Based on what we believe is a solid foundation, FY2021 marked a transition from a research-stage to a development-stage company. We established new research laboratories and administrative offices in Pittsburgh, PA, expanded our pipeline to include both rare disease and oncology, recruited clinical development and chemistry manufacturing and controls (“CMC”) teams, established offices in Cambridge, MA, nominated a development compound for our DM1 program, initiated good manufacturing practice (“GMP”) manufacturing scale up, finalized the formulation work for subcutaneous and intravenous routes, initiated PK/ADME studies with the DM1 development candidate, and initiated PK/pharmacodynamics (“PD”) studies to define the dosing regimen for initial human studies. In addition, we have continued to optimize candidates for our HD and KRAS programs, illustrating pharmacology in vivo in appropriate animal models of each. Additionally, in FY2021 we developed a proprietary genetic disease database with utility in prioritization of pipeline expansion and partnership opportunities.
We are developing precision genetic medicines targeting rare, monogenic diseases for which there are no approved therapies, as well as more common genetic disorders, including cancers that are resistant to current therapeutic approaches. Our disclosed pipeline includes therapeutic candidates for the treatment of DM1, HD, andas well as cancer-driving point mutations in KRAS, G12V and G12D, which are involved in many tumor types and have historically been “undruggable”.
Based on compelling results from in vitro and in vivo preclinical studies, we plan In October 2022, the Company announced plans to file an IND application for our DM1 investigational therapy inexpand its focus to include the fourth quarter of CY2022. We are targeting CY2023 to file an IND application for an investigational therapy to treat Huntington’s disease. Both are devastating systemic diseases with no effective therapies. Our oncology program has recently been announced (FY2021), together with in vivo activity illustrating allele-selective engagement of mutant KRAS at the DNA and RNA levels, with abrogation of downstream hyperactive signaling through multiple RAS pathway members, resulting in anti-tumor activity. We continue to improve upon our platform while concurrently developing programs, resulting in next-generation compounds that continue to make their way through preclinical development in a parallel manner. We have recently finalized an analysisadvancement of the entire known mutational databasedifferentiated gene editing capabilities of its platform. The Company is currently identifying and selected several additional high-valueevaluating multiple indications for screening andpotential future development.
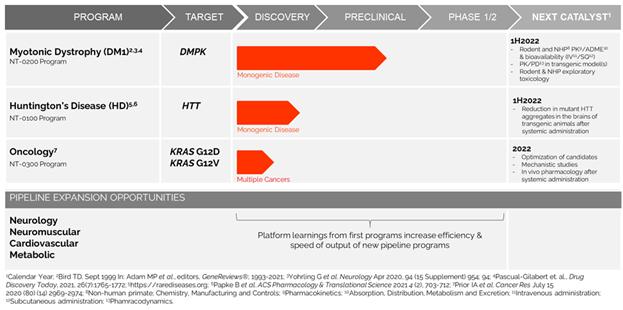
Figure 4. The initial pipeline in rare disease and oncology, with platform learnings increasing the efficiency and speed additional undisclosed programs, both internally developed and in discussions for co-development with partners.
We are poised to file a series of IND applications for indications with large unmet needs such as DM1, which is expected to reach IND application filing by the end of CY2022, HD expected to reach IND application in CY2023 and cancers (KRAS G12V and G12D mutations) likely thereafter.
1913