UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| | | | | |
|
| | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | |
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 20212023
| | | | | |
| or |
|
| FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM ___________ TO __________ |
| |
| COMMISSION FILE NUMBER | 001-38629 |
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) | | | | | |
| Pennsylvania | 83-0516635 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (IRS Employer Identification No.) |
2200 Energy Drive, Canonsburg, Pennsylvania 15317
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip code)
Registrant's telephone number, including area code: (724) 271-7600
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | | Trading Symbol | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock, no par value | | ETRN | | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files).Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer," "smaller reporting company" and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large Accelerated Filer | ☒ | | | Accelerated Filer | ☐ | | Emerging Growth Company | ☐ | |
| Non-Accelerated Filer | ☐ | | | Smaller Reporting Company | ☐ | | | | |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act.�� ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C.7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2021: $3.42023: $4.1 billion
The number of shares of common stock outstanding (in thousands), as of January 31, 2022: 432,6762024: 433,661
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The Company's definitive proxy statement relating to the 20222024 annual meeting of shareholders will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the close of the Company's fiscal year ended December 31, 20212023 and is incorporated by reference in Part III to the extent described therein.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
Table of Contents | | | | | | | | |
| | | Page No. |
| |
| |
| PART I |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| PART II |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| PART III |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| PART IV |
| | |
| | |
| | |
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
Glossary of Commonly Used Terms, Abbreviations and Measurements
2021 Water Services Agreement – that certain mixed-use water services agreement entered into on October 22, 2021 by the Company and EQT (as defined below), as subsequently amended, which upon its effectiveness, will replace the Water Services Letter Agreement (as defined below) and certain other existing Pennsylvania water services agreements.became effective on March 1, 2022.
Allowance for Funds Used During Construction (AFUDC) – carrying costs for the construction of certain long-lived regulated assets are capitalized and amortized over the related assets' estimated useful lives. The capitalized amount for construction of regulated assets includes interest cost and a designated cost of equity for financing the construction of these regulated assets.
Amended EQM Credit Facility – that certain Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 31, 2018, among EQM, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as the administrative agent, swing line lender, and a letter of credit (L/C) issuer, the lenders party thereto from time to time and any other persons party thereto from time to time (as amended by that certain First Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of March 30, 2020, by that certain Second Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated April 16, 2021, by that certain Third Amendment to the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of April 22, 2022, by that certain Fourth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 6, 2023, by that certain Fifth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of February 15, 2024, and as may be further amended, restated, amended and restated, supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time). For the avoidance of doubt, any reference to the Amended EQM Credit Facility as of any particular date shall mean the Amended EQM Credit Facility as in effect on such date.
Annual Revenue Commitments (ARC or ARCs) – contractual term in a water services agreement that obligates the customer to pay for a fixed amount of water services annually.
Appalachian Basin – the area of the United States composed of those portions of West Virginia, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland, Kentucky and Virginia that lie in the Appalachian Mountains.
associated gas – natural gas that is produced as a byproduct of principally oil production activities.
British thermal unit – a measure of the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one pound of water one-degree Fahrenheit.
Code – the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and the regulations and interpretations promulgated thereunder.
delivery point – the point where gas is delivered into a downstream gathering system or transmission pipeline.
Distribution – the distribution of 80.1% of the then-outstanding shares of common stock, no par value, of Equitrans Midstream Corporation (Equitrans Midstream common stock) to EQT shareholders of record as of the close of business on November 1, 2018.
EQGP – EQGP Holdings, LP and its subsidiaries. EQGP is a wholly owned subsidiary of Equitrans Midstream Corporation.
EQM – EQM Midstream Partners, LP and its subsidiaries. EQM is a wholly owned subsidiary of Equitrans Midstream Corporation.
EQM Merger – On June 17, 2020, pursuant to that certain Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of February 26, 2020, by and among the Company, EQM LP LLC (formerly, EQM LP Corporation), a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (EQM LP), LS Merger Sub, LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of EQM LP (Merger Sub), EQM and EQGP Services, LLC (the EQM General Partner), Merger Sub merged with and into EQM, with EQM continuing and surviving as an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
EQT – EQT Corporation (NYSE: EQT) and its subsidiaries.
EQT Global GGA – that certain Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement entered into on February 26, 2020 (the EQT Global GGA Effective Date) by the Company with EQT and certain affiliates of EQT for the provision of certain gas gathering services to EQT in the Marcellus and Utica Shales of Pennsylvania and West Virginia, as subsequently amended.
Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares – the Equitrans Midstream Corporation Series A Perpetual Convertible Preferred Shares, no par value.
firm contracts – contracts for gathering, transmission, storage and water services that reserve an agreed upon amount of pipeline or storage capacity regardless of the capacity used by the customer during each month, and generally obligate the customer to pay a fixed, monthly charge.
firm reservation fee revenues – contractually obligated revenues that include fixed monthly charges under firm contracts and fixed volumetric charges under MVC (as defined below) and ARC (as defined above) contracts.
gas – natural gas.
liquefied natural gas (LNG) – natural gas that has been cooled to minus 161 degrees Celsius for transportation, typically by ship. The cooling process reduces the volume of natural gas by 600 times.
local distribution company (LDC)(LDC or LDCs) – LDCs are companiesa company involved in the delivery of natural gas to consumers within a specific geographic area.
Minimum volume commitments (MVC or MVCs) – contracts for gathering or water services that obligate the customer to pay for a fixed amount of volumes daily, monthly, annually or over the life of the contract.
Mountain Valley Pipeline (MVP) – an estimated 300-mile, 42-inch diameter natural gas interstate pipeline with a targeted capacity of 2.0 Bcf per day that is designed to span from the Company's existing transmission and storage system in Wetzel County, West Virginia to Pittsylvania County, Virginia, providing access to the growing Southeast demand markets.
Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (MVP Joint Venture) – a joint venture formed among the Company and, as applicable, affiliates of each of NextEra Energy, Inc., Consolidated Edison, Inc. (Con Edison), AltaGas Ltd. and RGC Resources, Inc. that is constructing(RGC) for purposes of the MVP and the MVP Southgate (as defined below) projects.
MVP Southgate – a proposed 75-milean estimated 31-mile, 30-inch diameter natural gas interstate pipeline with a targeted capacity of 550,000 dekatherms per day that is contemplateddesigned to extendspan from the terminus of the MVP atin Pittsylvania County, Virginia to planned new delivery points in Rockingham and Alamance Counties,County, North Carolina. The project is subject to ongoing discussions between the MVP Joint Venture and the project shipper, Dominion Energy North Carolina, as discussed in "MVP Southgate Project" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in "Item 1. Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
natural gas liquids (NGLs) – those hydrocarbons in natural gas that are separated from the gas as liquids through the process of absorption, condensation, adsorption or other methods in gas processing plants. Natural gas liquids include ethane, propane, pentane, butane and iso-butane.
play – a proven geological formation that contains commercial amounts of hydrocarbons.
Predecessorperiod – the periods prior to the Separation Date (as defined below).
Preferred Interest – the preferred interest that the Company has in EQT Energy Supply, LLC (EES), a subsidiary of EQT.
Proxy Statement – the Company's definitive proxy statement relating to the 20222024 annual meeting of shareholders to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
receipt pointRager Mountain natural gas storage field incident – the point wherethat certain venting of natural gas is received by or intoin 2022 at a gathering system or transmission pipeline.storage well (well 2244) at Equitrans, L.P.'s Rager Mountain natural gas storage facility, located in Jackson Township, a remote section of Cambria County, Pennsylvania, which venting was successfully halted on November 19, 2022.
reservoir – a porous and permeable underground formation containing an individual and separate natural accumulation of producible hydrocarbons (crude oil and/or natural gas) which is confined by impermeable rock or water barriers and is characterized by a single natural pressure system.
Scope 1 emissions – direct greenhouse gas emissions from owned or controlled sources.
Scope 2 emissions – indirect greenhouse gas emissions from the generation of purchased energy.
Separation – the separation of EQT's midstream business, which was composed of the assets and liabilities of EQT's separately-operated natural gas gathering, transmission and storage and water services operations of EQT, from EQT's upstream business, which was composed of the natural gas, oil and natural gas liquids development, production and sales and commercial operations of EQT, which occurred on the Separation Date.
Separation Date – November 12, 2018.
throughput – the volume of natural gas transported or passing through a pipeline, plant, terminal or other facility during a particular period.
Water Services Letter Agreement –
5
wellhead – the equipment at the surface of a well used to control the well's pressure and the point at which the hydrocarbons and water exit the ground.
working gas – the volume of natural gas in the storage reservoir that can be extracted during the normal operation of the storage facility.
Unless the context otherwise requires, a reference to a "Note" herein refers to the accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statementsthe consolidated financial statements contained in Part II, "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
this Annual Report on Form 10-K and all references to "we," "us," "our" and "the Company" refer to Equitrans Midstream Corporation and its subsidiaries. | | | | | |
| Abbreviations | Measurements |
AROAROs – asset retirement obligations
| Btu = one British thermal unit |
ASC – Accounting Standards Codification | BBtu = billion British thermal units |
ASU – Accounting Standards Update | Bcf = billion cubic feet |
CERCLA – Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act | Mcf = thousand cubic feet |
DOT – United States Department of Transportation | MMBtu = million British thermal units |
EPA – United States Environmental Protection Agency | MMcf = million cubic feet |
FASB – Financial Accounting Standards Board | MMgal = million gallons |
FERC – United States Federal Energy Regulatory Commission | |
GAAP – United States Generally Accepted Accounting Principles | |
GHG – greenhouse gas | |
HCAHCAs – high consequence areaareas
| |
| |
IRS – United States Internal Revenue Service | |
MCAs – moderate consequence areas | |
NAAQS – National Ambient Air Quality Standards | |
NEPA – National Environmental Policy Act, as amended | |
NGA – Natural Gas Act of 1938, as amended | |
NGPA – Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978, as amended | |
NYMEX – New York Mercantile Exchange | |
NYSE – New York Stock Exchange | |
PHMSA – Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration of the DOT | |
RCRA – Resource Conservation and Recovery Act | |
SEC – United States Securities and Exchange Commission | |
| |
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
Cautionary Statements
Disclosures in this Annual Report on Form 10-K contain certain forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act), and Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the Securities Act). Statements that do not relate strictly to historical or current facts are forward-looking and usually identified by the use of words such as "aim," "anticipate," "approximate," "aspire," "assume," "believe," "budget," "continue," "could," "design," "estimate," "could,"expect," "would,"focused," "forecast," "goal," "guidance," "intend," "may," "objective," "opportunity," "outlook," "plan," "position," "potential," "predict," "project," "pursue," "scheduled," "seek," "should," "strategy," "strive," "target," "view," "will," "may," "forecast," "approximate," "expect," "project," "intend," "plan," "believe," "target"or "would" and other words of similar meaning in connection with any discussion of future operating or financial matters. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K include the matters discussed in the sections captioned "Strategy" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in Part I, "Item 1. Business" and "Outlook" in Part II, "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and the expectations of plans, strategies, objectives, and growth and anticipated financial and operational performance of Equitrans Midstream Corporation (together with its subsidiaries, Equitrans Midstream or the Company), including:including the following and/or statements with respect thereto, as applicable:
•guidance and any changes in such guidance regardingin respect of the Company’s gathering, transmission and storage and water services revenue and volume, including the anticipated effects associated with the EQT Global GGA and related documents entered into with EQT;GGA;
•projected revenue (including from firm reservation fees) and volumes, gathering rates, deferred revenues, expenses and contract liabilities, and the effects on liquidity, leverage, projected revenue, deferred revenue and contract liabilities associated with the EQT Global GGA and the MVP project (including changes in the targeted full in-service datetiming for such project);
•the ultimate gathering MVC fee relief, and timing thereof, provided to EQT under the EQT Global GGA and related agreements, including the exercise by EQTand timing of any cash-out option as an alternative to receiving a portion of such relief;step ups in MVC thereunder;
•the Company's ability to de-lever;de-lever and timing and means thereof;
•the ultimate financial, business, reputational and/or operational impacts resulting, directly or indirectly, from the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident;
•the weighted average contract life of gathering, transmission and storage contracts;
•infrastructure programs (including the targeted or ultimate timing, cost, capacity and sources of funding with respect to gathering, transmission and storage and water projects);
•the outcome of the Company's Board of Directors' strategic process with respect to the Company;
•the cost to construct or restore right-of-way for, capacity of, shippers for, timing and durability of regulatory approvals and concluding litigation, final design (including project scope, expansions, extensions or refinements and capital related thereto), ability and timing to contract additional capacity on, mitigate emissions from, and complete, and targeted in-service dates of, and completion (including potential timing of such completion) of current, planned or in-service projects or assets, in each case as applicable;
•the effect of the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023 on the MVP Joint Venture's ability to complete the MVP project;
•the ability to construct, complete and place in service the MVP project;
•the targeted timing and cost of completing, the MVP project (and risks related thereto), the realizability of the MVP performance award program, and the degree to which, if at all, the MVP PSU Amendment (as defined in Note 8) fosters the Company completing the MVP project safely and in compliance with environmental standards;
•the targeted total MVP project cost and schedule, including the timing for contractual obligations to commence, and the ability to continue construction, potential receipt of in-service authorization, and the realizability of the perceived benefits of the MVP project;
•finalizing the scope of the MVP Southgate and the ability to permit, construct, complete and place in service the MVP Southgate;
•the targeted total project cost and timing for completing (and ability to complete) MVP Southgate, including the satisfaction, if any, of conditions precedent with respect to the relevant precedent agreements, timing for forecasted
capital expenditures related thereto, and the realizability of the perceived benefits of the amended project, design, scope and provisions included in the relevant precedent agreements, and any potential extensions of the terms of the precedent agreements;
•the MVP Joint Venture's ability to execute any additional agreements for firm capacity for the MVP Southgate;
•the realizability of all or any portion of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment under the EQT Global GGA;
•the potential for future bipartisan support for, and the potential timing for, additional federal energy infrastructure permitting reform legislation to be enacted;
•the ultimate terms, partner relationships and structure of the MVP Joint Venture and ownership interests therein;
•the impact of changes in assumptions and estimates relating to the targetedpotential completion and full in-service datetiming of the MVP project (as well as changes in such timing) on, among other things, the fair value of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision of the EQT Global GGA, gathering rates, the amount of gathering MVC fee relief and the estimated transaction price allocated to the Company's remaining performance obligations under certain contracts with firm reservation fees and MVCs;
•the Company's ability to identify and complete opportunities to optimize its existing asset base and/or expansion projects in the Company's operating areas and in areas that would provide access to new markets;
•the Company's ability to provide producedbring, and mixedtargeted timing for bringing, in-service extensions and expansions of its mixed-use water handling servicessystem, and realize expansion opportunities;benefits therefrom in accordance with its strategy for its water services business segment;
•the Company's ability to identify and complete acquisitions and other strategic transactions, including joint ventures, effectively integrate transactions into the Company's operations, and achieve synergies, system optionality, accretion and other benefits associated with transactions, including through increased scale;
•any credit rating impacts associated withthe potential for the MVP project, EQM's leverage, customer credit ratings changes, defaults, acquisitions, dispositions and financings and any changes into impact EQM's credit ratings;ratings and the potential scope of any such impacts;
•the effect and outcome of futurecontractual disputes, litigation and other proceedings, including regulatory investigations and proceedings;
•the potential effects of any consolidation of or effected by upstream gas producers, including acquisitions of midstream assets, whether in or outside of the Appalachian Basin;
•the potential for, timing, amount and amounteffect of future issuances or repurchases of the Company's securities;
•the effects of conversion, if at all, of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares (as defined herein);
•the effects of seasonality;
•expected cash flows, cash flow profile (and support therefor from certain contract structures) and MVCs, including those associated with the EQT Global GGA, and the potential impacts thereon of the commission and in-service timing (or absence thereof) and cost of the MVP project;
•the ability to achieve, and time for achieving, Hammerhead pipeline full commercial in-service;
•projected capital contributions and capital and operating expenditures, including the amount and timing of reimbursable capital expenditures, capital budget and sources of funds for capital expenditures;
•the Company's ability to recoup replacement and related costs;
•future dividend amounts, timing and rates;
•changes in commodity prices and the effect of commodity pricesstatements regarding macroeconomic factors' effects on the Company's business;business, including future commodity prices, the impact of MVP in-service on commodity prices or natural gas volumes in the Appalachian Basin, and takeaway capacity constraints in the Appalachian Basin;
•beliefs regarding future decisions of customers in respect of production growth, curtailing natural gas production, timing of turning wells in line, rig and completion activity and related impacts on the Company's business;business, and the effect, if any, on such future decisions should the MVP be brought in-service, as well as the potential for increased volumes to flow to the Company's gathering and transmission system to supply the MVP following in-service;
•the Company's liquidity and financing position and requirements, including sources, availability and sufficiency;
•liquiditystatements regarding future interest rates and/or reference rates and financing requirements, including sources and availability;
•interest rates;the potential impacts thereof;
•the ability of the Company's subsidiaries (some of which are not wholly owned) to service debt under, and comply with the covenants contained in, their respective credit agreementsagreements;
•the MVP Joint Venture's ability to raise project-level debt, and the anticipated proceeds that the Company expects to timely extend and obtain modifications in terms under such agreements;receive therefrom;
•expectations regarding natural gas and water volumes in the Company's areas of operations;
•the Company's ability to achieve anticipated benefits associated with the execution of the EQT Global GGA and other commercial agreements;
•the impact on the Company and its subsidiaries of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, including, among other things, effects on demand for natural gas and the Company’s services, commodity prices, access to capital and costs which may be incurred as a result of, and potential need for compliance with, governmental (including state or local) regulations or orders which may be enacted and upheld with respect to testing and/or vaccination for COVID-19;
•the Company's ability to position itself for a lower carbon economy, achieve, and create value from, its environmental, social and governance (ESG) and sustainability initiatives, targets and aspirations (including targets and aspirations set forth in its climate policy) and the Company's ability to respond, and impacts of responding, to increasing stakeholder scrutiny in these areas;
•the effectiveness of the Company's information technology and operational technology systems and practices to detect and defend against evolving cyberattacks on United States critical infrastructure;
•the effects and associated cost of compliance with existing or new government regulationregulations including any quantification of potential impacts of regulatory matters related to climate change on the Company; and
•future tax rates, status and position.
The forward-looking statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from projected results. Accordingly, investors should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements as a prediction of actual results. The Company has based these forward-looking statements on management's current expectations and assumptions about future events. While the Company considers these expectations and assumptions to be reasonable, they are inherently subject to significant business, economic, competitive, regulatory, judicial, construction and other risks and uncertainties, many of which are difficult to predict and are beyond the Company's control.control, including, as it pertains to the MVP project, risks and uncertainties such as the physical construction conditions, including steep slopes and any further unexpected geological impediments, continued crew availability, ability to meet contractor draw down plans, and productivity realizable, project opposition, the receipt of certain time of year and other variances and approvals, if applicable, and weather. The risks and uncertainties that may affect the operations, performance and results of the Company's business and forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, those set forth under Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors," and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which such statement is made and the Company does not intend to correct or update any forward-looking statement, unless required by securities law, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. As forward-looking statements involve significant risks and uncertainties, caution should be exercised against placing undue reliance on such statements.
PART I
Item 1. Business
Overview of Operations and the Company
Equitrans Midstream is one of the largest natural gas gatherers in the U.S. and holds a significant transmission footprint in the Appalachian Basin. Equitrans Midstream, a Pennsylvania corporation, became an independent, publicly traded company on November 12, 2018 asand its common stock trades on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol "ETRN". The Company provides midstream services to its customers in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Ohio through its three primary assets: the gathering system, which includes predominantly dry gas gathering systems of high-pressure gathering lines; the transmission system, which includes FERC-regulated interstate pipelines and storage systems; and the water network, which primarily consists of water pipelines, storage and other facilities that support well completion and produced water handling activities.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company provided a resultmajority of the Separation (as defined below).
The Separation. On November 12, 2018, Equitrans Midstream, EQT and, for certain limited purposes, EQT Production Company, a wholly owned subsidiary of EQT, entered into a separation and distribution agreement (the Separation and Distribution Agreement), pursuant to which, among other things, EQT effected the separation of its midstream business, which was composed of the assets and liabilities of the separately-operated natural gas gathering, transmission and storage services and water services operations of EQT (the Midstream Business), from EQT's upstream business, which was composed ofunder long-term contracts that generally include firm reservation fee revenues. For the natural gas, oil and natural gas liquids development, production and sales and commercial operations of EQT (the Separation), to Equitrans Midstream, and distributed 80.1% of the then-outstanding shares of common stock, no par value, of Equitrans Midstream (Equitrans Midstream common stock) to EQT shareholders of record as of the close of business on November 1, 2018 (the Distribution).
In connection with the Separation, the Company acquired control of the entities conducting the Midstream Business. See Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the entities conducting the Midstream Business.
The Company's Post-Separation Relationship with EQT. The Company and EQT are separate companies with separate management teams and separate boards of directors. Although they operate separately, due to the approximately 5.3% of Equitrans Midstream's outstanding shares of common stock held by EQT as ofyear ended December 31, 2021, the Company and EQT are characterized for certain purposes as related parties. In connection with the Separation and Distribution, the Company and EQT executed the Separation and Distribution Agreement and various other agreements to effect the Separation. See Notes 1 and 8 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the relationship between the Company and EQT subsequent to the Separation.
EQGP Unit Purchases and Limited Call Right. On November 29, 2018, the Company entered into written agreements (the Unit Purchase Agreements) with certain investors owning an aggregate of 15,364,421 common units representing limited partner interests in EQGP (EQGP common units) for $20.00 per EQGP common unit that closed through a series of transactions ending on January 3, 2019 for an aggregate purchase price of $307.3 million (collectively, the EQGP Unit Purchases).
On December 31, 2018, the Company exercised a limited call right (the Limited Call Right) under EQGP's partnership agreement, pursuant to which, on January 10, 2019, the Company closed on the acquisition of the remaining 11,097,287 outstanding EQGP common units not owned by the Company or its affiliates for an aggregate purchase price of $221.9 million (such acquisition, together with the EQGP Unit Purchases, the EQGP Buyout), and EQGP became an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. See Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the EQGP Buyout.
EQM IDR Transaction. On February 22, 2019, Equitrans Midstream completed a simplification transaction pursuant to that certain Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of February 13, 2019 (the IDR Merger Agreement), by and among Equitrans Midstream and certain related parties, pursuant to which, among other things, (i) Equitrans Merger Sub, LP merged with and into EQGP (the Merger) with EQGP continuing as the surviving limited partnership and a wholly owned subsidiary of EQM, and (ii) each of (a) the IDRs in EQM, (b) the economic portion of the general partner interest in EQM and (c) the issued and outstanding EQGP common units were canceled, and, as consideration for such cancellation, certain affiliates of the Company received on a pro rata basis 80,000,000 newly-issued common units representing limited partner interests in EQM (EQM common units) and 7,000,000 newly-issued Class B units representing limited partner interests in EQM (Class B units), and EQGP Services, LLC (the EQM General Partner) retained the non-economic general partner interest in EQM (such transactions, collectively, the EQM IDR Transaction). Additionally, as part of the EQM IDR Transaction, the 21,811,643 EQM common units held by EQGP were canceled and 21,811,643 EQM common units were issued pro rata to certain subsidiaries of the Company. As a result of the EQM IDR Transaction, the EQM General Partner replaced EQM Midstream Services, LLC as the general partner of EQM. See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the EQM IDR Transaction.
EQM Series A Preferred Units. On March 13, 2019, EQM entered into a Convertible Preferred Unit Purchase Agreement, together with Joinder Agreements entered into on March 18, 2019, with certain investors (such investors, collectively, the Investors) to issue and sell in a private placement (the Private Placement) an aggregate of 24,605,291 Series A Perpetual Convertible Preferred Units (EQM Series A Preferred Units) representing limited partner interests in EQM for a cash purchase
price2023, approximately 70% of $48.77 per EQM Series A Preferred Unit, resulting in total gross proceedsthe Company's operating revenues were generated from firm reservation fee revenues. Generally, the Company is focused on utilizing contract structures reflecting long-term firm capacity, MVC or ARC commitments which are intended to provide support to its cash flow profile. The percentage of approximately $1.2 billion. The net proceeds from the Private Placement were used in partCompany's operating revenues that are generated by firm reservation fees (as well as the Company's revenue generally) may vary year to fund the purchase price in the Bolt-on Acquisition (as defined in Note 3) and to pay certain fees and expenses related to the Bolt-on Acquisition,year depending on various factors, including customer volumes and the remainder was usedrates realizable under the Company's contracts, including the EQT Global GGA (defined below) which provides for general partnership purposes. The Private Placement closed concurrently withperiodic gathering MVC fee declines through January 1, 2028 (with the closing offees then remaining fixed throughout the Bolt-on Acquisition on April 10, 2019. See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the EQM Series A Preferred Units, none of which remain outstanding, and Note 3 to the consolidated financial statement for further information on the Bolt-on Acquisition.
EQM Merger.On June 17, 2020, pursuant to that certain Agreement and Plan of Merger, datedremaining term). Additionally, as of February 26, 2020 (the EQM Merger Agreement), by and among the Company, EQM LP Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (EQM LP), LS Merger Sub, LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of EQM LP (Merger Sub), EQM and the EQM General Partner, Merger Sub merged with and into EQM (the EQM Merger), with EQM continuing and surviving as an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. Upon consummation of the EQM Merger, the Company acquired all of the outstanding EQM common units that the Company and its subsidiaries did not already own. Following the closing of the EQM Merger, EQM was no longer a publicly traded entity. See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the EQM Merger.
Preferred Restructuring Agreement.On February 26, 2020, the Company and EQM entered into a Preferred Restructuring Agreement (the Restructuring Agreement) with all of the Investors pursuant to which, at the effective time of the EQM Merger (the Effective Time): (i) EQM redeemed $600 million aggregate principal amount of the Investors' EQM Series A Preferred Units issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Restructuring Closing (as defined below), which occurred substantially concurrent with the closing of the EQM Merger, for cash at 101% of the EQM Series A Preferred Unit purchase price of $48.77 per such unit (the EQM Series A Preferred Unit Purchase Price) plus any accrued and unpaid distribution amounts and partial period distribution amounts, and (ii) immediately following such redemption, each remaining issued and outstanding EQM Series A Preferred Unit was exchanged for 2.44 shares of a newly authorized and created series of preferred stock, without par value, of Equitrans Midstream, convertible into Equitrans Midstream common stock (the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares) on a one for one basis, in each case,discussed below, in connection with MVP full in-service the occurrenceEQT Global GGA provides for more significant potential gathering MVC fee declines in certain contract years.
The Company's operations are focused primarily in southwestern Pennsylvania, northern West Virginia and southeastern Ohio, which are prolific resource development areas in the natural gas shale plays known as the Marcellus and Utica Shales. These regions are also the primary operating areas of EQT, the Company's largest customer, which was one of the “Series A Change of Control” (as definedlargest natural gas producers in the Fourth Amended and Restated AgreementUnited States based on average daily sales volumes as of Limited Partnership of EQM (as amended, the Former EQM Partnership Agreement)) that occurred upon the closingDecember 31, 2023. EQT accounted for approximately 61% of the EQM Merger (collectively,Company's revenues for the Restructuring and, the closing of the Restructuring, the Restructuring Closing). See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the Restructuring Agreement and the Restructuring.year ended December 31, 2023.
The EQT Global GGA. On February 26, 2020 (the EQT Global GGA Effective Date), the Company entered into a Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement (the(as subsequently amended, the EQT Global GGA) with EQT and certain affiliates of EQT for the provision by the Company of certain gas gathering services to EQT in the Marcellus and Utica Shales of Pennsylvania and West Virginia. The EQT Global GGA is intended to, among other things, incentivize combo and return-to-pad drilling by EQT. Pursuant to the EQT Global GGA, EQT is subject to an initial annual MVC of 3.0 Bcf per day that gradually steps up to 4.0 Bcf per day through December 2031 following the full in-service date of the MVP.MVP and the dedication of a substantial majority of EQT's core acreage in southwestern Pennsylvania and West Virginia. The EQT Global GGA runs from the EQT Global GGA Effective Date through December 31, 2035, and will renew annually thereafter unless terminated by EQT or the Company pursuant to its terms. Pursuant to the EQT Global GGA, the Company has certain obligations to build connections to connect EQT wells to its gathering system, which are subject to limitations, including geographical limitations in relation to the dedicated area, in Pennsylvania and West Virginia, as well as the distance of such connections to the Company's then-existing gathering system.system, which have provided and could further provide capital efficiencies to EQM. In addition to the fees related to gathering services, the EQT Global GGA provides for potential cash bonus payments payable by EQT to the Company during the period beginning on the first day of the calendar quarter in which the MVP full in-service date occurs through the calendar quarter ending December 31, 2024 (the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision). The potential cash bonus payments are conditioned upon the quarterly average of certain Henry Hub natural gas prices exceeding certain price thresholds.
TheUnder the EQT Global GGA, the performance obligation is to provide daily MVC capacity and as such the total consideration is allocated proportionally to the daily MVC over the life of the contract. In periods that the gathering MVC revenue billed will exceed the allocated consideration, the excess will be deferred to the contract liability and recognized in revenue when the performance obligation has been satisfied. While the 3.0 Bcf per day MVC capacity became effective on April 1, 2020, additional daily MVC capacity and the associated gathering MVC fees payable by EQT to the Company as set forth in the EQT Global GGA are subject to potential reductions for certainconditioned upon the full in-service date of the MVP. The performance obligation, the allocation of the total consideration over the life of the contract years as set forthand the gathering MVC fees payable by EQT under the contract have been in the past, and in the future could be, affected by changes in the timing of the full in-service date of the MVP.
Under the EQT Global GGA, conditioned to beginthe gathering MVC fee periodically declines through January 1, 2028 (with the fees then remaining fixed throughout the remaining term). Before January 1, 2026, beginning the first day of the quarter in which the full in-service date of the MVP occurs under the EQT Global GGA, the gathering MVC fees payable by EQT to the Company are subject to more significant potential declines for certain contract years as set forth in the EQT Global GGA, which, provideprior to EQT's exercise of the EQT Cash Option (defined below), provided for estimated aggregate fee relief of up to approximately $270 million in the first twelve-month period, up to approximately $230 million in the second twelve-month period and up to approximately $35 million in the third twelve-month period. Further,Given that the MVP full in-service date did not occur by January 1, 2022, on July 8, 2022, EQT irrevocably elected under the EQT Global GGA to forgo up to approximately $145 million of the potential gathering MVC fee relief in such first twelve-month period and up to approximately $90 million of the potential gathering MVC fee relief in such second twelve-month period in exchange for a cash payment from the Company to EQT in the amount of approximately $195.8 million (the EQT Cash Option). As a result of EQT exercising the EQT Cash Option (and payment by the Company thereof), the maximum aggregate potential fee relief applicable under the EQT Global GGA in such first twelve-month period and such second twelve-month period was reduced to be up to approximately $125 million and depending on the ultimate in-service date of the MVP, up to approximately $140 million, respectively. The gathering MVC fees and potential declines are subject to certain provisions related to inflation adjustment in accordance with the terms of the EQT Global GGA. Additionally, the EQT Global GGA provides for a fee credit to the gathering rate for certain gathered volumes that also receive separate transmission services under certain transmission contracts. In addition, given that the MVP full in-service date did not occur by January 1, 2022, EQT has an option, exercisable through December 31, 2022, to forgo approximately $145 million of the gathering fee relief in such first twelve-month period and approximately $90 million of the gathering fee relief in such second twelve-month period in exchange for a cash payment from the Company to EQT in the amount of approximately $196 million (the EQT Cash Option). See Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the EQT Global GGA.
Credit Letter Agreement. On February 26, 2020, in connection with the execution of the EQT Global GGA, the Company and EQT entered into a letter agreement (the Credit Letter Agreement) pursuant to which, among other things, (a) the Company
agreed to relieve certain credit posting requirements for EQT, in an amount up to approximately $250 million, under its commercial agreements with the Company, subject to EQT maintaining a minimum credit rating from two of three rating agencies of (i) Ba3 with Moody’s Investors Service (Moody's), (ii) BB- with S&P Global Ratings (S&P) and (iii) BB- with Fitch Investor Services (Fitch) and (b) the Company agreed to use commercially reasonable good faith efforts to negotiate similar credit support arrangements for EQT in respect of its commitments to the MVP Joint Venture.
Water Services Letter Agreement and 2021 Water Services Agreement. On February 26, 2020, the Company entered into a letter agreement with EQT relating to the provision of water services in Pennsylvania (such letter agreement, the Water Services Letter Agreement). Subject to the effect of the 2021 Water Services Agreement (as defined below), the Water Services Letter Agreement would have been effective as of the first day of the first month following the MVP full in-service date and would have expired on the fifth anniversary of such date. During each year of the Water Services Letter Agreement, EQT had agreed to pay the Company a minimum $60 million per year annual revenue commitment (ARC) for volumetric water services provided in Pennsylvania, all in accordance with existing water service agreements and new water service agreements entered into between the parties pursuant to the Water Services Letter Agreement (or the related agreements).
On October 22, 2021, the Company and EQT entered into a new 10-year, mixed-use water services agreement covering operations within a dedicated area in southwestern Pennsylvania (as subsequently amended, the 2021 Water Services Agreement). The 2021 Water Services Agreement, which, upon its effectiveness, replaces the Water Services Letter Agreement and certain other existing Pennsylvania water services agreements, will become effective with the commencement of water delivery service to a certain EQT well pad (anticipated in the first quarter of 2022). Pursuant to the 2021 Water Services Agreement, EQT has agreed to pay the Company a minimum ARC for water services equal to $40 million in each of the first five years of the 10-year contract term and equal to $35 million per year for the remaining five years of the contract term.
Share Purchase Agreements. On February 26, 2020, the Company entered into two share purchase agreements (the Share Purchase Agreements) with EQT, pursuant to which the Company agreed to (i) purchase 4,769,496 shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock (the Cash Shares) from EQT in exchange for approximately $46 million in cash, (ii) purchase 20,530,256 shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock (the Rate Relief Shares and, together with the Cash Shares, the Share Purchases) from EQT in exchange for a promissory note in the aggregate principal amount of approximately $196 million (which EQT subsequently assigned to EQM as consideration for certain commercial terms under the EQT Global GGA), and (iii) pay EQT cash in the amount of approximately $7 million (the Cash Amount). On March 5, 2020, the Company completed the Share Purchases and paid the Cash Amount. The Company used proceeds from the EQM Credit Facility (as defined in Note 11) to fund the purchase of the Cash Shares and to pay the Cash Amount in addition to other uses of proceeds. After the closing of the Share Purchases, the Company retired the Cash Shares and the Rate Relief Shares. On September 29, 2020, the Company made a prepayment to EQM of all principal, interest, fees and other obligations outstanding under the promissory note EQT assigned to EQM and the promissory note was terminated.
See also "Our exposure to commodity price risk may increase in the future and NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA.” included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of factors affecting the estimated fair value of the derivative asset attributable to the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision.
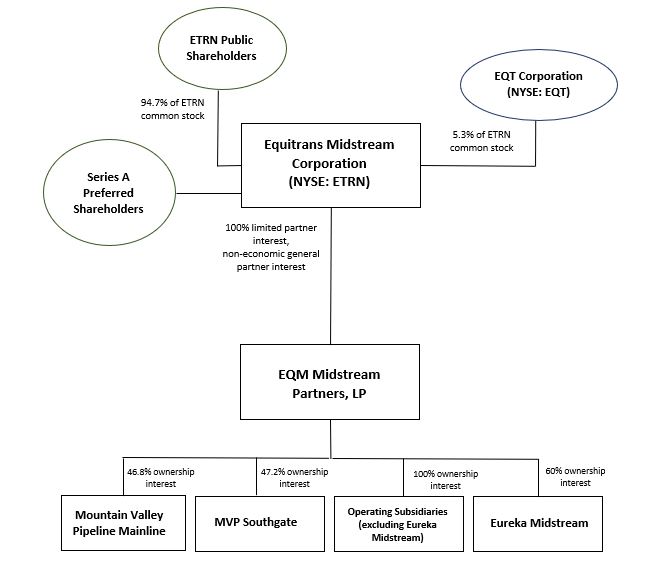
The following diagram depicts the Company's organizational and ownership structure as of December 31, 2021:2023:
Overview of Operations
The Company provides midstream services to its customers in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Ohio through its three primary assets: the gathering system, which includes predominantly dry gas gathering systems of high-pressure gathering lines; the transmission system, which includes FERC-regulated interstate pipelines and storage systems; and the water network, which primarily consists of water pipelines and other facilities that support well completion and produced water handling activities.
As of December 31, 2021, the Company provided a majority of its natural gas gathering, transmission and storage services under long-term contracts that generally include firm reservation fees. The Company maintains a stable cash flow profile, with approximately 64% of the Company's operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 2021 generated from firm reservation fees. The percentage of the Company's revenues that are generated by firm reservation fees is expected to increase in future years as a result of the 15-year term EQT Global GGA, which includes an MVC of 3.0 Bcf per day that became effective on April 1, 2020 and gradually steps up to 4.0 Bcf per day through December 2031 following the full in-service date of the MVP. These contract structures enhance the stability of the Company's cash flows and limit its exposure to customer volume variability.
The Company's operations are focused primarily in southwestern Pennsylvania, northern West Virginia and southeastern Ohio, which are prolific resource development areas in the natural gas shale plays known as the Marcellus and Utica Shales. These regions are also the primary operating areas of EQT, which was the largest natural gas producer in the United States based on average daily sales volumes as of December 31, 2021 and the Company's largest customer as of December 31, 2021. EQT accounted for approximately 59% of the Company's revenues for the year ended December 31, 2021.
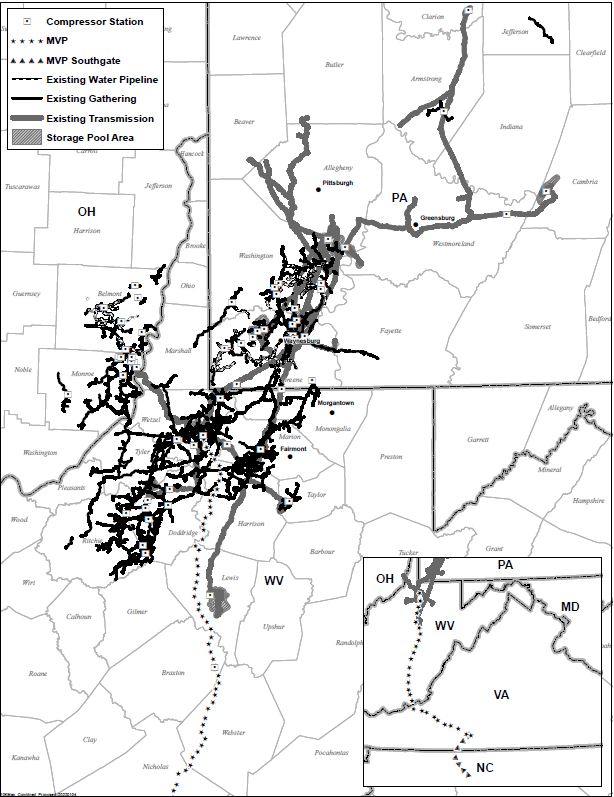
The following is a map of the Company's gathering, transmission and storage and water services operations as of December 31, 2021.2023. Also included are the MVP and MVP Southgate routes, which projects are discussed in "Strategy" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in Part I, "Item 1. Business."Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Business Segments
The Company reports its operations in three segments that reflect its three lines of business: Gathering, Transmission and Water. These segments include all of the Company's operations. For discussion of the composition of the three segments, see Notes 1 and 5 to the consolidated financial statements.
The Company's three business segments correspond to the Company's three primary assets: the gathering system, transmission and storage system and water service system. The following table summarizes the composition of the Company's operating revenues by business segment.
| | | | Years Ended December 31, | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Gathering operating revenues | Gathering operating revenues | 66 | % | | 67 | % | | 71 | % | Gathering operating revenues | 62 | % | | 66 | % | | 66 | % |
| Transmission operating revenues | Transmission operating revenues | 30 | % | | 26 | % | | 24 | % | Transmission operating revenues | 32 | % | | 30 | % | | 30 | % |
| Water operating revenues | Water operating revenues | 4 | % | | 7 | % | | 7 | % | Water operating revenues | 6 | % | | 4 | % | | 4 | % |
The Company's largest customer, EQT, accounted for approximately 59%61%, 64%61% and 69%59% of the Company's total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, respectively.
Gathering Customers. For the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, EQT accounted for approximately 59% of Gathering's throughput and approximately 62% of Gathering's revenues. Subject to certain exceptions and limitations, as of December 31, 2021,2023, Gathering (inclusive of acreage dedications to Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC (Eureka Midstream), a joint venture in which the Company is the operator and has a 60% interest and that owns a 265-mile gathering header pipeline system in Ohio and West Virginia that services both dry Utica and wet Marcellus Shale production)interest) had significant acreage dedications through which the Company has the right to elect to gather all natural gas produced from wells under dedicated areas in (i) Pennsylvania pursuant to agreements with EQT, including the EQT Global GGA, and agreements with certain other third parties, (ii) OhioWest Virginia pursuant to agreements with EQT, and other third parties, and (iii) West Virginia pursuant toincluding the EQT Global GGA, and agreements with certain other third parties, and (iii) Ohio pursuant to agreements with various third parties.
The Company provides gathering services in two manners: firm service and interruptible service. Firm service contracts are typically long-term and often include firm reservation fees, which are fixed, monthly charges for the guaranteed reservation of pipeline access. Revenues under firm reservation fees also include fixed volumetric charges under MVCs. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the gathering system had total contracted firm reservation capacity (including contracted MVCs) of approximately 7.07.7 Bcf per day (inclusive of Eureka Midstream contracted capacity), which included contracted firm reservation capacity of approximately 1.8 Bcf per day associated with the Company's high-pressure header pipelines. Including future capacity expected from expansion projects that are not yet fully constructed or not yet fully in-service for which the Company has executed firm contracts, the gathering system had total contracted firm reservation capacity (including contracted MVCs) of approximately 8.18.8 Bcf per day (inclusive of Eureka Midstream contracted capacity) as of December 31, 2021,2023, which included contracted firm reservation capacity of approximately 1.81.9 Bcf per day associated with the Company's high-pressure header pipelines. Volumetric-based fees can also be charged under firm contracts for each firm volume gathered, as well as for volumes gathered in excess of the firm contracted volume. Based on total projected contractual revenues, including projected contractual revenues from future capacity expected from expansion projects that are not yet fully constructed or not yet fully in-service for which the Company has executed firm contracts, the Company's firm gathering contracts had a weighted average remaining term of approximately 1413 years as of December 31, 2021.2023.
Interruptible service contracts include volumetric-based fees, which are charges for the volume of natural gas gathered and generally do not guarantee access to the pipeline. These contracts can be short- or long-term. To the extent that capacity reserved by customers with firm service contracts is not fully used or excess capacity exists, the gathering system can allocate capacity to interruptible services.
The Company generally does not take title to the natural gas gathered for its customers but retains a percentage of wellhead gas receipts to recover natural gas used to powerfuel certain of its compressor stations and meet other requirements on the Company's gathering systems.
Transmission Customers. For the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, EQT accounted for approximately 62%61% of Transmission's throughput and approximately 53%51% of Transmission's revenues. As of December 31, 2021,2023, Transmission had an acreage dedication from EQT through which the Company had the right to elect to transport all gas produced from wells drilled by EQT under dedicated areas in Allegheny, Washington and Greene Counties in Pennsylvania and Wetzel, Marion, Taylor, Tyler, Doddridge, Harrison and Lewis Counties in West Virginia. The Company's other customers include LDCs, marketers, producers and commercial and industrial users. The Company's transmission and storage system provides customers with
access to markets in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Ohio and to the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Midwestern and Gulf Coast markets through interconnect points with major interstate pipelines.
The Company provides transmission and storage services in two manners: firm service and interruptible service. Firm service contracts are typically long-term and often include firm reservation fees, which are fixed, monthly charges for the guaranteed reservation of pipeline and storage capacity. Volumetric-based fees can also be charged under firm contracts for firm volume transported or stored, as well as for volumes transported or stored in excess of the firm contracted volume. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the Company had firm capacity subscribed under firm transmission contracts of approximately 5.65.8 Bcf per day, which includes future capacity expected from expansion projects that are not yet fully constructed or not yet fully in-service for which the Company has executed firm transmission contracts and excludes 2.3approximately 2.6 Bcf per day of firm capacity commitments associated with the MVP and MVP Southgate projects. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the Company had firm storage capacity of approximately 29.8 Bcf subscribed under firm storage contracts. Based on total projected contractual revenues, including projected contractual revenues from future capacity expected from expansion projects that are not yet fully constructed or not yet fully in-service for which the Company has executed firm contracts, the Company's firm transmission and storage contracts had a weighted average remaining term of approximately 1312 years as of December 31, 2021.2023.
Interruptible service contracts include volumetric-based fees, which are charges for the volume of natural gas transported or stored and generally do not guarantee access to the pipeline or storage facility. These contracts can be short- or long-term. To the extent that capacity reserved by customers with firm service contracts is not fully used or excess capacity exists, the transmission and storage systems can allocate capacity to interruptible services.
The Company generally does not take title to the natural gas transported or stored for its customers but retains a percentage of gas receipts to recover natural gas used to powerfuel its compressor stations and meet other requirements of the Company's transmission and storage systems.
As of December 31, 2021,2023, approximately 97% of Transmission's contracted firm transmission capacity was subscribed by customers under negotiated rate agreements under its tariff, while the remainder was subscribed at discounted rates under its tariff, which are rates below the recourse rates and above a minimum level.tariff. As of December 31, 2021,2023, Transmission did not have anyhad minimal contracted firm transmission capacity subscribed at discounted rates and recourse rates under its tariff, which are the maximum rates an interstate pipeline may charge for its services under its tariff. See also "FERC Regulation" under "Regulatory Environment" below and "Our and the MVP Joint Venture's natural gas gathering, transmission and storage services, as applicable, are subject to extensive regulation by federal, state and local regulatory authorities. Changes in or additional regulatory measures adopted by such authorities, and related litigation, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends.” included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
Water Customers. For the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, EQT accounted for approximately 96% of Water's revenues. The Company has the exclusive right to provide fluid handling services to certain EQT-operated wells through 2029 (and thereafter such right continueswill continue on a month-to-month basis) within areas of dedication in Belmont County, Ohio, including the delivery of fresh water for well completion operations and the collection and recycling or disposal of flowback and produced water. The Company also provides water services to other customers operating in the Marcellus and Utica Shales. Upon commencement of the 2021 Water Services Agreement, the majority of the Company's water service revenues will be subject to an ARC with EQT.
See also "Water Services Letter Agreement" and "2021 Water Services Agreement" above for additional information on the Company's Water customers.
The Company's Assets
Gathering Assets. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the gathering system, inclusive of Eureka Midstream's gathering system, included approximately 1,1701,220 miles of high-pressure gathering lines, and 133138 compressor units with compression of approximately 491,000 horsepower and multiple interconnect points with the Company's transmission and storage system and to other interstate pipelines.
Transmission and Storage Assets. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the transmission and storage system included approximately 950940 miles of FERC-regulated, interstate pipelines that have interconnect points to seven interstate pipelines and multiple LDCs. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the transmission and storage system was supported by 4342 compressor units, with total throughput capacity of approximately 4.4 Bcf per day and compression of approximately 136,000135,000 horsepower, and 18 associated natural gas storage reservoirs, which had a peak withdrawal capacity of approximately 850820 MMcf per day and a working gas capacity of approximately 43 Bcf.
Water Assets. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the fresh water systems included approximately 200201 miles of pipeline that deliver fresh water from local municipal water authorities, the Monongahela River, the Ohio River, local reservoirs and several regional waterways. In addition, as of December 31, 2021,2023, the fresh water system assets included 23systems consisted of permanent, buried pipelines, surface pipelines, 17 fresh water impoundment facilities.
facilities, as well as pumping stations, which support water transportation throughout the systems, and take point facilities and measurement facilities, which support well completion activities. During 2021,2023, the Company began constructioncompleted the majority of athe main trunkline pipelines on the mixed water system in Greene County, Pennsylvania. The system hasincluding a targeted full in-service datepipeline that connects its two mixed water storage facilities. As of summer 2022 and is primarily supported byDecember 31, 2023, the 2021 Water Services Agreement. The mixed water system is designed to include 71included approximately 53 miles of
buried water pipeline and two water storage facilities with 350,000 barrels of capacity, andas well as two interconnects with the Company’s existing Pennsylvania fresh water systems and will provideprovides services to producers in southwestern Pennsylvania. As of December 31, 2021, the Company’sThe Company plans to continue to expand its mixed water system included approximately eight milesin 2024, including the completion of buried pipeline.a pipeline to serve a producer in West Virginia and a water pipeline, scheduled to be completed in the first quarter of 2025, to interconnect with the same producer's Pennsylvania mixed water network.
Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions
The Company's strategically-locatedstrategically located and integrated assets overlay core acreage in the Appalachian Basin. The location of the Company's assets allows its producer customers to access major demand markets in the U.S. The Company is one of the largest natural gas gatherers in the U.S., and its largest customer, EQT, was one of the largest natural gas producerproducers in the U.S. based on average daily sales volumes as of December 31, 2021. The Company maintains a stable cash flow profile, with approximately 64%2023 and EQT's public senior debt had investment grade credit ratings from Standard & Poor's Global Ratings (S&P), Fitch Ratings (Fitch) and Moody's Investors Service (Moody's) as of its operating revenues forthat date. For the year ended December 31, 20212023, approximately 70% of the Company's operating revenues were generated from firm reservation fees. Further, as discussed above,fee revenues. Generally, the Company is focused on utilizing contract structures reflecting long-term firm capacity, MVC or ARC commitments which are intended to provide support to its cash flow profile. The percentage of the Company's operating revenues that are generated by firm reservation fees is expected(as well as the Company's revenues generally) may vary year to increase in future years as a result ofyear depending on various factors, including customer volumes and the 15-year termrates realizable under the Company's contracts, including the EQT Global GGA which includes anprovides for periodic gathering MVC fee declines through January 1, 2028 (with the fee then remaining fixed throughout the remaining term). Additionally, as discussed above under "Overview of 3.0 Bcf per day that became effectivethe Company and Operations" in Part 1, "Item 1. Business" of this Annual Report on April 1, 2020 and gradually steps up to 4.0 Bcf per day through December 2031 following theForm 10-K, in connection with MVP full in-service date of the MVP. ThisEQT Global GGA provides for more significant potential gathering MVC fee declines in certain contract structure enhances the stability of the Company's cash flows and limits its exposure to customer volume variability.years.
Strategy.
The Company's principal strategystrategic aim is to achieve greater scale and scope, enhance the durability of its financial strength and to continue to work to position itself for a lower carbon economy, whicheconomy.
The Company's standalone strategy reflects its continued pursuit of organic growth projects, including completing and placing in service the Company expects will drive future growth and investment. The Company is implementing its strategy by continuingMVP, focusing on identifying opportunities to leverageuse its existing assets executeto deepen and grow its customer relationships at optimized levels of capital spending and taking into account the Company’s leverage, and continuing to prudently invest resources in its sustainability-oriented initiatives. The Company’s strategy also reflects its continued focus on its growth projects (including through potential expansionachieving a strong balance sheet, and extension opportunities), periodically evaluate strategically-alignedgiven the Company’s size, operating footprint and other factors considering inorganic growth opportunities, (whether within its existing footprint orsuch as to extend the Company's reachCompany’s operations into the southeast United States to become closer toand new, key demand markets, such as the Gulf of Mexico LNG export market), and focus on ESG and sustainability-oriented initiatives.Additionally,market.
In conjunction with the Company is also continuingworking to focus on strengthening its balance sheet through:
•highly predictable cash flows backed by firm reservation fees;
•actions to de-lever its balance sheet;
•disciplined capital spending;
•operating cost control; and
•an appropriate dividend policy.
As part of its approach to organic growth, the Company is focusedexecute on its projectsstandalone strategy, the Company’s Board of Directors has been engaged in a process with third parties that have expressed interest in strategic transactions involving the Company. The board has engaged outside advisors and assets outlined below, manythe process is ongoing. There is no assurance that such process will result in the execution, approval or completion of which are supported by contracts with firm capacityany specific transaction or MVC commitments.outcome.
The Company expects that the MVP, project (should it be placed in-service), together with the Hammerhead pipeline and Equitrans, L.P. Expansion Project (EEP), will primarily drive the Company's near-term organic growth, as discussed in further detail below. In particular, the Company believes that the MVP, among other benefits, will allow for greater natural gas production in the southwestern Appalachian Basin (and/or result in increased volumes flowing to the Company's gathering and transmission system given the Company's belief in the system's current unique positioning to provide the supply path to MVP). In addition, the Company continues to focus on de-levering its balance sheet (which the Company views as a critical strategic objective), including in connection with the MVP.
•Mountain Valley Pipeline. The MVP is being constructed by a joint venture among the Company and affiliates of each of NextEra Energy, Inc. (NEE), Consolidated Edison, Inc. (Con Edison), AltaGas Ltd. and RGC Resources, Inc. (RGC). As of December 31, 2021,2023, the Company owned an approximate 46.8%48.4% interest in the MVP project and will operate the MVP. The MVP is an estimated 300-mile, 42-inch diameter natural gas interstate pipeline with a targeted capacity of 2.0 Bcf per day that is designed to span from the Company's existing transmission and storage system in Wetzel County, West Virginia to Pittsylvania County, Virginia, providingwhich will provide access to the growing southeast demand markets.markets once it is placed in-service. The MVP Joint Venture has secured a total of 2.0 Bcf per day of firm capacity commitments at 20-year terms. Additional shippers have expressed interest in the MVP project and the MVP Joint Venture is evaluating an expansion opportunity that could add approximately 0.5 Bcf per day of capacity through the installation of incremental compression.
In October 2017, the FERC issued the Certificate of Public Convenience and Necessity (the Certificate) for the MVP. In the first quarter of 2018, the MVP Joint Venture received limited notice to proceed with certain construction activities from the FERC and commenced construction. However, the MVP project was repeatedly, significantly delayed and subject to cost increases because of legal and regulatory setbacks, particularly in respect of litigation in the U.S. Court of Appeals
for the Fourth Circuit (Fourth Circuit). Notwithstanding such prior setbacks, the MVP Joint Venture continued to engage in pursuing the authorizations necessary to complete the MVP project, including on February 28, 2023, the U.S. Department of the Interior’s Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) issuing a new Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement (2023 BiOp) for the MVP project and in May 2023, the U.S. Forest Service and Bureau of Land Management issuing authorizations related to MVP’s segment in the Jefferson National Forest (JNF).
On June 3, 2023, the President of the United States signed into law the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023 that, among other things, ratified and approved all permits and authorizations necessary for the construction and initial operation of the MVP, directed the applicable federal officials and agencies to maintain such authorizations, required the Secretary of the Army to issue not later than June 24, 2023 all permits or verifications necessary to complete construction of the MVP and allow for the MVP’s operation and maintenance, and divested courts of jurisdiction to review agency actions on approvals necessary for MVP construction and initial operation.
Thereafter, certain necessary authorizations were issued to the MVP Joint Venture, and the FERC authorized the MVP Joint Venture to resume all construction activities in all MVP project locations. After the Fourth Circuit issued a stay halting MVP project construction in the JNF and a stay of the 2023 BiOp, the U.S. Supreme Court vacated the stays on July 27, 2023. The MVP Joint Venture recommenced forward construction activity in August 2023.
Since then, the MVP Joint Venture has made substantial progress on completing the MVP. As of February 15, 2024, the MVP Joint Venture, among other things, has completed:
•approximately 300 miles of pipeline installed (less than 4 miles remaining to install);
•415 crossings (13 remaining);
•the hydrotesting of approximately 180 miles (approximately 125 miles remain to be tested, inclusive of interconnect piping);
•the purging and packing of the pipeline through to the second compressor station (total of approximately 77 miles);
•the commissioning of two of three MVP compressor stations; and
•restoration of a substantial portion of the pipeline right of way, with the remaining approximately 112 miles of pipeline restoration to occur following MVP in-service.
Forward progress slowed at the end of 2023 through early 2024 as a result of unforeseen challenging construction conditions, combined with unexpected and substantially adverse winter weather conditions throughout much of January 2024. As a result, the MVP Joint Venture retained a higher than planned contractor headcount through January into February to maintain the right of way and address weather-induced issues and also to be in a position to improve forward progress as soon as conditions became more favorable. While productivity has since improved at the end of January and into February 2024, the combined effect of these unforeseen challenges significantly slowed the previously anticipated pace of construction and adversely affected project cost. As a result, the Company is targeting MVP project completion and commissioning in the second quarter of 2024, at a total estimated project cost ranging from approximately $7.57 billion to approximately $7.63 billion (excluding allowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC)).
Based on such targeted completion timing and following in-service authorization from the FERC, the Company expects that MVP and MVP-related firm capacity contractual obligations would commence on June 1, 2024 (with certain MVC step ups and more significant gathering MVC fee declines under the EQT Global GGA commencing April 1, 2024).
As the MVP Joint Venture continues to diligently work towards responsibly completing the MVP project, it will
continue to prioritize the safety of its workforce, communities, and assets, and the project's compliance with applicable
environmental standards and regulations.
The targeted completion timing and cost, and accordingly the commencement of MVP and MVP-related firm capacity contractual obligations are subject to many factors, including the physical construction conditions, weather and productivity, many of which are beyond the Company's control.
activities fromFurther adverse developments however, whatever the FERC and commenced construction. Following a comprehensive review of all outstanding stream and wetland crossings acrosscause, affecting the approximately 300-mile MVP project route, on February 19, 2021, the MVP Joint Venture submitted (i) a joint application package to eachcould further increase project
costs and/or further delay completion or in-service of the Huntington, Pittsburghproject, and Norfolk Districts ofadversely affect the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (Army Corps)Company, including its
leverage levels and potential liquidity. See also "Expanding our business by constructing new midstream
assets subjects us to construction, business, economic, competitive, regulatory, judicial, environmental, political and
legal uncertainties that requested an Individual Permit from the Army Corps to effect approximately 300 water crossings utilizing open cut techniques (the Army Corps Individual Permit) and (ii) an application to amend the Certificate that seeks FERC authority to utilize alternative trenchless construction methods to effect approximately 120 water crossings. Related to seeking the Army Corps Individual Permit, on March 4, 2021, the MVP Joint Venture submitted applications to each of the West Virginia Department of Environmental Protection (WVDEP) and the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality (VADEQ) seeking Section 401 water quality certification approvals or waivers (such approvals or waivers, the State 401 Approvals), which State 401 Approvals were each received in December 2021. In early June 2021, the FERC issued a notice of schedule for the MVP Joint Venture's Certificate amendment application and the FERC issued an Environmental Assessment in mid-August 2021. As discussedare beyond our control." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on
Form 10-K. See also Part II, "Item 3. Legal Proceedings" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, on January 25, 2022, the MVP Joint Venture's authorizations related to the Jefferson National Forest (JNF) received from the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) were vacated and remanded on specific issues by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit (Fourth Circuit). As also discussed in Part I, "Item 3. Legal Proceedings" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, on February 2, 2022, the Fourth Circuit vacated and remanded on specific issues the Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement issued by the United States Department of the Interior's Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) for the MVP project. The MVP Joint Venture continues to review these recent decisions and evaluate the possible paths forward, which include working with the relevant federal agencies and consideration of potential legal appeals. As a result, the Company is not able to provide an update as to the in-service timing and overall cost for the project, except that the Company is no longer targeting a summer 2022 in-service date.
In addition to timely receiving, and subsequently maintaining, new authorizations in respect of the JNF, and a Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement, the MVP Joint Venture must, in order to complete the project, among other things, timely receive (i) the Army Corps Individual Permit (as well as timely receive, if necessary, certain other state-level approvals), and (ii) authorization from the FERC to amend the Certificate to utilize alternative trenchless construction methods for certain stream and wetland crossings, as well as any necessary extensions from FERC to complete the MVP project. The MVP Joint Venture also must (i) continue to have available the orders previously issued by the FERC, which are the subject of ongoing litigation, modifying its prior stop work orders and extending the MVP Joint Venture’s prescribed time to complete the MVP project; and (ii) timely receive authorization from the FERC to complete construction work in the portion of the project route currently remaining subject to the FERC’s previous stop work order and in the JNF. In each case, any such foregoing or other authorizations must remain in effect notwithstanding any pending or future challenge thereto. For further information regarding litigation and regulatory related delays affecting the completion of the MVP project, see Part I, "Item 3. Legal Proceedings" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. See also "The regulatory approval process for the construction of new midstream assets is very challenging, has significantly increased costs and delayed targeted in-service dates, and decisions by regulatory and judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings are likely to impact our or the MVP Joint Venture's ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvals and authorizations necessary to complete certain projects on the targeted time frame or at all or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects." included in "Item 1A. Risk Factors" for additional discussion.
On November 4, 2019, Con Edison exercised an option to cap its investment in the construction of the MVP project at approximately $530 million (excluding AFUDC). On May 4, 2023, RGC exercised an option for the Company to fund RGC's portion of future capital contributions with respect to the MVP project, which funding the Company commenced in June 2023 and will continue through the full in-service date of the MVP. The Company and NextEra Energy, Inc.NEE are obligated, and RGC, Resources, Inc., another memberprior to the exercise of the MVP Joint Venture owning an interest in the MVP project, hasits option described above had opted, to fund the shortfall in Con Edison's capital contributions on a pro rata basis. Following RGC's exercise of its option, the Company is also funding RGC's portion of Con Edison's shortfall. Such funding by the Company in respect of the Con Edison shortfall and funding by other membersRGC's portion of capital contributions has and will correspondingly increase the Company's and such other members' respective interests in the MVP project and decrease Con Edison's and RGC's respective interest, as applicable, in the MVP project. AsIf the project were to be completed in the second quarter of 2024 and at a result, depending ontotal project cost ranging from approximately $7.57 billion to approximately $7.63 billion (excluding AFUDC), the project's total cost, the Company'sCompany expects its equity ownership in the MVP project willwould progressively increase from approximately 48.4% to a percentage in excess of approximately 46.8%49.0%.
Through December 31, 2021,2023, the Company had funded approximately $2.5$3.4 billion of its then-estimated total capital contributions. During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company made approximately $284 million of capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture for the MVP project. For 2022,If the MVP project were to be completed in the second quarter of 2024 at a total project cost ranging from approximately $7.57 billion to approximately $7.63 billion (excluding AFUDC), the Company expects toit would make total capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture in 2024 of approximately $175$540 million to $225$575 million primarily related to work completedforward construction, and expects that it would incur a total of approximately $4.0 billion over the project's construction, inclusive of approximately $245 million in late 2021 and ongoing right-of-way maintenance.excess of the Company's ownership interest.
•Wellhead Gathering Expansion Projects and Hammerhead Pipeline. During the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, the Company invested approximately $224$267.7 million in gathering projects (inclusive of capital expenditures related to the noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream). For 2022,2024, the Company expects to invest approximately $270$225 million to
$320 $275 million in gathering projects (inclusive of expected capital expenditures of approximately $20$15 million related to the noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream). The primary projects include infrastructure expansion ofand optimization in core development areas in the Marcellus and Utica Shales in southwestern Pennsylvania, southeastern Ohio and northern West Virginia for EQT, Range Resources Corporation (Range Resources) and other producers. The Company has seen and expects that it will continue to see the benefits of return-to-pad drilling and system integrations in 2024, and estimates gathering capital expenditures required to maintain flat gathered volumes in a given year would be between approximately $200 million and $250 million for 2024.
The Hammerhead pipeline is a 1.6 Bcf per day gathering header pipeline that is primarily designed to connect natural gas produced in Pennsylvania and West Virginia to the MVP, Texas Eastern Transmission and DominionEastern Gas Transmission, is supported by a 20-year term, 1.2 Bcf per day, firm capacity commitment from EQT, and cost approximately $540 million. For more information, including regardingThe Company expects Hammerhead pipeline full commercial in-service statusto commence in conjunction with full MVP in-service and is focused on obtaining additional firm capacity commitments and/or additional interruptible volumes for the pipeline. During the fourth quarter of 2023, the Company provided firm and interruptible volumes from the Company's Hammerhead Gathering agreement with EQT and expects to continue the interruptible volumes up to the full commercial in-service date of the Hammerhead pipeline see "Outlook"when firm commitments will commence.
The Company also has an agreement with a producer customer to install approximately 32,000 horsepower booster compression to existing facilities. The project is backed by a long-term firm commitment and is expected to be in-service in "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysisthe first quarter of Financial Condition and Results2024. The majority of Operations."spend on the project was incurred in 2023.
•Transmission Projects and Equitrans Expansion ProjectProjects.. During the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, the Company invested approximately $26$84.2 million in transmission projects. For 2024, the Company expects to invest approximately $75 million to $85 million in transmission projects, including approximately $40 million to complete the EEP.Company's Ohio Valley Connector expansion project (OVCX). The Company expects OVCX will increase deliverability on the Company's existing Ohio Valley Connector pipeline (OVC) by approximately 350 MMcf per day, create new receipt and delivery transportation paths, and enhance long-term reliability. The project is primarily supported by new long-term firm capacity commitments of 330 MMcf per day, as well as an extension of approximately 1.0 Bcf per day of existing contracted mainline capacity for EQT. OVCX is designed to meet growing demand in key markets in the mid-continent and gulf
coast through existing interconnects with long-haul pipelines in Clarington, Ohio. On January 20, 2023, the FERC issued the Final Environmental Impact Statement for the project. On June 15, 2023, the FERC issued the Certificate of Public Convenience and Necessity for OVCX. On July 31, 2023, the FERC issued the Notice to Proceed and the Company commenced construction during the third quarter of 2023. The Company expects to invest a total of approximately $160 million in the project and is targeting the incremental capacity to be placed in-service during the second quarter of 2024. The OVCX project, as well as the Company's successful open season in 2023 for the available transmission capacity that was subject of the one-time transmission customer's contract buyout during the first quarter of 2023, is consistent with the Company's ongoing efforts to optimize existing assets and achieve capital efficiency.
The Company's EEP project is designed to provide north-to-south capacity on the mainline Equitrans, L.P. system, including primarily for deliveries to the MVP. A portion of the EEP commenced operations with interruptible service in the third quarter of 2019. The EEP provides capacity of approximately 600 MMcf per day and offers access to several markets through interconnects with Texas Eastern Transmission, DominionEastern Gas Transmission and Columbia Gas Transmission. Once theIn connection with MVP is fully placed in service,full in-service, firm transportation agreements for 550 MMcf per day of capacity will commence under 20-year terms.
For 2022, the Company expects to invest approximately $45 million in transmission projects, inclusive of capital expenditures expected for 2022 associated with the Company's Ohio Valley Connector expansion project (OVCX). OVCX will increase deliverability on the Company's existing Ohio Valley Connector pipeline (OVC) by approximately 350 MMcf per day, create new receipt and delivery transportation paths, and enhance long-term reliability. The project is supported by new long-term firm capacity commitments of 330 MMcf per day, as well as an extension of approximately 1.0 Bcf per day of existing contracted mainline capacity for EQT. OVCX is designed to meet growing demand in key markets in the mid-continent and gulf coast through existing interconnects with long-haul pipelines in Clarington, Ohio. The targeted in-service date for the incremental OVC capacity is the third quarter of 2023. The Company expects to invest approximately $160 million, which includes approximately $130 million for new compression. The project is consistent with the Company's ongoing efforts to optimize existing assets and achieve capital efficiency.
•MVP Southgate Project. In April 2018,December 2023, the MVP Joint Venture announced an amended MVP Southgate project in lieu of the original project. The amended project would extend approximately 31 miles from the terminus of the MVP in Pittsylvania County, Virginia to planned new delivery points in Rockingham County, North Carolina using 30-inch diameter pipe. The MVP Southgate project, which is a proposedwas announced in April 2018, previously contemplated an approximate 75-mile interstate pipeline that is contemplatedwas approved by the FERC to extend from the MVP at Pittsylvania County, Virginia to new delivery points in Rockingham and Alamance Counties, North Carolina. The MVP Southgate project is backed by a 300 MMcf per day firm capacity commitment from Dominion Energy North Carolina, and, as currently designed, reflects potential expansion capabilities that could provide up to 900 MMcf per day of total capacity. The Company is expected to operate the MVP Southgate project and owned a 47.2% interest in the MVP Southgate project as of December 31, 2021.
The MVP Joint Venture submittedhas entered into precedent agreements with each of Public Service Company of North Carolina, Inc. (PSNC), and Duke Energy Carolinas, LLC (Duke), which precedent agreements contemplate the MVP Southgate certificate applicationamended project (in lieu of the original project). In contrast to the FERC in November 2018. The Final Environmental Impact Statement for the MVP Southgateoriginal, lengthier project, was issued on February 14, 2020. In June 2020, the FERC issued the Certificate of Public Conveniencewhich traversed 155 water crossings and Necessity for the MVP Southgate; however, the FERC, while authorizing the project, directed the Office of Energy Projects not to issue a notice to proceed with construction until necessary federal permits are received for the MVP project and the Director of the Office of Energy Projects lifts the stop work order and authorizes the MVP Joint Venture to continue constructing the MVP project. On August 11, 2020, the North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality (NCDEQ) denied the MVP Southgate project'srequired an additional compressor station (the permit application for a Clean Water Act Section 401 Individual Water Quality Certification and Jordan Lake Riparian Buffer Authorization due to uncertainty surrounding the completion of the MVP project. On March 11, 2021, the Fourth Circuit, pursuant to an appeal filedwhich was denied by the MVP Joint Venture, vacated the NCDEQ's denial and remanded the matter to the NCDEQ for additional review. On April 29, 2021, the NCDEQ reissued its denial of the MVP Southgate project's application for a Clean Water Act Section 401 Individual Water Quality Certification and Jordan Lake Riparian Buffer Authorization. On December 3, 2021, the Virginia State Air Pollution Control Board deniedin 2021), the permitamended project would include substantially fewer water crossings (all of which would be evaluated for boring) and would not require a new compressor station. The new precedent agreements, among other things, collectively provide for 550,000 Dth per day of firm capacity commitments (whereas the original project was supported by a 300,000 Dth per day firm capacity commitment with PSNC, which has been superseded by the new precedent agreement with PSNC), are each for 20-year terms (subject to two potential five-year extensions), and describe certain conditions precedent to the parties’ respective obligations regarding MVP Southgate (including, among others, that both precedent agreements remain in full force and effect). Given the court-related construction stops experienced on MVP, the new precedent agreements also incorporate certain spending and termination protections which may be exercised in certain circumstances in accordance with the terms of the precedent agreements, including in connection with a delay, stay or vacatur of certain governmental authorizations. The MVP Joint Venture recently completed an open season for the MVP Southgate project’s Lambert compressor station, which decisionproject and expects to finalize the project scope in the coming months. The targeted completion timing for the project is June 2028, with the majority of the capital spend expected to occur in 2027.
The FERC previously conditioned its authorization on MVP Southgate being built and made available for service by June 18, 2023. On June 15, 2023, the MVP Joint Venture has appealed (and such appeal is pending). Seefiled a request with the discussionFERC for an extension of litigation and regulatory related delays affectingtime to June 18, 2026, to complete MVP Southgate, which the completionFERC granted on December 19, 2023. Project opponents filed a request for rehearing of the MVP Southgate project set forth in Part I, "Item 3. Legal Proceedings" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
GivenFERC's December 19, 2023 order. On February 20, 2024, the continually evolving regulatory and legal environment for greenfield pipeline construction projects, as well as factors specific toFERC denied the MVP and MVP Southgate projects, including the December 2021 compressor station state air permit denial, therehearing request. The MVP Joint Venture is evaluating the MVP Southgatepermitting and regulatory roadmap for the project, including engagingrequesting an updated completion due date.
•Water Operations. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company invested approximately $45.7 million in discussionsits water infrastructure, primarily to continue to construct the initial mixed-use water system buildout. The Company placed portions of the initial mixed-use water system in service during 2022 and its second above ground water storage facility into service in July 2023, which brings its total water storage capacity to 350,000 barrels. During 2023, the Company completed the majority of the main trunkline pipelines on the mixed water system, including a pipeline that connects its two mixed water storage facilities. In May 2023, the Company executed an agreement with Dominion Energy North Carolina regarding options with respecta producer customer to provide mixed-use water delivery service. The 10-year agreement is backed by a minimum volume commitment. For 2024, the Company expects to invest approximately $25 million to $35 million in its water operations, primarily related to the MVP Southgate project, including potentiallycontinued construction of its mixed-use water system buildout.
refining the project’s design and timing in lieu of pursuing the project as originally contemplated. Dominion Energy North Carolina’s obligations under the precedent agreement in support of the original project are subject to certain conditions, including that the MVP Joint Venture complete construction of the project facilities by June 1, 2022, which deadline is subject to extension by virtue of previously declared events of force majeure. The Company is unable to predict the results of the discussions between the MVP Joint Venture and Dominion Energy North Carolina, including any potential modifications to the project, or ultimate undertaking or completion of the project.
The MVP Southgate project, as originally designed, was estimated to cost a total of approximately $450 million to $500 million, a portion of which the Company expected to fund. During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company made approximately $4 million of capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture for the MVP Southgate project. For 2022, the Company expects to make capital contributions of approximately $5 million to the MVP Joint Venture for the MVP Southgate project.
•Water Operations. During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company invested approximately $35 million in its water infrastructure. For 2022, the Company expects to invest approximately $50 million in the operations of its water infrastructure in Pennsylvania, primarily for the construction of the mixed water system.
See "Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility" in Part II, "Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the Company's continued focus on ESG and sustainability matters which the Company believes will help to distinctively position the Company and create value.
Competitive Condition.Conditions. Key competitors for new natural gas gathering systems include companies that own major natural gas pipelines, independent gas gatherers and integrated energy companies. When compared to the Company or its customers, some of the Company's competitors have operations in multiple natural gas producing basins, have greater capital resources and access to, or control of, larger natural gas supplies. Natural gas producers that develop their own gas gathering systems or acquire such systems may also compete with the Company depending on the location of such systems relative to the Company's assets and existing agreements.
Competition for natural gas transmission and storage is primarily based on rates, customer commitment levels, timing, performance, commercial terms, reliability, service levels, location, reputation and fuel efficiencies. The Company's principal competitors in its transmission and storage market include companies that own major natural gas pipelines in the Marcellus and Utica Shales. In addition, the Company competes with companies that are building high-pressure gathering facilities that are able to transport natural gas to interstate pipelines without being subject to FERC jurisdiction. Major natural gas transmission companies that compete with the Company also have storage facilities connected to their transmission systems that compete with certain of the Company's storage facilities.
Key competition for water services includes natural gas producers that develop their own water distribution systems in lieu of employing the Company's water services assets and other natural gas midstream companies that offer water services. The Company's ability to attract customers to its water service business depends on its ability to evaluate and select suitable projects and to consummate transactions in a highly competitive environment.
Further, natural gas as a fuel competes with other forms of energy available to end-users, including coal, certain liquid fuels and, increasingly, renewable and alternative energy. Demand for renewable and alternative energy is increasing generally with changes in consumer preferences, governmental clean energy policies, and as renewable and alternative energy becomes more cost competitive with traditional fuels (including by technological advancement, legislation or government subsidies, as well as traditional supply and demand dynamics) and more widely available. Continued increases in the demand for renewable and alternative energy at the expense of natural gas (or increases in the demand for other sources of energy, particularly if prices for natural gas are elevated relative to other forms of energy as fuel) could lead to a reduction in demand for natural gas gathering, transmission and storage, and water services.
See also “Increased competition from other companies that provide gathering, transmission and storage, and water services, or from alternative fuel or energy sources, could negatively impact demand for our services, which could adversely affect our financial results.” included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Regulatory Environment
FERC Regulation. The Company's interstate natural gas transmission and storage operations are regulated by the FERC under the Natural Gas Act of 1938, as amended (NGA), the Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978, as amended (NGPA), and the regulations, rules and policies promulgated under those and other statutes. Certain portions of the Company's gathering operations are also currently rate-regulated by the FERC in connection with its interstate transmission operations. The Company's FERC-regulated operations are pursuant to tariffs approved by the FERC that establish rates (other than market-based rate authority), cost recovery mechanisms and terms and conditions of service to its customers. Generally, the FERC's authority extends to:
•rates and charges for the Company's natural gas transmission and storage services and FERC-regulated gathering services;
•certification and construction of new interstate transmission and storage facilities;
•abandonment of interstate transmission and storage services and facilities and certificated gathering facilities;
•maintenance of accounts and records;
•relationships between pipelines and certain affiliates;
•terms and conditions of services and service contracts with customers;
•depreciation and amortization policies;
•acquisitions and dispositions of interstate transmission and storage facilities; and
•initiation and discontinuation of interstate transmission and storage services.
The FERC regulates the rates and charges for transmission and storage in interstate commerce. Unless market-based rates have been approved by the FERC, the maximum applicable recourse rates and terms and conditions for service are set forth in the pipeline's FERC-approved tariff. Generally, the maximum filed recourse rates for interstate pipelines are based on the cost of providing service, including the recovery of a return on the pipeline's actual and prudent historical investment costs. Key determinants in the ratemaking process include the depreciated capital costs of the facilities, the costs of providing service, the allowed rate of return and income tax allowance, as well as volume throughput and contractual capacity commitment assumptions.
Interstate pipelines may not charge rates or impose terms and conditions of service that, upon review by the FERC, are found to be unjust or unreasonable, unduly discriminatory or preferential. Rate design and the allocation of costs also can affect a pipeline's profitability. While the ratemaking process establishes the maximum rate that can be charged, interstate pipelines such as the Company's transmission and storage system are permitted to discount their firm and interruptible rates without further FERC authorization down to a specified minimum level, provided they do not unduly discriminate. In addition, pipelines are allowed to negotiate different rates with their customers, under certain circumstances. Changes to rates or terms and conditions of service, and contracts can be proposed by a pipeline company under Section 4 of the NGA, or the existing interstate transmission and storage rates, or terms and conditions of service andand/or contracts may be challenged by a complaint filed by interested persons including customers, state agencies or the FERC under Section 5 of the NGA. Rate increases proposed by a pipeline may be allowed to become effective subject to refund and/or a period of suspension, while rates or terms and conditions of service that are the subject of a complaint under Section 5 of the NGA are subject to prospective change by the FERC. Rate increases proposed by a regulated interstate pipeline may be challenged and such increases may ultimately be rejected by the FERC.
The Company's interstate pipeline may also use negotiated rates that could involve rates above or below the recourse rate or rates that are subject to a different rate structure than the rates specified in the Company's interstate pipeline tariffs, provided that the affected customers are willing to agree to such rates and that the FERC has approved the negotiated rate agreement. A prerequisite for allowing the negotiated rates is that negotiated rate customers must have had the option to take service under the pipeline's recourse rates. As of December 31, 2021,2023, approximately 97% of the system's contracted firm transmission capacity was subscribed by customers under negotiated rate agreements under its tariff. Some negotiated rate transactions are designed to fix the negotiated rate for the term of the firm transportation agreement and the fixed rate is generally not subject to adjustment for increased or decreased costs occurring during the contract term.
The FERC’s regulations also extend to the terms and conditions set forth in agreements for transmission and storage services executed between interstate pipelines and their customers. These service agreements are required to conform, in all material respects, with the form of service agreements set forth in the pipeline's FERC-approved tariff. Non-conforming agreements must be filed with and accepted by the FERC. In the event that the FERC finds that an agreement is materially non-conforming, in whole or in part, it could reject, or require the Company to seek modification of, the agreement, or alternatively require the Company to modify its tariff so that the non-conforming provisions are generally available to all customers or class of customers.
The FERC’s jurisdiction also extends to the certification and construction of new interstate transmission and storage facilities, including, but not limited to, acquisitions, facility replacements and upgrades, expansions, and abandonment of facilities and services. While the FERC currently exercises jurisdiction over the rates and terms of service for the Company’s FERC-regulated gathering services, these gathering facilities may not be subject to the FERC’s certification and construction authority. Prior to commencing construction of new or existing interstate transmission and storage facilities, an interstate pipeline must obtain (except in certain circumstances, such as where the activity is permitted under the FERC’s regulations or is authorized under the operator’s existing blanket certificate issued by the FERC) a certificate authorizing the construction, or file to amend its existing certificate, from the FERC.
On April 19, 2018, the FERC issued a Notice of Inquiry (2018 Notice of Inquiry) seeking information regarding whether, and if so how, it should revise its approach under its currently effective policy statement on the certification of new natural gas transportation facilities (Certificate Policy Statement). The formal comment period in this proceeding closed on June 25, 2018. On February 18, 2021, the FERC issued another Notice of Inquiry in the same proceeding that modified and expanded the inquiry and renewed its request for public comment (together with the 2018 Notice of Inquiry, the Certificate Policy Statement NOI). The formal comment period closed May 26, 2021. On February 18, 2022, the FERC issued an Updated Certificate Policy Statement. The Company is evaluatingOn February 18, 2022, the FERC issued an interim GHG policy. On March 24, 2022, the FERC issued an order suspending the effectiveness of the Updated Certificate Policy Statement but at this time, itand the interim GHG policy and has taken no further action to date.
In 2024, there is not possible to predict the impacta possibility that the Updated Certificate Policy will have on the Company, if any.
In 2021,U.S. Congress did notcould pass legislation revising the NGA or other statutes that may impact the Company's existing facilities and operations or the ability to construct new facilities, though that remains a possibility in 2022.facilities. Potential areas of revision include, but are not limited to, (i) amending Section 5 of the NGA to allow the FERC to require a pipeline to make refunds from the date that a NGA Section 5 complaint was filed with the FERC if rates are later found to be unjust and unreasonable; (ii) amending
Section 7 of the NGA affecting the ability of companies to exercise eminent domain; and (iii) amending Section 19(b) of the NGA to provide the FERC additional time to act on requests for rehearing.
Party controlThe FERC’s assessment of greenhouse gas emissions in the NEPA review of pipeline certificate projects remains a divided issue among the Commissioners. In 2023, the FERC reached a compromise position among Acting Chairman Phillips and Commissioners Danly and Christie whereby the FERC will disclose the social cost of GHG calculations for informational purposes, but does not characterize the significance of the projects’ greenhouse gas emissions. This compromise position continued in the FERC’s 2023 Order on Remand in Rio Grande LNG, LLC in response to a U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia (D.C. Circuit) directive that the FERC address arguments regarding whether the social cost of carbon protocol is a generally accepted analytical tool for assessing the significance of greenhouse gas impacts. Commissioner Allison Clements has continued to file dissenting opinions opposing the Commission’s approach. The D.C. Circuit could decide several pending appeals in 2024 regarding the FERC’s treatment of greenhouse gas emissions in natural gas pipeline certificate reviews.
The FERC had four commissioners in 2023. However, Commissioner James Danly left the FERC at the FERC changed in 2021,end of 2023. On February 9, 2024, President Biden named Willie Phillips Chairman of the FERC. Commissioner Allison Clements’s term expires on June 30, 2024, and she has indicated that she will not seek another term, leaving the possibility that the FERC reestablished its full complementcould be without a quorum of fivethree members in 2024. If Congress does not confirm Commissioner Clements's replacement prior to expiration of her term, Commissioner Clements may remain in her position until the end of the current the U.S. Congress in January 2025. As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, President Biden has not yet nominated new commissioners. In 2021, FERC issued Order Nos. 871-B and -C (amending FERC regulations to prohibit the issuance of authorizations to proceed with construction while certain requests for rehearing are pending), demonstrated that it will consider climate change impacts in individual certificate proceedings, and incorporated enhanced environmental justice review in pipeline certificate orders. On February 18, 2022, the FERC issued an interim GHG policy. The Company is evaluating the interim GHG policy, but at this time, it is not possible to predict the impact that the interim GHG policy, or any future changes to that policy, will have on the Company, if any.
FERC Regulation of Gathering Rates and Terms of Service. Section 1(b) of the NGA exempts natural gas gathering facilities from regulation by the FERC under the NGA. While the FERC does not generally regulate the rates and terms of service over facilities determined to be performing a natural gas gathering function, it has traditionally regulated rates charged by interstate pipelines for gathering services performed on the pipeline's own gathering facilities when those gathering services are performed in connection with jurisdictional interstate transmission services. The Company currentlysubmitted an application to the FERC requesting authorization to abandon its low-pressure gathering facilities and services. On June 17, 2022 and December 16, 2022, the FERC issued orders authorizing Equitrans, L.P. to abandon these low-pressure gathering facilities, subject to certain conditions. In 2023, Equitrans, L.P. completed the abandonments of the remaining low-pressure gathering facilities and no longer maintains rates and terms of service in its tariff for unbundled gathering services performed on its gathering facilities in connection with theits transmission service. Just as with rates and terms of service for transmission and storage services, the Company's rates and terms of service for its FERC-regulated low-pressure gathering system may be challenged by complaint and are subject to prospective change by the FERC. The Company has submitted an application to the FERC requesting authorization to abandon these low-pressure gathering facilities and services. As of December 31, 2021, the application remained pending before the FERC.
The Company believes that its high-pressure gathering systems meet the traditional tests the FERC has used to establish a pipeline's status as an exempt gatherer not subject to regulation as a jurisdictional natural gas company. However, the distinction between FERC-regulated transmission services and federally unregulated gathering services is often the subject of litigation in the industry, so the classification and regulation of these systems are subject to change based on future determinations by the FERC, the courts or the U.S. Congress.
Pipeline Safety and Maintenance.The Company's interstate natural gas pipeline system isand natural gas storage assets are subject to regulation by the PHMSA. The PHMSA has established safety requirements pertaining to the design, installation, testing, construction, operation and maintenance of gas pipeline and storage facilities, including requirements that pipeline and storage operators develop a written qualification program for individuals performing covered tasks on pipeline facilities and implement pipeline and storage well integrity management programs. These integrity management plans require more frequent inspections and other preventive measures to ensure safe operation of oil and natural gas transportation pipelines and storage facilities in high population areas or facilities that are hard to evacuate and areas of daily concentrations of people.
Notwithstanding the investigatory and preventative maintenance costs incurred in the Company's performance of customary pipeline and storage management activities, the Company may incur significant additional expenses if anomalous pipeline or storage conditions are discovered or more stringent pipeline safety requirements are implemented. For example, in April 2016, the PHMSA published a notice of proposed rulemaking addressing several integrity management topics and proposing new requirements to address safety issues for natural gas transmission and gathering lines, along with certain storage facilities (the Mega Rule). The proposedPHMSA intended the Mega Rule wouldto strengthen existing integrity management requirements, expand assessment and repair requirements to pipelines in areas with medium population densities, and extend regulatory requirements to onshore gas gathering lines that are currently exempt. Part oneI of the Mega Rule was finalizedpromulgated on October 1, 2019, with an effective date of July 1, 2020 (see discussion below). Part three of the Mega RuleII was finalizedpromulgated on November 15, 2021, with an effective date of May 16, 2022 (see discussion below). Finally, Part twoIII of the Mega Rule will now be the final portion
addressed by a future rulemaking activity which remains under development, and no expected date for finalization has been released by PHMSA.
Further, in June 2016, then-President Obama signed the Protecting Our Infrastructure of Pipelines and Enhancing Safety Act of 2016 (the 2016 Pipeline Safety Act), extending the PHMSA's statutory mandate under prior legislation through 2019. In
addition, the 2016 Pipeline Safety Act empowered the PHMSA to address imminent hazards by imposing emergency restrictions, prohibitions and safety measures on owners and operators of gas or hazardous liquid pipeline facilities without prior notice or an opportunity for a hearing and also required the PHMSA to develop new safety standards for natural gas storage facilities by June 2018. Pursuant to those provisions of the 2016 Pipeline Safety Act, the PHMSA issued two separate Interim Final Rules in October 2016 anda final rule effective December 20162, 2019 that expanded the agency's authority to impose emergency restrictions, prohibitions and safety measures and issued a final rule effective March 13, 2020 that strengthened the rules related to underground natural gas storage facilities, including well integrity, wellbore tubing and casing integrity. The December 2016 Interim Final Rule, relating to underground gas storage facilities, went into effect in January 2017. PHMSA determined, however, that it would not issue enforcement citations to any operators for violations of provisions of the December 2016 Interim Final Rule that had previously been non-mandatory provisions of American Petroleum Institute Recommended Practices 1170 and 1171 until one year after PHMSA issued a final rule. The final rule related to underground gas storage facilities became effective as of March 13, 2020.integrity
Following the October 2016 Interim Final Rule, the PHMSA also published threefive final rules on pipeline safety applicable to the Company: "Enhanced Emergency Order Procedures;""Safety "Safety of Gas Transmission Pipelines: Maximum Allowable Operating Pressure Reconfirmation, Expansion of Assessment Requirements, and Other Related Amendments" (also known as the Mega Rule Part 1)I); and "Safety of Gas Gathering Pipelines: Extension of Reporting Requirements, Regulation of Large, High-Pressure Lines, and Other Related Amendments" (also known as the Mega Rule Part 3)II); and "Safety of Gas Transmission Pipelines: Repair Criteria, Integrity Management Improvements, Cathodic Protection, Management of Change, and Other Related Amendments" (also known as the Mega Rule Part III); and “Pipeline Safety: Requirement of Valve Installation and Minimum Rupture Detection Standards” (the valve rule). The Enhanced Emergency Order Procedures rule, which became effective on December 2, 2019, implements an existing statutory authorization for the PHMSA to issue emergency orders related to pipeline safety if an unsafe condition or practice, or a combination of unsafe conditions and practices, constitutes, or is causing an imminent hazard. The Safety of Gas Transmissions Pipelines rule,Mega Rule Part I, which went into effect on July 1, 2020, requires operators of certain gas transmission pipelines that have been tested or that have inadequate records to determine the material strength of their lines by reconfirming the Maximum Allowable Operating Pressure (MAOP), and establishes a new Moderate Consequence Area for determining regulatory requirements for gas transmission pipeline segments outside of high consequence areas. The rule also establishes new requirements for conducting baseline assessments, incorporates into the regulations industry standards and guidelines regarding design, construction and in-line inspections (ILI), and new requirements for data integration and risk analysis in integrity management programs, including seismicity, manufacturing and construction defects, and crack and crack-like defects, and includes several requirements that allow operators to notify the PHMSA of proposed alternative approaches to achieving the objectives of the minimum safety standards. The Safety of Gas Gathering Pipelines rule,Mega Rule Part II, which was finalized on November 15, 2021 and will gowent into effect on May 16, 2022, extends existing design, operational and maintenance, and reporting requirements to onshore natural gas gathering pipelines in rural areas. The rule requires operators of onshore gas gathering pipelines to report incidents and file annual reports (with the first annual reports submitted in Spring 2023), and creates new safety requirements that vary based on pipeline diameter and potential consequences of a failure. Mega Rule Part III, which was finalized on August 24, 2022, went into effect on May 24, 2023. The rule requires operators of certain transmission pipelines to assess their integrity management practices, and comply with enhanced corrosion control and mitigation timelines. It also establishes new requirements for pipeline inspections following an extreme weather event or natural disaster, and provides enhanced guidance for pipeline repairs. The valve rule requires the installation of remote operated rupture mitigation valves on new or entirely replaced transmission and storage lines when valves are installed to meet valve spacing requirements. In 2021,addition the valve rule includes requirements for operator actions to be taken when notified of a potential rupture that include notifying emergency response agencies and closing valves within a specified timeframe. In 2023, the Company did not incur material compliance costs in connection with complying with the PHMSA rules applicable to the Company. However, as discussed below, the Company does expect certain compliance costs to increase in the near future, and does not currently expectthe Company continues to assess the impact of compliance with these rules towhich could materially impact its future costs of operations and revenue from operations. However,For example, Mega Rule Part I requires MAOP reconfirmation of certain previously untested transmission pipeline segments, which are commonly referred to as ‘‘grandfathered’’ pipelines. The Company’s grandfathered pipeline MAOP reconfirmation efforts, which the Company will continuehas initiated, may result in unanticipated testing and/or replacement costs. When reconfirming MAOP on certain of the Company’s grandfathered pipeline segments the Company may be required to assessremove portions of pipelines for testing, shut in certain pipelines, and/or may face significant operational or technical challenges when performing either a pressure test or an ILI examination, which could result in substantial costs related thereto, or to repairs, remediation, or replacing existing pipelines, and/or other mitigating actions that may be determined to be necessary as a result of the impacttests, as well as lost cash flows resulting from shutting down the Company's pipelines during the pendency of any such actions, which could be material to capital expenditures, earnings and the Company's competitive position. Additionally, ensuring complete compliance with these rules on its future costs of operations and revenue from operations.
States are generally preempted by federal law in the area of pipeline safety, but state agencies may qualify to assume responsibility for enforcing federal regulations over intrastate pipelines. They may also promulgate additive pipeline safety regulations provided that the state standards are at least as stringent as the federal standards. Although many of the Company's natural gas facilities fall within a class that is not subject to integrity management requirements, the Company may incur significant costs and liabilities associated with repair, remediation, preventive or mitigation measures associated with its non-exempt transmission pipelines. The costs, if any, for repair, remediation, preventive or mitigating actions that may be
determined to be necessary as a result of the testing program, as well as lost cash flows resulting from shutting down the Company's pipelines during the pendency of any such actions, could be material to capital expenditures, earnings and the Company's competitive position.
Should the Company fail to comply with U.S. DOT regulations adopted under authority granted to the PHMSA, it could be subject to penalties and fines. The PHMSA has the statutory authority to impose civil penalties for pipeline safety violations up to a maximum of approximately $220,000$266,000 per day for each violation and approximately $2.2$2.6 million for a related series of violations. This maximum penalty authority established by statute will continue to be adjusted periodically to account for inflation. In addition, the Company could be required to make additional, unforeseen maintenance capital expenditures in the future for the above described or similarits regulatory compliance initiatives that are not reflected in its forecasted maintenance capital expenditures. The Company believes that its operations are in substantial compliance with all existing federal, state and local pipeline safety laws and regulations. However,initiatives. Additionally, the adoption of new laws and regulations, such as those proposed by PHMSA,the Mega Rule discussed above, could result in significant
added costs or delays to in service or the termination of projects, which could have a material adverse effect on the Company in the future.
On December 27, 2020, then-President Trump signed the "Protecting our Infrastructure of Pipelines and Enhancing Safety (PIPES Act) of 2020," which reauthorized the federal pipeline safety program that expired in 2019. The PIPES Act identifies areas where the U.S. Congress believed additional oversight, research, or regulations was needed. The PIPES Act includes new mandates for the PHMSA to require operators to update, as needed, their emergency response plans and operating and maintenance plans. The PIPES Act also requires operators to manage records and update, as necessary, their existing district regulator stations to eliminate a common mode of failure. The PHMSA will also require that leak detection and repair programs consider the environment, the use of advance lead detection practices and technologies, and that operators be able to locate and categorize all leaks that are hazardous to human safety, the environment, or that can become hazardous. The Company has not incurred and does not anticipate incurring material capital expenditures in connection with complying with the PIPES Act.
Cybersecurity. The U.S. government has continued to issue public warnings that indicate that energy assets might be specific targets of cyberattacks and, incyberattacks. In May and July 2021, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security's Transportation Safety Administration (the TSA) issued security directives (as well as subsequent revisions thereto) applicable to certain midstream companies requiring such companies to comply with mandatory reporting measures and undertake a number of specific cybersecurity enhancements for both information technology (IT) and operational technology (OT) systems. In both 2022 and 2023, the TSA released updated versions of the security directives, with the most recent versions requiring, among other things, the assessment of the effectiveness of our security measures. The Company continues to work with the TSA to ensure compliance with the security directives and is implementing the requirements of those security directives, as needed. While such implementation is utilizing significant internal resources, implementation as of the filing date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, hasimplementation of, and ongoing compliance with, our cybersecurity implementation program (CIP) and security directives have not materially adversely affected the Company's business and operations.
In March 2022, President Biden signed into law the Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022 (CIRCIA). CIRCIA directs the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) to promulgate regulations requiring certain entities to report to CISA certain cyber incidents. The Company expects that it will be subject to such regulations after they are promulgated and continues to monitor regulatory developments to ensure future compliance and assess the impact the compliance with these rules on its future costs of operations. As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, it is not possible to predict the ultimate impact such regulations may have on the Company’s business or operations.
The regulatory environment surrounding cybersecurity continues to evolve in ways that are frequently difficult to predict. We have been required and may further be required to expend additional resources as a result of current or new laws, regulations, directives or other requirements, or changes in the interpretation or enforcement practices thereof, related to cybersecurity, which could result in material compliance costs. Additionally, we may become subject to multiple incident reporting requirements and other cybersecurity obligations that could overlap or conflict with each other, resulting an increased risk of non-compliance or in different responses to the same incident. Any failure to remain in compliance with laws or regulations governing cybersecurity, including TSA security directives,the requirements contained in the Company’s CIP, may result in penalties, fines, enforcement actions, or mandated changes in our practices, which may have a material adverse effect on our business and operations.
For further information, see also "“Cyberattacks aimed at us or those third parties on which we rely, as well as any noncompliance by us or such third parties with applicable laws and regulations governing cybersecurity and/or data privacy, could materially adversely affect us."” under Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors."
OSHA Regulation.On September 9, 2021, President Biden announced a proposed new rule requiring that all employers with at least 100 employees require that their employees be fully vaccinated or require unvaccinated workers to produce a negative test result at least once a week. On November 4, 2021, the U.S. Department of Labor’s Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) issued an Emergency Temporary Standard (ETS) to carry out this mandate.
On January 13, 2022, the U.S. Supreme Court granted an application to stay the ETS pending disposition of petitions for review in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit. Effective January 26, 2022, OSHA withdrew the ETS as an enforceable emergency temporary standard, but did not withdraw the ETS as a proposed rule.
Should the ETS, or similar state or local requirement, take effect in the future, the Company expects it would be subject to such regulation concerning COVID-19 vaccination or testing. In that case, the Company may be required to implement a requirement that many or most employees get vaccinated, subject to limited exceptions, or be tested, resulting in additional costs to the Company. At this time, it is not possible to predict the impact that a vaccine or testing requirement would have on the Company or its workforce. Any such mandate may result in increased costs, operational disruptions or employee attrition, which could materially and adversely affect the Company’s business and results of operations.
OSHA has also implemented a National Emphasis Program in July 2021 that focuses on COVID-19. This program channels the agency’s resources toward inspections of employers with congregate work settings, to ensure they maintain safety protocols designed to limit the spread of the coronavirus (e.g., masking, social distancing). This program is not likely to impact the Company’s remote workers, but could result in increased inspections and fines at the Company’s congregate work settings.
OSHA is also focusing on hazards posed to workers by extreme heat. The Biden Administration has indicated that it considers heat-related illnesses to be a growing hazard because of climate change, has identified this area of policy as a priority for the Administration because of its disproportionate impact on communities of color.change. To combat this hazard, on September 1, 2021, the OSHA implemented an enforcement initiative prioritizing inspections of work activities when the heat index exceeds 80 degrees Fahrenheit. The OSHA is also developingfurther stepped-up enforcement in this area, announcing a National Emphasis Program for Outdoor and Indoor Heat-Related Hazards on April 8, 2022. In addition, the OSHA continues to make progress towards a formal national heat inspections and, on October 27,stress standard. In 2021,
the OSHA issued an Advanced Notice of Proposed Rulemaking on heat injury and illness prevention in outdoor and indoor work settings. This notice signals OSHA’s intentsettings and on August 24, 2023, the OSHA released options for a regulatory framework to issue a rule requiring employers to take certain precautions to avoid heat-related illnesses amongst their employees. As with OSHA’s COVID-19 enforcement initiatives, theseaddress heat stress in the workplace. These programs will not likely impact the Company’s remote employees, but could result in increased inspections and fines at the Company’s outdoor worksites.
Employee Health and Safety. As noted above, the Company is subject to a number of federal and state laws and regulations, including the federal Occupational Safety and Health Act and comparable state statutes, whose purpose is to protect the health and safety of workers. In addition, the OSHA hazard communication standard, the EPAU.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) community "right-to-know" regulations and comparable state laws and regulations require that information be maintained concerning hazardous materials used or produced in the Company's operations and that this information be provided to employees, state and local government authorities and citizens. The Company is confident that it is in substantial compliance with all applicable laws and regulations relating to worker health and safety.
Environmental Matters
General. The Company's operations are subject to stringent federal, state and local laws and regulations relating to the protection of the environment, which may have the following effects on the Company:
•requiring that the Company obtains various permits to conduct regulated activities;
•requiring the installation of pollution-control equipment or otherwise regulating the way the Company can handle or dispose of its wastes;
•limiting or prohibiting construction activities in sensitive areas, such as wetlands, water sources, or areas inhabited by endangered or threatened species; and
•requiring investigatory and remedial actions to mitigate or eliminate pollution conditions caused by the Company's operations or attributable to former operations.
In addition, the Company's operations and construction activities may be subject to county and local ordinances that restrict the time, place or manner in which those operations and activities may be conducted.
Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may trigger a variety of administrative, civil and criminal enforcement measures, including the assessment of monetary penalties, the imposition of investigatory and remedial obligations and the issuance of orders enjoining future operations or imposing additional compliance requirements. Also, certain environmental statutes impose strict, and in some cases joint and several, liability for the cleanup and restoration of sites where hydrocarbons or wastes have been disposed or otherwise released regardless of the fault of the current site owner or operator. Consequently, the Company may be subject to environmental liability at its currently owned or operated facilities for conditions caused by others prior to the Company's involvement.
The Company has implemented programs and policies designed to keep its pipelines and other facilities in compliance with existing environmental laws and regulations, and the Company does not believe that the cost of its compliance with such legal requirements will have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to its shareholders. Nonetheless, the trend in environmental regulation is to place more restrictions and limitations on activities that may affect the environment, and it is generally expected that such trend will likely increase under the Biden Administration. Thus, there can be no assurance as to the amount or timing of future expenditures for environmental compliance or remediation, and actual future expenditures may be significantly in excess of the amounts the Company currently anticipates.anticipates as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. For example, the Biden Administration has announced that it will be reviewing the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) for ozone and may make these standards more stringent. This could result in the areas in which the Company operates being designated as nonattainment areas. States that contain any areas designated as nonattainment areas will be required to develop implementation plans demonstrating how the areas will attain the applicable standard within a prescribed period of time. These plans may require the installation of
additional equipment to control emissions. The EPA did not make the ozone NAAQS more stringent when it reviewed them in 2020, but the Biden Administration has indicatedannounced that it will reconsider that decision.be commencing a review of these NAAQS. In addition, in November 2021,December 2023, the EPA issued a proposedfinal rule that would makemakes more stringent the volatile organic compound (VOC) and methane emissions limits on certain new and modified equipment in the oil and gas source category, including certain types of compressors and pneumatic pumps. The proposedfinal rule would also extendextends these requirements to existing sources for the first time. Some states are also enacting methane reduction programs. For example, Pennsylvania has a methane reduction framework for the oil and gas industry that will result in an existing source VOC regulation with the stated goal of reducing methane emissions from well sites, compressor stations and pipelines.
Compliance with these or other new regulations could, among other things, require installation of new emission controls on some of the Company's equipment, result in longer permitting timelines, and significantly increase the Company's capital expenditures and operating costs, which could adversely affect the Company's business. The Company continuously attempts to anticipate future regulatory requirements that might be imposed and works to remain in compliance with changing environmental laws and regulations and to minimize the costs of such compliance. While the Company believes that it is in substantial compliance with existing environmental laws and regulations, there is no assurance that the current conditions will continue in the future.
Additionally, on January 20, 2021, President Biden signed an executive order on "Protecting Public Health and the Environment and Restoring Science to Tackle the Climate Crisis," under which President Biden directed the heads of all federal agencies to review "all existing regulations, orders, guidance documents, policies, and any other similar agency actions (agency actions) promulgated, issued, or adopted" during the Trump Administration for consistency with the policies established in the Biden Administration order. Regulatory actions resulting from this review could adversely affect the Company’s business and results of operations, including by requiring additional capital expenditures and increasing operating costs.regulations.
The following is a discussion of several of the material environmental laws and regulations, as amended from time to time, that relate to the Company's business.
Hazardous Substances and Waste. The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA) and comparable state laws impose liability, without regard to fault or the legality of the original conduct, on certain classes of persons who are considered to be responsible for the release of a "hazardous substance" into the environment. These persons include current and prior owners or operators of the site where a release of hazardous substances occurred and companies that transported, disposed or arranged for the transportation or disposal of the hazardous substances found at the site. Under CERCLA, these "responsible persons" may be subject to strict and joint and several liability for the costs of cleaning up the hazardous substances that have been released into the environment, for damages to natural resources and for the costs of certain health studies. CERCLA also authorizes the EPA and, in some instances, third parties, to act in response to threats to the public health or the environment and to seek to recover from the responsible classes of persons the costs they incur. It is not uncommon for neighboring landowners and other third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by hazardous substances or other pollutants released into the environment. The Company generates materials in the course of its ordinary operations that are regulated as "hazardous substances" under CERCLA or similar state laws and, as a result,laws. The Company may be jointly and severally liable under CERCLA, or such laws, for all or part of the costs required to clean up sites at which these hazardous substances have been released into the environment.
In the ordinary course of the Company's operations, the Company generates wastes constituting solid wastes, and in some instances hazardous wastes, which are subject to the requirements of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) and comparable state statutes. While the RCRA regulates both solid and hazardous wastes, it imposes strict requirements on the generation, storage, treatment, transportation and disposal of hazardous wastes. While certain petroleum production wastes are excluded from RCRA's hazardous waste regulations, it is possible that these wastes will in the future be designated as "hazardous wastes" and be subject to more rigorous and costly disposal requirements, which could have a material adverse effect on the Company's maintenance capital expenditures and operating expenses.
The Company owns, leases or operates properties where petroleum hydrocarbons are being or have been handled for many years. The Company has generally utilized operating and disposal practices that are standard in the industry at the time, although petroleum hydrocarbons or other wastes may have been disposed of or released on or under the properties owned, leased or operated by the Company, or on or under the other locations where these petroleum hydrocarbons and wastes have been transported for treatment or disposal. Petroleum hydrocarbons or other wastes may have been disposed or released on certain of these properties by third parties that previously operated, owned or leased these properties and whose treatment and disposal or release of petroleum hydrocarbons and other wastes were not under the Company's control. These properties and the wastes disposed thereon may be subject to CERCLA, RCRA and analogous state laws. Under these laws, the Company could be required to remove or remediate previously disposed wastes (including wastes disposed of or released by prior owners or operators), to clean up contaminated property (including contaminated groundwater) or to perform remedial operations to prevent future contamination.
Air Emissions. The federal Clean Air Act and comparable state laws and regulations restrict the emission of air pollutants from various industrial sources, including the Company's compressor stations, and also impose various monitoring and reporting requirements. Such laws and regulations may require that the Company obtain pre-approval for the construction or modification of certain projects or facilities, obtain and strictly comply with air permits containing various emissions and operational limitations and utilize specific emission control technologies to limit emissions. The Company's failure to comply with these requirements could subject it to monetary penalties, injunctions, conditions or restrictions on operations and, potentially,
criminal enforcement actions. The Company may be required to incur certain capital expenditures in the future for air pollution control equipment in connection with obtaining and maintaining permits and approvals for air emissions.
These types of capital
expenditures could also be required in areas that are nonattainment for the ozone national ambient air quality standardsNAAQS depending on the design of the relevant state’s implementation plan to meet the air quality standards. The EPA did not make the ozone NAAQS more stringent when it reviewed them in 2020, and although the Biden Administration initially indicated that it would reconsider that decision, the EPA announced in August 2023 that it would cease its reconsideration and begin an entirely new review of the ozone NAAQS that would need to be completed by 2025 under the federal Clean Air Act. As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, it is not clear when the EPA will issue a notice of proposed rulemaking. If the ozone NAAQS are made more stringent, this could result in additional nonattainment areas being designated, which could in turn result in the Company being required to install additional pollution control equipment. Moreover, with regard to the 2015 ozone NAAQS, the EPA released a final rule in May 2023 called the Good Neighbor Plan that imposes a federal implementation plan in 23 states to address air pollution from those states that is contributing to downwind nonattainment of the 2015 ozone NAAQS in other states. The final rule establishes limitations on emissions of nitrogen oxides for certain industrial stationary sources in 23 states, including states in which the Company operates. The rule has been stayed in 12 states including West Virginia by seven different federal courts of appeals because the underlying disapproval of those states’ state implementation plans has been found likely to have been unlawful. The Good Neighbor Plan remains in effect in the remaining 11 states including Ohio, Pennsylvania and Virginia. The final Good Neighbor Plan has been challenged in various courts of appeals, including the D.C. Circuit. The D.C. Circuit denied a motion to stay the rule in September 2023, and some of the parties filed emergency stay applications with the U.S. Supreme Court in October 2023. The U.S. Supreme Court has scheduled oral argument on the emergency stay applications for February 21, 2024. As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, it is not clear how the U.S. Supreme Court will rule on the emergency stay application or how the other courts of appeals will rule on the challenges to the underlying disapproval of some states' implementation plans and on the Good Neighbor Plan itself. If the Good Neighbor Plan withstands these judicial challenges and remains in place in states in which the Company operates, the Company will be required to install additional pollution control equipment on certain of its assets, but the Company does not anticipate that compliance with the Good Neighbor Plan will have a material effect on the Company’s capital expenditures, earnings and competitive position.
In August 2023, an EPA issued final rule removing the “emergency” affirmative defense provision from the EPA’s Title V permit program regulations became effective. The EPA removed this provision from the permitting program because the agency found that these provisions conflicted with its current interpretation of the enforcement structure of the Clean Air Act. The EPA has directed states with similar emergency affirmative defense provisions in their Title V permitting programs to revise permits contains those provisions during permit renewals. The final rule has been challenged in the D.C. Circuit, but, as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, is in abeyance awaiting a decision in a separate D.C. Circuit case involving a different EPA rule that may have relevance to the challenge to the emergency defense rule. Although the EPA has stated that it “may” use its “case-by-case” enforcement discretion to determine whether to initiate enforcement as appropriate, this rule removes the automatic defense the Company could claim in an emergency situation and may make it more difficult to avoid liability for Title V permit violations.
On February 7, 2024, the EPA released a final rule revising the NAAQS for fine particulate matter (PM2.5). In the final rule, the EPA lowered the level of the annual NAAQS from 12.0 µg/m3 to 9.0 µg/m3. The new annual NAAQS could result in additional nonattainment areas being designated in areas in which the Company operates, which would result in new construction being more difficult in these areas. It would also result in states having to develop new state implementation plans setting forth the measures the state intends to take to attain the new annual standard, and it is possible that these new state implementation plans could require air pollution control devices to be installed on existing compression stations. The rule will take effect 60 days after it is published in the Federal Register, which had not occurred as of the filing of this Annual Report. It is not possible as of the filing date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K to predict the ultimate impact the revised annual PM2.5 NAAQS may have on the Company’s business or operations.
Future compliance with these requirements may require modifications to certain of the Company's operations, including the installation of new equipment to control emissions from the Company's compressors, that could result in significant costs, including increased capital expenditures and operating costs, and could adversely affect the Company's business.
Climate Change. The Company has announced a goalan aspiration of becoming net zero for scope 1 and 2 carbon emissions by 2050. The Company’s climate policy includes two interim emission reduction targets:goals: (i) a 50 percent reduction of its Scope 1 and Scope 2 methane emissions by 2030; and (ii) a 50 percent reduction of its total Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2040.
Legislative and regulatory measures to address climate change and GHG emissions are in various phases of discussion or implementation and will beare a major focus of the Biden Administration. On January 27, 2021, President Biden signed an executive
order on "Tackling the Climate Crisis at Home and Abroad." This executive order contains sweeping direction to the executive branch to address climate issues. Among other things,As discussed further below, the order put a "pause" on any new oil andconstruction of interstate natural gas leasestransportation pipelines pursuant to the NGA requires authorization from the FERC, and FERC actions are subject to review under NEPA. NEPA requires federal agencies, such as the FERC, to evaluate major federal actions having the potential to significantly affect the environment. On January 9, 2023, the White House Council on public lands or in offshore waters pending completionEnvironmental Quality published new interim guidance entitled “National Environmental Policy Act Guidance on Consideration of a review byGreenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change.” Generally, the Departmentinterim guidance calls for increased scrutiny of the Interior. A district court issued an injunction haltingGHG effects of proposed federal action, including requiring agencies to quantify the leasing pause, butproposed action’s GHG emissions and relevant climate impacts. The interim guidance and increased review of the Biden Administration is appealing that decision. UnderGHG impacts of federal action has the executive order,potential to significantly delay or limit, and significantly increase the Interior Department issued a reportcost of, development of midstream infrastructure. The EPA announced its Climate Enforcement and Compliance Strategy in November 2021September 2023, which directs all enforcement and compliance programs in responsethe EPA to this executive order that recommends increasingaddress climate change, wherever appropriate, in every matter within their jurisdiction. The Compliance Strategy also directs the oilEPA to prioritize enforcement and gas royalties associated with fossil fuels extracted from public landscompliance actions to mitigate climate change and offshore waters.
The EPA regulates GHG emissions from new and modified facilities that are potential major sources of criteria pollutants under the Clean Air Act's Prevention of Significant Deterioration and Title V programs and has adopted regulations that require, among other things, preconstruction and operating permits for certain large stationary sources and the monitoring and reporting of GHGs from certain onshore oil and natural gas production sources on an annual basis.
TheSince May 2016, the EPA regulateshas regulated methane and VOCs from the oil and gas sector through its new source performance standard program under the Clean Air Act. In May 2016, the EPA finalizedThese initial rules (Subpart OOOOa) that impose methane and VOC emissions limits on certain types of new and modified compressors and pneumatic pumps. The EPA finalized amendments to some requirements in these standards in March 2018, September 2018 and September 2020, including rescission of certain requirements and revisions to other requirements such as fugitive emissions monitoring frequency. In September 2020,December 2023, the EPA issued a final rule, (knownwhich as the Policy Rule) that "corrected" the regulations by removing the transmission and storage segments from the source category subject to the rule and removing the methane emissions limits from the rule. Congress revoked the Policy Rule through the Congressional Review Act, and President Biden signed this into law in June 2021. The Congressional Review Act action has the effect as though the Policy Rule never existed. The revocation of the Policy Rule didfiling of this Annual Report on Form 10-K has not affect Equitrans Midstream becauseyet been published in the Company never stopped complying with the Subpart OOOOa methane and VOC emissions limits. In November 2021, the EPA issued a proposed ruleFederal Register, that proposes to dodoes three things: (i) modifymodifies Subpart OOOOa to, among other things, increase fugitive emissions monitoring frequency; (ii) promulgatepromulgates a new Subpart OOOOb that would imposeimposes more stringent requirements on new and modified oil and gas sources;sources that commence construction or modification on or after December 6, 2022; and (iii) promulgatepromulgates an emissions guideline (a new Subpart OOOOc) that would provideprovides direction to the states to regulate VOC and methane emissions from existing sources in the sector for the first time. The proposed Subpart OOOOc would largelydirects states to regulate existing sources in largely the same manner in which new and modified sources are regulated.regulated under Subpart OOOOb. It is expected that some parties may challenge the final rule once it is published in the Federal Register. It is also expected that some parties may file petitions for reconsideration asking the EPA to reexamine certain parts of the final rule. If those challenges are filed and the proposed rule is finalized,withstands judicial review, or if the EPA decides against any changes to the final rule in response to petitions for reconsideration, the Company will be required to incur certain capital expenditures in the future for air pollution control equipment, increased fugitive emissions monitoring, and other requirements that could result in significant costs and could adversely affect the Company's business.
In addition,August 2022, the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) was enacted. Among other provisions, the IRA includes a methane fee that is imposed on certain types of facilities, including certain ones owned and/or operated by the Company. The IRA exempts from the methane fee those facilities that are subject to the EPA’s final methane rule (Subparts OOOOb and OOOOc discussed above), provided that the rule results in 2015,emission reductions that are at least equivalent to those that would be achieved under the U.S., Canada,November 2021 proposed rule (which is the case for new and modified sources and will be the U.K. participatedcase for existing sources unless a state is able to justify a lesser standard based on the Clean Air Act’s “remaining useful life and other factors” provision). The EPA published a proposed rule in the United Nations Conference on Climate Change, which ledFederal Register in January 2024. The proposed rule makes clear that the EPA does not think the exemption for existing sources that are subject to Subpart OOOOc would be available until state plans implementing OOOOc are approved and in effect in all states with sources subject to Subpart OOOOc. If the creationEPA finalizes this interpretation of the Paris Agreement. The Paris Agreement, which was signedIRA’s exemption, the methane fee could have a material effect on the Company until all states have finalized and had their plans approved by the U.S.EPA. Under the IRA, the Company could be liable for methane emissions from applicable facilities that are above 25,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent. These fees are written into the IRA and are: (1) $900 per ton for any tons over the threshold that are reported for calendar year 2024; (2) $1,200 per ton for any tons over the threshold that are reported for calendar year 2025; and (3) $1,500 per ton for any tons over the threshold that are reported for calendar year 2026 and each year thereafter. Even once all the states have approved state plans to implement Subpart OOOOc, it is possible that the Company could have operations in April 2016, requires countriesa state that implements less stringent emissions standards than the final Subpart OOOOc emissions guideline, in which case the exemption would not be available for applicable facilities in that state.
The IRA also directed the EPA to review and "represent a progression" in their intended nationally determined contributions (which set GHG emission reduction goals) every five years beginning in 2020. The United States withdrew from the Paris Agreement in 2020; however, President Biden signed an executive order on January 20, 2021, for the United States to rejoin the Paris Agreement. The United States participated in the United Nations Conference on Climate Change in Glasgow, Scotland in November 2021 and was oneamend Subpart W of the countries entering into a Global Methane Pledge. One of the key pieces of the U.S. Methane Emissions Reduction Action Plan that was announced is the EPA’s proposed methane rules forGreenhouse Gas Reporting Rule (which governs GHG emissions by the oil and gas sector. In April 2021, the United States announced its commitment to reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by 50 to 52 percent from 2005 levels by 2030.sector). The EPA issued a proposed rule amending Subpart W in August 2023. Depending on how the Subpart OOOOc of the EPA’s final rule and the Subpart W of the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Rule are finalized, there is a potential for
significant impacts on calculation of the Company’s IRA methane fee. In May 2023, the EPA proposed revised new source performance standards and an emissions guideline for certain new, modified, reconstructed, and existing natural gas-fired electric generating units. If finalized, this reduction isrule could have an impact on the demand for natural gas from the U.S. power sector, which could have an adverse effect on the demand for the Company’s business. State programs regulating GHG emissions from power plants, such as the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI), can also have the effect on the Company of reducing demand for natural gas by power plants. RGGI was found, however, to be achieved,unconstitutional in Pennsylvania in November 2023, but this decision is being appealed. Virginia also withdrew from the RGGI program effective January 1, 2024, but as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the decision has not yet been challenged in court.
California enacted two climate-related disclosure laws called the Climate Corporate Data Accountability Act (CCDAA) and the Climate-Related Financial Risk Act (CRFRA) on October 7, 2023. These laws may apply to the Company couldif we are considered to be “doing business in California” under the CCDAA and the CRFRA. Under the CCDAA, we may be required to reduce itsquantify and disclose certain GHG emissions data in accordance with the GHG Protocol, a standard developed by the World Resources Institute and the World Business Council for Sustainable Development beginning in 2026 (with the reporting of 2025 emissions data). These reports must be independently audited by a third-party assurance provider. The CRFRA may require us to prepare and submit a biennial report in accord with the framework of the Final Report and Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures disclosing the company’s climate-related financial risk, and the measures it has adopted to reduce and adapt to climate-related financial risk, with the first report due on January 1, 2026. These financial risk reports must be made available to the public on our website by the applicable compliance dates. There are annual fees associated with both the CCDAA and the CRFRA as well. The CCDAA and the CRFRA may cause us to incur additional (and potentially accelerate) compliance and reporting costs, certain of which could be material, including related to monitoring, collecting, analyzing and reporting new metrics and implementing systems and procuring additional necessary attestation. As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the California Air Resources Board has not yet issued proposed regulations to implement these two climate disclosure laws. Similarly, on March 21, 2022, the SEC released proposed rule changes that would increaserequire new climate-related disclosure in SEC filings, including certain climate-related metrics and GHG emissions. The SEC proposal, which as of the Company’s costfiling of environmental compliance.
The U.S. Congress, along with federal and state agencies, has also considered other measures to reduce the emissions of GHGs. Legislation or regulation that imposes a carbon tax on carbon emissions or that restricts those emissions could increase the Company's cost of environmental compliance through the Company's incurrence of increased non-income taxes or by requiring
the Company to install new equipment to reduce emissions from larger facilities and/or, depending on any future legislation, purchase emission allowances. The effect of climate change legislation or regulation on the Company's business is currently uncertain.uncertain as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. If the Company incurs additional costs to comply with such legislation or regulations, it may not be able to pass on the higher costs to its customers or recover all the costs related to complying with such requirements and any such recovery may depend on events beyond the Company's control, including the outcome of future rate proceedings before the FERC or state regulatory agencies and the provisions of any final legislation or implementing regulations. The Company's future results of operations, cash flows or financial condition could be adversely affected if such costs are not recovered through regulated rates or otherwise passed on to its customers. Additionally, the Company's producer customers may also be affected by legislation or regulation, which may, directly or indirectly, adversely impact their ability and willingness to produce natural gas and accordingly affect such producers' financial health or reduce the volumes delivered to the Company and demand for its services. Climate change and GHG legislation or regulation could delay or otherwise negatively affect efforts to obtain and maintain permits and other regulatory approvals for existing and new facilities, impose additional monitoring and reporting requirements or adversely affect demand for the natural gas the Company gathers, transports and stores. The effect on the Company of any new legislative or regulatory measures will depend on the particular provisions that are ultimately adopted.
See also “"Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing the financing of non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting the pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies, and alternative forms of energy) and, as well as physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers'customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services."” under Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" inof this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Water Discharges. The federal Clean Water Act and analogous state laws impose restrictions and strict controls regarding the discharge of pollutants or dredged and fill material into federal and state waters as well as waters of the United States, including adjacent wetlands. The discharge of pollutants into regulated waters is prohibited, except in accordance with the terms of permits issued by the EPA, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (Army Corps) or an analogous state agency. In September 2015, new EPA and Army Corps rules defining the scope of the EPA's and the Army Corps' jurisdiction became effective (the 2015 Clean Water Rule), however, the 2015 Clean Water Rule was promptly challenged in courts and was enjoined by judicial action
in some states. Further, in October 2019 the EPA issued a rule repealing the 2015 Clean Water Rule and recodifying the preexisting regulations. In June 2020, new EPA and Army Corps regulations narrowing the regulatory scope of the Clean Water Act became effective (the 2020 Navigable Waters Protection Rule). Like the 2015 Clean Water Rule, the 2020 Navigable Water Protection Rule was promptly challenged in courts and has been enjoined by judicial action in at least one state. On December 7, 2021, the EPA and the Army Corps published a proposed rule that would reinstate the pre-2015 definition of waters of the United States, updated to reflect recent U.S. Supreme Court decisions.decisions through that date. On December 30, 2022, the EPA and the Army Corps announced the final revised rule, which took effect on March 20, 2023. On May 25, 2023, the U.S. Supreme Court issued its ruling in Sackett v. EPA, U.S. Supreme Court Docket No. 21-454, holding that portions of the existing rules defining “waters of the United States” were invalid, and announcing a new definition of “waters.” On August 29, 2023, the EPA and the Army Corps issued a revised final rule designed to conform their regulations to the Sackett decision (the Conforming Rule), and the Conforming Rule took effect immediately upon its publication on September 8, 2023. However, the Conforming Rule itself does not define certain language from the U.S. Supreme Court’s ruling, and could be expanded or face additional legal challenges in the future. To the extent that any future rules expand the scope of the Clean Water Act's jurisdiction, or to the extent individual states choose to define their jurisdiction to include, and impose requirements on, waters previously regulated by the federal agencies, the Company could face increased costs and delays with respect to obtaining permits for activities in jurisdictional and non-jurisdictional waters, including wetlands.
Spill prevention, control and countermeasure requirements of federal laws require appropriate containment berms and similar structures to help prevent the contamination of regulated waters in the event of a hydrocarbon spill, rupture or leak. In addition, the Clean Water Act and analogous state laws require individual permits or coverage under general permits for discharges of storm water runoff from certain types of facilities. Federal and state regulatory agencies can impose administrative, civil and criminal penalties for non-compliance with discharge permits or other requirements of the Clean Water Act and analogous state laws. The Company believes that compliance with existing permits and foreseeable new permit requirements will not have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to its shareholders.
National Environmental Policy Act. The construction of interstate natural gas transportation pipelines pursuant to the NGA requires authorization from the FERC. The FERC actions are subject to the National Environmental Policy Act of 1978, as amended (NEPA). NEPA requires federal agencies, such as the FERC, to evaluate major federal actions having the potential to significantly affect the environment. In the course of such evaluations, an agency will either prepare an environmental assessment that examines the potential direct, indirect and cumulative effects of a proposed project or, if necessary, a more detailed Environmental Impact Statement. Any proposed plans for future construction activities that require FERC authorization will be subject to the requirements of NEPA. This process has the potential to significantly delay or limit, and significantly increase the cost of, development of midstream infrastructure. In September 2020, new Council on Environmental Quality regulations intended to streamline the NEPA evaluation process went into effect. TheseThose rules have been challenged in courts, although initial efforts to enjoin enforcement of the rule were unsuccessful. On January 20, 2020, President Biden issued an
Executive Order requiring a review of certain federal regulations, and in response the Council on Environmental Quality initiated a two-phase process to review NEPA regulations. Phase 1 of that process resulted in new regulations taking effect in May 2022, partially reverting NEPA regulations to rules that were in effect at the end of the Obama administration. On July 31, 2023, the Council on Environmental Quality published proposed Phase 2 revisions to NEPA regulations, including revisions to bring the regulations into compliance with changes made to NEPA by the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023, to increase substantive obligations placed on federal agencies in NEPA process, require consideration of climate change consequences, and require consideration of environmental justice, among other changes. The comment period for the proposed Phase 2 rules ended on September 29, 2023; a final rule is expected to follow.
Endangered Species Act. The federal Endangered Species Act (ESA) restricts activities that may adversely affect endangered and threatened species or their habitats. Federal agencies are required to ensure that any action authorized, funded or carried out by them is not likely to jeopardize the continued existence of listed species or modify their critical habitat. While some of the Company's facilities are located in areas that are designated as habitats for endangered or threatened species, the Company is confident that it is in substantial compliance with the ESA. The federal designation of previously unprotected species as being
endangered or threatened, or the federal designation of previously unprotected areas as a critical habitat for such species, has caused and could in the future cause the Company to incur additional costs, resulted in and could in the future result in delays in construction of pipelines and facilities, or cause the Company to become subject to operating restrictions in areas where the species are known or presumed to exist. For example, on September 14, 2022, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) proposed to list the Tricolored Bat (Perimyotis subflavus) as an endangered species; the Tricolored Bat is located in 39 states including North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and West Virginia. As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the FWS has not finalized that proposal, but an endangered species listing of the Tricolored Bat could limit development activities, particularly tree clearing, in areas where the bat is known or presumed to be present, including areas where we operate. The FWS continues to receive hundreds of petitions to consider listing additional species as endangered or threatened and is being regularly sued or threatened with lawsuits to address these petitions. Some of these legal actions may result in the listing of species located in areas in which the Company operates. Throughout 2020, the United StatesU.S. Department of Interior narrowed the ESA regulations and their applicability. These regulations have been challenged in the courts.
Environmental Justice. The federal government has made advancing environmental justice a priority and has announced a number of new initiatives in the area. Some of those initiatives could have impacts on the business of oil and gas companies, although the ultimate formamount of the federal government’s approach to these issues is unknown and the impact to the oil and gas industry remainsimpacts remain uncertain. The Biden Administration announced a renewed commitment to environmental justice in itsa day one executive order, on climate changeExecutive Order 13990: Protecting Public Health and the environmentEnvironment and Restoring Science to Tackle the Climate Crisis, and followed up that action with an executive order establishing newExecutive Order 14008: Tackling the Climate Crisis at Home and Abroad, which further solidified the administration’s commitment to addressing climate change and advancing environmental justice. Further, in April 2023, the Biden Administration issued Executive Order 14096: Revitalizing Our Nation’s Commitment to Environmental Justice for All, which reinforced the administration’s whole-of-government approach to advancing environmental justice. Since the beginning of the Biden Administration, numerous federal agencies have announced initiatives to prioritize environmental justice advisory committees tasked with helpingas they fulfill their missions.
On May 5, 2022, the government devise new environmental justice policies. Since that time, the White House Environmental Justice Advisory Committee has released recommendations that include new spending priorities, development of environmental justice impact assessment techniques, and legal enforcement recommendations. TheU.S. Department of Justice and the EPA Office of Enforcement and Compliance Assurance have issued policy statements indicating that both agencies will seek to enhance prosecution of(DOJ) launched a comprehensive environmental justice crimesenforcement strategy designed to guide the DOJ’s work and ensure use of all available tools to seek out wayspromote environmental justice. The strategy provides a roadmap for using DOJ’s civil and criminal enforcement authorities to addressadvance environmental justice through prioritizing enforcement of environmental and civil rights violations in overburdened communities. On the legal system.same day, DOJ also launched the Office of Environmental Justice, which has the mission of protecting overburdened and underserved communities from the harm caused by environmental crimes, pollution and climate change. The office serves as a central hub for implementing DOJ’s comprehensive environmental justice enforcement strategy and engages with all department entities to carry out this task.
Further, on September 24, 2022, the EPA launched the Office of Environmental Justice and External Civil Rights. In addition to providing resources and technical assistance on civil rights and environmental justice, the Office of Environmental Justice and External Civil Rights enforces federal civil rights laws, including Title VI of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, which prohibits discrimination by federal funding recipients.
In addition, the FERC has also issued a number of statements indicating that it will attempt to addressincreased its focus on environmental justice issues more substantially throughin its processes and analyses. For example, in March 2023, the FERC convened the Roundtable on Environmental Justice and Equity in Infrastructure Permitting as part of its two-year Equity Action Plan to promote equity and remove barriers that underserved communities, including environmental justice communities, face in the context of the FERC’s processes and policies in five focus areas.
Equitrans Midstream is aware of these changes regarding environmental justice-related policy making. Itand enforcement and is unclearin the process of assessing whether and how these new policies will be implemented, andthey may affect the Company. Equitrans Midstream will continue to monitor new developments and assess whether and how they may affect the Company.
States are also in the process of reexamining environmental justice law and policy. Pennsylvania’s then governor signed anExecutive Order 2021-07 in October 2021. The executive order in October 2021 creatingpermanently created an Office of Environmental Justice within the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection. It is tasked with revising Pennsylvania’sProtection, formally established the existent Environmental Justice Advisory Board, and created an Environmental Justice Interagency Council. In September 2023, the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection’s interim final Environmental Justice Policy became effective after an extensive public comment period. The interim final policy was subject to a public comment period that ended November 30, 2023, indicating the policy may be amended further. The prior policy had been in effect since 2004. Under the interim final policy, applications for certain Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection permits in environmental justice policiesareas would be subject to specified enhanced public participation requirements, and examining ways to advancethe agency would prioritize inspections and enforcement in environmental justice issues.areas. In Virginia, the legislature enacted the Environmental Justice Act of 2020, which requires state agencies to examine the environmental justice impacts of their actions and creates a council to recommend new environmental justice policies. Ohio andIn May 2023, the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality released for public comment draft guidance entitled Environmental Justice in the Permitting Process, which provides guidance to agency personnel on a permit evaluation process for permitting actions in environmental justice communities. Finalization of the guidance document remains pending. The West Virginia appearDepartment of Environmental Protection released draft Public Engagement Guidelines, which set forth guidance for agency public engagement efforts, for public comment in September 2023. The guidelines are pending finalization. Ohio appears to be monitoring developments at the EPA.EPA and other federal agencies. Many of the key issues before the states appear to be focused on enhancing public participation in permitting and other project development-related decisions. State agencies also appear to be considering new approaches to environmental justice in permitting decisions, potentially denying permits or other authorizations on environmental justice grounds. Equitrans MidstreamThe Company will continue to monitor state legal and regulatory developments in this area and respond as appropriate.
The majority of environmental justice litigation matters appear to be focused on whether state or federal agencies with permitting or other decision-making responsibility have adequately considered environmental justice issues during the decision-making process. Many advocacy organizations purportThese kinds of litigation, even if unsuccessful, present risks to raise environmental justice issues in connection with permitting legal challenges.the underlying project’s timeline and budget. Equitrans Midstream will continue to monitor these litigation-related developments.
Equitrans Midstream has a number of policies in place that addresstakes environmental justice issues. Oneissues seriously and is committed to supporting the communities in which the Company operates. In July 2022, the Company published its Environmental Justice Policy that reaffirms our commitment to providing reliable energy infrastructure in a safe and responsible manner while treating all people fairly. Additionally, one of the Company’s pillars of sustainability is stakeholder engagement, including engagement with the communities where Equitrans Midstream operates. In 2021,For example, Equitrans Midstream published itshas adopted a Stakeholder Engagement and Community Investment Policy, which emphasizes early and consistent community engagement throughout project development and operation, and it specifically prioritizes environmental justice and environmental stewardship. The Company has also adopted a Human Rights Policy committing the Company to safeguarding dignity and respect for all people throughout the Company’s value chain, including through community engagement and the prevention of discrimination.
Equitrans Midstream is in the process of developing a comprehensive environmental justice policy. The Company will continue that work, mindful of new developments at the federal, state, and local levels.
Seasonality
Weather affects natural gas demand for power generation and heating purposes. Peak demand for natural gas typically occurs during the winter months as a result of the heating load.
Human Capital Management
To ensure that we are well positioned to provide innovative solutions and reliable energy infrastructure services in a safe, efficient, and responsible manner and in a changing economic landscape focused on long-term, sustainable operations, the
Company seeks to employ a team of highly accomplished people who are dedicated to the Company’s success and to foster an engaging workplace environment that provides for competitive pay and benefits, attractive career development opportunities, and a collaborative, respectful culture.
As of December 31, 2021,2023, the Company had 766773 employees. During 2021,2023, the Company's overall turnover was just over6% (with more than 5% (with approximately 4.5% being voluntary turnover) of the total employee population.
Company Culture. The Company’s five core values of Safety, Integrity, Collaboration, Transparency, and Excellence shape its culture and identity and provide the framework for employee conduct and the Company’s relationships with its stakeholders.
The Company continues to utilize a cross-functional Culture Champions Group which solicits employee feedback on ways to further enhance corporate culture. In 2021, the Company completed its second anonymous culture survey and is in the process
31
Safety. Above all else, safety is the Company's main priority – this includes the safety of its employees, contractors, and communities – always. The Company is committed to maintaining a strong safety culture and continuing to identify and mitigate safety risks. The Health, Safety, SecuritySustainability and Environmental Committee of the Company's Board of Directors (Board) provides oversight for the Company's safety initiatives. The Company tracks numerous safety-related metrics to evaluate its safety performance and has incorporated safety metrics into the Company's annual incentive plan.
Diversity and Inclusion. The Company believes that diversity of thought and perspective and a team-based approach are essential to its continued success and the Company is committed, through its Inclusion Program and other initiatives, to continuing to build a diverse, inclusive, respectful, and safe workplace.During 2021,2023, the Company hosted, and more than 700300 employees attended, eight guest speakingfive educational sessions on inclusion topics; becametopics, including a Certified Age-Friendly Employer throughtraining on disability awareness and cognitive bias; implemented an automated resume redaction process for initial resume reviews during recruitment; promoted and obtained more than 50% employee participation in an Equitrans DEI Badge program whereby employees completed inclusion-focused courses to earn one of three badge levels (advocate, ambassador, and champion) to display in their email signatures and on LinkedIn; continued the Age-Friendly Institute and a Corporate Champion of the Wounded Warrior Project; signed the CEO Pledge through the CEO Actionannual mentor program for Diversity and Inclusion Coalition to publicly acknowledge the importance of diversity and inclusion; led a Pronouns Matter Campaign to encouragehigh potential underrepresented employees to select their preferred pronouns; provided a platform for employees to review inclusion-related contentbased on a bi-monthly basis; facilitated Unconscious Bias training for all employees;successful pilot program in 2022; and publishedcontinued to publish an Inclusion Scorecard to capture relevant employee demographics for discussion with leadership and for all employees to review.
The Company also partners with several diverse organizations to broaden and extend its recruitment efforts, including HBCUConnect.com (Historically Black Colleges and Universities Connect), DiversityJobs.com, RecruitMilitary.com and RetirementJobs.com.GettingHired.com (representing individuals with disabilities).
Total Rewards. The Company believes its employees are critical to its success and its total rewards and benefits are structured to attract and retain a talented and engaged workforce. These benefits include comprehensive health insurance for full- and part-time employees; a robust wellness program; annual flu immunizations and paid time off for COVID-19 vaccinations;immunizations; access to an Employee Assistance Program; tuition reimbursement; adoption assistance and paid new parent leave; paid time off for holidays, vacation, bereavement, jury duty, military and volunteer time; paid short- and long-term disability, life insurance, and business travel insurance; medical spending accounts for eligible retirees; competitive base salaries and an annual incentive plan and long-term incentive opportunities; and a robust retirement plan with generous company matching and non-elective contributions. In addition, the Company offers flexible work arrangements based on job duties, which the Company believes will increasingly enablerecognizes is enabling it to compete for talent on a broad geographic basis.
Talent Development. The Company believes it has a robust talent and leadership development framework. The Management DevelopmentHuman Capital and Compensation Committee of the Board overseesreviews and discusses with management the development program forhuman capital management matters relevant to the Company's executive officersCompany’s work force, including talent attraction and other key management personnel.retention. The Company provides technical, behavioral, and leadership training to multiple levels of Company leadersindividual contributors, managers, and managers,leaders, as well as customized, executive-level assessment, development, and developmentcoaching programs for senior leaders. Employees at all levels within the Company are encouraged to participate in relevant developmental opportunities through Company partnerships with external learning organizations and all employees are encouraged to complete an annual development plan.
Culture and Inclusion Council. The Company continues to utilize a cross-functional Culture and Inclusion Council (CIC) which solicits employee feedback on ways to further enhance corporate culture. In 2023, as part of its One Team philosophy, the Company emphasized internal relationships and connectedness in a hybrid person-centric work environment. The CIC hosted four regionally based networking opportunities for employees in Pennsylvania, Texas, and Florida; six Coffee Talks, which are virtual informational sessions on various Company or wellbeing topics; and seven Lunch with Leaders opportunities in which members of the leadership team take small groups of employees to lunch. The Company also continued to promote a flexible work environment for all employees, regardless of how or from where they work. This includes flexible temporary schedules when family or personal matters arise, and various permanent work schedule options based on the nature of the job and an employee’s personal preference. We encourage all employees, both field and non-field workers, to utilize flexibility opportunities as needed. As part of its person-centric work environment, the Company believes that nurturing relationships, supporting employees’ individual needs, and connecting with one another helps to foster a One Team environment to further drive efficiency and promote a stronger corporate culture long-term.
Additional Information. The Company publishes an annual Corporate Sustainability Report (CSR), which contains the most recent available data on a variety of topics, including those discussed above under the heading "Human Capital Management." Copies of the 20212023 CSR are available free of charge on the Company’s website (www.equitransmidstream.com) by selecting the "Sustainability" tab on the main page and then the "Sustainability Reporting" link. Information included in the CSR or our website is not incorporated into this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Availability of Reports
The Company makes certain filings with the SEC, including its Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and all amendments and exhibits to those reports, available free of charge through its website, www.equitransmidstream.com, as soon as reasonably practicable after they are filed with or furnished to the SEC. Reports filed with, or furnished to, the SEC are also available on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
In addition to the other information contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the following risk factors (and related summary) should be considered in evaluating our business and future prospects. The following discussion of risk factors, including the summary, contains forward-looking statements. The summary below is not exhaustive and is qualified by reference to the full set of risk factors set forth in this section.
The risk factors may be important for understanding any statement in this Annual Report on Form 10-K or elsewhere. The following information, including the full set of risk factors set forth in this section, should be read in conjunction with "Item 7. Management’sManagement's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and the financial statements and accompanying notes included in "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."Data" in Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Note that additional risks not presently known to us or that are currently considered immaterial as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K may also have a negative impact on our business and operations. If any of the events or circumstances described below actually occurs, our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends could suffer and the trading price of our common stock could decline.
Because of the following factors, as well as other variables affecting our results of operations, past performance may not be a reliable indicator of future performance, and historical trends should not be used to anticipate results or trends in future periods.
Summary of Risk Factors
The following is a summary of the most significant risks relating to our business activities that we have identified. If any of these risks actually occur, our business could be materially adversely affected. For a more complete understanding of our material risk factors, this summary should be read in conjunction with the detailed description of our risk factors which follows this section.
Risks Related to Our Operations
•We depend on EQT forgenerate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT and therefore are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT's drilling or completion activity or a greater focus of such activity on acreage not dedicated to us could adversely affect us.
•Decreases in production of natural gas inExpanding our areas of operation, and the lack of diversification of ourbusiness by constructing new midstream assets and geographic locations, could further adversely affect us.subjects us to risk.
•The regulatory approval process, including judicial review, for the construction of new midstreamtransmission assets is very challenging and has significantly impacted, and in the future could impact, our and the MVP Joint Venture's ability to obtain or maintain all approvals necessary to complete certain projects on timein a timely manner or at all.all or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects. If we do not complete expansionorganic growth projects, realize revenue generating volume growth on our systems, and/or identify and complete inorganic growth opportunities, our future growth may be limited. Further, there is no assurance as to the outcome of our Board of Directors' ongoing strategic process with respect to the Company.
•ReviewsDecreases or a lack of growth in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, and the lack of diversification of our assets, products and geographic locations, could further adversely affect us.
•Impairments of our assets, including property, plant, and equipment, intangible assets, goodwill intangible and other long-lived assets andour equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture, previously have resultedreduced, and if incurred in andthe future could result in significant impairment charges.reduce, our earnings.
•Cyberattacks aimed at us and/or third parties on which we rely, as well as any noncompliance by us or our third parties with applicable laws and regulations governing cybersecurity and/or data privacy, could materially adversely affect us.
•Our subsidiaries' significant indebtedness, and any future indebtedness, as well as the restrictions under our subsidiaries' debt agreements, could adversely affect us.
•We or our joint ventures may be unable to obtain financing on satisfactory terms and financing transactions may increase our financial leverage or cause dilution to our shareholders. A further downgrade of EQM’s credit ratings could impact our liquidity, access to capital, and costs of doing business.
•Increasing scrutiny and changing stakeholder expectations for ESG matters and sustainability practices may adversely affect us.
•Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks and physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.
•We face and will continue to face opposition to and negative public perception regarding the development of our expansion projects and the operation of our pipelines and facilities from various groups.
•Our subsidiaries' significant indebtedness, and any future indebtedness, as well as the restrictions under our subsidiaries' debt agreements, could adversely affect us.
•We may be unable to obtain financing on satisfactory terms and any financing transactions may increase our financial leverage or cause dilution to our shareholders. A further downgrade of EQM’s credit ratings, including in connection with the MVP project or customer credit ratings changes, could impact our liquidity, access to capital, and costs of doing business.
•Increased competition from other companies that provide gathering, transmission and storage, and water services, or from alternative fuel or energy sources, could have a negative impact on customer throughput and the demand for our services and could limit our ability to grow.
•We are exposed to the credit risk of our counterparties in the ordinary course of our business.
•We may not be able to realize the expected investment return under certain of our existing contracts, or renew or replace expiring contracts at favorable rates, on a long-term basis or at all.
•The ongoing outbreakall, and we have in the past been and may become subject to disagreements with counterparties on the interpretation of COVID-19 and its variant strains (or anyexisting or future pandemic) could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.contractual terms.
•Third-party pipelines and other facilities interconnected to our pipelines and facilities may become unavailable to transport or process natural gas.gas, or may not accept deliveries of natural gas from us or our joint ventures.
•Joint ventures that we have entered into (or may in the future enter into) might restrict our operational and corporate flexibility and divert our management’s time and our resources. We do not exercise control over our joint ventures or joint venture partners, and it may be difficult or impossible for us to cause these joint ventures or partners to take actions that we believe would be in our or the joint venture’s best interests.
•Acquisitions that we may makeStrategic transactions could reduce, rather than increase, our results of operations and liquidity, and adversely affect our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
•Expanding our business by constructing new midstream assets subjects us to risk, and weWe do not insure against all potential losses and could be seriously harmed by unexpected liabilities.
•Significant portions of our pipeline systems have been in service for several decades, and we are subject to numerous hazards, regulatory compliance obligations and operational risks.
•We do not own all of the land on which our assets are located, which could disrupt our operations and future development.
•The loss or disengagement of key personnel could adversely affect our ability to execute our plans.
•Our exposure to direct commodity price risk may increase in the future.
Legal and Regulatory Risk
•Our natural gas gathering, transmission and storage services are subject to extensive regulation. Changes in or additional regulatory measures, and related litigation, could have a material adverse effect on us.
•We may incur significant costs and liabilities as a result of adverse eventsperformance of our pipeline integrity management programs and increased maintenance or repair expenses and downtime or as a result ofcompliance with increasingly stringent pipeline safety regulation.regulations.
Risks Related to an Investment in Us
•For the taxable years prior to January 1, 2021, the tax treatment of EQM depended on its status as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes. If the IRS were to treat EQM as a corporation or if EQM becomes subject to additional amounts of entity-level taxation, it would reduce the amount of cash we have available to pay dividends to our shareholders.
•We face certain risks related to the tax treatment of EQM and any potential audit adjustment to EQM's income tax returns for tax years beginning after 2017.
•Our stock price has fluctuated and may further fluctuate significantly and yourour shareholders’ percentage of ownership in us may be diluted in the future.
•We cannot guarantee the timing, amount or payment of dividends on our common stock.
•Anti-takeover provisions contained in our governing documents and Pennsylvania law could impair an attempt to acquire us and our exclusive forum provision in our governing documents could discourage lawsuits against us and our directors and officers.
•Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares issued as part of the EQM Merger and the related Restructuring present a number of risks to current and future holders of our common stock.
Risks Related to the Separation
•We continue to face risks related to the Separation, including among others, those related to U.S. federal income taxes, contingent liabilities allocated to us following the Separation, EQT's obligations under certain Separation-related agreements and potential indemnification liabilities.
Risk Factors
Risks Related to Our Operations
We depend on EQT forgenerate a substantial majority of our revenues.revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT's drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results.
Historically, we have provided EQT a substantial percentage of its natural gas gathering, transmission and water services. EQT accounted for approximately 59%61% of our revenues for the year ended December 31, 2021.2023. We expect to continue to derive a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT for the foreseeable future, including as a result of the EQT Global GGA.future.
Given the scope of our business relationship with EQT, any event, whether in our areas of operations or otherwise, that adversely affects EQT'sEQT’s production (or the amount of its production which flows to our systems), financial condition, leverage, results of operations or cash flows may adversely affect us. Accordingly, we are subject to the business risks of EQT, including the following:
•prevailing and projected commodity prices, primarily natural gas and natural gas liquids (NGLs);
•natural gas price volatility or a sustained period of low commodity prices, and EQT’s utilization of financial hedges, which may have an adverse effect on, as applicable, EQT’s drilling operations, revenue, profitability, future rate of growth, creditworthiness and liquidity;
•decisions of EQT’s management in respect of curtailingto reduce, slow or maintain at relatively flat levels EQT’s natural gas production choke management, timingor to prioritize production away from our assets or obligations to build, which such decisions have been and may in the future be influenced by corporate capital allocation strategies, regional takeaway constraints, commodity prices, and/or other factors (as applicable); such decisions have in certain instances in the past directly and adversely impacted demand for our services and aspects of turning wellsour business, including, in line,combination with MVP project delays, the value potentially realizable under certain of our contracts, and rig and completion activity;
•a reduction in or slowing of EQT’s anticipated drilling and production schedule, which wouldfuture such decisions could (including, without limitation, as gathering fee declines take effect under the EQT Global GGA) directly and adversely impact demand forus and our services;
•the proximity, capacity, costbusiness, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and availability of gathering and transportation facilities, and other factors that result in differentials to benchmark prices;
•the availability and cost of capital to fund EQT’s operations and any changes in EQT’s credit ratings and the effects of EQT’s credit support obligations on such availability;
•the costs of producing natural gas and the availability and costs of drilling rigs and crews and other equipment;
•infrastructure capacity constraints and interruptions;
•geologic considerations;
•risks associated with the operation of EQT’s wells and facilities, including potential environmental liabilities;
•EQT’s ability to identify exploration, development and production opportunities based on market conditions;
•uncertainties inherent in projecting future rates of production, levels of reserves, and demand for natural gas, NGLs and oil;pay dividends to our shareholders;
•EQT’s ability to develop additional reserves that are economically recoverable, to optimize existing well production and to sustain production, including by use of large-scale, sequential, highly choreographed drilling and hydraulic fracturing, including combo and return-to-pad development;
•prevailing and projected commodity prices, primarily natural gas and natural gas liquids (NGLs), including their effect on EQT’s abilityhedge positions;
•natural gas price volatility or intentionperiods of low commodity prices, which may have an adverse effect on EQT’s drilling operations, revenue, profitability, future rate of growth, creditworthiness and liquidity;
•the proximity, capacity, cost and availability of gathering and transportation facilities, and other factors that result in differentials to develop additional reserves not covered by our assets or obligations to build;benchmark prices;
•the costs of producing natural gas, including the availability and costs of drilling rigs and crews and other equipment;
•geologic and reservoir risks and considerations;
•risks associated with the operation of EQT’s wells and facilities, including potential environmental liabilities;
•EQT’s ability to achieve anticipated efficiencies associated withidentify future exploration, development and production opportunities and midstream alternatives;
•uncertainties inherent in projecting future rates of production, levels of reserves, and demand for natural gas, NGLs and oil;
•EQT’s execution of its strategic plan execute onand additional strategic transactions, if any, and continue to execute on its de-levering plan;any;
•adverse effects of governmental and environmental regulation, including the availability of drilling permits, the regulation of hydraulic fracturing (including limitations in respect of engaging in hydraulic fracturing in specific areas), the potential removal of certain federal income tax deductions with respect to natural gas and oil exploration and development or additional state taxes on natural gas extraction, and changes in tax laws, and negative public perception, whether as a result of stakeholder focus on ESG and sustainability matters or otherwise, regarding EQT’s operations;
•the loss or disengagement of key personnel and/or the effectiveness of their replacements;
•EQT’s ability to achieve its ESG and sustainability targets; and
•risks associated with cybersecurity, environmental activists and other threats.
EQT may reduce its capital spending in the future based on various factors, including corporate capital allocation strategies, regional takeaway constraints, commodity prices or other factors. Unless we are successful in attracting significant new customers, our ability to maintain or increase the capacity subscribed and volumes transported or gathered under service arrangements on our gathering, transmission and storage and water systems will depend on receiving consistent or increasing commitments from EQT. While EQT has dedicated a significant amount of its acreage to us and executed long-term contracts with substantial firm reservation and MVCs on our systems, it may determine in the future that drilling in areas outside of our current areas of operations is strategically more attractive to it, and other than the firm reservations and MVCs, it is under no contractual obligation to maintain its production dedicated to us. Moreover, as disclosed on December 13, 2021, EQT’s corporate capital allocation strategy continues to focus on capital efficiency, reducing indebtedness to achieve investment grade metrics, returning capital to its shareholders and free cash flow generation as opposed to volume growth. A substantial reduction in the capacity subscribed or volumes transported or gathered on our systems by EQT (or sustained lack of growth in respect of such volumes) could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
As discussed under the heading "“Decreases or a lack of growth in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, whether as a result of regional takeaway constraints, producer corporate capital allocation strategies, lower regional natural gas prices, regional takeaway constraints,natural well decline, and/or other factors, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, our business and operating results and reduce our cash available to pay cash dividends to our shareholders." ”in Part I, "Item“Item 1A. Risk Factors"Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, there are a number of factors that could cause EQT and other producers to elect to reduce or maintain then-current levels of drilling activity or curtail production. Any sustained reductions in development or production activity in our areas of operation, particularly from EQT, or maintenance levels of production could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Additionally,Expanding our business by constructing new midstream assets subjects us to construction, business, economic, competitive, regulatory, judicial, environmental, political and legal uncertainties that are beyond our control.
Our growth strategy includes organic optimization of our existing assets and greenfield growth projects. The development and construction by us or our joint ventures of pipeline and water infrastructure and storage facilities and the executionoptimization of such assets involve numerous construction, business, economic, competitive, regulatory, judicial, environmental, political and legal uncertainties that are beyond our control, require the expenditure of significant amounts of capital and expose us to risks. Those risks include, but are not limited to: (i) physical construction conditions, such as topographical, or unknown or unanticipated geological, conditions and impediments; (ii) construction site access logistics; (iii) crew availability and productivity and ability to adhere to construction workforce drawdown plans; (iv) adverse weather conditions; (v) project opposition, including delays caused by landowners, advocacy groups or activists opposed to our projects and/or the natural gas industry through lawsuits or intervention in regulatory proceedings; (vi) environmental protocols and evolving regulatory or legal requirements and related impacts therefrom, including additional costs of compliance; (vii) the application of time of year or other regulatory restrictions affecting construction, (viii) failure to meet customer contractual requirements; (ix) environmental hazards; (x) vandalism; (xi) the lack of available skilled labor, equipment and materials (or escalating costs in respect thereof, including as a result of inflation); (xii) issues regarding availability of or access to connecting infrastructure; and (xiii) the inability to obtain necessary rights-of-way or approvals and permits from regulatory agencies on a timely basis or at all (and maintain such rights-of-way, approvals and permits once obtained, including by reason of judicial hostility or activism). Risks inherent in the construction of these types of projects, such as unanticipated geological conditions, challenging terrain in certain of our construction areas and severe or continuous adverse weather conditions, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, project timing, completion and cost, as well as increase the risk of loss of human life, personal injuries, significant damage to property or environmental pollution. Most notably, certain of these risks have been realized in the construction of the EQT Global GGA was based upon assumptions,MVP project, including regarding EQT’s forecasted drillingconstruction-related risks and production levelsadverse weather conditions, and volumes on our system, that our management believed appropriate atsuch risks or other risks may be realized in the time of execution. If anyfuture which may further adversely affect the timing and/or cost of the assumptions failMVP project.
Given such risks and uncertainties, our projects or those of our joint ventures may not be completed on schedule, within budgeted cost or at all. As a further example, public participation, including by pipeline infrastructure opponents, in the review and permitting process of projects, through litigation or otherwise, has previously introduced, and in the future can introduce, uncertainty and adversely affect project timing, completion and cost. See also “The regulatory approval process for the construction of new transmission assets is very challenging, and, as demonstrated with the MVP pipeline, has resulted in significantly increased costs and delayed targeted in-service dates, and decisions by regulatory and/or judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings relevant to the development of midstream assets, particularly any litigation instituted in the Fourth Circuit, such as regarding the MVP Southgate project and/or expansions or extensions of the MVP, are likely to impact our or the MVP Joint Venture's ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvals and authorizations, including as may be realizednecessary to complete certain projects in a timely manner or actual results differat all, or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects.” in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Further, civil protests regarding environmental justice and social issues or challenges in project permitting processes related to such issues, including proposed construction and location of infrastructure associated with fossil fuels, poses an increased risk and may lead to increased litigation, legislative and regulatory initiatives and review at federal, state, tribal and local levels of government or permitting delays that can prevent or delay the construction of such infrastructure and realization of associated revenues.
Additionally, construction expenditures on projects generally occur over an extended period, yet we will not receive revenues from, those assumptions,or realize any material increases in cash flow as has occurreda result of, the relevant project until it is placed into service. Moreover, our cash flow from a project may be delayed or may not meet our expectations, including as a result of taxes which could potentially be calculated based on excess expenditures, inclusive of maintenance, incurred during extended court-driven construction delays. Furthermore, we may construct facilities to capture anticipated future growth in production and/or demand in a region in which such growth does not materialize or is delayed beyond our expectations. As a result, new facilities may not be able to attract enough throughput to achieve our expected investment return. Such issues in respect of for example, the targeted full in-service date for the MVP, our ability to fully achieve the benefits we believed associated with the EQT Global GGA at the timeconstruction of its execution, as well asmidstream assets could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders, may be adversely affected. Further, if EQT's volumetric volumes on our systems do not meet levels we assumed atshareholders.
The regulatory approval process for the timeconstruction of executing the EQT Global GGAnew transmission assets is very challenging, and, during the period of such lower volumes, gathering fee reductions take effect in connectionas demonstrated with the fullMVP pipeline, has resulted in significantly increased costs and delayed targeted in-service datedates, and decisions by regulatory and/or judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings relevant to the development of midstream assets, particularly any litigation instituted in the Fourth Circuit, such as regarding the MVP Southgate project and/or expansions or extensions of the MVP, are likely to impact our or the MVP Joint Venture's ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvals and authorizations, including as may be necessary to complete certain projects in a timely manner or at all, or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects.
Certain of our projects require regulatory approval from federal, state and/or local authorities prior to and/or in the course of construction, including any extensions from, expansions of or additions to our and the MVP Joint Venture’s gathering, transmission and storage systems, as applicable. The approval process for certain projects has become increasingly slower and more difficult, due in part to federal, state and local concerns related to exploration and production, transmission and gathering activities and associated environmental impacts, and the increasingly negative public perception regarding, and opposition to, the oil and gas industry, including major pipeline projects like the MVP and MVP Southgate. Further, regulatory approvals and authorizations, even when obtained, have increasingly been subject to judicial challenge by activists requesting that issued approvals and authorizations be stayed and vacated.
Accordingly, authorizations needed for our or the MVP Joint Venture’s projects, including any expansion of the MVP project and the MVP Southgate project or other extensions, may not be granted or, if granted, such authorizations may include burdensome or expensive conditions or may later be stayed or revoked or vacated, as was repeatedly the case with the construction of the MVP project, particularly in respect of litigation in the Fourth Circuit. Significant delays in the regulatory approval process for projects, as well as stays and losses of critical authorizations and permits, should they be experienced, have the potential to significantly increase costs, delay targeted in-service dates and/or affect operations for projects (among other adverse effects), as has happened with the MVP and the originally contemplated MVP Southgate projects and could occur in the future in the case of authorizations required underfor our or the EQT Global GGA,MVP Joint Venture’s current or future projects, including in respect of developing expansions or extensions, such as expansion of the MVP project and the MVP Southgate project.
Any such adverse developments and uncertainties could adversely affect our ability, and/or, as applicable, the ability for the MVP Joint Venture and its owners, including us, to achieve expected investment returns, adversely affect our willingness or ability and/or that of our joint venture partners to continue to pursue projects, and/or cause impairments, including, as has occurred in the past, to our equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture.
We have experienced and may further experience increased opposition with respect to our and the MVP Joint Venture’s projects from activists in the form of lawsuits, intervention in regulatory proceedings and otherwise, which in the past resulted in adverse impacts to our business, financial condition, results of operations and liquidity. In particular, opponents were successful in past challenges with respect to the MVP project and two challenges with respect to MVP project authorizations remains outstanding as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K (see Part I, “Item 3. Legal Proceedings — Challenges to FERC Certificate, D.C. Circuit” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K). Opposition is ongoing regarding the MVP Southgate project and is expected for future projects, including any expansions of the MVP. If ongoing or future challenges were successful, it could result in significant, adverse impacts to our business, financial condition, results of operations and liquidity. Such opposition has made it increasingly difficult to complete projects and place them in service and, following any in-service, may also affect operations or affect extensions and/or expansions of projects. Further, such opposition and/or adverse court rulings and regulatory determinations may have the effect of increasing the timeframe on necessary agency action to address actual or perceived concerns in prior adverse court rulings, or may have the effect of increasing the risk that at a future point joint venture partners may elect not to continue to pursue or fund a project, which could, absent additional project sponsors, significantly imperil the ability to complete the project. See “We have entered into joint ventures, and may in the future enter into additional or modify existing joint ventures, that might restrict our operational and corporate flexibility and divert our management’s time and our resources. In addition, we exercise no control over joint venture partners and it may be difficult or impossible for us to cause these joint ventures or partners to take actions that we believe would be in our or the joint venture’s best interests and these joint ventures are subject to many of the same risks to which we are subject.”in Part I,
"Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Challenges to our projects have adversely affected and could adversely affect our business (including by increasing the possibility of investor activism), financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders may be adversely affected. See “EQT Global GGA” in Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.shareholders.
Decreases or a lack of growth in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, whether as a result of regional takeaway constraints, producer corporate capital allocation strategies, lower regional natural gas prices, regional takeaway constraints,natural well decline, and/or other factors, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, our business and operating results and reduce our cash available to pay cash dividends to our shareholders.shareholders.
Our business is dependent on continued natural gas production and the availability and development of reserves in our areas of operationoperation. Periods of higher natural gas prices have not caused our largest customers to materially increase their production forecasts. At various times our customers have previously announced, and may in the future announce, lower, flat or modest increases to production and development plansforecasts based on various factors, which could include (and have in the past included) regional takeaway capacity limitations (including without limitation the lack of completion of MVP), natural gas prices, access to capital, investor expectations regarding free cash flow, a desire to reduce or refinance leverage or other factors. See, for example, “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT's drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results.” in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Such decisions by our customers are impacted by various factors, including pricesaffect production levels and, accordingly, demand for natural gasour services and NGLs, which fluctuate,therefore our results of operations. Additionally, regional takeaway constraints, corporate capital allocation strategies or lower regional natural gas prices have caused and regional takeaway constraints.could cause producers to determine in the future that drilling activities in areas outside of our current areas of operation are strategically more attractive to them. Further reduction, or continued lack of growth, in the natural gas volumes supplied by our producer customers could limit our ability to grow, reduce throughput on our systems and adversely impact our business, including our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Prices for natural gas and NGLs, including regional basis differentials, have previously adversely affected, and may in the future adversely affect, the timing of development of additional reserves and production that is accessible by our pipeline and storage assets, which also negatively affects our water services business, and the creditworthiness of our customers. Lower natural gas prices, particularly in the Appalachian region, have in the past caused, and may in the future cause, certain producers, including certain of our customers, to determine to reduce or hold generally steady their rig count (and thereby delay or not increase production), delay turning wells in line, temporarily shut in portions of their production or otherwise take actions to slow production growth and/or maintain or reduce production, which when effected by our producer customers reduces the demand for, and usage of, our services. For instance, temporary production curtailments effected in 2020 by EQT and certain other of our customershave previously resulted in a decrease in our volumetric-based fee revenues for portions of 2020.revenues. An extended period of low natural gas prices and/or instability in natural gas prices in future periods, especially in the Appalachian region, or other factors could cause EQT or other producers to take similar actionscurtail production in the future, which could have a significant negative effect on the demand for our services, our volumetric-based fee revenue, and therefore our results of operations.
Additionally, although natural gas prices have increased from 2020 lows as of the filing date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, higher natural gas prices have not caused our largest customers to increase their production forecasts and, even if natural gas prices remain elevated, our customers may announce in the future lower, flat or modest increases to production forecasts based on various factors, which could include regional takeaway capacity limitations, access to capital, investor expectations regarding free cash flow, a desire to reduce or refinance leverage or other factors. See, for example, “We depend on EQT for a substantial majority of our revenues. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT’s drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) could adversely affect our business and operating results.” in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Such decisions by our customers affect production levels and, accordingly, demand for our services and therefore our results of operations. Additionally, lower regional natural gas prices (including regionally), corporate capital allocation strategies or regional takeaway constraints could cause producers to determine in the future that drilling activities in areas outside of our current areas of operation are strategically more attractive to them. Further reduction, or continued lack of growth, in the natural gas volumes supplied by our producer customers could result in reduced throughput on our systems and adversely impact our business, including our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Accordingly, maintainingMaintaining or increasing the contracted capacity or the volume of natural gas not subject to MVCs gathered, transported and stored on our systems and cash flows associated therewith is substantially dependent on our customers continually accessing additional reserves of natural gas in or accessible to our current areas of operations. For example, while EQT has dedicated production from a substantial portion of its leased properties to us, we have no control over the level of drilling activity in our areas of operation, the amount of reserves associated with wells connected to our gathering and transmission systems or the rate at which production from a well naturally declines over time. EQT and other producers may not develop the acreage they have dedicated to us for a variety of reasons, including, among other things, the availability and cost of capital, corporate capital allocation policies, producers’ focus on generating free cash flow and/or de-levering, prevailing and projected energy prices, hedging strategies and environmental or other governmental regulations. Our ability to obtain non-dedicated sources of natural gas is affected by the level of successful drilling activity near our systems and our ability to compete for volumes from successful new wells, and most development areas in our areas of operation are already dedicated to us or one of our competitors.
In addition, the amount of natural gas reserves underlying wells may also be less than anticipated, and the rate at which production from these reserves declines may be greater than anticipated. We do not obtain independent evaluations of natural gas reserves connected to our systems. Accordingly, we do not have independent estimates of total reserves connected to our systems or the anticipated life of such reserves. If the total reserves or estimated life of the reserves connected to our systems are less than we anticipate,anticipated based upon publicly available data provided by our producer customers, or the timeline for the development of reserves is longer than we anticipate, and we are unable to secure additional sources of natural gas, there could be a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
If new supplies of natural gas are not obtained to replace the natural decline in volumes from existing supply basins in our areas of operation, the overall volume of natural gas gathered, transported and stored on our systems would decline, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
The regulatory approval process for the construction of new midstream assets is very challenging, has significantly increased costs and delayed targeted in-service dates, and decisions by regulatory and judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings are likely to impact our or the MVP Joint Venture’s ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvals and authorizations necessary to complete certain projects on the targeted time frame or at all or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects.
Certain of our projects require regulatory approval from federal, state and/or local authorities prior to and/or in the course of construction, including any extensions from, expansions of or additions to our and the MVP Joint Venture’s gathering, transmission and storage systems, as applicable. The approval process for certain projects has become increasingly slower and more difficult, due in part to federal, state and local concerns related to exploration and production, transmission and gathering activities and associated environmental impacts, and the increasingly negative public perception regarding the oil and gas industry, including major pipeline projects like the MVP and MVP Southgate. Further, regulatory approvals and authorizations, even when obtained, have increasingly been subject to judicial challenge by activists requesting that issued approvals and authorizations be stayed and vacated.
Accordingly, authorizations needed for our projects, including the MVP and MVP Southgate projects, may not be granted or, if granted, such authorizations may include burdensome or expensive conditions or may later be stayed or revoked or vacated, as has been the case with certain authorizations in the past, including, most recently, in January and February 2022 with respect to certain approvals for the MVP project that the Fourth Circuit vacated.
In addition, significant delays in the regulatory approval process for projects, as well as stays and losses of critical authorizations and permits, including for the MVP and MVP Southgate projects, have significantly increased costs and delayed the targeted in-service dates for the projects, and further delays may cause similar adverse effects. Significant delays, such as that caused by the vacatur in January and February 2022 of certain approvals for the MVP project by the Fourth Circuit, and cost increases in turn could adversely affect our ability, and, in the case of the MVP and MVP Southgate projects, the ability for the MVP Joint Venture and its owners, including us, to achieve expected investment returns, adversely affect our willingness or ability and/or thatImpairments of our joint venture partners to continue to pursue projects, and/or further cause other-than-temporary declines in value to the Company's equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture. The MVPassets, including property, plant, and MVP Southgate projects in particular are subject to several agency actionsequipment, intangible assets, goodwill and judicial challenges (and will likely become subject to further actions and challenges), as described in more detail in “Item 3. Legal Proceedings” and "Strategy" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in “Item 1. Business.”
There is no guarantee that the MVP Joint Venture will ultimately (or timely) receive all necessary authorizations or that such authorizations will be maintained in effect following challenge, or even after projects are placed in service. Even if the MVP Joint Venture does succeed in resolving challenges or restoring or obtaining the necessary permits and other authorizations, this may not occur within the MVP Joint Venture’s then-targeted time frame for placing projects in service, prior to placing projects in service, or enable the MVP Joint Venture to meet the then-targeted project costs.
We have experienced and may further experience increased opposition from activists in the form of lawsuits, intervention in regulatory proceedings and otherwise, which has been and/or may be focused on the few remaining portions of the MVP project and which have resulted in significant, adverse decisions in respect of project authorizations. Such opposition has made it increasingly difficult to complete the project and place it in service within the then-targeted time frame or at all and, following any in-service, may also affect the ability to continue operating or effect extensions and/or expansions of the project. Further, such opposition and/or adverse court rulings and regulatory determinations may have the effect of increasing that risk that at a future point joint venture partners may elect not to continue to pursue or fund the project, which would, absent additional project sponsors, significantly imperil the ability to complete the project. See "We have entered into joint ventures, and may in the future enter into additional or modify existing joint ventures, that might restrict our operational and corporate flexibility and divert our management's time and our resources. In addition, we exercise no control over joint venture partners and it may be difficult or impossible for us to cause these joint ventures to take actions that we believe would be in our or the joint venture's best interest and these joint ventures are subject to many of the same operational risks to which we are subject." in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We also expect that other projects, such as the MVP Southgate, may be subject to similar heightened opposition. These and other challenges to our projects, particularly the MVP project, could adversely affect our business (including by increasing the possibility of investor activism), financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
The gathering fees payable by EQT to us set forth in the EQT Global GGA are subject to potential reductions for certain contract years set forth in the EQT Global GGA, conditioned to begin the first day of the quarter in which the full in-service date of the MVP occurs, which provide for estimated aggregate fee relief of approximately $270 million in the first twelve-month period, approximately $230 million in the second twelve-month period and approximately $35 million in the third twelve-month period. In addition, given that the MVP full in-service date did not occur by January 1, 2022, EQT has an option, exercisable through December 31, 2022, to forgo approximately $145 million of the gathering fee relief in such first twelve-month period and approximately $90 million of the gathering fee relief in such second twelve-month period in exchange for the EQT Cash Option. Among the benefits to us pursuant to the EQT Global GGA, EQT is subject to an initial annual MVC of 3.0 Bcf per day that became effective on April 1, 2020, which annual MVC gradually steps up to 4.0 Bcf per day through December 2031 following the full in-service date of the MVP. Delays in the MVP full in-service date affect our ability to achieve benefits associated with the execution of the EQT Global GGA. See “EQT Global GGA” in Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Reviews of our goodwill, intangible and other long-lived assets and equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture, previously have significantly reduced our earnings, and additional impairments could further reduce our earnings.
GAAP requires us to test certain assets for impairment on either an annual basis or when events or circumstances occur which indicate that the carrying value of such assets might be impaired. The outcome of such testing previously has resulted in, significant impairment charges, and reviewsin the future could result in, impairments of our assets, including our property, plant, and equipment, intangible assets, goodwill intangible and other long-lived assets andand/or our equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture could result in future significant impairment charges.
GAAP requires us to perform an assessment of goodwill at the reporting unit level for impairment at least annually and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value of a reporting unit is more likely than not less than its carrying amount.
We may perform either a qualitative or quantitative assessment of potential impairment. Our qualitative assessment of potential impairment may result in the determination that a quantitative impairment analysis is not necessary. Under this elective process, we assess qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events or circumstances leads us to determine that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount.Venture. If after assessing the totality of events or
circumstances, we determine that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is greater than its carrying amount, then performing a quantitative analysis is not required. However, if we conclude otherwise, then we perform a quantitative impairment analysis. If we choose not to perform a qualitative assessment, or if we choose to perform a qualitative assessment but are unable to qualitatively conclude that noan impairment has occurred, then we will performwould be required to take a quantitative assessment. In the case of a quantitative assessment, we estimate the fair value of the reporting unit with which the goodwill is associated and compare it to the carrying value. If the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairmentnoncash charge to goodwill is recognized for the excessearnings, which, if significant, could have a material adverse effect on our results of the reporting unit’s carrying value over its fair value.
Assessing goodwill for potential impairment requires significant judgmentsoperations and estimates by management. Fair value of the reporting unit to which goodwill is recorded is estimated using a combination of an income and market approach which, in the case of the income approach, applies significant inputs not observable in the public market (Level 3), including estimates and assumptions related to the use of an appropriate discount rate, future throughput volumes, the application of contractual terms providing for fee credit as necessary, operating costs, capital spending and changes in working capital, and, in the case of the market approach, applies metrics and multiples derived from comparable companies and reference transactions. The reporting unit to which goodwill is recorded as of December 31, 2021 is the EQM Opco reporting unit (as defined and discussed in Note 4).financial position. See Note 42 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information on our reporting units and impairmenta discussion of impairments previously recognized.
Further, the accounting estimates related to impairments are susceptible to change, including estimating fair value which requires considerable judgment. For goodwill, management’s estimate of a reporting unit’s future financial results is sensitive to changes in assumptions, such as changes in stock prices, weighted-average cost of capital, terminal growth rates and industry multiples. Similarly, cash flow estimates utilized for purposes of evaluating long-lived assets and equity method investments (such as in the MVP Joint Venture) require us to make projections and assumptions for many years into the future for pricing, demand, competition, operating costs, timing of operations, and other factors. We evaluate long-lived assets and equity method investments for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management’s judgment, that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable (meaning, in the case of its equity method investments,investment, that such investments haveinvestment has suffered other-than-temporary declines in value)value under ASC 323, Investments: Equity Method Investments and Joint Ventures (ASC 323)). With respect to property, plant and equipment and finite lived assets, asset recoverabilityWhen a quantitative assessment is measured by comparing the carrying value of the asset or asset group with its expected future pre-tax undiscounted cash flows. These cash flowperformed, we use estimates require us to make projections and assumptions for many years into the future for pricing, demand, competition, operating cost, commencement of operations, resolution of relevant legalin estimating our reporting units', our long-lived assets' and regulatory matters, and other factors. If the carrying amount exceeds the expected future undiscounted cash flows, we recognize an impairment equal to the excess of carrying value over fair value as determined by quoted market prices in active markets or present value techniques if quotes are unavailable. The determination of the fair value using present value techniques requires us to make projections and assumptions regarding the probability of a range of outcomes and the rates of interest used in the present value calculations. Any changes we make to these projections and assumptions could result in significant revisions to evaluations of recoverability and the recognition of additional impairments. The evaluation and measurement of impairments forour equity method investments involves similar uncertainties, judgmentsinvestment's fair values that we believe are reasonable and appropriate at that time; however assumptions and estimates as those applicable to other long-lived assets. If the equity method investment carrying value exceeds the fair value and it is determined that the decline in value is other-than-temporary, we will recognize an impairment equal to the excess of the carrying value over fair value. The fair value of equity method investments is generally estimated using an income approach under which significant judgments and assumptions include expected future cash flows, the appropriate discount rate and probability-weighted scenarios.
Estimates and assumptions used in reviews of our goodwill, intangible and other long-lived assets and equity method investments are inherently subjective, subject to significant business, economic, competitive regulatory, judicial and other risks that could materially affect the calculated fair values and require complex judgments. If actual results differ from the estimates or if assumptions are not realized (or if estimates or assumptions, such as of the probability of success of the projects toresulting conclusions regarding impairments, which an equity method investment relates, change), we may be required to recognize an impairment.
As of December 31, 2021, we had approximately $486.7 million of goodwill (all associated with the EQM Opco reporting unit) and $9.7 billion of other long-lived assets, which will be monitored for future impairment.
If the operations or projected operating results ofcould materially affect our businesses decline, we could incur additional goodwill, intangible asset, and property, plant and equipment impairment charges. Further, if we determine that the carrying value of long-lived assets is not recoverable or the value associated with our equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture has further suffered an other-than-temporary decline, we would also incur additional impairment charges. Future impairment charges could be significant and could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations for the period in which the impairment is recorded. As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we cannot predict the likelihood or magnitude of any future impairment.and financial position.
See Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements and “Outlook—Potential Future Impairments” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for additional information.
Cyberattacks aimed at us or those third parties on which we rely, as well as any noncompliance by us or such third parties with applicable laws and regulations governing cybersecurity and/or data privacy, could materially adversely affect us.
We have become increasingly dependent upon digital technologies, including information systems, infrastructure, and cloud applications, to conduct our business, and the maintenance of our financial and other records has long been dependent upon such technologies. Our business also involves collection, uses and other processing of personally identifiable information of our employees, contractors, land agreement counterparties, and other related parties by the Company and/or our third-party business partners. We depend on both our own systems, networks, and technology as well as the systems, networks and technology of our vendors, customers and other business partners. Our increasing reliance on digital technologies puts us at greater risk for system failures, disruptions, incidents, data breaches and cyberattacks (including through third parties with which we do business), which could significantly impair our ability to conduct our business. For instance, energyAdditionally, if our major customers or suppliers experience deliberate attacks on, or unintentional events affecting their digital technologies, it may reduce their ability to utilize our, or provide, services, which could have a material adverse impact on our operations and business. Energy industry participants, including midstream companies, have been the victims of high-profile ransomware attacks, and we expect to continue to be targeted by cyberattacks as a critical infrastructure company.
The U.S. government has continued to issue public warnings that indicate that energy assets might be specific targets of cyberattacks, and in May and July 2021, thecyberattacks. The TSA has issued a series of security directives (and subsequent amendments/revisions thereto) applicable to certain midstream companies, including us, requiring such companies to comply with mandatory reporting measures and undertake a number of specific cybersecurity enhancements for both IT and OT systems. In addition to the TSA security directives, there are multiple regulatory rulemaking processes, and contemplated legislation that may result in new regulations or requirements applicable to us. For additional information regarding cybersecurity matters applicable to us, including our TSA-approved CIP and laws and regulations such as the TSA security directives, see "Regulatory Environment" and "Cybersecurity" under Part I, “Item 1. Business” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We have been required and may further be required to expend additional resources as a result of current or new laws, regulations, directives or other requirements related to critical infrastructure cybersecurity. With the proliferation of regulations, we may become subject to overlapping or conflicting regulatory requirements. Any failure to remain in compliance with laws or regulations governing cybersecurity, including the TSA security directives, may result in penalties, fines, enforcement actions, or mandated changes in our practices, which may have a material adverse effect on our business and operations.
We rely on IT systems, some of which are managed by third parties that we do not control, that may also be, and may have been, susceptible to cyber threats and cyber-related risks described in this risk factor. While we and our third-party service providersthird parties that provide
services to us commit resources to the design, implementation and monitoring of our IT and OT systems, there is no guarantee that our or such third parties’ cybersecurity measures will provide absolute security.
Despite these measures, we may not be able to anticipate, detect or prevent all cyberattacks or incidents, particularly because the methodologies used by attackers change frequently or may not be recognized until launched, and because attackers are increasingly using tactics, techniques, and procedures designed to circumvent controls and avoid detection. Attacks may originate from outside or inside parties, hackers, criminal organizations, or other threat actors, including nation states. As a result, our ITartificial intelligence (“AI”) capabilities improve and OT systems (or those of third parties) that are designed to protect against cyber risksgain widespread use, we may not prevent or detect allexperience cyberattacks created using AI or incidents related to the use of AI, which may be difficult to detect and deliberatemitigate against.
Deliberate attacks on, or unintentional events or incidents affecting, our IT and OT systems or infrastructure or the systems or infrastructure of third parties could, depending on the extent or duration of the event, materially adversely affect us, including by leading to corruption, misappropriation or loss of our proprietary and sensitive data, delays (which could be significant) in the performance of services for our customers, difficulty in completing and settling transactions, challenges in maintaining our books and records, communication interruptions, environmental damage, regulatory scrutiny, personal injury or death, property damage and other operational disruptions, as well as damage to our reputation, financial condition and cash flows and potential legal claims and liabilities. Like other companies in the natural gas industry, we have identified and expect to continue to identify cyberattacks and incidents on our systems, but nonesystems. Additionally, we have received notification from third party service providers of certain such matters on their systems. None of the cyberattacks and incidents we have identified, or been notified of, to datethe filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K has had a material impact on our business or operations.
Further, as cyberattacks continue to evolve and increase in sophistication and volume, we have expended, and expect to continue to expend, additional resources relating to cybersecurity, including, as applicable, to continue to modify or enhance our preventive, protective, and response measures and/or to investigate and remediate potential vulnerabilities to or consequences of cyberattacks and incidents. There can be no assurance that any preventive, protective, response, or remedial measures will address or mitigate all threats that arise.
The regulatory landscape with regard to data privacy continues to develop. Newrapidly develop in foreign, federal and state jurisdictions. Compliance with new laws and regulations governing data privacy, as well as any unauthorized disclosure of personal information, is becoming increasingly complex and may potentially increase our compliance costs. Any failure by us, a company that we acquire, or one of our technology service providers,those third parties on which we rely, to comply with these laws and regulations, where applicable, could adversely affect us, including by resulting in reputational harm, penalties, regulatory investigations scrutiny, liabilities, legal claims and/or mandated changes in our business practices.
Increasing scrutiny and changing stakeholder expectations in respect of ESG and sustainability practices may adversely impact our business and our stock price and expose us to new or additional risks.
Companies across all industries are facing increasing scrutiny from stakeholders related to their ESG and sustainability practices. Investor advocacy groups, proxy advisory firms, certain institutional investors and lenders, investment funds and other influential investors and rating agencies are also increasingly focused on ESG and sustainability practices and matters and on the implications and social cost of their investments and loans. Stakeholders’ increased focus and activism related to ESG and sustainability matters may potentially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, and liquidity, as well as our stock price, and expose us to new or additional risks, including as described below.
Increased focus on ESG and sustainability matters, particularly with respect to climate change and related demand for renewable and alternative energy, may, among other things, hinder our access to capital given our fossil fuel-based operations and/or adversely affect demand for our services. See “Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing financing non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies and alternative forms of energy) and
physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.” and “Increased competition from other companies that provide gathering, transmission and storage, and water services, or from alternative fuel or energy sources, could negatively impact demand for our services, which could adversely affect our financial results.” under "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021. Additionally, pipeline infrastructure companies and projects, such as our MVP project, face increased legal scrutiny and risk, including litigation risk and enhanced and lengthier regulatory reviews by federal, state and/or environmental regulators, due to an increased focus on climate change and/or environmental justice policies and the fossil fuel industry.
We recognize that our shareholders, employees, customers, regulators, and other stakeholders expect us to continue to focus on long-term sustainable performance, including by addressing significant, relevant ESG factors, further working to prioritize sustainable energy practices, reducing our carbon footprint and promoting sustainability. We have incurred and expect to continue to incur costs and capital expenditures in doing so, and certain of such future costs and capital expenditures could be material. Further, if we do not adapt to or comply with investor or other stakeholder expectations and standards (or meet sustainability targets that we set), which are evolving, or if we are perceived not to have responded appropriately or quickly enough to growing concern for ESG and sustainability issues even if our actions are regulatorily and legally compliant, our business could suffer, including from reputational damage (and negative public perception regarding us or our industry may lead to additional regulatory scrutiny or other adverse developments). Additionally, activist shareholders may submit proposals to promote an ESG-related position. Responding to proxy contests and other actions by activist shareholders can be costly and time-consuming, disrupting our operations, causing reputational harm, and diverting the attention of our Board and senior management from the pursuit of business strategies.
In addition, as we continue to focus on long-term sustainable performance and address ESG factors, and as disclosure standards continue to evolve, including as a result of potential regulatory initiatives, we have expanded and expect to further expand our public disclosures in these areas. Such disclosures may reflect aspirational goals, targets, cost estimates and other expectations and assumptions, including over long timelines, which aspirational goals, targets, cost estimates, and other expectations and assumptions are necessarily uncertain and may not be realized. Failure to realize (or timely achieve progress on) such aspirational goals, targets, cost estimates, and other expectations or assumptions may adversely impact us. Further, a multitude of organizations that provide information to investors have developed ratings processes for evaluating companies on their approach to ESG and sustainability matters. Such ratings and reports are used by some investors to inform their investment and voting decisions. Unfavorable ESG ratings, or perceptions of us or our industry as a result of such ratings or our ESG and sustainability practices, may lead to increased negative investor and other stakeholder sentiment toward us or our customers, and to the allocation of investment capital to other industries and companies, which could negatively affect our stock price and access to and costs of capital.
The occurrence of any of the foregoing may adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and/or our stock price.
Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing financing non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies and alternative forms of energy) and physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.
Combating the effects of climate change continues to attract considerable attention in the United States and internationally, including from regulators, legislators, companies in a variety of industries, financial market participants and other stakeholders. Numerous proposals have been made and will likely continue to be made to monitor and limit existing emissions of GHGs, as well as to restrict or eliminate future emissions. Accordingly, our business and operations, and those of our producer customers, are subject to executive, regulatory, political, litigation, and financial risks associated with natural gas and the emission of GHGs.
While no comprehensive climate change legislation has been enacted at the federal level in the United States as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021, President Biden has made addressing climate change a priority of his administration, including by issuing in January 2021 an executive order recommitting the United States to the United-Nations-sponsored “Paris Agreement” (an international agreement for nations to limit GHG emissions) and announcing in April 2021 that the United States will target a 50-52% reduction in economy-wide GHG emissions by 2030 relative to 2005 levels. Accordingly, future federal GHG regulations of the oil and gas industry and legislation relating to climate change are likely. Moreover, federal regulators have taken (or announced that they plan to take or are contemplating) actions related to GHG regulations that have or may have a significant influence on our operations, including the EPA’s November 2021 proposed rule to regulate methane emissions from oil and natural gas sources and the FERC's ongoing evaluation of how to
treat GHGs for purposes of its environmental and certificate reviews. For additional information on GHG laws, regulations and other legal requirements applicable to us, see "Regulatory Environment" and "Environmental Matters" under "Item 1. Business."
The U.S. Congress, regulatory bodies and various states also have been evaluating and/or have implemented climate-related legislation and other regulatory initiatives that would further restrict emissions of GHGs, including the establishment of market-based cap-and-trade or carbon pricing programs or imposition of fees or taxes based on the emission of GHGs by certain facilities. For example, certain Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states in which we and/or the MVP Joint Venture operate, participate, and others are considering participating, in the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative agreement (RGGI) aimed at reducing carbon dioxide emissions from power plants, which could in turn lead to increased uncertainty with regard to demand for natural gas used in the generation of electricity.
Pennsylvania, which is home to our headquarters and many of our assets, approved Environmental Quality Board Final Rulemaking #7-599: CO2 Budget Trading Program (“RGGI Rules”) on September 1, 2021. This rulemaking would establish a cap on carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel plants and would authorize Pennsylvania to participate in RGGI. The RGGI Rules will not become effective until they are published by Pennsylvania’s Legislative Reference Bureau (“LRB”). Under Pennsylvania’s Regulatory Review Act, the LRB must provide the General Assembly time to review and reject the rulemaking before publishing the final rules. The Pennsylvania Senate and House passed concurrent resolutions disapproving the implementation of the RGGI Rules. However the Pennsylvania Governor vetoed those resolutions on January 10, 2022, leaving the Pennsylvania General Assembly with the opportunity to override that veto. The ongoing legislative review process means that the final RGGI Rules may not be promulgated until the second quarter of 2022, at the earliest. Additionally, it is anticipated that the RGGI Rules, if promulgated, will face legal challenges, which cast further uncertainty over the timing and implementation of the RGGI Rules.
Beyond Pennsylvania, it is likely that such regional and state efforts will continue and may establish additional requirements in states in which our assets are located regardless of federal action. For example, with respect to the footprints of MVP and MVP Southgate projects, North Carolina is considering rulemaking to join RGGI and Virginia currently is a member of RGGI. Virginia's recently elected governor, however, has issued an executive order calling on the state to begin the process of withdrawing from RGGI and rescinding its RGGI regulations. GHG restrictions, if implemented, may result in additional compliance obligations or taxes, and initiatives such as RGGI may adversely affect demand for natural gas and, therefore, negatively impact our producer customers, and in turn, the demand for our services. Any of these outcomes could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
There remains considerable uncertainty surrounding the timing, scope and potential impact of future action in the United States and internationally with respect to GHG emissions, including methane in particular. Although we continue to monitor legislative, regulatory and judicial developments in this area to assess potential impacts on our operations and otherwise take efforts and invest funds proactively to limit and reduce GHG emissions from our facilities, we cannot predict precisely what form future laws, regulations and legal requirements relating to climate change might take. Nor can we predict the stringency of any such requirements, when they might become effective or their exact effect on us. Further, laws, regulations and other legal requirements relating to climate change are constantly changing or being reinterpreted, and this may occur during the permitting and construction phases of our projects (which may last several years), as has been the case with our MVP and MVP Southgate projects. Generally, development and implementation of processes to comply with changing legal requirements is likely to be costly and time consuming. Further, compliance or noncompliance with existing or new climate change-focused regulations or other initiatives could adversely impact us by, among other things, imposing additional compliance obligations such as new emission control requirements, taxing the release of GHGs, causing longer permitting timelines, requiring that we purchase allowances for emissions, exposing us to regulatory penalties or affecting our reputation. Future laws, regulations and legal requirements designed to reduce GHG emissions also could make some of our activities, or those of our customers, uneconomic or less economically advantageous to maintain or operate, which may affect the estimated fair values of underlying assets and results of operations. Further, such future legislation and/or regulation may reduce the number of attractive business opportunities available to us. Additionally, climate change-focused regulations may adversely affect production of or demand for natural gas (such as by increasing the cost of producing natural gas or prompting consumers to use renewable fuels), which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. Although future laws, regulations and legal requirements relating to climate change could have a material impact on our industry and us, attempts at quantification are based on speculation of what may occur in the future. For example, based on several bills proposing the establishment of a carbon tax or carbon pricing that have been drafted across various jurisdictions, our preliminary estimate in 2021 of the potential increase in our operating cost upon the enactment of a carbon tax or carbon pricing ranged from approximately $2 million to approximately $96 million reflecting an assumed cost of carbon range and our estimated metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent Scope 1 and 2 emissions for 2020. However, these and any
other estimates we may make taking into account potential future laws, regulation or legal requirements are necessarily uncertain.
Litigation risks relating to climate change also are increasing. Parties have brought suit against the largest oil and natural gas exploration and production companies, alleging, among other things, that such companies created public nuisances by producing fuels that contributed to climate change effects, such as rising sea levels, and therefore are responsible for resultant roadway and infrastructure damages. Parties have also alleged that these companies have been aware of the adverse effects of climate change for some time but defrauded their investors and consumers by failing to adequately disclose those impacts. While we are not currently party to any such litigation, we or our customers could be named in future actions given that our business involves natural gas. Further, climate change-related factors may prompt governmental investigations or adversely affect the regulatory approval process for the construction and operation of midstream assets as, for example, opposition parties have cited our GHG operational emissions as a specific concern during comment periods for regulatory permit reviews.
Market forces driven by concern for climate change are affecting (and are expected to continue to affect) the availability and cost of capital to companies in the fossil fuel sector. For example, climate change activists continue to direct their attention towards, among other things, sources of funding for fossil fuel energy companies, which has resulted in certain financial institutions, funds and other sources of capital restricting or adding more burdensome terms to or altogether eliminating their investments in, or lending with respect to, fossil fuel energy-related activities and companies. Further, such institutions are increasingly allocating funds to those industries and companies perceived as having better growth opportunities and/or stronger ESG metrics and practices. Certain financial institutions, including some that are lenders under the Amended EQM Credit Facility (as defined in Note 11), have voluntarily adopted policies that have the effect of reducing the funding provided to the fossil fuel sector, and there is also a risk that financial institutions will in the future be required to adopt such policies. These market forces may adversely affect our ability to obtain financing in the future (and thus our pursuit of initiatives, such as growth projects) or achieve increases in our stock price, and these forces may also adversely affect our customers, which could result in, among other things, increased counterparty risk and/or decreased demand for our services. Further, demand for and development of lower carbon technologies and renewable and alternative energy is increasing as a result of concern regarding climate change, which may adversely affect demand for natural gas and accordingly our producer customers.
In addition to such transitional risks, climate change also may create physical risks to our business. Climate impacts, such as increasing temperatures, changing weather patterns, and more frequent or intense floods and storms, can pose serious challenges for our facilities, supply chains, employees, contractors, current and potential customers, and the communities in which we operate. In particular, our operations are primarily focused in the Appalachian Basin, which is a rain-susceptible region. Severe and repeated rainfall events above and beyond historical estimates and magnitudes because of climate change could cause damage to our physical assets, especially facilities located in low-lying areas near streams and riverbanks and pipelines situated in landslide-prone and rain susceptible regions, which may adversely affect our operations. We may not be able to pass on resultant higher costs to our customers or recover all costs related to mitigating these physical risks or repairing damage due to such events. Further, our ability to mitigate the adverse impacts of these events depends in part on the resilience of our facilities and the effectiveness of planning for disaster preparedness and response and business continuity, which plans may not fully encompass every potential climate-driven eventuality. Additionally, changing climate patterns could impact the demand for energy in the regions we currently and plan to serve. For example, extreme warm weather in the winter months may lead to decreased natural gas usage, which may affect our results of operations.
One or more of any such developments could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Negative public perception regarding us, MVP, MVP Southgate, other of our expansion projects, the midstream industry, and/or the natural gas industry in general have had and could continue to have an adverse effect on our operations and business, and negative public perception may increase the likelihood of governmental initiatives aimed at the natural gas industry.
Negative public perception regarding us, the MVP, MVP Southgate, other of our expansion projects, other industry participants and their projects and actions, the midstream industry and/or the natural gas industry in general resulting from, among other things, climate change, oil or produced water spills, gas and other hydrocarbon leaks, the explosion or location of natural gas transmission and gathering lines and other facilities, erosion and sedimentation issues, unpopular expansion projects, environmental justice concerns, and general concerns raised by activists about hydraulic fracturing and pipeline projects (as well as specific concerns raised in respect of particular pipeline projects), has led to, and may in the future lead to, increased regulatory scrutiny, which may, in turn, lead to new local, state and federal safety and environmental laws, regulations, guidelines, enforcement interpretations and/or adverse judicial rulings or regulatory actions. See the sections captioned "Regulatory Environment" and "Environmental Matters" under "Item 1. Business" as well as “Item 3. Legal Proceedings.” These actions have caused, and may continue to cause, operational delays or restrictions, increased construction and operating
costs, penalties under construction contracts, additional regulatory burdens and increased litigation. As discussed under “The regulatory approval process for the construction of new midstream assets is very challenging, has significantly increased costs and delayed targeted in-service dates, and decisions by regulatory and judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings are likely to impact our or the MVP Joint Venture's ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvals and authorizations necessary to complete certain projects on the targeted time frame or at all or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects,” there are several pending challenges to certain aspects of the MVP project and the MVP Southgate project that affect the MVP project and the MVP Southgate project, as applicable. Moreover, governmental authorities exercise considerable discretion in the timing and scope of permit issuance and the public may engage in the permitting process, including through intervention in the courts. Negative public perception could further cause the permits we and the MVP Joint Venture need to complete the expansion projects, including the MVP and MVP Southgate projects, and to conduct our and its respective operations to be denied, removed, withheld, delayed, stayed or burdened by requirements that restrict our and its respective abilities to profitably conduct business or make it more difficult to obtain the real property interests needed in order to operate relevant assets or complete planned growth projects, which could, among other adverse effects, affect project completion or subsequent operation, result in revenue loss or a reduction in our and the MVP Joint Venture’s customer bases.
Additionally, there have been initiatives at the federal, state and local levels aimed at the natural gas industry, including those to restrict the use of hydraulic fracturing. Adoption of legislation or regulations (which may be prompted by negative public perception) placing restrictions on hydraulic fracturing activities or other limitations with respect to the natural gas industry could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Our subsidiaries’ significant indebtedness, and any future indebtedness, as well as the restrictions under our subsidiaries’ debt agreements, could adversely affect our operating flexibility, business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Our subsidiaries have significant amounts of debt outstanding under the Amended EQM Credit Facility, the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility (as such terms are defined in Note 11)9) and the senior unsecured notes issued by EQM. See Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements for a discussion of the Amended EQM Credit Facility, the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility and the senior unsecured notes issued by EQM and see Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements for a discussion of the Fifth Amendment to the Amended EQM Credit Facility. The respective debt agreements of EQM and Eureka Midstream, LLC (Eureka), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eureka Midstream, contain various covenants and restrictive provisions that limit EQM’s and Eureka’s, as applicable, ability to, among other things:
•incur or guarantee additional debt;
•debt, make distributions on or redeem or repurchase units;
•units, incur or permit liens on assets;
•assets, enter into certain types of transactions with affiliates;
•affiliates, enter into burdensome agreements, subject to certain specified exceptions;
•exceptions, enter into certain mergers or acquisitions; and,
•dispose of all or substantially all of their respective assets.
See Note 11 to the consolidated financial statements for a discussion of the Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility. The Amended EQM Credit Facility contains certain negative covenants, that, among other things, establish for EQM a maximum Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) that varies over the course of the term ranging fromcould not more than 5.95exceed 5.85 to 1.00 to not more than 5.00for the quarter ended December 31, 2023, 6.00 to 1.00 for the quarter ending March 31, 2024, 6.25 to 1.00 for the quarter ending June 30, 2024, 5.85 to 1.00 for the quarter ending September 30, 2024, and 5.50 to 1.00 for quarters thereafter, with the then-applicable ratio being tested as of the end of each fiscal quarter (which in limited circumstances may be increased for certain measurement periods following the consummation of certain acquisitions).quarter. Under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility, Eureka is required to maintain a Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) of not more than 4.75 to 1.00 (or not more than 5.25 to 1.00 for certain measurement periods following the consummation of certain acquisitions). Additionally, as of the end of any fiscal quarter, Eureka may not permit the ratio of Consolidated EBITDA (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) for the four fiscal quarters then ending to Consolidated Interest Charges (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) to be less than 2.50 to 1.00. EQM’s and Eureka’s ability to meet these covenants can be affected by events beyond their respective control and we cannot assure our shareholders that EQM or Eureka will continue to meet these covenants.
In addition, the Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility each contain certain events of default, including the occurrence of a change of control.control (as defined in the applicable credit facility). Events beyond the control of EQM and Eureka (including changes in general economic and business conditions) and with respect to EQM, certain delays in the full in-service of the MVP project (absent mitigating actions by management), may affect the ability of EQM and Eureka to, as applicable, meet and comply with their respective financial obligations and covenants.
The provisions of the debt agreements may affect our ability to obtain future financing and pursue attractive business opportunities and our flexibility in planning for, and reacting to, changes in business conditions. In addition, a failure to comply
with the provisions of thethese debt agreements could result in an event of default, which could enable creditors to, subject to the terms and conditions of the applicable agreement, declare any outstanding principal of that debt, together with accrued and unpaid interest, to be immediately due and payable. If the payment of the debt is accelerated, our assets may be insufficient to repay such debt in full, and in turn our shareholders could experience a partial or total loss of their investments. The Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility each contain a cross default provision that applies to a default related to any other indebtedness the applicable borrower may have with an aggregate principal amount in excess of $25 million as to EQM, and $10 million as to Eureka.
We and our subsidiaries may in the future incur additional debt. Our and our subsidiaries’ levels of debt could have important consequences to us, including the following:
•that our ability to obtain additional financing, if necessary, for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions or other purposes may be impaired, or such financing may not be available on favorable terms;
•our funds available for operations, future business opportunities and dividends to our shareholders may be reduced by that portion of our cash flow required to make interest payments on our or our subsidiaries’ debt;
•we may be more vulnerable to competitive pressures or a downturn in our business or the economy generally; and
•our flexibility in responding to changing business and economic conditions may be limited.
Our ability to service our subsidiaries’ current, or our or our subsidiaries’ future respective debts, will depend upon, among other things, our future financial and operating performance, which will be affected by prevailing economic conditions and financial, business, regulatory and other factors, some of which are beyond our control. Further, we view de-levering our business as a critical strategic objective given that leverage levels affect the manner in which we may pursue strategic and organic initiatives, our ability to respond to market and competitive pressures, and the competition for investment capital. Our ability to de-lever and the pace thereof will depend on our future financial and operating performance, which will be affected by prevailing economic conditions and financial, business, regulatory and other factors (including particularly bringing the MVP in-service), as well as the MVP Joint Venture’s ability to execute on project-level financing, some of which are beyond our control.
If our operating results are not sufficient to service our subsidiaries’ current, or our or our subsidiaries’ future indebtedness, as applicable, or our operating results affect our ability to comply with covenants in our debt agreements, we will be forced to take actions such as seeking modifications to the terms of our debt agreements (for example, the Amended EQM Credit Facility has been amended to increase the Consolidated Leverage Ratio in the past), including providing guarantees, pledging assets as collateral, reducing dividends, reducing or delaying our business activities, acquisitions, investments or capital expenditures, selling assets or seeking additional equity or debt capital. We may not be able to timely effect any of these actions on satisfactory terms or at all. Further, if our operating results are not sufficient to enable de-levering or affect the pace of de-levering, or if MVP project-level financing is not realized, the manner in which we may pursue strategic and organic initiatives, address market and competitive pressures, and compete for investment capital may be adversely affected, absent additional actions to de-lever, which may not be available to us on satisfactory terms or at all.
Our subsidiaries’ current substantial indebtedness and the additional debt we and/or our subsidiaries will incur in the future for, among other things, working capital, repayment of existing indebtedness, capital expenditures, capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture, acquisitions or operating activities may adversely affect our liquidity and therefore our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
In addition, our subsidiaries’ significant indebtedness may be viewed negatively by credit rating agencies, which could result in increased costs for uscause our subsidiaries’ respective access to access the capital markets.markets to become more challenging. Any future additional downgrade of the debt issued by EQM could increase our capital costs or adversely affect our operating flexibility or ability to raise capital in the future. See "“A further downgrade of EQM'sEQM’s credit ratings including in connection with the MVP project or customer credit rating changes, which are determined by independent third parties, could impact our liquidity, access to capital, and costs of doing business."” in Part I, "Item“Item 1A. Risk Factors"Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Additionally, our ability to obtain financing in the future may be adversely affected by market forces driven by concern for climate change. See “Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing the financing of non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting the pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies, and alternative forms of energy) and, as well as physical risks that
could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.” in Part I, "Item“Item 1A. Risk Factors"Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
If we, our subsidiaries or our subsidiariesjoint ventures are unable to obtain needed capital or financing on satisfactory terms, our ability to execute our business strategy and pay dividends to our shareholders may be diminished. Additionally, financing transactions may increase our financial leverage or could cause dilution to our shareholders.
In order to fund our capital expenditures and capital contributions so to grow and maintain our asset base and complete expansion projects, including the MVP project, any expansion of the MVP project and the MVP Southgate projects, we will need to continue to make significant capital expenditures and capital contributions. If we do not make sufficient or effective capital expenditures and capital contributions, we will be unable to grow or maintain our business operations, which impacts our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
In order to fund our capital expenditures and capital contributions,project, as well as to fund potential strategic transactions, if any, we may use cash from our operations, incur borrowings under our subsidiaries’ credit facilities or through debt capital market transactions, enter into our ownnew credit arrangements or sell additional shares of our equity or a portion of our assets. Using cash from operations will reduce the cash we have available to pay dividends to our shareholders. Our andsubsidiaries’ or our subsidiaries’joint ventures’ ability to
obtain or maintain bank financing or to access the capital markets for debt offerings, or our ability to access the capital markets for future equity offerings, may be limited by, among other things our and as applicable, our subsidiaries’ or our joint ventures’ financial condition at the time of any such financing or offering, our andsubsidiaries’ or our subsidiaries’joint ventures’ credit ratings, as applicable, the covenants in our subsidiaries’ or our joint ventures’ debt agreements, the rights and preferences governing the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, the status of the MVP project, general economic conditions, market conditions in our industry, changes in law (including tax laws), and other contingencies and uncertainties that are beyond our control. Additionally, market forces are affecting (and are expected to continue to affect) the availability and cost of capital to companies in the fossil fuel sector. See “Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing the financing of non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting the pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies, and alternative forms of energy) and, as well as physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.” in Part I, "Item“Item 1A. Risk Factors"Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Even if we, our subsidiaries, or our subsidiariesjoint ventures are successful in obtaining funds through debt or equity financings, as applicable, the terms thereof could limit our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders and otherwise adversely affect us, such as by requiring additional or more restrictive covenants that impose operating and financial restrictions or, in the case of debt, requiring that collateral be posted to secure such debt. In addition, incurring additional debt may significantly increase our interest expense and financial leverage thereby limiting our ability to further borrow, and issuing additional equity may result in significant common shareholder dilution and increase the aggregate amount of cash required to maintain the then-current dividend rates, which could materially decrease our ability to pay dividends at the then-current dividend rates. If funding is not available to us, or our subsidiaries or joint ventures when needed, or is available only on unfavorable terms, we may be unable to execute our business plans, complete acquisitions or otherwise take advantage of business opportunities or respond to competitive pressures, any of which (or actions taken to attempt to address any such funding issue) could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. For example, our strategic plans reflect the potential to incur debt at the MVP Joint Venture following MVP in-service so to enhance our ability to de-lever and pace thereof. The MVP Joint Venture’s ability to incur debt is subject to many of the same factors and considerations, as applied to the MVP Joint Venture, as are described for us and our subsidiaries in this risk factor, as well as joint venture considerations described under “We have entered into joint ventures, and may in the future enter into additional or modify existing joint ventures, that might restrict our operational and corporate flexibility and divert our management’s time and our resources. In addition, we exercise no control over joint venture partners and it may be difficult or impossible for us to cause these joint ventures or partners to take actions that we believe would be in our or the joint venture’s best interests and these joint ventures are subject to many of the same risks to which we are subject.”in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and there is no assurance that debt at the MVP Joint Venture level, or related impacts or benefits, will be realized.
A further downgrade of EQM’s credit ratings including in connection with the MVP project or customer credit ratings changes, which are determined by independent third parties, could impact our liquidity, access to capital, and costs of doing business.
As of February 23, 2022,20, 2024, EQM’s credit ratings were Ba3 with a negativestable outlook, BB- with a stablenegative outlook and BB with a negative outlookon Rating Watch Positive from Moody’s, S&P and Fitch, respectively. EQM’s credit ratings have fluctuated (and may further fluctuate) depending on, among other things, EQM’s leverage, uncertainty around the full in-service datetiming and total project cost of the MVP project, and the credit profile of our customers.
EQM’s credit ratings are subject to further revision or withdrawal at any time by the assigning rating organization, and each rating should be evaluated independently of any other rating. We cannot ensure that a rating will remain in effect for any given period of time or that a rating will not be lowered or withdrawn entirely by a credit rating agency if, in its judgment, circumstances so warrant, including in connection with the MVP project, EQM's leverage or the creditworthiness of EQM’s customers. Credit rating agencies perform an independent analysis when assigning credit ratings. This analysis includes a
number of criteria such as business composition, market and operational risks, operational risks, various financial tests, ESG matters, as well as analysis of various financial metrics. Credit rating agencies continue to review the criteria for industry sectors and various debt ratings and may make changes to those criteria from time to time.
If any credit rating agency further downgrades or withdraws EQM’s ratings, including for reasons relating to the MVP project (such as for delays in the targeted full in-service date ofaffecting the MVP project or increases in such project’s targeted costs), EQM’s leverage or credit ratings of our customers, our and our subsidiaries’ respective access to the capital markets could become more challenging, borrowing costs will likely increase, our operating flexibility may be adversely affected, EQM may be required to provide additional credit assurance (the amount of which may be substantial), including the Cash Option Letter of Credit (as discussed in "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations"), in support of commercial agreements such as joint venture agreements, and the potential pool of investors and funding sources may decrease.
In order to be considered investment grade, EQM must be rated Baa3 or higher by Moody’s, BBB- or higher by S&P and BBB- or higher by Fitch. EQM’s non-investment grade credit ratings have resulted in greater borrowing costs, including under the Amended EQM Credit Facility, and increased collateral requirements, including under the MVP Joint Venture’s limited liability company agreement, than if EQM’s credit ratings were investment grade.
In addition to causing, among other impacts, higher borrowing costs and/or more restrictive terms associated with modifications to existing debt instruments, any further downgrade could also require additional or more restrictive covenants on future
indebtedness that impose operating and financial restrictions on us or our subsidiaries, certain of our subsidiaries to guarantee such debt and certain other debt, and certain of our subsidiaries to provide collateral to secure such debt.
Any increase in our financing costs resulting from a credit rating downgrade, and/or more restrictive covenants or the pledging of security, could adversely affect our ability to finance future operations.operations and limit our operating flexibility. If a credit rating downgrade and/or a resultant collateral requirement were to occur at a time when we are experiencing significant working capital requirements or otherwise lack liquidity, our business, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders could be adversely affected.
Increasing scrutiny and changing stakeholder expectations and disclosures in respect of ESG and sustainability practices may adversely impact our business and our stock price and impose additional costs or expose us to new or additional risks.
Companies across all industries are facing increasing scrutiny from stakeholders related to their ESG and sustainability practices. Investor advocacy groups, proxy advisory firms, certain institutional investors and lenders, investment funds and other influential investors and rating agencies are also increasingly focused on ESG and sustainability practices and matters and on the implications and social cost of their investments and loans. Increased focus related to ESG and sustainability matters may adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, and liquidity, as well as our stock price, and expose us to new or additional risks, including as described below.
Increased focus on ESG and sustainability matters, particularly with respect to climate change and related demand for renewable and alternative energy, may, among other things, hinder our access to capital given our fossil fuel-based operations and/or adversely affect demand for our services. See “Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing the financing of non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting the pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies, and alternative forms of energy), as well as physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.”in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Additionally, due to an increased focus on climate change and/or environmental justice policies, particularly as it relates to the fossil fuel industry, pipeline infrastructure companies and projects, as was the case with the MVP project, face increased legal scrutiny and execution risk, including related to litigation and enhanced and lengthier regulatory reviews by federal, state and/or environmental regulators.
We recognize that our shareholders, employees, customers, regulators, and other stakeholders expect us to continue to focus and report on long-term sustainable performance, including by addressing significant, relevant ESG factors, further working to prioritize sustainable energy practices, reducing our carbon footprint and promoting sustainability. We have incurred and expect to continue to incur costs and capital expenditures in doing so, and certain of such future costs and capital expenditures could be material, including because of increasing regulatory demands, which may not be consistent in their requirements. For example, California enacted two climate related disclosure laws called the Climate Corporate Data Accountability Act (“CCDAA”) and the Climate-Related Financial Risk Act (“CRFRA”) on October 7, 2023. Further, on March 21, 2022, the SEC released proposed rule changes that would require new climate-related disclosure in SEC filings. For additional information regarding the SEC’s climate related disclosures rule, the CCDAA and the CRFRA, please see “Regulatory Environment — Climate Change” under Part I, "Item 1. Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The CCDAA and the CRFRA would, and the SEC’s climate related disclosures rule if adopted as proposed would, cause us to incur additional (and potentially accelerate) compliance and reporting costs, certain of which could be material, including related to monitoring, collecting, analyzing and
reporting new metrics and implementing systems and procuring necessary attestations, as applicable. Such costs, or costs or impacts associated with any failures to comply with such or any similar laws, may adversely affect our future business, financial condition, results of operations, and liquidity.
Further, if we do not adapt to or comply with investor or other stakeholder expectations and standards, which are evolving, or if we are perceived not to have responded appropriately or quickly enough to growing concern for ESG and sustainability issues, our business could suffer, including from reputational damage (and negative public perception regarding us or our industry may lead to additional regulatory scrutiny or other adverse developments). We have disclosed aspirational goals, targets, potential financial impacts and other expectations and assumptions related to reducing our carbon footprint and promoting sustainability that are necessarily uncertain due to, among other things, long implementation timelines, and thus may not be realized. Failure to realize (or timely achieve progress on) such aspirational goals, targets, cost estimates, and other expectations or assumptions may adversely impact us. Our disclosures regarding aspirational goals, targets, cost estimates, and other expectations or assumptions, as applicable, could receive increased scrutiny by shareholders or regulators which may adversely impact us, including as a result of unforeseen events which may affect us.
Additionally, activist shareholders may submit proposals to promote or oppose an ESG-related position. Responding to such proposals, proxy contests and other actions by activist shareholders can be costly and time-consuming, disrupting our operations, causing reputational harm, and diverting the attention of our Board and senior management from the pursuit of business strategies. Further, a multitude of organizations that provide information to investors have developed ratings processes for evaluating companies on their approach to ESG and sustainability matters. Such ratings and reports are used by some investors to inform their investment and voting decisions. Favorable or unfavorable ESG ratings, or perceptions of us or our industry as a result of such ratings or our ESG and sustainability practices, may lead to increased negative investor and other stakeholder sentiment toward us or our customers, and to the allocation of investment capital to other industries and companies, which could negatively affect our stock price and access to and costs of capital.
The occurrence of any of the foregoing may adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and/or our stock price.
Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing the financing of non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting the pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies, and alternative forms of energy), as well as physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.
Combating the effects of climate change continues to attract considerable attention in the United States and internationally, including from regulators, legislators, companies in a variety of industries, financial market participants, and other stakeholders. Governmental, scientific, and public concern over the threat of climate change arising from GHG emissions has resulted in increasing risks and governmental actions that could have an adverse impact on our operations in the United States. Numerous proposals and regulations have been made and will continue to be made to monitor and limit existing GHG emissions, as well as to restrict or eliminate future emissions. Accordingly, our business and operations, and those in our value chain, including our producer customers, are subject to executive, regulatory, political, litigation, and financial risks associated with natural gas and the emission of GHGs.
At the federal level, the United States has taken steps to address climate change through legislative action, executive actions, and regulatory initiatives pursuant to existing statutes, such as the Clean Air Act. The EPA released in December 2023 its final rule, which has not yet been published in the Federal Register as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, regulating methane emissions from the oil and gas sector under the Clean Air Act. The Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 amended the Clean Air Act to require a “methane fee” for specific facilities that exceed GHG emission and/or methane intensity thresholds beginning in 2024. These new Clean Air Act regulations, as well as any other future laws or regulations that legislators or federal agencies may adopt, could have an adverse impact on our operations and results thereof. State and regional efforts could establish requirements in states in which our assets, employees or customers are located regardless of federal action.
States where our, the MVP Joint Venture’s or our customers’ assets are located have entered or sought to enter into the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI), which is a consortium of certain Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states that set declining limits on CO2 emissions from fossil fuel fired power plants. Initiatives such as RGGI, if enforceable in our areas of operation, may result in increased uncertainty regarding demand for natural gas used in the generation of electricity, including in our operating markets. Beyond regional and state efforts, nationally, demand for natural gas used in the generation of electricity could also be affected by federal action, such as the EPA’s proposed rulemaking to regulate GHG emissions from new and existing fossil fuel fired power plants.
There remains considerable uncertainty surrounding the timing, scope and potential impact of future state, national and international action with respect to GHG emissions, including methane in particular. Although we continue to monitor legislative, regulatory, and judicial developments in this area to assess potential impacts on our operations and otherwise take efforts and invest funds proactively to limit and reduce GHG emissions from our facilities, we cannot predict what form future laws, regulations, and legal requirements relating to climate change might take. Nor can we predict the stringency of any such requirements, when they might become effective, or their exact effect on us. Further, laws, regulations, and other legal requirements relating to climate change are constantly changing or being interpreted or reinterpreted, and this may occur during the permitting and construction phases of our projects, and may result in increased costs and delays. Generally, development and implementation of processes to comply with changing legal requirements are likely to be costly and time consuming. Laws, regulations and legal requirements designed to reduce GHG emissions also may: (i) make some of our activities, or those of our customers, uneconomic or less economically advantageous to maintain or operate, which may affect the estimated fair values of underlying assets and results of operations; (ii) reduce the number of attractive business opportunities available to us and discourage investments in our securities; (iii) impose additional and costly compliance obligations such as new emission control requirements, taxes, fees or other costs on the release of GHGs, cause longer permitting timelines, require that we purchase allowances for emissions, expose us to regulatory penalties or affect our reputation; and (iv) adversely affect production of or demand for natural gas (such as by increasing the cost of producing natural gas, increasing the cost of producing electricity with natural gas, or prompting consumers to use renewable fuels).
If any of the foregoing events were to occur, it may have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. Although future laws, regulations, and legal requirements relating to climate change could have a material impact on our industry and us, attempts at quantification are based on speculation of what may occur in the future which is inherently uncertain.
Litigation risks relating to climate change continue to increase. Parties have brought suit against certain large oil and natural gas exploration and production companies, alleging, among other things, that such companies created public nuisances by producing fuels that contributed to climate change effects, such as rising sea levels, and therefore are responsible for resultant damages. Parties have also alleged that these companies have been aware of the adverse effects of climate change for some time but misled their investors and consumers by failing to adequately disclose those impacts. While we are not currently party to any such litigation as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we, joint ventures in which we participate, or third parties with which we do business could be named in future actions given that our or their business involves natural gas. Further, climate change-related factors may prompt governmental investigations or adversely affect the regulatory approval process for the construction and operation of midstream assets, as, for example, opposition parties have cited, and are likely to cite in the future, our and/or the MVP Joint Venture's direct and/or indirect GHG emissions as a specific concern during comment periods for regulatory permit reviews.
Market forces driven by concern for climate change are also affecting (and are expected to continue to affect) the availability and cost of capital to companies in the fossil fuel sector. For example, climate change activists continue to direct their attention towards, among other things, sources of funding for fossil fuel energy companies, which has resulted in certain financial institutions, funds, and other sources of capital restricting or adding more burdensome terms to or altogether eliminating their investments in, or lending with respect to, fossil fuel energy-related activities and companies (as we have experienced with respect to the Amended EQM Credit Facility (as defined in Note 9), and in the future could experience). Further, such institutions are increasingly allocating funds to those industries and companies perceived as having better growth opportunities and/or stronger ESG metrics and practices. These market forces may adversely affect our ability to obtain financing in the future (and thus our pursuit of initiatives, such as growth projects) or achieve increases in our stock price, and these forces may also adversely affect our customers, which could result in, among other things, increased counterparty risk and/or decreased demand for our services. Further, the concern surrounding climate change is increasing demand for lower-carbon technologies and alternate forms of energy in the marketplace, which is driving innovation and investment in products that compete with natural gas. Continued momentum to develop and drive down the cost of competitive energy alternatives may adversely affect demand for natural gas and accordingly our producer customers.
In addition to such transitional risks, climate change also may create physical risks to our business. Climate impacts, such as increasing temperatures, changing weather patterns, and more frequent or intense floods and storms, can pose serious challenges for our facilities, supply chains, employees, contractors, current and potential customers, and the communities in which we operate. In particular, our operations are primarily located in the Appalachian Basin, which is a rain-susceptible region and given its geography there is inherent risk associated with landslides which could increase with climate change. Further, climate-induced rainfall events and severe storms above and beyond historical estimates, magnitudes, and frequency could exceed the pre-designed environmental controls in place on our construction projects, and/or cause pipeline slips or other damage to our physical assets, especially facilities located in low-lying areas near streams and riverbanks and pipelines situated in landslide-prone and rain-susceptible regions, which may adversely affect or temporarily interrupt our operations. We may not be able to pass on resultant financial impacts to our customers or recover all costs related to mitigating these physical risks or
repairing damage due to such events. Further, our ability to mitigate the adverse impacts of these events depends in part on the resilience of our environmental controls, facilities and the effectiveness of planning for disaster preparedness and response and business continuity, which plans may not fully encompass every potential climate-driven eventuality. Additionally, changing climate patterns could impact the demand for energy in the regions we currently and plan to serve. For example, extreme warm weather in the winter months may lead to decreased natural gas usage, which may affect our results of operations and financial condition.
One or more of any such developments could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
For additional information on GHG laws, regulations and other legal requirements applicable to us, see “Regulatory Environment — Environmental Matters” under “Item 1. Business” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Negative public perception regarding us, the MVP, MVP Southgate, other of our or the MVP Joint Venture’s extension or expansion projects, the midstream industry, and/or the natural gas industry in general have had and could continue to have an adverse effect on our operations and business, and negative public perception may increase the likelihood of governmental initiatives aimed at the natural gas industry.
Negative public perception regarding us, the MVP, MVP Southgate, other of our or the MVP Joint Venture’s extension or expansion projects and/or our industry, resulting from, among other things, concerns raised by advocacy groups regarding climate change; oil or produced water spills; gas and other hydrocarbon leaks; the explosion or location of natural gas transmission and gathering lines and other facilities; erosion and sedimentation issues; hydraulic fracturing, environmental justice concerns; as well as general and specific concerns relating to our operations or pipeline and expansion projects, has led to, and may in the future lead to, increased regulatory scrutiny, and/or new local, state, and federal safety and environmental laws, regulations, guidelines, enforcement interpretations and/or adverse judicial rulings or regulatory actions.
These actions have caused, and may continue to cause, operational delays or restrictions, increased construction and operating costs, penalties under construction contracts, additional regulatory burdens, and increased litigation. Moreover, governmental authorities exercise considerable discretion in the timing and scope of permit issuance, and the public may engage in the permitting process, including through intervention in the courts. Negative public perception could further cause the permits we and the MVP Joint Venture need to complete extension or expansion projects, including the MVP Southgate project and any expansion of the MVP, and to conduct our and its respective operations to be denied, removed, withheld, delayed, stayed or burdened by requirements that restrict our and its respective abilities to profitably conduct business or make it more difficult to obtain the real property interests needed to operate relevant assets or complete planned growth projects, which could, among other adverse effects, affect project completion or subsequent operation, result in revenue loss or a reduction in our and the MVP Joint Venture’s customer bases.
Furthermore, the 2024 election cycle will impact public policy initiatives at the federal and state level. In addition to the U.S. presidential election, all 435 seats in the U.S. House of Representatives and 34 U.S. Senate seats are subject to election. With the exception of Virginia, all of the states in our, or the MVP Joint Venture’s, operating area have elections that will determine control of state legislatures, including a gubernatorial election in North Carolina. The results of these elections will have a significant effect on the legislative and regulatory landscape for the natural gas industry. Additionally, there have been and continue to be certain initiatives at the federal, state and local levels aimed at the natural gas industry, including those to restrict the use of hydraulic fracturing as discussed in more detail in “The adoption of legislation relating to hydraulic fracturing and the enactment of new or increased severance taxes and impact fees on natural gas production could cause our current and potential customers to reduce the number of wells they drill in the Marcellus and Utica Shales or curtail production of existing wells connected to our assets. If reductions are significant for those or other reasons, the reductions could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.” in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Adoption of legislation or regulations (which may be prompted by negative public perception) placing restrictions on hydraulic fracturing activities or other limitations with respect to the natural gas industry could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
The lack of diversification of our assets, products and geographic locations could adversely affect us.
We rely exclusively on revenues generated from our gathering, transmission and storage and water systems, substantially all of which are located in the Appalachian Basin in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Ohio.Ohio, and as of December 31, 2023 dry natural gas comprised approximately 86% of our product portfolio. Due to our lack of diversification in assets, products and geographic location and continuing challenges tothe challenging environment for completing expansiontransmission projects such as the MVP and MVP Southgate, an adverse development in these businesses or our areas of operations, including adverse developments due to catastrophic events, pandemics, epidemics, weather, regulatory action, local prices, producer liquidity or production determinations, decreases in
demand for natural gas from the Appalachian Basin, takeaway capacity constraints from the Appalachian Basin (including as may remain long term notwithstanding any completion of MVP and limit our producer customers’ future ability to grow production volumes to then-existing pipeline capacity and consequently affect natural gas prices adversely within the Appalachian Basin) or increases in supply of natural gas from other natural gas or oil producing basins (such as if associated gas production were to continue to recover and return to or exceed pre-COVID-19 pandemic levels)from the Permian Basin) could have a more significant impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and our ability to pay dividends than if we maintained more diverse assets, products and locations.
We are exposed to the credit risk of our counterparties in the ordinary course ofand our business.credit risk management cannot completely eliminate such risk.
We are exposed to the risk of loss resulting from the nonpayment and/or nonperformance of our customers, suppliers, joint venture partners and other counterparties as further described in “Credit Risk” under Part II, “Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk.”Risk” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We extend credit to our customers as a normal part of our business. While we have established credit policies, including assessing the creditworthiness of our customers as permitted by our FERC-approved natural gas tariffs, and may require appropriate terms or credit support from them based on the results of such assessments, including in the form of prepayments, letters of credit, or guaranties, we may not adequately assess the creditworthiness of our existing or future customers.customers or any other party and our credit policies cannot completely eliminate credit risk. Pursuant to thecertain agreements with EQT, Global GGA and the Credit Letter Agreement, amongst other things, (a) we agreed to relieve certain credit posting requirements for EQT, in an amount up to approximately $250 million under its commercial agreements with us, subject to EQT maintaining a minimum credit rating from two of three rating agencies of (i) Ba3 with Moody’s, (ii) BB- with S&P and (iii) BB- with Fitch. As of February 23, 2022, EQT’s public debt had sub-investment gradeFitch, however, there can be no assurance that EQT will maintain sufficient credit ratings or such rating thresholds are protective against all credit risk in the case of BB+ with a positive outlook at S&P, Ba1 with a stable outlook at Moody’s, and BB+ with a stable outlook at Fitch. EQT.
Periods of natural gas price declines and sustained periods of low natural gas and NGL prices, previously have had, and could in the future have, an adverse effect on the creditworthiness of our customers, including their ability to pay firm reservation fees under long-term contracts. For example, thePeriods of low commodity price environment in 2019 and 2020prices have previously negatively impacted natural gas producers causing some producers significant economic stress including, in certain cases, to file for bankruptcy protection or to seek renegotiated contracts. We cannot predict the extent to which the businesses of our counterparties would be impacted if commodity prices decline, commodity prices are depressed for a sustained period of time, or other conditions in the energy industry were to deteriorate, nor can we estimate the impact such conditions would have on the abilities of our customers to perform under their gathering, transmission and storage and water services agreements with us. To the extent one or more of our counterparties is in financial distress or commences bankruptcy proceedings, contracts with these counterparties may be subject to renegotiation or rejection under applicable provisions of the United States Bankruptcy Code (Bankruptcy Code). Nonpayment and/or nonperformance by our counterparties and/or any unfavorable renegotiation or rejection of contracts under the Bankruptcy Code could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Our future growth may be limited and our cash flows adversely affected if we do not complete expansionorganic growth projects, realize revenue generating volume growth on our systems and/or identify and complete suitable acquisitions and otherinorganic strategic transactions and realize anticipated benefits therefrom, and we face and will continue to face opposition to the development of our expansion projects and the operation of our pipelines and facilities from various groups, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. Additionally, our Board of Directors is engaged in a process with third parties that have expressed interest in strategic transactions involving the Company, and there is no assurance as to the outcome of that process.
Our ability to grow organically depends primarily upon our ability to complete expansionorganic growth projects, such as the MVP and MVP Southgate projectsproject (and related extensions or expansions thereof), leverage our existing asset base to benefit our existing customer relationships and attract new customers, and realize increasing commitments and/or volume growth that result in an increase ingenerate revenue from customers. As gathering fee declines take effect under the EQT Global GGA, the failure to grow organically, including particularly the failure to achieve increasing commitments and/or volume growth that generate revenue, could adversely affect our cash flows and potentially our business. See, for example, “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we generate. We may be unable to complete successful, accretive expansion projects for many reasons, including, but not limitedare subject to the following:business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT's drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results.” in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Factors which may adversely affect our ability to grow organically include, among other things, any inability to:
•an inability to identify attractive expansionorganic growth projects;
•an inability to obtain and/or maintain necessary rights-of-way, real-estate rights or permits or other government approvals, including approvals by regulatory agencies;
•an inability to successfully integrate the infrastructure we build with our existing systems;
•an inability to obtain and/or maintain sources of fresh or produced water;
•an inability togenerate sufficient cash from our operations and/or raise financing for expansion projects on economically acceptable terms;terms for projects;
•incorrectrealize assumptions about volumes, revenues, costs, producer turn-in-lines and in-service timing, as well as potential growth; or
•an inability to secure or maintain adequate customer commitments, including to use the newly expanded facilities.
Additionally, we face and expect to continue to face staunch and protracted opposition to the development of expansion and extension projects (such as has been case with the MVP project)and MVP Southgate projects) and operation of our pipelines and facilities from environmental groups, certain landowners, local, regional and national groups opposed to the natural gas industry and/or fossil fuels generally, activists and other advocates. Such opposition has taken and will likely continue to take many forms, including organized protests, attempts to block, vandalize or sabotage our development or operations, intervention in regulatory or administrative proceedings involving our assets directly or indirectly, lawsuits legislation or other actions designed to prevent, disrupt or delay the development or operation of our assets and business.
Any event that delays or interrupts (or continues to delay or interrupt) the completion of expansion or extension projects, and/or revenues generated, or expected to be generated, by our operations or that causes us to make significant expenditures associated with delayed construction completion or not covered by insurance, could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
We also periodically evaluate inorganic growth opportunities, including additional interests in existing joint ventures. Our Board of Directors has been engaged in a process with third parties that have expressed interest in strategic transactions involving the Company. The board has engaged outside advisors and the process is ongoing. There is no guaranteeassurance that wesuch process will be able to identify, compete for and/or complete, suitable strategic transactions, or,result in the caseexecution, approval or completion of any such strategicspecific transaction achieve synergies or other potential benefits.outcome. See also “AcquisitionsStrategic transactions that we may makeenter into could reduce, rather than increase, our results of operations and liquidity, and adversely affect our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.” in Part I, "Item“Item 1A. Risk Factors"Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Failure to achieve growth could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Expanding our business by constructing new midstream assets subjects usWe have incurred and expect to risks.
Our growth strategy includes organic and greenfield growth projects. The development and construction of pipeline infrastructure and storage facilities and the optimization of such assets involve numerous regulatory, environmental, political and legal uncertainties that are beyond our control, and require the expenditure of significant amounts of capital and expose us to risks. Those risks include the failure to meet customer contractual requirements; delays caused by landowners; delays caused by advocacy groups or activists opposed to the natural gas industry through lawsuits or intervention in regulatory proceedings; environmental hazards; vandalism; adverse weather conditions; the performance of third-party contractors; delays caused by evolving regulatory or legal requirements; the lack of available skilled labor, equipment and materials (or escalating costs in respect thereof) and the inability to obtain necessary rights-of-way or approvals and permits from regulatory agencies on a timely basis or at all (and maintain such rights-of-way, approvals and permits once obtained). These types of projects may not be completed on schedule, within budgeted cost, or, in the case of the MVP Joint Venture may continue to be delayed and exceed the budgeted cost, or at all. For example, public participation, including by pipeline infrastructure opponents, in the review and permitting process of projects, through litigation or otherwise, can introduce uncertainty and adversely affect project timing, completion and cost. See also “The regulatory approval process for the construction of new midstream assets is very challenging, has significantly increasedincur costs and delayed targeted in-service dates, and decisions by regulatory and judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings are likely to impact our or the MVP Joint Venture's ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvals and authorizations necessary to complete certain projects on the targeted time frame or at all or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects.” in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Further, civil protests regarding environmental justice and social issues, including proposed construction and location of infrastructure associated with fossil fuels, may lead to increased litigation, legislative and regulatory initiatives and review at federal, state, tribal and local levels of government that could prevent or delay the construction of such infrastructure and realization of associated revenues.
Additionally, construction expenditures on projects may occur over an extended period, yet we will not receive revenues from, or realize any material increases in cash flowexpenses as a result of or arising in relation to the relevant project until it is placed into service. Moreover, our cash flow from a projectRager Mountain natural gas storage field incident in November 2022, which has included and may be delayedinclude potential additional regulatory penalties or may not meet our expectations. Furthermore, we may construct facilities to capture
anticipated future growth in production and/or demand in a region inother sanctions, which such growth does not materialize. As a result, new facilities may not be able to attract enough throughput to achieve our expected investment return. Such issues in respect of the construction of midstream assets could, depending on their scope and timing, materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
On November 6, 2022, we became aware of natural gas venting from a storage well (well 2244) at Equitrans, L.P.’s Rager Mountain natural gas storage facility, located in Cambria County, Pennsylvania, which venting was halted on November 19, 2022 (the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident). During and continuing since the occurrence of the incident, we have incurred costs and expenses relating to or arising out of the incident, including in connection with a root cause analysis of the incident, which was conducted by an independent, third-party company with expertise in reservoir management and well and corrosion engineering and which was submitted to the PHMSA in August 2023.
Although in October 2023, following authorization from the PHMSA of our injection plan for the Rager Mountain facility, we returned the Rager Mountain facility, other than well 2244 and two additional wells, to injection operations, as discussed in Part I, “Item 3. Legal Proceedings” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the PADEP, the PHMSA and other investigators are continuing to conduct civil and criminal investigations of the incident and we and our subsidiary Equitrans L.P., as applicable, are cooperating in such investigations. There can be no assurance as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K as to the outcome of any investigation or pending or future proceeding with respect to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, nor can there be any assurance regarding the scope of potential (or ultimately actual) financial or other impacts or sanctions to the Company as a result of such incident. Certain of the statutory provisions cited by the PADEP in certain notices of violation relating to the incident provide for a maximum penalty of up to $25,000 per day of violation, and if penalties are pursued and ultimately imposed related to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, the penalties are expected to result in monetary sanctions in excess of $300,000.
See also “We do not insure against all potential losses and could be seriously harmed by unexpected liabilities or the inability of our insurers to satisfy our claims.” in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors.”, and see also Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, Part I, “Item 3. Legal Proceedings” and Part II, “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information regarding the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident.
We are subject to numerous operational risks and hazards, and operational risks.as well as unforeseen interruptions.
Our business operations are subject to the inherent hazards and risks normally incidental to the gathering, transmission and storage of natural gas and performance of water services. These operating risks, some of which we have experienced and/or could experience in the future, include but are not limited to:
•aging infrastructure and mechanical or structural problems;
•security risks, including cybersecurity;
•pollution and other environmental risks;
•operator error;
•failure of equipment, facilities or new technology;
•damage to pipelines, wells and storage assets, facilities, equipment, environmental controls and surrounding properties, and pipeline blockages or other operational interruptions, caused or exacerbated by hurricanes, earthquakes, tornadoes, abnormal amounts of rainfall, floods and flash flooding, fires, droughts, landslides and other natural disasters andphenomena, weather conditions, acts of sabotage, vandalism and terrorism;
•inadvertent damage from construction, vehicles, and farm and utility equipment;
•uncontrolled releases of natural gas and other hydrocarbons or of fresh, mixed or produced water;water, or other hazardous materials;
•leaks, migrations or losses of natural gas as a result of the malfunction ofissues regarding pipeline and/or storage equipment or facilities and, including with respect to storage assets, as a result of undefined boundaries, geologic anomalies, limitations in then-applied industry-standard testing methodologies, operational practices (including as a result of regulatory requirements), natural pressure migration and wellbore migration;migration or other factors relevant to such storage assets;
•ruptures, fires, leaks and explosions;
•pipeline freeze offs due to cold weather; and
•other hazards that could also result in personal injury and loss of life, pollution to the environment and suspension of operations.
Any such events, certain of which we have experienced, and any of which we may experience in the future, could result in loss of human life, personal injuries, significant damage to property, environmental pollution, impairment or interruption, which could be significant, of our operations, regulatory investigations and penalties or other sanctions and substantial losses to us and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders, particularly if the event is not fully covered by insurance. See also “We do not insure against all potential losses and could be seriously harmed by unexpected liabilities or the inability of our insurers to satisfy our claims.” and “We have incurred and expect to continue to incur costs and expenses as a result of or arising in relation to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident in November 2022, which has included and may include potential additional regulatory penalties or other sanctions, which could, depending on their scope and timing, materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.”in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The location of certain segments of our systems in or near populated areas, including residential areas, commercial business centers and industrial sites, could increase the damages resulting from these risks. Accidents or other operating risks have resulted, and in the future could result, in loss of service available to our customers. Potential customerCustomer impacts arising from service interruptions on segments of our systems and/or our assets have included and/or may include, but are not limited to,without limitation and as applicable, curtailments, limitations on our ability to satisfy customer contractual requirements, obligations to provide reservation charge credits to customers in times of constrained capacity and solicitation of our existing customers by third parties for potential new projects that would compete directly with our existing services. Such circumstances could adversely impact our ability to retain customers and, as well as potentiallyhas been the case in certain instances in the past, negatively impact our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity andand/or ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Increased competition from other companies that provide gathering, transmission and storage, and water services, or from alternative fuel or energy sources, could negatively impact demand for our services, which could adversely affect our financial results.
Our ability to renew or replace existing contracts or add new contracts at rates sufficient to maintain or grow current revenues and cash flows could be adversely affected by the activities of our competitors. Our systems compete primarily with other interstate and intrastate pipelines and storage facilities in the gathering, transmission and storage of natural gas. Some of our competitors have greater financial resources and may be better positioned to compete, including if the midstream industry moves towards greater consolidation; further, some of such competitors may now, or in the future, have access to greater supplies of natural gas or water than we do. Some of these competitors may expand or construct gathering systems, transmission and storage systems and water systems that would create additional competition for the services we provide to our customers. In addition, certain of our customers, may developincluding EQT, have developed or acquireacquired their own gathering and water infrastructure, and may acquire or develop gathering, transmission or storage and/or water infrastructure in the future, which could have a negative impact on the demand for our services insteaddepending on the location of using ours.such systems relative to our assets and our producer customers’ drilling plans, commodity prices, existing contracts and other factors.
The policies of the FERC promoting competition in natural gas markets continue to have the effect of increasing the natural gas transmission and storage options for our customer base. As a result, we have experienced, and in the future could experience, “turnback” of firm capacity as existing agreements expire. If we are unable to remarket this capacity or can remarket it only at substantially discounted rates compared to previous contracts, we may have to bear the costs associated with the turned back capacity. Increased competition could reduce the volumes of natural gas transported or stored on our systems or, in cases where
we do not have long-term firm contracts, could force us to lower our transmission or storage rates. Increased competition could also adversely affect demand for our water services.
Further, natural gas as a fuel competes with other forms of energy available to end-users, including coal, liquid fuels and, increasingly, renewable and alternative energy. Demand for and development of renewable and alternative energy is increasing as a result of concern regarding climate change. Further, the availability of renewable and alternative energy is growing, and it continues to become more cost competitive with fossil fuels, including natural gas, and is growing more widely available.gas. Continued increases, whether driven by legislation, regulation or consumer preferences, in the availability and demand for renewable and alternative energy at the expense of natural gas (or increases in the demand for other sources of energy particularly if prices forrelative to natural gas significantly increase relative tobased on price and other forms of energy as fuel)factors) could adversely affect our producer customers and lead to a reduction in demand for our natural gas gathering, transmission and storage, and water services.
In addition, competition, including from renewable and alternative energy, could intensify the negative impact of factors that decrease demand for natural gas in the markets served by our systems, such as adverse economic conditions, weather, higher fuel costs and taxes or other governmental or regulatory actions that directly or indirectly increase the cost or limit the use of natural gas.
All of these competitive pressures could make it more difficult for us to retain our existing customers and/or attract new customers and/or additional volumes from existing customers as we seek to maintain and expand our business, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. In addition, competition, including from renewable and alternative energy, could intensify the negative impact of factors that decrease demand for natural gas in the markets served by our systems, such as adverse economic conditions, weather, higher fuel costs and taxes or other governmental or regulatory actions that directly or indirectly increase the cost or limit the use of natural gas.
We may not be able to renew or replace expiring contracts at favorable rates, on a long-term basis or at all.all, and disagreements have occurred and may arise with contractual counterparties on the interpretation of existing or future contractual terms.
One of our exposures to market risk occurs at the time our existing contracts expire and are subject to renegotiation and renewal. BasedAs these contracts expire, we may have to negotiate extensions or renewals with existing customers or enter into new contracts with existing customers or other customers. We may be unable to do so on total projected contractual revenues, including projected contractual revenues from future capacity expected from expansion projects that are not yet fully constructed for whichfavorable commercial terms, if at all. Further, we have executed firm contracts,also may be unable to maintain the economic structure of a particular contract with an existing customer or the overall mix of our firm gathering contracts and firm transmission and storage contracts had weighted average remaining terms of approximately 14 years and 13 years, respectively, as of December 31, 2021.contract portfolio. The extension or replacementrenewal of existing contracts and entry into new contracts depends on a number of factors beyond our control, including, but not limited to,to: (i) the level of existing and new competition to provide services to our markets; the(ii) macroeconomic factors affecting natural gas economics for our current and potential customers; (iii) the balance of supply and demand, on a short-term, seasonal and long-term basis, in our markets; (iv) the extent to which the customers in our markets are willing to contract on a long-term basis or require capacity on our systems; (v) customers’ existing and future downstream commitments; and (vi) the effects of federal, state or local regulations on the contracting practices of our customers and us. For more information related to contracting practices applicable to uscertain of our services, see “Regulatory Environment –— FERC Regulation” under Part I, “Item 1. Business.”Business” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Additionally, disagreements may arise with contractual counterparties on the interpretation of contractual provisions, as had been the case with EQT with the Hammerhead gathering contract, including during the negotiation, for example, of contract amendments required to be entered into upon the occurrence of specified events.
Any failure to extend or replace a significant portion of our existing contracts or to extend or replace our more significant contracts, or extending or replacing contracts at unfavorable or lower rates or with lower or no associated firm reservation fee revenues, or other disadvantageous terms relative to the prior contract structure, or disagreements or disputes on the interpretation of existing or future contractual terms, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
The ongoing outbreak of COVID-19 and its variant strains (or any future pandemic) could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Disruptions caused by pandemics, epidemics or disease outbreaks, such as COVID-19 and variants thereof, could materially affect the domestic and global economy, the natural gas industry, and/or us. The COVID-19 pandemic is ongoing and there is considerable uncertainty regarding the extent to which COVID-19 and variant strains will continue to spread and the effects of such continued spread.
Given the ongoing and dynamic nature of the circumstances, it is difficult to predict the further impact of the COVID-19 outbreak (or any other outbreak) on the domestic economy, the natural gas industry, and/or us; however, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be negatively affected in numerous ways, including, without limitation, that:
•demand for natural gas could be adversely affected, as was the case in 2020, which could negatively affect prices and forward prices for natural gas and our customers, including their development plans and, consequently, lead to curtailments or otherwise decrease demand for our services or heighten our exposure to customer risk;
•our operations, or those of our customers or suppliers, may be disrupted or become less efficient if a significant number of employees or contractors are unavailable due to illness;
•we, our customers and suppliers may be adversely affected due to the continued constraints on global supply chains resulting from the outbreak and may be adversely affected if the outbreak causes further or long delays in access to or
increases to cost of inventory, equipment or other items necessary to our, our customers’ or our suppliers’ respective businesses;
•legal and regulatory processes relevant to our operations may be disrupted or slowed, such as if relevant governmental authorities suffer reduced workforce availability due to the virus; and
•resultant disruption to, and instability in, financial and credit markets may adversely affect our access to capital, leverage and liquidity levels and credit ratings, as well as our counterparties’ access to capital, business continuity, financial stability, leverage and liquidity levels and credit ratings (which could heighten counterparty credit risk to which we are exposed in the ordinary course of our business).
Further, we could be affected by governmental mandates and responses to the pandemic. See “The loss or disengagement of key personnel could adversely affect our ability to execute our strategic, operational and financial plans.” in this Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Although we believe that we are following best practices under COVID-19 guidance and intend to continue to refine our practices as additional guidance is released, there is no guarantee that efforts by us or any other entity or authority to mitigate potential adverse impacts of the COVID-19 outbreak, whether on a local, state or national level, will be effective.
We also may incur additional costs to further attempt to mitigate potential impacts caused by COVID-19 related disruptions, which could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. Further, the COVID-19 outbreak (including federal, state and local governmental responses, broad economic impacts and market disruptions) has heightened and may further heighten many of the other risks set forth herein. The extent of the impact of COVID-19 on us will continue to depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted, including new information which may emerge concerning the severity of COVID-19, appearance or escalating circulation of new strains of the virus (including those with potential immune evasion or escape mutations), duration of the outbreak, and related economic effects and aftereffects (including on the natural gas industry), and actions taken to contain COVID-19 or its impact, including vaccine acceptance and mandates.
We may not be able to increase our customer throughput and resulting revenue due to competition and other factors, which could limit our ability to grow.
Our ability to increase our customer-subscribed capacity and throughput and resulting revenue is subject to numerous factors beyond our control, including competition from third-party producers’ existing contractual obligations to competitors, the location of our assets relative to those of competitors for existing or potential producer customers (or such producer customers’ own midstream assets), takeaway capacity constraints out of the Appalachian Basin, commodity prices, producers’ optionality in utilizing our (relative to third-party) systems to fill downstream commitments, and the extent to which we have available capacity when and where shippers require it. To the extent that we lack available capacity on our systems for volumes, or we cannot economically increase capacity, we may not be able to compete effectively with third-party systems for additional natural gas production in our areas of operation.operation and capacity constraints, as well as commodity prices, may, as has occurred in the past, adversely affect the degree to which natural gas production occurs in the Appalachian Basin, and relatedly the degree to which our systems are utilized.
Our efforts to attract new customers or larger commitments from existing customers may be adversely affected by our desire to provide services pursuant to long-term firm contracts and contracts with MVCs. Our potential customers may prefer to obtain services under other forms of contractual arrangements which could require volumetric exposure or potentially direct commodity exposure, and we may not be willing to agree to such other forms of contractual arrangements.
If third-party pipelines and other facilities interconnected to our pipelines and facilities become unavailable to transport or process natural gas or do not accept deliveries of natural gas from us, our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders could be adversely affected.
We depend on third-party pipelines and other facilities that provide receipt and delivery options to and from our transmission and storage system. For example, our and the MVP Joint Venture’s (once MVP is placed in-service) transmission, and our storage, system interconnects, as applicable, with the following third-party interstate pipelines: Transcontinental Gas Pipe Line Company, LLC (Transco), East Tennessee Natural Gas, Texas Eastern, DominionEastern Gas Transmission, Columbia Gas Transmission, Tennessee Gas Pipeline Company, Rockies Express Pipeline LLC, National Fuel Gas Supply Corporation and ET Rover Pipeline, LLC, as well as multiple distribution companies. Similarly, our gathering systems have multiple delivery interconnects to multiple interstate pipelines. In the event that our or the MVP Joint Venture's access to such systems is impaired (or any third party refuses to accept our or any of the amount of natural gas thatMVP Joint Venture's deliveries), our gathering systems can gather and transport previously has been, and inor the future wouldMVP Joint Venture's operations could be adversely affected, which hasresulting in adverse economic impact to us or the MVP Joint Venture. We have been affected by certain such circumstances in the past, which for example has reduced and could, as applicable, reduce revenues from our gathering activities as well as transmission and storage activities.
Because we do not own these third-party pipelines or facilities, their continuing operation isand access requirements are not within our control. If these or any other pipeline connections or facilities were to become unavailable for current or future volumes of natural gas due to repairs, damage to the facility, lack of capacity or any other reason, our (or, with MVP in-service, the MVP Joint Venture’s) ability to operate efficiently and continue shippingship natural gas to end markets could be restricted, as has occurred in the past. Any temporary or permanent interruption at any key pipeline interconnect or facility could have a material
adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
A substantial majority of the services we provide on our transmission and storage system are subject to long-term, fixed-price “negotiated rate” contracts that are subject to limited or no adjustment, even if our cost to perform such services exceeds the revenues received from such contracts, and, as a result, our costs could exceed our revenues received under such contracts, we could be unable to achieve the expected investment return under such contracts, and/or our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders could be adversely affected.
It is possible that costs to perform services under “negotiated rate” contracts could exceed the negotiated rates we have agreed to provide towith our customers. If this occurs, it could decrease the cash flow realized by our systems and, therefore, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. Under FERC policy, a regulated service provider and a customer may mutually agree to a “negotiated rate,” and that contract must be filed with and accepted by the FERC. As of December 31, 2021,2023, approximately 97% of the contracted firm transmission capacity on our system was subscribed under such “negotiated rate’’ contracts. Unless the parties to these “negotiated rate” contracts agree otherwise, the contracts generally may not be adjusted to account for increased costs that could
be caused by inflation, GHG emission cost (such as carbon taxes, fees, or assessments) or other factors relating to the specific facilities being used to perform the services.
We have entered into joint ventures, and may in the future enter into additional or modify existing joint ventures, that might restrict our operational and corporate flexibility and divert our management’s time and our resources. In addition, we exercise no control over joint venture partners and it may be difficult or impossible for us to cause these joint ventures or partners to take actions that we believe would be in our or the joint venture’s best interests and these joint ventures are subject to many of the same operational risks to which we are subject.
We have entered into joint ventures to construct the MVP and MVP Southgate projects and a joint venture relating to Eureka Midstream, and may in the future enter into additional joint venture arrangements with third parties.parties, including in respect of any expansion of the MVP. Joint venture arrangements may restrict our operational and corporate flexibility. Joint venture arrangements and dynamics can also divert management and operating resources in a manner that is disproportionate to our ownership percentage in such ventures. Because we do not control all of the decisions of the MVP Joint Ventureour joint ventures or the joint venture relating to Eureka Midstream,partners, it may be difficult or impossible for us to cause these joint ventures or partners to take actions that we believe would be in our or the joint venture’s best interests. Moreover, joint venture arrangements involve various risks and uncertainties, such as committing that we fund operating and/or capital expenditures, the timing and amount of which we may not control, and our joint venture partners may not act in a manner that we believe would be in our or the joint venture’s best interests, may elect not to support further pursuit of projects, and/or may not satisfy their financial obligations to the joint venture. The loss of joint venture partner support in further pursuing or funding a project may, and would in the case of the MVP project, significantly adversely affect the ability to complete the project. In addition, the operations of the MVP Joint Venture, Eureka Midstream and any joint ventures we may enter into in the future are subject to many of the same operational risks to which we are subject. For example, we may not be able to obtain financing at, or in respect of, a joint venture, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
AcquisitionsStrategic transactions that we may makeenter into could reduce, rather than increase, our results of operations and liquidity, and adversely affect our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Any completed acquisition involves potentialWe have, and may in the future, engage in acquisitions, dispositions, and other strategic transactions. These transactions involve risks that have impacted and may in the future impact our ability to realize a benefit from the transaction, including, among other things:
•potential risks (and as applicable): (i) an inability to obtain necessary regulatory and third-party approvals; (ii) the timing of and conditions imposed upon us by regulators in connection with such approvals; (iii) failure to realize assumptions about volumes, revenues, capital expenditures and costs, including synergies and potential growth;
• (iv) an inability to secure or maintain adequate customer commitments to use the acquired systems or facilities;
• (v) an inability to successfully integrate the assets or businesses we acquire;
• (vi) we could be required to contribute additional capital to support acquired businesses or assets, and we may assume liabilities that were not disclosed to us, for which we are not indemnified or insured or for which our indemnity or insurance is inadequate;
• (vii) the diversion of management’s and employees’ attention from other business concerns in a manner that is disproportionate to the relative size and impact of, or ownership percentage in, such acquired assets or entities; and
• (viii) unforeseen difficulties operating a larger organization or in new geographic areas, with new joint venture partners or new business lines.
If risks such as the above are realized, or if an acquisitiona strategic transaction fails to be accretive over the long term to our cash generated from operations on a per share basis, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
We do not insure against all potential losses and could be seriously harmed by unexpected liabilities.liabilities or the inability of our insurers to satisfy our claims.
We are not fully insured against all risks inherent in our business, including certain environmental accidents that might occur as well as many cyber events. We do not maintain insurance in the type to cover all possible risks of loss, including “wild well” coverage or certain damage caused by cyberattacks. In addition, we do not maintain business interruption insurance of the types and in amounts necessary to cover all possible risks of loss, like project delays caused by pandemics, cyberattacks, certain environmental incidents, governmental action or inaction. The occurrence of any risks not fully covered by insurance could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
We currentlyIn addition to requiring in many instances that we are named as additional insureds on policies maintained by vendors such as construction contractors, as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K we maintain excess liability insurance that covers our and our affiliates’ legal and contractual liabilities arising out of bodily injury, personal injury or property damage, including resulting loss of use, to third parties. This excess liability insurance includes coverage for sudden and accidental pollution liability but excludes: release of pollutants subsequent to their disposal; release of substances arising from the combustion of fuels that result in acidic deposition; and testing, monitoring, clean-up, containment, treatment or removal of pollutants from property owned, occupied by, rented to, used by or in the care, custody or control of us and our affiliates. We also maintain
coverage for us and our affiliates for physical damage to assets and resulting business interruption, including, in limited circumstances, certain damage caused by cyberattacks.
Most of our insurance is subject to deductibles or self-insured retentions. If a significant accident or event occurs for which we are not fully insured, it could adversely affect our operations, business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. We may not be able to maintain or obtain insurance of the types and in the amounts we desire at reasonable rates, and we have elected and may elect in the future to self-insure a portion of our asset portfolio. The insurance coverage we have obtained or may obtain may contain large deductibles or fail to cover certain hazards or cover all potential losses. In addition, for pre-Distribution losses, we share insurance coverage with EQT, and we will remain responsible for payment of any deductible or self-insured amounts under those insurance policies. To the extent we experience a pre-Distribution loss that would be covered under EQT’s insurance policies, our ability to collect under those policies may be reduced to the extent EQT erodes the limits under those policies.
Furthermore, any insurance company that provides coverage to us may experience negative developments that could impair its ability to pay any of our claims. As a result, we could be exposed to greater losses than anticipated and may have to obtain replacement insurance, if available, at a greater cost.
Significant portions of our pipeline systemsassets have been in service for several decades. There could be unknown events or conditions, or increased maintenance or repair expenses and downtime, associated with our pipelinesassets that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Significant portions of our transmission and storage system and FERC-regulated gathering system have been in service for several decades. The age and condition of these systems has contributed to, and could result in, adverse events, or increased maintenance or repair expenditures, and downtime associated with increased maintenance and repair activities.activities, as applicable. Any such adverse events or any significant increase in maintenance and repair expenditures or downtime, or related loss of revenue, due to the age or condition of our systems could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. See also,“We may incur significant costs and liabilities as a result of performance of our pipeline and storage integrity management programs and compliance with increasingly stringent safety regulation.” in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The loss or disengagement of key personnel or other workforce problems could adversely affect our ability to execute our strategic, operational and financial plans.
Our operations are dependent upon key management, technical and professional personnel, and one or more of these individuals could leave our employment.employment or become unavailable due to, among other things, pandemics or epidemics, natural disaster, war, act of terrorism, sustained illness or injury. The unexpected loss of the services and skills of one or more of these individuals could have a detrimental effect on us. In addition, the success of our operations depends, in part, on our ability to identify, attract, develop and retain experienced personnel. There iscontinues to be increased competition for experienced technical and other professionals, primarily in the corporate services functions, which could increase the costs associated with identifying, attracting and retaining such personnel. Additionally, a lack of employee engagement could lead to increased employee burnout, loss of productivity, increased propensity for errors, increased employee turnover, increased absenteeism, increased safety incidents and decreased customer satisfaction, which may in turn negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition. If we cannot identify, attract, develop, retain and engage key management, technical and professional personnel, along with other qualified employees, to support the various functions of our business, our ability to compete could be harmed.
On November 4, 2021, OSHA issued the ETS to carry out President Biden’s executive order requiring all employers with at least 100 employees to ensure that their employees are fully vaccinated or require unvaccinated workers to produce a negative test result at least once a week. On January 13, 2022, the U.S. Supreme Court granted an application to stay the ETS pending disposition of the applicants' petitions for review in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit. Effective January 26, 2022, OSHA withdrew the ETS as an enforceable emergency temporary standard, but did not withdraw the ETS as a proposed rule.
Should the ETS, or a similar state or local requirement, take effect in the future, the Company expects it would be subject to such regulation concerning COVID-19 vaccination or testing. In that case, the Company may be required to implement a requirement that many or most employees get vaccinated, subject to limited exceptions, or be tested. Such a mandate may result in increased costs, operational disruptions or employee attrition for the Company, which could be material. If we lose employees, it may be difficult in the current competitive labor market to find replacement employees, and this could have an adverse effect on future operations, revenues and costs, which could be material. Accordingly, implementation of and complying with the ETS or a similar state or local requirement could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Our exposure to direct commodity price risk may increase in the future.future and NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA.
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, 2020approximately 70%, 71% and 2019, approximately 64%, 66% and 58%, respectively, of our operating revenues were generated from firm reservation fees.fee revenues. Consequently, cash flows generated from such revenues generally had limited exposure to commodity price risks. However, cash flows that are not derived from firm reservation fees, such as those derived from our volumetric-based services, do create a level of exposure to commodity price risk in that producer customers may adjust their plans as a result of changes in the commodity price environment. Although our goal is to executecontinue to seek to contractually minimize our exposure to commodity price risk in the future by executing long-term firm reservation fee, MVC and MVCARC contracts with new or existing customers, in the future, our efforts to obtain such contractual terms may not be successful. In addition, we may acquire or develop additional midstream assets in the future that do not provide services primarily based on capacity reservation charges, MVCs, ARCs or other fixed fee arrangements and therefore may have a greater exposure to fluctuations in customer volume variability driven by commodity price risk than our current operations. Significantly greaterrisk. Our existing and future exposure, primarily through volumetric-based services, to the volatility of natural gas prices, including regional basis differentials with regard to natural gas prices, as a result of our contractsand any significant increase to such exposure could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Additionally, the EQT Global GGA provides for potential cash bonus payments payable by EQT to us during the period beginning on the first day of the calendar quarter in which the MVP full in-service date occurs through the calendar quarter ending December 31, 2024 (the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision). The fair value of the derivative asset attributable to the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision is largely determined by estimates of the NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas forward price curve and probability-weighted assumptions regarding MVP full in-service timing, and payments are conditioned upon the quarterly average of certain Henry Hub natural gas prices exceeding certain price thresholds. The NYMEX Henry Hub future price of natural gas is a widely used benchmark for the price of natural gas in the United States. Based on the Henry Hub natural gas forward strip prices as of February 18, 202216, 2024 and the terms of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision, any adverse change in assumptions regarding the MVP project may further decrease the estimated fair value of the derivative asset attributable to the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision, and such decrease may be substantial.adverse change or simply commodity prices on their own could ultimately result in further decreases to such estimated fair value, including to zero. Such changes in estimated fair value, if any, would be recognized in other income (expense) income,, net, on our statements of consolidated comprehensive income andincome. Depending on the future NYMEX Henry Hub prices, payments under the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision may not be triggered even if MVP were to be placed in-service (and, even if prices are sufficient to meet necessary thresholds, payments will not be triggered if the MVP is not placed in-service in or before the quarter ending December 31, 2024), which could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
We do not own all of the land on which our pipelines and facilities are located, which could disrupt our operations and future development.
We do not own all of the land on which our pipelines, storage systems and facilities have been constructed, and we have been, and in the future could be, subject to more onerous terms, and/or increased costs or delays, in retaining necessary landattempting (or by virtue of the need to attempt) to acquire or to maintain use if we do not have valid rights-of-way or easements, if such rights-of-way or easements lapse or terminate or if our facilities are not properly located within the boundariesrights to land. See “Item 2. Properties” in Part I of such rights-of-way or easements.this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information. Although many of these rights are perpetual in nature, we occasionally obtain the rights to construct and operate our pipelines and other facilities on land owned by third parties and governmental agencies for a specific period of time.time or in a manner in which certain facts could give rise to the presumption of the abandonment of the pipeline or other facilities. As has been the case in the past, if we were to be unsuccessful in negotiating or renegotiating rights-of-way or easements, we might have to institute condemnation proceedings on our FERC-regulated assets, the potential for which may have a negative effect on the timing and/or terms of FERC action on a project’s certification application and/or the timing of any authorized activities, or relocate our facilities for non-regulated assets. The FERC has announced a policy that would presumptively stay the effectiveness of certain future construction certificates, which may limit when we are able to exercise condemnation authority. It is possible that the U.S. Congress may amend Section 7 of the NGA to codify the FERC's presumptive stay or otherwise limit, modify, or remove the ability to utilize condemnation. It is also possible that a court may limit, modify or remove an operator’s ability to utilize condemnation under Section 7 of the NGA. A loss of rights-of-way, lease or easements or a relocation of our non-regulated assets could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. Additionally, even when we own an interest in the land on which our pipelines, storage systems and facilities have been constructed, agreements with correlative rights owners have caused us to, and in the future may require that we, relocate pipelines and facilities or shut in storage systems and facilities to facilitate the development of the correlative rights owners’ estate, or pay the correlative rights owners the lost value of their estate if they are not willing to accommodate development.
Legal and Regulatory Risk
Our and the MVP Joint Venture’s natural gas gathering, transmission and storage services, as applicable, are subject to extensive regulation by federal, state and local regulatory authorities. Changes in or additional regulatory measures adopted by such authorities, and related litigation, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends.
Our and the MVP Joint Venture’s interstate natural gas transmission and storage operations, as applicable, are regulated by the FERC under the NGA and the NGPA and the regulations, rules and policies promulgated under those and other statutes. Certain portions of our gathering operations are also currently regulated byOur and the FERC in connection with our interstate transmission operations. OurMVP Joint Venture’s FERC-regulated operations are pursuant to tariffs approved by the FERC that establish rates (other than market-based rate authority), cost recovery mechanisms and terms and conditions of service to our customers. The FERC’s authority extends to a variety of matters relevant to our operations. For additional information, see “Regulatory Environment—Environment — FERC Regulation” and “Regulatory Environment—FERC Regulation of Gathering Rates and Terms of Service” under “Item 1. Business.”Business” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Pursuant to the NGA, existing interstate transmission and storage rates, terms and conditions of service, and contracts may be challenged by complaint and are subject to prospective change by the FERC. Additionally, rate increases, changes to terms and conditions of service and contracts proposed by a regulated interstate pipeline may be protested and such actions can be delayed and may ultimately be rejected by the FERC. WeAs of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we and the MVP Joint
Venture currently hold authority from the FERC to charge and collect (i) “recourse rates,” which are the maximum rates an interstate pipeline may charge for its services under its tariff, (ii) “discount rates,” which are rates below the “recourse rates” and above a minimum level, (iii) “negotiated rates,” which involve rates that may be above or below the “recourse rates,” provided that the affected customers are willing to agree to such rates and that the FERC has approved the negotiated rate agreement, and (iv) market-based rates for some of our storage services from which we derive a small portion of our revenues. As of December 31, 2021,2023, approximately 97% of our contracted firm transmission capacity was subscribed by customers under negotiated rate agreements under our tariff, rather than recourse, discount or market-based rate contracts. There can be no guarantee that we or the MVP Joint Venture will be allowed to continue to operate under such rates or rate structures for the remainder of those assets’ operating lives. Customers, the FERC or other interested stakeholders, such as state regulatory agencies, may challenge our or the MVP Joint Venture’s rates offered to customers or the terms and conditions of service included in our tariffs. We do notNeither we nor the MVP Joint Venture have an agreement in place that would prohibit customers, including EQT or its affiliates, from challenging our or the MVP Joint Venture’s rates or tariffs. Any successful challenge against rates charged for our or the MVP Joint Venture’s transmission and storage services, as applicable, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Any changes to the FERC’s policies regarding the natural gas industry may have an impact on us, including the FERC’s approach to pro-competitive policies as it considers matters such as interstate pipeline rates and rules and policies that may affect rights of access to natural gas transmission capacity and transmission and storage facilities. The FERC and U.S. Congress may continue to evaluate changes in the NGA or new or modified FERC regulations or policies that may impact our or the MVP Joint Venture’s operations and affect our or the MVP Joint Venture’s ability to construct new facilities and the timing and cost of such new facilities, as well as the rates we chargecharged to our or the MVP Joint Venture’s customers and the services we provide.provided.
AOur and the MVP Joint Venture’s significant construction projectprojects generally requiresrequire review by multiple governmental agencies, including state and local agencies, whose cooperation is important in completing the regulatory process on schedule. Any agency’s delay in the issuance of, or refusal to issue, authorizations or permits, issuance of such authorizations or permits with unanticipated conditions, or the loss of a previously-issued authorization or permit, for one or more of these projects may mean that we will not be able to pursue these projects or that they will be constructed in a manner or with capital requirements that we did not anticipate.anticipate (as has been the case with our MVP project). Such delays, refusals, losses of permits, or resulting modifications to projects, certain of which we have experienced with respect to the MVP project and the originally contemplated MVP Southgate project, could materially and negatively impact the revenues and costs expected from these projects or cause us or our joint venture partners to abandon planned projects. For example, see “Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions” under “Item 1. Business.” and “Item 3. Legal Proceedings.” for a discussion of certain such regulatory matters relevant to the MVP and the MVP Southgate projects.
Failure to comply with applicable provisions of the NGA, the NGPA, federal pipeline safety laws and certain other laws, as well as with the regulations, rules, orders, restrictions and conditions associated with these laws, could result in the imposition of administrative and criminal remedies and civil penalties. For example, the FERC is authorized to impose civil penalties of up to approximately $1.3$1.5 million (adjusted periodically for inflation) per violation, per day for violations of the NGA, the NGPA or the rules, regulations, restrictions, conditions and orders promulgated under those statutes.
In addition, future federal, state or local legislation or regulations under which we or the MVP Joint Venture will operate our natural gas gathering, transmission and storage businesses may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
We are subject to stringent environmental and other laws and regulations that expose us to significant costs and liabilities that could exceed our expectations and affect our business. The current laws and regulations affecting our business are subject to change and in the future we may be subject to additional or revised laws, regulations and legal requirements, that could adversely impact our business.
Our operations are regulated extensively at the federal, state and local levels. For additional information on laws, regulations and other legal requirements applicable to us, see “Regulatory Environment” under “Item 1. Business.”Business” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Laws, regulations and other legal requirements applicable to our business, including relating to the environmental protection, health and safety, cybersecurity, as well
as climate change, have, among other things, increased, and in the future could continue to increase, our cost of compliance and doing business, including costs related to planning, designing, permitting, constructing, installing, operating, updating and/or abandoning gathering, transmission and water systems and pipelines, as well as storage systems. The need to comply with such laws, regulations and other legal requirements, and incidents of noncompliance, whether by us or third parties with whom we engage, has adversely affected and will likely continue to adversely affect our business, such as by, among other things and as applicable, resulting in increased costs, costly delays, operating restrictions and diversion of management time and resources in evaluating the ability to pursue projects, such as when new or additional permits or alternative construction methods are required. For example, as discussedsee Part I, “Item IA. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under “The regulatory approval process for the construction of new midstream assets is very challenging, has significantly increasedWe have incurred and expect to continue to incur costs and delayed targeted in-service dates,expenses as
a result of or arising in relation to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident in November 2022, which has included and decisions bymay include potential additional regulatory penalties or other sanctions, which could, depending on their scope and judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings are likely to impacttiming, materially adversely affect our or the MVP Joint Venture'sbusiness, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvalspay dividends to our shareholders.” and authorizations necessary to complete certain projects on the targeted time frame or at all or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects.”, there are several pending applications for and/or challenges to certain aspects of the MVP project and the MVP Southgate project that affect the MVP project and the MVP Southgate project, as applicable, including those litigation and regulatory-related delays discussed inPart I, “Item 3. Legal Proceedings.”Proceedings” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition, noncompliance with applicable laws, regulations or other legal requirements, including required permits and other approvals, has subjected and could subject us to, among other things, claims for personal injuries, property damage and other damages and, even if as a result of factors beyond our control and irrespective of our fault, could result in the suspension or termination of our operations and subject us to administrative, civil and criminal penalties and damages that could materially and negatively affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders. The risk of our incurring environmental costs and liabilities in connection with our operations is significant given our handling of natural gas, produced water and other hydrocarbons, as well as air emissions related to our operations. Risk is also present as a result of historical industry operations and waste disposal practices, and our handling of waste. These matters are subject to stringent and complex federal, state and local laws and regulations governing environmental protection and could affect our business in many ways. For example, an accidental release, irrespective of fault, from one of our pipelines or storage systems, has subjected and could subject us, as applicable, to substantial liabilities arising from environmental cleanup and restoration costs, claims made by neighboring landowners and other third parties for personal injury and property damage and fines or penalties for related violations of environmental laws or regulations. We may not be able to recover all or any of these costs from insurance. Further, we are generally responsible for all liabilities associated with the environmental condition of our facilities and assets, whether acquired or developed, regardless of when the liabilities arose and whether they are known or unknown. In connection with certain acquisitions and divestitures, we could acquire, or be required to provide indemnification against, environmental liabilities that could expose us to material losses, which may not be covered by insurance. In addition, the steps we could be required to takeneeded to bring certain facilities that arewere acquired into compliance have been expensive. In the future, steps to bring other acquired facilities into compliance could be prohibitively expensive, and we might be required to shut down, divest or alter the operation of those facilities, which might cause us to incur losses.
Laws, regulations and other legal requirements applicable to our business also are constantly changing, and implementation of compliant processes in response to such changes could be costly and time consuming. As an example, the FWS receives hundreds of petitions to consider listing of additional species as endangered or threatened and is regularly sued or threatened with lawsuits to address these petitions. Some of these legal actions have resulted, and may in the future result, in the listing of species located in our operating areas. Such designations of previously unprotected species as being endangered or threatened, or the designation of previously unprotected areas as a critical habitat for such species, has adversely affected and may in the future adversely affect our assets or projects. Additionally, as discussed under “Regulatory Environment” in “Item 1. Business”, in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, federal and state governments and agencies, including states where we operate, have made advancing environmental justice a priority. A significant number of current environmental justice initiatives focus on enhancing public participation in permitting and other project development-related decisions. WeOur projects and the MVP Joint Venture’s projects have been, and in the future may be, the target of objections to permits before state and federal agencies and related litigation brought by individuals or advocacy organizations that are purporting to raise environmental justice issues. In addition, various federal and state agencies have increased their focus on, and resources devoted to, environmental justice and certain agencies, including EPA and DOJ, have announced plans to seeksought out opportunities to address environmental justice issues through federal and state enforcement actions. Revised or additional laws, regulations or legal requirements (or interpretations thereof) that result in increased compliance costs, litigation or additional operating restrictions, particularly if those costs are not fully recoverable from our customers, or affect our customers’ production and operations, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
For information related to risks associated with laws and regulations concerning climate change, see “Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing the financing of non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting the pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies, and alternative forms of energy) and, as well as physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.”
We and our joint ventures may incur significant costs and liabilities as a result of adverse events orperformance of our pipeline and storage integrity management programs and compliance with increasingly stringent pipeline safety regulation, including pipeline integrity management program testing and related repairs.regulation.
The DOT, acting through PHMSA, hasand certain state agencies certificated by PHMSA, have adopted regulations requiring pipeline operators to develop an integrity management programsprogram for transmission pipelines located where a leak or rupture could harmimpact high population sensitive areas (also known as High Consequence Areas or HCAs) and newly defined Moderate Consequence Areas (MCAs), and an integrity management program for storage wells, unless the operator effectively demonstrates by a prescriptive risk assessment that the pipelinethese operational assets have mitigated risks that could not affect the area.these predefined areas, as applicable. The regulations require operators, including us, to perform ongoing assessments of pipeline and storage integrity; identify and characterize applicable threats to pipeline segments and storage wells that could impact a high population area;sensitive areas; confirm maximum allowable operating pressures; maintain and improve processes for data
collection, integration and analysis; repair and remediate pipelinesfacilities as necessary; and implement preventive and mitigating actions. In addition to population sensitive areas, PHMSA has also recently adopted regulations extending existing design, operational and maintenance, and reporting requirements to onshore gathering pipelines in rural areas. Finally, new PHMSA regulations require operators of certain transmission pipelines to assess their integrity management and maintenance practices, comply with enhanced corrosion control and mitigation timelines, and follow new requirements for pipeline inspections following an extreme weather event or natural disaster.
ChangesThe cost and financial impact of compliance will vary and depend on factors such as the number and extent of maintenance determined to be necessary as a result of the application of our integrity management programs, and such costs and financial impact could have a material adverse effect on us. Further, our pipeline and storage integrity management programs depend in part on inspection tools and methodologies developed, maintained, enhanced and applied, and certain testing conducted, by certain third parties, many of which are widely utilized within the natural gas industry. Advances in these tools and methodologies could identify potential and/or additional integrity issues for our assets. Consequently, we may incur additional costs and expenses to remediate those newly identified or potential issues, and we may not have the ability to timely comply with applicable laws and regulations. Additionally, pipeline and storage safety laws and regulations are subject to change and failures to comply with pipeline and storage safety laws and regulations, including changes in such laws and regulations or interpretations thereof that result in more stringent or costly safety standards, could have a material adverse effect on us. For more information on the laws, regulations and risks applicable to us, including risks associated with compliance with the Mega Rule, see “Regulatory Environment—PipelineEnvironment — Safety and Maintenance” under “Item 1. Business.”Business” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We may, and joint ventures of which we are the operator could, as is the case with the MVP Joint Venture, become subject to consent orders and agreements relating to integrity matters. On October 3, 2023, PHMSA issued a consent order incorporating the terms of a consent agreement entered into by PHMSA and the Company as the operator of the MVP project (the MVP Consent Agreement). The MVP Consent Agreement resolves the Notice of Proposed Safety Order (NOPSO) that PHMSA issued to the Company on August 11, 2023, for the MVP project, without admission or denial of any of the allegations in the NOPSO. The MVP Consent Agreement outlines the steps being taken by the MVP Joint Venture to responsibly complete construction, including, among other things, enhancing MVP’s existing coating, remediation and inspection processes, mandating or accelerating certain previously planned MVP inline inspections, accelerating the regulatory timeline for conducting cathodic protection surveys, and implementing additional measures to assess cathodic protection following MVP full in-service. The MVP Joint Venture has been conducting surveys and analyses and submitting reports to PHMSA in compliance with the requirements of the consent agreement. Failure to comply with the terms of the MVP Consent Agreement could have adverse effects on our business, including, in the case of the MVP Consent Agreement, adverse effects regarding MVP project completion.
The adoption of legislation relating to hydraulic fracturing and the enactment of new or increased severance taxes and impact fees on natural gas production could cause our current and potential customers to reduce the number of wells they drill in the Marcellus and Utica Shales or curtail production of existing wells.wells connected to our assets. If reductions are significant for those or other reasons, the reductions would likelycould have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Our assets are primarily located in the Marcellus Shale fairway in southwestern Pennsylvania and northern West Virginia and the Utica Shale fairway in southeastern Ohio, and a substantial majority of the production that we receive from customers is produced from wells completed using hydraulic fracturing. Hydraulic fracturing is an important and commonly used process in the completion of oil and gas wells, particularly in unconventional resource plays like the Marcellus and Utica Shales. Hydraulic fracturing is typically regulated by state oil and gas commissions and similar agencies, but several federal agencies have asserted regulatory authority over aspects of the process, including the EPA, which finalized effluent limit guidelines allowing zero discharge of wastewater from shale gas extraction operations to publicly owned treatment plants in 2016 in addition to existing limits on direct discharges. Additionally, in response to increased public concern regarding the alleged potential impacts of hydraulic fracturing, the EPA has asserted federal regulatory authority pursuant to the federal Safe Drinking Water Act over certain hydraulic fracturing activities involving the use of diesel fuels and published permitting guidance in February 2014 addressing the performance of such activities using diesel fuels.
The U.S. Congress has from time to time considered the adoption of legislation to provide for federal regulation of hydraulic fracturing, while a number of states, including those in which we operate, have adopted, and other states are considering adopting, regulations that could impose more stringent disclosure and/or well construction requirements on hydraulic fracturing operations. Some states, such as Pennsylvania, have imposed fees on the drilling of new unconventional oil and gas wells. Some states have elected, and other states could elect, to prohibit hydraulic fracturing altogether. The Biden Administration temporarily banned new leases for oilIn addition, there are regulations existing and gas drilling onproposed at the federal lands in January 2021, butand state level that ban was subsequently blocked by a federal court.could indirectly limit or affect hydraulic fracturing. Also, certain local governments have adopted, and others may adopt, ordinances within their jurisdictions regulating the time, place and manner of drilling activities in general or hydraulic fracturing activities in particular. Further, several federal governmental agencies, including the EPA, as well as certain states, have conducted reviews and studies on the environmental aspects of hydraulic fracturing, including the EPA. For example, in December 2016, the EPA issued its final report on a study it had conducted over several years regarding the effects of hydraulic fracturing on drinking water sources. The final report, contrary to several previously published draft reports issued by the EPA, found instances in which impacts to drinking water may occur. However, the report also noted significant data gaps that prevented the EPA from determining the extent or severity of these impacts. EPA has more recently sought input from states and stakeholders on approaches to management of wastewater produced from oil and gas extraction at onshore facilities, and published a summary of the input it received in May 2020.fracturing. The results of such reviews or studies have and could further spur initiatives to further regulate hydraulic fracturing.
State and federal regulatory agencies have focused on a possible connection between hydraulic fracturing-related activities and the increased occurrence of seismic activity (induced seismicity). In a few instances, operators of injection disposal wells in the vicinity of seismic events have been ordered to reduce injection volumes or suspend operations. Some state regulatory agencies, including those in Colorado, Ohio, Oklahoma and Texas, have modified their regulations to account for induced seismicity. While Pennsylvania is not one of the states where such regulation has been enacted, regulatory agencies at all levels are continuing to study the possible linkage between oil and gas activity and induced seismicity. These developments could result in additional regulation and restrictions on the use of injection disposal wells and hydraulic fracturing. Such regulations and restrictions could cause delays and impose additional costs and restrictions on our customers.
The adoption of new laws, regulations, ordinances, or executive actions at the federal, state or local levels imposing more stringent restrictions on hydraulic fracturing could make it more difficult for our customers to complete natural gas wells,
increase customers’ costs of compliance and doing business, and otherwise adversely affect the hydraulic fracturing services they perform, which could negatively impact demand for our gathering, transmission and storage, or water services.
Furthermore, the tax laws, rules and regulations that affect our customers are subject to change. For example, Pennsylvania’s governor has previouslyin Pennsylvania legislation was proposed legislation to impose a state severance tax on the extraction of natural resources, including natural gas produced from the Marcellus and Utica Shale formations, either in replacement of or in addition to the existing state impact fee. Pennsylvania’s legislature has not thus far advanced any of the governor’s severance tax proposals; however, severance tax legislation may continue to be proposed in future legislative sessions. Any such tax increase or change could adversely impact the earnings, cash flows and financial position of our customers and cause them to reduce their drilling in the areas in which we operate, which could negatively impact demand on our gathering, transmission and storage, and water services.
Risks Related to an Investment in Us
For the taxable years prior to January 1, 2021, the tax treatment of EQM depended on its status as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, as well as it not being subject to a material amount of entity-level taxation by individual states. If the IRS were to treat EQM as a corporation or if EQM becomes subject to additional amounts of entity-level taxation for state or foreign tax purposes for any open taxable year prior to January 1, 2021, it would reduce the amount of cash we have available to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Prior to the EQM Merger, EQM was a publicly traded partnership and the anticipated after-tax economic benefit of an investment in our shares depended largely on EQM being treated as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, which requires that 90% or more of EQM’s gross income for every taxable year consist of qualifying income, as defined in Section 7704 of the Code. As a result of the EQM Merger, the requirements under Section 7704 of the Code are no longer applicable to EQM for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2020.
Despite the fact that EQM is a limited partnership under Delaware law and has not elected to be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes, it is possible, under certain circumstances, that the IRS could determine on audit for taxable years prior to January 1, 2021 for EQM to be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes. For example, EQM would be treated as a corporation if the IRS determined that less than 90% of EQM’s gross income for any such taxable year consisted of qualifying income within the meaning of Section 7704 of the Code.
If EQM was treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes for any taxable year prior to January 1, 2021, EQM would be required to pay federal income tax on its taxable income at the corporate tax rate applicable to the relevant tax year and would likely pay state income taxes at varying rates. Distributions to us after the Separation Date would generally be taxed again as corporate distributions, and no income, gains, losses or deductions would flow through to us. Treatment of EQM as a corporation could result in a material reduction in the anticipated cash flow in the year of the payment to the IRS, potentially causing, among other things, a substantial reduction in the value of our shares.
If the IRS makes audit adjustments to EQM’s income tax returns for tax years beginning after 2017, the IRS (and some states) may assess and collect any resulting taxes (including any applicable penalties and interest) directly from EQM, in which case we may be required, and potentially former unitholders would be required, to reimburse EQM for such payments or, if EQM is required to bear such payments, such payments could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
Pursuant to the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015, if the IRS makes audit adjustments to EQM’s income tax return for tax years beginning after 2017, the IRS (and some states) may assess and collect any resulting taxes (including any applicable interest and penalties) directly from EQM. EQM will have a limited ability to shift any such tax liability to its general partner and unitholders, including us, in accordance with their interests in EQM during the year under audit, but there can be no assurance that EQM will be able to do so under all circumstances, or that EQM will be able to effect corresponding shifts in state income or similar tax liability resulting from the IRS adjustment in states in which EQM does business in the year under audit or in the adjustment year. As a result of the EQM Merger, we own all of the EQM common units. If EQM makes payments of taxes, penalties and interest resulting from audit adjustments with respect to tax periods beginning after 2017 and before 2021, we and potentially former unitholders may be required to reimburse it for such payment or, if EQM is required to bear such payments, such payments could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial position, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders.
In the event the IRS makes an audit adjustment to EQM’s income tax returns and EQM does not or cannot shift the liability to its unitholders in accordance with their interests in EQM during the year under audit, EQM will generally have the ability to
request that the IRS reduce the determined underpayment by reducing the suspended passive loss carryovers of EQM’s unitholders (without any compensation from EQM to such unitholders), to the extent such underpayment is attributable to a net
decrease in passive activity losses allocable to certain partners. Such reduction, if approved by the IRS, will be binding on any affected unitholders.
Our stock price has fluctuated and may fluctuate significantly.
The market price of our common stock has experienced substantial price volatility in the past and may continue to do so due to a number of factors, including the MVP project, some of which may be beyond our control. General market fluctuations, industry factors, such as climate change-related physical and transitional risks, and general economic and political conditions and events, such as economic slowdowns or recessions, as well as factors specific to our business (including the status of and cost to construct the MVP project and perceptions regarding our growth opportunities), have, as applicable, caused and could also continue to cause our stock price to decrease regardless of operating results. If we fail to meet expectations related to future growth, profitability, cash dividends, de-levering, strategic transactions or other market expectations, the market price of our common stock may decline significantly. Additionally, our stock price may be adversely affected by transactions in our common stock by significant shareholders, including EQT.
We expect that EQT will ultimately dispose of its ownership interest in us, representing approximately 5.3% of our outstanding common stock as of December 31, 2021, when it deems appropriate, but in no event later than November 12, 2023. There can be no assurance regarding the method by which EQT will dispose of its interest in or the actual timing of any such disposal.
However, any disposition by EQT, or any other significant shareholder, of our common stock in the public market, or the perception that such dispositions could occur, could adversely affect prevailing market prices for our common stock. Further, any delay by EQT in completing the disposition of its ownership interest in us could have an adverse effect on the market price for our common stock, which could affect investor confidence in us.
shareholders. A reduced stock price affects, among other things, our cost of capital and could affect our ability to execute on future strategic transactions, as well as increaseincreases opportunities for investor activism or unsolicited third-party activity affecting us.
We cannot guarantee the timing, amount or payment of dividends on our common stock, and we may further reduce the amount of the cash dividend that we pay on our common stock or may not pay any cash dividends at all to our shareholders. Our ability to declare and pay cash dividends to our shareholders, if any, in the future will depend on various factors, many of which are beyond our control.
We are not required to declare and pay dividends to our common shareholders, and ourshareholders. Our Board previously has reduced, and in the future may decide to further reduce, the amount of the cash dividend that we pay on our common stock orstock. Our Board may also decide not to declare any dividends in the future. Although we have in the past paid regular cash dividends, any payment of future dividends will be at the sole discretion of our Board and will depend upon many factors, including the Pennsylvania Business Corporation Law (PBCL), the financial condition, earnings, liquidity and capital requirements of our operating subsidiaries, covenants associated with certain debt obligations, legal requirements, our leverage, regulatory constraints and other factors deemed relevant by our Board. We are also may not entitled to pay any dividends on any junior securities, including any shares of our common stock, prior to paying the quarterly dividends payable to the holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, including any previously accrued and unpaid dividends.
YourOur shareholders’ percentage of ownership in us may be diluted in the future.
In theby future we may issue commonissuances of stock, orwhich could, among other equity to raise cash for our projects, operations, acquisitions or other purposes and may also acquire interests in other companies or assets by using one or more of cash, debt and/or our equity.
Any of these events may dilute your ownership interests in us, reducethings, have a dilutive effect on our earnings per common share and have an adverse effectrelated effects on the price of our common stock. The issuance of these new shares and the sale of additional shares from time to time could have the effect of depressing the market valueprice for our common stock. The increase in the number
Our shareholders’ percentage of shares of our common stock outstanding or the issuance of other equity of us, and any resulting dilution, may cause holders to sell shares of our common stock or may create the perception that such sales may occur, either of which may adversely affect the market for, and the market value of, our common stock.
Your percentage ownership in us may also be diluted because of equity issuances for acquisitions, capital market transactions or otherwise, including, without limitation, equity awards that we may grant to our directors, officers, and employees or otherwise as a result of equity issuances for acquisitions or capital market transactions.employees. Our Management DevelopmentHuman Capital and Compensation Committee and our Board have authority to grant share-based awards to our employees under employee benefit plans and, from time to time, we issue share-based awards to our employees under our employee benefit plans. Such awards will have a dilutive effect on our earnings per common share, which could adversely affect the market price of our common stock. From time to time, we issue share-based awards toEquity issuances may have a dilutive effect on our employees underearnings per share, which could adversely affect the market for and the market price of our employee benefits plans.
stock, and have a dilutive effect on our shareholders’ ownership interests in us.In addition, our Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation authorize us to issue, without the approval of our shareholders, one or more classes or series of preferred stock that have such designations, powers, preferences and relative, participating, optional and other special rights, including preferences over our common stock respecting dividends and distributions, as our Board generally may determine. The terms of one or more classes or series of preferred stock could dilute the voting power or reduce the value of our common stock. Similarly, the repurchase or redemption rights or liquidation preferences we could assign to holders of preferred stock could affect the residual value of our common stock.
As more fully described under “The Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares by virtue of their terms and preferences present a number of risks to current and future holders of our common stock.”, in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, upon the occurrence of certain events or the passage of time, the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares may be converted by the holder or us, as applicable, initially on a one-for-one basis in the case of certain conversions by holders, subject to certain anti-dilution adjustments and an adjustment for any dividends that have accrued but not been paid when due and partial period dividends. If we or a holder of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares convert Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares into common stock, the conversion will have a dilutive effect on our earnings per share of common stock, which could adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Anti-takeover provisions contained in our Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation and ThirdFifth Amended and Restated Bylaws, as well as provisions of Pennsylvania law, could impair an attempt to acquire us.us and limit the opportunity for our shareholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock.
Our Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation and ThirdFifth Amended and Restated Bylaws contain provisions that could have the effect of rendering more difficult or discouraging an acquisition of us deemed undesirable by our Board. These include provisions:
•authorizing blank check preferred stock, which we could issue with voting, liquidation, dividend and other rights superior to those of our common stock;
•limiting the liability of, and providing indemnification to, our directors and officers;
•specifying that our shareholders may take action only at a duly called annual or special meeting of shareholders and otherwise in accordance with our bylaws and prohibiting our shareholders from calling special meetings;
•requiring advance notice of proposals by our shareholders for business to be conducted at shareholder meetings and for nominations of candidates for election to our Board; and
•controlling the procedures for conduct of our Board and shareholder meetings and election and appointment of our directors.
These provisions, alone or together, could deter or delay hostile takeovers, proxy contests and changes in control or management of us. As a Pennsylvania corporation, we are also subject to provisions of Pennsylvania law, including certain provisions of Chapter 25 of the Pennsylvania Business Corporation Law (PBCL),PBCL, which, among other things, requires enhanced shareholder approval for certain transactions between us and a shareholder who is a party to the transaction or is treated differently from other shareholders and also prevents persons who become the beneficial owner of shares representing 20% or more of our voting power from engaging in certain business combinations without approval of our Board, and in some cases preventing consummation of the transaction for at least five years.
Any provision of our Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation, or ThirdFifth Amended and Restated Bylaws or Pennsylvania law that has the effect of delaying or deterring a change in control of us could limit the opportunity for our shareholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock and also could affect the price that some investors are willing to pay for our common stock.
Our ThirdFifth Amended and Restated Bylaws designate the state and federal courts sitting in the judicial district of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, County of Allegheny, as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our shareholders, which could discourage lawsuits againstand limit our shareholders’ ability to obtain a perceived favorable judicial forum for disputes with us, and our directors andor our officers.
Our ThirdFifth Amended and Restated Bylaws provide that, unless our Board otherwise determines, the state and federal courts sitting in the judicial district of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, County of Allegheny, will be the sole and exclusive forum for any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of us, any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any director or officer or other employee of ours to us or our shareholders, any action asserting a claim against us or any director or officer or other employee of us arising pursuant to any provision of the PBCL or our Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation or Thirdand Fifth Amended and Restated Bylaws or any action asserting a claim against us or any director or officer or other employee of ours governed by the internal affairs doctrine. The choice of forum provision set forth in our ThirdFifth Amended and Restated Bylaws does not apply to actions arising under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act.
When applicable, this exclusive forum provision may limit the ability of our shareholders to bring a claim in a judicial forum that such shareholders find favorable for disputes with us or our directors or officers, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and our directors and officers. Alternatively, if a court outside of Pennsylvania were to find this exclusive forum provision inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more of the specified types of actions or proceedings described above, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such matters in other jurisdictions, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares by virtue of their terms and preferences present a number of risks to current and future holders of our common stock.
Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares present a number of risks to current and future holders of our common stock, including a preference in favor of holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares in the payment of dividends on our common stock, the risk of dilution occurring as a result of the conversion of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares into our common stock and
the ability of the holders of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares to vote with the holders of our common stock on most matters, as well as the risk that the holders of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares will have certain other class voting rights with respect to any amendment to our organizational documents that would be adverse (other than in a de minimis manner) to any of the rights, preferences or privileges of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares.
We are party to a registration rights agreementRegistration Rights Agreement with certain holders of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares pursuant to which, among other things, we gave the Investorsinvestors certain rights to require us to file and maintain one or more registration statements with respect to the resale of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares and the shares of our common stock that are issuable upon conversion of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, and which, upon request by certain Investors partyShares. In July 2023, pursuant to thethis Registration Rights Agreement, will require uswe filed a registration statement with the SEC to initiate underwritten offerings for theregister up to 30,018,446 Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares and theup to 30,018,446 shares of our common stock that are issuable upon conversion of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares and use our best efforts to cause the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares to be listed on the securities exchange on which the shares of our common stock are then listed. See Note 2held by such certain investors party to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares.Registration Rights Agreement.
Risks Related to the Separation
If the Separation and Distribution, together with certain related transactions, does not continue to qualify as a transaction that is generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we, EQT, and our respective shareholders could be subject to significant tax liabilities and, in certain circumstances, we could be required to indemnify EQT for material taxes and other related amounts pursuant to indemnification obligations under the tax matters agreement.
It was a condition to the Distribution that (i) a private letter ruling from the IRS regarding the qualification of the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, as a transaction that is generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code and certain other U.S. federal income tax matters relating to the Separation and Distribution shall not have been revoked or modified in any material respect and (ii) EQT received an opinion of counsel with respect to certain tax matters relating to the qualification of the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, as a transaction described in Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code. The IRS private letter ruling is based upon and relies on, and the opinion of counsel is based upon and relies on, among other things, various facts and assumptions, as well as certain representations, statements and undertakings of EQT and us, including those relating to the past and future conduct of EQT and us. If any of these representations, statements or undertakings is, or becomes, inaccurate or incomplete, or if any representations or covenants contained in any of the Separation-related agreements and documents or in any documents relating to any IRS private letter ruling or opinion of counsel are breached, such IRS private letter ruling and/or opinion of counsel may be invalid and the conclusions reached therein could be jeopardized.
Notwithstanding receipt of the IRS private letter ruling and opinion of counsel, the IRS could determine that the Distribution and/or certain related transactions should be treated as taxable transactions for U.S. federal income tax purposes if it determines that any of the representations, assumptions or undertakings upon which such IRS private letter ruling or the opinion of counsel was based are false or have been violated. In addition, the IRS private letter ruling does not address all of the issues that are relevant to determining whether the Distribution, together with certain related transactions, continues to qualify as a transaction that is generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and the opinion of counsel represented the judgment of such counsel and is not binding on the IRS or any court and the IRS or a court may disagree with the conclusions in any opinion of counsel. Accordingly, notwithstanding receipt of an IRS private letter ruling or opinion of counsel, there can be no assurance that the IRS will not assert that the Distribution and/or certain related transactions do not qualify for the intended tax treatment or that a court would not sustain such a challenge. In the event the IRS were to prevail with such challenge we, EQT, and our respective shareholders could be subject to material U.S. federal income tax liability.
Even if the Distribution otherwise qualifies as generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Section 355 and Section 368(a)(1)(D) of the Code, it would result in a material U.S. federal income tax liability to EQT (but not to its shareholders) under Section 355(e) of the Code if one or more persons acquire, directly or indirectly, a 50-percent or greater interest (measured by either vote or value) in EQT’s stock or in the stock of us as part of a plan or series of related transactions that includes the Distribution, and we may be required to indemnify EQT for any such liability under the tax matters agreement entered into by EQT and us in connection with the Distribution. The process for determining whether an acquisition is part of a plan under these rules is complex, inherently factual in nature and subject to a comprehensive analysis of the facts and circumstances of the particular case. Notwithstanding the IRS private letter ruling and opinion of counsel described above, a sufficient change in ownership of EQT or our common stock may occur which could result in a material tax liability to EQT.
Under the tax matters agreement that EQT entered into with us, we may be required to indemnify EQT against any additional taxes and related amounts resulting from (i) an acquisition of all or a portion of our equity securities or assets, whether by merger or otherwise (and regardless of whether we participated in or otherwise facilitated the acquisition), (ii) other actions or failures to act by us or (iii) any of our representations, covenants or undertakings contained in any of the Separation-related
agreements and documents or in any documents relating to the IRS private letter ruling or the opinion of counsel being incorrect or violated. Any such indemnity obligations could be material.
If the IRS were to successfully assert that the EQM Merger or Share Purchasescertain share purchases from EQT in 2020 resulted in the Distribution and/or certain related transactions being treated as taxable transactions to EQT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we may be required to indemnify EQT for such taxes and related amounts.
Certain contingent liabilities allocated to us following the Separation may mature, resulting in material adverse impacts to our business.
There are several significant areas where the liabilities of EQT may become our obligations. For example, under the Code and the related rules and regulations, each corporation that was a member of the EQT consolidated U.S. federal income tax return group (EQT Tax Group) during a taxable period or portion of a taxable period ending on or before the effective date of the Distribution is jointly and severally liable for the U.S. federal income tax liability of the EQT consolidated U.S. federal income tax return groupTax Group for that taxable period. Consequently, if EQT is unable to pay the consolidated U.S. federal income tax liability for a pre-Separation period, we could be required to pay the amount of such tax, which could be substantial and in excess of the amount allocated to us under the tax matters agreement. Other provisions of federal law establish similar liability for other matters, including laws governing tax-qualified pension plans, as well as other contingent liabilities.
We or EQT may fail to perform under various transaction agreements that were executed as part of the Separation.
In connection with the Separation, we and EQT entered into a Separation and Distribution Agreement as well as various other agreements, including a tax matters agreement, an employee matters agreement and a shareholder and registration rights agreement with respect to EQT’s continuing ownership of our common stock. The Separation and Distribution Agreement, the tax matters agreement and the employee matters agreement determined the allocation of assets and liabilities between the companies following the Separation for those respective areas and include indemnification related to liabilities and obligations. If EQT is unable or unwilling to satisfy its obligations under these agreements, including its indemnification obligations, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
Potential indemnification liabilities to or from EQT pursuant to agreements relating to the Separation and Distribution could materially and adversely affect us.
The agreement that effected the Separation (the Separation and Distribution Agreement with EQTAgreement) provides for, among other things, provisions governing the relationship between us and EQT with respect to and resulting from the Separation. Among other things, the Separation and Distribution Agreement provides for indemnification obligations designed to make us financially responsible for substantially all liabilities that may exist relating to our business activities, whether incurred prior to or after the Separation, as well as those obligations of EQT assumed by us pursuant to the Separation and Distribution Agreement. If we are required to indemnify EQT under the circumstances set forth in the Separation and Distribution Agreement, we may be subject to substantial liabilities. See also the discussion of potential indemnification obligations under “If the Separation and Distribution, together with certain related transactions, does not continue to qualify as a transaction that is generally tax-free for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we, EQT, and our respective shareholders could be subject to significant tax liabilities and, in certain circumstances, we could be required to indemnify EQT for material taxes and other related amounts pursuant to indemnification obligations under the tax matters agreement.” in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Further, if EQT is unable or unwilling to satisfy its obligations under these agreements, including its indemnification obligations, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Due to the critical nature of our business to the U.S. economy and national energy security and the continuous threat of cyberattacks, we regard cybersecurity as a top tier enterprise risk. Cybersecurity is integrated into our enterprise risk management program, which includes quarterly technology and cybersecurity risk assessments. We use the results of the technology and cybersecurity risk assessments for risk-based decision making to determine actions and priorities for our cybersecurity program. The technology and cybersecurity risk assessment process includes an objective, risk-ranking process; documented mitigation activities; and action plans for those risks requiring additional mitigation. These activities consider safety implications, operational disruptions, and business and financial impacts. As part of the cybersecurity program, we regularly obtain threat intelligence from various sources, which sources originate from private, commercial, and independent entities. In addition, our IT leadership routinely conducts risk quantification, simulations, and assessment exercises. We regularly engage with relevant government agencies to report and share certain security information enabling us to benchmark our capabilities, establish appropriate program targets, and adapt to emerging cybersecurity issues.
To manage our cybersecurity risk, we practice cyber hygiene through, among other measures, identity and access management, vulnerability and patch management, and asset management programs. We also segment our informational and operational technologies, and leverage network micro-segmentation and combine this practice with zero-trust security concepts. Operationally, we continuously monitor for cyber intrusions and augment our internal resources and capabilities with third-party service providers. Multiple security technologies are employed to protect our systems, applications, and data, including
next generation firewalls, multi-factor authentication and access controls, and endpoint detection and response solutions. We have integrated our cloud-hosted services with our security operations center and have implemented measures aimed at securing our remote workforce. We measure our cybersecurity practices against the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework, relevant industry standards, and government regulations. We routinely engage independent third-party security firms to exercise and assess our cybersecurity capabilities.
Our information technology governance, including cybersecurity, is documented through written policies, procedures, guidelines, and standard operating procedures. All of our employees are required to undergo quarterly cybersecurity training. This training includes cybersecurity policies, cyber threats, and incorporating best practices into daily routines. Contractors and vendors that have access to our data, devices, or services are required to complete cybersecurity training prior to receiving access. Employees, vendors, and contractors with access to our operational technology network are required to undergo additional training specific to operational technology interactions. We maintain a Supplier Code of Conduct that is provided to our providers of materials and services during the onboarding process and that conveys our expectations regarding use and access requirements when using our technology resources.
We also manage cybersecurity risk through incident response strategies. We employ a fault-tolerant, highly available architecture and network segmentation as part of our containment strategy. We do not solely rely on architecture to ensure continuity and containment, and we employ additional technologies including, but not limited to, automated account disabling, automated device quarantining, network segment-isolation scripts, and cyber kill chain runbooks. We have implemented an Enterprise Data Backup Policy, which includes, among other activities, offsite backups, intra-day recovery points, and routine restoration of critical data. We use infrastructure-as-code to enable recovery of virtualized environments and employ data replication across multiple operating regions. We routinely exercise our recovery capabilities. Our Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan establishes a framework to manage the life cycle of a cyber event. Additionally, our Enterprise Crisis Management Plan provides a structure to assemble an enterprise crisis team in the event of a potential cyber related crisis. The crisis response team, including our Chief Information Officer (CIO), is responsible for managing the channels of communication pursuant to our Crisis Management Plan. This notification includes the notification or reporting of any significant cyber incidents to executive management. We periodically conduct cyber incident drills that include, as applicable, members of our Board of Directors, executives, certain business stakeholders, and legal and security partners, as necessary.
While we and third parties that provide services to us commit resources to the design, implementation and monitoring of our digital systems, there is no guarantee that our or our third parties’ cybersecurity measures will provide absolute security. Like other companies in the natural gas industry, we have identified and expect to continue to identify cyberattacks and incidents on our systems. Additionally, we have received notification from third-party service providers of certain such matters on their systems. None of the cyberattacks and incidents we have identified, or been notified of, to the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K has had a material impact on our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition. For more information regarding the risks associated with cybersecurity that may impact our business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition, see “Cyberattacks aimed at us or those third parties on which we rely, as well as any noncompliance by us or such third parties with applicable laws and regulations governing cybersecurity and/or data privacy, could materially adversely affect us.” included in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Given the importance to us of our cybersecurity program, in April 2022, our Board elected to exercise direct oversight of cybersecurity matters, rather than acting through its committees. The Board, as well as separately our executive management, receives, and has the opportunity to ask questions and raise discussion points regarding, management reports from the CIO and Senior Director of Cybersecurity and Network Operations on cybersecurity matters, as needed and no less than quarterly throughout the year, which reports include items such as cybersecurity updates, cybersecurity operational results, and audit findings. In addition, the Board and executive management receives and reviews the results of our cybersecurity risk and capabilities assessment on an annual basis.
The cybersecurity program is managed by our CIO and our Senior Director of Cybersecurity and Network Operations and reviewed and monitored by executive management, with oversight from the Board. Our CIO has significant expertise and more than 30 years of experience in information technology and cybersecurity including cloud technologies and reports to our Executive Vice President & Chief Legal Officer. Our Senior Director of Cybersecurity and Network Operations has more than two decades of experience in the fields of information technology and cybersecurity and holds cybersecurity certifications, including the Certified Information Systems Security Professional, Certified Cloud Security Professional, and GIAC Information Security Professional certifications. The CIO and Senior Director of Cybersecurity and Network Operations meet regularly with each other and members of their team to discuss cybersecurity threats, capabilities and program strategy. We have built in incident workflows that automatically provide notifications and escalate cybersecurity incidents. During an incident, the CIO acts as the incident commander and the Senior Director of Cybersecurity and Network Operations acts as operations section chief, working together to provider supervision over incident response.
Item 2. Properties
The Company leases its corporate headquarters office in Canonsburg, Pennsylvania.
The Company's real property falls into two categories: (i) parcels that it owns in fee and (ii) parcels in which its interest derives from leases, easements, rights-of-way, permits or licenses from landowners or governmental authorities permitting the use of such land for the Company's operations. Certain lands on which the Company's pipelines and facilities are located are owned by the Company in fee title, and the Company believes that it has satisfactory title to these lands. The remainder of thelands in all material respects. Other lands on which the Company's pipelines and facilities are located are held pursuant to surface leases or easements between the Company, as lessee or grantee, and the respective fee owners of the lands, as lessors or grantors. The Company has held, leased or owned many of these lands for many years without any material challenge known to the Company relating to the title to the land upon which the assets are located, and the Company believes that it has satisfactory leasehold estates, easement interests or fee ownership to such lands.lands in all material respects. The Company believes that it has satisfactory title to all of its material leases, easements, rights-of-way, permits and licenses in all material respects, and the Company has no knowledge of any material challenge to its title to such assets or their underlying fee title.
As contemplated under “We do not own all of the land on which our pipelines and facilities are located, which could disrupt our operations and future development," included in "Item 1A. Risk Factors," thereThere are, however, certain lands within the Company's storage pools and where the Company's pipelines and other facilities are located as to which it may not currently have vested real property rights as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, some of which are subject to ongoing acquisition negotiations or inverse condemnation proceedings. In accordance with Equitrans, L.P.'s FERC certificates, the geological formations within which its permitted storage facilities are located cannot be used by third parties in any way that would detrimentally affect its storage operations, and the Company has the power of eminent domain with respect to the acquisition of necessary real property rights to use such storage facilities. Certain property owners have initiated legal proceedings against the Company and its affiliates for trespass, inverse condemnation and other claims related to these matters, and there is no assurance that other property owners will not initiate similar legal proceedings against the Company and its affiliates prior to final resolution. See "We do not own all of the land on which our pipelines and facilities are located, which could disrupt our operations and future development." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
See Part I, "Item 1. Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the properties and their relatedCompany's business segments relevant to its property holdings and map of the Company's operations.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
In the ordinary course of business,From time to time, various legal and regulatory claims, investigations and proceedings are pending or threatened against the Company and its subsidiaries. While to the extent applicable the amounts claimed may be substantial, the Company is unable to predict with certainty the ultimate outcome of such claims, investigations and proceedings. The Company accrues legal and other direct costs related to loss contingencies when incurred. The Company establishes reserves whenever it believes it to bea reserve is appropriate for pending matters. Furthermore, after consultation with counsel and considering availablethe availability, if any, of insurance, the Company believes, although no assurance can be given, that the ultimate outcome of any matter currently pending against it or any of its consolidated subsidiaries as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K will not materially adversely affect its business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to its shareholders.
Arbitration Decision in Hammerhead Pipeline Dispute
See “Hammerhead Pipeline” under “Outlook” in “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” for additional information.
Environmental Proceedings
Pratt Storage Field. On October 31, 2018, a gas explosion occurred in Morgan Township, Greene County, Pennsylvania (the Incident). Following the explosion, the Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection (the PADEP), the Pennsylvania Public Utilities Commission and the PHMSA began investigating the Incident. In January 2020,October 2019, the PADEP notified the Company that it was required to submit an investigation report pursuant to the state’s gas migration regulations due to the Incident's proximity to the Company's Pratt Storage Field assets. The Company, while disputing the applicability of the regulations, submitted a report to the PADEP in MarchMay 2020. In September 2020, the PADEP responded to the Company’s investigation report with a request for additional information. The Company responded to the September 2020 request, but cannot predict whether any action will ultimately be brought byrequest. Over the next months the Company provided many responses to the PADEP’s continuing information requests.The PADEP or what the outcome of such an action would be. Ifissued a penalty is imposed, it could result in monetary sanctions in excess of $300,000. However,final report and closed its investigation and the Company does not believeexpect further inquiry from the PADEP on this matter. On October 23, 2023, the Company received permission from the FERC to plug and abandon the well in the Pratt Storage Field that is the penalty, if imposed, will have a material impact onsubject of the financial condition, results of operations or liquidityPADEP’s investigation of the Company.
Swarts Storage Field. On April 8, 2021, the PADEP notifiedAdditionally, the Company that it considered certain aspectsis continuing to defend in a civil litigation related to the Incident.
On October 30, 2023, the Company received a criminal complaint from the State Attorney General’s Office charging the Company with violations of the storage fieldClean Streams Law (the Pratt Complaint). In response to be outthe Pratt Complaint, the Company intends to fully assert its rights and defenses to the claims raised. The Pratt Complaint carries the possibility of compliance due to an alleged failure to plug or recondition wells within 2,000 feet of ongoing coal mining activities by CONSOL Energy Inc. and that a number of wells on the property allegedly did not meet current plugging standards. Themonetary
sanction, that if imposed could result in a fine in excess of $300,000. The Pratt Complaint could also cause reputational or other adverse impacts.
On December 29, 2022, the PHMSA issued the Company disputes these claimsa Notice of Proposed Safety Order that included proposed remedial requirements related to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, including, but not limited to, completing a root cause analysis. The Company addressed certain proposals in advance of an order from the agency. These efforts included conducting testing, evaluating other wells at the Rager field and ishiring a third-party specialist firm to undertake a root cause analysis, and subsequently on May 26, 2023, the PHMSA issued a consent order to the Company incorporating the terms of a consent agreement between the parties, which, among other things, required the completion of a root cause analysis and a remedial work plan, and specified that the Company may not resume injection operations at the Rager Mountain facility until authorized by the PHMSA. As discussed in “Transmission Results of Operation” in Part II, "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, in August 2023, the Company submitted a root cause analysis to the PHMSA in accordance with the consent order and later submitted a remedial work plan and, following completion of all actions in its remedial work plan, an injection plan to the PHMSA seeking authority to resume injections at Rager Mountain using all wells except three, which remain disconnected. On October 2, 2023, the PHMSA approved the Company’s injection plan. The Company began injections at Rager Mountain on October 5, 2023, subject to certain pressure restrictions and other requirements specified in the consent agreement between the PHMSA and the Company. On November 16, 2023, the PHMSA issued a letter to the Company approving the Company’s request to remove all pressure restrictions at the Rager Mountain facility. The Company plans to continue working with the PADEP and CONSOL Energy Inc.PHMSA, pursuant to resolve these issues. Based on the discussion withconsent order, regarding the PADEP, the Company anticipates a notice of violation (NOV) will be issued. remaining three wells.
If additional penalties are pursued and ultimately imposed related to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, the penalties, couldindividually and/or in the aggregate, are expected to result in monetary sanctions in excess of $300,000. However,While the Company does not believe that the penalties, if imposed, wouldwill have a material adverse impact on the Company's financial condition, results of operations or liquidity.liquidity, there can be no assurance as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K regarding the scope of potential (or ultimately actual) financial or other impacts to the Company as a result of the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident.
MVP Matters
The MVP Joint Venture is currently defendingThere remain certain agency actionslegal and judicial challengesregulatory matters relevant to the MVP any of which could affect the ability to complete or operate the project, including the following:
•Sierra Club, et al. Petitioners v. State Water Control Board, et al. Respondents and Mountain Valley Pipeline, Intervenor, Docket No. 21-2425, Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals (Fourth Circuit). On December 20, 2021, the Virginia Department of Environmental Quality (VADEQ) certified that the MVP project would satisfy Virginia’s water quality standards based on its comprehensive nine-month review of the MVP Joint Venture’s Joint Permit Application (VA 401 Permit). On December 22, 2021, Petitioners filed their petition challenging the VADEQ’s approval of the VA 401 Permit with the Fourth Circuit. On December 22, 2021, the Petitioners filed a request for an administrative stay with the VADEQ which was denied on January 4, 2022. On January 4, 2022, the Petitioners filed a petition with the Fourth Circuit seeking a judicial stay of the VA 401 Permit pending a decision on the merits. On February 11, 2022, Petitioners withdrew the stay petition. If the challenge were successful on its merits, it could result in the MVP Joint Venture's VA 401 Permit being delayed or vacated and/or additional legal proceedings, the outcome of which the Company cannot predict, and cause a delay or further delay in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project (and consequent impacts related to such delay), or otherwisecould have adverse effects.
•Sierra Club, et al. Petitioners v. West Virginia Department of Environmental Protection, et al. Respondents and Mountain Valley Pipeline, Intervenor, Docket No. 22-1008, Fourth Circuit. On December 30, 2021, the West Virginia Department of Environmental Protection (WVDEP) certified that the MVP project would satisfy West Virginia’s water quality standards based on its comprehensive nine-month review of the MVP Joint Venture’s Joint Permit Application (WV 401 Permit). On January 3, 2022, Petitioners filed their petition challenging the WVDEP’s approval of the WV 401 Permit with the Fourth Circuit. On January 4, 2022, the Petitioners filed a request for an administrative stay with the WVDEP which was denied on January 11, 2022. On January 11, 2022, Petitioners filed a petition with the Fourth Circuit seeking a judicial stay of the WV 401 Permit pending a decision on the merits. The stay petition was denied by the Fourth Circuit on February 8, 2022. If the challenge were successful on its merits, it could result in the MVP Joint Venture's WV 401 Permit being delayed or vacated and/or additional legal proceedings, the outcome of which the Company cannot predict, and cause a delay or further delay in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project (and consequent impacts related to such delay), or otherwise adverse effects.
•Jefferson National Forest Crossing and Associated Authorizations. In a different Fourth Circuit appeal, Sierra Club, et al. v. U.S. Forest Service, et al., consolidated under Case No. 17-2399, Fourth Circuit, filed in December 2017, the Sierra Club challenged a Bureau of Land Management (BLM) decision to grant a right-of-way to the MVP Joint Venture and a U.S. Forest Service (USFS) decision to amend its management plan to accommodate the MVP, both of which affect the MVP's approximate 3.5-mile segment in the Jefferson National Forest (JNF) in Virginia. On July 27, 2018, agreeing in part with the Sierra Club, the Fourth Circuit vacated the BLM and USFS decisions, finding fault with the BLM's analysis of the practicality of alternate routes and the USFS' analysis of erosion and sedimentation effects. The USFS published a draft Supplemental Environmental Impact Statement (SEIS) to the 2017 FERC Final Environmental Impact Statement for MVP in the Federal Register on September 25, 2020 with a public comment period that closed on November 9, 2020. On December 11, 2020, the USFS published a Final SEIS that addressed the issues raised in the prior proceedings and evaluated the most recent sedimentation analysis submitted to the agency consistent with the findings presented in MVP’s Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement issued by the Department of the Interior's Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS) on September 4, 2020. See Appalachian Voices, et al. v. U.S. Dep’t of Interior below for additional information. On January 11, 2021, the MVP Joint Venture received final approval of the Record of Decision from the USFS and, on January 15, 2021, the BLM issued the required right-of-way permit for the MVP’s 3.5-mile segment in the JNF in Virginia (the JNF Right-of-Way). On January 11, 2021, Sierra Club, et al. filed a petition with the Fourth Circuit to reverse the USFS approval of the Record of Decision and, on January 15, 2021, filed a petition with the Fourth Circuit challenging BLM’s grant of the JNF Right-of-Way. See Wild Virginia, et al. v. United States Forest Service, et al., No. 21-1039(L).The Fourth Circuit consolidated the challenges to the Record of Decision and the JNF Right-of-Way and briefing was completed. Oral argument occurred on October 29, 2021. On January 25, 2022, the Fourth Circuit, agreeing in part with the petitioners, vacated and remanded the Record of Decision and the JNF Right-of-Way, finding fault with (i) the USFS’ and BLM’s consideration of certain data from the U.S. Geological Survey and (ii) the USFS’ and BLM’s authorization of the use of conventional bores for stream crossings within the JNF based on a variance issued by the FERC, and, as a result of such issues, (iii) the USFS’ amendments in connection with the Record of Decision to the Jefferson Forest plan. The
vacatur of the Record of Decision and the JNF Right-of-Way may result in appellate and/or additional agency proceedings (the outcome of which the Company cannot predict) and has caused a delay in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project (and consequent impacts relating to such delay). The Company cannot predict whether and when any new authorizations will be received from the USFS and BLM and, if received, the result of any challenge to such authorizations.
On August 3, 2018, citing the court's vacatur and remand in Sierra Club, et al. v. U.S. Forest Service, et al., consolidated under Case No. 17-2399, the FERC issued a stop work order for the entire pipeline pending the agency actions on remand. The FERC modified its stop work order on August 29, 2018 to allow work to continue on all but approximately 25 miles of the project (the Exclusion Zone). On October 10, 2018, the Fourth Circuit granted a petition for rehearing filed by the MVP Joint Venture for the limited purpose of clarifying that the July 27, 2018 order did not vacate the portion of the BLM's Record of Decision authorizing a right-of-way and temporary use permit for the MVP to cross the Weston and Gauley Bridge Turnpike Trail in Braxton County, West Virginia. On October 15, 2018, the MVP Joint Venture filed with the FERC a request to further modify the August 3, 2018 stop work order to allow the MVP Joint Venture to complete the bore and install the pipeline under the Weston and Gauley Bridge Turnpike Trail. On October 24, 2018, the FERC granted the MVP Joint Venture's request to further modify the stop work order and authorize construction. Additionally, on October 9, 2020, the FERC authorized construction to resume project-wide (as it had been stopped by the FERC on October 15, 2019 in relation to a separate matter discussed below), other thaneffects with respect to the Exclusion Zone, which requires additional authorization. On December 17, 2020,project and consequently the FERC again modifiedCompany, including matters pending with the stop work order and authorized construction to resume in 17 miles of the Exclusion Zone. The Company cannot guarantee whether or when the FERC will act in respect of any or all of the remaining portions of the Exclusion Zone. The FERC's October 9, 2020 and December 17, 2020 actions are the subject of challenges filed by the Sierra Club in Sierra Club, et al. v. FERC, Case No. 20-1512 (consolidated with No. 21-1040), D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals on December 22, 2020 and January 25, 2021, respectively (a stay request filed by the Sierra Club on January 29, 2021 was denied by theU.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit (DCDistrict of Columbia (D.C. Circuit) on February 19, 2021). Briefing in Sierra Club, et al. v. FERC, Case No. 20-1512 (consolidated with No. 21-1040), D.C. Circuit Court of Appeals was completed in January 2022 and oral argument is scheduled for April 7, 2022. If any of the challenges to the FERC's October 9, 2020 and December 17, 2020 orders are successful, it could result in the FERC's orders being vacated and/or additional agency proceedings (the outcome of which the Company cannot predict) and cause a delay or further delay in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project (and consequent impacts relating to such delay), or otherwise adverse effects.
•Challenges to FERC Certificate, Court of Appeals for DCD.C. Circuit. Multiple parties have sought judicial review of the FERC'sFERC’s order issuing a certificate of public convenience and necessity to the MVP Joint Venture and/or the exercise by the MVP
Joint Venture of eminent domain authority. On February 19, 2019, the DCD.C. Circuit issued an order rejecting multiple consolidated petitions seeking direct review of the FERC order under the NGANatural Gas Act of 1938, as amended (NGA) and certain challenges to the exercise by the MVP Joint Venture of eminent domain authority in Appalachian Voices, et al. v. FERC, et al., consolidated under Case No. 17-1271. No petitions for rehearing or petitions for rehearing en banc were filed by the April 5, 2019 deadline. The mandate was issued on April 17, 2019. Another group of parties filed a complaint in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia asserting that the FERC'sFERC’s order issuing certificates is unlawful on constitutional and other grounds in Bold Alliance, et al. v. FERC, et al., Case No. 17-1822. The district court plaintiffs sought declaratory relief as well as an injunction preventing the MVP Joint Venture from developing its project or exercising eminent domain authority. In December 2017 and January 2018, the FERC and the MVP Joint Venture, respectively, moved to dismiss the petitions for lack of subject matter jurisdiction. The court granted the motion and dismissed plaintiffs'plaintiffs’ complaint on September 28, 2018. On October 26, 2018, plaintiffs appealed the decision in Case No. 17-1822 to the DCD.C. Circuit in Bold Alliance, et al. v. FERC, et al., Case No. 18-5322. On December 3, 2018, the FERC, as appellee, filed a joint motion with the appellants to hold Case No. 18-5322 in abeyance pending completion of the appeals of the final agency orders related to the MVP certificate in consolidated Case No. 17-1271 and Atlantic Coast Pipeline’s (ACP) certificate. The MVP Joint Venture filed a motion to dismiss the case as to some of the plaintiffs. On February 15, 2019, the DCD.C. Circuit entered an order holding this appeal in abeyance pending rulings on the appeals from the ACP and MVP FERC proceedings. AlthoughThe ACP petitioners on November 16, 2022, filed a joint motion for voluntary dismissal of all petitions for review pertaining to ACP, except for the membersBold Alliance proceeding. The court granted the motion on November 17, 2022. On January 5, 2023, the D.C. Circuit entered an order holding the Bold Alliance proceeding in abeyance pending further order of the ACP project announcedcourt and requiring the cancellationparties to file motions to govern future proceedings within 60 days of that project on July 5, 2020, ACP's proceeding remains pending.the U.S. Supreme Court disposition of the petition for writ of certiorari in Bohon et al. v. FERC et al., discussed below. On June 26, 2023, the court entered an order continuing the abeyance of Bold Alliance until 30 days after the disposition of Case No. 18-5322 remains in abeyance. 20-5203, discussed below.
Similarly, another group of parties filed a complaint in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia in Bohon et al. v. FERC et al., Case No. 20-00006,, asserting that the delegation of authority to the FERC under the NGA violates the nondelegation doctrine and separation-of-powers principle of the U.S. Constitution. The MVP Joint Venture and the FERC filed motions to dismiss which were granted by the court. On July 6, 2020, the landowners filed a notice of appeal to the DCD.C. Circuit in Case No. 20-5203. On November 30, 2020, appellants asked the DCD.C. Circuit to overturn the decision of the lower court. Oral argument before the DC Circuit was scheduled for March 29, 2021, but the court cancelled and held oral argument in abeyance and directed the parties to file motions to govern future proceedings following a decision by the U.S. Supreme Court in PennEast Pipeline Co. v. New Jersey, Case No. 19-1039, which decision was published on June 29, 2021. Briefing in Bohon et al. v. FERC et al., Case No.
20-00006 on the significance of the PennEast Pipeline Co. opinion was completed on July 29, 2021. The DCD.C. Circuit issued an order on September 15, 2021 denying appellants'appellants’ motion for summary reversal of the decision of the lower court and supplemental briefing was completed as of October 6, 2021. Oral argument occurred on DecemberOn June 21, 2022, the D.C. Circuit upheld the lower court’s decision to dismiss the lawsuit. On September 15, 20212022, the petitioners filed a petition for writ of certiorari with the U.S. Supreme Court. The FERC and the parties are awaiting a decision. Due to the uncertainty regarding the timing of permitting and the outcome of legal challenges facing the MVP project, on August 25, 2020, the MVP Joint Venture filed a request withresponses to the FERC for and, on October 9, 2020, the FERC granted, an extension of time to complete the MVP project for an additional two years through October 13,petition in November 2022. On December 22, 2020, a challengeApril 24, 2023, the U.S. Supreme Court granted the petition for certiorari, vacated the judgment, and remanded the case to the FERC’s actionD.C. Circuit for further consideration in light of the U.S. Supreme Court's April 14, 2023 opinion in Axon Enterprises, Inc. v. FTC. The D.C. Circuit subsequently issued an order authorizing, among other things, the parties to grant an extensionaddress in their supplemental briefing the implications of timeSection 324 of the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023 in addition to completeAxon. On October 24, 2023, the MVP project wasD.C. Circuit denied a stay motion filed by the petitioners. The parties filed their respective supplemental briefs on November 13, 2023. On November 26, 2023, the petitioners filed in the DC CircuitU.S. Supreme Court an “emergency” motion for an injunction requesting a judicial injunction on, or access to, the petitioners’ three properties pending resolution of their underlying claims in Sierra Club, et al. v. FERC, Case No. 20-1512 (consolidated with No. 21-1040, DC Circuit).the Bohon matter. On January 29, 2021, Sierra Club requestedDecember 5, 2023, Chief Justice John Roberts denied the application, without calling for a stay of the FERC’s action to grantresponse from the MVP Joint Venture an extension of timeor the federal government. On February 13, 2024, the D.C. Circuit affirmed and reinstated its June 21, 2022 judgment upholding the lower court's decision to completedismiss the MVP project fromlawsuit. If appealed to the DC Circuit, which stay request was denied byU.S. Supreme Court and the DC Circuitappeal were successful on February 19, 2021. Briefing inits merits, or if the Sierra Club, et al. v. FERC, Case No. 20-1512 (consolidated with No. 21-1040, D.C. Circuit)Bold Alliance , was completed in January 2022 and oral argument is scheduled for April 7, 2022. If any of these challengesappeal were successful, it could result in the MVP Joint Venture'sVenture’s certificate of public convenience and necessity being vacated and/or additional proceedings before the FERC, the outcome of which the Company cannot predict,ensure, and cause a delay or further delay in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project (and consequent impacts related to such delay), or otherwise have adverse effects.
•Appalachian Voices, et al. v. U.S. Dep’t of Interior, et al., Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals, Case No. 20-2159. In August 2019, Wild Virginia and certain other petitioners filed a petition in the Fourth Circuit in Wild Virginia et al. v. United States Department of the Interior; Case No. 19-1866, to challenge the MVP Joint Venture’s Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement issued by FWS which was approved in November 2017 (the Original BiOp). On October 11, 2019, the Fourth Circuit issued an order approving the petitioners’ requested stay of the Original BiOp and holding the litigation in abeyance until January 11, 2020. On October 15, 2019, the FERC issued an order requiring the MVP Joint Venture to cease all forward-construction progress (the FERC modified this order on October 9, 2020 and December 17, 2020, which the Sierra Club has appealed to the DC Circuit as discussed above under "Jefferson National Forest Crossing and Associated Authorizations"). On September 4, 2020, FWS issued the MVP Joint Venture a new Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement (the New BiOp) for the MVP project and the Fourth Circuit subsequently dismissed the litigation regarding the Original BiOp. On October 27, 2020, Appalachian Voices et al. filed a petition with the Fourth Circuit challenging the New BiOp and filed a request for an administrative stay of the New BiOp with FWS, which FWS subsequently denied. On November 2, 2020, the petitioners filed a motion to stay the New BiOp with the Fourth Circuit. On November 18, 2020, the Fourth Circuit issued an order denying the requested stay. The matter was fully briefed as of March 19, 2021. Oral argument occurred on October 29, 2021. On February 2, 2022, the Fourth Circuit vacated and remanded the New BiOp holding, in part, that the FWS did not adequately analyze the environmental context for species at issue. The vacatur of the New BiOp may result in appellate and/or additional agency proceedings (the outcome of which the Company cannot predict) and has caused a delay in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project (and consequent impacts relating to such delay). The Company cannot predict whether and when a new BiOp will be received from the FWS and, if received, the result of any challenge to such biological opinion.
Other Proceeding Relevant to the MVP Project
FERC Rulemaking on Construction Commencement. The MVP Joint Venture is a party to a FERC rulemaking proceeding that may potentially affect when the MVP Joint Venture is permitted to commence the crossings of streams and wetlands utilizing trenchless construction methods following the FERC’s issuance of its amended Certificate for the MVP project, as described above in "Strategy" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in "Item 1. Business." On May 4, 2021, the FERC issued Order No. 871-B. Order No. 871-B and its predecessors relate to an industry-wide rulemaking regarding construction commencement while a rehearing request is pending before the FERC. The MVP Joint Venture filed a request for clarification or rehearing of the certificate amendment aspects of Order No. 871-B with the FERC on June 3, 2021. The FERC issued Order No. 871-C on August 2, 2021. The Company cannot predict the impact of Order No. 871 and its progeny, or the FERC policies discussed in "Regulatory Environment - FERC Regulation" under "Item 1. Business.", on the MVP project, if any.
MVP Southgate Matters
The MVP Joint Venture is currently challenging or defending certain agency actions and judicial challenges to the MVP Southgate project that must be resolved in connection with the project, in addition to working to address matters affecting the MVP, including the following:
•Sierra Club et al. v. FERC; Case No. 20-1427, DC Circuit. On June 18, 2020, the FERC issued an order granting a certificate of public convenience and necessity for the MVP Southgate project. However, the FERC, while authorizing the project, directed the Office of Energy Projects not to issue a notice to proceed with construction until necessary federal permits are received for the MVP project and the Director of the Office of Energy Projects lifts the stop-work
order and authorizes the MVP Joint Venture to continue constructing the MVP project. Certain opposition parties subsequently requested rehearing of the certificate order. On August 20, 2020, the FERC issued an order denying requests for rehearing of that certificate order, and on September 17, 2020, the FERC issued an order addressing the arguments raised on rehearing. On October 9, 2020, Sierra Club, among other petitioners, filed an appeal of these orders with the DC Circuit. The matter has been fully briefed and oral argument was held on January 19, 2022 and the parties are awaiting a decision. If this challenge were successful, it could result in the MVP Southgate project’s certificate of public convenience and necessity being vacated and/or additional proceedings before the FERC, the outcome of which the Company cannot predict, and cause a further delay to the MVP Southgate project (and consequent impacts relating to such delay), or otherwise adverse effects.
•Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC v. North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality, No. 20-1971, Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals. On August 11, 2020, the North Carolina Department of Environmental Quality (NCDEQ) denied the MVP Southgate project’s application for a Clean Water Act Section 401 Individual Water Quality Certification and Jordan Lake Riparian Buffer Authorization and such denial was reissued by the NCDEQ on April 29, 2021. See "MVP Southgate Project" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in "Item 1. Business" for additional information. The Company is evaluating next steps, including the submission of a new application for a Clean Water Act Section 401 Individual Water Quality Certification and Jordan Lake Riparian Buffer Authorization for the MVP Southgate project, but cannot guarantee whether a new application, if submitted, will ultimately be approved or, if approved, whether conditions may be included as part of such approval or whether the application would then be further challenged.
•Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC v. State Air Pollution Control Board et al., U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit. On December 3, 2021, the Virginia State Air Pollution Control Board (VAPCB) voted 5-2 to deny the air permit for the MVP Southgate project’s Lambert Compressor Station (the Lambert Air Permit). On December 31, 2021, the MVP Joint Venture filed a Petition for Review in the Fourth Circuit to review the VAPCB’s December 3, 2021 denial of the Lambert Air Permit. The Company anticipates that the matter will be fully briefed by April 26, 2022. The Company cannot guarantee whether the MVP Joint Venture’s appeal will be successful and, if it were successful, and if the Lambert Air Permit were issued, that the decision or permit would not be further challenged and what the outcome or impact of any such challenge would be.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Information About Our Executive Officers
| | Name | Name | | Age | | Year Initially Elected as Executive Officer | | Title | Name | | Age | | Year Initially Elected as Executive Officer | | Title |
| Thomas F. Karam | Thomas F. Karam | | 63 | | 2018 | | Chief Executive Officer | Thomas F. Karam | | 65 | | 2018 | | Executive Chairman |
| Diana M. Charletta | Diana M. Charletta | | 49 | | 2018 | | President and Chief Operating Officer | Diana M. Charletta | | 51 | | 2018 | | President and Chief Executive Officer |
| Kirk R. Oliver | Kirk R. Oliver | | 64 | | 2018 | | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | Kirk R. Oliver | | 66 | | 2018 | | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
| Justin M. Macken | | Justin M. Macken | | 44 | | 2024 | | Executive Vice President, Pipeline Operations and Project Execution |
| Stephen M. Moore | Stephen M. Moore | | 62 | | 2019 | | Senior Vice President and General Counsel | Stephen M. Moore | | 64 | | 2019 | | Executive Vice President and Chief Legal Officer |
| Brian P. Pietrandrea | | 47 | | 2019 | | Vice President and Chief Accounting Officer |
| Nathan P. Tetlow | | Nathan P. Tetlow | | 46 | | 2024 | | Senior Vice President, Commercial Services |
Mr. Karam was appointed Chiefhas served as Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Equitrans Midstream in July 2019. Prior to that, Mr. Karamsince January 1, 2024, and previously served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Equitrans Midstream sincefrom September 2018 andthrough December 31, 2023, a Director on the Board since November 2018.2018 and Chairman of the Board since July 2019. Mr. Karam also served as President of Equitrans Midstream from September 2018 to July 2019. Prior to his service at Equitrans Midstream, he served as senior vice president, EQT and president, midstream from August 2018, serving in those capacities until the Separation. Mr. Karam served as chief executive officer and chairman of the EQM General Partner from July 2019 until the EQM Merger in June 2020, chairman, president and chief executive officer, from October 2018 to July 2019, and as president, chief executive officer and director, from August 2018 to October 2018. Additionally, he served as chairman, president and chief executive officer of the general partner of EQGP from October 2018 through the consummationEquitrans Midstream's acquisition of 100% of the limited partner interests in EQGP Buyout,in January 2019 (the EQGP Buyout), as well as president, chief executive officer and director from August 2018 to October 2018. Mr. Karam served on EQT’s board of directors from November 2017 until the Separation. Mr. Karam is the founder and served as chairman of Karbon Partners, LLC, which invests in, owns, constructs, and operates midstream energy assets, from April 2017 to August 2018. Mr. Karam previously served as the founder, chairman and chief executive officer of the general partner of PennTex Midstream Partners, LP (PennTex), a publicly traded master limited partnership with operations in North Louisiana and the Permian Basin from 2014 until its sale to Energy Transfer Partners in 2016. Preceding PennTex, he was the founder, chairman and chief executive officer of Laser Midstream Partners, LLC, one of
the first independent natural gas gathering systems in the northeast Marcellus Shale, from 2010 until 2012 when it was acquired by Williams Partners.
Ms. Charletta was appointedhas served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Equitrans Midstream since January 1, 2024 and previously served as President and Chief Operating Officer of Equitrans Midstream from July 2019 through December 31, 2023. The Board appointed Ms. Charletta as a Director in July 2019.April 2022. She was appointedpreviously served as Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer of Equitrans Midstream insince September 2018. She also served as executive vice president, chief operating officer and a director of the EQM General Partner from October 2018 through July 2019, when she was promoted to president and chief operating officer. She served as president, chief operating officer and director of the EQM General Partner through the EQM Merger. Ms. Charletta served as the executive vice president, chief operating officer and as a director of EQGP's general partner from October 2018 through the consummation of the EQGP Buyout. Ms. Charletta joined EQT in 2002 as a senior pipeline engineer and from that time held various management positions with increasing responsibility. She assumed the role of senior vice president of midstream operations of a subsidiary of EQT in December 2013 and was promoted to senior vice president of midstream engineering and construction in July 2017, a position she held until the Separation. Ms. Charletta also has served as a director of the Southern Gas Association, a natural gas trade association, since November 2022.
Mr. Oliver was appointedhas served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Equitrans Midstream since January 1, 2024, having previously served as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Equitrans Midstream infrom September 2018.2018 through December 31, 2023. He also served as senior vice president, chief financial officer and a director of the EQM General Partner from October 2018 through the EQM Merger. Mr. Oliver served as the senior vice president, chief financial officer and as a director of the general partner of EQGP from October 2018 through the EQGP Buyout. Prior to joining Equitrans Midstream, he was chief financial officer for UGI Corporation, which distributes, stores, transports and markets energy products and related services, from October 2012 through May 2018.
Mr. Macken has served as Executive Vice President, Pipeline Operations and Project Execution of Equitrans Midstream since January 1, 2024, having previously served as Equitrans Midstream's Senior Vice President of Gas Systems Planning and Engineering from September 2018 through December 31, 2023. Mr. Macken joined EQT in 2008 as manager of gas systems planning and engineering and was promoted to director of gas systems planning in 2010 and vice president of gas systems planning in 2014, a position he held until the Separation.
Mr. Moore was appointedhas served as Executive Vice President and Chief Legal Officer of Equitrans Midstream since January 1, 2024, having previously served as Senior Vice President and General Counsel of Equitrans Midstream infrom April 2019.2019 through
December 31, 2023. Prior to joining Equitrans Midstream, Mr. Moore was general counsel of PennTex Midstream Partners, LP, a publicly traded master limited partnership, from 2014 through 2017. From March 2018 to April 2019, Mr. Moore served as special projects counsel to UGI Corporation.
Mr. PietrandreaTetlow was appointedhas served as Senior Vice President, Commercial Services of Equitrans Midstream since January 1, 2024, having previously served as Vice President, Corporate Development and Chief Accounting Officer of Equitrans Midstream in August 2019. He also served as vice president and chief accounting officer of the EQM General PartnerInvestor Relations from August 2019 through the EQM Merger. Mr. Pietrandrea also served as controller of certain subsidiaries of Equitrans Midstream effective upon the Separation until his promotion in August 2019. Prior to joining Equitrans Midstream, Mr. Pietrandrea served in various roles of increasing responsibility at a subsidiary of EQT, including director, partnership accounting and reporting, from October 2013 through February 2017, controller, from March 2017 through February 2018, and vice president and controller from MarchNovember 2018 through December 31, 2023. Mr. Tetlow joined EQT in 2008 as a business specialist in the treasury department and held various management positions with increased responsibility. Mr. Tetlow was promoted to manager of corporate treasury in 2011 and became investor relations manager in 2012 and investor relations director in 2015, a position he held until the Separation.
All executive officers have executed agreements with the Company and serve at the pleasure of the Board. Officers are elected annually to serve during the ensuing year or until their successors are elected and qualified, or until their death, resignation or removal.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Equitrans Midstream common stock trades on the NYSE under the symbol "ETRN".
As of January 31, 2022,2024, there were 1,8271,626 shareholders of record of Equitrans Midstream common stock.
On January 24, 2022,23, 2024, the Board declared cash dividends for the fourth quarter of 20212023 of $0.15 per common share and $0.4873 per Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share, which dividends were paid on February 14, 20222024 to shareholders of record at the close of business on February 3, 2022.6, 2024.
As discussed under "We cannot guarantee the timing, amount or payment of dividends on our common stock, and we may further reduce the amount of the cash dividend that we pay on our common stock or may not pay any cash dividends at all to our shareholders. Our ability to declare and pay cash dividends to our shareholders, if any, in the future will depend on various factors, many of which are beyond our control.” included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors,"Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the amount and timing of dividends is subject to the discretion of the Board and depends upon business conditions, including, but not limited to, the financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and capital requirements of the Company's operating subsidiaries, covenants associated with certain debt obligations, legal requirements and strategic direction and other factors deemed relevant by the Board. The Board has the discretion to change the dividend at any time for any reason.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
See Part III, “Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for information relating to the Company’s equity compensation plans.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
See Notes 1 and 2 to the consolidated financial statements for a description of the Restructuring Agreement and Restructuring.
Market Repurchases
The Company did not have any repurchasessales of equityunregistered securities registered under Section 12 of the Exchange Act during the three months ended December 31, 2021.2023.
Market Repurchases
The following table sets forth the Company's repurchases of equity securities registered under Section 12 of the Exchange Act that occurred during the three months ended December 31, 2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | | Total number of shares purchased (a) | | Average price paid per share | | Total number of shares purchased as part of publicly announced plans or programs | | Approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the plans or programs |
| October 2023 (October 1 - October 31) | | — | | | $ | — | | | — | | | $ | — | |
| November 2023 (November 1 - November 30) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| December 2023 (December 1 - December 31) | | 161,466 | | | 10.25 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | 161,466 | | | $ | 10.25 | | | — | | | $ | — | |
(a) Reflects shares withheld by the Company to pay taxes upon vesting of restricted stock.
Stock Performance Graph
The graph below compares the cumulative thirty-seven monthfive-year total return provided to shareholders on Equitrans Midstream's common stock relative to the cumulative total returns of (i) the S&P 500 index and (ii) the Alerian US Midstream Energy Index. An investment of $100 (with reinvestment of all dividends) is assumed to have been made in Equitrans Midstream common stock on November 13, 2018, and with respect to each index Octoberbeginning on December 31, 2018, and relative performance is tracked through December 31, 2021.2023. 
| | | |
| | | | 11/13/2018 | | 12/31/2018 | | 12/31/2019 | | 12/31/2020 | 12/31/2021 | | | 12/31/2018 | | 12/31/2019 | | 12/31/2020 | 12/31/2021 | 12/31/2022 | 12/31/2023 |
| Equitrans Midstream Corporation | Equitrans Midstream Corporation | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 95.84 | | | $ | 71.75 | | | $ | 47.88 | | $ | 66.20 | |
| S&P 500 | S&P 500 | 100.00 | | | 92.82 | | | 122.05 | | | 144.51 | | 185.99 | |
| Alerian U.S. Midstream Energy | Alerian U.S. Midstream Energy | 100.00 | | | 89.60 | | | 103.54 | | | 77.70 | | 112.67 | |
|
Item 6. Reserved
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with “ItemPart I, "Item 1. Business,” “Item" Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors,”" and the consolidated financial statements, and the notes thereto, included in Part II, "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" ofin this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021.10-K.
The information covered in this section provides a comparison of material changes in the Company's results of operations and financial condition for fiscal year 2021 and2023 relative to fiscal year 2020.2022. For the discussion of fiscal year 20202022 relative to fiscal year 2019,2021, see Part II, "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" of the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2020,2022, filed with the SEC on February 23, 2021.21, 2023.
Executive Overview
Net lossincome (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders was $1,439.0$386.7 million, ($(3.32)$0.89 per diluted share)share, in 20212023 compared to net income attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders of $364.4$(327.9) million, ($1.060.76) per diluted share)share, in 2020.2022. The decreaseincrease resulted primarily from an impairment of the Company's equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture lowerincurred during the year ended December 31, 2022, higher equity income, from the Company's investment in the MVP Joint Venture, lowerhigher operating revenues, on Gathering (primarily due to impacts of the EQT Global GGA) and Water, higher net interest expense, higher other expense and additionala loss on extinguishment of debt charges,incurred during the year ended December 31, 2022 and higher income tax benefit, partially offset by lower income taxhigher operating expenses and higher net interest expense lower net income attributable to noncontrolling interest and transaction costs recorded during 2020. See. See Note 4 and Note 62 to the consolidated financial statements for a discussion of the impairment of the Company's equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture and deferred revenues underVenture.
As part of implementing the EQT Global GGA, respectively.
COVID-19 Update
While the COVID-19 pandemic is continuing, the outbreak has had, and continues to have, a minimal direct impactCompany's succession plan, on the Company’s overall operations. The Company continues to actively manage its response to the COVID-19 pandemic in collaboration with relevant parties and, given that the situation surrounding COVID-19 remains fluid, a number of Company-wide measures undertaken in response to COVID-19 remain in effect to continue to promote the safety and health of field and office-based employees and contractors.
On November 4, 2021, the U.S. Department of Labor's Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) issued an Emergency Temporary Standard (ETS) to carry out President Biden’s executive order requiring all employers with at least 100 employees to ensure that their employees are fully vaccinated or require unvaccinated workers to produce a negative test result at least once a week. On January 13, 2022, the U.S. Supreme Court granted an application to stay the ETS pending disposition1, 2024, Mr. Thomas F. Karam stepped down as Chief Executive Officer of the applicants' petitions for review inCompany and Diana M. Charletta, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit. Effective January 26, 2022, OSHA withdrew the ETS as an enforceable emergency temporary standard, but did not withdraw the ETS as a proposed rule. Should the ETS, or a similar state or local requirement, take effect in the future, the Company expects it would be subject to such regulation concerning COVID-19 vaccination or testing. In that case, the Company may be required to implement a requirement that many or most employees get vaccinated, subject to limited exceptions, or be tested, resulting in additional costs to the Company. At this time, it is not possible to predict the impact that a vaccine or testing requirement would have on the Company or its workforce. Any such mandate may result in increased costs, operational disruptions or employee attrition for the Company.See “The loss or disengagement of key personnel could adversely affect our ability to execute our strategic, operationalformer President and financial plans.” under "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021.
Notwithstanding the outbreak’s minimal direct impact to date on the Company’s overall operations, the Company acknowledges that the COVID-19 pandemic is still ongoingChief Operating Officer, became President and therefore the Company cannot predict that the pandemic, or further developments regarding variants of COVID-19 or other governmental action, will not have any impact in the future on the Company's business, results of operations or financial position. For further information regarding the potential impact of COVID-19 on the Company, see "The ongoing outbreak of COVID-19 and its variant strains (or any future pandemic) could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition." under "Item 1A. Risk Factors" and "Item 1. Business" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021.Chief Executive Officer.
Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility
The Company recognizes that the long-term interests of shareholders are served by managing ESG matters important to the Company’s stakeholders and working to be resilient and appropriately positioned in any environment, including a lower-carbon economy. The Company has, throughout its corporate history, embraced conductingembraces working to conduct business in a socially responsible and ethical manner by respecting all stakeholders, and is focused on identifying and executing on ESG and sustainability initiatives while further integrating corporate responsibility and ESG concerns into its business strategy and decision-making throughout the organization. The Company also is committed to continuing to operate with integrity, accountability and transparency. As a result, the Company anticipates that its allocation ofit will continue to prudently allocate capital resources to ESG and sustainability initiatives will increase in the future, which may include at increasing levels, which the Company believes will distinctively positionbenefit the Companysustainability of the Company's business and help to create value.
The Company believes that natural gas will remain a significant component of the global and national energy complex and will play a vital role in the transformation to a lower-carbon economy, notwithstanding increased demand for alternative energy sources. However,sources and negative sentiment with respect to natural gas, including natural gas infrastructure, from certain actors. Further, the Company believes that continued natural gas production and infrastructure growth are directly supportive of the United States' energy security, as evidenced by the historic inclusion of provisions mandating the completion of the MVP project in the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023. The Company also acknowledges the reality and risks of climate change as one of the mosta critical current issues. Asissue and, as an energy infrastructure company, the Company recognizes the ongoing developments and risks surrounding climate change, as well as corresponding potential opportunities, and that it must continue to focuschange. As a result, the Company is focused on long-term sustainable performance, including working to minimize impacts to the environment and society, such as by aggressively pursuing its
continuing to proactively pursue climate change mitigation targetsaspirations while also balancing the immediate and increasing need to deliver reliable, safe, and affordable natural gas energy in the United States now and in the future.
The Company is focused on incorporatingexecuting on sustainability initiatives while further integrating sustainability-focused risks and opportunities into the Company’s strategic and capital spending decision processes. In 2023, the Company focused primarily on developing the appropriate strategy and building the requisite programs and plans for achieving its GHG reduction goals. In January 2023, the Company announced its status as a founding member of the newly formed Appalachian Methane Initiative (AMI), a coalition of regional natural gas operators committed to further enhancing methane monitoring throughout the Appalachia Basin and facilitating additional methane emissions reduction in the region. Additionally, the Company’s GHG Committee developed a portfolio of 2024 capital projects that includes avoiding or eliminating methane emissions from both certain fixed and event-based sources. Further, the Company finalized its GHG Management program, providing the roadmap and accounting protocols for pursuing achievement of and reporting on progress towards its aspirational emissions targets. Additionally, aspects of the Company's compensation structure reflect sustainability-oriented goals and developments. For example, among other initiatives,the Human Capital and Compensation Committee of the Board determined to include the completion of certain scenario analyses under the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures framework, and the development of a related publishable report, as a metric in 2021 the Company made investmentsCompany’s 2023 short-term incentive compensation program applicable to replace certain high-bleed pneumatic devices with low-bleed pneumatic devices and replace certain gas-driven pneumatics with instrument air systems so as to reduce pneumatic methane emissions relative to 2019 levels in supportall employees,
including executives. The Company expects to continue to pursue strategic sustainability initiatives as appropriate, including with respect to climate change, and to incur costs and capital expenditures to do so,so. Costs and certain of such future costsexpenses associated with sustainability and capital expendituresESG matters could be material.
As discussed in “Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing the financing of non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting the pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies, and alternative forms of energy) and, as well as physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services.” in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” and “Regulatory Environment” in Part I, “Item 1. Business”, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the Company recognizes the evolving landscape of international accords and federal, state and local laws and regulations regarding GHG emissions or climate change initiatives. The Company also recognizes, as discussed in "Increasing scrutiny and changing stakeholder expectations and disclosures in respect of ESG and sustainability practices may adversely impact our business and our stock price and impose additional costs or expose us to new or additional risks." in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the changing expectations from a variety of stakeholders relating to ESG and sustainability practices.Changing market conditions, competition from lower emitting fuels, new laws and regulatory requirements, as well as unanticipated or inconsistent application of existing laws and regulations by administrative agencies, make it difficult to predict the long-term business impact of GHG emission and climate change initiatives on the Company’s liquidity, capital resources, results of operations and financial condition. However, the Company is taking steps to adjustprudently invest capital in furtherance of its approach to capital investment given regulatory changegoal of long-term sustainable operations and recognizes that responsive adaptation efforts are likely to be costly and time consuming.
Business Segment Results
Operating segments are revenue-producing components of an enterprise for which separate financial information is produced internally and is subject to evaluation by the chief operating decision maker in deciding how to allocate resources. Headquarters costs consist primarily of certain unallocated corporate expenses and transaction costs, and other unallocated corporate expenses.as applicable. Net interest expense, loss on extinguishment of debt, components of other income (expense) income,, net, and income tax expense (benefit) expense are managed on a consolidated basis. The Company has presented each segment's operating income (loss), unrealized (loss) gain on derivative instruments,other income (expense), net, equity income, impairment of equity method investment and various operational measures, as applicable, in the following sections. Management believes that the presentation of this information is useful to management and investors regarding the financial condition, results of operations and trends and uncertainties of its segments. The Company has reconciled each segment's operating income (loss) to the Company's consolidated operating income (loss) and net income (loss) income in Note 53 to the consolidated financial statements.
GATHERING RESULTS OF OPERATIONS | | | | Years Ended December 31, | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | | 2021 | | 2020 | | %
Change | | 2019 | | %
Change | | 2023 | | 2022 | | %
Change | | 2021 | | %
Change |
| FINANCIAL DATA | FINANCIAL DATA | (Thousands, except per day amounts) | FINANCIAL DATA | (Thousands, except per day amounts) |
Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | $ | 468,156 | | | $ | 595,720 | | | (21.4) | | | $ | 581,118 | | | 2.5 | |
| Volumetric-based fee revenues | 393,897 | | | 416,561 | | | (5.4) | | | 578,813 | | | (28.0) | |
Volumetric-based fee revenues (b) | |
| Total operating revenues | Total operating revenues | 862,053 | | | 1,012,281 | | | (14.8) | | | 1,159,931 | | | (12.7) | |
| Operating expenses: | Operating expenses: | |
| Operating and maintenance | Operating and maintenance | 99,625 | | | 87,388 | | | 14.0 | | | 96,740 | | | (9.7) | |
| Operating and maintenance | |
| Operating and maintenance | |
| Selling, general and administrative | Selling, general and administrative | 94,776 | | | 93,070 | | | 1.8 | | | 80,822 | | | 15.2 | |
| Separation and other transaction costs | — | | | 4,104 | | | (100.0) | | | 19,344 | | | (78.8) | |
| | Depreciation | |
| Depreciation | |
| Depreciation | Depreciation | 188,633 | | | 172,967 | | | 9.1 | | | 144,310 | | | 19.9 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 63,195 | | | 2.6 | | | 53,258 | | | 18.7 | |
| Impairments of long-lived assets | — | | | 55,581 | | | (100.0) | | | 854,307 | | | (93.5) | |
| | Total operating expenses | Total operating expenses | 447,853 | | | 476,305 | | | (6.0) | | | 1,248,781 | | | (61.9) | |
| Operating income (loss) | $ | 414,200 | | | $ | 535,976 | | | (22.7) | | | $ | (88,850) | | | 703.2 | |
| Total operating expenses | |
| Total operating expenses | |
| Operating income | |
| Other (expense) income, net (b) | $ | (16,362) | | | $ | 16,460 | | | (199.4) | | | $ | — | | | 100.0 | |
Other income (expense), net (c) | |
Other income (expense), net (c) | |
Other income (expense), net (c) | |
| | OPERATIONAL DATA | OPERATIONAL DATA | | | | | | |
| Gathering volumes (BBtu per day) | |
Firm capacity(c) | 5,216 | | | 4,652 | | | 12.1 | | | 3,351 | | | 38.8 | |
| OPERATIONAL DATA | |
| OPERATIONAL DATA | |
| Gathered volumes (BBtu per day) | |
| Gathered volumes (BBtu per day) | |
| Gathered volumes (BBtu per day) | |
Firm capacity (d) | |
Firm capacity (d) | |
Firm capacity (d) | |
| Volumetric-based services | Volumetric-based services | 3,098 | | | 3,553 | | | (12.8) | | | 4,493 | | | (20.9) | |
| Total gathered volumes | Total gathered volumes | 8,314 | | | 8,205 | | | 1.3 | | | 7,844 | | | 4.6 | |
| Capital expenditures(d) | $ | 223,807 | | | $ | 344,873 | | | (35.1) | | | $ | 834,712 | | | (58.7) | |
Capital expenditures(e) | |
Capital expenditures(e) | |
Capital expenditures(e) | |
(a)For the years ended December 31, 20212023, 2022 and 2020,2021, firm reservation fee revenues included approximately $11.3$4.1 million, $20.2 million and $15.0$11.3 million, respectively, of MVC unbilled revenues. There were no MVC unbilled revenues during
(b)For the year ended December 31, 2019.2023, volumetric-based fee revenues included a one-time contract buyout by a customer for approximately $5.0 million. For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022, and 2021, volumetric-based fee revenues included approximately $4.6 million, $4.2 million and $3.5 million, respectively, of MVC unbilled revenues.
(b)(c)Other income (expense) income,, net, includes the unrealized gain (loss) gain on derivative instruments associated with the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision.provision and gain on sale of gathering assets in 2022. See Note 1210 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.information on the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision.
(c)(d)Includes volumes up to the contractual MVC under agreements structured with MVCs. Volumes in excess of the contractual MVC are reported under Volumetric-basedvolumetric-based services.
(d)(e)Includes approximately $14.1$14.3 million, $41.6$20.3 million and $25.9$14.1 million of capital expenditures related to noncontrolling interestsinterest in Eureka Midstream for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, respectively.
Year Ended December 31, 20212023 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 20202022
Gathering operating revenues decreased by $150.2$20.4 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020.2022. Firm reservation fee revenues decreasedincreased by $127.6$10.0 million primarily due to $15.8 million of higher deferred revenue of $194.2 million primarily resulting from a cumulative adjustmentfirm reservation fees associated with certain potential contract extensionsthe EQT Global GGA due to assumption changes impacting the estimated total consideration underin the EQT Global GGA, partlyprior year and increased contracted capacity, partially offset by $54.3 million of increased MVC revenues resulting from the EQT Global GGA and $12.2 million of increased firm reservation revenues from other customers. See Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements forlower average rates on a discussion of deferred revenues under the EQT Global GGA.certain customer MVC. Volumetric-based fee revenues decreased by $22.7$30.4 million primarily due to lower gathered volumes resulting from reduced producer activity and lower effective rates, partially offset by higher compression revenues.
Gathering operating expenses decreaseda one-time contract buyout by $28.5a customer of approximately $5.0 million forand $4.7 million associated with firm and interruptible gathered volumes on Hammerhead. The Company expects interruptible volumes from the year ended December 31, 2021 comparedCompany's Hammerhead gathering agreement with EQT to continue up to the year ended December 31, 2020, primarily as a resultfull commercial in-service date of the impairments of gathering assets and customer-related intangible assets totaling $55.6 million, as described in Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements, and transaction costs associated with the EQM Merger and related transactions in 2020, partially offset by increases in operating and maintenance, selling, general andHammerhead pipeline when firm commitments will commence.
administrative, depreciationGathering operating expenses and amortization of intangible assets in 2021increased by $28.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to 2020. Operating and maintenance expense increased by $12.2 million primarily as a result of an increase in repairs and maintenance expense and personnel costs.the year ended December 31, 2022. Selling, general and administrative expenseexpenses increased by $1.7$31.1 million primarily due to legal feeshigher incentive compensation of $29.2 million, including $12.3 million associated with the Hammerhead pipeline arbitrationMVP PSU Program that included the impact of a cumulative catch-up since the inception of the award. Operating and maintenance expenses decreased by $4.3 million primarily due to lower operating expenses associated with the divestiture of the regulated low pressure gathering assets in June 2023 and lower repairs and maintenance expenses, partially offset by higher personnel costs.costs and higher property taxes. Depreciation expense increased by $15.7$1.5 million as a result of additional assets placed in-service.
See "Outlook" and Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements for further discussion"Overview of the impairment of long-lived assets. See alsoCompany and Operations" in Part II,1, "Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk"1. Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for discussions of certain customer production curtailments during 2020 and Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for discussions of the EQT Global GGA, and the transactions related thereto, including theperiodic gathering MVC fee relief to EQT thereunder. As was the case for the Gathering operating revenues during certain portions of 2021, the Company expectsdeclines and, additionally, discussion that the operating revenues resulting from the MVCs underin connection with MVP full in-service the EQT Global GGA will increase the proportion of the Company's total operating revenues that are firm reservation fee revenues, and correspondingly decrease the portion of the Company's total operating revenues that are volumetric-based fee revenues,provides for more significant potential gathering MVC fees declines in future periods.certain contract years. Firm reservation fee revenues under the Company’s Hammerhead gathering agreement with EQT are also expected to contribute to an increase in the Company’s firm reservation fee revenues following achievement of the Hammerhead pipeline full commercial in-service in conjunction with full MVP in-service. However, the percentage of the Company's operating revenues that are generated by firm reservation fees may vary year to year depending on various factors, including customer volumes and the rates realizable under the Company’s contracts, including the EQT Global GGA. See also “Outlook”"Commodity Price Risk" in Part II, "Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for aadditional information on factors that could affect the Company's operating revenues. Also, see Note 8 for further discussion ofon the arbitration decision issued in the Hammerhead pipeline dispute with EQT.MVP PSU Program.
TRANSMISSION RESULTS OF OPERATIONS | | | | Years Ended December 31, | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | | 2021 | | 2020 | | %
Change | | 2019 | | %
Change | | 2023 | | 2022 | | %
Change | | 2021 | | %
Change |
| FINANCIAL DATA | FINANCIAL DATA | (Thousands, except per day amounts) | FINANCIAL DATA | (Thousands, except per day amounts) |
| Firm reservation fee revenues | Firm reservation fee revenues | $ | 366,323 | | | $ | 364,533 | | | 0.5 | | | $ | 356,569 | | | 2.2 | |
| Volumetric-based fee revenues | 33,879 | | | 29,303 | | | 15.6 | | | 33,951 | | | (13.7) | |
Volumetric-based fee revenues (a) | |
| Total operating revenues | Total operating revenues | 400,202 | | | 393,836 | | | 1.6 | | | 390,520 | | | 0.8 | |
| Operating expenses: | Operating expenses: | |
| Operating and maintenance | |
| Operating and maintenance | |
| Operating and maintenance | Operating and maintenance | 33,883 | | | 37,635 | | | (10.0) | | | 33,989 | | | 10.7 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | Selling, general and administrative | 36,483 | | | 26,292 | | | 38.8 | | | 26,865 | | | (2.1) | |
| Depreciation | Depreciation | 55,310 | | | 54,540 | | | 1.4 | | | 51,935 | | | 5.0 | |
| Total operating expenses | Total operating expenses | 125,676 | | | 118,467 | | | 6.1 | | | 112,789 | | | 5.0 | |
| Operating income | Operating income | $ | 274,526 | | | $ | 275,369 | | | (0.3) | | | $ | 277,731 | | | (0.9) | |
| | Equity income | Equity income | $ | 17,579 | | | $ | 233,833 | | | (92.5) | | | $ | 163,279 | | | 43.2 | |
| Impairment of equity method investment | $ | (1,926,402) | | | $ | — | | | 100.0 | | | $ | — | | | — | |
| Equity income | |
| Equity income | |
| Impairments of equity method investment | |
| | OPERATIONAL DATA | OPERATIONAL DATA | | | | | | |
| Transmission pipeline throughput (BBtu per day) | |
| Firm capacity reservation | 2,960 | | | 2,932 | | | 1.0 | | | 2,823 | | | 3.9 | |
| Volumetric-based services | 11 | | | 16 | | | (31.3) | | | 90 | | | (82.2) | |
| OPERATIONAL DATA | |
| OPERATIONAL DATA | |
| Transmission pipeline throughput (BBtu per day): | |
| Transmission pipeline throughput (BBtu per day): | |
| Transmission pipeline throughput (BBtu per day): | |
Firm capacity (b) | |
Firm capacity (b) | |
Firm capacity (b) | |
| Interruptible capacity | |
| Total transmission pipeline throughput | Total transmission pipeline throughput | 2,971 | | | 2,948 | | | 0.8 | | | 2,913 | | | 1.2 | |
| | Average contracted firm transmission reservation commitments (BBtu per day) | Average contracted firm transmission reservation commitments (BBtu per day) | 4,082 | | | 4,087 | | | (0.1) | | | 3,966 | | | 3.1 | |
| Average contracted firm transmission reservation commitments (BBtu per day) | |
| Average contracted firm transmission reservation commitments (BBtu per day) | |
| Capital expenditures (a) | $ | 25,977 | | | $ | 45,219 | | | (42.6) | | | $ | 59,313 | | | (23.8) | |
Capital expenditures (c) | |
Capital expenditures (c) | |
Capital expenditures (c) | |
(a)For the year ended December 31, 2023, volumetric-based fee revenues included a one-time contract buyout by a customer for approximately $23.8 million.
(b)Firm capacity includes volumes associated with firm capacity contracts including volumes in excess of firm capacity.
(c)Transmission capital expenditures do not include aggregate capital contributions made to the MVP Joint Venture for the MVP and MVP Southgate projects of approximately $287.7$689.4 million, $272.8$199.6 million and $774.6$287.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, 2020respectively.
Year Ended December 31, 2023 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2022
Transmission operating revenues increased by $38.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. Firm reservation fee revenues decreased by $9.4 million primarily due to lower contracted capacity payments resulting from the one-time contract buyout that occurred during the first quarter of 2023. Volumetric-based fee revenues increased by $48.0 million primarily as a result of a one-time contract buyout by a customer of approximately $23.8 million and 2019, respectively.higher volumes in excess of firm capacity contracts.
Operating expenses increased by $41.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022. Operating and maintenance expense increased $21.8 million primarily due to operational efficiencies associated with operating activities with the Gathering segment for replenishment gas on the regulated low pressure gathering assets which were divested in June 2023, increased personnel costs and expenses associated with the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident. Selling, general and administrative expenses increased by $19.7 million resulting primarily from higher incentive compensation of $12 million, including $4.7 million associated with the MVP PSU Program that included the impact of a cumulative catch-up since the inception of the award, an increased reserve for bad debt expense and higher professional fees.
Regarding the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, the root cause analysis, which was conducted by an independent, third-party company with expertise in reservoir management and well and corrosion engineering, was submitted to the PHMSA in August 2023, which root cause analysis indicated that the direct cause of the venting from the relevant Rager Mountain facility storage well (well #2244) was due to corrosion caused by the infiltration of water, oxygen and debris into the well's annulus, and such corrosion resulted in a failure of the well casing. Based on results of an inventory verification test conducted after the venting incident was resolved, the Company’s initial gas loss estimate for well #2244 was approximately 1.29 Bcf. Following completion of the root cause analysis, the cumulative gas loss was determined to be approximately 1.164 Bcf, approximately 1.037 Bcf of which was vented to the atmosphere and roughly 0.127 Bcf was diverted to and contained within formation(s) located at approximately 1,800’ and/or 3,000’ below ground. Post-incident workstreams related to the safe and environmentally responsible operation of the Rager Mountain facility and other storage fields are ongoing.
The Company worked with various third-party experts to identify and address the causes and/or contributors to the November 2022 incident. The damaged casing on well #2244 has been replaced, and the well remains temporarily plugged. The Company intends to seek any necessary approval from PHMSA to perform certain capital activities to remediate well 2244 and ultimately return it to in-service. Additionally, several other Rager wells have undergone top joint casing replacements to address proactively less-aggressive corrosion that was identified. The Company also has performed supplemental evaluations and testing, including updated wireline logging, on all other wells at the Rager Mountain facility. In October 2023, following authorization from PHMSA of the Company's injection plan for the Rager Mountain facility, the Company returned the Rager Mountain facility, other than well #2244 and two additional wells, to injection operations, subject to certain operating pressure restrictions and other requirements specified in the consent agreement between the PHMSA and the Company. On November 16, 2023, the PHMSA issued a letter to the Company approving the Company's request to remove all pressure restrictions at the Rager Mountain facility. For additional information, see Part I, "Item 3. Legal Proceedings", Part I, "Item 1. Business" and "We have incurred and expect to continue to incur costs and expenses as a result of or arising in relation to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident in November 2022, which has included and may include potential additional regulatory penalties or other sanctions, which could, depending on their scope and timing, materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders." in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Equity income increased by $175.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022 due to the increase in the MVP Joint Venture's AFUDC on the MVP project resulting from the resumption of growth construction activities in 2023. Following MVP full in-service, the Company's equity income will be primarily derived from 20-year firm reservation contracts for the MVP project.
Impairments of equity method investment includes the separate impairments of the Company's equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture. See Note2 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
Year Ended December 31, 2021 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2020
Transmission operating revenues increased by $6.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020. Firm reservation fee revenues increased by $1.8 million primarily due to customers contracting for additional firm transmission capacity. Volumetric-based fee revenues increased $4.6 million primarily due to higher storage activities.
Operating expenses increased by $7.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 primarily as a result of higher selling, general and administrative expense resulting from increased professional service fees and personnel costs, partly offset by lower operating and maintenance expense primarily due to operational efficiencies.
Equity income decreased by $216.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 due to the decrease in the MVP Joint Venture's AFUDC on the MVP project.
In January 2021, the MVP Joint Venture temporarily suspended AFUDC on the MVP project due to a temporary reduction in growth construction activities. During the second quarter of 2021, the MVP Joint Venture resumed some AFUDC on the MVP project as certain growth construction activities resumed. The Company's equity income in future periods will be affected by the timing of the resumption of the remaining growth construction activities and associated AFUDC, and the timing of the completion of the MVP project, and such impact could be substantial.
Impairment of equity method investment includes the impairment of the Company's equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture during the fourth quarter of 2021. See Note 4 for further information.
WATER RESULTS OF OPERATIONS | | Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | %
Change | | 2019 | | %
Change |
| Years Ended December 31, | | | Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | %
Change | | 2021 | | %
Change |
| FINANCIAL DATA | FINANCIAL DATA | (Thousands) | FINANCIAL DATA | (Thousands) |
| Firm reservation fee revenues | Firm reservation fee revenues | $ | 5,063 | | | $ | 41,798 | | | (87.9) | | | $ | 11,190 | | | 273.5 | |
| Volumetric-based fee revenues | Volumetric-based fee revenues | 49,719 | | | 62,910 | | | (21.0) | | | 68,601 | | | (8.3) | |
| Total operating revenues | Total operating revenues | 54,782 | | | 104,708 | | | (47.7) | | | 79,791 | | | 31.2 | |
| Operating expenses: | Operating expenses: | |
| Operating and maintenance | Operating and maintenance | 19,810 | | | 29,131 | | | (32.0) | | | 34,638 | | | (15.9) | |
| Operating and maintenance | |
| Operating and maintenance | |
| Selling, general and administrative | Selling, general and administrative | 7,541 | | | 5,941 | | | 26.9 | | | 2,933 | | | 102.6 | |
| Depreciation | Depreciation | 25,233 | | | 30,880 | | | (18.3) | | | 26,915 | | | 14.7 | |
| Impairment of long-lived assets | Impairment of long-lived assets | 56,178 | | | — | | | 100.0 | | | — | | | 100.0 | |
| Total operating expenses | Total operating expenses | 108,762 | | | 65,952 | | | 64.9 | | | 64,486 | | | 2.3 | |
| Operating (loss) income | $ | (53,980) | | | $ | 38,756 | | | (239.3) | | | $ | 15,305 | | | 153.2 | |
| Operating income (loss) | |
| | OPERATIONAL DATA | OPERATIONAL DATA | |
| Water services volumes (MMgal) | |
Firm capacity reservation (a) | 105 | | | 697 | | | (84.9) | | | 249 | | | 179.9 | |
| OPERATIONAL DATA | |
| OPERATIONAL DATA | |
| Water services volumes (MMgal): | |
| Water services volumes (MMgal): | |
| Water services volumes (MMgal): | |
Firm capacity (a) | |
Firm capacity (a) | |
Firm capacity (a) | |
| Volumetric-based services | Volumetric-based services | 1,015 | | | 1,219 | | | (16.7) | | | 1,559 | | | (21.8) | |
| Total water volumes | Total water volumes | 1,120 | | | 1,916 | | | (41.5) | | | 1,808 | | | 6.0 | |
| | Capital expenditures | Capital expenditures | $ | 34,877 | | | $ | 11,905 | | | 193.0 | | | $ | 37,457 | | | (68.2) | |
| Capital expenditures | |
| Capital expenditures | |
(a) Includes volumes up to the contractual MVC under agreements structured with MVCs.MVCs or ARCs, as applicable. Volumes in excess of the contractual MVC are reported under Volumetric-based services.
Year Ended December 31, 20212023 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 20202022
Water operating revenues decreasedincreased by $49.9$18.0 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020.2022. Firm reservation fee revenues decreasedincreased by $36.7$5.3 million primarily as a result of decreasedincreased revenues due to a full year of ARCs associated with contractually lower MVCs.the 2021 Water Services Agreement. Volumetric-based fee revenues decreased $13.2increased by $12.7 million primarily due to lower volumes as a result of decreased producer activity and decreased realized rates on a per gallon basis.
Water operating expenses increased by $42.8$19.3 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020 primarily as a result of the impairment of long-lived assets totaling $56.2 million (as described in Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements) and higher selling,2022. Selling, general and administrative expense due to higher personnel costs and professional service fees, partly offsetincreased by lower operating and maintenance expense of $9.3$7.4 million primarily due to overall lower customer activity resulting in lower fresha contract asset write-down. Operating and maintenance expense increased by $5.9 million due to higher mixed-use water and produced water costs.storage expenses related to storage facilities placed in-service during the year ended December 31, 2023. Depreciation expense increased $6.0 million due to additional assets placed in-service.
The Company’s volumetric-based water services are directly associated with producers’ well completion activities and fresh and produced water needs (which are partiallyprimarily driven by horizontal lateral lengths and the number of completion stages per well). Therefore, the Water volumetric operating results traditionally fluctuate from year-to-year in response to producers’ well completion activities. The Company expects Water operating revenues to be higher for the year ending December 31, 2022 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2021 primarily due to the 2021 Water Services Agreement the Company entered into with EQT during the fourth quarter of 2021. The Company also expects that the revenues resulting from the ARC under the 2021 Water Services Agreement will increase the proportion of the Company's total water operating revenues that are firm reservation fee revenues, and correspondingly decrease the portion of the Company's total water operating revenues that are volumetric-based fee revenues, in future periods. See Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for further discussion of the 2021 Water Services Agreement.
Other Income Statement Items
Other Income (Expense) Income,, Net
Other income (expense) income,, net, decreased $33.3$10.6 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 compared to the year ended December 31, 20202022. The decrease was primarily due to a $1.5 million unrealized gain on derivative instruments during the year ended December 31, 2023 as compared to a result$9.6 million unrealized gain on derivative instruments during the year ended December 31, 2022, and a $3.7 million gain on the sale of a $32.8 millionnon-core gathering assets during the year ended December 31, 2022, partially offset by higher sublease income. The decrease in the fair value ofunrealized gains on derivative instruments was primarily due to changes in timing and probability-weighted assumptions regarding MVP project completion and changes in NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices associated with the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision relatedprovision.
See also "Our exposure to the impact of an assumed potential delaycommodity price risk may increase in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project, partially offset by an increase infuture and NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas future prices.
See also "Outlook"futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of factors affecting the estimated fair value of the derivative asset attributable to the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt
Loss on extinguishment of debt increased $16.2 million forDuring the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to2022, the year ended December 31, 2020. The Company incurred a loss on extinguishment of debt of $41.0approximately $24.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2021 related to the payment of the2022 Tender Offer premiumOffers (as defined in Note 9) for Senior Notes and open market repurchase premiums and fees, and write off of the respective unamortized discounts and financing costs related toassociated with the prepayment of the EQM Term Loans under, and termination of, the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement and purchase of portions of 2023, 2024 and 2025 Notes in thesuch Tender Offers. The Company incurred a loss on extinguishment of debt of $24.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2020 primarily related to the write off of unamortized discounts and financing costs on the ETRN Term Loan Credit Agreement. See Note 11 to the consolidated financial statements for additional discussion.
Net Interest Expense
Net interest expense increased by $71.3$32.6 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 compared to the year ended December 31, 20202022 primarily due to higherincreased interest expense of $88.3 millionrates and $48.2 million associated withborrowings under the 2021revolving credit facilities and interest on the 2022 Senior Notes and the 2020 Senior Notes, respectively, and decreased capitalized interest and AFUDC - debt of $13.6 million(as defined in the aggregate,Note 9), partially offset by lower interest expense of $79.7 million primarily associated with the terminationimpact of the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement2022 Tender Offers and the ETRN Term Loan Credit Agreement, decreased borrowings under the Amended EQM Credit Facility and lower interest onredemption of the 2023 Notes as a result of the Tender Offers.
As a result of the issuance of the 2021 Senior Notes, and after taking into account the use of those proceeds to pay off other outstanding debt, the Company expects interest expense for the periods after the issuance of the 2021 Senior Notes to continue to be higher than comparable prior year periods.effected in June 2023.
See also Note 119 and Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements for a discussion of certain of the Company's outstanding debt.
Income TaxesTax Expense (Benefit)
See Note 1412 to the consolidated financial statements for an explanation of the changes in income tax expense and effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 20212023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2020.
Net Income Attributable to Noncontrolling InterestsInterest
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interestsinterest decreased $200.4$2.7 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 compared to the year ended December 31, 20202022 primarily as a result of the reduction in noncontrolling interest in connection with the EQM Merger and the Restructuring.
The Company recordedlower net income attributable to noncontrolling interest for the third-party ownership interests in EQM (including the EQM Series A Preferred Units) through the closing of the EQM Merger. Upon the closing of the EQM Merger on June 17, 2020, the Company's remaining noncontrolling interest consists solely of the third-party ownership interest in Eureka Midstream.
Capital Expenditures
See "Investing Activities" and "Capital Requirements" under "Capital Resources and Liquidity" for a discussion of capital expenditures and capital contributions.
Outlook
The Company's strategically-locatedstrategically located and integrated assets overlay core acreage in the Appalachian Basin. The location of the Company's assets allows its producer customers to access major demand markets in the U.S. The Company is one of the largest natural gas gatherers in the U.S., and its largest customer, EQT, was one of the largest natural gas producerproducers in the U.S. based on average daily sales volumes as of December 31, 2021. The Company maintains a stable cash flow profile, with approximately 64%2023 and EQT's public senior debt had investment grade credit ratings from Standard & Poor's Global Ratings (S&P), Fitch Ratings (Fitch) and Moody's Investors Service (Moody's) as of its operating revenues forthat date. For the year ended December 31, 20212023, approximately 70% of the Company's operating revenues were generated byfrom firm reservation fees. Further,fee revenues. Generally, the Company is focused on utilizing contract structures reflecting long-term firm capacity, MVC or ARC commitments which are intended to provide support to its cash flow profile. The percentage of the Company's operating revenues that are generated by firm reservation fees is expected(as well as the Company's revenues generally) may vary year to increase in future years as a result ofyear depending on various factors, including customer volumes and the 15-year termrates realizable under the Company’s contracts, including the EQT Global GGA which includes anprovides for periodic gathering MVC fee declines through January 1, 2028 (with the fee then remaining fixed throughout the remaining term). Additionally, as discussed in "Overview of 3.0 Bcf per day that became effective on Aprilthe Company and Operations" in Part 1, 2020 and gradually steps up to 4.0 Bcf per day through December 2031 following the"Item 1. Business", in connection with MVP full in-service date of the MVP. ThisEQT Global GGA provides for more significant potential gathering MVC fee declines in certain contract structure enhances the stability of the Company's cash flows and limits its exposure to customer volume variability.years.
The Company's principal strategystrategic aim is to achieve greater scale and scope, enhance the durability of its financial strength and to continue to work to position itself for a lower carbon economy, whicheconomy.
The Company's standalone strategy reflects its continued pursuit of organic growth projects, including completing and placing in service the Company expects will drive future growth and investment. The Company is implementing its strategy by leveragingMVP, focusing on identifying opportunities to use its existing assets executingto deepen and grow its customer relationships at optimized levels of capital spending and taking into account the Company’s leverage, and continuing to prudently invest resources in its sustainability-oriented initiatives. The Company’s strategy also reflects its continued focus on its growth projects (including through potential expansionachieving a strong balance sheet, and extension opportunities), periodically evaluating strategically-alignedgiven the Company’s size, operating footprint and other factors considering inorganic growth opportunities, (whether within its existing footprint orsuch as to extend the Company's reachCompany’s operations’ into the southeast United States and to become closer tonew, key demand markets, such as the Gulf of Mexico LNG export market), and focusing on ESG and sustainability-oriented initiatives. Additionally,market.
In conjunction with the Company working to execute on its standalone strategy, the Company’s Board of Directors has been engaged in a process with third parties that have expressed interest in strategic transactions involving the Company. The board has engaged outside advisors and the process is also continuing to focus on strengthening its balance sheet through:
•highly predictable cash flows backed by firm reservation fees;
•actions to de-lever its balance sheet;
•disciplined capital spending;
•operating cost control; and
•an appropriate dividend policy.ongoing. There is no assurance that such process will result in the execution, approval or completion of any specific transaction or outcome.
As part of its approach to organic growth, the Company is focused on its projects and assets outlined in "Strategy" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in Part I, "Item 1. Business,"Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, many of which are supported by contracts with firm capacity, MVC or MVCARC commitments.
The Company expects that the MVP project (should it be placed in-service), together with the Hammerhead pipeline and EEP, will primarily drive the Company's organic growth.
EQT Global GGA. On February 27, 2020, the Company announced the EQT Global GGA, which is a 15-year contract that includes, among other things, a 3.0 Bcf per day MVC (which gradually steps up to 4.0 Bcf per day through December 2031 following the full in-service date of the MVP) and the dedication of a substantial majority of EQT’s core acreage in southwestern Pennsylvania and West Virginia to the Company. Under the EQT Global GGA, EQT will receive certain gathering fee relief over a period of three years, conditioned to begin the first day of the quarter in which the full in-service date of the MVP occurs, subject to any exercise of the EQT Cash Option (as further described in Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements). Further, the EQT Global GGA provides for a fee credit to the gathering rate for certain gathered volumes that also
receive separate transmission services under certain transmission contracts. The EQT Global GGA replaced 14 previous gathering agreements between EQT and the Company.
Under the EQT Global GGA, the performance obligation is to provide daily MVC capacity and as such the total consideration is allocated proportionally to the daily MVC over the life of the contract. In periods that the gathering MVC revenue billed will exceed the allocated consideration, the excess will be deferred to the contract liability and recognized in revenue when the performance obligation has been satisfied. While the 3.0 Bcf per day MVC capacity became effective on April 1, 2020, additional daily MVC capacity and the associated gathering MVC fees payable by EQT to the Company as set forth in the EQT Global GGA are conditioned upon the full in-service date of the MVP. There are ongoing legal and regulatory matters that affect the MVP project which have had and/or could have (as applicable) a material effect on the performance obligation, the allocation of the total consideration over the life of the contract and the gathering MVC fees payable by EQT under the contract.
Based on the Henry Hub natural gas forward strip prices as of February 18, 2022 and the terms of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision, and taking into account an assumed potential delay in the targeted full in-service date for the MVP project, the estimated fair value of the derivative asset attributable to the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision has decreased and any adverse change in assumptions regarding the MVP project would decrease the estimated fair value of the derivative asset attributable to the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision further, and such decrease may be substantial. For a discussion of the potential effect of hypothetical changes to the NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas future prices on the estimated fair value of the derivative asset attributable to the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision, see "Commodity Prices" in Part II, "Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Changes in estimated fair value are recognized in other (expense) income, net, on the Company’s statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
For a discussion of the Company's commercial relationship with EQT and related considerations, including risk factors, see Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors." See also Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information regarding the EQT Global GGA and the transactions related thereto. For further discussion on litigation and regulatory challenges affecting the MVP project, see "Strategy" under "Developments, Market Trends and Competitive Conditions" in "Item 1. Business" and "Item 3. Legal Proceedings."
Hammerhead Pipeline. On September 23, 2020, EQT and certain affiliates of EQT instituted arbitration proceedings against the Company by filing a Demand for Arbitration with the American Arbitration Association. The arbitration arose out of the Hammerhead gathering agreement, pursuant to which the Company agreed to construct the Hammerhead pipeline and gather gas for EQT. EQT sought a declaratory judgment that it could exercise an early termination right and purchase the Hammerhead pipeline and related facilities under the terms of the Hammerhead gathering agreement. With its Demand for Arbitration, EQT also sought emergency relief, asking that an emergency arbitrator: (i) resolve the parties’ dispute on the merits by October 1, 2020; or (ii) alternatively, toll the contractual deadline for EQT’s exercise of its termination right, which was set to expire on October 11, 2020, until after the parties’ dispute was resolved. On October 6, 2020, the emergency arbitrator issued an order denying EQT’s request for emergency resolution on the merits but tolling the early termination deadline until the arbitration was resolved. The Company’s answer to the Notice of Arbitration was filed on October 8, 2020, and the parties participated in an arbitration hearing from June 28, 2021 to July 2, 2021.
On October 25, 2021, the three-member panel appointed to arbitrate the dispute issued a binding arbitration decision in favor of the Company. The arbitration panel unanimously determined that, under the Hammerhead gathering agreement, although the in-service date for the Hammerhead pipeline was delayed beyond October 1, 2020, such delay was caused by or attributable to force majeure and, accordingly, that EQT has no early termination right under the Hammerhead gathering agreement relating to the timing of Hammerhead pipeline in-service or related right to purchase the Hammerhead gathering pipeline and associated facilities. Given the arbitration panel’s determinations, the Company will not be entitled to charge EQT monthly firm capacity reservation fees under the Hammerhead gathering agreement unless and until Hammerhead pipeline full commercial in-service is achieved (which the Company expects in conjunction with full MVP in-service).
Potential Future Impairments. The accounting estimates related to impairments are susceptible to change, including estimating fair value which requires considerable judgment. For goodwill, management’s estimate of a reporting unit’s future financial results is sensitive to changes in assumptions, such as changes in stock prices, weighted-average cost of capital, terminal growth rates and industry multiples. Similarly, cash flow estimates utilized for purposes of evaluating long-lived assets and equity method investment (such as in the MVP Joint Venture) require the Company to make projections and assumptions for many years into the future for pricing, demand, competition, operating costs, commencement of operations, resolution of relevant legal and regulatory matters, and other factors. The Company evaluates long-lived assets and equity method investments for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management’s judgment, that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable (meaning, in the case of its equity method investment, that such investment has suffered other-than-temporary declines in value under ASC 323). The Company believes the estimates and assumptions used in estimating its
reporting units’, its long-lived assets' and its equity investment's fair values are reasonable and appropriate as of December 31, 2021; however, assumptions and estimates are inherently subject to significant business, economic, competitive, regulatory, judicial and other risks that could materially affect the calculated fair values and the resulting conclusions regarding impairments, which could materially affect the Company’s results of operations and financial position. Additionally, actual results could differ from these estimates and assumptions may not be realized. The Company also continues to evaluate and monitor the ongoing legal and regulatory matters affecting the MVP and MVP Southgate projects, as further described in Part I, “Item 3. Legal Proceedings”Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Further adverse or delayed developments with respect to such matters or other adverse developments could require that the Company modify assumptions reflected in the probability-weighted scenarios of discounted future net cash flows (including with respect to the probability of success) utilized to estimate the fair value of its equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which could result in an other-than-temporary decline in value, resulting in an incremental impairment of that investment. See also Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements, as well as “Reviews of our goodwill, intangible and other long-lived assets and equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture have resulted in significant impairment charges, and reviews of our goodwill, intangible and other long-lived assets and equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture could result in future significant impairment charges.” included in “Item 1A. Risk Factors," and the Company's discussion of "Critical Accounting Estimates" included in "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation."
As of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the Company cannot predict the likelihood or magnitude of any future impairment. For information on the Company's past impairments, see Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements.
For a discussion of capital expenditures, see "Capital Requirements" under "Capital Resources and Liquidity" below.
Capital Resources and Liquidity
The Company's liquidity requirements are to finance its operations, its capital expenditures, potential acquisitions and other strategic transactions and capital contributions to joint ventures, including the MVP Joint Venture, to pay cash dividends and distributions, when declared and to satisfy any indebtedness obligations. Additionally, the Company or its affiliates may, at any time and from time to time, seek to retire or purchase outstanding debt through cash purchases and/or exchanges for equity or debt, in open-market purchases, privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. Such repurchases or exchanges, if any, will be upon such terms and at such prices as the Company may determine, and will depend on prevailing market conditions, the Company's other liquidity requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors and the amounts involved may be material. The Company's ability to meet these liquidity requirements depends on the Company's cash flow from operations, the continued ability of the Company to borrow under its subsidiaries' credit facilities and the Company's ability to raise capital in banking capital and othercapital markets. We believe that our cash on hand, and future cash generated from operations and future cash received from potential distributions from the MVP Joint Venture, together with available borrowing capacity under our subsidiaries' credit facilities and our access to banking and capital markets, will provide adequate resources to fund our short-term and long-term capital, operating and financing needs. However, cash flow, available borrowing capacity and capital raising activities may be affected by prevailing economic conditions in the natural gas industry and other financial and business factors, (including those market forcesincluding factors discussed in “Our business is subject to climate change-related transitional risks (including evolving climate-focused regulation and climate change-driven trends emphasizing financing non-fossil fuel businesses and prompting pursuit of emissions reductions, lower-carbon technologies and alternative forms of energy) and physical risks that could significantly increase our operating expenses and capital costs, adversely affect our customers’ development plans, and reduce demand for our products and services." included inPart I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report Form 10-K (for example, see “If we, our subsidiaries or our joint ventures are unable to obtain needed capital or financing on satisfactory terms, our ability to execute our business strategy and pay dividends to our shareholders may be diminished. Additionally, financing transactions may increase our
financial leverage or could cause dilution to our shareholders."), some of which are beyond the Company's control. The Company's available sources of liquidity include cash from operations, cash on hand, borrowings under its subsidiaries' revolving credit facilities, issuances of additional debt and issuances of additional equity securities. As of December 31, 2021, pursuant to the terms of the Amended EQM Credit Facility, EQM would have been able to borrow approximately $1.1 billion under the Amended EQM Credit Facility. The amount the Company is able to borrow under the Amended EQM Credit Facility is bounded by a maximum consolidated leverage ratio.ratio that could not exceed 5.85 to 1.00 for the quarter ended December 31, 2023, 6.00 to 1.00 for the quarter ending March 31, 2024, 6.25 to 1.00 for the quarter ending June 30, 2024, 5.85 to 1.00 for the quarter ending September 30, 2024, and 5.50 to 1.00 for quarters thereafter, with the then-applicable ratio being tested as of the end of each fiscal quarter. As of December 31, 2023, EQM had the ability to borrow approximately $0.4 billion under the Amended EQM Credit Facility. See Note 119 and Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements for further information regarding the Amended EQM Credit Facility. See also "Our subsidiaries’ significant indebtedness, and any future indebtedness, as well as the restrictions under our subsidiaries’ debt agreements, could adversely affect our operating flexibility, business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
See “Security Ratings” below for a discussion of EQM’s credit ratings during 2021.2023. Based on EQM's credit rating levels, EQM has delivered credit support to the MVP Joint Venture in the form of lettersa letter of credit, which in the case of theis for MVP project, isand was in the amount of approximately $219.7$104.7 million and is, in the case of the MVP Southgate, $14.2 million, in each case as of December 31, 2021 and which are subject to adjustment based on the applicable construction budget. In connection with delivering such letters2023. The letter of credit as replacement performance assurances, EQM's performance guarantees associated with the MVP and MVP Southgate projects were terminated. Additionally, pursuant to the EQT Global GGA, if EQM does not maintain minimum credit ratings from two of three credit rating agencies of at least Ba3 with respect to Moody's and BB- with respectthe MVP project is expected to S&P and Fitch, EQM will be obligatedfurther reduced as the Company contributes capital to provide additional credit support in an amount equal to approximately $196 million to EQT in supportfund MVP Holdco's remaining proportionate share of the potential payment obligation relatedconstruction budget, subject to a minimum-required level to be maintained through in-service of the EQT Cash Option (the Cash Option Letter of Credit).MVP project. See "A further downgrade of EQM’s credit ratings including in connection with the MVP project or customer credit ratings changes, which are determined by independent third parties, could impact our liquidity, access to capital, and costs of doing business." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors."Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. See Note 7 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on EQM's letters of credit.
76
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (Thousands) |
| Cash flows | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 1,016,078 | | | $ | 845,775 | | | $ | 1,168,768 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (1,070,082) | | | (567,037) | | | (572,969) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 244,983 | | | (345,501) | | | (669,161) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 190,979 | | | $ | (66,763) | | | $ | (73,362) | |
Operating Activities
Net cash flows provided by operating activities were $1,168.8increased approximately $170.3 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 as compared to $1,140.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020.2022. The increase was primarily driven by the payment of the EQT Cash
Option during the year ended December 31, 2022 and the timing of other working capital receipts and payments, partially offset by higher interest payments.
Investing Activities
Net cash flows used in investing activities were $573.0increased by $503.0 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 as compared to $729.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2020.2022. The decreaseincrease was primarily due to decreased capital expenditure spending on Eureka projects, the Hammerhead pipeline and various wellhead gathering and transmission projects, which was partially offset by an increase in capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture consistent with timing of the resumption of certain growth construction activities on the MVP project.Venture. See “Capital Requirements” below for a discussion of forecasted 20222024 capital expenditures and capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture.
Financing Activities
Net cash flows used inprovided by financing activities were $669.2$245.0 million for the year ended December 31, 20212023 as compared to $291.4net cash flows used in financing activities of $345.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2020.2022. For the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, the primary source of financing cash flows were proceeds from borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, while the primary uses of financing cash flows were repayments on borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, the payments of dividends to shareholders, the redemption of the 2023 Notes and distributions paid to noncontrolling interest. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the primary uses of financing cash flows were the payment for retirementpurchase of certain tranches of EQM's outstanding long-term indebtedness pursuant to the EQM Term Loans2022 Tender Offers and termination of the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement, netan open market purchase, repayments on borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, the Company's purchase of an aggregate principal amount of $500 million of EQM's 2023 Notes pursuant to the Tender Offers and the paymentpayments of dividends to shareholders, while the primary source of financing cash flows waswere the issuance of the 2021 Senior Notes. For the year ended December 31, 2020, the primary source of financing cash flows was net proceeds from the 20202022 Senior Notes issuance, whileand borrowings under the primary usesrevolving credit facilities.
Capital Requirements
The gathering, transmission and storage and water services businesses are capital intensive, requiring significant investment to develop new facilities and to maintain and upgrade existing operations.
The following represents the Company's material short-term and long-term cash requirements from contractual and other obligations as of December 31, 2021.2023.
| | | | Total | | 2022 | | 2023 – 2024 | | 2025 – 2026 | | 2027 + | | Total | | 2024 | | 2025 – 2026 | | 2027 – 2028 | | 2029 + |
| | | (Thousands) | | (Thousands) |
Long-term debt (a) | $ | 6,500,000 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,100,000 | | | $ | 1,200,000 | | | $ | 4,200,000 | |
Long-term debt, including current portion thereof (a) | |
| Credit facility borrowings (b) | |
Credit facility borrowings (b) | |
Credit facility borrowings (b) | Credit facility borrowings (b) | 505,000 | | | — | | | 505,000 | | | — | | | — | |
Interest payments on senior notes (c) | Interest payments on senior notes (c) | 2,646,375 | | | 340,375 | | | 630,854 | | | 519,031 | | | 1,156,115 | |
Purchase obligations (d) | Purchase obligations (d) | 3,943 | | | 1,273 | | | 2,232 | | | 438 | | | — | |
| Operating lease obligations (e) | 55,321 | | | 10,404 | | | 14,255 | | | 10,010 | | | 20,652 | |
Lease obligations (e) | |
Lease obligations (e) | |
Lease obligations (e) | |
Other liabilities (f) | Other liabilities (f) | 71,859 | | | 48,589 | | | 23,270 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total contractual and other obligations | Total contractual and other obligations | $ | 9,782,498 | | | $ | 400,641 | | | $ | 2,275,611 | | | $ | 1,729,479 | | | $ | 5,376,767 | |
(a)Includes $6.5approximately $6.4 billion in aggregate principal amount of EQM's senior notes as of December 31, 2021.2023. See Note 119 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
(b)Credit facility borrowings wereare classified based on the termination date of the credit facility agreements. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the Company had aggregate credit facility borrowings outstanding of approximately $225$915 million and $280$315 million under the Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility, respectively. See Note 119 and Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements for further information.
(c)Interest payments exclude interest related to the Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility as the interest rates on the credit facility borrowings are variable.
(d)Excludes purchase obligations of the MVP Joint Venture. Purchase obligations represent agreements to purchase goods or services that are enforceable, legally binding and specify all significant terms, including the approximate timing of the transaction. As of
December 31, 2021,2023, the Company's purchase obligations included commitments for capital expenditures, operating expenses and service contracts.
(e)Operating leasesLease obligations are primarily entered into for various office locations, compression equipment and compression equipment.a water storage facility.
(f)Other liabilities represent accruals for short-term employee compensation and estimated payouts for the Company's various liability award plans as of December 31, 2021.2023. See "Critical Accounting Estimates" below and Note 108 to the consolidated financial statements for discussion of factors that affect the ultimate amount of the payout of the Company's liability award plans.
Contractual and other obligations exclude purchase obligations of the MVP Joint Venture and dividends associated with the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares.
Capital expenditures in 2021 were2024 are expected to be approximately $286$325 million to $395 million (including approximately $14$15 million attributable to the noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream). Capital contributions toIf the MVP Joint Venture in 2021project were approximately $288 million. Capital expenditures in 2022 are expected to be completed in the second quarter of 2024 and at a total project cost ranging from approximately $365 million$7.57 billion to $415 million (including approximately $20 million attributable to$7.63 billion (excluding AFUDC), the noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream). The Company expects toit would make total capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture in 20222024 of approximately $175$540 million to $225$575 million for purposesprimarily related to forward construction of the MVP project related to work completed in late 2021 and ongoing work required for right-of-way maintenance and approximately $5 million for the MVP Southgate project. Capital contributions payable to the MVP Joint Venture are accrued upon the issuance of a capital call by the MVP Joint Venture. The Company's short-term and long-term capital investments may vary significantly from period to period based on the available investment opportunities, the timing of the construction of the MVP MVP Southgate and other projects, and maintenance needs. The Company expects to fund short-term and long-term capital expenditures and capital contributions primarily through cash on hand, cash generated from operations, available borrowing capacityborrowings under its subsidiaries' credit facilities and its access to banking and capital markets.
Credit Facility Borrowings
See Note 119 and Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements for discussion of the Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility, the prepayment and termination of the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement and Former Eureka Credit Facility.
Security Ratings
The table below sets forth the credit ratings for EQM's debt instruments at December 31, 2021.2023.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | EQM | | |
| | | Senior Notes | | |
| Rating Service | | | | | Rating | | Outlook | | | | |
| Moody's | | | | | Ba3 | | NegativeStable | | | | |
| S&P | | | | | BB- | | StableNegative | | | | |
| Fitch | | | | | BB | | NegativeN/A | | | | |
In January 2021, each of Moody's, S&P, andOn August 29, 2023, Fitch affirmed EQM's credit ratings in connection with the issuance of the 2021 Senior Notes. There were no changes to EQM's credit ratings during the year ended December 31, 2021.rating on Rating Watch Positive. EQM's credit ratings are subject to revision or withdrawal at any time by the assigning rating organization, and each rating should be evaluated independently of any other rating. The Company cannot ensure that a rating will remain in effect for any given period of time or that a rating will not be lowered or withdrawn entirely by a credit rating agency if, in its judgment, circumstances so warrant. If any credit rating agency downgrades or withdraws EQM's ratings, including for reasons relating to the MVP project (such as delays in the targeted full in-service date ofaffecting the MVP project or increases in such project’s targeted costs), EQM’s leverageleverage or credit ratings of the Company's customers, the Company's access to the capital markets could become more challenging, borrowing costs will likely increase, the Company may, depending on contractual provisions in effect at such time, be required to provide additional credit assurances (the amount of which may be substantial), including the Cash Option Letter of Credit, in support of commercial agreements such as joint venture agreements, and the potential pool of investors and funding sources may decrease. In order to be considered investment grade, a company must be rated Baa3 or higher by Moody's, BBB- or higher by S&P, or BBB- or higher by Fitch. All of EQM's credit ratings are considered non-investment grade.
Commitments and Contingencies
In the ordinary course of business,From time to time, various legal and regulatory claims and proceedings are pending or threatened against the Company and its subsidiaries. While the amounts claimed may be substantial, the Company is unable to predict with certainty
the ultimate outcome of such claims and proceedings. The Company accrues legal and other direct costs related to loss contingencies when incurred. The Company establishes reserves whenever it believes it to be appropriate for pending matters. Furthermore, after consultation with counsel and considering availablethe availability, if any, of insurance, the Company believes, although no assurance can be given, that the ultimate outcome of any matter currently pending against it or any of its consolidated subsidiaries as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K will not materially adversely affect its business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to its shareholders.
See "The regulatory approval process for the construction of new midstream assets is very challenging, has significantly increased costs and delayed targeted in-service dates, and decisions by regulatory and judicial authorities in pending or potential proceedings are likely to impact our or the MVP Joint Venture's ability to obtain or maintain in effect all approvals and authorizations necessary to complete certain projects on the targeted time frame or at all or our ability to achieve the expected investment returns on the projects." included in "Item 1A. Risk Factors," and seePart I, "Item 3. Legal Proceedings" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for discussion of litigation and regulatory proceedings, including related to the MVPRager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, and, MVP Southgate projects. further relating to that incident, "We have incurred and expect to continue to incur costs and expenses as a result of or arising in relation to the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident in November 2022, which has included and may include potential additional regulatory penalties or other sanctions, which could, depending on their scope and timing, materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and ability to pay dividends to our shareholders." under Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors," of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
See Note 1614 to the consolidated financial statements for further discussion of the Company's commitments and contingencies.
Dividends
On February 14, 2022,2024, the Company paid cash dividends for the fourth quarter of 20212023 of $0.15 per common share and $0.4873 per Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share to shareholders of record at the close of business on February 3, 2022.6, 2024.
For each quarter ending after March 31, 2024, the holders of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares will receive quarterly dividends at a rate per annum equal to the sum of (i) three-month CME Term SOFR, administered by CME Group Benchmark Administration, Ltd., plus a tenor spread adjustment of 0.26161% per annum as of the relevant determination date in respect of the applicable quarter and (ii) 8.15%; provided that such rate per annum in respect of periods after March 31, 2024 will not be less than 10.50%. As such, the Company expects dividends paid to holders of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares to be higher beginning in the third quarter of 2024.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
Recently issued accounting standards relevant to the Company are described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The Company's significant accounting policies are described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. Any new accounting policies or updates to existing accounting policies as a result of new accounting pronouncements have been included in the notes to the Company's consolidated financial statements. Preparation of financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenuesin the Company's consolidated financial statements and expenses and the related disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities.accompanying notes. The followingCompany's critical accounting policies discussed below are considered critical due to the significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of the Company's consolidated financial statements and the material impact on the results of operations or financial condition. Actual results could differ from those judgments and estimates.
Income Taxes. The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the Company's consolidated financial statements or tax returns.
The Company has federal and state net operating loss (NOL) carryforwards related to federal and various state jurisdictions. The federal, commonwealth of Virginia and state of West Virginia NOL carryforwards have no expiration, but utilization is limited to 80% of taxable income in the year of utilization. The Company's Pennsylvania NOL carryforwards expire between 2038 and 2041. In addition to the NOL carryforwards, the Company has deferred tax assets and liabilities principally resulting from its investment in partnerships.
The Company believes that it is more likely than not that the benefit from its federal and state NOL carryforwards and reversals of the investment in partnership deferred tax asset, net of offsetting deferred tax liabilities, will not be realized. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not (greater than 50%) that a tax benefit will not be realized. In evaluating the need for a valuation allowance, management considers available evidence, both positive and negative, including potential sources of taxable income, income available in carry-back periods, future reversals of taxable temporary differences, projections of taxable income and income from tax planning strategies. Positive evidence includes reversing temporary differences and projection of future profitability within the carry-forward period, including from tax planning strategies. Negative evidence includes historical pre-tax book losses and Pennsylvania NOL expirations. A review of positive and negative evidence regarding these tax benefits resulted in the conclusion that valuation allowances on the Company’s federal and state NOL carryforwards and reversals of the investment in partnership deferred tax asset, net of offsetting deferred tax liabilities, were warranted as it was more likely than not that these assets will not be realized.
Deferred tax assets for which no valuation allowance is recorded may not be realized, and changes in facts and circumstances may result in the establishment of a valuation allowance. Existing valuation allowances are re-examined under the same standards of positive and negative evidence that apply to valuation allowance establishment. If it is determined that it is more likely than not that a deferred tax asset for which a valuation is recorded will be realized, all or a portion of the valuation allowance may be released. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are also re-measured to reflect changes in underlying tax rates from tax law changes. Any determination to change the valuation allowance would impact the Company's income tax (benefit) expense in the period in which such a determination is made.
Tax benefits related to uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken on a tax return are recorded when such benefits meet a more likely than not threshold; otherwise, the tax benefit is recorded when the tax position has been effectively settled, either because the statute of limitations has expired or the appropriate taxing authority has completed its examination. Interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions are recognized as part of the provision for income taxes and are accrued in the period that such interest and penalties would be applicable under relevant tax law until such time that the related tax benefits are recognized.
The Company believes that accounting estimates related to income taxes are "critical accounting estimates" because the Company must assess the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered from future taxable income, exercise judgment when evaluating whether or not a valuation allowance must be established on deferred tax assets and exercise judgment regarding the amount of financial statement impact to record for uncertain tax positions. To the extent that a valuation allowance or an uncertain tax position is established or changed during a period, the Company records the impact within income tax (benefit) expense on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income. See Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Property, Plant and Equipment. Determination of depreciation expense requires judgment regarding the estimated useful lives and salvage values of property, plant and equipment. The Company has not historically experienced material changes in its results of operations from changes in the estimated useful lives or salvage values of its property, plant and equipment; however, these estimates are reviewed periodically, including each time Equitrans, L.P. files with the FERC for a change in its transmission storage and gatheringstorage rates. The Company believes that the accounting estimate related to depreciation expense is a "critical accounting estimate" because the assumptions used to estimate useful lives and salvage values of property, plant and equipment are susceptible to change. These assumptions affect depreciation expense and, if changed, could have a material effect on the Company's results of operations and financial position. See Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Impairments of Long-Lived Assets and Equity Method Investment. The Company evaluates long-lived assets and equity method investments for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management's judgment, that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable. With respect to property, plant and equipment and finite lived intangibles, asset recoverability is measured by comparing the carrying value of the asset or asset group with its expected future pre-tax undiscounted cash flows. Any accounting estimate related to an impairment of property, plant and equipment, finite-lived intangible assets, goodwill or an investment in an unconsolidated entity may require the Company's management to make assumptions about future cash flows, discount rates, the fair value of investments and whether losses in the value of its investments are other-than-temporary. Management's assumptions about future cash flows require significant judgment because, among other things, actual operating levels have been and are expected to differmay be different from estimated levels.
Goodwill is the cost of an acquisition less the fair value of the identifiable net assets of the acquired business. Goodwill is evaluated for impairment at least annually or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. TheWhen performing a quantitative assessment, the Company uses a combination of an income and market approach to estimate the fair value of its reporting units.
The Company believes that the accounting estimates related to impairments are "critical accounting estimates" because they require assumptions that are susceptible to change, including estimating fair value which requires considerable judgment. For example, in the case of goodwill, management’s estimate of a reporting unit’s future financial results is sensitive to changes in assumptions, such as changes in the Company's stock price, weighted-average cost of capital, terminal growth rates and industry multiples. TheWhen a quantitative assessment is performed, the Company believes theuses estimates and assumptions used in estimating its reporting units’ fair values that it believes are reasonable and appropriate;appropriate at that time; however, different assumptions and estimates could materially affect the calculated fair value and the resulting conclusion on impairment of whether goodwill is impaired, which could materially affect the Company’s results of operations and financial position. The Company performed a sensitivity analysis for the EQM Opco reporting unit (defined and discussed in Note 1), which is the only reporting unit with goodwill as of December 31, 2021, to quantify the effect of certain changes to assumptions used in goodwill assessment. It was determined that it would require more than a 1% increase to the weighted average cost of capital and more than a corresponding 1% decrease to the terminal cash flow growth rate in order for the Company to have recognized an impairment of goodwill as of December 31, 2021.
The Company’s investment in unconsolidated entitiesentity also requires considerable judgment to estimate fair value because the Company’s investment is not traded on an active market. When estimating the fair value of its equity method investment, the Company utilizes an income approach under which significant judgments and assumptions, including the discount rate and probability-weighted scenarios, are sensitive to change. For example, an increase of 25 basis points to the discount rate and a 5% decrease to the probability of success would have resulted in an increase to the impairment charge by $227.5 million or 11.8%. Additionally, the Company's investment in unconsolidated entitiesentity is susceptible to impairment risk from further
adverse macroeconomic conditions and/or other adverse factors (such as, in the case of the Company's equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture, permit and litigation matters impacting the MVP project). For example, adverse or delayed developments with respect to such matters or other adversefactors. Adverse developments could require that the Company modify assumptions reflected in the probability-weighted scenarios of discounted future net cash flows (including with respect to the probability of success)success prior to completion) utilized to estimate the fair value of its equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which could result in an incremental other-than-temporary impairment of that investment. While macroeconomic factors in and of themselves may not be a direct indicator of impairment, should an impairment indicator be identified in the future, macroeconomic factors such as changes in interest rates could ultimately impact the size and scope of any potential impairment.
See Notes 1 and 47 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Revenue Recognition. Revenue from the gathering, transmission and storage of natural gas is generally recognized when the service is provided. Revenue from water services is generally recognized when water is delivered. Contracts often contain fixed
and variable consideration. Fixed consideration primarily relates to firm reservation payments including MVCs.MVCs and ARCs. Variable consideration is generally dependent on volumes and recognized in the period they occur. From time to time, and at a minimum, atAt each reporting date and, as circumstances or events warrant, management reviews and updates as necessary, the assumptions utilized to estimate the total consideration for all contracts. For all contracts, theThe Company allocates the transaction price to each performance obligation based on the estimated relative standalone selling price. When applicable, the excess of consideration received over revenue recognized results in the deferral of those amounts until future periods based on a units of production or straight-line methodology as these methods appropriately match the consumption of services provided to the customer. The units of production methodology requires the use of production estimates that are uncertain and the use of judgment when developing estimates of future production volumes, thus impacting the rate of revenue recognition. Production estimates are monitored as circumstances and events warrant. Certain of the Company's gas gathering and water agreements have MVCs.MVCs or ARCs. If a customer under such an agreement fails to meet its MVC or ARC for a specified period (thus not exercising all the contractual rights to gathering and water services within the specified period, herein referred to as “breakage”), it is obligated to pay a contractually determined fee based upon the shortfall between the actual volumes and the MVC or ARC for the period contained in the contract. When management determines it is probable that the customer will not exercise all or a portion of its remaining rights, the Company recognizes revenue associated with such breakage amount in proportion to the pattern of exercised rights within the respective MVC or ARC period.
Revenue related to services provided but not yet billed is estimated each month. These estimates are generally based on contract data, preliminary throughput and allocation measurements. Final amounts for the current month are billed and collected in the following month. See Note 64 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
The Company records an allowance for credit losses on a quarterly basis in order to estimate uncollectible receivables. The Company's current expected credit loss (CECL) methodology considers risks of collection based on a customer’s current credit status. The standard requires an entity to assess whether financial assets share similar risk characteristics and, if so, group such assets in a pool. Customer balances are aggregated for evaluation based on their credit risk rating, which takes into account changes in economic factors that impact a customer’s ability to meet its financial obligations. The Company's CECL methodology assigns a reserve, even if remote, to each customer based on credit risk and the reserve is evaluated on a quarterly basis. In order to calculate the appropriate allowance, the Company utilizes an estimated loss rate factor based on a customer's credit rating for receivables and a risk-adjusted reserve based on the receivable aging schedule in order to account for the receivables which may be at a greater risk of collection. Customer credit risk ratings are updated quarterly and management has enabled a risk-responsive approach to changes in customer and economic factors. While the Company has not historically experienced material losses on uncollected receivables, a decline in the market price for natural gas affecting producer activity combined with additional customers on the Company's systems may result in a greater exposure to potential losses than management's current estimates.
The Company believes that the accounting estimates related to revenue recognition are "critical accounting estimates" because estimated relative standalone selling prices and volumes are subject to change based on actual measurements. In addition, the Company believes that the accounting estimates related to the allowance for credit losses are "critical accounting estimates" because the underlying assumptions used for the allowance can change and the actual mix of customers and their ability to pay may vary significantly from management's estimates, which could affect the collectability of customer receivables. These accounting estimates could potentially have a material effect on the Company's results of operations and financial position.
Share-Based Compensation.Income Taxes. The Company awards certain share-based compensation in connection with specific programsrecognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the formCompany's consolidated financial statements or tax returns.
The Company has federal and state of performance-based awardsWest Virginia net operating loss (NOL) carryforwards. The NOL carryforwards have no expiration, but utilization is limited to 80% of taxable income in the year of utilization. In addition to the NOL carryforwards, the Company has deferred tax assets and liabilities principally resulting from interest disallowance under Code Section 163(j) and investment in partnerships.
Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not (greater than 50%) that require judgmentsa tax benefit will not be realized. In evaluating the need for a valuation allowance, this requires significant judgment and estimates to determine their estimated fair value.management considers all available evidence, both positive and negative, including potential sources of taxable income, income available in carry-back periods, future reversals of taxable temporary differences, projections of taxable income and income from tax planning strategies. Positive evidence includes reversing temporary differences and projection of future profitability within the carry-forward period, including from tax planning strategies. Negative evidence includes historical pre-tax book losses.
Performance-based awards expected toDeferred tax assets for which no valuation allowance is recorded may not be satisfiedrealized, and changes in cashfacts and circumstances may result in the establishment of a valuation allowance. Existing valuation allowances are treated as liability awards and remeasured at fair value atre-examined under the end of each reporting period, recognizing a proportionate amount of the compensation expense for each period over the vesting period of the award. Performance-based awards expected to be satisfied in Company common stock are treated as equity awards and recorded based on an estimated grant date fair value over the vesting period of the award. Determination of the fairsame
valuestandards of positive and negative evidence that apply to valuation allowance establishment. If it is determined that it is more likely than not that a deferred tax asset for which a valuation allowance is recorded will be realized, all or a portion of the awards requires judgmentsvaluation allowance may be released. Deferred tax assets and estimates regarding, among other things, the appropriate methodologiesliabilities are also remeasured to followreflect changes in valuing the awards and the related inputs required by those valuation methodologies. The Company obtains a valuation at the grant date for equity awards and at each remeasurement date for liability awards based upon assumptions regarding risk-freeunderlying tax rates of return, expected volatilities, the expected term of the award and dividend yield, as applicable. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of valuation. Expected volatilities are based on historical volatility of the Company's common stock and, where applicable, the common stock of the peer group members at the time of valuation. The expected term represents the period of time elapsing during the applicable performance period. The dividend yield is based on the historical dividend yield of the Company's common stock adjusted for any expectedfrom tax law changes and where applicable, the common stock of the peer group members at the time of valuation.
For plans that include a performance condition that affects the number of shares that will ultimately vest, the probability that the performance condition will be achieved is reevaluated at the end of each reporting period and the payout multiplier is applied to the grant date fair value or measurement date fair value to record compensation expense, as applicable. For plans that include a market condition, compensation expense is based on a grant date fair value using a Monte Carlo simulation that remains constant throughout the vesting period for equity plans and a fair value using a Monte Carlo simulation remeasured at each reporting period for liability plans. Each plan subject to a market condition is accounted for separately for each vesting tranche of the award.any changes in uncertain tax benefits.
The Company believes that the accounting estimates related to share-based compensationincome taxes are "critical accounting estimates" because they may changethe Company must assess the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered from period to period basedfuture taxable income, and exercise judgment when evaluating whether or not a valuation allowance must be established on changes in assumptions about factors affecting the ultimate payout of awards, including the number of awards to ultimately vest and the market price and volatility of the Company's common stock.deferred tax assets. See Note 1012 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk. Changes in interest rates affect the amount of interest the Company earns on cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments and the interest rates EQM and Eureka pay on borrowings under their respective revolving credit facilities. The Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility provide for variable interest rates and thus expose the Company, through EQM and Eureka, to fluctuations in market interest rates. In addition, EQM's interest rates under the Amended EQM Credit Facility are impacted by changes in EQM's credit ratings (which changes may be caused by factors outside of EQM's control). Eureka's interest rates under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility are impacted by changes in Eureka's Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) which may fluctuate based on Eureka Midstream's distributions to its members, liquidity needs or operating results. Accordingly, changesif interest rates were to increase, our debt service obligations on the variable rate indebtedness would increase even though the amount borrowed remained the same, and our net income and cash flows, including cash available for servicing our indebtedness, will correspondingly decrease. Based on commitments as of December 31, 2023 and assuming all loans are fully drawn, each quarter point change in interest rates may impactwould result in a change of approximately $3.9 million in annual interest expense on indebtedness under the Company's results of operations and liquidity. Further, changesAmended EQM Credit Facility. Assuming all loans are fully drawn, each quarter point change in interest rates may affectwould result in a change of approximately $1.0 million in annual interest expense on indebtedness under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility. Further, regarding the dividend payable on Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares for quarters after March 31, 2024, changes in accordance with the Adjustable Interest Rate (LIBOR) Act (the LIBOR Act), and the rules implementing the LIBOR Act, three-month CME Term SOFR, administered by CME Group Benchmark Administration, LTD., plus a tenor spread adjustment of 0.26161% per annum, replaced, by operation of law, the three-month London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) to calculate dividends payable on the Series A Preferred Stock for each fiscal quarter ending after March 31, 2024. Fluctuations in three-month CME Term SOFR may affect such dividend (which will not be less than 10.50% under the Company's Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation), which could affect, among other things, the amount of cash the Company has available to make quarterly cash dividends to its shareholders. EQM's senior notes are fixed rate and thus do not expose the Company to fluctuations in market interest rates. Changes in interest rates do affect the fair value of EQM's fixed rate debt. See Note 11Notes 9 and 1210 to the consolidated financial statements for discussions of borrowings and for discussion of fair value measurements, respectively. EQM and Eureka may from time to time hedge the interest on portions of borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, as applicable, in order to manage risks associated with floating interest rates (however, thererates. However, the Company may be no assurance that suchnot maintain hedges willwith respect to all of its variable rate indebtedness, and any hedges it enters into may not fully mitigate its interest rate risk).risk
Credit Risk. The Company is exposed to credit risk, which is the risk that it may incur a loss if a counterparty fails to perform under a contract. The Company actively manages its exposure to credit risk associated with customers through credit analysis, credit approval and monitoring procedures. For certain transactions, the Company requests letters of credit, cash collateral, prepayments or guarantees as forms of credit support. Equitrans, L.P.'s FERC tariffs require tariff customers that do not meet specified credit standards to provide three months of credit support; however, the Company is exposed to credit risk beyond this three-month period when its tariffs do not require its customers to provide additional credit support. For some of the Company's long-term contracts associated with system expansions, it has entered into negotiated credit agreements that provide for other credit support if certain credit standards are not met. The Company has historically experienced only minimal credit losses in connection with its receivables.
The Company is exposed to the credit risk of its customers, such as EQT as ourincluding its largest customer, EQT, including as a result of changes in customer credit ratings, liquidity and access to capital markets. At December 31, 2021,In August 2023, Moody's upgraded EQT's public senior debt had non-investmentto an investment grade credit ratings. See "Credit Letter Agreement" includedrating and as of December 31, 2023, EQT's public debt has investment grade credit ratings from S&P, Fitch and Moody's. On February 26, 2020, in "Item 1. Business"connection with the execution of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for information regarding the EQT Global GGA, the Company and EQT entered into a letter agreement (the Credit Letter Agreement and associatedAgreement) pursuant to which, among other things, (a) the Company agreed to relieve certain credit posting requirements for EQT, in an amount up to approximately $250 million, under its commercial agreements with the Company, subject to EQT maintaining a minimum credit rating requirements.from two of three rating agencies of (i) Ba3 with Moody's, (ii) BB- with S&P and (iii) BB- with Fitch and (b) the Company agreed to use commercially reasonable good faith efforts to negotiate similar credit support arrangements for EQT in respect of its commitments to the MVP Joint Venture. In addition, EQT has guaranteed the payment obligations of certain of its subsidiaries, up to a maximum amount of $115 million, $131 million and $30 million related to gathering, transmission and water services, respectively, across all applicable contracts, for the benefit of the subsidiaries of the Company providing such services. See Note 1513 to the consolidated financial statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for further discussion of the Company's exposure to certain credit risk.
Commodity PricesPrice Risk. The Company's business is dependent on continued natural gas production and the availability and development of reserves in its areas of operation. Prices for natural gas and NGLs, including regional basis differentials, have previously adversely affected, and may in the future adversely affect, the timing of development of additional reserves and production that is accessible by the Company’s pipeline and storage assets, which also negatively affects the Company’s water services business, and the creditworthiness of the Company’s customers.
Lower natural gas prices, particularly in the Appalachian region, have increased from 2020 lowsin the past caused, and may in the future cause, producers such as EQT to determine to take actions to slow production growth and/or maintain flat or reduce production, which when effected by our producer customers limits growth in or may reduce the demand for, and usage of, our services. For instance, in certain periods of low natural gas prices prior to 2023, temporary production curtailments resulted in a decrease in our volumetric-based gathering fee revenues. Based on the forward price strip as of February 16, 2024, the filing dateCompany perceives continued risk that EQT and/or other producers could curtail production in 2024 or maintain at flat levels, which, depending on the nature and duration of any such curtailment, could have a significant negative effect on the demand for our services, our volumetric-based fee revenue, and therefore our results of operations, and any such maintenance may limit growth associated with our assets. See also “Decreases or a lack of growth in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, whether as a result of regional takeaway constraints, producer corporate capital allocation strategies, lower regional natural gas prices, natural well decline, and/or other factors, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, our business and operating results and reduce our cash available to pay cash dividends to our shareholders.”, "The lack of diversification of our assets, products and geographic locations could adversely affect us." and “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT's drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results.”, each included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Price declines and sustained periods of low natural gas and NGL prices could have an adverse effect on the creditworthiness of the Company's customers and related ability to pay firm reservation fees under long-term contracts and/or affect, as discussed above, activity levels and, accordingly, volumetric-based fees, which could affect the Company’s results of operations, liquidity or financial position. Credit risk and related management is further discussed under “Credit Risk” in Part II, “Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, higher10-K.
Increases in natural gas prices do not necessarily result in corresponding increases to the production forecasts of the Company's customers. Even when natural gas prices have not causedbeen commercially attractive, certain of the Company's largest customers to increase theirmaintained largely flat production forecasts in light of, among other things, the absence of incremental takeaway capacity from the Appalachian Basin and even if natural gas prices remain elevated, the Company's customers may announce in the future lower,still maintain flat or modest increases to production forecasts based on various factors, which could include regional takeaway capacity limitations, access to capital, investor expectations regarding free cash flow, a desire to reduce or refinance leverage or other factors. Additionally, prices may decline based on numerous factors, including levels of associated gas. See also “Decreases in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, whether as a result of producer corporate capital allocation strategies, lower regional natural gas prices, regional takeaway constraints, and/or other factors, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, our business and operating results and reduce our cash available to pay cash dividends to our shareholders.” and "The lack of diversification of our assets and geographic locations could adversely affect us." under "Item 1A. Risk Factors."
Lower natural gas prices, particularly in the Appalachian region, have in the past caused, and may in the future cause, certain producers, including customers of the Company, to determine to reduce or hold generally steady their rig count (and thereby delay or not increase production), delay turning wells in line, temporarily shut in portions of their production or otherwise take actions to slow production growth and/or reduce production, which when effected by the Company's producer customers reduces the demand for, and usage of, the Company’s services. For instance, temporary production curtailments effected in 2020 by EQT and certain other Company customers resulted in a decrease in the Company's volumetric-based fee revenues for portions of 2020. An extended period of low natural gas prices and/or instability in natural gas prices in future periods, especially in the Appalachian region, or other factors, could cause EQT or other producers to take similar actions in the future, which could have a significant negative effect on the demand for the Company's services and therefore its results of operations. Additionally, lower natural gas prices (including regionally), corporate capital allocation strategies or regional takeaway constraints, could cause producers to determine in the future that drilling activities in areas outside of the Company's current areas of operation are strategically more attractive to them.
Many of the Company’s customers, including EQT, have entered into long-term firm reservation gathering, transmission and water services contracts or contracts with MVCs or ARCs, as applicable, on the Company's systems and approximately 64%70% of the Company's operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 2021 was2023 were generated by firm reservation fees. As a result, thefee revenues. The Company believes that the effect of temporary declines in volumes of gas gathered, transported or stored onsuch contract structure is advantageous to its systems may be mitigated because firm reservation fee revenues are paid regardless of volumes supplied to the system by customers (althoughoverall business, although significant declines in gas production in the Company's areas of operations would likely adversely affect the Company's results of operations, financial condition and liquidity as approximately 36%30% of the Company’s operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 20212023 was generated by volumetric-based fee revenues).revenues. See "Our exposure to direct commodity price risk may increase in the future.future and NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA." and “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT’s drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results." underincluded in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors."
Price declines and sustained periods of low natural gas and NGL prices could have an adverse effect on the creditworthiness of the Company's customers and related ability to pay firm reservation fees under long-term contracts and/or affect, as discussed above, activity levels and, accordingly, volumetric-based fees, which could affect the Company’s results of operations, liquidity or financial position. For example, each of S&P, Moody's and Fitch took negative ratings actions on EQT during 2020, citing, among other things, lower natural gas price assumptions and financing needs (although all three ratings agencies later took positive action on EQT citing, among other things, subsequent debt reduction and improvementsFactors" in natural gas fundamentals). Credit risk and related management is further discussed above under “Credit Risk” in Part II, “Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Unless the Company is successful in attracting and retaining new customers, the Company's ability to maintain or increase the capacity subscribed and volumes transported, gathered or provided on its systems will be dependent on receiving consistent or increasing commitments and production from its existing customers, which may be impacted by commodity prices, including regional commodity prices and/or other factors, including corporate capital allocation strategies. While EQT has dedicated a substantial portion of its core acreage in southwestern Pennsylvania and West Virginia to the Company and has entered into long-term firm gathering and transmission contracts and contracts with MVCs on certain of the Company's systems, EQT may determine in the future that drilling or continuing to produce gas from existing wells in the Company's areas of operations is not economical above the amount to fulfill its required MVCs or otherwise strategically determine to curtail volumes on the Company's systems. Other than with respect to its MVCs and other firm commitments under existing contracts, EQT is under no contractual obligation to continue to develop its acreage dedicated to the Company. See also Note 6 to"Overview of the consolidated financial statementsCompany and Operations" in Part 1, "Item 1. Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the EQT Global GGA and the 2021 Water Services Agreement.GGA.
The fair value of the Company’s derivative instruments is, in part, determined by estimates of the NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas forward price curve. A hypothetical 10% increase in NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices would increase the valuation of the Company’s derivative instruments by approximately $5.9 million, while a hypothetical 10% decrease in
valuation of the Company’s derivative instruments by approximately $7.0 million, while a hypothetical 10% decrease in NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices would decrease the valuation of the Company’s derivative instruments by approximately $7.7$6.0 million. This fair value change assumes volatility based on prevailing market parameters at December 31, 2023. See Notes 1Note 10 and 6"Our exposure to commodity price risk may increase in the future and NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the consolidated financial statementsEQT Global GGA." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision.
For further discussion of commodity prices and related risks, see "Our exposure to direct commodity price risk may increase in the future," "Decreases in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, whether as a result of producer corporate capital allocation strategies, lower regional natural gas prices, regional takeaway constraints, and/or other factors, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, our business and operating results and reduce our cash available to pay cash dividends to our shareholders," and "The lack of diversification of our assets and geographic locations could adversely affect us." each under "Item 1A. Risk Factors".
Other Market Risks. The Amended EQM Credit Facility is underwritten by a syndicate of 14 financial institutions on and theafter October 31, 2023 and prior to April 30, 2025, and a syndicate of 13 financial institutions on and after April 30, 2025 and prior to April 30, 2026. The 2021 Eureka Credit Facility areis underwritten by syndicatesa syndicate of 21 and 16 financial institutions respectively, eachbefore November 13, 2024 and a syndicate of which14 financial institutions on and after November 13, 2024 and prior to November 13, 2025. Each financial institution is obligated to fund its pro rata portion of any borrowings by EQM or Eureka, as applicable. In each case, no one lender of the financial institutions in the syndicate holds more than 10% of such facility. EQM's and Eureka's respective large syndicate groups and relatively low percentage of participation by each lender is expected to limit the Company's and Eureka's respective exposure to disruption or consolidation in the banking industry. See Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements for further details.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
| | | | | |
| Page No. |
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB ID: 42) | |
Statements of Consolidated Comprehensive Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 20192021 | |
Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 20192021 | |
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 20212023 and 20202022 | |
Statements of Consolidated Shareholders' Equity and Mezzanine Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 20192021 | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Equitrans Midstream Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Equitrans Midstream Corporation (the Company) as of December 31, 20212023 and 2020,2022, the related statements of consolidated comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity and mezzanine equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021,2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 20212023 and 2020,2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2021,2023, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021,2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control-IntegratedControl—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 23, 202220, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit MattersMatter
The critical audit mattersmatter communicated below are mattersis a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that werewas communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relaterelates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit mattersmatter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit mattersmatter below, providing a separate opinionsopinion on the critical audit mattersmatter or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.it relates.
| | | | | |
| |
| |
| Valuation of EQM OpCo Reporting Unit GoodwillEquity Method Investment in Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (MVP Joint Venture) |
| |
| Description of the Matter | At December 31, 2021,2023, the Company had goodwillhas an investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which is constructing the Mountain Valley Pipeline, of approximately $486.7 million related to the EQM OpCo reporting unit.$1,832.3 million. As discussed in Notes 1, 2, and 47 to the consolidated financial statements goodwill is evaluatedthe Company accounts for its interest in the MVP Joint Venture under the equity method because it can exercise significant influence, but not control, over the MVP Joint Venture's operating and financial policies. The Company reviews its investment in the MVP Joint Venture for impairment at least annually and whenever events or changes in circumstancecircumstances indicate that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If, after assessing the totality of events or circumstances, the Company determines it is more likely than not that the fairmay have declined in value of a reporting unit is greater than its carrying amount, then a quantitative assessment is not required. However, if the Company concludes otherwise, a quantitative impairment analysis is performed. If the Company chooses not to perform a qualitative assessment, or if it chooses to perform a qualitative assessment but is unable to qualitatively conclude that no impairment has occurred, then the Company will perform a quantitative assessment. In the case of a quantitative impairment test, the Company estimates the fair value of the reporting unit with which the goodwill is associated and compares it tobelow the carrying value. If the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value,Adverse developments, including legal and regulatory matters, cost increases, and other unanticipated events may indicate an impairment charge is recognized forin value. During the excessyear ended December 31, 2023, the Company evaluated the developments around the MVP Joint Venture and concluded no impairment existed.
Auditing management’s evaluation of the reporting unit's carrying value over its fair value.
Auditing management’s quantitative goodwillMVP Joint Venture for indicators of impairment test for the EQM OpCo reporting unit was complex due to the significant estimationjudgment required, particularly related to determinelegal and regulatory matters, cost increases, and other developments that could impact the fair valueviability of that reporting unit. In particular, the fair value estimatesMountain Valley Pipeline project. The audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of that reporting unit were sensitive to significant assumptions, including assumptions regarding future throughput volumesmanagement’s monitoring of impairment indicators required a high degree of auditor judgement and operating costs, and discount rates, among others. These assumptions could be affected by factors such as unexpected future production curtailments by the Company’s customers that have contracts with volumetric-based fees or future market or economic conditions and industry and company-specific qualitative factors.
an increased extent of effort.
|
| |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s goodwill impairment review process, including controls over management’s review of the significant assumptions described above.
To test the estimated fair value of the Company’s EQM OpCo reporting unit for which a quantitative impairment test was performed, we performed audit procedures that included, among others, evaluating methodologies used and testing the significant assumptions discussed above and testing the underlying data used by the Company in its analyses for completeness and accuracy. We compared the significant assumptions used by management to current industry and economic trends and evaluated whether changes in those trends would affect the significant assumptions. We assessed the historical accuracy of management’s estimates and performed sensitivity analyses of significant assumptions to evaluate the changes in the fair value of the reporting unit that would result from changes in the assumptions. We involved our valuation specialists to assist in reviewing the valuation methodology and testing the discount rate assumption. Our procedures also included evaluating the sufficiency of the Company’s disclosures with respect to the valuation of EQM OpCo reporting unit goodwill described in Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements. |
| |
| | | | | |
| Valuation of Equity Method Investment in Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (MVP Joint Venture) |
| |
Description of the Matter | At December 31, 2021, the Company has an investment in the MVP Joint Venture of approximately $1.2 billion. As discussed in Notes 1 and 9 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company accounts for its interests in the MVP Joint Venture under the equity method because it has the ability to exercise significant influence, but not control, over the MVP Joint Venture's operating and financial policies. The Company reviews the carrying value of its investments in unconsolidated entities for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value may have declined in value. When there is evidence of loss in value that is other-than-temporary, the Company compares the investment's carrying value to its estimated fair value to determine whether impairment has occurred. If the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value, the Company estimates and recognizes an impairment loss equal to the difference between the investment's carrying value and fair value. During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company evaluated its investment in the MVP Joint Venture for impairment. As described in Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company identified as an indicator of an other-than-temporary decline in value the various uncertain legal outcomes and the potential impacts that certain unfavorable outcomes could have on the then targeted full in-service date for the MVP project and consequent timing for certain projects related thereto and total targeted MVP project costs. The Company also considered unfavorable decisions by the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit as supplemental evidence in evaluating its equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture as of December 31, 2021, to determine if the investment’s carrying value exceeded the fair value and, if so, whether that the decline in value was other-than-temporary. The Company used probability-weighted scenarios of discounted future cash flows to estimate the fair value of the investment. The Company considered scenarios under which ongoing or new legal and regulatory matters further delay the completion and increase the total costs of the project; all required legal and regulatory approvals and authorizations and certain compression expansion opportunities are realized; and the MVP project is canceled. As a result of the assessment, the Company recognized a pre-tax impairment charge of $1.9 billion that reduced the carrying value of its equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture to approximately $1.2 billion as of December 31, 2021. The use of probability-weighted, discounted cash flows requires management to make significant estimates regarding the likelihood of various scenarios utilized to determine the fair value estimate. Changes in the probability-weighted assumptions could have a significant impact on the fair value estimate, which is used to determine the amount of any impairment.
Auditing management’s evaluationmonitoring of impairment of the equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture was complex due to the significant judgment required to determine the fair value of the investment. In particular, the fair value estimates of the investment in the MVP Joint Venture were sensitive to significant assumptions, including assumptions regarding the probability-weighted, discounted cash flows. These assumptions could be affected by factors such as adverse macroeconomic conditions or other adverse factors such as permit and litigation matters impactingindicators for the MVP Joint Venture. The audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of management’s estimates and assumptions related to the likelihood of various probability-weighted scenarios required a high degree of auditor judgement and an increased extent of effort.
|
| | | | | |
| |
How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s equity method investment impairment evaluation process, including controls over management’s review of the significant assumptions described above.
To test the Company’s impairment evaluation related to its investment in the MVP Joint Venture, we performed audit procedures that included evaluating the methodologies used and testing significant assumptions and underlying data used by the Company in its analysesmanagement’s process for completeness and accuracy.identifying impairment indicators. We involved our valuation specialists to assist in reviewing the valuation methodology and testing the discount rate assumption.
Our audit procedures related to the probability-weighted forecasts of discounted future cash flows included, among others, procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of the probabilities assigned by management to various outcomes. We also performed procedures to assessassessed management’s consideration of potential changes in legal or regulatory trends, cost increases and other events and how such developments could impact significant assumptionsfactors that influence the in-service dates or viability of the project. We performed procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of key assumptions based upon management’s plans to resolve outstanding permitting issuesevaluated both supporting and performed reviews to identify any potential contrary evidence through reading information included in the Company’s press releases, regulatory filings, analyst and industry reports, internal communications to management and the Board of Directors, among others.evidence. Our procedures also included evaluating the sufficiency of the Company’s disclosures with respect to the valuation of the investment in the MVP Joint Venture described in Note 42 and 7 to the consolidated financial statements.
|
| | | | | |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP | |
| We have served as the Company's auditor since 2018. | |
| Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania | |
February 23, 2022 | 20, 2024 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Equitrans Midstream Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control overOver Financial Reporting
We have audited Equitrans Midstream Corporation's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021,2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control-IntegratedControl—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Equitrans Midstream Corporation (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021,2023, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 20212023 and 2020,2022, the related statements of consolidated comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity and mezzanine equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 20212023, and the related notes and our report dated February 23, 202220, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
| | | | | |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP | |
| Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania | |
February 23, 2022 | 20, 2024 |
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31,
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| | (Thousands, except per share amounts) |
| Operating revenues | $ | 1,317,037 | | | $ | 1,510,825 | | | $ | 1,630,242 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Operating and maintenance | 153,426 | | | 154,109 | | | 165,367 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 138,647 | | | 129,969 | | | 112,915 | |
| Separation and other transaction costs | — | | | 23,797 | | | 26,080 | |
| Depreciation | 270,404 | | | 259,613 | | | 227,364 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 63,195 | | | 53,258 | |
| | | | | |
| Impairments of long-lived assets | 56,178 | | | 55,581 | | | 969,258 | |
| Total operating expenses | 683,474 | | | 686,264 | | | 1,554,242 | |
| Operating income | 633,563 | | | 824,561 | | | 76,000 | |
Equity income (a) | 17,579 | | | 233,833 | | | 163,279 | |
| Impairment of equity method investment | (1,926,402) | | | — | | | — | |
| Other (expense) income, net | (16,104) | | | 17,225 | | | 2,661 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | (41,025) | | | (24,864) | | | — | |
| Net interest expense | (378,650) | | | (307,380) | | | (256,195) | |
| (Loss) income before income taxes | (1,711,039) | | | 743,375 | | | (14,255) | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense | (345,091) | | | 105,331 | | | 50,704 | |
| Net (loss) income | (1,365,948) | | | 638,044 | | | (64,959) | |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 14,530 | | | 214,912 | | | 138,784 | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to Equitrans Midstream | (1,380,478) | | | 423,132 | | | (203,743) | |
| Preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,760 | | | — | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | (1,438,990) | | | $ | 364,372 | | | $ | (203,743) | |
| | | | | |
(Loss) earnings per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - basic | $ | (3.32) | | | $ | 1.06 | | | $ | (0.80) | |
| (Loss) earnings per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - diluted | $ | (3.32) | | | $ | 1.06 | | | $ | (0.80) | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - basic | 433,008 | | | 343,935 | | | 254,884 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - diluted | 433,008 | | | 343,975 | | | 254,884 | |
| | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (1,365,948) | | | $ | 638,044 | | | $ | (64,959) | |
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax: | | | | | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $62, $70 and $70 | (175) | | | (203) | | | (517) | |
| Other comprehensive loss | (175) | | | (203) | | | (517) | |
| Comprehensive (loss) income | (1,366,123) | | | 637,841 | | | (65,476) | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | 14,530 | | | 214,912 | | | 138,784 | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,760 | | | — | |
| Comprehensive (loss) income attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | (1,439,165) | | | $ | 364,169 | | | $ | (204,260) | |
| | | | | |
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 1.80 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | (Thousands, except per share amounts) |
| Operating revenues | $ | 1,393,929 | | | $ | 1,357,747 | | | $ | 1,317,037 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Operating and maintenance | 177,972 | | | 154,667 | | | 153,179 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 187,374 | | | 128,472 | | | 137,056 | |
| | | | | |
| Depreciation | 279,386 | | | 272,195 | | | 270,404 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | |
| | | | | |
| Impairment of long-lived assets | — | | | — | | | 56,178 | |
| Total operating expenses | 709,551 | | | 620,153 | | | 681,636 | |
| Operating income | 684,378 | | | 737,594 | | | 635,401 | |
Equity income (a) | 175,215 | | | 168 | | | 17,579 | |
| Impairments of equity method investment | — | | | (583,057) | | | (1,926,402) | |
| Other income (expense), net | 3,222 | | | 13,871 | | | (47,546) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | (24,937) | | | (41,025) | |
| Net interest expense | (426,884) | | | (394,333) | | | (378,650) | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 435,931 | | | (250,694) | | | (1,740,643) | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense | (18,823) | | | 6,444 | | | (343,353) | |
| Net income (loss) | 454,754 | | | (257,138) | | | (1,397,290) | |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 9,525 | | | 12,204 | | | 14,530 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream | 445,229 | | | (269,342) | | | (1,411,820) | |
| Preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | 386,717 | | | $ | (327,854) | | | $ | (1,470,332) | |
| | | | | |
Earnings (loss) per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - basic | $ | 0.89 | | | $ | (0.76) | | | $ | (3.40) | |
| Earnings (loss) per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - diluted | $ | 0.89 | | | $ | (0.76) | | | $ | (3.40) | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - basic | 433,963 | | | 433,341 | | | 433,008 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - diluted | 436,132 | | | 433,341 | | | 433,008 | |
| | | | | |
| Statement of comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 454,754 | | | $ | (257,138) | | | $ | (1,397,290) | |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | | | | | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $19, $236 and $62 | 60 | | | 722 | | | 175 | |
| Other comprehensive income | 60 | | | 722 | | | 175 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 454,814 | | | (256,416) | | | (1,397,115) | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 9,525 | | | 12,204 | | | 14,530 | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | 386,777 | | | $ | (327,132) | | | $ | (1,470,157) | |
| | | | | |
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | |
(a)Represents equity income from Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (the MVP Joint Venture). See Note 9.7.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | | | | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | | (Thousands) | | (Thousands) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (1,365,948) | | | $ | 638,044 | | | $ | (64,959) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |
| Net income (loss) | |
| Net income (loss) | |
| Net income (loss) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | |
| Depreciation | |
| Depreciation | |
| Depreciation | Depreciation | 270,404 | | | 259,613 | | | 227,364 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 63,195 | | | 53,258 | |
| | Impairments of long-lived assets and equity method investments | 1,982,580 | | | 55,581 | | | 969,258 | |
| Deferred income taxes | (349,944) | | | 102,718 | | | 50,704 | |
| Equity income | (17,579) | | | (233,833) | | | (163,279) | |
| Other expense (income), net | 16,043 | | | (17,278) | | | (5,716) | |
| Provision for (recovery of) credit losses on accounts receivable and contract asset write-down | |
| Deferred income tax (benefit) expense | |
| Impairments of long-lived assets and equity method investment | |
Equity income (a) | |
| Other (income) expense, net | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | Loss on extinguishment of debt | 41,025 | | | 24,864 | | | — | |
| Non-cash long-term compensation expense | Non-cash long-term compensation expense | 14,921 | | | 12,301 | | | 2,786 | |
| Changes in other assets and liabilities: | Changes in other assets and liabilities: | |
| Accounts receivable | Accounts receivable | 64,172 | | | (37,810) | | | 17,523 | |
| Accounts receivable | |
| Accounts receivable | |
| Accounts payable | Accounts payable | (2,709) | | | (7,922) | | | (90,301) | |
| | Accrued interest | |
| Accrued interest | |
| Accrued interest | |
| Deferred revenue | |
| EQT Cash Option | |
| | Deferred revenue | 423,666 | | | 225,746 | | | — | |
| | Other assets and other liabilities | |
| Other assets and other liabilities | |
| Other assets and other liabilities | Other assets and other liabilities | 27,318 | | | 55,667 | | | (20,151) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | Net cash provided by operating activities | 1,168,768 | | | 1,140,886 | | | 976,487 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | Capital expenditures | (290,521) | | | (462,031) | | | (967,369) | |
| Capital expenditures | |
| Capital expenditures | |
| Capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture | Capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture | (287,665) | | | (272,801) | | | (774,593) | |
| Bolt-on Acquisition (defined in Note 3), net of cash acquired | — | | | — | | | (837,231) | |
| | Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest (defined in Note 1) | Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest (defined in Note 1) | 5,217 | | | 5,003 | | | 4,661 | |
| Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest (defined in Note 1) | |
| Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest (defined in Note 1) | |
| Proceeds from sale of gathering assets | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | Net cash used in investing activities | (572,969) | | | (729,829) | | | (2,574,532) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | |
| | Proceeds from revolving credit facility borrowings | Proceeds from revolving credit facility borrowings | 467,500 | | | 1,965,000 | | | 2,484,000 | |
| | Proceeds from revolving credit facility borrowings | |
| | Proceeds from revolving credit facility borrowings | |
| Payments on revolving credit facility borrowings | Payments on revolving credit facility borrowings | (750,000) | | | (2,080,000) | | | (2,495,500) | |
| Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt | Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt | 1,900,000 | | | 1,600,000 | | | 1,400,000 | |
| Debt discounts, debt issuance costs and credit facility origination fees | (29,904) | | | (26,720) | | | (2,870) | |
| Debt discounts, debt issuance costs and credit facility arrangement fees | |
| Payments for retirement of long-term debt | Payments for retirement of long-term debt | (1,936,250) | | | (594,000) | | | (34,325) | |
| Redemption of EQM Series A Preferred Units (defined in Note 1) | — | | | (617,338) | | | — | |
| Proceeds from issuance of EQM Series A Preferred Units, net of offering costs | — | | | — | | | 1,158,313 | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interests | (2,500) | | | (128,770) | | | (382,360) | |
| Distributions paid to holders of EQM Series A Preferred Units | — | | | (61,931) | | | (48,480) | |
| | Dividends paid to common shareholders | |
| Dividends paid to common shareholders | |
| Dividends paid to common shareholders | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares | Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares | (58,512) | | | (16,879) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to common shareholders | (259,495) | | | (278,395) | | | (448,128) | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest | |
| | Cash Shares and Cash Amount (defined in Note 6) | — | | | (52,323) | | | — | |
| Other items | |
| Other items | |
| Other items | |
| | Purchases of EQGP common units | — | | | — | | | (238,455) | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (669,161) | | | (291,356) | | | 1,392,195 | |
| | | Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | |
| | Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | |
| | Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | |
| | Net change in cash and cash equivalents | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | Net change in cash and cash equivalents | (73,362) | | | 119,701 | | | (205,850) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 208,023 | | | 88,322 | | | 294,172 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 134,661 | | | $ | 208,023 | | | $ | 88,322 | |
| | Cash paid during the period for: | |
| Cash paid during the year for: | |
| Cash paid during the year for: | |
| Cash paid during the year for: | |
| Interest, net of amount capitalized | Interest, net of amount capitalized | $ | 343,351 | | | $ | 249,302 | | | $ | 257,065 | |
| Income taxes | 3,500 | | | 3,709 | | | — | |
| Interest, net of amount capitalized | |
| Interest, net of amount capitalized | |
| Income taxes, net | |
| Non-cash activity during the period for: | |
| Issuance of Equitrans Midstream common stock pursuant to the EQM Merger (defined in Note 1), net of tax | $ | — | | | $ | 2,736,229 | | | $ | — | |
| Issuance of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares pursuant to the Restructuring Agreement | — | | | 667,214 | | | — | |
| Contract liability | — | | | 121,483 | | | — | |
| Separation-related adjustments | — | | | — | | | 93,666 | |
|
(a) Represents equity income from the MVP Joint Venture. See Note 7.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
DECEMBER 31,
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Thousands) |
| 2023 | | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
| ASSETS | ASSETS | |
| Current assets: | Current assets: | | | |
| Current assets: | |
| Current assets: | |
| Current assets: | |
| Current assets: | |
| Current assets: | |
| Current assets: | |
| Current assets: | |
| Current assets: | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 134,661 | | | $ | 208,023 | |
| Accounts receivable (net of allowance for credit losses of $2,696 and $4,699 as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively) | 252,301 | | | 290,446 | |
| Accounts receivable (net of allowance for credit losses of $6,429 and $3,031 as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively) | |
| Other current assets | Other current assets | 59,867 | | | 63,268 | |
| Total current assets | Total current assets | 446,829 | | | 561,737 | |
| | Property, plant and equipment | Property, plant and equipment | 9,004,602 | | | 8,835,652 | |
| Property, plant and equipment | |
| Property, plant and equipment | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation | Less: accumulated depreciation | (1,217,099) | | | (1,007,756) | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | Net property, plant and equipment | 7,787,503 | | | 7,827,896 | |
| | Investments in unconsolidated entity | 1,239,039 | | | 2,796,316 | |
Investment in unconsolidated entity (a) | |
Investment in unconsolidated entity (a) | |
Investment in unconsolidated entity (a) | |
| Goodwill | Goodwill | 486,698 | | | 486,698 | |
| Net intangible assets | Net intangible assets | 651,771 | | | 716,590 | |
| | Other assets | Other assets | 308,924 | | | 336,615 | |
| Other assets | |
| Other assets | |
| Total assets | Total assets | $ | 10,920,764 | | | $ | 12,725,852 | |
| | LIABILITIES, MEZZANINE EQUITY AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | LIABILITIES, MEZZANINE EQUITY AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | |
| LIABILITIES, MEZZANINE EQUITY AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | |
| LIABILITIES, MEZZANINE EQUITY AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | Current liabilities: | | | | Current liabilities: | | | |
| Current portion of revolving credit facility borrowings | $ | — | | | $ | 302,500 | |
| Current portion of long-term debt | |
| | Accounts payable | |
| Accounts payable | |
| Accounts payable | Accounts payable | 59,627 | | | 72,098 | |
| Capital contributions payable to the MVP Joint Venture | Capital contributions payable to the MVP Joint Venture | 72,188 | | | 10,723 | |
| Accrued interest | Accrued interest | 151,909 | | | 126,191 | |
| Accrued liabilities | Accrued liabilities | 83,852 | | | 83,366 | |
| Total current liabilities | Total current liabilities | 367,576 | | | 594,878 | |
| | Long-term liabilities: | |
| Revolving credit facility borrowings | |
| Revolving credit facility borrowings | |
| Revolving credit facility borrowings | Revolving credit facility borrowings | 505,000 | | | 485,000 | |
| Long-term debt | Long-term debt | 6,434,945 | | | 6,443,312 | |
| Contract liability | Contract liability | 821,342 | | | 398,750 | |
| Deferred income taxes | — | | | 345,896 | |
| | Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | |
| Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | |
| Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | 99,333 | | | 94,902 | |
| Total liabilities | Total liabilities | 8,228,196 | | | 8,362,738 | |
| | Mezzanine equity: | Mezzanine equity: | |
| Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, 30,018 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2021 and 2020 | 681,842 | | | 681,842 | |
| Mezzanine equity: | |
| Mezzanine equity: | |
| Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, 30,018 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | |
| Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, 30,018 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | |
| Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, 30,018 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | |
| | Shareholders' equity: | Shareholders' equity: | | | |
| Shareholders' equity: | |
| Shareholders' equity: | | | | |
| | Common stock, no par value, 432,522 and 432,470 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively | 3,957,756 | | | 3,941,295 | |
| Common stock, no par value, 433,505 and 432,781 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| Common stock, no par value, 433,505 and 432,781 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| Common stock, no par value, 433,505 and 432,781 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | |
| Retained deficit | Retained deficit | (2,428,171) | | | (728,959) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (2,054) | | | (2,229) | |
| Total common shareholders' equity | Total common shareholders' equity | 1,527,531 | | | 3,210,107 | |
| Noncontrolling interests | 483,195 | | | 471,165 | |
| Noncontrolling interest | |
| Total shareholders' equity | Total shareholders' equity | 2,010,726 | | | 3,681,272 | |
| Total liabilities, mezzanine equity and shareholders' equity | Total liabilities, mezzanine equity and shareholders' equity | $ | 10,920,764 | | | $ | 12,725,852 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY AND MEZZANINE EQUITY
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Mezzanine |
| | | Common Stock | | | | | | | | | | Equity |
| | | | | | | | | Accumulated Other | | | | | | Equitrans |
| | | | | | | Retained | | | | | | | Midstream |
| | | | Shares | | No | | Earnings | | Comprehensive | | Noncontrolling | | Total | | Preferred |
| | | | Outstanding | | Par Value | | (Deficit) | | Loss | | Interests | | Equity | | Shares |
| | | | (Thousands, except per unit and share amounts) | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2019 | | | 254,271 | | | $ | 425,370 | | | $ | 33,932 | | | $ | (1,509) | | | $ | 4,801,840 | | | $ | 5,259,633 | | | $ | — | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (203,743) | | | — | | | 138,784 | | | (64,959) | | | — | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $70 | | | — | | | — | | | 316 | | | (517) | | | — | | | (201) | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($1.76 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (448,567) | | | — | | | — | | | (448,567) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 474 | | | 2,531 | | | — | | | — | | | 255 | | | 2,786 | | | — | |
| Separation-related adjustments | | | — | | | (93,666) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (93,666) | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest unitholders ($4.595 per common unit for EQM) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (382,360) | | | (382,360) | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to holders of EQM Series A Preferred Units ($1.9703 per EQM Series A Preferred Unit) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (48,480) | | | (48,480) | | | — | |
| Issuance of EQM Series A Preferred Units, net of offering costs | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,158,313 | | | 1,158,313 | | | — | |
Bolt-on Acquisition (as defined in
Note 3) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 478,460 | | | 478,460 | | | — | |
| Purchase of EQGP common units | | | — | | | (38,648) | | | — | | | — | | | (199,807) | | | (238,455) | | | — | |
| Net changes in ownership of consolidated entities | | | — | | | 997,217 | | | — | | | — | | | (1,337,641) | | | (340,424) | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | | | 254,745 | | | $ | 1,292,804 | | | $ | (618,062) | | | $ | (2,026) | | | $ | 4,609,364 | | | $ | 5,282,080 | | | $ | — | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | — | | | — | | | 391,625 | | | — | | | 214,912 | | | 606,537 | | | 31,507 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $70 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (203) | | | — | | | (203) | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.90 per share) | | | (178) | | | — | | | (280,559) | | | — | | | — | | | (280,559) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 66 | | | 12,786 | | | — | | | — | | | 285 | | | 13,071 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest unitholders ($1.5475 per common unit for EQM) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (128,770) | | | (128,770) | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to holders of EQM Series A Preferred Units ($2.0728 per EQM Series A Preferred Unit) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (51,002) | | | (51,002) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($0.5623 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (16,879) | |
| Partial period distributions on EQM Series A Preferred Units converted in the EQM Merger (as defined in Note 1) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (10,929) | | | (10,929) | | | — | |
| Redemption of EQM Series A Preferred Units | | | — | | | — | | | (27,253) | | | — | | | (590,085) | | | (617,338) | | | — | |
| Restructuring Agreement (as defined in Note 1) | | | — | | | (100,524) | | | — | | | — | | | (579,157) | | | (679,681) | | | 667,214 | |
| EQM Merger | | | 203,137 | | | 2,736,229 | | | — | | | — | | | (2,993,453) | | | (257,224) | | | — | |
| Share Purchase Agreements (as defined in Note 6) | | | (25,300) | | | — | | | (190,992) | | | — | | | — | | | (190,992) | | | — | |
| Adoption of Topic 326 (as defined in Note 1) | | | — | | | — | | | (3,718) | | | — | | | — | | | (3,718) | | | — | |
| Balance at December 31, 2020 | | | 432,470 | | | $ | 3,941,295 | | | $ | (728,959) | | | $ | (2,229) | | | $ | 471,165 | | | $ | 3,681,272 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (1,438,990) | | | — | | | 14,530 | | | (1,424,460) | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $62 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 52 | | | 16,461 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 16,461 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,500) | | | (2,500) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | | | 432,522 | | | $ | 3,957,756 | | | $ | (2,428,171) | | | $ | (2,054) | | | $ | 483,195 | | | $ | 2,010,726 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY AND MEZZANINE EQUITY
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Mezzanine |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Equity |
| | | | | | | | | Accumulated Other | | | | | | Equitrans |
| | | Common Stock | | | | | | | | | Midstream |
| | | | Shares | | No | | Retained | | Comprehensive | | Noncontrolling | | Total | | Preferred |
| | | | Outstanding | | Par Value | | Deficit | | Loss | | Interest | | Equity | | Shares |
| | | | (Thousands, except per share amounts) | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2021 | | | 432,470 | | | $ | 3,941,295 | | | $ | (734,019) | | | $ | (2,229) | | | $ | 471,165 | | | $ | 3,676,212 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (1,470,332) | | | — | | | 14,530 | | | (1,455,802) | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax benefit of $62 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 52 | | | 14,623 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 14,623 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,500) | | | (2,500) | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per Share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | | | 432,522 | | | $ | 3,955,918 | | | $ | (2,464,573) | | | $ | (2,054) | | | $ | 483,195 | | | $ | 1,972,486 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (327,854) | | | — | | | 12,204 | | | (315,650) | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $236 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 722 | | | — | | | 722 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (261,163) | | | — | | | — | | | (261,163) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 259 | | | 18,209 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 18,209 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (16,000) | | | (16,000) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | 432,781 | | | $ | 3,974,127 | | | $ | (3,053,590) | | | $ | (1,332) | | | $ | 479,399 | | | $ | 1,398,604 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | — | | | — | | | 386,717 | | | — | | | 9,525 | | | 396,242 | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $19 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 60 | | | — | | | 60 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (265,333) | | | — | | | — | | | (265,333) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 724 | | | 40,558 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 40,558 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (26,320) | | | (26,320) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| Other items | | | — | | | (37,536) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (37,536) | | | — | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | 433,505 | | | $ | 3,977,149 | | | $ | (2,932,206) | | | $ | (1,272) | | | $ | 462,604 | | | $ | 1,506,275 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTSRecently Issued Accounting Standards
DECEMBER 31, 2021
1. Summary of Operations and Significant Accounting Policies
Organization
On November 12, 2018, Equitrans Midstream Corporation (together with its consolidated subsidiaries as applicable,Recently issued accounting standards relevant to the Company or Equitrans Midstream), EQT Corporation (EQT) and, for certain limited purposes, EQT Production Company, a wholly owned subsidiary of EQT, entered into a separation and distribution agreement (the Separation and Distribution Agreement), pursuant to which, among other things, EQT effected the separation of its midstream business, which was composed of the assets and liabilities of the separately-operated natural gas gathering, transmission and storage and water services operations of EQT (the Midstream Business), from EQT's upstream business, which was composed of the natural gas, oil and natural gas liquids development, production and sales and commercial operations of EQT (the Separation), and distributed 80.1% of the then-outstanding shares of common stock, no par value, of Equitrans Midstream (Equitrans Midstream common stock) to EQT shareholders of record as of the close of business on November 1, 2018 (the Distribution). As part of the Separation, EQT retained the remaining 19.9% of the then-outstanding shares in Equitrans Midstream.
Immediately following the Separation, the Company held investments in the entities then-conducting the Midstream Business, including limited and general partner interests in EQGP Holdings, LP (EQGP), which, as of the date of Separation, owned limited partner interests, the entire general partner interest and all of the incentive distribution rights (IDRs) in EQM Midstream Partners, LP (EQM). Following the closing of the EQGP Buyout (as defined and discussedare described in Note 2), EQGP became an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company on January 10, 2019.
The Company owns, operates, acquires and develops midstream assets in the Appalachian Basin. As of December 31, 2021, EQGP Services, LLC was EQM's general partner (the EQM General Partner) and was an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of Equitrans Midstream.
EQM Merger. On June 17, 2020, pursuant to that certain Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of February 26, 2020 (the EQM Merger Agreement), by and among the Company, EQM LP Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (EQM LP), LS Merger Sub, LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of EQM LP (Merger Sub), EQM and the EQM General Partner, Merger Sub merged with and into EQM (the EQM Merger), with EQM continuing and surviving as an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. Upon consummation of the EQM Merger, the Company acquired all of the outstanding EQM common units that the Company and its subsidiaries did not already own. Following the closing of the EQM Merger, EQM was no longer a publicly traded entity. See Note 2 for further information on the EQM Merger.
Preferred Restructuring Agreement. On February 26, 2020, Equitrans Midstream and EQM entered into a Preferred Restructuring Agreement (the Restructuring Agreement) with all of the holders of the Series A Perpetual Convertible Preferred Units representing limited partner interests in EQM (such units, EQM Series A Preferred Units and, such investors, collectively, the Investors), pursuant to which, at the effective time of the EQM Merger (the Effective Time): (i) EQM redeemed $600 million aggregate principal amount of the Investors' EQM Series A Preferred Units issued and outstanding immediately prior1 to the Restructuring Closing (as defined below), which occurred substantially concurrent with the closing of the EQM Merger, for cash at 101% of the EQM Series A Preferred Unit purchase price of $48.77 per such unit (the EQM Series A Preferred Unit Purchase Price) plus any accrued and unpaid distribution amounts and partial period distribution amounts, and (ii) immediately following such redemption, each remaining issued and outstanding EQM Series A Preferred Unit was exchanged for 2.44 shares of a newly authorized and created series of preferred stock, without par value, of Equitrans Midstream, convertible into Equitrans Midstream common stock (the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares) on a one for one basis, in each case, in connection with the occurrence of the “Series A Change of Control” (as defined in the Fourth Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of EQM (as amended, the Former EQM Partnership Agreement)) that occurred upon the closing of the EQM Merger (collectively, the Restructuring and, the closing of the Restructuring, the Restructuring Closing). See Note 2 for further information on the Restructuring Agreement.
Nature of Business
The Company provides midstream services to its customers in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Ohio through its 3 primary assets: the gathering system, which includes predominantly dry gas gathering systems of high-pressure gathering lines; the transmission system, which includes FERC-regulated interstate pipelines and storage systems; and the water network, which primarily consists of water pipelines and other facilities that support well completion activities and produced water handling activities.consolidated financial statements.
As of December 31, 2021,Critical Accounting Estimates
The Company's significant accounting policies are described in Note 1 to the gathering system, inclusive of Eureka Midstream's gathering system, included approximately 1,170 miles of high-pressure gathering lines with total contracted firm reservation capacity of approximately 7.0 billion cubic feet (Bcf) per day, which included contracted firm reservation capacity of approximately 1.8 Bcf per day associated with EQM's high-pressure header pipelines, 133 compressor units with compression of approximately 491,000 horsepower and multiple interconnect points with the Company's transmission and storage system and to other interstate pipelines.
As of December 31, 2021, the transmission and storage system included approximately 950 miles of FERC-regulated, interstate pipelines that have interconnect points to 7 interstate pipelines and multiple local distribution companies (LDCs). The transmission and storage system is supported by 43 compressor units, with total throughput capacity of approximately 4.4 Bcf per day and compression of approximately 136,000 horsepower, and 18 associated natural gas storage reservoirs, which have a peak withdrawal capacity of approximately 850 million cubic feet (MMcf) per day and a working gas capacity of approximately 43 Bcf, in each case as of December 31, 2021.
As of December 31, 2021, the Company's fresh water systems included approximately 200 miles of pipelines that deliver fresh and produced water from local municipalities' water authorities, the Monongahela River, the Ohio River, local reservoirs and several regional waterways. The fresh water delivery services systems consist of permanent, buried pipelines, surface pipelines, 23 fresh water impoundment facilities, as well as pumping stations, which support water transportation throughout the systems, and take point facilities and measurement facilities, which support well completion activities. As of December 31, 2021, the Company's mixed water system, which the Company began to construct in 2021, included approximately 8 miles of buried pipeline.
Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation. The consolidated financial statements, includewhich have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. Any new accounting policies or updates to existing accounting policies as a result of new accounting pronouncements have been included in the accounts of all entities in which the Company holds a controlling financial interest. For consolidated subsidiaries in which the Company’s ownership is less than 100%, the Company records noncontrolling interest relatednotes to the third-party ownership interests in those entities. Investments over which the Company can exert significant influence, but not control, over operating and financial policies are recorded under the equity method of accounting. Intercompany transactions have been eliminated for purposes of preparing theseCompany's consolidated financial statements. References in these financial statements to Equitrans Midstream or the Company refer collectively to Equitrans Midstream Corporation and, as applicable, its consolidated subsidiaries for all periods presented, unless otherwise indicated.
Segments. Operating segments are revenue-producing components of the enterprise for which separate financial information is produced internally and is subject to evaluation by the Company's chief operating decision maker in deciding how to allocate resources. The Company reports its operations in 3 segments that reflect its 3 lines of business of Gathering, Transmission and Water. The operating segments are evaluated based on their contribution to the Company's operating income and equity income. Transmission also includes the Company's investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which is accounted for as an equity investment as described in Note 9; as a result, Transmission's portion of the MVP Joint Venture's operating results is reflected in equity income and not in Transmission's operating income. All of the Company's operating revenues, income and assets are generated or located in the United States. See Note 5 for financial information by segment.
Reclassification: Certain previously reported amounts have been reclassified to conform to current year presentation.
Use of Estimates. The preparationPreparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts reported in thesethe Company's consolidated financial statements.statements and accompanying notes. The Company's critical accounting policies discussed below are considered critical due to the significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of the Company's consolidated financial statements and the material impact on the results of operations or financial condition. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash Equivalents. The Company classifies highly-liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less as cash equivalents. Interest earned on cash equivalents is recorded as a reduction to net interest expense on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Accounts Receivables. Tradejudgments and other receivables are stated at their historical carrying amount. Judgment is required to assess the ultimate realization of accounts receivable, including assessing the probability of collection and the creditworthiness of customers. The Company evaluates the allowance for credit losses on a quarterly basis in order to estimate uncollectible receivables.
Derivative Instruments. Derivative instruments are recorded on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as either an asset or liability measured at fair value. See Note 12.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments. Fair value represents the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the reporting date. The Company’s assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value at each reporting date are classified according to a hierarchy that prioritizes inputs and assumptions
underlying the valuation techniques. This fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs and consists of three broad levels:
•Level 1: Observable inputs that reflect unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets as of the reporting date.
•Level 2: Observable market-based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data. These are inputs other than quoted prices in active markets included in Level 1 that are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reporting date.
•Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data and may be used with internally developed methodologies that result in management’s best estimate of fair value.
The Company prioritizes valuation techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs. Assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based on the lowest priority level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgment and may affect the placement of assets and liabilities within the levels of the fair value hierarchy. Reclassifications of fair value between Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy, if applicable, are made at the end of each reporting period. See Note 12 for information regarding the fair value of financial instruments.estimates.
Property, Plant and Equipment. The Company'sDetermination of depreciation expense requires judgment regarding the estimated useful lives and salvage values of property, plant and equipment are stated at depreciated cost. Maintenance projects that do not increase the overall life of the related assets are expensed as incurred. Expenditures that extend the useful life of the asset are capitalized.equipment. The Company capitalized internal labor costshas not historically experienced material changes in its results of $50.8 million, $44.9 million and $47.6 millionoperations from changes in the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The Company capitalized interest, including the debt componentestimated useful lives or salvage values of Allowance for Funds Used During Construction (AFUDC), of $4.9 million, $18.6 million and $29.5 million in the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
The following table summarizes the Company'sits property, plant and equipment.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Thousands) |
| Gathering assets | $ | 6,911,268 | | | $ | 6,691,954 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (727,735) | | | (543,568) | |
| Net gathering assets | 6,183,533 | | | 6,148,386 | |
| Transmission and storage assets | 1,901,756 | | | 1,877,753 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (424,918) | | | (370,764) | |
| Net transmission and storage assets | 1,476,838 | | | 1,506,989 | |
| Water services assets | 176,245 | | | 251,885 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (60,379) | | | (90,841) | |
| Net water services assets | 115,866 | | | 161,044 | |
| Net other property, plant and equipment | 11,266 | | | 11,477 | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | $ | 7,787,503 | | | $ | 7,827,896 | |
Net other property, plant and equipment includes capitalized qualified implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract of $10.0 million and $8.8 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2021 and 2020. The Company finalized the implementation of certain portions of its enterprise resource planning system throughout 2021 and 2020 and amortized approximately $0.9 million and $0.5 million of implementation costs in the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Depreciation is recorded using composite rates on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the asset. The average depreciation rates for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 were 2.6%, 2.5% and 2.7%, respectively. The Company estimates that gathering and transmission pipelines have useful lives of 20 years to 50 years and compression equipment has useful lives of 20 years to 50 years. The Company estimates that water pipelines, pumping stations and impoundment facilities have useful lives of 10 years to 15 years. As circumstances warrant, depreciationequipment; however, these estimates are reviewed to determine if any changes in the underlying assumptions are necessary.periodically, including each time Equitrans, L.P., the Company's FERC-regulated
subsidiary, re-evaluates depreciation rates for its regulated property, plant and equipment each time it files with the FERC for a change in its transmission and storage and gathering rates.
Intangible Assets. Intangible assets are recorded under The Company believes that the acquisition method of accounting at their estimated fair values at the acquisition date, which are calculated as the present value of estimated future cash flows using a risk-adjusted discount rate. The Company's intangible assets are amortized on a straight-line basis. The estimated annual amortization expenseestimate related to depreciation expense is a "critical accounting estimate" because the intangible assets for eachassumptions used to estimate useful lives and salvage values of property, plant and equipment are susceptible to change. These assumptions affect depreciation expense and, if changed, could have a material effect on the next five years is $64.8 million.Company's results of operations and financial position. See Note 31 to the consolidated financial statements for further detail.
The following tables summarize the Company's intangible assets as of December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | December 31, 2021 |
| (In thousands) | | Useful Life | | Gross | | Accumulated Amortization(a) | | Net |
| Customer relationships | | 15 years | | $ | 623,199 | | | $ | (171,726) | | | $ | 451,473 | |
| Eureka Midstream-related customer relationships | | 10.75 years | | 237,000 | | | (48,144) | | | 188,856 | |
| Hornet Midstream-related customer relationships | | 7.25 years | | 74,000 | | | (62,558) | | | 11,442 | |
| | | | $ | 934,199 | | | $ | (282,428) | | | $ | 651,771 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | December 31, 2020 |
| (In thousands) | | Useful Life | | Gross | | Accumulated Amortization(a) | | Net |
| Customer relationships | | 15 years | | $ | 623,199 | | | $ | (130,180) | | | $ | 493,019 | |
| Eureka Midstream-related customer relationships | | 10.75 years | | 237,000 | | | (27,160) | | | 209,840 | |
| Hornet Midstream-related customer relationships | | 7.25 years | | 74,000 | | | (60,269) | | | 13,731 | |
| | | | $ | 934,199 | | | $ | (217,609) | | | $ | 716,590 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
(a)Impairment charge of $54.1 million is included within the Hornet Midstream-related customer relationships accumulated amortization. See Note 4 for furtheradditional information.
Goodwill and ImpairmentImpairments of Long-Lived Assets.Assets and Equity Method Investment. Goodwill is evaluated for impairment at least annually or whenever events or changes in circumstance indicate it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. The Company may perform either a qualitative assessment of potential impairment or proceed directly to a quantitative assessment of potential impairment. The Company's qualitative assessment of potential impairment may result in the determination that a quantitative impairment analysis is not necessary. Under this elective process, the Company assesses qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events or circumstances leads the Company to determine that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If after assessing the totality of events or circumstances, the Company determines it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is greater than its carrying amount, then a quantitative assessment is not required. However, if the Company concludes otherwise, a quantitative impairment analysis is performed.
If the Company chooses not to perform a qualitative assessment, or if it chooses to perform a qualitative assessment but is unable to qualitatively conclude that no impairment has occurred, then the Company will perform a quantitative assessment. In the case of a quantitative assessment, the Company estimates the fair value of the reporting unit with which the goodwill is associated and compares it to the carrying value. If the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairment charge is recognized for the excess of the reporting unit's carrying value over its fair value. See Note 4 for further detail.
The Company evaluates long-lived assets and equity method investments for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management's judgment, that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable. With respect to property, plant and equipment and finite lived intangibles, asset recoverability is measured by comparing the carrying value of the asset or asset group with its expected future pre-tax undiscounted cash flows. These cash flow estimatesAny accounting estimate related to an impairment of property, plant and equipment, finite-lived intangible assets, goodwill or an investment in an unconsolidated entity may require the CompanyCompany's management to make projections and assumptions for many years into theabout future for pricing, demand, competition, operating costs and other factors. If the carrying amount exceeds the expected future undiscounted cash flows, the Company recognizes an impairment equal to the excess of carrying value over fair value as determined by quoted market prices in active markets or present value techniques if quotes are unavailable. The determination ofdiscount rates, the fair value using presentof investments and whether losses in the value techniques requiresof its investments are other-than-temporary. Management's assumptions about future cash flows require significant judgment because, among other things, actual operating levels have been and may be different from estimated levels.
Goodwill is the cost of an acquisition less the fair value of the identifiable net assets of the acquired business. Goodwill is evaluated for impairment at least annually or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. When performing a quantitative assessment, the Company uses a combination of an income and market approach to make projectionsestimate the fair value of its reporting units.
The Company believes that the accounting estimates related to impairments are "critical accounting estimates" because they require assumptions that are susceptible to change, including estimating fair value which requires considerable judgment. For example, in the case of goodwill, management’s estimate of a reporting unit’s future financial results is sensitive to changes in assumptions, such as changes in the Company's stock price, weighted-average cost of capital, terminal growth rates and industry multiples. When a quantitative assessment is performed, the Company uses estimates and assumptions regardingin estimating its reporting units’ fair values that it believes are reasonable and appropriate at that time; however, different assumptions and estimates could materially affect the calculated fair value and the resulting conclusion of whether goodwill is impaired, which could materially affect the Company’s results of operations and financial position.
The Company’s investment in unconsolidated entity also requires considerable judgment to estimate fair value because the Company’s investment is not traded on an active market. When estimating the fair value of its equity method investment, the Company utilizes an income approach under which significant judgments and assumptions, including the discount rate and probability-weighted scenarios, are sensitive to change. Additionally, the Company's investment in unconsolidated entity is susceptible to impairment risk from adverse macroeconomic conditions and/or other adverse factors. Adverse developments could require that the Company modify assumptions reflected in the probability-weighted scenarios of discounted future net cash flows (including with respect to the probability of a rangesuccess prior to completion) utilized to estimate the fair value of outcomes and the rates of interest usedits equity method investment in the present value calculations. Any changes the Company makes to these projections and assumptionsMVP Joint Venture, which could result in significant revisionsan incremental other-than-temporary impairment of that investment. While macroeconomic factors in and of themselves may not be a direct indicator of impairment, should an impairment indicator be identified in the future, macroeconomic factors such as changes in interest rates could ultimately impact the size and scope of any potential impairment.
See Notes 1 and 7 to its evaluationsthe consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Revenue Recognition. Revenue from the gathering, transmission and storage of recoverability andnatural gas is generally recognized when the recognition of additional impairments. See Note 4 for further discussion on impairments of long-lived assets.service is provided. Revenue from water services is generally recognized when water is delivered. Contracts often contain fixed
Investments in Unconsolidated Entities. The Company accounts for the investments in its unconsolidated entities under the equity method. The Company’s pro-rata share of net income in the unconsolidated entities is included in equity income in the Company’s statements of consolidated comprehensive income. Contributions to or distributions from the unconsolidated entities and the Company’s pro-rata share of net income in the unconsolidated entities are recorded as adjustments to the investment balance. The Company reviews the carrying value of its investments in unconsolidated entities for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value may have declined in value. When there is evidence of loss in value that is other-than-temporary, the Company compares the investment's carrying value to its estimated fair value to determine whether impairment has occurred. If the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value, the Company estimates and recognizes an impairment loss equal to the difference between the investment's carrying value and fair value. See Notes 4 and 9 for further detail.
Preferred Interest. EQT Energy Supply, LLC(EES), a subsidiary of EQT, generates revenue by providing services to a local distribution company. The preferred interest that the Company has in EES (the Preferred Interest) is accounted for as a note receivable and is presented in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets with the current portion reported in other current assets. Distributions received from EES are recorded as a reduction to the Preferred Interest and as interest income, which is included in net interest expense in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income. The EES operating agreement provides for mandatory redemption of the Preferred Interest at the end of the preference period, which is expected to be December 31, 2034.
Unamortized Debt Discount and Issuance Costs. The Company amortizes debt discounts and issuance costs over the term of the related borrowing. Costs incurred from the issuance and/or extension, as applicable, of revolving credit facilities, including borrowings under the Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility (each as defined in Note 11), are presented in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets. Debt discounts and issuance costs for all other debt instruments are presented as a reduction to debt on the consolidated balance sheets. See Note 11 for further detail.
Leases. Right-of-use assets represent the right to use the underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent the obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. Right-of-use assets and lease liabilities are recognized on the consolidated balance sheets at the lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception based on whether the Company has the right to control the use of an identified asset, the right to obtain substantially all of the economic benefits from the use of the asset and the right to direct the use of the asset during the lease term and accounts for leases in accordance with ASC 842, Leases (ASC 842).
Leases in which the Company is the lessee that do not have a readily determinable implicit rate utilize an incremental borrowing rate, based on the information available at the lease commencement date, to determine the present value of lease payments. When a secured borrowing rate is not readily available, unsecured borrowing rates are adjusted for the effects of collateral to determine the incremental borrowing rate. The Company reassesses the incremental borrowing rate for any new and modified lease contracts as of the contract effective date. Lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term for operating leases. See Note 7.
Other Current Liabilities. The following table summarizes the Company's accrued liabilities as of December 31, 2021 and 2020.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | (Thousands) |
| Accrued employee compensation | $ | 50,372 | | | $ | 46,108 | |
| Non-income tax accruals | 19,972 | | | 19,492 | |
| Current portion of operating lease liabilities | 8,253 | | | 9,990 | |
| Other accrued liabilities | 5,255 | | | 7,776 | |
| Total accrued liabilities | $ | 83,852 | | | $ | 83,366 | |
Asset Retirement Obligations (AROs). The Company has AROs related to its water system impoundments and to one of its gathering compressor stations, for which the Company recorded an associated liability and capitalized a corresponding amount to asset retirement costs. The liabilityvariable consideration. Fixed consideration primarily relates to the expected future obligation to dismantle, reclaimfirm reservation payments including MVCs and dispose of these assetsARCs. Variable consideration is generally dependent on volumes and was estimated using the present value of expected future cash flows, adjusted for inflation and discounted at the Company's credit-adjusted, risk-free rate. The AROs are recorded in regulatory and other long-term liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets. Throughout 2021 and 2020, the Company undertook the reclamation process for certain water system impoundments, which reclamation process was completed as of December 31, 2021.
The following table presents changes in the Company's AROs during 2021 and 2020.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Thousands) |
| AROs at beginning of period | $ | 12,172 | | | $ | 12,301 | |
| | | |
| Liabilities settled | (1,609) | | | (724) | |
Revisions to estimated liabilities (a) | — | | | — | |
| Accretion expense | 678 | | | 595 | |
| AROs at end of period | $ | 11,241 | | | $ | 12,172 | |
(a)Revisions to estimated liabilities reflect changes in retirement cost assumptions and to the estimated timing of liability settlement.
The Company is not legally or contractually obligated to restore or dismantle its transmission and storage systems and its gathering systems, other than the one aforementioned gathering compressor station. The Company is legally required to operate and maintain these assets and intends to do so as long as supply and demand for natural gas exists, which the Company expects to continue into the foreseeable future. Therefore, the Company did not have any AROs related to its transmission and storage and gathering (other than the aforementioned gathering compressor station) assets as of December 31, 2021 and 2020.
Contingencies. The Company is involved in various regulatory and legal proceedings that arise in the ordinary course of business. A liability is recorded when the loss is probable and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company considers many factors when making such assessments, including historical knowledge and matter specifics. Estimates are developed through consultation with legal counsel and analysis of the potential results. See Note 16.
Regulatory Accounting. Equitrans, L.P. owns all of the Company's FERC-regulated transmission and storage operations as well as its FERC-regulated low-pressure gathering assets. Therefore, Equitrans, L.P. is subject to FERC regulation. Through the rate-setting process, rate regulation allows Equitrans, L.P. to recover the costs of providing regulated services plus an allowed return on invested capital. Regulatory accounting allows Equitrans, L.P. to defer expenses and income to its consolidated balance sheets as regulatory assets and liabilities when it is probable that those expenses and income will be allowed in the rate-setting process for a period other than the period that they would be reflected in a non-regulated entity's statements of consolidated comprehensive income. Regulatory assets and liabilities are recognized in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income inperiod they occur. At each reporting date and, as circumstances or events warrant, management reviews and updates the period thatassumptions utilized to estimate the underlying expenses and income are reflected in the rates charged to shippers and operators. Equitrans, L.P. expects to continue to be subject to rate regulation that will providetotal consideration for the recovery of deferred costs.
The following table summarizes Equitrans, L.P.'s regulatory assets and liabilities that are included in other assets and regulatory and other long-term liabilities, respectively, in the Company's consolidated balance sheets.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Thousands) |
| Regulatory assets: | | | |
Deferred taxes (a) | $ | 91,989 | | | $ | 89,243 | |
Other recoverable costs (b) | 3,654 | | | 4,960 | |
| Total regulatory assets | $ | 95,643 | | | $ | 94,203 | |
| Regulatory liabilities: | | | |
Deferred taxes (a) | $ | 9,727 | | | $ | 10,125 | |
On-going post-retirement benefits other than pension and other reimbursable costs (c) | 10,094 | | | 10,959 | |
| | | |
| Total regulatory liabilities | $ | 19,821 | | | $ | 21,084 | |
(a)The regulatory asset from deferred taxes is primarily related to a historical deferred income tax position and taxes on the equity component of AFUDC. The regulatory liability from deferred taxes relates to the revaluation of a historical difference between the regulatory and tax bases of regulated property, plant and equipment. Equitrans, L.P. expects to recover the amortization of the deferred tax positions ratably over the depreciable lives of the underlying assets. Equitrans, L.P. also expects to recover the taxes on the equity component of AFUDC through future rates over the depreciable lives of the underlying long-lived assets.
(b)The regulatory asset from other recoverable costs is primarily related to the costs associated with the Company's legacy post-retirement benefits plan.
(c)Equitrans, L.P. defers expenses for on-going post-retirement benefits other than pensions, which are subject to recovery in approved rates. The regulatory liability reflects lower cumulative actuarial expenses than the amounts recovered through rates.
The following tables present Equitrans, L.P.'s regulated operating revenues and operating expenses and property, plant and equipment included in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income and consolidated balance sheets, respectively.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (Thousands) |
| Operating revenues | $ | 403,634 | | | $ | 397,319 | | | $ | 396,847 | |
| Operating expenses | 135,888 | | | 124,206 | | | 210,861 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Thousands) |
| Property, plant and equipment | $ | 1,901,924 | | | $ | 1,878,312 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (424,918) | | | (370,815) | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | $ | 1,477,006 | | | $ | 1,507,497 | |
Gas imbalances occur when the actual amount of gas delivered from a pipeline system or storage facility varies from the amount of gas scheduled for delivery. The Company values gas imbalances due to/from shippers and operators at current index prices. Gas imbalances are settled in-kind, subject to the terms of the applicable FERC tariffs. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020, gas imbalance receivables were $1.9 million and $1.8 million, respectively, and are presented in other current assets, with offsetting amounts recorded to system gas, a component of property, plant and equipment, on the consolidated balance sheets. The Company classifies gas imbalances as current because they are expected to settle within one year.
Revenue Recognition. Revenue is measured based on considerations specific in a contract with a customer. The Company recognizes revenue under gathering, transmission and storage and water services contracts when it satisfies certain performance obligations, as discussed below.
The Company provides gathering, transmission and storage services in two manners: firm service and interruptible service. Firm service is provided under firm contracts, which are contracts for gathering, transmission or storage services that generally obligate the customer to pay a fixed, monthly charge to reserve an agreed upon amount of pipeline or storage capacity regardless of the capacity used by the customer during each month. Volumetric-based fees can also be charged under firm contracts for each firm volume transported, gathered or stored, as well as for volumes transported, gathered or stored in excess of the firm contracted volume, if capacity exists. Interruptible service contracts include volumetric-based fees, which are charges for the volume of gas gathered, transported or stored and generally do not guarantee access to the pipeline or storage facility. Firm and interruptible contracts can be short- or long-term in duration. Firm and interruptible transmission and storage service contracts are billed at the end of each calendar month, with payment typically due within 10 days. Firm and interruptible gathering contracts are billed on a one-month lag, with payment typically due within 21 days. Revenue related to gathering services provided but not yet billed is estimated each month. These estimates are generally based on contract data, preliminary throughput and allocation measurements.
Under a firm contract, the Company has a stand-ready obligation to provide the service over the life of the contract. The performance obligation for firm reservation fee revenue is satisfied over time as the pipeline capacity is made available to the customer. As such, the Company recognizes firm reservation fee revenue evenly over the contract period using a time-elapsed output method to measure progress. The performance obligation for volumetric-based fee revenue is generally satisfied upon the Company's monthly billing to the customer for volumes gathered, transported or stored during the month. The amount billed generally corresponds directly to the value of the Company's performance to date as the customer obtains value as each volume is gathered, transported or stored.
Water service revenues represent fees charged by the Company for the delivery of fresh and produced water to a customer at a specified delivery point and for the collection and recycling or disposal of flowback and produced water. The Company's water service revenues are generated under firm service and interruptible service contracts, which primarily utilize fixed prices per
volume delivered. Firm service provides water services under firm contracts to customers with priority. Interruptible service contracts generally do not guarantee access to the water facilities. For fresh and produced water delivery service contracts, the only performance obligation in each contract is for the Company to provide water (usually a minimum daily volume of water) to the customer at a designated delivery point. For flowback and produced water, the performance obligation is collection and disposal of the water, which typically occur within the same day. Water service contracts are billed on a monthly basis, with payment typically due within 30 days.
For all contracts, thecontracts. The Company allocates the transaction price to each performance obligation based on the estimated relative standalone selling price. When applicable, the excess of consideration received over revenue recognized results in the deferral of those amounts until future periods based on a units of production or straight-line methodology as these methods appropriately match the consumption of services provided to the customer. The units of production methodology requires the use of production estimates that are uncertain and the use of judgment when developing estimates of future production volumes, thus impacting the rate of revenue recognition. Production estimates are monitored as circumstances and events warrant.
Certain of the Company's gas gathering and water services agreements including the EQT Global GGA, are structured withhave MVCs which specify minimum quantities for which a customer will be charged regardless of quantities gathered or delivered under the contract. Revenue is recognized for MVCs when the performance obligation has been met, which is the earlier of when the gas is gathered or water provided, or when it is remote that the producer will be able to meet its MVC.ARCs. If a customer under such an agreement fails to meet its MVC or ARC for a specified period (thus not exercising all the contractual rights to gathering and water services within the specified period, herein referred to as “breakage”), it is obligated to pay a contractually determined fee based upon the shortfall between the actual volumes and the MVC or ARC for the period contained in the contract. When management determines it is probable that the customer will not exercise all or a portion of its remaining rights, the Company recognizes revenue associated with such breakage amount in proportion to the pattern of exercised rights within the respective MVC or ARC period.
Revenue related to services provided but not yet billed is estimated each month. These estimates are generally based on contract data, preliminary throughput and allocation measurements. Final amounts for the current month are billed and collected in the following month. See Note 6.4 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
AFUDC. The Company capitalizes the carrying costsrecords an allowance for credit losses on a quarterly basis in order to estimate uncollectible receivables. The Company's current expected credit loss (CECL) methodology considers risks of financing the construction of certain long-lived, regulated assets. Such costscollection based on a customer’s current credit status. The standard requires an entity to assess whether financial assets share similar risk characteristics and, if so, group such assets in a pool. Customer balances are amortized over the asset's estimated useful life and include interest costs (the debt component of AFUDC) and equity costs (the equity component of AFUDC).aggregated for evaluation based on their credit risk rating, which takes into account changes in economic factors that impact a customer’s ability to meet its financial obligations. The debt component of AFUDC is recorded asCompany's CECL methodology assigns a reductionreserve, even if remote, to net interest expenseeach customer based on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income,credit risk and the equity component of AFUDCreserve is recorded in other (expense) income, net,evaluated on a quarterly basis. In order to calculate the statements of consolidated comprehensive income. The debt component of AFUDCappropriate allowance, the Company utilizes an estimated loss rate factor based on a customer's credit rating for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020receivables and 2019 was $0.2 million, $0.3 million and $1.4 million, respectively, and the equity component of AFUDC for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019 was $0.3 million, $0.8 million and $5.7 million, respectively.
Share-Based Compensation. The Company recognizes share-based compensation expense based upon the estimated fair value of awards over the requisite service period. Time-based restricted units expected to be satisfied in cash are accounted for as liability awards recorded over the requisite service period, typically three years. The fair value of liability awards is remeasured at the end of each reporting perioda risk-adjusted reserve based on the closingreceivable aging schedule in order to account for the receivables which may be at a greater risk of collection. Customer credit risk ratings are updated quarterly and management has enabled a risk-responsive approach to changes in customer and economic factors. While the Company has not historically experienced material losses on uncollected receivables, a decline in the market price offor natural gas affecting producer activity combined with additional customers on the Company’s common stock. Time-based restricted stock awards expectedCompany's systems may result in a greater exposure to be satisfied inpotential losses than management's current estimates.
The Company common stockbelieves that the accounting estimates related to revenue recognition are accounted for as equity awards"critical accounting estimates" because estimated relative standalone selling prices and volumes are recorded over the requisite service period, typically three years,subject to change based on actual measurements. In addition, the grant date fair value. Director phantom units expectedCompany believes that the accounting estimates related to be satisfied in Company common stock vestthe allowance for credit losses are "critical accounting estimates" because the underlying assumptions used for the allowance can change and the actual mix of customers and their ability to pay may vary significantly from management's estimates, which could affect the collectability of customer receivables. These accounting estimates could potentially have a material effect on the dateCompany's results of grantoperations and are recorded based on the grant date fair value. The grant date fair value, in both cases, is determined based upon the closing price of the Company's common stock on the day before the grant date. Forfeitures are accounted for as they occur.
For plans that include a performance condition that affects the number of awards that will ultimately vest, the probability that the performance condition will be achieved is reevaluated at the end of each reporting period and the payout multiplier is applied to the grant date fair value or measurement date fair value to record compensation expense, as applicable. For plans that include a market condition, compensation expense is based on a grant date fair value using a Monte Carlo simulation that remains constant throughout the vesting period for equity plans and a fair value based on a Monte Carlo simulation remeasured at each reporting period for liability plans. Each plan subject to a market condition is accounted for separately for each vesting tranche of the award. See Note 10.financial position.
Income Taxes. The Company files a consolidated incomerecognizes deferred tax return for federal income taxesassets and the provision for income taxes is determined using the asset and liability approach of accounting for income taxes. Under this approach, the provision for income taxes represents income taxes paid or payable (or received or receivable) plus the change in deferred taxesliabilities for the current year. EQM is a limited partnership for U.S. federal and state incomeexpected future tax purposes. Eureka Midstream is a limited liability company for such purposes. EQM and Eureka Midstream are not subject to U.S. federal or state income taxes.
Allconsequences of Eureka Midstream's income is, and for the period prior to the closing of the EQM Merger all of EQM's income was,events that have been included in the Company's pre-tax income; however,consolidated financial statements or tax returns.
The Company has federal and state of West Virginia net operating loss (NOL) carryforwards. The NOL carryforwards have no expiration, but utilization is limited to 80% of taxable income in the Company does not record income tax expense on the portionsyear of its income attributableutilization. In addition to the noncontrolling member of Eureka Midstream and did not record income tax expense on the portions of its income attributable to the noncontrolling limited partners of EQM for the periods prior to the closing of the EQM Merger. This reduces the Company's effective tax rate in periods whenNOL carryforwards, the Company has consolidated pre-tax income and increases the effectivedeferred tax rate in periods when the Company has consolidated pre-tax loss.
Deferred taxes represent the future tax consequences of differences between the financial and tax bases of the Company's assets and liabilities. Deferred tax balances are adjusted for changesliabilities principally resulting from interest disallowance under Code Section 163(j) and investment in tax rates and tax laws when enacted. Deferred tax assets are reflected on the consolidated balance sheets for net operating losses, credits or other attributes generated by the Company. partnerships.
Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not (greater than 50%) that a tax benefit will not be realized. In evaluating the need for a valuation allowance, this requires significant judgment and management considers all available evidence, both positive and negative, including potential sources of taxable income, including income available in carry-back periods, future reversals of taxable temporary differences, projections of taxable income and income from tax planning strategies, as well as all available positivestrategies. Positive evidence includes reversing temporary differences and negative evidence.projection of future profitability within the carry-forward period, including from tax planning strategies. Negative evidence includes historical pre-tax book losses.
Deferred tax assets for which no valuation allowance is recorded may not be realized, and changes in facts and circumstances may result in the establishment of a valuation allowance. Existing valuation allowances are re-examined under the same
standards of positive and negative evidence that apply to valuation allowance establishment. If it is determined that it is more likely than not that a deferred tax asset for which a valuation allowance is recorded will be realized, all or a portion of the valuation allowance may be released. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are also re-measuredremeasured to reflect changes in underlying tax rates from tax law changes.
Tax benefits related to uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken on a tax return are recorded when such benefits meet a more likely than not threshold; otherwise, the tax benefit is recorded when the tax position has been effectively settled, either because the statute of limitations has expired or the appropriate taxing authority has completed its examination. Interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions are recognized as part of the provision for income taxes and are accrued in the period that such interest and penalties would be applicable under relevant tax law until such time that the related tax benefits are recognized. See Note 14.
Noncontrolling Interests. Noncontrolling interests represent the portion of the equity of consolidated entities that are not wholly owned by the Company. Noncontrolling interests are reported as a component of shareholders’ equity in the consolidated balance sheets and are adjusted by the amount of net income earned by the entities with noncontrolling interests, distributions paid to noncontrolling interest holderschanges and any changes in uncertain tax benefits.
The Company believes that accounting estimates related to income taxes are "critical accounting estimates" because the noncontrolling ownership percentages. AsCompany must assess the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered from future taxable income, and exercise judgment when evaluating whether or not a valuation allowance must be established on deferred tax assets. See Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk. Changes in interest rates affect the amount of interest the Company earns on cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments and the interest rates EQM and Eureka pay on borrowings under their respective revolving credit facilities. The Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility provide for variable interest rates and thus expose the Company, through EQM and Eureka, to fluctuations in market interest rates. In addition, EQM's interest rates under the Amended EQM Credit Facility are impacted by changes in EQM's credit ratings (which changes may be caused by factors outside of EQM's control). Eureka's interest rates under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility are impacted by changes in Eureka's Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) which may fluctuate based on Eureka Midstream's distributions to its members, liquidity needs or operating results. Accordingly, if interest rates were to increase, our debt service obligations on the variable rate indebtedness would increase even though the amount borrowed remained the same, and our net income and cash flows, including cash available for servicing our indebtedness, will correspondingly decrease. Based on commitments as of December 31, 2023 and assuming all loans are fully drawn, each quarter point change in interest rates would result in a change of approximately $3.9 million in annual interest expense on indebtedness under the Amended EQM Credit Facility. Assuming all loans are fully drawn, each quarter point change in interest rates would result in a change of approximately $1.0 million in annual interest expense on indebtedness under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility. Further, regarding the dividend payable on Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares for quarters after March 31, 2024, changes in accordance with the Adjustable Interest Rate (LIBOR) Act (the LIBOR Act), and 2020,the rules implementing the LIBOR Act, three-month CME Term SOFR, administered by CME Group Benchmark Administration, LTD., plus a tenor spread adjustment of 0.26161% per annum, replaced, by operation of law, the three-month London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) to calculate dividends payable on the Series A Preferred Stock for each fiscal quarter ending after March 31, 2024. Fluctuations in three-month CME Term SOFR may affect such dividend (which will not be less than 10.50% under the Company's noncontrollingSecond Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation), which could affect, among other things, the amount of cash the Company has available to make quarterly cash dividends to its shareholders. EQM's senior notes are fixed rate and thus do not expose the Company to fluctuations in market interest consistedrates. Changes in interest rates do affect the fair value of EQM's fixed rate debt. See Notes 9 and 10 to the consolidated financial statements for discussions of borrowings and fair value measurements, respectively. EQM and Eureka may from time to time hedge the interest on portions of borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, as applicable, in order to manage risks associated with floating interest rates. However, the Company may not maintain hedges with respect to all of its variable rate indebtedness, and any hedges it enters into may not fully mitigate its interest rate risk
Credit Risk. The Company is exposed to credit risk, which is the risk that it may incur a loss if a counterparty fails to perform under a contract. The Company actively manages its exposure to credit risk associated with customers through credit analysis, credit approval and monitoring procedures. For certain transactions, the Company requests letters of credit, cash collateral, prepayments or guarantees as forms of credit support. Equitrans, L.P.'s FERC tariffs require tariff customers that do not meet specified credit standards to provide three months of credit support; however, the Company is exposed to credit risk beyond this three-month period when its tariffs do not require its customers to provide additional credit support. For some of the third-party ownership interestCompany's long-term contracts associated with system expansions, it has entered into negotiated credit agreements that provide for other credit support if certain credit standards are not met.
The Company is exposed to the credit risk of its customers, including its largest customer, EQT, including as a result of changes in Eureka Midstream.customer credit ratings, liquidity and access to capital markets. In August 2023, Moody's upgraded EQT's public senior debt to an investment grade credit rating and as of December 31, 2023, EQT's public debt has investment grade credit ratings from S&P, Fitch and Moody's. On February 26, 2020, in connection with the execution of the EQT Global GGA, the Company and EQT entered into a letter agreement (the Credit Letter Agreement) pursuant to which, among other things, (a) the Company agreed to relieve certain credit posting requirements for EQT, in an amount up to approximately $250 million, under its commercial agreements with the Company, subject to EQT maintaining a minimum credit rating from two of three rating agencies of (i) Ba3 with Moody's, (ii) BB- with S&P and (iii) BB- with Fitch and (b) the Company agreed to use commercially reasonable good faith efforts to negotiate similar credit support arrangements for EQT in respect of its commitments to the MVP Joint Venture. In addition, EQT has guaranteed the payment obligations of certain of its subsidiaries, up to a maximum amount of $115 million, $131 million and $30 million related to gathering, transmission and water services, respectively, across all applicable contracts, for the benefit of the subsidiaries of the Company providing such services. See Note 13 to the consolidated financial statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for further discussion of the Company's exposure to certain credit risks.
Commodity Price Risk. The Company's business is dependent on continued natural gas production and the availability and development of reserves in its areas of operation. Prices for natural gas and NGLs, including regional basis differentials, have previously adversely affected, and may in the future adversely affect, timing of development of additional reserves and production that is accessible by the Company’s pipeline and storage assets, which also negatively affects the Company’s water services business, and the creditworthiness of the Company’s customers.
Lower natural gas prices, particularly in the Appalachian region, have in the past caused, and may in the future cause, producers such as EQT to determine to take actions to slow production growth and/or maintain flat or reduce production, which when effected by our producer customers limits growth in or may reduce the demand for, and usage of, our services. For the periodinstance, in certain periods of low natural gas prices prior to 2023, temporary production curtailments resulted in a decrease in our volumetric-based gathering fee revenues. Based on the closingforward price strip as of February 16, 2024, the Company perceives continued risk that EQT and/or other producers could curtail production in 2024 or maintain at flat levels, which, depending on the nature and duration of any such curtailment, could have a significant negative effect on the demand for our services, our volumetric-based fee revenue, and therefore our results of operations, and any such maintenance may limit growth associated with our assets. See also “Decreases or a lack of growth in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, whether as a result of regional takeaway constraints, producer corporate capital allocation strategies, lower regional natural gas prices, natural well decline, and/or other factors, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, our business and operating results and reduce our cash available to pay cash dividends to our shareholders.”, "The lack of diversification of our assets, products and geographic locations could adversely affect us." and “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT's drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results.”, each included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Price declines and sustained periods of low natural gas and NGL prices could have an adverse effect on the creditworthiness of the EQM MergerCompany's customers and related ability to pay firm reservation fees under long-term contracts and/or affect, as discussed above, activity levels and, accordingly, volumetric-based fees, which could affect the Company’s results of operations, liquidity or financial position. Credit risk and related management is further discussed under “Credit Risk” in Part II, “Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Increases in natural gas prices do not necessarily result in corresponding increases to the production forecasts of the Company's customers. Even when natural gas prices have been commercially attractive, certain of the Company's customers maintained largely flat production forecasts in light of, among other things, the absence of incremental takeaway capacity from the Appalachian Basin and the Company's customers may still maintain flat or modest increases to production forecasts based on various factors, which could include regional takeaway capacity limitations, access to capital, investor expectations regarding free cash flow, a desire to reduce or refinance leverage or other factors.
Additionally, lower natural gas prices (including regionally), corporate capital allocation strategies or regional takeaway constraints, could cause producers to determine in the future that drilling activities in areas outside of the Company's current areas of operation are strategically more attractive to them.
Many of the Company’s customers, including EQT, have entered into long-term firm reservation gathering, transmission and water services contracts or contracts with MVCs or ARCs, as applicable, on the Company's systems and approximately 70% of the Company's operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 2019,2023 were generated by firm reservation fee revenues. The Company believes that such contract structure is advantageous to its overall business, although significant declines in gas production in the Company's noncontrolling interests includedareas of operations would likely adversely affect the EQM common units not held byCompany's results of operations, financial condition and liquidity as approximately 30% of the Company or its affiliates. ForCompany’s operating revenues for the yearsyear ended December 31, 20212023 was generated by volumetric-based fee revenues. See "Our exposure to commodity price risk may increase in the future and 2020,NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA." and “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT’s drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
While EQT has dedicated a substantial portion of its core acreage in southwestern Pennsylvania and West Virginia to the Company and has entered into long-term firm gathering and transmission contracts and contracts with MVCs on certain of the Company's systems, EQT may determine in the future that drilling or continuing to produce gas from existing wells in the Company's areas of operations is not economical above the amount to fulfill its required MVCs or otherwise strategically determine to curtail volumes on the Company's systems. Other than with respect to its MVCs and other firm commitments under existing contracts, EQT is under no contractual obligation to continue to develop its acreage dedicated to the Company. See also "Overview of the Company and Operations" in Part 1, "Item 1. Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the period from April 10, 2019 toEQT Global GGA.
The fair value of the Company’s derivative instruments is, in part, determined by estimates of the NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas forward price curve. A hypothetical 10% increase in NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices would increase the valuation of the Company’s derivative instruments by approximately $5.9 million, while a hypothetical 10% decrease in
NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices would decrease the valuation of the Company’s derivative instruments by approximately $6.0 million. This fair value change assumes volatility based on prevailing market parameters at December 31, 2019,2023. See Note 10 and "Our exposure to commodity price risk may increase in the future and NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision.
Other Market Risks. The Amended EQM Credit Facility is underwritten by a syndicate of 14 financial institutions on and after October 31, 2023 and prior to April 30, 2025, and a syndicate of 13 financial institutions on and after April 30, 2025 and prior to April 30, 2026. The 2021 Eureka Credit Facility is underwritten by a syndicate of 16 financial institutions before November 13, 2024 and a syndicate of 14 financial institutions on and after November 13, 2024 and prior to November 13, 2025. Each financial institution is obligated to fund its pro rata portion of any borrowings by EQM or Eureka, as applicable. EQM's and Eureka's respective large syndicate groups and relatively low percentage of participation by each lender is expected to limit the Company's noncontrolling interests also included third-party ownership interestsand Eureka's respective exposure to disruption or consolidation in Eureka Midstream. For the period from January 1, 2020 throughbanking industry. See Note 9 to the closingconsolidated financial statements for further details.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
| | | | | |
| Page No. |
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB ID: 42) | |
| Statements of Consolidated Comprehensive Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | |
| Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | |
| Statements of Consolidated Shareholders' Equity and Mezzanine Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the EQM MergerShareholders and the period April 10, 2019 through December 31, 2019, the Company’s noncontrolling interests also included the EQM Series A Preferred Unitholders' interest in EQM's net income. For the period beginning January 1, 2019 and ending January 10, 2019, the Company's noncontrolling interests included third-party ownership interests in EQGP.
Earnings Per Share (EPS). Basic EPS is computed by dividing net (loss) income attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders by the weighted average numberBoard of sharesDirectors of Equitrans Midstream common stock outstanding duringCorporation
Opinion on the period. Diluted EPS is computed by dividing net (loss) income attributable to Equitrans Midstream byFinancial Statements
We have audited the weighted average number of sharesaccompanying consolidated balance sheets of Equitrans Midstream common stock outstandingCorporation (the Company) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related statements of consolidated comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity and mezzanine equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the assumed issuancerelated notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of all potentially dilutive securities. Each issuethe Company at December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of potential common sharesits operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 20, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is evaluated separatelyto express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in sequenceaccordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the most dilutivecurrent period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the least dilutive.audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The dilutive effectcommunication of share-based payment awardsthe critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and stock options is calculated usingwe are not, by communicating the treasury stock method,critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which assumes share purchases are calculated usingit relates.
| | | | | |
| |
| |
| Valuation of Equity Method Investment in Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (MVP Joint Venture) |
| |
| Description of the Matter | At December 31, 2023, the Company has an investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which is constructing the Mountain Valley Pipeline, of approximately $1,832.3 million. As discussed in Notes 1, 2, and 7 to the consolidated financial statements the Company accounts for its interest in the MVP Joint Venture under the equity method because it can exercise significant influence, but not control, over the MVP Joint Venture's operating and financial policies. The Company reviews its investment in the MVP Joint Venture for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value may have declined in value below the carrying value. Adverse developments, including legal and regulatory matters, cost increases, and other unanticipated events may indicate an impairment in value. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company evaluated the developments around the MVP Joint Venture and concluded no impairment existed.
Auditing management’s evaluation of the MVP Joint Venture for indicators of impairment was complex due to the significant judgment required, particularly related to legal and regulatory matters, cost increases, and other developments that could impact the viability of the Mountain Valley Pipeline project. The audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of management’s monitoring of impairment indicators required a high degree of auditor judgement and an increased extent of effort.
|
| |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s monitoring of impairment indicators for the MVP Joint Venture.
To test the Company’s impairment evaluation related to its investment in the MVP Joint Venture, we performed audit procedures that included evaluating management’s process for identifying impairment indicators. We assessed management’s consideration of potential changes in legal or regulatory trends, cost increases and other events and how such developments could impact factors that influence the viability of the project. We evaluated both supporting and contrary evidence. Our procedures also included evaluating the sufficiency of the Company’s disclosures with respect to the valuation of the investment in the MVP Joint Venture described in Note 2 and 7 to the consolidated financial statements.
|
| | |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP |
| We have served as the Company's auditor since 2018. |
| Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania |
| February 20, 2024 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the average share priceShareholders and the Board of Directors of Equitrans Midstream common stock duringCorporation
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Equitrans Midstream Corporation's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the applicable period. The Company uses the if-converted method to compute potential common shares from potentially dilutive convertible securities. Under the if-converted method, dilutive convertible securities are assumed to be converted from the dateCommittee of Sponsoring Organizations of the issuanceTreadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Equitrans Midstream Corporation (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related statements of consolidated comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity and mezzanine equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the resulting common shares arerelated notes and our report dated February 20, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the denominatoraccompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the diluted EPS calculationSecurities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the period being presented. Income attributable to preferred dividends on convertible preferred stockreliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that accumulated during the period is added back(1) pertain to the numerator for purposesmaintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the if-converted method. Diluted EPS also takes into considerationassets of the potential dilutioncompany; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
| | |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP |
| Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania |
| February 20, 2024 |
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31,
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | (Thousands, except per share amounts) |
| Operating revenues | $ | 1,393,929 | | | $ | 1,357,747 | | | $ | 1,317,037 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Operating and maintenance | 177,972 | | | 154,667 | | | 153,179 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 187,374 | | | 128,472 | | | 137,056 | |
| | | | | |
| Depreciation | 279,386 | | | 272,195 | | | 270,404 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | |
| | | | | |
| Impairment of long-lived assets | — | | | — | | | 56,178 | |
| Total operating expenses | 709,551 | | | 620,153 | | | 681,636 | |
| Operating income | 684,378 | | | 737,594 | | | 635,401 | |
Equity income (a) | 175,215 | | | 168 | | | 17,579 | |
| Impairments of equity method investment | — | | | (583,057) | | | (1,926,402) | |
| Other income (expense), net | 3,222 | | | 13,871 | | | (47,546) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | (24,937) | | | (41,025) | |
| Net interest expense | (426,884) | | | (394,333) | | | (378,650) | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 435,931 | | | (250,694) | | | (1,740,643) | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense | (18,823) | | | 6,444 | | | (343,353) | |
| Net income (loss) | 454,754 | | | (257,138) | | | (1,397,290) | |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 9,525 | | | 12,204 | | | 14,530 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream | 445,229 | | | (269,342) | | | (1,411,820) | |
| Preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | 386,717 | | | $ | (327,854) | | | $ | (1,470,332) | |
| | | | | |
Earnings (loss) per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - basic | $ | 0.89 | | | $ | (0.76) | | | $ | (3.40) | |
| Earnings (loss) per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - diluted | $ | 0.89 | | | $ | (0.76) | | | $ | (3.40) | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - basic | 433,963 | | | 433,341 | | | 433,008 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - diluted | 436,132 | | | 433,341 | | | 433,008 | |
| | | | | |
| Statement of comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 454,754 | | | $ | (257,138) | | | $ | (1,397,290) | |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | | | | | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $19, $236 and $62 | 60 | | | 722 | | | 175 | |
| Other comprehensive income | 60 | | | 722 | | | 175 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 454,814 | | | (256,416) | | | (1,397,115) | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 9,525 | | | 12,204 | | | 14,530 | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | 386,777 | | | $ | (327,132) | | | $ | (1,470,157) | |
| | | | | |
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | |
(a)Represents equity income from securities issued by subsidiaries that enable their holders to obtain the subsidiary's common stock.Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (the MVP Joint Venture). See Note 13.7.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | (Thousands) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 454,754 | | | $ | (257,138) | | | $ | (1,397,290) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation | 279,386 | | | 272,195 | | | 270,404 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | |
| Provision for (recovery of) credit losses on accounts receivable and contract asset write-down | 11,198 | | | 335 | | | (2,004) | |
| Deferred income tax (benefit) expense | (38,061) | | | 5,472 | | | (348,206) | |
| Impairments of long-lived assets and equity method investment | — | | | 583,057 | | | 1,982,580 | |
Equity income (a) | (175,215) | | | (168) | | | (17,579) | |
| Other (income) expense, net | (2,599) | | | (13,644) | | | 47,485 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | 24,937 | | | 41,025 | |
| Non-cash long-term compensation expense | 39,313 | | | 15,800 | | | 13,083 | |
| Changes in other assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | 21,947 | | | 22,523 | | | 66,176 | |
| Accounts payable | (4,156) | | | 12,667 | | | (2,709) | |
| | | | | |
| Accrued interest | (1,432) | | | (16,147) | | | 25,718 | |
| Deferred revenue | 328,013 | | | 346,491 | | | 423,666 | |
| EQT Cash Option | — | | | (195,820) | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Other assets and other liabilities | 38,111 | | | (19,604) | | | 1,600 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 1,016,078 | | | 845,775 | | | 1,168,768 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | (386,514) | | | (376,661) | | | (290,521) | |
| Capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture | (689,405) | | | (199,613) | | | (287,665) | |
| | | | | |
| Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest (defined in Note 1) | 5,837 | | | 5,518 | | | 5,217 | |
| Proceeds from sale of gathering assets | — | | | 3,719 | | | — | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (1,070,082) | | | (567,037) | | | (572,969) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Proceeds from revolving credit facility borrowings | 1,177,000 | | | 554,500 | | | 467,500 | |
| Payments on revolving credit facility borrowings | (482,000) | | | (524,500) | | | (750,000) | |
| Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt | — | | | 1,000,000 | | | 1,900,000 | |
| Debt discounts, debt issuance costs and credit facility arrangement fees | (3,362) | | | (19,880) | | | (29,904) | |
| Payments for retirement of long-term debt | (98,941) | | | (1,021,459) | | | (1,936,250) | |
| | | | | |
| Dividends paid to common shareholders | (259,920) | | | (259,650) | | | (259,495) | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares | (58,512) | | | (58,512) | | | (58,512) | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest | (26,320) | | | (16,000) | | | (2,500) | |
| | | | | |
| Other items | (2,962) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 244,983 | | | (345,501) | | | (669,161) | |
| | | | | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 190,979 | | | (66,763) | | | (73,362) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 67,898 | | | 134,661 | | | 208,023 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 258,877 | | | $ | 67,898 | | | $ | 134,661 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash paid during the year for: | | | | | |
| Interest, net of amount capitalized | $ | 422,817 | | | $ | 401,156 | | | $ | 343,351 | |
| Income taxes, net | 7,201 | | | 1,243 | | | 3,500 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
(a) Represents equity income from the MVP Joint Venture. See Note 7.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
DECEMBER 31,
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) |
| ASSETS | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 258,877 | | | $ | 67,898 | |
| Accounts receivable (net of allowance for credit losses of $6,429 and $3,031 as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively) | 258,264 | | | 246,887 | |
| Other current assets | 78,356 | | | 74,917 | |
| Total current assets | 595,497 | | | 389,702 | |
| | | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 9,745,298 | | | 9,365,051 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (1,752,914) | | | (1,480,720) | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | 7,992,384 | | | 7,884,331 | |
| | | |
Investment in unconsolidated entity (a) | 1,832,282 | | | 819,743 | |
| Goodwill | 486,698 | | | 486,698 | |
| Net intangible assets | 522,133 | | | 586,952 | |
| | | |
| Other assets | 280,432 | | | 278,159 | |
| Total assets | $ | 11,709,426 | | | $ | 10,445,585 | |
| | | |
| LIABILITIES, MEZZANINE EQUITY AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Current portion of long-term debt | $ | 299,731 | | | $ | 98,830 | |
| | | |
| Accounts payable | 60,884 | | | 60,528 | |
| Capital contributions payable to the MVP Joint Venture | 181,051 | | | 34,355 | |
| Accrued interest | 134,330 | | | 135,762 | |
| Accrued liabilities | 106,870 | | | 83,835 | |
| Total current liabilities | 782,866 | | | 413,310 | |
| Long-term liabilities: | | | |
| Revolving credit facility borrowings | 1,230,000 | | | 535,000 | |
| Long-term debt | 6,046,709 | | | 6,335,320 | |
| Contract liability | 1,296,039 | | | 968,535 | |
| | | |
| Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | 165,695 | | | 112,974 | |
| Total liabilities | 9,521,309 | | | 8,365,139 | |
| | | |
| Mezzanine equity: | | | |
| Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, 30,018 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | 681,842 | | | 681,842 | |
| | | |
| Shareholders' equity: | | | |
| | | |
| Common stock, no par value, 433,505 and 432,781 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | 3,977,149 | | | 3,974,127 | |
| Retained deficit | (2,932,206) | | | (3,053,590) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (1,272) | | | (1,332) | |
| Total common shareholders' equity | 1,043,671 | | | 919,205 | |
| Noncontrolling interest | 462,604 | | | 479,399 | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 1,506,275 | | | 1,398,604 | |
| Total liabilities, mezzanine equity and shareholders' equity | $ | 11,709,426 | | | $ | 10,445,585 | |
(a) Represents investment in the MVP Joint Venture. See Note 7.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY AND MEZZANINE EQUITY
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Mezzanine |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Equity |
| | | | | | | | | Accumulated Other | | | | | | Equitrans |
| | | Common Stock | | | | | | | | | Midstream |
| | | | Shares | | No | | Retained | | Comprehensive | | Noncontrolling | | Total | | Preferred |
| | | | Outstanding | | Par Value | | Deficit | | Loss | | Interest | | Equity | | Shares |
| | | | (Thousands, except per share amounts) | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2021 | | | 432,470 | | | $ | 3,941,295 | | | $ | (734,019) | | | $ | (2,229) | | | $ | 471,165 | | | $ | 3,676,212 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (1,470,332) | | | — | | | 14,530 | | | (1,455,802) | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax benefit of $62 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 52 | | | 14,623 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 14,623 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,500) | | | (2,500) | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per Share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | | | 432,522 | | | $ | 3,955,918 | | | $ | (2,464,573) | | | $ | (2,054) | | | $ | 483,195 | | | $ | 1,972,486 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (327,854) | | | — | | | 12,204 | | | (315,650) | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $236 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 722 | | | — | | | 722 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (261,163) | | | — | | | — | | | (261,163) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 259 | | | 18,209 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 18,209 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (16,000) | | | (16,000) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | 432,781 | | | $ | 3,974,127 | | | $ | (3,053,590) | | | $ | (1,332) | | | $ | 479,399 | | | $ | 1,398,604 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | — | | | — | | | 386,717 | | | — | | | 9,525 | | | 396,242 | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $19 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 60 | | | — | | | 60 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (265,333) | | | — | | | — | | | (265,333) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 724 | | | 40,558 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 40,558 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (26,320) | | | (26,320) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| Other items | | | — | | | (37,536) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (37,536) | | | — | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | 433,505 | | | $ | 3,977,149 | | | $ | (2,932,206) | | | $ | (1,272) | | | $ | 462,604 | | | $ | 1,506,275 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
Recently issued accounting standards relevant to the Company are described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The Company's significant accounting policies are described in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. Any new accounting policies or updates to existing accounting policies as a result of new accounting pronouncements have been included in the notes to the Company's consolidated financial statements. Preparation of financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts in the Company's consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. The Company's critical accounting policies discussed below are considered critical due to the significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of the Company's consolidated financial statements and the material impact on the results of operations or financial condition. Actual results could differ from those judgments and estimates.
Property, Plant and Equipment. Determination of depreciation expense requires judgment regarding the estimated useful lives and salvage values of property, plant and equipment. The Company has not historically experienced material changes in its results of operations from changes in estimated useful lives or salvage values of its property, plant and equipment; however, these estimates are reviewed periodically, including each time Equitrans, L.P. files with the FERC for a change in its transmission and storage rates. The Company believes that the accounting estimate related to depreciation expense is a "critical accounting estimate" because the assumptions used to estimate useful lives and salvage values of property, plant and equipment are susceptible to change. These assumptions affect depreciation expense and, if changed, could have a material effect on the Company's results of operations and financial position. See Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Impairments of Long-Lived Assets and Equity Method Investment. The Company evaluates long-lived assets and equity method investments for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management's judgment, that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable. With respect to property, plant and equipment and finite lived intangibles, asset recoverability is measured by comparing the carrying value of the asset or asset group with its expected future pre-tax undiscounted cash flows. Any accounting estimate related to an impairment of property, plant and equipment, finite-lived intangible assets, goodwill or an investment in an unconsolidated entity may require the Company's management to make assumptions about future cash flows, discount rates, the fair value of investments and whether losses in the value of its investments are other-than-temporary. Management's assumptions about future cash flows require significant judgment because, among other things, actual operating levels have been and may be different from estimated levels.
Goodwill is the cost of an acquisition less the fair value of the identifiable net assets of the acquired business. Goodwill is evaluated for impairment at least annually or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. When performing a quantitative assessment, the Company uses a combination of an income and market approach to estimate the fair value of its reporting units.
The Company believes that the accounting estimates related to impairments are "critical accounting estimates" because they require assumptions that are susceptible to change, including estimating fair value which requires considerable judgment. For example, in the case of goodwill, management’s estimate of a reporting unit’s future financial results is sensitive to changes in assumptions, such as changes in the Company's stock price, weighted-average cost of capital, terminal growth rates and industry multiples. When a quantitative assessment is performed, the Company uses estimates and assumptions in estimating its reporting units’ fair values that it believes are reasonable and appropriate at that time; however, different assumptions and estimates could materially affect the calculated fair value and the resulting conclusion of whether goodwill is impaired, which could materially affect the Company’s results of operations and financial position.
The Company’s investment in unconsolidated entity also requires considerable judgment to estimate fair value because the Company’s investment is not traded on an active market. When estimating the fair value of its equity method investment, the Company utilizes an income approach under which significant judgments and assumptions, including the discount rate and probability-weighted scenarios, are sensitive to change. Additionally, the Company's investment in unconsolidated entity is susceptible to impairment risk from adverse macroeconomic conditions and/or other adverse factors. Adverse developments could require that the Company modify assumptions reflected in the probability-weighted scenarios of discounted future net cash flows (including with respect to the probability of success prior to completion) utilized to estimate the fair value of its equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which could result in an incremental other-than-temporary impairment of that investment. While macroeconomic factors in and of themselves may not be a direct indicator of impairment, should an impairment indicator be identified in the future, macroeconomic factors such as changes in interest rates could ultimately impact the size and scope of any potential impairment.
See Notes 1 and 7 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Revenue Recognition. Revenue from the gathering, transmission and storage of natural gas is generally recognized when the service is provided. Revenue from water services is generally recognized when water is delivered. Contracts often contain fixed
and variable consideration. Fixed consideration primarily relates to firm reservation payments including MVCs and ARCs. Variable consideration is generally dependent on volumes and recognized in the period they occur. At each reporting date and, as circumstances or events warrant, management reviews and updates the assumptions utilized to estimate the total consideration for all contracts. The Company allocates the transaction price to each performance obligation based on the estimated relative standalone selling price. When applicable, the excess of consideration received over revenue recognized results in the deferral of those amounts until future periods based on a units of production or straight-line methodology as these methods appropriately match the consumption of services provided to the customer. The units of production methodology requires the use of production estimates that are uncertain and the use of judgment when developing estimates of future production volumes, thus impacting the rate of revenue recognition. Production estimates are monitored as circumstances and events warrant. Certain of the Company's gas gathering and water agreements have MVCs or ARCs. If a customer under such an agreement fails to meet its MVC or ARC for a specified period (thus not exercising all the contractual rights to gathering and water services within the specified period, herein referred to as “breakage”), it is obligated to pay a contractually determined fee based upon the shortfall between the actual volumes and the MVC or ARC for the period contained in the contract. When management determines it is probable that the customer will not exercise all or a portion of its remaining rights, the Company recognizes revenue associated with such breakage amount in proportion to the pattern of exercised rights within the respective MVC or ARC period.
Revenue related to services provided but not yet billed is estimated each month. These estimates are generally based on contract data, preliminary throughput and allocation measurements. Final amounts for the current month are billed and collected in the following month. See Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
The Company records an allowance for credit losses on a quarterly basis in order to estimate uncollectible receivables. The Company's current expected credit loss (CECL) methodology considers risks of collection based on a customer’s current credit status. The standard requires an entity to assess whether financial assets share similar risk characteristics and, if so, group such assets in a pool. Customer balances are aggregated for evaluation based on their credit risk rating, which takes into account changes in economic factors that impact a customer’s ability to meet its financial obligations. The Company's CECL methodology assigns a reserve, even if remote, to each customer based on credit risk and the reserve is evaluated on a quarterly basis. In order to calculate the appropriate allowance, the Company utilizes an estimated loss rate factor based on a customer's credit rating for receivables and a risk-adjusted reserve based on the receivable aging schedule in order to account for the receivables which may be at a greater risk of collection. Customer credit risk ratings are updated quarterly and management has enabled a risk-responsive approach to changes in customer and economic factors. While the Company has not historically experienced material losses on uncollected receivables, a decline in the market price for natural gas affecting producer activity combined with additional customers on the Company's systems may result in a greater exposure to potential losses than management's current estimates.
The Company believes that the accounting estimates related to revenue recognition are "critical accounting estimates" because estimated relative standalone selling prices and volumes are subject to change based on actual measurements. In addition, the Company believes that the accounting estimates related to the allowance for credit losses are "critical accounting estimates" because the underlying assumptions used for the allowance can change and the actual mix of customers and their ability to pay may vary significantly from management's estimates, which could affect the collectability of customer receivables. These accounting estimates could potentially have a material effect on the Company's results of operations and financial position.
Income Taxes. The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the Company's consolidated financial statements or tax returns.
The Company has federal and state of West Virginia net operating loss (NOL) carryforwards. The NOL carryforwards have no expiration, but utilization is limited to 80% of taxable income in the year of utilization. In addition to the NOL carryforwards, the Company has deferred tax assets and liabilities principally resulting from interest disallowance under Code Section 163(j) and investment in partnerships.
Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not (greater than 50%) that a tax benefit will not be realized. In evaluating the need for a valuation allowance, this requires significant judgment and management considers all available evidence, both positive and negative, including potential sources of taxable income, income available in carry-back periods, future reversals of taxable temporary differences, projections of taxable income and income from tax planning strategies. Positive evidence includes reversing temporary differences and projection of future profitability within the carry-forward period, including from tax planning strategies. Negative evidence includes historical pre-tax book losses.
Deferred tax assets for which no valuation allowance is recorded may not be realized, and changes in facts and circumstances may result in the establishment of a valuation allowance. Existing valuation allowances are re-examined under the same
standards of positive and negative evidence that apply to valuation allowance establishment. If it is determined that it is more likely than not that a deferred tax asset for which a valuation allowance is recorded will be realized, all or a portion of the valuation allowance may be released. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are also remeasured to reflect changes in underlying tax rates from tax law changes and any changes in uncertain tax benefits.
The Company believes that accounting estimates related to income taxes are "critical accounting estimates" because the Company must assess the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered from future taxable income, and exercise judgment when evaluating whether or not a valuation allowance must be established on deferred tax assets. See Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements for additional information.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk. Changes in interest rates affect the amount of interest the Company earns on cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments and the interest rates EQM and Eureka pay on borrowings under their respective revolving credit facilities. The Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility provide for variable interest rates and thus expose the Company, through EQM and Eureka, to fluctuations in market interest rates. In addition, EQM's interest rates under the Amended EQM Credit Facility are impacted by changes in EQM's credit ratings (which changes may be caused by factors outside of EQM's control). Eureka's interest rates under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility are impacted by changes in Eureka's Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) which may fluctuate based on Eureka Midstream's distributions to its members, liquidity needs or operating results. Accordingly, if interest rates were to increase, our debt service obligations on the variable rate indebtedness would increase even though the amount borrowed remained the same, and our net income and cash flows, including cash available for servicing our indebtedness, will correspondingly decrease. Based on commitments as of December 31, 2023 and assuming all loans are fully drawn, each quarter point change in interest rates would result in a change of approximately $3.9 million in annual interest expense on indebtedness under the Amended EQM Credit Facility. Assuming all loans are fully drawn, each quarter point change in interest rates would result in a change of approximately $1.0 million in annual interest expense on indebtedness under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility. Further, regarding the dividend payable on Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares for quarters after March 2020,31, 2024, changes in accordance with the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, ReferenceAdjustable Interest Rate Reform (Topic 848)(LIBOR) Act (the LIBOR Act), and the rules implementing the LIBOR Act, three-month CME Term SOFR, administered by CME Group Benchmark Administration, LTD., plus a tenor spread adjustment of 0.26161% per annum, replaced, by operation of law, the three-month London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) to calculate dividends payable on the Series A Preferred Stock for each fiscal quarter ending after March 31, 2024. Fluctuations in three-month CME Term SOFR may affect such dividend (which will not be less than 10.50% under the Company's Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation), which could affect, among other things, the amount of cash the Company has available to make quarterly cash dividends to its shareholders. EQM's senior notes are fixed rate and thus do not expose the Company to fluctuations in market interest rates. Changes in interest rates do affect the fair value of EQM's fixed rate debt. See Notes 9 and 10 to the consolidated financial statements for discussions of borrowings and fair value measurements, respectively. EQM and Eureka may from time to time hedge the interest on portions of borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, as applicable, in order to manage risks associated with floating interest rates. However, the Company may not maintain hedges with respect to all of its variable rate indebtedness, and any hedges it enters into may not fully mitigate its interest rate risk
Credit Risk. The Company is exposed to credit risk, which is the risk that it may incur a loss if a counterparty fails to perform under a contract. The Company actively manages its exposure to credit risk associated with customers through credit analysis, credit approval and monitoring procedures. For certain transactions, the Company requests letters of credit, cash collateral, prepayments or guarantees as forms of credit support. Equitrans, L.P.'s FERC tariffs require tariff customers that do not meet specified credit standards to provide three months of credit support; however, the Company is exposed to credit risk beyond this three-month period when its tariffs do not require its customers to provide additional credit support. For some of the Company's long-term contracts associated with system expansions, it has entered into negotiated credit agreements that provide for other credit support if certain credit standards are not met.
The Company is exposed to the credit risk of its customers, including its largest customer, EQT, including as a result of changes in customer credit ratings, liquidity and access to capital markets. In August 2023, Moody's upgraded EQT's public senior debt to an investment grade credit rating and as of December 31, 2023, EQT's public debt has investment grade credit ratings from S&P, Fitch and Moody's. On February 26, 2020, in connection with the execution of the EQT Global GGA, the Company and EQT entered into a letter agreement (the Credit Letter Agreement) pursuant to which, among other things, (a) the Company agreed to relieve certain credit posting requirements for EQT, in an amount up to approximately $250 million, under its commercial agreements with the Company, subject to EQT maintaining a minimum credit rating from two of three rating agencies of (i) Ba3 with Moody's, (ii) BB- with S&P and (iii) BB- with Fitch and (b) the Company agreed to use commercially reasonable good faith efforts to negotiate similar credit support arrangements for EQT in respect of its commitments to the MVP Joint Venture. In addition, EQT has guaranteed the payment obligations of certain of its subsidiaries, up to a maximum amount of $115 million, $131 million and $30 million related to gathering, transmission and water services, respectively, across all applicable contracts, for the benefit of the subsidiaries of the Company providing such services. See Note 13 to the consolidated financial statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for further discussion of the Company's exposure to certain credit risks.
Commodity Price Risk. The Company's business is dependent on continued natural gas production and the availability and development of reserves in its areas of operation. Prices for natural gas and NGLs, including regional basis differentials, have previously adversely affected, and may in the future adversely affect, timing of development of additional reserves and production that is accessible by the Company’s pipeline and storage assets, which also negatively affects the Company’s water services business, and the creditworthiness of the Company’s customers.
Lower natural gas prices, particularly in the Appalachian region, have in the past caused, and may in the future cause, producers such as EQT to determine to take actions to slow production growth and/or maintain flat or reduce production, which when effected by our producer customers limits growth in or may reduce the demand for, and usage of, our services. For instance, in certain periods of low natural gas prices prior to 2023, temporary production curtailments resulted in a decrease in our volumetric-based gathering fee revenues. Based on the forward price strip as of February 16, 2024, the Company perceives continued risk that EQT and/or other producers could curtail production in 2024 or maintain at flat levels, which, depending on the nature and duration of any such curtailment, could have a significant negative effect on the demand for our services, our volumetric-based fee revenue, and therefore our results of operations, and any such maintenance may limit growth associated with our assets. See also “Decreases or a lack of growth in production of natural gas in our areas of operation, whether as a result of regional takeaway constraints, producer corporate capital allocation strategies, lower regional natural gas prices, natural well decline, and/or other factors, have adversely affected, and in the future could adversely affect, our business and operating results and reduce our cash available to pay cash dividends to our shareholders.”, "The lack of diversification of our assets, products and geographic locations could adversely affect us." and “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT's drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results.”, each included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Price declines and sustained periods of low natural gas and NGL prices could have an adverse effect on the creditworthiness of the Company's customers and related ability to pay firm reservation fees under long-term contracts and/or affect, as discussed above, activity levels and, accordingly, volumetric-based fees, which could affect the Company’s results of operations, liquidity or financial position. Credit risk and related management is further discussed under “Credit Risk” in Part II, “Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Increases in natural gas prices do not necessarily result in corresponding increases to the production forecasts of the Company's customers. Even when natural gas prices have been commercially attractive, certain of the Company's customers maintained largely flat production forecasts in light of, among other things, the absence of incremental takeaway capacity from the Appalachian Basin and the Company's customers may still maintain flat or modest increases to production forecasts based on various factors, which could include regional takeaway capacity limitations, access to capital, investor expectations regarding free cash flow, a desire to reduce or refinance leverage or other factors.
Additionally, lower natural gas prices (including regionally), corporate capital allocation strategies or regional takeaway constraints, could cause producers to determine in the future that drilling activities in areas outside of the Company's current areas of operation are strategically more attractive to them.
Many of the Company’s customers, including EQT, have entered into long-term firm reservation gathering, transmission and water services contracts or contracts with MVCs or ARCs, as applicable, on the Company's systems and approximately 70% of the Company's operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 2023 were generated by firm reservation fee revenues. The Company believes that such contract structure is advantageous to its overall business, although significant declines in gas production in the Company's areas of operations would likely adversely affect the Company's results of operations, financial condition and liquidity as approximately 30% of the Company’s operating revenues for the year ended December 31, 2023 was generated by volumetric-based fee revenues. See "Our exposure to commodity price risk may increase in the future and NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA." and “We generate a substantial majority of our revenues from EQT. Therefore, we are subject to the business and liquidity risks of EQT, and any decrease in EQT’s drilling or completion activity (or significant production curtailments) or a shift in such activity away from our assets could adversely affect our business and operating results." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
While EQT has dedicated a substantial portion of its core acreage in southwestern Pennsylvania and West Virginia to the Company and has entered into long-term firm gathering and transmission contracts and contracts with MVCs on certain of the Company's systems, EQT may determine in the future that drilling or continuing to produce gas from existing wells in the Company's areas of operations is not economical above the amount to fulfill its required MVCs or otherwise strategically determine to curtail volumes on the Company's systems. Other than with respect to its MVCs and other firm commitments under existing contracts, EQT is under no contractual obligation to continue to develop its acreage dedicated to the Company. See also "Overview of the Company and Operations" in Part 1, "Item 1. Business" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the EQT Global GGA.
The fair value of the Company’s derivative instruments is, in part, determined by estimates of the NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas forward price curve. A hypothetical 10% increase in NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices would increase the valuation of the Company’s derivative instruments by approximately $5.9 million, while a hypothetical 10% decrease in
NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices would decrease the valuation of the Company’s derivative instruments by approximately $6.0 million. This fair value change assumes volatility based on prevailing market parameters at December 31, 2023. See Note 10 and "Our exposure to commodity price risk may increase in the future and NYMEX Henry Hub futures prices affect the fair value, and may affect the realizability, of potential cash payments to us by EQT pursuant to the EQT Global GGA." included in Part I, "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision.
Other Market Risks. The Amended EQM Credit Facility is underwritten by a syndicate of 14 financial institutions on and after October 31, 2023 and prior to April 30, 2025, and a syndicate of 13 financial institutions on and after April 30, 2025 and prior to April 30, 2026. The 2021 Eureka Credit Facility is underwritten by a syndicate of 16 financial institutions before November 13, 2024 and a syndicate of 14 financial institutions on and after November 13, 2024 and prior to November 13, 2025. Each financial institution is obligated to fund its pro rata portion of any borrowings by EQM or Eureka, as applicable. EQM's and Eureka's respective large syndicate groups and relatively low percentage of participation by each lender is expected to limit the Company's and Eureka's respective exposure to disruption or consolidation in the banking industry. See Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements for further details.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
| | | | | |
| Page No. |
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PCAOB ID: 42) | |
| Statements of Consolidated Comprehensive Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | |
| Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | |
| Statements of Consolidated Shareholders' Equity and Mezzanine Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Equitrans Midstream Corporation
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Equitrans Midstream Corporation (the Company) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related statements of consolidated comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity and mezzanine equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 20, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
| | | | | |
| |
| |
| Valuation of Equity Method Investment in Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (MVP Joint Venture) |
| |
| Description of the Matter | At December 31, 2023, the Company has an investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which is constructing the Mountain Valley Pipeline, of approximately $1,832.3 million. As discussed in Notes 1, 2, and 7 to the consolidated financial statements the Company accounts for its interest in the MVP Joint Venture under the equity method because it can exercise significant influence, but not control, over the MVP Joint Venture's operating and financial policies. The Company reviews its investment in the MVP Joint Venture for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the fair value may have declined in value below the carrying value. Adverse developments, including legal and regulatory matters, cost increases, and other unanticipated events may indicate an impairment in value. During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company evaluated the developments around the MVP Joint Venture and concluded no impairment existed.
Auditing management’s evaluation of the MVP Joint Venture for indicators of impairment was complex due to the significant judgment required, particularly related to legal and regulatory matters, cost increases, and other developments that could impact the viability of the Mountain Valley Pipeline project. The audit procedures to evaluate the reasonableness of management’s monitoring of impairment indicators required a high degree of auditor judgement and an increased extent of effort.
|
| |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s monitoring of impairment indicators for the MVP Joint Venture.
To test the Company’s impairment evaluation related to its investment in the MVP Joint Venture, we performed audit procedures that included evaluating management’s process for identifying impairment indicators. We assessed management’s consideration of potential changes in legal or regulatory trends, cost increases and other events and how such developments could impact factors that influence the viability of the project. We evaluated both supporting and contrary evidence. Our procedures also included evaluating the sufficiency of the Company’s disclosures with respect to the valuation of the investment in the MVP Joint Venture described in Note 2 and 7 to the consolidated financial statements.
|
| | |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP |
| We have served as the Company's auditor since 2018. |
| Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania |
| February 20, 2024 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Equitrans Midstream Corporation
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Equitrans Midstream Corporation's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Equitrans Midstream Corporation (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related statements of consolidated comprehensive income, cash flows and shareholders' equity and mezzanine equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes and our report dated February 20, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides practical expedientsa reasonable basis for contract modificationsour opinion.
Definition and certain hedging relationshipsLimitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
| | |
| /s/ Ernst & Young LLP |
| Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania |
| February 20, 2024 |
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31,
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | (Thousands, except per share amounts) |
| Operating revenues | $ | 1,393,929 | | | $ | 1,357,747 | | | $ | 1,317,037 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Operating and maintenance | 177,972 | | | 154,667 | | | 153,179 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 187,374 | | | 128,472 | | | 137,056 | |
| | | | | |
| Depreciation | 279,386 | | | 272,195 | | | 270,404 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | |
| | | | | |
| Impairment of long-lived assets | — | | | — | | | 56,178 | |
| Total operating expenses | 709,551 | | | 620,153 | | | 681,636 | |
| Operating income | 684,378 | | | 737,594 | | | 635,401 | |
Equity income (a) | 175,215 | | | 168 | | | 17,579 | |
| Impairments of equity method investment | — | | | (583,057) | | | (1,926,402) | |
| Other income (expense), net | 3,222 | | | 13,871 | | | (47,546) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | (24,937) | | | (41,025) | |
| Net interest expense | (426,884) | | | (394,333) | | | (378,650) | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 435,931 | | | (250,694) | | | (1,740,643) | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense | (18,823) | | | 6,444 | | | (343,353) | |
| Net income (loss) | 454,754 | | | (257,138) | | | (1,397,290) | |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 9,525 | | | 12,204 | | | 14,530 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream | 445,229 | | | (269,342) | | | (1,411,820) | |
| Preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | 386,717 | | | $ | (327,854) | | | $ | (1,470,332) | |
| | | | | |
Earnings (loss) per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - basic | $ | 0.89 | | | $ | (0.76) | | | $ | (3.40) | |
| Earnings (loss) per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders - diluted | $ | 0.89 | | | $ | (0.76) | | | $ | (3.40) | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - basic | 433,963 | | | 433,341 | | | 433,008 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding - diluted | 436,132 | | | 433,341 | | | 433,008 | |
| | | | | |
| Statement of comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 454,754 | | | $ | (257,138) | | | $ | (1,397,290) | |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | | | | | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $19, $236 and $62 | 60 | | | 722 | | | 175 | |
| Other comprehensive income | 60 | | | 722 | | | 175 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 454,814 | | | (256,416) | | | (1,397,115) | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | 9,525 | | | 12,204 | | | 14,530 | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | 386,777 | | | $ | (327,132) | | | $ | (1,470,157) | |
| | | | | |
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | |
(a)Represents equity income from Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (the MVP Joint Venture). See Note 7.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | (Thousands) |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 454,754 | | | $ | (257,138) | | | $ | (1,397,290) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation | 279,386 | | | 272,195 | | | 270,404 | |
| Amortization of intangible assets | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | | | 64,819 | |
| Provision for (recovery of) credit losses on accounts receivable and contract asset write-down | 11,198 | | | 335 | | | (2,004) | |
| Deferred income tax (benefit) expense | (38,061) | | | 5,472 | | | (348,206) | |
| Impairments of long-lived assets and equity method investment | — | | | 583,057 | | | 1,982,580 | |
Equity income (a) | (175,215) | | | (168) | | | (17,579) | |
| Other (income) expense, net | (2,599) | | | (13,644) | | | 47,485 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | 24,937 | | | 41,025 | |
| Non-cash long-term compensation expense | 39,313 | | | 15,800 | | | 13,083 | |
| Changes in other assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | 21,947 | | | 22,523 | | | 66,176 | |
| Accounts payable | (4,156) | | | 12,667 | | | (2,709) | |
| | | | | |
| Accrued interest | (1,432) | | | (16,147) | | | 25,718 | |
| Deferred revenue | 328,013 | | | 346,491 | | | 423,666 | |
| EQT Cash Option | — | | | (195,820) | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Other assets and other liabilities | 38,111 | | | (19,604) | | | 1,600 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 1,016,078 | | | 845,775 | | | 1,168,768 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | (386,514) | | | (376,661) | | | (290,521) | |
| Capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture | (689,405) | | | (199,613) | | | (287,665) | |
| | | | | |
| Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest (defined in Note 1) | 5,837 | | | 5,518 | | | 5,217 | |
| Proceeds from sale of gathering assets | — | | | 3,719 | | | — | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (1,070,082) | | | (567,037) | | | (572,969) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Proceeds from revolving credit facility borrowings | 1,177,000 | | | 554,500 | | | 467,500 | |
| Payments on revolving credit facility borrowings | (482,000) | | | (524,500) | | | (750,000) | |
| Proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt | — | | | 1,000,000 | | | 1,900,000 | |
| Debt discounts, debt issuance costs and credit facility arrangement fees | (3,362) | | | (19,880) | | | (29,904) | |
| Payments for retirement of long-term debt | (98,941) | | | (1,021,459) | | | (1,936,250) | |
| | | | | |
| Dividends paid to common shareholders | (259,920) | | | (259,650) | | | (259,495) | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares | (58,512) | | | (58,512) | | | (58,512) | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest | (26,320) | | | (16,000) | | | (2,500) | |
| | | | | |
| Other items | (2,962) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 244,983 | | | (345,501) | | | (669,161) | |
| | | | | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 190,979 | | | (66,763) | | | (73,362) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 67,898 | | | 134,661 | | | 208,023 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 258,877 | | | $ | 67,898 | | | $ | 134,661 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash paid during the year for: | | | | | |
| Interest, net of amount capitalized | $ | 422,817 | | | $ | 401,156 | | | $ | 343,351 | |
| Income taxes, net | 7,201 | | | 1,243 | | | 3,500 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
(a) Represents equity income from the MVP Joint Venture. See Note 7.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
DECEMBER 31,
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) |
| ASSETS | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 258,877 | | | $ | 67,898 | |
| Accounts receivable (net of allowance for credit losses of $6,429 and $3,031 as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively) | 258,264 | | | 246,887 | |
| Other current assets | 78,356 | | | 74,917 | |
| Total current assets | 595,497 | | | 389,702 | |
| | | |
| Property, plant and equipment | 9,745,298 | | | 9,365,051 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (1,752,914) | | | (1,480,720) | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | 7,992,384 | | | 7,884,331 | |
| | | |
Investment in unconsolidated entity (a) | 1,832,282 | | | 819,743 | |
| Goodwill | 486,698 | | | 486,698 | |
| Net intangible assets | 522,133 | | | 586,952 | |
| | | |
| Other assets | 280,432 | | | 278,159 | |
| Total assets | $ | 11,709,426 | | | $ | 10,445,585 | |
| | | |
| LIABILITIES, MEZZANINE EQUITY AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Current portion of long-term debt | $ | 299,731 | | | $ | 98,830 | |
| | | |
| Accounts payable | 60,884 | | | 60,528 | |
| Capital contributions payable to the MVP Joint Venture | 181,051 | | | 34,355 | |
| Accrued interest | 134,330 | | | 135,762 | |
| Accrued liabilities | 106,870 | | | 83,835 | |
| Total current liabilities | 782,866 | | | 413,310 | |
| Long-term liabilities: | | | |
| Revolving credit facility borrowings | 1,230,000 | | | 535,000 | |
| Long-term debt | 6,046,709 | | | 6,335,320 | |
| Contract liability | 1,296,039 | | | 968,535 | |
| | | |
| Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | 165,695 | | | 112,974 | |
| Total liabilities | 9,521,309 | | | 8,365,139 | |
| | | |
| Mezzanine equity: | | | |
| Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, 30,018 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022 | 681,842 | | | 681,842 | |
| | | |
| Shareholders' equity: | | | |
| | | |
| Common stock, no par value, 433,505 and 432,781 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | 3,977,149 | | | 3,974,127 | |
| Retained deficit | (2,932,206) | | | (3,053,590) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (1,272) | | | (1,332) | |
| Total common shareholders' equity | 1,043,671 | | | 919,205 | |
| Noncontrolling interest | 462,604 | | | 479,399 | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 1,506,275 | | | 1,398,604 | |
| Total liabilities, mezzanine equity and shareholders' equity | $ | 11,709,426 | | | $ | 10,445,585 | |
(a) Represents investment in the MVP Joint Venture. See Note 7.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY AND MEZZANINE EQUITY
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Mezzanine |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Equity |
| | | | | | | | | Accumulated Other | | | | | | Equitrans |
| | | Common Stock | | | | | | | | | Midstream |
| | | | Shares | | No | | Retained | | Comprehensive | | Noncontrolling | | Total | | Preferred |
| | | | Outstanding | | Par Value | | Deficit | | Loss | | Interest | | Equity | | Shares |
| | | | (Thousands, except per share amounts) | | |
| Balance at January 1, 2021 | | | 432,470 | | | $ | 3,941,295 | | | $ | (734,019) | | | $ | (2,229) | | | $ | 471,165 | | | $ | 3,676,212 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (1,470,332) | | | — | | | 14,530 | | | (1,455,802) | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax benefit of $62 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | | | 175 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | | | — | | | (260,222) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 52 | | | 14,623 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 14,623 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,500) | | | (2,500) | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per Share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | | | 432,522 | | | $ | 3,955,918 | | | $ | (2,464,573) | | | $ | (2,054) | | | $ | 483,195 | | | $ | 1,972,486 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | | | — | | | — | | | (327,854) | | | — | | | 12,204 | | | (315,650) | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $236 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 722 | | | — | | | 722 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (261,163) | | | — | | | — | | | (261,163) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 259 | | | 18,209 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 18,209 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (16,000) | | | (16,000) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | 432,781 | | | $ | 3,974,127 | | | $ | (3,053,590) | | | $ | (1,332) | | | $ | 479,399 | | | $ | 1,398,604 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
| Other comprehensive income (net of tax): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | | — | | | — | | | 386,717 | | | — | | | 9,525 | | | 396,242 | | | 58,512 | |
| Pension and other post-retirement benefits liability adjustment, net of tax expense of $19 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 60 | | | — | | | 60 | | | — | |
| Dividends on common shares ($0.60 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | (265,333) | | | — | | | — | | | (265,333) | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation plans, net | | | 724 | | | 40,558 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 40,558 | | | — | |
| Distributions paid to noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (26,320) | | | (26,320) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares ($1.9492 per share) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (58,512) | |
| Other items | | | — | | | (37,536) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (37,536) | | | — | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | 433,505 | | | $ | 3,977,149 | | | $ | (2,932,206) | | | $ | (1,272) | | | $ | 462,604 | | | $ | 1,506,275 | | | $ | 681,842 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
EQUITRANS MIDSTREAM CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2023
1. Summary of Operations and Significant Accounting Policies
Organization
Equitrans Midstream Corporation (together with its consolidated subsidiaries as applicable, the Company or Equitrans Midstream), a Pennsylvania corporation, is an independent, publicly traded company that owns, operates, acquires and develops midstream assets, in and originating from the Appalachian Basin. The Company's operating subsidiaries hold the majority of the Company's assets and there are substantially no assets at the Equitrans Midstream stand-alone entity.
Nature of Business
The Company's operating subsidiaries provide midstream services to the Company's customers in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Ohio through three primary assets: the gathering system, which includes predominantly dry gas gathering systems of high-pressure gathering lines; the transmission system, which includes Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) regulated interstate pipelines and storage systems; and the water network, which primarily consists of water pipelines, storage, and other facilities that support well completion activities and produced water handling activities.
As of December 31, 2023, the gathering system, inclusive of Eureka Midstream Holdings, LLC's (Eureka Midstream) gathering system, included approximately 1,220 miles of high-pressure gathering lines with total contracted firm reservation capacity of approximately 7.7 billion cubic feet (Bcf) per day, which included contracted firm reservation capacity of approximately 1.8 Bcf per day associated with the transitionCompany's high-pressure header pipelines, 138 compressor units with compression of approximately 491,000 horsepower and multiple interconnect points with the Company's transmission and storage system and to other interstate pipelines.
As of December 31, 2023, the transmission and storage system included approximately 940 miles of FERC-regulated, interstate pipelines that have interconnect points to seven interstate pipelines and multiple local distribution companies (LDCs). The transmission and storage system is supported by 42 compressor units, with total throughput capacity of approximately 4.4 Bcf per day and compression of approximately 135,000 horsepower, and 18 associated natural gas storage reservoirs, which have a peak withdrawal capacity of approximately 820 million cubic feet (MMcf) per day and a working gas capacity of approximately 43 Bcf, in each case as of December 31, 2023.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company's fresh water systems included approximately 201 miles of pipelines that deliver fresh water from referencelocal municipal water authorities, the Monongahela River, the Ohio River, local reservoirs and several regional waterways. The fresh water delivery services systems consist of permanent, buried pipelines, surface pipelines, 17 fresh water impoundment facilities, as well as pumping stations, which support water transportation throughout the systems, and take point facilities and measurement facilities, which support well completion activities. As of December 31, 2023, the mixed water system included approximately 53 miles of buried pipeline and two water storage facilities with 350,000 barrels of capacity, as well as two interconnects with the Company's existing Pennsylvania fresh water systems and provides services to producers in southwestern Pennsylvania. The Company plans to continue to expand its mixed water system in 2024, including the completion of a pipeline to serve a producer in West Virginia and an interconnect to access another producer's West Virginia water network.
Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of all entities in which the Company holds a controlling financial interest. For consolidated subsidiaries in which the Company’s ownership is less than 100%, the Company records noncontrolling interest related to the third-party ownership interests in those entities. Investments over which the Company can exert significant influence, but not control, over operating and financial policies are accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Intercompany transactions have been eliminated for purposes of preparing these consolidated financial statements. References in these financial statements to Equitrans Midstream or the Company refer collectively to Equitrans Midstream Corporation and its consolidated subsidiaries for all periods presented, unless otherwise indicated.
Segments. Operating segments are revenue-producing components of the enterprise for which separate financial information is produced internally and is subject to evaluation by the Company's chief operating decision maker in deciding how to allocate resources. The Company reports its operations in three segments that reflect its three lines of business of Gathering, Transmission and Water. The operating segments are evaluated based on their contribution to the Company's operating income and equity income. Transmission also includes the Company's investment in the MVP Joint Venture, which is accounted for as
an equity method investment as described in Note 7. Transmission's portion of the MVP Joint Venture's operating results is reflected in equity income and not in Transmission's operating income. All of the Company's operating revenues, income and assets are generated or located in the United States. See Note 3 for financial information by segment.
Reclassification. Certain previously reported amounts have been reclassified to conform to current year presentation.
Use of Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect amounts reported in these financial statements. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash Equivalents. The Company classifies highly-liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less as cash equivalents. Interest earned on cash equivalents is recorded as a reduction to net interest expense on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Accounts Receivables. Trade and other receivables are stated at their historical carrying amount. Judgment is required to determine the ultimate realization of accounts receivable, including assessing the probability of collection and the creditworthiness of customers. The Company evaluates the allowance for credit losses on a quarterly basis in order to estimate uncollectible receivables.
Other Current Assets. The following table summarizes the Company's other current assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022. | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) |
| Prepaid expenses | $ | 26,795 | | | $ | 23,346 | |
| Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision | 24,503 | | | — | |
| Inventory | 15,851 | | | 19,173 | |
| Unbilled revenue | 8,753 | | | 24,465 | |
| Other current assets | 2,454 | | | 7,933 | |
| Total other current assets | $ | 78,356 | | | $ | 74,917 | |
Derivative Instruments. Derivative instruments are recorded on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as either an asset or liability measured at fair value. Cash flows associated with derivative instruments and the related gains and losses are recorded as cash flows from operating activities on the Company's statement of consolidated cash flows. See Note 10.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments. Fair value represents the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the reporting date. The Company’s assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value at each reporting date are classified according to a hierarchy that prioritizes inputs and assumptions underlying the valuation techniques. This fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs and consists of three broad levels:
•Level 1: Observable inputs that reflect unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets as of the reporting date.
•Level 2: Observable market-based inputs or unobservable inputs that are corroborated by market data. These are inputs other than quoted prices in active markets included in Level 1 that are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reporting date.
•Level 3: Unobservable inputs that are not corroborated by market data and may be used with internally developed methodologies that result in management’s best estimate of fair value.
The Company prioritizes valuation techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs. Assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based on the lowest priority level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgment and may affect the placement of assets and liabilities within the levels of the fair value hierarchy. Reclassifications of fair value between Level 1, Level 2 and Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy, if applicable, are made at the end of each reporting period. See Note 10 for information regarding the fair value of financial instruments.
Property, Plant and Equipment. The Company's property, plant and equipment are stated at depreciated cost. Maintenance projects that do not increase the overall life of the related assets are expensed as incurred. Expenditures that extend the useful life of the asset are capitalized. The Company capitalized overhead, including internal labor costs, of $52.2 million, $47.3
million and $50.8 million in the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The Company capitalized interest, including the debt component of Allowance for Funds Used During Construction (AFUDC), of $11.4 million, $8.7 million and $4.9 million in the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
The following table summarizes the Company's property, plant and equipment.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) |
| Gathering assets | $ | 7,440,220 | | | $ | 7,176,011 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (1,113,967) | | | (919,465) | |
| Net gathering assets | 6,326,253 | | | 6,256,546 | |
| Transmission and storage assets | 2,001,489 | | | 1,928,894 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (531,259) | | | (475,688) | |
| Net transmission and storage assets | 1,470,230 | | | 1,453,206 | |
| Water services assets | 289,891 | | | 245,258 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (101,541) | | | (79,518) | |
| Net water services assets | 188,350 | | | 165,740 | |
| Other property, plant and equipment | 13,698 | | | 14,888 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (6,147) | | | (6,049) | |
| Net other property, plant and equipment | 7,551 | | | 8,839 | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | $ | 7,992,384 | | | $ | 7,884,331 | |
Property, plant and equipment includes capitalized qualified implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract of $7.9 million and $9.0 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2023 and 2022. The Company finalized the implementation of certain portions of its enterprise resource planning system throughout 2021 and amortized approximately $1.1 million, $1.0 million, and $0.9 million of implementation costs in the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Depreciation is recorded using composite rates on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the asset. The average depreciation rates for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 were 2.6%, 2.6% and 2.6%, respectively. The Company estimates that gathering and transmission pipelines have useful lives of 20 years to 50 years and compression equipment has useful lives of 20 years to 50 years. The Company estimates that water pipelines, pumping stations and impoundment facilities have useful lives of 10 years to 15 years. As circumstances warrant, depreciation estimates are reviewed to determine if any changes in the underlying assumptions are necessary. Equitrans, L.P., the Company's FERC-regulated subsidiary, re-evaluates depreciation rates for its regulated property, plant and equipment each time it files with the FERC for a change in transmission and storage rates.
Intangible Assets. Intangible assets are recorded under the acquisition method of accounting at their estimated fair values at the acquisition date, which are calculated as the present value of estimated future cash flows using a risk-adjusted discount rate. The Company's intangible assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over each intangible asset's estimated remaining useful life. The estimated annual amortization expense related to the intangible assets for each of the next five years is $64.8 million for years one through three and then $62.5 million in years four and five. The weighted average amortization period is approximately eight years.
The following tables summarize the Company's intangible assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | December 31, 2023 |
| (In thousands) | | Remaining Life | | Gross | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net |
| Customer relationships | | 9 years | | $ | 623,199 | | | $ | (254,819) | | | $ | 368,380 | |
| Eureka Midstream-related customer relationships | | 7 years | | 237,000 | | | (90,112) | | | 146,888 | |
| Hornet Midstream-related customer relationships | | 3 years | | 74,000 | | | (67,135) | | | 6,865 | |
| | | | $ | 934,199 | | | $ | (412,066) | | | $ | 522,133 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | December 31, 2022 |
| (In thousands) | | Remaining Life | | Gross | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net |
| Customer relationships | | 10 years | | $ | 623,199 | | | $ | (213,273) | | | $ | 409,926 | |
| Eureka Midstream-related customer relationships | | 8 years | | 237,000 | | | (69,128) | | | 167,872 | |
| Hornet Midstream-related customer relationships | | 4 years | | 74,000 | | | (64,846) | | | 9,154 | |
| | | | $ | 934,199 | | | $ | (347,247) | | | $ | 586,952 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Impairment of Goodwill and Long-Lived Assets. Goodwill is evaluated for impairment at least annually or whenever events or changes in circumstance indicate, in management's judgment, it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. The Company may perform either a qualitative assessment of potential impairment or proceed directly to a quantitative assessment of potential impairment. The Company assesses qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events or circumstances leads the Company to determine that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If, after assessing the totality of events or circumstances, the Company determines it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is greater than its carrying amount, then a quantitative assessment is not required. However, if the Company concludes otherwise, a quantitative impairment analysis is performed.
When the Company performs a quantitative assessment, the Company estimates the fair value of the reporting unit with which the goodwill is associated and compares it to the carrying value. If the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairment charge is recognized for the excess of the reporting unit's carrying value over its fair value.
The Company evaluates long-lived assets for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management's judgment, that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable. With respect to property, plant and equipment and finite lived intangibles, asset recoverability is measured by comparing the carrying value of the asset or asset group with its expected future pre-tax undiscounted cash flows. These cash flow estimates require the Company to make projections and assumptions for many years into the future for volumes, pricing, demand, competition, operating costs and other factors. If the carrying amount exceeds the expected future undiscounted cash flows, the Company recognizes an impairment equal to the excess of carrying value over fair value as determined by quoted market prices in active markets or present value techniques if quotes are unavailable. The determination of the fair value using present value techniques requires the Company to make projections and assumptions regarding the probability of a range of outcomes and the rates of interest used in the present value calculations. Any changes the Company makes to these projections and assumptions could result in significant revisions to its evaluations of recoverability and the recognition of additional impairments. See Note 2 for further detail.
Investment in Unconsolidated Entity. The Company accounts for investments in unconsolidated entities under the equity method. The Company’s pro-rata share of net income in unconsolidated entities is included in equity income in the Company’s statements of consolidated comprehensive income. Contributions to or distributions from unconsolidated entities and the Company’s pro-rata share of net income in unconsolidated entities are recorded as adjustments to the investment balance. The Company reviews the carrying value of investments in unconsolidated entities for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management's judgment, that the carrying value of such investment may have declined in value. When there is evidence of loss in value that is other-than-temporary, the Company compares the investment's carrying value to its estimated fair value to determine whether impairment has occurred. If the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value, the Company estimates and recognizes an impairment charge equal to the difference between the investment's carrying value and fair value. See Note 2 for further detail.
Preferred Interest. EQT Energy Supply, LLC(EES), a subsidiary of EQT, generates revenue by providing services to a local distribution company. The preferred interest that the Company has in EES (the Preferred Interest) is accounted for as a note receivable and is presented in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets with the current portion reported in other current assets. Distributions received from EES are recorded as a reduction to the Preferred Interest and as interest income, which is included in net interest expense in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income. The EES operating agreement provides for mandatory redemption of the Preferred Interest at the end of the preference period, which is expected to be discontinued. This guidance is applicableDecember 31, 2034. See Note 10 for further detail.
Unamortized Debt Discount and Issuance Costs. The Company amortizes debt discounts and issuance costs over the term of the related borrowing. Costs incurred from the arrangement, issuance and/or extension of revolving credit facilities, including the Amended EQM Credit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility (each as defined in Note 11)9), are presented in other assets in the consolidated balance sheets. Debt discounts and issuance costs for all other debt instruments are presented as a reduction to debt on the consolidated balance sheets. See Note 9 for further detail.
Leases. Right-of-use assets represent the right to use the underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent the obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. Right-of-use assets and lease liabilities are recognized on the
consolidated balance sheets at the lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception based on whether the Company has the right to control the use of an identified asset, the right to obtain substantially all of the economic benefits from the use of the asset and the right to direct the use of the asset during the lease term and accounts for leases in accordance with ASC 842, Leases (ASC 842).
Leases in which the Company is the lessee that do not have a readily determinable implicit rate utilize an incremental borrowing rate, based on the information available at the lease commencement date, to determine the present value of lease payments. When a secured borrowing rate is not readily available, unsecured borrowing rates are adjusted for the effects of collateral to determine the incremental borrowing rate. The Company reassesses the incremental borrowing rate for any new and modified lease contracts as of the contract effective date. Lease expense for operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Lease expense for finance leases includes the amortization of the right-of-use assets on a straight-line basis and the interest expense recognized on lease liabilities using the effective interest method over the lease term. See Note 5 for further detail.
Other Current Liabilities. The following table summarizes the Company's accrued liabilities as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 |
| | (Thousands) |
| Accrued employee compensation | $ | 52,263 | | | $ | 47,742 | |
| Non-income tax accruals | 21,851 | | | 20,629 | |
| Current portion of lease liabilities | 11,581 | | | 7,886 | |
| Current portion of contract liability | 5,061 | | | 4,552 | |
| Other accrued liabilities | 16,114 | | | 3,026 | |
| Total accrued liabilities | $ | 106,870 | | | $ | 83,835 | |
Asset Retirement Obligations (AROs). The Company has AROs related to its water system impoundments and facilities and to one of its gathering compressor stations, for which the Company recorded an associated liability and capitalized a corresponding amount to asset retirement costs. The liability relates to the expected future obligation to dismantle, reclaim and dispose of these assets and was estimated using the present value of expected future cash flows, adjusted for inflation, and discounted at the Company's credit-adjusted, risk-free rate. The AROs are recorded in regulatory and other long-term liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets.
The following table presents changes in the Company's AROs during 2023 and 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) |
| AROs at beginning of period | $ | 13,961 | | | $ | 11,241 | |
| Liabilities incurred | 2,154 | | | — | |
| Liabilities settled | (3,028) | | | (996) | |
| | | |
Revisions to estimated liabilities (a) | 306 | | | 3,153 | |
| Accretion expense | 862 | | | 563 | |
| AROs at end of period | $ | 14,255 | | | $ | 13,961 | |
(a)Revisions to estimated liabilities reflect changes in retirement cost assumptions and the estimated timing of liability settlement.
The Company is not legally or contractually obligated to restore or dismantle its transmission and storage systems and its gathering systems, other than the one aforementioned gathering compressor station. The Company is legally required to operate and maintain these assets and intends to do so as long as supply and demand for natural gas exists, which the Company expects to continue into the foreseeable future. Therefore, the Company did not have any AROs related to its transmission and storage and gathering (other than the aforementioned gathering compressor station) assets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
Contingencies. The Company is, from time to time, involved in various regulatory and legal proceedings. A liability is recorded when the loss is probable and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company considers many factors when
making such assessments, including historical knowledge and matter specifics. Estimates are developed through consultation with legal counsel and analysis of the potential results. See Note 14.
Regulatory Accounting. Equitrans, L.P. owns all of the Company's FERC-regulated transmission and storage operations. Through the rate-setting process, rate regulation allows Equitrans, L.P. to recover the costs of providing regulated services plus an allowed return on invested capital. Regulatory accounting allows Equitrans, L.P. to defer expenses and income to its consolidated balance sheets as regulatory assets and liabilities when it is probable that those expenses and income will be allowed in the rate-setting process for a period other than the period that they would be reflected in a non-regulated entity's statements of consolidated comprehensive income. Regulatory assets and liabilities are recognized in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income in the period that the underlying expenses and income are reflected in the rates charged to shippers and operators. Equitrans, L.P. expects to continue to be subject to rate regulation that will provide for the recovery of deferred costs.
The following table summarizes Equitrans, L.P.'s regulatory assets and liabilities that are included in other assets and regulatory and other long-term liabilities, respectively, in the Company's consolidated balance sheets.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) |
| Regulatory assets: | | | |
Deferred taxes (a) | $ | 123,128 | | | $ | 85,046 | |
Other recoverable costs (b) | 3,834 | | | 4,608 | |
| Total regulatory assets | $ | 126,962 | | | $ | 89,654 | |
| Regulatory liabilities: | | | |
Deferred taxes (a) | $ | 8,931 | | | $ | 9,329 | |
On-going post-retirement benefits other than pension and other reimbursable costs (c) | 19,862 | | | 19,251 | |
| | | |
| Total regulatory liabilities | $ | 28,793 | | | $ | 28,580 | |
(a)The regulatory asset from deferred taxes is primarily related to a historical deferred income tax position and taxes on the equity component of AFUDC. The regulatory liability from deferred taxes relates to the revaluation of a historical difference between the regulatory and tax bases of regulated property, plant and equipment. Equitrans, L.P. expects to recover the amortization of the deferred tax positions ratably over the depreciable lives of the underlying assets. Equitrans, L.P. also expects to recover the taxes on the equity component of AFUDC through future rates over the depreciable lives of the underlying long-lived assets.
(b)The regulatory asset from other recoverable costs is primarily related to the costs associated with the Company's legacy post-retirement benefits plan. Equitrans, L.P. expects to continue to recover these costs over the remaining 8.5 years.
(c)Equitrans, L.P. defers expenses for on-going post-retirement benefits other than pensions, which are subject to recovery in approved rates. The regulatory liability reflects lower cumulative actuarial expenses than the amounts recovered through rates. Equitrans, L.P. expects to continue to recover costs as long as the existing recourse rates provide for recovery.
The following tables present Equitrans, L.P.'s regulated operating revenues and operating expenses and property, plant and equipment included in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income and consolidated balance sheets, respectively. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (Thousands) |
| Operating revenues | $ | 446,184 | | | $ | 407,884 | | | $ | 403,634 | |
| Operating expenses | 169,449 | | | 137,782 | | | 135,888 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) |
| Property, plant and equipment | $ | 2,001,489 | | | $ | 1,928,898 | |
| Accumulated depreciation | (531,259) | | | (475,689) | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | $ | 1,470,230 | | | $ | 1,453,209 | |
Gas imbalances occur when the actual amount of gas delivered from a pipeline system or storage facility varies from the amount of gas scheduled for delivery. The Company values gas imbalances due to/from shippers and operators at current index prices. Gas imbalances are settled in-kind, subject to the terms of the applicable FERC tariffs. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, gas imbalance receivables were $1.3 million and $7.0 million, respectively, and are presented in other current assets, with offsetting amounts recorded to system gas, a component of property, plant and equipment, on the consolidated balance sheets. The Company classifies gas imbalances as current because they are expected to settle within one year.
Revenue Recognition. Revenue is measured based on considerations specific in a contract with a customer. The Company recognizes revenue under gathering, transmission and storage and water services contracts when it satisfies certain performance obligations, as discussed below.
The Company provides gathering, transmission and storage services in two manners: firm service and interruptible service. Firm service is provided under firm contracts, which are contracts for gathering, transmission or storage services that generally obligate the customer to pay a fixed, monthly charge to reserve an agreed upon amount of pipeline or storage capacity regardless of the capacity used by the customer during each month. Volumetric-based fees can also be charged under firm contracts for each firm volume transported, gathered or stored, as well as for each dividend following March 31, 2024volumes transported, gathered or stored in excess of the firm contracted volume, if capacity exists. Interruptible service contracts include volumetric-based fees, which are charges for the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares,volume of gas gathered, transported or stored and generally do not guarantee access to the pipeline or storage facility. Firm and interruptible contracts can be short- or long-term in duration. Firm and interruptible transmission and storage service contracts are billed at the end of each calendar month, with payment typically due within 10 days. Firm and interruptible gathering contracts are billed on a one-month lag, with payment typically due within 21 days. Revenue related to gathering services provided but not yet billed is estimated each month. These estimates are generally based on contract data, preliminary throughput and allocation measurements.
Under a firm contract, the Company has a stand-ready obligation to provide the service over the life of the contract. The performance obligation for firm reservation fee revenue is satisfied over time as the pipeline capacity is made available to the customer. As such, the Company recognizes firm reservation fee revenue evenly over the contract period using a time-elapsed output method to measure progress. The performance obligation for volumetric-based fee revenue is generally satisfied upon the Company's monthly billing to the customer for volumes gathered, transported or stored during the month. The amount billed generally corresponds directly to the value of the Company's performance to date as the customer obtains value as each volume is gathered, transported or stored.
Water service revenues represent fees charged by the Company for the delivery of fresh and produced water to a customer at a specified delivery point and for the collection and recycling or disposal of flowback and produced water. The Company's water service revenues are generated under firm service and interruptible service contracts, which primarily utilize fixed prices per volume delivered. Firm service provides water services under firm contracts to customers with priority. Interruptible service contracts generally do not guarantee access to the water facilities. For fresh and produced water delivery service contracts, the only performance obligation in each contract is for the Company to provide water (usually a minimum daily volume of water) to the customer at a designated delivery point. For flowback and produced water, the performance obligation is collection and disposal of the water, which typically occur within the same day. Water service contracts are billed on a monthly basis, with payment typically due within 30 days.
For all contracts, the Company allocates the transaction price to each performance obligation based on the estimated relative standalone selling price. When applicable, the excess of consideration received over revenue recognized results in the deferral of those amounts until future periods based on a units of production or straight-line methodology as these methods appropriately match the consumption of services provided to the customer. The units of production methodology requires the use of production estimates that are uncertain and the London Inter-Bank Offered Rate (LIBOR)use of judgment when developing estimates of future production volumes, thus impacting the rate of revenue recognition. Production estimates are monitored as circumstances and events warrant.
Certain of the Company's gas gathering and water services agreements, including the EQT Global GGA and the 2021 Water Services Agreement, are structured with MVCs or ARCs, as applicable, which specify minimum quantities for which a customer will be charged regardless of quantities gathered or delivered under the contract. Revenue is recognized for MVCs or
ARCs when the performance obligation has been met, which is the earlier of when the gas is gathered or water provided, or when it is remote that the producer will be able to meet its MVC or ARC. If a customer under such an agreement fails to meet its MVC or ARC for a specified period (thus not exercising all the contractual rights to gathering and water services within the specified period, herein referred to as “breakage”), it is obligated to pay a contractually determined fee based upon the shortfall between the actual volumes and the MVC or ARC for the period contained in the contract. See Note 4.
AFUDC. The Company capitalizes the carrying costs of financing the construction of certain long-lived, regulated assets. Such costs are amortized over the asset's estimated useful life and include interest costs (the debt component of AFUDC) and equity costs (the equity component of AFUDC). The debt component of AFUDC is recorded as a reference rate. The ASU was effective immediately butreduction to net interest expense on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income, and the equity component of AFUDC is only available through December 31, 2022. recorded in other income (expense), net, on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Share-Based Compensation. The Company recognizes share-based compensation cost based upon the estimated fair value of awards over the requisite service period. Time-based restricted units expected to be satisfied in cash are accounted for as liability awards recorded over the requisite service period, typically three years. The fair value of liability awards is currentlyremeasured at the end of each reporting period based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock. Time-based restricted stock awards expected to be satisfied in Company common stock are accounted for as equity awards and are recorded over the requisite service period, typically three years, based on the grant date fair value. Director phantom units expected to be satisfied in Company common stock vest on the date of grant and are recorded based on the grant date fair value. The grant date fair value, in both cases, is determined based upon the closing price of the Company's common stock on the day before the grant date. The Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur.
Performance-based awards expected to be satisfied in cash are accounted for as liability awards and remeasured at fair value at the end of each reporting period, recognizing a proportionate amount of the compensation cost for each period over the vesting period of the award.Performance-based awards expected to be satisfied in Company common stock are accounted for as equity awards and recorded based on an estimated grant date fair value over the vesting period of the award. For plans that include a performance condition that affects the number of awards that will ultimately vest, the probability that the performance condition will be achieved is reevaluated at the end of each reporting period and the payout multiplier is applied to the grant date fair value or measurement date fair value to record compensation cost, as applicable. Determination of the fair value of awards requires judgments and estimates regarding, among other things, the appropriate methodologies to follow in valuing the awards and the related inputs required by those valuation methodologies.
The Company obtains a valuation at each reporting date for liability awards and at the grant date for equity awards for plans that include a market condition based upon assumptions regarding risk-free rates of return, expected volatilities, the expected term of the award and dividend yield, as applicable. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of valuation. Expected volatilities are based on historical volatility of the Company's common stock and, where applicable, the common stock of the peer group members at the time of valuation. The expected term represents the period of time elapsing during the applicable performance period. The dividend yield is based on the historical dividend yield of the Company's common stock adjusted for any expected changes and, where applicable, the common stock of the peer group members at the time of valuation. Each plan subject to a market condition is accounted for separately for each vesting tranche of the award.
Dividends on awards are eligible to be paid in cash upon vesting on each share of common stock as dividends are declared on the Company's common stock during the vesting period. See Note 8 for further detail.
Income Taxes. The Company files a consolidated income tax return for federal income taxes and the provision for income taxes is determined using the asset and liability approach of accounting for income taxes. Under this approach, the provision for income taxes represents income taxes paid or payable (or received or receivable) plus the change in deferred taxes for the current year. EQM is a limited partnership for U.S. federal and state income tax purposes. Eureka Midstream is a limited liability company for such purposes. EQM and Eureka Midstream are not subject to U.S. federal or state income taxes.
All of Eureka Midstream's income is included in the Company's pre-tax income; however, the Company does not record income tax expense on the portions of its income attributable to the noncontrolling member of Eureka Midstream. This reduces the Company's effective tax rate in periods when the Company has consolidated pre-tax income and increases the effective tax rate in periods when the Company has consolidated pre-tax losses.
Deferred taxes represent the future tax consequences of differences between the financial and tax bases of the Company's assets and liabilities. Deferred tax balances are adjusted for changes in tax rates and tax laws when enacted. Deferred tax assets are reflected on the consolidated balance sheets for net operating losses, credits or other attributes generated by the Company. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not (greater than 50%) that a tax benefit will not be realized. In evaluating the potential impact of this standard on its financial statements.need for a valuation allowance, management considers all available evidence, both
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-06, Accounting for Convertible Instrumentspositive and Contractsnegative, including potential sources of taxable income, income available in an Entity’s Own Equity, which simplifies the accounting for convertible debtcarry-back periods, future reversals of taxable temporary differences, projections of taxable income and convertible preferred stock by removing the requirements to separately present certain conversion features in equity. In addition, the amendments in the ASU 2020-06 also simplify the guidance in ASC Subtopic 815-40, Derivatives and Hedging: Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity, by removing certain criteria that must be satisfied in order to classify a contract as equity. Finally, the amendments revise the guidance on calculating earnings per share, requiring use of the if-converted method for all convertible instruments and rescinding an entity’s ability to rebut the presumption of share settlement for instruments that may be settled in cash or other assets. The amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021. Adoption of the guidance must commence at the beginning of the annual fiscal year.income from tax planning strategies. The Company adopted this standard on January 1, 2022 and it had no impact on the Company's financial statements.
2. Investments in Consolidated, Non-Wholly Owned Entities
EQM IDR Transaction. On February 22, 2019, the Company completed a simplification transaction pursuant to that certain Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of February 13, 2019, by and among the Company and certain related parties, pursuant to which, among other things, (i) Equitrans Merger Sub, LP merged with and into EQGP (the IDR Merger) with EQGP continuing as the surviving limited partnership and a wholly owned subsidiary of EQM, and (ii) each of (a) the IDRs in EQM, (b) the economic portion of the general partner interest in EQM and (c) the issued and outstanding common units representing limited partner interests in EQGP (EQGP common units) were canceled, and, as consideration for such cancellation, certain wholly owned subsidiaries of the Company received on a pro rata basis 80,000,000 newly-issued EQM common units and 7,000,000 newly-issued Class B units representing limited partner interests in EQM (Class B units), and the EQM General Partner retained the non-economic general partner interest in EQM (such transactions, collectively, the EQM IDR Transaction). Additionally, as part of the EQM IDR Transaction, 21,811,643 EQM common units held by EQGP were canceled and 21,811,643 EQM common units were issued pro rata to certain wholly owned subsidiaries of the Company. As a result of the EQM IDR Transaction, the EQM General Partner replaced EQM Midstream Services, LLC as the general partner of EQM.
After giving effect to the EQM IDR Transaction, including the issuance of Class B units, the Company indirectly owned a total of 117,245,455 EQM common units and all of the Class B units.
EQM Series A Preferred Units.On March 13, 2019, EQM entered into a Convertible Preferred Unit Purchase Agreement, together with Joinder Agreements entered into on March 18, 2019, with the Investors to issue and sell in a private placement (the Private Placement) an aggregate of 24,605,291 EQM Series A Preferred Units for a cash purchase price of $48.77 per EQM Series A Preferred Unit, resulting in total gross proceeds of approximately $1.2 billion. The net proceeds from the Private Placement were used in part to fund the purchase price in the Bolt-on Acquisition and to pay certain fees and expenses related to the Bolt-on Acquisition, and the remainder was used for general partnership purposes. The Private Placement closed concurrently with the closing of the Bolt-on Acquisition on April 10, 2019, as discussed further in Note 3. See below for a discussion on the Preferred Restructuring Agreement.
EQM Merger. As discussed in Note 1, on June 17, 2020, the Company, EQM, EQM LP, Merger Sub and the EQM General Partner completed the EQM Merger, pursuant to which Merger Sub merged with and into EQM, with EQM continuing and surviving as an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. As a result of the EQM Merger, EQM is no longer a publicly traded entity.
At the Effective Time, subject to applicable tax withholding, (i) each outstanding EQM common unit, other than EQM common units owned by the Company and its subsidiaries, was converted into the right to receive 2.44 shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock (the Merger Consideration); (ii) (x) $600.0 million aggregate principal amount of the EQM Series A Preferred Units issued and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time were redeemed by EQM for cash at 101% of the EQM Series A Preferred Unit Purchase Price plus any accrued and unpaid distribution amounts and partial period distribution amounts, and (y) immediately following such redemption, each remaining issued and outstanding EQM Series A Preferred Unit was exchanged for 2.44 Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares; and (iii) each outstanding phantom unit relating to an EQM common unit issued pursuant to the Amended and Restated EQGP Services, LLC 2012 Long-Term Incentive Plan, dated as of February 22, 2019 (the EQM LTIP), and any other award issued pursuant to the EQM LTIP, whether vested or unvested, was converted into the right to receive, with respect to each EQM common unit subject thereto, the Merger Consideration (plus any accrued but unpaid amounts in relation to distribution equivalent rights). The limited partner interests in EQM owned by the Company and its subsidiaries (including the Class B units) remained outstanding as limited partner interests in the surviving entity. The EQM General Partner continued to own the non-economic general partner interest in the surviving entity.
No fractional shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock were issued in the EQM Merger; instead, all fractions of Equitrans Midstream common stock to which an EQM common unitholder otherwise would have been entitled were aggregated and the resulting fraction was rounded up to the nearest whole share of Equitrans Midstream common stock.
In connection with the EQM Merger at the Effective Time, the Company's omnibus and secondment agreements with EQM and certain other subsidiaries of the Company terminated, subject to the survival of certain license rights and indemnification obligations.
Because the Company controlled EQM both before and after the EQM Merger, the increase in the Company’s ownership interest in EQM resulting from the EQM Merger was accounted for as an equity transaction and reflected as a reduction of the noncontrolling interest associated with public ownership of EQM common units, offset by an increase in common stock, no par value. No gain or loss was recognized in the Company’s statements of consolidated comprehensive income as a result of the EQM Merger. In addition, the tax effects of the EQM Merger were reported as adjustments to deferred income taxes and Equitrans Midstream common stock, consistent with ASC 740, Income Taxes.
Immediately prior to the completion of the EQM Merger, the public limited partners collectively owned a 40.1% interest in EQM, excludingrecords the impact of the EQM Series A Preferred Units. The publicly-owned EQM common units, prior to completion of the EQM Merger, were reflectedvaluation allowances or any uncertain tax position within noncontrolling interest in the Company's consolidated balance sheets as of March 31, 2020. The portion of EQM earnings attributable to publicly-held EQM common units prior to completion of the EQM Merger was reflected in net income attributable to noncontrolling interests in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Additionally, for the period from January 1, 2020 to June 17, 2020, the Company determined that EQM was a variable interest entity. Through the Company's ownership and control of the general partner of EQM during that period, the Company had the power to direct the activities that most significantly affected EQM's economic performance. As a result of the EQM Merger, EQM is no longer a variable interest entity.
The Company recorded $23.8 million in expenses related to the EQM Merger and the EQT Global GGA (as defined in Note 4) during the year ended December 31, 2020. The expenses consisted of advisor, legal and accounting fees related to the transactions and are included in separation and other transaction costs intax expense (benefit) on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Preferred Restructuring Agreement. As discussedDeferred tax assets for which no valuation allowance is recorded may not be realized and changes in Note 1, on June 17, 2020, concurrently with the closing of the EQM Merger: (i) EQM redeemed $600 million aggregate principal amount of the EQM Series A Preferred Units issuedfacts and outstanding immediately prior to the Effective Time for cash at 101% of the EQM Series A Preferred Unit Purchase Price plus any accrued and unpaid distribution amounts and partial period distribution amounts, and (ii) immediately following such redemption, each remaining issued and outstanding EQM Series A Preferred Unit was exchanged for 2.44 Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, in each case, in connection with the occurrence of the “Series A Change of Control” (as definedcircumstances may result in the Former EQM Partnership Agreement) that occurred upon the closingestablishment of the EQM Merger. The Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares issued were not registereda valuation allowance. Existing valuation allowances are re-examined under the Securities Actsame standards of 1933, as amended (the Securities Act), in reliance upon the exemption provided in Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act and/or Regulation D promulgated thereunder.
On June 17, 2020, the Company paid cash of $617.3 millionpositive and negative evidence that apply to redeem $600 million aggregate principal amount of the Investors’ EQM Series A Preferred Units and pay partial period distributions on such EQM Series A Preferred Units. At the time of the redemption, the carrying value of the EQM Series A Preferred Units was $590.1 million, resulting invaluation allowance establishment. If it is determined that it is more likely than not that a premium over the carrying value of $27.3 million. The premium representeddeferred tax asset for which a return similar to distributions to the holders of the EQM Series A Preferred Units and, as such, reduced net income attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders, and wasvaluation is recorded in retained earnings (deficit) in the statements of consolidated shareholders' equity and mezzanine equity.
Pursuant to the Restructuring Agreement, in connection with the Restructuring Closing, the Company filed a statement with respect to shares, attaching a Certificate of Designations (the Certificate of Designations), with the Pennsylvania Department of State on June 17, 2020 to, among other things, authorize and establish the designations, rights and preferences of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares. On August 13, 2020, pursuant to the terms of the Certificate of Designations, the Company paid $10.9 million in the aggregate to holders of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares related to forgone partial period distributions on the EQM Series A Preferred Units that were converted into Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares in connection with the EQM Merger.
The Company's Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (the Restated Articles) set forth the designations, rights and preferences of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares.
The Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares were a new class of security as of June 2020. They rank pari passu with any other outstanding class or series of preferred stock of the Company and senior to Equitrans Midstream common stock with respect to dividend rights and rights upon liquidation. The Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares vote on an as-converted basis with Equitrans Midstream common stock and have certain other class voting rights with respect to any amendment to the Restated Articles that wouldwill be adverse (other than in a de minimis manner) to any of the rights, preferences or privileges of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares.
The holders of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares receive cumulative quarterly dividends at a rate per annum of 9.75% for each quarter ending on or before March 31, 2024, and thereafter quarterly dividends at a rate per annum equal to the sum of (i) three-month LIBOR as of the LIBOR Determination Date (as defined in the Restated Articles) in respect of the applicable quarter and (ii) 8.15%; provided that such rate per annum in respect of periods after March 31, 2024 will not be less than 10.50%. The Company is not permitted to pay any dividends on any junior securities, including on Equitrans Midstream common stock, prior to paying the quarterly dividends payable to the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, including any previously accrued and unpaid dividends.
Each holder of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares may elect to convertrealized, all or anya portion of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares owned by it into Equitrans Midstream common stock initiallyvaluation allowance may be released. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are also re-measured to reflect changes in underlying tax rates from tax law changes.
Tax benefits related to uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken on a one-for-one basis, subjecttax return are recorded when such benefits meet a more likely than not threshold; otherwise, the tax benefit is recorded when the tax position has been effectively settled, either because the statute of limitations has expired or the appropriate taxing authority has completed its examination. Interest and penalties related to certain anti-dilution adjustments and an adjustment for any dividends that have accrued but not been paid when due and partial period dividends (referred touncertain tax positions are recognized as the conversion rate), at any time (but not more often than once per fiscal quarter), provided that any conversion involves an aggregate number of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares of at least $20.0 million (calculated based on the closing price of Equitrans Midstream common stock on the trading day preceding noticepart of the conversion) or such lesser amount if such conversion relates to all of a holder’s remaining Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares or if such conversion is approved by the Company's Board of Directors (Board).
So long as the holders of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares have not elected to convert all of their Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares into Equitrans Midstream common stock, the Company may elect to convert all of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares into Equitrans Midstream common stock, at the then-applicable conversion rate, if (i) the shares of Equitrans Midstream common stockprovision for income taxes and are listed for, or admitted to, trading on a national securities exchange, (ii) the closing price per share of Equitrans Midstream common stock on the national securities exchange on which the shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock are listed for, or admitted to, trading exceeds $27.99 for the 20 consecutive trading days immediately preceding notice of the conversion, (iii) the average daily trading volume of the Equitrans Midstream common stock on the national securities exchange on which the shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock are listed for, or admitted to, trading exceeds 1,000,000 shares (subject to certain adjustments) of Equitrans Midstream common stock for the 20 consecutive trading days immediately preceding notice of the conversion, (iv) the Company has an effective registration statement on file with the SEC covering resales of the shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock to be received by such holders upon any such conversion and (v) the Company has paid all prior accumulated and unpaid dividends in cash in full to the holders.
Upon certain events involving a Change of Control (as definedaccrued in the Restated Articles) in which more than 90% ofperiod that such interest and penalties would be applicable under relevant tax law until such time that the consideration payable to the Company, or to the holders of Equitrans Midstream common stock, is payable in cash, the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares will automatically convert into Equitrans Midstream common stock at a conversion ratio equal to the greater of (i) the quotient of (a) the sum of (x) $19.99 (such price, the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share Issue Price) plus (y) any accrued and unpaid dividends as of such date, including any partial period dividends, with respect to the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, divided by (b) the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share Issue Price and (ii) the quotient of (a) the sum of (x)(1) the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share Issue Price multiplied by (2) 110% plus (y) any accrued and unpaid dividends on such date, including any partial period dividends with respect to the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, divided by (b) the volume weighted average price of the shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock for the 30-day period ending immediately prior to the execution of definitive documentation relating to the Change of Control.uncertain tax positions are resolved. See Note 12.
In connection with other Change of Control events that do not satisfy the 90% cash consideration threshold described above, in addition to certain other conditions, each holder of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares may elect to (i) convert all, but not less than all, of its Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares into Equitrans Midstream common stock at the then-applicable conversion rate, (ii) if the Company is not the surviving entity (or if the Company is the surviving entity, but Equitrans Midstream common stock will cease to be listed), require the Company to use commercially reasonable efforts to cause the surviving entity in any such transaction to deliver, in exchange for such holder's Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, a substantially equivalent security that has rights, preferences and privileges substantially equivalent to the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares (or if the Company is unable to cause such substantially equivalent securities to be issued, to exercise the option described in clause (i) or (iv) hereof or elect to convert such Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares at a conversion ratio reflecting a multiple of invested capital), (iii) if the Company is the surviving entity, continue to hold the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares or (iv) require the Company to redeem the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares at a price per share equal to 101% of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share Issue Price, plus accrued and unpaid dividends, including any partial period dividends, on the applicable Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares as of such date, which redemption price may be payable in cash, Equitrans Midstream common stock or a combination thereof at the election of the Board (and, if payable in Equitrans Midstream common stock, such Equitrans Midstream common stock will be issued at 95% of the volume-weighted average price of Equitrans Midstream common stock for the 20-day period ending on the fifth trading day immediately preceding the consummation of the Change of Control). Any holder of Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares that requires the Company to
redeem its Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares pursuant to clause (iv) above will have the right to withdraw such election with respect to all, but not less than all, of its Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares at any time prior to the fifth trading day immediately preceding the consummation of the Change of Control and instead elect to be treated in accordance with any of clauses (i), (ii) or (iii) above.
At any time on or after January 1, 2024, the Company will have the right, subject to applicable law, to redeem the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, in whole or in part, by paying cash for each Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share to be redeemed in an amount equal to the greater of (a) the sum of (i)(1) the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share Issue Price multiplied by (2) 110%, plus (ii) any accrued and unpaid dividends, including partial period dividends, with respect to the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares as of such date and (b) the amount the holder of such Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share would receive if such holder had converted such Equitrans Midstream Preferred Share into shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock at the then-applicable conversion ratio and the Company liquidated immediately thereafter.
Pursuant to the terms of the Restructuring Agreement, in connection with the Restructuring Closing, the Company entered into a registration rights agreement with the Investors (the Registration Rights Agreement) pursuant to which, among other things, the Company gave the Investors certain rights to require the Company to file and maintain one or more registration statements with respect to the resale of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares and the shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock that are issuable upon conversion of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares, and certain Investors have the right to require the Company to initiate underwritten offerings for the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares and the shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock that are issuable upon conversion of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, as a result of the Restructuring Closing, the Company recorded an increase in mezzanine equity of $667.2 million, a decrease in noncontrolling interest of $579.2 million and a decrease in common stock, no par value, of $100.5 million, net of deferred taxes of $12.5 million.
The Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares are considered redeemable securities under GAAP due to the possibility of redemption outside the Company’s control. They are therefore presented as temporary equity in the mezzanine equity section of the Company’s consolidated balance sheets and are not considered to be a component of shareholders’ equity on the consolidated balance sheets. The Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares were recorded at fair value as of the date of issuance, and income allocations increase the carrying value and declared dividends decrease the carrying value of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares. As the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares arewere not currently redeemable and notor probable of becoming redeemable as of December 31, 2023, adjustment to the initial carrying amount is not necessary and would only be required if it becomes probable that the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares would become redeemable.
Investment in EQGP
EQGP Unit Purchases. Noncontrolling InterestOn November 29, 2018,. Noncontrolling interest represents the Company entered into written agreements (the Unit Purchase Agreements) with certain investors owning an aggregate of 15,364,421 EQGP common units for $20.00 per EQGP common unit (the Purchase Price).
On December 31, 2018, the Company closed on the acquisition of an aggregate 14,560,281 EQGP common units pursuant to the Unit Purchase Agreements (the Initial Unit Purchase Closing) for an aggregate purchase price of $291.2 million. The Initial Unit Purchase Closing resulted in a reduction of additional paid-in capital of $46.8 million and a decrease in noncontrolling interest in consolidated subsidiaries of $244.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018.
On January 2, 2019 and January 3, 2019, the Company closed on the acquisitionportion of the remaining 804,140 EQGP common unitsequity of consolidated entities that the Company didare not purchase on December 31, 2018, pursuant to the Unit Purchase Agreements for an aggregate purchase price of $16.1 million (together with the Initial Unit Purchase Closing on December 31, 2018, the EQGP Unit Purchases).
EQGP Limited Call Right. Following the Initial Unit Purchase Closing, on December 31, 2018, the Company exercised a limited call right (the Limited Call Right and, together with the EQGP Unit Purchases, the EQGP Buyout) provided for in EQGP's agreement of limited partnership, dated as of October 12, 2018, pursuant to which the Company purchased all outstanding EQGP common units (other than thosewholly owned by the Company and its affiliates) atare reported as a component of shareholders’ equity in the Purchase Price. On January 10, 2019,consolidated balance sheets. Noncontrolling interest is adjusted by the amount of net income earned by the entities with noncontrolling interest, distributions paid to noncontrolling interest holders and any changes in the noncontrolling ownership percentages. For all periods presented, the Company's noncontrolling interest included third-party ownership interests in Eureka Midstream.
Earnings Per Share (EPS). Basic EPS is computed by dividing net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders by the weighted average number of shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted EPS is computed by dividing net income (loss) attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders by the weighted average number of shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock outstanding and the assumed issuance of all potentially dilutive securities. Each issue of potential common shares is evaluated separately in sequence from the most dilutive to the least dilutive. The dilutive effect of share-based payment awards and stock options is calculated using the treasury stock method, which assumes share purchases are calculated using the average share price of Equitrans Midstream common stock during the applicable period. The Company completed its exerciseuses the if-converted method to compute potential common shares from potentially dilutive convertible securities. Under the if-converted method, dilutive convertible securities are assumed to be converted from the date of the Limited Call Right by closingissuance and the resulting common shares are included in the denominator of the diluted EPS calculation for each applicable period. Income attributable to preferred dividends on convertible preferred stock that accumulated during the period is added back to the numerator for purposes of the if-converted method. See Note 11.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848), which provides practical expedients for contract modifications and certain hedging relationships associated with the transition from reference rates that are expected to be discontinued. This guidance is applicable to the calculation of each dividend following March 31, 2024 for the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares pursuant to the Company's Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation, as well as any Company contracts that use the London Inter-Bank Offered Rate as a reference rate. In December 2022, the FASB also issued ASU 2022-06, which amended Topic 848 to defer the sunset date to apply the practical expedients until December 31, 2024. The Company adopted this standard on April 1, 2023 and it had no impact on the acquisition onCompany's financial statements and related disclosures.
In November 2023, the remaining 11,097,287 outstanding EQGP common units not owned byFASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which provides improvements to reportable segment disclosures and is intended to enhance the Company or its affiliates for an aggregate purchase price of $221.9 million, and EQGP became an indirect, wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
In connection with the completion of the EQGP Buyout on January 10, 2019, certain non-employee members of the Board of Directors of EQGP's general partner stepped down from their roles and were paid the Purchase Price for each EQGP phantom unitdisclosures regarding significant segment expenses. The guidance is applicable to all public entities that they held, which was, in the aggregate, 29,829 EQGP phantom units, including accrued distributions.are required to report segment
In addition, on January 10, 2019, EQGP's omnibus agreementinformation in accordance with Equitrans Midstream was terminated.
Net Changes in Ownership of EQM
As a result of equity transactions relatingTopic 280 and is to the Company's investment in EQM, the Company adjusted its noncontrolling interest and common stock, no par value, balancesbe applied retrospectively to reflect the resulting changes in ownership. During the year ended December 31, 2020, as a result of the EQM Merger, the Company recorded,all prior periods presented in the aggregate,financial statements. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of adopting this standard on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes: Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which provides improvements to income tax disclosures and is intended to benefit investors by providing more detailed income tax disclosures that would be useful in making capital allocation decisions. The guidance is applicable to all public entities required to report income taxes in accordance with ASC 740 and should be applied prospectively, but retrospective application is permitted. The standard requires disaggregated information about a $2.7 billion increasereporting entity’s effective tax rate reconciliation, information on income taxes paid, and various other disclosure changes. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of common stock, no par value, a decrease in noncontrolling interest of $3.0 billionadopting this standard on its financial statements and an increase in deferred tax liability of $257.2 million. During the year ended December 31, 2019, as a result of the EQM IDR Transaction, the Company recorded, in the aggregate, a $997.2 million increase of common stock, no par value, a decrease in noncontrolling interest of $1.3 billion and a decrease in deferred tax asset of $340.4 million.related disclosures.
3.Mergers and Acquisitions
EQM Merger. See Note 2.
Bolt-on Acquisition. On March 13, 2019, the Company entered into a Purchase and Sale Agreement with North Haven Infrastructure Partners II Buffalo Holdings, LLC (NHIP), an affiliate of Morgan Stanley Infrastructure Partners, pursuant to which the Company acquired from NHIP a 60% Class A interest in Eureka Midstream and a 100% interest in Hornet Midstream (collectively, the Bolt-on Acquisition) for total consideration of approximately $1.04 billion, composed of approximately $852 million in cash, net of purchase price adjustments, and approximately $192 million in assumed pro-rata debt. At the time of the acquisition, Eureka Midstream owned an approximately 190-mile gathering header pipeline system in Ohio and West Virginia that services both dry Utica and wet Marcellus Shale production and Hornet Midstream owned an approximately 15-mile, high-pressure gathering system in West Virginia that connects to the Eureka Midstream system. The Bolt-on Acquisition closed on April 10, 2019 and was funded through proceeds from the Private Placement of the EQM Series A Preferred Units that closed concurrently with the Bolt-on Acquisition. See Note 2 for further information regarding the Private Placement.
At the closing of the Bolt-on Acquisition, a subsidiary of Hornet Midstream terminated all of its obligations under its term loan credit agreement and repaid the $28.2 million outstanding principal balance and $0.1 million in related interest and fees.
The Company recorded $17.0 million in acquisition-related expenses related to the Bolt-on Acquisition during the year ended December 31, 2019. The Bolt-on Acquisition acquisition-related expenses included $15.3 million for professional fees and $1.7 million for compensation arrangements during the year ended December 31, 2019, and are included in separation and other transaction costs in the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
The Bolt-on Acquisition was accounted for as a business combination using the acquisition method. As a result of the acquisition, the Company recognized $99.2 million of goodwill, which was allocated to the Gathering segment. Such goodwill primarily related to additional commercial opportunities, a diversified producer customer mix, increased exposure to dry Utica and wet Marcellus acreage and operating leverage within the Gathering segment. The purchase price allocation and related adjustments were finalized during the fourth quarter of 2019. The following table summarizes the final purchase price and allocation of the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the Bolt-on Acquisition as of April 10, 2019 by the Company, as well as certain measurement period adjustments made subsequent to the Company's initial valuation.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | Preliminary Purchase Price Allocation (As initially reported) | | Measurement Period Adjustments (a) | | Purchase Price Allocation (As adjusted) |
| Consideration given: | | | | | | |
Cash consideration (b) | | $ | 861,250 | | | $ | (11,404) | | | $ | 849,846 | |
| Buyout of portion of Eureka Midstream Class B units and incentive compensation | | 2,530 | | | — | | | 2,530 | |
| Total consideration | | 863,780 | | | (11,404) | | | 852,376 | |
| | | | | | |
| Fair value of liabilities assumed: | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities | | 52,458 | | | (9,857) | | | 42,601 | |
| Long-term debt | | 300,825 | | | — | | | 300,825 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | | 10,203 | | | — | | | 10,203 | |
| Amount attributable to liabilities assumed | | 363,486 | | | (9,857) | | | 353,629 | |
| | | | | | |
| Fair value of assets acquired: | | | | | | |
| Cash | | 15,145 | | | — | | | 15,145 | |
| Accounts receivable | | 16,817 | | | — | | | 16,817 | |
| Inventory | | 12,991 | | | (26) | | | 12,965 | |
| Other current assets | | 882 | | | — | | | 882 | |
| Net property, plant and equipment | | 1,222,284 | | | (8,906) | | | 1,213,378 | |
Intangible assets (c) | | 317,000 | | | (6,000) | | | 311,000 | |
| Deferred tax asset | | 5,773 | | | (5,268) | | | 505 | |
| Other assets | | 14,567 | | | — | | | 14,567 | |
| Amount attributable to assets acquired | | 1,605,459 | | | (20,200) | | | 1,585,259 | |
| | | | | | |
| Noncontrolling interests | | (486,062) | | | 7,602 | | | (478,460) | |
| | | | | | |
| Goodwill as of April 10, 2019 | | $ | 107,869 | | | $ | (8,663) | | | $ | 99,206 | |
Impairment of goodwill (d) | | | | | | (99,206) | |
| Goodwill as of December 31, 2019 | | | | | | $ | — | |
(a) The Company recorded measurement period adjustments to its preliminary acquisition date fair values due to the refinement of its valuation models, assumptions and inputs. The measurement period adjustments were based upon information obtained about facts and circumstances that existed at the acquisition date that, if known, would have affected the measurement of the amounts recognized at that date.
(b) The cash consideration for the Bolt-on Acquisition was adjusted by approximately $11.4 million related to working capital adjustments and the release of all escrowed indemnification funds to the Company.
(c) After considering the refinements to the valuation models, the Company estimated the fair value of the customer-related intangible assets acquired as part of the Bolt-on Acquisition to be $311.0 million. As a result, the fair value of the customer-related intangible assets was decreased by $6.0 million on September 30, 2019 with a corresponding increase to goodwill. In addition, the change to the provisional amount resulted in a decrease in amortization expense and accumulated amortization of approximately $0.4 million.
(d) During the third quarter of 2019, the Company identified impairment indicators that suggested the fair value of its goodwill was more likely than not below its carrying amount. As such, the Company performed an interim goodwill impairment assessment, which resulted in the Company recognizing impairment to goodwill of approximately $268.1 million, of which $99.2 million was associated with its Eureka/Hornet reporting unit, bringing the reporting unit's goodwill balance to zero. See Note 4 for further detail.
The estimated fair value of midstream facilities and equipment, generally consisting of pipeline systems and compression stations, was estimated using the cost approach. Significant unobservable inputs in the estimate of fair value under this approach included management's assumptions about the replacement costs for similar assets, the relative age of the acquired assets and any potential economic or functional obsolescence associated with the acquired assets. As a result, the estimated fair value of the midstream facilities and equipment represented a Level 3 fair value measurement.
As a result of the acquisition, the noncontrolling interest in Eureka Midstream was estimated to be $478.5 million. The fair value of the noncontrolling interest was calculated based on the enterprise value of Eureka Midstream and the percentage ownership not acquired by the Company. Significant unobservable inputs in the enterprise value of Eureka Midstream include
future revenue estimates and future cost assumptions. As a result, the fair value measurement is based on significant inputs that are not observable in the market and thus represents a Level 3 fair value measurement.
As part of the preliminary purchase price allocation, the Company identified intangible assets for customer relationships with third-party customers. The fair value of the customer relationships with third-party customers was determined using the income approach, which requires a forecast of the expected future cash flows generated and an estimated market-based weighted average cost of capital. Significant unobservable inputs in the determination of fair value include future revenue estimates, future cost assumptions and estimated customer retention rates. As a result, the estimated fair value of the identified intangible assets represents a Level 3 fair value measurement. The Company previously utilized a useful life of 20 years for the Eureka Midstream- and Hornet Midstream-related intangible assets. As a result of then-expected changes in cash flows due to decreases in producer activity driven by lower natural gas prices in periods subsequent to the Bolt-on Acquisition closing, as of April 1, 2020, the Company prospectively changed the remaining useful life of the Eureka Midstream-related intangible assets to 10.75 years, increasing the expected annual amortization expense by $9.1 million. In addition, as a result of then-expected reductions in future cash flows, as of October 1, 2019, the useful life of the Hornet Midstream-related intangible assets was prospectively changed to 7.25 years.
In conjunction with the Bolt-on Acquisition, the Company recorded tax deductible goodwill of $43.0 million. The Company does not have tax basis on the portion attributable to the former noncontrolling limited partners of EQM.
Post-Acquisition Operating Results. Subsequent to the completion of the Bolt-on Acquisition, Eureka Midstream and Hornet Midstream collectively contributed the following to both the Gathering segment and the Company's consolidated operating results for the period from April 10, 2019 through December 31, 2019.
| | | | | | | | |
(in thousands) | | April 10, 2019 Through December 31, 2019 |
Operating revenues | | $ | 97,123 | |
Operating loss attributable to Equitrans Midstream | | $ | (94,551) | |
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | | $ | (21,291) | |
Net loss attributable to Equitrans Midstream | | $ | (80,631) | |
Unaudited Pro Forma Information. The following unaudited pro forma combined financial information presents the Company's results as though the EQGP Buyout, EQM IDR Transaction and Bolt-on Acquisition had been completed at January 1, 2019. The pro forma combined financial information has been included for comparative purposes and is not necessarily indicative of the results that might have actually occurred had the EQGP Buyout, EQM IDR Transaction and Bolt-on Acquisition taken place on January 1, 2019; furthermore, the financial information is not intended to be a projection of future results.
| | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except per share data) | | December 31, 2019 | | |
Pro forma operating revenues | | $ | 1,661,822 | | | |
Pro forma net loss | | $ | (44,167) | | | |
Pro forma net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | $ | 126,558 | | | |
Pro forma net loss attributable to Equitrans Midstream | | $ | (170,725) | | | |
Pro forma loss per share (basic) | | $ | (0.67) | | | |
Pro forma loss per share (diluted) | | $ | (0.67) | | | |
4. Impairments of Long-Lived Assets and Equity Method Investment
Goodwill. The three reporting units to which the Company hadCompany's goodwill during 2019 were (i) the Ohio gathering assets that were acquired in certain prior acquisitions (collectively, Rice Retained Midstream), (ii) the Pennsylvania gathering assets acquired by EQM from Rice Midstream Partners LP (n/k/a RM Partners LP) (RMP) and its general partner (RMP PA Gas Gathering reporting unit) and (iii) the Ohio and West Virginia gathering assets acquired in the Bolt-on Acquisition (Eureka/Hornet, collectivelybalance is associated entirely with Rice Retained Midstream and RMP PA Gas Gathering, the Reporting Units).
During the third quarter of 2019, the Company identified impairment indicators in the form of significant declines in the unit price of EQM common units and corresponding market capitalization, primarily as a result of continued suppressed natural gas prices and decreased producer drilling activity. Management considered these declines as indicators that the fair value of goodwill was more likely than not below the carrying amounts for the respective Reporting Units. As such, the performance of an interim goodwill impairment assessment was required. In estimating the fair value of each of the Reporting Units, the Company used a combination of the income approach and the market approach. The Company used the income approach’s
discounted cash flow method, which applies significant inputs not observable in the public market (Level 3), including estimates and assumptions related to the use of an appropriate discount rate, future throughput volumes, operating costs, capital spending and changes in working capital. The Company used the market approach’s comparable company and reference transaction methods. The comparable company method evaluates the value of a company using metrics of other businesses of similar size and industry. The reference transaction method evaluates the value of a company based on pricing multiples derived from similar transactions entered into by similar companies.
As of August 31, 2019, the Company determined that the fair value of Rice Retained Midstream was greater than its carrying value; however, the carrying values of RMP PA Gas Gathering and Eureka/Hornet were each greater than their respective fair values. As a result, the Company recognized impairment of goodwill of $168.9 million and $99.2 million on RMP PA Gas Gathering and Eureka/Hornet, respectively. The non-cash impairment charges are included in the impairments of long-lived assets line on the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
During the fourth quarter of 2019, as of the date of the Company’s annual goodwill impairment assessment, the Company concluded the performance of a quantitative impairment assessment was required. Factors contributing to this conclusion were the continued decline of the Company's market capitalization in the fourth quarter and the sustained declines in producer drilling activity driven by market conditions including natural gas pricing.
Consistent with the third quarter 2019 interim goodwill impairment assessment, the Company used the income approach’s discounted cash flow method and the market approach’s comparable company and reference transaction methods. During the Company’s fourth quarter 2019 impairment assessment, the Company determined that the carrying values of RMP PA Gas Gathering and Rice Retained Midstream were each greater than their respective fair values. As a result, the Company recognized impairment of goodwill of $433.2 million and $150.5 million on RMP PA Gas Gathering and Rice Retained Midstream, respectively. The non-cash impairment charge is included in the impairments of long-lived assets line on the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
The following table summarizes the carrying amount of goodwill associated with the Company's Reporting Units for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | EQM Opco(a) | | Rice Retained Midstream | | | | Eureka/Hornet | | Total |
| (Thousands) |
| Gross Goodwill | $ | 1,350,721 | | | $ | 150,489 | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,501,210 | |
| Accumulated impairment losses | (261,941) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (261,941) | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Goodwill as of January 1, 2019 | 1,088,780 | | | 150,489 | | | | | — | | | 1,239,269 | |
| Add: goodwill associated with Bolt-on Acquisition | — | | | — | | | | | 99,206 | | | 99,206 | |
| Less: impairment of goodwill | (602,082) | | | (150,489) | | | | | (99,206) | | | (851,777) | |
| Goodwill as of December 31, 2019 | 486,698 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 486,698 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Goodwill as of December 31, 2020 | 486,698 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 486,698 | |
| Goodwill as of December 31, 2021 | $ | 486,698 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | 486,698 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Gross Goodwill | $ | 1,350,721 | | | $ | 150,489 | | | | | $ | 99,206 | | | $ | 1,600,416 | |
| Accumulated impairment losses | (864,023) | | | (150,489) | | | | | (99,206) | | | (1,113,718) | |
| Goodwill as of December 31, 2021 | $ | 486,698 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | — | | | $ | 486,698 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
(a) Effective on the EQT Global GGA Effective Date, the RMP PA Gas Gathering reporting unit was merged with and into the EQM Opco reporting unit, with the EQM Opco reporting unit surviving.
On February 26, 2020 (the EQT Global GGA Effective Date), the Company (through EQM) entered into a Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement (as amended, the EQT Global GGA) with EQT for the provision of certain gas gathering services to EQT in the Marcellus and Utica Shales of Pennsylvania and West Virginia (as further discussed in Note 6). Prior to the EQT Global GGA Effective Date, the Company operated 3 reportable operating segments and 7 reporting units, which are one level below the operating segment level and are generally based on how segment management reviews the Company's operating results. Commencing with the EQT Global GGA Effective Date, the Company reduced its reporting units from 7 to 6 and maintained its 3 reportable operating segments. As of the EQT Global GGA Effective Date, the only reporting unit to which the Company had goodwill recorded was the RMP PA Gas Gathering reporting unit. As a result of the EQT Global GGA, the assets under, and operations associated with, the RMP PA Gas Gathering reporting unit and the reporting unit associated with the gas gathering and compression activities of EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, an indirect wholly owned
subsidiary of the Company, (EQM Opco reporting unit), were combined to service a collective minimum volume commitment (MVC) under the agreement. Therefore, effective on the EQT Global GGA Effective Date, the RMP PA Gas Gatheringand such reporting unit was merged with and intois included within the EQM Opco reporting unit,Gathering segment. The following table summarizes the carrying amount of goodwill associated with the EQM OpcoCompany's reporting unit surviving.units as of December 31, 2023 and 2022.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | |
| (Thousands) |
| Gross Goodwill | $ | 1,350,721 | | | $ | 1,350,721 | |
| Accumulated impairment losses | (864,023) | | | (864,023) | |
| Balance as of end of period | $ | 486,698 | | | $ | 486,698 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
There was no impairment to goodwill recorded during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
During the firstfourth quarter of 2020,2023, the Company identifiedperformed a qualitative impairment indicators inassessment. As a result of the form of significant declines in the unit price of EQM common units and corresponding market capitalization. Management considered these declines as indicatorsassessment, it was determined that it was not more likely than not that the fair value of the RMP PA Gas GatheringEQM Opco reporting unit may have been belowwas less than its carrying amount and the performance of an interim quantitative goodwillas such, no further impairment assessmenttesting was required. Additionally, as a result of the combination of the RMP PA Gas Gathering reporting unit and the EQM Opco reporting unit, the Company tested both the RMP PA Gas Gathering and the merged EQM Opco reporting units for goodwill impairment. In estimating the fair value of the RMP PA Gas Gathering and the merged EQM Opco reporting units, the Company used a combination of the income approach and the market approach, both as described above.
As a result of the interim assessment, the Company determined that the fair values of the RMP PA Gas Gathering reporting unit and the merged EQM Opco reporting unit, as applicable, were greater than their respective carrying values. No impairment to goodwill was recorded during the three months ended March 31, 2020. The Company believes the estimates and assumptions used in estimating its reporting units’ fair values are reasonable and appropriate; however, different assumptions and estimates could materially affect the calculated fair values of the RMP PA Gas Gathering reporting unit and the merged EQM Opco reporting unit and the resulting conclusions on impairment of goodwill, which could materially affect the Company’s results of operations and financial position. Additionally, actual results could differ from these estimates and assumptions may not be realized.
necessary. During the fourth quarter of 2020,2022, the Company performed a quantitative impairment assessment as required as part of the annual goodwill impairment assessment. As a result of the annual assessment, the Company determined that the fair value of the EQM Opco reporting unit was greater than its carrying value. No impairment to goodwill was recorded as a result of
The Company believes the annual impairment assessment.
As of December 31, 2021, the Company's goodwill balance wasestimates and assumptions used in estimating its reporting unit's fair values are reasonable and appropriate; however, different assumptions and estimates, including those that could be driven by risks associated entirely with the EQM Opco reporting unit. During the fourth quarter of 2021, the Company performed a quantitative impairment assessment as required as part of the annual goodwill impairment assessment. As a result of the annual assessment, the Company determined that the fair value of the EQM Opco reporting unit was greater than its carrying value. No impairment to goodwill was recorded as a result of the impairment assessment. However, the EQM Opco reporting unit is susceptible to impairment risk from future adverse market or economic conditions and Company-specificCompany specific qualitative factors, contractual changes or modifications or other adverse factors such as unexpected future production curtailmentscurtailment by customers, could materially affect the Company's customers that have contracts with volumetric-based fees. Any such adverse changes in the future could reduce the underlying cash flows used to estimatecalculated fair value and could result in a decline in fair value that could trigger future impairment charges relating toof the EQM Opco reporting unit.unit and the resulting conclusions on impairment of goodwill, which could materially affect the Company’s results of operations and financial position. Additionally, actual results could differ from these estimates and assumptions may not be realized.
Long-Lived Assets. During the third quarter of 2019, the Company assessed its long-lived asset groups for impairment due to the triggering events described in the 2019 interim goodwill impairment summary above. As a result of the recoverability test, management determined that the carrying value of certain long-lived assets associated with Eureka/Hornet (specifically, Hornet Midstream customer-related intangible assets) were not recoverable. The Company estimated the fair value of the Hornet Midstream-related intangible assets and determined that the fair value was not in excess of the assets’ carrying value, which resulted in an impairment charge of approximately $36.4 million related to certain of such intangible assets within the Company's Gathering segment. The non-cash impairment charge is included in the impairments of long-lived assets line on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income. During the fourth quarter of 2019, a triggering event occurred as a result of the Company's annual goodwill impairment evaluation, which required the Company to perform a recoverability test on its long-lived assets. No impairment to long-lived assets was recorded as a result of the recoverability test.
During 2019, the Company reassessed its asset groupings for its regulated pipelines due to certain regulatory ratemaking policy changes affecting the regulated pipelines, changes in strategic focus and plans for segmentation of operations. Prior to the second quarter of 2019, the Company defined its regulated asset grouping to include the FERC-regulated transmission and storage assets, integrated with the low-pressure assets due to overlapping operations, a shared costs structure and similar ratemaking structures. During the second quarter of 2019, Equitrans, L.P. reached a settlement related to its FERC Form 501-G report, which was focused solely on the Company’s FERC-regulated transmission and storage assets. Further, management increased its operational focus and emphasis on high-pressure gathering assets as illustrated by the consummation of the Bolt-on Acquisition. As a result of these regulatory changes and shift in operational focus, beginning with the second quarter of 2019, the Company grouped its FERC-regulated assets in two asset groupings: FERC-regulated transmission and storage assets and FERC-regulated low-pressure gathering assets. Upon the change in asset grouping, management evaluated whether any indicators of impairment were present and, in conjunction with the evaluation, the Company determined that the carrying values for the non-core FERC-regulated low-pressure gathering assets exceeded their undiscounted cash flows. Additionally,
following the settlement related to the FERC Form 501-G report, management did not, and currently does not plan to, seek to recover the deficient cash flows through a future rate proceeding. The Company therefore estimated the fair values of FERC-regulated low-pressure gathering assets and determined that their fair values were not in excess of the assets’ carrying values, which resulted in recognized impairments of property and equipment of approximately $81.0 million during 2019 related to the assets within the Company's Gathering segment. As a result of the impairment, the assets carry no book value. The non-cash impairment charge is included in the impairments of long-lived assets line on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
As of March 31, 2020, the Company performed a recoverability test of the Hornet Midstream long-lived assets due to decreased producer activity. As a result of the recoverability test, management determined that the carrying value of the Hornet Midstream long-lived assets (which consisted of gathering assets and customer-related intangible assets) was not recoverable under ASC 360, Impairment Testing: Long-Lived Assets Classified as Held and Used. During the first quarter of 2020, the Company estimated the fair value of the Hornet Midstream asset group and determined that the fair value was not in excess of the assets’ carrying value, which resulted in impairment charges of approximately $37.9 million to the gathering assets and approximately $17.7 million to the customer-related intangible assets both within the Company’s Gathering segment. The non-cash impairment charges were recognized during the first quarter of 2020 and are included in the impairments of long-lived assets line on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
As of June 30, 2021, the Company performed a recoverability test of the Equitrans Water Services (OH) LLC (Ohio Water) long-lived assets due to decreased producer activity in Ohio within the Company's Water segment. As a result of the recoverability test, management determined that the carrying value of the Ohio Water long-lived assets was not recoverable under ASC 360, Impairment Testing: Long-Lived Assets Classified as Held and Used. The Company estimated the fair value of the Ohio Water asset group and determined that the fair value was less than the assets’ carrying value, which resulted in impairment charges of approximately $56.2 million to the Ohio Water assets within the Company's Water segment. The non-cash impairment charge was recognized during the second quarter of 2021 and is included in the impairmentsimpairment of long-lived assets line on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Equity Method Investment. The Company is also required to evaluate its equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture to determine whether it is impaired under ASC 323, Investments - Equity Method and Joint Ventures. The standard for determining whether an impairment must be recorded under ASC 323, Investments: Equity Method Investments and Joint Ventures (ASC 323) is whether there occurred an other-than-temporary decline in value. The Company monitorsreviews the carrying value of investments in unconsolidated entities for impairment recorded under ASC 323 whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate, in management's judgment, that may indicate the carrying value of such investment may have experienced an other-than-temporary decline in value. The fair value of an equity method investment is generally estimated using an income approach under which significant judgments and assumptions include expected future cash flows, the appropriate discount rate and probability-weighted scenarios.
Events or circumstances that may be indicative of an other-than-temporary decline in value of an equity method investment include, but are not limited to:
•a prolonged period of time that the fair value is below the investor’s carrying value;
•the current expected financial performance is significantly worse than anticipated when the investor originally invested in the investee;
•adverse regulatory action is expected to substantially reduce the investee’s product demand or profitability;
•the investee has lost significant customers or suppliers with no immediate prospects for replacement;
•the investee’s discounted or undiscounted cash flows are below the investor’s carrying amount; and
•the investee’s industry is declining and significantly lags the performance of the economy as a whole.
The estimates that the Company makes with respect to its equity method investment are based upon assumptions that management believes are reasonable, and the impact of variations in these estimates or the underlying assumptions could be material. Additionally, if any joint venture to which the investment relates recognizes an impairment under ASC 360, the Company would be required to record its proportionate share of such impairment loss and would also evaluate such investment for an other-than-temporary decline in value under ASC 323.
During 2020, the MVP Joint Venture received certain adverse court rulings in the U.S. Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals. As a result, the Company evaluated its equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture for impairment during the fourth quarter of 2020 and determined that the fair value of the investment continued to exceed the carrying value and, therefore, no impairment was necessary. The Company estimated the fair value of its investment in the MVP Joint Venture using an income
approach that primarily considered probability-weighted scenarios of discounted future net cash flows based on the most recent estimate of total project costs and revenues as of December 31, 2020. These scenarios reflected assumptions and judgments regarding various future court decisions and regulatory authorizations and the impact that those decisions and authorizations may have on the timing and extent of the Company’s investment, including scenarios assuming the full resolution of permitting issues. The Company’s analysis took into account, among other things, growth expectations from additional compression expansion opportunities. The Company generally used an after-tax discount rate of 5.5% in the analysis derived based on a market participant approach. Based on the Company’s then expectations for the MVP Joint Venture's projects, and taking into account, among other things, regulatory considerations, public support for the MVP project by the Chairman of the U.S. Senate Committee on Energy and Natural Resources, and other publicly available information, the Company assigned higher probabilities for scenarios under which the Company received all required legal and regulatory approvals and authorizations and certain compression expansion opportunities are realized. A low probability was assigned to the scenario under which the project is cancelled.
During the fourth quarter of 2021, certain legal challenges before the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit (Fourth Circuit) regarding regulatory authorizations previously granted to the MVP Joint Venture were completed, other than the issuance of decisions in those matters. In connection with the completion of those proceedings, the Company identified as an indicator of an other-than-temporary decline in value the various uncertain legal outcomes and the potential impacts that certain unfavorable outcomes could have on the then targetedthen-targeted full in-service date for the MVP project and consequent timing for certain projects related thereto and total targeted MVP project costs. In January 2022, the Fourth Circuit vacated and remanded the MVP Joint Venture's authorizationsthen-authorizations related to the Jefferson National Forest (JNF) received from the Bureau of Land Management and the U.S. Forest Service and, in February 2022, the Fourth Circuit vacated and remanded the Biologicalthen-Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement issued by the U.S. Department of the Interior’s Fish and Wildlife Service for the MVP project. The Company considered these unfavorable decisions by the Fourth Circuit as supplemental evidence in evaluating its equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture as of December 31, 2021, to determine if the investment’s carrying value exceeded the fair value and, if so, whether that the decline in value was other-than-temporary.
The Company estimated the fair value of its investment in the MVP Joint Venture using an income approach that primarily considered revised probability-weighted scenarios of discounted future net cash flows based on the estimates of total project costs and revenues. These scenarios reflected assumptions and judgments regarding the ultimate outcome of further matters relating to, orpotential delays and cost increases resulting from the January and February 2022 Fourth Circuit rulings, as well as various other ongoingthen-ongoing legal and regulatory matters affecting the MVP and MVP Southgate projects.projects (as defined herein). Such assumptions and judgments also included certain additional potential delays and related cost increases that could result from unfavorable decisions on these proceedings and matters. The Company’s analysis also took into account, among other things, probability-weighted growth expectations from additional compression expansion opportunities. The Company generally used an after-tax discount rate of 5.5 percent5.5% in the analysis derived based on a market participant approach. The Company considered scenarios under which ongoingthen-ongoing or new legal and regulatory matters furtherfurthered delay the completion and increaseincreased the total costs of the project; all required legal and regulatory approvals and authorizations and certain compression expansion opportunities are realized; and the MVP project is canceled. As a result of the assessment, the Company recognized a pre-tax impairment charge of approximately $1.9 billion that reduced the carrying value of its equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture to approximately $1.2 billion as of December 31, 2021.billion. Given the significant assumptions and judgments used in estimating the fair value of the Company's investment in the MVP Joint Venture, the fair value of the investment in the MVP Joint Venture represents a Level 3 measurement.
There isDuring the third quarter of 2022 assessment, the Company identified an increased risk thatof further permitting delays resulting primarily from legal developments and regulatory uncertainties, as well as macroeconomic pressures primarily due to increased interest rates impacting the Company’sdiscount rate used within the estimated fair value of its investment in the MVP Joint Venture. The Company considered these factors to be indicators of a decline in value. As such, the Company evaluated if the carrying value of its equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture may be furtherexceeded the fair value and, if so, whether that decline in value was other-than-temporary, and thus the equity method investment was impaired in the future. There are ongoing (and may be future) legal and regulatory matters related to the MVP project, any of which could affect the ability to complete or operate the project, as well as legal and regulatory matters related to the MVP Southgate project that must be resolved in connection with the project. Assumptions and estimates utilized in assessingunder ASC 323.
The Company estimated the fair value of the Company’sits investment in the MVP Joint Venture may change depending onusing an income approach generally consistent with that described above, except that the nature or timingCompany generally used an after-tax discount rate of resolutions to7.5% in the legal and regulatory matters oranalysis derived based on other relevant developments. Adversea market participant approach. As a result of the assessment, the Company recognized a pre-tax impairment charge of approximately $583.1 million.
Future adverse developments, as well as potential macroeconomic factors, including other-than-temporary market fluctuations, changes in circumstances relevant to the likelihood of project or expansion completioninterest rates, cost increases and other unanticipated events could prompt the Company,result in future assessments, to apply a lower probability of project or expansion completion and such changes in assumptions or estimates (including probability) could have a material adverse effect on the fair valueadditional impairment of the Company's equity method investment in the MVP Joint VentureVenture. While macroeconomic factors in and potentially resultof themselves may not be a direct
indicator of impairment, should an impairment indicator be identified in an additional impairment, whichthe future, these macroeconomic factors could have a material adverse effect onultimately impact the Company's resultssize and scope of operations and financial position.any potential impairment.
5.3. Financial Information by Business Segment
The Company reports its operations in 3three segments that reflect its 3three lines of business of Gathering, Transmission and Water, which reflects the manner in which management evaluates the business for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Refer to Note 1 for discussion on business segments.
| | | | Years Ended December 31, | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | | (Thousands) | | (Thousands) |
| Revenues from customers: | Revenues from customers: | | | Revenues from customers: | | | | | |
| Gathering | $ | 862,053 | | | $ | 1,012,281 | | | $ | 1,159,931 | |
| Transmission | 400,202 | | | 393,836 | | | 390,520 | |
Gathering (a) | |
Transmission (a) | |
| Water | Water | 54,782 | | | 104,708 | | | 79,791 | |
| Total operating revenues | Total operating revenues | $ | 1,317,037 | | | $ | 1,510,825 | | | $ | 1,630,242 | |
| Operating income (loss): | Operating income (loss): | | | | | | Operating income (loss): | | | | | |
Gathering (a) | $ | 414,200 | | | $ | 535,976 | | | $ | (88,850) | |
Gathering | |
| Transmission | Transmission | 274,526 | | | 275,369 | | | 277,731 | |
Water (b) | Water (b) | (53,980) | | | 38,756 | | | 15,305 | |
Headquarters (c) | Headquarters (c) | (1,183) | | | (25,540) | | | (128,186) | |
| Total operating income | Total operating income | $ | 633,563 | | | $ | 824,561 | | | $ | 76,000 | |
| | Reconciliation of operating income to net (loss) income: | Reconciliation of operating income to net (loss) income: | |
| Reconciliation of operating income to net (loss) income: | |
| Reconciliation of operating income to net (loss) income: | |
Equity income (d) | Equity income (d) | $ | 17,579 | | | $ | 233,833 | | | $ | 163,279 | |
Impairment of equity method investment (d) | (1,926,402) | | | — | | | — | |
Other (expense) income, net (e) | (16,104) | | | 17,225 | | | 2,661 | |
Equity income (d) | |
Equity income (d) | |
Impairments of equity method investment (d) | |
Other income (expense), net (e) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | Loss on extinguishment of debt | (41,025) | | | (24,864) | | | — | |
| Net interest expense | Net interest expense | (378,650) | | | (307,380) | | | (256,195) | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense | Income tax (benefit) expense | (345,091) | | | 105,331 | | | 50,704 | |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (1,365,948) | | | $ | 638,044 | | | $ | (64,959) | |
| Net income (loss) | |
(a)Impairments of long-lived assets of $55.6 million and $854.3 million forFor the yearsyear ended December 31, 20202023, volumetric-based fee revenues associated with Gathering and 2019, respectively, wereTransmission included in Gathering operating income (loss). See Note 4one-time contract buyouts by a customer for further information.approximately $5.0 million and $23.8 million, respectively.
(b)ImpairmentsImpairment of long-lived assets of $56.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 waswere included in Water operating income (loss). See Note 42 for further information.
(c)Includes separation and other transaction costs and othercertain unallocated corporate expenses.
(d)Equity income and impairmentimpairments of equity method investment are included in the Transmission segment.
(e)Includes unrealized (loss)gains (losses) on derivative instruments and, for the year ended December 31, 2022, gain on derivative instrumentssale of gathering assets recorded in the Gathering segment.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, | | |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | |
| | (Thousands) | | |
| Segment assets: | | | | | | | |
| Gathering | $ | 7,638,877 | | | $ | 7,739,836 | | | $ | 7,572,911 | | | |
Transmission (a) | 2,769,097 | | | 4,357,382 | | | 3,903,707 | | | |
| Water | 151,151 | | | 185,802 | | | 202,440 | | | |
| Total operating segments | 10,559,125 | | | 12,283,020 | | | 11,679,058 | | | |
| Headquarters, including cash | 361,639 | | | 442,832 | | | 362,651 | | | |
| Total assets | $ | 10,920,764 | | | $ | 12,725,852 | | | $ | 12,041,709 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, | | |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| | (Thousands) | | |
| Segment assets: | | | | | | | |
| Gathering | $ | 7,612,820 | | | $ | 7,610,233 | | | $ | 7,600,637 | | | |
Transmission (a) | 3,369,718 | | | 2,333,896 | | | 2,769,097 | | | |
| Water | 217,225 | | | 218,680 | | | 151,151 | | | |
| Total operating segments | 11,199,763 | | | 10,162,809 | | | 10,520,885 | | | |
| Headquarters, including cash | 509,663 | | | 282,776 | | | 361,639 | | | |
| Total assets | $ | 11,709,426 | | | $ | 10,445,585 | | | $ | 10,882,524 | | | |
(a)The equity investment in the MVP Joint Venture is included in the Transmission segment.
| | | | Years Ended December 31, | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | | (Thousands) | | (Thousands) |
| Depreciation: | Depreciation: | | | Depreciation: | | | | | |
| Gathering | Gathering | $ | 188,633 | | | $ | 172,967 | | | $ | 144,310 | |
| Transmission | Transmission | 55,310 | | | 54,540 | | | 51,935 | |
| Water | Water | 25,233 | | | 30,880 | | | 26,915 | |
| Headquarters | Headquarters | 1,228 | | | 1,226 | | | 4,204 | |
| Total | Total | $ | 270,404 | | | $ | 259,613 | | | $ | 227,364 | |
| Expenditures for segment assets: | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures: | |
Gathering (a) | |
Gathering (a) | |
Gathering (a) | Gathering (a) | $ | 223,807 | | | $ | 344,873 | | | $ | 834,712 | |
Transmission (b) | Transmission (b) | 25,977 | | | 45,219 | | | 59,313 | |
| Water | Water | 34,877 | | | 11,905 | | | 37,457 | |
| Headquarters | Headquarters | 1,494 | | | 4,004 | | | 9,779 | |
Total (c) | Total (c) | $ | 286,155 | | | $ | 406,001 | | | $ | 941,261 | |
(a)Includes approximately $14.1$14.3 million, $41.6$20.3 million and $25.9$14.1 million of capital expenditures related to noncontrolling interestsinterest in Eureka Midstream for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, respectively.
(b)Transmission capital expenditures do not include aggregate capital contributions made to the MVP Joint Venture for the MVP and MVP Southgate projects of approximately $287.7$689.4 million, $272.8$199.6 million and $774.6$287.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, respectively.
(c)The Company accrues capital expenditures when the work has been completed but the associated bills have not yet been paid. Accrued capital expenditures are excluded from the statements of consolidated cash flows until they are paid. The net impact of non-cash capital expenditures, including the effect of accrued capital expenditures, assumed capital expenditures associated with the Bolt-on Acquisition, transfers to/from inventory as assets are completed/assigned to a project and capitalized share-based compensation costs, was $4.4$(11.1) million, $56.0$8.2 million and $26.1$4.4 million at December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, respectively.
4. Revenue from Contracts with Customers
For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, 2020 and 2019,substantially all revenues recognized on the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income arewere from contracts with customers. As of December 31, 20212023 and 2020,2022, all receivables recorded on the Company's consolidated balance sheets represent performance obligations that have been satisfied and for which an unconditional right to consideration exists.
Summary of disaggregated revenues. The tables below provide disaggregated revenue information by business segment.
| | Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
| Gathering | | Transmission | | Water | | Total |
| (Thousands) |
| Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | | Year Ended December 31, 2023 |
| Gathering | | | Gathering | | Transmission | | Water | | Total |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | $ | 468,156 | | | $ | 366,323 | | | $ | 5,063 | | | $ | 839,542 | |
| Volumetric-based fee revenues | 393,897 | | | 33,879 | | | 49,719 | | | 477,495 | |
Volumetric-based fee revenues (b) | |
| Total operating revenues | Total operating revenues | $ | 862,053 | | | $ | 400,202 | | | $ | 54,782 | | | $ | 1,317,037 | |
| | Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| Gathering | | Transmission | | Water | | Total |
| (Thousands) |
| Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | | Year Ended December 31, 2022 |
| Gathering | | | Gathering | | Transmission | | Water | | Total |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | $ | 595,720 | | | $ | 364,533 | | | $ | 41,798 | | | $ | 1,002,051 | |
| Volumetric-based fee revenues | 416,561 | | | 29,303 | | | 62,910 | | | 508,774 | |
Volumetric-based fee revenues (b) | |
| Total operating revenues | Total operating revenues | $ | 1,012,281 | | | $ | 393,836 | | | $ | 104,708 | | | $ | 1,510,825 | |
| | Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| Gathering | | Transmission | | Water | | Total |
| (Thousands) |
| Year Ended December 31, 2021 | | | Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
| Gathering | | | Gathering | | Transmission | | Water | | Total |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | Firm reservation fee revenues (a) | $ | 581,118 | | | $ | 356,569 | | | $ | 11,190 | | | $ | 948,877 | |
| Volumetric-based fee revenues | 578,813 | | | 33,951 | | | 68,601 | | | 681,365 | |
Volumetric-based fee revenues (b) | |
| Total operating revenues | Total operating revenues | $ | 1,159,931 | | | $ | 390,520 | | | $ | 79,791 | | | $ | 1,630,242 | |
(a) For the years ended December 31, 20212023, 2022 and 2020,2021, firm reservation fee revenues associated with Gathering included approximately $11.3$4.1 million, $20.2 million and $15.0$11.3 million, respectively, of MVC unbilled revenues. There were no MVC unbilled revenues associated with Gathering during
(b) For the year ended December 31, 2019.2023, volumetric-based fee revenues associated with Gathering and Transmission included one-time contract buyouts by a customer for approximately $5.0 million and $23.8 million, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, volumetric-based fee revenues associated with Gathering included approximately $4.6 million, $4.2 million and $3.5 million, respectively, of MVC unbilled revenues.
Contract assets. The Company recognizes contract assets primarily in instances where billing occurs subsequent to revenue recognition and the Company's right to invoice the customer is conditioned on something other than the passage of time. The Company's contract assets primarily consist of revenue recognized under contracts containing MVCs (whereby management has concluded (i) it is probable there will be a MVC deficiency payment at the end of the then-current MVC period, which is typically the period beginning at the inception of such contracts through the successive twelve-month periods after that date, and (ii) that a significant reversal of revenue recognized currently for the future MVC deficiency payment will not occur), as well as certain other contractual commitments. As a result, the Company's contract assets related to the Company's future MVC deficiency payments are generally expected to be collected within the next twelve months and are primarily included in other current assets in the Company's consolidated balance sheets until such time as the MVC deficiency payments are invoiced to the customer.
The following table presents changes in the Company's unbilled revenuecontract assets balance during the years ended December 31, 20212023 and 2020:2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Unbilled Revenue | | |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | |
| | (Thousands) | | |
| Balance as of beginning of period | | $ | 18,618 | | | $ | — | | | |
Revenue recognized in excess of amounts invoiced (a) | | 26,779 | | | 28,446 | | | |
Minimum volume commitments invoiced (b) | | (28,442) | | | (9,828) | | | |
Amortization (c) | | (183) | | | — | | | |
| Balance as of end of period | | $ | 16,772 | | | $ | 18,618 | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Contract Assets |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| | (Thousands) | | |
| Balance as of beginning of period | | $ | 27,493 | | | $ | 16,772 | | | |
Revenue recognized in excess of amounts invoiced (a) | | 12,233 | | | 30,477 | | | |
Minimum volume commitments invoiced (b) | | (27,945) | | | (19,256) | | | |
Amortization (c) | | (658) | | | (500) | | | |
| Balance as of end of period | | $ | 11,123 | | | $ | 27,493 | | | |
| | | | | | |
(a) Primarily includes revenues associated with MVCs that are generally included in firm reservation fee revenues within the Gathering and Water segments. During the year ended December 31, 2021, also includes other contractual commitments of approximately $6.4 million.
(b) Unbilled revenues are transferred to accounts receivable once the Company has an unconditional right to consideration from the customer.
(c) Amortization of capitalized contract costs paid to customers over the expected life of the agreement.
Contract liabilities. The Company's contract liabilities consist of deferred revenue primarily associated with the EQT Global GGA, including advance payments from EQT associated with the Rate Relief Shares (as defined below) acquired by the Company as consideration for certain commercial terms and the initial fair value of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision (as defined below). The contract liabilities are classified as current or non-current according to when such amounts are expected to be recognized. As of December 31, 2021, total contract liabilities were $822.4 million, of which $1.1 million was classified as current and recorded in accrued liabilities and $821.3 million was classified as non-current and recorded in contract liability on the Company's consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31,On February 26, 2020 the contract liabilities were $398.8 million, which was recorded in contract liability on the Company's consolidated balance sheets.
Contracts requiring advance payments and the recognition of contract liabilities are evaluated to determine whether the advance payments provide the Company with a significant financing benefit. This determination requires significant judgment and is based on the combined effect of the expected length of time between when the Company transfers the promised goods or services to the customer and when the customer pays for those goods or services and the prevailing interest rates. The Company has assessed the EQT Global GGA and determined that this agreement does not contain a significant financing component.
The following table presents changes in the Company's contract liability balances during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Contract Liability |
| | | | 2021 | | 2020 |
| | | | (Thousands) |
| Balance as of beginning of period | | | | $ | 398,750 | | | $ | — | |
Amounts recorded during the period (a) | | | | 300,496 | | | 398,750 | |
Change in estimated variable consideration (b) | | | | 123,707 | | | — | |
Amounts transferred during the period (c) | | | | (537) | | | — | |
| Balance as of end of period | | | | $ | 822,416 | | | $ | 398,750 | |
| | | | | | |
(a) Includes deferred billed revenue during the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020 primarily associated with the EQT Global GGA.
(b) Change in estimated variable consideration represents the increase in total deferred revenue required for gathering MVC revenue with a declining rate structure, resulting from contractual amendments that required total estimated gathering consideration to be reduced. See 'EQT Global GGA' discussion below for additional information on the contractual amendments.
(c) Deferred revenues are recognized as revenue upon satisfaction of the Company's performance obligation to the customer.
Summary of remaining performance obligations.The following table summarizes the estimated transaction price allocated to the Company's remaining performance obligations under all contracts with firm reservation fees and MVCs as of December 31, 2021 that the Company will invoice or transfer from contract liabilities and recognize in future periods.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2025 | | 2026 | | Thereafter | | Total |
| | (Thousands) |
| Gathering firm reservation fees | $ | 88,587 | | | $ | 105,667 | | | $ | 157,484 | | | $ | 149,923 | | | $ | 141,091 | | | $ | 1,277,200 | | | $ | 1,919,952 | |
| Gathering revenues supported by MVCs | 441,202 | | | 454,236 | | | 426,929 | | | 445,958 | | | 457,120 | | | 3,462,805 | | | 5,688,250 | |
| Transmission firm reservation fees | 362,096 | | | 358,222 | | | 375,984 | | | 362,814 | | | 357,910 | | | 3,222,117 | | | 5,039,143 | |
| Water revenues supported by MVCs | 33,313 | | | 37,500 | | | 37,500 | | | 37,500 | | | 37,500 | | | 193,750 | | | 377,063 | |
Total (a) | $ | 925,198 | | | $ | 955,625 | | | $ | 997,897 | | | $ | 996,195 | | | $ | 993,621 | | | $ | 8,155,872 | | | $ | 13,024,408 | |
(a) Includes assumptions regarding timing for placing certain projects in-service. Such assumptions may not be realized and delays in the in-service dates for projects have substantially altered, and additional delays may further substantially alter, the remaining performance obligations for certain contracts with firm reservation fees and/or MVCs. The MVP Joint Venture is accounted for as an equity investment and those amounts are not included in the table above.
Based on total projected contractual revenues, including projected contractual revenues from future capacity expected from expansion projects that are not yet fully constructed for which the Company has executed firm contracts, the Company's firm gathering contracts and firm transmission and storage contracts had weighted average remaining terms of approximately 14 years and 13 years, respectively, as of December 31, 2021.
EQT Global GGA. On the(the EQT Global GGA Effective Date,Date), the Company entered into a
Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement (as amended, the EQT Global GGAGGA) with EQT and certain of its affiliates for the
provision by the Company of certain gas gathering services to EQT in the Marcellus and Utica Shales of Pennsylvania and West Virginia. Pursuant to the EQT Global GGA, EQT is subject to an initial annual MVCThe Company's contract liabilities consist of 3.0 Bcf per day that gradually steps up to 4.0 Bcf per day through December 2031 following the full in-service date of the MVP. The EQT Global GGA runs from the EQT Global GGA Effective Date through December 31, 2035, and will renew annually thereafter unless terminated by EQT or the Company pursuant to its terms. Pursuant to the EQT Global GGA, the Company has certain obligations to build connections to connect EQT wells to the Company's gathering system, which are subject to geographical limitations in relation to the dedicated area in Pennsylvania and West Virginia, as well as the distance of such connections to the Company's then-existing gathering system. Management has estimated the total consideration expected to be received over the life of the EQT Global GGA, including gathering MVCdeferred revenue primarily associated with a declining rate structure, the gathering fee credit for certain gathered volumes that also receive separate transmission services under certain transmission contracts (including the FTS (defined below)), the fair value of the Rate Relief Shares (as defined below) and the initial fair value of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision. From time to time, and at a minimum, at each reporting date, management reviews and updates, as necessary, the assumptions utilized to estimate the total consideration of the EQT Global GGA. The total consideration is allocated proportionally to the performance obligation under the contract, which is to provide daily MVC capacity over the life of the contract, in order to recognize revenue in accordance with ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. The performance obligations will be satisfied during the life of the contract based on a units of production methodology for the daily MVC capacity provided to EQT. Due to the declining rate structure, there will be periods during which the billable gathering MVC revenue will exceed the allocated consideration to the performance obligation, which will result in billable gathering
MVC revenue being deferred to the contract liability. The deferred consideration amounts are deferred until recognized in revenue when the associated performance obligation has been satisfied andContract liabilities are classified as current or non-current according to when such amounts are expected to be recognized. In addition
On July 8, 2022, the Company received written notice from EQT, pursuant to the estimated total consideration allocated to the daily MVC, the EQT Global GGA, includes other fees based on variable or volumetric-based services that will be recognizedof EQT’s irrevocable election under the agreement to forgo up to approximately $145 million of potential gathering MVC fee relief in the first twelve-month period the services are provided. The Company applied judgment in determining the balance sheet classification of the elements of the EQT Global GGA and Share Purchase Agreements (as defined below) under the applicable accounting guidance.
The gathering MVC fees payable by EQT to the Company set forth in the EQT Global GGA are subject to potential reductions for certain contract years as set forth in the EQT Global GGA, conditioned to beginbeginning the first day of the quarter in which the full in-service date of the MVP occurs, which provide for estimated aggregate fee relief of approximately $270 million in the first twelve-month period, approximately $230 million in the second twelve-month period and approximately $35 million in the third twelve-month period. Further, the EQT Global GGA provides for a fee credit to the gathering rate for certain gathered volumes that also receive separate transmission services under certain transmission contracts. In addition, given that the MVP full in-service date did not occur by January 1, 2022, EQT has an option until December 31, 2022,occurs and up to forgo approximately $145 million of the gathering fee relief in such first twelve-month period and approximately $90 million of thepotential gathering MVC fee relief in the second such second twelve-month period in exchange for a cash payment from the Company to EQT in the amount of approximately $196$195.8 million (the EQT Cash Option). As considerationa result of EQT’s election to forgo potential rate relief in exchange for the additional rate relief subjectcash option payment, the Company recorded a reduction to the EQT Cash Option, the Company purchased shares of its common stock (see Rate Relief Shares discussed and defined below) from EQT. The consideration received for future contractual rate relief associated with the Rate Relief Shares was recorded at a fair valuecontract liability of approximately $121.5 million as a contract liability in accordance with ASC 606 and will be recognized as revenue over$195.8 million. The Company utilized borrowings under the life of the contract.Amended EQM Credit Facility to effect such payment to EQT on October 4, 2022.
During the fourth quarter of 2021, the Company entered into two amendments to an agreement for firm transportation service (FTS) with EQT that, subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions, would have the effect of extending the primary term of the FTS. As a result of the potential extension, management reassessed the expected gathering MVC fee credit assumptions and, as a result of the impacts to such assumptions, the total consideration expected under the EQT Global GGA was reduced. The Company recognized a cumulative adjustment that decreased revenue and increased contract liability by $123.7 million, respectively, during the year ended December 31, 2021. The cumulative adjustment had no impact to the amount billed to and cash collected from EQT under the EQT Global GGA.
The EQT Global GGA provides for potential cash bonus payments payable by EQT to the Company during the period beginning on the first day of the calendar quarter in which the MVP full in-service date occurs through the calendar quarter ending December 31, 2024 (the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision). The potential cash bonus payments are conditioned upon the quarterly average of certain Henry Hub natural gas prices exceeding certain price thresholds. The Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision meets the definition of an embedded derivative that was required to be bifurcated from the host contract and accounted for separately in accordance with ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging. The embedded derivative was recorded as a derivative asset at its estimated fair value at inception of approximately $51.5 million and as part of the contract liability to be included in the total consideration to be allocated to the performance obligation under ASC 606. Subsequent changes to the fair value of the derivative instrument through the end of the contract are recognized in other (expense) income, net, on the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Water Services Letter Agreement and 2021 Water Services Agreement. On February 26, 2020, the Company entered into a letter agreement with EQT relating to the provision of water services in Pennsylvania (such letter agreement, the Water Services Letter Agreement). Subject to the effect of the 2021 Water Services Agreement (as defined below), the Water Services Letter Agreement would have been effective as of the first day of the first month following the MVP full in-service date and would have expired on the fifth anniversary of such date. During each year of the Water Services Letter Agreement, EQT had agreed to pay the Company a minimum $60 million per year Annual Revenue Commitment (ARC) for volumetric water services provided in Pennsylvania, all in accordance with existing water service agreements and new water service agreements entered into between the parties pursuant to the Water Services Letter Agreement (or the related agreements).
On October 22, 2021, the Company and EQT entered into a new 10-year, mixed-use water services agreement covering operations within a dedicated area in southwestern Pennsylvania (as subsequently amended, the 2021 Water Services Agreement). The 2021 Water Services Agreement which upon its effectiveness, replacesbecame effective on March 1, 2022 and replaced the Water Services Letter Agreementletter agreement for water services entered into with EQT in February 2020 and certain other existing Pennsylvania water services agreements, will become effective with the commencement of water delivery service to a certain EQT well pad (anticipated in the first quarter of 2022).agreements. Pursuant to the 2021 Water Services Agreement, EQT has agreed to pay the Company a minimum ARC for water services equal to $40 million in each of the first five years of the 10-year contract term and equal to $35 million per year for the remaining five years of the contract term.
Share Purchase Agreements. On February 26, 2020,The following table presents changes in the Company entered into 2 share purchase agreements (the Share Purchase Agreements) with EQT, pursuant to whichCompany's contract liability balances during the Company agreed to (i) purchase 4,769,496 shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock (the Cash Shares) from EQT in exchange for approximately $46 million in cash, (ii) purchaseyears ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
20,530,256 shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock (the Rate Relief Shares | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Contract Liability |
| | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | |
| | | | (Thousands) |
| Balance as of beginning of period | | | | $ | 973,087 | | | $ | 822,416 | | | |
Amounts recorded during the period (a) | | | | 338,860 | | | 359,797 | | | |
Change in estimated variable consideration (b) | | | | (5,331) | | | (11,761) | | | |
Amounts transferred during the period (c) | | | | (5,516) | | | (1,545) | | | |
| EQT Cash Option | | | | — | | | (195,820) | | | |
| Balance as of end of period | | | | $ | 1,301,100 | | | $ | 973,087 | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
(a) Includes deferred billed revenue during the years ended December 31, 2023 and together2022 primarily associated with the Cash Shares, the Share Purchases) from EQT in exchange for a promissory note in the aggregate principal amount of approximately $196 million (which EQT subsequently assigned to EQM as consideration for certain commercial terms under the EQT Global GGA),GGA.
(b) For the year ended December 31, 2023, the change in estimated variable consideration represents the decrease in total deferred revenue due to changes in MVP timing assumptions. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the change in estimated variable consideration represents the decrease in total deferred revenue required for gathering MVC revenue with a declining rate structure, resulting from the EQT Cash Option election that required total estimated gathering consideration to be increased and (iii) pay EQT cashfrom contractual amendments that required total estimated gathering consideration to be reduced.
(c) Deferred revenues are recognized as revenue upon satisfaction of the Company's performance obligation to the customer.
Summary of remaining performance obligations.The following table summarizes the estimated transaction price allocated to the Company's remaining performance obligations under all contracts with firm reservation fees, MVCs and/or ARCs as of December 31, 2023 that the Company will invoice or transfer from contract liabilities and recognize in future periods.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 | | Thereafter | | Total |
| | (Thousands) |
| Gathering firm reservation fees | $ | 162,177 | | | $ | 176,657 | | | $ | 167,163 | | | $ | 160,370 | | | $ | 156,747 | | | $ | 1,568,133 | | | $ | 2,391,247 | |
| Gathering revenues supported by MVCs | 427,513 | | | 457,339 | | | 489,679 | | | 487,710 | | | 485,079 | | | 2,685,762 | | | 5,033,082 | |
| Transmission firm reservation fees | 397,514 | | | 400,073 | | | 400,429 | | | 399,680 | | | 396,999 | | | 2,765,237 | | | 4,759,932 | |
| Water revenues supported by ARCs/MVCs | 45,706 | | | 48,441 | | | 45,159 | | | 44,065 | | | 45,706 | | | 120,938 | | | 350,015 | |
Total (a) | $ | 1,032,910 | | | $ | 1,082,510 | | | $ | 1,102,430 | | | $ | 1,091,825 | | | $ | 1,084,531 | | | $ | 7,140,070 | | | $ | 12,534,276 | |
(a) Includes assumptions regarding timing for placing certain projects in-service. Such assumptions may not be realized and delays in the amountin-service dates for projects have substantially altered, and additional delays may further substantially alter, the remaining performance obligations for certain contracts with firm reservation fees and/or MVCs and/or ARCs. The MVP Joint Venture is accounted for as an equity method investment and those amounts are not included in the table above.
Based on total projected contractual revenues, including projected contractual revenues from future capacity expected from expansion projects that are not yet fully constructed or not yet fully in-service for which the Company has executed firm contracts, the Company's firm gathering contracts and firm transmission and storage contracts had weighted average remaining terms of approximately $7 million (the Cash Amount). On March 5, 2020, the Company completed the Share Purchases13 years and paid the Cash Amount. The Company used proceeds from the EQM Credit Facility (defined in Note 11) to fund the purchase12 years, respectively, as of the Cash Shares and to pay the Cash Amount in addition to other uses of proceeds. After the closing of the Share Purchases, the Company retired the Cash Shares and the Rate Relief Shares. Additionally, the Company recorded a $17.2 million deferred tax liability in conjunction with the Rate Relief Shares. On September 29, 2020, the Company made a prepayment to EQM of all principal, interest, fees and other obligations outstanding under the promissory note EQT assigned to EQM and the promissory note was terminated.December 31, 2023.
7.5. Leases
The Company has certain facility and compressor operating lease contracts that are classified as operating leases and one lease contract for the rental of a water storage facility classified as a financing lease in accordance with ASC 842. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are considered short-term, and are not recorded on the balance sheet. Instead, the short-term leases are recognized in expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Upon the adoption of ASC 842 on January 1, 2019, the Companyterm and are not recorded an operating lease right-of-use asset and a corresponding operating lease liability of $49.7 million on its consolidated balance sheets, reflecting the then present value of future lease payments on the Company's facility and compressor lease contracts.balance sheet. As of December 31, 20212023 and 2020,2022, the Company had no lease contracts classified as financing leases and was not a lessor;the lessor to any arrangement; however, the Company was party to acertain subleasing arrangementarrangements whereby the Company, as sublessor, agreed to sublet leased office space to a third party.
The following table summarizes lease cost for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019:2021: | | Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (Thousands) |
| Years Ended December 31, | | | Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
| Operating lease cost | Operating lease cost | $ | 12,571 | | | $ | 14,464 | | | $ | 12,858 | |
| Finance lease cost: | |
| Amortization of leased assets | |
| Amortization of leased assets | |
| Amortization of leased assets | |
| Interest on lease liabilities | |
| Short-term lease cost | Short-term lease cost | 6,057 | | | 5,075 | | | 4,642 | |
| Variable lease cost | Variable lease cost | 7 | | | 168 | | | 321 | |
| Sublease income | Sublease income | (492) | | | (583) | | | (445) | |
| Total lease cost | Total lease cost | $ | 18,143 | | | $ | 19,124 | | | $ | 17,376 | |
Operating lease expense related to the Company's compressor lease contracts and facility lease contracts is reported in operating and maintenance expense and selling, general and administrative expense, respectively, on the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income. Finance lease expense related to the Company's water storage facility contract amortization and interest is reported in operating and maintenance expense and net interest expense, respectively, on the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
ForThe following table summarizes the cash paid for operating and finance lease liabilities for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019, cash paid for operating lease liabilities was $12.8 million, $14.8 million and $12.3 million, respectively, which was reported in cash flows provided by operating activities on the statements of consolidated cash flows.2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (Thousands) |
| Operating lease liabilities | $ | 10,923 | | | $ | 10,484 | | | $ | 12,792 | |
| Finance lease liabilities | 2,021 | | | 670 | | | — |
The operating lease right-of-use assets are reported in other assets and the current and noncurrent portions of the operating lease liabilities are reported in accrued liabilities and regulatory and other long-term liabilities, respectively, on the consolidatedfollowing table summarizes balance sheets. sheet information related to our leases is as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | December 31, |
| | Balance Sheet Classification | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | | (Thousands) |
| Assets: | | | | | | |
| Operating lease right-of-use | | Other assets | | $ | 37,598 | | | $ | 35,969 | |
| Finance lease | | Other assets | | 14,061 | | | 15,683 | |
| Total right-of-use assets | | | | $ | 51,659 | | | $ | 51,652 | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Current operating | | Accrued liabilities | | $ | 10,284 | | | $ | 6,682 | |
| Current finance | | Accrued liabilities | | 1,297 | | | 1,203 | |
| Non-current operating | | Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | | 28,889 | | | 30,272 | |
| Non-current finance | | Regulatory and other long-term liabilities | | 13,434 | | | 14,660 | |
| Total lease liabilities | | | | $ | 53,904 | | | $ | 52,817 | |
As of December 31, 20212023 and 2020, the operating lease right-of-use assets were $43.4 million and $53.2 million, respectively, and operating lease liabilities were $44.4 million and $53.4 million, respectively, of which $8.3 million and $10.0 million, respectively, was classified as current. As of December 31, 2021 and 2020,2022, the weighted average remaining operating lease terms were sevensix years and eightseven years, respectively, and the weighted average discount rates were 6.1% and 5.9%, respectively. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the remaining finance lease term was nine years and ten years, respectively, and the discount rate was 5.8% and 5.7%5.9%, respectively.
The following table summarizes undiscounted cash flows owed by the Company to lessors pursuant to noncancelable contractual agreements in effect as of December 31, 20212023 and related imputed interest.
| | December 31, 2021 |
| (Thousands) |
| 2022 | $ | 10,404 | |
| 2023 | 8,065 | |
| Operating Leases | | | Operating Leases | | Finance Leases |
| Year ending December 31, | | Year ending December 31, | (Thousands) |
| 2024 | 2024 | 6,190 | |
| 2025 | 2025 | 4,970 | |
| 2026 | 2026 | 5,040 | |
| 2027 | |
| 2028 | |
| Thereafter | Thereafter | 20,652 | |
| Total | Total | 55,321 | |
| Less: imputed interest | Less: imputed interest | 10,911 | |
| Present value of operating lease liability | $ | 44,410 | |
| Present value of lease liabilities | |
8.6. Related Party Transactions
Related Party Transactions with EQT
As of December 31, 2021, EQT remained a related party to the Company due to its ownership of 22,796,026 shares of Equitrans Midstream common stock, which represented an approximately 5.3% ownership interest in the Company, excluding the impact of the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares. In the ordinary course of business, the Company engaged, and continues to engage, as applicable,engages in transactions with EQT and its affiliates, including but not limited to, entering into new or amending existing gathering agreements, transportation service and precedent agreements, storage agreements andand/or water services agreements.
Related Party Transactions with EQM
ETRN EQM Omnibus Agreements. Pursuant to an omnibus agreement with EQM, the EQM General Partner (as successor to the former EQM general partner) and the Company (the ETRN Omnibus Agreement), the Company performed centralized corporate, general and administrative services for EQM. In exchange, EQM reimbursed the Company for the expenses incurredagreements, however, based solely on information reported by the CompanyEQT in providing these services. In connectiona Schedule 13G/A filed with the entry by EQM and the Company into an Assignment and Bill of SaleSEC on March 31, 2019, the ETRN Omnibus AgreementApril 28, 2022, EQT was amended and restated, to, among other things, govern the Company's use, and payment for such use, of the acquired assets following their conveyance to EQM under the Assignment and Bill of Sale. In connection with the EQM Merger, the ETRN Omnibus Agreement terminated at the Effective Time, subject to the survival of certain license rights and indemnification obligations. See Note 2.
Secondment Agreement. Pursuant tono longer a secondment agreement, employeesrelated party of the Company as of April 22, 2022 and its affiliates were, priorthe amounts disclosed related to the closing of the EQM Merger, seconded to EQM to provide operating and other servicesEQT below are accordingly presented with respect to EQM's business under the direction, supervision and control of EQM. EQM reimbursed the Company and its affiliates for the services provided by the seconded employees. The expenses forfull 2021 period during which EQM reimbursed the Company and its affiliates were not necessarily reflective of the actual expenses that EQM would incur onEQT was considered a stand-alone basis. EQM is unable to estimate what those expenses would be on a stand-alone basis. In connection with the EQM Merger, the Company's secondment agreement with EQM terminated at the Effective Time. See Note 2.
Summary of Related Party Transactionsrelated party.
The following table summarizes the Company's related party transactions.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (Thousands) |
| Operating revenues | $ | 777,276 | | | $ | 964,220 | | | $ | 1,122,626 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Separation and other transaction costs | — | | | — | | | (1,440) | |
Equity income (a) | 17,579 | | | 233,833 | | | 163,279 | |
| | | | | |
| Interest income from the Preferred Interest | 5,767 | | | 6,053 | | | 6,324 | |
| | | | | |
Capital contributions to the MVP Joint Venture (a) | (287,665) | | | (272,801) | | | (774,593) | |
| Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest | 5,217 | | | 5,003 | | | 4,661 | |
| Net distributions to EQT | — | | | — | | | (93,666) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2021 | | |
| | (Thousands) |
| Operating revenues | | | $ | 777,276 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Interest income from the Preferred Interest | | | 5,767 | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Principal payments received on the Preferred Interest | | | 5,217 | | | |
| | | | | |
(a)The MVP Joint Venture. Associated with the Company's ownershipThe Company has an equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture. See Note 9 for further detail.The MVP Joint Venture is constructing the Mountain Valley Pipeline and is developing the MVP Southgate project, each discussed in more detail below. The Company maintains separate ownership interests in and is expected to operate the two MVP Joint Venture projects.
The following table summarizes the Company's related party receivables and payables.Mountain Valley Pipeline. | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Thousands) |
| Accounts receivable | $ | 190,410 | | | $ | 199,674 | |
| Contract asset | 2,246 | | | 2,207 | |
| Investments in unconsolidated entity | 1,239,039 | | | 2,796,316 | |
| Preferred Interest | 99,838 | | | 105,056 | |
| | | |
| Capital contributions payable to the MVP Joint Venture | 72,188 | | | 10,723 | |
| Contract liability | 818,658 | | | 398,750 | |
9. Investment in Unconsolidated Entity
The MVP Joint Venture is constructing the Mountain Valley Pipeline (MVP), an estimated 300-mile natural gas interstate pipeline that is designed to span from northern West Virginia to southern Virginia. The Company will operate the MVP and owned a 46.8%48.4% interest in the MVP project as of December 31, 2021.2023. On November 4, 2019, Consolidated Edison, Inc. (Con Edison) exercised an option to cap its investment in the construction of the MVP project at approximately $530 million (excluding AFUDC). On May 4, 2023, RGC Resources, Inc. (RGC) also exercised an option for the Company to fund RGC's portion of future capital contributions with respect to the MVP project, which funding the Company commenced in June 2023 and will continue through the full in-service date of the MVP. The Company and NextEra Energy, Inc. are obligated to, and RGC Resources, Inc., another memberprior to the exercise of the MVP Joint Venture owning an interest in the MVP project, hasits option described above had opted to, fund the shortfall in Con Edison's capital contributions, on a pro rata basis. Following RGC's exercise of its option, the Company is also funding RGC's portion of Con Edison's shortfall. Such funding by the Company in respect of the Con Edison shortfall and funding by other membersRGC's portion of capital contributions has and will correspondingly increase the Company's and such other funding members' respective interests in the MVP project and decrease Con Edison's interestand RGC's respective interests, as applicable, in the MVP project.
On June 3, 2023, the President of the United States signed into law the Fiscal Responsibility Act of 2023 that, among other things, ratified and approved all permits and authorizations necessary for the construction and initial operation of the MVP, directed the applicable federal officials and agencies to maintain such authorizations, required the Secretary of the Army to issue not later than June 24, 2023 all permits or verifications necessary to complete construction of the MVP and allow for the MVP’s operation and maintenance, and divested courts of jurisdiction to review agency actions on approvals necessary for MVP construction and initial operation. Thereafter, certain necessary authorizations were issued to the MVP Joint Venture, and the FERC authorized the MVP Joint Venture to resume all construction activities in all MVP project locations. After the Fourth Circuit issued a stay halting MVP project construction in the Jefferson National Forest and a stay of the 2023 Biological Opinion and Incidental Take Statement, the U.S. Supreme Court vacated the stays on July 27, 2023. The MVP Joint Venture recommenced forward construction activity in August 2023.
Construction on the MVP project occurred throughout the late summer, fall and into the 2023-2024 winter season, and as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K is continuing. The MVP project made substantial progress after resuming construction in late summer 2023. Forward progress, however, slowed at the end of 2023 through early 2024 as a result of unforeseen challenging construction conditions, combined with unexpected and substantially adverse winter weather conditions throughout much of January. As a result, dependingthe MVP Joint Venture retained a higher than planned contractor headcount through January into February to maintain the right of way and address weather-induced issues and also to be in a position to improve forward progress as soon as conditions became more favorable. While productivity has since improved at the end of January and into February, the combined effect of these unforeseen challenges significantly slowed the previously anticipated pace of construction and adversely affected project cost. As a result, the Company is now targeting MVP project completion and commissioning in the second quarter of 2024, at a total estimated project cost ranging from approximately $7.57 billion to approximately $7.63 billion (excluding allowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC)).
Based on such targeted completion timing and following in-service authorization from the project'sFERC, the Company expects that MVP and MVP-related firm capacity contractual obligations would commence on June 1, 2024 (with certain MVC step ups and more significant gathering MVC fee declines under the EQT Global GGA commencing April 1, 2024). Such targeted completion timing and cost, and accordingly the commencement of contractual obligations, are subject to certain factors, including the physical construction conditions including hard rock and steep terrain, weather and productivity, many of which are beyond the Company’s control. If the project were to be completed in the second quarter of 2024 and at a total estimated project cost ranging from approximately $7.57 billion to approximately $7.63 billion (excluding AFUDC), the Company'sCompany expects its equity ownership in the MVP project willwould progressively increase from approximately 48.4% to a percentage in excess of approximately 46.8%49.0%.
The MVP Joint Venture is a variable interest entity because it has insufficient equity to finance its activities during the construction stage of the project. The Company is not the primary beneficiary of the MVP Joint Venture because the Company does not have the power to direct the activities that most significantly affect the MVP Joint Venture's economic performance. Certain business decisions, such as decisions to make distributions of cash, require a greater than 66 2/3% ownership interest approval, and no one member owns more than a 66 2/3% interest.
In April 2018, Upon completion of the MVP project, the Company expects the MVP Joint Venture announced the MVP Southgate project, which isto no longer be a proposed 75-mile interstate pipeline that is contemplatedvariable interest entity because it will have sufficient equity to extend from the MVP at Pittsylvania County, Virginiafinance its activities, including accessing capital markets and returning a portion of invested capital to new delivery points in Rockingham and Alamance Counties, North Carolina. The Company is expected to operate the MVP Southgate pipeline and owned a 47.2% interest in the MVP Southgate project as of December 31, 2021. The MVP Joint Venture is evaluating the MVP Southgate project, including engaging in discussions with the project shipper, Dominion Energy North Carolina, regarding options with respect to the project, including potentially refining the project’s design and timing in lieu of pursuing the project as originally contemplated. Dominion Energy North Carolina’s obligations under the precedent agreement in support of the original project are subject to certain conditions, including that the MVP Joint Venture complete construction of the project facilities by June 1, 2022, which deadline is subject to extension by virtue of previously declared events of force majeure. The Company is unable to predict the results of the discussions between the MVP Joint Venture and Dominion Energy North Carolina, including any potential modifications to the project, or ultimate undertaking or completion of the project.its owners.
In November 2021,December 2023, the MVP Joint Venture issued a capital call notice for the funding of the MVP project to MVP Holdco, LLC (MVP Holdco), a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, for $72.0$181.1 million, of which $52.9 million and $19.1 million was paid in January 2022 and February 2022, respectively.2024. The capital contributions payable and the corresponding increase to the investment balance are reflected on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2021.2023. In January 2024, the MVP Joint Venture issued a capital call notice for the funding of the MVP project to MVP Holdco for $113.6 million, which was paid in February 2024.
Pursuant to the MVP Joint Venture's limited liability company agreement, MVP Holdco is obligated to provide performance assurances in respect of the MVP project, which may take the form of a guarantee from EQM (provided that EQM's debt is rated as investment grade in accordance with the requirements of the MVP Joint Venture's limited liability company agreement), a letter of credit or cash collateral, in favor of the MVP Joint Venture to provide assurance as to the funding of MVP Holdco's proportionate share of the construction budget for the MVP project. As of December 31, 2023, the letter of credit with respect to the MVP project was in the amount of approximately $104.7 million. The letter of credit with respect to the MVP project is expected to be further reduced as the Company contributes capital to fund MVP Holdco's remaining proportionate share of the construction budget, subject to a minimum-required level to be maintained through in-service of the MVP project.
The following tables summarize the condensed financial statements of the MVP Joint Venture in relation to the MVP project.
Condensed Balance Sheets | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | |
| (Thousands) |
| Current assets | $ | 349,417 | | | $ | 71,535 | |
| Non-current assets | 8,480,539 | | | 6,737,064 | |
| Total assets | $ | 8,829,956 | | | $ | 6,808,599 | |
| | | |
| Current liabilities | $ | 371,508 | | | $ | 118,679 | |
| Equity | 8,458,448 | | | 6,689,920 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 8,829,956 | | | $ | 6,808,599 | |
Condensed Statements of Operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | | | | |
| (Thousands) |
| Operating (expenses) income | $ | (199) | | | $ | 20 | | | $ | (399) | |
| Other income | 4,792 | | | 335 | | | 18 | |
| AFUDC – debt | 108,681 | | | — | | | 11,452 | |
| AFUDC – equity | 253,602 | | | — | | | 26,722 | |
| | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 366,876 | | | $ | 355 | | | $ | 37,793 | |
The Company's ownership interest in the MVP Joint Venture related to the MVP project is significant for the year ended December 31, 2023 as defined by the SEC's Regulation S-X Rule 1-02(w). Accordingly, as required by Regulation S-X Rule 3-09, the Company has included audited financial statements of the MVP Joint Venture, with respect to the MVP project, as of and for the year ended December 31, 2023 as Exhibit 99.1 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
MVP Southgate Project. In April 2018, the MVP Joint Venture announced the MVP Southgate project (MVP Southgate) as a contemplated interstate pipeline that was approved by the United States FERC and designed to extend approximately 75 miles from the MVP in Pittsylvania County, Virginia to new delivery points in Rockingham and Alamance Counties, North Carolina using 24-inch and 16-inch diameter pipe.
In addition, pursuantlate December 2023, following completion of its negotiations with each of Public Service Company of North Carolina, Inc. (PSNC) and Duke Energy Carolinas, LLC (Duke), the MVP Joint Venture entered into precedent agreements with each of PSNC and Duke. The precedent agreements contemplate an amended project (in lieu of the original project). The amended project would extend approximately 31 miles from the terminus of the MVP in Pittsylvania County, Virginia to planned new delivery points in Rockingham County, North Carolina using 30-inch diameter pipe.
The Company is expected to operate the MVP Southgate pipeline and owned a 47.2% interest in the MVP Southgate project as of December 31, 2023. The amended MVP Southgate is estimated to cost a total of approximately $370 million, excluding AFUDC and certain costs incurred for purposes of the original project. The Company expects to fund its proportionate share through capital contributions made to the MVP Joint Venture. The targeted completion timing for the project is June 2028, with the majority of the capital spend expected to occur in 2027.
Pursuant to the MVP Joint Venture's limited liability company agreement, MVP Holdco is obligated to provide performance assurances in respect of MVP Southgate, which performance assurances may take the form of a guarantee from EQM (provided that EQM's debt is rated as investment grade in accordance with the requirements of the MVP Joint Venture's limited liability company agreement), a letter of credit or cash collateral.
Based on EQM's credit rating levels in the first quarter of 2020, EQM delivered replacement credit support to the MVP Joint Venture in the form of letters of credit in the amounts of approximately $220.2 million and On April 6, 2023, EQM’s $14.2 million with respect to the MVP and MVP Southgate projects, respectively. In connection with delivering such letters of credit as replacement performance assurances, EQM's performance guarantees associated with the MVP and MVP Southgate projects were terminated. As of December 31, 2021, the letter of credit with respect to the MVP Southgate project was interminated, following the amount of approximately $219.7 million.determination to temporarily defer partners’ obligations to post performance assurances with respect to the MVP Southgate project, which may be reinstated upon further developments. Upon the FERC’s initial release to begin construction of the MVP Southgate project, the Company’s current letter of credit to support MVP Southgate will be terminated, and the Company will be obligated to deliver a new letter of credit (or provide anotheran allowable form of performance assurance)assurance in an amount equal to 33% of MVP Holdco’s proportionate share of the remaining capital obligations for the MVP Southgate project under the applicable construction budget.
The following tables summarize the condensed consolidated financial statements
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Unaudited) | | |
| (Thousands) |
| Current assets | $ | 148,820 | | | $ | 146,054 | |
| Non-current assets | 6,432,288 | | | 5,848,298 | |
| Total assets | $ | 6,581,108 | | | $ | 5,994,352 | |
| | | |
| Current liabilities | $ | 160,331 | | | $ | 217,086 | |
| Equity | 6,420,777 | | | 5,777,266 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 6,581,108 | | | $ | 5,994,352 | |
Condensed Statements of Consolidated Operations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (Unaudited) | | | | |
| (Thousands) |
| Operating expenses | $ | (399) | | | $ | (360) | | | $ | (2,416) | |
| Other income | 18 | | | 288 | | | 6,243 | |
| Net interest income | 11,452 | | | 150,995 | | | 105,382 | |
| AFUDC – equity | 26,722 | | | 352,323 | | | 245,890 | |
| | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 37,793 | | | $ | 503,246 | | | $ | 355,099 | |
The Company's ownership interest in the MVP Joint Venture related to the MVP project is significant for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 as defined by the SEC’s Regulation S-X Rule 1-02(w). Accordingly, as required by Regulation S-X Rule 3-09, the Company has included audited financial statements of the MVP Joint Venture, with respect to the MVP project, as of December 31, 2020 and for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 as Exhibit 99.1 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
10.8. Share-based Compensation Plans
The Company maintains employee share-based compensation plans for restricted stock, restricted stock units, performance awards, stock options and other equity or cash-based awards as governed by the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2018 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended (the 2018 Plan), which was effective as of November 12, 2018. Non-employee members of the Company's Board receive phantom units in connection with their board service payable in Company common stock upon the director's termination of services from the Board. The 2018 Plan's term is through the 2028 shareholders' meeting and the maximum number of shares of common stock that may be issued and as to which awards may be granted under the 2018 Plan is 38,592,386 shares.
InThe Company also has remaining obligations pertaining to the settlement of unexercised stock options of former employees and outstanding phantom unit awards to certain directors, which were granted in accordance with an Employee Matters Agreement by and between the Company and EQT entered into on November 12, 2018 in connection with the Separation (Employee Matters Agreement),. Pursuant to the Employee Matters Agreement, previously outstanding share-based compensation
awards granted under EQT's equity compensation programs prior to the Separation and held by certain executives and employees of the Company and EQT were adjusted to reflect the impact of the Separation on these awards. To preserve the aggregate intrinsic value of EQT awards held prior to the Separation, as measured immediately before and immediately after the Separation (excluding EQT option awards which were converted in accordance with the conversion provisions set forth in the Employee Matters Agreement), each holder of EQT share-based compensation awards generally received an adjusted award consisting of both a share-based compensation award denominated in EQT equity and a share-based compensation award denominated in Company equity. These awards were adjusted in accordance with the basket method, resulting in participants retaining one unit of the existing EQT incentive award while receiving an additional 0.8 units of a Company-based award and included awards that were share-settled and awards satisfied in cash, which were treated as liability awards. The Company recognizes share-based compensation expense related to unvested awards held by its employees, no matter which entity settles the obligation.
Changes in performance and the number of outstanding awards can impact the ultimate amountnumber of the Company's performance awards to be settled. Share-based awards to be settled in Equitrans Midstream common stock upon settlement are funded by shares acquired by the Company in the open market or from any other person, stock issued directly by the Company or any combination of the foregoing. Share counts for share-based compensation discussed herein represent outstanding shares to be remitted by the Company to (i) its employees in connection with compensation programs adopted by the Company and (ii) employees of the Company and EQT (or, as applicable, former employees of the Company or EQT) pursuant to the Employee Matters Agreement.
The following table summarizes the components of share-based compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019.2021.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (Thousands) |
| | | | | |
| 2017 Incentive PSU Program | — | | | — | | | (893) | |
| 2018 Incentive PSU Program | — | | | 698 | | | (360) | |
| 2019 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program | 984 | | | 4,935 | | | — | |
| 2020 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program | 1,297 | | | 2,317 | | | — | |
| 2021 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program | 5,940 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| 2018 EQT Value Driver Performance Share Unit Award Program | — | | | — | | | 637 | |
| Restricted stock awards | 11,268 | | | 7,422 | | | 5,197 | |
| Other programs, including non-employee director awards | 3,205 | | | 1,577 | | | 1,833 | |
| Total share-based compensation expense | $ | 22,694 | | | $ | 16,949 | | | $ | 6,414 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (Thousands) |
| | | | | |
| 2023 PSU Program | 4,800 | | | — | | | — | |
| 2022 PSU Program | 6,077 | | | 5,672 | | | — | |
| 2021 MVP PSU Program | 20,576 | | | — | | | — | |
| 2021 PSU Program | 2,083 | | | 1,527 | | | 5,940 | |
| 2020 PSU Program | — | | | (221) | | | 1,297 | |
| 2019 PSU Program | — | | | — | | | 984 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Restricted stock awards | 15,186 | | | 7,840 | | | 11,268 | |
| Other programs, including non-employee director awards | 1,416 | | | 1,132 | | | 1,367 | |
| Total share-based compensation expense | $ | 50,138 | | | $ | 15,950 | | | $ | 20,856 | |
The Company capitalizes compensation cost for its share-based compensation awards based on an employee's job function. Capitalized compensation costs for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 2020 and 2019 were $4.2$5.0 million, $1.9$2.0 million and ($0.5)$4.2 million, respectively. The Company recorded $2.0$2.9 million, $0.2$1.0 million, and $0.7$2.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, respectively, of tax expense for excess tax benefits related to share-based compensation plans.
Performance Share Unit Programs – Equity & Liability
The Company assumed portions of the 2017 EQT Incentive Performance Share Unit Program (2017 Incentive PSU Program) and the 2018 EQT Incentive Performance Share Unit Program (2018 Incentive PSU Program) at the Separation Date.
The Management DevelopmentHuman Capital and Compensation Committee of the Company's Board (the(referred to herein as the Compensation Committee) adopted the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2019 Performance Share Unit Program (the 2019 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program), the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2020 Performance Share Unit Program (the 2020 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program) and, the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2021 Performance Share Unit Program (the 2021 PSU Program), the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2022 Performance Share Unit Program (the 2022 PSU Program) and the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2023 Performance Share Unit Program (the 2023 PSU Program).
The 2017 Incentive2019 PSU Program, the 2018 Incentive2020 PSU Program, the 2021 PSU Program, the 2022 PSU Program and the 2023 PSU Program (collectively, the EQT Incentive PSU Programs), the 2019 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program, the 2020 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program and the 2021 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program (collectively, the Equitrans Midstream PSU Programs) are referred to herein as the Incentive PSU Programs. The Incentive PSU Programs vest in both equity and liability awards.
The Company established the Equitrans Midstream PSU Programs to provide long-term incentive opportunities to key employees to further align their interests with those of the Company's shareholders and with the strategic objectives of the Company. The performance period for each of the awards under the Incentive PSU Programs, except for the 2020 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program, is 36 months, with vesting occurring upon payment following the expiration of the performance period, subject to continued service through such vesting date. The awards under the 2020 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program may bewere earned over four separate performance periods as follows: (i) 20% for each of the
three calendar years that occuroccurred following the vesting commencement date (i.e., the 2020, 2021 and 2022 calendar years) and (ii) 40% for the cumulative three-year period following the vesting commencement date (i.e., January 1, 2020 through December 31, 2022), with vesting occurring upon payment following the expiration of the cumulative three-year performance period, subject to continued service through such vesting date.
The 2019 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program awards granted in 2020, 2021 and 2022 were or will be earned based on the level of Equitrans Midstream total shareholder return (TSR) relative to a predefined peer group. The PSU Program awards granted in 2023 will be earned based upon the level of TSR relative to a predefined peer group, the achievement of certain levels of free cash flow before changes in working capital, and the cumulative Equitrans Midstream total shareholder return.
number of ESG-related projects completed, in each case during the performance period and, in the case of free cash flow before changes in working capital, on an annual basis within such performance period. The Equitrans Midstream PSU Program awards grantedCompany commences recording compensation cost for the free cash flow before changes in 2020 and 2021 will be earned based onworking capital performance condition when the level of Equitrans Midstream total shareholder return relative to a predefined peer group (with respect to the 2020 Equitrans Midstream PSU Program awards not to exceed 100% if the Company's total shareholder return is less than zero percent).targets have been established for each annual period.
The payout factor for the Equitrans Midstream PSU Programs varyvaries between zero and 200% of the number of outstanding units, each contingent on the applicable performance metrics. The Company recorded the portionsportion of the Incentive PSU Programs containing a market condition that are to be settled in stock as equity awards using a grant date fair value determined through a Monte Carlo simulation, which projects the common stock price for EQT or the Company as applicable, and theirits peers at the ending point of the applicable performance period. The Incentive PSU Programs containing a market condition also included awards to be settled in cash and, therefore, were recorded at fair value as of the measurement date determined through a Monte Carlo simulation, which projects the common stock price for EQT or the Company as applicable, and theirits peers at the ending point of the applicable performance period. The expected share prices were generated using each company'sthe Company's annual volatility for the expected term and the commensurate three-year or two-year risk-free rates (each shown in the chart below) for equity awards and liability awards, respectively. The vesting of units under each Incentiveof the PSU ProgramPrograms occurs upon payment following the expiration of the applicable performance period, subject to continued service through such date, and the satisfaction of the underlying performance or market condition.
The following table provides detailed information on each award:summarizes all PSU Programs to be settled in stock and classified as equity awards:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Incentive PSU Program | | Settled In | | Accounting Treatment | | Fair Value (a) | | | | Vested/ Payment Date | | Awards Paid | | Value
(Millions) | | Unvested/ Expected Payment Date | | Awards Outstanding as of December 31, 2021 (b) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2017 | | Stock | | Equity | | $ | 120.60 | | | | | February 2020 | | 66,822 | | | $ | 8.1 | | | N/A | | N/A |
| 2017 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | 13.36 | | | | | February 2020 | | 146,387 | | | 2.0 | | | N/A | | N/A |
| 2018 | | Stock | | Equity | | $ | 76.53 | | | | | February 2021 | | 40,349 | | 3.1 | | | N/A | | N/A |
| 2018T1 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | 8.04 | | | | | February 2021 | | 40,769 | | 0.3 | | | N/A | | N/A |
| 2018T2 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | — | | | | | February 2021 | | — | | | — | | | N/A | | N/A |
| 2019 | | Stock | | Equity | | $ | 15.03 | | | | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | First Quarter of 2022 | | 474,488 | |
| 2019 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | — | | | | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | First Quarter of 2022 | | 209,525 | |
| 2020 | | Stock | | Equity | | $ | 5.59 | | | | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | First Quarter of 2023 | | 703,583 | |
| 2020 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | 7.19 | | | | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | First Quarter of 2023 | | 406,050 | |
| 2021 | | Stock | | Equity | | $ | 8.77 | | | | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | First Quarter of 2024 | | 1,481,126 | |
| 2021 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | 13.73 | | | | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | First Quarter of 2024 | | 856,190 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Non-vested Shares | | Weighted Average Fair Value Per Share | | Aggregate Fair Value |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2020 | | 1,300,567 | | | $ | 13.78 | | | $ | 17,925,467 | |
| Granted | | 1,540,230 | | | 8.77 | | | 13,507,817 | |
| Vested | | (85,872) | | | 76.53 | | | (6,571,784) | |
| Forfeited | | (95,729) | | | 8.45 | | | (808,857) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | | 2,659,196 | | | $ | 9.05 | | | $ | 24,052,643 | |
| Granted | | 1,274,910 | | | 14.86 | | | 18,945,163 | |
| Vested | | (474,488) | | | 15.03 | | | (7,131,551) | |
| | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | | 3,459,618 | | | $ | 10.37 | | | $ | 35,866,255 | |
| Granted | | 1,523,826 | | | 8.04 | | | 12,247,293 | |
| Vested | | (703,583) | | | 5.59 | | | (3,931,628) | |
| | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | | 4,279,861 | | | $ | 10.32 | | | $ | 44,181,920 | |
As of December 31, 2023, $15.6 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested PSU Programs to be settled in stock was expected to be recognized over a remaining weighted average vesting term of approximately one year.
The following table summarizes all PSU Programs to be settled in cash and classified as liability awards:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Non-vested Units | | Weighted Average Fair Value Per Unit | | Aggregate Fair Value |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2020 | | 712,595 | | | $ | 11.85 | | | $ | 8,441,384 | |
| Granted | | 873,460 | | | 8.77 | | | 7,660,244 | |
| Vested | | (87,145) | | | 33.87 | | | (2,951,624) | |
| Forfeited | | (27,145) | | | 8.23 | | | (223,349) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | | 1,471,765 | | | $ | 8.78 | | | $ | 12,926,655 | |
| Granted | | 717,930 | | | 14.86 | | | 10,668,440 | |
| Vested | | (226,135) | | | 14.67 | | | (3,318,009) | |
| Forfeited | | (85,758) | | | 10.81 | | | (927,125) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | | 1,877,802 | | | $ | 10.30 | | | $ | 19,349,961 | |
| Granted | | 625,009 | | | 8.04 | | | 5,023,320 | |
| Vested | | (389,160) | | | 5.59 | | | (2,174,332) | |
| Forfeited | | (82,236) | | | 10.69 | | | (878,913) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | | 2,031,415 | | | $ | 10.50 | | | $ | 21,320,036 | |
(a)Grant date fair value was determined using a Monte Carlo simulation for equity awards. For unvested liability awards, the fair value was determined using a Monte Carlo simulation asThe payout factor of the measurement date. For vested liability awards,free cash flow before changes in working capital performance metric covering the fair value is equal to the Company’s stock price at the endfirst annual period of the 2023 PSU Program was achieved at a performance period.
(b)Representsof 200%, subject to final certification by the number of outstanding unitsCompensation Committee. The total liability recorded for the cash-settled PSU Programs was $6.9 million and $3.9 million as of December 31, 2021, adjusted for forfeitures, to be settled in stock or cash.2023 and 2022, respectively.
Fair value is estimated using a Monte Carlo simulation valuation method with the following weighted average assumptions:
| | For Incentive PSU Programs Issued During the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| For PSU Programs Issued During the Years Ended December 31, | | | For PSU Programs Issued During the Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Accounting Treatment | Accounting Treatment | Liability (a) | | Equity | | Liability (a) | | Equity | | | Equity | Accounting Treatment | Liability (a) | | Equity | | Liability (a) | | Equity | | Liability (a) | | | Equity |
| Risk-free rate | Risk-free rate | 0.67 | % | | 0.16 | % | | 0.28 | % | | 0.39 | % | | | 2.54 | % | Risk-free rate | 4.20 | % | | 4.48 | % | | 4.25 | % | | 1.16 | % | | 4.65 | % | | | 0.16 | % |
| Dividend yield | Dividend yield | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | | N/A | Dividend yield | N/A | | N/A | | | N/A |
| Volatility factor | Volatility factor | 61.0 | % | | 61.0 | % | | 42.0 | % | | 53.0 | % | | | 30.0 | % | Volatility factor | 47.7 | % | | 57.8 | % | | 58.4 | % | | 54.0 | % | | 58.4 | % | | | 61.0 | % |
| Expected term | Expected term | 2 years | | 3 years | | 1 year | | 3 years | | | 3 years | Expected term | 2 years | | 3 years | | 2 years | | 3 years | | 1 year | | | 3 years |
(a)Information shown for the valuation of the liability plan valuations is as of the measurement date.
Restricted Stock Awards – Equity
The Company granted 660,250, 491,640 and 344,796A summary of restricted stock equity awardsaward activity during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 2020 and 2019, respectively, to key employeesis presented below. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-vested Shares | | Weighted Average Fair Value Per Share | | Aggregate Fair Value |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2021 | 841,068 | | | $ | 17.08 | | | $ | 14,366,346 | |
| Granted | 660,250 | | | 8.04 | | | 5,308,410 | |
| Vested | (58,185) | | | 44.20 | | | (2,572,026) | |
| Forfeited | (49,732) | | | 11.17 | | | (555,522) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 1,393,401 | | | $ | 11.88 | | | $ | 16,547,208 | |
| Granted | 546,520 | | | 10.34 | | | 5,651,017 | |
| Vested | (293,281) | | | 17.81 | | | (5,223,311) | |
| | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | 1,646,640 | | | $ | 10.31 | | | $ | 16,974,914 | |
| Granted | 1,646,000 | | | 6.23 | | | 10,254,580 | |
| Vested | (870,970) | | | 10.89 | | | (9,481,533) | |
| | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | 2,421,670 | | | $ | 7.33 | | | $ | 17,747,961 | |
The restricted stock granted will beequity grants generally become fully vested at the end of the three-yearservice period commencing with the vesting commencement date, assuming continued service through such date.
As of December 31, 2021, $5.52023, $9.1 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested restricted stock equity awards was expected to be recognized over a remaining weighted average vesting term of approximately 1.241.6 years.
A summary of restricted stock equity award activity during the year ended December 31, 2021 is presented below. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-vested Shares (a) | | Weighted Average Fair Value | | Aggregate Grant Date Fair Value |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2021 | 841,068 | | | $ | 17.08 | | | $ | 14,366,346 | |
| | | | | |
| Granted | 660,250 | | | 8.04 | | | 5,308,410 | |
| Vested | (58,185) | | | 44.20 | | | (2,572,026) | |
| Forfeited | (49,732) | | | 11.17 | | | (555,522) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 1,393,401 | | | $ | 11.88 | | | $ | 16,547,208 | |
(a)Non-vested shares outstanding at December 31, 2021 will be settled by the Company once vested, assuming continued service through such date.
Restricted Stock Unit Awards – Liability
The Company granted 430,800, 455,619, and 271,233A summary of restricted stock unit liability awardsaward activity during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 2020 and 2019, respectively, to key employees of the Company. is presented below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-vested Units | | Weighted Average
Fair Value Per Unit | | Aggregate Fair Value |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2021 | 877,596 | | | $ | 15.46 | | | $ | 13,565,895 | |
| Granted | 430,800 | | | 8.06 | | | 3,472,652 | |
| Vested | (190,036) | | | 20.76 | | | (3,944,942) | |
| Forfeited | (38,656) | | | 10.73 | | | (414,837) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 1,079,704 | | | $ | 11.74 | | | $ | 12,678,768 | |
| Granted | 380,250 | | | 9.77 | | | 3,716,834 | |
| Vested | (267,642) | | | 16.82 | | | (4,502,803) | |
| Forfeited | (45,043) | | | 10.00 | | | (450,504) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | 1,147,269 | | | $ | 9.97 | | | $ | 11,442,295 | |
| Granted | 1,136,000 | | | 6.25 | | | 7,102,647 | |
| Vested | (403,261) | | | 11.98 | | | (4,832,392) | |
| Forfeited | (79,118) | | | 7.26 | | | (574,614) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | 1,800,890 | | | $ | 7.30 | | | $ | 13,137,936 | |
The restricted stock units granted will beunit grants generally become fully vested at the end of the three-yearservice period commencing with the vesting commencement date, assuming continued service through such date. The total liability recorded for these restricted stock units was $7.9$10.9 million and $4.5$6.5 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
MVP PSU Program
In December 2021, at the recommendation of the Compensation Committee and approval of the Board, the Company granted a special, one-time, performance award program designed to reward all employees should the Company’s most complex and strategically significant project, the MVP project, be placed in-service (the MVP PSU Program). The Company granted 1,450,110 shares to all participants in the 2018 Plan as of November 1, 2021 (LTIP Participants), except the Company’s named executive officers (NEOs) and certain other senior leaders (collectively, the Senior Executives), and 1,158,030 shares to the Senior Executives. The MVP PSU Program awards were granted on December 6, 2021 and 2020, respectively.will be paid in Company common stock, contingent on the MVP Joint Venture being authorized by the FERC to commence service on the MVP (such authorization, the In-Service Date) on or before a specified expiration date of January 1, 2024 (the Expiration Date, the now inapplicability of which is discussed below), subject to continued service through the applicable payment date:
A summary•As to shares issued to the LTIP Participants, 100% will be paid on the date selected by the Company that is not later than 90 days after the In-Service Date;
•As to shares issued to the Senior Executives:
•50% will be paid on the date selected by the Company that is not later than 90 days after the In-Service Date;
•25% will be paid on the date selected by the Company that is not later than 30 days after the first anniversary of restricted stock unit liability award activity during the year ended December 31, 2021In-Service Date; and
•25% will be paid on the date selected by the Company that is presented below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-vested Shares (a) | | Weighted Average Fair Value | | Aggregate Grant Date Fair Value |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2021 | 877,596 | | | $ | 15.46 | | | $ | 13,565,895 | |
| | | | | |
| Granted | 430,800 | | | 8.06 | | | 3,472,652 | |
| Vested | (190,036) | | | 20.76 | | | (3,944,942) | |
| Forfeited | (38,656) | | | 10.73 | | | (414,837) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 1,079,704 | | | $ | 11.74 | | | $ | 12,678,768 | |
(a)The achievement of the MVP Joint Venture being authorized by the FERC to commence service on the MVP on or before the Expiration Date represented a performance condition as defined by ASC 718, Non-vested shares outstandingShare-based Compensation, that should be assessed at the end of each reporting period as to whether the performance condition is probable of being achieved. Due to the graded vesting of the MVP PSU Program awards to the Senior Executives, the Company recognizes compensation cost over the requisite service period for each separately vested tranche of the award as though each award was, in substance, its own award. In June 2023, the performance condition associated with the MVP PSU Program awards was deemed to be probable. During the year ended December 31, 2021 will be settled by2023, the Company once vested, assuming continuedrecognized compensation cost of approximately $20.6 million that includes the impact of a cumulative catch-up to reflect the requisite service through suchperiod of each award that has been provided to date. As of December 31, 2023, there was approximately $3.6 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested MVP PSU Program awards that is expected to be recognized over a remaining weighted average vesting term of approximately 0.6 years.
Value DriverIn connection with considering the Company’s ongoing efforts to complete the MVP project, the Board took note of the significant legal and regulatory obstacles that delayed progress on the MVP project that were outside of the control of the Company, particularly since the inception of the MVP PSU Program, the efforts undertaken by many of the Company’s employees, including the NEOs, to overcome these obstacles, and ongoing risks. The Board also was focused on and sought to promote the Company's top priority of completing the MVP project safely and in compliance with applicable environmental standards. Taking into account these factors, the proximity of the Expiration Date, and noting the potential that the Expiration Date could distract from, or be cited by project opponents as a distraction from, a focus on safety and environmental compliance, the Board, on July 26, 2023, with the recommendation of the Compensation Committee, approved an amendment to the MVP PSU Program to eliminate the Expiration Date as a term of the MVP PSU Program and all award agreements thereunder (the MVP PSU Amendment).
Accordingly, the Equitrans Midstream Corporation Senior Executive 2021 MVP Performance Share UnitUnits Award Programs
UnderAgreements to which the 2018 EQT Value DriverNEOs are parties and the Equitrans Midstream Corporation LTIP Participant 2021 MVP Performance Share UnitUnits Award Program (the 2018 EQT VDA), 50%Agreements were amended to reflect the elimination of the awards confirmed vested upon payment followingExpiration Date, and the first anniversarycalculation of shares retained in the event of a participant’s termination due to death, disability or retirement also was clarified. All other terms of the grant date,award agreements remain in full force and effect.
The MVP PSU Amendment resulted in a change to the remaining 50%original performance condition of the awards confirmed vested upon payment followingMVP PSU Program. As such, the second anniversary ofCompany accounted for the grant date subjectMVP PSU Amendment as a Type Ι modification in accordance with ASC 718, which did not result in any additional compensation cost related to continued service through such dates.the awards.
The following table provides detailed information on the 2018 EQT VDA award:MVP PSU Program as of December 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| EQT VDA Program | | Settled In | | Accounting Treatment | | Fair Value per Unit (a) | | Vested/ Payment Date | | Cash Paid
(Millions) | | Unvested/ Expected Payment Date | | Awards Outstanding as of
December 31, 2021 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2018 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | 20.02 | | | February 2019 | | $ | 4.1 | | | N/A | | N/A |
| 2018 | | Cash | | Liability | | $ | 13.36 | | | February 2020 | | $ | 2.3 | | | N/A | | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| MVP PSU Program | | Non-vested Shares | | Grant Date Fair Value (a) | | Fair Value (Thousands) | | Requisite Service Period | | Unrecognized Compensation Cost (Thousands) | | |
| LTIP Participants | | 1,362,243 | | | $9.59 | | $ | 13,064 | | | 28 months | | $ | 883 | | | |
| Senior Executives T1 | | 579,015 | | | $9.59 | | 5,553 | | | 28 months | | 381 | | | |
| Senior Executives T2 | | 289,511 | | | $9.59 | | 2,776 | | | 40 months | | 948 | | | |
| Senior Executives T3 | | 289,504 | | | $9.59 | | 2,776 | | | 52 months | | 1,382 | | | |
(a)The fair value per unit is Determined based onupon the closing price of the Company's common stock price on the measurementday before the grant date.
Non-Qualified Stock Options
In connection with the Separation, the Company assumed stock options related to EQT share-based compensation awards. Stock options outstanding and exercisable as of December 31, 2021 were 464,876, have a weighted average exercise price of $38.55 and expire between 20222024 and 2028. There was2028 and there are no unrecognized compensation costs remaining related to these options. A summary of stock option activity during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 2020 and 2019. There were no unrecognized compensation costs related to outstanding non-vested stock options asis presented below. | | | | | | | | |
| | Options |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2021 | | 464,876 | |
| | |
| Expired | | — | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | | 464,876 | |
| | |
| Expired | | (94,132) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | | 370,744 | |
| | |
| Expired | | (83,207) | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | | 287,537 | |
Phantom Units
The Company grants phantom unit awards to certain non-employee directors thatwho serve or at the time of grant served on the Board. Director phantom units expected to be satisfied in Company common stock vest on the date of grant and are recorded based on the grant date fair value, which is determined based upon the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the trading day before the grant date. The value of director phantom units is paid in Company common stock upon the director's termination of service on the Board. Prior to the completion of the EQGP Buyout and the EQM Merger, respectively, EQGP's general partner and EQM's general partner, as applicable, granted phantom unit awards to certain non-employee directors of EQGP's general partner and EQM's general partner, respectively. A total of 512,440 Equitrans Midstream non-employee director share-based awards including accrued dividends were outstanding as of December 31, 2021.
A summary of phantom units' activity for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 20192021 is presented below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Grants | | Weighted Average Fair Value | | Compensation Expense (Millions) | | Grants | | Weighted Average Fair Value | | Compensation Expense (Millions) | | Grants | | Weighted Average Fair Value | | Compensation Expense (Millions) |
| Equitrans Midstream phantom units | 149,280 | | | $ | 8.04 | | | $ | 1.2 | | | 92,760 | | | $ | 11.51 | | | $ | 1.1 | | | 45,000 | | | $ | 20.02 | | | $ | 0.9 | |
EQGP phantom units (a) | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | 8,500 | | | $ | 20.00 | | | $ | 0.2 | |
EQM phantom units(b) | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | 9,540 | | | $ | 29.91 | | | $ | 0.3 | | | 5,910 | | | $ | 43.25 | | | $ | 0.3 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| Equitrans Midstream phantom units | | |
| Units | | Weighted Average
Fair Value Per Share | | Aggregate Fair Value | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2021 | 318,605 | | | $ | 16.43 | | | $ | 5,234,709 | | | | | | | |
| Granted | 177,156 | | | 8.16 | | | 1,445,036 | | | | | | | |
| Distributions | (16,957) | | | 20.29 | | | (343,982) | | | | | | | |
| Dividends | 33,636 | | | 8.88 | | | 298,813 | | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2021 | 512,440 | | | $ | 12.95 | | | $ | 6,634,576 | | | | | | | |
| Granted | 141,778 | | | 10.03 | | | 1,422,140 | | | | | | | |
| Distributions | (104,603) | | | 14.75 | | | (1,542,823) | | | | | | | |
| Dividends | 37,533 | | | 7.86 | | | 294,990 | | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2022 | 587,148 | | | $ | 11.60 | | | $ | 6,808,883 | | | | | | | |
| Granted | 265,115 | | | 5.17 | | | 1,371,610 | | | | | | | |
| Distributions | (78,840) | | | 7.56 | | | (595,686) | | | | | | | |
| Dividends | 63,591 | | | 7.30 | | | 464,084 | | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2023 | 837,014 | | | $ | 9.62 | | | $ | 8,048,891 | | | | | | | |
(a)In connection with the completion of the EQGP Buyout, the non-employee directors of EQGP's general partner were paid the Purchase Price for each EQGP phantom unit that they held. See Note 2.
(b)In connection with the closing of the EQM Merger, the non-employee directors of the EQM General Partner received the Merger Consideration for each EQM phantom unit that they held. See Note 2.
20222024 Awards
Effective in January 2022,February 2024, the Compensation Committee adopted the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 20222024 Performance Share Unit Program (2022(2024 PSU Program) under the 2018 Plan. The 20222024 PSU Program was established to align the interests of key employees with the interests of shareholders and the strategic objectives of the Company.
In January 2022, 1,997,750 units were granted Awards under the 20222024 PSU Program. Program, consisting of both equity and liability awards, are expected to be granted in the first quarter of 2024.
The vesting of the units under the 20222024 PSU Program will occur upon payment after the expiration of the Performance Period,performance period, which is January 1, 20222024 to December 31, 2024,2026, assuming continued employment with the Company. The payout will vary between zero and 200% of the number of outstanding units contingent upon the level of total shareholder return relative to a predefined peer group, the achievement of certain levels of free cash flow before changes in working capital and planning and executing on certain methane emissions mitigation projects, in each case during the Performance Period. If earned atperformance period and, in the target payout levelcase of 100%, 1,274,910 of the 2022 PSU Program units are expectedfree cash flow before changes in working capital, on an annual basis within such performance period.
The Company also expects to be distributed in Company common stock and 722,840 of the 2022 PSU Program units are expected to be paid in cash.
In January 2022, 546,520grant restricted stock equity and 310,320 restricted stock unit liability awards were granted.in the first quarter of 2024. The restricted stock equity awards and restricted stock unit liability awards will be fully vested at the end of the three-year period commencing on January 1, 2022,2027, assuming continued employment with the Company.
Employee Savings Plan
For the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, the Company recognized expense related to its defined contribution plan of $7.6$8.2 million, $8.1$8.0 million and $7.8$7.6 million, respectively.
9. Debt
The following table presents the Company's and its consolidated subsidiaries' outstanding debt as of December 31, 20212023 and 2020.2022.
| | December 31, 2023 | | | December 31, 2023 | | December 31, 2022 |
| Principal | | | Principal | | Carrying Value(a) | | Fair Value(b) | | Principal | | Carrying Value(a) | | Fair Value(b) |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
| | Amended EQM Credit Facility | |
| | Amended EQM Credit Facility | |
| | Amended EQM Credit Facility | |
| 2021 Eureka Credit Facility | |
| Total credit facility borrowings | |
| | | December 31, 2021 | | December 31, 2020 |
| | Principal | | Carrying Value(a) | | Fair Value(b) | | Principal | | Carrying Value(a) | | Fair Value(b) |
EQM 4.75% Senior Notes due 2023 (c) | |
| | (Thousands) |
| | Amended EQM Credit Facility | $ | 225,000 | | | $ | 225,000 | | | $ | 225,000 | | | $ | 485,000 | | | $ | 485,000 | | | $ | 485,000 | |
Eureka Credit Facility (c) | 280,000 | | | 280,000 | | | 280,000 | | | 302,500 | | | 302,500 | | | 302,500 | |
| Total credit facility borrowings | $ | 505,000 | | | $ | 505,000 | | | $ | 505,000 | | | $ | 787,500 | | | $ | 787,500 | | | $ | 787,500 | |
EQM 4.75% Senior Notes due 2023 (c) | |
| | | Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,400,000 | | | 1,397,768 | | | 1,400,000 | |
EQM 4.75% Senior Notes due 2023 (c) | |
| EQM 4.00% Senior Notes due 2024 | EQM 4.00% Senior Notes due 2024 | 500,000 | | | 498,014 | | | 522,695 | | | 500,000 | | | 497,245 | | | 515,455 | |
| EQM 6.00% Senior Notes due 2025 | |
| EQM 4.125% Senior Notes due 2026 | EQM 4.125% Senior Notes due 2026 | 500,000 | | | 495,816 | | | 517,695 | | | 500,000 | | | 494,966 | | | 512,285 | |
| EQM 6.50% Senior Notes due 2027 | |
| EQM 7.50% Senior Notes due 2027 | |
| EQM 5.50% Senior Notes due 2028 | |
| EQM 4.50% Senior Notes due 2029 | EQM 4.50% Senior Notes due 2029 | 800,000 | | | 790,927 | | | 834,856 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| EQM 4.75% Senior Notes due 2023 | 600,000 | | | 598,088 | | | 628,380 | | | 1,100,000 | | | 1,094,235 | | | 1,162,590 | |
| EQM 7.50% Senior Notes due 2030 | |
| EQM 4.75% Senior Notes due 2031 | EQM 4.75% Senior Notes due 2031 | 1,100,000 | | | 1,087,493 | | | 1,166,220 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| EQM 5.50% Senior Notes due 2028 | 850,000 | | | 842,657 | | | 939,684 | | | 850,000 | | | 841,538 | | | 933,980 | |
| EQM 6.50% Senior Notes due 2048 | EQM 6.50% Senior Notes due 2048 | 550,000 | | | 539,778 | | | 673,458 | | | 550,000 | | | 539,393 | | | 582,995 | |
| EQM 6.00% Senior Notes due 2025 | 700,000 | | | 692,662 | | | 763,091 | | | 700,000 | | | 690,565 | | | 767,375 | |
| EQM 6.50% Senior Notes due 2027 | 900,000 | | | 889,510 | | | 1,014,417 | | | 900,000 | | | 887,602 | | | 1,020,060 | |
| | Total debt | |
| Less current portion of long-term debt | |
| Total long-term debt | Total long-term debt | $ | 6,500,000 | | | $ | 6,434,945 | | | $ | 7,060,496 | | | $ | 6,500,000 | | | $ | 6,443,312 | | | $ | 6,894,740 | |
(a)Carrying values of the senior notes and term loans represent principal amount less unamortized debt issuance costs and debt discounts.
(b)See Note 1210 for a discussion of fair value measurements.
(c)Includes aggregate borrowings outstanding onSee "2023 Senior Notes Redemption" below for discussion of the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility (as defined below) asredemption of the then-outstanding 2023 Notes (defined herein).
As of December 31, 20212023, the combined aggregate amounts of maturities for long-term debt, including the current portion thereof, were as follows: $0.3 billion in 2024, $0.4 billion in 2025, $0.5 billion in 2026, $1.4 billion in 2027, $0.85 billion in 2028 and on$2.95 billion in 2029 and thereafter.
EQM Revolving Credit Facility. On October 6, 2023 (the Fourth Amendment Date), EQM entered into an amendment (the Fourth Amendment) to the Former EurekaThird Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 31, 2018 (as amended, supplemented or otherwise modified, the Amended EQM Credit Facility), among EQM, as borrower, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as the administrative agent, swing line lender and an L/C issuer, the lenders party thereto from time to time and any other persons party thereto from time to time. The Fourth Amendment extended the stated maturity date of the Amended EQM Credit Facility with such extension only applicable for the lenders approving the Fourth Amendment, from April 30, 2025 to April 30, 2026. After giving effect to such extension contemplated by the Fourth Amendment, EQM had or, as applicable, has aggregate commitments available under the Amended EQM Credit Facility of approximately $2.16 billion before October 31, 2023, approximately $1.55 billion in aggregate commitments available on and after October 31, 2023 and prior to April 30, 2025, and approximately $1.45 billion in aggregate commitments available on and after April 30, 2025 and prior to April 30, 2026.
As of December 31, 2023, the Company had aggregate commitments available under the Amended EQM Credit Facility of approximately $1.55 billion. As of December 31, 2023, EQM had $915 million of borrowings and approximately $105.8 million of letters of credit outstanding under the Amended EQM Credit Facility. The amount EQM is able to borrow under the Amended EQM Credit Facility is bounded by a maximum Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined below)in the Amended EQM Credit Facility), and as of October 1, 2023 (the MVP Mobilization Effective Date), such maximum Consolidated Leverage Ratio permitted with respect to the fiscal quarter ending December 30, 2020.31, 2023 and the end of each of EQM's three
consecutive fiscal quarters thereafter was 5.85 to 1.00, with the then-applicable ratio being tested as of the end of the applicable fiscal quarter. As of December 31, 2021,2023, EQM had the combined aggregate amounts of maturities for long-term debt were as follows: zero in 2022, $0.6ability to borrow approximately $0.4 billion in 2023, $0.5 billion in 2024, $0.7 billion in 2025, $0.5 billion in 2026 and $4.2 billion in 2027 and thereafter.
Equitrans Midstream Term Loan Facility. In December 2018, Equitrans Midstream entered into a term loan credit agreement (as amended in May 2019, the ETRN Term Loan Credit Agreement) that provided for a senior secured term loan facility in an aggregate principal amount of $600 million (the ETRN Term Loans). The Company received net proceeds from the ETRN Term Loans of $568.1 million, inclusive of a discount of $18.0 million and estimated debt issuance costs of $13.9 million. The net proceeds were primarily used to fund the EQGP Buyout, including certain fees, costs and expenses in connection therewith, and the remainder was used for general corporate purposes. On March 3, 2020, EQM drew $650.0 million under the EQM Credit Facility (defined below) and transferred such funds to the Company, pursuant to a senior unsecured term loan agreement with the Company. The Company utilized a portion of such funds to pay off all of the amounts outstanding under the ETRN Term Loans and the ETRN Term Loan Credit Agreement was terminated. As a result, the Company wrote off $24.4 million of unamortized discount and financing costs related to the ETRN Term Loan Credit Agreement. The write off charge is included in the loss on early extinguishment of debt line on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income. On September 29, 2020, the Company made a prepayment to EQM of all principal, interest, fees and other obligations outstanding under the senior unsecured term loan agreement and terminated the agreement. During the period from January 1, 2020 to March 3, 2020, the weighted average annual interest rate was approximately 6.2%. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the weighted average annual interest rate was approximately 6.8%.
Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility.In October 2018, Equitrans Midstream entered into a senior secured revolving credit facility agreement that provided for $100 million in borrowing capacity (the Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility). Equitrans Midstream amended the Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility on December 31, 2018 to, among other things, permit the incurrence of the borrowings under the ETRN Term Loan Credit Agreement. The Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility, which was available for general corporate purposes and to fund ongoing working capital requirements, was terminated on March 3, 2020 in conjunction with the Company's termination of the ETRN Term Loan Credit Agreement (see above). As a result, the Company wrote off $0.5 million of unamortized financing costs related to the Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility. The write off charge is included in the loss on early extinguishment of debt line on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
The Company had no borrowings and no letters of credit outstanding under the Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility during the period from January 1, 2020 to March 3, 2020. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the maximum outstanding borrowings under the Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility was $44 million, the average daily balance was approximately $3.2 million and the weighted average annual interest rate was 4.2%. Commitment fees paid to maintain credit availability under the Equitrans Midstream Credit Facility were approximately $0.1 million for the period from January 1, 2020 to March 3, 2020, and $0.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019.
EQM Revolving Credit Facility. On October 31, 2018, EQM amended and restated its unsecured revolving credit facility to increase the borrowing capacity from $1 billion to $3 billion and extend the term to October 2023 (the EQM Credit Facility). On March 30, 2020, EQM entered into an amendment (the First Amendment) to the EQM Credit Facility (as amended, the First Amended EQM Credit Facility) which, among other things, amended certain defined terms and negative covenants in the EQM Credit Facility. On April 16, 2021, EQM entered into a second amendment (the Second Amendment) to the EQM Credit Facility (as amended by the First Amendment and the Second Amendment, the Amended EQM Credit Facility). The Second Amendment amended, among other things:
•certain defined terms, including:
•the definition of “Applicable Rate” in the First Amended EQM Credit Facility such that: (i) Base Rate Loans (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) bear interest at a base rate plus a margin of 0.125% to 2.000% determined on the basis of EQM’s then-current credit ratings and (ii) Eurodollar Rate Loans (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) bear interest at a Eurodollar Rate (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) plus a margin of 1.125% to 3.000% also determined on the basis of EQM’s then-current credit ratings; and
•the definition of “Qualified Project” in the First Amended EQM Credit Facility and certain related definitions, which, collectively, have the effect of removing the designation of the MVP project and the Hammerhead pipeline as Qualified Projects on a go-forward basis after March 31, 2021 under the Amended EQM Credit Facility, and eliminating certain addbacks to Consolidated EBITDA (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) that previously were available in connection with the MVP project and the Hammerhead pipeline; and
•the financial covenant under the First Amended EQM Credit Facility, pursuant to which, except for certain measurement periods following the consummation of certain acquisitions during which the Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) cannot exceed the greater of 5.50 to 1.00 or the maximum ratio otherwise permitted under the Amended EQM Credit Facility for the applicable period, the Consolidated Leverage Ratio cannot exceed, (i) for each fiscal quarter ending on and after June 30, 2021 and on or prior to September 30, 2022, 5.95 to 1.00, (ii) for the fiscal quarter ending on December 31, 2022, 5.25 to 1.00, and (iii) for each fiscal quarter ending after December 31, 2022, 5.00 to 1.00.
The Second Amendment also reduced the aggregate commitments available under the Amended EQM Credit Facility to $2.25 billion, and the commitment of each lender thereunder was reduced accordingly on a pro rata basis.
The Amended EQM Credit Facility is available for general partnership purposes, including to purchase assets, to make investments, to fund working capital requirements and capital expenditures and to pay distributions. Subject to satisfaction of certain conditions, the Amended EQM Credit Facility has an accordion feature that allows EQM to increase the available borrowings under the facility by up to an additional $750 million. The Amended EQM Credit Facility has a sublimit of up to $250 million for same-day swing line advances and a sublimit of up to $400 million for letters of credit. In addition, EQM has the ability to request that one or more lenders make available term loans under the Amended EQM Credit Facility subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions (which term loans would be secured by cash, qualifying investment grade securities or a combination thereof). The Company’s obligations in respect of the revolving borrowings made under the Amended EQM Credit Facility are unsecured.Facility. As of December 31, 2021, no term loans were outstanding under the Amended EQM Credit Facility.
As of December 31, 2021,2022, EQM had approximately $225$240 million of borrowings and approximately $234.9 million of letters of credit outstanding under the Amended EQM Credit Facility. AsFor the avoidance of December 31, 2020, EQM had approximately $485 million of borrowings and $246 million of letters of credit outstanding underdoubt, any reference to the First Amended EQM Credit Facility as of any particular date shall mean the Amended EQM Credit Facility as in effect on such date.
See Note 15 for discussion of the Fifth Amendment to the Amended EQM Credit Facility.
During the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, the maximum outstanding borrowings were $915 million, $315 million and $525 million, $2,040 million and $1,690 million, respectively;respectively, the average daily balances were approximately $354 million, $193 million and $395 million, $852 million and $846 million, respectively;respectively, and the weighted average annual interest rates were approximately 2.6%8.1%, 2.9%4.5% and 3.6%2.6%, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, commitment fees of $7.4$7.6 million, $7.2$8.4 million and $4.6$7.4 million, respectively, were paid to maintain credit availability under the Amended EQM Credit Facility.
Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement. In August 2019, EQM entered into a term loan agreement (the 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement) that provided for unsecured As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, no term loans (the EQM Term Loans) in an aggregate principal amount of $1.4 billion. On March 30, 2020, EQM entered into an amendment to the 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement (as amended, the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement) which, among other things, amended certain defined terms and negative covenants in the 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement.
On January 8, 2021, EQM (i) applied a portion of the proceeds from the issuance of the 2021 Senior Notes (as defined below) to prepay all principal, interest, fees and other obligationswere outstanding under the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement and (ii) terminated the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement and the loan documents associated therewith. EQM repaid outstanding loans with a principal amount of $1.4 billion in connection with the termination of the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement. Prior to its termination in January 2021, the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement would have matured in August 2022.
The Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement provided EQM with the right to request incremental term loans in an aggregate amount of up to $300 million, subject to, among other things, obtaining additional commitments from existing lenders or commitments from new lenders. As of December 31, 2020, EQM had $1.4 billion of borrowings outstanding under the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement. During the period from January 1, 2021 through January 7, 2021, the weighted average annual interest rate was approximately 2.4%. During the year ended December 30, 2020 and for the applicable portions of the year ended December 31, 2019, the weighted average annual interest rates were approximately 2.7% and 3.3%, respectively.Credit Facility.
Eureka Credit Facilities. On May 13, 2021, Eureka Midstream, LLC (Eureka), a wholly owned subsidiary of Eureka Midstream, repaid all outstanding principal borrowings plus accrued and unpaid interest under and terminated its credit facility with ABN AMRO Capital USA LLC, as administrative agent, the lenders party thereto from time to time and any other persons party thereto from time to time (the Former Eureka Credit Facility). No early termination or prepayment penalties were incurred as a result of the termination of the Former Eureka Credit Facility or the repayment of outstanding amounts under the facility. In connection with the termination of the Former Eureka Credit Facility, all guaranties and liens securing the obligations under the Former Eureka Credit Facility were terminated and released. Prior to its termination, the Former Eureka Credit Facility was scheduled to mature on August 25, 2021.
In conjunction with the termination of, and to fund the repayment of all outstanding amounts under the Former Eureka Credit Facility, on May 13, 2021, Eureka entered into a $400 million senior secured revolving credit facility withSumitomo Mitsui Banking Corporation, as administrative agent, the lenders party thereto from time to time and any other persons party thereto from time to time (the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility). The 2021On March 29, 2023, Eureka Credit Facility matures on November 13, 2024, and is available for general business purposes, including financing maintenance and expansion capital expenditures relatedentered into an amendment (the First Eureka Amendment) to the Eureka system and providing working capital for Eureka’s operations. Subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions, the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility hasthat replaced the London Interbank Offered Rate with the Secured Overnight Financing Rate as the benchmark rate for borrowings, including a credit spread adjustment of 0.10% for all applicable interest periods, as well as for daily swing line borrowings. On October 5, 2023, Eureka entered into an accordion feature that allowsamendment (the Second Eureka Amendment) to increase the available borrowings under the facility to an amount no greater than $500 million of total commitments. The 2021 Eureka Credit Facility also has a sublimit of up to $20 million for same-day swing line advances.
Underthat extended the termsstated maturity date of the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility, with such extension only applicable for the lenders approving the Second Eureka can obtain base rate loans or Eurodollar rate loans. Base rate loans are denominated in dollars and bear interest at an adjusted base rate, which is equalAmendment, from November 13, 2024 to the highest of (i) the prime rate as quoted by the Wall Street Journal, (ii) the one-month Adjusted Eurodollar Rate (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) plus 1.0% or (iii) the Federal Funds effective rate plus 0.5% per annum; plus the Applicable Margin (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility). Eurodollar rate loans bear interest at the Adjusted Eurodollar Rate per annum, which rate isNovember 13, 2025. Any reference to be determined by the administrative agent pursuant to a prescribed calculation based on the ICE Benchmark Administration LIBOR Rate for committed loans, and the 30-day rate of interest per annum appearing in Bloomberg Page BBAM1 as the London interbank offered rate for deposits in dollars for swing line advances, plus the Applicable Margin. The Applicable Margin ranges from 1.00% to 2.25% in the case of base rate loans and from 2.00% to 3.25% in the case of Eurodollar rate loans, in each case, depending on Eureka's consolidated leverage ratio.
The 2021 Eureka Credit Facility contains negative covenants that, among other things, limit restricted payments, the incurrence of debt, dispositions, mergers and fundamental changes, securities issuances and transactions with affiliates, in each case and as applicable, subject to certain specified exceptions. In addition, the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility contains certain specified eventsas of default such as insolvency, nonpayment of scheduled principal or interest obligations, loss and failure to replace certain material contracts, change of control and cross-default related to the acceleration or default of certain other financial obligations.
Underany particular date shall mean the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility Eureka is required to maintain a Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as definedas in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) of not more than 4.75 to 1.00 (or not more than 5.25 to 1.00 for certain measurement periods following the consummation of certain acquisitions), tested as of the end of each fiscal quarter. If Eureka has issued senior notes of $200 million or more in the aggregate as of the end of any fiscal quarter, then foreffect on such fiscal quarter and for each fiscal quarter thereafter, Eureka is required to maintain a Consolidated Leverage Ratio of not more than 5.25 to 1.00 and will not permit the ratio of senior indebtedness to four-quarter Consolidated EBITDA (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) as of the end of any such quarter to exceed 3.50 to 1.00. Additionally, as of the end of any fiscal quarter, Eureka will not permit the ratio of Consolidated EBITDA for the four fiscal quarters then ending to Consolidated Interest Charges (as defined in the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility) to be less than 2.50 to 1.00. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary, the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility provides Eureka with an equity cure right if it fails to abide by such financial covenants.date.
As of December 31, 2021,2023 and 2022, Eureka had approximately $280$315 million and $295 million, respectively, of borrowings outstanding under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility. As ofDuring the years ended December 31, 2020, Eureka had approximately $303 million2023 and 2022, the maximum amount of outstanding borrowings under the Former2021 Eureka Credit Facility.Facility at any time was approximately $315 million and $295 million, the average daily balance was approximately $310 million and $281 million, and Eureka incurred interest at a weighted average annual interest rate of approximately 7.8% and 4.4%, respectively. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, commitment fees of $0.4 million and $0.5 million were paid to maintain credit availability under the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2021, the maximum amount of outstanding borrowings under either of the Former Eureka credit facilitiesCredit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility at any time was approximately $315 million, the average daily balance was approximately $301 million and Eureka incurred interest at a weighted average annual interest rate of approximately 2.5%. For the year ended December 31, 2021, commitment fees of $0.5 million were paid to maintain credit availability under the Former Eureka credit facilities. DuringCredit Facility and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility.
2023 Senior Notes Redemption. On June 21, 2023 (the Redemption Date), EQM redeemed in full its then-outstanding 4.75% Senior Notes due 2023 (the 2023 Notes) in the aggregate principal amount of $98.9 million, pursuant the Indenture, dated as of August 1, 2014, by and between EQM, the subsidiary guarantors party thereto and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. (BNYMTC), as trustee, as supplemented by that certain Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 25, 2018, by and between the EQM and BNYMTC, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 2023 Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the Redemption Date. Upon the redemption by EQM of the 2023 Notes, the Third Supplemental Indenture was discharged and ceased to be of further effect except as to rights thereunder. EQM utilized cash on hand to effect the redemption on the Redemption Date.
2022 Senior Notes. On June 7, 2022, EQM completed a private offering of $500 million aggregate principal amount of new 7.50% senior notes due 2027 (the 2027 Notes) and $500 million aggregate principal amount of new 7.50% senior notes due 2030 (the 2030 Notes and, together with the 2027 Notes, the 2022 Senior Notes) and received net proceeds from the offering of approximately $984.5 million (excluding costs related to the 2022 Tender Offers discussed below), inclusive of a discount of approximately $12.5 million and debt issuance costs of approximately $3.0 million.
The 2022 Senior Notes were issued under and are governed by an indenture, dated June 7, 2022 (the 2022 Indenture), between EQM and U.S. Bank Trust Company, National Association, as trustee. The 2022 Indenture contains covenants that limit EQM’s ability to, among other things, incur certain liens securing indebtedness, engage in certain sale and leaseback transactions, and
enter into certain consolidations, mergers, conveyances, transfers or leases of all or substantially all of EQM’s assets. The 2027 Notes will mature on June 1, 2027 and interest on the 2027 Notes is payable semi-annually on June 1 and December 1 of each year, commencing December 1, 2022. The 2030 Notes will mature on June 1, 2030 and interest on the 2030 Notes is payable semi-annually on June 1 and December 1 of each year, commencing December 1, 2022.
EQM used the net proceeds from the offering of the 2022 Senior Notes and cash on hand to purchase (i) an aggregate principal amount of approximately $501.1 million of its outstanding 2023 Notes pursuant to a tender offer for any and all of the outstanding 2023 Notes (the Any and All Tender Offer) and an open market purchase following the expiration of the Any and All Tender Offer, and (ii) an aggregate principal amount of $300 million of its outstanding 6.00% notes due 2025 (2025 Notes), and an aggregate principal amount of $200 million of its outstanding 4.00% notes due 2024 (2024 Notes), pursuant to tender offers (the Maximum Tender Offers, together with the Any and All Tender Offer, the 2022 Tender Offers) for the 2025 Notes and 2024 Notes, which such Maximum Tender Offers reflected a maximum aggregate principal amount of 2025 Notes and 2024 Notes to be purchased of $500 million (such amount, the Aggregate Maximum Principal Amount).
2022 Tender Offers. On June 6, 2022, the Any and All Tender Offer expired and, on June 7, 2022 and June 9, 2022, EQM purchased an aggregate principal amount of approximately $496.8 million of 2023 Notes at an aggregate cost of approximately $506.7 million pursuant to the Any and All Tender Offer. On June 10, 2022, which was after the closing of the Any and All Tender Offer, EQM also repurchased an aggregate principal amount of approximately $4.3 million of 2023 Notes in the open market at an aggregate cost of approximately $4.4 million. On June 13, 2022, which was the early tender deadline for the Maximum Tender Offers, the Aggregate Maximum Principal Amount was fully subscribed by the 2024 Notes and 2025 Notes then tendered, and, on June 14, 2022, EQM purchased an aggregate principal amount of $200 million of 2024 Notes and $300 million of 2025 Notes at an aggregate cost of approximately $509 million (inclusive of the applicable early tender premium for the 2024 Notes and 2025 Notes described in that certain Offer to Purchase of EQM dated May 31, 2022, as amended).
The Company incurred a loss on the extinguishment of debt of approximately $24.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2020,2022 related to the payment of the 2022 Tender Offers and foropen market repurchase premiums and fees, and write off of the period from April 10, 2019 through December 31, 2019,respective unamortized discounts and financing costs associated with the maximumpurchase of portions of 2023, 2024 and 2025 Notes in the 2022 Tender Offers. This amount is included in the loss on extinguishment of outstanding borrowings underdebt line on the Former Eureka Credit Facility at any time were approximately $323 million and $293 million, respectively, the average daily balances were approximately $301 million and $288 million, respectively, and Eureka incurred interest at weighted average annual interest ratesstatements of approximately 2.6% and 4.2%, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2020 and for the period from April 10, 2019 through December 31, 2019, commitment fees of $0.6 million and $0.4 million were paid to maintain credit availability under the Former Eureka Credit Facility, respectively.consolidated comprehensive income.
2021 Senior Notes. During the first quarter of 2021, EQM issued, in a private offering, $800 million aggregate principal amount of new 4.50% senior notes due 2029 (the 2029 Notes) and $1,100 million aggregate principal amount of new 4.75% senior notes due 2031 (the 2031 Notes and, together with the 2029 Notes, the 2021 Senior Notes) and received net proceeds from the offering of approximately $1,876.5 million (excluding costs related to the 2021 Tender Offers discussed below), inclusive of a discount of $19 million and debt issuance costs of $4.5 million. EQM used the net proceeds from the offering of the 2021 Senior Notes and cash on hand to repay all outstanding borrowings under the term loan agreement EQM entered into in August 2019 (as amended, the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement,Agreement), to purchase an aggregate principal amount of $500 million of its outstanding 4.75% notes due 2023 (2023 Notes)Notes pursuant to tender offers for certain of EQM's outstanding indebtedness (such tender offers, the 2021 Tender Offers), and for general partnership purposes.
The 2021 Senior Notes were issued under and are governed by an indenture, dated January 8, 2021 (the 2021 Indenture), between EQM and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. The 2021 Indenture contains covenants that limit EQM’s ability to, among other things, incur certain liens securing indebtedness, engage in certain sale and leaseback transactions, and enter into certain consolidations, mergers, conveyances, transfers or leases of all or substantially all of EQM’s assets. The 2029 Notes will mature on January 15, 2029 and interest on the 2029 Notes is payable semi-annually on January 15 and July 15 of each year, commencing July 15, 2021. The 2031 Notes will mature on January 15, 2031 and interest on the 2031 Notes is payable semi-annually on January 15 and July 15 of each year, commencing July 15, 2021.
The 2021 Senior Notes are unsecured and rank equally with all of EQM’s existing and future senior obligations. The 2021 Senior Notes are senior in right of payment to any of EQM’s future obligations that are, by their terms, expressly subordinated in right of payment to the 2021 Senior Notes. The 2021 Senior Notes are effectively subordinated to EQM’s secured obligations, if any, to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such obligations, and structurally subordinated to all indebtedness and obligations, including trade payables, of EQM’s subsidiaries, other than any subsidiaries that may guarantee the 2021 Senior Notes in the future. EQM may, at its option, redeem some or all of the 2029 Notes and the 2031 Notes, in whole or in part, at any time prior to their maturity at the applicable redemption price as set forth in the 2021 Indenture.
Upon the occurrence of a Change of Control Triggering Event (as defined in the 2021 Indenture), EQM may be required to offer to purchase the 2021 Senior Notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2021 Senior Notes repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the repurchase date.
The 2021 Indenture contains certain events of default, including the following: (i) default in the payment of interest on such 2021 Senior Notes when due that continues for 30 days; (ii) default in the payment of principal of or premium, if any, on any such 2021 Senior Notes when due, whether at its stated maturity, upon redemption or otherwise; (iii) failure by EQM or any subsidiary guarantor, if any, to comply for 90 days with the other agreements with respect to such 2021 Senior Notes contained in the 2021 Indenture after written notice by the trustee or by the holders of at least 25% in principal amount of the outstanding 2021 Senior Notes of such series; (iv) certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization of EQM or any subsidiary guarantor, if any, that is one of EQM’s Significant Subsidiaries (as defined in the 2021 Indenture); and (v) if such 2021 Senior Notes are guaranteed by a subsidiary guarantor that is one of EQM’s Significant Subsidiaries, (a) the guarantee of that subsidiary guarantor ceases to be in full force and effect, except as otherwise provided in the 2021 Indenture; (b) the guarantee of that subsidiary guarantor is declared null and void in a judicial proceeding; or (c) that subsidiary guarantor denies or disaffirms its obligations under the 2021 Indenture or its guarantee.
If an event of default occurs and is continuing with respect to any of the 2021 Senior Notes, the trustee or the holders of at least 25% in aggregate principal amount of the then outstanding 2021 Senior Notes of such series may declare the 2021 Senior Notes of such series to be due and payable. Upon such a declaration, such principal, premium, if any, and accrued and unpaid interest on such 2021 Senior Notes will be due and payable immediately. If an event of default relating to certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization occurs, all outstanding 2021 Senior Notes will become due and payable immediately without further action or notice on the part of the trustee or any holders of the 2021 Senior Notes.
Tender Offers. On January 15, 2021 (the 2021 early tender deadline), the maximum principal amount for the 2021 Tender Offers was fully subscribed by the 2023 Notes tendered as of the 2021 early tender deadline and on January 20, 2021, EQM purchased an aggregate principal amount of $500 million of 2023 Notes at an aggregate cost of approximately $537 million (inclusive of the applicable early tender premium for the 2023 Notes described in that certain Offer to Purchase of EQM dated January 4, 2021, as amended, plus accrued interest).
The Company incurred a loss on the extinguishment of debt of $41.0 million during the first quarter of 2021 related to the payment of the premium in the 2021 Tender Offer premiumOffers and write off of unamortized discounts and financing costs related to the prepayment of the EQM Term Loansloans under, and termination of, the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement and purchase of 2023 Notes in the 2021 Tender Offers. This amount is included in the loss on extinguishment of debt line on the statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
2020 Senior Notes. During the second quarter of 2020, EQM issued $700 million aggregate principal amount of new 6.00% senior unsecured notes due July 1, 2025 and $900 million aggregate principal amount of new 6.50% senior unsecured notes due July 1, 2027 (collectively, the 2020 Senior Notes) and received net proceeds from the offering of approximately $1,576.1 million, inclusive of a discount of $20.0 million and debt issuance costs of $3.9 million. A portion of the net proceeds were used to repay a portion of the borrowings outstanding under the First Amended EQM Credit Facility, and the remainder was used for general partnership purposes.
The 2020 Senior Notes were issued under and are governed by an indenture, dated June 18, 2020 (the 2020 Indenture), between EQM and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. The 2020 Indenture contains covenants that limit EQM's ability to, among other things, incur certain liens securing indebtedness, engage in certain sale and leaseback
transactions, and enter into certain consolidations, mergers, conveyances, transfers or leases of all or substantially all of EQM's assets. Upon the occurrence of a Change of Control Triggering Event (as defined in the 2020 Indenture), EQM may be required to offer to purchase the 2020 Senior Notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2020 Senior Notes repurchased, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the repurchase date.
The 2020 Senior Notes are unsecured and rank equally with all of EQM’s existing and future senior obligations. The 2020 Senior Notes are senior in right of payment to any of EQM’s future obligations that are, by their terms, expressly subordinated in right of payment to the 2020 Senior Notes. The 2020 Senior Notes are effectively subordinated to EQM’s secured obligations, if any, to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such obligations, and structurally subordinated to all indebtedness and obligations, including trade payables, of EQM’s subsidiaries, other than any subsidiaries that may guarantee the 2020 Senior Notes in the future.
The 2020 Indenture contains certain events of default, including the following: (1) default in the payment of interest on such 2020 Senior Notes when due that continues for 30 days; (2) default in the payment of principal of or premium, if any, on any such 2020 Senior Notes when due, whether at its stated maturity, upon redemption or otherwise; (3) failure by EQM or any subsidiary guarantor, if any, to comply for 90 days with the other agreements with respect to such 2020 Senior Notes contained in the 2020 Indenture after written notice by the trustee or by the holders of at least 25% in principal amount of the outstanding 2020 Senior Notes of such series; (4) certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization of EQM or any subsidiary guarantor, if any, that is one of EQM’s Significant Subsidiaries (as defined in the 2020 Indenture); and (5) if such 2020 Senior Notes are guaranteed by a subsidiary guarantor that is one of EQM’s Significant Subsidiaries, (a) the guarantee of that subsidiary guarantor ceases to be in full force and effect, except as otherwise provided in the 2020 Indenture; (b) the guarantee of that subsidiary guarantor is declared null and void in a judicial proceeding; or (c) that subsidiary guarantor denies or disaffirms its obligations under the 2020 Indenture or its guarantee.
If an event of default occurs and is continuing with respect to any of the 2020 Senior Notes, the trustee or the holders of at least 25% in aggregate principal amount of the then outstanding 2020 Senior Notes of such series may declare the 2020 Senior Notes of such series to be due and payable. Upon such a declaration, such principal, premium, if any, and accrued and unpaid interest on such 2020 Senior Notes will be due and payable immediately. If an event of default relating to certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization occurs, all outstanding 2020 Senior Notes will become due and payable immediately without further action or notice on the part of the trustee or any holders of the 2020 Senior Notes.
As of December 31, 2021,2023, EQM and Eureka were in compliance with all debt provisions and covenants.
12.10. Fair Value Measurements
Assets Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis. The Company records derivative instruments at fair value on a gross basis in its consolidated balance sheets. The EQT Global GGA provides for potential cash bonus payments payable by EQT to the Company during the period beginning on the first day of the calendar quarter in which the MVP full in-service date occurs through the calendar quarter ending December 31, 2024 (the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision). The potential cash bonus payments are conditioned upon the quarterly average of certain Henry Hub natural gas prices exceeding certain price thresholds. The Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision is accounted for as described in Note 6, isa derivative instrument and recorded at its estimated fair value using a Monte Carlo simulation model. Significant inputs used in the fair value measurement include NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices as of the date of valuation, probability-weighted assumptions regarding in-service timing for the MVP project completion, risk-free interest rates based on U.S. Treasury rates, expected volatility of NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices and an estimated credit spread of EQT. The probability-weighted assumptions regarding MVP project completion, utilizing internally developed methodologies, and the expected volatility of NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas futures prices used in the valuation methodology represents arepresent significant unobservable inputinputs causing the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision to be designated as a Level 3 fair value measurement. An expected average volatility of approximately 39%47.5% was utilized in the valuation model, which is based on market-quoted volatilities of relevant NYMEX Henry Hub natural gas forward prices.
As of December 31, 2021 and 2020,2023, the fair valuesvalue of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision were $51.6was $24.5 million, and $68.0 million, respectively, which werewas recorded in other current assets on the Company's consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2022, the fair value of the Henry Hub cash bonus payment provision was $23.0 million, which was recorded in other assets on the Company's consolidated balance sheets. During the years ended December 31, 20212023, 2022 and 2020,2021, the Company recognized a lossgain of $16.4$1.5 million, a gain of $9.6 million and a gainloss of $16.5$47.8 million, respectively, representing the change in estimated fair value of the derivative instrument during the respective period. The (loss) gain is reflectedperiods and these amounts are recorded in other income (expense) income,, net, in the Company's statements of consolidated comprehensive income.
Other Financial Instruments. The carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable amounts due to/from related parties and accounts payable approximate fair value due to the short maturity of the instruments; as such, their fair values are Level 1 fair value measurements.instruments. The carrying values of borrowings under the Amended EQM Credit Facility, the Former Eureka Credit Facility (prior to its termination), and the 2021 Eureka Credit Facility and the Amended 2019 EQM Term Loan Agreement (prior to its termination) approximate fair value as the interest rates are based on prevailing market rates; these are considered Level 1 fair value measurements.rates. As EQM's borrowings under its senior notes are not actively traded, their fair values are estimated using an income approach model that applies a discount rate based on prevailing market rates for debt with similar remaining time-to-maturity and credit risk; as such, their fair values are Level 2 fair value measurements. See Note 119 for further information on the fair value of the Company’s outstanding debt. The fair value of the Preferred Interest is a Level 3 fair value measurement and is estimated using an income approach model that applies a market-based discount rate. As of
December 31, 20212023 and 2020,2022, the estimated fair values of the Preferred Interest were approximately $117$90.7 million and $127$95.2 million, respectively, and the carrying values of the Preferred Interest were approximately $100$88.5 million and $105$94.3 million, respectively.
13.11. Earnings (Loss) Earnings Per Share
The following tables set forth the computation of the basic and diluted (loss) earnings per share attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders forFor the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Basic | | Diluted | | Basic | | Diluted | | Basic | | Diluted |
| (In thousands, except per share data) |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (1,365,948) | | | (1,365,948) | | | $ | 638,044 | | | $ | 638,044 | | | $ | (64,959) | | | $ | (64,959) | |
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests (excluding EQM Series A Preferred Units) | 14,530 | | | 14,530 | | | 167,553 | | | 167,553 | | | 64,803 | | | 64,803 | |
| Less: EQM Series A Preferred Units interest in net income | — | | | — | | | 47,359 | | | 47,359 | | | 73,981 | | | 73,981 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Less: Preferred dividends | 58,512 | | | 58,512 | | | 58,760 | | | 58,760 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | (1,438,990) | | | $ | (1,438,990) | | | $ | 364,372 | | | $ | 364,372 | | | $ | (203,743) | | | $ | (203,743) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | 433,008 | | | 433,008 | | | 343,935 | | | 343,935 | | | 254,884 | | | 254,884 | |
Dilutive securities (a) | — | | | — | | | — | | | 40 | | | — | | | — | |
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | 433,008 | | | 433,008 | | | 343,935 | | | 343,975 | | | 254,884 | | | 254,884 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per share of common stock attributable to Equitrans Midstream common shareholders | $ | (3.32) | | | $ | (3.32) | | | $ | 1.06 | | | $ | 1.06 | | | $ | (0.80) | | | $ | (0.80) | |
(a) For the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company excluded 30,278 (in thousands), 30,835 (in thousands), and 30,556 (in thousands), respectively, of weighted average anti-dilutive securities related to the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares and stock-based compensation awards. Forawards from the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company excluded 16,512 (in thousands)computation of diluted weighted average anti-dilutive securities related to the Equitrans Midstream Preferred Shares and stock-based compensation awards. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company excluded 5 (in thousands) of weighted average anti-dilutive securities related to stock-based compensation awards. See Note 10 for information on the Company's stock awards. Additionally, for the applicable periods, EQM's dilutive securities issued and outstanding prior to the EQM Merger did not have a material impact on the Company's diluted earnings per share.
Preferred dividends include a $27.3 million premium recognized on the redemption of the EQM Series A Preferred Units as part of the Restructuring Closing during the year ended December 31, 2020.common shares.
The Company grants Equitrans Midstream phantom units to certain non-employee directors that will be paid in Equitrans Midstream common stock upon the director's termination of service on the Board. As there are no remaining service, performance or market conditions related to these awards, 498, 288750, 595 and 208498 (in thousands) Equitrans Midstream phantom units were included in the computation of basic and diluted weighted average common shares outstanding for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, respectively. See Note 108 for information on Equitrans Midstream phantom units.
14.12. Income Taxes
The following table summarizes income tax (benefit) expense for the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019.2021.
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (Thousands) |
| Years Ended December 31, | | | Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
| Current income tax expense: | Current income tax expense: | |
| Federal | |
| Federal | |
| Federal | Federal | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| State | State | 4,853 | | | 2,613 | | | — | |
| Total current income tax expense | Total current income tax expense | 4,853 | | | 2,613 | | | — | |
| Deferred income tax (benefit) expense: | |
| Deferred income tax expense (benefit): | |
| Federal | |
| Federal | |
| Federal | Federal | (274,857) | | | 81,206 | | | 30,975 | |
| State | State | (75,087) | | | 21,512 | | | 19,729 | |
| Total deferred income tax (benefit) expense | Total deferred income tax (benefit) expense | (349,944) | | | 102,718 | | | 50,704 | |
| Total income tax (benefit) expense | Total income tax (benefit) expense | $ | (345,091) | | | $ | 105,331 | | | $ | 50,704 | |
The following table summarizes differences between income tax expense (benefit) expense and amounts computed at the applicable federal statutory rate on pre-tax income for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2023 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| (Thousands) |
| Income tax expense (benefit) at statutory rate | $ | 91,546 | | | $ | (52,646) | | | $ | (365,535) | |
| Valuation allowances | (99,802) | | | 49,799 | | | 106,886 | |
| State income tax expense (benefit) | 17,738 | | | 9,440 | | | (81,573) | |
| Noncontrolling interest share of earnings | (2,000) | | | (2,563) | | | (3,051) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| AFUDC - equity | (25,575) | | | 11 | | | (2,595) | |
| Unrecognized tax benefit - statute of limitations lapse | (7,426) | | | — | | | — | |
| Other | 6,696 | | | 2,403 | | | 2,515 | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense | $ | (18,823) | | | $ | 6,444 | | | $ | (343,353) | |
| Effective tax rate | (4.3) | % | | (2.6) | % | | 19.7 | % |
For the year ended December 31, 2023, the effective tax rate was lower than the federal and state statutory rates primarily due to the impact of changes in the valuation allowance that limit tax benefits for the Company's federal and state deferred tax assets and the impact of projected AFUDC - equity from the MVP project. For the year ended December 31, 2023, the effective tax rate was lower than the year ended December 31, 2022, primarily due to the impact of projected AFUDC - equity from the MVP project and the impact of changes in the valuation allowance, partially offset by higher state tax expense caused by the effects of a difference between the current and deferred applicable rates.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, the effective tax rate was lower than the federal and state statutory rates due to the increase in the valuation allowances that limit tax benefits for the Company's federal and state deferred tax assets, primarily due to the impairment of the Company's equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture and its impact on the loss before income taxes and deferred income tax assets. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the effective tax rate was lower than the year ended December 31, 2021, 2020primarily due to the lower 2022 impairment of the Company's equity method investment in the MVP Joint Venture and 2019.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (Thousands) |
| Income tax (benefit) expense at statutory rate | $ | (359,318) | | | $ | 156,109 | | | $ | (2,993) | |
| Valuation allowance | 97,634 | | | — | | | — | |
| State income tax (benefit) expense | (80,277) | | | 19,058 | | | 15,587 | |
| Noncontrolling interests' share of earnings | (3,051) | | | (45,132) | | | (29,145) | |
| Impairment of goodwill | — | | | — | | | 78,177 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| AFUDC - equity | (2,595) | | | (28,346) | | | (14,127) | |
| Other | 2,516 | | | 3,642 | | | 3,205 | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense | $ | (345,091) | | | $ | 105,331 | | | $ | 50,704 | |
| Effective tax rate | 20.2 | % | | 14.2 | % | | (355.7) | % |
For the year ended December 31, 2021, the effective tax rate was lower than the federal and state statutory rates due to the increase in the valuation allowances that limit tax benefits for the Company's federal and state deferred tax assets. For the year ended December 31, 2021, the effective tax rate was higher than the year ended December 31, 2020assets, primarily due to the EQM Merger impact on noncontrolling interest and the decrease in MVP Joint Venture AFUDC on the construction
to the impairment of the Company's equity method investment (see Note 4) and its impact onin the loss before income taxes. Noncontrolling interest and AFUDC – equity increase the effective tax rate in periods with a loss before income taxes.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, the effective tax rate was higher than the year ended December 31, 2019 primarily due to the impairment of goodwill (see Note 4) in 2019MVP Joint Venture and its impact on the loss before income taxes and noncontrolling interest. The effective tax rate was lower for the year ended December 31, 2019 as a result of the portion of goodwill for which there was no tax basis, partially offset by the impact of noncontrolling interest and AFUDC – equity. The net impact of the impairment of goodwill, including its impact todeferred income tax expense at the statutory rate, state income tax expense, noncontrolling interests' share of earnings and impairment of goodwill was a reduction to income tax expense of approximately $43.0 million. The impact of AFUDC – equity increased for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to prior periods primarily as a result of increases in the Company's pro-rata share of the MVP Joint Venture's AFUDC on the construction of the MVP.
For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, the effective tax rates were lower than the federal and state statutory rates because the Company does not record income tax expense for the applicable periods on the portions of its income attributable to the noncontrolling member of Eureka Midstream and did not record income tax expense on the portion of its income attributable to noncontrolling limited partners of EQM for the periods prior to the closing of the EQM Merger.
The following table summarizes the components of net deferred tax (liabilities) assets.
| | December 31, |
| 2021 | | 2020 |
| (Thousands) |
| December 31, | | | December 31, |
| 2023 | | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (Thousands) | | | (Thousands) |
| Deferred income tax assets: | Deferred income tax assets: | |
| Investment in partnerships | Investment in partnerships | $ | 67,153 | | | $ | — | |
| Investment in partnerships | |
| Investment in partnerships | |
| Section 163(j) interest limitation | |
| Net operating loss carryforwards | Net operating loss carryforwards | 51,231 | | | 54,925 | |
| Other | |
| Total deferred tax assets | Total deferred tax assets | 118,384 | | | 54,925 | |
| Valuation allowance | Valuation allowance | (97,634) | | | — | |
| Net deferred tax asset | Net deferred tax asset | 20,750 | | | 54,925 | |
| Deferred income tax liabilities: | Deferred income tax liabilities: | |
| | Investment in partnerships | |
| | Investment in partnerships | |
| | Investment in partnerships | Investment in partnerships | — | | | (379,432) | |
| Deferred revenue | Deferred revenue | (17,120) | | | (18,257) | |
| Other | Other | (3,630) | | | (3,132) | |
| Total deferred income tax liability | (20,750) | | | (400,821) | |
| Total deferred income tax liabilities | |
| | Net deferred income tax asset (liability) | $ | — | | | $ | (345,896) | |
| Net deferred income tax liability | |
| Net deferred income tax liability | |
| Net deferred income tax liability | |
|
As ofDuring the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, the change in the Company's investment in partnerships was primarily impacted by tax depreciation in excess of book depreciation and certain state tax items, partially offset by the impacts of capitalized interest and deferred revenue. The change in certain state tax items had a corresponding reduction to common stock, no par value of $37.5 million.
The following table provides details related to our net operating losses (NOL) and valuation allowances as of:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | Expiration Period | 2023 | | 2022 | |
| | | (Thousands) | |
| NOL carryforwards | | | | | | |
| U.S. federal net operating losses | | Indefinite | $ | 35,161 | | | $ | 61,710 | | |
| Pennsylvania net operating losses | | 2040 - 2042 | — | | | 6,792 | | |
| Other state net operating losses | | Indefinite | 1,507 | | | 3,137 | | |
| Total NOL carryforwards | | | 36,668 | | | 71,639 | | |
| | | | | | |
| Valuation allowance on NOL carryforwards | | | | | | |
| Federal | | | $ | (18,061) | | | $ | (61,710) | | |
| State | | | (1,150) | | | (9,929) | | |
| Total valuation allowance on NOL carryforwards | | | (19,211) | | | (71,639) | | |
For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company has federal NOL of $34.5 million and state NOL of $16.7 million related to various state jurisdictions with a corresponding full valuation allowance of $34.5 million and $16.7 million, respectively. The Company also hashad a valuation allowance related to itsfederal and state interest disallowances under Internal Revenue Code (Code) Section 163(j) of $36.5 million in each case. The Company also had a valuation allowance related to certain investment in partnership deferred tax assets, net of offsetting deferred tax liability, of $46.4 million. As offor the years ended December 31, 2020, the Company had federal NOL2023 and 2022, of $41.4$1.2 million and state NOL of $13.5$48.5 million, related to various state jurisdictions. The federal and commonwealth of Virginia and state of West Virginia NOL carryforwards have no expiration, but utilization is limited to 80% of taxable income in the year of utilization. The Company's Pennsylvania NOL carryforwards expire between 2038 and 2041 and utilization is limited to 40% of taxable income in the year of utilization.respectively.
For the year ended December 31, 2021,2023, the Company believes that it is more likely than not that the benefit from a portion of its federal and state NOL carryforwards, and reversals of the investment in partnership deferred tax asset,assets related to interest disallowance under Code Section 163(j), and certain
state deferred tax assets, net of offsetting deferred tax liabilities, will not be realized.realized and accordingly, the Company maintains related valuation allowances. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not (greater than 50%) that a tax benefit will not be realized. In evaluating the need for a valuation allowance, management considers available evidence, both positive and negative, including potential sources of taxable income, income available in carry-back periods, future reversals of taxable temporary differences, projections of taxable income and income from tax planning strategies. Positive evidence includes reversing temporary differences and projection of future profitability within the carry-forward period, including from tax planning strategies. Negative evidence includes historical pre-tax book losses and Pennsylvania NOL expirations.losses. A review of positive and negative evidence regarding these tax benefits resulted in the conclusion that valuation allowances on a portion of the Company’s federal and state NOL carryforwards and reversals of the investment in partnership deferred tax asset, net of offsetting deferred tax liabilities, were warranted as it was more likely than not that these assets will not be realized. Any determination to change the valuation allowance would impact the Company's income tax expense in the period in which such a determination is made.
The Company has not identified any uncertain tax positionsfollowing table summarizes the difference in the valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 or 2019.2023, 2022 and 2021:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Additions |
| | Beginning Balance | | Credited to Costs and Expenses | | Ending Balance |
| | (Thousands) |
| 2023 | | | | | | |
Deferred tax asset valuation allowance (a) | | $ | 156,685 | | | $ | (99,802) | | | $ | 56,883 | |
| 2022 | | | | | | |
Deferred tax asset valuation allowance (a) | | $ | 106,886 | | | $ | 49,799 | | | $ | 156,685 | |
| 2021 | | | | | | |
Deferred tax asset valuation allowance (a) | | $ | — | | | $ | 106,886 | | | $ | 106,886 | |
| | | | | | |
(a) Deducted from related assets.
The following table sets forth the reconciliation of gross unrecognized tax benefits and summarizes specific line items as of:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2023 | | | | |
| | (Thousands) |
| Beginning balance, January 1 | | $ | — | | | | | |
| Additions for tax positions taken in current year | | 17,465 | | | | | |
| Additions for tax positions taken in prior year | | 55,612 | | | | | |
| Lapse in statute of limitations | | (7,782) | | | | | |
| Ending balance, December 31 | | $ | 65,295 | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| If recognized, affects the effective tax rate (including valuation allowances) | | $ | 31,378 | | | | | |
| Recorded as an offset to related deferred tax assets and liabilities in Consolidated Balance Sheets | | $ | 32,557 | | | | | |
There were no gross unrecognized tax benefits during the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company recorded unrecognized tax benefits related to the deductibility of capitalized interest and certain state tax items. As of December 31, 2023, it is reasonably possible that the amount of unrecognized tax benefits will decrease by approximately $3.6 million within the next twelve months due to the expiration of statutes of limitation and is anticipated to impact the effective tax rate before considering the impact of valuation allowances.
The Company recorded interest and penalties associated with unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $1.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2023. The Company did not recognize interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021.
The Company is not subject to federal or state income tax examination by tax authorities for years before 2018.2020.
15.13. Concentrations of Credit Risk
The Company is exposed to the credit risk of its customers, including EQT, its largest customer, other producers, natural gas marketers, distribution companies and other end users. For the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019,2021, EQT accounted for approximately 59%61%, 64%61% and 69%59%, respectively, of the Company's total revenues across all of the Company's operating segments. As of December 31, 2021, EQT2023, EQT's public debt had investment grade credit ratings of BB+ from S&P, (with a positive outlook), Ba1 from Moody's (with a stable outlook)Fitch and BB+ from Fitch (with a stable outlook), each of which were considered non-investment grade. As of December 31, 2020, EQT's credit ratings with each of S&P, Moody's and Fitch were considered non-investment grade.Moody's.
As of December 31, 20212023 and 2020,2022, EQT accounted for 75%approximately 69% and 68%72%, respectively, of the Company's accounts receivable balances, while various other natural gas marketers and producers accounted for the majority of the remaining accounts receivable balances. To manage the credit risk related to transactions with marketers, the Company engages with only those that
meet specified criteria for credit and liquidity strength and actively monitors accounts with marketers. In connection with its assessment of marketer credit and liquidity strength, the Company may request a letter of credit, guarantee, performance bond or other credit enhancement. The Company did not experience significant defaults on accounts receivable during the years ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 2019.2021.
16.14. Commitments and Contingencies
In the ordinary course of business,From time to time, various legal and regulatory claims, investigations and proceedings are pending or threatened against the Company and its subsidiaries. While to the extent applicable the amounts claimed may be substantial, the Company is unable to predict with certainty the ultimate outcome of such claims, investigations and proceedings. The Company accrues legal and other direct costs related to loss contingencies when incurred. The Company establishes reserves whenever it believes it to bea reserve is appropriate for pending matters. Furthermore, after consultation with counsel and considering availablethe availability, if any, of insurance, the Company believes, although no assurance can be given, that the ultimate outcome of any matter currently pending against it or any of its consolidated subsidiaries as of the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K will not materially adversely affect its business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to its shareholders.
The Company has established a regulatory reserve in connection with the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, which is included in regulatory and other long-term liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022. The ultimate regulatory costs and expenses as a result of the Rager Mountain natural gas storage field incident, may exceed such reserve and, if significant individually or in the aggregate, could have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to the Company's shareholders.
The Company is subject to federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations. These laws and regulations, which are constantly changing, can require expenditures for remediation and, in certain instances, have resulted and can result in assessment of fines. The Company has established procedures for the ongoing evaluation of its operations to seek to identify potential environmental exposures and to ensurepromote compliance with regulatory requirements. The estimated costs associated with identified situations requiring remedial action are accrued; however, when recoverable through future regulated rates, certain of these costs are deferred as regulatory assets. OngoingThrough December 31, 2023, ongoing expenditures for compliance with current environmental laws and regulations, including investments in facilities to meet environmental requirements, have not been material. ManagementBased on applicable environmental laws and regulations, management believes that required expenditures in respect of such current environmental laws and regulationsthereof will not be significantly different in either nature or amount in the future and, based on such current environmental laws and regulations, does not know of any future environmental liabilities that will have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to the Company's shareholders.shareholders (however, the Company cautions that the ultimate expenditures related to or arising out of the Rager Mountain incident may affect the nature and magnitude of future expenditures, and such expenditures and the ultimate impact of the Rager Mountain incident are not yet known). Nonetheless, the trend in environmental regulation is to place more restrictions and limitations on activities that may affect the environment, and it is generally expected that such trend will likely increase in the future. Thus, compliance with future environmental laws and regulations in the future could result in significant costs and could have a material adverse effect on the Company's business, financial condition, results of operations, liquidity or ability to pay dividends to the Company's shareholders. The Company has identified situations that require remedial action for which approximately $0.2 million, in each case, is included in regulatory and other long-term liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, respectively.
Purchase obligations represent agreements to purchase goods or services that are enforceable, legally binding and specify all significant terms, including the approximate timing of the transaction. As of December 31, 2021,2023, the Company had approximately $3.9$5.2 million of purchase obligations, which included commitments for capital expenditures, operating expenses and service contracts.
For information related to operating lease rental payments for office locations and compressors, see Note 75.
See Note 97 for discussion of the letters of credit to support MVP Holdco's performance assurances to the MVP Joint Venture guarantees and letters of credit. See Note 6 for a description of the EQT Global GGA.Venture.
15. Subsequent Events
Fifth Amendment to EQM Revolving Credit Facility. On February 15, 2024 (the Fifth Amendment Date), EQM entered into an amendment (the Fifth Amendment) to the Amended EQM Credit Facility. The Fifth Amendment, among other things, amended the financial covenant, such that the Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) (i) as of March 31, 2024, cannot exceed 6.00 to 1.00, (ii) as of June 30, 2024, cannot exceed 6.25 to 1.00, (iii) as of September 30, 2024, cannot exceed 5.85 to 1.00 and (iv) as of the end of each fiscal quarter thereafter, cannot exceed 5.50 to 1.00.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Not applicable.None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Company's Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer, an evaluation of the Company's disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (Exchange Act)), was conducted as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on that evaluation, the Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of the end of the period covered by this report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting. There were no changes in internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act) that occurred during the fourth quarter of 20212023 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. The management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company's internal control system is designed to provide reasonable assurance to the management and Board of the Company regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Accordingly, even effective controls can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
The management of the Company assessed the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021.2023. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013). Based on this assessment, management concluded that the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021.2023.
Ernst & Young LLP (Ernst & Young), the independent registered public accounting firm that audited the Company's consolidated financial statements, has issued an attestation report on the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Ernst & Young's attestation report on the Company's internal control over financial reporting appears in Part II, "Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated by reference herein.
Item 9B. Other Information
Not applicable.During the three months ended December 31, 2023, no director or officer of the Company subject to Section 16 of the Exchange Act adopted, terminated or modified a ‘Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement’ or ‘non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement,’ as each term is defined in Item 408(a) of Regulation S-K.
Item 1.01. Entry Into a Material Definitive Agreement.
Fifth Amendment to Revolving Credit Agreement
On the Fifth Amendment Date, EQM, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, entered into the Fifth Amendment to the Amended EQM Credit Facility. The Fifth Amendment, among other things, amended the financial covenant, such that the Consolidated Leverage Ratio (as defined in the Amended EQM Credit Facility) (i) as of March 31, 2024, cannot exceed 6.00 to 1.00, (ii) as of June 30, 2024, cannot exceed 6.25 to 1.00, (iii) as of September 30, 2024, cannot exceed 5.85 to 1.00 and (iv) as of the end of each fiscal quarter thereafter, cannot exceed 5.50 to 1.00.
The Fifth Amendment is attached as Exhibit 10.1(f) to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and incorporated into this Item 1.01 by reference. The foregoing summary has been included to provide investors and security holders with information regarding certain of the terms of the Fifth Amendment and is qualified in its entirety by the terms and conditions of the Fifth Amendment and the Amended EQM Credit Facility. It is not intended to provide any other factual information about the Company or its subsidiaries and affiliates, including EQM.
Relationships.
Certain of the lenders under the Amended EQM Credit Facility and their respective affiliates have, from time to time, performed, and may in the future perform, various financial advisory, commercial and/or investment banking services for the Company and/or its affiliates, for which they have received or may receive customary fees and expenses. Certain affiliates of
such lenders have acted, and may in the future act, as underwriters, agents, arrangers or lenders, as applicable, in respect of certain of the Company’s and/or its subsidiaries’ and/or affiliates’ debt or equity issuances or credit facilities.
Item 2.03.Creation of a Direct Financial Obligation or an Obligation under an Off-Balance Sheet Arrangement of a Registrant.
The information set forth under Item 1.01 above is incorporated into this Item 2.03 by reference.
Item 9.01. Financial Statements and Exhibits.
(d) Exhibits
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | | Description |
| | Fifth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of February 15, 2024, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, the lender parties thereto and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent. |
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by Item 10 is incorporated by reference from the information under the captions "PROXY STATEMENT SUMMARY," "ITEM NO. 1 - ELECTION OF DIRECTORS," "EQUITY OWNERSHIP" AND "CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND BOARD MATTERS", to the extent applicable, in the Proxy Statement and under the caption "Information About Our Executive Officers" in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Equitrans Midstream has a written Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that applies to Equitrans Midstream's Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer), Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer), Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting Officer) and others. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on Equitrans Midstream's website at www.equitransmidstream.com (accessible by clicking on the "About" link on the main page followed by the "Governance" link), and a printed copy will be delivered free of charge on request by writing to the corporate secretary at Equitrans Midstream Corporation, c/o Corporate Secretary, 2200 Energy Drive, Canonsburg, Pennsylvania 15317. Any amendments to, or waivers from, a provision of the Company's Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that applies to the Company's Principal Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer and that relatesrelate to any element of the code of ethics enumerated in paragraph (b) of Item 406 of Regulation S-K shall be disclosed by posting such information on the Company's website at www.equitransmidstream.com.
Information required by Item 401 of Regulation S-K with respect to executive officers is included after Item 4 at the end of Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the caption "Information About Our Executive Officers" and is incorporated herein by reference.
The Company has adopted insider trading policies and procedures governing the purchase, sale and/or other disposition of the Company's securities by directors, officers and employees that are reasonably designed to promote compliance with insider trading laws, rules and regulations and applicable listing standards.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by Item 11 is incorporated by reference from the information under the captions "CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND BOARD MATTERS," "DIRECTORS' COMPENSATION" and "EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION INFORMATION" in the Proxy Statement.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by Item 12 is incorporated by reference from the information under the captions "EQUITY OWNERSHIP" and "SECURITIES AUTHORIZED FOR ISSUANCE UNDER EQUITY COMPENSATION PLANS" in the Proxy Statement.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions and Director Independence
The information required by Item 13 is incorporated by reference from the information under the captions "ITEM NO. 1 - ELECTION OF DIRECTORS" and "CORPORATE GOVERNANCE AND BOARD MATTERS" in the Proxy Statement.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information required by Item 14 is incorporated by reference from the information under the caption "ITEM NO. 45 - RATIFICATION OF APPOINTMENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM" in the Proxy Statement.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) Documents filed as part of this report
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 1 | | Financial Statements | Page
Reference | | | | | |
| Statements of Consolidated Comprehensive Income for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 20192021 | | | | | | |
| Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 20192021 | | | | | | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 20212023 and 20202022 | | | | | | |
| Statements of Consolidated Shareholders' Equity and Mezzanine Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2021, 20202023, 2022 and 20192021 | | | | | | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| 2 | | Financial Statement Schedules | | | | | | |
| | All schedules are omitted since the subject matter thereof is either not present or is not present in amounts sufficient to require submission of the schedules. | |
| The financial statements of the MVP Joint Venture, Series A are included in this filing as Exhibit 99.1 pursuant to Rule 3-09 of Regulation S-X. | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 3 | | Exhibits | |
| The exhibits referenced below are filed (or, as applicable, furnished) as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. | |
In reviewing any agreements incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K or filed with this Form 10-K, please remember that such agreements are included to provide information regarding their terms. They are not intended to be a source of financial, business or operational information about the Company or any of its subsidiaries or affiliates. The representations, warranties and covenants contained in these agreements are made solely for purposes of the agreements and are made as of specific dates; are solely for the benefit of the parties; may be subject to qualifications and limitations agreed upon by the parties in connection with negotiating the terms of the agreements, including being made for the purpose of allocating contractual risk between the parties instead of establishing matters as facts; and may be subject to standards of materiality applicable to the contracting parties that differ from those applicable to investors or security holders. Investors and security holders should not rely on the representations, warranties and covenants or any description thereof as characterizations of the actual state of facts or condition of the Company or any of its subsidiaries or affiliates or, in connection with acquisition agreements, of the assets to be acquired. Moreover, information concerning the subject matter of the representations, warranties and covenants may change after the date of the agreements. Accordingly, these representations and warranties alone may not describe the actual state of affairs as of the date they were made or at another time.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | | Document Description | | Method of Filing |
| | Separation and Distribution Agreement, dated as of November 12, 2018, by and among EQT Corporation, Equitrans Midstream Corporation and, solely for certain limited purposes therein, EQT Production Company. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | Tax Matters Agreement, dated as of November 12, 2018, by and between EQT Corporation and Equitrans Midstream Corporation. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.3 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | Employee Matters Agreement, dated as of November 12, 2018, by and between EQT Corporation and Equitrans Midstream Corporation. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.4 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated as of March 13, 2019, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP and North Haven Infrastructure Partners II Buffalo Holdings, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on March 15, 2019. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of February 26, 2020, by and among Equitrans Midstream Corporation, EQM LP Corporation, LS Merger Sub, LLC, EQM Midstream Partners, LP and EQGP Services, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on February 28, 2020. |
| | Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of Equitrans Midstream Corporation. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on April 28, 2021. |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | ThirdFifth Amended and Restated Bylaws of Equitrans Midstream Corporation. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.33.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on April 28, 2021.December 14, 2022. |
| | | | |
| | Indenture, dated as of August 1, 2014, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP), as issuer, the subsidiaries of EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP) party thereto, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on August 1, 2014. |
| | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of August 1, 2014, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP), as issuer, the subsidiaries of EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP) party thereto, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on August 1, 2014. |
| | Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 4, 2016, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP), as issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on November 4, 2016. |
| | | | |
| | Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 25, 2018, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP), as issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on June 25, 2018. |
| | Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 25, 2018, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP), as issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on June 25, 2018. |
| | Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 25, 2018, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP (formerly known as EQT Midstream Partners, LP), as issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.6 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on June 25, 2018. |
| | | Shareholder and Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of November 12, 2018, by and between EQT Corporation and Equitrans Midstream Corporation. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018.
| | Description of Certain of Registrant's Securities. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 4.8.4.6. |
| | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of June 17, 2020, by and among Equitrans Midstream Corporation and the Investors party thereto. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on June 17, 2020. |
| | Indenture, dated as of June 18, 2020, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on June 18, 2020. |
| | Indenture, dated as of January 8, 2021, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on January 8, 2021. |
| | Indenture, dated as of June 7, 2022, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP and U.S. Bank Trust Company, National Association, as trustee. | | | | | | | | | | | | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on June 7, 2022. |
| | Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 31, 2018, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and an L/C Issuer, and the other lenders party thereto. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on October 31, 2018. |
| | First Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of March 30, 2020, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, the lender parties thereto and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on March 30, 2020. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Second Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of April 16, 2021, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, the lender parties thereto and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on April 19, 2021. |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | SubleaseThird Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, effectivedated as of March 1, 2011,April 22, 2022, by and between Equitrans, L.P.among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, the lender parties thereto and EQT Production Company.Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1210.1 to Amendment No. 2 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form S-1/A Registration Statement (#333-179487)8-K (#001-38629) filed on May 10, 2012.April 25, 2022. |
| | Fourth Amendment of Subleaseto Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of April 5, 2012,October 6, 2023, by and between Equitrans, L.P.among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, the lender parties thereto and EQT Production Company.Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to Amendment No. 2 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form S-1/A Registration Statement (#333-179487) filed on May 10, 2012. |
| | | | |
| | Second Amended and Restated Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement, dated as of March 31, 2017, by and between Rice Drilling D LLC and EQM Olympus Midstream LLC (formerly known as Rice Olympus Midstream LLC). Specific items in this exhibit have been redacted, as marked by three asterisks [***], because confidential treatment for those items has been granted by the SEC. The redacted material has been separately filed with the SEC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 10-Q (#001-35574) for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2018. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2020, by and between EQM Olympus Midstream, LLC and Rice Drilling D LLC. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.4(b). |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of February 18, 2021, by and between EQM Olympus Midstream, LLC and Rice Drilling D LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of February 1, 2022, by and between EQM Olympus Midstream, LLC and Rice Drilling D LLC. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.4(d). |
| | Secondment Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2018, by and among Equitrans Midstream Corporation, EQM Midstream Partners, LP, and EQM Midstream Services, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.310.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018.October 10, 2023. |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | Fifth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated OmnibusCredit Agreement, dated as of March 31, 2019,February 15, 2024, by and among Equitrans Midstream Corporation, EQM Midstream Partners, LP, EQGP Services, LLCthe lender parties thereto and for limited purposes, EQM Midstream Services, LLC.Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent. | | Incorporated herein by reference toFiled herewith as Exhibit 10.6 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019.10.1(f). |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | Third Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC, dated as of April 6, 2018, by and among MVP Holdco, LLC, US Marcellus Gas Infrastructure, LLC, WGL Midstream MVP LLC (formerly WGL Midstream, Inc.), Con Edison Gas Pipeline and Storage, LLC, RGC Midstream, LLC and Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC. Specific items in this exhibit have been redacted, as marked by three asterisks [***], because confidential treatment for those items has been granted by the SEC. The redacted material has been separately filed with the SEC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 10-Q/A (#001-35574) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2018. |
| | First Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC, dated as of February 5, 2020, by and among MVP Holdco, LLC, US Marcellus Gas Infrastructure, LLC, WGL Midstream MVP LLC (formerly WGL Midstream, Inc.), Con Edison Gas Pipeline and Storage, LLC, RGC Midstream, LLC and Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.21(b) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2019. |
| | Amended and Restated Omnibus Agreement, dated November 13, 2018, among EQT Corporation, EQM Midstream Partners, LP and EQM Midstream Services, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | Second Amended and Restated Omnibus Agreement, dated November 13, 2018, among EQT Corporation, RM Partners LP, EQM Midstream Management LLC, and EQM Poseidon Midstream LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to EQM Midstream Partners, LP's Form 8-K (#001-35574) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | Transportation Service Agreement Applicable to Firm Transportation Service Under Rate Schedule FTS, Contract No. EQTR 20242-852, dated as of September 24, 2014, and Exhibit A amended August 12, 2020 and Exhibit C amended April 1, 2019 by and between Equitrans, L.P. and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Filed herewithIncorporated herein by reference as Exhibit 10.10(a). to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | Transportation Service Agreement Applicable to Firm Transportation Service Under Rate Schedule FTS, Contract No. EQTR 20242-852, dated as of September 24, 2014 as Amended December 6, 2021 by and between Equitrans L.P and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Filed herewithIncorporated herein by reference as Exhibit 10.10(b). to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | Transportation Service Agreement Applicable to Firm Transportation Service Under Rate Schedule FTS, Contract No. EQTR 20242-852, dated as of September 24, 2014 as amended December 6, 2021 by and between Equitrans L.P and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Filed herewithIncorporated herein by reference as Exhibit 10.10(c). to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | Transportation Service Agreement Applicable to Firm Transportation Service Under Rate Schedule FTS, Contract No. EQTR19837-1296, dated as of January 8, 2016 and amended December 6, 2021, by and between Equitrans, L.P. and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Filed herewithIncorporated herein by reference as Exhibit 10.11.10.11 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation Amended and Restated Directors’ Deferred Compensation Plan. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2018 Long-Term Incentive Plan. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to Registration Statement on Form S-8 (File No. 333-228337) filed on November 9, 2018. |
| | First Amendment to the Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2018 Long-Term Incentive Plan. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on June 17, 2020. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of August 9, 2018, with Thomas F. Karam. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.57 to Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (#001-38629) filed on October 18, 2018. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of September 4, 2018, with Kirk R. Oliver. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.58 to Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (#001-38629) filed on October 18, 2018. |
| | Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of January 15, 2019, with Diana M. Charletta | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on January 22, 2019. |
| | First Amendment, dated February 20, 2023, to Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of January 15, 2019, with Diana M. Charletta. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.14(b) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of January 15, 2019, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Diana M. Charletta. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on September 7, 2023. |
| | Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2018, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Thomas F. Karam. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | First Amendment, dated as of February 20, 2023, to Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2018, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Thomas F. Karam. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.15(b) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2018, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Thomas F. Karam. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on September 7, 2023. |
| | Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2018, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Kirk R. Oliver. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | First Amendment, dated as of February 20, 2023, to Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2018, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Kirk R. Oliver. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16(b) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Second Amendment to Amended and Restated Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2018, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Kirk R. Oliver. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on September 7, 2023 |
| | Letter Agreement, dated April 2, 2019, with Stephen M. Moore. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019. |
| | Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated April 15, 2019, with Stephen M. Moore. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019. |
| | First Amendment, dated as of February 20, 2023, to Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated April 15, 2019, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Stephen M. Moore. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.18(b) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Second Amendment to Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of April 15, 2019, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Stephen M. Moore. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on September 7, 2023. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Form of Agreement of Assignment of Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on November 13, 2018. |
| | Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Change of ControlNon-Competition Agreement, dated as of April 14, 2020,February 20, 2023, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Brian P. Pietrandrea. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | First Amendment to Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of February 20, 2023, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Brian P. Pietrandrea. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1710.6 to Form 10-Q8-K (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020.filed on September 7, 2023. |
| | Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of July 26, 2023, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Nathan P. Tetlow. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.16(a). |
| | First Amendment to Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of July 26, 2023, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Nathan P. Tetlow. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.16(b). |
| | Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of July 26, 2023, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Justin S. Macken. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.17(a). |
| | First Amendment to Confidentiality, Non-Solicitation and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of July 26, 2023, by and between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Justin S. Macken. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.17(b). |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Director and/or Executive Officer Indemnification Agreement. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to Registration Statement on Form 10-12B/A (#001-38629) filed on October 18, 2018. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2019 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.7(a) to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Standard) under 2018 Long-Term Incentive Plan (2019 grants). | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.7(b) to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019. |
| | Form of Participant Award Agreement under the 2019 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.7(c) to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019. |
| | | Amendment to 2018 EQT Incentive Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019.
| | | | |
| | Amended and Restated Equitrans Midstream Corporation Short-Term Incentive Plan. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Director Participant Award Agreement. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2019. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2020 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020. |
| | Form of Participant Award Agreement under 2020 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement (2020 Awards). | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020. |
| | Preferred Restructuring Agreement, dated as of February 26, 2020, by and among Equitrans Midstream Corporation, EQM Midstream Partners, LP and the Investors party thereto. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on February 28, 2020. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement, dated as of February 26, 2020, by and among EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQT Energy, LLC and EQM Gathering Opco, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Form 8-K/A (#001-38629) filed on March 13, 2020. |
| | First Amendment to Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2020, by and among EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQT Energy, LLC and EQM Gathering Opco, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2020. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of February 23, 2021, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC and EQT Energy, LLC | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of February 2, 2021, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of February 9, 2021, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQM Olympus Midstream, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQT Energy, LLC and Rice Drilling D LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of February 3, 2021, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of July 10, 2021, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of August 25, 2021, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of September 13, 2021, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2021. |
| | Second Amendment to Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement, dated as of December 6, 2021, by and among EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQT Energy, LLC and EQM Gathering Opco, LLC. | | Filed herewith asIncorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.34(j). to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Third Amendment to Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2021, by and among EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQT Energy, LLC and EQM Gathering Opco, LLC. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.34(k). |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of November 1, 2020, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4510.34(k) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2020.2021. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of February 4,December 14, 2022, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.31(q) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Filed herewithFourth Amendment to Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement, dated as of January 23, 2023, by and among EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQT Energy, LLC and EQM Gathering Opco, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.34(m).10.31(r) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of January 23, 2023, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.31(s) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of January 27, 2023, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.31(t) to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of June 1, 2023, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.01 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2023. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of October 3, 2023, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2023. |
| | Fifth Amendment to Gas Gathering and Compression Agreement, dated as of October 4, 2023, by and among EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQT Energy, LLC and EQM Gathering Opco, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2023. |
| | Letter Agreement, dated as of October 5, 2023, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, Equitrans, L.P., EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2023. |
| | Amended and Restated Letter Agreement, dated as of October 12, 2023, by and among EQM Gathering Opco, LLC, EQT Corporation, EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, and EQT Energy, LLC | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2023. |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | Credit Letter Agreement, dated as of February 26, 2020, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP and EQT Corporation. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2020. |
| | | Water Services Letter Agreement, dated as of February 26, 2020, by and among EQT Production Company, Rice Drilling B LLC, EQM Gathering Opco, LLC and Equitrans Water Services (PA) LLC. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Form 8-K/A (#001-38629) filed on March 13, 2020.
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Purchase Agreement, dated June 16, 2020, by and between EQM Midstream Partners, LP and J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, as representative of the several initial purchasers named on Schedule 1 thereto. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on June 18, 2020. |
| | Purchase Agreement, dated January 4, 2021, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, Equitrans Midstream Corporation (for certain limited purposes) and Barclays Capital Inc., as representative of the several initial purchasers named on Schedule 1 thereto. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on January 5, 2021. |
| | | | |
| | Purchase Agreement, dated May 31, 2022, by and among EQM Midstream Partners, LP, Equitrans Midstream Corporation Executive Short-Term Incentive Plan (2021).(for certain limited purposes) and BofA Securities Inc., as representative of the several initial purchasers named on Schedule 1 thereto. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.4610.1 to Form 10-K8-K (#001-38629) filed on February 23, 2021.June 2, 2022. |
| | | | |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2021 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.47 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) filed on February 23, 2021. |
| | Form of Participant Award Agreement under 2021 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.48 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) filed on February 23, 2021. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement (2021 Awards). | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.49 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) filed on February 23, 2021. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Senior Executive 2021 MVP Performance Share Units Award Agreement. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on December 7, 2021. |
| | | | |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Senior Executive 2021 MVP Performance Share Units Award Agreement Notice. | | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.02 to Form 10-Q (#001-38629) for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2023. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2022 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Filed herewith asIncorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.44.10.44 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | Form of Participant Award Agreement under 2022 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Filed herewith asIncorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.45.10.45 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement (2022 Awards). | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.46 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2021. |
| | | | |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation Employee Stock Purchase Plan. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on April 27, 2022. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2023 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.47 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Form of Participant Award Agreement under 2023 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.48 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Restricted Stock Award Agreement (2023 Awards). | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.49 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation Second Amended and Restated Executive Short-Term Incentive Plan | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.50 to Form 10-K (#001-38629) for the year ended December 31, 2022. |
| | Transition Agreement between Equitrans Midstream Corporation and Thomas F. Karam. | | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (#001-38629) filed on September 7, 2023. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation 2024 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.45. |
| | Form of Participant Award Agreement under 2024 Performance Share Unit Program. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.46. |
| | Form of Equitrans Midstream Corporation Amended and Restated Executive Short-Term Incentive PlanRestricted Stock Award Agreement (2024 Awards). | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 10.47. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation Corporate Stock Trading Policy, effective February 7, 2024, and related Addendum for Section 16 Reporting Officers and Directors. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 19.1. |
| | Schedule of Subsidiaries. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 21.1. |
| | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 23.1. |
| | Consent of Independent Auditors (Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC - Series A). | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 23.2. |
| | Rule 13(a)-14(a) Certification of Principal Executive Officer. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 31.1. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Rule 13(a)-14(a) Certification of Principal Financial Officer. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 31.2. |
| | Section 1350 Certification of Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer. | | Furnished herewith as Exhibit 32. |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation Compensation Recoupment Policy, Amended and Restated as of October 24, 2023. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 97. |
| | Mountain Valley Pipeline, LLC (Series A) financial statements. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 99.1. |
| 101 | | | Inline Interactive Data File. | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 101. |
| 104 | | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) | | Filed herewith as Exhibit 104. |
* Management contract and compensatory arrangement in which any director or any named executive officer participates
** Schedules and exhibits have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K. Equitrans Midstream Corporation hereby undertakes to furnish supplemental copies of any of the omitted schedules and exhibits upon request by the SEC.
# Certain portions of the exhibits that are not material and is of the type Equitrans Midstream treats as confidential have been redacted pursuant to Item 601(b)(10)(iv) of Regulation S-K. Copies of the unredacted exhibits will be furnished to the SEC upon request.
## Certain personally identifiable information has been omitted from this exhibit pursuant to Item 601(a)(6) of Regulation S-K.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | |
| | Equitrans Midstream Corporation |
| | (Registrant) |
| | |
| | | |
| | By: | /s/ KIRK R. OLIVER |
| | | Kirk R. Oliver |
| | | SeniorExecutive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
| | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
/s/ THOMAS F. KARAMDIANA M. CHARLETTA | | President and Chief Executive | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
Thomas F. KaramDiana M. Charletta | | Officer and Chairman | | |
| | (Principal Executive Officer) | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ KIRK R. OLIVER | | SeniorExecutive Vice President and Chief | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| Kirk R. Oliver | | Chief Financial Officer | | |
| | (Principal Financial Officer) | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ BRIAN P. PIETRANDREA | | Vice President and Chief | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| Brian P. Pietrandrea | | Accounting Officer | | |
| | (Principal Accounting Officer) | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ VICKY A. BAILEY | | Director | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| Vicky A. Bailey | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ SARAH M. BARPOULIS | | Director | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| Sarah M. Barpoulis | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ KENNETH M. BURKE | | Director | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| Kenneth M. Burke | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ PATRICIA K. COLLAWNTHOMAS F. KARAM | | DirectorExecutive Chairman | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
Patricia K. CollawnThomas F. Karam | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ MARGARET K. DORMAN | | Director | | February 23, 2022 |
Margaret K. Dorman | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ D. MARK LELAND | | Director | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| D. Mark Leland | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ NORMAN J. SZYDLOWSKI | | Director | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| Norman J. Szydlowski | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ ROBERT F. VAGT | | Director | | February 23, 202220, 2024 |
| Robert F. Vagt | | | | |