Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D. C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to .
Commission File Number 0-23827
PC CONNECTION, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 02-0513618 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
730 Milford Road Merrimack, New Hampshire | 03054 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code (603) 683-2000
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, $.01 par value | Nasdaq Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
(Title of Class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
YES ¨ NO þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
YES ¨ NO þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
YES þ NO ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer þ | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | Smaller reporting company ¨ | |||
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
YES ¨ NO þ
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s voting shares of common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant on June 30, 2008, based on $9.31 per share, the last reported sale price on the Nasdaq Global Select Market on that date, was $88,664,139.
The number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock, as of March 4, 2009:
Class | Number of Shares | |
| Common Stock, $.01 par value | 27,012,729 |
The following documents are incorporated by reference into the Annual Report on Form 10-K: Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2009 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Report.
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||
| PART I | ||||
ITEM 1. | 1 | |||
ITEM 1A. | 10 | |||
ITEM 1B. | 16 | |||
ITEM 2. | 16 | |||
ITEM 3. | 17 | |||
ITEM 4. | 17 | |||
| PART II | ||||
ITEM 5. | 18 | |||
ITEM 6. | 21 | |||
ITEM 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 23 | ||
ITEM 7A. | 40 | |||
ITEM 8. | 40 | |||
ITEM 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | 40 | ||
ITEM 9A. | 40 | |||
ITEM 9B. | 43 | |||
| PART III | ||||
ITEM 10. | 44 | |||
ITEM 11. | 44 | |||
ITEM 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | 44 | ||
ITEM 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | 44 | ||
ITEM 14. | 44 | |||
| PART IV | ||||
ITEM 15. | 45 | |||
| 52 | ||||
Table of Contents
PART I
| Item 1. | Business |
GENERAL
We are a leading direct marketer of a wide range of information technology, or IT, products and services, including computer systems, software and peripheral equipment, networking communications, and other products and accessories that we purchase from manufacturers, distributors, and other suppliers. We also offer a growing range of installation, configuration, repair, and other services performed by our personnel and third-party providers. We operate through three primary business segments: (1) consumers and small- to medium-sized businesses, or SMB, through our PC Connection Sales subsidiaries, (2) large enterprise customers, or Large Account, through our MoreDirect subsidiary, and (3) federal, state, and local government and educational institutions, or Public Sector, through our GovConnection subsidiary. Our principal customers are SMBs (comprised of 20 to 1,000 employees), medium-to-large corporate accounts, and government and educational institutions. We generate sales through (i) outbound telemarketing and field sales contacts by sales representatives focused on the business, education, and government markets, (ii) our websites, and (iii) inbound calls from customers responding to our catalogs and other advertising media. We offer a broad selection of over 150,000 products targeted for business use at competitive prices, including products from Acer, Apple, Cisco Systems, Hewlett-Packard, IBM, Lenovo, Microsoft, Sony, Symantec, and Toshiba. Our most frequently ordered products are carried in inventory and are typically shipped to customers the same day the order is received.
Since our founding in 1982, we have consistently served our customers’ needs by providing innovative, reliable, and timely service and technical support, and by offering an extensive assortment of branded products through knowledgeable, well-trained sales and support teams. Our strategy’s effectiveness is reflected in the recognition we have received, including being named to the Fortune 1000 and the VARBusiness 500 for each of the last eight years. In 2008, we were awarded first place by InformationWeek in the Supply Chain Innovation and Retail Industry categories and were ranked #8 overall among the nation’s most innovative companies by InformationWeek.
We believe that our consistent customer focus has also resulted in strong brand name recognition and a broad and loyal customer base. Approximately 91% of our net sales in the year ended December 31, 2008 were made to customers who had previously purchased products from us. We believe we also have strong relationships with vendors, resulting in favorable product allocations and marketing assistance.
Our marketing efforts are targeted at SMBs, government and educational institutions, and medium-to-large corporate accounts. As of December 31, 2008, we employed 712 sales representatives, including 186 new sales representatives with less than 12 months of outbound telemarketing experience with us. Sales representatives are responsible for managing corporate and public sector accounts and focus on outbound sales calls to prospective customers. We believe that increasing our sales representatives’ productivity is important to our future success, and we have increased our investments in this area accordingly.
We market our products and services through our websites: www.pcconnection.com, www.macconnection.com, www.moredirect.com, and www.govconnection.com. Our websites provide customers and prospective customers with product information and enable customers to place electronic orders for products. For the fiscal year 2008, Internet sales processed directly online were $515.7 million, or 29.4% of net sales, compared to 29.6% in 2007.
We publish several catalogs, including PC Connection®, focusing on PCs and compatible products, and MacConnection®, focusing on Apple personal computers and compatible products. We also issue, from time to time, specialty catalogs, including GovConnection catalogs directed to government and educational institutions. With concise product descriptions, relevant technical information, and illustrations, along with toll-free telephone numbers for ordering, our catalogs are recognized as a leading source for personal computer hardware, software, and other related products. We distributed approximately 12 million catalogs in 2008.
1
Table of Contents
Additional financial information regarding our business segments and geographic data about our customers and assets is contained in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations in Item 7 of Part II, and Note 15 to our Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We are subject to the informational requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, and accordingly, we file reports, proxy and information statements, and other information with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC. Such reports and information can be read and copied at the public reference facilities maintained by the SEC at the Public Reference Room, 100 F Street, NE, Washington, D.C. 20549. Information regarding the operation of the Public Reference Room may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains a website (http://www.sec.gov) that contains such reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. We maintain a website with the address www.pcconnection.com. We are not including the information contained in our website as part of, or incorporating by reference into, this annual report on Form 10-K. We make available free of charge through our website our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, and current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to these reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file these materials with, or otherwise furnish them to, the SEC.
MARKET AND COMPETITION
We generate approximately 52% of our sales from the SMB market, 27% from medium-to-large corporate accounts (Fortune 1000), and 21% from government agencies and educational organizations. The overall U.S. IT market that we serve is estimated to be in excess of $200 billion.
The largest segment of this market is served by local and regional “value added resellers,” or VARs, many of whom we believe are transitioning from the hardware and software business to IT services, which generally have higher margins. We have transitioned from an end-user or desktop-centric computing supplier to a network or enterprise-wide computing supplier. We have also partnered with third-party technology and telecommunications service providers. We now offer our customers access to the same services and technical expertise as local and regional VARs, but with more extensive product selection at lower prices.
Intense competition for customers has led manufacturers of PCs and related products to use all available channels, including direct marketers, to distribute products. Certain manufacturers who have traditionally used resellers to distribute their products have established their own direct marketing operations, including sales through the Internet. Nonetheless, we believe that these manufacturers of PCs and related products will continue to provide us and other third-party direct marketers favorable product allocations and marketing support.
We believe new entrants to the direct marketing channel must overcome a number of obstacles, including:
| • | the substantial time and resources required to build a customer base of meaningful size and profitability for cost-effective operation; |
| • | the high costs of developing the information and operating infrastructure required by direct marketers; |
| • | the advantages enjoyed by larger and more established competitors in terms of purchasing and operating efficiencies; |
| • | the difficulty of building relationships with manufacturers to achieve favorable product allocations and attractive pricing terms; and |
| • | the difficulty of identifying and recruiting management personnel with significant direct marketing experience in the industry. |
2
Table of Contents
BUSINESS STRATEGIES
Our objective is to become the principal supplier of IT products and solutions, including personal computers and related products and services, to our customers. The key elements of our business strategies include:
| • | Providing consistent customer service before, during, and after the sale. We believe that we have earned a reputation for providing superior customer service by consistently focusing on our customers’ needs. We deliver value to our customers through high-quality service and technical support provided by our knowledgeable, well-trained personnel. We also have efficient delivery programs and offer our customers reasonable return policies. |
| • | Offering a broad product selection at competitive prices. We offer a wide assortment of IT products and solutions, including personal computers and related products and networking products, at competitive prices. Our merchandising programs feature products that provide customers with aggressive price and performance and the convenience of one-stop shopping for their personal computer and related needs. |
| • | Simplifying technology products procurement for corporate customers.We offer Internet-based procurement options that simplify the process and lower the cost of procurement for our customers. Our Large Account subsidiary, MoreDirect, specializes in Internet-based solutions and provides electronic integration with its customers and suppliers. |
| • | Maintaining a strong brand name and customer awareness. Since our founding in 1982, we have built a strong brand name and customer awareness. We have been named to the Fortune 1000 and the VARBusiness 500 for each of the last eight years, and in 2007 Forbes Magazine acknowledged us as one of America’s most trustworthy companies. Our mailing list includes more than 4,200,000 names, of which approximately 370,000 have purchased products from us during the last 12 months. |
| • | Maintaining long-standing vendor relationships. We have a history of strong relationships with vendors, and were among the first direct marketers qualified by manufacturers to market computer systems to end users. We provide our vendors with both information concerning customer preferences and an efficient channel for the advertising and distribution of their products. |
GROWTH STRATEGIES
Our growth strategies are to increase revenues derived from broader product and service offerings, increased penetration of our existing customers, and expanded customer base. The key elements of our growth strategies include:
| • | Expanding product, solution, and service offerings. We offer our customers an extensive range of IT products, solutions, and services, and continually evaluate and add new products and services, as they become available or in response to customer demand. We work closely with vendors to identify and source first-to-market product offerings at aggressive prices. We offer a growing range of installation, configuration, repair, and other services performed by our personnel and third-party providers, and seek to become a total IT solution provider to our customers. |
| • | Targeting customer segments. Through targeted marketing, we seek to expand the number of our active customers and generate additional sales from existing customers. We have developed specialty catalogs featuring product offerings designed to address the needs of specific customer populations, including new product inserts targeted to purchasers of graphics, server, and networking products. We also utilize internet marketing campaigns that focus on select markets. |
| • | Pursuing strategic acquisitions and alliances. We seek acquisitions and alliances that add new customers, strengthen our product offerings, add management talent, and produce operating results which are accretive to our core business earnings. |
| • | Increasing productivity of our sales representatives. We believe that higher sales productivity is the key to leveraging our expense structure and driving future profitability improvements. We invest |
3
Table of Contents
significant resources in training new sales representatives, and provide ongoing training to experienced personnel. Our training and evaluation programs are focused towards assisting our sales personnel in understanding and anticipating clients’ IT needs, with the goal of fostering loyal client relationships. We are currently undertaking a major modification and upgrade of our sales order and customer management system that are expected to improve sales productivity beginning in the second half of 2009. Significant sales growth over the long term will also likely require us to add sales representatives in the future. |
SERVICE AND SUPPORT
Since our founding in 1982, our primary objective has been to provide products that meet the demands and needs of customers and to supplement those products with up-to-date product information and excellent customer service and support. We believe that offering our customers superior value, through a combination of product knowledge, consistent and reliable service, and leading products at competitive prices, differentiates us from other direct marketers and provides the foundation for developing a broad and loyal customer base.
We invest in training programs for our service and support personnel, with an emphasis on putting customer needs and service first. We provide toll-free technical support from 9:00 a.m. through 5:30 p.m. Eastern Time, Monday through Friday. Product support technicians assist callers with questions concerning compatibility, installation, determination of defects, and more difficult questions relating to product use. The product support technicians authorize customers to return defective or incompatible products to either the manufacturer or to us for warranty service. In-house technicians perform both warranty and non-warranty repair on most major systems and hardware products.
Using our customized information system, we send our customer orders either to our distribution center or to our drop-ship suppliers, depending on product availability, for processing immediately after a customer receives a credit approval. At our distribution center, we also perform custom configuration of computer systems as requested by our customers, which typically consists of the installation of memory, accessories, and/or software purchased. Our customers may select the method of delivery that best meets their needs and is most cost effective, ranging from expedited overnight delivery for urgently-needed items to ground freight, generally used for heavier, more bulky items. Through our Everything Overnight® service, orders accepted up to 7:00 p.m. Eastern Time can be shipped for overnight delivery.
Our inventory stocking levels are based on three primary criteria. First, we stock and maintain a large quantity of products that sell through quickly (such as notebook and desktop systems, printers, and monitors). Second, we stock products obtained through opportunistic purchases (including first-to-market and end-of-life special promotions, and popular products with limited availability). Third, we stock products in common demand, such as components we use to configure systems prior to shipping, for which we want to avoid shortages. Inventory stocking decisions are made generally independent of the level of shipping service, as expedited shipping, including overnight delivery, is available through the majority of our drop-ship suppliers as well as through our warehouse.
MARKETING AND SALES
We sell our products through our direct marketing channels to SMBs, government and educational institutions, and medium-to-large corporate accounts. We strive to be the primary supplier of IT products and solutions, including personal computers and related products, to our existing customers and to our expanding customer base. We use multiple marketing approaches to reach existing and prospective customers, including:
| • | outbound telemarketing and field sales; |
| • | Web and print media advertising; |
| • | marketing programs targeted to specific customer populations; and |
4
Table of Contents
| • | catalogs and inbound telesales. |
All of our marketing approaches emphasize our broad product offerings, fast delivery, customer support, competitive pricing, and our increasing range of service solutions.
We believe that our ability to establish and maintain long-term customer relationships and to encourage repeat purchases is largely dependent on the strength of our sales personnel and programs. Because our customers’ primary contact with us is through our sales representatives, we are committed to maintaining a qualified, knowledgeable, and motivated sales staff with its principal focus on customer service.
Sales Channels.The following table sets forth our percentage of net sales by sales channel:
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Sales Channel | |||||||||
Outbound Telemarketing and Field Sales | 69 | % | 68 | % | 66 | % | |||
Online Internet | 29 | 30 | 31 | ||||||
Inbound Telesales | 2 | 2 | 3 | ||||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
Outbound Telemarketing and Field Sales. We seek to build loyal relationships with potential high-volume customers by assigning them to individual account managers. We believe that customers respond favorably to one-on-one relationships with personalized, well-trained account managers. Once established, these one-on-one relationships are maintained and enhanced through frequent telecommunications and targeted catalogs and other marketing materials designed to meet each customer’s specific IT needs. We pay most of our account managers a base annual salary plus incentive compensation. Incentive compensation is tied to gross profit dollars produced by the individual account manager. Account managers historically have significantly increased productivity after approximately twelve months of training and experience. At December 31, 2008, we employed 712 sales representatives, including 186 with less than twelve months of outbound telemarketing experience with us.
Online Internet. (www.pcconnection.com, www.macconnection.com, www.moredirect.com, and www.govconnection.com) We provide product descriptions and prices of generally all products online. Our PC Connection website also provides updated information for more than 140,000 items and on-screen images for more than 100,000 items. We offer, and continuously update, selected product offerings and other special buys. We believe our websites are an important sales source and communication tool for improving customer service.
Our MoreDirect subsidiary’s business process and operations are primarily Web based. During 2008, approximately two-thirds of MoreDirect’s orders were received via the Internet. Most of its corporate customers utilize a customized Web page to quickly search, source, and track IT products. MoreDirect’s website aggregates the current available inventories of its largest IT suppliers into a single on-line source for its corporate customers. Its custom designed Internet-based system, TRAXX™, provides corporate buyers with comparative pricing from several suppliers as well as special pricing arranged through the manufacturer.
The Internet supports three key business initiatives for us:
| • | Customer choice—We have built our business on the premise that our customers should be able to choose how they interact with us, be it by telephone, over the Internet, e-mail, fax, or mail. |
| • | Lowering transactions costs—Our website tools include robust product search features and Internet Business Accounts (customized Web pages), which allow customers to quickly and |
5
Table of Contents
easily find information about products of interest to them. If customers still have questions, they may call into our Telesales Representatives or Account Managers. Such phone calls are typically shorter and have higher close rates than calls from customers who have not first visited our websites. |
| • | Leveraging the time of experienced sales representatives—Our investments in technology-based sales and service programs allow our sales representatives more time to build and maintain relationships with our customers and help them to solve their business problems. |
Inbound Telesales. Our inbound sales representatives answer customer telephone calls generated by our catalogs and other advertising programs. These representatives also assist customers in making purchasing decisions, process product orders, and respond to customer inquiries on order status, product pricing, and availability. Using our proprietary information systems, sales representatives can quickly access customer records which detail purchase history and billing and shipping information, expediting the ordering process. Our inbound sales have decreased in recent years reflecting our focus on more diverse marketing strategies and programs designed to reach our business customers, as well as increased Internet usage by our customers.
Business Segments. We conduct our business operations through three primary business segments: (1) SMB, (2) Large Account, and (3) Public Sector.
SMB Segment. Our principal target customers in this segment are small-to-medium-sized business customers with 20 to 1,000 employees, although we continue to sell to consumers. Our primary means of marketing to this segment incorporate all three sales channels—outbound telemarketing, primarily to our business customers; inbound telesales, particularly to our consumer group and very small business customers; and online Internet sales to both consumer and business customers.
Large Account Segment. Through our MoreDirect subsidiary’s custom designed Web-based system, we are able to offer our larger corporate customers an efficient and effective method of sourcing, evaluating, purchasing, and tracking a wide variety of IT products and services. MoreDirect’s strategy is to be the primary single source procurement portal for its large corporate customers. MoreDirect’s sales representatives typically have ten to twenty years of experience and are located strategically across the United States. This allows them to work directly with customers, often on site. MoreDirect generally places its product orders with manufacturers and/or distribution companies for drop shipment directly to its customers.
Public Sector Segment. We use a combination of outbound telemarketing, including some on-site sales solicitation by field sales account managers, and online Internet sales through Internet Business Accounts, to reach these customers. Through our GovConnection subsidiary, we target each of the four distinct market sectors within this segment—federal government, higher educational institutions, school grades K-12, and state and local governments.
The following table sets forth the relative distribution of our net sales by business segment:
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Business Segment | |||||||||
SMB | 52 | % | 54 | % | 54 | % | |||
Large Account | 27 | 29 | 30 | ||||||
Public Sector | 21 | 17 | 16 | ||||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
Catalog Distribution. Our two principal catalogs are PC Connection® for the PC market and MacConnection® for the Apple market. In 2008, we published twelve editions of each. We distribute catalogs to purchasers on our in-house mailing list as well as to other prospective customers. In addition, we
6
Table of Contents
distribute specialty catalogs to educational and government customers and prospects on a periodic basis. We also distribute our monthly catalogs customized with special covers and inserts, offering a wide assortment of special offers on products in specific areas such as graphics, server/netcom, and mobile computing, or for specific customers, such as developers.
Specialty Marketing. Our specialty marketing activities include direct mail, other inbound and outbound telemarketing services, bulletin board services, package inserts, fax broadcasts, and electronic mail. We also market call-answering and fulfillment services to certain product vendors.
Customers. We maintain an extensive database of customers and prospects currently aggregating more than 4,200,000 names. Approximately 91% of our net sales in the year ended December 31, 2008 were made to customers who had previously purchased products from us. Except for sales to the federal government, which accounted for approximately 8% of consolidated revenues, no single customer accounted for more than 2% of our consolidated revenue in 2008. The loss of any single customer will not have a material adverse effect on any of our business segments. In addition, we do not have individual orders in our backlog that are material to our business. We typically ship products within hours of receipt of orders.
PRODUCTS AND MERCHANDISING
We continuously focus on expanding the breadth of our product offerings. We currently offer our customers over 150,000 information technology products designed for business applications from more than 1,400 manufacturers, including hardware and peripherals, accessories, networking products, and software. We select the products we sell based upon their technology and effectiveness, market demand, product features, quality, price, margins, and warranties. As part of our merchandising strategy, we also offer products related to PCs, such as digital cameras and digital media players.
The following table sets forth our percentage of net sales (in dollars) of notebooks and personal digital assistants, or PDAs, video, imaging and sound, desktops and servers, software, and other major product categories:
| PERCENTAGE OF NET SALES | |||||||||
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Notebooks and PDAs | 15 | % | 16 | % | 17 | % | |||
Video, Imaging and Sound | 15 | 14 | 13 | ||||||
Desktops/Servers | 13 | 14 | 14 | ||||||
Software | 13 | 13 | 13 | ||||||
Net/Com Products | 10 | 8 | 8 | ||||||
Printers and Printer Supplies | 9 | 10 | 10 | ||||||
Storage Devices | 9 | 9 | 9 | ||||||
Memory and System Enhancements | 4 | 5 | 5 | ||||||
Accessories/Other | 12 | 11 | 11 | ||||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
We offer a 30-day right of return generally limited to defective merchandise. Returns of non-defective products are subject to restocking fees. Substantially all of the products marketed by us are warranted by the manufacturer. We generally accept returns directly from the customer and then either credit the customer’s account or ship the customer a similar product from our inventory.
PURCHASING AND VENDOR RELATIONS
During the year ended December 31, 2008, we shipped approximately half of our purchases directly to our distribution facility in Wilmington, Ohio. For the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, product purchases from Ingram Micro, Inc., our largest vendor, accounted for 24%, 24%, and 27%, respectively, of our total product purchases. Purchases from Tech Data Corporation comprised 17% of our total product purchases in
7
Table of Contents
each of the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006. Purchases from Hewlett Packard, or HP, constituted 12%, 14%, and 15% of our total product purchases in 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively. No other vendor accounted for more than 10% of our total product purchases in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006. We believe that, while we may experience some short-term disruption, alternative sources for products obtained from Ingram Micro, Tech Data, and HP are available to us.
Many product suppliers reimburse us for advertisements or other cooperative marketing programs in our catalogs and other marketing vehicles. Reimbursements may be in the form of discounts, advertising allowances, and/or rebates. We also receive allowances from certain vendors based upon the volume of purchases or sales of the vendors’ products by us.
Some of our vendors offer limited price protection in the form of rebates or credits against future purchases. We may also participate in end-of-life product and other special purchases which may not be eligible for price protection.
We believe that we have excellent relationships with our vendors. We generally pay vendors within stated terms, or earlier when favorable discounts are offered. We believe that because of our volume purchases we are able to obtain product pricing and terms that are competitive with those available to other major direct marketers. Although brand names and individual product offerings are important to our business, we believe that competitive products are available in substantially all of the merchandise categories offered by us.
DISTRIBUTION
We fulfill orders from customers both from products we hold in inventory and through drop shipping arrangements with manufacturers and distributors. At our approximately 205,000 square foot distribution and fulfillment complex in Wilmington, Ohio, we receive and ship inventory, configure computer systems, and process returned products. Orders are transmitted electronically from our various sales facilities to our Wilmington distribution center after credit approval, where packing documentation is printed automatically and order fulfillment takes place. Our customers are given several shipping options, ranging from expedited overnight delivery through our Everything Overnight® service to normal ground freight service. Through our Everything Overnight® service, orders accepted up until 7:00 p.m. Eastern Time, are generally shipped for overnight delivery via United Parcel Service (“UPS”) or FedEx Corporation. Upon request, orders may also be shipped by other common carriers. Given the significant reduction in shipping services by DHL in 2008, UPS has become our primary shipping provider.
We also place product orders directly with manufacturers and/or distribution companies for drop shipment by those manufacturers and/or suppliers directly to customers. Our MoreDirect subsidiary generally utilizes drop shipping for all product orders. Order status with distributors is tracked online, and in all circumstances, a confirmation of shipment from manufacturers and/or distribution companies is received prior to initial recording of the transaction. At the end of each financial reporting period, revenue is adjusted pursuant to Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 104, “Revenue Recognition,” (“SAB 104”) to reflect the anticipated receipt of products by the customers in the period. Products drop shipped by suppliers were 55% of net sales in 2008 and 51% of net sales in 2007. In future years, we expect that products drop shipped from suppliers will continue to increase, both in dollars and as a percentage of net sales, as we seek to lower our overall inventory and distribution costs while maintaining excellent customer service.
Certain of our larger customers occasionally request special staged delivery arrangements under which either we or our distribution partners set aside and temporarily hold inventory on our customer’s behalf. Such orders are firm delivery orders, and customers generally pay under normal credit terms, regardless of delivery. Revenue on such transactions is not recorded until shipment to their final destination as requested by the customer. Inventory held for such staged delivery requests aggregated $11.0 million at December 31, 2008.
We maintain inventories of fast moving products to meet customer demand, representing products that account for a high percentage of our ongoing product sales transactions and sales dollars. We may also, from
8
Table of Contents
time to time, make large inventory purchases of certain first-to-market products or end-of-life products to obtain favorable purchasing discounts. We also maintain sufficient inventory levels of common-demand components and accessories used for configuration services.
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS
All of our subsidiaries, except for MoreDirect, utilize centralized management information systems principally comprised of applications software running on IBM i5 and p5 computers and Microsoft Windows 2003-based servers, which we have customized for our use. These systems permit centralized management of key functions, including order taking and processing, inventory and accounts receivable management, purchasing, sales, and distribution, and the preparation of daily operating control reports on key aspects of the business. We also operate advanced telecommunications equipment to support our sales and customer service operations. Key elements of the telecommunications systems are integrated with our computer systems to provide timely customer information to sales and service representatives, and to facilitate the preparation of operating and performance data.
MoreDirect has developed a custom designed Internet-based system, TRAXX™, which comprises applications software running on Linux servers. This system is an integrated application of sales order processing, integrated supply chain visibility, and full EDI links with major manufacturers’ distribution partners for product information, availability, pricing, ordering, delivery, and tracking, including related accounting functions.
We believe our customized information systems enable us to improve our productivity, ship customer orders on a same-day basis, respond quickly to changes in our industry, and provide high levels of customer service.
Our success is dependent in large part on the accuracy and proper use of our information systems, including our telephone systems, to manage our inventory and accounts receivable collections, to purchase, sell, and ship our products efficiently and on a timely basis, and to maintain cost-efficient operations. We have undertaken a significant upgrade of our sales processing systems, which is expected to be completed in the second half of 2009. We expect to continually upgrade our information systems in the future to more effectively manage our operations and customer database.
COMPETITION
The direct marketing and sale of information technology products, including personal computers and related products, is highly competitive. We compete with other direct marketers of IT products, including CDW Corporation and Insight Enterprises, Inc., who are much larger than we are. We also compete with:
| • | certain product manufacturers that sell directly to customers, such as Dell Inc., as well as some of our own suppliers, such as HP, Lenovo, and Apple; |
| • | distributors that sell directly to certain customers; |
| • | local and regional VARs; |
| • | various franchisers, office supply superstores, and national computer retailers; and |
| • | companies with more extensive websites and commercial online networks. |
Additional competition may arise if other new methods of distribution, such as broadband electronic software distribution, emerge in the future. We compete not only for customers, but also for favorable product allocations and cooperative advertising support from product manufacturers. Several of our competitors are larger and have substantially greater financial resources than we do.
We believe that price, product selection and availability, and service and support are the most important competitive factors in our industry.
9
Table of Contents
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS
Our trademarks include PC Connection®, GovConnection®, MacConnection®, and MoreDirect®, and their related logos; Everything Overnight®, The Connection®, Raccoon Character®, Service Connection®, HealthConnection™, ProConnection™, TRAXX™, Graphics Connection®, Education Connection®, Get Connected®, Connect®, and Your Brands, Your Way, Next Day®. We intend to use and protect these and our other marks, as we deem necessary. We believe our trademarks have significant value and are an important factor in the marketing of our products. We do not maintain a traditional research and development group, but we work closely with computer product manufacturers and other technology developers to stay abreast of the latest developments in computer technology, with respect to the products we both sell and use.
WORK FORCE
As of December 31, 2008, we employed 1,625 persons, of whom 878 (including 166 management and support personnel) were engaged in sales related activities, 120 were engaged in providing IT services and customer service and support, 308 were engaged in purchasing, marketing, and distribution related activities, 105 were engaged in the operation and development of management information systems, and 214 were engaged in administrative and finance functions. We consider our employee relations to be good. Our employees are not represented by a labor union, and we have never experienced a labor related work stoppage.
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
Statements contained or incorporated by reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K that are not based on historical fact are “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Exchange Act. These forward-looking statements regarding future events and our future results are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts, and projections and the beliefs and assumptions of management including, without limitation, our expectations with regard to the industry’s rapid technological change and exposure to inventory obsolescence, availability and allocations of goods, reliance on vendor support and relationships, competitive risks, pricing risks, and the overall level of economic activity and the level of business investment in information technology products. Forward-looking statements may be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as “may,” “could,” “will,” “expect,” “estimate,” “anticipate,” “continue,” or similar terms, variations of such terms or the negative of those terms.
We cannot assure investors that our assumptions and expectations will prove to have been correct. Important factors could cause our actual results to differ materially from those indicated or implied by forward-looking statements. Such factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include those factors discussed below. We undertake no intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business, financial condition, or results of operations would likely suffer.
We have experienced variability in sales, and there is no assurance that we will be able to maintain profitable operations.
Several factors have caused our sales and results of operations to fluctuate and we expect these fluctuations to continue on a quarterly basis. Causes of these fluctuations include:
| • | changes in the overall level of economic activity; |
| • | the condition of the personal computer industry in general; |
| • | changes in the level of business investment in information technology products; |
| • | shifts in customer demand for hardware and software products; |
| • | variations in levels of competition; |
10
Table of Contents
| • | industry shipments of new products or upgrades; |
| • | the timing of new merchandise and catalog offerings; |
| • | fluctuations in response rates; |
| • | fluctuations in postage, paper, shipping, and printing costs and in merchandise returns; |
| • | adverse weather conditions that affect response, distribution, or shipping; |
| • | changes in our product offerings; and |
| • | changes in vendor distribution of products. |
Our results also may vary based on our ability to hire and retain sales representatives and other essential personnel, as well as our success in integrating acquisitions into our business, and their relative costs.
We base our operating expenditures on sales forecasts. If our revenues do not meet anticipated levels in the future, we may not be able to reduce our staffing levels and operating expenses in a timely manner to avoid significant losses from operations.
Should our financial performance not meet expectations and our stock price continue to trade at current levels, we may be required to record an additional significant charge to earnings for impairment of goodwill and other intangibles.
In accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards, (“SFAS”) 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangibles,” we test goodwill for impairment on an annual basis, and more frequently if potential impairment indicators arise. We determined that the fair values of our SMB and Public Sector segments’ goodwill were lower than the carrying values as of December 31, 2008, and accordingly the carrying values of those segments’ goodwill were written off, resulting in a significant non-cash charge to earnings. Although we determined that the fair value of our Large Account segment’s goodwill exceeded its carrying value, should this segment’s financial performance not meet expectations, we would likely adjust downward expected future operating results. Such adjustment may result in a determination that our carrying values for goodwill and other non-amortizing intangibles for that segment exceed fair values. This determination may in turn require that we record an additional significant non-cash charge to earnings to reduce the $50.2 million aggregate carrying amount of goodwill and other intangibles in the Large Account operating segment, resulting in a negative effect on our results of operations.
The current volatility in economic conditions and the financial markets may adversely affect our access to capital and credit markets.
The current volatility and disruption to the capital and credit markets has reached nearly unprecedented levels and has significantly adversely impacted economic conditions, resulting in additional significant recessionary pressures and further declines in consumer confidence and economic growth.
These conditions have also resulted in a substantial tightening of the credit markets, including lending by financial institutions which is a source of capital for our borrowing and liquidity. This tightening of the credit markets has increased the cost of capital and reduced the availability of credit. It is difficult to predict how long the current economic and capital and credit market conditions will continue, the extent to which they will continue to deteriorate, and to which our business may be adversely affected. However, if current levels of economic and capital and credit market disruption and volatility worsen, we are likely to experience an adverse impact, which may be material, on our business, the cost of and access to capital and credit markets, and our results of operations.
11
Table of Contents
We may experience a reduction in the incentive programs offered to us by our vendors.
Some product manufacturers and distributors provide us with incentives such as supplier reimbursements, payment discounts, price protection, rebates, and other similar arrangements. The increasingly competitive computer hardware market has already resulted in the following:
| • | reduction or elimination of some of these incentive programs; |
| • | more restrictive price protection and other terms; and |
| • | reduced advertising allowances and incentives, in some cases. |
Many product suppliers provide us with advertising allowances, and in exchange, we feature their products in our catalogs and other marketing vehicles. These vendor allowances, to the extent that they represent specific reimbursements of incremental and identifiable costs, are offset against selling, general, and administrative, or SG&A, expenses. Advertising allowances that cannot be associated with a specific program funded by an individual vendor or that exceed the fair value of advertising expense associated with that program are classified as offsets to cost of sales or inventory. In the past, we have experienced a decrease in the level of vendor consideration available to us from certain manufacturers. The level of such consideration we receive from some manufacturers may decline in the future. Such a decline could decrease our gross margin and have a material adverse effect on our earnings and cash flows.
We face many competitive risks.
The direct marketing industry and the computer products retail business, in particular, are highly competitive. We compete with consumer electronics and computer retail stores, including superstores. We also compete with other direct marketers of hardware and software and computer related products, including CDW Corporation, Insight Enterprises, Inc., and Dell Inc., who are much larger than we are. Certain hardware and software vendors, such as HP, Lenovo, and Apple, who provide products to us, are also selling their products directly to end users through their own catalogs, stores, and via the Internet. We compete not only for customers, but also for advertising support from personal computer product manufacturers. Some of our competitors have larger catalog circulations and customer bases and greater financial, marketing, and other resources. In addition, some of our competitors offer a wider range of products and services than we do and may be able to respond more quickly to new or changing opportunities, technologies, and customer requirements. Many current and potential competitors also have greater name recognition, engage in more extensive promotional activities, and adopt pricing policies that are more aggressive than ours. We expect competition to increase as retailers and direct marketers who have not traditionally sold computers and related products enter the industry.
In addition, product resellers and direct marketers are combining operations or acquiring or merging with other resellers and direct marketers to increase efficiency. Moreover, current and potential competitors have established or may establish cooperative relationships among themselves or with third parties to enhance their products and services. Accordingly, it is possible that new competitors or alliances among competitors may emerge and acquire significant market share.
We cannot provide assurance that we can continue to compete effectively against our current or future competitors. If we encounter new competition or fail to compete effectively against our competitors, our business may be harmed.
We face and will continue to face significant price competition.
Generally, pricing is very aggressive in the personal computer industry, particularly in this current economic environment, and we expect pricing pressures to escalate if economic conditions worsen. An increase in price competition could result in a reduction of our profit margins. There can be no assurance that we will be able to offset the effects of price reductions with an increase in the number of customers, higher sales, cost reductions, or otherwise. Also, our sales of personal computer hardware products are generally producing lower profit margins
12
Table of Contents
than those associated with software products. Such pricing pressures could result in an erosion of our market share, reduced sales, and reduced operating margins, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
The failure to comply with our public sector contracts could result in, among other things, fines or liabilities.
Revenues from the public sector segment are derived from sales to federal, state, and local government departments and agencies, as well as to educational institutions, through various contracts and open market sales. Government contracting is a highly regulated area. Noncompliance with government procurement regulations or contract provisions could result in civil, criminal, and administrative liability, including substantial monetary fines or damages, termination of government contracts, and suspension, debarment, or ineligibility from doing business with the government. Our current arrangements with these government agencies allow them to cancel orders with little or no notice and do not require them to purchase products from us in the future. The effect of any of these possible actions by any government department or agency could adversely affect our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
We are exposed to inventory obsolescence due to the rapid technological changes occurring in the personal computer industry.
The market for personal computer products is characterized by rapid technological change and the frequent introduction of new products and product enhancements. Our success depends in large part on our ability to identify and market products that meet the needs of customers in that marketplace. In order to satisfy customer demand and to obtain favorable purchasing discounts, we have and may continue to carry increased inventory levels of certain products. By so doing, we are subject to the increased risk of inventory obsolescence. Also, in order to implement our business strategy, we intend to continue, among other things, placing larger than typical inventory stocking orders of selected products and increasing our participation in first-to-market purchase opportunities. We may also, from time to time, make large inventory purchases of certain end-of-life products and market products on a private-label basis, which would increase the risk of inventory obsolescence. In addition, we sometimes acquire special purchase products without return privileges. There can be no assurance that we will be able to avoid losses related to obsolete inventory. In addition, manufacturers are limiting return rights and are taking steps to reduce their inventory exposure by supporting “configure-to-order” programs authorizing distributors and resellers to assemble computer hardware under the manufacturers’ brands. These trends reduce the costs to manufacturers and shift the burden of inventory risk to resellers like us, which could negatively impact our business.
We acquire products for resale from a limited number of vendors. The loss of any one of these vendors could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We acquire products for resale both directly from manufacturers and indirectly through distributors and other sources. The five vendors supplying the greatest amount of goods to us constituted 70%, 74%, and 70% of our total product purchases in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively. Among these five vendors, purchases from Ingram represented 24%, 24%, and 27% of our total product purchases in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively. Purchases from Tech Data comprised 17% of our total product purchases in each of the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006. Purchases from HP represented 12%, 14%, and 15% of our total product purchases in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively. No other vendor supplied more than 10% of our total product purchases in the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006. If we were unable to acquire products from Ingram, HP, or Tech Data, we could experience a short-term disruption in the availability of products, and such disruption could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and cash flows.
Substantially all of our contracts and arrangements with our vendors that supply significant quantities of products are terminable by such vendors or us without notice or upon short notice. Most of our product vendors provide us with trade credit, of which the net amount outstanding at December 31, 2008 was $101.8 million.
13
Table of Contents
Termination, interruption, or contraction of relationships with our vendors, including a reduction in the level of trade credit provided to us, could have a material adverse effect on our financial position.
Some product manufacturers either do not permit us to sell the full line of their products or limit the number of product units available to direct marketers such as us. An element of our business strategy is to continue increasing our participation in first-to-market purchase opportunities. The availability of certain desired products, especially in the direct marketing channel, has been constrained in the past. We could experience a material adverse effect to our business if we are unable to source first-to-market purchase or similar opportunities, or if we face the reemergence of significant availability constraints.
We could experience system failures which would interfere with our ability to process orders.
We depend on the accuracy and proper use of our management information systems, including our telephone system. Many of our key functions depend on the quality and effective utilization of the information generated by our management information systems, including:
| • | our ability to manage inventory and accounts receivable collection; |
| • | our ability to purchase, sell, and ship products efficiently and on a timely basis; and |
| • | our ability to maintain operations. |
Our management information systems require continual upgrades to most effectively manage our operations and customer database. Although we maintain some redundant systems, with full data backup, a substantial interruption in management information systems or in telephone communication systems, including those resulting from natural disasters as well as power loss, telecommunications failure, or similar events, would substantially hinder our ability to process customer orders and thus could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We are dependent on key personnel.
Our future performance will depend to a significant extent upon the efforts and abilities of our senior executives. The competition for qualified management personnel in the computer products industry is very intense, and the loss of service of one or more of these persons could have an adverse effect on our business. Our success and plans for future growth will also depend on our ability to hire, train, and retain skilled personnel in all areas of our business, including sales representatives and technical support personnel. There can be no assurance that we will be able to attract, train, and retain sufficient qualified personnel to achieve our business objectives.
The methods of distributing personal computers and related products are changing, and such changes may negatively impact us and our business.
The manner in which personal computers and related products are distributed and sold is changing, and new methods of distribution and sale, such as online shopping services, have emerged. Hardware and software manufacturers have sold, and may intensify their efforts to sell, their products directly to end users. From time to time, certain manufacturers have instituted programs for the direct sales of large order quantities of hardware and software to certain major corporate accounts. These types of programs may continue to be developed and used by various manufacturers. Some of our vendors, including Apple, HP, and Lenovo, currently sell some of their products directly to end users and have stated their intentions to increase the level of such direct sales. In addition, manufacturers may attempt to increase the volume of software products distributed electronically to end users. An increase in the volume of products sold through or used by consumers of any of these competitive programs or distributed electronically to end users could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We depend heavily on third-party shippers to deliver our products to customers.
Many of our customers elect to have their purchases shipped by an interstate common carrier, such as UPS or FedEx Corporation. A strike or other interruption in service by these shippers could adversely affect our ability to market or deliver products to customers on a timely basis.
14
Table of Contents
We may experience potential increases in shipping, paper, and postage costs, which may adversely affect our business if we are not able to pass such increases on to our customers.
Shipping costs are a significant expense in the operation of our business. Increases in postal or shipping rates and paper costs could significantly impact the cost of producing and mailing our catalogs and shipping customer orders. Postage prices and shipping rates increase periodically, and we have no control over future increases. We have a long-term contract with UPS, and believe that we have negotiated favorable shipping rates with our carriers. We generally invoice customers for shipping and handling charges. There can be no assurance that we will be able to pass on to our customers the full cost, including any future increases in the cost, of commercial delivery services.
We also incur substantial paper and postage costs related to our marketing activities, including producing and mailing our catalogs. Paper prices historically have been cyclical, and we have experienced substantial increases in the past. Significant increases in postal or shipping rates and paper costs could adversely impact our business, financial condition, and results of operations, particularly if we cannot pass on such increases to our customers or offset such increases by reducing other costs.
We rely on the continued development of electronic commerce and Internet infrastructure development.
We have had an increasing level of sales made via the Internet in part because of the growing use and acceptance of the Internet by end users. Sales of computer products via the Internet represent a significant and increasing portion of overall computer product sales. Growth of our Internet sales is dependent on potential customers using the Internet in addition to traditional means of commerce to purchase products. We cannot accurately predict the rate at which they will do so.
Our success in growing our Internet business will depend in large part upon the development of an increasingly sophisticated infrastructure for providing Internet access and services. If the number of Internet users or their use of Internet resources continues to grow rapidly, such growth may overwhelm the existing Internet infrastructure. Our ability to increase the speed with which we provide services to customers and to increase the scope of such services ultimately is limited by, and reliant upon, the sophistication, speed, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of the networks operated by third parties, and these networks may not continue to be developed or be available at prices consistent with our required business model.
We face many uncertainties relating to the collection of state sales and use tax.
We collect and remit sales and use taxes in states in which we have either voluntarily registered or have a physical presence. Various states have sought to impose on direct marketers the burden of collecting state sales and use taxes on the sales of products shipped to their residents. In 1992, the United States Supreme Court affirmed its position that it is unconstitutional for a state to impose sales or use tax collection obligations on an out-of-state mail-order company whose only contacts with the state are limited to the distribution of catalogs and other advertising materials through the mail and the subsequent delivery of purchased goods by United States mail or by interstate common carrier. However, legislation that would expand the ability of states to impose sales and use tax collection obligations on direct marketers has been introduced in Congress on many occasions. Additionally, certain states have adopted rules that require companies and their affiliates to register in those states as a condition of doing business with those state agencies.
Moreover, due to our presence on various forms of electronic media and other operational factors, our contacts with many states may exceed the limited contacts involved in the Supreme Court case. We cannot predict the level of contacts that is sufficient to permit a state to impose on us a sales or use tax collection obligation. Two of our competitors have elected to collect sales and use taxes in all states. If the Supreme Court changes its position, or if legislation is passed to overturn the Supreme Court’s decision, or if a court were to determine that our contacts with a state exceed the constitutionally permitted contacts, the expansion of a sales or use tax collection obligation on us in states to which we ship products would result in additional administrative expenses to us, could result in tax liability for past sales as well as price increases to our customers, and could reduce future sales.
15
Table of Contents
Privacy concerns with respect to list development and maintenance may materially adversely affect our business.
We mail catalogs and send electronic messages to names in our proprietary customer database and to potential customers whose names we obtain from rented or exchanged mailing lists. World-wide public concern regarding personal privacy has subjected the rental and use of customer mailing lists and other customer information to increased scrutiny. Any domestic or foreign legislation enacted limiting or prohibiting these practices could negatively affect our business.
We are controlled by two principal stockholders.
Patricia Gallup and David Hall, our two principal stockholders, beneficially own or control, in the aggregate, approximately 64% of the outstanding shares of our common stock. Because of their beneficial stock ownership, these stockholders can continue to elect the members of the Board of Directors and decide all matters requiring stockholder approval at a meeting or by a written consent in lieu of a meeting. Similarly, such stockholders can control decisions to adopt, amend, or repeal our charter and our bylaws, or take other actions requiring the vote or consent of our stockholders and prevent a takeover of us by one or more third parties, or sell or otherwise transfer their stock to a third party, which could deprive our stockholders of a control premium that might otherwise be realized by them in connection with an acquisition of our Company. Such control may result in decisions that are not in the best interest of our public stockholders. In connection with our initial public offering, the principal stockholders placed substantially all shares of common stock beneficially owned by them into a voting trust, pursuant to which they are required to agree as to the manner of voting such shares in order for the shares to be voted. Such provisions could discourage bids for our common stock at a premium as well as have a negative impact on the market price of our common stock.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None.
| Item 2. | Properties |
In November 1997 we entered into a fifteen year lease for our corporate headquarters and telemarketing center located at 730 Milford Road, Merrimack, New Hampshire 03054-4631, with an affiliated entity, G&H Post, which is related to us through common ownership. The total lease is valued at approximately $7.0 million, based upon an independent property appraisal obtained at the date of lease, and interest is calculated at an annual rate of 11%. The lease, as amended, requires us to pay our proportionate share of real estate taxes and common area maintenance charges as either additional rent or directly to third-parties and also to pay insurance premiums for the leased property. We have the option to renew the lease for two additional terms of five years each. The lease has been recorded as a capital lease in the financial statements.
In August 2008, our subsidiary Merrimack Services Corporation entered into a lease agreement with G&H Post, which is related to us through common ownership, for an office facility adjacent to our corporate headquarters. The lease has a term of ten years and provides Merrimack Services Corporation an option to renew the lease for two additional two-year terms, at the then comparable market rate. The lease requires us to pay our proportionate share of real estate taxes and common area maintenance charges as either additional rent or directly to third-parties and also to pay insurance premiums for the leased property. The lease has been recorded as an operating lease in the financial statements.
We also lease 205,000 square feet in two facilities in Wilmington, Ohio, which houses our distribution and order fulfillment operations. The leases governing these two facilities expire in the fourth quarter of 2009 and the first quarter of 2010 and contain provisions to renew for additional terms. We also operate sales and support offices in Keene and Portsmouth, New Hampshire; Marlborough, Massachusetts; Rockville, Maryland; Fairfield, Connecticut; Sioux City, South Dakota; Addison, Texas; and Boca Raton, Florida, and lease facilities at these
16
Table of Contents
locations. Leasehold improvements associated with these properties are amortized over the terms of the leases or their useful lives, whichever is shorter. We believe that existing or otherwise available distribution facilities in Wilmington, Ohio will be sufficient to support our anticipated needs through the next twelve months and beyond.
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
We are subject to audits by states on sales and income taxes, unclaimed property, and other assessments. A comprehensive multi-state unclaimed property audit is in progress, and total accruals for unclaimed property aggregated $2.5 million at December 31, 2008. While management believes that known and estimated liabilities have been adequately provided for, it is too early to determine the ultimate outcome of such audits. Such outcome could have a material negative impact on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
We are subject to various legal proceedings and claims which have arisen during the ordinary course of business. In the opinion of management, the outcome of such matters is not expected to have a material effect on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
| Item 4. | Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders |
There were no matters submitted during the fourth quarter of 2008 to a vote of security holders.
Executive Officers of PC Connection
Our executive officers and their ages as of March 4, 2009 are as follows:
Name | Age | Position | ||
| Patricia Gallup | 54 | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Jack Ferguson | 70 | Executive Vice President, Treasurer, and Chief Financial Officer | ||
| Timothy McGrath | 50 | Executive Vice President, PC Connection Enterprises | ||
| Bradley Mousseau | 57 | Senior Vice President, Human Resources |
Patricia Gallup is a co-founder of PC Connection and has served as Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board since September 2002. Ms. Gallup also assumed the role of President upon the resignation of our president in March 2003. Ms. Gallup served as Chairman from June 2001 to August 2002. Ms. Gallup has served as a member of our executive management team since its inception in 1982.
Jack Fergusonhas served as Executive Vice President since May 2007, as Chief Financial Officer since December 2005, and as Treasurer since November 1997. Mr. Ferguson served as Senior Vice President from April 2006 to May 2007 and as Vice President from December 2005 to April 2006. Mr. Ferguson served as Interim Chief Financial Officer from October 2004 to December 2005 and as Director of Finance from December 1992 to November 1997. Prior to joining our company, Mr. Ferguson was a partner with Deloitte & Touche LLP, an international accounting firm.
Timothy McGrath has served as Executive Vice President, PC Connection Enterprises since May 2007. Mr. McGrath served as Senior Vice President, PC Connection Enterprises from December 2006 to May 2007 and as President of PC Connection Sales Corporation, our largest sales subsidiary, from August 2005 to December 2006. Prior to joining our company, Mr. McGrath served from 2002 to 2005 in a variety of senior management positions at Insight Enterprises, Inc. Initially he served as President of Comark, a division of Insight, and later as Executive Vice President of Sales. Mr. McGrath served in various executive sales positions at Comark Inc. from 1999 to 2002, which was purchased by Insight Enterprises, Inc. in April 2002.
Bradley Mousseau has served as Senior Vice President, Human Resources since April 2006. Mr. Mousseau served as Vice President, Human Resources from January 2000 to April 2006. Prior to joining our company, Mr. Mousseau served as Vice President of Global Workforce Strategies for Systems & Computer Technology Corporation from April 1997 to January 2000.
17
Table of Contents
PART II
| Item 5. | Market for the Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters, and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information
Our common stock commenced trading on March 3, 1998, on the Nasdaq Global Select Market under the symbol “PCCC.” As of March 4, 2009, there were 27,012,729 shares outstanding of our common stock held by approximately 100 stockholders of record and 2,050 beneficial holders.
The following table sets forth for the fiscal periods indicated the range of high and low sales prices for our common stock on the Nasdaq Global Select Market.
2008 | High | Low | ||||
Quarter Ended: | ||||||
December 31 | $ | 6.73 | $ | 3.10 | ||
September 30 | 9.64 | 6.04 | ||||
June 30 | 12.07 | 6.60 | ||||
March 31 | 13.19 | 7.85 | ||||
2007 | High | Low | ||||
Quarter Ended: | ||||||
December 31 | $ | 16.09 | $ | 11.18 | ||
September 30 | 15.52 | 11.16 | ||||
June 30 | 15.44 | 10.85 | ||||
March 31 | 18.80 | 12.97 | ||||
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We anticipate that we will generally retain future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of our business, and we have no current plans to pay cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Our secured credit agreement contains restrictions that may limit our ability to pay dividends in the future.
Share Repurchase Authorization
On March 28, 2001, our Board of Directors authorized the spending of up to $15.0 million to repurchase our common stock. Share purchases will be made in the open market from time to time depending on market conditions. Our current bank line of credit, however, limits repurchases made after June 2005 to $10.0 million without bank approval of higher amounts.
During the year ended December 31, 2008, we repurchased an aggregate of 195,994 shares for $1.4 million. As of December 31, 2008, we had repurchased an aggregate of 558,411 shares for $3.7 million. The maximum approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the program without further bank approval is $8.6 million. We have issued nonvested shares from treasury stock and have reflected upon vesting the net remaining balance of treasury stock on the consolidated balance sheet. In addition, we withheld 14,852 shares, having an aggregate fair value of $0.1 million, upon the vesting of stock awards to satisfy related employee tax obligations during the year ended December 31, 2008. Such transactions were recognized as a repurchase of common stock and returned to treasury but do not apply against authorized repurchase limits under our bank line agreement and Board of Directors’ authorization.
18
Table of Contents
The following table provides information about our purchases during the quarter ended December 31, 2008, of equity securities that we registered pursuant to Section 12 of the Exchange Act:
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased (1) | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Maximum Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Program(2) | |||||
10/01/08 – 10/31/08 | — | — | — | $ | 11,569,537 | ||||
11/01/08 – 11/30/08 | 50,031 | 3.76 | 50,031 | $ | 11,381,321 | ||||
12/01/08 – 12/31/08 | 32,824 | 4.45 | 26,211 | $ | 11,265,683 | ||||
Total | 82,855 | 4.08 | 76,242 | $ | 11,265,683 | ||||
| (1) | In December 2008, an employee withheld 6,613 shares from his nonvested stock award to satisfy income tax obligations due upon the vesting of the award. |
| (2) | On March 28, 2001, our Board of Directors announced approval of a share repurchase program of our common stock having an aggregate value of up to $15.0 million. Share purchases are made in open market transactions from time to time depending on market conditions. The Program does not have a fixed expiration date. |
19
Table of Contents
Stock Performance Graph
The following performance graph and related information shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Exchange Act, each as amended, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate it by reference into such filing.
The following stock performance graph compares cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock for the period from December 31, 2003 through December 31, 2008 with the cumulative total return for (i) the Russell 2000 Index and (ii) our Peer Group. This graph assumes the investment of $100 on December 31, 2003 in our common stock, the Russell 2000 Index, and our Peer Group and assumes dividends are reinvested. Our Peer Group consists of Insight Enterprises, Inc., PC Mall, Inc., Systemax, Inc, and Zones, Inc.
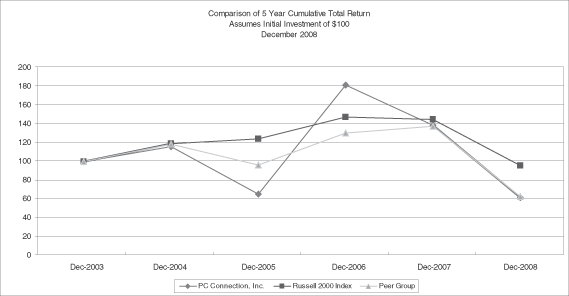
| Base Period Dec-03 | Indexed Returns | ||||||||||||||
| Years Ended | |||||||||||||||
Company Name / Index | Dec-04 | Dec-05 | Dec-06 | Dec-07 | Dec-08 | ||||||||||
PC Connection, Inc. | 100 | 15.75 | (43.49 | ) | 175.60 | (23.47 | ) | (54.89 | ) | ||||||
Russell 2000 Index | 100 | 18.33 | 4.56 | 18.35 | (1.55 | ) | (33.80 | ) | |||||||
Peer Group | 100 | 18.23 | (18.57 | ) | 34.62 | 5.71 | (53.99 | ) | |||||||
20
Table of Contents
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The following selected financial and operating data should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements and the Notes thereto, and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and other financial information included elsewhere in this Form 10-K.
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except per share and selected operating data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated Income Statement Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,753,680 | $ | 1,785,379 | $ | 1,635,651 | $ | 1,444,297 | $ | 1,353,834 | ||||||||||
Cost of sales | 1,538,836 | 1,566,409 | 1,435,400 | 1,280,701 | 1,201,780 | |||||||||||||||
Gross profit | 214,844 | 218,970 | 200,251 | 163,596 | 152,054 | |||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 186,728 | 181,640 | 173,927 | 151,981 | 132,729 | |||||||||||||||
Goodwill impairment(1) | 8,807 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Special charges(2) | 1,431 | 541 | 2,391 | 2,127 | 5,232 | |||||||||||||||
Income from operations | 17,878 | 36,789 | 23,933 | 9,488 | 14,093 | |||||||||||||||
Interest expense | (681 | ) | (932 | ) | (1,828 | ) | (1,447 | ) | (1,385 | ) | ||||||||||
Other, net | 811 | 764 | 121 | 89 | 152 | |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 18,008 | 36,621 | 22,226 | 8,130 | 12,860 | |||||||||||||||
Income tax provision | (7,642 | ) | (13,626 | ) | (8,450 | ) | (3,683 | ) | (4,556 | ) | ||||||||||
Net income | $ | 10,366 | $ | 22,995 | $ | 13,776 | $ | 4,447 | $ | 8,304 | ||||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | .39 | $ | .86 | $ | .54 | $ | .18 | $ | .33 | ||||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | .39 | $ | .85 | $ | .54 | $ | .18 | $ | .33 | ||||||||||
Selected Operating Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Catalogs distributed | 12,210,000 | 13,804,000 | 15,326,000 | 27,467,000 | 31,125,000 | |||||||||||||||
Orders entered(3) | 1,444,000 | 1,480,000 | 1,528,000 | 1,439,000 | 1,281,000 | |||||||||||||||
Average order size(3) | $ | 1,401 | $ | 1,408 | $ | 1,241 | $ | 1,166 | $ | 1,230 | ||||||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Working capital | $ | 174,207 | $ | 156,532 | $ | 126,965 | $ | 100,893 | $ | 103,637 | ||||||||||
Total assets | 378,167 | 380,879 | 346,684 | 337,705 | 286,542 | |||||||||||||||
Short-term debt: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current maturities of capital lease obligations: | ||||||||||||||||||||
To affiliate | 699 | 527 | 464 | 416 | 373 | |||||||||||||||
To third party | — | — | 395 | 412 | 391 | |||||||||||||||
Notes payable | — | — | — | 19,975 | 4,810 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term debt: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Capital lease obligations, less current maturities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
To affiliate | 3,610 | 4,309 | 4,836 | 5,299 | 5,715 | |||||||||||||||
To third party | — | — | — | 396 | 841 | |||||||||||||||
Total stockholders’ equity | 235,324 | 224,310 | 196,904 | 171,399 | 166,158 | |||||||||||||||
21
Table of Contents
| (1) | See Note 2, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets,” to our Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion of the non-cash goodwill impairment charge. |
| (2) | Our 2008 and 2007 special charges consist of $1,431 and $541, respectively, related to management restructuring costs, classified as workforce reductions, in the below Notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our 2006 special charges consist of $520 for the cost of workforce reductions, $1,500 related to our settlement with the Department of Justice (“DOJ”) on our 2003 General Services Administration (“GSA”) audit matter, and $371 related to the temporary retention of certain Amherst employees and facilities subsequent to the purchase of certain assets of Amherst Technologies, or the Amherst Transaction. Our 2005 special charges consist of $1,071 for the cost of workforce reductions and $1,056 incurred related to the temporary retention of certain Amherst employees and facilities subsequent to the Amherst Transaction. Our 2004 special charges consist of $860 for the cost of workforce reductions, $101 for the remaining uninsured portion of a 2003 employee defalcation, $3,559 related to our review of the 2003 GSA contract cancellation and costs related to securing a new schedule, $512 in professional fees related to a review of certain prior year rebate-related transactions, and $200 related to a litigation settlement. |
| (3) | Does not reflect cancellations or returns. |
22
Table of Contents
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
Our management’s discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations include the identification of certain trends and other statements that may predict or anticipate future business or financial results that are subject to important factors that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those indicated. See “Item 1A. Risk Factors.”
OVERVIEW
We are a leading direct marketer of a wide range of information technology, or IT, products and services—including computer systems, software and peripheral equipment, networking communications, and other products and accessories that we purchase from manufacturers, distributors, and other suppliers. We also offer a growing range of installation, configuration, repair, and other services performed by our personnel and third-party providers. We operate through three primary business segments: (a) consumers and small- to medium-sized businesses, or SMBs, through our PC Connection Sales subsidiaries, (b) large enterprise customers, or Large Account, through our MoreDirect subsidiary, and (c) federal, state, and local government and educational institutions, or Public Sector, through our GovConnection subsidiary.
We generate sales through (i) outbound telemarketing and field sales contacts by account managers focused on the business, education, and government markets, (ii) our websites, and (iii) inbound calls from customers responding to our catalogs and other advertising media.
As a value added reseller in the IT supply chain, we do not manufacture IT hardware or software. We are dependent on our suppliers that consist of manufacturers and distributors that historically have sold only to resellers rather than directly to end users. Certain manufacturers have on many occasions attempted to sell directly to our customers, thereby eliminating our role. Consolidation in this industry is more evident than ever, as further streamlining of our supply chain occurs. If more of our suppliers were to succeed in selling to our customers directly, including the electronic distribution of software products, our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows could be negatively affected.
Market conditions and technology advances significantly affect the demand for our products and services. Virtual delivery of software products and advanced Internet technology providing customers enhanced functionality have substantially increased customer expectations, requiring us to invest more heavily in our own IT development to meet these new demands. As buying trends change and electronic commerce continues to grow, customers become more sophisticated and have more choices than ever before. Customers are also better able to make price comparisons through the Internet, thereby increasing price competition. These conditions could have a negative effect on our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The primary challenges we face in effectively managing our business are (1) maintaining or increasing our revenues in the face of a worsening global recession, while at the same time, maintaining, if not improving, our gross profit margins in all three business segments, (2) recruiting, retaining, and improving the productivity of our sales personnel, and (3) effectively controlling our SG&A expenses over an expected lower sales base. With declines in spending projected in the overall IT industry, any significant sales growth for us must come through increased market share. Competition is expected to be even more intense in the future, which could put more pressure on margins. Given the softness in customer demand, management implemented cost reductions beginning late in the third quarter of 2008 to reduce expenses to be in line with lower sales volumes. We lowered headcount in sales support areas and implemented various cost reduction programs that are expected to result in annualized savings of $6 million. Given the continued decline in the demand environment, we implemented further cost reductions in the first quarter of 2009 which we believe could result in additional savings of up to $16 million in 2009. We expect to record severance charges of up to $0.6 million in connection with this action.
We believe that more of our customers are seeking total IT solutions, rather than simply specific IT products. Through the formation of our services subsidiary, ProConnection, Inc., we are able to provide customers complete IT solutions, from identifying their needs, to designing, developing, and managing the
23
Table of Contents
integration of products and services to implement their IT projects. Such service offerings carry much higher margins than traditional product sales. Additionally, the technical certifications of our service engineers permit us to offer higher-end, more complex products that also carry higher gross margins. We expect these service offerings and technical certifications to continue to play a role in sales generation and gross margins in this competitive environment.
We seek to recruit, retain, and increase the productivity of our sales personnel through training, mentoring, financial incentives based on performance, and updating and streamlining our information systems to make our operations more efficient. We are currently undertaking a major modification and upgrade of our sales order and customer management system that are expected to improve sales productivity beginning in the second half of 2009. In addition, as stated above, we continue to actively monitor and manage our expense structure in order to obtain better leverage of our operating costs.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following table sets forth information derived from our consolidated statements of income expressed as a percentage of net sales for the periods indicated.
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
Net sales (in millions) | $ | 1,753.7 | $ | 1,785.4 | $ | 1,635.7 | ||||||
Net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
Gross profit | 12.3 | 12.3 | 12.2 | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 10.7 | 10.2 | 10.6 | |||||||||
Goodwill impairment | 0.5 | — | — | |||||||||
Special charges | 0.1 | — | 0.1 | |||||||||
Income from operations | 1.0 | 2.1 | 1.5 | |||||||||
Net sales decreased by $31.7 million year over year in 2008 as increased Public Sector revenues were offset by revenue declines in the SMB and Large Account segments. Operating margins decreased year over year due to the goodwill impairment charge and higher operating costs, which we attribute to increased IT investments in sales support systems and higher personnel costs.
Sales Distribution
The following table sets forth our percentage of net sales by business segment and product mix:
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Business Segment | |||||||||
SMB | 52 | % | 54 | % | 54 | % | |||
Large Account | 27 | 29 | 30 | ||||||
Public Sector | 21 | 17 | 16 | ||||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
Product Mix | |||||||||
Notebooks and PDAs | 15 | % | 16 | % | 17 | % | |||
Video, Imaging and Sound | 15 | 14 | 13 | ||||||
Desktop/Servers | 13 | 14 | 14 | ||||||
Software | 13 | 13 | 13 | ||||||
Net/Com Products | 10 | 8 | 8 | ||||||
Printers and Printer Supplies | 9 | 10 | 10 | ||||||
Storage Devices | 9 | 9 | 9 | ||||||
Memory and System Enhancements | 4 | 5 | 5 | ||||||
Accessories/Other | 12 | 11 | 11 | ||||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
24
Table of Contents
We experienced year-over-year sales declines in 2008 in all but three product categories, which we attribute to the weakened economy and the associated decline in IT spending. Our highest year-over-year growth category was Net/Com Products, which grew 27% in 2008 compared to the prior year, reflecting industry demand for total IT solutions products. Sales of Accessories/Other also grew 4% year over year, primarily due to increased sales of consumer electronics and power management products.
Gross Profit Margins
The following table summarizes our overall gross profit margins, as a percentage of net sales, for the last three years:
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Segment | |||||||||
SMB | 13.9 | % | 13.4 | % | 13.3 | % | |||
Large Account | 11.0 | 11.2 | 10.8 | ||||||
Public Sector | 9.6 | 10.5 | 11.2 | ||||||
Total | 12.3 | % | 12.3 | % | 12.2 | % | |||
Consolidated gross profit dollars decreased in 2008 by $4.1 million compared to 2007 primarily due to the decline in net sales, as consolidated gross profit margin was unchanged year over year. Gross profit margins were unchanged as lower invoice product margins in 2008 were offset by increased vendor consideration recorded as a reduction to cost of sales compared to 2007.
Cost of Sales and Certain Other Costs
Cost of sales includes the invoice cost of the product, direct costs of packaging, inbound and outbound freight, and provisions for inventory obsolescence, adjusted for discounts, rebates, and other vendor allowances, including those pursuant to Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue No. 02-16, “Accounting by a Customer (Including a Reseller) for Certain Consideration Received from a Vendor” (“EITF 02-16”). Direct operating expenses relating to our purchasing function and receiving, inspection, internal transfer, warehousing, packing and shipping, and other expenses of our distribution center are included in SG&A expenses. Accordingly, our gross margins may not be comparable to those of other entities who include all of the costs related to their distribution network in cost of goods sold. Such costs, as a percentage of net sales for the periods reported, are as follows:
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||
| 0.69 | % | 0.65 | % | 0.67 | % | ||
Operating Expenses
The following table breaks out our more significant operating expenses for the last three years (in millions of dollars):
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
Personnel costs | $ | 124.0 | $ | 121.4 | $ | 117.3 | ||||||
Advertising | 19.5 | 19.9 | 13.3 | |||||||||
Facilities operations | 9.5 | 9.1 | 9.0 | |||||||||
Credit card fees | 7.7 | 8.0 | 8.1 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 7.0 | 6.8 | 7.0 | |||||||||
Professional fees | 8.1 | 5.4 | 5.8 | |||||||||
Bad debts | 1.7 | 1.0 | 2.3 | |||||||||
Other—net | 9.2 | 10.0 | 11.1 | |||||||||
Total | $ | 186.7 | $ | 181.6 | $ | 173.9 | ||||||
Percentage of net sales | 10.7 | % | 10.2 | % | 10.6 | % | ||||||
25
Table of Contents
Operating income in 2008 declined compared to 2007 due to higher personnel costs, increased professional fees, and the goodwill impairment charge. Professional fees increased due to increased IT investments in sales support systems. We are currently undertaking a major modification and upgrade of our sales order processing and customer management system that are expected to improve sales productivity in the second half of 2009. While we plan to continue our focus on controlling discretionary expenditures, we expect that our SG&A expense may vary depending on changes in sales volume, as well as the levels of continued investments in key growth initiatives such as enhancing our sales training, improving marketing programs, and deploying next generation technology to support the sales organization.
Personnel costs represent the majority of our operating expenses, with sales personnel representing the largest portion of these costs. The year-over-year increase in personnel costs resulted from annual merit increases, higher share-based compensation, and the hiring of services personnel in 2008. Increased bad debt expense also negatively affected operating income.
YEAR-OVER-YEAR COMPARISONS
Year Ended December 31, 2008 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2007
Net sales decreased 1.8% to $1,753.7 million in 2008 from $1,785.4 million in 2007 due to decreases in the SMB and Large Account segments. Changes in net sales and gross profit by business segment are shown in the following table (dollars in millions):
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of Net Sales | Amount | % of Net Sales | % Change | |||||||||||
Sales: | |||||||||||||||
SMB | $ | 919.1 | 52.4 | % | $ | 964.5 | 54.0 | % | (4.7 | %) | |||||
Large Account | 475.3 | 27.1 | 514.8 | 28.8 | (7.7 | ) | |||||||||
Public Sector | 359.3 | 20.5 | 306.1 | 17.2 | 17.4 | ||||||||||
| �� | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,753.7 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,785.4 | 100.0 | % | (1.8 | %) | |||||
Gross Profit: | |||||||||||||||
SMB | $ | 128.0 | 13.9 | % | $ | 129.3 | 13.4 | % | (1.0 | %) | |||||
Large Account | 52.5 | 11.0 | 57.5 | 11.2 | (8.7 | ) | |||||||||
Public Sector | 34.3 | 9.6 | 32.2 | 10.5 | 6.5 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 214.8 | 12.3 | % | $ | 219.0 | 12.3 | % | (1.9 | %) | |||||
| • | Net sales for the SMB segment decreased across most product and customer sectors. Corporate sales declined by 4% year over year, reflecting the continued softening in IT spending by small- and medium-sized businesses. Consumer sales continued to decline, reflecting our focus on more diverse marketing programs designed to reach our business customers and the general decline in consumer spending. Average annualized sales productivity decreased 6% year over year in 2008 compared to 2007. Sales representatives for our SMB segment totaled 453 at December 31, 2008, compared to 470 at December 31, 2007. |
| • | Net sales for the Large Account segment decreased year over year, reflecting the industry-wide decline in IT spending by large account customers. Sales representatives for our Large Account segment totaled 94 at December 31, 2008, compared to 96 at December 31, 2007. Average annualized sales productivity increased year over year by 2% in 2008 reflecting improved sales processes and reduced headcount. |
| • | Net sales for the Public Sector segment in 2008 increased by 17.4% year over year primarily due to increased sales made under existing federal government contracts. Average annualized sales |
26
Table of Contents
productivity in 2008 increased by 4% year over year largely due to the success of our federal sales representatives. Sales representatives for our Public Sector segment totaled 165 at December 31, 2008, up from 117 at December 31, 2007. Most of the year-over-year headcount increase resulted from sales representatives hired in December 2008 at our new sales site in South Dakota. |
Gross profit decreased in dollars in 2008 compared to 2007 as shown by the following:
| • | Gross profit for the SMB segment declined year over year in 2008 due to decreased net sales, as gross profit margins increased over the same period. We attribute the increase in gross profit margin to additional vendor consideration, offset partially by increased competitive pricing pressures in 2008 compared to the prior year. |
| • | Gross profit for the Large Account segment decreased year over year in both dollars and as a percentage of net sales. The decline in gross profit margins was attributable to aggressive competitive pricing as large account customers increasingly curtailed IT spending in the second half of 2008. Additional vendor consideration partially offset such pricing pressure. |
| • | Gross profit for the Public Sector segment increased in dollars in 2008 but decreased as a percentage of net sales compared to 2007. Declines in invoice product and freight margins and lower agency fee revenues, which are recorded on a net basis, adversely impacted gross profit margins in 2008 compared to the prior year. |
Selling, general and administrative expensesincreased in dollars and as a percentage of sales in 2008 compared to 2007.
SG&A expenses attributable to our operating segments and Headquarters/Other group are summarized below (dollars in millions):
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of Net Sales | Amount | % of Net Sales | % Change | |||||||||||
SMB | $ | 110.2 | 12.0 | % | $ | 105.0 | 10.9 | % | 5.0 | % | |||||
Large Account | 30.3 | 6.4 | 29.0 | 5.6 | 4.5 | ||||||||||
Public Sector | 35.0 | 9.7 | 30.6 | 10.0 | 14.4 | ||||||||||
Headquarters/Other | 11.2 | 17.0 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 186.7 | 10.6 | % | $ | 181.6 | 10.2 | % | 2.8 | % | |||||
| • | SG&A expenses for the SMB segment increased year over year in both dollars and as a percentage of net sales. Increased personnel costs, higher bad debt expense, and additional usage of centralized headquarter services led to increased operating expenses in 2008. Despite a decrease in variable compensation associated with lower gross margins, personnel expense increased due to the higher travel and training costs experienced in 2008. The operating costs of corporate headquarters and other support functions are charged to the reportable operating segments based on their estimated usage of the underlying functions. |
| • | SG&A expenses for the Large Account segment increased in dollars and as a percentage of net sales compared to the prior year period. Additional usage of centralized headquarter services was partly offset by reduced variable compensation associated with lower gross margins in 2008 compared to the prior year period. |
| • | SG&A expenses for the Public Sector segment increased in dollars but decreased as a percentage of net sales in 2008 due to the leveraging of such expenses over a larger sales base. The year-over-year dollar |
27
Table of Contents
increase was attributable to increased usage of centralized headquarter services and incremental variable compensation associated with higher gross profit dollars in 2008 compared to the prior year. |
| • | SG&A expenses for the Headquarters/Other group decreased in dollars year over year as increased usage by the operating segments offset increased investments in information technology systems, annual merit increases, and higher share-based compensation expense in 2008 compared to the prior year. As discussed in Note 15, “Segment and Related Disclosures” to the Consolidated Financial Statements,the “Headquarters/Other” group provides services to the three reportable operating segments in areas such as finance, human resources, information technology, product management, and marketing. Most of the operating costs associated with such corporate headquarters functions are charged to the operating segments based on their estimated usage of the underlying functions. Certain headquarters costs relating to executive oversight functions are not allocated to the operating segments and are included in this group’s expenses. |
Goodwill impairment charges totaling $8.8 million, $5.4 million net of taxes, were recorded in the year ended December 31, 2008. We did not record any impairment charges in 2007. As discussed in Note 2, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the 2008 non-cash impairment charges represented the entire goodwill balances carried by our SMB and Public Sector segments. Goodwill impairment, pre-tax by segment, for the year ended December 31, 2008 is summarized below(dollars in millions):
| 2008 | |||
Public Sector | $ | 7.6 | |
SMB | 1.2 | ||
Total | $ | 8.8 | |
Special charges totaled $1.4 million and $0.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Such charges related to management restructuring costs, classified as workforce reductions in the table below. A roll forward of liabilities related to special charges for the two years ended December 31, 2008, is shown below (dollars in millions):
| Workforce Reduction | ||||
Balance, December 31, 2006 | $ | 0.2 | ||
Charges | 0.5 | |||
Cash Payments | (0.2 | ) | ||
Balance, December 31, 2007 | $ | 0.5 | ||
Charges | 1.4 | |||
Cash Payments | (0.6 | ) | ||
Liabilities at December 31, 2008 | $ | 1.3 | ||
Income from operations decreased by $18.9 million to $17.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, from $36.8 million in 2007. Income from operations as a percentage of net sales decreased from 2.1% in 2007 to 1.0% in 2008. This decrease was attributable to the decrease in net sales, goodwill impairment charges, and increased operating expenses in 2008 as a percentage of net sales, as discussed above.
Interest expensewas $0.7 million in 2008 compared to $0.9 million in 2007. Interest expense decreased in 2008 due to lower borrowing levels in 2008 compared to the prior year, as well as reduced interest expense associated with our capital lease in 2008 compared to 2007. Interest and other income was largely unchanged year over year despite higher cash balances maintained in 2008 compared to 2007 due to lower interest rates received on such balances in 2008 compared to the prior year.
28
Table of Contents
Our effective tax rate was 42.4% for 2008 and 37.2% for 2007. Our higher effective tax rate in 2008 was generally due to increased state tax expense associated with filing in additional states as a result of our business expansion, as well as a reduction in state credit carryforwards. Our 2007 tax rate was favorably impacted by the consolidated filing of certain state income tax returns. We anticipate that our effective tax rate will be in the range of 40.0% to 41.0% in 2009.
Net incomedecreased by $12.6 million to $10.4 million in 2008 from $23.0 million in 2007, principally as a result of the decrease in income from operations.
Year Ended December 31, 2007 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2006
Net sales increased 9.2% to $1,785.4 million in 2007 from $1,635.7 million in 2006 due to increases in all three business segments. Changes in net sales and gross profit by business segment are shown in the following table (dollars in millions):
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of Net Sales | Amount | % of Net Sales | % Change | |||||||||||
Sales: | |||||||||||||||
SMB | $ | 964.5 | 54.0 | % | $ | 887.0 | 54.2 | % | 8.7 | % | |||||
Large Account | 514.8 | 28.8 | 482.9 | 29.5 | 6.6 | ||||||||||
Public Sector | 306.1 | 17.2 | 265.8 | 16.3 | 15.2 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,785.4 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,635.7 | 100.0 | % | 9.2 | % | |||||
Gross Profit: | |||||||||||||||
SMB | $ | 129.3 | 13.4 | % | $ | 118.3 | 13.3 | % | 9.3 | % | |||||
Large Account | 57.5 | 11.2 | 52.3 | 10.8 | 9.9 | ||||||||||
Public Sector | 32.2 | 10.5 | 29.7 | 11.2 | 8.4 | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 219.0 | 12.3 | % | $ | 200.3 | 12.2 | % | 9.3 | % | |||||
| • | Net sales for our SMB segment benefited from our 17% growth in corporate outbound sales in 2007 compared to 2006. We believe such growth is attributable to this segment’s sales representatives adding new customers and acquiring a greater share of existing customers’ IT purchases. Sales growth was adversely impacted by a decline in consumer sales, as both inbound telephone sales and internet consumer sales decreased year over year in 2007. These changes reflect our continued focus on more diverse marketing strategies and programs designed to reach our business customers. Average annualized sales productivity in 2007 increased by 10% compared to 2006 in the SMB segment due to increased tenure of our sales representatives. Sales representatives for our SMB segment totaled 470 at December 31, 2007, compared to 473 at December 31, 2006. |
| • | Net sales for our Large Account segment increased year over year as its seasoned sales representatives increased sales to existing customers and added new accounts. Sales representatives for our Large Account segment totaled 105 at December 31, 2007, down from 119 at the end of 2006. Average annualized sales productivity in 2007 improved year over year by 18%, reflecting the success of this segment’s consultative sales and solutions selling model. |
| • | Net sales for our Public Sector segment increased year over year due to the additional sales made in 2007 under recently awarded federal and higher education contracts. Average annualized sales productivity in 2007 increased by 10% year over year reflecting the improvement in average sales representative tenure. Sales representatives for our Public Sector segment totaled 117 at December 31, 2007, up from 110 at December 31, 2006. |
29
Table of Contents
Gross profit increased in dollars in 2007 compared to 2006 in all three business segments as shown by the following:
| • | Gross profit for our SMB segment increased year over year primarily due to increased net sales, as gross profit margins were unchanged year over year. Increased vendor consideration recorded as an offset to cost of sales was largely offset in 2007 by lower customer invoice margins compared to the prior year. Invoice margins were adversely impacted by several large sales of video product to three commercial customers. |
| • | Gross profit for our Large Account segment increased year over year due to larger net sales and improved gross profit margins. Gross profit margins increased in 2007 by 34 basis points as a percentage of sales compared to 2006 due to larger net sales of software referral and other agency fees and increased levels of higher-margin service revenues. |
| • | Gross profit for our Public Sector segment increased in dollars year over year due to larger net sales. Gross profit margins declined year over year due to reduced levels of higher-margin agency fee transactions. Invoice product margins were generally unchanged in 2007 compared to the prior year. |
Selling, general and administrative expensesincreased in dollars but decreased as a percentage of sales in 2007 from 2006.
We revised in the third quarter of 2007 our reporting of operating segments. Under this revised reporting structure, logistics and centralized headquarters functions that were formerly provided by the SMB segment to the Public Sector and Large Account segments were separated from the SMB segment. The centralized headquarters functions provide services in areas such as finance, human resources, information technology, legal, communications, and marketing. Most of the operating costs associated with the corporate headquarters functions are charged to the reportable operating segments based on their estimated usage of the underlying functions. Certain of the headquarters costs relating to executive oversight functions are not allocated to the operating segments and are included under the heading of “Headquarters/Other” in the table below.
SG&A expenses attributable to our operating segments and Headquarters/Other group are summarized below (dollars in millions):
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of Net Sales | Amount | % of Net Sales | % Change | |||||||||||
SMB | $ | 105.0 | 10.9 | % | $ | 105.2 | 11.9 | % | (0.2 | )% | |||||
Large Account | 29.0 | 5.6 | 27.8 | 5.8 | 4.3 | ||||||||||
Public Sector | 30.6 | 10.0 | 33.2 | 12.5 | (7.8 | ) | |||||||||
Headquarters/Other | 17.0 | 7.7 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 181.6 | 10.2 | % | $ | 173.9 | 10.6 | % | 4.4 | % | |||||
| • | SG&A expenses for our SMB segment decreased slightly in dollars year over year as a reduction in allocation expense of centralized headquarter services offset increased variable compensation associated with higher gross profits and increased net advertising expense. The operating costs of corporate headquarters and other support functions are charged to the reportable operating segments based on their estimated usage of the underlying functions. Net advertising expense, charged primarily to our SMB segment, increased due to our recording of substantially all vendor consideration as a reduction to inventory purchases, rather than a reduction of advertising expense, as discussed earlier. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales decreased year over year in 2007 due to improved personnel expense leverage and cost reductions in other areas. |
30
Table of Contents
| • | SG&A expenses for our Large Account segment increased in dollars but decreased as a percentage of net sales in 2007 compared to the prior year. The dollar increase resulted primarily from incremental sales compensation associated with higher sales levels. |
| • | SG&A expenses for our Public Sector segment decreased in both dollars and as a percentage of net sales in 2007 compared to the prior year. The year-over-year improvements are attributable to decreases in state compliance expense and centralized headquarters expense allocation. Net advertising expense increased due to our recording of substantially all vendor consideration as a reduction to inventory purchases, rather than a reduction of advertising expense, as discussed earlier. |
| • | SG&A expenses for our Headquarters/Other group (which represent those costs not allocated to the operating segments) increased in dollars year over year as a result of changes in our allocation process which led to certain headquarters costs relating to executive oversight functions no longer being allocated to the operating segments, as discussed above. |
Special charges totaled $0.5 million and $2.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. We recorded charges of $0.5 million in each of 2007 and 2006 related to management restructuring costs, classified as workforce reductions in the table below. In 2006, we also recorded a charge of $1.5 million related to our settlement with the DOJ on our 2003 GSA audit matter and a charge of $0.4 million related to the temporary retention of Amherst employees and facilities subsequent to the completion of the Amherst Transaction.
A roll forward of liabilities related to special charges for the two years ended December 31, 2007, is shown below (dollars in millions). The beginning balance of $1.1 million for the GSA matter was recorded as a component of cost of sales.
| Workforce Reduction | Amherst Transaction | GSA Matter | Other | Total | |||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2005 | $ | 0.9 | $ | 0.1 | $ | 1.1 | $ | — | $ | 2.1 | |||||||||
Charges | 0.5 | 0.4 | 1.5 | — | 2.4 | ||||||||||||||
Cash Payments | (1.2 | ) | (0.5 | ) | (2.6 | ) | — | (4.3 | ) | ||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2006 | $ | 0.2 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.2 | |||||||||
Charges | 0.5 | — | — | — | 0.5 | ||||||||||||||
Cash Payments | (0.2 | ) | — | — | — | (0.2 | ) | ||||||||||||
Liabilities at December 31, 2007 | $ | 0.5 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.5 | |||||||||
Income from operations increased by $12.9 million to $36.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2007, from $23.9 million in 2006. Income from operations as a percentage of net sales increased from 1.5% in 2006 to 2.1% in 2007. This increase was attributable to the increase in net sales, reduction in operating expenses as a percentage of net sales, and reduction in special charges as discussed above.
Interest expensewas $0.9 million in 2007 compared to $1.8 million in 2006. Interest expense decreased in 2007 due to lower average borrowings in 2007 as compared to the prior year.
Our effective tax rate was 37.2% for 2007 and 38.0% for 2006. Our 2007 tax rate was favorably impacted by the consolidated filing of certain state income tax returns.
Net incomeincreased by $9.2 million to $23.0 million in 2007 from $13.8 million in 2006, principally as a result of the increase in income from operations.
31
Table of Contents
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Liquidity Overview
Our primary sources of liquidity have historically been internally generated funds from operations and borrowings under our bank line of credit. We have used those funds to meet our capital requirements, which consist primarily of working capital for operational needs, capital expenditures for computer equipment and software used in our business, repurchases of common stock for treasury, and as opportunities arise, possible acquisitions of new businesses.
We believe that funds generated from operations, together with available credit under our bank line of credit and inventory trade credit agreements, will be sufficient to finance our working capital, capital expenditure, and other requirements for at least the next twelve calendar months. We expect our capital needs for 2009 to consist primarily of capital expenditures of $8.0 to $10.0 million and payments on capital and contractual obligations of approximately $4.5 million. We expect to meet our cash requirements for 2009 through a combination of cash on hand, cash generated from operations and, if necessary, borrowings on our bank line of credit, as follows:
| • | Cash on Hand. At December 31, 2008, we had approximately $47.0 million in unrestricted accounts. |
| • | Cash Generated from Operations. We expect to generate cash flows from operations in excess of operating cash needs by generating earnings and balancing net changes in inventories and receivables with compensating changes in payables to generate a positive cash flow. Historically, we have consistently generated positive cash flows from operations. |
| • | Credit Facilities. As of December 31, 2008, no borrowings were outstanding against our $50.0 million bank line of credit. This line of credit can be increased, at our option, to $80.0 million for approved acquisitions or other uses authorized by the bank. Borrowings are, however, limited by certain minimum collateral and earnings requirements, as described more fully below. |
Our ability to continue funding our planned growth, both internally and externally, is dependent upon our ability to generate sufficient cash flow from operations or to obtain additional funds through equity or debt financing, or from other sources of financing, as may be required. While at this time we do not anticipate needing any additional sources of financing to fund our operations, if demand for IT products continues to decline, our cash flows from operations may be substantially affected. See also related risks listed below under “Item 1A. Risk Factors.”
Summary Sources and Uses of Cash
The following table summarizes our sources and uses of cash over the last three years (in millions):
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 45.2 | $ | 0.4 | $ | 26.4 | ||||||
Net cash used for investing activities | (10.3 | ) | (7.0 | ) | (8.0 | ) | ||||||
Net cash (used for) provided by financing activities | (1.6 | ) | 2.8 | (10.6 | ) | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 33.3 | $ | (3.8 | ) | $ | 7.8 | |||||
Cash provided by operating activities increased substantially in 2008 compared to the prior years. Operating cash flow in 2008 resulted primarily from net income before non-cash goodwill impairment and depreciation, as well as decreases in accounts receivables and inventory. Accounts receivable decreased by $16.3 million in 2008 from the prior year-end level due to the decline in net sales experienced in 2008. Days sales outstanding increased to 45 days at December 31, 2008, compared to 43 days at December 31, 2007, as a result of increased sales in 2008 to public sector customers, who generally have longer payment terms compared to our corporate customers. Despite worsening economic conditions, our corporate customers continue to pay within terms.
32
Table of Contents
Inventory decreased by $15.3 million in 2008 due partly to the shipment of staged customer roll-outs in the first quarter of 2008 and as a result of management actions taken in the fourth quarter of 2008 to adjust inventory levels in line with decreased revenues. Increased drop-shipments also contributed to reduced inventory levels as we drop-shipped 55% of net sales in 2008, compared to 51% in 2007. Inventory days improved to 14 days at December 31, 2008, compared to 16 days at December 31, 2007. Cash flow provided by operations for the year ended December 31, 2007, resulted primarily from net income before depreciation and an increase in accrued expenses, offset by increases in accounts receivable and inventory. Cash flow provided by operations for the year ended December 31, 2006, resulted primarily from net income before depreciation and a decrease in inventory, offset partially by an increase in accounts receivable.
At December 31, 2008, we had $101.8 million in outstanding accounts payable. Such accounts are generally paid within 30 days of incurrence, or earlier when favorable cash discounts are offered. This balance will be financed by cash flows from operations or short-term borrowings under the line of credit. This amount includes $13.5 million payable to two financial institutions under inventory trade credit agreements we use to finance our purchase of certain inventory, secured by the inventory so financed. We believe we will be able to meet our obligations under our accounts payable with cash flows from operations and our existing line of credit.
Cash used for investing activities increased by $3.3 million in 2008 compared to 2007. These activities include our capital expenditures in the three years presented, primarily for computer equipment and capitalized internally-developed software. In 2008, we completed an extensive desktop upgrade and increased year over year our investments in sales system enhancements, that together accounted for the majority of this year-over-year increase.
Cash used for financing activitiesin 2008 was attributable largely to our repurchase of common stock. We repurchased 195,994 shares at a total cost of $1.4 million in 2008 (an average price of $7.39 per share). In addition, we withheld 14,852 shares, having an aggregate fair value of $0.1 million, upon the vesting of stock awards to satisfy related employee tax obligations during the year ended December 31, 2008. These repurchases were placed in treasury and are available for future equity grants or retirement. Cash provided by financing activities in 2007 related primarily to proceeds of $2.9 million from option exercises in 2007. In 2006, cash was used for financing activities with the pay down in our net borrowings of $20.0 million under our bank line of credit, partially offset by proceeds of $9.7 million from option exercises in 2006.
Debt Instruments, Contractual Agreements, and Related Covenants
Below is a summary of certain provisions of our credit facilities and other contractual obligations. For more information about the restrictive covenants in our debt instruments and inventory financing agreements, see “Factors Affecting Sources of Liquidity.” For more information about our obligations, commitments, and contingencies, see our consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes included in this annual report.
Bank Line of Credit. Our bank line of credit provides us with a borrowing capacity of up to $50.0 million at the prime rate (3.25% at December 31, 2008). In addition, we have the option to increase the facility by an additional $30.0 million, based on sufficient levels of trade receivables to meet borrowing base requirements, and depending on meeting minimum EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) and equity requirements, described below under “Factors Affecting Sources of Liquidity.” The facility also gives us the option of obtaining Eurodollar Rate Loans in multiples of $1.0 million for various short-term durations. Substantially all of our assets are collateralized as security for this facility, and all of our subsidiaries are guarantors under the line of credit. At December 31, 2008, the entire $50 million facility was available for borrowing.
This facility, which matures in October 2012, operates under an automatic cash management program whereby disbursements in excess of available cash are added as borrowings at the time disbursement checks clear the bank, and available cash receipts are first applied against any outstanding borrowings and then invested in short-term qualified cash investments. Accordingly, borrowings under the line are classified as current.
33
Table of Contents
Inventory Trade Credit Agreements. We have additional security agreements with two financial institutions to facilitate the purchase of inventory from various suppliers under certain terms and conditions. These agreements allow a collateralized first position in certain branded products inventory financed by these financial institutions. Although the agreements provide for up to 100% financing on the purchase price, up to an aggregate of $45.0 million, any outstanding financing must be fully secured by available inventory. We do not pay any interest or discount fees on such inventory financing; such costs are borne by the suppliers as an incentive for us to purchase their products. Amounts outstanding under such facilities, equal to $13.5 million as of December 31, 2008, are recorded in accounts payable, and the inventory financed is classified as inventory on the consolidated balance sheet.
Contractual Obligations. The following table sets forth information with respect to our long-term obligations payable in cash as of December 31, 2008 (in thousands):
| Payments Due By Period | |||||||||||||||
| Total | Less Than 1 Year | 1 – 3 Years | 3 – 5 Years | More Than 5 Years | |||||||||||
Contractual Obligations: | |||||||||||||||
Capital lease obligations (1) | $ | 5,601 | $ | 1,139 | $ | 2,278 | $ | 2,184 | — | ||||||
Operating lease obligations(2) | 7,147 | 2,991 | 2,386 | 736 | 1,034 | ||||||||||
Sports marketing commitments | 1,601 | 367 | 654 | 580 | — | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 14,349 | $ | 4,497 | $ | 5,318 | $ | 3,500 | $ | 1,034 | |||||
| (1) | Including interest, excluding taxes, insurance, and common area maintenance charges. |
| (2) | Excluding taxes, insurance, and common area maintenance charges. |
Due to the uncertainty with respect to the timing of future cash flows associated with our unrecognized tax benefits at December 31, 2008, we are unable to make reasonably reliable estimates of the period of cash settlement with the respective taxing authority. Therefore, $3.4 million of unrecognized tax benefits, including interest and penalties, have been excluded from the contractual obligations table above. See Note 11 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion on income taxes.
Capital Leases. We have a fifteen-year lease for our corporate headquarters with an affiliated company related through common ownership. In addition to the rent payable under the facility lease, we are required to pay real estate taxes, insurance, and common area maintenance charges.
Operating Leases. We also lease facilities from our principal stockholders and facilities and equipment from third parties under non-cancelable operating leases. See “Contractual Obligations” above for lease commitments under these leases.
Sports Marketing Commitments. We have entered into multi-year sponsorship agreements with the Boston Red Sox and the New England Patriots that extend to 2010 and 2013, respectively. These agreements, which grant us various marketing rights and seating arrangements, require annual payments aggregating from $0.3 million to $0.4 million per year.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements. We do not have any other off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have, a current or future material effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures, or capital resources.
Factors Affecting Sources of Liquidity
Internally Generated Funds. The key factors affecting our internally generated funds are our ability to minimize costs and fully achieve our operating efficiencies, timely collection of our customer receivables, and management of our inventory levels.
34
Table of Contents
Bank Line of Credit. Our credit facility contains certain financial ratios and operational covenants and other restrictions (including restrictions on additional debt, guarantees, stock repurchases, dividends and other distributions, investments, and liens) with which we and all of our subsidiaries must comply. Any failure to comply with these covenants would not only prevent us from borrowing additional funds under this line of credit, but would also constitute a default. This credit facility contains two financial tests:
| • | The funded debt ratio (defined as the average outstanding advances under the line for the quarter, divided by the consolidated EBITDA for the trailing four quarters) must not be more than 2.0 to 1.0. We did not have any outstanding borrowings under the credit facility in the fourth quarter of 2008, and accordingly the funded debt ratio did not limit potential borrowings at December 31, 2008. Future decreases in our consolidated EBITDA, however, could limit our potential borrowings under the credit facility. |
| • | Minimum Consolidated Net Worth must be at least $150.0 million, plus 50% of consolidated net income for each quarter, beginning with the quarter ended March 31, 2007. Such amount was calculated at December 31, 2008, as $173.6 million, whereas our actual consolidated stockholders’ equity at this date was $235.3 million. |
The borrowing base under this facility is set at 80% of qualified commercial receivables, plus 50% of qualified government receivables. As of December 31, 2008, the entire $50.0 million facility was available for borrowing.
Inventory Trade Credit Agreements. These agreements contain similar financial ratios and operational covenants and restrictions as those contained in our bank line of credit described above. Such agreements also contain cross-default provisions whereby a default under the bank agreement would also constitute a default under these agreements. Financing under these agreements is limited to the purchase of specific branded products from authorized suppliers, and amounts outstanding must be fully collateralized by inventories of those products on hand.
Capital Markets. Our ability to raise additional funds in the capital market depends upon, among other things, general economic conditions, the condition of the information technology industry, our financial performance and stock price, and the state of the capital markets.
APPLICATION OF CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
The SEC requires that all registrants disclose their most “critical accounting policies.” A “critical accounting policy” has been defined as one that is both important to the portrayal of the registrant’s financial condition and results and requires management’s most difficult, subjective or complex judgments, often as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain. Further, “critical accounting policies” are those that are reflective of significant judgments and uncertainties, and potentially result in materially different results under different assumptions and conditions.
We believe that our accounting policies described below fit the definition of “critical accounting policies.” We have reviewed our policies for the year ended December 31, 2008, and determined that they remain our most critical accounting policies.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue on product sales is recognized at the point in time when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, delivery has occurred, and there is a reasonable assurance of collection of the sales proceeds. We generally obtain oral or written purchase authorizations from our customers for a specified amount of product at a specified price. Because we either (i) have a general practice of covering customer losses while products are in-transit despite title transferring at the point of shipment or (ii) have FOB—destination specifically set out in our arrangements with certain customers, delivery is deemed to have occurred at the point in time when the product is received by the customer.
35
Table of Contents
We provide our customers with a limited thirty-day right of return generally limited to defective merchandise. Revenue is recognized at delivery and a reserve for sales returns is recorded. We have demonstrated the ability to make reasonable and reliable estimates of product returns in accordance with SFAS 48, “Revenue Recognition When Right of Return Exists,” based on significant historical experience. We record our sales reserves as offsets to accounts receivable and, for customers who have already paid, as credits to accrued expenses. At December 31, 2008, we recorded sales reserves of $2.1 million and $0.4 million as components of accounts receivable and accrued expenses, respectively. At December 31, 2007, we recorded sales reserves of $2.1 million and $0.3 million as components of accounts receivable and accrued expenses, respectively.
All amounts billed to a customer in a sale transaction related to shipping and handling, if any, represent revenues earned for the goods provided, and these amounts have been classified as “net sales.” Costs related to such shipping and handling billings are classified as “cost of sales.” Sales are reported net of sales, use, or other transaction taxes that are collected from customers and remitted to taxing authorities.
Revenue for third-party service contracts is recorded on a net sales recognition basis because we do not assume the risks and rewards of ownership in these transactions. For such contracts, we evaluate whether the sales of such services should be recorded as gross sales or net sales as required under the guidelines described in SAB 104, “Revenue Recognition” and EITF Issue No. 99-19, “Reporting Revenue Gross as a Principal versus Net as an Agent.” Under gross sales recognition, we are the primary obligor, and the entire selling process is recorded in sales with our cost to the third-party service provider recorded as a cost of sales. Under net sales recognition, we are not the primary obligor, and the cost to the third-party service provider is recorded as a reduction to sales, with no cost of goods sold, thus leaving the gross profit as the reported net sale for the transaction.
Similarly, we recognize revenue from agency sales transactions on a net sales basis. In agency sales transactions, we facilitate product sales by equipment and software manufacturers directly to our customers and receive agency, or referral, fees for such transactions. We do not take title to the products or assume any maintenance or return obligations in these transactions; title is passed directly from the supplier to our customer.
Net amounts included in revenue for such third-party service contracts and agency sales transactions were $13.3 million, $14.3 million, and $10.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.
Although service revenues represent a small percentage of our consolidated revenues, we offer a growing range of services, including installation, configuration, repair, and other services performed by our personnel and third-party providers. If a service is performed in conjunction with the delivery of hardware, software, or another service, then we determine whether an item included in such multiple-element arrangements constitutes a separate deliverable, in accordance with EITF 00-21, “Accounting for Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables.”
In these arrangements, an element is separated as a deliverable only when the following three conditions are met:
| • | The delivered item(s) has value to the customer on a standalone basis; |
| • | There is objective and reliable evidence of the fair value of the undelivered item; and |
| • | If the arrangement includes a general right of return relative to the delivered item, delivery or performance of the undelivered item(s) is considered probable and substantially under our control. |
Accounts Receivable
We perform ongoing credit evaluations of our customers and adjust credit limits based upon payment history and customers’ current creditworthiness. Our allowance is generally computed by (1) applying specific
36
Table of Contents
percentage reserves on accounts that are past due; and (2) specifically reserving for customers known to be in financial difficulty. Therefore, if the financial condition of certain of our customers were to deteriorate, or if we noted there was a lengthening of the timing of the settlement of receivables that was symptomatic of a general deterioration in the ability of our customers to pay, we would have to increase our allowance for doubtful accounts. This would negatively impact our earnings. Our cash flows would be impacted to the extent that receivables could not be collected.
In addition to accounts receivable from customers, we record receivables from our vendors/suppliers for cooperative advertising, price protection, supplier reimbursements, rebates, and other similar arrangements. A portion of such receivables is estimated based on information available from our vendors at discrete points in time. While such estimates have historically approximated actual cash received, an unanticipated change in a promotional program could give rise to a reduction in the receivable. This could negatively impact our earnings and our cash flows.
Considerable judgment is used in assessing the ultimate realization of customer receivables and vendor/supplier receivables, including reviewing the financial stability of a customer, vendor information, and gauging current market conditions. If our evaluations are incorrect, we may incur additional charges in the future on our consolidated statements of income.
Vendor Allowances
We receive allowances from merchandise vendors for price protections, discounts, product rebates, and other programs. These allowances are treated as a reduction of the vendor’s prices and are recorded as adjustments to cost of sales or inventory, as applicable. We also receive vendor co-op advertising funding for our catalogs and other programs. Vendors have the ability to place advertisements in the catalogs or fund other advertising activities for which we receive advertising allowances. These vendor allowances, to the extent that they represent specific reimbursements of the underlying incremental and identifiable costs, are offset against SG&A expense on the consolidated statements of income. Advertising allowances that cannot be associated with a specific program funded by an individual vendor or that exceed the fair value of advertising expense associated with that program are classified as offsets to cost of inventory purchases in accordance with EITF 02-16. Our vendor partners generally consolidate their funding of advertising and other marketing programs, and as a result, we classify substantially all vendor allowances as a reduction of cost of inventory purchases rather than a reduction of advertising expense. The level of allowances received from certain merchandise vendors has declined in past years and may do so again. Such a decline could have a material impact on gross margin and operating income.
Inventories—Merchandise
Inventories (all finished goods) consisting of software packages, computer systems, and peripheral equipment are stated at cost (determined under a weighted-average cost method which approximates the first-in, first-out method) or market, whichever is lower. Inventory quantities on hand are reviewed regularly, and provisions are made for obsolete, slow moving, and non-salable inventory, based primarily on management’s forecast of customer demand for those products in inventory. The IT industry is characterized by rapid technological change and new product development that could result in increased obsolescence of inventory on hand. Increased obsolescence or decreased customer demand beyond management’s expectations could require additional provisions. This could negatively impact our earnings. Our obsolescence charges have historically ranged between $5.6 million and $6.6 million per annum. Historically, there have been no unusual charges precipitated by specific technological or forecast issues.
Contingencies
From time to time we are subject to potential claims and assessments from third parties. We continually assess whether or not such claims have merit and warrant accrual under the “probable and estimable” criteria of
37
Table of Contents
SFAS No. 5, “Accounting for Contingencies.” We are also subject to audits by states on sales and income taxes, unclaimed property, and other assessments. A multi-state unclaimed property audit is currently in progress, and certain sales tax audits may be imminent. While management believes that known liabilities have been adequately provided for, it is too early to determine the ultimate outcome of such audits. Such outcome could have a material negative impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
Value of Goodwill and Long-Lived Assets, Including Intangibles
We recorded a non-cash goodwill impairment charge of $8.8 million in the year ended December 31, 2008 to write-off the entire goodwill balances held by the SMB and Public Sector segments. Our Large Account segment, however, continues to carry $50.2 million of goodwill and other intangible assets. While we believe that our future estimates are reasonable, different assumptions regarding items such as future cash flows and the volatility inherent in markets which we serve could materially affect our valuations and result in impairment charges against the carrying value of those remaining assets in our Large Account segment.
We carry a variety of long-lived assets on our consolidated balance sheet. These are all currently classified as held for use. These include property and equipment, identifiable intangibles, and goodwill. An impairment review is undertaken on (1) an annual basis for assets such as goodwill and indefinite lived intangible assets; and (2) on an event-driven basis for all long-lived assets (including indefinite lived intangible assets and goodwill) when facts and circumstances suggest that cash flows emanating from such assets may be diminished. We historically have reviewed the carrying value of all these assets based partly on our projections of anticipated cash flows—projections which are, in part, dependent upon anticipated market conditions, operational performance, and legal status. Any impairment charge that is recorded negatively impacts our earnings. Cash flows are generally not impacted.
Employee Compensation and Benefits
Our employee compensation model has several elements that we consider variable. These include our obligation to our employees for health care. We have selected a plan that results in our being self-insured up to certain stop-loss limits. Accordingly, we have to estimate the amount of health care claims outstanding at a given point in time. These estimates are based on historical experience and could be subject to change. Such change could negatively impact both our earnings and our cash flows.
Share-Based Compensation
Prior to January 1, 2006, we accounted for employee stock options using the intrinsic value method in accordance with Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 25, “Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees”. The intrinsic value method requires that compensation expense be measured by the difference between the fair value of our common stock and the strike price of the option as of a measurement date. Effective January 1, 2006, we adopted SFAS No. 123 (revised 2004), “Share-Based Payment,” (“SFAS 123(R)”) using the modified prospective application method. SFAS 123(R) requires a company to measure the grant date fair value of equity awards given to employees and recognize that cost, adjusted for forfeitures, over the period that such services are performed in its consolidated financial statements (as further described in Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements). SFAS 123(R) requires forfeitures to be estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures experienced differ from these estimates. We elected to use the criteria in SFAS 123(R) to establish the beginning balance of the additional paid-in capital pool related to the tax effects of employee share-based compensation.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred income tax assets and liabilities for the differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities that will result in taxable or deductible amounts in the future, based on enacted tax laws and rates anticipated to be applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. On January 1, 2007, we adopted Financial Accounting Standards Boards (“FASB”) Interpretation No. 48, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement
38
Table of Contents
No. 109” (“FIN 48”). We account for uncertain tax positions in accordance with FIN 48. Accordingly, we report a liability for unrecognized tax benefits resulting from uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. We recognize interest and penalties, if any, related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
RECENTLY ISSUED FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements” (“SFAS 157”). This Statement defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value, and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. SFAS 157 does not require any new fair value measurements but rather applies under other accounting pronouncements that require or permit fair value measurements. SFAS 157 is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007. In February 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. 157-2 (“FSP 157-2”). FSP 157-2 delayed the effective date of SFAS 157 for all nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a recurring basis (at least annually), until fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. These nonfinancial items include assets and liabilities such as reporting units measured at a fair value in a goodwill impairment test and nonfinancial assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination. As such, we partially adopted SFAS 157 on January 1, 2008, and it did not have a significant impact on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
In October 2008, the FASB issued FSP 157-3 “Determining the Fair Value of a Financial Asset When the Market for That Asset Is Not Active” (“FSP 157-3”). FSP 157-3 clarifies the application of SFAS 157 in a market that is not active, and addresses application issues such as the use of internal assumptions when relevant observable data does not exist, the use of observable market information when the market is not active, and the use of market quotes when assessing the relevance of observable and unobservable data. FSP 157-3 is effective for all periods presented in accordance with SFAS 157. The adoption of FSP 157-3 did not have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements or the fair values of our financial assets and liabilities.
In February 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” (“SFAS 159”), which permits companies to voluntarily choose to measure specified financial instruments and other items at fair value on a contract-by-contract basis. If the fair value option is elected, subsequent changes in fair value will be required to be reported in earnings each reporting period. This Statement is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007 and interim periods within those fiscal years. We have elected not to measure any eligible items at fair value. Accordingly, the adoption of SFAS 159 did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 141 (revised 2007), “Business Combinations” (“SFAS No. 141(R)”). Under SFAS 141(R), an entity is required to recognize the assets acquired, liabilities assumed, contractual contingencies, and contingent consideration at their fair value on the acquisition date. It further requires that acquisition-related costs be recognized separately from the acquisition and expensed as incurred; that restructuring costs generally be expensed in periods subsequent to the acquisition date; and that changes in accounting for deferred tax asset valuation allowances and acquired income tax uncertainties after the measurement period be recognized as a component of provision for taxes. This Statement is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and is to be applied prospectively. We are currently assessing the potential impact SFAS 141(R) will have on our financial statements.
INFLATION
We have historically offset any inflation in operating costs by a combination of increased productivity and price increases, where appropriate. We do not expect inflation to have a significant impact on our business in the foreseeable future.
39
Table of Contents
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk |
We invest cash balances in excess of operating requirements in short-term securities, generally with maturities of 90 days or less. In addition, our unsecured credit agreement provides for borrowings which bear interest at variable rates based on the prime rate. We believe the effect, if any, of reasonably possible near-term changes in interest rates on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows should not be material. Our credit agreement exposes earnings to changes in short-term interest rates since interest rates on the underlying obligations are variable. No borrowings were outstanding pursuant to the credit agreement as of December 31, 2008, and our average outstanding borrowing during 2008 was minimal. Accordingly, the change in earnings resulting from a hypothetical 10% increase or decrease in interest rates would not be material.
| Item 8. | Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
The information required by this Item is included in this Report beginning at page F-1.
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
Not applicable.
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Management’s Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company’s management, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2008. The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) promulgated under the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures. The Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives as described above. Based on this evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this report, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) or 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the Company’s principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the Company’s board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and includes those policies and procedures that: (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and
40
Table of Contents
directors of the Company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The Company’s management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008. In making this assessment, the Company’s management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission inInternal Control-Integrated Framework.
Based on our assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2008, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
The Company’s Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm has issued an audit report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008. This report appears below.
41
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
PC Connection, Inc.
Merrimack, NH
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of PC Connection, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2008, based on criteria established inInternal Control—Integrated Frameworkissued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company’s board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on the criteria established inInternal Control—Integrated Frameworkissued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule as of and for the year ended December 31, 2008 of the Company and our report dated March 16, 2009 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and financial statement schedule.
Deloitte & Touche LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
March 16, 2009
42
Table of Contents
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
No change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting occurred during the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2008, that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
| Item 9B. | Other information |
None.
43
Table of Contents
PART III
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers, and Corporate Governance |
The information included under the headings, “Executive Officers of PC Connection” in Item 4 of Part I hereof and “Information Concerning Directors, Nominees, and Executive Officers,” “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” “Code of Business Conduct and Ethics,” and “Board Committees—Audit Committee” in our definitive Proxy Statement for our 2009 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on June 17, 2009 (the “Proxy Statement”) is incorporated herein by reference. We anticipate filing the Proxy Statement within 120 days after December 31, 2008. With the exception of the foregoing information and other information specifically incorporated by reference into this Form 10-K, the Proxy Statement is not being filed as a part hereof.
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The information included under the headings “Executive Compensation,” “Director Compensation,” “Compensation Committee and Interlocks and Insider Participation,” and “Compensation Committee Report” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The information included under the headings “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information included under the headings “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and “Director Independence” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
The information included under the heading “Principal Accountant Fees and Services” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
44
Table of Contents
PART IV
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
| (a) | List of Documents Filed as Part of this Report: |
| (1) | Consolidated Financial Statements |
The consolidated financial statements listed below are included in this document.
Consolidated Financial Statements | Page References | |
| F-2 | ||
| F-3 | ||
| F-4 | ||
| F-5 | ||
| F-6 | ||
| F-7 |
| (2) | Consolidated Financial Statement Schedule: |
The following Consolidated Financial Statement Schedule, as set forth below, is filed with this report:
Schedule | Page Reference | |
| S-1 |
All other schedules have been omitted because they are either not applicable or the relevant information has already been disclosed in the financial statements.
| (3) | Supplementary Data |
Not applicable.
45
Table of Contents
| (b) | Exhibits |
The exhibits listed below are filed herewith or are incorporated herein by reference to other filings.
EXHIBIT INDEX
Exhibits | ||
| 3.2(5) | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Registrant, as amended. | |
| 3.4(27) | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Registrant. | |
| 4.1(1) | Form of specimen certificate for shares of Common Stock, $0.01 par value per share, of the Registrant. | |
| 9.1(1) | Form of 1998 PC Connection Voting Trust Agreement among the Registrant, Patricia Gallup individually and as a trustee, and David Hall individually and as trustee. | |
| 10.1(1) | Form of Registration Rights Agreement among the Registrant, Patricia Gallup, David Hall, and the 1998 PC Connection Voting Trust. | |
| 10.2(5) | 1997 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| 10.3(24) | 2007 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| 10.4(20) | Amended and Restated 1997 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended. | |
| 10.5(25) | Form of Incentive Stock Option Agreement for 2007 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| 10.6(25) | Form of Nonstatutory Stock Option Agreement for 2007 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| 10.7(25) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement for 2007 Stock Incentive Plan. | |
| 10.8(19) | PC Connection, Inc. Discretionary Bonus Plan. | |
| 10.9(1) | Employment Agreement, dated as of January 1, 1998, between the Registrant and Patricia Gallup. | |
| 10.10(29) | Employment Agreement, dated as of May 12, 2008, between the Registrant and Timothy McGrath. | |
| 10.11(29) | Severance Agreement, dated as of October 9, 2001, between the Registrant and Bradley Mousseau. | |
| 10.12(31) | Separation Agreement, dated October 14, 2008, by and between the Registrant and David Beffa-Negrini. | |
| 10.13(12) | Agreement for Inventory Financing, dated as of October 31, 2002, by and among the Registrant, Merrimack Services Corporation, GovConnection, Inc., MoreDirect, Inc., and IBM Credit Corporation. | |
| 10.14(12) | Guaranty, dated as of November 14, 2002, entered into by Registrant in connection with the Agreement for Inventory Financing, dated as of October 31, 2002, by and among the Registrant, Merrimack Services Corporation, GovConnection, Inc., MoreDirect, Inc., and IBM Credit Corporation. | |
| 10.15(12) | Guaranty, dated as of November 14, 2002, entered into by PC Connection Sales Corporation in connection with the Agreement for Inventory Financing, dated as of October 31, 2002, by and among the Registrant, Merrimack Services Corporation, GovConnection, Inc., MoreDirect, Inc., and IBM Credit Corporation. | |
46
Table of Contents
Exhibits | ||
| 10.16(12) | Acknowledgement, Waiver, and Amendment to Agreement for Inventory Financing, dated as of November 25, 2003, by and among the Registrant, Merrimack Services Corporation, GovConnection, Inc., MoreDirect, Inc., and IBM Credit LLC. | |
| 10.17(20) | Second Amendment, dated May 9, 2004, to the Agreement for Inventory Financing between the Registrant and its subsidiaries Merrimack Services Corporation, GovConnection, Inc., and MoreDirect, Inc., and IBM Credit LLC. | |
| 10.18(20) | Third Amendment, dated May 27, 2005, to the Agreement for Inventory Financing between the Registrant and its subsidiaries Merrimack Services Corporation, GovConnection, Inc., and MoreDirect, Inc., and IBM Credit LLC. | |
| 10.19(16) | Second Amended and Restated Credit and Security Agreement, dated June 29, 2005, among Citizens Bank of Massachusetts, as lender and as agent, other financial institutions party thereto from time to time, as lenders, PC Connection, Inc., as borrower, GovConnection, Inc., Merrimack Services Corporation, PC Connection Sales Corporation, PC Connection Sales of Massachusetts, Inc., and MoreDirect, Inc., each as guarantors. | |
| 10.20(26) | Third Amendment, dated October 15, 2007, to the Second Amended and Restated Credit and Security Agreement by and among the Registrant and certain subsidiary guarantors, and RBS Citizens, National Association, successor by merger to Citizens Bank of Massachusetts, as lender and agent. | |
| 10.21(17) | Bill of Sale, dated October 21, 2005, between PC Connection, Inc. and IBM Credit, LLC. | |
| 10.22(1) | Amended and Restated Lease between the Registrant and G&H Post, LLC, dated December 29, 1997, for property located at Route 101A, Merrimack, New Hampshire. | |
| 10.23(2) | Amendment No. 1 to Amended and Restated Lease between the Registrant and G&H Post, LLC, dated December 29, 1998, for property located at Route 101A, Merrimack, New Hampshire. | |
| 10.24 | Amendment No. 2 to Amended and Restated Lease between the Registrant and G&H Post, LLC, dated December 29, 1998, for property located at Route 101A, Merrimack, New Hampshire. | |
| 10.25(30) | Lease between the Merrimack Services Corporation and G&H Post LLC, dated August 11, 2008, for property located at Merrimack, New Hampshire. | |
| 10.26(1) | Lease between the Registrant and Miller-Valentine Partners, dated September 27, 1990, as amended, for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.27(4) | Third Amendment, dated June 26, 2000, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and EWE Warehouse Investments V, LTD., dated September 27, 1990, for property located at 2840 Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.28(9) | Fourth Amendment, dated July 31, 2002, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and EWE Warehouse Investments V, LTD., dated September 27, 1990, for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.29(14) | Fifth Amendment, dated February 28, 2005, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and EWE Warehouse Investments V, LTD., dated September 27, 1990, for property located at 2780-2880 Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.30(22) | Sixth Amendment, dated October 26, 2006, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and EWE Warehouse Investments V, LTD., dated September 27, 1990, for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
47
Table of Contents
Exhibits | ||
| 10.31 | Seventh Amendment, dated January 28, 2009, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and EWE Warehouse Investments V, LTD., dated September 27, 1990, for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.32(3) | Assignment of Lease Agreements, dated December 13, 1999, between Micro Warehouse, Inc. (assignor) and the Registrant (assignee), for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.33(6) | First Amendment, dated June 19, 2001, to the Assignment of Lease Agreements, dated as of December 13, 1999, between Micro Warehouse Inc. (assignor) and Merrimack Services Corporation for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.34(12) | Second Amendment, dated April 24, 2003, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services and EWE Warehouse Investments V, LTD., dated December 13, 1999, for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.35(20) | Third Amendment, dated November 11, 2005, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and EWE Warehouse Investments V, LTD., dated December 13, 1999, for property located at Old State Route 73, Wilmington, Ohio. | |
| 10.36(4) | Lease between ComTeq Federal, Inc. and Rockville Office/Industrial Associates dated December 14, 1993, for property located at 7503 Standish Place, Rockville, Maryland. | |
| 10.37(4) | First Amendment, dated November 1, 1996, to the Lease Agreement between ComTeq Federal, Inc. and Rockville Office/Industrial Associates, dated December 14, 1993, for property located in Rockville, Maryland. | |
| 10.38(4) | Second Amendment, dated March 31, 1998, to the Lease Agreement between ComTeq Federal, Inc. and Rockville Office/Industrial Associates, dated December 14, 1993, for property located in Rockville, Maryland. | |
| 10.39(4) | Third Amendment, dated August 31, 2000, to the Lease Agreement between ComTeq Federal, Inc. and Rockville Office/Industrial Associates, dated December 14, 1993, property located in Rockville, Maryland. | |
| 10.40(9) | Fourth Amendment, dated November 20, 2002, to the Lease Agreement between GovConnection, Inc. (formerly known as ComTeq Federal, Inc.) and Metro Park I, LLC (formerly known as Rockville Office/Industrial Associates), dated December 14, 1993, for property located in Rockville, Maryland. | |
| 10.41(20) | Fifth Amendment, dated December 12, 2005, to the Lease Agreement between GovConnection, Inc. and Metro Park I, LLC, dated December 14, 1993, for property located in Rockville, Maryland. | |
| 10.42(32) | Sixth Amendment, dated September 18, 2008, to the Lease Agreement between GovConnection, Inc. and Metro Park I, LLC, dated December 14, 1993, for property located in Rockville, Maryland. | |
| 10.43(4) | Lease between Merrimack Services Corporation and Schleicher & Schuell, Inc., dated November 16, 2000, for property located at 10 Optical Avenue, Keene, New Hampshire. | |
| 10.44(21) | First Amendment, dated April 21, 2006, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and Whatman, Inc. successor-by-merger to Schleicher & Schuell, Inc., dated November 16, 2000, for property located at 10 Optical Avenue, Keene, New Hampshire. | |
48
Table of Contents
Exhibits | ||
| 10.45(28) | Second Amendment, dated January 31, 2008, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and East Keene RE LLC, successor-in-interest to Whatman, Inc., dated November 16, 2006, for property located at 10 Optical Avenue, Keene, New Hampshire. | |
| 10.46(10) | Lease between GovConnection, Inc. and Fairhaven Investors Limited Partnership, dated April 30, 2003, for property located at 2150 Post Road, Fairfield, Connecticut. | |
| 10.47(15) | First Amendment, dated April 14, 2005, to the Lease Agreement between GovConnection, Inc. and Fairhaven Investors Limited Partnership, dated May 1, 2003, for property located in Fairhaven, Connecticut. | |
| 10.48(13) | Fifth Amendment, dated September 24, 2004, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and Bronx II, LLC, dated October 27, 1988, as amended for property located in Marlborough, MA. | |
| 10.49(28) | Sixth Amendment, dated February 29, 2008, to the Lease Agreement between Merrimack Services Corporation and RFP Lincoln 293, LLC, assignee of the leasehold interest of Bronx II, LLC, dated October 27, 1988, as amended for property located in Marlborough, MA. | |
| 10.50(14) | Lease between MoreDirect, Inc. and Boca Technology Center, LLC, dated February 14, 2005, for property located in Boca Raton, Florida. | |
| 10.51(14) | Sublease between Merrimack Services Corporation and 222 International, LP, dated March 4, 2005, for property located in Portsmouth, New Hampshire. | |
| 10.52(20) | Lease between MoreDirect, Inc. and RMC Midway Walnut, LP, dated January 6, 2006, for property located at 14295 Midway Road, Addison, Texas. | |
| 10.53(20) | Lease between PC Connection Sales of Massachusetts, Inc. and RMC Midway Walnut, LP, dated January 6, 2006, for property located at 14295 Midway Road, Addison, Texas. | |
| 10.54(23) | Release and Settlement Agreement, dated December 1, 2006, by and between the United States of America and GovConnection, Inc. | |
| 10.55 | Summary of Compensation for Executive Officers. | |
| 10.56 | Summary of Compensation for Non-Employee Directors. | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of Registrant. | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP. | |
| 31.1 | Certification of the Company’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 31.2 | Certification of the Company’s Executive Vice President, Treasurer, and Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.1 | Certification of the Company’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.2 | Certification of the Company’s Executive Vice President, Treasurer, and Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference from the exhibits filed with the Company’s registration statement (333-41171) on Form S-1 filed under the Securities Act of 1933. |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on March 31, 1999. |
49
Table of Contents
| (3) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K/A Amendment No. 1, File Number 0-23827, filed on April 4, 2000. |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on March 30, 2001. |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s proxy statement pursuant to Section 14(a), File Number 0-23827, filed on April 17, 2001. |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, File Number 0-23827, filed on August 14, 2001. |
| (7) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on April 1, 2002. |
| (8) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, dated April 5, 2002. |
| (9) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on March 31, 2003. |
| (10) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, File Number 0-23827, filed on August 13, 2003. |
| (11) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, File number 0-23827, filed November 20, 2003. |
| (12) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on March 30, 2004. |
| (13) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, File Number 0-23827, filed November 15, 2004. |
| (14) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on March 31, 2006. |
| (15) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on May 16, 2005. |
| (16) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, filed on July 6, 2005. |
| (17) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, filed on October 27, 2005. |
| (18) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on November 14, 2005. |
| (19) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, filed on December 30, 2005. |
| (20) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on March 30, 2006. |
| (21) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on August 11, 2006. |
| (22) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, filed on October 31, 2007. |
| (23) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, filed on December 7, 2006. |
| (24) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s proxy statement pursuant to Section 14(a), File Number 0-23827, filed on April 30, 2007. |
| (25) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on August 10, 2007. |
| (26) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on November 13, 2007. |
| (27) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, filed on January 9, 2008. |
| (28) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s annual report on Form 10-K, File Number 0-23827, filed on March 14, 2008. |
50
Table of Contents
| (29) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on May 12, 2008. |
| (30) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on August 11, 2008. |
| (31) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s current report on Form 8-K, filed on October 17, 2008. |
| (32) | Incorporated by reference from exhibits filed with the Company’s quarterly report on Form 10-Q, filed on November 10, 2008. |
51
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15 (d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| PC CONNECTION, INC. | ||||||||
| Date: March 16, 2009 | By: | /s/ PATRICIA GALLUP | ||||||
Patricia Gallup Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | ||||||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Name | Title | Date | ||
/s/ PATRICIA GALLUP Patricia Gallup | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | March 16, 2009 | ||
/s/ JACK FERGUSON Jack Ferguson | Executive Vice President, Treasurer, and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | March 16, 2009 | ||
/s/ BRUCE BARONE Bruce Barone | Director | March 16, 2009 | ||
/s/ JOSEPH BAUTE Joseph Baute | Director | March 16, 2009 | ||
/s/ DAVID BEFFA-NEGRINI David Beffa-Negrini | Director | March 16, 2009 | ||
/s/ DAVID HALL David Hall | Director | March 16, 2009 | ||
/s/ DONALD WEATHERSON Donald Weatherson | Director | March 16, 2009 | ||
52
Table of Contents
PC CONNECTION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
F-1
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
PC Connection, Inc.
Merrimack, NH
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of PC Connection, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the related consolidated statements of income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of PC Connection, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
As discussed in Note 1, the Company adopted the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board Interpretation No. 48,Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109, effective January 1, 2007.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on the criteria established inInternal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated March 16, 2009 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Deloitte & Touche LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
March 16, 2009
F-2
Table of Contents
PC CONNECTION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(amounts in thousands, except per share data)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
Current Assets: | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 47,003 | $ | 13,741 | ||||
Accounts receivable, net | 185,885 | 202,216 | ||||||
Inventories—merchandise | 60,813 | 76,090 | ||||||
Deferred income taxes | 4,244 | 2,858 | ||||||
Income taxes receivable | 1,448 | 345 | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 3,626 | 4,322 | ||||||
Total current assets | 303,019 | 299,572 | ||||||
Property and equipment, net | 24,483 | 20,831 | ||||||
Goodwill | 48,060 | 56,867 | ||||||
Other intangibles, net | 2,220 | 3,291 | ||||||
Other assets | 385 | 318 | ||||||
Total Assets | $ | 378,167 | $ | 380,879 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
Current maturities of capital lease obligation to affiliate | $ | 699 | $ | 527 | ||||
Accounts payable | 101,783 | 111,140 | ||||||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | 19,993 | 20,557 | ||||||
Accrued payroll | 6,337 | 10,816 | ||||||
Total current liabilities | 128,812 | 143,040 | ||||||
Capital lease obligation to affiliate, less current maturities | 3,610 | 4,309 | ||||||
Deferred income taxes | 6,183 | 5,436 | ||||||
Other liabilities | 4,238 | 3,784 | ||||||
Total Liabilities | $ | 142,843 | $ | 156,569 | ||||
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 13) | ||||||||
Stockholders’ Equity: | ||||||||
Preferred Stock, $.01 par value, 10,000 shares authorized, none issued | — | — | ||||||
Common Stock, $.01 par value, 100,000 shares authorized, 27,326 and 27,252 issued, 26,834 and 26,925 outstanding at December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007, respectively | 273 | 273 | ||||||
Additional paid-in capital | 95,997 | 94,132 | ||||||
Retained earnings | 142,336 | 131,970 | ||||||
Treasury stock at cost | (3,282 | ) | (2,065 | ) | ||||
Total Stockholders’ Equity | 235,324 | 224,310 | ||||||
Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $ | 378,167 | $ | 380,879 | ||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-3
Table of Contents
PC CONNECTION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(amounts in thousands, except per share data)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,753,680 | $ | 1,785,379 | $ | 1,635,651 | ||||||
Cost of sales | 1,538,836 | 1,566,409 | 1,435,400 | |||||||||
Gross profit | 214,844 | 218,970 | 200,251 | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 186,728 | 181,640 | 173,927 | |||||||||
Goodwill impairment | 8,807 | — | — | |||||||||
Special charges | 1,431 | 541 | 2,391 | |||||||||
Income from operations | 17,878 | 36,789 | 23,933 | |||||||||
Interest expense | (681 | ) | (932 | ) | (1,828 | ) | ||||||
Other, net | 811 | 764 | 121 | |||||||||
Income before taxes | 18,008 | 36,621 | 22,226 | |||||||||
Income tax provision | (7,642 | ) | (13,626 | ) | (8,450 | ) | ||||||
Net income | $ | 10,366 | $ | 22,995 | $ | 13,776 | ||||||
Earnings per common share: | ||||||||||||
Basic | $ | .39 | $ | .86 | $ | .54 | ||||||
Diluted | $ | .39 | $ | .85 | $ | .54 | ||||||
Shares used in computation of earnings per common share: | ||||||||||||
Basic | 26,828 | 26,785 | 25,516 | |||||||||
Diluted | 26,896 | 27,024 | 25,731 | |||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Table of Contents
PC CONNECTION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(amounts in thousands)
| Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Retained Earnings | Treasury Shares | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
Balance—January 1, 2006 | 25,622 | $ | 256 | $ | 77,884 | $ | 95,545 | (362 | ) | $ | (2,286 | ) | $ | 171,399 | ||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under stock incentive plans, including income tax benefits | 1,210 | 12 | 11,066 | — | — | — | 11,078 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 30 | 1 | 232 | — | — | — | 233 | |||||||||||||||||
Nonvested stock awards | — | — | (63 | ) | — | 10 | 63 | — | ||||||||||||||||
Stock compensation expense | — | — | 418 | — | — | — | 418 | |||||||||||||||||
Net income and comprehensive income | — | — | — | 13,776 | — | — | 13,776 | |||||||||||||||||
Balance—December 31, 2006 | 26,862 | 269 | 89,537 | 109,321 | (352 | ) | (2,223 | ) | 196,904 | |||||||||||||||
Cumulative effect of change in accounting principle | — | — | — | (346 | ) | — | — | (346 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under stock incentive plans, including income tax benefits | 364 | 4 | 3,880 | — | — | — | 3,884 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 26 | — | 294 | — | — | — | 294 | |||||||||||||||||
Nonvested stock awards | — | — | (158 | ) | — | 25 | 158 | — | ||||||||||||||||
Stock compensation expense | — | — | 579 | — | — | — | 579 | |||||||||||||||||
Net income and comprehensive income | — | — | — | 22,995 | — | — | 22,995 | |||||||||||||||||
Balance—December 31, 2007 | 27,252 | 273 | 94,132 | 131,970 | (327 | ) | (2,065 | ) | 224,310 | |||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under stock incentive plans, including income tax deficiencies | 33 | — | 105 | — | — | — | 105 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 41 | — | 257 | — | — | — | 257 | |||||||||||||||||
Nonvested stock awards | — | — | (320 | ) | — | 46 | 320 | — | ||||||||||||||||
Stock compensation expense | — | — | 1,823 | — | — | — | 1,823 | |||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock for Treasury | — | — | — | — | (211 | ) | (1,537 | ) | (1,537 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Net income and comprehensive income | — | — | — | 10,366 | — | — | 10,366 | |||||||||||||||||
Balance—December 31, 2008 | 27,326 | $ | 273 | $ | 95,997 | $ | 142,336 | (492 | ) | $ | (3,282 | ) | $ | 235,324 | ||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Table of Contents
PC CONNECTION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(amounts in thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 10,366 | $ | 22,995 | $ | 13,776 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Goodwill impairment | 8,807 | — | — | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 6,965 | 6,781 | 7,049 | |||||||||
Provision for doubtful accounts | 2,277 | 1,587 | 2,885 | |||||||||
Stock compensation expense | 1,823 | 579 | 418 | |||||||||
Loss on disposal of fixed assets | 614 | 68 | 86 | |||||||||
Deferred income taxes | (639 | ) | 670 | 2,179 | ||||||||
Income tax (deficiency) benefit from equity award transactions | (98 | ) | 974 | 1,338 | ||||||||
Excess tax benefit from exercise of stock options | (3 | ) | (447 | ) | (240 | ) | ||||||
Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
Accounts receivable | 14,054 | (33,581 | ) | (10,582 | ) | |||||||
Inventories | 15,277 | (6,683 | ) | 5,967 | ||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (407 | ) | (158 | ) | 1,452 | |||||||
Other non-current assets | (67 | ) | 37 | 4 | ||||||||
Accounts payable | (9,191 | ) | 163 | (3,436 | ) | |||||||
Accrued expenses and other liabilities | (4,623 | ) | 7,448 | 5,466 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 45,155 | 433 | 26,362 | |||||||||
Cash Flows from Investing Activities: | ||||||||||||
Purchases of property and equipment | (10,370 | ) | (7,066 | ) | (7,981 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of property and equipment | 44 | — | 21 | |||||||||
Net cash used for investing activities | (10,326 | ) | (7,066 | ) | (7,960 | ) | ||||||
Cash Flows from Financing Activities: | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from short-term borrowings | 37,343 | 53,280 | 402,039 | |||||||||
Repayment of short-term borrowings | (37,343 | ) | (53,280 | ) | (422,014 | ) | ||||||
Purchase of treasury shares | (1,537 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Repayment of capital lease obligations | (527 | ) | (859 | ) | (828 | ) | ||||||
Exercise of stock options | 203 | 2,910 | 9,740 | |||||||||
Issuance of stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 257 | 294 | 233 | |||||||||
Net share settlement obligation | 34 | — | — | |||||||||
Excess tax benefit from exercise of stock options | 3 | 447 | 240 | |||||||||
Net cash (used for) provided by financing activities | (1,567 | ) | 2,792 | (10,590 | ) | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 33,262 | (3,841 | ) | 7,812 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | 13,741 | 17,582 | 9,770 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | $ | 47,003 | $ | 13,741 | $ | 17,582 | ||||||
Non-cash Financing Activity: | ||||||||||||
Issuance of nonvested stock from treasury | $ | 320 | $ | 158 | $ | 63 | ||||||
Supplemental Cash Flow Information: | ||||||||||||
Income taxes paid | $ | 10,083 | $ | 9,688 | $ | 5,160 | ||||||
Interest paid | 581 | 779 | 1,713 | |||||||||
Purchase accounting adjustment | — | — | 47 | |||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Table of Contents
PC CONNECTION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(amounts in thousands, except per share data)
| 1. | SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
PC Connection, Inc. is a leading direct marketer of a wide range of IT products and services—including computer systems, software and peripheral equipment, networking communications, warranty, configuration and other services, and other products and accessories that we purchase from manufacturers, distributors, and other suppliers. We operate through three primary business segments: (1) consumers and small- to medium-sized businesses, or SMB, through our PC Connection Sales subsidiaries, (2) large enterprise customers, or Large Account, through our MoreDirect subsidiary, and (3) federal, state, and local government and educational institutions, or Public Sector, through our GovConnection subsidiary.
The following is a summary of our significant accounting policies.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of PC Connection, Inc. and its subsidiaries. Intercompany transactions and balances are eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates in the Preparation of Financial Statements
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions. These estimates and assumptions affect the amounts reported in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue on product sales is recognized at the point in time when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, delivery has occurred, and there is a reasonable assurance of collection of the sales proceeds. We generally obtain oral or written purchase authorizations from our customers for a specified amount of product at a specified price. Because we either (i) have a general practice of covering customer losses while products are in-transit despite title transferring at the point of shipment or (ii) have FOB—destination specifically set out in our arrangements with federal agencies and certain commercial customers, delivery is deemed to have occurred at the point in time when the product is received by the customer.
We provide our customers with a limited thirty-day right of return generally limited to defective merchandise. Revenue is recognized at delivery and a reserve for sales returns is recorded. We have demonstrated the ability to make reasonable and reliable estimates of product returns in accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 48, “Revenue Recognition When Right of Return Exists,” based on significant historical experience. We record our sales reserves as offsets to accounts receivable and, for customers who have already paid, as credits to accrued expenses. At December 31, 2008, we recorded sales reserves of $2,128 and $404 as components of accounts receivable and accrued expenses, respectively. At December 31, 2007, we recorded sales reserves of $2,143 and $309 as components of accounts receivable and accrued expenses, respectively.
All amounts billed to a customer in a sale transaction related to shipping and handling, if any, represent revenues earned for the goods provided, and these amounts have been classified as “net sales.” Costs related to such shipping and handling billings are classified as “cost of sales.” Sales are reported net of sales, use, or other transaction taxes that are collected from customers and remitted to taxing authorities.
F-7
Table of Contents
Revenue for third-party service contracts is recorded on a net sales recognition basis because we do not assume the risks and rewards of ownership in these transactions. For such contracts, we evaluate whether the sales of such services should be recorded as gross sales or net sales as required under the guidelines described in Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 104, “Revenue Recognition” and Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue No. 99-19, “Reporting Revenue Gross as a Principal versus Net as an Agent.” Under gross sales recognition, we are the primary obligor, and the entire selling process is recorded in sales with our cost to the third-party service provider recorded as a cost of sales. Under net sales recognition, we are not the primary obligor, and the cost to the third-party service provider is recorded as a reduction to sales, with no cost of goods sold, thus leaving the gross profit as the reported net sale for the transaction.
Similarly, we recognize revenue from agency sales transactions on a net sales basis. In agency sales transactions, we facilitate product sales by equipment and software manufacturers directly to our customers and receive agency, or referral, fees for such transactions. We do not take title to the products or assume any maintenance or return obligations in these transactions; title is passed directly from the supplier to our customer.
Net amounts included in revenue for such third-party service contracts and agency sales transactions were $13,250, $14,332, and $10,776 for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.
Although service revenues represent a small percentage of our consolidated revenues, we offer a growing range of services, including installation, configuration, repair, and other services performed by our personnel and third-party providers. If a service is performed in conjunction with the delivery of hardware, software, or another service, then we determine whether an item included in such multiple-element arrangements constitutes a separate deliverable, in accordance with EITF 00-21, “Accounting for Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables.”
In these arrangements, an element is separated as a deliverable only when the following three conditions are met:
| • | The delivered item(s) has value to the customer on a standalone basis; |
| • | There is objective and reliable evidence of the fair value of the undelivered item; and |
| • | If the arrangement includes a general right of return relative to the delivered item, delivery or performance of the undelivered item(s) is considered probable and substantially under our control. |
Cost of Sales and Certain Other Costs
Cost of sales includes the invoice cost of the product, direct costs of packaging, inbound and outbound freight, and provisions for inventory obsolescence, adjusted for discounts, rebates, and other vendor allowances, including those pursuant to EITF Issue No. 02-16, “Accounting by a Customer (Including a Reseller) for Certain Consideration Received from a Vendor.” Direct operating expenses relating to our purchasing function and receiving, inspection, internal transfer, warehousing, packing and shipping, and other operating expenses of our distribution center are included in selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expenses. Total direct operating expenses relating to these functions included in SG&A expenses for the three years ended December 31, 2008 are shown below:
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||
| $ | 12,125 | $ | 11,529 | $ | 10,878 | ||
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider all highly liquid short-term investments with original maturities of 90 days or less to be cash equivalents. The carrying value of our cash equivalents approximates fair value. The majority of payments due
F-8
Table of Contents
from credit card processors and banks for third-party credit card and debit card transactions process within one to five business days. All credit card and debit card transactions that process in less than seven days are classified as cash and cash equivalents. Amounts due from banks for these transactions classified as cash totaled $2,684 and $2,626 at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Accounts Receivable
We perform ongoing credit evaluations of our customers and adjust credit limits based on payment history and customer creditworthiness. We maintain an allowance for estimated doubtful accounts based on our historical experience and the customer credit issues identified. We monitor collections regularly and adjust the allowance for doubtful accounts as necessary to recognize any changes in credit exposure.
Inventories—Merchandise
Inventories (all finished goods) consisting of software packages, computer systems, and peripheral equipment, are stated at cost (determined under a weighted-average cost method which approximates the first-in, first-out method) or market, whichever is lower. Inventory quantities on hand are reviewed regularly, and allowances are maintained for obsolete, slow moving, and nonsalable inventory.
Vendor Allowances
We receive allowances from merchandise vendors for price protections, discounts, product rebates, and other programs. These allowances are treated as a reduction of the vendor’s prices and are recorded as adjustments to cost of sales or inventory, as applicable. Allowances for product rebates that require certain volumes of product sales or purchases are recorded only after the related milestones are met.
Advertising Costs and Allowances
Costs of producing and distributing catalogs are charged to expense in the period in which the catalogs are first issued. Other advertising costs are expensed as incurred.
Vendors have the ability to place advertisements in our catalogs or fund other advertising activities for which we receive advertising allowances. These vendor allowances, to the extent that they represent specific reimbursements of the underlying incremental and identifiable costs, are offset against SG&A expenses. Advertising allowances that cannot be associated with a specific program funded by an individual vendor or that exceed the fair value of advertising expense associated with that program are classified as offsets to cost of sales or inventory in accordance with EITF 02-16. Our vendor partners generally consolidate their funding of advertising and other marketing programs, and as a result, we classify substantially all vendor consideration as a reduction of cost of inventory purchases rather than a reduction of advertising expense. Advertising expense, which is classified as a component of SG&A expenses, totaled $19,470, $19,853, and $13,252, for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization is provided for financial reporting purposes over the estimated useful lives of the assets ranging from three to seven years. Computer software, including licenses and internally developed software, is capitalized and amortized over lives ranging from three to five years, except that certain capitalized internally developed software is expensed for income tax reporting purposes. Depreciation is provided using the straight-line method for property. Leasehold improvements and facilities under capital leases are amortized over the terms of the related leases or their useful lives, whichever is shorter, whereas for income tax reporting purposes, they are amortized over the applicable tax lives. When events or circumstances indicate a potential impairment,
F-9
Table of Contents
we evaluate the carrying value of property and equipment based upon current and anticipated undiscounted cash flows, and recognize an impairment when it is probable that such estimated future cash flows will be less than the asset carrying value. We did not recognize any impairment of fixed assets in 2008, 2007, or 2006.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
Our intangible assets consist of (1) goodwill, which is not amortized; (2) indefinite lived intangibles, which consist of certain trademarks that are not subject to amortization; and (3) amortizing intangibles, which consist of customer lists and a licensing agreement, which are being amortized over their useful lives.
Note 2 describes SFAS No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” (“SFAS 142”), and the annual impairment methodology that we employ on January 1 of each year in calculating the recoverability of goodwill. This same impairment test will be performed at other times during the course of a year should an event occur which suggests that the recoverability of goodwill should be challenged. Non-amortizing intangibles are also subject to annual impairment tests and interim tests if conditions require. We performed the first step of the impairment test required under SFAS 142 as of December 31, 2008, and found a potential impairment of the goodwill balances held by our SMB and Public Sector segments. As a result, we completed the prescribed second step to measure the amount of the impairment and determined that the carrying amounts of each reporting units’ goodwill to be fully impaired. Accordingly, we recognized an impairment loss equal to the entire goodwill balance held by each of the two segments in the fourth quarter of 2008.
Amortizing intangibles are evaluated for impairment using the methodology set forth in SFAS No. 144, “Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-lived Assets,” (“SFAS 144”). Recoverability of these assets is assessed only when events have occurred that may give rise to impairment. When a potential impairment has been identified, forecasted undiscounted net cash flows of the operations to which the asset relates are compared to the current carrying value of the long-lived assets present in that operation. If such cash flows are less than such carrying amounts, long-lived assets including such intangibles, are written down to their respective fair values.
Income Taxes
We recognize deferred income tax assets and liabilities for the differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities that will result in taxable or deductible amounts in the future, based on enacted tax laws and rates anticipated to be applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to affect taxable income. On January 1, 2007, we adopted Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Interpretation No. 48, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109” (“FIN 48”). We account for uncertain tax positions in accordance with FIN 48. Accordingly, we report a liability for unrecognized tax benefits resulting from uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. We recognize interest and penalties, if any, related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
Concentrations
Concentrations of credit risk with respect to trade account receivables are limited due to the large number of customers comprising our customer base. Ongoing credit evaluations of customers’ financial condition are performed by management on a regular basis.
During the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, product purchases from Ingram Micro, Inc., our largest vendor, accounted for approximately 24%, 24%, and 27%, respectively, of our total product purchases. Purchases from Tech Data Corporation comprised 17% of our total product purchases in each of 2008, 2007, and 2006. Purchases from Hewlett-Packard Company constituted 12%, 14%, and 15% of our total product purchases in 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively. No other vendor supplied more than 10% of our total product purchases 2008, 2007, and 2006.
F-10
Table of Contents
No single customer, other than the federal government, accounted for more than 3% of total net sales in 2008, 2007, and 2006. Net sales to the federal government in 2008, 2007, and 2006 were $134,836, $98,543, and $72,550, or 7.7%, 5.5%, and 4.4% of total net sales, respectively.
Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per common share is computed using the weighted average number of shares outstanding. Diluted earnings per share is computed using the weighted average number of shares outstanding adjusted for the incremental shares attributed to options outstanding to purchase common stock and nonvested stock, if dilutive.
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted earnings per share:
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Numerator: | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 10,366 | $ | 22,995 | $ | 13,776 | |||
Denominator: | |||||||||
Denominator for basic earnings per share | 26,828 | 26,785 | 25,516 | ||||||
Dilutive effect of employee equity awards | 68 | 239 | 215 | ||||||
Denominator for diluted earnings per share | 26,896 | 27,024 | 25,731 | ||||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||
Basic | $ | .39 | $ | .86 | $ | .54 | |||
Diluted | $ | .39 | $ | .85 | $ | .54 | |||
For the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, the following weighted average unexercised stock options and other common stock equivalents were excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share because the effect would have been anti-dilutive:
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||
Anti-dilutive stock options | 788 | 272 | 1,361 |
Stock-Based Compensation
Effective January 1, 2006, we adopted SFAS No. 123 (revised 2004), “Share-Based Payment,” (“SFAS 123(R)”) using the modified prospective application method. SFAS 123(R) requires a company to measure the grant date fair value of equity awards given to employees and recognize that cost, adjusted for forfeitures, over the period that such services are performed in its consolidated financial statements (described in Note 10). SFAS 123(R) requires forfeitures to be estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures experienced differ from these estimates.
Share Repurchase Authorization
On March 28, 2001, our Board of Directors authorized the spending of up to $15,000 to repurchase our common stock. Share purchases will be made in the open market from time to time depending on market conditions. Our current bank line of credit, however, limits repurchases made after June 2005 to $10,000 without bank approval of higher amounts.
During the year ended December 31, 2008, we repurchased an aggregate of 196 shares for $1,449. As of December 31, 2008, we had repurchased an aggregate of 558 shares for $3,734. The maximum approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the program without further bank approval is $8,551. We have issued nonvested shares from treasury stock and have reflected upon vesting the net remaining balance of
F-11
Table of Contents
treasury stock on the consolidated balance sheet. In addition, we withheld 15 shares, having an aggregate fair value of $88, upon the vesting of nonvested stock to satisfy related employee tax obligations during the year ended December 31, 2008. Such transactions were recognized as a repurchase of common stock and returned to treasury but do not apply against authorized repurchase limits under our bank line agreement and Board of Directors’ authorization.
Recently Issued Financial Accounting Standards
In September 2006, the FASB issued SFAS No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements” (“SFAS 157”). This Statement defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value, and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. SFAS 157 does not require any new fair value measurements but rather applies under other accounting pronouncements that require or permit fair value measurements. SFAS 157 is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007. In February 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. 157-2 (“FSP 157-2”). FSP 157-2 delays the effective date of SFAS 157 for all nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a recurring basis (at least annually), until fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. These nonfinancial items include assets and liabilities such as reporting units measured at a fair value in a goodwill impairment test and nonfinancial assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination. As such, we partially adopted SFAS 157 on January 1, 2008, and it did not have a significant impact on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
In October 2008, the FASB issued FSP 157-3 “Determining the Fair Value of a Financial Asset When the Market for That Asset Is Not Active” (“FSP 157-3”). FSP 157-3 clarifies the application of SFAS 157 in a market that is not active, and addresses application issues such as the use of internal assumptions when relevant observable data does not exist, the use of observable market information when the market is not active, and the use of market quotes when assessing the relevance of observable and unobservable data. FSP 157-3 is effective for all periods presented in accordance with SFAS 157. The adoption of FSP 157-3 did not have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements or the fair values of our financial assets and liabilities.
In February 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” (“SFAS 159”), which permits companies to voluntarily choose to measure specified financial instruments and other items at fair value on a contract-by-contract basis. If the fair value option is elected, subsequent changes in fair value will be required to be reported in earnings each reporting period. This Statement is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007 and interim periods within those fiscal years. We have elected not to measure any eligible items at fair value. Accordingly, the adoption of SFAS 159 did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 141 (revised 2007), “Business Combinations” (“SFAS 141(R)”). Under SFAS 141(R), an entity is required to recognize the assets acquired, liabilities assumed, contractual contingencies, and contingent consideration at their fair value on the acquisition date. It further requires that acquisition-related costs be recognized separately from the acquisition and expensed as incurred; that restructuring costs generally be expensed in periods subsequent to the acquisition date; and that changes in accounting for deferred tax asset valuation allowances and acquired income tax uncertainties after the measurement period be recognized as a component of provision for taxes. This Statement is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and is to be applied prospectively. We are currently assessing the potential impact SFAS 141(R) will have on our financial statements.
| 2. | GOODWILL AND OTHER INTANGIBLE ASSETS |
We account for goodwill and intangible assets in accordance with SFAS 142. Under SFAS 142, goodwill and certain intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized but are subject to an annual impairment test, and more frequently, if events or circumstances occur that would indicate a potential decline in our fair value. We have identified four reporting units, consisting of our three operating segments and the Headquarters/Other
F-12
Table of Contents
group, which provides services in areas such as finance, human resources, information technology, and executive oversight functions (See Note 15). We perform the assessment annually as of January 1, and on an interim basis if potential impairment indicators arise, and determine the fair value of the reporting units using established income and market valuation approaches.
We completed our annual goodwill and indefinite lived trademark impairment tests on the first day of 2006, 2007, and 2008 and determined that the fair value of each reporting unit exceeded its carrying value and as a result, no impairments resulted. During the third quarter of 2008, we experienced declines in both net sales and the market value of our common stock. We deemed these declines to be a triggering event under SFAS 142, and accordingly, performed an interim impairment test. As a result of this interim test, we determined that we passed step one of the goodwill impairment test prescribed by SFAS 142 for all reporting units. During the fourth quarter, we continued to experience declines in our net sales and stock market value. We deemed these declines to be a triggering event under SFAS 142 as of December 31, 2008. We performed the first step of the impairment test required under SFAS 142, and found that the fair values of the SMB and Public Sector reporting units were less than the respective carrying values and thus a potential impairment of goodwill existed for both reporting units. Accordingly, we proceeded to the second step of the impairment test under SFAS 142 to measure the amount, if any, of the impairment loss. The second step of the impairment test compares the implied fair value of a reporting unit’s goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. If the reporting unit’s carrying amount exceeds the implied fair value, a loss is recognized to the extent of such excess. Under the second step, we found a zero implied fair value of goodwill for the SMB and Public Sector reporting units, and as a result, we recognized an impairment loss of $8,807, $5,383 net of taxes, in our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2008. The fair value of the Large Account reporting unit exceeded its carrying value, and accordingly there was no need to perform the second step of the impairment test for the Large Account unit.
We determined the fair values of our reporting units by preparing a discounted cash flow analysis using updated forward looking projections of each unit’s expected future operating results. The significant assumptions used in our discounted cash flow analysis include: net income, the discount rate used to present value future cash flows, working capital requirements, and terminal growth rates. Net income assumptions include sales growth, gross margin, and SG&A growth assumptions which are generally based on historical trends. The discount rate used is a “market participant” weighted average cost of capital (“WAAC”) and was 13.5% at December 31, 2008. Working capital requirements were estimated at 7.5% of revenues. We have performed a sensitivity analysis on our significant assumptions and have determined that a reasonable, negative change in its assumptions, as follows, would not impact our conclusion: reduce net income by 10%, increase the WAAC by 100 basis points, or reduce terminal sales growth rate by 20%.
A rollforward of the carrying amount of goodwill for the year ended December 31, 2008 by operating segment is as follows:
| SMB | Large Account | Public Sector | Total | ||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2007 | $ | 1,173 | $ | 48,060 | $ | 7,634 | $ | 56,867 | |||||||
Impairment loss | (1,173 | ) | — | (7,634 | ) | (8,807 | ) | ||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2008 | $ | — | $ | 48,060 | $ | — | $ | 48,060 | |||||||
Intangible assets not subject to amortization consisted of trademarks of $1,190 at both December 31, 2008 and 2007. Intangible assets subject to amortization at December 31, 2008 consisted of customer lists of $941 and a licensing agreement of $89 (net of accumulated amortization of $4,278 and $386, respectively). Intangible assets subject to amortization at December 31, 2007 consisted of customer lists of $1,893 and a licensing agreement of $208 (net of accumulated amortization of $3,326 and $267, respectively). Amortization expense related to intangible assets is recorded on a straight-line basis. For the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, we recorded amortization expense of $1,071, $1,071, and $1,064, respectively.
F-13
Table of Contents
The estimated amortization expense relating to customer lists and licensing agreements for each of the three succeeding years and thereafter is as follows:
For the Year Ending December 31, | |||
2009 | $ | 942 | |
2010 | 88 | ||
2011 and thereafter | — | ||
In accordance with SFAS 144, we also tested for potential impairment of our long-lived assets. We determined that the undiscounted cash flows expected from the use of these assets exceeded the carrying values of such assets, and as a result, concluded that no impairment was indicated. We also assessed the fair values of our other significant assets, including property, plant, and equipment, in accordance with SFAS 144, and determined that the undiscounted cash flows expected from the use of these assets exceeded the carrying amounts of such assets. As a result, we concluded that no impairment was indicated for our long-lived assets.
| 3. | FAIR VALUE |
SFAS 157 establishes a fair value hierarchy that requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. Observable inputs are obtained from independent sources and can be validated by a third party, whereas unobservable inputs reflect assumptions regarding what a third party would use in pricing an asset or liability. A financial instrument’s categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. SFAS 157 establishes three levels of inputs that may be used to measure fair value:
Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2—Include other inputs that are directly or indirectly observable in the marketplace.
Level 3—Unobservable inputs which are supported by little or no market activity.
In accordance with SFAS 157, we measure our cash equivalents at fair value and are classified within Level 1 or Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy. The classification has been determined based on the manner in which we value our cash equivalents, primarily using quoted market prices or alternative pricing sources. Assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis consisted of the following types of instruments and were reported as cash equivalents as of December 31, 2008:
Fair Value Measurements at Reporting Date Using
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Instruments (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | 12/31/08 Total Balance | |||||||||
Assets | ||||||||||||
Cash Equivalents: | ||||||||||||
Bank time deposits | $ | — | $ | 10,094 | $ | — | $ | 10,094 | ||||
Money market fund deposits | 36,909 | — | — | 36,909 | ||||||||
Total assets measured at fair value | 36,909 | $ | 10,094 | — | $ | 47,003 | ||||||
F-14
Table of Contents
| 4. | ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE |
Accounts receivable consisted of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
Trade | $ | 178,998 | $ | 194,116 | ||
Advertising consideration | 4,196 | 4,272 | ||||
Vendor returns, rebates, and other | 7,711 | 9,699 | ||||
Due from employees | 206 | 216 | ||||
Due from affiliates | 2 | 1 | ||||
Total | 191,113 | 208,304 | ||||
Less allowances for: | ||||||
Sales returns | 2,128 | 2,143 | ||||
Doubtful accounts | 3,100 | 3,945 | ||||
Accounts receivable, net | $ | 185,885 | $ | 202,216 | ||
| 5. | PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT |
Property and equipment consisted of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
Facilities and equipment under capital lease | $ | 7,215 | $ | 8,447 | ||
Leasehold improvements | 7,436 | 6,881 | ||||
Furniture and equipment | 26,397 | 26,444 | ||||
Computer software, including licenses and internally-developed software | 42,324 | 36,371 | ||||
Automobiles | 215 | 215 | ||||
Total | 83,587 | 78,358 | ||||
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | 59,104 | 57,527 | ||||
Property and equipment, net | $ | 24,483 | $ | 20,831 | ||
We recorded depreciation and amortization expense, including capital lease amortization, of $5,894, $5,710, and $5,985 for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.
| 6. | SPECIAL CHARGES |
In 2008 and 2007, we recorded charges of $1,431 and $541, respectively, related to management restructuring costs, classified as workforce reductions in the table below.
In 2006, we recorded a charge of $1,500 related to our settlement with the Department of Justice (“DOJ”) on our 2003 General Services Administration (“GSA”) audit matter. We also recorded in 2006 a charge of $520 related to management restructuring costs and a charge of $371 related to the temporary retention of certain Amherst employees and facilities subsequent to our Amherst Transaction.
A rollforward of liabilities related to special charges for the three years ended December 31, 2008 is shown below. The beginning balance as of January 1, 2006 for the GSA matter was recorded in prior periods as a component of cost of sales. We concluded a settlement of this matter with the DOJ in the fourth quarter of 2006.
| Workforce Reductions | Amherst Transaction | GSA Matter | Total | |||||||||
Balance, January 1, 2006 | 866 | 132 | 1,050 | 2,048 | ||||||||
Charges | 520 | 371 | 1,500 | 2,391 | ||||||||
Cash Payments | (1,201 | ) | (503 | ) | (2,550 | ) | (4,254 | ) | ||||
F-15
Table of Contents
| Workforce Reductions | Amherst Transaction | GSA Matter | Total | |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2006 | 185 | — | — | 185 | ||||||||||
Charges | 541 | — | — | 541 | ||||||||||
Cash Payments | $ | (185 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (185 | ) | ||||
Balance, December 31, 2007 | 541 | — | — | 541 | ||||||||||
Charges | 1,431 | — | — | 1,431 | ||||||||||
Cash Payments | (708 | ) | — | — | (708 | ) | ||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2008 | $ | 1,264 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,264 | ||||||
Liabilities at December 31, 2008 consist of $955 of accrued payroll and $309 of non-current other liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet. Liabilities at December 31, 2007 are included in accrued payroll on the consolidated balance sheet.
| 7. | BANK BORROWINGS |
We have a $50,000 credit facility collateralized by substantially all of our business assets. This facility can be increased, at our option, to $80,000 for approved acquisitions or other uses authorized by the bank at substantially the same terms. Amounts outstanding under this facility bear interest at the prime rate (3.25% at December 31, 2008). The facility also gives us the option of obtaining Eurodollar Rate Loans in multiples of $1,000 for various short-term durations. The credit facility includes various customary financial ratios and operating covenants, including minimum net worth and maximum funded debt ratio requirements, and restrictions on the payment of dividends to shareholders, repurchase of our common stock, and default acceleration provisions, none of which we believe significantly restricts our operations. Funded debt ratio is the ratio of average outstanding advances under the credit facility to EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest Expense, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization). The maximum allowable funded debt ratio under the agreement is 2.0 to 1.0. We did not have any borrowings outstanding under the credit facility in the fourth quarter of 2008, and accordingly such financial ratio did not limit potential borrowings at December 31, 2008. Future decreases in our consolidated EBITDA, however, could limit our potential borrowings under the credit facility.
No borrowings were outstanding under this credit facility at December 31, 2008 and 2007, and accordingly the entire $50,000 facility was available for borrowing at both dates. The credit facility matures on October 15, 2012, at which time amounts outstanding become due.
Certain information with respect to short-term borrowings was as follows:
Year ended December 31, | Weighted Average Interest Rate | Maximum Amount Outstanding | Average Amount Outstanding | ||||||
2008 | 6.9 | % | $ | 9,687 | $ | 167 | |||
2007 | 7.4 | 18,651 | 497 | ||||||
2006 | 6.3 | 41,648 | 13,550 | ||||||
| 8. | TRADE CREDIT AGREEMENTS |
At December 31, 2008 and 2007, we had security agreements with two financial institutions to facilitate the purchase of inventory from various suppliers under certain terms and conditions. The agreements allow a collateralized first position in certain branded products inventory financed by the financial institutions up to an aggregated amount of $45,000. The cost of such financing under these agreements is borne by the suppliers by discounting their invoices to the financial institutions as an incentive for us to purchase their products. We do not pay any interest or discount fees on such inventory financing. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, accounts payable included $13,499 and $12,197, respectively, owed to these financial institutions.
F-16
Table of Contents
| 9. | CAPITAL LEASE |
In November 1997 we entered into a fifteen-year lease for our corporate headquarters with an affiliated company related to us through common ownership. We occupied the facility upon completion of construction in late November 1998, and the lease payments commenced in December 1998.
Annual lease payments under the terms of the lease, as amended, are approximately $911 for the first five years of the lease, increasing to $1,025 for years six through ten and $1,139 for years eleven through fifteen. The lease requires us to pay our proportionate share of real estate taxes and common area maintenance charges either directly to providers or as additional rent and also to pay insurance premiums for the leased property. We have the option to renew the lease for two additional terms of five years each. The lease has been recorded as a capital lease.
The net book value of capital lease assets was $2,365 and $2,846 as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Future aggregate minimum annual lease payments under the capital lease at December 31, 2008 are as follows:
Year Ending December 31 | Payments | ||
2009 | $ | 1,139 | |
2010 | 1,139 | ||
2011 | 1,139 | ||
2012 | 1,139 | ||
2013 | 1,045 | ||
2014 and thereafter | — | ||
Total minimum payments (excluding taxes, maintenance, and insurance) | 5,601 | ||
Less amount representing interest | 1,292 | ||
Present value of minimum lease payments | 4,309 | ||
Less current maturities (excluding interest) | 699 | ||
Long-term portion | $ | 3,610 | |
| 10. | STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY AND SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION |
Preferred Stock
Our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation (the “Restated Certificate”) authorized the issuance of up to 10,000 shares of preferred stock, $.01 par value per share (the “Preferred Stock”). Under the terms of the Restated Certificate, the Board is authorized, subject to any limitations prescribed by law, without stockholder approval, to issue by a unanimous vote such shares of Preferred Stock in one or more series. Each such series of Preferred Stock shall have such rights, preferences, privileges, and restrictions, including voting rights, dividend rights, redemption privileges, and liquidation preferences, as shall be determined by the Board. There were no preferred shares outstanding at 2008 and 2007.
Equity Compensation Plan Descriptions
In November 1997 the Board adopted and the stockholders approved the 1997 Stock Incentive Plan (the “1997 Plan”), which became effective on the closing of our initial public offering in 1998. Under the terms of the 1997 Plan, we were authorized, for a ten-year period, to grant incentive stock options, non-statutory stock options, stock appreciation rights, performance shares, and awards of nonvested and vested stock. The 1997 Plan expired in November 2007. Under such plan, options to purchase 798 shares remain outstanding as of December 31, 2008.
F-17
Table of Contents
In April 2007 the Board adopted the 2007 Stock Incentive Plan (the “2007 Plan”), which the stockholders approved in June 2007. The purpose of the 2007 Plan is to advance the interests of our stockholders by enhancing our ability to attract, retain, and motivate persons who are expected to make important contributions to our success and to better align the interests of such persons with those of our stockholders. Under the terms of the 2007 Plan, we are authorized, for a ten-year period, to grant options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, and other stock-based awards to employees, officers, directors, consultants, and advisors. A total of 500 shares were authorized for issuance by stockholders. In 2008, grants made under the 2007 Plan aggregated 412 shares, leaving 88 shares as eligible for issuance as of December 31, 2008.
1997 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In November 1997 the Board adopted and the stockholders approved the 1997 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “Purchase Plan”), which became effective on February 1, 1999. The Purchase Plan authorizes the issuance of common stock to participating employees. Under the Purchase Plan, as amended, our employees are eligible to purchase company stock at 95% of the purchase price as of the last business day of the six-month period. Such discount level allows us to avoid recognition of stock compensation expense associated with the purchase of common stock under the Purchase Plan. An aggregate of 838 shares of common stock has been reserved for issuance under the Purchase Plan, of which 741 shares have been purchased.
Accounting for Share-Based Compensation
We account for share-based compensation in accordance with SFAS 123(R), which requires a company to measure the grant date fair value of equity awards given to employees and recognize that cost, adjusted for forfeitures, over the period that services are performed. This Standard is a revision of SFAS 123 and supersedes APB 25 and its related interpretations. We adopted the provisions of SFAS 123(R) using the modified prospective application method and used the criteria in SFAS 123(R) to establish the beginning balance of the additional paid-in capital pool related to the tax effects of employee share-based compensation.
In 2006 and 2007, we recorded share-based compensation costs as a component of SG&A expenses. In 2008, we recorded $1,484 of share-based compensation as a component of SG&A expenses and $339 as special charges related to management restructurings. We did not grant any stock options in 2006. In 2007 and 2008, we granted stock options that vest over varying periods of up to four years and have contractual lives of ten years.
We employed the Black-Scholes option valuation model to assess the grant date fair value of each option grant and have elected to value each grant as a single award. The application of this model requires certain key input assumptions, including expected volatility, option term, and risk-free interest rates. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of our common stock. The expected term of options is estimated using the historical exercise behavior of employees and directors. The risk-free interest rate for periods within the contractual life of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve corresponding to the stock option’s average life. The key weighted-average assumptions we used to apply this pricing model for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006 were as follows:
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||
Risk-free interest rate | 3.04% | 4.55% | — | |||
Volatility | 57.89% | 62.60% | — | |||
Expected life of option grants | 4.8 years | 5.2 years | — | |||
Dividend yield | 0% | 0% | — |
F-18
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes the components of share-based compensation recorded as expense for the three years ended December 31, 2008:
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
Stock options | $ | 883 | $ | 474 | $ | 413 | ||||||
Nonvested shares | 940 | 105 | 5 | |||||||||
Pre-tax compensation expense | 1,823 | 579 | 418 | |||||||||
Tax benefit | (544 | ) | (95 | ) | (55 | ) | ||||||
Net effect on net income | $ | 1,279 | $ | 484 | $ | 363 | ||||||
We have historically settled stock option exercises with newly issued common shares. The intrinsic value of options exercised in the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006 was $2,873 and $3,710, respectively. The following table summarizes our stock option exercises for the year ended December 31, 2008:
| 2008 | |||
Options exercised | 33 | ||
Cash proceeds from options exercised | $ | 204 | |
Intrinsic value of options exercised | $ | 83 | |
Tax benefit realized from options exercised | $ | 16 | |
The following table sets forth our stock option activity for the year ended December 31, 2008:
| Option Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (Years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||
Outstanding, January 1, 2008 | 876 | $ | 12.99 | ||||||||
Granted | 187 | 8.76 | |||||||||
Exercised | (33 | ) | 6.13 | ||||||||
Expired | (44 | ) | 16.85 | ||||||||
Outstanding, December 31, 2008 | 986 | $ | 12.25 | 6.14 | $ | 10 | |||||
Vested and expected to vest | 909 | $ | 12.41 | 5.91 | $ | 10 | |||||
Exercisable, December 31, 2008 | 578 | $ | 13.72 | 4.36 | $ | 10 | |||||
The weighted-average grant date fair values of options granted in 2008 and 2007 were $4.49 and $7.65, respectively. Total exercisable options and their weighted average exercise price at December 31, 2007 and 2006 were 536 shares at $14.48 and 819 shares at $14.07, respectively. Unearned compensation cost related to the unvested portion of outstanding stock options as of December 31, 2008 was $1,327 and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 2.5 years.
We have issued nonvested stock awards from treasury stock in each of the three years ended December 31, 2008. Recipients of nonvested stock possess the rights of stockholders, including voting rights and the right to receive dividends. We recognize expense associated with stock awards ratably over the respective vesting periods. The fair value of nonvested stock was determined using the end of day market value of our common stock on the grant date. The following table summarizes our nonvested shares activity as of December 31, 2008:
| Shares | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
Nonvested at January 1, 2008 | 32 | $ | 12.39 | |||
Awarded | 225 | 9.04 | ||||
Vested | (73 | ) | 9.62 | |||
Nonvested at December 31, 2008 | 184 | $ | 9.40 | |||
F-19
Table of Contents
The weighted-average grant-date fair values of nonvested stock granted in 2007 and 2006 were $13.13 and $9.92, respectively. The total fair value of nonvested shares that vested in 2008 and 2007 and were $416 and $33, respectively. Unearned compensation costs related to the nonvested portion of outstanding nonvested stock as of December 31, 2008 was $1,007 and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 2.7 years.
| 11. | INCOME TAXES |
The provision for income taxes consisted of the following:
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||
Current: | ||||||||||
Federal | $ | 7,289 | $ | 11,027 | $ | 5,765 | ||||
State | 1,104 | 935 | 506 | |||||||
Total current | 8,393 | 11,962 | 6,271 | |||||||
Deferred: | ||||||||||
Federal | (960 | ) | 1,581 | 1,968 | ||||||
State | 209 | 83 | 211 | |||||||
Net deferred | (751 | ) | 1,664 | 2,179 | ||||||
Net provision | $ | 7,642 | $ | 13,626 | $ | 8,450 | ||||
The components of the deferred taxes at December 31, 2008 and 2007 are as follows:
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
Current: | ||||||||
Provisions for doubtful accounts | $ | 1,161 | $ | 1,482 | ||||
Inventory costs capitalized for tax purposes | 79 | 147 | ||||||
Inventory and sales returns reserves | 585 | 598 | ||||||
Deductible expenses, primarily employee-benefit related | 373 | 105 | ||||||
State tax contingency and other accruals | 1,437 | 63 | ||||||
Other | 609 | 463 | ||||||
Net deferred tax asset—current | $ | 4,244 | $ | 2,858 | ||||
Non-Current: | ||||||||
Compensation under non-statutory stock option agreements | $ | 404 | $ | 153 | ||||
State tax loss carryforwards | 1,127 | 1,414 | ||||||
State tax credit carryforwards | 608 | 1,268 | ||||||
Goodwill and other intangibles | (4,672 | ) | (6,633 | ) | ||||
Property and equipment | (3,910 | ) | (2,470 | ) | ||||
FIN 48 gross up for federal benefit | 770 | 636 | ||||||
Capitalized software | 668 | 618 | ||||||
Deferred revenue | 262 | 347 | ||||||
State tax contingency and other accruals | — | 1,314 | ||||||
Subtotal | (4,743 | ) | (3,353 | ) | ||||
Valuation allowance | (1,440 | ) | (2,083 | ) | ||||
Net deferred tax liability—non-current | (6,183 | ) | (5,436 | ) | ||||
Net deferred tax liability | $ | (1,939 | ) | $ | (2,578 | ) | ||
The state tax credit carryforwards are available to offset future state income taxes in years with sufficient state income levels to create creditable tax and within the applicable carryforward period for these credits. Total tax credit carryforwards aggregated $935 and $1,268 at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. These credits
F-20
Table of Contents
are subject to a five-year carryforward period, with $401 expiring beginning in 2009 and $280 in 2010, $172 in 2011, and $82 expiring in 2013. Additionally, certain of our subsidiaries have state net operating loss carryforwards aggregating $21,267 at December 31, 2008, and representing state tax benefits, net of federal taxes, of approximately $1,127. These loss carryforwards are subject to five- and twenty-year carryforward periods, with $64, $65, $195, $53, and $121 expiring from 2009 through 2013, respectively, and $629 expiring after 2013. We have provided valuation allowances of $1,440 and $2,083 at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, against the state tax credit and state tax loss carryforwards, representing the portion of carryforward credits and losses that we believe are not likely to be realized. The net change in the valuation allowance in 2008 included a reduction of $643 related to the utilization and expiration of state net operating loss carryforwards and state tax credit carryforwards. The net change in the valuation allowance in 2007 included a reduction of $349 related to the expiration of state net operating loss carryforwards and state tax credit carryforwards.
The reconciliation of our 2008, 2007, and 2006 income tax provision to the statutory federal tax rate is as follows:
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Statutory tax rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | |||
State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 5.0 | 2.6 | 3.2 | ||||||
Nondeductible expenses | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.4 | ||||||
Other—net | 1.2 | (0.9 | ) | (1.6 | ) | ||||
Effective income tax rate | 42.4 | % | 37.2 | % | 38.0 | % | |||
We file one consolidated United States federal income tax return that includes all of our subsidiaries as well as several consolidated, combined, and separate company returns in many U.S. state tax jurisdictions. The tax years 2005-2007 remain open to examination by the major state taxing jurisdictions in which we file. An Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) audit of the 2005 tax year was settled in 2008. It resulted in an increase in taxable income in 2006 by $325; the IRS asserted that $325 was the punitive portion of a GSA settlement, of which $1,510 was accrued and deducted in 2006. We paid $2,550 to the GSA in 2006 to settle all claims made after a GSA contract administration review. The tax and interest on the $325 adjustment totaled $127 and was paid in September 2008. The tax years 2006-2007 remain open to examination by the IRS.
Effective January 1, 2007, we adopted the provisions of FIN 48, and we continue to follow the accounting pronouncement for uncertain tax positions. A reconciliation of unrecognized tax benefits for 2008 and 2007 is as follows:
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
Balance at January 1, | $ | 2,368 | $ | 1,222 | ||||
Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 128 | 179 | ||||||
Additions based on tax positions of prior years | 96 | 987 | ||||||
Reductions for tax positions of prior years for: | ||||||||
Lapses of applicable statute of limitations | (317 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||
Balance at December 31 | $ | 2,275 | $ | 2,368 | ||||
We have elected to continue our historic treatment for interest and penalties, recognizing potential interest and penalties related to unrecognized income tax benefits as a component of income tax expense, and the corresponding accrual is included as a component of our liability for unrecognized income tax benefits. During the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, we recognized additional liabilities of $556 and $1,389, respectively, for unrecognized income tax positions relating to tax positions taken in the current and prior
F-21
Table of Contents
periods. Such amounts include $332 and $185, respectively, of interest and penalties. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, interest aggregated $849 and $840, respectively, and penalties aggregated $312 and $292, respectively. In addition, we reduced our unrecognized tax benefits by $303 for interest and penalties related to lapses of applicable statute of limitations. As of December 31, 2008, unrecognized tax benefits of $1,737 would favorably affect our effective tax rate, if recognized.
We do not anticipate that total unrecognized tax benefits will change significantly due to the settlement of audits, expiration of statute of limitations, or other reasons prior to December 31, 2009.
| 12. | EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLAN |
We have a contributory profit-sharing and employee savings plan covering all qualified employees. No contributions to the profit-sharing element of the plan were made by us in 2008, 2007, or 2006. Effective January 1, 2007, we amended our defined contribution plan to require the automatic enrollment of new employees. We made matching contributions to the employee savings element of such plan of $1,103, $979, and $831 in 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.
| 13. | COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
Operating Leases
In August 2008, we entered into an operating lease agreement with our principal stockholders for an office facility adjacent to our corporate headquarters. The lease has a term of ten years and provides us the option to renew for two additional two-year terms. The lease requires us to pay our proportionate share of real estate taxes and common area maintenance charges either as additional rent or directly to third-parties and also to pay insurance premiums for the leased property. We also lease an office facility from our principal stockholders under a one-year noncancelable operating lease, scheduled to expire in 2009. This lease agreement requires us to pay all real estate taxes and insurance premiums related thereto. We also lease several other buildings from our principal stockholders on a month-to-month basis. We believe that the above leasing transactions were consummated on terms equivalent to those that prevail in arm’s-length transactions.
In addition, we lease office, distribution facilities, and equipment from unrelated parties with remaining terms of one to six years.
Future aggregate minimum annual lease payments under these leases at December 31, 2008 are as follows:
Year Ending December 31 | Related Parties | Others | Total | ||||||
2009 | $ | 308 | $ | 2,683 | $ | 2,991 | |||
2010 | 225 | 1,109 | 1,334 | ||||||
2011 | 225 | 827 | 1,052 | ||||||
2012 | 225 | 286 | 511 | ||||||
2013 | 225 | — | 225 | ||||||
2014 and thereafter | 1,034 | — | 1,034 | ||||||
Total rent expense aggregated $3,723, $3,548, and $3,780 for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively, under the terms of the leases described above. Such amounts included $358, $381, and $386 in 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively, paid to related parties.
Sports Marketing Agreements
We have entered into multi-year sponsorship agreements with the Boston Red Sox and the New England Patriots that extend to 2012 and 2013, respectively. These agreements grant us various marketing rights and seating arrangements.
F-22
Table of Contents
Future aggregate minimum annual payments required under these agreements at December 31, 2008 are as follows:
Year Ending December 31 | Total | ||
2009 | $ | 367 | |
2010 | 379 | ||
2011 | 275 | ||
2012 | 285 | ||
2013 | 295 | ||
2014 and thereafter | — | ||
Total marketing expense payments under agreements with these organizations aggregated $1,530, $1,869, and $1,944 for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively, under the terms of the agreements described above.
Contingencies
We are subject to various legal proceedings and claims which have arisen during the ordinary course of business. In the opinion of management, the outcome of such matters is not expected to have a material effect on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
We are subject to audits by states on sales and income taxes, unclaimed property, and other assessments. A comprehensive multi-state unclaimed property audit is currently in progress, and total accruals for unclaimed property aggregated $2,542 at December 31, 2008. While management believes that known and estimated liabilities have been adequately provided for, it is too early to determine the ultimate outcome of such audits. Such outcome could have a material negative impact on our financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
| 14. | OTHER RELATED-PARTY TRANSACTIONS |
As described in Notes 9 and 13, we have leased certain facilities from related parties. Other related-party transactions include the transactions summarized below. We believe such transactions were consummated on terms equivalent to those that prevail in arm’s-length transactions. Related parties consist primarily of affiliated companies related to us through common ownership.
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Revenue: | |||||||||
Sales of services to affiliated companies | $ | 22 | $ | 35 | $ | 62 | |||
| 15. | SEGMENT AND RELATED DISCLOSURES |
SFAS No. 131, “Disclosures About Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information,” requires that public companies report profits and losses and certain other information on their “reportable operating segments” in their annual and interim financial statements. Our Chief Operating Decision Maker (“CODM”) evaluates operations and allocates resources based on a measure of operating income. The internal organization used by our CODM to assess performance and allocate resources determines the basis for our reportable operating segments. Our CODM is our Chief Executive Officer.
Our operations are organized under three reportable operating segments—the “SMB” segment, which serves small- and medium-sized businesses, as well as consumers; the “Large Account” segment, which serves medium-to-large corporations; and the “Public Sector” segment, which serves federal, state, and local government and educational institutions—together with our Headquarters/Other group that provide services in
F-23
Table of Contents
areas such as finance, human resources, information technology, legal, product management, communications, and marketing. Most of the operating costs associated with the Headquarters/Other group functions are charged to the reportable operating segments based on their estimated usage of the underlying functions. We report these charges to the operating segments as “Allocations.” Certain of the headquarters costs relating to executive oversight functions that are not allocated to the operating segments are included under the heading of “Headquarters/Other” in the tables below.
Net sales represent net sales to external customers and exclude inter-segment product revenues, as they are not reviewed by our CODM. In addition, our CODM reviews income tax expense on a consolidated basis, and accordingly, we do not report income tax expense by operating segment. Segment information applicable to our reportable operating segments for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006 is shown below:
| Year Ended December 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||
| SMB Segment | Large Account Segment | Public Sector Segment | Headquarters/ Other | Consolidated | |||||||||||||||
Net Sales | $ | 919,056 | $ | 475,298 | $ | 359,326 | $ | 1,753,680 | |||||||||||
Operating income (loss) before allocations | $ | 62,826 | $ | 25,107 | $ | 6,035 | $ | (76,090 | ) | $ | 17, 878 | ||||||||
Allocations | (46,222 | ) | (2,921 | ) | (14,338 | ) | 63,481 | — | |||||||||||
Operating income (loss) | $ | 16,604 | $ | 22,186 | $ | (8,303 | ) | $ | (12,609 | ) | $ | 17, 878 | |||||||
Net interest expense and other, net | 130 | ||||||||||||||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 18,008 | |||||||||||||||||
Selected Operating Expense: | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 286 | $ | 1,320 | $ | 162 | $ | 5,197 | $ | 6,965 | |||||||||
Goodwill impairment | 1,173 | — | 7,634 | — | 8,807 | ||||||||||||||
Special charges | 12 | — | 43 | 1,376 | $ | 1,431 | |||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 148,665 | $ | 162,362 | $ | 65,942 | $ | 1,198 | $ | 378,167 | |||||||||
Goodwill | — | 48,060 | — | — | 48,060 | ||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SMB Segment | Large Account Segment | Public Sector Segment | Headquarters/ Other | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
Net Sales | $ | 964,503 | $ | 514,770 | $ | 306,106 | $ | 1,785,379 | ||||||||||||
Operating income (loss) before allocations | $ | 64,699 | $ | 29,156 | $ | 12,991 | $ | (70,057 | ) | $ | 36,789 | |||||||||
Allocations | (40,447 | ) | (1,182 | ) | (11,386 | ) | 53,015 | — | ||||||||||||
Operating income (loss) | $ | 24,252 | $ | 27,974 | $ | 1,605 | $ | (17,042 | ) | $ | 36,789 | |||||||||
Net interest expense and other, net | (168 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 36,621 | ||||||||||||||||||
Selected Operating Expense: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 303 | $ | 1,305 | $ | 114 | $ | 5,059 | $ | 6,781 | ||||||||||
Special charges | — | 541 | — | — | 541 | |||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 140,234 | $ | 154,031 | $ | 53,844 | $ | 32,770 | $ | 380,879 | ||||||||||
Goodwill | 1,173 | 48,060 | �� | 7,634 | — | 56,867 | ||||||||||||||
F-24
Table of Contents
| Year Ended December 31, 2006 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SMB Segment | Large Account Segment | Public Sector Segment | Headquarters/ Other | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
Net Sales | $ | 887,040 | $ | 482,850 | $ | 265,761 | $ | 1,635,651 | ||||||||||||
Operating income (loss) before allocations | $ | 59,534 | $ | 25,273 | $ | 8,629 | $ | (69,503 | ) | $ | 23,933 | |||||||||
Allocations | (46,481 | ) | (863 | ) | (13,493 | ) | 60,837 | — | ||||||||||||
Operating income (loss) | $ | 13,053 | $ | 24,410 | $ | (4,864 | ) | $ | (8,666 | ) | $ | 23,933 | ||||||||
Net interest expense and other, net | (1,707 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Income before taxes | $ | 22,226 | ||||||||||||||||||
Selected Operating Expense: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | $ | 269 | $ | 1,434 | $ | 121 | $ | 5,225 | $ | 7,049 | ||||||||||
Special charges | 44 | 1,384 | 9 | 954 | 2,391 | |||||||||||||||
Our operating segments’ assets presented above are primarily accounts receivables, intercompany receivables, goodwill and, other tangibles. Assets for the Headquarters/Other group are managed by corporate headquarters, including cash, inventory, and property and equipment. Total assets for the Headquarters/Other group are presented net of intercompany balances eliminations of $128,618 and $75,020 for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Our capital expenditures are largely comprised of IT hardware and software purchased to maintain or upgrade our management information systems. These systems serve all of our subsidiaries, to varying degrees, and as a result, our CODM does not evaluate capital expenditures on a segment basis.
Senior management also monitors revenue by product mix (Notebooks and PDAs; Desktops and Servers; Storage Devices; Software; Net/Com Products; Printers and Printer Supplies; Video, Imaging, and Sound; Memory and System Enhancements; and Accessories/Other).
Net sales by segment and product mix are presented below:
| Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
Segment (excludes transfers between segments) | |||||||||
SMB | $ | 919,056 | $ | 964,503 | $ | 887,040 | |||
Large Account | 475,298 | 514,770 | 482,850 | ||||||
Public Sector | 359,326 | 306,106 | 265,761 | ||||||
Total | $ | 1,753,680 | $ | 1,785,379 | $ | 1,635,651 | |||
Product Mix | |||||||||
Notebooks and PDAs | $ | 270,808 | $ | 290,709 | $ | 283,203 | |||
Desktop/Servers | 233,349 | 250,767 | 229,407 | ||||||
Storage Devices | 152,650 | 161,073 | 139,807 | ||||||
Software | 225,297 | 226,106 | 203,985 | ||||||
Net/Com Products | 184,106 | 144,654 | 137,867 | ||||||
Printers and Printer Supplies | 159,414 | 170,963 | 164,683 | ||||||
Video, Imaging, and Sound | 260,702 | 259,140 | 212,338 | ||||||
Memory and System Enhancements | 63,438 | 84,966 | 80,789 | ||||||
Accessories/Other | 203,916 | 197,001 | 183,572 | ||||||
Total | $ | 1,753,680 | $ | 1,785,379 | $ | 1,635,651 | |||
F-25
Table of Contents
Substantially, all of our net sales in 2008, 2007, and 2006 were made to customers located in the United States. Shipments to customers located in foreign countries aggregated less than 1% in 2008, 2007, and 2006. All of our assets at December 31, 2008 and 2007 were located in the United States. Our primary target customers are SMBs comprised of 20 to 1,000 employees, federal, state, and local government agencies, educational institutions, and medium-to-large corporate accounts. No single customer other than the federal government accounted for more than 3% of total net sales in 2008, 2007, and 2006. Net sales to the federal government in 2008, 2007, and 2006 were $134,836, $98,543, and $72,550, or 7.7%, 5.5%, and 4.4% of total net sales, respectively.
| 16. | SELECTED UNAUDITED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL RESULTS |
The following table sets forth certain unaudited quarterly data of the Company for each of the quarters since January 2007. This information has been prepared on the same basis as the annual financial statements and all necessary adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, have been included in the amounts stated below to present fairly the selected quarterly information when read in conjunction with the annual financial statements and the notes thereto included elsewhere in this document. The quarterly operating results are not necessarily indicative of future results of operations.
| Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2008 | June 30, 2008 | September 30, 2008 | December 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||
Net Sales | $ | 423,724 | $ | 449,399 | $ | 441,444 | $ | 439,113 | ||||||||
Cost of Sales | 370,980 | 392,559 | 388,121 | 387,176 | ||||||||||||
Gross Profit | 52,744 | 56,840 | 53,323 | 51,937 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 45,393 | 48,173 | 46,872 | 46,290 | ||||||||||||
Goodwill impairment | — | — | — | 8,807 | ||||||||||||
Special charges | — | — | 1,431 | — | ||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 7,351 | 8,667 | 5,020 | (3,160 | ) | |||||||||||
Interest expense | (162 | ) | (199 | ) | (187 | ) | (133 | ) | ||||||||
Other, net | 159 | 205 | 246 | 201 | ||||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 7,348 | 8,673 | 5,079 | (3,092 | ) | |||||||||||
Income tax (provision) benefit | (2,574 | ) | (3,586 | ) | (1,865 | ) | 383 | |||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 4,774 | $ | 5,087 | $ | 3,214 | $ | (2,709 | ) | |||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding: | ||||||||||||||||
Basic | 26,860 | 26,807 | 26,835 | 26,808 | ||||||||||||
Diluted | 26,974 | 26,930 | 26,892 | 26,808 | ||||||||||||
Earnings per common share: | ||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.12 | $ | (.10 | ) | |||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.12 | $ | (.10 | ) | |||||||
F-26
Table of Contents
| Quarters Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2007 | June 30, 2007 | September 30, 2007 | December 31, 2007 | |||||||||||||
Net Sales | $ | 398,180 | $ | 441,122 | $ | 456,470 | $ | 489,607 | ||||||||
Cost of Sales | 348,265 | 387,082 | 398,940 | 432,122 | ||||||||||||
Gross Profit | 49,915 | 54,040 | 57,530 | 57,485 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 44,193 | 45,005 | 45,572 | 46,870 | ||||||||||||
Special charges | — | — | — | 541 | ||||||||||||
Income from operations | 5,722 | 9,035 | 11,958 | 10,074 | ||||||||||||
Interest expense | (208 | ) | (242 | ) | (218 | ) | (264 | ) | ||||||||
Other, net | 201 | 260 | 192 | 111 | ||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 5,715 | 9,053 | 11,932 | 9,921 | ||||||||||||
Income tax provision | (2,330 | ) | (3,300 | ) | (4,247 | ) | (3,749 | ) | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,385 | $ | 5,753 | $ | 7,685 | $ | 6,172 | ||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding: | ||||||||||||||||
Basic | 26,680 | 26,798 | 26,814 | 26,844 | ||||||||||||
Diluted | 27,005 | 26,995 | 27,017 | 27,052 | ||||||||||||
Earnings per common share: | ||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.21 | $ | 0.29 | $ | 0.23 | ||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.21 | $ | 0.28 | $ | 0.23 | ||||||||
F-27
Table of Contents
PC CONNECTION, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
SCHEDULE II—VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
(amounts in thousands)
Description | Balance at Beginning of Period | Charged to Costs and Expenses | Deductions- Write-Offs | Balance at End of Period | |||||||||
Allowance for Sales Returns | |||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2006 | $ | 2,288 | $ | 33,796 | $ | (33,856 | ) | $ | 2,228 | ||||
Year Ended December 31, 2007 | 2,228 | 39,226 | (39,311 | ) | 2,143 | ||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2008 | 2,143 | 34,651 | (34,666 | ) | 2,128 | ||||||||
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | |||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2006 | $ | 3,628 | $ | 2,885 | $ | (2,400 | ) | $ | 4,113 | ||||
Year Ended December 31, 2007 | 4,113 | 1,587 | (1,755 | ) | 3,945 | ||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2008 | 3,945 | 2,277 | (3,122 | ) | 3,100 | ||||||||
Inventory Valuation Reserve | |||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2006 | $ | 1,549 | $ | 6,563 | $ | (6,957 | ) | $ | 1,155 | ||||
Year Ended December 31, 2007 | 1,155 | 6,546 | (6,496 | ) | 1,205 | ||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2008 | 1,205 | 6,171 | (6,224 | ) | 1,152 | ||||||||
S-1