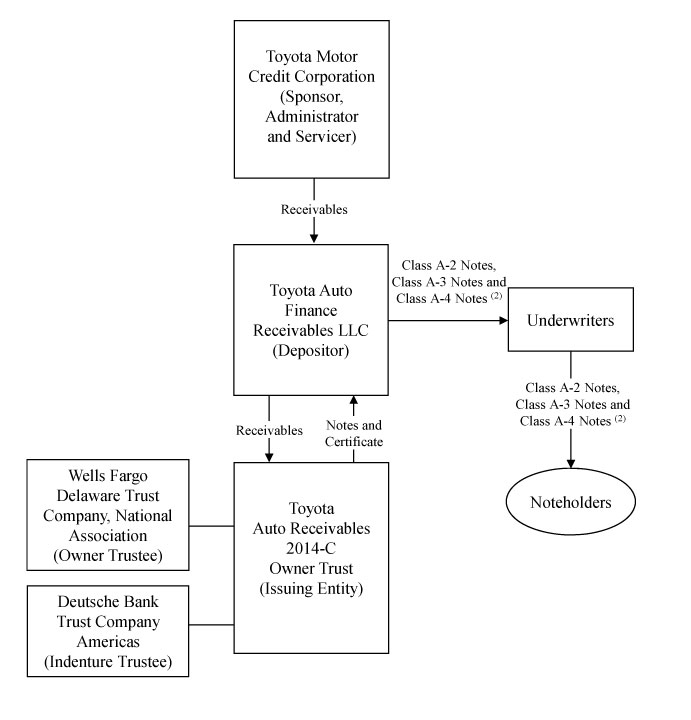
Toyota Auto Receivables Trusts
Asset Backed Notes
Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC
Depositor
Toyota Motor Credit Corporation
Sponsor, Administrator and Servicer of the Asset Backed Notes and
Issuer of the TMCC Demand Notes
You should review carefully the factors described under “Risk Factors” beginning on page 14 of this prospectus and in the related prospectus supplement. This prospectus does not contain complete information about the offering of the securities. You are urged to read both this prospectus and the related prospectus supplement that will provide additional information about the securities being offered to you. No one may use this prospectus to offer and sell the securities unless it is accompanied by the related prospectus supplement. Neither the SEC nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved the securities or determined that this prospectus or the prospectus supplement is accurate or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense. Notes of a given series issued by an issuing entity will be obligations of that issuing entity only. The notes represent obligations of the related issuing entity only and do not represent the obligations of or interests in Toyota Motor Credit Corporation, Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC, Toyota Financial Services Corporation, Toyota Financial Services Americas Corporation, Toyota Motor Corporation, Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc. or any of their affiliates. Neither the securities nor the receivables owned by the issuing entity are insured or guaranteed by any governmental agency. The TMCC Demand Notes will be obligations solely of Toyota Motor Credit Corporation and will not be obligations of, or directly or indirectly guaranteed by, Toyota Motor Corporation, Toyota Financial Services Corporation or any of their affiliates. The TMCC Demand Notes will have the benefit of credit support agreements as described under “TMCC Demand Notes—Credit Support” in this prospectus. | The Issuing Entities – • A new issuing entity will be formed to issue each series of notes. • The assets of each issuing entity: – will be described in a related prospectus supplement; – will be primarily a pool of retail installment sales contracts secured by new or used automobiles and light duty trucks; – may include credit enhancement described in a related prospectus supplement; and – will include related assets such as: • security interests in the financed vehicles; • proceeds from claims on related insurance policies; • amounts deposited in specified bank accounts; and • all proceeds of the foregoing. The Notes – • The notes will be asset backed securities sold periodically in one or more series; • will be paid only from the assets of the related issuing entity, including any related credit enhancement and any funds in accounts pledged to the issuing entity; • will be issued in one or more classes; and • will be treated as indebtedness of the related issuing entity. The amounts and prices of each offering of notes will be determined at the time of sale and will be described in a prospectus supplement that will be attached to this prospectus. The TMCC Demand Notes – • will be unsecured general obligations of Toyota Motor Credit Corporation; and • will rank pari passu with all other unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness of Toyota Motor Credit Corporation outstanding from time to time. The date of this prospectus is October 3, 2014. |
IMPORTANT NOTICE ABOUT INFORMATION PRESENTED IN THIS
PROSPECTUS AND THE ACCOMPANYING PROSPECTUS SUPPLEMENT
Information about the notes is provided in two separate documents that progressively provide more detail:
| | · | this prospectus, which provides general information, some of which may not apply to a particular series of notes including your series; and |
| | · | the accompanying prospectus supplement, which will describe the specific terms of your series of notes including: |
| | — | the timing of interest and principal payments; |
| | — | the priority of interest and principal payments for each class of offered notes; |
| | — | financial and other information about the receivables and other related assets owned by the issuing entity; |
| | — | information about the credit enhancement for each class of offered notes; and |
| | — | the method for selling the notes. |
You should rely only on the information provided in this prospectus and the accompanying prospectus supplement, including any information incorporated by reference. No one has been authorized to provide you with different information. The notes are not being offered in any state where their offer is not permitted.
Cross references in this prospectus and in the prospectus supplement have been provided to captions in these materials where you can find further related discussions of a particular topic. The Table of Contents beginning on page 4 of this prospectus provides the pages on which these captions are located.
You can find a listing of the pages where capitalized terms used in this prospectus are defined under the caption “Index of Defined Terms” beginning on page 100 in this prospectus.
Whenever we use words like “intends,” “anticipates” or “expects” or similar words in this prospectus, we are making a forward-looking statement, or a projection of what we think will happen in the future. Forward-looking statements are inherently subject to a variety of circumstances, many of which are beyond our control and could cause actual results to differ materially from what we anticipate. Any forward-looking statements in this prospectus speak only as of the date of this prospectus. We do not assume any responsibility to update or review any forward-looking statement contained in this prospectus to reflect any change in our expectation about the subject of that forward-looking statement or to reflect any change in events, conditions or circumstances on which we have based any forward-looking statement, except to the extent required by law. For the avoidance of doubt, the “safe harbor” provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 do not apply to forward-looking statements made in this prospectus.
INCORPORATION OF CERTAIN DOCUMENTS BY REFERENCE
RELATING TO NOTES ISSUED BY TOYOTA AUTO RECEIVABLES TRUSTS
The Securities and Exchange Commission (which we refer to in this prospectus as the SEC) allows us to “incorporate by reference” information filed with it by Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC on behalf of an issuing entity, which means that we can disclose important information to you by referring you to those documents. The information incorporated by reference is considered to be part of this prospectus. Information that we file later with the SEC will automatically update the information in this prospectus. In all cases, you should rely on the later information over different information included in this prospectus or the related prospectus supplement. We incorporate by reference any future annual, monthly or current SEC reports and proxy materials filed by or on behalf of an issuing entity until we terminate our offering of the notes by that issuing entity.
If you have received a copy of this prospectus and the related prospectus supplement, you may request a copy of any document that we have incorporated by reference in this prospectus or the prospectus supplement, excluding any exhibit to the document unless the exhibit is specifically incorporated by reference in the document, at no cost by contacting Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC at the following address or telephone number: Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC, 19851 South Western Avenue, Torrance, California 90501; telephone: (310) 468-7333.
INCORPORATION OF CERTAIN DOCUMENTS BY REFERENCE
RELATING TO DEMAND NOTES ISSUED BY TOYOTA MOTOR CREDIT CORPORATION
We also incorporate by reference (i) the annual report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2014, (ii) the quarterly report on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended June 30, 2014 and (iii) the current report on Form 8-K filed on September 16, 2014, each as filed by Toyota Motor Credit Corporation with the SEC under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”).
We also incorporate by reference each document that TMCC will file with the SEC under Sections 13(a), 13(c), 14 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act after the date of this prospectus until the offering of the notes is completed, except for any portion of a document that is not “filed” under the Exchange Act.
You may request a copy of any document that we have incorporated by reference in this prospectus relating to the demand notes issued by Toyota Motor Credit Corporation, excluding any exhibit to the document unless the exhibit is specifically incorporated by reference in the document, at no cost by contacting TMCC at the following address or telephone number: Toyota Motor Credit Corporation, 19001 South Western Avenue, Torrance, California 90501; telephone: (310) 468-1310.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Prospectus
| | Page |
| 7 |
RISK FACTORS | 14 |
THE SPONSOR, ADMINISTRATOR, SERVICER AND ISSUER OF THE TMCC DEMAND NOTES | 30 |
Underwriting of Motor Vehicle Retail Installment Sales Contracts | 30 |
Electronic Contracts and Electronic Contracting | 32 |
Servicing of Motor Vehicle Retail Installment Sales Contracts | 32 |
Securitization Experience | 33 |
THE DEPOSITOR | 34 |
THE ISSUING ENTITY | 34 |
THE ISSUING ENTITY PROPERTY | 35 |
THE OWNER TRUSTEE AND THE INDENTURE TRUSTEE | 36 |
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR NOTES | 36 |
THE RECEIVABLES POOLS | 37 |
DELINQUENCIES, REPOSSESSIONS AND NET LOSSES | 39 |
WEIGHTED AVERAGE LIVES OF THE NOTES | 39 |
POOL FACTORS AND TRADING INFORMATION | 41 |
USE OF PROCEEDS | 41 |
DESCRIPTION OF THE NOTES | 41 |
General | 41 |
Principal and Interest on the Notes | 42 |
The Indenture | 42 |
The Indenture Trustee | 47 |
CERTAIN INFORMATION REGARDING THE NOTES | 47 |
Fixed Rate Notes | 47 |
Floating Rate Notes | 47 |
Derivative and Other Cash Flow Enhancement Arrangements | 53 |
Revolving Period | 54 |
Prefunding Period | 54 |
Book Entry Registration | 54 |
Definitive Securities | 58 |
List of Securityholders | 59 |
Reports to Securityholders | 60 |
DESCRIPTION OF THE TRANSFER AND SERVICING AGREEMENTS | 61 |
Sale and Assignment of Receivables | 61 |
Accounts | 63 |
Servicing Procedures | 64 |
Insurance on Financed Vehicles | 66 |
Collections | 66 |
Advances | 67 |
Servicing Compensation and Payment of Expenses | 68 |
Payments | 69 |
Credit and Cash Flow Enhancement | 69 |
Net Deposits | 72 |
Statements to Trustees and Issuing Entity | 72 |
Evidence as to Compliance | 72 |
Certain Matters Regarding the Servicer; Servicer Liability | 73 |
Servicer Default | 73 |
Rights Upon Servicer Default | 74 |
Waiver of Past Defaults | 74 |
Amendment | 74 |
Non-Petition | 75 |
Payment of Notes | 76 |
Depositor Liability | 76 |
Termination | 76 |
Administration Agreement | 77 |
CERTAIN LEGAL ASPECTS OF THE RECEIVABLES | 78 |
General | 78 |
Security Interests | 78 |
Repossession | 80 |
Notice of Sale; Reinstatement and Redemption Rights | 80 |
Deficiency Judgments and Excess Proceeds | 81 |
Certain Bankruptcy Considerations | 81 |
Dodd-Frank Act Orderly Liquidation Authority Provisions | 82 |
Consumer Protection Laws | 84 |
Forfeiture for Drug, RICO and Money Laundering Violations | 86 |
Other Limitations | 87 |
TMCC Demand Notes | 87 |
Issuer of the TMCC Demand Notes | 87 |
General | 88 |
Removal of Demand Notes Indenture Trustee; Successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee | 89 |
Successor Corporation | 89 |
TMCC Statement as to Compliance | 89 |
Supplemental Demand Notes Indentures | 89 |
Events of Default Under the Demand Notes Indenture | 90 |
| | 91 |
Absence of Covenants | 92 |
Defeasance and Discharge of Demand Notes Indenture | 92 |
Regarding the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee | 92 |
Credit Support | 92 |
Governing Law | 93 |
Where You can Find More Information | 93 |
Experts | 93 |
CERTAIN FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES | 94 |
Tax Characterization of the Issuing Entity | 94 |
| | 94 |
Tax Consequences to Owners of the Notes | 95 |
CERTAIN STATE TAX CONSEQUENCES | 98 |
ERISA CONSIDERATIONS | 98 |
PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION | 98 |
LEGAL OPINIONS | 99 |
INDEX OF DEFINED TERMS | 100 |
SUMMARY OF TERMS
The following information highlights selected information from this document and provides a general overview of the terms of the securities. To understand all of the terms of the offering of the notes, you should read carefully this entire document and the accompanying prospectus supplement. Both documents contain information you should consider when making your investment decision.
| Issuing Entity | The trust to be formed for each series of notes. The issuing entity will be formed by a trust agreement between the depositor and the owner trustee of the issuing entity. |
| Depositor | Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC, a wholly owned, limited purpose subsidiary of Toyota Motor Credit Corporation. The principal executive offices of Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC are located at 19851 South Western Avenue, Torrance, California 90501, its telephone number is (310) 468-7333 and its facsimile number is (310) 468-6194. |
Sponsor, Administrator, Servicer and Issuer | |
| of the TMCC Demand Notes | Toyota Motor Credit Corporation (“TMCC”). The principal executive offices of TMCC are located at 19001 South Western Avenue, Torrance, California 90501, its telephone number is (310) 468-1310 and its facsimile number is (310) 468-6194. |
| Indenture Trustee | An indenture trustee will be named in the prospectus supplement for each series. |
| Owner Trustee | An owner trustee for each issuing entity that issues a series of securities will be named in the prospectus supplement for that series. |
| Securities | A series of securities will include one or more classes of notes. Notes of a series will be issued pursuant to an indenture. |
A series of securities will also include one or more certificates representing the undivided ownership interest in the related issuing entity. The certificates will not be offered.
Holders of certain classes of notes may have the right to receive their payments before holders of other classes of notes are paid. This is referred to as “sequential payment.” In addition, payments on certain classes of notes may be subordinated to payments to senior classes of notes. This is referred to as “subordination.” The prospectus supplement will describe the payment priorities and any subordination provisions that apply to a class of notes.
Terms—The terms of each class of notes in a series will be described in the prospectus supplement including:
| | • | stated principal amount of the notes; |
| | • | interest rate or formula for determining the interest rate (which may be fixed, variable, adjustable or some combination of these rates); and |
| | • | the ability of holders of a class to direct the indenture trustee or owner trustee to take specific remedies. |
A class of notes may differ from other classes of notes in certain respects including:
| | • | timing and priority of payments; |
| | • | interest rate or formula; |
| | • | amount of principal or interest payments; |
| | • | whether interest or principal will be payable to holders of the class if certain events occur; |
| | • | the right to receive collections from designated portions of the receivables owned by the issuing entity; and |
| | • | the ability of holders of a class to direct the indenture trustee or owner trustee to take specified remedies. |
Form—If you acquire a beneficial ownership interest in the notes of a series, you will generally hold them through The Depository Trust Company in the United States or Clearstream Banking, société anonyme or the Euroclear Bank S.A./N.V, as operator for the Euroclear System. This is referred to as “book entry” form. As long as the notes are held in book entry form, you will not receive a definitive certificate representing the notes.
For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Book-Entry Registration” in this prospectus.
Denomination—Notes will be issued in the denominations specified in the related prospectus supplement.
| TMCC Demand Notes | If so specified in the related prospectus supplement, the TMCC demand notes will be issued, in the form of fully registered definitive notes without interest coupons, by TMCC pursuant to the demand notes indenture and purchased by the applicable issuing entity. The TMCC demand notes will be |
unsecured general obligations of TMCC and will rank pari passu with all other unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness of TMCC outstanding from time to time. No noteholder will have any direct interest in the TMCC demand notes or have any direct rights under the TMCC demand notes or the demand notes indenture. The applicable issuing entity will be the only holder of TMCC demand notes, and the noteholders will be secured by the TMCC demand notes.
For additional information regarding the terms and conditions of any TMCC demand notes, you should refer to the related prospectus supplement and “TMCC Demand Notes” in this prospectus.
| The Issuing Entity Property | The assets of each issuing entity: |
| | • | will be described in the prospectus supplement; |
| | • | will primarily be a pool of retail installment sales contracts (the “receivables”) secured by new or used automobiles and light duty trucks (“financed vehicles”) and amounts due or collected under the contracts on or after a specified cutoff date; |
| | • | may include credit or cash flow enhancement as described in the related prospectus supplement; and |
| | • | will include related assets such as: |
| | — | security interests in the financed vehicles; |
| | — | proceeds from claims on related insurance policies; |
| | — | amounts deposited in bank accounts specified in the related prospectus supplement; and |
| | — | all proceeds of the foregoing. |
For additional information regarding the assets of the issuing entity, you should refer to “The Issuing Entity Property” in this prospectus and “The Issuing Entity” in the related prospectus supplement.
Purchasers of new and used automobiles and light duty trucks often finance their purchases by entering into retail installment sales contracts with Toyota, Lexus and Scion dealers who then sell the contracts to TMCC. The purchasers of the financed vehicles are referred to as the “obligors” under the receivables. The terms of the contracts must meet requirements specified by TMCC.
On or before the date the notes of a series are issued, TMCC will sell a specified amount of receivables to Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC, the depositor. The depositor will, in turn, sell the receivables to the issuing entity. The sale by
the depositor to the issuing entity will be documented under a sale and servicing agreement among the depositor, the servicer and the issuing entity.
The receivables to be sold by TMCC to the depositor and, in turn, sold to the issuing entity will be selected based on criteria specified in the sale and servicing agreement. These criteria will be described in the related prospectus supplement.
Except to the extent otherwise specified in the related prospectus supplement, the issuing entity will use collections on the receivables to pay interest and principal to holders of each class of notes. The prospectus supplement will describe whether:
| | • | collections received each month will be passed through or paid to holders of notes on a monthly basis; or |
| | • | whether payments will instead be made on a quarterly, semi-annual, annual or other basis. |
If payments are made other than monthly, or if the servicer may not temporarily commingle collections with its own funds, the issuing entity will need to invest the collections until the relevant payment date. These investments must satisfy criteria specified in the related sale and servicing agreement. In some cases, and if specified in the related prospectus supplement, the investments will be demand notes issued by TMCC. These demand notes will be unsecured general obligations of TMCC and will rank equally with all other outstanding senior unsecured debt of TMCC.
If so specified in the related prospectus supplement, the related issuing entity may invest in demand notes of TMCC even if payments to holders of the issuing entity’s notes are to be paid monthly. If so specified in the related prospectus supplement, the related issuing entity may invest amounts on deposit in any reserve account in demand notes of TMCC.
If so specified in the related prospectus supplement, the related issuing entity may issue to TMCC, or any creditworthy third party, a revolving liquidity note as a form of liquidity enhancement.
For additional information regarding the terms and conditions of any TMCC demand notes and any revolving liquidity note, you should refer to “TMCC Demand Notes” and “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements–Credit and Cash Flow Enhancement–Revolving Liquidity Note” in this prospectus.
| Prefunding | If specified in a prospectus supplement, on the applicable closing date, the depositor will make a deposit into a prefunding account from proceeds received from the sale of the related notes, in an amount that will be specified in the |
| | related prospectus supplement, but not to exceed 50% of the proceeds of the offering. Amounts on deposit in the prefunding account will be used to purchase additional receivables, which will be required to have the same eligibility criteria and general characteristics as the initial pool of receivables during the period to be specified in the related prospectus supplement, which may not exceed one year from the date of issuance of the related notes. Any amounts remaining on deposit in the prefunding account following the end of the specified prefunding period will be transferred to the related collection account and included as part of available amounts on the next succeeding payment date or applied to specific classes of notes as described in the prospectus supplement. |
| Revolving Period | If specified in a prospectus supplement, during the period beginning on the related closing date and ending on the payment date to be specified in the related prospectus supplement, which may not exceed three years from the date of issuance of the related notes, all amounts that represent principal collections on the receivables that otherwise would become principal distributable amounts on the next related payment date will instead be used to purchase additional receivables, which will be required to have the same eligibility criteria and general characteristics as the initial pool of receivables or such other characteristics as described in the related prospectus supplement. |
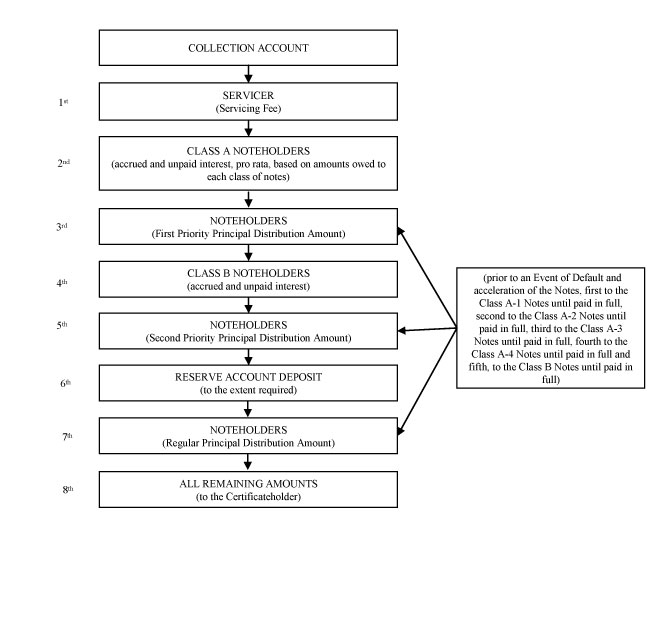
| Credit and Cash Flow Enhancement | The issuing entities may include certain features designed to provide protection to one or more classes of notes. These features are referred to as “credit enhancement.” Credit enhancement may include any one or more of the following: |
| | • | sequential payment or other payment prioritization of certain classes; |
| | • | subordination of one or more classes of notes; |
| | • | one or more reserve accounts; |
| | • | overcollateralization (i.e., the amount by which the principal amount of the receivables exceeds the principal amount of all the issuing entity’s outstanding notes); |
| | • | letters of credit, cash collateral accounts or other credit facilities; |
| | • | guaranteed investment contracts; |
| | • | excess interest collections (i.e., the excess of interest collections on the receivables over servicing fees, interest on the issuing entity’s notes and any amounts required to be deposited in a reserve account, if any). |
In addition, the issuing entity may include certain features designed to ensure the timely payment of amounts owed to noteholders. These features may include any one or more of the following:
| | • | yield maintenance agreements; |
| | • | currency or interest rate swap or cap transactions; |
| | • | ability to issue revolving liquidity notes to creditworthy third parties or TMCC; or |
The specific terms of any credit or cash flow enhancement applicable to an issuing entity or to the notes issued by an issuing entity will be described in detail in the related prospectus supplement, including any limitations or exclusions from coverage.
| Servicing | TMCC will be appointed to act as servicer for the receivables. In that capacity, the servicer will handle all collections, administer defaults and delinquencies and otherwise service the contracts. The issuing entity will pay the servicer a monthly fee equal to a percentage of the total principal balance of the receivables at the beginning of the preceding month specified in the related prospectus supplement. The servicer will also receive additional servicing compensation in the form of investment earnings, late fees, extension fees and other administrative fees and expenses or similar charges received by the servicer during such month. |
| Advances | If specified in the related prospectus supplement, the servicer may be obligated to advance to the issuing entity interest on the receivables that is due but unpaid by the obligor. In addition, the servicer may be obligated to advance to the issuing entity due but unpaid principal of any receivables that are classified as actuarial receivables rather than as simple interest receivables. The servicer will not be required to make any advance if it determines that it will not be able to recover an advance from an obligor. The issuing entity will reimburse the servicer from late collections on the receivables for which the servicer has made advances, or from collections generally if the servicer determines that an advance will not be recoverable with respect to such receivable. |
For additional information regarding advances and reimbursement of advances, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Advances” in this prospectus.
| Optional Redemption | The servicer may purchase all of the receivables remaining in the issuing entity on any payment date when the outstanding aggregate principal balance of the receivables is equal to or less than the percentage specified in the related prospectus supplement of the original total principal balance of the receivables as of the related cutoff date, which would cause the issuing entity to redeem outstanding notes prior to their final scheduled payment dates. |
For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Termination” in this prospectus.
| Changes in Payment Priorities | Each prospectus supplement will provide a description of the conditions under which changes in the priority of payments to noteholders would be made on any given payment date. |
| Removal of Pool Assets | Each prospectus supplement will provide a description of the circumstances under which receivables may or are required to be removed from the related issuing entity. |
| Tax Status | Special tax counsel to the issuing entity will be required to deliver an opinion that: |
| | • | the notes held by parties unaffiliated with the issuing entity will be characterized as debt for federal income tax purposes; and |
| | • | the issuing entity will not be characterized as an association (or a publicly traded partnership) taxable as a corporation for federal income tax purposes. |
By purchasing a note you will be agreeing to treat the note as indebtedness for tax purposes. You should consult your own tax advisor regarding the federal tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of the notes, and the tax consequences arising under the laws of any state or other taxing jurisdiction.
For additional information regarding the application of Federal and state tax laws, you should refer to “Certain Federal Income Tax Consequences” and “Certain State Tax Consequences” in this prospectus.
| ERISA Considerations | Notes will generally be eligible for purchase by employee benefit plans. For additional information regarding the ERISA eligibility of any class of notes, you should refer to “ERISA Considerations” in this prospectus and the related prospectus supplement. |
RISK FACTORS
You should consider the following risk factors in deciding whether to purchase notes of any class. In addition, you should consider the risk factors described under “Risk Factors” in the related prospectus supplement for a description of further material risks to your investment in the notes.
You must rely for repayment only upon payments from the issuing entity’s assets which may not be sufficient to make full payments on your notes. | The notes represent interests solely in the issuing entity or indebtedness of the issuing entity and will not be insured or guaranteed by the depositor, sponsor, administrator, servicer or any of their respective affiliates, any governmental entity, the related trustee or any other person or entity other than the issuing entity. The only sources of payment on your notes are payments received on the receivables and, if and to the extent available, any credit or cash flow enhancement for the issuing entity, including amounts on deposit in the reserve account, if any, established for that issuing entity. If the available credit enhancement is exhausted, your notes will be paid solely from current distributions on the receivables. In limited circumstances, the issuing entity will also have access to the funds in a yield maintenance account or have the benefit of overcollateralization to provide limited protection against low-interest yielding receivables. |
| | For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Credit and Cash Flow Enhancement—Yield Maintenance Account” and “Yield Maintenance Agreement” in this prospectus. |
You may experience reduced returns on your investments resulting from prepayments on the receivables, the use of a prefunding account, events of default, optional redemption, repurchases of receivables or early termination of the issuing entity. | You may receive payment of principal on your notes earlier than you expected for the reasons described below. As a result, you may not be able to reinvest the principal paid to you earlier than you expected at a rate of return that is equal to or greater than the rate of return, or effective yield, on your notes. In addition, an issuing entity may contain a feature known as a prefunding account from which specified funds will be used to purchase additional receivables after the date the notes are issued. To the extent all of those funds are not used by the end of the specified period to purchase new receivables, those funds will be used to make payments on the notes. In that event, you would receive payments on your notes earlier than expected. Unless otherwise described in the related prospectus supplement, TMCC, as servicer, or the depositor, under certain circumstances, may be required to repurchase certain receivables as a result of breaches of certain representations and warranties or covenants. The servicer or an affiliate may also be permitted to purchase all of the receivables remaining in the issuing entity on any payment date if the aggregate outstanding principal balance of the receivables, as of the last day of the related collection period, is less than or equal to the percentage specified in the related prospectus supplement of the aggregate outstanding principal balance of the receivables as of the related cutoff date. Further, the receivables sold to the issuing entity related to a series of notes may be prepaid, in full or in part. The rate of prepayments on the receivables may be influenced by a variety of economic, social and other factors in addition to those described above. For these reasons, the servicer cannot predict |
| | the actual prepayment rates for the receivables. You will bear any reinvestment risks resulting from prepayments on the receivables and the corresponding acceleration of payments on the related notes. The final payment of each class of notes is expected to occur prior to its scheduled final payment date because of the prepayment and reallocation considerations described above. For additional information, you should refer to “Weighted Average Lives of the Notes” in this prospectus. |
The issuing entity’s security interests in financed vehicles may be unenforceable or defeated. | The certificates of title for vehicles financed by TMCC name TMCC as the secured party. The certificates of title for financed vehicles under contracts assigned to the issuing entity will not be amended to identify the issuing entity as the new secured party because it would be administratively burdensome to do so. However, financing statements showing the transfer to the issuing entity of TMCC’s and the depositor’s interest in the receivables and the transfer to the indenture trustee of the issuing entity’s interest in the receivables will be filed with the appropriate governmental authorities. TMCC, as servicer, will retain the documentation for the receivables and the certificates of title. |
| | Because of these arrangements, another person could acquire an interest in the receivables and the financed vehicles that is judged by a court of law to be superior to the issuing entity’s or the indenture trustee’s interest. Examples of these persons are other creditors of the obligor, a subsequent purchaser of a financed vehicle or another lender who finances the vehicle. Some of the ways this could happen are described under “Certain Legal Aspects of the Receivables” in this prospectus. In some circumstances, either the depositor or the servicer will be required to purchase receivables if a security interest superior to the claims of others has not been properly established and maintained. The details of this obligation are described under “Certain Legal Aspects of the Receivables” in this prospectus. |
If the servicer does not maintain control of the receivables evidenced by electronic contracts, the issuing entity may not have a perfected security interest in those receivables. | As described in “The Sponsor, Administrator, Servicer and Issuer of the TMCC Demand Notes—Electronic Contracts and Electronic Contracting” in this prospectus, for some receivables, TMCC acquires possession of the related contracts from dealers and converts them to electronic form and maintains control of the electronic copies through TMCC’s own technology system. Other receivables may be originated electronically through a third-party custodian using the third-party custodian’s technology system. Both of these technology systems are designed to enable TMCC to perfect its security interest in the receivables evidenced by electronic contracts by satisfying the Uniform Commercial Code’s requirements for “control” of electronic chattel paper. In order for TMCC to have “control” of an electronic contract, (a) there must be a “single authoritative copy” of the electronic contract that is readily distinguishable from all other copies and which identifies TMCC as the owner, (b) all other copies of the electronic contract must indicate that they are not the “authoritative copy” of the electronic contract, (c) any revisions to the authoritative copy of the electronic |
| | contract must be readily identifiable as either authorized or unauthorized revisions, and (d) authorized revisions of the electronic contract cannot be made without TMCC’s participation. However, it is possible that another person could acquire an interest in an electronic contract that is superior to TMCC’s interest (and accordingly the issuing entity’s interest). This could occur if TMCC ceases to have “control” over the electronic contract that is maintained by TMCC or on behalf of TMCC by the third-party custodian and another party purchases that electronic contract (without knowledge that such purchase violates TMCC’s rights in the electronic contract) and obtains “control” over the electronic contract. TMCC also could lose control over an electronic contract if through fraud, forgery, negligence or error, or as a result of a computer virus or a failure of or weakness in TMCC’s or the third-party custodian’s technology system, as applicable, a person other than TMCC were able to modify or duplicate the authoritative copy of the contract. Although TMCC will perfect its assignment of its security interest in the electronic contracts to the issuing entity by filing financing statements, the fact that TMCC may not have a security interest in the receivables perfected by control may affect the priority of the issuing entity’s security interest in the receivables. The issuing entity’s interest in the receivables could be junior to another party with a perfected security interest in the inventory of the originating dealer. There can be no assurances that the third-party’s technology system will perform as represented to the servicer in maintaining the systems and controls required to provide assurance that TMCC maintains control over an electronic contract. In that event, there may be delays in obtaining copies of the electronic contract or confirming ownership and control of the electronic contract. TMCC and the depositor will represent that TMCC has a perfected security interest in the receivables to the extent evidenced by electronic contracts by means of control and that the security interest has been transferred to the depositor and thereafter to the issuing entity. From time to time, the receivables evidenced by electronic contracts may be amended, including, without limitation, by extensions of the final maturity date. To the extent any of those amendments is evidenced in tangible form, TMCC and the depositor will represent that TMCC has a perfected security interest in the receivables (consisting of the electronic contract and tangible amendment) by possession of the tangible amendment and control of the electronic contract. However, the law governing the perfection of security interests in electronic contracts by control is relatively recent. As a result, there is a risk that the systems employed by TMCC or |
| | the third-party to maintain control of the electronic contracts may not be sufficient as a matter of law to give TMCC (and accordingly, the issuing entity) a perfected security interest in the receivables evidenced by electronic contracts. As a result of the foregoing, TMCC (and accordingly, the issuing entity) may not have a perfected security interest in certain receivables or its interest, although perfected, could be junior to that of another party. Either circumstance could affect TMCC’s ability on behalf of the issuing entity to repossess and sell the underlying financed vehicles. Therefore, you may be subject to delays in payment on your notes and you may incur losses on your investment in the notes. |
The bankruptcy of your issuing entity could result in losses or delays in payments on your notes. | If your issuing entity becomes subject to bankruptcy proceedings, you could experience losses or delays in the payments on your notes as a result of, among other things, an “automatic stay,” which prevents secured creditors from exercising remedies against a debtor in bankruptcy without permission from the applicable court, and provisions of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code that permit substitution of collateral in limited circumstances. |
The bankruptcy of TMCC or the depositor could result in losses or delays in payments on the notes. | If TMCC or the depositor becomes subject to bankruptcy proceedings, you could experience losses or delays in the payments on your notes. TMCC will sell the receivables to the depositor, and the depositor will in turn transfer the receivables to the issuing entity. However, if TMCC or the depositor becomes subject to a bankruptcy proceeding, the court in the bankruptcy proceeding could conclude that TMCC or the depositor effectively still owns the receivables by concluding that the sale to the depositor by TMCC or the transfer to the issuing entity by the depositor was not a “true sale” or that the depositor should be consolidated with TMCC for bankruptcy purposes or that the issuing entity should be consolidated with the depositor for bankruptcy purposes. If a court were to reach this conclusion, you could experience losses or delays in payments on the notes as a result of, among other things: |
| | The depositor will take steps in structuring each transaction described in this prospectus to minimize the risk that a court would consolidate the depositor with TMCC or consolidate the issuing entity with the depositor for bankruptcy purposes or conclude that the sale of receivables to the depositor was not a “true sale.” For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Legal Aspects of the Receivables—Certain Bankruptcy Considerations” in this prospectus. |
Failure to pay principal on your notes will not constitute an event of default until maturity. | The amount of principal required to be paid to the noteholders will generally be limited to amounts available in the collection account (and the reserve account or other forms of credit or cash flow enhancement, if any). Therefore, the failure to pay principal of your notes generally will not result in the occurrence of an event of default until the final scheduled payment date for your notes. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Notes—The Indenture—Events of Default; Rights Upon Event of Default” in this prospectus. |
Receivables that fail to comply with consumer protection laws may be unenforceable, which may result in losses on your investment. | Numerous federal and state consumer protection laws regulate consumer contracts such as the receivables. If any of the receivables do not comply with one or more of these laws, the servicer may be prevented from or delayed in collecting the receivables. If that happens, payments on the securities could be delayed or reduced. The depositor, originator and servicer will make representations and warranties relating to the receivables’ compliance with law and the issuing entity’s ability to enforce the contracts. If the depositor breaches any of these representations or warranties, the issuing entity’s sole remedy will be to require the depositor to repurchase the affected receivables. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Legal Aspects of the Receivables—Consumer Protection Laws” in this prospectus. |
The regulatory environment in which TMCC operates could have a material adverse effect on its business and operating results. | As a provider of finance, insurance and other payment and vehicle protection products, TMCC operates in a highly regulated environment. Federal regulatory agencies have issued numerous rulemakings to implement various requirements of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, but many of these rules remain in proposed form. Agencies have issued rules establishing a comprehensive framework for the regulation of derivatives, prohibiting proprietary trading by entities affiliated with an insured depository institution, providing for the regulation of non-bank financial institutions that pose systemic risk, and requiring sponsors of asset-backed securities to retain an ownership stake in securitization transactions. The absence of final rules, in some cases, and the complexity of some of the proposed rules make it difficult to estimate their financial, compliance or operational impacts. Accordingly, compliance with applicable law in this highly regulated and developing environment is costly and can affect operating results. Compliance requires forms, processes, procedures, controls and the infrastructure to support these requirements. Compliance may create operational constraints and |
| | place limits on pricing, as the laws and regulations in the financial services industry are designed primarily for the protection of consumers. Changes in regulation could restrict TMCC’s ability to operate its business as currently operated, could impose substantial additional costs or require it to implement new processes, which could adversely affect TMCC’s business, prospects, financial performance or financial condition. The failure to comply could result in significant statutory civil and criminal fines, penalties, monetary damages, attorneys’ fees and costs, restrictions on TMCC’s ability to operate its business, possible revocation of licenses and damage to TMCC’s reputation, brand and valued customer relationships. Any such costs, restrictions or damage could adversely affect TMCC’s business, prospects, financial performance or financial condition. |
There may be potential adverse effects on the servicer, the receivables and your notes in the event any Toyota, Lexus or Scion models are subject to recalls. | Toyota Motor Sales, U.S.A., Inc. (“TMS”) periodically conducts vehicle recalls which could include temporary suspensions of sales and production of certain Toyota, Lexus and Scion models. Because TMCC’s business is substantially dependent upon the sale of Toyota, Lexus and Scion vehicles, these events or similar future events could adversely affect TMCC’s business. A decline in values of used Toyota, Lexus and Scion vehicles would have a negative effect on realized values and return rates which, in turn, could increase credit losses to TMCC. Further, TMCC and its affiliates may be or may become subject to litigation or governmental investigations and may thus become subject to judgments, fines or other penalties. These factors could affect sales of Toyota, Lexus and Scion vehicles and, accordingly, could have a negative effect on TMCC’s operating results and financial condition. If the demand for used Toyota, Lexus or Scion vehicles decreases due to recalls or other factors, the resale value of the vehicles related to the receivables may also decrease. As a result, the amount of proceeds received upon the liquidation or other disposition of financed vehicles may decrease. A decrease in the level of sales, including as a result of the actual or perceived quality, safety or reliability of Toyota, Lexus and Scion vehicles, will have a negative impact on the level of TMCC’s financing volume, insurance volume, earnings assets and revenues. The credit performance of TMCC’s dealer and consumer lending portfolios may also be adversely affected. In addition, as a result of recalls, if any, obligors of receivables may be more likely to be delinquent in or default on payments on their receivables. If any of these events materially affect collections on the receivables securing your notes, you may experience delays in payments or principal losses on your notes if the available credit enhancement has been exhausted. |
There may be potential adverse effects of credit ratings-related matters on the servicer. | Several credit rating agencies rate the long-term corporate credit and/or debt of TMCC and its affiliates. The credit ratings of TMCC depend, in large part, on the existence of the credit support arrangements with Toyota Financial Services Corporation and Toyota Motor Corporation (“TMC”) and on the financial condition and operating results of TMC. If these arrangements (or replacement arrangements acceptable to the applicable rating agencies) become unavailable to TMCC, or if the credit ratings of the credit support providers were lowered, |
| | TMCC’s credit ratings would be adversely impacted. The cost and availability of financing is influenced by credit ratings, which are intended to be an indicator of the creditworthiness of a particular company, security or obligation. Credit rating agencies which rate the credit of TMC and its affiliates, including TMCC, may qualify or alter ratings at any time. Global economic conditions and other geopolitical factors may directly or indirectly affect such ratings. Any downgrade in the sovereign credit ratings of the United States or Japan may directly or indirectly have a negative effect on the ratings of TMC and TMCC. Downgrades or placement on review for possible downgrades could result in an increase in TMCC’s borrowing costs as well as reduced access to global unsecured debt capital markets. In addition, depending on the level of the downgrade, TMCC may be required to post an increased amount of cash collateral under certain of its derivative agreements. These factors would have a negative impact on TMCC’s competitive position, operating results and financial condition. |
Funds held by the servicer that are intended to be used to make payments on the notes may be exposed to a risk of loss. | Subject to any conditions specified in the related prospectus supplement, the servicer generally may retain all payments and proceeds collected on the receivables during each collection period. The servicer is generally not required to segregate those funds from its own accounts until the funds are deposited in the collection account on or prior to each payment date. Until any collections or proceeds are deposited into the collection account, the servicer will be able to invest those amounts for its own benefit at its own risk. The issuing entity and noteholders are not entitled to any amount earned on the funds held by the servicer. If the servicer does not deposit the funds in the collection account as required on any payment date, the issuing entity may be unable to make the payments owed on your notes. |
A servicer default may result in additional costs, increased servicing fees by a substitute servicer or a diminution in servicing performance, including higher delinquencies and defaults, either of which may have an adverse effect on your notes. | If a servicer default occurs, the indenture trustee or the specified noteholders in a given series of notes may remove the servicer without the consent of the owner trustee or the certificateholders. In the event of the removal of the servicer and the appointment of a successor servicer, we cannot predict: In addition, the noteholders of the controlling class specified in the related prospectus supplement have the ability, with some exceptions, to waive defaults by the servicer. Furthermore, the indenture trustee or the noteholders of the controlling class specified in the related prospectus supplement may experience difficulties in appointing a successor servicer and during any transition phase it is possible that normal servicing activities could be disrupted, resulting in increased delinquencies and/or defaults on the receivables. |
Paying the servicer a fee based on a percentage of the receivables may result in the inability to obtain a successor servicer. | Because the servicer is paid its basic servicing fee based on a percentage of the aggregate outstanding amount of the receivables, the fee the servicer receives each month will be reduced as the size of the pool decreases over time. At some point, if the need arises to obtain a successor servicer, the fee that such successor servicer would earn might not be sufficient to induce a potential successor servicer to agree to service the remaining receivables in the pool. Also if there is a delay in obtaining a successor servicer, it is possible that normal servicing activities could be disrupted during this period, resulting in increased delinquencies and/or defaults on the receivables. |
The insolvency or bankruptcy of the servicer could delay the appointment of a successor servicer or reduce payments on your notes. | In the event of default by the servicer resulting solely from certain events of insolvency or the bankruptcy of the servicer, a court, conservator, receiver or liquidator may have the power to prevent either the indenture trustee or the noteholders of the controlling class specified in the related prospectus supplement from appointing a successor servicer or prevent the servicer from appointing a sub-servicer, as the case may be, and delays in the collection of payments on the receivables may occur. Any delay in the collection of payments on the receivables may delay or reduce payments to noteholders. |
Losses and delinquencies on the receivables may differ from TMCC’s historical loss and delinquency levels. | We cannot guarantee that the delinquency and loss levels of the receivables in the pool owned by an issuing entity will correspond to the delinquency and loss levels TMCC has experienced in the past on its loan portfolio. There is a risk that delinquencies and losses could increase or decline for various reasons including changes in underwriting standards or changes in local, regional or national economies. |
If the issuing entity enters into a currency or an interest rate swap, payments on the notes will be dependent on payments made under the swap agreement. | If the issuing entity enters into a currency swap, interest rate swap or a combined currency and interest rate swap, its ability to protect itself from shortfalls in cash flow caused by currency or interest rate changes will depend to a large extent on the terms of the swap agreement and whether the swap counterparty performs its obligations under the swap. If the issuing entity does not receive the payments it expects from the swap counterparty, the issuing entity may not have adequate funds to make all payments to noteholders when due, if ever. If the issuing entity issues notes with adjustable interest rates, interest will be due on the notes at adjustable rates, while interest will be earned on the receivables at fixed rates. In this circumstance, the issuing entity may enter into an interest rate swap to reduce its exposure to changes in interest rates. An interest rate swap requires one party to make payments to the other party in an amount calculated by applying an interest rate (for example a floating rate) to a specified notional amount in exchange for the other party making a payment calculated by applying a different interest rate (for example a fixed rate) to the same notional amount. For example, if the issuing entity issues $100 million of notes bearing interest at a floating LIBOR rate, it might enter into a swap agreement under which the issuing entity would pay interest to the swap counterparty in an amount equal to an agreed upon fixed rate on $100 million in exchange for receiving interest on $100 million at the floating LIBOR rate. The $100 million would be the “notional” amount because it is |
| | used simply to make the calculation. In an interest rate swap, no principal payments are exchanged. If the issuing entity issues notes denominated in a currency other than U.S. dollars, the issuing entity will need to make payments on the notes in a currency other than U.S. dollars, as described in the related prospectus supplement. Payments collected on the receivables, however, will be made in U.S. dollars. In this circumstance, the issuing entity may enter into a currency swap to reduce its exposure to changes in currency exchange rates. A currency swap requires one party to provide a specified amount of a currency to the other party at specified times in exchange for the other party providing a different currency at a predetermined exchange ratio. For example, if the issuing entity issues notes denominated in Swiss Francs, it might enter into a swap agreement with a swap counterparty under which the issuing entity would use the collections on the receivables to pay U.S. dollars to the swap counterparty in exchange for receiving Swiss Francs at a predetermined exchange rate to make the payments owed on the notes. In some cases, an issuing entity may enter into a currency or interest rate swap with TMCC as the swap counterparty. The terms of any swap will be described in more detail in the related prospectus supplement. |
Termination of a swap agreement and the inability to locate a replacement swap counterparty may cause termination of the issuing entity and sale of its assets. | A swap agreement may be terminated if particular events occur. Most of these events are generally beyond the control of the issuing entity or the swap counterparty. If an event of default under a swap agreement occurs and the indenture trustee is not able to assign the swap agreement to another party, obtain a swap agreement on substantially the same terms or is unable to establish any other arrangement consistent with the rating agencies’ criteria, the indenture trustee may terminate the swap agreement, which may result in an event of default under the related indenture if specified in the related prospectus supplement. It is impossible to predict how long it would take to sell the assets of the issuing entity. Some of the possible adverse consequences of a sale of the assets of the issuing entity are: |
| | average lives of the notes and could reduce the return on your notes. |
| | Additional information about termination of the issuing entity and sale of the issuing entity’s assets, including a description of how the proceeds of a sale would be distributed will be included in the related prospectus supplement. Any swap agreement involves risk. An issuing entity will be exposed to this risk should it use this mechanism. For this reason, only investors capable of understanding these risks should invest in the notes. You are strongly urged to consult with your financial advisors before deciding to invest in the notes if a swap is involved. |
Paid-ahead simple interest contracts may affect the weighted average lives of the notes. | If an obligor on a simple interest contract makes a payment on the contract ahead of schedule (for example, because the obligor intends to go on vacation), the weighted average life of the notes could be affected. This is because the additional scheduled payments will be treated as a principal prepayment and applied to reduce the principal balance of the related contract and the obligor will generally not be required to make any scheduled payments during the period for which it was paid ahead. During this paid ahead period, interest will continue to accrue on the principal balance of the contract, as reduced by the application of the additional scheduled payments, but the obligor’s contract would not be considered delinquent during this period. While the servicer may be required to make interest advances during this period, no principal advances will be made. Furthermore, when the obligor resumes his required payments, the payments so paid may be insufficient to cover the interest that has accrued since the last payment by the obligor. This situation will continue until the regularly scheduled payments are once again sufficient to cover all accrued interest and to reduce the principal balance of the contract. The payment by the issuing entity of the paid ahead principal amount on the notes will generally shorten the weighted average lives of the notes. However, depending on the length of time during which a paid ahead simple interest contract is not amortizing as described above, the weighted average lives of the notes may be extended. In addition, to the extent the servicer makes advances on a paid ahead simple interest contract which subsequently goes into default, the loss on this contract may be larger than would have been the case had advances not been made because liquidation proceeds for the contract will be applied first to reimburse the servicer its advances. TMCC’s portfolio of retail installment sales contracts has historically included simple interest contracts which have been paid ahead by one or more scheduled monthly payments. There can be no assurance as to the number of contracts in the issuing entity which may become paid ahead simple interest contracts as described above or the number or the principal amount of the scheduled payments which may be paid ahead. |
The ratings for the notes may be lowered or withdrawn at any time and do not consider the suitability of the notes for you. | The ratings assigned to the notes by any rating agency will be based on, among other things, the adequacy of the assets of the issuing entity, any credit enhancement for a series of notes and any other information such rating agency considers material to such determination. A security rating is not a recommendation to buy, sell or hold the notes. The rating considers only the likelihood that the issuing entity will pay interest on time and will ultimately pay principal in full or make full distributions of note balances. Ratings on the notes do not address the timing of distributions of principal on the notes prior to their applicable final scheduled payment date. The ratings do not consider the prices of the notes or their suitability to a particular investor. The ratings may be lowered or withdrawn at any time. If any rating agency changes its rating or withdraws its rating, no one has an obligation to provide additional credit enhancement or to restore the original rating. |
The rating of a swap counterparty or the issuer of demand notes may affect the ratings of the notes. | If an issuing entity enters into a swap or invests in TMCC demand notes, any rating agencies rating the notes will consider the provisions of the swap agreement or the demand notes and any ratings assigned to the swap counterparty and TMCC, as issuer of the demand notes in rating the notes. TMCC may also be the swap counterparty. A downgrade, suspension or withdrawal of the rating of the debt of TMCC by any rating agency may result in the downgrade, suspension or withdrawal of the rating assigned by that rating agency to any class (or all classes) of notes. A downgrade, suspension or withdrawal of the rating assigned by any rating agency to a class of notes would likely have adverse consequences on their liquidity or market value. To provide some protection against the adverse consequences of a downgrade, the swap counterparty will be required to take one of the following actions if any rating agency rating its debt reduces its debt ratings below certain levels: If TMCC is the swap counterparty, it may be able to cure the effects of a downgrade by taking the actions described above. However, if TMCC is both the demand note issuer and the swap counterparty, these actions may not be sufficient to prevent a downgrade of the ratings of the notes. Any currency or interest rate swap or demand notes involve a degree of counterparty credit risk. An issuing entity will be exposed to this risk should it use any of these mechanisms. For this reason, only investors capable of understanding these risks should invest in the notes. You are strongly urged to consult with your financial advisors before |
| | deciding to invest in the notes if a swap or demand notes are involved. |
The rating of a third party credit enhancement provider may affect the ratings of the notes. | If an issuing entity enters into any third party credit enhancement arrangement, any rating agencies rating the issuing entity’s notes will consider the provisions of the arrangement and any rating of any third party credit enhancement provided. If any rating agency rating the notes downgrades the debt rating of any third party credit provider, it is also likely to downgrade the rating of the notes. Any downgrade in the rating of the notes could have severe adverse consequences on their liquidity or market value. |
Dependence on a revolving liquidity note to fund certain shortfalls presents counterparty risk, risk of change of yields of the notes and risk of loss in connection with breach of funding obligation. | General. If an issuing entity enters into a revolving liquidity note agreement, any rating agencies rating the issuing entity’s notes will consider the provisions of the revolving liquidity note and any rating of the holder of the revolving liquidity note in rating the notes. TMCC may be the holder of the revolving liquidity note. If any rating agency rating the notes downgrades the debt rating of the holder of the revolving liquidity note, it is also likely to downgrade the rating of the notes. Any downgrade in the rating of the notes could have severe adverse consequences on their liquidity or market value. Counterparty Risk; Performance Risk. The amounts available to the issuing entity to pay interest and principal of the notes may depend in part on the operation of the revolving liquidity note agreement and the performance of the obligations of the holder of the revolving liquidity note under the revolving liquidity note agreement. On any payment date on which available collections are insufficient to fund payments of interest on and principal of the notes, the issuing entity may be dependent on receiving payments from the holder of the revolving liquidity note, to make payments on the notes to the extent there are no amounts, or insufficient amounts, then on deposit in the reserve account to fund the shortfalls. If the holder of the revolving liquidity note fails to fund any requested draw, the amount of credit enhancement available in the current or any future period may be reduced and you may experience delays and/or reductions in the interest and principal payments on your notes. This is particularly true because these funding obligations could arise under circumstances where there are no amounts on deposit in the reserve account and current collections are insufficient to fund the shortfalls or to start making deposits into the reserve account to be available to make payments in future periods. A failure by the holder of the revolving liquidity note to fund draws will cause you to experience delays and/or reductions in interest and principal payments on your notes. Investors should make their own determinations as to the likelihood of performance by the holder of the revolving liquidity note of its obligations under the revolving liquidity note agreement. An event of default may affect weighted average life and yield. If the holder of the revolving liquidity note defaults on its |
| | obligation to fund the entire undrawn amount of the revolving liquidity note in connection with a downgrade or breach of funding obligation, this default may constitute an event of default that will cause the priority of payments of all notes to change. Thereafter, all classes of notes may be exposed to the risk of additional shortfalls and losses, and, even if sufficient collections are thereafter available to fund payment in full of all classes of notes, this change in the priority of payments will change the timing of the repayment in full relative to the respective final scheduled payment dates of each class, with corresponding negative effects on the yields to the holders of each class. |
Proceeds of the liquidation of the assets of the related issuing entity may not be sufficient to pay your notes in full. | If so directed by the holders of the requisite percentage of outstanding notes of a series (or, if so specified in the related prospectus supplement, the requisite percentage of outstanding notes of the controlling class of a series), following an acceleration of the notes upon an event of default, the indenture trustee will liquidate the assets of the issuing entity only in limited circumstances. However, there is no assurance that the amount received from liquidation will be equal to or greater than the aggregate principal amount of the notes. Therefore, upon an event of default, there can be no assurance that sufficient funds will be available to repay you in full. This deficiency will be more severe in the case of any notes where the aggregate principal amount of the notes exceeds the aggregate principal balance of the receivables. |
The purchase of additional receivables after the closing date may adversely affect the characteristics of the receivables held by the issuing entity or the average life of and rate of return on the notes. | If so specified in the related prospectus supplement, an issuing entity may use amounts on deposit of principal collections received on its receivables to purchase additional receivables from the depositor after the related closing date during a specified revolving period. All additional receivables purchased from the depositor must meet the selection criteria applicable to the receivables purchased by the issuing entity on the closing date. The credit quality of the additional receivables may be lower than the credit quality of the initial receivables, however, and could adversely affect the performance of the related receivables pool. In addition, the rate of prepayments on the additional receivables may be higher than the rate of prepayments on the initial receivables, which could reduce the average life of and rate of return on your notes. You will bear all reinvestment risk associated with any prepayment of your notes. |
| Because the notes are in book entry form, your rights can only be exercised indirectly. | Because the notes will be issued in book entry form, you will be required to hold your interest in the notes through The Depository Trust Company in the United States, or Clearstream Banking, société anonyme or the Euroclear Bank S.A./N.V, as operator for the Euroclear System or their successors or assigns. Transfers of interests in the notes within The Depository Trust Company, Clearstream Banking, société anonyme or the Euroclear System must be made in accordance with the usual rules and operating procedures of those systems. So long as the notes are in book entry form, you will not be entitled to receive a definitive note representing your interest. The notes will remain in book entry form except in the limited circumstances described under “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Book Entry Registration” in the related prospectus supplement. Unless and |
| | until the notes cease to be held in book entry form, the indenture trustee will not recognize you as a “noteholder,” as the term is used in the indenture. As a result, you will only be able to exercise the rights of noteholders indirectly through The Depository Trust Company (if in the United States) and its participating organizations, or Clearstream Banking, société anonyme and the Euroclear Bank S.A./N.V, as operator for the Euroclear System and their participating organizations. Holding the notes in book entry form could also limit your ability to pledge your notes to persons or entities that do not participate in The Depository Trust Company, Clearstream Banking, société anonyme or the Euroclear System and to take other actions that require a physical certificate representing the notes. Interest and principal on the notes will be paid by the issuing entity to The Depository Trust Company as the record holder of the notes while they are held in book entry form. The Depository Trust Company will credit payments received from the issuing entity to the accounts of its participants which, in turn, will credit those amounts to noteholders either directly or indirectly through indirect participants. This process may delay your receipt of principal and interest payments from the issuing entity. |
The inability to acquire subsequent receivables may result in possible prepayments on the notes. | If so disclosed in the related prospectus supplement, an issuing entity may agree to buy additional receivables from the depositor after the closing date. The number of receivables that the depositor has to sell depends on its ability to acquire additional receivables which, in turn, is affected by, among other things, the number of financed vehicles sold. The number of financed vehicles sold is affected by a variety of factors, including interest rates, unemployment levels, the rate of inflation and consumer perception of economic conditions generally. If the full amount deposited on the closing date for the purpose of purchasing additional receivables from the depositor cannot be used for that purpose during the specified period, all remaining monies will be applied as a mandatory prepayment of a designated class or classes of notes. For additional information, you should refer to “The Receivables Pools—Prefunding” in this prospectus. |
The amounts received upon disposition of the financed vehicles may be adversely affected by a variety of factors, including discount pricing incentives, marketing incentive programs and other used car market factors which may increase the risk of loss on your notes. | The market for used Toyota, Lexus or Scion vehicles could be adversely affected by factors such as governmental action, changes in consumer demand, styling changes (including future plans for new Toyota, Lexus and Scion product introductions), recalls, the actual or perceived quality, safety or reliability of Toyota, Lexus and Scion vehicles, used vehicle supply (such as an overabundance of used cars in the marketplace), the level of current used vehicle values, fuel prices, new vehicle pricing, new vehicle incentive programs, new vehicle sales, increased competition, decreased or delayed new vehicle production due to natural disasters, supply chain interruptions or other events and economic conditions generally. Any such adverse change could result in reduced proceeds upon the liquidation or other disposition of financed vehicles, and therefore could result in reduced proceeds on defaulted |
| | receivables. If losses on the receivables exceed the credit enhancement available for your series of notes, you may suffer a loss on your investment. Discount pricing incentives or other marketing incentive programs on new cars by TMS, TMCC or by their competitors that effectively reduce the prices of new cars may have the effect of reducing demand by consumers for used cars. Additionally, the pricing of used vehicles is affected by the supply and demand for those vehicles, which, in turn, is affected by consumer tastes, economic factors (including the price of gasoline), the introduction and pricing of new car models, the actual or perceived quality, safety or reliability of vehicles and other factors. The reduced demand for used cars resulting from discount pricing incentives or other marketing incentive programs introduced by TMS, TMCC or any of their competitors or other factors may reduce the prices consumers will be willing to pay for used cars, including vehicles that secure the receivables. As a result, the proceeds received by the issuing entity upon any repossession of financed vehicles may be reduced and may not be sufficient to pay the underlying receivables. The servicer manages the market for used Toyota, Lexus and Scion vehicles through certain programs described herein, but there can be no assurance that such efforts will continue to be successful. |
The return on the notes could be reduced by shortfalls due to the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act. | The Servicemembers Civil Relief Act, as amended (the “Relief Act”), provides, and similar laws of many states may provide, relief to obligors who enter active military service (including national guard members) and to obligors in reserve status who are called to active duty after the origination of their receivables. In addition, relief may also be granted to obligors who are dependents of persons eligible for Relief Act benefits. Global conflicts and tensions may continue to involve military operations that will increase the number of U.S. citizens who have been called or will be called to active duty. The Relief Act provides, generally, that an obligor who is covered by the Relief Act may not be charged interest on the related receivable in excess of 6% per annum during the period of the obligor’s active duty. These shortfalls are not required to be paid by the obligor at any future time. The servicer is not required to advance these shortfalls as delinquent payments. Any resulting shortfalls in interest or principal will reduce the amount available for distribution, on your notes. Any such interest shortfall will be paid in subsequent periods to the extent of available funds before payments of principal are made on the notes and may result in extending the anticipated maturity of your class of notes or possibly result in a loss in the absence of sufficient credit enhancement. The Relief Act also limits the ability of the servicer to repossess the financed vehicle securing a receivable during the related obligor’s period of active duty and, in some cases, may require the servicer to extend the maturity of the receivable, lower the monthly payments and readjust the payment schedule for a period of time after the completion of the obligor’s military service. |
| | In addition, the servicer may elect to reduce the interest rate on receivables affected by the application of the Relief Act to a rate that is lower than the maximum rate prescribed by the application of the Relief Act and may readjust the payment schedule for any receivable that is affected by the application of the Relief Act until the maturity of the receivable. The servicer may also elect to pay off the existing receivable and have the related obligor enter into a new loan reflecting the payment terms permissible under the Relief Act. In this case, the servicer would deposit an amount equal to the remaining outstanding principal balance of the original receivable into the related collection account and remove such receivable from the related issuing entity. In addition, pursuant to laws of various states, payments on retail installment sales contracts or installment loans, such as the receivables by residents in those states who are called into active duty with the National Guard or the reserves, will be deferred under certain circumstances. These state laws may also limit the ability of the servicer to repossess the financed vehicle securing a receivable. As a result of the Relief Act and similar state legislation or regulations and as a result of the servicer’s ability to further lower the interest rate on the affected receivables, there may be delays or reductions in payment of, and increased losses on the receivables and you may suffer a loss on your notes. We do not know how many receivables have been or may be affected by the application of the Relief Act. |
THE SPONSOR, ADMINISTRATOR, SERVICER AND ISSUER OF THE TMCC DEMAND NOTES
Toyota Motor Credit Corporation (“TMCC”) was incorporated in California in 1982, and commenced operations in 1983. The address of TMCC’s principal executive offices is 19001 South Western Avenue, Torrance, California 90501. TMCC is owned by Toyota Financial Services Americas Corporation, a California corporation, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of Toyota Financial Services Corporation, a Japanese corporation (“TFSC”). TFSC, in turn, is a wholly owned subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation, a Japanese corporation (“TMC”). TFSC manages TMC’s worldwide finance operations. TMCC is marketed under the brands of Toyota Financial Services and Lexus Financial Services.
On April 28, 2014, TMCC issued a press release announcing that, as part of TMC’s planned consolidation of its three separate North American headquarters for manufacturing, sales and marketing to a single new headquarters facility in Plano, Texas, TMCC’s corporate headquarters would move from Torrance, California, to Plano, Texas, beginning in 2017.
TMCC provides a variety of finance and insurance products to authorized Toyota (including Scion) and Lexus vehicle dealers or dealer groups and, to a lesser extent, other domestic and import franchise dealers (collectively, the “Dealers”) and their customers in the United States (excluding Hawaii) (the “U.S.A.”) and Puerto Rico. In addition, TMCC also provides financing to industrial equipment dealers and their customers in the U.S.A. The Dealers will originate, and TMCC will purchase, the Receivables in the ordinary course of business pursuant to dealer agreements (the “Dealer Agreements”). TMCC’s products fall primarily into the following categories:
| | · | Finance – TMCC acquires a broad range of retail finance products including consumer and commercial installment sales contracts (collectively referred to as “retail contracts”) in the U.S.A. and Puerto Rico and leasing contracts accounted for as either direct finance leases or operating leases (“lease contracts”) from vehicle and industrial equipment dealers in the U.S.A. TMCC also provides dealer financing, including wholesale financing (also referred to as floorplan financing), working capital loans, revolving lines of credit and real estate financing to vehicle and industrial equipment dealers in the U.S.A. and Puerto Rico. |
| | · | Insurance – Through a wholly owned subsidiary, TMCC provides marketing, underwriting, and claims administration related to covering certain risks of vehicle dealers and their customers in the U.S.A. TMCC also provides coverage and related administrative services to certain of its affiliates in the U.S.A. |
TMCC primarily acquires retail contracts, lease contracts and insurance contracts from vehicle dealers through 30 dealer sales and services offices (“DSSOs”) and services the contracts through three regional customer service centers (“CSCs”) located throughout the U.S.A. Contract acquisition and servicing for commercial vehicles and industrial equipment dealers are performed at TMCC’s headquarters in Torrance, California. The DSSOs primarily support vehicle dealer financing needs by providing services such as acquiring retail and lease contracts from vehicle dealers, financing inventories, and financing other dealer activities and requirements such as business acquisitions, facilities refurbishment, real estate purchases and working capital requirements. The DSSOs also provide support for TMCC’s insurance products sold in the U.S.A. The CSCs support customer account servicing functions such as collections, lease terminations, and administration of both retail contract customers and lease contract customer accounts. The Central region CSC also supports insurance operations by providing agreement and claims administrative services.
Underwriting of Motor Vehicle Retail Installment Sales Contracts
TMCC purchases retail installment sales contracts secured by new or used automobile and light duty trucks from Dealers located throughout the U.S.A. and Puerto Rico. Dealers originate these Receivables in accordance with TMCC’s requirements as specified in existing agreements between TMCC and the Dealers. The Receivables are purchased in accordance with TMCC’s underwriting guidelines. TMCC acquires possession of the retail installment sales contracts that are not originated electronically from Dealers and generally converts such retail installment sales contracts to electronic form and maintains control of the electronic copies. TMCC uses a
proprietary credit scoring system to evaluate an applicant’s risk profile. Factors used by the credit scoring system (based on the applicant’s credit history) include the term of the contract, ability to pay, debt ratios, amount financed relative to the value of the vehicle to be financed and credit bureau attributes, such as number of trade lines, utilization ratio, and number of credit inquiries.
Applications are received by TMCC either from Dealers or directly from consumers when submitted online through TMCC’s online credit application. In the case of online credit applications, the consumer simultaneously applies to the related Dealer and TMCC. Applications received from Dealers include the applicant’s name, address, residential status, source and amount of monthly income and amount of monthly rent or mortgage payment. In 2011, TMCC completed its transition to a new online loan origination system (“carLOS”) for contract acquisition from the previous system (“OSCAR”). Applications received from consumers also include the applicant’s name, address, residential status, source and amount of monthly income and amount of monthly rent or mortgage payment. Upon receipt of the credit application, both OSCAR and carLOS automatically generate and transmit credit bureau requests to one or more of the major credit bureaus, which provide a credit report to TMCC.
Credit applications are then subject to systematic evaluation. Both OSCAR and carLOS evaluate each application to determine if it qualifies for auto-decisioning using specific requirements and without manual intervention. OSCAR and carLOS first review the application for compliance with TMCC credit policies (such as OFAC, social security, fraud, identity theft and address discrepancies) and then review selected factors of the application in a matrix. These factors include FICO®, VantageScore® and internal credit scores, payment-to-income ratios, loan-to-value ratio, full credit history, term and new versus used status. carLOS sends specific credit scoring attributes of an application (such as delinquency history, number of vehicles financed and utilization ratio) to an external decision engine that mirrors what was previously done internally within OSCAR. The external decision engine can reflect changes to TMCC’s credit scorecards and decisioning strategies more easily than OSCAR. In both systems, typically, the highest quality credit applications are approved automatically. The automated approval process approves only the applicant’s credit eligibility. carLOS has the capability of performing automated declines of applications, typically those which are the most risky and of the lowest quality of credit applications received. The automated declines consider factors including term, amount of advance, payment to income ratio and FICO® score.
Credit analysts (located at the DSSOs) approve or reject all credit applications that are not auto-decisioned, and may also approve an application that has been the subject of an automated decline under carLOS. Failure to be automatically approved through auto-decisioning does not mean that an application does not meet TMCC’s underwriting guidelines.
Credit analysts are assigned approval levels for maximum amount financed, maximum percentage advanced, payment-to-income ratio, and maximum term. Senior personnel may approve applications that have not been approved by a credit analyst or were not originally approved by a credit analyst. Purchasing standards are not strict limits or requirements and may be overridden for a number of compensating reasons determined in the judgment of the analyst or more senior personnel evaluating the application, including demonstrated ability to pay, strong credit history, and prior favorable TMCC financing experience with the applicant.
A credit analyst decisions applications based on an evaluation that considers an applicant’s creditworthiness and may consider an applicant’s projected ability to meet the monthly obligation, which is derived, among other things, from the amount financed and the term. TMCC’s proprietary scoring system assists the credit analyst in the credit review process. The system calculates and assigns a payment probability and a credit grade. To calculate the payment probability, key data from credit bureaus are combined with data from customer applications, including ratios such as vehicle payment to income and total debt payments to income. These and other factors are weighted by a statistically validated credit scoring process to produce the payment probability and credit grade.
A credit analyst will verify information contained in the credit application if the application presents an elevated level of credit risk. At any time during the credit decisioning process, the credit analyst may elect to counter the offer to extend credit. A countered credit decision is a credit application that could be purchased upon satisfaction of modified contract terms not originally submitted by the Dealer.
The final credit decision is made based upon the degree of credit risk perceived by the credit analyst after assessing the strengths and weaknesses of the application. Additionally, an Equal Credit Opportunity Act adverse action notice is sent to the customer specifying the reasons for the denial of, or counteroffer to, the application for credit. When a customer application is approved, the Dealer is required to submit specific contract documentation in accordance with TMCC procedures.
TMCC utilizes a tiered pricing program for retail installment sales contracts. The program matches contract interest rates with customer risk as defined by credit bureau scores and other factors for a range of price and risk combinations. Each application is assigned a credit tier. Rates vary based on credit tier, term, loan-to-value and collateral, including whether a new or used vehicle is financed. In addition, special rates may apply as a result of promotional activities or exceptions granted by TMCC on a case-by-case basis. TMCC reviews and adjusts interest rates based on competitive and economic factors and distributes the rates, by tier, to Dealers.
TMCC regularly reviews and analyzes its portfolio of Receivables to evaluate the effectiveness of its underwriting guidelines and purchasing criteria. If external economic factors, credit losses or delinquency experience, market conditions or other factors change, TMCC may adjust its underwriting guidelines and purchasing criteria in order to change the asset quality of its portfolio or to achieve other goals and objectives. Any adjustments to TMCC’s underwriting guidelines or purchasing criteria will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement.
TMCC’s retail installment sales contracts require Obligors to possess physical damage insurance and to provide evidence of such insurance upon TMCC’s request. The terms of each Receivable allow, but do not require, TMCC to obtain any such coverage on behalf of the Obligor. In accordance with its normal servicing procedures, TMCC currently does not obtain insurance coverage on behalf of the Obligor.
Electronic Contracts and Electronic Contracting
For receivables that are not originated electronically, TMCC typically acquires possession of the retail installment sales contracts from Dealers, converts such retail installment sales contracts to electronic form and maintains control of the electronic copies (“Converted Electronic Contracts”) through TMCC’s technology system that permits storage, access and administration of these Converted Electronic Contracts.
Beginning in 2011, TMCC began to engage a number of Dealers in the United States in electronic contracting, under which the related contracts are evidenced by an electronic record and are electronically signed by the related Obligors (the “Original Electronic Contracts”). TMCC has contracted with a third-party to facilitate the process of creating and storing Original Electronic Contracts. The third-party’s technology system permits transmission, storage, access and administration of Original Electronic Contracts and is comprised of proprietary and third-party software, hardware, network communications equipment, lines and services, computer servers, data centers, support and maintenance services, security devices and other related technology materials that enable electronic contracting in the automobile retail industry. The third-party’s system allows for the transmission, storage, access and administration of Original Electronic Contracts. Through use of the third-party’s system, a Dealer originates electronic retail installment contracts and then transfers these electronic contracts to TMCC.
Both TMCC’s system for Converted Electronic Contracts and the third-party system for Original Electronic Contracts use a combination of technological and administrative features that are designed to (i) designate a single copy of the record or records comprising an electronic contract as being the single authoritative copy of the receivable, (ii) manage access to and the expression of the authoritative copy, (iii) identify TMCC as the owner of record of the authoritative copy and (iv) in the case of Original Electronic Contracts, provide a means for transferring record ownership of, and the exclusive right of access to, the authoritative copy from the current owner of record to a successor owner of record.
Servicing of Motor Vehicle Retail Installment Sales Contracts
TMCC is the servicer of the Receivables (in such capacity, the “Servicer”). Each of the three customer service centers services the finance contracts using the same servicing system and procedures, for all open accounts. TMCC monitors bankruptcy administration, including related post-charge-off and recovery activities, and manages the remediation (if applicable) and liquidation of each Receivable. TMCC considers an Obligor to be past due if less than 90% of a regularly scheduled payment is received by the due date. TMCC uses an on-line collection and
auto dialer system that prioritizes collection efforts and signals TMCC collections personnel to make telephone contact with delinquent Obligors. TMCC engages a third party vendor to mail written communications. Collection efforts are based on risk and behavioral scoring models (which analyze borrowers’ past payment performance, vehicle valuation and credit scores to predict future payment behavior and loss probabilities). In accordance with its Customary Servicing Practices, TMCC may offer Obligors due date changes and payment deferrals over the course of the contract for Obligors with temporary financial hardships. Deferral approval is based on risk-based scoring for each account. TMCC generally determines whether to commence repossession efforts after a Receivable is 82 days past due. Repossessed vehicles are held in inventory to comply with statutory requirements and then sold at private auctions, unless public auctions are required by applicable law. Any unpaid amounts remaining after sale or after full charge-off are pursued by TMCC to the extent practical and legally permissible. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Legal Aspects of the Receivables—Deficiency Judgments and Excess Proceeds” in this prospectus. Any surplus amounts remaining after sale fees and expenses have been paid, and any reserve charge-backs and/or dealer guarantees, are refunded to the customers. Collections of deficiencies and refunds of surplus are administered at a centralized facility. TMCC’s policy is to charge-off a finance contract in its servicing system as soon as disposition of the vehicle has been completed and sales proceeds have been received, but TMCC may in some circumstances charge-off a finance contract prior to repossession. In the case of uncollectible accounts, charge-off of a finance contract will occur prior to repossession. When repossession and disposition of the collateral has not been completed, TMCC’s policy is to charge-off the account as soon as TMCC determines that the vehicle cannot be recovered, but not later than when the contract is 120 days delinquent. Prior to the fourth quarter of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, a vehicle lease contract or retail installment sales contract was considered contractually delinquent when it was 150 days past due. Beginning with the fourth quarter of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2010, TMCC changed its charge-off policy so that contracts were charged-off at 120 days past due rather than 150 days past due. This change resulted in an increase in charge-offs in respect of vehicle leases and retail installment sales contracts of $38 million for the quarter ended March 31, 2010.
As described in each Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Servicer is generally obligated to manage, service, administer and make collections on the Receivables with reasonable care, using that degree of skill and attention that the Servicer exercises with respect to comparable automotive receivables that it services for itself or others (“Customary Servicing Practices”). As part of its Customary Servicing Practices, the Servicer may implement new programs, whether on an intermediate, pilot or permanent basis, or on a regional or nationwide basis, or modify its standards, policies and procedures as long as, in each case, the Servicer implements such programs or modifies its standards, policies and procedures in respect of comparable assets serviced for itself in the ordinary course of business. For example, the Servicer has in the past granted deferrals, extensions and other administrative relief to obligors living in areas affected by natural disasters.
As also described in each Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Servicer may, in accordance with its Customary Servicing Practices, waive any prepayment charge, late payment charge or any other fees that may be collected in the ordinary course of servicing the Receivables. In addition, to the extent provided in each Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Servicer also will be authorized to offer and grant extensions, rebates or adjustments on a Receivable in accordance with its Customary Servicing Practices, without the prior consent of the owner trustee, indenture trustee or any registered holder of the Securities (each, a “Securityholder”), subject to the terms described under “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Servicing Procedures” in this prospectus.
Securitization Experience
TMCC utilizes the asset-backed securities markets as a complement to its core unsecured funding programs, to secure an alternate source of liquidity, and to gain access to a unique investor base. TMCC currently maintains a shelf registration statement (with the depositor listed as the registrant) with the SEC relating to the issuance of securities secured by retail finance receivables. Additional information regarding TMCC’s securitization experience will be described under “The Sponsor, Administrator and Servicer” in the related Prospectus Supplement.
TMCC indirectly originates all Receivables in each asset pool to be securitized in the ordinary course of its business. For additional information regarding the selection criteria used in selecting the asset pool to be securitized, you should refer to “The Receivables Pools” in this prospectus. TMCC engages one of the selected underwriters of the related securities to assist in structuring the transaction based on the forecasted cash flows of the pool and to determine class sizes and average lives based on current market conditions.
THE DEPOSITOR
Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC (“TAFR LLC” or the “Depositor”) was formed in the State of Delaware on December 22, 2000, as a wholly owned, limited purpose subsidiary of TMCC. The principal executive offices of the Depositor are located at 19851 S. Western Avenue EF 12, Torrance, California, 90501, Attn: President, and its telephone number is (310) 468-7333.
The Depositor was organized primarily for the purpose of acquiring installment sales contracts similar to the Receivables and associated rights from TMCC, selling the Receivables and installment sales contracts similar to the Receivables to an Issuing Entity, causing the issuance of securities similar to the notes and certificates and engaging in related transactions. Initially, the Depositor will also own the Certificate issued by the Issuing Entity. TAFR LLC’s limited liability company agreement limits the Depositor’s activities to the purposes indicated above and to any activities incidental to and necessary for such purposes (including repurchase obligations for breaches of representations and warranties regarding Receivables). Other than the obligation to obtain the consent of the holder of record of the Certificates (the “Certificateholder”) with respect to amendments to the related trust agreement or other consent rights given to the holder of the residual interest in the related Issuing Entity, the Depositor will have no ongoing duties with respect to each Issuing Entity.
The limited liability company agreement of the Depositor includes requirements for independent directors, extensive corporate separateness covenants and restrictions on its permitted corporate functions (including on its ability to borrow money or incur debts), all of which are designed to prevent the consolidation of the assets of the Depositor with those of any of TMCC, any of its affiliates or of the related Issuing Entities in the event of a bankruptcy or insolvency proceeding of TMCC, such other affiliated entity or the related Issuing Entities.
THE ISSUING ENTITY
The Depositor will establish each issuing entity (each, an “Issuing Entity”) pursuant to a Trust Agreement (as amended and supplemented from time to time, the “Trust Agreement”).
The terms of each series of notes (the “Notes”) or certificates (the “Certificates” and, together with the Notes, the “Securities”) issued by each Issuing Entity, and additional information concerning the assets of each Issuing Entity and any applicable credit enhancement will be described in a supplement to this prospectus (a “Prospectus Supplement”).
The Issuing Entity for each series will not engage in any activity other than:
| | (i) | issuing the Notes and the Certificates; |
| | (ii) | entering into and performing its obligations under any currency exchange rate or interest rate swap agreement between the Issuing Entity and a counterparty; |
| | (iii) | acquiring the Receivables and the other assets of the Issuing Entity from the Depositor in exchange for the Notes and the Certificates; |
| | (iv) | assigning, granting, transferring, pledging, mortgaging and conveying the Issuing Entity’s property pursuant to the related Indenture; |
| | (v) | managing and distributing to the holders of the Certificates any portion of the Issuing Entity’s property released from the lien of the related Indenture; |
| | (vi) | entering into and performing its obligations under the financing documents; |
| | (vii) | engaging in other activities that are necessary, suitable or convenient to accomplish the activities listed in clauses (i) through (vi) above or are incidental to or connected with those activities; |
| | (viii) | engaging in any other activities as may be required, to the extent permitted under the related financing documents, to conserve the Issuing Entity’s property and the making of distributions to the holders of the Notes and Certificates; and |
| | (ix) | engaging in ancillary or related activities as specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. |
Each Issuing Entity will be structured as a bankruptcy remote, special purpose entity. Each Sale and Servicing Agreement, Trust Agreement, Indenture, Receivables Purchase Agreement and Administration Agreement (collectively, the “Transfer and Servicing Agreements”) will contain a non-petition clause, whereunder all applicable parties covenant not to institute any bankruptcy or insolvency proceedings (or take any related actions) against either the applicable Issuing Entity or the Depositor at any time in connection with any obligations relating to the related Notes or any of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements.
For additional information regarding permissible activities of or restrictions on each Issuing Entity, you should refer to “Description of the Notes—The Indenture—Certain Covenants” in this prospectus.
THE ISSUING ENTITY PROPERTY
The property of each Issuing Entity will include a pool (a “Receivables Pool”) of retail installment sales contracts (the “Receivables”) between Dealers and the obligors (the “Obligors”) of new and used automobiles and light duty trucks (the “Financed Vehicles”) and all payments due on such Receivables on and after the applicable cutoff date (the “Cutoff Date”), as specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. The Dealers will originate, and TMCC will purchase, the Receivables of each Receivables Pool in the ordinary course of business pursuant to Dealer Agreements. On the applicable Closing Date, TMCC will transfer the Receivables to the Depositor and the Depositor will sell the Receivables comprising the related initial Receivables Pool to the Issuing Entity pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement among the Depositor, the Servicer and the Issuing Entity (as amended and supplemented from time to time, the “Sale and Servicing Agreement”); provided that if so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, subsequent sales of additional Receivables by the Depositor may occur during a Revolving Period or Prefunding Period.
The property of each Issuing Entity will also include (i) such amounts as from time to time may be held in separate accounts established and maintained by the Servicer or Depositor with the indenture trustee pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement; (ii) security interests in the vehicles financed by the Receivables (the “Financed Vehicles”) and any accessions thereto; (iii) the rights to proceeds from claims on certain physical damage, credit life and disability insurance policies covering the Financed Vehicles or the Obligors, as the case may be; (iv) the right of the Depositor to receive any proceeds from Dealer Recourse, if any, on Receivables or Financed Vehicles; (v) the rights of the Depositor under the Sale and Servicing Agreement; (vi) the right to realize upon any property (including the right to receive future Liquidation Proceeds) that will have secured a Receivable and that will have been repossessed by or on behalf of the applicable Issuing Entity; and (vii) any and all proceeds of clauses (i) through (vi) above. Various forms of credit enhancement may be used to provide credit enhancement for the benefit of holders of the related Securities, including a Yield Maintenance Account or a Reserve Account. The property of the Issuing Entity is referred to herein as the “Trust Estate.”
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Issuing Entity property may also include the rights of the Issuing Entity and powers of the applicable trustee under the Swap Agreement, and the amounts payable to the Issuing Entity under the Swap Agreement, and the rights of the Issuing Entity and the powers of the related trustee under the Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement, and the amounts so funded by the holder of the Revolving Liquidity Note under such Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement.
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, TMCC Demand Notes will be issued by TMCC and purchased by the related Issuing Entity. The TMCC Demand Notes will be unsecured general obligations of TMCC and will rank equally with all other outstanding unsecured and unsubordinated debt of TMCC. For additional information regarding the TMCC Demand Notes, you should refer to “TMCC Demand Notes” in this prospectus and, if applicable, in the related Prospectus Supplement.
THE OWNER TRUSTEE AND THE INDENTURE TRUSTEE
An owner trustee for each Issuing Entity and an indenture trustee under any Indenture pursuant to which Notes are issued will be specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. An owner trustee’s or indenture trustee’s liability in connection with the issuance and, if applicable, the sale of the related Securities is limited solely to the express obligations of such owner trustee or indenture trustee described in the related Trust Agreement, and/or Sale and Servicing Agreement or Indenture, as applicable. An owner trustee or indenture trustee may resign at any time by so notifying the Issuing Entity, in which event the Servicer, or its successor, will be obligated to appoint a successor thereto. Any rating agency engaged by TMCC to rate the Notes of a series (each, a “Rating Agency”) will also be notified of such resignation. The administrator of an Issuing Entity may also remove an owner trustee or indenture trustee that ceases to be eligible to continue in such capacity under the related Trust Agreement or the Indenture or becomes insolvent or legally unable to act. In such circumstances, the Servicer or the administrator, as the case may be, will be obligated to appoint a successor thereto. Any resignation or removal of an owner trustee and appointment of a successor owner trustee will not become effective until acceptance of the appointment by the successor owner trustee pursuant to the Trust Agreement. No resignation or removal of the indenture trustee and no appointment of a successor indenture trustee will become effective until the acceptance of appointment by the successor indenture trustee pursuant to the Indenture.
The Issuing Entity will cause the administrator to indemnify the indenture trustee against any and all loss, liability or expense (including attorneys’ fees and expenses) incurred by it in connection with the administration of the applicable Issuing Entity and the performance of its duties under the Indenture, the Sale and Servicing Agreement or any other Transfer and Servicing Agreement. The indenture trustee will notify the Issuing Entity and the administrator promptly of any claim for which it may seek indemnity; provided, that, failure by the indenture trustee to provide such notification will not relieve the Issuing Entity or the administrator of its obligations under the Indenture if no prejudice to the Issuing Entity or the administrator will have resulted from such failure. Neither the Issuing Entity nor the administrator need reimburse any expense or indemnify against any loss, liability or expense incurred by the indenture trustee through the indenture trustee’s own willful misconduct, negligence or bad faith.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION ABOUT YOUR NOTES
The Issuing Entity—The indenture trustee will provide to Noteholders (which will be Cede & Co. as the nominee of DTC unless Definitive Notes are issued under the limited circumstances described in this prospectus) unaudited monthly and annual reports concerning the Receivables and certain other matters. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Reports to Securityholders” and “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Evidence as to Compliance” in this prospectus. If and for so long as any Notes are listed on an exchange and the rules of such exchange so require, each such report (including a statement of the outstanding principal amount of each class of Notes) also will be delivered to such exchange on the related Payment Date or other date for delivery of such reports. Copies of such reports may be obtained at no charge at the offices specified in the related Prospectus Supplement.
The Depositor—Toyota Auto Finance Receivables LLC, as Depositor, has filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) a registration statement on Form S-3 (the “Registration Statement”) under the Securities Act of 1933 (the “Securities Act”) of which this prospectus forms a part. The Registration Statement is available for inspection without charge at the public reference facilities maintained at the principal office of the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You may obtain information on the operation of the SEC’s reference room by calling the SEC at (800) SEC-0330. You may obtain copies of such materials at prescribed rates by writing to the Public Reference Section of the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. The SEC also maintains a website (http://www.sec.gov) that contains reports, registration statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC using the SEC’s Electronic Data Gathering Analysis and Retrieval system (commonly known as EDGAR). All reports filed by the Depositor may be found on EDGAR, or any successor electronic filing website, filed under the name of the Depositor and under the SEC Central Index Key (CIK) 0001131131, and all reports filed with respect to each Issuing Entity will be filed under registration file number 333-188672 plus the applicable serial tag number. Copies of the transaction agreements relating to the Notes will also be filed with the SEC on EDGAR under the registration number shown above.
For the time period that each Issuing Entity is required to report under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), the Depositor, on behalf of the Issuing Entity of the related series, will file the reports required under Section 13(a), 13(c), 14 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act. These reports include (but are not limited to):
| | · | Reports on Form 8-K (Current Report) including as Exhibits to the Form 8-K the transaction agreements or other documents specified in the related Prospectus Supplement; |
| | · | Reports on Form 8-K (Current Report), following the occurrence of events specified in Form 8-K requiring disclosure, which are required to be filed within the time-frame specified in Form 8-K related to the type of event; |
| | · | Reports on Form 10-D (Asset-Backed Issuer Distribution Report), containing the distribution and pool performance information required on Form 10-D, which are required to be filed 15 days following the payment date specified in the related Prospectus Supplement; and |
| | · | Report on Form 10-K (Annual Report), containing the items specified in Form 10-K with respect to a fiscal year, and the items required pursuant to Items 1122 and 1123 of Regulation AB of the Exchange Act. |
Unless specifically stated in the report, the report and any information included in the report will neither be examined nor reported on by an independent public accountant. Each Issuing Entity formed by the Depositor will have a separate file number assigned by the SEC, which unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, is not available until filing of the final Prospectus Supplement related to the series. Unless a technical problem occurs with the EDGAR system, reports filed with the SEC with respect to an Issuing Entity after the final Prospectus Supplement is filed will be available under the Issuing Entity’s specific number, which will be a series number assigned to the file number of the Depositor shown above.
The distribution and pool performance reports filed on Form 10-D will be forwarded to each Securityholder as specified under “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Reports to Securityholders” in this prospectus. The Depositor will post reports on its website located at “www.toyotafinancial.com” as soon as reasonably practicable after such reports are filed with the SEC.
Static Pool Data—Static pool data with respect to the delinquency, cumulative loss and prepayment data for each Issuing Entity (i) by vintage origination year for TMCC and/or (ii) by prior securitized pools of TMCC, as applicable, will be presented in an appendix to the related Prospectus Supplement.
If and for so long as Notes are listed on an exchange and the rules of such exchange so require, the related Prospectus Supplement will include the address of an office in the jurisdictions specified by the rules of such exchange at which copies of the Registration Statement filed by TAFR LLC (including all documents incorporated in the Registration Statement) can be obtained for so long as those Notes are outstanding. If so required by the rules of such exchange, copies of those documents will also be filed with such exchange for so long as those Notes are outstanding. Copies of the transaction agreements relating to the Notes will also be filed with the SEC and with any such exchange that so requires.
THE RECEIVABLES POOLS
The Receivables Pool for each Issuing Entity will include the Receivables purchased as of the applicable Cutoff Date. The Receivables will have been originated by Dealers in accordance with TMCC’s requirements and subsequently purchased by TMCC. The Receivables evidence the indirect financing made available by TMCC to the related Obligors in connection with the purchase by such Obligors of the Financed Vehicles. On or before the date of initial issuance of the Notes (the “Closing Date”), TMCC will sell the Receivables comprising the related initial Receivables Pool to the Depositor pursuant to the receivables purchase agreement (the “Receivables Purchase Agreement”) between the Depositor and TMCC, provided that if so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Issuing Entity may subsequently purchase additional Receivables from the Depositor during a specified
Revolving Period or Prefunding Period. The Depositor will, in turn, sell the Receivables to the Issuing Entity pursuant to the related Transfer and Servicing Agreement. During the term of the related Transfer and Servicing Agreement, neither the Depositor nor TMCC may substitute any other retail installment sales contract for any Receivable sold to the Issuing Entity.
The Receivables in each Receivables Pool will have been purchased by TMCC from Dealers in the ordinary course of business. The Receivables are purchased from Dealers pursuant to Dealer Agreements. TMCC purchases Receivables originated in accordance with its credit standards which are based upon the vehicle buyer’s ability and willingness to repay the obligation as well as the value of the vehicle being financed, as described under “The Sponsor, Administrator, Servicer and Issuer of the TMCC Demand Notes—Underwriting of Motor Vehicle Retail Installment Sales Contracts” in this prospectus.
The Receivables to be held by each Issuing Entity for inclusion in a Receivables Pool will be selected from TMCC’s portfolio of automobile and/or light duty truck retail installment sales contracts that meet several criteria. These criteria require that each Receivable (i) is secured by a new or used vehicle, (ii) was originated in the United States, (iii) provides for monthly payments that fully amortize the amount financed over its original term to maturity (except for minimally different payments in the first or last month in the life of the Receivable and except pursuant to the Servicer’s Customary Servicing Practices, including permitted modifications that re-amortize the term of the Receivable), and (iv) satisfies the other criteria, if any, described in the related Prospectus Supplement, which may include original term to maturity, percentage by principal balance of the Receivables of types of vehicles, geographic location, percentage by principal balance of the Receivables of new vehicles and used vehicles, credit grade, remaining term to maturity, delinquency status, date of origination and contractual annual percentage rate. No selection procedures believed by the Depositor to be adverse to the Noteholders of any series will be used in selecting the related Receivables.
Each Receivable will provide for the allocation of payments according to (i) the simple interest method (“Simple Interest Receivables”) or (ii) the “actuarial” method (“Actuarial Receivables”).
Simple Interest Receivables. Payments on Simple Interest Receivables will be applied first to interest accrued through the date immediately preceding the date of payment and then to unpaid principal. Accordingly, if an Obligor pays an installment before its due date, the portion of the payment allocable to interest for the payment period will be less than if the payment had been made on the due date, the portion of the payment applied to reduce the principal balance will be correspondingly greater, and the principal balance will be amortized more rapidly than scheduled. Conversely, if an Obligor pays an installment after its due date, the portion of the payment allocable to interest for the payment period will be greater than if the payment had been made on the due date, the portion of the payment applied to reduce the principal balance will be correspondingly less, and the principal balance will be amortized more slowly than scheduled, in which case a larger portion of the principal balance may be due on the final scheduled payment date for the related Receivable. No adjustment to the scheduled monthly payments is made in the event of early or late payments, although in the case of late payments the Obligor may be subject to a late charge.
Actuarial Receivables. An Actuarial Receivable provides for amortization of the loan over a series of fixed level monthly installments. Each Scheduled Payment is deemed to consist of an amount of interest equal to 1/12 of the stated annual percentage rate (“APR”) of the Receivable multiplied by the scheduled principal balance of the Receivable and an amount of principal equal to the remainder of the Scheduled Payment. No adjustment to the scheduled monthly payments is made in the event of early or late payments, although in the case of late payments the Obligor may be subject to a late charge.
Additional information with respect to each Receivables Pool will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement, including, to the extent appropriate, the composition, the distribution by APR and by the states of origination, the portion of such Receivables Pool consisting of Actuarial and of Simple Interest Receivables and the portion of such Receivables Pool secured by new vehicles and by used vehicles. If a substantial portion of the Receivables in a Receivable Pool consist of Receivables evidenced by electronic contracts, the portion of the Receivables Pool evidenced by electronic contracts will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement. The related Prospectus Supplement will also include static pool information regarding pools of assets related to certain previously issued series of Notes.
Prefunding. An Issuing Entity may enter into an agreement with the Depositor, in which the Depositor will sell additional Receivables to the Issuing Entity after the Closing Date. The transfer of Receivables to the Issuing Entity after the Closing Date is known as a prefunding feature. Any subsequent Receivables will be required to conform to the requirements described in the related Prospectus Supplement. If a prefunding feature is used, the indenture trustee will be required to deposit all or a portion of the proceeds of the sale of the Notes of the series in a segregated account. The subsequent Receivables will be transferred to the Issuing Entity in exchange for money released from that segregated account. Any transfer of Receivables must occur within a specified period. If all of the monies originally deposited in the segregated account are not used by the end of the specified period, all remaining monies will be applied as a mandatory prepayment of a designated class or classes of Notes.
DELINQUENCIES, REPOSSESSIONS AND NET LOSSES
Certain information concerning TMCC’s experience pertaining to delinquencies, repossessions and net losses with respect to its portfolio of new and used retail automobile and/or light duty truck receivables (including receivables previously sold that TMCC continues to service) will be described in each Prospectus Supplement. There can be no assurance that the delinquency, repossession and net loss experience on any Receivables Pool will be comparable to prior experience or to such information.
WEIGHTED AVERAGE LIVES OF THE NOTES
Information regarding maturity and prepayment considerations with respect to each series of Notes will be described under “Weighted Average Lives of the Notes” in the related Prospectus Supplement and “Risk Factors — You may experience reduced returns on your investments resulting from prepayments on the receivables, events of default, optional redemption, repurchases of receivables or early termination of the issuing entity” in this prospectus. The weighted average lives of the Notes of any series will generally be influenced by the rate at which the principal balances of the related Receivables are paid, which payment may be in the form of scheduled amortization or prepayments. For this purpose, the term “prepayments” includes prepayments in full, partial prepayments (including those related to rebates of extended warranty contract costs and insurance premiums), liquidations due to default, as well as receipts of proceeds from physical damage, theft, credit life and credit disability insurance policies and repurchases or purchases by the Depositor or TMCC of certain Receivables for administrative reasons or for breaches of representations and warranties. The term “weighted average life” corresponds to the average amount of time during which each dollar of principal of a Receivable is outstanding.
All of the Receivables will be prepayable at any time without penalty to the Obligor. However, a partial prepayment received on an Actuarial Receivable made by an Obligor will not be applied to reduce the outstanding principal balance of that Receivable on the Payment Date following the Collection Period in which they were received but will be retained and applied towards payments due in later Collection Periods. If prepayments in full are received on an Actuarial Receivable or if full or partial prepayments are received on the Simple Interest Receivables, the actual weighted average life of the Receivables may be shorter than the scheduled weighted average life of the Receivables described in the related Prospectus Supplement. The rate of prepayment of automotive receivables is influenced by a variety of economic, social and other factors, including the fact that an Obligor generally may not sell or transfer the Financed Vehicle securing a Receivable without the consent of the Servicer. A prepayment may also occur if an Obligor refinances a Receivable. Refinancings may occur more frequently in a declining interest rate environment.
Under certain circumstances, the Depositor or Servicer will be obligated to repurchase Receivables from a given Issuing Entity pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement as a result of breaches of certain representations and warranties or covenants. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Sale and Assignment of Receivables” and “—Servicing Procedures” in this prospectus. In addition, pursuant to agreements between TMCC and the Dealers, each Dealer is obligated to repurchase from TMCC contracts that do not meet certain representations and warranties made by such Dealer (such Dealer repurchase obligations are referred to in this prospectus as “Dealer Recourse”). Such representations and warranties relate primarily to the origination of the contracts and the perfection of the security interests in the related Financed Vehicles, and do not relate to the creditworthiness of the related Obligors or the collectibility of such contracts. Although the Dealer Agreements with respect to the Receivables will not be assigned to the Issuing Entity, TMCC’s interest in any Dealer Recourse will be assigned, and the related Sale and Servicing Agreement will
require that TMCC deposit any recovery in respect of any Receivable pursuant to any Dealer Recourse in the related Collection Account. The sales by the Dealers of installment sales contracts to TMCC do not generally provide for recourse against the Dealers for unpaid amounts in the event of a default by an Obligor under such retail installment sales contract, other than in connection with the breach of the foregoing representations and warranties. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Sale and Assignment of Receivables” and “—Servicing Procedures” in this prospectus.
The effective yield on, and average lives of, a series of Notes will depend on, among other things, the amount of payments (including prepayments) on or in respect of the related Receivables and the rate at which such payments are made to such Noteholders. The timing of changes in the rate of payments in respect of the Receivables also may affect significantly an investor’s actual yield to maturity and the average lives of a series of Notes. A substantial increase in the rate of payments on or in respect of the related Receivables (including liquidation or other disposition of Financed Vehicles) may shorten the final maturities of, and may significantly affect the yields on, the related series of Notes.
An investor’s expected yield will be affected by:
| | · | the price paid for the Notes of a series, |
| | · | the rate of prepayments of the related Receivables, and |
| | · | the investor’s assumed reinvestment rate. |
These factors do not operate independently, but are interrelated. For example, if prepayments on the related Receivables are slower than anticipated, an investor’s yield may be lower if interest rates are higher than anticipated and higher if interest rates are lower than anticipated. Conversely, if prepayments on the related Receivables are faster than anticipated, an investor’s yield may be higher if interest rates are higher than anticipated and lower if interest rates are lower than anticipated.
Early retirement of the Notes will occur if the Servicer, or any successor to the Servicer, exercises its option to purchase all of the Receivables remaining in the Issuing Entity when the Pool Balance is equal to or less than the percentage specified in the related Prospectus Supplement of the Pool Balance as of the Cutoff Date. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Termination” in this prospectus. Certain Events of Default could result in liquidation of the assets of the Issuing Entity and acceleration of the related Notes. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Notes—The Indenture—Events of Default; Rights upon Event of Default” in this prospectus. For additional information regarding events that would result in a termination of a swap, you should refer to “The Swap Agreement” in the related Prospectus Supplement. If the Issuing Entity is party to a Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement, events resulting in termination of the Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement may also result in liquidation of the assets of the Issuing Entity and acceleration of the related Notes.
Any reinvestment risk resulting from the rate of prepayments of the Receivables and the payment of such prepayments to Noteholders will be borne entirely by the Noteholders.
In light of the above considerations, there can be no assurance as to the amount of principal payments to be made on the Notes of a given series on each Payment Date, since the amount will depend, in part, on the amount of principal collected on the related Receivables Pool during the applicable Collection Period. No prediction can be made as to the actual prepayment experience on the Receivables, and any reinvestment risks resulting from a faster or slower incidence of prepayment of Receivables will be borne entirely by the Noteholders of a given series.
The related Prospectus Supplement may describe certain additional information with respect to the maturity and prepayment considerations applicable to the particular Receivables Pool and the related series of Notes.
POOL FACTORS AND TRADING INFORMATION
The “Note Pool Factor” is a seven digit decimal which the Servicer will compute prior to each payment with respect to each class of Notes. The Note Pool Factor represents the remaining outstanding principal amount of a class of Notes, as of the close of business on the applicable Payment Date, as a fraction of the initial outstanding principal amount of such class of Notes. Each Note Pool Factor will initially be 1.0000000 and thereafter will decline to reflect reductions in the outstanding principal amount of the applicable class of Notes. A Noteholder’s portion of the aggregate outstanding principal amount of the related class of Notes is the product of (i) the original denomination of such Noteholder’s Note and (ii) the applicable Note Pool Factor.
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement with respect to each Issuing Entity, the Noteholders will receive reports on or about each Payment Date concerning (i) with respect to the Collection Period immediately preceding such Payment Date, payments received on the Receivables, the Pool Balance, each Note Pool Factor and various other items of information, and (ii) with respect to the Collection Period second preceding such Payment Date, as applicable, amounts allocated or paid on the preceding Payment Date and any reconciliation of such amounts with information provided by the Servicer prior to such current Payment Date. In addition, Securityholders of record during any calendar year will be furnished information for tax reporting purposes not later than the latest date permitted by law. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Reports to Securityholders” in this prospectus.
USE OF PROCEEDS
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, each Issuing Entity will use the net proceeds from the sale of the Notes of a given series to purchase Receivables from the Depositor and to make the initial deposit into any related Reserve Account or Yield Maintenance Account, if applicable.
DESCRIPTION OF THE NOTES
General
With respect to each Issuing Entity that issues Notes, one or more classes (each, a “class”) of Notes of the related series will be issued pursuant to the terms of an indenture (the “Indenture”), a form of which has been filed as an exhibit to the Registration Statement of which this prospectus forms a part. The following summary does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and is qualified in its entirety by reference to, all the provisions of the Notes and the Indenture.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, each class of Notes will initially be represented by one or more Notes registered in the name of the nominee of DTC (together with any successor depository selected by the Issuing Entity, the “Depository”) except as described below. Notes will be available for purchase in the denominations specified in the related Prospectus Supplement in book entry form only (unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement). The Depositor has been informed by DTC that DTC’s nominee will be Cede & Co., unless another nominee is specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. Accordingly, such nominee is expected to be the holder of record of the Notes (a “Noteholder”) of each class. Unless and until Definitive Notes are issued under the limited circumstances described in this prospectus or in the related Prospectus Supplement, no Noteholder will be entitled to receive a physical certificate representing a Note. All references in this prospectus and in the related Prospectus Supplement to actions by Noteholders refer to actions taken by DTC upon instructions from its participating organizations (the “DTC Participants”) and all references in this prospectus and in the related Prospectus Supplement to payments, notices, reports and statements to Noteholders refer to payments, notices, reports and statements to DTC or its nominee, as the registered holder of the Notes, for distribution to Noteholders in accordance with DTC’s procedures with respect thereto. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Book Entry Registration” and “—Definitive Securities” in this prospectus.
Principal and Interest on the Notes
The related Prospectus Supplement will describe the timing and priority of payment, seniority, allocations of losses, interest rate (the “Interest Rate”) and amount of or method of determining payments of principal and interest (or, where applicable, of principal or interest only) on each class of Notes of a given series, including during any periods of payments of interest only or principal only. Payments of interest on and principal of any Notes will be made on the dates specified in the related Prospectus Supplement (each, a “Payment Date”) in such amounts as are described in the Prospectus Supplement. The right of holders of any class of Notes to receive payments of principal and interest may be senior or subordinate to the rights of holders of any other class or classes of Notes of such series. Payments of interest on the Notes will generally be made prior to payments of principal. With respect to holders of one or more classes of Notes so designated in the related Prospectus Supplement, during a Revolving Period, only payments of interest will be made on the Notes. A series may include one or more classes of Notes (the “Strip Notes”) entitled to (i) principal payments with disproportionate, nominal or no interest payments or (ii) interest payments with disproportionate, nominal or no principal payments. Each class of Notes may have a different Interest Rate, which may be a fixed, variable or adjustable Interest Rate (and which may be zero for certain classes of Strip Notes), or any combination of the foregoing. The related Prospectus Supplement will specify the Interest Rate for each class of Notes of a given series or the method for determining such Interest Rate. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Fixed Rate Notes” and “—Floating Rate Notes” in this prospectus. One or more classes of Notes of a series may be redeemable in whole or in part, including as a result of the Servicer exercising its option to purchase the related Receivables Pool or other early termination of the related Issuing Entity. Noteholders will not be able to cause the Issuing Entity to redeem their Notes.
One or more classes of Notes of a given series may have fixed principal payment schedules, in the manner and to the extent described in the related Prospectus Supplement. Noteholders of such Notes would be entitled to receive as payments of principal on any given Payment Date the amounts described on such fixed principal payment schedule.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, payments to Noteholders of all classes within a series in respect of interest will have the same priority. Under certain circumstances, however, on any Payment Date the amount available for such payments could be less than the amount of interest payable on the Notes. If this is the case, each class of Noteholders will receive its ratable share (based upon the aggregate amount of interest due to such class of Noteholders) of the aggregate amount of interest available for payment on the Notes. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Payments” and “—Credit and Cash Flow Enhancement” in this prospectus.
If a series of Notes includes two or more classes of Notes, the sequential order and priority of payment in respect of principal and interest, and any schedule or formula or other provisions applicable to the determination of such schedule or formula, of each such class will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement. Payments in respect of principal and interest of any class of Notes will be made on a pro rata basis among all the Noteholders of such class.
The Indenture
Modification of Indenture. If an Issuing Entity has issued Notes pursuant to an Indenture, the Issuing Entity and the applicable indenture trustee may, with the consent of the holders of a majority of the holders of the most senior class or classes of Notes of a series (as long as any Notes of such class or classes are outstanding), and thereafter, in the order of seniority, each other then most senior class or classes of Notes of a series, if any, described in the related Prospectus Supplement, as long as they are outstanding (such Notes, the “Controlling Class”), execute a supplemental indenture to add provisions to, change in any manner or eliminate any provisions of, the related Indenture, or modify (except as provided below) in any manner the rights of the related Noteholders. Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, for purposes of determining whether the Noteholders of the requisite percentage of the outstanding amount of the Controlling Class of Notes or any class of Notes have given any request, demand, authorization, direction, notice, consent, or waiver under the Indenture or the related Transfer and Servicing Agreements, Notes held or owned by the Issuing Entity, any other obligor upon the Notes, TAFR LLC, TMCC or any affiliate will be disregarded and deemed not to be “outstanding.”
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Issuing Entity and the applicable indenture trustee may also enter into supplemental indentures with prior notice to the Rating Agencies, and without obtaining the consent of the Noteholders or Certificateholders of the related series, for the purpose of adding any provisions to or changing in any manner or eliminating any of the provisions of the related Indenture or of modifying in any manner the rights of such Noteholders; provided, that either (i) an officer’s certificate has been delivered by the Servicer to the related owner trustee and the related indenture trustee certifying that such officer reasonably believes that such supplemental indenture will not materially and adversely affect the interest of any such Noteholder or (ii) the related indenture trustee has been provided a letter from each applicable Rating Agency to the effect that such action will not result in the reduction or withdrawal of any rating it currently assigns to any class of Notes of the related series, or each other Rating Agency has been provided with 10 days prior notice of the proposed supplemental indenture and each such other Rating Agency has not notified the Indenture Trustee that such action might or would result in the reduction or withdrawal of the rating it has currently assigned to any class of Notes of the related series.
Additionally, unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Issuing Entity and the applicable indenture trustee may also enter into supplemental indentures, without obtaining the consent of the Noteholders or Certificateholders of the related series, but with prior notice to the Rating Agencies, for the purpose of, among other things, correcting or amplifying the description of the collateral, evidencing the assumption of the Issuing Entity’s obligations under the Indenture, the Notes and the Certificates, as applicable, by a permitted successor to the Issuing Entity, adding additional covenants of the Issuing Entity for the benefit of the related Noteholders and/or Swap Counterparty, surrendering rights of the Issuing Entity, conveying, or otherwise transferring or pledging, property to or with the related indenture trustee, evidencing and providing for the appointment of a successor indenture trustee or adding or changing any of the provisions of the Indenture as necessary and permitted to facilitate the administration by more than one indenture trustee, and modifying, eliminating or adding to the provisions of the Indenture in order to comply with the Trust Indenture Act of 1939, as amended.
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement and subject to the terms described in the following paragraph, the Issuing Entity and the applicable indenture trustee, also may, with prior notice to the Rating Agencies, enter into an indenture or indentures supplemental to the related indenture for the purpose of adding any provisions to or changing in any manner or eliminating any of the provisions of such indenture or of modifying in any manner the rights of the Noteholders under such indenture; provided, that Noteholders evidencing at least a majority of the outstanding principal amount of the Controlling Class, acting as a single class have consented to such amendment.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement with respect to a series of Notes, without the consent of the holder of each such outstanding Note affected thereby, no supplemental indenture will: (i) change the due date of any installment of principal of or interest on any such Note or reduce the principal amount of any such Note, the interest rate specified thereon or the redemption price with respect thereto or change any place of payment where or the coin or currency in which any such Note or any interest thereon is payable; (ii) impair the right to institute suit for the enforcement of certain provisions of the related Indenture regarding payment; (iii) reduce the percentage of the aggregate amount of the outstanding Notes of such series, the consent of the holders of which is required for any such supplemental indenture or the consent of the holders of which is required for any waiver of compliance with certain provisions of the related Indenture or of certain defaults under the related Indenture and their consequences as provided for in such Indenture; (iv) modify or alter the provisions of the related Indenture regarding the voting of Notes held by the applicable Issuing Entity, any other obligor on such Notes, the Depositor or an affiliate of any of them; (v) reduce the percentage of the aggregate outstanding amount of such Notes, the consent of the holders of which is required to direct the related indenture trustee to sell or liquidate the Trust Estate if the proceeds of such sale would be insufficient to pay the principal amount and accrued but unpaid interest on the outstanding Notes of such series; (vi) decrease the percentage of the aggregate principal amount of such Notes required to amend the sections of the related Indenture which specify the applicable percentage of aggregate principal amount of the Notes of such series necessary to amend such Indenture or certain other related agreements; or (vii) permit the creation of any lien ranking prior to or on a parity with the lien of the related Indenture with respect to any of the collateral for such Notes or, except as otherwise permitted or contemplated in such Indenture, terminate the lien of such Indenture on any such collateral or deprive the holder of any such Note of the security afforded by the lien of such Indenture.
Events of Default; Rights Upon Event of Default. With respect to the Notes of a given series, unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, “Events of Default” under the related Indenture will consist of: (i) a default for five business days or more in the payment of any interest on any such Note of the Controlling Class; (ii) a default in the payment of the principal of any such Note on the related final scheduled Payment Date; (iii) a default in the observance or performance of any covenant or agreement of the applicable Issuing Entity made in the related Indenture which materially and adversely affects interests of the Noteholders and the continuation of any such default for a period of 90 days after written notice of such default is given to such Issuing Entity by the applicable indenture trustee or to such Issuing Entity and such indenture trustee by the holders of at least a majority of the principal amount of such Notes of the Controlling Class then outstanding acting together as a single class; (iv) any representation or warranty made by such Issuing Entity in the related Indenture or in any certificate delivered pursuant thereto or in connection therewith having been incorrect in a material respect as of the time made which materially and adversely affects the interests of the Noteholders, and such breach not having been cured within 60 days after written notice of such breach is given to such Issuing Entity by the applicable indenture trustee or to such Issuing Entity and such indenture trustee by the holders at least a majority of the principal amount of such Notes of the Controlling Class then outstanding acting together as a single class; or (v) certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency, receivership or liquidation of the applicable Issuing Entity (which, if involuntary, remains unstayed for more than 90 days).
Notwithstanding the foregoing, the amount of principal required to be paid to Noteholders of such series under the related Indenture will generally be limited to amounts available to be deposited in the Collection Account. Therefore, unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the failure to pay principal on a class of Notes generally will not result in the occurrence of an Event of Default until the final scheduled Payment Date for such class of Notes. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if a delay in or failure of performance referred to under clauses (i) through (iv) above was caused by force majeure or other similar occurrence, the grace period described in the applicable clause will be extended for a period of 30 calendar days. In addition, as described below, following the occurrence of an Event of Default (other than an Event of Default related to the failure to make required payments) and acceleration of the maturity of the Notes, the indenture trustee is not required to sell the assets of the Issuing Entity (as described above under “The Issuing Entity Property” in this prospectus), and the indenture trustee may sell the assets of the related Issuing Entity only after meeting requirements specified in the Indenture. Under those circumstances, even if the maturity of the Notes has been accelerated, there may not be any funds to pay the principal owed on the Notes.
If an Event of Default should occur and be continuing with respect to the Notes of any series, the related indenture trustee or holders of a majority in principal amount of such Notes of the Controlling Class then outstanding acting together as a single class may declare the principal of such Notes to be immediately due and payable. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, such declaration may be rescinded by the holders of a majority in principal amount of such Notes of the Controlling Class then outstanding acting together as a single class if:
(i) the Issuing Entity has paid or deposited with the indenture trustee a sum sufficient to pay:
| | (A) | all payments of principal of and interest on the Notes and all other amounts that would then be due on such Notes if the Event of Default giving rise to such acceleration had not occurred; and |
| | (B) | all sums paid by the indenture trustee under the related Indenture or the owner trustee under the related Trust Agreement and the reasonable compensation, expenses, disbursements and advances of the indenture trustee and the owner trustee and their respective agents and counsel; and |
| | (ii) | all Events of Default, other than the nonpayment of the principal or interest of the Notes that has become due solely by such acceleration, have been cured or waived. |
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, an Event of Default during a Revolving Period may cause the early termination of such Revolving Period and the commencement of payments of principal on the Notes.
If the Notes of any series are due and payable following an Event of Default with respect thereto, the related indenture trustee may institute proceedings to collect amounts due, exercise remedies as a secured party, including foreclosure or sale of the related Trust Estate or elect to have the applicable Issuing Entity maintain possession of such Trust Estate and continue to apply proceeds from the Trust Estate as if there had been no declaration of acceleration. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, however, such indenture trustee is prohibited from selling the related Trust Estate following an Event of Default, other than a default in the payment of any principal on the final scheduled Payment Date of such Note or a default for five days or more in the payment of any interest on any Note of the Controlling Class of such series, unless (i) the holders of all such outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class consent to such sale, (ii) the proceeds of such sale are sufficient to pay in full the principal of and the accrued interest on such outstanding Notes at the date of such sale or (iii) such indenture trustee determines that the proceeds of the Trust Estate would not be sufficient on an ongoing basis to make all payments on such Notes as such payments would have become due if such obligations had not been declared due and payable, and such indenture trustee obtains the consent of the holders of 66 2/3% of the aggregate outstanding principal amount of such Notes of the Controlling Class. Unless otherwise specified in the Prospectus Supplement, in the event of the sale of the Trust Estate by the indenture trustee following an Event of Default, the Noteholders will receive notice and opportunity to submit a bid in respect of such sale.
If an Event of Default occurs and is continuing and the indenture trustee has actual knowledge of such Event of Default, the indenture trustee will be obligated to mail to each Noteholder notice of the Event of Default within 90 days of the discovery of such Event of Default. Except in the case of an Event of Default in payment of principal on the final scheduled Payment Date of such Note or interest on any Note of the Controlling Class of such series (including payments pursuant to the mandatory redemption provisions of such Note), the indenture trustee may withhold the notice to Noteholders if and so long as a committee of its officers in good faith determines that withholding the notice is in the best interests of Noteholders.
Subject to the provisions of the applicable Indenture relating to the duties of the related indenture trustee, if an Event of Default occurs and is continuing with respect to a series of Notes, the related indenture trustee will be under no obligation to exercise any of the rights or powers under the Indenture at the request or direction of any of the holders of such Notes, if the related indenture trustee reasonably believes it will not be adequately indemnified against the costs, expenses and liabilities which might be incurred by it in complying with such request. Subject to the provisions for indemnification and certain limitations contained in the related Indenture, the holders of not less than a majority of the principal amount of the outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class of a given series will have the right to direct the time, method and place of conducting any proceeding or any remedy available to the applicable indenture trustee, and the holders of a majority in principal amount of such Notes of the Controlling Class then outstanding may, in certain cases, waive any default under the related Indenture, except a default in the deposit of collections or other required amounts, any required payment from amounts held in any Trust Account in respect of amounts due on the Notes, payment of principal or interest or a default in respect of a covenant or provision of such Indenture that cannot be modified without the waiver or consent of all the holders of such outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class.
Any Notes owned by the Depositor, the Servicer or any of their affiliates will be entitled to equal and proportionate benefits under the Indenture, except that such Notes, while owned by the Depositor, the Servicer or any of their affiliates, will not be considered to be outstanding for the purpose of determining whether the requisite percentage of Noteholders have given any request, demand, authorization, direction, notice, consent or other action under the Indenture.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, no holder of a Note of any series will have the right to institute any proceeding with respect to the related Indenture, unless (i) such holder previously has given to the applicable indenture trustee written notice of a continuing Event of Default, (ii) the holders of not less than 25% in principal amount of the outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class of such series have made written request to such indenture trustee to institute such proceeding in its own name as indenture trustee, (iii) such holder or holders have offered such indenture trustee reasonable indemnity, (iv) such indenture trustee has for 30 days failed to institute such proceeding and (v) no direction inconsistent with such written request has been given to such indenture trustee during such 30 day period by the holders of a majority in principal amount of such outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class.
In addition, each indenture trustee and the related Noteholders by accepting the related Notes, covenants that they will not at any time institute against the applicable Issuing Entity or the Depositor any bankruptcy, reorganization or other proceeding under any federal or state bankruptcy or similar law.
With respect to any Issuing Entity, neither the related indenture trustee nor the related owner trustee in its individual capacity, nor any holder of a Certificate representing an ownership interest in such Issuing Entity nor any of their respective owners, beneficiaries, agents, officers, directors, employees, affiliates, successors or assigns will, in the absence of an express agreement to the contrary, be personally liable for the payment of the principal of or interest on the related Notes or for the agreements of such Issuing Entity contained in the applicable Indenture.
Certain Covenants. Each Indenture will provide that the related Issuing Entity may not consolidate with or merge into any other entity, unless, among other things, (i) the entity formed by or surviving such consolidation or merger is organized under the laws of the United States, any state or the District of Columbia, (ii) such entity expressly assumes such Issuing Entity’s obligation to make due and punctual payments upon the Notes of the related series and the performance or observance of every agreement and covenant of such Issuing Entity under the Indenture, (iii) no Event of Default has occurred and be continuing immediately after such merger or consolidation, (iv) such Issuing Entity has been advised that the rating of the Notes of such series then in effect would not be reduced or withdrawn by the Rating Agencies as a result of such merger or consolidation and (v) such Issuing Entity has received an opinion of counsel to the effect that such consolidation or merger would have no material adverse tax consequence to the Issuing Entity or to any related Noteholder or Certificateholder.
Each Issuing Entity will not, among other things, (i) except as expressly permitted by the applicable Indenture, the applicable Transfer and Servicing Agreements or certain related documents with respect to such Issuing Entity (collectively, the “Related Documents”), sell, transfer, exchange or otherwise dispose of any of the assets of such Issuing Entity, (ii) claim any credit on or make any deduction from the principal and interest payable in respect of the Notes of the related series (other than amounts withheld under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (referred to in this prospectus as the “Code”) or applicable state law) or assert any claim against any present or former holder of such Notes because of the payment of taxes levied or assessed upon such Issuing Entity, (iii) except as expressly permitted by the Related Documents, dissolve or liquidate in whole or in part, (iv) permit the validity or effectiveness of the related Indenture to be impaired or permit any person to be released from any covenants or obligations with respect to such Notes under such Indenture except as may be expressly permitted thereby or (v) permit any lien, charge, excise, claim, security interest, mortgage or other encumbrance to be created on or extend to or otherwise arise upon or burden the assets of such Issuing Entity or any part thereof, or any interest in the assets of the Issuing Entity or the proceeds thereof.
No Issuing Entity may engage in any activity other than as specified in this prospectus or in the related Prospectus Supplement. No Issuing Entity will incur, assume or guarantee any indebtedness other than indebtedness incurred pursuant to the related Notes and the related Indenture, pursuant to any Advances made to it by the Servicer or otherwise in accordance with the Related Documents.
Annual Compliance Statement. Each Issuing Entity will be required to file annually with the related indenture trustee a written statement as to the fulfillment of its obligations under the Indenture.
Indenture Trustee’s Annual Report. The indenture trustee for each Issuing Entity will be required to distribute each year to all related Noteholders a brief report relating to its eligibility and qualification to continue as indenture trustee under the related Indenture, any amounts advanced by it under the Indenture, the amount, interest rate and maturity date of certain indebtedness owing by such Issuing Entity to the applicable indenture trustee in its individual capacity, the property and funds physically held by such indenture trustee as such and any action taken by it that materially affects the related Notes and that has not been previously reported.
Satisfaction and Discharge of Indenture. An Indenture will be discharged with respect to the collateral securing the related Notes upon the delivery to the related indenture trustee for cancellation of all such Notes or, with certain limitations, upon deposit with such indenture trustee of funds sufficient for the payment in full of all such Notes.
The Indenture Trustee
The indenture trustee for a series of Notes will be specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. The indenture trustee for any series generally may resign at any time. Upon resignation of the indenture trustee, the Issuing Entity will be obligated to appoint a successor thereto for such series. The Issuing Entity or administrator may also remove any such indenture trustee if such indenture trustee ceases to be eligible to continue as such under the related Indenture or if such indenture trustee becomes bankrupt or insolvent. In such circumstances, the Issuing Entity will be obligated to appoint a successor thereto for the applicable series of Notes. Any resignation or removal of the indenture trustee and appointment of a successor thereto for any series of Notes will not become effective until acceptance of the appointment by such successor.
CERTAIN INFORMATION REGARDING THE NOTES
Fixed Rate Notes
Any class of Notes (other than certain classes of Strip Notes) may bear interest at a fixed rate per annum (“Fixed Rate Notes”) or at a variable or adjustable rate per annum (“Floating Rate Notes”), as more fully described below and in the related Prospectus Supplement. Each class of Fixed Rate Notes will bear interest at the applicable per annum Interest Rate or Pass Through Rate, as the case may be, specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. Unless otherwise described in the related Prospectus Supplement, interest on each class of Fixed Rate Notes will be computed on the basis of a 360 day year of twelve 30 day months. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Notes—Principal and Interest on the Notes” and “Description of the Certificates—Payments of Principal and Interest” in this prospectus.
Floating Rate Notes
Each class of Floating Rate Notes will bear interest during each applicable Interest Period at a rate per annum determined by reference to an interest rate basis (the “Base Rate”), plus or minus the Spread, if any, or multiplied by the Spread Multiplier, if any, in each case as specified in the related Prospectus Supplement.
The “Spread” is the number of basis points to be added to or subtracted from the related Base Rate applicable to such Floating Rate Notes. The “Spread Multiplier” is the percentage of the related Base Rate applicable to such Floating Rate Notes by which such Base Rate will be multiplied to determine the applicable interest rate on such Floating Rate Notes. The “Index Maturity” is the period to maturity of the instrument or obligation with respect to which the Base Rate will be calculated.
The related Prospectus Supplement will designate one of the following Base Rates as applicable to a given Floating Rate Note: (i) the CD Rate (a “CD Rate Note”), (ii) the Commercial Paper Rate (a “Commercial Paper Rate Note”), (iii) the Federal Funds Rate (a “Federal Funds Rate Note”), (iv) LIBOR (a “LIBOR Note”) or (v) the Treasury Rate (a “Treasury Rate Note”).
“H.15(519)” means the weekly statistical release designated as H.15(519) published by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, available through the world wide web site of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System at http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/current/default.htm, or any successor site or publication. “H.15 Daily Update” means the daily update of H.15(519), available through the world wide web site of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System at http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/ default.htm, or any successor site or publication. “Interest Reset Date” will be the first day of the applicable Interest Reset Period, or such other day as may be specified in the related Prospectus Supplement with respect to a class of Floating Rate Notes.
Each related Prospectus Supplement will specify whether the rate of interest on the related Floating Rate Notes will be reset daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, semiannually, annually or such other specified period (each, an “Interest Reset Period”) and the dates on which such Interest Rate will be reset (each, an “Interest Reset Date”). Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Interest Reset Date will be, in the case of Floating Rate Notes which reset: (i) daily, each Business Day; (ii) weekly, the Wednesday of each week (with the
exception of weekly reset Treasury Rate Notes which will reset the Tuesday of each week, except as specified below); (iii) monthly, the third Wednesday of each month; (iv) quarterly, the third Wednesday of March, June, September and December of each year; (v) semiannually, the third Wednesday of the two months specified in the related Prospectus Supplement; and (vi) annually, the third Wednesday of the month specified in the related Prospectus Supplement.
The interest rate that will take effect with respect to a Floating Rate Note on an Interest Reset Date will be the rate determined as of the applicable interest determination date (each, an “Interest Determination Date”). Unless otherwise indicated in the related Prospectus Supplement: the Interest Rate Determination Date with respect to an Interest Reset Date for CD Rate Notes, Commercial Paper Rate Notes and Federal Funds Rate Notes will be such Interest Reset Date; the Interest Determination Date with respect to an Interest Reset Date for LIBOR Notes will be the second London Business Day preceding such Interest Reset Date; the Interest Determination Date with respect to an Interest Reset Date for Treasury Rate Notes will be the day of the week on which Treasury bills normally would be auctioned (Treasury bills are normally sold at auction on Monday of each week, unless that day is a legal holiday, in which case the auction is normally held on the following Tuesday, except that such auction may be held on the preceding Friday); provided, however, that if, as a result of a legal holiday, an auction is held on the Friday of the week preceding an Interest Reset Date, the related Interest Determination Date will be such preceding Friday; and provided, further, that if an auction falls on any Interest Reset Date, then the Interest Reset Date will instead be the first Business Day following such auction.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, if any Interest Reset Date for any Floating Rate Note would otherwise be a day that is not a Business Day, such Interest Reset Date will be postponed to the next succeeding day that is a Business Day, except that in the case of a Floating Rate Note as to which LIBOR is an applicable Base Rate, if such Business Day falls in the next succeeding calendar month, such Interest Reset Date will be the immediately preceding Business Day. Unless specified otherwise in the related Prospectus Supplement, “Business Day” means a day other than a Saturday, a Sunday, a legal holiday or a day on which commercial banks in New York, New York, or San Francisco, California are authorized or obligated by law, regulation, executive order or decree to be closed. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, with respect to determining the Interest Reset Date for Notes as to which LIBOR is an applicable Base Rate, the definition of Business Day will also include all London Business Days. “London Business Day” means any day (a) on which commercial banks are open for business, including dealings in such Index Currency in London and (b) if the Index Currency is the Euro a day on which the Trans European Automated Real time Gross Settlement Express Transfer System (“TARGET system”) is open and on which commercial banks and foreign exchange markets settle payments in London and New York.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, if any Payment Date for any Floating Rate Note (other than the Final Payment Date) would otherwise be a day that is not a Business Day, such Payment Date will be the next succeeding day that is a Business Day except that in the case of a Floating Rate Note as to which LIBOR is the applicable Base Rate, if such Business Day falls in the next succeeding calendar month, such Payment Date will be the immediately preceding Business Day. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, if the final Payment Date of a Floating Rate Note falls on a day that is not a Business Day, the payment of principal, premium, if any, and interest will be made on the next succeeding Business Day, and no interest on such payment will accrue for the period from and after such Final Payment Date.
Except as otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, each Floating Rate Note will accrue interest on an “Actual/360” basis, an “Actual/Actual” basis, or a “30/360” basis, in each case as specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. For Floating Rate Notes calculated on an Actual/360 basis and Actual/Actual basis, accrued interest for each Interest Period will be calculated by multiplying (i) the face amount of such Floating Rate Note; (ii) the applicable interest rate, and (iii) the actual number of days in the related Interest Period, and dividing the resulting product by 360 or 365, as applicable (or, with respect to an Actual/Actual basis Floating Rate Note, if any portion of the related Interest Period falls in a leap year, the product of (i) and (ii) above will be multiplied by the sum of (X) the actual number of days in that portion of such Interest Period falling in a leap year divided by 366 and (Y) the actual number of days in that portion of such Interest Period falling in a non-leap year divided by 365). For Floating Rate Notes calculated on a 30/360 basis, accrued interest for an Interest Period will be computed on the basis of a 360 day year of twelve 30 day months, irrespective of how many days are actually in such Interest Period. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, with respect to any Floating Rate Note that accrues
interest on a 30/360 basis, if any Payment Date including the related Final Payment Date falls on a day that is not a Business Day, the related payment of principal or interest will be made on the next succeeding Business Day as if made on the date such payment was due, and no interest will accrue on the amount so payable for the period from and after such Payment Date. The “Interest Period” with respect to any class of Floating Rate Notes will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement.
As specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, Floating Rate Notes of a given class may also have either or both of the following (in each case expressed as a rate per annum): (i) a maximum limitation, or ceiling, on the rate at which interest may accrue during any interest period and (ii) a minimum limitation, or floor, on the rate at which interest may accrue during any interest period. In addition to any maximum interest rate that may be applicable to any class of Floating Rate Notes, the interest rate applicable to any class of Floating Rate Notes will in no event be higher than the maximum rate permitted by applicable law, as the same may be modified by United States law of general application.
Each Issuing Entity with respect to which a class of Floating Rate Notes will be issued will appoint, and enter into agreements with, a calculation agent (each, a “Calculation Agent”) to calculate interest rates on each such class of Floating Rate Notes issued with respect thereto. The related Prospectus Supplement will describe the identity of the Calculation Agent for each such class of Floating Rate Notes of a given series, which may be the related indenture trustee with respect to such series. All determinations of interest by the Calculation Agent will, in the absence of manifest error, be conclusive for all purposes and binding on the holders of Floating Rate Notes of a given class. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, all percentages resulting from any calculation on Floating Rate Notes will be rounded to the nearest one hundred thousandth of a percentage point, with five one millionths of a percentage point rounded upwards (e.g., 9.876545% (or .09876545) would be rounded to 9.87655% (or .0987655)), and all dollar amounts used in or resulting from such calculation on Floating Rate Notes will be rounded to the nearest cent (with one half cent being rounded upward).
CD Rate Notes. Each CD Rate Note will bear interest for each Interest Reset Period at the interest rate calculated with reference to the CD Rate and the Spread or Spread Multiplier, if any, specified in such Note and in the related Prospectus Supplement.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the “CD Rate” for each Interest Reset Period will be the rate as of the second Business Day prior to the Interest Reset Date for such Interest Reset Period (a “CD Rate Determination Date”) for negotiable United States dollar certificates of deposit having the Index Maturity specified in the related Prospectus Supplement as published in H.15(519), as defined above, under the heading “Floating Rate Notes.”
The following procedures will be followed if the CD Rate cannot be determined as described above:
| | (1) | If the rate referred to above is not so published by 3:00 p.m., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, then the CD Rate on the applicable CD Rate Determination Date will be the rate for negotiable United States dollar certificates of deposit of the Index Maturity specified in the related Prospectus Supplement as published in H.15 Daily Update (as defined above), or other recognized electronic source used for the purpose of displaying the applicable rate, under the caption “CDs (secondary market)”. |
| | (2) | If the rate referred to in clause (1) above is not so published by 3:00 p.m., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, then the CD Rate on the applicable CD Rate Determination Date will be the rate calculated by the Calculation Agent as the arithmetic mean of the secondary market offered rates as of 10:00 a.m., New York City time, on the applicable CD Rate Determination Date of three leading nonbank dealers in negotiable United States dollar certificates of deposit in the City of New York selected by the Calculation Agent for negotiable United States dollar certificates of deposit of major United States money market banks for negotiable certificates of deposit with a remaining maturity closest to the Index Maturity specified in the related Prospectus Supplement in an amount that is representative for a single transaction in that market at the time. |
| | (3) | If the dealers selected by the Calculation Agent are not quoting as described in clause (2) above, the CD Rate on the applicable CD Rate Determination Date will be the rate in effect on the applicable CD Rate Determination Date. |
The “Calculation Date” pertaining to any CD Rate Determination Date will be the first to occur of (a) the tenth calendar day after such CD Rate Determination Date or, if such day is not a business day, the next succeeding business day or (b) the Business Day preceding the applicable Payment Date.
Commercial Paper Rate Notes. Each Commercial Paper Rate Note will bear interest for each Interest Reset Period at the interest rate calculated with reference to the Commercial Paper Rate and the Spread or Spread Multiplier, if any, specified in such Note and in the related Prospectus Supplement.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the “Commercial Paper Rate” for each Interest Reset Period will be determined by the Calculation Agent for such Commercial Paper Rate Note as of the second Business Day prior to the Interest Reset Date for such Interest Reset Period (a “Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date”) and will be the Money Market Yield, as defined below, on the applicable Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date of the rate for commercial paper having the Index Maturity specified in the related Prospectus Supplement published in H.15(519) under the heading “Commercial Paper—Nonfinancial.”
The following procedures will be followed if the Commercial Paper Rate cannot be determined as described above:
| | (1) | If the rate referred to above is not published by 3:00 p.m., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, then the Commercial Paper Rate will be the Money Market Yield on the applicable Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date of the rate for commercial paper having the Index Maturity specified in the related Prospectus Supplement published in H.15 Daily Update, or other recognized electronic source for the purpose of displaying the applicable rate under the caption “Commercial Paper—Nonfinancial.” |
| | (2) | If by 3:00 p.m., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date the Commercial Paper Rate is not yet published in either H.15(519) or H.15 Daily Update, then the Commercial Paper Rate for the applicable Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date will be calculated by the Calculation Agent as the Money Market Yield of the arithmetic mean of the offered rates at approximately 11:00 a.m., New York City time, on the applicable Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date of three leading dealers of United States dollar commercial paper in The City of New York, which may include the Calculation Agent and its affiliates, selected by the Calculation Agent for commercial paper having the Index Maturity designated in the related Prospectus Supplement placed for industrial issuers whose bond rating is “Aa” or the equivalent from a nationally recognized securities rating organization. |
| | (3) | If the dealers selected by the Calculation Agent are not quoting as mentioned in clause (2) above, the Commercial Paper Rate determined on the applicable Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date will be the rate in effect on the applicable Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date. |
“Money Market Yield” means a yield (expressed as a percentage rounded upward to the nearest one hundred-thousandth of a percentage point) calculated in accordance with the following formula:
| Money Market Yield = | | X 100 |
| 360 - (D x M) |
where “D” refers to the applicable per annum rate for commercial paper quoted on a bank discount basis and expressed as a decimal, and “M” refers to the actual number of days in the Interest Period for which interest is being calculated.
The “Calculation Date” pertaining to any Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date will be the first to occur of (a) the tenth calendar day after such Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date or, if such day is not a business day, the next succeeding business day or (b) the second business day preceding the related Payment Date.
Federal Funds Rate Notes. Each Federal Funds Rate Note will bear interest for each Interest Reset Period at the interest rate calculated with reference to the Federal Funds Rate and the Spread or Spread Multiplier, if any, specified in such Note and in the related Prospectus Supplement.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the “Federal Funds Rate” for each Interest Reset Period will be the effective rate as of the first Business Day prior to the Interest Reset Date for such Interest Reset Period (a “Federal Funds Rate Determination Date” for United States dollar federal funds as published in H.15(519) for that day opposite the caption “EFFECT,” as displayed on Reuters Screen FEDFUNDS1 Page or any other page as may replace the applicable page on that service.
The following procedures will be followed if the Federal Funds Rate cannot be determined as described above:
| | (1) | If the rate referred to above does not appear on Reuters Screen FEDFUNDS1 Page or is not so published by 3:00 p.m., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, the Federal Funds Rate for the applicable Federal Funds Rate Determination Date will be the rate on the applicable Federal Funds Rate Determination Date for United States dollar federal funds published in H.15 Daily Update, or other recognized electronic source for the purpose of displaying the applicable rate under the heading “Federal Funds (Effective).” |
| | (2) | If the Federal Funds Rate is not so published by 3:00 p.m., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, the Federal Funds Rate for the applicable Federal Funds Rate Determination Date will be calculated by the Calculation Agent as the arithmetic mean of the rates for the last transaction in overnight United States dollar federal funds arranged by three leading brokers of United States dollar federal funds transactions in The City of New York, which may include the Calculation Agent and its affiliates, selected by the Calculation Agent before 9:00 a.m., New York City time on the applicable Federal Funds Rate Determination Date. |
| | (3) | If the brokers so selected by the Calculation Agent are not quoting as mentioned in clause (2) above, the Federal Funds Rate for the applicable Federal Funds Rate Determination Date will be the Federal Funds Rate in effect on the applicable Federal Funds Rate Determination Date. |
The “Calculation Date” pertaining to any Federal Funds Rate Determination Date will be the first to occur of (a) the tenth calendar day after such Federal Funds Rate Determination Date or, if such day is not a business day, the next succeeding business day or (b) the second business day preceding the related Payment Date.
LIBOR Notes. Each LIBOR Note will bear interest for each Interest Reset Period at the interest rate calculated with reference to LIBOR and the Spread or Spread Multiplier, if any, specified in such Note and in the related Prospectus Supplement.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, with respect to LIBOR indexed to the offered rates for U.S. dollar deposits, “LIBOR” for each Interest Reset Period will be determined by the Calculation Agent for any LIBOR Note to be the rate for deposits in the Index Currency having the Index Maturity designated in the related Prospectus Supplement commencing on the second “London Business Day” (as defined above) immediately following the applicable Interest Determination Date that appears on the Reuters Screen LIBOR 01 Page as of 11:00 a.m. London time, on the applicable Interest Determination Date.
The following procedures will be followed if LIBOR cannot be determined as described above:
| | (1) | With respect to an Interest Determination Date on which fewer than two offered rates appear, or no rate appears, as the case may be, on the Reuters Screen LIBOR 01 Page as specified above, LIBOR |
for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the rate calculated by the Calculation Agent as the arithmetic mean of at least two quotations obtained by the Calculation Agent after requesting the principal London offices of each of four major reference banks in the London interbank market, which may include the Calculation Agent and its affiliates, as selected by the Calculation Agent, to provide the Calculation Agent with its offered quotation for deposits in the Index Currency for the period of the Index Maturity designated in the related Prospectus Supplement, commencing on the second London Business Day immediately following the applicable Interest Determination Date, to prime banks in the London interbank market at approximately 11:00 a.m., London time, on such Interest Determination Date and in a principal amount that is representative for a single transaction in the applicable Index Currency in that market at that time. If at least two such quotations are provided, LIBOR determined on the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the arithmetic mean of the quotations.
| | (2) | If fewer than two quotations referred to in clause (1) above are provided, LIBOR determined on the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the rate calculated by the Calculation Agent as the arithmetic mean of the rates quoted at approximately 11:00 a.m., or such other time specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, in the applicable Principal Financial Center, on the applicable Interest Determination Date by three major banks, which may include the Calculation Agent and its affiliates, in that Principal Financial Center selected by the Calculation Agent for loans in the Index Currency to leading European banks, having the Index Maturity designated in the related Prospectus Supplement and in a principal amount that is representative for a single transaction in the Index Currency in that market at that time. |
| | (3) | If the banks so selected by the calculation agent are not quoting as mentioned in clause (2) above, LIBOR for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be LIBOR in effect on the applicable Interest Determination Date. |
“Index Currency” means the currency specified in the related Prospectus Supplement as the currency for which LIBOR will be calculated. If no currency is specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Index Currency will be United States dollars.
“Principal Financial Center” means, unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the capital city of the country issuing the Index Currency relates, except that with respect to United States dollars, Australian dollars, Canadian dollars, euros, South African Rand and Swiss Francs, the Principal Financial Center will be the City of New York, Sydney, Toronto, London, Johannesburg and Zurich, respectively.
Treasury Rate Notes. Each Treasury Rate Note will bear interest for each Interest Reset Period at the interest rate calculated with reference to the Treasury Rate and the Spread or Spread Multiplier, if any, specified in such Note and in the related Prospectus Supplement determined on the “Treasury Rate Determination Date” specified in such Prospectus Supplement.
Unless specified otherwise in the related Prospectus Supplement, the “Treasury Rate” for each Interest Period means the rate from the auction held on the applicable Interest Determination Date (“Auction”) of direct obligations of the United States (“Treasury Bills”) having the Index Maturity specified in the applicable pricing supplement under the caption “INVEST RATE” on the display on the Reuters Screen USAUCTION10 Page or the Reuters Screen USAUCTION11 Page opposite the “Designated Maturity.”
The following procedures will be followed if the Treasury Rate cannot be determined as described above:
| | (1) | If the rate described above is not so published by 3:00 P.M., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, the Treasury Rate for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the Bond Equivalent Yield of the rate for the applicable Treasury Bills as published in H.15 Daily Update, or other recognized electronic source used for the purpose of displaying the applicable rate, under the caption “U.S. Government Securities/Treasury Bills/Auction High.” |
| | (2) | If the rate described in clause (1) above is not so published by 3:00 P.M., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, the Treasury Rate for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the Bond Equivalent Yield of the auction rate of the applicable Treasury Bills announced by the United States Department of the Treasury. |
| | (3) | If the rate described in clause (2) above is not announced by the United States Department of the Treasury, or if the Auction is not held, the Treasury Rate for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the Bond Equivalent Yield of the rate on the applicable Interest Determination Date of Treasury Bills having the Index Maturity specified in the applicable pricing supplement published in H.15(519) under the caption “U.S. Government Securities/Treasury Bills/Secondary Market.” |
| | (4) | If the rate described in clause (3) above is not so published by 3:00 P.M., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, the Treasury Rate for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the rate on the applicable Interest Determination Date of the applicable Treasury Bills as published in H.15 Daily Update, or other recognized electronic source used for the purpose of displaying the applicable rate, under the caption “U.S. Government Securities/Treasury Bills/Secondary Market.” |
| | (5) | If the rate described in clause (4) above is not so published by 3:00 P.M., New York City time, on the related Calculation Date, the Treasury Rate for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the rate on the applicable Interest Determination Date calculated by the calculation agent as the Bond Equivalent Yield of the arithmetic mean of the secondary market bid rates, as of approximately 3:30 P.M., New York City time, on the applicable Interest Determination Date, of three primary United States government securities dealers, which may include the calculation agent or its affiliates, selected by the calculation agent, for the issue of Treasury Bills with a remaining maturity closest to the Index Maturity specified in the applicable pricing supplement. |
| | (6) | If the dealers selected by the calculation agent are not quoting as described in clause (5) above, the Treasury Rate for the applicable Interest Determination Date will be the rate in effect on the applicable Interest Determination Date. |
“Bond Equivalent Yield” means a yield calculated in accordance with the following formula and expressed as a percentage:
Bond Equivalent Yield = | | X 100 |
| 360 - (D x M) |
where “D” refers to the applicable per annum rate for Treasury Bills quoted on a bank discount basis, “N” refers to 365 or 366, as the case may be, and “M” refers to the actual number of days in the interest period for which interest is being calculated.
The “Calculation Date” pertaining to any Treasury Rate Determination Date will be the first to occur of (a) the tenth calendar day after such Treasury Rate Determination Date or, if such a day is not a Business Day, the next succeeding Business Day or (b) the second Business Day preceding the date any payment is required to be made for any period following the applicable Interest Reset Date.
Derivative and Other Cash Flow Enhancement Arrangements
The Issuing Entity may also include one or more derivative or other cash flow arrangements to ensure the timely payment of interest on the Notes of a series or any class of Notes. Such arrangements may include maturity liquidity facilities, interest rate cap or floor agreements or interest rate or currency swap agreements. The type of arrangements, if any, for a series of Notes or class of Notes, along with a description of the provider of such arrangements (which may include TMCC), will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement.
Revolving Period
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Sale and Servicing Agreement for any series may provide that all or a portion of the principal collected on the Receivables may be applied by the indenture trustee to acquire subsequent Receivables during a specified period rather than used to distribute payments of principal to holders of one or more classes of securities of such series during that period. The duration of any such Revolving Period (a “Revolving Period”) will not exceed three years. The related Prospectus Supplement will specify the percentage of the aggregate principal balance of the Receivables represented by the Revolving Period and the maximum amount of additional Receivables that may be acquired during the Revolving Period, in each case, to the extent determinable. Any specified Revolving Period would be followed by an “Amortization Period,” during which Noteholders would receive payments in respect of principal. Any Revolving Period may terminate earlier than its scheduled end date upon the occurrence of certain events specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. Any such termination of a Revolving Period would result in earlier than expected principal repayment of the Notes.
Prefunding Period
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, on the Closing Date, a portion of the proceeds specified in the related Prospectus Supplement received from the sale of the applicable Notes and Certificates will be deposited into a segregated prefunding account. The related Prospectus Supplement also will specify the percentage of the aggregate principal balance of the Receivables represented by the prefunded amount. Following the Closing Date, and continuing until the date specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, commonly referred to as a prefunding period, the Issuing Entity will have the ability to purchase additional Receivables to the extent there are sufficient funds on deposit in the related prefunding account. The prefunding period will be no longer than one year. If all of the monies originally deposited in the segregated account are not used by the end of the specified period, all remaining monies will be applied as a mandatory prepayment of a designated class or classes of Notes. Any prefunding period may terminate prior to the end of the specified period and result in earlier than expected principal repayment of one or more classes of Notes specified in the related Prospectus Supplement upon the occurrence of certain events to be described in the related Prospectus Supplement. In addition, the related Prospectus Supplement will specify any limitation on the ability of the sponsor or Depositor to add assets and the requirements for assets that may be added to the pool.
Book Entry Registration
General
Upon issuance, unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, all notes in book-entry form having the same original issue date, Maturity and otherwise having identical terms and provisions will be represented by one or more fully registered global notes. Each global note will be deposited with, or on behalf of, the Depository Trust Company (“DTC”), as depository, registered in the name of DTC or a nominee of DTC.
Except as described below, a global note may not be transferred except as a whole: (1) by DTC to a nominee of DTC; (2) by a nominee of DTC to DTC or another nominee of DTC; (3) by DTC or any nominee to a successor of DTC or a nominee of the successor.
So long as DTC or its nominee is the registered owner of a global note, DTC or its nominee, as the case may be, will be the sole holder of the notes in book-entry form represented by the global note for all purposes under the Indenture. Except as otherwise provided in this section, the actual purchasers, or “Beneficial Owners,” of the global note or notes representing notes in book-entry form will not be entitled to receive physical delivery of notes in certificated form and will not be considered to be the holders of the notes for any purpose under the Indenture, and no global note representing notes in book-entry form will be exchangeable or transferable. Accordingly, each person owning a beneficial interest in a global note must rely on the procedures of DTC and, if a person is not a participant, on the procedures of the participant through which the person owns its interest in order to exercise any rights of a holder under the Indenture.
We may elect to allow Beneficial Owners to hold their interest in a Global Note held by DTC through Clearstream Banking, société anonyme (“Clearstream”) or Euroclear Bank S.A./N.V., as operator of the Euroclear
system (“Euroclear”), if they are participants in those systems, or indirectly through organizations that are participants in those systems. Clearstream and Euroclear will hold interests on behalf of their customers through accounts held in Clearstream’s and Euroclear names on the books of their respective depositaries, which in turn will hold the interests in the depositaries’ names on the books of DTC.
We understand that under existing industry practices, if we request any action of holders or if an owner of a beneficial interest in a global note desires to give or take any action that a holder is entitled to give or take under the Indenture, DTC would authorize the participants holding the relevant beneficial interests to give or take the desired action, and the participants would authorize Beneficial Owners owning through the participants to give or take the desired action or would otherwise act upon the instructions of Beneficial Owners. Euroclear operator or Clearstream, as the case may be, will take action on behalf of their participants only in accordance with its relevant rules and procedures and subject to its respective depositaries’ ability to effect such actions on its behalf through DTC.
The laws of some jurisdictions require that certain purchasers of securities take physical delivery of the securities in definitive certificated form. These limits and laws may impair the ability to transfer beneficial interests in a global note representing notes in book-entry form. Further, because DTC can act only on behalf of its participants, who in turn act on behalf of indirect participants, the ability of Beneficial Owners to pledge their interest in the notes to persons or entities that do not participate in the DTC system, or otherwise take action with respect to such interest, may be limited by the lack of a definitive certificate of such interest.
Settlement Procedures
The initial depository for the notes will be DTC. The depository will act as securities depository for the notes in book-entry form. The notes in book-entry form will be issued as fully registered securities registered in the name of Cede & Co., the depository’s nominee or such other name as may be requested by an authorized representative of DTC. One global note will be issued to represent each $500,000,000 of aggregate principal amount of notes of the same issue. Additional global notes will be issued to represent any remaining principal amount of the issue.
Purchases of notes in book-entry form under DTC’s system must be made by or through direct participants, which will receive a credit for notes in book-entry form on DTC’s records. The ownership interest of each Beneficial Owner is in turn recorded on the records of direct participants and indirect participants. Beneficial Owners of notes in book-entry form will not receive written confirmation from DTC of their purchase, but Beneficial Owners are expected to receive written confirmations providing details of the transaction, as well as periodic statements of their holdings, from the direct or indirect participants through which the Beneficial Owner entered into the transaction. Transfers of ownership interests in a global note representing notes in book-entry form are accomplished by entries made on the books of participants acting on behalf of the Beneficial Owners. Beneficial Owners of a global note representing notes in book-entry form will not receive notes in certificated form representing their ownership interests in the notes, unless use of the book-entry system for notes in book-entry form is discontinued.
To facilitate subsequent transfers, all global notes representing notes in book-entry form which are deposited with DTC are registered in the name of DTC’s partnership nominee, Cede & Co. or such other name as may be requested by an authorized representative of DTC. The deposit of global notes with DTC and their registration in the name Cede & Co. or such other DTC nominee effect no change in beneficial ownership. DTC has no knowledge of the actual Beneficial Owners of the global notes representing the notes in book-entry form; DTC’s records reflect only the identity of the direct participants to whose accounts the notes in book-entry form are credited, which may or may not be the Beneficial Owners. The participants will remain responsible for keeping account of their holdings on behalf of their customers and for forwarding all notices concerning the notes to their customers.
Conveyance of notices and other communications by DTC to direct participants, by direct participants to indirect participants, and by direct participants and indirect participants to Beneficial Owners will be governed by arrangements among them, subject to any statutory or regulatory requirements as may be in effect from time to time.
Redemption notices will be sent to DTC. If less than all of the notes in book-entry form within an issue are being redeemed, DTC’s practice is to determine by lot the amount of the interest of each direct participant in the issue to be redeemed.
Neither DTC nor Cede & Co. (nor any other DTC nominee) will consent or vote with respect to the global notes representing the notes in book-entry form unless authorized by a direct participant in accordance with DTC’s procedures. Under its usual procedures, DTC mails an omnibus proxy to us as soon as possible after the applicable record date. The omnibus proxy assigns Cede & Co.’s consenting or voting rights to those direct participants, identified in a listing attached to the omnibus proxy, to whose accounts the notes in book-entry form are credited on the applicable record date.
So long as DTC, or its nominee, is a registered owner of the global notes representing the notes in book-entry form, we will make principal, premium, if any, and interest payments on the global notes representing the notes in book-entry form to DTC. DTC’s practice is to credit direct participants’ accounts upon DTC’s receipt of funds and corresponding detail information from TAFR LLC or the indenture trustee, on the applicable payment date in accordance with their respective holdings shown on DTC’s records. Payments by participants to Beneficial Owners will be governed by standing instructions and customary practices, as is the case with securities held for the accounts of customers in bearer form or registered in “street name,” and will be the responsibility of the participant and not of DTC, the indenture trustee or TAFR LLC, subject to any statutory or regulatory requirements as may be in effect from time to time. Payment of principal, premium, if any, and interest to DTC is the responsibility of TAFR LLC or the indenture trustee. Disbursement of such payments to direct participants is the responsibility of DTC, and disbursement of payments to the Beneficial Owners is the responsibility of direct participants and indirect participants. Distributions with respect to Notes held through Clearstream or Euroclear will be credited, to the extent received by their respective depositaries, to the cash accounts of their participants in accordance with the relevant system’s rules and procedures.
DTC may discontinue providing its services as securities depository with respect to the notes in book-entry form at any time by giving reasonable notice to TAFR LLC or the indenture trustee. Under these circumstances, if a successor securities depository is not obtained, notes in certificated form are required to be printed and delivered.
We may decide (subject to the procedures of the securities depository) to discontinue use of a system of book-entry transfers through the depository or a successor securities depository. In that event, notes in definitive certificated form will be printed and delivered.
If DTC is at any time unwilling or unable to continue as depository and a successor depository is not appointed by us within 90 days, we will issue notes in certificated form in exchange for the notes represented by the global notes. In addition, we may at any time and in our sole discretion determine (subject to the procedures of the securities depositary) to discontinue use of a global note and, in that event, will issue notes in certificated form in exchange for the notes represented by the global note. Notes so issued will be issued in minimum denominations as provided in the related Prospectus Supplement and will be issued in registered form only, without coupons.
Secondary Market Trading
Because the purchaser determines the place of delivery, it is important to establish at the time of trading of any notes where both the purchaser’s and seller’s accounts are located to ensure that settlement can be made on the desired value date.
Trading between participants of DTC, or “DTC Participants.” Secondary market sales of notes held in DTC between DTC Participants will occur in the ordinary way in accordance with DTC rules and will be settled using the procedures applicable to United States corporate debt obligations.
Trading between participants of Euroclear, or “Euroclear Participants” and/or participants of Clearstream, or “Clearstream Participants.” Secondary market sales of beneficial interests in the notes held through Euroclear or Clearstream to purchasers that will hold beneficial interests through Euroclear or Clearstream will be conducted in accordance with the normal rules and operating procedures of Euroclear and Clearstream and will be settled using the procedures applicable to conventional eurobonds.
Trading between DTC Seller and Euroclear/Clearstream Purchaser. When book-entry interests in notes are to be transferred from the account of a DTC Participant to the account of a Euroclear or Clearstream accountholder, the purchaser must first send instructions to the Euroclear operator or Clearstream through a participant at least one business day (European time) prior to the settlement date, in accordance with its rules and procedures and within its established deadlines (European time). Clearstream Participants and Euroclear Participants may not deliver instructions directly to DTC. Euroclear or Clearstream will then instruct its depositary to receive the notes and make payment for them. On the settlement date, the depositary will make payment to the DTC Participant’s account and the notes will be credited to the depositary’s account. After settlement has been completed, DTC will credit the notes to the U.S. depositary for Euroclear or Clearstream, as the case may be. Euroclear operator or Clearstream will credit the notes, in accordance with its usual procedures, to the participant’s account, and the participant will then credit the purchaser’s account. These securities credits will appear the next business day (European time) after the settlement date. The cash debit from the account of Euroclear or Clearstream will be back-valued to the value date (which will be the preceding business day (European time) if settlement occurs in New York). If settlement is not completed on the intended value date (i.e., the trade fails), the cash debit will instead be valued at the actual settlement date. Since the settlement will occur during New York business hours, a DTC Participant selling an interest in the notes can use its usual procedures for transferring notes to the U.S. depositary for Euroclear or Clearstream, as the case may be, for the benefit of Euroclear Participants or Clearstream Participants. The DTC seller will receive the sale proceeds on the settlement date. Thus, to the DTC seller, a cross-market sale will settle no differently than a trade between two DTC Participants.
Trading between a Euroclear or Clearstream Seller and a DTC Purchaser. Due to time zone differences in their favor, Euroclear Participants and Clearstream Participants can use their usual procedures to transfer notes through the applicable U.S. depositary to a DTC Participant. The seller must first send instructions to Euroclear or Clearstream through a participant at least one business day (European time) prior to the settlement date. Euroclear or Clearstream will then instruct its U.S. Depositary to credit the notes to the DTC Participant’s account and receive payment. The payment will be credited in the account of the Euroclear or Clearstream Participant on the following business day (European time), but the receipt of the cash proceeds will be back-valued to the value date (which will be the preceding business day (European time) if settlement occurs in New York). If settlement is not completed on the intended value date (i.e., the trade fails), the receipt of the cash proceeds will instead be valued at the actual settlement date.
Although the foregoing sets out the procedures of Euroclear, Clearstream and DTC in order to facilitate the transfers of interests in the notes among participants of DTC, Clearstream and Euroclear, none of Euroclear, Clearstream or DTC is under any obligation to perform or continue to perform such procedures, and such procedures may be discontinued at any time. Neither we nor any agent or any paying agent, any underwriter or any affiliate of any of the above, or any person by whom any of the above is controlled for the purposes of the Securities Act will have any responsibility for the performance by DTC, Euroclear and Clearstream or their respective direct or indirect participants or accountholders of their respective obligations under the rules and procedures governing their operations or for the sufficiency for any purpose of the arrangements described above.
The Clearing Systems
DTC. DTC, the world’s largest securities depository, is a limited -purpose trust company organized under the New York Banking Law, a “banking organization” within the meaning of the New York Banking Law, a member of the Federal Reserve System, a “clearing corporation” within the meaning of the New York Uniform Commercial Code, and a “clearing agency” registered pursuant to the provisions of Section 17A of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. DTC holds and provides asset servicing for over 3.5 million issues of U.S. and non-U.S. equity issues, corporate and municipal debt issues, and money market instruments (from over 100 countries) that DTC Direct Participants deposit with DTC. DTC also facilitates the post-trade settlement among DTC Direct Participants of sales and other securities transactions in deposited securities, through electronic computerized book-entry transfers and pledges between DTC Direct Participants’ accounts. This eliminates the need for physical movement of securities certificates. DTC Direct Participants include both U.S. and non-U.S. securities brokers and dealers, banks, trust companies, clearing corporations, and certain other organizations. DTC is a wholly-owned subsidiary of The Depository Trust & Clearing Corporation (“DTCC”). DTCC is the holding company for DTC, National Securities Clearing Corporation and Fixed Income Clearing Corporation, all of which are registered clearing agencies. DTCC is owned by the users of its regulated subsidiaries. Access to the DTC system is also
available to others such as both U.S. and non-U.S. securities brokers and dealers, banks, trust companies, and clearing corporations that clear through or maintain a custodial relationship with a DTC Direct Participant, either directly or indirectly. The DTC Rules applicable to DTC Direct Participants are on file with the Securities and Exchange Commission. More information about DTC can be found at www.dtcc.com.
Clearstream. Clearstream advises that it is incorporated under the laws of Luxembourg as a professional depository. Clearstream holds securities for its participating organizations (“Clearstream Participants”) and facilitates the clearance and settlement of securities transactions between Clearstream Participants through electronic book- entry changes in accounts of Clearstream Participants, thereby eliminating the need for physical movement of certificates. Clearstream provides to Clearstream Participants, among other things, services for safekeeping, administration, clearance and settlement of internationally traded securities and securities lending and borrowing. Clearstream interfaces with domestic markets in several countries. As a professional depository in Luxembourg, Clearstream is subject to regulation by the Commission de Surveillance du Secteur Financier. Clearstream Participants are recognized financial institutions around the world, including underwriters, securities brokers and dealers, banks, trust companies, clearing corporations and certain other organizations and may include the agents. Indirect access to Clearstream is also available to other institutions such as banks, brokers, dealers and trust companies that clear through or maintain a custodial relationship with a Clearstream Participant either directly or indirectly. Distributions with respect to the notes held beneficially through Clearstream will be credited to cash accounts of Clearstream Participants in accordance with its rules and procedures, to the extent received by the U.S. Depositary for Clearstream.
Euroclear. Euroclear holds securities and book-entry interests in securities for participants of Euroclear (“Euroclear Participants”) and facilitates the clearance and settlement of securities transactions between Euroclear Participants, and between Euroclear Participants and participants of certain other securities intermediaries through electronic book-entry changes in accounts of such participants or other securities intermediaries. Euroclear provides Euroclear Participants, among other things, with safekeeping, administration, clearance and settlement, securities lending and borrowing and related services. Euroclear Participants include investment banks, securities brokers and dealers, banks, central banks, supranationals, custodians, investment managers, corporations, trust companies and certain other organizations, and may include the agents. Non-participants in Euroclear may hold and transfer beneficial interests in a global note through accounts with a Euroclear Participant or any other securities intermediary that holds a book-entry interest in a global note through one or more securities intermediaries standing between such other securities intermediary and Euroclear. Securities clearance accounts and cash accounts with the Euroclear Operator are governed by the Terms and Conditions Governing Use of Euroclear and the related Operating Procedures of the Euroclear System, and applicable Belgian law (collectively, the “Terms and Conditions”). The Terms and Conditions govern transfers of securities and cash within Euroclear, withdrawals of securities and cash from Euroclear, and receipts of payments with respect to securities in Euroclear. All securities in Euroclear are held on a fungible basis without attribution of specific certificates to specific securities clearance accounts. The Euroclear Operator acts under the Terms and Conditions only on behalf of Euroclear Participants, and has no record of or relationship with persons holding through Euroclear Participants. Distributions with respect to notes held beneficially through Euroclear will be credited to the cash accounts of Euroclear Participants in accordance with the Terms and Conditions, to the extent received by the U.S. Depository for Euroclear.
Although DTC, Clearstream and Euroclear have agreed to these procedures in order to facilitate transfers of Securities among participants of DTC, Clearstream and Euroclear, they are under no obligation to perform or continue to perform such procedures and such procedures may be discontinued at any time. Information concerning DTC, Clearstream, and Euroclear in this prospectus has been obtained from sources we believe to be reliable, but we take no responsibility for the accuracy thereof.
Definitive Securities
The Certificates of a given series will be issued in fully registered, certificated form (“Definitive Certificates”). Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Notes of a given series will be issued in fully registered, certificated form (“Definitive Notes” and together with the Definitive Certificates, collectively referred to in this prospectus as “Definitive Securities”) to Noteholders or their respective nominees, rather than to DTC or its nominee, only if (i) DTC is no longer willing or able to discharge properly its responsibilities as depository with respect to such Notes and such administrator or trustee is unable to locate a
qualified successor (and if it is an administrator that has made such determination, such administrator so notifies the applicable trustee in writing), (ii) the Depositor or the administrator or trustee, as applicable, at its option, elects to terminate the book entry system through DTC or (iii) after the occurrence of an Event of Default or a Servicer Default with respect to such Notes, holders representing at least a majority of the outstanding principal amount of the Notes of the Controlling Class of such series, acting together as a single class, advise the applicable trustee through DTC in writing that the continuation of a book entry system through DTC (or a successor to DTC) with respect to such Notes is no longer in the best interest of the holders of such Notes.
Upon the occurrence of any event described in the immediately preceding paragraph, the applicable indenture trustee will be required to notify all applicable Noteholders of a given series through Participants of the availability of Definitive Notes. Upon surrender by DTC of the definitive certificates representing the corresponding Notes and receipt of instructions for re-registration, the applicable indenture trustee will reissue such Notes as Definitive Notes to such Noteholders.
Payments of principal of, and interest on, such Definitive Notes will thereafter be made by the applicable trustee or indenture trustee in accordance with the procedures described in the related Indenture or the related Trust Agreement, as applicable, directly to holders of Definitive Notes in whose names the Definitive Notes were registered at the close of business on the applicable Record Date specified for such Notes in the related Prospectus Supplement. Such payments will be made by check mailed to the address of such holder as it appears on the register maintained by the applicable indenture trustee. The final payment on any such Definitive Note, however, will be made only upon presentation and surrender of such Definitive Note at the office or agency specified in the notice of final payment to the applicable Noteholders. The applicable indenture trustee will provide such notice to the applicable Noteholders not less than 15 or more than 30 days prior to the date on which such final payment is expected to occur.
Definitive Securities will be transferable and exchangeable at the offices of the applicable trustee or of a registrar named in a notice delivered to holders of Definitive Securities. No service charge will be imposed for any registration of transfer or exchange, but the applicable trustee may require payment of a sum sufficient to cover any tax or other governmental charge imposed in connection therewith.
List of Securityholders
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement with respect to the Notes of any series, three or more holders of the Notes of such series or one or more holders of such Notes evidencing not less than 25% of the aggregate outstanding principal amount of such Notes may, by written request to the related indenture trustee, obtain access to the list of all Noteholders maintained by such indenture trustee for the purpose of communicating with other Noteholders with respect to their rights under the related Indenture or under such Notes. Such indenture trustee may elect not to afford the requesting Noteholders access to the list of Noteholders if it agrees to mail the desired communication or proxy, on behalf of and at the expense of the requesting Noteholders, to all Noteholders of such series.
The Depositor or an affiliate will be the initial Certificateholder for any series.
The Trust Agreement and Indenture will not provide for the holding of annual or other meetings of Securityholders.
Reports to Securityholders
With respect to each series of Securities, on or prior to each Payment Date, the Servicer will prepare and provide to the related indenture trustee and the owner trustee a statement to be delivered to the related Noteholders and Certificateholders, respectively, on such Payment Date. With respect to each series of Securities, each such statement to be delivered to Securityholders will include (to the extent applicable) the following information (and any other information so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement) as to the Notes of such series and as to the Certificates of such series with respect to such Payment Date or the period since the previous Payment Date, as applicable:
| | (i) | the amount of the payment allocable to the principal amount of each class of Notes; |
| | (ii) | the amount of the payment allocable to interest on each class of Notes; |
| | (iii) | the applicable reserve account draw amount, if any, the balance on deposit in the Reserve Account on that Payment Date after giving effect to withdrawals therefrom and deposits thereto in respect of that Payment Date and the change in that balance from the immediately preceding Payment Date; |
| | (iv) | the number of Receivables, the Pool Balance and the Adjusted Pool Balance as of the close of business on the first day and the last day of the related Collection Period; |
| | (v) | the aggregate outstanding principal amount and the Note Pool Factor for each class of Notes, before and after giving effect to all payments in respect of principal on such Payment Date; |
| | (vi) | the amount of the Basic Servicing Fee paid to the Servicer, the amount of any unpaid Basic Servicing Fee, if any, and the change in that amount from that of the prior Payment Date and the amount of any additional servicing compensation paid to the Servicer, each with respect to the related Collection Period; |
| | (vii) | the Base Rate for the immediately succeeding Interest Period; |
| | (viii) | the Interest Rate for the Interest Period relating to the succeeding Payment Date for any class of Notes of such series with variable or adjustable rates; |
| | (ix) | the Noteholders’ Interest Carryover Shortfall, the Noteholders’ Principal Carryover Shortfall (each as defined in the related Prospectus Supplement), if any, in each case as applicable to the Notes, and the change in such amounts from the preceding statement; |
| | (x) | the amount of Advances, if any, made in respect of the related Receivables and the related Collection Period and the amount of unreimbursed Advances on such Payment Date; |
| | (xi) | the balance of any related Reserve Account, Prefunding Account, Yield Maintenance Account, currency swap, interest rate swap or other interest rate protection agreements or other credit or liquidity enhancement (including a Revolving Liquidity Note, surety bond or cash collateral account), on such date, (i) before giving effect to changes thereto on that date and the amount of those changes and (ii) after giving effect to changes thereto on that date and the amount of those changes; |
| | (xii) | the Available Collections (as that term is defined in the Prospectus Supplement); |
| | (xiii) | payments to and from third party credit or cash flow enhancement providers, if any; |
| | (xiv) | delinquency and loss information on the Receivables for the related Collection Period; |
| | (xv) | any material change in practices with respect to charge-offs, collection and management of delinquent Receivables, and the effect of any grace period, re-aging, re-structure, partial payments or other practices on delinquency and loss experience; |
| | (xvi) | any material modifications, extensions or waivers to Receivables terms, fees, penalties or payments during the Collection Period; |
| | (xvii) | any material breaches of representations, warranties or covenants contained in the Transfer and Servicing Agreements; |
| | (xviii) | any new issuance of notes or other securities backed by the Receivables; |
| | (xix) | any material change in the underwriting, origination or acquisition of Receivables; and |
| | (xx) | such other information as may be specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. |
Within the prescribed period of time for tax reporting purposes after the end of each calendar year during the term of each Issuing Entity, the applicable trustee will mail to each person who at any time during such calendar year has been a Securityholder with respect to such Issuing Entity and received any payment thereon a statement containing certain information for the purposes of such Securityholder’s preparation of federal income tax returns. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Federal Income Tax Consequences” in this prospectus.
DESCRIPTION OF THE TRANSFER AND SERVICING AGREEMENTS
The following summary describes certain terms of each of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements. Forms of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements have been filed as exhibits to the Registration Statement of which this prospectus forms a part. The provisions of any of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements may differ in non-material respects from those described in this prospectus and, if so, will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement. This summary does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by reference to, all the provisions of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements. If an Issuing Entity includes a Revolving Period, the related Prospectus Supplement and Transfer and Servicing Agreements will describe the allocations and application to be made in respect of principal during and after such Revolving Period.
Sale and Assignment of Receivables
On or prior to the Closing Date specified with respect to any given Issuing Entity in the related Prospectus Supplement, TMCC will sell and assign to the Depositor, without recourse, pursuant to a Receivables Purchase Agreement, its entire interest in the Receivables comprising the related Receivables Pool, including the security interests in the Financed Vehicles. On the Closing Date, the Depositor will transfer and assign to the applicable Issuing Entity, without recourse, pursuant to a Sale and Servicing Agreement, its entire interest in the Receivables comprising the related Receivables Pool, including its security interests in the related Financed Vehicles. Each such Receivable will be identified in the transfer notice (the “Transfer Notice”) delivered to the Issuer pursuant to such Sale and Servicing Agreement. The applicable Issuing Entity will pledge its assets, including the Receivables, to the applicable indenture trustee, for the benefit of the Noteholders. The applicable indenture trustee will, concurrently with such transfer and assignment, on behalf of the Issuing Entity, execute and deliver the related Notes and/or Certificates. Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the net proceeds received from the sale of the Notes of a given series will be applied to the purchase of the related Receivables from TMCC and, to the extent specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, to make any required initial deposit into the Reserve Account, Prefunding Account or Yield Maintenance Account. If an Issuing Entity includes a Revolving Period, provision for acquisition of additional Receivables by the Issuing Entity will be made in the applicable Receivables Purchase Agreement and Sale and Servicing Agreement.
TMCC, pursuant to each Receivables Purchase Agreement, and the Depositor, pursuant to each Sale and Servicing Agreement, will represent and warrant, with respect to whether, among other things: (i) the information provided in the related Transfer Notice is true and correct in all material respects as of the Cutoff Date, and no selection procedures adverse to the Noteholders have been utilized in selecting the Receivables; (ii) the terms of
each Receivable require the related Obligor to possess physical damage insurance which covers the Financed Vehicle in accordance with TMCC’s normal requirements; (iii) as of the applicable Closing Date, to the best of its knowledge, the related Receivables are free and clear of all security interests, liens, charges and encumbrances (other than tax liens, mechanics’ liens and any liens that attach to a Receivable or any property, as the context may require, by operation of law) that are prior to, or of the same priority with, the security interests in the Financed Vehicles granted by the related Receivables, and no offsets, defenses or counterclaims have been asserted or threatened; (iv) as of the Closing Date, each of such Receivables is secured by a first priority perfected security interest in favor of TMCC in the Financed Vehicle or all necessary and appropriate actions have been taken to perfect a first priority security interest; (v) each related Receivable, at the time it was originated, complied and, as of the Closing Date, complies in all material respects with applicable federal and state laws, including, without limitation, consumer credit, truth in lending, equal credit opportunity and disclosure laws; and (vi) any other representations and warranties that may be described in the related Prospectus Supplement are true and correct in all material respects.
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, by the last day of the second month following the discovery by or notice to the Depositor of a breach of any representation or warranty of the Depositor that materially and adversely affects the interests of the related Issuing Entity in any Receivable, the Depositor, unless the breach is cured in all material respects, will repurchase such Receivable (a “Warranty Receivable”) from such Issuing Entity and, pursuant to the Receivables Purchase Agreement, TMCC will purchase such Warranty Receivable from the Depositor, at a price equal to the Warranty Purchase Payment for such Receivable. The “Warranty Purchase Payment” (1) for an Actuarial Receivable, will be equal to (a) the sum of (i) all remaining Scheduled Payments (and any applicable amounts in the Yield Maintenance Account, if any), (ii) all past due Scheduled Payments for which an Advance has not been made, (iii) all outstanding Advances made by the Servicer in respect of such Actuarial Receivable and (iv) an amount equal to any reimbursements of outstanding Advances made by the Servicer with respect to such Actuarial Receivable from collections made on or in respect of other Receivables, minus (b) the sum of (i) the rebate, if any, paid to the Obligor on an Actuarial Receivable on or before the date of such purchase and (ii) any other proceeds previously received (e.g., insurance or other proceeds in respect of the liquidation of such Actuarial Receivable) to the extent applied to reduce the Principal Balance of such Actuarial Receivable and (2) for a Simple Interest Receivable, will be equal to its unpaid principal balance, plus interest thereon at a rate equal to the sum of the Interest Rate or Pass Through Rate specified in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement and the Servicing Fee Rate to the last day of the Collection Period relating to such repurchase. This repurchase obligation will constitute the sole remedy available to the Noteholders, the indenture trustee or the Issuing Entity for any such uncured breach by the Depositor. The obligation of the Depositor to repurchase a Receivable will not be conditioned on performance by TMCC of its obligation to purchase such Receivable from the Depositor pursuant to the Receivables Purchase Agreement.
Pursuant to each Sale and Servicing Agreement, to ensure uniform quality in servicing both the Receivables and the Servicer’s own portfolio of automobile and/or light duty truck installment sales contracts, as well as to reduce administrative costs, the Depositor and each Issuing Entity will designate the Servicer as custodian to maintain possession or, in the case of electronic contracts, control (directly, or through an agent), on behalf of such Issuing Entity, of the related installment sales contracts and any other documents relating to the Receivables. In performing its duties as custodian, the Servicer will act with reasonable care, using that degree of skill and attention that the Servicer exercises with respect to the Receivable files relating to comparable automotive Receivables that the Servicer services for itself or others. The Servicer will make available to the related Issuing Entity and the related Indenture Trustee a list of the locations of the Receivable files and the related accounts, records and computer systems maintained by the Servicer at such times during normal business hours as instructed by the related Issuing Entity or the related Indenture Trustee with reasonable advance notice. The Receivables will not be physically segregated from other automobile and/or light duty truck installment sales contracts of the Servicer, or those which the Servicer services for others, to reflect the transfer to the related Issuing Entity. However, UCC financing statements reflecting the sale and assignment of the Receivables by TMCC to the Depositor and by the Depositor to the applicable Issuing Entity and the pledge of the Receivables by the applicable Issuing Entity to the applicable indenture trustee will be filed, and the respective accounting records and computer files of TMCC and the Depositor will reflect such sale and assignment. The Depositor, or the Servicer on behalf of the Depositor, will be responsible for maintaining such perfected security interest through the filing of continuation statements or amended financing statements, as applicable. Because the Receivables will remain in the possession or control of the Servicer or its agent and will not be stamped or otherwise marked to reflect the assignment to the
indenture trustee, if a subsequent purchaser were able to take physical possession or, in the case of electronic Receivables, control of the Receivables without knowledge of the assignment, the indenture trustee’s interest in the Receivables could be defeated. For additional information, you should refer to “Risk Factors—The issuing entity’s security interests in financed vehicles may be unenforceable or defeated” and “Certain Legal Aspects of the Receivables—Security Interests” in this prospectus. In addition, under certain circumstances the indenture trustee’s security interest in collections that have been received by the Servicer but not yet remitted to the related Collection Account could be defeated.
Accounts
With respect to each Issuing Entity that issues Notes, the Servicer will establish and maintain with the related indenture trustee one or more accounts (each, a “Collection Account”), in the name of the indenture trustee on behalf of the related Noteholders and the Swap Counterparty, into which payments made on or with respect to the related Receivables, and all amounts released from any Yield Maintenance Account, Reserve Account, Prefunding Account or other form of credit enhancement will be deposited for payment to the related Noteholders.
If so provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Servicer will establish for each series of Notes an additional account (the “Payahead Account”), in the name of the related indenture trustee, into which, to the extent required by the Sale and Servicing Agreement, early payments by or on behalf of Obligors on Actuarial Receivables will be deposited until such time as the related payment becomes due. Until such time as payments ahead are transferred from the Payahead Account to a Collection Account, they will not constitute collected interest or collected principal and will not be available for payment to the applicable Noteholders or Certificateholders. The Payahead Account will initially be maintained with the applicable indenture trustee.
Any other accounts to be established with respect to an Issuing Entity, including any Yield Maintenance Account or any Reserve Account will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement.
For any series of Notes, funds in the related Collection Account not allocated for the purchase of additional Receivables during any Revolving Period, any Yield Maintenance Account, the Reserve Account and such other accounts as may be identified in the related Prospectus Supplement (collectively, the “Trust Accounts”) will be invested, at the direction of the Seller or the Servicer, as provided in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, in Eligible Investments.
“Eligible Investments” will be specified in the related Transfer and Servicing Agreements and are generally limited to investments acceptable to the Rating Agencies rating such Notes as being consistent with the rating of such Notes. Commercial paper issued by TMCC or its affiliates will be Eligible Investments, subject to satisfying criteria applicable to Eligible Investments. If specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, demand notes issued by TMCC will be Eligible Investments. Except as described below or in the related Prospectus Supplement, Eligible Investments are limited to obligations or securities that mature on or before the next Payment Date for such series. However, to the extent permitted by the Rating Agencies, funds in any Trust Account may be invested in securities that will not mature prior to the date of the next payment with respect to such Notes and will not be sold to meet any shortfalls. Thus, the amount of cash in any Reserve Account at any time may be less than the balance of the amount specified for such purpose. If the amount required to be withdrawn from any Reserve Account or drawn down on a Revolving Liquidity Note (at which time the Reserve Account may be unfunded) to cover shortfalls in collections on the related Receivables (as provided in the related Prospectus Supplement) exceeds the amount of cash in the Reserve Account, a temporary shortfall in the amounts paid to the related Noteholders could result, which could, in turn, increase the average life of the Notes of such series. Except as otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, investment earnings on funds deposited in the Trust Accounts, net of losses and investment expenses (collectively, “Investment Earnings”), will be released to the Servicer on each Payment Date as additional servicing compensation, or to the Seller (in the case of Investment Earnings in the Reserve Account).
The Trust Accounts will be maintained as Eligible Deposit Accounts. “Eligible Deposit Account” means either (a) a segregated account with an Eligible Institution or (b) a segregated trust account with the corporate trust department of a depository institution organized under the laws of the United States of America or any one of the states thereof or the District of Columbia (or any domestic branch of a foreign bank), having corporate trust powers and acting as trustee for funds deposited in such account, so long as any of the securities of such depository
institution have a credit rating from Standard & Poor’s Ratings Services, a Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC business, of at least BBB, if it is a Rating Agency, and a credit rating from each other Rating Agency in one of its generic rating categories which signifies investment grade. “Eligible Institution” means, with respect to an Issuing Entity, a depository institution or trust company (which may be the owner trustee, the indenture trustee or any of their respective affiliates) organized under the laws of the United States of America or any one of the states thereof or the District of Columbia (or any domestic branch of a foreign bank), (i) which has either (A) a long term unsecured debt rating acceptable to the Rating Agencies or (B) a short term unsecured debt rating or certificate of deposit rating acceptable to the Rating Agencies and (ii) whose deposits are insured by the FDIC. Except as otherwise provided in the Sale and Servicing Agreement, in the event that the Collection Account maintained with the Indenture Trustee is no longer an Eligible Deposit Account, then the Servicer will, with the Indenture Trustee’s assistance as necessary, use reasonable efforts to cause the Collection Account to be moved to an Eligible Institution within thirty days.
Servicing Procedures
The Servicer, for the benefit of each Issuing Entity, will manage, service, administer and make collections on the Receivables (other than Administrative Receivables and Warranty Receivables) with reasonable care, using that degree of skill and attention that the Servicer exercises with respect to all comparable motor vehicle retail installment sales contracts that it services for itself or others. The Servicer’s duties will include collection and posting of all payments, responding to inquiries of Obligors or by federal, state or local government authorities with respect to the Receivables, investigating delinquencies, sending payment coupons to Obligors, reporting tax information to Obligors in accordance with its Customary Servicing Practices, policing the collateral, accounting for collections and furnishing monthly and annual statements to the indenture trustee and owner trustee with respect to distributions, generating federal income tax information, making Advances and performing the other duties specified in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement. The Servicer will, in accordance with its Customary Servicing Practices, have full power and authority, acting alone, to do any and all things in connection with such managing, servicing, administration and collection that it may deem necessary or desirable. Without limiting the generality of the foregoing, the Servicer will be authorized and empowered to execute and deliver, on behalf of itself, each Issuing Entity, the owner trustee, the indenture trustee, the related Securityholders or any of them, any and all instruments of satisfaction or cancellation, or of partial or full release or discharge and all other comparable instruments, with respect to the Receivables and the Financed Vehicles. The Servicer is authorized to commence, in its own name or in the name of the related Issuing Entity, a legal proceeding to enforce a defaulted Receivable or to commence or participate in a legal proceeding (including without limitation a bankruptcy proceeding) relating to or involving a Receivable, including a defaulted Receivable. If the Servicer commences or participates in such a legal proceeding in its own name, the related Issuing Entity will be deemed to have automatically assigned, solely for the purpose of collection on behalf of the party retaining an interest in such Receivable, such Receivable and the other related property of the Issuing Entity with respect to such Receivable to the Servicer for purposes of commencing or participating in any such proceeding as a party or claimant. The Servicer is also authorized and empowered under each Sale and Servicing Agreement to execute and deliver in the Servicer’s name any notices, demands, claims, complaints, responses, affidavits or other documents or instruments in connection with any such proceeding. If in any enforcement suit or legal proceeding it will be held that the Servicer may not enforce a Receivable on the grounds that it will not be a real party in interest or a holder entitled to enforce such Receivable, the owner trustee on behalf of the related Issuing Entity will, at the Servicer’s expense and written direction, take steps to enforce such Receivable, including bringing suit in its name or the name of the Issuing Entity, the indenture trustee, the related Noteholders or the related Certificateholders. The owner trustee on behalf of the related Issuing Entity is required to furnish the Servicer with any powers of attorney and other documents and take any other steps which the Servicer may deem necessary or appropriate to enable the Servicer to carry out its servicing and administrative duties under the Sale and Servicing Agreement.
The Servicer will make reasonable efforts to collect all payments due with respect to the Receivables held by any Issuing Entity and will, consistent with the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, follow the collection procedures it follows with respect to comparable motor vehicle retail installment sales contracts it services for itself and others.
Consistent with its normal procedures, the Servicer will be authorized to grant certain rebates, adjustments or extensions with respect to the Receivables without the prior written consent of the owner trustee or the indenture
trustee. However, if the amount of any Scheduled Payment due in a subsequent Collection Period is reduced as a result of any modification to the related APR or the Amount Financed, an increase in the total number of Scheduled Payments or an extension of the maturity of a Receivable beyond the end of the Collection Period related to the final scheduled maturity date for the latest maturing class of Notes of the related series, as described in the related Prospectus Supplement (the “Final Scheduled Maturity Date”), the Servicer will be obligated either to purchase such Receivable, as described below, or make Advances on each subsequent Payment Date in amounts equal to the amount of any reduction to the related Scheduled Payments to be paid by the related Obligors during the subsequent Collection Periods, provided that the Servicer will have no such obligation to repurchase a Receivable, or make Advances in respect thereof, as a result of any such extension of the maturity of such Receivable if it is required to grant such extension under law or pursuant to a court order. However, the Servicer may, if a default, breach, violation, delinquency or event permitting acceleration under the terms of any Receivable has occurred or, in the judgment of the Servicer, is imminent:
| | (A) | extend such Receivable for credit related reasons that would be acceptable to the Servicer with respect to comparable new, or used automobile or light-duty truck receivables that it services for itself, but only if the final scheduled payment date of such Receivable as extended would not be later than the last day of the Collection Period preceding the Final Scheduled Maturity Date for the related series; or |
| | (B) | reduce an Obligor’s monthly payment amount in the event of a prepayment resulting from refunds of credit life and disability insurance premiums and service contracts and make similar adjustments in an Obligor’s payment terms to the extent required by law; |
Additionally, if at the end of the scheduled term of any Receivable, the outstanding principal amount of the Receivable is such that the final payment to be made by the related Obligor is larger than the regularly scheduled payment of principal and interest made by such Obligor, the Servicer may permit such Obligor to pay such remaining principal amount in more than one payment of principal and interest, provided that the last such payment will be due on or prior to the last day of the Collection Period preceding the Final Scheduled Maturity Date for the related series. The Servicer may, in accordance with its Customary Servicing Practices, waive any prepayment charge, late payment charge or any other fees that may be collected in the ordinary course of servicing the Receivables.
In the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Servicer will covenant that except as otherwise contemplated in such Sale and Servicing Agreement, (i) it will not release any Financed Vehicle from the security interest granted in the related Receivable except (a) in the event of payment in full by or on behalf of the Obligor thereunder or payment in full less a deficiency which the Servicer would not attempt to collect in accordance with its Customary Servicing Practices, (b) in connection with repossession or (c) as may be required by an insurer in order to receive proceeds from any insurance policy covering such Financed Vehicle; (ii) it will do nothing to impair the rights of the Securityholders in the Receivables and (iii) it will not amend any Receivable such that the total number of Scheduled Payments, the Amount Financed or the APR is altered or the maturity of a Receivable is extended beyond the Final Scheduled Maturity Date unless it is making Advances corresponding to reductions to Scheduled Payments as described above. By the last day of the second Collection Period following the Collection Period in which the Depositor, the Servicer, the indenture trustee or the owner trustee discovers or receives notice of a breach of any such covenant that materially and adversely affects the interests of the Securityholders in a Receivable, the Servicer, unless the breach is cured in all material respects, will purchase the Receivable (an “Administrative Receivable”) from the trustee at a price equal to the Administrative Purchase Payment for such Receivable. The “Administrative Purchase Payment” (1) for an Actuarial Receivable, will be equal to (a) the sum of (i) all remaining Scheduled Payments (plus any amounts on deposit in the applicable Yield Maintenance Account), (ii) an amount equal to any reimbursements of outstanding Advances made by the Servicer with respect to such Actuarial Receivable from collections on or in respect of other Receivables and (iii) all past due Scheduled Payments for which an Advance has not been made, minus (b) all Payments Ahead with respect to such Receivable then on deposit in the Payahead Account and the Rebate, if any, paid to the Obligor on an Actuarial Receivable on or before the date of such purchase and (2) for a Simple Interest Receivable, will be equal to its unpaid Principal Balance, plus interest thereon at a rate equal to the sum of the contract rate or Pass Through Rate specified in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement and the Servicing Fee Rate to the last day of the Collection Period relating to such purchase. Upon the purchase of any Administrative Receivable, the Servicer will for all purposes of the Sale and Servicing
Agreement be deemed to have released all claims for the reimbursement of outstanding Advances made in respect of such Receivable. This purchase obligation will constitute the sole remedy available to the Securityholders, the Issuing Entity, the indenture trustee or the owner trustee for any such uncured breach by the Servicer.
If the Servicer determines that eventual payment in full of a Receivable is unlikely, the Servicer will follow its normal practices and procedures to recover all amounts due upon such Receivable, including the repossession and disposition of the related Financed Vehicle at a public or private sale, or the taking of any other action permitted by applicable law. For additional information, you should refer to “Certain Legal Aspects of the Receivables” in this prospectus.
Insurance on Financed Vehicles
Each Receivable requires the related Obligor to possess physical damage insurance which covers loss or damage to the Financed Vehicle in an amount not less than the actual cash value thereof pursuant to which TMCC is named as a loss payee. Since the Obligors may select their own insurers to provide the requisite coverage, the specific terms and conditions of their policies may vary. The terms of each Receivable allow, but do not require, TMCC to obtain any such coverage on behalf of the Obligor. In accordance with its normal servicing procedures, TMCC currently does not obtain insurance coverage on behalf of the Obligor. TMCC currently does not monitor ongoing insurance compliance in connection with its customary servicing procedures. In the event that the failure of an Obligor to maintain any such required insurance results in a shortfall in amounts to be paid to Securityholders, to the extent such shortfall is not covered by amounts on deposit in the Reserve Account or other methods of credit enhancement, the Securityholders could suffer a loss on their investment.
Collections
With respect to each Issuing Entity, the Servicer will deposit all payments on the related Receivables (from whatever source) and all proceeds of such Receivables collected during each collection period specified in the related Prospectus Supplement (each, a “Collection Period”) into the related Collection Account.
For as long as (i) TMCC is the Servicer, (ii) a Servicer Default or an Event of Default has not occurred and is not continuing and (iii) the short-term unsecured debt of TMCC is rated in the highest category of, or is otherwise acceptable to, each Rating Agency rating the Notes (or alternative arrangements acceptable to the Rating Agencies are made) (the “Monthly Remittance Condition”), the Servicer may retain all payments on or in respect of the Receivables received from Obligors and all proceeds of Receivables collected during each Collection Period without segregation in its own accounts until deposited in the related Collection Account on or prior to the related Payment Date. However, if the Monthly Remittance Condition is not met, the Servicer will deposit all such payments and proceeds into the related Collection Account not later than two Business Days after identification. However, pending deposit into the Collection Account, collections may be invested by the Servicer at its own risk and for its own benefit and will not be segregated from its own funds, and the Servicer, at its own risk and for its own benefit, may instruct the indenture trustee to invest amounts held in the Collection Account or the Payahead Account from the time deposited until the related Payment Date in Eligible Investments. The Depositor or the Servicer, as the case may be, will remit the aggregate Warranty Purchase Payments and Administrative Purchase Payments of any Receivables to be purchased from the Issuing Entity into the Collection Account on or prior to the related Payment Date. If the Servicer were unable to remit such funds, Noteholders might incur a loss. For additional information, you should refer to “Risk Factors—Funds held by the servicer that are intended to be used to make payments on the securities may be exposed to a risk of loss” in this prospectus.
To the extent described in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Servicer may, in order to satisfy the requirements described above, obtain a letter of credit, guarantee, insurance policy or surety bond or make a deposit of cash or securities as provided in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement for the benefit of the related Issuing Entity to secure timely remittances of collections on the related Receivables and payment of the aggregate Warranty Purchase Payments and Administrative Purchase Payments with respect to Receivables required to be repurchased by the Depositor or the Servicer, as applicable.
Collections on or in respect of a Receivable made during a Collection Period (including Warranty Purchase Payments and Administrative Purchase Payments) which are not late fees, extension fees or certain other similar fees or charges will be applied first to any outstanding Advances made by the Servicer with respect to such Receivable, and then to the related Scheduled Payment. Any collections on or in respect of a Receivable remaining after such applications will be considered an “Excess Payment.” Excess Payments constituting a prepayment in full of Actuarial Receivables and any Excess Payments relating to Simple Interest Receivables will be applied as a prepayment in respect of such Receivable (each, a “Prepayment”). All other Excess Payments in respect of Actuarial Receivables will be held by the Servicer (or if the Servicer has not satisfied the conditions in clauses (i) through (iii) in the second preceding paragraph, deposited in the Payahead Account), as a Payment Ahead. On the records and computer systems maintained by the Servicer, Excess Payments in respect of a Simple Interest Receivable that do not constitute a prepayment in full typically result in future payments not being due on such Receivable in the amount of such Excess Payments.
Advances
The related Prospectus Supplement may specify that the Servicer is permitted or required to make advances of interest or principal payments on the Receivables. If the related Prospectus Supplement does not specify that the Servicer is required to make advances, then the Servicer is not required, but may be permitted, to make the advances described below or any other advances in respect of interest or principal payments on the Receivables.
If provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, if the Scheduled Payment due on an Actuarial Receivable (other than an Administrative Receivable or a Warranty Receivable) is not received in full by the end of the month in which it is due, whether as the result of any extension granted to the Obligor or otherwise, the amount of Payments Ahead, if any, not previously applied with respect to such Actuarial Receivable, will be applied by the Servicer to the extent of the shortfall and the Payments Ahead will be reduced accordingly. If any shortfall remains and if so provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Servicer will make an advance to the Issuing Entity in an amount equal to the amount of such shortfall (each, an “Actuarial Advance”). The Servicer will not be obligated to make an Actuarial Advance to the extent that it determines, in its sole discretion, that such Actuarial Advance will not be recovered from subsequent collections on or in respect of the related Actuarial Receivable. All Actuarial Advances will be reimbursable to the Servicer, without interest, if and when a payment relating to a Receivable with respect to which an Actuarial Advance has previously been made is subsequently received (other than from Administrative Purchase Payments). Upon the determination by the Servicer that reimbursement from the preceding source is unlikely, it will be entitled to recover unreimbursed Actuarial Advances from collections on or in respect of other Receivables.
In addition, if provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, if the Scheduled Payment on a Simple Interest Receivable (other than an Administrative Receivable or a Warranty Receivable) is not received in full by the end of the month in which it is due, the Servicer will, subject to the limitations described below, advance to the Issuing Entity an amount with respect to such Simple Interest Receivable equal to the product of the Principal Balance of such Simple Interest Receivable as of the first day of the related Collection Period and one twelfth of its APR minus the amount of interest actually received on such Simple Interest Receivable during the related Collection Period (each, a “Simple Interest Advance” and, together with the Actuarial Advances, the “Advances”). If such a calculation results in a negative number, an amount equal to such negative amount will be paid to the Servicer in reimbursement of outstanding Simple Interest Advances. In addition, in the event that a Simple Interest Receivable becomes a Liquidated Receivable, the amount of accrued and unpaid interest thereon (but not including interest for the current Collection Period) will, up to the amount of all outstanding Simple Interest Advances in respect of such Simple Interest Receivable, be withdrawn from the related Collection Account and paid to the Servicer in reimbursement of such outstanding Simple Interest Advances. No advances of principal will be made with respect to Simple Interest Receivables. The Servicer will not be obligated to make a Simple Interest Advance (other than in respect of an interest shortfall arising from the prepayment of a Simple Interest Receivable) to the extent that it determines, in its sole discretion, that such Simple Interest Advance will not be recovered from subsequent collections on or in respect of the related Simple Interest Receivable. All Simple Interest Advances will be reimbursable to the Servicer, without interest, when a payment relating to a Receivable with respect to which a Simple Interest Advance has previously been made is subsequently received (other than from Administrative Purchase Payments). Upon the determination by the Servicer that reimbursement from the preceding source is
unlikely, it will be entitled to recover unreimbursed Simple Interest Advances from collections on or in respect of other Receivables.
If provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Servicer will also be required to make Advances with respect to each Receivable that it does not purchase as described above under “—Servicing Procedures” as to which it has made any modification that reduces the amount of Scheduled Payments to be paid by the related Obligor during subsequent Collection Periods.
If provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Servicer will make all Advances by depositing into the related Collection Account an amount equal to the aggregate of the Actuarial Advances and Simple Interest Advances due in respect of a Collection Period on or prior to the related Payment Date. The related Prospectus Supplement will describe the provisions to be contained in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement with regard to the applicable dates when Advances must be deposited into the related Collection Account.
Servicing Compensation and Payment of Expenses
Unless otherwise specified in the Prospectus Supplement with respect to any Issuing Entity, the Servicer will be entitled to receive the servicing fees for each Collection Period, as compensation for services rendered, in an amount generally equal to one-twelfth of the product of (a) the servicing fee rate as described in the related Prospectus Supplement (the “Servicing Fee Rate”), and (b) the Pool Balance as of the first day of the related Collection Period (the “Basic Servicing Fee”).
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement with respect to a given Issuing Entity, the Servicer will also be entitled to collect and retain any late fees, extension fees and other administrative fees or similar charges allowed by applicable law with respect to the related Receivables as additional servicing compensation (the “Supplemental Servicing Fee” and, together with the Basic Servicing Fee, the “Total Servicing Fee”) and will be entitled to reimbursement from the Issuing Entity for certain liabilities. The Total Servicing Fee (together with any portion of all servicing fees that remains unpaid from prior Payment Dates) will be paid or retained by the Servicer as provided in the related Prospectus Supplement. The Servicer (or the Seller, in the case of the Reserve Account) may also be entitled to receive any interest earned during a Collection Period from the investment of monies in the Trust Accounts. Payments by or on behalf of Obligors will be allocated to scheduled payments and late fees and other charges in accordance with the Servicer’s Customary Servicing Practices.
The Total Servicing Fee will compensate the Servicer for performing the functions of a third party servicer of Receivables as an agent for their beneficial owner, including collecting and posting all payments, responding to inquiries of Obligors on the Receivables, investigating delinquencies, providing payment information, paying costs of collections and policing the collateral. The Servicing Fee also will compensate the Servicer for administering the particular Receivables Pool, including making Advances, accounting for collections and furnishing monthly and annual statements to the related owner trustee and indenture trustee with respect to payments and generating federal income tax information for such Issuing Entity and for the related Noteholders and Certificateholders. The Total Servicing Fee also will reimburse the Servicer for certain taxes, the fees of the related owner trustee and indenture trustee, if any, accounting fees, outside auditor fees, data processing costs and other costs incurred in connection with administering the applicable Receivables Pool.
The “Pool Balance” will equal the aggregate Principal Balance of the Receivables. The “Principal Balance” of a Receivable as of any date will equal the Amount Financed (as defined in the related Transfer and Servicing Agreement) minus the sum of (i) in the case of an Actuarial Receivable, that portion of all Scheduled Payments due on or prior to such date allocable to principal, computed in accordance with the actuarial method, (ii) in the case of a Simple Interest Receivable, that portion of all Scheduled Payments actually received on or prior to such date allocable to principal, (iii) any Warranty Purchase Payment or Administrative Purchase Payment with respect to such Receivable allocable to principal (to the extent not included in clauses (i) and (ii) above) and (iv) any Prepayments or other payments applied to reduce the unpaid principal balance of such Receivable (to the extent not included in clauses (i), (ii) and (iii) above).
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the initial aggregate Principal Balance of the Receivables to be sold to the Issuing Entity on the Closing Date will be discounted to reflect the present value of all scheduled payments due on the Receivables that have not been applied on or prior to the Cutoff Date.
Payments
With respect to each series of Securities, beginning on the Payment Date specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, payments of principal and interest (or, where applicable, of principal or interest only) on each class of such Securities entitled thereto will be made by the applicable indenture trustee to the Noteholders and by the applicable owner trustee to the Certificateholders of such series. The timing, calculation, allocation, order, source, priorities of and requirements for all payments to each class of Noteholders and all payments to each class of Certificateholders of such series will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement.
With respect to each Issuing Entity, on each Payment Date collections received on the related Receivables during the preceding Collection Period will be withdrawn from the related Collection Account, based upon information provided by the Servicer, and will be paid to the Noteholders and/or Certificateholders to the extent provided in the related Prospectus Supplement. Credit enhancement, such as a Reserve Account, will be available to cover any shortfalls in the amount available for payment to the Noteholders on such date to the extent specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. As more fully described in the related Prospectus Supplement, and unless otherwise specified in such Prospectus Supplement, (i) payments in respect of principal of a class of Notes of a given series will be subordinate to payments in respect of interest on such class; (ii) unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, payments in respect of the Certificates of such series will be subordinate to payments in respect of Notes of such series; and (iii) payments in respect of one or more classes of Notes of such series may be subordinated to payments in respect of other classes of Notes of such series.
Credit and Cash Flow Enhancement
The amounts and types of credit and cash flow enhancement arrangements and the provider thereof, if applicable, with respect to each class of Notes of a given series, if any, will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement. If and to the extent provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, credit and cash flow enhancement may be in the form of sequential payment of certain classes of Notes, subordination of one or more classes of Notes, Reserve Accounts, Yield Maintenance Accounts and yield maintenance agreements, overcollateralization, letters of credit, cash collateral accounts, surety bonds, guaranteed investment contracts, repurchase obligations, cash deposits, credit or liquidity facilities (including the issuance by an Issuing Entity of a Revolving Liquidity Note), excess interest, or currency or interest rate swap agreements, as may be described in the related Prospectus Supplement or any combination of two or more of the foregoing. If specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, credit or cash flow enhancement for a class of Notes may cover one or more other classes of Notes of the same series.
The presence of a Reserve Account and other forms of credit enhancement for the benefit of any class or series of Notes is intended to enhance the likelihood of receipt by the Noteholders of such class or series of the full amount of principal and interest due thereon and to decrease the likelihood that such Noteholders will experience losses. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the credit enhancement for a class or series of Notes will not provide protection against all risks of loss and will not guarantee repayment of the entire principal amount and interest thereon. If losses occur that exceed the amount covered by any credit enhancement or that are not covered by any credit enhancement, Noteholders of any class or series will bear their allocable share of deficiencies, as described in the related Prospectus Supplement. In addition, if a form of credit enhancement covers more than one class of Notes, Noteholders of any such class will be subject to the risk that such credit enhancement will be exhausted by the claims of Noteholders of other classes.
Sequential Payment of Certain Classes of Notes. The notes are entitled to receive distributions in accordance with various priorities for payment of principal as described in the related Prospectus Supplement. Distributions of principal on classes of notes having an earlier priority of payment will be affected by the rates of prepayment of the Receivables early in the life of the asset pool. The timing of commencement of principal distributions and the weighted average lives of classes of Notes with a later priority of payment will be affected by
the rates of prepayment of the Receivables both before and after the commencement of principal distributions on those classes of Notes.
Subordination of Principal and Interest. As further described in the related Prospectus Supplement, payments of principal or interest on certain classes of Notes will be subordinated to payments of principal or interest on other classes of Notes.
Reserve Account. If so provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Depositor or a third party will establish and own for a series or class of Notes an account, as specified in the related Prospectus Supplement (the “Reserve Account”), which will be maintained with the related indenture trustee. Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Reserve Account will be funded by an initial deposit by the Depositor or a third party on the Closing Date in the amount described in the related Prospectus Supplement (the “Reserve Account Initial Deposit”). To the extent provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, the amount on deposit in the Reserve Account will be increased on each Payment Date thereafter up to the Specified Reserve Account Balance (as defined in the related Prospectus Supplement) by the deposit to the Reserve Account of the amount of collections on the related Receivables remaining on each such Payment Date after the payment of all other required payments on such date. The related Prospectus Supplement will describe the circumstances and manner under which payments may be made out of the Reserve Account, either to holders of the Notes covered thereby or to the Depositor or a third party.
Yield Maintenance Account. A “Yield Maintenance Account” may be established with respect to any class or series of Notes. The terms relating to any such account will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement. Each Yield Maintenance Account will be designed to hold funds to be applied by the related indenture trustee, to provide payments to Noteholders in respect of Receivables that have APRs less than the sum of the Pass Through Rate or Interest Rate specified in the related Prospectus Supplement plus the Servicing Fee Rate specified in the related Prospectus Supplement (the “Required Rate”). Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, each Yield Maintenance Account will be maintained with the same entity with which the related Collection Account is maintained and will be created with an initial deposit in an amount and by the Depositor or other person specified in the related Prospectus Supplement.
On each Payment Date, the related indenture trustee will transfer to the Collection Account from monies on deposit in the Yield Maintenance Account an amount specified in the related Prospectus Supplement (the “Yield Maintenance Deposit”) in respect of the Receivables having APRs less than the Required Rate for such Payment Date. Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, amounts on deposit on any Payment Date in the Yield Maintenance Account in excess of the “Required Yield Maintenance Amount” specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, after giving effect to all payments to be made on such Payment Date, will be released to the Depositor. Monies on deposit in the Yield Maintenance Account may be invested in Eligible Investments under the circumstances and in the manner described in the related Trust Agreement. Any monies remaining on deposit in the Yield Maintenance Account upon the termination of the Issuing Entity also will be released to the Depositor.
Yield Maintenance Agreement. If a Yield Maintenance Account is established with respect to any class or series of Notes that allows or requires any party to make deposits into such Yield Maintenance Account after the Closing Date, TMCC, the Depositor, any third party responsible for such deposits and the related owner trustee or indenture trustee, as the case may be, will enter into a “Yield Maintenance Agreement” pursuant to which, on each Payment Date, such party will deposit into the Yield Maintenance Account the difference between the amount held on deposit in the Yield Maintenance Account as of such Payment Date and the Required Yield Maintenance Amount, in each case determined after giving effect to all required withdrawals from the Yield Maintenance Account on such Payment Date.
Overcollateralization. Overcollateralization is the amount by which the principal amount of the Receivables owned by an Issuing entity exceeds the principal amount of all of the Issuing Entity’s outstanding Securities. Overcollateralization may be used as credit enhancement and/or to provide limited protection against losses and low-interest receivables.
Letter of Credit. A letter of credit, which will be issued by a bank or other financial institution, may be issued in a maximum amount which may be permanently reduced as draws are made or may be replenished as
previous draws are repaid from certain excess cash amounts generated by the Receivables. Draws may be made to cover shortfalls generally in collections, with respect to particular types of shortfalls such as those due to particular types of losses or with respect to specific situations such as shortfalls in amounts necessary to pay current interest.
Cash Collateral Account. The Prospectus Supplement may provide that upon the occurrence of an event of default by the Servicer, a segregated cash collateral account may be established as security for the Servicer’s obligations under the Sale and Servicing Agreement.
Surety Bond. The Prospectus Supplement may provide that the Issuing Entity enter into agreements (i.e. obtain a “Surety Bond” agreement) with an insurer pursuant to which the insurer guarantees payments of principal and/or interest on the Notes. If on any date specified in the Prospectus Supplement the amount on deposit in the Collection Account, after giving effect to all amounts deposited to or payable from a Payahead Account, any prefunding account or yield maintenance account or a capitalized interest agreement with respect to the related Payment Date, is less than the sum of the Servicing Fee, and amounts due to Noteholders on the related Payment Date, the indenture trustee by delivering a notice to the insurer will demand payment under any such Surety Bond in an amount equal to the deficiency. The related Prospectus Supplement will describe the circumstances and manner under which payments may be made under any such Surety Bond, either to Noteholders, or the owner trustee or the indenture trustee.
Guaranteed Investment Contracts. Specified Available Collections (as that term is defined in the Prospectus Supplement) may be invested under a guaranteed investment contract issued by an insurance company, financial institution or other entity.
Repurchase Obligations. Pursuant to agreements between TMCC and the Dealers, each Dealer is obligated to repurchase from TMCC contracts that do not meet certain representations and warranties made by such Dealer. Such representations and warranties relate primarily to the origination of the contracts and the perfection of the security interests in the related Financed Vehicles, and do not relate to the creditworthiness of the related Obligors or the collectibility of such contracts. Although the Dealer Agreements with respect to the Receivables will not be assigned to the Issuing Entity, TMCC’s interest in any Dealer Recourse will be assigned, and the related Sale and Servicing Agreement will require that TMCC deposit any recovery in respect of any Receivable pursuant to any Dealer Recourse in the related Collection Account. However, the representations and warranties of the Dealers in the Dealer Agreements will not be incorporated in the Transfer and Servicing Agreements for any series of Notes and TMCC will not represent or warrant in the Transfer and Servicing Agreements that the representations and warranties of the Dealers in the Dealer Agreements are true and correct. Thus, TMCC will not be obligated to repurchase any Receivables upon a breach of representation or warranty by the related Dealer.
In addition, the Depositor and TMCC will make representations and warranties relating to the Receivables’ compliance with law and the Issuing Entity’s ability to enforce the Contracts. If the Depositor breaches any of these representations or warranties, the Issuing Entity’s sole remedy will be to require the Depositor to repurchase the affected Receivables. Under certain circumstances, the Servicer will be obligated to repurchase Receivables from a given Issuing Entity pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement as a result of breaches of certain representations and warranties or covenants. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Sale and Assignment of Receivables” and “—Servicing Procedures” in this prospectus.
Cash Deposits. The Depositor may fund accounts or may otherwise provide cash deposits to provide additional funds that may be applied to make payments on the Notes issued by the Issuing Entity. Any such arrangements will be disclosed in the related Prospectus Supplement.
Revolving Liquidity Note. If so provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, and a Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement (the “Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement”), the Issuing Entity will issue a Revolving Liquidity Note (the “Revolving Liquidity Note”) to TMCC, or a creditworthy third party. The related Prospectus Supplement will describe the circumstances and manner under which amounts may be drawn down under the Revolving Liquidity Note to make payments either to holders of the Notes covered thereby or to the Depositor or a third party.
Excess Interest. More interest is expected to be paid by the Obligors in respect of the Receivables than is necessary to pay the related servicing fee, trustee fees and expenses, and interest on the Notes for each payment period, as described in the related Prospectus Supplement. Any such excess in interest payments from Obligors will serve as additional credit enhancement.
Derivative Agreements. If specified in a related Prospectus Supplement, an Issuing Entity may enter into one or more currency or interest rate swap agreements to reduce its exposure to changes in currency exchange rates or interest rate risks, as applicable, or to offset basis risk between Receivables that pay based on one index and Notes that pay based on a different index.
Net Deposits
As an administrative convenience, unless the Servicer is required to remit collections daily (as described under “—Collections” above), the Servicer will be permitted to make the deposit of collections, aggregate Advances and Administrative Purchase Amounts for any Issuing Entity for or with respect to the related Collection Period on a monthly basis and net of payments to be made to the Servicer for such Issuing Entity with respect to such Collection Period. The Servicer may cause to be made a single, net transfer from the Collection Account to the Payahead Account, if any, or vice versa. The Servicer, however, will account to the owner trustee, any indenture trustee, the Noteholders and the Certificateholders with respect to each Issuing Entity as if all deposits, payments and transfers were made individually. If the related Payment Dates are not the same for all classes of Notes, all distributions, deposits or other remittances made on a Payment Date will be treated as having been distributed, deposited or remitted on the same Payment Date for the applicable Collection Period for purposes of determining other amounts required to be distributed, deposited or otherwise remitted on a Payment Date.
Statements to Trustees and Issuing Entity
On a Business Day in each month that precedes each Payment Date (each a “Determination Date” to be specified in the related Prospectus Supplement), the Servicer will provide to the applicable indenture trustee and the applicable owner trustee a statement setting forth with respect to a series of Securities substantially the same information as is required to be provided in the periodic reports provided to Securityholders of such series described under “Certain Information Regarding the Notes—Reports to Securityholders” in this prospectus.
Evidence as to Compliance
Each Sale and Servicing Agreement will provide that a firm of nationally recognized independent accountants will furnish to the related Issuing Entity, administrator, indenture trustee and owner trustee annually a statement as to compliance in all material respects by the Servicer during the preceding twelve months (or, in the case of the first such certificate, from the applicable Closing Date, which may be a longer or shorter period) with certain standards relating to the servicing of the applicable Receivables.
Each Sale and Servicing Agreement will also provide for delivery to the related Issuing Entity, indenture trustee and owner trustee, substantially simultaneously with the delivery of such accountants’ statement referred to above, of a certificate signed by an officer of the Servicer stating that the Servicer has fulfilled its obligations under the Sale and Servicing Agreement throughout the preceding twelve months (or, in the case of the first such certificate, from the Closing Date) in all material respects or, if there has been a material default in the fulfillment of any such obligation, describing each such default. The Servicer has agreed to give each indenture trustee and each owner trustee notice of certain Servicer Defaults under the related Sale and Servicing Agreement.
Each Sale and Servicing Agreement will require the Servicer to furnish to the related Issuing Entity and the indenture trustee any report or information required to facilitate compliance by the Issuing Entity with Subpart 229.1100 – Asset Backed Securities (Regulation AB), 17 C.F.R. §§229.1100-229.1123, as that regulation may be amended from time to time, and subject to such clarification and interpretation as have been provided by the SEC in the adopting release (Asset-Backed Securities, Securities Act Release No. 33-8518.70 Fed. Reg. 1.506.1.531 (January 7, 2005)) or by the staff of the Commission, or as may be provided by the Commission or its staff from time to time.
Copies of such statements and certificates may be obtained by Noteholders by a request in writing addressed to the applicable indenture trustee.
Certain Matters Regarding the Servicer; Servicer Liability
Each Sale and Servicing Agreement will provide that TMCC may not resign from its obligations and duties as Servicer under the Sale and Servicing Agreement, except upon determination that TMCC’s performance of such duties is no longer permissible under applicable law, except as provided in the immediately following paragraph. No such resignation will become effective until the related indenture trustee or a successor servicer has assumed TMCC’s servicing obligations and duties under such Sale and Servicing Agreement.
Under the circumstances specified in each Sale and Servicing Agreement, any entity into which the Servicer may be merged or consolidated, or any entity resulting from any merger or consolidation to which the Servicer is a party, or any entity succeeding to all or substantially all of the business of the Servicer will be the successor of the Servicer under such Sale and Servicing Agreement.
Each Sale and Servicing Agreement will further provide that neither the Servicer nor any of its directors, officers, employees and agents will be under any liability to the related Issuing Entity or the related Noteholders or Certificateholders for taking any action or for refraining from taking any action pursuant to such Sale and Servicing Agreement or for errors in judgment; except that neither the Servicer nor any such person will be protected against any liability that would otherwise be imposed by reason of willful misfeasance, bad faith or negligence in the performance of the Servicer’s duties under the Sale and Servicing Agreement or by reason of reckless disregard of its obligations and duties under the Sale and Servicing Agreement. In addition, each Sale and Servicing Agreement will provide that the Servicer is under no obligation to appear in, prosecute or defend any legal action that is not incidental to the Servicer’s servicing responsibilities under such Sale and Servicing Agreement and that, in its opinion, may cause it to incur any expense or liability.
Upon a termination of the Servicer, the indenture trustee will select and appoint a successor servicer to perform the outgoing Servicer’s duties and undertake its responsibilities and liabilities. The appointed successor servicer must be an established financial institution with a net worth of at least $25,000,000 and whose regular business includes the servicing of contracts. The successor servicer will hold all the rights of the outgoing Servicer under the Transfer and Servicing Agreements and will be entitled to receive the servicing fee described in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement. No successor servicer appointed in accordance with the Transfer and Servicing Agreements may resign from its duties unless the law prohibits it from continuing to perform such duties.
Upon the termination or resignation of the Servicer, the outgoing Servicer will transfer all cash amounts that are to be held by the successor servicer to the successor servicer and will provide the successor servicer with all information regarding the Receivable files that is required for the proper servicing of the Receivables. All reasonable and documented costs, expenses and fees incurred in connection with the transfer of Receivable files to the successor servicer under the provisions described in this paragraph will be paid by the outgoing Servicer. The owner trustee and the indenture trustee will provide prompt written notice of any resignation or termination of the Servicer to the Certificateholders and Noteholders, respectively, upon either occurrence.
Servicer Default
Except as otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, “Servicer Default” under each Sale and Servicing Agreement will consist of (1) any failure by the Servicer (or the Depositor, so long as TMCC is the Servicer) to deliver to the applicable owner trustee or indenture trustee for deposit in any of the Trust Accounts any required payment or to direct the applicable owner trustee or indenture trustee to make any required distributions therefrom, which failure continues unremedied for five Business Days after receipt by the Servicer of written notice of such failure given (a) to the Servicer (or the Depositor, so long as TMCC is the Servicer) by the applicable owner trustee or indenture trustee or (b) to the Depositor or the Servicer, as the case may be, and to the applicable owner trustee and indenture trustee, by the holders of Notes of the related series evidencing not less than a majority of the principal amount of such outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class; (2) any failure by the Servicer duly to observe or perform in any material respect any other covenant or agreement in such Sale and Servicing Agreement, which failure materially and adversely affects the rights of the Noteholders or the Certificateholders of the related series
and which continues unremedied for 90 days after the giving of written notice of such failure (A) to the Servicer or the Depositor, as the case may be, by the applicable owner trustee or indenture trustee or (B) to the Servicer or the Depositor, as the case may be, and to the applicable owner trustee and indenture trustee, by the holders of Notes of the related series evidencing not less than a majority of the principal amount of such outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class; and (3) the occurrence of an Insolvency Event with respect to the Servicer. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if a delay in or failure of performance referred to under clause (1) or (2) above was caused by force majeure or other similar occurrences, the grace period described in clauses (1) and (2) will be extended for an additional period of 60 calendar days. Upon the occurrence of any such event, the Servicer will not be relieved from using all commercially reasonable efforts to perform its obligations in a timely manner in accordance with the terms of the Servicing Agreement, and the Servicer will provide to the owner trustee, the indenture trustee, the Depositor and the Securityholders prompt notice of such failure or delay by it, together with a description of its efforts to so perform its obligations. The applicable Rating Agencies will be given prompt written notice of the occurrence of a Servicer Default.
“Insolvency Event” means, with respect to any Person, any of the following events or actions: certain events of insolvency, readjustment of debt, marshaling of assets and liabilities or similar proceedings with respect to such Person and certain actions by such Person indicating its insolvency, reorganization pursuant to bankruptcy proceedings or inability to pay its obligations.
Rights Upon Servicer Default
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, as long as a Servicer Default under a Sale and Servicing Agreement remains unremedied, the related indenture trustee or holders of Notes of the related series evidencing not less than a majority of principal amount of such Notes of the Controlling Class then outstanding, acting together as a single class, may terminate all the rights and obligations of the Servicer under such Sale and Servicing Agreement (except for obligations that expressly survive termination), whereupon such indenture trustee or a successor servicer appointed by such indenture trustee will succeed to all the responsibilities, duties and liabilities of the Servicer under such Sale and Servicing Agreement and will be entitled to similar compensation arrangements. If the Servicer becomes a debtor in bankruptcy or, if not eligible to be a debtor in bankruptcy, becomes the subject of insolvency proceedings, and no Servicer Default other than such commencement of a bankruptcy or insolvency proceeding has occurred, such indenture trustee or such Noteholders may be unable to effect a transfer of servicing. In the event that such indenture trustee is unwilling or unable to so act, it may appoint, or petition a court of competent jurisdiction for the appointment of, a successor with a net worth of at least $50,000,000 and whose regular business includes the servicing of automobile and/or light duty truck receivables. Such indenture trustee may make such arrangements for compensation to be paid, which in no event may be greater than the servicing compensation to the Servicer under such Sale and Servicing Agreement. Notwithstanding such termination, the Servicer will be entitled to payment of certain amounts payable to it prior to such termination for services rendered prior to such termination.
Waiver of Past Defaults
With respect to each Issuing Entity that has issued Notes, unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement (i) the holders of Notes evidencing not less than a majority of the principal amount of the then outstanding Notes of the Controlling Class of the related series, acting together as a single class, may, on behalf of all such Noteholders, waive any default by the Servicer in the performance of its obligations under the related Sale and Servicing Agreement and its consequences, except a Servicer Default in making any required deposits to or payments from any of the Trust Accounts in accordance with such Sale and Servicing Agreement. No such waiver will impair such Noteholders’ rights with respect to subsequent defaults.
Amendment
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, each of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements may be amended by the parties thereto, without the consent of the related Noteholders or Certificateholders, to cure any ambiguity, to correct or supplement any provisions in the Transfer and Servicing Agreements or for the purpose of adding any provisions to or changing in any manner or eliminating any of the provisions of such Transfer and Servicing Agreements or of modifying in any manner the rights of such
Noteholders; provided, that either (i) an officer’s certificate has been delivered by the Servicer to the relevant trustees certifying that such officer reasonably believes that such supplemental indenture will not materially and adversely affect the interest of any such Noteholder or (ii) the relevant indenture trustee has been provided a letter from each applicable Rating Agency to the effect that such amendment will not result in the reduction or withdrawal of any rating it currently assigns to any class of Notes of the related series, or each other Rating Agency has been provided with 10 days prior notice of the proposed amendment and each such other Rating Agency has not notified the relevant trustee that the proposed amendment might or would result in the reduction or withdrawal of the rating it has currently assigned to any class of Notes of the related series.
Each Transfer and Servicing Agreement may also be amended by the parties thereto without the consent of any Noteholder or Certificateholder for the purpose of changing the formula or percentage for determining the Specified Reserve Account Balance, the manner in which a Reserve Account is funded, changing the remittance schedule for deposit of collections in accounts or changing the definition of Eligible Investments if the relevant trustee has been provided a letter from each applicable Rating Agency to the effect that such amendment will not result in the reduction or withdrawal of any rating it currently assigns to any class of Notes of the related Series, or each other Rating Agency has been provided with 10 days’ prior notice of the amendment and each such other Rating Agency has not notified the relevant trustee that the amendment might or would result in the reduction or withdrawal of the rating it has currently assigned to any class of Notes of the related Series.
Unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Transfer and Servicing Agreements may also be amended by the parties thereto, with the consent of the related indenture trustee and with prior notice to the Rating Agencies, for the purpose of adding any provisions to or changing in any manner or eliminating any of the provisions of any such agreement or of modifying in any manner the rights of the Noteholders or Certificateholders under such agreement; provided, that if the interests of the Noteholders are materially and adversely affected, the Noteholders evidencing at least a majority of the outstanding principal amount of each class of Notes of the Controlling Class of the related series, acting as a single class have consented to such amendment.
However, no amendment to a Transfer and Servicing Agreement may (x) increase or reduce in any manner the amount of, or accelerate or delay the timing of, collections of payments on the related Receivables or distributions that are required to be made for the benefit of such Noteholders or Certificateholders without the consent of all Noteholders and Certificateholders adversely affected thereby, or (y) reduce the percentage of the Notes or Certificates of such series which are required to consent to any such amendment without the consent of the Noteholders and Certficateholders adversely affected thereby; provided, that any amendment referred to in clause (x) or (y) above will be deemed to not adversely affect any Noteholder if the relevant trustee has been provided a letter from each applicable Rating Agency to the effect that such amendment will not result in the reduction or withdrawal of the rating it has currently assigned to the Notes of that class, or each other Rating Agency has been provided with 10 days prior notice of the amendment and each such other Rating Agency has not notified the relevant trustee that the amendment might or would result in the reduction or withdrawal of the rating it has currently assigned to the Notes of that class. No amendment referred to in clause (x) in the immediately preceding sentence will be permitted unless an officer’s certificate has been delivered by the Servicer to the relevant trustees certifying that such officer reasonably believes that such proposed amendment will not materially and adversely affect the interest of any such Noteholder whose consent was not obtained.
Non-Petition
Each Trust Agreement will provide that the applicable owner trustee does not have the power to commence a voluntary proceeding in bankruptcy with respect to the related Issuing Entity without the unanimous prior approval of all Certificateholders (including the Depositor) of such Issuing Entity and the delivery to such owner trustee by each such Certificateholder (including the Depositor) of a certificate certifying that such Certificateholder reasonably believes that such Issuing Entity is insolvent.
In addition, each Transfer and Servicing Agreement will include an agreement of each party thereto that such party will not commence bankruptcy proceedings against the Issuing Entity or the Depositor in connection with any obligations relating to the Certificates, the Notes, such Agreement or any of the other related agreements prior to the date which is one year and one day after the termination of the Indenture.
Payment of Notes
Upon the payment in full of all outstanding Notes of a given series and the satisfaction and discharge of the related Indenture, the related owner trustee will succeed to all the rights of the indenture trustee, and the Certificateholders of such series will succeed to all the rights of the Noteholders of such series, under the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, except as otherwise provided in such Sale and Servicing Agreement.
Depositor Liability
Under each Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Depositor will agree to be liable directly to an injured party solely to the extent described in such Sale and Servicing Agreement.
Termination
With respect to each Issuing Entity, the obligations of the Servicer, the Depositor, the related owner trustee and the related indenture trustee, as the case may be, pursuant to the Transfer and Servicing Agreements will terminate upon the earlier of (i) the maturity or other liquidation of the last related Receivable and the disposition of any amounts received upon liquidation of any property remaining in the Issuing Entity and (ii) the payment to Noteholders, if any, and Certificateholders of the related series of all amounts required to be paid to them pursuant to the Transfer and Servicing Agreements.
The related indenture trustee will give written notice of termination to each Noteholder of record. The final distribution to any Noteholder will be made only upon surrender and cancellation of that holder’s Note at any office or agency of the related indenture trustee specified in the notice of termination. Any funds remaining in the Issuing Entity, after the related indenture trustee has taken measures to locate Noteholders as described in the related Sale and Servicing Agreement or Indenture and those measures have failed, will be distributed, subject to applicable law, as provided in the Indenture or the Trust Agreement, as applicable.
Unless otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, in order to avoid excessive administrative expense, the Servicer, or an affiliate, will have the option to purchase from each Issuing Entity, on any Payment Date, the Receivables remaining in the related Issuing Entity if, as of the last day of the related Collection Period, the related Pool Balance is equal to or less than the percentage specified in the related Prospectus Supplement of the Pool Balance on the related Cutoff Date, but in any case an amount at least equal to the unpaid principal amount of the outstanding Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon and, if so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, any amounts payable to the swap counterparty. The related owner trustee or indenture trustee will give written notice of termination to each Securityholder.
If specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, if a default under the Revolving Liquidity Note occurs, the principal of each class of Notes may become immediately payable and the Issuing Entity will terminate upon payment of all amounts due to the Noteholders. In such event, the indenture trustee will be obligated to liquidate the assets of the Issuing Entity and the proceeds therefrom (and amounts held in related accounts) will be applied to pay the Notes of the related series in full, to the extent of amounts available therefor. Similarly, if so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, if a Swap Termination or an Event of Default occurs during a Revolving Period, such Swap Termination or Event of Default may cause the early termination of the Revolving Period and the commencement of payments of principal on the Notes.
Upon termination of any Issuing Entity, the related owner trustee will, or will direct the related indenture trustee to, promptly sell the assets of such Issuing Entity (other than the Trust Accounts) in a commercially reasonable manner and on commercially reasonable terms. The proceeds from any such sale, disposition or liquidation of the Trust Estate of such Issuing Entity will be treated as collections on such Receivables and deposited in the related Collection Account. With respect to any Issuing Entity, if the proceeds from the liquidation of the related Trust Estate and any amounts on deposit in the related Reserve Account, if any, Yield Maintenance Account, if any, Payahead Account, if any, and Collection Account are not sufficient to pay the Notes in full, the amount of principal returned to Noteholders of the related series will be reduced and some or all of such Noteholders will incur a loss.
As more fully described in the related Prospectus Supplement, any outstanding Notes of the related series will be redeemed concurrently with any of the events specified above and the subsequent payment to the related Certificateholders of all amounts required to be paid to them pursuant to the applicable Trust Agreement will effect early retirement of the Certificates of such series.
Administration Agreement
TMCC, in its capacity as administrator, will enter into an agreement (as amended and supplemented from time to time, an “Administration Agreement”) with each Issuing Entity that issues Notes and the related indenture trustee pursuant to which the administrator will agree, to the extent provided in such Administration Agreement, to provide the notices and to perform other administrative obligations required by the related Indenture.
In addition, and unless otherwise specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, it will be the obligation of the administrator to:
| | · | pay the related indenture trustee the compensation provided for in the related Indenture; |
| | · | reimburse each indenture trustee for its reasonable expenses, disbursements and advances incurred by each such indenture trustee in accordance with the Indenture, except any such expense, disbursement or advance as may be attributable to its willful misconduct, negligence or bad faith; |
| | · | reimburse each owner trustee for its reasonable expenses, disbursements and advances incurred by each such owner trustee in accordance with the Trust Agreement, except any such expenses, disbursement or advance as may be attributable to its willful misconduct, gross negligence or bad faith; and |
| | · | indemnify each owner trustee and indenture trustee for, and hold them harmless against, any loss, liability or expense incurred without negligence (or gross negligence, in the case of an owner trustee) or bad faith on its part, arising out of or in connection with the acceptance or administration of the transactions contemplated by the applicable agreements, including the reasonable costs and expenses of defending itself against any claim or liability in connection with the exercise or performance of any of its powers or duties under the related Indenture or Trust Agreement, as applicable, to the extent it is entitled to such indemnification under the related Indenture, with respect to each indenture trustee, and under the related Trust Agreement, with respect to each owner trustee. |
The obligations of the administrator with respect to the owner trustee and indenture trustee will survive the termination of the Administration Agreement.
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement with respect to any such Issuing Entity, as compensation for the performance of the administrator’s obligations under the applicable Administration Agreement and as reimbursement for its expenses related thereto, the administrator will be entitled to a monthly administration fee of such amount as may be described in the related Prospectus Supplement (the “Administration Fee”), which fee will be paid by the Servicer. If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the administrator, pursuant to an Administration Agreement, will deliver appropriate draw requests under a Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement for execution and delivery by the indenture trustee 24 or more hours before the Servicer is required to put cash in the Collection Account.
The administrator may not resign or be removed until (i) a successor administrator is appointed by the Issuing Entity, (ii) such successor administrator has agreed in writing to be bound by the terms of the Administration Agreement in the same manner as the administrator and (iii) each applicable Rating Agency has confirmed to the related owner trustee that the proposed appointment of the successor administrator will not result in a reduction or withdrawal of any rating then assigned by such Rating Agency to the Notes issued by the related Issuing Entity or each other Rating Agency has been provided 10 days’ prior notice of the proposed appointment of the successor administrator and each such other Rating Agency has not notified the owner trustee or the Depositor that such action will result in a reduction or withdrawal of any rating then assigned by it to the related Notes.
Under the circumstances specified in each Administration Agreement, any entity into which the administrator may be merged or consolidated, or any entity resulting from any merger or consolidation to which the administrator is a party, or any entity succeeding to all or substantially all of the business of the administrator will be the successor of the administrator under such Administration Agreement.
The Administration Agreement may be amended by a written amendment signed by the Issuing Entity, the administrator, the owner trustee and the indenture trustee, but without the consent of the Noteholders or the Certificateholders, for the purpose of adding any provisions to or modifying or changing in any manner or eliminating any of the provisions of the Administration Agreement; provided, however, that an Officer’s Certificate is delivered by the Servicer to the Indenture Trustee in connection with such amendment certifying that either (i) such officer reasonably believes such amendment will not, adversely affect in any material respect the interests of any Noteholder or (ii) (x) has received a letter from each applicable Rating Agency to the effect that such Rating Agency will not reduce or withdraw the rating it has then currently assigned to any Class of Notes as a result of such amendment or (y) has provided each other Rating Agency with 10 days’ prior notice of such amendment and each such other Rating Agency has not notified the Indenture Trustee that such amendment might or would result in the reduction or withdrawal of the rating it has then currently assigned to any Class of Notes.
CERTAIN LEGAL ASPECTS OF THE RECEIVABLES
General
The transfer of the Receivables to the applicable Issuing Entity and the pledge of the Receivables to the applicable Indenture Trustee, the perfection of the security interests in the Receivables and the enforcement of rights to realize on the Financed Vehicles as collateral for the Receivables are subject to a number of federal and state laws, including the UCC as in effect in various states. The Servicer and the Depositor will take the actions described below to perfect the rights of the applicable indenture trustee in the Receivables. If another party purchases (including the taking of a security interest in) the Receivables for new value in the ordinary course of its business, without actual knowledge of the Issuing Entity’s interest, and takes possession or, in the case of electronic Receivables, control of the Receivables, that purchaser would acquire an interest in the Receivables superior to the interest of the Issuing Entity and the Indenture Trustee.
Security Interests
General. In states in which retail installment sales contracts such as the Receivables evidence the credit sale of automobiles and/or light duty trucks by dealers to Obligors, the contracts also constitute personal property security agreements and include grants of security interests in the vehicles under the applicable UCC. Perfection of security interests in financed automobiles and/or light duty trucks is generally governed by the motor vehicle registration laws of the state in which the vehicle is located. In most states, a security interest in an automobile or light duty truck is perfected by obtaining possession of the certificate of title to the Financed Vehicle or by a notation of the secured party’s lien on the vehicle’s certificate of title, as applicable.
All retail installment sales contracts acquired by TMCC from Dealers name TMCC as obligee or assignee and as the secured party. TMCC’s possession of tangible contracts and its control of electronic contracts will perfect its interest in the contracts against the Dealers and their creditors and also provide TMCC priority over any prior secured creditors, such as an inventory financer, that has a security interest in the contracts. TMCC also takes all actions necessary under the laws of the state in which the related Financed Vehicle is located to perfect its security interest in that Financed Vehicle, including, where applicable, having a notation of its lien recorded on the related certificate of title or with the department of motor vehicles and, where applicable, obtaining possession of that certificate of title. Because TMCC continues to service the contracts as Servicer under the Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Obligors on the contracts will not be notified of the sale from TMCC to the Depositor or the sale from the Depositor to the related Issuing Entity.
Perfection. Pursuant to the related Receivables Purchase Agreement, TMCC will sell and assign its security interest in the Financed Vehicles to the Depositor and, with respect to each Issuing Entity, pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Depositor will sell and assign its security interest in the Financed Vehicles to that Issuing Entity. Each Issuing Entity will pledge its security interest in the Financed Receivables to
the applicable indenture trustee. However, because of the administrative burden and expense, none of TMCC, the Depositor, the related Issuing Entity or the related indenture trustee will amend any certificate of title to identify that Issuing Entity or the applicable indenture trustee as the new secured party on such certificate of title relating to a Financed Vehicle. However, UCC financing statements with respect to the transfer to the Depositor of TMCC’s security interest in the Financed Vehicles, the transfer to the Issuing Entity of the Depositor’s security interest in the Financed Vehicles and the transfer to the applicable indenture trustee of the Issuing Entity’s security interest in the Financed Vehicles will be filed with the appropriate governmental authorities. In addition, the Servicer will continue to hold any certificates of title relating to the vehicles in its possession as custodian for the Depositor and that Issuing Entity pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Sale and Assignment of Receivables” in this prospectus.
In most states, an assignment of contracts and interests in motor vehicles such as that under each Receivables Purchase Agreement or each Sale and Servicing Agreement is an effective conveyance of a security interest without amendment of any lien noted on a vehicle’s certificate of title, and the assignee succeeds thereby to the assignor’s rights as secured party. In those states, the Issuing Entity’s or the applicable indenture trustee’s security interest will not be noted on a vehicle’s certificate of title, but the Issuing Entity will have a perfected security interest in the vehicles. The security interest of such Issuing Entity and the applicable indenture trustee in the vehicle could be defeated through fraud or negligence because neither the Issuing Entity nor the applicable indenture trustee will be listed as lienholder on the certificates of title. In those states, in the absence of fraud or forgery by the vehicle owner or the Servicer or administrative error by state or local agencies, the notation of TMCC’s lien on the certificates of title will be sufficient to protect that Issuing Entity against the rights of subsequent purchasers of a Financed Vehicle or subsequent lenders who take a security interest in a Financed Vehicle. In each Receivables Purchase Agreement, TMCC will represent and warrant, and in each Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Depositor will represent and warrant, that it has taken all action necessary to obtain a perfected security interest in each Financed Vehicle. If there are any Financed Vehicles as to which TMCC failed to obtain and assign to the Depositor a perfected security interest, the security interest of the Depositor would be subordinate to, among others, subsequent purchasers of the Financed Vehicles and holders of perfected security interests in the Financed Vehicles. To the extent that failure has a material and adverse effect on the Issuing Entity’s interest in the related Receivables, however, it would constitute a breach of the warranties of TMCC under the related Receivables Purchase Agreement or the Depositor under the related Sale and Servicing Agreement. Accordingly, pursuant to the related Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Depositor would be required to repurchase the related Receivable from the Issuing Entity and, pursuant to the related Receivables Purchase Agreement, TMCC would be required to purchase that Receivable from the Depositor, in each case unless the breach was cured. Pursuant to each Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Depositor will assign its rights to the related Issuing Entity or cause TMCC to purchase the Receivable under the related Receivables Purchase Agreement. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Sale and Assignment of Receivables” and “Risk Factors—The issuing entity’s security interests in financed vehicles may be unenforceable or defeated” in this prospectus.
The requirements for the creation, perfection, transfer and release of liens in financed vehicles generally are governed by state law, and these requirements vary on a state-by-state basis. Failure to comply with these detailed requirements could result in liability to the trust or the release of the lien on the vehicle or other adverse consequences. For example, the State of New York passed legislation allowing a dealer of used motor vehicles to have the lien of a prior lienholder in a motor vehicle released, and to have a new certificate of title with respect to that motor vehicle reissued without the notation of the prior lienholder’s lien, upon submission to the Commissioner of the New York Department of Motor Vehicles of evidence that the prior lien has been satisfied without any signature or formal release by the prior lienholder. It is possible that, as a result of fraud, forgery, negligence or error, a lien on a financed vehicle could be released without prior payment in full of the receivable.
Continuity of Perfection. Under the laws of most states, the perfected security interest in a vehicle would continue for up to four months after the vehicle is moved to a state that is different from the one in which it is initially registered and the owner thereof re-registers the vehicle in the new state. A majority of states generally require surrender of a certificate of title to re-register a vehicle. In those states that require a secured party to hold possession of the certificate of title to maintain perfection of the security interest, the secured party would learn of the re-registration through the request from the Obligor under the related installment sale contract to surrender
possession of the certificate of title. In the case of vehicles registered in states providing for the notation of a lien on the certificate of title but not possession by the secured party (such as Texas), the secured party would receive notice of surrender from the state of re-registration if the security interest is noted on the certificate of title. Thus, the secured party would have the opportunity to re-perfect its security interest in the vehicle in the state of relocation. However, these procedural safeguards will not protect the secured party if through fraud, forgery or administrative error, the debtor somehow procures a new certificate of title that does not list the secured party’s lien. Additionally, in states that do not require a certificate of title for registration of a motor vehicle, re-registration could defeat perfection. In the ordinary course of servicing the Receivables, TMCC will take steps to effect re-perfection upon receipt of notice of re-registration or information from the Obligor as to relocation. Similarly, when an Obligor sells a Financed Vehicle, TMCC must surrender possession of the certificate of title or will receive notice as a result of its lien noted on the certificate of title and accordingly will have an opportunity to require satisfaction of the related Receivable before release of the lien. Under each Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Servicer will be obligated to take appropriate steps, at the Servicer’s expense, to maintain perfection of security interests in the Financed Vehicles and will be obligated to purchase the related Receivable if it fails to do so and that failure has a material and adverse effect on the Issuing Entity’s interest in the Receivable.
Priority of Liens Arising by Operation of Law. Under the laws of most states (including California), liens for repairs performed on a motor vehicle and liens for unpaid taxes take priority over even a perfected security interest in a financed vehicle. The Code also grants priority to specified federal tax liens over the lien of a secured party. The laws of some states and federal law permit the confiscation of vehicles by governmental authorities under some circumstances if used in unlawful activities, which may result in the loss of a secured party’s perfected security interest in the confiscated vehicle. For additional information, you should refer to “Forfeiture for Drug, RICO and Money Laundering Violations” in this prospectus. TMCC will represent and warrant to the Depositor in each Receivables Purchase Agreement, and the Depositor will represent and warrant to the Issuing Entity in each Sale and Servicing Agreement, that, as of the related Closing Date, each security interest in a Financed Vehicle is prior to all other present liens (other than tax liens and any other liens that arise by operation of law) upon and security interests in that Financed Vehicle. However, liens for repairs or taxes could arise, or the confiscation of a Financed Vehicle could occur, at any time during the term of a Receivable. No notice will be given to the owner trustee, the indenture trustee, any Noteholders or the Certificateholders in respect of a given Issuing Entity if that a lien arises or confiscation occurs which would not give rise to the Depositor’s repurchase obligation under the related Sale and Servicing Agreement or TMCC’s repurchase obligation under the related Receivables Purchase Agreement.
Repossession
In the event of default by an Obligor, the holder of the related retail installment sale contract has all the remedies of a secured party under the UCC, except where specifically limited by other state laws. Among the UCC remedies, the secured party has the right to perform repossession by self-help means, unless it would constitute a breach of the peace or is otherwise limited by applicable state law. Unless a vehicle financed by TMCC is voluntarily surrendered, self-help repossession is the method employed by TMCC in most states and is accomplished simply by retaking possession of the Financed Vehicle. In cases where an Obligor objects or raises a defense to repossession, or if otherwise required by applicable state law, a court order must be obtained from the appropriate state court, and that vehicle must then be recovered in accordance with that order. In some jurisdictions, the secured party is required to notify that Obligor of the default and the intent to repossess the collateral and to give that Obligor a time period within which to cure the default prior to repossession. In some states, an Obligor has right to reinstate its contract and recover the collateral by paying the delinquent installments and other amount due.
Notice of Sale; Reinstatement and Redemption Rights
In the event of default by an Obligor under a retail installment sales contract, some jurisdictions require that the Obligor be notified of the default and be given a time period within which to cure the default prior to repossession. Generally, this right of cure may only be exercised on a limited number of occasions during the term of the related contract.
The UCC and other state laws require the secured party to provide an Obligor with reasonable notice of the date, time and place of any public sale and/or the date after which any private sale of the collateral may be held. In
most states, under certain circumstances after any such financed vehicle has been repossessed, the related Obligor may reinstate the related contract by paying the delinquent installments and other amounts due. Additionally, in most states, an Obligor has the right to redeem the collateral prior to actual sale by paying the secured party the unpaid principal balance of the obligation, accrued interest on the obligation plus reasonable expenses for repossessing, holding and preparing the collateral for disposition and arranging for its sale, plus, in some jurisdictions, reasonable attorneys’ fees. In some states, an Obligor has the right to redeem the collateral prior to actual sale by payment of delinquent installments or the unpaid balance.
Deficiency Judgments and Excess Proceeds
The proceeds of resale of the vehicles generally will be applied first to the expenses of resale and repossession and then to the satisfaction of the indebtedness. While some states impose prohibitions or limitations on deficiency judgments if the net proceeds from resale do not cover the full amount of the indebtedness, a deficiency judgment can be sought in those states that do not prohibit or limit those judgments. In addition to the notice requirement described above, the UCC requires that every aspect of the sale or other disposition, including the method, manner, time, place and terms, be “commercially reasonable.” Generally, courts have held that when a sale is not “commercially reasonable,” the secured party loses its right to a deficiency judgment. However, the deficiency judgment would be a personal judgment against the Obligor for the shortfall, and a defaulting Obligor can be expected to have very little capital or sources of income available following repossession. Therefore, in many cases, it may not be useful to seek a deficiency judgment or, if one is obtained, it may be settled at a significant discount or be uncollectible. In addition, the UCC permits the Obligor or other interested party to recover for any loss caused by noncompliance with the provisions of the UCC. Also, prior to a sale, the UCC permits the Obligor or other interested person to prohibit the secured party from disposing of the collateral if it is established that the secured party is not proceeding in accordance with the “default” provisions under the UCC.
Occasionally, after resale of a repossessed vehicle and payment of all expenses and indebtedness, there is a surplus of funds. In that case, the UCC requires the creditor to remit the surplus to any holder of a subordinate lien with respect to that vehicle or if no such lienholder exists, the UCC requires the creditor to remit the surplus to the Obligor.
Certain Bankruptcy Considerations
In structuring the transactions contemplated in this prospectus, the Depositor has taken steps that are intended to make it unlikely that the voluntary or involuntary application for relief by TMCC under the United States Bankruptcy Code or similar applicable state laws (collectively, “Insolvency Laws”) will result in consolidation of the assets and liabilities of the Depositor or the Issuing Entity with those of TMCC. These steps include the creation of the Depositor as a wholly owned, limited purpose subsidiary pursuant to a limited liability company agreement containing certain limitations (including requiring that the Depositor must at all times have at least one “Independent Manager” and restrictions on the nature of the Depositor’s business and on its ability to commence a voluntary case or proceeding under any Insolvency Law without the affirmative vote of a majority of its managers, including each Independent Manager). However, delays in payments on a series of Notes and possible reductions in the amount of those payments could occur if:
| | 1. | a court were to conclude that the assets and liabilities of the Depositor should be consolidated with those of TMCC in the event of the application of applicable Insolvency Laws to TMCC; |
| | 2. | a filing were made under any Insolvency Law by or against the Depositor ore the related Issuing Entity; and |
| | 3. | an attempt were made to litigate any of the foregoing issues. |
On a Closing Date, counsel to the Depositor will give an opinion to the effect that, based on a reasoned analysis of analogous case law (although there is no precedent based on directly similar facts), and, subject to facts, assumptions and qualifications specified in the opinion and applying the principles described in the opinion, in the event of a voluntary or involuntary bankruptcy case in respect of the Depositor under Title 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code at a time when the Depositor was insolvent, the property of the Issuing Entity would not properly
be substantively consolidated with the property of the estate of the Depositor. Among other things, that opinion will assume that each of the Depositor and the Issuing Entity will follow specified procedures in the conduct of its affairs, including maintaining records and books of account separate from those of the other, refraining from commingling its assets with those of the other, and refraining from holding itself out as having agreed to pay, or being liable for, the debt of the other. The Depositor and the Issuing Entity intend to follow these and other procedures related to maintaining their separate corporate identities. However, there can be no assurance that a court would not conclude that the assets and liabilities of the Depositor should be consolidated with those of the Issuing Entity.
TMCC will warrant in each Receivables Purchase Agreement that the sale of the related Receivables by it to the Depositor is a valid sale. Notwithstanding the foregoing, if TMCC were to become a debtor in a bankruptcy case, a court could take the position that the sale of Receivables to the Depositor should instead be treated as a pledge of those Receivables to secure a borrowing of TMCC. In addition, if the transfer of Receivables to the Depositor is treated as a pledge instead of a sale, a tax or government lien on the property of TMCC arising before the transfer of a Receivable to the Depositor may have priority over the Depositor’s interest in that Receivable. In addition, while TMCC is the Servicer, cash collections on the Receivables may be commingled with the funds of TMCC and, in the event of that bankruptcy of TMCC, the Issuing Entity may not have a perfected interest in those collections.
TMCC and the Depositor will treat the transactions described in this prospectus as a sale of the Receivables to the Depositor, so that the automatic stay provisions of the United States Bankruptcy Code should not apply to the Receivables in the event that TMCC were to become a debtor in a bankruptcy case.
Dodd-Frank Act Orderly Liquidation Authority Provisions
General. On July 21, 2010, President Obama signed into law the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”). The Dodd-Frank Act, among other things, gives the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) authority to act as receiver of certain bank holding companies, financial companies and their respective subsidiaries in specific situations under the Orderly Liquidation Authority (“OLA”) provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act. The proceedings, standards, powers of the receiver and many substantive provisions of the OLA differ from those of the United States Bankruptcy Code in several respects. In addition, because the legislation remains subject to clarification through FDIC regulations and has yet to be applied by the FDIC in any receivership, it is unclear what impact these provisions will have on any particular company, including TMCC, the Depositor, any Issuing Entity or any of their respective creditors.
Potential Applicability to TMCC, the Depositor and Issuing Entities. There is uncertainty about which companies will be subject to the OLA rather than the United States Bankruptcy Code. For a company to become subject to the OLA, the Secretary of the Treasury (in consultation with the President of the United States) must determine, among other things, that such company is in default or in danger of default, that the company’s failure and its resolution under the United States Bankruptcy Code “would have serious adverse effects on financial stability in the United States,” that no viable private sector alternative is available to prevent the default of the company and an OLA proceeding would mitigate these adverse effects.
TMCC’s senior unsecured debt is currently given an investment grade rating. TMCC’s business is generally limited to providing retail financing, dealer financing and certain other financial products and services to vehicle and industrial equipment dealers and their customers and marketing, underwriting and administering insurance agreements related to covering certain risks of vehicle dealers and their customers. TMCC has many competitors in these businesses with substantial resources. There can be no assurance, however, that circumstances will not change in the future or that, regardless of the nature and scope of TMCC’s business and competitive market, the Secretary would not determine that the failure of TMCC would have serious adverse effects on financial stability in the United States.
Under certain circumstances, if TMCC were determined to be a “covered financial company,” the applicable Issuing Entity or the Depositor could also be subject to the provisions of the OLA as a “covered subsidiary” of TMCC. For a covered subsidiary to be considered a covered financial company for purposes of the OLA and therefore be subject to receivership under the OLA, (1) the FDIC would have to be appointed as receiver
for TMCC under the OLA as described above, (2) the FDIC and the Secretary of the Treasury would have to jointly determine that (a) such Issuing Entity or Depositor, as applicable, is in default or in danger of default, (b) appointment of the FDIC as receiver of the covered subsidiary would avoid or mitigate serious adverse effects on the financial stability or economic conditions of the United States and (c) such appointment would facilitate the orderly liquidation of TMCC. To mitigate the likelihood that an Issuing Entity or the Depositor would be subject to the OLA, no Issuing Entity intends to issue non-investment grade debt and the Depositor will not issue any debt. Moreover, each Issuing Entity will own a relatively small amount of the Receivables originated and serviced by TMCC and each Issuing Entity and the Depositor will be structured as a separate legal entity from TMCC and other Issuing Entities sponsored by TMCC. Notwithstanding the foregoing, because of the novelty of the Dodd-Frank Act and the OLA provisions, the uncertainty of the Secretary of the Treasury’s determination and the fact that such determination would be made in the future under potentially different circumstances, no assurance can be given that the OLA provisions would not apply to TMCC, a particular Issuing Entity or the Depositor or, if it were to apply, that the timing and amounts of payments to the related series of Noteholders would not be less favorable than under the United States Bankruptcy Code.
FDIC’s Repudiation Power Under the OLA. If the FDIC were appointed receiver of TMCC or of a covered subsidiary, including the applicable Issuing Entity or the Depositor, under the OLA, the FDIC would have various powers under the OLA, including the power to repudiate any contract to which TMCC or such covered subsidiary was a party, if the FDIC determined that performance of the contract was burdensome to the estate and that repudiation would promote the orderly administration of TMCC’s or such covered subsidiary’s affairs, as applicable. In January 2011, the acting General Counsel of the FDIC (the “FDIC Counsel”) issued an advisory opinion confirming, among other things, its intended application of the FDIC’s repudiation power under OLA. In that advisory opinion, the FDIC Counsel stated that nothing in the Dodd-Frank Act changes the existing law governing the separate existence of separate entities under other applicable law. As a result, the FDIC Counsel was of the opinion that the FDIC as receiver for a covered financial company, which could include TMCC or its subsidiaries (including the Depositor or the applicable Issuing Entity), cannot repudiate a contract or lease unless it has been appointed as receiver for that entity or the separate existence of that entity may be disregarded under other applicable law. In addition, the FDIC Counsel was of the opinion that until such time as the FDIC Board of Directors adopts a regulation further addressing the application of Section 210(c) of the Dodd-Frank Act, if the FDIC were to become receiver for a covered financial company, which could include TMCC or its subsidiaries (including the Depositor or the applicable Issuing Entity), the FDIC will not, in the exercise of its authority under Section 210(c) of the Dodd-Frank Act, reclaim, recover, or recharacterize as property of that covered financial company or the receivership any asset transferred by that covered financial company prior to the end of the applicable transition period of a regulation provided that such transfer satisfies the conditions for the exclusion of such assets from the property of the estate of that covered financial company under the United States Bankruptcy Code. Although this advisory opinion does not bind the FDIC or its Board of Directors, and could be modified or withdrawn in the future, the advisory opinion also states that the FDIC Counsel will recommend that the FDIC Board of Directors incorporates a transition period of 90 days for any provisions in any further regulations affecting the statutory power to disaffirm or repudiate contracts. As no such regulations have been proposed, the foregoing FDIC Counsel’s interpretation currently remains in effect. The advisory opinion also states that the FDIC staff anticipates recommending consideration of future regulations related to the Dodd-Frank Act. To the extent any future regulations or subsequent FDIC actions in an OLA proceeding involving TMCC or its subsidiaries (including the Depositor or your Issuing Entity), are contrary to this advisory opinion, payment or distributions of principal and interest on the Securities issued by the applicable Issuing Entity would be delayed and could be reduced.
We will structure the transfers of Receivables under the Receivables Purchase Agreement and the Sale and Servicing Agreement with the intent that they would be characterized as legal true sales under applicable state law and that the Receivables would not be included in the transferor’s bankruptcy estate under the United States Bankruptcy Code. If the transfers are so characterized, based on the FDIC Counsel of the FDIC’s advisory opinion rendered in January 2011 and other applicable law, the FDIC would not be able to recover the transferred Receivables using its repudiation power. However, if the FDIC were to successfully assert that the transfers of Receivables were not legal true sales and should instead be characterized as a security interest to secure loans, and if the FDIC repudiated those loans, the purchasers of the Receivables or the Noteholders, as applicable, would have a claim for their “actual direct compensatory damages,” which claim would be no less than the amount lent plus interest accrued to the date the FDIC was appointed receiver. In addition, to the extent that the value of the collateral securing the loan exceeds such amount, the purchaser or the Noteholders, as applicable, would also have a
claim for any interest that accrued after such appointment at least through the date of repudiation or disaffirmance. In addition, even if the FDIC were to unsuccessfully challenge that the transfers were not legal true sales or that the FDIC would not repudiate a legal true sale, Noteholders could suffer delays in the payments on their Notes.
Also assuming that the FDIC were appointed receiver of TMCC or of a covered subsidiary, including the applicable Issuing Entity or the Depositor, under the OLA, the FDIC’s repudiation power would extend to continuing obligations of TMCC or that covered subsidiary, as applicable, including its obligations to repurchase Receivables for breach of representation or warranty as well as its obligation to service the Receivables. If the FDIC were to exercise this repudiation power, Noteholders would not be able to compel TMCC or any applicable covered subsidiary to repurchase Receivables for breach of representation and warranty and instead would have a claim for damages in TMCC’s or that covered subsidiary’s receivership, as applicable, and thus would suffer delays and may suffer losses of payments on their Notes. Noteholders would also be prevented from replacing the Servicer during the stay. In addition, if the FDIC were to repudiate TMCC’s obligations as Servicer, there may be disruptions in servicing as a result of a transfer of servicing to a third party and Noteholders may suffer delays or losses of payments on their Notes. In addition, there are other statutory provisions under the OLA enforceable by the FDIC under which, if the FDIC takes action, payments or distributions of principal and interest on the Notes issued by the related Issuing Entity would be delayed and may be reduced.
In addition, under the OLA, none of the parties to the Receivables Purchase Agreement, Sale and Servicing Agreement, the Administration Agreement and the Indenture could exercise any right or power to terminate, accelerate, or declare a default under those contracts, or otherwise affect TMCC’s or a covered subsidiary’s rights under those contracts without the FDIC’s consent for 90 days after the receiver is appointed. During the same period, the FDIC’s consent would also be needed for any attempt to obtain possession of or exercise control over any property of TMCC or of a covered subsidiary. The requirement to obtain the FDIC’s consent before taking these actions relating to a covered financial company’s contracts or property is comparable to the “automatic stay” in bankruptcy.
If an Issuing Entity were to become subject to the OLA, the FDIC may repudiate the debt of such Issuing Entity. In such an event, the related series of Noteholders would have a secured claim in the receivership of such Issuing Entity for “actual direct compensatory damages” as described above, but delays in payments on such series of Notes would occur and possible reductions in the amount of those payments could occur. In addition, for a period of 90 days after a receiver was appointed, Noteholders would be stayed from accelerating the debt or exercising any remedies under the Indenture.
FDIC’s Avoidance Power Under the OLA. Under statutory provisions of the OLA similar to those of the United States Bankruptcy Code, the FDIC could avoid transfers of Receivables that are deemed “preferential.” On July 15, 2011, the FDIC Board of Directors issued a final rule (the “Final Rule”) which, among other things, clarifies that the treatment of preferential transfers under the OLA was intended to be consistent with, and should be interpreted in a manner consistent with, the related provisions under the United States Bankruptcy Code. The Final Rule became effective on August 15, 2011. Based on the Final Rule, a transfer of the Receivables perfected by the filing of a UCC financing statement against TMCC, the Depositor and the applicable Issuing Entity as provided in the applicable Transfer and Servicing Agreements would not be avoidable by the FDIC as a preference under the OLA. For additional information, you should refer to “—Bankruptcy Considerations” above.
Consumer Protection Laws
Numerous federal and state consumer protection laws and related regulations impose substantial requirements upon lenders and servicers involved in consumer finance. These laws include the Truth in Lending Act, the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, the Federal Trade Commission Act, the Fair Credit Billing Act, the Fair Credit Reporting Act, the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (the “FDCPA”), the Magnuson Moss Warranty Act, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau’s Regulations B and Z, the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, the Servicemembers’ Civil Relief Act (the “Relief Act”) and similar state laws protecting servicemembers, the National Consumer Credit Protection Act, the Texas Consumer Credit Code, the Dodd-Frank Act, state adoptions of the National Consumer Act and of the Uniform Consumer Credit Code and state motor vehicle retail installment sales acts and other similar laws. Many states have adopted “lemon laws” that provide redress to consumers who purchase a vehicle that remains out of compliance with its manufacturer’s warranty after a specified number of attempts to correct a
problem or a specified time period. Also, state laws impose finance charge ceilings and other restrictions on consumer transactions and require contract disclosures in addition to those required under federal law. These requirements impose specific statutory liabilities upon creditors who fail to comply with their provisions. In some cases, this liability could affect an assignee’s ability to enforce consumer finance contracts such as the Receivables.
Any licensing requirements of the applicable Issuing Entity are governed by state and sometimes local law, and these requirements vary on a jurisdiction-by-jurisdiction basis. For example, the City of New York passed legislation requiring a purchaser of delinquent loans to be licensed as a debt collector. It is not clear what delinquent means under that law. It is possible that, as a result of not being properly licensed under a state or local law, the applicable Issuing Entity could be subject to liability or other adverse consequences.
With respect to used vehicles, the Federal Trade Commission’s Rule on Sale of Used Vehicles (the “FTC Rule”) requires all sellers of used vehicles to prepare, complete and display a “Buyers Guide” which explains the warranty coverage for such vehicles. The Federal Magnuson-Moss Warranty Act and state lemon laws may impose further obligations on motor vehicle dealers. Holders of the Receivables may have liability or claims and defenses under those statutes, the FTC Rule and similar state statutes.
The so called “Holder in Due Course” Rule of the Federal Trade Commission (the “HDC Rule”), the provisions of which are generally duplicated by the Uniform Consumer Credit Code, other statutes or the common law in some states, has the effect of subjecting a seller (and specified creditors and their assignees) in a consumer credit transaction to all claims and defenses which the Obligor in the transaction could assert against the seller of the goods. Liability under the HDC Rule is limited to the amounts paid by the Obligor under the contract, and the holder of the Receivable may also be unable to collect any balance remaining due under that contract from the Obligor.
Most of the Receivables will be subject to the requirements of the HDC Rule. Accordingly, each Issuing Entity, as holder of the related Receivables, will be subject to any claims or defenses that the purchaser of the applicable Financed Vehicle may assert against the seller of the related Financed Vehicle. For each Obligor, these claims are limited to a maximum liability equal to the amounts paid by the Obligor on the related Receivable. Under most state motor vehicle dealer licensing laws, sellers of motor vehicles are required to be licensed to sell motor vehicles at retail sale. Furthermore, federal odometer regulations promulgated under the Motor Vehicle Information and Cost Savings Act require that all sellers of new and used vehicles furnish a written statement signed by the seller certifying the accuracy of the odometer reading. If the seller is not properly licensed or if a written odometer disclosure statement was not provided to the related Obligor, the Obligor may be able to assert a defense against the seller of the vehicle. If an Obligor were successful in asserting any of those claims or defenses, that claim or defense would constitute a breach of the Depositor’s representations and warranties under the related Sale and Servicing Agreement and a breach of TMCC’s warranties under the related Receivables Purchase Agreement and would, if the breach materially and adversely affects the Receivable or the interest of the Noteholders, create an obligation of the Depositor and TMCC, respectively, to repurchase the Receivable unless the breach is cured. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Sale and Assignment of Receivables” in this prospectus.
Courts have applied general equitable principles to secured parties pursuing repossession and litigation involving deficiency balances. These equitable principles may have the effect of relieving an Obligor from some or all of the legal consequences of a default. Any such shortfall, to the extent not covered by amounts payable to the Noteholders from amounts on deposit in the related Reserve Account or from coverage provided under any other credit enhancement mechanism, could result in losses to the Noteholders.
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”), which was created by the Dodd-Frank Act, is responsible for implementing and enforcing various federal consumer protection laws and supervising certain depository institutions and non-depository institutions offering financial products and services to consumers, including automobile loans and leases. The CFPB has broad regulatory examination and enforcement powers over consumer financial products and services (which include, among others, retail and lease contracts that TMCC purchases) and supervisory authority over certain depository institutions and non-depository institutions. While TMCC is not currently subject to the CFPB’s supervisory authority, the CFPB has recently proposed rules that, if enacted in their proposed form, would expand the scope of the CFPB’s supervisory and examination authority to include larger participants in the auto lending and leasing markets, including TMCC. The CFPB has issued public
guidance regarding compliance with the fair lending requirements of the Equal Credit Opportunity Act, and its implementing regulation, for automobile lenders. The guidance raises fair lending concerns relating to the practices of permitting automobile dealers to negotiate a consumer contract rate that is higher than the rate the lender provides to the dealer. This increased rate is typically called “dealer markup” or “dealer participation.” The CFPB has been conducting fair lending examinations and investigations of automobile lenders and their dealer participation policies and other compensation practices. In addition, the CFPB has recently indicated an intention to prescribe rules implementing the FDCPA that would apply to first-party creditors such as TMCC. First-party creditors are expressly excluded from the scope of the FDCPA, but the CFPB is proposing to use its rule-making authority on the prohibition of unfair, deceptive or abusive acts and practices to apply the rules more broadly.
The CFPB, together with the U.S. Department of Justice, have requested that TMCC provide certain information about TMCC’s purchases of auto loans from dealers and discretionary pricing practices. TMCC is voluntarily cooperating with the request for information. The CFPB has also recently begun reviews concerning certain other automobile lending practices, including the sale of extended warranties, credit insurance and other add-on products. If any of these practices were found to violate applicable laws, the Depositor could be obligated to repurchase from the Issuing Entity any Receivable that fails to comply with law. In addition, TMCC, the Depositor or the Issuing Entity could possibly be subject to claims by the Obligors on those Receivables, and any relief granted by a court could potentially adversely affect the Issuing Entity. For additional discussion of how a failure to comply with consumer protection laws may impact the Issuing Entity, the Receivables or your investment in the Notes, see “Risk Factors—Receivables that fail to comply with consumer protection laws may be unenforceable, which may result in losses on your investment” in this prospectus.
In addition, the CFPB and the Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”) have recently become more active in investigating the products, services and operations of credit providers, including banks and other finance companies engaged in auto finance activities. Both the FTC and CFPB announced various enforcement actions against lenders in the past few years involving significant penalties, consent orders, cease and desist orders and similar remedies. If similar action is taken against the products, services and operations that TMCC offers, TMCC may be required to cease or alter certain business practices, which could have a material effect on TMCC’s financial condition, liquidity and results of operations.
TMCC regularly evaluates how to comply with CFPB fair lending guidance, which compliance includes periodically performing reviews of TMCC’s lending and servicing policies and analyses of both dealer-specific and portfolio-wide loan pricing data for potential disparities resulting from dealer participation and compensation policies. Depending upon the results of these reviews and analyses or any regulatory agency actions, TMCC voluntarily may be taking, may consider taking, or may be required to take, corrective actions, including modifying the interest rate or making payments with respect to certain Receivables. Certain corrective actions may result in TMCC, as Servicer, being required under the related Sale and Servicing Agreement to repurchase the affected Receivables. See “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Servicing Procedures” in this prospectus for a discussion of purchase obligations of the Servicer.
TMCC and the Depositor will represent and warrant under each Receivables Purchase Agreement and each Sale and Servicing Agreement, as applicable, that each Receivable complies with all requirements of law in all material respects. Accordingly, if an Obligor has a claim against such Issuing Entity for violation of any law and such claim materially and adversely affects such Issuing Entity’s interest in a Receivable, such violation would constitute a breach of the representations and warranties of TMCC under the Receivables Purchase Agreement and the Depositor under such Sale and Servicing Agreement and would create an obligation of TMCC and the Depositor to repurchase the Receivable unless the breach is cured. For additional information, you should refer to “Description of the Transfer and Servicing Agreements—Sale and Assignment of Receivables” in this prospectus.
Forfeiture for Drug, RICO and Money Laundering Violations
Federal law provides that property purchased or improved with assets derived from criminal activity or otherwise tainted, or used in the commission of certain offenses can be seized and ordered forfeited to the United States of America. The offenses that can trigger such a seizure and forfeiture include, among others, violations of the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act, the Bank Secrecy Act, the anti-money laundering laws and
regulations, including the USA Patriot Act of 2001 and the regulations issued pursuant thereto, as well as the narcotic drug laws. In many instances, the United States may seize the property even before a conviction occurs.
Other Limitations
In addition to the laws limiting or prohibiting deficiency judgments, numerous other statutory provisions, including federal bankruptcy laws and related state laws, may interfere with or affect the ability of a secured party to realize upon collateral or to enforce a deficiency judgment. For example, in a Chapter 13 proceeding under the United States Bankruptcy Code, a court may prevent a creditor from repossessing a vehicle and, as part of the repayment plan, reduce the amount of the secured indebtedness to the market value of the vehicle at the time of bankruptcy (as determined by the court), leaving the creditor as a general unsecured creditor for the remainder of the indebtedness. A bankruptcy court may also reduce the monthly payments due under a contract or change the rate of interest and time of repayment of the indebtedness.
Under the terms of the Relief Act, an Obligor who enters the military service (including members of the Army, Navy, Air Force, Marines, National Guard, and officers of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and U.S. Public Health Service assigned to duty with the military) after the origination of that Obligor’s Receivable (including an Obligor who is a member of the National Guard or is in reserve status at the time of the origination of the Obligor’s Receivable and is later called to active duty) may not be charged interest and fees above an annual rate of 6% during the period of that Obligor’s active duty status after a request for relief by the Obligor. The Relief Act provides for extension of payments during a period of service upon request of the Obligor. Interest and fees at a rate in excess of 6% that would have been incurred but for the Relief Act are forgiven. It is possible that the foregoing could have an effect on the ability of the Servicer to collect the full amount of interest owing on some of the Receivables. In addition, the Relief Act and the laws of some states, including California, New York and New Jersey, impose limitations that would impair the ability of the Servicer to repossess the released Financed Vehicle during the Obligor’s period of active duty status and, under certain circumstances, during an additional period thereafter. Thus, if that Receivable goes into default, there may be delays and losses occasioned by the inability to exercise the Issuing Entity’s rights with respect to the Receivable and the related Financed Vehicle in a timely fashion.
Any shortfall pursuant to either of the two preceding paragraphs, to the extent not covered by amounts payable to the Noteholders or Certificateholders from amounts on deposit in the related Reserve Account or from coverage provided under any other credit enhancement mechanism, could result in losses to the Noteholders and Certificateholders. For additional information, you should refer to “Risk Factors—The return on the notes could be reduced by shortfalls due to the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act” in this prospectus.
TMCC DEMAND NOTES
The following summary describes certain terms of demand notes that may be issued from time to time by TMCC (the “TMCC Demand Notes”). TMCC Demand Notes will be issued under a Demand Notes Indenture (the “Demand Notes Indenture”), between TMCC and the trustee under the Demand Notes Indenture (in such capacity, the “Demand Notes Indenture Trustee”). The characteristics of any particular series of TMCC Demand Notes and the provisions of any particular Demand Notes Indenture will be more fully described in the related Prospectus Supplement. In addition, this summary does not purport to be complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by reference to, the provisions of any Demand Notes Indenture that is entered into by the related Issuing Entity.
Issuer of the TMCC Demand Notes
TMCC provides a variety of finance and insurance products, including retail financing, leasing, dealer financing, insurance products and services to vehicle and industrial equipment dealers and their customers.
TMCC was incorporated in California in 1982 and began operations in 1983. TMCC’s principal executive offices are located at 19001 South Western Avenue, Torrance, California 90501, and TMCC’s telephone number is (310) 468-1310.
TMCC is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Toyota Financial Services Americas Corporation, a holding company owned 100% by Toyota Financial Services Corporation (“TFSC”). TFSC, in turn, is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation (“TMC”). TFSC was incorporated in July 2000 and its corporate headquarters is located in Nagoya, Japan. The purpose of TFSC is to control and manage Toyota’s finance operations worldwide.
For additional information regarding TMCC, you should refer to “The Sponsor, Administrator, Servicer and Issuer of the TMCC Demand Notes,” “TMCC Demand Notes—Where You Can Find More Information” and “Incorporation of Certain Documents by Reference Relating to Demand Notes Issued by TMCC” in this prospectus.
General
Collections in respect of the Receivables will be applied to make payments of interest and principal of each class of Notes. If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, payments of interest and/or principal of one or more classes of Notes may be made on a quarterly, semi-annual or annual basis, and not simply as a pass through of collections received during a particular month. In order to make distributions of principal and/or interest on a basis other than monthly, the indenture trustee will be required to invest amounts otherwise payable as principal or interest of the specified classes of Notes in highly rated investments maturing on or just prior to specified Payment Dates and bearing interest at rates specified in the related Prospectus Supplement as directed by the Servicer. The indenture trustee may invest some or all such funds in TMCC Demand Notes. The indenture trustee may invest in TMCC Demand Notes even if payments to holders of such securities are to be paid monthly. If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the TMCC Demand Notes will be an Eligible Investment.
The outstanding principal amount of the TMCC Demand Notes purchased with collections will change from time to time, depending on the amount of collections invested. The aggregate principal amount of TMCC Demand Notes that may be issued under any Demand Notes Indenture will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement. Interest on the TMCC Demand Notes will be paid at rates and on terms described in the related Prospectus Supplement. Different forms of TMCC Demand Notes may be used to represent investments of Collections relating to interest and investments of Collections relating to principal. TMCC Demand Notes representing investments of Collections relating to interest will mature on or before the dates on which interest is to be paid to Noteholders. TMCC Demand Notes representing investments of Collections relating to principal will mature on or before the dates on which principal is to be paid to Noteholders. In addition, the indenture trustee will generally have the right to demand payment of the TMCC Demand Notes in connection with the reduction of TMCC’s rating to a level below that specified in the related Prospectus Supplement or upon the occurrence of other events specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. For additional information, you should refer to “Risk Factors—The rating of a swap counterparty or the issuer of demand notes may affect the ratings of the notes” in this prospectus. The payment terms relating to the TMCC Demand Notes will be described in detail in the related Prospectus Supplement.
TMCC Demand Notes will be unsecured general obligations of TMCC and will rank pari passu with all other unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness of TMCC outstanding from time to time. TMCC Demand Notes will not be subject to redemption by TMCC and will not have the benefit of any sinking fund.
Any TMCC Demand Notes will be issued only in fully registered form without interest coupons, and payment of principal of and interest on TMCC Demand Notes will be made by the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee as paying agent by wire transfer to an account maintained by the indenture trustee, as the holder of the TMCC Demand Notes.
No Noteholder will have a direct interest in any TMCC Demand Notes or have any direct rights under the TMCC Demand Notes or the Demand Notes Indenture. The Issuing Entity will be the only holder of the TMCC Demand Notes, which it will hold for the benefit of the Noteholders. In the event any vote or other action, including action upon the occurrence of an Event of Default under the Demand Notes Indenture, is required or permitted by the holders of the TMCC Demand Notes under the Demand Notes Indenture, the Issuing Entity as such holder will be permitted to vote or take such other action as it deems fit. However, the Issuing Entity will be permitted, but not required, to seek the direction of the Noteholders before taking any such action, all as further described in the related Prospectus Supplement. References under this caption to “holders of the TMCC Demand Notes” and phrases of similar import will be to the Issuing Entity as the holder of the TMCC Demand Notes.
If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Issuing Entity may invest in TMCC Demand Notes even if payments on Notes of the related series are to be paid monthly. If so specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Issuing Entity may invest amounts on deposit in any Reserve Account in TMCC Demand Notes.
Removal of Demand Notes Indenture Trustee; Successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee
The Demand Notes Indenture Trustee may resign by providing written notice to TMCC and the Issuing Entity, as holder of the TMCC Demand Notes. The Issuing Entity, as holder of the TMCC Demand Notes, may remove the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee by written notice thereto and to TMCC, and may appoint a successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee. TMCC may remove the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee in the event that: (a) the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee fails to continue to satisfy the criteria for eligibility to act as Demand Notes Indenture Trustee; (b) the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee is adjudged a bankrupt or insolvent; (c) a receiver or other public officer takes charge of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee or its property; or (d) the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee otherwise becomes incapable of acting in such capacity.
If the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee resigns, is removed or is unable to act as Demand Notes Indenture Trustee for any reason, TMCC will promptly appoint a successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, unless the Issuing Entity has already done so. Within one year after a successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee takes office, the Issuing Entity may appoint a successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee to replace any successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee appointed by TMCC. Any resignation or removal of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee and appointment of a successor Demand Notes Indenture Trustee will become effective only upon such successor’s acceptance of such appointment and the payment of outstanding fees and expenses due to the prior Demand Notes Indenture Trustee as described in the Demand Notes Indenture.
Successor Corporation
The Demand Notes Indenture provides that TMCC may consolidate with, or sell, lease or convey all or substantially all of its assets to, or merge with or into, any other corporation, provided, that in any such case: (i) either TMCC will be the continuing corporation, or the successor corporation will be a corporation organized and existing under the laws of the United States or any state thereof and will expressly assume, by execution and delivery to the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee of a supplemental Demand Notes Indenture in form satisfactory thereto, all of the obligations of TMCC under the TMCC Demand Notes and the Demand Notes Indenture; and (ii) TMCC or such successor corporation, as the case may be, will not, immediately after such merger or consolidation, or such sale, lease or conveyance, be in default in the performance of any such obligation. Subject to certain limitations in the Demand Notes Indenture, the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee may receive from TMCC an officer’s certificate and an opinion of counsel as conclusive evidence that any such consolidation, merger, sale, lease or conveyance, and any such assumption, complies with the provisions of the Demand Notes Indenture.
TMCC Statement as to Compliance
TMCC will deliver to the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, within 120 days after the end of each fiscal year, a written statement signed by the principal executive officer, the principal financial officer or the principal accounting officer of the Company, stating that:
| | · | a review of the activities of TMCC during such year and of its performance under the Demand Notes Indenture has been made under his or her supervision, and (b) to the best of his or her knowledge, based on such review, (i) TMCC has complied with all the conditions and covenants imposed on it under the Demand Notes Indenture throughout such year, or, if there has been a default in the fulfillment of any such condition or covenant, specifying each such default known to him or her and the nature and status thereof, and (ii) no event has occurred and is continuing which is, or after notice or lapse of time or both would become, an event of default under the Demand Notes Indenture, or, if such an event has occurred and is continuing, specifying each such event known to him and the nature and status thereof. |
| | · | TMCC will deliver to the Trustee, within five days after the occurrence thereof, written notice of any event which after notice or lapse of time or both would become an event of default under the Demand Notes Indenture. |
Supplemental Demand Notes Indentures
Supplemental Demand Notes Indentures may be entered into by TMCC and the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee without the consent of the holder of the TMCC Demand Notes (a) to cure any ambiguity, to correct or
supplement any provisions in a Supplemental Demand Notes Indenture that may be inconsistent with any other provision of such Supplemental Demand Notes Indenture or to add any other provision with respect to matters or questions arising under the Demand Notes Indenture which are not inconsistent with the provisions thereof, provided that any such action will not, in the good faith judgment of the parties, materially and adversely affect the interest of any holder of TMCC Demand Notes or any Noteholder and the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee will be furnished an opinion of counsel to the effect that such amendment will not materially and adversely affect the interest of any Noteholder, and (b) for purposes of appointing a successor trustee under a Demand Notes Indenture or in connection with any merger or consolidation of TMCC or the transfer or lease of the assets of TMCC in their entirety, in each case in accordance with the provisions of the Demand Notes Indenture. In addition, supplemental Demand Notes Indentures may be entered into by TMCC and the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee with the consent of the holder of the TMCC Demand Notes (which consent will not be given except at the written direction of Holders of at least 25% in aggregate principal amount of the Notes issued by an Issuing Entity acting as a single class) for the purpose of adding any provisions to or changing in any manner or eliminating any other provisions of the Demand Notes Indenture or of modifying in any manner the rights with respect to the TMCC Demand Notes, provided that no supplemental Demand Notes Indenture may, among other things, reduce the principal amount of or interest on any TMCC Demand Notes, change the maturity date for the payment of the principal, the date on which interest will be payable or other terms of payment or reduce the percentage of holders of TMCC Demand Notes necessary to modify or alter the Demand Notes Indenture, without the consent of each Holder of Securities affected thereby.
Events of Default Under the Demand Notes Indenture
The Demand Notes Indenture defines an Event of Default with respect to the TMCC Demand Notes as being any one of the following events: (i) default in payment of principal on the TMCC Demand Notes and continuance of such default for a period of 10 days; (ii) default in payment of any interest on the TMCC Demand Notes and continuance of such default for a period of 30 days; (iii) default in the performance, or breach, of any other covenant or warranty of TMCC in the Demand Notes Indenture continued for 90 days after appropriate notice; and (iv) certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization. If an Event of Default occurs and is continuing, the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee or the holders of at least 25% in aggregate principal amount of TMCC Demand Notes may declare the TMCC Demand Notes to be due and payable.
At any time after such a declaration of acceleration with respect to TMCC Demand Notes has been made and before a judgment or decree for payment of the money due has been obtained by the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, the holders of not less than a majority in principal amount of the outstanding TMCC Demand Notes, by written notice to TMCC and the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, may rescind and annul such declaration and its consequences if:
| | · | TMCC has paid or deposited with the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee a sum of money sufficient to pay: |
| | § | all sums paid or advanced by the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee hereunder and the reasonable compensation, expenses, disbursements and advances of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, its agents and counsel; |
| | § | all due and overdue installments of interest on all TMCC Demand Notes; |
| | § | the principal of any TMCC Demand Notes which have become due otherwise than by such declaration of acceleration and interest thereon at the rate borne by or provided for in such TMCC Demand Notes; and |
| | § | to the extent that payment of such interest is lawful, interest upon overdue installments of interest at the rate borne by or provided for in such TMCC Demand Notes; and |
| | · | all Events of Default under the Demand Notes Indenture with respect to TMCC Demand Notes, other than the non-payment of the principal of, and interest on TMCC Demand Notes |
which will has become due solely by such declaration of acceleration, has been cured or waived as provided in the Demand Notes Indenture.
Any past default with respect to the TMCC Demand Notes may be waived by the holders of a majority in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding TMCC Demand Notes, except in a case of failure to pay principal of or interest on the TMCC Demand Notes for which payment has not been subsequently made or a default in respect of a covenant or provision of the Demand Notes Indenture which cannot be modified or amended without the consent of the holder of each outstanding TMCC Demand Note. TMCC will be required to file with the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee annually an officer’s certificate as to the absence of certain defaults. The Demand Notes Indenture Trustee may withhold notice to holders of the TMCC Demand Notes of any default with respect to such series (except in payment of principal or interest) if it in good faith determines that it is in the interest of such holders to do so.
If there is a default in the payment of interest or principal on any TMCC Demand Note and such default continues for a period of 30 days in the case of interest or a period of 10 days in the case of principal, TMCC will, upon demand of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, pay to the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, for the benefit of the holders of such TMCC Demand Notes, the whole amount of money then due and payable with respect to such TMCC Demand Notes with interest upon the overdue principal and, to the extent that payment of such interest will be legally enforceable, upon any overdue installments of interest at the rate borne by or provided for in such TMCC Demand Notes, and, in addition thereto, such further amount of money as will be sufficient to cover the costs and expenses of collection, including the reasonable compensation, expenses, disbursements and advances of the Trustee, its agents and counsel.
If TMCC fails to pay the money it is required to pay the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee as stated in the preceding paragraph upon the demand of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, in its own name and as trustee of an express trust, may institute a judicial proceeding for the collection of the money so due and unpaid, and may prosecute such proceeding to judgment or final decree, and may enforce the same against TMCC or any other obligor upon such TMCC Demand Notes and collect the money adjudged or decreed to be payable in the manner provided by law out of the property of TMCC or any other obligor upon such TMCC Demand Notes wherever situated.
If an Event of Default with respect to TMCC Demand Notes occurs and is continuing, the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee may in its discretion proceed to protect and enforce its rights and the rights of the holders of TMCC Demand Notes by such appropriate judicial proceedings as the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee will deem most effectual to protect and enforce any such rights, whether for the specific enforcement of any covenant or agreement in the Demand Notes Indenture or such TMCC Demand Notes or in aid of the exercise of any power granted herein or therein, or to enforce any other proper remedy.
Subject to the provisions of the Demand Notes Indenture relating to the duties of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee in case an Event of Default will occur and be continuing, the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee will be under no obligation to exercise any of its rights or powers under the Demand Notes Indenture at the request or direction of any of the holders of TMCC Demand Notes, unless such holders have offered to the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee indemnity or security satisfactory to it against the costs, expenses and liabilities which might be incurred by it in compliance with such request or direction. The Demand Notes Indenture Trustee may consult with counsel and the written advice of such counsel or any opinion of counsel will be full and complete authorization and protection in respect of any action taken, suffered or omitted by it hereunder in good faith and in reliance thereon. The Demand Notes Indenture Trustee will not be liable for any action it takes or omits to take in good faith which it believes to be authorized or within its rights or powers. Subject to provisions in the Demand Notes Indenture for the indemnification of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee and to certain other limitations, the holders of a majority in principal amount of the outstanding TMCC Demand Notes will have the right to direct the time, method and place of conducting any proceeding for any remedy available to the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, or exercising any Issuing Entity or power conferred on the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee with respect to the TMCC Demand Notes.
Absence of Covenants
The provisions of the Demand Notes Indenture do not contain any covenants that limit the ability of TMCC to subject its properties to liens, to enter into any type of transaction or business or to secure any of its other indebtedness without providing security for the TMCC Demand Notes. The provisions of the Demand Notes Indenture do not afford the holders of the TMCC Demand Notes protection in the event of a highly leveraged transaction, reorganization, restructuring, change in control, merger or similar transaction or other event.
Defeasance and Discharge of Demand Notes Indenture
TMCC may satisfy and discharge its obligations under the Demand Notes Indenture by delivering to the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee for cancellation all outstanding TMCC Demand Notes, or depositing with the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee money sufficient to pay the principal of and interest on the outstanding TMCC Demand Notes on the date on which any such payments are due and payable in accordance with the terms of the Demand Notes Indenture and the TMCC Demand Notes, and in each case by satisfying certain additional conditions in the Demand Notes Indenture. However, in the case of any such deposit, certain of TMCC’s obligations under the Demand Notes Indenture (including the obligation to pay the principal and interest on the outstanding TMCC Demand Notes) will continue until all of the TMCC Demand Notes are paid in full.
Regarding the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee
The Demand Notes Indenture Trustee may be the applicable trustee and/or indenture trustee. The Demand Notes Indenture contains certain limitations on the right of the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee, should it become a creditor of TMCC, to obtain payment of claims in certain cases, or to realize on certain property received in respect of any such claim as security or otherwise. The Demand Notes Indenture Trustee is permitted to engage in other transactions with TMCC; provided, however, that if the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee acquires any conflicting interest it must eliminate such conflict or resign.
The Demand Notes Indenture provides that, in case an Event of Default has occurred and is continuing, the Demand Notes Indenture Trustee is required to use the degree of care and skill of a prudent person in the conduct of his or her own affairs in the exercise of its powers.
Credit Support
TMCC has entered into a Credit Support Agreement with TFSC (the “TMCC Credit Support Agreement”), in which TFSC agreed to:
| | · | maintain 100% ownership of TMCC; |
| | · | cause TMCC and its subsidiaries to have a tangible net worth (where tangible net worth means the aggregate amount of issued capital, capital surplus and retained earnings less any intangible assets) of at least $100,000; and |
| | · | make sufficient funds available to TMCC so that TMCC will be able to service the obligations arising out of its own bonds, debentures, notes (including the TMCC Demand Notes) and other investment securities and commercial paper (collectively, “TMCC Securities”). |
The agreement is not a guarantee by TFSC of the TMCC Demand Notes or any other TMCC Securities or other obligations of TMCC. The agreement is governed by, and construed in accordance with, the laws of Japan.
TFSC has entered into a Credit Support Agreement with TMC (the “TMC Credit Support Agreement”), in which TMC agreed to:
| | · | maintain 100% ownership of TFSC; |
| | · | cause TFSC and its subsidiaries to have a certain minimum tangible net worth (where tangible net worth means the aggregate amount of issued capital, capital surplus and retained earnings less any intangible assets); and |
| | · | make sufficient funds available to TFSC so that TFSC will be able to (i) service the obligations arising out of its own bonds, debentures, notes and other investment securities and commercial paper and (ii) honor its obligations incurred as a result of guarantees or credit support agreements that it has extended (the “TFSC Securities”). |
The agreement is not a guarantee by TMC of any securities or obligations of TFSC. TMC’s obligations under the agreement rank pari passu with its senior unsecured debt obligations. The agreement is governed by, and construed in accordance with, the laws of Japan.
Holders of TMCC Securities, including any Issuing Entity holding TMCC Demand Notes, will have the right to claim directly against TFSC and TMC to perform their respective obligations under the credit support agreements by making a written claim together with a declaration to the effect that the holder will have recourse to the rights given under the credit support agreement. If TFSC and/or TMC receives such a claim from any holder of TMCC Securities, TFSC and/or TMC will indemnify, without any further action or formality, the holder against any loss or damage resulting from the failure of TFSC and/or TMC to perform any of their respective obligations under the credit support agreements. The holder of TMCC Securities who made the claim may then enforce the indemnity directly against TFSC and/or TMC.
Either TFSC or TMCC may terminate the TMCC Credit Support Agreement upon 30 days written notice to the other, with a copy to each rating agency that has issued a rating in respect of TMCC or any TMCC Securities upon the request of TFSC or TMCC. Similarly, either TMC or TFSC may terminate the TMC Credit Support Agreement upon 30 days written notice to the other, with a copy to each rating agency that has issued a rating in respect of TFSC or any TFSC Securities upon the request of TMC or TFSC. Termination will not take effect, however, unless (1) all TMCC Securities or TFSC Securities, as the case may be, issued on or prior to the date of the termination notice have been repaid or (2) each relevant rating agency has confirmed that the debt ratings of all such securities will be unaffected by the termination. In addition, with certain exceptions, the TMCC Credit Support Agreement and TMC Credit Support Agreement may be modified only by the written agreement of the applicable parties thereto.
TMC files reports and other information with the SEC, which can be read and copied at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington D.C. 20549. You may obtain information about the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. TMC’s electronic SEC filings are available on the Internet through the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
Governing Law
The Demand Notes Indenture and the TMCC Demand Notes will be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of the State of New York.
Where You can Find More Information
TMCC files annual, quarterly and current reports and other information with the SEC. You may read and copy TMCC’s SEC filings at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington D.C. 20549. You may obtain information about the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. TMCC’s electronic SEC filings are available on the Internet through the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
The consolidated financial statements incorporated, with respect to the TMCC Demand Notes, in this prospectus by reference to the annual report on Form 10-K of TMCC for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2014, have been so incorporated in reliance on the report of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
CERTAIN FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSEQUENCES
The following discussion of the anticipated material federal income tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of the Notes and the Certificates of any series, to the extent it relates to matters of law or legal conclusions with respect thereto, represents the opinion of tax counsel to each Issuing Entity with respect to the related series on the material matters associated with those consequences, subject to the qualifications described in this prospectus. “Tax Counsel” with respect to each Issuing Entity will be specified in the related Prospectus Supplement. The discussion does not purport to deal with federal income tax consequences applicable to all categories of investors, some of which may be subject to special rules and does not address which forms should be used to report information related to Notes and Certificates to the Internal Revenue Service, which we refer to in this prospectus as the “IRS.” For example, it does not discuss the tax treatment of Noteholders or Certificateholders that are insurance companies, regulated investment companies or dealers in securities. Moreover, there are no cases or Internal Revenue Service rulings on similar transactions involving both debt and equity interests issued by an Issuing Entity with terms similar to those of the notes and the certificates. As a result, the IRS may disagree with all or one or more parts of the discussion below. It is suggested that prospective investors consult their own tax advisors in determining the federal, state, local, foreign and any other tax consequences to them of the purchase, ownership and disposition of the Notes and the Certificates.
The following discussion is based upon current provisions of the Code, the Treasury regulations promulgated under the Code and judicial or ruling authority, all of which are subject to change, which change may be retroactive. Each Issuing Entity will be provided with an opinion of Tax Counsel regarding the federal income tax matters discussed below.
An opinion of Tax Counsel, however, is not binding on the IRS or the courts. No ruling on any of the issues discussed below will be sought from the IRS. For purposes of the following discussion, references to the Issuing Entity, the Notes, the Certificates and related terms, parties and documents will be deemed to refer to each Issuing Entity and the Notes, Certificates and related terms, parties and documents applicable to that Issuing Entity.
Tax Characterization of the Issuing Entity
The following discussion of the material anticipated federal income tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of the Notes and the Certificates of an Issuing Entity nominally referred to as an “owner trust” in the related Prospectus Supplement (an “Owner Trust”), to the extent it relates to matters of law or legal conclusions with respect thereto, represents the opinion of Tax Counsel to each Owner Trust with respect to the related series on the material matters associated with those consequences, subject to the qualifications described in this prospectus. In addition, Tax Counsel has prepared or reviewed the statements in this prospectus under the heading “Certain Federal Income Tax Consequences” and is of the opinion that those statements are correct in all material respects. Those statements are intended as an explanatory discussion of the related federal income tax matters affecting investors, but do not purport to furnish information in the level of detail or with the attention to an investor’s specific tax circumstances that would be provided by an investor’s own tax advisor. Accordingly, it is suggested that each investor consult its own tax advisor with regard to the tax consequences to it of investing in Notes or Certificates.
Tax Counsel will deliver its opinion that an Owner Trust will not be an association (or publicly traded partnership) taxable as a corporation for federal income tax purposes. This opinion will be based on the assumption that the terms of the Transfer and Servicing Agreement will be complied with, and on Tax Counsel’s conclusion that the nature of the income of the Issuing Entity will exempt it from the rule that some publicly traded partnerships are taxable as corporations.
If the Owner Trust were taxable as a corporation for federal income tax purposes, the Issuing Entity would be subject to corporate income tax on its taxable income. The Issuing Entity’s taxable income would include all its income on the Receivables, possibly reduced by its interest expense on the Notes. Any corporate income tax could materially reduce cash available to make payments on the Notes and the Certificates.
Tax Consequences to Owners of the Notes
Treatment of the Notes as Indebtedness. The Depositor and any Noteholders will agree, and the beneficial owners of the Notes (which we refer to in this prospectus as the “Note Owners”) will agree by their purchase of Notes, to treat the Notes as debt for federal income tax purposes. Except as otherwise provided in the related Prospectus Supplement, Tax Counsel will deliver its opinion that the Notes will be classified as debt for federal income tax purposes. The discussion below assumes this characterization of the Notes is correct.
OID, Etc. The discussion below assumes that all payments on the Notes are denominated in U.S. dollars, and that the Notes are not Strip Notes. Moreover, subject to the discussion below for short-term notes, the discussion assumes that the interest formula for the Notes meets the requirements for “qualified stated interest” under Treasury regulations (the “OID regulations”) relating to original issue discount (“OID”), and that any OID on the Notes (i.e., any excess of the principal amount of the Notes over their issue price) does not exceed a de minimis amount (i.e., 0.25% of their principal amount multiplied by the number of full years included in determining their term), all within the meaning of the OID regulations. In determining whether any OID on the Notes is de minimis, the Depositor expects to use a reasonable assumption regarding prepayments (a “Prepayment Assumption”) to determine the weighted average maturity of the Notes. If these conditions are not satisfied with respect to any given series of Notes, additional tax considerations with respect to those Notes will be disclosed in the related Prospectus Supplement.
Interest Income on the Notes. Based on the above assumptions, except as discussed in the following paragraph, the Notes will not be considered issued with OID. The stated interest on the Notes will be taxable to a Note Owner as ordinary interest income when received or accrued in accordance with that Note Owner’s method of tax accounting. Under the OID regulations, the Note Owner of a Note issued with a de minimis amount of OID must include that OID in income, on a pro rata basis, as principal payments are made on the Note. Subject to a statutorily defined de minimis rule for market discount and a required election for premium, absent an exception based on a taxpayer’s unique circumstances, a purchaser who buys a Note for more or less than its principal amount will be subject, respectively, to the premium amortization or market discount rules of the Code.
The Note Owner of a Note that has a fixed maturity date of not more than one year from the issue date of that note (a “Short-Term Note”) may be subject to special rules. An accrual basis Note Owner of a Short-Term Note (and some cash method Note Owners, including regulated investment companies, as described in Section 1281 of the Code) is required to report interest income as interest accrues on a straight-line basis or under a constant yield method over the term of each interest period. Other cash basis Note Owners of a Short-Term Note are required to report interest income as interest is paid (or, if earlier, upon the taxable disposition of the Short-Term Note). However, a cash basis Note Owner of a Short-Term Note reporting interest income as it is paid may be required to defer a portion of any interest expense otherwise deductible on indebtedness incurred to purchase or carry the Short-Term Note until the taxable disposition of the Short-Term Note. A cash basis Note Owner that is not required to report interest income as it accrues under Section 1281 may elect to accrue interest income on all nongovernment debt obligations with a term of one year or less, in which case the Note Owner would not be subject to the interest expense deferral rule referred to in the preceding sentence. Certain special rules apply if a Short-Term Note is purchased for more or less than its principal amount.
Sale or Other Disposition. If a Note Owner sells a Note, the Note Owner will recognize gain or loss in an amount equal to the difference between the amount realized on the sale and the Note Owner’s adjusted tax basis in the Note. The adjusted tax basis of a Note to a particular Note Owner will equal the Note Owner’s cost for the Note, increased by any market discount, acquisition discount and OID previously included in income by that Note Owner with respect to the note and decreased by the amount of bond premium, if any, previously amortized and by the amount of payments of principal and OID previously received by that Note Owner with respect to that Note. Any gain or loss, and any gain or loss recognized on a prepayment of the Notes, will be capital gain or loss if the Note was held as a capital asset, except for gain representing accrued interest and accrued market discount not previously included in income. Except for an annual $3,000 exception applicable to individuals, capital losses may be used only to offset capital gains or gains treated as capital gains.
Net Investment Income. A tax of 3.8% is imposed on the “net investment income” of certain U.S. individuals, trusts and estates. Among other items, net investment income generally includes gross income from
interest and net gain attributable to the disposition of certain property, less certain deductions. Note Owners that are U.S. Persons should consult their own tax advisors regarding the possible implications of this tax in their particular circumstances.
Foreign Owners. Except as described below with respect to backup withholding or FATCA (defined below), interest paid (or accrued) to a Note Owner who is not a U.S. Person (a “Foreign Owner”) will be considered “portfolio interest,” and not subject to United States federal income tax and withholding tax if the interest is not effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business within the United States by the Foreign Owner and:
| | 1. | the Foreign Owner is not actually or constructively a “10 percent shareholder” of the Issuing Entity or the Depositor (including a holder of 10% or more of the outstanding certificates issued by the Issuing Entity) or a “controlled foreign corporation” with respect to which the Issuing Entity or the Depositor is a “related person” within the meaning of the Code; |
| | 2. | the Foreign Owner is not a bank receiving interest described in Section 881(c)(3)(A) of the Code; |
| | 3. | the interest is not contingent interest described in Section 871(h)(4) of the Code; and |
| | 4. | the Foreign Owner does not bear specified relationships to any certificateholder. |
To qualify for the portfolio interest exemption, the Foreign Owner must provide the applicable trustee or other person who is otherwise required to withhold U.S. tax with respect to the notes with an appropriate statement (on Form W-8BEN, Form W-8BEN-E or applicable similar or successor forms), signed under penalty of perjury, certifying that the Note Owner is a Foreign Owner and providing the Foreign Owner’s name and address. Interest paid to a Foreign Owner is also not subject to United States federal withholding tax if such interest is effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business within the United States by the Foreign Owner and such foreign person submits a properly executed Form W-8ECI (or applicable successor form). If a note is held through a securities clearing organization or other financial institution, the organization or institution may provide the relevant signed statement to the withholding agent; in that case, however, the Foreign Owner must provide the security clearing organization or other financial institution with a Form W-8BEN, Form W-8BEN-E, Form W-8ECI or applicable similar or successor form. A Form W-8BEN, Form W-8BEN-E and Form W-8ECI remains in effect for a period beginning on the date the form is signed and ending on the last day of the third succeeding calendar year, absent a change in circumstances causing any information on the form to be incorrect. Under certain circumstances, the Form W-8BEN and Form W-8BEN-E can remain in effect indefinitely. The Foreign Owner must notify the person to whom it provided the Form W-8BEN, Form W-8BEN-E, Form W-8ECI or applicable similar or successor form of any changes to the information on the Form or applicable similar or successor form. If interest paid to a Foreign Owner is not considered portfolio interest and is not effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business within the United States by the Foreign Owner, then it will be subject to United States federal income and withholding tax at a rate of 30 percent, unless reduced or eliminated pursuant to an applicable tax treaty. In order to claim the benefit of any applicable tax treaty, the Foreign Owner must provide the applicable trustee or other person who is required to withhold U.S. tax with respect to the notes with an appropriate statement (on Form W-8BEN, Form W-8BEN-E or applicable similar or successor form), signed under penalties of perjury, certifying that the Foreign Owner is entitled to benefits under the treaty.
Except as described below with respect to backup withholding or FATCA, any capital gain realized on the sale, redemption, retirement or other taxable disposition of a Note by a Foreign Owner will be exempt from United States federal income and withholding tax, provided that (1) the gain is not effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States by the Foreign Owner and (2) in the case of an individual Foreign Owner, the Foreign Owner is not present in the United States for 183 days or more during the taxable year of disposition.
If interest paid to a Foreign Owner or gain on the sale, redemption, retirement or other taxable disposition of a Note is effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business within the United States by the Foreign Owner, then although the foreign person will be exempt from the withholding of tax previously
discussed if an appropriate statement is provided, such foreign person generally will be subject to United States federal income tax on such interest, including OID, or gain at applicable graduated federal income tax rates. In addition, if the Foreign Owner is a foreign corporation, it may be subject to a branch profits tax equal to 30% of the “effectively connected earnings and profits” within the meaning of the Code for the taxable year, as adjusted for certain items, unless such Foreign Owner qualifies for a lower rate under an applicable tax treaty.
As used in this prospectus, a “U.S. Person” means:
| | 1. | a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| | 2. | an entity treated as a corporation or a partnership for United States federal income tax purpose created or organized under the laws of the United States, any state thereof, or the District of Columbia; |
| | 3. | an estate, the income of which from sources outside the United States is includible in gross income for federal income tax purposes regardless of its connection with the conduct of a trade or business within the United States; or |
| | 4. | a trust if (a) a court within the U.S. is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust and one or more United States persons have authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust or (b) such trust was in existence on August 20, 1996 and is eligible to elect, and has made a valid election, to be treated as a U.S. Person despite not meeting the requirements of clause (a). |
Backup Withholding. Each Note Owner (other than an exempt Note Owner such as a tax-exempt organization, qualified pension and profit- sharing trust, individual retirement account or nonresident alien who provides certification as to status as a nonresident) will be required to provide, under penalties of perjury, a certificate (on Form W-9) providing the Note Owner’s name, address, correct federal taxpayer identification number and a statement that the Note Owner is not subject to backup withholding. Should a nonexempt Note Owner fail to provide the required certification, amounts otherwise payable to the Note Owner may be subject to backup withholding tax, and the Issuing Entity will be required to withhold and remit the withheld amount to the IRS. Any such amount withheld would be credited against the Note Owner’s federal income tax liability.
Possible Alternative Treatments of the Notes. If, contrary to the opinion of Tax Counsel, the IRS successfully asserted that one or more of the notes did not represent debt for federal income tax purposes, the notes might be treated as equity interests in the Issuing Entity. If so treated, the Issuing Entity might be taxable as a corporation with the adverse consequences described above (and the taxable corporation would not be able to reduce its taxable income by deductions for interest expense on notes recharacterized as equity). Alternatively, and most likely in the view of Tax Counsel, the Issuing Entity might be treated as a partnership (including a publicly traded partnership) that would not be taxable as a corporation. Nonetheless, treatment of the notes as equity interests in a publicly traded partnership could have adverse tax consequences to some Note Owners. For example, income to some tax-exempt entities (including pension funds) may be “unrelated business taxable income,” income to Foreign Owners may be subject to U.S. income tax and withholding taxes and cause Foreign Owners to be subject to U.S. tax return filing and withholding requirements, and individual Note Owners might be subject to some limitations on their ability to deduct their share of Issuing Entity expenses.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance. In addition to the rules described above regarding the potential imposition of U.S. withholding taxes on payments to non-U.S. persons, withholding taxes could also be imposed under the new Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (“FATCA”) regime. FATCA was enacted in the United States in 2010 as part of the Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment Act (the “HIRE Act”) as a way to encourage tax reporting and compliance with respect to ownership by U.S. persons of assets through foreign accounts. Under FATCA, foreign financial institutions (defined broadly to include hedge funds, private equity funds, mutual funds, securitization vehicles and other investment vehicles) must comply with new information gathering and reporting rules with respect to their U.S. account holders and investors and may be required to enter into agreements with the IRS pursuant to which such foreign financial institutions must gather and report certain information to the IRS and
withhold U.S. tax from certain payments made by it. Foreign financial institutions that fail to comply with the FATCA requirements will be subject to a new 30% withholding tax on U.S. source payments, including interest, OID and gross proceeds from the sale of any equity or debt instruments of U.S. issuers. Payments of interest or OID to foreign non-financial entities and gross proceeds will also be subject to a withholding tax of 30% if the entity does not certify that it does not have any substantial U.S. owner or provide the name, address and TIN of each substantial U.S. owner. The FATCA withholding tax will apply regardless of whether the payment would otherwise be exempt from U.S. nonresident withholding tax (e.g., under the portfolio interest exemption or as capital gain) and regardless of whether the foreign financial institution is the beneficial owner of such payment. Pursuant to final regulations, although FATCA withholding tax currently applies to payments of interest on debt instruments issued after June 30, 2014, the withholding tax on gross proceeds from a disposition of debt instruments to which the FATCA provisions apply will not be imposed prior to January 1, 2017. Prospective investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the HIRE Act.
Reportable Transactions. A penalty in the amount of $10,000 in the case of a natural person and $50,000 in any other case is imposed on any taxpayer that fails to timely file an information return with the IRS with respect to a “reportable transaction” (as defined in Section 6011 of the Code). The rules defining “reportable transactions” are complex, but include (and are not limited to) transactions that result in certain losses that exceed threshold amounts. Prospective investors are advised to consult their own tax advisers regarding any possible disclosure obligations in light of their particular circumstances.
CERTAIN STATE TAX CONSEQUENCES
The above discussion does not address the tax treatment of any Owner Trust, Notes or Note Owners under any state or local tax laws. The activities to be undertaken by the Servicer in servicing and collecting the Receivables will take place in various states and, therefore, many different state and local tax regimes potentially apply to different portions of these transactions. Prospective investors are urged to consult with their tax advisors regarding the state and local tax treatment of any Owner Trust as well as any state and local tax consequences for them purchasing, holding and disposing of Notes or Certificates.
You should consult your tax advisor with respect to the tax consequences to you of the purchase, ownership and disposition of notes, including the tax consequences under state, local, foreign and other tax laws and the possible effects of changes in federal or other tax laws.
ERISA CONSIDERATIONS
The Notes issued by the related Issuing Entity will generally be eligible for purchase by pension, profit-sharing or other employee benefit plans that are subject to Title I of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended (“ERISA”), IRAs, Keogh Plans and other plans covered by Section 4975 of the Code and entities deemed to hold the plan assets of the foregoing (each, a “Plan”). The “ERISA Considerations” section of each related Prospectus Supplement includes a detailed description of the ERISA implications for each series of Notes.
PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION
On the terms and conditions described in an underwriting agreement with respect to the Notes (the “Underwriting Agreement”), the Depositor will agree to cause the related Issuing Entity to sell to the underwriters named in the related Underwriting Agreement and in the related Prospectus Supplement, and each of such underwriters will severally agree to purchase, the principal amount of each class of Notes of the related series described in the related Underwriting Agreement and in the related Prospectus Supplement.
In the Underwriting Agreement with respect to any given series of Notes, the several underwriters will agree, subject to the terms and conditions described in the related Underwriting Agreement, to purchase all the Notes described in such Underwriting Agreement which are offered hereby and by the related Prospectus Supplement if any of such Notes are purchased.
Each Prospectus Supplement will either (i) describe the price at which each class of Notes being offered by such Prospectus Supplement will be offered to the public and any concessions that may be offered to certain dealers participating in the offering of such Notes or (ii) specify that the related Notes are to be resold by the underwriters in negotiated transactions at varying prices to be determined at the time of such sale. After the initial public offering of any such Notes, such public offering prices and such concessions may be changed.
Each Underwriting Agreement will provide that TMCC and the Depositor will indemnify the underwriters against certain civil liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act, or contribute to payments the several underwriters may be required to make in respect of such civil liabilities.
Each Issuing Entity may, from time to time, invest the funds in its Trust Accounts in Eligible Investments acquired from such underwriters or from the Depositor.
Pursuant to each Underwriting Agreement with respect to a given series of Notes, the closing of the sale of any class of Notes subject to such Underwriting Agreement will be conditioned on the closing of the sale of all other such classes of Notes of that series.
If specified in the related Prospectus Supplement, the Depositor or its affiliate may place all or a portion of a class or classes of Notes of the related series directly or through a placement agent. The Depositor or its affiliate also may retain all or a portion of a class or classes of Notes of the related series for its own account. Some or all of such retained Notes may be resold by the Depositor or its affiliate at any time on or after the applicable Closing Date in one or more negotiated transactions at varying prices to be determined at the time of sale.
The place and time of delivery for the Notes in respect of which this prospectus is delivered will be described in the related Prospectus Supplement.
If the related Prospectus Supplement specified that the applicable Issuing Entity will hold TMCC Demand Notes, the TMCC Demand Notes will be issued by TMCC and will be sold directly to the applicable Issuing Entity. The TMCC Demand Notes will not be sold directly to any investor other than the applicable Issuing Entity. A Noteholder of Notes issued by an Issuing Entity which holds TMCC Demand Notes will be an indirect holder of those TMCC Demand Notes.
LEGAL OPINIONS
Certain legal matters relating to the Notes of any series will be passed upon for the related Issuing Entity, the Depositor and the Servicer by Bingham McCutchen LLP. In addition, certain United States federal income tax and other matters will be passed upon for the related Issuing Entity by Bingham McCutchen LLP.
INDEX OF DEFINED TERMS
| 30/360 | 48 | | DSSOs | 30 |
| Actual/360 | 48 | | DTC | 54 |
| Actual/Actual | 48 | | DTC Participants | 41 |
| Actuarial Advance | 67 | | DTCC | 57 |
| Actuarial Receivables | 38 | | Eligible Deposit Account | 63 |
| Administration Agreement | 77 | | Eligible Institution | 64 |
| Administration Fee | 77 | | Eligible Investments | 63 |
| Administrative Purchase Payment | 65 | | ERISA | 98 |
| Administrative Receivable | 65 | | Euroclear | 55 |
| Advances | 67 | | Euroclear Participants | 58 |
| Amortization Period | 54 | | Excess Payment | 67 |
| APR | 38 | | Exchange Act | 37 |
| Auction | 52 | | FATCA | 97 |
| Base Rate | 47 | | FDCPA | 84 |
| Basic Servicing Fee | 68 | | FDIC | 82 |
| Beneficial Owners | 54 | | FDIC Counsel | 83 |
| Bond Equivalent Yield | 53 | | Federal Funds Rate | 51 |
| Business Day | 48 | | Federal Funds Rate Determination Date | 51 |
| Calculation Agent | 49 | | Federal Funds Rate Note | 47 |
| Calculation Date | 50, 51, 53 | | Final Rule | 84 |
| carLOS | 31 | | Final Scheduled Maturity Date | 65 |
| CD Rate | 49 | | financed vehicles | 9 |
| CD Rate Determination Date | 49 | | Financed Vehicles | 35 |
| CD Rate Note | 47 | | Fixed Rate Notes | 47 |
| Certificateholder | 34 | | Floating Rate Notes | 47 |
| Certificates | 34 | | Foreign Owner | 96 |
| CFPB | 85 | | FTC | 86 |
| class | 41 | | FTC Rule | 85 |
| Clearstream | 54 | | H.15 Daily Update | 47 |
| Closing Date | 37 | | H.15(519) | 47 |
| Code | 46 | | HDC Rule | 85 |
| Collection Account | 63 | | HIRE Act | 97 |
| Collection Period | 66 | | Indenture | 41 |
| Commercial Paper Rate | 50 | | Indenture Trustee | 36 |
| Commercial Paper Rate Determination Date | 50 | | Index Currency | 52 |
| Commercial Paper Rate Note | 47 | | Index Maturity | 47 |
| Controlling Class | 42 | | Insolvency Event | 74 |
| credit enhancement | 11 | | Insolvency Laws | 81 |
| CSCs | 30 | | Interest Determination Date | 48 |
| Customary Servicing Practices | 33 | | Interest Period | 49 |
| Cutoff Date | 35 | | Interest Rate | 42 |
| Dealer Agreements | 30 | | Interest Reset Date | 47 |
| Dealer Recourse | 39 | | Interest Reset Period | 47 |
| Dealers | 30, 35 | | Investment Earnings | 63 |
| Definitive Certificates | 58 | | Issuer | 34 |
| Definitive Notes | 58 | | Issuing Entity | 34 |
| Definitive Securities | 58 | | LIBOR | 51 |
| Demand Notes Indenture | 87 | | LIBOR Note | 47 |
| Demand Notes Indenture Trustee | 87 | | London Business Day | 48 |
| Depositor | 34 | | Money Market Yield | 50 |
| Depository | 41 | | Monthly Remittance Condition | 66 |
| Determination Date | 72 | | Note Owners | 95 |
| Dodd-Frank Act | 82 | | Note Pool Factor | 41 |
| noteholder | 26 | | Servicer | 32 |
| Noteholder | 41 | | Servicer Default | 73 |
| Notes | 34 | | Servicing Fee Rate | 68 |
| obligors | 9 | | Short-Term Note | 95 |
| Obligors | 35 | | Simple Interest Advance | 67 |
| OID | 95 | | Simple Interest Receivables | 38 |
| OID regulations | 95 | | Spread | 47 |
| OLA | 82 | | Spread Multiplier | 47 |
| OSCAR | 31 | | Strip Notes | 42 |
| Owner Trust | 94 | | Supplemental Servicing Fee | 68 |
| Payahead Account | 63 | | Surety Bond | 71 |
| Payment Date | 42 | | TAFR LLC | 34 |
| Plan | 98 | | TARGET system | 48 |
| Pool Balance | 68 | | Tax Counsel | 94 |
| Prepayment | 67 | | TFSC | 30, 87 |
| Prepayment Assumption | 95 | | TFSC Securities | 93 |
| prepayments | 39 | | TMC | 19, 30, 87 |
| Principal Balance | 68 | | TMC Credit Support Agreement | 92 |
| Principal Financial Center | 52 | | TMCC | 7, 30 |
| Prospectus Supplement | 34 | | TMCC Credit Support Agreement | 92 |
| Rating Agency | 36 | | TMCC Demand Notes | 10, 87 |
| receivables | 9 | | TMCC Securities | 92 |
| Receivables | 35 | | TMS | 19 |
| Receivables Pool | 35 | | Total Servicing Fee | 68 |
| Receivables Purchase Agreement | 37 | | Transfer and Servicing Agreements | 35 |
| Registration Statement | 36 | | Transfer Notice | 61 |
| Related Documents | 46 | | Treasury Bills | 52 |
| Relief Act | 28, 84 | | Treasury Rate | 52 |
| Required Rate | 70 | | Treasury Rate Determination Date | 52 |
| Required Yield Maintenance Amount | 70 | | Treasury Rate Note | 47 |
| Reserve Fund | 70 | | Trust Accounts | 63 |
| Reserve Fund Initial Deposit | 70 | | Trust Agreement | 34 |
| Revolving Liquidity Note | 71 | | Trust Estate | 35 |
| Revolving Liquidity Note Agreement | 71 | | Trustee | 36 |
| Revolving Period | 11 | | U.S.A. | 30 |
| Sale and Servicing Agreement | 35 | | Underwriting Agreement | 98 |
| SEC | 2, 36 | | Warranty Purchase Payment | 62 |
| Securities | 34 | | Warranty Receivable | 62 |
| Securities Act | 36 | | weighted average life | 39 |
| securityholder | 26 | | Yield Maintenance Account | 70 |
| Securityholder | 33 | | Yield Maintenance Agreement | 70 |
| Securityholders | 36 | | Yield Maintenance Deposit | 70 |