TABLE OF CONTENTS | |||
Page | |||
1 | |||
3 | |||
3 | |||
28 | |||
76 | |||
76 | |||
78 | |||
78 | |||
78 | |||
79 | |||
79 | |||
79 | |||
80 | |||
88 | |||
89 | |||
110 | |||
110 | |||
110 | |||
111 | |||
112 | |||
112 | |||
112 | |||
113 | |||
113 | |||
113 | |||
114 | |||
114 | |||
116 | |||
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K and the information incorporated by reference in this Annual Report contain(this "Annual Report"), contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or Exchange Act,as amended, (the "Exchange Act"), that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. AllThe forward-looking statements are contained principally in Part I, Item 1. “Business,” Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors,” and Part II, Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” but are also contained elsewhere in this Annual Report. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by the words “may,” “might,” “will,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “objective,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “project,” “potential,” “continue” and “ongoing,” or the negative of these terms, or other thancomparable terminology intended to identify statements relatedabout the future. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to present facts, current conditionsbe materially different from the information expressed or historical facts,implied by these forward-looking statements. Although we believe that we have a reasonable basis for each forward-looking statement contained in this Annual Report, we caution you that these statements are based on Form 10-K, including but not limiteda combination of facts and factors currently known by us and our expectations of the future, about which we cannot be certain. Forward-looking statements include statements about:
1
You should refer to Item 1A. “Risk Factors” in this Annual Report for a discussion of important risks and uncertaintiesfactors that couldmay cause our actual results to differ materially from the results discussed in thethose expressed or implied by our forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements, include, but are not limited to, the possibility that we may not succeed in developing EggPC cell derived eggs that can be fertilized; the risks implicit in the development process of preparing bovine and human EggPC derived eggs for fertilization; regulatory risks associated with obtaining authorization to fertilize human EggPCSM cells for research; the possibility that international in vitro fertilization (“IVF”) clinics that we work with may determine not to provide or continue providing the OvaPrime or AUGMENT treatments, or to delay providing such treatments, or to limit the population of patients receiving the treatments based on clinical efficacy, safety or commercial, logistic, economic, available data, regulatory or other reasons; challenges associated with enrolling and completing clinical trials, and the possibility that the results may not be favorable; the science underlying our treatments (including OvaPrime treatment, OvaTure treatment and AUGMENT treatment), which is unproven; scientific and regulatory challenges associated with characterizing and fertilizing an EggPC cell-derived egg; our ability to obtain regulatory approval or licenses where necessary for our treatments; risks associated with reliance on third parties, in particular our partner IVF clinics and the contract research organizations and academic partners that we plan to work with in our OvaTure development efforts; our ability to develop our treatments on the timelines we expect, if at all; our ability to commercialize our treatments on the timelines we expect, if at all, as well as other risks described under "Risk Factors" and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. As a result of these and other factors, we may not actually achievecannot assure you that the plans, intentions or expectations disclosedforward-looking statements in this Annual Report will prove to be accurate. Furthermore, if our forward-looking statements andprove to be inaccurate, the inaccuracy may be material. In light of the significant uncertainties in these forward-looking statements, you should not place undue reliance onregard these statements as a representation or warranty by us or any other person that we will achieve our forward-looking statements. Ourobjectives and plans in any specified time frame, or at all. The forward-looking statements do not reflectin this Annual Report represent our views as of the potential impactdate of any future acquisitions, mergers, dispositions, joint ventures or investmentsthis Annual Report. We anticipate that subsequent events and developments may cause our views to change. However, while we may make. We do not assume anyelect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, we undertake no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. You should, therefore, not rely on these forward-looking statements as representing our views as of any date subsequent to the date of this Annual Report.
As used herein, the words “Tempest,” “we,” “us,” “our,” and "company" refer to Tempest Therapeutics, Inc. and its direct and indirect subsidiaries, as applicable.
2
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company moving into late-stage development with a diverse portfolio of novel targeted and immune-mediated product candidates with the potential to be first-in-class treatments for a wide range of cancers. The company’s programs range from early research to the lead program, TPST-1120, that is poised to begin a pivotal study in first-line liver cancer. Our philosophy is to build a company based upon not only good ideas and creative science, but also upon the efficient translation of those ideas into therapies that will improve patients’ lives. Each of our programs are designed to provide different and independent approaches to fighting cancer, providing a portfolio of truly diversified assets.
Our two clinical-stage therapeutic product candidates are TPST-1120 and TPST-1495, which we believe are the first clinical-stage molecules designed to inhibit their respective targets.
TPST-1120 is a company focused onselective antagonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (“PPARα”). On October 11, 2023, we announced new and updated positive results from the discoveryplanned data analysis of the ongoing global randomized Phase 1b/2 trial of TPST-1120 combined with the standard-of-care first-line regimen of atezolizumab and development of new treatment options for women and families strugglingbevacizumab in patients with infertility. OvaScience is leveraging the breakthrough discovery of egg precursor,advanced or EggPC
In addition to the overall data, the new biomarker subpopulation findings are poor, however,consistent with the mechanism of action of TPST-1120: patients with b-catenin activating mutations (21% in this study or n=7) showed a confirmed ORR of 43% and a disease control rate (“DCR”) of 100% in the TPST-1120 arm; and distinct from the control arm, the TPST-1120 arm was consistently active across PD-L1 negative tumors with a confirmed ORR of 27% in the TPST-1120 arm, compared to a reduced ORR of 7% for the control arm.
These randomized data build upon clinical data from Phase 1 trials that were reported at a podium presentation at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (“ASCO”) annual meeting in June 2022. RECIST responses were also observed in this study at the two highest TPST-1120 doses, administered in combination with nivolumab, for an average live birth rate per cycleORR of 28 percentthose cohorts of 30% (3 of 10 patients), including in patients who previously progressed on anti-PD-1 (-L1) therapy. We believe the next step in TPST-1120 development is a pivotal Phase 3 trial in first-line HCC and are planning to meet with the FDA in 2024 in order to advance that goal. In addition, given the totality of the data, we are considering pursuing development of TPST-1120 for use in kidney cancer (“RCC”) and potentially other indications.
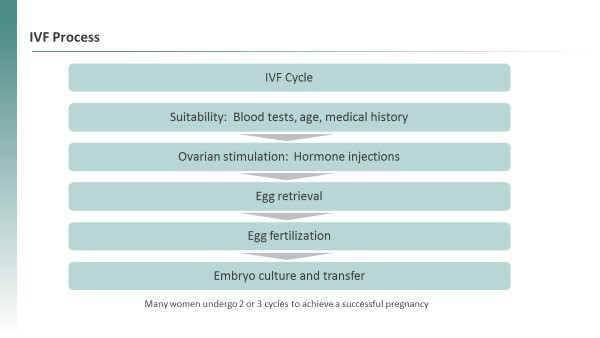
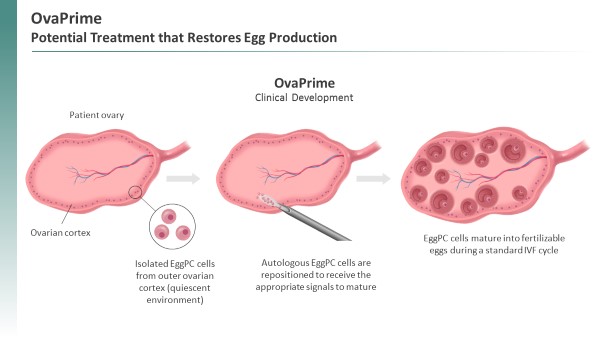
Our second clinical program, TPST-1495, a dual antagonist of the EP2 and EP4 receptors of prostaglandin E2, is in an ongoing Phase 1 combination trial in patients with endometrial cancer. Data from the TPST-1495 Phase 1 trial was presented at the ASCO annual meeting in June 2023. Additionally, we are planning to advance TPST-1495 in a new indication, Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (“FAP”), for which there are no approved therapies. Given that prostaglandin signaling is implicated in FAP and based on positive preclinical data in a CDC report. For womenrelevant mouse model, we believe there is strong mechanistic support for this approach. We are working with Diminished Ovarian Reserve, including those with Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (POI) or Poor Ovarian Reserve (POR), IVF is largely ineffective. In these women, the average live birth rate per cycle is only six percent. Market research suggests that many patients with POI or POR resort to a donor egg or adoption, with some giving up on having a child altogether (Fulcrum Research Group). Other women are unable or unwilling to undergo hormone stimulation, which is a required component of standard IVF treatment. The EggPC cell technology has the potential to offer new treatment options to these women.
3
Beyond these clinical programs, we plan to continue to leverage our drug development and matured in vitro into healthy, fertilizable eggs. This potential treatment may be an option for all women undergoing IVF, which represents approximately 1.9 million women per year globally.

Our Pipeline
Our product development pipeline consists of the ovary usingfollowing orally-available therapies, which if approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the "FDA"), we believe will be first in class:

1. Timing is an antibody that binds specificallyestimate based on current projections and status of programs
2. Estimated for either year-end 2024 or the first quarter of 2025, subject to discussions with FDA.
3. Received initial approval from NCI; study start subject to final approval.
Strategy
Our team has come together to build an integrated company to deliver meaningful therapies to cancer patients by leveraging our collective capabilities and experience. We expect to build value for our stockholders with the following over-arching strategy:
4
Clinical Programs
TPST-1120: PPARαTranscription Factor Antagonist
TPST-1120, a restorepotentially first-in-class oral small molecule antagonist of PPARα, has completed a woman’s egg production,Phase 1a/b trial, and is currently being studied in clinical development. With OvaPrime,an ongoing randomized Phase 1b/2 trial. The Phase 1a/b trial was a woman’s own EggPC cells are isolated frommulticenter, open-label, dose-escalation, that evaluated TPST-1120 as both a niche within her ovary where they are
Tumors evolve to promote their own survival by alternating energy sources, promoting angiogenesis and evading immune recognition. PPARα is a transcription factor that is activated through binding of long-chain fatty acid ligands, which in turn regulates the expression of genes that control glucose and lipid homeostasis, inflammation, proliferation, differentiation and cell death. Included among these regulated genes are those that enable fatty acid oxidation, or FAO, and β-oxidation metabolic pathways in cellular peroxisomes and in mitochondria. An FAO metabolic profile is associated with tumor proliferation, induction of angiogenesis and immune suppression. Published studies and internal Tempest analyses of over 9,000 primary ovarian insufficiency (POI)or metastatic tumor samples in the Human Cancer Genome public database reveal a metabolic gene expression profile characterized by increased PPARα, FAO genes and secondarily, assess changeslipogenesis associated with increased metastatic potential and reduced survival enrichment among multiple cancers, including HCC, CCA, breast carcinoma, colorectal adenocarcinoma, RCC, lung adenocarcinoma and prostate adenocarcinoma. TPST-1120 is designed to block the pathways that support tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis and immune suppression, resulting in women’s hormone levels, follicular developmentreduced disease and occurrencepatient benefit.

5
Summary of pregnancy.
We have conducted pre-clinical pharmacology studies along with pharmacokinetics, or PK, and toxicology studies with TPST-1120 to the EggPC cells, while the other ovary is exposed to the EggPC vehicle as a means to have each subject serve as her own control. Results betweensupport its ongoing evaluation for the treatment and control ovary are examined for relevant endpoints such as antral follicle counts.
Immune checkpoint blockade enhances anti-tumor immunity by restoring the activity of cytotoxic T (Teff) cells. Emerging experimental results suggest that inhibiting FAO with a PPARα antagonist may target resistance mechanisms to both anti-PD-L1/PD-1 and anti-VEGF therapies, supporting the combination of TPST-1120 with either or both therapies. We have conducted preclinical studies showing that while both TPST-1120 or anti-PD-1 monotherapy inhibited outgrowth of established flank MC38 tumors, the combination of these two agents resulted in synergistic anti-tumor activity. In addition, MC38 tumor-bearing mice cured by the combination therapy, unlike age-matched naïve control mice, were completely resistant to tumor growth when rechallenged with autologous MC38 tumor cells, demonstrating that TPST-1120 in combination with anti-PD-1 induced lasting tumor-specific immune memory. In addition, activating mutations in the Wnt/B-catenin pathway represent the most frequently dysregulated pathway in HCC. Such mutations render a tumor cell reintroduction, OvaPrime was generally safedependent upon FAO for its energy source, and well-tolerated. Amongin preclinical studies, Tempest has shown reduction and long-term durable cures in mice bearing Wnt/B-catenin activated HCC tumors treated with TPST-1120 and an immune checkpoint inhibitor. The promise of these pre-clinical results have been observed in the first 20 patients evaluable for safety six-months post-EggPC cell reintroduction, there were no treatment related serious adverse events (SAEs) and no adverse events (AEs) related to the EggPC cells. There were seven mild AEs, four of which were deemed unrelated to OvaPrime and three of which were related to the standard laparoscopic procedure used to reintroduce EggPC cells into the ovary. No patients discontinued treatment because of an AE. The mean duration of follow-up among these 20 patients was nine months.
Efficacy in Syngeneic β-Catenin-driven Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model

Tumor resistance to anti-angiogenic drugs is also associated with elevated lipogenesis and FAO, primarily through the vascular regression and hypoxic environment that this class of therapies engenders. In response, tumor cells can switch to FAO as a readoutmechanism of secondary endpoints byresistance against anti-angiogenic therapy. In a preclinical study, we confirmed that combination of TPST-1120 with tyrosine kinase inhibitor-, or TKI-, based anti-angiogenesis therapy confers potent anti-tumor activity.
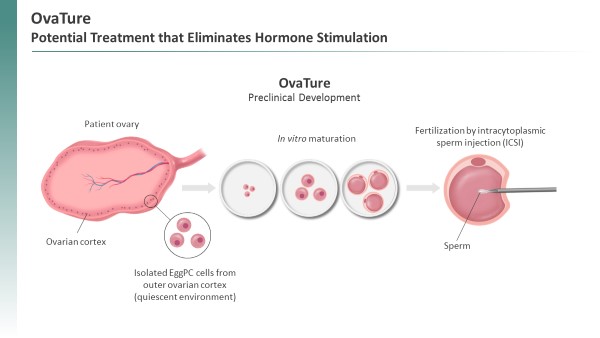
The preclinical data for TPST-120 are consistent with the end of the third quarter of 2019. However, based on preliminary blinded data we do not expect this Phase 1 clinical trial to produce strong signals on any of our secondary endpoints. We believe this may be due to the delivery of a sub-optimal EggPC cell dose.
6
the potential evaluation of developmental competence.
Overview of TPST-1120 Clinical Trials
We completed a Phase 1a/b study of TPST-1120 and a randomized Phase 1b/2 clinical study is ongoing. We have released positive data from both studies and expect updated data from the OvaTure Collaboration rather than underPhase 1b/2 clinical study in 2024. The Phase 1a/b trial evaluated both monotherapy and combination therapy with the OvaXon joint venture. We areanti-PD-1 agent nivolumab in discussionspatients with Intrexon regardingadvanced solid tumors that our PPARα-dependent transcriptome analysis of diverse human cancers revealed favor the futureusage of FAO. Results from both the monotherapy and the combination arms were presented in an oral presentation at the ASCO conference in 2022.
TPST-1120 demonstrated monotherapy clinical benefit in patients with late-line, treatment-refractory cancers where objective responses (RECIST v1.1) would not be expected, including pancreatic, CCA, and colorectal cancers ("CRC"). Results showed that 53% (10/19) of patients experienced clinical benefit in the form of disease control, including tumor shrinkage in 21% of the OvaXon joint venture.
In the combination therapy portion of the OvaTure Collaboration, effective 90 days following notice.trial, 15 evaluable patients with heavily pretreated RCC, HCC and CCA were treated with oral twice-daily TPST-1120 and the anti-PD-1 therapy, nivolumab. All the HCC and RCC patients had received an approved anti-PD-1 therapy in at least one prior line of therapy and discontinued that treatment due to disease progression. We believe thatobserved objective responses (RECIST v1.1) in two patients with late-line RCC who had previously progressed on anti-PD-1 therapy without having achieved an objective response (ORR 50%, n=2/4, in evaluable RCC patients), and we can best continueobserved mixed response in a third RCC IO-refractory patient with significant reduction (>30%) in the target lesion, but the appearance of new disease precluded designation as a RECIST PR. A third RECIST response was observed in a patient with late-line, heavily pre-treated CCA, a tumor type generally not responsive to anti-PD-1 therapy alone. All the RECIST responses were observed at the two highest doses.

Notably, one RCC patient who achieved a response after treatment with TPST-1120 and nivolumab had previously been treated with nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab without experiencing an objective response and progressed on treatment, followed by further progression of cancer on both cabozantinib and everolimus. The initial RECIST PR was seen at the first on-study assessment at eight weeks and included a response in all target lesions as well as complete radiographic resolution of multiple sites of metastatic disease (see CT scan below) and has been confirmed at subsequent assessments beyond 12 months.
7
Partial Response in Late-Line RCC Patient Treated with TPST-1120
and Nivolumab Combination Therapy

Randomized Data in HCC
On October 11, 2023, we announced updated positive results from the planned data analysis from the ongoing global randomized Phase 1b/2 trial of TPST-1120, combined with the standard-of-care first-line regimen of atezolizumab and bevacizumab, in patients with advanced or metastatic HCC. The study is comparing the TPST-1120 arm to standard of care alone, and enrolled 40 patients randomized to the TPST-1120 arm and 30 patients randomized to the control arm. With a median follow-up of 9.2 and 9.9 months for the TPST-1120 arm and standard-of-care arm, respectively, the data showed a 30% confirmed ORR achieved in the TPST-1120 arm compared to 13.3% for atezolizumab and bevacizumab in the control arm, a substantial increase specific to the TPST-1120 arm as compared to the previously released interim data cut of 17.5% in the TPST-1120 arm versus 10.3% in the control arm. The results also showed a favorable progression free survival and OS hazard ratio for the TPST-1120 arm as compared to the standard-of-care control arm. In the TPST-1120 arm 40% of patients remained on treatment versus 16.7% in the control arm, while 72.5% of the TPST-1120 arm patients remained on study versus 46.7% in the control arm.

1. Data not provided by Roche
New biomarker subpopulation findings are consistent with the mechanism of action of TPST-1120. Patients with b-catenin activating mutations (21% in this study (n=7)) showed an increased confirmed ORR of 43% and a disease control rate (“DCR”) of 100% in the TPST-1120 arm. In addition, and distinct from the control arm, the TPST-1120 arm was consistently active across
8
PD-L1 negative tumors with a confirmed ORR of 27% in the TPST-1120 arm, compared to a reduced ORR of 7% for the control arm. We expect updated data to be available in 2024.


Early in the development of OvaTureTPST-1120, given the expression profile and attributes of PPARα, we selected HCC, RCC and CAA as cancers of interest and checkpoint inhibitors and anti-angiogenic therapeutics as potential companion therapies with the goal
9
to maximize the opportunity to bring meaningful benefit to patients with these cancers. Based on the pre-clinical and clinical data released to date, we believe that the emerging clinical benefit profile of TPST-1120 for patients shows alignment with these predictions, and we look forward to the potential benefit TPST-1120 could bring to patients with these cancers.
We own worldwide rights to TPST-1120, and have filed and been issued patents, including composition of matter, pharmaceutical compositions, and related methods of use, which are expected to expire between December 2033 and November 2043, without giving effect to any patent term extensions.
TPST-1495: Dual EP2/EP4 Prostaglandin Receptor Antagonist
Our second clinical molecule is TPST-1495, a potentially first-in-class, oral, small molecule dual antagonist of the prostaglandin E2, or PGE2, receptors, EP2 and EP4. TPST-1495 is engineered to inhibit only these receptors while sparing the homologous - but differentially active - EP1 and EP3 receptors.
There is extensive literature demonstrating that PGE2 both enhances tumor proliferation and inhibits anti-cancer immune function; it is known from the scientific literature that many tumors express elevated levels of the cyclooxygenase enzymes that produce PGE2. Elevated expression of COX-2 and overproduction of PGE2 is correlated with progression of diverse malignancies by building out our internal capabilitiesstimulating tumor cell proliferation, survival, evasion and expertise undermetastasis as well as host angiogenesis. In addition, PGE2 suppresses anti-tumor immunity by inhibiting the leadershipfunction of Dr. James Lillie, our Chief Scientific Officer,critical anti-tumor immune effector cell populations such as dendritic cells, natural killer ("NK cells"), T cells, and engagingM1 macrophages, while promoting the activity of suppressive immune cell populations including myeloid-derived suppressor cells ("MDSCs"), M2 macrophages, and regulatory T cells. Recent studies have also shown that increased expression of COX-2 and production of PGE2 can play a role in the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy and in the development of adaptive resistance to therapy. This body of literature provides the scientific rationale for developing therapeutics that maximally inhibit the prostaglandin pathway, as well as for combining TPST-1495 with immune checkpoint inhibitor monoclonal antibodies.
We conducted preclinical studies to evaluate TPST-1495, including its ability to reverse PGE2-mediated suppression of primary human monocyte to dendritic cell differentiation and activation in vitro, as well as comparisons to other agents designed to operate in the same pathway such as a single EP4 antagonist and, as described, COX2.
We have also conducted preclinical studies to evaluate TPST-1495 in a spontaneous APCMin/+ mouse model of FAP that demonstrated a significant survival advantage in comparison to other inhibitors in the prostaglandin pathway.

Source: Francica et al., Cancer Res Commun; 3(8) August 2023 https://doi.org/10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0249
10
Overview of Ongoing TPST-1495 Clinical Trials
TPST-1495 was evaluated in a first-in-human, Phase 1, multicenter, open-label, schedule and dose optimization trial in subjects with late-stage solid tumor cancers that are deemed incurable. Study objectives include evaluation of safety, tolerability, PK, PD, and preliminary anti-tumor activity of TPST-1495 as monotherapy and in combination with the checkpoint inhibitor, pembrolizumab. TPST-1495 has been evaluated on a once daily (“QD”) or twice daily (“BID”) schedule and with continuous or intermittent administration as monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab. Results from the Phase 1 study were presented at ASCO 2023. The data showed that in a diverse and treatment-refractory patient population, treatment with TPST-1495 as a monotherapy and in combination with pembrolizumab resulted in tumor shrinkage and prolonged stable disease in certain patients, as well as a durable confirmed partial response (“PR”) in a combination therapy patient with microsatellite stable colorectal cancer (“MSS CRC”), an indication not normally responsive to immunotherapy. The safety profile for TPST-1495 monotherapy on the recommended once-daily schedule was tolerable, with predominantly Grade 1-2 treatment related adverse events (“TRAEs”), including abdominal pain (17.9% All Grade and 0% Grade 3+), nausea (20.5% All Grade and 0% Grade 3+), and diarrhea (15.4% All Grade and 2.6% Grade 3+). For the combination with pembrolizumab, the most common TRAEs were nausea (29.2% All Grade and 0% Grade 3+), fatigue (20.8% All Grade and 4.2% Grade 3+) and diarrhea (20.8% All Grade, 0% Grade 3+). No TRAEs of Grade ≥4 were reported. On the recommended once-daily schedule, the DCR by RECIST v1.1 was 44% for patients on monotherapy TPST-1495 and 40.9% for patients on TPST-1495 with pembrolizumab (including a confirmed PR in a patient with MSS CRC and a stable disease rate of 36.4%). An ongoing combination arm in patients with endometrial cancer is expected to complete and data will be reported in 2024.
Our preclinical results in the APCMin/+ lead us to consider the application of TPST-1495 in familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome (“FAP”). FAP is a hereditary condition characterized by the development of numerous polyps in the colon and rectum. These polyps have the potential to become cancerous if left untreated. FAP is caused by mutations in the APC gene, which normally helps regulate cell growth and division in the intestinal lining. Individuals with FAP have a significantly increased risk of developing colorectal cancer at a young age, often before the age of 40. Additionally, FAP can lead to the development of polyps in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as other non-gastrointestinal tumors. Management of FAP typically involves regular surveillance with colonoscopies and surgical intervention to remove the polyps and reduce the risk of cancer. Currently, there are no systemic therapies approved to treat FAP. We are working with the Cancer Prevention Clinical Trials Network on a National Cancer Institute (“NCI”)-funded Phase 2 study, and subject to final approval of NCI, plan to start the study in 2024.
We own worldwide rights to TPST-1495, and have filed and been issued patents, including composition of matter and pharmaceutical compositions, which are expected to expire between April 2038 and October 2042, without giving effect to any patent term extensions.
Discovery Research
Our Discovery Research team is dedicated to identifying and validating novel therapeutic targets in oncology. We are not bound to a single technology platform, which allows us the scientific freedom to pursue targets and modalities that we believe have the highest probability to benefit patients. Rigorous medicinal chemistry and a broad set of preclinical validation studies are conducted to further evaluate lead compounds and inform decision-making for advancement into clinical development. Collaboration with academic institutions, contract research organizations that have specific, complementary capabilities(“CROs”), and strategic partners provides opportunity to enrich our own,pipeline, as well, asenhancing our academic collaborators.

License Agreements
In February 2018,2021, we provided Intrexon with written notice of termination of the OvaTure Collaboration, effective 90 days following notice. The OvaTure Collaboration provided for Intrexon to deliver laboratory and animal data to support OvaTure development, and provided that upon the delivery of laboratory and animal data, we would incur an obligation to pay Intrexon a mid-single digit royalty on net sales of any OvaTure fertility treatment in the future, and the exact royalty will depend upon the timing of the completion of the milestone. The royalty will apply if Intrexon intellectual property is utilized in the continued development of OvaTure.
11
trial, and we retain global development and commercialization rights to TPST-1120. Pursuant to the agreement, Roche provides us with notice of the amount of TPST-1120 required and the delivery timeline, and we supply the TPST-1120. All rights to invention and discoveries relating solely to TPST-1120 or biomarkers solely related to TPST-1120 made during any study will be our technologyexclusive property. All data generated in the field utilizing Intrexon's synthetic biology platform.
The agreement applies on a study-by-study basis until the futurelast treatment of the OvaXon joint venture.
Sales and Marketing
We recordedintend to retain significant development and commercial rights to our initial investment in OvaXon as an equity method investment in December 2013. As of December 31, 2017product candidates and, 2016,if marketing approval is obtained, to commercialize our equity investment in OvaXon was $0.1 million and included within other current assetsproduct candidates on our consolidated balance sheets. We and Intrexon both made additional contributions of $1.1 million and $1.8 million for the years ending December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Manufacturing
We do not own or operate, and currently have no plans to establish, any manufacturing facilities. We rely and expect to continue to rely, on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates for preclinical and clinical testing, as well as for commercial manufacture if any of our product candidates obtain marketing approval. We also rely, and expect to continue to rely, on third parties to package, label, store and distribute our investigational product candidates, as well as for our commercial products if marketing approval is obtained. We have internal personnel and utilize consultants with extensive technical, manufacturing, analytical and quality experience to oversee contract manufacturing and testing activities. We will continue to workexpand and strengthen our network of third-party providers but may also consider investing in internal manufacturing capabilities in the future if there is a technical need, or a strategic or financial benefit.
Manufacturing is subject to extensive regulations that impose procedural and documentation requirements. At a minimum these regulations govern record keeping, manufacturing processes and controls, personnel, quality control and quality assurance. Our systems, procedures and contractors are required to comply with these regulations and are assessed through regular monitoring and formal audits.
Competition
The biopharmaceutical and immuno-oncology industries are characterized by intense competition and rapid innovation. Any product candidates that we successfully develop and commercialize will have to compete with existing and future new therapies. While we believe that our technology, development experience and scientific knowledge provide us with competitive advantages, we face potential competition from many different sources, including large and specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, academic research institutions, government agencies and public and private research institutions that conduct research, seek patent protection, and establish collaborative arrangements for research, development, manufacturing and commercialization.
12
If our TPST-1120, TPST-1495, or any future product candidates are approved for the FDA under its available procedurestreatment of tumors, they may compete with other products used to determinetreat such diseases. There are a variety of treatments used for cancerous tumors that include chemotherapy drugs, small molecules, monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, bi-specific antibodies, cell therapies, oncolytic viruses and vaccines, as well as other approaches. In addition, there are several competitors in clinical development for the most appropriate regulatory pathway for potential entry intotreatment of HCC, RCC, cholangiocarcinoma, and other indications that we may be targeting with TPST-1120 and TPST-1495, including companies such as Ono, Adlai Nortye, Merck, Roche, Exelixis, and AstraZeneca.
TPST-1120, our small molecule designed to be a selective antagonist of PPARα, is the U.S. market.
Many of our competitors, either alone or (ii)with strategic partners, have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than we do. Accordingly, our competitors may be more successful than us in research and development, manufacturing, preclinical testing, conducting clinical trials, obtaining approval for treatments and achieving widespread market acceptance, rendering our treatments obsolete or non-competitive. Merger and acquisition activity in the eventbiotechnology and biopharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of a material breach that is not cured within 30 days. During the Initial Term, IVF Japan Group will payour competitors. These companies also compete with us a fixed amount of $1,000 per AUGMENT cyclein recruiting and will reimburse usretaining qualified scientific and management personnel, establishing clinical trial sites and patient registration for all lab operationsclinical trials and personnel costs, which we anticipateacquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs. Smaller or early-stage companies may also prove to be approximately $0.2 million forsignificant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies.
Our commercial opportunity could be substantially limited if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are more effective, safer, less toxic, more convenient or less expensive than our comparable products. In geographies that are critical to our commercial success, competitors may also obtain regulatory approvals before us, resulting in our competitors building a strong market position in advance of the Initial Term,entry of our products. The key competitive factors affecting the success of all our programs are likely to be their efficacy, safety, convenience and are payableavailability of reimbursement. In addition, our ability to compete may be affected in nonrefundable quarterly installments on the first day of each quarter. The IVF Japan Group is also responsible to reimburse us for the cost of materials for AUGMENT for all cycles in excess of 100 which are estimated at $2,000 per cycle. We will retain the worldwide commercialization rights for AUGMENT outside of Japan.
Intellectual Property
We strive to use AUGMENTprotect and enhance the proprietary technology, inventions and improvements that are commercially important to our business, including obtaining, maintaining, and defending our patent rights. Our policy is to seek to protect our proprietary position by, among other methods, filing patent applications and obtaining issued patents in Japan was made by the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology (JSOG). In some other countries, there
As of February 20, 2018, we own or have exclusively licensed 65December 31, 2023, our patent portfolio consisted of issued patents in 44 countries and jurisdictions and have more than 170 applications pending in more than 130 countries (including applications directly filed in countries and applications filed in regional patent offices); communications indicating allowance have been received for three of these applications.
With respect to TPST-1120, as of December 31, 2023, we own issued patents and pending patent applications pending with patent officesin the United States, Europe, China, Japan, and other markets outside of the U.S. whichUnited States as well as one pending PCT application. The issued
13
United States patents covering TPST-1120 as composition of matter, pharmaceutical compositions, and related methods of use are owned by MGH, twoexpected to expire in December 2033, absent any patent term extensions for regulatory delay. Any additional patents that may issue from these pending patent applications are expected to expire between December 2033 and November 2043, absent any patent term adjustments or patent term extensions for regulatory delay.
With respect to TPST-1495, as of December 31, 2023, we own issued patents including one U.S.and pending patent co-owned by MGHapplications in the United States, Europe, China, Japan, and The President and Fellows of Harvard College, or Harvard, one pending U.S. non-provisional application co-owned by MGH and Harvard, and seventeen applications pending in patent officesother markets outside of the U.S. whichUnited States as well as one pending PCT application. The issued United State patents covering TPST-1495 as composition of matter, pharmaceutical composition, and related methods of use are co-ownedexpected to expire between April 2038 and April 2039, absent any patent term extensions for regulatory delay. Any additional patents that may issue from these pending patent applications are expected to expire between April 2038 and November 2043, absent any patent term adjustments or patent term extensions for regulatory delay.
As of December 31, 2023, our patent portfolio also included pending patent applications in the United States and Europe that are exclusively licensed to us by MGHthe University of California at Berkeley. The licensed patent applications do not cover any of our current product candidates.
We also possess substantial know-how and Harvard.
With respect to our product candidates and processes that we have licensed from MGH is directedintend to female germline stem cells, includingdevelop and commercialize in the normal course of business, we intend to pursue patent protection covering, when possible, compositions, methods of isolating such female germline stem cellsuse, dosing, and various usesformulations. We may also pursue patent protection with respect to manufacturing and drug development processes and technologies.
Issued patents can provide protection for such female germline stem cells, including methods for IVF, methods for egg production, methods to treat infertilityvarying periods of time, depending upon the date of filing of the patent application, the date of patent issuance and methods to restore ovarian function. This family includes issuedthe legal term of patents in the U.S., Canada and 30 European countries allin which they are obtained. In general, patents issued for patent applications filed in the United States can provide exclusionary rights for 20 years from the earliest effective filing date. The term of which will expireUnited States patents may be extended by delays encountered during prosecution that are caused by the USPTO, also known as patent term adjustment. In addition, in May 2025. We believecertain instances, the term of an issued United States patent that somecovers or claims an FDA approved product can be extended to recapture a portion of the term effectively lost as a result of the FDA regulatory review period, which is called patent term extension. The restoration period cannot be longer than five years and the total patent term, including the restoration period, must not exceed 14 years following FDA approval. The term of patents outside of this family providethe United States varies in accordance with the laws of the foreign jurisdiction, but typically is also 20 years from the earliest effective filing date. However, the actual protection for therapeutic compositions comprising EggPC cells, whichafforded by a patent varies on a product-by-product basis, from country-to-country and depends upon many factors, including the type of patent, the scope of its coverage, the availability of regulatory-related extensions, the availability of legal remedies in a particular country and the validity and enforceability of the patent.
The patent positions of companies like ours are referred togenerally uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. No consistent policy regarding the scope of claims allowable in patents in the patents as female germline stem cells,field of oncology has emerged in the United States. The relevant patent laws and that sometheir interpretation outside of the United States are also uncertain. Changes in either the patent laws or their interpretation in the United States and other countries may diminish our ability to protect our technology or product candidates and could affect the value of such intellectual property. In particular, our ability to stop third parties from making, using, selling, offering to sell, or importing products that infringe our intellectual property will depend in part on our success in obtaining and enforcing patent claims that cover our technology, inventions, and improvements. We cannot guarantee that patents will be granted with respect to any of this family provide protection for elements of the manufacturing process for obtaining such therapeutic compositions.
Moreover, even its issued patents and any additional patents claiming prioritymay not guarantee us the right to practice our technology in relation to the underlying provisional applications, will expire in April 2032 unless patent term extension is granted. We believe that these patents,commercialization of its products. Patent and any patents issuing from this family, provide protection for AUGMENT and several important aspects thereof.
14
commercializing our product candidates and know-how. Trade secrets and know-how can be difficult to protect. We seek to protectpracticing our proprietary technology, and processes, in part, by confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measuresissued patents may be breached andchallenged, invalidated, or circumvented, which could limit our ability to stop competitors from marketing related products or could limit the term of patent protection that otherwise may exist for its product candidates. In addition, the scope of the rights granted under any issued patents may not provide us with protection or competitive advantages against competitors with similar technology. Furthermore, our competitors may independently develop similar technologies that are outside the scope of the rights granted under any issued patents. For these reasons, we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets and know-how may otherwise become known or may be independently discovered by competitors. To the extent that our consultants, contractors or collaborators use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the rights in related or resulting know-how and inventions.
Government Regulation
Government authorities in the need for hormonal hyperstimulation for egg retrieval. We anticipate that price also will be an important competitive factor for all our fertility treatment options. At this time, we cannot evaluate how our
FDA Approval Process
In the United States, pharmaceutical products are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (“FFDCA”), and other federal and state statutes and regulations govern, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, storage, recordkeeping, approval, labeling, promotion and marketing, distribution, post-approval monitoring and reporting, sampling and import and export of drugs, biologicspharmaceutical products. Failure to comply with applicable U.S. requirements may subject a company to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as clinical hold, FDA refusal to approve pending a New Drug Applications ("NDA") warning or untitled letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties and medical devices, as well as other types of medical productscriminal prosecution.
Our investigational medicines and procedures. Most countries also have rules relatingany future investigational medicines must be approved by the FDA pursuant to procurement and use of human tissues or cells, and rules relating to assisted human reproduction. Although the specific rules vary country by country, in general different levels of regulation are applicable depending on the nature of the treatment, the level of risk involved, and/or its intended uses. Some classes of products (e.g., treatments regulated as drugs or biologicsan NDA before they may be legally marketed in the United States, or treatments regulated as medicinal products inStates. The process generally involves the EU) requirefollowing:
15
The preclinical and clinical testing and approval requirements. In these jurisdictions,process requires substantial time, effort and financial resources, and we cannot be certain that any approvals for our product candidates will be granted on a timely basis, or at all.
Preclinical Studies
Before testing any drug product candidates in humans, the developmentproduct candidate must undergo rigorous preclinical testing. Preclinical tests include laboratory evaluation of product chemistry, formulation and marketing of such therapies generally do not requiretoxicity, as well as in vitro and animal studies to assess the potential for adverse events and in some cases to establish a rationale for therapeutic use. The conduct of the preclinical tests must comply with federal regulations and requirements, including GLP. An IND sponsor must submit the results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information, analytical data, any available clinical trialsdata or pre-reviewliterature and approval of a marketing application by the relevant regulatory authority. In addition, although many such therapies are still subject to post-marketing requirements, these requirements typically are substantially reduced as comparedplans for clinical studies, among other things, to the requirementsFDA as part of an IND. An IND is a request for drugs, biologics, medicinal products or medical devices.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials involve the administration of the United States. We metinvestigational new drug to healthy volunteers or patients under the supervision of a qualified investigator, generally a physician not employed by or under the trial sponsor’s control. Clinical trials must be conducted: (i) in compliance with federal regulations; (ii) in compliance with GCP, an international standard meant to protect the FDArights and health of patients and to define the roles of clinical trial sponsors, administrators and monitors; as well as (iii) under protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the trial, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated in the second quarter of 2017 regarding AUGMENT,trial. Each protocol involving testing on U.S. patients and will continue to work with the FDA under its available procedures to determine the most appropriate regulatory pathway for potential entry into the U.S. market. We cannot provide any assurance, however, that the FDA will ultimately change the position taken in the "untitled" letter. In March 2018, Health Canada informed us that performing AUGMENT violates Canada's Assisted Human Reproduction Act, and requested that we cease offering AUGMENT in Canada. Accordingly, we are no longer making AUGMENT available in Canada while we consider next steps.
Furthermore, each EU member state inclinical trial must be reviewed and approved by an IRB for each institution at which the clinical trial will be conducted. Underconducted to ensure that the new Regulation on Clinical Trials, which is expectedrisks to take effectindividuals participating in the clinical trials are minimized and are reasonable in relation to anticipated benefits. The IRB also approves the informed consent form that must be provided to each clinical trial subject or after October 2018, there will be a centralized application procedure where one
There also are requirements governing the reporting of ongoing clinical trials and completed clinical trial results to public registries. Information about certain clinical trials, including clinical trial results, must be notifiedsubmitted within specific timeframes for publication on the www.clinicaltrials.gov website. Information related to the product, patient population, phase of investigation, clinical trial sites and investigators and other aspects of the clinical trial is then made public as part of the registration. Disclosure of the results of these clinical trials can be delayed in certain circumstances for up to two years after the date of completion of the trial.
16
A sponsor who wishes to conduct a clinical trial outside of the United States may, but need not, obtain FDA authorization to conduct the clinical trial under an IND. If a foreign clinical trial is not conducted under an IND, the sponsor may submit data from the clinical trial to the FDA in support of an NDA. The FDA will accept a well-designed and well-conducted foreign clinical trial not conducted under an IND if the clinical trial was conducted in accordance with GCP requirements, and the FDA is able to validate the data through an onsite inspection if deemed necessary.
Clinical trials are generally conducted in three sequential phases, known as Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3:
These Phases may overlap or be combined. For example, a Phase 1/2 clinical trial may contain both a dose-escalation stage and a dose expansion stage, the latter of which may confirm tolerability at the recommended dose for expansion in future clinical trials (as in traditional Phase 1 clinical trials) and provide insight into the anti-tumor effects of the investigational therapy in selected subpopulation(s).
Typically, during the development of oncology therapies, all subjects enrolled in Phase 1 clinical trials are disease-affected patients and, as a medicinal product EMA,result, considerably more information on clinical activity may be collected during such trials than during Phase 1 clinical trials for non-oncology therapies. A single Phase 3 or Phase 2 trial with other confirmatory evidence may be sufficient in rare instances to provide substantial evidence of effectiveness (generally subject to the requirement of additional post-approval studies). The manufacturer of an investigational drug in a phase 2 or 3 clinical trial for a serious or life-threatening disease is required to make available, such as by posting on its website, its policy on evaluating and national medicines regulatorsresponding to requests for expanded access.
Phase 1, Phase 2, Phase 3 and other types of clinical trials may not be completed successfully within any specified period, if at all. The FDA, the EU provideIRB, or the opportunity for dialogue and guidancesponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including non-compliance with regulatory requirements or a finding that the development program. Atpatients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution if the EMA level, thisclinical trial is usually donenot being conducted in accordance with the formIRB’s requirements or if the drug has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients. Additionally, some clinical trials are overseen by an independent group of scientific advice, which is givenqualified experts organized by the Scientific Advice Working Partyclinical trial sponsor, known as a data safety monitoring board or committee. This group provides authorization for whether a trial may move forward at designated checkpoints based on access to certain data from the trial.
Concurrent with clinical trials, companies usually complete additional animal studies and must develop additional information about the chemistry and physical characteristics of the Committeedrug as well as finalize a process for Medicinal Products for Human Use, or CHMP. A fee is incurredmanufacturing the product in commercial quantities in accordance with each scientific advice procedure. Advice from the EMA is typically provided based on questions concerning, for example,cGMP requirements. The manufacturing process must be capable of consistently producing quality (chemistry, manufacturing and controls testing), nonclinical testing and clinical studies, and pharmacovigilance plans and risk-management programs. Advice is not legally binding with regard to any future marketing authorization applicationbatches of the product concerned. To date, we haveand, among other things, companies must develop methods for testing the identity, strength, quality, potency and purity of the final product. Additionally, appropriate packaging must be selected and tested, and
17
stability studies must be conducted to demonstrate that the investigational medicines do not initiated any scientific advice procedures or other discussions with the EMA or any national regulatory authorities in the EU.
FDA Review Process
After completion of the required clinical testing, we must obtain aan NDA is prepared and submitted to the FDA. FDA approval of an NDA is required before marketing authorization before weof the product may place a medicinal product on the marketbegin in the EU. ThereU.S. An NDA must include the results of all preclinical, clinical and other testing and a compilation of data relating to the product’s pharmacology, chemistry, manufacture and controls. To support marketing approval, the data submitted must be sufficient in quality and quantity to establish the safety and efficacy of the investigational product to the satisfaction of the FDA. FDA approval of an NDA must be obtained before a drug may be marketed in the United States. The cost of preparing and submitting an NDA is substantial. Under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (“PDUFA”), each NDA must be accompanied by a substantial user fee. The FDA adjusts the PDUFA user fees on an annual basis. Fee waivers or reductions are variousavailable in certain circumstances, including a waiver of the application procedures available,fee for the first application filed by a small business. Additionally, no user fees are assessed on NDAs for products designated as orphan drugs, unless the product also includes a non-orphan indication. The applicant under an approved NDA is also subject to an annual program fee.
The FDA reviews each submitted NDA before it determines whether to file it and may request additional information. The FDA must make a decision on whether to file an NDA within 60 days of receipt, and such decision could include a refusal to file by the FDA. Once the submission is filed, the FDA begins an in-depth review of an NDA. The FDA has agreed to certain performance goals in the review of an NDA. Most applications for standard review drug products are reviewed within ten to twelve months; most applications for priority review drugs are reviewed in six to eight months. Priority review can be applied to drugs that the FDA determines may offer significant improvement in safety or effectiveness compared to marketed products or where no adequate therapy exists. The review process for both standard and priority review may be extended by the FDA for three additional months to consider certain late-submitted information, or information intended to clarify information already provided in the submission. The FDA does not always meet its goal dates for standard and priority timeframes for an NDA, and the review process can be extended by FDA requests for additional information or clarification.
The FDA may also refer applications for novel drug products, or drug products that present difficult questions of safety or efficacy, to an outside advisory committee—typically a panel that includes clinicians and other experts—for review, evaluation and a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions, if any. The FDA is not bound by the recommendation of an advisory committee, but it generally follows such recommendations.
Before approving an NDA, the FDA will conduct a pre-approval inspection of the manufacturing facilities for the new product to determine whether they comply with cGMP requirements. The FDA will not approve the product unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications. The FDA also typically inspects clinical trial sites to ensure compliance with GCP requirements and the integrity of the data supporting safety and efficacy.
After the FDA evaluates an NDA and the manufacturing facilities, it issues either an approval letter or a complete response letter. A complete response letter ("CRL"), generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing, or information, in order for the FDA to reconsider the application, such as additional clinical data, additional pivotal clinical trial(s), and/or other significant and time-consuming requirements related to clinical trials, preclinical studies or manufacturing. If a CRL is issued, the applicant may resubmit an NDA addressing all of the deficiencies identified in the letter, withdraw the application, engage in formal dispute resolution or request an opportunity for a hearing. The FDA has committed to reviewing resubmissions in two or six months depending on the type of information included. Even if such data and information are submitted, the FDA may decide that an NDA does not satisfy the criteria for approval.
As a potential condition of an NDA approval, the FDA may require a REMS to help ensure that the benefits of the drug outweigh the potential risks to patients. A REMS can include medication guides, communication plans for healthcare professionals and elements to assure a product’s safe use ("ETASU"). An ETASU can include, but is not limited to, special training or certification
18
for prescribing or dispensing the product, involved. Alldispensing the product only under certain circumstances, special monitoring and the use of patient-specific registries. The requirement for a REMS can materially affect the potential market and profitability of the product. Moreover, the FDA may require substantial post-approval testing and surveillance to monitor the product’s safety or efficacy.
Changes to some of the conditions established in an approved application, proceduresincluding changes in indications, labeling, or manufacturing processes or facilities, require submission and FDA approval of an applicationNDA supplement or, in some case, a new NDA, before the change can be implemented. An NDA supplement for a new indication typically requires clinical data similar to that in the common technical document,original application, and the FDA uses the same procedures and actions in reviewing NDA supplements as it does in reviewing NDAs.
Orphan Drug Designation
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan drug designation to drugs intended to treat a rare disease or CTD, format,condition, which includes the submission of detailed information about the manufacturing and quality of the product, and non-clinical and clinical trial information. There is an increasing trendgenerally a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the EU towards greater transparency and, while the manufacturing or quality information is currently generally protected as confidential information, the EMA and national regulatory authorities are now liable to disclose much of the non-clinical and clinical information in marketing authorization dossiers, including the full clinical trial reports, in response to freedom of information requests after the marketing authorization has been granted. Clinical trial reports will also be posted on the EMA's website following the grant, denial or withdrawal of a marketing authorization application, subject to procedures for limited redactions and protection against unfair commercial use.
Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting an NDA. After the FDA grants orphan drug designation, the identity of the drug and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review and approval process.
If a product that has orphan designation subsequently receivedreceives the first FDA approval for the disease or condition for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to a seven-year exclusive marketing period in the U.S. for that product, for that indication. During the seven-year exclusivity period, the FDA may not approve any other applications to market the same drug for the same disease, except in limited circumstances, such as a showing of clinical superiority to the product with orphan drug exclusivity by means of greater effectiveness, greater safety, or providing a major contribution to patient care, or in instances of drug supply issues. Orphan drug exclusivity does not prevent the FDA from approving a different drug for the same disease or condition, or the same drug for a different disease or condition. Other benefits of orphan drug designation include tax credits for certain research and an exemption from the NDA user fee.
Expedited Development and Review Programs
The FDA is authorized to designate certain products for expedited review if they are intended to address an "untitled" letter questioningunmet medical need in the statustreatment of AUGMENTa serious or life-threatening disease or condition.
Fast Track Designation
Fast track designation may be granted for products that are intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition for which there is no effective treatment and preclinical or clinical data demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs for the condition. Fast track designation applies to both the product and the specific indication for which it is being studied. The sponsor of an investigational drug product may request that the FDA designate the drug candidate for a specific indication as a section 361 HCT/P,fast track drug concurrent with, or after, the submission of the IND for the drug candidate. The FDA must determine if the drug candidate qualifies for fast track designation within 60 days of receipt of the sponsor’s request. For fast track products, sponsors may have greater interactions with the FDA and advising usthe FDA may initiate review of sections of a fast track product’s NDA before the application is complete. This rolling review is available if the FDA determines, after preliminary evaluation of clinical data submitted by the sponsor, that a fast track product may be effective. The sponsor must also provide, and the FDA must approve, a schedule for the submission of the remaining information and the sponsor must pay applicable user fees. At the time of an NDA filing, the FDA will determine whether to filegrant priority review designation. Additionally, fast track designation may be withdrawn if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process.
Breakthrough Therapy Designation
19
Breakthrough therapy designation may be granted for products that are intended, alone or in combination with one or more other products, to treat a serious or life-threatening condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the product may demonstrate substantial improvement over currently approved therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints. Under the breakthrough therapy program, the sponsor of a new drug candidate may request that the FDA designate the candidate for a specific indication as a breakthrough therapy concurrent with, or after, the submission of an IND for the potential fertility treatment, following which we suspended our commercialization effortsdrug candidate. The FDA must determine if the drug product qualifies for breakthrough therapy designation within 60 days of receipt of the sponsor’s request. The FDA may take certain actions with respect to breakthrough therapies, including holding meetings with the sponsor throughout the development process, providing timely advice to the product sponsor regarding development and approval, involving more senior staff in the United States. We believereview process, assigning a cross-disciplinary project lead for the review team and taking other steps to design the clinical studies in an efficient manner.
Priority Review
Priority review may be granted for products that AUGMENTare intended to treat a serious or life-threatening condition and, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in safety and effectiveness compared to available therapies. The FDA will attempt to direct additional resources to the evaluation of an application designated for priority review in an effort to facilitate the review.
Accelerated Approval
Accelerated approval may be granted for products that are intended to treat a serious or life-threatening condition and that generally provide a meaningful therapeutic advantage to patients over existing treatments. A product eligible for accelerated approval may be approved on the basis of either a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality, that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. In clinical trials, a surrogate endpoint is a measurement of laboratory or clinical signs of a disease or condition that substitutes for a direct measurement of how a patient feels, functions or survives. The accelerated approval pathway is most often used in settings in which the course of a disease is long, and an extended period of time is required to measure the intended clinical benefit of a product, even if the effect on the surrogate or intermediate clinical endpoint occurs rapidly. Thus, accelerated approval has been used extensively in the development and approval of products for treatment of a variety of cancers in which the goal of therapy is generally to improve survival or decrease morbidity and the duration of the typical disease course requires lengthy and sometimes large studies to demonstrate a clinical or survival benefit. The accelerated approval pathway is contingent on a sponsor’s agreement to conduct additional post-approval confirmatory studies to verify and describe the product’s clinical benefit. These confirmatory trials must be completed with due diligence and, in some cases, the FDA may require that the trial be designed, initiated and/or fully enrolled prior to approval. Failure to conduct required post-approval studies, or to confirm a clinical benefit during post-marketing studies, would allow the FDA to withdraw the product from the market on an expedited basis. All promotional materials for product candidates approved under accelerated regulations are subject to prior review by the FDA.
Even if a product qualifies for one or more of these programs, the FDA may later decide that the product no longer meets the conditions for qualification or the time period for FDA review or approval may not be shortened. Furthermore, fast track designation, breakthrough therapy designation, priority review and accelerated approval do not change the standards for approval, but may expedite the development or approval process.
Pediatric Information
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act ("PREA"), an NDA or supplements to an NDA must contain data to assess the safety and effectiveness of the drug for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the drug is safe and effective. The FDA may grant full or partial waivers, or deferrals, for submission of data. Unless otherwise required by regulation, PREA does not apply to any drug for an indication for which orphan designation has been granted, with certain exceptions.
20
The Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act ("BPCA"), provides NDA holders a six-month extension of any exclusivity—patent or nonpatent—for a drug if certain conditions are met. Conditions for exclusivity include the FDA’s determination that information relating to the use of a new drug in the pediatric population may produce health benefits in that population, the FDA making a written request for pediatric studies, and the applicant agreeing to perform, and reporting on, the requested studies within the statutory timeframe. Applications under the BPCA are treated as priority applications, with all of the benefits that designation confers.
Post-Approval Requirements
Once an NDA is approved, a product will be subject to certain post-approval requirements. For instance, the FDA closely regulates the post-approval marketing and promotion of drugs, including standards and regulations for direct-to-consumer advertising, off-label promotion, industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities and promotional activities involving the internet. Drugs may be marketed only for the approved indications and in a manner consistent with the approved labeling.
Adverse event reporting and submission of periodic reports are required following FDA approval of an NDA. The FDA also may require post-marketing testing, known as phase 4 testing, REMS, and surveillance to monitor the effects of an approved product, or the FDA may place conditions on an approval that could meetrestrict the criteriadistribution or use of the product. In addition, quality control, drug manufacture, packaging and labeling procedures must continue to conform to cGMP after approval. Drug manufacturers and certain of their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies. Registration with the FDA subjects entities to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA, during which the Agency inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMP. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the areas of production and quality-control to maintain compliance with cGMP. Regulatory authorities may withdraw product approvals or request product recalls if a company fails to comply with regulatory standards, if it encounters problems following initial marketing, or if previously unrecognized problems are subsequently discovered.
Once an approval is granted, the FDA may withdraw the approval if compliance with regulatory requirements and standards is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing processes or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in revisions to the approved labeling to add new safety information, imposition of post-market studies or clinical studies to assess new safety risks or imposition of distribution or other restrictions under a REMS program. Other potential consequences include, among other things:
The Hatch-Waxman Act Orange Book Listing
Under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, commonly referred to as the Hatch Waxman Amendments, NDA applicants are required to identify to the FDA each patent whose claims cover the applicant’s drug or approved method of using the drug. Upon approval of a drug, the applicant must update its listing of patents to the NDA in timely fashion and each of the patents listed in the application for regulationthe drug is then published in the FDA’s Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations, commonly known as the Orange Book.
21
Drugs listed in the Orange Book can, in turn, be cited by potential generic competitors in support of approval of an abbreviated new drug application ("ANDA"). An ANDA provides for marketing of a drug product that has the same active ingredient(s), strength, route of administration, and dosage form as the listed drug and has been shown through bioequivalence testing to be therapeutically equivalent to the listed drug. An approved ANDA product is considered to be therapeutically equivalent to the listed drug. Other than the requirement for bioequivalence testing, ANDA applicants are not required to conduct, or submit results of, pre-clinical or clinical tests to prove the safety or effectiveness of their drug product. Drugs approved under the ANDA pathway are commonly referred to as “generic equivalents” to the listed drug and can often be substituted by pharmacists under prescriptions written for the original listed drug pursuant to each state’s laws on drug substitution.
The ANDA applicant is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents identified for the reference listed drug in the Orange Book. Specifically, the applicant must certify to each patent in one of the following ways: (i) the required patent information has not been filed; (ii) the listed patent has expired; (iii) the listed patent has not expired but will expire on a particular date and approval is sought after patent expiration; or (iv) the listed patent is invalid or will not be infringed by the new product. A certification that the new product will not infringe the already approved product’s listed patents, or that such patents are invalid, is called a Paragraph IV certification. For patents listed that claim an approved method of use, under certain circumstances the ANDA applicant may also elect to submit a section 361 HCT/P, butviii statement certifying that its proposed ANDA label does not contain (or carves out) any language regarding the patented method-of-use rather than certify to a listed method-of-use patent. If the applicant does not challenge the listed patents through a Paragraph IV certification, the ANDA application will not be approved until all the listed patents claiming the referenced product have expired. If the ANDA applicant has provided a Paragraph IV certification to the FDA, the applicant must also send notice of the Paragraph IV certification to the NDA-holder and patentee(s) once the ANDA has been accepted for filing by the FDA (referred to as the “notice letter”). The NDA and patent holders may then initiate a patent infringement lawsuit in response to the notice letter. The filing of a patent infringement lawsuit within 45 days of the receipt of a Paragraph IV certification automatically prevents the FDA from approving the ANDA until the earlier of 30 months from the date the notice letter is received, expiration of the patent, the date of a settlement order or consent decree signed and entered by the court stating that the patent that is the subject of the certification is invalid or not infringed, or a decision in the patent case that is favorable to the ANDA applicant.
The ANDA application also will not be approved until any applicable non-patent exclusivity listed in the Orange Book for the referenced product has expired. In some instances, an ANDA applicant may receive approval prior to expiration of certain non-patent exclusivity if the applicant seeks, and the FDA permits, the omission of such exclusivity-protected information from the ANDA prescribing information.
Exclusivity
Upon an NDA approval of a new chemical entity ("NCE"), which is a drug that contains no active moiety that has been approved by the FDA in any other NDA, that drug receives five years of marketing exclusivity during which the FDA cannot receive any ANDA seeking approval of a generic version of that drug unless the application contains a Paragraph IV certification, in which case the application may be submitted one year prior to expiration of the NCE exclusivity. If there is no guaranteelisted patent in the Orange Book, there may not be a Paragraph IV certification, and, thus, no ANDA for a generic version of the drug may be filed before the expiration of the exclusivity period.
Certain changes to an approved drug, such as the approval of a new indication, the approval of a new strength, and the approval of a new condition of use, are associated with a three-year period of exclusivity from the date of approval during which the FDA cannot approve an ANDA for a generic drug that includes the change. In some instances, an ANDA applicant may receive approval prior to expiration of the three-year exclusivity if the applicant seeks, and the FDA would agreepermits, the omission of such exclusivity-protected information from the ANDA package insert.
Patent Term Extension
The Hatch Waxman Amendments permit a patent term extension as compensation for patent term lost during the FDA regulatory review process. Patent term extension, however, cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the
22
product’s approval date. After an NDA approval, owners of relevant drug patents may apply for the extension. The allowable patent term extension is calculated as half of the drug’s testing phase (the time between an IND application and an NDA submission) and all of the review phase (the time between an NDA submission and approval) up to a maximum of five years. The time can be reduced for any time the FDA determines that the applicant did not pursue approval with our classification of AUGMENT or any of our potential fertility treatments. We metdue diligence.
The United States Patent and Trademark Office ("USPTO"), in consultation with the FDA, inreviews and approves the second quarterapplication for any patent term extension or restoration. However, the USPTO may not grant an extension because of, 2017 regarding AUGMENT,for example, failing to exercise due diligence during the testing phase or regulatory review process, failing to apply within applicable deadlines, failing to apply prior to expiration of relevant patents or otherwise failing to satisfy applicable requirements. Moreover, the applicable time period or the scope of patent protection afforded could be less than requested.
The total patent term after the extension may not exceed 14 years, and will continueonly one patent can be extended. The application for the extension must be submitted prior to work with the FDA under its available procedures to determine the most appropriate regulatory pathway for potential entry into the U.S. market.
Coverage, Pricing, and local authorities in addition to the FDA or EMA. Reimbursement
In the United States this likely includesand in foreign markets, sales of pharmaceutical products depend, in part, on the extent to which third-party payors provide coverage and establish adequate reimbursement levels for such products. In the United States, third-party payors include federal and state healthcare programs, private managed care providers, health insurers and other organizations. Adequate coverage and reimbursement from governmental healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid in the United States, and commercial payors are critical to new product acceptance.
There is significant uncertainty related to third-party payor coverage and reimbursement of newly approved products. In the United States, for example, principal decisions about reimbursement for new products are typically made by the Centers for Medicare and& Medicaid Services, ("CMS"), other divisions ofor CMS, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services such as the Office of Inspector General,(“HHS”). CMS decides whether and the U.S. Department of Justiceto what extent a new product will be covered and individual U.S. Attorney offices within the Department of Justice, as well as statereimbursed under Medicare, and local governments,private third-party payors often follow CMS’s decisions regarding coverage and ex-US equivalents. Our operations in the relevant jurisdictions must comply with all of these applicable requirements or we may be unablereimbursement to conduct our business or may face civil or criminal sanctions.
Increasingly, third-party payors are requiring that drug companies provide them with predetermined discounts from list prices and are challenging the prices charged for medical products. Further, such third party payors are increasingly challenging the price, and examining the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness,reviewing the cost effectiveness of medical product candidates. There may be especially significant delays in obtaining coverage and reimbursement for newly approved drugs. Third-party payors may limit coverage to specific product candidates on an approved list, known as a formulary, which might not include all FDA-approved drugs for a particular indication.
Outside the United States, the commercialization of therapeutics is generally subject to extensive governmental price controls and other market regulations, and we believe the increasing emphasis on cost containment initiatives in Europe, Canada and other countries has, and will continue to, put pressure on the pricing and usage of therapeutics such as our product candidates.
Other Healthcare Laws
23
In addition to FDA restrictions on marketing of pharmaceutical products, several other types of state and federal laws have been applied to restrict certain general business and marketing practices in the safetypharmaceutical industry in recent years. These laws include anti-kickback statutes, false claims statutes and efficacy,other healthcare laws and regulations.
The federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, knowingly and willfully offering, paying, soliciting or receiving remuneration to induce, or in return for, purchasing, leasing, ordering or arranging for the purchase, lease or order of medicalany healthcare item or service reimbursable under Medicare, Medicaid, or other federally financed healthcare programs. This statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between pharmaceutical manufacturers on the one hand and prescribers, purchasers and formulary managers, among others, on the other. Although there are a number of statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors protecting certain common activities from prosecution or other regulatory sanctions, the exceptions and safe harbors are drawn narrowly, and practices that involve remuneration intended to induce prescribing, purchases or recommendations may be subject to scrutiny if they do not qualify for an exception or safe harbor. In addition, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to commit a violation.
Federal civil and criminal false claims laws, including the federal civil False Claims Act, prohibit any person or entity from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, a false claim for payment to the federal government, or knowingly making, or causing to be made, a false statement to have a false claim paid. This includes claims made to programs where the federal government reimburses, such as Medicare and Medicaid, as well as programs where the federal government is a direct purchaser, such as when it purchases off the Federal Supply Schedule. Recently, several pharmaceutical and other healthcare companies have been prosecuted under these laws for allegedly inflating drug prices they report to pricing services, which in turn were used by the government to set Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement rates, and for allegedly providing free product to customers with the expectation that the customers would bill federal programs for the product. In addition, certain marketing practices, including off-label promotion, may also violate false claims laws. Additionally, the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the federal civil False Claims Act. Most states also have statutes or regulations similar to the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and civil False Claims Act, which apply to items and services reimbursed under Medicaid and other state programs, or, in several states, apply regardless of the payor.
Other federal statutes pertaining to healthcare fraud and abuse include the civil monetary penalties statute, which prohibits, among other things, the offer or payment of remuneration to a Medicaid or Medicare beneficiary that the offerer or payor knows or should know is likely to influence the beneficiary to order a receive a reimbursable item or service from a particular supplier, and the additional federal criminal statutes created by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 ("HIPAA"), which prohibits, among other things, knowingly and willfully executing or attempting to execute a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or obtain by means of false or fraudulent pretenses, representations or promises any money or property owned by or under the control of any healthcare benefit program in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items or services. Similar to the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to commit a violation.
Further, pursuant to the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation (the “Affordable Care Act” or the “ACA”), CMS has issued a final rule that requires manufacturers of prescription drugs to collect and report information on certain payments or transfers of value to physicians (defined to include doctors, dentists, optometrists, podiatrists and chiropractors), other healthcare professionals (such as physicians assistants and nurse practitioners), and teaching hospitals, as well as investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members. The reports must be submitted on an annual basis. The reported data is made available in searchable form on a public website on an annual basis. Failure to submit required information may result in civil monetary penalties.
HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act and its implementing regulations, imposes obligations, including mandatory contractual terms, on covered entities, business associates and their covered subcontractors with respect to safeguarding the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information.
24
In addition, several states now require prescription drug companies to report certain expenses relating to the marketing and promotion of drug products and procedures.
Efforts to ensure that business arrangements with third parties comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations involve substantial costs. If a drug company’s operations are found to be in violation of any such requirements, it may be subject to significant penalties, including civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, imprisonment, the curtailment or restructuring of its operations, loss of eligibility to obtain approvals from the FDA, exclusion from participation in government contracting, healthcare reimbursement or other federal or state government healthcare programs, including Medicare and Medicaid, integrity oversight and reporting obligations, imprisonment, and reputational harm. Although effective compliance programs can mitigate the risk of investigation and prosecution for violations of these laws, these risks cannot be entirely eliminated. Any action for an alleged or suspected violation can cause a drug company to incur significant legal expenses and divert management’s attention from the operation of the business, even if such action is successfully defended.
U.S. Healthcare Reform
In the EUUnited States there have been, and elsewhere,continue to be, proposals by the federal government, state governments, influenceregulators and third-party payors to control or manage the increased costs of health care and, more generally, to reform the U.S. healthcare system. The pharmaceutical industry has been a particular focus of these efforts and has been significantly affected by major legislative initiatives. For example, in March 2010, the ACA was enacted, which intended to broaden access to health insurance, reduce or constrain the growth of healthcare spending, enhance remedies against fraud and abuse, add new transparency requirements for the healthcare and health insurance industries, impose new taxes and fees on the health industry and impose additional health policy reforms, substantially changed the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and significantly impacts the U.S. pharmaceutical industry. The ACA, among other things, (i) subjected therapeutic biologics to potential competition by lower-cost biosimilars by creating a licensure framework for follow-on biologic products, (ii) proscribed a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs and therapeutic biologics that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected, (iii) increased the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extended the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, (iv) established annual nondeductible fees and taxes on manufacturers of certain branded prescription drugs and therapeutic biologics, apportioned among these entities according to their market share in certain government healthcare programs, (v) established a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% (now 70%) point of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs and therapeutic biologics to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs and therapeutic biologics to be covered under Medicare Part D, (vi) expanded eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs by, among other things, allowing states to offer Medicaid coverage to additional individuals and by adding new mandatory eligibility categories for individuals with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty level, thereby potentially increasing manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability, (vii) expanded the entities eligible for discounts under the Public Health program, (viii) created a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research, and (ix) established a Center for Medicare Innovation at CMS to test innovative payment and service delivery models to lower Medicare and Medicaid spending, potentially including prescription drug spending.
There have been judicial, executive brand, and Congressional challenges to certain aspects of the ACA, to repeal or replace certain aspects, of the ACA. By way of example, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (the "Tax Act"), was enacted and included,
25
among other things, a provision that repealed, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the ACA on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year that is commonly referred to as the “individual mandate.” There have been subsequent challenges to the constitutionality of the ACA following the repeal of the individual mandate. On June 17, 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court dismissed a challenge on procedural grounds that argued the ACA is unconstitutional in its entirety because the individual mandate was repealed by Congress. In addition, on August 16, 2022, President Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, or IRA, into law, which among other things, extends enhanced subsidies for individuals purchasing health insurance coverage in ACA marketplaces through plan year 2025. The IRA also eliminates the “donut hole” under the Medicare Part D program beginning in 2025 by significantly lowering the beneficiary maximum out-of-pocket cost and creating a new manufacturer discount program. However, it is possible that the ACA will be subject to judicial or Congressional challenges in the future. It is unclear how such challenges will impact the ACA. Tempest cannot predict the ultimate content, timing or effect of any healthcare reform legislation or the impact of potential legislation on its business.
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the ACA was enacted to reduce healthcare expenditures. On August 2, 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011, was enacted which, among other things, included aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year. These reductions went into effect on April 1, 2013 and, due to subsequent legislative amendments to the statute will remain in effect through 2031, unless additional Congressional action is taken. Under current legislation, the actual reduction in Medicare payments will vary from 1% in 2022 to up to 4% in the final fiscal year of this sequester.
Moreover, on January 2, 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several types of providers, including hospitals, imaging centers and cancer treatment centers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. If federal spending is further reduced, anticipated budgetary shortfalls may also impact the ability of relevant agencies, such as the FDA or the National Institutes of Health to continue to function at current levels. Amounts allocated to federal grants and contracts may be reduced or eliminated. These reductions may also impact the ability of relevant agencies to timely review and approve research and development, manufacturing, and marketing activities, which may delay Tempest’s ability to develop, market and sell any products Tempest may develop.
Moreover, payment methodologies may be subject to changes in healthcare legislation and regulatory initiatives. For example, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 (“MMA”), changed the way Medicare covers and pays for pharmaceutical products. The legislation expanded Medicare coverage for drug purchases by the elderly and introduced a new reimbursement methodology based on average sales prices for physician-administered drugs. In addition, this legislation provided authority for limiting the number of drugs that will be covered in any therapeutic class. While the MMA only applies to drug benefits for Medicare beneficiaries, private payors often follow Medicare coverage policy and payment limitations in setting their own reimbursement rates. Therefore, any reduction in reimbursement that results from the MMA may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors.
Recently there has been heightened governmental scrutiny over the manner in which manufacturers set prices for their marketed products, which has resulted in several Congressional inquiries and proposed and enacted federal and state legislation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to product pricing, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drug products. At the federal level, in July 2021, the Biden administration released an executive order, “Promoting Competition in the American Economy,” with multiple provisions aimed at prescription drugs. In response to Biden’s executive order, on September 9, 2021, HHS released a Comprehensive Plan for Addressing High Drug Prices that outlines principles for drug pricing reform and sets out a variety of potential legislative policies that Congress could pursue as well as potential administrative actions HHS can take to advance these principles. In addition, the IRA, among other things, (i) directs HHS to negotiate the price of medical productscertain high-expenditure, single-source drugs and proceduresbiologics covered under Medicare, and subject drug manufacturers to civil monetary penalties and a potential excise tax by offering a price that is not equal to or less than the negotiated “maximum fair price” for such drugs and biologics under the law, and (ii) imposes rebates with respect to certain drugs and biologics covered under Medicare Part B or Medicare Part D to penalize price increases that outpace inflation. The IRA permits HHS to implement many of these provisions through their pricing and reimbursement rules and control of national healthcare systems that fund a large part of consumers' medical costs. Some jurisdictions operate positive and negative list systems under which treatments or procedures
26
guidance, as opposed to regulation, for the initial years. These provisions will take effect progressively starting in fiscal year 2023, although they may be marketed only aftersubject to legal challenges. It is currently unclear how the IRA will be implemented but is likely to have a significant impact on the pharmaceutical industry. Further, the Biden administration released an additional executive order on October 14, 2022, directing HHS to submit a report on how the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation can be further leveraged to test new models for lowering drug costs for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. It is unclear whether this executive order or similar policy initiatives will be implemented in the future. At the state level, legislatures are increasingly passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical and biological product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement price has been agreed upon. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval,constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and, in some cases, designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing.
Additionally, on May 30, 2018, the Trickett Wendler, Frank Mongiello, Jordan McLinn, and Matthew Bellina Right to Try Act of these countries may require the completion of2017 was signed into law. The law, among other things, provides a federal framework for certain patients to access certain investigational new drug products that have completed a phase 1 clinical trial and that are undergoing investigation for FDA approval. Under certain circumstances, eligible patients can seek treatment without enrolling in clinical trials that compareand without obtaining FDA authorization under an FDA expanded access program; however, manufacturers are not obligated to provide investigational new drug products under the cost-effectiveness of our particular treatments or procedurescurrent federal right to currently available therapies. Other countries allow medical companies to fix their own prices, but monitortry law.
Employees and control company profits. The downward pressure on healthcare costs has become very intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new treatments and procedures.
As of December 31, 2017,2023, we had 36 full-time employees.17 employees, including 14 holding Ph.D., M.D., JD, LL.M., and/or MBA degrees, our employees have established internal expertise in chemistry, biochemistry, molecular biology, immunology, pharmacology, toxicology, pre-clinical development, regulatory and quality, translational medicine, and early-to-late-stage clinical development, as well as finance, business development and strategic transactions. None of our employees are represented by a labor union or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. agreements. We will continue to add experienced and talented scientists in areas, such as medicinal chemistry, that we believe are critical for the discovery of highly differentiated small-molecule compounds.
Compensation and Benefits
We consider a number of measures and objectives in managing our relationship withhuman capital assets, including, among others, employee engagement, development and training, talent acquisition and retention, employee safety and wellness, diversity and inclusion, and compensation and pay equity. We provide our employees with salaries and bonuses intended to be good.
Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI)
We were incorporated underbelieve that a diverse workforce is important to our success and we are fundamentally committed to creating and maintaining a work environment in which employees are treated fairly, with dignity, decency, respect and in accordance with all applicable laws. We understand that varied perspectives lead to the lawsbest ideas and outcomes. We believe that by creating a workplace where every individual can feel welcome and valued, we will be better able to achieve our corporate objectives. All employees must adhere to a code of the State of Delaware in April 2011 under the name Ovastem, Inc.business conduct and changed our name to OvaScience, Inc. in May 2011. Our principal executive offices are located at 9 4th Avenue, Waltham, Massachusetts 02451,ethics and our telephone numberemployee handbook, which combined, define standards for appropriate behavior. Our recruitment, hiring, development, training, compensation, and advancement is (617) 500-2802. based on qualifications, performance, skills, and experience without regard to gender, gender identity, sexual orientation, race, or ethnicity. People of color and those who are part of underrepresented groups in the biotech industry are encouraged to apply for open positions.
Available Information
27
Our internet website address is www.ovascience.com. Thewww.Tempesttx.com. In addition to the information about us and our subsidiaries contained on, or thatin this Annual Report, information about us can be accessed through,found on our website. Our website and information included in or linked to our website isare not a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We have included our website address in this Annual Report solely as an inactive textual reference.
Our annual reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reportsquarterly reports on Form 10-Q, and Current Reportscurrent reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, are available free of charge through our website as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC"). Additionally, the SEC onmaintains an internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information. The address of the Investors section of ourSEC’s website at www.ovascience.com or by contacting our Corporate Communications department at (617) 500-2802. The contents of our website are not incorporated by reference into this report and you should not consider information provided on our website to be part of this report.
ITEM 1A. Risk Factors
Our business is subjectinvolves significant risks, some of which are described below. You should carefully consider the risks described below, together with all of the other information contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the financial statements and the related notes. Any of these events could cause the trading price of our common stock to numerous risks. We cautiondecline, which would cause you thatto lose all or part of your investment. The occurrence of any of the following important factors, among others,risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth prospects or cause our actual results to differ materially from those expressedcontained in forward-looking statements we have made by us or onmay make from time to time.
Summary of Selected Risks Associated with Our Business
Our business is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, any one of which could materially adversely affect our behalf in filingsbusiness, financial condition, operating results, and prospects. You should read this summary together with the SEC, press releases, communicationsmore detailed description of each risk factor contained below.
28
Risks Related to Our Financial Position and NeedCapital Needs
We have a history of operating losses, and we may not achieve or sustain profitability. We anticipate that we will continue to incur losses for Additional Capitalthe foreseeable future. If we fail to obtain additional funding to conduct our planned research and
29
development efforts, we could be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our product development programs or commercial development efforts.
We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company with a limited operating history. Biotechnology product development is a highly speculative undertaking and involves a substantial degree of risk. Our earlyoperations to date have been limited primarily to organizing and staffing, business planning, raising capital, acquiring and developing product and technology rights, manufacturing, and conducting research and development activities for our product candidates. We have never generated any revenue from product sales and we have not obtained regulatory approvals for any of our product candidates. We incurred net losses of $29.5 million and $35.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively. As of December 31, 2023, we had an accumulated deficit of $165.3 million. Substantially all of our operating losses have resulted from costs incurred in connection with our research and development programs and from general and administrative costs associated with our operations. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and operating losses over the next several years and for the foreseeable future as we continue to conduct research and development, clinical testing, regulatory compliance activities, manufacturing activities, and, if any of our product candidates is approved, sales and marketing activities. Our prior losses, combined with our expected future losses, have had and will continue to have an adverse effect on our stockholders’ equity and working capital.
We will need to raise additional funding to finance our operations, which may not be available on acceptable terms or at all. Failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed may force us to delay, limit or terminate our product development efforts or other operations.
Our operations have consumed significant amounts of cash since inception. We expect our expenses to continue to increase in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we conduct clinical trials of, and seek marketing approval for, our product candidates, including later stage clinical trials such as our potential pivotal Phase 3 trial in first-line HCC, subject to our discussions with the FDA, and advance our other programs. Developing pharmaceutical products, including conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials, is a very time-consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes years to complete. Other unanticipated costs may also arise. Because the design and outcome of our ongoing and anticipated clinical trials are highly uncertain, we cannot reasonably estimate the actual amount of resources and funding that will be necessary to successfully complete the development and commercialization of any product candidate we develop. Moreover, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations and planned research and clinical development activities. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
the timing, progress, costs and results of our ongoing preclinical studies and clinical trials of our product candidates;
the scope, progress, results and costs of preclinical development, laboratory testing and clinical trials of other product candidates that we may pursue;
• our ability to establish collaborations on favorable terms, if at all;
• the costs, timing and outcome of regulatory review of our product candidates;
• the costs and timing of future commercialization activities, including product manufacturing, marketing, sales, reimbursement and distribution, for any of our product candidates for which we may receive marketing approval;
• the revenue, if any, received from commercial sales of our product candidates for which we may receive marketing approval;
• the cost of any milestone and royalty payments with respect to any approved product candidates;
• the costs and timing of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our intellectual property rights and defending any intellectual property-related claims;
30
• the costs of operating as a public company; and
• the extent to which we acquire or in-license other product candidates and technologies.
We may never generate the necessary data or results required to obtain regulatory approval in order to generate revenue from product sales. In addition, our product candidates, if approved, may not achieve commercial success. Our commercial revenues, if any, will be derived from sales of products that we do not expect to be commercially available for several years, if at all. Accordingly, we will need to continue to rely on our cash and cash equivalents and additional financing to achieve our business objectives.
As of December 31, 2023, we had cash and cash equivalents of $39.2 million. We believe that our cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2023, will fund our current operating plans through at least the next 12 months from the date the financial statements were issued. We have based this assessment on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and it is possible that we will not achieve the progress that we expect with these funds because the actual costs and timing of clinical development and regulatory and commercial activities are difficult to predict and are subject to substantial risks and delays, and that we will use our capital resources sooner than we currently expect. This estimate does not reflect any additional expenditures that may result from any further strategic transactions to expand and diversify our product pipeline, including acquisitions of assets, businesses, rights to products, product candidates or technologies or strategic alliances or collaborations that we may pursue.
Accordingly, we will require substantial additional capital to develop our product candidates. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If we require additional capital at a time when investment in our industry or in the marketplace in general is limited, we might not be able to raise funding on favorable terms, if at all. Our ability to raise additional capital may be adversely impacted by potential worsening global economic conditions, inflation expectations, and the recent disruptions to and volatility in the credit and financial markets in the United States and worldwide resulting from public health crises and geopolitical tensions, such as the Russia-Ukraine war and the war in Israel. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or on acceptable terms, we could be forced to delay, reduce, or explore other strategic options for our research and development programs or other opportunities, or even our operations. If we do not obtain additional financing and are required to terminate our operations, our stockholders will lose their investment.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish proprietary rights.
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate substantial product revenue, we expect to finance our cash needs through public or private equity or debt financings, third-party funding, marketing and distribution arrangements, as well as other collaborations, strategic alliances and licensing arrangements, or any combination of these approaches. We do not have any committed external source of funds. In July 2021, we entered into Sales Agreement, or the ATM Agreement, with Jefferies LLC, for an at-the-market offering program that allows us to sell up to an aggregate of $100 million of our common stock. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest may be further diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a stockholder. In addition, we may issue equity or debt securities as consideration for obtaining rights to additional compounds.
Debt and equity financings, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as redeeming our shares, making investments, incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures, declaring dividends or placing limitations on our ability to acquire, sell or license intellectual property rights and other operating restrictions that could negatively impact our ability to conduct our business. For example, our obligations under the loan and security agreement, or Loan Agreement, with Oxford Finance LLC, or Oxford Finance, are secured by a security interest in all of our assets, including our intellectual property. In addition, the Loan Agreement contains customary covenants that, subject to specific exceptions, restrict our ability to, among other things, declare dividends or redeem or repurchase equity interests, incur additional liens, make loans and investments, incur additional indebtedness, engage in mergers, acquisitions and asset sales, transact with affiliates, undergo a change in control, add or change business locations, or engage in businesses that are not related to its existing business.
31
In addition, if we raise additional capital through future collaborations, strategic alliances or third-party licensing arrangements, we may have to relinquish future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates, or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us.
If we are unable to raise additional capital when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our drug development or future commercialization efforts, or grant rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise develop and market ourselves.
The terms of the Loan Agreement with Oxford Finance provide Oxford with a lien against all of our assets, including our intellectual property, and contains financial covenants and other restrictions on our actions that may limit our operational flexibility or otherwise adversely affect our results of operations.
In January 2021, we entered into a Loan Agreement with Oxford Finance that provided us with up to $35.0 million of borrowing capacity across three potential tranches, which was subsequently amended in December 2022. The initial tranche of $15.0 million was funded at the closing of the Loan Agreement. As of December 31, 2023, a total of $10.0 million in borrowing capacity remained available at the option of Oxford Finance. Our overall leverage and certain obligations and affirmative and negative covenants contained in the related documentation could adversely affect our financial health and business and future operations by limiting our ability to, among other things, satisfy our obligations under the Loan Agreement, refinance our debt on terms acceptable to us or at all, plan for and adjust to changing business, industry and market conditions, use our available cash flow to fund future acquisitions and make dividend payments, and obtain additional financing for working capital, to fund growth or for general corporate purposes, even when necessary to maintain adequate liquidity.
If we default under the Loan Agreement, Oxford Finance may accelerate all of our repayment obligations and exercise all of their rights and remedies under the Loan Agreement and applicable law, potentially requiring us to renegotiate our agreement on terms less favorable to us. In addition, since the borrowings under the Loan Agreement are secured by a lien on our assets, including our intellectual property, Oxford Finance would be able to foreclose on our assets if we do not cure any default or pay any amounts due and payable under the Loan Agreement. Further, if we are liquidated, the lenders’ right to repayment would be senior to the rights of the holders of our common stock to receive any proceeds from the liquidation. Oxford Finance could declare a default upon the occurrence of an event of default, including events that they interpret as a material adverse change as defined in the Loan Agreement, payment defaults or breaches of certain affirmative and negative covenants, thereby requiring us to repay the loan immediately. Any declaration by Oxford Finance of an event of default could significantly harm our business and prospects and could cause the price of our common stock to decline. Additionally, if we raise any additional debt financing, the terms of such additional debt could further restrict our operating and financial flexibility.
Our limited operating history may make it difficult for you to evaluate the success of our business to date and to assess our future viability.
Our operations to date have been limited to organizing and staffing, business planning, raising capital, acquiring our corporate strategy, including a shift to focus on the advancement of OvaPrime and OvaTure, which are in clinicaltechnology, identifying potential product candidates, undertaking research and preclinical development, respectively.studies of our product candidates, manufacturing, and establishing licensing arrangements. We cannot assure you that this shift will be successful. Anyhave not yet demonstrated the ability to complete clinical trials of our product candidates, obtain marketing approvals, manufacture a commercial scale product or conduct sales and marketing activities necessary for successful commercialization. Consequently, any predictions you make about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be if we were inhad a later stage of development.
In addition, as a new and rapidly evolving fields. For example, to execute our business, plan, we will need to be successful in a range of challenging activities, including clinical trials of OvaPrime, development of OvaTure, obtaining any required approvals, manufacturing, marketing and selling those potential fertility treatments that we successfully develop, and addressing the challenges of foreign operations.
Our ability to utilize our net operating loss carryforwards and tax credit carryforwards may be subject to limitations.
32
Our ability to use our federal and state net operating losses (“NOLs”) to offset potential future taxable income and related income taxes that would otherwise be due is dependent upon our generation of future taxable income, and we cannot predict with certainty when, or whether, we will generate sufficient taxable income to use all of our NOLs.
Under Section 382 and Section 383 of the Code and corresponding provisions of state law, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change,” its ability to use its pre-change NOL carryforwards and other pre-change tax attributes (such as research tax credits) to offset its post-change income or taxes may be limited. A Section 382 “ownership change” is generally defined as a greater than 50 percentage point change (by value) in its equity ownership by certain stockholders over a three-year period. We may have incurred significant losses sinceexperienced ownership changes in the past, including as a result of the merger with Millendo, and may experience ownership changes in the future due to subsequent shifts in our inception. stock ownership (some of which are outside of our control). Furthermore, the merger constituted an ownership change (within the meaning of Section 382 of the Code) of Millendo which may have eliminated or otherwise substantially limited our ability to use Millendo’s federal and state NOLs to offset our future taxable income. Consequently, even if we achieve profitability, we may not be able to utilize a material portion of Private Tempest’s, Millendo’s or our combined NOL carryforwards and other tax attributes, which could have a material adverse effect on cash flow and results of operations. Similar provisions of state tax law may also apply to limit our ability to use of accumulated state tax attributes. There is also a risk that due to regulatory changes, such as suspensions on the use of NOLs, or other unforeseen reasons, our existing NOLs could expire or otherwise be unavailable to offset future income tax liabilities.
Risks Related to Our Business and Strategy
We expect to incur lossesexpand our development and regulatory capabilities, and as a result, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth, which could disrupt our operations.
We expect to experience significant growth in the number of our employees and the scope of our operations, particularly in the areas of product candidate development, growing our capability to conduct clinical trials, and, if approved, through commercialization of our product candidates. To manage our anticipated future growth, we must continue to implement and improve our managerial, operational and financial systems, expand our facilities and continue to recruit and train additional qualified personnel, or contract with third parties to provide these capabilities. Due to our limited financial resources and the limited experience of our management team in managing a company with such anticipated growth, we may not be able to effectively manage the expansion of our operations or recruit and train additional qualified personnel. The expansion of our operations may lead to significant costs and may divert our management and business development resources. Any inability to manage growth could delay the execution of our business plans or disrupt our operations.
We must attract and retain highly skilled employees to succeed.
To succeed, we must recruit, retain, manage and motivate qualified clinical, scientific, technical and management personnel, and we face significant competition for experienced personnel. If we do not succeed in attracting and retaining qualified personnel, particularly at the management level, it could adversely affect our ability to execute our business plan, harm our results of operations and increase our capabilities to successfully commercialize our product candidates. In particular, we believe that our future success is highly dependent upon the contributions of our senior management, particularly our Chief Executive Officer and President, Stephen Brady and our Chief Medical Officer, Sam Whiting. The loss of services of Messrs. Brady or Whiting, or any of our other senior management, could delay or prevent the successful development of our product pipeline, completion of our planned clinical trials or the commercialization of our product candidates, if approved. The competition for qualified personnel in the biotechnology field is intense and as a result, we may be unable to continue to attract and retain qualified personnel necessary for the foreseeable futuredevelopment of our business or to recruit suitable replacement personnel.
Many of the other biotechnology companies that we compete against for qualified personnel have greater financial and other resources, different risk profiles and a longer history in the industry than we do. They also may never achieve or maintain profitability.provide more diverse opportunities and better chances for career advancement. Some of these characteristics may be more appealing to high-quality candidates than
33
what we have incurred significantto offer. If we are unable to continue to attract and retain high-quality personnel, the rate and success at which we can discover and develop product candidates and our business will be limited.
Future acquisitions or strategic alliances could disrupt our business and harm our financial condition and results of operations.
We may acquire additional businesses or drugs form strategic alliances or create joint ventures with third parties that we believe will complement or augment our existing business. If we acquire businesses with promising markets or technologies, we may not be able to realize the benefit of acquiring such businesses if we are unable to successfully integrate them with our existing operations and company culture. We may encounter numerous difficulties in developing, manufacturing and marketing any new drugs resulting from a strategic alliance or acquisition that delay or prevent us from realizing their expected benefits or enhancing our business. We cannot assure you that, following any such acquisition, we will achieve the expected synergies to justify the transaction. The risks we face in connection with acquisitions, include:
Our failure to building outaddress these risks or other problems encountered in connection with our international infrastructure.
Risks Related to Our Product Development and Regulatory Approval
If we are unable to develop, obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize TPST-1495, TPST-1120, or any of our future product candidates, or if we experience significant expensesdelays in doing so, our business will be materially harmed.
We plan to invest a substantial amount of our efforts and increasing operating lossesfinancial resources in our current lead product candidates, TPST-1495, a dual EP2/EP4 prostaglandin (“PGE2”) receptor antagonist, and TPST-1120, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (“PPARα”) antagonist for the foreseeable future. treatment of various cancers. We have initiated Phase 1 clinical trials of TPST-1495 and
34
TPST-1120 for the treatment of advanced solid tumors. We intend to request meetings with FDA during 2024 to discuss a potential pivotal Phase 3 trial design for TPST-1120 for HCC, but the FDA may not agree that we are ready for such meetings, and may require that we conduct additional dose optimization or Phase 2 development work prior to proceeding to a Phase 3 trial. Any delay in our ability to proceed to a pivotal trial for TPST-1120 will add time and expense to the development pathway and adversely impact the timing and potential for profitability. Our ability to generate product revenue will depend heavily on the successful development and eventual commercialization of TPST-1495 and TPST-1120 and any future product candidates, which may never occur. We currently generate no revenue from sales of any product and we may never be able to develop or commercialize a marketable product.
Each of our programs and product candidates will require further clinical and/or preclinical development, regulatory approval in multiple jurisdictions, obtaining preclinical, clinical and commercial manufacturing supply, capacity and expertise, building of a commercial organization, substantial investment and significant marketing efforts before we generate any revenue from product sales. TPST-1495 and TPST-1120 and any future product candidates must be authorized for marketing by the FDA, the Health Products and Food Branch of Health Canada (“HPFB”), the European Medicines Agency (“EMA”), and certain other foreign regulatory agencies before we may commercialize any of our product candidates in the United States, Canada, European Union, or other jurisdictions.
The net losses we incur may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter. We anticipatesuccess of TPST-1495 and TPST-1120 and any future product candidates depends on multiple factors, including:
35
If we do not succeed in one or more of these factors in a timely manner or at all, we could experience significant delays or an inability to successfully commercialize our product candidates, which would materially harm our business. If we do not receive regulatory approvals for our product candidates, we may not be able to continue our operations.
Success in preclinical studies and earlier clinical trials for our product candidates may not be indicative of the results that may be obtained in later clinical trials, which may delay or prevent obtaining regulatory approval.
Clinical development is expensive and can take many years to complete, and our outcome is inherently uncertain. Failure can occur at any time during the clinical trial process. Success in preclinical studies and early clinical trials may not be predictive of results in later-stage clinical trials, and successful results from early or small clinical trials may not be replicated or show as favorable an outcome in later-stage or larger clinical trials, even if successful. We will be required to demonstrate through adequate and well-controlled clinical trials that our product candidates are safe and effective for their intended uses before we can seek regulatory approvals for their commercial sale. The conduct of Phase 3 trials and academic partners;the submission of a New Drug Application (“NDA”) is a complicated process. We have not previously completed any pivotal clinical trials, have limited experience in preparing, submitting and supporting regulatory filings, and have not previously submitted an NDA. Consequently, we may be unable to successfully and efficiently execute and complete necessary clinical trials and other requirements in a way that leads to NDA submission and approval of any product candidate we are developing.
Even if our clinical trials demonstrate acceptable safety and efficacy of TPST-1495 and TPST-1120 or any future product candidates and such product candidates receive regulatory approval, the labeling we obtain through negotiations with the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities may not include data on secondary endpoints and may not provide us with a competitive advantage over other products approved for the same or similar indications.
Many companies in the biotechnology industry have suffered significant setbacks in late-stage clinical trials after achieving positive results in early-stage development, and there is a high failure rate for product candidates proceeding through clinical trials. In addition, different methodologies, assumptions and applications we utilize to assess particular safety or efficacy parameters may yield different statistical results. Even if we believe the data collected from clinical trials of our product candidates are promising, these data may not be sufficient to support approval by the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities. Preclinical and clinical data can be interpreted in different ways. Accordingly, the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities could interpret these data in different ways from us or our partners, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. If our study data does not consistently or sufficiently demonstrate the safety or efficacy of any of our product candidates, including TPST-1495 and TPST-1120, to the satisfaction of the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities, then the regulatory approvals for such product candidates could be significantly delayed as we work to meet approval requirements, or, if we are not able to meet these requirements, such approvals could be withheld or withdrawn.
If we encounter difficulties enrolling patients in our clinical trials, our clinical development activities could be delayed or otherwise adversely affected.
36
We may experience difficulties in patient enrollment in our clinical trials for a variety of reasons. The timely completion of clinical trials in accordance with our protocols depends, among other things, on our ability to enroll a sufficient number of patients who remain in the study until our conclusion. The enrollment of patients depends on many factors, including:
Delays or failures in planned patient enrollment or retention may result in increased costs, program delays or both, which could have a harmful effect on our ability to develop our product candidates or could render further development impossible. For example, the impact of public health crises or geopolitical tensions, such as the Russia-Ukraine war and the war in Israel, may delay or prevent patients from enrolling or from receiving treatment in accordance with the protocol and the required timelines, which could delay our clinical trials, or prevent us from completing our clinical trials at all.
In addition, our clinical trials will compete with other clinical trials for product candidates that are in the same therapeutic areas as our product candidates, and this competition will reduce the number and types of patients available to us because some patients who might have opted to enroll in our trials may instead opt to enroll in a trial being conducted by one of our competitors. Since the number of qualified clinical investigators is limited, some of our clinical trial sites are also being used by some of our competitors, which may reduce the number of patients who are available for our clinical trials in that clinical trial site.
Moreover, because our product candidates represent unproven methods for cancer treatment, potential patients and their doctors may be inclined to use existing therapies rather than enroll patients in our clinical trials.
Interim and preliminary data from our clinical trials that we may announce or publish from time to time may change as more patient data becomes available and are subject to audit and verification procedures that could result in material changes in the final data.
From time to time, we may publish interim or preliminary data from our clinical studies. Interim data from clinical trials that we may complete are subject to the risk that one or more of the clinical outcomes may materially change as patient enrollment continues and more patient data become available.
Preliminary or interim data also remain subject to audit and verification procedures that may result in the final data being materially different from the preliminary data we previously published. As a result, interim and preliminary data should be viewed with caution until the final data is available. Adverse differences between preliminary or interim data and final data could significantly harm our business prospects.
We currently are investigating TPST-1120 and TPST-1495 in combination with other approved therapies, and we may in the future investigate product candidates in combination with other approved and unapproved therapies, which exposes us to additional risks.
We are currently investigating and may continue to investigate one or more of our product candidates in combination with one or more other approved or unapproved therapies to treat cancers. Even if any product candidate we develop were to receive
37
marketing approval or be commercialized for use in combination with other existing therapies, we would continue to be subject to the risks that the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities outside of the United States could revoke approval of the therapy used in combination with our product or that safety, efficacy, manufacturing or supply issues could arise with any of those existing therapies, including shortages of those products for use in our intended clinical trials. If the therapies we use in combination with our product candidates are replaced as the standard of care for the indications we choose for any of our product candidates, the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require us to conduct additional clinical trials. The occurrence of any of these risks could result in our own products, if approved, being removed from the market or being less successful commercially. We also may choose to evaluate our current product candidates or any other future product candidates in combination with one or more cancer therapies that have not yet been approved for marketing by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. We will not be able to market and sell our current product candidates or any product candidate we develop in combination with an unapproved cancer therapy for a combination indication if that unapproved therapy does not ultimately obtain marketing approval either alone or in combination with our product. In addition, unapproved cancer therapies face the same risks described with respect to our product candidates currently in development and clinical trials, including the potential for serious adverse effects, delay in their clinical trials and lack of FDA approval. If the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities do not approve these other products or revoke their approval of, or if safety, efficacy, quality, manufacturing or supply issues arise with, the products we choose to evaluate in combination with our product candidate we develop, we may be unable to obtain approval of or market such combination therapy.
Even if we complete the necessary preclinical studies and clinical trials, we cannot predict when, or if, we will obtain regulatory approval to commercialize a product candidate and the approval may be for a narrower indication than we seek.
Prior to commercialization, TPST-1495, TPST-1120 and any future product candidates must be approved by the FDA pursuant to an NDA in the United States and pursuant to similar marketing applications by the HPFB, EMA and similar regulatory authorities outside the United States. The process of obtaining marketing approvals, both in the United States and abroad, is expensive and takes many years, if approval is obtained at all, and can vary substantially based upon a variety of factors, including the type, complexity and novelty of the product candidates involved. Failure to obtain marketing approval for a product candidate will prevent us from commercializing the product candidate. We have not received approval to market TPST-1495, TPST-1120 or any future product candidates from regulatory authorities in any jurisdiction. We have no experience in submitting and supporting the applications necessary to gain marketing approvals, and, in the event regulatory authorities indicate that we may submit such applications, we may be unable to do so as quickly and efficiently as desired. Securing marketing approval requires the submission of extensive preclinical and clinical data and supporting information to regulatory authorities for each therapeutic indication to establish the product candidate’s safety and efficacy. Securing marketing approval also requires the submission of information about the product manufacturing process to, and inspection of manufacturing facilities by, the regulatory authorities. Our product candidates may not be effective, may be only moderately effective or may prove to have undesirable or unintended side effects, toxicities or other characteristics that may preclude us from obtaining marketing approval or prevent or limit commercial use. Regulatory authorities have substantial discretion in the approval process and may refuse to accept or file any application or may decide that our data is insufficient for approval and require additional preclinical, clinical or other studies. In addition, varying interpretations of the data obtained from preclinical and clinical testing could delay, limit or prevent marketing approval of a product candidate.
Approval of TPST-1495 and TPST-1120 and any future product candidates may be delayed or refused for many reasons, including:
38
Even if our product candidates meet their pre-specified safety and efficacy endpoints in clinical trials, the regulatory authorities may not complete their review processes in a timely manner and may not consider such clinical trial results sufficient to grant, or we may not be able to obtain, regulatory approval. Additional delays may result if an FDA Advisory Committee or other regulatory authority recommends non-approval or restrictions on approval. In addition, we may experience delays or rejections based upon additional government regulation from future legislation or administrative action, or changes in regulatory authority policy during the period of product development, clinical trials and the review process.
Regulatory authorities also may approve a product candidate for more limited indications than requested or they may impose significant limitations in the form of narrow indications, warnings, contraindications or Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (“REMS”). These regulatory authorities may also grant approval subject to the performance of costly post-marketing clinical trials. In addition, regulatory authorities may not approve the labeling claims that are necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of our product candidates. Any of the foregoing scenarios could materially harm the commercial prospects for our product candidates and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
TPST-1495, TPST-1120 and any future product candidates may cause undesirable and/or unforeseen side effects or be perceived by the public as unsafe, which could delay or prevent their advancement into clinical trials or regulatory approval, limit the commercial potential or result in significant negative consequences.
As is the case with pharmaceuticals generally, it is likely that there may be side effects and adverse events associated with our product candidates’ use. Results of our clinical trials could reveal a high and unacceptable severity and prevalence of side effects or unexpected characteristics. As we continue developing our product candidates and initiate clinical trials of our additional product candidates, serious adverse events (“SAEs”), undesirable side effects, relapse of disease or unexpected characteristics may emerge causing us to abandon these product candidates or limit their development to more narrow uses or subpopulations in which the SAEs or undesirable side effects or other characteristics are less prevalent, less severe or more acceptable from a risk-benefit perspective or in which efficacy is more pronounced or durable.
If any such adverse events occur, our clinical trials could be suspended or terminated and the FDA, the HPFB, the European Commission, the EMA or other regulatory authorities could order us to cease further development of, or deny approval of, our product candidates for any or all targeted indications. Even if we can demonstrate that all future serious adverse events are not product-related, such occurrences could affect patient recruitment or the ability of enrolled patients to complete the trial. Moreover, if we elect, or are required, to not initiate, delay, suspend or terminate any future clinical trial of any of our product candidates, the commercial prospects of such product candidates may be harmed and our ability to generate product revenues from any of these product candidates may be delayed or eliminated. Any of these occurrences may harm our ability to develop other product candidates, and may adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects significantly, including our ability to successfully sign collaboration or license agreements with external partners. Other treatments for cancers that utilize prostaglandin E2 antagonist or a PPARα antagonist or similar mechanism of action could also
39
generate data that could adversely affect the clinical, regulatory or commercial perception of TPST-1495 and TPST-1120 and any future product candidates.
Additionally, if any of our product candidates receives marketing approval, the FDA could require us to adopt a REMS to ensure that the benefits of the product outweigh our risks, which may include, for example, a Medication Guide outlining the risks of the product for distribution to patients and a communication plan to health care practitioners, or other elements to assure safe use of the OvaPrime and OvaTure treatments;product.
Furthermore, if we or others later identify undesirable side effects caused by our product candidates, several potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
Any of these occurrences may harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects significantly.
We may not be successful in our efforts to expand our pipeline of product candidates and develop marketable products.
Because we have limited financial and managerial resources, we focus on research programs and product candidates that we identify for specific indications. Our business depends on our successful development and commercialization of the limited number of internal product candidates we are researching or have in preclinical development. Even if we are successful in continuing to build our pipeline, development of the potential product candidates that we identify will require substantial investment in additional clinical development, management of clinical, preclinical and manufacturing activities, regulatory approval in multiple jurisdictions, obtaining manufacturing supply capability, building a commercial organization, and significant marketing efforts before we generate any revenue from product sales. Furthermore, such product candidates may not be suitable for clinical development, including as a result of their harmful side effects, limited efficacy or other characteristics that indicate that they are unlikely to be products that will receive marketing approval and achieve market acceptance. If we cannot develop further product candidates, we may not be able to obtain product revenue in future periods, which would adversely affect our business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
Although our pipeline includes multiple programs, we are primarily focused on our lead product candidates, TPST-1495 and TPST-1120, and we may forego or delay pursuit of opportunities with other product candidates or for other indications that later prove to have greater commercial potential. Our resource allocation decisions may cause us to fail to capitalize on viable commercial products or profitable market opportunities. Our spending on current and future research and development programs and product candidates for specific indications may not yield any commercially viable products. Our understanding and evaluation of biological targets for the discovery and development of new product candidates may fail to identify challenges encountered in subsequent preclinical and clinical development. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential or target market for a particular product candidate, we may relinquish valuable rights to that product candidate through collaboration, licensing or other royalty arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights.
Any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval will be subject to extensive post-marketing regulatory requirements and could be subject to post-marketing restrictions or withdrawal from the market, and we may be subject to
40
penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems with our product candidates, when and if any of them are approved.
Our product candidates and the activities associated with their development and potential commercialization, including their testing, manufacturing, recordkeeping, labeling, storage, approval, advertising, promotion, sale and distribution, are subject to comprehensive regulation by the FDA and other U.S. and international sales,regulatory authorities. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration and listing requirements, requirements relating to manufacturing, including current Good Manufacturing Practices (“cGMP”), quality control, quality assurance and corresponding maintenance of records and documents, including periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities and requirements regarding the distribution of samples to providers and recordkeeping. In addition, manufacturers of drug products and their facilities are subject to continual review and periodic, unannounced inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with cGMP.
The FDA may also impose requirements for costly post-marketing studies or clinical trials and surveillance to monitor the safety or efficacy of any approved product. The FDA closely regulates the post-approval marketing and promotion of drugs to ensure that they are marketed in a manner consistent with the provisions of the approved labeling. The FDA imposes stringent restrictions on manufacturers’ communications regarding use of their products. If we promote our product candidates in a manner inconsistent with FDA-approved labeling or otherwise not in compliance with FDA regulations, we may be subject to enforcement action. Violations of the FFDCA relating to the promotion of prescription drugs may lead to investigations alleging violations of federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws, as well as state consumer protection laws and similar laws in international jurisdictions.
In addition, later discovery of previously unknown adverse events or other problems with our product candidates, manufacturers or manufacturing andprocesses, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may yield various results, including:
41
The occurrence of any event or penalty described above may inhibit our ability to commercialize our fertility treatments;
Non-compliance with Canadian and European requirements regarding safety monitoring or pharmacovigilance, and with requirements related to the development of products for the pediatric population, can also result in significant financial penalties.
Our failure to obtain regulatory approval in international jurisdictions would prevent us from marketing our product candidates outside the United States.
To market and sell TPST-1495, TPST-1120 and any future product candidates in other jurisdictions, we must obtain separate marketing approvals and comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements. The approval procedure varies among countries and can involve additional testing. The time and data required to obtain approval may differ substantially from that required to obtain FDA approval. The regulatory approval process outside the United States generally includes all of the risks associated with obtaining FDA approval. In addition, in many countries outside the United States, we must secure product reimbursement approvals before regulatory authorities will approve the product for sale in that country. Failure to obtain foreign regulatory approvals or non-compliance with foreign regulatory requirements could result in significant delays, difficulties and costs for us and could delay or prevent the introduction of our product candidates in certain countries.
If we fail to comply with the regulatory requirements in international markets and receive applicable marketing approvals, our target market will be reduced and our ability to realize the full market potential of our product candidates will be harmed and our business will be adversely affected. We may not obtain foreign regulatory approvals on a timely basis, if at all. Our failure to obtain approval of any of our product candidates by regulatory authorities in another country may significantly diminish the commercial prospects of that product candidate and our business prospects could decline.
Risks Related to Commercialization and Manufacturing
The commercial success of our product candidates, including TPST-1495 and TPST-1120, will depend upon their degree of market acceptance by providers, patients, patient advocacy groups, third-party payors and the general medical community.
Even if the requisite approvals from the FDA, the HPFB, the EMA and other regulatory authorities internationally are obtained, the commercial success of our product candidates will depend, in part, on the acceptance of providers, patients and third-party payors of drugs designed to act as a dual antagonist of EP2 and EP4 and PPARα antagonists in general, and our product candidates in particular, as medically necessary, cost-effective and safe. In addition, we may face challenges in seeking to establish and grow sales of TPST-1495 and TPST-1120 or any future product candidates. Any product that we commercialize may not gain acceptance by providers, patients, patient advocacy groups, third-party payors and the general medical community. If these products do not achieve an adequate level of acceptance, we may not generate significant product revenue and may not become profitable.
Even if a potential product displays a favorable efficacy and safety profile in preclinical studies and clinical trials, market acceptance of the product will not be fully known until after it is launched.
42
The pricing, insurance coverage and reimbursement status of newly approved products is uncertain. Failure to obtain or maintain adequate coverage and reimbursement for our product candidates, if approved, could limit our ability to market those products and decrease our ability to generate product revenue.
Successful sales of our product candidates, if approved, depend on the availability of coverage and adequate reimbursement from third-party payors including governmental healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, managed care organizations and commercial payors, among others. Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of any product candidates for which we obtain regulatory approval. In addition, because our product candidates represent new approaches to the treatment of cancer, we cannot accurately estimate the potential revenue from our product candidates.
We expect that coverage and reimbursement by third-party payors will be essential for most patients to be able to afford these treatments. Accordingly, sales of our product candidates will depend substantially, both domestically and internationally, on the extent to which the costs of our product candidates will be paid by health maintenance, managed care, pharmacy benefit and similar healthcare management organizations, or will be reimbursed by government payors, private health coverage insurers and other third-party payors. Even if coverage is provided, the established reimbursement amount may not be high enough to allow us to establish or maintain pricing sufficient to realize a sufficient return on our investment.
There is significant uncertainty related to the insurance coverage and reimbursement of newly approved products. In the United States, third-party payors, including private and governmental payors, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs, play an important role in determining the extent to which new drugs will be covered and reimbursed. The Medicare program covers certain individuals aged 65 or older, disabled or suffering from end-stage renal disease. The Medicaid program, which varies from state-to-state, covers certain individuals and families who have limited financial means. The Medicare and Medicaid programs increasingly are used as models for how private payors and other government payors develop their coverage and reimbursement policies for drugs. One payor’s determination to provide coverage for a drug product, however, does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage for the drug product. Further, a payor’s decision to provide coverage for a drug product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be approved.
In addition to government and private payors, professional organizations such as the American Medical Association, can influence decisions about coverage and reimbursement for new products by determining standards for care. In addition, many private payors contract with commercial vendors who sell software that provide guidelines that attempt to limit utilization of, and therefore reimbursement for, certain products deemed to provide limited benefit compared to existing alternatives. Such organizations may set guidelines that limit reimbursement or utilization of our product candidates, if approved. Even if favorable coverage and reimbursement status is attained for one or more product candidates for which our collaborators receive regulatory approval, less favorable coverage policies and reimbursement rates may be implemented in the future.
Outside the United States, international operations are generally subject to extensive governmental price controls and other market regulations, and we believe the increasing emphasis on cost-containment initiatives in Europe, Canada and other countries has and will continue to put pressure on the pricing and usage of therapeutics such as our product candidates. In many countries, particularly the countries of the EU, the prices of medical products are subject to varying price control mechanisms as part of national health systems. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after the receipt of marketing approval for a product. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval in some countries, we may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost-effectiveness of our product candidate to other available therapies. In general, the prices of products under such systems are substantially lower than in the United States. Other countries allow companies to fix their own prices for products, but monitor and control company profits. Additional foreign price controls or other changes in pricing regulation could restrict the amount that we are able to charge for our product candidates. Accordingly, in markets outside the United States, the reimbursement for our product candidates may be reduced compared with the United States and may be insufficient to generate commercially reasonable revenues and profits.
Moreover, increasing efforts by government and other third-party payors, in the United States and internationally, to cap or reduce healthcare costs may cause such payors to limit both coverage and the level of reimbursement for new products approved and, as a result, they may not cover or provide adequate payment for our product candidates. We expect to experience pricing pressures
43
in connection with the sale of any of our product candidates due to the trend toward managed healthcare, the increasing influence of certain third-party payors, such as health maintenance organizations, and additional legislative changes. The downward pressure on healthcare costs in general, particularly prescription drugs and surgical procedures and other treatments, has become very intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new products into the healthcare market. Recently there have been instances in which third-party payors have refused to reimburse treatments for patients for whom the treatment is indicated in the FDA-approved product labeling. Even if we are successful in obtaining FDA approval to commercialize our product candidates, we cannot guarantee that we will be able to secure reimbursement for all patients for whom treatment with our product candidates is indicated.
If third parties on which we depend to conduct our planned preclinical studies or clinical trials do not perform as contractually required, fail to satisfy regulatory or legal requirements or miss expected deadlines, our development program could be delayed with adverse effects on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We rely on third party CROs, CMOs, consultants and others to design, conduct, supervise and monitor key activities relating to, testing, discovery, manufacturing, preclinical studies and clinical trials of our fertility treatments;
If we cannot contract with acceptable third parties on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, or if these third parties do not carry out their contractual duties, satisfy legal and regulatory requirements for the conduct of preclinical studies or clinical trials or meet expected deadlines, our clinical development programs could be delayed and otherwise adversely affected. In all events, we are responsible for ensuring that each of our preclinical studies and clinical trials is conducted in accordance with the general investigational plan and protocols for the trial, as well as in accordance with GLP, GCP and other applicable laws, regulations and standards. Our reliance on third parties that we do not control does not relieve us of these responsibilities and requirements. The FDA and other regulatory authorities enforce GCP through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators and trial sites. If we or any required approvals fromof these third parties fails to comply with applicable GCP, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA or similarcomparable foreign regulatory authorities may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our marketing applications. We cannot assure you that upon inspection by a given regulatory authority, such regulatory authority will determine that any of our clinical trials have complied with GCP. In addition, our clinical trials must be conducted with product produced in accordance with cGMP. Our failure to comply with these regulations may require us to repeat clinical trials, which could delay or prevent the receipt of regulatory approvals. Any such event could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We face significant competition in an environment of rapid technological change, and it is possible that our competitors may achieve regulatory approval before us or develop therapies that are more advanced or effective than our therapies, which may harm our business, financial condition and our ability to successfully market or commercialize TPST-1495, TPST-1120, and any future product candidates.
The biopharmaceutical industry, and the immuno-oncology industry specifically, is characterized by intense competition and rapid innovation. We are aware of other companies focused on developing cancer therapies in various indications. We may also face competition from large and specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, academic research institutions, government agencies outsideand public and private research institutions that conduct research, seek patent protection, and establish collaborative arrangements for research, development, manufacturing and commercialization.
44
Many of our potential competitors, alone or with their strategic partners, may have substantially greater financial, technical and other resources than we do, such as larger research and development, clinical, marketing and manufacturing organizations. Mergers and acquisitions in the United States, whichbiotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of competitors. Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if competitors develop and commercialize products that are safer, more effective, have fewer or less severe side effects, are more convenient or are less expensive than any product candidates that we refer to as Foreign Regulatory Authorities,may develop. Competitors also may obtain FDA or other regulatory approval for their products more rapidly than we may obtain approval for our potential fertility treatments;
To become and remain profitable, we must develop and eventually commercialize our potential fertility treatmentsproduct candidates with significant market potential, including OvaPrime and OvaTure, and determine strategies to scale our treatments commercially. Thiswhich will require us to be successful in a range of challenging activities. These activities include, among other things, completing preclinical studies and initiating and completing clinical trials of our product candidates, obtaining marketing approval for our treatments, obtainingthese product candidates, manufacturing, marketing and selling those products that are approved and satisfying any necessary regulatory approvals and successfully commercializing, either alone or with partners.post marketing requirements. We may never succeed in any or all of these activities and, even if we do, we may never generate revenues that are significant or large enough to achieve profitability. If we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a quarterly or annual basis. Our failure to become and remain profitable would decrease the value of our companycommon stock and could impair our ability to raise capital, maintain our research and development efforts, expand our business or continue our operations.
We may fail to achieve sufficient revenues from our fertility treatments to achieve profitability on our expected timelines or at all. We will need to continue to rely on additional financingthird parties to achievemanufacture our business objectives. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
We must currently rely on outside vendors to manufacture supplies and process our product candidates. We have not yet manufactured or potential fertility treatments or grant licensesprocessed our product candidates on terms thata commercial scale and may not be favorableable to us.
We do not yet have sufficient information to reliably estimate the memberscost of the commercial manufacturing and processing of our board of directorsproduct candidates, and certain of the underwriters fromactual cost to manufacture and process our January 2015 follow-on public offeringproduct candidates could materially and adversely affect the commercial viability of our common stock by investors alleging violations of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. The plaintiffs’ motion for class certification has been denied, and the court has entered summary judgment dismissing the claims of all but one of the plaintiffs. The remaining plaintiff has also filed a substantially similar putative class action complaint in the U.S. District Court for the District of Massachusetts. On March 24, 2017, a second purported shareholder class action lawsuit was filed against us and certain of our present and former officers alleging violations of Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
45
Our contract manufacturers would also be successfully commercialized.
The manufacture of drugs is complex, and our third-party manufacturers may encounter difficulties in production. If any of our third-party manufacturers encounter such difficulties, our ability to provide adequate supply of our product candidates for clinical trials, our ability to obtain marketing approval, or our ability to provide supply of our product candidates for patients, if we have successfully developed fertilizable, mature eggs until we have successfully fertilized them,approved, could be delayed or stopped.
We intend to establish manufacturing relationships with a limited number of suppliers to manufacture raw materials, the drug substance and we may never succeed in fertilizing human or bovine EggPC cell-derived eggs. We may find that there are important criteriafinished product of any product candidate for developmental competence thatwhich we are responsible for preclinical or clinical development. Each supplier may require licenses to manufacture such components if such processes are not observing,owned by the supplier or that elementsin the public domain. As part of any marketing approval, a manufacturer and its processes are required to be qualified by the criteria for maturity that we have observed are inadequately developed for fertilization. To date, our effortsFDA prior to fertilize bovine EggPC cell-derived eggs have failed. Further, we will require authorizationregulatory approval. If supply from the approved vendor is interrupted, there could be a significant disruption in commercial supply. An alternative vendor would need to be qualified through an NDA supplement which could result in further delay. The FDA or other regulatory bodiesagencies outside of the United States may also require additional studies if a new supplier is relied upon for commercial production. Switching vendors may involve substantial costs and is likely to attemptresult in a delay in our desired clinical and commercial timelines.
The process of manufacturing drugs is complex, highly regulated and subject to fertilizemultiple risks. Manufacturing drugs is highly susceptible to product loss due to contamination, equipment failure, improper installation or operation of equipment, vendor or operator error, inconsistency in yields, variability in product characteristics and difficulties in scaling the production process. Even minor deviations from normal manufacturing processes could result in reduced production yields, product defects and other supply disruptions. If microbial, viral or other contaminations are discovered at the facilities of our manufacturers, such facilities may need to be closed for an extended period of time to investigate and remedy the contamination, which could delay clinical trials and adversely harm our business. Moreover, if the FDA determines that our CMOs are not in compliance with FDA laws and regulations, including those governing cGMP, the FDA may deny an NDA approval until the deficiencies are corrected or we replace the manufacturer in our NDA with a human Egg PC cell-derived egg before we can test any eggsmanufacturer that is in compliance. In addition, approved products and the facilities at which they are manufactured are required to maintain ongoing compliance with extensive FDA requirements and the requirements of other similar agencies, including ensuring that quality control and manufacturing procedures conform to cGMP requirements. As such, our CMOs are subject to continual review and periodic inspections to assess compliance with cGMP. Furthermore, although we do mature. Therenot have day-to-day control over the operations of our CMOs, we are significant aspects of OvaTure that will require additional innovationresponsible for us to continue its development. The recent nature of the scientific discoveries underlying OvaTure, the need for additional innovationensuring compliance with applicable laws and the absence of information about egg precursor cell technology from human clinical trials all increase theregulations, including cGMP.
In addition, there are risks associated with this potential fertility treatment. In any event, we believe that it will be costly and time consuming to develop and successfully commercialize OvaTure, and we may not succeed in doing so.
46
We believe that we will rely upon a limited number of manufacturers for our product candidates, which may include single-source suppliers for the various steps of manufacture. This reliance on a limited number of manufacturers and the complexity of drug manufacturing and the difficulty of scaling up a manufacturing process could cause the delay of clinical trials, regulatory submissions, required approvals or commercialization of our other fertility treatments would result in significant delays or may requireproduct candidates, cause us to abandonincur higher costs and prevent us from commercializing our product candidates successfully. Furthermore, if our suppliers fail to deliver the required commercial quantities of materials on a timely basis and at commercially reasonable prices, and we are unable to secure one or more clinical trials altogether. Enrollment delaysreplacement suppliers capable of production in a timely manner at a substantially equivalent cost, our clinical trials may result in increased development costs for ourbe delayed or we could lose potential fertility treatments, which would cause the value of our company to decline and limit our ability to obtain additional financing.
If we are unable to establish sales and marketing capabilities or enter into additional agreements with third parties to market and sell and market our potential fertility treatments,product candidates, we may be unable to generate any revenues.
We currently do not have an organization for the sales, marketing and distribution of TPST-1495, TPST-1120 or any future product candidates, and the cost of establishing and maintaining such an organization may exceed the cost-effectiveness of doing so. To market any products that may be successful in commercializing them.
Any future strategic alliance partners may not dedicate sufficient resources to the commercialization of our product candidates or may otherwise fail in their commercialization due to factors beyond our control. If we are unable to establish effective alliances to enable the sale of our product candidates to healthcare professionals and in geographical regions, including the United States, that will not be covered by our marketing and sales force, or if our potential future strategic alliance partners do not successfully commercialize the product candidates, our ability to generate revenues from product sales will be adversely affected.
If we are unable to establish adequate sales, marketing and distribution services, our treatment revenuescapabilities, whether independently or the profitability of these treatment revenues to us are likely to be lower than if we were to market and sell any potential fertility treatment ourselves. In addition,with third parties, we may not be successful in entering into arrangementsable to generate sufficient product revenue and may not become profitable. We will be competing with many companies that currently have extensive and well-funded marketing and sales operations. Without an internal team or the support of a third partiesparty to sellperform marketing and market our potential fertility treatments orsales functions, we may be unable to do so on terms that are favorable to us. We likely will have limited control over such third parties, and any of them may fail to devote the necessary resources and attention to sell and market our potential fertility treatments effectively and in compliance with applicable laws.
We may not be successful in obtaining necessary rightsfinding strategic collaborators for continuing development of certain of our future product candidates or successfully commercializing or competing in the market for certain indications.
In the future, we may decide to additionalcollaborate with non-profit organizations, universities and pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for the development and potential commercialization of existing and new product candidates. We face significant competition in seeking appropriate collaborators. Whether we reach a definitive agreement for a collaboration will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the collaborator’s resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration and the proposed collaborator’s evaluation of a number of factors. Those factors may include the design or results of clinical trials, the likelihood of approval by the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside the United States, the potential market for the subject product candidate, the costs and complexities of manufacturing and delivering such product candidate to patients, the potential of competing drugs, the existence of uncertainty with respect to our ownership of technology, which can exist if there is a challenge to such ownership without regard to the merits of the challenge and industry and market conditions generally. The collaborator may also consider alternative product candidates or technologies or potential fertility treatments, including from our scientific founders,for similar indications that may be available to collaborate on and whether such a collaboration could be more attractive than the one for our development pipeline through acquisitions and in-licenses.
47
We may not be able to negotiate collaborations on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to do so, we may have to curtail the development of the product candidate for which we are seeking to collaborate, reduce or delay our development program or one or more of our other development programs, delay our potential commercialization or reduce the scope of any sales or marketing activities, or increase our expenditures and undertake development or commercialization activities at our expense. If we elect to increase our expenditures to fund development or commercialization activities on our product candidates, we may need to obtain additional capital, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at all. If we do not have sufficient funds, we may not be able to further develop our product candidates or bring them to market and generate product revenue.
The success of any potential collaboration arrangements will depend heavily on the efforts and activities of our collaborators. Collaborators generally have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to these collaborations. Disagreements between parties to a competitive advantage over us due to their size, cash resources and greatercollaboration arrangement regarding clinical development and commercialization capabilities.matters can lead to delays in the development process or commercializing the applicable product candidate and, in some cases, termination of such collaboration arrangements. These disagreements can be difficult to resolve if neither of the parties has final decision-making authority. Collaborations with pharmaceutical or biotechnology companies and other third parties often are terminated or allowed to expire by the other party. Any such termination or expiration, or any failure by our partners to perform their obligations under collaboration agreements, would adversely affect us financially and could harm our business reputation or negatively impact our ability to successfully develop, obtain regulatory approvals for and commercialize our product candidates.
Risks Related to Government Regulation
The FDA regulatory approval process is lengthy and time consuming, and we may experience significant delays in the clinical development and regulatory approval of our product candidates.
Obtaining FDA approval is unpredictable, typically takes many years following the commencement of clinical trials and depends upon numerous factors, including the type, complexity and novelty of the product candidates involved. In addition, approval policies, regulations or the type and amount of clinical data necessary to gain approval may change during the course of a product candidate’s clinical development and may vary among jurisdictions, which may cause delays in the approval or the decision not to approve an application. Regulatory authorities have substantial discretion in the approval process and may refuse to accept any application or may decide that our data are insufficient for approval and require additional preclinical, clinical or other data. Even if we eventually complete clinical testing and receive approval for our product candidates, the FDA may approve our product candidates for a more limited indication or a narrower patient population than originally requested or may impose other prescribing limitations or warnings that limit the product’s commercial potential. We have not submitted for, or obtained, regulatory approval for any product candidate, and it is possible that none of our product candidates will ever obtain regulatory approval. Further, development of our product candidates and/or regulatory approval may be delayed for reasons beyond our control.
We may also experience delays in obtaining regulatory approvals, including but not limited to:
48
We could also encounter delays if physicians encounter unresolved ethical issues associated with enrolling patients in clinical trials of our product candidates in lieu of prescribing existing treatments that have established safety and efficacy profiles. Further, a clinical trial may be suspended or terminated by us, the IRBs for the institutions in which such trials are being conducted or by
49
the FDA or other regulatory authorities due to a number of factors, including failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or our clinical protocols, inspection of the clinical trial operations or trial site by the FDA or other regulatory authorities resulting in the imposition of a clinical hold, safety issues or adverse side effects, failure to demonstrate a benefit from using a product candidate, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions, lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial, or based on a recommendation by the Data Safety Monitoring Committee. If we experience termination of, or delays in the completion of, any clinical trial of our product candidates, the commercial prospects for our product candidates will be harmed, and our ability to generate product revenue will be delayed. In addition, any delays in completing our clinical trials will increase our costs, slow down our product development and approval process and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenue.
Many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our product candidates.
We may seek Breakthrough Therapy designation or Fast Track designation by the FDA for one or more of our product candidates but may not receive such designation. Even if we secure such designation, it may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review or approval process and it does not increase the likelihood that our product candidates will receive marketing approval.
We may seek Breakthrough Therapy or Fast Track designation for some of our product candidates. If a product candidate is intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition and clinical or preclinical data demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs for this condition, the product candidate may be eligible for Fast Track designation. The benefits of Fast Track designation include more frequent meetings with FDA to discuss the drug’s development plan and ensure collection of appropriate data needed to support drug approval, more frequent written communication from FDA about such things as the design of the proposed clinical trials and use of biomarkers, eligibility for Accelerated Approval and Priority Review, if relevant criteria are met, and rolling review, which means that a drug company can submit completed sections of our NDA for review by FDA, rather than waiting until every section of our NDA is completed before the entire application can be reviewed. NDA review usually does not begin until the entire application has been submitted to the FDA.
A breakthrough therapy is defined as a drug that is intended, alone or in combination with one or more other drugs or biologics, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. Drugs designated as breakthrough therapies by the FDA may be eligible for all features of Fast Track designation, intensive guidance on an efficient drug development program, beginning as early as Phase 1, and organizational commitment involving senior managers at FDA.
The FDA has broad discretion whether or not to grant these designations, so even if we believe a particular product candidate is eligible, we cannot assure that the FDA would decide to grant the designation. Even if we obtain Fast Track designation and/or Breakthrough Therapy designation for one or more of our product candidates, it may not experience a faster development process, review or approval compared to non-expedited FDA review procedures. In addition, the FDA may withdraw Fast Track designation or Breakthrough Therapy designation if it believes that the designation is no longer supported. These designations do not guarantee qualification for the FDA’s priority review procedures or a faster review or approval process.
50
We may attempt to secure FDA approval of our product candidates through the accelerated approval pathway. If we are unable to obtain accelerated approval, we may be required to conduct additional preclinical studies or clinical trials beyond those that we currently contemplate, which could increase the expense of obtaining, and delay the receipt of, necessary marketing approvals.
We are developing certain product candidates for the treatment of serious conditions, and therefore may decide to seek approval of such product candidates under the FDA’s accelerated approval pathway. A product may be eligible for accelerated approval if it is designed to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and provides a meaningful therapeutic benefit over existing treatments based upon a determination that the product candidate has an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability of or lack of alternative treatments. For example, we continuethe purposes of accelerated approval, a surrogate endpoint is a marker, such as a laboratory measurement, radiographic image, physical sign, or other measure that is thought to work collaboratively withpredict clinical benefit, but is not itself a measure of clinical benefit.
The accelerated approval pathway may be used in cases in which the advantage of a new drug over available therapy may not be a direct therapeutic advantage, but is a clinically important improvement from a patient and public health perspective. If granted, accelerated approval is usually contingent on the sponsor’s agreement to conduct, in a diligent manner, additional post-approval confirmatory studies to verity and describe the drug’s anticipated effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit. In some cases, the FDA may require that the trial be designed, initiated, and/or fully enrolled prior to approval. If the sponsor fails to conduct such studies in a timely manner, or if such post-approval studies fail to verify the drug’s predicted clinical benefit, or if other evidence demonstrates that our scientific founders. These scientists continueproduct candidate is not shown to be activesafe and effective under the conditions of use, the FDA may withdraw its approval of the drug on an expedited basis.
If we decide to submit an NDA seeking accelerated approval or receive an expedited regulatory designation for any of our product candidates, there can be no assurance that such submission or application will be accepted or that any expedited development, review or approval will be granted on a timely basis, or at all. If any of our competitors were to receive full approval on the basis of a confirmatory trial for an indication for which we are seeking accelerated approval before we receive accelerated approval, the indication we are seeking may no longer qualify as a condition for which there is an unmet medical need and accelerated approval of our product candidate would be more difficult or may not occur.
Failure to obtain accelerated approval or any other form of expedited development, review or approval for our product candidates would result in a longer time period to commercialization of such product candidate, if any, and could increase the cost of development of such product candidate harm our competitive position in the fieldmarketplace.
We may be unsuccessful in obtaining Orphan Drug Designation for our product candidates or transfer of infertilitydesignations obtained by others for future product candidates, and, may develop new potential fertility treatments or intellectual property based on their continued research relating to infertility. The rights to new inventions by our scientific founders generally belong to the hospitals and academic institutions at which they are employed and are not subject to license or other rights in our favor. In the event that our scientific founders, or other third party scientists or entities, develop potential fertility treatments or intellectual property that
The FDA may designate drugs intended to treat relatively small patient populations as orphan drugs. Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a drug as an orphan drug if it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is defined as a patient population of fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States, or a patient population greater than 200,000 in the United States when there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making available the drug in the United States will be recovered from sales in the United States for that drug. Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting an NDA. In the United States, Orphan Drug Designation entitles a party to financial incentives such acquisitionas opportunities for tax credits for qualified clinical research costs and exemption from prescription drug user fees. Generally, if a drug with an Orphan Drug Designation subsequently receives the first marketing approval for the indication for which it has such designation, the drug is entitled to a period of marketing exclusivity, which precludes FDA from approving another marketing application for the same drug and indication for that time period, except in limited circumstances. If a competitor is able to obtain orphan drug exclusivity prior to us for a product that constitutes the same active moiety and treats the same indications as our product candidates, we may
51
not be able to obtain approval of our drug by the applicable regulatory authority for a significant period of time unless we are able to show that our drug is clinically superior to the approved drug. The applicable period is seven years in the United States.
We may seek Orphan Drug Designation for one or in-license. Our failuremore of our product candidates in the United States as part of our business strategy. However, Orphan Drug Designation does not guarantee future orphan drug marketing exclusivity. Even after an orphan drug is approved, the FDA can also subsequently approve a later application for the same drug for the same condition if the FDA concludes that the later drug is clinically superior in that it is shown to reach an agreement for any applicable potential fertility treatment or intellectual property could resultbe safer in a third party acquiringsubstantial portion of the related rights and thereby harm our business.
Moreover, orphan drug exclusive marketing rights in the United States may be unwilling to assignlost if the FDA later determines that the request for designation was materially defective or license rights to us. We also may be unable to license or acquire relevant potential fertility treatments on terms that would allow us to make an appropriate return on our investment.
Enacted and future legislation may increase the difficulty and cost for us to commercialize and obtain marketing approval of our product candidates and may affect the prices we may set.
Existing regulatory policies may change, and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent, limit or delay regulatory approval of our product candidates. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or if we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we may lose any marketing approval that we may have obtained, and we may not achieve or sustain profitability.
In March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, or collectively the Affordable Care Act (“ACA”), was enacted to broaden access to health insurance, reduce or constrain the growth of healthcare spending, enhance remedies against fraud and abuse, add new transparency requirements for health care and health insurance industries, impose new taxes and fees on the health industry and impose additional health policy reforms. The ACA contains provisions that may potentially affect the profitability of our product candidates, if approved, including, for example, increased rebates for products sold to Medicaid programs, extension of Medicaid rebates to Medicaid managed care plans, mandatory discounts for certain Medicare Part D beneficiaries and annual fees based on pharmaceutical companies’ share of sales to federal health care programs, and expansion of the entities eligible for discounts under the 340B Drug Pricing Program.
While Congress has not passed legislation to comprehensively repeal the ACA, legislation affecting the ACA has been signed into law, including the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, which eliminated, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the ACA on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year, which is commonly referred to as the “individual mandate.” On June 17, 2021, the U.S. Supreme Court dismissed the most recent judicial challenge to the ACA brought by several states without specifically ruling on the constitutionality of the law. In addition, on August 16, 2022, President Biden signed the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 ("IRA") into law, which among other things, extends enhanced subsidies for individuals purchasing health insurance coverage in ACA through plan year 2025. The IRA also reduces the "donut hole" under the Medicare Part D program beginning in 2025 by significantly lowering the beneficiary maximum out-of-pocket cost and through a newly established manufacturer discount program. In the future, there may be other efforts to challenge, repeal or replace the ACA. It is unclear how many such challenges and the healthcare reform measures of the Biden administration will impact the ACA and our business. We are continuing to monitor any changes to the ACA that, in turn, may potentially impact our business in the future.
Recently, the cost of prescription pharmaceuticals has been the subject of considerable discussion in the United States at both the federal and state levels. While several proposed reform measures will require Congress to pass legislation to become effective, Congress and the Biden administration have each indicated that it will seek new legislative and/or administrative measures to address prescription drug costs. Since the Presidential inauguration, the Biden administration has taken several executive actions
52
that signal changes in policy from the prior administration. For example, on July 9, 2021, President Biden signed an executive order to promote competition in the U.S. economy that included several initiatives aimed prescription drugs. Among other provisions, the executive order directed the Secretary of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services ("HHS") to issue a report to the White House that includes a plan to, among other things, reduce prices for prescription drugs, including prices paid by the federal government for such drugs. In response to Biden’s executive order, on September 9, 2021, HHS released a Comprehensive Plan for Addressing High Drug Prices that outlines principles for drug pricing reform and sets out a variety of potential legislative policies that Congress could pursue as well as potential administrative actions HHS can take to advance these principles. In addition, the IRA, among other things, (1) directs HHS to negotiate the price of certain single-source drugs and biologics covered under Medicare and (2) imposes rebates under Medicare Part B and Medicare Part D to penalize price increases that outpace inflation. These provisions will take effect progressively starting in fiscal year 2023, although they may be subject to legal challenges. It is currently unclear how the IRA will be implemented but is likely to have a significant impact on the pharmaceutical industry. Further, the Biden administration released an additional executive order on October 14, 2022, directing HHS to submit a report on how the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation can be further leveraged to test new models for lowering drug costs for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. It is unclear whether this executive order or similar policy initiatives will be implemented in the future. At the state level, legislatures and agencies are increasingly passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control spending on and patient out-of-pocket costs for drug products. These measures include constraints on pricing, discounting and reimbursement; restrictions on certain product access and marketing; cost disclosure and transparency measures that require detailed reporting of drug pricing and marketing information both at product launch and in the event of a price increase; and, in some cases, measures designed to encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing.
We expect that the ACA and the IRA, as well as other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, may result in more rigorous coverage criteria and in additional downward pressure on the price that we receive for any approved product. Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare or other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors. The implementation of cost containment measures or other healthcare reforms may prevent us from being able to generate revenue, attain profitability, or commercialize our product candidates.
Legislative and regulatory proposals have also been made to expand post-approval requirements and restrict sales and promotional activities for pharmaceutical products. We cannot be sure whether additional legislative changes will be enacted, or whether FDA regulations, guidance or interpretations will be changed, or what the impact of such changes on the marketing approvals of our product candidates, if any, may be. In addition, increased scrutiny by the U.S. Congress of the FDA’s approval process may significantly delay or prevent marketing approval, as well as subject us to more stringent product labeling and post-marketing testing and other requirements.
The FDA’s ability to review and approve new products may be hindered by a variety of factors, including budget and funding levels, ability to hire and retain key personnel, statutory, regulatory and policy changes and global health concerns.
The ability of the FDA to review and approve new products can be affected by a variety of factors, including government budget and funding levels, statutory, regulatory and policy changes, the FDA’s ability to hire and retain key personnel and accept the payment of user fees, and other events that may otherwise affect the FDA’s ability to perform routine functions. In addition, government funding of other government agencies that fund research and development activities is subject to the political process, which is inherently fluid and unpredictable. Disruptions at the FDA and other agencies may also slow the time necessary for new drugs to be reviewed and/or approved by necessary government agencies, which would adversely affect our business. For example, over the last several years the U.S. government has shut down several times and certain regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, have had to furlough critical employees and stop critical activities.
The ability of the FDA and other government agencies to properly administer their functions is highly dependent on the levels of government funding and the ability to fill key leadership appointments, among various factors. Delays in filling or replacing key positions could significantly impact the ability of the FDA and other agencies to fulfill their functions, and could greatly impact healthcare and the pharmaceutical industry.
53
We are subject to stringent and evolving U.S. and foreign laws, regulations, and rules, contractual obligations, industry standards, policies and other obligations related to data privacy and security, and our failure to comply with them could harm our business.
We collect, receive, store, process, generate, use, transfer, disclose, make accessible, protect, secure, dispose of, transmit, and share (collectively, process) a large quantity of sensitive information, including confidential business and patient health information in connection with our preclinical and clinical studies. Our data processing activities subject us to numerous data privacy and security obligations, such as various laws, regulations, guidance, industry standards, external and internal privacy and security policies, contractual requirements, and other obligations relating to data privacy and security.
In the United States, there are numerous federal and state privacy and data security laws and regulations governing the processing of personal data, including health information privacy laws, security breach notification laws, consumer protection laws, and other similar laws (e.g., wiretapping laws). Each of these laws is subject to varying interpretations and constantly evolving. In addition, we obtain health information from third parties (including research institutions from which it obtains clinical trial data) that are subject to privacy and security requirements under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”), which imposes specific requirements relating to the privacy, security, and transmission of protected health information.
Certain states have also adopted comprehensive privacy laws and regulations that impose certain obligations on covered businesses, including providing specific disclosures in privacy notices and affording residents with certain rights concerning their personal data. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act, as amended by the California Privacy Rights Act (“CPRA”) (collectively, the “CCPA”) gives California residents expanded rights to suitableaccess and delete their personal data, opt out of certain personal data sharing, and receive detailed information about how their personal information is used. The CCPA provides for civil penalties for violations, as well as a private right of action for data breaches that is expected to increase data breach litigation. Although the CCPA exempts some data processed in the context of clinical trials, the CCPA may increase our compliance costs and potential fertility treatmentsliability. Similar laws are being considered in several other states, as well as at the federal and local levels, and we expect more states to pass similar laws in the future.
Outside the United States, an increasing number of laws, regulations, and industry standards govern data privacy and security. For example, in Canada, the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (“PIPEDA”) and similar provincial laws may impose obligations with respect to processing personal data, including health-related information. PIPEDA requires companies to obtain an individual’s consent when collecting, using or disclosing that individual’s personal data. Individuals have the right to access and challenge the accuracy of their personal data held by an organization, and personal data may only be used for the purposes for which it was collected. If an organization intends to use personal data for another purpose, it must again obtain that individual’s consent. Failure to comply with PIPEDA could result in significant fines and penalties.
As another example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (the “EU GDPR”) and the United Kingdom’s GDPR (together with EU GDPR, “GDPR”) also impose strict requirements for processing personal data and substantial fines for breaches and violations (for example, under the EU GDPR, up to the greater of €20 million or 4% of our annual worldwide gross revenue). Additionally, under GDPR, companies may face temporary or definitive bans on reasonable terms,data processing and other corrective action or private litigation related to processing of personal data brought by classes of data subjects or consumer protection organizations authorized at law to represent their interests.
Further, Europe and other jurisdictions have enacted laws requiring data to be localized or limiting the transfer of personal data to other countries. In particular, the European Economic Area (EEA) and the UK have significantly restricted the transfer of personal data to the United States and other countries whose privacy laws it generally believes are inadequate. Other jurisdictions may adopt similarly stringent interpretations of their data localization and cross-border data transfer laws. If there is no lawful manner for us to transfer personal data from the EEA, the UK or other jurisdictions to the United States, or if the requirements for a legally-compliant transfer are too onerous, we could face significant adverse consequences, including the interruption or degradation of our operations, the need to relocate part of or all of our business or data processing activities to other jurisdictions (such as Europe) at significant expense, increased exposure to regulatory actions, substantial fines and penalties, the inability to
54
transfer data and work with partners, vendors and other third parties, and injunctions against our processing or transferring of personal data necessary to operate our business.
In addition to data privacy and security laws, we are contractually subject to industry standards adopted by industry groups and, we may become subject to such obligations in the future. We are also bound by contractual obligations related to data privacy and security, and our efforts to comply with such obligations may not be successful. We publish privacy policies, marketing materials and other statements regarding data privacy and security. If these policies, materials or statements are found to be deficient, lacking in transparency, deceptive, unfair, or misrepresentative of our practices, we may be subject to investigation, enforcement actions by regulators or other adverse consequences.
Compliance with these obligations is a rigorous and time-intensive process, and we may be required to put in place additional mechanisms designed to ensure compliance with these obligations. If we fail (or are perceived to have failed) to comply with any such obligations, we may face significant consequences, including without limitation government enforcement actions (e.g., investigations, fines and penalties, audits, inspections); litigation (including class-action claims) and mass arbitration demands); additional reporting requirements and/or oversight; bans on processing personal data; orders to destroy or not use personal data; imprisonment of company officials; or other consequences that could adversely affect our business, financial condition and prospectsresults of operations.
If our information technology systems or those of third parties upon which we rely, or our data, are or were compromised, we could experience adverse consequences, including disclosure of sensitive information, damage to our reputation, and significant financial and legal exposure.
Cyberattacks, malicious internet-based activity, online and offline fraud, and other similar activities threaten the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of our sensitive information and information technology systems, and those of the third parties upon which we rely. These threats are increasing in their frequency, sophistication and intensity, have become increasingly difficult to detect, and come from a variety of sources, including traditional computer “hackers,” threat actors, “hacktivists,” organized criminal threat actors, personnel (such as through theft or misuse), sophisticated nation states, and nation-state-supported actors. Some actors now engage and are expected to continue to engage in cyberattacks, including without limitation nation-state actors for growthgeopolitical reasons and in conjunction with military conflicts and defense activities. During times of war and other major conflicts, we and the third parties upon which we rely may be vulnerable to a heightened risk of these attacks, including retaliatory cyberattacks, that could suffer.
Cyberattacks could include wrongful conduct by hostile foreign governments, industrial espionage, wire fraud and other forms of cyber fraud, the deployment of harmful malware, denial-of-service attacks, social engineering attacks (including through deep-fakes, which may be increasingly more difficult to identify as fake, and phishing attacks), malicious code (such as viruses and worms), credential stuffing attacks, credential harvesting, ransomware attacks, supply-chain attacks, software bugs, server malfunctions, software or hardware failures, loss of data, attacks enhanced or facilitated by artificial intelligence or other information technology assets, fraud or other means to threaten confidentiality, integrity and availability of our sensitive information. We face substantial competition, including fromand the third parties upon which we rely may also experience telecommunications failures, natural disasters, terrorism, war and other similar threats.
In particular, severe ransomware attacks are becoming increasingly prevalent and can lead to significant interruptions in our operations, ability to provide our products or services, loss of sensitive information and income, reputational harm, and diversion of funds. Extortion payments may alleviate the negative impact of a ransomware attack, but we may be unwilling or unable to make such payments due to, for example, applicable laws or regulations prohibiting such payments.
As more established infertility treatments,of our employees work remotely, the risk of a cybersecurity incident potentially occurring, and our investment in risk mitigations against such as standard IVF,an incident, is increasing. For example, there has been an increase in phishing and spam emails as well as advancessocial engineering attempts from “hackers.” Future or past business transactions (such as acquisitions or integrations) could expose us to additional cybersecurity risks and vulnerabilities, as our systems could be negatively affected by vulnerabilities
55
present in new artificial reproductive technologies, whichacquired or integrated entities’ systems and technologies. Furthermore, we may resultdiscover security issues that were not found during due diligence of such acquired or integrated entities, and it may be difficult to integrate companies into our information technology environment and security program.
In addition, we rely on third parties and their technology to operate critical business systems to process sensitive information, including our CROs, CMOs and other contractors, consultants and law and accounting firms. Our ability to monitor these third parties’ information security practices is limited, and these third parties may not have adequate information security measures in others discovering, developingplace. If these third parties experience a security incident or commercializing potential fertility treatments beforeother interruption, we could experience adverse consequences. While we may be entitled to damages if our third-party partners fail to satisfy their privacy or more successfully thansecurity-related obligations to us, any award may be insufficient to cover our damages, or we do.
Although we devote resources to protect our information systems, we realize that cyberattacks are a number of fertility treatmentsthreat, and there can be no assurance that are generally acceptedour efforts will prevent information security breaches. We take steps designed to detect, mitigate, and remediate vulnerabilities in our information systems (such as our and the medicalthird parties’ upon which we rely hardware and patient communities,software). We may not, however, detect and remediate all such vulnerabilities including fertility drugs, IUIon a timely basis. Further, we may experience delays in developing and IVF. Competition in the infertility market is largely based on pregnancydeploying remedial measures and live birth rates and side effects of treatment on patients. Accordingly, our success is highly dependent on our ability to develop potential fertility treatments that improve pregnancy and live birth rates and reduce risks and side effects, as compared to existing treatments. The ability of any potential fertility treatment that we successfully develop to reduce the overall costs associated with IVF also will be an important competitive factor.
Any of the shortcomingspreviously identified or similar threats could cause a security incident or other interruption that could result in unauthorized, unlawful, or accidental acquisition, modification, destruction, loss, alteration, encryption, disclosure of, IVF.or access to our sensitive information or our information technology systems, or those of the third parties upon whom we rely. A security incident or other interruption could disrupt our ability (and that of third parties upon whom we rely) to provide our services.
We may expend significant resources or modify our business activities (including our clinical trial activities) to try to protect against security incidents. Certain data privacy and security obligations may require us to implement and maintain specific security measures or industry-standard or reasonable security measures to protect our information technology systems and sensitive information. Applicable data privacy and security obligations may require us to notify relevant stakeholders, including affected individuals, customers, regulators, and investors, of security incidents. Such disclosures are costly, and the disclosure or the failure to comply with such requirements could lead to adverse consequences.
A successful or perceived security incident experienced by us or the third parties upon which we rely could cause serious negative consequences for us, including, without limitation, the disruption of operations, the misappropriation of sensitive information, disclosure of corporate strategic plans, material disruption of our development programs and our business operations, government enforcement actions (e.g., investigations, fines, penalties, audits, inspections), additional reporting requirements and/or oversight, restrictions on processing sensitive information, litigation, indemnification obligations, reputational harm, negative publicity, and other harms. For example, the loss of data from preclinical studies or clinical trials could result in significant delays in our regulatory approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. To the extent that any disruption or security incident were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our sensitive information or applications, or inappropriate disclosure of such information, we could incur liability, our competitive position could be harmed and the further development and commercialization of our product candidates could be significantly delayed.
Our employees, principal investigators, CROs, CMOs and consultants may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including non-compliance with regulatory standards and requirements and insider trading.
We are exposed to the risk of fraud or other misconduct by our employees, principal investigators, consultants and commercial partners. Misconduct by these parties could include intentional failures to comply with the regulations of FDA and non-U.S. regulators, to provide accurate information to the FDA and non-U.S. regulators, to comply with healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations in the United States and abroad, to report financial information or data accurately or disclose unauthorized activities to us. In particular, sales, marketing and business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws
56
and regulations intended to prevent fraud, misconduct, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, sales commission, customer incentive programs and other business arrangements. Such misconduct could also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical studies, which could result in regulatory sanctions and could cause serious harm to our reputation. It is not always possible to identify and deter employee misconduct, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to comply with these laws or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are awarenot successful in defending or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, including the imposition of a numbersignificant fines or other sanctions.
Obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval of companiesour product candidates in one jurisdiction does not mean that we will be successful in obtaining regulatory approval of our product candidates in other jurisdictions.
Obtaining and laboratories that are currently developing potential fertility treatments intended to identify high quality embryos for usemaintaining regulatory approval of our product candidates in IVF, a university study of the transfer of granulosa cell mitochondria into eggs, a university study using pronuclear transfer for improvement in IVF success rates and a university study of induced pluriopotent stem cells, or iPS, shows that iPS cells can be generated from somatic cells and programmed to become differentiated cells, which can include germ line cells such as oocytes. Novocellus Ltd. is developing an embryo viability test, using culture media, to aid in the selection of embryos used in IVF. FertiliTech and Auxogyn, Inc. are developing hardware and software that analyzes embryo development against cell division timing parameters to help identify the highest quality embryo within a group of embryos. If successfully developed, these potential fertility treatments could improve outcomes and alleviate some of the other shortcomings of standard IVF, thereby decreasing the need for our potential fertility treatments. Fertility Focus, along with its strategic partner Norgenix, are developing a fertiloscope for the early diagnosis of, and immediate corrective surgery for, the physical causes of infertility. Molecular diagnostic companies like Reprogenetics are developing novel preimplantation genetic diagnosis and screening methods to detect chromosomal and genetic disorders of embryos prior to transfer back to the women. Testing embryos in this manner may increase the likelihood of pregnancy, reduce the chances of pregnancy loss, and improve the odds of delivery. At this time, we cannot evaluate how our potential fertility treatments, if successfully developed and commercialized, would compare technologically, clinically or commercially to any other potential fertility treatments being developed or to be marketed by competitors. There can be no assuranceone jurisdiction does not guarantee that we will be able to compete effectively. OvaXon is engagedobtain or maintain regulatory approval in gene editing, which isany other jurisdiction, while a rapidly evolving field. OvaXon could potentially have competitorsfailure or delay in bothobtaining regulatory approval in the United States and internationally, including major multinational pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and universities and other research institutions. Some of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies we expect OvaXon to compete with include GlaxoSmithKline plc, Sangamo BioSciences Inc., HemaQuest Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., and Novartis AG.
We may not obtain approvals from regulatory authorities outside the United States on a timely basis, if at all. Approval by the FDA foralso submit marketing applications in the United States does not ensure approval by regulatoryother countries. Regulatory authorities in other countries or jurisdictions and approval by one regulatory authority outside the United States does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other countries or jurisdictions or by the FDA.
Our operations and criminal penalties.
Healthcare providers and third-party payors will play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of any product candidates for which we anticipate very limited third party coverage and reimbursement, including from federal healthcare programs, for any of our potential fertility treatments and services, ourobtain marketing approval. Our future arrangements with third partyproviders, third-party payors and IVF clinics and physicians may exposecustomers will subject us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations that may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we market, sell and distribute OvaPrime, OvaTure and any other future potential fertility treatments and servicesproduct candidates for which we obtain marketing approval.
Restrictions under applicable U.S. federal and state fraud and abusehealthcare laws and regulations that may be applicable to our business include the following:
57