UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
FOR ANNUAL AND TRANSITION REPORTS PURSUANT TO SECTIONS 13 OR 15(d)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
| | | |
þ | | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | | For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 20092010 |
o | | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | | For the Transition Period From to |
Commission file number 1-10235
IDEX CORPORATION
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
| | | |
Delaware
| | 36-3555336 |
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization) | | 36-3555336
(I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) |
630 Dundee Road, Northbrook,1925 West Field Court, Lake Forest, Illinois
(Address of principal executive offices)
| | 6006260045
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number:
(847) 498-7070
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | |
Title of Each Class | | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| |
| Common Stock, par value $.01 per share | | New York Stock Exchange
and Chicago Stock Exchange |
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 ofRegulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes oþ No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 ofRegulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of thisForm 10-K or any amendment to thisForm 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| | | |
| Large accelerated filer þ | Accelerated filer o | Non-accelerated filer o | Smaller reporting company o |
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined inRule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes o No þ
The aggregate market value of the voting stock (based on the June 30, 20092010 closing price of $36.84)$28.57) held by non-affiliates of IDEX Corporation was $1,953,103,845.$2,292,832,953.
The number of shares outstanding of IDEX Corporation’s common stock, par value $.01 per share (the “Common Stock”), as of February 18, 201017, 2011 was 81,000,45182,441,446 (net of treasury shares).
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the 20092010 Annual Report to stockholders of IDEX Corporation (“the 20092010 Annual Report”) are incorporated by reference in Part II of thisForm 10-K and portions of the Proxy Statement of IDEX Corporation (the “2010“2011 Proxy Statement”) with respect to the 20102011 annual meeting of stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of thisForm 10-K.
PART I
IDEX Corporation (“IDEX” or the “Company”) is a Delaware Corporationcorporation incorporated on September 24, 1987. The Company is an applied solutions business that sells an extensive array of pumps, flow meters and other fluidics systems and components and engineered products to customers in a variety of markets around the world. All of the Company’s business activities are carried out through wholly-owned subsidiaries.
IDEX has four reportable business segments: Fluid & Metering Technologies, Health & Science Technologies, Dispensing Equipment, and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products. Reporting units in the Fluid & Metering Technologies segment include Banjo, Energy, (Corken, Faure Herman, Liquid Controls, S.A.M.P.I., Sponsler and Toptech products), Industrial Process Technology, (IDEX AODD (Pumper Parts, Versa-Matic and Warren Rupp products), Richter, Sanitary (Knight, Quadro and Wright Flow products), and Viking (Blagdon and Viking products)Chemical, Food & Pharmaceuticals (“CFP”) and Water (ADS, IETG, iPEK, and Pulsafeeder products)& Waste Water (“Water”). Reporting units in the Health & Science Technologies segment include IDEX Health & Science Technologies (“HST”IH&S”) Core (Eastern Plastics, Innovadyne, Isolation Technologies, Rheodyne, Sapphire, Semrock, Precision Polymer Engineering Semrock, Systec(“PPE”), previously referred to as Seals, Ltd, Gast and Upchurch Scientific products), Gast (Gast and Jun-Air products), and Micropump (Ismatec, Micropump and Trebor products).Micropump. The Dispensing Equipment segment is a reporting unit and includes FAST & Fluid Management and Fluid Management products.unit. Reporting units in the Fire &Safety/Diversified Products segment include Fire Suppression, (Class 1, Godiva and Hale products), Rescue Tools (Dinglee, Hurst, Lukas and Vetter products) and Band-It.
IDEX believes that each of its reporting units is a leader in its product and service areas. The Company also believes that its strong financial performance has been attributable to its ability to design and engineer specialized quality products, coupled with its ability to identify and successfully consummate and integrate strategic acquisitions.
FLUID & METERING TECHNOLOGIES SEGMENT
The Fluid & Metering Technologies segmentSegment designs, produces and distributes positive displacement pumps, flow meters, injectors, and other fluid-handling pump modules and systems and provides flow monitoring and other services for the water and wastewater.wastewater industries. Fluid & Metering Technologies application-specific pump and metering solutions serve a diverse range of end markets, including industrial infrastructure (fossil fuels, refined & alternative fuels, and water & wastewater), chemical processing, agricultural, food & beverage, pulp & paper, transportation, plastics & resins, electronics & electrical, construction & mining, pharmaceutical & bio-pharmaceutical, machinery and numerous other specialty niche markets. Fluid & Metering Technologies accounted for 48% of IDEX’s sales and 44% of IDEX’s operating income in 2009,2010, with approximately 46%47% of its sales to customers outside the U.S.
Banjo. Banjo is a provider of special purpose, severe-duty pumps, valves, fittings and systems used in liquid handling. Banjo is based in Crawfordsville, Indiana and its products are used in agricultural and industrial applications. Approximately 11% of Banjo’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Energy. Energy includes the Company’s Corken, Faure Herman, Liquid Controls, S.A.M.P.I., Sponsler and Toptech businesses. Energy is a leading supplier of flow meters, electronic registration and control products, rotary vane and turbine pumps, reciprocating piston compressors, and terminal automation control systems. Headquartered in Lake Bluff, Illinois (Liquid Controls and Sponsler products), Energy has additional facilities in Longwood, Florida and Zwijndrech, Belgium (Toptech products); Oklahoma City, Oklahoma (Corken products); La Ferté Bernard, France and Houston, Texas (Faure Herman products); Vadodara, Gujarat, India (Liquid Controls products); and Altopascio, Italy (S.A.M.P.I. products). Applications for Liquid Controls and S.A.M.P.I. positive displacement flow meters, electronic, registration and control products include mobile and stationary metering installations for wholesale and retail distribution of petroleum and liquefied petroleum gas, aviation refueling, and industrial metering and dispensing of liquids and gases. Corken products consist of positive-displacement rotary vane pumps, single and multistage regenerative turbine pumps, and small horsepower reciprocating piston compressors, while Sponsler products consist of precision turbine flow meters to meet all flow applications, including low-flow applications where viscosity, corrosive media, extreme temperature or hazardous materials are
1
factors.compressors. Toptech supplies terminal automation hardware and software to control and manage inventories, as well as transactional data and invoicing, to customers in the oil, gas and refined-fuels markets. In February 2007, IDEX acquired Faure Herman is a leading supplier of ultrasonic and helical turbine flow meters used in the custody transfer and control of high value fluids and gases. Approximately 54%55% of Energy’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Industrial Process Technologies.Chemical, Food & Pharmaceuticals. Industrial Process Technologies (“IPT”)CFP includes the Company’s IDEX AODD,Quadro, Richter, SanitaryViking and VikingWarren Rupp businesses. IPTCFP is a leading producer of air-operated and motor-driven double-diaphragm pumps and
1
replacement parts; a leading provider of premium quality lined pumps, valves and control equipment for the chemical, fine chemical and pharmaceutical industries; a leading manufacturer of pumps and dispensing equipment for industrial laundries, commercial dishwashing and chemical metering;industries and a leading provider of particle control solutions for the pharmaceutical &and bio-pharmaceutical markets. IDEX AODDQuadro’s products (which also include Pumper Parts, Versa-Matic and Warren Rupp products) are used for abrasive and semisolid materials as well as for applications where product degradation is a concern or where electricity is not available or should not be used. Market’s served by IDEX AODD products include chemical, paint, food processing, electronics, construction, utilities, mining and industrial maintenance. Richter’s corrosion resistant fluoroplastic lined products offer superior solutions for demanding applications in the process industry. Sanitary’s products (which include Knight, QuadroFitzpatrick, Inc. (“Fitzpatrick”) and Wright Flow products) consist of rotary lobe pumps, stainless-steel centrifugal and positive displacement pumps, and pump replacement parts and customized size reduction, roll compaction and drying systems for the beverage, food processing, pharmaceutical, cosmetics and other industries that require sanitary processing, as well as products for fine milling, emulsification and special handling of liquid and solid particulates for laboratory, pilot phase and production scale processing. Richter’s corrosion resistant fluoroplastic lined products offer superior solutions for demanding applications in the process industry. Viking’s products consist of external gear pumps, strainers and reducers, and related controls used for transferring and metering thin and viscous liquids sold under the Viking® brand and air-operated double-diaphragm pumps sold under the Blagdon® brand. Markets served by Viking products include chemical, petroleum, pulp & paper, plastics, paints, inks, tanker trucks, compressor, construction, food & beverage, personal care, pharmaceutical and biotech. IPTWarren Rupp products (which also include Pumper Parts and Versa-Matic products) are used for abrasive and semisolid materials as well as for applications where product degradation is a concern or where electricity is not available or should not be used. Markets served by Warren Rupp products include chemical, paint, food processing, electronics, construction, utilities, mining and industrial maintenance.CFP maintains operations in Mansfield, Ohio (IDEX AODD)Muskego, Wisconsin; Elmhurst, Illinois; Waterloo, Ontario, Canada; and Eastbourne, East Sussex, England (Quadro); Kampen, Germany,Germany; Nanjing, China, and Coimbatore, India (Richter); Lake Forest, California, Unanderra, New South Wales, Australia, Mississauga, Ontario, Canada, Eastbourne, East Sussex, England, Muskego, Wisconsin and Windsor, Ontario, Canada (Sanitary); and Cedar Falls, Iowa (Richter, SanitaryQuadro and Viking); and Mansfield, Ohio (Warren Rupp);. IPTCFP uses primarily independent distributors to sell and market its products. Approximately 53% of IPT’s 2009CFP’s 2010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Water and& Waste Water (“Water”).Water. Water includes the Company’s ADS, IETG, iPEK, Knight and Pulsafeeder businesses. Water is a leading provider of metering technology &and flow monitoring products and underground surveillance services for water and& wastewater markets, as well as a leading manufacturer of pumps and dispensing equipment for industrial laundries, commercial dishwashing and chemical metering; and a provider of metering pumps, special-purpose rotary pumps, peristaltic pumps, fully integrated pump and metering systems, custom chemical-feed systems, electronic controls and dispensing equipment. ADSADS’s products and services provide comprehensive integrated solutions that enable industry, municipalities and government agencies to analyze and measure the capacity, quality and integrity of wastewater collection systems, including the maintenance and construction of such systems. IETGIETG’s products and services enable water companies to effectively manage their water distribution and sewerage networks, while its surveillance service specializes in underground asset detection and mapping for utilities and other private companies. iPEK supplies remote controlled systems used for infrastructure inspection. Knight is a leading manufacturer of pumps and dispensing equipment for industrial laundries, commercial dishwashing and chemical metering. Pulsafeeder products are used to introduce precise amounts of fluids into processes to manage water quality and chemical composition, and itsas well as peristaltic pumps. Its markets include water &and wastewater treatment, oil & gas, power generation, pulp & paper, chemical &and hydrocarbon processing, and swimming pools. Water maintains operations in Huntsville, Alabama,Alabama; Sydney, New South Wales, Australia,Australia; Melbourne, Victoria, Australia,Australia; and Auckland, New Zealand (ADS),; Leeds, England (IETG),; Hirschegg, AustriaAustria; and Sulzberg, Germany (iPEK); Lake Forest, California; Mississauga, Ontario, Canada; Eastbourne, East Sussex, England;,Unanderra, New South Wales, Australia, and Ciudad Juarez, Chihuahua, Mexico(Maquila Arrangement)(Knight); Rochester, New York, andYork; Punta Gorda, FloridaFlorida; Loveland, Ohio; and Milan, Italy (Pulsafeeder). Approximately 37%41% of Water’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
HEALTH & SCIENCE TECHNOLOGIES SEGMENT
The Health & Science Technologies Segment designs, produces and distributes a wide range of precision fluidics and sealing solutions, including very high precision, low-flow rate pumping solutions required in analytical instrumentation, clinical diagnostics and drug discovery, high performance molded and extruded, biocompatible medical devices and implantables, air compressors used in medical, dental and industrial applications, and precision gear
2
and peristaltic pump technologies that meet exacting OEM specifications. The segment accounted for 23%26% of both IDEX’s sales and 28% of operating income in 2009,2010, with approximately 39%45% of its sales to customers outside the U.S.
2
HST Core.IDEX Health & Science. HST CoreIH&S consists of the IDEX Health & Science (“IHS”) and Semrock business units. IHS is a consolidation of the Company’s Eastern Plastics, Innovadyne, Isolation Technologies, Rheodyne, Ismatec, Sapphire Engineering, Systec and Upchurch Scientific businesses and has facilities in Rohnert Park, California (Innovadyne, Rheodyne and Systec products); Bristol, Connecticut (Eastern Plastics products); Glattbrugg, Switzerland and Wertheim-Mondfeld, Germany (Ismatec products); Middleboro, Massachusetts (Isolation Technologies and Sapphire Engineering products); and Oak Harbor, Washington (Upchurch Scientific and Ismatec products). Rheodyne and Systec products include injectors, valves, fittings and accessories for the analytical instrumentation market. Rheodyne and Systec products are used by manufacturers of high pressure liquid chromatography equipment servicing the pharmaceutical, biotech, life science, food & beverage, and chemical markets. Ismatec is a manufacturer of peristaltic metering pumps, analytical process controllers, and sample preparation systems. Sapphire Engineering and Upchurch Scientific products include fluidic components and systems for the analytical, biotech and diagnostic instrumentation markets, such as fittings, precision-dispensing pumps and valves, tubing and integrated tubing assemblies, filter sensors and other micro-fluidic and nano-fluidic components. Markets for Sapphire Engineering and Upchurch Scientific products include pharmaceutical, drug discovery, chemical, biochemical processing, genomics/proteomics research, environmental labs, food/agriculture, medical lab, personal care, and plastics/polymer/rubber production. Eastern Plastics products, which consist of high-precisionhigh- precision integrated fluidics and associated engineered plastics solutions. Eastern Plastics productssolutions, are used in a broad set of end markets including medical diagnostics, analytical instrumentation, and laboratory automation. In October 2007, the Company acquired Isolation Technologies a leading developer ofproducts include advanced column hardware and accessories for the High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)high performance liquid chromatography (“HPLC”) market. HPLC instruments are used in a variety of analytical chemistry applications, with primary commercial applications including drug discovery and quality control measurements for pharmaceutical and food/beverage testing. Approximately 44% of IH&S’s 2010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Semrock.Semrock which was acquired in October 2008, is a provider of optical filters for biotech and analytical instrumentation in the life sciences markets. Semrock’s optical filters are produced usingstate-of-the-art manufacturing processes which enable it to offer its customers significant improvements in instrument performance and reliability. Semrock is located in Rochester, New York. Approximately 35%39% of HST Core’s 2009Semrock’s 2010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Precision Polymer Engineering (PPE). PPE, which was acquired in April 2010 and is located in Blackburn, England, is a provider of proprietary high performance seals and advanced sealing solutions for a diverse range of global industries and applications, including hazardous duty, analytical instrumentation, semiconductor/solar, process technologies, pharmaceutical, electronics, and food applications. Approximately 83% of PPE’s 2010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Gast. Gast includes the Company’s Gast and Jun-Air businesses. The Gast business is a leading manufacturer of air-moving products, including air motors, low-range and medium-range vacuum pumps, vacuum generators, regenerative blowers and fractional horsepower compressors. Gast products are used in a variety of long-life applications requiring a quiet, clean source of moderate vacuum or pressure. Markets served by Gast products include medical equipment, environmental equipment, computers & electronics, printing machinery, paint mixing machinery, packaging machinery, graphic arts, and industrial manufacturing. Based in Benton Harbor, Michigan, Gast also has a facility in Redditch, England. Jun-Air is a provider of low-decibel, ultra-quiet vacuum compressors suitable for medical, dental and laboratory applications. BasedJun-Air has locations in Norresundby, Denmark Jun-Air has additional operations inand Lyon, France,France; and Dankeryd, The Netherlands. Approximately 32%29% of Gast’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Micropump. Micropump includes the Company’s Ismatec, Micropump and Trebor businesses. Micropump, headquartered in Vancouver, Washington, is a leader in small, precision-engineered, magnetically and electromagnetically driven rotary gear, piston and centrifugal pumps. Micropump products are used in low-flow abrasive and corrosive applications. Markets served by Micropump products include printing machinery, medical equipment, paints & inks, chemical processing, pharmaceutical, refining, laboratory, electronics, pulp & paper, water treatment, textiles, peristaltic metering pumps, analytical process controllers and sample preparation systems. Ismatec, a leading manufacturer of peristaltic metering pumps, analytical process controllers, and sample preparation systems, has facilities in Glattbrugg, Switzerland and Wertheim-Mondfeld, Germany. Located in Salt Lake City, Utah, the Trebor business is a leader in high-purity fluid handling products, including air-operated diaphragm pumps and deionized water-heating systems. Trebor products are used in manufacturing of semiconductors, disk drives and flat panel displays. Approximately 67%68% of Micropump’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
3
DISPENSING EQUIPMENT SEGMENT
The Dispensing Equipment Segment produces precision equipment for dispensing, metering and mixing colorants paints, and hair colorants and other personal care productspaints used in a variety of retail and commercial
3
businesses around the world. The segment accounted for 9%8% of IDEX’s sales and 7% of IDEX’s operating income in 2009,2010, with approximately 64%67% of its sales to customers outside the U.S.
Dispensing Equipment is a leading American, European and Asianglobal supplier of precision-designed tinting, mixing, dispensing and measuring equipment for auto refinishing and architectural paints and personal care products.paints. Dispensing Equipment equipment isproducts are used in retail and commercial stores, hardware stores, home centers, department stores, automotive body shops as well aspoint-of-purchase dispensers and mixing equipment for the personal care and health and beauty industry. Dispensing Equipment is currently pursuing opportunities to use its precision mixing, dispensing and measuring expertise in the food and beverage areas.dispensers. Dispensing Equipment is headquartered in Wheeling, Illinois, with additional operations in Sassenheim, The Netherlands,Netherlands; Unanderra, Australia; Gennevilliers, France; Milan, Italy; Torun, Poland; Barcelona, Spain; and Scarborough, Ontario, Canada. Approximately 64% of Dispensing Equipment’s 2009 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
FIRE & SAFETY/DIVERSIFIED PRODUCTS SEGMENT
The Fire & Safety/Diversified Products Segment produces firefighting pumps and controls, rescue tools, lifting bags and other components and systems for the fire and rescue industry, and engineered stainless steel banding and clamping devices used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications. The segment accounted for 20%18% of IDEX’s sales and 26%21% of IDEX’s operating income in 2009,2010, with approximately 53%55% of its sales to customers outside the U.S.
Fire Suppression. Fire Suppression includes the Company’s Class 1, Hale and Godiva businesses, which produce truck-mounted and portable fire pumps, stainless steel valves, foam and compressed air foam systems, pump modules and pump kits, electronic controls and information systems, conventional and networked electrical systems, and mechanical components for the fire, rescue and specialty vehicle markets. Fire Suppression’s customers are primarily OEMs. Fire Suppression is headquartered in Ocala, Florida (Class 1 products)1), with additional facilities located in Conshohocken, Pennsylvania (Hale products)(Hale); Neenah, Wisconsin (Class 1 products)and Hale); and Warwick, England (Godiva products)(Godiva). Approximately 34%37% of Fire Suppression’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Rescue Tools. Rescue toolsTools includes the Company’s Dinglee, Hurst, Lukas and Vetter businesses, which produce hydraulic, battery, gas and electric-operated rescue equipment, hydraulic re-railing equipment, hydraulic tools for industrial applications, recycling cutters, pneumatic lifting and sealing bags for vehicle and aircraft rescue, environmental protection and disaster control, and shoring equipment for vehicular or structural collapse. Markets served by Rescue Tools products include public and private fire and rescue organizations. Rescue Tools has facilities in Shelby, North Carolina (Hurst products)(Hurst); Tianjin, China (Dinglee products)(Dinglee); Erlangen, Germany (Lukas products)(Lukas); and Zulpich, Germany (Vetter products)(Vetter). Approximately 77%79% of Rescue Tools’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
Band-It. Band-It is a leading producer of high-quality stainless steel banding, buckles and clamping systems. The BAND-IT® brand is highly recognized worldwide. Band-It products are used for securing exhaust system heat and sound shields, industrial hose fittings, traffic signs and signals, electrical cable shielding, identification and bundling, and numerous other industrial and commercial applications. Markets for Band-It products include transportation equipment, oil & gas, general industrial maintenance, electronics, electrical, communications, aerospace, utility, municipal and subsea marine. Band-It is based in Denver, Colorado, with additional operations in Staveley Near Chesterfield, Derbyshire, England, and Singapore. Approximately 42% of Band-It’s 20092010 sales were to customers outside the U.S.
GENERAL ASPECTS APPLICABLE TO THE COMPANY’S BUSINESS SEGMENTS
Competitors
The Company’s businesses participate in highly competitive markets. IDEX believes that the principal points of competition are product quality, price, design and engineering capabilities, product development, conformity to customer specifications, quality of post-sale support, timeliness of delivery, and effectiveness of our distribution channels.
4
Principal competitors of the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment are the Pump Solutions Group (Blackmer and Wilden products) of Dover Corporation (with respect to pumps and small horsepower compressors used in liquified petroleum gas distribution facilities, rotary gear pumps, and air-operated double-diaphragm
4
pumps); the Milton Roy unit of United Technologies Corporation (with respect to metering pumps and controls); and Tuthill Corporation (with respect to rotary gear pumps).
Principal competitors of the Health & Science Technologies Segment are the Thomas division of Gardner Denver, Inc. (with respect to vacuum pumps and compressors); Dionex Corporation (with respect to analytical instrumentation); Parker Hannifin (with respect to sealing devices); and Valco Instruments Co., Inc. (with respect to fluid injectors and valves).
The principal competitor of the Dispensing Equipment Segment is CPS Color Group Oy, which is owned by Nordic Capital (with respect to dispensing and mixing equipment for the paint industry).
The principal competitors of the Fire & Safety/Diversified Products Segment are Waterous Company, a unit of American Cast Iron Pipe Company (with respect to truck-mounted firefighting pumps), Holmatro, Inc. (with respect to rescue tools), and Panduit Corporation (with respect to stainless steel bands, buckles and tools).
Employees
At December 31, 2009,2010, the Company had approximately 5,3005,966 employees. Approximately 8% were represented by labor unions with various contracts expiring through February 2012. Management believes that the Company’s relationship with their employees is good. The Company historically has been able to satisfactorily renegotiate its collective bargaining agreements, with its last work stoppage in March 1993.
Suppliers
The Company manufactures many of the parts and components used in its products. Substantially all materials, parts and components purchased by the Company are available from multiple sources.
Inventory and Backlog
The Company regularly and systematically adjusts production schedules and quantities based on the flow of incoming orders. Backlogs typically are limited to 1one to 11/2one and a half months of production. While total inventory levels also may be affected by changes in orders, the Company generally tries to maintain relatively stable inventory levels based on its assessment of the requirements of the various industries served.
Raw Materials
The Company uses a wide variety of raw materials which are generally available from a number of sources. As a result, shortages from any single supplier have not had, and are not likely to have a material impact on operations.
Shared Services
The Company has two production facilities in Suzhou, China, that support multiple IDEX business units. IDEX also has personnel in China, India and Singapore that provide sales and marketing, product design and engineering, and sourcing support to IDEX business units, as well as personnel in various locations in Europe, South America, the Middle East and Japan to support sales and marketing efforts of IDEX businesses in those regions.
Segment Information
For segment financial information for the years 2010, 2009, 2008, and 2007,2008, see the table titled “Company and Business Segment Financial Information” presented on page 1718 in Part II. Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and Note 1311 of the “NotesNotes to Consolidated Financial Statements” on page 48Statements in Part II. Item 8. Financial“Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.Data”.
5
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The following table sets forth the names of the executive officers of the Company, their ages, years of service, the positions held by them, and their business experience during the past 5 years.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Years of
| | | | | | Years of
| | |
Name | | Age | | Service | | Position | | Age | | Service | | Position |
| |
| Lawrence D. Kingsley | | 47 | | 5 | | Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer | | 48 | | 6 | | Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer |
| Dominic A. Romeo | | 50 | | 6 | | Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | | 51 | | 7 | | Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
| Harold Morgan | | 52 | | 2 | | Vice President-Human Resources | |
| Kevin G. Hostetler | | | 42 | | 5 | | Vice President-Group Executive Fluid & Metering Technologies |
| John L. McMurray | | 59 | | 17 | | Vice President-Group Executive Process Technologies | | 60 | | 18 | | Vice President-Corporate |
| Heath A. Mitts | | 39 | | 4 | | Vice President-Corporate Finance | | 40 | | 5 | | Vice President-Corporate Finance |
| Harold Morgan | | | 52 | | 3 | | Vice President-Human Resources |
| Frank J. Notaro | | 46 | | 12 | | Vice President-General Counsel and Secretary | | 47 | | 13 | | Vice President-General Counsel and Secretary |
| Daniel J. Salliotte | | 43 | | 5 | | Vice President-Strategy and Business Development | | 44 | | 6 | | Vice President-Strategy and Business Development |
| Andrew K. Silvernail | | | 39 | | 2 | | Vice President-Group Executive Health & Science Technologies, Global Dispensing and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products |
| Michael J. Yates | | 44 | | 4 | | Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer | | 45 | | 5 | | Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer |
| Kevin G. Hostetler | | 41 | | 4 | | Vice President, Group Executive Fluid and Metering Technologies | |
| Andrew K. Silvernail | | 38 | | 1 | | Vice President, Group Executive Health and Science Technologies and Global Dispensing | |
Mr. Kingsley has been Chairman of the Board since April 2006. He was appointed to the position of President and Chief Executive Officer in March 2005. Mr. Kingsley was hired as Chief Operating Officer in August 2004.
Mr. Romeo has been Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of the Company since January 2004. As previously announced in December 2010, Mr. Romeo is retiring in February 2011.
Mr. Hostetler has been Vice President-Group Executive Fluid & Metering Technologies since February 2010. Mr. Hostetler joined IDEX in July 2005 as President of the Energy Group and was appointed Vice President, Group Executive and President Energy and Water and IDEX Asia in December 2008.
Mr. McMurray has served as Vice President-Corporate since February 2010 with responsibilities for operational excellence, supply chain and environment and health and safety. Prior to that, Mr. McMurray was Vice President-Group Executive from August 2003. Mr. McMurray will be retiring in April 2011.
Mr. Mitts has been Vice President-Corporate Finance since September 2005. In December 2010, the Company announced that Mr. Mitts is succeeding Mr. Romeo as Chief Financial Officer in February 2011.
Mr. Morgan has been Vice President-Human Resources of the Company since June 2008. From February 2003 to June 2008, Mr. Morgan was Senior Vice President and Chief Administrative Officer for Bally Total Fitness Corporation.
Mr. McMurray has been Vice President-Group Executive Process Technologies since August 2003. In February 2010, IDEX announced that Mr. McMurray will be retiring in April 2011. He will remain a corporate officer through his retirement with responsibilities for operational excellence, supply chain and environment, health and safety through his retirement date.
Mr. Mitts has been Vice President-Corporate Finance since September 2005. Prior to joining IDEX, Mr. Mitts was Chief Financial Officer of PerkinElmer’s Asia operations, based out of Singapore, from February 2002 to September 2005.
Mr. Notaro has served as Vice President-General Counsel and Secretary since March 1998.
Mr. Salliotte has been Vice President-Strategy and Business Development of the Company since October 2004.
Mr. Yates was appointed Vice-President and Chief Accounting Officer in February 2010. Mr. Yates was hired asSilvernail has been Vice President-Controller in October 2005. Prior to joining IDEX, Mr. Yates was a Senior Manager at PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP from November 1999 to October 2005.
Mr. Hostetler was appointed Vice President, Group Executive Fluid and Metering Technologies in February 2010. Mr. Hostetler joined IDEX in July 2005 as President of the Liquid Controls Group and was then appointed Vice President, Group Executive and President Energy and Water and IDEX Asia in December 2008. Prior to joining IDEX, Mr. Hostetler was General Manager, Assembly Solutions at Ingersoll-Rand.
6
Mr. Silvernail was appointed Vice President, GroupPresident-Group Executive Health and& Science Technologies, and Global Dispensing inand Fire & Safety/Diversified Products since January 2011. From February 2010. From January 20092010 to FebruaryDecember 2010, Mr. Silvernail was Vice President, GroupPresident-Group Executive Health & Sciences Technologies and Global Dispensing. Mr. Silvernail joined IDEX in January 2009 as Vice President-Group Executive Health & Science Technologies. Prior to joining IDEX, Mr. Silvernail served as Group President at Rexnord Industries from April 2005 to August 2008 and Group Vice President of Business Development at Newell Rubbermaid from September 2002 to February 2005.2008.
Mr. Yates has been Vice-President and Chief Accounting Officer since February 2010. Mr. Yates was hired as Vice President-Controller in October 2005.
6
The Company’s executive officers are elected at a meeting of the Board of Directors immediately following the annual meeting of stockholders, and they serve until the next annual meeting of the Board, or until their successors are duly elected.
Public Filings
Copies of the Company’s annual report onForm 10-K, quarterly reports onForm 10-Q, current reports onForm 8-K and amendments to those reports are made available free of charge at www.idexcorp.com as soon as reasonably practicable after being filed electronically with the SEC. Our reports are also available free of charge on the SEC’s website, www.sec.gov. The information on the Company’s website is not incorporated into thisForm 10-K.
For an enterprise as diverse and complex as the Company, a wide range of factors could materially affect future developments and performance. In addition to the factors affecting specific business operations identified in connection with the description of thesethose operations and the financial results of these operations elsewhere in this report, the most significant factors affecting our operations include the following:
THE RECENT FINANCIAL CRISIS AND CURRENT UNCERTAINTY IN GLOBAL ECONOMIC CONDITIONS COULD NEGATIVELY AFFECT OUR BUSINESS, RESULTS OF OPERATIONS, FINANCIAL CONDITION OR CASH FLOWS.
The recent financial crisis affecting the banking system and financial markets and the current uncertainty in global economic conditions have resulted in a tightening in the credit markets, a low level of liquidity in many financial markets, and extreme volatility in credit, equity and fixed income markets. There could be a number of follow-on effects from these economic developments on our business, including insolvency of key suppliers resulting in product delays; inability of customers to obtain credit to finance purchases of our productsand/or customer insolvencies; decreased customer confidence; and decreased customer demand, including order delays or cancellations.
CHANGES IN U.S. OR INTERNATIONAL ECONOMIC CONDITIONS COULD ADVERSELY AFFECT THE PROFITABILITY OF ANY OF OUR BUSINESSES.
In 2009, 53%2010, 51% of the Company’s revenue was derived from domestic operations while 47%49% was international.derived from international operations. The Company’s largest markets include life sciences &and medical technologies, fire and rescue, petroleum LPG, paint and coatings, chemical processing and water &and wastewater treatment. A slowdown in the economy and in particular any of these specific end markets could directly affect the Company’s revenue stream and profitability.
POLITICAL CONDITIONS IN FOREIGN COUNTRIES IN WHICH WE OPERATE COULD ADVERSELY AFFECT OUR BUSINESS.
In 2009,2010, approximately 47%49% of our total sales were to customers outside the U.S. We expect our international operations and export sales to continue to contribute to earningsbe significant for the foreseeable future. Both theour sales from international operations and export sales are subject in varying degrees to risks inherent in doing business outside the United States. SuchThese risks include the following:
• possibility of unfavorable circumstances arising from host country laws or regulations;
• risks of economic instability;
• currency exchange rate fluctuations and restrictions on currency repatriation;
7
• potential negative consequences from changes to taxation policies;
• the disruption of operations from labor and political disturbances;
• changes in tariff and trade barriers and import or export licensing requirements; and,
• insurrection or war.
| | |
| • | possibility of unfavorable circumstances arising from host country laws or regulations; |
|
| • | risks of economic instability; |
|
| • | currency exchange rate fluctuations and restrictions on currency repatriation; |
|
| • | potential negative consequences from changes to taxation policies; |
|
| • | the disruption of operations from labor and political disturbances; |
|
| • | changes in tariff and trade barriers and import or export licensing requirements; and, |
|
| • | insurrection or war. |
We cannot predict the impact such future, largely unforeseeable events might have on the Company’s operations.
AN INABILITY TO CONTINUE TO DEVELOP NEW PRODUCTS CAN LIMIT THE COMPANY’S REVENUE AND PROFITABILITY.
The Company’s organic growthrevenue grew organically by 12% in 2010, but was down 14% in 2009 and flat in 2008.2009. Approximately 20%19% of our revenue was derived from new products developed over the past three years. Our ability to continue to grow organically is tied to our ability to continue to develop new products.
7
OUR GROWTH STRATEGY INCLUDES ACQUISITIONS AND WE MAY NOT BE ABLE TO MAKE ACQUISITIONS OF SUITABLE CANDIDATES OR INTEGRATE ACQUISITIONS SUCCESSFULLY.
Our historical growth has included, and our future growth is likely to continue to include in large part our acquisition strategy and the successful integration of acquired businesses into our existing operations.
acquisitions. We intend to continue to seek additional acquisition opportunities both to expand into new markets and to enhance our position in existing markets throughout the world. We cannot be assured, however, that we will be able to successfully identify suitable candidates, negotiate appropriate acquisition terms, obtain financing which may be needed to consummate suchthose acquisitions, complete proposed acquisitions, successfully integrate acquired businesses into our existing operations or expand into new markets. In addition, we cannot assure you that any acquisition, once successfully integrated, will perform as planned, be accretive to earnings, or prove to be beneficial to our operations and cash flow.
Acquisitions involve numerous risks, including the assumption of undisclosed or unindemnified liabilities, difficulties in the assimilation of the operations, technologies, services and products of the acquired companies and the diversion of management’s attention from other business concerns. In addition, prior acquisitions have resulted, and future acquisitions could result, in the incurrence of substantial additional indebtedness and other expenses. Once integrated, acquired operations may not achieve levels of revenues, profitability or productivity comparable with those achieved by our existing operations, or otherwise perform as expected.
THE MARKETS WE SERVE ARE HIGHLY COMPETITIVE. THIS COMPETITION COULD LIMIT THE VOLUME OF PRODUCTS THAT WE SELL AND REDUCE OUR OPERATING MARGINS.
Most of our products are sold in competitive markets. We believe that the principal points of competition in our markets are product quality, price, design and engineering capabilities, product development, conformity to customer specifications, quality of post-sale support, timeliness of delivery, and effectiveness of our distribution channels. Maintaining and improving our competitive position will require continued investment by us in manufacturing, engineering, quality standards, marketing, customer service and support, and our distribution networks. We cannot be assured that we willmay not be successful in maintaining our competitive position. Our competitors may develop products that are superior to our products, or may develop methods of more efficiently and effectively providing products and services or may adapt more quickly than us to new technologies or evolving customer requirements. Pricing pressures also could cause us to adjust the prices of certain of our products to stay competitive. We cannot be assured that we willmay not be able to compete successfully with our existing competitors or with new competitors. Failure to continue competing successfully could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flow.
8
WE ARE DEPENDENT ON THE AVAILABILITY OF RAW MATERIALS, PARTS AND COMPONENTS USED IN OUR PRODUCTS.
While we manufacture many of the parts and components used in our products, we require substantial amounts of raw materials and purchase some parts and components from suppliers. The availability and prices for raw materials, parts and components may be subject to curtailment or change due to, among other things, suppliers’ allocations to other purchasers, interruptions in production by suppliers, changes in exchange rates and prevailing price levels. Any change in the supply of, or price for, these raw materials or parts and components could materially affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flow.
SIGNIFICANT MOVEMENTS IN FOREIGN CURRENCY EXCHANGE RATES MAY HARM OUR FINANCIAL RESULTS.
We are exposed to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, particularly with respect to the Euro, Canadian Dollar, British Pound and Chinese Renminbi. Any significant change in the value of the currencies of the countries in which we do business against the U.S. Dollar could affect our ability to sell products competitively and control our cost structure, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flow. For additional detail related to this risk, see Part II. Item 7A. Quantitative“Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk.Risk”.
8
AN UNFAVORABLE OUTCOME WITH REGARDS TOOF ANY OF OUR PENDING CONTINGENCIES OR LITIGATION COULD ADVERSELY AFFECT OUR BUSINESS, FINANCIAL CONDITION, RESULTS OF OPERATIONS AND CASH FLOW.
We currently are involved in certain legal and regulatory proceedings. Where it is reasonably possible to do so, we accrue estimates of the probable costs for the resolution of these matters. These estimates are developed in consultation with outside counsel and are based upon an analysis of potential results, assuming a combination of litigation and settlement strategies. It is possible, however, that future operating results for any particular quarter or annual period could be materially affected by changes in our assumptions or the effectiveness of our strategies related to these proceedings. For additional detail related to this risk, see Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
WE COULD BE ADVERSELY AFFECTED BY RAPID CHANGES IN INTEREST RATES.
Our profitability may be adversely affected during any period of an unexpected or rapid increase in interest rates. The Company’s interest rate exposure was primarily related to the $400.1 million of total debt outstanding at December 31, 2009. The majority of the debt is priced at interest rates that float with the market. In order to mitigate this interest exposure, the Company entered into interest rate exchange agreements that effectively converted $345.0 million of our floating-rate debt to a fixed rate. A 50 basis point movement in the interest rate on the remaining $55.1 million floating-rate debt would result in an approximate $0.3 million annualized increase or decrease in interest expense and cash flow. For additional detail related to this risk, see Part II. Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk.“Legal Proceedings”.
OUR INTANGIBLE ASSETS ARE A SIGNIFICANT PORTION OF OUR TOTAL ASSETS AND A WRITE-OFF OF OUR INTANGIBLE ASSETS COULD CAUSE A MAJORADVERSELY IMPACT ON THE COMPANY’SOUR OPERATING RESULTS AND SIGNIFICANTLY REDUCE OUR NET WORTH.
Our total assets reflect substantial intangible assets, primarily goodwill and identifiable intangible assets. At December 31, 2009,2010, goodwill and intangible assets totaled $1,180.4$1,207.0 million and $281.4 million, respectively. These goodwill and intangible assets result from our acquisitions, representing the excess of cost over the fair value of the tangible assets we have acquired. Annually, or when certain events occur that require a more current valuation, we assess whether there has been an impairment in the value of our goodwill or intangible assets. If future operating performance at one or more of our reporting units were to fall significantly below forecast levels, we could be required to reflect, under current applicable accounting rules, a non-cash charge to operating income for an impairment. Any determination requiring the write-off of a significant portion of the goodwill or intangible assets could have a material negative effect on our results of operations and total capitalization. In accordance with Accounting
9
Standards Codification (“ASC”), 350, “Intangibles — Goodwill and Other”, the Company concluded that events had occurred and circumstances had changed in 2008 which required the Company to record a goodwill impairment of $30.1 million at Fluid Management, a reporting unit within the Company’s Dispensing Equipment Segment. See Note 5 in Part II. Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data for further discussion on goodwill and intangible assets.
| |
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments. |
The Company has received no written comments regarding its periodic or current reports from the staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission that were issued 180 days or more preceding the end of its 2009 calendar year and that remain unresolved.
The Company’s principal plants and offices have an aggregate floor space area of approximately 4.0 million square feet, of which 2.5 million square feet (62%) is located in the U.S. and approximately 1.5 million square feet (38%) is located outside the U.S., primarily in Germany (8%), Italy (7%), the U.K. (6%), China (4%) and Australia (4%The Netherlands (2%). These facilities are considered to be suitable and adequate for their operations. Management believes we can meet the expected demand increase over the near term with our existing facilities, especially given our operational improvement initiatives that usually increase capacity. The Company’s executive office occupies approximately 26,00032,165 square feet of leased space in Northbrook,Lake Forest, Illinois.
Approximately 2.82.9 million square feet (69%(73%) of the principal plant and office floor area is owned by the Company, and the balance is held under lease. Approximately 1.81.9 million square feet (44%(48%) of the principal plant and office floor area is held by business units in the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment; 0.80.7 million square feet (19%(18%) is held by business units in the Health & Science Technologies Segment; 0.60.5 million square feet (16%(12%) is held by business units in the Dispensing Equipment Segment; and 0.70.8 million square feet (18%(19%) is held by business units in the Fire & Safety/Diversified Products Segment.
| |
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings. |
The Company and sixnine of its subsidiaries are presently named as defendants in a number of lawsuits claiming various asbestos-related personal injuries, allegedly as a result of exposure to products manufactured with components that contained asbestos. SuchThese components were acquired from third party suppliers, and were not manufactured by any of the subsidiaries. To date, the majority of the Company’s settlements and legal costs, except for costs of coordination, administration, insurance investigation and a portion of defense costs, have been covered in full by insurance subject to applicable deductibles. However, the Company cannot predict whether and to what extent insurance will be available to continue to cover such settlements and legal costs, or how insurers may respond
9
to claims that are tendered to them.
Claims have been filed in jurisdictions throughout the United States. Most of the claims resolved to date have been dismissed without payment. The balance have been settled for various insignificant amounts. Only one case has been tried, resulting in a verdict for the Company’s business unit.
No provision has been made in the financial statements of the Company, other than for insurance deductibles in the ordinary course, and the Company does not currently believe the asbestos-related claims will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial position, results of operations or cash flow.
The Company is also party to various other legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business, none of which is expected to have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flow.
| |
| Item 4. | Reserved.(Removed and Reserved). |
10
PART II
| |
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related ShareholderStockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities. |
Information regarding the prices of, and dividends on, the Common Stock, and certain related matters, is incorporated herein by reference to “Shareholder Information” on the inner back cover of the 2009 Annual Report.
The principal market for the Company’s Common Stock is the New York Stock Exchange, but the Common Stock is also listed on the Chicago Stock Exchange. As of February 18, 2010,17, 2011, Common Stock was held by approximately 7,000 shareholders and there were 81,000,45182,441,446 shares of Common Stock outstanding, net of treasury shares.
The high and low sales prices of the Common Stock per share and the dividends paid per share during the last two years is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | | | | | | | Dividends
| | | | | | | | | Dividends
| |
| | | High | | | Low | | | Per Share | | | High | | | Low | | | Per Share | |
| |
| First Quarter | | $ | 33.66 | | | $ | 28.09 | | | $ | 0.12 | | | $ | 26.24 | | | $ | 16.67 | | | $ | 0.12 | |
| Second Quarter | | | 35.54 | | | | 28.49 | | | | 0.15 | | | | 26.18 | | | | 19.67 | | | | 0.12 | |
| Third Quarter | | | 36.24 | | | | 27.54 | | | | 0.15 | | | | 29.71 | | | | 22.16 | | | | 0.12 | |
| Fourth Quarter | | | 40.29 | | | | 35.08 | | | | 0.15 | | | | 32.85 | | | | 26.08 | | | | 0.12 | |
Our payment of dividends in the future will be determined by our Board of Directors and will depend on business conditions, our earnings and other factors.
For information pertaining to issuable securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans and the related weighted average exercise price, see Part III, Item 12, “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters”.Matters.”
The following table provides information about the Company purchases of equity securities that are registered by the Company pursuant to Section 12 of the Exchange ActCommon Stock during the quarter ended December 31, 2009:2010:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Total Number of
| | | Maximum Dollar
| |
| | | | | | | | | Shares Purchased as
| | | Value that May Yet
| |
| | | | | | | | | Part of Publicly
| | | be Purchased Under
| |
| | | Total Number of
| | | Average Price
| | | Announced Plans
| | | the Plans
| |
Period | | Shares Purchased | | | Paid per Share | | | or Programs(1) | | | or Programs(1) | |
| |
October 1, 2009 to
October 31, 2009 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
November 1, 2009 to
November 30, 2009 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
December 1, 2009 to
December 31, 2009 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Total Number of
| | | Maximum Dollar
| |
| | | | | | | | | Shares Purchased as
| | | Value that May Yet
| |
| | | | | | | | | Part of Publicly
| | | be Purchased Under
| |
| | | Total Number of
| | | Average Price
| | | Announced Plans
| | | the Plans
| |
| Period | | Shares Purchased | | | Paid per Share | | | or Programs(1) | | | or Programs(1) | |
| |
October 1, 2010 to
October 31, 2010 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
November 1, 2010 to
November 30, 2010 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
December 1, 2010 to
December 31, 2010 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 75,000,020 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | On April 21, 2008, IDEX’sthe Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $125.0 million of its outstanding common shares either in the open market or through private transactions. |
1110
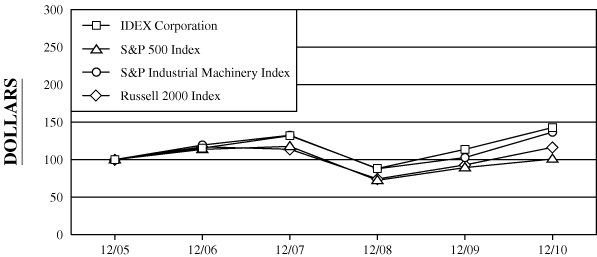
Performance Graph.The following table compares total shareholder returns over the last five years to the Standard & Poor’s (the “S&P”) 500 Index, the S&P 600 Small Cap Industrial Machinery Index and the Russell 2000 Index assuming the value of the investment in IDEXour Common Stock and each index was $100 on December 31, 2004.2005. Total return values for IDEXour Common Stock, the S&P 500 Index, S&P 600 Small Cap Industrial Machinery Index and the Russell 2000 Index were calculated on cumulative total return values assuming reinvestment of dividends. The shareholder return shown on the graph below is not necessarily indicative of future performance.

| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 12/04 | | | 12/05 | | | 12/06 | | | 12/07 | | | 12/08 | | | 12/09 | | | 12/05 | | | 12/06 | | | 12/07 | | | 12/08 | | | 12/09 | | | 12/10 |
| IDEX Corporation | | | $ | 100.00 | | | | $ | 101.48 | | | | $ | 117.04 | | | | $ | 133.81 | | | | $ | 89.44 | | | | $ | 115.37 | | | | $ | 100.00 | | | | $ | 115.33 | | | | $ | 131.86 | | | | $ | 88.14 | | | | $ | 113.69 | | | | $ | 142.77 | |
| S&P 500 Index | | | | 100.00 | | | | | 103.00 | | | | | 117.03 | | | | | 121.16 | | | | | 74.53 | | | | | 92.01 | | | | | 100.00 | | | | | 113.62 | | | | | 117.63 | | | | | 72.36 | | | | | 89.33 | | | | | 100.75 | |
| S&P Industrial Machinery Index | | | | 100.00 | | | | | 107.84 | | | | | 128.76 | | | | | 142.85 | | | | | 94.67 | | | | | 110.77 | | | | | 100.00 | | | | | 119.40 | | | | | 132.46 | | | | | 87.79 | | | | | 102.71 | | | | | 136.65 | |
| Russell 2000 Index | | | | 100.00 | | | | | 103.32 | | | | | 120.89 | | | | | 117.57 | | | | | 76.65 | | | | | 95.98 | | | | | 100.00 | | | | | 117.00 | | | | | 113.79 | | | | | 74.19 | | | | | 92.90 | | | | | 116.40 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
1211
| |
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data.(1) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands, except per share data) | | 2009 | | 2008(2) | | 2007(2) | | 2006(2) | | 2005(2) | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
| |
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | | | $ | 1,358,631 | | | $ | 1,154,940 | | | $ | 1,011,253 | | | $ | 1,513,073 | | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | | | $ | 1,358,631 | | | $ | 1,154,940 | |
| Gross profit | | | 522,386 | | | | 597,433 | | | | 566,161 | | | | 474,172 | | | | 415,625 | | | | 618,483 | | | | 522,386 | | | | 597,433 | | | | 566,161 | | | | 474,172 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | 325,453 | | | | 343,392 | | | | 313,366 | | | | 260,201 | | | | 232,935 | | | | 358,272 | | | | 325,453 | | | | 343,392 | | | | 313,366 | | | | 260,201 | |
| Goodwill impairment | | | — | | | | 30,090 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 30,090 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Restructuring expenses | | | 12,079 | | | | 17,995 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 11,095 | | | | 12,079 | | | | 17,995 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Operating income | | | 184,854 | | | | 205,956 | | | | 252,795 | | | | 213,971 | | | | 182,690 | | | | 249,116 | | | | 184,854 | | | | 205,956 | | | | 252,795 | | | | 213,971 | |
| Other income — net | | | 1,151 | | | | 5,123 | | | | 3,434 | | | | 1,040 | | | | 557 | | |
| Other income (expense) — net | | | | (1,092 | ) | | | 1,151 | | | | 5,123 | | | | 3,434 | | | | 1,040 | |
| Interest expense | | | 17,178 | | | | 18,852 | | | | 23,353 | | | | 16,353 | | | | 14,370 | | | | 16,150 | | | | 17,178 | | | | 18,852 | | | | 23,353 | | | | 16,353 | |
| Provision for income taxes | | | 55,436 | | | | 65,201 | | | | 78,457 | | | | 67,038 | | | | 59,215 | | | | 74,774 | | | | 55,436 | | | | 65,201 | | | | 78,457 | | | | 67,038 | |
| Income from continuing operations | | | 113,391 | | | | 127,026 | | | | 154,419 | | | | 131,620 | | | | 109,662 | | | | 157,100 | | | | 113,391 | | | | 127,026 | | | | 154,419 | | | | 131,620 | |
Income/(loss) from discontinuedoperations-net of tax | | | — | | | | — | | | | (719 | ) | | | 12,949 | | | | 1,228 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (719 | ) | | | 12,949 | |
| Net income | | | 113,391 | | | | 127,026 | | | | 153,700 | | | | 144,569 | | | | 110,890 | | | | 157,100 | | | | 113,391 | | | | 127,026 | | | | 153,700 | | | | 144,569 | |
FINANCIAL POSITION | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current assets | | $ | 451,712 | | | $ | 480,688 | | | $ | 617,622 | | | $ | 400,724 | | | $ | 336,250 | | | $ | 692,758 | | | $ | 451,712 | | | $ | 480,688 | | | $ | 617,622 | | | $ | 400,724 | |
| Current liabilities | | | 189,682 | | | | 219,869 | | | | 198,953 | | | | 187,252 | | | | 153,296 | | | | 353,668 | | | | 189,682 | | | | 219,869 | | | | 198,953 | | | | 187,252 | |
| Working capital | | | 262,030 | | | | 260,819 | | | | 418,669 | | | | 213,472 | | | | 182,954 | | | | 339,090 | | | | 262,030 | | | | 260,819 | | | | 418,669 | | | | 213,472 | |
| Current ratio | | | 2.4 | | | | 2.2 | | | | 3.1 | | | | 2.1 | | | | 2.2 | | | | 2.0 | | | | 2.4 | | | | 2.2 | | | | 3.1 | | | | 2.1 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 25,525 | | | | 28,358 | | | | 26,496 | | | | 21,198 | | | | 22,532 | | | | 32,769 | | | | 25,525 | | | | 28,358 | | | | 26,496 | | | | 21,198 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 56,346 | | | | 48,599 | | | | 38,038 | | | | 29,956 | | | | 26,254 | | | | 58,108 | | | | 56,346 | | | | 48,599 | | | | 38,038 | | | | 29,956 | |
| Total assets | | | 2,098,157 | | | | 2,151,800 | | | | 1,970,078 | | | | 1,653,637 | | | | 1,229,459 | | | | 2,381,695 | | | | 2,098,157 | | | | 2,151,800 | | | | 1,970,078 | | | | 1,653,637 | |
| Total borrowings | | | 400,100 | | | | 554,000 | | | | 454,731 | | | | 361,980 | | | | 160,043 | | | | 527,895 | | | | 400,100 | | | | 554,000 | | | | 454,731 | | | | 361,980 | |
| Shareholders’ equity | | | 1,268,104 | | | | 1,144,783 | | | | 1,143,207 | | | | 962,088 | | | | 808,289 | | | | 1,375,660 | | | | 1,268,104 | | | | 1,144,783 | | | | 1,143,207 | | | | 962,088 | |
PERFORMANCE MEASURES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Percent of net sales: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross profit | | | 39.3 | % | | | 40.1 | % | | | 41.7 | % | | | 41.0 | % | | | 41.1 | % | | | 40.9 | % | | | 39.3 | % | | | 40.1 | % | | | 41.7 | % | | | 41.0 | % |
| SG&A expenses | | | 24.5 | | | | 23.1 | | | | 23.1 | | | | 22.5 | | | | 23.0 | | | | 23.7 | | | | 24.5 | | | | 23.1 | | | | 23.1 | | | | 22.5 | |
| Operating income | | | 13.9 | | | | 13.8 | | | | 18.6 | | | | 18.5 | | | | 18.1 | | | | 16.5 | | | | 13.9 | | | | 13.8 | | | | 18.6 | | | | 18.5 | |
| Income before income taxes | | | 12.7 | | | | 12.9 | | | | 17.1 | | | | 17.2 | | | | 16.7 | | | | 15.3 | | | | 12.7 | | | | 12.9 | | | | 17.1 | | | | 17.2 | |
| Income from continuing operations | | | 8.5 | | | | 8.5 | | | | 11.4 | | | | 11.4 | | | | 10.8 | | | | 10.4 | | | | 8.5 | | | | 8.5 | | | | 11.4 | | | | 11.4 | |
| Effective tax rate | | | 32.8 | | | | 33.9 | | | | 33.7 | | | | 33.7 | | | | 35.1 | | | | 32.2 | | | | 32.8 | | | | 33.9 | | | | 33.7 | | | | 33.7 | |
Return on average assets(3)(2) | | | 5.3 | | | | 6.2 | | | | 8.5 | | | | 9.1 | | | | 9.1 | | | | 7.0 | | | | 5.3 | | | | 6.2 | | | | 8.5 | | | | 9.1 | |
| Borrowings as a percent of capitalization | | | 24.0 | | | | 32.6 | | | | 28.5 | | | | 27.3 | | | | 16.5 | | | | 27.7 | | | | 24.0 | | | | 32.6 | | | | 28.5 | | | | 27.3 | |
Return on average shareholders’ equity(3)(2) | | | 9.4 | | | | 11.1 | | | | 14.7 | | | | 14.9 | | | | 14.6 | | | | 11.9 | | | | 9.4 | | | | 11.1 | | | | 14.7 | | | | 14.9 | |
PER SHARE DATA(5)(4) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| — income from continuing operations | | $ | 1.41 | | | $ | 1.55 | | | $ | 1.90 | | | $ | 1.65 | | | $ | 1.41 | | | $ | 1.93 | | | $ | 1.41 | | | $ | 1.55 | | | $ | 1.90 | | | $ | 1.65 | |
| — net income | | | 1.41 | | | | 1.55 | | | | 1.89 | | | | 1.81 | | | | 1.43 | | | | 1.93 | | | | 1.41 | | | | 1.55 | | | | 1.89 | | | | 1.81 | |
| Diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| — income from continuing operations | | | 1.40 | | | | 1.53 | | | | 1.88 | | | | 1.62 | | | | 1.39 | | | | 1.90 | | | | 1.40 | | | | 1.53 | | | | 1.88 | | | | 1.62 | |
| — net income | | | 1.40 | | | | 1.53 | | | | 1.87 | | | | 1.78 | | | | 1.40 | | | | 1.90 | | | | 1.40 | | | | 1.53 | | | | 1.87 | | | | 1.78 | |
| Cash dividends declared | | | .48 | | | | .48 | | | | .48 | | | | .40 | | | | .32 | | | | .60 | | | | .48 | | | | .48 | | | | .48 | | | | .40 | |
| Shareholders’ equity | | | 15.66 | | | | 14.26 | | | | 14.01 | | | | 11.94 | | | | 10.21 | | | | 16.76 | | | | 15.66 | | | | 14.26 | | | | 14.01 | | | | 11.94 | |
| Stock price | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| — high | | | 32.85 | | | | 40.75 | | | | 44.99 | | | | 35.65 | | | | 30.22 | | | | 40.29 | | | | 32.85 | | | | 40.75 | | | | 44.99 | | | | 35.65 | |
| — low | | | 16.67 | | | | 17.70 | | | | 30.41 | | | | 26.00 | | | | 24.33 | | | | 27.54 | | | | 16.67 | | | | 17.70 | | | | 30.41 | | | | 26.00 | |
| — close | | | 31.15 | | | | 24.15 | | | | 36.13 | | | | 31.61 | | | | 27.41 | | | | 39.12 | | | | 31.15 | | | | 24.15 | | | | 36.13 | | | | 31.61 | |
| Price/earnings ratio at year end | | | 22 | | | | 16 | | | | 19 | | | | 20 | | | | 20 | | | | 21 | | | | 22 | | | | 16 | | | | 19 | | | | 20 | |
Other Data | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Employees at year end | | | 5,300 | | | | 5,813 | | | | 5,009 | | | | 4,863 | | | | 4,263 | | | | 5,966 | | | | 5,300 | | | | 5,813 | | | | 5,009 | | | | 4,863 | |
| Shareholders at year end | | | 7,000 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 6,700 | | | | 6,700 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 7,000 | | | | 6,700 | |
| Shares outstanding (in 000s)(4): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares outstanding (in 000s)(3): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| — basic | | | 79,716 | | | | 81,123 | | | | 80,666 | | | | 79,527 | | | | 77,088 | | | | 80,466 | | | | 79,716 | | | | 81,123 | | | | 80,666 | | | | 79,527 | |
| — diluted | | | 80,727 | | | | 82,320 | | | | 82,086 | | | | 80,976 | | | | 79,080 | | | | 81,983 | | | | 80,727 | | | | 82,320 | | | | 82,086 | | | | 80,976 | |
| At year end (net of treasury) | | | 80,970 | | | | 80,302 | | | | 81,579 | | | | 80,546 | | | | 79,191 | | | | 82,070 | | | | 80,970 | | | | 80,302 | | | | 81,579 | | | | 80,546 | |
| | |
| (1) | | For additional detail, see Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II. Item 8. Financial“Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.Data”. |
| |
| (2) | | Certain prior year amounts have been restated to reflect theLast-In-First-Out (LIFO) toFirst-In-First-Out (FIFO) inventory costing change. |
|
(3) | | Return calculated based on income from continuing operations. |
| |
(4)(3) | | All share and per share data has been restated to reflect thethree-for-two stock splits effected in the form of a 50% stock dividend in May of 2007. |
| |
(5)(4) | | Adjusted to reflect the accounting guidance provided in ASCAccounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 260, “Earnings Per Share”. |
1312
| |
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations. |
Cautionary Statement Under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act
The “Liquidity and Capital Resources” section of thisThis management’s discussion and analysis, including, without limitations the section entitled “Historical Overview and Outlook” and other portions of our operationsthis report contain forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. These statements may relate to, among other things, capital expenditures, cost reductions, cash flow, and operating improvements and are indicated by words or phrases such as “anticipate,” “estimate,” “plans,” “expects,” “projects,” “should,” “will,” “management believes,” “the Company believes,” “we believe,” “the Company intends” and similar words or phrases. These statements are subject to inherent uncertainties and risks that could cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated at the date of this filing. The risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to, the following: economic and political consequences resulting from terrorist attacks and wars; levels of industrial activity and economic conditions in the U.S. and other countries around the world; pricing pressures and other competitive factors, and levels of capital spending in certain industries — all of which could have a material impact on our order rates and results, particularly in light of the low levels of order backlogs we typically maintain; our ability to make acquisitions and to integrate and operate acquired businesses on a profitable basis; the relationship of the U.S. dollar to other currencies and its impact on pricing and cost competitiveness; political and economic conditions in foreign countries in which we operate; interest rates; capacity utilization and the effect this has on costs; labor markets; market conditions and material costs; and developments with respect to contingencies, such as litigation and environmental matters. The forward-looking statements included here are only made as of the date of this report, and we undertake no obligation to publicly update them to reflect subsequent events or circumstances. Investors are cautioned not to rely unduly on forward-looking statements when evaluating the information presented here.
Historical Overview and Outlook
IDEX Corporation is an applied solutions company specializing in fluid and metering technologies, health and science technologies, dispensing equipment, and fire, safety and other diversified products built to its customers’ specifications. Our products are sold in niche markets to a wide range of industries throughout the world. Accordingly, our businesses are affected by levels of industrial activity and economic conditions in the U.S. and in other countries where we do business and by the relationship of the U.S. dollar to other currencies. Levels of capacity utilization and capital spending in certain industries and overall industrial activity are among the factors that influence the demand for our products.
The Company consists of four reportingreportable segments: Fluid & Metering Technologies, Health & Science Technologies, Dispensing Equipment and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products.
The Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment designs, produces and distributes positive displacement pumps, flow meters, injectors, and other fluid-handling pump modules and systems and provides flow monitoring and other services for water and wastewater. The Health & Science Technologies Segment designs, produces and distributes a wide range of precision fluidics solutions, including very high precision, low-flow rate pumping solutions required in analytical instrumentation, clinical diagnostics and drug discovery, high performance molded and extruded, biocompatible medical devices and implantables, air compressors used in medical, dental and industrial applications, and precision gear and peristaltic pump technologies that meet exacting OEM specifications. The Dispensing Equipment Segment produces precision equipment for dispensing, metering and mixing colorants paints, and hair colorants and other personal care productspaints used in a variety of retail and commercial businesses around the world. The Fire & Safety/Diversified Products Segment produces firefighting pumps and controls, rescue tools, lifting bags and other components and systems for the fire and rescue industry, and engineered stainless steel banding and clamping devices used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
Some of our key 2010 financial highlights are as follows:
| | |
| • | Sales of $1.51 billion rose 14%; organic sales — excluding acquisitions and foreign currency translation — were up 12%. |
|
| • | Gross margins improved 160 basis points to 40.9% of sales |
13
| | |
| • | Operating margins at 16.5% increased 260 basis points compared to 2009. |
|
| • | Net income increased 39% to $157.1 million. |
|
| • | Diluted EPS of $1.90 increased 50 cents compared to 2009. |
For 2011, the Company is expected to grow organically in the mid to high single digits with acquisition-related growth projected at approximately 4 percent for transactions completed in 2010 and two acquisitions to be completed in the first quarter of 2011. Based on the Company’s current outlook, for the full year 2011, we are forecasting fully diluted EPS of $2.23 to $2.33.
Results of Operations
On July 1, 2009 the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) ASC became the authoritative source of accounting principals to be applied to financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. In accordance with the ASC, citations to accounting literature in this report are to the relevant topic of the ASC or are presented in plain English.
14
The following is a discussion and analysis of our financial position and results of operations for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009.2010. For purposes of this discussion and analysis section, reference is made to the table on page 1716 and the Consolidated Statements of Operations in Part II. Item 8. Financial“Financial Statements and Supplementary DataData” on page 28. We changed our method26.
Performance in 2010 Compared with 2009
Sales in 2010 of accounting$1,513.1 million were 14% higher than the $1,329.7 million recorded a year ago. This increase reflects a 12% increase in organic sales and 3% from four acquisitions (PPE — April 2010, OBL — July 2010, Periflo — September 2010 and Fitzpatrick — November 2010), partially offset by 1% unfavorable foreign currency translation. Organic sales increased in Fluid & Metering Technologies, Health & Science Technologies and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products segments, but were flat in the Dispensing Equipment segment. Domestic organic sales were up 9% versus the prior year, while international organic sales increased 15% in 2010. Organic sales to customers outside the U.S. represented 49% of total sales in 2010 and 46% in 2009.
In 2010, Fluid & Metering Technologies contributed 48% of sales and 44% of operating income; Health & Science Technologies accounted for inventory26% of sales and 28% of operating income; Dispensing Equipment accounted for 8% of sales and 7% of operating income; and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products represented 18% of sales and 21% of operating income.
Fluid & Metering Technologies sales of $729.9 million in 2010 increased $88.8 million, or 14%, compared with 2009. This reflects a 13% increase in organic sales and 2% for acquisitions (OBL, Periflo and Fitzpatrick), partially offset by 1% unfavorable foreign currency translation. The increase in organic growth was driven by strong global growth across energy, chemical, food & pharma and water & wastewater markets. In 2010, organic sales increased approximately 13% domestically and 14% internationally. Organic sales to customers outside the U.S. were approximately 46% of total segment sales in 2010 and 41% in 2009.
Health & Science Technologies sales of $397.2 million increased $92.9 million, or 31%, in 2010 compared with last year. This change reflects a 21% increase in organic growth and a 10% increase from the LIFO methodacquisition of PPE. The increase in organic sales reflects market strength across all Health & Science Technologies products. In 2010, organic sales increased 14% domestically and 32% internationally. Organic sales to customers outside the FIFO method effective January 1,U.S. were approximately 43% of total segment sales in 2010 and 40% in 2009.
Dispensing Equipment sales of $125.3 million decreased $2.0 million, or 2%, in 2010 compared with the prior year. This change reflects 2% unfavorable foreign currency translation, while organic growth was flat in 2010 compared to 2009. The Dispensing Equipment Segment experienced strength in Asia and parts of Eastern Europe, offset by softness in North America and Western Europe. Organic domestic sales decreased 9% compared with 2009, while organic international sales increased 5%. Organic sales to customers outside the U.S. were 67% of total segment sales in 2010 and applied this66% in 2009.
Fire & Safety/Diversified Products sales of $265.5 million increased $2.7 million, or 1%, in 2010 compared with 2009. Organic sales activity increased 2%, while foreign currency translation accounted for a 1% decrease. The increase in organic business growth was driven by higher demand for engineered band clamping systems, partially offset by weakness in fire suppression. In 2010, organic sales decreased 3% domestically and increased 7%
14
internationally. Organic sales to customers outside the U.S. were 56% of total segment sales in 2010 and 55% in 2009.
Gross profit of $618.5 million in 2010 was $96.1 million, or 18%, higher than 2009. As a percent of sales, gross profit was 40.9% in 2010, which represented a 160 basis-point increase from 39.3% in 2009. The increase in gross margin primarily reflects higher sales volume, cost reductions due to our restructuring initiatives and change in accounting principle retrospectivelyproduct mix.
Selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expenses increased to all prior periods presented herein (see Note 2$358.3 million in Part II. Item 8.2010 from $325.5 million in 2009. The $32.8 million increase reflects approximately $22.0 million for volume related expenses and $10.8 million for incremental costs associated with the acquisitions of PPE in April 2010, OBL in July 2010, Periflo in September 2010 and Fitzpatrick in November 2010. As a percent of net sales, SG&A expenses were 23.7% for 2010 and 24.5% in 2009.
In 2010, the Company recorded pre-tax restructuring expenses totaling $11.1 million, while $12.1 million was recorded in 2009. These restructuring expenses were mainly attributable to employee severance related to employee reductions across various functional areas and facility closures resulting from the Company’s cost savings initiatives. These initiatives included severance benefits for 215 employees in 2010 and 478 in 2009. The Company has completed these employee reductions in 2010 and expects severance payments to be fully paid by the end of 2011 using cash from operations.
Operating income increased $64.3 million, or 35%, to $249.1 million in 2010 from $184.9 million in 2009. This increase primarily reflects an increase in volume, changes in product mix and cost reductions due to our restructuring initiatives. Operating margins in 2010 were 16.5% of sales compared with 13.9% recorded in 2009.
In the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment, operating income of $131.9 million and operating margins of 18.1% in 2010 were up from the $100.3 million and 15.6% recorded in 2009, principally due to higher sales and cost reduction initiatives. In the Health & Science Technologies Segment, operating income of $82.3 million and operating margins of 20.7% in 2010 were up from the $51.7 million and 17.0% recorded in 2009 due to higher volume and cost reduction initiatives. In the Dispensing Equipment Segment, operating income of $19.5 million and operating margins of 15.6% in 2010 were up from the $15.1 million and 11.9% recorded in 2009 due to cost reduction initiatives and improved productivity. Operating income and operating margins in the Fire &Safety/Diversified Products Segment of $62.8 million and 23.7%, respectively, were higher than the $59.9 million and 22.8% recorded in 2009, due to higher volume and favorable mix.
Other expense was $1.1 million in 2010 compared with a $1.2 million gain in 2009, due to unfavorable foreign currency translation.
Interest expense decreased to $16.2 million in 2010 from $17.2 million in 2009. The decrease was principally due to lower debt levels and a lower interest rate environment.
The provision for income taxes increased to $74.8 million in 2010 from $55.4 million in 2009. The effective tax rate decreased to 32.2% in 2010 from 32.8% in 2009, due to changes in the mix of global pre-tax income among taxing jurisdictions.
Net income for 2010 was $157.1 million, 39% higher than the $113.4 million earned in 2009. Diluted earnings per share in 2010 of $1.90 increased $0.50, or 36%, compared with last year.
15
Company and Business Segment Financial Statements and Supplementary Data).Information
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31,(1) | |
| | | 2010 | | | 2009 | | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales(2) | | $ | 729,945 | | | $ | 641,108 | | | $ | 697,702 | |
Operating income(3) | | | 131,944 | | | | 100,289 | | | | 123,801 | |
Operating margin(3) | | | 18.1 | % | | | 15.6 | % | | | 17.7 | % |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 1,111,085 | | | $ | 1,043,082 | | | $ | 1,070,348 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 33,134 | | | | 32,584 | | | | 26,276 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 17,308 | | | | 12,867 | | | | 13,859 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales(2) | | $ | 397,198 | | | $ | 304,329 | | | $ | 331,591 | |
Operating income(3) | | | 82,332 | | | | 51,712 | | | | 58,297 | |
Operating margin(3) | | | 20.7 | % | | | 17.0 | % | | | 17.6 | % |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 648,400 | | | $ | 567,096 | | | $ | 594,459 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 16,012 | | | | 14,293 | | | | 11,806 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 7,516 | | | | 6,365 | | | | 5,365 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales(2) | | $ | 125,320 | | | $ | 127,279 | | | $ | 163,861 | |
Operating income (loss)(3)(4) | | | 19,490 | | | | 15,147 | | | | (10,748 | ) |
Operating margin(3)(4) | | | 15.6 | % | | | 11.9 | % | | | (6.6 | )% |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 205,540 | | | $ | 164,979 | | | $ | 179,800 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 3,753 | | | | 3,124 | | | | 3,986 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 1,129 | | | | 864 | | | | 2,528 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales(2) | | $ | 265,501 | | | $ | 262,809 | | | $ | 300,462 | |
Operating income(3) | | | 62,844 | | | | 59,884 | | | | 74,310 | |
Operating margin(3) | | | 23.7 | % | | | 22.8 | % | | | 24.7 | % |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 278,567 | | | $ | 285,893 | | | $ | 286,482 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 4,885 | | | | 5,328 | | | | 5,288 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 3,513 | | | | 3,686 | | | | 4,743 | |
| Total IDEX | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales | | $ | 1,513,073 | | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | |
| Operating income | | | 249,116 | | | | 184,854 | | | | 205,956 | |
| Operating margin | | | 16.5 | % | | | 13.9 | % | | | 13.8 | % |
| Total assets | | $ | 2,381,695 | | | $ | 2,098,157 | | | $ | 2,151,800 | |
Depreciation and amortization(5) | | | 58,108 | | | | 56,346 | | | | 48,599 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 32,769 | | | | 25,525 | | | | 28,358 | |
| | |
| (1) | | Data includes acquisition of Fitzpatrick (November 2010), Periflo (September 2010), OBL (July 2010), IETG (October 2008), iPEK (October 2008), Richter (October 2008) and ADS (January 2008) in the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment and PPE (April 2010), Innovadyne (November 2008) and Semrock (October 2008) in the Health & Science Technologies Segment from the date of acquisition. |
|
| (2) | | Segment net sales include intersegment sales. |
|
| (3) | | Segment operating income excludes unallocated corporate operating expenses. |
|
| (4) | | Segment operating income includes $30.1 million goodwill impairment charge in 2008 for Fluid Management. |
|
| (5) | | Excludes amortization of debt issuance expenses. |
16
Performance in 2009 Compared with 2008
Sales in 2009 of $1,329.7 million were 11% lower than the $1,489.5 million recorded a year ago.in 2008. This decrease reflects a 14% decrease in organic sales and 2% unfavorable foreign currency translation, partially offset by a 5% increase from fourfive acquisitions (Richter — October 2008, iPEK — October 2008, IETG — October 2008, and Semrock — October 2008 and Innovadyne — November 2008). Organic sales decreased in all four of the Company’s reportingreportable segments. Domestic organic sales were down 13% versus the prior year, while international organic sales were down 15% in 2009. Sales to customers outside the U.S. represented 47% of total sales in both 2009 and 2008.
In 2009, Fluid & Metering Technologies contributed 48% of sales and 44% of operating income; Health & Science Technologies accounted for 23% of both sales and operating income; Dispensing Equipment accounted for 9% of sales and 7% of operating income; and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products represented 20% of sales and 26% of operating income.
Fluid & Metering Technologies sales of $641.1 million in 2009 decreased $56.6 million, or 8%, compared with 2008. This reflects a 16% decline in organic sales and 1% of unfavorable foreign currency translation, partially offset by a 9% increase for acquisitions (Richter, iPEK and IETG). The decrease in organic growth was driven by weakness in chemical, energy, water and wastewater markets. In 2009, organic sales declined approximately 16% both domestically and internationally. SalesOrganic sales to customers outside the U.S. were approximately 46%41% of total segment sales in 2009 and 41%43% in 2008.
Health & Science Technologies sales of $304.3 million decreased $27.3 million, or 8%, in 2009 compared with last year.2008. This change represents a 12% decrease in organic volume and 1% unfavorable foreign currency translation, partially offset by a 5% increase from the acquisitionacquisitions of Semrock.Semrock and Innovadyne. The decrease in organic sales reflectsreflected market softness in both core and non-coreacross the Health & Science Technologies businesses. In 2009, organic sales decreased 13% domestically and 10% internationally. SalesOrganic sales to customers outside the U.S. were approximately 39%40% of total segment sales in both 2009 and 38% in 2008.
Dispensing Equipment sales of $127.3 million decreased $36.6 million, or 22%, in 2009 compared with the prior year. Organic sales decreased 18%, while foreign currency translation accounted for 4% of the decrease. The decrease in organic growth was due to continued deterioration in capital spending in the European and North American markets. Organic domestic sales increased 8% compared with 2008, while organic international sales decreased 27%. SalesOrganic sales to customers outside the U.S. were 64%66% of total segment sales in 2009, down from 74%73% in 2008.
Fire & Safety/Diversified Products sales of $262.8 million decreased $37.7 million, or 13%, in 2009 compared with 2008. Organic sales activity decreased 9%, while foreign currency translation accounted for 4% of the decrease. The decrease in organic business growth was driven by lower demand for engineered band clamping systems and lower levels of municipal spending. In 2009, organic sales decreased 12% domestically and 7% internationally. SalesOrganic sales to customers outside the U.S. were 53%55% of total segment sales in 2009 and 54%53% in 2008.
Gross profit of $522.4 million in 2009 was $75.0 million, or 13%, lower than 2008. As a percent of sales, gross profit was 39.3% in 2009, which represented an 80 basis-point decrease from 40.1% in 2008. The decrease in gross margin primarily reflects lower volume and product mix.
Selling, general and administrative (SG&A)SG&A expenses decreased to $325.5 million in 2009 from $343.4 million in 2008. The $17.9 million decrease reflects approximately $40.7 million for restructuring related savings and volume related expenses, partially offset by a $22.8 million increase for incremental costs associated with recently acquired businesses. As a percent of net sales, SG&A expenses were 24.5% for 2009 and 23.1% in 2008.
15
In 2009, the Company concluded that the fair value of each of its reporting units was in excess of its carrying value as of October 31, 2009, and thus no goodwill impairment was identified. However, a 10% decrease in fair value of the Banjo or the Water reporting units within the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment could potentially result in a goodwill impairment charge at these reporting units. The total goodwill balance for these two reporting units as of October 31, 2009 was $288.7 million. In 2008, the Company recorded a goodwill impairment charge of $30.1 million. The Company concluded in accordance with ASC 350 that events had occurred and circumstances had changed which required the Company to perform an interim period goodwill impairment test at Fluid Management, a reporting unit in 2008 within the Company’s Dispensing Equipment Segment. Fluid Management had experienced a downturn in capital spending by its customer base and thea loss of market share. The Company performed an impairment test and compared the fair
17
value of the reporting unit to its carrying value. It was determined that the fair value of Fluid Management was less than the carrying value of the net assets. The excess of the fair value of the reporting unit over the amounts assigned to its assets and liabilities is the implied fair value of goodwill. The Company’s analysis resulted in an implied fair value of goodwill of $21.2 million.
In 2009 and 2008, the Company recorded pre-tax restructuring expenses totaling $12.1 million and $18.0 million, respectively, for employee severance related to employee reductions across various functional areas and facility closures resulting from the Company’s cost savings initiatives. These initiatives included severance benefits for 478 employees in 2009 and 380 in 2008. The Company is anticipating the employee reductions to be completed by mid 2010 with an expected additional total cost of $4.0 — $5.0 million in 2010, with severance payments expected to be fully paid by the end of 2011 using cash from operations.
Operating income decreased $21.1 million, or 10%, to $184.9 million in 2009 from $206.0 million in 2008. This decrease primarily reflects a decrease in volume, partially offset by the goodwill impairment charge in 2008 and the impact from acquisitions. Operating margins in 2009 were 13.9% of sales compared with 13.8% recorded in 2008.
In the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment, operating income of $100.3 million and operating margins of 15.6% in 2009 were down from the $123.8 million and 17.7% recorded in 2008 principally due to lower sales. In the Health & Science Technologies Segment, operating income of $51.7 million and operating margins of 17.0% in 2009 were down from the $58.3 million and 17.6% recorded in 2008 due to lower volume. In the Dispensing Equipment Segment, operating income of $15.1 million and operating margins of 11.9% in 2009 were up from the $10.7 million of operating loss recorded in 2008, due to thea goodwill impairment charge in 2008, partially offset by continued deterioration in the North American and European markets. Operating income and operating margins in the Fire & Safety/Diversified Products Segment of $59.9 million and 22.8%, respectively, were lower than the $74.3 million and 24.7% recorded in 2008, due primarily to lower volume and unfavorable product mix.
16
Company and Business Segment Financial Information
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31,(1) | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008(6) | | | 2007(6) | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales(2) | | $ | 641,108 | | | $ | 697,702 | | | $ | 570,307 | |
| Operating income(3) | | | 100,289 | | | | 123,801 | | | | 119,060 | |
| Operating margin(3) | | | 15.6 | % | | | 17.7 | % | | | 20.9 | % |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 1,043,082 | | | $ | 1,070,348 | | | $ | 698,286 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 32,584 | | | | 26,276 | | | | 16,797 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 12,867 | | | | 13,859 | | | | 11,407 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales(2) | | $ | 304,329 | | | $ | 331,591 | | | $ | 327,170 | |
| Operating income(3) | | | 51,712 | | | | 58,297 | | | | 61,473 | |
| Operating margin(3) | | | 17.0 | % | | | 17.6 | % | | | 18.8 | % |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 567,096 | | | $ | 594,459 | | | $ | 542,427 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 14,293 | | | | 11,806 | | | | 11,156 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 6,365 | | | | 5,365 | | | | 5,342 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales(2) | | $ | 127,279 | | | $ | 163,861 | | | $ | 177,948 | |
| Operating income (loss)(3)(4) | | | 15,147 | | | | (10,748 | ) | | | 39,179 | |
| Operating margin(3)(4) | | | 11.9 | % | | | (6.6 | )% | | | 22.0 | % |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 164,979 | | | $ | 179,800 | | | $ | 236,751 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 3,124 | | | | 3,986 | | | | 3,151 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 864 | | | | 2,528 | | | | 2,832 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales(2) | | $ | 262,809 | | | $ | 300,462 | | | $ | 288,424 | |
| Operating income(3) | | | 59,884 | | | | 74,310 | | | | 66,287 | |
| Operating margin(3) | | | 22.8 | % | | | 24.7 | % | | | 23.0 | % |
| Identifiable assets | | $ | 285,893 | | | $ | 286,482 | | | $ | 312,603 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 5,328 | | | | 5,288 | | | | 5,676 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 3,686 | | | | 4,743 | | | | 3,532 | |
| Company | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | | | $ | 1,358,631 | |
| Operating income | | | 184,854 | | | | 205,956 | | | | 252,795 | |
| Operating margin | | | 13.9 | % | | | 13.8 | % | | | 18.6 | % |
| Total assets | | $ | 2,098,157 | | | $ | 2,151,800 | | | $ | 1,970,078 | |
| Depreciation and amortization(5) | | | 56,346 | | | | 48,599 | | | | 38,038 | |
| Capital expenditures | | | 25,525 | | | | 28,358 | | | | 26,496 | |
| | |
(1) | | Data includes acquisition of IETG (October 2008), iPEK (October 2008), Richter (October 2008), ADS (January 2008), Quadro (June 2007), Faure Herman (February 2007), in the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment and Semrock (October 2008), Isolation Technologies (October 2007), in the Health & Science Technologies Segment from the date of acquisition. |
|
(2) | | Segment net sales include intersegment sales. |
|
(3) | | Segment operating income excludes unallocated corporate operating expenses. |
|
(4) | | Segment operating income includes $30.1 million goodwill impairment charge in 2008 for Fluid Management. |
|
(5) | | Excludes amortization of debt issuance expenses. |
|
(6) | | Certain prior year amounts have been restated to reflect the LIFO to FIFO inventory costing change. |
17
Other income of $1.2 million in 2009 was $3.9 million lower than the $5.1 million in 2008, due to unfavorable foreign currency translation and lower interest income.
Interest expense decreased to $17.2 million in 2009 from $18.9 million in 2008. The decrease was due to a lower interest rate environment, the retirementreplacement of the $150.0 million senior notes toof debt with a lower interest rate borrowing in February 2008 and the conversion of $350.0 million floating-rate debt into fixed-rates.
The provision for income taxes decreased to $55.4 million in 2009 from $65.2 million in 2008. The effective tax rate decreased to 32.8% in 2009 from 33.9% in 2008, due to changes in the mix of global pre-tax income among taxing jurisdictions.
Net income for 2009 was $113.4 million, 11% lower than the $127.0 million earned in the same period of 2008. Diluted earnings per share in 2009 of $1.40 decreased $0.13, or 8%, compared with the same period last year.2008.
Performance in 2008 Compared with 2007
Sales in 2008 of $1,489.5 million were 10% higher than the $1,358.6 million recorded in 2007. Seven acquisitions (Quadro — June 2007, Isolation Technologies — October 2007, ADS — January 2008, Richter — October 2008, iPEK — October 2008, IETG — October 2008 and Semrock — October 2008) completed since 2007 accounted for an improvement of 9%, foreign currency translation accounted for 1%, while organic sales were flat. Organic sales increased in the Fluid & Metering Technologies and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products segments, but were down in the Health & Science Technologies and Dispensing Equipment segments. Domestic organic sales were down 3% versus the prior year, while international organic sales were up 4% over the prior year. Sales to customers outside the U.S. represented 47% of total sales in 2008 and 46% in 2007.
In 2008, Fluid & Metering Technologies contributed 47% of sales and 50% of operating income; Health & Science Technologies accounted for 22% of sales and 24% of operating income; Dispensing Equipment accounted for 11% of sales and (4)% of operating income; and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products represented 20% of sales and 30% of operating income.
Fluid & Metering Technologies sales of $697.7 million in 2008 rose $127.4 million, or 22%, compared with 2007. The acquisition of Quadro, ADS, Richter, iPEK and IETG accounted for 18% of the increase, while organic growth increased 4%. In 2008, organic sales grew approximately 2% domestically and 6% internationally. Sales to customers outside the U.S. were approximately 41% of total segment sales in 2008 and 42% in 2007.
Health & Science Technologies sales of $331.6 million increased $4.4 million, or 1%, in 2008 compared with last year. The acquisition of Isolation Technologies and Semrock accounted for 4% of the increase partially offset by a 3% decrease in organic volume. In 2008, organic sales decreased 2% domestically and 5% internationally. Sales to customers outside the U.S. were approximately 39% of total segment sales in 2008 and 2007.
Dispensing Equipment sales of $163.9 million decreased $14.1 million, or 8%, in 2008 compared with the prior year. Organic sales decreased 13%, while foreign currency translation accounted for an increase of 5%. Organic domestic sales decreased 35% compared with 2007, while organic international sales were essentially flat. Sales to customers outside the U.S. were 74% of total segment sales in 2008, up from 63% in 2007.
Fire & Safety/Diversified Products sales of $300.5 million increased $12.0 million, or 4%, in 2008 compared with 2007. Organic sales activity increased 3%, while foreign currency translation accounted for 1%. In 2008, organic sales decreased 4% domestically, while organic international sales increased 11%. Sales to customers outside the U.S. were 54% of total segment sales in 2008 and 49% in 2007.
Gross profit of $597.4 million in 2008 was $31.3 million, or 6%, higher than 2007. As a percent of sales, gross profit was 40.1% in 2008, which represented a 160 basis-point decrease from 41.7% in 2007. The decrease in gross margin primarily reflects product mix, inventory fair value expense, higher material costs and the effect from recent acquisitions.
SG&A expenses increased to $343.4 million in 2008 from $313.4 million in 2007. This increase primarily relates to our recent acquisitions. As a percent of net sales, SG&A expenses were 23.1% for both 2008 and 2007.
18
In 2008 the Company recorded a goodwill impairment charge of $30.1 million. The Company concluded in accordance with ASC 350 that events had occurred and circumstances had changed which required the Company to perform an interim period goodwill impairment test at Fluid Management, a reporting unit within the Company’s Dispensing Equipment Segment. Fluid Management had experienced a downturn in capital spending by its customer base and the loss of market share. The Company performed an impairment test and compared the fair value of the reporting unit to its carrying value. It was determined that the fair value of Fluid Management was less than the carrying value of the net assets. The excess of the fair value of the reporting unit over the amounts assigned to its assets and liabilities is the implied fair value of goodwill. The Company’s analysis resulted in an implied fair value of goodwill of $21.2 million.
In October 2008, the date of our annual impairment test, the Company updated certain forecasts to reflect, among other things, the global economic downturn and other considerations. Because of these changes in circumstances, as of December 31, 2008 the Company reassessed the likelihood of any further impairment of our reporting units. No goodwill impairments were identified. However, further changes in our forecasts or changes in key assumptions could cause book values of certain reporting units to exceed their fair values which could have resulted in goodwill impairment charges in future periods. Except for two of our reporting units within the Fluid & Metering Technologies segment, a 10% decrease in the fair value of our reporting units did not result in goodwill impairment based on carrying values at December 31, 2008. The two reporting units which could have potentially resulted in a goodwill impairment if a 10% decrease in fair value were realized had a total goodwill balance of $204.2 million.
In 2008, the Company recorded pre-tax restructuring expenses totaling $18.0 million. These restructuring expenses were related to the Company’s restructuring program, which includes the previously announced cessation of manufacturing operations in its Dispensing Equipment segment’s Milan, Italy facility. The expenses recorded in 2008 included costs related to involuntary terminations and other direct costs associated with implementing these initiatives.
Operating income decreased $46.8 million, or 19%, to $206.0 million in 2008 from $252.8 million in 2007. This decrease consists of $18.0 million for restructuring-related charges, $30.1 million for a goodwill impairment charge, $10.6 million from the effect of the 2008 acquisitions and $4.1 million for the acquisition related inventory fair value expense, partially offset by $16.0 million in savings attributable to strategic sourcing and other operational excellence initiatives. Operating margins in 2008 were 13.8% of sales compared with 18.6% in 2007. The decrease in operating margins was primarily due to the impact of the restructuring-related and goodwill impairment charges, as well as expenses associated with recent acquisitions, partially offset by an increase in volume.
In the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment, operating income of $123.8 million in 2008 was up from the $119.1 million recorded in 2007 principally due to increased volume, partially offset by the restructuring-related charges. Operating margins for Fluid & Metering Technologies of 17.7% in 2008 were down from 20.9% in 2007, primarily due to the impact of acquisitions and the restructuring-related charges. In the Health & Science Technologies Segment, operating income of $58.3 million and operating margins of 17.6% in 2008 were down from the $61.5 million and 18.8% recorded in 2007, principally due to recent acquisitions and the restructuring-related charges. In the Dispensing Equipment Segment, an operating loss of $10.7 million and operating margins of (6.6)% in 2008 were down from the $39.2 million and 22.0% recorded in 2007, due to lower volume as a result of continued deterioration in capital spending for both North American and European markets, the restructuring-related and goodwill impairment charges and selective material cost increases. Operating income and operating margins in the Fire & Safety/Diversified Products Segment of $74.3 million and 24.7%, respectively, were higher than the $66.3 million and 23.0% recorded in 2007, due primarily to favorable product mix, partially offset by restructuring-related charges.
Other income of $5.1 million in 2008 was $1.7 million higher than the $3.4 million in 2007, due to favorable foreign currency translation and higher interest income.
Interest expense decreased to $18.9 million in 2008 from $23.4 million in 2007. The decrease was due to a lower interest rate environment, the retirement of the $150.0 million senior notes to a lower interest rate and the conversion of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt.
19
The provision for income taxes decreased to $65.2 million in 2008 from $78.5 million in 2007. The effective tax rate increased to 33.9% in 2008 from 33.7% in 2007, due to changes in the mix of global pre-tax income among taxing jurisdictions.
Income from continuing operations in 2008 was $127.0 million, 18% lower than the $154.4 million earned in 2007. Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations in 2008 of $1.53 decreased $0.35, or 19%, compared with the same period of 2007.
Loss from discontinued operations in 2007 was $0.7 million or $0.01 per share, which resulted from the operations for Halox. The 2007 loss includes $0.7 million loss from operations and a $0.1 million loss from the sale of Halox, offset by a $0.1 million income adjustment from the sale of Lubriquip.
Net income for 2008 was $127.0 million, 17% lower than the $153.7 million earned in the same period of 2007. Diluted earnings per share in 2008 of $1.53 decreased $0.34, or 18%, compared with the same period last year.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
At December 31, 2009,2010, working capital was $262.0$339.1 million and the Company’s current ratio was 2.42.0 to 1. Cash flows from operating activities decreased $10.5$28.1 million, or 5%13%, to $212.5$184.5 million in 2009.2010, primarily due to the settlement of the forward starting interest rate contract entered into during 2010 in connection with the $300.0 million 4.5% Senior Notes issued in December 2010.
Cash flows from operations were more than adequate to fund capital expenditures of $32.8 million and $25.5 million in 2010 and $28.4 million in 2009, and 2008, respectively. Capital expenditures were generally for machinery and equipment that improved productivity and tooling to support the global sourcing initiatives, although a portion was for business system technology and replacement of equipment and facilities. Management believes that the Company has ample capacity in its plants and equipment to meet expected needs for future growth in the intermediate term.
The Company acquired ADSPPE in January 2008April 2010 for cash consideration of $156.1 million, Richter in October 2008 for cash consideration of $93.3$51.3 million and the assumption of approximately $8.7$2.7 million in debt related items, iPEKOBL in October 2008July 2010 for cash consideration of $43.1$15.4 million, Periflo in September 2010 for cash consideration of $4.3 million and Fitzpatrick in November 2010 for cash consideration of $20.3 million and the assumption of approximately $1.4$0.4 million in debt related items, IETG in October 2008 for cash consideration of $35.0 million and the assumption of approximately $1.9 million in debt related items, Semrock in October 2008 for cash consideration of $60.6 million and Innovadyne Technologies, Inc (“Innovadyne”) for cash consideration of $3.3 million. Approximately $155.0 million of theitems. The cash payment for ADSPPE was financed bywith borrowings under the Company’s credit facility, of which $140.0 million was reflected as restrictedwhile the other acquisitions were paid with cash at December 31, 2007. Approximately $63.7 million, $33.2 million, $20.5 million, $60.0 million and $3.3 million of the cash payments for the acquisitions of Richter, iPEK, IETG, Semrock and Innovadyne, respectively, were financed by borrowings under the Company’s credit facility.from operations.
18
The Company maintains a $600.0 million unsecured domestic, multi-currency bank revolving credit facility (“Credit Facility”), which expires on December 21, 2011. At December 31, 20092010, there was $298.7$27.8 million outstanding under the Credit Facility and outstanding letters of credit totaled approximately $7.1 million.Facility. The net available borrowing under the Credit Facility as of December 31, 2009,2010, was approximately $294.2$572.2 million. Interest is payable quarterly on the outstanding borrowings at the bank agent’s reference rate. Interest on borrowings based on LIBOR plus an applicable margin is payable on the maturity date of the borrowing, or quarterly from the effective date for borrowings exceeding three months. The applicable margin is based on the Company’s senior, unsecured, long-term debt rating and can range from 24 basis points to 50 basis points. Based on the Company’s BBBcredit rating at December 31, 2009,2010, the applicable margin was 40 basis points. An annual Credit Facility fee, also based on the Company’s credit rating, is currently 10 basis points and is payable quarterly.
At December 31, 2009 the Company had one interest rate exchange agreement related to the Credit Facility. The interest rate exchange agreement, expiring in January 2011, effectively converted $250.0 million of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt at an interest rate of 3.25%. The fixed rate noted above is comprised of the fixed rate on the interest rate exchange agreement and the Company’s current margin of 40 basis points on the Credit Facility.
There are two financial covenants that the Company is required to maintain in connection with the Credit Facility and Term Loan. As defined in the agreement, the minimum interest coverage ratio (operating cash flow to
20
interest) is 3.0 to 1 and the maximum leverage ratio (outstanding debt to operating cash flow) is 3.25 to 1. At December 31, 2009, the Company was in compliance with both of these financial covenants.
On April 18, 2008, the Company completed a $100.0 million unsecured senior bank term loan agreement (“Term Loan”), with covenants consistent with the existing Credit Facility and a maturity on December 21, 2011. At December 31, 2009,2010, there was $95.0$90.0 million outstanding under the Term Loan with $5.0 million included within short term borrowings. Interest under the Term Loan is based on the bank agent’s reference rate or LIBOR plus an applicable margin and is payable at the end of the selected interest period, but at least quarterly. The applicable margin is based on the Company’s senior, unsecured, long-term debt rating and can range from 45 to 100 basis points. Based on the Company’s current debt rating, the applicable margin is 80 basis points. The Term Loan requires repaymentsa repayment of $5.0 million and $7.5 million in April of 2010 and 2011, respectively, with the remaining balance due on December 21, 2011. The Company used the proceeds from the Term Loan to pay down existing debt outstanding under the Credit Facility. The Company currently maintains an interest rate exchange agreement related to the Term Loan which expires in December 2011. WithThis interest rate exchange agreement has a current notional amount of $95.0$90.0 million, the agreement effectively converted the $100.0 million of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt at an interest rate of 4.00%. The fixed rate is comprised of the fixed rate on the interest rate exchange agreement and the Company’s current margin of 80 basis points on the Term Loan.
On June 9, 2010, the Company completed a private placement of €81.0 million ($96.8 million) aggregate principal amount of 2.58% Series 2010 Senior Euro Notes due June 9, 2015 (“2.58% Senior Euro Notes”) pursuant to a Master Note Purchase Agreement, dated June 9, 2010 (the “Purchase Agreement”). The Purchase Agreement provides for the issuance of additional series of notes in the future. The 2.58% Senior Euro Notes bear interest at a rate of 2.58% per annum and will mature on June 9, 2015. The 2.58% Senior Euro Notes are unsecured obligations of the Company and rank pari passu in right of payment with all of the Company’s other senior debt. The Company may at any time prepay all or any portion of the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes; provided that such portion is greater than 5% of the aggregate principal amount of Notes then outstanding under the Purchase Agreement. In the event of a prepayment, the Company will pay an amount equal to par plus accrued interest plus a make-whole premium. The Purchase Agreement contains certain covenants that restrict the Company’s ability to, among other things, transfer or sell assets, create liens and engage in certain mergers or consolidations. In addition, the Company must comply with a leverage ratio and interest coverage ratio as set forth in the Purchase Agreement. The Purchase Agreement provides for customary events of default. In the case of an event of default arising from specified events of bankruptcy or insolvency, all outstanding 2.58% Senior Euro Notes will become due and payable immediately without further action or notice. In the case of payment events of defaults, any holder of the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes affected thereby may declare all the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes held by it due and payable immediately. In the case of any other event of default, a majority of the holders of the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes may declare all the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes to be due and payable immediately. The Company used a portion of the proceeds from the private placement to pay down existing debt outstanding under the Credit Facility that had previously been denominated in Euros, with the remainder being available for ongoing business activities.
On December 6, 2010, the Company completed a public offering of $300.0 million 4.5% Notes due December 15, 2020 (“4.5% Senior Notes”). The net proceeds from the offering of approximately $295.7 million, after deducting the $1.6 million issuance discount, the $1.9 million underwriting commission and estimated offering expenses of approximately $0.8 million, was used to repay $250.0 million of outstanding indebtedness under the Credit Facility. The balance of the net proceeds will be used for general corporate purposes. The 4.5% Senior Notes will bear interest at a rate of 4.5% per annum, which is payable semi-annually in arrears each June 15 and December 15, beginning June 15, 2011. The Company may redeem all or part of the 4.5% Senior Notes at any time prior to maturity at the redemption prices set forth in the Note Indenture (“Indenture”) governing the
19
4.5% Senior Notes. The Company may issue additional debt from time to time pursuant to the Indenture. The Indenture and 4.5% Senior Notes contain covenants that limit the Company’s ability to, among other things, incur certain liens securing indebtedness, engage in certain sale-leaseback transactions, and enter into certain consolidations, mergers, conveyances, transfers or leases of all or substantially all the Company’s assets. The terms of the 4.5% Senior Notes also require the Company to make an offer to repurchase 4.5% Senior Notes upon a change of control triggering event (as defined in the Indenture) at a price equal to 101% of their principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest if any.
On April 15, 2010, the Company entered into a forward starting interest rate contract with a notional amount of $300.0 million with a settlement date in December 2010. This contract was entered into in anticipation of the issuance of the $300.0 million 4.5% Senior Notes and was designed to lock in the market interest rate as of April 15, 2010. The Company settled this interest rate contract in December 2010, resulting in a $31.0 million payment. The $31.0 million will be amortized into interest expense over the 10 year term of the 4.5% Senior Notes yielding an effective interest rate of 5.8%.
There are two key financial covenants that the Company is required to maintain in connection with the Credit Facility, Term Loan, and 2.58% Senior Euro Notes. There are no financial covenants relating to the 4.5% Senior Notes. The most restrictive financial covenants under these debt instruments require a minimum interest coverage ratio (operating cash flow to interest) of 3.0 to 1 and a maximum leverage ratio (outstanding debt to operating cash flow) of 3.25 to 1. At December 31, 2010, the Company was in compliance with both of these financial covenants. The Company expects to be in compliance with both of these key financial covenants throughout 2011.
On April 21, 2008, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $125.0 million of its outstanding common shares. Repurchases under the new program will be funded with cash flow generation, and made from time to time in either the open market or through private transactions. The timing, volume, and nature of share repurchases will be at the discretion of management, dependent on market conditions, other priorities for cash investment, applicable securities laws, and other factors, and may be suspended or discontinued at any time. In 2008, 2.3 million shares were purchased at a cost of $50.0 million; noNo shares were purchased in 2010 or 2009.
Despite the downturn in global financial markets during 2008 and 2009, the Company has not experienced any liquidity issues and we continue toWe expect that our current liquidity, notwithstanding these adverse market conditions,cash and cash that will be generated from operations during 2011 will be sufficient to meet our operating cash requirements, planned capital expenditures, interest on all borrowings, required debt repayments, any authorized share repurchases, planned capital expenditures,pension and postretirement funding requirements and annual dividend payments to holders of commonthe Company’s stock during the next twelve months. InAdditionally, in the event that suitable businesses are available for acquisition upon terms acceptable to the Board of Directors,terms, we may obtain all or a portion of the financing for thethese acquisitions through the incurrence of additional long-term borrowings. However, in lightOur current intention, if the available terms and conditions are acceptable, is to enter into a new revolving credit facility agreement during 2011 since the existing Credit Facility matures on December 21, 2011. As of recent adverse events in global financialDecember 31, 2010, $27.8 million is outstanding under the existing Credit Facility and economic conditions, we cannot$90.0 million is outstanding under the Term Loan and both are classified as short term borrowings on the Balance Sheet. We expect our cash and cash from operations to be certain that additional financing will be available on satisfactory terms, if at all.adequate to repay these balances during 2011.
Contractual Obligations, Commitments and Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Our contractual obligations and commercial commitments include pension and postretirement medical benefit plans, rental payments under operating leases, payments under capital leases, and other long-term obligations arising in the ordinary course of business. There are no identifiable events or uncertainties, including the lowering of our credit rating that would accelerate payment or maturity of any of these commitments or obligations.
The following table summarizes our significant contractual obligations and commercial commitments at December 31, 2009,2010, and the future periods in which such obligations are expected to be settled in cash. In addition, the table reflects the timing of principal and interest payments on outstanding borrowings. Additional detail
2120
regarding these obligations is provided in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II. Item 8. Financial“Financial Statements and Supplementary Data,Data”, as referenced in the table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Less
| | | | | | More
| | | | | Less
| | | | | | More
| |
| | | | | Than
| | 1-3
| | 3-5
| | Than
| | | | | Than
| | 1-3
| | 3-5
| | Than
| |
Payments Due by Period | | Total | | 1 Year | | Years | | Years | | 5 Years | | | Total | | 1 Year | | Years | | Years | | 5 Years | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Borrowings (Note 6)(1) | | $ | 415,918 | | | $ | 20,949 | | | $ | 394,969 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | |
Borrowings(1) | | | $ | 677,156 | | | $ | 139,347 | | | $ | 32,538 | | | $ | 138,333 | | | $ | 366,938 | |
| Interest rate exchange agreements | | | 10,497 | | | | — | | | | 10,497 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,365 | | | | 2,365 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Operating lease commitments (Note 9) | | | 33,181 | | | | 8,582 | | | | 10,458 | | | | 5,273 | | | | 8,868 | | |
| Capital lease obligations(2) | | | 3,965 | | | | 587 | | | | 780 | | | | 780 | | | | 1,818 | | |
| Purchase obligations(3) | | | 71,404 | | | | 66,070 | | | | 5,221 | | | | 113 | | | | — | | |
| Pension obligations | | | 91,600 | | | | 7,700 | | | | 16,700 | | | | 18,500 | | | | 48,700 | | |
| Income tax obligations (ASC 740)(4) | | | 5,285 | | | | 283 | | | | 2,949 | | | | 389 | | | | 1,664 | | |
| Operating lease commitments | | | | 35,321 | | | | 9,679 | | | | 12,668 | | | | 6,057 | | | | 6,917 | |
Capital lease obligations(2) | | | | 3,808 | | | | 793 | | | | 981 | | | | 718 | | | | 1,316 | |
Purchase obligations(3) | | | | 76,629 | | | | 63,084 | | | | 2,514 | | | | 11,031 | | | | — | |
| Pension and post-retirement obligations | | | | 96,100 | | | | 8,600 | | | | 17,600 | | | | 19,500 | | | | 50,400 | |
Income tax obligations(4) | | | | 6,440 | | | | 1,319 | | | | 4,201 | | | | 204 | | | | 716 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total contractual obligations(5) | | $ | 631,850 | | | $ | 104,171 | | | $ | 441,574 | | | $ | 25,055 | | | $ | 61,050 | | |
Total contractual obligations(5) | | | $ | 897,819 | | | $ | 225,187 | | | $ | 70,502 | | | $ | 175,843 | | | $ | 426,287 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | Includes interest payments based on contractual terms and current interest rates for variable debt. |
| |
| (2) | | ComprisedConsists primarily of property leases. |
| |
| (3) | | ComprisedConsists primarily of inventory commitments. |
| |
| (4) | | Excludes interest and penalties. |
| |
| (5) | | Comprised ofComprises liabilities recorded on the balance sheet of $477,236,$492,878, and obligations not recorded on the balance sheet of $154,614.$404,941. |
Critical Accounting Policies
We believe that the application of the following accounting policies, which are important to our financial position and results of operations, requires significant judgments and estimates on the part of management. For a summary of all of our accounting policies, including the accounting policies discussed below, see Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II. Item 8. Financial“Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.Data”.
Revenue recognition — The Company recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery has occurred, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectibility of the sales price is reasonably assured. For product sales, delivery does not occur until the products have been shipped and risk of loss has been transferred to the customer. Revenue from services is recognized when the services are provided or ratably over the contract term. Some arrangements with customers may include multiple deliverables, including the combination of products and services. In such cases, the Company has identified these as separate elements in accordance withASC985-65-25 “Revenue Recognition-Multiple-Element Arrangements-Recognition” and recognizes revenue consistent with the policy for each separate element based on the fair value of each accounting unit. Revenues from certain long-term contracts are recognized on thepercentage-of-completion method.Percentage-of-completion is measured principally by the percentage of costs incurred to date for each contract to the estimated total costs for such contract at completion. Provisions for estimated losses on uncompleted long-term contracts are made in the period in which such losses are determined. Due to uncertainties inherent in the estimation process, it is reasonably possible that completion costs, including those arising from contract penalty provisions and final contract settlements, will be revised in the near-term. Such revisions to costs and income are recognized in the period in which the revisions are determined.
The Company records allowances for discounts, product returns and customer incentives at the time of sale as a reduction of revenue as such allowances can be reliably estimated based on historical experience and known trends. The Company also offers product warranties and accrues its estimated exposure for warranty claims at the time of sale based upon the length of the warranty period, warranty costs incurred and any other related information known to the Company.
21
Share-based compensation — The Company accounts for stock-based employee compensation under the fair value recognition and measurement provisions of ASC Topic 718 “Compensation — Stock Compensation” and
22
applies the Binomial lattice option-pricing model to determine the fair value of options. The Binomial lattice option-pricing model incorporates certain assumptions, such as the expected volatility, risk-free interest rate, expected dividend yield, expected forfeiture rate and expected life of options, in order to arrive at a fair value estimate. As a result, share-based compensation expense, as calculated and recorded under ASC 718 could have been impacted if other assumptions were used. Furthermore, if the Company used different assumptions in future periods, share-based compensation expense could be impacted in future periods. See Note 1613 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II. Item 8. Financial“Financial Statements and Supplementary DataData” for additional information.
Inventory — The Company states inventories at the lower of cost or market. Cost, which includes material, labor, and factory overhead, is determined on a FIFO basis. We changed our method of accounting for inventory from the LIFO method to the FIFO method effective January 1, 2009 and applied this change in accounting principle retrospectively to all prior periods presented herein (see Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II. Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data). We make adjustments to reduce the cost of inventory to its net realizable value, if required, for estimated excess, obsolescence or impaired balances. Factors influencing these adjustments include changes in market demand, product life cycle and engineering changes.
Goodwill, long-lived and intangible assets — The Company evaluates the recoverability of certain noncurrent assets utilizing various estimation processes. An impairment of a long-lived asset exists when the asset’s carrying amount exceeds its fair value, and is recorded when the carrying amount is not recoverable through future operations. An intangible asset or goodwill impairment exists when the carrying amount of intangible assets and goodwill exceeds its fair value. Assessments of possible impairments of goodwill, long-lived or intangible assets are made when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the asset may not be recoverable through future operations. Additionally, testing for possible impairment of recorded goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible asset balances is performed annually. The amount and timing of impairment charges for these assets require the estimation of future cash flows and the fair value of the related assets.
The Company’s business acquisitions result in recording goodwill and other intangible assets, which affect the amount of amortization expense and possible impairment expense that the Company will incur in future periods. The Company follows the guidance prescribed in ASC 350, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” to test goodwill and intangible assets for impairment. Annually, on October 31st,31 or more frequently if triggering events occur, the Company compares the fair value of their reporting units to the carrying value of each reporting unit to determine if a goodwill impairment exists.
The Company determines the fair value of each reporting unit utilizing an income approach (discounted cash flows) weighted 50% and a market approach consisting of a comparable public company EBITDA multiples methodology weighted 50%. To determine the reasonableness of the calculated fair values, the Company reviews the assumptions to ensure that neither the income approach nor the market approach yielded significantly different valuations.
The key assumptions are updated each year for each reporting unit for the income and market methodology used to determine fair value. Various assumptions are utilized including forecasted operating results, annual operating plans, strategic plans, economic projections, anticipated future cash flows, the weighted average cost of capital, comparable transactions, market data and EBITDA multiples. The assumptions that have the most significant effect on the fair value calculation are the weighted average cost of capital, the EBITDA multiples and terminal growth rates. The 20092010 and 20082009 ranges for these three assumptions utilized by the Company are as follows:
| | | | | |
| Assumptions: | | 20092010 Range
| | 20082009 Range
|
|
Assumptions | | | | |
| Weighted average cost of capital | | 12.1% to 13.9% | | 11.0% to 13.7% | | 12.6% to 13.9% |
| EBITDA multiples | | 9.0x to 11.0x12.0x | | 5.8x9.0x to 9.0x11.0x |
| Terminal growth rates | | 3.0% to 3.5% | | 3.0% to 3.5% |
The Company concluded that the fair value of each of its reporting units was substantially in excess of its carrying value as of October 31, 2009,2010, and thus no goodwill impairment was identified. However, a 10% decrease in fair value of the
23
Banjo or the Water reporting units within the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment could potentially result in a goodwill impairment charge at these reporting units. The total goodwill balance for these two reporting units as of October 31, 2009 was $288.7 million.
Income taxes — The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with ASC 740 — “Income Taxes”. Under ASC 740, deferred income tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the estimated future tax effects
22
of differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities based on currently enacted tax laws. The Company’s tax balances are based on management’s interpretation of the tax regulations and rulings in numerous taxing jurisdictions. Future tax authority rulings and changes in tax laws and future tax planning strategies could affect the actual effective tax rate and tax balances recorded by the Company.
Contingencies and litigation —We are currently involved in certain legal and regulatory proceedings and, as required and where it is reasonably possible to do so, we accrue estimates of the probable costs for the resolution of these matters. These estimates are developed in consultation with outside counsel and are based upon an analysis of potential results, assuming a combination of litigation and settlement strategies. It is possible, however, that future operating results for any particular quarterly or annual period could be materially affected by changes in our assumptions or the effectiveness of our strategies related to these proceedings.
Defined benefit retirement plans — — The plan obligations and related assets of the defined benefit retirement plans are presented in Note 1714 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II. Item 8. Financial“Financial Statements and Supplementary Data. PlanData”. Level 1 assets which consist primarily of marketable equity and debt instruments, are valued using unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets in active markets. Level 2 assets are valued using quoted prices or other observable inputs for similar assets. Level 3 assets are valued using unobservable inputs, but reflect the assumptions market quotations.participants would use in pricing the assets. Plan obligations and the annual pension expense are determined by consulting with actuaries using a number of assumptions provided by the Company. Key assumptions in the determination of the annual pension expense include the discount rate, the rate of salary increases, and the estimated future return on plan assets. To the extent actual amounts differ from these assumptions and estimated amounts, results could be adversely affected.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2009,January 2010, the FASBFinancial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued ASU2009-05,2010-06, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (Topic 820) — Measuring Liabilities at Fair Value”. ASU2009-05 provides clarification regarding valuation techniques when a quoted price in an active market for an identical liability is not available in addition to treatment of the existence of restrictions that prevent the transfer of a liability. ASU2009-05 also clarifies that both a quoted price in an active market for an identical liability at the measurement date and the quoted price for an identical liability when traded as an asset in an active market (when no adjustments to the quoted price of the asset are required) are Level 1 fair value measurements. This standard is effective for the first reporting period, including interim periods, beginning after issuance. Adoption of ASU2009-05 did not have a material effect on the consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows of the Company.
In July 2009, the ASC became the authoritative source of accounting principals to be applied to financial statements prepared in accordance with principles generally accepted in the U.S. In accordance with the ASC, citations to accounting literature in this report are to the relevant topic of the ASC or are presented in plain English. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for interim and annual periods ending after September 15, 2009. The Company adopted this standard on its effective date.
In May 2009, the FASB issued an update to ASC 855 “Subsequent Events.” This standard establishes general standards of accounting forUpdate provides amendments to Subtopic820-10 and disclosure of events that occur after the balance sheet date, but before the financial statements are issued or available to be issued (“subsequent events”). This standard requires disclosure of the date through which the entity has evaluated subsequent events and the basis for that date. For public entities, this is the date the financial statements are issued. This standard does not apply to subsequent events or transactions that arerelated guidance within the scope of other principles generally accepted in the U.S. and will not result in significant changes in the subsequent events reported by the Company. This standard is effective for interim or annual periods ending after June 15, 2009. The Company adopted this standard on its effective date.
In April 2009, the FASB issued an update to ASC 820 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” and ASC 270 “Interim Reporting.” This standard requires disclosures about fair value of financial instruments in interim and
24
annual financial statements. This standard is effective for periods ending after June 15, 2009. The Company adopted this standard on its effective date.
In December 2008, the FASB issued ASC 715 “Compensation-Retirement Benefits.” This standard provides additional guidance on employers’ disclosures about the plan assets of defined benefit pension or other postretirement plans. ASC 715 requires disclosures about how investment allocation decisions are made, the fair value of each major category of plan assets, valuation techniques used to develop fair value measurements of plan assets, the impact of measurements on changes in plan assets when using significant unobservable inputs and significant concentrations of risk in the plan assets. These disclosures are required for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2009. The Company adopted this standard on its effective date.
In June 2008, the FASB issued an update to ASC 260 “Earnings Per Share.” This standard addresses whether instruments granted in share-based payment transactions are participating securities prior to vesting and, therefore, need to be included in the allocation in computing earnings per share under the two-class method described in ASC 260. The FASB concluded that all outstanding unvested share-based payment awards that contain rights to nonforfeitable dividends participate in undistributed earnings with common shareholders. If awards are considered participating securities, the Company is required to apply the two-class method of computing basic and diluted earnings per share. The Company determined that its outstanding unvested shares are participating securities. Accordingly, effective January 1, 2009, earnings per common share are computed using the two-class method prescribed by ASC 260. All previously reported earnings per common share data has been retrospectively adjusted to conform to the new computation method (see EPS in Note 1).
In December 2007, the FASB issued an update to ASC 805 “Business Combinations.” The objective of the standard is to establish principles and requirements for how an acquirer in a business combination recognizes and measures in its financial statements, the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any controlling interest; recognizes and measures the goodwill acquired in the business combination or a gain from a bargain purchase; and determines what information to disclose to enable users of the financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. This standard is to be applied prospectively to business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after an entity’s fiscal year that begins after December 15, 2008. Upon adoption, ASC 805 did not have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or cash flows. However, depending on the nature of an acquisition or the quantity of acquisitions entered into after the adoption, ASC 805 may significantly impact the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or cash flows when compared to acquisitions accounted for under prior U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”) to require disclosure of the transfers in and resultout of Levels 1 and 2 and a schedule for Level 3 that separately identifies purchases, sales, issuances and settlements and requires more detailed disclosures regarding valuation techniques and inputs. The new disclosures and clarifications of existing disclosures were effective for the Company’s fiscal year 2010, except for the disclosures about purchases, sales, issuances and settlements in more earnings volatility and generally lower earnings duethe roll forward of activity in Level 3 fair value measurements, which will be effective for the Company’s fiscal year 2011. See Note 7 of the Notes to among other items,Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II, Item 8 of this report for disclosures associated with the expensingadoption of deal costs and restructuring costs of acquired companies.this standard that were effective in 2010.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In October 2009, the FASB issued ASUNo. 2009-13, “Revenue Recognition (Topic 605) — Multiple-Deliverable Revenue Arrangements.” ASUNo. 2009-13 addresses the accounting for multiple-deliverable arrangements to enable vendors to account for products or services (deliverables) separately rather than as a combined unit. This guidance establishes a selling price hierarchy for determining the selling price of a deliverable, which is based on: (a) vendor-specific objective evidence; (b) third-party evidence; or (c) estimates. This guidance also eliminates the residual method of allocation and requires that arrangement consideration be allocated at the inception of the arrangement to all deliverables using the relative selling price method. In addition, this guidance significantly expands required disclosures related to a vendor’s multiple-deliverable revenue arrangements.ASUNo. 2009-13 is effective prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or materially modified in fiscal years beginning on or after June 15, 2010 and early adoption is permitted. A company may elect, but will not be required, to adopt the amendments in ASUNo. 2009-13 retrospectively for all prior periods. Management is currently evaluating the requirements of ASUNo. 2009-13 and has not yet determined the impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
2523
| |
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk. |
The Company is subject to market risk associated with changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates. We may, from time to time, enter into foreign currency forward contracts and interest rate exchange agreements on our debt when we believe there is a financial advantage in doing so. A treasury risk management policy, adopted by the Board of Directors, describes the procedures and controls over derivative financial and commodity instruments, including foreign currency forward contracts and interest rate swaps.exchange agreements. Under the policy, we do not use derivative financial or commodity derivative instruments for trading purposes, and the use of these instruments is subject to strict approvals by senior officers. Typically, the use of derivative instruments is limited to foreign currency forward contracts and interest rate exchange agreements on the Company’s outstanding long-term debt. The Company’s exposure related to derivative instruments is, in the aggregate, not material to its financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The Company’s foreign currency exchange rate risk is limited principally to the Euro, Canadian Dollar, British Pound and Chinese Renminbi. We manage our foreign exchange risk principally through invoicing our customers in the same currency as the source of our products. The effect of transaction gains and losses is reported within “Otherincome-net” income (expense)-net” on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The Company’s interest rate exposure is primarily related to the $400.1 million of total debt outstanding at December 31, 2009. The majority of the debt is priced at interest rates that float with the market. In order to mitigate this interest exposure, the Company entered into interest rate exchange agreements that effectively converted $345.0 million of our floating-rate debt outstanding at December 31, 2009 to a fixed-rate. A 50-basis point movement in the interest rate on the remaining $55.1 million floating-rate debt would result in an approximate $0.3 million annualized increase or decrease in interest expense and cash flows.
2624
| |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data. |
IDEX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands except share and per share amounts) | | | (In thousands except share and per share amounts) | |
| |
ASSETS | ASSETS | ASSETS |
| Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 73,526 | | | $ | 61,353 | | | $ | 235,136 | | | $ | 73,526 | |
| Receivables — net | | | 183,178 | | | | 205,269 | | | | 213,553 | | | | 183,178 | |
| Inventories | | | 159,463 | | | | 181,200 | | | | 196,546 | | | | 159,463 | |
| Other current assets | | | 35,545 | | | | 32,866 | | | | 47,523 | | | | 35,545 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | 451,712 | | | | 480,688 | | | | 692,758 | | | | 451,712 | |
| Property, plant and equipment — net | | | 178,283 | | | | 186,283 | | | | 188,562 | | | | 178,283 | |
| Goodwill | | | 1,180,445 | | | | 1,167,063 | | | | 1,207,001 | | | | 1,180,445 | |
| Intangible assets — net | | | 281,354 | | | | 303,226 | | | | 281,392 | | | | 281,354 | |
| Other noncurrent assets | | | 6,363 | | | | 14,540 | | | | 11,982 | | | | 6,363 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 2,098,157 | | | $ | 2,151,800 | | | $ | 2,381,695 | | | $ | 2,098,157 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade accounts payable | | $ | 73,020 | | | $ | 87,304 | | | $ | 104,055 | | | $ | 73,020 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 98,730 | | | | 117,186 | | | | 117,879 | | | | 98,730 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | 8,346 | | | | 5,856 | | | | 119,445 | | | | 8,346 | |
| Dividends payable | | | 9,586 | | | | 9,523 | | | | 12,289 | | | | 9,586 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 189,682 | | | | 219,869 | | | | 353,668 | | | | 189,682 | |
| Long-term borrowings | | | 391,754 | | | | 548,144 | | | | 408,450 | | | | 391,754 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | | 148,806 | | | | 141,984 | | | | 148,534 | | | | 148,806 | |
| Other noncurrent liabilities | | | 99,811 | | | | 97,020 | | | | 95,383 | | | | 99,811 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 830,053 | | | | 1,007,017 | | | | 1,006,035 | | | | 830,053 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 9) | | | | | | | | | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 8) | | | | | | | | | |
| Shareholders’ equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred stock: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Authorized: 5,000,000 shares, $.01 per share par value; Issued: none | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Common stock: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Authorized: 150,000,000 shares, $.01 per share par value; Issued: 83,510,320 shares at December 31, 2009 and 82,786,045 shares at December 31, 2008 | | | 835 | | | | 828 | | |
| Authorized: 150,000,000 shares, $.01 per share par value; Issued: 84,636,668 shares at December 31, 2010 and 83,510,320 shares at December 31, 2009 | | | | 846 | | | | 835 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | | | 401,570 | | | | 377,154 | | | | 441,271 | | | | 401,570 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 896,977 | | | | 822,286 | | | | 1,005,040 | | | | 896,977 | |
| Treasury stock at cost: 2,540,052 shares at December 31, 2009 and 2,483,955 shares at December 31, 2008 | | | (56,706 | ) | | | (55,393 | ) | |
| Treasury stock at cost: 2,566,985 shares at December 31, 2010 and 2,540,052 shares at December 31, 2009 | | | | (58,788 | ) | | | (56,706 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | 25,428 | | | | (92 | ) | | | (12,709 | ) | | | 25,428 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total shareholders’ equity | | | 1,268,104 | | | | 1,144,783 | | | | 1,375,660 | | | | 1,268,104 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | | $ | 2,098,157 | | | $ | 2,151,800 | | | $ | 2,381,695 | | | $ | 2,098,157 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
2725
IDEX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | | | For the Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands except per share amounts) | | | (In thousands except per share amounts) | |
| |
| Net sales | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | | | $ | 1,358,631 | | | $ | 1,513,073 | | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | |
| Cost of sales | | | 807,275 | | | | 892,038 | | | | 792,470 | | | | 894,590 | | | | 807,275 | | | | 892,038 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Gross profit | | | 522,386 | | | | 597,433 | | | | 566,161 | | | | 618,483 | | | | 522,386 | | | | 597,433 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | 325,453 | | | | 343,392 | | | | 313,366 | | | | 358,272 | | | | 325,453 | | | | 343,392 | |
| Goodwill impairment | | | — | | | | 30,090 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 30,090 | |
| Restructuring expenses | | | 12,079 | | | | 17,995 | | | | — | | | | 11,095 | | | | 12,079 | | | | 17,995 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating income | | | 184,854 | | | | 205,956 | | | | 252,795 | | | | 249,116 | | | | 184,854 | | | | 205,956 | |
| Other income — net | | | 1,151 | | | | 5,123 | | | | 3,434 | | |
| Other income (expense) — net | | | | (1,092 | ) | | | 1,151 | | | | 5,123 | |
| Interest expense | | | 17,178 | | | | 18,852 | | | | 23,353 | | | | 16,150 | | | | 17,178 | | | | 18,852 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | | | 168,827 | | | | 192,227 | | | | 232,876 | | |
| Income before income taxes | | | | 231,874 | | | | 168,827 | | | | 192,227 | |
| Provision for income taxes | | | 55,436 | | | | 65,201 | | | | 78,457 | | | | 74,774 | | | | 55,436 | | | | 65,201 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Income from continuing operations | | | 113,391 | | | | 127,026 | | | | 154,419 | | |
| Net loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | | | — | | | | — | | | | (719 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 113,391 | | | $ | 127,026 | | | $ | 153,700 | | | $ | 157,100 | | | $ | 113,391 | | | $ | 127,026 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | 1.41 | | | $ | 1.55 | | | $ | 1.90 | | |
| Discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | (0.01 | ) | |
| Earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic earnings per common share | | | $ | 1.93 | | | $ | 1.41 | | | $ | 1.55 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 1.41 | | | $ | 1.55 | | | $ | 1.89 | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | 1.40 | | | $ | 1.53 | | | $ | 1.88 | | |
| Discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | (0.01 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 1.40 | | | $ | 1.53 | | | $ | 1.87 | | |
| Diluted earnings per common share | | | $ | 1.90 | | | $ | 1.40 | | | $ | 1.53 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 79,716 | | | | 81,123 | | | | 80,666 | | | | 80,466 | | | | 79,716 | | | | 81,123 | |
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 80,727 | | | | 82,320 | | | | 82,086 | | | | 81,983 | | | | 80,727 | | | | 82,320 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
2826
IDEX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | | | | | | | | | | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Net Actuarial
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Income (Loss) | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Losses and
| | Cumulative
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Net Actuarial
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Prior Service
| | Unrealized
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Losses and
| | Cumulative
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Costs on
| | Loss
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Prior Service
| | Unrealized
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Pensions
| | on
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Costs on
| | Loss
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | and Other
| | Derivatives
| | | | | | | | | | | | | Pensions
| | on
| | | | | |
| | | Common
| | | | | | Post-
| | Designated
| | | | | | | | | | | | | and Other
| | Derivatives
| | | | | |
| | | Stock and
| | | | Cumulative
| | Retirement
| | as Cash
| | | | Total
| | | Common
| | | | | | Post-
| | Designated
| | | | | |
| | | Additional
| | Retained
| | Translation
| | Benefit
| | Flow
| | Treasury
| | Shareholders’
| | | Stock and
| | | | Cumulative
| | Retirement
| | as Cash
| | | | Total
| |
| | | Paid-In Capital | | Earnings | | Adjustment | | Plans | | Hedges | | Stock | | Equity | | | Additional
| | Retained
| | Translation
| | Benefit
| | Flow
| | Treasury
| | Shareholders’
| |
| | | (In thousands except share and per share amounts) | | | Paid-In Capital | | Earnings | | Adjustment | | Plans | | Hedges | | Stock | | Equity | |
| | | (In thousands except share and per share amounts) | |
Balance, December 31, 2006, as previously stated | | $ | 317,955 | | | $ | 638,579 | | | $ | 52,295 | | | $ | (26,309 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | (3,248 | ) | | $ | 979,272 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Impact of adopting change in accounting related to inventory (see Note 2) | | | — | | | | (17,331 | ) | | | 147 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (17,184 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2006, as restated | | $ | 317,955 | | | $ | 621,248 | | | $ | 52,442 | | | $ | (26,309 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | (3,248 | ) | | $ | 962,088 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | — | | | | 153,700 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 153,700 | | |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | | — | | | | — | | | | 33,573 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 33,573 | | |
| Adjustment to pension and other benefit liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5,934 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5,934 | | |
| | | | | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 39,507 | | |
| | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 193,207 | | |
| | | | | |
| Cumulative effect of change in accounting for uncertainties in income taxes (ASC 740 — See Note 11) | | | — | | | | (1,204 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,204 | ) | |
| Issuance of 892,438 shares of common stock from exercise of stock options and deferred compensation plans | | | 16,742 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 16,742 | | |
| Share-based compensation | | | 12,570 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 12,570 | | |
| Unvested shares surrendered for tax withholding | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,195 | ) | | | (1,195 | ) | |
| Cash dividends declared-$.48 per common share outstanding | | | — | | | | (39,001 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (39,001 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2007 | | $ | 347,267 | | | $ | 734,743 | | | $ | 86,015 | | | $ | (20,375 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | (4,443 | ) | | $ | 1,143,207 | | | $ | 347,267 | | | $ | 734,743 | | | $ | 86,015 | | | $ | (20,375 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | (4,443 | ) | | $ | 1,143,207 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | — | | | | 127,026 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 127,026 | | | | — | | | | 127,026 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 127,026 | |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | | — | | | | — | | | | (45,863 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (45,863 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (45,863 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (45,863 | ) |
| Adjustment to pension and other benefit liabilities | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (13,279 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (13,279 | ) | |
| Unrealized derivative losses | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (6,642 | ) | | | — | | | | (6,642 | ) | |
| Net change in retirement obligations (net of tax benefit of $7.7 million) | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (13,279 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (13,279 | ) |
| Net change on derivatives designated as cash flow hedges (net of tax benefit of $3.7 million) | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (6,642 | ) | | | — | | | | (6,642 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (65,784 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (65,784 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 61,242 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 61,242 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Cumulative effect of change in measurement date of foreign plans under ASC 715 | | | — | | | | (351 | ) | | | 52 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (299 | ) | | | — | | | | (351 | ) | | | 52 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (299 | ) |
| Issuance of 597,863 shares of common stock from exercise of stock options and deferred compensation plans | | | 15,701 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,701 | | | | 15,701 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,701 | |
| Share-based compensation | | | 15,014 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,014 | | | | 15,014 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,014 | |
| Repurchase of 2.3 million shares of common stock | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (50,000 | ) | | | (50,000 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (50,000 | ) | | | (50,000 | ) |
| Unvested shares surrendered for tax withholding | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (950 | ) | | | (950 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (950 | ) | | | (950 | ) |
| Cash dividends declared — $.48 per common share outstanding | | | — | | | | (39,132 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (39,132 | ) | | | — | | | | (39,132 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (39,132 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2008 | | $ | 377,982 | | | $ | 822,286 | | | $ | 40,204 | | | $ | (33,654 | ) | | $ | (6,642 | ) | | $ | (55,393 | ) | | $ | 1,144,783 | | | $ | 377,982 | | | $ | 822,286 | | | $ | 40,204 | | | $ | (33,654 | ) | | $ | (6,642 | ) | | $ | (55,393 | ) | | $ | 1,144,783 | |
| | | | | | �� | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | — | | | | 113,391 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 113,391 | | | | — | | | | 113,391 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 113,391 | |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | | — | | | | — | | | | 19,195 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 19,195 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 19,195 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 19,195 | |
| Amortization of retirement obligations | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 6,396 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 6,396 | | |
| Unrealized loss on derivatives designated as cash flow hedges | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (71 | ) | | | — | | | | (71 | ) | |
| Net change in retirement obligations (net of tax expense of $3.5 million) | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 6,396 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 6,396 | |
| Net change on derivatives designated as cash flow hedges (net of tax benefit of $0.1 million) | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (71 | ) | | | — | | | | (71 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25,520 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25,520 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 138,911 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 138,911 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Issuance of 744,827 shares of common stock from issuance of unvested shares, exercise of stock options and deferred compensation plans | | | 8,713 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 8,713 | | | | 8,713 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 8,713 | |
| Share-based compensation | | | 15,710 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,710 | | | | 15,710 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 15,710 | |
| Unvested shares surrendered for tax withholding | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,313 | ) | | | (1,313 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,313 | ) | | | (1,313 | ) |
| Cash dividends declared — $.48 per common share outstanding | | | — | | | | (38,700 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (38,700 | ) | | | — | | | | (38,700 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (38,700 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2009 | | $ | 402,405 | | | $ | 896,977 | | | $ | 59,399 | | | $ | (27,258 | ) | | $ | (6,713 | ) | | $ | (56,706 | ) | | $ | 1,268,104 | | | $ | 402,405 | | | $ | 896,977 | | | $ | 59,399 | | | $ | (27,258 | ) | | $ | (6,713 | ) | | $ | (56,706 | ) | | $ | 1,268,104 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | | — | | | | 157,100 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 157,100 | |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (21,097 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (21,097 | ) |
| Net change in retirement obligations (net of tax benefit of $1.7 million) | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,830 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,830 | ) |
| Net change on derivatives designated as cash flow hedges (net of tax benefit of $11.9 million) | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (14,210 | ) | | | — | | | | (14,210 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (38,137 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 118,963 | |
| | | | | |
| Issuance of 1,222,274 shares of common stock from issuance of unvested shares, exercise of stock options and deferred compensation plans | | | | 22,354 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 22,354 | |
| Share-based compensation | | | | 17,358 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 17,358 | |
| Unvested shares surrendered for tax withholding | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,082 | ) | | | (2,082 | ) |
| Cash dividends declared — $.60 per common share outstanding | | | | — | | | | (49,037 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (49,037 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance, December 31, 2010 | | | $ | 442,117 | | | $ | 1,005,040 | | | $ | 38,302 | | | $ | (30,088 | ) | | $ | (20,923 | ) | | $ | (58,788 | ) | | $ | 1,375,660 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
2927
IDEX CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Years Ended December 31, | | | For The Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Cash flows from operating activities of continuing operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 113,391 | | | $ | 127,026 | | | $ | 153,700 | | | $ | 157,100 | | | $ | 113,391 | | | $ | 127,026 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss from discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | 719 | | |
| Loss (gain) on sale of fixed assets | | | 447 | | | | — | | | | (371 | ) | |
| Loss on sale of fixed assets | | | | 12 | | | | 447 | | | | — | |
| Goodwill impairment | | | — | | | | 30,090 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 30,090 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 31,850 | | | | 30,989 | | | | 28,316 | | | | 32,367 | | | | 31,850 | | | | 30,989 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | | | 24,496 | | | | 17,610 | | | | 9,722 | | | | 25,741 | | | | 24,496 | | | | 17,610 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance expenses | | | 308 | | | | 288 | | | | 460 | | | | 547 | | | | 308 | | | | 288 | |
| Share-based compensation expense | | | 15,710 | | | | 15,014 | | | | 12,570 | | | | 17,358 | | | | 15,710 | | | | 15,014 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | | 1,081 | | | | (10,817 | ) | | | 1,470 | | | | (7,336 | ) | | | 1,081 | | | | (10,817 | ) |
| Excess tax benefit from share-based compensation | | | (2,762 | ) | | | (3,134 | ) | | | (5,390 | ) | | | (3,457 | ) | | | (2,762 | ) | | | (3,134 | ) |
| Forward starting interest rate contract | | | | (30,970 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| Changes in (net of the effect from acquisitions): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Receivables | | | 26,069 | | | | 19,667 | | | | (8,714 | ) | | | (22,162 | ) | | | 26,069 | | | | 19,667 | |
| Inventories | | | 23,149 | | | | (4,389 | ) | | | (191 | ) | | | (26,651 | ) | | | 23,149 | | | | (4,389 | ) |
| Trade accounts payable | | | (16,310 | ) | | | (6,385 | ) | | | 808 | | | | 21,432 | | | | (16,310 | ) | | | (6,385 | ) |
| Accrued expenses | | | (14,294 | ) | | | 1,215 | | | | 4,141 | | | | 17,941 | | | | (14,294 | ) | | | 1,215 | |
| Other — net | | | 9,397 | | | | 5,886 | | | | 1,754 | | | | 2,555 | | | | 9,397 | | | | 5,886 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash flows provided by operating activities of continuing operations | | | 212,532 | | | | 223,060 | | | | 198,994 | | |
| Cash flows from investing activities of continuing operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchases of property, plant and equipment | | | (25,059 | ) | | | (27,837 | ) | | | (24,498 | ) | |
| Net cash flows provided by operating activities | | | | 184,477 | | | | 212,532 | | | | 223,060 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash purchases of property, plant and equipment | | | | (31,740 | ) | | | (25,059 | ) | | | (27,837 | ) |
| Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | | | — | | | | (392,825 | ) | | | (86,207 | ) | | | (91,286 | ) | | | — | | | | (392,825 | ) |
| Proceeds from the sale of discontinued businesses | | | — | | | | — | | | | 326 | | |
| Proceeds from fixed assets disposals | | | 3,582 | | | | — | | | | 288 | | | | 720 | | | | 3,582 | | | | — | |
| Changes in restricted cash | | | — | | | | 140,005 | | | | (140,005 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 140,005 | |
| Other — net | | | 1,860 | | | | — | | | | 1,500 | | | | — | | | | 1,860 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash flows used in investing activities of continuing operations | | | (19,617 | ) | | | (280,657 | ) | | | (248,596 | ) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities of continuing operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash flows used in investing activities | | | | (122,306 | ) | | | (19,617 | ) | | | (280,657 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowings under credit facilities for acquisitions | | | — | | | | 180,665 | | | | 209,132 | | | | 53,866 | | | | — | | | | 180,665 | |
| Borrowings under credit facilities and term loan | | | 70,114 | | | | 483,044 | | | | 46,947 | | | | 7,685 | | | | 70,114 | | | | 483,044 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of 2.58% Senior Euro Notes | | | | 96,762 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Payments under credit facilities and term loan | | | (225,604 | ) | | | (413,207 | ) | | | (166,423 | ) | | | (331,632 | ) | | | (225,604 | ) | | | (413,207 | ) |
| Payment of senior notes | | | — | | | | (150,000 | ) | | | — | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of 4.5% Senior Notes | | | | 298,427 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Payment of 6.875% Senior Notes | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (150,000 | ) |
| Debt issuance costs | | | | (2,685 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| Dividends paid | | | (38,637 | ) | | | (39,398 | ) | | | (37,267 | ) | | | (46,334 | ) | | | (38,637 | ) | | | (39,398 | ) |
| Distributions to discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | (664 | ) | |
| Proceeds from stock option exercises | | | 7,694 | | | | 10,421 | | | | 13,996 | | | | 18,057 | | | | 7,694 | | | | 10,421 | |
| Excess tax benefit from share-based compensation | | | 2,762 | | | | 3,134 | | | | 5,390 | | | | 3,457 | | | | 2,762 | | | | 3,134 | |
| Purchase of common stock | | | — | | | | (50,000 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (50,000 | ) |
| Other — net | | | (1,313 | ) | | | (1,980 | ) | | | (241 | ) | | | (2,082 | ) | | | (1,313 | ) | | | (1,980 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash flows (used in) provided by financing activities of continuing operations | | | (184,984 | ) | | | 22,679 | | | | 70,870 | | |
| Cash flows from discontinued operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities of discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | (869 | ) | |
| Net cash used in investing activities of discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities of discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | 867 | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash flows used in discontinued operations | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2 | ) | |
| Net cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities | | | | 95,521 | | | | (184,984 | ) | | | 22,679 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | | 4,242 | | | | (6,486 | ) | | | 3,548 | | | | 3,918 | | | | 4,242 | | | | (6,486 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash | | | 12,173 | | | | (41,404 | ) | | | 24,814 | | | | 161,610 | | | | 12,173 | | | | (41,404 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | 61,353 | | | | 102,757 | | | | 77,943 | | | | 73,526 | | | | 61,353 | | | | 102,757 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | | $ | 73,526 | | | $ | 61,353 | | | $ | 102,757 | | | $ | 235,136 | | | $ | 73,526 | | | $ | 61,353 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental cash flow information | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash paid for: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest | | $ | 17,311 | | | $ | 20,139 | | | $ | 22,974 | | | $ | 16,776 | | | $ | 17,311 | | | $ | 20,139 | |
| Income taxes | | | 50,796 | | | | 72,074 | | | | 78,052 | | | | 73,867 | | | | 50,796 | | | | 72,074 | |
| Significant non-cash activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Debt acquired with acquisition of business | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,571 | | | | 758 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Capital expenditures included in accounts payable | | | 466 | | | | 521 | | | | 561 | | |
| Issuance of unvested shares | | | 5,131 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5,603 | | | | 5,131 | | | | — | |
| Non-cash capital expenditures | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,437 | | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
3028
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| |
| 1. | Significant Accounting Policies |
Business
IDEX Corporation is an applied solutions company specializing in fluid and metering technologies, health and science technologies, dispensing equipment, and fire, safety and other diversified products built to its customers’ specifications. Its products are sold in niche markets to a wide range of industries throughout the world. The Company’s products include industrial pumps, compressors, flow meters, injectors and valves, and related controls for use in a wide variety of process applications; precision fluidics solutions, including pumps, valves, degassing equipment, corrective tubing, fittings, and complex manifolds, as well as specialty medical equipment and devices used in life science applications; precision-engineered equipment for dispensing, metering and mixing paints, and personal care products;paints; refinishing equipment; and engineered products for industrial and commercial markets, including fire and rescue, transportation equipment, oil and gas, electronics, and communications. These activities are grouped into four reportable segments: Fluid & Metering Technologies, Health & Science Technologies, Dispensing Equipment, and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the Company and its subsidiaries. All intercompany transactions and accounts have been eliminated.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, and reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates. The principal areas of estimation reflected in the financial statements are revenue recognition, sales returns and allowances, allowance for doubtful accounts, inventory valuation, recoverability of long-lived assets, performing annual goodwill and intangible and long lived asset impairment analyses, income taxes, product warranties, derivatives, contingencies and litigation, insurance-related items, share-based compensation and defined benefit retirement plans.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, delivery has occurred, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectibilitycollectability of the sales price is reasonably assured. For product sales, delivery does not occur until the products have been shipped and risk of loss has been transferred to the customer. Revenue from services is recognized when the services are provided or ratably over the contract term. Some arrangements with customers may include multiple deliverables, including the combination of products and services. In such cases the Company has identified these as separate elements in accordance with ASCAccounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 985 and recognizes revenue consistent with the policy for each separate element based on the fair value of each accounting unit. Revenues from certain long-term contracts are recognized on thepercentage-of-completion method.Percentage-of-completion is measured principally by the percentage of costs incurred to date for each contract to the estimated total costs for such contract at completion. Provisions for estimated losses on uncompleted long-term contracts are made in the period in which such losses are determined. Due to uncertainties inherent in the estimation process, it is reasonably possible that completion costs, including those arising from contract penalty provisions and final contract settlements, will be revised in the near-term. Such revisions to costs and income are recognized in the period in which the revisions are determined.
The Company records allowances for discounts, product returns and customer incentives at the time of sale as a reduction of revenue as such allowances can be reliably estimated based on historical experience and known trends. The Company also offers product warranties and accrues its estimated exposure for warranty claims at the time of
29
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
sale based upon the length of the warranty period, warranty costs incurred and any other related information known to the Company.
31
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
Shipping and Handling Costs
Shipping and handling costs are included in cost of sales and are recognized as a period expense during the period in which they are incurred.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)Advertising Costs
Advertising costs of $11.0 million, $11.4 million and $11.1 million for the twelve months ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively are expensed as incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with an original maturity of three90 days or fewer monthsless to be cash and cash equivalents.
Inventories
The Company states inventories at the lower of cost or market. Cost, which includes material, labor, and factory overhead, is determined on a FIFO basis. We changed our method of accounting for inventory from the LIFO method to the FIFO method effective January 1, 2009 and applied this change in accounting principle retrospectively to all prior periods presented herein (see Note 2). We make adjustments to reduce the cost of inventory to its net realizable value, if required, at the business unit level for estimated excess, obsolescence or impaired balances. Factors influencing these adjustments include changes in market demand, product life cycle and engineering changes.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment upon the occurrence of events or changes in circumstances that indicate that the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable, as measured by comparing their net book value to the projected undiscounted future cash flows generated by their use. Impaired assets are recorded at their estimated fair value using a discounted cash flow analysis.
Goodwill and Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
The Company reviews the carrying value of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets annually on October 31st,31, or upon the occurrence of events or changes in circumstances that indicate that the carrying value of the goodwill or intangible assets may not be recoverable, in accordance with ASC 350. The Company evaluates the recoverability of each of these assets based on the estimated fair value of each of the eleventhirteen reporting units and indefinite-lived intangible asset. See Note 54 for a further discussion on goodwill and intangible assets.
Borrowing Expenses
Expenses, inclusive of commissions and professional fees, incurred in securing and issuing debt are amortized over the life of the related borrowing and are included in Interest expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Earnings per Common Share
Earnings per common share (“EPS”) is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of shares of common stock (basic) plus common stock equivalents and unvested shares (diluted) outstanding during the year. Common stock equivalents consist of stock options and deferred compensation units (“DCUs”) and have been included in the calculation of weighted average shares outstanding using the treasury stock method.
30
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
ASC 260 concludes that all outstanding unvested share-based payment awards that contain rights to nonforfeitable dividends participate in undistributed earnings with common shareholders. If awards are considered participating securities, the Company is required to apply the two-class method of computing basic and diluted earnings per share. The Company has determined that its outstanding unvested shares are participating securities. Accordingly, effective January 1, 2009, earnings per common share were computed using the two-class method prescribed by ASC 260. All previously reported earnings per common share data has been retrospectively adjusted to conform to the new computation method. Net income attributable to common shareholders was reduced by $1.4 million, $0.8 million and $0.9 million in 2010, 2009 and $0.8 million in December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively.
32
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Basic weighted average shares outstanding reconciles to diluted weighted average shares outstanding as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 79,716 | | | | 81,123 | | | | 80,666 | | | | 80,466 | | | | 79,716 | | | | 81,123 | |
| Dilutive effect of stock options, DCUs and unvested shares | | | 1,011 | | | | 1,197 | | | | 1,420 | | | | 1,517 | | | | 1,011 | | | | 1,197 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 80,727 | | | | 82,320 | | | | 82,086 | | | | 81,983 | | | | 80,727 | | | | 82,320 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Options to purchase approximately 0.2 million, 2.2 million 3.3 million and 1.73.3 million shares of common stock as of December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 2007,2008, respectively, were not included in the computation of diluted EPS because the exercise price was greater than the average market price of the Company’s common stock and, therefore, the effect of their inclusion would have been antidilutive.
Share-Based Compensation
The Company accounts for share-based payments in accordance with ASC 718. Accordingly, the Company expenses the fair value of awards made under its share-based compensation plans. That cost is recognized in the consolidated financial statements over the requisite service period of the grants. See Note 1613 for further discussion on share-based compensation.
Depreciation and Amortization
Property and equipment are stated at cost, with depreciation and amortization provided using the straight-line method over the following estimated useful lives:
| | | | | |
| Land improvements | | | 8 to 12 years | |
| Buildings and improvements | | | 8 to 30 years | |
Machinery and& equipment and engineering drawings | | | 3 to 12 years | |
| Office and transportation equipment | | | 3 to 10 years | |
Certain identifiable intangible assets are amortized over their estimated useful lives using the straight-line method. The estimated useful lives used in the computation of amortization of identifiable intangible assets are as follows:
| | | | | |
| Patents | | | 5 to 17 years | |
| Trade names | | | 3 to 20 years | |
| Customer relationships | | | 3 to 20 years | |
| Non-compete agreements | | | 2 to 5 years | |
| Unpatented technology and other | | | 54 to 20 years | |
31
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Research and Development Expenditures
Costs associated with research and development are expensed in the period incurred and are included in “Cost of sales” within the Consolidated Statements of Operations. Research and development expenses, which include costs associated with developing new products and major improvements to existing products were $31.8 million, $29.6 million and $29.5 million in 2010, 2009 and $28.1 million in 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively.
Foreign Currency Translation
The functional currency of substantially all operations outside the United States is the respective local currency. Accordingly, those foreign currency balance sheet accounts have been translated using the exchange rates in effect as of the balance sheet date. Income statement amounts have been translated using the average exchange rate for the year. The gains and losses resulting from changes in exchange rates from year to year have been reported
33
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
in “Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)” in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The effect of transaction gains and losses is reported within “Otherincome-net” income (expense)-net” on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Income Taxes
Income tax expense includes United States, state, local and international income taxes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the tax consequences of temporary differences between the financial reporting and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities.liabilities and for loss carryforwards. The tax rate used to determine the deferred tax assets and liabilities is the enacted tax rate for the year and manner in which the differences are expected to reverse. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount that will more likely than not be realized.
Concentration of Credit Risk
The Company is not dependent on a single customer, the largest of which accounted for less than 3%2% of net sales for all years presented.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2009,January 2010, the FASB issued ASU2009-05,2010-06, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (Topic 820) — Measuring Liabilities at Fair Value”. ASU” This Update provides amendments to Subtopic2009-05820-10 provides clarificationand related guidance within GAAP to require disclosure of the transfers in and out of Levels 1 and 2 and a schedule for Level 3 that separately identifies purchases, sales, issuances and settlements and requires more detailed disclosures regarding valuation techniques when a quoted price in an active market for an identical liability is not available in addition to treatmentand inputs. The new disclosures and clarifications of the existence of restrictions that prevent the transfer of a liability. ASU2009-05 also clarifies that both a quoted price in an active market for an identical liability at the measurement date and the quoted price for an identical liability when traded as an asset in an active market (when no adjustments to the quoted price of the asset are required) are Level 1 fair value measurements. This standard isexisting disclosures were effective for the first reporting period, including interim periods, beginning after issuance. Adoption of ASU2009-05 did not have a material effect onCompany’s fiscal year 2010, except for the consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows of the Company.
In July 2009, the ASC became the authoritative source of accounting principals to be applied to financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. In accordance with the ASC, citations to accounting literature in this report are to the relevant topic of the ASC or are presented in plain English. This standard is effective for financial statements issued for interimdisclosures about purchases, sales, issuances and annual periods ending after September 15, 2009. The Company adopted this standard on its effective date.
In May 2009, the FASB issued an update to ASC 855 “Subsequent Events.” This standard establishes general standards of accounting for and disclosure of events that occur after the balance sheet date, but before the financial statements are issued or available to be issued (“subsequent events”). This standard requires disclosure of the date through which the entity has evaluated subsequent events and the basis for that date. For public entities, this is the date the financial statements are issued. This standard does not apply to subsequent events or transactions that are within the scope of other GAAP and will not result in significant changessettlements in the subsequent events reported by the Company. This standard is effective for interim or annual periods ending after June 15, 2009. The Company adopted this standard on its effective date.
In April 2009, the FASB issued an update to ASC 820 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” and ASC 270 “Interim Reporting.” This standard requires disclosures about fair valueroll forward of financial instrumentsactivity in interim and annual financial statements. This standard is effective for periods ending after June 15, 2009. The Company adopted this standard on its effective date.
In December 2008, the FASB issued ASC 715 “Compensation-Retirement Benefits.” This standard provides additional guidance on employers’ disclosures about the plan assets of defined benefit pension or other postretirement plans. ASC 715 requires disclosures about how investment allocation decisions are made, the fair value of each major category of plan assets, valuation techniques used to developLevel 3 fair value measurements, of plan assets, the
34
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
impact of measurements on changes in plan assets when using significant unobservable inputs and significant concentrations of risk inwhich will be effective for the plan assets. TheseCompany’s fiscal year 2011. See Note 7 for disclosures are required for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2009. The Company adoptedassociated with the adoption of this standard on itsthat were effective date.
In June 2008, the FASB issued an update to ASC 260 “Earnings Per Share.” This standard addresses whether instruments granted in share-based payment transactions are participating securities prior to vesting and, therefore, need to be included in the allocation in computing earnings per share under the two-class method described in ASC 260. The FASB concluded that all outstanding unvested share-based payment awards that contain rights to nonforfeitable dividends participate in undistributed earnings with common shareholders. If awards are considered participating securities, the Company is required to apply the two-class method of computing basic and diluted earnings per share. The Company determined that its outstanding unvested shares are participating securities. Accordingly, effective January 1, 2009, earnings per common share are computed using the two-class method prescribed by ASC 260. All previously reported earnings per common share data has been retrospectively adjusted to conform to the new computation method (see EPS in Note 1).
In December 2007, the FASB issued an update to ASC 805 “Business Combinations.” The objective of the standard is to establish principles and requirements for how an acquirer in a business combination recognizes and measures in its financial statements, the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any controlling interest; recognizes and measures the goodwill acquired in the business combination or a gain from a bargain purchase; and determines what information to disclose to enable users of the financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. This standard is to be applied prospectively to business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after an entity’s fiscal year that begins after December 15, 2008. Upon adoption, ASC 805 did not have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or cash flows. However, depending on the nature of an acquisition or the quantity of acquisitions entered into after the adoption, ASC 805 may significantly impact the Company’s consolidated results of operations, financial position or cash flows when compared to acquisitions accounted for under prior U.S. GAAP and result in more earnings volatility and generally lower earnings due to, among other items, the expensing of deal costs and restructuring costs of acquired companies.2010.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In October 2009, the FASB issued ASUNo. 2009-13, “Revenue Recognition (Topic 605) — Multiple-Deliverable Revenue Arrangements.” ASUNo. 2009-13 addresses the accounting for multiple-deliverable arrangements to enable vendors to account for products or services (deliverables) separately rather than as a combined unit. This guidance establishes a selling price hierarchy for determining the selling price of a deliverable, which is based on: (a) vendor-specific objective evidence; (b) third-party evidence; or (c) estimates. This guidance also eliminates the residual method of allocation and requires that arrangement consideration be allocated at the inception of the arrangement to all deliverables using the relative selling price method. In addition, this guidance significantly expands required disclosures related to a vendor’s multiple-deliverable revenue arrangements. ASUNo. 2009-13 is effective prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or materially modified in fiscal years beginning on or after June 15, 2010 and early adoption is permitted. A company may elect, but will not be required,
32
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
to adopt the amendments in ASUNo. 2009-13 retrospectively for all prior periods. Management is currently evaluating the requirements of ASUNo. 2009-13 and has not yet determined the impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost, which includes material, labor, and factory overhead, is determined on a FIFO basis.
Prior to January 1, 2009, we valued certain inventories under the LIFO cost method. As of January 1, 2009, we changed our method of accounting for these inventories from the LIFO method to the FIFO method. As of
35
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
December 31, 2008, the inventories for which the LIFO method of accounting was applied represented approximately 85% of total net inventories. We believe that this change is to a preferable method which better reflects the current cost of inventory on our consolidated balance sheets. Additionally, this change conforms all of our worldwide inventories to a consistent inventory costing method and provides better comparability to our peers. We applied this change in accounting principle retrospectively to all prior periods presented herein in accordance with ASC 250 “Accounting Changes and Error Corrections.” As a result of this accounting change, our retained earnings as of December 31, 2006 decreased to $621.2 million using the FIFO method from $638.6 million as originally reported using the LIFO method. The following tables summarize the effect of the accounting change on our consolidated financial statements.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, 2009 | |
| | | Computed
| | | | | | | |
| | | Under Prior
| | | Effect of
| | | As Computed
| |
| | | Method | | | Change | | | Under FIFO | |
| | | (Thousands, except per share data) | |
| |
Statement of Operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of sales | | $ | 803,536 | | | $ | 3,739 | | | $ | 807,275 | |
| Income taxes | | | 56,662 | | | | (1,226 | ) | | | 55,436 | |
| Net income | | | 115,904 | | | | (2,513 | ) | | | 113,391 | |
| Earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic | | | 1.44 | | | | (0.03 | ) | | | 1.41 | |
| Diluted | | | 1.43 | | | | (0.03 | ) | | | 1.40 | |
Statement of Cash Flows: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | 115,904 | | | | (2,513 | ) | | | 113,391 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | | 2,307 | | | | (1,226 | ) | | | 1,081 | |
| Changes in inventories | | | 19,410 | | | | 3,739 | | | | 23,149 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 212,532 | | | | — | | | | 212,532 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, 2008 | |
| | | Computed
| | | | | | As Computed
| |
| | | Under Prior
| | | Effect of
| | | Under
| |
| | | Method | | | Change | | | FIFO | |
| | | (Thousands, except per share data) | |
| |
Statement of Operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of sales | | $ | 885,562 | | | $ | 6,476 | | | $ | 892,038 | |
| Income taxes | | | 67,343 | | | | (2,142 | ) | | | 65,201 | |
| Net income | | | 131,360 | | | | (4,334 | ) | | | 127,026 | |
| Earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic | | | 1.60 | | | | (0.05 | ) | | | 1.55 | |
| Diluted | | | 1.59 | | | | (0.06 | ) | | | 1.53 | |
Statement of Cash Flows: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | 131,360 | | | | (4,334 | ) | | | 127,026 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 601 | | | | 614 | | | | 1,215 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | | (8,196 | ) | | | (2,621 | ) | | | (10,817 | ) |
| Changes in inventories | | | (9,659 | ) | | | 5,270 | | | | (4,389 | ) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 224,131 | | | | (1,071 | ) | | | 223,060 | |
36
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, 2007 | |
| | | Computed
| | | | | | | |
| | | Under Prior
| | | Effect of
| | | As Computed
| |
| | | Method | | | Change | | | Under FIFO | |
| | | (Thousands, except per share data) | |
| |
Statement of Operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of sales | | $ | 790,182 | | | $ | 2,288 | | | $ | 792,470 | |
| Income taxes | | | 79,300 | | | | (843 | ) | | | 78,457 | |
| Net income | | | 155,145 | | | | (1,445 | ) | | | 153,700 | |
| Earnings per common share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic | | | 1.91 | | | | (0.02 | ) | | | 1.89 | |
| Diluted | | | 1.89 | | | | (0.02 | ) | | | 1.87 | |
Statement of Cash Flows: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | 155,145 | | | | (1,445 | ) | | | 153,700 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | | 2,449 | | | | (979 | ) | | | 1,470 | |
| Changes in inventories | | | (3,502 | ) | | | 3,311 | | | | (191 | ) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 198,107 | | | | 887 | | | | 198,994 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, 2009 | | | As of December 31, 2008 | |
| | | Computed
| | | | | | As Computed
| | | Computed
| | | | | | As Computed
| |
| | | Under
| | | Effect of
| | | Under
| | | Under Prior
| | | Effect of
| | | Under
| |
| Balance Sheet: | | Prior Method | | | Change | | | FIFO | | | Method | | | Change | | | FIFO | |
| |
| Inventories | | $ | 196,162 | | | $ | (36,699 | ) | | $ | 159,463 | | | $ | 214,160 | | | $ | (32,960 | ) | | $ | 181,200 | |
| Other current assets (prepaid taxes) | | | 25,876 | | | | 9,669 | | | | 35,545 | | | | 24,423 | | | | 8,443 | | | | 32,866 | |
| Accrued expenses (income tax payable) | | | 98,116 | | | | 614 | | | | 98,730 | | | | 116,572 | | | | 614 | | | | 117,186 | |
| Deferred income tax liability | | | 151,158 | | | | (2,352 | ) | | | 148,806 | | | | 144,336 | | | | (2,352 | ) | | | 141,984 | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | | 59,137 | | | | 262 | | | | 59,399 | | | | 39,873 | | | | 331 | | | | 40,204 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 922,600 | | | | (25,623 | ) | | | 896,977 | | | | 845,396 | | | | (23,110 | ) | | | 822,286 | |
Since mid-2008, we haveThe Company has recorded restructuring costsexpenses as a result of cost reduction efforts and facility closings. Accruals have been recorded based on these costs and primarily consist of employee termination benefits. We record accrualsexpenses for employee termination benefits based on the guidance of ASC 420, “Exit or Disposal Cost Obligations.” These expenses are included in Restructuring expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations while the related restructuring accruals are included in Accrued expenses in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
2009 Initiatives
During the year ended December 31, 2009,2010, the Company recorded an additional $11.1 million of pre-tax restructuring expenses totaling $12.1 millionrelated to our 2009 restructuring initiative for employee severance related to employee reductions across various functional areas as well as facility closures resulting from the Company’s cost savings initiatives. These initiatives included severance benefits for 478 employees. The Company is anticipating the employee reductions to be completed by mid 2010 with an expected additional total cost of $4.0 — $5.0 million in 2010, with severance payments expected to be fully paid by the end of 2011 using cash from operations.
37
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
2008 Initiatives
In 2008,2009, the Company recorded pre-tax restructuring expenses totaling $18.0$12.1 million for employee severance related to employee reductions across various functional areas as well as facility closures resulting from our cost savings initiatives. These initiativesthis same initiative. The 2009 initiative included severance benefits for 380approximately 700 employees. These employee reductions
Pre-tax restructuring expenses, by segment, for the year ended December 31, 2010, were completed by the end of 2008.as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Severance
| | | | | | | |
| | | Costs | | | Exit Costs | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | $ | 2,630 | | | $ | 320 | | | $ | 2,950 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | 3,511 | | | | 1,650 | | | | 5,161 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | 641 | | | | — | | | | 641 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | 589 | | | | — | | | | 589 | |
| Corporate/Other | | | 1,754 | | | | — | | | | 1,754 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total restructuring costs | | $ | 9,125 | | | $ | 1,970 | | | $ | 11,095 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pre-tax restructuring expenses, by segment, for the year ended December 31, 2009, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Severance
| | | | | | | |
| | | Costs | | | Exit Costs | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | $ | 2,694 | | | $ | 1,364 | | | $ | 4,058 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | 2,201 | | | | 1,303 | | | | 3,504 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | 1,155 | | | | 860 | | | | 2,015 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | 1,308 | | | | — | | | | 1,308 | |
| Corporate/Other | | | 488 | | | | 706 | | | | 1,194 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total restructuring costs | | $ | 7,846 | | | $ | 4,233 | | | $ | 12,079 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pre-tax restructuring expenses, by segment, for the year ended December 31, 2008, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Severance
| | | | | | | |
| | | Costs | | | Exit Costs | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | $ | 3,978 | | | $ | 1,177 | | | $ | 5,155 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | 3,226 | | | | 1,015 | | | | 4,241 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | 4,256 | | | | 1,311 | | | | 5,567 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | 723 | | | | — | | | | 723 | |
| Corporate/Other | | | 1,898 | | | | 411 | | | | 2,309 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total restructuring costs | | $ | 14,081 | | | $ | 3,914 | | | $ | 17,995 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Restructuring accruals of $6.9 million and $9.3 million at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively, are reflected in Accrued expenses in our Consolidated Balance Sheets as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008
| | | 2009
| | | | |
| | | Initiatives | | | Initiatives | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| BALANCE AT JANUARY 1, 2008 | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Restructuring costs/reversals | | | 17,995 | | | | — | | | | 17,995 | |
| Payments/utilization | | | (8,732 | ) | | | — | | | | (8,732 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2008 | | | 9,263 | | | | — | | | | 9,263 | |
| Restructuring costs/reversals | | | 828 | | | | 11,251 | | | | 12,079 | |
| Acquisition related | | | — | | | | 3,927 | | | | 3,927 | |
| Payments/utilization | | | (10,091 | ) | | | (8,300 | ) | | | (18,391 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2009 | | $ | — | | | $ | 6,878 | | | $ | 6,878 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
3833
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Restructuring accruals of $3.5 million and $6.9 million at December 31, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively, are reflected in Accrued expenses in our Consolidated Balance Sheets as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009
| | | 2008
| | | | |
| | | Initiatives | | | Initiatives | | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| BALANCE AT JANUARY 1, 2009 | | $ | — | | | $ | 9,263 | | | $ | 9,263 | |
| Restructuring costs | | | 11,251 | | | | 828 | | | | 12,079 | |
| Acquisition related | | | 3,927 | | | | — | | | | 3,927 | |
| Payments/utilization | | | (8,300 | ) | | | (10,091 | ) | | | (18,391 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2009 | | | 6,878 | | | | — | | | | 6,878 | |
| Restructuring costs | | | 11,095 | | | | — | | | | 11,095 | |
| Payments/utilization | | | (14,430 | ) | | | — | | | | (14,430 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2010 | | $ | 3,543 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,543 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
4.3. | Balance Sheet Components |
The components of certain balance sheet accounts at December 31, 20092010 and 20082009 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| RECEIVABLES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Customers | | $ | 185,926 | | | $ | 205,776 | | | $ | 212,899 | | | $ | 185,926 | |
| Other | | | 3,412 | | | | 5,093 | | | | 5,976 | | | | 3,412 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 189,338 | | | | 210,869 | | | | 218,875 | | | | 189,338 | |
| Less allowance for doubtful accounts | | | 6,160 | | | | 5,600 | | | | 5,322 | | | | 6,160 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total receivables — net | | $ | 183,178 | | | $ | 205,269 | | | $ | 213,553 | | | $ | 183,178 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| INVENTORIES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Raw materials and components parts | | $ | 101,314 | | | $ | 110,290 | | | $ | 141,316 | | | $ | 113,777 | |
| Work in process | | | 18,978 | | | | 22,483 | | | | 24,757 | | | | 20,669 | |
| Finished goods | | | 39,171 | | | | 48,427 | | | | 51,747 | | | | 43,626 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total inventories | | $ | 159,463 | | | $ | 181,200 | | |
| Total | | | | 217,820 | | | | 178,072 | |
| Less inventory reserves | | | | 21,274 | | | | 18,609 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Totalinventories-net | | | $ | 196,546 | | | $ | 159,463 | |
| | | | | | | |
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT | | | | | | | | | |
| Land and improvements | | | $ | 23,956 | | | $ | 19,776 | |
| Buildings and improvements | | | | 127,272 | | | | 125,735 | |
| Machinery and equipment | | | | 253,193 | | | | 235,219 | |
| Office and transportation equipment | | | | 95,141 | | | | 91,706 | |
| Engineering drawings | | | | 1,456 | | | | 1,869 | |
| Construction in progress | | | | 7,003 | | | | 9,360 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | | | | 508,021 | | | | 483,665 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | | 319,459 | | | | 305,382 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total property, plant and equipment — net | | | $ | 188,562 | | | $ | 178,283 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT | | | | | | | | |
| Land and improvements | | $ | 19,776 | | | $ | 19,918 | |
| Buildings and improvements | | | 125,735 | | | | 119,549 | |
| Machinery and equipment | | | 235,219 | | | | 246,052 | |
| Office and transportation equipment | | | 91,706 | | | | 92,555 | |
| Engineering drawings | | | 1,869 | | | | 2,510 | |
| Construction in progress | | | 9,360 | | | | 14,334 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 483,665 | | | | 494,918 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | 305,382 | | | | 308,635 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total property, plant and equipment — net | | $ | 178,283 | | | $ | 186,283 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| ACCRUED EXPENSES | | | | | | | | |
| Payroll and related items | | $ | 39,315 | | | $ | 45,162 | |
| Management incentive compensation | | | 12,157 | | | | 10,078 | |
| Income taxes payable | | | 3,757 | | | | 8,275 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | | 56 | | | | 1,471 | |
| Insurance | | | 4,375 | | | | 9,964 | |
| Warranty | | | 4,383 | | | | 3,751 | |
| Deferred revenue | | | 4,480 | | | | 2,600 | |
| Restructuring | | | 6,878 | | | | 9,263 | |
| Other | | | 23,329 | | | | 26,622 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total accrued expenses | | $ | 98,730 | | | $ | 117,186 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
3934
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| ACCRUED EXPENSES | | | | | | | | | |
| Payroll and related items | | | $ | 46,937 | | | $ | 39,315 | |
| Management incentive compensation | | | | 19,985 | | | | 12,157 | |
| Income taxes payable | | | | 6,126 | | | | 3,757 | |
| Deferred income taxes | | | | 723 | | | | 56 | |
| Insurance | | | | 5,544 | | | | 4,375 | |
| Warranty | | | | 3,831 | | | | 4,383 | |
| Deferred revenue | | | | 7,172 | | | | 4,480 | |
| Restructuring | | | | 3,543 | | | | 6,878 | |
| Interest rate exchange agreement | | | | 2,328 | | | | — | |
| Liability for uncertain tax positions | | | | 1,647 | | | | 313 | |
| Other | | | | 20,043 | | | | 23,016 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total accrued expenses | | | $ | 117,879 | | | $ | 98,730 | |
| | | | | | | |
| OTHER NONCURRENT LIABILITIES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension and retiree medical obligations | | $ | 67,426 | | | $ | 76,488 | | | $ | 74,559 | | | $ | 67,426 | |
| Liability for uncertain tax positions | | | 6,398 | | | | 4,758 | | | | 5,912 | | | | 6,398 | |
| Derivative financial instruments | | | 10,497 | | | | 10,098 | | |
| Interest rate exchange agreement | | | | — | | | | 10,497 | |
| Deferred revenue | | | 5,353 | | | | 479 | | | | 4,225 | | | | 5,353 | |
| Other | | | 10,137 | | | | 5,197 | | | | 10,687 | | | | 10,137 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total other noncurrent liabilities | | $ | 99,811 | | | $ | 97,020 | | | $ | 95,383 | | | $ | 99,811 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
5.4. | Goodwill and Intangible Assets |
The changes in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, by business segment, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fluid &
| | Health &
| | | | Fire & Safety/
| | | | | Fluid &
| | Health &
| | | | Fire & Safety/
| | | |
| | | Metering
| | Science
| | Dispensing
| | Diversified
| | | | | Metering
| | Science
| | Dispensing
| | Diversified
| | | |
| | | Technologies | | Technologies | | Equipment | | Products | | Total | | | Technologies | | Technologies | | Equipment | | Products | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Goodwill | | $ | 341,521 | | | $ | 353,060 | | | $ | 137,390 | | | $ | 151,707 | | | $ | 983,678 | | | $ | 531,046 | | | $ | 391,654 | | | $ | 133,560 | | | $ | 147,552 | | | $ | 1,203,812 | |
| Accumulated impairment losses | | | (6,659 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (6,659 | ) | | | (6,659 | ) | | | — | | | | (30,090 | ) | | | — | | | | (36,749 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT JANUARY 1, 2008 | | | 334,862 | | | | 353,060 | | | | 137,390 | | | | 151,707 | | | | 977,019 | | |
| Acquisitions (Note 14) | | | 202,549 | | | | 39,551 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 242,100 | | |
| Foreign currency translation | | | (11,841 | ) | | | (35 | ) | | | (3,830 | ) | | | (4,155 | ) | | | (19,861 | ) | |
| Purchase price adjustments | | | (1,183 | ) | | | (922 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (2,105 | ) | |
| Goodwill impairment | | | — | | | | — | | | | (30,090 | ) | | | — | | | | (30,090 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2008 | | | 524,387 | | | | 391,654 | | | | 103,470 | | | | 147,552 | | | | 1,167,063 | | |
| BALANCE AT JANUARY 1, 2009 | | | | 524,387 | | | | 391,654 | | | | 103,470 | | | | 147,552 | | | | 1,167,063 | |
| Foreign currency translation | | | 7,164 | | | | 298 | | | | 1,503 | | | | 1,562 | | | | 10,527 | | | | 7,164 | | | | 298 | | | | 1,503 | | | | 1,562 | | | | 10,527 | |
| Purchase price adjustments | | | 2,428 | | | | 427 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,855 | | | | 2,428 | | | | 427 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,855 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2009 | | $ | 533,979 | | | $ | 392,379 | | | $ | 104,973 | | | $ | 149,114 | | | $ | 1,180,445 | | | | 533,979 | | | | 392,379 | | | | 104,973 | | | | 149,114 | | | | 1,180,445 | |
| Acquisitions (Note 12) | | | | 15,828 | | | | 29,653 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 45,481 | |
| Foreign currency translation | | | | (7,890 | ) | | | (768 | ) | | | (6,193 | ) | | | (4,074 | ) | | | (18,925 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2010 | | | $ | 541,917 | | | $ | 421,264 | | | $ | 98,780 | | | $ | 145,040 | | | $ | 1,207,001 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
ASC 350 requires that goodwill be tested for impairment at the reporting unit level on an annual basis and between annual tests if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair
35
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
value of the reporting unit below its carrying value. Goodwill represents the purchase price in excess of the net amount assigned to assets acquired and liabilities assumed.
Goodwill and other acquired intangible assets with indefinite lives were tested for impairment as of October 31, 2009,2010, the Company’s annual impairment assessment date. In 2009,2010, there were no triggering events or change in circumstances that would have required a review other than as of our annual test date. The Company concluded that the fair value of each of the reporting units and indefinite-lived intangible assets was in excess of the carrying value as of October 31, 2009. However, a 10% decrease in the fair value of the Banjo or the Water reporting units within the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment could potentially result in a goodwill impairment charge at these reporting units. The total goodwill balance for these two reporting units as of October 31, 2009 was $288.7 million.
In 2008 in accordance with ASC 350, the Company concluded that Fluid Management, a reporting unit within the Company’s Dispensing Equipment segment, experienced a downturn in capital spending by its customer base and the loss of market share which required the Company to perform an interim period goodwill impairment test.
40
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The Company performed the first step of the two-step impairment test and compared the fair value of the reporting unit to its carrying value. Consistent with the Company’s approach in its annual impairment testing, in assessing the fair value of the Fluid Management reporting unit, the Company considered both the market approach and income approach. In 2008 under the market approach, the fair value of the reporting unit is based on comparing the reporting unit to comparable publicly traded companies or comparable entities which have been recently acquired in arms-length transactions. Under the income approach, the fair value of the reporting unit is based on the present value of estimated future cash flows. The income approach is dependent on a number of significant management assumptions including estimates of operating results, capital expenditures, other operating costs and discount rates. Due to current conditions within the market and the specific reporting unit, weighting was equally attributed to both the market and income approaches (50% each) in arriving at the fair value of the reporting unit. The Company determined that the fair value of the Fluid Management reporting unit was less than the carrying value of the net assets of the reporting unit, and thus the Company performed step two of the impairment test.
In step two of the impairment test, the Company determined the implied fair value of the goodwill and compared it to the carrying value of the goodwill. The Company allocated the current fair value of the Fluid Management reporting unit to all of its assets and liabilities as if the reporting unit had presently been acquired in a business combination. The excess of the fair value of the reporting unit over the fair value of its identifiable assets and liabilities is the implied fair value of goodwill. The Company’s step two analysis resulted in an implied fair value of goodwill of $21.2 million, and as a result, the Company recognized an impairment charge of $30.1 million in the third quarter of 2008.2010.
The following table provides the gross carrying value and accumulated amortization for each major class of intangible asset at December 31, 20092010 and 2008:2009:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | At December 31, 2009 | | At December 31, 2008 | | | | | At December 31, 2010 | | | | At December 31, 2009 | |
| | | Gross
| | | | | | Weighted
| | Gross
| | | | | | | Gross
| | | | | | Weighted
| | Gross
| | | | | |
| | | Carrying
| | Accumulated
| | | | Average
| | Carrying
| | Accumulated
| | | | | Carrying
| | Accumulated
| | | | Average
| | Carrying
| | Accumulated
| | | |
| | | Amount | | Amortization | | Net | | Life | | Amount | | Amortization | | Net | | | Amount | | Amortization | | Net | | Life | | Amount | | Amortization | | Net | |
| |
| Amortizable intangible assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Patents | | $ | 9,914 | | | $ | (4,289 | ) | | $ | 5,625 | | | | 11 | | | $ | 11,795 | | | $ | (5,550 | ) | | $ | 6,245 | | | $ | 9,906 | | | $ | (5,052 | ) | | $ | 4,854 | | | | 11 | | | $ | 9,914 | | | $ | (4,289 | ) | | $ | 5,625 | |
| Trade names | | | 63,589 | | | | (10,144 | ) | | | 53,445 | | | | 15 | | | | 62,805 | | | | (6,310 | ) | | | 56,495 | | | | 69,043 | | | | (13,769 | ) | | | 55,274 | | | | 15 | | | | 63,589 | | | | (10,144 | ) | | | 53,445 | |
| Customer relationships | | | 157,890 | | | | (32,422 | ) | | | 125,468 | | | | 12 | | | | 156,216 | | | | (16,601 | ) | | | 139,615 | | | | 169,065 | | | | (47,686 | ) | | | 121,379 | | | | 11 | | | | 157,890 | | | | (32,422 | ) | | | 125,468 | |
| Non-compete agreements | | | 4,268 | | | | (3,356 | ) | | | 912 | | | | 4 | | | | 4,569 | | | | (2,989 | ) | | | 1,580 | | | | 4,087 | | | | (3,501 | ) | | | 586 | | | | 4 | | | | 4,268 | | | | (3,356 | ) | | | 912 | |
| Unpatented technology | | | 36,047 | | | | (6,240 | ) | | | 29,807 | | | | 14 | | | | 35,527 | | | | (2,939 | ) | | | 32,588 | | | | 43,206 | | | | (9,407 | ) | | | 33,799 | | | | 14 | | | | 36,047 | | | | (6,240 | ) | | | 29,807 | |
| Other | | | 6,236 | | | | (2,239 | ) | | | 3,997 | | | | 10 | | | | 6,282 | | | | (1,679 | ) | | | 4,603 | | | | 5,957 | | | | (2,557 | ) | | | 3,400 | | | | 10 | | | | 6,236 | | | | (2,239 | ) | | | 3,997 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total amortizable intangible assets | | | 277,944 | | | | (58,690 | ) | | | 219,254 | | | | | | | | 277,194 | | | | (36,068 | ) | | | 241,126 | | | | 301,264 | | | | (81,972 | ) | | | 219,292 | | | | | | | | 277,944 | | | | (58,690 | ) | | | 219,254 | |
| Banjo trade name | | | 62,100 | | | | — | | | | 62,100 | | | | | | | | 62,100 | | | | — | | | | 62,100 | | | | 62,100 | | | | — | | | | 62,100 | | | | | | | | 62,100 | | | | — | | | | 62,100 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 340,044 | | | $ | (58,690 | ) | | $ | 281,354 | | | | | | | $ | 339,294 | | | $ | (36,068 | ) | | $ | 303,226 | | | $ | 363,364 | | | $ | (81,972 | ) | | $ | 281,392 | | | | | | | $ | 340,044 | | | $ | (58,690 | ) | | $ | 281,354 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The Banjo trade name is an indefinite lived intangible asset which is tested for impairment on an annual basis.basis on October 31. Amortization of intangible assets was $25.7 million, $24.5 million and $17.6 million in 2010, 2009 and $9.7 million in 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively. Amortization expense for each of the next five years is estimated to be approximately $25.0$27.0 million annually.
41
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Borrowings at December 31, 20092010 and 20082009 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Credit facility | | $ | 298,732 | | | $ | 448,763 | | |
| Term loan | | | 95,000 | | | | 100,000 | | |
| Credit Facility | | | $ | 27,842 | | | $ | 298,732 | |
| Term Loan | | | | 90,000 | | | | 95,000 | |
| 2.58% Senior Euro Notes | | | | 107,341 | | | | — | |
| 4.5% Senior Notes | | | | 298,427 | | | | — | |
| Other borrowings | | | 6,368 | | | | 5,237 | | | | 4,285 | | | | 6,368 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total borrowings | | | 400,100 | | | | 554,000 | | | | 527,895 | | | | 400,100 | |
| Less current portion | | | 8,346 | | | | 5,856 | | | | 119,445 | | | | 8,346 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total long-term borrowings | | $ | 391,754 | | | $ | 548,144 | | | $ | 408,450 | | | $ | 391,754 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The Company maintains a $600.0 million unsecured domestic, multi-currency bank revolving credit facility (“Credit Facility”), which expires on December 21, 2011. In 2008, the Credit Facility was amended to allow the
36
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Company to designate certain foreign subsidiaries as designated borrowers. Upon approval from the lenders, the designated borrowers will bewere allowed to receive loans under the Credit Facility. A designated borrower sublimit was established as the lesser of the aggregate commitments or $100.0 million. As of the amendment date, Fluid Management Europe B.V., (FME)(“FME”) was approved by the lenders as a designated borrower. FME’sOn March 16, 2010, IDEX UK Ltd. (“IDEX UK”) was also approved by the lenders as a designated borrower which allowed them to receive loans under the Credit Facility. FME had no borrowings under the Credit Facility as of December 31, 2010, while $48.7 million was outstanding as of December 31,2009. This balance was repaid with proceeds from the €81.0 million 2.58% Senior Euro Notes. IDEX UK’s borrowings included within short term borrowings under the Credit Facility at year endDecember 31, 2010 were approximately $48.7£18.0 million (Euro 34($27.8 million). As the FMEIDEX UK’s borrowings under the Credit Facility are EuroBritish Pound denominated and the cash flows that will be used to make payments of principal and interest are predominately denominatedgenerated in Euros,British Pound, the Company does not anticipate any significant foreign exchange gains or losses in servicing this debt.
At December 31, 20092010 there was $298.7$27.8 million outstanding under the Credit Facility and outstanding letters of credit totaled approximately $7.1 million.Facility. The net available borrowing under the Credit Facility as of December 31, 2009,2010, was approximately $294.2$572.2 million. Interest is payable quarterly on the outstanding borrowings at the bank agent’s reference rate. Interest on borrowings, based on LIBOR plus an applicable margin, is payable on the maturity date of the borrowing, or quarterly from the effective date for borrowings exceeding three months. The applicable margin is based on the Company’s senior, unsecured, long-term debt rating and can range from 24 basis points to 50 basis points. Based on the Company’s BBBcredit rating at December 31, 2009,2010, the applicable margin was 40 basis points. An annual Credit Facility fee, also based on the Company’s credit rating, is currently 10 basis points and is payable quarterly.
At December 31, 2009 the Company had one interest rate exchange agreement related to the Credit Facility. The interest rate exchange agreement, expiring in January 2011, effectively converted $250.0 million of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt at an interest rate of 3.25%. The fixed rate noted above is comprised of the fixed rate on the interest rate exchange agreement and the Company’s current margin of 40 basis points on the Credit Facility.
On February 15, 2008, the Company retired its $150.0 million senior notes using proceeds available under the Company’s Credit Facility.
On April 18, 2008, the Company completed a $100.0 million unsecured senior bank term loan agreement (“Term Loan”), with covenants consistent with the existing Credit Facility and a maturity on December 21, 2011. At December 31, 2009,2010, there was $95.0$90.0 million outstanding under the Term Loan with $5.0 million included within short term borrowings. Interest under the Term Loan is based on the bank agent’s reference rate or LIBOR plus an applicable margin and is payable at the end of the selected interest period, but at least quarterly. The applicable margin is based on the Company’s senior, unsecured, long-term debt rating and can range from 45 to 100 basis points. Based on the Company’s current debt rating, the applicable margin is 80 basis points. The Term Loan requires repaymentsa repayment of $5.0 million and $7.5 million in April of 2010 and 2011, respectively, with the remaining
42
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
balance due on December 21, 2011. The Company used the proceeds from the Term Loan to pay down existing debt outstanding under the Credit Facility.
The Company currently maintains an interest rate exchange agreement related to the Term Loan thatwhich expires in December 2011. WithThis interest rate exchange agreement has a current notional amount of $95.0$90.0 million, the agreement effectively converted $100.0 million of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt at an interest rate of 4.00%. The fixed rate is comprised of the fixed rate on the interest rate exchange agreement and the Company’s current margin of 80 basis points on the Term Loan.
On June 9, 2010, the Company completed a private placement of €81.0 million ($96.8 million) aggregate principal amount of 2.58% Series 2010 Senior Euro Notes due June 9, 2015 (“2.58% Senior Euro Notes”) pursuant to a Master Note Purchase Agreement, dated June 9, 2010 (the “Purchase Agreement”). The Purchase Agreement provides for the issuance of additional series of notes in the future. The 2.58% Senior Euro Notes bear interest at a rate of 2.58% per annum and will mature on June 9, 2015. The 2.58% Senior Euro Notes are unsecured obligations of the Company and rank pari passu in right of payment with all of the Company’s other senior debt. The Company may at any time prepay all or any portion of the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes; provided that such portion is greater than 5% of the aggregate principal amount of Notes then outstanding under the Purchase Agreement. In the event of a prepayment, the Company will pay an amount equal to par plus accrued interest plus a make-whole premium. The Purchase Agreement contains certain covenants that restrict the Company’s ability to, among other things, transfer or sell assets, create liens and engage in certain mergers or consolidations. In addition, the Company must comply with a leverage ratio and interest coverage ratio as set forth in the Purchase Agreement. The Purchase Agreement provides for customary events of default. In the case of an event of default arising from specified events of bankruptcy or insolvency, all outstanding 2.58% Senior Euro Notes will become due and payable immediately without further action or notice. In the case of payment events of defaults, any holder of the 2.58% Senior Euro
37
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Notes affected thereby may declare all the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes held by it due and payable immediately. In the case of any other event of default, a majority of the holders of the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes may declare all the 2.58% Senior Euro Notes to be due and payable immediately. The Company used a portion of the proceeds from the private placement to pay down existing debt outstanding under the Credit Facility that had previously been denominated in Euros, with the remainder being available for ongoing business activities.
On December 6, 2010, the Company completed a public offering of $300.0 million 4.5% Notes due December 15, 2020 (“4.5% Senior Notes”). The net proceeds from the offering of approximately $295.7 million, after deducting the $1.6 million issuance discount, the $1.9 million underwriting commission and estimated offering expenses of approximately $0.8 million, was used to repay $250.0 million of outstanding indebtedness under the Credit Facility. The balance of the net proceeds will be used for general corporate purposes. The 4.5% Senior Notes will bear interest at a rate of 4.5% per annum, which is payable semi-annually in arrears each June 15 and December 15, beginning June 15, 2011. The Company may redeem all or part of the 4.5% Senior Notes at any time prior to maturity at the redemption prices set forth in the Note Indenture (“Indenture”) governing the 4.5% Senior Notes. The Company may issue additional debt from time to time pursuant to the Indenture. The Indenture and 4.5% Senior Notes contain covenants that limit the Company’s ability to, among other things, incur certain liens securing indebtedness, engage in certain sale-leaseback transactions, and enter into certain consolidations, mergers, conveyances, transfers or leases of all or substantially all the Company’s assets. The terms of the 4.5% Senior Notes also require the Company to make an offer to repurchase 4.5% Senior Notes upon a change of control triggering event (as defined in the Indenture) at a price equal to 101% of their principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest if any.
On April 15, 2010, the Company entered into a forward starting interest rate contract with a notional amount of $300.0 million with a settlement date in December 2010. This contract was entered into in anticipation of the issuance of the $300.0 million 4.5% Senior Notes and was designed to lock in the market interest rate as of April 15, 2010. The Company settled this interest rate contract in December 2010, resulting in a $31.0 million payment. The $31.0 million will be amortized into interest expense over the 10 year term of the 4.5% Senior Notes yielding an effective interest rate of 5.8%.
Other borrowings of $6.4$4.3 million at December 31, 20092010 was comprised of capital leases as well as debt at international locations maintained for working capital purposes. Interest is payable on the outstanding debt balances at the international locations at rates ranging from 0.8%1.0% to 4.0%7.28% per annum.
There are two key financial covenants that the Company is required to maintain in connection with the Credit Facility, Term Loan, and Term Loan. As defined in2.58% Senior Euro Notes. There are no financial covenants relating to the agreement, the4.5% Senior Notes. The most restrictive financial covenants under these debt instruments require a minimum interest coverage ratio (operating cash flow to interest) isof 3.0 to 1 and thea maximum leverage ratio (outstanding debt to operating cash flow) isof 3.25 to 1. At December 31, 2009,2010, the Company was in compliance with both of these financial covenants.
Total borrowings at December 31, 20092010 have scheduled maturities as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| 2010 | | $ | 8,346 | | |
| 2011 | | | 389,083 | | | $ | 119,445 | |
| 2012 | | | 330 | | | | 472 | |
| 2013 | | | 309 | | | | 338 | |
| 2014 | | | 320 | | | | 295 | |
| 2015 | | | | 107,647 | |
| Thereafter | | | 1,712 | | | | 299,698 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total borrowings | | $ | 400,100 | | | $ | 527,895 | |
| | | | | | | |
38
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| |
7.6. | Derivative Instruments |
The Company enters into cash flow hedges to reduce the exposure to variability in certain expected future cash flows. The type of cash flow hedges the Company enters into includes foreign currency contracts and interest rate exchange agreements that effectively convert a portion of floating-rate debt to fixed-rate debt and are designed to reduce the impact of interest rate changes on future interest expense.
The effective portion of gains or losses on interest rate exchange agreements is reported in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders’ equity and reclassified into net income in the same period or periods in which the hedged transaction affects net income. The remaining gain or loss in excess of the cumulative change in the present value of future cash flows or the hedged item, if any, is recognized into net income during the period of change.
Fair values relating to derivative financial instruments reflect the estimated amounts that the Company would receive or pay to sell or buy the contracts based on quoted market prices of comparable contracts at each balance sheet date.
At December 31, 2009,2010, the Company had twoone interest rate exchange agreements.agreement. The first interest rate exchange agreement, expiring in January 2011, effectively converted $250.0 million of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt at an interest rate of 3.25%. The second interest rate exchange agreement, expiring December 2011, with a current notional amount of $95.0$90.0 million, effectively converted $100.0 million of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt at an interest rate of 4.00%. The fixed rate is comprisedconsists of the fixed rate on the interest rate exchange agreements and the Company’s current margin of 40 basis points for the Credit Facility and 80 basis points on the Term Loan.
Expiring in January 2011, the interest rate exchange agreement related to the Credit Facility was settled in December 2010. The interest rate exchange agreement effectively converted $250.0 million of floating-rate debt into fixed-rate debt at an interest rate of 3.25%.
Based on interest rates at December 31, 2010, approximately $5.9 million of the amount included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders’ equity at December 31, 2010 will be recognized to net income over the next 12 months as the underlying hedged transactions are realized. The $5.9 million is comprised of $2.3 million from the interest rate exchange agreement and $3.6 million from the forward starting interest rate contract.
At December 31, 2010, the Company had foreign currency exchange contracts with an aggregate notional amount of $2.5 million to manage its exposure to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. The change in fair market value of these contracts for the twelve months ended December 31, 2010 was immaterial.
The following table sets forth the fair value amounts of derivative instruments held by the Company as of December 31, 2010 and 2009:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fair Value-Assets (Liabilities) | | | |
| | | December 31,
| | | December 31,
| | | Balance Sheet
|
| | | 2010 | | | 2009 | | | Caption |
| | | (In thousands) | | | |
| |
| Interest rate exchange agreement | | $ | (2,328 | ) | | $ | — | | | Accrued expenses |
| Interest rate exchange agreement | | | — | | | | (10,497 | ) | | Other noncurrent liabilities |
| Foreign exchange contracts | | | 176 | | | | — | | | Other current assets |
4339
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Based on interest rates at December 31, 2009, approximately $9.3 million of the amount included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders’ equity at December 31, 2009 will be recognized to net income over the next 12 months as the underlying hedged transactions are realized.
The following table set’s forth the fair value amounts of derivative instruments held by the Company as of December 31, 2009 and 2008:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fair Value-Liabilities | | | |
| | | December 31,
| | | December 31,
| | | Balance Sheet
|
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | Caption |
| | | (In thousands) | | | |
| |
| Interest rate contracts | | $ | 10,497 | | | $ | 10,098 | | | Other noncurrent liabilities |
| Foreign exchange contracts | | | — | | | | 272 | | | Accrued expenses |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 10,497 | | | $ | 10,370 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The following table summarizes the gain (loss) recognized and the amounts and location of income (expense) and gain (loss) reclassified into income for interest rate contracts and foreign currency contracts for the year ended December 31, 20092010 and 2008:2009:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Gain (Loss) Recognized in
| | Income (Expense)
| | | | Gain (Loss) Recognized in
| | (Expense)
| | |
| | | Other Comprehensive
| | and Gain (Loss)
| | | | Other Comprehensive
| | and Gain (Loss)
| | |
| | | Income (Loss) | | Reclassified into Income | | Income
| | Income | | Reclassified into Income | | Income
|
| | | Year Ended December 31, | | Statement
| | Twelve Months Ended December 31, | | Statement
|
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2009 | | 2008 | | Caption | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2009 | | Caption |
| | | (In thousands) | | | | | | (In thousands) | | | | |
| |
| Interest rate contracts | | $ | (8,509 | ) | | $ | (9,743 | ) | | $ | (8,111 | ) | | $ | 348 | | | Interest expense | |
| Interest rate agreements | | | $ | (31,792 | ) | | $ | (8,509 | ) | | $ | (8,805 | ) | | $ | (8,111 | ) | | Interest expense |
| Interest rate agreements | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (440 | ) | | | — | | | Miscellaneous loss |
| Foreign exchange contracts | | | 1,187 | | | | (307 | ) | | | 899 | | | | (19 | ) | | Sales | | | 126 | | | | 1,187 | | | | 126 | | | | 899 | | | Sales |
| |
8.7. | Fair Value Measurements |
ASC 820“Fair “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures”defines fair value, provides guidance for measuring fair value and requires certain disclosures. This standard discusses valuation techniques, such as the market approach (comparable market prices), the income approach (present value of future income or cash flow), and the cost approach (cost to replace the service capacity of an asset or replacement cost). The standard utilizes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three broad levels. The following is a brief description of those three levels:
| | |
| | • | Level 1: Observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| |
| | • | Level 2: Inputs, other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. These include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active. |
| |
| | • | Level 3: Unobservable inputs that reflect the reporting entity’s own assumptions. |
The following table summarizes the basis used to measure the Company’s financial assets and liabilities(liabilities) at fair value on a recurring basis in the balance sheet at December 31, 20092010 and 2008:2009:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Basis of Fair Value Measurements |
| | | Balance at
| | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
| | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| | | (In thousands) |
| |
| Money market investment | | $ | 9,186 | | | $ | 9,186 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Interest rate exchange agreement derivative financial instruments | | $ | 10,497 | | | | — | | | $ | 10,497 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Basis of Fair Value Measurements | |
| | | Balance at
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2010 | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Money market investments | | $ | 96,730 | | | $ | 96,730 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Interest rate agreements | | $ | (2,328 | ) | | | — | | | $ | (2,328 | ) | | | — | |
| Foreign currency contracts | | $ | 176 | | | | — | | | $ | 176 | | | | — | |
44
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Money market investment | | $ | 9,186 | | | $ | 9,186 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Interest rate agreements | | $ | (10,497 | ) | | | — | | | $ | (10,497 | ) | | | — | |
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at
| | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
| | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| | | (In thousands) |
| |
| Interest rate exchange agreement derivative financial instruments | | $ | 10,098 | | | | — | | | $ | 10,098 | | | | — | |
| Foreign currency contracts | | $ | 272 | | | | — | | | $ | 272 | | | | — | |
There were no transfers of assets or liabilities between Level 1 and Level 2 in 2010 or 2009.
In determining the fair value of the Company’s interest rate exchange agreement derivatives, the Company uses a present value of expected cash flows based on market observable interest rate yield curves commensurate
40
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
with the term of each instrument and the credit default swap market to reflect the credit risk of either the Company or the counterparty.
The carrying value of our cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued expenses approximates their fair values because of the short term nature of these instruments. At December 31, 2009,2010, the fair value of our Credit Facility, and Term Loan, 2.58% Senior Euro Notes and 4.5% Senior Notes, based on thequoted market prices and current market rates for debt with similar credit risk and maturity, was approximately $375.6$515.5 million compared to the carrying value of $393.7$523.6 million.
| |
9.8. | Commitments and Contingencies |
At December 31, 2009, total future minimum rental payments under noncancelable operatingThe Company leases primarily forcertain office facilities, warehouses and data processing equipment were $33.2 million. The future minimum rental commitments for each of the next five years and thereafter are as follows: 2010 — $8.6 million; 2011 — $5.9 million; 2012 — $4.5 million; 2013 — $3.1 million; 2014 — $2.2 million; thereafter — $8.9 million.
under operating leases. Rental expense from continuing operations totaled $13.9 million, $12.2 million $12.6 million and $11.6$12.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively.
The aggregate future minimum lease payments for operating and 2007, respectively.capital leases as of December 31, 2010 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Operating | | | Capital | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| 2011 | | $ | 9,679 | | | $ | 793 | |
| 2012 | | | 7,371 | | | | 567 | |
| 2013 | | | 5,297 | | | | 414 | |
| 2014 | | | 3,339 | | | | 359 | |
| 2015 | | | 2,718 | | | | 359 | |
| 2016 and thereafter | | | 6,917 | | | | 1,316 | |
Warranty costs are provided for at time of sale. The warranty provision is based on historical costs and adjusted for specific known claims. A roll forward of the warranty reserve is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Beginning balance January 1 | | $ | 4,383 | | | $ | 3,751 | |
| Provision for warranties | | | 4,331 | | | | 4,507 | |
| Claim settlements | | | (4,665 | ) | | | (3,918 | ) |
| Other adjustments | | | (218 | ) | | | 43 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Ending balance December 31 | | $ | 3,831 | | | $ | 4,383 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
41
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The Company is a party to various legal proceedings involving employment, contractual, product liability and other matters,arising in the ordinary course of business, none of which is expected to have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, results of operations financial condition, or cash flows.flow.
| |
10.9. | Common and Preferred Stock |
On April 21, 2008, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $125.0 million of its outstanding common shares either in the open market or through private transactions. In 2008, the Company purchased a total of 2.3 million shares at a cost of approximately $50.0 million. No shares were purchased in 2010 and 2009.
At December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, the Company had 150 million shares of authorized common stock, with a par value of $.01 per share and 5 million shares of authorized preferred stock with a par value of $.01 per share. No preferred stock was issued as of December 31, 20092010 and 2008.2009.
Pretax income for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 20072008 was taxed in the following jurisdictions:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Domestic | | $ | 114,389 | | | $ | 120,962 | | | $ | 162,880 | | | $ | 161,573 | | | $ | 114,389 | | | $ | 120,962 | |
| Foreign | | | 54,438 | | | | 71,265 | | | | 69,996 | | | | 70,301 | | | | 54,438 | | | | 71,265 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 168,827 | | | $ | 192,227 | | | $ | 232,876 | | | $ | 231,874 | | | $ | 168,827 | | | $ | 192,227 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The provision (benefit) for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008, was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2010 | | | 2009 | | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Current | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | $ | 59,384 | | | $ | 34,921 | | | $ | 47,594 | |
| State and local | | | 4,548 | | | | 2,704 | | | | 6,542 | |
| Foreign | | | 18,178 | | | | 16,730 | | | | 21,882 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current | | | 82,110 | | | | 54,355 | | | | 76,018 | |
| Deferred | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | | (6,550 | ) | | | 1,658 | | | | (10,099 | ) |
| State and local | | | (293 | ) | | | 110 | | | | (503 | ) |
| Foreign | | | (493 | ) | | | (687 | ) | | | (215 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total deferred | | | (7,336 | ) | | | 1,081 | | | | (10,817 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total provision for income taxes | | $ | 74,774 | | | $ | 55,436 | | | $ | 65,201 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
4542
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The provision (benefit) for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007, was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Current | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | $ | 34,921 | | | $ | 47,594 | | | $ | 50,045 | |
| State and local | | | 2,704 | | | | 6,542 | | | | 5,522 | |
| Foreign | | | 16,730 | | | | 21,882 | | | | 21,420 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current | | | 54,355 | | | | 76,018 | | | | 76,987 | |
| Deferred | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | | 1,658 | | | | (10,099 | ) | | | 4,198 | |
| State and local | | | 110 | | | | (503 | ) | | | 400 | |
| Foreign | | | (687 | ) | | | (215 | ) | | | (3,128 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total deferred | | | 1,081 | | | | (10,817 | ) | | | 1,470 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total provision for income taxes | | $ | 55,436 | | | $ | 65,201 | | | $ | 78,457 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax assets (liabilities) related to the following at December 31, 20092010 and 20082009 were:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Employee and retiree benefit plans | | $ | 24,075 | | | $ | 29,197 | | | $ | 17,764 | | | $ | 24,075 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | (167,345 | ) | | | (170,652 | ) | | | (179,889 | ) | | | (167,345 | ) |
| Inventories | | | 7,240 | | | | 5,596 | | | | 6,934 | | | | 7,240 | |
| Allowances and accruals | | | 7,589 | | | | 7,434 | | | | 16,690 | | | | 7,589 | |
| Interest rate exchange agreement | | | | 11,995 | | | | 3,783 | |
| Other | | | (2,633 | ) | | | 4,076 | | | | 1,617 | | | | (6,416 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | (131,074 | ) | | $ | (124,349 | ) | | $ | (124,889 | ) | | $ | (131,074 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The deferred tax assets and liabilities recognized in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 20092010 and 20082009 were:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Deferred tax asset — other current assets | | $ | 17,615 | | | $ | 11,469 | | | $ | 23,829 | | | $ | 17,615 | |
| Deferred tax asset — other noncurrent assets | | | 173 | | | | 7,637 | | | | 539 | | | | 173 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total deferred tax assets | | | 17,788 | | | | 19,106 | | | | 24,368 | | | | 17,788 | |
| Deferred tax liability — accrued expenses | | | (56 | ) | | | (1,471 | ) | | | (723 | ) | | | (56 | ) |
| Noncurrent deferred tax liability — deferred income taxes | | | (148,806 | ) | | | (141,984 | ) | | | (148,534 | ) | | | (148,806 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | | | (148,862 | ) | | | (143,455 | ) | | | (149,257 | ) | | | (148,862 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net deferred tax liabilities | | $ | (131,074 | ) | | $ | (124,349 | ) | | $ | (124,889 | ) | | $ | (131,074 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
46
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The provision for income taxes differs from the amount computed by applying the statutory federal income tax rate to pretax income. The computed amount and the differences for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, 2008, and 20072008 are shown in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Pretax income | | $ | 168,827 | | | $ | 192,227 | | | $ | 232,876 | | | $ | 231,874 | | | $ | 168,827 | | | $ | 192,227 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for income taxes: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Computed amount at statutory rate of 35% | | $ | 59,089 | | | $ | 67,280 | | | $ | 81,507 | | | $ | 81,156 | | | $ | 59,089 | | | $ | 67,280 | |
| State and local income tax (net of federal tax benefit) | | | 1,829 | | | | 3,925 | | | | 3,849 | | | | 2,766 | | | | 1,829 | | | | 3,925 | |
Taxes onnon-U.S.earnings-net of foreign tax credits | | | (4,117 | ) | | | (5,191 | ) | | | (407 | ) | | | (8,545 | ) | | | (4,117 | ) | | | (5,191 | ) |
| U.S. business tax credits | | | (754 | ) | | | (857 | ) | | | (679 | ) | | | (935 | ) | | | (754 | ) | | | (857 | ) |
| Domestic activities production deduction | | | (1,925 | ) | | | (2,291 | ) | | | (2,450 | ) | | | (4,720 | ) | | | (1,925 | ) | | | (2,291 | ) |
Revaluation of deferred taxes fornon-U.S. rate changes | | | — | | | | — | | | | (4,535 | ) | |
| Other | | | 1,314 | | | | 2,335 | | | | 1,172 | | | | 5,052 | | | | 1,314 | | | | 2,335 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total provision for income taxes | | $ | 55,436 | | | $ | 65,201 | | | $ | 78,457 | | | $ | 74,774 | | | $ | 55,436 | | | $ | 65,201 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The Company has not provided an estimate for any U.S. or additional foreign taxes on undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries that might be payable if these earnings were repatriated since the Company considers these amounts to be permanently invested.
43
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
We adopted the provisions of ASC 740 on January 1, 2007. In accordance with ASC 740, the Company recognized a cumulative-effect adjustment of $1.2 million, increasing its liability for unrecognized tax benefits, interest, and penalties and reducing the January 1, 2007 balance of retained earnings.NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 20072008 are shown in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Unrecognized tax benefits beginning balance | | $ | 4,009 | | | $ | 5,938 | | | $ | 5,485 | | | $ | 5,285 | | | $ | 4,009 | | | $ | 5,938 | |
| Gross increases for tax positions of prior years | | | 2,138 | | | | 2,571 | | | | 2,943 | | | | 3,049 | | | | 2,138 | | | | 2,571 | |
| Gross decreases for tax positions of prior years | | | — | | | | (1,836 | ) | | | (432 | ) | | | (675 | ) | | | — | | | | (1,836 | ) |
| Settlements | | | (628 | ) | | | (993 | ) | | | (1,952 | ) | | | (517 | ) | | | (628 | ) | | | (993 | ) |
| Lapse of statute of limitations | | | (234 | ) | | | (1,671 | ) | | | (106 | ) | | | (702 | ) | | | (234 | ) | | | (1,671 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits ending balance | | $ | 5,285 | | | $ | 4,009 | | | $ | 5,938 | | | $ | 6,440 | | | $ | 5,285 | | | $ | 4,009 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
We recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense. As of December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 20072008 we had approximately $0.9$0.8 million, $0.9 million and $1.0$0.9 million, respectively, of accrued interest related to uncertain tax positions. As of December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 20072008 we had approximately $0.4 million, $0.2 million and $0.2 million, respectively, of accrued penalties related to uncertain tax positions.
The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits that would affect our effective tax rate if recognized is $5.8 million, $4.4 million as of December 31, 2009,and $3.1 million as of December 31, 2008 and $2.5 million as of2010, December 31, 2007.2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively. The tax years2005-20082005-2009 remain open to examination by major taxing jurisdictions. Due to the potential for resolution of federal, state and foreign examinations, and the expiration of various statutes of limitation, it is reasonably possible that the Company’s gross unrecognized tax benefits balance may change within the next twelve months by a range of zero to $0.3$1.6 million.
47
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
The Company had loss carry forwards for U.S. federal andNOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)non-U.S. purposes
at December 31, 2010 of $3.5 and $13.7 million respectively, and as of December 31, 2009, $2.2 million and $12.5 million, respectively. The federal loss carry forwards are available for use against the Company’s consolidated federal taxable income and expire between 2023 and 2030. The entire balance of thenon-U.S. losses is available to be carried forward, with $9.5 million of these losses beginning to expire during the years 2012 through 2019. The remaining $4.2 million of such losses can be carried forward indefinitely. At December 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company had a foreign capital loss carry forward of approximately $1.3 million and 2008,$2.3 million respectively. The foreign capital loss can be carried forward indefinitely. At December 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company has a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset attributable to the foreign capital loss of $0.4 million and $0.6 million, respectively. At December 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company had state net operating loss carry forwards of approximately $12.7$18.7 million and $14.3 million, respectively. At December 31, 2009 and 2008 the Company had foreign net operating loss carry forwards of approximately $12.5 million and $9.7 million, respectively. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the Company had a foreign capital loss carry forward of approximately $2.3 million and $3.8$12.7 million, respectively. If unutilized, the state net operating loss will expire between 2016 and 2028. Neither the foreign net operating loss nor the foreign capital loss has an expiration date.2029. At December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, the Company recorded a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset attributable to the state net operating loss of $0.2$0.4 million and $0.4 million, respectively. The Company has not recorded a valuation allowance against the foreign net operating loss at either December 31, 2009 or 2008. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the Company has a valuation allowance against the deferred tax asset attributable to the foreign capital loss of $0.6 million and $1.1$0.2 million, respectively.
The components of Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) for 2009, 2008 and 2007 follow:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Unrealized losses on derivatives | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pretax amount | | $ | (127 | ) | | $ | (10,370 | ) | | $ | — | |
| Tax benefit | | | 56 | | | | 3,728 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Aftertax amount | | $ | (71 | ) | | $ | (6,642 | ) | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pension and other post-retirement plans | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pretax amount | | $ | 9,863 | | | $ | (20,996 | ) | | $ | 10,097 | |
| Tax benefit (provision) | | | (3,467 | ) | | | 7,717 | | | | (4,163 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Aftertax amount | | $ | 6,396 | | | $ | (13,279 | ) | | $ | 5,934 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pretax amount | | $ | 19,195 | | | $ | (45,863 | ) | | $ | 33,573 | |
| Tax benefit (provision) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Aftertax amount | | $ | 19,195 | | | $ | (45,863 | ) | | $ | 33,573 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjustments are generally not adjusted for income taxes as they relate to indefinite investments in non-US subsidiaries.
| |
13.11. | Business Segments and Geographic Information |
IDEX has four reportable business segments: Fluid & Metering Technologies, Health & Science Technologies, Dispensing Equipment, and Fire & Safety/Diversified Products. Reporting units in the Fluid & Metering Technologies segment include Banjo, Energy,Banjo; Energy; Chemical, Food & Pharmaceuticals; and Water and IPT.& Waste Water. Reporting units in the Health & Science Technologies segmentSegment include HST Core, Gast,IDEX Health & Science; Semrock; PPE; Gast; and Micropump. Reporting units in theThe Dispensing Equipment segment include the Fluid Management businesses.Segment is a reporting unit. Reporting units in the Fire & Safety/Diversified Products segmentSegment include Fire Suppression,Suppression; Rescue ToolsTools; and Band-It.
The Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment designs, produces and distributes positive displacement pumps, flow meters, injectors, and other fluid-handling pump modules and systems and provides flow monitoring and other services for water and& wastewater. The Health & Science Technologies Segment designs, produces and distributes a
44
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
wide range of precision fluidics and sealing solutions, including very high precision, low-flow rate pumping solutions required in analytical instrumentation, clinical diagnostics and drug discovery, high performance molded and extruded,
48
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
biocompatible medical devices and implantables, air compressors used in medical, dental and industrial applications, and precision gear and peristaltic pump technologies that meet exacting OEM specifications. The Dispensing Equipment Segment produces precision equipment for dispensing, metering and mixing colorants paints, and hair colorants and other personal care productspaints used in a variety of retail and commercial businesses around the world. The Fire &Safety/Diversified Products Segment produces firefighting pumps and controls, rescue tools, lifting bags and other components and systems for the fire and rescue industry, and engineered stainless steel banding and clamping devices used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications.
Information on the Company’s business segments from continuing operations is presented below, based on the nature of products and services offered. The Company evaluates performance based on several factors, of which operating income is the primary financial measure. Intersegment sales are accounted for at fair value as if the sales were to third parties.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008(5) | | 2007(5) | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| NET SALES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| External customers | | $ | 640,242 | | | $ | 696,641 | | | $ | 568,622 | | | $ | 729,233 | | | $ | 640,242 | | | $ | 696,641 | |
| Intersegment sales | | | 866 | | | | 1,061 | | | | 1,685 | | | | 712 | | | | 866 | | | | 1,061 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total segment sales | | | 641,108 | | | | 697,702 | | | | 570,307 | | | | 729,945 | | | | 641,108 | | | | 697,702 | |
| Health & Science Technologies: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| External customers | | | 299,336 | | | | 328,514 | | | | 323,639 | | | | 393,481 | | | | 299,336 | | | | 328,514 | |
| Intersegment sales | | | 4,993 | | | | 3,077 | | | | 3,531 | | | | 3,717 | | | | 4,993 | | | | 3,077 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total segment sales | | | 304,329 | | | | 331,591 | | | | 327,170 | | | | 397,198 | | | | 304,329 | | | | 331,591 | |
| Dispensing Equipment: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| External customers | | | 127,279 | | | | 163,861 | | | | 177,948 | | | | 125,127 | | | | 127,279 | | | | 163,861 | |
| Intersegment sales | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 193 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total segment sales | | | 127,279 | | | | 163,861 | | | | 177,948 | | | | 125,320 | | | | 127,279 | | | | 163,861 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| External customers | | | 262,804 | | | | 300,455 | | | | 288,422 | | | | 265,232 | | | | 262,804 | | | | 300,455 | |
| Intersegment sales | | | 5 | | | | 7 | | | | 2 | | | | 269 | | | | 5 | | | | 7 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total segment sales | | | 262,809 | | | | 300,462 | | | | 288,424 | | | | 265,501 | | | | 262,809 | | | | 300,462 | |
| Intersegment eliminations | | | (5,864 | ) | | | (4,145 | ) | | | (5,218 | ) | | | (4,891 | ) | | | (5,864 | ) | | | (4,145 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total net sales | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | | | $ | 1,358,631 | | | $ | 1,513,073 | | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| OPERATING INCOME(1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
OPERATING INCOME(1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | $ | 100,289 | | | $ | 123,801 | | | $ | 119,060 | | | $ | 131,944 | | | $ | 100,289 | | | $ | 123,801 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | 51,712 | | | | 58,297 | | | | 61,473 | | | | 82,332 | | | | 51,712 | | | | 58,297 | |
| Dispensing Equipment(2) | | | 15,147 | | | | (10,748 | ) | | | 39,179 | | |
Dispensing Equipment(2) | | | | 19,490 | | | | 15,147 | | | | (10,748 | ) |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | 59,884 | | | | 74,310 | | | | 66,287 | | | | 62,844 | | | | 59,884 | | | | 74,310 | |
| Corporate office and other(3) | | | (42,178 | ) | | | (39,704 | ) | | | (33,204 | ) | |
Corporate office and other(3) | | | | (47,494 | ) | | | (42,178 | ) | | | (39,704 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total operating income | | $ | 184,854 | | | $ | 205,956 | | | $ | 252,795 | | | $ | 249,116 | | | $ | 184,854 | | | $ | 205,956 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
4945
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008(5) | | 2007(5) | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | $ | 1,043,082 | | | $ | 1,070,348 | | | $ | 698,286 | | | $ | 1,111,085 | | | $ | 1,043,082 | | | $ | 1,070,348 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | 567,096 | | | | 594,459 | | | | 542,427 | | | | 648,400 | | | | 567,096 | | | | 594,459 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | 164,979 | | | | 179,800 | | | | 236,751 | | | | 205,540 | | | | 164,979 | | | | 179,800 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | 285,893 | | | | 286,482 | | | | 312,603 | | | | 278,567 | | | | 285,893 | | | | 286,482 | |
| Corporate office and other(3) | | | 37,107 | | | | 20,711 | | | | 180,011 | | |
Corporate office and other(3) | | | | 138,103 | | | | 37,107 | | | | 20,711 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 2,098,157 | | | $ | 2,151,800 | | | $ | 1,970,078 | | | $ | 2,381,695 | | | $ | 2,098,157 | | | $ | 2,151,800 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| DEPRECIATION AND AMORTIZATION(4) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
DEPRECIATION AND AMORTIZATION(4) | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | $ | 32,584 | | | $ | 26,276 | | | $ | 16,797 | | | $ | 33,134 | | | $ | 32,584 | | | $ | 26,276 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | 14,293 | | | | 11,806 | | | | 11,156 | | | | 16,012 | | | | 14,293 | | | | 11,806 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | 3,124 | | | | 3,986 | | | | 3,151 | | | | 3,753 | | | | 3,124 | | | | 3,986 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | 5,328 | | | | 5,288 | | | | 5,676 | | | | 4,885 | | | | 5,328 | | | | 5,288 | |
| Corporate office and other | | | 1,017 | | | | 1,243 | | | | 1,258 | | | | 324 | | | | 1,017 | | | | 1,243 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total depreciation and amortization | | $ | 56,346 | | | $ | 48,599 | | | $ | 38,038 | | | $ | 58,108 | | | $ | 56,346 | | | $ | 48,599 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| CAPITAL EXPENDITURES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fluid & Metering Technologies | | $ | 12,867 | | | $ | 13,859 | | | $ | 11,407 | | | $ | 17,308 | | | $ | 12,867 | | | $ | 13,859 | |
| Health & Science Technologies | | | 6,365 | | | | 5,365 | | | | 5,342 | | | | 7,516 | | | | 6,365 | | | | 5,365 | |
| Dispensing Equipment | | | 864 | | | | 2,528 | | | | 2,832 | | | | 1,129 | | | | 864 | | | | 2,528 | |
| Fire & Safety/Diversified Products | | | 3,686 | | | | 4,743 | | | | 3,532 | | | | 3,513 | | | | 3,686 | | | | 4,743 | |
| Corporate office and other | | | 1,743 | | | | 1,863 | | | | 3,383 | | | | 3,303 | | | | 1,743 | | | | 1,863 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total capital expenditures | | $ | 25,525 | | | $ | 28,358 | | | $ | 26,496 | | | $ | 32,769 | | | $ | 25,525 | | | $ | 28,358 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | Segment operating income excludes net unallocated corporate operating expenses. |
| |
| (2) | | Segment operating income includes $30.1 million goodwill impairment charge in 2008 for Fluid Management. |
| |
| (3) | | Includes intersegment eliminations. |
| |
| (4) | | Excludes amortization of debt issuance expenses. |
|
(5) | | Certain prior year amounts have been restated to reflect the LIFO to FIFO inventory costing change. |
5046
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Information about the Company’s operations in different geographical regions for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 20072008 is shown below. Net sales were attributed to geographic areas based on location of the customer, and no country outside the U.S. was greater than 10% of total revenues.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| NET SALES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | $ | 698,822 | | | $ | 793,872 | | | $ | 734,877 | | | $ | 766,067 | | | $ | 698,822 | | | $ | 793,872 | |
| Europe | | | 361,774 | | | | 386,864 | | | | 340,543 | | | | 402,056 | | | | 361,774 | | | | 386,864 | |
| Other countries | | | 269,065 | | | | 308,735 | | | | 283,211 | | | | 344,950 | | | | 269,065 | | | | 308,735 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total net sales | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | | | $ | 1,358,631 | | | $ | 1,513,073 | | | $ | 1,329,661 | | | $ | 1,489,471 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| LONG-LIVED ASSETS — PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | $ | 105,165 | | | $ | 111,252 | | | $ | 110,371 | | | $ | 108,951 | | | $ | 105,165 | | | $ | 111,252 | |
| Europe | | | 61,766 | | | | 65,208 | | | | 54,401 | | | | 68,756 | | | | 61,766 | | | | 65,208 | |
| Other countries | | | 11,352 | | | | 9,823 | | | | 8,227 | | | | 10,855 | | | | 11,352 | | | | 9,823 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total long-lived assets | | $ | 178,283 | | | $ | 186,283 | | | $ | 172,999 | | |
| Total long-lived assets — net | | | $ | 188,562 | | | $ | 178,283 | | | $ | 186,283 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
All of the Company’s acquisitions have been accounted for under ASC 805, Business Combinations. Accordingly, the accounts of the acquired companies, after adjustments to reflect fair values assigned to assets and liabilities, have been included in the consolidated financial statements from their respective dates of acquisition.
2010 Acquisitions
On April 15, 2010, the Company acquired the stock of PPE, previously referred to as Seals, Ltd, a leading provider of proprietary high performance seals and advanced sealing solutions for a diverse range of global industries, including analytical instrumentation, semiconductor/solar and process technologies. PPE consists of the Polymer Engineering and Perlast divisions. PPE’ Polymer Engineering division focuses on sealing solutions for hazardous duty applications. The Perlast division produces highly engineered seals for analytical instrumentation, pharmaceutical, electronics, and food applications. Headquartered in Blackburn, England, PPE operates as part of the Health & Science Technologies Segment with annual revenues of approximately $32.0 million (£21 million). The Company acquired PPE for an aggregate purchase price of $54.0 million, consisting of $51.3 million in cash and the assumption of approximately $2.7 million of debt related items. The cash payment was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $29.7 million and $17.2 million, respectively. The $29.7 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
On July 21, 2010, the Company acquired the stock of OBL, S.r.l. (“OBL”), a leading provider of mechanical and hydraulic diaphragm pumps. OBL provides polymer blending systems and related accessories for a diverse range of global industries, including water, waste water, oil and gas, petro-chemical and power generation markets. Headquartered in Milan, Italy, with annual revenues of approximately $10.9 million (€8.5 million), OBL operates within IDEX’s Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment as part of the Water & Waste Water reporting unit. The Company acquired OBL for cash consideration of $15.4 million. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $7.7 million and $4.0 million, respectively. The $7.7 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
47
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
On September 17, 2010, the Company acquired the assets of Periflo, a leading provider of peristaltic pumps for the industrial and municipal water & wastewater markets. Periflo offers a complete family of peristaltic hose pumps for a wide variety of applications. Headquartered in Loveland, Ohio, with annual revenues of approximately $3.5 million, Periflo operates within IDEX’s Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment as part of the Water & Waste Water reporting unit. The Company acquired Periflo for cash consideration of $4.3 million. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $2.5 million and $0.7 million, respectively. The $2.5 million of goodwill is deductible for tax purposes.
On November 1, 2010, the Company acquired the stock of Fitzpatrick, a global leader in the design and manufacture of process technologies for the pharmaceutical, food and personal care markets. Fitzpatrick designs and manufactures customized size reduction, roll compaction and drying systems to support their customers’ product development and manufacturing processes. Fitzpatrick expands the capability of IDEX’s Quadro Engineering business by adding coarse particle sizing, roll compaction and drying systems to Quadro’s fine particle processing. Headquartered in Elmhurst, Illinois, Fitzpatrick has annual revenues of approximately $22.0 million. Fitzpatrick operates in the Chemical Food & Pharmaceutical reporting unit within the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment. The Company acquired Fitzpatrick for cash consideration of approximately $20.3 million. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $5.6 million and $8.0 million, respectively. The $5.6 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
The purchase price for 2010 acquisitions has been allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on estimated fair values at the date of the acquisition. For certain acquisitions that occurred in 2010, the Company is in the process of obtaining or finalizing appraisals of tangible and intangible assets and it is continuing to evaluate the initial purchase price allocations, as of the acquisition date, which will be adjusted as additional information relative to the fair values of the assets and liabilities of the businesses become known. Accordingly, management has used their best estimate in the initial purchase price allocation as of the date of these financial statements.
The allocation of the acquisition costs to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, based on their estimated fair values were as follows:
| | | | | |
| | | 2010 | |
| | | In thousands | |
| |
| Current assets, net of cash acquired | | $ | 25,231 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | 18,344 | |
| Goodwill | | | 45,481 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 29,861 | |
| Other assets | | | 2,950 | |
| | | | | |
| Total assets acquired | | | 121,867 | |
| Total liabilities assumed | | | (30,581 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Net assets acquired | | $ | 91,286 | |
| | | | | |
Acquired intangible assets consist of trademarks, customer relationships, unpatented technology and non-compete agreements, which are being amortized over a life of 2-15 years. The goodwill recorded for the acquisitions reflects the strategic fit and revenue and earnings growth potential of these businesses.
The Company incurred $4.0 million of acquisition related transaction costs in 2010, relating to completed, pending and potential transactions that ultimately were not completed.
2008 Acquisitions
On January 1, 2008, the Company acquired the stock of ADS, a provider of metering technology and flow monitoring services for water and& wastewater markets. ADS is headquartered in Huntsville, Alabama, with regional
48
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
sales and service offices throughout the United States and Australia. With annual revenues of approximately $70.0 million, ADS operates as part of the Water reporting unit within the Company’s Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment. The Company acquired ADS for an aggregate purchase pricecash consideration of $156.1 million, consisting entirely of cash.million. Approximately $155.0 million of the cash payment was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility, of which $140.0 million was reflected as restricted cash at December 31, 2007.Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $102.1 million and $51.9 million, respectively. The $102.1 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
On October 1, 2008, the Company acquired the stock of Richter, a provider of premium quality lined pumps, valves and control equipment for the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Richter’s corrosion resistant fluoroplastic lined products offer solutions for demanding applications in the process industry. Headquartered in Kempen, Germany, with facilities in China, India and the U.S., Richter has annual revenues of approximately $53.0 million. Richter operates as part of the IPTChemical, Food & Pharmaceutical reporting unit within the Company’s Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment. The Company acquired Richter for an aggregate purchase price of $102.0 million, consisting of $93.3 million in cash and the assumption of approximately $8.7 million of debt related items. Approximately $63.7 million of the cash payment was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $57.8 million and $32.7 million, respectively. The $57.8 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
On October 14, 2008, the Company acquired the stock of iPEK, a provider of systems focused on infrastructure analysis, specifically wastewater collection systems. iPEK is a developer of remote controlled systems for infrastructure inspection. Headquartered in Hirschegg, Austria, iPEK has annual revenues of approximately $25.0 million. iPEK operates as part of the Water reporting unit within the Company’s Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment and is expected to leverage the ADS acquisition which was completed in January 2008.Segment. The Company acquired iPEK for an aggregate purchase price of $44.5 million, consisting of $43.1 million in cash and the assumption of approximately $1.4 million of debt related items. Approximately $33.2 million of the cash payment was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets
51
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
recognized as part of this transaction were $21.1 million and $17.8 million, respectively. Of the $21.1 million of goodwill, approximately $20.0 million is expected to be deductible for tax purposes.
On October 16, 2008, the Company acquired the stock of IETG, a provider of flow monitoring and underground utility surveillance services for the water and& wastewater markets. IETG products and services enable water companies to effectively manage their water distribution and sewerage networks, while its surveillance service specializes in underground asset detection and mapping for utilities and other private companies. Headquartered in Leeds, United Kingdom, IETG has annual revenues of approximately $26.0 million. IETG operates as part of the Water reporting unit within IDEX’s Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment. The Company acquired IETG for an aggregate purchase price of $36.9 million, consisting of $35.0 million in cash and the assumption of approximately $1.9 million of debt related items. Approximately $20.5 million of the cash payment was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $24.0 million and $9.2 million, respectively. The $24.0 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
On October 20, 2008, the Company acquired the stock of Semrock, a provider of optical filters for biotech and analytical instrumentation in the life sciences markets. Semrock’s products are used in the biotechnology and analytical instrumentation industries. Semrock produces optical filters usingstate-of-the-art manufacturing processes which enable them to offer significant improvements in the performance and reliability of their customers’ instruments. Headquartered in Rochester, New York, Semrock has annual revenues of approximately $21.0 million. Semrock operates as part of the HST Core reporting unit within the Company’s Health & Science Technologies Segment. The Company acquired Semrock for an aggregate purchase pricecash consideration of $60.6 million, consisting entirely of cash.million. Approximately $60.0 million of the cash payment was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $38.1 million and $20.0 million, respectively. The $38.1 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
49
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
On November 14, 2008, the Company acquired the stock of Innovadyne, a provider of nanoliter dispensing instruments for the life sciences industry. Innovadyne’s products are used for assay miniaturization across a broad range of disciplines including High Throughput Screening, Assay Development, PCR/Sequencing, and Protein Crystallography. Innovadyne operates as part of the HST CoreIH&S reporting unit within the Company’s Health & Science Technologies Segment. The Company acquired Innovadyne for an aggregate purchase pricecash consideration of $3.3 million, consisting entirely of cash. Approximately $3.3 million of the cash paymentwhich was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $1.4 million and $1.1$1.2 million, respectively. The $1.4 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
On February 14, 2007,The allocation of the Companyacquisition costs to the assets acquired the stockand liabilities assumed, based on their estimated fair values were as follows:
| | | | | |
| | | 2008 | |
| | | In thousands | |
| |
| Current assets, net of cash acquired | | $ | 81,969 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | | | 25,558 | |
| Goodwill | | | 244,519 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 132,791 | |
| Other assets | | | 800 | |
| | | | | |
| Total assets acquired | | | 485,637 | |
| Total liabilities assumed | | | (94,266 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Net assets acquired | | $ | 391,371 | |
| | | | | |
Acquired intangible assets consist of Faure Herman,patents, trademarks, customer relationships, unpatented technology and non-compete agreements, which are being amortized over a leading providerlife of ultrasonic and helical turbine flow meters used2-17 years. The 2008 acquisitions resulted in the custody transfer and controlrecognition of high value fluids and gases. Headquartered in La Ferté Bernard, France, Faure Herman has sales offices in Europe and North America, with annual revenues of approximately $22.0 million. Faure Herman operates as part of the Company’s Energy reporting unit within its Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment. The Company acquired Faure Herman for an aggregate purchase price of $25.9 million, consisting of $24.3 million in cash and the assumption of approximately $1.6goodwill totaling $244.5 million, of debt. Approximately $12.9which $20.0 million of the cash payment was financed with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $13.4 million and $7.7 million, respectively. The $13.4 million of goodwill is not deductible for tax purposes.
On June 12, 2007, the Company acquired the assets of Quadro, a leading provider of particle control solutions for the pharmaceutical and bio-pharmaceutical markets. Quadro’s core capabilities include fine milling, emulsification and special handling of liquid and solid particulates for laboratory, pilot phase and production scale processing within the pharmaceutical and bio-pharmaceutical markets. Headquartered in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, Quadro, with annual revenues of approximately $25.0 million, operates as part of the IPT reporting unit within the Company’s Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment. The Company acquired Quadro for a purchase price of $32.2 million, consisting entirely of cash. Approximately $11.3 million of the cash payment was financed
52
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
with borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $12.1 million and $10.9 million, respectively. Of the $12.1 million of goodwill, approximately $8.9 million is expected to be deductible for tax purposes.
On October 18, 2007, the Company acquired the assets of Isolation Technologies, a leading developer of advanced column hardware and accessories for the High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) market. HPLC instruments are used in a variety of analytical chemistry applications, with primary commercial applications including drug discovery and quality control measurements for pharmaceutical and food/beverage testing. Isolation Technologies, with annual revenues of approximately $12.0 million, operates as part of the HST Core reporting unit in the Company’s Health and Science Technologies Segment. The Company acquired Isolation Technologies for a purchase price of $30.2 million, consisting entirely of cash. Approximately $29.7 million of the cash payment was financed by borrowings under the Company’s Credit Facility. Goodwill and intangible assets recognized as part of this transaction were $17.9 million and $8.7 million, respectively. The $17.9 million of goodwill is deductible for tax purposes.
The resultsgoodwill recorded for the acquisitions reflects the strategic fit and revenue and earnings growth potential of operations for these acquisitions have been included within the Company’s financial results from the date of the acquisition. The Company does not consider these acquisitions to be material to its results of operations for any of the periods presented.businesses.
| |
15. | Discontinued Operations |
On August 13, 2007, the Company completed the sale of Halox, its chemical and electrochemical systems product line operating as part of the Fluid & Metering Technologies Segment.
Summarized results of the Company’s discontinued operations are as follows:
| | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended
| |
| | | December 31, 2007 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Revenue | | $ | 1,428 | |
| | | | | |
| Loss from discontinued operations before income taxes | | $ | (1,106 | ) |
| Income tax benefit (provision) | | | 387 | |
| | | | | |
| Loss from discontinued operations | | $ | (719 | ) |
| | | | | |
| |
16.13. | Share-Based Compensation |
The Company maintains two share-based compensation plans for executives, non-employee directors, and certain key employees which authorize the granting of stock options, unvested shares, unvested share units, and other types of awards consistent with the purpose of the plans. The number of shares authorized for issuance under the Company’s plans as of December 31, 20092010 totals 7.110.6 million, of which 1.74.3 million shares were available for future issuance. Stock options granted under these plans are generally non-qualified, and are granted with an exercise price equal to the market price of the Company’s stock at the date of grant. Substantially all of the options issued to employees prior to 2005 become exercisable in five equal installments, while the majority of options issued to employees in 2005 and after become exercisable in four equal installments, beginning one year from the date of grant, and generally expire 10 years from the date of grant. Stock options granted to non-employee directors cliff vest after one or two years. Unvested share and unvested share unit awards generally cliff vest after three or four years for employees, and three years for non-employee directors. The Company issued 264,915, 273,000 583,000 and 134,000583,000 of unvested shares as compensation to key employees in 2010, 2009 2008 and 2007,2008, respectively. Of the shares granted in 2008, 242,800 of the shares vest 50% on April 8, 2011 and 50% on April 8, 2013, but such vesting may be accelerated if the Company’s share price for any five consecutive trading days equals or exceeds $65.90 (twice the closing price of the shares on the date of grant). Also, 12,333 of the 2008 shares issued vested on April 8, 2009 with
53
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
another 12,333 vesting on April 8, 2010 and 49,334 vesting on April 8, 2011. The unvested shares granted in 2009 and 2007 and the remaining unvested shares granted in 2008 contain a cliff vesting feature and vest either three or four years after the grant date for employees and three years for non-employee directors.
All unvested shares carry dividend and voting rights, and the sale of the shares is restricted prior to the date of vesting.
50
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The Company accounts for share-based payments in accordance with ASC 718. Accordingly, the Company expenses the fair value of awards made under its share-based plans. That cost is recognized in the consolidated financial statements over the requisite service period of the grants.
Weighted average option fair values and assumptions for the period specified are disclosed in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| |
| Weighted average fair value of grants | | $ | 5.32 | | | $ | 8.81 | | | $ | 9.55 | | | $ | 9.56 | | | $ | 5.32 | | | $ | 8.81 | |
| Dividend yield | | | 2.35 | % | | | 1.46 | % | | | 1.37 | % | | | 1.51 | % | | | 2.35 | % | | | 1.46 | % |
| Volatility | | | 32.53 | % | | | 31.51 | % | | | 30.59 | % | | | 33.43 | % | | | 32.53 | % | | | 31.51 | % |
| Risk-free interest rate | | | 0.69 | % - 4.63% | | | 1.68 | % - 5.33% | | | 4.23 | % - 4.92% | | | 0.32 | % - 5.67% | | | 0.69 | % - 4.63% | | | 1.68 | % - 5.33% |
| Expected life (in years) | | | 5.85 | | | | 5.28 | | | | 4.64 | | | | 5.98 | | | | 5.85 | | | | 5.28 | |
The assumptions are as follows:
| | |
| | • | The Company estimated volatility using its historical share price performance over the contractual term of the option. |
| |
| | • | The Company uses historical data to estimate the expected life of the option. The expected life assumption for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 20072008 is an output of the Binomial lattice option-pricing model, which incorporates vesting provisions, rate of voluntary exercise and rate of post-vesting termination over the contractual life of the option to define expected employee behavior. |
| |
| | • | The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for periods within the contractual life of the option. For the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 2008 and 2007,2008, we present the range of risk-free one-year forward rates, derived from the U.S. treasury yield curve, utilized in the Binomial lattice option-pricing model. |
| |
| | • | The expected dividend yield is based on the Company’s current dividend yield as the best estimate of projected dividend yield for periods within the contractual life of the option. |
The Company’s policy is to recognize compensation cost on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period for the entire award. Additionally, the Company’s general policy is to issue new shares of common stock to satisfy stock option exercises or grants of unvested shares.
Total compensation cost for stock options is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Cost of goods sold | | $ | 945 | | | $ | 1,043 | | | $ | 999 | | | $ | 804 | | | $ | 945 | | | $ | 1,043 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | 6,288 | | | | 7,175 | | | | 7,330 | | | | 6,923 | | | | 6,288 | | | | 7,175 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total expense before income taxes | | | 7,233 | | | | 8,218 | | | | 8,329 | | | | 7,727 | | | | 7,233 | | | | 8,218 | |
| Income tax benefit | | | (2,322 | ) | | | (2,585 | ) | | | (3,032 | ) | | | (2,450 | ) | | | (2,322 | ) | | | (2,585 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total expense after income taxes | | $ | 4,911 | | | $ | 5,633 | | | $ | 5,297 | | | $ | 5,277 | | | $ | 4,911 | | | $ | 5,633 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
5451
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Total compensation cost for unvested shares is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Cost of goods sold | | $ | 248 | | | $ | 79 | | | $ | 28 | | | $ | 311 | | | $ | 248 | | | $ | 79 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | | 8,229 | | | | 6,717 | | | | 4,213 | | | | 8,382 | | | | 8,229 | | | | 6,717 | |
| Restructuring expenses | | | | 938 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total expense before income taxes | | | 8,477 | | | | 6,796 | | | | 4,241 | | | | 9,631 | | | | 8,477 | | | | 6,796 | |
| Income tax benefit | | | (1,444 | ) | | | (1,108 | ) | | | (827 | ) | | | (2,097 | ) | | | (1,444 | ) | | | (1,108 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total expense after income taxes | | $ | 7,033 | | | $ | 5,688 | | | $ | 3,414 | | | $ | 7,534 | | | $ | 7,033 | | | $ | 5,688 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Recognition of compensation cost was consistent with recognition of cash compensation for the same employees. Compensation cost capitalized as part of inventory was immaterial.
As of December 31, 2009,2010, there was $10.3 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to stock options that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.3 years. As of December 31, 2009,2010, there was $11.7$9.7 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested shares that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.11.0 years.
A summary of the Company’s stock option activity as of December 31, 2009,2010, and changes during the year ended December 31, 20092010 is presented in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Weighted
| | Weighted-Average
| | Aggregate
| | | | | Weighted
| | Weighted-Average
| | Aggregate
| |
| | | | | Average
| | Remaining
| | Intrinsic
| | | | | Average
| | Remaining
| | Intrinsic
| |
Stock Options | | Shares | | Price | | Contractual Term | | Value | | | Shares | | Price | | Contractual Term | | Value | |
| |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2009 | | | 5,485,896 | | | $ | 25.87 | | | | 6.55 | | | $ | 16,785,351 | | |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2010 | | | | 5,793,028 | | | $ | 25.14 | | | | 6.40 | | | $ | 40,557,217 | |
| Granted | | | 1,195,780 | | | | 20.25 | | | | | | | | | | | | 947,275 | | | | 31.85 | | | | | | | | | |
| Exercised | | | (473,208 | ) | | | 16.22 | | | | | | | | | | | | (956,256 | ) | | | 19.85 | | | | | | | | | |
| Forfeited/Expired | | | (415,440 | ) | | | 30.85 | | | | | | | | | | | | (379,824 | ) | | | 30.97 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2009 | | | 5,793,028 | | | $ | 25.14 | | | | 6.40 | | | $ | 40,557,214 | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2010 | | | | 5,404,223 | | | $ | 26.85 | | | | 6.29 | | | $ | 66,329,686 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2009 | | | 5,590,573 | | | $ | 25.14 | | | | 6.31 | | | $ | 39,209,262 | | |
| Exercisable at December 31, 2009 | | | 3,500,837 | | | $ | 24.08 | | | | 5.04 | | | $ | 27,821,826 | | |
| Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2010 | | | | 5,227,778 | | | $ | 26.81 | | | | 6.21 | | | $ | 64,381,855 | |
| Exercisable at December 31, 2010 | | | | 3,262,249 | | | $ | 26.02 | | | | 4.97 | | | $ | 42,741,628 | |
The intrinsic value for stock options outstanding and exercisable is defined as the difference between the market value of the Company’s common stock as of the end of the period, and the grant price. The total intrinsic value of options exercised in 2010, 2009 and 2008, and 2007, was $14.4 million, $5.3 million $10.4 million and $17.3$10.4 million, respectively. In 2010, 2009 2008 and 2007,2008, cash received from options exercised was $18.1 million, $7.7 million $10.4 million and $14.0$10.4 million, respectively, while the actual tax benefit realized for the tax deductions from stock options exercised totaled $5.2 million, $1.9 million $3.1 million and $6.3$3.1 million, respectively.
5552
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
A summary of the Company’s unvested share activity as of December 31, 2009,2010, and changes during the year ending December 31, 20092010 is presented in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Weighted-Average
| | | | | Weighted-Average
| |
| | | | | Grant Date Fair
| | | | | Grant Date Fair
| |
Unvested Shares | | Shares | | Value | | | Shares | | Value | |
| |
| Nonvested at January 1, 2009 | | | 903,200 | | | $ | 31.57 | | |
| Nonvested at January 1, 2010 | | | | 920,599 | | | $ | 29.58 | |
| Granted | | | 273,419 | | | | 20.34 | | | | 264,915 | | | | 31.90 | |
| Vested | | | (219,282 | ) | | | 26.32 | | | | (173,703 | ) | | | 32.38 | |
| Forfeited | | | (36,738 | ) | | | 29.24 | | | | (61,714 | ) | | | 27.89 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Nonvested at December 31, 2009 | | | 920,599 | | | | 29.58 | | |
| Nonvested at December 31, 2010 | | | | 950,097 | | | | 29.83 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Generally, unvestedUnvested share grants accrue dividends and their fair value is equal to the market price of the Company’s stock at the date of the grant.
| |
17.14. | Retirement Benefits |
The Company sponsors several qualified and nonqualified pension plans and other postretirement plans for its employees. The Company uses a measurement date of December 31 for its defined benefit pension plans and post retirement medical plans. In 2008, theThe Company adoptedemploys the measurement date provisions of ASC 715, “Compensation-Retirement Benefits”. Those provisions, which require the measurement date of plan assets and liabilities to coincide with the sponsor’s year end.
53
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following table provides a reconciliation of the changes in the benefit obligations and fair value of plan assets over the two-year period ended December 31, 2009,2010, and a statement of the funded status at December 31 for both years.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefits | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | Other Benefits | |
| | | U.S. | | | Non-U.S. | | | U.S. | | | Non-U.S. | | | 2009 | | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| CHANGE IN BENEFIT OBLIGATION | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Obligation at January 1 | | $ | 72,689 | | | $ | 36,811 | | | $ | 71,507 | | | $ | 34,711 | | | $ | 21,767 | | | $ | 21,890 | |
| ASC 715 measurement date adjustment | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 589 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Service cost | | | 1,551 | | | | 824 | | | | 1,765 | | | | 932 | | | | 468 | | | | 607 | |
| Interest cost | | | 4,375 | | | | 2,122 | | | | 4,484 | | | | 1,901 | | | | 1,018 | | | | 1,328 | |
| Plan amendments | | | — | | | | — | | | | 501 | | | | 9 | | | | (2,932 | ) | | | — | |
| Benefits paid | | | (4,233 | ) | | | (1,563 | ) | | | (4,761 | ) | | | (1,475 | ) | | | (1,135 | ) | | | (1,058 | ) |
| Actuarial gain (loss) | | | 7,817 | | | | (1,253 | ) | | | (551 | ) | | | (1,563 | ) | | | (1,418 | ) | | | (445 | ) |
| Currency translation | | | — | | | | 1,845 | | | | — | | | | (6,377 | ) | | | 291 | | | | (555 | ) |
| Acquisitions | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 8,043 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Curtailments/settlements | | | (987 | ) | | | — | | | | (256 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Other | | | — | | | | 556 | | | | — | | | | 41 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Obligation at December 31 | | $ | 81,212 | | | $ | 39,342 | | | $ | 72,689 | | | $ | 36,811 | | | $ | 18,059 | | | $ | 21,767 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
56
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefits | | | | | | | Pension Benefits | | Other Benefits | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | Other Benefits | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | | | | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| | |
| CHANGE IN BENEFIT OBLIGATION | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Obligation at January 1 | | | $ | 81,212 | | | $ | 39,342 | | | $ | 72,689 | | | $ | 36,811 | | | $ | 18,059 | | | $ | 21,767 | |
| Service cost | | | | 1,665 | | | | 719 | | | | 1,551 | | | | 824 | | | | 528 | | | | 468 | |
| Interest cost | | | | 4,525 | | | | 2,148 | | | | 4,375 | | | | 2,122 | | | | 1,008 | | | | 1,018 | |
| Plan amendments | | | | 101 | | | | 128 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (400 | ) | | | (2,932 | ) |
| Benefits paid | | | | (3,567 | ) | | | (1,542 | ) | | | (4,233 | ) | | | (1,563 | ) | | | (842 | ) | | | (1,135 | ) |
| Actuarial (gain) loss | | | | 6,166 | | | | 3,561 | | | | 7,817 | | | | (1,253 | ) | | | 1,598 | | | | (1,418 | ) |
| Currency translation | | | | — | | | | (2,117 | ) | | | — | | | | 1,845 | | | | 117 | | | | 291 | |
| Curtailments/settlements | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (987 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Other | | | | — | | | | 6 | | | | — | | | | 556 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Obligation at December 31 | | | $ | 90,102 | | | $ | 42,245 | | | $ | 81,212 | | | $ | 39,342 | | | $ | 20,068 | | | $ | 18,059 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| CHANGE IN PLAN ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at January 1 | | $ | 39,974 | | | $ | 11,975 | | | $ | 63,612 | | | $ | 18,301 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 53,210 | | | $ | 15,376 | | | $ | 39,974 | | | $ | 11,975 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Actual return on plan assets | | | 9,638 | | | | 1,848 | | | | (19,523 | ) | | | (1,670 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5,631 | | | | 1,842 | | | | 9,638 | | | | 1,848 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Employer contributions | | | 8,818 | | | | 1,812 | | | | 902 | | | | 1,432 | | | | 1,135 | | | | 1,058 | | | | 2,873 | | | | 1,765 | | | | 8,818 | | | | 1,812 | | | | 842 | | | | 1,135 | |
| Benefits paid | | | (4,233 | ) | | | (1,563 | ) | | | (4,761 | ) | | | (1,475 | ) | | | (1,135 | ) | | | (1,058 | ) | | | (3,567 | ) | | | (1,542 | ) | | | (4,233 | ) | | | (1,563 | ) | | | (842 | ) | | | (1,135 | ) |
| Currency translation | | | — | | | | 1,279 | | | | — | | | | (4,587 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (381 | ) | | | — | | | | 1,279 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Settlements | | | (987 | ) | | | — | | | | (256 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (987 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Other | | | — | | | | 25 | | | | — | | | | (26 | ) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | — | | | | 340 | | | | — | | | | 25 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at December 31 | | $ | 53,210 | | | $ | 15,376 | | | $ | 39,974 | | | $ | 11,975 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 58,147 | | | $ | 17,400 | | | $ | 53,210 | | | $ | 15,376 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Funded status at December 31 | | $ | (28,002 | ) | | $ | (23,966 | ) | | $ | (32,715 | ) | | $ | (24,836 | ) | | $ | (18,059 | ) | | $ | (21,767 | ) | | $ | (31,955 | ) | | $ | (24,845 | ) | | $ | (28,002 | ) | | $ | (23,966 | ) | | $ | (20,068 | ) | | $ | (18,059 | ) |
| COMPONENTS ON THE CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | $ | (601 | ) | | $ | (1,032 | ) | | $ | (651 | ) | | $ | (876 | ) | | $ | (968 | ) | | $ | (1,303 | ) | | $ | (657 | ) | | $ | (653 | ) | | $ | (601 | ) | | $ | (1,032 | ) | | $ | (999 | ) | | $ | (968 | ) |
| Noncurrent liabilities | | | (27,401 | ) | | | (22,934 | ) | | | (32,064 | ) | | | (23,960 | ) | | | (17,091 | ) | | | (20,464 | ) | | | (31,298 | ) | | | (24,192 | ) | | | (27,401 | ) | | | (22,934 | ) | | | (19,069 | ) | | | (17,091 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net liability at December 31 | | $ | (28,002 | ) | | $ | (23,966 | ) | | $ | (32,715 | ) | | $ | (24,836 | ) | | $ | (18,059 | ) | | $ | (21,767 | ) | | $ | (31,955 | ) | | $ | (24,845 | ) | | $ | (28,002 | ) | | $ | (23,966 | ) | | $ | (20,068 | ) | | $ | (18,059 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accumulated benefit obligation for all defined benefit pension plans was $114.8$126.4 million and $103.3$114.8 million at December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, respectively.
The weighted average assumptions used in the measurement of the Company’s benefit obligation at December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | U.S. Plans | | | Non-U.S. Plans | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | 2009 | | | 2008 | |
| |
| Discount rate | | | 5.80 | % | | | 6.30 | % | | | 5.88 | % | | | 5.73 | % |
| Rate of compensation increase | | | 3.89 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 3.35 | % | | | 3.17 | % |
The pretax amounts recognized in Accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefits | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | Other Benefits | |
| | | U.S. | | | Non-U.S. | | | U.S. | | | Non-U.S | | | 2009 | | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Prior service cost (credit) | | $ | 735 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 1,047 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | (2,966 | ) | | $ | (330 | ) |
| Net loss | | | 38,043 | | | | 5,466 | | | | 41,403 | | | | 7,662 | | | | 661 | | | | 1,991 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 38,778 | | | $ | 5,474 | | | $ | 42,450 | | | $ | 7,670 | | | $ | (2,305 | ) | | $ | 1,661 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | U.S. Plans | | | Non-U.S. Plans | |
| | | 2010 | | | 2009 | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| |
| Discount rate | | | 5.20 | % | | | 5.80 | % | | | 5.35 | % | | | 5.88 | % |
| Rate of compensation increase | | | 3.90 | % | | | 3.89 | % | | | 3.37 | % | | | 3.35 | % |
57
54
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The pretax amounts recognized in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) as of December 31, 2010 and 2009 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefits | | | | | | | |
| | | 2010 | | | 2009 | | | Other Benefits | |
| | | U.S. | | | Non-U.S. | | | U.S. | | | Non-U.S | | | 2010 | | | 2009 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Prior service cost (credit) | | $ | 597 | | | $ | 131 | | | $ | 735 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | (3,044 | ) | | $ | (2,966 | ) |
| Net loss | | | 38,813 | | | | 7,629 | | | | 38,043 | | | | 5,466 | | | | 2,313 | | | | 661 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 39,410 | | | $ | 7,760 | | | $ | 38,778 | | | $ | 5,474 | | | $ | (731 | ) | | $ | (2,305 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The amounts in Accumulated other comprehensive lossincome (loss) as of December 31, 2009,2010, that are expected to be recognized as components of net periodic benefit cost during 20102011 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Non-U.S.
| | Other
| | | | | | | Non-U.S.
| | Other
| | | |
| | | U.S. Pension
| | Pension Benefit
| | Post-Retirement
| | | | | U.S. Pension
| | Pension Benefit
| | Post-Retirement
| | | |
| | | Benefit Plans | | Plans | | Benefit Plans | | Total | | | Benefit Plans | | Plans | | Benefit Plans | | Total | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Prior service cost (credit) | | $ | 228 | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | (305 | ) | | $ | (76 | ) | | $ | 178 | | | $ | 9 | | | $ | (346 | ) | | $ | (159 | ) |
| Net loss (gain) | | | 4,279 | | | | 308 | | | | (45 | ) | | | 4,542 | | |
| Net loss | | | | 4,146 | | | | 415 | | | | 190 | | | | 4,751 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 4,507 | | | $ | 309 | | | $ | (350 | ) | | $ | 4,466 | | | $ | 4,324 | | | $ | 424 | | | $ | (156 | ) | | $ | 4,592 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The following tables provide the components of, and the weighted average assumptions used to determine, the net periodic benefit cost for the plans in 2010, 2009 2008 and 2007:2008:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefits | | | Pension Benefits | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Service cost | | $ | 1,551 | | | $ | 824 | | | $ | 1,765 | | | $ | 932 | | | $ | 1,876 | | | $ | 874 | | | $ | 1,665 | | | $ | 719 | | | $ | 1,551 | | | $ | 824 | | | $ | 1,765 | | | $ | 932 | |
| Interest cost | | | 4,375 | | | | 2,122 | | | | 4,484 | | | | 1,901 | | | | 4,288 | | | | 1,626 | | | | 4,525 | | | | 2,148 | | | | 4,375 | | | | 2,122 | | | | 4,484 | | | | 1,901 | |
| Expected return on plan assets | | | (3,505 | ) | | | (780 | ) | | | (5,169 | ) | | | (1,017 | ) | | | (5,242 | ) | | | (1,075 | ) | | | (4,396 | ) | | | (945 | ) | | | (3,505 | ) | | | (780 | ) | | | (5,169 | ) | | | (1,017 | ) |
| Net amortization | | | 5,299 | | | | 370 | | | | 2,244 | | | | 381 | | | | 2,730 | | | | 715 | | | | 4,401 | | | | 302 | | | | 5,299 | | | | 370 | | | | 2,244 | | | | 381 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net periodic benefit cost | | $ | 7,720 | | | $ | 2,536 | | | $ | 3,324 | | | $ | 2,197 | | | $ | 3,652 | | | $ | 2,140 | | | $ | 6,195 | | | $ | 2,224 | | | $ | 7,720 | | | $ | 2,536 | | | $ | 3,324 | | | $ | 2,197 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Other Benefits | | | Other Benefits | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Service cost | | $ | 468 | | | $ | 607 | | | $ | 611 | | | $ | 528 | | | $ | 468 | | | $ | 607 | |
| Interest cost | | | 1,018 | | | | 1,328 | | | | 1,230 | | | | 1,008 | | | | 1,018 | | | | 1,328 | |
| Net amortization | | | (385 | ) | | | 137 | | | | 227 | | | | (370 | ) | | | (385 | ) | | | 137 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net periodic benefit cost | | $ | 1,101 | | | $ | 2,072 | | | $ | 2,068 | | | $ | 1,166 | | | $ | 1,101 | | | $ | 2,072 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | U.S. Plans | | Non-U.S. Plans | | U.S. Plans | | Non-U.S. Plans | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 | |
| |
| Discount rate | | | 6.30 | % | | | 6.40 | % | | | 5.80 | % | | | 5.73 | % | | | 5.48 | % | | | 4.80 | % | | | 5.80 | % | | | 6.30 | % | | | 6.40 | % | | | 5.88 | % | | | 5.73 | % | | | 5.48 | % |
| Expected return on plan assets | | | 8.50 | % | | | 8.50 | % | | | 8.50 | % | | | 6.05 | % | | | 5.82 | % | | | 6.00 | % | | | 8.50 | % | | | 8.50 | % | | | 8.50 | % | | | 6.28 | % | | | 6.05 | % | | | 5.82 | % |
| Rate of compensation increase | | | 4.00 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 3.17 | % | | | 3.92 | % | | | 3.72 | % | | | 3.89 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 4.00 | % | | | 3.35 | % | | | 3.17 | % | | | 3.92 | % |
5855
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following table provides pretax amounts recognized in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in 2009:2010:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefits | | | Pension Benefits | |
| | | | | | | Other
| | | | | | | Other
| |
| | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | Benefits | | | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | Benefits | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Net gain (loss) in current year | | $ | (1,683 | ) | | $ | 2,320 | | | $ | 1,418 | | |
| Net loss in current year | | | $ | (4,931 | ) | | $ | (2,663 | ) | | $ | (1,598 | ) |
| Prior service cost | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,932 | | | | (101 | ) | | | (128 | ) | | | 400 | |
| Amortization of prior service cost (credit) | | | 312 | | | | 1 | | | | (304 | ) | | | 239 | | | | 5 | | | | (324 | ) |
| Amortization of net loss (gain) | | | 4,986 | | | | 369 | | | | (81 | ) | | | 4,161 | | | | 297 | | | | (46 | ) |
| Exchange rate effect on amounts in OCI | | | — | | | | (418 | ) | | | 11 | | | | — | | | | 204 | | | | (6 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | $ | 3,615 | | | $ | 2,272 | | | $ | 3,976 | | | $ | (632 | ) | | $ | (2,285 | ) | | $ | (1,574 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The discount rates for our plans are derived by matching the plan’s cash flows to a yield curve that provides the equivalent yields on zero-coupon bonds for each maturity. The discount rate selected is the rate that produces the same present value of cash flows.
In selecting the expected rate of return on plan assets, the Company considers the historical returns and expected returns on plan assets. The expected returns are evaluated using asset return class, variance and correlation assumptions based on the plan’s target asset allocation and current market conditions.
Prior service costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over the average remaining service period of active participants. Gains and losses in excess of 10% of the greater of the benefit obligation or the market value of assets are amortized over the average remaining service period of active participants. Costs of bargaining unit-sponsored multi-employer plans and defined contribution plans were $7.2 million, $9.6 million and $9.8 million for 2010, 2009 and $9.4 million for 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively.
For measurement purposes, a 7.6%7.9% weighted average annual rate of increase in the per capita cost of covered health care benefits was assumed for 2009.2010. The rate was assumed to decrease gradually each year to a rate of 5.40%4.50% for 2015,2028, and remain at that level thereafter. Assumed health care cost trend rates have a significant effect on the amounts reported for the health care plans. A 1% increase in the assumed health care cost trend rates would increase the service and interest cost components of the net periodic benefit cost by $0.1 million and the health care component of the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation by $1.5 million. A 1% decrease in the assumed health care cost trend rate would decrease the service and interest cost components of the net periodic benefit cost by $0.1 million and the health care component of the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation by $1.2$1.3 million.
Plan Assets
The Company’s pension plan weighted average asset allocations at December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, by asset category, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | 2008 | | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| |
| Equity securities | | | 66 | % | | | 53 | % | | | 67 | % | | | 66 | % |
| Fixed income securities | | | 34 | | | | 43 | | | | 33 | | | | 34 | |
| Other | | | — | | | | 4 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
5956
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following table summarizestables summarize the basis used to measure defined benefit plans’ assets at fair value at December 31, 2010 and 2009:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Basis of Fair Value Measurement | | | Basis of Fair Value Measurement | |
| | | Outstanding Balances | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | | Outstanding Balances | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Equities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Equity | | | $ | 13,644 | | | $ | 13,644 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Absolute return funds(1) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | $ | 11,107 | | | $ | 11,107 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | | 38,325 | | | | 18,549 | | | | 19,776 | | | | — | |
| Non U.S. | | | 6,749 | | | | 6,749 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 22,838 | | | | 17,400 | | | | 5,438 | | | | — | |
| Absolute return funds(1) | | | 49,386 | | | | 17,930 | | | | 31,456 | | | | — | | |
| Other(2) | | | 1,343 | | | | 1,343 | | | | — | | | | — | | |
Other(2) | | | | 740 | | | | 740 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 68,585 | | | $ | 37,129 | | | $ | 31,456 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 75,547 | | | $ | 50,333 | | | $ | 25,214 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Basis of Fair Value Measurement | |
| | | Outstanding Balances | | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
| |
| Equities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | $ | 11,107 | | | $ | 11,107 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Non U.S. | | | 6,749 | | | | 6,749 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Absolute return funds(1) | | | 49,386 | | | | 17,930 | | | | 31,456 | | | | — | |
Other(2) | | | 1,344 | | | | 1,344 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | $ | 68,586 | | | $ | 37,130 | | | $ | 31,456 | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | Primarily funds invested by managers that have a global mandate with the flexibility to allocate capital broadly across a wide range of asset classes and strategies including, but not limited to equities, fixed income, commodities, interest rate futures, currencies and other securities to outperform an agreed benchmark with specific return and volatility targets. |
| |
| (2) | | Primarily cash and cash equivalents. |
Equities that are valued using quoted prices are valued at the published market prices. Equities in a common collective trust or a registered investment company that are valued using significant other observable inputs are valued at the net asset value (NAV)(“NAV”) provided by the fund administrator. The NAV is based on value of the underlying assets owned by the fund minus its liabilities. Fixed income securities that are valued using significant other observable inputs are valued at prices obtained from independent financial service industry-recognized vendors.
Investment Policies and Strategies
The investment objectives of the Company’s plan assets are to earn the highest possible rate of return consistent with the tolerance for risk as determined periodically by the Company in its role as a fiduciary. The general guidelines of asset allocation of fund assets are that “equities” will represent from 55% to 75% of the market value of total fund assets with a target of 66%, and “fixed income” obligations, including cash, will represent from 25% to 45% with a target of 34%. The term “equities” includes common stock, convertible bonds and convertible stock. The term “fixed income” includes preferred stockand/or contractual payments with a specific maturity date. The Company strives to maintain asset allocations within the designated ranges by conducting periodic reviews of fund allocations and plan liquidity needs, and rebalancing the portfolio accordingly. The total fund performance is monitored and results measured using a 3- to5-year moving average against long-term absolute and relative return objectives to meet actuarially determined forecasted benefit obligations. No restrictions are placed on the selection of individual investments by the qualified investment fund managers. The performance of the investment fund
57
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
managers is reviewed on a regular basis, using appointed professional independent advisors. As of December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, there were no shares of the Company’s stock held in plan assets.
Cash Flows
The Company expects to contribute approximately $4.7$7.9 million to its defined benefit plans and $1.0 million to its other postretirement benefit plans in 2010.2011. The Company also expects to contribute approximately $11.8$12.3 million to its defined contribution plans in 2010.
60
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
2011.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Estimated Future Benefit Payments
The future estimated benefit payments for the next five years and the five years thereafter are as follows: 2010 — $7.7 million; 2011 — $8.0$8.6 million; 2012 — $8.7$8.8 million; 2013 — $8.6$8.8 million; 2014-$9.92014 — $10.0 million; 2015 — $9.5 million; 2016 to 20192020 — $48.7$50.4 million.
| |
18.15. | Quarterly Results of Operations (Unaudited) |
The following table summarizes the unaudited quarterly results of operations for the years ended December 31, 20092010 and 2008.2009.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 Quarters | | 2008 Quarters(1) |
| | | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth | | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth |
| |
| Net sales | | $ | 326,613 | | | $ | 336,455 | | | $ | 323,249 | | | $ | 343,344 | | | $ | 371,662 | | | $ | 397,310 | | | $ | 365,193 | | | $ | 355,306 | |
| Gross profit | | | 123,194 | | | | 131,101 | | | | 129,058 | | | | 139,033 | | | | 152,480 | | | | 161,510 | | | | 147,784 | | | | 135,659 | |
| Operating income(2) | | | 39,161 | | | | 46,735 | | | | 46,517 | | | | 52,441 | | | | 65,412 | | | | 72,110 | | | | 30,804 | | | | 37,630 | |
| Net income | | $ | 22,605 | | | $ | 27,922 | | | $ | 29,777 | | | $ | 33,087 | | | $ | 39,603 | | | $ | 45,060 | | | $ | 19,883 | | | $ | 22,480 | |
| Basic EPS | | $ | .28 | | | $ | .35 | | | $ | .37 | | | $ | .41 | | | $ | .49 | | | $ | .55 | | | $ | .24 | | | $ | .28 | |
| Diluted EPS | | $ | .28 | | | $ | .34 | | | $ | .37 | | | $ | .40 | | | $ | .48 | | | $ | .54 | | | $ | .24 | | | $ | .27 | |
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding | | | 79,513 | | | | 79,675 | | | | 79,740 | | | | 79,937 | | | | 81,067 | | | | 81,322 | | | | 81,572 | | | | 80,529 | |
| Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | | | 80,219 | | | | 80,507 | | | | 80,879 | | | | 81,303 | | | | 82,288 | | | | 82,746 | | | | 82,957 | | | | 81,289 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2010 Quarters | | | 2009 Quarters | |
| | | First | | | Second | | | Third | | | Fourth | | | First | | | Second | | | Third | | | Fourth | |
| |
| Net sales | | $ | 355,598 | | | $ | 378,526 | | | $ | 373,731 | | | $ | 405,218 | | | $ | 326,613 | | | $ | 336,455 | | | $ | 323,249 | | | $ | 343,344 | |
| Gross profit | | | 147,541 | | | | 154,821 | | | | 154,133 | | | | 161,988 | | | | 123,194 | | | | 131,101 | | | | 129,058 | | | | 139,033 | |
| Operating income | | | 57,893 | | | | 62,780 | | | | 62,439 | | | | 66,004 | | | | 39,161 | | | | 46,735 | | | | 46,517 | | | | 52,441 | |
| Net income | | | 36,625 | | | | 40,398 | | | | 38,564 | | | | 41,513 | | | | 22,605 | | | | 27,922 | | | | 29,777 | | | | 33,087 | |
| Basic EPS | | $ | .45 | | | $ | .50 | | | $ | .47 | | | $ | .51 | | | $ | .28 | | | $ | .35 | | | $ | .37 | | | $ | .41 | |
| Diluted EPS | | $ | .45 | | | $ | .49 | | | $ | .47 | | | $ | .50 | | | $ | .28 | | | $ | .34 | | | $ | .37 | | | $ | .40 | |
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding | | | 80,080 | | | | 80,369 | | | | 80,517 | | | | 80,899 | | | | 79,513 | | | | 79,675 | | | | 79,740 | | | | 79,937 | |
| Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | | | 81,509 | | | | 81,800 | | | | 81,938 | | | | 82,686 | | | | 80,219 | | | | 80,507 | | | | 80,879 | | | | 81,303 | |
| | |
(1)16. | | Certain prior year amounts have been restated to reflect the LIFO to FIFO inventory costing change. Statements (continue |
|
(2) | | Third quarter 2008 operating income includes a $30.1 million goodwill impairment charge for Fluid Management.Subsequent Events |
On January 20, 2011, the Company acquired Advanced Thin Films, LLC (“AT Films”) for cash consideration of approximately $32.0 million. AT Films, with annual revenues of approximately $9.0 million, specializes in optical components and coatings for applications in the fields of scientific research, defense, aerospace, telecommunications and electronics manufacturing. AT Films’ core competence is in the design and manufacture of filters, splitters, reflectors and mirrors with the precise physical properties required to support their customers’ most challenging and cutting-edge optical applications. Headquartered in Boulder, Colorado, AT Films will operate within the Health & Science Technologies Segment as a part of the IDEX optical products platform.
On January 25, 2011, the Company entered into a merger agreement to acquire Microfluidics International Corporation (“Microfluidics”) at a price of $1.35 net per share in cash. The transaction is expected to close in the first quarter of 2011. With annual revenues of approximately $16.0 million, Microfluidics is a global leader in the design and manufacture of laboratory and commercial equipment used in the production of micro and nano scale materials for the pharmaceutical and chemical markets. Microfluidics is the exclusive producer of the Microfluidizer® family of high shear fluid processors for uniform particle size reduction, robust cell disruption and nanoparticle creation. Microfluidics’ product and service offerings will enhance the Company’s micro fluidics and micro particle technology position. Microfluidics is headquartered in Newton, MA.
While allocation of the purchase price is not complete, the Company believes that the majority of the purchase price will be allocated to goodwill and intangibles assets for both acquisitions.
6158
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of IDEX Corporation
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of IDEX Corporation and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009.2010. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of the Company as of December 31, 20092010 and 2008,2009, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009,2010, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
As discussed in Note 2, in 2009, the Company changed its method of accounting for approximately 85% of its net inventories from thelast-in, first-out method to thefirst-in, first-out method and, retrospectively, adjusted the 2008 and 2007 financial statements for the change.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009,2010, based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated February 26, 2010,24, 2011, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Deloitte & Touche LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 26, 201024, 2011
6259
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of IDEX Corporation
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of IDEX Corporation and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2009,2010, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. As described in Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management excluded from its assessment the internal control over financial reporting at Precision Polymer Engineering Limited (“PPE”), which was acquired on April 15, 2010, OBL, S.r.l. (“OBL”), which was acquired on July 21, 2010, Periflo, which was acquired on September 17, 2010, and Fitzpatrick, Inc. (“Fitzpatrick”), which was acquired on November 1, 2010. These exclusions constitute 7.6% and 5.6% of net and total assets, respectively, 2.7% of net sales, and 2.8% of net income of the consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2010. Accordingly, our audit did not include the internal control over financial reporting at PPE, OBL, Periflo, and Fitzpatrick. The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company’s board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“generally accepted accounting principles”). A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009,2010, based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule as of and for the year ended December 31, 2009,2010, of the Company and our report dated February 26, 2010,24, 2011, expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule and included an explanatory paragraph referring to the Company’s change in the method of accounting for 85% of the Company’s net inventories from thelast-in, first-out method to thefirst-in, first-out method in 2009.schedule.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Deloitte & Touche LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 26, 201024, 2011
6360
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Internal control over financial reporting refers to the process designed by, or under the supervision of, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, and effected by our board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, and includes those policies and procedures that:
| | |
| | • | Pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; |
| |
| | • | Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and |
| |
| | • | Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Internal control over financial reporting cannot provide absolute assurance of achieving financial reporting objectives because of its inherent limitations. Internal control over financial reporting is a process that involves human diligence and compliance and is subject to lapses in judgment and breakdowns resulting from human failures. Internal control over financial reporting also can be circumvented by collusion or improper management override. Because of such limitations, there is a risk that material misstatements may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by internal control over financial reporting. However, these inherent limitations are known features of the financial reporting process. Therefore, it is possible to design into the process safeguards to reduce, though not eliminate, this risk. Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting for the Company. Management has used the framework set forth in the report entitled “Internal Control — Integrated Framework” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission to assess the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Management has concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2009.2010.
The Company completed the acquisitions of PPE in April 2010, OBL in July 2010, Periflo in September 2010 and Fitzpatrick in November 2010. Due to the timing of the acquisitions, management has excluded these acquisitions from our evaluation of effectiveness of internal controls over financial reporting. This exclusion represented 2.7% of total sales and 2.8% of net income as well as 7.6% of net assets and 5.6% of total assets for the year ended December 31, 2010.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009,2010, has been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which appears herein.
Lawrence D. Kingsley
Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer
Dominic A. Romeo
Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
Northbrook,Lake Forest, Illinois
February 26, 201024, 2011
6461
| |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure. |
None.
| |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures. |
The Company maintains disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the Company’s Exchange Act reports is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
As required by SECRule 13a-15(b), the Company carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on the foregoing, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective.effective as of December 31, 2010.
The information set forth under the captions “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” and “Management’sManagement’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting”Reporting appearing on pages 62-64page 61 of Part II. Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Datathis report is incorporated hereininto this Item 9A by reference.
There has been no change in the Company’s internal controlscontrol over financial reporting during the Company’s most recent fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
| |
| Item 9B. | Other Information. |
None.
PART III
| |
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance. |
Information under the headings “Election of Directors” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” and the information under the subheading “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Committees,” in the Company’s 20102011 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference. Information regarding executive officers of the Company is located in Part I. Item 1. of this report under the caption “Executive Officers of the Registrant.”
The Company has adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics applicable to the Company’s directors, officers (including the Company’s principal executive officer, and principal financial &officer and principal accounting officer) and employees. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, along with the Audit Committee Charter, Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee Charter, Compensation Committee Charter and Corporate Governance Guidelines are available on the Company’s website atwww.idexcorp.com.
In the event that we amend or waive any of the provisions of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics applicable to our principal executive officer, or principal financial &officer or principal accounting officer, we intend to disclose the same on the Company’s website.
| |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation. |
Information under the heading “Executive Compensation” in the Company’s 20102011 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
6562
| |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters. |
Information under the heading “Security Ownership” and the information under the subheading “Equity Compensation Plans” in the Company’s 20102011 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table sets forth certain information with respect to the Company’s equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2010.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Number of Securities
| | | Weighted-Average
| | | Number of Securities
| |
| | | To be Issued Upon
| | | Exercise Price of
| | | Remaining Available for
| |
| | | Exercise of
| | | Outstanding
| | | Future Issuance Under
| |
| | | Outstanding Options,
| | | Options, Warrants
| | | Equity Compensation
| |
| Plan Category | | Warrants and Rights | | | and Rights | | | Plans(1)(2) | |
| |
| Equity compensation plans approved by the Company’s shareholders | | | 6,379,628 | | | $ | 26.85 | | | | 4,288,413 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 6,379,628 | | | $ | 26.85 | | | | 4,288,413 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | |
| (1) | | Excludes securities to be issued upon the exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights. |
|
| (2) | | All Deferred Compensation Units (“DCUs”) issued under the Directors Deferred Compensation Plan and Deferred Compensation Plan for Non-officer Presidents are to be issued under the Company’s Incentive Award Plan and any DCUs remaining in these plans were eliminated by shareholder approval on April 8, 2008. DCUs issued under the Deferred Compensation Plan for Officers continue to be issued under the Incentive Award Plan. |
The number of DCUs is determined by dividing the amount deferred by the closing price of the Company’s Common Stock the day before the date of deferral. The DCUs are entitled to receive dividend equivalents which are reinvested in DCUs based on the same formula for investment of a participant’s deferral. Since deferred compensation is payable upon separation of service within the meaning of Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code, no benefits are payable prior to the date that is six months after the date of separation of service, or the date of death of the employee, if earlier.
| |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence. |
No certain relationships exist. Information under the heading “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Committees” in the Company’s 20102011 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
| |
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
Information under the heading “Principal Accountant Fees and Services” in the Company’s 20102011 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
63
PART IV
| |
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule. |
(A) 1. Financial Statements
Consolidated financial statements filed as part of this report are listed under Part II. Item 8. “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this Annual Report onForm 10-K..
2. Financial Statement Schedule
| | | | | |
| | | 20092010 Form
|
| | | 10-K Page |
| |
| Schedule II — Valuation and Qualifying Accounts | | | 6765 | |
All other schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, not required, or because the required information is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements of the Company or the Notes thereto.
3. Exhibits
The exhibits filed with this report are listed on the “Exhibit Index.”
(B) Exhibit Index
Reference is made to the Exhibit Index beginning on page 6967 hereof.
6664
Schedule
IDEX CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2010, 2009 2008 AND 20072008
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Charged
| | | | | | | | | | Charged
| | | | | | | |
| | | Balance
| | to Costs
| | | | | | Balance
| | Balance
| | to Costs
| | | | | | Balance
| |
| | | Beginning
| | and
| | | | | | End of
| | Beginning
| | and
| | | | | | End of
| |
Description | | of Year | | Expenses(1) | | Deductions(2) | | Other(3) | | Year | | of Year | | Expenses(1) | | Deductions(2) | | Other(3) | | Year | |
| | | (In thousands) | | | | | | (In thousands) | | | | | |
| |
| Year Ended December 31, 2010: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deducted from assets to which they apply: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable reserves | | | $ | 6,160 | | | $ | 945 | | | $ | 1,879 | | | $ | 96 | | | $ | 5,322 | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2009: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deducted from assets to which they apply: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable reserves | | $ | 5,600 | | | $ | 1,789 | | | $ | 617 | | | $ | (612 | ) | | $ | 6,160 | | | | 5,600 | | | | 1,789 | | | | 617 | | | | (612 | ) | | | 6,160 | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2008: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deducted from assets to which they apply: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable reserves | | | 5,746 | | | | 1,379 | | | | 1,621 | | | | 96 | | | | 5,600 | | | | 5,746 | | | | 1,379 | | | | 1,621 | | | | 96 | | | | 5,600 | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2007: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deducted from assets to which they apply: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable reserves | | | 3,545 | | | | 2,636 | | | | 625 | | | | 190 | | | | 5,746 | | |
| | |
| (1) | | Includes provision for doubtful accounts, sales returns and sales discounts granted to customers. |
| |
| (2) | | Represents uncollectible accounts, net of recoveries. |
| |
| (3) | | Represents acquisition, divestiture, translation and reclassification adjustments. |
6765
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
IDEX CORPORATION
Dominic A. Romeo
Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
Date: February 26, 201024, 2011
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | |
Signature | | Title | | Date |
| |
| | | | | |
/s/ LAWRENCE D. KINGSLEY
Lawrence D. Kingsley | | Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ DOMINIC A. ROMEO
Dominic A. Romeo | | Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ MICHAEL J. YATES
Michael J. Yates | | Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting Officer) | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ BRADLEY J. BELL
Bradley J. Bell | | Director | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ RUBY R. CHANDY
Ruby R. Chandy | | Director | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ WILLIAM M. COOK
William M. Cook | | Director | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ FRANK S. HERMANCE
Frank S. Hermance | | Director | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ GREGORY F. MILZCIK
Gregory F. Milzcik | | Director | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | |
/s/ ERNEST J. MROZEK
Ernest J. Mrozek | | Director | | February 24, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ NEIL A. SPRINGER
Neil A. Springer | | Director | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
| | | | | |
/s/ MICHAEL T. TOKARZ
Michael T. Tokarz | | Director | | February 26, 201024, 2011 |
6866
Exhibit Index
| | | | | |
Exhibit
| | |
Number | | Description |
| |
| | 3 | .1 | | Restated Certificate of Incorporation of IDEX Corporation (formerly HI, Inc.) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of IDEX, et al., Registration No. 33-21205, as filed on April 21, 1988) |
| | 3 | .1(a) | | Amendment to Restated Certificate of Incorporation of IDEX Corporation (formerly HI, Inc.) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.1 (a) to the Quarterly Report of IDEX on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 1996, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 3 | .1(b) | | Amendment to Restated Certificate of Incorporation of IDEX Corporation (formerly HI, Inc.) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.1 (b) to the Current Report of IDEX on Form 8-K March 24, 2005, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 3 | .2 | | Amended and Restated By-Laws of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.2 to Post-Effective Amendment No. 2 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of IDEX, et al., Registration No. 33-21205, as filed on July 17, 1989) |
| | 3 | .2(a) | | Amended and Restated Article III, Section 13 of the Amended and Restated By-Laws of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.2 (a) to Post-Effective Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of IDEX, et al., Registration No. 33-21205, as filed on February 12, 1990) |
| | 4 | .1 | | Restated Certificate of Incorporation and By-Laws of IDEX Corporation (filed as Exhibits No. 3.1 through 3.2 (a)) |
| | 4 | .4 | | Specimen Certificate of Common Stock of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.3 to the Registration Statement on Form S-2 of IDEX, et al., Registration No. 33-42208, as filed on September 16, 1991) |
| | 4 | .5 | | Credit Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2006, among IDEX Corporation, Bank of America N.A. as Agent and Issuing Bank, and the Other Financial Institutions Party Hereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report of IDEX on Form 8-K dated December 22, 2006, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 4 | .5(a) | | Amendment No. 2 to Credit Agreement, dated as of September 29, 2008, among IDEX Corporation, Bank of America N.A. as Agent and Issuing Bank, and the other financial institutions party hereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.3 (a) to the Quarterly Report of IDEX on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2008, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 4 | .6 | | Credit Lyonnais Uncommitted Line of Credit, dated as of December 3, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6 to the Annual Report of IDEX on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2001, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 4 | .6(a) | | Amendment No. 8 dated as of December 12, 2007 to the Credit Lyonnais Uncommitted Line of Credit Agreement dated December 3, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6 (a) to the Annual Report of IDEX on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 4 | .7 | | Term Loan Agreement, dated April 18, 2008, among IDEX Corporation, Bank of America N.A. as Agent, and the other financial institutions party hereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 to the Current Report of IDEX on Form 8-K dated April 18, 2008, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 10 | .1** | | Revised and Restated IDEX Management Incentive Compensation Plan for Key Employees Effective January 1, 2003 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report of IDEX on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2003, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| | 10 | .2** | | Form of Indemnification Agreement of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.23 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of IDEX, et al., Registration No. 33-28317, as filed on April 26, 1989) |
69
| | | | |
Exhibit
| | |
Number | | Description |
| |
| 3.1 | 10 | .3*Restated Certificate of Incorporation of IDEX Corporation (formerly HI, Inc.) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.1 to the Registration Statement onForm S-1 of IDEX, et al., RegistrationNo. 33-21205, as filed on April 21, 1988) |
| 3.1(a) | | Amendment to Restated Certificate of Incorporation of IDEX Corporation (formerly HI, Inc.) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.1 (a) to the Quarterly Report of IDEX onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 1996, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 3.1(b) | | Amendment to Restated Certificate of Incorporation of IDEX Corporation (formerly HI, Inc.) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.1 (b) to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K March 24, 2005, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 3.2 | | Amended and Restated By-Laws of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.2 to Post-Effective Amendment No. 2 to the Registration Statement onForm S-1 of IDEX, et al., RegistrationNo. 33-21205, as filed on July 17, 1989) |
| 3.2(a) | | Amended and Restated Article III, Section 13 of the Amended and Restated By-Laws of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 3.2 (a) to Post-Effective Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement onForm S-1 of IDEX, et al., RegistrationNo. 33-21205, as filed on February 12, 1990) |
| 4.1 | | Restated Certificate of Incorporation and By-Laws of IDEX Corporation (filed as Exhibits No. 3.1 through 3.2 (a)) |
| 4.4 | | Specimen Certificate of Common Stock of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.3 to the Registration Statement onForm S-2 of IDEX, et al., RegistrationNo. 33-42208, as filed on September 16, 1991) |
| 4.5 | | Credit Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2006, among IDEX Corporation, Bank of America N.A. as Agent and Issuing Bank, and the Other Financial Institutions Party Hereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K dated December 22, 2006, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 4.5(a) | | Amendment No. 2 to Credit Agreement, dated as of September 29, 2008, among IDEX Corporation, Bank of America N.A. as Agent and Issuing Bank, and the other financial institutions party hereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.3 (a) to the Quarterly Report of IDEX onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2008, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 4.6 | | Credit Lyonnais Uncommitted Line of Credit, dated as of December 3, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6 to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2001, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 4.6(a) | | Amendment No. 8 dated as of December 12, 2007 to the Credit Lyonnais Uncommitted Line of Credit Agreement dated December 3, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6 (a) to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007, CommissionFile No. 1-10235) |
| 4.7 | | Term Loan Agreement, dated April 18, 2008, among IDEX Corporation, Bank of America N.A. as Agent, and the other financial institutions party hereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K dated April 18, 2008, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 4.8 | | Master Note Purchase Agreement, dated June 9, 2010 with respect to €81,000,000 2.58% Series 2010 Senior Notes due June 9, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.1 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K filed June 14, 2010, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 4.9 | | Indenture between IDEX Corporation and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, dated as of December 6, 2010 (Debt Securities) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.1 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K filed December 7, 2010, CommissionFile No. 1-10235) |
| 4.10 | | First Supplemental Indenture between IDEX Corporation and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, dated as of December 6, 2010 (as to 4.5% Senior Notes due 2010) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.2 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K filed December 7, 2010, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
67
| | |
Exhibit
| | |
| Number | | Description |
|
| 10.1** | | Revised and Restated IDEX Management Incentive Compensation Plan for Key Employees Effective January 1, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K filed on March 1, 2010, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10.2** | | Form of Indemnification Agreement of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.23 to the Registration Statement onForm S-1 of IDEX, et al., RegistrationNo. 33-28317, as filed on April 26, 1989) |
| 10.3** | | IDEX Corporation Amended and Restated Stock Option Plan for Outside Directors adopted by resolution of the Board of Directors dated as of January 25, 2000 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 of the Quarterly Report of IDEX onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2000, Commission FileNo. 10-10235)1-10235) |
| 10 | .3(a)10.3(a)** | | First Amendment to IDEX Corporation Amended and Restated Stock Option Plan for Outside Directors, adopted by resolution of the Board of Directors dated as of November 20, 2003 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 (a) to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003) |
| 10 | .4*10.4** | | Non-Qualified Stock Option Plan for Non-Officer Key Employees of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.15 to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1992, Commission FileNo. 1-102351)1-10235) |
| 10 | .5*10.5** | | Third Amended and Restated 1996 Stock Option Plan for Non-Officer Key Employees of IDEX Corporation dated January 9, 2003 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registration Statement onForm S-8 of IDEX, RegistrationNo. 333-104768, as filed on April 25, 2003) |
| 10 | .6*10.6** | | Non-Qualified Stock Option Plan for Officers of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.16 to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1992, Commission FileNo. 1-102351)1-10235) |
| 10 | .7*10.7** | | First Amended and Restated 1996 Stock Plan for Officers of IDEX Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 to the Quarterly Report of IDEX onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 1998, Commission FileNo. 1-102351)1-10235) |
| 10 | .8*10.8** | | 2001 Stock Plan for Officers dated March 27, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.2 to the Quarterly Report of IDEX onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2001, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .9*10.9** | | IDEX Corporation Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.17 to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1992, Commission FileNo. 1-102351)1-10235) |
| 10 | .10*10.10** | | Second Amended and Restated IDEX Corporation Directors Deferred Compensation Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.14 (b)10.14(b) to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1997, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .11*10.11** | | IDEX Corporation 1996 Deferred Compensation Plan for Officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.8 to the Registration Statement onForm S-8 of IDEX, et al., RegistrationNo. 333-18643, as filed on December 23, 1996) |
| 10 | .11(a)10.11(a)** | | First Amendment to the IDEX Corporation 1996 Deferred Compensation Plan for Officers, dated March 23, 2004 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 to the Quarterly Report of IDEX onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2004)2004, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .12*10.12** | | IDEX Corporation 1996 Deferred Compensation Plan for Non-Officer Presidents (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 4.7 to the Registration Statement onForm S-8 of IDEX, et al., RegistrantNo. 333-18643, as filed on December 23, 1996) |
| 10 | .13*10.13** | | Letter Agreement between IDEX Corporation and John L. McMurray, dated April 24, 2000 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1710.13 (a) to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2001, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .14*10.14** | | LetterEmployment Agreement between IDEX Service Corporation and Dominic A. Romeo, dated Decembereffective March 1, 20032010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.2110.1 to the AnnualCurrent Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005)8-K filed March 1, 2010, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
68
| | |
Exhibit
| | |
| Number | | Description |
| |
10 | .15*10.15** | | Employment Agreement between IDEX Corporation and Lawrence D. Kingsley, dated July 21, 2004 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 to the Quarterly Report of IDEX onForm 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2004)2004, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .15(a)10.15(a)** | | First Amendment to Employment Agreement between IDEX Corporation and Lawrence D. Kingsley, dated March 22, 2005 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 (a) to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K dated March 24, 2005, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
70
| | | | |
Exhibit
| | |
Number
| | Description
|
|
| 10 | .16*10.16** | | Form Stock Option Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K dated March 24, 2005, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .17*10.17** | | Form Unvested Stock Agreement (incorporated by reference to Appendix A of the Proxy Statement of IDEX, Corporation, dated February 25, 2005, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .18*10.18** | | IDEX Corporation Incentive Award Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K dated March 24, 2005, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .19*10.19** | | Letter Agreement between IDEX Corporation and Frank J. Notaro, dated April 24, 2000 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.25 to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .20*10.20** | | Definitive agreement to acquire Nova Technologies Corporation, dated November 13, 2007, (incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K dated November 16, 2007, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .21*10.21** | | IDEX Corporation Incentive Award Plan (as Amended and Restated) (incorporated by reference to Appendix A of the Proxy Statement of IDEX, Corporation, filed March 7, 2008, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .22*10.22** | | IDEX Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement with Lawrence Kingsley, dated April 8, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report of IDEX Corporation onForm 8-K, dated April 8, 2008, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .23*10.23** | | IDEX Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement with Dominic Romeo, dated April 8, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Current Report of IDEX Corporation onForm 8-K, dated April 8, 2008, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .24*10.24** | | Form of IDEX Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement, dated April 8, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Current Report of IDEX Corporation onForm 8-K, dated April 8, 2008, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10 | .25*10.25** | | Second Amendment to Employment Agreement between IDEX Corporation and Lawrence D. Kingsley, dated December 8, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.28 to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| *10 | .26*10.26** | | Letter Agreement between IDEX Corporation and Harold Morgan, dated June 6, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.26 to the Annual Report of IDEX onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10.27** | | Amendment to Agreement between IDEX Corporation, IDEX Service Corporation and Dominic A. Romeo, dated December 20, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K filed December 23, 2010, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10.28** | | Letter Agreement between IDEX Corporation and Frank J. Notaro, dated September 30, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.1 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K filed October 1, 2010, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| 10.29** | | Letter Agreement between IDEX Corporation and Harold Morgan, dated September 30, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 10.2 to the Current Report of IDEX onForm 8-K filed October 1, 2010, Commission FileNo. 1-10235) |
| *10.30** | | Third Amended and Restated IDEX Corporation Directors Deferred Compensation Plan |
| *10.31** | | Merger and Restatement of IDEX Corporation Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, the IDEX Corporation 1996 Deferred Compensation Plan for Officers and the IDEX Corporation 1996 Deferred Compensation Plan for Non- Officer Presidents |
| *12 | | | Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges |
| *13 | | | The portions of IDEX Corporation’s 2009 Annual Report to Shareholders, which are specifically incorporated by reference. |
| 18 | | | Letter from Deloitte and Touche, LLP regarding change in accounting principle hereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit No. 18 to the Quarterly Report of IDEX on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2009, Commission File No. 1-10235) |
| *21 | | | Subsidiaries of IDEX |
69
| | *23 | |
Exhibit
| | |
| Number | | Description |
|
| *23 | | Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP |
| *31 | .131.1 | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant toRule 13a-14 (a) orRule 15d-14(a)15d-14 (a) |
| *31 | .231.2 | | Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant toRule 13a-14 (a) orRule 15d-14(a)15d-14 (a) |
| *32 | .1**32.1 | | Certification pursuant to Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code |
| *32 | .2**32.2 | | Certification pursuant to Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code |
| ****101 | | The following materials from IDEX Corporation’s Annual Report onForm 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010 formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Statements of Operations for the three years ended December 31, 2010, (ii) the Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 31, 2010 and 2009, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the three years ended December 31, 2010, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the three years ended December 31, 2010, (v) Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements, and (vi) Financial Statement Schedule of Valuation and Qualifying Accounts. |
| | |
| * | | Filed herewithherewith. |
| |
| ** | | Management contract or compensatory plan or agreement. |
|
| *** | | Furnished herewith. |
|
| **** | | In accordance with Rule 406T ofRegulation S-T, the XBRL related information in Exhibit 101 to this Annual Report onForm 10-K shall not be deemed to be “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, or otherwise subject to the liability of that section, and shall not be part of any registration statement or other document filed under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except as shall be expressly set forth by specific reference in such filing. |
7170

