UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
| |
| [X] | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 or 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 20132014
OR
|
| |
| [ ] | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number 1-3523
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
| | |
| Kansas | | 48-0290150 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
|
| | |
| 818 South Kansas Avenue, Topeka, Kansas 66612 | | (785) 575-6300 |
| (Address, including Zip code and telephone number, including area code, of registrant’s principal executive offices) |
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(b) of the Act:
|
| | |
| Common Stock, par value $5.00 per share | | New York Stock Exchange |
| (Title of each class) | | (Name of each exchange on which registered) |
Securities registered pursuant to section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer (as defined in Rule 405 of the Act). Yes X No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes No X
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes X No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes X No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Check one:
Large accelerated filer X Accelerated filer Non-accelerated filer Smaller reporting company
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes No X
The aggregate market value of the voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $4,056,844,230$4,936,929,569 at June 30, 2013.2014.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
|
| | |
| Common Stock, par value $5.00 per share | | 128,791,042132,137,563 shares |
| (Class) | | (Outstanding at February 18, 2014)17, 2015) |
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE:
|
| | |
| Description of the document | | Part of the Form 10-K |
Portions of the Westar Energy, Inc. definitive proxy statement to be used in connection with the registrant’s 20142015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders | | Part III (Item 10 through Item 14) (Portions of Item 10 are not incorporated by reference and are provided herein) |
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
| | |
| | | Page |
| | | |
| Item 1. | | |
| Item 1A. | | |
| Item 1B. | | |
| Item 2. | | |
| Item 3. | | |
| Item 4. | | |
| | | |
| Item 5. | | |
| Item 6. | | |
| Item 7. | | |
| Item 7A. | | |
| Item 8. | | |
| Item 9. | | |
| Item 9A. | | |
| Item 9B. | | |
| | | |
| Item 10. | | |
| Item 11. | | |
| Item 12. | | |
| Item 13. | | |
| Item 14. | | |
| | | |
| Item 15. | | |
| |
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
The following is a glossary of frequently used abbreviations or acronyms that are found throughout this report.
|
| | |
| Abbreviation or Acronym | | Definition |
| AFUDC | | Allowance for funds used during construction |
| ARO | | Asset retirement obligation |
| BACT | | Best Available Control Technology |
| BNSF | | BNSF Railway Company |
| Btu | | British thermal units |
CAMR | | Clean Air Mercury Rule |
| CCB | | Coal combustion byproductbyproducts |
| CO | | Carbon monoxide |
CO2 | | Carbon dioxide |
| COLI | | Corporate-owned life insurance |
| CSAPR | | Cross-State Air Pollution Rule |
Dodd-Frank ActCWA | | Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer ProtectionClean Water Act |
| DOE | | Department of Energy |
| DSPP | | Direct Stock Purchase Plan |
| ECRR | | Environmental Cost Recovery Rider |
| EPA | | Environmental Protection Agency |
| EPS | | Earnings per share |
| FERC | | Federal Energy Regulatory Commission |
| Fitch | | Fitch Ratings |
| GAAP | | Generally Accepted Accounting Principles |
| GHG | | Greenhouse gas |
| IM | | Integrated Marketplace |
| IRS | | Internal Revenue Service |
| JEC | | Jeffrey Energy Center |
| KCC | | Kansas Corporation Commission |
| KCPL | | Kansas City Power & Light Company |
| KDHE | | Kansas Department of Health and Environment |
| KGE | | Kansas Gas and Electric Company |
| La Cygne | | La Cygne Generating Station |
| LTISA Plan | | Long-Term Incentive and Share Award Plan |
| MATS | | Mercury and Air Toxics Standards |
| MMBtu | | Millions of BtuBritish thermal units |
| Moody’s | | Moody’s Investors Service |
| MW | | Megawatt(s) |
| MWh | | Megawatt hour(s) |
| NAAQS | | National Ambient Air Quality Standards |
| NDT | | Nuclear Decommissioning Trust |
| NEIL | | Nuclear Electric Insurance Limited |
| NOx | | Nitrogen oxides |
| NRC | | Nuclear Regulatory Commission |
NSPS | | New Source Performance Standard |
| PCB | | Polychlorinated biphenyl |
| PM | | Particulate matter |
| PRB | | Powder River Basin |
| Prairie Wind | | Prairie Wind Transmission, LLC |
| PSD | | Prevention of Significant Deterioration |
| RECA | | Retail energy cost adjustment |
|
| | |
| RSU | | Restricted share unit |
| RTO | | Regional Transmission Organization |
| S&P | | Standard & Poor’s Ratings Services |
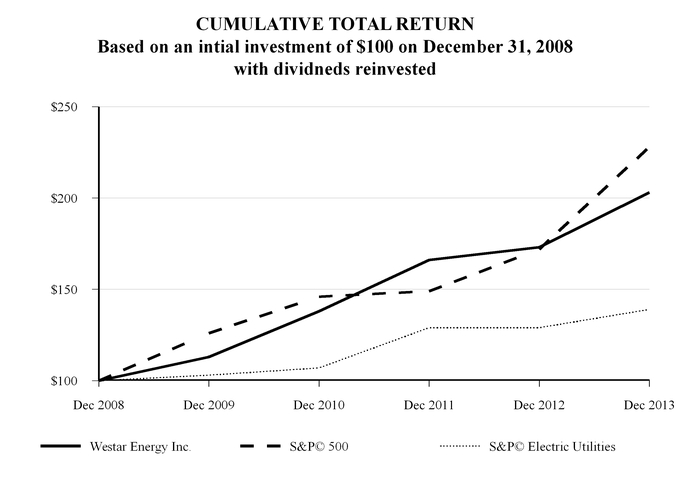
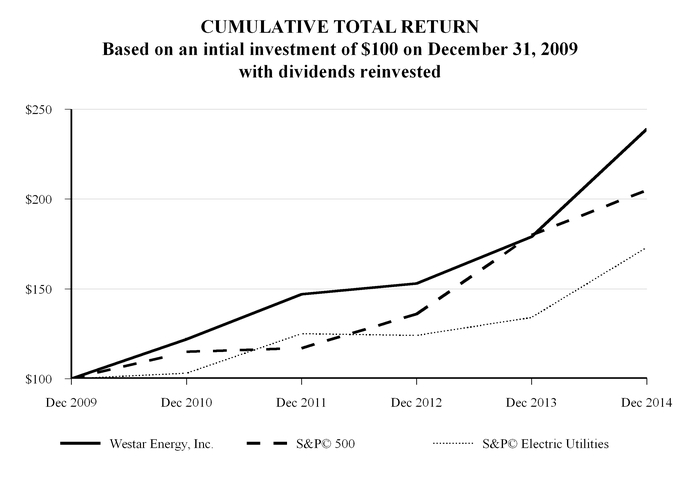
| S&P 500 | | Standard & Poor’s 500 Index |
| S&P Electric Utilities | | Standard & Poor’s Electric Utility Index |
SCR | | Selective catalytic reduction |
| SEC | | Securities and Exchange Commission |
SO2 | | Sulfur dioxide |
| SPP | | Southwest Power Pool, Inc. |
| SSCGP | | Southern Star Central Gas Pipeline |
Staff | | Staff of the Securities Exchange Commission |
| VaR | | Value-at-Risk |
| VIE | | Variable interest entity |
| Wolf Creek | | Wolf Creek Generating Station |
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Certain matters discussed in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are "forward-looking statements." The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 has established that these statements qualify for safe harbors from liability. Forward-looking statements may include words like we "believe," "anticipate," "target," "expect," "estimate," "intend" and words of similar meaning. Forward-looking statements describe our future plans, objectives, expectations or goals. Such statements address future events and conditions concerning matters such as, but not limited to:
| |
| - | amount, type and timing of capital expenditures, |
| |
| - | liquidity and capital resources, |
| |
| - | possible corporate restructurings, acquisitions and dispositions, |
| |
| - | compliance with debt and other restrictive covenants, |
| |
| - | interest rates and dividends, |
| |
| - | the overall economy of our service area and its impact on our customers' demand for electricity and their ability to pay for service. |
What happens in each case could vary materially from what we expect because of such things as:
| |
| - | the risk ofrisks related to operating in a heavily regulated industry that is subject to frequent and uncertainunpredictable political, legislative, judicial and regulatory developments, at any levelwhich can impact our operations, results of government that can affect our revenuesoperations, and costs,financial condition, |
| |
| - | the difficulty of predicting the amountmagnitude and timing of changes in demand for electricity, including with respect to emerging competing services and technologies and conservation and energy efficiency measures, |
| |
| - | the impact of weather conditions, and their effect onincluding as it relates to sales of electricity as well as onand prices of energy commodities, |
| |
| - | equipment damage from storms and extreme weather, |
| |
| - | economic and capital market conditions, including the impact of inflation or deflation, changes in interest rates, the cost and availability of capital and the market for trading wholesale energy, |
| |
| - | the impact of changes in market conditions on employee benefit liability calculations and funding obligations, as well as actual and assumed investment returns on invested plan assets, |
| |
| - | the impact of changes in estimates regarding our Wolf Creek Generating Station (Wolf Creek) decommissioning obligation, |
| |
| - | the existence or introduction of competition into markets in which we operate, |
| |
| - | the impact of frequently changing laws and regulations relating to air and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, water emissions, waste management and other environmental matters, |
| |
| - | risks associated with execution of our planned capital expenditure program, including timing and receipt of regulatory approvals necessary for planned construction and expansion projects as well as the ability to complete planned construction projects within the terms and time frames anticipated, |
| |
| - | cost, availability and timely provision of equipment, supplies, labor and fuel we need to operate our business, |
| |
| - | availability of generating capacity and the performance of our generating plants, |
| |
| - | changes in regulation of nuclear generating facilities and nuclear materials and fuel, including possible shutdown or required modification of nuclear generating facilities, |
| |
| - | additional regulation due to Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) oversight to ensure the safe operation of Wolf Creek, either related to Wolf Creek's performance, or potentially relating to events or performance at a nuclear plant anywhere in the world, |
| |
| - | uncertainty regarding the establishment of interim or permanent sites for spent nuclear fuel storage and disposal, |
| |
| - | homeland and information and operating systems security considerations, |
| |
| - | changes in accounting requirements and other accounting matters, |
| |
| - | changes in the energy markets in which we participate resulting from the development and implementation of real time and next day trading markets, and the effect of the retroactive repricing of transactions in such markets following execution because of changes or adjustments in market pricing mechanisms by regional transmission organizations (RTOs) and independent system operators, |
| |
| - | reduced demand for coal-based energy because of actual or potential climate impacts and development of alternate energy sources, |
| |
| - | current and future litigation, regulatory investigations, proceedings or inquiries, |
| |
| - | other circumstances affecting anticipated operations,cost of fuel used in generation and wholesale electricity sales and costs,prices, and |
| |
| - | other factors discussed elsewhere in this report, including in "Item 1A. Risk Factors" and "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and in other reports we file from time to time with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). |
These lists are not all-inclusive because it is not possible to predict all factors. This report should be read in its entirety. No one section of this report deals with all aspects of the subject matter. The reader should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statement, as forward-looking statements speak only as of the date such statements were made. We undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statement to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which such statement was made.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
GENERAL
Overview
We are the largest electric utility in Kansas. Unless the context otherwise indicates, all references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to "the company," "we," "us," "our" and similar words are to Westar Energy, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. The term "Westar Energy" refers to Westar Energy, Inc., a Kansas corporation incorporated in 1924, alone and not together with its consolidated subsidiaries.
We provide electric generation, transmission and distribution services to approximately 693,000698,000 customers in Kansas. Westar Energy provides these services in central and northeastern Kansas, including the cities of Topeka, Lawrence, Manhattan, Salina and Hutchinson. Kansas Gas and Electric Company (KGE), Westar Energy's wholly ownedwholly-owned subsidiary, provides these services in south-central and southeastern Kansas, including the city of Wichita. Both Westar Energy and KGE conduct business using the name Westar Energy. Our corporate headquarters is located at 818 South Kansas Avenue, Topeka, Kansas 66612.
Strategy
We expect to continue operating as a vertically integrated, regulated, electric utility. Significant elements of our strategy include maintaining a flexible and diverse energy supply portfolio. In doing so, we continue to make environmental upgrades to our coal-fired power plants, develop renewable generation, build and upgrade our electrical infrastructure and develop systems and programs with regard to how our customers use energy.energy and interact with us.
OPERATIONS
General
As noted above, we supply electric energy at retail to customers in Kansas. We also supply electric energy at wholesale to municipalities and electric cooperatives in Kansas, and have contracts for the sale or purchase of wholesale electricity with other utilities.
Following is the percentage of our revenues by customer classification. Classification of customers as residential, commercial and industrial requires judgment and our classifications may be different from other companies. Assignment of tariffs is not dependent on classification.
| | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Residential | | 31 | % | | 32 | % | | 32 | % | | 31 | % | | 31 | % | | 32 | % |
| Commercial | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % |
| Industrial | | 16 | % | | 16 | % | | 16 | % | | 16 | % | | 16 | % | | 16 | % |
| Wholesale | | 15 | % | | 14 | % | | 16 | % | | 15 | % | | 15 | % | | 14 | % |
| Transmission | | 9 | % | | 9 | % | | 7 | % | | 9 | % | | 9 | % | | 9 | % |
| Other | | 1 | % | | 1 | % | | 1 | % | | 1 | % | | 1 | % | | 1 | % |
| Total | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % |
The percentage of our retail electricity sales by customer class was as follows.
| | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Residential | | 34 | % | | 34 | % | | 35 | % | | 34 | % | | 34 | % | | 34 | % |
| Commercial | | 38 | % | | 38 | % | | 37 | % | | 38 | % | | 38 | % | | 38 | % |
| Industrial | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % | | 28 | % |
| Total | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % |
GenerationGenerating Capability and Firm Capacity Purchases
We have 6,5716,645 megawatts (MW) of accredited generating capacitycapability in service. See "Item 2. Properties" for additional information about our generating units. We own electricity generating facilities orFurther, we purchase electricity pursuant to long-term contracts from renewable generation facilities with an installed design capacity of 664521 MW. Because of the intermittent nature of wind generation, only 14 MW of accreditedOur generating capacity is associated with wind generation facilities. Our capacitycapability and net generation by fuel type are summarized below.
| | | Fuel Type | | Capacity(MW) | | Percent of Total Capacity | | Net Generation (MWh) | | Percent of Total Net Generation | | Capability (MW) | | Percent of Total Capability | | Net Generation (MWh) | | Percent of Total Net Generation |
| Coal | | 3,424 |
| | 52 | % | | 20,677,415 |
| | 73 | % | | 3,415 |
| | 48 | % | | 19,495,473 |
| | 71 | % |
| Nuclear | | 547 |
| | 8 | % | | 3,369,101 |
| | 12 | % | | 549 |
| | 8 | % | | 4,022,443 |
| | 15 | % |
| Natural gas/diesel | | 2,599 |
| | 39 | % | | 1,785,382 |
| | 6 | % | | 2,532 |
| | 35 | % | | 1,379,927 |
| | 5 | % |
| Renewable | | 1 |
| | <1% |
| | 426,919 |
| | 2 | % | | 670 |
| | 9 | % | | 2,393,744 |
| | 9 | % |
| Renewable purchase contracts | | 13 |
| | <1% |
| | 1,894,308 |
| | 7 | % | |
| Total | | 6,584 |
| | 100 | % | | 28,153,125 |
| | 100 | % | | 7,166 |
| | 100 | % | | 27,291,587 |
| | 100 | % |
In November, 2013 weWe have entered into atwo unrelated renewable energy purchase agreement.agreements. Under theeach agreement, we plan to purchase an additional 200 MW of installed designed capacity, for a total of 400 MW. One agreement is to be deliveredprovide this generating capability by the end of 2015 while the other is to provide additional generating capability by the end of 2016.
Our aggregate 20132014 peak system net load of 5,1865,226 MW occurred in July 2013.August 2014. Because of the intermittent nature of wind generation, only 58 MW of net accredited generating capacity is associated with our wind generation facilities. Our net accredited generating capacity, combined with firm capacity purchases and sales and potentially interruptible load, provided a capacity margin of 19% above system peak responsibility at the time of our 20132014 peak system net load, which satisfied Southwest Power Pool, Inc. (SPP) planning requirements.
Under wholesale agreements, we provide firm generating capacity to other entities as set forth below.
|
| | | | | |
| Utility (a) | | Capacity (MW) | | Expiration |
Oklahoma Municipal Power Authority | | 61 |
| | December 2013 |
| Midwest Energy, Inc. | | 75 |
| | December 2015 |
| Midwest Energy, Inc. | | 120 |
| | May 2017 |
| Midwest Energy, Inc. | | 35 |
| | May 2017 |
| Mid-Kansas Electric Company, LLC | | 174 |
| | January 2019 |
| Kansas Power Pool | | 59 |
| | March 2020December 2022 |
| Midwest Energy, Inc. | | 150 |
| | May 2025 |
| Other | | 133 |
| | December 2013 – May 2015 |
| Total | | 687616 |
| | |
_______________
| |
| (a) | Under a wholesale agreement that expires in May 2039, we provide base load capacity to the city of McPherson, Kansas, and in return the city provides peaking capacity to us. During 20132014, we provided approximately 89 MW to, and received approximately 148 MW from, the city. The amount of base load capacity provided to the city is based on a fixed percentage of its annual peak system load. The city is a full requirements customer of Westar Energy. The agreement for the city to provide capacity to us is treated as a capital lease. |
Fossil Fuel Generation
The effectiveness of a fuel to produce heat is measured in British thermal units (Btu). The higher the Btu content of a fuel, the smaller volume of fuel required to produce a given amount of electricity. We measure the quantity of heat consumed during the generation of electricity in millions of BtuBritish thermal units (MMBtu).
Coal
Jeffrey Energy Center (JEC): The three coal-fired units at JEC have an aggregate capacity of 2,155 MW, of which we own or consolidate through a variable interest entity (VIE) a combined 92% share, or 1,983 MW. We have a long-term coal supply contract with Alpha Natural Resources, Inc. to supply coal to JEC from surface mines located in the Powder River Basin (PRB) in Wyoming. The contract contains a schedule of minimum annual MMBtu quantities. All of the coal used at JEC is purchased under this contract, which expires December 31, 2020. The contract provides for price escalation based on certain costs of production. The price for quantities purchased in excess of the scheduled annual minimum is subject to renegotiation every five years to provide an adjusted price for the ensuing five years that reflects the market prices at the time of renegotiation. The most recent price adjustment was effective January 1, 2013.
The BNSF Railway Company (BNSF) and Union Pacific Railroad Company transport coal to JEC under a long-term rail transportation contract. The contract term continues through December 31, 2020, at which time we plan to enter into a new contract. The contract price is subject to price escalation based on certain costs incurred by the railroads.
The average delivered cost of coal consumed at JEC during 20132014 was approximately $1.77 per MMBtu, or $29.22$29.16 per ton.
La Cygne Generating Station (La Cygne): The two coal-fired units at La Cygne have an aggregate generating capacity of 1,4181,416 MW. Our share of the units is 50%, or 708 MW, of which we either own directly or consolidate through a VIE a 50% share, or 709 MW.VIE. La Cygne uses primarily PRB coal but one of the two units also uses a small portion of locally-mined coal. The operator of La Cygne, Kansas City Power & Light Company (KCPL), arranges coal purchases and transportation services for La Cygne. Approximately 70%90%, 40%50% and 20%15% of La Cygne's PRB coal requirements are under contract for 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2016,2017, respectively. About 80% of those commitments under contract for 2014 are fixed price95%, 85% and all45% of those commitments under contract are fixed price for 2015, 2016 and 2016.2017, respectively. As the PRB coal contracts expire, we anticipate that KCPL will negotiate new supply contracts or purchase coal on the spot market.
All of the La Cygne PRB coal is transported under KCPL's rail transportation agreements with BNSF through 2018 and Kansas City Southern Railroad through 2020. During 20132014, our share of average delivered cost of coal consumed at La Cygne was approximately $2.06 per MMBtu, or $35.81$35.76 per ton.
Lawrence and Tecumseh Energy Centers: Lawrence and Tecumseh Energy Centers have an aggregate generating capacity of 732724 MW. We purchase PRB coal for these energy centers under a contract with Arch Coal, Inc., which we expect to provide that provides for 100% of the coal requirements for these facilities through 2014.2017. BNSF transports coal for these energy centers under a contract that expires in December 2020, at which time we plan to enter into a new contract.2020.
During 2013,2014, the average delivered cost of coal consumed in the Lawrence units was approximately $1.78$1.68 per MMBtu, or $31.43$29.81 per ton. The average delivered cost of coal consumed in the Tecumseh units was approximately $1.74$1.67 per MMBtu, or $30.96$29.75 per ton.
Natural Gas
We use natural gas as a primary fuel at our Gordon Evans, Murray Gill, Hutchinson, Spring Creek and Emporia Energy Centers, at the State Line facility and in the gas turbine units at Tecumseh Energy Center. We can also use natural gas as a supplemental fuel in the coal-fired units at Lawrence and Tecumseh Energy Centers. During 2013,2014, we consumed 19.015.3 million MMBtu of natural gas for a total cost of $83.8$87.1 million, or approximately $4.41$5.71 per MMBtu. Natural gas accounted for approximately 7%6% of the total MMBtu of fuel we consumed and approximately 16%17% of our total fuel expense in 2013.2014. From time to time, we may enter into contracts, including the use of derivatives, in an effort to manage the cost of natural gas. For additional information about our exposure to commodity price risks, see "Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk."
We maintain a natural gas transportation arrangement for Hutchinson Energy Center with Kansas Gas Service. The agreement has historically expired on April 30 of each year and is renegotiated for an additional one year term. We meet a portion of our natural gas transportation requirements for Gordon Evans, Murray Gill, Lawrence, Tecumseh and Emporia Energy Centers through firm natural gas transportation capacity agreements with Southern Star Central Gas Pipeline (SSCGP). We meet all of the natural gas transportation requirements for the State Line facility through a firm transportation agreement with SSCGP. The firm transportation agreement that serves Gordon Evans and Murray Gill Energy Centers extends throughexpires in April 1, 2020, and the agreement for Lawrence and Tecumseh Energy Centers expires in April 1, 2030. The agreement for the State Line facility extends through July 30,August 2017, while the agreement for Emporia Energy Center is in place until December 1, 2028, and is renewable for five-year terms thereafter. We meet all of the natural gas transportation requirements for Spring Creek Energy Center through an interruptible month-to-month transportation agreement with ONEOK Gas Transportation, LLC.
Diesel
We use diesel to start some of our coal generating stations, as a primary fuel in the Hutchinson No. 4 combustion turbine and in our diesel generators. We purchase No. 2 diesel in the spot market. We maintain quantities in inventory that we believe will allow us to facilitate economic dispatch of power and satisfy emergency requirements. We do not use significant amounts of diesel in our operations.
Nuclear Generation
General
Wolf Creek is a 1,1641,168 MW nuclear power plant located near Burlington, Kansas. KGE owns a 47% interest in Wolf Creek, or 547549 MW. Wolf Creek's operating license, issued by the NRC, is effective until 2045. Wolf Creek Nuclear Operating Corporation, an operating company owned by each of the plant's owners in proportion to their ownership share of the plant, operates the plant. The plant's owners pay operating costs proportionate to their respective ownership share.
Fuel Supply
Wolf Creek has on hand or under contract all of the uranium and conversion services needed to operate through September 2016 and approximately 70% of the uranium and conversion services needed after that date through March 2021. The owners also have under contract all of the uranium enrichment and fabrication services required to operate Wolf Creek through March 2027 and September 2025, respectively. All such agreements have been entered into in the ordinary course of business.
Operations and Regulation
Plant performance, including extended or unscheduled shutdowns of Wolf Creek, could cause us to purchase replacement power, rely more heavily on our other generating units and/or reduce amounts of power available for us to sell in the wholesale market. Plant performance also affects the degree of regulatory oversight and related costs. In early 2014, Wolf Creek will undergounderwent a planned maintenance outage. Because the outage iswas not part of a refueling outage, the related costs will bewere expensed as incurred. We expect ourOur share of the outage to becosts were approximately $9.0$8.7 million. The next refueling and maintenance outage is planned for the first quarter of 2015.
Wolf Creek normally operates on an 18-month planned refueling and maintenance outage schedule. As authorized by our regulators, incremental maintenance costs of planned refueling and maintenance outages are deferred and amortized ratably over the period between planned outages. During outages at the plant, we meet our electric demand primarily with our other generating unitsrefueling and by purchasing power.maintenance outages.
The NRC evaluates, monitors and rates various inspection findings and performance indicators for Wolf Creek based on safety significance. Although not expected, the NRC could impose an unscheduled plant shutdown due to security or safety concerns. Those concerns need not be related to Wolf Creek specifically, but could be due to concerns about nuclear power generally or circumstances at other nuclear plants in which we have no ownership.
See Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Commitments and Contingencies," for additional information regarding our nuclear operations.
Wind Generation
As discussed under "Environmental Matters—Renewable Energy Standard" below,in Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, "Commitments and Contingencies," Kansas law requiresspecifies that a portion of our energy supply resources consist of a certain amount ofbe from renewable sources. For us, wind has been the primary source of renewable energy. As of December 31, 2013,2014, we owned approximately 149 MW of designed installed wind capacity and had under contract the purchase of wind energy produced from approximately 715915 MW of designed installed wind capability. Of the 715915 MW under contract, 200515 MW are currently in operation and 400 MW are associated with an agreement pursuant to which a generation provider isagreements that are scheduled to deliver power beginning in late 2015 and 2016.
Other Fuel Matters
The table below provides our weighted average cost of fuel, including transportation costs.
| | | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Per MMBtu: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Nuclear | $ | 0.75 |
| | $ | 0.70 |
| | $ | 0.68 |
| $ | 0.66 |
| | $ | 0.75 |
| | $ | 0.70 |
|
| Coal | 1.82 |
| | 1.86 |
| | 1.74 |
| 1.80 |
| | 1.82 |
| | 1.86 |
|
| Natural gas | 4.41 |
| | 3.20 |
| | 4.81 |
| 5.71 |
| | 4.41 |
| | 3.20 |
|
| Diesel | 22.89 |
| | 23.12 |
| | 19.33 |
| 21.31 |
| | 22.89 |
| | 23.12 |
|
| All generating stations | 1.91 |
| | 1.84 |
| | 1.92 |
| 1.90 |
| | 1.91 |
| | 1.84 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Per MWh Generation: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Nuclear | $ | 7.86 |
| | $ | 7.28 |
| | $ | 7.15 |
| $ | 6.79 |
| | $ | 7.86 |
| | $ | 7.28 |
|
| Coal | 20.26 |
| | 20.59 |
| | 19.30 |
| 20.04 |
| | 20.26 |
| | 20.59 |
|
| Natural gas/diesel | 46.38 |
| | 33.29 |
| | 52.65 |
| 62.84 |
| | 46.38 |
| | 33.29 |
|
| All generating stations | 20.45 |
| | 19.65 |
| | 20.60 |
| 20.27 |
| | 20.45 |
| | 19.65 |
|
Our wind production has no associated fuel costs and is, therefore, not included in the table above.
Purchased Power
In addition to generating electricity, we also purchase power. Factors that cause us to purchase power include contractual arrangements, planned and unscheduled outages at our generating plants, favorable wholesale energy prices compared to our costs of production, weather conditions and other factors. Transmission constraints may limit our ability to bring purchased electricity into our control area, potentially requiring us to curtail or interrupt our customers as permitted by our tariffs. In 20132014, purchased power comprised approximately 18%27% of our total fuel and purchased power expense. Our weighted average cost of purchased power per Megawatt hour (MWh) was $37.26 in 2014, $33.63 in 2013, and $26.41 in 2012 and $34.27 in 2011.
Transmission
Regional Transmission Organization
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) requires owners of regulated transmission assets to allow third parties nondiscriminatory access to their transmission systems. We are a member of the SPP RTO and transferred the functional control of our transmission system, including the approval of transmission service, to the SPP. The SPP coordinates the operation of our transmission system within an interconnected transmission system that covers all or portions of nine states. The SPP collects revenues for the use of each transmission owner's transmission system. Transmission customers transmit power purchased and generated for sale or bought for resale in the wholesale market throughout the entire SPP system. Transmission capacity is sold on a first come/first served non-discriminatory basis. All transmission customers are charged rates applicable to the transmission system in the zone where energy is delivered, including transmission customers that may sell power inside our certificated service territory. The SPP then distributes as revenue to transmission owners the amounts it collects from transmission users less an amount it retains to cover administrative expenses.
Southwest Power Pool Integrated Market in SPP
The SPP is scheduled to launch anlaunched their new Integrated Marketplace (IM) in March 2014. The SPP IM will beis similar to other organized power markets currently operating in other RTOs. The SPP IM will changeimpacts how we currentlycommit and sell the output from our generation facilities and buy power to meet the needs of our customers. The SPP will havehas the authority to start and stop generating units participating in the market and will selectselects the lowest cost resource mix to meet the needs of the various SPP customers while ensuring reliable operations of the transmission system. As with other organized markets, there will be additional market related products, revenues,
Transmission Investments
We own a 50% interest in Prairie Wind Transmission, LLC (Prairie Wind), which is a joint venture between us and charges. Westar recently submitted the necessary regulatory filings seekingElectric Transmission America, LLC, which itself is a joint venture between affiliates of American Electric Power Company, Inc. and Berkshire Hathaway Energy Company. In 2014, Prairie Wind completed construction on, and energized, a 108 mile 345 kV double-circuit transmission line that is now being used to recognize the associated revenues and chargesprovide transmission service in the prices we charge our customers, similar to our current retail energy cost adjustment tariff.SPP.
In 2011, the FERC issued Order No. 1000, which revised the FERC's existing regulations governing the process for planning enhancements and expansions of the electric transmission grid, along with the corresponding process for allocating the costs of such expansions. Among other things, Order No. 1000 sets forth a framework pursuant to which certain transmission projects that are approved by the RTOs, including the SPP, become subject to a competitive bidding process whereby qualified entities can build and own the transmission facilities, even if the entities are not located in the service territory covered by the transmission facilities. This process is complicated, and is governed by Order No. 1000 and the tariff each RTO has with the FERC. In addition, notwithstanding the competitive processes created by Order No. 1000, incumbent utilities maintain a right of first refusal for certain transmission projects, depending on, among other things, the date by which the projects must be completed, the size of the projects and whether the incumbent utilities have pre-existing facilities that are being impacted by the projects.
TableWe are actively participating in the SPP’s transmission planning activities and implementation of ContentsOrder No. 1000. We believe we have opportunities to develop transmission infrastructure, including projects pursuant to which we as the incumbent have a right of first refusal and those projects that are subject to the Order No. 1000 competitive processes. However, due in part to the long term nature of transmission planning activities, coupled with the fact that Order No. 1000 is in its very early stages, we are unable to predict the impact of Order No. 1000. Accordingly, in our forecasted capital expenditure table, there are no dollars of investment associated with Order No. 1000 projects.
Regulation and Our Prices
Kansas law gives the Kansas Corporation Commission (KCC) general regulatory authority over our retail prices, extensions and abandonments of service and facilities, the classification of accounts, the issuance of some securities and various other matters. We are also subject to the jurisdiction of FERC, which has authority over wholesale electricity sales, including prices, the transmission of electric power and the issuance of some securities. We are subject to the jurisdiction of the NRC for nuclear plant operations and safety. Regulatory authorities have established various methods permitting adjustments to our prices for the recovery of costs. For portions of our cost of service, regulators allow us to adjust our prices periodically through the application of formulae that track changes in our costs, which reduce the time between making expenditures or investments and reflecting them in the prices we charge customers. However, for the remaining portions of our cost of service, we must file a general rate review, which lengthens the period of time between when we make and recover expenditures and a return on our investments. See Note 3 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Rate Matters and Regulation," for information regarding our rate proceedings with the KCC and FERC.
Environmental Matters
General
We are subject to various federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations. Environmental laws and regulations affecting our operations are overlapping, complex, subject to changes, have become more stringent over time and are expensive to implement. Such laws and regulations relate primarily to air quality, water quality, the use of water and the handling, disposal and clean-up of hazardous and non-hazardous substances and wastes.wastes, including coal combustion byproducts (CCBs). These laws and regulations oftentimes require a lengthy and complex process for obtaining licenses, permits and approvals from governmental agencies for new, existing or modified facilities. If we fail to comply with such laws, regulations and permits, or fail to obtain and maintain necessary permits, we could be fined or otherwise sanctioned by regulators, and such fines or the cost of sanctions may not be recoverable in our prices. We have incurred and will continue to incur significant capital and other expenditures to comply with environmental laws and regulations.
We are currently permitted to recover certain of these costs through the environmental cost recovery rider (ECRR), which, in comparison to a general rate review, reduces the amount of time it takes to begin collecting in retail prices the costs associated with capital expenditures for qualifying environmental improvements. However, there can be no assurance thatWe are not allowed to use the ECRR to collect approximately $610.0 million of the projected capital investment associated with environmental upgrades at La Cygne. In November 2013, the KCC issued an order allowing us to increase our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades through June 30, 2013, and to reflect cost reductions elsewhere. The new prices were expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $30.7 million.
Our estimated capital expenditures associated with environmental improvements for 2015-2017 appear in the following table. We prepare these estimates for planning purposes and revise them from time to time.
|
| | | | |
| Year | | Total |
| | | (In Thousands) |
| 2015 | | $ | 85,400 |
|
| 2016 | | 26,800 |
|
| 2017 | | 14,500 |
|
| Total | | $ | 126,700 |
|
To change our prices to collect increased operating and maintenance costs, we must file a general rate review with the KCC. We intend to file our next general rate review in March 2015. Costs to comply with existing or future environmental laws and regulations will notcould have a material adverse effect on our operations or consolidated financial results. Certain key environmental issues, laws and regulations facingIn addition, the installation of new equipment may cause us are described further below.
Air Emissions
We must comply with the federal Clean Air Act, state laws and implementing federal and state regulations that impose, among other things, limitations on emissions generated from our operations, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), mercury and acid gases.
Emissions from our generating facilities, including PM, SO2 and NOx, have been determined by regulation to reduce visibility by causing or contributingthe net production, reliability and availability of our plants. Furthermore, enhancements to regional haze. Under federal laws, such as the Clean Air Visibility Rule, and pursuant to an agreement with the Kansas Department of Health and Environment (KDHE) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), we are required to install, operate and maintain controls to reduce emissions found to cause or contribute to regional haze. In addition, our power plants, that burn fossil fuels emit carbon dioxide,even if they result in greater efficiency, can trigger a regulatory review, which is also regulated under the Clean Air Act and for which the EPA is presently developing regulations.could result in increased costs or other operational requirements.
Sulfur DioxideSee “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Nitrogen Oxide
Through the combustionAnalysis of fossil fuels at our generating facilities, we emit SO2 Financial Condition and NOx. FederalResults of Operations - Environmental Regulation,” “Item 1A. Risk Factors" and stateNotes 3 and 13 to Consolidated Financial Statements, “Rate Matters and Regulation - KCC Proceedings - Environmental Costs” and “Commitments and Contingencies - Environmental Matters,” respectively, for more information regarding environmental trends, risks and laws and regulations, including those noted above, and permits issued to us limit the amount of these substances we can emit. If we exceed these limits we could be subject to fines and penalties. In order to meet SO2 and NOx regulations applicable to our generating facilities, we use low-sulfur coal and natural gas and have equipped some of our generating facilities with equipment to control such emissions.
We are subject to the SO2 allowance and trading program under the federal Clean Air Act Acid Rain Program. Under this program, each unit must have enough allowances to cover its SO2 emissions for that year. In 2013, we had adequate SO2 allowances to meet planned generation and we expect to have enough to cover emissions under this program in 2014.
Cross-State Air Pollution Rule
In 2011, the EPA finalized the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) requiring 28 states, including Kansas, Missouri and Oklahoma, to further reduce power plant emissions of SO2 and NOx beginning January 2012, with further reductions required beginning January 2014. In August 2012, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit vacated CSAPR and remanded the rule to the EPA to promulgate a replacement. This decision is now under review by the U.S. Supreme Court. We cannot at this time predict the outcome of the U.S. Supreme Court's review; however, based on our current and planned environmental controls, if the regulations were to be reinstated or replaced, either in part or in whole, we do not believe the impact on our operations and consolidated financial results would be material.
National Ambient Air Quality Standards
Under the federal Clean Air Act, the EPA sets National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for certain emissions considered harmful to public health and the environment, including two classes of PM, NOx (a precursor to ozone), CO and SO2, which result from fossil fuel combustion. Areas meeting the NAAQS are designated attainment areas while those that do not meet the NAAQS are considered nonattainment areas. Each state must develop a plan to bring nonattainment areas into compliance with the NAAQS. NAAQS must be reviewed by the EPA at five-year intervals. KDHE, our state environmental regulatory agency, proposed to designate portions of the Kansas City area nonattainment for the eight-hour ozone standard. The EPA has not acted on KDHE's proposed designation of the Kansas City area and it is uncertain when, or if, such a designation might occur. The Wichita area also exceeded the eight-hour ozone standard and could be designated nonattainment in the future potentially impacting our operations.
In September 2011, the President instructed the EPA not to implement its more stringent 2008 Ozone Standard since a new NAAQS for ozone was due to be proposed in 2013 and finalized in 2014. We are waiting on this new standard and cannot at this time predict the impact it may have on our operations, but it could be material.
In December 2012, the EPA strengthened an existing NAAQS for one class of PM. By the end of 2014, the EPA anticipates making final attainment/nonattainment designations under this rule and expects to issue a final implementation rule. We are currently evaluating the rule, however, we cannot at this time predict the impact it may have on our operations or consolidated financial results, but it could be material.
In 2010 the EPA strengthened the NAAQS for both NOx and SO2. We continue to communicate with our regulators regarding these standards and are currently evaluating what impact this could have on our operations and consolidated financial results. If we are required to install additional equipment to control emissions at our facilities, the revised NAAQS could have a material impact on our operations and consolidated financial results.
Mercury and Other Air Emissions
The operation of power plants results in emissions of mercury, acid gases and other air toxics. In 2012, the EPA's Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) for power plants became effective, replacing the prior federal Clean Air Mercury Rule (CAMR) and requiring significant reductions in mercury, acid gases and other emissions. We expect to be compliant with the new standards by April 2016 as approved by KDHE. We continue to evaluate the new standards and believe that our related investment will be approximately $17.0 million.
Greenhouse Gases
Byproducts of burning coal and other fossil fuels include carbon dioxide (CO2) and other gases referred to as greenhouse gases (GHGs), which are believed by many to contribute to climate change. The EPA has proposed using the federal Clean Air Act to limit CO2 and other GHG emissions, and other measures are being imposed or offered by individual states, municipalities and regional agreements with the goal of reducing GHG emissions.
In January 2014, the EPA re-proposed a New Source Performance Standard (NSPS) that would limit CO2 emissions for new coal and natural gas fueled generating units. The re-proposal would limit CO2 emissions to 1,000 lbs per MWh generated for larger natural gas units and 1,100 lbs per MWh generated for smaller natural gas units and coal units. Final regulations are expected later in 2014. The EPA was also directed to issue proposed standards addressing CO2 emissions for modified, reconstructed and existing power plants by June 2014, issue final rules by June 2015, and require that states submit their implementation plans to the EPA no later than June 2016. We cannot at this time determine the impact of such proposals on our operations and consolidated financial results, but we believe the costs to comply could be material.
Under regulations known as the Tailoring Rule, the EPA regulates GHG emissions from certain stationary sources. The regulations are being implemented pursuant to two federal Clean Air Act programs which impose recordkeeping and monitoring requirements and also mandate the implementation of best available control technology (BACT) for projects that cause a significant increase in GHG emissions (defined to be more than 75,000 tons or more per year or 100,000 tons or more per year, depending on various factors). The EPA has issued guidance on what BACT entails for the control of GHGs and individual states are now required to determine what controls are required for facilities within their jurisdiction on a case-by-case basis. We cannot at this time determine the impact of these regulations on our future operations and consolidated financial results, but we believe the cost of compliance with the regulations could be material.
Water
We discharge some of the water used in our operations. This water may contain substances deemed to be pollutants. Revised rules governing such discharges from coal-fired power plants are expected to be issued by the EPA in 2014. Although we cannot at this time determine the timing or impact of compliance with any new regulations, more stringent regulations could have a material impact on our operations and consolidated financial results.
In 2011, the EPA issued a proposed rule that would increase the requirements for cooling intake structures at power plants over concerns about impacts to aquatic life. We are currently evaluating the proposed rule as well as recent nationally-issued information requests from the EPA. The EPA is required to finalize the rule by April 2014; however, because the rule has yet to be finalized, we cannot predict the impact it may have on our operations or consolidated financial results, but it could be material.
Regulation of Coal Combustion Byproducts
In the course of operating our coal generation plants, we produce coal combustion byproducts (CCBs), including fly ash, gypsum and bottom ash. We recycle some of our ash production, principally by selling to the aggregate industry. In 2010, the EPA proposed a rule to regulate CCBs at the federal level, which we believe might impair our ability to recycle ash or require additional CCB handling, processing and storage equipment, or both. The EPA has agreed, subject to court approval, to issue a final rule in 2014. While we cannot at this time estimate the impact and costs associated with future regulations of CCBs, we believe the impact on our operations and consolidated financial results could be material.regulations.
Renewable Energy Standard
Kansas law mandates that we maintain a minimum amount of renewable energy sources. Through 2015, net renewable generation capability must be 10% of the average peak retail demand for the three prior years, subject to limited exceptions. This requirement increases to 15% for years 2016 through 2019 and 20% for 2020 and thereafter. With our existing wind generation facilities, supply contracts and renewable energy credits, we are able to satisfy the net renewable generation requirement through 2015. With our agreementagreements to purchase an additional 200400 MW of installed design capcaitycapacity from a wind generation facilityfacilities beginning in late2015 through 2016, we expect to meet the increased requirements through 2020.for 2020 and thereafter. If we are unable to meet future requirements, our operations and consolidated financial results could be adversely impacted.
Environmental Costs
As discussed above, environmental laws and regulations affecting our operations are evolving and becoming more stringent. As a result, we are making and will continue to make significant capital and operating expenditures to reduce regulated emissions. The amount of these expenditures could change materially depending on the timing and nature of required investments, the specific outcomes resulting from existing regulations, new regulations, legislation and the manner in which we operate our plants. The degree to which we will need to reduce certain emissions and the timing of when such emissions controls may be required is uncertain. Additionally, our ability to access capital markets and the availability of materials, equipment and contractors may affect the timing and amount of these capital investments.
We are not allowed to use the ECRR to collect approximately $610.0 million of the projected capital investment associated with environmental upgrades at La Cygne. In November 2013, the KCC issued an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades and to reflect cost reductions elsewhere. The new prices are expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $30.7 million. To change our prices to collect increased operating and maintenance costs, we must file a general rate review with the KCC.
Our estimated capital expenditures associated with environmental improvements for 2014-2016 appear in the following table. We prepare these estimates for planning purposes and revise them from time to time.
|
| | | | |
| Year | | Total |
| | | (In Thousands) |
| 2014 | | $ | 237,000 |
|
| 2015 | | 112,000 |
|
| 2016 | | 21,900 |
|
| Total | | $ | 370,900 |
|
In addition to the capital investment, in the event we install new equipment, such equipment may cause us to incur significant increases in annual operating and maintenance expenses and may reduce the net production, reliability and availability of the plants. Furthermore, enhancements to our power plants, even if they result in greater efficiency, can trigger a new source review, which could require additional control equipment. In order to change our prices to recognize increased operating and maintenance costs, we must file a general rate review with the KCC.
EPA Consent Decree
As part of a 2010 settlement of a lawsuit filed by the Department of Justice on behalf of the EPA, we are installing selective catalytic reduction (SCR) equipment on one of three JEC coal units by the end of 2014, which we estimate will cost approximately $230.0 million. We are installing less expensive NOx reduction equipment on the other two units to satisfy other terms of the settlement. We plan to complete these projects in 2014 and recover the costs to install these systems through our ECRR, but such recovery remains subject to the approval of our regulators.
Safety and Health Regulation
The safety and health of our employees is vital to our business. We are subject to a number of federal and state laws and regulations, including the Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970. We believe we have appropriate measures in place to ensurepromote the safety and health of our employees and to monitor our compliance with such laws and regulations.
Information Technology
SafeguardingWe rely upon information technology networks and systems is importantto process, transmit and store electronic information, and to manage or support a variety of business processes and activities, including the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity, supply chain functions and the invoicing and collection of payments from our customers. Cybersecurity breaches, criminal activity, terrorist attacks and other disruptions to our information technology infrastructure could interfere with our operations, could expose us or our customers or employees to a risk of loss and could expose us to liability or regulatory penalties or cause us reputational damage or other harm to our business. There are risks associated with the unauthorized access, theft or accidental release of electronic data, which may result in the misappropriation or corruption of our information or cause operational disruptions. We believe these risks are getting increasingly larger and more sophisticated. We believe that we have taken appropriate measures to secure our information infrastructure from attacks or breachesnetwork and from accidental release of information,systems, but notwithstanding such measures may not be sufficient, especially due to the increasing sophistication of potential attacks may result in remaining vulnerabilities.cyberattacks. See Item 1A, "Risk Factors,""Item 1A. Risk Factors" for additional information.
SEASONALITY
Our electricity sales and revenues are seasonal, with the third quarter typically accounting for the greatest of each. Our electricity sales are impacted by weather conditions, the economy of our service territory and other factors affecting customers' demand for electricity.
EMPLOYEES
As of February 18, 2014,17, 2015, we had 2,302 employees. In 2013, we negotiated2,411 employees, 1,283 of which were covered by a contract extension with Locals 304 and 1523 of the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers that extends through June 30, 2017. The contract covers 1,256 employees as of February 18, 2014.
ACCESS TO COMPANY INFORMATION
Our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and Current Reports on Form 8-K are available free of charge either on our Internet website at www.westarenergy.com or through requests addressed to our investor relations
department. These reports are available as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. The information contained on our Internet website is not part of this document.
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE COMPANY
|
| | | | | | | |
| Name | | Age | | Present Office | | Other Offices or Positions Held During the Past Five Years |
| | | | | | | |
| Mark A. Ruelle | | 5253 |
| | Director, President and Chief Executive Officer (since August 2011) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Director, President and Chief Financial Officer (May 2011 to July 2011) Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (January 2003 to April 2011) |
Douglas R. SterbenzBruce A. Akin | | 50 |
| | ExecutiveSenior Vice President, and Chief Operating OfficerPower Delivery (since July 2007)January 2015) | |
Westar Energy, Inc.
Vice President, Power Delivery (February 2012 to December 2014)
Vice President, Operations Strategy and Support (July 2007 to February 2012) |
GregJerl L. Banning | | 54 |
| | Senior Vice President, Operations Support and Administration
(since January 2015) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Vice President, Human Resources and IT (January 2014 to December 2014) Vice President, Human Resources (February 2010 to December 2013) |
| John T. Bridson | | 45 |
| | Senior Vice President, Generation and Marketing (since January 2015) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Vice President, Generation (February 2011 to December 2014) Executive Director, Generation (May 2010 to February 2011) Executive Director, Lawrence Energy Center (January 2007 to May 2010) |
| Gregory A. Greenwood | | 4849 |
| | Senior Vice President, Strategy (since August 2011) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Vice President, Major Construction Projects (December 2009 to July 2011) Vice President, Generation Construction (August 2006 to December 2009)
|
| Anthony D. Somma | | 5051 |
| | Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer (since August 2011) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Vice President, Treasurer (February 2009 to July 2011) Treasurer (August 2006 to February 2009)
|
| Larry D. Irick | | 5758 |
| | Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary (since February 2003) | | |
| Kevin L. Kongs | | 5152 |
| | Vice President, Controller (since November 2013) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Assistant Controller (October 2006 to November 2013)
|
Executive officers serve at the pleasure of the board of directors. There are no family relationships among any of the executive officers, nor any arrangements or understandings between any executive officer and other persons pursuant to which he was appointed as an executive officer.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
We operate in market and regulatory environments that involve significant risks, many of which are beyond our control. In addition to other information in this Form 10-K, including "Item 1. Business" and "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and in other documents we file with the SEC from time to time, the following factors may affect our results of operations, our cash flows and the market pricesvalue of our publicly tradedequity and debt securities. These factors may cause results to differ materially from those expressed in any forward-looking statements made by us or on our behalf. The factors listed below are not intended to be an exhaustive discussion of all such risks, and the statements below must be read together with factors discussed elsewhere in this document and in our other filings with the SEC.
Weather conditions, including mild and severe weather, may adversely impact our consolidated financial results.
Weather conditions directly influence the demand for electricity. Our customers use electricity for heating in winter months and cooling in summer months. Because of air conditioning demand, typically we produce our highest revenues in the third quarter. Milder temperatures reduce demand for electricity and have a corresponding affectimpact on our revenues. Unusually mild weather in the future could adversely affect our consolidated financial results.
In addition, severe weather conditions can produce storms that can inflict extensive damage to our equipment and facilities, which can require us to incur additional operating and maintenance expense and additional capital expenditures. Our prices may not always be adjusted timely andor adequately to reflect these higher costs. Additionally, because many of our power plants use water for cooling, persistent or severe drought conditions could result in limited power production. High water conditions can also impair planned deliveries of fuel to our plants.
Our prices are subject to regulatory review and may not prove adequate to recover our costs and provide a fair return.
We must obtain from state and federal regulators the authority to establish terms and prices for our services. The KCC and, for most of our wholesale customers, FERC, use a cost-of-service approach that takes into account operating expenses, fixed obligations and recovery of and return on capital investments. Using this approach, the KCC and FERC set prices at levels calculated to recover such costs and a permitted return on investment. Except for wholesale transactions for which the price is not so regulated, and except to the extent the KCC and FERC permit us to modify our prices through the application of formulae that track changes in certain of our costs, our prices generally remain fixed until changed following a rate review. Further, the adjustments may be modified, limited or eliminated by regulatory or legislative actions. We may apply to change our prices or intervening parties may request that our prices be reviewed for possible adjustment.
Rate proceedings through which our prices and terms of service are determined typically involve numerous parties including electricity consumers, consumer advocates and governmental entities, some of whom take positions adverse to us. In addition, regulators' decisions may be appealed to the courts by us or other parties to the proceedings. These factors may lead to uncertainty and delays in implementing changes to our prices or terms of service. There can be no assurance that our regulators will find all of our costs to have been prudently incurred. A finding that costs have been imprudently incurred can lead to disallowance of recovery for those costs. Further, the prices approved by the applicable regulatory body may not be sufficient for us to recover our costs and to provide for an adequate return on and of capital investments.
We cannot predict the outcome of any rate review or the actions of our regulators. The outcome of rate proceedings, or delays in implementing price changes to reflect changes in our costs, could have a material affect on our consolidated financial results.
Our costs of compliance with environmental laws and regulations, including those relating to greenhouse gas emissions, are significant, and the future costs of compliance with environmental laws and regulations could adversely affectimpact our operations and consolidated financial results.
We are subject to extensive federal, state and local environmental statutes, ruleslaws and regulations relating to air quality, water quality, the use of water, the handling, disposal and clean-up of hazardous and non-hazardous substances and wastes, natural resources and health and safety. Compliance with these legal requirements, which change frequently and have tended to become more restrictive, requires us to commit significant capital and operating resources toward permitting, emission fees, environmental monitoring, installation and operation of air and water quality control equipment and purchases of air emission allowances and/or offsets. These laws and regulations oftentimes require a lengthy and complex process for obtaining licenses, permits and approvals from governmental agencies for new, existing or modified facilities. If we fail to comply with such laws, regulations and permits, or fail to obtain and maintain necessary permits, we could be fined or otherwise sanctioned by regulators, and such fines or the cost of sanctions may not be recoverable in our prices.
Costs of compliance with environmental laws and regulations or fines or penalties resulting from non-compliance, if not recovered in our prices, could adversely affectimpact our operations and/or consolidated financial results, especially if emission and/or discharge limits are tightened, more extensive permitting requirements are imposed, additional substances become regulated andor the number and types of assets we operate increases. We cannot estimate our compliance costs or any possible fines or penalties with certainty, or the degree to which such costs might be recovered in our prices, due to our inability to predict the requirements and timing of implementation of environmental rules or regulations. See "Item“Item 1. Business - Environmental Matters,” “Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Executive Summary—Current Trends—Operations-Executive Summary-Current Trends-Environmental Regulation” and Notes 3 and 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, “Rate Matters and Regulation - KCC Proceedings - Environmental Regulation—Air Emissions"Costs” and “Commitments and Contingencies - Environmental Matters,” respectively, for additional information.
In addition, we combust large amounts of fossil fuels as we produce electricity. This results in significant emissions of COcarbon dioxide (CO2) and other GHGsgreenhouse gases (GHGs) through the operation of our power plants. Federal legislation has been in the past, and is expectedmay in the future to be, introduced in Congress to regulate the emission of GHGs and numerous states and regions have adopted programs to stabilize or reduce GHG emissions.
The EPA regulates, and intends to regulate further, GHGs under the Clean Air Act. Under regulations finalized in 2010, the EPA is regulating GHG emissions from certain stationary sources, such as power plants. Under the current regulations, any source that emits at least 75,000 tons per year of GHGs is required to have a Title V operating permit under the Clean Air Act. Sources that already have a Title V permit would have GHG provisions added to their permits upon renewal. Additionally, Prevention of Significant Deterioration Program permits for new major sources of GHG emissions and GHG sources that undergo major modifications are required to implement BACT for the control of GHG emissions. The EPA has issued guidance on what BACT entails for the control of GHGs and individual states are now required to determine what controls are required for facilities within their jurisdiction on a case-by-case basis. These regulations could have a material impact on our operations or require us to incur substantial costs. Additionally,In particular, in January 2014, the EPA re-proposed an NSPSNew Source Performance Standard that would limit CO2 emissions for new coal and natural gas fueled electric generating units. This proposal isIn June 2014, the EPA issued proposed CO2 emissions rules, called the Clean Power Plan, for existing, modified and reconstructed power plants. The EPA expects to finalize the Clean Power Plan by summer of 2015; states would be expected to become a final rule in 2014.propose by summer 2016 their plans to implement it, which could require us to make efficiency improvements to our existing facilities, among other things. See Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, “Commitments and Contingencies-Environmental Matters” for additional information. We are currently evaluating the proposalproposed rules, and believe it could impact our future generation plansthese rules, if it becomes a final rule. In addition, the EPA is also expected to proposefinalized in June 2014, a GHG NSPS for existing units that couldtheir current form, would likely have a material impact on our operations, future generation plants and/or results of operations.
Further, in the course of operating our coal generation plants, we produce CCBs, including fly ash, gypsum and bottom ash, which we must handle, recycle, process or dispose of. We recyclehistorically have recycled some of our ash production, principally by selling to the aggregate industry. In 2010,December 2014, the EPA proposedissued a final rule to regulatethat regulates CCBs as non-hazardous solid waste under Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. The final rule will impact the manner in which we believe might impairdispose of CCBs, and it may adversely impact our ability to recycle ash or require additional CCB handling, processing and storage equipment, or both. See Note 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, “Commitments and Contingencies-Environmental Matters” for additional information. The EPA has agreed, subject to court approval, to issue a finalimpact of this rule in 2014. While we cannot at this time estimate the impact and costs associated with future regulations of CCBs, we believe the impact on our operations and consolidated financial results could be material.
We could be subject to penalties as a result of mandatory reliability standards, which could adversely affect our consolidated financial results.
As a result of the Energy Policy Act of 2005, owners and operators of the bulk power transmission system, including Westar Energy and KGE, are subject to mandatory reliability standards promulgated by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation and enforced by FERC. If we were found to be out of compliance with the mandatory reliability standards, we could be subject to sanctions, including substantial monetary penalties, which we might not be able to recover in the prices we charge our customers. This could have a material affectadverse effect on our consolidated financial results.
Adverse economic conditions could adversely impact our operations and consolidated financial results.
Our operations are affectedimpacted by economic conditions. Adverse general economic conditions including a prolonged recession or capital market disruptions may:
reduce demand for our service;
increase delinquencies or non-payment by customers;
adversely impact the financial condition of suppliers, which may in turn limit our access to inventory or capital equipment or increase our costs; and
increase deductibles and premiums and result in more restrictive policy terms under insurance policies regarding risks we typically insure against, or make insurance claims more difficult to collect.
In the opposite,addition, unexpectedly strong economic conditions can result in increased costs and shortages. Any of the aforementioned events, and others we may not be able to identify, could have an adverse impact on our consolidated financial results.
We are exposed to various risks associated with the ownership and operation of Wolf Creek, any of which could adversely impact our consolidated financial results.
Through KGE's ownership interest in Wolf Creek, we are subject to the risks of nuclear generation, which include:
the risks associated with storing, handling and disposing of radioactive materials and the current lack of a long-term off-site disposal solution for radioactive materials;
limitations on the amounts and types of insurance commercially available to cover losses that might arise in connection with nuclear operations;
uncertainties with respect to the technological and financial aspects of decommissioning Wolf Creek at the end of its life; and
costs of measures associated with public safety.
The NRC has authority to impose licensing and safety-related requirements for the operation of nuclear generation facilities. In the event of non-compliance, the NRC has authority to impose fines or shut down a unit, or both, depending upon its assessment of the severity of the situation, until compliance is achieved. Revised safety requirements enacted by the NRC could necessitate substantial capital expenditures at Wolf Creek.
If anAn incident did occur at Wolf Creek it could have a material affectimpact on our consolidated financial results. Furthermore, the non-compliance of other nuclear facilities operators with applicable regulations or the occurrence of a serious nuclear incident at other facilities anywhere in the world could result in increased regulation of the industry as a whole, which could in turn increase Wolf Creek's compliance costs and impact our consolidated financial results. Such events could also result in a shutdown of Wolf Creek.
In addition, in the event of an extended or unscheduled outage at Wolf Creek, we would be required to generate power from more costly generating units, purchase power in the open market to replace the power normally produced at Wolf Creek and have less power available for sale into the wholesale market. If we were unable to recover these costs in the prices we charge customers, such events would likely have an adverse impact on our consolidated financial results.
Significant decisions about capital investments are based on forecasts of long-term demand for energy incorporating assumptions about multiple, uncertain factors. Our actual experience may differ significantly from our assumptions, which may adversely impact our consolidated financial results.
We attempt to forecast demand to determine the timing and adequacy of our energy and energy delivery resources. Long-term forecasts involve risks because they rely on assumptions we make concerning uncertain factors including weather, technological change, environmental and other regulatory requirements, economic conditions, social pressures and the responsiveness of customers' electricity demand to conservation measures and prices. Both actual future demand and our ability to satisfy such demand depend on these and other factors and may vary materially from our forecasts. If our actual experience varies significantly from our forecasts, our consolidated financial results may be adversely affected.impacted.
Our planned capital investment for the next few years is large in relation to our size, subjecting us to significant risks.
Our anticipated capital expenditures for 20142015 through 20162017 are approximately $2.1 billion.$2.0 billion. In addition to risks discussed above associated with recovering capital investments through our prices, and risks associated with our reliance on the capital markets and short-term credit to fund those investments, our capital expenditure program poses risks, including, but not necessarily limited to:
shortages, disruption in the delivery and inconsistent quality of equipment, materials and labor;
contractor or supplier non-performance;
delays in or failure to receive necessary permits, approvals and other regulatory authorizations;
impacts of new and existing laws and regulations, including environmental and health and safety laws, regulations and permit requirements;
adverse weather;
unforeseen engineering problems or changes in project design or scope;
environmental and geological conditions; and
unanticipated cost increases with respect to labor or materials, including basic commodities needed for our infrastructure such as steel, copper and aluminum.
These and other factors, or any combination of them, could cause us to defer or limit our capital expenditure program and could adversely impact our consolidated financial results.
Our ability to fund our capital expenditures and meet our working capital and liquidity needs may be limited by conditions in the bank and capital markets, or by our credit ratings or the market price of Westar Energy's common stock. Further, capital market conditions can cause fluctuations in the values of assets set aside for employee benefit obligations and the Wolf Creek nuclear decommissioning trust (NDT) and may increase our funding requirements related to these obligations.
To fund our capital expenditures and for working capital and liquidity, we rely on access to capital markets and to short-term credit. Disruption in capital markets, deterioration in the financial condition of the financial institutions on which we rely, any credit rating downgrade or any decrease in the market price of Westar Energy's common stock may make capital more difficult and costly for us to obtain, may restrict liquidity available to us, may require us to defer or limit capital investments or impact operations or may reduce the value of our financial assets. These and other related effects may have an adversecould adversely impact on our business and consolidated financial results, including our ability to pay dividends and to make investments or undertake programs necessary to meet regulatory mandates and customer demand.
Further, we have significant future financial obligations with respect to employee benefit obligations and the Wolf Creek NDT. The value of the assets needed to meet those obligations are subject to market fluctuations and will yield uncertain returns, which may fall below our expectations for meeting our obligations. Additionally, inflation and changes in interest rates affectimpact the value of future liabilities. In general, when interest rates decline, the value of future liabilities increase. While the KCC allows us to implement a regulatory accounting mechanism to track certain of our employee benefit plan expenses, this mechanism does not allow us to make automatic price adjustments. Only in future rate proceedings may we be allowed to adjust our prices to reflect changes in our funding requirements. Further, the tracking mechanism for these benefit plan expenses is part of our overall rate structure, and as such, it is subject to KCC review and may be modified, limited or eliminated in the future. If these assets are not managed successfully, our consolidated financial results and cash flows could be adversely affected.impacted.
SecurityPhysical and cyber security breaches, criminal activity, terrorist attacks and other disruptions to our facilities or our information technology infrastructure could directly or indirectly interfere with our operations, could expose us or our customers or employees to a risk of loss and could expose us to liability or regulatory penalties or cause reputational damage and other harm to our business.
We rely upon information technology networks and systems to process, transmit and store electronic information, and to manage or support a variety of business processes and activities, including the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity, supply chain functions, and the invoicing and collection of payments from our customers. We also use information technology systems to record, process and summarize financial information and results of operations for internal reporting purposes and to comply with financial reporting, legal and tax requirements. Our technology networks and systems collect and store sensitive data including system operating information, proprietary business information belonging to us and third parties and personal information belonging to our customers and employees.
Our information technology networks and infrastructure may be vulnerable to damage, disruptions or shutdowns due to attacks by hackers or breaches due to employee error or malfeasance or other disruptions during software or hardware upgrades, telecommunication failures or natural disasters or other catastrophic events. These attacks or breaches could, among other things, result in the erasure of data or render our equipment unusable. The occurrence of any of these events could impact the reliability of our generation, transmission and distribution systems; could impact our ability to conduct business in the ordinary course; could expose us, our customers or our employees to a risk of loss or misuse of information; and could result in legal claims or proceedings, liability or regulatory penalties against us, damage our reputation or otherwise harm our business. We cannot accurately assess the probability that a security breach may occur, despite the measures that we take to prevent such
a breach, and we are unable to quantify the potential impact of such an event. We can provide no assurance that we will identify and remedy all security or system vulnerabilities or that unauthorized access or error will be identified and remedied.
Additionally, we cannot predict the impact that any future information technology or terrorist attack may have on the energy industry in general. Our facilities could be direct targets or indirect casualties of such attacks. The effects of such attacks could include disruption to our generation, transmission and distribution systems or to the electrical grid in general, and could increase the cost of insurance coverage or result in a decline in the U.S. economy.
Equipment failures and other events beyond our control may cause extended or unplanned plant outages, which may adversely impact our consolidated financial results.
The generation, distribution and transmission of electricity require the use of expensive and complicated equipment, much of which is aged, and all of which requires significant ongoing maintenance. Our power plants and equipment are subject to extended or unplanned outages because of equipment failure, weather, transmission system disruption, operator error, contractor or subcontractor failure and other factors beyond our control. In such events, we must either produce replacement power from our other plants, which may be less efficient or more expensive to operate, purchase power from others at unpredictable and potentially higher costs in order to meet our sales obligations, or suffer outages. Such events could also limit our ability to make sales to customers. Therefore, the occurrence of extended or unplanned outages could adversely affect our consolidated financial results.
Our regulated business model may be threatened by technological advancements that could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Significant technological advancements are taking place in the electric industry, including advancements related to self-generation and distributed energy technologies such as fuel cells, micro turbines, wind turbines and solar cells. Adoption of these technologies may increase because of advancements or government subsidies reducing the cost of generating electricity through these technologies to a level that is competitive with our current methods of generating electricity. There is also a perception that generating electricity through these technologies is more environmentally friendly than generating electricity with fossil-fuels.fossil fuels. Increased adoption of these technologies could reduce electricity demand and the pool of customers from whom fixed costs are recovered, resulting in under recovery of our fixed costs. Increased self-generation and the related use of net energy metering, which allows self-generating customers to receive bill credits for surplus power, could put upward price pressure on our remaining customers because self-generating customers do not currently pay a share of the costs necessary to operate our transmission and distribution system.customers. If we were unable to adjust our prices to reflect reduced electricity demand and increased self-generation and net energy metering, our financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
| | | | | | | | Unit Capacity (MW) By Owner | | | | | Unit Capability (MW) By Owner (a) |
| Name | Location | Unit No. | Year Installed | Principal Fuel | Westar Energy | KGE | Total Company | Location | Unit No. | Year Installed | Principal Fuel | Westar Energy | KGE | Total Company |
| Central Plains Wind Farm | Wichita County, Kansas | | (a) | 2009 | Wind | — | Wichita County, Kansas | | (a) | 2009 | Wind | 99 | — | 99 |
| Emporia Energy Center: | Emporia, Kansas | | | Emporia, Kansas | | |
| Combustion Turbines | | 1 | | 2008 | Gas | 45 | — | 45 | | 1 | | 2008 | Gas | 45 | — | 45 |
| | | 2 | | 2008 | Gas | 45 | — | 45 | | 2 | | 2008 | Gas | 45 | — | 45 |
| | | 3 | | 2008 | Gas | 44 | — | 44 | | 3 | | 2008 | Gas | 44 | — | 44 |
| | | 4 | | 2008 | Gas | 46 | — | 46 | | 4 | | 2008 | Gas | 46 | — | 46 |
| | | 5 | | 2008 | Gas | 157 | — | 157 | | 5 | | 2008 | Gas | 157 | — | 157 |
| | | 6 | | 2009 | Gas | 153 | — | 153 | | 6 | | 2009 | Gas | 155 | — | 155 |
| | | 7 | | 2009 | Gas | 156 | — | 156 | | 7 | | 2009 | Gas | 156 | — | 156 |
| Flat Ridge Wind Farm | Barber County, Kansas | | (a) | 2009 | Wind | 1 | — | 1 | Barber County, Kansas | | (a) | 2009 | Wind | 50 | — | 50 |
| Gordon Evans Energy Center: | Colwich, Kansas | | | Colwich, Kansas | | |
| Steam Turbines | | 1 | | 1961 | Gas | — | 152 | | 1 | | 1961 | Gas | — | 152 |
| | | 2 | | 1967 | Gas | — | 372 | | 2 | | 1967 | Gas | — | 370 |
| Combustion Turbines | | 1 | | 2000 | Gas | 68 | — | 68 | | 1 | | 2000 | Gas | 73 | — | 73 |
| | | 2 | | 2000 | Gas | 66 | — | 66 | | 2 | | 2000 | Gas | 71 | — | 71 |
| | | 3 | | 2001 | Gas | 148 | — | 148 | | 3 | | 2001 | Gas | 148 | — | 148 |
| Hutchinson Energy Center: | Hutchinson, Kansas | | | Hutchinson, Kansas | | |
| Steam Turbine | | 4 | | 1965 | Gas | 171 | — | 171 | | 4 | | 1965 | Gas | 176 | — | 176 |
| Combustion Turbines | | 1 | | 1974 | Gas | 56 | — | 56 | | 1 | | 1974 | Gas | 56 | — | 56 |
| | | 2 | | 1974 | Gas | 52 | — | 52 | | 2 | | 1974 | Gas | 52 | — | 52 |
| | | 3 | | 1974 | Gas | 57 | — | 57 | | 3 | | 1974 | Gas | 57 | — | 57 |
| | | 4 | | 1975 | Diesel | 71 | — | 71 | | 4 | | 1975 | Diesel | 71 | — | 71 |
| Jeffrey Energy Center (92%): | St. Marys, Kansas | | | St. Marys, Kansas | | |
| Steam Turbines | | 1 | (b) | 1978 | Coal | 517 | 144 | 661 | | 1 | (b) | 1978 | Coal | 517 | 144 | 661 |
| | | 2 | (b) | 1980 | Coal | 515 | 143 | 658 | | 2 | (b) | 1980 | Coal | 515 | 143 | 658 |
| | | 3 | (b) | 1983 | Coal | 520 | 144 | 664 | | 3 | (b) | 1983 | Coal | 520 | 144 | 664 |
| La Cygne Station (50%): | La Cygne, Kansas | | | La Cygne, Kansas | | |
| Steam Turbines | | 1 | (b) | 1973 | Coal | — | 368 | | 1 | (b) | 1973 | Coal | — | 367 |
| | | 2 | (c) | 1977 | Coal | — | 341 | | 2 | (c) | 1977 | Coal | — | 341 |
| Lawrence Energy Center: | Lawrence, Kansas | | | Lawrence, Kansas | | |
| Steam Turbines | | 3 | | 1954 | Coal | 49 | — | 49 | | 3 | | 1954 | Coal | 48 | — | 48 |
| | | 4 | | 1960 | Coal | 107 | — | 107 | | 4 | | 1960 | Coal | 104 | — | 104 |
| | | 5 | | 1971 | Coal | 374 | — | 374 | | 5 | | 1971 | Coal | 370 | — | 370 |
| Murray Gill Energy Center: | Wichita, Kansas | | | Wichita, Kansas | | |
| Steam Turbines | | 1 | | 1952 | Gas | — | 37 | | 3 | | 1956 | Gas | — | 104 |
| | | 2 | | 1954 | Gas | — | 48 | | 4 | | 1959 | Gas | — | 90 |
| | | 3 | | 1956 | Gas | — | 93 | |
| | | 4 | | 1959 | Gas | — | 90 | |
| Spring Creek Energy Center: | Edmond, Oklahoma | | | Edmond, Oklahoma | | |
| Combustion Turbines | | 1 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 68 | — | 68 | | 1 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 68 | — | 68 |
| | | 2 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 68 | — | 68 | | 2 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 68 | — | 68 |
| | | 3 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 67 | — | 67 | | 3 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 67 | — | 67 |
| | | 4 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 68 | — | 68 | | 4 | (d) | 2001 | Gas | 68 | — | 68 |
| State Line (40%): | Joplin, Missouri | | | Joplin, Missouri | | |
| Combined Cycle | | 2-1 | (b) | 2001 | Gas | 64 | — | 64 | | 2-1 | (b) | 2001 | Gas | 61 | — | 61 |
| | | 2-2 | (b) | 2001 | Gas | 65 | — | 65 | | 2-2 | (b) | 2001 | Gas | 62 | — | 62 |
| | | 2-3 | (b) | 2001 | Gas | 72 | — | 72 | | 2-3 | (b) | 2001 | Gas | 70 | — | 70 |
| Tecumseh Energy Center: | Tecumseh, Kansas | | | — | | Tecumseh, Kansas | | |
| Steam Turbines | | 7 | | 1957 | Coal | 72 | — | 72 | | 7 | | 1957 | Coal | 72 | — | 72 |
| | | 8 | | 1962 | Coal | 130 | — | 130 | | 8 | | 1962 | Coal | 130 | — | 130 |
| Wolf Creek Generating Station (47%): | Burlington, Kansas | | | Burlington, Kansas | | |
| Nuclear | | 1 | (b) | 1985 | Uranium | — | 547 | | 1 | (b) | 1985 | Uranium | — | 549 |
| Total | | | | 4,092 | 2,479 | 6,571 | | | | 4,241 | 2,404 | 6,645 |
| (a) Westar Energy owns Central Plains Wind Farm, which has an installed design capacity of 99 MW. Westar Energy owns 50% and purchases the other 50% of the generation from Flat Ridge Wind Farm pursuant to a purchase power agreement with BP Alternative Energy North. In total, it has an installed design capacity of 100 MW. | |
| (a) Capability (except for wind generating facilities) represents accredited net generating capacity approved by the SPP. Capability for our wind generating facilities represents the installed design capacity. Due to the intermittent nature of wind generation, these facilities are only associated with a total of 22 MW of accredited generating capacity. | | (a) Capability (except for wind generating facilities) represents accredited net generating capacity approved by the SPP. Capability for our wind generating facilities represents the installed design capacity. Due to the intermittent nature of wind generation, these facilities are only associated with a total of 22 MW of accredited generating capacity. |
(b) Westar Energy jointly owns State Line (40%) while KGE jointly owns La Cygne unit 1 (50%) and Wolf Creek (47%). We jointly own and consolidate as a VIE 92% of JEC. Unit capacity amounts reflect our ownership and leased percentages only. | (c) In 1987, KGE entered into a sale-leaseback transaction involving its 50% interest in the La Cygne unit 2. We consolidate the leasing entity as a VIE as discussed in Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Variable Interest Entities." | (d) We acquired Spring Creek Energy Center in 2006. |
We own and have in service approximately 6,300 miles of transmission lines, approximately 24,000 miles of overhead distribution lines and approximately 4,7004,800 miles of underground distribution lines.
Substantially all of our utility properties are encumbered by first priority mortgages pursuant to which bonds have been issued and are outstanding.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
Information on legal proceedings is set forth in Notes 3, 13 and 15 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Rate Matters and Regulation," "Commitments and Contingencies" and "Legal Proceedings," respectively, which are incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not Applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
STOCK TRADING
Westar Energy's common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange and traded under the ticker symbol WR. As of February 18, 201417, 2015, Westar Energy had 19,43618,557 common shareholders of record. For information regarding quarterly common stock price ranges for 20132014 and 20122013, see Note 19 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Quarterly Results (Unaudited)."
STOCK PERFORMANCE GRAPH
The following graph compares the performance of Westar Energy's common stock during the period that began on December 31, 20082009, and ended on December 31, 20132014, to the performance of the Standard & Poor's 500 Index (S&P 500) and the Standard & Poor's Electric Utility Index (S&P Electric Utilities). The graph assumes a $100 investment in Westar Energy's common stock and in each of the indices at the beginning of the period and a reinvestment of dividends paid on such investments throughout the period.
| | | | Dec 2008 | Dec 2009 | Dec 2010 | Dec 2011 | Dec 2012 | Dec 2013 | Dec 2009 | Dec 2010 | Dec 2011 | Dec 2012 | Dec 2013 | Dec 2014 |
| Westar Energy Inc. | $100 | $113 | $138 | $166 | $173 | $203 | |
| Westar Energy, Inc. | | $100 | $122 | $147 | $153 | $179 | $239 |
S&P© 500 | $100 | $126 | $146 | $149 | $172 | $228 | $100 | $115 | $117 | $136 | $180 | $205 |
S&P© Electric Utilities | $100 | $103 | $107 | $129 | $139 | $100 | $103 | $125 | $124 | $134 | $173 |
DIVIDENDS
Holders of Westar Energy's common stock are entitled to dividends when and as declared by Westar Energy's board of directors.
Quarterly dividends on common stock have historically been paid on or about the first business day of January, April, July and October to shareholders of record as of or about the ninth day of the preceding month. Westar Energy's board of directors reviews the common stock dividend policy from time to time. Among the factors the board of directors considers in determining Westar Energy's dividend policy are earnings, cash flows, capitalization ratios, regulation, competition and financial loan covenants. In 20132014, Westar Energy's board of directors declared four quarterly dividends of $0.340.35 per share, reflecting an annual dividend of $1.361.40 per share, compared to four quarterly dividends of $0.330.34 per share in 20122013, reflecting an annual dividend of $1.321.36 per share. On February 26, 2014,25, 2015, Westar Energy's board of directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.35$0.36 per share payable to shareholders on April 1, 2014.2015. The indicated annual dividend rate is $1.40$1.44 per share.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Income Statement Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total revenues | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
| | $ | 2,170,991 |
| | $ | 2,056,171 |
| | $ | 1,858,231 |
| $ | 2,601,703 |
| | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
| | $ | 2,170,991 |
| | $ | 2,056,171 |
|
Net income (a) | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
| | 236,180 |
| | 208,624 |
| | 141,330 |
| 322,325 |
| | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
| | 236,180 |
| | 208,624 |
|
| Net income attributable to common stock | 292,520 |
| | 273,530 |
| | 229,269 |
| | 202,926 |
| | 174,105 |
| 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 273,530 |
| | 229,269 |
| | 202,926 |
|
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | $ | 9,597,111 |
| | $ | 9,265,231 |
| | $ | 8,682,851 |
| | $ | 8,079,638 |
| | $ | 7,525,483 |
| $ | 10,347,001 |
| | $ | 9,597,138 |
| | $ | 9,265,231 |
| | $ | 8,682,851 |
| | $ | 8,079,638 |
|
Long-term obligations (b)(a) | 3,495,292 |
| | 3,124,831 |
| | 2,818,030 |
| | 2,808,560 |
| | 2,610,315 |
| 3,461,779 |
| | 3,495,292 |
| | 3,124,831 |
| | 2,818,030 |
| | 2,808,560 |
|
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Common Stock Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings per share available for common stock (c) | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.95 |
| | $ | 1.81 |
| | $ | 1.58 |
| $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.95 |
| | $ | 1.81 |
|
| Diluted earnings per share available for common stock | 2.27 |
| | 2.15 |
| | 1.93 |
| | 1.80 |
| | 1.58 |
| 2.35 |
| | 2.27 |
| | 2.15 |
| | 1.93 |
| | 1.80 |
|
| Dividends declared per share | 1.36 |
| | 1.32 |
| | 1.28 |
| | 1.24 |
| | 1.20 |
| 1.40 |
| | 1.36 |
| | 1.32 |
| | 1.28 |
| | 1.24 |
|
| Book value per share | 23.88 |
| | 22.89 |
| | 22.03 |
| | 21.25 |
| | 20.59 |
| 25.02 |
| | 23.88 |
| | 22.89 |
| | 22.03 |
| | 21.25 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Average equivalent common shares outstanding (in thousands) (d) (e) | 127,463 |
| | 126,712 |
| | 116,891 |
| | 111,629 |
| | 109,648 |
| |
| Average equivalent common shares outstanding (in thousands) (b) (c) (d) | | 130,015 |
| | 127,463 |
| | 126,712 |
| | 116,891 |
| | 111,629 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | The 2009 amount represents income from continuing operations. |
| |
(b) | Includes long-term debt, net, current maturities of long-term debt, capital leases, and, for 2010 through 2013, long-term debt of VIEs, net and current maturities of long-term debt of VIEs. See Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Variable Interest Entities," for additional information regarding VIEs. |
| |
(c) | We recorded basic EPS available for common stock from continuing operations of $1.28 in 2009 using the two-class method. See Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies-Earnings Per Share," for additional information regarding the two-class method. |
| |
(d)(b) | In 2010, Westar Energy issued and sold approximately 3.1 million shares of common stock realizing proceeds of $54.7 million. |
| |
(e)(c) | In 2011, Westar Energy issued and sold approximately 13.6 million shares of common stock realizing proceeds of $294.9 million. |
| |
| (d) | In 2014, Westar Energy issued and sold approximately 3.4 million shares of common stock realizing proceeds of $87.7 million. |
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Certain matters discussed in Management's Discussion and Analysis are "forward-looking statements." The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 has established that these statements qualify for safe harbors from liability. Forward-looking statements may include words like we "believe," "anticipate," "target," "expect," "estimate," "intend" and words of similar meaning. Forward-looking statements describe our future plans, objectives, expectations or goals. See "Forward Looking"Forward-Looking Statements" above for additional information.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
Description of Business
We are the largest electric utility in Kansas. We produce, transmit and sell electricity at retail to approximately 693,000698,000 customers in Kansas under the regulation of the KCC. We also supply electric energy at wholesale to municipalities and electric cooperatives in Kansas under the regulation of FERC. We have contracts for the sale or purchase of wholesale electricity with other utilities.
Earnings Per Share
Following is a summary of our net income and basic EPSearnings per share (EPS) for the years ended December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
| | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | 2014 | | 2013 | | Change |
| | | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) | | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income attributable to common stock | | $ | 292,520 |
| | $ | 273,530 |
| | $ | 18,990 |
| | $ | 313,259 |
| | $ | 292,520 |
| | $ | 20,739 |
|
| Earnings per common share, basic | | 2.29 |
| | 2.15 |
| | 0.14 |
| | 2.40 |
| | 2.29 |
| | 0.11 |
|
Net income attributed to common stock and basic EPS for the year ended December 31, 2013,2014 increased due primarily to higher prices and lower selling, general and administrative expenses. Lower electricity sales as a result of cooler weather and reducedincreased demand for electricity served to partially offset the aforementioned increases.from our industrial customers. See the discussion under "—Operating Results" below for additional information.
Key Factors Affecting Our Performance
The principal business, economic and other factors that affect our operations and financial performance include:
weather conditions;
the economy;
customer conservation efforts;
the performance, operation and maintenance of our electric generating facilities and network;
conditions in the fuel, wholesale electricity and energy markets;
rate and other regulations and costs of addressing public policy initiatives including environmental laws and regulations;
the availability of and our access to liquidity and capital resources; and
capital market conditions.
Strategy
We expect to continue operating as a vertically integrated, regulated, electric utility. Significant elements of our strategy include maintaining a flexible and diverse energy supply portfolio. In doing so, we continue to make environmental upgrades to our coal-fired power plants, develop renewable generation, build and upgrade our electrical infrastructure and develop systems and programs with regard to how our customers use energy.energy and interact with us.
Current Trends
Environmental Regulation
We are subject to various federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations. Environmental laws and regulations affecting our operations which relate primarilyare overlapping, complex, subject to air quality, water quality, the use of water, and the handling, disposal and clean-up of hazardous and non-hazardous substances and wastes, continue to evolve andchanges, have become more stringent over time and costly over time. We have incurredare expensive to implement. There are variety of final and will continue to incur significant capital and other expenditures, and may potentially need to limit the use of some of our power plants, to comply with existing and new environmentalproposed laws and regulations. While certain of these costs are recoverable through the ECRR and ultimately we expect all such costs to be reflected in the prices we are allowed to charge, we cannot assureregulations that all such costs will be recovered or that they will be recovered incould have a timely manner. See Note 13 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements, "Commitments and Contingencies," for additional information regarding environmental laws and regulations.
Air Emissions
The operation of power plants results in emissions of mercury, acid gases and other air toxics. In 2012, the EPA's MATS for power plants became effective, replacing the prior federal CAMR and requiring significant reductions in mercury, acid gases and other emissions. We expect to be compliant with the new standards by April 2016 as approved by KDHE. We continue to evaluate the new standards and believe that our related investment will be approximately $17.0 million.
Greenhouse Gases
In January 2014, the EPA re-proposed a NSPS that would limit CO2 emissions for new coal and natural gas fueled generating units. The re-proposal would limit CO2 emissions to 1,000 lbs per MWh generated for larger natural gas units and 1,100 lbs per MWh generated for smaller natural gas units and coal units. Final regulations are expected later in 2014. The EPA was also directed to issue proposed standards addressing CO2 emissions for modified, reconstructed and existing power plants by June 2014, issue final rules by June 2015, and require that states submit their implementation plans to the EPA no later than June 2016. We cannot at this time determine the impact of such proposalsmaterial adverse effect on our operations and consolidated financial results, but we believeincluding those relating to:
further regulation of GHGs by the costsEPA, including pursuant to complythe Clean Power Plan, and future legislation that could be material.proposed by the U.S. Congress;
Undervarious proposed and expected regulations known as the Tailoring Rule, the EPA regulates GHGgoverning air emissions from certain stationary sources. The regulations are being implemented pursuantincluding, those relating to two federal Clean Air Act programs which impose recordkeeping and monitoring requirements and also mandate the implementation of BACT for projects that cause a significant increase in GHG emissions (defined to be more than 75,000 tons or more per year or 100,000 tons or more per year, depending on various factors). The EPA has issued guidance on what BACT entails for the control of GHGs and individual states are now required to determine what controls are required for facilities within their jurisdiction on a case-by-case basis. We cannot at this time determine the impact of these regulations on our future operations and consolidated financial results, but we believe the costs to comply with the regulations could be material.
Regulation of Coal Combustion Byproducts
In the course of operating our coal generation plants, we produce CCBs, including fly ash, gypsum and bottom ash. We recycle some of our ash production, principally by selling to the aggregate industry. In 2010, the EPA proposed a rule to regulate CCBs, which we believe might impair our ability to recycle ash or require additional CCB handling, processing and storage equipment, or both. The EPA has agreed, subject to court approval, to issue a final rule in 2014. While we cannot at this time estimate the impact and costs associated with future regulations of CCBs, we believe the impact on our operations and consolidated financial results could be material.
National Ambient Air Quality Standards (particularly those relating to particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, ozone, carbon monoxide and sulfur dioxide) and the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule;
Underour water discharges, including under Section 316(b) of the federal Clean AirWater Act the EPA sets NAAQS for certain emissions considered harmful to public health(CWA) and the environment, including two classesdefinition of PM, NOx (a precursor to ozone), CO and SO2, which result from fossil fuel combustion. Areas meeting the NAAQS are designated attainment areas while those that do not meet the NAAQS are considered nonattainment areas. Each state must develop a plan to bring nonattainment areas into compliance with the NAAQS. NAAQS must be reviewed by EPA at five-year intervals. KDHE proposed to designate portionsWaters of the Kansas City area nonattainmentUnited States for the eight-hour ozone standard. The EPA has not acted on KDHE's proposed designationpurposes of the Kansas City areaCWA;
the regulation of CCB; and it is uncertain when, or if, such a designation might occur. The Wichita area also exceeded the eight-hour ozone standard and could be designated nonattainment in the future potentially impacting our operations.
applicable renewable energy standards.
In September 2011,See and Notes 3 and 13 to the President instructed the EPA not to implement its more stringent 2008 Ozone Standard sinceConsolidated Financial Statements, “Rate Matters and Regulation – KCC Proceeding – Environmental Costs” and “Commitments and Contingencies—Environmental Matters,” respectively, for a new NAAQS for ozone was due to be proposed in 2013discussion of environmental costs, laws, regulations and finalized in 2014. We are waiting on this new standard and cannot at this time predict the impact it may have on our operations, but it could be material.other contingencies.
In December 2012, the EPA strengthened an existing NAAQS for one class of PM. By the end of 2014, the EPA anticipates making final attainment/nonattainment designations under this rule and expects to issue a final implementation rule. We are currently evaluating the rule, however, we cannot at this time predict the impact it may have on our operations or consolidated financial results, but it could be material.
In 2010, the EPA strengthened the NAAQS for both NOx and SO2. We continue to communicate with our regulators regarding these standards and are currently evaluating what impact this could have on our operations and consolidated financial results. If we are required to install additional equipment to control emissions at our facilities, the revised NAAQS could have a material impact on our operations and consolidated financial results.
Water
We discharge some of the water used in our operations. This water may contain substances deemed to be pollutants. Revised rules governing such discharges from coal-fired power plants are expected to be issued by the EPA in 2014. Although we cannot at this time determine the timing or impact of compliance with any new regulations, more stringent regulations could have a material impact on our operations and consolidated financial results.
In 2011, the EPA issued a proposed rule that would increase the requirements for cooling water intake structures at power plants over concerns about impacts to aquatic life. We are currently evaluating the proposed rule as well as recent nationally-issued information requests from the EPA. The EPA is required to finalize the rule by April 2014; however, because the rule has yet to be finalized, we cannot predict the impact it may have on our operations or consolidated financial results, but it could be material.
Renewable Energy Standard
Kansas law mandates that we maintain a minimum amount of renewable energy sources. Through 2015, net renewable generation capacity must be 10% of the average peak retail demand for the three prior years, subject to limited exceptions. This requirement increases to 15% for years 2016 through 2019 and 20% for 2020 and thereafter. With our existing wind generation facilities, supply contracts and renewable energy credits, we are able to satisfy the net renewable generation requirement through 2015. With our agreementagreements to purchase an additional 200400 MW of installed design capacity from a wind generation facilityfacilities beginning in late2015 through 2016, we expect to meet the increased requirements through 2020.for 2020 and thereafter. If we are unable to meet future requirements, our operations and consolidated financial results could be adversely impacted.
Regulation of Nuclear Generating Station
Additional regulation of Wolf Creek resulting from NRC oversight of the plant's performance or from changing regulations generally, including those that could potentially result from natural disasters or any event that might occur at any nuclear power plant anywhere in the world, may result in increased net operating expenses and capital expenditures. We cannot estimate the cost associated with such increases, but they could be material to our operations and consolidated financial results.
We expect future increases in operating costs due to increased NRC oversight and efforts to comply with new industry-wide regulations adopted by the NRC in 2012. Future extended or unscheduled shutdowns of Wolf CreekWe cannot estimate the cost associated with such increases, but they could cause usbe material to our operations and consolidated financial results.
purchase replacement power, rely more heavily on our other generating units and reduce amounts of power available for us to sell in the wholesale market.
Allowance for Funds Used During Construction
AFUDCAllowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC) represents the allowed cost of capital used to finance utility construction activity. We compute AFUDC by applying a composite rate to qualified construction work in progress. We credit other income (for equity funds) and interest expense (for borrowed funds) for the amount of AFUDC capitalized as construction cost on the accompanying consolidated statements of income as follows:
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Borrowed funds | $ | 11,706 |
| | $ | 10,399 |
| | $ | 5,589 |
| $ | 12,044 |
| | $ | 11,706 |
| | $ | 10,399 |
|
| Equity funds | 14,143 |
| | 11,706 |
| | 5,550 |
| 17,029 |
| | 14,143 |
| | 11,706 |
|
| Total | $ | 25,849 |
| | $ | 22,105 |
| | $ | 11,139 |
| $ | 29,073 |
| | $ | 25,849 |
| | $ | 22,105 |
|
| Average AFUDC Rates | 4.8 | % | | 5.0 | % | | 3.6 | % | 6.7 | % | | 4.8 | % | | 5.0 | % |
We expect AFUDC for both borrowed funds and equity funds to fluctuatebe lower over the next several years as we executemajor projects within our capital expenditure program.program have been completed.
Interest Expense
We expect interest expense to increase over the next several years as we issue new debt securities to fund our capital expenditure program. We continue to believe this increase will be reflected in the prices we are permitted to charge customers, as cost of capital will be a component of future rate proceedings and is also recognized in some of the other rate adjustments we are permitted to make. In addition, short-term interest rates are extremely low by historical standards. We cannot predict to what extent these conditions will continue. See Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Long-Term Debt" for additional information regarding the issuance of long-term debt.
Outstanding Shares of Common Stock
We expect the number of outstanding shares of Westar Energy common stock to increase through 2015 as we issue additional shares previously priced through forward sales agreements to fund our capital expenditure program. See Note 16 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Common and Preferred Stock," for additional information regarding our share issuances.
Customer Growth and Usage
Residential customer additions have slowedmoderated since the 2008 recession and residential electricity demand has stabilized and is growing modestly. Overall retail sales have grown as well, and are approaching pre-recession levels. We believe that, in the near-term, our overall retail sales growth will be between 1% and 2% driven by industrial demand and stable to slightly declining due principally to the effects of the economic downturnresidential and energy efficiency measures.commercial growth. Absent an economic recovery to conditions similar to those preceding the downturn,2008 recession, we believe such customer additionslong-term retail sales growth will continuebe about 0.50% to be significantly lower than historical levels.0.75% per year. In addition, with the numerous energy efficiency policy initiatives promulgated through federal, state and local governments, as well as industry initiatives, environmental regulations and the need to strengthen and modernize the grid, which will increase price pressure, we believe customers will continue to adopt more energy efficiency and conservation measures, which will slow or possibly suppress the rategrowth of demand for electricity.
20142015 Outlook
In 2014,2015, we expect to maintain our current business strategy and regulatory approach. Subject to regulatory approvals, we anticipate annualized price increases of approximately $50.0 million from formulae that track changes in certain of our costs, as well as a $30.7 million general price increase authorized by the KCC in November 2013. Assuming normal weather in line with the historical average, we expect 20142015 retail electricity sales to be between about 0.5% to 1.0%1.5% higher than weather-normalized 2013weather normalized 2014 sales.
In addition to updating prices through various cost recovery mechanisms, we anticipate increased operating and maintenance expenses, including maintenance costs for our power plants, and higher selling,will be filing a general and administrative expenses.rate case in early March 2015 with the KCC, with new prices expected to be effective in the fourth quarter.
Absent increases in SPP transmission expense and property taxestax expense, which are increasing at a much higher rate than inflation and are offset with higher revenues pursuant to our regulatory mechanisms.mechanisms, we anticipate operating and maintenance and selling, general and administrative expenses to be lower in 2015 as compared to 2014. To help fund our
capital spending as provided under "—Future Cash Requirements" below, in 2015 we plan to settle forward transactions covering approximately 9.2 million shares of our common stock sales that were priced in prior periods, and utilize short-term borrowings and we expect to issue common stock to settle forward sale transactions.
In March 2014, the SPPby issuing commercial paper until permanent financing is expected to launch an IM similar to other organized power markets currently operating in other RTOs. As a result, we expect an increase in revenues and a corresponding increase in fuel and purchased power expense. Further, additional products may result in increased derivative activity, currently presented in other assets and liabilities, for which we will receive regulatory treatment.
place.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
Our discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations are based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in conformity with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," contains a summary of our significant accounting policies, many of which require the use of estimates and assumptions by management. The policies highlighted below have an impact on our reported results that may be material due to the levels of judgment and subjectivity necessary to account for uncertain matters or their susceptibility to change.
Regulatory Accounting
We currently apply accounting standards that recognize the economic effects of rate regulation. Accordingly, we have recorded regulatory assets and liabilities when required by a regulatory order or based on regulatory precedent. Regulatory assets represent incurred costs that have been deferred because they are probable of future recovery in our prices. Regulatory liabilities represent probable future reductions in revenue or refunds to customers.
The deferral of costs as regulatory assets is appropriate only when the future recovery of such costs is probable. In assessing probability, we consider such factors as specific regulatory orders, regulatory precedent and the current regulatory environment. WereIf we to deem it no longer probable that we would recover such costs, we would record a charge against income in the amount of the related regulatory assets.
As of December 31, 20132014, we had recorded regulatory assets currently subject to recovery in future prices of approximately $755.4859.8 million and regulatory liabilities of $329.6343.5 million, as discussed in greater detail in Note 3 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Rate Matters and Regulation."
Pension and Post-retirement Benefit Plans Actuarial Assumptions
We and Wolf Creek calculate our pension benefit and post-retirement medical benefit obligations and related costs using actuarial concepts within the guidance provided by applicable GAAP.
In accounting for our retirement plans and post-retirement benefits, we make assumptions regarding the valuation of benefit obligations and the performance of plan assets. The reported costs of our pension plans are impacted by estimates regarding earnings on plan assets, contributions to the plan, discount rates used to determine our projected benefit obligation and pension costs and employee demographics including age, life expectancy and compensation levels and employment periods. Changes in these assumptions result primarily in changes to regulatory assets, regulatory liabilities or the amount of related pension and post-retirement benefit liabilities reflected on our consolidated balance sheets. Such changes may also require cash contributions.
The following table shows the impact of a 0.5% change in our pension plan discount rate, salary scale and rate of return on plan assets.
| | | Actuarial Assumption | | Change in Assumption | | Change in Projected Benefit Obligation (a) | | Annual Change in Projected Pension Costs (a) | | Change in Assumption | | Change in Projected Benefit Obligation (a) | | Annual Change in Projected Pension Costs (a) |
| | | (Dollars In Thousands) | | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Discount rate | | 0.5% decrease | | $ | 70,159 |
| | $ | 6,721 |
| | 0.5% decrease | | $ | 100,210 |
| | $ | 9,530 |
|
| | | 0.5% increase | | (63,319 | ) | | (6,234 | ) | | 0.5% increase | | (88,880 | ) | | (8,559 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Salary scale | | 0.5% decrease | | (17,359 | ) | | (3,392 | ) | | 0.5% decrease | | (17,433 | ) | | (3,552 | ) |
| | | 0.5% increase | | 17,686 |
| | 3,491 |
| | 0.5% increase | | 18,405 |
| | 3,778 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| Rate of return on plan assets | | 0.5% decrease | | — |
| | 3,359 |
| | 0.5% decrease | | — |
| | 3,698 |
|
| | | 0.5% increase | | — |
| | (3,359 | ) | | 0.5% increase | | — |
| | (3,698 | ) |
_______________
| |
| (a) | Increases or decreases due to changes in actuarial assumptions result primarily in changes to regulatory assets and liabilities. |
The following table shows the impact of a 0.5% change in the discount rate and rate of return on plan assets and a 1% change in the annual medical trend on our post-retirement benefit plans.
| | | Actuarial Assumption | | Change in Assumption | | Change in Projected Benefit Obligation (a) | | Annual Change in Projected Post-retirement Costs (a) | | Change in Assumption | | Change in Projected Benefit Obligation (a) | | Annual Change in Projected Post-retirement Costs (a) |
| | | (Dollars In Thousands) | | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Discount rate | | 0.5% decrease | | $ | 8,174 |
| | $ | 436 |
| | 0.5% decrease | | $ | 9,294 |
| | $ | 496 |
|
| | | 0.5% increase | | (7,702 | ) | | (446 | ) | | 0.5% increase | | (8,388 | ) | | (457 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Rate of return on plan assets | | 0.5% decrease | | — |
| | 521 |
| | 0.5% decrease | | — |
| | 552 |
|
| | | 0.5% increase | | — |
| | (519 | ) | | 0.5% increase | | — |
| | (552 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Annual medical trend | | 1.0% decrease | | (1,804 | ) | | (261 | ) | | 1.0% decrease | | 97 |
| | 16 |
|
| | | 1.0% increase | | 1,996 |
| | 292 |
| | 1.0% increase | | (108 | ) | | (16 | ) |
_______________
| |
| (a) | Increases or decreases due to changes in actuarial assumptions result primarily in changes to regulatory assets and liabilities. |
Revenue Recognition
Electricity Sales
We record revenue at the time we deliver electricity to customers. We determine the amounts delivered to individual customers through systematic monthly readings of customer meters. At the end of each month, we estimate how much electricity we have delivered since the prior meter reading and record the corresponding unbilled revenue.
Our unbilled revenue estimate is affected by factors including fluctuations in energy demand, weather, line losses and changes in the composition of customer classes. We recorded estimated unbilled revenue of $61.0 million as of December 31, 2014 and $60.1 million as of December 31, 2013 and $62.5 million as of December 31, 2012.
Income Taxes
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, we recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. We recognize the future tax benefits to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not. We amortize deferred investment tax credits over the lives of the related properties as required by tax laws and regulatory practices. We recognize production tax credits in the year that electricity is generated to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not.
We record deferred tax assets to the extent capital losses, operating losses, or tax credits will be carried forward to future periods. However, when we believe based on available evidence that we do not, or will not, have sufficient future capital gains or taxable income in the appropriate taxing jurisdiction to realize the entire benefit during the applicable carryforward period, we record a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset.
The application of income tax law is complex. Laws and regulations in this area are voluminous and often ambiguous. Accordingly, we must make judgments regarding income tax exposure. Interpretations of and guidance surrounding income tax laws and regulations change over time. As a result, changes in our judgments can materially affect amounts we recognize in our consolidated financial statements. See Note 10, of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Taxes," for additional detail on our accounting for income taxes.
Asset Retirement Obligations
Legal Liability
We have recognized legal obligations associated with the disposal of long-lived assets that result from the acquisition, construction, development or normal operation of such assets. Concurrent with the recognition of the liability, the estimated cost of the asset retirement obligation (ARO) is capitalized and depreciated over the remaining life of the asset. We estimate our AROs based on the fair value of the AROs we incurred at the time the related long-lived assets were either acquired, placed in service or when regulations establishing the obligation became effective.
We initially recorded AROs at fair value for the estimated cost to decommission Wolf Creek (our 47% share), retire our wind generating facilities, dispose of asbestos insulating material at our power plants, remediate ash disposal ponds and dispose of polychlorinated biphenyl contaminated oil. In determining our AROs, we make assumptions regarding probable future disposal costs. A change in these assumptions could have a significant impact on the AROs reflected on our consolidated balance sheets.
As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, we have recorded AROs of $160.7230.7 million and $152.6160.7 million, respectively. For additional information on our legal AROs, see Note 14 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Asset Retirement Obligations."
Non-Legal Liability - Cost of Removal
We collect in our prices the costs to dispose of plant assets that do not represent legal retirement obligations. As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, we had $114.188.2 million and $129.0114.1 million, respectively, in amounts collected, but not yet spent, for removal costs classified as a regulatory liability.
Contingencies and Litigation
We are currently involved in certain legal proceedings and have estimated the probable cost for the resolution of these claims. These estimates are based on an analysis of potential results, assuming a combination of litigation and settlement strategies. It is possible that our future consolidated financial results could be materially affected by changes in our assumptions. See Notes 13 and 15 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Commitments and Contingencies" and "Legal Proceedings," for additional information.
OPERATING RESULTS
We evaluate operating results based on EPS. We have various classifications of revenues, defined as follows:
Retail: Sales of electricity to residential, commercial and industrial customers. Classification of customers as residential, commercial or industrial requires judgment and our classifications may be different from other companies. Assignment of tariffs is not dependent on classification.
Other retail: Salesretail sales of electricity include lighting for lighting public streets and highways, net of revenue subject to refund.
Wholesale: Sales of electricity to electric cooperatives, municipalities, and other electric utilities and RTOs, the prices for which are either based on cost or prevailing market prices as prescribed by FERC authority. Margins realizedRevenues from these sales serve to offsetare either included in the retail prices through eitherenergy cost adjustment or used in the RECA ordeterminations of base rates at the time of our next general rate case.
Transmission: Reflects transmission revenues, including those based on tariffs with the SPP.
Other: Miscellaneous electric revenues including ancillary service revenues and rent from electric property leased to others. This category also includes transactions unrelated to the production of our generating assets and fees we earn for services that we provide for third parties.
Electric utility revenues are impacted by things such as rate regulation, fuel costs, technology, customer behavior, the economy and competitive forces. Changing weather also affects the amount of electricity our customers use as electricity sales are seasonal. As a summer peaking utility, the third quarter typically accounts for our greatest electricity sales. Hot summer temperatures and cold winter temperatures prompt more demand, especially among residential and commercial customers, and to a lesser extent, industrial customers. Mild weather reduces customer demand. Our wholesale revenues are impacted by, among other factors, demand, cost and availability of fuel and purchased power, price volatility, available generation capacity, transmission availability and weather.
20132014 Compared to 20122013
Below we discuss our operating results for the year ended December 31, 20132014, compared to the results for the year ended December 31, 20122013. Significant changes in results of operations shown in the table immediately below are further explained in the descriptions that follow.
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change | 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| REVENUES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Residential | $ | 728,852 |
| | $ | 714,562 |
| | $ | 14,290 |
| | 2.0 |
| $ | 793,586 |
| | $ | 728,852 |
| | $ | 64,734 |
| | 8.9 |
|
| Commercial | 667,106 |
| | 640,654 |
| | 26,452 |
| | 4.1 |
| 727,964 |
| | 667,106 |
| | 60,858 |
| | 9.1 |
|
| Industrial | 374,825 |
| | 368,909 |
| | 5,916 |
| | 1.6 |
| 414,997 |
| | 374,825 |
| | 40,172 |
| | 10.7 |
|
| Other retail | 8,939 |
| | (5,845 | ) | | 14,784 |
| | 252.9 |
| (24,180 | ) | | 8,939 |
| | (33,119 | ) | | (370.5 | ) |
| Total Retail Revenues | 1,779,722 |
| | 1,718,280 |
| | 61,442 |
| | 3.6 |
| 1,912,367 |
| | 1,779,722 |
| | 132,645 |
| | 7.5 |
|
| Wholesale | 348,239 |
| | 316,353 |
| | 31,886 |
| | 10.1 |
| 392,730 |
| | 348,239 |
| | 44,491 |
| | 12.8 |
|
| Transmission (a) | 210,281 |
| | 193,797 |
| | 16,484 |
| | 8.5 |
| 256,838 |
| | 210,281 |
| | 46,557 |
| | 22.1 |
|
| Other | 32,412 |
| | 33,040 |
| | (628 | ) | | (1.9 | ) | 39,768 |
| | 32,412 |
| | 7,356 |
| | 22.7 |
|
| Total Revenues | 2,370,654 |
| | 2,261,470 |
| | 109,184 |
| | 4.8 |
| 2,601,703 |
| | 2,370,654 |
| | 231,049 |
| | 9.7 |
|
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fuel and purchased power | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
| | 44,807 |
| | 7.6 |
| 705,450 |
| | 634,797 |
| | 70,653 |
| | 11.1 |
|
| SPP network transmission costs | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
| | 12,057 |
| | 7.2 |
| 218,924 |
| | 178,604 |
| | 40,320 |
| | 22.6 |
|
| Operating and maintenance | 359,060 |
| | 342,055 |
| | 17,005 |
| | 5.0 |
| 367,188 |
| | 359,060 |
| | 8,128 |
| | 2.3 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
| | 2,129 |
| | 0.8 |
| 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 13,849 |
| | 5.1 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 224,133 |
| | 226,012 |
| | (1,879 | ) | | (0.8 | ) | 250,439 |
| | 224,133 |
| | 26,306 |
| | 11.7 |
|
| Taxes other than income tax | 122,282 |
| | 104,269 |
| | 18,013 |
| | 17.3 |
| 140,302 |
| | 122,282 |
| | 18,020 |
| | 14.7 |
|
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,791,469 |
| | 1,699,337 |
| | 92,132 |
| | 5.4 |
| 1,968,745 |
| | 1,791,469 |
| | 177,276 |
| | 9.9 |
|
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 579,185 |
| | 562,133 |
| | 17,052 |
| | 3.0 |
| 632,958 |
| | 579,185 |
| | 53,773 |
| | 9.3 |
|
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Investment earnings | 10,056 |
| | 7,411 |
| | 2,645 |
| | 35.7 |
| 10,622 |
| | 10,056 |
| | 566 |
| | 5.6 |
|
| Other income | 35,609 |
| | 35,378 |
| | 231 |
| | 0.7 |
| 31,522 |
| | 35,609 |
| | (4,087 | ) | | (11.5 | ) |
| Other expense | (18,099 | ) | | (19,987 | ) | | 1,888 |
| | 9.4 |
| (18,389 | ) | | (18,099 | ) | | (290 | ) | | (1.6 | ) |
| Total Other Income | 27,566 |
| | 22,802 |
| | 4,764 |
| | 20.9 |
| 23,755 |
| | 27,566 |
| | (3,811 | ) | | (13.8 | ) |
| Interest expense | 182,167 |
| | 176,337 |
| | 5,830 |
| | 3.3 |
| 183,118 |
| | 182,167 |
| | 951 |
| | 0.5 |
|
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 424,584 |
| | 408,598 |
| | 15,986 |
| | 3.9 |
| 473,595 |
| | 424,584 |
| | 49,011 |
| | 11.5 |
|
| Income tax expense | 123,721 |
| | 126,136 |
| | (2,415 | ) | | (1.9 | ) | 151,270 |
| | 123,721 |
| | 27,549 |
| | 22.3 |
|
| NET INCOME | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
| | 18,401 |
| | 6.5 |
| 322,325 |
| | 300,863 |
| | 21,462 |
| | 7.1 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 1,027 |
| | 14.0 |
| 9,066 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 723 |
| | 8.7 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY, INC. | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
| | 17,374 |
| | 6.3 |
| 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 20,739 |
| | 7.1 |
|
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | 1,616 |
| | (1,616 | ) | | (100.0 | ) | |
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO COMMON STOCK | $ | 292,520 |
| | $ | 273,530 |
| | $ | 18,990 |
| | 6.9 |
| |
| BASIC EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 0.14 |
| | 6.5 |
| $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 0.11 |
| | 4.8 |
|
| DILUTED EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 0.12 |
| | 5.6 |
| $ | 2.35 |
| | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 0.08 |
| | 3.5 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | ReflectsIncludes revenue from an SPP network transmission tariff corresponding to our SPP network transmission costs. These costs, less administration fees of $39.151.0 million and $27.239.1 million, were returned to us as revenue in 20132014 and 20122013, respectively.
|
Rate Case Agreement
In November 2013, the KCC issued an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades, as discussed below, and to reflect cost reductions elsewhere. The new prices arewere expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $30.7 million.
In April 2012, the KCC issued an order authorizing higher revenues to recover higher expenses primarily for increased tree trimming to enhance reliability and increased pension costs resulting from the consequences of the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent low interest rate environment in accordance with the regulatory mechanism in place to account for such pension costs. As a result of this order, we expect selling, general and administrative expense to increase $32.1 million and the cost of operating and maintaining our distribution system to increase $10.9 million on an annualized basis. In addition, we revised our depreciation rates to reflect changes in the estimated useful lives of some of our assets. The change in estimate will decrease annual depreciation expense by $43.6 million. However, decreased depreciation expense as a result of lower depreciation rates will be offset by additional depreciation related to additions to property, plant and equipment. Because the aforementioned changes were implemented shortly after the KCC issued its order, our 2012 consolidated financial results do not reflect the full annual impact of the changes.
Gross Margin
Fuel and purchased power costs fluctuate with electricity sales and unit costs. As permitted by regulators, we adjust our retail prices to reflect changes in the costs of fuel and purchased power. Fuel and purchased power costs for wholesale customers are recovered at prevailing market prices or based on a predetermined formula with a price adjustment approved by FERC. As a result, changes in fuel and purchased power costs are offset in revenues with minimal impact on net income. In addition, SPP network transmission costs fluctuate due primarily to investments by us and other members of the SPP for upgrades to the transmission grid within the SPP RTO. As with fuel and purchased power costs, changes in SPP network transmission costs are mostly reflected in the prices we charge customers with minimal impact on net income. For these reasons, we believe gross margin is useful for understanding and analyzing changes in our operating performance from one period to the next. We calculate gross margin as total revenues, including transmission revenues, less the sum of fuel and purchased power costs and amounts billed by the SPP for network transmission costs. Accordingly, gross margin reflects transmission revenues and costs on a net basis. The following table summarizes our gross margin for the years ended December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change | 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Revenues | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
| | $ | 109,184 |
| | 4.8 | $ | 2,601,703 |
| | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 231,049 |
| | 9.7 |
| Less: Fuel and purchased power expense | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
| | 44,807 |
| | 7.6 | 705,450 |
| | 634,797 |
| | 70,653 |
| | 11.1 |
| SPP network transmission costs | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
| | 12,057 |
| | 7.2 | 218,924 |
| | 178,604 |
| | 40,320 |
| | 22.6 |
| Gross Margin | $ | 1,557,253 |
| | $ | 1,504,933 |
| | $ | 52,320 |
| | 3.5 | $ | 1,677,329 |
| | $ | 1,557,253 |
| | $ | 120,076 |
| | 7.7 |
The following table reflects changes in electricity sales for the years ended December 31, 20132014 and 20122013. No electricity sales are shown for transmission or other as they are not directly related to the amount of electricity we sell.
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change | 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Thousands of MWh) | | | (Thousands of MWh) | |
| ELECTRICITY SALES: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Residential | 6,523 |
| | 6,684 |
| | (161 | ) | | (2.4 | ) | 6,580 |
| | 6,523 |
| | 57 |
| | 0.9 |
| Commercial | 7,480 |
| | 7,581 |
| | (101 | ) | | (1.3 | ) | 7,521 |
| | 7,480 |
| | 41 |
| | 0.5 |
| Industrial | 5,407 |
| | 5,588 |
| | (181 | ) | | (3.2 | ) | 5,601 |
| | 5,407 |
| | 194 |
| | 3.6 |
| Other retail | 86 |
| | 85 |
| | 1 |
| | 1.2 |
| 86 |
| | 86 |
| | — |
| | — |
| Total Retail | 19,496 |
| | 19,938 |
| | (442 | ) | | (2.2 | ) | 19,788 |
| | 19,496 |
| | 292 |
| | 1.5 |
| Wholesale | 8,593 |
| | 7,719 |
| | 874 |
| | 11.3 |
| 9,544 |
| | 8,593 |
| | 951 |
| | 11.1 |
| Total | 28,089 |
| | 27,657 |
| | 432 |
| | 1.6 |
| 29,332 |
| | 28,089 |
| | 1,243 |
| | 4.4 |
Gross margin increased due primarily to higher retail revenues, that wereprincipally the result of higher retail prices. Average retail prices offset partiallywere about 6% higher than 2013, resulting from recovery of investments we made in our transmission infrastructure and air quality controls at our power plants. Retail revenues were also impacted by lower retail electricity sales. The lower retailmore electricity sales were attributableresulting principally to cooler summer weather, which particularly impacted residential and commercial electricity sales. As measured by cooling degree days, 2013 was 23% cooler than the prior year. Contributing also to the decrease in retailfrom increased sales was the reduced demand, primarily from several largeto industrial customers.
Income from operations is the most directly comparable measure to our presentation of gross margin that is calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP in our consolidated statements of income. Our presentation of gross margin should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for income from operations. Additionally, our presentation of gross margin may not be comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies. The following table reconciles income from operations with gross margin for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Gross margin | $ | 1,677,329 |
| | $ | 1,557,253 |
| | $ | 120,076 |
| | 7.7 |
| Less: Operating and maintenance expense | 367,188 |
| | 359,060 |
| | 8,128 |
| | 2.3 |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 13,849 |
| | 5.1 |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | 250,439 |
| | 224,133 |
| | 26,306 |
| | 11.7 |
| Taxes other than income tax | 140,302 |
| | 122,282 |
| | 18,020 |
| | 14.7 |
| Income from operations | $ | 632,958 |
| | $ | 579,185 |
| | $ | 53,773 |
| | 9.3 |
Operating Expenses and Other Income and Expense Items
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Operating and maintenance expense | $ | 367,188 |
| | $ | 359,060 |
| | $ | 8,128 |
| | 2.3 |
Operating and maintenance expense increased due principally to:
a $6.4 million increase in operating and maintenance costs at our plants primarily for planned outages at our coal fired plants;
a $4.3 million increase in operating and maintenance costs to enhance reliability of our transmission systems; and,
an approximately $3.9 million increase in costs at Wolf Creek attributable primarily to a planned outage in the first and second quarters of 2014; however,
partially offsetting these increases was a $7.8 million decrease in amounts expensed for previously deferred storm costs.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | $ | 286,442 |
| | $ | 272,593 |
| | $ | 13,849 |
| | 5.1 |
Depreciation and amortization expense increased due to plant additions, including air quality controls, and transmission facilities as well as increased amortization related primarily to implementing new software systems.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | $ | 250,439 |
| | $ | 224,133 |
| | $ | 26,306 |
| | 11.7 |
Selling, general and administrative expense increased due primarily to:
higher labor and employee benefit costs of $10.6 million;
a $6.1 million increase in fees related primarily to implementing new software systems; and,
an increase in the allowance for uncollectible accounts of $2.7 million.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Taxes other than income tax | $ | 140,302 |
| | $ | 122,282 |
| | $ | 18,020 |
| | 14.7 |
Taxes other than income tax increased due primarily to a $16.2 million increase in property taxes, which are offset in retail revenues.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Other income | $ | 31,522 |
| | $ | 35,609 |
| | $ | (4,087 | ) | | (11.5 | ) |
Other income decreased due primarily to our having recorded about $6.9 million less in COLI benefits. The decrease was partially offset by our having recorded $2.9 million more in equity AFUDC.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Income tax expense | $ | 151,270 |
| | $ | 123,721 |
| | $ | 27,549 |
| | 22.3 |
Income tax expense increased due primarily to higher income before income taxes.
2013 Compared to 2012
Below we discuss our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2013, compared to the results for the year ended December 31, 2012. Significant changes in results of operations shown in the table immediately below are further explained in the descriptions that follow.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| REVENUES: | | | | | | | |
| Residential | $ | 728,852 |
| | $ | 714,562 |
| | $ | 14,290 |
| | 2.0 |
|
| Commercial | 667,106 |
| | 640,654 |
| | 26,452 |
| | 4.1 |
|
| Industrial | 374,825 |
| | 368,909 |
| | 5,916 |
| | 1.6 |
|
| Other retail | 8,939 |
| | (5,845 | ) | | 14,784 |
| | 252.9 |
|
| Total Retail Revenues | 1,779,722 |
| | 1,718,280 |
| | 61,442 |
| | 3.6 |
|
| Wholesale | 348,239 |
| | 316,353 |
| | 31,886 |
| | 10.1 |
|
| Transmission (a) | 210,281 |
| | 193,797 |
| | 16,484 |
| | 8.5 |
|
| Other | 32,412 |
| | 33,040 |
| | (628 | ) | | (1.9 | ) |
| Total Revenues | 2,370,654 |
| | 2,261,470 |
| | 109,184 |
| | 4.8 |
|
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | | | |
| Fuel and purchased power | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
| | 44,807 |
| | 7.6 |
|
| SPP network transmission costs | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
| | 12,057 |
| | 7.2 |
|
| Operating and maintenance | 359,060 |
| | 342,055 |
| | 17,005 |
| | 5.0 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
| | 2,129 |
| | 0.8 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 224,133 |
| | 226,012 |
| | (1,879 | ) | | (0.8 | ) |
| Taxes other than income tax | 122,282 |
| | 104,269 |
| | 18,013 |
| | 17.3 |
|
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,791,469 |
| | 1,699,337 |
| | 92,132 |
| | 5.4 |
|
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 579,185 |
| | 562,133 |
| | 17,052 |
| | 3.0 |
|
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | | | |
| Investment earnings | 10,056 |
| | 7,411 |
| | 2,645 |
| | 35.7 |
|
| Other income | 35,609 |
| | 35,378 |
| | 231 |
| | 0.7 |
|
| Other expense | (18,099 | ) | | (19,987 | ) | | 1,888 |
| | 9.4 |
|
| Total Other Income (Expense) | 27,566 |
| | 22,802 |
| | 4,764 |
| | 20.9 |
|
| Interest expense | 182,167 |
| | 176,337 |
| | 5,830 |
| | 3.3 |
|
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 424,584 |
| | 408,598 |
| | 15,986 |
| | 3.9 |
|
| Income tax expense | 123,721 |
| | 126,136 |
| | (2,415 | ) | | (1.9 | ) |
| NET INCOME | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
| | 18,401 |
| | 6.5 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 1,027 |
| | 14.0 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY. INC. | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
| | 17,374 |
| | 6.3 |
|
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | 1,616 |
| | (1,616 | ) | | (100.0 | ) |
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO COMMON STOCK | $ | 292,520 |
| | $ | 273,530 |
| | $ | 18,990 |
| | 6.9 |
|
| BASIC EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 0.14 |
| | 6.5 |
|
| DILUTED EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 0.12 |
| | 5.6 |
|
______________
| |
| (a) | Includes revenue from an SPP network transmission tariff corresponding to our SPP network transmission costs. These costs, less administration fees of $39.1 million and $27.2 million, respectively, were returned to us as revenue in 2013 and 2012, respectively. |
Rate Case Agreement
In April 2012, the KCC issued an order authorizing higher revenues to recover higher expenses primarily for increased tree trimming to enhance reliability and increased pension costs resulting from the consequences of the 2008 financial crisis and subsequent low interest rate environment in accordance with the regulatory mechanism in place to account for such pension costs. As a result of this order, we expected selling, general and administrative expense to increase $32.1 million and the cost of operating and maintaining our distribution system to increase $10.9 million on an annualized basis. In addition, we revised our depreciation rates to reflect changes in the estimated useful lives of some of our assets. The change in estimate decreased annual depreciation expense by $43.6 million. However, decreased depreciation expense as a result of lower depreciation rates were offset by additional depreciation related to additions to property, plant and equipment. Because the aforementioned changes were implemented shortly after the KCC issued its order, our 2012 consolidated financial results do not reflect the full annual impact of the changes.
Gross Margin
The following table summarizes our gross margin for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Revenues | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
| | $ | 109,184 |
| | 4.8 |
| Less: Fuel and purchased power expense | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
| | 44,807 |
| | 7.6 |
| SPP network transmission costs | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
| | 12,057 |
| | 7.2 |
| Gross Margin | $ | 1,557,253 |
| | $ | 1,504,933 |
| | $ | 52,320 |
| | 3.5 |
The following table reflects changes in electricity sales for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012. No electricity sales are shown for transmission or other as they are not directly related to the amount of electricity we sell.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Thousands of MWh) | | |
| ELECTRICITY SALES: | | | | | | | |
| Residential | 6,523 |
| | 6,684 |
| | (161 | ) | | (2.4 | ) |
| Commercial | 7,480 |
| | 7,581 |
| | (101 | ) | | (1.3 | ) |
| Industrial | 5,407 |
| | 5,588 |
| | (181 | ) | | (3.2 | ) |
| Other retail | 86 |
| | 85 |
| | 1 |
| | 1.2 |
|
| Total Retail | 19,496 |
| | 19,938 |
| | (442 | ) | | (2.2 | ) |
| Wholesale | 8,593 |
| | 7,719 |
| | 874 |
| | 11.3 |
|
| Total | 28,089 |
| | 27,657 |
| | 432 |
| | 1.6 |
|
Gross margin increased due primarily to higher retail revenues that were the result of higher prices offset partially by lower retail electricity sales. The lower retail electricity sales were attributable principally to cooler summer weather, which particularly impacted residential and commercial electricity sales. As measured by cooling degree days, 2013 was 23% cooler than the prior year. Contributing also to the decrease in retail sales was the reduced demand, primarily from several large industrial customers.
The following table reconciles income from operations with gross margin for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Gross margin | $ | 1,557,253 |
| | $ | 1,504,933 |
| | $ | 52,320 |
| | 3.5 |
|
| Less: Operating and maintenance expense | 359,060 |
| | 342,055 |
| | 17,005 |
| | 5.0 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization expense | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
| | 2,129 |
| | 0.8 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative expense | 224,133 |
| | 226,012 |
| | (1,879 | ) | | (0.8 | ) |
| Taxes other than income tax | 122,282 |
| | 104,269 |
| | 18,013 |
| | 17.3 |
|
| Income from operations | $ | 579,185 |
| | $ | 562,133 |
| | $ | 17,052 |
| | 3.0 |
|
Operating Expenses and Other Income and Expense Items
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Operating and maintenance expense | $ | 359,060 |
| | $ | 342,055 |
| | $ | 17,005 |
| | 5.0 |
Operating and maintenance expense increased due principally to:
higher costs for tree trimming, pursuant to authorized rate recovery, and other distribution reliability activities of $11.8 million; and
higher costs at Wolf Creek of $5.0 million, due principally to higher amortization of refueling outage costs and recognition of costs incurred during an unscheduled maintenance outage in 2013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | $ | 272,593 |
| | $ | 270,464 |
| | $ | 2,129 |
| | 0.8 |
Depreciation and amortization expense increased due to additional depreciation expense resulting primarily from increased plant additions at our power plants, including air quality controls, and the addition of transmission facilities. Partially offsetting this increase was a result of our having reduced depreciation rates in mid 2012 to reflect changes in the estimated useful lives of some of our assets.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | $ | 224,133 |
| | $ | 226,012 |
| | $ | (1,879 | ) | | (0.8 | ) |
Selling, general and administrative expense decreased due primarily to:
lower post-retirement and other employee benefit costs of $8.6 million due principally to restructuring insurance contracts; and,
lower labor cost of $2.3 million, which in part reflects expenses recorded in 2012 related to sustainable cost reduction activities; however,
partially offsetting these decreases were higher pension costs of $12.3 million, most of which were offset with higher revenues. These increased pension cost were principally a consequence of the 2008 financial market downturn and the subsequent low interest rate environment.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Taxes other than income tax | $ | 122,282 |
| | $ | 104,269 |
| | $ | 18,013 |
| | 17.3 |
Taxes other than income tax increased due primarily to an $18.2 million increase in property taxes, which are offset in retail revenues.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Investment earnings | $ | 10,056 |
| | $ | 7,411 |
| | $ | 2,645 |
| | 35.7 |
Investment earnings increased due principally to:
$1.2 million increase in earnings from our investment in Prairie Wind Transmission, LLC;Wind; and,
$1.4 million of additional gains on investments in a trust to fund retirement benefits.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Interest expense | $ | 182,167 |
| | $ | 176,337 |
| | $ | 5,830 |
| | 3.3 |
Interest expense increased due to our recording $10.5 million in interest principally related to additional debt issued to fund capital investment. Partially offsetting this increase was a $2.2 million decrease of interest expense on long-term debt of VIEs and a $1.3 million decrease for capitalized interest.
2012 Compared to 2011
Below we discuss our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to the results for the year ended December 31, 2011. Significant changes in results of operations shown in the table immediately below are further explained in the descriptions that follow.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| REVENUES: | | | | | | | |
| Residential | $ | 714,562 |
| | $ | 693,388 |
| | $ | 21,174 |
| | 3.1 |
|
| Commercial | 640,654 |
| | 604,626 |
| | 36,028 |
| | 6.0 |
|
| Industrial | 368,909 |
| | 347,881 |
| | 21,028 |
| | 6.0 |
|
| Other retail | (5,845 | ) | | (8,964 | ) | | 3,119 |
| | 34.8 |
|
| Total Retail Revenues | 1,718,280 |
| | 1,636,931 |
| | 81,349 |
| | 5.0 |
|
| Wholesale | 316,353 |
| | 346,948 |
| | (30,595 | ) | | (8.8 | ) |
| Transmission (a) | 193,797 |
| | 154,569 |
| | 39,228 |
| | 25.4 |
|
| Other | 33,040 |
| | 32,543 |
| | 497 |
| | 1.5 |
|
| Total Revenues | 2,261,470 |
| | 2,170,991 |
| | 90,479 |
| | 4.2 |
|
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | | | |
| Fuel and purchased power | 589,990 |
| | 630,793 |
| | (40,803 | ) | | (6.5 | ) |
| SPP network transmission costs | 166,547 |
| | 132,164 |
| | 34,383 |
| | 26.0 |
|
| Operating and maintenance | 342,055 |
| | 332,989 |
| | 9,066 |
| | 2.7 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 270,464 |
| | 285,322 |
| | (14,858 | ) | | (5.2 | ) |
| Selling, general and administrative | 226,012 |
| | 184,695 |
| | 41,317 |
| | 22.4 |
|
| Taxes other than income tax | 104,269 |
| | 92,599 |
| | 11,670 |
| | 12.6 |
|
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,699,337 |
| | 1,658,562 |
| | 40,775 |
| | 2.5 |
|
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 562,133 |
| | 512,429 |
| | 49,704 |
| | 9.7 |
|
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | | | |
| Investment earnings | 7,411 |
| | 9,301 |
| | (1,890 | ) | | (20.3 | ) |
| Other income | 35,378 |
| | 8,652 |
| | 26,726 |
| | 308.9 |
|
| Other expense | (19,987 | ) | | (18,398 | ) | | (1,589 | ) | | (8.6 | ) |
| Total Other Income (Expense) | 22,802 |
| | (445 | ) | | 23,247 |
| | (b) |
|
| Interest expense | 176,337 |
| | 172,460 |
| | 3,877 |
| | 2.2 |
|
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 408,598 |
| | 339,524 |
| | 69,074 |
| | 20.3 |
|
| Income tax expense | 126,136 |
| | 103,344 |
| | 22,792 |
| | 22.1 |
|
| NET INCOME | 282,462 |
| | 236,180 |
| | 46,282 |
| | 19.6 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 7,316 |
| | 5,941 |
| | 1,375 |
| | 23.1 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY. INC. | 275,146 |
| | 230,239 |
| | 44,907 |
| | 19.5 |
|
| Preferred dividends | 1,616 |
| | 970 |
| | 646 |
| | 66.6 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO COMMON STOCK | $ | 273,530 |
| | $ | 229,269 |
| | $ | 44,261 |
| | 19.3 |
|
| BASIC EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.95 |
| | $ | 0.20 |
| | 10.3 |
|
| DILUTED EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.93 |
| | $ | 0.22 |
| | 11.4 |
|
______________
| |
(a) | Reflects revenue from an SPP network transmission tariff corresponding to our SPP network transmission costs. These costs, less administration fees of $27.2 million and $18.6 million, respectively, were returned to us as revenue.
|
| |
(b) | Change greater than 1,000%. |
Gross Margin
The following table summarizes our gross margin for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Revenues | $ | 2,261,470 |
| | $ | 2,170,991 |
| | $ | 90,479 |
| | 4.2 |
|
| Less: Fuel and purchased power expense | 589,990 |
| | 630,793 |
| | (40,803 | ) | | (6.5 | ) |
| SPP network transmission costs | 166,547 |
| | 132,164 |
| | 34,383 |
| | 26.0 |
|
| Gross Margin | $ | 1,504,933 |
| | $ | 1,408,034 |
| | $ | 96,899 |
| | 6.9 |
|
The following table reflects changes in electricity sales for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011. No electricity sales are shown for transmission or other as they are not directly related to the amount of electricity we sell.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Thousands of MWh) | | |
| ELECTRICITY SALES: | | | | | | | |
| Residential | 6,684 |
| | 6,986 |
| | (302 | ) | | (4.3 | ) |
| Commercial | 7,581 |
| | 7,573 |
| | 8 |
| | 0.1 |
|
| Industrial | 5,588 |
| | 5,589 |
| | (1 | ) | | (a) |
|
| Other retail | 85 |
| | 88 |
| | (3 | ) | | (3.4 | ) |
| Total Retail | 19,938 |
| | 20,236 |
| | (298 | ) | | (1.5 | ) |
| Wholesale | 7,719 |
| | 8,215 |
| | (496 | ) | | (6.0 | ) |
| Total | 27,657 |
| | 28,451 |
| | (794 | ) | | (2.8 | ) |
Gross margin increased due primarily to higher retail revenues that were the result of higher prices offset partially by lower retail electricity sales. The lower retail electricity sales were attributable principally to moderate weather, which particularly impacted residential electricity sales. In 2012, cooling degree days were similar to 2011; however, cooling degree days during the third quarter of 2012 were 9% lower than the same period of 2011.
The following table reconciles income from operations with gross margin for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Gross margin | $ | 1,504,933 |
| | $ | 1,408,034 |
| | $ | 96,899 |
| | 6.9 |
|
| Less: Operating and maintenance expense | 342,055 |
| | 332,989 |
| | 9,066 |
| | 2.7 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization expense | 270,464 |
| | 285,322 |
| | (14,858 | ) | | (5.2 | ) |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | 226,012 |
| | 184,695 |
| | 41,317 |
| | 22.4 |
|
| Taxes other than income tax | 104,269 |
| | 92,599 |
| | 11,670 |
| | 12.6 |
|
| Income from operations | $ | 562,133 |
| | $ | 512,429 |
| | $ | 49,704 |
| | 9.7 |
|
Operating Expenses and Other Income and Expense Items
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Operating and maintenance expense | $ | 342,055 |
| | $ | 332,989 |
| | $ | 9,066 |
| | 2.7 |
Operating and maintenance expense increased due principally to:
higher costs for tree trimming, pursuant to authorized rate recovery, and other electrical system reliability activities of $5.9 million; and
higher costs at Wolf Creek of $4.6 million, which were the result primarily of maintenance costs incurred during an unscheduled outage.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Depreciation and amortization expense | $ | 270,464 |
| | $ | 285,322 |
| | $ | (14,858 | ) | | (5.2 | ) |
Depreciation and amortization expense decreased as a result of our having reduced depreciation rates to reflect changes in the estimated useful lives of some of our assets. Partially offsetting this decrease was additional depreciation expense associated primarily with additions at our power plants, including air quality controls, and the addition of transmission facilities.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | $ | 226,012 |
| | $ | 184,695 |
| | $ | 41,317 |
| | 22.4 |
Selling, general and administrative expense increased due primarily to:
our having reversed $22.0 million of previously accrued liabilities in 2011 as a result of settling litigation;
higher pension and other employee benefit costs of $20.2 million pursuant to authorized rate recovery;
our having recorded $4.5 million of expense as a result of sustainable cost reduction activities; and
a $2.1 million increase in the amortization of previously deferred amounts associated with various energy efficiency programs, which we recover in retail revenues; however,
partially offsetting these increases was a $9.4 million decrease in legal fees that was the result principally of arbitration and litigation that occurred in 2011.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Taxes other than income tax | $ | 104,269 |
| | $ | 92,599 |
| | $ | 11,670 |
| | 12.6 |
Taxes other than income tax increased due primarily to a $9.2 million increase in property taxes, which is offset in retail revenues.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Investment earnings | $ | 7,411 |
| | $ | 9,301 |
| | $ | (1,890 | ) | | (20.3 | ) |
Investment earnings decreased due principally to:
our having recorded a $7.2 million gain on the sale of a non-utility investment in 2011; however,
partially offsetting this item was our having recorded $4.5 million of additional gains on investments in a trust to fund retirement benefits and a $1.7 million increase in earnings from our investment in Prairie Wind Transmission, LLC.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Other income | $ | 35,378 |
| | $ | 8,652 |
| | $ | 26,726 |
| | 308.9 |
Other income increased due principally to:
our having recorded an additional $17.4 million in COLI (corporate-owned life insurance) benefits;
a $6.2 million increase in equity AFUDC, which reflects more construction activity; and
our having recorded an additional $3.1 million related to the sale of oil inventory.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Income tax expense | $ | 126,136 |
| | $ | 103,344 |
| | $ | 22,792 |
| | 22.1 |
Income tax expense increased due principally to higher income before income taxes.
Financial Condition
A number of factors affected amounts recorded on our balance sheet as of December 31, 20132014, compared to December 31, 20122013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Fuel inventory and supplies | $ | 239,511 |
| | $ | 249,016 |
| | $ | (9,505 | ) | | (3.8 | ) |
Fuel inventory and supplies decreased due principally to a $16.7 million decrease in coal inventory, due to a price reduction in the cost of coal and reduced transportation costs. This decrease was partially offset by a $6.8 million increase in materials and supplies as a result of higher inventory replacement costs as well as materials purchased for spring 2014 outages.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 7,551,916 |
| | $ | 7,013,765 |
| | $ | 538,151 |
| | 7.7 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 8,162,908 |
| | $ | 7,551,916 |
| | $ | 610,992 |
| | 8.1 |
Property, plant and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation, increased due primarily to plant additions at our power plants, includingfor air quality controls, additional transmission facilities and the addition of transmission facilities.a revision to our ARO to decommission Wolf Creek.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Property, plant and equipment of variable interest entities, net | $ | 296,626 |
| | $ | 321,975 |
| | $ | (25,349 | ) | | (7.9 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Property, plant and equipment of variable interest entities, net | $ | 278,573 |
| | $ | 296,626 |
| | $ | (18,053 | ) | | (6.1 | ) |
Property, plant and equipment of variable interest entities,VIEs, net of accumulated depreciation, decreased due to deconsolidating a rail car lease as discussed in Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Variable Interest Entities," and normal depreciation of these assets.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change | 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Regulatory assets | $ | 755,414 |
| | $ | 1,002,672 |
| | $ | (247,258 | ) | | (24.7 | ) | $ | 859,778 |
| | $ | 755,414 |
| | $ | 104,364 |
| | 13.8 |
| Regulatory liabilities | 329,556 |
| | 323,175 |
| | 6,381 |
| | 2.0 |
| 343,485 |
| | 329,556 |
| | 13,929 |
| | 4.2 |
| Net regulatory assets | $ | 425,858 |
| | $ | 679,497 |
| | $ | (253,639 | ) | | (37.3 | ) | $ | 516,293 |
| | $ | 425,858 |
| | $ | 90,435 |
| | 21.2 |
Total regulatory assets decreasedincreased due primarily to the following reasons:
a $265.1$158.5 million decreaseincrease in deferred employee benefit costs, due primarilyprincipally to decreased pension and post-retirement benefit obligations as a result of increasesdecrease in the discount rates used to calculate our and Wolf Creek's benefits obligations;pension benefit obligations and the adoption of updated mortality tables. However, this increase was partially offset by the following items:
a $9.6$22.1 million decrease in amounts previously deferred for storm costs;fuel expense;
a $5.3$17.9 million decrease in amounts deferred for Wolf Creek refueling and maintenance outages; and
a $9.8 million decrease in amounts due from customers for future income taxes; and
a $4.4 million decrease in amounts deferred for energy efficiency costs; however,
partially offsetting decreases were a $17.9 million, $14.9 million and $12.7 million increase in amounts deferred for fuel expense, for the Wolf Creek outage and for property taxes, respectively.taxes.
RegulatoryTotal regulatory liabilities increased due primarily to the following reasons:
a $24.9$25.2 million increase in jurisdictional AFUDC, which is AFUDC that is accrued subsequent to the fair value oftime costs are included in our prices and prior to the NDTtime associated costs are placed into service; and, an $8.3
a $17.9 million increase in other post-retirement costs. Partiallyrefund obligations related to amounts we have collected from our customers in excess of our actual cost of fuel and purchased power; however,
partially offsetting this increasethese increases was a $14.8$25.9 million decrease in amounts collected but not yet spent to dispose of plant assets.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Short-term debt | $ | 134,600 |
| | $ | 339,200 |
| | $ | (204,600 | ) | | (60.3 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Short-term debt | $ | 257,600 |
| | $ | 134,600 |
| | $ | 123,000 |
| | 91.4 |
Short-term debt decreasedincreased due to decreasesincreases in issuances of commercial paper. Proceeds from issuances of long-term debt were usedpaper to temporarily fund capital expenditures, to repay short-term debt, which had been used primarily to purchase capital equipment,borrowings under Westar Energy's revolving credit facilities, to redeem bonds anddebt on an interim basis, for working capital andand/or for other general corporate purposes.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 250,000 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 250,000 |
| |
|
| Long-term debt, net | 2,968,958 |
| | 2,819,271 |
| | 149,687 |
| | 5.3 |
| Total long-term debt | $ | 3,218,958 |
| | $ | 2,819,271 |
| | $ | 399,687 |
| | 14.2 |
Total long-term debt increased due to the issuance of $500.0 million principal amount of first mortgage bonds. This increase was partially offset by our redemption of two pollution control bond issues with an aggregate principal amount of
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | — |
| | $ | 250,000 |
| | $ | (250,000 | ) | | (100.0 | ) |
| Long-term debt, net | 3,215,539 |
| | 2,968,958 |
| | 246,581 |
| | 8.3 |
|
| Total long-term debt | $ | 3,215,539 |
| | $ | 3,218,958 |
| | $ | (3,419 | ) | | (0.1 | ) |
In 2014, Westar Energy and KGE issued $180.0 million and $250.0 million, respectively, in principal amount of first mortgage bonds. Proceeds of these issuances were used to retire $250.0 millon of Westar Energy first mortgage bonds and redeem three KGE pollution control bond series with principal amount of $177.5 million. Both the issuance and redemptions are further discussed inFor more information on our long-term debt, see Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, “Long-Term"Long-term Debt.”"
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change | 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Current maturities of long-term debt of variable interest entities | $ | 27,479 |
| | $ | 25,942 |
| | $ | 1,537 |
| | 5.9 |
| $ | 27,933 |
| | $ | 27,479 |
| | $ | 454 |
| | 1.7 |
|
| Long-term debt of variable interest entities | 194,802 |
| | 222,743 |
| | (27,941 | ) | | (12.5 | ) | 166,565 |
| | 194,802 |
| | (28,237 | ) | | (14.5 | ) |
| Total long-term debt of variable interest entities | $ | 222,281 |
| | $ | 248,685 |
| | $ | (26,404 | ) | | (10.6 | ) | $ | 194,498 |
| | $ | 222,281 |
| | $ | (27,783 | ) | | (12.5 | ) |
Total long-term debt of variable interest entitiesVIEs decreased due principally to the VIEs that hold the JEC and La Cygne leasehold interests having made principal payments totaling $25.4$27.2 million.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Deferred income tax liabilities | $ | 1,361,418 |
| | $ | 1,197,837 |
| | $ | 163,581 |
| | 13.7 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Deferred income tax liabilities | $ | 1,475,487 |
| | $ | 1,363,148 |
| | $ | 112,339 |
| | 8.2 |
Long-term deferred income tax liabilities increased due primarily to the use of bonus and accelerated depreciation methods during the year.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2013 | | 2012 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Accrued employee benefits | $ | 331,558 |
| | $ | 564,870 |
| | $ | (233,312 | ) | | (41.3 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Accrued employee benefits | $ | 532,622 |
| | $ | 331,558 |
| | $ | 201,064 |
| | 60.6 |
Accrued employee benefits decreasedincreased due primarily to lowerhigher pension and post-retirement benefit obligations as a result of increasesdecreases in the discount rates used to calculate our and Wolf Creek's benefits obligations.pension benefit obligations and the adoption of updated mortality tables.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| 2014 | | 2013 | | Change | | % Change |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Asset retirement obligations | $ | 230,668 |
| | $ | 160,682 |
| | $ | 69,986 |
| | 43.6 |
Asset retirement obligations increased due primarily to a $50.7 million revision in our ARO to decommission Wolf Creek. For additional information, see Note 14 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Asset Retirement Obligations."
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Overview
Available sources of funds to operate our business include internally generated cash, short-term borrowings under Westar Energy's commercial paper program and revolving credit facilities and access to capital markets. We expect to meet our day-to-day cash requirements including, among other items, fuel and purchased power, dividends, interest payments, income taxes and pension contributions, using primarily internally generated cash and short-term borrowings. To meet the cash requirements for our capital investments, we expect to use internally generated cash, short-term borrowings and proceeds from the issuance of debt and equity securities in the capital markets. When such balances are of sufficient size and it makes economic sense to do so, we also use proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt and equity securities to repay short-term borrowings, which are principally related to investments in capital equipment and the redemption of bonds and for working capital and general corporate purposes. For additional information on our future cash requirements, see "—Future Cash Requirements" below.
In 2014,2015, we expect to continue our significant capital spending program and plan to contribute to our pension trust. We continue to believe that we will have the ability to pay dividends. Uncertainties affecting our ability to meet cash requirements include, among others, factors affecting revenues described in "Item 1A. Risk Factors" and "—Operating Results" above, economic conditions, regulatory actions, compliance with environmental regulations and conditions in the capital markets. For additional information on our future cash requirements, see "—Future Cash Requirements" below.
Capital Structure
As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, our capital structure, excluding short-term debt, was as follows:
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| Common equity | 47% | | 49% | 49% | | 47% |
| Noncontrolling interests | <1% | | <1% | <1% | | <1% |
| Long-term debt, including VIEs | 53% | | 51% | 51% | | 53% |
Short-Term Borrowings
In 2011, Westar Energy entered intomaintains a commercial paper program pursuant to which it may issue commercial paper up to a maximum aggregate amount outstanding at any one time of $1.0 billion. This program is supported by Westar Energy's revolving credit facilities. Maturities of commercial paper issuances may not exceed 365 days from the date of issuance and proceeds from such issuances will be used to temporarily fund capital expenditures, to repay borrowings under Westar Energy's revolving credit facilities,redeem debt on an interim basis, for working capital and/or for other general corporate purposes. As of February 18, 201417, 2015, Westar Energy had issued $177.8$402.3 million of commercial paper.paper issued and outstanding.
Westar Energy has two revolving credit facilities in the amounts of $730.0 million and $270.0 million. In July 2013,September 2014, Westar Energy extended the term of the $730.0 million facility by one year to terminate in September 2017, and2018, $81.4 million of which will expire in September 2017. In February 2014, Westar Energy extended the term of theits $270.0 million credit facility to February 2017, provided that $20.0 million of this facilitywhich will terminate in February 2016. As long as there is no default under the facility,facilities, the $730.0 million facility may be extended an additional yeartwo years and the aggregate amount of borrowings under the $730.0 million and $270.0 million facilities may be increased to $1.0 billion and $400.0 million, respectively, subject to lender participation. All borrowings under the facilities are secured by KGE first mortgage bonds. Total combined borrowings under the revolving credit facilities and the commercial paper program may not exceed $1.0 billion at any given time. As of February 18, 201417, 2015, no amounts were borrowed and $18.5$15.4 million of letters of credit had been issued under the $730.0 million facility. No amounts were borrowed and no letters of credit were issued under the $270.0 million facility as of the same date.
A default by Westar Energy or KGE under other indebtedness totaling more than $25.0 million would be a default under both revolving credit facilities. Westar Energy is required to maintain a consolidated indebtedness to consolidated capitalization ratio of 65% or less at all times. At December 31, 20132014, our ratio was 53%52%. See Note 8 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Short-Term Debt," for additional information regarding our short-term borrowings.
Long-Term Debt Financing
We have $250.0In January 2015, Westar Energy redeemed $125.0 million in outstanding aggregate principal amount of first mortgage bonds that are due July 1, 2014. We expect to issue additional long-term debt to redeem those bonds before the maturity date thereof.
In August 2013, Westar Energy issued $250.0 million principal amount of first mortgage bonds bearing stated interest of 4.625%at 5.95% and maturing in September 2043.January 2035.
In June 2013,July 2014, KGE redeemed two pollution control bond series with an aggregate principal amount of $100.0 million and stated interest rates of 5.60% and 6.00%.
In March 2013, Westar Energy issued $250.0 million in principal amount of first mortgage bonds bearing stated interest at 4.30% and maturing July 2044. The proceeds were used to retire Westar Energy first mortgage bonds in a principal amount of $250.0 million with a stated interest of 6.00% maturing in July 2014.
In May 2014, Westar Energy issued $180.0 million in principal amount of first mortgage bonds bearing stated interest at 4.10% and maturing in April 2043. These bonds constitute a further issuance of a series of bonds initially issued in March 2013 in a principal amount of $250.0 million. Proceeds from these issuancesthe May 2014 issuance were used to repay short-term debt, which had been used primarily to purchase capital equipment,in June 2014 to redeem bondsthree KGE pollution control bond series totaling $177.5 million principal amount at stated interest rates between 5.00% and for working capital and general corporate purposes.5.30%.
As of December 31, 20132014, we had $121.9 million of variable rate, tax-exempt bonds. While the interest rates for these bonds have been extremely low, we continue to monitor the credit markets and evaluate our options with respect to these bonds.
The Westar Energy and KGE mortgages each contain provisions restricting the amount of first mortgage bonds that can be issued by each entity. We must comply with such restrictions prior to the issuance of additional first mortgage bonds or other secured indebtedness.
Under the Westar Energy mortgage, the issuance of bonds is subject to limitations based on the amount of bondable property additions. In addition, so long as any bonds issued prior to January 1, 1997 remain outstanding, the mortgage prohibits additional first mortgage bonds from being issued, except in connection with certain refundings, unless Westar Energy's unconsolidated net earnings available for interest, depreciation and property retirement (which as defined, does not include earnings or losses attributable to the ownership of securities of subsidiaries), for a period of 12 consecutive months within 15 months preceding the issuance, are not less than the greater of twice the annual interest charges on or 10% of the principal amount of all first mortgage bonds outstanding after giving effect to the proposed issuance. As of December 31, 20132014, approximately $505.3$743.2 million principal amount of additional first mortgage bonds could be issued under the most restrictive provisions in the mortgage, except in connection with certain refundings.
Under the KGE mortgage, the issuance of bonds is subject to limitations based on the amount of bondable property additions. In addition, the mortgage prohibits additional first mortgage bonds from being issued, except in connection with certain refundings, unless KGE's net earnings before income taxes and before provision for retirement and depreciation of property for a period of 12 consecutive months within 15 months preceding the issuance are not less than either two and one-half times the annual interest charges on or 10% of the principal amount of all KGE first mortgage bonds outstanding after giving effect to the proposed issuance. As of December 31, 20132014, approximately $1.1$1.3 billion principal amount of additional KGE first mortgage bonds could be issued under the most restrictive provisions in the mortgage.
Some of our debt instruments contain restrictions that require us to maintain leverage ratios as defined in the credit agreements. We calculate these ratios in accordance with the agreements and they are used to determine compliance with our various debt covenants. We were in compliance with these covenants as of December 31, 2013.2014.
Impact of Credit Ratings on Debt Financing
Moody's Investors Service (Moody's), Standard & Poor's Ratings Services (S&P) and Fitch Ratings (Fitch) are independent credit-rating agencies that rate our debt securities. These ratings indicate each agency's assessment of our ability to pay interest and principal when due on our securities.
In general, more favorable credit ratings increase borrowing opportunities and reduce the cost of borrowing. Under Westar Energy's revolving credit facilities and commercial paper program, our cost of borrowings is determined in part by credit ratings. However, Westar Energy's ability to borrow under the credit facilities and commercial paper program are not conditioned on maintaining a particular credit rating. We may enter into new credit agreements that contain credit rating conditions, which could affect our liquidity and/or our borrowing costs.
Factors that impact our credit ratings include a combination of objective and subjective criteria. Objective criteria include typical financial ratios, such as total debt to total capitalization and funds from operations to total debt, among others, future capital expenditures and our access to liquidity including committed lines of credit. Subjective criteria include such items as the quality and credibility of management, the political and regulatory environment we operate in and an assessment of our governance and risk management practices.
In January 2014, Moody's upgraded its ratings for Westar Energy and KGE first mortgage bonds to A2 from A3. In February 2013,April 2014, S&P revised its criteria for rating utility first mortgage bonds and, as a result, upgraded its ratings for Westar Energy and KGE first mortgage bonds/senior secured debtbonds to A-A from BBB+. Additionally, in April 2013, S&P affirmedA-. In June 2014, Fitch revised its ratingsrating for Westar EnergyEnergy's and KGE and raised itsKGE's outlook to positive from stable.
As of February 18, 201417, 2015, our ratings with the agencies are as shown in the table below.
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Westar Energy First Mortgage Bond Rating | | KGE First Mortgage Bond Rating | | Westar Energy Commercial Paper | | Rating Outlook |
| Moody’s | A2 | | A2 | | P-2 | | Stable |
| S&P | A-A | | A-A | | A-2 | | PositiveStable |
| Fitch | A- | | A- | | F2 | | StablePositive |
Common and Preferred Stock
Common Stock
Westar Energy's Restated Articles of Incorporation, as amended, provide for 275.0 million authorized shares of common stock. As of December 31, 20132014, Westar Energy had 128.3131.7 million shares issued and outstanding.
In September 2013, Westar Energy entered into two forward sale agreements with two banks. Under the terms of the agreements, the banks, as forward sellers, borrowed 8.0 million shares of Westar Energy's common stock from third parties and sold them to a group of underwriters for $31.15 per share. Pursuant to over-allotment options granted to the underwriters, the underwriters purchased in October 2013 an additional 0.9 million shares from the banks as forward sellers, increasing the total number of shares under the forward sale agreements to approximately 8.9 million. The underwriters received a commission equal to 3.5% of the sales price of all shares sold under the agreements.each agreement. Westar Energy must settle such transactions within 24 months.months of the applicable agreement.
In March 2013, Westar Energy entered into a new, three-year sales agency financing agreement and master forward sale confirmationagreement with a bank, similar to the sales agency financing agreement and master forward sale confirmation entered into in April 2010.bank. The maximum amount that Westar Energy may offer and sell under the March 2013 master agreements is the lesser of an aggregate of $500.0 million or approximately 25.0 million shares, subject to adjustment for share splits, share combinations and share dividends. Under the terms of the sales agency financing agreement, Westar Energy may offer and sell shares of its common stock from time to time. In addition, under the terms of the March 2013 sales agency financing agreement and master forward sale confirmation, Westar Energy may from time to time enter into one or more forward sale transactions with the bank, as forward purchaser, and the bank will borrow shares of Westar Energy's common stock from third parties and sell them through its agent. The agent receives a commission equal to 1% of the sales price of all shares sold under the agreements. Westar Energy must settle the forward sale transactions within 18 months of the date each transaction is entered.
In April 2010, Westar Energy entered into a three-year Sales Agency Financing Agreementsales agency financing agreement and master forward sale agreement with a bank that was terminated in March 2013. The maximum amount that Westar Energy could offer and sell under the agreements was the lesser of an aggregate of $500.0 million or approximately 22.0 million shares, subject to adjustment for share splits, share combinations and share dividends. Under the terms of the Sales Agency Financing Agreement, Westar Energy could offer and sell shares of its common stock from timeTerms under these agreements are generally similar to time through the broker dealer subsidiary, as agent. The broker dealer received a commission equal to 1% of the sales price of all shares sold under the agreement. In addition, under the terms of the Sales Agency Financing Agreement and forward sale agreement, Westar Energy could from time to time enter into one or more forward sale transactions with the bank, as forward purchaser, and the bank will borrow shares of Westar Energy's common stock from third parties and sell them through its broker dealer. Westar Energy was required to settle the forward sale transactions within 18 months of the date each transaction was entered. In 2011 and 2010, Westar Energy entered into and settled forward sale transactions with respect to an aggregate of approximately 5.4 million shares of common stock for proceeds of approximately $118.3 million.
During 2013 and 2012, Westar Energy entered into additional forward sale transactions with respect to an aggregate of approximately 2.5 million and 1.8 million shares of common stock respectively, under the March 2013 and April 2010agreements described above.
The following table summarizes our common stock activity pursuant to the three forward sale agreements. During 2013, Westar Energy settled 1.1 million shares, resulting in 3.1 million shares under the March 2013 and April 2010 agreements that had not settled as of December 31, 2013. In February 2014, Westar Energy settled 0.3 million shares with a physical settlement amount of approximately $9.2 million.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Shares that could be settled at beginning of year | 12,052,976 |
| | 1,753,415 |
| | — |
|
| Transactions entered | — |
| | 11,367,673 |
| | 1,753,415 |
|
| Transactions settled (a) | 2,892,476 |
| | 1,068,112 |
| | — |
|
| Shares that could be settled at end of year (b) | 9,160,500 |
| | 12,052,976 |
| | 1,753,415 |
|
| _______________ | | | | | |
| (a) The shares settled during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, were settled with a physical settlement amount of approximately $82.9 million and $27.0 million, respectively. |
| (b) Assuming physical share settlement of the 9.2 million shares associated with the forward sale transactions that could be settled as of December 31, 2014, Westar Energy would have received aggregate proceeds of approximately $258.3 million based on a weighted average forward price of $28.20 per share. In February 2015, Westar Energy settled 0.2 million shares with a physical settlement amount of approximately $7.5 million. |
The forward sale transactions are entered into at market prices; therefore, the forward sale agreements have no initial fair value. Westar Energy does not receive any proceeds from the sale of common stock under the forward sale agreements until transactions are settled. Upon settlement, Westar Energy will record the forward sale agreements within equity. Except in specified circumstances or events that would require physical share settlement, Westar Energy is able to elect to settle any forward sale transactions by means of physical share, cash or net share settlement, and is also able to elect to settle the forward sale transactions in whole, or in part, earlier than the stated maturity dates. Currently, Westar Energy anticipates settling the forward sale transactions through physical share settlement. The shares under the forward sale agreements are initially priced when the transactions are entered into and are subject to certain fixed pricing adjustments during the term of the agreements. Accordingly, assuming physical share settlement, Westar Energy's net proceeds from the forward sale transactions will represent the prices established by the forward sale agreements applicable to the time periods in which physical settlement occurs.
Assuming physical share settlement of the approximately 12.1 million shares associated with all forward sale transactions as of December 31, 2013, Westar Energy would have received aggregate proceeds of approximately $358.3 million based on a weighted average forward price of $29.73 per share.
Westar Energy used the proceeds from the issuance of common stocktransactions described above to repay short-term borrowings, with such borrowed amounts principally related toused for investments in capital equipment, as well as for working capital and general corporate purposes.
Preferred Stock Redemption46
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Rate | | Shares | | Principal Outstanding | | Call Price | | Premium | | Total Cost to Redeem |
| (Dollars in Thousands) |
| 4.50% | | 121,613 |
| | $ | 12,161 |
| | 108.0% | | $ | 973 |
| | $ | 13,134 |
|
| 4.25% | | 54,970 |
| | 5,497 |
| | 101.5% | | 82 |
| | 5,579 |
|
| 5.00% | | 37,780 |
| | 3,778 |
| | 102.0% | | 76 |
| | 3,854 |
|
| | | 214,363 |
| | $ | 21,436 |
| | | | $ | 1,131 |
| | $ | 22,567 |
|
Summary of Cash Flows
| | | | | Year Ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | | (In Thousands) | | (In Thousands) |
| Cash flows from (used in): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | | $ | 702,803 |
| | $ | 599,106 |
| | $ | 462,696 |
| | $ | 824,355 |
| | $ | 702,803 |
| | $ | 599,106 |
|
| Investing activities | | (641,901 | ) | | (797,337 | ) | | (701,516 | ) | | (838,748 | ) | | (641,901 | ) | | (797,337 | ) |
| Financing activities | | (62,244 | ) | | 200,521 |
| | 241,431 |
| | 14,462 |
| | (62,244 | ) | | 200,521 |
|
| Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents | | $ | (1,342 | ) | | $ | 2,290 |
| | $ | 2,611 |
| | $ | 69 |
| | $ | (1,342 | ) | | $ | 2,290 |
|
Cash Flows from Operating Activities
Cash flows from operating activities increased $103.7121.6 million in 20132014 compared to 20122013 due principally to our having received $384.2 million more from retail and wholesale customers. This increase was offset partially by our having paid $227.4 million more for fuel and purchased power.
Cash flows from operating activities increased $103.7 million in 2013 compared to 2012 due principally to our having received about $74.3 million more from retail and wholesale customers, our having paid approximately $40.9 million less for pension and post retirement contributions, our having paid $29.7 million in 2012 to settle treasury yield hedge transactions, and our receiving $9.6 million more in COLIcorporate owned life insurance (COLI) death proceeds. Increases were offset partially by our having paid approximately $65.6 million more for the planned Wolf Creek refueling and maintenance outage.
The $136.4 million increase in 2012 compared to 2011 was due principally to our having paid approximately $100.9 million less for fuel and purchased power, our having received about $96.3 million more from retail customers and our having paid $56.3 million in 2011 to settle litigation. Increases were offset partially by our having received approximately $42.0 million less from wholesale customers, our having paid $29.7 million in 2012 to settle treasury yield hedge transactions, our having received $13.1 million less in income tax refunds and our having contributed $10.3 million more to pension and post-retirement benefit plans.
Cash Flows used in Investing Activities
Cash flows used in investing activities increased $196.8 million from 2013 to 2014 due primarily to decreased proceeds from investment in COLI of $104.4 million and increased investment in property, plant and equipment of $72.0 million.
Cash flows used in investing activities decreased $155.4$155.4 million from 2012 to 2013 due primarily to increased proceeds from investment in corporate owned life insuranceCOLI of $114.1 million and decreased investment in property, plant and equipment of $30.1 million.
Cash flows used in investing activities increased $95.8 million from 2011 to 2012 due primarily to our having invested an additional $112.8 million in additions to property, plant and equipment, which was attributable principally to additions at our power plants, including air quality controls, and the addition of transmission facilities. The increased investment in 2012 was partially offset by our having received $32.2 million more in proceeds from our investment in COLI.
Cash Flows from (used in) Financing Activities
Cash flows from financing activities increased $76.7 million in 2014 compared to 2013. The increase was due primarily to our having borrowed $327.6 million more in short-term debt, our having repaid $104.2 million less for borrowings against the cash surrender value of COLI, and also an increase in issuances of common stock of $54.8 million. This was partially offset by our having paid $327.5 million more to retire, and our having received $74.4 million less from issuances of, long-term debt.
Cash flows from financing activities decreased $262.8$262.8 million in 2013 compared to 2012.2012. The decrease was due primarily to our having borrowed $258.1 million less in short term debt and our having repaid $110.6 million more for borrowings against the cash surrender value of corporate owned life insurance.COLI. This decrease was partially offset by our having paid $120.6 million less to retire long-term debt.
The $40.9 million decrease in 2012 compared to 2011 was due principally to our having received $287.9 million less in proceeds from the issuance of common stock, which was attributable principally to our having issued shares in 2011 to settle forward transactions, and our having retired $220.2 million more of long-term debt due to favorable conditions in the capital markets. Contributing to the decrease was our having repaid $31.4 million more for borrowings against the cash surrender value of COLI, our having established a $22.6 million restricted cash account to fund the redemption of preferred stock and our having paid $19.9 million more for dividends as a result principally of our having increased our common stock dividend from $1.28 per share in 2011 to $1.32 per share in 2012. Partially offsetting the decreases was our having received $541.4 million in proceeds from long-term debt issuances. The proceeds were used to repay short-term debt, which was used to purchase capital equipment, to redeem bonds, and for working capital and general corporate purposes.
Future Cash Requirements
Our business requires significant capital investments. Through 2016,2017, we expect to need cash primarily for utility construction programs designed to improve and expand facilities related to providing electric service, which include, but are not limited to, expenditures for environmental projects at our coal-fired power plants, new transmission lines and other improvements to our power plants, transmission and distribution lines and equipment. We expect to meet these cash needs with internally generated cash, short-term borrowings and the issuance of securities in the capital markets.
We have incurred and expect to continue to incur significant costs to comply with existing and future environmental laws and regulations, which are subject to changing interpretations and amendments. Changes to environmental regulations could result in significantly more stringent laws and regulations or interpretations thereof that could affect us and our industry in particular. These laws, regulations and interpretations could result in more stringent terms in our existing operating permits or a failure to obtain new permits could cause a material increase in our capital or operational costs and could otherwise have a material effect on our operations and consolidated financial results.
Capital expenditures for 20132014 and anticipated capital expenditures, including costs of removal, for 20142015 through 20162017 are shown in the following table.
| | | | Actual | | | | | | | Actual | | Projected |
| | 2013 | | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2016 | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2016 | | 2017 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Generation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Replacements and other | $ | 201,395 |
| | $ | 181,600 |
| | $ | 173,100 |
| | $ | 136,800 |
| $ | 206,674 |
| | $ | 175,200 |
| | $ | 181,100 |
| | $ | 140,900 |
|
| Environmental | 262,441 |
| | 237,000 |
| | 112,000 |
| | 21,900 |
| 237,959 |
| | 85,400 |
| | 26,800 |
| | 14,500 |
|
| Nuclear fuel | 4,129 |
| | 52,900 |
| | 28,600 |
| | 30,200 |
| 41,873 |
| | 15,700 |
| | 28,800 |
| | 46,500 |
|
| Transmission (a) | 168,662 |
| | 179,100 |
| | 186,900 |
| | 203,400 |
| 187,957 |
| | 198,600 |
| | 205,300 |
| | 216,100 |
|
| Distribution | 107,993 |
| | 137,200 |
| | 147,700 |
| | 157,300 |
| 135,654 |
| | 165,500 |
| | 171,700 |
| | 189,200 |
|
| Other | 35,478 |
| | 26,200 |
| | 30,700 |
| | 41,400 |
| 41,936 |
| | 51,600 |
| | 47,300 |
| | 63,800 |
|
| Total capital expenditures | $ | 780,098 |
| | $ | 814,000 |
| | $ | 679,000 |
| | $ | 591,000 |
| $ | 852,053 |
| | $ | 692,000 |
| | $ | 661,000 |
| | $ | 671,000 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | In addition to amounts listed, we are investingmade an $8.0 million investment in Prairie Wind Transmission. In 2013, we incurred $4.0 million of expenditures related to this investment. In 2014 we plan to incur expenditures related to Prairie Wind Transmission of $6.7 million.in 2014. We do not anticipate any further investment related to Prairie Wind Transmission in 2015 and 2016.through 2017. |
We prepare these estimates for planning purposes and revise them from time to time. Actual expenditures will differ, perhaps materially, from our estimates due to changing regulatory requirements, changing costs, delays or advances in engineering, construction or permitting, changes in the availability and cost of capital and other factors discussed in "Item 1A. Risk Factors." We and our generating plant co-owners periodically evaluate these estimates and this may result in possibly material changes in actual costs. In addition, these amounts do not include any estimates for potential new environmental requirements.
We will also need significant amounts of cash in the future to meet our long-term debt obligations. The principal amounts of our long-term debt maturities as of December 31, 20132014, are as follows.
| | | Year | | Long-term debt | | Long-term debt of VIEs | | Long-term debt | | Long-term debt of VIEs |
| | | (In Thousands) | | (In Thousands) |
| 2014 | | $ | 250,000 |
| | $ | 27,479 |
| |
| 2015 | | — |
| | 27,933 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 27,933 |
|
| 2016 | | — |
| | 28,309 |
| | — |
| | 28,309 |
|
| 2017 | | 125,000 |
| | 26,842 |
| | 125,000 |
| | 26,842 |
|
| 2018 | | 300,000 |
| | 28,538 |
| | 300,000 |
| | 28,538 |
|
| 2019 | | | 300,000 |
| | 31,485 |
|
| Thereafter | | 2,549,440 |
| | 82,581 |
| | 2,501,940 |
| | 51,097 |
|
| Total maturities | | $ | 3,224,440 |
| | $ | 221,682 |
| | $ | 3,226,940 |
| | $ | 194,204 |
|
Pension Obligation
The amount we contribute to our pension plan for future periods is not yet known, however, we expect to fund our pension plan each year at least to a level equal to current year pension expense. We must also meet minimum funding requirements under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act, as amended by the Pension Protection Act. We may contribute additional amounts from time to time as deemed appropriate.
We contributed $27.526.4 million to our pension trust in 20132014 and $56.727.5 million in 20122013. We expect to contribute approximately $30.842.0 million in 20142015. In 20132014 and 20122013, we also funded $7.67.1 million and $13.97.6 million, respectively, of Wolf Creek's pension plan contributions. In 20142015, we plan to contribute $5.4$4.7 million to fund Wolf Creek's pension plan contributions. See Notes 11 and 12 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Employee Benefit Plans" and "Wolf Creek Employee Benefit Plans," for additional discussion of Westar Energy and Wolf Creek benefit plans, respectively.
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
As discussed under "—Common Stock" above and in Note 16 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Common and Preferred Stock," Westar Energy entered into several forward sale agreements with banks in 2013. The forward sale agreements are off-balance sheet arrangements. We also have off-balance sheet arrangements in the form of operating leases and letters of credit entered into in the ordinary course of business. We did not have any additional off-balance sheet arrangements as of December 31, 20132014.
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS AND COMMERCIAL COMMITMENTS
In the course of our business activities, we enter into a variety of contracts and commercial commitments. Some of these result in direct obligations reflected on our consolidated balance sheets while others are commitments, some firm and some based on uncertainties, not reflected in our underlying consolidated financial statements.
Contractual Cash Obligations
The following table summarizes the projected future cash payments for our contractual obligations existing as of December 31, 20132014.
| | | | Total | | 2014 | | 2015 - 2016 | | 2017 - 2018 | | Thereafter | Total | | 2015 | | 2016 - 2017 | | 2018 - 2019 | | Thereafter |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Long-term debt (a) | $ | 3,224,440 |
| | $ | 250,000 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 425,000 |
| | $ | 2,549,440 |
| $ | 3,226,940 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 125,000 |
| | $ | 600,000 |
| | $ | 2,501,940 |
|
| Long-term debt of VIEs (a) | 221,682 |
| | 27,479 |
| | 56,242 |
| | 55,380 |
| | 82,581 |
| 194,204 |
| | 27,933 |
| | 55,151 |
| | 60,023 |
| | 51,097 |
|
| Interest on long-term debt (b) | 2,698,143 |
| | 173,875 |
| | 317,749 |
| | 308,093 |
| | 1,898,426 |
| 2,898,604 |
| | 167,699 |
| | 332,178 |
| | 286,597 |
| | 2,112,130 |
|
| Interest on long-term debt of VIEs | 50,209 |
| | 12,183 |
| | 19,128 |
| | 12,594 |
| | 6,304 |
| 38,025 |
| | 10,430 |
| | 15,776 |
| | 9,312 |
| | 2,507 |
|
| Long-term debt, including interest | 6,194,474 |
| | 463,537 |
| | 393,119 |
| | 801,067 |
| | 4,536,751 |
| 6,357,773 |
| | 206,062 |
| | 528,105 |
| | 955,932 |
| | 4,667,674 |
|
| Pension and post-retirement benefit expected contributions (c) | 39,700 |
| | 39,700 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| 47,300 |
| | 47,300 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Capital leases (d) | 99,044 |
| | 6,464 |
| | 11,070 |
| | 9,375 |
| | 72,135 |
| 86,664 |
| | 6,379 |
| | 11,001 |
| | 9,624 |
| | 59,660 |
|
| Operating leases (e) | 65,588 |
| | 14,384 |
| | 22,212 |
| | 13,631 |
| | 15,361 |
| 53,583 |
| | 12,396 |
| | 18,994 |
| | 13,078 |
| | 9,115 |
|
| Other obligations of VIEs (f) | 14,980 |
| | 1,038 |
| | 3,626 |
| | 10,316 |
| | — |
| 13,942 |
| | 1,076 |
| | 8,310 |
| | 4,556 |
| | — |
|
| Fossil fuel (g) | 1,287,180 |
| | 199,289 |
| | 350,411 |
| | 347,846 |
| | 389,634 |
| 1,189,900 |
| | 203,033 |
| | 409,771 |
| | 354,417 |
| | 222,679 |
|
| Nuclear fuel (h) | 282,569 |
| | 42,196 |
| | 39,303 |
| | 44,806 |
| 39,443 |
| 156,264 |
| 157,931 |
| | 13,621 |
| | 54,099 |
| | 19,375 |
| | 70,836 |
|
| Transmission service (i) | 33,791 |
| | 7,267 |
| | 12,133 |
| | 5,399 |
| | 8,992 |
| 33,949 |
| | 9,491 |
| | 9,590 |
| | 6,861 |
| | 8,007 |
|
| Unconditional purchase obligations | 312,171 |
| | 258,293 |
| | 46,415 |
| | 7,463 |
| | — |
| 482,880 |
| | 406,859 |
| | 48,774 |
| | 27,247 |
| | — |
|
| Total contractual obligations (j) | $ | 8,329,497 |
| | $ | 1,032,168 |
| | $ | 878,289 |
| | $ | 1,239,903 |
| | $ | 5,179,137 |
| $ | 8,423,922 |
| | $ | 906,217 |
| | $ | 1,088,644 |
| | $ | 1,391,090 |
| | $ | 5,037,971 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | See Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Long-Term Debt," for individual maturities. |
| |
| (b) | We calculate interest on our variable rate debt based on the effective interest rates as of December 31, 20132014. |
| |
| (c) | Our contribution amounts for future periods are not yet known. See Notes 11 and 12 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Employee Benefit Plans" and "Wolf Creek Employee Benefit Plans," for additional information regarding pension and post-retirement benefits. |
| |
| (d) | Includes principal and interest on capital leases. |
| |
| (e) | Includes leases for operating facilities, operating equipment, office space, office equipment, vehicles and rail cars as well as other miscellaneous commitments. |
| |
| (f) | See Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, “Variable Interest Entities,” for additional information on VIEs. |
| |
| (g) | Coal and natural gas commodity and transportation contracts. |
| |
| (h) | Uranium concentrates, conversion, enrichment fabrication and spent nuclear fuel disposal.fabrication. |
| |
| (i) | Includes obligations to SPP for transmission service payments. See Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Commitments and Contingencies," for additional information. |
| |
| (j) | We have $1.9$1.5 million of unrecognized income tax benefits, including interest, that are not included in this table because we cannot reasonably estimate the timing of the cash payments to taxing authorities assuming those unrecognized income tax benefits are settled at the amounts accrued as of December 31, 20132014. |
Commercial Commitments
Our commercial commitments as of December 31, 20132014, consist of outstanding letters of credit that expire in 2014,2015, some of which automatically renew annually. The letters of credit are comprised of $11.7$9.2 million related to new transmission projects, $3.3$3.9 million related to energy marketing and trading activities, $0.8 million related to workers' compensation and $3.4$2.4 million related to other operating activities, for a total outstanding balance of $19.2$16.3 million.
OTHER INFORMATION
Changes in Prices
KCC Proceedings
We filedplan to file an application with the KCC in February 2014early March 2015 to adjust our prices to include updated transmission costs as reflectedthe additional investment in our transmission formula rate effective in January 2014 discussed below. If approved, we estimate that the new prices will increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $43.6 million.La Cygne environmental upgrades, investment to extend the life of Wolf Creek and programs to improve reliability. We expect the KCC to issue an order on our request in March 2014.by late October 2015.
In December 2013,2014, the KCC approved an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include costs incurred for property taxes. The new prices were effective in January 20142015 and are expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $12.7$4.9 million.
In November 2013,October 2014, the KCC issuedapproved an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades and to reflect cost reductions elsewhere.previously deferred amounts associated with various energy efficiency programs. The new prices arewere effective in November 2014 and we estimate this will decrease our annual retail revenues by a total of approximately $5.0 million.
We, KCC staff and a consumer advocate joined in a request filed with the KCC to defer depreciation expense and carrying costs related to our capital investment associated with environmental upgrades at La Cygne until new retail prices become effective following a general rate case expected to be filed in March 2015. We estimate our share of these deferred costs will be approximately $20.0 million and we expect to begin deferring these costs in March 2015. In September 2014, the KCC issued an order approving the joint application that will allow us to include these deferred costs in our next general rate case, which is expected to increase our annual revenues by approximately $4.0 million.
In June 2014, the KCC issued an order to adjust our prices to include updated transmission costs as reflected in the TFR discussed below. The new prices were effective in April 2014 and we estimate this will increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $30.7$41.0 million.
In May 2013,2014, the KCC issued an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include costs associated with 2012 investments into comply with environmental projects. The newrequirements during 2013. New prices were effective in June 20132014 and are expected towe estimate this will increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $27.3 million.
In March 2013, we adjusted our prices to included updated transmission costs as reflected in the transmission formula rate discussed below. The KCC issued an order in July 2013 approving our adjustment which is expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $11.8$11.0 million.
FERC Proceedings
In October 2013,August 2014, the KCC filed a challenge with the FERC regarding rate making as it pertains to the cost of interstate electrical transmission service we postedoperate. The KCC is requesting that we lower our updated transmission formula ratereturn on equity by nearly two percentage points, which would result in reductions of the TFR revenue requirement if granted. If we are unable to reach a settlement, the FERC will schedule a hearing.
Our TFR that includes projected 2014 transmission capital expenditures and operating costs. The updated rate wascosts became effective in January 2014 and iswere expected to increase our annual transmission revenues by approximately $44.3 million.
Our transmission formula rate that includes projected 2013 transmission capital expenditures and operating costs was effective in January 2013 and is expected to increase our annual transmission revenues by approximately $12.2 million. This updated rate provided the basis for our request withto the KCC to adjust our retail prices to include updated transmission costs as discussed above.
Our TFR that includes projected 2015 transmission capital expenditures and operating costs became effective in January 2015 and is expected to decrease our annual transmission revenues by approximately $4.6 million.
Wolf Creek Outage
Wolf Creek normally operates on an 18-month planned refueling and maintenance outage schedule. However, as a result of an unscheduled maintenance outage at Wolf Creek in 2012 coupled with the longer than planned refueling and maintenance outage in 2011, we were able to defer the fall 2012 plannedWolf Creek has since operated on a longer refueling and maintenance outage toschedule. After the first quarter of 2013. The next planned refueling and maintenance outage, will beoccurring in the first quarter of 2015. During2015, Wolf Creek will revert back to the normal 18-month refueling and maintenance outage schedule. In order to revert to the normal schedule, Wolf Creek underwent a planned maintenance outage in the first quarter of 2014, Wolf Creek will undergo a planned maintenance outage.2014. The outage iswas not part of a refueling outage and therefore will bewas expensed as incurred. We expect ourOur share of the 2014 outage costs to bewas approximately $9.0$8.7 million.
New Financial Regulation
In 2010, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (Dodd-Frank Act) was signed into law. Although the Dodd-Frank Act is focused primarily on the regulation and oversight of financial institutions, it also calls for new regulation of the derivatives markets, including mandatory clearing of certain swaps, exchange trading, margin requirements and other transparency requirements, which could impact our operations and consolidated financial results. We do not expect compliance with related regulations to have a significant impact on our business.
Stock-Based Compensation
We use two types of restricted share units (RSUs) for our stock-based compensation awards; those with service requirements and those with performance measures. See Note 11 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Employee Benefit Plans," for additional information. Total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with only service requirements was $4.4 million as of December 31, 20132014, and we expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.71.9 years. Total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with performance measures was $4.03.8 million as of December 31, 20132014, and we expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.7 years.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Our fuel procurement and energy marketing activities involve primary market risk exposures, including commodity price risk, credit risk and interest rate risk. Commodity price risk is the potential adverse price impact related to the purchase or sale of electricity and energy-related products. Credit risk is the potential adverse financial impact resulting from non-performance by a counterparty of its contractual obligations. Interest rate risk is the potential adverse financial impact related to changes in interest rates. In addition, our investments in trusts to fund nuclear plant decommissioning and to fund non-qualified retirement benefits give rise to security price risk. Many of the securities in these trusts are exposed to price fluctuations in the capital markets.
Commodity Price Risk
We engage in both financial and physical trading with the goal of managing our commodity price risk, enhancing system reliability and increasing profits. We procure and trade electricity, coal, natural gas and other energy-related products by utilizing energy commodity contracts and a variety of financial instruments, including futures contracts, options and swaps.
We use various types of fuel, including coal, natural gas, uranium and diesel to operate our plants and also purchase power to meet customer demand. Our prices and consolidated financial results are exposed to market risks from commodity price changes for electricity and other energy-related products as well as from interest rates. Volatility in these markets impacts our costs of purchased power, costs of fuel for our generating plants and our participation in energy markets. We strive to manage our customers' and our exposure to these market risks through regulatory, operating and financing activities and, when we deem appropriate, we economically hedge a portion of these risks through the use of derivative financial instruments for non-trading purposes.
Factors that affect our commodity price exposure are the quantity and availability of fuel used for generation, the availability of our power plants and the quantity of electricity customers consume. Quantities of fossil fuel we use to generate electricity fluctuate from period to period based on availability, price and deliverability of a given fuel type, as well as planned and unscheduled outages at our generating plants that use fossil fuels. Our commodity price exposure is also affected by our nuclear plant refueling and maintenance schedule. Our customers' electricity usage also varies based on weather, the economy and other factors.
We trade various types of fuel primarily to reduce exposure related to the volatility of commodity prices. A significant portion of our coal requirements is purchased under long-term contracts to hedge much of the fuel exposure for customers. If we were unable to generate an adequate supply of electricity for our customers, we would purchase power in the wholesale market to the extent it is available, subject to possible transmission constraints, and/or implement curtailment or interruption procedures as permitted in our tariffs and terms and conditions of service.
One way by which we manage and measure the commodity price risk of our trading portfolio is by using a variance/covariance value-at-risk (VaR) model. In addition to VaR, we employ additional risk control processes such as stress testing, daily loss limits, credit limits and position limits. We expect to use similar control processes in the future. The use of VaR requires assumptions, including the selection of a confidence level and a measure of volatility associated with potential losses and the estimated holding period. We express VaR as a potential dollar loss based on a 95% confidence level using a one-day holding period and a 20-day historical observation period. It is possible that actual results may differ significantly from assumptions. Accordingly, VaR may not accurately reflect our levels of exposure. The energy trading and market-based wholesale portfolio VaR amounts for 20132014 and 20122013 were as follows:
| | | | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| High | $ | 205 |
| | $ | 309 |
| $ | 614 |
| | $ | 205 |
|
| Low | 9 |
| | 10 |
| 14 |
| | 9 |
|
| Average | 83 |
| | 84 |
| 76 |
| | 83 |
|
Interest Rate Risk
We have entered into numerous fixed and variable rate debt obligations. For details, see Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Long-Term Debt." We manage our interest rate risk related to these debt obligations by limiting our exposure to variable interest rate debt, diversifying maturity dates and entering into treasury yield hedge transactions. We may also use other financial derivative instruments such as interest rate swaps. We compute and present information about the sensitivity to changes in interest rates for variable rate debt and current maturities of fixed rate debt by assuming a 100 basis point change in the current interest rates applicable to such debt over the remaining time the debt is outstanding.
We had approximately $534.0$407.5 million of variable rate debt and current maturities of fixed rate debt as of December 31, 20132014. A 100 basis point change in interest rates applicable to this debt would impact income before income taxes on an annualized basis by approximately $2.8$4.0 million. As of December 31, 20132014, we had $121.9 million of variable rate bonds insured by bond insurers. Interest rates payable under these bonds are normally set through periodic auctions. However, conditions in the credit markets over the past few years caused a dramatic reduction in the demand for auction bonds, which led to failed auctions. The contractual provisions of these securities set forth an indexing formula method by which interest will be paid in the event of an auction failure. Depending on the level of these reference indices, our interest costs may be higher or lower than what they would have been had the securities been auctioned successfully. Additionally, should insurers of those bonds experience a decrease in their credit ratings, such event could increase our borrowing costs. Furthermore, a decline in interest rates generally can serve to increase our pension and post-retirement benefit obligations.
Security Price Risk
We maintain the NDT, as required by the NRC and Kansas statute, to fund certain costs of nuclear plant decommissioning. As of December 31, 20132014, investments in the NDT were allocated 50% to equity securities, 26% to debt securities, 10% to combination debt/equityequity/other securities, 9% to alternative investments, 5% to real estate securities and less than 1% to cash equivalents. As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, the fair value of the NDT investments was $175.6185.0 million and $150.8175.6 million, respectively. Changes in interest rates and/or other market changes resulting in a 10% decrease in the value of the securities would have resulted in a $17.6an $18.5 million decrease in the value of the NDT as of December 31, 20132014.
We also maintain a trust to fund non-qualified retirement benefits. As of December 31, 20132014, investments in the trust were comprised of 65% equity securities, 35% debt securities and less than 1% cash equivalents. The fair value of the investments in this trust was $35.5 million as of December 31, 2014, and $34.9 million as of December 31, 2013, and $43.5 million as of December 31, 2012. Changes in interest rates and/or other market changes resulting in a 10% decrease in the value of the securities would have resulted in a $3.5 million decrease in the value of the trust as of December 31, 20132014.
By maintaining diversified portfolios of securities, we seek to maximizeoptimize the returns to fund the aforementioned obligations within acceptable risk tolerances, including interest rate risk. However, many of the securities in the portfolios are exposed to price fluctuations in the capital markets. If the value of the securities diminishes, the cost of funding the obligations rises. We actively monitor the portfolios by benchmarking the performance of the investments against relevant indices and by maintaining and periodically reviewing the asset allocations in relation to established policy targets. Our exposure to security price risk related to the NDT is in part mitigated because we are currently allowed to recover decommissioning costs in the prices we charge our customers.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
|
| |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS | PAGE |
| |
| |
| Financial Statements: | |
| Westar Energy, Inc. and Subsidiaries: | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Financial Schedules: | |
| |
SCHEDULES OMITTED
The following schedules are omitted because of the absence of the conditions under which they are required or the information is included in our consolidated financial statements and schedules presented:
I, III, IV and V.
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
We are responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the company’s board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and includes those policies and procedures that:
Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company;
Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and
Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
We assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 20132014. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control-Integrated Framework.Commission. Based on the assessment, we concluded that, as of December 31, 20132014, our internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria. Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an audit report on the company’s internal control over financial reporting.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Westar Energy, Inc.
Topeka, Kansas
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2013,2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (1992) (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying management’s report on internal control over financial reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company's principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company's board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013,2014, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (1992)(2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule of the Company as of and for the year ended December 31, 20132014 of the Company and our report dated February 26, 201425, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and financial statement schedule.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Kansas City, Missouri
February 26, 201425, 2015
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Westar Energy, Inc.
Topeka, Kansas
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 20132014 and 2012,2013, and the related consolidated statements of income, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2013.2014. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 20132014 and 2012,2013, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2013,2014, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013,2014, based on the criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (1992)(2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and ourour report dated February 26, 201425, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Kansas City, Missouri
February 26, 201425, 2015
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Par Values)
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| ASSETS | | | | | | |
| CURRENT ASSETS: | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 4,487 |
| | $ | 5,829 |
| $ | 4,556 |
| | $ | 4,487 |
|
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $4,596 and $4,916, respectively | 250,036 |
| | 224,439 |
| |
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $5,309 and $4,596, respectively | | 267,327 |
| | 250,036 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | 239,511 |
| | 249,016 |
| 247,406 |
| | 239,511 |
|
| Deferred tax assets | 37,927 |
| | — |
| 29,636 |
| | 37,954 |
|
| Prepaid expenses | 15,821 |
| | 15,847 |
| 15,793 |
| | 15,821 |
|
| Regulatory assets | 135,408 |
| | 114,895 |
| 105,549 |
| | 135,408 |
|
| Other | 23,608 |
| | 33,049 |
| 30,655 |
| | 23,608 |
|
| Total Current Assets | 706,798 |
| | 643,075 |
| 700,922 |
| | 706,825 |
|
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET | 7,551,916 |
| | 7,013,765 |
| 8,162,908 |
| | 7,551,916 |
|
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT OF VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES, NET | 296,626 |
| | 321,975 |
| 278,573 |
| | 296,626 |
|
| OTHER ASSETS: | | | | | | |
| Regulatory assets | 620,006 |
| | 887,777 |
| 754,229 |
| | 620,006 |
|
| Nuclear decommissioning trust | 175,625 |
| | 150,754 |
| 185,016 |
| | 175,625 |
|
| Other | 246,140 |
| | 247,885 |
| 265,353 |
| | 246,140 |
|
| Total Other Assets | 1,041,771 |
| | 1,286,416 |
| 1,204,598 |
| | 1,041,771 |
|
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 9,597,111 |
| | $ | 9,265,231 |
| $ | 10,347,001 |
| | $ | 9,597,138 |
|
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | |
| CURRENT LIABILITIES: | | | | | | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 250,000 |
| | $ | — |
| $ | — |
| | $ | 250,000 |
|
| Current maturities of long-term debt of variable interest entities | 27,479 |
| | 25,942 |
| 27,933 |
| | 27,479 |
|
| Short-term debt | 134,600 |
| | 339,200 |
| 257,600 |
| | 134,600 |
|
| Accounts payable | 233,351 |
| | 180,825 |
| 219,351 |
| | 233,351 |
|
| Accrued dividends | 43,604 |
| | 41,743 |
| 44,971 |
| | 43,604 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 69,742 |
| | 58,624 |
| 74,356 |
| | 69,769 |
|
| Accrued interest | 80,457 |
| | 77,891 |
| 79,707 |
| | 80,457 |
|
| Regulatory liabilities | 35,982 |
| | 37,557 |
| 55,142 |
| | 35,982 |
|
| Other | 80,184 |
| | 84,359 |
| 90,571 |
| | 80,184 |
|
| Total Current Liabilities | 955,399 |
| | 846,141 |
| 849,631 |
| | 955,426 |
|
| LONG-TERM LIABILITIES: | | | | | | |
| Long-term debt, net | 2,968,958 |
| | 2,819,271 |
| 3,215,539 |
| | 2,968,958 |
|
| Long-term debt of variable interest entities, net | 194,802 |
| | 222,743 |
| 166,565 |
| | 194,802 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | 1,361,418 |
| | 1,197,837 |
| 1,475,487 |
| | 1,363,148 |
|
| Unamortized investment tax credits | 192,265 |
| | 191,512 |
| 211,040 |
| | 192,265 |
|
| Regulatory liabilities | 293,574 |
| | 285,618 |
| 288,343 |
| | 293,574 |
|
| Accrued employee benefits | 331,558 |
| | 564,870 |
| 532,622 |
| | 331,558 |
|
| Asset retirement obligations | 160,682 |
| | 152,648 |
| 230,668 |
| | 160,682 |
|
| Other | 69,924 |
| | 74,336 |
| 75,799 |
| | 68,194 |
|
| Total Long-Term Liabilities | 5,573,181 |
| | 5,508,835 |
| 6,196,063 |
| | 5,573,181 |
|
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (See Notes 13 and 15) |
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| EQUITY: | | | | | | |
| Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity: | | | | | | |
| Common stock, par value $5 per share; authorized 275,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding 128,254,229 shares and 126,503,748 shares, respective to each date | 641,271 |
| | 632,519 |
| |
| Common stock, par value $5 per share; authorized 275,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding 131,687,454 shares and 128,254,229 shares, respective to each date | | 658,437 |
| | 641,271 |
|
| Paid-in capital | 1,696,727 |
| | 1,656,972 |
| 1,781,120 |
| | 1,696,727 |
|
| Retained earnings | 724,776 |
| | 606,649 |
| 855,299 |
| | 724,776 |
|
| Total Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity | 3,062,774 |
| | 2,896,140 |
| 3,294,856 |
| | 3,062,774 |
|
| Noncontrolling Interests | 5,757 |
| | 14,115 |
| 6,451 |
| | 5,757 |
|
| Total Equity | 3,068,531 |
| | 2,910,255 |
| 3,301,307 |
| | 3,068,531 |
|
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | $ | 9,597,111 |
| | $ | 9,265,231 |
| $ | 10,347,001 |
| | $ | 9,597,138 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| REVENUES | $ | 2,601,703 |
| | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
|
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | |
| Fuel and purchased power | 705,450 |
| | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
|
| SPP network transmission costs | 218,924 |
| | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
|
| Operating and maintenance | 367,188 |
| | 359,060 |
| | 342,055 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 250,439 |
| | 224,133 |
| | 226,012 |
|
| Taxes other than income tax | 140,302 |
| | 122,282 |
| | 104,269 |
|
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,968,745 |
| | 1,791,469 |
| | 1,699,337 |
|
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 632,958 |
| | 579,185 |
| | 562,133 |
|
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | |
| Investment earnings | 10,622 |
| | 10,056 |
| | 7,411 |
|
| Other income | 31,522 |
| | 35,609 |
| | 35,378 |
|
| Other expense | (18,389 | ) | | (18,099 | ) | | (19,987 | ) |
| Total Other Income (Expense) | 23,755 |
| | 27,566 |
| | 22,802 |
|
| Interest expense | 183,118 |
| | 182,167 |
| | 176,337 |
|
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 473,595 |
| | 424,584 |
| | 408,598 |
|
| Income tax expense | 151,270 |
| | 123,721 |
| | 126,136 |
|
| NET INCOME | 322,325 |
| | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 9,066 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY, INC. | 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
|
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 1,616 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO COMMON STOCK | $ | 313,259 |
|
| $ | 292,520 |
| | $ | 273,530 |
|
| BASIC AND DILUTED EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY (see Note 2): | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 2.35 |
| | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| AVERAGE EQUIVALENT COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING | 130,014,941 |
| | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
|
| DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 1.40 |
| | $ | 1.36 |
| | $ | 1.32 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 322,325 |
| | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
|
| Amortization of nuclear fuel | 26,051 |
| | 22,690 |
| | 24,369 |
|
| Amortization of deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) |
| Amortization of corporate-owned life insurance | 20,202 |
| | 15,149 |
| | 28,792 |
|
| Non-cash compensation | 7,280 |
| | 8,188 |
| | 7,255 |
|
| Net deferred income taxes and credits | 151,451 |
| | 123,307 |
| | 126,248 |
|
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | (875 | ) | | (576 | ) | | (1,698 | ) |
| Allowance for equity funds used during construction | (17,029 | ) | | (14,143 | ) | | (11,706 | ) |
| Changes in working capital items: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (17,291 | ) | | (24,649 | ) | | 2,408 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | (8,773 | ) | | 10,124 |
| | (19,227 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses and other | 36,717 |
| | (12,316 | ) | | (3,630 | ) |
| Accounts payable | 6,189 |
| | 7,856 |
| | (19,161 | ) |
| Accrued taxes | 6,596 |
| | 14,218 |
| | 11,937 |
|
| Other current liabilities | (31,624 | ) | | (52,829 | ) | | (105,169 | ) |
| Changes in other assets | 6,378 |
| | (4,167 | ) | | 13,015 |
|
| Changes in other liabilities | 35,811 |
| | 41,990 |
| | (1,758 | ) |
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities | 824,355 |
| | 702,803 |
| | 599,106 |
|
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Additions to property, plant and equipment | (852,052 | ) | | (780,098 | ) | | (810,209 | ) |
| Purchase of securities - trusts | (9,075 | ) | | (66,668 | ) | | (20,473 | ) |
| Sale of securities - trusts | 11,125 |
| | 81,994 |
| | 21,604 |
|
| Investment in corporate-owned life insurance | (16,250 | ) | | (17,724 | ) | | (18,404 | ) |
| Proceeds from investment in corporate-owned life insurance | 43,234 |
| | 147,658 |
| | 33,542 |
|
| Proceeds from federal grant | — |
| | 876 |
| | 4,775 |
|
| Investment in affiliated company | (8,000 | ) | | (4,947 | ) | | (8,669 | ) |
| Other investing activities | (7,730 | ) | | (2,992 | ) | | 497 |
|
| Cash Flows used in Investing Activities | (838,748 | ) | | (641,901 | ) | | (797,337 | ) |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Short-term debt, net | 122,406 |
| | (205,241 | ) | | 52,900 |
|
| Proceeds from long-term debt | 417,943 |
| | 492,347 |
| | 541,374 |
|
| Retirements of long-term debt | (427,500 | ) | | (100,000 | ) | | (220,563 | ) |
| Retirements of long-term debt of variable interest entities | (27,479 | ) | | (25,942 | ) | | (28,114 | ) |
| Repayment of capital leases | (3,340 | ) | | (2,995 | ) | | (2,679 | ) |
| Borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | 59,766 |
| | 59,565 |
| | 67,791 |
|
| Repayment of borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | (41,249 | ) | | (145,418 | ) | | (34,838 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | 875 |
| | 576 |
| | 1,698 |
|
| Preferred stock redemption | — |
| | — |
| | (22,567 | ) |
| Issuance of common stock | 87,669 |
| | 32,906 |
| | 6,996 |
|
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | (1,030 | ) | | (2,419 | ) | | (3,295 | ) |
| Cash dividends paid | (171,507 | ) | | (162,904 | ) | | (158,182 | ) |
| Other financing activities | (2,092 | ) | | (2,719 | ) | | — |
|
| Cash Flows from (used in) Financing Activities | 14,462 |
| | (62,244 | ) | | 200,521 |
|
| NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | 69 |
| | (1,342 | ) | | 2,290 |
|
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS: | | | | | |
| Beginning of period | 4,487 |
| | 5,829 |
| | 3,539 |
|
| End of period | $ | 4,556 |
| | $ | 4,487 |
| | $ | 5,829 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| REVENUES | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
| | $ | 2,170,991 |
|
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | |
| Fuel and purchased power | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
| | 630,793 |
|
| SPP network transmission costs | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
| | 132,164 |
|
| Operating and maintenance | 359,060 |
| | 342,055 |
| | 332,989 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
| | 285,322 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 224,133 |
| | 226,012 |
| | 184,695 |
|
| Taxes other than income tax | 122,282 |
| | 104,269 |
| | 92,599 |
|
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,791,469 |
| | 1,699,337 |
| | 1,658,562 |
|
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 579,185 |
| | 562,133 |
| | 512,429 |
|
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | |
| Investment earnings | 10,056 |
| | 7,411 |
| | 9,301 |
|
| Other income | 35,609 |
| | 35,378 |
| | 8,652 |
|
| Other expense | (18,099 | ) | | (19,987 | ) | | (18,398 | ) |
| Total Other Income (Expense) | 27,566 |
| | 22,802 |
| | (445 | ) |
| Interest expense | 182,167 |
| | 176,337 |
| | 172,460 |
|
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 424,584 |
| | 408,598 |
| | 339,524 |
|
| Income tax expense | 123,721 |
| | 126,136 |
| | 103,344 |
|
| NET INCOME | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
| | 236,180 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 5,941 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY, INC. | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
| | 230,239 |
|
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | 1,616 |
| | 970 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO COMMON STOCK | $ | 292,520 |
|
| $ | 273,530 |
| | $ | 229,269 |
|
| BASIC AND DILUTED EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY (see Note 2): | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.95 |
|
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.93 |
|
| AVERAGE EQUIVALENT COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
| | 116,890,552 |
|
| DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 1.36 |
| | $ | 1.32 |
| | $ | 1.28 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
| | $ | 236,180 |
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
| | 285,322 |
|
| Amortization of nuclear fuel | 22,690 |
| | 24,369 |
| | 21,151 |
|
| Amortization of deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) |
| Amortization of corporate-owned life insurance | 15,149 |
| | 28,792 |
| | 25,650 |
|
| Non-cash compensation | 8,188 |
| | 7,255 |
| | 8,422 |
|
| Net deferred income taxes and credits | 123,307 |
| | 126,248 |
| | 111,723 |
|
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | (576 | ) | | (1,698 | ) | | (1,180 | ) |
| Allowance for equity funds used during construction | (14,143 | ) | | (11,706 | ) | | (5,550 | ) |
| Gain on sale of non-utility investment | — |
| | — |
| | (7,246 | ) |
| Gain on settlement of contractual obligations with former officers | — |
| | — |
| | (22,039 | ) |
| Changes in working capital items: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (24,649 | ) | | 2,408 |
| | (1,638 | ) |
| Fuel inventory and supplies | 10,124 |
| | (19,227 | ) | | (21,485 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses and other | (12,316 | ) | | (3,630 | ) | | (50,138 | ) |
| Accounts payable | 7,856 |
| | (19,161 | ) | | 3,008 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 14,218 |
| | 11,937 |
| | 18,633 |
|
| Other current liabilities | (52,829 | ) | | (105,169 | ) | | (107,012 | ) |
| Changes in other assets | (4,167 | ) | | 13,015 |
| | (10,167 | ) |
| Changes in other liabilities | 41,990 |
| | (1,758 | ) | | (15,443 | ) |
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities | 702,803 |
| | 599,106 |
| | 462,696 |
|
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Additions to property, plant and equipment | (780,098 | ) | | (810,209 | ) | | (697,451 | ) |
| Purchase of securities - trusts | (66,668 | ) | | (20,473 | ) | | (49,737 | ) |
| Sale of securities - trusts | 81,994 |
| | 21,604 |
| | 47,534 |
|
| Investment in corporate-owned life insurance | (17,724 | ) | | (18,404 | ) | | (19,214 | ) |
| Proceeds from investment in corporate-owned life insurance | 147,658 |
| | 33,542 |
| | 1,295 |
|
| Proceeds from federal grant | 876 |
| | 4,775 |
| | 8,561 |
|
| Investment in affiliated company | (4,947 | ) | | (8,669 | ) | | (1,943 | ) |
| Proceeds from sale of non-utility investments | — |
| | — |
| | 9,246 |
|
| Other investing activities | (2,992 | ) | | 497 |
| | 193 |
|
| Cash Flows used in Investing Activities | (641,901 | ) | | (797,337 | ) | | (701,516 | ) |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Short-term debt, net | (205,241 | ) | | 52,900 |
| | 54,081 |
|
| Proceeds from long-term debt | 492,347 |
| | 541,374 |
| | — |
|
| Retirements of long-term debt | (100,000 | ) | | (220,563 | ) | | (371 | ) |
| Retirements of long-term debt of variable interest entities | (25,942 | ) | | (28,114 | ) | | (30,159 | ) |
| Repayment of capital leases | (2,995 | ) | | (2,679 | ) | | (2,233 | ) |
| Borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | 59,565 |
| | 67,791 |
| | 67,562 |
|
| Repayment of borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | (145,418 | ) | | (34,838 | ) | | (3,421 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | 576 |
| | 1,698 |
| | 1,180 |
|
| Preferred stock redemption | — |
| | (22,567 | ) | | — |
|
| Issuance of common stock | 32,906 |
| | 6,996 |
| | 294,942 |
|
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | (2,419 | ) | | (3,295 | ) | | (1,917 | ) |
| Cash dividends paid | (162,904 | ) | | (158,182 | ) | | (138,233 | ) |
| Other financing activities | (2,719 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Cash Flows (used in) from Financing Activities | (62,244 | ) | | 200,521 |
| | 241,431 |
|
| NET (DECREASE) INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | (1,342 | ) | | 2,290 |
| | 2,611 |
|
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS: | | | | | |
| Beginning of period | 5,829 |
| | 3,539 |
| | 928 |
|
| End of period | $ | 4,487 |
| | $ | 5,829 |
| | $ | 3,539 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(Dollars in Thousands)
| | | | Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders | | | | | Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders | | | | |
| | Cumulative preferred stock shares | | Cumulative preferred stock | | Common stock shares | | Common stock | | Paid-in capital | | Retained earnings | | Non-controlling interests | | Total equity | Cumulative preferred stock shares | | Cumulative preferred stock | | Common stock shares | | Common stock | | Paid-in capital | | Retained earnings | | Non-controlling interests | | Total equity |
| Balance as of December 31, 2010 | 214,363 |
| | $ | 21,436 |
| | 112,128,068 |
| | $ | 560,640 |
| | $ | 1,398,580 |
| | $ | 423,647 |
| | $ | 6,070 |
| | $ | 2,410,373 |
| |
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 230,239 |
| | 5,941 |
| | 236,180 |
| |
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 12,951,207 |
| | 64,756 |
| | 230,186 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 294,942 |
| |
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 619,121 |
| | 3,096 |
| | 4,331 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,427 |
| |
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,141 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (3,141 | ) | |
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (970 | ) | | — |
| | (970 | ) | |
Dividends on common stock
($1.28 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (151,700 | ) | | — |
| | (151,700 | ) | |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,367 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,367 |
| |
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,180 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,180 |
| |
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,917 | ) | | (1,917 | ) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | 214,363 |
| | 21,436 |
| | 125,698,396 |
| | 628,492 |
| | 1,639,503 |
| | 501,216 |
| | 10,094 |
| | 2,800,741 |
| 214,363 |
| | $ | 21,436 |
| | 125,698,396 |
| | $ | 628,492 |
| | $ | 1,639,503 |
| | $ | 501,216 |
| | $ | 10,094 |
| | $ | 2,800,741 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 275,146 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 282,462 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 275,146 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 282,462 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 242,463 |
| | 1,212 |
| | 5,784 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 6,996 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 242,463 |
| | 1,212 |
| | 5,784 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 6,996 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 562,889 |
| | 2,815 |
| | 6,274 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,089 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 562,889 |
| | 2,815 |
| | 6,274 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,089 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) |
| Stock Redemption | (214,363 | ) | | (21,436 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (21,436 | ) | |
| Stock redemption | | (214,363 | ) | | (21,436 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (21,436 | ) |
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,616 | ) | | — |
| | (1,616 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,616 | ) | | — |
| | (1,616 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.32 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (168,097 | ) | | — |
| | (168,097 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (168,097 | ) | | — |
| | (168,097 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
|
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,295 | ) | | (3,295 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,295 | ) | | (3,295 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | — |
| | — |
| | 126,503,748 |
| | 632,519 |
| | 1,656,972 |
| | 606,649 |
| | 14,115 |
| | 2,910,255 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 126,503,748 |
| | 632,519 |
| | 1,656,972 |
| | 606,649 |
| | 14,115 |
| | 2,910,255 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 292,520 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 300,863 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 292,520 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 300,863 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 1,256,391 |
| | 6,282 |
| | 26,624 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 32,906 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 1,256,391 |
| | 6,282 |
| | 26,624 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 32,906 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 494,090 |
| | 2,470 |
| | 7,171 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,641 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 494,090 |
| | 2,470 |
| | 7,171 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,641 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.36 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (174,393 | ) | | — |
| | (174,393 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (174,393 | ) | | — |
| | (174,393 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
|
| Deconsolidation of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (14,282 | ) | | (14,282 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| �� | — |
| | — |
| | (14,282 | ) | | (14,282 | ) |
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,419 | ) | | (2,419 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,419 | ) | | (2,419 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | — |
| | $ | — |
| | 128,254,229 |
| | $ | 641,271 |
| | $ | 1,696,727 |
| | $ | 724,776 |
| | $ | 5,757 |
| | $ | 3,068,531 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 128,254,229 |
| | 641,271 |
| | 1,696,727 |
| | 724,776 |
| | 5,757 |
| | 3,068,531 |
|
| Net income | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 313,259 |
| | 9,066 |
| | 322,325 |
|
| Issuance of stock | | — |
| | — |
| | 3,026,239 |
| | 15,131 |
| | 72,538 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 87,669 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | | — |
| | — |
| | 406,986 |
| | 2,035 |
| | 7,120 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,155 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,092 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,092 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.40 per share) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (182,736 | ) | | — |
| | (182,736 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,193 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,193 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 875 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 875 |
|
| Deconsolidation of noncontrolling interests | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (7,342 | ) | | (7,342 | ) |
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,030 | ) | | (1,030 | ) |
| Other | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,241 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (1,241 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | | — |
| | $ | — |
| | 131,687,454 |
| | $ | 658,437 |
| | $ | 1,781,120 |
| | $ | 855,299 |
| | $ | 6,451 |
| | $ | 3,301,307 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
We are the largest electric utility in Kansas. Unless the context otherwise indicates, all references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to "the company," "we," "us," "our" and similar words are to Westar Energy, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. The term "Westar Energy" refers to Westar Energy, Inc., a Kansas corporation incorporated in 1924,, alone and not together with its consolidated subsidiaries.
We provide electric generation, transmission and distribution services to approximately 693,000698,000 customers in Kansas. Westar Energy provides these services in central and northeastern Kansas, including the cities of Topeka, Lawrence, Manhattan, Salina and Hutchinson. Kansas Gas and Electric Company (KGE), Westar Energy's wholly-owned subsidiary, provides these services in south-central and southeastern Kansas, including the city of Wichita. Both Westar Energy and KGE conduct business using the name Westar Energy. Our corporate headquarters is located at 818 South Kansas Avenue, Topeka, Kansas 66612.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAPgenerally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for the United States of America. Our consolidated financial statements include all operating divisions, majority owned subsidiaries and variable interest entities (VIEs) of which we maintain a controlling interest or are the primary beneficiary reported as a single reportable segment. Undivided interests in jointly-owned generation facilities are included on a proportionate basis. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Management's Estimates
When we prepare our consolidated financial statements, we are required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the date of our consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. We evaluate our estimates on an ongoing basis, including those related to depreciation, unbilled revenue, valuation of investments, forecasted fuel costs included in our retail energy cost adjustment (RECA) billed to customers, income taxes, pension and post-retirement benefits, our asset retirement obligations (AROs) including the decommissioning of Wolf Creek Generating Station (Wolf Creek), environmental issues, VIEs, contingencies and litigation. Actual results may differ from those estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Regulatory Accounting
We apply accounting standards that recognize the economic effects of rate regulation. Accordingly, we have recorded regulatory assets and liabilities when required by a regulatory order or based on regulatory precedent. See Note 3, "Rate Matters and Regulation," for additional information regarding our regulatory assets and liabilities.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider investments that are highly liquid and have maturities of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Fuel Inventory and Supplies
We state fuel inventory and supplies at average cost. Following are the balances for fuel inventory and supplies stated separately.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Fuel inventory | $ | 78,368 |
| | $ | 94,664 |
| $ | 70,416 |
| | $ | 78,368 |
|
| Supplies | 161,143 |
| | 154,352 |
| 176,990 |
| | 161,143 |
|
| Total | $ | 239,511 |
| | $ | 249,016 |
| |
| Fuel inventory and supplies | | $ | 247,406 |
| | $ | 239,511 |
|
Property, Plant and Equipment
We record the value of property, plant and equipment, including that of VIEs, at cost. For plant, cost includes contracted services, direct labor and materials, indirect charges for engineering and supervision and an allowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC). AFUDC represents the allowed cost of capital used to finance utility construction activity. We compute AFUDC by applying a composite rate to qualified construction work in progress. We credit other income (for equity funds) and interest expense (for borrowed funds) for the amount of AFUDC capitalized as construction cost on the accompanying consolidated statements of income as follows:
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Borrowed funds | $ | 11,706 |
| | $ | 10,399 |
| | $ | 5,589 |
| $ | 12,044 |
| | $ | 11,706 |
| | $ | 10,399 |
|
| Equity funds | 14,143 |
| | 11,706 |
| | 5,550 |
| 17,029 |
| | 14,143 |
| | 11,706 |
|
| Total | $ | 25,849 |
| | $ | 22,105 |
| | $ | 11,139 |
| $ | 29,073 |
| | $ | 25,849 |
| | $ | 22,105 |
|
| Average AFUDC Rates | 4.8% | | 5.0 | % | | 3.6 | % | 6.7 | % | | 4.8 | % | | 5.0 | % |
We charge maintenance costs and replacements of minor items of property to expense as incurred, except for maintenance costs incurred for our planned refueling and maintenance outages at Wolf Creek. As authorized by regulators, we defer and amortize to expense ratably over the period between planned outages incremental maintenance costs incurred for such outages. When a unit of depreciable property is retired, we charge to accumulated depreciation the original cost less salvage value.
Depreciation
We depreciate utility plant using a straight-line method. The depreciation rates are based on an average annual composite basis using group rates that approximated 2.4% in 2014, 2.5% in 2013, and 2.6% in 2012 and 3.0% in 2011.
Depreciable lives of property, plant and equipment are as follows.
|
| | | | |
| | | Years |
| Fossil fuel generating facilities | | 6 | to | 78 |
| Nuclear fuel generating facility | | 55 | to | 71 |
| Wind generating facilities | | 19 | to | 20 |
| Transmission facilities | | 15 | to | 75 |
| Distribution facilities | | 22 | to | 68 |
| Other | | 5 | to | 30 |
Nuclear Fuel
We record as property, plant and equipment our share of the cost of nuclear fuel used in the process of refinement, conversion, enrichment and fabrication. We reflect this at original cost and amortize such amounts to fuel expense based on the quantity of heat consumed during the generation of electricity as measured in millions of British thermal units (MMBtu). The accumulated amortization of nuclear fuel in the reactor was $72.3 million as of December 31, 2014, and $46.2 million as of December 31, 2013, and $69.2 million as of December 31, 2012. The cost of nuclear fuel charged to fuel and purchased power expense was $27.3 million in 2014, $26.5 million in 2013, and $28.3 million in 2012 and $24.6 million in 2011.
Cash Surrender Value of Life Insurance
We recorded on our consolidated balance sheets in other long-term assets the following amounts related to corporate-owned life insurance (COLI) policies.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Cash surrender value of policies | $ | 1,289,457 |
| | $ | 1,370,788 |
| $ | 1,306,777 |
| | $ | 1,289,457 |
|
| Borrowings against policies | (1,156,341 | ) | | (1,241,343 | ) | (1,173,956 | ) | | (1,156,341 | ) |
| Corporate-owned life insurance, net | $ | 133,116 |
| | $ | 129,445 |
| $ | 132,821 |
| | $ | 133,116 |
|
We record as income increases in cash surrender value and death benefits. We offset against policy income the interest expense that we incur on policy loans. Income from death benefits is highly variable from period to period.
Revenue Recognition
We record revenue at the time we deliver electricity to customers. We determine the amounts delivered to individual customers through systematic monthly readings of customer meters. At the end of each month, we estimate how much electricity we have delivered since the prior meter reading and record the corresponding unbilled revenue.
Our unbilled revenue estimate is affected by factors including fluctuations in energy demand, weather, line losses and changes in the composition of customer classes. We recorded estimated unbilled revenue of $61.0 million as of December 31, 2014, and $60.1 million as of December 31, 2013, and $62.5 million as of December 31, 2012.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
We determine our allowance for doubtful accounts based on the age of our receivables. We charge receivables off when they are deemed uncollectible, which is based on a number of factors including specific facts surrounding an account and management's judgment.
Income Taxes
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, we recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. We recognize the future tax benefits to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not. We amortize deferred investment tax credits over the lives of the related properties as required by tax laws and regulatory practices. We recognize production tax credits in the year that electricity is generated to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not.
We record deferred tax assets to the extent capital losses, operating losses, or tax credits will be carried forward to future periods. However, when we believe based on available evidence that we do not, or will not, have sufficient future capital gains or taxable income in the appropriate taxing jurisdiction to realize the entire benefit during the applicable carryforward period, we record a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset.
The application of income tax law is complex. Laws and regulations in this area are voluminous and often ambiguous. Accordingly, we must make judgments regarding income tax exposure. Interpretations of and guidance surrounding income tax laws and regulations change over time. As a result, changes in our judgments can materially affect amounts we recognize in our consolidated financial statements. See Note 10, "Taxes," for additional detail on our accounting for income taxes.
Sales Tax
We account for the collection and remittance of sales tax on a net basis. As a result, we do not reflect sales tax in our consolidated statements of income.
Earnings Per Share
We have participating securities in the form of unvested restricted share units (RSUs) with nonforfeitable rights to dividend equivalents that receive dividends on an equal basis with dividends declared on common shares. As a result, we apply the two-class method of computing basic and diluted earnings per share (EPS).
Under the two-class method, we reduce net income attributable to common stock by the amount of dividends declared in the current period. We allocate the remaining earnings to common stock and RSUs to the extent that each security may share in earnings as if all of the earnings for the period had been distributed. We determine the total earnings allocated to each security by adding together the amount allocated for dividends and the amount allocated for a participation feature. To compute basic EPS, we divide the earnings allocated to common stock by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted EPS includes the effect of potential issuances of common shares resulting from our forward sale agreements and RSUs with forfeitable rights to dividend equivalents. We compute the dilutive effect of potential issuances of common shares using the treasury stock method.
The following table reconciles our basic and diluted EPS from net income.
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| Net income | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
| | $ | 236,180 |
| $ | 322,325 |
| | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 5,941 |
| 9,066 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
|
| Net income attributable to Westar Energy, Inc. | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
| | 230,239 |
| 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
|
| Less: Preferred dividends | — |
| | 1,616 |
| | 970 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 1,616 |
|
| Net income allocated to RSUs | 810 |
| | 778 |
| | 772 |
| 790 |
| | 810 |
| | 778 |
|
| Net income allocated to common stock | $ | 291,710 |
| | $ | 272,752 |
| | $ | 228,497 |
| $ | 312,469 |
| | $ | 291,710 |
| | $ | 272,752 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average equivalent common shares outstanding – basic | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
| | 116,890,552 |
| 130,014,941 |
| | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
|
| Effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | | | | | | |
| RSUs | 17,195 |
| | 97,757 |
| | 188,025 |
| 181,397 |
| | 17,195 |
| | 97,757 |
|
| Forward sale agreements | 818,505 |
| | 89,160 |
| | 1,211,645 |
| 2,628,187 |
| | 818,505 |
| | 89,160 |
|
| Weighted average equivalent common shares outstanding – diluted (a) | 128,298,694 |
| | 126,898,786 |
| | 118,290,222 |
| 132,824,525 |
| | 128,298,694 |
| | 126,898,786 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Earnings per common share, basic | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.95 |
| $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| Earnings per common share, diluted | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
| | $ | 1.93 |
| $ | 2.35 |
| | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | For the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012, we had no antidilutive shares.securities. |
Supplemental Cash Flow Information
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| CASH PAID FOR (RECEIVED FROM): | | | | | |
| Interest on financing activities, net of amount capitalized | $ | 148,691 |
| | $ | 143,564 |
| | $ | 145,570 |
|
| Interest on financing activities of VIEs | 13,892 |
| | 16,214 |
| | 18,167 |
|
| Income taxes, net of refunds | (11 | ) | | (4,378 | ) | | (17,519 | ) |
| NON-CASH INVESTING TRANSACTIONS: | | | | | |
| Property, plant and equipment additions | 127,544 |
| | 89,354 |
| | 105,435 |
|
| Property, plant and equipment of VIEs | (14,282 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| NON-CASH FINANCING TRANSACTIONS: | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock for reinvested dividends and compensation plans | 9,641 |
| | 9,089 |
| | 7,427 |
|
| Deconsolidation of VIEs | (14,282 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Assets acquired through capital leases | 334 |
| | 10,683 |
| | 43,011 |
|
Investment Earnings - SaleWe plan to file an application with the KCC in early March 2015 to adjust our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades, investment to extend the life of Non-utility InvestmentWolf Creek and programs to improve reliability. We expect the KCC to issue an order on our request by late October 2015.
In December 2014, the KCC approved an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include costs incurred for property taxes. The new prices were effective in January 2015 and are expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $4.9 million.
In October 2014, the KCC approved an order to adjust our prices to include previously deferred amounts associated with various energy efficiency programs. The new prices were effective in November 2014 and we estimate this will decrease our annual retail revenues by a total of approximately $5.0 million.
We, KCC staff and a consumer advocate joined in a request filed with the KCC to defer depreciation expense and carrying costs related to our capital investment associated with environmental upgrades at La Cygne until new retail prices become effective following a general rate case expected to be filed in March 2015. We estimate our share of these deferred costs will be approximately $20.0 million and we expect to begin deferring these costs in March 2015. In September 2014, the KCC issued an order approving the joint application that will allow us to include these deferred costs in our next general rate case, which is expected to increase our annual revenues by approximately $4.0 million.
In June 2014, the KCC issued an order to adjust our prices to include updated transmission costs as reflected in the TFR discussed below. The new prices were effective in April 2014 and we estimate this will increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $41.0 million.
In May 2014, the KCC issued an order to adjust our prices to include costs associated with investments to comply with environmental requirements during 2013. New prices were effective in June 2014 and we estimate this will increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $11.0 million.
FERC Proceedings
In August 2014, the KCC filed a challenge with the FERC regarding rate making as it pertains to the cost of interstate electrical transmission service we operate. The KCC is requesting that we lower our transmission return on equity by nearly two percentage points, which would result in reductions of the TFR revenue requirement if granted. If we are unable to reach a settlement, the FERC will schedule a hearing.
Our TFR that includes projected 2014 transmission capital expenditures and operating costs became effective January 2014 and were expected to increase annual transmission revenues by approximately $44.3 million. This updated rate provided the basis for our request to the KCC to adjust our retail prices to include updated transmission costs discussed above.
Our TFR that includes projected 2015 transmission capital expenditures and operating costs became effective in January 2015 and is expected to decrease our annual transmission revenues by approximately $4.6 million.
Wolf Creek Outage
Wolf Creek normally operates on an 18-month planned refueling and maintenance outage schedule. However, as a result of an unscheduled maintenance outage at Wolf Creek in 2012 coupled with the longer than planned refueling and maintenance outage in 2011, we recordedWolf Creek has since operated on a $7.2 million gain onlonger refueling and maintenance outage schedule. After the salenext planned refueling and maintenance outage, occurring in the first quarter of 2015, Wolf Creek will revert back to the normal 18-month refueling and maintenance outage schedule. In order to revert to the normal schedule, Wolf Creek underwent a planned maintenance outage in the first quarter of 2014. The outage was not part of a non-utility investment.
refueling outage and therefore was expensed as incurred. Our share of the 2014 outage costs was approximately $8.7 million.
3. RATE MATTERS AND REGULATIONStock-Based Compensation
Regulatory AssetsWe use two types of restricted share units (RSUs) for our stock-based compensation awards; those with service requirements and Regulatory Liabilitiesthose with performance measures. See Note 11 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Employee Benefit Plans," for additional information. Total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with only service requirements was $4.4 million as of December 31, 2014, and we expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.9 years. Total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with performance measures was $3.8 million as of December 31, 2014, and we expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.7 years.
Regulatory assets represent incurred
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Our fuel procurement and energy marketing activities involve primary market risk exposures, including commodity price risk, credit risk and interest rate risk. Commodity price risk is the potential adverse price impact related to the purchase or sale of electricity and energy-related products. Credit risk is the potential adverse financial impact resulting from non-performance by a counterparty of its contractual obligations. Interest rate risk is the potential adverse financial impact related to changes in interest rates. In addition, our investments in trusts to fund nuclear plant decommissioning and to fund non-qualified retirement benefits give rise to security price risk. Many of the securities in these trusts are exposed to price fluctuations in the capital markets.
Commodity Price Risk
We engage in both financial and physical trading with the goal of managing our commodity price risk, enhancing system reliability and increasing profits. We procure and trade electricity, coal, natural gas and other energy-related products by utilizing energy commodity contracts and a variety of financial instruments, including futures contracts, options and swaps.
We use various types of fuel, including coal, natural gas, uranium and diesel to operate our plants and also purchase power to meet customer demand. Our prices and consolidated financial results are exposed to market risks from commodity price changes for electricity and other energy-related products as well as from interest rates. Volatility in these markets impacts our costs that have been deferred because they are probable of future recoverypurchased power, costs of fuel for our generating plants and our participation in customer prices. Regulatory liabilities represent probable future reductions in revenue or refundsenergy markets. We strive to customersmanage our customers' and our exposure to these market risks through regulatory, operating and financing activities and, when we deem appropriate, we economically hedge a portion of these risks through the use of derivative financial instruments for non-trading purposes.
Factors that affect our commodity price setting process. Regulatory assetsexposure are the quantity and liabilities reflectedavailability of fuel used for generation, the availability of our power plants and the quantity of electricity customers consume. Quantities of fossil fuel we use to generate electricity fluctuate from period to period based on availability, price and deliverability of a given fuel type, as well as planned and unscheduled outages at our consolidated balance sheets aregenerating plants that use fossil fuels. Our commodity price exposure is also affected by our nuclear plant refueling and maintenance schedule. Our customers' electricity usage also varies based on weather, the economy and other factors.
We trade various types of fuel primarily to reduce exposure related to the volatility of commodity prices. A significant portion of our coal requirements is purchased under long-term contracts to hedge much of the fuel exposure for customers. If we were unable to generate an adequate supply of electricity for our customers, we would purchase power in the wholesale market to the extent it is available, subject to possible transmission constraints, and/or implement curtailment or interruption procedures as follows.permitted in our tariffs and terms and conditions of service.
One way by which we manage and measure the commodity price risk of our trading portfolio is by using a variance/covariance value-at-risk (VaR) model. In addition to VaR, we employ additional risk control processes such as stress testing, daily loss limits, credit limits and position limits. We expect to use similar control processes in the future. The use of VaR requires assumptions, including the selection of a confidence level and a measure of volatility associated with potential losses and the estimated holding period. We express VaR as a potential dollar loss based on a 95% confidence level using a one-day holding period and a 20-day historical observation period. It is possible that actual results may differ significantly from assumptions. Accordingly, VaR may not accurately reflect our levels of exposure. The energy trading and market-based wholesale portfolio VaR amounts for 2014 and 2013 were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Regulatory Assets: | | | |
| Deferred employee benefit costs | $ | 277,122 |
| | $ | 542,174 |
|
| Amounts due from customers for future income taxes, net | 163,742 |
| | 169,091 |
|
| Depreciation | 71,047 |
| | 73,672 |
|
| Debt reacquisition costs | 63,882 |
| | 67,721 |
|
| Ad valorem tax | 34,492 |
| | 21,812 |
|
| Wolf Creek outage | 29,026 |
| | 14,143 |
|
| Treasury yield hedges | 27,594 |
| | 28,573 |
|
| Asset retirement obligations | 23,555 |
| | 22,633 |
|
| Retail energy cost adjustment | 22,138 |
| | 4,262 |
|
| Disallowed plant costs | 15,964 |
| | 16,106 |
|
| Energy efficiency program costs | 14,477 |
| | 18,835 |
|
| Storm costs | 1,483 |
| | 11,076 |
|
| Other regulatory assets | 10,892 |
| | 12,574 |
|
| Total regulatory assets | $ | 755,414 |
| | $ | 1,002,672 |
|
| | | | |
| Regulatory Liabilities: | | | |
| Removal costs | $ | 114,148 |
| | $ | 128,971 |
|
| Deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback | 86,551 |
| | 92,046 |
|
| Nuclear decommissioning | 43,272 |
| | 25,937 |
|
| La Cygne dismantling costs | 20,505 |
| | 18,093 |
|
| Other post-retirement benefits costs | 19,000 |
| | 10,722 |
|
| Retail energy cost adjustment | 15,414 |
| | 16,595 |
|
| Kansas tax credits | 11,076 |
| | 10,781 |
|
| Jurisdictional allowance for funds used during construction | 7,893 |
| | 4,457 |
|
| Gain on sale of oil | 4,278 |
| | 6,219 |
|
| Fuel supply and electricity contracts | 2,635 |
| | 4,387 |
|
| Other regulatory liabilities | 4,784 |
| | 4,967 |
|
| Total regulatory liabilities | $ | 329,556 |
| | $ | 323,175 |
|
|
| | | | | | | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| High | $ | 614 |
| | $ | 205 |
|
| Low | 14 |
| | 9 |
|
| Average | 76 |
| | 83 |
|
Below we summarize the natureInterest Rate Risk
We have entered into numerous fixed and period of recovery for eachvariable rate debt obligations. For details, see Note 9 of the regulatory assets listedNotes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Long-Term Debt." We manage our interest rate risk related to these debt obligations by limiting our exposure to variable interest rate debt, diversifying maturity dates and entering into treasury yield hedge transactions. We may also use other financial derivative instruments such as interest rate swaps. We compute and present information about the sensitivity to changes in interest rates for variable rate debt and current maturities of fixed rate debt by assuming a 100 basis point change in the table above.current interest rates applicable to such debt over the remaining time the debt is outstanding.
Deferred employee benefit costs:We had approximately $407.5 million of variable rate debt and current maturities of fixed rate debt as of IncludesDecember 31, 2014. A 100 basis point change in interest rates applicable to this debt would impact income before income taxes on an annualized basis by approximately $4.0 million. As of December 31, 2014, we had $223.5121.9 million of variable rate bonds insured by bond insurers. Interest rates payable under these bonds are normally set through periodic auctions. However, conditions in the credit markets over the past few years caused a dramatic reduction in the demand for auction bonds, which led to failed auctions. The contractual provisions of these securities set forth an indexing formula method by which interest will be paid in the event of an auction failure. Depending on the level of these reference indices, our interest costs may be higher or lower than what they would have been had the securities been auctioned successfully. Additionally, should insurers of those bonds experience a decrease in their credit ratings, such event could increase our borrowing costs. Furthermore, a decline in interest rates generally can serve to increase our pension and post-retirement benefit obligationsobligations.
Security Price Risk
We maintain the NDT, as required by the NRC and Kansas statute, to fund certain costs of nuclear plant decommissioning. As of December 31, 2014, investments in the NDT were allocated 50% to equity securities, 26% to debt securities, 10% to combination debt/equity/other securities, 9% to alternative investments, 5% to real estate securities and less than 1% to cash equivalents. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the fair value of the NDT investments was $53.7185.0 million for actual pension expenseand $175.6 million, respectively. Changes in excessinterest rates and/or other market changes resulting in a 10% decrease in the value of the amountsecurities would have resulted in an $18.5 million decrease in the value of such expense recognizedthe NDT as of December 31, 2014.
We also maintain a trust to fund non-qualified retirement benefits. As of December 31, 2014, investments in setting our prices.the trust were comprised of 65% equity securities, 35% debt securities and less than 1% cash equivalents. The fair value of the investments in this trust was $35.5 million as of December 31, 2014, and $34.9 million as of December 31, 2013. Changes in interest rates and/or other market changes resulting in a 10% decrease from 2012in the value of the securities would have resulted in a $3.5 million decrease in the value of the trust as of December 31, 2014.
By maintaining diversified portfolios of securities, we seek to 2013 is primarily attributableoptimize the returns to fund the aforementioned obligations within acceptable risk tolerances, including interest rate risk. However, many of the securities in the portfolios are exposed to price fluctuations in the capital markets. If the value of the securities diminishes, the cost of funding the obligations rises. We actively monitor the portfolios by benchmarking the performance of the investments against relevant indices and by maintaining and periodically reviewing the asset allocations in relation to established policy targets. Our exposure to security price risk related to the favorable increaseNDT is in part mitigated because we are currently allowed to recover decommissioning costs in the funded statusprices we charge our customers.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
|
| |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS | PAGE |
| |
| |
| Financial Statements: | |
| Westar Energy, Inc. and Subsidiaries: | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Financial Schedules: | |
| |
SCHEDULES OMITTED
The following schedules are omitted because of the absence of the conditions under which they are required or the information is included in our consolidated financial statements and schedules presented:
I, III, IV and V.
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
We are responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the company’s board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and includes those policies and procedures that:
Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company;
Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and
Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
We assessed the effectiveness of our and Wolf Creek's pension and post-retirement plans. Duringinternal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. In making this assessment, we will amortize to expense approximately $24.9 millionused the criteria set forth in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the benefit obligations and approximately $9.8 million ofTreadway Commission. Based on the excess pension expense. As authorized in the April 2012 Kansas Corporation Commission (KCC) order discussed below,assessment, we are amortizing the excess pension expenseconcluded that, as of December 31, 2014, our internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria. Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an audit report on the time of our filing with the KCCcompany’s internal control over a financial reporting.five-year period. We do not earn a return on this asset.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Amounts due from customers
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Westar Energy, Inc.
Topeka, Kansas
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company's management is responsible for future income taxes, net: Inmaintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying management’s report on internal control over financial reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with various orders,the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we have reducedplan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our pricesaudit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company's principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company's board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the income tax benefits associatedtransactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with certain income tax deductions, thereby passinggenerally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on these benefitsthe financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to customers aterror or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the time we receive them. We believe it is probableeffectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the net future increasescontrols may become inadequate because of changes in income taxes payable will be recovered from customers when these temporary income tax benefits reverse in future periods. We have recorded a regulatory asset, netconditions, or that the degree of compliance with the regulatory liability, for these amounts on which we do not earn a return. We also have recorded a regulatory liability for our obligation to customers for income taxes recovered in earlier periods when corporate income tax rates were higher than current income tax rates. This benefit will be returned to customers as these temporary differences reverse in future periods. The income tax-related regulatory assets and liabilities as well as unamortized investment tax credits are also temporary differences for which deferred income taxes have been provided. These items are measured by the expected cash flows to be receivedpolicies or settled in future prices. We do not earn a return on this asset.
procedures may deteriorate.
Depreciation: RepresentsIn our opinion, the difference between regulatory depreciation expense and depreciation expense we record forCompany maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting purposes. We earn a returnas of December 31, 2014, based on this asset and amortize the difference overcriteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the lifeCommittee of Sponsoring Organizations of the related plant.
Treadway Commission.
Debt reacquisition costs: Includes costs incurred to reacquire and refinance debt. These costs are amortized overWe have also audited, in accordance with the termstandards of the new debt. We do not earn a returnPublic Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule of the Company as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014 of the Company and our report dated February 25, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on this asset.
those financial statements and financial statement schedule.
Ad valorem tax: Represents actual costs incurred for property taxes in excess of amounts collected in our prices. We expect to recover these amounts in our prices over a one-year period. We do not earn a return on this asset.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Wolf Creek outage: We defer the expenses associated with Wolf Creek's scheduled refueling and maintenance outages and amortize these expenses during the period between planned outages. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Kansas City, Missouri
Treasury yield hedges: Represents the effective portion of losses on treasury yield hedge transactions. This amount will be amortized to interest expense over the term of the related debt. See Note 4, "Financial Instruments and Trading Securities—Cash Flow Hedges," for additional information regarding our treasury yield hedge transactions. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Asset retirement obligations: Represents amounts associated with our AROs as discussed in Note 14, "Asset Retirement Obligations." We recover these amounts over the life of the related plant. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Retail energy cost adjustment: We are allowed to adjust our retail prices to reflect changes in the cost of fuel and purchased power needed to serve our customers. This item represents the actual cost of fuel consumed in producing electricity and the cost of purchased power in excess of the amounts we have collected from customers. We expect to recover in our prices this shortfall over a one-year period. We have two retail jurisdictions, each with a separate cost of fuel. For the reporting period, this resulted in us simultaneously reporting both a regulatory asset and a regulatory liability for this item. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Disallowed plant costs: Originally there was a decision to disallow certain costs related to the Wolf Creek plant. Subsequently, in 1987, the KCC revised its original conclusion and provided for recovery of an indirect disallowance with no return on investment. This regulatory asset represents the present value of the future expected revenues to be provided to recover these costs, net of the amounts amortized.
Energy efficiency program costs: We accumulate and defer for future recovery costs related to our various energy efficiency programs. We will amortize such costs over a one-year period. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Storm costs: We accumulated and deferred for future recovery costs related to restoring our electric transmission and distribution systems from damages sustained during unusually damaging storms. We will amortize the remaining costs over a two-year period and no longer earn a return on this asset.
February 25, 2015
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Other regulatory assets:Wes Includes various regulatory assetstar Energy, Inc.
Topeka, Kansas
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of income, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that individuallywe plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are smallfree of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the total regulatory asset balance. Other regulatory assets have various recovery periods. We do not earnbasic consolidated financial statements taken as a return on any of these assets.
whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
Below we summarizeWe have also audited, in accordance with the nature and period of amortization for eachstandards of the regulatory liabilities listedPublic Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on the criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the table above.Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 25, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Removal costs: Represents amounts collected, but not yet spent, to dispose of plant assets that do not represent legal retirement obligations. This liability will be discharged as removal costs are incurred.
Deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback: Represents the gain KGE recorded on the 1987 sale and leaseback of its 50% interest in La Cygne Generation Station (La Cygne) unit 2. We amortize the gain over the lease term.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Nuclear decommissioning: We have a legal obligation to decommission Wolf Creek at the end of its useful life. This amount represents the difference between the fair value of the assets held in a decommissioning trust and the amount recorded for our ARO. See Note 4, "Financial Instruments and Trading Securities," Note 5, "Financial Investments" and Note 14, "Asset Retirement Obligations," for information regarding our nuclear decommissioning trust (NDT) and our ARO.
Kansas City, Missouri
La Cygne dismantling costs: We are contractually obligated to dismantle a portion of La Cygne unit 2. This item represents amounts collected but not yet spent to dismantle this unit and the obligation will be discharged as we dismantle the unit.
Other post-retirement benefits costs: Includes $6.7 million for post-retirement obligations and $12.3 million of other post-retirement benefits expense recognized in setting our prices in excess of actual other post-retirement benefits expense. We amortize the amount over a five-year period.
Retail energy cost adjustment: We are allowed to adjust our retail prices to reflect changes in the cost of fuel and purchased power needed to serve our customers. We bill customers based on our estimated costs. This item represents the amount we collected from customers that was in excess of our actual cost of fuel and purchased power. We will refund to customers this excess recovery over a one-year period. We have two retail jurisdictions, each with a separate cost of fuel. For the reporting period, this resulted in us simultaneously reporting both a regulatory asset and a regulatory liability for this item.
Kansas tax credits: This item represents Kansas tax credits on investments in utility plant. Amounts will be credited to customers subsequent to their realization over the remaining lives of the utility plant giving rise to the tax credits.
Jurisdictional allowance for funds used during construction: This item represents AFUDC that is accrued subsequent to the time the associated construction charges are included in our rates and prior to the time the charges are placed in service. The AFUDC is amortized to depreciation expense over the useful life of the asset that is placed in service.
Gain on sale of oil: We discontinued the use of a certain type of oil in our plants. As a result, we sold this oil inventory for a gain. This item represents the remaining portion of the gain that will be refunded to customers over a three-year period.
Fuel supply and electricity contracts: We use fair value accounting for some of our fuel supply and electricity contracts. This represents the non-cash net gain position on fuel supply and electricity contracts that are recorded at fair value. Under the RECA, fuel supply contract market gains accrue to the benefit of our customers.
Other regulatory liabilities: Includes various regulatory liabilities that individually are relatively small in relation to the total regulatory liability balance. Other regulatory liabilities will be credited over various periods.
February 25, 2015
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Par Values)
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| CURRENT ASSETS: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 4,556 |
| | $ | 4,487 |
|
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $5,309 and $4,596, respectively | 267,327 |
| | 250,036 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | 247,406 |
| | 239,511 |
|
| Deferred tax assets | 29,636 |
| | 37,954 |
|
| Prepaid expenses | 15,793 |
| | 15,821 |
|
| Regulatory assets | 105,549 |
| | 135,408 |
|
| Other | 30,655 |
| | 23,608 |
|
| Total Current Assets | 700,922 |
| | 706,825 |
|
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET | 8,162,908 |
| | 7,551,916 |
|
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT OF VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES, NET | 278,573 |
| | 296,626 |
|
| OTHER ASSETS: | | | |
| Regulatory assets | 754,229 |
| | 620,006 |
|
| Nuclear decommissioning trust | 185,016 |
| | 175,625 |
|
| Other | 265,353 |
| | 246,140 |
|
| Total Other Assets | 1,204,598 |
| | 1,041,771 |
|
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 10,347,001 |
| | $ | 9,597,138 |
|
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | |
| CURRENT LIABILITIES: | | | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | — |
| | $ | 250,000 |
|
| Current maturities of long-term debt of variable interest entities | 27,933 |
| | 27,479 |
|
| Short-term debt | 257,600 |
| | 134,600 |
|
| Accounts payable | 219,351 |
| | 233,351 |
|
| Accrued dividends | 44,971 |
| | 43,604 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 74,356 |
| | 69,769 |
|
| Accrued interest | 79,707 |
| | 80,457 |
|
| Regulatory liabilities | 55,142 |
| | 35,982 |
|
| Other | 90,571 |
| | 80,184 |
|
| Total Current Liabilities | 849,631 |
| | 955,426 |
|
| LONG-TERM LIABILITIES: | | | |
| Long-term debt, net | 3,215,539 |
| | 2,968,958 |
|
| Long-term debt of variable interest entities, net | 166,565 |
| | 194,802 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | 1,475,487 |
| | 1,363,148 |
|
| Unamortized investment tax credits | 211,040 |
| | 192,265 |
|
| Regulatory liabilities | 288,343 |
| | 293,574 |
|
| Accrued employee benefits | 532,622 |
| | 331,558 |
|
| Asset retirement obligations | 230,668 |
| | 160,682 |
|
| Other | 75,799 |
| | 68,194 |
|
| Total Long-Term Liabilities | 6,196,063 |
| | 5,573,181 |
|
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (See Notes 13 and 15) |
|
| |
|
|
| EQUITY: | | | |
| Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity: | | | |
| Common stock, par value $5 per share; authorized 275,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding 131,687,454 shares and 128,254,229 shares, respective to each date | 658,437 |
| | 641,271 |
|
| Paid-in capital | 1,781,120 |
| | 1,696,727 |
|
| Retained earnings | 855,299 |
| | 724,776 |
|
| Total Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity | 3,294,856 |
| | 3,062,774 |
|
| Noncontrolling Interests | 6,451 |
| | 5,757 |
|
| Total Equity | 3,301,307 |
| | 3,068,531 |
|
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | $ | 10,347,001 |
| | $ | 9,597,138 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| REVENUES | $ | 2,601,703 |
| | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
|
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | |
| Fuel and purchased power | 705,450 |
| | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
|
| SPP network transmission costs | 218,924 |
| | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
|
| Operating and maintenance | 367,188 |
| | 359,060 |
| | 342,055 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 250,439 |
| | 224,133 |
| | 226,012 |
|
| Taxes other than income tax | 140,302 |
| | 122,282 |
| | 104,269 |
|
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,968,745 |
| | 1,791,469 |
| | 1,699,337 |
|
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 632,958 |
| | 579,185 |
| | 562,133 |
|
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | |
| Investment earnings | 10,622 |
| | 10,056 |
| | 7,411 |
|
| Other income | 31,522 |
| | 35,609 |
| | 35,378 |
|
| Other expense | (18,389 | ) | | (18,099 | ) | | (19,987 | ) |
| Total Other Income (Expense) | 23,755 |
| | 27,566 |
| | 22,802 |
|
| Interest expense | 183,118 |
| | 182,167 |
| | 176,337 |
|
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 473,595 |
| | 424,584 |
| | 408,598 |
|
| Income tax expense | 151,270 |
| | 123,721 |
| | 126,136 |
|
| NET INCOME | 322,325 |
| | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 9,066 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY, INC. | 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
|
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 1,616 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO COMMON STOCK | $ | 313,259 |
|
| $ | 292,520 |
| | $ | 273,530 |
|
| BASIC AND DILUTED EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY (see Note 2): | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 2.35 |
| | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| AVERAGE EQUIVALENT COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING | 130,014,941 |
| | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
|
| DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 1.40 |
| | $ | 1.36 |
| | $ | 1.32 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 322,325 |
| | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
|
| Amortization of nuclear fuel | 26,051 |
| | 22,690 |
| | 24,369 |
|
| Amortization of deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) |
| Amortization of corporate-owned life insurance | 20,202 |
| | 15,149 |
| | 28,792 |
|
| Non-cash compensation | 7,280 |
| | 8,188 |
| | 7,255 |
|
| Net deferred income taxes and credits | 151,451 |
| | 123,307 |
| | 126,248 |
|
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | (875 | ) | | (576 | ) | | (1,698 | ) |
| Allowance for equity funds used during construction | (17,029 | ) | | (14,143 | ) | | (11,706 | ) |
| Changes in working capital items: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (17,291 | ) | | (24,649 | ) | | 2,408 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | (8,773 | ) | | 10,124 |
| | (19,227 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses and other | 36,717 |
| | (12,316 | ) | | (3,630 | ) |
| Accounts payable | 6,189 |
| | 7,856 |
| | (19,161 | ) |
| Accrued taxes | 6,596 |
| | 14,218 |
| | 11,937 |
|
| Other current liabilities | (31,624 | ) | | (52,829 | ) | | (105,169 | ) |
| Changes in other assets | 6,378 |
| | (4,167 | ) | | 13,015 |
|
| Changes in other liabilities | 35,811 |
| | 41,990 |
| | (1,758 | ) |
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities | 824,355 |
| | 702,803 |
| | 599,106 |
|
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Additions to property, plant and equipment | (852,052 | ) | | (780,098 | ) | | (810,209 | ) |
| Purchase of securities - trusts | (9,075 | ) | | (66,668 | ) | | (20,473 | ) |
| Sale of securities - trusts | 11,125 |
| | 81,994 |
| | 21,604 |
|
| Investment in corporate-owned life insurance | (16,250 | ) | | (17,724 | ) | | (18,404 | ) |
| Proceeds from investment in corporate-owned life insurance | 43,234 |
| | 147,658 |
| | 33,542 |
|
| Proceeds from federal grant | — |
| | 876 |
| | 4,775 |
|
| Investment in affiliated company | (8,000 | ) | | (4,947 | ) | | (8,669 | ) |
| Other investing activities | (7,730 | ) | | (2,992 | ) | | 497 |
|
| Cash Flows used in Investing Activities | (838,748 | ) | | (641,901 | ) | | (797,337 | ) |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Short-term debt, net | 122,406 |
| | (205,241 | ) | | 52,900 |
|
| Proceeds from long-term debt | 417,943 |
| | 492,347 |
| | 541,374 |
|
| Retirements of long-term debt | (427,500 | ) | | (100,000 | ) | | (220,563 | ) |
| Retirements of long-term debt of variable interest entities | (27,479 | ) | | (25,942 | ) | | (28,114 | ) |
| Repayment of capital leases | (3,340 | ) | | (2,995 | ) | | (2,679 | ) |
| Borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | 59,766 |
| | 59,565 |
| | 67,791 |
|
| Repayment of borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | (41,249 | ) | | (145,418 | ) | | (34,838 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | 875 |
| | 576 |
| | 1,698 |
|
| Preferred stock redemption | — |
| | — |
| | (22,567 | ) |
| Issuance of common stock | 87,669 |
| | 32,906 |
| | 6,996 |
|
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | (1,030 | ) | | (2,419 | ) | | (3,295 | ) |
| Cash dividends paid | (171,507 | ) | | (162,904 | ) | | (158,182 | ) |
| Other financing activities | (2,092 | ) | | (2,719 | ) | | — |
|
| Cash Flows from (used in) Financing Activities | 14,462 |
| | (62,244 | ) | | 200,521 |
|
| NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | 69 |
| | (1,342 | ) | | 2,290 |
|
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS: | | | | | |
| Beginning of period | 4,487 |
| | 5,829 |
| | 3,539 |
|
| End of period | $ | 4,556 |
| | $ | 4,487 |
| | $ | 5,829 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders | | | | |
| | Cumulative preferred stock shares | | Cumulative preferred stock | | Common stock shares | | Common stock | | Paid-in capital | | Retained earnings | | Non-controlling interests | | Total equity |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | 214,363 |
| | $ | 21,436 |
| | 125,698,396 |
| | $ | 628,492 |
| | $ | 1,639,503 |
| | $ | 501,216 |
| | $ | 10,094 |
| | $ | 2,800,741 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 275,146 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 282,462 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 242,463 |
| | 1,212 |
| | 5,784 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 6,996 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 562,889 |
| | 2,815 |
| | 6,274 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,089 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) |
| Stock redemption | (214,363 | ) | | (21,436 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (21,436 | ) |
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,616 | ) | | — |
| | (1,616 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.32 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (168,097 | ) | | — |
| | (168,097 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
|
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,295 | ) | | (3,295 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | — |
| | — |
| | 126,503,748 |
| | 632,519 |
| | 1,656,972 |
| | 606,649 |
| | 14,115 |
| | 2,910,255 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 292,520 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 300,863 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 1,256,391 |
| | 6,282 |
| | 26,624 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 32,906 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 494,090 |
| | 2,470 |
| | 7,171 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,641 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.36 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (174,393 | ) | | — |
| | (174,393 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
|
| Deconsolidation of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| �� | — |
| | — |
| | (14,282 | ) | | (14,282 | ) |
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,419 | ) | | (2,419 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | — |
| | — |
| | 128,254,229 |
| | 641,271 |
| | 1,696,727 |
| | 724,776 |
| | 5,757 |
| | 3,068,531 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 313,259 |
| | 9,066 |
| | 322,325 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 3,026,239 |
| | 15,131 |
| | 72,538 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 87,669 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 406,986 |
| | 2,035 |
| | 7,120 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,155 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,092 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,092 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.40 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (182,736 | ) | | — |
| | (182,736 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,193 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,193 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 875 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 875 |
|
| Deconsolidation of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (7,342 | ) | | (7,342 | ) |
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,030 | ) | | (1,030 | ) |
| Other | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,241 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (1,241 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | — |
| | $ | — |
| | 131,687,454 |
| | $ | 658,437 |
| | $ | 1,781,120 |
| | $ | 855,299 |
| | $ | 6,451 |
| | $ | 3,301,307 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
We are the largest electric utility in Kansas. Unless the context otherwise indicates, all references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to "the company," "we," "us," "our" and similar words are to Westar Energy, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. The term "Westar Energy" refers to Westar Energy, Inc., a Kansas corporation incorporated in 1924, alone and not together with its consolidated subsidiaries.
We provide electric generation, transmission and distribution services to approximately 698,000 customers in Kansas. Westar Energy provides these services in central and northeastern Kansas, including the cities of Topeka, Lawrence, Manhattan, Salina and Hutchinson. Kansas Gas and Electric Company (KGE), Westar Energy's wholly-owned subsidiary, provides these services in south-central and southeastern Kansas, including the city of Wichita. Both Westar Energy and KGE conduct business using the name Westar Energy. Our corporate headquarters is located at 818 South Kansas Avenue, Topeka, Kansas 66612.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for the United States of America. Our consolidated financial statements include all operating divisions, majority owned subsidiaries and variable interest entities (VIEs) of which we maintain a controlling interest or are the primary beneficiary reported as a single reportable segment. Undivided interests in jointly-owned generation facilities are included on a proportionate basis. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Management's Estimates
When we prepare our consolidated financial statements, we are required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the date of our consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. We evaluate our estimates on an ongoing basis, including those related to depreciation, unbilled revenue, valuation of investments, forecasted fuel costs included in our retail energy cost adjustment (RECA) billed to customers, income taxes, pension and post-retirement benefits, our asset retirement obligations (AROs) including the decommissioning of Wolf Creek Generating Station (Wolf Creek), environmental issues, VIEs, contingencies and litigation. Actual results may differ from those estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Regulatory Accounting
We apply accounting standards that recognize the economic effects of rate regulation. Accordingly, we have recorded regulatory assets and liabilities when required by a regulatory order or based on regulatory precedent. See Note 3, "Rate Matters and Regulation," for additional information regarding our regulatory assets and liabilities.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider investments that are highly liquid and have maturities of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Fuel Inventory and Supplies
We state fuel inventory and supplies at average cost. Following are the balances for fuel inventory and supplies stated separately.
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Fuel inventory | $ | 70,416 |
| | $ | 78,368 |
|
| Supplies | 176,990 |
| | 161,143 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | $ | 247,406 |
| | $ | 239,511 |
|
Property, Plant and Equipment
We record the value of property, plant and equipment, including that of VIEs, at cost. For plant, cost includes contracted services, direct labor and materials, indirect charges for engineering and supervision and an allowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC). AFUDC represents the allowed cost of capital used to finance utility construction activity. We compute AFUDC by applying a composite rate to qualified construction work in progress. We credit other income (for equity funds) and interest expense (for borrowed funds) for the amount of AFUDC capitalized as construction cost on the accompanying consolidated statements of income as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Borrowed funds | $ | 12,044 |
| | $ | 11,706 |
| | $ | 10,399 |
|
| Equity funds | 17,029 |
| | 14,143 |
| | 11,706 |
|
| Total | $ | 29,073 |
| | $ | 25,849 |
| | $ | 22,105 |
|
| Average AFUDC Rates | 6.7 | % | | 4.8 | % | | 5.0 | % |
We charge maintenance costs and replacements of minor items of property to expense as incurred, except for maintenance costs incurred for our planned refueling and maintenance outages at Wolf Creek. As authorized by regulators, we defer and amortize to expense ratably over the period between planned outages incremental maintenance costs incurred for such outages. When a unit of depreciable property is retired, we charge to accumulated depreciation the original cost less salvage value.
Depreciation
We depreciate utility plant using a straight-line method. The depreciation rates are based on an average annual composite basis using group rates that approximated 2.4% in 2014, 2.5% in 2013 and 2.6% in 2012.
Depreciable lives of property, plant and equipment are as follows.
|
| | | | |
| | | Years |
| Fossil fuel generating facilities | | 6 | to | 78 |
| Nuclear fuel generating facility | | 55 | to | 71 |
| Wind generating facilities | | 19 | to | 20 |
| Transmission facilities | | 15 | to | 75 |
| Distribution facilities | | 22 | to | 68 |
| Other | | 5 | to | 30 |
Nuclear Fuel
We record as property, plant and equipment our share of the cost of nuclear fuel used in the process of refinement, conversion, enrichment and fabrication. We reflect this at original cost and amortize such amounts to fuel expense based on the quantity of heat consumed during the generation of electricity as measured in millions of British thermal units (MMBtu). The accumulated amortization of nuclear fuel in the reactor was $72.3 million as of December 31, 2014, and $46.2 million as of December 31, 2013. The cost of nuclear fuel charged to fuel and purchased power expense was $27.3 million in 2014, $26.5 million in 2013 and $28.3 million in 2012.
Cash Surrender Value of Life Insurance
We recorded on our consolidated balance sheets in other long-term assets the following amounts related to corporate-owned life insurance (COLI) policies.
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Cash surrender value of policies | $ | 1,306,777 |
| | $ | 1,289,457 |
|
| Borrowings against policies | (1,173,956 | ) | | (1,156,341 | ) |
| Corporate-owned life insurance, net | $ | 132,821 |
| | $ | 133,116 |
|
We record as income increases in cash surrender value and death benefits. We offset against policy income the interest expense that we incur on policy loans. Income from death benefits is highly variable from period to period.
Revenue Recognition
We record revenue at the time we deliver electricity to customers. We determine the amounts delivered to individual customers through systematic monthly readings of customer meters. At the end of each month, we estimate how much electricity we have delivered since the prior meter reading and record the corresponding unbilled revenue.
Our unbilled revenue estimate is affected by factors including fluctuations in energy demand, weather, line losses and changes in the composition of customer classes. We recorded estimated unbilled revenue of $61.0 million as of December 31, 2014, and $60.1 million as of December 31, 2013.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
We determine our allowance for doubtful accounts based on the age of our receivables. We charge receivables off when they are deemed uncollectible, which is based on a number of factors including specific facts surrounding an account and management's judgment.
Income Taxes
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, we recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. We recognize the future tax benefits to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not. We amortize deferred investment tax credits over the lives of the related properties as required by tax laws and regulatory practices. We recognize production tax credits in the year that electricity is generated to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not.
We record deferred tax assets to the extent capital losses, operating losses, or tax credits will be carried forward to future periods. However, when we believe based on available evidence that we do not, or will not, have sufficient future capital gains or taxable income in the appropriate taxing jurisdiction to realize the entire benefit during the applicable carryforward period, we record a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset.
The application of income tax law is complex. Laws and regulations in this area are voluminous and often ambiguous. Accordingly, we must make judgments regarding income tax exposure. Interpretations of and guidance surrounding income tax laws and regulations change over time. As a result, changes in our judgments can materially affect amounts we recognize in our consolidated financial statements. See Note 10, "Taxes," for additional detail on our accounting for income taxes.
Sales Tax
We account for the collection and remittance of sales tax on a net basis. As a result, we do not reflect sales tax in our consolidated statements of income.
Earnings Per Share
We have participating securities in the form of unvested restricted share units (RSUs) with nonforfeitable rights to dividend equivalents that receive dividends on an equal basis with dividends declared on common shares. As a result, we apply the two-class method of computing basic and diluted earnings per share (EPS).
To compute basic EPS, we divide the earnings allocated to common stock by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted EPS includes the effect of potential issuances of common shares resulting from our forward sale agreements and RSUs with forfeitable rights to dividend equivalents. We compute the dilutive effect of potential issuances of common shares using the treasury stock method.
The following table reconciles our basic and diluted EPS from net income.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| Net income | $ | 322,325 |
| | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 9,066 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
|
| Net income attributable to Westar Energy, Inc. | 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
|
| Less: Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 1,616 |
|
| Net income allocated to RSUs | 790 |
| | 810 |
| | 778 |
|
| Net income allocated to common stock | $ | 312,469 |
| | $ | 291,710 |
| | $ | 272,752 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Weighted average equivalent common shares outstanding – basic | 130,014,941 |
| | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
|
| Effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | |
| RSUs | 181,397 |
| | 17,195 |
| | 97,757 |
|
| Forward sale agreements | 2,628,187 |
| | 818,505 |
| | 89,160 |
|
| Weighted average equivalent common shares outstanding – diluted (a) | 132,824,525 |
| | 128,298,694 |
| | 126,898,786 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Earnings per common share, basic | $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| Earnings per common share, diluted | $ | 2.35 |
| | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | For the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, we had no antidilutive securities. |
KCC Proceedings
We plan to file an application with the KCC in early March 2015 to adjust our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades, investment to extend the life of Wolf Creek and programs to improve reliability. We expect the KCC to issue an order on our request by late October 2015.
In December 2014, the KCC approved an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include costs incurred for property taxes. The new prices were effective in January 2015 and are expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $4.9 million.
In October 2014, the KCC approved an order to adjust our prices to include previously deferred amounts associated with various energy efficiency programs. The new prices were effective in November 2014 and we estimate this will decrease our annual retail revenues by a total of approximately $5.0 million.
We, KCC staff and a consumer advocate joined in a request filed with the KCC to defer depreciation expense and carrying costs related to our capital investment associated with environmental upgrades at La Cygne until new retail prices become effective following a general rate case expected to be filed in March 2015. We estimate our share of these deferred costs will be approximately $20.0 million and we expect to begin deferring these costs in March 2015. In September 2014, the KCC issued an order approving the joint application that will allow us to include these deferred costs in our next general rate case, which is expected to increase our annual revenues by approximately $4.0 million.
In June 2014, the KCC issued an order to adjust our prices to include updated transmission costs as reflected in the TFR discussed below. The new prices were effective in April 2014 and we estimate this will increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $41.0 million.
In May 2014, the KCC issued an order to adjust our prices to include costs associated with investments to comply with environmental requirements during 2013. New prices were effective in June 2014 and we estimate this will increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $11.0 million.
FERC Proceedings
In August 2014, the KCC filed a challenge with the FERC regarding rate making as it pertains to the cost of interstate electrical transmission service we operate. The KCC is requesting that we lower our transmission return on equity by nearly two percentage points, which would result in reductions of the TFR revenue requirement if granted. If we are unable to reach a settlement, the FERC will schedule a hearing.
Our TFR that includes projected 2014 transmission capital expenditures and operating costs became effective January 2014 and were expected to increase annual transmission revenues by approximately $44.3 million. This updated rate provided the basis for our request to the KCC to adjust our retail prices to include updated transmission costs discussed above.
Our TFR that includes projected 2015 transmission capital expenditures and operating costs became effective in January 2015 and is expected to decrease our annual transmission revenues by approximately $4.6 million.
Wolf Creek Outage
Wolf Creek normally operates on an 18-month planned refueling and maintenance outage schedule. However, as a result of an unscheduled maintenance outage at Wolf Creek in 2012 coupled with the longer than planned refueling and maintenance outage in 2011, Wolf Creek has since operated on a longer refueling and maintenance outage schedule. After the next planned refueling and maintenance outage, occurring in the first quarter of 2015, Wolf Creek will revert back to the normal 18-month refueling and maintenance outage schedule. In order to revert to the normal schedule, Wolf Creek underwent a planned maintenance outage in the first quarter of 2014. The outage was not part of a refueling outage and therefore was expensed as incurred. Our share of the 2014 outage costs was approximately $8.7 million.
Stock-Based Compensation
We use two types of restricted share units (RSUs) for our stock-based compensation awards; those with service requirements and those with performance measures. See Note 11 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Employee Benefit Plans," for additional information. Total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with only service requirements was $4.4 million as of December 31, 2014, and we expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.9 years. Total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with performance measures was $3.8 million as of December 31, 2014, and we expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.7 years.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Our fuel procurement and energy marketing activities involve primary market risk exposures, including commodity price risk, credit risk and interest rate risk. Commodity price risk is the potential adverse price impact related to the purchase or sale of electricity and energy-related products. Credit risk is the potential adverse financial impact resulting from non-performance by a counterparty of its contractual obligations. Interest rate risk is the potential adverse financial impact related to changes in interest rates. In addition, our investments in trusts to fund nuclear plant decommissioning and to fund non-qualified retirement benefits give rise to security price risk. Many of the securities in these trusts are exposed to price fluctuations in the capital markets.
Commodity Price Risk
We engage in both financial and physical trading with the goal of managing our commodity price risk, enhancing system reliability and increasing profits. We procure and trade electricity, coal, natural gas and other energy-related products by utilizing energy commodity contracts and a variety of financial instruments, including futures contracts, options and swaps.
We use various types of fuel, including coal, natural gas, uranium and diesel to operate our plants and also purchase power to meet customer demand. Our prices and consolidated financial results are exposed to market risks from commodity price changes for electricity and other energy-related products as well as from interest rates. Volatility in these markets impacts our costs of purchased power, costs of fuel for our generating plants and our participation in energy markets. We strive to manage our customers' and our exposure to these market risks through regulatory, operating and financing activities and, when we deem appropriate, we economically hedge a portion of these risks through the use of derivative financial instruments for non-trading purposes.
Factors that affect our commodity price exposure are the quantity and availability of fuel used for generation, the availability of our power plants and the quantity of electricity customers consume. Quantities of fossil fuel we use to generate electricity fluctuate from period to period based on availability, price and deliverability of a given fuel type, as well as planned and unscheduled outages at our generating plants that use fossil fuels. Our commodity price exposure is also affected by our nuclear plant refueling and maintenance schedule. Our customers' electricity usage also varies based on weather, the economy and other factors.
We trade various types of fuel primarily to reduce exposure related to the volatility of commodity prices. A significant portion of our coal requirements is purchased under long-term contracts to hedge much of the fuel exposure for customers. If we were unable to generate an adequate supply of electricity for our customers, we would purchase power in the wholesale market to the extent it is available, subject to possible transmission constraints, and/or implement curtailment or interruption procedures as permitted in our tariffs and terms and conditions of service.
One way by which we manage and measure the commodity price risk of our trading portfolio is by using a variance/covariance value-at-risk (VaR) model. In addition to VaR, we employ additional risk control processes such as stress testing, daily loss limits, credit limits and position limits. We expect to use similar control processes in the future. The use of VaR requires assumptions, including the selection of a confidence level and a measure of volatility associated with potential losses and the estimated holding period. We express VaR as a potential dollar loss based on a 95% confidence level using a one-day holding period and a 20-day historical observation period. It is possible that actual results may differ significantly from assumptions. Accordingly, VaR may not accurately reflect our levels of exposure. The energy trading and market-based wholesale portfolio VaR amounts for 2014 and 2013 were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| High | $ | 614 |
| | $ | 205 |
|
| Low | 14 |
| | 9 |
|
| Average | 76 |
| | 83 |
|
Interest Rate Risk
We have entered into numerous fixed and variable rate debt obligations. For details, see Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, "Long-Term Debt." We manage our interest rate risk related to these debt obligations by limiting our exposure to variable interest rate debt, diversifying maturity dates and entering into treasury yield hedge transactions. We may also use other financial derivative instruments such as interest rate swaps. We compute and present information about the sensitivity to changes in interest rates for variable rate debt and current maturities of fixed rate debt by assuming a 100 basis point change in the current interest rates applicable to such debt over the remaining time the debt is outstanding.
We had approximately $407.5 million of variable rate debt and current maturities of fixed rate debt as of December 31, 2014. A 100 basis point change in interest rates applicable to this debt would impact income before income taxes on an annualized basis by approximately $4.0 million. As of December 31, 2014, we had $121.9 million of variable rate bonds insured by bond insurers. Interest rates payable under these bonds are normally set through periodic auctions. However, conditions in the credit markets over the past few years caused a dramatic reduction in the demand for auction bonds, which led to failed auctions. The contractual provisions of these securities set forth an indexing formula method by which interest will be paid in the event of an auction failure. Depending on the level of these reference indices, our interest costs may be higher or lower than what they would have been had the securities been auctioned successfully. Additionally, should insurers of those bonds experience a decrease in their credit ratings, such event could increase our borrowing costs. Furthermore, a decline in interest rates generally can serve to increase our pension and post-retirement benefit obligations.
Security Price Risk
We maintain the NDT, as required by the NRC and Kansas statute, to fund certain costs of nuclear plant decommissioning. As of December 31, 2014, investments in the NDT were allocated 50% to equity securities, 26% to debt securities, 10% to combination debt/equity/other securities, 9% to alternative investments, 5% to real estate securities and less than 1% to cash equivalents. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the fair value of the NDT investments was $185.0 million and $175.6 million, respectively. Changes in interest rates and/or other market changes resulting in a 10% decrease in the value of the securities would have resulted in an $18.5 million decrease in the value of the NDT as of December 31, 2014.
We also maintain a trust to fund non-qualified retirement benefits. As of December 31, 2014, investments in the trust were comprised of 65% equity securities, 35% debt securities and less than 1% cash equivalents. The fair value of the investments in this trust was $35.5 million as of December 31, 2014, and $34.9 million as of December 31, 2013. Changes in interest rates and/or other market changes resulting in a 10% decrease in the value of the securities would have resulted in a $3.5 million decrease in the value of the trust as of December 31, 2014.
By maintaining diversified portfolios of securities, we seek to optimize the returns to fund the aforementioned obligations within acceptable risk tolerances, including interest rate risk. However, many of the securities in the portfolios are exposed to price fluctuations in the capital markets. If the value of the securities diminishes, the cost of funding the obligations rises. We actively monitor the portfolios by benchmarking the performance of the investments against relevant indices and by maintaining and periodically reviewing the asset allocations in relation to established policy targets. Our exposure to security price risk related to the NDT is in part mitigated because we are currently allowed to recover decommissioning costs in the prices we charge our customers.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
|
| |
| TABLE OF CONTENTS | PAGE |
| |
| |
| Financial Statements: | |
| Westar Energy, Inc. and Subsidiaries: | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Financial Schedules: | |
| |
SCHEDULES OMITTED
The following schedules are omitted because of the absence of the conditions under which they are required or the information is included in our consolidated financial statements and schedules presented:
I, III, IV and V.
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
We are responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the company’s board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and includes those policies and procedures that:
Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company;
Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and
Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
We assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on the assessment, we concluded that, as of December 31, 2014, our internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria. Our independent registered public accounting firm has issued an audit report on the company’s internal control over financial reporting.
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Westar Energy, Inc.
Topeka, Kansas
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying management’s report on internal control over financial reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company's principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company's board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule of the Company as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014 of the Company and our report dated February 25, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and financial statement schedule.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Kansas City, Missouri
February 25, 2015
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Westar Energy, Inc.
Topeka, Kansas
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of income, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Westar Energy, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on the criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 25, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Kansas City, Missouri
February 25, 2015
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Par Values)
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| CURRENT ASSETS: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 4,556 |
| | $ | 4,487 |
|
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $5,309 and $4,596, respectively | 267,327 |
| | 250,036 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | 247,406 |
| | 239,511 |
|
| Deferred tax assets | 29,636 |
| | 37,954 |
|
| Prepaid expenses | 15,793 |
| | 15,821 |
|
| Regulatory assets | 105,549 |
| | 135,408 |
|
| Other | 30,655 |
| | 23,608 |
|
| Total Current Assets | 700,922 |
| | 706,825 |
|
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET | 8,162,908 |
| | 7,551,916 |
|
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT OF VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES, NET | 278,573 |
| | 296,626 |
|
| OTHER ASSETS: | | | |
| Regulatory assets | 754,229 |
| | 620,006 |
|
| Nuclear decommissioning trust | 185,016 |
| | 175,625 |
|
| Other | 265,353 |
| | 246,140 |
|
| Total Other Assets | 1,204,598 |
| | 1,041,771 |
|
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 10,347,001 |
| | $ | 9,597,138 |
|
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | |
| CURRENT LIABILITIES: | | | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | — |
| | $ | 250,000 |
|
| Current maturities of long-term debt of variable interest entities | 27,933 |
| | 27,479 |
|
| Short-term debt | 257,600 |
| | 134,600 |
|
| Accounts payable | 219,351 |
| | 233,351 |
|
| Accrued dividends | 44,971 |
| | 43,604 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 74,356 |
| | 69,769 |
|
| Accrued interest | 79,707 |
| | 80,457 |
|
| Regulatory liabilities | 55,142 |
| | 35,982 |
|
| Other | 90,571 |
| | 80,184 |
|
| Total Current Liabilities | 849,631 |
| | 955,426 |
|
| LONG-TERM LIABILITIES: | | | |
| Long-term debt, net | 3,215,539 |
| | 2,968,958 |
|
| Long-term debt of variable interest entities, net | 166,565 |
| | 194,802 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | 1,475,487 |
| | 1,363,148 |
|
| Unamortized investment tax credits | 211,040 |
| | 192,265 |
|
| Regulatory liabilities | 288,343 |
| | 293,574 |
|
| Accrued employee benefits | 532,622 |
| | 331,558 |
|
| Asset retirement obligations | 230,668 |
| | 160,682 |
|
| Other | 75,799 |
| | 68,194 |
|
| Total Long-Term Liabilities | 6,196,063 |
| | 5,573,181 |
|
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (See Notes 13 and 15) |
|
| |
|
|
| EQUITY: | | | |
| Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity: | | | |
| Common stock, par value $5 per share; authorized 275,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding 131,687,454 shares and 128,254,229 shares, respective to each date | 658,437 |
| | 641,271 |
|
| Paid-in capital | 1,781,120 |
| | 1,696,727 |
|
| Retained earnings | 855,299 |
| | 724,776 |
|
| Total Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders’ Equity | 3,294,856 |
| | 3,062,774 |
|
| Noncontrolling Interests | 6,451 |
| | 5,757 |
|
| Total Equity | 3,301,307 |
| | 3,068,531 |
|
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | $ | 10,347,001 |
| | $ | 9,597,138 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| REVENUES | $ | 2,601,703 |
| | $ | 2,370,654 |
| | $ | 2,261,470 |
|
| OPERATING EXPENSES: | | | | | |
| Fuel and purchased power | 705,450 |
| | 634,797 |
| | 589,990 |
|
| SPP network transmission costs | 218,924 |
| | 178,604 |
| | 166,547 |
|
| Operating and maintenance | 367,188 |
| | 359,060 |
| | 342,055 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 250,439 |
| | 224,133 |
| | 226,012 |
|
| Taxes other than income tax | 140,302 |
| | 122,282 |
| | 104,269 |
|
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,968,745 |
| | 1,791,469 |
| | 1,699,337 |
|
| INCOME FROM OPERATIONS | 632,958 |
| | 579,185 |
| | 562,133 |
|
| OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): | | | | | |
| Investment earnings | 10,622 |
| | 10,056 |
| | 7,411 |
|
| Other income | 31,522 |
| | 35,609 |
| | 35,378 |
|
| Other expense | (18,389 | ) | | (18,099 | ) | | (19,987 | ) |
| Total Other Income (Expense) | 23,755 |
| | 27,566 |
| | 22,802 |
|
| Interest expense | 183,118 |
| | 182,167 |
| | 176,337 |
|
| INCOME BEFORE INCOME TAXES | 473,595 |
| | 424,584 |
| | 408,598 |
|
| Income tax expense | 151,270 |
| | 123,721 |
| | 126,136 |
|
| NET INCOME | 322,325 |
| | 300,863 |
| | 282,462 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 9,066 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY, INC. | 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
|
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 1,616 |
|
| NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO COMMON STOCK | $ | 313,259 |
|
| $ | 292,520 |
| | $ | 273,530 |
|
| BASIC AND DILUTED EARNINGS PER AVERAGE COMMON SHARE OUTSTANDING ATTRIBUTABLE TO WESTAR ENERGY (see Note 2): | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 2.35 |
| | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| AVERAGE EQUIVALENT COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING | 130,014,941 |
| | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
|
| DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 1.40 |
| | $ | 1.36 |
| | $ | 1.32 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 322,325 |
| | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 286,442 |
| | 272,593 |
| | 270,464 |
|
| Amortization of nuclear fuel | 26,051 |
| | 22,690 |
| | 24,369 |
|
| Amortization of deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) | | (5,495 | ) |
| Amortization of corporate-owned life insurance | 20,202 |
| | 15,149 |
| | 28,792 |
|
| Non-cash compensation | 7,280 |
| | 8,188 |
| | 7,255 |
|
| Net deferred income taxes and credits | 151,451 |
| | 123,307 |
| | 126,248 |
|
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | (875 | ) | | (576 | ) | | (1,698 | ) |
| Allowance for equity funds used during construction | (17,029 | ) | | (14,143 | ) | | (11,706 | ) |
| Changes in working capital items: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (17,291 | ) | | (24,649 | ) | | 2,408 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | (8,773 | ) | | 10,124 |
| | (19,227 | ) |
| Prepaid expenses and other | 36,717 |
| | (12,316 | ) | | (3,630 | ) |
| Accounts payable | 6,189 |
| | 7,856 |
| | (19,161 | ) |
| Accrued taxes | 6,596 |
| | 14,218 |
| | 11,937 |
|
| Other current liabilities | (31,624 | ) | | (52,829 | ) | | (105,169 | ) |
| Changes in other assets | 6,378 |
| | (4,167 | ) | | 13,015 |
|
| Changes in other liabilities | 35,811 |
| | 41,990 |
| | (1,758 | ) |
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities | 824,355 |
| | 702,803 |
| | 599,106 |
|
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Additions to property, plant and equipment | (852,052 | ) | | (780,098 | ) | | (810,209 | ) |
| Purchase of securities - trusts | (9,075 | ) | | (66,668 | ) | | (20,473 | ) |
| Sale of securities - trusts | 11,125 |
| | 81,994 |
| | 21,604 |
|
| Investment in corporate-owned life insurance | (16,250 | ) | | (17,724 | ) | | (18,404 | ) |
| Proceeds from investment in corporate-owned life insurance | 43,234 |
| | 147,658 |
| | 33,542 |
|
| Proceeds from federal grant | — |
| | 876 |
| | 4,775 |
|
| Investment in affiliated company | (8,000 | ) | | (4,947 | ) | | (8,669 | ) |
| Other investing activities | (7,730 | ) | | (2,992 | ) | | 497 |
|
| Cash Flows used in Investing Activities | (838,748 | ) | | (641,901 | ) | | (797,337 | ) |
| CASH FLOWS FROM (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | | | |
| Short-term debt, net | 122,406 |
| | (205,241 | ) | | 52,900 |
|
| Proceeds from long-term debt | 417,943 |
| | 492,347 |
| | 541,374 |
|
| Retirements of long-term debt | (427,500 | ) | | (100,000 | ) | | (220,563 | ) |
| Retirements of long-term debt of variable interest entities | (27,479 | ) | | (25,942 | ) | | (28,114 | ) |
| Repayment of capital leases | (3,340 | ) | | (2,995 | ) | | (2,679 | ) |
| Borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | 59,766 |
| | 59,565 |
| | 67,791 |
|
| Repayment of borrowings against cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance | (41,249 | ) | | (145,418 | ) | | (34,838 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation excess tax benefits | 875 |
| | 576 |
| | 1,698 |
|
| Preferred stock redemption | — |
| | — |
| | (22,567 | ) |
| Issuance of common stock | 87,669 |
| | 32,906 |
| | 6,996 |
|
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | (1,030 | ) | | (2,419 | ) | | (3,295 | ) |
| Cash dividends paid | (171,507 | ) | | (162,904 | ) | | (158,182 | ) |
| Other financing activities | (2,092 | ) | | (2,719 | ) | | — |
|
| Cash Flows from (used in) Financing Activities | 14,462 |
| | (62,244 | ) | | 200,521 |
|
| NET INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | 69 |
| | (1,342 | ) | | 2,290 |
|
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS: | | | | | |
| Beginning of period | 4,487 |
| | 5,829 |
| | 3,539 |
|
| End of period | $ | 4,556 |
| | $ | 4,487 |
| | $ | 5,829 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(Dollars in Thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Westar Energy, Inc. Shareholders | | | | |
| | Cumulative preferred stock shares | | Cumulative preferred stock | | Common stock shares | | Common stock | | Paid-in capital | | Retained earnings | | Non-controlling interests | | Total equity |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | 214,363 |
| | $ | 21,436 |
| | 125,698,396 |
| | $ | 628,492 |
| | $ | 1,639,503 |
| | $ | 501,216 |
| | $ | 10,094 |
| | $ | 2,800,741 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 275,146 |
| | 7,316 |
| | 282,462 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 242,463 |
| | 1,212 |
| | 5,784 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 6,996 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 562,889 |
| | 2,815 |
| | 6,274 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,089 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (3,490 | ) |
| Stock redemption | (214,363 | ) | | (21,436 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (21,436 | ) |
| Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,616 | ) | | — |
| | (1,616 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.32 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (168,097 | ) | | — |
| | (168,097 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,203 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,698 |
|
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3,295 | ) | | (3,295 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | — |
| | — |
| | 126,503,748 |
| | 632,519 |
| | 1,656,972 |
| | 606,649 |
| | 14,115 |
| | 2,910,255 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 292,520 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 300,863 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 1,256,391 |
| | 6,282 |
| | 26,624 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 32,906 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 494,090 |
| | 2,470 |
| | 7,171 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,641 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,719 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.36 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (174,393 | ) | | — |
| | (174,393 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,103 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 576 |
|
| Deconsolidation of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| �� | — |
| | — |
| | (14,282 | ) | | (14,282 | ) |
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,419 | ) | | (2,419 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | — |
| | — |
| | 128,254,229 |
| | 641,271 |
| | 1,696,727 |
| | 724,776 |
| | 5,757 |
| | 3,068,531 |
|
| Net income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 313,259 |
| | 9,066 |
| | 322,325 |
|
| Issuance of stock | — |
| | — |
| | 3,026,239 |
| | 15,131 |
| | 72,538 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 87,669 |
|
| Issuance of stock for compensation and reinvested dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 406,986 |
| | 2,035 |
| | 7,120 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,155 |
|
| Tax withholding related to stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,092 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,092 | ) |
Dividends on common stock
($1.40 per share) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (182,736 | ) | | — |
| | (182,736 | ) |
| Stock compensation expense | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,193 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,193 |
|
| Tax benefit on stock compensation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 875 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 875 |
|
| Deconsolidation of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (7,342 | ) | | (7,342 | ) |
| Distributions to shareholders of noncontrolling interests | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,030 | ) | | (1,030 | ) |
| Other | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,241 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (1,241 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | — |
| | $ | — |
| | 131,687,454 |
| | $ | 658,437 |
| | $ | 1,781,120 |
| | $ | 855,299 |
| | $ | 6,451 |
| | $ | 3,301,307 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
We are the largest electric utility in Kansas. Unless the context otherwise indicates, all references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to "the company," "we," "us," "our" and similar words are to Westar Energy, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. The term "Westar Energy" refers to Westar Energy, Inc., a Kansas corporation incorporated in 1924, alone and not together with its consolidated subsidiaries.
We provide electric generation, transmission and distribution services to approximately 698,000 customers in Kansas. Westar Energy provides these services in central and northeastern Kansas, including the cities of Topeka, Lawrence, Manhattan, Salina and Hutchinson. Kansas Gas and Electric Company (KGE), Westar Energy's wholly-owned subsidiary, provides these services in south-central and southeastern Kansas, including the city of Wichita. Both Westar Energy and KGE conduct business using the name Westar Energy. Our corporate headquarters is located at 818 South Kansas Avenue, Topeka, Kansas 66612.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of Consolidation
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) for the United States of America. Our consolidated financial statements include all operating divisions, majority owned subsidiaries and variable interest entities (VIEs) of which we maintain a controlling interest or are the primary beneficiary reported as a single reportable segment. Undivided interests in jointly-owned generation facilities are included on a proportionate basis. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Management's Estimates
When we prepare our consolidated financial statements, we are required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the date of our consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. We evaluate our estimates on an ongoing basis, including those related to depreciation, unbilled revenue, valuation of investments, forecasted fuel costs included in our retail energy cost adjustment (RECA) billed to customers, income taxes, pension and post-retirement benefits, our asset retirement obligations (AROs) including the decommissioning of Wolf Creek Generating Station (Wolf Creek), environmental issues, VIEs, contingencies and litigation. Actual results may differ from those estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Regulatory Accounting
We apply accounting standards that recognize the economic effects of rate regulation. Accordingly, we have recorded regulatory assets and liabilities when required by a regulatory order or based on regulatory precedent. See Note 3, "Rate Matters and Regulation," for additional information regarding our regulatory assets and liabilities.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider investments that are highly liquid and have maturities of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Fuel Inventory and Supplies
We state fuel inventory and supplies at average cost. Following are the balances for fuel inventory and supplies stated separately.
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Fuel inventory | $ | 70,416 |
| | $ | 78,368 |
|
| Supplies | 176,990 |
| | 161,143 |
|
| Fuel inventory and supplies | $ | 247,406 |
| | $ | 239,511 |
|
Property, Plant and Equipment
We record the value of property, plant and equipment, including that of VIEs, at cost. For plant, cost includes contracted services, direct labor and materials, indirect charges for engineering and supervision and an allowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC). AFUDC represents the allowed cost of capital used to finance utility construction activity. We compute AFUDC by applying a composite rate to qualified construction work in progress. We credit other income (for equity funds) and interest expense (for borrowed funds) for the amount of AFUDC capitalized as construction cost on the accompanying consolidated statements of income as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (Dollars In Thousands) |
| Borrowed funds | $ | 12,044 |
| | $ | 11,706 |
| | $ | 10,399 |
|
| Equity funds | 17,029 |
| | 14,143 |
| | 11,706 |
|
| Total | $ | 29,073 |
| | $ | 25,849 |
| | $ | 22,105 |
|
| Average AFUDC Rates | 6.7 | % | | 4.8 | % | | 5.0 | % |
We charge maintenance costs and replacements of minor items of property to expense as incurred, except for maintenance costs incurred for our planned refueling and maintenance outages at Wolf Creek. As authorized by regulators, we defer and amortize to expense ratably over the period between planned outages incremental maintenance costs incurred for such outages. When a unit of depreciable property is retired, we charge to accumulated depreciation the original cost less salvage value.
Depreciation
We depreciate utility plant using a straight-line method. The depreciation rates are based on an average annual composite basis using group rates that approximated 2.4% in 2014, 2.5% in 2013 and 2.6% in 2012.
Depreciable lives of property, plant and equipment are as follows.
|
| | | | |
| | | Years |
| Fossil fuel generating facilities | | 6 | to | 78 |
| Nuclear fuel generating facility | | 55 | to | 71 |
| Wind generating facilities | | 19 | to | 20 |
| Transmission facilities | | 15 | to | 75 |
| Distribution facilities | | 22 | to | 68 |
| Other | | 5 | to | 30 |
Nuclear Fuel
We record as property, plant and equipment our share of the cost of nuclear fuel used in the process of refinement, conversion, enrichment and fabrication. We reflect this at original cost and amortize such amounts to fuel expense based on the quantity of heat consumed during the generation of electricity as measured in millions of British thermal units (MMBtu). The accumulated amortization of nuclear fuel in the reactor was $72.3 million as of December 31, 2014, and $46.2 million as of December 31, 2013. The cost of nuclear fuel charged to fuel and purchased power expense was $27.3 million in 2014, $26.5 million in 2013 and $28.3 million in 2012.
Cash Surrender Value of Life Insurance
We recorded on our consolidated balance sheets in other long-term assets the following amounts related to corporate-owned life insurance (COLI) policies.
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Cash surrender value of policies | $ | 1,306,777 |
| | $ | 1,289,457 |
|
| Borrowings against policies | (1,173,956 | ) | | (1,156,341 | ) |
| Corporate-owned life insurance, net | $ | 132,821 |
| | $ | 133,116 |
|
We record as income increases in cash surrender value and death benefits. We offset against policy income the interest expense that we incur on policy loans. Income from death benefits is highly variable from period to period.
Revenue Recognition
We record revenue at the time we deliver electricity to customers. We determine the amounts delivered to individual customers through systematic monthly readings of customer meters. At the end of each month, we estimate how much electricity we have delivered since the prior meter reading and record the corresponding unbilled revenue.
Our unbilled revenue estimate is affected by factors including fluctuations in energy demand, weather, line losses and changes in the composition of customer classes. We recorded estimated unbilled revenue of $61.0 million as of December 31, 2014, and $60.1 million as of December 31, 2013.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
We determine our allowance for doubtful accounts based on the age of our receivables. We charge receivables off when they are deemed uncollectible, which is based on a number of factors including specific facts surrounding an account and management's judgment.
Income Taxes
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, we recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. We recognize the future tax benefits to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not. We amortize deferred investment tax credits over the lives of the related properties as required by tax laws and regulatory practices. We recognize production tax credits in the year that electricity is generated to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not.
We record deferred tax assets to the extent capital losses, operating losses, or tax credits will be carried forward to future periods. However, when we believe based on available evidence that we do not, or will not, have sufficient future capital gains or taxable income in the appropriate taxing jurisdiction to realize the entire benefit during the applicable carryforward period, we record a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset.
The application of income tax law is complex. Laws and regulations in this area are voluminous and often ambiguous. Accordingly, we must make judgments regarding income tax exposure. Interpretations of and guidance surrounding income tax laws and regulations change over time. As a result, changes in our judgments can materially affect amounts we recognize in our consolidated financial statements. See Note 10, "Taxes," for additional detail on our accounting for income taxes.
Sales Tax
We account for the collection and remittance of sales tax on a net basis. As a result, we do not reflect sales tax in our consolidated statements of income.
Earnings Per Share
We have participating securities in the form of unvested restricted share units (RSUs) with nonforfeitable rights to dividend equivalents that receive dividends on an equal basis with dividends declared on common shares. As a result, we apply the two-class method of computing basic and diluted earnings per share (EPS).
To compute basic EPS, we divide the earnings allocated to common stock by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted EPS includes the effect of potential issuances of common shares resulting from our forward sale agreements and RSUs with forfeitable rights to dividend equivalents. We compute the dilutive effect of potential issuances of common shares using the treasury stock method.
The following table reconciles our basic and diluted EPS from net income.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (Dollars In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| Net income | $ | 322,325 |
| | $ | 300,863 |
| | $ | 282,462 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 9,066 |
| | 8,343 |
| | 7,316 |
|
| Net income attributable to Westar Energy, Inc. | 313,259 |
| | 292,520 |
| | 275,146 |
|
| Less: Preferred dividends | — |
| | — |
| | 1,616 |
|
| Net income allocated to RSUs | 790 |
| | 810 |
| | 778 |
|
| Net income allocated to common stock | $ | 312,469 |
| | $ | 291,710 |
| | $ | 272,752 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Weighted average equivalent common shares outstanding – basic | 130,014,941 |
| | 127,462,994 |
| | 126,711,869 |
|
| Effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | |
| RSUs | 181,397 |
| | 17,195 |
| | 97,757 |
|
| Forward sale agreements | 2,628,187 |
| | 818,505 |
| | 89,160 |
|
| Weighted average equivalent common shares outstanding – diluted (a) | 132,824,525 |
| | 128,298,694 |
| | 126,898,786 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Earnings per common share, basic | $ | 2.40 |
| | $ | 2.29 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
| Earnings per common share, diluted | $ | 2.35 |
| | $ | 2.27 |
| | $ | 2.15 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | For the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, we had no antidilutive securities. |
Supplemental Cash Flow Information
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| CASH PAID FOR (RECEIVED FROM): | | | | | |
| Interest on financing activities, net of amount capitalized | $ | 160,292 |
| | $ | 148,691 |
| | $ | 143,564 |
|
| Interest on financing activities of VIEs | 12,183 |
| | 13,892 |
| | 16,214 |
|
| Income taxes, net of refunds | 458 |
| | (11 | ) | | (4,378 | ) |
| NON-CASH INVESTING TRANSACTIONS: | | | | | |
| Property, plant and equipment additions | 143,192 |
| | 127,544 |
| | 89,354 |
|
| Property, plant and equipment of VIEs | (7,342 | ) | | (14,282 | ) | | — |
|
| NON-CASH FINANCING TRANSACTIONS: | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock for reinvested dividends and compensation plans | 9,155 |
| | 9,641 |
| | 9,089 |
|
| Deconsolidation of VIEs | (7,342 | ) | | (14,282 | ) | | — |
|
| Assets acquired through capital leases | 8,717 |
| | 334 |
| | 10,683 |
|
New Accounting Pronouncements
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP for the United States of America. To address current issues in accounting, regulatory bodies have issued the following new accounting pronouncements that may affect our accounting and/or disclosure.
Extraordinary and Unusual Items
In January 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued guidance that eliminates the accounting concept of extraordinary items. The objective of the new guidance is to reduce complexity in accounting standards while maintaining or improving the usefulness of information provided. The guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. We have elected to adopt effective January 1, 2015, without a material impact to our financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
In May 2014, the FASB issued guidance that addresses revenue from contracts with customers. The objective of the new guidance is to establish principles to report useful information to users of financial statements about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue from contracts with customers. This guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016. Early application of the standard is not permitted. The standard permits the use of either the retrospective application or cumulative effect transition method. We have not yet selected a transition method or determined the impact on our consolidated financial statements but we do not expect it to be material.
3. RATE MATTERS AND REGULATION
Regulatory Assets and Regulatory Liabilities
Regulatory assets represent incurred costs that have been deferred because they are probable of future recovery in customer prices. Regulatory liabilities represent probable future reductions in revenue or refunds to customers through the price setting process. Regulatory assets and liabilities reflected on our consolidated balance sheets are as follows.
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Regulatory Assets: | | | |
| Deferred employee benefit costs | $ | 435,590 |
| | $ | 277,122 |
|
| Amounts due from customers for future income taxes, net | 153,984 |
| | 163,742 |
|
| Depreciation | 68,422 |
| | 71,047 |
|
| Debt reacquisition costs | 61,079 |
| | 63,882 |
|
| Ad valorem tax | 39,428 |
| | 34,492 |
|
| Treasury yield hedges | 26,614 |
| | 27,594 |
|
| Asset retirement obligations | 26,106 |
| | 23,555 |
|
| Disallowed plant costs | 15,809 |
| | 15,964 |
|
| Wolf Creek outage | 11,165 |
| | 29,026 |
|
| Energy efficiency program costs | 8,933 |
| | 14,477 |
|
| Retail energy cost adjustment | — |
| | 22,138 |
|
| Other regulatory assets | 12,648 |
| | 12,375 |
|
| Total regulatory assets | $ | 859,778 |
| | $ | 755,414 |
|
| | | | |
| Regulatory Liabilities: | | | |
| Removal costs | $ | 88,242 |
| | $ | 114,148 |
|
| Deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback | 81,055 |
| | 86,551 |
|
| Nuclear decommissioning | 43,641 |
| | 43,272 |
|
| Retail energy cost adjustment | 33,274 |
| | 15,414 |
|
| Jurisdictional allowance for funds used during construction | 33,103 |
| | 7,893 |
|
| La Cygne leasehold dismantling costs | 22,918 |
| | 20,505 |
|
| Other post-retirement benefits costs | 15,473 |
| | 19,000 |
|
| Kansas tax credits | 12,725 |
| | 11,076 |
|
| Gain on sale of oil | 2,337 |
| | 4,278 |
|
| Fuel supply and electricity contracts | 1,738 |
| | 2,635 |
|
| Other regulatory liabilities | 8,979 |
| | 4,784 |
|
| Total regulatory liabilities | $ | 343,485 |
| | $ | 329,556 |
|
Below we summarize the nature and period of recovery for each of the regulatory assets listed in the table above.
Deferred employee benefit costs: Includes $399.8 million for pension and post-retirement benefit obligations and $35.8 million for actual pension expense in excess of the amount of such expense recognized in setting our prices. The increase from 2013 to 2014 is attributable primarily to a decrease in the discount rates used to calculate our and Wolf Creek's pension benefit obligations and the adoption of updated mortality tables. During 2015, we will amortize to expense approximately $39.5 million of the benefit obligations and approximately $9.8 million of the excess pension expense. We are amortizing the excess pension expense over a five-year period. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Amounts due from customers for future income taxes, net: In accordance with various orders, we have reduced our prices to reflect the income tax benefits associated with certain income tax deductions, thereby passing on these benefits to customers at the time we receive them. We believe it is probable that the net future increases in income taxes payable will be recovered from customers when these temporary income tax benefits reverse in future periods. We have recorded a regulatory asset, net of the regulatory liability, for these amounts. We also have recorded a regulatory liability for our obligation to customers for income taxes recovered in earlier periods when corporate income tax rates were higher than current income tax rates. This benefit will be returned to customers as these temporary differences reverse in future periods. The income tax-related regulatory assets and liabilities as well as unamortized investment tax credits are also temporary differences for which deferred income taxes have been provided. These items are measured by the expected cash flows to be received or settled in future prices. We do not earn a return on this net asset.
Depreciation: Represents the difference between regulatory depreciation expense and depreciation expense we record for financial reporting purposes. We earn a return on this asset and amortize the difference over the life of the related plant.
Debt reacquisition costs: Includes costs incurred to reacquire and refinance debt. These costs are amortized over the term of the new debt. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Ad valorem tax: Represents actual costs incurred for property taxes in excess of amounts collected in our prices. We expect to recover these amounts in our prices over a one-year period. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Treasury yield hedges: Represents the effective portion of losses on treasury yield hedge transactions. This amount will be amortized to interest expense over the term of the related debt. See Note 4, "Financial Instruments and Trading Securities—Cash Flow Hedges," for additional information regarding our treasury yield hedge transactions. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Asset retirement obligations: Represents amounts associated with our AROs as discussed in Note 14, "Asset Retirement Obligations." We recover these amounts over the life of the related plant. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Disallowed plant costs: Originally there was a decision to disallow certain costs related to the Wolf Creek plant. Subsequently, in 1987, the KCC revised its original conclusion and provided for recovery of an indirect disallowance with no return on investment. This regulatory asset represents the present value of the future expected revenues to be provided to recover these costs, net of the amounts amortized.
Wolf Creek outage: We defer the expenses associated with Wolf Creek's scheduled refueling and maintenance outages and amortize these expenses during the period between planned outages. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Energy efficiency program costs: We accumulate and defer for future recovery costs related to our various energy efficiency programs. We will amortize such costs over a one-year period. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Retail energy cost adjustment: We are allowed to adjust our retail prices to reflect changes in the cost of fuel and purchased power needed to serve our customers. This item represents the actual cost of fuel consumed in producing electricity and the cost of purchased power in excess of the amounts we have collected from customers. We expect to recover in our prices this shortfall over a one-year period. We do not earn a return on this asset.
Other regulatory assets: Includes various regulatory assets that individually are small in relation to the total regulatory asset balance. Other regulatory assets have various recovery periods. We do not earn a return on any of these assets.
Below we summarize the nature and period of amortization for each of the regulatory liabilities listed in the table above.
Removal costs: Represents amounts collected, but not yet spent, to dispose of plant assets that do not represent legal retirement obligations. This liability will be discharged as removal costs are incurred.
Deferred regulatory gain from sale leaseback: Represents the gain KGE recorded on the 1987 sale and leaseback of its 50% interest in La Cygne Generating Station (La Cygne) unit 2. We amortize the gain over the lease term.
Nuclear decommissioning: We have a legal obligation to decommission Wolf Creek at the end of its useful life. This amount represents the difference between the fair value of the assets held in a decommissioning trust and the amount recorded for the accumulated accretion and depreciation expense associated with our ARO. See Note 4, 5 and 14, "Financial Instruments and Trading Securities," "Financial Investments" and "Asset Retirement Obligations," respectively, for information regarding our nuclear decommissioning trust (NDT) and our ARO.
Retail energy cost adjustment: We are allowed to adjust our retail prices to reflect changes in the cost of fuel and purchased power needed to serve our customers. We bill customers based on our estimated costs. This item represents the amount we collected from customers that was in excess of our actual cost of fuel and purchased power. We will refund to customers this excess recovery over a one-year period.
Jurisdictional allowance for funds used during construction: This item represents AFUDC that is accrued subsequent to the time the associated construction charges are included in our rates and prior to the time the charges are placed in service. The AFUDC is amortized to depreciation expense over the useful life of the asset that is placed in service.
La Cygne leasehold dismantling costs: We are contractually obligated to dismantle a portion of La Cygne unit 2. This item represents amounts collected but not yet spent to dismantle this unit and the obligation will be discharged as we dismantle the unit.
Other post-retirement benefits costs: Represents amount of other post-retirement benefits expense recognized in setting our prices in excess of actual other post-retirement benefits expense. We amortize the amount over a five-year period.
Kansas tax credits: This item represents Kansas tax credits on investments in utility plant. Amounts will be credited to customers subsequent to their realization over the remaining lives of the utility plant giving rise to the tax credits.
Gain on sale of oil: We discontinued the use of a certain type of oil in our plants. As a result, we sold this oil inventory for a gain. This item represents the remaining portion of the gain that will be refunded to customers over a three-year period.
Fuel supply and electricity contracts: We use fair value accounting for some of our fuel supply and electricity contracts. This represents the non-cash net gain position on fuel supply and electricity contracts that are recorded at fair value. Under the RECA, fuel supply contract market gains accrue to the benefit of our customers.
Other regulatory liabilities: Includes various regulatory liabilities that individually are relatively small in relation to the total regulatory liability balance. Other regulatory liabilities will be credited over various periods.
KCC Proceedings
General and Abbreviated Rate Reviews
We, staff of the Kansas Corporation Commission (KCC) and a consumer advocate joined in a request filed with the KCC to defer depreciation expense and carrying costs related to our capital investment associated with environmental upgrades at La Cygne until new retail prices become effective following a general rate case expected to be filed in March 2015. We estimate our share of these deferred costs will be approximately $20.0 million and we expect to begin deferring these costs in March 2015. In September 2014, the KCC issued an order approving the joint application that will allow us to include these deferred costs in our next general rate case, which is expected to increase our annual revenues by approximately $4.0 million.
In November 2013, the KCC issued an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades, as discussed below, and to reflect cost reductions elsewhere. The new prices arewere expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $30.7 million.
In April 2012, the KCC issued an order expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $50.0 million. In addition, we revised our depreciation rates to reflect changes in the estimated useful lives of some of our depreciable assets. The change in estimate will decreasedecreased annual depreciation expense by $43.6 million. The new prices were effective shortly after having received the order.
Environmental Costs
In August 2011, the KCC issued an order ruling that Kansas City Power & Light Company's (KCPL) decision to make environmental upgrades at La Cygne to comply with environmental regulations is prudent and the $1.2 billion project cost estimate is reasonable. We have a 50% interest in La Cygne and intervened in the proceeding. The KCC denied our request to collect our approximately $610.0 million share of the capital investment for the environmental upgrades through our environmental cost recovery rider (ECRR). However, as noted above, we received an order regarding an abbreviated rate review to update our prices to include a portion of the capital costs associated with the project. We will request to collect our remaining investment in La Cygne environmental upgrades as part of a general rate case expected to be filed in March 2015.
We also make annual filings with the KCC to adjust our prices to include costs associated with investments in air quality equipment made during the prior year. In the most recent three years, the KCC issued orders related to such filings allowing us to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately:
$11.0 million effective in June 2014;
$27.3 million effective in June 2013; and
$19.5 million effective in June 2012; and
$10.4 million effective in June 2011.
Transmission Costs
We make annual filings with the KCC to adjust our prices to include updated transmission costs as reflected in our transmission formula rate discussed below. In the most recent three years, the KCC issued orders related to such filings allowing us to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately:
$41.0 million effective in April 2014;
$11.8 million effective in March 2013; and
$36.7 million effective in April 2012; and
$17.4 million effective in April 2011.
Energy Efficiency
We make annual filings with the KCC to adjust our prices to include previously deferred amounts associated with various energy efficiency programs. In the most recent three years, the KCC issued orders related to such filings allowingauthorizing us to adjust our annual retail revenues by approximately:
$5.0 million decrease effective in November 2014;
$1.3 million decrease effective in November 2013; and
$1.1 million increase effective in October 2012; and
$4.9 million increase effective in November 2011.
Property Tax Surcharge
We make annual filings with the KCC to adjust our prices to include the cost incurred for property taxes. In the most recent three years, the KCC issued orders related to such filings allowing us to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately:
$15.212.7 million effective in January 2013;2014;
$15.2 million effective in January 2013; and
$5.9 million effective in January 2012; and.
$0.7 million effective in January 2011.
FERC Proceedings
In October of each year, we post an updated transmission formula rate that includes projected transmission capital expenditures and operating costs for the following year. This rate provides the basis for our annual request with the KCC to adjust our retail prices to include updated transmission costs as noted above. In the most recent three years, we posted our transmission formula rate which was expected to increase our annual transmission revenues by approximately:
$44.3 million effective in January 2014;
$12.2 million effective in January 2013; and
$38.2 million effective in January 2012; and.
$15.9 million effectiveIn August 2014, the KCC filed a challenge with the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) regarding rate making as it pertains to the cost of interstate electrical transmission service we operate. The KCC is requesting that we lower our transmission return on equity by nearly two percentage points, which would result in January 2011.
reductions of the TFR revenue requirement if granted. We are currently in settlement discussions. If we are unable to reach a settlement, FERC may schedule a hearing.
4. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS AND TRADING SECURITIES
Values of Financial and Derivative Instruments
GAAP establishes a hierarchical framework for disclosing the transparency of the inputs utilized in measuring assets and liabilities at fair value. Our assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgment and may affect the classification of assets and liabilities within the fair value hierarchy levels. The three levels of the hierarchy and examples are as follows:
Level 1 - Quoted prices are available in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. The types of assets and liabilities included in level 1 are highly liquid and actively traded instruments with quoted prices, such as equities listed on public exchanges.
Level 2 - Pricing inputs are not quoted prices in active markets, but are either directly or indirectly observable. The types of assets and liabilities included in level 2 are typically measured at net asset value, comparable to actively traded securities or contracts, such as treasury securities with pricing interpolated from recent trades of similar securities, or priced with models using highly observable inputs.
Level 3 - Significant inputs to pricing have little or no transparency. The types of assets and liabilities included in level 3 are those with inputs requiring significant management judgment or estimation. Level 3 includes investments in private equity, real estate securities and other alternative investments, which are measured at net asset value.
We record cash and cash equivalents, short-term borrowings and variable rate debt on our consolidated balance sheets at cost, which approximates fair value. We measure the fair value of fixed rate debt, a level 2 measurement, based on quoted market prices for the same or similar issues or on the current rates offered for instruments of the same remaining maturities and redemption provisions. The recorded amount of accounts receivable and other current financial instruments approximates fair value.
All of our level 2 investments are held in investment funds that are measured at fair value using daily net asset values. In addition, we maintain certain level 3 investments in private equity, alternative investments and real estate securities that are also measured at fair value using net asset value, but require significant unobservable market information to measure the fair value of the underlying investments. The underlying investments in private equity are measured at fair value utilizing both market- and income-based models, public company comparables, investment cost or the value derived from subsequent financings. Adjustments are made when actual performance differs from expected performance; when market, economic or company-specific conditions change; and when other news or events have a material impact on the security. The underlying alternative investments include collateralized debt obligations, mezzanine debt and a variety of other investments. The fair value of these investments is measured using a variety of primarily market-based models utilizing inputs such as security prices, maturity, call features, ratings and other developments related to specific securities. The underlying real estate investments are measured at fair value using a combination of market- and income-based models utilizing market discount rates, projected cash flows and the estimated value into perpetuity.
We measure fair value based on information available as of the measurement date. The following table provides the carrying values and measured fair values of our fixed-rate debt.
| | | | As of December 31, 2013 | | As of December 31, 2012 | As of December 31, 2014 | | As of December 31, 2013 |
| | Carrying Value | | Fair Value | | Carrying Value | | Fair Value | Carrying Value | | Fair Value | | Carrying Value | | Fair Value |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Fixed-rate debt | $ | 3,102,500 |
| | $ | 3,294,209 |
| | $ | 2,702,500 |
| | $ | 3,178,752 |
| $ | 3,105,000 |
| | $ | 3,488,410 |
| | $ | 3,102,500 |
| | $ | 3,294,209 |
|
| Fixed-rate debt of VIEs | 221,682 |
| | 241,241 |
| | 247,624 |
| | 275,341 |
| 194,204 |
| | 213,579 |
| | 221,682 |
| | 241,241 |
|
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
The following table provides the amounts and their corresponding level of hierarchy for our assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Nuclear Decommissioning Trust: | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | $ | — |
| | $ | 49,957 |
| | $ | 5,817 |
| | $ | 55,774 |
|
| International equity | — |
| | 31,816 |
| | — |
| | 31,816 |
|
| Core bonds | — |
| | 18,107 |
| | — |
| | 18,107 |
|
| High-yield bonds | — |
| | 12,902 |
| | — |
| | 12,902 |
|
| Emerging market bonds | — |
| | 11,055 |
| | — |
| | 11,055 |
|
| Other fixed income | — |
| | 4,690 |
| | — |
| | 4,690 |
|
| Combination debt/equity/other fund | — |
| | 17,093 |
| | — |
| | 17,093 |
|
| Alternative investments | — |
| | — |
| | 15,675 |
| | 15,675 |
|
| Real estate securities | — |
| | — |
| | 8,511 |
| | 8,511 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 2 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2 |
|
| Total Nuclear Decommissioning Trust | 2 |
| | 145,620 |
| | 30,003 |
| | 175,625 |
|
| Trading Securities: (a) | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | — |
| | 18,075 |
| | — |
| | 18,075 |
|
| International equity | — |
| | 4,519 |
| | — |
| | 4,519 |
|
| Core bonds | — |
| | 12,166 |
| | — |
| | 12,166 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 166 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 166 |
|
| Total Trading Securities | 166 |
| | 34,760 |
| | — |
| | 34,926 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | $ | 168 |
| | $ | 180,380 |
| | $ | 30,003 |
| | $ | 210,551 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Nuclear Decommissioning Trust: | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | $ | — |
| | $ | 56,157 |
| | $ | 4,899 |
| | $ | 61,056 |
|
| International equity | — |
| | 30,041 |
| | — |
| | 30,041 |
|
| Core bonds | — |
| | 28,350 |
| | — |
| | 28,350 |
|
| High-yield bonds | — |
| | 8,782 |
| | — |
| | 8,782 |
|
| Emerging market bonds | — |
| | 6,428 |
| | — |
| | 6,428 |
|
| Combination debt/equity fund | — |
| | 8,194 |
| | — |
| | 8,194 |
|
| Real estate securities | — |
| | — |
| | 7,865 |
| | 7,865 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 38 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 38 |
|
| Total Nuclear Decommissioning Trust | 38 |
| | 137,952 |
| | 12,764 |
| | 150,754 |
|
| Trading Securities: | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | — |
| | 22,470 |
| | — |
| | 22,470 |
|
| International equity | — |
| | 5,744 |
| | — |
| | 5,744 |
|
| Core bonds | — |
| | 15,104 |
| | — |
| | 15,104 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 166 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 166 |
|
| Total Trading Securities | 166 |
| | 43,318 |
| | — |
| | 43,484 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | $ | 204 |
| | $ | 181,270 |
| | $ | 12,764 |
| | $ | 194,238 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2014 | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Nuclear Decommissioning Trust: | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | $ | — |
| | $ | 54,925 |
| | $ | 6,047 |
| | $ | 60,972 |
|
| International equity funds | — |
| | 30,791 |
| | — |
| | 30,791 |
|
| Core bond fund | — |
| | 19,289 |
| | — |
| | 19,289 |
|
| High-yield bond fund | — |
| | 13,198 |
| | — |
| | 13,198 |
|
| Emerging market bond fund | — |
| | 10,988 |
| | — |
| | 10,988 |
|
| Other fixed income fund | — |
| | 4,779 |
| | — |
| | 4,779 |
|
| Combination debt/equity/other funds | — |
| | 18,141 |
| | — |
| | 18,141 |
|
| Alternative investment fund | — |
| | — |
| | 16,970 |
| | 16,970 |
|
| Real estate securities fund | — |
| | — |
| | 9,548 |
| | 9,548 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 340 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 340 |
|
| Total Nuclear Decommissioning Trust | 340 |
| | 152,111 |
| | 32,565 |
| | 185,016 |
|
| Trading Securities: | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | — |
| | 18,698 |
| | — |
| | 18,698 |
|
| International equity fund | — |
| | 4,252 |
| | — |
| | 4,252 |
|
| Core bond fund | — |
| | 12,379 |
| | — |
| | 12,379 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 168 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 168 |
|
| Total Trading Securities | 168 |
| | 35,329 |
| | — |
| | 35,497 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | $ | 508 |
| | $ | 187,440 |
| | $ | 32,565 |
| | $ | 220,513 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Nuclear Decommissioning Trust: | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | $ | — |
| | $ | 49,957 |
| | $ | 5,817 |
| | $ | 55,774 |
|
| International equity funds | — |
| | 31,816 |
| | — |
| | 31,816 |
|
| Core bond fund | — |
| | 18,107 |
| | — |
| | 18,107 |
|
| High-yield bond fund | — |
| | 12,902 |
| | — |
| | 12,902 |
|
| Emerging market bond fund | — |
| | 11,055 |
| | — |
| | 11,055 |
|
| Other fixed income fund | — |
| | 4,690 |
| | — |
| | 4,690 |
|
| Combination debt/equity/other funds | — |
| | 17,093 |
| | — |
| | 17,093 |
|
| Alternative investment fund | — |
| | — |
| | 15,675 |
| | 15,675 |
|
| Real estate securities fund | — |
| | — |
| | 8,511 |
| | 8,511 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 2 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2 |
|
| Total Nuclear Decommissioning Trust | 2 |
| | 145,620 |
| | 30,003 |
| | 175,625 |
|
| Trading Securities: | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | — |
| | 18,075 |
| | — |
| | 18,075 |
|
| International equity fund | — |
| | 4,519 |
| | — |
| | 4,519 |
|
| Core bond fund | — |
| | 12,166 |
| | — |
| | 12,166 |
|
| Cash equivalents | 166 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 166 |
|
| Total Trading Securities | 166 |
| | 34,760 |
| | — |
| | 34,926 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | $ | 168 |
| | $ | 180,380 |
| | $ | 30,003 |
| | $ | 210,551 |
|
_______________
| |
(a) | The decrease in the fair value of trading securities was due to withdrawing $15.3 million. |
The following table provides reconciliations of assets and liabilities held in the NDT measured at fair value using significant level 3 inputs for the years ended December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
| | | | Domestic Equity | | Alternative Investments | | Real Estate Securities | | Net Balance | Domestic Equity Funds | | Alternative Investment Fund | | Real Estate Securities Fund | | Net Balance |
| | | (In Thousands) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | | $ | 5,817 |
| | $ | 15,675 |
| | $ | 8,511 |
| | $ | 30,003 |
|
| Total realized and unrealized gains included in: | | | | | | | | |
| Regulatory liabilities | | 391 |
| | 1,295 |
| | 1,037 |
| | 2,723 |
|
| Purchases | | 335 |
| | — |
| | 351 |
| | 686 |
|
| Sales | | (496 | ) | | — |
| | (351 | ) | | (847 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | | $ | 6,047 |
| | $ | 16,970 |
| | $ | 9,548 |
| | $ | 32,565 |
|
| | (In Thousands) | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | $ | 4,899 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 7,865 |
| | $ | 12,764 |
| $ | 4,899 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 7,865 |
| | $ | 12,764 |
|
| Total realized and unrealized gains included in: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Regulatory liabilities | 940 |
| | 675 |
| | 646 |
| | 2,261 |
| 940 |
| | 675 |
| | 646 |
| | 2,261 |
|
| Purchases | 341 |
| | 15,000 |
| | 287 |
| | 15,628 |
| 341 |
| | 15,000 |
| | 287 |
| | 15,628 |
|
| Sales | (363 | ) | | — |
| | (287 | ) | | (650 | ) | (363 | ) | | — |
| | (287 | ) | | (650 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | $ | 5,817 |
| | $ | 15,675 |
| | $ | 8,511 |
| | $ | 30,003 |
| $ | 5,817 |
| | $ | 15,675 |
|
| $ | 8,511 |
|
| $ | 30,003 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | $ | 3,931 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 7,095 |
| | $ | 11,026 |
| |
| Total realized and unrealized gains included in: | | | | | | | | |
| Regulatory liabilities | 90 |
| | — |
| | 770 |
| | 860 |
| |
| Purchases | 891 |
| | — |
| | 320 |
| | 1,211 |
| |
| Sales | (13 | ) | | — |
| | (320 | ) | | (333 | ) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | $ | 4,899 |
| | $ | — |
|
| $ | 7,865 |
|
| $ | 12,764 |
| |
Portions of the gains and losses contributing to changes in net assets in the above table are unrealized. The following table summarizes the unrealized gains and losses we recorded to regulatory liabilities on our consolidated financial statements during the years ended December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, attributed to level 3 assets and liabilities.
| | | | Domestic Equity | | Alternative Investments | | Real Estate Securities | | Net Balance | Domestic
Equity Funds | | Alternative Investment Fund | | Real Estate
Securities Fund | | Net
Balance |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | | $ | (105 | ) | | $ | 1,296 |
| | $ | 685 |
| | $ | 1,876 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2013 | $ | 577 |
| | $ | 675 |
| | $ | 359 |
| | $ | 1,611 |
| 577 |
| | 675 |
| | 359 |
| | 1,611 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2012 | 77 |
| | — |
| | 451 |
| | 528 |
| |
Some of our investments in the NDT and our trading securities portfolio are measured at net asset value, do not have readily determinable fair values and are either with investment companies or companies that follow accounting guidance consistent with investment companies. In certain situations these investments may have redemption restrictions. The following table provides additional information on these investments.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2013 | | As of December 31, 2012 | | As of December 31, 2013 |
| | Fair Value | | Unfunded Commitments | | Fair Value | | Unfunded Commitments | | Redemption Frequency | | Length of Settlement |
| | (In Thousands) | | | | |
| Nuclear Decommissioning Trust: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | $ | 5,817 |
| | $ | 2,683 |
| | $ | 4,899 |
| | $ | 1,024 |
| | (a) | | (a) |
| Alternative investments | 15,675 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (b) | | (b) |
| Real estate securities | 8,511 |
| | — |
| | 7,865 |
| | — |
| | Quarterly | | 80 days |
| Total Nuclear Decommissioning Trust | $ | 30,003 |
| | $ | 2,683 |
| | $ | 12,764 |
| | $ | 1,024 |
| | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trading Securities: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | $ | 18,075 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 22,470 |
| | $ | — |
| | Upon Notice | | 1 day |
| International equity | 4,519 |
| | — |
| | 5,744 |
| | — |
| | Upon Notice | | 1 day |
| Core bonds | 12,166 |
| | — |
| | 15,104 |
| | — |
| | Upon Notice | | 1 day |
| Total Trading Securities | 34,760 |
| | — |
| | 43,318 |
| | — |
| | | | |
| Total | $ | 64,763 |
| | $ | 2,683 |
| | $ | 56,082 |
| | $ | 1,024 |
| | | | |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, 2014 | | As of December 31, 2013 | | As of December 31, 2014 |
| | Fair Value | | Unfunded Commitments | | Fair Value | | Unfunded Commitments | | Redemption Frequency | | Length of Settlement |
| | (In Thousands) | | | | |
| Nuclear Decommissioning Trust: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | $ | 6,047 |
| | $ | 2,348 |
| | $ | 5,817 |
| | $ | 2,683 |
| | (a) | | (a) |
| Alternative investment fund | 16,970 |
| | — |
| | 15,675 |
| | — |
| | (b) | | (b) |
| Real estate securities fund | 9,548 |
| | — |
| | 8,511 |
| | — |
| | Quarterly | | 80 days |
| Total Nuclear Decommissioning Trust | $ | 32,565 |
| | $ | 2,348 |
| | $ | 30,003 |
| | $ | 2,683 |
| | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trading Securities: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | $ | 18,698 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 18,075 |
| | $ | — |
| | Upon Notice | | 1 day |
| International equity funds | 4,252 |
| | — |
| | 4,519 |
| | — |
| | Upon Notice | | 1 day |
| Core bond fund | 12,379 |
| | — |
| | 12,166 |
| | — |
| | Upon Notice | | 1 day |
| Total Trading Securities | 35,329 |
| | — |
| | 34,760 |
| | — |
| | | | |
| Total | $ | 67,894 |
| | $ | 2,348 |
| | $ | 64,763 |
| | $ | 2,683 |
| | | | |
_______________
| |
| (a) | This investment is in three long-term private equity funds that do not permit early withdrawal. Our investments in these funds cannot be distributed until the underlying investments have been liquidated which may take years from the date of initial liquidation. One fund hasTwo funds have begun to make distributions and we expect the other to begin in 2014.distributions. Our initial investment in the third fund occurred in the 3rdthird quarter of 2013. This fund's term will be 15 years, subject to the General Partner'sgeneral partner's right to extend the term for up to three additional one-year periods. |
| |
| (b) | This fund has an initial lock-up period of 24 months.months, which began in April 2013. Redemptions are allowed, on a quarterly basis, after 24 months at the sole discretion of the fund's board of directors. A 65-day notice of redemption is required. There is a holdback on final redemptions. |
Nonrecurring Fair Value Measurements
We have recognized legal obligations associated with the disposal of long-lived assets that result from the acquisition, construction, development or normal operations of such assets. In 2013, we recorded no additional AROs. In 2012, we recorded $3.1 million of additional AROs. We initially record AROs at fair value for the estimated cost to satisfy the retirement obligation.
We measure the fair value of AROs by estimating the cost to satisfy the retirement obligation then discounting that value at a risk- and inflation-adjusted rate. To determine the cost to satisfy the retirement obligation, experts reporting to the Chief Operating Officer must estimate the cost of basic inputs such as labor, energy, materials, timing and disposal and make assumptions on the method of disposal or decommissioning. Our estimates are validated with contractor estimates and when we satisfy other similar obligations. We estimate the cost to satisfy the 2012 ARO layer is approximately $3.1 million.
To determine the appropriate discount rate, we use observable inputs such as inflation rates, short and long-term yields for U.S. government securities and our nonperformance risk. Due to the significant unobservable inputs required in our measurement, we have determined that our fair value measurements of our AROs are level 3 in the fair value hierarchy. For additional information on our AROs, see Note 14, "Asset Retirement Obligations."
Derivative Instruments
Cash Flow Hedges
In 2011, we entered into treasury yield hedge transactions to hedge our interest rate risk associated with a $125.0 million portion of a forecasted issuance of fixed rate debt. These transactions were designated and qualified as cash flow hedges and measured at fair value by estimating the net present value of a series of payments using market-based models with observable inputs such as the spread between the 30-year U.S Treasury bill yield and the contracted, fixed yield. As a result of regulatory accounting treatment, we report the effective portion of the gains or losses on these derivative instruments as a regulatory liability or regulatory asset and amortize such amounts to interest expense over the term of the related debt. During the first quarter ofIn 2012, we settled the treasury yield hedge transactions for a cost of $29.7 million, which will be amortized to interest expense over the 30-year term of the debt issued in March 2012. See Note 9, "Long-Term Debt" for additional information regarding the debt issuance. As of December 31, 20132014 and 2012,2013, we had recorded $27.6$26.6 million and $28.6$27.6 million, respectively, as a regulatory asset.
Price Risk
We use various types of fuel, including coal, natural gas, uranium and diesel to operate our plants and also purchase power to meet customer demand. Our prices and consolidated financial results are exposed to market risks from commodity price changes for electricity and other energy-related products as well as from interest rates. Volatility in these markets impacts our costs of purchased power, costs of fuel for our generating plants and our participation in energy markets. We strive to manage our customers' and our exposure to these market risks through regulatory, operating and financing activities and, when we deem appropriate, we economically hedge a portion of these risks through the use of derivative financial instruments for non-trading purposes.
Interest Rate Risk
We have entered into numerous fixed and variable rate debt obligations. For details, see Note 9, "Long-Term Debt." We manage our interest rate risk related to these debt obligations by limiting our exposure to variable interest rate debt, diversifying maturity dates and entering into treasury yield hedge transactions. We may also use other financial derivative instruments such as interest rate swaps.
5. FINANCIAL INVESTMENTS
We report our investments in equity and debt securities at fair value and use the specific identification method to determine their realized gains and losses. We classify these investments as either trading securities or available-for-sale securities as described below.
Trading Securities
We hold equity and debt investments which we classify as trading securities in a trust used to fund certain retirement benefit obligations. These obligations oftotaled $29.8 million and $27.0 million and $30.0 million as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, respectively. For additional information on our benefit obligations, see Note 11, "Employee Benefit Plans."
As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, we measured the fair value of trust assets at $34.9$35.5 million and $43.534.9 million, respectively. We include unrealized gains or losses on these securities in investment earnings on our consolidated statements of income. For the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012, we recorded unrealized gains of $2.6 million, $6.7 million $4.1 million and $0.3$4.1 million, respectively.
Available-for-Sale Securities
We hold investments in a trust for the purpose of funding the decommissioning of Wolf Creek. We have classified these investments as available-for-sale and have recorded all such investments at their fair market value as of December 31, 2013,2014 and December 31, 2012. As of December 31, 2013, the fair value of available-for-sale bond funds was $46.8 million. The NDT did not have investments in debt securities outside of investment funds as of December 31, 2013.
Using the specific identification method to determine cost, we realized gains on our available-for-sale securities of $0.1 million in 2014, $5.3 million in 2013, and $0.6 million in 2012 and $1.3 million in 2011. We record net realized and unrealized gains and losses in regulatory liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets. This reporting is consistent with the method we use to account for the decommissioning costs we recover in our prices. Gains or losses on assets in the trust fund are recorded as increases or decreases, respectively, to regulatory liabilities and could result in lower or higher funding requirements for decommissioning costs, which we believe would be reflected in the prices paid by our customers.
The following table presents the cost, gross unrealized gains and losses, fair value and allocation of investments in the NDT fund as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Gross Unrealized | | | | |
| Security Type | | Cost | | Gain | | Loss | | Fair Value | | Allocation |
| | | (Dollars In Thousands) | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | 40,976 |
| | $ | 14,799 |
| | $ | (1 | ) | | $ | 55,774 |
| | 32 | % |
| International equity | | 26,581 |
| | 5,266 |
| | (31 | ) | | 31,816 |
| | 18 | % |
| Core bonds | | 18,287 |
| | — |
| | (180 | ) | | 18,107 |
| | 10 | % |
| High-yield bonds | | 12,275 |
| | 627 |
| | — |
| | 12,902 |
| | 7 | % |
| Emerging market bonds | | 12,207 |
| | — |
| | (1,152 | ) | | 11,055 |
| | 6 | % |
| Other fixed income | | 4,684 |
| | 6 |
| | — |
| | 4,690 |
| | 3 | % |
| Combination debt/equity/other fund | | 14,964 |
| | 2,380 |
| | (251 | ) | | 17,093 |
| | 10 | % |
| Alternative investments | | 15,000 |
| | 675 |
| | — |
| | 15,675 |
| | 9 | % |
| Real estate securities | | 10,268 |
| | — |
| | (1,757 | ) | | 8,511 |
| | 5 | % |
| Cash equivalents | | 2 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2 |
| | <1% |
|
| Total | | $ | 155,244 |
| | $ | 23,753 |
| | $ | (3,372 | ) | | $ | 175,625 |
| | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | 53,598 |
| | $ | 7,458 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 61,056 |
| | 41 | % |
| International equity | | 28,248 |
| | 1,793 |
| | — |
| | 30,041 |
| | 20 | % |
| Core bonds | | 27,309 |
| | 1,041 |
| | — |
| | 28,350 |
| | 19 | % |
| High-yield bonds | | 8,022 |
| | 760 |
| | — |
| | 8,782 |
| | 6 | % |
| Emerging market bonds | | 6,080 |
| | 348 |
| | — |
| | 6,428 |
| | 4 | % |
| Combination debt/equity fund | | 8,074 |
| | 120 |
| | — |
| | 8,194 |
| | 5 | % |
| Real estate securities | | 9,981 |
| | — |
| | (2,116 | ) | | 7,865 |
| | 5 | % |
| Cash equivalents | | 38 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 38 |
| | <1% |
|
| Total | | $ | 141,350 |
| | $ | 11,520 |
| | $ | (2,116 | ) | | $ | 150,754 |
| | 100 | % |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Gross Unrealized | | | | |
| Security Type | | Cost | | Gain | | Loss | | Fair Value | | Allocation |
| | | (Dollars In Thousands) | | |
| As of December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | | $ | 46,126 |
| | $ | 14,853 |
| | $ | (7 | ) | | $ | 60,972 |
| | 33 | % |
| International equity funds | | 27,521 |
| | 3,683 |
| | (413 | ) | | 30,791 |
| | 17 | % |
| Core bond fund | | 18,811 |
| | 478 |
| | — |
| | 19,289 |
| | 10 | % |
| High-yield bond fund | | 13,342 |
| | — |
| | (144 | ) | | 13,198 |
| | 7 | % |
| Emerging market bond fund | | 12,556 |
| | — |
| | (1,568 | ) | | 10,988 |
| | 6 | % |
| Other fixed income fund | | 4,798 |
| | — |
| | (19 | ) | | 4,779 |
| | 3 | % |
| Combination debt/equity/other funds | | 14,975 |
| | 3,786 |
| | (620 | ) | | 18,141 |
| | 10 | % |
| Alternative investment fund | | 15,000 |
| | 1,970 |
| | — |
| | 16,970 |
| | 9 | % |
| Real estate securities fund | | 10,619 |
| | — |
| | (1,071 | ) | | 9,548 |
| | 5 | % |
| Cash equivalents | | 340 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 340 |
| | <1% |
|
| Total | | $ | 164,088 |
| | $ | 24,770 |
| | $ | (3,842 | ) | | $ | 185,016 |
| | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | | $ | 40,976 |
| | $ | 14,799 |
| | $ | (1 | ) | | $ | 55,774 |
| | 32 | % |
| International equity funds | | 26,581 |
| | 5,266 |
| | (31 | ) | | 31,816 |
| | 18 | % |
| Core bond fund | | 18,287 |
| | — |
| | (180 | ) | | 18,107 |
| | 10 | % |
| High-yield bond fund | | 12,275 |
| | 627 |
| | — |
| | 12,902 |
| | 7 | % |
| Emerging market bond fund | | 12,207 |
| | — |
| | (1,152 | ) | | 11,055 |
| | 6 | % |
| Other fixed income fund | | 4,684 |
| | 6 |
| | — |
| | 4,690 |
| | 3 | % |
| Combination debt/equity/other funds | | 14,964 |
| | 2,380 |
| | (251 | ) | | 17,093 |
| | 10 | % |
| Alternative investment fund | | 15,000 |
| | 675 |
| | — |
| | 15,675 |
| | 9 | % |
| Real estate securities fund | | 10,268 |
| | — |
| | (1,757 | ) | | 8,511 |
| | 5 | % |
| Cash equivalents | | 2 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2 |
| | <1% |
|
| Total | | $ | 155,244 |
| | $ | 23,753 |
| | $ | (3,372 | ) | | $ | 175,625 |
| | 100 | % |
The following table presents the fair value and the gross unrealized losses of the available-for-sale securities held in the NDT fund aggregated by investment category and the length of time that individual securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Less than 12 Months | | 12 Months or Greater | | Total |
| | Fair Value | | Gross Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Gross Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Gross Unrealized Losses |
| | (In Thousands) |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | $ | 59 |
| | $ | (1 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 59 |
| | $ | (1 | ) |
| International equity | 6,244 |
| | (31 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 6,244 |
| | (31 | ) |
| Core bonds | 18,107 |
| | (180 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 18,107 |
| | (180 | ) |
| Emerging market bonds | 11,055 |
| | (1,152 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 11,055 |
| | (1,152 | ) |
| Combination debt/equity/other funds | 6,283 |
| | (251 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 6,283 |
| | (251 | ) |
| Real estate securities | — |
| | — |
| | 8,511 |
| | (1,757 | ) | | 8,511 |
| | (1,757 | ) |
| Total | $ | 41,748 |
| | $ | (1,615 | ) | | $ | 8,511 |
| | $ | (1,757 | ) | | $ | 50,259 |
| | $ | (3,372 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| As of December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | |
| |
|
| Real estate securities | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 7,865 |
| | $ | (2,116 | ) | | $ | 7,865 |
| | $ | (2,116 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Less than 12 Months | | 12 Months or Greater | | Total |
| | Fair Value | | Gross Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Gross Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Gross Unrealized Losses |
| | (In Thousands) |
| As of December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 263 |
| | $ | (7 | ) | | $ | 263 |
| | $ | (7 | ) |
| International equity funds | 5,905 |
| | (413 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 5,905 |
| | (413 | ) |
| High-yield bond fund | 13,198 |
| | (144 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 13,198 |
| | (144 | ) |
| Emerging market bond fund | — |
| | — |
| | 10,988 |
| | (1,568 | ) | | 10,988 |
| | (1,568 | ) |
| Other fixed income fund | 4,779 |
| | (19 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 4,779 |
| | (19 | ) |
| Combination debt/equity/other funds | — |
| | — |
| | 5,892 |
| | (620 | ) | | 5,892 |
| | (620 | ) |
| Real estate securities fund | — |
| | — |
| | 9,548 |
| | (1,071 | ) | | 9,548 |
| | (1,071 | ) |
| Total | $ | 23,882 |
| | $ | (576 | ) | | $ | 26,691 |
| | $ | (3,266 | ) | | $ | 50,573 |
| | $ | (3,842 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | |
| |
|
| Domestic equity funds | $ | 59 |
| | $ | (1 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 59 |
| | $ | (1 | ) |
| International equity funds | 6,244 |
| | (31 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 6,244 |
| | (31 | ) |
| Core bond fund | 18,107 |
| | (180 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 18,107 |
| | (180 | ) |
| Emerging market bond fund | 11,055 |
| | (1,152 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 11,055 |
| | (1,152 | ) |
| Combination debt/equity/other funds | 6,283 |
| | (251 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 6,283 |
| | (251 | ) |
| Real estate securities fund | — |
| | — |
| | 8,511 |
| | (1,757 | ) | | 8,511 |
| | (1,757 | ) |
| Total | $ | 41,748 |
| | $ | (1,615 | ) | | $ | 8,511 |
| | $ | (1,757 | ) | | $ | 50,259 |
| | $ | (3,372 | ) |
6. PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
The following is a summary of our property, plant and equipment balance.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Electric plant in service | $ | 9,753,787 |
| | $ | 9,389,192 |
| $ | 10,620,292 |
| | $ | 9,753,787 |
|
| Electric plant acquisition adjustment | 802,318 |
| | 802,318 |
| 802,318 |
| | 802,318 |
|
| Accumulated depreciation | (3,971,735 | ) | | (3,791,545 | ) | (4,112,483 | ) | | (3,971,735 | ) |
| | 6,584,370 |
| | 6,399,965 |
| 7,310,127 |
| | 6,584,370 |
|
| Construction work in progress | 904,586 |
| | 532,332 |
| 773,144 |
| | 904,586 |
|
| Nuclear fuel, net | 62,960 |
| | 81,468 |
| 79,637 |
| | 62,960 |
|
| Net property, plant and equipment | $ | 7,551,916 |
| | $ | 7,013,765 |
| $ | 8,162,908 |
| | $ | 7,551,916 |
|
The following is a summary of property, plant and equipment of VIEs.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Electric plant of VIEs | $ | 513,793 |
| | $ | 543,548 |
| $ | 497,999 |
| | $ | 513,793 |
|
| Accumulated depreciation of VIEs | (217,167 | ) | | (221,573 | ) | (219,426 | ) | | (217,167 | ) |
| Net property, plant and equipment of VIEs | $ | 296,626 |
| | $ | 321,975 |
| $ | 278,573 |
| | $ | 296,626 |
|
We revised our depreciation rates to reflect changes in the estimated useful lives of some of our assets in 2012. We recorded depreciation expense on property, plant and equipment of $263.8 million in 2014, $249.9 million in 2013, and $247.8 million in 2012 and $262.6 million in 2011. Approximately $9.7 million, $9.8$9.7 million and $9.8 million of depreciation expense in 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012, respectively, was attributable to property, plant and equipment of VIEs.
7. JOINT OWNERSHIP OF UTILITY PLANTS
Under joint ownership agreements with other utilities, we have undivided ownership interests in four electric generating stations. Energy generated and operating expenses are divided on the same basis as ownership with each owner reflecting its respective costs in its statements of income and each owner responsible for its own financing. Information relative to our ownership interests in these facilities as of December 31, 20132014, is shown in the table below.
| | | Plant | | In-Service Dates | | Investment | | Accumulated Depreciation | | Construction Work in Progress | | Net MW | | Ownership Percentage | | In-Service Dates | | Investment | | Accumulated Depreciation | | Construction Work in Progress | | Net MW | | Ownership Percentage |
| | | (Dollars in Thousands) | | | (Dollars in Thousands) | |
| La Cygne unit 1 (a) | | June 1973 | | $ | 334,054 |
| | $ | 151,674 |
| | $ | 280,688 |
| | 368 | | 50 | | June 1973 | | $ | 345,866 |
| | $ | 157,550 |
| | $ | 368,445 |
| | 367 | | 50 |
| JEC unit 1 (a) | | July 1978 | | 530,407 |
| | 194,944 |
| | 166,073 |
| | 661 | | 92 | | July 1978 | | 789,142 |
| | 189,973 |
| | 11,150 |
| | 661 | | 92 |
| JEC unit 2 (a) | | May 1980 | | 504,508 |
| | 190,660 |
| | 13,138 |
| | 658 | | 92 | | May 1980 | | 540,871 |
| | 190,769 |
| | 3,189 |
| | 658 | | 92 |
| JEC unit 3 (a) | | May 1983 | | 713,937 |
| | 296,278 |
| | 1,906 |
| | 664 | | 92 | | May 1983 | | 709,497 |
| | 309,540 |
| | 3,246 |
| | 664 | | 92 |
| Wolf Creek (b) | | Sept. 1985 | | 1,596,382 |
| | 773,724 |
| | 144,083 |
| | 547 | | 47 | | Sept. 1985 | | 1,818,005 |
| | 788,602 |
| | 73,333 |
| | 549 | | 47 |
| State Line (c) | | June 2001 | | 110,408 |
| | 48,357 |
| | 305 |
| | 201 | | 40 | | June 2001 | | 100,671 |
| | 53,347 |
| | 22 |
| | 193 | | 40 |
| Total | | $ | 3,789,696 |
| | $ | 1,655,637 |
| | $ | 606,193 |
| | 3,099 | | | $ | 4,304,052 |
| | $ | 1,689,781 |
| | $ | 459,385 |
| | 3,092 | |
_______________
| |
| (a) | Jointly owned with KCPL. Our 8% leasehold interest in JECJeffrey Energy Center (JEC) that is consolidated as a VIE is reflected in the net megawatts (MW) and ownership percentage provided above, but not in the other amounts in the table. |
| |
| (b) | Jointly owned with KCPL and Kansas Electric Power Cooperative, Inc. |
(c) Jointly owned with Empire District Electric Company.
We include in operating expenses on our consolidated statements of income our share of operating expenses of the above plants. Our share of fuel expense for the above plants is generally based on the amount of power we take from the respective plants. Our share of other transactions associated with the plants is included in the appropriate classification on our consolidated financial statements.
In addition, we also consolidate a VIE that holds our 50% leasehold interest in La Cygne unit 2, which represents 341 MW of net capacity. The VIE's investment in the 50% interest was $392.1 million and accumulated depreciation was $187.4$194.5 million as of December 31, 20132014. We include these amounts in property, plant and equipment of variable interest entities,VIEs, net on our consolidated balance sheets. See Note 17, "Variable Interest Entities," for additional information about VIEs.
8. SHORT-TERM DEBT
In July 2013September 2014, Westar Energy extended the term of its $730.0 million revolving credit facility to terminate in September 20172018., $81.4 million of which will expire in September 2017. As long as there is no default under the facility, Westar Energy may extend the facility up to an additional yeartwo years and may increase the aggregate amount of borrowings under the facility to $1.0 billion, both subject to lender participation. All borrowings under the facility are secured by KGE first mortgage bonds. As of December 31, 20132014, no amounts had been borrowed and $18.415.6 million of letters of credit had been issued under this revolving credit facility. As of December 31, 20122013, noneno amounts had been borrowed and $13.818.4 million of letters of credit had been issued under this revolving credit facility.
In 2011, Westar Energy entered into a revolving credit facility with a syndicate of banks for $270.0 million. In February 2014, Westar Energy extended the term of the $270.0 million revolving credit facility to February 2017, provided thatof which $20.0 million of this facility will terminate in February 2016. AsSo long as there is no default under the facility, Westar Energy may increase the aggregate amount of borrowings under the facility to $400.0 million, subject to lender participation. All borrowings under the facility are secured by KGE first mortgage bonds. As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, Westar Energy had no borrowed amounts or letters of credit outstanding under this revolving credit facility.
In 2011, Westar Energy entered intomaintains a commercial paper program pursuant to which it may issue commercial paper up to a maximum aggregate amount outstanding at any one time of $1.0 billion. This program is supported by Westar Energy's revolving credit facilities. Maturities of commercial paper issuances may not exceed 365 days from the date of issuance and proceeds from such issuances will be used to temporarily fund capital expenditures, to repay borrowings under Westar Energy's revolving credit facilities,redeem debt on an interim basis, for working capital and/or for other general corporate purposes. Westar Energy had issued$257.6 million and $134.6 million and $339.2 millionof commercial paper issued and outstanding as of December 31, 20132014 and 2012,2013, respectively.
In addition, total combined borrowings under Westar Energy's commercial paper program and revolving credit facilities may not exceed $1.0 billion at any given time. The weighted average interest rate on short-term borrowings outstanding as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, was 0.52% and December 31, 2012, was 0.28% and 0.46%, respectively. Additional information regarding our short-term debt is as follows.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Weighted average short-term debt outstanding during the year | $ | 228,352 |
| | $ | 298,907 |
| $ | 232,336 |
| | $ | 228,352 |
|
| Weighted daily average interest rates during the year, excluding fees | 0.39 | % | | 0.55 | % | 0.30 | % | | 0.39 | % |
Our interest expense on short-term debt was $2.0 million in 2014, $2.4 million in 2013, and $3.2 million in 2012 and $3.9 million in 2011.
9. LONG-TERM DEBT
Outstanding Debt
The following table summarizes our long-term debt outstanding.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Westar Energy | | | | | | |
| First mortgage bond series: | | | | | | |
| 6.00% due 2014 | $ | 250,000 |
| | $ | 250,000 |
| $ | — |
| | $ | 250,000 |
|
| 5.15% due 2017 | 125,000 |
| | 125,000 |
| 125,000 |
| | 125,000 |
|
| 8.625% due 2018 | 300,000 |
| | 300,000 |
| 300,000 |
| | 300,000 |
|
| 5.10% due 2020 | 250,000 |
| | 250,000 |
| 250,000 |
| | 250,000 |
|
| 5.95% due 2035 | 125,000 |
| | 125,000 |
| 125,000 |
| | 125,000 |
|
| 5.875% due 2036 | 150,000 |
| | 150,000 |
| 150,000 |
| | 150,000 |
|
| 4.125% due 2042 | 550,000 |
| | 550,000 |
| 550,000 |
| | 550,000 |
|
| 4.10% due 2043 | 250,000 |
| | — |
| 430,000 |
| | 250,000 |
|
| 4.625% due 2043 | 250,000 |
| | — |
| 250,000 |
| | 250,000 |
|
| | 2,250,000 |
| | 1,750,000 |
| 2,180,000 |
| | 2,250,000 |
|
| Pollution control bond series: | | | | | | |
| Variable due 2032, 0.12% as of December 31, 2013; 0.32% as of December 31, 2012 | 45,000 |
| | 45,000 |
| |
| Variable due 2032, 0.12% as of December 31, 2013; 0.26% as of December 31, 2012 | 30,500 |
| | 30,500 |
| |
| Variable due 2032, 0.06% as of December 31, 2014; 0.12% as of December 31, 2013 | | 45,000 |
| | 45,000 |
|
| Variable due 2032, 0.08% as of December 31, 2014; 0.12% as of December 31, 2013 | | 30,500 |
| | 30,500 |
|
| | 75,500 |
| | 75,500 |
| 75,500 |
| | 75,500 |
|
| | | | | | | |
| KGE | | | | | | |
| First mortgage bond series: | | | | | | |
| 6.70% due 2019 | 300,000 |
| | 300,000 |
| 300,000 |
| | 300,000 |
|
| 6.15% due 2023 | 50,000 |
| | 50,000 |
| 50,000 |
| | 50,000 |
|
| 6.53% due 2037 | 175,000 |
| | 175,000 |
| 175,000 |
| | 175,000 |
|
| 6.64% due 2038 | 100,000 |
| | 100,000 |
| 100,000 |
| | 100,000 |
|
| 4.30% due 2044 | | 250,000 |
| | — |
|
| | 625,000 |
| | 625,000 |
| 875,000 |
| | 625,000 |
|
| Pollution control bond series: | | | | | | |
| Variable due 2027, 0.10% as of December 31, 2013; 0.26% as of December 31, 2012 | 21,940 |
| | 21,940 |
| |
| Variable due 2027, 0.08% as of December 31, 2014; 0.10% as of December 31, 2013 | | 21,940 |
| | 21,940 |
|
| 5.30% due 2031 | 108,600 |
| | 108,600 |
| — |
| | 108,600 |
|
| 5.30% due 2031 | 18,900 |
| | 18,900 |
| — |
| | 18,900 |
|
| 4.85% due 2031 | 50,000 |
| | 50,000 |
| 50,000 |
| | 50,000 |
|
| 5.60% due 2031 | — |
| | 50,000 |
| |
| 6.00% due 2031 | — |
| | 50,000 |
| |
| 5.00% due 2031 | 50,000 |
| | 50,000 |
| — |
| | 50,000 |
|
| Variable due 2032, 0.10% as of December 31, 2013; 0.26% as of December 31, 2012 | 14,500 |
| | 14,500 |
| |
| Variable due 2032, 0.10% as of December 31, 2013; 0.26% as of December 31, 2012 | 10,000 |
| | 10,000 |
| |
| Variable due 2032, 0.08% as of December 31, 2014; 0.10% as of December 31, 2013 | | 14,500 |
| | 14,500 |
|
| Variable due 2032, 0.08% as of December 31, 2014; 0.10% as of December 31, 2013 | | 10,000 |
| | 10,000 |
|
| | 273,940 |
| | 373,940 |
| 96,440 |
| | 273,940 |
|
| | | | | | | |
| Total long-term debt | 3,224,440 |
| | 2,824,440 |
| 3,226,940 |
| | 3,224,440 |
|
| Unamortized debt discount (a) | (5,482 | ) | | (5,169 | ) | (11,401 | ) | | (5,482 | ) |
| Long-term debt due within one year | (250,000 | ) | | — |
| — |
| | (250,000 | ) |
| Long-term debt, net | $ | 2,968,958 |
|
| $ | 2,819,271 |
| $ | 3,215,539 |
|
| $ | 2,968,958 |
|
| | | | | | | |
| Variable Interest Entities | | | | | | |
| 6.99% due 2014 (b) | 316 |
| | 866 |
| — |
| | 316 |
|
| 5.92 % due 2019 (b) | 13,243 |
| | 17,630 |
| |
| 5.92% due 2019 (b) | | 8,413 |
| | 13,243 |
|
| 5.647% due 2021 (b) | 208,123 |
| | 229,128 |
| 185,791 |
| | 208,123 |
|
| Total long-term debt of variable interest entities | 221,682 |
| | 247,624 |
| 194,204 |
| | 221,682 |
|
| Unamortized debt premium (a) | 599 |
| | 1,061 |
| 294 |
| | 599 |
|
| Long-term debt of variable interest entities due within one year | (27,479 | ) |
| (25,942 | ) | (27,933 | ) |
| (27,479 | ) |
| Long-term debt of variable interest entities, net | $ | 194,802 |
|
| $ | 222,743 |
| $ | 166,565 |
|
| $ | 194,802 |
|
_______________
(a) We amortize debt discounts and premiums to interest expense over the term of the respective issues.
(b) Portions of our payments related to this debt reduce the principal balances each year until maturity.
The Westar Energy and KGE mortgages each contain provisions restricting the amount of first mortgage bonds that could be issued by each entity. We must comply with such restrictions prior to the issuance of additional first mortgage bonds or other secured indebtedness.
The amount of Westar Energy first mortgage bonds authorized by its Mortgage and Deed of Trust, dated July 1, 1939, as supplemented, is subject to certain limitations as described below. The amount of KGE first mortgage bonds authorized by the KGE Mortgage and Deed of Trust, dated April 1, 1940, as supplemented and amended, is limited to a maximum of $3.5 billion, unless amended further. First mortgage bonds are secured by utility assets. Amounts of additional bonds that may be issued are subject to property, earnings and certain restrictive provisions, except in connection with certain refundings, of each mortgage. As of December 31, 20132014, approximately $505.3$743.2 million principal amount of additional first mortgage bonds could be issued under the most restrictive provisions in Westar Energy's mortgage. As of December 31, 20132014, approximately $1.1$1.3 billion principal amount of additional KGE first mortgage bonds could be issued under the most restrictive provisions in KGE's mortgage.
As of December 31, 20132014, we had $121.9$121.9 millionof variable rate, tax-exempt bonds.While the interest rates for these bonds have been extremely low, we continue to monitor the credit markets and evaluate our options with respect to these bonds.
In August 2013,January 2015, Westar Energy issued $250.0redeemed $125.0 million in principal amount of first mortgage bonds bearing stated interest at 4.625%5.95% and maturing September 2043.January 2035.
In June 2013,July 2014, KGE redeemed two pollution control bond series with an aggregate principal amount of $100.0issued $250.0 million and stated interest rates at 5.60% and 6.00%.
In March 2013, Westar Energy issued $250.0 millionin principal amount of first mortgage bonds bearing stated interest at 4.10%4.30% and maturing April 2043.July 2044, the proceeds of which were used to retire Westar Energy first mortgage bonds in a principal amount of $250.0 million with a stated interest of 6.00% maturing in July 2014.
In May 2012,2014, Westar Energy issued $300.0$180.0 million in principal amount of first mortgage bonds at a discount yielding 4.157%, bearing stated interest at 4.125%4.10% and maturing in March 2042.April 2043. These bonds constitute a further issuance of a series of bonds initially issued in March 20122013 in thea principal amount of $250.0$250.0 million. Proceeds from the May 2014 issuance were used in June 2014 to redeem three KGE pollution control bond series totaling $177.5 million, principal amount at a discount yielding 4.13%,stated interest rates between 5.00% and 5.30%.
In August 2013, Westar Energy issued $250.0 million principal amount of first mortgage bonds bearing stated interest at 4.125%4.625% and maturing in March 2042.September 2043.
In May 2012, Westar EnergyJune 2013, KGE redeemed $150.0 million aggregatetwo pollution control bond series with a principal amount of 6.10% first mortgage bonds. Additionally, in $100.0 million and stated interest rates at 5.60% and 6.00%.
In March 20122013, Westar Energy redeemed $57.2issued $250.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.00% pollution controlfirst mortgage bonds bearing stated interest at 4.10% and KGE redeemed $13.3 million aggregate principal amount of 5.10% pollution control bonds.maturing April 2043.
Proceeds from issuances were used to repay short-term debt, which was used to purchase capital equipment, to redeem bonds and for working capital and general corporate purposes.
Maturities
The principal amounts of our long-term debt maturities as of December 31, 20132014, are as follows.
| | | Year | | Long-term debt | | Long-term debt of VIEs | | Long-term debt | | Long-term debt of VIEs |
| | | (In Thousands) | | (In Thousands) |
| 2014 | | $ | 250,000 |
| | $ | 27,479 |
| |
| 2015 | | — |
| | 27,933 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 27,933 |
|
| 2016 | | — |
| | 28,309 |
| | — |
| | 28,309 |
|
| 2017 | | 125,000 |
| | 26,842 |
| | 125,000 |
| | 26,842 |
|
| 2018 | | 300,000 |
| | 28,538 |
| | 300,000 |
| | 28,538 |
|
| 2019 | | | 300,000 |
| | 31,485 |
|
| Thereafter | | 2,549,440 |
| | 82,581 |
| | 2,501,940 |
| | 51,097 |
|
| Total maturities | | $ | 3,224,440 |
| | $ | 221,682 |
| | $ | 3,226,940 |
| | $ | 194,204 |
|
Interest expense on long-term debt was $158.8 million in 2014, $154.9 million in 2013, and $145.6 million in 2012 and $142.6 million in 2011. Interest expense on long-term debt of VIEs was $11.4 million in 2014, $13.0 million in 2013, and $15.1 million in 2012 and $16.8 million in 2011.
10. TAXES
Income tax expense is comprised of the following components.
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Income Tax Expense (Benefit): | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current income taxes: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | 135 |
| | $ | (691 | ) | | $ | (8,575 | ) | $ | 416 |
| | $ | 135 |
| | $ | (691 | ) |
| State | 279 |
| | 579 |
| | 196 |
| (597 | ) | | 279 |
| | 579 |
|
| Deferred income taxes: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Federal | 102,030 |
| | 102,960 |
| | 93,089 |
| 124,923 |
| | 102,030 |
| | 102,960 |
|
| State | 24,443 |
| | 26,300 |
| | 21,337 |
| 29,657 |
| | 24,443 |
| | 26,300 |
|
| Investment tax credit amortization | (3,166 | ) | | (3,012 | ) | | (2,703 | ) | (3,129 | ) | | (3,166 | ) | | (3,012 | ) |
| Income tax expense | $ | 123,721 |
| | $ | 126,136 |
| | $ | 103,344 |
| $ | 151,270 |
| | $ | 123,721 |
| | $ | 126,136 |
|
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are reflected on our consolidated balance sheets as follows.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Current deferred tax assets | $ | 37,927 |
| | $ | — |
| $ | 29,636 |
| | $ | 37,954 |
|
| Other current liabilities | — |
| | 8,654 |
| |
| Non-current deferred tax liabilities | 1,361,418 |
| | 1,197,837 |
| 1,475,487 |
| | 1,363,148 |
|
| Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | 1,323,491 |
| | $ | 1,206,491 |
| $ | 1,445,851 |
| | $ | 1,325,194 |
|
The tax effect of the temporary differences and carryforwards that comprise our deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are summarized in the following table.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | |
| Tax credit carryforward (a) | $ | 212,635 |
| | $ | 199,160 |
| $ | 257,827 |
| | $ | 212,635 |
|
| Net operating loss carryforward (b) | 110,588 |
| | 111,869 |
| 179,285 |
| | 108,885 |
|
| Deferred employee benefit costs | 85,720 |
| | 191,997 |
| 158,102 |
| | 85,720 |
|
| Deferred state income taxes | 57,243 |
| | 55,577 |
| 66,557 |
| | 57,243 |
|
| Deferred regulatory gain on sale-leaseback | 38,124 |
| | 40,543 |
| 35,706 |
| | 38,124 |
|
| Deferred compensation | | 29,315 |
| | 30,022 |
|
| Alternative minimum tax carryforward (c) | 35,666 |
| | 36,471 |
| 24,114 |
| | 35,666 |
|
| Deferred compensation | 30,022 |
| | 28,319 |
| |
| Accrued liabilities | 17,396 |
| | 15,969 |
| 23,048 |
| | 17,396 |
|
| Disallowed costs | 11,453 |
| | 12,083 |
| 10,829 |
| | 11,453 |
|
| LaCygne dismantling cost | 8,110 |
| | 7,156 |
| 9,064 |
| | 8,110 |
|
| Capital loss carryforward (d) | 3,447 |
| | 11,509 |
| 1,981 |
| | 3,447 |
|
| Other | 20,058 |
| | 13,741 |
| 27,689 |
| | 20,058 |
|
| Total gross deferred tax assets | 630,462 |
| | 724,394 |
| 823,517 |
| | 628,759 |
|
| Less: Valuation allowance (e) | 3,504 |
| | 13,812 |
| 1,981 |
| | 3,504 |
|
| Deferred tax assets | $ | 626,958 |
| | $ | 710,582 |
| $ | 821,536 |
| | $ | 625,255 |
|
| | | | | | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Accelerated depreciation | $ | 1,390,669 |
| | $ | 1,255,892 |
| $ | 1,664,367 |
| | $ | 1,390,669 |
|
| Acquisition premium | 171,907 |
| | 179,920 |
| 163,894 |
| �� | 171,907 |
|
| Deferred employee benefit costs | | 158,102 |
| | 85,720 |
|
| Amounts due from customers for future income taxes, net | 163,742 |
| | 169,091 |
| 153,984 |
| | 163,742 |
|
| Deferred employee benefit costs | 85,720 |
| | 191,997 |
| |
| Deferred state income taxes | 51,504 |
| | 50,134 |
| 59,170 |
| | 51,504 |
|
| Debt reacquisition costs | | 20,102 |
| | 19,985 |
|
| Storm costs | | 15,713 |
| | 21,165 |
|
| Pension expense tracker | 21,230 |
| | 22,437 |
| 14,187 |
| | 21,230 |
|
| Storm costs | 21,165 |
| | 4,373 |
| |
| Debt reacquisition costs | 19,985 |
| | 22,313 |
| |
| Other | 24,527 |
| | 20,916 |
| 17,868 |
| | 24,527 |
|
| Total deferred tax liabilities | $ | 1,950,449 |
| | $ | 1,917,073 |
| $ | 2,267,387 |
| | $ | 1,950,449 |
|
| | | | | | | |
| Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | 1,323,491 |
| | $ | 1,206,491 |
| $ | 1,445,851 |
| | $ | 1,325,194 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | Based on filed tax returns and amounts expected to be reported in current year tax returns (December 31, 20132014), we had available federal general business tax credits of $50.273.5 million and state investment tax credits of $162.4184.3 million. The federal general business tax credits were primarily generated from affordable housing partnerships in which we sold the majority of our interests in 2001.production tax credits. These tax credits expire beginning in 2020 and ending in 20332034. The state investment tax credits expire beginning in 2017 and ending in 20292030. |
| |
| (b) | As of December 31, 20132014, we had a federal net operating loss carryforward of $277.6452.8 million, which is available to offset federal taxable income. The net operating losses will expire beginning in 2031 and ending in 20322034. |
| |
| (c) | As of December 31, 20132014, we had available an alternative minimum tax credit carryforward of $35.7$24.1 million,, which has an unlimited carryforward period. |
| |
| (d) | As of December 31, 20132014, we had an unused capital loss carryforward of $8.7$5.0 million that is available to offset future capital gains. The capital losses will expire in 2016. |
| |
| (e) | As we do not expect to realize any significant capital gains in the future, we have established a valuation allowance of $3.52.0 million. The total valuation allowance related to the deferred tax assets was $2.0 million as of December 31, 2014, and $3.5 million as of December 31, 2013, and $13.8 million as of December 31, 2012. |
In accordance with various orders, we have reduced our prices to reflect the income tax benefits associated with certain accelerated income tax deductions. We believe it is probable that the net future increases in income taxes payable will be recovered from customers when these temporary income tax benefits reverse. We have recorded a regulatory asset for these amounts. We also have recorded a regulatory liability for our obligation to reduce the prices charged to customers for deferred income taxes recovered from customers at corporate income tax rates higher than current income tax rates. The price reduction will occur as the temporary differences resulting in the excess deferred income tax liabilities reverse. The income tax-related regulatory assets and liabilities as well as unamortized investment tax credits are also temporary differences for which deferred income taxes have been provided. The net deferred income tax liability related to these temporary differences is classified above as amounts due from customers for future income taxes, net.
Our effective income tax rates are computed by dividing total federal and state income taxes by the sum of such taxes and net income. The difference between the effective income tax rates and the federal statutory income tax rates are as follows.
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Statutory federal income tax rate | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % |
| Effect of: |
| |
| |
| | | | | |
| State income taxes | | 4.0 |
| | 3.8 |
| | 4.3 |
|
| Corporate-owned life insurance policies | (5.4 | ) | | (4.9 | ) | | (4.5 | ) | (4.0 | ) | | (5.4 | ) | | (4.9 | ) |
| State income taxes | 3.8 |
| | 4.3 |
| | 4.1 |
| |
| Production tax credits | (2.3 | ) | | (2.4 | ) | | (2.9 | ) | (2.1 | ) | | (2.3 | ) | | (2.4 | ) |
| Flow through depreciation for plant-related differences | 2.2 |
| | 1.4 |
| | 1.8 |
| 2.0 |
| | 2.2 |
| | 1.4 |
|
| AFUDC equity | (1.2 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | (1.3 | ) | | (1.2 | ) | | (1.0 | ) |
| Amortization of federal investment tax credits | | (0.7 | ) | | (0.7 | ) | | (0.7 | ) |
| Capital loss utilization carryforward | (1.1 | ) | | (0.3 | ) | | (0.5 | ) | (0.3 | ) | | (1.1 | ) | | (0.3 | ) |
| Amortization of federal investment tax credits | (0.7 | ) | | (0.7 | ) | | (0.8 | ) | |
| Liability for unrecognized income tax benefits | 0.1 |
| | 0.2 |
| | — |
| (0.2 | ) | | 0.1 |
| | 0.2 |
|
| Other | (1.3 | ) | | (0.7 | ) | | (1.2 | ) | (0.5 | ) | | (1.3 | ) | | (0.7 | ) |
| Effective income tax rate | 29.1 | % | | 30.9 | % | | 30.4 | % | 31.9 | % | | 29.1 | % | | 30.9 | % |
We file income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction as well as various state and foreign jurisdictions. The income tax returns we file will likely be audited by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or other tax authorities. With few exceptions, the statute of limitations with respect to U.S. federal, state and local, or non-U.S. income tax examinations by tax authorities remains open for tax year 20082011 and forward.
The IRS has examined our federal income tax return filed for tax year 2010 and the amended federal income tax returnsEffective January 1, 2014, we filed for tax years 2007, 2008 and 2009. The examination results, which were approvedadopted new regulations released by the Joint Committee on Taxation of the U.S. Congress and accepted by the IRS in April 2013, did not have a significant impact on our consolidated statements of income or cash flows.
On September 13, 2013, the IRS and United States Treasury Department released final regulations regarding the deduction and capitalization of expenditures related to tangible property, including the tax treatment of, among other things, materials and supplies and the determination of whether expenditures with respect to tangible property are a deductible repair or must be capitalized, and re-proposed regulations regarding dispositions of property under the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System. The regulations are generally effective for tax years beginning on or after January 1, 2014, but may be adopted in earlier years under certain circumstances. On January 24, 2014, the IRS issued transition guidance that provides the procedures for taxpayers to change their method of accounting to comply with the regulations. We intend to adopt the guidance effective January 1, 2014. We do not expect the adoption of thethese regulations todid not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
The liability for unrecognized income tax benefits increased from $1.2 million at December 31, 2012, to $1.7 million at December 31, 2013. The net increase in the liability for unrecognized income tax benefits was largely attributable to tax positions taken with respect to the capitalization of plant related expenditures. We do not expect significant changes in the liability for unrecognized income tax benefits in the next 12 months. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amounts of unrecognized income tax benefits is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Liability for unrecognized income tax benefits as of January 1 | $ | 1,219 |
| | $ | 2,483 |
| | $ | 1,888 |
|
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 224 |
| | 373 |
| | 967 |
|
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | 325 |
| | — |
| | 939 |
|
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (65 | ) | | (1,637 | ) | | (563 | ) |
| Settlements | — |
| | — |
| | (748 | ) |
| Liability for unrecognized income tax benefits as of December 31 | $ | 1,703 |
| | $ | 1,219 |
| | $ | 2,483 |
|
The liability for unrecognized income tax benefits, as disclosed above, is net of reductions to deferred tax assets for credit carryforwards of $0.3 million and $0.2 million as of December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. There were no reductions to deferred tax assets for credit carryforwards as of December 31, 2013. The amounts of unrecognized income tax benefits that, if recognized, would favorably impact ourAdditionally, also effective income tax rate, were $2.4 million, $2.0 million and $1.2 million (net of tax) as of December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Interest related to income tax uncertainties is classified as interest expense and accrued interest liability. During 2013 and 2012 ,January 1, 2014, we did not reverse any interest expense previously recorded for income tax uncertainties. During 2011, we reversed interest expense previously recorded for income tax uncertainties of $0.2 million. As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we had $0.2 million accrued for interest on our liability related to unrecognized income tax benefits. We accrued no penalties at either December 31, 2013 or 2012.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we had recorded $1.5 million for probable assessments of taxes other than income taxes.
In July 2013, theimplemented new FASB issued new accounting guidance on presentingregarding the presentation of an unrecognized tax benefit when a net operating loss carryforward exists.benefit. An unrecognized tax benefit should be presented in the financial statements as a reduction to a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward. To the extent a net operating loss carryforward issuch tax assets are not available to settle any additional income taxes that would result from the disallowance of a tax position at the reporting date;date, the unrecognized tax benefit should be presented in the financial statements as a liability and should not be combined with deferred tax assets. TheWe adopted this guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2013. This guidance iswith retrospective application to prior periods and it did not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial results.statements.
The unrecognized income tax benefits increased from $1.7 million at December 31, 2013, to $3.2 million at December 31, 2014. The increase for unrecognized income tax benefits was largely attributable to tax positions taken with respect to research and experimental tax credits. We do not expect significant changes in the unrecognized income tax benefits in the next 12 months. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amounts of unrecognized income tax benefits is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (In Thousands) |
| Unrecognized income tax benefits as of January 1 | $ | 1,703 |
| | $ | 1,219 |
| | $ | 2,483 |
|
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 872 |
| | 224 |
| | 373 |
|
| Additions for tax positions of prior years | 813 |
| | 325 |
| | — |
|
| Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (200 | ) | | (65 | ) | | (1,637 | ) |
| Settlements | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Unrecognized income tax benefits as of December 31 | $ | 3,188 |
| | $ | 1,703 |
| | $ | 1,219 |
|
The amounts of unrecognized income tax benefits that, if recognized, would favorably impact our effective income tax rate, were $3.2 million, $2.4 million and $2.0 million (net of tax) as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Interest related to income tax uncertainties is classified as interest expense and accrued interest liability. As of December 31, 2014, we had no amounts accrued for interest related to unrecognized income tax benefits, compared to $0.2 million as of December 31, 2013. We accrued no penalties at either December 31, 2014 or 2013.
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, we had recorded $1.5 million for probable assessments of taxes other than income taxes.
11. EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
Pension and Post-Retirement Benefit Plans
We maintain a qualified non-contributory defined benefit pension plan covering substantially all of our employees. For the majority of our employees, pension benefits are based on years of service and an employee's compensation during the 60 highest paid consecutive months out of 120 before retirement. Non-union employees hired after December 31, 2001, and union employees hired after December 31, 2011, are covered by the same defined benefit pension plan; however, their benefits are derived from a cash balance account formula. We also maintain a non-qualified Executive Salary Continuation Plan for the benefit of certain retired executive officers. We have discontinued accruing any future benefits under this non-qualified plan.
The amount we contribute to our pension plan for future periods is not yet known, however, we expect to fund our pension plan each year at least to a level equal to current year pension expense. We must also meet minimum funding requirements under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act, as amended by the Pension Protection Act. We may contribute additional amounts from time to time as deemed appropriate.
In addition to providing pension benefits, we provide certain post-retirement health care and life insurance benefits for substantially all retired employees. We accrue and recover in our prices the costs of post-retirement benefits during an
employee's years of service. We expectIn 2014 and prior years, our retirees were covered under a health insurance policy. In January 2015, we began giving our retirees a fixed annual allowance, which provides them the flexibility to fund our post-retirement plan each year at leastobtain health coverage in the marketplace that is tailored to a level equal to current year post-retirement expense.their needs.
As a co-owner of Wolf Creek, KGE is indirectly responsible for 47% of the liabilities and expenses associated with the Wolf Creek pension and post-retirement benefit plans. See Note 12, "Wolf Creek Employee Benefit Plans," for information about Wolf Creek's benefit plans.
The following tables summarize the status of our pension and post-retirement benefit plans.
| | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| As of December 31, | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Change in Benefit Obligation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligation, beginning of year | $ | 928,708 |
| | $ | 876,308 |
| | $ | 152,564 |
| | $ | 150,078 |
| $ | 823,780 |
| | $ | 928,708 |
| | $ | 133,061 |
| | $ | 152,564 |
|
| Service cost | 21,420 |
| | 19,556 |
| | 2,028 |
| | 2,057 |
| 16,218 |
| | 21,420 |
| | 1,381 |
| | 2,028 |
|
| Interest cost | 38,520 |
| | 39,576 |
| | 6,007 |
| | 6,298 |
| 41,600 |
| | 38,520 |
| | 6,351 |
| | 6,007 |
|
| Plan participants’ contributions | — |
| | — |
| | 2,961 |
| | 2,987 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 4,232 |
| | 2,961 |
|
| Benefits paid (a) | (36,529 | ) | | (60,229 | ) | | (10,968 | ) | | (9,799 | ) | |
| Benefits paid | | (39,225 | ) | | (36,529 | ) | | (12,184 | ) | | (10,968 | ) |
| Actuarial (gains) losses | (128,339 | ) | | 53,497 |
| | (19,531 | ) | | 943 |
| 188,272 |
| | (128,339 | ) | | 16,509 |
| | (19,531 | ) |
| Benefit obligation, end of year (b) | $ | 823,780 |
| | $ | 928,708 |
| | $ | 133,061 |
| | $ | 152,564 |
| |
| Amendments | | — |
| | — |
| | (7,834 | ) | | — |
|
| Benefit obligation, end of year (a) | | $ | 1,030,645 |
| | $ | 823,780 |
| | $ | 141,516 |
| | $ | 133,061 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Change in Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets, beginning of year | $ | 547,931 |
| | $ | 481,077 |
| | $ | 106,793 |
| | $ | 91,858 |
| $ | 609,817 |
| | $ | 547,931 |
| | $ | 121,766 |
| | $ | 106,793 |
|
| Actual return on plan assets | 68,151 |
| | 67,328 |
| | 17,361 |
| | 10,673 |
| 61,291 |
| | 68,151 |
| | 7,189 |
| | 17,361 |
|
| Employer contributions | 27,500 |
| | 56,700 |
| | 5,318 |
| | 10,803 |
| 26,400 |
| | 27,500 |
| | — |
| | 5,318 |
|
| Plan participants’ contributions | — |
| | — |
| | 2,830 |
| | 2,845 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 4,074 |
| | 2,830 |
|
| Benefits paid (a) | (33,765 | ) | | (57,174 | ) | | (10,536 | ) | | (9,386 | ) | |
| Benefits paid | | (36,367 | ) | | (33,765 | ) | | (11,680 | ) | | (10,536 | ) |
| Fair value of plan assets, end of year | $ | 609,817 |
| | $ | 547,931 |
| | $ | 121,766 |
| | $ | 106,793 |
| $ | 661,141 |
| | $ | 609,817 |
| | $ | 121,349 |
| | $ | 121,766 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Funded status, end of year | $ | (213,963 | ) | | $ | (380,777 | ) | | $ | (11,295 | ) | | $ | (45,771 | ) | $ | (369,504 | ) | | $ | (213,963 | ) | | $ | (20,167 | ) | | $ | (11,295 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts Recognized in the Balance Sheets Consist of: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liability | $ | (2,740 | ) | | $ | (2,870 | ) | | $ | (242 | ) | | $ | (298 | ) | $ | (2,716 | ) | | $ | (2,740 | ) | | $ | (246 | ) | | $ | (242 | ) |
| Noncurrent liability | (211,223 | ) | | (377,907 | ) | | (11,053 | ) | | (45,473 | ) | (366,788 | ) | | (211,223 | ) | | (19,921 | ) | | (11,053 | ) |
| Net amount recognized | $ | (213,963 | ) | | $ | (380,777 | ) | | $ | (11,295 | ) | | $ | (45,771 | ) | $ | (369,504 | ) | | $ | (213,963 | ) | | $ | (20,167 | ) | | $ | (11,295 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts Recognized in Regulatory Assets Consist of: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net actuarial loss | $ | 186,365 |
| | $ | 383,365 |
| | $ | (18,890 | ) | | $ | 12,436 |
| |
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | | $ | 329,572 |
| | $ | 186,365 |
| | $ | (2,253 | ) | | $ | (18,890 | ) |
| Prior service cost | 3,393 |
| | 3,994 |
| | 13,942 |
| | 16,467 |
| 2,867 |
| | 3,393 |
| | 3,585 |
| | 13,942 |
|
| Transition obligation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 325 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net amount recognized | $ | 189,758 |
| | $ | 387,359 |
| | $ | (4,948 | ) | | $ | 29,228 |
| $ | 332,439 |
| | $ | 189,758 |
| | $ | 1,332 |
| | $ | (4,948 | ) |
_______________
| |
| (a) | In 2012 certain former employees received a one-time lump sum payment of their pension benefits totaling $26.1 million.
|
| |
(b) | As of December 31, 20132014 and 2012,2013, pension benefits include non-qualified benefit obligations of $27.0$29.8 million and $30.027.0 million, respectively, which are funded by a trust containing assets of $34.9$35.5 million and $43.534.9 million, respectively, classified as trading securities. The assets in the aforementioned trust are not included in the table above. See Notes 4 and 5, "Financial Instruments and Trading Securities" and "Financial Investments," respectively, for additional information regarding these amounts. |
| | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| As of December 31, | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Pension Plans With a Projected Benefit Obligation In Excess of Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 823,780 |
| | $ | 928,708 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| $ | 1,030,645 |
| | $ | 823,780 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Fair value of plan assets | 609,817 |
| | 547,931 |
| | — |
| | — |
| 661,141 |
| | 609,817 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension Plans With an Accumulated Benefit Obligation In Excess of Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 732,150 |
| | $ | 806,888 |
| | — |
| | — |
| $ | 914,800 |
| | $ | 732,150 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Fair value of plan assets | 609,817 |
| | 547,931 |
| | — |
| | — |
| 661,141 |
| | 609,817 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Post-retirement Plans With an Accumulated Post-retirement Benefit Obligation In Excess of Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated post-retirement benefit obligation | — |
| | — |
| | $ | 133,061 |
| | $ | 152,564 |
| — |
| | — |
| | $ | 141,516 |
| | $ | 133,061 |
|
| Fair value of plan assets | — |
| | — |
| | 121,766 |
| | 106,793 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 121,349 |
| | 121,766 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-Average Actuarial Assumptions used to Determine Net Periodic Benefit Obligation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discount rate | 5.07 | % | | 4.13 | % | | 4.88 | % | | 3.99 | % | 4.17 | % | | 5.07 | % | | 4.10 | % | | 4.88 | % |
| Compensation rate increase | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — |
| | — |
| 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — |
| | — |
|
We use a measurement date of December 31 for our pension and post-retirement benefit plans. The discount rate used to determine the current year pension obligation and the following year's pension expense is based on a bond selection-settlement portfolio approach. This approach develops a discount rate by selecting a portfolio of high quality, non-callable corporate bonds that generate sufficient cash flow to provide for the projected benefit payments of the plan. After the bond portfolio is selected, a single interest rate is determined that equates the present value of the plan's projected benefit payments discounted at this rate with the market value of the bonds selected. The decrease in the discount rates used as of December 31, 2014, increased the pension and post-retirement benefit obligations by approximately $123.5 million and $11.2 million, respectively.
We utilize actuarial assumptions about mortality to calculate the pension and post-retirement benefit obligations. In 2014, revised mortality tables were published which reflect improved life expectancies based on past experience and future projections. We adopted the revised mortality tables as of December 31, 2014, resulting in an increase to the pension and post-retirement benefit obligations by approximately $58.6 million and $5.9 million, respectively.
We amortize prior service cost on a straight-line basis over the average future service of the active employees (plan participants) benefiting under the plan at the time of the amendment. We amortize the net actuarial gain or loss on a straight-line basis over the average future service of active plan participants benefiting under the plan without application of an amortization corridor. The KCC allows us to record a regulatory asset or liability to track the cumulative difference between current year pension and post-retirement benefits expense and the amount of such expense recognized in setting our prices. We accumulate such regulatory asset or liability between general rate reviews and amortize the accumulated amount as part of resetting our base prices. Following is additional information regarding our pension and post-retirement benefit plans.
| | | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| Year Ended December 31, | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | | (Dollars in Thousands) | | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Components of Net Periodic Cost (Benefit): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Service cost | | $ | 21,420 |
| | $ | 19,556 |
| | $ | 16,076 |
| | $ | 2,028 |
| | $ | 2,057 |
| | $ | 1,803 |
| | $ | 16,218 |
| | $ | 21,420 |
| | $ | 19,556 |
| | $ | 1,381 |
| | $ | 2,028 |
| | $ | 2,057 |
|
| Interest cost | | 38,520 |
| | 39,576 |
| | 40,045 |
| | 6,007 |
| | 6,298 |
| | 6,793 |
| | 41,600 |
| | 38,520 |
| | 39,576 |
| | 6,351 |
| | 6,007 |
| | 6,298 |
|
| Expected return on plan assets | | (33,405 | ) | | (32,283 | ) | | (31,087 | ) | | (6,691 | ) | | (5,491 | ) | | (5,002 | ) | | (36,438 | ) | | (33,405 | ) | | (32,283 | ) | | (6,576 | ) | | (6,691 | ) | | (5,491 | ) |
| Amortization of unrecognized: | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transition obligation, net | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 325 |
| | 3,912 |
| | 3,911 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 325 |
| | 3,912 |
|
| Prior service costs | | 601 |
| | 612 |
| | 1,213 |
| | 2,524 |
| | 2,524 |
| | 2,524 |
| | 526 |
| | 601 |
| | 612 |
| | 2,524 |
| | 2,524 |
| | 2,524 |
|
| Actuarial loss, net | | 33,914 |
| | 32,778 |
| | 23,659 |
| | 1,125 |
| | 1,503 |
| | 702 |
| | 19,362 |
| | 33,914 |
| | 32,778 |
| | (742 | ) | | 1,125 |
| | 1,503 |
|
| Net periodic cost before regulatory adjustment | | 61,050 |
| | 60,239 |
| | 49,906 |
| | 5,318 |
| | 10,803 |
| | 10,731 |
| | 41,268 |
| | 61,050 |
| | 60,239 |
| | 2,938 |
| | 5,318 |
| | 10,803 |
|
| Regulatory adjustment (a) | | 3,693 |
| | (6,523 | ) | | (22,098 | ) | | 2,922 |
| | 23 |
| | 1,344 |
| | 15,479 |
| | 3,693 |
| | (6,523 | ) | | 4,499 |
| | 2,922 |
| | 23 |
|
| Net periodic cost | | $ | 64,743 |
| | $ | 53,716 |
| | $ | 27,808 |
| | $ | 8,240 |
| | $ | 10,826 |
| | $ | 12,075 |
| | $ | 56,747 |
| | $ | 64,743 |
| | $ | 53,716 |
| | $ | 7,437 |
| | $ | 8,240 |
| | $ | 10,826 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other Changes in Plan Assets and Benefit Obligations Recognized in Regulatory Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current year actuarial (gain)/loss | | $ | (163,086 | ) | | $ | 18,451 |
| | $ | 97,429 |
| | $ | (30,201 | ) | | $ | (4,239 | ) | | $ | 10,421 |
| | $ | 162,569 |
| | $ | (163,086 | ) | | $ | 18,451 |
| | $ | 15,896 |
| | $ | (30,201 | ) | | $ | (4,239 | ) |
| Amortization of actuarial (loss) | | (33,914 | ) | | (32,778 | ) | | (23,659 | ) | | (1,125 | ) | | (1,503 | ) | | (702 | ) | | (19,362 | ) | | (33,914 | ) | | (32,778 | ) | | 742 |
| | (1,125 | ) | | (1,503 | ) |
| Current year prior service cost | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 4,451 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (7,834 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Amortization of prior service costs | | (601 | ) | | (612 | ) | | (1,213 | ) | | (2,525 | ) | | (2,524 | ) | | (2,524 | ) | | (526 | ) | | (601 | ) | | (612 | ) | | (2,524 | ) | | (2,525 | ) | | (2,524 | ) |
| Amortization of transition obligation | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (325 | ) | | (3,912 | ) | | (3,911 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (325 | ) | | (3,912 | ) |
| Total recognized in regulatory assets | | $ | (197,601 | ) | | $ | (14,939 | ) | | $ | 72,557 |
| | $ | (34,176 | ) | | $ | (12,178 | ) | | $ | 7,735 |
| | $ | 142,681 |
| | $ | (197,601 | ) | | $ | (14,939 | ) | | $ | 6,280 |
| | $ | (34,176 | ) | | $ | (12,178 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total recognized in net periodic cost and regulatory assets | | $ | (132,858 | ) | | $ | 38,777 |
| | $ | 100,365 |
| | $ | (25,936 | ) | | $ | (1,352 | ) | | $ | 19,810 |
| | $ | 199,428 |
| | $ | (132,858 | ) | | $ | 38,777 |
| | $ | 13,717 |
| | $ | (25,936 | ) | | $ | (1,352 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-Average Actuarial Assumptions used to Determine Net Periodic Cost (Benefit): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discount rate | | 4.13 | % | | 4.50 | % | | 5.35 | % | | 3.99 | % | | 4.25 | % | | 5.00 | % | | 5.07 | % | | 4.13 | % | | 4.50 | % | | 4.88 | % | | 3.99 | % | | 4.25 | % |
| Expected long-term return on plan assets | | 6.50 | % | | 6.50 | % | | 6.50 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 6.50 | % | | 6.50 | % | | 6.50 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % |
| Compensation rate increase | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — |
| | — |
| | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — | % |
_______________
| |
| (a) | The regulatory adjustment represents the difference between current period pension or post-retirement benefit expense and the amount of such expense recognized in setting our prices. |
We estimate that we will amortize the following amounts from regulatory assets into net periodic cost in 20142015.
| | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Actuarial loss (gain) | $ | 19,362 |
| | $ | (742 | ) | |
| Actuarial loss | | $ | 32,131 |
| | $ | 379 |
|
| Prior service cost | 525 |
| | 2,524 |
| 520 |
| | 455 |
|
| Total | $ | 19,887 |
| | $ | 1,782 |
| $ | 32,651 |
| | $ | 834 |
|
We base the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets on historical and projected rates of return for current and planned asset classes in the plans' investment portfolios. We select assumed projected rates of return for each asset class after analyzing long-term historical experience and future expectations of the volatility of the various asset classes. Based on target asset allocations for each asset class, we develop an overall expected rate of return for the portfolios, adjusted for historical and expected experience of active portfolio management results compared to benchmark returns and for the effect of expenses paid from plan assets.
For measurement purposes, the assumed annual health care cost growth rates were as follows.
|
| | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Health care cost trend rate assumed for next year | 7.5% | | 8.0% |
| Rate to which the cost trend rate is assumed to decline (the ultimate trend rate) | 5.0% | | 5.0% |
| |
| |
|
| Year that the rate reaches the ultimate trend rate | 2019 | | 2019 |
|
| | | |
| As of December 31, |
| 2014 (a) | | 2013 |
| Health care cost trend rate assumed for next year | — | | 7.5% |
| Rate to which the cost trend rate is assumed to decline (the ultimate trend rate) | — | | 5.0% |
| | | |
| Year that the rate reaches the ultimate trend rate | — | | 2019 |
_______________
| |
| (a) | Amounts are zero due to a change in our post retirement medical plan, effective January 2015, whereby we began to offer retirees a fixed cost allowance to obtain health coverage. |
The health care cost trend rate affects the projected benefit obligation. A 1% change in assumed health care cost growth rates would have effects shown in the following table.
| | | | One-Percentage- Point Increase | | One-Percentage- Point Decrease | One-Percentage- Point Increase | | One-Percentage- Point Decrease |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Effect on total of service and interest cost | $ | 153 |
| | $ | (136 | ) | $ | 134 |
| | $ | (120 | ) |
Effect on post-retirement benefit obligation | 2,098 |
| | (1,901 | ) | — |
| | — |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | Amounts are zero due to a change in our post retirement medical plan, effective January 2015, whereby we began to offer retirees a fixed cost allowance to obtain health coverage. |
Plan Assets
We believe we manage pension and post-retirement benefit plan assets in a prudent manner with regard to preserving principal while providing reasonable returns. We have adopted a long-term investment horizon such that the chances and duration of investment losses are carefully weighed against the long-term potential for appreciation of assets. Part of our strategy includes managing interest rate sensitivity of plan assets relative to the associated liabilities. The primary objective of the pension plan is to provide a source of retirement income for its participants and beneficiaries, and the primary financial objective of the plan is to improve its funded status. The primary objective of the post-retirement benefit plan is growth in assets and preservation of principal, while minimizing interim volatility, to meet anticipated claims of plan participants. We delegate the management of our pension and post-retirement benefit plan assets to independent investment advisors who hire and dismiss investment managers based upon various factors. The investment advisors striveare instructed to diversify investments across asset classes, sectors and manager styles to minimize the risk of large losses, based upon objectives and risk tolerance specified by management, which include allowable and/or prohibited investment types. We measure and monitor investment risk on an ongoing basis through quarterly investment portfolio reviews and annual liability measurements.
As noted above, weWe have established certain prohibited investments for our pension and post-retirement benefit plans. Such prohibited investments include loans to the company or its officers and directors as well as investments in the company's debt or equity securities, except as may occur indirectly through investments in diversified mutual funds. In addition, to reduce concentration of risk, the pension plan will not invest in any fund that holds more than 25% of its total assets to be invested in the securities of one or more issuers conducting their principal business activities in the same industry. This restriction does not apply to investments in securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. government or its agencies.
Target allocations for our pension plan assets are about approximately 39% to debt securities, 39% to equity securities, 12% to alternative investments such as real estate securities, hedge funds and private equity investments, and the remaining 10% to a fund which provides tactical portfolio overlay by investing in debt and equity securities. Our investments in equity include investment funds with underlying investments in domestic and foreign large-, mid- and small-cap companies, derivatives related to such holdings, private equity investments including late-stage venture investments and other investments. Our investments in debt include core and high-yield bonds. Core bonds are comprised of investment funds with underlying investments in investment grade debt securities of corporate entities, obligations of U.S. and foreign governments and their agencies and other debt securities. High-yield bonds include investment funds with underlying investments in non-investment grade debt securities of corporate entities, obligations of foreign governments and their agencies, private debt securities and other debt securities. Real estate securities consist primarily of funds invested in core real estate throughout the U.S. while alternative funds invest in wide ranging investments including equity and debt securities of domestic and foreign corporations, debt securities issued by U.S. and foreign governments and their agencies, structured debt, warrants, exchange-traded funds, derivative instruments, private investment funds and other investments.
Target allocations for our post-retirement benefit plan assets are 65% to equity securities and 35% to debt securities. Our investments in equity securities include investment funds with underlying investments primarily in domestic and foreign
large-, mid- and small-cap companies. Our investments in debt securities include a core bond fund with underlying investments in investment grade debt securities of domestic and foreign corporate entities, obligations of U.S. and foreign governments and their agencies, private placement securities and other investments.
Similar to other assets measured at fair value, GAAP establishes a hierarchal framework for disclosing the transparency of the inputs utilized in measuring pension and post-retirement benefit plan assets at fair value. From time to time, the pension and post-retirement benefits trusts may buy and sell investments resulting in changes within the hierarchy. See Note 4, "Financial Instruments and Trading Securities," for a description of the hierarchal framework.
All level 2 pension investments are held in investment funds that are measured at fair value using daily net asset values as reported by the trustee, except for $47.4$59.0 million as of December 31, 20132014, invested directly in long-term U.S. Treasury securities. We also maintain certain level 3 investments in private equity, alternative investments and real estate securities that are also measured at fair value using net asset value, but require significant unobservable market information to measure the fair value of the underlying investments. The underlying investments in private equity are measured at fair value utilizing both market- and income-based models, public company comparables, investment cost or the value derived from subsequent financings. Adjustments are made when actual performance differs from expected performance; when market, economic or company-specific conditions change; and when other news or events have a material impact on the security. The underlying alternative investments include collateralized debt obligations, mezzanine debt and a variety of other investments. The fair value of these investments is measured using a variety of primarily market-based models utilizing inputs such as security prices, maturity, call features, ratings and other developments related to specific securities. The underlying real estate investments are measured at fair value using a combination of market- and income-based models utilizing market discount rates, projected cash flows and the estimated value into perpetuity.
The following table provides the fair value of our pension plan assets and the corresponding level of hierarchy as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | — |
| | $ | 161,272 |
| | $ | 22,488 |
| | $ | 183,760 |
|
| International equity | | — |
| | 75,872 |
| | — |
| | 75,872 |
|
| Core bonds | | — |
| | 191,506 |
| | — |
| | 191,506 |
|
| High-yield bonds | | — |
| | 20,796 |
| | — |
| | 20,796 |
|
| Emerging market bonds | | — |
| | 13,113 |
| | — |
| | 13,113 |
|
| Combination debt/equity fund | | — |
| | 58,336 |
| | — |
| | 58,336 |
|
| Alternative investments | | — |
| | — |
| | 39,171 |
| | 39,171 |
|
| Real estate securities | | — |
| | — |
| | 24,022 |
| | 24,022 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 3,241 |
| | — |
| | 3,241 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 524,136 |
| | $ | 85,681 |
| | $ | 609,817 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | — |
| | $ | 129,501 |
| | $ | 18,493 |
| | $ | 147,994 |
|
| International equity | | — |
| | 67,743 |
| | — |
| | 67,743 |
|
| Core bonds | | — |
| | 178,784 |
| | — |
| | 178,784 |
|
| High-yield bonds | | — |
| | 19,070 |
| | — |
| | 19,070 |
|
| Emerging market bonds | | — |
| | 14,276 |
| | — |
| | 14,276 |
|
| Combination debt/equity fund | | — |
| | 50,750 |
| | — |
| | 50,750 |
|
| Alternative investments | | — |
| | — |
| | 45,535 |
| | 45,535 |
|
| Real estate securities | | — |
| | — |
| | 20,927 |
| | 20,927 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 2,852 |
| | — |
| | 2,852 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 462,976 |
| | $ | 84,955 |
| | $ | 547,931 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2014 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | | $ | — |
| | $ | 160,574 |
| | $ | 23,996 |
| | $ | 184,570 |
|
| International equity fund | | — |
| | 82,604 |
| | — |
| | 82,604 |
|
| Core bond funds | | — |
| | 224,740 |
| | — |
| | 224,740 |
|
| High-yield bond fund | | — |
| | 20,412 |
| | — |
| | 20,412 |
|
| Emerging market bond fund | | — |
| | 14,685 |
| | — |
| | 14,685 |
|
| Combination debt/equity/other fund | | — |
| | 61,632 |
| | — |
| | 61,632 |
|
| Alternative investment funds | | — |
| | — |
| | 41,141 |
| | 41,141 |
|
| Real estate securities fund | | — |
| | — |
| | 26,439 |
| | 26,439 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 4,918 |
| | — |
| | 4,918 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 569,565 |
| | $ | 91,576 |
| | $ | 661,141 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | | $ | — |
| | $ | 161,272 |
| | $ | 22,488 |
| | $ | 183,760 |
|
| International equity fund | | — |
| | 75,872 |
| | — |
| | 75,872 |
|
| Core bond funds | | — |
| | 191,506 |
| | — |
| | 191,506 |
|
| High-yield bond fund | | — |
| | 20,796 |
| | — |
| | 20,796 |
|
| Emerging market bond fund | | — |
| | 13,113 |
| | — |
| | 13,113 |
|
| Combination debt/equity/other fund | | — |
| | 58,336 |
| | — |
| | 58,336 |
|
| Alternative investment funds | | — |
| | — |
| | 39,171 |
| | 39,171 |
|
| Real estate securities fund | | — |
| | — |
| | 24,022 |
| | 24,022 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 3,241 |
| | — |
| | 3,241 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 524,136 |
| | $ | 85,681 |
| | $ | 609,817 |
|
The following table provides a reconciliation of pension plan assets measured at fair value using significant level 3 inputs for the years ended December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
| | | | Domestic Equity | | Alternative Funds | | Real Estate Securities | | Total | Domestic Equity Funds | | Alternative Investment Funds | | Real Estate Securities Fund | | Total |
| | | (In Thousands) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | | $ | 22,488 |
| | $ | 39,171 |
| | $ | 24,022 |
| | $ | 85,681 |
|
| Actual gain (loss) on plan assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Relating to assets still held at the reporting date | | (154 | ) | | 1,970 |
| | 2,630 |
| | 4,446 |
|
| Relating to assets sold during the period | | 1,365 |
| | — |
| | 29 |
| | 1,394 |
|
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net | | 297 |
| | — |
| | (242 | ) | | 55 |
|
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | | $ | 23,996 |
| | $ | 41,141 |
| | $ | 26,439 |
| | $ | 91,576 |
|
| | (In Thousands) | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | $ | 18,493 |
| | $ | 45,535 |
| | $ | 20,927 |
| | $ | 84,955 |
| $ | 18,493 |
| | $ | 45,535 |
| | $ | 20,927 |
| | $ | 84,955 |
|
| Actual gain (loss) on plan assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Relating to assets still held at the reporting date | 3,845 |
| | 1,936 |
| | 3,307 |
| | 9,088 |
| 3,845 |
| | 1,936 |
| | 3,307 |
| | 9,088 |
|
| Relating to assets sold during the period | — |
| | 826 |
| | — |
| | 826 |
| — |
| | 826 |
| | — |
| | 826 |
|
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net | 150 |
| | (9,126 | ) | | (212 | ) | | (9,188 | ) | 150 |
| | (9,126 | ) | | (212 | ) | | (9,188 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | $ | 22,488 |
| | $ | 39,171 |
| | $ | 24,022 |
| | $ | 85,681 |
| $ | 22,488 |
| | $ | 39,171 |
| | $ | 24,022 |
| | $ | 85,681 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | $ | 15,375 |
| | $ | 40,716 |
| | $ | 18,848 |
| | $ | 74,939 |
| |
| Actual gain (loss) on plan assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Relating to assets still held at the reporting date | (25 | ) | | 4,819 |
| | 2,296 |
| | 7,090 |
| |
| Relating to assets sold during the period | 53 |
| | — |
| | (27 | ) | | 26 |
| |
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net | 3,090 |
| | — |
| | (190 | ) | | 2,900 |
| |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | $ | 18,493 |
| | $ | 45,535 |
| | $ | 20,927 |
| | $ | 84,955 |
| |
The following table provides the fair value of our post-retirement benefit plan assets and the corresponding level of hierarchy as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
| | | As of December 31, 2014 | | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | | | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | | | $ | — |
| | $ | 63,600 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 63,600 |
|
| International equity fund | | | — |
| | 14,783 |
| | — |
| | 14,783 |
|
| Core bond funds | | | — |
| | 42,390 |
| | — |
| | 42,390 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | 576 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | | $ | — |
| | $ | 121,349 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 121,349 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | | | | | | | |
| | | (In Thousands) | | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | — |
| | $ | 64,080 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 64,080 |
| |
| International equity | | — |
| | 16,018 |
| | — |
| | 16,018 |
| |
| Core bonds | | — |
| | 41,092 |
| | — |
| | 41,092 |
| |
| Domestic equity funds | | | $ | — |
| | $ | 64,080 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 64,080 |
|
| International equity fund | | | — |
| | 16,018 |
| | — |
| | 16,018 |
|
| Core bond funds | | | — |
| | 41,092 |
| | — |
| | 41,092 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | 576 |
| | — |
| | 576 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 121,766 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 121,766 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 121,766 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 121,766 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | — |
| | $ | 55,441 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 55,441 |
| |
| International equity | | — |
| | 14,037 |
| | — |
| | 14,037 |
| |
| Core bonds | | — |
| | 36,738 |
| | — |
| | 36,738 |
| |
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 577 |
| | — |
| | 577 |
| |
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 106,793 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 106,793 |
| |
Cash Flows
The following table shows the expected cash flows for our pension and post-retirement benefit plans for future years.
| | | Expected Cash Flows | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets |
| | | (In Millions) | | (In Millions) |
| Expected contributions: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2014 | | $ | 30.8 |
| | | | $ | 2.9 |
| | | |
| 2015 | | | $ | 42.0 |
| | | | $ | — |
| | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Expected benefit payments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2014 | | $ | (35.4 | ) | | $ | (2.8 | ) | | $ | (8.7 | ) | | $ | (0.2 | ) | |
| 2015 | | (36.9 | ) | | (2.8 | ) | | (9.1 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | $ | (35.1 | ) | | $ | (2.8 | ) | | $ | (8.2 | ) | | $ | (0.2 | ) |
| 2016 | | (39.2 | ) | | (2.8 | ) | | (9.3 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (37.3 | ) | | (2.8 | ) | | (8.3 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| 2017 | | (41.5 | ) | | (2.7 | ) | | (9.6 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (39.5 | ) | | (2.8 | ) | | (8.4 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| 2018 | | (44.5 | ) | | (2.7 | ) | | (9.8 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (41.9 | ) | | (2.7 | ) | | (8.6 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| 2019 - 2023 | | (257.9 | ) | | (12.8 | ) | | (49.7 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | |
| 2019 | | | (44.2 | ) | | (2.7 | ) | | (8.7 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| 2020-2024 | | | (257.8 | ) | | (13.0 | ) | | (43.5 | ) | | (1.0 | ) |
Savings Plans
We maintain a qualified 401(k) savings plan in which most of our employees participate. We match employees' contributions in cash up to specified maximum limits. Our contributions to the plan are deposited with a trustee and invested at the direction of plan participants into one or more of the investment alternatives we provide under the plan. Our contributions totaled $7.0 million in 2014, $6.9 million in 2013, and $7.1 million in 2012 and $7.0 million in 2011.
Stock-Based Compensation Plans
We have a long-term incentive and share award plan (LTISA Plan), which is a stock-based compensation plan in which employees and directors are eligible for awards. The LTISA Plan was implemented as a means to attract, retain and motivate employees and directors. Under the LTISA Plan, we may grant awards in the form of stock options, dividend equivalents, share appreciation rights, RSUs, performance shares and performance share units to plan participants. InUp to May 20118.25 million, Westar Energy shareholders approved an increase in the number of shares of common stock that may be granted under the LTISA Plan to 8.25 million shares from 5.0 million shares.Plan. As of December 31, 20132014, awards of approximately 4.95.0 million shares of common stock had been made under the plan.
All stock-based compensation is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized as an expense in the consolidated statement of income over the requisite service period. The requisite service periods range from one to ten years. The table below shows compensation expense and income tax benefits related to stock-based compensation arrangements that are included in our net income.
| | | | Year Ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Compensation expense | $ | 8,121 |
| | $ | 7,203 |
| | $ | 8,367 |
| $ | 7,193 |
| | $ | 8,121 |
| | $ | 7,203 |
|
| Income tax benefits related to stock-based compensation arrangements | 3,212 |
| | 2,849 |
| | 3,309 |
| 2,845 |
| | 3,212 |
| | 2,849 |
|
We use RSU awards for our stock-based compensation awards. RSU awards are grants that entitle the holder to receive shares of common stock as the awards vest. These RSU awards are defined as nonvested shares and do not include restrictions once the awards have vested. In 2011, outstanding RSUs with only service requirements previously awarded to our former chief executive officer that were subject to forfeiture were modified to provide for the vesting upon his retirement in July 2011 of a prorated number of the RSUs based on the number of days from the grant date of the RSUs to his retirement date. In addition, outstanding RSUs with performance measures previously awarded to our former chief executive officer were modified to provide for the vesting on the scheduled vesting date, subject to the satisfaction of the applicable performance criteria, of a prorated number of the target RSUs based on the number of days from the grant date of the RSUs to his retirement date. We recorded compensation expense of $2.8 million in 2011 related to these modifications.
RSU awards with only service requirements vest solely upon the passage of time. We measure the fair value of these RSU awards based on the market price of the underlying common stock as of the grant date. RSU awards with only service conditions that have a graded vesting schedule are recognized as an expense in the consolidated statement of income on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period for the entire award. Nonforfeitable dividend equivalents, or the rights to receive cash equal to the value of dividends paid on Westar Energy's common stock, are paid on these RSUs during the vesting period.
RSU awards with performance measures vest upon expiration of the award term. The number of shares of common stock awarded upon vesting will vary from 0% to 200% of the RSU award, with performance tied to our total shareholder return relative to the total shareholder return of our peer group. We measure the fair value of these RSU awards using a Monte Carlo simulation technique that uses the closing stock price at the valuation date and incorporates assumptions for inputs of the expected volatility and risk-free interest rates. Expected volatility is based on historical volatility over three years using daily stock price observations. The risk-free interest rate is based on treasury constant maturity yields as reported by the Federal Reserve and the length of the performance period. For the 2014 valuation, inputs for expected volatility ranged from 15.2% to 23.3% and the risk-free interest rate was approximately 0.3%. For the 2013 valuation, inputs for expected volatility ranged from 15.0% to 23.5% and the risk-free interest rate was approximately 0.3%. For the 2012 valuation, inputs for expected volatility ranged from 17.6% to 33.6% and the risk-free interest rate was approximately 0.4%. For these RSU awards, dividend equivalents accumulate over the vesting period and are paid in cash based on the number of shares of common stock awarded upon vesting.
During the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012, our RSU activity for awards with only service requirements was as follows:follows.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| | (Shares In Thousands) | (Shares In Thousands) |
| Nonvested balance, beginning of year | 351.1 |
| | $ | 25.47 |
| | 368.5 |
| | $ | 23.83 |
| | 600.4 |
| | $ | 21.50 |
| 352.5 |
| | $ | 28.38 |
| | 351.1 |
| | $ | 25.47 |
| | 368.5 |
| | $ | 23.83 |
|
| Granted | 139.6 |
| | 31.06 |
| | 131.0 |
| | 27.82 |
| | 284.1 |
| | 26.30 |
| 131.5 |
| | 34.53 |
| | 139.6 |
| | 31.06 |
| | 131.0 |
| | 27.82 |
|
| Vested | (125.5 | ) | | 23.22 |
| | (127.8 | ) | | 23.34 |
| | (187.3 | ) | | 23.50 |
| (118.2 | ) | | 26.19 |
| | (125.5 | ) | | 23.22 |
| | (127.8 | ) | | 23.34 |
|
| Forfeited | (12.7 | ) | | 28.35 |
| | (20.6 | ) | | 24.40 |
| | (328.7 | ) | | 24.37 |
| (23.6 | ) | | 30.00 |
| | (12.7 | ) | | 28.35 |
| | (20.6 | ) | | 24.40 |
|
| Nonvested balance, end of year | 352.5 |
| | 28.38 |
| | 351.1 |
| | 25.47 |
| | 368.5 |
| | 23.83 |
| 342.2 |
| | 31.38 |
| | 352.5 |
| | 28.38 |
| | 351.1 |
| | 25.47 |
|
Total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with only service requirements was $4.4 million and $4.4 million as of December 31, 2014 and 2013., respectively. We expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.71.9 years. The total fair value of RSUs with only service requirements that vested during the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012, was $3.73.9 million, $3.7 million and $4.83.7 million, respectively.
During the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012, our RSU activity for awards with performance measures was as follows:follows.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Shares | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| | (Shares In Thousands) | (Shares In Thousands) |
| Nonvested balance, beginning of year | 340.1 |
| | $ | 29.20 |
| | 324.2 |
| | $ | 28.31 |
| | 348.4 |
| | $ | 24.98 |
| 350.1 |
| | $ | 30.35 |
| | 340.1 |
| | $ | 29.20 |
| | 324.2 |
| | $ | 28.31 |
|
| Granted | 134.4 |
| | 31.54 |
| | 122.3 |
| | 28.84 |
| | 244.4 |
| | 31.26 |
| 126.1 |
| | 35.97 |
| | 134.4 |
| | 31.54 |
| | 122.3 |
| | 28.84 |
|
| Vested | (112.5 | ) | | 28.29 |
| | (88.2 | ) | | 25.46 |
| | (119.5 | ) | | 24.12 |
| (108.2 | ) | | 30.56 |
| | (112.5 | ) | | 28.29 |
| | (88.2 | ) | | 25.46 |
|
| Forfeited | (11.9 | ) | | 30.45 |
| | (18.2 | ) | | 29.00 |
| | (149.1 | ) | | 28.72 |
| (22.9 | ) | | 30.70 |
| | (11.9 | ) | | 30.45 |
| | (18.2 | ) | | 29.00 |
|
| Nonvested balance, end of year | 350.1 |
| | 30.35 |
| | 340.1 |
| | 29.20 |
| | 324.2 |
| | 28.31 |
| 345.1 |
| | 32.31 |
| | 350.1 |
| | 30.35 |
| | 340.1 |
| | 29.20 |
|
As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, total unrecognized compensation cost related to RSU awards with performance measures was $4.03.8 million and $3.54.0 million, respectively. We expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted-average period of 1.7 years. The total fair value of RSUs with performance measures that vested during the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012, was $2.30.5 million, $3.6$2.3 million and $3.6 million, respectively.
Another component of the LTISA Plan is the Executive Stock for Compensation program under which, in the past, eligible employees were entitled to receive deferred common stock in lieu of current cash compensation. Although this plan was discontinued in 2001, dividends will continue to be paid to plan participants on their outstanding plan balance until distribution. Plan participants were awarded 551403 shares of common stock for dividends in 2014, 551 shares in 2013, and 666 shares in 2012 and 4,757 shares in 2011. Participants received common stock distributions of 1,944 shares in 2014, 3,456 shares in 2013, and 1,461 shares in 2012 and 67,426 shares in 2011.
Income tax benefits resulting from income tax deductions in excess of the related compensation cost recognized in the financial statements is classified as cash flows from financing activities in the consolidated statements of cash flows.
12. WOLF CREEK EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
Pension and Post-retirement Benefit Plans
As a co-owner of Wolf Creek, KGE is indirectly responsible for 47% of the liabilities and expenses associated with the Wolf Creek pension and post-retirement benefit plans. KGE accrues its 47% share of Wolf Creek's cost of pension and post-retirement benefits during the years an employee provides service. The following tables summarize the status of KGE's 47% share of the Wolf Creek pension and post-retirement benefit plans. | | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| As of December 31, | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Change in Benefit Obligation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligation, beginning of year | $ | 176,891 |
| | $ | 161,396 |
| | $ | 11,020 |
| | $ | 10,129 |
| $ | 162,820 |
| | $ | 176,891 |
| | $ | 10,010 |
| | $ | 11,020 |
|
| Service cost | 6,835 |
| | 6,062 |
| | 206 |
| | 191 |
| 5,695 |
| | 6,835 |
| | 173 |
| | 206 |
|
| Interest cost | 7,562 |
| | 7,537 |
| | 413 |
| | 411 |
| 8,469 |
| | 7,562 |
| | 464 |
| | 413 |
|
| Plan participants’ contributions | — |
| | — |
| | 696 |
| | 608 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 766 |
| | 696 |
|
Benefits paid (a) | (4,349 | ) | | (8,569 | ) | | (1,022 | ) | | (988 | ) | (5,039 | ) | | (4,349 | ) | | (1,292 | ) | | (1,022 | ) |
| Actuarial (gains) losses | (24,119 | ) | | 9,815 |
| | (1,303 | ) | | 669 |
| 38,375 |
| | (24,119 | ) | | (1,881 | ) | | (1,303 | ) |
| Amendments | — |
| | 650 |
| | — |
| | — |
| |
| Benefit obligation, end of year | $ | 162,820 |
| | $ | 176,891 |
| | $ | 10,010 |
| | $ | 11,020 |
| $ | 210,320 |
| | $ | 162,820 |
| | $ | 8,240 |
| | $ | 10,010 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Change in Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets, beginning of year | $ | 98,051 |
| | $ | 80,727 |
| | $ | 13 |
| | $ | 4 |
| $ | 114,734 |
| | $ | 98,051 |
| | $ | 17 |
| | $ | 13 |
|
| Actual return on plan assets | 13,166 |
| | 11,764 |
| | — |
| | — |
| 7,626 |
| | 13,166 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Employer contributions | 7,624 |
| | 13,887 |
| | 330 |
| | 389 |
| 7,089 |
| | 7,624 |
| | 515 |
| | 330 |
|
| Plan participants' contributions | — |
| | — |
| | 696 |
| | 608 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 766 |
| | 696 |
|
| Benefits paid | (4,107 | ) | | (8,327 | ) | | (1,022 | ) | | (988 | ) | (4,789 | ) | | (4,107 | ) | | (1,292 | ) | | (1,022 | ) |
| Fair value of plan assets, end of year | $ | 114,734 |
| | $ | 98,051 |
| | $ | 17 |
| | $ | 13 |
| $ | 124,660 |
| | $ | 114,734 |
| | $ | 6 |
| | $ | 17 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Funded status, end of year | $ | (48,086 | ) | | $ | (78,840 | ) | | $ | (9,993 | ) | | $ | (11,007 | ) | $ | (85,660 | ) | | $ | (48,086 | ) | | $ | (8,234 | ) | | $ | (9,993 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts Recognized in the Balance Sheets Consist of: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liability | $ | (237 | ) | | $ | (243 | ) | | $ | (614 | ) | | $ | (625 | ) | $ | (247 | ) | | $ | (237 | ) | | $ | (575 | ) | | $ | (614 | ) |
| Noncurrent liability | (47,849 | ) | | (78,597 | ) | | (9,379 | ) | | (10,382 | ) | (85,413 | ) | | (47,849 | ) | | (7,659 | ) | | (9,379 | ) |
| Net amount recognized | $ | (48,086 | ) | | $ | (78,840 | ) | | $ | (9,993 | ) | | $ | (11,007 | ) | $ | (85,660 | ) | | $ | (48,086 | ) | | $ | (8,234 | ) | | $ | (9,993 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amounts Recognized in Regulatory Assets Consist of: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net actuarial loss | $ | 29,203 |
| | $ | 64,535 |
| | $ | 2,076 |
| | $ | 3,643 |
| $ | 65,049 |
| | $ | 29,203 |
| | $ | 29 |
| | $ | 2,076 |
|
| Prior service cost | 617 |
| | 675 |
| | — |
| | — |
| 559 |
| | 617 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Transition obligation | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1 |
| |
| Net amount recognized | $ | 29,820 |
| | $ | 65,210 |
| | $ | 2,076 |
| | $ | 3,644 |
| $ | 65,608 |
| | $ | 29,820 |
| | $ | 29 |
| | $ | 2,076 |
|
_______________
| |
(a) | In 2012 certain former employees received a one-time lump sum payment of their pension benefits. Our share of the payment totaled $4.9 million.
|
| | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| As of December 31, | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Pension Plans With a Projected Benefit Obligation In Excess of Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 162,820 |
| | $ | 176,891 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| $ | 210,320 |
| | $ | 162,820 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Fair value of plan assets | 114,734 |
| | 98,051 |
| | — |
| | — |
| 124,660 |
| | 114,734 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension Plans With an Accumulated Benefit Obligation In Excess of Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 137,459 |
| | $ | 141,722 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| $ | 179,228 |
| | $ | 137,459 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Fair value of plan assets | 114,734 |
| | 98,051 |
| | — |
| | — |
| 124,660 |
| | 114,734 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Post-retirement Plans With an Accumulated Post-retirement Benefit Obligation In Excess of Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated post-retirement benefit obligation | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 10,010 |
| | $ | 11,020 |
| $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 8,240 |
| | $ | 10,010 |
|
| Fair value of plan assets | — |
| | — |
| | 16 |
| | 13 |
| — |
| | — |
| | 6 |
| | 16 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-Average Actuarial Assumptions used to Determine Net Periodic Benefit Obligation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discount rate | 5.11 | % | | 4.16 | % | | 4.70 | % | | 3.78 | % | 4.20 | % | | 5.11 | % | | 3.89 | % | | 4.70 | % |
| Compensation rate increase | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — |
| | — |
| 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — |
| | — |
|
Wolf Creek uses a measurement date of December 31 for its pension and post-retirement benefit plans. The discount rate used to determine the current year pension obligation and the following year's pension expense is based on a bond selection-settlement portfolio approach. This approach develops a discount rate by selecting a portfolio of high quality, non-callable corporate bonds that generate sufficient cash flow to provide for the projected benefit payments of the plan. After the bond portfolio is selected, a single interest rate is determined that equates the present value of the plan's projected benefit payments discounted at this rate with the market value of the bonds selected. The decrease in the discount rates used as of December 31, 2014, increased Wolf Creek's pension and post-retirement benefit obligations by approximately $26.9 million and $0.6 million, respectively.
Wolf Creek utilizes actuarial assumptions about mortality to calculate the pension and post-retirement benefit obligations. In 2014, revised mortality tables were published which reflect improved life expectancies based on past experience and future projections. Wolf Creek adopted the revised mortality tables as of December 31, 2014, resulting in an increase to the pension and post-retirement benefit obligations by approximately $11.3 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
The prior service cost (benefit) is amortized on a straight-line basis over the average future service of the active employees (plan participants) benefiting under the plan at the time of the amendment. The net actuarial gain or loss is amortized on a straight-line basis over the average future service of active plan participants benefiting under the plan without application of an amortization corridor. Following is additional information regarding KGE's 47% share of the Wolf Creek pension and other post-retirement benefit plans.
| | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| Year Ended December 31, | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| | (Dollars in Thousands) | (Dollars in Thousands) |
| Components of Net Periodic Cost (Benefit): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Service cost | $ | 6,835 |
| | $ | 6,062 |
| | $ | 4,957 |
| | $ | 206 |
| | $ | 191 |
| | $ | 165 |
| $ | 5,695 |
| | $ | 6,835 |
| | $ | 6,062 |
| | $ | 173 |
| | $ | 206 |
| | $ | 191 |
|
| Interest cost | 7,562 |
| | 7,537 |
| | 7,370 |
| | 413 |
| | 411 |
| | 458 |
| 8,469 |
| | 7,562 |
| | 7,537 |
| | 464 |
| | 413 |
| | 411 |
|
| Expected return on plan assets | (7,373 | ) | | (6,577 | ) | | (5,904 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| (8,084 | ) | | (7,373 | ) | | (6,577 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Amortization of unrecognized: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transition obligation, net | — |
| | — |
| | 52 |
| | — |
| | 57 |
| | 58 |
| — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 57 |
|
| Prior service costs | 58 |
| | 6 |
| | 16 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| 58 |
| | 58 |
| | 6 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Actuarial loss, net | 5,421 |
| | 5,366 |
| | 3,586 |
| | 265 |
| | 234 |
| | 227 |
| 2,987 |
| | 5,421 |
| | 5,366 |
| | 165 |
| | 265 |
| | 234 |
|
| Net periodic cost before regulatory adjustment | 12,503 |
| | 12,394 |
| | 10,077 |
| | 884 |
| | 893 |
| | 908 |
| 9,125 |
| | 12,503 |
| | 12,394 |
| | 802 |
| | 884 |
| | 893 |
|
| Regulatory adjustment (a) | (641 | ) | | (1,776 | ) | | (2,546 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| 2,328 |
| | (641 | ) | | (1,776 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net periodic cost | $ | 11,862 |
| | $ | 10,618 |
| | $ | 7,531 |
| | $ | 884 |
| | $ | 893 |
| | $ | 908 |
| $ | 11,453 |
| | $ | 11,862 |
| | $ | 10,618 |
| | $ | 802 |
| | $ | 884 |
| | $ | 893 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other Changes in Plan Assets and Benefit Obligations Recognized in Regulatory Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current year actuarial (gain)/loss | $ | (29,911 | ) | | $ | 4,629 |
| | $ | 29,124 |
| | $ | (1,303 | ) | | $ | 669 |
| | $ | (360 | ) | |
| Amortization of actuarial loss | (5,421 | ) | | (5,366 | ) | | (3,586 | ) | | (265 | ) | | (234 | ) | | (227 | ) | |
| Current year actuarial (gain) loss | | $ | 38,833 |
| | $ | (29,911 | ) | | $ | 4,629 |
| | $ | (1,881 | ) | | $ | (1,303 | ) | | $ | 669 |
|
| Amortization of actuarial loss (gain) | | (2,987 | ) | | (5,421 | ) | | (5,366 | ) | | (165 | ) | | (265 | ) | | (234 | ) |
| Current year prior service cost | — |
| | 650 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| — |
| | — |
| | 650 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Amortization of prior service cost | (58 | ) | | (6 | ) | | (16 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| (58 | ) | | (58 | ) | | (6 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Amortization of transition obligation | — |
| | — |
| | (52 | ) | | — |
| | (57 | ) | | (58 | ) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (57 | ) |
| Total recognized in regulatory assets | $ | (35,390 | ) | | $ | (93 | ) | | $ | 25,470 |
| | $ | (1,568 | ) | | $ | 378 |
| | $ | (645 | ) | $ | 35,788 |
| | $ | (35,390 | ) | | $ | (93 | ) | | $ | (2,046 | ) | | $ | (1,568 | ) | | $ | 378 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total recognized in net periodic cost and regulatory assets | $ | (23,528 | ) | | $ | 10,525 |
| | $ | 33,001 |
| | $ | (684 | ) | | $ | 1,271 |
| | $ | 263 |
| $ | 47,241 |
| | $ | (23,528 | ) | | $ | 10,525 |
| | $ | (1,244 | ) | | $ | (684 | ) | | $ | 1,271 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-Average Actuarial Assumptions used to Determine Net Periodic Cost: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discount rate | 4.16 | % | | 4.55 | % | | 5.45 | % | | 3.78 | % | | 4.10 | % | | 4.90 | % | 5.11 | % | | 4.16 | % | | 4.55 | % | | 4.70 | % | | 3.78 | % | | 4.10 | % |
| Expected long-term return on plan assets | 7.50 | % | | 7.50 | % | | 7.50 | % | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| 7.50 | % | | 7.50 | % | | 7.50 | % | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Compensation rate increase | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | The regulatory adjustment represents the difference between current period pension or post-retirement benefit expense and the amount of such expense recognized in setting our prices. |
We estimate that we will amortize the following amounts from regulatory assets into net periodic cost in 20142015.
| | | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Actuarial loss | $ | 2,987 |
| | $ | 165 |
| $ | 5,930 |
| | $ | 2 |
|
| Prior service cost | 58 |
| | — |
| 57 |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 3,045 |
| | $ | 165 |
| $ | 5,987 |
| | $ | 2 |
|
The expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is based on historical and projected rates of return for current and planned asset classes in the plans' investment portfolios. Assumed projected rates of return for each asset class were selected after analyzing long-term historical experience and future expectations of the volatility of the various asset classes. Based on target asset allocations for each asset class, the overall expected rate of return for the portfolios was developed, adjusted for historical and expected experience of active portfolio management results compared to benchmark returns and for the effect of expenses paid from plan assets.
For measurement purposes, the assumed annual health care cost growth rates were as follows.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| Health care cost trend rate assumed for next year | 7.5 | % | | 8.0 | % | 7.0 | % | | 7.5 | % |
| Rate to which the cost trend rate is assumed to decline (the ultimate trend rate) | 5.0 | % | | 5.0 | % | 5.0 | % | | 5.0 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Year that the rate reaches the ultimate trend rate | 2019 |
| | 2019 |
| 2019 |
| | 2019 |
|
The health care cost trend rate affects the projected benefit obligation. A 1% change in assumed health care cost growth rates would have effects shown in the following table.
| | | | One-Percentage- Point Increase | | One-Percentage- Point Decrease | One-Percentage- Point Increase | | One-Percentage- Point Decrease |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Effect on total of service and interest cost | $ | (9 | ) | | $ | 9 |
| $ | (8 | ) | | $ | 8 |
|
| Effect on post-retirement benefit obligation | (102 | ) | | 97 |
| (111 | ) | | 113 |
|
Plan Assets
ItsWolf Creek's pension and post-retirement plan investment strategy is to manage assets in a prudent manner with regard to preserving principal while providing reasonable returns. It has adopted a long-term investment horizon such that the chances and duration of investment losses are carefully weighed against the long-term potential for appreciation of assets. Part of its strategy includes managing interest rate sensitivity of plan assets relative to the associated liabilities. The primary objective of the pension plan is to provide a source of retirement income for its participants and beneficiaries, and the primary financial objective of the plan is to improve its funded status. The primary objective of the post-retirement benefit plan is growth in assets and preservation of principal, while minimizing interim volatility, to meet anticipated claims of plan participants. Wolf Creek delegates the management of its pension and post-retirement benefit plan assets to independent investment advisors who hire and dismiss investment managers based upon various factors. The investment advisors striveare instructed to diversify investments across asset classes, sectors and manager styles to minimize the risk of large losses, based upon objectives and risk tolerance specified by Wolf Creek, which include allowable and/or prohibited investment types. It measures and monitors investment risk on an ongoing basis through quarterly investment portfolio reviews and annual liability measurements.
The target allocations for Wolf Creek's pension plan assets are 31% to international equity securities, 25% to domestic equity securities, 25% to debt securities, 10% to real estate securities, 5% to commodity investments and 4% to other investments. The investments in both international and domestic equity include investments in large-, mid- and small-cap companies, private equity funds and investment funds with underlying investments similar to those previously mentioned. The investments in debt include core and high-yield bonds. Core bonds include funds invested in investment grade debt securities of corporate entities, obligations of U.S. and foreign governments and their agencies and private debt securities. High-yield bonds include a fund with underlying investments in non-investment grade debt securities of corporate entities, private placements and bank debt. Real estate securities include funds invested in commercial and residential real estate properties while commodity investments include funds invested in commodity-related instruments.
All of Wolf Creek's pension plan assets are recorded at fair value using daily net asset values as reported by the trustee. However, level 3 investments in real estate funds and alternative funds are invested in underlying investments that are illiquid and require significant judgment when measuring them at fair value using market- and income-based models. Significant unobservable inputs for underlying real estate investments include estimated market discount rates, projected cash flows and estimated value into perpetuity. Alternative funds invest in a wide range of investments typically with low correlations to traditional investments.
Similar to other assets measured at fair value, GAAP establishes a hierarchal framework for disclosing the transparency of the inputs utilized in measuring pension and post-retirement benefit plan assets at fair value. From time to time, the Wolf Creek pension trust may buy and sell investments resulting in changes within the hierarchy. See Note 4, "Financial Instruments and Trading Securities," for a description of the hierarchal framework.
The following table provides the fair value of KGE's 47% share of Wolf Creek's pension plan assets and the corresponding level of hierarchy as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | — |
| | $ | 30,599 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 30,599 |
|
| International equity | | — |
| | 36,868 |
| | — |
| | 36,868 |
|
| Core bonds | | — |
| | 26,926 |
| | — |
| | 26,926 |
|
| Real estate securities | | — |
| | 5,440 |
| | 5,094 |
| | 10,534 |
|
| Commodities | | — |
| | 5,245 |
| | — |
| | 5,245 |
|
| Alternative investments | | — |
| | — |
| | 4,147 |
| | 4,147 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 415 |
| | — |
| | 415 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 105,493 |
| | $ | 9,241 |
| | $ | 114,734 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity | | $ | — |
| | $ | 24,305 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 24,305 |
|
| International equity | | — |
| | 30,484 |
| | — |
| | 30,484 |
|
| Core bonds | | — |
| | 24,763 |
| | — |
| | 24,763 |
|
| Real estate securities | | — |
| | 4,972 |
| | 4,541 |
| | 9,513 |
|
| Commodities | | — |
| | 4,789 |
| | — |
| | 4,789 |
|
| Alternative investments | | — |
| | — |
| | 3,900 |
| | 3,900 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 297 |
| | — |
| | 297 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 89,610 |
| | $ | 8,441 |
| | $ | 98,051 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2014 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | | $ | — |
| | $ | 31,580 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 31,580 |
|
| International equity funds | | — |
| | 38,624 |
| | — |
| | 38,624 |
|
| Core bond funds | | — |
| | 31,854 |
| | — |
| | 31,854 |
|
| Real estate securities fund | | — |
| | 6,313 |
| | 5,649 |
| | 11,962 |
|
| Commodities fund | | — |
| | 5,887 |
| | — |
| | 5,887 |
|
| Alternative investment fund | | — |
| | — |
| | 4,309 |
| | 4,309 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 444 |
| | — |
| | 444 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 114,702 |
| | $ | 9,958 |
| | $ | 124,660 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| As of December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | |
| Assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic equity funds | | $ | — |
| | $ | 30,599 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 30,599 |
|
| International equity funds | | — |
| | 36,868 |
| | — |
| | 36,868 |
|
| Core bond funds | | — |
| | 26,926 |
| | — |
| | 26,926 |
|
| Real estate securities fund | | — |
| | 5,440 |
| | 5,094 |
| | 10,534 |
|
| Commodities fund | | — |
| | 5,245 |
| | — |
| | 5,245 |
|
| Alternative investment fund | | — |
| | — |
| | 4,147 |
| | 4,147 |
|
| Cash equivalents | | — |
| | 415 |
| | — |
| | 415 |
|
| Total Assets Measured at Fair Value | | $ | — |
| | $ | 105,493 |
| | $ | 9,241 |
| | $ | 114,734 |
|
The following table provides a reconciliation of KGE's 47% share of Wolf Creek's pension plan assets measured at fair value using significant level 3 inputs for the years ended December 31, 20132014 and 20122013.
| | | | | | | | | Real Estate Securities Fund | | Alternative Investment Fund | | Total |
| | Real Estate Securities | | Alternative Investments | | Total | (In Thousands) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | | $ | 5,094 |
| | $ | 4,147 |
| | $ | 9,241 |
|
| Actual gain on plan assets: | | | | | | |
| Relating to assets still held at the reporting date | | 555 |
| | 162 |
| | 717 |
|
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 | | $ | 5,649 |
| | $ | 4,309 |
| | $ | 9,958 |
|
| | (In Thousands) | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | $ | 4,541 |
| | $ | 3,900 |
| | $ | 8,441 |
| $ | 4,541 |
| | $ | 3,900 |
| | $ | 8,441 |
|
| Actual gain (loss) on plan assets: | | | | | | |
| Actual gain on plan assets: | |
| | | | |
| Relating to assets still held at the reporting date | 553 |
| | 247 |
| | 800 |
| 553 |
| | 247 |
| | 800 |
|
| Balance as of December 31, 2013 | $ | 5,094 |
| | $ | 4,147 |
| | $ | 9,241 |
| $ | 5,094 |
| | $ | 4,147 |
| | $ | 9,241 |
|
| | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | $ | 3,630 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 3,630 |
| |
| Actual gain (loss) on plan assets: |
| | | | | |
| Relating to assets still held at the reporting date | (411 | ) | | 23 |
| | (388 | ) | |
| Relating to assets sold during the period | 755 |
| | — |
| | 755 |
| |
| Purchases, issuances and settlements, net | 567 |
| | 3,877 |
| | 4,444 |
| |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | $ | 4,541 |
| | $ | 3,900 |
| | $ | 8,441 |
| |
Cash Flows
The following table shows our expected cash flows for KGE's 47% share of Wolf Creek's pension and post-retirement benefit plans for future years.
| | | Expected Cash Flows | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits | | Pension Benefits | | Post-retirement Benefits |
| | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets | | To/(From) Trust | | (From) Company Assets |
| | | (In Millions) | | (In Millions) |
| Expected contributions: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2014 | | $ | 5.4 |
| | | | $ | 0.6 |
| | | |
| 2015 | | | $ | 4.7 |
| | | | $ | 0.6 |
| | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Expected benefit payments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2014 | | $ | (4.6 | ) | | $ | (0.2 | ) | | $ | (0.6 | ) | | $ | — |
| |
| 2015 | | (5.3 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.7 | ) | | — |
| | $ | (5.4 | ) | | $ | (0.2 | ) | | $ | (0.6 | ) | | $ | — |
|
| 2016 | | (6.1 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.8 | ) | | — |
| | (6.1 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | — |
|
| 2017 | | (7.0 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.8 | ) | | — |
| | (6.8 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | — |
|
| 2018 | | (7.8 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.8 | ) | | — |
| | (7.5 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | — |
|
| 2019 - 2022 | | (53.0 | ) | | (1.3 | ) | | (4.4 | ) | | — |
| |
| 2019 | | | (8.2 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.7 | ) | | — |
|
| 2020 - 2024 | | | (51.0 | ) | | (1.1 | ) | | (3.2 | ) | | — |
|
Savings Plan
Wolf Creek maintains a qualified 401(k) savings plan in which most of its employees participate. They matchWolf Creek matches employees' contributions in cash up to specified maximum limits. Wolf Creek's contributions to the plan are deposited with a trustee and invested at the direction of plan participants into one or more of the investment alternatives provided under the plan. KGE's portion of the expense associated with Wolf Creek's matching contributions was $1.4 million in 20132014, $1.31.4 million in 20122013 and $1.3 million in 20112012.
13. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Purchase Orders and Contracts
As part of our ongoing operations and capital expenditure program, we have purchase orders and contracts, excluding fuel and transmission, which are discussed below under "—Fuel, Purchased Power and Transmission Commitments." These commitments relate to purchase obligations issued and outstanding at year-end.
The yearly detail of the aggregate amount of required payments as of December 31, 20132014, was as follows.
| | | | Committed Amount | Committed Amount |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| 2014 | $ | 258,293 |
| |
| 2015 | 20,653 |
| $ | 406,859 |
|
| 2016 | 25,762 |
| 39,551 |
|
| 2017 | | 9,223 |
|
| Thereafter | 7,463 |
| 27,247 |
|
| Total amount committed | $ | 312,171 |
| $ | 482,880 |
|
Federal Clean Environmental Matters
Air ActEmissions
We must comply with the federal Clean Air Act, state laws and implementing federal and state regulations that impose, among other things, limitations on emissions generated from our operations, including sulfur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter (PM), nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), mercury and acid gases.
Emissions from our generating facilities, including PM, SO2 and NOx, have been determined by regulation to reduce visibility by causing or contributing to regional haze. Under federal laws, such as the Clean Air Visibility Rule, and pursuant to an agreement with the Kansas Department of Health and Environment (KDHE) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), we are required to install, operate and maintain controls to reduce emissions found to cause or contribute to regional haze.
Sulfur Dioxide and Nitrogen Oxide
Through the combustion of fossil fuels at our generating facilities, we emit SO2 and NOx. Federal and state laws and regulations, including those noted above, and permits issued to us limit the amount of these substances we can emit. If we exceed these limits, we could be subject to fines and penalties. In order to meet SO2 and NOx regulations applicable to our generating facilities, we use low-sulfur coal and natural gas and have equipped the majority of our fossil fuel generating facilities with equipment to control such emissions.
We are subject to the SO2 allowance and trading program under the federal Clean Air Act Acid Rain Program. Under this program, each unit must have enough allowances to cover its SO2 emissions for that year. In 2014, we had adequate SO2 allowances to meet planned generation and we expect to have enough to cover emissions under this program in 2015.
Cross-State Air Pollution Rule
In 2011, the EPA finalized the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) requiring 28 states, including Kansas, Missouri and Oklahoma, to further reduce emissions of SO2, NOx and fine PM. In April 2014, the U.S. Supreme Court reversed a 2012 decision by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit that had vacated CSAPR and remanded CSAPR back to the U.S. Court of Appeals for further proceedings consistent with the U.S. Supreme Court decision. In June 2014, the U.S. Department of Justice, on behalf of the EPA, filed a motion to lift the CSAPR stay. In October 2014, the U.S. Court of Appeals granted the motion to lift the CSAPR stay and established a schedule to hear arguments on the remaining outstanding issues beginning in March 2015. During the CSAPR stay, we installed various emission controls at our generation facilities and have projects for additional controls in progress or planned that will reduce the impact of CSAPR. We are unable to determine the full impact of reinstatement of CSAPR until the U.S. Court of Appeals and the EPA take further action, however, we are prepared to comply with CSAPR in its current form.
National Ambient Air Quality Standards
Under the federal Clean Air Act, the EPA sets National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for certain emissions considered harmful to public health and the environment, including two classes of PM, NOx (a precursor to ozone), CO and SO2, which result from fossil fuel combustion. Areas meeting the NAAQS are designated attainment areas while those that do not meet the NAAQS are considered nonattainment areas. Each state must develop a plan to bring nonattainment areas into compliance with the NAAQS. NAAQS must be reviewed by the EPA at five-year intervals. KDHE, our state environmental regulatory agency, proposed to designate portions of the Kansas City area nonattainment for the eight-hour ozone standard, which has the potential to impact our operations.standard. The EPA has not acted on KDHE's proposed designation of the Kansas City area and it is uncertain when, or if, such a designation might occur. The Wichita area also exceeded the eight-hour ozone standard and could be designated nonattainment in the future potentially impacting our operations.
In December 2012, the EPA strengthened an existing NAAQS for one class of PM. By the end of 2014, the EPA anticipates making final attainment/nonattainment Nonattainment designations under this rule and expects to issueon areas that impact our operations could have a final implementation rule. We are currently evaluating the rule and thematerial impact it may have on our operations or consolidated financial results.
In 2010,, the EPA strengthened the NAAQS for both NOx and SO2. We continue to communicate with our regulators regarding these standards and are currently evaluating what impact this could have on our operations.operations and consolidated financial results. If we are required to install additional equipment to control emissions at our facilities, the revised NAAQS could have a material impact on our operations and consolidated financial results.
In December 2014, the EPA published a proposed rule revising NAAQS for ozone and to make certain other changes, including extending the ozone monitoring season by at least one month. The EPA intends to issue a final rule regarding the ozone NAAQS by October 2015 and make attainment/nonattainment designations for any revised standards by October 2017. We are currently reviewing this proposed new standard and cannot at this time predict the impact it may have on our operations, but it could be material.
In December 2012, the EPA strengthened an existing NAAQS for one class of PM. In December 2014, the EPA designated the entire state of Kansas as unclassifiable/in attainment with the standard. We cannot at this time predict the impact this designation may have on our operations or consolidated financial results, but it could be material.
Mercury and Air Toxics Standards
The operation of power plants results in emissions of mercury, acid gases and other air toxics. In 2012, the EPA's Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) for power plants became effective, replacing the prior federal Clean Air Mercury Rule and requiring significant reductions in mercury, acid gases and other emissions. Several lawsuits challenging MATS have been filed by other parties and consolidated into a single proceeding before the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit. In April 2014, the U.S. Court of Appeals issued an opinion upholding MATS. In July 2014, numerous states and two trade groups petitioned the U.S. Supreme Court to review this opinion, and in November 2014, the U.S. Supreme Court agreed to such review. The U.S. Supreme Court is expected to rule by June 2015; however, we currently cannot predict the outcome of this litigation, or its impact, if any, on our MATS compliance planning. Nonetheless, we expect to be compliant with the MATS in its current form by April 2016 as currently approved by KDHE. We currently believe that our related investment, based on MATS in its current form, will not be significant.
Greenhouse Gases
Byproducts of burning coal and other fossil fuels include carbon dioxide (CO2) and other gases referred to as greenhouse gases (GHGs), which are believed by many to contribute to climate change. The EPA is currently, and has further proposed, using the federal Clean Air Act to limit CO2 and other GHG emissions, and other measures are being imposed or offered by individual states, municipalities and regional agreements with the goal of reducing GHG emissions.
In January 2014, the EPA re-proposed a New Source Performance Standard that would limit CO2 emissions for new coal and natural gas fueled electric generating units. The re-proposal would limit CO2 emissions to 1,000 lbs per Megawatt hour (MWh) generated for larger natural gas units and 1,100 lbs per MWh generated for smaller natural gas units and coal units. The EPA issued proposed standards addressing CO2 emissions for modified, reconstructed and existing power plants in June 2014. The standards for existing plants is known as the Clean Power Plan. The EPA anticipates issuing final rules for new, modified, reconstructed and existing power plants by summer 2015 and requiring states to submit their implementation state plans to the EPA by no later than summer 2016. The EPA is expected to propose in summer 2015 a federal plan that will implement the Clean Power Plan to be used for states that fail to submit adequate state plans, with such federal plan expected to be finalized by summer 2016. While the Clean Power Plan is not yet final, various legal and judicial challenges to it have been filed. We cannot at this time determine the impact of such proposals on our operations or consolidated financial results, but we believe the costs to comply could be material.
Under regulations formerly known as the Tailoring Rule, the EPA regulates GHG emissions from certain stationary sources. The regulations are implemented pursuant to two federal Clean Air Act programs, the Prevention of Significant Deterioration (PSD) and Title V Operating Permit Programs, that impose recordkeeping and monitoring requirements and also mandate the implementation of best available control technology (BACT) for projects that cause a significant increase in GHG emissions (currently defined to be more than 75,000 tons or more per year or 100,000 tons or more per year, depending on various factors). In June 2014, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that the EPA had exceeded its statutory authority in issuing the Tailoring Rule by regulating under the PSD program sources based solely on their GHG emissions. However, the U.S. Supreme Court also held that the EPA could impose GHG BACT requirements for sources already required to implement PSD for other pollutants. Therefore, if future modifications to our sources require PSD review for other pollutants, it may also trigger GHG BACT requirements. The EPA has issued guidance on what BACT entails for the control of GHGs and individual states are now required to determine what controls are required for facilities within their jurisdiction on a case-by-case basis. We cannot at this time determine the impact of these regulations on our future operations or consolidated financial results as the rule has not been finalized, but we believe the cost of compliance with the regulations could be material.
Water
We discharge some of the water used in our operations. This water may contain substances deemed to be pollutants. Revised rules governing such discharges from coal-fired power plants are expected to be issued by the EPA by the end of September 2015. Although we cannot at this time determine the timing or impact of compliance with any new regulations, more stringent regulations could have a material impact on our operations or consolidated financial results.
In October 2014, the EPA’s final standards for cooling intake structures at power plants to protect aquatic life took effect. The standards, based on Section 316(b) of the federal Clean Water Act (CWA), require subject facilities to choose among seven Best Technology Available options to reduce fish impingement. In addition, some facilities must conduct studies to assist permitting authorities to determine whether and what site-specific controls, if any, would be required to reduce entrainment of aquatic organisms. Our current analysis indicates this rule will not have a significant impact on our coal plants that employ cooling towers. Biological monitoring may be required for LaCygne and Wolf Creek. We are currently evaluating the rule's impact on those two plants and cannot predict the resulting impact on our operations or consolidated financial results, but we do not expect it to be material.
In April 2014, the EPA along with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers issued a proposed rule defining the Waters of the United States for purposes of the CWA. This rulemaking has the potential to impact all programs under the CWA. Expansion of regulated waterways is possible under the proposal, which could impact several permitting programs. Although we cannot at this time determine the timing or impact of compliance with any new regulations, more stringent regulations could have a material impact on our operations or consolidated financial results.
Regulation of Coal Combustion Byproducts
In the course of operating our coal generation plants, we produce coal combustion byproducts (CCBs), including fly ash, gypsum and bottom ash. We recycle some of our ash production, principally by selling to the aggregate industry. In 2010, the EPA proposed a rule to regulate CCB by the federal government. The EPA released a pre-publication version of the rule in December 2014, which we believe will require additional CCB handling, processing and storage equipment and potential closure of certain ash disposal areas, but it has not yet published the final rule. While we cannot at this time estimate the impact and costs associated with future regulations of CCB, we believe the impact on our operations or consolidated financial results could be material.
Environmental Projects
We will continue to make significant capital and operating expenditures at our power plants to reduce regulated emissions. The amount of these expenditures could change materially depending on the timing and nature of required investments, the specific outcomes resulting from existing regulations, new regulations, legislation and the manner in which we operate the plants. In addition to the capital investment, in the event we install new equipment, such equipment may cause us to incur significant increases in annual operating and maintenance expense and may reduce the net production, reliability and availability of the plants. The degree to which we will need to reduce emissions and the timing of when such emissions controls may be required is uncertain. Additionally, our ability to access capital markets and the availability of materials, equipment and contractors may affect the timing and ultimate amount of such capital investments.
InWe are currently permitted to recover certain of these costs through the ECRR, which, in comparison to a general rate review, the ECRR reduces the amount of time it takes to begin collecting in retail prices the costs associated with capital expenditures for qualifying environmental improvements. We are not allowed to use the ECRR to collect approximately $610.0 million of the projected capital investment associated with the environmental upgrades at La Cygne. In November 2013, the KCC issued an order allowing us to adjust our prices to include the additional investment in the La Cygne environmental upgrades and to reflect cost reductions elsewhere. The new prices are expected to increase our annual retail revenues by approximately $30.7 million. For additional information regarding our abbreviated rate review, see Note 3, "Rate Matters and Regulation." To change our prices to collect increased operating and maintenance costs, we must file a general rate review with the KCC. We intend to file our next general rate review in March 2015. In addition, the installation of new equipment may cause us to reduce the net production, reliability and availability of our plants. Furthermore, enhancements to our power plants, even if they result in greater efficiency, can trigger a regulatory review, which could result in increased costs or other operational requirements. For additional information regarding our abbreviated rate review, see Note 3, "Rate Matters and Regulation."
Air EmissionsEPA Consent Decree
The operationAs part of power plants resultsa 2010 settlement of a lawsuit filed by the U.S. Department of Justice on behalf of the EPA, we completed installation of selective catalytic reduction equipment on one of our three JEC coal units in emissionsDecember 2014, at a cost of mercury, acid gases andapproximately $225.0 million. We also completed installation of less expensive NOx reduction equipment on the other air toxics. In 2012,two units to satisfy other terms of the EPA's Mercury and Air Toxics Standards (MATS) for power plants became effective, replacingsettlement. We plan to recover the prior federal Clean Air Mercury Rule (CAMR) and requiring significant reductions in mercury, acid gases and other emissions. We expectcosts of installing these systems through our ECRR, but such recovery remains subject to be compliant with the new standards by April 2016 as approved by KDHE. We continue to evaluate the new standards and believe thatapproval of our related investment will be approximately $17.0 million.regulators.
Greenhouse Gases
Under regulations known as the Tailoring Rule, the EPA is regulating greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from certain stationary sources. The regulations are being implemented pursuant to two federal Clean Air Act programs which impose recordkeeping and monitoring requirements and also mandate the implementation of best available control technology (BACT) for projects that cause a significant increase in GHG emissions (defined to be more than 75,000 tons or more per year or 100,000 tons or more per year, depending on various factors). The EPA has issued guidance on what BACT entails for the control of GHGs and individual states are now required to determine what controls are required for facilities within their jurisdiction on a case-by-case basis. We cannot at this time determine the impact of these regulations on our operations and consolidated financial results, but we believe the cost of compliance with the regulations could be material.
Renewable Energy Standard
Kansas law mandates that we maintain a minimum amount of renewable energy sources. Through 2015, net renewable generation capacity must be 10% of the average peak retail demand for the three prior years, subject to limited exceptions. This requirement increases to 15% for years 2016 through 2019 and 20% for 2020 and thereafter. In 2012, we began purchasing under 20-year supply contracts the renewable energy produced from approximately 370 MW of additionalWith our existing wind generation which, together with existing facilities, supply contracts and renewable energy credits, will allow uswe are able to satisfy the net renewable generation requirement through 2015. With our agreementagreements to purchase an additional 200400 MW of installed design capacity from a wind generation facilityfacilities beginning in late2015 through 2016, we expect to meet the increased requirements through 2020.for 2020 and thereafter. If we are unable to meet future requirements, our operations and consolidated financial results could be adversely impacted.
EPA Consent Decree
As part of a 2010 settlement of a lawsuit filed by the Department of Justice on behalf of the EPA, we are installing selective catalytic reduction (SCR) equipment on one of three JEC coal units by the end of 2014, which we estimate will cost approximately $230.0 million. We are installing less expensive NOx reduction equipment on the other two units to satisfy other terms of the settlement. We plan to complete these projects in 2014 and recover the costs to install these systems through our ECRR, but such recovery remains subject to the approval of our regulators.
FERC Investigation
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) opened a non-public investigation of our use of transmission service between July 2006 and February 2008. In May 2009, FERC staff alleged that we improperly used secondary network transmission service to facilitate off-system wholesale power sales in violation of applicable FERC orders and Southwest Power Pool (SPP) tariffs and that we received $14.3 million of unjust profits through such activities. Based on our response to these allegations, FERC staff substantially revised downward its preliminary conclusions to allege that we received $0.9 million of unjust profits and failed to pay $0.8 million to the SPP for transmission service. As of December 31, 2012, we had recorded a liability of $1.6 million related to the potential settlement of this investigation and the risks of litigating this matter to a final outcome. We settled with FERC in January 2013 for $1.6 million.
Nuclear Decommissioning
Nuclear decommissioning is a nuclear industry term for the permanent shutdown of a nuclear power plant and the removal of radioactive components in accordance with Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) requirements. The NRC will terminate a plant's license and release the property for unrestricted use when a company has reduced the residual radioactivity of a nuclear plant to a level mandated by the NRC. The NRC requires companies with nuclear plants to prepare formal financial plans to fund nuclear decommissioning. These plans are designed so that sufficient funds required for nuclear decommissioning will be accumulated prior to the expiration of the license of the related nuclear power plant. Wolf Creek files a nuclear decommissioning site study with the KCC every three years.
The KCC reviews nuclear decommissioning plans in two phases. Phase one is the approval of the revisedupdated nuclear decommissioning study including the estimated costs to decommission the plant. Phase two involves the review and approval of a funding schedule prepared by the owner of the plant detailing how it plans to fund the future-year dollar amount of its pro rata share of the decommissioning costs.
In 20112014 we revised, Wolf Creek updated the nuclear decommissioning cost study. Based on the study, our share of decommissioning costs, including decontamination, dismantling and site restoration, is estimated to be $296.2 million.approximately $360.0 million. This amount compares to the prior site study estimate of $279.0296.2 million. The site study cost estimate represents the estimate to decommission Wolf Creek as of the site study year. The actual nuclear decommissioning costs may vary from the estimates because of changes in regulations and technologies as well as changes in costs for labor, materials and equipment.
We are allowed to recover nuclear decommissioning costs in our prices over a period equal to the operating license of Wolf Creek, which is through 2045. The NRC requires that funds sufficient to meet nuclear decommissioning obligations be held in a trust. We believe that the KCC approved funding level will also be sufficient to meet the NRC requirement. Our consolidated financial results would be materially affected if we were not allowed to recover in our prices the full amount of the funding requirement.
We recovered in our prices and deposited in an external trust fund for nuclear decommissioning approximately $2.8 million in 2014, $2.9 million in 2013, $3.2 million in 2012 and $3.2 million in 20112012. We record our investment in the NDT fund at fair value, which approximated $175.6185.0 million and $150.8175.6 million as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, respectively.
Storage of Spent Nuclear Fuel
Under the Nuclear Waste Policy Act of 1982,, the Department of Energy (DOE) is responsible for the permanent disposal of spent nuclear fuel. Wolf Creek payspaid into a federal Nuclear Waste Fund administered by the DOE a quarterly fee for the future disposal of spent nuclear fuel. In November 2013, a federal court of appeals ruled that the DOE must stop collecting this fee effective May 2014. Our share of the fee, calculated as one tenth of a cent for each kilowatt-hour of net nuclear generation delivered to customers, was $3.0$0.8 million in 2013, $3.62014, $3.0 million in 20122013 and $3.1$3.6 million in 2011.2012. We include these costs in fuel and purchased power expense on our consolidated statements of income. As of November 2013, a federal court of appeals ruled that the DOE must stop collecting this fee.
In 2010, the DOE filed a motion with the NRC to withdraw its then pending application to construct a national repository for the disposal of spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste at Yucca Mountain, Nevada. An NRC board denied the DOE's motion to withdraw its application and the DOE appealed that decision to the full NRC. In 2011, the NRC issued an evenly split decision on the appeal and also ordered the licensing board to close out its work on the DOE's application by the end of 2011 due to a lack of funding. These agency actions prompted the States of Washington and South Carolina, and a county in South Carolina, to file a lawsuit in a federal Court of Appeals asking the court to compel the NRC to resume its license review and to issue a decision on the license application. In August 2013, the court ordered the NRC to resume its review of the DOE's application. Wolf Creek has an on-site storage facility designed to hold all spent fuel generated at the plant through 2025 and believes it will be able to expand on-site storage as needed past 2025. We cannot predict when, or if, an alternative disposal site will be available to receive Wolf Creek's spent nuclear fuel and will continue to monitor this activity.
Wolf Creek disposes of most of its low-level radioactive waste at an existing third-party repository in Utah, which we expect will remain available to Wolf Creek. Wolf Creek also contracts with a waste processor to process, take title and dispose in another state most of the remainder of Wolf Creek's low-level radioactive waste. Should on-site waste storage be needed in the future, Wolf Creek has storage capacity on site adequate for aboutapproximately four years of plant operations and believes it willwould be able to expand that storage capacity if needed.
Nuclear Insurance
We maintain nuclear liability, property and business interruption insurance for Wolf Creek. These policies contain certain industry standard terms, conditions and exclusions, including, but not limited to, ordinary wear and tear and war. An industry aggregate limit of $3.2 billion plus any reinsurance, indemnity or any other source recoverable by Nuclear Electric Insurance Limited (NEIL), our property and business interruption insurance provider, exists for acts of terrorism affecting Wolf Creek or any other NEIL insured plant within 12 months from the date of the first act. The $3.2 billion maximum recovery limit is not applicable, however, in the event of a "certified act of terrorism" as defined in the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act of 2002, as amended by the Terrorism Risk Insurance Program Reauthorization Act of 2007. In addition, we may be required to participate in industry-wide retrospective assessment programs as discussed below.
Nuclear Liability Insurance
Pursuant to the Price-Anderson Act, which has been reauthorized through December 31, 2025, by the Energy Policy Act of 2005,, we are required to insure against public liability claims resulting from nuclear incidents to the current limit of public liability, which is approximately $13.6 billion.$13.6 billion. This limit of liability consists of the maximum available commercial insurance of $375.0$375.0 million and the remaining $13.2$13.2 billion is provided through mandatory participation in an industry-wide retrospective assessment program. In addition, Congress could impose additional revenue-raising measures to pay claims. Under this retrospective assessment program, the owners of Wolf Creek are jointly and severally subject to an assessment of up to $127.3$127.3 million (our share is $59.8 million)$59.8 million), payable at no more than $19.0$19.0 million (our share is $8.9 million)$8.9 million) per incident per year per reactor. Both the total and yearly assessment is subject to an inflationary adjustment every five years with the next adjustment in 2018.2018.
Nuclear Property and Business Interruption Insurance
The owners of Wolf Creek carry decontamination liability, premature nuclear decommissioning liability and property damage insurance for Wolf Creek totaling approximately $2.8 billion.$2.8 billion. In the event of an accident, insurance proceeds must first be used for reactor stabilization and site decontamination in accordance with a plan mandated by the NRC. Our share of any remaining proceeds can be used to pay for property damage or, if certain requirements are met, including decommissioning the plant, toward a shortfall in the NDT fund. The owners also carry additional insurance with NEIL to cover costs of replacement power and other extra expenses incurred during a prolonged outage resulting from accidental property damage at Wolf Creek. If significant losses were incurred at any of the nuclear plants insured under the NEIL policies, we may be subject to retrospective assessments under the current policies of approximately $34.4$39.5 million (our share is $16.1$18.6 million).
Accidental Nuclear Outage Insurance
Although we maintain various insurance policies to provide coverage for potential losses and liabilities resulting from an accident or an extended outage, our insurance coverage may not be adequate to cover the costs that could result from a catastrophic accident or extended outage at Wolf Creek. Any substantial losses not covered by insurance, to the extent not recoverable in our prices, would have a material effect on our consolidated financial results.
Fuel, Purchased Power and Transmission Commitments
To supply a portion of the fuel requirements for our power plants, the owners of Wolf Creek have entered into various contracts to obtain nuclear fuel and we have entered into various contracts to obtain coal and natural gas. Some of these contracts contain provisions for price escalation and minimum purchase commitments. As of December 31, 20132014, our share of Wolf Creek's nuclear fuel commitments was approximately $41.327.1 million for uranium concentrates expiring in 2017, $6.14.1 million for conversion expiring in 2017, $109.093.3 million for enrichment expiring in 2025 and $41.133.3 million for fabrication expiring in 2023.
As of December 31, 20132014, our coal and coal transportation contract commitments under the remaining terms of the contracts were approximately $900.6 million1.1 billion. The contracts are for plants that we operate and expire at various times through 20212020.
As of December 31, 20132014, our natural gas transportation contract commitments under the remaining terms of the contracts were approximately $117.2118.5 million. The natural gas transportation contracts provide firm service to several of our natural gas burning facilities and expire at various times through 2030.
We have power purchase power agreements with the owners of fivesix separate wind generation facilities with installed design capacities of 715915 MW expiring in 2028 through 2036. Of the 715915 MW under contract, 200400 MW are associated with an agreementagreements pursuant to which a generation provider isproviders are scheduled to deliver power beginning in 2015 and 2016. Each of the agreements provide for our receipt and purchase of energy produced at a fixed price per unit of output. We estimate that our annual cost of energy purchased from these wind generation facilities will be approximately $68.2$68.2 million. in 2015 and approximately $110.0 million for the next several years thereafter.
We have acquired rights to transmit a total of 306 MW of power.MW. Agreements providing transmission capacity for approximately 200 MW expire in 2016 while the remaining 106 MW expire in 2022. As of December 31, 20132014, we are committed to spend approximately $33.834.0 million over the remaining terms of these agreements.
14. ASSET RETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS
Legal Liability
We have recognized legal obligations associated with the disposal of long-lived assets that result from the acquisition, construction, development or normal operation of such assets. The recording of AROs for regulated operations has no income statement impact due to the deferral of the adjustments through the establishment of a regulatory asset.asset or an offset to a regulatory liability.
We initially recorded AROs at fair value for the estimated cost to decommission Wolf Creek (KGE's 47% share), retire our wind generation facilities, dispose of asbestos insulating material at our power plants, remediate ash disposal ponds and dispose of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-contaminated oil.
The following table summarizes our legal AROs included on our consolidated balance sheets in long-term liabilities.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Beginning ARO | $ | 152,648 |
| | $ | 142,508 |
| $ | 160,682 |
| | $ | 152,648 |
|
| Increase in nuclear decommissioning ARO liability | | 50,683 |
| | — |
|
| Increase in other ARO liabilities | | 9,580 |
| | — |
|
| Liabilities settled | (973 | ) | | (1,389 | ) | (593 | ) | | (973 | ) |
| Accretion expense | 9,007 |
| | 8,454 |
| 10,316 |
| | 9,007 |
|
| Revisions in estimated cash flows | — |
| | 3,075 |
| |
| Ending ARO | $ | 160,682 |
| | $ | 152,648 |
| $ | 230,668 |
| | $ | 160,682 |
|
Wolf Creek filed a nuclear decommissioning cost study with the KCC in 2014. As a result of the study, we recorded a $50.7 million increase in our ARO to reflect revisions to the estimated costs to decommission Wolf Creek.
Conditional ARO refers to a legal obligation to perform an asset retirement activity in which the timing and/or method of settlement are conditional on a future event that may or may not be within the control of the entity. We determined that our conditional AROs include the retirement of our wind generation facilities, disposal of asbestos insulating material at our power plants, the remediation of ash disposal ponds and the disposal of PCB-contaminated oil.
We have an obligation to retire our wind generation facilities and remove the foundations. The ARO related to our wind generation facilities was determined based upon the date each wind generation facility was placed into service.
The amount of the retirement obligation related to asbestos disposal was recorded as of 1990, the date when the EPA published the "National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants: Asbestos NESHAP Revision; Final Rule."
We operate, as permitted by the state of Kansas, ash landfills at several of our power plants. The retirement obligation for the ash landfills was determined based upon the date each landfill was originally placed in service.
PCB-contaminated oil is contained within company electrical equipment, primarily transformers. The PCB retirement obligation was determined based upon the PCB regulations that originally became effective in 1978.
Non-Legal Liability - Cost of Removal
We collect in our prices the costs to dispose of plant assets that do not represent legal retirement obligations. As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, we had $114.188.2 million and $129.0114.1 million, respectively, in amounts collected, but not yet spent, for removal costs classified as a regulatory liability.
15. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
In 2011, we reached agreements with two former executive officers settling all contractual obligations related to their previous employment. The agreements required us to make payments totaling approximately $57.0 million, pay approximately $8.4 million for their legal fees and expenses, and release deferred stock for compensation shares. We also reversed the remaining approximately $22.0 million of previously accrued liabilities in 2011, which reduced selling, general and administrative expense reported on our consolidated statement of income.
We and our subsidiaries are involved in various other legal, environmental and regulatory proceedings. We believe that adequate provisions have been made and accordingly believe that the ultimate disposition of such matters will not have a material effect on our consolidated financial results. See Note 3, "Rate Matters and Regulation," and Note 13, "Commitments and Contingencies," for additional information.
16. COMMON AND PREFERRED STOCK
Common Stock
General
In 2011, Westar Energy shareholders approved an amendment to its Restated Articles of Incorporation to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized to be issued from 150.0 million to 275.0 million. As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, Westar Energy had issued 128.3131.7 million shares and 126.5128.3 million shares, respectively.
Westar Energy has a direct stock purchase plan (DSPP). Shares of common stock sold pursuant to the DSPP may be either original issue shares or shares purchased in the open market. During 20132014 and 20122013, Westar Energy issued 0.70.5 million shares and 0.80.7 million shares, respectively, through the DSPP and other stock-based plans operated under the LTISA Plan. As of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013, a total of 2.01.6 million shares and 1.52.0 million shares, respectively, were available under the DSPP registration statement.
Issuances
In September 2013, Westar Energy entered into two forward sale agreements with two banks. Under the terms of the agreements, the banks, as forward sellers, borrowed 8.0 million shares of Westar Energy's common stock from third parties and sold them to a group of underwriters for $31.15 per share. Pursuant to over-allotment options granted to the underwriters, the underwriters purchased in October 2013 an additional 0.9 million shares from the banks as forward sellers, increasing the total number of shares under the forward sale agreements to approximately 8.9 million. The underwriters received a commission equal to 3.5% of the sales price of all shares sold under theeach agreement. Westar Energy is required tomust settle such transactions within 24 months.months of the applicable agreement.
In March 2013, Westar Energy entered into a new, three-year sales agency financing agreement and master forward sale confirmationagreement with a bank, similar to the sales agency financing agreement and master forward sale confirmation entered into in April 2010.bank. The maximum amount that Westar Energy may offer and sell under the March 2013 master agreements is the lesser of an aggregate of $500.0 million or approximately 25.0 million shares, subject to adjustment for share splits, share combinations and share dividends. Under the terms of the sales agency financing agreement, Westar Energy may offer and sell shares of its common stock from time to time. In addition, under the terms of the March 2013 sales agency financing agreement and master forward sale confirmation, Westar Energy may from time to time enter into one or more forward sale transactions with the bank, as forward purchaser and the bank will borrow shares of Westar Energy's common stock from third parties and sell them through its agent. The agent receives a commission equal to 1% of the sales price of all shares sold under the agreements. Westar Energy must settle the forward sale transactions within 18 months of the date each transaction is entered. Under the terms of March 2013 agreements and
In April 2010, agreements, during the year ended December 31, 2013, Westar Energy entered into transactionsa three-year sales agency financing agreement and master forward sale agreement with respect toa bank that was terminated in March 2013. The maximum amount that Westar Energy could offer and sell under the agreements was the lesser of an aggregate of $500.0 million or approximately 2.522.0 million shares, ofsubject to adjustment for share splits, share combinations and share dividends. Terms under these agreements were generally similar to the March 2013 agreements described above.
The following table summarizes our common stock and settled 1.1 million shares that had a 2012 vintage. As of December 31, 2013, 3.1 million shares could have been settled. In February 2014, Westar Energy settled 0.3 million shares with a physical settlement amount of approximately $9.2 million.
Assuming physical share settlement ofactivity pursuant to the approximately 12.1 million shares associated with allthree forward sale transactions as of December 31, 2013, Westar Energy would have received aggregate proceeds of approximately $358.3 million based on a weighted average forward price of $29.73 per share.agreements.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Shares that could be settled at beginning of year | 12,052,976 |
| | 1,753,415 |
| | — |
|
| Transactions entered | — |
| | 11,367,673 |
| | 1,753,415 |
|
| Transactions settled (a) | 2,892,476 |
| | 1,068,112 |
| | — |
|
| Shares that could be settled at end of year (b) | 9,160,500 |
| | 12,052,976 |
| | 1,753,415 |
|
| _______________ | | | | | |
| (a) The shares settled during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, were settled with a physical settlement amount of approximately $82.9 million and $27.0 million, respectively. |
| (b) Assuming physical share settlement of the 9.2 million shares associated with the forward sale transactions that could be settled as of December 31, 2014, Westar Energy would have received aggregate proceeds of approximately $258.3 million based on a weighted average forward price of $28.20 per share. In February 2015, Westar Energy settled 0.2 million shares with a physical settlement amount of approximately $7.5 million. |
The forward sale transactions are entered into at market prices; therefore, the forward sale agreements have no initial fair value. Westar Energy does not receive any proceeds from the sale of common stock under the forward sale agreements until transactions are settled. Upon settlement, Westar Energy will record the forward sale agreements within equity. Except in specified circumstances or events that would require physical share settlement, Westar Energy is able to elect to settle any forward sale transactions by means of physical share, cash or net share settlement, and is also able to elect to settle the forward sale transactions in whole, or in part, earlier than the stated maturity dates. Currently, Westar Energy anticipates settling the forward sale transactions through physical share settlement. The shares under the forward sale agreements are initially priced when the transactions are entered into and are subject to certain fixed pricing adjustments during the term of the agreements. Accordingly, assuming physical share settlement, Westar Energy's net proceeds from the forward sale transactions will represent the prices established by the forward sale agreements applicable to the time periods in which physical settlement occurs.
Westar Energy used the proceeds from the transactions described above to repay short-term borrowings, with such borrowed amounts principally used for investments in capital equipment, as well as for working capital and general corporate purposes.
Preferred Stock Redemption
In May 2012, Westar Energy provided an irrevocable notice of redemption to holders of all of Westar Energy's preferred shares. Accordingly, we reduced preferred equity to zero, recognized the obligation to redeem the preferred shares as a liability and recognized the redemption premium as a preferred stock dividend. Payment was due to holders of the preferred shares effective July 1, 2012. The table below shows the redemption amounts for all series of preferred stock.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Rate | | Shares | | Principal Outstanding | | Call Price | | Premium | | Total Cost to Redeem |
| (Dollars in Thousands) |
| 4.50% | | 121,613 |
| | $ | 12,161 |
| | 108.0% | | $ | 973 |
| | $ | 13,134 |
|
| 4.25% | | 54,970 |
| | 5,497 |
| | 101.5% | | 82 |
| | 5,579 |
|
| 5.00% | | 37,780 |
| | 3,778 |
| | 102.0% | | 76 |
| | 3,854 |
|
| | | 214,363 |
| | $ | 21,436 |
| | | | $ | 1,131 |
| | $ | 22,567 |
|
17. VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
In determining the primary beneficiary of a VIE, we assess the entity's purpose and design, including the nature of the entity's activities and the risks that the entity was designed to create and pass through to its variable interest holders. A reporting enterprise is deemed to be the primary beneficiary of a VIE if it has (a) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the VIE's economic performance and (b) the obligation to absorb losses or right to receive benefits from the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE. Accounting guidance effective January 1,in 2010 requires the primary beneficiary of a VIE to consolidate the VIE. The trusts holding our 8% interest in JEC and our 50% interest in La Cygne unit 2 and railcars we use to transport coal to some of our power plants are VIEs of which we are the primary beneficiary.
We assess all entities with which we become involved to determine whether such entities are VIEs and, if so, whether or not we are the primary beneficiary of the entities. We also continuously assess whether we are the primary beneficiary of the VIEs with which we are involved. Prospective changes in facts and circumstances may cause us to reconsider our determination as it relates to the identification of the primary beneficiary.
8% Interest in Jeffrey Energy Center
Under an agreement that expires in January 2019, we lease an 8% interest in JEC from a trust. The trust was financed with an equity contribution from an owner participant and debt issued by the trust. The trust was created specifically to purchase the 8% interest in JEC and lease it to a third party, and does not hold any other assets. We meet the requirements to be considered the primary beneficiary of the trust. In determining the primary beneficiary of the trust, we concluded that the activities of the trust that most significantly impact its economic performance and that we have the power to direct include (1) the operation and maintenance of the 8% interest in JEC, (2) our ability to exercise a purchase option at the end of the agreement at the lesser of fair value or a fixed amount and (3) our option to require refinancing of the trust's debt. We have the potential to receive benefits from the trust that could potentially be significant if the fair value of the 8% interest in JEC at the end of the agreement is greater than the fixed amount. The possibility of lower interest rates upon refinancing the debt also creates the potential for us to receive significant benefits.
50% Interest in La Cygne Unit 2
Under an agreement that expires in September 2029, KGE entered into a sale-leaseback transaction with a trust under which the trust purchased KGE's 50% interest in La Cygne unit 2 and subsequently leased it back to KGE. The trust was financed with an equity contribution from an owner participant and debt issued by the trust. The trust was created specifically to purchase the 50% interest in La Cygne unit 2 and lease it back to KGE, and does not hold any other assets. We meet the requirements to be considered the primary beneficiary of the trust. In determining the primary beneficiary of the trust, we concluded that the activities of the trust that most significantly impact its economic performance and that we have the power to direct include (1) the operation and maintenance of the 50% interest in La Cygne unit 2, (2) our ability to exercise a purchase option at the end of the agreement at the lesser of fair value or a fixed amount and (3) our option to require refinancing of the trust's debt. We have the potential to receive benefits from the trust that could potentially be significant if the fair value of the 50% interest in La Cygne unit 2 at the end of the agreement is greater than the fixed amount. The possibility of lower interest rates upon refinancing the debt also creates the potential for us to receive significant benefits.
Railcars
WeUnder two separate agreements, we leased railcars from an unrelated trusttrusts to transport coal to some of our power plants. We consolidated the trusttrusts as a VIEVIEs until the agreementagreements expired in May 2013.2013 and November 2014. As a result of deconsolidating the trust,trusts, property, plant and equipment of VIEs, net and noncontrolling interests decreased $14.3 million.million in 2013 and $7.3 million in 2014.
We also lease railcars from another unrelated trust under an agreement that expires in November 2014. The trust was financed with an equity contribution from an owner participant and debt issued by the trust. The trust was created specifically to purchase the railcars and lease them to us, and does not hold any other assets. We meet the requirements to be considered the primary beneficiary of this trust. In determining the primary beneficiary of the trust, we concluded that the activities of the trust that most significantly impact its economic performance and that we have the power to direct include the operation, maintenance and repair of the railcars and our ability to exercise a purchase option at the end of the agreements at the lesser of fair value or a fixed amount. We have the potential to receive benefits from the trust that could potentially be significant if the fair value of the railcars at the end of the agreements is greater than the fixed amount. Our agreement with this trust also includes renewal options during which time we would pay a fixed amount of rent. We have the potential to receive benefits from the trust during the renewal period if the fixed amount of rent is less than the amount we would be required to pay under a new agreement.
Financial Statement Impact
We have recorded the following assets and liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets related to the VIEs described above.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | |
| Property, plant and equipment of variable interest entities, net | $ | 296,626 |
| | $ | 321,975 |
| $ | 278,573 |
| | $ | 296,626 |
|
| Regulatory assets (a) | 6,792 |
| | 5,810 |
| 7,882 |
| | 6,792 |
|
| | | | | | | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt of variable interest entities | $ | 27,479 |
| | $ | 25,942 |
| $ | 27,933 |
| | $ | 27,479 |
|
| Accrued interest (b) | 3,472 |
| | 3,948 |
| 2,961 |
| | 3,472 |
|
| Long-term debt of variable interest entities, net | 194,802 |
| | 222,743 |
| 166,565 |
| | 194,802 |
|
_______________
(a) Included in long-term regulatory assets on our consolidated balance sheets.
(b) Included in accrued interest on our consolidated balance sheets.
All of the liabilities noted in the table above relate to the purchase of the property, plant and equipment. The assets of the VIEs can be used only to settle obligations of the VIEs and the VIEs' debt holders have no recourse to our general credit. We have not provided financial or other support to the VIEs and are not required to provide such support. We did not record any gain or loss upon initial consolidation of the VIEs.
18. LEASES
Operating Leases
We lease office buildings, computer equipment, vehicles, railcars and other property and equipment. These leases have various terms and expiration dates ranging from one to 20 years.
In determining lease expense, we recognize the effects of scheduled rent increases on a straight-line basis over the minimum lease term. Rental expense and estimated future commitments under operating leases are as follows.
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | Total Operating Leases | | Total Operating Leases |
| | | (In Thousands) | | (In Thousands) |
| Rental expense: | | | | |
| 2011 | | $ | 17,577 |
| |
| 2012 | | 17,080 |
| | $ | 17,080 |
|
| 2013 | | 16,484 |
| | 16,484 |
|
| 2014 | | | 14,143 |
|
| | | | | |
| Future commitments: | | | | |
| 2014 | | $ | 14,384 |
| |
| 2015 | | 11,980 |
| | $ | 12,396 |
|
| 2016 | | 10,232 |
| | 10,434 |
|
| 2017 | | 8,383 |
| | 8,560 |
|
| 2018 | | 5,248 |
| | 7,148 |
|
| 2019 | | | 5,930 |
|
| Thereafter | | 15,361 |
| | 9,115 |
|
| Total future commitments | | $ | 65,588 |
| | $ | 53,583 |
|
Capital Leases
We identify capital leases based on defined criteria. For both vehicles and computer equipment, new leases are signed each month based on the terms of master lease agreements. The lease term for vehicles is from two to eight years depending on the type of vehicle. Computer equipment has a lease term of three to five years.
In 2012, we signed an agreement to lease electrical facilities that connect a wind generating facility to the transmission system. The agreement extends through August 2032, at which time it may be extended or we may exercise an option to purchase the line. The terms of the agreement meet the criteria of a capital lease; therefore, we recorded an $8.3 million capital lease.
Assets recorded under capital leases including the 2012 lease described above presented as generation plant, are listed below.
| | | | As of December 31, | As of December 31, |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | (In Thousands) | (In Thousands) |
| Vehicles | $ | 12,141 |
| | $ | 12,594 |
| $ | 18,819 |
| | $ | 12,141 |
|
| Computer equipment | 1,758 |
| | 1,423 |
| 1,504 |
| | 1,758 |
|
| Generation plant | 48,346 |
| | 48,346 |
| 40,049 |
| | 48,346 |
|
| Accumulated amortization | (10,493 | ) | | (6,928 | ) | (11,741 | ) | | (10,493 | ) |
| Total capital leases | $ | 51,752 |
| | $ | 55,435 |
| $ | 48,631 |
| | $ | 51,752 |
|
Capital leases are treated as operating leases for rate making purposes. Minimum annual rental payments, excluding administrative costs such as property taxes, insurance and maintenance, under capital leases are listed below.
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | Total Capital Leases | | Total Capital Leases |
| | | (In Thousands) | | (In Thousands) |
| 2014 | | $ | 6,464 |
| |
| 2015 | | 5,891 |
| | $ | 6,379 |
|
| 2016 | | 5,179 |
| | 5,717 |
|
| 2017 | | 4,711 |
| | 5,284 |
|
| 2018 | | 4,664 |
| | 5,131 |
|
| 2019 | | | 4,493 |
|
| Thereafter | | 72,135 |
| | 59,660 |
|
| | | 99,044 |
| | 86,664 |
|
| Amounts representing imputed interest | | (44,992 | ) | | (34,922 | ) |
| Present value of net minimum lease payments under capital leases | | 54,052 |
| | 51,742 |
|
| Less: Current portion | | 3,249 |
| | 3,833 |
|
| Total long-term obligation under capital leases | | $ | 50,803 |
| | $ | 47,909 |
|
19. QUARTERLY RESULTS (UNAUDITED)
Our business is seasonal in nature and, in our opinion, comparisons between the quarters of a year do not give a true indication of overall trends and changes in operations.
| | | 2013 | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth | |
| 2014 | | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth |
| | (In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) | (In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues (a) | $ | 546,212 |
| | $ | 569,589 |
| | $ | 694,974 |
| | $ | 559,878 |
| $ | 628,556 |
| | $ | 612,668 |
| | $ | 764,040 |
| | $ | 596,439 |
|
| Net income (a) | 53,256 |
| | 69,451 |
| | 135,095 |
| | 43,061 |
| 70,970 |
| | 55,822 |
| | 149,760 |
| | 45,773 |
|
| Net income attributable to Westar Energy, Inc. (a) | 51,144 |
| | 67,188 |
| | 133,125 |
| | 41,062 |
| 68,955 |
| | 53,473 |
| | 147,382 |
| | 43,449 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Per Share Data (a): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Earnings available | $ | 0.40 |
| | $ | 0.53 |
| | $ | 1.04 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
| $ | 0.53 |
| | $ | 0.41 |
| | $ | 1.13 |
| | $ | 0.33 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Earnings available | $ | 0.40 |
| | $ | 0.52 |
| | $ | 1.04 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
| $ | 0.52 |
| | $ | 0.40 |
| | $ | 1.10 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash dividend declared per common share | $ | 0.34 |
| | $ | 0.34 |
| | $ | 0.34 |
| | $ | 0.34 |
| $ | 0.35 |
| | $ | 0.35 |
| | $ | 0.35 |
| | $ | 0.35 |
|
| Market price per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| High | $ | 33.35 |
| | $ | 34.96 |
| | $ | 34.31 |
| | $ | 32.56 |
| $ | 35.33 |
| | $ | 38.24 |
| | $ | 38.23 |
| | $ | 43.15 |
|
| Low | $ | 28.59 |
| | $ | 30.13 |
| | $ | 29.79 |
| | $ | 29.95 |
| $ | 31.67 |
| | $ | 34.51 |
| | $ | 33.76 |
| | $ | 33.73 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | Items are computed independently for each of the periods presented and the sum of the quarterly amounts may not equal the total for the year. |
| | | 2012 | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth | |
| 2013 | | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth |
| | (In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) | (In Thousands, Except Per Share Amounts) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues (a) | $ | 475,677 |
| | $ | 566,262 |
| | $ | 695,758 |
| | $ | 523,772 |
| $ | 546,212 |
| | $ | 569,589 |
| | $ | 694,974 |
| | $ | 559,878 |
|
| Net income (a) | 29,237 |
| | 64,462 |
| | 141,067 |
| | 47,695 |
| 53,256 |
| | 69,451 |
| | 135,095 |
| | 43,061 |
|
| Net income attributable to common stock (a) | 27,282 |
| | 61,361 |
| | 139,281 |
| | 45,607 |
| |
| Net income attributable to Westar Energy, Inc. (a) | | 51,144 |
| | 67,188 |
| | 133,125 |
| | 41,062 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Per Share Data (a): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Earnings available | $ | 0.21 |
| | $ | 0.48 |
| | $ | 1.10 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
| $ | 0.40 |
| | $ | 0.53 |
| | $ | 1.04 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Earnings available | $ | 0.21 |
| | $ | 0.48 |
| | $ | 1.09 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
| $ | 0.40 |
| | $ | 0.52 |
| | $ | 1.04 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash dividend declared per common share | $ | 0.33 |
| | $ | 0.33 |
| | $ | 0.33 |
| | $ | 0.33 |
| $ | 0.34 |
| | $ | 0.34 |
| | $ | 0.34 |
| | $ | 0.34 |
|
| Market price per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| High | $ | 29.13 |
| | $ | 30.17 |
| | $ | 33.04 |
| | $ | 30.29 |
| $ | 33.35 |
| | $ | 34.96 |
| | $ | 34.31 |
| | $ | 32.56 |
|
| Low | $ | 27.12 |
| | $ | 26.80 |
| | $ | 28.96 |
| | $ | 27.33 |
| $ | 28.59 |
| | $ | 30.13 |
| | $ | 29.79 |
| | $ | 29.95 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | Items are computed independently for each of the periods presented and the sum of the quarterly amounts may not equal the total for the year. |
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
We maintain a set of disclosure controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in reports that we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (Exchange Act), is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in Securities and Exchange CommissionSEC rules and forms. In addition, the disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to management, including the chief executive officer and the chief financial officer, allowing timely decisions regarding required disclosure. As of the end of the period covered by this report, based on an evaluation carried out under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the chief executive officer and the chief financial officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures, the chief executive officer and the chief financial officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
In 2013 we completed the implementation a new Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system for our financial, accounting, and supply chain functions that changes our business and financial transaction processes used in those functions. This implementation represents a change in our internal control over financial reporting. In connection with this implementation, we updated our internal controls over financial reporting, as necessary, to accommodate modifications to our business processes and accounting procedures.
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the three months ended December 31, 20132014, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
See "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" for Management's Annual Report On Internal Control Over Financial Reporting and the Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm's report with respect to the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.Investors should note that we announce material financial information in SEC filings, press releases and public conference calls. In accordance with SEC guidance, we may also use the Investor Relations section of our website (http://www.WestarEnergy.com, under “Investors”) to communicate with investors about our company. It is possible that the financial and other information we post there could be deemed to be material information. The information on our website is not part of this document.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS AND EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The information concerning directors required by Item 401 of Regulation S-K will be included under the caption Election of Directors in our definitive Proxy Statement for our 20142015 Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A (20142015 Proxy Statement), and that information is incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K. Information concerning executive officers required by Item 401 of Regulation S-K is located under Part I, Item 1 of this Form 10-K. The information required by Item 405 of Regulation S-K concerning compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act will be included under the caption Additional Information - Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance in our 20142015 Proxy Statement, and that information is incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K. The information required by Item 406, 407(c)(3), (d)(4) and (d)(5) of Regulation S-K will be included under the captioncaptions Election of Directors - Corporate Governance Matters and - Board Meetings and Committee Assignmentsin our 20142015 Proxy Statement, and that information is incorporated by reference in this Form 10‑K.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by Item 11 will be set forth in our 20142015 Proxy Statement under the captions Compensation Discussion and Analysis, Compensation Committee Report, Compensation of Executive Officers, Director Compensation and Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation, and that information is incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
The information required by Item 12 will be set forth in our 20142015 Proxy Statement under the captions Beneficial Ownership of Voting Securities and Equity Compensation Plan Information, and that information is incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
The information required by Item 13 will be set forth in our 20142015 Proxy Statement under the caption Election of Directors - Corporate Governance Matters, and that information is incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by Item 14 will be set forth in our 20142015 Proxy Statement under the caption of Ratification and Confirmation of Deloitte and Touche LLP as Our Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm for 20142015 and its subsections captioned Independent Registered Accounting Firm Fees and Audit Committee Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures, and that information is incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS INCLUDED HEREIN
Westar Energy, Inc.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 20132014 and 20122013
Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for the years ended December 31, 20132014, 20122013 and 20112012
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
SCHEDULES
Schedule II - Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
Schedules omitted as not applicable or not required under the Rules of Regulation S-X: I, III, IV and V.
EXHIBIT INDEX
All exhibits marked "I" are incorporated herein by reference. All exhibits marked with "*" are management contracts or compensatory plans or arrangements required to be identified by Item 15(a)(3) of Form 10-K. All exhibits marked "#" are filed with this Form 10-K.
Description
|
| | | | |
1(a) | | Amendment to Sales Agency Financing Agreement, dated May 26, 2010, among Westar Energy, Inc., BNY Mellon Capital Markets, LLC, and The Bank of New York Mellon (filed as Exhibit 1(a) to the Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2012 filed on August 7, 2012) | | I |
1(b) | | Second Amendment to Sales Agency Financing Agreement, dated May 9, 2012, among Westar Energy, Inc., BNY Mellon Capital Markets, LLC, and The Bank of New York Mellon (filed as Exhibit 1(b) to the Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2012 filed on May 9, 2012) | | I |
1(c)1(a) | | Sales Agency Financing Agreement, dated March 21, 2013, with BNY Mellon Capital Markets, LLC and The Bank of New York Mellon (filed as Exhibit 1.1 to the Form 8-K filed on March 22, 2013) | | I |
| 3(a) | | By-laws of Westar Energy, Inc., as amended April 28, 2004 (filed as Exhibit 3(a) to the Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2004 filed on August 4, 2004) | | I |
| 3(b) | | Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc., as amended through May 25, 1988 (filed as Exhibit 4 to the Form S-8 Registration Statement, SEC File No. 33-23022 filed on July 15, 1988) | | I |
| 3(c) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3 to the Form 10-K405 for the period ended December 31, 1998 filed on April 14, 1999) | | I |
| 3(d) | | Certificate of Correction to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3(b) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 1991 filed on March 30, 1992) | | I |
| 3(e) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3(c) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 1994 filed on March 30, 1995) | | I |
| 3(f) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3 to the Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 1994 filed on August 11, 1994) | | I |
| 3(g) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3(a) to the Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 1996 filed on August 14, 1996) | | I |
| 3(h) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3 to the Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 1998 filed on May 12, 1998) | | I |
|
| | | | |
| 3(i) | | Form of Certificate of Designations for 7.5% Convertible Preference Stock (filed as Exhibit 99.4 to the Form 8-K filed on November 17, 2000) | | I |
| 3(j) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3(l) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2002 filed on April 11, 2003) | | I |
|
| | | | |
| 3(k) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3(m) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2002 filed on April 11, 2003) | | I |
| 3(l) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3(m) to the Form S-3 Registration Statement No. 333-125828 filed on June 15, 2005) | | I |
| 3(m) | | Certificate of Amendment to Restated Articles of Incorporation of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 3(m) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 filed on February 23, 2012) | | #I |
| 3(n) | | Form of Certificate of Decertification of Preference Shares (filed as Exhibit 3(n) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2011 filed on February 23, 2012 | | #I |
| 4(a) | | Mortgage and Deed of Trust dated July 1, 1939 between Westar Energy, Inc. and Harris Trust and Savings Bank, Trustee (filed as Exhibit 4(a) to Registration Statement No. 33-21739) | | I |
| 4(b) | | First and Second Supplemental Indentures dated July 1, 1939 and April 1, 1949, respectively (filed as Exhibit 4(b) to Registration Statement No. 33-21739) | | I |
| 4(c) | | Sixth Supplemental Indenture dated October 4, 1951 (filed as Exhibit 4(b) to Registration Statement No. 33-21739) | | I |
| 4(d) | | Fourteenth Supplemental Indenture dated May 1, 1976 (filed as Exhibit 4(b) to Registration Statement No. 33-21739) | | I |
| 4(e) | | Twenty-Eighth Supplemental Indenture dated July 1, 1992 (filed as Exhibit 4(o) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 1992 filed on March 30, 1993) | | I |
| 4(f) | | Twenty-Ninth Supplemental Indenture dated August 20, 1992 (filed as Exhibit 4(p) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 1992 filed on March 30, 1993) | | I |
| 4(g) | | Thirtieth Supplemental Indenture dated February 1, 1993 (filed as Exhibit 4(q) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 1992 filed on March 30, 1993) | | I |
| 4(h) | | Thirty-First Supplemental Indenture dated April 15, 1993 (filed as Exhibit 4(r) to the Form S-3 Registration Statement No. 33-50069 filed on August 24, 1993) | | I |
| 4(i) | | Thirty-Second Supplemental Indenture dated April 15, 1994 (filed as Exhibit 4(s) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 1994 filed on March 30, 1995) | | I |
| 4(j) | | Senior Indenture dated August 1, 1998 (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 1998 filed on August 12, 1998) | | I |
| 4(k) | | Form of Senior Note (included in Exhibit 4(j)) | | I |
| 4(l) | | Thirty-Fourth Supplemental Indenture dated June 28, 2000 (filed as Exhibit 4(v) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2000 filed on April 2, 2001) | | I |
| 4(m) | | Thirty-Fifth Supplemental Indenture dated May 10, 2002 between Westar Energy, Inc. and BNY Midwest Trust Company, as Trustee (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2002 filed on May 15, 2002) | | I |
| 4(n) | | Thirty-Sixth Supplemental Indenture dated as of June 1, 2004, between Westar Energy, Inc. and BNY Midwest Trust Company (as successor to Harris Trust and Savings Bank), to its Mortgage and Deed of Trust dated July 1, 1939 (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on January 18, 2005) | | I |
| 4(o) | | Thirty-Seventh Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 17, 2004, between Westar Energy, Inc. and BNY Midwest Trust Company (as successor to Harris Trust and Savings Bank), to its Mortgage and Deed of Trust dated July 1, 1939 (filed as Exhibit 4.2 to the Form 8-K filed on January 18, 2005) | | I |
| 4(p) | | Thirty-Eighth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of January 18, 2005, between Westar Energy, Inc. and BNY Midwest Trust Company (as successor to Harris Trust and Savings Bank), to its Mortgage and Deed of Trust dated July 1, 1939 (filed as Exhibit 4.3 to the Form 8-K filed on January 18, 2005) | | I |
| 4(q) | | Thirty-Ninth Supplemental Indenture dated June 30, 2005 between Westar Energy, Inc. and BNY Midwest Trust Company (as successor to Harris Trust and Savings Bank) to its Mortgage and Deed of Trust dated July 1, 1939 (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on July 1, 2005) | | I |
| 4(r) | | Fortieth Supplemental Indenture dated May 15, 2007 between Westar Energy, Inc. and The Bank of New York Trust Company, N.A. (as successor to Harris Trust and Savings Bank) to its Mortgage and Deed of Trust dated July 1, 1939 (filed as Exhibit 4.16 to the Form 8-K filed on May 16, 2007) | | I |
| 4(s) | | Form of First Mortgage Bonds, 6.10% Series Due 2047 (contained in Exhibit 4(r)) | | I |
| 4(t) | | Forty-First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 25, 2008 by and among Westar Energy, Inc., The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. and Judith L. Bartolini (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on November 24, 2008) | | I |
|
| | | | |
| 4(u) | | Form of Forty-Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 1, 2012 by and among Westar Energy, Inc., The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. and Judith L. Bartolini (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on February 29, 2012) | | I |
|
| | | | |
| 4(v) | | Form of Forty-Second Supplemental (Reopening) Indenture, dated as of May 17, 2012 by and among Westar Energy, Inc., The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. and Judith L. Bartolini (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on May 16, 2012) | | I |
| 4(w) | | Form of Forty-Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 28, 2013, by and between Westar Energy, Inc. and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as successor trustee to Harris Trust and Savings Bank (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on March 22, 2013)
| | I |
| 4(x) | | Form of Forty-Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of August 19, 2013, by and between Westar Energy, Inc. and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as successor trustee to Harris Trust and Savings Bank (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on August 14, 2013) | | I |
4(y) | | Fifty-Eighth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of February 12, 2013, by and among Kansas Gas and Electric Company, The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. and Richard Tarnas (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to the Form 8-K filed on February 15, 2013) | | I |
| | | | | |
| | | Instruments defining the rights of holders of other long-term debt not required to be filed as Exhibits will be furnished to the Commission upon request. | | |
| | | | | |
| 10(a) | | Executive Salary Continuation Plan of Western Resources, Inc., as revised, effective September 22, 1995 (filed as Exhibit 10(j) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 1995 filed on March 27, 1996)* | | I |
| 10(b) | | Long-Term Incentive and Share Award Plan (filed as Exhibit 10(a) to the Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 1996 filed on August 14, 1996)* | | I |
| 10(c) | | Amendment to Long-Term Incentive and Share Award Plan (filed as Exhibit 10 to the Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2011)* | | I |
| 10(d) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of Restricted Share Units Award (Grant Dates Prior to February 26, 2014) (filed as Exhibit 10(aq) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2009, filed on February 25, 2010)* | | I |
| 10(e) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of Performance Based Restricted Share Units Award (Grant Dates Prior to February 26, 2014) (filed as Exhibit 10(ar) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2009 filed on February 25, 2010)* | | I |
| 10(f) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of Restricted Share Units Award (Grant Dates February 26, 2014 Forward)* | | # |
| 10(g) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of Performance Based Restricted Share Units Award (Grant Dates February 26, 2014 Forward)* | | # |
| 10(h) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Non-Employee Director Deferred Compensation Plan, as amended and restated, dated as of October 20, 2004 (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on October 21, 2004)* | | I |
10(d)10(i) | | Resolutions of the Westar Energy, Inc. Board of Directors regarding Non-Employee Director Compensation, approved on September 2, 2004 (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on December 17, 2004)* | | I |
10(e) | | Form of Change in Control Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on January 26, 2006)* | | I |
10(f) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of Restricted Share Units Award (filed as Exhibit 10(aq) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2009, filed on February 25, 2010) | | I |
10(g) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of Performance Based Restricted Share Units Award (filed as Exhibit 10(ar) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2009 filed on February 25, 2010) | | I |
10(h) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of First Transition Performance Based Restricted Share Units Award (filed as Exhibit 10(as) to the form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2009 filed on February 25, 2010) | | I |
10(i) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Form of Second Transition Performance Based Restricted Share Units Award (filed as Exhibit 10(at) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2009 filed on February 25, 2010) | | I |
| 10(j) | | Form of Amended and Restated Change in Control Agreement with Officers of Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10(au) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2009 filed on February 25, 2010)* | | I |
| 10(k) | | Westar Energy, Inc. Retirement Benefit Restoration Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2010)* | | I |
| 10(l) | | Westar Energy, Inc. 401(k) Benefit Restoration Plan* | | # |
| 10(m) | | Credit Agreement dated as of February 18, 2011, among Westar Energy, Inc., and several banks and other financial institutions or entities from time to time parties to the Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on February 22, 2011) | | I |
10(m) | | Amendment to Long-Term Incentive and Share Award Plan (filed as Exhibit 10 to the Form 8-K filed on May 6, 2011) | | I |
| 10(n) | | Amendment to Restricted Share Units Awards betweenFirst Extension Agreement dated as of February 12, 2013, among Westar Energy, Inc. and William B. Mooreseveral banks and other financial institutions party thereto (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on July 6, 2011)February 15, 2013) | | I |
| 10(o) | | Second Extension Agreement dated as of February 14, 2014, among Westar Energy, Inc. and several banks and other financial institutions or entities from time to time parties to the Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10(v) to the Form 10-K for the period ended December 31, 2013 filed on February 26, 2014) | | I |
| 10(p) | | Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of September 29, 2011, among Westar Energy, Inc. and several banks and other financial institutions or entities from time to time parties to the Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on September 29, 2011) | | I |
10(p)10(q) | | First Extension Agreement dated as of February 12,July 19, 2013, among Westar Energy, Inc. and several banks and other financial institutions party theretoor entities from time to time parties to the Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.110(a) to the Form 8-K10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2014 filed on February 15, 2013)November 5, 2014) | | I |
10(q)10(r) | | Second Extension Agreement dated as of September 18, 2014, among Westar Energy, Inc. and several banks and other financial institutions or entities from time to time parties to the Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10(b) to the Form 10-Q for the period ended September 30, 2014 filed on November 5, 2014) | | I |
| 10(s) | | Master Confirmation for Forward Stock Sale Transactions, dated March 21, 2013, between Westar Energy, Inc. and The Bank of New York Mellon (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on March 22, 2013) | | I |
10(r) |
| | | | |
| 10(t) | | Confirmation of Forward Sale Transaction, dated September 24, 2013, between JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, London Branch and Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on September 27, 2013) | | I |
|
| | | | |
10(s)10(u) | | Confirmation of Forward Sale Transaction, dated September 24, 2013, between Wells Fargo Bank, National Association and Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Form 8-K filed on September 27, 2013) | | I |
10(t)10(v) | | Confirmation of Additional Forward Stock Sale Transaction, dated October 16, 2013, between JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, London Branch and Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Form 8-K filed on October 17, 2013) | | I |
10(u)10(w) | | Confirmation of Additional Forward Stock Sale Transaction, dated October 16, 2013, between Wells Fargo Bank, National Association and Westar Energy, Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to the Form 8-K filed on October 17, 2013) | | I |
10(v) | | Second Extension Agreement dated as of February 14, 2014, among Westar Energy, Inc. and several banks and other forward institutions or entities from time to time parties to the Agreement | | # |
12(a)12 | | Computations of Ratio of Consolidated Earnings to Fixed Charges | | # |
12(b) | | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2007 (filed as Exhibit 12.1 to the Form 8-K filed on May 10, 2007) | | I |
| 21 | | Subsidiaries of the Registrant | | # |
| 23 | | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP | | # |
| 31(a) | | Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | | # |
| 31(b) | | Certification of Principal Accounting Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | | # |
| 32 | | Certifications pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (furnished and not to be considered filed as part of the Form 10-K) | | # |
| 101.INS | | XBRL Instance Document | | # |
| 101.SCH | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | | # |
| 101.CAL | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | | # |
| 101.DEF | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | | # |
| 101.LAB | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | | # |
| 101.PRE | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | | # |
WESTAR ENERGY, INC.
SCHEDULE II — VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
| | | Description | | Balance at Beginning of Period | | Charged to Costs and Expenses | | Deductions (a) | | Balance at End of Period | | Balance at Beginning of Period | | Charged to Costs and Expenses | | Deductions (a) | | Balance at End of Period |
| | | (In Thousands) | |
| Year ended December 31, 2011 | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowances deducted from assets for doubtful accounts | | $ | 5,729 |
| | $ | 8,774 |
| | $ | (7,119 | ) | | $ | 7,384 |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | (In Thousands) |
| Year ended December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowances deducted from assets for doubtful accounts | | $ | 7,384 |
| | $ | 6,617 |
| | $ | (9,085 | ) | | $ | 4,916 |
| | $ | 7,384 |
| | $ | 6,617 |
| | $ | (9,085 | ) | | $ | 4,916 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowances deducted from assets for doubtful accounts | | $ | 4,916 |
| | $ | 7,039 |
| | $ | (7,359 | ) | | $ | 4,596 |
| | $ | 4,916 |
| | $ | 7,039 |
| | $ | (7,359 | ) | | $ | 4,596 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowances deducted from assets for doubtful accounts | | | $ | 4,596 |
| | $ | 9,752 |
| | $ | (9,039 | ) | | $ | 5,309 |
|
_______________
| |
| (a) | Result from write-offs of accounts receivable. |
SIGNATURE
Pursuant to the requirements of Sections 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
| | | | | | |
| | | | | WESTAR ENERGY, INC. |
| | | | | | | |
| Date: | | February 26, 201425, 2015 | | By: | | /s/ ANTHONY D. SOMMA |
| | | | | | | Anthony D. Somma |
| | | | | | | Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
| | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
/S/ MARK A. RUELLE | | Director, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Mark A. Ruelle) | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ ANTHONY D. SOMMA | | Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Anthony D. Somma) | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ CHARLES Q. CHANDLER IV | | Chairman of the Board | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Charles Q. Chandler IV) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ MOLLIE H. CARTER | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Mollie H. Carter) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ R. A. EDWARDS III | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (R. A. Edwards III) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ JERRY B. FARLEY | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Jerry B. Farley) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ RICHARD L. HAWLEY | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Richard L. Hawley) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ B. ANTHONY ISAAC | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (B. Anthony Isaac) | | | | |
| | | | |
/S/ ARTHUR B. KRAUSE
| | Director | | February 26, 2014 |
(Arthur B. Krause) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ SANDRA A. J. LAWRENCE | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Sandra A. J. Lawrence) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ MICHAEL F. MORRISSEY | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (Michael F. Morrissey) | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ S. CARL SODERSTROM JR. | | Director | | February 26, 201425, 2015 |
| (S. Carl Soderstrom Jr.) | | | | |