
Use these links to rapidly review the document
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Acceleron Pharma Inc. Index to Financial Statements
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 7,September 6, 2013
Registration No. 333- 333-190417
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Amendment No. 2
to
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
ACCELERON PHARMA INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | 2836 (Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) | 27-0072226 (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
128 Sidney Street
Cambridge, MA 02139
(617) 649-9200
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including
area code, of registrant's principal executive offices)
John L. Knopf, Ph.D.
Chief Executive Officer and President
128 Sidney Street
Cambridge, MA 02139
(617) 649-9200
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including
area code, of agent for service)
| Copies to: | ||||
Marc Rubenstein, Esq. Ropes & Gray LLP Prudential Tower 800 Boylston Street Boston, MA 02199 (617) 951-7000 | John D. Quisel, Ph.D., Esq. Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary Acceleron Pharma Inc. 128 Sidney Street Cambridge, MA 02139 (617) 649-9200 | Jonathan L. Kravetz, Esq. Brian P. Keane, Esq. Mintz, Levin, Cohn, Ferris, Glovsky and Popeo, P.C. One Financial Center Boston, MA 02111 (617) 542-6000 | ||
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to public:
As soon as practicable after this Registration Statement is declared effective.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. o
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. o
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. o
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer o | Non-accelerated filer ý (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company o |
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
| Title of each class of securities to be registered | Proposed maximum aggregate offering price(1) | Amount of registration fee | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Common stock, $0.001 par value | $74,750,000 | $10,196 | ||
| ||||
| Title of Each Class of Securities to be Registered | Amount to be Registered(1) | Proposed Maximum Offering Price Per Share | Proposed Maximum Aggregate Offering Price(2) | Amount of Registration Fee(3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Common Stock, $0.001 par value per share | 5,347,500 | $15.00 | $80,212,500 | $10,941 | ||||
| ||||||||
The Registrant hereby amends this Registration Statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the Registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this Registration Statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until the Registration Statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
The information in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and it is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted.
SUBJECT TO COMPLETION, DATED AUGUST 7,SEPTEMBER 6, 2013
PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS

4,650,000 Shares
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Common Stock
$ per share
This is the initial public offering of our common stock. We are selling 4,650,000 shares of our common stock. We currently expect the initial public offering price to be between $$13.00 and $$15.00 per share of common stock.
We have granted the underwriters an option to purchase up to 697,500 additional shares of common stock to cover over-allotments.
We have applied to have our common stock listed on the NASDAQ Global Market under the symbol "XLRN".
We are an "emerging growth company" as that term is used in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 and, as such, have elected to comply with certain reduced public company reporting requirements for this prospectus and future filings.
Investing in our common stock involves risk. See "Risk Factors" beginning on page 12.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or passed on the adequacy or accuracy of this prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
| | Per share | Total | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Public Offering Price | $ | $ | ||
| Underwriting Discounts and | $ | $ | ||
| Proceeds to Acceleron (before expenses) | $ | $ |
Our collaboration partner, Celgene Corporation, has agreed to purchase $$10.0 million of our common stock in a separate private placement concurrent with the completion of this offering at a price per share equal to the initial public offering price. The sale of such shares will not be registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
The underwriters expect to deliver the shares of common stock to investors on or about , 2013 through the book-entry facilities of The Depositary Trust Company.
| Citigroup | Leerink Swann |
Piper Jaffray
JMP Securities
, 2013
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | Page | |
|---|---|---|
Summary | 1 | |
The Offering | 8 | |
Summary Financial Data | 10 | |
Risk Factors | 12 | |
Series E Conversion | 37 | |
Use of Proceeds | 38 | |
Dividend Policy | 39 | |
Capitalization | 40 | |
Dilution | 42 | |
Selected Financial Data | 44 | |
Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 46 | |
Business | ||
Management | ||
Executive and Director Compensation | ||
Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions | ||
Principal Stockholders | ||
Description of Capital Stock | ||
Shares Eligible for Future Sale | ||
Material United States Federal Income Tax Considerations for Non-U.S. Holders | ||
Underwriting | ||
Legal Matters | ||
Experts | ||
Where You Can Find More Information |
We are responsible for the information contained in this prospectus and in any free-writing prospectus we prepare or authorize. We have not authorized anyone to provide you with different information, and we take no responsibility for any other information others may give you. We are not, and the underwriters are not, making an offer to sell these securities in any jurisdiction where the offer or sale is not permitted. You should not assume that the information contained in this prospectus is accurate as of any date other than the date on the cover of this prospectus.
We own or have rights to trademarks, service marks and trade names that we use in connection with the operation of our business, including our corporate name, logos and website names. Other trademarks, service marks and trade names appearing in this prospectus are the property of their respective owners. The trademarks that we own include Acceleron®. Solely for convenience, some of the trademarks, service marks and trade names referred to in this prospectus are listed without the ® and ™ symbols, but we will assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights to our trademarks, service marks and trade names.
This summary highlights information contained in other parts of this prospectus. Because it is only a summary, it does not contain all of the information that you should consider before investing in shares of our common stock and it is qualified in its entirety by, and should be read in conjunction with, the more detailed information appearing elsewhere in this prospectus. You should read the entire prospectus carefully, especially "Risk Factors" and "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations", before deciding to buy shares of our common stock. Unless the context requires otherwise, references in this prospectus to "Acceleron", "we", "us" and "our" refer to Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Overview
We are a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of novel protein therapeutics for cancer and rare diseases. Our research focuses on the biology of the Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-b) protein superfamily, a large and diverse group of molecules that are key regulators in the growth and repair of tissues throughout the human body. We are leaders in understanding the biology of the TGF-b superfamily and in targeting these pathways to develop important new medicines. By coupling our discovery and development expertise, including our proprietary knowledge of the TGF-b superfamily, with our internal protein engineering and manufacturing capabilities, we have built a highly productive research and development platform that has generated innovative clinical and preclinical protein therapeutic candidates with novel mechanisms of action.
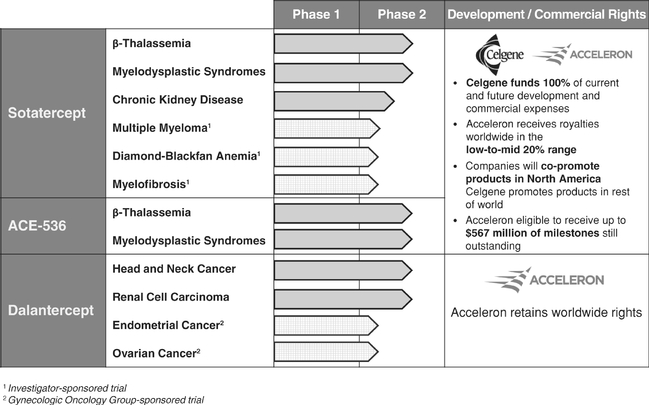
We have three internally discovered protein therapeutic candidates that are currently being studied in 12 ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, focused on cancer and rare diseases. These differentiated protein therapeutic candidates have the potential to significantly improve clinical outcomes for patients.
The Acceleron Discovery and Development Platform: Novel Approaches to Potent Biology
We focus on discovering and developing protein therapeutics that target a group of approximately 30 secreted proteins, or ligands, that are collectively referred to as the TGF-b superfamily. These ligands bind to subsets of 12 different receptors on the surface of cells, triggering intracellular changes in gene expression that guide cell growth and differentiation. The TGF-b superfamily ligands and their receptors represent a diverse and under-explored set of drug targets with the potential to yield therapeutics that modulate the growth and repair of diseased cells and tissues.
Members of the TGF-b superfamily are now recognized as important regulators of red blood cell formation. We have shown that inhibition of members of the TGF-b superfamily ameliorates anemia in mouse models ofb-thalassemia and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). These red blood cell disorders are generally unresponsive to currently approved drugs. Based on our findings, we are developing two protein therapeutic candidates, sotatercept and ACE-536, each of which is currently in Phase 2 clinical trials to treat patients with these diseases.
Members of the TGF-b superfamily also play a significant role in regulating blood vessel formation. We and our academic collaborators have shown that mice with a defect in a particular receptor for members of the TGF-b superfamily are resistant to tumor growth due to reduced blood vessel formation in the tumor. We have used this insight to design our anti-angiogenic agent, dalantercept, which is currently in Phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of cancer.
Sotatercept and ACE-536: Novel Protein Therapeutic
Candidates in Phase 2 Clinical Trials forb-thalassemia and MDS
Together with our collaboration partner, Celgene Corporation, we are developing sotatercept and ACE-536, our lead protein therapeutic candidates, to treat anemia and associated complications in patients withb-thalassemia and MDS. Clinical trials are underway in other diseases as well.
Sotatercept and ACE-536 have already shown promising biological activity in initial clinical trials. We and Celgene have conducted six clinical trials with sotatercept in over 160 healthy volunteers and cancer patients. We have conducted one clinical trial with ACE-536 in healthy volunteers. In these studies, both sotatercept and ACE-536 caused a dose-dependent increase in the number of red blood cells. Based on these results, we and Celgene have initiated Phase 2 clinical trials with each of these protein therapeutic candidates inb-thalassemia and MDS. We and Celgene plan to initiate Phase 3 clinical trials for one or both of these protein therapeutic candidates in one or both ofb-thalassemia and MDS by the end of 2014 or early 2015.
b-thalassemia
b-thalassemia is a hereditary disease arising from defects in genes involved in the production of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for carrying oxygen in red blood cells. During red blood cell formation in the bone marrow, these genetic defects cause most of the cells to die before they mature into fully functional red blood cells. As a consequence, patients withb-thalassemia have anemia, a lower than normal number of red blood cells, and many patients experience a broad array of complications arising from their disease, including an enlarged spleen, skeletal deformities and serious organ damage, such as liver fibrosis and heart failure, resulting from the accumulation of iron. There is no approved drug and no effective drug therapy for the anemia ofb-thalassemia. Frequent blood transfusions are used to manage the treatment of anemia in patients withb-thalassemia, but further contribute to the accumulation of iron and associated organ toxicities.
We and Celgene have shown that sotatercept and ACE-536 increase the production of red blood cells by promoting their maturation in the bone marrow. We believe this mechanism of action may be particularly beneficial for patients suffering from diseases, such asb-thalassemia, that are characterized by diminished red blood cell maturation. In a mouse model ofb-thalassemia, the mouse version of ACE-536 demonstrated broad disease modifying effects. In this model, the mouse version of ACE-536 increased red blood cell production, reduced spleen size, increased bone density and reduced levels of iron in the kidney and liver.
The Thalassaemia International Federation estimates that there are approximately 300,000 patients worldwide withb-thalassemia, approximately 20,000 of which are in the United States and Europe, who are dependent on frequent blood transfusions. We estimate that there are at least as manyb-thalassemia patients who do not receive frequent blood transfusions. Many of these patients have hemoglobin levels that are approximately half that of normal individuals and experience significant complications from the disease.
Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
MDS are a group of heterogeneous hematologic diseases characterized by abnormal proliferation and differentiation of blood precursor cells, including red blood cell precursors, in the bone marrow. This leads to anemia, which is present in the vast majority of MDS patients at the time of diagnosis. Much like the anemia ofb-thalassemia, the anemia of MDS is characterized by an over-abundance of early stage red blood cell precursors, a large proportion of which fails to mature into functional red blood cells during the later phases of the red blood cell formation process. Drugs that stimulate the production of early stage red blood cell precursors, such as recombinant erythropoietin, are often used to treat anemia in MDS patients, yet many do not experience a substantial improvement of their
anemia with these drugs. Although not approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with MDS, these products generate an estimated $500 to $700 million in annual U.S. sales from use in these patients, according to our market research.
Additional Opportunities for Sotatercept
Although sotatercept and ACE-536 have similar effects on red blood cells, sotatercept has also been shown to increase bone mass in humans and to inhibit tumor growth in mouse models of multiple myeloma, a cancer of the bone marrow. To take advantage of these additional activities, sotatercept is being studied in an investigator-sponsored Phase 2 trial in multiple myeloma patients. Additionally, many patients with chronic kidney disease suffer from both anemia and bone loss. Celgene is conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial of sotatercept in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Our Partnership With Celgene
We are developing sotatercept and ACE-536 through our exclusive worldwide collaborations with Celgene. As of January 1, 2013, Celgene became responsible for paying 100% of worldwide development costs for both programs. Additionally, we may receive up to $567.0 million of potential development, regulatory and commercial milestone payments and, if these protein therapeutic candidates are commercialized, we will receive a royalty on net sales in the low-to-mid 20% range. If approved, we also will co-promote sotatercept and ACE-536 in North America, for which our commercialization costs will be entirely funded by Celgene.
Dalantercept: Novel Protein Therapeutic Candidate in Phase 2 Clinical Trials for Cancer
Our third clinical stage protein therapeutic candidate, dalantercept, is designed to inhibit blood vessel formation in tumors through a mechanism that is distinct from, and potentially synergistic with, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway inhibitors, the dominant class of cancer drugs that inhibit blood vessel formation. The VEGF pathway inhibitors collectively generate worldwide sales in excess of $8 billion annually. We are developing dalantercept primarily for use in combination with these successful products to produce better outcomes for cancer patients.
Inhibiting Angiogenesis to Limit Tumor Growth
Angiogenesis is a process by which new blood vessels are formed. Angiogenesis can be simplified to two major stages—the proliferative stage followed by the maturation stage. During the proliferative stage, vascular endothelial cells, the cells lining the inside of the blood vessels, increase in number. This proliferative stage is followed by the maturation stage during which the endothelial cells coalesce to form tubes which are then stabilized through the recruitment of perivascular cells that form an outer layer of the blood vessels resulting in fully formed, functional vessels.
Tumors depend on angiogenesis to form new blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to feed the rapidly growing malignant cells. The principal molecule driving the proliferative stage of angiogenesis in tumors is a protein called VEGF. Inhibiting VEGF-driven angiogenesis to control tumor growth has become an important and widely-used approach to cancer treatment. There are several FDA-approved cancer drugs that inhibit the VEGF pathway. Despite the success of these drugs, many patients fail to respond or develop resistance to VEGF pathway inhibitor therapy, resulting in an unmet need for new therapies to inhibit angiogenesis by a different mechanism.
We are using our knowledge of the TGF-b superfamily to develop dalantercept, a novel protein therapeutic candidate targeting the maturation stage of angiogenesis. Recently, the activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) has been recognized as an important regulator of the maturation stage of angiogenesis. ALK1 is one of the 12 receptors for ligands in the TGF-b superfamily and is found primarily on endothelial cells. The importance of the ALK1 pathway in angiogenesis was discovered in
part through research into a genetic disease in which patients manifest vascular defects, including a reduced ability to form capillary beds, which are the networks of small blood vessels that connect arteries to veins and are necessary for nutrient and waste exchange in tissues. This research revealed that these patients have only one of two functional copies of the ALK1 gene. The resulting decreased signaling through the ALK1 receptor inhibits blood vessel maturation, leading to the reduced formation of capillary beds.
Opportunities for Dalantercept
We reasoned that leveraging the biology of the ALK1 pathway to inhibit maturation of blood vessels could impair the growth of tumors by limiting the development of capillary beds within the tumor. To test this hypothesis, mice with a predisposition to develop tumors were bred to have only one copy, rather than two copies, of the ALK1 gene that normally occur. In response to the loss of half of the ALK1 genes, tumor growth and size and blood vessel density in the tumor were reduced by half. We have also shown in two mouse cancer models that treatment with dalantercept decreases metastases. This is in contrast to VEGF pathway inhibitors, many of which have been shown to increase metastases in mouse cancer models. These results and additional research in the field have established the ALK1 signaling pathway as a promising target for developing a new class of anti-angiogenesis agents, ALK1 pathway inhibitors. We are developing dalantercept to treat cancer by inhibiting the ligands of the TGF-b superfamily that signal through the ALK1 receptor.
We believe one promising opportunity for dalantercept will be its use in combination with VEGF pathway inhibitors because these agents target distinct sequential steps in tumor angiogenesis. Moreover, we believe that dalantercept sensitizes blood vessels to increase the effects of treatment with VEGF pathway inhibitors. A combination of ALK1 and VEGF pathway inhibitors could have application in a number of different oncology indications where VEGF pathway inhibitors are currently used, such as non-small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer and renal cell carcinoma and we are considering future trials in these indications.
We have completed a Phase 1 trial of dalantercept and are pursuing a program of ongoing and planned Phase 2 trials seeking to demonstrate single agent activity of dalantercept for advanced solid tumors and activity of dalantercept in combination with approved VEGF pathway inhibitors or chemotherapy in advanced solid tumors. We currently are testing dalantercept as a single agent in a Phase 2 clinical trial in patients with squamous cell cancer of the head and neck and in a Phase 2 combination clinical trial with the VEGF pathway inhibitor axitinib in patients with renal cell carcinoma.
We have not entered into a partnership for dalantercept and retain worldwide rights to this program.
Our Clinical Stage Pipeline
The development status of our three clinical stage protein therapeutic candidates is summarized below:
Our Strategy
Our goal is to be a leader in the discovery, development and commercialization of novel protein therapeutics for cancer and rare diseases. Key components of our strategy are:
additional protein therapeutic candidates for the treatment of cancer and diseases involving fibrosis.
Risk Factors
An investment in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. Any of the factors set forth under "Risk Factors" may limit our ability to successfully execute our business strategy. You should carefully consider all of the information set forth in this prospectus and, in particular, should evaluate the specific factors set forth under "Risk Factors" in deciding whether to invest in our common stock. Among these important risks are the following:
Implications of Being an Emerging Growth Company
As a company with less than $1.0 billion in revenue during our most recently completed fiscal year, we qualify as an "emerging growth company" as defined in Section 2(a) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, which we refer to as the Securities Act, as modified by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, or the JOBS Act. As an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of specified reduced disclosure and other requirements that are otherwise applicable, in general, to public companies that are not emerging growth companies. These provisions include:
We may take advantage of these exemptions for up to five years or such earlier time that we are no longer an emerging growth company. We would cease to be an emerging growth company if we have more than $1.0 billion in annual revenues as of the end of a fiscal year, if we are deemed to be a large-accelerated filer under the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or if we issue more than $1.0 billion of non-convertible debt over a three-year-period.
The JOBS Act permits an emerging growth company to take advantage of an extended transition period to comply with new or revised accounting standards applicable to public companies. We are choosing to "opt out" of this provision.
Corporate Information
We were incorporated in the state of Delaware in June 2003 as Phoenix Pharma, Inc., and we subsequently changed our name to Acceleron Pharma Inc. and commenced operations in February 2004. Our principal executive offices are located at 128 Sidney Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139, and our telephone number is (617) 649-9200. Our Internet website iswww.acceleronpharma.com. The information on, or that can be accessed through, our website is not part of this prospectus, and you should not rely on any such information in making the decision whether to purchase our common stock.
Common stock offered by us | 4,650,000 shares | |
Common stock to be outstanding after this offering | 25,705,604 shares | |
Common stock to be outstanding after this offering and the concurrent private placement | 26,419,889 shares | |
Option to purchase additional shares | The underwriters have an option for a period of 30 days to purchase up to 697,500 additional shares of our common stock to cover over-allotments, if any. | |
Use of proceeds | We estimate that the net proceeds from this offering will be approximately | |
Risk factors | You should read the "Risk Factors" section of this prospectus for a discussion of factors to consider carefully before deciding to invest in shares of our common stock. | |
Proposed NASDAQ Global Market symbol | XLRN |
The number of shares of common stock to be outstanding after this offering and the concurrent private placement is based on 81,867,37821,055,604 shares of common stock outstanding as of March 31,June 30, 2013 and excludes the following:
Unless otherwise indicated, all information in this prospectus reflects or assumes the following:
The following summary financial data for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 are derived from our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The summary financial data as of March 31,June 30, 2013 and for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013 have been derived from our unaudited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. These unaudited financial statements have been prepared on a basis consistent with our audited financial statements and, in our opinion, contain all adjustments, consisting only of normal and recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair presentation of such financial data. You should read this data together with our audited financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus and the information under the captions "Selected Financial Data" and "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations". Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of our future results, and our operating results for the three-monthsix-month period ended March 31,June 30, 2013 are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2013 or any other interim periods or any future year or period.
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(in thousands, except per share data) | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Collaboration revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | 2,375 | $ | 12,515 | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | 4,765 | $ | 35,406 | ||||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 4,760 | 5,558 | 949 | 2,497 | 4,760 | 5,558 | 2,599 | 6,034 | ||||||||||||||||||
Contract manufacturing | 1,745 | — | — | — | 1,745 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Total revenue | 80,911 | 15,254 | 3,324 | 15,012 | 80,911 | 15,254 | 7,364 | 41,440 | ||||||||||||||||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Research and development | 32,713 | 35,319 | 8,212 | 8,780 | 32,713 | 35,319 | 16,925 | 17,691 | ||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 8,142 | 8,824 | 2,045 | 3,096 | 8,142 | 8,824 | 4,276 | 6,461 | ||||||||||||||||||
Cost of contract manufacturing revenue | 1,500 | — | — | — | 1,500 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 42,355 | 44,143 | 10,257 | 11,876 | 42,355 | 44,143 | 21,201 | 24,152 | ||||||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (6,933 | ) | 3,136 | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (13,837 | ) | 17,288 | ||||||||||||||
Total other expense, net | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (655 | ) | (1,489 | ) | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (1,151 | ) | (2,563 | ) | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.20 | $ | (6.21 | ) | $ | (1.50 | ) | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | 0.80 | $ | (24.84 | ) | $ | (11.91 | ) | $ | 0.19 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 0.19 | $ | (6.21 | ) | $ | (1.50 | ) | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | 0.78 | $ | (24.84 | ) | $ | (11.91 | ) | $ | 0.17 | |||||
Weighted-average number of common shares used in computing net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 9,313 | 9,605 | 9,579 | 9,740 | 2,328 | 2,401 | 2,395 | 2,437 | ||||||||||||||||||
Diluted | 10,863 | 9,605 | 9,579 | 9,740 | 2,716 | 2,401 | 2,395 | 4,434 | ||||||||||||||||||
Pro forma net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders(1): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||
Diluted | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||
Pro forma weighted-average number of common shares used in computing pro forma net income (loss) per share: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 82,267 | 81,859 | 21,155 | 21,045 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted | 82,267 | 88,651 | 21,155 | 23,062 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| | March 31, 2013 | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(in thousands) | Actual | Pro forma(2) | Pro forma, as adjusted(3)(4) | Actual | Pro forma(2) | Pro forma, as adjusted(3)(4) | ||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 38,510 | $ | 38,510 | $ | 28,465 | $ | 28,465 | $ | 96,253 | ||||||||||
Total assets | 48,447 | 48,447 | 40,023 | 40,023 | 107,811 | |||||||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 37,279 | 37,279 | 16,786 | 16,786 | 16,786 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term deferred revenue | 6,670 | 6,670 | 6,668 | 6,668 | 6,668 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term notes payable | 14,717 | 14,717 | 12,869 | 12,869 | 12,869 | |||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | 1,022 | — | 1,009 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 5,935 | 5,935 | 6,381 | 6,381 | 6,381 | |||||||||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock | 272,980 | — | 279,823 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Total stockholders' deficit | (292,868 | ) | (18,866 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Total stockholders' (deficit) equity | (286,100 | ) | (5,268 | ) | 62,520 | |||||||||||||||
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties described below together with all of the other information contained in this prospectus, including our financial statements and the related notes appearing at the end of this prospectus, before deciding to invest in our common stock. If any of the following risks actually occurs, our business, prospects, operating results and financial condition could suffer materially, the trading price of our common stock could decline and you could lose all or part of your investment. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently believe to be immaterial may also adversely affect our business.
Risks related to our financial position and need for additional capital
We have incurred net operating losses since our inception and anticipate that we will continue to incur substantial operating losses for the foreseeable future. We may never achieve or sustain profitability.
We have incurred net losses during most fiscal periods since our inception. As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had an accumulated deficit of $292.9$286.1 million. We do not know whether or when we will become profitable. To date, we have not commercialized any products or generated any revenues from the sale of products, and we do not expect to generate any product revenues in the foreseeable future. Our losses have resulted principally from costs incurred in our discovery and development activities.
We anticipate that our expenses will increase in the future as we expand our discovery, research, development, manufacturing and commercialization activities. However, we also anticipate that these increased expenses will be partially offset by milestone payments we expect to receive under our agreements with Celgene and potentially by payments we may receive under new collaboration arrangements we may enter into with third parties for dalantercept or other protein therapeutic candidates. If we do not receive the anticipated milestone payments or do not enter into partnerships for dalantercept or other protein therapeutic candidates on acceptable terms, our operating losses will substantially increase over the next several years as we execute our plan to expand our discovery, research, development, manufacturing and commercialization activities. There can be no assurance that we will enter into a new collaboration or achieve milestones and, therefore, no assurance our losses will not increase prohibitively in the future.
To become and remain profitable, we or our partners must succeed in developing our protein therapeutic candidates, obtaining regulatory approval for them, and manufacturing, marketing and selling those products for which we or our partners may obtain regulatory approval. We or they may not succeed in these activities, and we may never generate revenue from product sales that is significant enough to achieve profitability. Even if we achieve profitability in the future, we may not be able to sustain profitability in subsequent periods. Our failure to become or remain profitable would depress our market value and could impair our ability to raise capital, expand our business, discover or develop other protein therapeutic candidates or continue our operations. A decline in the value of our company could cause you to lose all or part of your investment.
We will require substantial additional financing to achieve our goals, and a failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed could force us to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or commercialization efforts.
As of March 31,June 30, 2013, our cash and cash equivalents were $38.5$28.5 million. We believe that we will continue to expend substantial resources for the foreseeable future developing dalantercept and new protein therapeutic candidates. These expenditures will include costs associated with research and development, potentially acquiring new technologies, conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials, potentially obtaining regulatory approvals and manufacturing products, as well as marketing and selling
products approved for sale, if any. In addition, other unanticipated costs may arise. Because the outcome of our planned and anticipated clinical trials is highly uncertain, we cannot reasonably estimate the actual amounts necessary to successfully complete the development and commercialization of our protein therapeutic candidates.
Celgene pays development, manufacturing and commercialization and certain patent costs for sotatercept and ACE-536. Other than those costs, our future capital requirements depend on many factors, including:
Based on our current operating plan, we believe that the net proceeds we receive from this offering and the concurrent private placement, together with receipt of anticipated milestone payments and our existing cash and cash equivalents will be sufficient to fund our projected operating requirements through the first half of 2015. However, our operating plan may change as a result of many factors currently unknown to us, and we may need additional funds sooner than planned. In addition, we may seek additional capital due to favorable market conditions or strategic considerations even if we believe we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. Additional funds may not be available when we need them on terms that are acceptable to us, or at all. If adequate funds are not available to us on a timely basis, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate preclinical studies, clinical trials or other development activities for one or more of our protein therapeutic candidates or delay, limit, reduce or terminate our establishment of sales and marketing capabilities or other activities that may be necessary to commercialize our protein therapeutic candidates.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our existing stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies or protein therapeutics on unfavorable terms to us.
We may seek additional capital through a variety of means, including through private and public equity offerings and debt financings. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a stockholder. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take certain actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If we raise additional funds through strategic partnerships with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies or protein therapeutics, or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financing when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or
commercialization efforts for dalantercept or any protein therapeutics other than sotatercept or ACE-536, or grant rights to develop and market protein therapeutics that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Risks Related to Regulatory Review and Approval of Our Protein Therapeutic Candidates
If we or our partners do not obtain regulatory approval for our current and future protein therapeutics, our business will be adversely affected.
Our protein therapeutic candidates will be subject to extensive governmental regulations relating to, among other things, development, clinical trials, manufacturing and commercialization. In order to obtain regulatory approval for the commercial sale of any protein therapeutic candidates, we or our partners must demonstrate through extensive preclinical studies and clinical trials that the protein therapeutic candidate is safe and effective for use in each target indication. Clinical testing is expensive, time-consuming and uncertain as to outcome. We or our partners may gain regulatory approval for sotatercept, ACE-536, dalantercept, or any other protein therapeutic candidate in some but not all of the territories available or some but not all of the target indications, resulting in limited commercial opportunity for the approved protein therapeutics, or we or they may never obtain regulatory approval for these protein therapeutic candidates.
Delays in the commencement, enrollment or completion of clinical trials of our protein therapeutic candidates could result in increased costs to us as well as a delay or failure in obtaining regulatory approval, or prevent us from commercializing our protein therapeutic candidates on a timely basis, or at all.
We cannot guarantee that clinical trials will be conducted as planned or completed on schedule, if at all. A failure of one or more clinical trials can occur at any stage of testing. Events that may prevent successful or timely commencement, enrollment or completion of clinical development include:
Delays, including delays caused by the above factors, can be costly and could negatively affect our or Celgene's ability to complete a clinical trial. If we or Celgene are not able to successfully complete clinical trials, we will not be able to obtain regulatory approval and will not be able to commercialize our protein therapeutic candidates.
Clinical failure may occur at any stage of clinical development, and because our protein therapeutic candidates are in an early stage of development, there is a high risk of failure, and we may never succeed in developing marketable products or generating product revenue.
Our early encouraging preclinical and clinical results for sotatercept, ACE-536 and dalantercept are not necessarily predictive of the results of our ongoing or future clinical trials. Promising results in preclinical studies of a drug candidate may not be predictive of similar results in humans during clinical trials, and successful results from early clinical trials of a drug candidate may not be replicated in later and larger clinical trials or in clinical trials for different indications. If the results of our or our partners' ongoing or future clinical trials are inconclusive with respect to the efficacy of our protein therapeutic candidates or if we or they do not meet the clinical endpoints with statistical significance or if there are safety concerns or adverse events associated with our protein therapeutic candidates, we or our partner may be prevented or delayed in obtaining marketing approval for our protein therapeutic candidates. In addition, data obtained from trials and studies are susceptible to varying interpretations, and regulators may not interpret our data as favorably as we do, which may delay or prevent regulatory approval. Alternatively, even if we or our partners obtain regulatory approval, that approval may be for indications or patient populations that are not as broad as intended or desired or may require labeling that includes significant use or distribution restrictions or safety warnings. We or our partners may also be required to perform additional or unanticipated clinical trials to obtain approval or be subject to additional post-marketing testing requirements to maintain regulatory approval. In addition, regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval of a product or impose restrictions on its distribution, such as in the form of a modified risk evaluation and mitigation strategy.
If we or any of our partners violate the guidelines pertaining to promotion and advertising of any of our protein therapeutics, if approved, we or they may be subject to disciplinary action by the FDA's Office of Prescription Drug Promotion (OPDP) or other regulatory authorities.
The FDA's Office of Prescription Drug Promotion, or OPDP, is responsible for reviewing prescription drug advertising and promotional labeling to ensure that the information contained in these materials is not false or misleading. There are specific disclosure requirements, and the applicable regulations mandate that advertisements cannot be false or misleading or omit material facts about the product. Prescription drug promotional materials must present a fair balance between the drug's effectiveness and the risks associated with its use. Most warning letters from OPDP cite inadequate disclosure of risk information.
OPDP prioritizes its actions based on the degree of risk to the public health, and often focuses on newly introduced drugs and those associated with significant health risks. There are two types of letters that OPDP typically sends to companies that violate its drug advertising and promotional guidelines: notice of violation letters, or untitled letters, and warning letters. In the case of an untitled letter, OPDP typically alerts the drug company of the violation and issues a directive to refrain from future violations, but does not typically demand other corrective action. A warning letter is typically issued in cases that are more serious or where the company is a repeat offender. Although we have not received
any such letters from OPDP, we or any partner may inadvertently violate OPDP's guidelines in the future and be subject to a OPDP untitled letter or warning letter, which may have a negative impact on our business.
If we or our partners fail to obtain regulatory approval in jurisdictions outside the United States, we and they will not be able to market our products in those jurisdictions.
We and our partners intend to market our protein therapeutic candidates, if approved, in international markets. Such marketing will require separate regulatory approvals in each market and compliance with numerous and varying regulatory requirements. The approval procedures vary from country-to-country and may require additional testing. Moreover, the time required to obtain approval may differ from that required to obtain FDA approval. In addition, in many countries outside the United States, a protein therapeutic must be approved for reimbursement before it can be approved for sale in that country. Approval by the FDA does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other countries or jurisdictions, and approval by one foreign regulatory authority does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other foreign countries or by the FDA. The foreign regulatory approval process may include all of the risks associated with obtaining FDA approval. We or our partners may not obtain foreign regulatory approvals on a timely basis, if at all. We or our partners may not be able to file for regulatory approvals and may not receive necessary approvals to commercialize our products in any market.
Even if we or our partners receive regulatory approval for our protein therapeutic candidates, such products will be subject to ongoing regulatory review, which may result in significant additional expense. Additionally, our protein therapeutic candidates, if approved, could be subject to labeling and other restrictions, and we or our partners may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or experience unanticipated problems with our products.
Any regulatory approvals that we or our partners receive for our protein therapeutic candidates may also be subject to limitations on the approved indicated uses for which the product may be marketed or to conditions of approval, or contain requirements for potentially costly post-marketing testing, including Phase 4 clinical trials, and surveillance to monitor safety and efficacy. In addition, if the FDA approves any of our protein therapeutic candidates, the manufacturing processes, labeling, packaging, distribution, adverse event reporting, storage, advertising, promotion and recordkeeping for the product will be subject to extensive and ongoing regulatory requirements. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration, as well as continued compliance with current good manufacturing practice, or cGMP, and GCP, for any clinical trials that we or our partners conduct post-approval.
Later discovery of previously unknown problems with an approved protein therapeutic, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing operations or processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in, among other things:
The FDA's policies may change and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent, limit or delay regulatory approval of our protein therapeutic candidates. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we or our partners are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we or our partners may lose any marketing approval that may have been obtained and we may not achieve or sustain profitability, which would adversely affect our business.
Risks Related to Our Reliance on Third Parties
We are dependent on Celgene for the successful development and commercialization of two of our three clinical stage protein therapeutic candidates, sotatercept and ACE-536. If Celgene does not devote sufficient resources to the development of these candidates, is unsuccessful in its efforts, or chooses to terminate its agreements with us, our business will be materially harmed.
We have entered into collaboration agreements with Celgene to develop and commercialize sotatercept and ACE-536. Pursuant to the sotatercept agreement, responsibility for all clinical and other product development activities and for manufacturing sotatercept has been transferred to Celgene. For ACE-536, we are responsible for conducting the two ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, and we are also responsible for manufacturing supplies for Phase 1 and Phase 2 studies. Celgene will be responsible for all clinical development and manufacturing activities after such studies are completed. As of January 1, 2013, Celgene became responsible for paying 100% of worldwide development costs for sotatercept and ACE-536. We will co-promote sotatercept and ACE-536, if approved by the FDA and its counterparties, in North America. Celgene will be responsible for all commercialization costs, including the cost of our promotion activities.
Celgene is obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize sotatercept and ACE-536. Celgene may determine that it is commercially reasonable to develop and commercialize only sotatercept or ACE-536 and discontinue the development or commercialization of the other protein therapeutic candidate, or Celgene may determine that it is not commercially reasonable to continue development of one or both of sotatercept and ACE-536. In the event of any such decision, we may be unable to progress the discontinued candidate or candidates ourselves. In addition, under our collaboration agreements, once Celgene takes over development activities of a protein therapeutic candidate, it may determine the development plan and activities for that protein therapeutic candidate. We may disagree with Celgene about the development strategy it employs, but we will have no rights to impose our development strategy on Celgene. Similarly, Celgene may decide to seek regulatory approval for, and limit commercialization of, either or both of sotatercept and ACE-536 to narrower indications than we would pursue. We would be prevented from developing or commercializing a candidate in an indication that Celgene has chosen not to pursue.
This partnership may not be scientifically or commercially successful due to a number of important factors, including the following:
existing products, lenalidomide and azacitidine, for certain MDS patients for which sotatercept and ACE-536 are also being developed.
We and Celgene rely on third parties to conduct preclinical studies and clinical trials for our protein therapeutic candidates, and if they do not properly and successfully perform their obligations to us, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approvals for our protein therapeutic candidates.
We design the clinical trials for dalantercept and will do so for any future unpartnered protein therapeutic candidates, and we will continue to work with Celgene on trials for sotatercept and ACE-536. However, we and Celgene rely on CROs and other third parties to assist in managing, monitoring and otherwise carrying out many of these trials. We and Celgene compete with many other companies for the resources of these third parties. The third parties on whom we and Celgene rely generally may terminate their engagements at any time, and having to enter into alternative arrangements would delay development and commercialization of our protein therapeutic candidates.
The FDA and foreign regulatory authorities require compliance with regulations and standards, including GCP, for designing, conducting, monitoring, recording, analyzing, and reporting the results of clinical trials to assure that the data and results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of trial participants are protected. Although we and Celgene rely on third parties to conduct many of our and their clinical trials, we and Celgene are responsible for ensuring that each of these clinical trials is conducted in accordance with its general investigational plan, protocol and other requirements.
If these third parties do not successfully carry out their duties under their agreements, if the quality or accuracy of the data they obtain is compromised due to their failure to adhere to clinical trial protocols or to regulatory requirements, or if they otherwise fail to comply with clinical trial protocols or meet expected deadlines, the clinical trials of our protein therapeutic candidates may not
meet regulatory requirements. If clinical trials do not meet regulatory requirements or if these third parties need to be replaced, preclinical development activities or clinical trials may be extended, delayed, suspended or terminated. If any of these events occur, we or Celgene may not be able to obtain regulatory approval of our protein therapeutic candidates on a timely basis or at all.
We and Celgene intend to rely on third-party manufacturers to make our protein therapeutics, and any failure by a third-party manufacturer may delay or impair our and Celgene's ability to complete clinical trials or commercialize our protein therapeutic candidates.
Manufacturing biologic drugs is complicated and is tightly regulated by the FDA, the European Medicines Agency, or EMA, and comparable regulatory authorities around the world. We currently manufacture drug substance for our preclinical studies, Phase 1 clinical trials and Phase 2 clinical trials of ACE-536 and dalantercept. For Phase 3 and commercial supply of our products that we have not partnered, we expect to use contract manufacturing organizations. Successfully transferring complicated manufacturing techniques to contract manufacturing organizations and scaling up these techniques for commercial quantities will be time consuming and we may not be able to achieve such transfer. Moreover, the market for contract manufacturing services for protein therapeutics is highly cyclical, with periods of relatively abundant capacity alternating with periods in which there is little available capacity. If any need we or Celgene have for contract manufacturing services increases during a period of industry-wide tight capacity, we or Celgene may not be able to access the required capacity on a timely basis or on commercially viable terms.
In addition, we contract with fill & finishing providers with the appropriate expertise, facilities and scale to meet our needs. Failure to maintain cGMP can result in a contractor receiving FDA sanctions, which can impact our and Celgene's contractors' ability to operate or lead to delays in our clinical development programs. We believe that our current fill & finish contractors are operating in accordance with cGMP, but we can give no assurance that FDA or other regulatory agencies will not conclude that a lack of compliance exists. In addition, any delay in contracting for fill & finish services, or failure of the contract manufacturer to perform the services as needed, may delay clinical trials, registration and launches. Any such issues may have a substantial negative effect on our business.
For our two lead products, sotatercept and ACE-536, we rely on our collaboration partner Celgene to produce, or contract for the production of, bulk drug substance and finished drug product for late stage clinical trials and for commercial supplies of any approved candidates. Any failure by Celgene or by third-parties with which Celgene contracts may delay or impair the ability to complete late stage clinical trials or commercialize either or both of sotatercept and ACE-536, if approved.
We produced drug substance for preclinical and Phase 1 and 2 clinical trials for sotatercept and ACE-536. Celgene is now responsible for manufacturing sotatercept and will be responsible for manufacturing ACE-536 for future late-stage clinical trials. Celgene generally does not perform the manufacture of the drug substance or drug product for either sotatercept or ACE-536 itself. Celgene has used and may continue to use contract manufacturers for the manufacture of drug substance and drug product for sotatercept and we have no expectation that Celgene plans to perform the manufacture of bulk drug substance or drug product for either sotatercept or ACE-536 in the future. However, Celgene would have the right to manufacture sotatercept or ACE-536, itself or through the use of contract manufacturers. We understand that they have entered into a manufacturing arrangement for Phase 2 supplies of sotatercept bulk drug substance with contract manufacturers with considerable biotherapeutics manufacturing experience, including manufacturing monoclonal antibodies through processes similar to those used for sotatercept. To date they have not entered into an arrangement with a third party to manufacture supplies of sotatercept or ACE-536 for Phase 3 trials or commercial sales. If they are unable to contract at the appropriate time with a manufacturer willing and able to manufacture sufficient quantities of sotatercept and ACE-536 to meet Phase 3 and
commercial demand, either for technical or business reasons, the development and commercialization of sotatercept and ACE-536 may be delayed.
We may not be successful in establishing and maintaining additional strategic partnerships, which could adversely affect our ability to develop and commercialize products, negatively impacting our operating results.
In addition to our current collaborations with Celgene, a part of our strategy is to strategically evaluate and, as deemed appropriate, enter into additional partnerships in the future when strategically attractive, including potentially with major biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies. We face significant competition in seeking appropriate partners for our protein therapeutic candidates, and the negotiation process is time-consuming and complex. In order for us to successfully partner our protein therapeutic candidates, potential partners must view these protein therapeutic candidates as economically valuable in markets they determine to be attractive in light of the terms that we are seeking and other available products for licensing by other companies. Even if we are successful in our efforts to establish new strategic partnerships, the terms that we agree upon may not be favorable to us, and we may not be able to maintain such strategic partnerships if, for example, development or approval of a protein therapeutic is delayed or sales of an approved product are disappointing. Any delay in entering into new strategic partnership agreements related to our protein therapeutic candidates could delay the development and commercialization of our protein therapeutic candidates and reduce their competitiveness even if they reach the market.
If we fail to establish and maintain additional strategic partnerships related to our protein therapeutic candidates, we will bear all of the risk and costs related to the development of any such protein therapeutic candidate, and we may need to seek additional financing, hire additional employees and otherwise develop expertise for which we have not budgeted. This could negatively affect the development of any unpartnered protein therapeutic candidate.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we are unable to obtain or protect intellectual property rights related to our protein therapeutic candidates, we may not be able to compete effectively.
We rely upon a combination of patents, trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements to protect the intellectual property related to our platform technology and protein therapeutic candidates. The patent position of biotechnology companies is generally uncertain because it involves complex legal and factual considerations. The standards applied by the United States Patent and Trademark Office, or USPTO, and foreign patent offices in granting patents are not always applied uniformly or predictably. For example, there is no uniform worldwide policy regarding patentable subject matter or the scope of claims allowable in biotechnology patents. The patent applications that we own or in-license may fail to result in issued patents with claims that cover our protein therapeutic candidates in the United States or in other countries. There is no assurance that all potentially relevant prior art relating to our patents and patent applications has been found. We may be unaware of prior art that could be used to invalidate an issued patent or prevent our pending patent applications from issuing as patents. Even if patents do successfully issue and even if such patents cover our protein therapeutic candidates, third parties may challenge their validity, enforceability or scope, which may result in such patents being narrowed or invalidated. Furthermore, even if they are unchallenged, our patents and patent applications may not adequately protect our intellectual property, provide exclusivity for our protein therapeutic candidates or prevent others from designing around our claims. Any of these outcomes could impair our ability to prevent competition from third parties, which may have an adverse impact on our business.
If patent applications we hold or have in-licensed with respect to our platform or protein therapeutic candidates fail to issue, if their breadth or strength of protection is threatened, or if they
fail to provide meaningful exclusivity for our protein therapeutic candidates, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us. Several patent applications covering our protein therapeutic candidates have been filed recently. We cannot offer any assurances about which, if any, patents will issue, the breadth of any such patents or whether any issued patents will be found invalid and unenforceable or will be threatened by third parties. Any successful challenge to these patents or any other patents owned by or licensed to us could deprive us of rights necessary for the successful commercialization of any protein therapeutic candidate that we or our partners may develop. Since patent applications in the United States and most other countries are confidential for a period of time after filing, and some remain so until issued, we cannot be certain that we were the first to file any patent application related to a protein therapeutic candidate. Furthermore, if third parties have filed such patent applications, an interference proceeding in the United States can be initiated by the USPTO or a third party to determine who was the first to invent any of the subject matter covered by the patent claims of our applications. In addition, patents have a limited lifespan. In the United States, the natural expiration of a patent is generally 20 years after it is filed. Various extensions may be available; however, the life of a patent and the protection it affords is limited. If we encounter delays in obtaining regulatory approvals, the period of time during which we could market a protein therapeutic under patent protection could be reduced. Even if patents covering our protein therapeutic candidates are obtained, once the patent life has expired for a product, we may be open to competition from biosimilar products.
Any loss of patent protection could have a material adverse impact on our business. We and our partner may be unable to prevent competitors from entering the market with a product that is similar to or the same as our protein therapeutics. In addition, the royalty we would receive under our collaboration agreements with Celgene for sotatercept and ACE-536 would be reduced by 50% if such product ceases to be covered by a valid claim of our patents even if no competitor with a similar product has entered the market.
Third-party claims of intellectual property infringement or misappropriation may prevent or delay our development and commercialization efforts.
Our commercial success depends in part on us and our partners not infringing the patents and proprietary rights of third parties. There is a substantial amount of litigation, both within and outside the United States, involving patent and other intellectual property rights in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, including patent infringement lawsuits, interferences, oppositions and inter partes reexamination proceedings before the USPTO and corresponding foreign patent offices. Numerous U.S. and foreign issued patents and pending patent applications owned by third parties exist in the fields in which we and our partners are developing and may develop our protein therapeutic candidates. As the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries expand and more patents are issued, the risk increases that our protein therapeutic candidates may be subject to claims of infringement of the patent rights of third parties.
Third parties may assert that we are employing their proprietary technology without authorization. There may be third-party patents or patent applications with claims to materials, formulations, methods of manufacture or methods for treatment related to the use or manufacture of our protein therapeutic candidates, that we failed to identify. For example, applications filed before November 29, 2000 and certain applications filed after that date that will not be filed outside the United States remain confidential until issued as patents. Except for the preceding exceptions, patent applications in the United States and elsewhere are generally published only after a waiting period of approximately 18 months after the earliest filing. Therefore, patent applications covering our platform technology or our protein therapeutic candidates could have been filed by others without our knowledge. Additionally, pending patent applications which have been published can, subject to certain limitations, be later amended in a manner that could cover our platform technologies, our protein therapeutic candidates or the use or manufacture of our protein therapeutic candidates.
If any third-party patents were held by a court of competent jurisdiction to cover aspects of our materials, formulations, methods of manufacture or methods for treatment, the holders of any such patents would be able to block our ability to develop and commercialize the applicable protein therapeutic candidate until such patent expired or unless we or our partners obtain a license. These licenses may not be available on acceptable terms, if at all. Even if we or our partners were able to obtain a license, the rights may be nonexclusive, which could result in our competitors gaining access to the same intellectual property. Ultimately, we or our partners could be prevented from commercializing a product, or be forced to cease some aspect of our business operations, if, as a result of actual or threatened patent infringement claims, we or our partners are unable to enter into licenses on acceptable terms. If Celgene is required to enter a license agreement with a third party in order to import, develop, manufacture or commercialize sotatercept or ACE-536, the royalty rate and sales milestone payments that we could receive may be reduced by up to 50%. This could harm our business significantly.
Parties making claims against us or our partners may obtain injunctive or other equitable relief, which could effectively block our or our partners' ability to further develop and commercialize one or more of our protein therapeutic candidates. Defending against claims of patent infringement or misappropriation of trade secrets could be costly and time consuming, regardless of the outcome. Thus, even if we were to ultimately prevail, or to settle at an early stage, such litigation could burden us with substantial unanticipated costs. In addition, litigation or threatened litigation could result in significant demands on the time and attention of our management team, distracting them from the pursuit of other company business. In the event of a successful claim of infringement against us or our partners, we may have to pay substantial damages, including treble damages and attorneys' fees for willful infringement, pay royalties, redesign our infringing products or obtain one or more licenses from third parties, which may be impossible or require substantial time and monetary expenditure.
We may face a claim of misappropriation if a third party believes that we inappropriately obtained and used trade secrets of such third party. If we are found to have misappropriated a third party's trade secrets, we may be prevented from further using such trade secrets, limiting our ability to develop our protein therapeutic candidates, and we may be required to pay damages.
During the course of any patent or other intellectual property litigation, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, rulings on motions, and other interim proceedings in the litigation. If securities analysts or investors regard these announcements as negative, the perceived value of our protein therapeutics, programs, or intellectual property could be diminished. Accordingly, the market price of our common stock may decline.
We have in-licensed a portion of our intellectual property, and, if we fail to comply with our obligations under these arrangements, we could lose such intellectual property rights or owe damages to the licensor of such intellectual property.
We are a party to a number of license agreements that are important to our business, and we may enter into additional license agreements in the future. Our discovery and development platform is built, in part, around patents exclusively in-licensed from academic or research institutions. Certain of our in-licensed intellectual property also covers sotatercept and dalantercept. See "Business—Intellectual Property—In-Licenses" for a description of our license agreements with the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research and the Salk Institute for Biological Studies.
Our existing license agreements impose, and we expect that future license agreements will impose, various diligence, milestone payment, royalty and other obligations on us. If there is any conflict, dispute, disagreement or issue of non-performance between us and our licensing partners regarding our rights or obligations under the license agreements, including any such conflict, dispute or disagreement arising from our failure to satisfy payment obligations under any such agreement, we may owe damages, our licensor may have a right to terminate the affected license, and our and our partners'
ability to utilize the affected intellectual property in our drug discovery and development efforts, and our ability to enter into collaboration or marketing agreements for an affected protein therapeutic candidate, may be adversely affected.
For example, the Salk Institute for Biological Studies recently filed a lawsuit against us alleging under one of our license agreements with them, which pertains to ActRIIB, its entitlement to a further share of certain payments received by us under our now-terminated agreement with Shire AG and a share of certain payments received by us under our on-going collaboration agreement with Celgene in connection with ACE-536. Although we and Salk have agreed that ACE-536 is not covered by any patent rights licensed from Salk, an unfavorable outcome in this litigation may lead to us owing significant damages to Salk and higher-than-anticipated future payments under this license in connection with development milestone payments that we may receive from Celgene. It is possible that Salk may seek to terminate the license covering the receptor. We do not believe that such a termination would have a material impact on our business or the development of any of our products. The patents under this license covered only one of our protein therapeutic candidates, ACE-031, the development of which has been discontinued. See "Business—Legal Proceedings" for a description of this proceeding.
Confidentiality agreements with employees and third parties may not prevent unauthorized disclosure of trade secrets and other proprietary information.
In addition to the protection afforded by patents, we rely on trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements to protect proprietary know-how that is not patentable or that we elect not to patent, processes for which patents are difficult to enforce and any other elements of our platform technology and discovery and development processes that involve proprietary know-how, information or technology that is not covered by patents. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, and outside scientific advisors, contractors and collaborators. Although we use reasonable efforts to protect our trade secrets, our employees, consultants, contractors, or outside scientific advisors might intentionally or inadvertently disclose our trade secret information to competitors. In addition, competitors may otherwise gain access to our trade secrets or independently develop substantially equivalent information and techniques.
Enforcing a claim that a third party illegally obtained and is using any of our trade secrets is expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the United States sometimes are less willing than U.S. courts to protect trade secrets. Misappropriation or unauthorized disclosure of our trade secrets could impair our competitive position and may have a material adverse effect on our business
Risks Related to Commercialization of Our Protein Therapeutic Candidates
Our future commercial success depends upon attaining significant market acceptance of our protein therapeutic candidates, if approved, among physicians, patients, health care payers and, in cancer markets, acceptance by the operators of major cancer clinics.
Even if we or our partners obtain regulatory approval for sotatercept, ACE-536, dalantercept or any other protein therapeutics that we may develop or acquire in the future, the product may not gain market acceptance among physicians, health care payors, patients and the medical community. Market acceptance of any approved products depends on a number of factors, including:
Market acceptance is critical to our ability to generate significant revenue. Any protein therapeutic candidate, if approved and commercialized, may be accepted in only limited capacities or not at all. If any approved products are not accepted by the market to the extent that we expect, we may not be able to generate significant revenue and our business would suffer.
Reimbursement may be limited or unavailable in certain market segments for our protein therapeutic candidates, which could make it difficult for us to sell our products profitably.
Market acceptance and sales of any approved protein therapeutics will depend significantly on the availability of adequate coverage and reimbursement from third-party payers and may be affected by existing and future health care reform measures. Government authorities and third-party payors, such as private health insurers and health maintenance organizations, decide which drugs they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels. Reimbursement by a third-party payer may depend upon a number of factors, including the third-party payor's determination that use of a product is:
Obtaining coverage and reimbursement approval for a product from a government or other third party payer is a time consuming and costly process that could require us to provide supporting scientific, clinical and cost-effectiveness data for the use of our products to the payer. We or our partners may not be able to provide data sufficient to gain acceptance with respect to coverage and reimbursement. We cannot be sure that coverage or adequate reimbursement will be available for any of our protein therapeutic candidates. Also, we cannot be sure that reimbursement amounts will not reduce the demand for, or the price of, our products. If reimbursement is not available or is available only to limited levels, we may not be able to commercialize certain of our products. In addition in the United States, third-party payers are increasingly attempting to contain health care costs by limiting both coverage and the level of reimbursement of new drugs. As a result, significant uncertainty exists as to whether and how much third-party payers will reimburse patients for their use of newly approved drugs, which in turn will put pressure on the pricing of drugs.
Price controls may be imposed in foreign markets, which may adversely affect our future profitability.
In some countries, particularly member states of the European Union, the pricing of prescription drugs is subject to governmental control. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after receipt of marketing approval for a product. In addition, there can be considerable pressure by governments and other stakeholders on prices and reimbursement levels, including as part of cost containment measures. Political, economic and regulatory developments may further complicate pricing negotiations, and pricing negotiations may
continue after reimbursement has been obtained. Reference pricing used by various European Union member states and parallel distribution, or arbitrage between low-priced and high-priced member states, can further reduce prices. In some countries, we or our partners may be required to conduct a clinical trial or other studies that compare the cost-effectiveness of our protein therapeutic candidates to other available therapies in order to obtain or maintain reimbursement or pricing approval. Publication of discounts by third-party payers or authorities may lead to further pressure on the prices or reimbursement levels within the country of publication and other countries. If reimbursement of our products is unavailable or limited in scope or amount, or if pricing is set at unsatisfactory levels, our business could be adversely affected.
The impact of recent healthcare reform legislation and other changes in the healthcare industry and in healthcare spending on us is currently unknown, and may adversely affect our business model.
Our revenue prospects could be affected by changes in healthcare spending and policy in the United States and abroad. We operate in a highly regulated industry and new laws, regulations or judicial decisions, or new interpretations of existing laws, regulations or decisions, related to health care availability, the method of delivery or payment for health care products and services could negatively impact our business, operations and financial condition. There is significant interest in promoting health care reform, as evidenced by the enactment in the United States of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act in 2010. It is likely that federal and state legislatures within the United States and foreign governments will continue to consider changes to existing health care legislation. We cannot predict the reform initiatives that may be adopted in the future or whether initiatives that have been adopted will be repealed or modified. The continuing efforts of the government, insurance companies, managed care organizations and other payers of healthcare services to contain or reduce costs of healthcare may adversely affect:
We face substantial competition, which may result in others discovering, developing or commercializing products before, or more successfully, than we do.
Our future success depends on our or our partners' ability to demonstrate and maintain a competitive advantage with respect to the design, development and commercialization of our protein therapeutic candidates. Our objective is to design, develop and commercialize new products with superior efficacy, convenience, tolerability and safety. In many cases, the protein therapeutics that we commercialize with our strategic partners or on our own will compete with existing, market-leading products.
There are products currently approved to treat patients with MDS, including iron chelation therapy, immunomodulators and various chemotherapeutic agents. In addition, erythropoiesis stimulating agents and red blood cell transfusions are extensively used to treat anemia in MDS. ACE-536 or sotatercept, if approved, will compete with these therapies. In addition, one or more products not currently approved for the treatment of anemia in MDS may in the future be granted marketing approval for the treatment of anemia in MDS or other conditions for which ACE-536 or sotatercept might be approved, including Aranesp®, being developed by Amgen, which is in Phase 3 trials. While there are currently no drug products approved for the treatment of anemia inb-thalassemia, red blood cell transfusions are extensively used and sotatercept or ACE-536, if approved, would compete with this therapy. In addition, HQK-1001, a fetal hemoglobin stimulating agent being
developed by HemaQuest Pharmaceuticals, has completed a Phase 1/2 clinical trial and an investigator sponsored Phase 2 clinical trial in patients withb-thalassemia. Further, the future approval, in one or more regions, of a biosimilar product to one of our products could create substantial competition and have a material impact on our business.
Sotatercept or ACE-536, if approved for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced anemia or anemia of chronic kidney disease, would compete with erythropoiesis-stimulating agents, such as Epogen® and Aranesp®, marketed by Amgen, and Procrit®, marketed by Johnson & Johnson, that are currently approved for the treatment of chemotherapy-induced anemia or anemia of chronic kidney disease and other therapies in development including oral, small molecule treatments being developed by Astellas Pharma and Fibrogen designed to increase the body's production of erythropoietin.
While we anticipate that dalantercept, if approved for the treatment of cancer, would likely be approved in combination with certain VEGF pathway inhibitors that are currently approved for the treatment of various cancer types, dalantercept would compete with other products, including other angiogenesis inhibitors, approved for the treatment of these cancers.
Many of our potential competitors have significantly greater financial, manufacturing, marketing, drug development, technical and human resources than we do. Large pharmaceutical companies, in particular, have extensive experience in clinical testing, obtaining regulatory approvals, recruiting patients and in manufacturing pharmaceutical products. These companies also have significantly greater research and marketing capabilities than we do and may also have products that have been approved or are in late stages of development, and have collaborative arrangements in our target markets with leading companies and research institutions. Established pharmaceutical companies may also invest heavily to accelerate discovery and development of novel compounds or to in-license novel compounds that could make the protein therapeutics that we develop obsolete. As a result of all of these factors, our competitors may succeed in obtaining patent protection and/or FDA approval or discovering, developing and commercializing protein therapeutics before we do. In addition, any new product that competes with an approved product must demonstrate compelling advantages in efficacy, convenience, tolerability and safety in order to overcome price competition and to be commercially successful. If we are not able to compete effectively against potential competitors, our business will not grow and our financial condition and operations will suffer.
Our protein therapeutics may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that delay or prevent their regulatory approval or limit their commercial potential.
Undesirable side effects caused by our protein therapeutics could cause us, Celgene or regulatory authorities to interrupt, delay or halt clinical trials and could result in the denial of regulatory approval by the FDA or other regulatory authorities and potential products liability claims. We and Celgene are currently conducting a number of Phase 2 trials for our clinical stage protein therapeutic candidates. Serious adverse events deemed to be caused by our protein therapeutics could have a material adverse effect on the development of our protein therapeutic candidates and our business as a whole. The most common adverse event to date in the clinical trials evaluating the safety and efficacy of our protein therapeutic candidates has been hypertension in our clinical trials for sotatercept and fluid retention in our clinical trials for dalantercept. Our understanding of the relationship between our protein therapeutic candidates and these events may change as we gather more information, and additional unexpected adverse events may occur. There can be no assurance that additional adverse events associated with our protein therapeutic candidates will not be observed. Recently, we discontinued the development of ACE-031, another of our clinical stage protein therapeutics that binds to ligands of the TGF-b superfamily. Clinical development of ACE-031 was put on clinical hold in 2011 due to preliminary safety observations in patients. After gathering further information from animal toxicology studies, we and our ACE-031 partner, Shire AG, determined that the risk-benefit profile of ACE-031 was not appropriate for the intended patient population, boys aged four and older with a genetic
muscle wasting disease, and we discontinued development of this protein therapeutic candidate. As is typical in drug development, we have a program of ongoing toxicology studies in animals for our other clinical stage protein therapeutics and cannot provide assurance that the findings from such studies or any ongoing or future clinical trials will not adversely affect our clinical development activities.
If we or others identify undesirable side effects caused by our protein therapeutic candidates either before or after receipt of marketing approval, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
Any of these events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of our protein therapeutics and could substantially increase commercialization costs.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
If we fail to attract and keep senior management and key scientific personnel, we may be unable to successfully develop our protein therapeutics, conduct our clinical trials and commercialize our protein therapeutic candidates.
We are highly dependent on members of our senior management, including John L. Knopf, Ph.D., our Chief Executive Officer and President and one of our founders. The loss of the services of any of these persons could impede the achievement of our research, development and commercialization objectives. We do not maintain "key person" insurance for any of our executives or other employees.
Recruiting and retaining qualified scientific, clinical, manufacturing, sales and marketing personnel will also be critical to our success. We may not be able to attract and retain these personnel on acceptable terms given the competition among numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for similar personnel. We also experience competition for the hiring of scientific and clinical personnel from universities and research institutions. In addition, we rely on consultants and advisors, including scientific and clinical advisors, to assist us in formulating our research and development and commercialization strategy. Our consultants and advisors, including our scientific co-founders, may be employed by employers other than us and may have commitments under consulting or advisory contracts with other entities that may limit their availability to us.
Our employees may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including noncompliance with regulatory standards and requirements and insider trading.
We are exposed to the risk of employee fraud or other misconduct. Misconduct by employees could include intentional failures to comply with FDA regulations, to provide accurate information to the FDA, to comply with manufacturing standards we have established, to comply with federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations, to report financial information or data accurately or to disclose unauthorized activities to us. In particular, sales, marketing and business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws and regulations intended to prevent fraud, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit
a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, sales commission, customer incentive programs and other business arrangements. Employee misconduct could also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical trials, which could result in regulatory sanctions and serious harm to our reputation. It is not always possible to identify and deter employee misconduct, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to be in compliance with such laws or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, including the imposition of significant fines or other sanctions.
We may encounter difficulties in managing our growth and expanding our operations successfully.
As we seek to advance our protein therapeutic candidates through clinical trials and commercialization, we will need to expand our development, regulatory, manufacturing, marketing and sales capabilities or contract with third parties to provide these capabilities for us. As our operations expand, we expect that we will need to manage additional relationships with various strategic partners, suppliers and other third parties. Future growth will impose significant added responsibilities on members of management. Our future financial performance and our ability to commercialize our protein therapeutic candidates and to compete effectively will depend, in part, on our ability to manage any future growth effectively. To that end, we must be able to manage our development efforts and clinical trials effectively and hire, train and integrate additional management, administrative and, if necessary, sales and marketing personnel. We may not be able to accomplish these tasks, and our failure to accomplish any of them could prevent us from successfully growing our company.
If product liability lawsuits are brought against us, we may incur substantial liabilities and may be required to limit commercialization of our protein therapeutics.
We face an inherent risk of product liability as a result of the clinical testing of our protein therapeutic candidates and will face an even greater risk if we commercialize any products. For example, we may be sued if any product we develop allegedly causes injury or is found to be otherwise unsuitable during product testing, manufacturing, marketing or sale. Any such product liability claims may include allegations of defects in manufacturing, defects in design, a failure to warn of dangers inherent in the product, negligence, strict liability, and a breach of warranties. Claims could also be asserted under state consumer protection acts. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against product liability claims, we may incur substantial liabilities or be required to limit commercialization of our protein therapeutic candidates. Even a successful defense would require significant financial and management resources. Regardless of the merits or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
Failure to obtain and retain sufficient product liability insurance at an acceptable cost to protect against potential product liability claims could prevent or inhibit the commercialization of products we develop. We currently carry product liability insurance covering our clinical trials in the amount of $10 million in the aggregate. Although we maintain such insurance, any claim that may be brought against us could result in a court judgment or settlement in an amount that is not covered, in whole or in part, by our insurance or that is in excess of the limits of our insurance coverage. Our insurance policies also have various exclusions, and we may be subject to a product liability claim for which we have no coverage. We will have to pay any amounts awarded by a court or negotiated in a settlement that exceed our coverage limitations or that are not covered by our insurance, and we may not have, or be able to obtain, sufficient capital to pay such amounts.
We must comply with environmental laws and regulations, and failure to comply with these laws and regulations could expose us to significant liabilities.
We use hazardous chemicals and radioactive and biological materials in certain aspects of our business and are subject to a variety of federal, state and local laws and regulations governing the use, generation, manufacture, distribution, storage, handling, treatment and disposal of these materials. Although we believe our safety procedures for handling and disposing of these materials and waste products comply with these laws and regulations, we cannot eliminate the risk of accidental injury or contamination from the use, manufacture, distribution, storage, handling, treatment or disposal of hazardous materials. In the event of contamination or injury, or failure to comply with environmental, occupational health and safety and export control laws and regulations, we could be held liable for any resulting damages and any such liability could exceed our assets and resources. We are uninsured for third-party contamination injury.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock and This Offering
We are eligible to be treated as an "emerging growth company" as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, and we cannot be certain if the reduced disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an "emerging growth company", as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, or the JOBS Act. For as long as we continue to be an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including (1) not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, which we refer to as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, (2) reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in this prospectus and our periodic reports and proxy statements and (3) exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. In addition, as an emerging growth company, we are only required to provide two years of audited financial statements and two years of selected financial data in this prospectus. We could be an emerging growth company for up to five years, although circumstances could cause us to lose that status earlier, including if the market value of our common stock held by non-affiliates exceeds $700.0 million as of any June 30 before that time or if we have total annual gross revenue of $1.0 billion or more during any fiscal year before that time, in which cases we would no longer be an emerging growth company as of the following December 31 or, if we issue more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt during any three-year period before that time, we would cease to be an emerging growth company immediately. Even after we no longer qualify as an emerging growth company, we may still qualify as a "smaller reporting
company" which would allow us to take advantage of many of the same exemptions from disclosure requirements, including not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we may rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
Under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies can also delay adopting new or revised accounting standards until such time as those standards apply to private companies. We have irrevocably elected not to avail ourselves of this exemption from new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, will be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies.
We do not know whether a market will develop for our common stock or what the market price of our common stock will be and, as a result, it may be difficult for you to sell your shares of our common stock.
Before this offering, there was no public trading market for our common stock. If a market for our common stock does not develop or is not sustained, it may be difficult for you to sell your shares of common stock at an attractive price, or at all. Further, an inactive market may also impair our ability to raise capital by selling shares of our common stock and may impair our ability to enter into strategic partnerships or acquire companies or products by using our shares of common stock as consideration. We cannot predict the prices at which our common stock will trade. It is possible that in one or more future periods our results of operations may be below the expectations of public market analysts and investors and, as a result of these and other factors, the price of our common stock may fall.
The market price of our common stock may be highly volatile, and you may not be able to resell your shares at or above the initial public offering price.
The initial public offering price for our shares will be determined by negotiations between us and the representatives of the underwriters and may not be indicative of prices that will prevail in the trading market. The market price of shares of our common stock could be subject to wide fluctuations in response to many risk factors listed in this section, and others beyond our control, including:
In addition, the stock market has recently experienced significant volatility, particularly with respect to pharmaceutical, biotechnology and other life sciences company stocks. The volatility of pharmaceutical, biotechnology and other life sciences company stocks often does not relate to the operating performance of the companies represented by the stock. As we operate in a single industry, we are especially vulnerable to these factors to the extent that they affect our industry or our products, or to a lesser extent our markets. In the past, securities class action litigation has often been initiated against companies following periods of volatility in their stock price. This type of litigation could result in substantial costs and divert our management's attention and resources, and could also require us to make substantial payments to satisfy judgments or to settle litigation.
Our principal stockholders and management own a significant percentage of our stock and will be able to exercise significant influence over matters subject to stockholder approval.
As of June 1,30, 2013, our executive officers, directors and principal stockholders, together with their respective affiliates, owned approximately 86%87% of our common stock, including shares subject to outstanding options and warrants that are exercisable within 60 days after such date, and we expect that upon completion of this offering and the concurrent private placement to Celgene, that same group will continue to hold at least %72% of our outstanding common stock. Accordingly, even after this offering, these stockholders will be able to exert a significant degree of influence over our management and affairs and over matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of our board of directors and approval of significant corporate transactions. This concentration of ownership could have the effect of entrenching our management and/or the board of directors, delaying or preventing a change in our control or otherwise discouraging a potential acquirer from attempting to obtain control of us, which in turn could have a material and adverse effect on the fair market value of our common stock.
A significant portion of our total outstanding shares may be sold into the public market in the near future, which could cause the market price of our common stock to drop significantly, even if our business is doing well.
Sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market could occur at any time after the expiration of the lock-up agreements described in the "Underwriting" section of this prospectus. These sales, or the market perception that the holders of a large number of shares intend to sell shares, could reduce the market price of our common stock. After this offering and the concurrent private placement, we will have 26,419,889 shares of common stock outstanding. This includes the 4,650,000 shares that we are selling in this offering, which may be resold in the public market immediately.immediately and approximately 714,285 shares being sold in the concurrent private placement (assuming an initial public offering price of $14.00 per share, the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), which will be freely tradeable six months after the closing of the concurrent private placement. The remaining 21,055,604 shares, or %80% of our outstanding shares after this offering and the concurrent private placement, are currently restricted as a result of securities laws or lock-up agreements but will be able to be sold,
lock-up agreements but will be able to be sold, subject to any applicable volume limitations under federal securities laws with respect to affiliate sales, in the near future as set forth below.
Number of Shares and % of Total Outstanding | Date Available for Sale into Public Market | |
|---|---|---|
| 946,284 shares, or | On the date of this prospectus | |
18,197 shares, or | 90 days after the date of this prospectus | |
20,091,123 shares, or 76% | 180 days after the date of this prospectus, due to lock-up agreements between the holders of these shares and the underwriters. However, the representatives of the underwriters can waive the provisions of these lock-up agreements and allow these stockholders to sell their shares at any time. |
In addition, as of March 31,June 30, 2013, there were 4,046,4531,011,590 shares subject to outstanding warrants, 14,765,6953,677,965 shares subject to outstanding options and an additional 610,1001,500,000 shares reserved for future issuance under our employee benefit plans that will become eligible for sale in the public market to the extent permitted by any applicable vesting requirements, the lock-up agreements and Rules 144 and 701 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. Moreover, after this offering and the concurrent private placement, holders of an aggregate of 81,867,37818,694,861 shares of our common stock and holders of warrants to purchase 4,046,453131,378 shares of our common stock will have rights, subject to some conditions, to require us to file registration statements covering their shares or to include their shares in registration statements that we may file for ourselves or other stockholders. If such holders, by exercising their registration rights, cause a large number of securities to be registered and sold into the public market, these sales could have an adverse effect on the market price for our common stock. We also intend to register all shares of common stock that we may issue under our employee benefit plans, including our 2013 Omnibus Long-TermEquity Incentive Plan. Once we register these shares and they are issued in accordance with the terms of the plans, they can be freely sold in the public market upon issuance, subject to the lock-up agreements and the restrictions imposed on our affiliates under Rule 144. For more information, see "Shares Eligible for Future Sale—Rule 144".
You will incur immediate and substantial dilution as a result of this offering.
If you purchase common stock in this offering, assuming a public offering price of $ ,$14.00, the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover of this prospectus, you will incur immediate and substantial dilution of $$11.63 per share, representing the difference between the assumed initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share and our pro forma net tangible book value per share after giving effect to this offering, and the concurrent private placement to Celgene and the conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock upon the closing of this offering. Moreover, we issued warrants and options in the past to acquire common stock at prices significantly below the assumed initial public offering price. As of March 31,June 30, 2013, there were 4,046,4531,011,590 shares subject to outstanding warrants and 14,765,6953,677,965 shares subject to outstanding options. To the extent that these outstanding warrants or options are ultimately exercised, you will incur further dilution.
We have broad discretion in the use of net proceeds from this offering and may not use them effectively.
We currently intend to use the net proceeds from this offering to fund the continued clinical development of dalantercept and to continue to discover and develop other protein therapeutics in our pipeline and for working capital and other general corporate purposes, including funding the costs of operating a public company. See "Use of Proceeds." Any remaining amounts will be used for general corporate purposes, general and administrative expenses, capital expenditures, working capital and prosecution and maintenance of our intellectual property. Although we currently intend to use the net
proceeds from this offering in such a manner, we will have broad discretion in the application of the
net proceeds. Our failure to apply these funds effectively could affect our ability to continue to develop and commercialize our protein therapeutic candidates.
We will incur increased costs as a result of being a public company and our management expects to devote substantial time to public company compliance programs.
As a public company, we will incur significant legal, insurance, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. In addition, our administrative staff will be required to perform additional tasks. For example, in anticipation of becoming a public company, we will need to adopt additional internal controls and disclosure controls and procedures, retain a transfer agent, adopt an insider trading policy and bear all of the internal and external costs of preparing and distributing periodic public reports in compliance with our obligations under the securities laws. We intend to invest resources to comply with evolving laws, regulations and standards, and this investment will result in increased general and administrative expenses and may divert management's time and attention from product development activities. If our efforts to comply with new laws, regulations and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies due to ambiguities related to practice, regulatory authorities may initiate legal proceedings against us and our business may be harmed. In connection with this offering, we are increasing our directors' and officers' insurance coverage, which will increase our insurance cost. In the future, it will be more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain coverage. These factors could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified members of our board of directors, particularly to serve on our audit committee and compensation committee, and qualified executive officers.
In addition, in order to comply with the requirements of being a public company, we may need to undertake various actions, including implementing new internal controls and procedures and hiring new accounting or internal audit staff. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires that we maintain effective disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting. We are continuing to develop and refine our disclosure controls and other procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or the Commission, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the Commission's rules and forms, and that information required to be disclosed in reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as amended, or the Exchange Act, is accumulated and communicated to our principal executive and financial officers. Any failure to develop or maintain effective controls could adversely affect the results of periodic management evaluations. In the event that we are not able to demonstrate compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, that our internal control over financial reporting is perceived as inadequate, or that we are unable to produce timely or accurate financial statements, investors may lose confidence in our operating results and the price of our ordinary shares could decline. In addition, if we are unable to continue to meet these requirements, we may not be able to remain listed on NASDAQ.
We are not currently required to comply with the Commission's rules that implement Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and are therefore not yet required to make a formal assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting for that purpose. Upon becoming a public company, we will be required to comply with certain of these rules, which will require management to certify financial and other information in our quarterly and annual reports and provide an annual management report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting commencing with our second annual report. This assessment will need to include the disclosure of any material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting identified by our management or our independent registered public accounting firm. We are just beginning the costly and challenging process of implementing the system and processing documentation needed to comply with such requirements.
We may not be able to complete our evaluation, testing and any required remediation in a timely fashion.
Our independent registered public accounting firm will not be required to formally attest to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting until the later of our second annual report or the first annual report required to be filed with the Commission following the date we are no longer an "emerging growth company" as defined in the JOBS Act. We cannot assure you that there will not be material weaknesses or significant deficiencies in our internal controls in the future.
We do not expect to pay any cash dividends for the foreseeable future.
You should not rely on an investment in our common stock to provide dividend income. We do not anticipate that we will pay any cash dividends to holders of our common stock in the foreseeable future. Instead, we plan to retain any earnings to maintain and expand our operations. In addition, our ability to pay cash dividends is currently prohibited by the terms of our debt financing arrangement, and any future debt financing arrangement may contain terms prohibiting or limiting the amount of dividends that may be declared or paid on our common stock. Accordingly, investors must rely on sales of their common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any return on their investment. As a result, investors seeking cash dividends should not purchase our common stock.
Provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, our amended and restated by-laws and Delaware law may have anti-takeover effects that could discourage an acquisition of us by others, even if an acquisition would be beneficial to our stockholders, and may prevent attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, amended and restated by-laws and Delaware law contain provisions that may have the effect of delaying or preventing a change in control of us or changes in our management. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and by-laws, which will become effective upon the closing of this offering, include provisions that:
These provisions, alone or together, could delay or prevent hostile takeovers and changes in control or changes in our management.
In addition, because we are incorporated in the state of Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which limits the ability of stockholders owning in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock to merge or combine with us.
Any provision of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or amended and restated by-laws or Delaware law that has the effect of delaying or deterring a change in control could limit the opportunity for our stockholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock, and could also affect the price that some investors are willing to pay for our common stock.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation designates the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware as the sole and exclusive forum for certain types of actions and proceedings that may be initiated by our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders' ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers or employees.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that, subject to limited exceptions, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for (1) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (2) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers or other employees to us or our stockholders, (3) any action asserting a claim against us arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or our amended and restated by-laws, or (4) any other action asserting a claim against us that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our capital stock shall be deemed to have notice of and to have consented to the provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation described above. This choice of forum provision may limit a stockholder's ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or our directors, officers or other employees, which may discourage such lawsuits against us and our directors, officers and employees. Alternatively, if a court were to find these provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation inapplicable to, or unenforceable in respect of, one or more of the specified types of actions or proceedings, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such matters in other jurisdictions, which could adversely affect our business and financial condition.
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are neither historical facts nor assurances of future performance. Instead, they are based on our current beliefs, expectations and assumptions regarding the future of our business, future plans and strategies, our clinical results and other future conditions. The words "anticipate", "believe", "estimate", "expect", "forecast", "goal", "intend", "may", "plan", "predict", "project", "target", "potential", "will", "would", "could", "should", "continue", "contemplate", or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words.
The forward-looking statements in this prospectus include, among other things, statements about:
We may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements, and you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. Actual results or events could differ materially from the plans, intentions and expectations disclosed in the forward-looking statements we make. We have included important factors in the cautionary statements included in this prospectus, particularly in the "Risk Factors" section, that we believe could cause actual results or events to differ materially from the forward-looking statements that we make. Our forward-looking statements do not reflect the potential impact of any future acquisitions, mergers, dispositions, joint ventures or investments we may make.
The forward-looking statements in this prospectus represent our views as of the date of this prospectus. We anticipate that subsequent events and developments will cause our views to change. However, while we may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, we have no current intention of doing so except to the extent required by applicable law. You should, therefore, not rely on these forward-looking statements as representing our views as of any date subsequent to the date of this prospectus.
Immediately prior toUpon the completion of this offering, each outstanding share of Series E preferred stock issued on June 10, 2010 will be converted into approximately 1.73 shares of common stock and each outstanding share of Series E preferred stock issued as of July 9, 2010 will convert into approximately 1.70 shares of common stock determined by dividing (1) the Special Series E Liquidation Payment, which is equal to a preference of 22%, compounded annually on the initial per share investment amount ($3.14)12.56), accrued from June 10, 2010,the date the shares were issued, through the closing date of this offering, and which is currently estimated to be $ ,September 23, 2013, by (2) the initial public offering price of a share of our common stock in this offering. The number of shares of common stock into which each share of Series E preferred stock will convert is also expressed with the following formula:
--------------------------------------- the initial public offering price |
| Where | ||
x = | the number of days elapsed since | |
The estimated Special Series E Liquidation Payment is based upon an assumed pricingclosing date of this offering of ,September 23, 2013. If the pricingclosing date for this offering occurs before or after such date, the aggregate number of shares of Common into which the outstanding Series E conversion amount per sharepreferred stock will convert will be less or more, as applicable, than such estimated amount by approximately $800 shares per day.
Assuming an initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, the 802,957 outstanding shares of Series E preferred stock will convert into 1,381,806 shares of common stock, and 21,055,604 shares of common stock will be outstanding immediately after the conversion of the Series E preferred stock and our other series of preferred stock, but before this offering and the concurrent private placement.
Because the number of shares of common stock into which each share of Series E preferred stock is convertible will be determined by reference to the initial public offering price in this offering, a change in the assumed initial public offering price would have a corresponding impact on the number of outstanding shares of common stock presented in this prospectus after giving effect to this offering and the concurrent private placement. The following number of shares of common stock would be outstanding immediately after the conversion of the Series E preferred stock and our other series of preferred stock, but before this offering and the concurrent private placement, assuming the initial public offering prices for our common stock shown below:
| |||||||||||||
| | Assumed Initial Public Offering Price | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | $12.00 | $13.00 | $15.00 | $16.00 | |||||||||
Shares Outstanding | 21,285,940 | 21,161,929 | 20,963,511 | 20,882,904 | |||||||||
We estimate that the net proceeds of the sale of 4,650,000 shares of common stock in this offering will be approximately $$57.8 million at an assumed initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. If the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option in full, we estimate that the net proceeds will be approximately $$66.9 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. Each $1.00 increase or decrease in the assumed initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share would increase or decrease our net proceeds by $approximately $4.3 million, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
We are undertaking this offering in order to access the public capital markets and to increase our liquidity. We intend to use the net proceeds from this offering as follows:
The expected use of the net proceeds from this offering represents our intentions based upon our current plans and business conditions, which could change in the future as our plans and business conditions evolve. The amounts and timing of our actual expenditures depend on numerous factors, including the ongoing status of and results from our clinical trials and other studies, the progress of our preclinical development efforts and any unforeseen cash needs. As a result, our management will have broad discretion in applying the net proceeds of this offering. Although we may use a portion of the net proceeds of this offering for the acquisition or licensing, as the case may be, of product candidates, technologies, compounds, other assets or complementary businesses, we have no current understandings, agreements or commitments to do so.
Pending the use of the proceeds from this offering, we intend to invest the net proceeds in short-term, interest-bearing, investment-grade securities, certificates of deposit or government securities.
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our common stock. We currently intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings, if any, to fund the development and expansion of our business and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. In addition, our ability to pay cash dividends is currently prohibited by the terms of our debt financing arrangements, and any future debt financing arrangement may contain terms prohibiting or limiting the amount of dividends that may be declared or paid on our common stock. Any future determination to pay dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors.
The following table sets forth our cash and cash equivalents and capitalization as of March 31,June 30, 2013:
You should read this information together with our audited financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus and the information set forth under the heading "Selected Financial Data" and "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations".
| | As of June 30, 2013 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Actual | Pro Forma | Pro Forma, as Adjusted(1) | |||||||
| | (in thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 28,465 | $ | 28,465 | $ | 96,253 | ||||
Notes payable, net of current portion | $ | 12,869 | $ | 12,869 | $ | 12,869 | ||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | 1,009 | — | — | |||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 6,381 | 6,381 | 6,381 | |||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock | 279,823 | — | — | |||||||
Stockholders' (deficit) equity: | ||||||||||
Undesignated preferred stock, $0.001 par value: | — | — | — | |||||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 104,013,161 shares authorized, actual and pro forma; 2,447,195 shares issued and outstanding, actual and 21,055,604 shares issued and outstanding, pro forma; 175,000,000 shares authorized and 26,419,889 shares issued and outstanding, pro forma as adjusted(2) | 3 | 22 | 27 | |||||||
Additional paid-in capital | — | 150,411 | 218,194 | |||||||
Accumulated deficit | (286,103 | ) | (155,701 | ) | (155,701 | ) | ||||
Total stockholders' (deficit) equity | (286,100 | ) | (5,268 | ) | 62,520 | |||||
Total capitalization | $ | 13,982 | $ | 13,982 | $ | 81,770 | ||||
| | As of March 31, 2013 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Actual | Pro Forma | Pro Forma, as Adjusted(1) | |||||||
| | (in thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 38,510 | $ | 38,510 | $ | |||||
Notes payable, net of current portion | $ | 14,717 | $ | 14,717 | $ | |||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | 1,022 | — | ||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 5,935 | 5,935 | ||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock | 272,980 | — | ||||||||
Stockholders' (deficit) equity: | ||||||||||
Undesignated preferred stock, $0.001 par value: | — | — | ||||||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 104,013,161 shares authorized, actual and pro forma; 9,748,650 shares issued and outstanding, actual and 81,867,378 shares issued and outstanding, pro forma; shares authorized and shares issued and outstanding, pro forma as adjusted(2) | 10 | 82 | ||||||||
Additional paid-in capital | — | 149,838 | ||||||||
Accumulated deficit | (292,878 | ) | (168,786 | ) | ||||||
Total stockholders' (deficit) equity | (292,868 | ) | (18,866 | ) | ||||||
Total capitalization | $ | 1,786 | $ | 1,786 | $ | |||||
equity by approximately $$4.3 million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set
forth on the cover of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
If you invest in our common stock in this offering, your interest will be diluted to the extent of the difference between the initial public offering price per share of our common stock in this offering and the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share of our common stock after this offering.
We had a historical net tangible book value of $(292.9)$(286.1) million, or $(30.04)$(116.91) per share of common stock, as of March 31,June 30, 2013. Historical net tangible book value per share is equal to our total tangible assets, less total liabilities and preferred stock, divided by the number of outstanding shares of our common.common stock. As of March 31,June 30, 2013, the pro forma net tangible book value of our common stock was $(18.9)$(5.3) million, or $(0.23)$(0.25) per share of common stock, taking into account the expected conversion of our outstanding preferred stock into common stock and the conversion of our outstanding warrants to purchase our preferred stock into warrants to purchase common stock, prior to the completion of this offering. After giving further effect to (1) the sale of 4,650,000 shares of common stock in this offering, after deducting estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, at an assumed initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus, and (2) the sale by us of 714,285 shares of our common stock in the concurrent private placement at the initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share, assuming an initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of March 31,June 30, 2013 would have been approximately $$62.5 million, or approximately $$2.37 per share of common stock. This represents an immediate increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value of $$2.62 per share to our existing stockholders and an immediate dilution of $$11.63 per share to investors participating in this offering. The following table illustrates this per share dilution:
Assumed initial public offering price per share | $ | $ | 14.00 | |||||||||||
Historical net tangible book value per share as of March 31, 2013 | $ | (30.04 | ) | |||||||||||
Historical net tangible book value per share as of June 30, 2013 | $ | (116.91 | ) | |||||||||||
Increase attributable to the conversion of outstanding preferred stock and reclassification of preferred stock warrants | $ | 116.66 | ||||||||||||
Pro forma net tangible book value per share as of March 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||||
Pro forma net tangible book value per share as of June 30, 2013 | $ | (0.25 | ) | |||||||||||
Increase in net tangible book value per share attributable to new investors | $ | 2.62 | ||||||||||||
Pro forma net tangible book value per share after this offering | $ | 2.37 | ||||||||||||
Dilution per share to new investors | $ | $ | 11.63 | |||||||||||
Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share would increase (decrease) our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value by approximately $$4.3 million, the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share by approximately $$0.16 per share and the dilution to investors purchasing shares in this offering by approximately $$0.84 per share, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of June 30, 2013 will increase to $71.6 million, or $2.64 per share, representing an increase to existing stockholders of $2.89 per share, and there will be an immediate dilution of $11.36 per share to new investors.
The following table summarizes, on a pro forma as adjusted basis as of March 31,June 30, 2013, the differences between the number of shares of common stock purchased from us, the total consideration and the average price per share paid by existing stockholders (giving effect to the conversion of all outstanding shares of our preferred stock into 72,118,72818,608,409 shares of common stock prior to the completion of this offering) and by investors participating in this offering, after deducting underwritingbut excluding the common
stock to be sold in the concurrent private placement, before deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses, at an assumed initial public offering price of $$14.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus.
| | Shares purchased | Total consideration | | Shares purchased | Total consideration | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Average price per share | Average price per share | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | Number | Percent | Amount | Percent | Number | Percent | Amount | Percent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Existing stockholders | % | $ | % | $ | 21,055,604 | 81.9 | % | $ | 144,814,759 | 69.0 | % | $ | 6.88 | |||||||||||||||||||
New investors | % | % | $ | 4,650,000 | 18.1 | % | 65,100,000 | 31.0 | % | $ | 14.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 100 | % | $ | 100 | % | 25,705,604 | 100 | % | $ | 209,914,759 | 100 | % | $ | 8.17 | ||||||||||||||||||
The number of shares of common stock to be outstanding after this offering is based on the number of shares outstanding as of March 31,June 30, 2013 and excludes the following:
If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of , 2013 will increase to $ million, or $ per share, representing an increase to existing stockholders of $ per share, and there will be an immediate dilution of an additional $ per share to new investors.
Furthermore, we may choose to raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities due to market conditions or strategic considerations even if we believe we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. New investors will experience further dilution if any of our outstanding options or warrants are exercised, new options are issued and exercised under our equity incentive plans or we issue additional shares of common stock, other equity securities or convertible debt securities in the future.
The information set forth below should be read in conjunction with the "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" section of this prospectus and with our financial statements and notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus. The selected financial data in this section are not intended to replace the financial statements and are qualified in their entirety by the financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus.
The selected statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) data for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2011 and 2012 have been derived from our audited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. The selected statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) data for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013 and the balance sheet data as of March 31,June 30, 2013 have been derived from our unaudited financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. In our opinion, these unaudited financial statements have been prepared on a basis consistent with our audited financial statements and contain all adjustments, consisting only of normal and recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair presentation of such financial data. Our historical results for any prior period are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected in any future period, and our interim period results are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for a full year or any other interim period.
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(in thousands, except per share data) | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Collaboration revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | 2,375 | $ | 12,515 | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | 4,765 | $ | 35,406 | ||||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 4,760 | 5,558 | 949 | 2,497 | 4,760 | 5,558 | 2,599 | 6,034 | ||||||||||||||||||
Contract manufacturing | 1,745 | — | — | — | 1,745 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Total revenue | 80,911 | 15,254 | 3,324 | 15,012 | 80,911 | 15,254 | 7,364 | 41,440 | ||||||||||||||||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Research and development | 32,713 | 35,319 | 8,212 | 8,780 | 32,713 | 35,319 | 16,925 | 17,691 | ||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 8,142 | 8,824 | 2,045 | 3,096 | 8,142 | 8,824 | 4,276 | 6,461 | ||||||||||||||||||
Cost of contract manufacturing revenue | 1,500 | — | — | — | 1,500 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 42,355 | 44,143 | 10,257 | 11,876 | 42,355 | 44,143 | 21,201 | 24,152 | ||||||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (6,933 | ) | 3,136 | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (13,837 | ) | 17,288 | ||||||||||||||
Total other expense, net | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (655 | ) | (1,489 | ) | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (1,151 | ) | (2,563 | ) | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.20 | $ | (6.21 | ) | $ | (1.50 | ) | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | 0.80 | $ | (24.84 | ) | $ | (11.91 | ) | $ | 0.19 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 0.19 | $ | (6.21 | ) | $ | (1.50 | ) | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | 0.78 | $ | (24.84 | ) | $ | (11.91 | ) | $ | 0.17 | |||||
Weighted-average number of common shares used in computing net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 9,313 | 9,605 | 9,579 | 9,740 | 2,328 | 2,401 | 2,395 | 2,437 | ||||||||||||||||||
Diluted | 10,863 | 9,605 | 9,579 | 9,740 | 2,716 | 2,401 | 2,395 | 4,434 | ||||||||||||||||||
Pro forma net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders(1): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||
Diluted | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||
Pro forma weighted-average number of common shares used in computing pro forma net income (loss) per share: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 82,267 | 81,859 | 21,155 | 21,045 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted | 82,267 | 88,651 | 21,155 | 23,062 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| | December 31, | | December 31, | | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | March 31, 2013 | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 65,037 | $ | 39,611 | $ | 38,510 | $ | 65,037 | $ | 39,611 | $ | 28,465 | ||||||||
Total assets | 73,789 | 49,212 | 48,447 | 73,789 | 49,212 | 40,023 | ||||||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 23,853 | 38,802 | 37,279 | 23,853 | 38,802 | 16,786 | ||||||||||||||
Long term deferred revenue | 33,350 | 6,760 | 6,670 | 33,350 | 6,760 | 6,668 | ||||||||||||||
Long-term notes payable | — | 16,525 | 14,717 | — | 16,525 | 12,869 | ||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | 1,046 | 1,422 | 1,022 | 1,046 | 1,422 | 1,009 | ||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 3,347 | 5,229 | 5,935 | 3,347 | 5,229 | 6,381 | ||||||||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock | 241,549 | 268,610 | 272,980 | 241,549 | 268,610 | 279,823 | ||||||||||||||
Total stockholder's deficit | (232,691 | ) | (290,973 | ) | (292,868 | ) | (232,691 | ) | (290,973 | ) | (286,100 | ) | ||||||||
MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations together with the section entitled "Selected Financial Data" and our financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. This discussion and other parts of this prospectus contain forward-looking statements that involve risk and uncertainties, such as statements of our plans, objectives, expectations and intentions. Our actual results could differ materially from those discussed in these forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, those discussed in the "Risk Factors" section.
Overview
We are a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of novel protein therapeutics for cancer and rare diseases. Our research focuses on the biology of the Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-b) protein superfamily, a large and diverse group of molecules that are key regulators in the growth and repair of tissues throughout the human body. We are leaders in understanding the biology of the TGF-b superfamily and in targeting these pathways to develop important new medicines. By coupling our discovery and development expertise, including our proprietary knowledge of the TGF-b superfamily, with our internal protein engineering and manufacturing capabilities, we have built a highly productive research & development platform that has generated innovative protein therapeutic candidates with novel mechanisms of action. These differentiated protein therapeutic candidates have the potential to significantly improve clinical outcomes for patients with cancer and rare diseases.
We have three internally discovered protein therapeutic candidates that are currently being studied in 12 ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, focused on cancer and rare diseases. Our two most advanced protein therapeutic candidates, sotatercept and ACE-536, promote red blood cell production through a novel mechanism. Together with our collaboration partner, Celgene Corporation, which we refer to as Celgene, we are developing sotatercept and ACE-536 to treat anemia and associated complications in patients withb-thalassemia and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), red blood cell disorders that are generally unresponsive to currently approved drugs. Our third clinical stage protein therapeutic candidate, dalantercept, is designed to inhibit blood vessel formation through a mechanism that is distinct from, and potentially synergistic with, the dominant class of cancer drugs that inhibit blood vessel formation, the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway inhibitors. We are developing dalantercept primarily for use in combination with these successful products to produce better outcomes for cancer patients.
We are developing sotatercept and ACE-536 through our exclusive worldwide collaborations with Celgene. As of January 1, 2013, Celgene became responsible for paying 100% of worldwide development costs for both programs. We may receive up to $567.0 million of potential development, regulatory and commercial milestone payments still outstanding and, if these protein therapeutic candidates are commercialized, we will receive a royalty on net sales in the low-to-mid 20% range. We also will co-promote sotatercept and ACE-536 in North America, if approved, for which our commercialization costs will be entirely funded by Celgene. We have not entered into a partnership for dalantercept and retain worldwide rights to this program.
To date, our operations have been primarily funded by $105.1 million in equity investments from venture investors, $39.2 million in equity investments from our partners and $186.5$188.9 million in upfront payments, milestones, and net research and development payments from our strategic partners.
We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses over at least the next several years. We expect our expenses will increase substantially in connection with our ongoing activities, as we:
We will not generate revenue from product sales unless and until we or a partner successfully complete development and obtain regulatory approval for one or more of our protein therapeutic candidates, which we expect will take a number of years and is subject to significant uncertainty. All current and future development and commercialization costs for sotatercept and ACE-536 are paid by Celgene. If we obtain regulatory approval for dalantercept or any future protein therapeutic candidate, we expect to incur significant commercialization expenses related to product sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution to the extent that such costs are not paid by future partners. We will seek to fund our operations through the sale of equity, debt financings or other sources, including potential additional collaborations. However, we may be unable to raise additional funds or enter into such other arrangements when needed on favorable terms, or at all. If we fail to raise capital or enter into such other arrangements as, and when, needed, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development or commercialization of one or more of our protein therapeutics.
Our ability to generate product revenue and become profitable depends upon our and our partners' ability to successfully commercialize products. We expect to incur losses for the foreseeable future, and we expect these losses to increase as we continue our development of, and seek regulatory approvals for, our protein therapeutics and potentially begin to commercialize any approved products. For a description of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with product development, see "Risk Factors".
Financial Operations Overview
Revenue
Collaboration Revenue
We have not generated any revenue from the sale of products. Our revenue to date has been predominantly derived from collaboration revenue, which includes license and milestone revenues and cost sharing revenue, generated through collaboration and license agreements with partners for the development and commercialization of our protein therapeutics. Cost sharing revenue represents amounts reimbursed by our collaboration partners for expenses incurred by us for research and development activities and, potentially, co-promotion activities, under our collaboration agreements. Cost sharing revenue is recognized in the period that the related activities are performed. To the extent that we reimburse collaborators for costs incurred in connection with activities performed by them, we record these costs as a reduction of cost-sharing revenue.
Contract Manufacturing Revenue
We have generated contract manufacturing revenue in the past but have no current contract manufacturing arrangements. Contract manufacturing revenue consists of revenue received for producing bulk drug substance for third parties other than our partners.
Costs and Expenses
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs directly incurred by us for the development of our protein therapeutic candidates, which include:
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Costs for certain development activities are recognized based on an evaluation of the progress to completion of specific tasks using information and data provided to us by our vendors and our clinical sites.
We cannot determine with certainty the duration and completion costs of the current or future clinical trials of our protein therapeutic candidates or if, when, or to what extent we will generate revenues from the commercialization and sale of any of our protein therapeutic candidates for which we or any partner obtain regulatory approval. We or our partners may never succeed in achieving regulatory approval for any of our protein therapeutic candidates. The duration, costs and timing of clinical trials and development of our protein therapeutic candidates will depend on a variety of factors, including:
A change in the outcome of any of these variables with respect to the development of a protein therapeutic candidate could mean a significant change in the costs and timing associated with the development of that protein therapeutic candidate. For example, if the FDA, or another regulatory authority were to require us to conduct clinical trials beyond those that we currently anticipate will be required for the completion of the clinical development of protein therapeutics, or if we experience significant delays in the enrollment in any clinical trials, we could be required to expend significant additional financial resources and time on the completion of clinical development.
From inception through March 31,June 30, 2013, we have incurred $260.0$268.9 million in research and development expenses. We plan to increase our research and development expenses for the foreseeable future as we continue the development of our TGF-b platform protein therapeutics, the discovery and development of preclinical protein therapeutics, and the development of sotatercept, ACE-536 and dalantercept. Beginning January 1, 2013, expenses associated with sotatercept and ACE-536 are reimbursed 100% by Celgene. These reimbursements are recorded as revenue. Of the 12 Phase 2 clinical trials that are underway for sotatercept, ACE-536 and dalantercept, we are expensing the costs of six clinical trials of ACE-536 and dalantercept, of which the two for ACE-536 are reimbursed by Celgene.
We manage certain activities such as clinical trial operations, manufacture of protein therapeutic candidates, and preclinical animal toxicology studies through third-party CROs. The only costs we track by each protein therapeutic candidate are external costs such as services provided to us by CROs, manufacturing of preclinical and clinical drug substance, and other outsourced research and development expenses. We do not assign or allocate to individual development programs internal costs such as salaries and benefits, facilities costs, lab supplies and the costs of preclinical research and studies. Our external research and development expenses for sotatercept, ACE-536, dalantercept and ACE-031 (for which development was suspended in April 2013) during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013 are as follows:
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(in thousands) | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Sotatercept(1) | $ | 974 | $ | 6 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 974 | $ | 6 | $ | 6 | $ | 1 | ||||||||||
ACE-536(1) | 681 | 2,885 | 579 | 703 | 681 | 2,885 | 1,136 | 1,750 | ||||||||||||||||||
Dalantercept | 1,323 | 3,422 | 465 | 1,076 | 1,323 | 3,422 | 1,229 | 2,152 | ||||||||||||||||||
ACE-031(2) | 4,240 | 3,453 | 309 | 502 | 4,240 | 3,453 | 1,418 | 1,001 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total direct research and development expenses | 7,218 | 9,766 | 1,353 | 2,281 | 7,218 | 9,766 | 3,789 | 4,904 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other expenses(3) | 25,495 | 25,553 | 6,859 | 6,499 | 25,495 | 25,553 | 13,136 | 12,787 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total research and development expenses | $ | 32,713 | $ | 35,319 | $ | 8,212 | $ | 8,780 | $ | 32,713 | $ | 35,319 | $ | 16,925 | $ | 17,691 | ||||||||||
Contract Manufacturing Expenses
Contract manufacturing expenses consist primarily of costs incurred for the production of bulk drug substance for third parties other than our partners. The costs generally include employee-related expenses including salary and benefits, direct materials and overhead costs including rent, depreciation, utilities, facility maintenance and insurance. We do not have any current contract manufacturing arrangements.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and related costs for personnel, including stock-based compensation and travel expenses for our employees in executive, operational, finance and human resource functions and other general and administrative expenses including directors' fees and professional fees for accounting and legal services.
After the completion of this offering, we will experience increased expenses related to audit, legal, regulatory and tax-related services associated with maintaining compliance with exchange listing and Securities and Exchange Commission requirements, director and officer insurance premiums, and investor relations costs associated with being a public company. We anticipate that our general and administrative expenses will increase in the future as we increase our headcount to support our continued research and development and potential commercialization of our protein therapeutics. Additionally, if and when we believe regulatory approval of a protein therapeutic candidate appears likely, to the extent that we are undertaking commercialization of such protein therapeutic candidate ourselves, we anticipate an increase in payroll and related expenses as a result of our preparation for commercial operations.
Other Expense, Net
Other expense, net consists primarily of interest expense from our venture debt facility, interest income earned on cash and cash equivalents, and the re-measurement gain or loss associated with the change in the fair value of our preferred stock and common stock warrant liabilities.
We use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate the fair value of the warrants. We base the estimates in the Black-Scholes option pricing model, in part, on subjective assumptions, including stock price volatility, risk-free interest rate, dividend yield, and the fair value of the preferred stock or common stock underlying the warrants.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our management's discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based on our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, and expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in our financial statements. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments, including those related to revenue recognition, accrued expenses and stock-based compensation. We also utilize significant estimates and assumptions in determining the fair value of our common stock and the fair value of our liability-classified warrants to purchase preferred stock and common stock. We base our estimates on historical experience, known trends and events, and various other factors that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
While our significant accounting policies are described in more detail in the notes to our financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus, we believe the following accounting policies to be most critical to the judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
We have primarily generated revenue through collaboration arrangements with strategic partners for the development and commercialization of our protein therapeutics.
We recognize revenue in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 605,Revenue Recognition. Accordingly, revenue is recognized for each unit of accounting when all of the following criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the fee is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectability is reasonably assured.
Amounts received prior to satisfying the revenue recognition criteria are recorded as deferred revenue on our balance sheets. Amounts expected to be recognized as revenue within the 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, current portion and amounts not expected to be recognized as revenue within the 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, net of current portion.
Under collaboration agreements, we may receive payments for non-refundable up-front fees, milestone payments upon achieving significant development events, research and development reimbursements and royalties on future product sales. These payments are received in connection with the deliverables contained in the arrangements which may include (1) licenses, or options to obtain licenses, to our technology, (2) research and development activities performed for the collaboration partner, (3) participation on joint committees and (4) manufacturing clinical or preclinical material.
Effective January 1, 2011, we adopted Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2009-13,Multiple-Deliverable Revenue Arrangements, which amends ASC Topic 605-25,Revenue Recognition—Multiple Element Arrangements. This guidance applies to new arrangements as well as existing agreements that are significantly modified after January 1, 2011.
The application of the multiple element guidance requires subjective determinations, and requires management to make judgments about the individual deliverables, and whether such deliverables are separable from the other aspects of the contractual relationship. Deliverables are considered separate units of accounting provided that: (1) the delivered item(s) has value to the customer on a stand-alone basis and (2) if the arrangement includes a general right of return relative to the delivered item(s), delivery or performance of the undelivered item(s) is considered probable and substantially in our control. In determining the units of accounting, management evaluates certain criteria, including whether the deliverables have stand-alone value, based on the consideration of the relevant facts and circumstances for each arrangement, such as the research, manufacturing and commercialization capabilities of the collaboration partner and the availability of the associated expertise in the general marketplace. In addition, we consider whether the collaboration partner can use the other deliverable(s) for their intended purpose without the receipt of the remaining element(s), whether the value of the deliverable is dependent on the undelivered item(s), and whether there are other vendors that can provide the undelivered element(s).
Arrangement consideration that is fixed or determinable is allocated among the separate units of accounting using the relative selling price method, and the applicable revenue recognition criteria, as described above, are applied to each of the separate units of accounting in determining the appropriate period or pattern of recognition. We determine the estimated selling price for deliverables within each agreement using vendor-specific objective evidence (VSOE) of selling price, if available, third-party evidence (TPE) of selling price if VSOE is not available, or management's best estimate of selling price (BESP) if neither VSOE nor TPE is available. Subsequent to the adoption of ASU 2009-13, we typically use BESP to estimate the selling price of the deliverables. Determining the BESP for a unit of accounting requires significant judgment. In developing the BESP for a unit of accounting, we consider applicable market conditions and relevant entity-specific factors, including factors that were contemplated in negotiating the agreement with the customer and estimated costs. We validate the BESP for units of accounting by evaluating whether changes in the key assumptions used to determine the BESP will have a significant effect on the allocation of arrangement consideration between multiple units of accounting.
Our agreements may contain options which provide the collaboration partner the right to obtain additional licenses. Options are considered substantive if, at the inception of the arrangement, we are at risk as to whether the collaboration partner will choose to exercise the option. Factors that we consider in evaluating whether an option is substantive include the overall objective of the arrangement, the benefit the collaborator might obtain from the arrangement without exercising the
option, the cost to exercise the option and the likelihood that the option will be exercised. For arrangements under which an option is considered substantive, we do not consider the item underlying the option to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and the associated option fees are not included in allocable arrangement consideration, assuming the option is not priced at a significant and incremental discount. Conversely, for arrangements under which an option is not considered substantive or if an option is priced at a significant and incremental discount, we would consider the item underlying the option to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and a corresponding amount would be included in allocable arrangement consideration.
We typically receive up-front, non-refundable payments when licensing our intellectual property in conjunction with a research and development agreement. When we believe the license to our intellectual property has stand-alone value, we generally recognize revenue attributed to the license upon delivery. When we believe the license to our intellectual property does not have stand-alone value from the other deliverables to be provided in the arrangement, we generally recognize revenue attributed to the license on a straight-line basis over our contractual or estimated performance period, which is typically the term of our research and development or manufacturing obligations. We continually evaluate these periods, and will adjust the period of revenue recognition if circumstances change.
Research and development funding is recognized as revenue in the period that the related services are performed. When we act as the principal under our collaboration arrangements, we record payments received for the reimbursement of research and development costs as cost-sharing revenue. To the extent that we reimburse the collaborator for costs incurred, we record these costs as a reduction of cost-sharing revenue.
We periodically review the basis for our estimates, and we may change the estimates if circumstances change. These changes can significantly increase or decrease the amount of revenue recognized. As we apply our policy to our collaboration arrangements we make judgments which affected the pattern of revenue recognition. For instance, in our arrangement with Celgene, we are obligated to provide research and development services. We are recognizing revenue over the estimated period of our performance of the research and development services, which was estimated to end in December 2014, the expected completion date of the proof-of-concept trials for ACE-536 under the Celgene collaboration. Another instance relates to our arrangement with Shire AG, where in April 2013, we and Shire determined not to further advance the development of ACE-031 or back-up compounds and Shire terminated our collaboration agreement effective as of June 30, 2013.
In addition to up-front payments and research and development funding, we may also be entitled to milestone payments that are contingent upon achievement of a predefined objective. At the inception of each arrangement that includes milestone payments, we evaluate whether the milestone is substantive and at-risk. This evaluation includes an assessment of whether (1) the consideration is commensurate with either the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, or the enhancement of the value of the delivered item(s) as a result of a specific outcome resulting at least in part from the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, (2) the consideration relates solely to past performance, and (3) the consideration is reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. We evaluate factors such as the scientific, regulatory, commercial and other risks that must be overcome to achieve the respective milestone, the level of effort and investment required to achieve the respective milestone, and whether the milestone consideration is reasonable relative to all deliverables and payment terms in the arrangement in making this assessment. On the milestone achievement date, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met and the milestone is deemed substantive and at-risk, we recognize the payment as license and milestone revenue. For milestones that are not deemed substantive and at-risk, where payment is reasonably assured, we recognize the milestone payment over the remaining service period.
Sales and commercial milestones and royalties will be recognized when and if earned, provided collectability is reasonably assured.
Clinical Trial Accruals and Related Expenses
We accrue and expense costs for clinical trial activities performed by third parties, including CROs and clinical investigators, based upon estimates made as of the reporting date of the work completed over the life of the individual study in accordance with agreements established with CROs and clinical trial sites. Some CROs invoice us on a monthly basis, while others invoice upon achievement of milestones and the expense is recorded as services are rendered. We determine the estimates of clinical activities incurred at the end of each reporting period through discussion with internal personnel and outside service providers as to the progress or stage of completion of trials or services, as of the end of each reporting period, pursuant to contracts with numerous clinical trial centers and CROs and the agreed upon fee to be paid for such services. The significant factors considered in estimating accruals include the number of patients enrolled and the percentage of work completed to date. Costs of setting up clinical trial sites for participation in the trials that are paid for in advance are expensed over the estimated set-up period. While the set-up periods vary from one arrangement to another, such set-up periods generally take approximately three months. Set-up activities include clinical site identification, institutional review board, or IRB, submissions, regulatory submissions, clinical investigator kick-off meetings and pre-study site visits. Clinical trial site costs related to patient enrollments are accrued as patients are entered into the trial.
Stock-Based Compensation
We account for our stock-based awards in accordance with ASC Topic 718,Compensation—Stock Compensation, or ASC 718, which requires all stock-based payments to employees, including grants of employee stock options and modifications to existing stock options, to be recognized in the statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) based on their fair values. We recognize the compensation cost of awards subject to service-based vesting conditions over the requisite service period, which is generally equal to the vesting term. For awards subject to both performance and service-based vesting conditions, we recognize compensation cost using an accelerated recognition method when it is probable that the performance condition will be achieved. We account for stock-based awards to non-employees using the fair value method. Stock options granted to non-employees are subject to periodic revaluation over their vesting terms and stock-based compensation cost is recognized using an accelerated recognition method.
We estimate the fair value of our stock-based awards to employees and non-employees using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which requires the input of highly subjective assumptions, including (1) the expected volatility of our stock, (2) the expected term of the award, (3) the risk-free interest rate and (4) expected dividends. Due to the lack of a public market for our common stock and resulting lack of company-specific historical and implied volatility data, we have based our estimate of expected volatility on the historical volatility of a group of similar companies that are publicly traded. For these analyses, we have selected companies with characteristics that we believe are comparable to ours, including enterprise value, risk profiles, position within the industry, and with historical share price information sufficient to meet the expected life of the stock-based awards. We compute the historical volatility data using the daily closing prices for the selected companies' shares during the equivalent period as the calculated expected term of our stock-based awards. We will continue to apply this process until a sufficient amount of historical information regarding the volatility of our own stock price becomes available. We have estimated the expected life of our employee stock options using the "simplified" method, whereby, the expected life equals the average of the vesting term and the original contractual term of the option. The risk-free interest rates for periods within the expected life of the option are based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect during the period the options were granted.
We also estimate forfeitures at the time of grant, and revise those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from estimates. We use historical data to estimate pre-vesting option forfeitures to the extent that actual forfeitures differ from our estimates, the difference is recorded as a cumulative adjustment in the period the estimates were revised. Stock-based compensation expense recognized in the financial statements is based on awards that are ultimately expected to vest.
We have computed the estimated fair value of stock options at the date of grant using the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
Expected volatility | 66.0 | % | 69.0 | % | 66.9 | % | n/a | 66.0 | % | 69.0 | % | 66.9 | % | 70.3 | % | |||||||||
Expected term (in years) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | n/a | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.1 | % | 0.9 | % | 1.2 | % | n/a | 1.1 | % | 0.9 | % | 0.9 | % | 1.4 | % | |||||||||
Expected dividend yield | — | — | — | n/a | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation totaled approximately $1.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 and $0.4$0.9 million for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013. As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had $4.0$3.6 million of unrecognized compensation expense, net of related forfeiture estimates, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average remaining vesting period of approximately 2.72.5 years. We expect the impact of our stock-based compensation expense for stock-based awards granted to employees and non-employees to grow in future periods due to the potential increases in the value of our common stock and headcount.
The following table summarizes by grant date the number of shares of common stock underlying stock options granted from January 1, 2012 through March 31,June 30, 2013, as well as the associated per share exercise price and the retrospective estimated fair value per share of our common stock on the date of grant:
Date of Grant | Number of shares subject to awards | Exercise price per share(1) | Retrospective fair value per share on date of grant(2) | Number of Shares Subject to Awards | Exercise Price Per Share(1) | Retrospective Fair Value Per Share on Date of Grant(2) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
March 1, 2012 | 91,000 | $ | 1.32 | $ | 1.45 | 22,750 | $ | 5.28 | $ | 5.80 | ||||||||||
June 7, 2012 | 954,000 | $ | 1.32 | $ | 1.53 | 238,500 | $ | 5.28 | $ | 6.12 | ||||||||||
September 6, 2012 | 81,000 | $ | 1.32 | $ | 1.53 | 20,250 | $ | 5.28 | $ | 6.12 | ||||||||||
November 13, 2012 | 1,000,000 | $ | 1.32 | $ | 1.97 | 250,000 | $ | 5.28 | $ | 7.88 | ||||||||||
December 12, 2012 | 762,000 | $ | 1.78 | $ | 1.97 | 190,500 | $ | 7.12 | $ | 7.88 | ||||||||||
June 6, 2013 | 8,750 | $ | 9.64 | n/a | ||||||||||||||||
Determination of the Fair Value of Common Stock on Grant Dates
Our audit committee recommended, and our board of directors determined, the fair value of our common stock considering, in part, the work of an independent third party valuation specialist. The board determined the estimated per share fair value of our common stock at various dates considering contemporaneous valuations performed in accordance with the guidance outlined in the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants Practice Aid,Valuation of Privately-Held Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation, also known as the Practice Aid. We engaged the valuation firm to perform contemporaneous valuations as of December 21, 2011, December 12, 2012, and March 31, 2013 and June 6, 2013. In conducting the contemporaneous valuations, the valuation firm considered all objective and subjective factors that we believed to be relevant for each valuation conducted, including our best estimate of our business condition, prospects and operating performance at each valuation date. Within the contemporaneous valuations performed, a range of factors, assumptions and methodologies were used. The significant factors included:
The dates of our contemporaneous valuations have not always coincided with the dates of our stock option grants. In determining the exercise prices of the stock options set forth in the table above, our board of directors considered, among other things, the most recent contemporaneous valuations of our common stock and our assessment of additional objective and subjective factors we believed were relevant as of the grant date. The additional factors considered when determining any changes in fair value between the most recent contemporaneous valuation and the grant dates included our stage of research and preclinical development, our operating and financial performance and current business conditions.
There are significant judgments and estimates inherent in the determination of the fair value of our common stock. These judgments and estimates include assumptions regarding our future operating performance, the time to completing an IPO or other liquidity event, the related company valuations associated with such events, and the determinations of the appropriate valuation methods at each valuation date. If we had made different assumptions, our stock-based compensation expense, net
income (loss) and net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders could have been different.
In early May 2013, based on the progress of our clinical pipeline, overall capital market conditions and the improving market for biopharmaceutical IPOs, our board of directors determined and directed management to begin preparation and submission of a confidential draft registration statement for an IPO. We selected underwriters and held an organizational meeting in June 2013. We believe these events increased the probability of an early IPO scenario and therefore in connection with the preparation of our financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2012, we retrospectively re-assessed the estimated fair value of our common stock for financial reporting purposes at interim dates between the contemporaneous valuations where there were stock option grants. For these interim periods, we adjusted the fair value based on market conditions, progress made in our development programs and whether we achieved company milestones.
Common Stock Valuation Methodologies
These contemporaneous and retrospective valuations were prepared in accordance with the guidelines in the Practice Aid, which prescribes several valuation approaches for setting the value of an enterprise, such as the cost, market and income approaches, and various methodologies for allocating the value of an enterprise to its common stock. We generally used the market approach, in particular the guideline company and precedent transaction methodologies, based on inputs from comparable public companies' equity valuations and comparable acquisition transactions, to estimate the enterprise value of our company.
Methods Used to Allocate Our Enterprise Value to Classes of Securities
In accordance with the Practice Aid, we considered the various methods for allocating the enterprise value across our classes and series of capital stock to determine the fair value of our common stock at each valuation date. The methods we considered consisted of the following:
We used the PWERM to allocate the enterprise values to the common stock for each valuation date. Under this method, the value of the common stock is estimated based upon an analysis of future values for our company assuming various investment outcomes, the timing of which is based, in part, on the plans of our board of directors and management. Under this approach, share value is derived from the probability-weighted present value of expected future investment returns, considering each of the possible outcomes available to us, as well as the economic and control rights of each share class. The fair value of our common stock was estimated using a probability-weighted analysis of the present value of the returns afforded to common stockholders under several future stockholder exit or liquidity event scenarios, either through (1) an IPO; (2) an acquisition or sale of our company at a premium to the
cumulative liquidation preference of the preferred stockholders; or (3) a sale of our company at a value below the cumulative liquidation preference of the preferred stockholders.
The individual stockholder exit or liquidity scenarios considered in each analysis depended on the specific facts and circumstances, internal and external, present as of each valuation date. The future projected enterprise value used to value our common stock in the IPO scenarios and the sale scenarios were estimated by application of the market approach based on certain key assumptions, including the following:
The present values of our common stock under each scenario were then calculated by applying a risk-adjusted discount rate and then probability-weighting those present values based on our estimate of the relative probability of each scenario.
Finally, the estimated fair value of our common stock was reduced by a discount for lack of marketability. A discount is appropriate because our common stock is unregistered, and the holder of a minority interest in the common stock may not influence the timing of a liquidity event for our company. Our estimate of the appropriate discount for lack of marketability took into consideration put option methodologies consistent with the Practice Aid. We selected a smaller discount after taking into account empirical studies of restricted stock issued by publicly-traded companies.
March 1, 2012 Common Stock Valuation
We performed a retrospective valuation of our common stock as of March 1, 2012, and determined the fair value to be $1.45$5.80 per share as of that date. For the retrospective valuation at March 1, 2012, significant assumptions for the PWERM included the probability of occurrence of each scenario, timing to the liquidity event, discount rate and discount for lack of marketability. The specific facts and circumstances considered in assessing these key valuation assumptions included those noted in the following table:
March 1, 2012 Major Assumptions | IPO Short Term | IPO Long Term | Sale— High | Sale— Low | Sales Below Liquidation Preference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Probability of scenario | 20 | % | 20 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | 10 | % | ||||||
Discount for lack of marketability | — | — | 5 | % | 5 | % | n/a | |||||||||
Timeline to liquidity (in years) | 1.8 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.0 | |||||||||||
Discount rate—common stock | 30 | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | n/a | |||||||
In applying the market approach to estimate our future enterprise values under the IPO exit scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 1.8 years under a short term scenario or 2.3 years in the IPO long term scenario. We considered our development pipeline and our collaborations as of the valuation date. The selected enterprise value in the short-term scenario was based on the pre-money IPO market data for transactions between the third quartile and the maximum of the observed range. The selected aggregate enterprise value in the long-term scenario was based on consideration of the high-end of the observed range of transaction values and assumed our most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression.
In applying the market approach to estimate our aggregate future enterprise values under the two sale scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 2.5 years
for the high-case scenario and the low-case scenario. The selected enterprise value utilized in the low-case scenario considered the median of the observed range of comparable transaction values. The selected enterprise value for the high-case scenario was based on the comparable transaction values between the third quartile and the high-end of the observed range. We assumed we would make significant progress and achieve certain key milestones with respect to our development pipeline by the time a sale was consummated, including assumptions that our three most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression, one or more additional compounds would enter Phase 1 trials and several other compounds would be nominated for pre-Investigational New Drug activities.
In the sale at a price below liquidation preference scenario, a sale of our existing research and intellectual property was assumed in 3.0 years, at a value that would not allow the preferred stockholders to realize their full liquidation preference resulting in no value to common stockholders.
Under all the exit scenarios considered in the PWERM, the fair value of our common stock was calculated using the estimated future enterprise valuations, a risk-adjusted discount rate of 30.0% based on the inherent risk of a hypothetical investment in our common stock, and a discount for lack of marketability which was 0% in the IPO scenarios and 5% in all other assumed liquidity events. The risk-adjusted discount rate was based on consideration of the weighted-average cost of capital for comparable biotechnology companies adjusted for company specific risk factors, the venture capital rates of return detailed in the Practice Aid, and an analysis of other quantitative and qualitative factors considered pertinent to estimating the discount rate. The resulting value, which represented the estimated fair value of our common stock as of March 1, 2012, was $1.45$5.80 per share.
June 7, 2012 and September 6, 2012 Common Stock Valuation
We performed a retrospective valuation of our common stock as of June 7, 2012, and determined the fair value to be $1.53$6.12 per share as of that date. For the retrospective valuation at June 7, 2012, significant assumptions for the PWERM included the probability of occurrence of each scenario, timing to the liquidity event, discount rate and discount for lack of marketability. The specific facts and circumstances in assessing these key valuation assumptions included those noted in the following table:
June 7, 2012 Major Assumptions | IPO Short Term | IPO Long Term | Sale— High | Sale— Low | Sales Below Liquidation Preference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Probability of scenario | 25 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | 20 | % | 5 | % | ||||||
Discount for lack of marketability | — | — | 5 | % | 5 | % | n/a | |||||||||
Timeline to liquidity (in years) | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.0 | |||||||||||
Discount rate—common stock | 30 | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | n/a | |||||||
In applying the market approach to estimate our future enterprise values under the IPO exit scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 1.5 years under a short term scenario or 2.0 years in the IPO long term scenario. We considered our development pipeline and our collaborations as of the valuation date. The selected enterprise value in the short-term scenario was based on the pre-money IPO market data for transactions between the third quartile and the maximum of the observed range. The selected aggregate enterprise value in the long-term scenario was based on consideration of the high-end of the observed range of transaction values and assumed our most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression.
In applying the market approach to estimate our aggregate future enterprise values under the two sale scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 2.5 years for the high-case scenario and the low-case scenario. The selected enterprise value utilized in the low-case scenario considered the median of the observed range of comparable transaction values. The selected enterprise value for the high-case scenario was based on the comparable transaction values
between the third quartile and the high-end of the observed range. We assumed we would make significant progress and achieve certain key milestones with respect to our development pipeline by the time a sale was consummated, including assumptions that our three most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression, one or more additional compounds would enter Phase 1 trials and several other compounds would be nominated for pre-IND activities.
In the sale at a price below liquidation preference scenario, a sale of our existing research and intellectual property was assumed in 3.0 years, at a value that would not allow the preferred stockholders to realize their full liquidation preference resulting in no value to common stockholders.
Under all the exit scenarios considered in the PWERM, the fair value of our common stock was calculated using the estimated future enterprise valuations, a risk-adjusted discount rate of 30% based on the inherent risk of a hypothetical investment in our common stock, and a discount for lack of marketability which was decreased to 0% in the long-term IPO scenarios and remained 5% in all other assumed liquidity events. The risk-adjusted discount rate was based on consideration of the weighted-average cost of capital for comparable biotechnology companies adjusted for company specific risk factors, the venture capital rates of return detailed in the Practice Aid, and an analysis of other quantitative and qualitative factors considered pertinent to estimating the discount rate. The resulting value, which represented the estimated fair value of our common stock as of June 7, 2012, was $1.53$6.12 per share.
The estimated per share fair value of our common stock calculated in our valuation as of June 7, 2012 of $1.53$6.12 per share increased from the March 1, 2012 valuation of $1.45$5.80 per share primarily due to the following factors:
As a result of the fact that the number of stock option grants were not significant on September 6, 2012, we utilized the June 7, 2012 valuation to determine the retrospective fair value of our common stock in September 2012.
November 13, 2012 and December 12, 2012 Common Stock Valuation
We performed a retrospective valuation of our common stock as of November 13, 2012, and determined the fair value to be $1.97$7.88 per share as of that date. For the retrospective valuation at November 13, 2012, significant assumptions for the PWERM included the probability of occurrence of each scenario, timing to the liquidity event, discount rate and discount for lack of marketability. The specific facts and circumstances considered in assessing these key valuation assumptions included those noted in the following table:
November 13, 2012 Major Assumptions | IPO Short Term | IPO Long Term | Sale— High | Sale— Low | Sales Below Liquidation Preference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Probability of scenario | 30 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | 15 | % | 5 | % | ||||||
Discount for lack of marketability | — | — | 5 | % | 5 | % | n/a | |||||||||
Timeline to liquidity (in years) | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | |||||||||||
Discount rate—common stock | 30 | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | n/a | |||||||
In applying the market approach to estimate our future enterprise values under the IPO exit scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 1.0 years under a short term scenario or 1.5 years in the IPO long term scenario due to improvement in IPO market conditions for companies in our industry. We considered our development pipeline and our collaborations as of the valuation date. The selected enterprise value in the short-term scenario was based on the pre-money IPO market data for transactions between the third quartile and the maximum of the observed range. The selected aggregate enterprise value in the long-term scenario was based on consideration of the high-end of the observed range of transaction values and assumed our most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression.
In applying the market approach to estimate our aggregate future enterprise values under the two sale scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 2.0 years for the high-case scenario and the low-case scenario. The selected enterprise value utilized in the low-case scenario considered the median of the observed range of comparable transaction values. The selected enterprise value for the high-case scenario was based on the comparable transaction values between the third quartile and the high-end of the observed range. We assumed we would make significant progress and achieve certain key milestones with respect to our development pipeline by the time a sale was consummated, including assumptions that our three most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression, one or more additional compounds would enter Phase 1 trials and several other compounds would be nominated for pre-IND activities.
In the sale at a price below liquidation preference scenario, a sale of our existing research and intellectual property was assumed in 2.5 years, at a value that would not allow the preferred stockholders to realize their full liquidation preference resulting in no value to common stockholders.
Under all the exit scenarios considered in the PWERM, the fair value of our common stock was calculated using the estimated future enterprise valuations, a lower risk-adjusted discount rate of 25% based on a reduction in the inherent risk of a hypothetical investment in our common stock, and a discount for lack of marketability which remained 0% in the IPO scenarios and remained 5% in all other assumed liquidity events. The risk-adjusted discount rate was based on consideration of the weighted-average cost of capital for comparable biotechnology companies adjusted for company specific risk factors, the venture capital rates of return detailed in the Practice Aid, and an analysis of other quantitative and qualitative factors considered pertinent to estimating the discount rate. The resulting value, which represented the estimated fair value of our common stock as of November 13, 2012, was $1.97$7.88 per share.
The estimated per share fair value of our common stock calculated in our valuation as of November 13, 2012 of $1.97$7.88 per share increased from the June 7, 2012 retrospective valuation estimate of $1.49$6.12 per share primarily due to the following factors:
As a result of the fact that there were no material changes to our business from November 13, 2012 to December 12, 2012, we utilized the November 13, 2012 valuation to determine the exercise price of option grants in December.
March 31, 2013 Common Stock Valuation
We performed a retrospectivecontemporaneous valuation of our common stock as of March 31, 2013, and determined the fair value to be $2.17$8.68 per share as of that date. For the retrospective valuation at March 31, 2013, significant assumptions for the PWERM included the probability of occurrence of each scenario, timing
scenario, timing to the liquidity event, discount rate and discount for lack of marketability. The specific facts and circumstances considered in assessing these key valuation assumptions included those noted in the following table:
March 31, 2013 Major Assumptions | IPO Short Term | IPO Long Term | Sale— High | Sale— Low | Sales Below Liquidation Preference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Probability of scenario | 50 | % | 10 | % | 20 | % | 15 | % | 5 | % | ||||||
Discount for lack of marketability | — | — | 5 | % | 5 | % | n/a | |||||||||
Timeline to liquidity (in years) | 0.6 | 1.0 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.3 | |||||||||||
Discount rate—common stock | 25 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | n/a | |||||||
In applying the market approach to estimate our future enterprise values under the IPO exit scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 7 months under a short term scenario and 1.0 years in the IPO long term scenario. We considered our development pipeline and our collaborations as of the valuation date. The selected enterprise value in the short-term scenario was based on the pre-money IPO market data for transactions between the third quartile and the maximum of the observed range. The selected aggregate enterprise value in the long-term scenario was based on consideration of the high-end of the observed range of transaction values and assumed our most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression.
In applying the market approach to estimate our aggregate future enterprise values under the two trade sale scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 1.8 years for the high-case scenario and 2.0 years the low-case scenario. The selected enterprise value utilized in the low-case scenario considered the median of the observed range of comparable transaction values. The selected enterprise value for the high-case scenario was based on the comparable transaction values between the third quartile and the high-end of the observed range. We assumed we would make significant progress and achieve certain key milestones with respect to our development pipeline by the time a trade sale was consummated, including assumptions that our three most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression, one or more additional compounds would enter Phase 1 trials and several other compounds would be nominated for pre-IND activities.
In the sale at a price below liquidation preference scenario, a sale of our existing research and intellectual property was assumed in 2.3 years, at a value that would not allow the preferred stockholders to realize their full liquidation preference resulting in no value to common stockholders.
Under all the exit scenarios considered in the PWERM, the fair value of our common stock was calculated using the estimated future enterprise valuations, a lower risk-adjusted discount rate of 25% based on a reduction to the inherent risk of a hypothetical investment in our common stock, and a discount for lack of marketability which remained at 0% in the IPO scenarios and remained 5% in all other assumed liquidity events. The risk-adjusted discount rate was based on consideration of the weighted-average cost of capital for comparable biotechnology companies adjusted for company specific risk factors, the venture capital rates of return detailed in the Practice Aid, and an analysis of other quantitative and qualitative factors considered pertinent to estimating the discount rate. The resulting value, which represented the estimated fair value of our common stock as of March 31, 2013, was $2.17$8.68 per share.
The estimated per share fair value of our common stock calculated in our valuation as of March 31, 2013 of $2.17$8.68 per share increased from the November 13, 2012 valuation of $1.97$7.88 per share primarily due to the following factors:
June 6, 2013 Common Stock Valuation
We performed a contemporaneous valuation of our common stock as of June 6, 2013, and determined the fair value to be $9.64 per share as of that date.
For the contemporaneous valuation at June 6, 2013, significant assumptions for the PWERM included the probability of occurrence of each scenario, timing to the liquidity event, discount rate and discount for lack of marketability. The specific facts and circumstances considered in assessing these key valuation assumptions included those noted in the following table:
June 6, 2013 Major Assumptions | IPO Short Term | IPO Long Term | Sale— High | Sale— Low | Sales Below Liquidation Preference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Probability of scenario | 60 | % | 10 | % | 15 | % | 10 | % | 5 | % | ||||||
Discount for lack of marketability | — | — | 5 | % | 5 | % | n/a | |||||||||
Timeline to liquidity (in years) | 0.4 | 0.8 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.1 | |||||||||||
Discount rate—common stock | 25 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | 25 | % | n/a | |||||||
In applying the market approach to estimate our future enterprise values under the IPO exit scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 5 months under a short term scenario and 10 months in the IPO long term scenario. We considered our development pipeline and our collaborations as of the valuation date. The selected enterprise value in the short-term scenario was based on the pre-money IPO market data for transactions between the third quartile and the maximum of the observed range. The selected aggregate enterprise value in the long-term scenario was based on consideration of the high-end of the observed range of transaction values and assumed our most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression.
In applying the market approach to estimate our aggregate future enterprise values under the two trade sale scenarios, as described previously, it was assumed that a liquidity event would occur in 1.6 years for the high-case scenario and 1.8 years the low-case scenario. The selected enterprise value utilized in the low-case scenario considered the median of the observed range of comparable transaction values. The selected enterprise value for the high-case scenario was based on the comparable transaction values between the third quartile and the high-end of the observed range. We assumed we would make significant progress and achieve certain key milestones with respect to our development pipeline by the time a trade sale was consummated, including assumptions that our three most advanced development projects would continue their positive clinical progression, one or more additional compounds would enter Phase 1 trials and several other compounds would be nominated for pre-IND activities.
In the sale at a price below liquidation preference scenario, a sale of our existing research and intellectual property was assumed in 2.1 years, at a value that would not allow the preferred stockholders to realize their full liquidation preference resulting in no value to common stockholders.
Under all the exit scenarios considered in the PWERM, the fair value of our common stock was calculated using the estimated future enterprise valuations, a lower risk-adjusted discount rate of 25% based on a reduction to the inherent risk of a hypothetical investment in our common stock, and a discount for lack of marketability which remained at 0% in the IPO scenarios and remained 5% in all
other assumed liquidity events. The risk-adjusted discount rate was based on consideration of the weighted-average cost of capital for comparable biotechnology companies adjusted for company specific risk factors, the venture capital rates of return detailed in the Practice Aid, and an analysis of other quantitative and qualitative factors considered pertinent to estimating the discount rate. The resulting value, which represented the estimated fair value of our common stock as of June 6, 2013, was $9.64 per share.
The estimated per share fair value of our common stock calculated in our valuation as of June 6, 2013 of $9.64 per share increased from the March 31, 2013 valuation of $8.68 per share primarily due to the following factors:
Initial public offering price
In consultation with the underwriters for this offering, we determined the estimated price range for this offering, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus. In comparison, our estimate of the fair value of our common stock was $9.64 per share as of June 6, 2013. As is typical in initial public offerings, the estimated price range for this offering was not derived using a formal determination of fair value, but was determined by negotiation between us and the underwriters. Among the factors that were considered in setting this range were the following:
The midpoint of the estimated price range for this offering reflects a significant increase over the estimated valuation as of June 6, 2013 of $9.64 per share. The price range for this offering is in excess of our prior valuations. We believe the difference is due to the following factors:
There are significant additional judgments and estimates inherent in the determination of these valuations. These judgments and estimates include assumptions regarding our future performance, including the successful enrollment and completion of our clinical studies as well as the determination of the appropriate valuation methods. If we had made different assumptions, our stock-based compensation expense could have been different. The foregoing valuation methodologies are not the only methodologies available and they will not be used to value our common stock once this offering is complete. We cannot make assurances as to any particular valuation for our common stock. Accordingly, investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on the foregoing valuation methodologies as an indicator of future stock prices.
Warrants to Purchase Preferred Stock and Common Stock
As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had warrants outstanding to purchase shares of Series B, Series C-1 and Series D-1 preferred stock and common stock. Freestanding warrants that are related to the purchase of redeemable preferred stock are classified as liabilities and recorded at fair value regardless of the timing of the redemption feature or the redemption price or the likelihood of redemption. The warrants are subject to re-measurement at each balance sheet date and any change in fair value is recognized as a component of other income (expense), net. We measure the fair value of our warrants to purchase preferred stock using a Black-Scholes option pricing model. The warrants to purchase shares of our common stock contain a provision requiring an adjustment to the number of shares in the event we issue common stock, or securities convertible into or exercisable for common stock, at a price
per share lower than the warrant exercise price. The anti-dilution feature requires the warrants to be classified as liabilities and measured at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized as a component of other income (expense). The fair value of the warrants to purchase common stock on the date of issuance and on each re-measurement date for those warrants to purchase common stock are classified as liabilities and are estimated using the Monte Carlo simulation framework. The Company estimated that there would be up to three future financing events over the remaining life of the warrants to purchase common stock. Any modifications to the warrant liabilities are recorded in earnings during the period of the modification. The significant assumptions used in estimating the fair value of our warrant liabilities include the exercise price, volatility of the stock underlying the warrant, risk-free interest rate, estimated fair value of the stock underlying the warrant, and the estimated life of the warrant.
The consummation of this offering will result in the conversion of all classes of our preferred stock into common stock. Upon such conversion of the underlying classes of preferred stock, pursuant to the terms of the preferred stock warrants, the remaining warrants to purchase Series B, C-1 and D-1 preferred stock will be classified as a component of equity and no longer be subject to re-measurement.
Emerging Growth Company Status
The Jumpstart our Business Startups Act of 2012, or the JOBS Act, permits an "emerging growth company" such as us to take advantage of an extended transition period to comply with new or revised accounting standards applicable to public companies. We are choosing to "opt out" of this provision and, as a result, we will comply with new or revised accounting standards as required when they are adopted. This decision to opt out of the extended transition period under the JOBS Act is irrevocable.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the ThreeSix Months Ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013
| | Three months ended March 31, | | Six Months Ended June 30, | | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Increase (Decrease) | Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Collaboration revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 2,375 | $ | 12,515 | $ | 10,140 | $ | 4,765 | $ | 35,406 | $ | 30,641 | ||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 949 | 2,497 | 1,548 | 2,599 | 6,034 | 3,435 | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue | 3,324 | 15,012 | 11,688 | 7,364 | 41,440 | 34,076 | ||||||||||||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Research and development | 8,212 | 8,780 | 568 | 16,925 | 17,691 | 766 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 2,045 | 3,096 | 1,051 | 4,276 | 6,461 | 2,185 | ||||||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 10,257 | 11,876 | 1,619 | 21,201 | 24,152 | 2,951 | ||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | (6,933 | ) | 3,136 | 10,069 | (13,837 | ) | 17,288 | 31,125 | ||||||||||||
Other income (expense), net | (655 | ) | (1,489 | ) | (834 | ) | (1,151 | ) | (2,563 | ) | (1,412 | ) | ||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 9,235 | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | $ | 29,713 | ||||||
Revenue. We recognized revenue of $15.0$41.4 million in the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, compared to $3.3$7.4 million in the same period in 2012. This $11.7$34.1 million increase was primarily due to the $10.0 million milestone payment received in connection with our Celgene collaboration for the first patient dosed in a Phase 2 trial in ACE-536.ACE-536 and recognizing an additional $20.5 million of deferred revenue because Shire ended our collaboration as of June 30, 2013. The remaining increase was
primarily due to an increase in net cost-sharing revenue of $1.5$3.4 million due primarily to Celgene assuming 100% of the costs of development for these protein therapeutic candidates as of January 1, 2013.
The following table shows revenue from all sources for the periods presented.
| | Three months ended March 31, | | Six Months Ended June 30, | | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Increase (Decrease) | Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
Collaboration revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Celgene: | ||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 470 | $ | 10,631 | $ | 10,161 | $ | 955 | $ | 11,084 | $ | 10,129 | ||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 487 | 2,166 | 1,679 | 1,260 | 5,329 | 4,069 | ||||||||||||||
Total Celgene | 957 | 12,797 | 11,840 | 2,215 | 16,413 | 14,198 | ||||||||||||||
Shire: | ||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | 1,905 | 1,884 | (21 | ) | 3,810 | 24,322 | 20,512 | |||||||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 462 | 331 | (131 | ) | 1,339 | 705 | (634 | ) | ||||||||||||
| �� | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total Shire | 2,367 | 2,215 | (152 | ) | 5,149 | 25,027 | 19,878 | |||||||||||||
Total collaboration revenue | 3,324 | 15,012 | 11,688 | 7,364 | 41,440 | 34,076 | ||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 3,324 | $ | 15,012 | $ | 11,688 | $ | 7,364 | $ | 41,440 | $ | 34,076 | ||||||||
Research and Development Expenses. Research and development expenses were $8.8$17.7 million in the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, compared to $8.2$16.9 million in the same period in 2012. This $0.6$0.8 million increase was primarily due to an increase in expenses associated with clinical activity totaling $1.2$2.4 million, partially offset by a reduction in preclinical animal studies totaling $0.6$1.6 million.
General and Administrative Expenses. General and administrative expenses were $3.1$6.5 million in the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, compared to $2.0$4.3 million for the same period in 2012. This $1.1$2.2 million increase was primarily related to higher professional fees for legal services in connection with our litigation (see "Business—Litigation") and for legal and financial consulting services in connection with business development activities totaling $0.8$1.5 million and higher total compensation expenses totaling $0.3$0.7 million.
Other Expense, Net. Other expense, net was $1.5$2.6 million in the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, compared to $0.7$1.2 million for the same period in 2012. This $0.8$1.4 million increase was primarily due to higher expense associated with the increase in fair value of the liability for warrants to purchase common stock of $0.5$0.8 million and an increase in interest expense of $0.3$0.7 million due to a higher average outstanding debt balance in the first quarterhalf of 2013.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2011 and 2012
| | Year ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, | | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Increase (Decrease) | Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Collaboration revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | (64,710 | ) | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | (64,710 | ) | ||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 4,760 | 5,558 | 798 | 4,760 | 5,558 | 798 | ||||||||||||||
Contract manufacturing | 1,745 | — | (1,745 | ) | 1,745 | — | (1,745 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total revenue | 80,911 | 15,254 | (65,657 | ) | 80,911 | 15,254 | (65,657 | ) | ||||||||||||
Costs and operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Research and development | 32,713 | 35,319 | 2,606 | 32,713 | 35,319 | 2,606 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 8,142 | 8,824 | 682 | 8,142 | 8,824 | 682 | ||||||||||||||
Cost of contract manufacturing revenue | 1,500 | — | (1,500 | ) | 1,500 | — | (1,500 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 42,355 | 44,143 | 1,788 | 42,355 | 44,143 | 1,788 | ||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (67,445 | ) | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (67,445 | ) | ||||||||||
Other expense, net | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (1,403 | ) | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (1,403 | ) | ||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (68,848 | ) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (68,848 | ) | ||||
Revenue. We recognized revenue of $15.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to $80.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2011. The $65.6 million decrease in revenue in 2012 was primarily due to a decrease of $64.7 million in license and milestone revenue, because during 2011, upon signing the ACE-536 Celgene collaboration and amending the sotatercept agreement, we recognized upfront payments and deferred revenue totaling $54.8 million. During 2011, we also recognized the remaining $2.4 million of deferred revenue from the Alkermes collaboration. Also, in 2012 we did not recognize any milestone payments compared to $7.0 million during 2011. The decrease in license and milestone revenue was offset by higher 2012 cost-sharing revenue due primarily to lower reimbursements paid to Shire for ACE-031. We also recognized $1.7 million for a contract manufacturing project during 2011.
The following table shows revenue from all sources for the periods presented.
| | Year ended December 31, | | Year Ended December 31, | | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Increase (Decrease) | Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
Collaboration revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Celgene: | ||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 63,607 | $ | 2,035 | $ | (61,572 | ) | $ | 63,607 | $ | 2,035 | $ | (61,572 | ) | ||||||
Cost-sharing, net | (121 | ) | 2,879 | 3,000 | (121 | ) | 2,879 | 3,000 | ||||||||||||
Total Celgene | 63,486 | 4,914 | (58,572 | ) | 63,486 | 4,914 | (58,572 | ) | ||||||||||||
Shire: | ||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | 8,392 | 7,661 | (731 | ) | 8,392 | 7,661 | (731 | ) | ||||||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 4,148 | 2,679 | (1,469 | ) | 4,148 | 2,679 | (1,469 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total Shire | 12,540 | 10,340 | (2,200 | ) | 12,540 | 10,340 | (2,200 | ) | ||||||||||||
Alkermes: | ||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | 2,407 | — | (2,407 | ) | 2,407 | — | (2,407 | ) | ||||||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 733 | — | (733 | ) | 733 | — | (733 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total Alkermes | 3,140 | — | (3,140 | ) | 3,140 | — | (3,140 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total collaboration revenue | 79,166 | 15,254 | (63,912 | ) | 79,166 | 15,254 | (63,912 | ) | ||||||||||||
Contract manufacturing revenue | 1,745 | — | (1,745 | ) | 1,745 | — | (1,745 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 80,911 | $ | 15,254 | $ | (65,657 | ) | $ | 80,911 | $ | 15,254 | $ | (65,657 | ) | ||||||
Research and Development Expenses. Research and development expenses were $35.3 million in the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to $32.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2011. This $2.6 million increase was primarily due to increases in expenses related to preclinical animal toxicology studies of $2.6 million, patent-related legal services of $0.9 million, external testing of $0.6 million, clinical trial activities of $0.5 million, contract labor of $0.5 million, outsourced research of $0.3 million and management bonuses of $0.3 million partially offset by decreases in expenses related to depreciation of $1.3 million, contract manufacturing of $0.7 million, supplies of $0.4 million, and in-licensing of $0.5 million.
General and Administrative Expenses. General and administrative expenses were $8.8 million in the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to $8.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2011. This $0.7 million increase was primarily related to higher professional fees for legal costs of $0.4 million in connection with litigation activities and higher compensation costs of $0.3 million.
Cost of Contract Manufacturing Revenue. There was no cost of contract manufacturing revenue for the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2011. This decrease was due to there being no contract manufacturing services provided during 2012.
Other Expense, Net. Other expense, net was $3.7 million in the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to $2.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2011. The increase was primarily due to a $1.8 million increase in fair value of the liability for warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock and common stock.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We have incurred losses and cumulative negative cash flows from operations since our inception in June 2003, and as of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had an accumulated deficit of $292.9$286.1 million. We anticipate that we will continue to incur losses for at least the next several years. We expect that our research and development and general and administrative expenses will continue to increase and, as a result, we will need additional capital to fund our operations, which we may raise through a combination of the sale of equity, debt financings or other sources, including potential additional collaborations.
To date, our operations have been funded by $105.1 million in equity investments from venture investors, $39.2 million in equity investments from our partners, and $186.5$188.9 million in upfront payments, milestones, and net research and development payments from our partners.
As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had $38.5$28.5 million in cash and cash equivalents. Cash in excess of immediate requirements is invested in accordance with our investment policy, primarily with a view to liquidity and capital preservation. Currently, our funds are held in money market mutual funds consisting of U.S. government-backed securities.
We entered into a new venture debt facility on June 7, 2012 and, as of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had $20.0 million in venture debt outstanding. After an interest-only period, we began paying down principal on the debt facility in July 2013. Interest accrues at a rate of 8.5% per annum and is payable monthly. The debt facility also included a closing fee of $0.2 million and is also subject to an additional deferred payment of $1.2 million with the final payment. We are amortizing the cost over the 42 months of loan resulting in an effective interest rate of approximately 11.8%. We are not subject to any financial covenants and the debt facility is secured by a lien on all of our property as of, or acquired after, June 7, 2012, except for intellectual property. The debt facility matures in December 2015.
Cash Flows
The following table sets forth the primary sources and uses of cash for each of the periods set forth below:
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(in thousands) | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating activities | $ | 9,056 | $ | (38,884 | ) | $ | (11,821 | ) | $ | (735 | ) | $ | 9,056 | $ | (38,884 | ) | $ | (21,509 | ) | $ | (10,747 | ) | ||||
Investing activities | (27 | ) | (441 | ) | (8 | ) | (80 | ) | (27 | ) | (441 | ) | (302 | ) | (125 | ) | ||||||||||
Financing activities | 21,092 | 13,899 | (2,460 | ) | (286 | ) | 21,092 | 13,899 | 13,757 | (274 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 30,121 | $ | (25,426 | ) | $ | (14,289 | ) | $ | (1,101 | ) | $ | 30,121 | $ | (25,426 | ) | $ | (8,054 | ) | $ | (11,146 | ) | ||||
Operating Activities. The significant decrease in net cash used in operating activities for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, compared to the three months ended March 31,June 30, 2012, is primarily due to the receipt of a $10.0 million milestone payment from Celgene in the first quarter of 2013. The significant decrease in cash provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to the year ended December 31, 2011, is primarily due to the upfront and milestone payments of $32.5 million related to the ACE-536 Agreement received during 2011.
Net cash used in operating activities was $0.7$10.7 million for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, and consisted primarily of net income of $1.6$14.7 million adjusted for non-cash items including an increase in fair value of warrants of $1.1$1.5 million, stock-based compensation expense of $0.4$0.9 million, depreciation and amortization of $0.4 million, forgiveness of the related party receivable of $0.2 million, and accretion of deferred interest of $0.1$0.2 million, offset by a net increase in operating assets and liabilitiesamortization of $4.1 million. The significant items in the change indeferred debt issuance costs of $0.2 million offset
operating assets and liabilities include a decrease in deferred revenue of $2.5 million due to the ongoing recognition of revenue deferred in connection with up-front payments for the Celgene and Shire collaboration agreements and a decrease in accrued expenses of $0.7 million. Other components of the change in operating assets and liabilities include an increase in prepaid expenses and other currents assets of $0.3 million, an increase in collaboration receivables of $0.2 million, a decrease in accounts payable of $0.2 million and a decrease in deferred rent of $0.1 million.
Net cash used in operating activities was $11.8 million for the three months ended March 31, 2012 and consisted primarily of a net loss of $7.6 million adjusted for non-cash items including an increase in the fair value of warrants of $0.5 million, stock-based compensation expense of $0.3 million, depreciation and amortization of $0.5 million and accretion of deferred interest of $0.1 million, andby a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities of $5.5$28.9 million. The significant items in the change in operating assets and liabilities include a decrease in deferred revenue of $2.4$25.4 million due primarily to the recognition of $22.4 million of deferred revenue for the Shire collaboration agreement which was terminated effective June 30, 2013. Other components of the change in operating assets and liabilities include a decrease in accrued expenses of $2.0 million, an increase in collaboration receivables of $1.6 million, an increase in accounts payable of $0.3 million and a decrease in deferred rent of $0.2 million.
Net cash used in operating activities was $21.5 million for the six months ended June 30, 2012 and consisted primarily of a net loss of $15.0 million adjusted for non-cash items including an increase in the fair value of warrants of $0.7 million, stock-based compensation expense of $0.5 million, depreciation and amortization of $0.8 million and accretion of deferred interest of $0.2 million, and a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities of $8.8 million. The significant items in the change in operating assets and liabilities include a decrease in deferred revenue of $4.8 million due to the ongoing recognition of revenue deferred in connection with up-front payments for the Celgene and Shire collaboration agreements, a decrease in accounts payable of $1.1$1.5 million and an increase in prepaid expenses and other current assets of $1.3$1.2 million. Other components of the change in operating assets and liabilities include an increase in collaboration receivables of $0.3$0.9 million, a decrease in accrued expenses of $0.3 million and a decrease in deferred rent of $0.1$0.2 million.
Net cash used in operating activities was $38.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 and is primarily due to a net loss of $32.6 million adjusted for non-cash items including an increase in the fair value of warrants of $2.3 million, stock-based compensation of $1.2 million, depreciation and amortization of $1.3 million, and accretion of deferred interest of $0.3 million and a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities of $11.5 million. The significant items in the change in operating assets and liabilities include a decrease in deferred revenue of $9.7 million due to the ongoing recognition of revenue deferred in connection with up-front payments for the Celgene and Shire collaboration agreements, a decrease in accounts payable of $1.3 million and an increase in collaboration receivables of $1.1 million, offset in part by an increase in accrued expenses of $1.6 million. Other components of the change in operating assets and liabilities include an increase in prepaid expenses and other current assets of $0.6 million and a decrease in deferred rent of $0.5 million.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $9.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2011 and is primarily due to net income of $36.3 million, which was impacted by non-cash items including depreciation and amortization of $3.1 million, stock-based compensation of $1.4 million, an increase in the fair value of warrants of $0.5 million, accretion of deferred interest of $0.3 million and amortization of debt discount of $0.2 million and a net decrease in operating assets and liabilities of $32.8 million. The significant items in the change in operating assets and liabilities include a decrease in deferred revenue of $35.1 million due primarily to the acceleration of deferred revenue associated with the Celgene collaboration upfront payments as a result of the modification of the collaboration agreement, as well as a decrease in accrued expenses of $2.8 million, offset in part by a decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets of $2.6 million and a decrease in collaboration receivables of $1.8 million. Other components of the change in operating assets and liabilities include an increase in accounts payable of $0.3 million and an increase in deferred rent of $0.2 million.
Investing Activities. Net cash used in investing activities was $0.1 million for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013 and relates to$0.3 million for the purchasesix months ended June 30, 2012 and consisted of purchases of property and equipment. Net cash used in investing activities for the three months ended March 31, 2012 wasde minimis.
Net cash used in investing activities was $27,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011 and $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 and consisted of purchases of property and equipment.
Financing Activities. Net cash used inprovided by financing activities was $2.5$13.8 million for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and consisted primarilyof $19.9 million in net proceeds received from the drawdown of our new venture debt line in June 2012, offset by $6.2 million of principal payments made to pay down aour previous
venture debt facility.line. Net cash used in financing activities was $0.3 million for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013 and consisted primarily of a payment we made to repurchase and retire redeemable convertible preferred stock, common stock and warrants to purchase common stock.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $21.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2011 and consisted primarily of $30.4 million of net proceeds received from the sale of 9,704,756 shares of our Series F preferred stock, as well as $0.2 million received from the exercise of stock options and warrants to purchase common stock, offset in part by $9.5 million of principal payments made to pay down a previous venture debt facility.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $13.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2012 and consisted of $19.9 million in net proceeds received from the drawdown of our new venture debt line in June 2012, as well as $0.2 million received from the exercise of stock options and warrants to purchase common stock, offset by $6.2 million of principal payments made to pay down our previous venture debt line.
Operating Capital Requirements
To date, we have not generated any revenue from product sales. We do not know when, or if, we will generate any revenue from product sales. We will not generate revenue from product sales unless and until we or our partners obtain regulatory approval of and commercialize one of our current or future protein therapeutics. We anticipate that we will continue to generate losses for the foreseeable future, and we expect the losses to increase as we continue the development of, and seek and obtain regulatory approvals for, dalantercept and any future protein therapeutics, and begin to commercialize any approved products. We are subject to all of the risks incident in the development of protein therapeutics, and we may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other unknown factors that may adversely affect our business. Upon the closing of this offering, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company. We anticipate that we will need additional funding in connection with our continuing operations.
We believe that the net proceeds we receive from this offering and the concurrent private placement, together with receipt of anticipated milestone payments and our existing cash and cash equivalents will be sufficient to fund our projected operating requirements through the first half of 2015. However, we will require additional capital for the further development of our existing protein therapeutic candidates and may also need to raise additional funds sooner to pursue other development activities related to additional protein therapeutic candidates.
Until we can generate a sufficient amount of revenue from our products, if ever, we expect to fund our operations through a combination of equity offerings, or debt financings or other sources including potential additional collaborations. Additional capital may not be available on favorable terms, if at all. If we are unable to raise additional capital in sufficient amounts or on terms acceptable to us, we may have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue the development or commercialization of one or more of our protein therapeutic candidates. If we raise additional funds through the issuance of additional debt or equity securities, it could result in dilution to our existing stockholders and increased fixed payment obligations, and these securities may have rights senior to those of our common stock. If we incur indebtedness, we could become subject to covenants that would restrict our operations and potentially impair our competitiveness, such as limitations on our ability to incur additional debt, limitations on our ability to acquire, sell or license intellectual property rights and other operating restrictions that could adversely impact our ability to conduct our business. We may not be able to
enter into new collaboration arrangements for any of our proprietary protein therapeutic candidates. Any of these events could significantly harm our business, financial condition and prospects.
Our forecast of the period of time through which our financial resources will be adequate to support our operations is a forward-looking statement and involves risks and uncertainties, and actual
results could vary as a result of a number of factors. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and we could utilize our available capital resources sooner than we currently expect. Our future funding requirements, both near and long-term, will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The following is a summary of our long-term contractual cash obligations as of December 31, 2012.
(in thousands) | Total | Less than 1 Year | 1 to 3 Years | 3 to 5 Years | More than 5 Years | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Operating lease obligations(1) | $ | 23,979 | $ | 4,522 | $ | 8,628 | $ | 7,876 | $ | 2,953 | ||||||
Less: sublease income(2) | (1,407 | ) | (583 | ) | (824 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Venture debt facility(3) | 24,320 | 5,304 | 19,016 | — | — | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 46,892 | $ | 9,243 | $ | 26,820 | $ | 7,876 | $ | 2,953 | ||||||
We also have obligations to make future payments to third party licensors that become due and payable on the achievement of certain development, regulatory and commercial milestones. We have not included these commitments on our balance sheet or in the table above because the achievement and timing of these milestones is not fixed or determinable. These commitments include the following:
We enter into contracts in the normal course of business with CROs for clinical trials and clinical supply manufacturing and with vendors for preclinical safety and research studies, research supplies and other services and products for operating purposes. These contracts generally provide for termination on notice, and therefore are cancelable contracts and not included in the table of contractual obligations and commitments.
Net Operating Loss (NOL) Carryforwards
We have deferred tax assets of approximately $68.2 million as of December 31, 2012, which have been fully offset by a valuation allowance due to uncertainties surrounding our ability to realize these tax benefits. The deferred tax assets are primarily composed of federal and state tax net operating loss,
or NOL, carryforwards and research and development tax credit carryforwards. As of December 31, 2012, we had federal NOL carryforwards of approximately $93.3 million and state NOL carryforwards of $75.1 million available to reduce future taxable income, if any. These federal NOL carryforwards expire at various times through 2032 and the state NOL carryforwards expire at various times through 2032. In general, if we experience a greater than 50 percent aggregate change in ownership of certain significant stockholders over a three-year period, or a Section 382 ownership change, utilization of our pre-change NOL carryforwards are subject to an annual limitation under Section 382 of the Internal
Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and similar state laws. Such limitations may result in expiration of a portion of the NOL carryforwards before utilization and may be substantial. If we experience a Section 382 ownership change in connection with this offering or as a result of future changes in our stock ownership, some of which changes are outside our control, the tax benefits related to the NOL carryforwards may be limited or lost.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have during the periods presented, and we do not currently have, any off-balance sheet arrangements, as defined in the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risks
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates. As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had cash and cash equivalents of $38.5$28.5 million. Our cash equivalents are invested in money market mutual funds consisting of U.S. government-backed securities. Our primary exposure to market risk is interest rate sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates, particularly because our investments are in short-term securities. Due to the short-term duration of our investment portfolio and the low risk profile of our investments, an immediate 100 basis point change in interest rates would not have a material effect on the fair market value of our portfolio.
Overview
We are a clinical stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of novel protein therapeutics for cancer and rare diseases. Our research focuses on the biology of the Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-b) protein superfamily, a large and diverse group of molecules that are key regulators in the growth and repair of tissues throughout the human body. We are leaders in understanding the biology of the TGF-b superfamily and in targeting these pathways to develop important new medicines. By coupling our discovery and development expertise, including our proprietary knowledge of the TGF-b superfamily, with our internal protein engineering and manufacturing capabilities, we have built a highly productive discovery and development platform that has generated innovative protein therapeutic candidates with novel mechanisms of action. These differentiated protein therapeutic candidates have the potential to significantly improve clinical outcomes for patients with cancer and rare diseases.
We focus on discovering and developing protein therapeutics that target a group of approximately 30 secreted proteins, or ligands, that are collectively referred to as the TGF-b superfamily. These ligands bind to subsets of 12 different receptors on the surface of cells, triggering intra-cellular changes in gene expression that guide cell growth and differentiation. The TGF-b superfamily ligands and their receptors represent an under-explored and diverse set of drug targets with the potential to yield therapeutics that modulate the growth and repair of diseased cells and tissues.
We have three internally discovered protein therapeutic candidates that are currently being studied in 12 ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, focused on cancer and rare diseases. Our two most advanced protein therapeutic candidates, sotatercept and ACE-536, promote red blood cell production through a novel mechanism. Together with our collaboration partner, Celgene Corporation, we are developing sotatercept and ACE-536 to treat anemia and associated complications in patients withb-thalassemia and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS). These red blood cell disorders are generally unresponsive to currently approved drugs. Our third clinical stage protein therapeutic candidate, dalantercept, is designed to inhibit blood vessel formation through a mechanism that is distinct from, and potentially synergistic with, the dominant class of cancer drugs that inhibit blood vessel formation, the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway inhibitors. We are developing dalantercept primarily for use in combination with these products to produce better outcomes for cancer patients. We estimate that we have spent approximately $116.3 million on research and development from 2010 through 2012.
Sotatercept and ACE-536 have already shown promising biological activity in our initial clinical trials. We and Celgene have conducted six human clinical trials with sotatercept in over 160 healthy volunteers and cancer patients. We have conducted one clinical trial with ACE-536 in healthy volunteers. In these studies, both sotatercept and ACE-536 caused a dose-dependent increase in the number of red blood cells. Based on these results, we and Celgene have initiated Phase 2 clinical trials with each of these protein therapeutic candidates inb-thalassemia and MDS. In the ongoing trial of sotatercept in patients withb-thalassemia, we have observed encouraging, dose-dependent increases in hemoglobin in a subset of patients at the two lowest dose levels. We and Celgene plan to initiate Phase 3 clinical trials for one or both of these protein therapeutic candidates in one or both ofb-thalassemia and MDS by the end of 2014 or early 2015.
With respect to our third clinical stage protein therapeutic candidate, dalantercept, we have conducted a Phase 1 clinical trial and we are pursuing a program of ongoing Phase 2 trials. In our Phase 1 clinical trial in patients with advanced solid tumors, of the 29 evaluable patients treated, one had a partial response and 13 had stable disease, according to RECIST criteria. In our current Phase 2 program, we are studying the single agent activity of dalantercept in patients with advanced head and neck cancer, and we are studying dalantercept in combination with an approved VEGF pathway inhibitor in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.
We are developing sotatercept and ACE-536 through our exclusive worldwide collaborations with Celgene. As of January 1, 2013, Celgene became responsible for paying 100% of worldwide development costs for both programs. We may receive up to an additional $567.0 million of potential development, regulatory and commercial milestone payments and, if these protein therapeutic candidates are commercialized, we will receive a royalty on net sales in the low-to-mid 20% range. We will co-promote sotatercept and ACE-536, if approved, in North America for which our commercialization costs will be entirely funded by Celgene.
We have not entered into a partnership for dalantercept and retain worldwide rights to this program.
To date, our operations have been funded primarily by $105.1 million in equity investments from venture investors, $39.2 million in equity investments from our collaboration partners Celgene and Alkermes, Inc. ("Alkermes") and $186.5$188.9 million in upfront payments, milestones, and net research and development payments from our collaboration partners.
Our Strategy
Our goal is to be a leader in the discovery, development and commercialization of novel protein therapeutics for cancer and rare diseases. Key components of our strategy are:
The Acceleron Discovery Platform: Novel Approaches to Potent Biology
Since our founding, we have focused on developing protein therapeutics that target a group of approximately 30 secreted proteins, or ligands, that are collectively referred to as the TGF-b superfamily. These ligands bind to subsets of 12 different receptors on the surface of cells, triggering intra-cellular changes in gene expression that guide cell growth and differentiation. The TGF-b superfamily ligands and their receptors represent a diverse and underexplored set of drug targets with the potential to yield potent therapeutics for the growth and repair of diseased cells and tissues. Applying our proprietary discovery and development platform, including our knowledge of the biology of the TGF-b superfamily and its receptors, we have generated a robust pipeline of innovative clinical and preclinical protein therapeutic candidates targeting key mechanisms underlying cancer and rare diseases.
Our Focus—The TGF-b Superfamily
On a daily basis, the human body must orchestrate the growth and differentiation of cells to maintain and repair its cells and organ systems. Stem cells and precursor cells are undifferentiated cell types that reside in most tissues of the body. When tissue growth or regeneration is required, these undifferentiated cells divide and, through a series of intermediate stages, give rise to new, fully differentiated cells that build or repair the affected tissue. Decades of research have identified the TGF-b superfamily and its associated receptors as key regulators of the growth and differentiation of stem and precursor cells.
Until recently, regulation of the erythropoietin pathway was the primary therapeutic approach to stimulate red blood cell formation. Members of the TGF-b superfamily are now recognized as important regulators of red blood cell formation. We have shown that inhibition of members of the TGF-beta superfamily ameliorates anemia in mouse models ofb-thalassemia and MDS. Based on our findings, we are developing two protein therapeutic candidates, sotatercept and ACE-536, each of which is currently in Phase 2 clinical trials to treat patients with these diseases.
Members of the TGF-b superfamily also play a significant role in regulating blood vessel formation. We and our academic collaborators have shown that mice with a genetic defect in a particular receptor for members of the TGF-b superfamily are resistant to tumor growth due to reduced blood vessel formation in the tumor. We have used this insight to design our Phase 2 anti-angiogenic agent, dalantercept, for the treatment of cancer.
Members of the family are also significant regulators of muscle development. A genetic defect in a TGF-b superfamily ligand, known as myostatin, causes profound increases in skeletal muscle. A naturally occurring mutation in myostatin has been identified in animals, such as "double-muscled" breeds of cattle and in the "bully whippet" offspring of whippet racing dogs, which have been selectively bred to have increased muscle mass or function. Furthermore, a mutation in myostatin has been identified in a human family, members of which exhibit exceptional musculature and strength. We are actively working on preclinical programs to increase muscle mass and strength.
Ligands of the TGF-b superfamily cause these profound biological effects by altering gene expression in target cells. As shown in the illustration below, a ligand of the superfamily initiates intracellular signaling by binding to a receptor that is located on the surface of a target cell. Upon binding to the ligand, the receptor activates specific transcription factors inside the target cell, which
are called Smad proteins. The activated Smad proteins regulate gene expression and guide cellular growth and differentiation.
The TGF-b superfamily ligands are divided into subgroups termed the activins, the Growth and Differentiation Factors (GDFs), the Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs) and the TGF-b subgroup (for which the superfamily is named). Our clinical stage protein therapeutic candidates focus on the activin, GDF and BMP subgroups.
We believe that, by employing our proprietary discovery and development platform, we can design protein therapeutic candidates that alter TGF-b superfamily signaling and unlock the therapeutic potential of this group of proteins.
Acceleron Approach
By combining the powerful biology of the TGF-b superfamily with our discovery and development expertise and our internal protein engineering and manufacturing capabilities, we have built a robust clinical and preclinical pipeline of protein therapeutic candidates targeting key mechanisms underlying cancer and rare diseases.
We have taken a comprehensive, receptor-focused approach to access the biology of the TGF-b superfamily. We recognized that the 12 receptors for the superfamily act as control points for the ligands and therefore represent an attractive approach for pharmacological intervention. We have in-licensed patent rights for nine of the 12 receptors and systematically evaluated interactions between each receptor and a comprehensive panel of ligands. In the body, these ligands are naturally regulated by trap proteins that bind to the ligands thereby blocking ligand-receptor interactions and diminishing signaling in the cell. To mimic this natural regulatory approach, we have built our protein therapeutic candidates using the ligand-binding part of the receptors, depicted in the upper part of the figure below, as traps that capture the relevant groups of ligands in each biological process. We link the ligand-binding portion, the extracellular domain, of these receptors to the portion of a human antibody known as the Fc domain, depicted in the lower part of the figure below, which confers favorable pharmaceutical properties. The resulting "fused" proteins can be administered by simple intravenous or
subcutaneous injection and reside in the blood for sufficient periods of time to permit dosing on a weekly or monthly basis.
Protein therapeutics constructed this way are referred to as "receptor fusion proteins" or "ligand traps". Some of the most successful protein therapeutics on the market belong to this category including Enbrel® (etanercept), Eylea® (aflibercept) and Orencia® (abatacept).
As shown in the figure below, our receptor fusion proteins act as ligand traps by binding to ligands of the TGF-b superfamily, preventing those ligands from binding to the cell surface receptors, and thereby preventing activation of Smad proteins in the target cell.
To take full advantage of our proprietary discovery and development platform, we have developed an integrated set of technologies and capabilities to rapidly and cost-effectively create, test and advance multiple protein therapeutic candidates. Our protein engineering expertise allows us to create and optimize our receptor fusion proteins. We have developed the capability to generate recombinant cell lines that produce our protein therapeutic candidates, and assess the activity of these molecules in animals using our internal animal pharmacology facility or the capabilities of our academic collaborators. We have also invested in infrastructure to manufacture Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical material quickly and flexibly using our internal current good manufacturing practices, or cGMP, compliant protein production facility to support clinical development of our protein therapeutic candidates.
We use our integrated platform of research, development and manufacturing technologies to rapidly and cost-effectively create, test and advance our protein therapeutic candidates. Our robust clinical and preclinical pipeline is focused on areas of high-unmet medical need, particularly in the areas of cancer and rare diseases.
Our Product Pipeline
We have three clinical stage protein therapeutic candidates in twelve ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, of which three are Celgene-sponsored trials, four are Acceleron sponsored trials, three are investigator sponsored trials and two are collaborative group-sponsored trials.
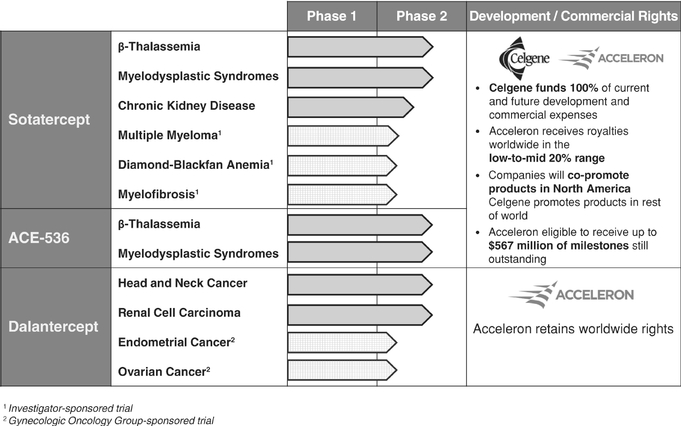
Sotatercept and ACE-536
Anemia in Patients withb-thalassemia and MDS
Erythropoiesis, the process by which precursor cells proliferate and differentiate to give rise to red blood cells, is one of the most important and active processes in human biology. The primary role of red blood cells is to carry and deliver oxygen to other cells throughout the body. At any given time, there are approximately 25 trillion red blood cells in normal adult circulation which account for roughly 25% of the body's total number of cells. The human body produces 2.4 million new red blood cells each second. Red blood cell formation starts in the bone marrow with cells referred to as red blood cell precursors. These precursor cells go through many rounds of cellular proliferation, combined with cellular differentiation, to become more specialized cells to carry out their role as mature, functional red blood cells. We believe this highly active process of red blood cell production is normally tightly controlled by positive and negative regulators of the erythropoietic process. Erythropoietin is a positive regulator that stimulates proliferation of early red blood cell precursor cells, the BFU-E and CFU-E cells depicted in the figure below. Based on our research, it is now recognized that certain ligands in the TGF-b superfamily are negative regulators of red blood cell precursors, starting with the Pro-E cells and those that follow, as depicted in the figure below. These members of the TGF-b superfamily
restrain the maturation of these precursors into later stage precursors and ultimately into functional red blood cells (RBCs).
Depiction of Normal Erythropoiesis
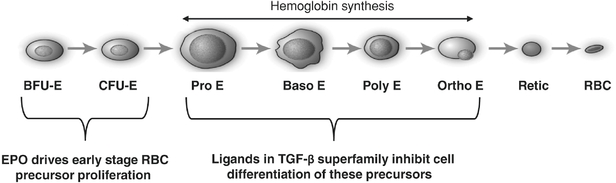
In certain diseases, the highly active process of red blood cell production does not function properly, leading to a reduction in the number of functional red blood cells, a condition known as anemia. Anemia in some disease settings is currently treated by the use of erythropoiesis stimulating agents, such as recombinant erythropoietin, that stimulate proliferation of early stage precursors of red blood cells. However, in certain diseases, such asb-thalassemia and MDS, anemia is caused by defects in the production of late stage red blood cell precursors, which is known as ineffective erythropoiesis.
Anemias caused by ineffective erythropoiesis are not well-treated by current therapies. As shown in the illustration below, ineffective erythropoiesis is characterized by an over-abundance of early stage red blood cell precursors and a decreased ability of late stage precursor cells to properly differentiate into healthy, functional red blood cells. The resulting anemia stimulates the body's overproduction of erythropoietin, which exacerbates the over-abundance of early stage precursors. Because the defective step in ineffective erythropoiesis lies downstream of the early stage precursors, the increase in the number of these cells fails to resolve the anemia.
Depiction of Ineffective Erythropoiesis
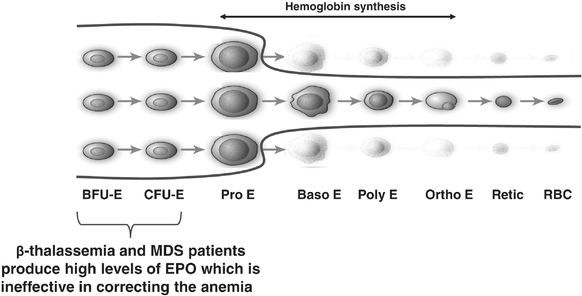
Based on our preclinical research, we believe that TGF-b superfamily ligands function as negative regulators of erythropoiesis by inhibiting the maturation of these early stage red blood cell precursors. Both sotatercept and ACE-536 are ligand traps designed to inhibit these negative regulators of late stage red blood cell precursors and promote their maturation into functional red blood cells.
We are developing sotatercept and ACE-536, through our collaborations with Celgene, as treatments for anemia in diseases in which erythropoiesis-stimulating agents are either not approved or are not well-suited to treat the underlying anemia. In diseases such asb-thalassemia and MDS in which anemia is caused by ineffective erythropoiesis, we believe both sotatercept and ACE-536 may help correct this defective process. Although similar in terms of their effects on red blood cells, there are differences in how these two protein therapeutic candidates bind to and inhibit ligands. Unlike ACE-536, sotatercept binds to and inhibits activin A, a TGF-b superfamily ligand, and has been shown to increase bone mass and inhibit the growth of tumors in mouse cancer models. Given its effects on bone, sotatercept is being studied in patients with chronic kidney disease, where it has the potential to treat both anemia and mineral and bone disorder. In addition, in preclinical studies, sotatercept inhibits the growth of myeloma cells. Therefore, sotatercept is also being studied in multiple myeloma patients to inhibit tumor growth and improve the anemia and the bone loss associated with the disease.
b-thalassemia
The thalassemias comprise a heterogeneous group of disorders arising from defects in the genes that encode the proteins that comprise hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a four-subunit protein complex formed of twoa-subunits and twob-subunits, each with an iron-containing heme group that binds to and carries oxygen molecules within red blood cells. There are two main classifications of thalassemia,a-thalassemia andb-thalassemia, depending on whether the genetic defect lies in the gene encoding thea-subunit or theb-subunit.b-thalassemia is particularly prevalent throughout the Mediterranean region, Middle East, and Southeast Asia, and, due to migration and immigration, is now a global disease. The Thalassaemia International Federation estimates that there are approximately 300,000 patients worldwide withb-thalassemia, approximately 20,000 of which are in the United States and Europe, who are dependent on frequent blood transfusions. We estimate that there are at least as manyb-thalassemia patients in the same regions who are not transfusion dependent and not included in these estimates. Many of these patients have hemoglobin levels that are approximately half that of normal individuals and experience significant complications of the disease.
Anemia ofb-thalassemia is primarily a result of ineffective erythropoiesis. The genetic defect leads to decreased production of theb-subunits of hemoglobin resulting in an excess amount of thea-subunits. The excess freea-subunits form aggregates, called hemichromes, which damage the maturing red blood cells, leading to increased cell death in the later stages of red blood cell maturation. These hemichromes are responsible for the ineffective erythropoiesis ofb-thalassemia.
Patients with the most severe form ofb-thalassemia produce few, if any,b-subunits, resulting in an increased amount of freea-subunits and consequently a high number of hemichromes. These patients typically present with life-threatening anemia within the first year of life and require regular and lifelong red blood cell transfusions, usually every 2 to 4 weeks. Because red blood cells contain significant amounts of iron, this intensive transfusion regimen contributes to a condition known as iron overload, which is the principal cause of mortality. Consequently, therapy to reduce iron overload, called iron chelation therapy, is also part of standard treatment in these patients and typically begins after patients have received approximately 20 transfusions during their lifetime. Iron chelation therapy alone costs between $25,000 and $40,000 per year and yet does not treat the underlying anemia. The course of the disease depends largely on whether patients are maintained on an adequate transfusion and iron chelation regimen. Poor compliance with transfusion and/or iron chelation is associated with a poor prognosis and shortened survival. However, even with the standard of care, patients are at risk of infection from transfusions as well as toxicities related to iron chelation therapy.
Patients with an intermediate form ofb-thalassemia, who are not necessarily dependent on frequent transfusions early in life, nevertheless suffer from a wide range of debilitating conditions. The ongoing ineffective erythropoiesis leads to various complications affecting a wide range of organ systems. By the second decade of life, most of these patients' hemoglobin levels have declined to the
6-8 g/dL range, or approximately half that of normal individuals. In an attempt to correct this chronic anemia, the body produces high levels of erythropoietin resulting in a continued stimulation of the early red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow. The number of these precursors grows to such an extent in the bone marrow that it leads to skeletal deformities, porosity of the long bones, and bone fractures. Splenomegaly, or enlargement of the spleen, is the result in part of continuous clearance by the spleen of the malformed red blood cells damaged by hemichromes. This commonly leads patients to require removal of their spleen, which in turn leads to worsening of other complications, such as blood clots. Iron overload is another significant complication even in the absence of red blood cell transfusions. This is due to increased intestinal iron absorption as a result of the ongoing ineffective erythropoiesis. Patients also suffer from various endocrine disorders due, in large part, to the accumulation of iron in the endocrine glands. Importantly, iron can also accumulate in the liver and heart, leading to severe complications such as liver fibrosis and heart failure.
No drug is approved to treat the anemia ofb-thalassemia. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is viewed as the only curative approach forb-thalassemia, although this option is limited by the availability of appropriate donors and by risks, including death, associated with the bone marrow transplant procedure. Consequently this treatment is used only in the most severely affected patients.
Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Myelodysplastic syndromes, or MDS, are a group of heterogeneous hematologic diseases characterized by abnormal proliferation and differentiation of blood precursor cells, including red blood cell precursors, in the bone marrow. This leads to peripheral reductions in red blood cells, often accompanied by decreases in white blood cells and platelets, as well as a risk of disease progression to acute myeloid leukemia. Anemia is present in the vast majority of MDS patients at the time of diagnosis. MDS is primarily a disease of the elderly, with 88% of cases diagnosed in individuals 60 years of age or older. Cancer surveillance databases estimate the annual incidence of MDS in the United States at 10,000 to 15,000 cases and the overall U.S. prevalence at approximately 30,000 to 60,000 patients.
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation represents the only treatment modality with curative potential, although the relatively high morbidity and mortality of this approach limits its use. Approximately 23% of MDS patients are categorized as intermediate-2 to high risk. These patients are typically treated with inhibitors of DNA methyltransferase such as Vidaza® (2012 U.S. sales of $324 million for MDS) or Dacogen® (2012 U.S. sales of $233 million for MDS). Of the remaining 77% of patients categorized as low to intermediate-1 risk, approximately 10% have a specific chromosomal mutation and are typically treated with Revlimid® (2012 U.S. sales of $257 million for MDS). The remaining 67% of patients typically receive red blood cell transfusions or erythropoiesis stimulating agents, though erythropoiesis stimulating agents are not approved by the FDA or the EMA for the treatment of anemia in MDS patients. Our internal market research estimates that erythropoiesis stimulating agents generate $500 to $700 million in annual U.S. sales from their use in this disease.
The anemia in MDS is primarily due to ineffective erythropoiesis and a significant number of MDS patients have serum erythropoietin levels substantially above the normal range, indicating that the anemia in these MDS patients is not a consequence of erythropoietin deficiency. Approximately 50% of MDS patients are unresponsive to the administration of recombinant erythropoietin and instead require red blood cell transfusions, which can increase the risk of infection and iron-overload related toxicities. Treatment-resistant anemia resulting from ineffective erythropoiesis is a major cause of morbidity in MDS patients.
Chronic Kidney Disease
Anemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease. Because erythropoietin is produced in the kidney, patients with chronic kidney disease do not produce adequate amounts of erythropoietin, which leads to anemia. Additional serious complications of chronic kidney disease include a condition known as chronic kidney disease mineral and bone disorder that occurs when the diseased kidneys fail to maintain proper levels of calcium and phosphorous in the blood, leading to abnormal bone hormone levels. It is a common problem in people with chronic kidney disease and affects almost all patients receiving dialysis. These patients' bones gradually become thin and weak and the risk of fractures increases. According to the United States Renal Data System, there are over 400,000 chronic kidney disease patients receiving dialysis in the United States. Erythropoiesis stimulating agents have been approved for this indication for over twenty years. Sotatercept has the potential to differentiate itself from erythropoiesis stimulating agents in this patient population because of its positive effects on bone metabolism observed following the administration of sotatercept in preclinical models, healthy volunteers and cancer patients.
Sotatercept Clinical and Preclinical Development
Sotatercept is a soluble receptor fusion protein consisting of the extracellular domain of the activin receptor type IIA (ActRIIA) linked to the Fc domain of human IgG1. Sotatercept acts as a protein trap for TGF-b superfamily ligands that signal through the ActRIIA receptor. Sotatercept has increased red blood cells in multiple clinical trials.
Ongoing Phase 2 Clinical Trials of Sotatercept
Our collaboration partner, Celgene, is currently conducting three Phase 2 clinical trials of sotatercept in patients withb-thalassemia, MDS and chronic kidney disease. We understand that Celgene plans to submit applications for orphan drug designation of sotatercept for the treatment ofb-thalassemia and for the treatment of MDS. Through collaborations with leading academic institutions, Celgene is also overseeing three investigator-sponsored trials.
Celgene-Sponsored Clinical Trials
b-thalassemia. Celgene is conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial of sotatercept designed as an ascending dose study to determine the safety and efficacy of sotatercept in adults withb-thalassemia. The dose levels to be studied are 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5 mg/kg given subcutaneously once every three weeks for a period of 6 cycles with continued treatment at the discretion of the investigator for up to 22 months. Each cohort includes six or more patients receiving a single dose level during the dose escalation phase, followed by an expansion phase at a selected dose level in up to ten additional patients. The first patient in the trial was first dosed in November 2012. Celgene has completed enrolling the 0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg cohorts and is now enrolling patients in the 0.5 mg/kg cohort. Based on the safety, tolerability and effects observed to date, Celgene is in the process of amending the protocol for the trial to potentially study higher dose levels. The primary outcome measure of the trial is to identify a safe dose level and to measure efficacy (1) in transfusion dependent patients by a reduction of transfusion burden by³20% compared to the pretreatment transfusion burden for each patient and (2) in non-transfusion dependent patients by an increase in hemoglobin level by³1 g/dL compared to the baseline hemoglobin, sustained for 12 weeks. This trial will also evaluate as exploratory endpoints the effects of sotatercept on iron overload, which is an important cause of morbidity and mortality associated withb-thalassemia, and bone metabolism. The trial is being conducted in six sites in Italy, France, and the United Kingdom and may enroll up to 28 patients.
As shown below, in the ongoing Phase 2 clinical trial of sotatercept inb-thalassemia patients, sotatercept has generated encouraging dose-dependent increases in hemoglobin levels in patients who
are non-transfusion dependent based on preliminary data from the two lowest dose levels. In these charts, each line represents an individual patient's change in hemoglobin levels from his or her baseline value. As shown in the charts below, one patient who received 0.1 mg/kg of sotatercept exhibited at least a 1 g/dL increase in hemoglobin from their baseline level while at a dose level of 0.3 mg/kg all five patients in the cohort achieved at least a 1 g/dL increase. As Celgene continues to dose escalate in this trial, we expect to see greater increases in hemoglobin levels; however, the number of patients in each cohort is limited, and preliminary results may not be indicative of future results. If this activity is confirmed with an acceptable safety profile, we and Celgene plan to initiate pivotal trial(s) inb-thalassemia by the end of 2014 or early 2015. At the dose levels that have been studied to date, we have not yet observed an effect in the transfusion dependent patients. Based on currently projected timelines, which are subject to change, we expect additional data from this clinical trial to become available as follows: additional interim data in the fourth quarter of 2013, data from the completed dose escalation portion of the clinical trial in the second quarter of 2014, and final data in the fourth quarter of 2014.
Hemoglobin Change from Baseline for Evaluable Non-Transfusion Dependent Patients
(Interim Data as of July 3, 2013)
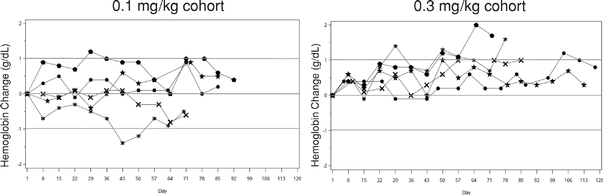
MDS. Celgene is conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial of sotatercept for the treatment of anemia in patients with low-or intermediate-1 risk MDS. The dose levels to be studied are 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5 mg/kg given subcutaneously once every three weeks for five cycles, and up to three additional cycles for late responders, with continued treatment at the discretion of the investigator. Each cohort may include up to 20 patients receiving a single dose level during the dose escalation phase, followed by an expansion phase at a selected dose level in up to 15 additional patients. The first patient in the trial was first dosed in December 2012. Celgene has currently completed the 0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg cohorts and is now enrolling patients in the 0.5 mg/kg cohort. Based on the safety, tolerability and effects observed to date, Celgene is in the process of amending the protocol for this trial to potentially study higher dose levels. The primary outcome measure is erythroid hematological improvement (HI-E). For patients who require transfusions of <4 units of red blood cells in the eight weeks prior to dosing, HI-E is an increase in hemoglobin of³1.5 g/dL sustained over a period³8 weeks in the absence of red blood cell transfusions. For subjects that require transfusions of³4 units of red blood cells in the eight weeks prior to dosing, HI-E is a decrease of³4 units of red blood cells transfused over a period of eight weeks compared to the number of units transfused in the eight weeks prior to treatment. This trial will also evaluate the effects of sotatercept on iron overload and bone metabolism. The trial is being conducted at up to 23 sites in the United States and France and may enroll up to 75 patients. Based on currently projected timelines, which are subject to change, we expect additional data from this clinical trial to become available as follows: data from the completed dose escalation portion of the clinical trial in the second quarter of 2014, and final data in the fourth quarter of 2014.
Chronic Kidney Disease. Celgene is conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial with sotatercept designed as a randomized, placebo-controlled dose escalation study to evaluate the pharmacokinetics, safety, efficacy, tolerability and pharmacodynamics of sotatercept for the correction of anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis. The first patient in the trial was first dosed in August 2010. The first dose level was 0.1 mg/kg administered subcutaneously as a single dose. Subsequent dose levels to be studied are 0.3, 0.5 and 0.7 mg/kg administered subcutaneously once every four weeks for up to eight cycles. Each cohort will include up to 12 (nine sotatercept-treated and three placebo-treated) patients receiving a single dose level during the dose escalation phase, followed by an additional cohort at a selected dose level. Celgene has completed enrollment in the 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5 mg/kg cohorts and is now enrolling patients in the 0.7 mg/kg cohort. Based on the safety, tolerability, and effects observed to date, Celgene is in the process of amending the protocol for this trial to study an additional cohort dosed at 0.7 mg/kg administered subcutaneously every two weeks. The primary endpoints are pharmacokinetics and safety. Other endpoints include effects on hemoglobin and serum markers of bone metabolism. The trial is being conducted at up to 21 sites in the United States and may enroll up to 56 patients.
Celgene has submitted applications with regulatory authorities in Europe for a Phase 2 study of sotatercept in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis, which, if successful is expected to enable a Phase 3 trial. The protocol has not yet received ethics committee and regulatory approval and therefor is still subject to change. This trial is expected to begin by the end of 2013.
Sotatercept Investigator Sponsored Trials
Through collaborations with leading academic institutions, Celgene is overseeing investigator-sponsored trials in multiple myeloma, Diamond-Blackfan anemia and myelofibrosis.
Completed Clinical Trials
Six human clinical trials of sotatercept, including Phase 1 clinical trials in healthy volunteers and Phase 2 clinical trials of patients with multiple myeloma, breast cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer, collectively involving over 160 patients have been conducted to date. In healthy volunteers, we observed increases in red blood cells and hemoglobin. The mean change in hemoglobin for the patients who received a single dose of 1.0 mg/kg was almost 3 g/dL, which is similar to receiving a transfusion of three units of blood. We have also shown that in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with multiple myeloma receiving melphalan, prednisolone and thalidomide, sotatercept produced
dose-dependent increases in hemoglobin. In the placebo and 0.1 mg/kg sotatercept cohorts, none of the patients achieved at least a 1.5 g/dL increase in hemoglobin at day 29 of the trial compared to their baseline levels. In the 0.3 and 0.5 mg/kg sotatercept cohorts, 13% and 38% of the patients, respectively, achieved at least a 1.5 g/dL increase in hemoglobin at day 29 of the trial compared to their baseline levels. In a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial in breast cancer patients who had anemia due to myelosuppressive chemotherapy, sotatercept produced dose-dependent increases in hemoglobin levels. In both the placebo and 0.1 mg/kg sotatercept cohorts, 20% of the patients had their hemoglobin levels increase to at least 11 g/dL maintained for 28 days in the absence of a red blood cell transfusion or use of an erythropoiesis stimulating agent. In the 0.3 mg/kg cohort, 22% of the patients achieved this outcome and in the 0.5 mg/kg cohort, 75% of the patients achieved this threshold. In a randomized, dose-ranging Phase 2 trial of sotatercept in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer, sotatercept, administered at a fixed dose of 15 or 30 mg given subcutaneously every six weeks, produced increases in hemoglobin. In patients who did not receive red blood cell transfusions within the first four weeks, the change from baseline was at least 1 g/dL of hemoglobin for 40% of patients at week 2 and 16% of patients at week four. Given the results of these trials, we and Celgene may decide to pursue further clinical development in the future in one or more of these indications.
Safety
Across the completed clinical trials, sotatercept has been generally well-tolerated. In studies with healthy volunteers, the only treatment-related serious adverse event was a report of persistent, progressive high blood pressure in one subject. While the precise cause of elevated blood pressure cannot be determined, it was an expected consequence of elevated red blood cell levels that occurred in this subject. Commonly observed adverse events included headache, infection, dizziness, hypertension, hot flush, tingling, muscle spasms, limb injury, fatigue and asthenia. In three studies of patients with cancer (myeloma, breast and lung cancer), one sudden death was reported in a myeloma patient. The event was evaluated as probably related to the concurrent anti-myeloma therapy of melphalan, prednisolone and thalidomide and possibly related to sotatercept. One patient with advanced breast cancer experienced serious adverse events of perforated gastric ulcer and peptic ulcer disease that were evaluated as possibly related to sotatercept. One patient with advanced lung cancer experienced a serious adverse event of a cerebrovascular accident (blockage of a blood vessel in the brain) that was suspected as related to treatment.
Among the ongoing clinical trials managed by Celgene, as of July 31, 2013, no treatment-related serious adverse events have been reported in the MDS trial. In theb-thalassemia trial, two patients have exhibited serious adverse events that were suspected as related to sotatercept: bone pain and superficial thrombophlebitis (an inflamed blood clot in a superficial vein). In the anemia of chronic kidney disease trial, two patients have experienced serious adverse events that were suspected as related to sotatercept: atrial fibrillation and worsening anemia.
Sotatercept Investigational New Drug (IND) Applications
Sotatercept is the subject of three separate company-sponsored U.S. IND applications. We submitted the first IND to the FDA on March 13, 2006 for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. There are currently no studies being conducted under this IND. We submitted the second IND to the FDA on March 27, 2009 to assess the use of sotatercept for the treatment of anemia in various cancer-related indications. We transferred sponsorship of both INDs to Celgene on January 19, 2010. Under the second IND, sotatercept is currently being studied in patients with lower-risk MDS. A third IND was submitted by Celgene to the FDA on January 25, 2010 to assess sotatercept for the treatment of anemia in patients with end-stage renal disease. In addition, sotatercept is being studied in Europe under two separate Clinical Trial Applications (CTAs). The first CTA is for a Phase 2 study for the treatment of anemia in adult patients withb-thalassemia, submitted to France on December 28,
2011, to the United Kingdom on July 26, 2012, to Italy on July 27, 2012, and to Greece on November 23, 2012. The second CTA is for a Phase 2 study for the treatment of anemia in patients with lower-risk MDS, submitted to France on October 10, 2012. Sotatercept is also being studied in the United States under three investigator-sponsored INDs.
Preclinical Studies
In preclinical studies, RAP-011 (the mouse equivalent of sotatercept) was evaluated in a broad range of animal pharmacology studies to assess its biological effects. RAP-011 has been shown to increase red blood cell counts in mice, rats, and monkeys. RAP-011 showed increased hemoglobin and red blood cell counts in mouse models ofb-thalassemia and MDS, demonstrating decreased ineffective erythropoiesis in these models. RAP-011 was also able to prevent chemotherapy-induced anemia in a mouse model of this condition and was able to correct anemia in a mouse model of chronic kidney disease. RAP-011 increased bone mineral density in ovariectomized mice and has demonstrated positive effects in mice on bone lesions and bone metastases in a number of cancer models including models of multiple myeloma.
ACE-536 Clinical and Preclinical Development
ACE-536 is a soluble receptor fusion protein consisting of a modified extracellular domain of the activin receptor type IIB (ActRIIB) linked to the Fc domain of human IgG1.
Ongoing Phase 2 Clinical Trials of ACE-536
We are conducting Phase 2 clinical trials of ACE-536 in patients withb-thalassemia and in patients with MDS. The FDA has granted orphan designation for ACE-536 for the treatment ofb-thalassemia and for the treatment of MDS.
b-thalassemia. We are conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial of ACE-536, designed as an ascending dose trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy in patients withb-thalassemia. The dose levels to be studied are 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1 mg/kg given subcutaneously once every three weeks for up to 85 days. Each cohort will include three to six patients receiving a single dose level during the dose escalation phase. This will be followed by an expansion phase at a selected dose level in up to 20 patients. The first patient in the trial was first dosed in March 2013. We have completed enrollment of the 0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg cohorts and are currently enrolling patients in the 0.6 mg/kg cohort. The primary outcome measure is the proportion of patients who have an increase in hemoglobin of³1.5 g/dL from baseline for³14 days (in the absence of red blood cell transfusions) in non-transfusion dependent patients or a³20% reduction in red blood cell transfusion burden compared to the pretreatment transfusion burden in transfusion dependent patients. This trial will also examine the effects of ACE-536 on iron overload, an important cause of morbidity and mortality inb-thalassemia patients. Secondary endpoints include markers of serum iron and hemolysis. The trial is being conducted at up to six sites in Italy, and we plan to include additional sites in Europe and may enroll up to 50 patients. Based on currently projected timelines, which are subject to change, we expect additional data from this clinical trial to become available as follows: data from the completed dose escalation portion of the clinical trial during the second quarter of 2014, and final data in the fourth quarter of 2014.
MDS. We are conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial of ACE-536 designed as an ascending dose trial in patients with low or intermediate-1 risk MDS. The dose levels to be studied are 0.125, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1 mg/kg given subcutaneously once every three weeks for up to 85 days. Each cohort will include three to six patients receiving a single dose level during the dose escalation phase. This will be followed by an expansion phase at a selected dose level in up to 30 patients. Based on the safety, tolerability, and effects observed to date, we are in the process of amending the protocol to potentially study higher
dose levels. The first patient in the trial was first dosed in January 2013. We have currently completed enrollment in the 0.125, 0.25 and 0.5 mg/kg cohorts and are now enrolling patients in the 0.75 mg/kg cohort. The primary outcome measure is the proportion of patients who have an increase of hemoglobin³1.5 g/dL from baseline for 14 days in the absence of red blood cell transfusions in non-transfusion dependent patients or a³50% reduction of red blood cell transfusions over a period of eight weeks compared to pretreatment transfusion burden in transfusion-dependent patients. This trial will also examine the effects of ACE-536 on iron overload. The trial is being conducted at up to nine sites in Germany and may enroll up to 60 patients. Based on currently projected timelines, which are subject to change, we expect additional data from this clinical trial to become available as follows: data from the completed dose escalation portion of the clinical trial during the second quarter of 2014, and final data in the fourth quarter of 2014.
Completed Phase 1 Clinical Trial
ACE-536 was studied in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, ascending dose Phase 1 clinical trial in 32 healthy volunteers. ACE-536 produced dose-dependent increases in hemoglobin and red blood cells. The proportion of subjects with a hemoglobin increase of³1.0 g/dL increased on a dose-dependent basis, with approximately 80% of subjects in the 0.25 mg/kg dose level achieving this threshold.
Safety
In the completed Phase 1 clinical trial in healthy volunteers, ACE-536 was well-tolerated. No ACE-536 related serious adverse events were reported in the completed Phase 1 clinical trial. Commonly observed possibly or probably treatment-related adverse events included injection site bruising, injection site blemish, dry skin, numbness, muscle spasms, muscle pain, generalized itchiness and raised rash. In the ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, there have been no ACE-536 related serious adverse events reported as of July 31, 2013.
ACE-536 Investigational New Drug (IND) Applications
ACE-536 is being studied in the United States under an IND that we submitted to the FDA on June 14, 2011. The indication identified in the IND is for the treatment of anemia in patients with MDS. No studies are being conducted under this IND at this time. In addition, ACE-536 is being studied in Europe under two separate Clinical Trial Applications (CTAs). The first is for a Phase 2 study for the treatment of anemia in adult patients withb-thalassemia, submitted to Italy on August 29, 2012, to Turkey on June 14, 2013, and to Greece on July 2, 2013. The second is for a Phase 2 study for the treatment of anemia in patients with low- or intermediate-1 risk MDS, submitted to Germany on August 21, 2012.
Preclinical Studies
A number of preclinical pharmacology studies have been conducted with ACE-536 or its mouse version, RAP-536, that demonstrate its effects on red blood cells, hemoglobin and hematocrit. Collectively ACE-536 and RAP-536 have shown activity in mouse models ofb-thalassemia, MDS, chemotherapy-induced anemia, acute blood loss and renal anemia.
b-thalassemia. RAP-536 has been evaluated in a series of studies using a mouse model ofb-thalassemia. These mice carry deletion mutations in theb-globin genes, resulting in a deficiency ofb-globin protein and hematologic abnormalities very similar to those seen in humanb-thalassemia patients, including severe anemia and the formation of hemichromes resulting in ineffective erythropoiesis. These mice also exhibit severe complications common in patients with thalassemia, such as an enlarged spleen, bone loss and iron overload. In these mice, RAP-536 treatment improved
numerous hematologic parameters, including significant increases in red blood cell count, hemoglobin levels, and hematocrit, decreased serum erythropoietin, normalized red blood cell size, and reduced red blood cell breakdown, as measured by serum bilirubin.
Representative blood smears were taken from theb-thalassemia mouse studies for both the placebo-treated animals and the RAP-536 treated animals. As shown in the image below, RAP-536 improved red blood cell morphology by reducing the number of poorly formed and damaged red blood cells, and reducing the amount of cellular debris that results from dying red blood cells.
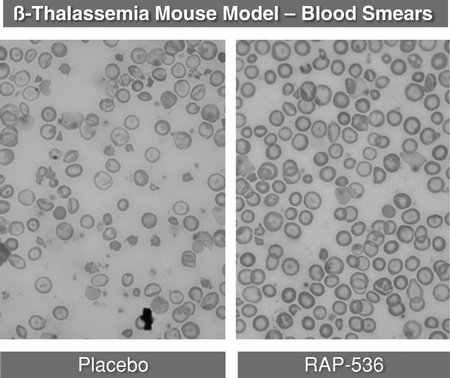
Importantly, RAP-536 improved the maturation of later stage red blood cell precursor populations, in the bone marrow and spleen, with concomitant reductions in the earlier-stage red blood cell precursor populations. We believe RAP-536 reduced the ineffective erythropoiesis by decreasing the formation of harmful hemichromes.
This reduction in ineffective erythropoiesis reduced severe and common complications of the disease in mice, evidenced by reduced iron deposition in organs, reduced spleen weights and normalized bone density. Based on the numerous beneficial effects of RAP-536 in this mouse model ofb-thalassemia, we believe that it is modifying the disease and has the potential to do so in human patients.
MDS. In a mouse model of MDS, RAP-536 treated animals had statistically significant increases in red blood cell count, hemoglobin levels and hematocrit compared to controls. Additionally, RAP-536 reduced the ineffective erythropoiesis as evidenced by the improvement in the ratio of red blood cell precursors to other cells in the bone marrow.
Taken together, our clinical and preclinical results suggest that ACE-536 could be a meaningful novel therapy to treat anemia.
Dalantercept
Inhibiting Angiogenesis to Limit Tumor Growth
Angiogenesis is a process by which new blood vessels are formed. Angiogenesis can be simplified to two major stages—the proliferative stage followed by the maturation stage. During the proliferative stage, vascular endothelial cells, the cells lining the inside of the blood vessels, multiply in number and migrate to the site where a new vessel will be formed. This proliferative stage is followed by the maturation stage during which the endothelial cells coalesce to form tubes which are then stabilized through the recruitment of perivascular cells that form an outer layer of the blood vessels resulting in fully formed, functional vessels.
Tumors depend on angiogenesis to form new blood vessels to supply nutrients and oxygen to feed the rapidly growing malignant cells. The principal molecule driving the proliferative stage of angiogenesis in tumors is a protein called vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Inhibiting VEGF-driven angiogenesis to control tumor growth has become an important and widely-used approach to cancer treatment. There are several FDA-approved cancer drugs that inhibit the VEGF pathway, with over $8 billion in aggregate worldwide sales. Despite the success of these drugs, many patients fail to respond or develop resistance to VEGF pathway inhibitor therapy, resulting in an unmet need for new therapies to inhibit angiogenesis by a different mechanism.
We are using our knowledge of the TGF-b superfamily to develop dalantercept, a novel protein therapeutic candidate targeting the maturation stage of angiogenesis. Recently, the activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) has been recognized as a key regulator of the maturation stage of angiogenesis. ALK1 is one of the 12 receptors for ligands in the TGF-b superfamily and is found primarily on endothelial cells. The importance of the ALK1 pathway in angiogenesis was discovered, in part, through research into the genetic basis of the disease hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia 2 (HHT-2) in which patients manifest vascular defects including reduced ability to form capillary beds, which are the networks of small blood vessels that connect arteries to veins and are necessary for nutrient and waste exchange in tissues. This research revealed that these patients have only one of two functional copies of the ALK1 gene.
We reasoned that leveraging the biology of the ALK1 pathway to inhibit maturation of blood vessels could impair the growth of tumors by limiting the development of capillary beds within the tumor. To test this hypothesis, mice with a predisposition to develop tumors were bred to have only one, rather than two copies, of the ALK1 gene. In response to the loss of half of the ALK1 genes, tumor growth and size and blood vessel density in the tumor were reduced by half. These results and additional research in the field have established the ALK1 signaling pathway as a promising target for developing a new class of anti-angiogenesis agents—ALK1 pathway inhibitors.
We believe one promising opportunity for dalantercept will be its use in combination with VEGF pathway inhibitors because these agents target distinct sequential steps in angiogenesis. Moreover, we and others have hypothesized that agents, such as dalantercept, that inhibit vessel maturation are able to sensitize the tumor vasculature to the anticancer effects of VEGF pathway inhibition. We believe that newly formed blood vessels become more resistant to VEGF pathway inhibitors as they mature. Therefore we believe that by preventing blood vessel maturation, dalantercept may maintain newly formed vessels in an immature state that increases their susceptibility to VEGF pathway inhibitors.
We and our academic collaborators have also shown in two mouse cancer models that treatment with dalantercept decreases metastases. This is in contrast to VEGF pathway inhibitors that increase metastases in mouse cancer models.
We believe that a combination of ALK1 and VEGF pathway inhibitors could have application in a number of different oncology indications where VEGF pathway inhibitors are currently used. The currently approved VEGF pathway inhibitors include Avastin® (bevacizumab), Nexavar® (sorafenib),
Sutent® (sunitinib), Inlyta® (axitinib), and Votrient® (pazopanib). Four large markets for which these drugs have been approved are non-small cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, renal cell carcinoma and liver cancer.
Dalantercept Clinical and Preclinical Development
Dalantercept is comprised of the extracellular domain of the ALK1 receptor linked to the Fc domain of IgG1. Dalantercept acts as a ligand trap for ligands in the TGF-b superfamily that signal through the ALK1 receptor. We have completed a Phase 1 trial of dalantercept and are pursuing a program of ongoing and planned Phase 2 trials seeking to demonstrate single agent activity of dalantercept for advanced solid tumors and activity of dalantercept in combination with approved VEGF pathway inhibitors or chemotherapy in advanced solid tumors.
Ongoing Phase 2 Clinical Trials of Dalantercept
We are currently conducting two Phase 2 clinical trials of dalantercept in head and neck cancer and renal cell carcinoma. Additionally, through collaborations with a National Cancer Institute funded collaborative research group, the Gynecologic Oncology Group, we are overseeing an additional two Phase 2 clinical trials. We plan to submit applications for orphan designation of dalantercept for those indications or subsets of indications that meet FDA requirements for orphan status.
Acceleron Sponsored Clinical Trials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. We are conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial of dalantercept as a single agent in an ascending dose trial in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. The first patient in the trial was first dosed in October 2011. After an initial cohort of two patients treated at a fixed dose level of 80 mg, we amended the
trial and began recruitment of patients under the amended protocol in the first quarter of 2012 to study the dose level of 0.6 mg/kg given subcutaneously once every three weeks. The protocol was subsequently amended to increase the dose level of dalantercept to 1.2 mg/kg. Patients continue to receive dalantercept until there is disease progression (either clinically or as measured by analysis of radiographic imaging according to RECIST criteria) or dalantercept is no longer tolerated. The primary outcome measure is objective response rate as measured by RECIST criteria, and there are a number of secondary outcome measures of tumor response. The trial is being conducted in 12 centers in the United States, and we completed enrollment in July 2013 with a total of 46 patients, including two patients treated at the 80 mg dose, 13 at the 0.6 mg/kg dose, and 31 at the 1.2 mg/kg dose. Of these 46 patients, 3236 patients (one patient at 80 mg, 13 patients at 0.6 mg/kg, and 1822 patients at 1.2 mg/kg) were evaluable for radiological response according to RECIST criteria as of July 16,August 22, 2013. The preliminary data for these 3236 patients are as follows: no patients at 80 mg, three patients (23%) at 0.6 mg/kg and sixeight patients (33%(36%) at 1.2 mg/kg achieved stable disease as their best response at the beginning of their third cycle and, at the 1.2 mg/kg dose level, one patient (6%(5%) achieved a partial response. None of these patients achieved a complete response. These preliminary data suggest dalantercept has dose dependent but modest single agent activity in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. We believe the greatest potential for dalantercept will be in combination with VEGF pathway inhibitors or in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Renal Cell Carcinoma. We are conducting a two-part Phase 2 clinical trial of dalantercept in combination with axitinib, an approved VEGF pathway inhibitor, in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Part one of this trial is designed as a single-arm dose escalation and expansion stage with the primary endpoint of evaluating the safety and tolerability of various dose levels of dalantercept in combination with axitinib to select a dose level of dalantercept (in combination with axitinib) for further study if merited. The dose levels of dalantercept to be studied are 0.6, 0.9, 1.2, and 1.5 mg/kg given subcutaneously once every three weeks. Each cohort will include up to six patients receiving a single dose level during the dose escalation phase, followed by an expansion phase in up to 20 additional patients. The first patient in the trial was first dosed in January 2013. Patients continue to receive dalantercept and axitinib until there is disease progression (either clinically or as measured by RECIST criteria) or the combination is no longer tolerated. Enrollment at the two lowest dose levels has been completed, with four patients enrolled at the 0.6 mg/kg dose level of dalantercept and four patients enrolled at the 0.9 mg/kg dose level. We are now enrolling patients at the 1.2 mg/kg dose level of dalantercept. Based on the safety, tolerability and effects observed to date, we are in the process of amending the protocol to potentially study dalantercept in combination with other VEGF pathway inhibitors. Once a maximum tolerated dose level is determined in this first part of the trial, a dose level for the expansion phase will be selected and additional patients will be enrolled at that selected dose level. Up to a total of 44 patients may be enrolled in the dose escalation and expansion part of the trial. Part two of the trial will be a randomized comparison of the selected dose of dalantercept in combination with axitinib versus axitinib alone with a total of 112 patients. The primary endpoint of part two of the trial will be progression-free survival. The trial is currently being conducted in 7 sites in the United States.
We believe that early preliminary data from this trial is encouraging. As of August 1, 2013, four
Four patients were enrolled in the 0.6 mg/kg dose group and each patient's response as of August 28, 2013 according to RECIST is described below. Percentage decreases in tumor size are reported relative to the baseline measurement at the beginning of the study.
axitinib, the target tumors in the liver decreased in size by 15% at treatment cycle 3 and by 29% at cycle 5. This patient remains on study.
Of the fourFour patients enrolled at the 0.9 mg/kg dose level, only one patient as of August 1, 2013 has been evaluated for tumor response.level. All four patients at the 0.9 mg/kg dose level remain on study. Each patient's response as of August 28, 2013 according to RECIST is described below.
Based on currently projected timelines, which are subject to change, we expect to initiate part two of this trial in the first quarter of 2014, which, if successful, we expect would enable a Phase 3 trial. We expect dose escalation data to be available when we initiate part two of the trial.
Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) Sponsored Trials
The Gynecologic Oncology Group, one of the National Cancer Institute's funded collaborative cancer research groups, is sponsoring two Phase 2 clinical trials to study the activity of dalantercept as a single agent. The first of these is a trial in patients with recurrent or persistent endometrial cancer and the second trial is in patients with recurrent or persistent ovarian cancer. Both of these clinical trials are designed as two-part studies. If there is sufficient activity in the first part of the trial, additional patients will be enrolled in the second, expanded part of the trial. We anticipate that we may receive notification from the GOG by the end of 2013 if there is sufficient activity to enroll additional patients in the second part of the endometrial cancer trial. We anticipate that in late 2013 or early 2014, we may receive notification from the GOG if there is sufficient activity to enroll additional patients in the second part of the ovarian cancer trial.
Phase 1 Trial Results
A Phase 1 ascending dose trial evaluated the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics and anti-tumor activity of dalantercept in patients with advanced solid tumors. Dalantercept was given subcutaneously approximately once every three weeks until disease progression. Thirty-seven patients were enrolled in dose groups at 0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 1.6, 3.2 and 4.8 mg/kg. In this trial, dalantercept demonstrated
anti-tumor activity based on decreases or stabilization of tumor size. As shown in the figure below, out of the 29 evaluable patients treated, one (3%) had a partial response and 13 (45%) had stable disease according to RECIST criteria. Of the 13 who experienced stable disease, eight experienced stable disease for at least three months. Treatment continued until the patient experienced progressive disease.
The figure below displays each patient's best overall response by the maximum percent change decrease in target lesion size. The dose level each patient received is shown below their bar.
Best Overall Response by the Maximum Percent Change Decrease in Target Lesion Size According to RECIST v1.1 Criteria
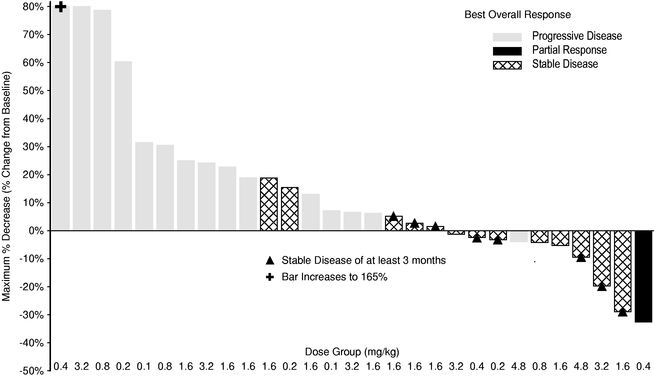
In addition to these effects on tumor size, dalantercept demonstrated likely anti-angiogenic activity evidenced by a reduction of tumor metabolic activity as well as decreases in tumor blood flow. Lastly, some patients were observed to have dilated blood vessels in the skin, similar to those in HHT-2 patients, suggesting ALK1 pathway inhibition.
Safety
In clinical trials to date, dalantercept has been generally well-tolerated. In the initial Phase 1 clinical trial in advanced cancer patients, five patients out of 37 experienced serious adverse events deemed treatment-related that were reported as left ventricular dysfunction, fatigue, fluid overload, and congestive heart failure. Two of these patients had prior coronary artery disease. In subsequent trials fluid overload has been successfully managed with diuretics. As of July 31, 2013 the following treatment related adverse events have been observed in our ongoing clinical trials. Two patients in the head and neck cancer clinical trial have experienced serious adverse events of fluid accumulation around the lungs that were determined to be possibly related to dalantercept. Another patient in the head and neck trial has experienced serious adverse events of tracheal obstruction and pulmonary edema that were determined to be possibly related to dalantercept. In the clinical trial of patients with endometrial
cancer, six patients have experienced treatment-related serious adverse events reported as fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity, fluid accumulation around the lungs, rectal fistula, gastric bleeding, vomiting, anemia, and shortness of breath. In the clinical trial of patients with ovarian cancer, one patient has experienced treatment related serious adverse events reported as hypokalemia (decreased potassium), anorexia, dehydration and increased creatinine. No treatment related serious adverse events have been observed in the renal cell carcinoma trial.
Dalantercept Investigational New Drug (IND) Applications
Dalantercept is being studied in the United States under an IND that we submitted to the FDA on July 29, 2009 for the treatment of patients with advanced solid tumors or multiple myeloma. Dalantercept is also being studied in the United States under two INDs sponsored by the Gynecologic Oncology Group: the first was submitted on August 2, 2012 for the treatment of recurrent/persistent endometrial carcinoma and the second submitted on September 25, 2012 for the treatment of recurrent/persistent ovarian carcinoma.
Preclinical Studies
We have demonstrated that dalantercept as a single agent inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis in a variety of mouse models of cancer. Importantly, we have shown that dalantercept is a potent inhibitor of the maturation stage of angiogenesis. This is in contrast with VEGF pathway inhibitors that target the proliferative stage of angiogenesis.
We also demonstrated that dalantercept in combination with a VEGF pathway inhibitor provides enhanced anti-tumor effects. In mice bearing human renal cell carcinoma xenografts, we and our academic collaborators have shown that simultaneous administration of both dalantercept and sunitinib, a VEGF-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, had substantially greater efficacy than either agent alone. In another mouse model of human renal cell carcinoma that develops resistance to sunitinib, tumor growth was blocked by the simultaneous administration of dalantercept. The figures below summarize those results.
| Dalantercept/Sunitinib Combination Exceeds Activity of Either Alone (Mouse Model of Renal Cell Carcinoma (A498)) | Dalantercept/Sunitinib Combination Slows Tumor Growth in a Sunitinib Resistant Model (Mouse Model of Renal Cell Carcinoma (786O)) | |
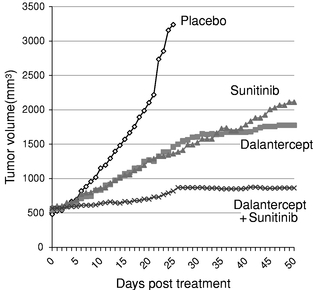 | 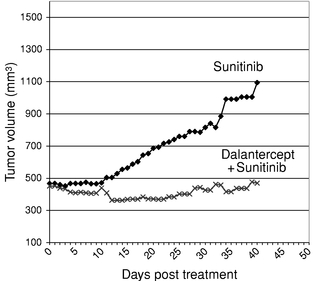 | |
Collaboration with Drs. Wang, Bhatt, Mier, Atkins; Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston | ||
Development Objectives
For sotatercept and ACE-536, our development strategy, determined in collaboration with Celgene, for bothb-thalassemia and MDS is to conduct similar clinical trials with each protein therapeutic candidate in each disease essentially in parallel. For each disease, we and Celgene will review the data from both studies and determine which, if either, protein therapeutic candidate to move forward into subsequent, pivotal studies. It is our goal to initiate the Phase 3 clinical trials for one or both protein therapeutic candidates in one or both of these diseases by the end of 2014 or early 2015.
For dalantercept, our development strategy is to continue the renal cell carcinoma trial and to initiate during 2014 part two of the trial that compares the combination of dalantercept and axitinib to axitinib alone. We will also work toward completion of the ongoing single agent trial in head and neck cancer. We expect to initiate, during the third quarter of 2014, additional randomized, controlled trials of dalantercept in cancer patients in combination with an approved VEGF pathway inhibitor. We are currently planning trials of dalantercept plus sorafenib compared to sorafenib alone in first-line hepatocellular carcinoma (a form of liver cancer), dalantercept plus bevacizumab plus standard therapy compared to bevacizumab plus standard therapy in non-small cell lung cancer, and dalantercept plus bevacizumab plus standard therapy compared to bevacizumab plus standard therapy in colorectal cancer.
Our Preclinical Pipeline
We are using our discovery platform and knowledge of the TGF-b superfamily to design and evaluate promising new protein therapeutic candidates that inhibit ligands of the TGF-b superfamily. We have preclinical stage protein therapeutic candidates in our pipeline that have shown promising activity in animal models such as:
We are preparing production-grade cell lines for the manufacture of two protein therapeutic candidates to enable further preclinical evaluation of safety and efficacy that will, if successful, form the basis for an investigational new drug application and the initiation of clinical trials. One of these protein therapeutic candidates is ACE-083, an agent being developed for localized treatment of muscle loss in conditions such as muscular dystrophies. We expect to initiate a clinical trial with ACE-083 by the end of 2014.
Our Strategic Partnerships
Collaborations with corporate partners have provided us with significant funding and access to our partners' scientific, development, regulatory and commercial capabilities. We have received more than $225.0 million from our collaborations with Celgene, Alkermes and Shire.
Celgene
On February 20, 2008 we entered into an agreement, which we refer to as the Sotatercept Agreement, with Celgene Corporation, under which we granted to Celgene worldwide rights to sotatercept. On August 2, 2011 we entered into a second agreement with Celgene for ACE-536, which we refer to as the ACE-536 Agreement under which we granted to Celgene worldwide rights to ACE-536 and also amended certain terms of the Sotatercept Agreement. These agreements provide Celgene exclusive licenses for these protein therapeutic candidates in all indications, as well as exclusive rights to obtain a license to certain future compounds.
Sotatercept Agreement. Under the terms of the Sotatercept Agreement, we and Celgene are collaborating on the development and commercialization of sotatercept. We also granted Celgene an option to license discovery stage compounds against three specified targets. Celgene paid $45.0 million and bought $5.0 million of equity upon execution of the Sotatercept Agreement and, as of March 31,June 30, 2013, we have received $34.0$34.2 million in research and development funding and milestone payments for the sotatercept program.
We retained responsibility for research, development through the end of Phase 2a clinical trials, as well as manufacturing the clinical supplies for these trials. These activities are substantially complete. Celgene is conducting the current Phase 2 trials forb-thalassemia, MDS and chronic kidney disease and will be responsible for any future clinical trials for sotatercept as well as for all future manufacture of sotatercept. We are eligible to receive future development, regulatory and commercial milestones of up to $367.0 million for the sotatercept program and up to an additional $348.0 million for each of the three discovery stage programs. None of the three discovery stage programs has advanced to the stage to achieve payment of a milestone, nor do we expect any such milestone payments in the near future.
ACE-536 Agreement. Under the terms of the ACE-536 Agreement, we and Celgene are collaborating in the development and commercialization of ACE-536. We also granted Celgene an option to license products for which Acceleron files an investigational new drug application for the treatment of anemia. Celgene paid $25.0 million to us upon execution of the ACE-536 Agreement in August 2011 and, as of March 31,June 30, 2013, we have received $25.0$25.2 million in research and development funding and milestone payments for the ACE-536 program.
Under this agreement, we retained responsibility for research, development through the end of Phase 1 and the two ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials in MDS andb-thalassemia, as well as manufacturing the clinical supplies for these studies. Celgene will conduct subsequent Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials. Acceleron will manufacture ACE-536 for all Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials, and Celgene will have responsibility for the manufacture of ACE-536 for Phase 3 clinical trials and commercial supplies. We are eligible to receive future development, regulatory and commercial milestones of up to $200.0 million for the ACE-536 program.
Both Agreements. Under each agreement, the conduct of the collaboration is managed by a Joint Development Committee and Joint Commercialization Committee. Other than with respect to certain matters related to our conduct of Phase 2 trials, in the event of a deadlock of a committee, the resolution of the relevant issue is determined by Celgene. Prior to January 1, 2013, Celgene paid the majority of development costs under the Sotatercept and ACE-536 Agreements. As of January 1, 2013, Celgene became responsible for paying 100% of worldwide development costs for both programs. Celgene will be responsible for all commercialization costs worldwide. We are obligated to co-promote sotatercept, ACE-536 and future products, in each case if approved, under both agreements in North America, and Celgene will pay all costs related thereto. We will receive tiered royalties in the low-to-mid 20% range on net sales of sotatercept and ACE-536. The royalty schedules for sotatercept and ACE-536 are the same. Celgene is obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize sotatercept and ACE-536. Celgene may determine that it is commercially reasonable to develop and commercialize only sotatercept or ACE-536 and discontinue the development or commercialization of the other protein therapeutic candidate, or Celgene may determine that it is not commercially reasonable to continue development of one or both of sotatercept and ACE-536. In the event of any such decision, we may be unable to progress the discontinued candidate or candidates ourselves. The agreements are terminable by either party upon a breach that is uncured and continuing or by Celgene for convenience on a country by country or product by product basis, or in its entirety. Celgene may also terminate the agreement, in its entirety or on a product by product basis, for failure of a product to meet a development or clinical trial endpoint. Termination for cause by us or termination by Celgene for convenience or failure to meet an endpoint will have the effect of
terminating the applicable license, while termination for cause by Celgene will have the effect of reducing remaining royalties by a certain percentage.
Other Collaborations
Alkermes. On December 3, 2009, we entered into a Collaboration and License Agreement with Alkermes relating to a proprietary technology platform for extending the circulating half-life of certain proteins. Under the terms of the agreement, we granted Alkermes worldwide rights to apply this
technology to proteins outside of the TGF-b superfamily in return for an upfront license payment. We are entitled to future development, regulatory and sales milestones and mid-single digit royalties on product sales for each drug developed and commercialized by Alkermes using this technology. To our knowledge, Alkermes is not currently developing any products using this technology.
Shire. On September 8, 2010, we entered into an agreement with Shire AG for the joint development and commercialization of ACE-031, a clinical stage protein therapeutic candidate. We granted Shire an exclusive license in markets outside of North America. Under the terms of the agreement, Shire made an upfront cash payment of $45.0 million. We received $8.3 million in research and development payments from Shire during the term of the agreement. In April 2013, we and Shire determined not to further advance the development of ACE-031, and Shire terminated our collaboration agreement, effective as of June 30, 2013 and all rights reverted to us. We currently have no plans to continue the development of ACE-031.
Competition
The development and commercialization of new drugs is highly competitive. We and our collaborators will face competition with respect to all protein therapeutics we may develop or commercialize in the future from pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies worldwide. Many of the entities developing and marketing potentially competing products have significantly greater financial resources and expertise than we do in research and development, manufacturing, preclinical testing, conducting clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approvals and marketing. Our commercial opportunity will be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are more effective, have fewer side effects, are more convenient or are less expensive than any products that we may develop.
If our clinical stage protein therapeutics are approved, they will compete with currently marketed drugs and therapies used for treatment of the following indications, and potentially with drug candidates currently in development for the same indications:
b-thalassemia
If either sotatercept or ACE-536 is approved for the treatment of patients withb-thalassemia, it would compete with:
MDS
If either sotatercept or ACE-536 is approved for the treatment of patients with MDS, it would compete with the following:
Chronic Kidney Disease
If either sotatercept or ACE-536 is approved for the treatment of anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease, it would compete primarily with erythropoiesis stimulating agents that have been approved to treat these patients for over 20 years. In 2011, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) changed the reimbursement practice for erythropoiesis stimulating agents in chronic kidney disease patients on dialysis, which has led to changes in the way erythropoiesis stimulating agents are used in clinical practice, including decreasing the number of patients treated with erythropoiesis stimulating agents as well as decreasing the average dose and duration of therapy. These changes and the anticipated future introduction of biosimilar erythropoiesis stimulating agents are expected to generate additional price pressure in this market. Additionally, we are aware that Astellas Pharma and Fibrogen are developing oral, small molecule treatments that increase the production of erythropoietin to treat patients with anemia.
Oncology Therapies
We are developing dalantercept to be used in combination with VEGF pathway inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. If dalantercept is approved, it would compete with:
In addition to the therapies mentioned above, there are many generic chemotherapy agents and other regimens commonly used to treat various types of cancer, including renal cell carcinoma, head and neck, endometrial and ovarian cancer.
The key competitive factors affecting the success of any approved product will be its efficacy, safety profile, price, method of administration and level of promotional activity.
Commercialization
We retain co-promotion rights with our collaboration partner, Celgene, for both sotatercept and ACE-536 in North America, and under the terms of our agreements with Celgene, our commercialization costs will be entirely funded by Celgene. We also currently retain worldwide commercialization rights for our oncology protein therapeutic candidate, dalantercept. We intend to build a hematology and oncology focused, specialty sales force in North America and, possibly, other markets to effectively support the commercialization of these and future products. We believe that a specialty sales force will be sufficient to target key prescribing physicians in hematology and oncology. We currently do not have any sales or marketing capabilities or experience. We will establish the required capabilities within an appropriate time frame ahead of any product approval and commercialization to support a product launch. If we are not able to establish sales and marketing capabilities or are not successful in commercializing our future products, either on our own or through collaborations with Celgene, any future product revenue will be materially adversely affected.
Intellectual Property
Our commercial success depends in part on our ability to obtain and maintain proprietary protection for our protein therapeutics, novel biological discoveries, screening and drug development technology, to operate without infringing on the proprietary rights of others and to prevent others from infringing our proprietary rights. Our policy is to seek to protect our proprietary position by, among other methods, filing U.S. and foreign patent applications related to our proprietary technology, inventions and improvements that are important to the development and implementation of our business. We also rely on trade secrets, know-how, continuing technological innovation and potential in-licensing opportunities to develop and maintain our proprietary position. Additionally, we expect to benefit from a variety of statutory frameworks in the United States, Europe and other countries that relate to the regulation of biosimilar molecules and orphan drug status. These statutory frameworks provide periods of non-patent-based exclusivity for qualifying molecules. See "Government Regulations".
Our patenting strategy is focused on our protein therapeutics. We seek composition-of-matter and method-of-treatment patents for each such protein in key therapeutic areas. We also seek patent protection with respect to companion diagnostic methods and compositions and treatments for targeted patient populations. We have sought patent protection alone or jointly with our collaborators, as dictated by our collaboration agreements.
Our patent estate, on a worldwide basis, includes approximately 75 issued patents and approximately 300 pending patent applications, with pending and issued claims relating to all of our current clinical stage protein therapeutic candidates, sotatercept, ACE-536 and dalantercept. Of these, approximately 20 issued patents cover the nine receptors for the TGF-b superfamily that we have selected as the core focus of our discovery approach. These figures include in-licensed patents and patent applications to which we hold exclusive commercial rights.
Individual patents extend for varying periods of time depending on the date of filing of the patent application or the date of patent issuance and the legal term of patents in the countries in which they are obtained. Generally, patents issued from applications filed in the United States are effective for twenty years from the earliest non-provisional filing date. In addition, in certain instances, a patent term can be extended to recapture a portion of the term effectively lost as a result of the FDA regulatory review period, however, the restoration period cannot be longer than five years and the total patent term including the restoration period must not exceed 14 years following FDA approval. The duration of foreign patents varies in accordance with provisions of applicable local law, but typically is also twenty years from the earliest international filing date. Our issued patents with respect to our receptor-focused platform will expire on dates ranging from 2013 to 2018, and, our issued patents and
pending applications with respect to our protein therapeutic candidates will expire on dates ranging from 2026 to 2033, exclusive of possible patent term extensions, However, the actual protection afforded by a patent varies on a product by product basis, from country to country and depends upon many factors, including the type of patent, the scope of its coverage, the availability of extensions of patent term, the availability of legal remedies in a particular country and the validity and enforceability of the patent.
National and international patent laws concerning protein therapeutics remain highly unsettled. No consistent policy regarding the patent-eligibility or the breadth of claims allowed in such patents has emerged to date in the United States, Europe or other countries. Changes in either the patent laws or in interpretations of patent laws in the United States and other countries can diminish our ability to protect our inventions and enforce our intellectual property rights. Accordingly, we cannot predict the breadth or enforceability of claims that may be granted in our patents or in third-party patents. The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are characterized by extensive litigation regarding patents and other intellectual property rights. Our ability to maintain and solidify our proprietary position for our drugs and technology will depend on our success in obtaining effective claims and enforcing those claims once granted. We do not know whether any of the patent applications that we may file or license from third parties will result in the issuance of any patents. The issued patents that we own or may receive in the future, may be challenged, invalidated or circumvented, and the rights granted under any issued patents may not provide us with sufficient protection or competitive advantages against competitors with similar technology. Furthermore, our competitors may be able to independently develop and commercialize similar drugs or duplicate our technology, business model or strategy without infringing our patents. Because of the extensive time required for clinical development and regulatory review of a drug we may develop, it is possible that, before any of our drugs can be commercialized, any related patent may expire or remain in force for only a short period following commercialization, thereby reducing any advantage of any such patent. The patent positions for our most advanced programs are summarized below:
Sotatercept Patent Coverage
We hold two issued patents covering the sotatercept composition of matter in the United States, one issued patent in Europe (registered in most countries of the European Patent Convention) and additional patents issued or pending in many other major jurisdictions worldwide, including Japan, China, South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, Russia, Israel and India. The expected expiration date for these composition of matter patents is 2026 plus any extensions of term available under national law.
We hold two issued patents covering the treatment of anemia by administration of sotatercept in the United States and similar patents issued or pending in many other major jurisdictions worldwide, including Europe, Japan, China, South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, Russia, Israel and India. The expected expiration date for these composition of matter patents is 2027 exclusive of possible patent term extensions.
We also hold patents and patent applications directed to a variety of other uses for sotatercept, including the reduction of tumor cell burden in multiple myeloma.
ACE-536 Patent Coverage
We hold two issued patents covering the ACE-536 composition of matter in the United States, and additional patents issued or pending in many other major jurisdictions worldwide, including Europe, Japan, China, South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, Russia and India. The expected expiration dates for these composition of matter patents are 2028 and 2029, exclusive of possible patent term extensions.
We hold one issued patent covering the treatment of anemia by administration of ACE-536 in the United States and similar patents issued or pending in other major jurisdictions worldwide, including
Europe, Japan, China, South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, Russia and India. The expected expiration date for these method of treatment patents is 2029 exclusive of possible patent term extensions.
Dalantercept Patent Coverage
We hold one issued patent covering the dalantercept composition of matter in the United States, which is expected to expire in 2029, exclusive of possible patent term extensions, and we hold additional pending patent applications. We hold additional issued patents and pending patent applications covering composition of matter in many other major jurisdictions worldwide, including Europe, Japan, China, South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, Russia and India. The expected expiration dates for these patent filings claiming the dalantercept composition of matter, if issued, are either 2027 or 2029, exclusive of possible patent term extensions.
We hold one issued patent covering the treatment of tumor angiogenesis by administration of dalantercept in the United States and similar patents issued or pending in other major jurisdictions worldwide, including Europe, Japan, China, South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, Russia and India. The expected expiration date for these method of treatment patents is 2027, exclusive of possible patent term extensions.
We also hold patent applications directed to a variety of other uses for dalantercept, including the treatment of renal cell carcinoma with a combination of dalantercept and a VEGF-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor. This patent application is jointly invented and owned with the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, or BIDMC, and we have secured an exclusive license to the BIDMC rights. The expected expiration date for these patent applications, should they issue as patents, is 2033 plus any extensions of term available under national law.
Trade Secrets
In addition to patents, we rely upon unpatented trade secrets and know-how and continuing technological innovation to develop and maintain our competitive position. We seek to protect our proprietary information, in part, using confidentiality agreements with our commercial partners, collaborators, employees and consultants and invention assignment agreements with our employees. These agreements are designed to protect our proprietary information and, in the case of the invention assignment agreements, to grant us ownership of technologies that are developed through a relationship with a third party. These agreements may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors. To the extent that our commercial partners, collaborators, employees and consultants use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the rights in related or resulting know-how and inventions.
In-Licenses
Effective June 21, 2012, we entered into a license agreement with the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, or BIDMC, to obtain worldwide, exclusive rights under patent filings jointly invented by us and BIDMC. The patent rights relate to the treatment of renal cell cancer by combination therapy with dalantercept and VEGF-receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). The intellectual property includes one pending U.S. patent filing and one pending PCT (international) patent filing. If issued, the patents are predicted to expire in 2033. Under the agreement, BIDMC retained rights, on behalf of itself and other non-profit academic institutions, to practice under the licensed rights for non-profit purposes. The license rights granted to us are further subject to any rights the United States Government may have in such licensed rights due to its sponsorship of research that led to the creation of the licensed rights. We agreed to pay BIDMC specified development and sales milestone payments aggregating up to $1.0 million. In addition, we are required to pay BIDMC royalties in the low single-
digits on worldwide net product sales of drug labeled for treatment regimens that are claimed in the licensed patents. The agreement terminates upon the expiration of the last valid claim of the licensed patent rights. We may terminate the agreement at any time by giving BIDMC advance written notice. The agreement may also be terminated by BIDMC in the event of a material breach by us or in the event we become subject to specified bankruptcy or similar circumstances. In any termination event, we retain our joint ownership of the patent rights and a worldwide non-exclusive license with right to sublicense.
In August 6, 2010, we entered into an amended and restated license agreement with the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research, or LICR, to obtain worldwide, exclusive rights under patent filings solely owned by LICR and patent rights jointly invented by us and LICR. The LICR-owned patent rights relate to the first cloning of the type I activin receptors, ALK1, ALK2, ALK3, ALK4, ALK5 and ALK6, and include claims to nucleic acids, proteins and antibodies with respect to each of the foregoing. These patent rights expire between the years 2013 and 2018. The license excludes the rights with regard to anti-ALK2 antibodies. The joint patent rights relate to the treatment of pancreatic tumors with dalantercept and, if issued, such patent rights are expected to expire in 2029. Under the agreement, LICR retained rights, on behalf of itself and other non-profit academic institutions, to practice under the licensed rights for non-profit purposes. We agreed to pay LICR specified development and sales milestone payments aggregating up to $1.6 million for dalantercept. In addition, we are required to pay LICR royalties in the low single-digits on worldwide net product sales of products claimed in the licensed patents, with royalty obligations continuing at a 50% reduced rate for eight years after patent expiration. If we sublicense the LICR patent rights, we will owe LICR a percentage of sublicensing revenue, excluding payments based on the level of sales, profits or other levels of commercialization. The agreement terminates upon the expiration of royalty obligations. We may terminate the agreement at any time by giving LICR advance written notice. The agreement may also be terminated by LICR in the event of a material breach by us or in the event we become subject to specified bankruptcy or similar circumstances. In any termination we retain our joint ownership right in the jointly owned patent filings.
In August 2010, we entered into two amended and restated license agreements with the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, or Salk, providing rights under U.S. patent filings solely owned by Salk. The agreements for the licensed patent rights relate to the first cloning of the type II activin receptors, human ActRIIA and frog ActRIIB, respectively, and include claims to vertebrate homolog nucleic acids and proteins with respect to each of the foregoing. These patent rights expire between the years 2016 and 2017. One of these agreements relates to ActRIIA and sotatercept; the other agreement relates to ActRIIB, ACE-536 and the discontinued program ACE-031. The licenses granted are exclusive as to the therapeutic products that are covered by the patents and non-exclusive as to diagnostic products and other products that are developed using the Salk patent rights. If we sublicense the Salk patent rights, we will owe Salk a percentage of sublicensing revenue, excluding payments based on sales. Under the agreements, Salk retained rights, on behalf of itself and other non-profit academic institutions, to practice under the licensed rights for non-profit purposes. We agreed to pay Salk specified development milestone payments totaling up to $2.0 million for sotatercept and $0.7 million for ACE-536. In addition, we are required to pay Salk royalties in the low single-digits on worldwide net product sales by us or our sublicensees of products claimed in the licensed patents, or derived from use of the licensed patent rights, with royalty obligations continuing at a reduced rate for a period of time after patent expiration. The agreements terminate upon the expiration of royalty obligations. We may terminate either agreement at any time by giving Salk advance written notice. Either agreement may also be terminated by Salk in the event of a material breach by us or in the event we become subject to bankruptcy or similar circumstances.
Government Regulation
The preclinical studies and clinical testing, manufacture, labeling, storage, record keeping, advertising, promotion, export, marketing and sales, among other things, of our protein therapeutic candidates and future products, are subject to extensive regulation by governmental authorities in the United States and other countries. In the United States, pharmaceutical products are regulated by the FDA under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and other laws, including, in the case of biologics, the Public Health Service Act. We expect sotatercept, ACE-536, and dalantercept to be regulated by the FDA as biologics and to be reviewed by the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) as proteins intended for therapeutic use. Protein therapeutics require the submission of a Biologics License Application, or BLA, and approval by the FDA prior to being marketed in the U.S. Manufacturers of protein therapeutics may also be subject to state regulation. Failure to comply with FDA requirements, both before and after product approval, may subject us or our partners, contract manufacturers, and suppliers to administrative or judicial sanctions, including FDA refusal to approve applications, warning letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, fines and/or criminal prosecution.
The steps required before a biologic may be approved for marketing of an indication in the United States generally include:
Preclinical studies include laboratory evaluation of product chemistry, toxicity and formulation as well as animal studies to assess the potential safety and efficacy of the biologic candidate. Preclinical studies must be conducted in compliance with FDA regulations regarding GLPs. The results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information and analytical data, are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND. Some preclinical testing may continue even after the IND is submitted. In addition to including the results of the preclinical testing, the IND will also include a protocol detailing, among other things, the objectives of the clinical trial, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated if the first phase or phases of the clinical trial lends themselves to an efficacy determination. The IND will automatically become effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless the FDA within the 30-day time period places the IND on clinical hold because of its concerns about the drug candidate or the conduct of the trial described in the clinical protocol included in the IND. The IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before clinical trials can proceed.
All clinical trials must be conducted under the supervision of one or more qualified principal investigators in accordance with GCPs. They must be conducted under protocols detailing the objectives
of the applicable phase of the trial, dosing procedures, research subject selection and exclusion criteria and the safety and effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. Each protocol must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND, and progress reports detailing the status of the clinical trials must be submitted to the FDA annually. Sponsors also must timely report to the FDA serious and unexpected adverse reactions, any clinically important increase in the rate of a serious suspected adverse reaction over that listed in the protocol or investigator's brochure, or any findings from other studies or animal or in vitro testing that suggest a significant risk in humans exposed to the drug. An institutional review board, or IRB, at each institution participating in the clinical trial must review and approve the protocol before a clinical trial commences at that institution, approve the information regarding the trial and the consent form that must be provided to each research subject or the subject's legal representative, and monitor the study until completed.
Clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap and different trials may be initiated with the same drug candidate within the same phase of development in similar or differing patient populations. Phase 1 trials may be conducted in a limited number of patients, but are usually conducted in healthy volunteer subjects. The drug candidate is initially tested for safety and, as appropriate, for absorption, metabolism, distribution, excretion, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics.
Phase 2 usually involves trials in a larger, but still limited, patient population to evaluate preliminarily the efficacy of the drug candidate for specific, targeted indications to determine dosage tolerance and optimal dosage and to identify possible short-term adverse effects and safety risks.
Phase 3 trials are undertaken to further evaluate clinical efficacy of a specific endpoint and to test further for safety within an expanded patient population at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites. Phase 1, Phase 2, or Phase 3 testing might not be completed successfully within any specific time period, if at all, with respect to any of our protein therapeutic candidates. Results from one trial are not necessarily predictive of results from later trials. Furthermore, the FDA or the sponsor may suspend clinical trials at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution if the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB's requirements or if the drug candidate has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients.
The results of the preclinical studies and clinical trials, together with other detailed information, including information on the manufacture and composition of the product, are submitted to the FDA as part of a BLA requesting approval to market the drug candidate for a proposed indication. Under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act, as re-authorized most recently in July 2012, the fees payable to the FDA for reviewing a BLA, as well as annual fees for commercial manufacturing establishments and for approved products, can be substantial. The fee for review of an application that requires clinical data, such as a BLA, for the one year period ending September 30, 2013, is almost $2.0 million, subject to certain limited deferrals, waivers, and reductions that may be available. The fees typically increase each year. Each BLA submitted to the FDA for approval is reviewed for administrative completeness and reviewability within 60 days following receipt by the FDA of the application. If the BLA is found complete, the FDA will file the BLA, triggering a full review of the application. The FDA may refuse to file any BLA that it deems incomplete or not properly reviewable at the time of submission. The FDA's established goal is to review 90% of priority BLA applications within six months after the application is accepted for filing and 90% of standard BLA applications within 10 months of the acceptance date, whereupon a review decision is to be made. The FDA, however, may not approve a drug candidate within these established goals and its review goals are subject to change from time to time. Further, the outcome of the review, even if generally favorable, may not be an actual approval but a "complete response letter" that describes additional work that must be done before the application can be approved. Before approving a BLA, the FDA may inspect the facility or facilities at
which the product is manufactured and will not approve the product unless the facility complies with cGMPs. The FDA may deny approval of a BLA if applicable statutory or regulatory criteria are not satisfied, or may require additional testing or information, which can extend the review process. FDA approval of any application may include many delays or never be granted. If a product is approved, the approval may impose limitations on the uses for which the product may be marketed, may require that warning statements be included in the product labeling, may require that additional studies be conducted following approval as a condition of the approval, and may impose restrictions and conditions on product distribution, prescribing, or dispensing in the form of a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy, or REMS, or otherwise limit the scope of any approval. The FDA must approve a BLA supplement or a new BLA before a product may be marketed for other uses or before certain manufacturing or other changes may be made. Further post-marketing testing and surveillance to monitor the safety or efficacy of a product is required. Also, product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or if safety or manufacturing problems occur following initial marketing. In addition, new government requirements may be established that could delay or prevent regulatory approval of our protein therapeutic candidates under development.
As part of the recently-enacted Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010, under the subtitle of Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009, or the BPCI, a statutory pathway has been created for licensure, or approval, of biological products that are biosimilar to, and possibly interchangeable with, earlier biological products licensed under the Public Health Service Act. Also under the BPCI, innovator manufacturers of original reference biological products are granted 12 years of exclusivity before biosimilars can be approved for marketing in the United States. The objectives of the BPCI are conceptually similar to those of the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, commonly referred to as the "Hatch-Waxman Act", which established abbreviated pathways for the approval of drug products. The implementation of an abbreviated approval pathway for biological products is under the direction of the FDA and is currently being developed. In late 2010, the FDA held a hearing to receive comments from a broad group of stakeholders regarding the implementation of the BPCI. Since that hearing in 2010, the FDA, in February 2012 and February 2013, has issued several draft guidances for industry related to the BPCI, addressing scientific, quality and procedural issues relevant to an abbreviated application for a biosimilar product. The approval of a biologic product biosimilar to one of our products could have a material adverse impact on our business as it may be significantly less costly to bring to market and may be priced significantly lower than our products.
Both before and after the FDA approves a product, the manufacturer and the holder or holders of the BLA for the product are subject to comprehensive regulatory oversight. For example, quality control and manufacturing procedures must conform, on an ongoing basis, to cGMP requirements, and the FDA periodically inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMPs. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to spend time, money and effort to maintain cGMP compliance.
Orphan Drug Act
The Orphan Drug Act provides incentives to manufacturers to develop and market drugs for rare diseases and conditions affecting fewer than 200,000 persons in the United States at the time of application for orphan drug designation. Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting a BLA. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review and approval process. If a product that has orphan drug designation subsequently receives the first FDA approval for the disease for which it has such designation, the holder of the approval is entitled to a seven-year exclusive marketing period in the United States for that product except in very limited circumstances. For example, a drug that the FDA considers to be clinically superior to, or different from, another approved orphan drug, even though for the same indication, may also obtain approval in the United States during the seven-year exclusive marketing period. In addition, holders of exclusivity for orphan drugs are expected to assure the availability of sufficient quantities of their orphan drugs to meet the needs of patients. Failure to do so could result in the withdrawal of marketing exclusivity for the drug. ACE-536 has Orphan drug designation in the United States for two indications.
Legislation similar to the Orphan Drug Act has been enacted outside the U.S., including in the EU. The orphan legislation in the EU is available for therapies addressing chronic debilitating or life-threatening conditions that affect five or fewer out of 10,000 persons or are financially not viable to develop. The market exclusivity period is for ten years, although that period can be reduced to six years if, at the end of the fifth year, available evidence establishes that the product is sufficiently profitable not to justify maintenance of market exclusivity. The market exclusivity may be extended to 12 years if sponsors complete a pediatric investigation plan agreed upon with the relevant committee of the EMA.
Expedited Review and Approval
The FDA has various programs, including Fast Track, priority review, and accelerated approval, which are intended to expedite or simplify the process for reviewing drugs, and/or provide for the approval of a drug on the basis of a surrogate endpoint. Even if a drug qualifies for one or more of these programs, the FDA may later decide that the drug no longer meets the conditions for qualification or that the time period for FDA review or approval will be shortened. Generally, drugs that are eligible for these programs are those for serious or life-threatening conditions, those with the potential to address unmet medical needs and those that offer meaningful benefits over existing treatments. For example, Fast Track is a process designed to facilitate the development and expedite the review of drugs to treat serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions and fill unmet medical needs. Priority review is designed to give drugs that offer major advances in treatment or provide a treatment where no adequate therapy exists an initial review within six months as compared to a standard review time of ten months. Although Fast Track and priority review do not affect the standards for approval, the FDA will attempt to facilitate early and frequent meetings with a sponsor of a Fast Track designated drug and expedite review of the application for a drug designated for priority review. Accelerated approval provides for an earlier approval for a new drug that is intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and that fills an unmet medical need based on a surrogate endpoint. A surrogate endpoint is a laboratory measurement or physical sign used as an indirect or substitute measurement representing a clinically meaningful outcome. As a condition of approval, the FDA may require that a sponsor of a drug candidate receiving accelerated approval perform post-marketing clinical trials to confirm the clinically meaning full outcome as predicted by the surrogate marker trial.
In the recently enacted Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act, or FDASIA, Congress encouraged the FDA to utilize innovative and flexible approaches to the assessment of products under accelerated approval. The law requires the FDA to issue related draft guidance within a year after the law's enactment and also promulgate confirming regulatory changes. For example, sponsors may request that their drug be designated as a Breakthrough Therapy. A request for Breakthrough Therapy designation should be submitted concurrently with, or as an amendment to an IND, ideally no later than the end-of-Phase 2 meeting with FDA. FDA has recently issued guidance related to this designation and has already granted the designation to some 20 new drugs.
Pediatric Exclusivity and Pediatric Use
Under the Best Pharmaceuticals for Children Act, or BPCA, certain drugs may obtain an additional six months of exclusivity, if the sponsor submits information requested in writing by the FDA, or a Written Request, relating to the use of the active moiety of the drug in children. The FDA may not issue a Written Request for studies on unapproved or approved indications or where it determines that information relating to the use of a drug in a pediatric population, or part of the pediatric population, may not produce health benefits in that population.
We have not received a Written Request for such pediatric studies, although we may ask the FDA to issue a Written Request for such studies in the future. To receive the six-month pediatric market exclusivity, we would have to receive a Written Request from the FDA, conduct the requested studies
in accordance with a written agreement with the FDA or, if there is no written agreement, in accordance with commonly accepted scientific principles, and submit reports of the studies. A Written Request may include studies for indications that are not currently in the labeling if the FDA determines that such information will benefit the public health. The FDA will accept the reports upon its determination that the studies were conducted in accordance with and are responsive to the original Written Request or commonly accepted scientific principles, as appropriate, and that the reports comply with the FDA's filing requirements.
In addition, the Pediatric Research Equity Act, or PREA, requires a sponsor to conduct pediatric studies for most drugs and biologicals, for a new active ingredient, new indication, new dosage form, new dosing regimen or new route of administration. Under PREA, original NDAs, BLAs and supplements thereto must contain a pediatric assessment unless the sponsor has received a deferral or waiver. The required assessment must include the evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of the product for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations and support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. The sponsor or FDA may request a deferral of pediatric studies for some or all of the pediatric subpopulations. A deferral may be granted for several reasons, including a finding that the drug or biologic is ready for approval for use in adults before pediatric studies are complete or that additional safety or effectiveness data needs to be collected before the pediatric studies begin. After April 2013, the FDA must send a non-compliance letter to any sponsor that fails to submit the required assessment, keep a deferral current or fails to submit a request for approval of a pediatric formulation.
As part of the FDASIA, Congress made a few revisions to BPCA and PREA, which were slated to expire on September 30, 2012, and made both laws permanent.
Reimbursement
In both domestic and foreign markets, sales and reimbursement of any approved products will depend, in part, on the extent to which the costs of such products will be covered by third-party payors, such as government health programs, commercial insurance and managed healthcare organizations. These third-party payors are increasingly challenging the prices charged for medical products and services and imposing controls to manage costs. The containment of healthcare costs has become a priority of federal and state governments and the prices of drugs have been a focus in this effort. Governments have shown significant interest in implementing cost-containment programs, including price controls, restrictions on reimbursement and requirements for substitution of generic products. Adoption of price controls and cost-containment measures, and adoption of more restrictive policies in jurisdictions with existing controls and measures, could further limit our net revenue and results. In addition, there is significant uncertainty regarding the reimbursement status of newly approved healthcare products. We may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in order to demonstrate the cost-effectiveness of our products. If third-party payors do not consider our products to be cost-effective compared to other therapies, the payors may not cover our products after approved as a benefit under their plans or, if they do, the level of payment may not be sufficient to allow us to sell our products on a profitable basis.
Within the United States, if we obtain appropriate approval in the future to market any of our current protein therapeutic candidates, we may seek approval and coverage for those products under Medicaid, Medicare and the Public Health Service (PHS) pharmaceutical pricing program and also seek to sell the products to federal agencies.
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that is administered by the states for low income and disabled beneficiaries. Under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program, manufacturers are required to pay a rebate for each unit of product reimbursed by the state Medicaid programs. The amount of the rebate
for each product is set by law and may be subject to an additional discount if certain pricing increases more than inflation.
Medicare is a federal program administered by the federal government that covers individuals age 65 and over as well as those with certain disabilities. Medicare Part D provides coverage to enrolled Medicare patients for self-administered drugs (i.e., drugs that do not need to be administered by a physician). Medicare Part D is administered by private prescription drug plans approved by the U.S. government and each drug plan establishes its own Medicare Part D formulary for prescription drug coverage and pricing, which the drug plan may modify from time-to-time.
Medicare Part B covers most injectable drugs given in an in-patient setting, and some drugs administered by a licensed medical provider in hospital outpatient departments and doctors offices. Medicare Part B is administered by Medicare Administrative Contractors, which generally have the responsibility of making coverage decisions. Subject to certain payment adjustments and limits, Medicare generally pays for Part B covered drugs based on a percentage of manufacturer-reported average sales price.
Drug products are subject to discounted pricing when purchased by federal agencies via the Federal Supply Schedule (FSS). FFS participation is required for a drug product to be covered and paid for by certain federal agencies and for coverage under Medicaid, Medicare Part B and the PHS pharmaceutical pricing program. FSS pricing is negotiated periodically with the Department of Veterans Affairs. FSS pricing is intended to not exceed the price that a manufacturer charges its most-favored non-federal customer for its product. In addition, prices for drugs purchased by the Veterans Administration, Department of Defense (including drugs purchased by military personnel and dependents through the TRICARE retail pharmacy program), Coast Guard, and PHS are subject to a cap on pricing (known as the "federal ceiling price") and may be subject to an additional discount if pricing increases more than inflation.
To maintain coverage of drugs under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program, manufacturers are required to extend discounts to certain purchasers under the PHS pharmaceutical pricing program. Purchasers eligible for discounts include hospitals that serve a disproportionate share of financially needy patients, community health clinics and other entities that receive health services grants from the PHS.
The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 provides funding for the federal government to compare the effectiveness of different treatments for the same illness. A plan for the research will be developed by the Department of Health and Human Services, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the National Institutes for Health, and periodic reports on the status of the research and related expenditures will be made to Congress. Although the results of the comparative effectiveness studies are not intended to mandate coverage policies for public or private payors, it is not clear what effect, if any, the research will have on the sales of any product, if any such product or the condition that it is intended to treat is the subject of a study. It is also possible that comparative effectiveness research demonstrating benefits in a competitor's product could adversely affect the sales of any of our approved protein therapeutics. If third-party payors do not consider our products to be cost-effective compared to other available therapies, they may not cover our products as a benefit under their plans or, if they do, the level of payment may not be sufficient to allow us to sell our products on a profitable basis.
The United States and state governments continue to propose and pass legislation designed to reduce the cost of healthcare. In March 2010, the United States Congress enacted the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act which includes changes to the coverage and payment for drug products under government health care programs. Adoption of other new legislation at the federal or state level could further limit reimbursement for pharmaceuticals.
Outside the United States, ensuring adequate coverage and payment for our products will face challenges. Pricing of prescription pharmaceuticals is subject to governmental control in many countries. Pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can extend well beyond the receipt of regulatory marketing approval for a product and may require us to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost effectiveness of our protein therapeutic candidates or products to other available therapies. The conduct of such a clinical trial could be expensive and result in delays in our commercialization efforts. Third-party payors are challenging the prices charged for medical products and services, and many third-party payors limit reimbursement for newly-approved health care products. Recent budgetary pressures in many European Union countries are also causing governments to consider or implement various cost-containment measures, such as price freezes, increased price cuts and rebates. If budget pressures continue, governments may implement additional cost-containment measures. Cost-control initiatives could decrease the price we might establish for products that we may develop or sell, which would result in lower product revenues or royalties payable to us. There can be no assurance that any country that has price controls or reimbursement limitations for pharmaceutical products will allow favorable reimbursement and pricing arrangements for any of our products.
Foreign Regulation
In addition to regulations in the United States, we will be subject to a variety of foreign regulations governing clinical trials and commercial sales and distribution of our protein therapeutic candidates. Whether or not we obtain FDA approval for a protein therapeutic candidate, we must obtain approval from the comparable regulatory authorities of foreign countries or economic areas, such as the European Union, before we may commence clinical trials or market products in those countries or areas. The approval process and requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials, product licensing, pricing and reimbursement vary greatly from place to place, and the time may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval.
Certain countries outside of the United States have a process that requires the submission of a clinical trial application much like an IND prior to the commencement of human clinical trials. In Europe, for example, a clinical trial application, or CTA, must be submitted to the competent national health authority and to independent ethics committees in each country in which a company intends to conduct clinical trials. Once the CTA is approved in accordance with a country's requirements, clinical trial development may proceed in that country. In all cases, the clinical trials must be conducted in accordance with good clinical practices, or GCPs and other applicable regulatory requirements.
Under European Union regulatory systems, a company may submit marketing authorization applications either under a centralized or decentralized procedure. The centralized procedure is compulsory for medicinal products produced by biotechnology or those medicinal products containing new active substances for specific indications such as the treatment of AIDS, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, viral diseases and designated orphan medicines, and optional for other medicines which are highly innovative. Under the centralized procedure, a marketing application is submitted to the European Medicines Agency where it will be evaluated by the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use and a favorable opinion typically results in the grant by the European Commission of a single marketing authorization that is valid for all European Union member states within 67 days of receipt of the opinion. The initial marketing authorization is valid for five years, but once renewed is usually valid for an unlimited period. The decentralized procedure provides for approval by one or more "concerned" member states based on an assessment of an application performed by one member state, known as the "reference" member state. Under the decentralized approval procedure, an applicant submits an application, or dossier, and related materials to the reference member state and concerned member states. The reference member state prepares a draft assessment and drafts of the related materials within 120 days after receipt of a valid application. Within 90 days of receiving the reference member state's assessment report, each concerned member state must decide whether to
approve the assessment report and related materials. If a member state does not recognize the marketing authorization, the disputed points are eventually referred to the European Commission, whose decision is binding on all member states.
As in the United States, we may apply for designation of a product as an orphan drug for the treatment of a specific indication in the European Union before the application for marketing authorization is made. Orphan drugs in Europe enjoy economic and marketing benefits, including up to 10 years of market exclusivity for the approved indication unless another applicant can show that its product is safer, more effective or otherwise clinically superior to the orphan designated product.
Additional Regulation
We are also subject to regulation under the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Environmental Protection Act, the Toxic Substances Control Act, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act and other present and potential federal, state or local regulations. These and other laws govern our use, handling and disposal of various biological and chemical substances used in, and waste generated by our operations. Our research and development involves the controlled use of hazardous materials, chemicals and viruses. Although we believe that our safety procedures for handling and disposing of such materials comply with the standards prescribed by state and federal regulations, the risk of accidental contamination or injury from these materials cannot be completely eliminated. In the event of such an accident, we could be held liable for any damages that result and any such liability could exceed our resources.
There have been a number of federal and state proposals during the last few years regarding the pricing of pharmaceutical and biological products, government control and other changes to the healthcare system of the U.S. It is uncertain what legislative proposals will be adopted or what actions federal, state or private payers for medical goods and services may take in response to any healthcare reform proposals or legislation. We cannot predict the effect medical or healthcare reforms may have on our business, and no assurance can be given that any such reforms will not have a material adverse effect.
Manufacturing
We currently manufacture drug substance for our preclinical studies, Phase 1 clinical trials and Phase 2 clinical trials of ACE-536 and dalantercept. We manufacture material compliant to U.S. and European cGMP at our 12,000 square foot multi-product facility located at our corporate headquarters in Cambridge, Massachusetts. We have the capabilities to manufacture receptor fusion proteins, monoclonal antibodies, and other protein therapeutics.
Our manufacturing facility is based on single use, disposable technology to maximize the focus of personnel and other resources on the production process, minimizing the need for cleaning and sterilization while optimizing the efficiency of product change-over. The facility consists of four independent clean rooms totaling 4,000 square feet. The facility includes one 250 liter and one 1,000 liter single use bioreactor and has space for two additional 1,000 liter bioreactors.
Over 20 fulltime employees focus on our process development and manufacturing activities. We believe that our strategic investment in manufacturing capabilities allows us to advance our protein therapeutic candidates at a more rapid pace and provides us with more portfolio flexibility than if we used a contract manufacturer. The facility produces drug substance in a cost-effective manner while allowing us to retain control over the process and provides an ability to balance the requirements of multiple programs and avoid costly commitments of funds before clinical data are available.
Our manufacturing capabilities encompass the full manufacturing process through quality control and quality assurance. These groups are integrated with our project teams from discovery through
development. This structure enables us to efficiently transfer research stage lead molecules into manufacturing. We have designed our manufacturing facility and processes to provide maximum flexibility and rapid change over for the manufacture of different protein therapeutic candidates. We outsource fill-finish, packaging, labeling, shipping, and distribution.
We manufacture our protein therapeutic candidates using readily available raw materials and well established manufacturing procedures based on a standardized process modified for each of our protein therapeutic candidates. We produce our proteins in bioreactors using Chinese hamster ovary cells that have been genetically engineered to produce our specific protein therapeutic candidates. We then purify the proteins using industry standard methods, which include affinity chromatography and ultrafiltration operations. Processes developed within our facility have been successfully transferred to commercial facilities based on stainless steel bioreactors. We have conducted comparability characterization on sotatercept between our Phase 2 material and material made at a commercial manufacturer and found them to be comparable.
We believe that we can scale our manufacturing processes to support our clinical development programs and the potential commercialization of our protein therapeutic candidates. For our early phase protein therapeutic candidates, we intend to continue to manufacture drug substance for preclinical testing and Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical development at our current facilities. As ACE-536 progresses to Phase 3 clinical trials, we intend to transfer the process for Phase 3 production to Celgene, under the terms of our collaboration agreements. We have already successfully transferred the manufacturing process for sotatercept to Celgene, and we expect Celgene will use a contract manufacturer for Phase 3 and commercial supply of sotatercept and ACE-536.
Employees
As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had 7879 full-time employees, 6364 of whom are involved in research, development or manufacturing, and 20 of whom have Ph.D. or M.D. degrees. We have no collective bargaining agreements with our employees and we have not experienced any work stoppages. We consider our relations with our employees to be good.
Facilities
Our corporate, research and development, manufacturing, and clinical trial operations are located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. We lease approximately 94,500 square feet of office and laboratory space in three adjacent buildings with aggregate monthly net-rent expense of approximately $0.4 million. We have sublet approximately 14,000 square feet of space in one of our leased buildings. Two leases expire in September 2018 and one lease expires in May 2015. We believe our facilities are adequate for our current needs and that suitable additional substitute space would be available if needed.
Legal Proceedings
On October 18, 2012, the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, which we refer to as Salk, filed a complaint in the Massachusetts Superior Court for Suffolk County, alleging that we breached one of our two licensing agreements with Salk. The licensing agreement in dispute provides us with a license with respect to certain of Salk's U.S. patents related to the ActRIIB activin receptor proteins. Salk contends that, under the licensing agreement, we owed Salk a greater share of the upfront payment that we received under our now-terminated agreement with Shire AG regarding ACE-031 and a share of the upfront payment and development milestone payments that we have received under our ongoing collaboration agreement with Celgene regarding ACE-536. Salk is seeking a total of approximately $10.5 million plus interest in payment and a 15% share of future development milestone payments received under our agreement with Celgene regarding ACE-536. We contend that no additional
amounts are due to Salk and that we have complied with all of our payment obligations under the applicable Salk license agreement.
We moved to dismiss the complaint on December 3, 2012. The Court denied our motion on February 28, 2013. On March 14, 2013, Acceleron answered the complaint and asserted patent invalidity counterclaims. On the basis of those counterclaims, Acceleron removed the action on March 28, 2013 to the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. The parties have since reached an agreement on a stipulation as to certain patent issues raised in the action, and Acceleron has dismissed its counterclaims. The Court held an initial scheduling conference on May 30, 2013, and the parties have begun fact discovery. The case is currently scheduled for trial in September 2014. We intend to defend our position vigorously.
Executive Officers, Significant Employees and Directors
Below is a list of the names, ages as of August 1, 2013 and positions, and a brief account of the business experience of the individuals who serve as our executive officers and directors as of the date of this prospectus. Our certificate of incorporation will provide that our board of directors will be divided into three class of directors, with the classes as nearly equal in number as possible. Upon completion of this offering, each of our directors identified below will serve in the class indicated. Subject to any earlier resignation or removal in accordance with the terms of our certificate of incorporation and by-laws that we expect to be in effect upon the closing of this offering, our Class I directors will serve until the first annual meeting of stockholders following the completion of this offering; our Class II directors will serve until the second annual meeting of stockholders following the completion of this offering; and our Class III directors will serve until the third annual meeting of stockholders following the completion of this offering.
Name | Age | Position | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
John L. Knopf, Ph.D. | 61 | Chief Executive Officer and President; Director (Class | |||
Kevin F. McLaughlin | 57 | Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer | |||
Matthew L. Sherman, M.D. | 57 | Senior Vice President and Chief Medical Officer | |||
Steven D. Ertel | 44 | Senior Vice President and Chief Business Officer | |||
Ravindra Kumar, Ph.D. | 53 | Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer | |||
Robert J. Steininger II | 58 | Senior Vice President, Manufacturing | |||
John D. Quisel, J.D., Ph.D. | 42 | Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary | |||
Anthony B. Evnin, Ph.D. | 72 | Director (Class | |||
Jean M. George | 55 | Director (Class | |||
George Golumbeski, Ph.D. | 56 | Director (Class | |||
Carl L. Gordon, Ph.D., CFA* | 48 | Director | |||
Edwin M. Kania, Jr. | 56 | Director (Class | |||
Tom Maniatis, Ph.D. | 70 | Director (Class | |||
Terrance G. McGuire | 57 | Director (Class | |||
Richard F. Pops | 51 | Director (Class | |||
Joseph S. Zakrzewski | 50 | Director (Class | |||
John L. Knopf, Ph.D. co-founded Acceleron in 2003 and is our Chief Executive Officer and President. Dr. Knopf served on our board of directors from 2003 to 2004, and has served from 2007 to the present. Prior to founding Acceleron, Dr. Knopf served as Site Head of the Wyeth Research facilities in Cambridge, MA and Vice President of Metabolic and Respiratory Disease. Dr. Knopf was an early key scientist at Genetics Institute (GI) from 1982 to 1998, where he participated in the development of pioneering biopharmaceutical products including the first treatment for hemophilia, recombinant factor VIIIRecombinate® and helped establish GI as a premier biopharmaceutical company. While at GI, he established a structure-based small molecule discovery group. Dr. Knopf is the author of several key scientific manuscripts in the area of signal transduction, and is named as an inventor of several patents. Dr. Knopf received a BS in biology from SUNY Stonybrook and his Ph.D. in biology at SUNY Buffalo. We believe Dr. Knopf's extensive experience and knowledge of biopharmaceuticals and our company qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Kevin F. McLaughlin joined Acceleron in November 2010 and is our Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer. He most recently served, from 2009 through 2010, as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Qteros, Inc. He was a co-founder of Aptius
Education, Inc. and from 2007 through 2009 he worked as the Chief Operating Officer and a director. From 1996 through 2007, Mr. McLaughlin held several executive positions with PRAECIS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. He joined PRAECIS as their first Chief Financial Officer where he had responsibility for private financings, partnership financings, the company's initial public offering and subsequent stock offering. Later, Mr. McLaughlin became COO, and then President and CEO, and he served as a member of the board of directors. In this capacity he was responsible for negotiating the sale of the company to GlaxoSmithKline. He began his career in senior financial roles at Prime Computer and Computervision Corporation. Mr. McLaughlin received a BS in business from Northeastern University and an MBA from Babson College.
Matthew L. Sherman, M.D. joined Acceleron in May 2006 and is our Senior Vice President and Chief Medical Officer. Previously, he served as Senior Vice President and Chief Medical Officer at Synta Pharmaceuticals where he was responsible for clinical research, clinical operations, biostatistics, data management, regulatory affairs, quality assurance and program management. Prior to that, Dr. Sherman worked at Genetics Institute and Wyeth Pharmaceuticals in various capacities including Therapeutic Area Director for Oncology. While at Wyeth, Dr. Sherman provided senior oncology and hematology leadership for worldwide clinical development for both small molecule and biologic therapeutics, including the submission and approval of Mylotarg® by the FDA. He has published numerous papers and book chapters in the field of oncology and clinical development and is named as an inventor of several patents. Dr. Sherman is board certified in Medical Oncology and Internal Medicine and held various clinical positions at Harvard Medical School with corresponding hospital appointments at the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women's Hospital. Dr. Sherman received an SB in chemistry from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and an MD from Dartmouth Medical School.
Steven D. Ertel joined Acceleron in January 2006 and is our Senior Vice President and Chief Business Officer. Mr. Ertel established our business development function and currently leads our business development, commercial strategy and program management functions. Mr. Ertel has over 20 years of experience in the biotechnology industry at Vivus, Inc., Genentech, Inc., Biogen Idec, Inc., and Synta. His responsibilities at these companies included program management for preclinical and clinical stage programs, commercial strategy for clinical stage programs, market launch of a novel biologic agent, and business development. Mr. Ertel began his career in the venture capital industry at Oxford Bioscience Partners. Mr. Ertel received a BSE in biomedical engineering from Duke University and an MBA from the Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania.
Ravindra Kumar, Ph.D. joined Acceleron in March 2004 and is currently our Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer. Dr. Kumar established and currently leads our discovery research. Previously, Dr. Kumar worked for 12 years at Genetics Institute and Wyeth Pharmaceuticals. At Genetics Institute, Dr. Kumar was a key member of the Small Molecule Drug Discovery group and was responsible for cell biology. Following the integration of discovery functions from GI and Wyeth Pharmaceuticals, Dr. Kumar served as Senior Scientist in the Biological Chemistry group. Dr. Kumar is the author of several key scientific manuscripts in the area of protein glycosylation and is named as an inventor of several patents. Dr. Kumar received his BS in chemistry from Rohilkhand University, his MS in chemistry from Meerut University, his Ph.D. from University of New Brunswick and he completed his post-doctoral fellowship at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, in Bronx, NY.
Robert J. Steininger II joined Acceleron in March 2007 and is our Senior Vice President of Manufacturing. He currently serves as a director of the Massachusetts Accelerator for Biomanufacturing, PBE Corporation and Sunopro. He was previously the Vice President of Process Sciences at Millennium Pharmaceuticals. In this capacity, he was responsible for managing the processes for the bulk production of both large and small molecule clinical candidates. Mr. Steininger also served as a Vice President within the Millennium Product and Portfolio Management organization. Prior to joining Millennium, he held multiple roles at GI from 1984 to 2000, including Director of
Clinical Production, Director of Process Technology, Director of Regulatory Affairs, and Senior Director of Research, Genomics. Mr. Steininger received a SB in chemistry from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and an MS in chemical engineering from the University of California, Berkeley.
John D. Quisel, J.D., Ph.D. joined Acceleron in October 2006 and is our Vice President and General Counsel and Secretary. Prior to joining us, Dr. Quisel worked at the Boston office of Ropes & Gray LLP and, prior to that, the Boston office of Foley Hoag LLP. In his work at law firms, Dr. Quisel has, through strategic in-licensing and protection of internal research programs, assembled and licensed product and platform focused intellectual property portfolios for numerous biotechnology ventures. Over his entire career, Dr. Quisel's experience spans many aspects of biotechnology law, including the negotiation of intellectual property licenses and product development collaborations, patent prosecution and litigation. Dr. Quisel received an AB in biology from Harvard University, an MS in biology from Stanford University, a Ph.D. in biology from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and a J.D. from Harvard Law School.
Anthony B. Evnin, Ph.D. has served as a member of our board of directors since 2004. Since 1975, Dr. Evnin has been a Partner at Venrock, Inc. and then VR Management, LLC, both part of Venrock Associates, a venture capital firm, where he focuses largely on life sciences investments and, in particular, biotechnology investments. Before this, he served as a manager of business development at Story Chemical Corporation and a research scientist at Union Carbide Corporation. Dr. Evnin currently serves on the boards of AVEO Pharmaceuticals, Infinity Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Constellation Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Metabolex, Inc. During the last five years, Dr. Evnin served as a director of Altea Therapeutics Corporation, Celladon Corporation, Kenet, Inc., Boston-Power, Inc., Memory Pharmaceuticals Corp., Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Renovis, Inc., Icagen, Inc., Coley Pharmaceutical Group, Inc., and Pharmos Corporation. Dr. Evnin is a Trustee of The Rockefeller University and of The Jackson Laboratory, Trustee Emeritus of Princeton University, a Member of the Boards of Overseers and Managers of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, and a Director of the New York Genome Center. Dr. Evnin received an AB in chemistry from Princeton University and a Ph.D. in chemistry from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. We believe Dr. Evnin's substantial experience as an investor in, and director of, early stage biopharmaceutical companies, as well as his expertise in corporate strategy at a publicly traded biopharmaceutical company qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Jean M. George has served as a member of our board of directors since 2005. Since 2002, Ms. George has been a Managing Director at Advanced Technology Ventures (ATV), and, concurrently since April 2013, Ms. George has been a Managing Director at LSV Capital Management. She joined ATV in 2002 and serves as the firm's East Coast lead partner for healthcare investments. Prior to joining ATV, Ms. George was a Director at BancBoston Ventures, where she led the health care team's investment activity in NuGenesis Technologies Corp., Microbia, Inc., Syntonix Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Neurometrix, Inc. Before BancBoston Ventures, she worked at Genzyme Corporation from 1988 to 1998, where she held a variety of operational roles in marketing, product development, and business development, including Vice President of Global Sales and Marketing. She also worked as a Vice President and Founder of Genzyme's Tissue Repair Division. She is currently a Director of Calithera Biosciences, Hydra Biosciences, Inc., Zeltiq Aesthetics, Inc. and Portola Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ms. George was a Director of Hypnion, Inc., Critical Therapeutics, Inc. and Proteolix, Inc. She was named a member of the Scientific Advisory Board for the Massachusetts Life Sciences Center. Ms. George received a BS in biology from the University of Maine and an MBA from Simmons College Graduate School of Management. We believe that Ms. George's executive experience in the life sciences and therapeutic device industries qualifies her to serve as a member of our board of directors.
George Golumbeski, Ph.D. has served as a member of our board of directors since 2011. Since 2009, Dr. Golumbeski has been a Senior Vice President of Business Development for Celgene Corporation, where he is responsible for the full array of business development activities, including
identification and evaluation of opportunities, structuring and negotiating transactions, in-licensing, M&A, out-licensing, and alliance management. At Celgene, these activities are focused primarily within the therapeutic areas of oncology and inflammation. From 2008 to 2009, Dr. Golumbeski served as the CEO of Nabriva Therapeutics AG. Prior to Nabriva, Dr. Golumbeski served as Vice President of Business Development, Licensing and Strategy for Novartis-Oncology. During his tenure at Novartis, Dr. Golumbeski's group closed a significant number of collaboration agreements which bolstered the development pipeline. Earlier in his career, Dr. Golumbeski held senior positions at Elan Pharmaceuticals and at Schwarz Pharma, where he led the effort to in-license rotigotine and lacosamide (now both approved agents). Dr. Golumbeski received a BA in biology from the University of Virginia and a Ph.D. in genetics from the University of Wisconsin-Madison. We believe that Dr. Golumbeski's experience as an officer of other pharmaceutical companies, as well as Dr. Golumbeski's extensive experience in research and development and corporate leadership positions, qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Carl L. Gordon, Ph.D., CFA has served as a member of our board of directors since 2006. Dr. Gordon has served as a General Partner and Co-Head of Private Equity of OrbiMed Advisors LLC, or OrbiMed, which he co-founded in 1998. From 1995 to 1997 he was a senior biotechnology analyst at Mehta and Isaly, and from 1993 to 1995 he was a Fellow at The Rockefeller University. Dr. Gordon currently serves on the board of directors of Selecta Biosciences, Singulex, Inc. and other companies. He has also served on the boards Complete Genomics, Inc., BioCryst Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Arius Research, Inc. and numerous other companies. Dr. Gordon received a BS in chemistry from Harvard and a Ph.D in molecular biology from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. We believe that Dr. Gordon's venture capital experience, expertise in the scientific field of molecular biology and financial credentials qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Edwin M. Kania, Jr. has served as a member of our board of directors since 2004. Since 2000, Mr. Kania has been Managing Partner and the Chairman of Flagship Ventures, a Boston-based venture capital firm that he co-founded and that also manages the Applied Genomic Technology Capital Fund, L.P. (AGTC Fund) as well as funds raised by OneLiberty Ventures. Prior to co-founding Flagship Ventures, Mr. Kania was a General Partner at OneLiberty Ventures and its predecessor firm, Morgan Holland Ventures which he joined in 1985. Mr. Kania currently serves on the boards of several private companies. Mr. Kania has also served on the boards of Aspect Medical, EXACT Sciences and other public and private companies. Mr. Kania's direct investment experience covers over 100 companies, and he has been intimately involved in the launch and development of more than a dozen companies as the founding, lead or co-lead investor, and has on occasion assumed operating roles in support of management. Mr. Kania received a BS in physics from Dartmouth College and an MBA from Harvard Business School. We believe that Mr. Kania's extensive experience investing in, guiding and leading start-up and early phase companies qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Tom Maniatis, Ph.D. co-founded Acceleron in 2003 and has served as a member of our board of directors and chairman of our Scientific Advisory Board since 2003. Since 2010 he has been a Professor and Chair of the Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biophysics at the Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons. Prior to working at Columbia, Dr. Maniatis was a professor at Harvard University where he studied the mechanisms of transcription and RNA splicing in eukaryotes. Dr. Maniatis currently serves on the board of Constellation Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Dr. Maniatis is also a co-founder of Genetics Institute and ProScript Inc., where he served on the board of directors. Dr. Maniatis is a member of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, and has received numerous awards for his research contributions, including the Eli Lilly Research Award in Microbiology and Immunology, the Richard Lounsbery Award for Biology and Medicine from the U.S. and French National Academies of Science, and the 2012 Lasker-Koshland Special Achievement Award in Medical Science. Dr. Maniatis received a BA in biology, an MS in chemistry from the University of Colorado at Boulder, and a Ph.D. in molecular biology from Vanderbilt University. We believe Dr. Maniatis's
extensive experience and knowledge of biopharmaceuticals and the biopharmaceutical industry qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Terrance G. McGuire has served as a member of our board of directors since 2005. Mr. McGuire co-founded Polaris Partners in 1996 and is currently one of their general partners. Prior to starting Polaris Partners, Mr. McGuire spent seven years at Burr, Egan, Deleage & Co., investing in early stage medical and information technology companies. He currently serves on the board of directors of Adimab/Arsanis, Aero Designs/Wiki Cells, Arsenal Medical/480 Biomedical, Iora Health, Ironwood Pharmaceuticals, Life Line Screening, MicroCHIPS, NextCode, Pulmatrix, SustainX, and Trevena. He has served on the board of directors of numerous other companies, including Remon Medical Technologies, GlycoFi, Akamai Technologies, Aspect Medical Systems, Cubist Pharmaceuticals, Transform Pharma, and deCODE genetics. Mr. McGuire is the former chairman of the National Venture Capital Association, chairman of the board of the Thayer School of Engineering at Dartmouth College, and a member of the boards of The David H. Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and The Arthur Rock Center for Entrepreneurship at Harvard Business School. Mr. McGuire received a BS in physics and economics from Hobart College, an MS in engineering from The Thayer School at Dartmouth College, and an MBA from Harvard Business School. We believe that Mr. McGuire's extensive experience as a venture capitalist focused on the biotechnology industry, as well as Mr. McGuire's many years of experience helping companies evolve from the start-up phase to successful public companies qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Richard F. Pops has served as a member of our board of directors since 2004. Since 2011, Mr. Pops has served as Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the board of Alkermes plc, the parent company of Alkermes. From 2009 to 2011, Mr. Pops served as Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Alkermes, from 2007 to 2009 he served as the Chairman of the board of Alkermes, and from 1991 through 2007 he served as the Chief Executive Officer of Alkermes. Mr. Pops also serves on the board of directors of Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., Epizyme Inc., the Biotechnology Industry Organization (BIO) and Pharmaceutical Researcher and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA). He has previously served on the board of directors of Sirtris Pharmaceuticals from 2004 to 2008, and CombinatoRx, Inc. from 2001 to 2009. Mr. Pops also served on the board of directors of Reliant Pharmaceuticals, a privately held pharmaceutical company purchased by GlaxoSmithKline in 2007, and on the advisory board of Polaris Venture Partners. He was a member of the Harvard Medical School Board of Fellows from 2002 through June 2012. Mr. Pops received a BA in economics from Stanford University. We believe that Mr. Pops leadership experience and industry knowledge qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Joseph S. Zakrzewski has served as a member of our board of directors since 2011. Since 2010, Mr. Zakrzewski has been Executive Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Amarin Corporation. From 2007 to 2010, Mr. Zakrzewski served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Xcellerex. From 2005 to 2007, Mr. Zakrzewski served as the Chief Operating Officer of Reliant Pharmaceuticals, overseeing the launch of Omacor®, a drug to treat elevated triglyceride levels. From 1988 to 2004, Mr. Zakrzewski served in a variety of positions at Eli Lilly and Company including as Vice President, Corporate Business Development from 2003 through 2004. In addition, Mr. Zakrzewski served as a Venture Partner with OrbiMed in 2010 and 2011. Mr. Zakrzewski also currently serves on the board of directors of Amarin and Insulet Corporation and has also served on the board of directors of Xcellerex, Azelon/Zelos Therapeutics and Promedior. Mr. Zakrzewski received a BS in Chemical Engineering and an MS in Biochemical Engineering from Drexel University as well as an MBA in Finance from Indiana University. We believe that Mr. Zakrzewski's substantial experience as an executive officer of other pharmaceutical companies, as well as Mr. Zakrzewski's service as on boards of directors of other pharmaceutical companies qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Board Composition
Our board of directors is currently comprised of 10 members. However, we expect that, effective upon the completion of this offering, Dr. Gordon will resign from our board of directors and we will reduce the size of our board from 10 to nine. Our board of directors has determined that each of Ms. George and Messrs Evnin, Golumbeski, Kania, Maniatis, McGuire, Pops and Zakrzewski is independent for NASDAQ purposes. The members of our board of directors were elected in compliance with the provisions of the voting agreement among us and our major stockholders. The voting agreement will terminate upon the closing of this offering and we will have no further contractual obligations regarding the election of our directors. See "Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions". Our directors hold office until their successors have been elected and qualified or until their earlier death, resignation or removal. There are no family relationships among any of our directors or executive officers.
Board Committees
Our board of directors has three standing committees: the audit committee, the compensation committee and the nominating and corporate governance committee.
Audit Committee
Our audit committee is composed of Anthony B. Evnin, Ph.D., Jean M. George and Joseph S. Zakrzewski, with Dr. Evnin serving as chairman of the committee. Our board of directors has determined that each member of the audit committeeMr. Zakrzewski meets the independence requirements of Rule 10A-3 under the Exchange Act and the applicable listing standards of NASDAQ. We expect that a majority of our audit committee members will be independent within 90 days of this prospectus. Our board of directors has determined that Joseph S. Zakrzewski is an "audit committee financial expert" within the meaning of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, regulations and applicable listing standards of NASDAQ. The audit committee's responsibilities include:
Compensation Committee
Our compensation committee is composed of Edwin M. Kania, Jr., Tom Maniatis, Ph.D. and Joseph S. Zakrzewski, with Mr. Kania serving as chairman of the committee. Our board of directors has determined that each member of the compensation committee is "independent" as defined under the applicable listing standards of NASDAQ. The compensation committee's responsibilities include:
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee
Our nominating and corporate governance committee is composed of Anthony B. Evnin, Ph.D., Jean M. George and Terrance G. McGuire, with Ms. George serving as chairman of the committee. Our board of directors has determined that each member of the nominating and corporate governance committee is "independent" as defined under the applicable listing standards of NASDAQ. The nominating and corporate governance committee's responsibilities include:
Our board of directors may establish other committees from time to time.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
None of the members of our compensation committee has at any time during the prior three years been one of our officers or employees. None of our executive officers currently serves, or in the past fiscal year has served, as a member of the board of directors or compensation committee of any entity that has one or more executive officers serving on our board of directors or compensation committee. For a description of transactions between us and members of our compensation committee and affiliates of such members, please see "Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions."
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
We have adopted a code of business conduct and ethics that applies to all of our employees, officers and directors, including those officers responsible for financial reporting. Upon the closing of this offering, our code of business conduct and ethics will be available on our website. We intend to disclose any amendments to the code, or any waivers of its requirements, on our website.
EXECUTIVE AND DIRECTOR COMPENSATION
Overview
The following discussion relates to the compensation of our founder, Chief Executive Officer and President, John L. Knopf, Ph.D., and our two most highly compensated executive officers (other than our chief executive officer), Matthew L. Sherman, M.D., our Chief Medical Officer and Senior Vice President, and John D. Quisel, J.D., Ph.D., our General Counsel, Vice President and Secretary, who are collectively referred to in this prospectus as our named executive officers. Each year, our compensation committee and board of directors review and determine the compensation of our named executive officers. Our executive compensation program is designed to attract and retain a highly skilled team of key executives and to align the compensation of our executives with the interests of our shareholders by rewarding the achievement of short- and long-term strategic financial goals, which we believe serves to enhance short- and long-term value creation for our shareholders.
Elements of Executive Compensation
The compensation of our named executive officers consists of base salary, annual cash bonuses, equity awards and employee benefits that are made available to all salaried employees. Our named executive officers are also entitled to certain compensation and benefits upon certain terminations of employment and certain change in control transactions pursuant to employment agreements.
Base Salaries. Base salaries for our named executive officers are determined based on the scope of each officer's responsibilities along with his respective experience and contributions to the company. Base salaries for our named executive officers are determined annually by our compensation committee, subject to review and approval by our board of directors. When reviewing base salaries for increase, our compensation committee takes factors into account such as each officer's experience and individual performance, the company's performance as a whole, data from surveys of compensation paid by comparable companies, and general industry conditions, but does not assign any specific weighting to any factor. For 2012, our board of directors approved a base salary of $400,000 for Dr. Knopf, $364,270 for Dr. Sherman and $310,000 for Dr. Quisel, representing an increase of 5.88%, 3.00% and 3.08%, respectively, from the base salary for each such executive in 2011.
Annual Cash Bonuses. Our annual cash bonus program promotes and rewards the achievement of key strategic and business goals. For fiscal 2012, the target annual bonus as a percentage of base salary for each of Dr. Knopf, Dr. Sherman and Dr. Quisel was 50%, 30% and 30%, respectively.
At the beginning of fiscal 2012, our compensation committee established corporate performance goals, each having a designated weighting, that related to key strategic and financial goals of the company, including the initiation or completion of certain trials related to our clinical pipeline, the creation of a strategic plan to maximize business development efforts, and the achievement of other financial and business objectives, including maintenance of a certain level of cash reserves and creating certain strategic partnerships. At the end of the 2012 fiscal year, our compensation committee met and evaluated the performance of the company against the specified performance goals. Based on its evaluation, the compensation committee recommended full payment of 2012 annual bonuses at the target level for all employees covered under this program, including our named executive officers, which payments were approved by our board of directors. Accordingly, each of Drs. Knopf, Sherman and Quisel received a cash bonus for 2012 equal to $200,000, $109,281 and $93,000, respectively.
Equity Awards. Our named executive officers participate in our Acceleron Pharma Inc. 2003 Stock Option and Restricted Stock Plan, which we refer to as the "2003 Plan". See "—2003 Plan" below for additional details about the 2003 Plan. Each of our named executive officers received a grant of stock options during fiscal 2012. Grants under the 2003 Plan, including those made to our named executive officers, generally consist of stock option awards subject to time-based vesting. Awards that are subject
to time-based vesting generally vest either in quarterly installments over four years or vest as to 25% of the shares subject to the option after one year and thereafter continue to vest in quarterly installments over the following three years, generally subject to continued employment. Stock options subject to time- and performance-based vesting were granted under the 2003 Plan to Dr. Knopf in 2012. This option award vests based on the achievement by the company of certain financial goals or milestones related to clinical trials and, after the achievement of the applicable goal or milestone, quarterly over three years, with all such stock options, to the extent unvested, vesting in full on September 6, 2016, generally subject to Dr. Knopf's continued employment. Option awards serve to align the interests of our named executive officers with our shareholders, because no value is created unless the value of our common stock appreciates after grant. They also encourage retention through the use of time-based vesting. Pursuant to agreements with certain members of senior management, including our named executive officers, a portion of the executive's stock option and restricted stock awards will vest automatically as of the date of a change of control and all or a portion of the executive's stock option and restricted stock awards may vest upon certain terminations of employment.
Benefits. We provide modest benefits to our named executive officers. These benefits and perquisites, such as participation in our 401(k) plan and basic health and welfare benefit coverage, are available to all of our eligible employees.
Employment Agreements and Change of Control Agreements. Drs. Knopf, Sherman and Quisel have entered into employment agreements with us that include severance, change of control, and restrictive covenant provisions. We believe that change of control arrangements provide our executives with security that will likely reduce any reluctance they may have to pursue a change of control transaction that could be in the best interests of our stockholders. We also believe that reasonable severance and change of control benefits are necessary in order to attract and retain high-quality executive officers.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth information about certain compensation awarded or paid to our named executive officers for the 2012 fiscal year.
Name and Principal Position | Year | Salary ($)(1) | Option Awards ($)(2) | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($)(3) | Total ($) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
John L. Knopf, Ph.D. | 2012 | 400,000 | 1,355,300 | 200,000 | 1,955,300 | |||||||||||
Chief Executive Officer and President | ||||||||||||||||
Matthew L. Sherman, M.D. | 2012 | 364,270 | 124,550 | 109,281 | 598,101 | |||||||||||
Chief Medical Officer & Senior Vice President | ||||||||||||||||
John D. Quisel, J.D., Ph.D. | 2012 | 310,000 | 158,415 | 93,000 | 561,415 | |||||||||||
General Counsel, Vice President and Secretary | ||||||||||||||||
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
The following table sets forth information regarding equity awards held by our named executive officers as of December 31, 2012.
OPTION AWARDS
Name | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Exercisable | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Unexercisable | Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned Options (#) | Option Exercise Price ($)(5) | Option Expiration Date(6) | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Exercisable | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Unexercisable | Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned Options (#) | Option Exercise Price ($)(5) | Option Expiration Date(6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
John L. Knopf | 50,000 | (1) | — | — | 0.10 | 2/2/2015 | 12,500 | (1) | — | — | 0.40 | 2/2/2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 50,000 | (2) | — | — | 0.10 | 3/29/2016 | 12,500 | (2) | — | — | 0.40 | 3/29/2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 400,000 | (2) | — | — | 0.45 | 1/31/2017 | 100,000 | (2) | — | — | 1.80 | 1/31/2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,050,000 | (2) | — | — | 1.27 | 3/27/2018 | 262,500 | (2) | — | — | 5.08 | 3/27/2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 137,500 | (2) | 62,500 | (2) | — | 1.47 | 2/4/2020 | 34,375 | (2) | 15,625 | (2) | — | 5.88 | 2/4/2020 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 175,000 | (2) | 175,000 | (2) | — | 0.97 | 12/2/2020 | 43,750 | (2) | 43,750 | (2) | — | 3.88 | 12/2/2020 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 50,000 | (2) | 150,000 | (2) | — | 1.32 | 12/16/2021 | 12,500 | (2) | 37,500 | (2) | — | 5.28 | 12/16/2021 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 34,375 | (2) | 515,625 | (2) | — | 1.32 | 11/13/2022 | 8,594 | (2) | 128,906 | (2) | — | 5.28 | 11/13/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | 150,000 | (3) | 1.32 | 11/13/2022 | — | — | 37,500 | (3) | 5.28 | 11/13/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | 150,000 | (3) | 1.32 | 11/13/2022 | — | — | 37,500 | (3) | 5.28 | 11/13/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| — | — | 150,000 | (4) | 1.32 | 11/13/2022 | — | — | 37,500 | (4) | 5.28 | 11/13/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Matthew L. Sherman | 239,062 | (1) | — | — | 0.12 | 5/31/2016 | 59,765 | (1) | — | — | 0.48 | 5/31/2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 131,250 | (2) | — | — | 0.45 | 1/31/2017 | 32,812 | (2) | — | — | 1.80 | 1/31/2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 140,000 | (2) | — | — | 1.27 | 3/27/2018 | 35,000 | (2) | — | — | 5.08 | 3/27/2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 75,000 | (2) | 75,000 | (2) | — | 0.97 | 12/2/2020 | 18,750 | (2) | 18,750 | (2) | — | 3.88 | 12/2/2020 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 12,500 | (2) | 37,500 | (2) | — | 1.32 | 12/16/2021 | 3,125 | (2) | 9,375 | (2) | — | 5.28 | 12/16/2021 | |||||||||||||||||||
| — | 100,000 | (2) | — | 1.78 | 12/12/2022 | — | 25,000 | (2) | — | 7.12 | 12/12/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||
John D. Quisel | 110,000 | (1) | — | — | 0.23 | 11/15/2016 | 27,500 | (1) | — | — | 0.92 | 11/15/2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 10,000 | (2) | — | — | 0.45 | 6/12/2017 | 2,500 | (2) | — | — | 1.80 | 6/12/2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 30,000 | (2) | — | — | 1.27 | 3/27/2018 | 7,500 | (2) | — | — | 5.08 | 3/27/2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 50,000 | (2) | — | — | 1.47 | 12/17/2018 | 12,500 | (2) | — | — | 5.88 | 12/17/2018 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 75,000 | (2) | 25,000 | (2) | — | 1.47 | 12/2/2019 | 18,750 | (2) | 6,250 | (2) | — | 5.88 | 12/2/2019 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 125,000 | (2) | 125,000 | (2) | — | 0.97 | 12/2/2020 | 31,250 | (2) | 31,250 | (2) | — | 3.88 | 12/2/2020 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 18,748 | (2) | 56,252 | (2) | — | 1.32 | 12/16/2021 | 4,687 | (2) | 14,063 | (2) | — | 5.28 | 12/16/2021 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 12,500 | (2) | 87,500 | (2) | — | 1.32 | 6/7/2022 | 3,125 | (2) | 21,875 | (2) | — | 5.28 | 6/7/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||
| — | 50,000 | (2) | — | 1.78 | 12/12/2022 | — | 12,500 | (2) | — | 7.12 | 12/12/2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Retirement Benefits
We do not maintain any qualified or non-qualified defined benefit plans or supplemental executive retirement plans that cover our named executive officers. We offer a tax-qualified retirement plan, which we refer to as our 401(k) plan, to eligible employees, including our named executive officers. Our 401(k) plan permits eligible employees to defer up to 100% of their annual eligible compensation, subject to certain limitations imposed by the Internal Revenue Service. Employees' elective deferrals are immediately fully vested and non-forfeitable in this plan. We may, but are not required to, make discretionary matching contributions and other employer contributions on behalf of eligible employees under this plan. We did not make any matching or other contributions on behalf of eligible employees in fiscal year 2012.
Employment Agreements
We have entered into amended and restated employment agreements with each of Drs. Knopf, Sherman and Quisel, each providing for an initiala base salary of $400,000, $364,270 and $310,000, respectively, and a discretionary bonus based on performance goals in accordance with our annual cash bonus program. Each agreement also provides for certain payments and benefits upon a qualifying termination of the executive's employment and a change of control, as described below.
Change of Control. At the time of the consummation of a change of control, 50%, in the case of Dr. Knopf, and 25%, in the case of Drs. Sherman and Quisel, of any unvested restricted stock and stock options then held by suchthe executive that were granted on or prior to the effective date of the executive's amended and restated employment agreement (referred to as the amendment date) will vest.
Termination of Employment Without Cause or for Good Reason Following a Change of Control. If, within one year after the consummation of a change of control, the executive's employment is terminated by us (or our successor) other than for cause or the executive terminates his employment for good reason (as such terms are defined in the respective agreements),executive's employment agreement): (1) we will pay the executive a lump sum payment equal to the product of 1.5 times, in the case of Dr. Knopf, or one times, in the case of Drs. Sherman and Quisel, (x) the sum of executive's then-current annual base salary and an amount equal toplus 100% of the executive's target bonus for the year in which the termination occurs, (2) 100% of any unvested restricted stockequity and unvested stock optionsequity-based awards held by the executive at the time of such termination
will fully vest, and (3) if the executive elects under COBRA or any successor law to continue participation in our group health and/or dental plans in which the executive was participating
prior to such termination, the companywe will pay or, at itsour option reimburse the executive for, the full premium cost of that participation for 18 months, in the case of Dr. Knopf, or 12 months, in the case of Drs. Sherman and Quisel, following the date the executive's employment terminates or, if earlier, until the date the executive becomes eligible to enroll in such plans of a new employer. We will also pay the executive any base salary earned but not paid and any vacation time accrued but not used, in each case as of the termination date.
Termination of Employment Without Cause or for Good Reason. If the executive's employment is terminated by us other than for cause or the executive terminates his employment for good reason (as such terms are defined in the respective agreements)executive's employment agreement) under circumstances other than as described in the preceding paragraph,paragraph: (1) we will continue to pay the executive his base salary for a period of 1218 months, in the case of Dr. Knopf, and Dr. Sherman, and sixor 12 months, in the case of Dr.Drs. Sherman and Quisel, in accordance with our payroll policy, and (2) any unvested restricted stock or stock option awards the executive holds at the time of such termination of employment that are subject only to time-based vesting and that were granted on or prior to the amendment date will vest to the extent such restricted stock or stock option awardawards would have otherwise vested over the 12 months, nine months or six months, in the case of each of Dr. Knopf, Dr. Sherman, or Dr. Quisel, respectively, following such termination of employment, and (3) if the executive elects under COBRA or any successor law to continue participation in our group health and/or dental plans in which the executive was participating prior to such termination, we will pay or, at our option reimburse the executive for, the full premium cost of that participation for 18 months, in the case of Dr. Knopf, or 12 months, in the case of Drs. KnopfSherman and Sherman, or six months, in the case of Dr. Quisel. We will also pay the executive any base salary earned but not paid and any vacation time accrued but not used, in each case as of the termination date.
Termination of Employment Due to Death or Disability. If the executive's employment terminates due to the executive's death or disability, all unvested restricted shares and stock options then held by the executive that were granted on or prior to the amendment date will vest as of the date of termination. In the event of the executive'ssuch a termination of employment due to the executive's disability, to the extent we do not maintain a disability plan providing for continuation of the executive's base salary for one year following the date of such termination, during this period we will pay the executive, at the time the executive's base salary would otherwise have been paid, an amount equal to the excess of 100% of the executive's base salary over the disability insurance benefits, if any, actually paid to the executive. We will also pay the executive any base salary earned but not paid and any vacation time accrued but not used, in each case as of the termination date.
Severance Subject to Release of Claims and Compliance With Restrictive Covenants. Our obligation to provide the executive with any severance payments or other benefits under the employment agreement is conditioned on the executive signing an effective release of claims in our favor and the executive's continued full performance of his obligations under the Employee Confidentiality, Non-Compete and Proprietary Information Agreement relating to confidentiality, noncompetition and nonsolicitation.
Other Termination of Employment. If the executive's employment is terminated for any reason other than by us without cause, by the executive for good reason, or due to the executive's death or disability, the executive will only be entitled to receive earned but unpaid base salary and any accrued but not used vacation as of the termination date.
280G Gross-Up.Gross-up. IfIn the event that a change in ownership or control of the company under Section 280G of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, and the regulations thereunder, occurs on or before the second anniversary of the amendment date, if any portion of the payments made pursuant to the executive's employment agreementsagreement or otherwise constitutes an "excess parachute payment" within the meaning of Section 280G of the Internal Revenue Code, we will pay the executive an
additional amount that after reduction forthe imposition of all taxes with respect to such gross-up payment equals the excise tax with respect to the excess parachute payment.
Table If the change in ownership or control occurs after the second anniversary of Contentsthe amendment date and any portion of the payments made pursuant to the employment agreement or otherwise constitutes an excess parachute payment, the executive will be entitled to receive an amount of such payments reduced so that no portion of the payments would constitute an excess parachute payment, or the amount otherwise payable to the executive under the employment agreement or otherwise reduced by all applicable taxes, including the excise tax, whichever amount results in the greater amount payable to the executive.
Executive Loan
We and Dr. Knopf are parties to a Secured Promissory Note dated January 28, 2008 and amended on November 13, 2012, pursuant to which we made a loan to Dr. Knopf with a principal balance of $200,000 and an interest rate of 3.11% per annum. As of March 31,June 30, 2013, the outstanding principal balance of the note together with the accrued and unpaid interest thereon was approximately $235,000. The outstanding principal balance and accrued and unpaid interest on the note was forgiven immediately prior to the public filing of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
2012 Director Compensation
The following table sets forth information concerning the compensation earned by our directors during 2012. Dr. Knopf receives no additional compensation for his service as a director, and, consequently, is not included in this table. The compensation received by Dr. Knopf as an employee during 2012 is included in the "Summary Compensation Table" above.
Name | Fees Paid in Cash ($)(1) | Option Awards ($)(2) | Total ($) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Richard F. Pops | 30,000 | — | 30,000 | |||||||
Tom Maniatis | 20,000 | — | 20,000 | |||||||
Wylie W. Vale | 10,000 | — | 10,000 | |||||||
Joseph S. Zakrzewski | 25,000 | — | 25,000 | |||||||
Our board of directors has adopted a non-employee director compensation policy, effective as of the completion of this offering, that is designed to provide a total compensation package that enables us to attract and retain, on a long-term basis, high caliber non-employee directors. Under the policy, all non-employee directors will be paid cash compensation from and after the completion of this offering, as set forth below:
| | Annual Retainer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Board of Directors: | ||||
All non-employee members | $ | 35,000 | ||
Additional retainer for Lead Independent Director | $ | 15,000 | ||
Audit Committee: | ||||
Chairman | $ | 15,000 | ||
Non-Chairman members | $ | 7,500 | ||
Compensation Committee: | ||||
Chairman | $ | 10,000 | ||
Non-Chairman members | $ | 5,000 | ||
Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee: | ||||
Chairman | $ | 7,500 | ||
Non-Chairman members | $ | 3,750 | ||
Under our non-employee director compensation policy, each person who is initially appointed or elected to the board of directors will be eligible to receive a grant of stock options to purchase 20,000 shares of our common stock under our 2013 Equity Incentive Plan on the date he or she first becomes a non-employee director, which will vest annually in equal installments over a three-year period. In addition, each continuing non-employee director will be eligible to receive an annual option grant to purchase 10,000 shares of our common stock, which will vest in full on the first anniversary of the grant date. The options will be granted at fair market value on the date of grant.
Equity and Incentive Plans
2003 Plan
The 2003 Plan, which became effective December 17, 2003, provides for the grant of options to purchase shares of our common stock and for the grant or sale of restricted stock to key employees and directors of, and consultants and advisors to, us and our affiliates who, in the opinion of the compensation committee, are in a position to contribute significantly to our success and the success of our affiliates. The summary of the 2003 Plan is not a complete description of all provisions of the 2003 Plan and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the 2003 Plan, which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
The 2003 Plan is administered by our compensation committee, which has authority to determine eligibility for and grant awards and to determine the terms and conditions of all awards, including the time or times upon which awards vest or become exercisable and remain exercisable.
Authorized Shares. Subject to adjustment, the maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be delivered in satisfaction of awards under the 2003 Plan is 19,750,0004,937,500 shares. Shares of our common stock to be issued under the 2003 Plan may be authorized but unissued shares of our common stock or previously issued shares acquired by the company.
Stock Options. The compensation committee determines the exercise price of each stock option, which will not be less than the fair market value of a share of our common stock on the date of grant.
Unless otherwise provided by our compensation committee, a participant's unvested stock options will immediately terminate upon the participant's cessation of employment, and vested stock options will remain outstanding for three months or one year (in the case of death) (or, in each case, until the applicable expiration date, if earlier). If the compensation committee determines that the cessation of a participant's employment resulted for reasons that cast such discredit on the participant as to justify immediate termination of stock options, all stock options then held by the participant will immediately terminate upon such termination of employment, whether or not vested.
Restricted Stock. The compensation committee may grant or sell restricted stock to any participant (including, but not limited to, upon the exercise of options to purchase common stock) subject to the conditions and restrictions and for such purchase price, if any, as determined by the compensation committee. A participant will have all the rights of a shareholder with respect to shares of restricted stock granted or sold to the participant under the 2003 Plan. Unless the compensation committee determines otherwise, upon the cessation of a participant's employment for any reason, including death, the company will have the right (but not the obligation) to reacquire any shares of restricted stock outstanding at the participant's original purchase price, if any, for such shares. If there is no purchase price, restricted stock will be forfeited upon such termination of employment.
Covered Transactions. Unless an award agreement provides otherwise, in the event of a covered transaction (as defined in the 2003 Plan) in which there is an acquiring or surviving entity, the compensation committee may provide for the assumption or substitution of some or all outstanding awards by the acquiring or surviving entity. If the awards are not so assumed or substituted, and except as otherwise provided in an award agreement, each stock option will vest and become fully exercisable prior to the covered transaction and the stock option will terminate upon consummation of the covered transaction. In the case of restricted stock, the compensation committee may require that any amounts delivered, exchanged or otherwise paid in respect of such stock in connection with the covered transaction be placed in escrow or otherwise made subject to such restrictions as the compensation committee deems appropriate. Under the 2003 Plan, a covered transaction generally includes a consolidation, merger or similar transaction in which the company is not the surviving entity, a sale or transfer of all or substantially all of our assets or a dissolution or liquidation of our company.
Following this offering, all equity-based awards will be granted under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan described below.
2013 Equity Incentive Plan
Prior to the completion of this offering, our board of directors intends to adopthas adopted the Acceleron Pharma Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan or the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan and, following this offering, all equity-based awards will be granted under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan. As of the date of this prospectus, no awards have been made under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan. The following summary describes what we anticipate to be the material terms of the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan. This summary of the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan is not a complete description of all provisions of the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan, which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
Plan Administration. The 2013 Equity Incentive Plan is administered by our compensation committee. Our compensation committee has the authority to, among other things, interpret the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan, determine eligibility for, grant and determine the terms of awards under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan, and to do all things necessary to carry out the purposes of the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan. Our compensation committee's determinations under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan are conclusive and binding.
Authorized Shares. Subject to adjustment, the maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be delivered in satisfaction of awards under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan is ,1,344,116, plus 155,884 shares of our common stock that are available for grant under the 2003 Plan on the date the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan is adopted. The number of shares of our common stock available for issuance under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan will be automatically increased annually on each January 1st, from January 1, 2014 through January 1, 2023, in an amount equal to the least of
Shares of our common stock to be issued under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan may be authorized but unissued shares of our common stock or previously issued shares acquired by us. Any shares of our common stock underlying awards that are settled in cash or otherwise expire, terminate, or are forfeited prior to the issuance of stock will again be available for issuance under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan.
Individual Limits. The maximum number of shares of our common stock subject to stock options and the maximum number of shares of our common stock subject to stock appreciation rights that may be granted to any person in any calendar year is each 1,000,000 shares. The maximum number of shares of our common stock subject to other awards that may be granted to any person in any calendar year is 500,000 shares.
Eligibility. Our compensation committee will select participants from among our key employees, directors, consultants and advisors and of our affiliates who are in a position to contribute significantly to the success of the company and its affiliates. Eligibility for options intended to be incentive stock options, or ISOs, is limited to employees of the company or certain affiliates.
Types of Awards. The 2013 Equity Incentive Plan provides for grants of stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted and unrestricted stock, stock units, performance awards and other awards convertible into or otherwise based on shares of our common stock. Dividend equivalents may also be provided in connection with an award under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan.
Vesting. Our compensation committee has the authority to determine the vesting schedule applicable to each award, and to accelerate the vesting or exercisability of any award.
Termination of Employment. Our compensation committee will determine the effect of termination of employment or service on an award. Unless otherwise provided by our compensation committee or in an award agreement, upon a termination of a participant's employment all unvested options then held by the participant and other awards requiring exercise will terminate and all other unvested awards will be forfeited and all vested stock options and stock appreciation rights then held by the participant will remain outstanding for three months or one year in the case of death or, in each case, until the applicable expiration date, if earlier. All stock options and stock appreciation rights held by a participant immediately prior to the participant's termination of employment will immediately terminate upon termination of employment if the termination is for cause as defined in the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan or occurs in circumstances that would have constituted grounds for the participant's employment to be terminated for cause, in the determination of the Administrator.
Performance Criteria. The 2013 Equity Incentive Plan provides for the grant of performance awards that are made based upon, and subject to achieving, "performance objectives". Performance objectives with respect to those awards that are intended to qualify as "performance-based compensation" for purposes of Section 162(m) of the Code, or Section 162(m) are limited to an objectively determinable measure or measures of performance relating to any or any combination of the following (measured either absolutely or by reference to an index or indices and determined either on a consolidated basis or, as the context permits, on a divisional, subsidiary, line of business, project or geographical basis or in combinations thereof): sales; revenues; assets; expenses; earnings before or after deduction for all or any portion of interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization or equity expense, whether or not on a continuing operations or an aggregate or per share basis; return on equity, investment, capital, capital employed or assets; one or more operating ratios; operating income or profit, including on an after-tax basis; net income; borrowing levels, leverage ratios or credit rating; market share; capital expenditures; cash flow; stock price; stockholder return; sales of particular products or services; customer acquisition or retention; acquisitions and divestitures (in whole or in part); joint ventures, strategic alliances, licenses or collaborations; spin-offs, split-ups and the like; reorganizations; recapitalizations, restructurings, financings (issuance of debt or equity) or refinancings; manufacturing or process development; or achievement of clinical trial or research objectives, regulatory or other filings or approvals or other product development milestones.
To the extent consistent with the requirements for satisfying the performance-based compensation exception under Section 162(m), our compensation committee may provide in the case of any award intended to qualify for such exception that one or more of the performance objectives applicable to an award will be adjusted in an objectively determinable manner to reflect events (for example, the impact of charges for restructurings, discontinued operations, mergers, acquisitions, extraordinary items, and other unusual or non-recurring items, and the cumulative effects of tax on accounting changes, each as defined by U.S. generally accepted accounting principles) occurring during the performance period of such award that affect the applicable performance objectives.
Transferability. Awards under the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan may not be transferred except by will or by the laws of descent and distribution, unless (for awards other than ISOs) otherwise provided by our compensation committee.
Covered Transactions. In the event of a consolidation, merger or similar transaction, a sale or transfer of all or substantially all of our assets or our dissolution or liquidation, our compensation committee may, among other things, provide for continuation or assumption of outstanding awards, for new grants in substitution of outstanding awards, for the accelerated vesting or delivery of shares under awards or for a cash-out of outstanding awards, in each case on such terms and with such restrictions as it deems appropriate. Except as our compensation committee may otherwise determine, awards not assumed will automatically terminate and in the case of outstanding shares of restricted stock, will automatically be forfeited upon the consummation of such covered transaction.
Adjustment. In the event of a stock dividend, stock split or combination of shares including a reverse stock split, recapitalization or other change in our capital structure that constitutes an equity restructuring within the meaning of the Financial Accounting Standards Board, Accounting Standards Codification Topic 718,Compensation—Stock Compensation, our compensation committee will make appropriate adjustments to the maximum number of shares that may be delivered under, and the individual share limits included in, the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan, and will also make appropriate adjustments to the number and kind of shares of stock or securities subject to awards, the exercise prices of such awards or any other terms of awards affected by such change. Our compensation committee will also make the types of adjustments described above to take into account distributions and other events other than those listed above if it determines that such adjustments are appropriate to avoid distortion and preserve the value of awards.
Amendment and Termination. Our compensation committee will be able to amend the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan or outstanding awards, or terminate the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan as to future grants of awards, except that our compensation committee will not be able to alter the terms of an award if it would affect materially and adversely a participant's rights under the award without the participant's consent (unless expressly provided in the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan or the right to alter the terms of an award was expressly reserved by our compensation committee at the time the award was granted). Stockholder approval will be required for any amendment to the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan to the extent such approval is required by law, including the Code or applicable stock exchange requirements.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
Prior to the completion of this offering, our board of directors intends to adopthas adopted an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the "ESPP") as a means of permitting our eligible employees, including our named executive officers, to acquire shares of our common stock. Two hundred seventy five thousand shares of our common stock will be available for issuance under the ESPP. Under the ESPP, eligible employees of the company may purchase shares of our common stock during pre-specified purchase periods at a price equal to the lesser of 85% of the fair market value of a share of our common stock at the beginning of the purchase period or 85% of the fair market value of a share of our common stock at the end of the purchase period. As of the date of this prospectus, our board of directors has not determined the date on which the initial purchase period will commence under the ESPP, although the initial purchase period will not commence prior to the completion of this offering.
2013 Cash Bonus Program
Our named executive officers are each entitled to participate in our annual cash bonus program for fiscal 2013. As with our 2012 program described above under "—Executive Compensation—Elements of Executive Compensation—Annual Cash Bonus", 2013 cash bonus awards will be determined based on the achievement of pre-established corporate performance goals. The corporate performance goals for 2013 under this program include key strategic and financial goals related to research and the company's clinical pipeline, process development and manufacturing, business development and the achievement of financial objectives. As in 2012, the target cash bonus for Dr. Knopf is 50% of base salary, and the target cash bonus for each of Drs. Sherman and Quisel is 30% of base salary.
Acceleron Pharma Inc. Cash Incentive Plan
Prior to the completion of this offering, our board of directors intends to adopt the Acceleron Pharma Inc. Cash Incentive Plan, or the Cash Incentive Plan. Starting with our 2014 fiscal year, annual award opportunities for executive officers, including our named executive officers, and other key employees will be granted under the Cash Incentive Plan. The following summary describes what we anticipate to be the material terms of the Cash Incentive Plan. This summary is not a complete
description of all provisions of the Cash Incentive Plan and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the Cash Incentive Plan, which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
Administration. The Cash Incentive Plan will be administered by our compensation committee. Our compensation committee has authority to interpret the Cash Incentive Plan, and any interpretation or decision by the compensation committee with regard to any questions arising under the Cash Incentive Plan will be final and conclusive on all participants.
Eligibility. Executive officers and other key employees of the Company and our subsidiaries will be selected from time to time by the compensation committee to participate in the Cash Incentive Plan.
Awards. Award opportunities under the Cash Incentive Plan will be granted by our compensation committee prior to, or within a specified period of time following the beginning of, the fiscal year of the Company (or other performance period selected by the compensation committee). The compensation committee will establish the performance criteria applicable to the award, the amount or amounts payable if the performance criteria are achieved, and such other terms and conditions as the compensation committee deems appropriate. The Cash Incentive Plan permits the grant of awards that are intended to qualify as exempt performance-based compensation under Section 162(m) as well as awards that are not intended to so qualify. Any awards that are intended to qualify as performance-based compensation will be administered in accordance with the requirements of Section 162(m).
Performance Criteria. Awards under the Cash Incentive Plan will be made based on, and subject to achieving, "performance criteria" established by our compensation committee. Performance criteria for awards intended to qualify as performance-based compensation for purposes of Section 162(m) are limited to the objectively determinable measures of performance relating to any or any combination of the following (measured either absolutely or by reference to an index or indices or the performance of one or more companies and determined either on a consolidated basis or, as the context permits, on a divisional, subsidiary, line of business, project or geographical basis or in combinations thereof): sales; revenues; assets; expenses; earnings before or after deduction for all or any portion of interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization or equity expense, whether or not on a continuing operations or an aggregate or per share basis; return on equity, investment, capital, capital employed or assets; one or more operating ratios; operating income or profit, including on an after-tax basis; net income; borrowing levels, leverage ratios or credit rating; market share; capital expenditures; cash flow; stock price; stockholder return; sales of particular products or services; customer acquisition or retention; acquisitions and divestitures (in whole or in part); joint ventures, strategic alliances, licenses or collaborations; spin-offs, split-ups and the like; reorganizations; recapitalizations, restructurings, financings (issuance of debt or equity) or refinancings; manufacturing or process development; or achievement of clinical trial or research objectives, regulatory or other filings or approvals or other product development milestones.
To the extent consistent with the requirements of Section 162(m), the compensation committee may establish that in the case of any award intended to qualify as exempt performance-based compensation under Section 162(m), that one or more of the performance criteria applicable to such award be adjusted in an objectively determinable manner to reflect events (for example, the impact of charges for restructurings, discontinued operations, mergers, acquisitions, extraordinary items, and other unusual or non-recurring items, and the cumulative effects of tax on accounting changes, each as defined by U.S. generally accepted accounting principles) occurring during the performance period of such award that affect the applicable performance criteria.
Payment. A participant will be entitled to payment under an award only if all conditions to payment have been satisfied in accordance with the Cash Incentive Plan and the terms of the award.
Following the close of the performance period, our compensation committee will determine (and, to the extent required by Section 162(m), certify) whether and to what extent the applicable performance criteria have been satisfied. Our compensation committee will then determine the actual payment, if any, under each award. Our compensation committee has the sole and absolute discretion to reduce (including to zero) the actual payment to be made under any award. Our compensation committee will determine the payment dates for awards under the Cash Incentive Plan. Our compensation committee may permit a participant to defer payment of an award.
Payment Limits. The maximum payment to any participant under the Cash Incentive Plan in any fiscal year will in no event exceed $$1 million.
Recovery of Compensation. Awards under the Cash Incentive Plan will be subject to forfeiture, termination and rescission, and a participant who receives a payment pursuant to the Cash Incentive Plan will be obligated to return to us such payment, to the extent provided by our compensation committee in an award agreement, pursuant to Company policy relating to the recovery of erroneously-paid incentive compensation, or as otherwise required by law or applicable stock exchange listing standards.
Amendment and Termination. Our compensation committee may amend the Cash Incentive Plan at any time, provided that any amendment will be approved by our stockholders if required by Section 162(m). Our compensation committee may terminate the Cash Incentive Plan at any time.
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The following is a description of transactions, since January 1, 2012, to which we have been a party, in which the amount involved exceeded or will exceed $120,000, and in which any related person had a direct or indirect material interest.
Indemnification Agreements
Prior to the completion of this offering, we expect to enterWe have entered into indemnification agreements with each of our directors and executive officers. These agreements will require us to indemnify these individuals and, in certain cases, affiliates of such individuals, to the fullest extent permissible under Delaware law against liabilities that may arise by reason of their service to us or at our direction, and to advance expenses incurred as a result of any proceeding against them as to which they could be indemnified.
Registration Rights Agreement
In connection with our Series F preferred stock financing, on December 22, 2011, we entered into an amended and restated registration rights agreement with the holders of all of our then-outstanding shares of preferred stock including certain of our named executive officers and entities with which certain of our directors are affiliated. The agreement provides that these holders have the right to demand that we file a registration statement with respect to the common stock issued upon conversion of our preferred stock. These holders may also request that shares of common stock held by them be included in certain registration statements that we are otherwise filing. See "Description of Capital Stock—Registration Rights".
Right of First Refusal and Co-Sale Agreement
In connection with our Series F preferred stock financing, on December 22, 2011, we entered into an amended and restated right of first refusal and co-sale agreement with the holders of all of our then-outstanding shares of preferred stock including certain of our named executive officers and entities with which certain of our directors are affiliated. Pursuant to the terms of this agreement, in the event of a proposed sale of shares of our common or preferred stock, the seller was required to first offer such shares to the company and to the other investors, subject to certain conditions and restrictions. This agreement will terminate upon the completion of this offering.
Voting Agreement
In connection with our Series F preferred stock financing on December 22, 2011, we entered into an amended and restated voting agreement with the holders of all of our then-outstanding shares of preferred stock including certain of our named executive officers and entities with which certain of our directors are affiliated, with respect to the election of directors and certain other matters. All of our current directors were elected pursuant to the terms of this agreement. This agreement will terminate upon the completion of this offering.
Investor Rights Agreement
In connection with our Series F preferred stock financing, on December 22, 2011, we entered into an amended and restated investor rights agreement with the holders of all of our then-outstanding shares of preferred stock including certain of our named executive officers and entities with which certain of our directors are affiliated. Pursuant to the terms of this agreement, we granted our investors certain information rights as well as the right to participate pro rata in any future private financing rounds. This agreement will terminate upon the completion of this offering.
Transactions with Our Executive Officers, Directors and 5% Stockholders
On March 13, 2013, we repurchased shares of our common and preferred stock, as well as warrants to purchase shares of our common stock, from UBS Juniper Crossover Fund, LLC, an affiliate of OrbiMed Advisors and of Dr. Gordon, for $300,000 in aggregate.
On January 28, 2008, we entered into a secured promissory note with our chief executive offer,officer, which was amended on November 13, 2012, with a principal balance of $200,000 and an interest rate of 3.11% per annum. The note iswas secured by a pledge of shares of the company's stock under a pledge agreement dated January 28, 2008. The terms of the note provideprovided that it willwould mature on January 28, 2014, or be forgiven upon the occurrence of certain corporate events, including the filing of a registration statement with the SEC. Immediately prior to the filing of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, the outstanding principal balance and accrued and unpaid interest on the note was forgiven. See "Executive Compensation—Executive Loan".
Related Person Transactions Policy
We have adopted a related person transaction approval policy that will govern the review of related person transactions following the closing of this offering. Pursuant to this policy, if we want to enter into a transaction with a related person or an affiliate of a related person, our General Counsel will review the proposed transaction to determine, based on applicable NASDAQ and SEC rules, if such transaction requires pre-approval by the audit committee and/or board of directors. If pre-approval is required, such matters will be reviewed at the next regular or special audit committee and/or board of directors meeting. We may not enter into a related person transaction unless our General Counsel has either specifically confirmed in writing that no further reviews are necessary or that all requisite corporate reviews have been obtained.
The following table sets forth information relating to the beneficial ownership of our common stock as of August 1, 2013, by: each person, or group of affiliated persons, known by us to beneficially own more than 5% of our outstanding shares of common stock; each of our directors; each of our named executive officers; and all directors and executive officers as a group.
The number of shares beneficially owned by each entity, person, director or executive officer is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC, and the information is not necessarily indicative of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under such rules, beneficial ownership includes any shares over which the individual has sole or shared voting power or investment power as well as any shares that the individual has the right to acquire within 60 days of JuneAugust 1, 2013 through the exercise of any stock option, warrants or other rights. Except as otherwise indicated, and subject to applicable community property laws, the persons named in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock held by that person.
The percentage of shares beneficially owned is computed on the basis of 81,867,37821,055,604 shares of our common stock outstanding as of March 31,June 30, 2013, which reflects the assumed conversion of all of our outstanding shares of preferred stock into an aggregate of 72,118,72818,608,409 shares of common stock, at an assumed one to one conversion factor for our Series E preferred stock. For a description of the conversion, upon the completion of this offering, of shares of our Series E preferred stock into shares of common stock, see "Series E Conversion". Shares of our common stock that a person has the right to acquire within 60 days of JuneAugust 1, 2013 are deemed outstanding for purposes of computing the percentage ownership of the person holding such rights, but are not deemed outstanding for purposes of computing the percentage ownership of any other person, except with respect to the percentage
ownership of all directors and executive officers as a group. Unless otherwise indicated below, the address for each beneficial owner listed is c/o John Quisel, 128 Sidney Street, Cambridge, MA 02139.
| | | Percentage of shares beneficially owned | | Percentage of shares beneficially owned | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Name and address of beneficial owner | Number of shares beneficially owned | Before offering | After offering | Number of shares beneficially owned | Before offering | After offering and concurrent private placement | ||||||||||||||
5% or greater stockholders: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Polaris Venture Partners, and related funds(1) | 12,847,236 | 15.6 | % | 3,336,798 | 15.7 | % | 12.5 | % | ||||||||||||
650 East Kendall Street, 4th Floor | ||||||||||||||||||||
Venrock Partners, and related funds(2) | 10,200,454 | 12.4 | % | 2,635,936 | 12.4 | % | 9.9 | % | ||||||||||||
55 Cambridge Parkway, Suite 100 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Advanced Technology Ventures, and related funds(3) | 10,308,659 | 12.5 | % | 2,677,948 | 12.6 | % | 10.1 | % | ||||||||||||
500 Boylston Street, Suite 1380 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Celgene Corporation(4) | 10,095,187 | 12.3 | % | 2,549,301 | 12.1 | % | 12.3 | % | ||||||||||||
86 Morris Avenue | ||||||||||||||||||||
Flagship Ventures(5) | 9,105,926 | 11.1 | % | 2,276,479 | 10.8 | % | 8.6 | % | ||||||||||||
1 Memorial Drive | ||||||||||||||||||||
OrbiMed Advisors LLC(6) | 8,738,944 | 10.6 | % | 2,289,352 | 10.8 | % | 8.6 | % | ||||||||||||
601 Lexington Avenue, 54th Floor | ||||||||||||||||||||
Directors and named executive officers: | ||||||||||||||||||||
John L. Knopf, Ph.D.(7) | 3,070,623 | 3.7 | % | 769,155 | 3.6 | % | 2.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Anthony B. Evnin, Ph.D.(8) | 10,200,454 | 12.4 | % | 2,635,936 | 12.4 | % | 9.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Jean M. George(9) | 10,308,659 | 12.5 | % | 2,677,948 | 12.6 | % | 10.1 | % | ||||||||||||
George Golumbeski, Ph.D. | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Carl L. Gordon, Ph.D., CFA(10) | 8,738,944 | 10.6 | % | 2,289,352 | 10.8 | % | 8.6 | % | ||||||||||||
Edwin M. Kania, Jr.(11) | 9,105,926 | 11.1 | % | 2,276,479 | 10.8 | % | 8.6 | % | ||||||||||||
Terrance G. McGuire(12) | 12,847,236 | 15.6 | % | 3,336,798 | 15.7 | % | 12.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Tom Maniatis, Ph.D.(13) | 995,417 | 1.2 | % | 248,854 | 1.2 | % | * | |||||||||||||
Richard F. Pops(14) | 179,167 | * | 44,791 | * | * | |||||||||||||||
Joseph S. Zakrzewski(15) | 62,500 | * | 15,625 | * | * | |||||||||||||||
Matthew L. Sherman, M.D.(16) | 883,750 | 1.1 | % | 220,937 | 1.0 | % | * | |||||||||||||
John Quisel, J.D., Ph.D.(17) | 539,057 | * | 134,764 | * | * | |||||||||||||||
All executive officers and directors as a group (16 persons)(18) | 59,382,232 | 69.7 | % | 59,382,232 | 72.5 | % | 57.8 | % | ||||||||||||
stock, 3,134783 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series D preferred stock, 9,4594,080 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series E preferred stock, 6,3701,592 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series F preferred stock, and warrants exercisable for 10,1032,525 shares of common stock held by Venrock Entrepreneurs Fund IV, L.P. (Venrock Entrepreneurs, and together with Venrock Partners and Venrock IV, the Venrock Entities). The sole general partner of Venrock IV is Venrock Management IV, LLC (VM4). The sole general partner of Venrock Partners is Venrock Partners Management, LLC (VPM). The sole general partner of Venrock Entrepreneurs is VEF Management IV, LLC (VEFM4). VM4, VPM and VEFM4 disclaim beneficial ownership over all shares held by the Venrock Entities, except to the extent of their indirect pecuniary interests therein. Anthony B. Evnin, Ph.D., a director of the Company, is a member of VM4, VPM and VEFM4 and as such, he may be deemed to have voting and investment power with respect to these shares. Dr. Evnin disclaims beneficial ownership of these shares except to the extent of his indirect pecuniary interest therein.
preferred stock, 1,344 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series D preferred stock, 4,7612,053 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series E preferred stock, 2,195548 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series F preferred stock, and warrants exercisable for 5,0851,271 shares of common stock held by ATV Entrepreneurs VI, L.P. (ATV VI-E) and (vii) 16,5154,128 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series A preferred stock held by ATV Alliance 2003, L.P. (ATV A 2003). ATV Associates VII, L.L.C (ATV A VII) is the general partner of ATV VII, ATV VII-B, ATV VII-C and ATV VII-E and exercises voting and dispositive authority over the shares held by ATV VII, ATV VII-B, ATV VII-C and ATV VII-E. Voting and dispositive decisions of ATV A VII are made collectively by Michael A. Carusi, Jean M. George (one of our directors), Steven N. Baloff, Robert C. Hower and William C. Wiberg (collectively, the ATV A VII Managing Directors). ATV A VII and each of the ATV A VII Managing Directors disclaim beneficial ownership of the shares held by ATV VII, ATV VII-B, ATV VII-C and ATV VII-E except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. ATV Associates VI, L.L.C (ATV A VI) is the general partner of ATV VI and ATV VI-E and exercises voting and dispositive authority over the shares held by ATV VI and ATV VI-E. Voting and dispositive decisions of ATV A VI are made collectively by Michael A. Carusi, Steven N. Baloff, Pieter J. Schiller , Robert C. Hower and William C. Wiberg (collectively, the ATV A VI Managing Directors). ATV A VI and each of the ATV A VI Managing Directors disclaim beneficial ownership of the shares held by ATV VI and ATV VI-E except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. ATV Alliance Associates, L.L.C. (ATV Alliance, LLC) is the general partner of ATV A 2003 and exercises voting and dispositive authority over the shares held by ATV A 2003. Voting and dispositive decisions of ATV Alliance, LLC are made by Jean M. George (one of our directors). ATV Alliance, LLC and Jean M. George disclaim beneficial ownership of the shares held by ATV A 2003 except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein.
of common stock issuable upon conversion of series B preferred stock, 701,678175,419 shares of common
stock issuable upon conversion of series C preferred stock, 93,77123,442 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series D preferred stock and warrants exercisable for 451,603112,900 shares of common stock held by OPI II, and (iv) 1,688,406422,101 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series B preferred stock, 262,72165,680 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series C preferred stock, 35,1108,777 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of series D preferred stock, 14,382 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the series E preferred stock and warrants exercisable for 169,09042,271 shares of common stock held by OPI QP. OrbiMed Advisors LLC, or OrbiMed, a registered investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended, is the managing member of OrbiMed Capital GP II LLC, which is the general partner of OPI II and OPI QP (collectively, the OrbiMed Funds). Mr. Samuel D. Isaly is the managing member of and owner of a controlling interest in OrbiMed. Accordingly, OrbiMed and Mr. Isaly may be deemed to have voting and investment power over the shares held by OrbiMed Funds noted above. OrbiMed and Mr. Isaly disclaim beneficial ownership with respect to such shares, except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein, if any.
General
The following description of our capital stock is intended as a summary only and is qualified in its entirety by reference to our restated certificate of incorporation and restated by-laws that will be in effect at the closing of this offering, which will be filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, and to the applicable provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law. We refer in this section to our restated certificate of incorporation as our certificate of incorporation, and we refer to our amended and restated by-laws as our by-laws. The description of our capital stock reflects changes to our capital structure that will occur upon the closing of this offering.
Upon the closing of this offering and the filing of our restated certificate of incorporation, our authorized capital stock will consist of 175,000,000 shares of our common stock, par value $0.001 per share, and 25,000,000 shares of our preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share, all of which preferred stock will be undesignated.
As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had issued and outstanding:
Upon closing of this offering, all outstanding warrants to purchase shares of preferred stock will convert into warrants to purchase an aggregate of 565,495141,370 shares of common stock.
The amounts above do not give effect to our anticipated 1-for reverse split.
As of March 31,June 30, 2013, we had 144222 stockholders of record.
Common Stock
Dividend Rights. Subject to preferences that may apply to shares of preferred stock outstanding at the time, holders of outstanding shares of common stock will be entitled to receive dividends out of assets legally available at the times and in the amounts as the board of directors may from time to time determine.
Voting Rights. Each outstanding share of common stock will be entitled to one vote on all matters submitted to a vote of stockholders. Holders of shares of our common stock shall have no cumulative voting rights.
Preemptive Rights. Our common stock will not be entitled to preemptive or other similar subscription rights to purchase any of our securities.
Conversion or Redemption Rights. Our common stock will be neither convertible nor redeemable.
Liquidation Rights. Upon our liquidation, the holders of our common stock will be entitled to receive pro rata our assets which are legally available for distribution, after payment of all debts and other liabilities and subject to the prior rights of any holders of preferred stock then outstanding.
Listing. We intend to list our common stock on the NASDAQ Global Market under the symbol XLRN.
Preferred Stock
Our board of directors may, without further action by our stockholders, from time to time, direct the issuance of shares of preferred stock in series and may, at the time of issuance, determine the designations, powers, preferences, privileges, and relative participating, optional or special rights as well as the qualifications, limitations or restrictions thereof, including dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption and liquidation preferences, any or all of which may be greater than the rights of the common stock. Satisfaction of any dividend preferences of outstanding shares of preferred stock would reduce the amount of funds available for the payment of dividends on shares of our common stock. Holders of shares of preferred stock may be entitled to receive a preference payment in the event of our liquidation before any payment is made to the holders of shares of our common stock. Under certain circumstances, the issuance of shares of preferred stock may render more difficult or tend to discourage a merger, tender offer or proxy contest, the assumption of control by a holder of a large block of our securities or the removal of incumbent management. Upon the affirmative vote of a majority of the total number of directors then in office, our board of directors, without stockholder approval, may issue shares of preferred stock with voting and conversion rights which could adversely affect the holders of shares of our common stock and the market value of our common stock. Upon consummation of this offering, there will be no shares of preferred stock outstanding, and we have no present intention to issue any shares of preferred stock.
Registration Rights
We are party to an amended and restated registration rights agreement, with the holders of shares of our common stock issuable upon conversion of the shares of preferred stock. These shares will represent approximately %72% of our outstanding common stock after this offering and the concurrent private placement, or %70% if the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option.
Under the amended and restated registration rights agreement, holders of registrable shares can demand that we file a registration statement or request that their shares be included on a registration statement that we are otherwise filing, in either case, registering the resale of their shares of common stock. These registration rights are subject to conditions and limitations, including the right, in certain circumstances, of the underwriters of an offering to limit the number of shares included in such registration and our right, in certain circumstances, not to effect a requested S-1 or S-3 registration within 60 days before or six months following the Company's estimated date of filing of a registration statement pertaining to an underwritten public offering of securities for the account of the Company offering of our securities, including this offering.
Demand Registration Rights
Following the six-month anniversary of the completion of this offering, the holders of at least a majority of the registrable shares may require us to file a registration statement under the Securities Act at our expense with respect to the resale of their registrable shares, and we are required to use our best efforts to effect the registration.
Piggyback Registration Rights
If we propose to register any of our securities under the Securities Act for our own account or the account of any other holder, the holders of registrable shares are entitled to notice of such registration and to request that we include registrable shares for resale on such registration statement, subject to the right of any underwriter to limit the number of shares included in such registration. We will pay all registration expenses, other than underwriting discounts and commissions, related to any demand or piggyback registration. The amended and restated registration rights agreement contains customary cross-indemnification provisions, pursuant to which we are obligated to indemnify the selling stockholders, in the event of misstatements or omissions in the registration statement attributable to us except in the event of fraud and they are obligated to indemnify us for misstatements or omissions attributable to them. The registration rights will not terminate until all registrable shares have been sold or no longer qualify as registrable shares.
Anti-Takeover Effects of Our Certificate of Incorporation and Our By-Laws
Our certificate of incorporation and by-laws will contain certain provisions that are intended to enhance the likelihood of continuity and stability in the composition of the board of directors and which may have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a future takeover or change in control of the company unless such takeover or change in control is approved by the board of directors.
These provisions include:
Classified Board. Our certificate of incorporation will provide that our board of directors will be divided into three classes of directors, with the classes as nearly equal in number as possible. As a result, approximately one-third of our board of directors will be elected each year. The classification of directors will have the effect of making it more difficult for stockholders to change the composition of our board. Our certificate of incorporation will also provide that, subject to any rights of holders of preferred stock to elect additional directors under specified circumstances, the number of directors will be fixed exclusively pursuant to a resolution adopted by our board of directors. Upon completion of this offering, we expect that our board of directors will have nine members.
Action by Written Consent; Special Meetings of Stockholders. Our certificate of incorporation will provide that stockholder action can be taken only at an annual or special meeting of stockholders and cannot be taken by written consent in lieu of a meeting once investment funds affiliated with the Sponsor cease to beneficially own more than 50% of our outstanding shares. Our certificate of incorporation and the by-laws will also provide that, except as otherwise required by law, special meetings of the stockholders can only be called by the chairman or vice-chairman of the board, the chief executive officer, or pursuant to a resolution adopted by a majority of the board of directors or, until the date that investment funds affiliated with the Sponsor cease to beneficially own more than 50% of our outstanding shares, at the request of holders of 50% or more of our outstanding shares. Except as described above, stockholders will not be permitted to call a special meeting or to require the board of directors to call a special meeting.
Removal of Directors. Our certificate of incorporation will provide that our directors may be removed only for cause by the affirmative vote of at least 75% of the voting power of our outstanding shares of capital stock, voting together as a single class. This requirement of a supermajority vote to remove directors could enable a minority of our stockholders to prevent a change in the composition of our board.
Advance Notice Procedures. Our by-laws will establish an advance notice procedure for stockholder proposals to be brought before an annual meeting of our stockholders, including proposed nominations of persons for election to the board of directors. Stockholders at an annual meeting will only be able to consider proposals or nominations specified in the notice of meeting or brought before the meeting by
or at the direction of the board of directors or by a stockholder who was a stockholder of record on the record date for the meeting, who is entitled to vote at the meeting and who has given our Secretary timely written notice, in proper form, of the stockholder's intention to bring that business before the meeting. Although the by-laws will not give the board of directors the power to approve or disapprove stockholder nominations of candidates or proposals regarding other business to be conducted at a special or annual meeting, the by-laws may have the effect of precluding the conduct of certain business at a meeting if the proper procedures are not followed or may discourage or deter a potential acquiror from conducting a solicitation of proxies to elect its own slate of directors or otherwise attempting to obtain control of the company.
Super Majority Approval Requirements. The Delaware General Corporation Law generally provides that the affirmative vote of a majority of the shares entitled to vote on any matter is required to amend a corporation's certificate of incorporation or by-laws, unless either a corporation's certificate of incorporation or by-laws requires a greater percentage. Our certificate of incorporation and by-laws will provide that the affirmative vote of holders of at least 75% of the total votes eligible to be cast in the election of directors will be required to amend, alter, change or repeal specified provisions once investment funds affiliated with the Sponsor cease to beneficially own more than 50% of our outstanding shares. This requirement of a supermajority vote to approve amendments to our certificate of incorporation and by-laws could enable a minority of our stockholders to exercise veto power over any such amendments.
Authorized but Unissued Shares. Our authorized but unissued shares of common stock and preferred stock will be available for future issuance without stockholder approval. These additional shares may be utilized for a variety of corporate purposes, including future public offerings to raise additional capital, corporate acquisitions and employee benefit plans. The existence of authorized but unissued shares of common stock and preferred stock could render more difficult or discourage an attempt to obtain control of a majority of our common stock by means of a proxy contest, tender offer, merger or otherwise.
Exclusive Forum. Our certificate of incorporation will provide that, subject to limited exceptions, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for (1) any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf, (2) any action asserting a claim of breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of our directors, officers or other employees to us or our stockholders, (3) any action asserting a claim against us arising pursuant to any provision of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our certificate of incorporation or our by-laws, or (4) any other action asserting a claim against us that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring any interest in shares of our capital stock shall be deemed to have notice of and to have consented to the provisions of our certificate of incorporation described above. Although we believe these provisions benefit us by providing increased consistency in the application of Delaware law for the specified types of actions and proceedings, the provisions may have the effect of discouraging lawsuits against our directors and officers. The enforceability of similar choice of forum provisions in other companies' certificates of incorporation has been challenged in legal proceedings, and it is possible that, in connection with one or more actions or proceedings described above, a court could find the choice of forum provisions contained in our certificate of incorporation to be inapplicable or unenforceable.
Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law
Upon completion of this offering, we will be subject to the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law. In general, Section 203 prohibits a publicly-held Delaware corporation from engaging in a "business combination" with an "interested stockholder" for a three-year period following the time that this stockholder becomes an interested stockholder, unless the
business combination is approved in a prescribed manner. A "business combination" includes, among other things, a merger, asset or stock sale or other transaction resulting in a financial benefit to the interested stockholder. An "interested stockholder" is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, owns, or did own within three years prior to the determination of interested stockholder status, 15% or more of the corporation's voting stock.
Under Section 203, a business combination between a corporation and an interested stockholder is prohibited unless it satisfies one of the following conditions: before the stockholder became interested, the board of directors approved either the business combination or the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder; upon consummation of the transaction which resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the time the transaction commenced, excluding for purposes of determining the voting stock outstanding, shares owned by persons who are directors and also officers, and employee stock plans, in some instances; or at or after the time the stockholder became interested, the business combination was approved by the board of directors of the corporation and authorized at an annual or special meeting of the stockholders by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock which is not owned by the interested stockholder.
A Delaware corporation may "opt out" of these provisions with an express provision in its original certificate of incorporation or an express provision in its certificate of incorporation or by-laws resulting from a stockholders' amendment approved by at least a majority of the outstanding voting shares. We have not opted out of these provisions. As a result, mergers or other takeover or change in control attempts of us may be discouraged or prevented.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
The transfer agent and registrar for our common stock is .Computershare Trust Company, N.A. The transfer agent and registrar's address is .250 Royall Street Canton, Massachusetts 02021.
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. Future sales of our common stock, including shares issued upon the exercise of outstanding options or warrants, in the public market after this offering, or the perception that those sales may occur, could cause the prevailing market price for our common stock to fall or impair our ability to raise equity capital in the future. As described below, only a limited number of shares of our common stock will be available for sale in the public market for a period of several months after completion of this offering due to contractual and legal restrictions on resale described below. Future sales of our common stock in the public market either before (to the extent permitted) or after restrictions lapse, or the perception that those sales may occur, could adversely affect the prevailing market price of our common stock at such time and our ability to raise equity capital at a time and price we deem appropriate.
Sale of Restricted Shares
As of March 31,June 30, 2013, based on the number of shares of our common stock then outstanding, upon the closing of this offering and the concurrent private placement and assuming (1) the conversion of our outstanding preferred stock into common stock, (2) no exercise of the underwriters' option to purchase additional shares of common stock, and (3) no exercise of outstanding options or warrants, we would have had outstanding an aggregate of approximately 26,419,889 shares of common stock. Of these shares, all of the 4,650,000 shares of common stock to be sold in this offering, and any shares sold upon exercise of the underwriters' option to purchase additional shares will be freely tradable in the public market without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, unless the shares are held by any of our "affiliates" as such term is defined in Rule 144 of the Securities Act. The approximately 714,285 shares being sold in the concurrent private placement (assuming an initial public offering price of $14.00 per share, the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover of this prospectus) will be freely tradeable six months after the closing of the concurrent private placement. All remaining shares of common stock held by existing stockholders immediately prior to the completion of this offering will be "restricted securities" as such term is defined in Rule 144. These restricted securities were issued and sold by us, or will be issued and sold by us, in private transactions and are eligible for public sale only if registered under the Securities Act or if they qualify for an exemption from registration under the Securities Act, including the exemptions provided by Rule 144 or Rule 701, which rules are summarized below.
As a result of the lock-up agreements referred to below and the provisions of Rule 144 and Rule 701 under the Securities Act, the shares of our common stock (excluding the shares sold in this offering)offering and the concurrent private placement) that will be available for sale in the public market are as follows:
| Approximate Number of Shares | First Date Available for Sale into Public Market | |
|---|---|---|
946,284 | On the date of this prospectus | |
18,197 | 90 days after the date of this prospectus | |
20,091,123 | 180 days after the date of this prospectus upon expiration of the lock-up agreements referred to below, subject in some cases to applicable volume limitations under Rule 144 |
Lock-up Agreements
In connection with this offering, we, our officers and directors, certain of our officersemployees and stockholders holding approximately %95% of our shares of common stock outstanding as of March 31,June 30, 2013 (assuming conversion of all of our outstanding shares of preferred stock), have agreed, subject to
certain exceptions, with the underwriters not to dispose of or hedge any shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable for shares of common stock during the period from the date of the lock-up agreement continuing through the date 180 days after the date of this prospectus, except with the prior written consent of Citigroup Global Markets Inc. and Leerink Swann LLC, the representatives of the underwriters. The representatives of the underwriters have advised us that they
have no current intent or arrangement to release any of the shares subject to the lock-up agreements prior to the expiration of the lock-up period.
Following the lock-up periods set forth in the agreements described above, and assuming that the representatives of the underwriters do not release any parties from these agreements, all of the shares of our common stock that are restricted securities or are held by our affiliates as of the date of this prospectus will be eligible for sale in the public market in compliance with Rule 144 under the Securities Act.
In addition, pursuant to each of our amended and restated investors' rights agreement and amended and restated right of first refusal and co-sale agreement, the parties thereto have agreed that, if requested in writing by the representatives of the underwriters of the initial public offering of our securities, they will not sell, make any short sale of, grant any option for the purchase of, or otherwise dispose of any shares of our stock during the same 180-day restricted period referred to above. We expect the representatives of the underwriters to invoke this written request prior to the completion of this offering and, accordingly, that the parties to these agreements will be subject to the related transaction restrictions. Holders of approximately 20,091,123 shares of common stock (including shares of our preferred stock that will be converted into shares of our common stock upon completion of this offering), or %76% of our outstanding shares of common stock on an as converted basis, are, collectively subject to lock-up restrictions as parties to these agreements or lock-up agreements with the underwriters.
Rule 144
In general, under Rule 144, as currently in effect, once we have been subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, for at least 90 days, a person (or persons whose shares are required to be aggregated) who is not deemed to have been one of our "affiliates" for purposes of Rule 144 at any time during the three months preceding a sale, and who has beneficially owned restricted securities within the meaning of Rule 144 for at least six months, including the holding period of any prior owner other than one of our "affiliates," is entitled to sell those shares in the public market (subject to the lock-up agreement referred to above, if applicable) without complying with the manner of sale, volume limitations or notice provisions of Rule 144, but subject to compliance with the public information requirements of Rule 144. If such a person has beneficially owned the sales proposed to be sold for at least one year, including the holding period of any prior owner other than "affiliates", then such person is entitled to sell such shares in the public market without complying with any of the requirements of Rule 144 (subject to the lock-up agreement referred to above, if applicable). In general, under Rule 144, as currently in effect, once we have been subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Exchange Act for at least 90 days, our "affiliates", as defined in Rule 144, who have beneficially owned the shares proposed to be sold for at least six months are entitled to sell in the public market, upon expiration of any applicable lock-up agreements and within any three-month period, a number of those shares of our common stock that does not exceed the greater of: 1% of the number of common shares then outstanding, which will equal approximately 264,200 shares of common stock immediately after this offering and the concurrent private placement (calculated on the basis of the number of shares of our common stock outstanding as of March 31,June 30, 2013 and the assumptions described above); or the average weekly trading volume of our common stock on the NASDAQ Global Market during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to such sale.
Such sales under Rule 144 by our "affiliates" or persons selling shares on behalf of our "affiliates" are also subject to certain manner of sale provisions, notice requirements and to the availability of current public information about us. Notwithstanding the availability of Rule 144, the holders of substantially all of our restricted securities have entered into lock-up agreements as referenced above
and their restricted securities will become eligible for sale (subject to the above limitations under Rule 144) upon the expiration of the restrictions set forth in those agreements.
Rule 701
In general, under Rule 701 as currently in effect, any of our employees, directors, officers, consultants or advisors who acquired common stock from us in connection with a written compensatory stock or option plan or other written agreement in compliance with Rule 701 under the Securities Act before the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part (to the extent such common stock is not subject to a lock-up agreement) is entitled to rely on Rule 701 to resell such shares beginning 90 days after we become subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Exchange Act in reliance on Rule 144, but without compliance with the holding period requirements contained in Rule 144. Accordingly, subject to any applicable lock-up agreements, beginning 90 days after we become subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, under Rule 701 persons who are not our "affiliates", as defined in Rule 144, may resell those shares without complying with the minimum holding period or public information requirements of Rule 144, and persons who are our "affiliates" may resell those shares without compliance with Rule 144's minimum holding period requirements (subject to the terms of the lock-up agreement referred to below, if applicable).
Equity Incentive Plans
We intend to file with the SEC a registration statement under the Securities Act covering the shares of common stock that we may issue upon exercise of outstanding options reserved for issuance under our 2003 Stock Option and Restricted Stock Plan and 2013 Equity Incentive Plan. Such registration statement is expected to be filed and become effective after the completion of this offering prior to the end of our fiscal year. Accordingly, shares registered under such registration statement will be available for sale in the open market following its effective date, subject to Rule 144 volume limitations and the lock-up agreements described above, if applicable.
MATERIAL UNITED STATES FEDERAL INCOME TAX
CONSIDERATIONS FOR NON-U.S. HOLDERS
The following is a summary of the material U.S. federal income and estate tax considerations relating to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common stock by Non-U.S. Holders (defined below). This summary does not purport to be a complete analysis of all the potential tax considerations relevant to Non-U.S. Holders of our common stock. This summary is based upon the Internal Revenue Code, the Treasury regulations promulgated or proposed thereunder and administrative and judicial interpretations thereof, all as of the date hereof and all of which are subject to change at any time, possibly on a retroactive basis.
This summary assumes that shares of our common stock are held as "capital assets" within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Internal Revenue Code (generally, property held for investment). This summary does not purport to deal with all aspects of U.S. federal income and estate taxation that might be relevant to particular Non-U.S. Holders in light of their particular investment circumstances or status, nor does it address specific tax considerations that may be relevant to particular persons (including, for example, financial institutions, broker-dealers, insurance companies, partnerships or other pass-through entities, certain U.S. expatriates, tax-exempt organizations, pension plans, "controlled foreign corporations", "passive foreign investment companies", corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid U.S. federal income tax, persons in special situations, such as those who have elected to mark securities to market or those who hold common stock as part of a straddle, hedge, conversion transaction, synthetic security or other integrated investment, or holders subject to the alternative minimum or the newly effective 3.8% Medicare tax on net investment income). In addition, except as explicitly addressed herein with respect to estate tax, this summary does not address estate and gift tax considerations or considerations under the tax laws of any state, local or non-U.S. jurisdiction.
For purposes of this summary, a "Non-U.S. Holder" means a beneficial owner of common stock that for U.S. federal income tax purposes is not classified as a partnership and is not:
If an entity that is classified as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds our common stock, the tax treatment of persons treated as its partners for U.S. federal income tax purposes will generally depend upon the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. Partnerships and other entities that are classified as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes and persons holding our common stock through a partnership or other entity classified as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes are urged to consult their own tax advisors.
There can be no assurance that the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) will not challenge one or more of the tax consequences described herein, and we have not obtained, nor do we intend to obtain a ruling from the IRS with respect to the U.S. federal income or estate tax consequences to a Non-U.S. Holder of the purchase, ownership or disposition of our common stock.
THIS SUMMARY IS FOR GENERAL INFORMATION ONLY AND IS NOT INTENDED TO BE TAX ADVICE. NON-U.S. HOLDERS ARE URGED TO CONSULT THEIR TAX ADVISORS CONCERNING THE U.S. FEDERAL INCOME AND ESTATE TAXATION, STATE, LOCAL AND NON-U.S. TAXATION AND OTHER TAX CONSEQUENCES TO THEM OF THE PURCHASE, OWNERSHIP AND DISPOSITION OF OUR COMMON STOCK.
Distributions on Our Common Stock
As discussed under "Dividend Policy" above, we do not currently expect to pay dividends. In the event that we do make a distribution of cash or property with respect to our common stock, any such distributions generally will constitute dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits, if any, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. If a distribution exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits, the excess will constitute a return of capital and will first reduce the holder's adjusted tax basis in our common stock, but not below zero. Any remaining excess will be treated as capital gain, subject to the tax treatment described below in "—Gain on Sale, Exchange or Other Taxable Disposition of Our Common Stock". Any such distribution would also be subject to the discussion below under the section titled "—Additional Withholding and Reporting Requirements".
Dividends paid to a Non-U.S. Holder generally will be subject to a 30% U.S. federal withholding tax unless such Non-U.S. Holder provides us or our agent, as the case may be, with the appropriate IRS Form W-8, such as:
The certification requirement described above must be provided to us or our agent prior to the payment of dividends and must be updated periodically. The certification also may require a Non-U.S. Holder that provides an IRS form or that claims treaty benefits to provide its U.S. taxpayer identification number. Special certification and other requirements apply in the case of certain Non-U.S. Holders that hold shares of our common stock through intermediaries or are pass-through entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
Each Non-U.S. Holder is urged to consult its own tax advisor about the specific methods for satisfying these requirements. A claim for exemption will not be valid if the person receiving the applicable form has actual knowledge or reason to know that the statements on the form are false.
If dividends are effectively connected with a trade or business in the United States of a Non-U.S. Holder (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, attributable to a U.S. permanent establishment), the Non-U.S. Holder, although exempt from the withholding tax described above (provided that the certifications described above are satisfied), generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on such dividends on a net income basis in the same manner as if it were a resident of the United States. In addition, if a Non-U.S. Holder is treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the Non-U.S. Holder may be subject to an additional "branch profits tax" equal to 30% (unless reduced by an applicable income treaty) of its earnings and profits in respect of such effectively connected dividend income.
Non-U.S. Holders that do not timely provide us or our agent with the required certification, but which are eligible for a reduced rate of U.S. federal withholding tax pursuant to an income tax treaty, may obtain a refund or credit of any excess amount withheld by timely filing an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS.
Gain on Sale, Exchange or Other Taxable Disposition of Our Common Stock
Subject to the discussion below under the section titled "—Additional Withholding and Reporting Requirements", in general, a Non-U.S. Holder will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax or withholding tax on gain realized upon such holder's sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of shares of our common stock unless (1) such Non-U.S. Holder is an individual who is present in the United States for 183 days or more in the taxable year of disposition, and certain other conditions are met, (2) we are or have been a "United States real property holding corporation", as defined in the Internal Revenue Code (a USRPHC), at any time within the shorter of the five-year period preceding the disposition and the Non-U.S. Holder's holding period in the shares of our common stock, and certain other requirements are met, or (3) such gain is effectively connected with the conduct by such Non-U.S. Holder of a trade or business in the United States (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, is attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by such Non-U.S. Holder in the United States).
If the first exception applies, the Non-U.S. Holder generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at a rate of 30% (or at a reduced rate under an applicable income tax treaty) on the amount by which such Non-U.S. Holder's capital gains allocable to U.S. sources exceed capital losses allocable to U.S. sources during the taxable year of the disposition. If the third exception applies, the Non-U.S. Holder generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax with respect to such gain on a net income basis in the same manner as if it were a resident of the United States and a Non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes may also be subject to a branch profits tax with respect to any earnings and profits attributable to such gain at a rate of 30% (or at a reduced rate under an applicable income tax treaty).
Generally, a corporation is a USRPHC only if the fair market value of its U.S. real property interests (as defined in the Internal Revenue Code) equals or exceeds 50% of the sum of the fair market value of its worldwide real property interests plus its other assets used or held for use in a trade or business. Although there can be no assurance in this regard, we believe that we are not, and do not anticipate becoming, a USRPHC. However, because the determination of whether we are a USRPHC depends on the fair market value of our U.S. real property interests relative to the fair market value of other business assets, there can be no assurance that we will not become a USRPHC in the future. Even if we became a USRPHC, a Non-U.S. Holder would not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on a sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of our common stock by reason of our status as USRPHC so long as our common stock is regularly traded on an established securities market at any time during the calendar year in which the disposition occurs and such Non-U.S. Holder does not own and is not deemed to own (directly, indirectly or constructively) more than 5% of our common stock at any time during the shorter of the five year period ending on the date of disposition and the holder's holding period. However, no assurance can be provided that our common stock will be regularly traded on an established securities market for purposes of the rules described above. Prospective investors are encouraged to consult their own tax advisors regarding the possible consequences to them if we are, or were to become, a USRPHC.
Additional Withholding and Reporting Requirements
Legislation enacted in March 2010 and related Treasury guidance (commonly referred to as FATCA) will impose, in certain circumstances, U.S. federal withholding at a rate of 30% on payments of (1) dividends on our common stock on or after January 1, 2014, and (2) gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of our common stock on or after January 1, 2017. In the case of payments made to a "foreign financial institution" as defined under FATCA (including, among other entities, an investment fund), as a beneficial owner or as an intermediary, the tax generally will be imposed, subject to certain exceptions, unless such institution (1) enters into (or is otherwise subject to) and complies with an agreement with the U.S. government (a "FATCA Agreement") or (2) complies with applicable
foreign law enacted in connection with an intergovernmental agreement between the United States and a foreign jurisdiction (an "IGA"), in either case to, among other things, collect and provide to the U.S. or other relevant tax authorities certain information regarding U.S. account holders of such institution. In the case of payments made to a foreign entity that is not a foreign financial institution (as a beneficial owner), the tax generally will be imposed, subject to certain exceptions, unless such foreign entity provides the withholding agent with a certification that it does not have any "substantial U.S. owner" (generally, any specified U.S. person that directly or indirectly owns more than a specified percentage of such entity) or that identifies its substantial U.S. owners. If our common stock is held through a foreign financial institution that enters into (or is otherwise subject to) a FATCA Agreement, such foreign financial institution (or, in certain cases, a person paying amounts to such foreign financial institution) generally will be required, subject to certain exceptions, to withhold such tax on payments of dividends and proceeds described above made to (1) a person (including an individual) that fails to comply with certain information requests or (2) a foreign financial institution that has not entered into (and is not otherwise subject to) a FATCA Agreement and is not required to comply with FATCA pursuant to applicable foreign law enacted in connection with an IGA.
Prospective investors should consult their own tax advisors regarding the possible impact of these rules on their investment in our common stock, and the entities through which they hold our common stock, including, without limitation, the process and deadlines for meeting the applicable requirements to prevent the imposition of this 30% withholding tax under FATCA.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
We must report annually to the IRS and to each Non-U.S. Holder the gross amount of the distributions on our common stock paid to the holder and the tax withheld, if any, with respect to the distributions. Non-U.S. Holders may have to comply with specific certification procedures to establish that the holder is not a United States person (as defined in the Internal Revenue Code) in order to avoid backup withholding at the applicable rate, currently 28%, with respect to dividends on our common stock. Dividends paid to Non-U.S. Holders subject to the U.S. withholding tax, as described above under the section titled "—Distributions on Our Common Stock", generally will be exempt from U.S. backup withholding.
Information reporting and backup withholding will generally apply to the proceeds of a disposition of our common stock by a Non-U.S. Holder effected by or through the U.S. office of any broker, U.S. or foreign, unless the holder certifies its status as a Non-U.S. Holder and satisfies certain other requirements, or otherwise establishes an exemption. Generally, information reporting and backup withholding will not apply to a payment of disposition proceeds to a Non-U.S. Holder where the transaction is effected outside the United States through a non-U.S. office of a broker. However, for information reporting purposes, dispositions effected through a non-U.S. office of a broker with substantial U.S. ownership or operations generally will be treated in a manner similar to dispositions effected through a U.S. office of a broker. Prospective investors should consult their own tax advisors regarding the application of the information reporting and backup withholding rules to them.
Copies of information returns may be made available to the tax authorities of the country in which the Non-U.S. Holder resides or, in which the Non-U.S. Holder is incorporated, under the provisions of a specific treaty or agreement.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules from a payment to a Non-U.S. Holder can be refunded or credited against the Non-U.S. Holder's U.S. federal income tax liability, if any, provided that an appropriate claim is timely filed with the IRS.
Federal Estate Tax
Common stock owned (or treated as owned) by an individual who is not a citizen or a resident of the United States (as defined for U.S. federal estate tax purposes) at the time of death will be included in the individual's gross estate for U.S. federal estate tax purposes unless an applicable estate or other tax treaty provides otherwise, and therefore, may be subject to U.S. federal estate tax.
Citigroup Global Markets Inc. and Leerink Swann LLC are acting as joint book-running managers of the offering and as representatives of the underwriters named below. Subject to the terms and conditions stated in the underwriting agreement dated the date of this prospectus, each underwriter named below has severally agreed to purchase, and we have agreed to sell to that underwriter, the number of shares set forth opposite the underwriter's name.
Underwriter | Number of Shares | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Citigroup Global Markets Inc. | ||||
Leerink Swann LLC | ||||
JMP Securities LLC | ||||
Piper Jaffray & Co. | ||||
Total | 4,650,000 | |||
The underwriting agreement provides that the obligations of the underwriters to purchase the shares included in this offering are subject to approval of legal matters by counsel and to other conditions. The underwriters are obligated to purchase all the shares (other than those covered by the over-allotment option described below) if they purchase any of the shares.
Shares sold by the underwriters to the public will initially be offered at the initial public offering price set forth on the cover of this prospectus. Any shares sold by the underwriters to securities dealers may be sold at a discount from the initial public offering price not to exceed $ per share. If all the shares are not sold at the initial offering price, the underwriters may change the offering price and the other selling terms. The representatives have advised us that the underwriters do not intend to make sales to discretionary accounts.
If the underwriters sell more shares than the total number set forth in the table above, we have granted to the underwriters an option, exercisable for 30 days from the date of this prospectus, to purchase up to 697,500 additional shares at the public offering price less the underwriting discount. The underwriters may exercise the option solely for the purpose of covering over-allotments, if any, in connection with this offering. To the extent the option is exercised, each underwriter must purchase a number of additional shares approximately proportionate to that underwriter's initial purchase commitment. Any shares issued or sold under the option will be issued and sold on the same terms and conditions as the other shares that are the subject of this offering.
We, our officers and directors, certain of our employees and stockholders holding substantially all of our other stockholderscommon stock on an as-converted basis prior to this offering have agreed that, for a period of 180 days from the date of this prospectus, we and they will not, without the prior written consent of Citigroup and Leerink, dispose of or hedge any shares or any securities convertible into or exchangeable for our common stock. Citigroup and Leerink in their sole discretion may release any of the securities subject to these lock-up agreements at any time, which, in the case of officers and directors, shall be with notice.
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our shares. Consequently, the initial public offering price for the shares was determined by negotiations between us and the representatives. Among the factors considered in determining the initial public offering price were our results of operations, our current financial condition, our future prospects, our markets, the economic conditions in and future prospects for the industry in which we compete, our management, and currently prevailing general conditions in the equity securities markets, including current market valuations of publicly traded companies considered comparable to our company. We cannot assure you, however, that the price at which the shares will sell in the public market after this offering will not be lower than
the initial public offering price or that an active trading market in our shares will develop and continue after this offering.
We have applied to have our shares listed on the NASDAQ Global Market under the symbol XLRN.
The following table shows the underwriting discounts and commissions that we are to pay to the underwriters in connection with this offering. These amounts are shown assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters' over-allotment option.
| | Paid by Acceleron | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | No Exercise | Full Exercise | |||||
Per share | $ | $ | |||||
Total | $ | $ | |||||
We estimate that our portion of the total expenses of this offering will be $ .approximately $2.8 million.
We have also agreed to reimburse the underwriters for certain of their expenses in an amount up to $30,000 as set forth in the underwriting agreement.
In connection with the offering, the underwriters may purchase and sell shares in the open market. Purchases and sales in the open market may include short sales, purchases to cover short positions, which may include purchases pursuant to the over-allotment option, and stabilizing purchases.
Purchases to cover short positions and stabilizing purchases, as well as other purchases by the underwriters for their own accounts, may have the effect of preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of the shares. They may also cause the price of the shares to be higher than the price that would otherwise exist in the open market in the absence of these transactions. The underwriters may conduct these transactions on the NASDAQ Global Market, in the over-the-counter market or
otherwise. If the underwriters commence any of these transactions, they may discontinue them at any time.
Conflicts of Interest
The underwriters are full service financial institutions engaged in various activities, which may include securities trading, commercial and investment banking, financial advisory, investment management, principal investment, hedging, financing and brokerage activities. Certain of the underwriters and their respective affiliates may, from time to time, engage in transactions with and perform services for us in the ordinary course of their business for which they may receive customary fees and reimbursement of expenses. In the ordinary course of their various business activities, the underwriters and their respective affiliates may make or hold a broad array of investments and actively trade debt and equity securities (or related derivative securities) and financial instruments (which may include bank loans and/or credit default swaps) for their own account and for the accounts of their customers and may at any time hold long and short positions in such securities and instruments. Such investments and securities activities may involve securities and/or instruments of ours or our affiliates. The underwriters and their affiliates may also make investment recommendations and/or publish or express independent research views in respect of such securities or financial instruments and may hold, or recommend to clients that they acquire, long and/or short positions in such securities and instruments.
We have agreed to indemnify the underwriters against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act, or to contribute to payments the underwriters may be required to make because of any of those liabilities.
Notice to Prospective Investors in the European Economic Area
In relation to each member state of the European Economic Area that has implemented the Prospectus Directive (each, a relevant member state), with effect from and including the date on which the Prospectus Directive is implemented in that relevant member state (the relevant implementation date), an offer of shares described in this prospectus may not be made to the public in that relevant member state other than:
provided that no such offer of shares shall require us or any underwriter to publish a prospectus pursuant to Article 3 of the Prospectus Directive.
For purposes of this provision, the expression an "offer of securities to the public" in any relevant member state means the communication in any form and by any means of sufficient information on the terms of the offer and the shares to be offered so as to enable an investor to decide to purchase or subscribe for the shares, as the expression may be varied in that member state by any measure implementing the Prospectus Directive in that member state, and the expression "Prospectus Directive" means Directive 2003/71/EC (and amendments thereto, including the 2010 PD Amending Directive, to the extent implemented in the relevant member state) and includes any relevant implementing measure in the relevant member state. The expression 2010 PD Amending Directive means Directive 2010/73/EU.
The sellers of the shares have not authorized and do not authorize the making of any offer of shares through any financial intermediary on their behalf, other than offers made by the underwriters
with a view to the final placement of the shares as contemplated in this prospectus. Accordingly, no purchaser of the shares, other than the underwriters, is authorized to make any further offer of the shares on behalf of the sellers or the underwriters.
Notice to Prospective Investors in the United Kingdom
This prospectus is only being distributed to, and is only directed at, persons in the United Kingdom that are qualified investors within the meaning of Article 2(1)(e) of the Prospectus Directive that are also (i) investment professionals falling within Article 19(5) of the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (Financial Promotion) Order 2005 (the Order) or (ii) high net worth entities, and other persons to whom it may lawfully be communicated, falling within Article 49(2)(a) to (d) of the Order (each such person being referred to as a "relevant person"). This prospectus and its contents are confidential and should not be distributed, published or reproduced (in whole or in part) or disclosed by recipients to any other persons in the United Kingdom. Any person in the United Kingdom that is not a relevant person should not act or rely on this document or any of its contents.
Notice to Prospective Investors in France
Neither this prospectus nor any other offering material relating to the shares described in this prospectus has been submitted to the clearance procedures of theAutorité des Marchés Financiersor of the competent authority of another member state of the European Economic Area and notified to theAutorité des Marchés Financiers. The shares have not been offered or sold and will not be offered or sold, directly or indirectly, to the public in France. Neither this prospectus nor any other offering material relating to the shares has been or will be:
Such offers, sales and distributions will be made in France only:
The shares may be resold directly or indirectly, only in compliance with articles L.411-1, L.411-2, L.412-1 and L.621-8 through L.621-8-3 of the FrenchCode monétaire et financier.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Australia
No prospectus or other disclosure document (as defined in the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) of Australia ("Corporations Act")) in relation to the common stock has been or will be lodged with the Australian Securities & Investments Commission ("ASIC"). This document has not been lodged with
ASIC and is only directed to certain categories of exempt persons. Accordingly, if you receive this document in Australia:
Notice to Prospective Investors in Hong Kong
The shares may not be offered or sold in Hong Kong by means of any document other than (i) in circumstances which do not constitute an offer to the public within the meaning of the Companies Ordinance (Cap. 32, Laws of Hong Kong), or (ii) to "professional investors" within the meaning of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571, Laws of Hong Kong) and any rules made thereunder, or (iii) in other circumstances which do not result in the document being a "prospectus" within the meaning of the Companies Ordinance (Cap. 32, Laws of Hong Kong) and no advertisement, invitation or document relating to the shares may be issued or may be in the possession of any person for the purpose of issue (in each case whether in Hong Kong or elsewhere), which is directed at, or the contents of which are likely to be accessed or read by, the public in Hong Kong (except if permitted to do so under the laws of Hong Kong) other than with respect to shares which are or are intended to be disposed of only to persons outside Hong Kong or only to "professional investors" within the meaning of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571, Laws of Hong Kong) and any rules made thereunder.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Japan
The shares offered in this prospectus have not been and will not be registered under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law of Japan. The shares have not been offered or sold and will not be offered or sold, directly or indirectly, in Japan or to or for the account of any resident of Japan (including any corporation or other entity organized under the laws of Japan), except (i) pursuant to an exemption from the registration requirements of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law and (ii) in compliance with any other applicable requirements of Japanese law.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Singapore
This prospectus has not been registered as a prospectus with the Monetary Authority of Singapore. Accordingly, this prospectus and any other document or material in connection with the offer or sale, or invitation for subscription or purchase, of the shares may not be circulated or distributed, nor may
the shares be offered or sold, or be made the subject of an invitation for subscription or purchase, whether directly or indirectly, to persons in Singapore other than (i) to an institutional investor under Section 274 of the Securities and Futures Act, Chapter 289 of Singapore (the SFA), (ii) to a relevant person pursuant to Section 275(1), or any person pursuant to Section 275(1A), and in accordance with the conditions specified in Section 275 of the SFA or (iii) otherwise pursuant to, and in accordance with the conditions of, any other applicable provision of the SFA, in each case subject to compliance with conditions set forth in the SFA.
Where the shares are subscribed or purchased under Section 275 of the SFA by a relevant person which is:
shares, debentures and units of shares and debentures of that corporation or the beneficiaries' rights and interest (howsoever described) in that trust shall not be transferred within six months after that corporation or that trust has acquired the shares pursuant to an offer made under Section 275 of the SFA except:
The validity of the issuance of our common stock offered in this prospectus will be passed upon for us by Ropes & Gray LLP, Boston, Massachusetts. Certain legal matters in connection with this offering will be passed upon for the underwriters by Mintz, Levin, Cohn, Ferris, Glovsky and Popeo, P.C., Boston, Massachusetts.
The financial statements of Acceleron Pharma Inc. at December 31, 2011 and 2012, and for the years then ended, appearing in this Prospectus and Registration Statement have been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report thereon appearing elsewhere herein, and are included in reliance upon such report given on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the shares of common stock offered hereby. This prospectus, which constitutes a part of the registration statement, does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement or the exhibits and schedules filed therewith. For further information with respect to us and the common stock offered hereby, reference is made to the registration statement and the exhibits and schedules filed therewith. Statements contained in this prospectus regarding the contents of any contract or any other document that is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement are not necessarily complete, and each such statement is qualified in all respects by reference to the full text of such contract or other document filed as an exhibit to the registration statement. A copy of the registration statement and the exhibits and schedules filed therewith may be inspected without charge at the public reference room maintained by the SEC, located at 100 F Street N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549, and copies of all or any part of the registration statement may be obtained from such offices upon the payment of the fees prescribed by the SEC. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information about the public reference room. The SEC also maintains a website that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding registrants that file electronically with the SEC. The address is www.sec.gov.
Upon completion of this offering, we will become subject to the information and periodic reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and, in accordance therewith, will file periodic reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. Such periodic reports, proxy statements and other information will be available for inspection and copying at the public reference room and website of the SEC referred to above.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Index to Financial Statements
| | Pages | |
|---|---|---|
Report of | F-2 | |
Balance | F-3 | |
Statements of | F-4 | |
Statements of | F-5 | |
Statements of | F-7 | |
Notes to | F-8 |
Report of independent registered public accounting firmIndependent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of Acceleron Pharma Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the related statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss), redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders' deficit, and cash flows for the years then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Acceleron Pharma Inc. at December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
July 3, 2013, except for Note 16,
as to which the date is
September 5, 2013
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Balance sheetsSheets
(Inamounts in thousands except share and per share data)
| | December 31, | March 31, 2013 | December 31, | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | Actual | Pro Forma | 2011 | 2012 | Actual | Pro Forma | ||||||||||||||||||
| | | | (unaudited) | | | (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 65,037 | $ | 39,611 | $ | 38,510 | $ | 38,510 | $ | 65,037 | $ | 39,611 | $ | 28,465 | $ | 28,465 | ||||||||||
Collaboration receivables (includes related party amounts of $1,024, $1,840 and $2,419 at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31, 2013, respectively) | 1,660 | 2,776 | 2,999 | 2,999 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Collaboration receivables (includes related party amounts of $1,024, $1,840 and $3,329 at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and June 30, 2013, respectively) | 1,660 | 2,776 | 4,340 | 4,340 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Related party receivable | — | — | 235 | 235 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1,044 | 1,474 | 1,746 | 1,746 | 1,044 | 1,474 | 1,288 | 1,288 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total current assets | 67,741 | 43,861 | 43,490 | 43,490 | 67,741 | 43,861 | 34,098 | 34,098 | ||||||||||||||||||
Property and equipment, net | 4,911 | 4,059 | 3,916 | 3,916 | 4,911 | 4,059 | 3,734 | 3,734 | ||||||||||||||||||
Restricted cash | 912 | 913 | 913 | 913 | 912 | 913 | 913 | 913 | ||||||||||||||||||
Related party receivables | 225 | 233 | — | — | 225 | 233 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Other assets | — | 146 | 128 | 128 | — | 146 | 1,283 | 1,283 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 73,789 | $ | 49,212 | $ | 48,447 | $ | 48,447 | $ | 73,789 | $ | 49,212 | $ | 40,023 | $ | 40,023 | ||||||||||
Liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders' deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 1,914 | $ | 642 | $ | 395 | $ | 395 | $ | 1,914 | $ | 642 | $ | 955 | $ | 955 | ||||||||||
Accrued expenses (includes related party amounts of $833, $861, and $861 at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31, 2013, respectively) | 4,513 | 6,153 | 5,409 | 5,409 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Accrued expenses (includes related party amounts of $833, $861, and $0 at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and June 30, 2013, respectively) | 4,513 | 6,153 | 5,311 | 5,311 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Deferred revenue | 10,946 | 27,840 | 25,414 | 25,414 | 10,946 | 27,840 | 2,525 | 2,525 | ||||||||||||||||||
Deferred rent | 483 | 499 | 499 | 499 | 483 | 499 | 499 | 499 | ||||||||||||||||||
Notes payable, net of discount | 5,997 | 3,668 | 5,562 | 5,562 | 5,997 | 3,668 | 7,496 | 7,496 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 23,853 | 38,802 | 37,279 | 37,279 | 23,853 | 38,802 | 16,786 | 16,786 | ||||||||||||||||||
Deferred revenue, net of current portion | 33,350 | 6,760 | 6,670 | 6,670 | 33,350 | 6,760 | 6,668 | 6,668 | ||||||||||||||||||
Deferred rent, net of current portion | 3,335 | 2,837 | 2,712 | 2,712 | 3,335 | 2,837 | 2,587 | 2,587 | ||||||||||||||||||
Notes payable, net of current portion and discount | — | 16,525 | 14,717 | 14,717 | — | 16,525 | 12,869 | 12,869 | ||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | 1,046 | 1,422 | 1,022 | — | 1,046 | 1,422 | 1,009 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 3,347 | 5,229 | 5,935 | 5,935 | 3,347 | 5,229 | 6,381 | 6,381 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | 64,931 | 71,575 | 68,335 | 67,313 | 64,931 | 71,575 | 46,300 | 45,291 | ||||||||||||||||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock (Note 8) | 241,549 | 268,610 | 272,980 | — | 241,549 | 268,610 | 279,823 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders' deficit: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value: 104,013,161 shares authorized; 9,573,972, 9,728,763, and 9,748,650 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012, and March 31, 2013, respectively, and 81,867,378 shares outstanding at March 31, 2013 (pro forma) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 82 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value: 104,013,161 shares authorized; 2,393,458, 2,432,155, and 2,447,195 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012, and June 30, 2013, respectively, and 21,055,604 shares outstanding at June 30, 2013 (pro forma) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Additional paid-in capital | — | — | — | 149,838 | — | — | — | 150,411 | ||||||||||||||||||
Accumulated deficit | (232,701 | ) | (290,983 | ) | (292,878 | ) | (168,786 | ) | (232,694 | ) | (290,976 | ) | (286,103 | ) | (155,701 | ) | ||||||||||
Total stockholders' deficit | (232,691 | ) | (290,973 | ) | (292,868 | ) | (18,866 | ) | (232,691 | ) | (290,973 | ) | (286,100 | ) | (5,268 | ) | ||||||||||
Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders' deficit | $ | 73,789 | $ | 49,212 | $ | 48,447 | $ | 48,447 | $ | 73,789 | $ | 49,212 | $ | 40,023 | $ | 40,023 | ||||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
Statements of operationsOperations and comprehensive income (loss)
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(Inamounts in thousands except per share data)
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
| | | | (unaudited) | | | (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Collaboration revenue: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | 2,375 | $ | 12,515 | $ | 74,406 | $ | 9,696 | $ | 4,765 | $ | 35,406 | ||||||||||
Cost-sharing, net | 4,760 | 5,558 | 949 | 2,497 | 4,760 | 5,558 | 2,599 | 6,034 | ||||||||||||||||||
Contract manufacturing | 1,745 | — | — | — | 1,745 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Total revenue(1) | 80,911 | 15,254 | 3,324 | 15,012 | 80,911 | 15,254 | 7,364 | 41,440 | ||||||||||||||||||
Costs and expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Research and development | 32,713 | 35,319 | 8,212 | 8,780 | 32,713 | 35,319 | 16,925 | 17,691 | ||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 8,142 | 8,824 | 2,045 | 3,096 | 8,142 | 8,824 | 4,276 | 6,461 | ||||||||||||||||||
Cost of contract manufacturing revenue | 1,500 | — | — | — | 1,500 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Total costs and expenses | 42,355 | 44,143 | 10,257 | 11,876 | 42,355 | 44,143 | 21,201 | 24,152 | ||||||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (6,933 | ) | 3,136 | 38,556 | (28,889 | ) | (13,837 | ) | 17,288 | ||||||||||||||
Other (expense) income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other expense, net | (485 | ) | (2,255 | ) | (454 | ) | (1,066 | ) | (485 | ) | (2,255 | ) | (697 | ) | (1,422 | ) | ||||||||||
Interest income | 17 | 91 | 28 | 12 | 17 | 91 | 53 | 20 | ||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense | (1,822 | ) | (1,529 | ) | (229 | ) | (435 | ) | (1,822 | ) | (1,529 | ) | (507 | ) | (1,161 | ) | ||||||||||
Total other expense, net | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (655 | ) | (1,489 | ) | (2,290 | ) | (3,693 | ) | (1,151 | ) | (2,563 | ) | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Reconciliation of net income (loss) to net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs on redeemable convertible preferred stock | (21,757 | ) | (27,061 | ) | (6,747 | ) | (6,756 | ) | (21,757 | ) | (27,061 | ) | (13,545 | ) | (13,599 | ) | ||||||||||
Gain on extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | — | — | 2,765 | — | — | — | 2,765 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) applicable to participating securities | (12,645 | ) | — | — | — | (12,645 | ) | — | — | (3,428 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders—basic | $ | 1,864 | $ | (59,643 | ) | $ | (14,335 | ) | $ | (2,344 | ) | $ | 1,864 | $ | (59,643 | ) | $ | (28,533 | ) | $ | 463 | |||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs on redeemable convertible preferred stock | (21,757 | ) | (27,061 | ) | (6,747 | ) | (6,756 | ) | (21,757 | ) | (27,061 | ) | (13,545 | ) | (13,599 | ) | ||||||||||
Gain on extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | — | — | 2,765 | — | — | — | 2,765 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) applicable to participating securities | (12,395 | ) | — | — | — | (12,395 | ) | — | — | (3,125 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders—diluted | $ | 2,114 | $ | (59,643 | ) | $ | (14,335 | ) | $ | (2,344 | ) | $ | 2,114 | $ | (59,643 | ) | $ | (28,533 | ) | $ | 766 | |||||
Net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders: (Note 2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.20 | $ | (6.21 | ) | $ | (1.50 | ) | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | 0.80 | $ | (24.84 | ) | $ | (11.91 | ) | $ | 0.19 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 0.19 | $ | (6.21 | ) | $ | (1.50 | ) | $ | (0.24 | ) | $ | 0.78 | $ | (24.84 | ) | $ | (11.91 | ) | $ | 0.17 | |||||
Weighted-average number of common shares used in computing net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 9,313 | 9,605 | 9,579 | 9,740 | 2,328 | 2,401 | 2,395 | 2,437 | ||||||||||||||||||
Diluted | 10,863 | 9,605 | 9,579 | 9,740 | 2,716 | 2,401 | 2,395 | 4,434 | ||||||||||||||||||
Pro forma net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders (unaudited): (Note 2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.77 | ||||||||||||||||
Diluted | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.70 | ||||||||||||||||
Pro forma weighted-average number of common shares used in computing proforma net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders (unaudited) : | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | 82,267 | 81,859 | 21,155 | 21,045 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted | 82,267 | 88,651 | 21,155 | 23,062 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) Includes related party revenue (Note 15) | $ | 64,220 | $ | 4,914 | $ | 958 | $ | 12,798 | $ | 64,220 | $ | 4,914 | $ | 2,215 | $ | 16,413 | ||||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Statements of redeemable convertible preferred stockRedeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and stockholders' deficitStockholders' Deficit
(Inamounts in thousands except share data)
| | Series A Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series B Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series C Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series C-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series D Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series D-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series A Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series B Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series C Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series C-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series D Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series D-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2010 | 25,643,980 | $ | 57,433 | 16,816,810 | $ | 55,880 | 11,912,333 | $ | 48,726 | 1,831,502 | $ | 7,571 | 939,847 | $ | 2,989 | 2,547,771 | $ | 8,392 | 6,410,976 | $ | 57,433 | 4,204,185 | $ | 55,880 | 2,978,062 | $ | 48,726 | 457,875 | $ | 7,571 | 234,940 | $ | 2,989 | 636,942 | $ | 8,392 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series E redeemable convertible preferred stock net of issuance costs of $201 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series F redeemable convertible preferred stock net of issuance costs of $92 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs related to redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | 4,616 | — | 5,584 | — | 5,594 | — | 908 | — | 668 | — | 1,736 | — | 4,616 | — | 5,584 | — | 5,594 | — | 908 | — | 668 | — | 1,736 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compensation expense associated with stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Grant of stock options to nonemployees | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ecercise of common warrants | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2011 | 25,643,980 | 62,049 | 16,816,810 | 61,464 | 11,912,333 | 54,320 | 1,831,502 | 8,479 | 939,847 | 3,657 | 2,547,771 | 10,128 | 6,410,976 | 62,049 | 4,204,185 | 61,464 | 2,978,062 | 54,320 | 457,875 | 8,479 | 234,940 | 3,657 | 636,942 | 10,128 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs related to redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | 4,616 | — | 5,580 | — | 5,589 | — | 908 | — | 668 | — | 1,736 | — | 4,616 | — | 5,580 | — | 5,589 | — | 908 | — | 668 | — | 1,736 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compensation expense associated with stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2012 | 25,643,980 | 66,665 | 16,816,810 | 67,044 | 11,912,333 | 59,909 | 1,831,502 | 9,387 | 939,847 | 4,325 | 2,547,771 | 11,864 | 6,410,976 | 66,665 | 4,204,185 | 67,044 | 2,978,062 | 59,909 | 457,875 | 9,387 | 234,940 | 4,325 | 636,942 | 11,864 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs related to redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | 1,159 | — | 1,386 | — | 1,391 | — | 226 | — | 166 | — | 434 | — | 2,321 | — | 2,872 | — | 2,775 | — | 451 | — | 332 | — | 868 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase and retirement of redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | — | (558,964 | ) | (2,267 | ) | (86,977 | ) | (445 | ) | — | — | (11,624 | ) | (54 | ) | — | — | — | — | (139,741 | ) | (2,267 | ) | (21,744 | ) | (445 | ) | — | — | (2,906 | ) | (54 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of warrants to purchase convertible preferred stock | 186,674 | 678 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 46,668 | 678 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compensation expense associated with stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at March 31, 2013 (unaudited) | 25,830,654 | 68,502 | 16,257,846 | 66,163 | 11,825,356 | 60,855 | 1,831,502 | 9,613 | 928,223 | 4,437 | 2,547,771 | 12,298 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at June 30, 2013 (unaudited) | 6,457,644 | 69,664 | 4,064,444 | 67,649 | 2,956,318 | 62,239 | 457,875 | 9,838 | 232,034 | 4,603 | 636,942 | 12,732 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of redeemable convertible preferred stock into common stock (unaudited) | (25,830,654 | ) | (68,502 | ) | (16,257,846 | ) | (66,163 | ) | (11,825,356 | ) | (60,855 | ) | (1,831,502 | ) | (9,613 | ) | (928,223 | ) | (4,437 | ) | (2,547,771 | ) | (12,298 | ) | (6,457,644 | ) | (69,665 | ) | (4,064,444 | ) | (67,650 | ) | (2,956,339 | ) | (62,239 | ) | (457,875 | ) | (9,838 | ) | (232,055 | ) | (4,603 | ) | (636,942 | ) | (12,732 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reclassification of warrants to purchase shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock into warrants to purchase common stock (unaudited) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pro forma, March 31, 2013 (unaudited) | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pro forma, June 30, 2013 (unaudited) | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Statements of redeemable convertible preferred stockRedeemable Convertible Preferred Stock and stockholders' deficitStockholders' Deficit (continued)
(Inamounts in thousands except share data)
| | Series E Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series F Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | | | | | | | Series E Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Series F Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | | | | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Total Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Common Stock | | | | Total Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock | Common Stock | | | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | $0.001 Par Value | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Total Stockholders' Deficit | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | Value | Number of Shares | $0.001 Par Value | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Total Stockholders' Deficit | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2010 | 3,264,333 | $ | 8,423 | — | $ | — | $ | 189,414 | 9,045,983 | $ | 10 | $ | — | $ | (248,827 | ) | $ | (248,817 | ) | 816,060 | $ | 8,423 | — | $ | — | $ | 189,414 | 2,261,461 | $ | 3 | $ | — | $ | (248,820 | ) | $ | (248,817 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series E redeemable convertible preferred stock net of issuance costs of $201 | — | — | 9,704,756 | 30,378 | 30,378 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series F redeemable convertible preferred stock net of issuance costs of $92 | — | — | 2,426,171 | 30,378 | 30,378 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs related to redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | 2,511 | — | 140 | 21,757 | — | — | (1,617 | ) | (20,140 | ) | (21,757 | ) | — | 2,511 | — | 140 | 21,757 | — | — | (1,617 | ) | (20,140 | ) | (21,757 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compensation expense associated with stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,212 | — | 1,212 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,212 | — | 1,212 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Grant of stock options to nonemployees | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 215 | — | 215 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 215 | — | 215 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options | — | — | — | — | — | 378,992 | — | 190 | — | 190 | — | — | — | — | — | 94,748 | — | 190 | — | 190 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Ecercise of common warrants | — | — | — | — | — | 148,997 | — | (0 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 37,249 | — | (0 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 36,266 | 36,266 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 36,266 | 36,266 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2011 | 3,264,333 | 10,934 | 9,704,756 | 30,518 | 241,549 | 9,573,972 | 10 | — | (232,701 | ) | (232,691 | ) | 816,060 | 10,934 | 2,426,171 | 30,518 | 241,549 | 2,393,458 | 3 | — | (232,694 | ) | (232,691 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs related to redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | 2,459 | — | 5,505 | 27,061 | — | — | (1,361 | ) | (25,700 | ) | (27,061 | ) | — | 2,459 | — | 5,505 | 27,061 | — | — | (1,361 | ) | (25,700 | ) | (27,061 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compensation expense associated with stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,206 | — | 1,206 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,206 | — | 1,206 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options | — | — | — | — | — | 154,791 | — | 155 | — | 155 | — | — | — | — | — | 38,697 | — | 155 | — | 155 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (32,582 | ) | (32,582 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (32,582 | ) | (32,582 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2012 | 3,264,333 | 13,393 | 9,704,756 | 36,023 | 268,610 | 9,728,763 | 10 | — | (290,983 | ) | (290,973 | ) | 816,060 | 13,393 | 2,426,171 | 36,023 | 268,610 | 2,432,155 | 3 | — | (290,976 | ) | (290,973 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs related to redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | 619 | — | 1,375 | 6,756 | — | — | (3,214 | ) | (3,542 | ) | (6,756 | ) | — | 1,231 | — | 2,749 | 13,599 | — | — | (3,747 | ) | (9,852 | ) | (13,599 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase and retirement of redeemable convertible preferred stock | (52,413 | ) | (224 | ) | (19,300 | ) | (74 | ) | (3,064 | ) | (2,888 | ) | — | 2,772 | — | 2,772 | (13,103 | ) | (224 | ) | (4,825 | ) | (74 | ) | (3,064 | ) | (722 | ) | — | 2,773 | — | 2,773 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of warrants to purchase convertible preferred stock | — | — | — | — | 678 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 678 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Compensation expense associated with stock options | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 428 | — | 428 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 948 | — | 948 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options | — | — | — | — | — | 22,775 | — | 14 | — | 14 | — | — | — | — | — | 15,762 | — | 26 | — | 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,647 | 1,647 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 14,725 | 14,725 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at March 31, 2013 (unaudited) | 3,211,920 | 13,788 | 9,685,456 | 37,324 | 272,980 | 9,748,650 | 10 | — | (292,878 | ) | (292,868 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at June 30, 2013 (unaudited) | 802,957 | 14,400 | 2,421,346 | 38,698 | 279,823 | 2,447,195 | 3 | — | (286,103 | ) | (286,100 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of redeemable convertible preferred stock into common stock (unaudited) | (3,211,920 | ) | (13,788 | ) | (9,685,456 | ) | (37,324 | ) | (272,980 | ) | 72,118,728 | 72 | 148,816 | 124,092 | 272,980 | (802,957 | ) | (14,400 | ) | (2,421,346 | ) | (38,698 | ) | (279,823 | ) | 18,608,409 | 19 | 149,402 | 130,402 | 279,823 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reclassification of warrants to purchase shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock into warrants to purchase common stock (unaudited) | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,022 | — | 1,022 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,009 | — | 1,009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pro forma, March 31, 2013 (unaudited) | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | $ | — | 81,867,378 | $ | 82 | $ | 149,838 | $ | (168,786 | ) | $ | (18,866 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pro forma, June 30, 2013 (unaudited) | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | $ | — | 21,055,604 | $ | 22 | $ | 150,411 | $ | (155,701 | ) | $ | (5,268 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Statements of cash flowsCash Flows
(Inamounts in thousands)
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
| | | | (unaudited) | | | (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Operating activities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (7,588 | ) | $ | 1,647 | $ | 36,266 | $ | (32,582 | ) | $ | (14,988 | ) | $ | 14,725 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 3,134 | 1,293 | 476 | 224 | 3,134 | 1,293 | 829 | 449 | ||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 1,427 | 1,206 | 261 | 428 | 1,427 | 1,206 | 528 | 948 | ||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of debt discount | 162 | 51 | 25 | — | 162 | 51 | 51 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of deferred interest | 271 | 335 | 68 | 86 | 271 | 335 | 164 | 171 | ||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of deferred debt issuance costs | 79 | 84 | 20 | 18 | 79 | 84 | 48 | 177 | ||||||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of warrants | 481 | 2,258 | 454 | 1,067 | 481 | 2,258 | 696 | 1,500 | ||||||||||||||||||
Gain on retirement of warrants | — | — | — | (76 | ) | — | — | — | (76 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Forgiveness of related party receivable | — | — | — | 237 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 2,564 | (594 | ) | (1,288 | ) | (272 | ) | 2,564 | (594 | ) | (1,196 | ) | 38 | |||||||||||||
Collaboration receivables | 1,836 | (1,116 | ) | (282 | ) | (223 | ) | 1,836 | (1,116 | ) | (917 | ) | (1,564 | ) | ||||||||||||
Related party receivable | (6 | ) | (8 | ) | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | (6 | ) | (8 | ) | (4 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||||||
Accounts payable | 334 | (1,272 | ) | (1,133 | ) | (247 | ) | 334 | (1,272 | ) | (1,457 | ) | 314 | |||||||||||||
Accrued expenses | (2,773 | ) | 1,640 | (342 | ) | (744 | ) | (2,773 | ) | 1,640 | (265 | ) | (2,006 | ) | ||||||||||||
Deferred revenue | (35,130 | ) | (9,696 | ) | (2,375 | ) | (2,516 | ) | (35,130 | ) | (9,696 | ) | (4,765 | ) | (25,406 | ) | ||||||||||
Deferred rent | 211 | (482 | ) | (115 | ) | (125 | ) | 211 | (482 | ) | (233 | ) | (250 | ) | ||||||||||||
Restricted cash | 200 | (1 | ) | — | — | 200 | (1 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 9,056 | (38,884 | ) | (11,821 | ) | (735 | ) | 9,056 | (38,884 | ) | (21,509 | ) | (10,747 | ) | ||||||||||||
Investing activities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchases of property and equipment | (27 | ) | (441 | ) | (8 | ) | (80 | ) | (27 | ) | (441 | ) | (302 | ) | (125 | ) | ||||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (27 | ) | (441 | ) | (8 | ) | (80 | ) | (27 | ) | (441 | ) | (302 | ) | (125 | ) | ||||||||||
Financing activities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Financing Activities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from issuance of redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs | 30,378 | — | — | — | 30,378 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from long-term debt, net of issuance costs | — | 19,935 | — | — | — | 19,935 | 19,945 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Payments of long-term debt | (9,476 | ) | (6,191 | ) | (2,462 | ) | — | (9,476 | ) | (6,191 | ) | (6,191 | ) | — | ||||||||||||
Payments made to repurchase redeemable convertible preferred stock, common stock and warrants to purchase common stock | — | — | — | (300 | ) | — | — | — | (300 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from exercise of stock options and warrants to purchase common stock | 190 | 155 | 2 | 14 | 190 | 155 | 3 | 26 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 21,092 | 13,899 | (2,460 | ) | (286 | ) | 21,092 | 13,899 | 13,757 | (274 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 30,121 | (25,426 | ) | (14,289 | ) | (1,101 | ) | 30,121 | (25,426 | ) | (8,054 | ) | (11,146 | ) | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 34,916 | 65,037 | 65,037 | 39,611 | 34,916 | 65,037 | 65,037 | 39,611 | ||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 65,037 | $ | 39,611 | $ | 50,748 | $ | 38,510 | $ | 65,037 | $ | 39,611 | $ | 56,983 | $ | 28,465 | ||||||||||
Supplemental discussion of cash flow information: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 1,461 | $ | 1,065 | $ | 164 | $ | 435 | $ | 1,461 | $ | 1,065 | $ | 357 | $ | 850 | ||||||||||
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Supplemental Disclosure of Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of dividends, interest, redemption value, and issuance costs on preferred stock | $ | 21,757 | $ | 27,061 | $ | 6,747 | $ | 6,756 | $ | 21,757 | $ | 27,061 | $ | 13,545 | $ | 13,599 | ||||||||||
Cashless exercise of warrants | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 678 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 678 | ||||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements
Years endedEnded December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the three months ended March 31,Six Months Ended June 30, 2012 and 2013
(Informationinformation as of March 31,June 30, 2013 and for the threesix months
ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013 and 2012 is unaudited)
1. Nature of businessBusiness
Acceleron Pharma Inc. (Acceleron or the Company) was incorporated in the state of Delaware on June 13, 2003, as Phoenix Pharma, Inc. The Company subsequently changed its name to Acceleron Pharma Inc. and commenced operations in February 2004. The Company is a Cambridge, Massachusetts-based biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of novel protein therapeutics for cancer and rare diseases. The Company's research focuses on the biology of the Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-b) protein superfamily, a large and diverse group of molecules that regulate the growth and repair of tissues throughout the human body. By coupling its discovery and development expertise, including its proprietary knowledge of the TGF-b superfamily, with internal protein engineering and manufacturing capabilities, the Company has built a highly productive research and development platform that has generated numerous innovative protein therapeutics with novel mechanisms of action. The Company has internally discovered three protein therapeutics that are currently being studied in 12 ongoing Phase 2 clinical trials, focused on the areas of cancer and rare diseases.
The Company is subject to risks common to companies in the biotechnology industry, including, but not limited to, risk that the Company never achieves profitability, the need for substantial additional financing, risk of relying on third parties, risks of clinical trial failures, dependence on key personnel, protection of proprietary technology and compliance with government regulations.
Liquidity
As of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, the Company had an accumulated deficit of $291.0 million and $292.9$286.1 million, respectively, and will require substantial additional capital to fund its research and development. The Company believes that its cash resources of $39.6 million at December 31, 2012 will be sufficient to allow the Company to fund its current operating plan through January 1, 2014; however, the Company will be required to raise additional capital to fund operations beyond this time. As the Company continues to incur losses, a transition to profitability is dependent upon the successful development, approval and commercialization of its product candidates and the achievement of a level of revenues adequate to support the Company's cost structure. The Company may never achieve profitability, and unless and until it does, the Company will continue to need to raise additional capital. Management intends to fund future operations through the sale of equity, debt financings or other sources, including potential additional collaborations. There can be no assurances, however, that additional funding will be available on terms acceptable to the Company, or at all.
2. Summary of significant accounting policiesSignificant Accounting Policies
The accompanying financial statements reflect the application of certain significant accounting policies as described below and elsewhere in these notes to the financial statements. The Company believes that a significant accounting policy is one that is both important to the portrayal of the Company's financial condition and results, and requires management's most difficult, subjective, or complex judgments, often as the result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policiesSignificant Accounting Policies (continued)
Basis of presentationPresentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (GAAP). Any reference in these notes to applicable guidance is meant to refer to the authoritative United States generally accepted accounting principles as found in the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) and Accounting Standards Update (ASU) of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
Unaudited interim financial informationInterim Financial Information
The accompanying interim balance sheet as of March 31,June 30, 2013, the statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) and statements of cash flows for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the statement of redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders' deficit for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, and the financial data and other information disclosed in these notes related to the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013 are unaudited. The unaudited interim financial statements have been prepared on the same basis as the audited annual financial statements, and, in the opinion of management, reflect all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for the fair presentation of the Company's financial position as of March 31,June 30, 2013, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013. The results for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the year ending December 31, 2013, any other interim periods, or any future year or period.
Unaudited pro forma informationPro Forma Information
On June 6, 2013, the Company's board of directors (the Board) authorized management of the Company to pursue the filing of a registration statement with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for the Company to sell shares of its common stock to the public. The unaudited pro forma balance sheet and the unaudited pro forma statement of redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders' equity as of March 31,June 30, 2013 reflect the automatic conversion, at the closing of an initial public offering (IPO) of the Company's common stock, of all outstanding shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock into 72,118,72818,608,409 shares of common stock based on the shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock outstanding at March 31,June 30, 2013, which assumes a 1:1 conversion ratio, and the automatic conversion of warrants to purchase 565,495141,370 shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock into warrants to purchase 565,495141,370 shares of common stock based on the warrants outstanding at March 31,June 30, 2013.
Unaudited pro forma net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders is computed using the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding after giving pro forma effect to the conversion of all redeemable convertible preferred stock during the year ended December 31, 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013 into shares of the Company's common stock, assuming a 1:1 conversion ratio, as if such conversion had occurred at the beginning of the period presented, or the date of original issuance, if later. Upon conversion of the redeemable convertible preferred stock into shares of the Company's common stock in the event of an IPO, the holders of the redeemable convertible preferred stock are not entitled to receive undeclared dividends. Accordingly, the impact of the accretion of unpaid and undeclared dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs, has been excluded from the determination of basic and diluted loss per share. The gain recognized upon the extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred stock during the threesix months ended
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
March 31, June 30, 2013 has also been excluded from the determination of net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders. Additionally, the gains (losses) associated with the changes in the fair value of the warrants to purchase redeemable preferred stock
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
has been excluded from the determination of net income (loss) as these remeasurements would not be required when the warrants to purchase shares of preferred stock become warrants to purchase common stock.
Further, the cumulative accretion of unpaid and undeclared dividends has been reflected as an increase to additional-paid-in-capital and accumulated deficit in the accompanying unaudited pro forma statement of redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders' deficit March 31,for the six months ended June 30, 2013.
As noted above, the unaudited pro forma information reflects the automatic conversion, at the closing of an IPO of the Company's common stock, of all redeemable convertible preferred stock into shares of common stockstock. The conversion has been performedreflected assuming a 1:11-to-1 conversion ratio; however, in certain events, as described in Note 8,ratio for all series of redeemable convertible preferred stock, except for the Series E redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series E Preferred Stock), which may convert into common stock at a ratio greater than 1:1,1-to-1, based on a formula driven by the date on which the Company completes an IPO and the price of such offering. For purposes of the unaudited pro forma information included within these financial statements, the conversion of the Series E Preferred Stock has been reflected assuming a weighted-average conversion ratio of 1.72-to-1, which was calculated assuming an IPO price of $14.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the range set forth on the front cover of the Company's prospectus and an estimated closing date for an IPO of September 23, 2013. See Note 8 for further discussion of the Series E Preferred Stock conversion feature as well as a discussion of the rights and preferences of the redeemable convertible preferred stock, including the conversion rights.stock.
Use of estimatesEstimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts expensed during the reporting period. Actual results could materially differ from those estimates.
Management considers many factors in selecting appropriate financial accounting policies and controls, and in developing the estimates and assumptions that are used in the preparation of these financial statements. Management must apply significant judgment in this process. In addition, other factors may affect estimates, including: expected business and operational changes, sensitivity and volatility associated with the assumptions used in developing estimates, and whether historical trends are expected to be representative of future trends. The estimation process often may yield a range of potentially reasonable estimates of the ultimate future outcomes and management must select an amount that falls within that range of reasonable estimates. This process may result in actual results differing materially from those estimated amounts used in the preparation of the financial statements if these results differ from historical experience, or other assumptions do not turn out to be substantially accurate, even if such assumptions are reasonable when made. In preparing these financial statements, management used significant estimates in the following areas, among others: revenue recognition, stock-based compensation expense, the determination of the fair value of stock-based awards, the fair value of liability-classified warrants, accrued expenses, and the recoverability of the Company's net deferred tax assets and related valuation allowance.
The Company utilizes significant estimates and assumptions in determining the fair value of its common stock. The Board determined the estimated fair value of the Company's common stock based on a number of objective and subjective factors, including external market conditions affecting the
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
biotechnology industry sector and the prices at which the Company sold shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock, the superior rights and preferences of securities senior to the Company's common stock at the time, and the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an IPO or sale of the Company.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
The Company utilized various valuation methodologies in accordance with the framework of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants' Technical Practice Aid,Valuation of Privately-Held Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation, to estimate the fair value of its common stock. Each valuation methodology includes estimates and assumptions that require the Company's judgment. These estimates and assumptions include a number of objective and subjective factors, including external market conditions affecting the biotechnology industry sector, the prices at which the Company sold shares of preferred stock, the superior rights and preferences of securities senior to the Common Stock at the time and the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an IPO or sale. Significant changes to the key assumptions used in the valuations could result in different fair values of common stock at each valuation date.
Reclassifications
The Company has reclassified certain prior period amounts in the balance sheet as of December 31, 2011, totaling $0.5 million related to deferred rent from long-term to short-term to conform to the current period presentation. This reclassification had no impact on the previously reported results of operations or cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2011.
Collaboration receivableReceivable
Credit is extended to customers based upon an evaluation of the customer's financial condition. Collaboration receivables are recorded at net realizable value. The Company does not charge interest on past due balances. Collaboration receivables are determined to be past due when the payment due date is exceeded. The Company utilizes a specific identification accounts receivable reserve methodology based on a review of outstanding balances and previous activities to determine the allowance for doubtful accounts. The Company charges off uncollectible receivables at the time the Company determines the receivable is no longer collectible. The Company did not have an allowance for doubtful accounts at December 31, 2011 or 2012 or at March 31,June 30, 2013.
Segment informationInformation
Operating segments are identified as components of an enterprise about which separate discrete financial information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision maker, or decision making group, in making decisions on how to allocate resources and assess performance. The Company's chief operating decision maker is the chief executive officer. The Company and the chief executive officer view the Company's operations and manage its business as one operating segment. All material long-lived assets of the Company reside in the United States. The Company does use contract research organizations (CROs) and research institutions located outside the United States. Some of these expenses are subject to collaboration reimbursement which is presented as a component of cost sharing, net in the statement of operations and comprehensive income (loss).
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Cash and cash equivalentsCash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of 90 days or less at acquisition to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include cash held in banks and amounts held in interest-bearing money market accounts. Cash equivalents are carried at cost, which approximates their fair market value.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
Concentrations of credit riskCredit Risk and off-balance sheet riskOff-Balance Sheet Risk
The Company has no off-balance sheet risk, such as foreign exchange contracts, option contracts, or other foreign hedging arrangements. Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk are primarily cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash and accounts receivable. The Company maintains its cash and cash equivalent balances in the form of money market accounts with financial institutions that management believes are creditworthy. The Company's investment policy includes guidelines on the quality of the institutions and financial instruments and defines allowable investments that the Company believes minimizes the exposure to concentration of credit risk.
The Company routinely assesses the creditworthiness of its customers and collaboration partners. The Company has not experienced any material losses related to receivables from individual customers and collaboration partners, or groups of customers. The Company does not require collateral. Due to these factors, no additional credit risk beyond amounts provided for collection losses is believed by management to be probable in the Company's accounts receivable.
Deferred IPO issuance costsIssuance Costs
Deferred issuance costs, which primarily consist of direct incremental legal and accounting fees relating to the IPO, are capitalized. The deferred issuance costs will be offset against IPO proceeds upon the consummation of the offering. In the event the offering is terminated, or delayed more than 90 days, deferred offering costs will be expensed. No amounts were deferred as of December 31, 2011 or 2012 or as2012. As of March 31, 2013.June 30, 2013, $1.3 million of deferred issuance costs were recorded in other long-term assets in the accompanying balance sheet.
Disclosure of fair valueFair Value of financial instrumentsFinancial Instruments
The carrying amounts of the Company's financial instruments, which include cash, cash equivalents, collaboration receivables, accounts payable, accrued expenses and notes payable, approximated their fair values at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, due to the short-term nature of these instruments, and for the notes payable, the interest rates the Company believes it could obtain for borrowings with similar terms. See discussion below on the determination of the fair value of the Company's preferred and common stock warrants.
The Company has evaluated the estimated fair value of financial instruments using available market information and management's estimates. The use of different market assumptions and/or estimation methodologies could have a significant effect on the estimated fair value amounts.
Fair value measurementsValue Measurements
ASC Topic 820,Fair Value Measurement (ASC 820), establishes a fair value hierarchy for instruments measured at fair value that distinguishes between assumptions based on market data (observable
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(observable inputs) and the Company's own assumptions (unobservable inputs). Observable inputs are inputs that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability based on market data obtained from sources independent of the Company. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect the Company's assumptions about the inputs that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, and are developed based on the best information available in the circumstances.
ASC 820 identifies fair value as the exchange price, or exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
market participants. As a basis for considering market participant assumptions in fair value measurements, ASC Topic 820 establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between the following:
To the extent that the valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by the Company in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level 3. A financial instrument's level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Items measured at fair value on a recurring basis include warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock and warrants to purchase common stock (Note 6). During the periods presented, the Company has not changed the manner in which it values assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value using Level 3 inputs.
The following tables set forth the Company's financial instruments carried at fair value using the lowest level of input applicable to each financial instrument as of December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013 (in thousands):
| | December 31, 2011 | December 31, 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Quoted prices in active markets for identical items (Level 1) | Significant other observable inputs (Level 2) | Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) | Total | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Items (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 61,269 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 61,269 | $ | 61,269 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 61,269 | ||||||||||
Restricted cash | 912 | — | — | 912 | 912 | — | — | 912 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 62,181 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 62,181 | $ | 62,181 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 62,181 | ||||||||||
Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,046 | $ | 1,046 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,046 | $ | 1,046 | ||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | — | — | 3,347 | 3,347 | — | — | 3,347 | 3,347 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,393 | $ | 4,393 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4,393 | $ | 4,393 | ||||||||||
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policiesSignificant Accounting Policies (continued)
| | December 31, 2012 | December 31, 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Quoted prices in active markets for identical items (Level 1) | Significant other observable inputs (Level 2) | Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) | Total | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Items (Level 1) | Significant other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 36,847 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 36,847 | $ | 36,847 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 36,847 | ||||||||||
Restricted cash | 913 | — | — | 913 | 913 | — | — | 913 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 37,760 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 37,760 | $ | 37,760 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 37,760 | ||||||||||
Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,422 | $ | 1,422 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,422 | $ | 1,422 | ||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | — | — | 5,229 | 5,229 | — | — | 5,229 | 5,229 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,651 | $ | 6,651 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,651 | $ | 6,651 | ||||||||||
| | March 31, 2013 | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Quoted prices in active markets for identical items (Level 1) | Significant other observable inputs (Level 2) | Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) | Total | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Items (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 36,855 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 36,855 | $ | 24,861 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 24,861 | ||||||||||
Restricted cash | 913 | — | — | 913 | 913 | — | — | 913 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 37,768 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 37,768 | $ | 25,774 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 25,774 | ||||||||||
Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase redeemable convertible preferred stock | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,022 | $ | 1,022 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,009 | $ | 1,009 | ||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | — | — | 5,935 | 5,935 | — | — | 6,381 | 6,381 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,957 | $ | 6,957 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 7,390 | $ | 7,390 | ||||||||||
The following table sets forth a summary of changes in the fair value of the Company's preferred and common stock warrant liability, which represents a recurring measurement that is classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy, wherein fair value is estimated using significant unobservable inputs (in thousands):
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 3,912 | $ | 4,393 | $ | 4,393 | $ | 6,651 | $ | 3,912 | $ | 4,393 | $ | 4,393 | $ | 6,651 | ||||||||||
Change in fair value | 481 | 2,258 | 454 | 1,067 | 481 | 2,258 | 696 | 1,500 | ||||||||||||||||||
Exercises | — | — | — | (678 | ) | — | — | — | (678 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Repurchases | — | — | — | (83 | ) | — | — | — | (83 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Ending balance | $ | 4,393 | $ | 6,651 | $ | 4,847 | $ | 6,957 | $ | 4,393 | $ | 6,651 | $ | 5,089 | $ | 7,390 | ||||||||||
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policiesSignificant Accounting Policies (continued)
The money market funds noted above are included in cash and cash equivalents in the accompanying balance sheets. The Company recognizes transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy as of the end of the reporting period. There were no transfers within the hierarchy during the years ended December 31, 2011 or 2012 or during the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013.
The fair value of the warrants on the date of issuance and on each re-measurement date for those warrants classified as liabilities is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. This method of valuation involves using inputs such as the fair value of the Company's various classes of preferred stock, stock price volatility, the contractual term of the warrants, risk free interest rates, and dividend yields. Due to the nature of these inputs, the valuation of the warrants is considered a Level 3 measurement. See Note 6 for further discussions of the accounting for the warrants, as well as for a summary of the significant inputs and assumptions used to determine the fair value of the warrants.
The Company measures eligible assets and liabilities at fair value, with changes in value recognized in earnings. Fair value treatment may be elected either upon initial recognition of an eligible asset or liability or, for an existing asset or liability, if an event triggers a new basis of accounting. The Company did not elect to remeasure any of its existing financial assets or liabilities, and did not elect the fair value option for any financial assets and liabilities transacted in the years ended December 31, 2011 or 2012 or the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013.
Property and equipmentEquipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost. Maintenance and repairs that do not improve or extend the lives of the respective assets are expensed to operations as incurred. Upon disposal, retirement or sale the related cost and accumulated depreciation is removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is included in the results of operations. Depreciation and amortization is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, which are as follows:
Asset | Estimated | |
|---|---|---|
Computer equipment and software | 3 years | |
Office and laboratory equipment | 3 years | |
Leasehold improvements | Shorter of the useful life or remaining lease term |
The Company reviews long-lived assets when events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value of the assets may not be recoverable. Recoverability is measured by comparison of the book values of the assets to future net undiscounted cash flows that the assets are expected to generate. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the book value of the assets exceed their fair value, which is measured based on the projected discounted future net cash flows arising from the assets. No impairment losses have been recorded during the years ended December 31, 2011 or 2012 or the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
Revenue recognitionRecognition
The company has primarily generated revenue through collaboration, license and research arrangements with collaboration partners for the development and commercialization of protein therapeutics.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
The Company recognizes revenue in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 605,Revenue Recognition. Accordingly, revenue is recognized for each unit of accounting when all of the following criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the fee is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectability is reasonably assured.
Amounts received prior to satisfying the revenue recognition criteria are recorded as deferred revenue in the Company's balance sheets. Amounts expected to be recognized as revenue within the 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, current portion. Amounts not expected to be recognized as revenue within the 12 months following the balance sheet date are classified as deferred revenue, net of current portion.
Multiple element revenue arrangementsElement Revenue Arrangements
The Company enters into collaboration agreements from time to time, which are more fully described in Note 10. The arrangements generally contain multiple elements or deliverables, which may include (1) licenses, or options to obtain licenses, to the Company's technology, (2) research and development activities performed for the collaboration partner, (3) participation on Joint Development Committees, and (4) manufacturing clinical or preclinical material. Payments pursuant to these arrangements typically include non-refundable, up-front payments, milestone payments upon achieving significant development events, research and development reimbursements, sales milestones, and royalties on future product sales.
Effective January 1, 2011, the Company adopted ASU No. 2009-13,Multiple-Deliverable Revenue Arrangements (ASU 2009-13), which amends Topic 605-25,Revenue Recognition—Multiple Element Arrangements (ASC 605-25). The Company applies this guidance to new arrangements as well as existing agreements that are significantly modified after January 1, 2011. For agreements that are significantly modified, the Company determines the estimated selling price for the remaining undelivered elements as of the date of the material modification and allocates arrangement consideration based upon the estimated selling price to the undelivered elements.
The application of the multiple element guidance requires subjective determinations, and requires management to make judgments about the individual deliverables, and whether such deliverables are separable from the other aspects of the contractual relationship. Deliverables are considered separate units of accounting provided that: (1) the delivered item(s) has value to the customer on a stand-alone basis and (2) if the arrangement includes a general right of return relative to the delivered item(s), delivery or performance of the undelivered item(s) is considered probable and substantially in the control of the Company. In determining the units of accounting, management evaluates certain criteria, including whether the deliverables have stand-alone value, based on the consideration of the relevant facts and circumstances for each arrangement, such as the research, manufacturing and commercialization capabilities of the collaboration partner and the availability of the associated expertise in the general marketplace. In addition, the Company considers whether the collaboration
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
partner can use the other deliverable(s) for their intended purpose without the receipt of the remaining element(s), whether the value of the deliverable is dependent on the undelivered item(s) and whether there are other vendors that can provide the undelivered element(s). Arrangement consideration that is fixed or determinable is allocated among the separate units of accounting using the relative selling
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
price method, and the applicable revenue recognition criteria, as described above, are applied to each of the separate units of accounting in determining the appropriate period or pattern of recognition.
The Company determines the estimated selling price for deliverables within each agreement using vendor-specific objective evidence (VSOE) of selling price, if available, third-party evidence (TPE) of selling price if VSOE is not available, or management's best estimate of selling price (BESP) if neither VSOE nor TPE is available. Subsequent to the adoption of ASU 2009-13, the Company typically uses BESP to estimate the selling price of the deliverables. Determining the BESP for a unit of accounting requires significant judgment. In developing the BESP for a unit of accounting, the Company considers applicable market conditions and relevant entity-specific factors, including factors that were contemplated in negotiating the agreement with the customer and estimated costs. The Company validates the BESP for units of accounting by evaluating whether changes in the key assumptions used to determine the BESP will have a significant effect on the allocation of arrangement consideration between multiple units of accounting.
The Company typically receives up-front, non-refundable payments when licensing its intellectual property in conjunction with a collaboration agreement. When management believes the license to its intellectual property does not have stand-alone value from the other deliverables to be provided in the arrangement, the Company generally recognizes revenue attributed to the license on a straight-line basis over the contractual or estimated performance period, which is typically the term of the Company's research and development or manufacturing obligations. The Company continually evaluates these periods, and will adjust the period of revenue recognition if circumstances change. When management believes the license to its intellectual property has stand-alone value, the Company generally recognizes revenue attributed to the license upon delivery.
Research and development funding is recognized as revenue in the period that the related services are performed. When the Company acts as the principal under its collaboration agreements, it records payments received for the reimbursement of research and development costs as cost-sharing revenue in the statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss). To the extent that the Company reimburses the collaborator for costs incurred, the Company records these costs as a reduction of cost-sharing revenue.
The Company's agreements may contain options which provide the collaboration partner the right to obtain additional licenses. Options are considered substantive if, at the inception of the arrangement, the Company is at risk as to whether the collaboration partner will choose to exercise the option. Factors considered in evaluating whether an option is substantive include the overall objective of the arrangement, the benefit the collaborator might obtain from the arrangement without exercising the option, the cost to exercise the option and the likelihood that the option will be exercised. For arrangements under which an option is considered substantive, the Company does not consider the item underlying the option to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and the associated option fees are not included in allocable arrangement consideration, assuming the option is not priced at a significant and incremental discount. Conversely, for arrangements under which an option is not
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
considered substantive or if an option is priced at a significant and incremental discount, the Company would consider the item underlying the option to be a deliverable at the inception of the arrangement and a corresponding amount would be included in allocable arrangement consideration.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Effective January 1, 2011, the Company adopted ASU No. 2010-17,Revenue Recognition—Milestone Method (ASU 2010-17). At the inception of each arrangement that includes milestone payments, the Company evaluates, with respect to each milestone, whether the milestone is substantive and at-risk. This evaluation includes an assessment of whether (a) the consideration is commensurate with either (1) the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, or (2) the enhancement of the value of the delivered item(s) as a result of a specific outcome resulting at least in part from the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, (b) the consideration relates solely to past performance, and (c) the consideration is reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. The Company evaluates factors such as the scientific, regulatory, commercial, and other risks that must be overcome to achieve the respective milestone, the level of effort and investment required to achieve the respective milestone, and whether the milestone consideration is reasonable relative to all deliverables and payment terms in the arrangement in making this assessment. On the milestone achievement date, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met and the milestone is deemed substantive and at-risk, the Company recognizes the payment as license and milestone revenue. For milestones that are not deemed substantive and at-risk, where payment is reasonably assured, the Company recognizes the milestone payment over the remaining service period.
Sales and commercial milestones and royalties will be recognized when and if earned, provided collectability is reasonably assured.
Contract manufacturing revenueManufacturing Revenue
Contract manufacturing revenue is recognized upon delivery of the product in accordance with the terms of the contract, which specifies when transfer of title and risk of loss occurs.
Research and development expensesDevelopment Expenses
Research and development costs are charged to expense as costs are incurred in performing research and development activities. Research and development costs include all direct costs, including salaries, stock compensation and benefits for research and development personnel, outside consultants, costs of clinical trials, sponsored research, clinical trials insurance, other outside costs, depreciation and facility costs related to the development of drug candidates. The Company records up-front, non-refundable payments made to outside vendors, or other payments made in advance of services performed or goods being delivered, as prepaid expenses, which are expensed as services are performed or the goods are delivered.
Certain research and development projects are, or have been, partially funded by collaboration agreements, and the expenses related to these activities are included in research and development costs. The Company records the related reimbursement of research and development under these agreements as revenue, as more fully described above and in Note 10.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
Stock-based compensationStock-Based Compensation
At December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, the Company had one stock-based compensation plan, which is more fully described in Note 11. The Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with the provisions of ASC Topic 718,Compensation—Stock Compensation (ASC 718),
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
which requires the recognition of expense related to the fair value of stock-based compensation awards in the statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss).
For stock options issued to employees and members of the Board for their services on the Board, the Company estimates the grant date fair value of each option using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The use of the Black-Scholes option-pricing model requires management to make assumptions with respect to the expected term of the option, the expected volatility of the common stock consistent with the expected life of the option, risk-free interest rates and expected dividend yields of the common stock. For awards subject to service-based vesting conditions, the Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense, net of estimated forfeitures, equal to the grant date fair value of stock options on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting term. For awards subject to both performance and service-based vesting conditions, the Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense using an accelerated recognition method when it is probable that the performance condition will be achieved. Forfeitures are required to be estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates.
Share-based payments issued to non-employees are recorded at their fair values, and are periodically revalued as the equity instruments vest and are recognized as expense over the related service period in accordance with the provisions of ASC 718 and ASC Topic 505,Equity. For stock-based awards granted to non-employees, the Company recognizes stock-based compensation expense using an accelerated recognition method.
See Note 11 for a discussion of the assumptions used by the Company in determining the grant date fair value of options granted under the Black-Scholes option pricing model, as well as a summary of the stock option activity under the Company's stock-based compensation plan for the year ended December 31, 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013.
Income taxesTaxes
Income taxes are recorded in accordance with ASC Topic 740,Income Taxes (ASC 740), which provides for deferred taxes using an asset and liability approach. The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the difference between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Valuation allowances are provided, if based upon the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
The Company accounts for uncertain tax positions in accordance with the provisions of ASC 740. When uncertain tax positions exist, the Company recognizes the tax benefit of tax positions to the extent that the benefit will more likely than not be realized. The determination as to whether the tax benefit will more likely than not be realized is based upon the technical merits of the tax position as well as consideration of the available facts and circumstances. As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, and March 31,June 30, 2013, the Company does not have any significant uncertain tax positions.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Net income (loss) per shareIncome (Loss) Per Share
Net income (loss) per share information is determined using the two-class method, which includes the weighted-average number of common stock outstanding during the period and other securities that participate in dividends (a participating security). The Company's redeemable convertible preferred stock are participating securities as defined by ASC 260-10,Earnings Per Share.
Under the two-class method, basic net income (loss) per share applicable to common stockholders is computed by dividing the net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the reporting period. Diluted net income (loss) per share is computed using the more dilutive of (1) the two-class method or (2) the if-converted method. The Company allocates net income first to preferred stockholders based on dividend rights under the Company's articles of incorporation and then to preferred and common stockholders based on ownership interests. Net losses are not allocated to preferred stockholders as they do not have an obligation to share in the Company's net losses.
Diluted net income (loss) per share gives effect to all potentially dilutive securities, including redeemable convertible preferred stock, and shares issuable upon the exercise of outstanding warrants and stock options, using the treasury stock method. For the year ended December 31, 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012, and 2013, the Company has excluded the effects of all potentially dilutive shares, which include redeemable convertible preferred stock, warrants for redeemable convertible preferred stock, warrants for common stock and outstanding common stock options, from the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding as their inclusion in the computation for all periods would be anti-dilutive due to net losses.
The following common stock equivalents were excluded from the calculation of diluted net income (loss) per share for the periods indicated because including them would have had an anti-dilutive effect (in thousands):
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding stock options | — | 14,920 | 12,605 | 14,766 | — | 3,730 | 3,363 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Common stock warrants | 3,497 | 3,537 | 3,537 | 3,481 | 874 | 884 | 884 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock | — | 72,662 | 72,662 | 72,119 | — | 18,166 | 18,166 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Preferred stock warrants | — | 992 | 992 | 566 | — | 248 | 248 | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3,497 | 92,111 | 89,796 | 90,932 | 874 | 23,028 | 22,661 | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Unaudited pro forma net income (loss) per sharePro Forma Net Income (Loss) Per Share
Unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net income (loss) per share has been computed using the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding after giving pro forma effect to the conversion of all shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock into shares of common stock and the
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies (continued)
conversion of all warrants to purchase shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock into warrants to purchase common stock, as if such conversion had occurred as of the date of original issuance. Upon conversion of the redeemable convertible preferred stock into common stock in the event of an IPO, the holders of the redeemable convertible preferred stock are not entitled to receive undeclared dividends. Accordingly, the impact of the accretion of unpaid and undeclared dividends, interest, redemption value and issuance costs, has been excluded from the determination of net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders as the holders of the redeemable convertible preferred stock are
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
not entitled to receive undeclared dividends upon such conversion. The gain recognized upon the extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred stock during the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013 has also been excluded from the determination of net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders. Additionally, the gains (losses) associated with the changes in the fair value of the warrants to purchase redeemable preferred stock has been excluded from the determination of net income (loss) as these remeasurements would not be required when the warrants to purchase shares of preferred stock become warrants to purchase common stock.
A reconciliation of the pro forma net income (loss) per share is as follows (in thousands, except per share data):
| | Year ended December 31, 2012 | Three months ended March 31, 2013 | Year Ended December 31, 2012 | Six Months Ended June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Numerator: | ||||||||||||||
Net loss applicable to common stockholders | $ | (59,643 | ) | $ | (2,344 | ) | $ | (59,643 | ) | $ | 463 | |||
Accretion and dividends on redeemable convertible preferred stock | 27,061 | 6,756 | 27,061 | 13,599 | ||||||||||
Gain on extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred stock | — | (2,765 | ) | — | (2,765 | ) | ||||||||
Net (loss) income applicable to participating securities | — | 3,428 | ||||||||||||
Change in the fair value of warrants | 2,258 | 1,067 | 2,258 | 1,500 | ||||||||||
Pro forma net income (loss) applicable to common stockholders | $ | (30,324 | ) | $ | 2,714 | $ | (30,324 | ) | $ | 16,225 | ||||
Denominator: | ||||||||||||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding—basic | 9,605 | 9,740 | 2,401 | 2,437 | ||||||||||
Adjustment for assumed conversion of redeemable convertible preferred shares | 72,662 | 72,119 | 18,754 | 18,608 | ||||||||||
Weighted-average number of common shares used in computing pro forma net income (loss) per share—basic | 82,267 | 81,859 | 21,155 | 21,045 | ||||||||||
Weighted-average number of common shares issuable upon exercise of outstanding stock options, based on treasury stock method | — | 5,553 | — | 1,654 | ||||||||||
Weighted-average number of common shares issuable upon exercise of outstanding warrants, based on treasury stock method | — | 1,239 | — | 363 | ||||||||||
Weighted-average number of common shares used in computing pro forma net income (loss) per share—diluted | 82,267 | 88,651 | 21,155 | 23,062 | ||||||||||
Pro forma net income (loss) per share applicable to common shareholders—basic | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.77 | ||||
Pro forma net income (loss) per share applicable to common shareholders—diluted | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (1.43 | ) | $ | 0.70 | ||||
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
2. Summary of significant accounting policiesSignificant Accounting Policies (continued)
Comprehensive income (loss)Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) is defined as the change in equity of a business enterprise during a period from transactions, other events, and circumstances from non-owner sources. Comprehensive income (loss) consists of net income (loss) and other comprehensive income (loss), which includes certain changes in equity that are excluded from net income (loss). Comprehensive income (loss) has been disclosed in the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) and equals the Company's net income (loss) for all periods presented.
Subsequent eventsEvents
The Company considers events or transactions that occur after the balance sheet date but prior to the issuance of the financial statements to provide additional evidence relative to certain estimates or to identify matters that require additional disclosure. See Note 16.
Application of newNew or revised accounting standardsRevised Accounting Standards
On April 5, 2012, the Jump-Start Our Business Startups Act (the JOBS Act) was signed into law. The JOBS Act contains provisions that, among other things, reduce certain reporting requirements for an "emerging growth company." As an emerging growth company the Company has elected to not take advantage of the extended transition period afforded by the JOBS Act for the implementation of new or revised accounting standards, and as a result, will comply with new or revised accounting standards on the relevant dates on which adoption of such standards is required for non-emerging growth companies.
Recently adopted accounting pronouncementsAdopted Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the FASB or other standard setting bodies and adopted by the Company as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the Company believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
3. Property and equipment, netEquipment, Net
Property and equipment, net, consists of the following (in thousands):
| | December 31, | | December 31, | | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | March 31, 2013 | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
Computer equipment and software | $ | 728 | $ | 919 | $ | 919 | $ | 728 | $ | 919 | $ | 919 | ||||||||
Office equipment | 179 | 179 | 190 | 179 | 179 | 190 | ||||||||||||||
Laboratory equipment | 11,692 | 11,815 | 11,885 | 11,692 | 11,815 | 11,936 | ||||||||||||||
Leasehold improvements | 10,060 | 10,088 | 10,088 | 10,060 | 10,088 | 10,088 | ||||||||||||||
Construction in progress | 162 | 8 | 7 | 162 | 8 | 0 | ||||||||||||||
Total property and equipment | 22,821 | 23,009 | 23,089 | 22,821 | 23,009 | 23,133 | ||||||||||||||
Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (17,910 | ) | (18,950 | ) | (19,173 | ) | (17,910 | ) | (18,950 | ) | (19,399 | ) | ||||||||
Property and equipment, net | $ | 4,911 | $ | 4,059 | $ | 3,916 | $ | 4,911 | $ | 4,059 | $ | 3,734 | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization expense was $3.1 million, $1.3 million, $0.5$0.8 million and $0.2$0.4 million for the years ending December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, respectively.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
4. Restricted cashCash
As of December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, the Company maintained letters of credit totaling $0.9 million held in the form of a money market account as collateral for the Company's facility lease obligations and its credit cards.
5. Accrued expensesExpenses
Accrued expenses consist of the following (in thousands):
| | December 31, | | December 31, | | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | March 31, 2013 | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
Collaboration expense | $ | 1,042 | $ | 1,000 | $ | 1,052 | $ | 1,042 | $ | 1,000 | $ | 247 | ||||||||
Research and development related | 570 | 1,282 | 897 | 570 | 1,282 | 616 | ||||||||||||||
Employee compensation | 1,963 | 2,448 | 1,097 | 1,963 | 2,448 | 1,577 | ||||||||||||||
Legal | 209 | 419 | 1,302 | |||||||||||||||||
Professional services | 368 | 607 | 1,920 | |||||||||||||||||
Other | 729 | 1,004 | 1,061 | 570 | 816 | 951 | ||||||||||||||
| $ | 4,513 | $ | 6,153 | $ | 5,409 | $ | 4,513 | $ | 6,153 | $ | 5,311 | |||||||||
6. Warrants
Below is a summary of the number of shares issuable upon exercise of outstanding warrants and the terms and accounting treatment for the outstanding warrants (in thousands, except per share data):
| | | | | | | Balance sheet classification | | | | | | Balance Sheet Classification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Warrants as of | Weighted- average exercise price per share | | Warrants as of | Weighted- Average Exercise Price Per Share | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | December 31, | | | December 31, | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | December 31, 2011 | December 31, 2012 | March 31, 2013 | | March 31, 2013 | December 31, 2011 | December 31, 2012 | June 30, 2013 | | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| | 2011 | 2012 | Weighted- average exercise price per share | 2011 | 2012 | Weighted- Average Exercise Price Per Share | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrant to purchase Series A Preferred Stock | 426 | 426 | — | $ | 1.00 | February 28, 2013 | N/A(2) | 107 | 107 | — | $ | 4.00 | February 28, 2013 | N/A(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase Series B Preferred Stock | 128 | 128 | 128 | 1.85 | December 21, 2013 | Liability | 32 | 32 | 32 | 7.40 | December 21, 2013 | Liability | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase Series C-1 Preferred Stock | 183 | 183 | 183 | 2.73 | June 25, 2019 | Liability | 46 | 46 | 46 | 10.92 | June 25, 2019 | Liability | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase Series D-1 Preferred Stock | 255 | 255 | 255 | 3.14 | March 18, 2020 | Liability | Liability | Liability | 64 | 64 | 64 | 12.56 | March 18, 2020 | Liability | Liability | Liability | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 3,486 | 3,486 | 3,430 | 1.47 | June 10, 2020 - July 9, 2020 | Liability | Liability | Liability | 872 | 872 | 858 | 5.88 | June 10, 2020 - July 9, 2020 | Liability | Liability | Liability | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 51 | 51 | 51 | 1.00 - 1.85 | March 31, 2015 - December 31, 2017 | Equity | Equity | Equity(1) | 13 | 13 | 13 | 4.00 - 7.40 | March 31, 2015 - December 31, 2017 | Equity | Equity | Equity(2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
All warrants | 4,529 | 4,529 | 4,047 | $ | 1.64 | 1,134 | 1,134 | 1,013 | $ | 6.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In connection with various financing transactions that were consummated in periods prior to December 31, 2011, the Company issued warrants for the purchase of up to 426,000106,500 shares of the Company's Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series A Preferred Stock), 127,56831,891 shares of the Company's Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series B Preferred Stock), 183,15045,786 shares of the Company's Series C-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series C-1 Preferred Stock), and 254,77763,693 shares of the Company's Series D-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series D-1 Preferred Stock). Each warrant was immediately exercisable. The warrants to purchase Series A and Series B Preferred Stock expire seven years from the original date of issuance, while the
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
6. Warrants (continued)
Series A and Series B Preferred Stock expire seven years from the original date of issuance, while the warrants to purchase Series C-1 and Series D-1 Preferred Stock expire ten years from the original date of issuance. The warrants to purchase shares of the Company's preferred stock have an exercise price equal to the original issuance price of the underlying instrument. Each warrant is exercisable on either a physical settlement or net share settlement basis and the redemption provisions are outside the control of the Company. Upon the conversion of the Series A Preferred Stock and/or Series B Preferred Stock and/or Series C-1 Preferred Stock and/or Series D-1 Preferred Stock into shares of common stock, the associated warrants to purchase shares of the Company's preferred stock are will become exercisable for shares of common stock.
The Company follows the provisions of ASC Topic 480,Issuer's Accounting for Freestanding Warrants and Other Similar Instruments on Shares that Are Redeemable, which requires that warrants to purchase redeemable preferred stock be classified as liabilities. In addition, the value of the warrants is remeasured to the then-current fair value at each reporting date. Changes in fair value are recorded to other income (expense), net. For the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the Company remeasured the fair value of all of its outstanding warrants to purchase shares of the Company's preferred stock, using current assumptions, resulting in an increase in fair value of $0.5$0.1 million, $2.3$0.4 million, $0.5$0.1 million and $1.1$0.3 million, respectively, which was recorded in other expense net in the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss). The Company will continue to re-measure the fair value of the liability associated with the warrants to purchase shares of Series B Preferred Stock, Series C-1 Preferred Stock, and Series D-1 Preferred Stock at the end of each reporting period until the earlier of the exercise or expiration of the applicable warrants or until such time that the underlying preferred stock is reclassified to permanent equity.
In December 2012, the Company modified the warrant to purchase 426,000106,500 shares of Series A Preferred Stock and extended the expiration date from December 21, 2012 to February 28, 2013. During the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, the holder of the warrant exercised the warrant on a net basis, resulting in the issuance of 186,67446,668 shares of Series A Preferred Stock. Upon exercise, the Company re-measured the fair value of the warrant and recorded the resulting increase in fair value of $0.1 million as other expense in the accompanying statement of operations and comprehensive income for the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013.
In connection with the Series E redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series E Preferred Stock) financing transactions that took place in June 2010 and July 2010, the Company issued warrants to purchase up to 3,486,395871,580 shares of common stock. Each warrant was immediately exercisable and expires ten years from the original date of issuance. The warrants to purchase shares of the Company's common stock have an exercise price equal to the estimated fair value of the underlying instrument as of the initial date such warrants were issued. Each warrant is exercisable on either a physical settlement or net share settlement basis from the date of issuance. The warrant agreement contains a provision requiring an adjustment to the number of shares in the event the Company issues common stock, or securities convertible into or exercisable for common stock, at a price per share lower than the warrant exercise price. The Company concluded the anti-dilution feature required the warrants to be classified as liabilities under ASC Topic 815,Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity's Own Equity (ASC 815). The warrants are measured at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized as a gain or loss to other income (expense) in the statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) for each reporting period thereafter. The fair value of the common stock warrants were recorded as a discount to the preferred stock issued of $3.0 million, and the preferred stock is being accreted to the redemption value. On December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, the Company remeasured the
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
6. Warrants (continued)
fair value of the outstanding warrants, using current assumptions, resulting in an increase in fair value of $0.3 million, $1.9 million and $0.8$1.2 million, respectively, which was recorded in other expense in the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013. The Company will continue to re-measure the fair value of the liability associated with the warrants to purchase common stock at the end of each reporting period until the earlier of the exercise or the expiration of the applicable warrants. On March 31, 2013, the Company retired 55,97913,994 warrants to purchase common stock as a consequence of a repurchase of shares from an investor. All remaining outstanding warrants were fully vested and exercisable as of December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013.
In connection with various financing transactions that were consummated in periods prior to December 31, 2011, the Company issued warrants to purchase up to 50,54212,634 shares of common stock. The awards of warrants to purchase shares of common stock are accounted for as equity instruments. The warrants are exercisable at any time through their respective expiration dates. The fair value at issuance was calculated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, and was charged to interest expense during the periods the related debt was outstanding.
The Company issued warrants to purchase up to 165,55341,388 shares of common stock in periods prior to December 31, 2011 in exchange for consulting services provided by a third party pursuant to stand-alone award agreements that are independent of an equity incentive plan. The warrants vested upon achievement of four milestones and were outstanding for approximately seven years from the date of issuance. During the year ended December 31, 2011, the holder exercised 165,55341,388 warrants to purchase common stock on a net basis resulting in the issuance of 148,99737,249 shares of common stock. There were no exercises, cancellations, or expirations of warrants during the yearsyear ended December 31, 2012.
Fair valueValue
The fair value of the warrants to purchase preferred stock on the date of issuance and on each re-measurement date for those warrants to purchase preferred stock classified as liabilities, is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. This method of valuation involves using inputs such as the fair value of the Company's various classes of preferred stock and common stock, stock price volatility, contractual term of the warrants, risk free interest rates, and dividend yields. The fair value of the warrants to purchase common stock on the date of issuance and on each re-measurement date for those warrants to purchase common stock are classified as liabilities and are estimated using the Monte Carlo simulation framework, which incorporated three future financing events over the remaining life of the warrants to purchase common stock. Due to the nature of these inputs and the valuation techniques utilized, the valuation of the warrants to purchase preferred stock and common stock are considered a Level 3 measurement (Note 2).
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
6. Warrants (continued)
The fair value of each warrant to purchase shares of the Company's Series A Preferred Stock was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012(1) | 2012 | 2013(2) | 2011 | 2012(1) | 2012 | 2013(2) | ||||||||||||||||||
Fair value of underlying instrument | $ | 1.69 | $ | 2.31 | $ | 1.73 | n/a | $ | 6.76 | $ | 9.24 | $ | 7.64 | n/a | ||||||||||||
Expected volatility | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 67.0 | % | n/a | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 66.8 | % | n/a | ||||||||||||
Expected term (in years) | 1.16 | 0.16 | 0.73 | n/a | 1.16 | 0.16 | 0.48 | n/a | ||||||||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 0.12 | % | 0.04 | % | 0.17 | % | n/a | 0.12 | % | 0.04 | % | 0.16 | % | n/a | ||||||||||||
Expected dividend yield | — | % | — | % | — | % | n/a | — | % | — | % | — | % | n/a | ||||||||||||
The fair value of each warrant to purchase shares of the Company's Series B Preferred Stock was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Fair value of underlying instrument | $ | 1.89 | $ | 2.49 | $ | 1.95 | $ | 2.79 | $ | 7.56 | $ | 9.96 | $ | 8.40 | $ | 11.28 | ||||||||||
Expected volatility | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 67.0 | % | 69.2 | % | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 66.8 | % | 70.4 | % | ||||||||||
Expected term (in years) | 1.98 | 0.97 | 1.73 | 0.73 | 1.98 | 0.97 | 1.48 | 0.48 | ||||||||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 0.25 | % | 0.16 | % | 0.33 | % | 0.13 | % | 0.25 | % | 0.16 | % | 0.27 | % | 0.10 | % | ||||||||||
Expected dividend yield | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||
The fair value of each warrant to purchase shares of the Company's Series C-1 Preferred Stock was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Fair value of underlying instrument | $ | 2.21 | $ | 2.76 | $ | 2.36 | $ | 3.09 | $ | 8.84 | $ | 11.04 | $ | 9.52 | $ | 11.96 | ||||||||||
Expected volatility | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 67.0 | % | 69.2 | % | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 66.8 | % | 70.4 | % | ||||||||||
Expected term (in years) | 7.46 | 6.46 | 7.21 | 6.21 | 7.46 | 6.46 | 6.96 | 5.96 | ||||||||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.35 | % | 0.95 | % | 1.61 | % | 1.01 | % | 1.35 | % | 0.95 | % | 1.11 | % | 1.69 | % | ||||||||||
Expected dividend yield | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||
The fair value of each warrant to purchase shares of the Company's Series D-1 Preferred Stock was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Fair value of underlying instrument | $ | 2.21 | $ | 2.63 | $ | 2.36 | $ | 3.09 | $ | 8.84 | $ | 10.52 | $ | 9.12 | $ | 12.28 | ||||||||||
Expected volatility | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 67.0 | % | 69.2 | % | 66.0 | % | 69.1 | % | 66.8 | % | 70.4 | % | ||||||||||
Expected term (in years) | 8.22 | 7.22 | 7.97 | 6.97 | 8.22 | 7.22 | 7.72 | 6.72 | ||||||||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.62 | % | 1.18 | % | 1.92 | % | 1.24 | % | 1.62 | % | 1.18 | % | 1.39 | % | 1.96 | % | ||||||||||
Expected dividend yield | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
6. Warrants (continued)
Fair valueValue of underlying instrumentUnderlying Instrument
The Company estimated the fair value of its shares of Series A Preferred Stock, Series B-1 Preferred Stock, Series C-1 Preferred Stock and Series D-1 Preferred Stock as of December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013 using the PWERM.
Expected volatilityVolatility
The Company estimated the expected volatility based on actual historical volatility of the stock price of similar companies with publicly-traded equity securities. The Company calculated the historical volatility of the selected companies by using daily closing prices over a period of the expected term of the associated award. The companies were selected based on their enterprise value, risk profiles, position within the industry, and with historical share price information sufficient to meet the expected term of the associated award. A decrease in the selected volatility would decrease the fair value of the underlying instrument.
Expected termTerm
The Company based the expected term on the actual remaining contractual term of each respective warrant. A decrease in the expected term would decrease the fair value of the underlying instrument.
Risk-free interest rateRisk-Free Interest Rate
The Company estimated the risk-free interest rate in reference to the yield on U.S. Treasury securities with a maturity date commensurate with the expected term of the associated award. A decrease in the selected risk-free rate would decrease the fair value of the underlying instrument.
Expected dividend yieldDividend Yield
The Company estimated the expected dividend yield based on consideration of its historical dividend experience and future dividend expectations. The Company has not historically declared or paid dividends to stockholders. Moreover, it does not intend to pay dividends in the future, but instead expects to retain any earnings to invest in the continued growth of the business. Accordingly, the Company assumed an expected dividend yield of 0.0%.
7. Commitments and contingenciesContingencies
Operating leasesLeases
The Company leases its facilities under non-cancelable operating leases that expire at various dates through May 2018. All of the Company's leases contain escalating rent clauses, which require higher rent payments in future years. The Company expenses rent on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease, including any rent-free periods. In addition, the Company received certain leasehold improvement incentives, and recorded these incentives as deferred rent, which is amortized as a reduction of rent expense over the life of the lease. Rent expense of approximately $3.6 million, $3.5 million, $0.9$1.7 million and $0.9$1.7 million were incurred during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, respectively.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
7. Commitments and contingenciesContingencies (continued)
Future annual minimum lease payments as of December 31, 2012, are as follows (in thousands):
2013 | $ | 4,522 | ||
2014 | 4,522 | |||
2015 | 4,106 | |||
2016 | 3,938 | |||
2017 | 3,938 | |||
2018 | 2,953 | |||
Total | $ | 23,979 | ||
In February 2011, the Company entered into a sublease agreement for a portion of one of its facility leases. The tenant will pay rent on the lease from February 28, 2011 until May 30, 2015. The Company will continue to utilize the remaining portion of the leased property.
Future annual minimum sublease payments as of December 31, 2012, are as follows (in thousands):
2013 | $ | 583 | ||
2014 | 583 | |||
2015 | 241 | |||
Total | $ | 1,407 | ||
Legal proceedingsProceedings
On October 18, 2012, the Salk Institute for Biological Studies (Salk) filed a complaint in the Massachusetts Superior Court for Suffolk County, alleging that the Company breached one of the Company's two licensing agreements with Salk. The licensing agreement in dispute provides the Company with a license with respect to certain of Salk's U.S. patents related to the ActRIIB activin receptor proteins. Salk contends that, under the licensing agreement, the Company owed Salk a greater share of the upfront payment that it received under its now-terminated agreement with Shire AG regarding ACE-031 and a share of the upfront payment and development milestone payments that the Company has received under its ongoing collaboration agreement with Celgene regarding ACE-536. Salk is seeking a total of approximately $10.5 million plus interest in payment and a 15% share of future development milestone payments received under the agreement with Celgene regarding ACE-536. The Company contends that no additional amounts are due to Salk and that it has complied with all of its payment obligations under the applicable Salk license agreement.
The Company moved to dismiss the complaint on December 3, 2012. The Court denied the Company's motion on February 28, 2013. On March 14, 2013, Acceleron answered the complaint and asserted patent invalidity counterclaims. On the basis of those counterclaims, Acceleron removed the action on March 28, 2013 to the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. The parties have since reached an agreement on a stipulation as to certain patent issues raised in the action, and Acceleron has dismissed its counterclaims. The Court held an initial scheduling conference on May 30, 2013, and the parties have begun fact discovery. The case is currently scheduled for trial in September 2014. The Company intends to defend its position vigorously.
The Company evaluated the suit under ASC Topic 450,Contingencies, as a loss contingency. The estimated loss from a loss contingency shall be accrued if information available before the financial
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
7. Commitments and contingenciesContingencies (continued)
statements are issued indicates that it is probable a liability had been incurred at the date of the financial statements, and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. Because the Company believes that the potential for an unfavorable outcome is not probable, it has not established a reserve with respect to the dispute as of December 31, 2012 or March 31,June 30, 2013.
The Company's estimates can be affected by various factors. As of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, management has determined a loss is reasonably possible. Although the Company believes it would successfully defend the lawsuit, the Company has in the past participated in settlement discussions with Salk. Accordingly, the Company has estimated the range of possible losses as of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013 to be between $0 and $10.5 million plus interest.
Other
The Company is also party to various agreements, principally relating to licensed technology, that require future payments relating to milestones not met at December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, or royalties on future sales of specified products. No milestone or royalty payments under these agreements are expected to be payable in the immediate future. See Note 10 for discussion of these arrangements.
The Company enters into standard indemnification agreements in the ordinary course of business. Pursuant to the agreements, the Company indemnifies, holds harmless, and agrees to reimburse the indemnified party for losses suffered or incurred by the indemnified party, generally the Company's business partners or customers, in connection with any U.S. patent or any copyright or other intellectual property infringement claim by any third party with respect to the Company's products. The term of these indemnification agreements is generally perpetual any time after execution of the agreement. The maximum potential amount of future payments the Company could be required to make under these indemnification agreements is unlimited. The Company has never incurred costs to defend lawsuits or settle claims related to these indemnification agreements.
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stockConvertible Preferred Stock
As of December 31, 2012, and June 30, 2013 the authorized capital stock of the Company included 74,077,227 shares of preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share, of which: (i)(1) 26,069,980 shares have been designated as Series A Preferred Stock, (ii)(2) 16,944,378 shares have been designated as Series B Preferred Stock, (iii)(3) 11,923,077 shares have been designated as Series C redeemable convertible (Series C Preferred Stock), (iv)(4) 2,014,652 shares have been designated as Series C-1 Preferred Stock, (iv)(5) 955,414 shares have been designated as Series D redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series D Preferred Stock), (v)(6) 2,802,548 shares have been designated as Series D-1 Preferred Stock, (vi)(7) 3,662,422 shares have been designated as Series E Preferred Stock, and (vii)(8) 9,704,756 shares have been designated as Series F redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series F Preferred Stock, and all collectively the "Preferred Stock").
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stockConvertible Preferred Stock (continued)
The Company's Preferred Stock consisted of the following (in thousands, except share and per share data):
| | December 31, | | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | March 31, 2013 | |||||||
Series A Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 26,069,980 shares authorized, 25,643,980 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 25,830,654 shares at March 31, 2013, at redemption value | $ | 62,049 | $ | 66,665 | $ | 68,502 | ||||
Series B Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 16,944,378 shares authorized, 16,816,810 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 16,257,846 shares at March 31, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 61,464 | 67,044 | 66,163 | |||||||
Series C Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 11,923,077 shares authorized, 11,912,333 shares issued, and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 11,825,356 shares at March 31, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 54,320 | 59,909 | 60,855 | |||||||
Series C-1 Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 2,014,652 shares authorized, 1,831,502 issued, and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31, 2013, at redemption value | 8,479 | 9,387 | 9,613 | |||||||
Series D Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 955,414 shares authorized, 939,847 shares issued, and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 928,223 shares at March 31, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 3,657 | 4,325 | 4,437 | |||||||
Series D-1 Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 2,802,548 shares authorized, 2,547,771 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31, 2013, at redemption value | 10,128 | 11,864 | 12,298 | |||||||
Series E Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 3,662,422 shares authorized, 3,264,333 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012, and 3,211,920 shares at March 31, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 10,934 | 13,393 | 13,788 | |||||||
Series F Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 9,704,756 shares authorized, 9,704,756 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 9,685,456 shares at March 31, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 30,518 | 36,023 | 37,324 | |||||||
Total redeemable convertible preferred stock | $ | 241,549 | $ | 268,610 | $ | 272,980 | ||||
| | December 31, | | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | June 30, 2013 | |||||||
Series A Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 26,069,980 shares authorized, 6,410,976 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 6,457,644 shares at June 30, 2013, at redemption value | $ | 62,049 | $ | 66,665 | $ | 69,664 | ||||
Series B Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 16,944,378 shares authorized, 4,204,185 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 4,064,444 shares at June 30, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 61,464 | 67,044 | 67,649 | |||||||
Series C Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 11,923,077 shares authorized, 2,978,062 shares issued, and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 2,956,318 shares at June 30, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 54,320 | 59,909 | 62,239 | |||||||
Series C-1 Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 2,014,652 shares authorized, 457,875 issued, and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and June 30, 2013, at redemption value | 8,479 | 9,387 | 9,838 | |||||||
Series D Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 955,414 shares authorized, 234,940 shares issued, and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 232,034 shares at June 30, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 3,657 | 4,325 | 4,603 | |||||||
Series D-1 Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 2,802,548 shares authorized, 636,942 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and June 30, 2013, at redemption value | 10,128 | 11,864 | 12,732 | |||||||
Series E Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 3,662,422 shares authorized, 816,060 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012, and 802,957 shares at June 30, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 10,934 | 13,393 | 14,400 | |||||||
Series F Preferred Stock, $0.001 par value: 9,704,756 shares authorized, 2,426,171 issued and outstanding at December 31, 2011 and 2012 and 2,421,346 shares at June 30, 2013, at redemption value(2) | 30,518 | 36,023 | 38,698 | |||||||
Total redeemable convertible preferred stock | $ | 241,549 | $ | 268,610 | $ | 279,823 | ||||
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stockConvertible Preferred Stock (continued)
The holders of the Company's Preferred Stock have rights and preferences as specified below.
Dividends
The holders of the Company's Preferred Stock are entitled to receive, when and as declared by the Board, preferential cumulative dividends at the rate of 8% per share per annum of the stated value thereof. Such dividends shall be cumulative and shall accrue from the original issue date, whether or not earned or declared, and whether or not in any fiscal year there shall be net profits or surplus available for the payment of dividends in such fiscal year. No dividends or other distributions will be made with respect to the common stock until all declared dividends on the Preferred Stock have been paid. Additionally, if the Board declares a dividend with respect to the common stock, the Board must also declare at the same time, a dividend to the holders of the Preferred equal to the dividend that would have been payable if the outstanding Preferred Stock had been converted into shares of common stock. No dividends have been declared or paid by the Company through March 31,June 30, 2013.
Liquidation
In the event of any liquidation, dissolution, or winding up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary, the holders of Series F Preferred Stock are entitled to receive an amount equal to the greater of (a) $3.14$12.56 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment, plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid, or (b) an amount per share as would have been payable had each share been converted to common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. No payment shall be made to the holders of Series A, Series B, Series C, Series C-1, Series D, Series D-1 and Series E Preferred Stock or common stock unless and until full payment has been made to the holders of Series F Preferred Stock.
After payment has been made to the holders of Series F Preferred Stock, the holders of Series E Preferred Stock are entitled to receive an amount equal to the greater of (a) the Special Series E Liquidation Payment (as defined below), plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid, or (b) an amount per share as would have been payable had each share been converted to common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. No payment shall be made to the holders of Series A, Series B, Series C, Series C-1, Series D and Series D-1 Preferred Stock or common stock unless and until full payment has been made to the holders of Series E Preferred Stock.
The Special Series E Liquidation Payment is equal to a preference calculated as a 22% annually compounded return on the initial per share investment amount of $3.14$12.56 per share from the date of issuance to the date of an initial public offering, subject to appropriate adjustments.
After payment has been made to the holders of Series F and Series E Preferred Stock, the holders of Series D and Series D-1 Preferred Stock are entitled to receive an amount equal to the greater of (a) $3.14$12.56 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment, plus any dividends accrued or declared but unpaid, or (b) an amount per share as would have been payable had each share been converted to common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. No payment shall be made to the holders of Series A, Series B, Series C and Series C-1 Preferred Stock or common stock unless and until full payment has been made to the holders of Series D and Series D-1 Preferred Stock.
After payment has been made to the holders of Series F, Series E, Series D, and Series D-1 Preferred Stock, the holders of Series C and Series C-1 Preferred Stock are entitled to receive an amount equal to the greater of (a) $2.73$10.92 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment for Series C-1 Preferred Stock and $2.60 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment, for Series C Preferred Stock,
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stockConvertible Preferred Stock (continued)
Preferred Stock and $10.40 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment, for Series C Preferred Stock, plus any dividends accrued or declared but unpaid, or (b) an amount per share as would have been payable had each share been converted to common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. No payment shall be made to the holders of Series A and Series B Preferred Stock or common stock unless and until full payment has been made to the holders of Series C and Series C-1 Preferred Stock.
After payment has been made to the holders of Series F, Series E, Series D, Series D-1, Series C and Series C-1 Preferred Stock, the holders of Series B Preferred Stock are entitled to receive, an amount equal to the greater of (a) $1.85$7.40 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment, plus any dividends accrued or declared but unpaid, or (b) an amount per share as would have been payable had each share been converted to common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. No payment shall be made to the holders of Series A Preferred Stock or of common stock unless and until full payment has been made to the holders of Series B Preferred Stock.
After payment has been made to the holders of Series F, Series E, Series D, Series D-1, Series C, Series C-1 and Series B Preferred Stock, the holders of Series A Preferred Stock are entitled to receive, in preference to the holders of common stock, an amount equal to the greater of (a) $1.00$4.00 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment, plus any dividends accrued or declared but unpaid, or (b) an amount per share as would have been payable had each share been converted to common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. No payment shall be made to the holders of common stock unless and until full payment has been made to the holders of Series A Preferred Stock.
The remaining assets of the Company available for distribution, after distribution to the holders of Series F, Series E, Series D, Series D-1, Series C, Series C-1, Series B and Series A Preferred Stock shall be distributed ratably among the holders of common stock.
Voting
The holders of the Preferred Stock are entitled to vote, together with the holders of common stock, on all matters submitted to stockholders for a vote. The holders of the Preferred Stock are entitled to the number of votes equal to the number of shares of common stock into which each share of the Preferred Stock is convertible at the time of such vote. On various matters submitted to the stockholders for a vote, certain series of Preferred Stock are entitled to separate votes.
Conversion
Voluntary
Each share of Preferred Stock is convertible at the option of the holder into such number of shares of common stock as is determined by dividing $1.00$4.00 in the case of Series A Preferred Stock, $1.85$7.40 in the case of Series B Preferred Stock, $2.60$10.40 in the case of Series C Stock, $2.73$10.92 in the case of Series C-1 Stock, $3.14$12.56 in the case of Series D and D-1 Preferred Stock, $3.14$12.56 in the case of Series E Stock, and $3.14$12.56 in the case of Series F Stock by the conversion prices in effect at the time of conversion. As of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, the conversion rate for all series of Preferred Stock is 1:1, but is subject to adjustment in the future upon the occurrence of certain events.
Mandatory
Each share of Preferred Stock shall be automatically converted into shares of common stock at the conversion price in effect at the time of conversion, upon (i)(1) the closing of an IPO of the Company's
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stockConvertible Preferred Stock (continued)
common stock in which the price is greater than $9.42$37.68 per share, adjusted for certain dilutive events, and which results in gross proceeds of at least $50.0 million.
Each share of Preferred Stock shall be automatically converted into shares of common stock at the conversion price in effect at the time of conversion, upon (i)(1) the closing of an IPO of the Company's common stock in which the price is between $3.70$14.80 and $9.42$37.68 per share, adjusted for certain dilutive events, and which results in gross proceeds of at least $50.0 million, and (ii)(2) the election by the holders of at least two-thirds of the outstanding shares of the respective series of Series B Preferred Stock, Series C Preferred Stock, Series D Preferred Stock, Series E Preferred Stock, and Series F Preferred Stock, voting as a single class.
Each share of Preferred Stock shall be automatically converted into shares of common stock at the conversion price in effect at the time of conversion, upon (i)(1) the closing of an IPO of the Company's common stock in which the price is less than $3.70$14.80 per share, adjusted for certain dilutive events, and which results in gross proceeds of at least $50.0 million, and (ii)(2) the election by the holders of at least two-thirds of the outstanding shares of Series B Preferred Stock, and (iii)(3) the election by the holders of at least 60% of the outstanding shares of the respective series of Series C Preferred Stock, Series D Preferred Stock, Series E Preferred Stock, and Series F Preferred Stock voting as a single class.
In the event of a closing of an IPO of the Company's common stock not meeting the criteria discussed above, and the election by the holders of at least two thirds of the outstanding shares of the respective series of Series B Preferred Stock, Series C Preferred Stock, Series D Preferred Stock, Series E Preferred Stock, and Series F Preferred Stock voting as a single class, each share of Preferred Stock shall be automatically converted into shares of common stock at the conversion price in effect at the time of conversion, upon.
In the event of an automatic conversion of the Preferred Stock upon the closing of an IPO in which the per-share price is less than $9.42,$37.68, adjusted for certain dilutive events, each share of Series E Preferred stock will be converted into common stock at the greater of (i)(1) the number of shares which would be received under the conversion price in effect at the time of the offering based upon the conversion features noted above, or (ii)(2) a ratio determined by dividing (1) the Special Series E Liquidation Payment, accrued from the issuance date through the date of an IPO, by (2) the price of aper share of ourthe Company's common stock in an IPO. Because the number of shares of common stock into which a share of Series E Preferred Stock is convertible will be determined by reference to the IPO price and the date of conversion, the Company is unable to currently estimate the conversion ratio as of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013. As such, forFor purposes of the unaudited pro forma financial information included within these financial statements, the conversion of all redeemable convertible preferred stockthe Series E Preferred Stock has been performed assuming a weighted-average conversion ratio of 1.72-to-1, which was calculated assuming an IPO price of $14.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the range set forth on the front cover of the Company's prospectus and an estimated closing date for an IPO of September 23, 2013. Based on these assumptions, the 802,957 outstanding shares of Series E Preferred Stock as of June 30, 2013 will convert into 1,381,806 shares of common stock has been calculated assuming a 1:1 conversion ratio.stock.
Special mandatoryMandatory
In the event that any holder of shares of Preferred Stock does not participate in a Qualified Financing (as defined) by purchasing, in the aggregate, in such Qualified Financing and within the time period specified by the Company, such holder's pro rata amount, then such holder's shares of preferred stock will automatically convert into common stock at the respective Conversion Price (as defined).
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
8. Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (continued)
The Company evaluated each series of its Preferred Stock and determined that each individual series is considered an equity host under ASC 815. In making this determination, the Company's analysis followed the whole instrument approach which compares an individual feature against the
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stock (continued)
entire preferred stock instrument which includes that feature. The Company's analysis was based on a consideration of the economic characteristics and risks of each series of Preferred Stock. More specifically, the Company evaluated all of the stated and implied substantive terms and features, including: (i)(1) whether the Preferred Stock included redemption features, (ii)(2) how and when any redemption features could be exercised, (iii)(3) whether the holders of Preferred Stock were entitled to dividends, (iv)(4) the voting rights of the Preferred Stock and (v)(5) the existence and nature of any conversion rights. As a result of the Company's conclusion that the Preferred Stock represents an equity host, the conversion feature of all series of Preferred Stock is considered to be clearly and closely related to the associated Preferred Stock host instrument. Accordingly, the conversion feature of all series of Preferred Stock is not considered an embedded derivative that requires bifurcation.
The Company accounts for potential beneficial conversion features under FASB ASC Topic 470-20,Debt with Conversion and Other Options. At the time of each of the issuances of Preferred Stock, the Company's common stock into which each series of the Company's Preferred Stock is convertible had an estimated fair value less than the effective conversion prices of the Preferred Stock. Therefore, there was no intrinsic value on the respective commitment dates.
As noted above, in certain events, the Series E Preferred Stock may convert to common stock on a basis higher than 1:1,1-to-1, based on a formula driven by the date on which the Company completes an IPO and the price of such offering. The Company concluded, in accordance with the provisions of ASC 470, that as the changes to the conversion terms would be triggered by a future event that is outside of the Company's control, this represents a contingent conversion option, and, therefore, should not be recognized until and unless the triggering event occurs. Assuming an IPO of $14.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, the 802,957 outstanding shares of Series E Preferred Stock as of June 30, 2013 will convert into 1,381,806 shares of common stock. Using the assumed conversion ratio, the Company evaluated whether a beneficial conversion feature may be required to be recorded with respect to the Series E Preferred Stock when the triggering event occurs, measured based on the number of shares of common stock assumed to be issuable upon the resolution of the contingency multiplied by the commitment date fair value of the common stock less the proceeds of the Series E Preferred Stock financing. Based upon this assessment, the Company determined that no beneficial conversion feature is required to be recognized.
Redemption
The Company shall be required to redeem all, but not less than all, of the outstanding shares of the Series F Preferred Stock, as applicable, in three equal installments at the written election of holders of 83% of the outstanding shares of Series F Preferred Stock at any time on or after the date that is 90 days before the fifth anniversary of the original issue date of the Company's Series F Preferred Stock, which is September 22, 2016. The redemption price per share of Series F Preferred Stock shall be equal to (i) $3.14(1) $12.56 for the Series F Preferred Stock (the Series F Base Redemption Price) adjusted for certain dilutive events, plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid on such share on the applicable redemption date, plus (ii)(2) an additional amount computed similar to interest payable on the Series F Base Redemption Price at the rate equal to simple interest of 10% per annum from the date of issuance of such shares.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
8. Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (continued)
After full redemption of the Series F Preferred Stock, the Company shall be required to redeem all, but not less than all, of the outstanding shares of the Series E Preferred Stock, in three equal installments at the written election of holders of 75% of the outstanding shares of Series E Preferred Stock at any time on or after the date that is 90 days before the fifth anniversary of the original issue date of the Company's Series F Preferred Stock. The redemption price per share of Series E Preferred Stock shall be equal to (i) $3.14(1) $12.56 for the Series E Preferred Stock (the Series E Base Redemption Price) adjusted for certain dilutive events, plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid on such share on the applicable redemption date, plus (ii)(2) an additional amount computed similar to interest payable on the Series E Base Redemption Price at the rate equal to simple interest of 10% per annum from the date of issuance of such shares.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stock (continued)
After full redemption of the Series F and Series E Preferred Stock, the Company shall be required to redeem all, but not less than all, of the outstanding shares of the Series D and Series D-1 Preferred Stock, as applicable, in three equal installments at the written election of holders of 85% of the outstanding shares of Series D and Series D-1 Preferred Stock at any time on or after the date that is 90 days before the fifth anniversary of the original issue date of the Company's Series F Preferred Stock. The redemption price per share of Series D Preferred Stock shall be equal to (i) $3.14(1) $12.56 for the Series D and D-1 Preferred Stock (the Series D Base Redemption Price) adjusted for certain dilutive events, plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid on such share on the applicable redemption date, plus (ii)(2) an additional amount computed similar to interest payable on the Series D Base Redemption Price at the rate equal to simple interest of 10% per annum from the date of issuance of such shares.
After full redemption of the Series F, Series E, Series D, and Series D-1 Preferred Stock, the Company shall be required to redeem all, but not less than all, of the outstanding shares of the Series C Preferred Stock, as applicable, in three equal installments at the written election of holders of two-thirds of the outstanding shares of Series C and Series C-1 Preferred Stock at any time on or after the date that is 90 days before the fifth anniversary of the original issue date of the Company's Series F Preferred Stock. The redemption price per share shall be equal to (i) $2.60(1) $10.40 in the case of Series C Preferred Stock and $2.73$10.92 in the case of Series C-1 Preferred Stock (the Series C Base Redemption Price), adjusted for certain dilutive events, plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid on such share on the applicable redemption date, plus (ii)(2) an additional amount computed similar to interest payable on the Series C Base Redemption Price at the rate equal to simple interest of 10% per annum from the date of issuance of such shares.
After full redemption of the Series F, Series E, Series D, Series D-1, Series C, and Series C-1 Preferred Stock, the Company shall be required to redeem all, but not less than all, of the outstanding shares of the Series B Preferred Stock, as applicable, in three equal installments at the written election of holders of two-thirds of the outstanding shares of Series B Preferred Stock at any time on or after the date that is 90 days before the fifth anniversary of the original issue date of the Company's Series F Preferred Stock. The redemption price per share shall be equal to (i) $1.85(1) $7.40 for the Series B Preferred Stock (the Series B Base Redemption Price), adjusted for certain dilutive events, plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid on such share on the applicable redemption date, plus (ii)(2) an additional amount computed similar to interest payable on the Series B Base Redemption Price at the rate equal to simple interest of 10% per annum from the date of issuance of such shares.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
8. Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (continued)
After full redemption of the Series F, Series E, Series D, Series D-1, Series C, Series C-1, and Series B Preferred Stock, the Company shall be required to redeem all, but not less than all, of the outstanding shares of the Series A Preferred Stock, as applicable, in three equal installments at the written election of holders of two-thirds of the outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock at any time on or after the date that is 90 days before the fifth anniversary of the original issue date of the Company's Series F Preferred Stock. The redemption price per share shall be equal to (i) $1.00(1) $4.00 for the Series A Preferred Stock (the Series A Base Redemption Price), adjusted for certain dilutive events, plus all dividends accrued or declared but unpaid on such share on the applicable redemption date, plus (ii)(2) an additional amount computed similar to interest payable on the Series A Base Redemption Price at the rate equal to simple interest of 10% per annum from the date of issuance of such shares.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
8. Redeemable convertible preferred stock (continued)
As the Preferred Stock may become redeemable upon an event that is outside of the control of the Company, the Preferred Stock has been classified outside of permanent equity.
9. Common stockStock
As of December 31, 2012 and June 30, 2013, the authorized capital stock of the Company included 104,013,161 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share.
General
The voting, dividend and liquidation rights of the holders of shares of common stock are subject to and qualified by the rights, powers and preferences of the holders of the Preferred Stock. The common stock has the following characteristics:
Voting
The holders of shares of common stock are entitled to one vote for each share of common stock held at all meetings of stockholders and written actions in lieu of meetings.
Dividends
The holders of shares of common stock are entitled to receive dividends, if and when declared by the Board. Cash dividends may not be declared or paid to holders of shares of common stock until paid on each series of outstanding Preferred Stock in accordance with their respective terms. No dividends have been declared or paid by the Company through March 31,June 30, 2013.
Liquidation
After payment to the holders of shares of Preferred Stock of their liquidation preferences, the holders of shares of common stock are entitled to share ratably in the Company's remaining assets available for distribution to stockholders, in the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company or upon the occurrence of a deemed liquidation event.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
9. Common stockStock (continued)
Reserved for future issuanceFuture Issuance
There were 9,573,972, 9,728,7632,393,458, 2,432,155 and 9,748,6502,447,195 common shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2011 and 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, respectively. The Company has reserved for future issuance the following number of shares of common stock (in thousands):
| | December 31, | March 31, 2013 | December 31, | June 30, 2013 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2012 | 2012 | ||||||||||||
Conversion of Series A Preferred Stock | 25,644 | 25,831 | 6,411 | 6,458 | ||||||||||
Conversion of Series B Preferred Stock | 16,817 | 16,258 | 4,204 | 4,064 | ||||||||||
Conversion of Series C Preferred Stock | 11,912 | 11,825 | 2,978 | 2,956 | ||||||||||
Conversion of Series C-1 Preferred Stock | 1,832 | 1,832 | 458 | 458 | ||||||||||
Conversion of Series D Preferred Stock | 940 | 928 | 235 | 232 | ||||||||||
Conversion of Series D-1 Preferred Stock | 2,548 | 2,548 | 637 | 637 | ||||||||||
Conversion of Series E Preferred Stock | 3,264 | 3,212 | 816 | 803 | ||||||||||
Conversion of Series F Preferred Stock | 9,705 | 9,685 | 2,426 | 2,421 | ||||||||||
Warrants to purchase Preferred Stock | 991 | 565 | 248 | 141 | ||||||||||
Outstanding stock options to purchase common stock | 14,920 | 14,766 | 3,730 | 3,678 | ||||||||||
Shares available for future issuance under stock option plan | 478 | 610 | 120 | 156 | ||||||||||
Warrants to purchase common stock | 3,537 | 3,481 | 884 | 870 | ||||||||||
Additional shares reserved for unissued, but designated, Preferred Stock | 1,416 | 1,416 | 55,912 | 56,048 | ||||||||||
Total shares of authorized common stock reserved for future issuance | 94,004 | 92,957 | 79,059 | 78,922 | ||||||||||
10. Significant agreementsAgreements
Celgene
Overview
On February 20, 2008 the Company entered into a collaboration, license, and option agreement (the Sotatercept Agreement) with Celgene Corporation (Celgene) relating to sotatercept. On August 2, 2011, the Company entered into a second collaboration, license and option agreement with Celgene for ACE-536 (the ACE-536 Agreement), and also amended certain terms of the Sotatercept Agreement. These agreements provide Celgene exclusive licenses for Sotatercept and ACE-536 in all indications, as well as exclusive rights to obtain a license to certain future compounds. Celgene is a global biopharmaceutical company primarily engaged in the discovery, development and commercialization of innovative therapies designed to treat cancer and immune-inflammatory related diseases.
Sotatercept agreementAgreement
Under the terms of the Sotatercept Agreement, the Company and Celgene collaborate worldwide for the joint development and commercialization of sotatercept. The Company also granted Celgene an option to license three discovery stage compounds. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company and Celgene will jointly develop, manufacture and commercialize sotatercept. Celgene paid $45.0 million of nonrefundable, upfront license and option payments to the Company upon the closing of the Sotatercept Agreement.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
10. Significant agreementsAgreements (continued)
The Company retained responsibility for research, development through the end of Phase 2a clinical trials, as well as manufacturing the clinical supplies for these trials. These activities were substantially completed in 2011. Celgene is conducting the ongoing Phase 2 trials for myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), chronic kidney disease, andb-thalassemia and will be responsible for any Phase 3 clinical trials, as well as additional Phase 2 clinical trials, and will be responsible for overseeing the manufacture of Phase 3 and commercial supplies by third party contract manufacturing organizations. Under the agreement, the Company was eligible to receive clinical milestones of up to $88.0 million, regulatory milestones of up to $272.0 million, and commercial milestones of up to $150.0 million for sotatercept. Clinical milestone payments are triggered upon initiation of a defined phase of clinical research for a product candidate. Regulatory milestone payments are triggered upon the acceptance of the marketing application and upon the approval to market a product candidate by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or other global regulatory authorities. Commercial milestone payments are triggered when an approved pharmaceutical product reaches certain defined levels of net sales by Celgene in countries outside of North America. In addition, to the extent sotatercept is commercialized, the Company would be entitled to receive tiered royalty payments in the low-to-mid twenty percent range of net sales from sales generated from all geographies. Royalty payments are subject to certain reductions, including for entry of a generic product onto the market.
Additionally, for three named discovery-stage option programs the Company was eligible to receive option fees of up to $30.0 million, clinical milestones of up to $53.3 million, regulatory milestones of up to $204.0 million, and commercial milestones of up to $150.0 million for each option program. Clinical milestone payments are triggered upon initiation of a defined phase of clinical research for a product candidate. Regulatory milestone payments are triggered upon the acceptance of the marketing application and upon the approval to market a product candidate by the FDA or other global regulatory authorities. Commercial milestone payments are triggered when an approved pharmaceutical product reaches certain defined levels of net sales by Celgene in countries outside of North America. Option fee payments are triggered upon license of any of the option programs by Celgene. In addition, to the extent an option compound is commercialized, the Company would be entitled to receive tiered royalty payments in the low-to-mid twenty percent range of net sales from sales generated from all geographies. Royalty payments are subject to certain reductions, including for entry of a generic product onto the market. None of the three discovery stage programs has advanced to the stage to achieve payment of a milestone.
In connection with entering into the Sotatercept Agreement, Celgene purchased 1,831,502457,875 shares of Series C-1 Preferred Stock at the aggregate purchase price of $5.0 million. The Series C-1 Preferred Stock was purchased at an amount that was deemed to represent fair value at the time of purchase. In the event that the Company's IPO results in gross proceeds of at least $35.0 million, Celgene has committed to purchase, in a private offering concurrently with the IPO, shares of common stock equal to $10.0 million at the issuance price per share at the IPO if the gross proceeds from the IPO are greater than $50.0 million or twenty percent (20%) of the gross proceeds if the IPO raises less than $50.0 million.
Commensurate with the execution of the ACE-536 Agreement described below, the Company and Celgene agreed to modify the terms of the Sotatercept Agreement. The modified terms included: (1) a change to the responsibility for development costs to align with the ACE-536 Agreement, with Celgene responsible for more than half of the worldwide costs through December 31, 2012, and 100% of the
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
10. Significant agreementsAgreements (continued)
development costs thereafter, (2) future contingent development milestones for sotatercept were amended to a two-category (oncology and non-oncology) structure with potential future clinical milestones of $27.0 million and regulatory milestones of $190.0 million from a four-category (various cancer indications) structure and, (3) future contingent development milestones for option compounds were amended to a two-category (oncology and non-oncology) structure with potential future clinical milestones of $25.5 million and regulatory milestones of $142.5 million from a four-category (various cancer indications) structure, and (4) an option to buy down tiered royalty payments on both Sotatercept and ACE-536 with a one-time $25.0 million payment on or prior to January 1, 2013. The potential commercial milestones remained unchanged. To date, the Company has received $33.9$34.2 million in research and development funding and milestone payments for sotatercept under the original and modified agreements. The next likely clinical milestone payment would be $7.0 million and result from Celgene's start of a Phase 2b clinical trial in chronic kidney disease.
The Sotatercept Agreement will expire on a country-by-country basis on the occurrence of both of the following: (a)(1) the expiration of the royalty term with respect to all license products in such country, and (b)(2) the exercise or forfeiture by Celgene of its option with regard to each option compound. The royalty term for each licensed product in each country outside North America is the period commencing with first commercial sale of the applicable licensed product in the applicable country and ending on the latest of expiration of specified patent coverage or a specified period of years. The royalty term for each licensed product in North America is the period commencing with the first commercial sale in North America and ending, on a licensed product and country-by-country basis on the date which commercialization of such licensed product has ceased. The term for each option compound runs for a specified period of years unless Celgene exercises its option, in which case the compound becomes a licensed product, or forfeits its option by failing to make certain payments following the achievement of certain milestones in early clinical development of the option compound.
Celgene has the right to terminate the agreement with respect to one or more licensed targets or in its entirety, upon 180 days' notice (or 45 days' notice if the licensed product has failed to meet certain end point criteria with respect to clinical trials or other development activities). The agreement may also be terminated in its entirety by either Celgene or the Company in the event of a material breach by the other party or in the event of a bankruptcy filing of the other party. There are no cancellation, termination or refund provisions in this arrangement that contain material financial consequences to the Company.
ACE-536 agreementAgreement
Under the terms of the ACE-536 Agreement, the Company and Celgene collaborate worldwide for the joint development and commercialization of ACE-536. The Company also granted Celgene an option for future products Acceleron files an Investigational New Drug application for the treatment of anemia. Celgene paid $25.0 million on the closing of the ACE-536 Agreement in August, 2011.
The Company retains responsibility for research, development through the end of Phase 1 and initial Phase 2 clinical trials, as well as manufacturing the clinical supplies for these studies. Celgene will conduct subsequent Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical studies. Acceleron will manufacture ACE-536 for the Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials and Celgene will be responsible for overseeing the manufacture of Phase 3 and commercial supplies by third party contract manufacturing organizations. The Company is eligible to receive clinical milestones of up to $32.5 million, regulatory milestones of up to
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
10. Significant agreementsAgreements (continued)
$105.0 million and commercial milestones of up to $80.0 million for ACE-536. The Company will receive additional, lower development, regulatory, and commercial milestones for any additional products for the treatment of anemia on which Celgene exercises an option. Clinical milestone payments are triggered upon initiation of a defined phase of clinical research for a product candidate. Regulatory milestone payments are triggered upon the acceptance of the marketing application and upon approval to market a protein therapeutic candidate by the FDA or other global regulatory authorities. Commercial milestone payments are triggered when an approved pharmaceutical product reaches certain defined levels of net sales by Celgene in countries outside of North America. In addition, to the extent ACE-536 is commercialized, the Company would be entitled to receive tiered royalty payments in the low-to-mid twenty percent range of net sales from sales generated from all geographies. Royalty payments are subject to certain reductions, including for entry of a generic product onto the market. To date,Through June 30, 2013, the Company has received $23.3$25.2 million in research and development funding and milestone payments for ACE-536. The next likely clinical milestone payment would be $15.0 million and result from the start of a Phase 3 study in MDS orb-thalassemia. The Company has not yet identified additional compounds for the treatment of anemia. Accordingly, there is no assurance that the Company will generate future value from additional programs.
The ACE-536 Agreement will expire on a country-by-country basis on the occurrence of both of the following: (a)(1) the expiration of the royalty term with respect to all license products in such country, and (b)(2) the end of the option term. The royalty term for each licensed product in each country outside North America is the period commencing with first commercial sale of the applicable licensed product in the applicable country and ending on the latest of expiration of specified patent coverage or a specified period of years. The royalty term for each licensed product in North America is the period commencing with the first commercial sale in North America and ending, on a licensed product and country-by-country basis on the date which commercialization of such licensed product has ceased. The option term runs until the later of (a)(1) the date on which no development or commercialization activities are ongoing or are expected to commence for any licensed products under the ACE-536 Agreement; (b)(2) the date on which (i) no development or commercialization activities are ongoing or are expected to commence for any licensed products under the Sotatercept Agreement and (ii) all option rights under the Sotatercept Agreement have been forfeited with respect to each option compound where Celgene has made a payment with respect to such compound; and (c)(3) the royalty term for all licensed products under the ACE-536 Agreement and the Sotatercept Agreement has ended; provided that if at the time the option term would otherwise end any option compounds under the ACE-536 Agreement are in clinical development the option term shall continue until Celgene's rights to such compound are either exercised or forfeited.
Celgene has the right to terminate the ACE-536 Agreement with respect to one or more licensed targets or in its entirety, upon 180 days' notice (or 45 days' notice if the licensed product has failed to meet certain end point criteria with respect to clinical trials or other development activities), provided that Celgene may not terminate the ACE-536 Agreement prior to the completion of the on-going ACE-536b-thalassemia and ACE-536 MDS Phase 2 clinical trials, except under certain conditions. The agreement may also be terminated in its entirety by either Celgene or the Company in the event of a material breach by the other party or in the event of a bankruptcy filing of the other party. There are no cancellation, termination or refund provisions in this arrangement that contain material financial consequences to the Company.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
10. Significant agreementsAgreements (continued)
Both agreementsAgreements
The Company and Celgene shared development costs under the Sotatercept and ACE-536 Agreements through December 31, 2012. As of January 1, 2013, Celgene is responsible for paying 100% of worldwide development costs under both agreements. Celgene will be responsible for all commercialization costs worldwide. The Company has the right to co-promote sotatercept, ACE-536 and future products under both agreements in North America. Celgene's option to buy down royalty rates for sotatercept and ACE-536 expired unexercised and, therefore, the Company will receive tiered royalties in the low-to-mid twenty percent range on net sales of sotatercept and ACE-536. The royalty schedules for sotatercept and ACE-536 are the same.
Accounting analysisAnalysis
Prior to 2011, the Company accounted for the Sotatercept Agreement, as a multiple element arrangement under ASC 605-25 (prior to the amendments of ASU 2009-13). The Company identified the following deliverables under the arrangement; 1)(1) the license to the ActRIIA compound, 2)(2) right to license option program compounds, 3)(3) participation in the joint development committee, 4)(4) participation in the joint commercialization committee and 5)(5) research and development activities. Under the provisions of ASC 605-25, applicable to the arrangement, since the Company could not establish VSOE for the undelivered elements, the Company was required to recognize the initial consideration, consisting of the $45.0 million of nonrefundable upfront license and option payments, over the period the undelivered elements were to be delivered, which was initially estimated to be 15 years. As of the date of the modification of the agreement, there was approximately $34.7 million of deferred revenue under the arrangement.
As a result of the material modifications to the cost sharing obligations, milestone payments structure and royalty payment structure, the Company concluded the modification represented a significant modification under ASU 2009-13, which required the Company to apply the updated provisions of ASU 2009-13 subsequent to the modification.
Because the ACE-536 Agreement and the amendment to the Sotatercept Agreement were negotiated in contemplation of each other, and the Company had not yet completed all of its obligations pursuant to the Sotatercept Agreement, the agreements were considered one arrangement for accounting purposes. The deliverables under the combined arrangement include: (1) licenses to develop and commercialize sotatercept and ACE-536, (2) performance of research and development services, (3) participation on the joint development committees, and (4) the performance of manufacturing services to provide clinical material to Celgene. The Company has determined the option to future products related to the treatment of anemia represents a substantive option. The Company is under no obligation to discover, develop or deliver any new compounds that modulate anemia and Celgene is not contractually obligated to exercise the option. As a result, the Company is at risk as to whether Celgene will exercise the option.
All of these deliverables identified in the arrangement were deemed to have stand-alone value and to meet the criteria to be accounted for as separate units of accounting under ASC 605-25. Factors considered in making this determination included, among other things, the subject of the licenses, the nature of the research and development services, and the capabilities of Celgene.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
10. Significant agreementsAgreements (continued)
The total arrangement consideration of $77.7 million under the ACE-536 Agreement and amended Sotatercept Agreement consisted of (1) the $25.0 million up-front payment for the license of ACE-536, (2) the remaining deferred revenue from the Sotatercept Agreement of $34.7 million, and (3) estimated payments for development activities and manufacturing services of $18.0 million. The Company used its BESP for each of the undelivered elements as the Company did not have VSOE or TPE of selling price for each deliverable. The Company's BESP considered its development plan for the compounds, expected manufacturing services, and reimbursement from Celgene (reimbursement of more than half of development expenses through December 31, 2012 and 100% thereafter). The Company determined its BESP for each of the undelivered elements under the arrangements as of the arrangement execution date as follows:
After determining BESP of the undelivered elements, the residualremaining consideration of $49.5 million was recognized upon execution of the arrangements. The difference between the estimated payments of $18.0 million and the estimated selling prices which totaled $28.2 million, using BESP, for undelivered elements was $10.2 million. This amount was deferred at inception and will be recognized as the undelivered elements are delivered, using the proportional performance method, or ratably in the case of performance on the Joint Development Committee.
During 2011, the Company achieved a $7.5 million clinical milestone under its ACE-536 Agreement, related to the dosing of the first patient in a multiple-dose clinical trial. The Company evaluated the milestone and determined that it was not substantive, as there was no significant uncertainty to achieving the milestone upon execution of the ACE-536 Agreement. As such, the Company allocated the $7.5 million payment based on the allocation of arrangement consideration determined at the execution date of the ACE-536 Agreement and amended Sotatercept Agreement. Based on this allocation, the Company recognized $4.8 million of the payment upon achievement, with the remaining $2.7 million recognized as revenue as the undelivered elements are delivered, consistent with the treatment of the up-front payment. During 2011, the Company achieved a $7.0 million clinical milestone under its Sotatercept Agreement, related to the dosing of the first patient for a Phase 2b clinical trial. The Company evaluated the milestone and deemed it to be substantive and consistent with the definition of a milestone included in ASU 2010-17 and, accordingly, recognized the $7.0 million payment in revenue during the year ended in December 31, 2011. During January 2013, the Company achieved a $10.0 million clinical milestone under its ACE-536 Agreement, related to the dosing of the first patient for a Phase 2 clinical trial. The Company evaluated the milestone and deemed it to be substantive and consistent with the definition of a milestone included in ASU 2010-17 and, accordingly, recognized the $10.0 million payment in revenue during the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013. The remaining development milestones under the ACE-536 and Sotatercept Agreements were deemed to be substantive and consistent with the definition of a milestone included in ASU 2010-17 and, accordingly, the Company will recognize payments related to the achievement of such milestones, if any, when such milestone is achieved. Factors considered in this determination included scientific and regulatory risks that must be overcome to achieve the milestones, the level of effort and
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
10. Significant agreementsAgreements (continued)
effort and investment required to achieve each milestone, and the monetary value attributed to each milestone. During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the Company recognized $54.8 million, $2.0 million, $0.5$1.0 million and $0.6$1.1 million, respectively, of the total deferred revenue as license and milestone revenue in the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss).
Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, Celgene and the Company share development costs, with Celgene responsible for substantially more than half of the costs for sotatercept and ACE-536 until December 31, 2012 and 100% of the costs from January 1, 2013 and thereafter. Payments from Celgene with respect to research and development costs incurred by the Company are recorded as cost-sharing revenue. Payments by the Company to Celgene for research and development costs incurred by Celgene are recorded as a reduction to cost-sharing revenue. During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013 the Company recorded net cost-sharing revenue of $(0.1) million, $2.9 million, $0.5$1.3 million and $2.2$5.3 million, respectively, which includes payments to Celgene of $2.8 million, $2.8 million, $0.7$1.3 million and zero, respectively which were recorded as contra-revenue.
Other agreementsAgreements
Shire licenseLicense
In September 2010, the Company entered into a license and collaboration agreement granting Shire AG the exclusive right to develop, manufacture and commercialize ActRIIB compounds in territories outside North America. Shire also received the right to conduct research and manufacture commercial supplies in North America for ActRIIB compounds. The lead ActRIIB compound was designated ACE-031. Under the initial development plan, the companies share the costs associated with developing and commercializing ACE-031, in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. In September 2010, Shire made a nonrefundable, up-front license payment to the Company of $45.0 million. In accordance with the Company's revenue recognition policy prior to the adoption of ASU 2009-13, the up-front license payment of $45.0 million was deferred, and will be recognized as revenue ratably over three years, which represented the original period over which the Company expected to perform and deliver research and development and manufacturing services. On February 8, 2011, the FDA placed ACE-031 on clinical hold. The Company re-assessed the duration of its deliverables under the license agreement and estimated the new term to be approximately five years. The adjustment was treated as a change in accounting estimate with the remaining deferred revenue of $38.8 million at February 8, 2011, recognized prospectively over the new period of research and development and manufacturing services. In April 2013, the Company and Shire determined not to further pursue development of ACE-031 and Shire sent the Company a notice of termination for the ACE-031 collaboration. The collaboration terminated effective June 30, 2013. At December 31, 2012, the Company had classified the remaining deferred revenue as current in the balance sheet. Upon the effectiveness of the termination of the Shire Agreement in the second quarter of 2013, the Company accelerated the recognition of $22.4 million of remaining deferred revenue from upfront non-refundable payments received under the Shire Agreement as it had no further obligation for deliverables under the Shire Agreement. During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the Company recognized $8.4 million, $7.7 million, $1.9$3.8 million and $1.9$24.3 million, respectively of the
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
10. Significant Agreements (continued)
up-front, non-refundable payments as license and milestone revenue in the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss).
The agreement also included contingent milestone payments, based on the achievement of development milestones totaling $223.8 million and commercial milestones of $228.8 million for ActRIIB compounds. The milestones under the Shire Agreement were deemed to be substantive and consistent with the definition of a milestone included in ASU 2010-17 and, accordingly, the Company recognized payments related to the achievement of such milestones, if any, when such milestone was achieved. Factors considered in this determination included scientific and regulatory risks that must be
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
10. Significant agreements (continued)
overcome to achieve the milestones, the level of effort and investment required to achieve each milestone, and the monetary value attributed to each milestone.
Pursuant to the terms of the agreement, Shire and the Company shared development costs, with Shire responsible for 65% of the costs for ACE-031 and 55% of the costs for licensed compounds other than ACE-031. Payments from Shire with respect to research and development costs incurred by the Company are recorded as cost-sharing revenue. Payments by the Company to Shire for research and development costs incurred by Shire are recorded as a reduction to cost-sharing revenue. During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the Company recorded net cost-sharing revenue of $4.1 million, $2.7 million, $0.5$1.3 million, $0.3$0.7 million, respectively, which includes payments to Shire of $2.0 million, $0.7 million, $0.2$0.4 million, $0.2 million, respectively, which are recorded as contra-revenue in the accompanying statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss).
In April 2013, the Company and Shire determined not to further pursue development of ACE-031 and Shire sent the Company a notice of termination for the ACE-031 collaboration. The collaboration will terminate effective June 30, 2013. At December 31, 2012, the Company had classified the remaining deferred revenue as current in the balance sheet. Upon notification from Shire, the Company evaluated the remaining obligations under the agreement, and has determined it will recognize the remaining deferred revenue of $22.4 million by June 30, 2013 upon the effectiveness of the termination.
Alkermes licenseLicense
In December 2009, the Company entered into a Collaboration and License Agreement with Alkermes Plc. (Alkermes) relating to a proprietary technology platform for extending the circulating half-life of certain proteins. Under the terms of the agreement, Alkermes paid the Company an up-front cash payment of $2.0 million in December 2009, which was deferred and recognized as license revenue ratably over the estimated research and development term. In addition, Alkermes purchased 2,547,771636,942 shares of Series D-1 Preferred Stock at a per share price of $3.14,$12.56, resulting in gross proceeds to the Company of $8.0 million. The Company determined that the price of $3.14$12.56 paid by Alkermes included a premium of $0.58$2.32 per share over the fair value of the Series D-1 Preferred Stock of $2.56$10.24 as calculated by the Company in its contemporaneous stock valuation. Accordingly, the Company has recognized the premium of $1.5 million as additional license revenue on a straight-line basis over the term discussed above. In October 2011, Alkermes discontinued development of the compounds being investigated under the license agreement, and as a result, the Company recognized the remaining $2.4 million of the up-front payment as revenue, as it had no further obligations under the arrangement, though the license continues.
As the principal in the collaboration, Acceleron recognized cost-sharing revenue for reimbursement payments from Alkermes. During the year ended December 31, 2011, the Company recognized net cost-sharing revenue of $0.7 million. No amounts were recognized in subsequent periods.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
10. Significant Agreements (continued)
ImmunoGen services agreementServices Agreement
In October 2010, the Company entered into a Biopharmaceutical Services Agreement with ImmunoGen, Inc. Acceleron agreed to develop and manufacture an ImmunoGen product. The
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
10. Significant agreements (continued)
Company determined the arrangement should be accounted for as a service arrangement, using the proportional performance method. Accordingly, the Company recognized revenue as the underlying performance criteria were met. The costs associated with the services were charged to operations as incurred. As of December 31, 2011, the work was completed, and the Company recorded revenue of $1.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2011.
Other
The Company entered into a license agreement with a non-profit institution for an exclusive, sublicensable, worldwide, royalty-bearing license to certain patents developed by the institution (Primary Licensed Products). In addition, the Company was granted a non-exclusive, non-sub-licensable license for Secondary Licensed Products. As compensation for the licenses, the Company issued 250,000 shares of its common stock to the institution, the fair value of which was $25,000, and was expensed during 2004, to research and development expense. We also agreed to pay specified development milestone payments totaling up to $2.0 million for sotatercept and $0.7 million for ACE-536. In addition, the Company is obligated to pay milestone fees based on the Company's research and development progress, and U.S. sublicensing revenue ranging from 10%-25%, as well as a royalty ranging from 1.0%-3.5% of net sales on any products developed under the licenses. During 2011 and 2012, the Company paid and expensed milestones and fees defined under the agreement totaling $0.1 million and zero, respectively. The Company also paid $0.5 million and zero in 2011 and 2012, respectively, based on the receipt of U.S. sublicensing revenue, which is recorded as research and development expense.
The Company entered into another license agreement with certain individuals for an exclusive, sublicensable, worldwide, royalty-bearing license to certain patents developed by the individuals. We agreed to pay specified development and sales milestone payments aggregating up to $1.0 million relating to the development and commercialization of dalantercept. In addition, we are required to pay royalties in the low single-digits on worldwide net product sales of dalantercept, with royalty obligations continuing at a 50% reduced rate for a period of time after patent expiration. If we sublicense our patent rights, we will owe a percentage of sublicensing revenue, excluding payments based on the level of sales, profits or other levels of commercialization. During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the Company did not reach any milestones defined under the agreement and, therefore, no amounts have been paid or expensed.
During 2012, the Company executed a license agreement with a research institution for an exclusive, sublicensable, worldwide, royalty-bearing license. The Company is obligated to pay development milestones and commercial milestone fees totaling up to $1.0 million. Under the agreement, if the Company uses the inventors in the clinical research, the development milestones are waived and commercial milestones shall change to $0.8 million plus any waived milestones. The Company will also pay $25,000 annually upon first commercial sale as well as royalties of 1.5% of net sales on any products developed under the patents. During the year ended December 31, 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the Company did not reach any milestones defined under the agreement and, therefore, no amounts have been paid or expensed.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
11. Stock-based compensationStock-Based Compensation
The Company's 2003 Stock Option and Restricted Stock Plan (the 2003 Plan) provides for the issuance of stock options, restricted stock awards, and restricted stock to employees, officers, directors, consultants, and key personnel of the Company as determined by the Board. As of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, the total number of shares of common stock which may be issued under the 2003 Plan was 19,750,000.4,937,500. The number of options available for future grant was 478,171119,542 and 610,100155,884 at December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, respectively. This number can be increased by the Board, subject to the approval of the shareholders
The Company has not granted unrestricted stock awards under the Plan since its inception. Stock options carry an exercise price equal to the estimated fair value of the Company's common stock on the date of grant. Options generally expire ten years following the date of grant. Stock options and restricted stock awards typically vest over four years, but vesting provisions can vary based on the discretion of the Board.
Shares of the Company's common stock underlying any awards that are forfeited, canceled, withheld upon exercise of an option, or settlement of an award to cover the exercise price or tax withholding, reacquired by the Company prior to vesting, satisfied without the issuance of shares of the Company's common stock, or otherwise terminated other than by exercise will be added back to the shares of common stock available for issuance under the 2003 Plan. Shares available for issuance under the 2003 Plan may be authorized but unissued shares of the Company's common stock or shares of the Company's common stock that have been reacquired by the Company.
During 2010, the Company modified the awards of three employees that left the Company. The modifications all related to the term of vested options post termination. The changes ranged from 3.5 years to the remaining life of the option. Awards were reviewed under ASC 718, and the fair value of the unvested options that were modified will be re-measured and the expense adjusted at each reporting period. During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, non-employee stock compensation expense of $0.2 million and $36,000 respectively, was recorded.
The Company recognized stock-based compensation expense totaling $1.4 million, $1.2 million, $0.3$0.5 million and $0.4$0.9 million during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, respectively.
Total compensation cost recognized for all stock-based compensation awards in the statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) is as follows (in thousands):
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Research and development | $ | 686 | $ | 514 | $ | 118 | $ | 151 | $ | 686 | $ | 514 | $ | 237 | $ | 311 | ||||||||||
General and administrative | 741 | 692 | 143 | 277 | 741 | 692 | 291 | 637 | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,427 | $ | 1,206 | $ | 261 | $ | 428 | $ | 1,427 | $ | 1,206 | $ | 528 | $ | 948 | |||||||||||
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
11. Stock-based compensationStock-Based Compensation (continued)
The fair value of each option issued to employees was estimated at the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions (in thousands):
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
Fair value of the underlying instrument | $ | 1.32 | $ | 1.97 | $ | 1.45 | n/a | |||||||||||||||||||
Expected volatility | 66.0 | % | 69.0 | % | 66.9 | % | n/a | 66.0 | % | 69.0 | % | 66.9 | % | 70.3 | % | |||||||||||
Expected term (in years) | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | n/a | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.07 | % | 0.89 | % | 1.17 | % | n/a | 1.1 | % | 0.9 | % | 0.9 | % | 1.4 | % | |||||||||||
Expected dividend yield | — | % | — | % | — | % | n/a | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | |||||||||||
Fair valueValue of underlying instrumentUnderlying Instrument
The Company estimates the fair value of its stock-based awards to employees using the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
Expected volatilityVolatility
The Company estimated the expected volatility based on actual historical volatility of the stock price of similar companies with publicly-traded equity securities. The Company calculated the historical volatility of the selected companies by using daily closing prices over a period of the expected term of the associated award. The companies were selected based on their enterprise value, risk profiles, position within the industry, and with historical share price information sufficient to meet the expected term of the associated award. A decrease in the selected volatility would decrease the fair value of the underlying instrument.
Expected termTerm
The Company estimates the expected life of its employee stock options using the "simplified" method, as prescribed in Staff Accounting Bulletin (SAB) No. 107, whereby, the expected life equals the arithmetic average of the vesting term and the original contractual term of the option due to its lack of sufficient historical data.
Risk-free interest rateRisk-Free Interest Rate
The Company estimated the risk-free interest rate in reference to the yield on U.S. Treasury securities with a maturity date commensurate with the expected term of the associated award. A decrease in the selected risk-free rate would decrease the fair value of the underlying instrument.
Expected dividend yieldDividend Yield
The Company estimated the expected dividend yield based on consideration of its historical dividend experience and future dividend expectations. The Company has not historically declared or paid dividends to stockholders. Moreover, it does not intend to pay dividends in the future, but instead expects to retain any earnings to invest in the continued growth of the business. Accordingly, the Company assumed an expected dividend yield of 0.0%.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
11. Stock-based compensationStock-Based Compensation (continued)
Stock optionsOptions
The following table summarizes the stock option activity under the 2003 Plan during the year ended December 31, 2012 and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013 (in thousands):
| | Number of grants | Weighted- average exercise price per share | Weighted- average contractual life (in years) | Aggregate intrinsic value(a) | Number of Grants | Weighted- Average Exercise Price Per Share | Weighted- Average Contractual Life (in years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value(1) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Outstanding at December 31, 2011 | 12,602 | $ | 0.94 | 6.88 | $ | 4,968 | 3,151 | $ | 3.76 | 6.88 | $ | 4,968 | ||||||||||||||
Granted | 2,888 | $ | 1.44 | 722 | $ | 5.76 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Exercised | (155 | ) | $ | 1.01 | (39 | ) | $ | 4.04 | ||||||||||||||||||
Canceled or forfeited | (415 | ) | $ | 1.08 | (104 | ) | $ | 4.32 | ||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | 14,920 | 1.04 | 6.62 | $ | 13,946 | 3,730 | $ | 4.16 | 6.62 | $ | 13,946 | |||||||||||||||
Granted | — | $ | — | 9 | $ | 9.64 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Exercised | (23 | ) | $ | 0.59 | (16 | ) | $ | 1.64 | ||||||||||||||||||
Canceled or forfeited | (132 | ) | $ | 1.10 | (45 | ) | $ | 4.32 | ||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding at March 31, 2013 | 14,766 | 1.04 | 6.44 | $ | 16,754 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Outstanding at June 30, 2013 | 3,678 | $ | 4.16 | 6.24 | $ | 20,145 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2012 | 9,517 | $ | 0.89 | 5.32 | $ | 10,250 | 2,379 | $ | 3.56 | 5.32 | $ | 10,250 | ||||||||||||||
Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2012 | 14,546 | $ | 1.03 | 6.55 | $ | 13,722 | 3,637 | $ | 4.12 | 6.55 | $ | 13,722 | ||||||||||||||
Exercisable at March 31, 2013 | 9,874 | $ | 0.91 | 5.29 | $ | 12,462 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Exercisable at June 30, 2013 | 2,567 | $ | 3.72 | 5.24 | $ | 15,248 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Vested and expected to vest at March 31, 2013(b) | 14,457 | $ | 1.03 | 6.38 | $ | 16,510 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Vested and expected to vest at June 30, 2013(2) | 3,613 | $ | 4.12 | 6.19 | $ | 19,886 | ||||||||||||||||||||
During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, the Company granted stock options to purchase an aggregate of 1,336,700 shares of its common stock, 2,888,000 shares of its common stock,334,175, 722,000, 261,250 and 91,0008,750 shares of its common stock, respectively, with a weighted-average grant date fair values of options granted of $1.28, $1.80$5.12, $7.20, $6.08 and $1.45,$9.64, respectively. No options were granted during the three months ended March 31, 2013.
During the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013, current and former employees of the Company exercised a total of 379,000, 155,000, 7,000,94,748, 38,697, 1,750, and 23,00015,762 options, respectively, resulting in total proceeds of $0.2 million, $0.2 million, $2,000 and $13,000,$26,000, respectively.
The intrinsic value of options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2012, and the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, was $47,000 and $26,000,$110,105, respectively.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statementsFinancial Statements (continued)
11. Stock-based compensationStock-Based Compensation (continued)
As of December 31, 2012, there was $4.4 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to unvested stock options that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.9 years. As of March 31,June 30, 2013, there was $4.0$3.6 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to unvested stock options that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.72.5 years.
12. 401(k) savings planSavings Plan
In 2004, the Company established a defined-contribution savings plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code (the 401(k) Plan). The 401(k) Plan covers all employees who meet defined minimum age and service requirements, and allows participants to defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pretax basis. The Company has not made any contributions to the 401(k) Plan to date.
13. Income taxesTaxes
The Company provides for income taxes under ASC 740. Under ASC 740, the liability method is used in accounting for income taxes. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities, and are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that will be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse.
For the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, the Company did not record a current or deferred income tax expense or benefit.
The Company's income (loss) before income taxes was $36.3 million and $(32.6) million for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012, respectively, and was generated entirely in the United States.
Deferred taxes are recognized for temporary differences between the basis of assets and liabilities for financial statement and income tax purposes. The significant components of the Company's deferred tax assets are comprised of the following (in thousands):
| | Year ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||
U.S. and state net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 20,016 | $ | 35,584 | $ | 20,016 | $ | 35,584 | ||||||
Research and development credits | 5,383 | 5,384 | 5,383 | 5,384 | ||||||||||
Deferred revenue | 25,690 | 21,882 | 25,690 | 21,882 | ||||||||||
Accruals and other temporary differences | 5,889 | 5,333 | 5,889 | 5,333 | ||||||||||
Total deferred tax assets | 56,978 | 68,183 | 56,978 | 68,183 | ||||||||||
Less valuation allowance | (56,978 | ) | (68,183 | ) | (56,978 | ) | (68,183 | ) | ||||||
Net deferred tax assets | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
The Company has evaluated the positive and negative evidence bearing upon the realizability of its deferred tax assets. Based on the Company's history of operating losses, the Company has concluded that it is more likely than not that the benefit of its deferred tax assets will not be realized. Accordingly, the Company has provided a full valuation allowance for deferred tax assets as of
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
13. Income taxes (continued)
December 31, 2011 and 2012. The valuation allowance increased by $11.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2012, due primarily to the generation of net operating losses during the period. The
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
13. Income Taxes (continued)
valuation allowance decreased by $14.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2011, due primarily to the utilization of net operating losses during the period.
A reconciliation of income tax expense computed at the statutory federal income tax rate to income taxes as reflected in the financial statements is as follows:
| | Year ended December 31, | Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||
Federal income tax expense at statutory rate | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | ||||||
State income tax, net of federal benefit | 5.0 | % | 4.2 | % | 5.0 | % | 4.2 | % | ||||||
Permanent differences | 1.5 | % | (3.4 | )% | 1.5 | % | (3.4 | )% | ||||||
Research and development credit | (1.0 | )% | — | % | (1.0 | )% | — | % | ||||||
Other | — | % | (0.4 | )% | — | % | (0.4 | )% | ||||||
Change in valuation allowance | (39.5 | )% | (34.4 | )% | (39.5 | )% | (34.4 | )% | ||||||
Effective income tax rate | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||||
As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, the Company had U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards of $53.6 million and $93.3 million, respectively, which may be available to offset future income tax liabilities and expire at various dates through 2032. As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, the Company also had U.S. state net operating loss carryforwards of $35.8 million and $75.4 million, respectively, which may be available to offset future income tax liabilities and expire at various dates through 2032. As a result of the up-front payment pursuant to the Company's collaboration agreement with Celgene, the Company expects that it will use a significant portion of its net operating loss carryforwards in 2011.
As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, the Company had federal research and development tax credit carryforwards of $3.8 million and $3.8 million, respectively, available to reduce future tax liabilities which expire at various dates through 2032. As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, the Company had state research and development tax credit carryforwards of approximately $2.4 million and $2.4 million, respectively, available to reduce future tax liabilities which expire at various dates through 2027.
Under the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, the net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards are subject to review and possible adjustment by the Internal Revenue Service and state tax authorities. Net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards may become subject to an annual limitation in the event of certain cumulative changes in the ownership interest of significant shareholders over a three-year period in excess of 50 percent, as defined under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code, respectively, as well as similar state provisions. This could limit the amount of tax attributes that can be utilized annually to offset future taxable income or tax liabilities. The amount of the annual limitation is determined based on the value of the Company immediately prior to the ownership change. Subsequent ownership changes may further affect the limitation in future years. The Company has completed several financings since its inception which may have resulted in a change in control as defined by Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code, or could result in a change in control in the future.
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
13. Income taxes (continued)
The Company will recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense. As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, the Company had no accrued interest or penalties related to uncertain tax positions and no amounts have been recognized in the Company's statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss).
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
13. Income Taxes (continued)
For all years through December 31, 2012, the Company generated research credits but has not conducted a study to document the qualified activities. This study may result in an adjustment to the Company's research and development credit carryforwards; however, until a study is completed and any adjustment is known, no amounts are being presented as an uncertain tax position for these two years. A full valuation allowance has been provided against the Company's research and development credits and, if an adjustment is required, this adjustment would be offset by an adjustment to the deferred tax asset established for the research and development credit carryforwards and the valuation allowance.
The Company files income tax returns in the United States, and various state jurisdictions. The federal and state income tax returns are generally subject to tax examinations for the tax years ended December 31, 2009 through December 31, 2012. To the extent the Company has tax attribute carryforwards, the tax years in which the attribute was generated may still be adjusted upon examination by the Internal Revenue Service, state or foreign tax authorities to the extent utilized in a future period.
14. Long-term debtLong-Term Debt
On June 26, 2009, the Company entered into a Senior Loan Agreement (the 2009 Senior Loan Agreement) with three lenders that provides for a total funding commitment of $10.0 million. The Company was required to make payments over 36 months, the first 6 payments of which were interest only, and the principal balance plus accrued interest was payable over the remaining 30 months. Interest accrued at 12.70% per annum. The Company was not subject to any financial covenants under this arrangement. The 2009 Senior Loan Agreement was secured by substantially all of the assets of the Company other than intellectual property and certain permanent capital improvements to the leased facilities. In accordance with the 2009 Senior Loan Agreement, the Company issued warrants to purchase 183,15045,786 shares of Series C-1 Preferred Stock with a fair value at issuance of $0.3 million. The fair value of the warrants, which was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model on the date of issue was treated as a discount to the debt and accreted to interest expense using the effective interest method. As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, the outstanding balance under the 2009 Senior Loan Agreement was $2.3 million and zero, respectively.
On March 18, 2010, the Company entered into a loan modification agreement (the 2010 Loan Modification Agreement) with the same three lenders as the 2009 Senior Loan Agreement. The 2010 Loan Modification Agreement provides for an additional funding commitment of $10.0 million. As of December 31, 2011 and 2012, the outstanding balance under the 2010 Loan Modification Agreement was $3.2 million and zero, respectively. The Company was required to make payments over 27 months, the first 3 payments of which were interest only, and the principal balance plus accrued interest was payable over the remaining 24 months. Interest accrued at 15.00% per annum. The Company was not subject to any financial covenants under this arrangement. The 2010 Loan Modification Agreement was secured by substantially all of the assets of the Company other than intellectual property and certain permanent capital improvements to the leased facilities. In accordance with the 2010 Loan Modification Agreement, the Company issued warrants to purchase 254,77763,693 shares of Series D-1 Preferred Stock
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
14. Long-term debt (continued)
with a fair value at issuance of $0.5 million. The fair value of the warrants, which was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, on the date of issue was treated as a discount to the debt and accreted to interest expense using the effective interest method.
On June 7, 2012, the Company entered into a loan and security agreement (the Loan Agreement) with the same three lenders, pursuant to which the Company received a loan in the aggregate principal
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
14. Long-Term Debt (continued)
amount of $20.0 million. The Company is required to repay the aggregate principal balance under the Loan Agreement in 42 months. The first 12 payments are interest only and the remaining 30 payments are equal monthly installments of principal plus interest. The Loan Agreement provided that the interest only period could be extended under certain circumstances. As of December 31 2012 and March 31, 2013, theThe Company did not expect to trigger the requirements for an extension of the interest only period.and will begin paying principal in July 2013.
Per annum interest is payable at the 8.5%. The Loan Agreement also included a closing fee of $0.2 million. The Company is amortizing the cost over the 42 months of loan. The Loan Agreement is also subject to an additional deferred payment of $1.2 million due with the final payment. The Company is recording the deferred payment to interest expense over the term of the Loan Agreement. The resulting effective interest rate is approximately 11.8%. The company is not subject to any financial covenants and the Loan Agreement is secured by a lien on all of the Company's personal property as of, or acquired after, the date of the Loan Agreement, except for intellectual property.
The Loan Agreement defines events of default, including the occurrence of an event that results in a material adverse effect upon the Company's business operations, properties, assets or condition (financial or otherwise), its ability to perform its obligations under and in accordance with the terms of the Loan Agreement, or upon the ability of the lenders to enforce any of their rights or remedies with respect to such obligations, or upon the collateral under the Loan Agreement or upon the liens of the lenders on such collateral or upon the priority of such liens. The lenders also received a right, to purchase at fair value, up to $2.0 million of equity of the Company sold in any sale by the Company to third parties of equity securities resulting in at least $5.0 million in net cash proceeds to the Company, subject to certain exceptions. As of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, there have been no events of default under the loan. As of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, the principal balance outstanding was $20.0 million.
At December 31, 2012, future minimum payments related to long-term debt were as follows (in thousands):
Year ending December 31: | ||||
2013 | $ | 5,304 | ||
2014 | 8,908 | |||
2015 | 10,108 | |||
Less amounts representing interest | (3,120 | ) | ||
Less Deferred Fee | (1,200 | ) | ||
Future minimum principal payments | 20,000 | |||
Less current portion | 3,668 | |||
Noncurrent financing obligations | $ | 16,332 | ||
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
15. Related party transactionsParty Transactions
Celgene Corporation (Celgene)
In connection with its entry into the collaboration agreement with Celgene, on February 2008, the Company sold Celgene 1,831,502457,875 shares of its Series C-1 Preferred Stock. As part of the Company's June 2010 Series E financing, Celgene purchased 145,98536,496 shares of Series E Preferred Stock and received warrants to purchase 155,91638,979 shares of common stock. As part of the Company's December 2011 Series F financing, Celgene purchased 7,961,7841,990,446 shares of Series F Preferred Stock. As a result of these
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
15. Related Party Transactions (continued)
transactions, Celgene owned 9.9% and 10.0% of the Company's fully diluted equity as of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, respectively. Refer to Note 10 for additional information regarding this collaboration agreement.
During the year ended December 31, 2012, the Company recognized $4.9 million in collaboration revenue under the Celgene collaboration arrangement and, as of December 31, 2012, had $10.3 million of deferred revenue related to the Celgene collaboration arrangement. During the threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2013, the Company recognized $12.8$16.4 million in collaboration revenue under the Celgene collaboration arrangement and, as of March 31,June 30, 2013, had $9.6$9.2 million of deferred revenue related to the Celgene collaboration arrangement.
The Company recognized following revenuesrevenue from Celgene during the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2012 and threesix months ended March 31,June 30, 2012 and 2013 as follows (in thousands):
| | Year ended December 31, | Three months ended March 31, | Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | 2011 | 2012 | 2012 | 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||
License and milestone | $ | 63,607 | $ | 2,035 | $ | 470 | $ | 10,631 | $ | 63,607 | $ | 2,035 | $ | 955 | $ | 11,084 | ||||||||||
Cost sharing, net | (121 | ) | 2,879 | 488 | 2,166 | (121 | ) | 2,879 | 1,260 | 5,329 | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | 63,486 | $ | 4,914 | $ | 958 | $ | 12,797 | $ | 63,486 | $ | 4,914 | $ | 2,215 | $ | 16,413 | |||||||||||
Alkermes
One of the Company's directors is also the Chairman, President, and Chief Executive Officer of Alkermes plc, the parent company of Alkermes, with which the Company entered into a collaboration agreement during 2009.
As of December 31, 2012 and June 30, 2013, Alkermes held 2,781,005695,250 shares of the Company's Preferred Stock and warrants to purchase 170,49742,624 shares of common stock. For the year ended December 31, 2011, Alkermes paid the Company $0.7 million for research services. No such fees were paid to the Company during 2012 or 2013.
Related-party receivableRelated-Party Receivable
On January 28, 2008, the Company issued a secured promissory note (the Note Receivable) in the amount of $0.2 million to the current chief executive officer of the Company (the CEO). The Note Receivable bears interest at an annual interest rate of 3.11% and was initially repayable on the earlier of January 28, 2011, or the date prior to the date that the Company files a registration statement with the SEC, covering shares of its common stock. The Note Receivable is secured by shares of the Company's common stock owned by the CEO. On December 22, 2010, the term was extended until
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to financial statements (continued)
15. Related party transactions (continued)
January 28, 2014, or the date prior to the date that the Company files a registration statement with the SEC covering shares of its common stock.
In November 2012, the Company further modified the terms of the Note Receivable, such that in the event that an acquisition event occurs or the company files a registration statement with the SEC on or before the maturity date, the unpaid principal and interest will be forgiven. The Company evaluated the forgiveness provisions and determined that forgiveness was not probable as of December 31, 2012, or March 31, 2013, and as such, continued to record the Note Receivable as an asset at December 31, 2012 2012. As a result of the Company's filing of a registration statement with the SEC on August 6, 2013 which triggered the forgiveness of the Note Receivable, the Company expensed the unpaid principal
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements (continued)
15. Related Party Transactions (continued)
and March 31,interest expense totaling $0.2 million as compensation expense during the six months ended June 30, 2013.
16. Subsequent eventsEvents
The Company has completed an evaluation of all subsequent events after the audited balance sheet date of December 31, 2012 and the unaudited balance sheet date of March 31,June 30, 2013 through July 3,September 5, 2013, the date this Registration Statement on Form S-1 was submitted to the SEC, to ensure that this filing includes appropriate disclosure of events both recognized in the financial statements as of December 31, 2012 and March 31,June 30, 2013, and events which occurred subsequently but were not recognized in the financial statements. The Company has concluded that no subsequent events have occurred that require disclosure, except as disclosed within these financial statements.statements and except as described below.
On September 4, 2013, the Board approved the following actions, which were approved by the stockholders on the same day:
On September 4, 2013, the Board also approved for filing immediately following the effectiveness of the Company's registration statement in connection with its IPO, the Restated Certificate of Incorporation to increase the authorized number of shares of common stock from 104,013,161 to 175,000,000, to authorize 25,000,000 shares of undesignated preferred stock, par value $0.001 per share, and to eliminate all references to the previously designated Series Preferred Stock. This Restated Certificate of Incorporation was approved by the stockholders on September 4, 2013.
4,650,000 Shares
Acceleron Pharma Inc.
Common Stock

PRELIMINARY PROSPECTUS
, 2013
| Citigroup | Leerink Swann |
Piper Jaffray
JMP Securities
Through and including , 2013 (25 days after the commencement of this offering), all dealers that effect transactions in shares of our common stock, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This delivery is in addition to a dealer's obligation to deliver a prospectus when acting as an underwriter and with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 13. Other expensesExpenses of issuanceIssuance and distributionDistribution
The following table sets forth the costs and expenses, other than the underwriting discounts and commissions, payable by the registrant in connection with the sale of common stock being registered. All amounts are estimates except for the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, registration fee, the FINRA filing fee and NASDAQ listing fee.
Item | Amount to be paid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
SEC registration fee | $ | 10,196 | ||
FINRA filing fee | 11,713 | |||
NASDAQ listing fee | 25,000 | |||
Printing and engraving expenses | * | |||
Legal fees and expenses | * | |||
Accounting fees and expenses | * | |||
Transfer Agent fees and expenses | * | |||
Miscellaneous expenses | * | |||
Total | $ | * | ||
Item | Amount to be paid | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
SEC registration fee | $ | 10,941 | ||
FINRA filing fee | 11,713 | |||
NASDAQ listing fee | 125,000 | |||
Blue Sky fees and expenses | 15,000 | |||
Printing and engraving expenses | 250,000 | |||
Legal fees and expenses | 1,150,000 | |||
Accounting fees and expenses | 800,000 | |||
Transfer Agent fees and expenses | 15,000 | |||
Miscellaneous expenses | 377,346 | |||
Total | $ | 2,755,000 | ||
Item 14. Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Section 145 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware provides as follows:
A corporation shall have the power to indemnify any person who was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding, whether civil, criminal, administrative or investigative (other than an action by or in the right of the corporation) by reason of the fact that the person is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation, or is or was serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise, against expenses (including attorneys' fees), judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by him in connection with such action, suit or proceeding if the person acted in good faith and in a manner the person reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interest of the corporation, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe his conduct was unlawful. The termination of any action, suit or proceeding by judgment, order, settlement, conviction or upon a plea of nolo contendere or its equivalent shall not, of itself, create a presumption that the person did not act in good faith and in a manner which the person reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation, and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had reasonable cause to believe that his conduct was unlawful.
A corporation shall have the power to indemnify any person who was or is a party or is threatened to be made a party to any threatened, pending or completed action or suit by or in the right of the corporation to procure a judgment in its favor by reason of the fact that the person is or was a director, officer, employee or agent of the corporation, or is or was serving at the request of the corporation as a director, officer, employee or agent of another corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust or other enterprise against expenses (including attorneys' fees) actually and reasonably incurred by him in connection with the defense or settlement of such action or suit if the person acted in good faith and in a manner the person reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the corporation and except that no indemnification shall be made with respect to any claim, issue or
II-1
matter as to which such person shall have been adjudged to be liable to the corporation unless and
II-1
only to the extent that the Court of Chancery or the court in which such action or suit was brought shall determine upon application that, despite the adjudication of liability but in view of all the circumstances of the case, such person is fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnity for such expenses which the Court of Chancery or such other court shall deem proper.
As permitted by the Delaware General Corporation Law, we have included in our restated certificate of incorporation a provision to eliminate the personal liability of our directors for monetary damages for breach of their fiduciary duties as directors, subject to certain exceptions. In addition, our restated certificate of incorporation and by-laws provide that we are required to indemnify our officers and directors under certain circumstances, including those circumstances in which indemnification would otherwise be discretionary, and we are required to advance expenses to our officers and directors as incurred in connection with proceedings against them for which they may be indemnified.
We intend to enter into indemnification agreements with our directors and officers. These agreements will provide broader indemnity rights than those provided under the Delaware General Corporation Law and our restated certificate of incorporation. The indemnification agreements are not intended to deny or otherwise limit third-party or derivative suits against us or our directors or officers, but to the extent a director or officer were entitled to indemnity or contribution under the indemnification agreement, the financial burden of a third-party suit would be borne by us, and we would not benefit from derivative recoveries against the director or officer. Such recoveries would accrue to our benefit but would be offset by our obligations to the director or officer under the indemnification agreement.
The underwriting agreement provides that the underwriters are obligated, under certain circumstances, to indemnify our directors, officers and controlling persons against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act. Reference is made to the form of underwriting agreement filed as Exhibit 1.1 hereto.
We maintain directors' and officers' liability insurance for the benefit of our directors and officers.
Item 15. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
In the three years preceding the filing of this registration statement, we have issued the following securities that were not registered under the Securities Act. The following share numbers do not reflect the 1-for-1-for-4 reverse split of our common stock or the conversion of our preferred stock into common stock.
Sales of Capital Stock
On December 22, 2011, we issued 9,704,756 shares of Series F Convertible preferred stock for total consideration of $30,472,934.
On June 10, 2010 and July 9, 2010, we issued 2,660,962 and 603,371 respectively, shares of Series E Convertible preferred stock for total consideration of 8,355,421$8,355,421 and 1,894,585$1,894,585 respectively.
Issuances of preferred stock were exempt pursuant to Rule 506 and Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933.
Sales of Warrants
On June 10, 2010, in connection with the issuance of our Series E Convertible preferred stock, we issued warrants to purchase 3,486,395 shares of our common stock.
Sales of warrants were exempt pursuant to Rule 506 and Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933.
II-2
Grants and Exercises of Stock Options
From January 1, 2013 through March 31,June 30, 2013, we did not grantgranted options to purchase a total of 35,000 shares of our common stock to employees.employees at a weighted-average price of $2.41 per share. During the same period, we issued 22,77563,048 shares of common stock upon the exercise of options to purchase such shares of common stock at a weighted average price of $0.59$0.41 per share.
In 2012, we granted options to purchase a total of 2,248,0002,888,000 shares of our common stock to employees, at a weighted averageweighted-average price of $1.44 per share. In 2012, we issued 154,791 shares of common stock upon the exercise of options to purchase such shares of common stock at a weighted averageweighted-average price of $1.01 per share.
In 2011, we granted options to purchase a total of 1,366,7001,336,700 shares of our common stock to employees, at a weighted averageweighted-average price of $1.28 per share. In 2011, we issued 378,992 shares of common stock upon the exercise of options to purchase such shares of common stock at a weighted averageweighted-average price of $0.50 per share.
In 2010, we granted options to purchase a total of 4,249,544 shares of our common stock to employees, at a weighted averageweighted-average price of $1.05 per share. In 2010, we issued 155,252 shares of common stock upon the exercise of options to purchase such shares of common stock at a weighted averageweighted-average price of $0.56 per share.
Option grants and the issuances of common stock upon exercise of such options were exempt pursuant to Rule 701 and Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933.
Item 16. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
| Exhibit number | Description of exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Form of Underwriting Agreement | ||
3.1 | ** | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation | |
3.2 | Amendment to Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, filed September 5, 2013 | ||
3.3 | Form of Restated Certificate of Incorporation | ||
** | Amended and Restated By-laws | ||
** | Form of Amended and Restated By-laws | ||
4.1 | Form of Common Stock Certificate | ||
4.2 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement | |
4.3 | ** | Form of Warrant to Purchase Stock, issued to Series E Investors as of June 10, 2010 and July 9, 2010 | |
4.4 | ** | Form of Common Stock Warrant Certificate, issued to General Electric Capital Corporation as of March 28, 2007 | |
5.1 | Opinion of Ropes & Gray LLP | ||
10.1 | ** | Form of Director Indemnification Agreement | |
10.2 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Voting Agreement | |
II-3
| Exhibit number | Description of exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ** | Amended and Restated Right of First Refusal and Co-sale Agreement, dated as of December 22, 2011 | ||
10.4 | ** | Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated as of December 22, 2011 | |
10.5 | ** | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of June 7, 2012, among Oxford Finance LLC, the Lenders listed on Schedule 1.1, Silicon Valley Bank, MidCap Financial SBIC, LP, and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.6 | + | Collaboration, License and Option Agreement between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and Celgene Corporation, dated February 20, 2008, and amended August 2, 2011 | |
10.7 | +** | Amended and Restated License Agreement between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research Ltd., dated August 6, 2010 | |
10.8 | +** | Exclusive License Agreement between Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated June 21, 2012 | |
10.9 | + | Collaboration, License and Option Agreement between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and Celgene Corporation, dated August 2, 2011 | |
10.10 | ** | Exclusive License Agreement between Salk Institute for Biological Studies and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated as of August 10, 2010 | |
10.11 | ** | Amended and Restated License Agreement between Salk Institute for Biological Studies and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated as of August 11, 2010 | |
10.12 | ** | Indenture of Lease between Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated May 20, 2008 | |
10.13 | ** | Form of Acceleron Pharma Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive Plan | |
10.14 | ** | Form of Acceleron Pharma Inc. Cash Incentive Plan | |
10.15 | ** | Acceleron Pharma Inc. 2003 Stock Option and Restricted Stock Plan | |
10.16 | ** | Promissory Note by and between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and John Knopf, dated as of January 28, 2008, and amended November 13, 2012 | |
10.17 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between John Knopf and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.18 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between Matthew L. Sherman and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.19 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between John D. Quisel and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.20 | Employee Stock Purchase Plan | ||
23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP | ||
23.2 | Consent of Ropes & Gray LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1) | ||
24.1 | ** | Power of Attorney (included on signature page) | |
II-4
Schedules not listed above have been omitted because the information required to be set forth therein is not applicable or is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto.
II-4
The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes to provide to the underwriters at the closing specified in the underwriting agreement certificates in such denominations and registered in such names as required by the underwriters to permit prompt delivery to each purchaser.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes:
(1) That for purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the Registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act of 1933 shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective.
(2) That for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
II-5
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Registrant has duly caused this Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-1 to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the city of Cambridge, Commonwealth of Massachusetts, on AugustSeptember 6th, 2013.
| ACCELERON PHARMA INC. | ||||
By: | /s/ JOHN KNOPF, PH.D. John L. Knopf, Ph.D. Chief Executive Officer and President | |||
Signatures and Power of Attorney
We, the undersigned directors and officers of Acceleron Pharma Inc. (the "Company"), hereby severally constitute and appoint John L. Knopf, Kevin F. McLaughlin and John D. Quisel, and each of them singly, our true and lawful attorneys, with full power to them, and to each of them singly, to sign for us and in our names in the capacities indicated below, the registration statement on Form S-1 filed herewith, and any and all pre-effective and post-effective amendments to said registration statement, and any registration statement filed pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, in connection with the registration under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, of equity securities of the Company, and to file or cause to be filed the same, with all exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as each of us might or could do in person, and hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys, and each of them, or their substitute or substitutes, shall do or cause to be done by virtue of this Power of Attorney.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act, this Amendment No. 2 to Registration Statement on Form S-1 has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /s/ JOHN KNOPF, PH.D. John L. Knopf, Ph.D. | Chief Executive Officer and President (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
Kevin F. McLaughlin | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
Anthony B. Evnin, Ph.D. | Director | |||
* Jean M. George | Director | September 6, 2013 | ||
* George Golumbeski, Ph.D. | Director | September 6, 2013 | ||
* Carl L. Gordon, Ph.D., CFA | Director | September 6, 2013 |
II-6
Signature | Title | Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Edwin M. Kania, Jr. | Director | |||
Tom Maniatis, Ph.D. | Director | |||
Terrance G. McGuire | Director | |||
Richard F. Pops | Director | |||
Joseph S. Zakrzewski | Director |
| *by: | /s/ JOHN KNOPF, PH.D. Attorney-in-Fact |
II-7
| Exhibit number | Description of exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 | Form of Underwriting Agreement | ||
3.1 | ** | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation | |
3.2 | Amendment to Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, filed September 5, 2013 | ||
3.3 | Form of Restated Certificate of Incorporation | ||
** | Amended and Restated By-laws | ||
** | Form of Amended and Restated By-laws | ||
4.1 | Form of Common Stock Certificate | ||
4.2 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement | |
4.3 | ** | Form of Warrant to Purchase Stock, issued to Series E Investors as of June 10, 2010 and July 9, 2010 | |
4.4 | ** | Form of Common Stock Warrant Certificate, issued to General Electric Capital Corporation as of March 28, 2007 | |
5.1 | Opinion of Ropes & Gray LLP | ||
10.1 | ** | Form of Director Indemnification Agreement | |
10.2 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Voting Agreement | |
10.3 | ** | Amended and Restated Right of First Refusal and Co-sale Agreement, dated as of December 22, 2011 | |
10.4 | ** | Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated as of December 22, 2011 | |
10.5 | ** | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of June 7, 2012, among Oxford Finance LLC, the Lenders listed on Schedule 1.1, Silicon Valley Bank, MidCap Financial SBIC, LP, and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.6 | + | Collaboration, License and Option Agreement between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and Celgene Corporation, dated February 20, 2008, and amended August 2, 2011 | |
10.7 | +** | Amended and Restated License Agreement between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research Ltd., dated August 6, 2010 | |
10.8 | +** | Exclusive License Agreement between Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated June 21, 2012 | |
10.9 | + | Collaboration, License and Option Agreement between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and Celgene Corporation, dated August 2, 2011 | |
10.10 | ** | Exclusive License Agreement between Salk Institute for Biological Studies and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated as of August 10, 2010 | |
10.11 | ** | Amended and Restated License Agreement between Salk Institute for Biological Studies and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated as of August 11, 2010 | |
10.12 | ** | Indenture of Lease between Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Acceleron Pharma Inc., dated May 20, 2008 | |
10.13 | ** | Form of Acceleron Pharma Inc. 2013 Equity Incentive | |
II-8
| Exhibit number | Description of exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ** | Form of Acceleron Pharma Inc. Cash Incentive Plan | ||
10.15 | ** | Acceleron Pharma Inc. 2003 Stock Option and Restricted Stock Plan | |
10.16 | ** | Promissory Note by and between Acceleron Pharma Inc. and John Knopf, dated as of January 28, 2008, and amended November 13, 2012 | |
10.17 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between John Knopf and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.18 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between Matthew L. Sherman and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.19 | ** | Form of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between John D. Quisel and Acceleron Pharma Inc. | |
10.20 | Employee Stock Purchase Plan | ||
23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP | ||
23.2 | Consent of Ropes & Gray LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1) | ||
24.1 | ** | Power of Attorney (included on signature page) | |
II-9