UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
| | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2024
or
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to .
Commission File Number 001-34956
CONN’S, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | | | | |
| Delaware | | 06-1672840 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
| | |
| 2445 Technology Forest Blvd., Suite 800, The Woodlands, TX | | 77381 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (936) 230-5899
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | CONN | NASDAQ Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | | Accelerated filer | ý |
| | | | |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| | | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant's executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ý
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates as of July 31, 2023, was $46.1 million based on the closing price of the registrant’s common stock as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market on such date.
There were 24,885,975 shares of common stock, $0.01 par value per share, outstanding on April 15, 2024.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Certain information required to be furnished pursuant to Part III of this Form 10-K is set forth in, and is hereby incorporated by reference herein from, Conn’s definitive proxy statement for its 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, to be filed by Conn’s with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after January 31, 2024.
CONN’S INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED JANUARY 31, 2024
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Page No. |
| PART I | |
| ITEM 1. | | |
| ITEM 1A. | | |
| ITEM 1B. | | |
| ITEM 1C. | | |
| ITEM 2. | | |
| ITEM 3. | | |
| ITEM 4. | | |
| PART II | |
| ITEM 5. | | |
| ITEM 6. | | |
| ITEM 7. | | |
| ITEM 7A. | | |
| ITEM 8. | | |
| ITEM 9. | | |
| ITEM 9A. | | |
| ITEM 9B. | | |
| ITEM 9C. | | |
| PART III | |
| ITEM 10. | | |
| ITEM 11. | | |
| ITEM 12. | | |
| ITEM 13. | | |
| ITEM 14. | | |
| PART IV | |
| ITEM 15. | | |
| |
| ITEM 16. | | |
| |
This Annual Report on Form 10-K includes our trademarks such as “Conn’s,” “Conn’s HomePlus,” “Badcock,” “Badcock Home Furniture & more,” “YE$ YOU’RE APPROVED,” “YES Money,” “YE$ Money,” “YES Lease,” “YE$ Lease,” “Dreamspot,” “Just Right,” “Legends Signature,” “Protect-it,” “Protect·it,” “Stanhope,” “Stanhope Quality Through Generations,” and our logos, which are protected under applicable intellectual property laws and are the property of Conn’s, Inc. This report also contains trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights of other companies, which are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, trademarks and trade names referred to in this Annual Report may appear without the ® or TM symbols, but such references are not intended to indicate, in any way, that we will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights or the rights of the applicable licensor to these trademarks and trade names.
References to “we,” “our,” “us,” “the Company,” “Conn’s” or “CONN” refer to Conn’s, Inc. and, as apparent from the context, its consolidated bankruptcy-remote variable-interest entities (“VIEs”), and its wholly-owned subsidiaries.
PART I
Forward-Looking Statements
This report contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws, including but not limited to, the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, that involve risks and uncertainties. Such forward-looking statements include statements regarding benefits of the W.S. Badcock acquisition, integration plans and expected synergies, information concerning our future financial performance, business strategy, plans, goals and objectives. Statements containing the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “project,” “should,” “predict,” “will,” “potential,” or the negative of such terms or other similar expressions are generally forward-looking in nature and not historical facts. Such forward-looking statements are based on our current expectations. We can give no assurance that such statements will prove to be correct, and actual results may differ materially. A wide variety of potential risks, uncertainties, and other factors could materially affect our ability to achieve the results either expressed or implied by our forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to: our ability to integrate the W.S. Badcock business, the possibility that our stockholders may not approve the issuance of non-voting common stock required for conversion of the preferred stock issued in connection with the W.S. Badcock acquisition, the risk that any announcement relating to the W.S. Badcock acquisition could have adverse effects on the market price of Conn’s common stock, the risk that the W.S. Badcock acquisition could have an adverse effect on our ability to retain customers and retain and hire key personnel and maintain relationships with suppliers and customers, our ability to achieve cost-cutting synergies, our inability to operate the combined company as effectively and efficiently as expected, our inability to achieve the intended benefits of the W.S. Badcock acquisition for any other reason, general economic conditions impacting our customers or potential customers; our ability to execute periodic securitizations of future originated customer loans on favorable terms; our ability to continue existing customer financing programs or to offer new customer financing programs; changes in the delinquency status of our credit portfolio; unfavorable developments in ongoing litigation; increased regulatory oversight; higher than anticipated net charge-offs in the credit portfolio; the success of our planned opening of new stores; expansion of our e-commerce business; technological and market developments and sales trends for our major product offerings; our ability to manage effectively the selection of our major product offerings; our ability to protect against cyber-attacks or data security breaches and to protect the integrity and security of individually identifiable data of our customers and employees; our ability to fund our operations, capital expenditures, debt repayment and expansion from cash flows from operations, borrowings from our Revolving Credit Facility (as defined herein), BRF Term Loan (as defined herein), and Delayed Draw Term Loan (as defined hearein); proceeds from accessing debt or equity markets; the effects of epidemics or pandemics; and other risks detailed in Part I, Item 1A, Risk Factors, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and other reports filed with the SEC. If one or more of these or other risks or uncertainties materialize (or the consequences of such a development changes), or should our underlying assumptions prove incorrect, actual outcomes may vary materially from those reflected in our forward-looking statements. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this report. We disclaim any intention or obligation to update publicly or revise such statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, or to provide periodic updates or guidance. All forward-looking statements attributable to us, or to persons acting on our behalf, are expressly qualified in their entirety by these cautionary statements.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS.
Company Overview
Conn’s, Inc., a Delaware corporation, is a holding company with no independent assets or operations other than its investments in its subsidiaries. References to “we,” “our,” “us,” “the Company,” “Conn’s” or “CONN” refer to Conn’s, Inc. and, as apparent from the context, its subsidiaries. Conn’s is a leading specialty retailer that offers a broad selection of quality, branded durable consumer goods and related services in addition to proprietary credit solutions for its core consumers. We operate an integrated and scalable business through our retail stores and websites. Our complementary product offerings include furniture and mattresses, home appliances, consumer electronics, home office products, accessories and seasonal items from leading global brands across a wide range of price points. Our credit offerings provide financing solutions to a large, under-served population of consumers who typically have limited credit alternatives. We provide customers the opportunity to comparison shop across brands with confidence in our competitive prices as well as affordable monthly payment options, fast delivery and installation in the majority of our markets and product repair service. We believe our large, attractively merchandised stores and credit solutions offer a distinctive value proposition compared to other retailers that target our core customer demographic.
Our fiscal year ends on January 31. References to a fiscal year refer to the calendar year in which the fiscal year ends.
On December 18, 2023, we announced the acquisition of W.S. Badcock LLC (“Badcock”). Founded in 1904, Badcock operates nearly 380 stores in eight southeastern states comprised of approximately 60 corporate locations and 300 independent dealer owned stores. The stores are branded “Badcock Home Furniture & more” and provide customers with furniture, appliances, bedding, electronics, home office equipment, accessories, and seasonal items. Badcock offers customers affordable payment plans, including Badcock Easy Purchase, an in-house payment solution. The transaction brings together two highly
complementary companies with significant reach across 15 states and powered by best-in-class payment offerings, compelling eCommerce capabilities, and a premium shopping experience.
As of December 18, 2023, the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed exceeded the value of the consideration given and as such, we recorded a bargain purchase gain net of deferred taxes of $104.9 million. The results of Badcock included in our financial statements for the fiscal year ended 2024 includes transactions from December 18, 2023 to January 31, 2024.
Operating Segments
We operate two reportable segments: retail and credit. Information regarding segment performance is included in Part II, Item 7., Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, and Part II, Item 8. in Note 14, Segment Information, of the Consolidated Financial Statements of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Retail Segment. Conn's began as a small plumbing and heating business in 1890 and started selling home appliances to the retail market in 1937 through one store located in Beaumont, Texas. As of January 31, 2024, including Badcock locations, we operated 552 retail stores, of which 244 are corporate owned and 308 are dealer owned and are located in 15 states across the southeast United States. Our Conn's stores typically range in size from 25,000 to 50,000 square feet and are predominantly located in areas densely populated by our core customers. Our Badcock stores are typically range in size from 10,000 to 25,000 square feet and are predominantly located in more rural areas. The dealer owned stores are owned and operated by entrepreneurs and we sell our Badcock products through their stores paying a commission upon delivery of the sold product.
We utilize a merchandising strategy that offers a wide range of quality, name brand and private brand products across a broad spectrum of price points. This wide selection allows us to offer products and price points that appeal to the majority of our core consumers. Our primary retail product categories include:
•Home appliance, including refrigerators, freezers, washers, dryers, dishwashers and ranges. We offer brands such as Samsung, LG, General Electric, and Frigidaire.
•Furniture and mattress, including furniture and related accessories for the living room, dining room and bedroom, as well as both lay flat mattresses and mattress in a box offerings. We offer furniture brands such as Corinthian and Catnapper, and mattress brands such as Tempur-Pedic, Simmons Beautyrest and Nectar.
•Consumer electronics, including LED, OLED, QLED, 4K Ultra HD, 8K televisions, home theater audio, video game consoles, arcade gaming products, and portable audio equipment. We offer brands such as Samsung, LG, Sony, Bose and Microsoft Xbox.
•Home office, including computers, tablets, monitors and accessories. We offer brands such as HP, Apple, and Microsoft.
We strive to ensure that our customers’ shopping experience at Conn’s is equal to, or exceeds, their experience with other providers of durable consumer goods targeting our core customer demographic. We offer a high level of customer service through our commissioned and trained sales force, fast delivery and installation in the majority of our markets and product repair or replacement services for most items sold in our stores. We also sell and offer our services through our websites, conns.com and badcock.com. Flexible payment alternatives offered through our proprietary in-house credit programs and third-party financing alternatives provide our customers the ability to make aspirational purchases. We believe our extensive brand and product selection, competitive pricing, financing alternatives and supporting services, combined with our customer service-focused store, delivery and service associates make us an attractive alternative to appliance and electronics superstores, furniture and mattress stores, department stores, and other national, regional, local and internet retailers. We believe our attractive credit programs generate strong customer loyalty and repeat business.
Credit Segment. Our in-house consumer credit programs are an integral part of our business and are a major driver of customer loyalty. We believe our in-house credit programs are a significant competitive advantage that we have developed over our 50-plus years in providing credit. We have developed proprietary underwriting models that provide standardized credit decisions, including down payment, limit amounts and credit terms, based on customer risk and income level. We use our proprietary auto-decision algorithms as well as in-depth evaluations of creditworthiness performed by qualified in-house credit underwriters to complete all credit decisions. In order to improve the speed and consistency of underwriting decisions, we continually review our auto-decision algorithms. Additionally, we provide access to alternative financing options to a wider range of consumers through our relationship with third-party payment solution providers. These third parties manage their own respective underwriting decisions and are responsible for their own collections. Our in-house credit programs and access to third-party payment solutions allows us to provide credit to a large and under-served customer base and differentiates us from our competitors that do not offer similar programs.
Our goal is to provide every customer that enters our stores or applies for credit on our website an affordable monthly payment option. Currently, we make the following payment options available to our customers based on a review of their credit worthiness:
•For customers with credit scores that are typically above 650, we offer special no-interest or lower interest option financing programs on select products through a Conn’s branded revolving credit card from Synchrony or we may offer an in-house financing program;
•For customers with credit scores that are typically between 550 and 650, we offer our proprietary in-house financing program, which is a fixed term, fixed payment installment and consumer loan contract and may also include special no-interest or lower interest options; and
•For customers that do not qualify for our credit programs, we offer a lease-to-own payment option through an arrangement with our third-party lease-to-own providers.
We continuously evaluate alternative financing programs that may give us the ability to provide more customers with the ability to purchase the products and services we offer.
Our retail business and credit business operate independently from each other. The retail segment is not involved in credit approval decisions or collections. Decisions to extend consumer credit to our retail customers under our in-house programs are made by our internal credit underwriting department. In addition to underwriting, we manage the collection process of our in-house consumer credit portfolio. Sales financed through our in-house credit programs are secured by the products purchased, which we believe gives us a distinct advantage over other creditors when pursuing collections. The products we sell and finance are typically necessities for the home.
We mitigate credit risk by originating to a significant number of customers who have purchased from us in the past. These repeat customers have historically exhibited a lower probability of default than new customers. For fiscal year 2024 and 2023, 58% and 47%, respectively, of our originations were to repeat customers who financed a subsequent purchase through our in-house credit programs more than five months after financing an initial purchase through our in-house credit programs. As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, 54% and 55%, respectively, of balances due under our in-house credit programs were from repeat customers who have previously financed with us.
Industry and Market Overview
The products we sell are typically considered home necessities, used by our customers in their everyday lives. Many factors influence sales, including consumer confidence, economic conditions, and household formations. We also benefit from the introduction of new products and technologies driving consumers to upgrade existing appliances, electronics and home office products.
As of January 31, 2024, we operated 213 of our 552 stores in Texas and Florida. According to the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Economic Analysis (the “Bureau of Economic Analysis”), Texas and Florida were the second and eighth largest states by nominal GDP in 2023. In addition, from calendar year 2018 to 2023, Texas and Florida experienced population growth of 6.6% and 6.4% compared to the United States (“U.S.”) population growth of 2.5% over the same period.
Furniture and Mattress. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, personal consumption expenditures for household furniture and mattresses were $160.0 billion for calendar year 2023, a decrease of 25.6% from $215.0 billion in 2022. The household furniture and mattress market is highly fragmented with sales coming from manufacturer-owned stores, independent dealers, furniture centers, specialty sleep product stores, national and local chains, mass market retailers, department stores, internet retailers, and, to a lesser extent, home improvement centers, decorator showrooms, wholesale clubs and catalog retailers. For fiscal year 2024, Conn's generated 39.0% of total product sales from the sale of furniture and mattresses. The furniture and mattress category generated our highest individual product category gross margin. Given our ability to provide customer financing and fast delivery, we believe that we have strong competitive advantages and significant growth opportunities in this market and expect to continue to grow the balance of sale of our furniture and mattress product category. Product design, innovation and technological advancements have been key drivers of sales in this market.
Home Appliance. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, personal consumption expenditures for home appliances were $84.5 billion for calendar year 2023, an increase of 9.5% from $77.2 billion in 2022. Major household appliances, such as refrigerators and washer/dryers, accounted for 87.0% of this total at $73.4 billion in 2023. For fiscal year 2024, Conn's generated 37.5% of total product sales from the sale of home appliances. The retail appliance market is large and concentrated among a few major dealers, with sales coming primarily from home improvement centers, large appliance and electronics superstores, national chains, warehouse clubs, department stores, regional chains, local dealers/single-store operators, manufacturer-direct websites and internet retailers.
Key drivers of sales in the appliance market include product design and innovation, brand and quality. We carry products with features that include large-capacity, high-efficiency laundry appliances, refrigerator design innovation, technological advancements such as smart home connectivity and variations on these features from leading brands.
Consumer Electronics and Home Office. According to the Bureau of Economic Analysis, electronics spending was $419.4 billion for calendar year 2023, an increase of 11.2% from $377.1 billion for calendar year 2022. Televisions accounted for $34.4 billion of the overall personal consumption expenditures, versus $45.2 billion in the prior year. Personal computers and peripheral equipment accounted for $95.7 billion of the overall expenditures, compared to $83.9 billion in the prior year. For fiscal year 2024, Conn's generated 12.2% of total product sales from the sale of consumer electronics and 4.2% of total product sales from the sale of home office products. The electronics market is highly fragmented with sales coming from large appliance and electronics superstores, national chains, warehouse clubs, regional chains, local dealers/single-store operators, manufacturer-direct websites, manufacturer-direct stores, consumer electronics departments of selected department and discount stores and internet retailers.
Technological advancements and the introduction of new products largely drive demand in the electronics market. Historically, industry growth has been fueled primarily by the introduction of products that incorporate new technologies and advances in existing technologies, including 4K Ultra HD, OLED, QLED, and mini-LED televisions, gaming products, video game consoles, home theater and computers. New technologies offer better clarity and quality of video, increased computer processing speed, and support increased availability of 4K content and other significant advantages.
Consumer Credit. Based on data from the Federal Reserve System, estimated total consumer credit outstanding, which primarily excludes loans secured by real estate, was $5.0 trillion as of December 31, 2023, an increase of 4.2% from $4.8 trillion at December 31, 2022. Consumers obtain credit from banks, credit unions, finance companies and non-financial businesses that offer credit, including retailers. The credit obtained takes many forms, including revolving (e.g., credit cards) and fixed-term (e.g., automobile loans), and at times is secured by the products being purchased.
Competition. Our competitive strength is based on offering financing options, including our proprietary in-house credit programs, to our core customers, enhanced customer service and customer shopping experience through our unique sales force training and product knowledge, fast delivery capabilities, low payment guarantee, and product repair service. Currently, we compete against a diverse group of retailers, including national mass merchants such as Wal-Mart, Target, Sam’s Club, and Costco, specialized national retailers such as Best Buy, Ashley Furniture and Mattress Firm, home improvement stores such as Lowe’s and Home Depot, and locally-owned regional or independent retail specialty stores that sell furniture and mattresses, home appliances, and consumer electronics similar, and often identical, to those items we sell. We also compete with internet retailers such as Amazon, Wayfair and manufacturer-direct websites. In addition, there are few barriers to entry into our current and contemplated markets, and new competitors may enter our current or future markets at any time. Certain of our competitors offer third party financing or provide other forms of credit, which compete with our in-house credit programs for credit-constrained consumers. We also compete against companies offering credit-constrained consumers products for the home similar to those offered by us under weekly or monthly lease-to-own payment options. Competitors include Aaron’s and Rent-A-Center, as well as many smaller, independent companies.
Customers
We have a well-defined core consumer base that is comprised of working individuals who typically earn between $25,000 to $60,000 in annual income, live in densely populated and mature neighborhoods or more rural locations, and typically shop at our stores to replace older household goods with newer items. Our product line is comprised of durable home necessities which enables us to appeal to a diverse range of cultural and socioeconomic backgrounds and to operate stores in diverse markets. No single customer accounts for more than 10% of our total revenues and we do not have a significant concentration of sales with any individual customer. Therefore, the loss of any one customer would not have a material impact on our business.
Seasonality
Our business is seasonal which typically means that a higher portion of sales and operating profit are realized during the fourth quarter due primarily to the holiday shopping season. In addition, during the first quarter, our portfolio performance benefits from the timing of personal income tax refunds received by our customers, which typically results in higher cash collection rates.
Merchandising
Vendors. We purchase products from a wide range of manufacturers and distributors. Our pricing arrangements with these manufacturers and distributors typically cover a one-year time period and are renewable at the option of the parties. Similar to other specialty retailers, we purchase a significant portion of our total inventory from a limited number of vendors. During fiscal year 2024, 67.9% of our total inventory purchases were from six vendors, including 31.3%, 18.5% and 11.1% of our total inventory purchases from Samsung, LG and GE, respectively. The loss of any one or more of these key vendors or our failure
to establish and maintain relationships with these and other vendors could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. Our relationships with our vendors allowed us to maintain a competitive in-stock position.
Merchandise. We focus on providing a selection of quality merchandise at a wide range of price points to appeal to a broad range of potential customers. We primarily sell brand name merchandise with manufacturer’s warranties. Our established relationships with furniture and mattress, home appliance and consumer electronics vendors give us purchasing power that allows us to offer name brand appliances and electronics at prices that are competitive with national retailers and provides us a competitive selling advantage over smaller independent retailers. Additionally, we provide fast and accurate delivery to our customers, giving us a competitive advantage over most other retailers of our product categories in the marketplace today.
Credit Operations - Installment Loans
General. We sell our products by offering our customers financing through our proprietary in-house credit programs, the use of third-party financing, and by taking cash or credit card payments. For the fiscal year 2024, approximately 61.3% of purchases were financed through our proprietary in-house credit programs, approximately 23.1% of purchases were financed through the use of third-party financing and lease-to-own, and approximately 15.6% of purchases were made with cash or credit card.
Underwriting. Decisions to extend credit to our retail customers are made by our internal credit underwriting department, which is separate and distinct from our other operations, including credit monitoring and collections and retail sales. In addition to auto-decision algorithms, we employ a team of credit underwriting personnel of approximately 45 individuals to make credit granting decisions using our proprietary underwriting process. Our underwriting process considers one or more of the following elements: credit bureau information; income and address verification; current income and debt levels; a review of the customer’s previous credit history with us; and the particular products being purchased. Our underwriting models determine the finance terms, including down payment, limit amounts and credit terms. During fiscal year 2024, of the credit applications received, 80.1% were auto decisioned. The remaining credit decisions were based on the evaluation of the customer’s creditworthiness in combination with requiring additional documentation from the applicant. These credit applicants may have past credit problems, lack credit history or be potential fraudulent applications, requiring us to use stricter underwriting criteria. The additional requirements include verification of employment and recent work history, heightened ID verification and potentially a required down payment. Our underwriting employees are trained and monitored to ensure they follow our methodology in approving credit.
Part of our ability to control delinquency and net charge-off is based on the total approval amount, the finance product offering, i.e. interest free period or down payment amounts, the maximum contract terms we allow and the purchase money security interest that we obtain in the product financed, which reduce our credit risk and increase our customers’ ability and willingness to meet their future obligations. We require the customer to provide proof of property insurance coverage on all purchases financed through our credit offerings to offset potential losses relating to theft or damage of the product financed. We do not require customers to purchase property insurance from us if they have or acquire such insurance from another third-party.
Credit monitoring and collections. Our collection activities involve a combination of efforts that take place in our San Antonio collection center and our first party agency in India. As of January 31, 2024, we employed approximately 350 full and part time individual collectors and support personnel who service our active customer credit portfolio. We also utilize collection agencies to service portions of our charged-off portfolio, which provide approximately 150 additional agents. Our in-house, credit-financed sales are secured by the products purchased, which we believe gives us a distinct advantage over other creditors when pursuing collections, especially given that many of the products we finance are generally necessities for the home. We utilize a credit collection strategy that includes telephone calls and messages, internal collectors that contact borrowers, collection letters, e-mails, text messages and third-party legal services that process claims and attend bankruptcy hearings and voluntary repossession. Our employees are trained to follow our methodology in collecting our accounts and charging off any uncollectible accounts based on pre-determined aging criteria, depending on their area of responsibility. All collection personnel are required to complete classroom training, which includes negotiation techniques and credit policy training to ensure customer retention and compliance with debt collection regulations. Post-graduation, the collection trainees undergo skill assessment training, coaching and call monitoring within their respective departments. Our personnel are required to complete regular refresher training and testing.
We closely monitor the credit portfolio to identify delinquent accounts early and dedicate resources to contact customers concerning past due accounts. We believe that our unique underwriting models, secured interest in the products financed, required down payments and credit limits, local presence, ability to work with customers relative to their product and service needs, and our flexible financing alternatives help mitigate the loss experience on our portfolio.
Customers can make payments through our web portal, over the phone, by ACH, third-party bill pay arrangements, by mail to our lock box or in-person at our store locations. During fiscal year 2024, we received 18.9% of the payments on credit accounts in our store locations, which helps us maintain a relationship with the customer that keeps losses lower while encouraging repeat purchases. We may extend or “re-age” a portion of our delinquent customer accounts as a part of our normal collection procedures to protect our investment. Generally, extensions are granted to customers who have experienced a financial
difficulty (such as the temporary loss of employment), which is subsequently resolved and when the customer indicates a willingness and ability to resume making monthly payments. These re-ages involve modifying the payment terms to defer a portion of the cash payments currently required of the debtor to help the debtor improve his or her financial condition and eventually be able to pay the account balance. Our re-aging of customer accounts does not change the interest rate or the total principal amount due from the customer and typically does not reduce the monthly contractual payments. We typically charge the customer an extension fee, where permitted, which approximates the interest owed for the time period the contract was past due. Our re-age programs consist of extensions and two payment updates, which include unilateral extensions to customers who make two full payments in three calendar months in certain states. During the second quarter of fiscal year 2021, we changed our re-age policy to increase the number of days required for a customer to qualify for a unilateral re-age. Re-ages are not granted to debtors who demonstrate a lack of intent or ability to service the obligation or have reached our limits for account re-aging. To a much lesser extent, we may provide the customer the ability to re-age their obligation by refinancing the account, which does not change the total principal amount due from the customer but does reduce the monthly contractual payments and extends the term. Under these options the customer must demonstrate a willingness and ability to resume making contractual monthly payments.
We deem an account to be uncollectible and charge it off when the account is more than 209 days past due at the end of a month. Our credit and accounting staff consistently monitor trends in charge-offs by examining the various characteristics of the charge-offs, including by market, product type, customer credit and income information, down payment amounts and other identifying information. We track our charge-offs both gross, before recoveries, and net, after recoveries. We periodically adjust our credit granting, collection and charge-off policies based on this information. It is to our advantage to manage the portfolio to balance the combined servicing costs and net losses on the credit portfolio with the benefit of repeat retail sales. We may incur higher servicing costs in order to build customer relationships that may result in future retail sales. Collection activity continues after an account is charged off by both internal staff and third-party collection agencies who are typically paid on a contingency basis.
Credit Operations - Revolving Accounts
Badcock Credit. In conjunction with our acquisition of Badcock in December 2023, we acquired open revolving accounts which differ from Conn's traditional installment loan accounts. These revolving accounts were originated under Badcock's proprietary underwriting models. Badcock's customer base is similar to Conn's and generally seeks payment options to help acquire furniture, appliances and home goods. While revolving accounts remain open even while carrying a zero balance, balances are typically paid over an 18 month period. Each month the customer is billed for that month's required minimum payment. As long as a customer is not delinquent, additional purchases can be made on the revolving credit account up to the maximum credit limit established at origination. Once an account becomes delinquent, the customer is no longer eligible to make future purchases using that account. The revolving accounts are charged-off after no payment has been received for 360 days. We account for these accounts under the fair value accounting option which adjusts the balance each reporting period to reflect the present value of the future cash flows associated with the accounts and is included in other revenue. Cash payments, charge-offs, reages and current macro conditions impact the valuation of the receivables. Management intends to offer our installment loan products in all Badcock stores during 2024.
Store Operations
Stores. We operate retail stores in 15 states. The following table summarizes the number of standalone corporate owned and dealer owned stores in operation at January 31, 2024 in each of our markets:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Geographic Location | | Number of Locations | | Retail Square Feet | | Other
Square Feet |
| Alabama | | 44 | | | 744,753 | | | 228,018 | |
| Arizona | | 10 | | | 352,449 | | | 69,570 | |
| Colorado | | 7 | | | 243,383 | | | 47,623 | |
| Florida | | 138 | | | 2,161,971 | | | 580,441 | |
| Georgia | | 88 | | | 1,192,636 | | | 299,691 | |
| Louisiana | | 11 | | | 434,225 | | | 71,901 | |
| Mississippi | | 9 | | | 175,079 | | | 57,783 | |
| Nevada | | 3 | | | 118,511 | | | 26,072 | |
| New Mexico | | 5 | | | 173,067 | | | 28,314 | |
| North Carolina | | 72 | | | 1,362,370 | | | 419,843 | |
| Oklahoma | | 4 | | | 135,215 | | | 27,740 | |
| South Carolina | | 45 | | | 715,087 | | | 214,592 | |
| Tennessee | | 28 | | | 570,142 | | | 156,576 | |
| Texas | | 75 | | | 2,670,362 | | | 416,543 | |
| Virginia | | 13 | | | 285,758 | | | 74,845 | |
| Store totals | | 552 | | | 11,335,008 | | | 2,719,552 | |
| Distribution and Service Centers and Cross-dock Facilities (excluding cross-docks within stores) | | 25 | | | — | | | 5,743,354 | |
| Corporate and Administrative Offices | | 6 | | | — | | | 248,340 | |
Total (1) | | 583 | | | 11,335,008 | | | 8,711,246 | |
(1)Includes 308 dealer owned stores.
Our stores have an average selling space of approximately 37,000 square feet, plus a storage area for fast-moving and smaller products that customers prefer to carry out rather than wait for in-home delivery. Fifteen of our retail stores also contain cross-dock facilities.
We continuously evaluate our existing and potential sites to position our stores in desirable locations and relocate stores that are not properly positioned. We typically lease rather than purchase our stores, distribution and service centers and cross-dock facilities to retain the flexibility of managing our financial commitment to a location if we later decide that a store or market is performing below our standards or the market would be better served by a relocation. We currently lease most of our locations.
Personnel and compensation. We staff a typical corporate owned store with a store manager, an assistant manager, an average of 12 sales personnel and other support staff, including cashiers and porters based on store size and location. Managers have an average tenure with us of approximately four years and typically have prior sales floor experience. In addition to store managers, we have 17 district managers.
We compensate the majority of our sales associates on a straight commission arrangement. Store managers and assistant store managers receive a salary and are eligible for a bonus. We believe that our store compensation plans, which are primarily tied to sales and KPI metrics, generally help us attract and motivate employees.
Personnel located in our dealer-run stores are employed and compensated by the dealers under their separate arrangements. We pay the dealers a commission for selling our products including warranty and insurance products, which is meant to compensate the dealers for their efforts.
Advertising
We design our marketing programs to increase awareness of our brand, grow consideration, drive traffic demand to our website and stores which all ultimately lead to growing sales and building customer loyalty. We employ a multi-touch media approach utilizing direct mail, video, digital channels, and radio. Our promotional programs include various product discount promotions, various financing offers and free product promotions.
E-Commerce
We are focused on expanding the capabilities of our website to generate customer traffic for both our digital and physical stores. Our websites provide new and existing customers with the ability to purchase substantially all of our product offerings, view prices, apply for credit and make payments on their credit accounts. We update our websites regularly to reflect new products, product availability and current promotional offers. Our websites are a significant component of our advertising strategy. We believe our websites represent a possible source for future sales and growth in our credit collections. We are focused on improving the customer experience by making it easier for customers to apply for and be approved for credit on-line. We offer credit-qualified customers the ability to complete an entire purchase transaction financed online through our proprietary in-house credit programs. Our websites averaged approximately 78,000 credit applications per month during fiscal year 2024. This compares to average monthly website applications of approximately 60,000 and 74,000 during fiscal year 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Our websites are supported by a call center, allowing us to better assist customers with their credit and product needs.
Distribution and Inventory Management
We currently operate 14 regional distribution centers, one service center, 10 smaller cross-dock facilities and 15 stores with cross-dock facilities. This enables us to deliver products to our customers quickly, reduces inventory requirements at the individual stores, and facilitates regional inventory and accounting controls.
In our retail stores, we maintain an inventory of certain fast-moving items and products that the customer is likely to carry out of the store. Our inventory management system and the use of scanning technology in our distribution centers allow us to determine, on a real-time basis, the location of any product we sell. If we do not have a product at the desired retail store at the time of sale, we can typically provide it through one of our distribution centers.
We primarily use third-party providers to move products from distribution centers to stores and between markets to meet customer needs. We outsource our in-home deliveries to third-party providers and, for many purchases, we offer fast delivery to our customers. These third-party providers use a fleet of home delivery vehicles that enables a highly trained staff of delivery and installation specialists to quickly complete the sales process and provide a high-quality customer experience. We also may receive a delivery fee based on the products sold and the services needed to complete the delivery.
Product Support Services
Delivery and installation. We provide home delivery and installation services in the markets in which we operate. We believe fast and accurate delivery of our products is a highly valued service to our customers.
Credit insurance. Through third-party insurance companies, we offer property, life, disability and involuntary unemployment credit insurance, which we collectively refer to as credit insurance, at most of our stores on sales financed through our in-house credit programs. These insurance products protect the customer’s purchase by covering their payments on their credit account if covered events occur. Property insurance purchased through us can be canceled at any time with proof of alternative coverage. We receive sales commissions from the third-party insurance companies at the time we sell the coverage, and we may receive retrospective commissions, which are additional commissions paid by the insurance carrier if insurance claims are less than earned premiums.
We require proof of property insurance on all purchases financed through our in-house credit offerings; however, we do not require that customers purchase this insurance from us if they have or acquire such insurance from another third-party provider. Premiums charged on the credit products we sell are regulated and vary by state.
Product repair service. We believe that providing product repair and replacement services is an important differentiation and reinforces customer loyalty. We provide in-home and shop repair services for most of the products we sell and primarily service products purchased from us. Customer repair needs are primarily serviced with an employee-based technician workforce. We believe this staffing model allows us to control the post-sale customer service experience.
Repair service agreements. Customers may purchase repair service agreements that we sell for third-party insurers at the time a product is purchased. These agreements broaden and extend the period of covered manufacturer warranty service for up to four years from the date of purchase, depending on the product, and protect the customer against repair costs. Customers may finance the cost of the agreements along with the purchase price of the associated product.
We have contracts with third-party insurers that issue the initial repair service agreements to cover the costs of repairs performed under these agreements. The initial service agreement is between the customer and the third-party insurance company, and, through our agreements with the third-party insurance company, we provide service when it is needed under each agreement sold. We receive a commission on the sale of the contract and we may receive retrospective commissions, which are additional commissions paid by the insurance carrier over time if the cost of repair claims are less than earned premiums. Additionally, we bill the insurance company for the cost of the service work that we perform.
Human Capital Management
We employ approximately 4,500 full-time employees and 150 part-time employees in the U.S. across 15 states, all of whom are expected to be guided by our values and by an underlying set of ethical principles. Incorporated into our Code of Business Conduct & Ethics, our values and principles define our culture and strengthen our workforce. We strive to demonstrate to our customers, stockholders, business partners, communities and employees that we are worthy of their trust and continually strive to enhance our brand reputation. We invest in employees at all levels who are expected to integrate our values and principles in all that we do.
Our Board of Directors oversees human capital management activities (including assessing the effectiveness of employee programs and advising management with regard to the quality of the workforce to carry out our strategic goals and overall human resource strategies) and other committees of the Board of Directors also have responsibilities that impact our human capital management as outlined in their respective charters. Our Human Resources function has management responsibility for advising and assisting the business on human resource matters and executing our overall human capital management strategies.
We are committed to fostering work environments that value diversity and inclusion. A variety of perspectives enriches our culture, leads to innovative solutions for our business and enables us to better meet the needs of a diverse customer base and reflects the communities we serve. Our aim is to develop inclusive leaders and an inclusive culture, while also recruiting, developing, mentoring, training, and retaining a diverse workforce.
We strive to engage and retain our employees throughout the employment life-cycle with effective recruiting and onboarding; competitive pay, benefits and other rewards; mandatory and optional programs for professional development and career advancement; compliance training; and a safe, healthy and respectful workplace.
We maintain an Ethics Hotline that is available to all employees to report (anonymously if desired) any matter of concern. Communications to the hotline are routed to appropriate functions (whether Human Resources, Legal or other departments) for investigation and resolution. In addition, any stockholder or other interested party may send communications to the Board of Directors, either individually or as a group.
Regulation
The extension of credit to consumers is a highly regulated area of our business. Numerous federal and state laws impose disclosure and other requirements and limitations on the origination, servicing and enforcement of retail installment sale accounts, revolving credit accounts and consumer loans as well as our acts and practices in connection with these activities. Applicable federal laws include, but are not limited to, the Truth in Lending Act (“TILA”), the Equal Credit Opportunity Act (“ECOA”), the Fair Credit Reporting Act (“FCRA”), the Fair Debt Collection Practices Act (“FDCPA”), the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (“TCPA”), the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (“GLBA”), the Electronic Fund Transfer Act (“EFTA”), the Military Lending Act (“MLA”), the Servicemembers Civil Relief Act (“SCRA”) and the implementing regulations of the foregoing statutes. The Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”) has broad consumer protection enforcement authority under Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act (“FTCA”), which prohibits “unfair or deceptive acts or practices in or affecting commerce.” The FTC also can enforce specific consumer protection statutes, such as the ECOA, FCRA, FDCPA, TCPA, GLBA, EFTA, MLA, SCRA and TILA, and has authority to issue regulations in respect of certain of these.
The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (“CFPB”) was created in 2010 upon the enactment of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (“Dodd-Frank Act”). The CFPB has rulemaking and enforcement authority over nonbanks engaging in offering or providing a consumer financial product or service (such as extending credit and servicing loans) as well as any affiliate of such “covered person” that acts as a “service provider” to such covered person. The federal consumer financial laws over which the CFPB has enforcement and rulemaking authority include TILA, ECOA, FCRA, FDCPA, and GLBA as well as authority under Title X of the Dodd-Frank Act to prohibit “unfair, deceptive or abusive acts or practices” (“UDAAP”) in connection with consumer financial products and services. The scope of UDAAP is broad and often uncertain, but the CFPB has been active in enforcing UDAAP claims. The CFPB has broad power to impose civil monetary penalties, restitution, and other corrective action under the various laws described above and, for this reason, poses a significant regulatory risk to the origination, servicing, and collection of our various credit offerings.
In addition to its rule making and enforcement authority described in the preceding paragraph, the CFPB also has supervisory and examination authority over mortgage lending, payday lending, and private student lending, as well as “larger participants” in other markets for consumer financial products or services (including debt collection), and any covered person if the CFPB has “reasonable cause to determine” that such covered person is engaging, or has engaged, in conduct that poses risks to consumers with regard to the offering or provision of consumer financial products or services, whether based on consumer complaints or “information from other sources.” Although we are not automatically subject to CFPB supervisory or examination authority based on the foregoing categories, the CFPB has authority to investigate and take enforcement action against us with respect to any alleged violation by us of a federal consumer financial law over which the CFPB has jurisdiction, including the prohibition on UDAAP. The mere receipt by us of a “civil investigative demand” from the CFPB requiring
production of documents, written responses, reports or oral testimony could result in required public disclosure, adverse publicity, and substantial cost to us regardless of the outcome. The CFPB may become more active in its investigations and enforcement due to changes in the political landscape.
Regulatory rulemaking by the CFPB could adversely affect origination, servicing, and collection of our retail installment sale and consumer loan products by making it more difficult and costly for us to offer, service or collect these products. In addition, CFPB rulemaking could make it possible, or easier for our customers to bring class action claims against us, or prohibit or limit the use of arbitration clauses and class action waivers, both of which we include in our installment contracts and loan agreements.
In Texas, Oklahoma, Louisiana and Tennessee, Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., an affiliate of Conn Appliances, Inc., offers a consumer loan product to our customers. In conjunction with our direct loan program, Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., Conn Appliances, Inc., and Conn Credit I, LP, each hold consumer lender licenses as required by their respective state laws. For customers of most stores located outside of Texas, Oklahoma, Louisiana, and Tennessee, Conn Appliances, Inc. offers a retail installment sale contract.
W.S. Badcock LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Conn’s Inc., offers a retail revolving credit product in Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Virginia, holding related licenses in both Florida and South Carolina, as required.
State laws impose disclosure and other requirements and limitations on retail installment sale contracts and consumer loan agreements and impose maximum amounts of finance charges and interest, as well as regulation of other fees and charges, together with restrictions on credit terms, collection and enforcement and other aspects of extending and collecting consumer credit. State consumer finance laws vary from state to state. The originating and servicing of consumer loans typically requires state licensing which entails heightened supervision, examination, and other requirements which may not be applicable to retail sellers extending credit under retail installment sale contracts. Pursuant to the Dodd-Frank Act, state attorneys general and designated state consumer finance regulatory agencies may enforce specified federal consumer finance laws and impose penalties and remedies for their violation. We routinely review our contracts and procedures to ensure compliance with applicable consumer credit laws. Failure on our part to comply with applicable laws could expose us to consumer litigation and government enforcement action, possibly resulting in substantial penalties and claims for damages and, in certain circumstances, may subject us to injunctions, require us to refund finance charges already paid, forgo finance charges not yet paid under credit accounts, change our credit extension, servicing, collection, and marketing practices or a combination of the foregoing. We believe that we are in substantial compliance with all applicable federal and state consumer credit and collection laws.
Our sale of credit insurance products, insured by an unaffiliated third-party insurance provider, that include property, life, disability and involuntary unemployment credit insurance is also highly regulated. These products are only offered with a retail installment sales, retail revolving credit sale, or loan contract agreement purchase. State laws currently impose disclosure obligations and other restrictions with respect to our sales of these products, impose limitations on the amount of premiums that we may charge and require licensing of certain of our employees and operating entities. State laws with respect to these products vary from state to state. Failure to comply with these laws could expose us to consumer litigation and government enforcement action, possibly resulting in substantial penalties and claims for damages, and in certain circumstances, may subject us to injunctions or require us to refund premiums or change our policies and procedures with respect to these products and the marketing of these products or a combination of the foregoing. We believe that we are in substantial compliance with all applicable federal and state consumer credit and collection laws.
In conjunction with the sale of merchandise, we offer our customers the opportunity to purchase repair service agreements on specified products. These contracts are entered into between the customer and an unaffiliated third-party service provider. The contracts enable the customer to obtain repair and/or replacement of certain eligible products in the event of specified failures as described in the terms and conditions of the contract. The service provider, which is financially and legally obligated to perform under these contracts, has entered into a contract with our affiliate to administer the contracts. We post descriptions of these contracts and links to the contract terms on our website. Service contracts require payment of a segregated fee which may be paid by cash, check or financed by customers entering into retail installment sale contracts with Conn Appliances, Inc. loan agreements with Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., or retail revolving credit agreements with W.S. Badcock LLC. The federal Magnusson-Moss Warranty Act governs written warranties and service contracts. For service contracts entered into with Texas customers, state law requires registration of the service provider and Conn Appliances, Inc. as an administrator, a reimbursement insurance policy and other requirements on the service provider, responsibilities on service contract sellers, record-keeping requirements, restrictions on the sale or marketing of service contracts, required contract terms and disclosures, and cancellation requirements, among other requirements and prohibitions. Other states vary in their regulation of these contracts. Violation of these laws can result in injunctive relief, civil penalties, and/or other remedies. We believe that we are in substantial compliance with all applicable federal and state consumer credit and collection laws.
Tradenames and Trademarks
We have registered the trademarks “Conn’s,” “Conn’s HomePlus,” “Badcock,” “Badcock Home Furniture & more,” “YE$ YOU’RE APPROVED,” “YES Money,” “YE$ Money,” “YES Lease,” “YE$ Lease,” “Dreamspot,” “Just Right,” “Legends Signature,” “Protect-it,” “Protect·it,” “Stanhope,” “Stanhope Quality Through Generations,” and our logos, which are protected under applicable intellectual property laws and are the property of Conn’s, Inc. Our trademark registrations generally last for ten-year periods and are renewed prior to expiration for additional ten-year periods.
Available Information
We are subject to reporting requirements of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (“Exchange Act”), and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder. The Exchange Act requires us to file reports, proxy and other information statements and other information with the SEC. You may also obtain these materials electronically by accessing the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
The Board of Directors of the Company (“Board of Directors”) has adopted a code of business conduct and ethics for our employees, code of ethics for our Chief Executive Officer and senior financial professionals and a code of business conduct and ethics for our Board of Directors. A copy of these codes are published on our website at www.conns.com under “Investor Relations — Corporate Governance.” We intend to make all required disclosures concerning any amendments to, or waivers from, these codes on our website. In addition, we make available, free of charge on our website, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and amendments to these reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file this material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. You may review these documents, under the heading “Investor Relations — SEC Filings,” by accessing our website at www.conns.com.
We make available on our website at www.conns.com under “Investor Relations — Asset Backed Securities” updated monthly reports to the holders of our asset-backed notes. This information reflects the performance of the securitized portfolio only, in contrast to the financial statements contained herein, which reflect the performance of all of the Company’s outstanding receivables, including those originated subsequent to those included in the securitized portfolio.
Our website and the information contained on our website is not incorporated in this Annual Report on Form 10-K or any other document filed with the SEC.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS.
You should consider carefully the risks described below and other information presented in this Form 10-K, including Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and the consolidated financial statements and related notes included in this Form 10-K, as well as information provided in other reports, registration statements and materials that we file with the SEC and the other information incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K. If any of the risks described below or elsewhere in this Form 10-K were to materialize, our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows or prospects could be materially adversely affected. In such case, the trading price of our common stock could decline and you could lose part or all of your investment. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, prospects or stock price, which we refer to collectively as a material adverse effect on us (or comparable phrases).
Summary Risk Factors
Risks Related to Our Business
•An economic downturn, pandemics or epidemics, war, including a potential escalation of the current conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, or other events may affect consumer purchases from us as well as their ability to repay their credit obligations to us, which could result in a material adverse effect on us.
•We may not be able to open new stores or profitably operate recently opened stores in existing, adjacent or new geographic markets.
•Our inability to access our Revolving Credit Facility or the capital markets on favorable terms or at all may have a material adverse effect on us.
•Our existing and future levels of indebtedness could adversely affect our financial health, ability to obtain financing in the future, ability to react to changes in our business and ability to fulfill our obligations under such indebtedness.
•We may not be successful in integrating our recently acquired lease-to-own platform into our existing business or performing in-house lease-to-own transactions and our failure to do so could negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition.
•Our debt securities may receive ratings that may increase our borrowing costs.
•We might not be able to access the securitization market for capital from time to time in the future, which may require us to seek alternative and more costly sources of financing.
•One of our operating subsidiaries may be required to repurchase certain finance receivables if representations and warranties about the quality and nature of such receivables are breached, which may negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
•A decrease in our credit sales, a decline in credit quality of our customers or other factors outside of our control could lead to a decrease in our product sales and profitability.
•Covenants in our debt agreements impose various operating and financial restrictions on us, and if we are not able to comply with such covenants, our lenders could accelerate our indebtedness, proceed against certain collateral we have provided or exercise other remedies, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
•Increased borrowing costs may negatively impact our results of operations.
•Deterioration in the performance of our customer receivables portfolio could materially adversely affect our liquidity position and profitability.
•In deciding whether to extend credit to customers, we rely on the accuracy and completeness of information furnished to us by or on behalf of our credit customers, and we assume certain behavior and attributes on the basis of prior customers. If we and our systems are unable to detect any misrepresentations in this information, or if our assumptions prove inaccurate, it may have a material adverse effect on us.
•Our policy of re-aging certain delinquent borrowers affects our delinquency statistics and the timing and amount of our write-offs, and may lead to higher delinquency statistics in the future, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
•We rely on internal models to manage risk and to provide accounting estimates. We could suffer a material adverse effect if those models do not provide reliable accounting estimates or predictions of future activity.
•We benefit from the collection of customer and non-customer recoveries on our customer accounts receivables. Our inability to continue to collect these recoveries could adversely affect our financial results.
•Our reported results require the judgment of management, and we could be subject to risks associated with these judgments or could be adversely affected by the implementation of new, or changes in the interpretation of existing, accounting principles or financial reporting requirements.
•Changes in customer demand and product mix could materially adversely affect our business.
•We may experience significant price pressures over the life cycle of our products from competing technologies and our competitors.
•A disruption in our relationships with, the operations of, or the supply of product from any of our key suppliers, including those suppliers and manufacturers located in Asia and Mexico, whether due to pandemics or epidemics, geopolitical conflict, including a potential escalation of the current conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, or otherwise, could have a material adverse effect on us.
•Failure to maintain sound business and contractual relationships with our dealers may have a material adverse effect on our business and our consolidated financial positions, results of operations and cash flows.
•Our failure to operate our dealer network in a manner that does not implicate federal and state franchise laws may adversely affect our business, prospects, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
•We may be held responsible by third parties, regulators, or courts for the action of, or failure to act, by our dealers and their employees, which could expose us possible fines, other liabilities or bad publicity or damage to our brands.
•Disputes with our dealers could have a materially adversely affect on our business.
•Our stores are concentrated in the southern region of the U.S., especially Texas and Florida, which subjects us to regional risks, such as the economy, regulatory, outbreaks, the performance of energy markets, extreme weather conditions, hurricanes and other natural or man-made disasters.
•Our information technology systems for our key business processes are vulnerable to damage that could harm our business.
•Our information technology systems may not be adequate to meet our evolving business and emerging regulatory needs and the failure to successfully implement new systems could negatively impact our business and financial results.
•If we cannot continue to offer third party payment solutions for customers who do not qualify for our proprietary credit offerings, our business may be impaired.
•If we are unable to continue to offer third-party repair service agreements to our customers, we could incur additional costs or repair expenses, which could materially adversely affect us.
•Our costs to protect our intellectual property rights, infringement of which could impair our name and reputation, could be significant.
•Failure to protect the security of our customers’, employees’ or suppliers’ information or failure to comply with data privacy and protection laws could expose us to litigation, compromise the integrity of our products, damage our reputation and materially adversely affect us.
•Failure to successfully utilize and manage e-commerce, and to compete effectively with the growing e-commerce sector, could materially adversely affect our business and prospects.
•If we fail to maintain adequate systems and processes to detect and prevent fraudulent activity, including in our e-commerce business, our business could be materially adversely impacted.
•Because we maintain a significant supply of cash and inventories in our stores, we may be subject to employee and third-party robberies, burglaries, thefts, riots and looting, and may be subject to liability as a result of crimes at our stores.
•We face risks with respect to product liability claims and product recalls, which could materially adversely affect our reputation, our business, and our consolidated results of operations.
Risks Associated with the Badcock Acquisition
•We may not be able to successfully integrate the Badcock business and our failure to do so could negatively impact our business and financial results.
•We may fail to realize all of the anticipated benefits of the acquisition.
•We have incurred substantial transaction fees and costs in connection with the acquisition.
•We may not be able to retain key personnel following the acquisition.
•The market price of our common stock after the acquisition may be affected by factors different from those affecting the shares of our common stock historically.
•Conn’s preferred shares received by holders of the W.S. Badcock LLC interests in connection with the acquisition and the class of non-voting common stock convertible therefrom have different rights from the Conn’s common stock.
•We may fail to receive sufficient stockholder support for establishing the class of non-voting common stock or the related conversion of the preferred shares into such new class which could result in us paying a dividend in respect of the preferred shares.
Risks Related to Laws and Regulation
•We may expand our retail, credit, or lease-to-own offerings and become subject to different operating, regulator or legal requirements
•Our business could be materially adversely affected by changes in consumer protection laws and regulations.
•Regulatory agencies may reshape consumer financial laws and there continues to be uncertainty as to how such actions will impact our business.
•Judicial or administrative decisions, CFPB rule-making or amendments to the Federal Arbitration Act could render the arbitration agreements we use illegal or unenforceable.
•We are required to comply with laws and regulations regulating extensions of credit, lease-to-own transactions, and other dealings with customers and our failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations, or any adverse change in those laws or regulations, could have a negative impact on our business.
•We face the risk of litigation resulting from calls and text messages in violation of the TCPA.
•A large number of our stores are located in the State of Texas and State of Florida, which subjects us to concentrated regulatory risks.
Risks Related to Our Business
An economic downturn, pandemics or epidemics, war, including a potential escalation of the current conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, or other events may affect consumer purchases from us as well as their ability to repay their credit obligations to us, which could result in a material adverse effect on us. Many factors affect consumer spending, including regional or world events, war, diseases, outbreaks or epidemics, including a potential escalation of the current conflicts in the Ukraine and the Middle East, conditions in financial markets, local, state and national budgets and fiscal operations and conditions, general business conditions, interest rates, inflation, energy prices, consumer debt levels, the availability of consumer credit, taxation, unemployment trends and other matters that influence consumer confidence. Consumer purchases of our products and customers making payments to us decline during periods when disposable income is lower or periods of actual or perceived unfavorable economic conditions. Decreases in consumer confidence, instability in financial markets and political environment and volatile oil prices have negatively impacted our markets and may present significant challenges to our operations in the future. Additionally, we believe a portion of our customer base continues to experience significant economic challenges and uncertainty, including stagnant incomes, and that those challenges could be intensified by various macroeconomic factors, including increasing inflationary pressures and significant recent disruption in financial markets in connection with the COVID-19 pandemic, increased unemployment, rising interest rates, increases in the cost of energy, and other factors.
We may not be able to open new stores or profitably operate recently opened stores in existing, adjacent or new geographic markets. There are a number of factors that could affect our ability to successfully execute on new and recently opened stores, including:
•Difficulties associated with the hiring, training and retention of skilled personnel, including store managers;
•The availability of financial resources;
•The availability of favorable sites in existing, adjacent or new markets on terms, including price, consistent with our business plan;
•Competition in existing, adjacent or new markets;
•Competitive conditions, consumer tastes and discretionary spending patterns in adjacent or new markets that are different from those in our existing markets or changes in competitive conditions, consumer tastes and discretionary spending patterns in our existing markets;
•A lack of consumer demand for our products or financing programs at levels that can support store growth or the profitability of existing stores;
•Inability to make customer financing programs available that allow consumers to purchase products at levels that can support store growth;
•An inability to manage a greater number of new customers from new stores;
•Limitations created by covenants and conditions under our debt agreements, including our Revolving Credit Facility, and our asset-backed notes;
•An inability or unwillingness of vendors to supply product on credit, on a timely basis or at competitive prices;
•An inability to secure consumer lending licenses in new or adjacent states or markets;
•The failure to open enough stores in new markets to achieve a sufficient market presence and realize the benefits of leveraging our advertising and distribution systems;
•Unfamiliarity with local real estate markets and demographics in adjacent and new markets;
•Problems in adapting our distribution and other operational and management systems to an expanded network of stores; and
•Higher costs for direct mail, television, newspaper, digital, radio and out-of-home targeted advertising.
These and other similar factors may also limit the ability of any newly opened stores to achieve sales and profitability levels consistent with our projections or comparable with our existing stores or to become profitable at all. As a result, we may determine that we need to close or reduce the hours of operation of certain stores, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
If we are unable to effectively manage growth of our business, our revenues may not increase, our cost of operations may rise and our results of operations may decline. In connection with our growth, we will face various associated business risks, including the risk that our management, financial controls and information systems will be inadequate to support expansion. Our growth will require management to expend significant time, effort, and additional resources to ensure the continuing adequacy of our financial controls, operating procedures, information systems, product purchasing, warehousing and
distribution systems and employee training programs. While we have engaged in and focused on these elements, we cannot predict whether we will be able to effectively manage the increased demand resulting from expansion in current markets or into new markets, or respond on a timely basis to the changing demands that our expansion will impose on our management, financial controls and information systems. If we fail to successfully manage the challenges of growth, do not continue to improve our systems and controls or encounter unexpected difficulties during expansion, we could be materially adversely affected.
Our inability to access our Revolving Credit Facility or the capital markets on favorable terms or at all may have a material adverse effect on us. We generally finance our operations primarily through a combination of cash flow generated from operations, borrowings under our Revolving Credit Facility, and securitizations of customer receivables through the capital markets. Our ability to access capital through our existing Revolving Credit Facility, raise additional capital by expanding our Revolving Credit Facility, or undertake future securitization or other debt or equity transactions on economically favorable terms or at all, depends in large part on factors that are beyond our control, including:
•Conditions in the securities and finance markets generally, and for securitized instruments in particular;
•A negative bias toward our industry by capital market participants;
•Our credit rating or the credit rating of any securities we may issue;
•General economic conditions and the results of our earnings, cash flows and balance sheet;
•Security or collateral requirements;
•The credit quality and performance of our customer receivables;
•Regulatory restrictions applicable to us;
•Our overall business and industry prospects;
•Our overall sales performance, profitability, cash flow, balance sheet quality, regulatory restrictions;
•Our ability to provide or obtain financial support for required credit enhancement;
•Our ability to adequately service our financial instruments;
•Our ability to make required representations and warranties;
•Our ability to meet debt covenant requirements; and
•Prevailing interest rates, including rising interest rates.
If adequate capital is not available at the time we need it, we may have to curtail future growth or change our expansion plans, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
We use our customer receivables, in addition to our inventory, as collateral to support our capital needs. As the aggregate amount and performance of our customer receivables has fluctuated, from time to time we have required amendments to our credit facilities in order to stay in compliance with our obligations thereunder. If we require such amendments in the future and are unable to obtain them, or if we are unable to arrange substitute financing facilities or other sources of capital, then we may be unable to continue drawing funds under our Revolving Credit Facility, which would force us to limit or cease offering credit through our finance programs. Likewise, if the borrowing base under our Revolving Credit Facility is reduced, or otherwise becomes unavailable, or we are unable to arrange substitute financing facilities or other sources of capital, we may have to limit the amount of credit that we make available through our customer credit programs. A reduction in our ability to offer customer credit could have a material adverse effect on us. Further, our inability, or limitations on our ability, to obtain funding through securitization facilities or other sources may materially adversely affect our ability to provide additional credit to existing customers, which could have a material adverse effect on our profitability under our credit programs if such existing customers fail to repay outstanding credit. Additionally, the inability of any of the financial institutions providing our financing facilities to fund their respective commitments could materially adversely affect our ability to fund our credit programs, capital expenditures and other general corporate needs.
Our existing and future levels of indebtedness could adversely affect our financial health, ability to obtain financing in the future, ability to react to changes in our business and ability to fulfill our obligations under such indebtedness. As of January 31, 2024, we had aggregate outstanding indebtedness, including under our Revolving Credit Facility, Term Loan and various classes of asset-backed notes, of $1,008.7 million. This level of indebtedness could:
•Make it more difficult for us to satisfy our obligations with respect to our outstanding notes, Revolving Credit Facility, Term Loan and other indebtedness, resulting in possible defaults on and acceleration of such indebtedness;
•Require us to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to the payment of principal and interest on our indebtedness, thereby reducing the availability of such cash flows to fund working capital, acquisitions, new store openings, capital expenditures and other general corporate purposes;
•Limit our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, acquisitions, new store openings, capital expenditures, debt service requirements and other general corporate purposes;
•Limit our ability to refinance indebtedness or cause the associated costs of such refinancing to increase;
•Increase our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions, including interest rate fluctuations (because a portion of our borrowings are at variable rates of interest); and
•Place us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors with proportionately less debt or comparable debt at more favorable interest rates which, as a result, may be better positioned to withstand economic downturns.
Any of the foregoing impacts of our level of indebtedness could have a material adverse effect on us.
We may not be successful in integrating our acquired lease-to-own platform into our existing business or performing in-house lease-to-own transactions and our failure to do so could negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition. The rollout of our in-house lease-to-own program is subject to a number of risks including those around technology, underwriting and customer uptake. If our in-house lease-to-own program is delayed, encounters unforeseen costs, or is not received well by our customers, it may have a negative impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our debt securities may receive ratings that may increase our borrowing costs. We may elect to issue securities for which we may seek to obtain a rating from a rating agency. It is possible, however, that one or more rating agencies may independently determine to assign a rating to any of our issued debt securities. If any ratings are assigned to any of our debt, or the asset-backed notes or other securities with a rating, such ratings, if they are lower than market expectations or are subsequently lowered or withdrawn, whether as a result of our actions or factors which are beyond our control, could increase our future borrowing costs and impair our ability to access capital and credit markets on terms commercially acceptable to us, or at all. Inability to access the credit markets on acceptable terms, if at all, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
We might not be able to access the securitization market for capital from time to time in the future, which may require us to seek alternative and more costly sources of financing. We have successfully consummated a number of securitization transactions, however, there can be no assurances that we will be able to complete additional securitization transactions if securitization markets become constrained. Additional or prolonged disruptions in the securitization market, such as a recession could preclude our ability to use securitization as a financing source, or could render it an inefficient source of financing making us more dependent on alternative sourcing of financing that might not be as favorable as securitizations or might be otherwise unfavorable or unavailable altogether.
Securitization structures are subject to an evolving regulatory environment that may affect the availability and attractiveness of securitization as a financing option. In the U.S., following the economic recession that began in 2009, there has been increased political and regulatory scrutiny of the asset-backed securities industry, which has resulted in increased regulation. The impact of such regulations on investors in securitization markets and the incentives for certain investors to hold asset-backed securities remain unclear, and may have a material adverse effect on the liquidity of such securities, which could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity. Additionally, rules from various agencies now require sponsors of asset-backed securities to retain an ownership stake in securitization transactions. Any adverse changes to these regulations could effectively limit our access to securitization as a source of financing or alter the structure of securitizations, which could pose risks to our participation in any securitizations or could reduce or eliminate the economic incentives to us of participating in securitizations.
One of our operating subsidiaries may be required to repurchase certain finance receivables if representations and warranties about the quality and nature of such receivables are breached, which may negatively impact our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity. We have entered into certain financing arrangements, including issuances of asset-backed notes (collectively, “Financing Transactions”), that are secured by retail installment contracts and direct consumer loans originated by our operating subsidiaries (the “Receivables”). In connection with the Financing Transactions, our operating subsidiaries sold the Receivables to certain of our wholly-owned special purpose VIEs and made certain representations and warranties about the quality and nature of the Receivables.
If there is a breach of those representations and warranties, one of our operating subsidiaries may be obligated to repurchase the affected Receivables. If our operating subsidiary is required to repurchase Receivables that were previously sold in connection with the Financing Transactions, this could have a materially adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition, and liquidity.
A decrease in our credit sales, a decline in credit quality of our customers or other factors outside of our control could lead to a decrease in our product sales and profitability. A significant portion of our credit portfolio is comprised of credit
provided to customers considered to be sub-prime borrowers who have limited credit history, low income or past credit problems. Entering into credit arrangements with such customers entails a higher risk of customer default, higher delinquency rates and higher losses than extending credit to more creditworthy customers. While we believe that our pricing and the underwriting criteria and collection methods we employ enable us to effectively and appropriately manage the higher risks inherent in issuing credit to sub-prime customers, no assurance can be given that such pricing and underwriting criteria and methods will afford adequate protection against such risks. We have experienced volatility in delinquency and charge-off rates on our customer receivables, each of which has the effect of decreasing our profitability. Some of our customer receivables become delinquent from time to time. Some accounts end up in default, due to various factors, such as general and local economic conditions, including the impact of rising interest rates, living costs and unemployment rates. If we continue to expand into new markets, we will obtain new customer receivables that may present a higher risk than our existing customer receivables since new customer receivables do not have an established credit history with us.
If we reduce the amount of credit we grant to our customers (whether due to financial or regulatory constraints, including regulatory constraints relating to interest rates), or if our customers curtail entering into credit arrangements with us, whether as a result of prolonged economic uncertainty in the U.S., increases in unemployment or other factors, we likely would sell fewer products, which could result in a material adverse effect on us. Further, because a significant number of payments we receive on credit accounts are made in person by customers in one of our store locations, any decrease in credit sales could reduce traffic in our stores and result in lower revenues. A decline in the credit quality of our credit accounts could also cause an increase in our credit losses, which would result in an adverse effect on our earnings. A decline in credit quality could also lead to stricter underwriting criteria which could have a negative impact on net sales.
We maintain an allowance for doubtful accounts on the installment loans included in our customer accounts receivable. If the allowance for doubtful accounts is inadequate, we would recognize losses in excess of the allowance, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
Covenants in our debt agreements impose various operating and financial restrictions on us, and if we are not able to comply with such covenants, our lenders could accelerate our indebtedness, proceed against certain collateral we have provided or exercise other remedies, which could have a material adverse effect on us. The covenants in our Revolving Credit Facility, Term Loan, Delayed Draw Term Loan, and the indenture governing our asset-backed notes contain a number of restrictions that impose operating and financial restrictions on us and may limit our ability to execute our growth strategy or engage in acts that may be in our long-term best interest, including restrictions on our ability to incur additional indebtedness, grant liens on assets, make distributions on equity interests, dispose of assets, make loans, pay other indebtedness, engage in mergers, and other matters. In addition, we must maintain compliance with certain financial covenants. Our ability to meet those financial covenants can be affected by events beyond our control, and we may be unable to meet them.
A breach of the covenants could result in an event of default under our Revolving Credit Facility, Term Loan, Delayed Draw Term Loan, or the indentures governing our asset-backed notes. Such a default may allow the applicable creditors to accelerate any related debt and may result in the acceleration of any other debt to which a cross-default provision applies. Furthermore, if we are unable to repay the amounts due and payable under our Revolving Credit or Term Loan, the lenders thereunder could proceed against the collateral granted to them to secure that indebtedness, which could have a material adverse effect on us. In the event our lenders accelerate the repayment of our borrowings, we may not have sufficient funds to repay that indebtedness.
Increased borrowing costs will negatively impact our results of operations. Because most of our consumer credit programs have interest rates equal to the highest rate allowable under applicable state law, we would generally not be able to pass higher borrowing costs along to future consumer credit customers and our results of operations could be negatively impacted. The interest rates on our Revolving Credit Facility are variable based upon an applicable margin determined by a pricing grid plus a base rate, and increases in such rates would reduce our margins. The level of interest rates in the market in general will impact the interest rate on any debt instruments we issue in the future. Additionally, we may issue debt securities or enter into credit facilities under which we pay interest at a higher rate than we have historically paid, which would further reduce our earnings and negatively impact our results of operations.
Deterioration in the performance of our customer receivables portfolio could materially adversely affect our liquidity position and profitability. Our liquidity position and profitability are heavily dependent on our ability to collect our customer receivables. If the performance of our customer receivables portfolio were to substantially deteriorate, that could have a material adverse effect on the liquidity available to us and our ability to comply with the covenants and borrowing base calculations under our Revolving Credit Facility, and our earnings may decline due to higher provisions for bad debt expense, higher servicing costs, higher net charge-off rates and lower interest and fee income.
Our ability to collect from credit customers may be impaired by store closings. In the event of store closings, credit customers may not pay balances in a timely fashion, or may not pay at all, since a large number of our customers remit payments in store and have not traditionally made payments to a non-store location.
In deciding whether to extend credit to customers, we rely on the accuracy and completeness of information furnished to us by or on behalf of our credit customers, and we assume certain behavior and attributes on the basis of prior customers. If we and our systems are unable to detect any misrepresentations in this information, or if our assumptions prove inaccurate, it may have a material adverse effect on us. In deciding whether to extend credit to customers, we rely heavily on information furnished to us by or on behalf of our credit customers, including employment and personal financial information, and our ability to validate such information through third-party services. We also assume certain behavior and attributes observed for prior customers. Our ability to effectively manage our credit risk could be impaired, and could have a material adverse effect on us, if a significant percentage of our credit customers intentionally or negligently misrepresent any of this information, and our systems do not detect such misrepresentations, or if unexpected changes in behavior caused by macroeconomic conditions, changes in consumer preferences, availability of alternative products or other factors cause our assumptions to be inaccurate.
Our policy of re-aging certain delinquent borrowers affects our delinquency statistics and the timing and amount of our write-offs, and may lead to higher delinquency statistics in the future, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial results. Re-aging is offered to certain of our past-due customers if they meet the conditions of our re-age policy. Our decision to offer a delinquent customer a re-age program is based on that borrower’s specific condition, our history with the borrower, the amount of the loan and various other factors. When we re-age a customer’s account, we move the account from a delinquent status to a current status. Management exercises a considerable amount of discretion over the re-aging process and has the ability to re-age an account multiple times during its life. Treating an otherwise uncollectible account as current affects our delinquency statistics, as well as impacts the timing and amount of charge-offs and, potentially, our future financial results. If these accounts had been charged off sooner, our net loss rates for earlier periods might have been higher. If the customer defaults on the re-aged account, our re-aging may have simply postponed a delinquency, and our future delinquency statistics will be correspondingly higher.
If we fail to properly staff and train our collections personnel or timely contact delinquent borrowers, the number of delinquent customer receivables eventually being charged off could increase. We contact customers with delinquent credit account balances soon after the account becomes delinquent. During periods of increased delinquencies, it is important that we are proactive in dealing with customers rather than simply allowing customer receivables to go to charge-off. Historically, when our servicing becomes involved at an earlier stage of delinquency with credit counseling and workout programs, there is a greater likelihood that the customer receivable will not be charged off.
The success of our collection efforts depends on our collection center being properly staffed and our staff being properly trained to assist borrowers in bringing delinquent balances current and ultimately avoiding charge-off. If we do not properly staff and train our collections personnel, or if we incur any downtime or other issues with our information systems that assist us with our collection efforts, then the number of accounts in a delinquent status or charged-off could increase. In addition, managing a substantially higher volume of delinquent customer receivables typically increases our operational costs. A rise in delinquencies or charge-offs could result in a material adverse effect on us.
We rely on internal models to manage risk and to provide accounting estimates. We could suffer a material adverse effect if those models do not provide reliable accounting estimates or predictions of future activity. We make significant use of business and financial models in connection with our efforts to measure and monitor our risk exposures and to manage our credit portfolio. For example, we use models as a basis for credit underwriting decisions, portfolio delinquency, charge-off and collection expectations and other market risks, based on economic factors and our experience. The information provided by these models is used in making business decisions relating to strategies, initiatives, transactions and pricing, as well as the size of our allowance for doubtful accounts, among other accounting estimates.
Models are inherently imperfect predictors of actual results because they are based on current and historical data available to us and our assumptions about factors such as credit demand, payment rates, default rates, delinquency rates and other factors that may overstate or understate future experience. Our models could produce unreliable results for a number of reasons, including the limitations of historical data to predict results due to unprecedented or unforeseen events or circumstances, invalid or incorrect assumptions underlying the models, the need for manual adjustments in response to rapid changes in economic conditions, changes in credit policies, incorrect coding of the models, incorrect data being used by the models or inappropriate application of a model to products or events outside of the model’s intended use. In particular, models are less dependable when the prevailing economic environment is different than historical experience.
In addition, we continually receive new economic data. Our critical accounting estimates, such as the size of our allowance for doubtful accounts, are subject to change, often significantly, due to the nature and magnitude of changes in economic conditions. However, there is generally a lag between the availability of this economic information and the preparation of corresponding internal models. When economic conditions change quickly or in unforeseen ways, there is increased risk that the assumptions and inputs reflected in our models are not representative of current economic conditions.
Changes in the economy, regulatory landscape, credit policies and practices, and the credit and capital markets have required, and will continue to require, frequent adjustments to our models and the application of greater management judgment in the
interpretation and adjustment of the results produced by our models, including in connection with market uncertainty. The application of greater management judgment reflects the need to take into account updated information while continuing to maintain controlled processes for model updates, including model development, testing, independent validation and implementation. As a result of the time and resources, including technical and staffing resources, that are required to perform these processes effectively, it may not be possible to replace existing models quickly enough to ensure that they will always properly account for the impacts of recent information and actions.
If circumstances prove our models to be undependable or not representative of our results, then we may deem it necessary to increase our allowance for doubtful accounts in the future. If our actual charge-offs exceed the assumption used to establish the allowance, our provision for losses would increase and could result in a material adverse effect on us.
We benefit from the collection of customer and non-customer recoveries on our customer accounts receivables. Our inability to continue to collect these recoveries could adversely affect our financial results. Once an account is charged-off, we continue to pursue collections from various recovery sources, including the customer, various state taxing jurisdictions in which sales tax was remitted and our third party insurance and warranty carriers that sold insurance and warranty products. If we are unable to continue to pursue our collections efforts as a result of operational, legislative, contractual or other changes, our financial results could be adversely affected.
Our reported results require the judgment of management, and we could be subject to risks associated with these judgments or could be adversely affected by the implementation of new, or changes in the interpretation of existing, accounting principles or financial reporting requirements. The preparation of our financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the dates of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting periods. In addition, we prepare our financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”), and GAAP and its interpretations are subject to change over time. If new rules, different judgments, or interpretations of existing rules require us to change our financial reporting, our results of operations and financial condition could be materially adversely affected, and we could be required to restate historical financial reporting.
Some of our customers may be recent immigrants and some may not be US citizens. Changes in immigration policies that affect states that share a border with Mexico may negatively impact our retail sales. We follow customer identification procedures including accepting government-issued picture identification, but we do not verify the immigration status of our customers. If we or the retail credit offering sector receive negative publicity around making loans to potentially undocumented immigrants, it may draw additional attention from regulatory agencies or advocacy groups, which may harm our sales and collections results. While our credit models look to approve customers who have stability of residency and employment, it is possible that a significant change in immigration patterns, policies or enforcement could cause our customers to reduce their business with us, or not engage in business transactions with us, and cause a reduction in sales or an increase in account delinquencies. Changes in immigration policies that affect states that share a border with Mexico may continue to create sales challenges and to negatively impact our retail sales in stores along the Mexican border. There is no assurance that a significant change in US immigration patterns, laws, regulations or enforcement will not occur, and any such significant change could have a material adverse impact on us.
If we lose key management or are unable to attract and retain the qualified sales and credit granting and collection personnel required for our business, our operating results could suffer. Our success depends to a significant degree on the skills, experience and continued service of our key executives and the identification of suitable successors for them. While our key executives are subject to non-competition restrictions and other negative contractual covenants, if we lose the services of any of these individuals and we are unable to identify a suitable successor, or if one or more of them or other key personnel decide to join a competitor or otherwise compete directly or indirectly with us, our business and operations could be harmed, and we could have difficulty in implementing our strategy. In addition, our sales and credit operations are largely dependent upon our labor force. As our business grows, and as we incur turnover in current positions, we will need to locate, hire and retain additional qualified sales personnel in a timely manner and develop, train and manage an increasing number of management level sales associates and other employees. Additionally, if we are unable to attract and retain qualified credit granting and collection personnel, our ability to perform quality underwriting of new credit transactions and maintain workloads for our collections personnel at a manageable level could be materially adversely affected, and our operations could be materially adversely impacted, resulting in higher delinquency and net charge-offs on our credit portfolio. Competition for qualified employees could require us to pay higher wages, and increases in the federal, state or local minimum wage or other employee benefits costs could increase our operating expenses. If we are unable to attract and retain personnel as needed in the future or our operating expenses increase, our net sales and operating results could suffer.
We depend on hiring an adequate number of hourly employees to run our business and are subject to government regulations concerning these and our other employees, including wage and hour regulations. Our workforce is comprised primarily of employees who work on an hourly basis. In certain markets where we operate, there is significant competition for hourly employees. The lack of availability of an adequate number of hourly employees or an increase in wages and benefits to
current employees could have a material adverse effect on us. We are subject to applicable rules and regulations relating to our relationship with our employees, including wage and hour regulations, health and workers’ compensation benefits, unemployment taxes, overtime and working conditions and immigration status. Accordingly, legislated increases in the federal, state or local minimum wage, as well as increases in additional labor cost components such as employee benefit costs, workers’ compensation insurance rates, compliance costs and fines, would increase our labor costs, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
We face significant competition from national, regional, local and internet retailers of furniture and mattresses, home appliances, and consumer electronics. The retail market for consumer electronics, furniture and mattresses is highly fragmented and intensely competitive and the market for home appliances is concentrated among a few major dealers. We currently compete against a diverse group of retailers, including national mass merchants, specialized national retailers, home improvement stores, and locally-owned regional or independent retail specialty stores that sell furniture and mattresses, home appliances, and consumer electronics, similar, and often identical, to those items we sell. We also compete with retailers that market products using store catalogs and the internet. In addition, there are few barriers to entry into our current and contemplated markets, and new competitors may enter our current or future markets at any time. Additionally, we compete to some extent against companies offering weekly or monthly lease-to-own payment options to credit-constrained consumers for products for the home similar to those offered by us.
We may not be able to compete successfully against existing and future competitors. Some of our competitors have financial resources that may be substantially greater than ours and they may be able to purchase inventory at lower costs and better endure economic downturns. If we cannot offer competitive prices to our customers, our sales may decline or we may be required to accept lower profit margins. Our competitors may respond more quickly to new or emerging technologies and may have greater resources to devote to promotion and sale of products and services. If two or more competitors consolidate their businesses or enter into strategic partnerships, they may be able to compete more effectively against us.
Our existing competitors or new entrants into our industry may use a number of different strategies to compete against us, including:
•Expansion by our existing competitors or entry by new competitors into markets where we currently operate;
•Lower pricing;
•Aggressive advertising and marketing;
•Extension of credit to customers on terms more favorable than we offer;
•Extension of credit options to customers with lower credit quality than qualifies for the credit programs we offer;
•Larger store size, or innovative store formats, which may result in greater operational efficiencies; and
•Adoption of improved retail sales methods.
Competition from any of these sources could cause us to lose market share, sales and customers, limit our ability to attract new customers, increase expenditures or reduce prices, any of which could have a material adverse effect on us.
Changes in customer demand and product mix could materially adversely affect our business. Our products must appeal to a broad range of consumers whose preferences cannot be predicted with certainty and are subject to change. Our ability to maintain and increase sales depends to a large extent on the introduction and availability of new products and technologies and our ability to respond timely to customer demands and preferences for such new products. It is possible that the introduction of new products will never achieve widespread consumer acceptance or will be supplanted by alternative products and technologies that do not offer us a similar sales opportunity or are sold at lower price points or margins. We may be unable to anticipate these buying patterns, which could result in a material adverse effect on us. In addition, we often make commitments to purchase products from our vendors several months in advance of proposed delivery dates. Significant deviation from the projected demand for products that we sell could affect our inventory strategies, which may have an adverse effect on us, either from lost sales or lower margins due to the need to reduce prices to dispose of excess inventory.
We may experience significant price pressures over the life cycle of our products from competing technologies and our competitors. Prices for many of our products decrease over their life cycle. Such decreases often result in decreased gross profit margins. Suppliers may also take various steps, including manufacturing lower-cost inventory in higher volumes, to increase their own profitability, which may negatively impact our margins and, as a result, our profitability. Typically, new products, such as OLED, QLED, and 8K are introduced at relatively high price points that are then gradually reduced as the product becomes mainstream. To sustain same store sales growth, unit sales must increase at a rate greater than the decline in product prices. The affordability of products helps drive unit sales growth. However, as a result of relatively short product life cycles in the consumer electronics industry, which limit the amount of time available for sales volume to increase, combined with rapid price erosion in the industry, retailers are challenged to maintain overall gross margin levels and positive same store
sales. We continue to adjust our marketing strategies to address this challenge through the introduction of new product categories, new products within our existing categories and product innovations. If we fail to accurately anticipate the introduction of new technologies, we may possess significant amounts of obsolete inventory that can only be sold at substantially lower prices than we anticipated. In addition, we may not be able to maintain our historical margin levels in the future due to increased sales of lower margin products, such as personal electronics products, and declines in average selling prices of key products, such as consumer electronics and home appliances. If sales of lower margin items continue to increase and replace sales of higher margin items, or if our consumer electronics products average selling prices decrease due to the maturity of their life cycle, our gross margin and overall gross profit levels may be materially adversely affected.
A disruption in our relationships with, the operations of, or the supply of product from any of our key suppliers, including those suppliers and manufacturers located in Asia and Mexico, whether due to pandemics or epidemics, geopolitical conflict, including a potential escalation of the current conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, or otherwise, could have a material adverse effect on us. The success of our business and growth strategies depends to a significant degree on our relationships with our suppliers, particularly our brand name suppliers. We do not have long-term supply agreements or exclusive arrangements with a number of our vendors. We typically order our inventory through the issuance of individual purchase orders to vendors. We have limited contractual assurance of the continued supply of merchandise we currently, or would like to, offer our customers. We also rely on our suppliers for funds in the form of vendor allowances. We may be subject to rationing by suppliers with respect to a number of limited distribution items. In addition, while we purchase products from approximately 200 manufacturers and distributors, we rely heavily on a relatively small number of suppliers. For example, during fiscal year 2024, 67.9% of our total inventory purchases were from six vendors. The loss of any one or more of our key suppliers or failure to establish and maintain relationships with these and other vendors, and limitations on the availability of inventory or repair parts, could have a material adverse effect on our supply and assortment of products, as we may not be able to find suitable replacements to supply products at competitive prices, and on our results of operations and financial condition.
If one of our vendors were to go out of business or were to be unable to fund amounts due to us, including payments due for returns of product and warranty claims, it could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. Catastrophic or other unforeseen events, including pandemics or epidemics, whether inside or outside the U.S., and geopolitical conflict, including the ongoing conflicts in Ukraine and the Middle East, could materially adversely impact the supply and delivery to us of products manufactured far from our sales facilities, including manufacturers or suppliers located in Asia and Mexico, which could materially adversely impact our results of operations. In addition, because many of the products we sell are manufactured outside of the U.S., we may experience labor unrest or an increase in the cost of imported vendor products, or an inability to secure imported merchandise, as a result of border taxes, tariffs, or trade disputes at any time for reasons beyond our control. Any slow-downs, disruptions or strikes at any of the ports may have a material adverse effect on our relationships with our customers and our business, potentially resulting in canceled orders by customers and reduced revenues and earnings. If imported merchandise becomes more expensive, unavailable or difficult to obtain, we may not be able to meet the demands of our customers. Products from alternative sources may also be more expensive than those our vendors currently import.
Our ability to enter new markets successfully depends, to a significant extent, on the willingness and ability of our vendors to supply merchandise to additional distribution centers and stores. If vendors are unwilling or unable to supply some or all of their products to us at acceptable prices in one or more markets, we could be materially adversely affected.
Furthermore, we rely on credit from vendors to purchase our products. A substantial change in credit terms from vendors or vendors’ willingness to extend credit to us, including providing inventory under consignment arrangements, would reduce our ability to obtain the merchandise that we sell, which could have a material adverse effect on us. In addition, if our vendors fail to continue to offer vendor allowances, or we are restricted in our ability to earn such funds, our results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Turmoil in financial markets and economic disruptions around the world may also negatively impact our suppliers’ access to capital and liquidity with which to maintain their inventory, production levels, and product quality, and operate their businesses, all of which could materially adversely affect our supply chain. It may also cause them to change their pricing policies, which could adversely impact demand for their products. Economic disruptions and market instability may make it difficult for us and our suppliers to accurately forecast future product demand trends, which could cause us to carry too much or too little merchandise in various product categories. In addition, to the extent that any manufacturer utilizes labor practices that are not commonly accepted in the U.S., we could be materially adversely affected by any resulting negative publicity.
Failure to maintain sound business and contractual relationships with our dealers may have a material adverse effect on our business and our consolidated financial position, results of operations, and cash flows. Our financial success depends in significant part on our ability to maintain sound business relationships with our dealers. The support of our dealers is also critical for the success of our marketing programs and any new strategic initiatives we seek to undertake. Deterioration in our relationships with our dealers or the failure of our dealers to support our marketing programs and strategic initiatives could have
a material adverse effect on our business and our consolidated financial position, results of operations, and cash flows. In addition, the failure of our dealers to continue or renew their agreements could have a material adverse effect on our business and our ability to enforce the dealers’ contractual obligations.
Our failure to operate our dealer network in a manner that does not implicate federal and state franchise laws may adversely affect our business, prospects, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. As operated now, our dealer program is not a franchise subject to franchise laws and regulations enacted by a number of states and rules promulgated by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (collectively, the “Franchise Laws”). However, if the relationship between us and our dealers should be deemed to constitute a franchise under the Franchise Laws or otherwise violate one or more of the Franchise Laws, we and our operations could be negatively affected including requiring us to incur substantial additional costs which could adversely affect us and our business, prospects, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Additionally, we could face the prospect that discontented dealers could use such violations as the basis for seeking to terminate its dealership agreement or to initiate claims against us for alleged prior failure to comply with the Franchise Laws. We may also face enforcement actions by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission and state governmental agencies, which may seek fines and other remedies available to these agencies under such Franchise Laws. If our dealer program were determined to be a franchise subject to the Franchise Laws, as a franchisor, we would be more susceptible to the risk of adverse legislation or regulations being enacted in the future and we cannot predict how existing or future laws or regulations will be administered or interpreted. Additionally, we cannot predict the amount of future expenditures that may be required in order to comply with any such laws or regulations. Companies that operate franchise systems may be subject to claims arising out of violations of laws and regulations at their franchised locations, including, without limitation, for allegedly being a joint employer with a franchisee. Litigation may lead to a decline in the sales and operating results of our Badcock stores and divert management resources regardless of whether the allegations in such litigation are valid or whether Badcock is liable.
We may be held responsible by third parties, regulators, or courts for the action of, or failure to act, by our dealers and their employees which could expose us to possible fines, other liabilities, bad publicity or damage to our brands.
We grant our dealers a limited license to use our registered service marks and, accordingly, there is risk that one or more of the dealers may be identified as being controlled by us. Third parties, regulators, or courts may seek to hold us responsible for the actions or failures to act by our dealers. Thus, the failure of our dealers to comply with laws and regulations may expose us to liability and damages that may have an adverse effect on our business.
Our dealers operate their businesses under our brands. Because our dealers are independent third parties with their own financial objectives, actions taken by them, including breaches of their contractual obligations, and negative publicity associated with these actions, could adversely affect our reputation and brands more broadly. Any actions as a result of conduct by our dealers, their employees or otherwise which negatively impacts our reputation and brands may result in fewer customers and lower revenues and profits for us.
Disputes with our dealers may have a material adverse effect on our business. From time to time, we engage in disputes with some of our dealers, and some of these disputes result in litigation or arbitration proceedings. Disputes with our dealers may require us to incur significant legal fees, subject us to damages, and occupy a disproportionate amount of management’s time. A material increase in the number of these disputes, or unfavorable outcomes in these disputes, may have a material adverse effect on our business. To the extent we have disputes with our dealers, our relationships with our dealers could be negatively impacted, which could hurt our growth prospects or negatively impact our financial performance.
Our same store sales fluctuate significantly. Our same store sales have fluctuated significantly from quarter to quarter historically and may fluctuate in the future. A number of factors have historically affected, or may in the future affect, our same store sales, including:
•Changes in competition, such as pricing pressure, and the opening of new stores by competitors in our markets;
•General economic conditions;
•Economic challenges faced by our customer base;
•Our Badcock acquisition;
•New product introductions;
•Changes in our marketing programs;
•Consumer trends;
•Changes in our merchandise mix;
•Changes in the relative sales price points of our major product categories;
•Underwriting standards for our customers purchasing merchandise on credit;
•Our ability to offer credit programs attractive to our customers;
•The impact of any new stores on our existing stores;
•Our ability to manage our supply chain and inventory as a result of relocations of and restructurings to our distribution centers;
•Weather events and conditions in our markets;
•Pandemics, epidemics or outbreaks;
•Timing of promotional events;
•Timing, location and participants of major sporting events;
•The number of new store openings;
•The percentage of our stores that are mature stores that tend to be smaller or have fewer assortment of higher margin products, such as furniture;
•The locations of our stores and the traffic drawn to those areas;
•How often we update our stores;
•Our ability to execute our business strategy effectively;
•Staffing levels; and
•Lease-to-own penetration rates.
In the past we have been named as a defendant in multiple securities class action lawsuits. Potential similar or related litigation or investigations could result in substantial damages and may divert management’s time and attention from our business.
These lawsuits or future such lawsuits could result in the diversion of management’s time and attention away from business operations, which could harm our business and also harm our relationships with existing customers and vendors. They may also materially damage our reputation and the value of our brand. Our legal expenses incurred in defending these lawsuits, or future such lawsuits, have been, and could be, significant, and rulings against us, or settlements, could have a material adverse effect on us.
There can be no assurance that any litigation to which we are, or in the future may become, a party will be resolved in our favor. These lawsuits and any other lawsuits that we may become party to are subject to inherent uncertainties, and the costs to us of defending litigation matters will depend upon many unknown factors. Any claim that is successfully decided against us may require us to pay substantial damages, including punitive damages, and other related fees, or prevent us from selling certain of our products. Regardless of whether lawsuits are resolved in our favor or if we are the plaintiff or the defendant in the litigation, any lawsuits to which we are or may become a party will likely be expensive and time consuming to defend or resolve.
Pending litigation relating to the sale of credit insurance and the sale of repair service agreements in the retail industry could have a material adverse effect on us. State attorneys generals and private plaintiffs have filed lawsuits against other retailers relating to improper practices in connection with the sale of credit insurance and repair service agreements in several jurisdictions around the country. We offer credit insurance in our stores on sales financed under our credit programs and require customers to purchase credit insurance from us, or provide evidence from a third-party insurance provider, at their election, in connection with sales of merchandise on credit. Therefore, similar litigation could be brought against us. While we believe we are in full compliance with applicable laws and regulations, if we are found liable in any future lawsuit regarding credit insurance or repair service agreements, we could be required to pay substantial damages or incur substantial costs as part of an out-of-court settlement or require us to modify or suspend certain operations, any of which could have a material adverse effect on us. An adverse judgment or any negative publicity associated with our repair service agreements or any potential credit insurance litigation could also affect our reputation, which could have a negative impact on our cash flow and results of operations.
Pending or unforeseen litigation and the potential for adverse publicity associated with litigation could have a material adverse effect on us. We are involved from time to time in various legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of our business, including primarily commercial, consumer finance, debt collections, product liability, employment and intellectual property claims. We currently do not expect the outcome of any pending matters to have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations, financial position or cash flows. Litigation, however, is inherently unpredictable, and it is possible that the ultimate outcome of one or more pending claims asserted against us, or claims that may be asserted in the
future that we are currently not aware of, or adverse publicity resulting from any such litigation, could adversely impact our business, reputation, sales, profitability, cash flows and financial condition.
In recent years many participants in the manufacturing, retail and software industries have been the target of patent litigation claimants making demands or filing claims based upon alleged patent infringement through the manufacturing and selling, either in merchandise or through software and internet websites, of product or merely providing access through website portals. We, in conjunction with multiple other parties, have been (and remain) the targets of such claims. While we believe that we have not violated or infringed any third-party alleged patent rights, and intend to defend vigorously any such claims, the cost to defend, settle or pay any such claims could be substantial and could have a material adverse effect on us.
Failure to effectively manage our costs could have a material adverse effect on our profitability. Certain elements of our cost structure are largely fixed in nature. Consumer spending remains uncertain, which makes it more challenging for us to maintain or increase our operating income. The competitiveness in our industry and increasing price transparency means that the focus on achieving efficient operations is greater than ever. As a result, we must continuously focus on managing our cost structure. Failure to manage our labor and benefit rates, advertising and marketing expenses, operating leases, charge-offs, other store expenses or indirect spending could materially adversely affect us.
Our stores are concentrated in the southern region of the U.S., especially Texas and Florida, which subjects us to regional risks, such as the economy, regulatory, outbreaks, the performance of energy markets, extreme weather conditions, hurricanes and other natural or man-made disasters. If the southern region of the U.S. suffers an economic downturn, increased regulation or any other adverse regional event, such as an outbreak, a collapse of the oil and gas market, or inclement weather, it could have a material adverse effect on us as a result of the concentration of our stores in such region. Several of our competitors operate stores in various regions across the U.S. and thus may not be as vulnerable to the risks associated with operating in a concentrated region. The states and the local economies where many of our stores are located are dependent, to a degree, on the oil and gas industries, which can be very volatile due to fluctuations of commodities prices or other causes. Because of fears of climate change and adverse effects of drilling explosions and oil spills, legislation has been considered, and governmental regulations and orders have been issued, which, combined with the local economic and employment conditions caused by both, could materially adversely impact the oil and gas industries and the economic health of areas in which a significant number of our stores are located.
Acts of violence at or threatened against our stores or the centers in which they are located, including active shooter situations, protests and terrorism, could unfavorably impact our sales, which could have a material adverse effect on us. Any act of violence at or threatened against our stores or the centers in which they are located, including active shooter situations, protests and terrorist activities, may result in restricted access to our stores and/or store closures in the short-term, and in the long-term, may cause our customers to avoid our stores. Any such situation could adversely impact cash flows and make it more difficult to fully staff our stores, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our information technology systems for our key business processes are vulnerable to damage that could harm our business. Our ability to operate our business, including our ability to manage our credit and collections, operations and inventory levels, largely depends on the efficient operation of our computer hardware and software systems. We use management information systems, including our credit underwriting, loan management, inventory management and collections systems, to track inventory information at the store level, communicate customer information, aggregate daily sales and expense information and manage our credit portfolio, including processing credit applications and managing collections. In addition, we license these systems from third parties. These systems and our operations are subject to damage or interruption from, among other things:
•Power loss, computer systems failures and internet, telecommunications or data network failures;
•Operator negligence, unauthorized access or improper operation by, or supervision of, employees;
•Physical and electronic loss of data or security breaches, misappropriation and similar events;
•Computer viruses;
•Intentional acts of vandalism and similar events;
•Failures on behalf of third parties from which we license certain of these systems to provide timely, quality and regular access to or maintenance of such systems; and
•Hurricanes, fires, floods and other natural disasters.
In addition, the software that we have developed internally to use in our daily operations may contain undetected errors that could cause our network to fail or our expenses to increase. Any failure of our owned or licensed systems due to any of these or other causes could cause an interruption in our operations and result in reduced net sales and results of operations. Though we have implemented contingency and disaster recovery processes in the event of one or several technology failures, any unforeseen failure, interruption or compromise of our systems or our security measures could adversely affect our business and
harm our reputation. The risk of possible failures or interruptions may not be adequately addressed by us or the third-parties on which we rely, and such failures or interruptions could occur. The occurrence of any failures or interruptions could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our information technology systems may not be adequate to meet our evolving business and emerging regulatory needs and the failure to successfully implement new systems, including to integrate Badcock and achieve anticipated synergies, could negatively impact our business and financial results. We are investing capital in new information technology systems and implementing modifications and upgrades to existing systems to support our growth and integrate Badcock. These investments include replacing legacy systems, making changes to existing systems, building redundancies, acquiring new systems and hardware with updated functionality, and integrating Badcock systems to achieve synergies. We are taking actions to ensure the successful implementation of these initiatives, including the testing of new systems and the transfer of existing data, with minimal disruptions to our business and collections, but there can be no guarantee of success. These efforts may take longer and may require greater financial and other resources than anticipated, may cause distraction of key personnel, may cause disruptions to our existing systems and our business, and may not provide the anticipated benefits. Any disruption in our information technology systems, or our inability to improve, or failure to upgrade, integrate or expand our systems to meet our evolving business and emerging regulatory requirements, could impair our ability to achieve critical strategic initiatives and could have a material adverse effect on us.
We could lose our access to customer and credit data sources, which could cause us competitive harm and have a material adverse effect on us. We are heavily dependent on customer and credit data provided by third party providers. Our data providers could stop providing data, provide untimely, incorrect or incomplete data, or increase the costs for their data for a variety of reasons, including a perception that our systems are insecure as a result of a data security breach or regulatory concerns or for competitive reasons. We could also become subject to increased legislative, regulatory or judicial restrictions or mandates on the collection, disclosure or use of such data, in particular if such data is not collected by our providers in a way that allows us to legally use the data. If we were to lose access to this external data or if our access or use were restricted or were to become less economical or desirable, our business would be negatively impacted, which would adversely affect our operating results and financial condition. We cannot provide assurance that we will be successful in maintaining our relationships with these external data source providers or that we will be able to continue to obtain data from them on acceptable terms or at all. Furthermore, we cannot provide assurance that we will be able to obtain comparable data from alternative sources on favorable terms or at all if our current sources become unavailable.
If we cannot continue to offer third party payment solutions for customers who do not qualify for our proprietary credit offerings, our business may be impaired. Currently, if a customer does not qualify for our credit offering for a particular purchase in our stores, but qualifies with a payment solutions provider not affiliated with us but with whom we have a commercial relationship, then we sell the applicable merchandise to such payment solutions provider, which leases the merchandise to the customer under a lease-to-own arrangement, and we record a cash sale. In fiscal year 2024, our third-party payment solution providers providing lease-to-own arrangements, represented approximately 8.5% of our retail revenue. Our third-party payment and credit solutions providers’ business models are subject to various risks that are outside of our control. If, as a result of any of these risks, our third-party payment and credit solutions providers are unable to, or otherwise determine not to continue operating with us at a level or on terms similar to the level or on terms we have historically operated, or if we are unable to establish new partnerships with different providers on favorable terms or at all, then we could lose sales or revenue, our financial results could be adversely affected, our ability to execute our growth plan could be impeded and we could otherwise suffer a material adverse effect.
If we are unable to continue to offer third-party repair service agreements to our customers, we could incur additional costs or repair expenses, which could materially adversely affect us. There are a limited number of insurance carriers that provide repair service agreement programs. If repair service agreement programs become unavailable from our current providers for any reason, we may be unable to provide repair service agreements to our customers on the same or similar terms, or at all. Even if we are able to obtain a substitute provider, higher premiums may be required, which could have a material adverse effect on our profitability if we are unable to pass along the increased cost of such coverage to our customers. Inability to maintain the repair service agreement program could cause fluctuations in our repair expenses, impact our credit portfolio losses, and cause greater volatility of earnings and could require us to become the obligor under new contracts we sell.
If we are unable to maintain group credit insurance policies from insurance carriers, which allow us to offer their credit insurance products to our customers purchasing our merchandise on credit, our revenues may be reduced or our credit losses may increase. There are a limited number of insurance carriers that provide credit insurance coverage for sale to our customers. If credit insurance becomes unavailable for any reason we may be unable to offer substitute coverage on the same or similar terms, or at all. Even if we are able to obtain substitute coverage, it may be at higher rates or reduced coverage, which could affect customer acceptance of these products, reduce our revenues or increase our credit losses.
We utilize a limited number of home delivery service providers. The loss of any one provider could have a material negative impact on our home delivery operations. If our third-party merchandise delivery services are unable to meet our promised
delivery schedule, unable to maintain expense controls, or cease operations, our net sales may decline due to a decline in customer satisfaction, and profitability levels may be negatively impacted. For many purchases, we offer next day delivery to our customers that we outsource to one of our third-party delivery service providers. The loss of any one service provider, or the failure to establish and maintain relationships with these or other similar service providers, could have a material negative impact on our home delivery operations. These third-parties are subject to risks that are beyond our control and, if they fail to timely or satisfactorily deliver our products, we may lose business from customers in the future and could suffer damage to our reputation. The loss of customers or damage to our reputation could have a material adverse effect on us. Further, if our third-party delivery service providers are unable to maintain expense controls, our profitability and results of operations may be negatively impacted.
Changes in trade policy, currency exchange rate fluctuations and other factors beyond our control could materially adversely affect our business. A significant portion of our inventory is manufactured or assembled overseas in Asia and in Mexico. Changes in U.S. and foreign governments’ trade policies have resulted in, and may continue to result in, tariffs on imports into and exports from the U.S. Throughout 2018 and 2019, the U.S. imposed tariffs on imports from several countries, including China. While the impact of the tariffs was minimal to the Company in fiscal year 2023 and 2024, because many of the products that we sell are manufactured in foreign jurisdictions, including China, other such tariffs could have a negative impact on our business in the future. The current and any future administrations in Washington, D.C. may likely take a different view on tariffs with China and other countries. In addition, if the U.S. were to withdraw from or materially modify international trade agreements, similar to the replacement of the North American Free Trade Agreement with the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement in November 2018, certain foreign-sourced goods that we sell may no longer be available at commercially attractive prices or at all, resulting in a material adverse effect on us. Additionally, currency fluctuations, including a devaluation of the U.S. dollar, border taxes, import tariffs, or other factors beyond our control may increase the cost of items we purchase or create shortages of these items, which in turn could have a material adverse effect on us. Conversely, significant reductions in the cost of these items in U.S. dollars may cause a significant reduction in the retail prices of those products, resulting in a material adverse effect on us.
Our costs to protect our intellectual property rights, infringement of which could impair our name and reputation, could be significant. We believe that our success and ability to compete depends in part on consumer identification of the name “Conn’s” and “Badcock” and other trademark registrations and we rely on such trademark registrations and common law rights to protect the distinctiveness of our brands. We intend to protect vigorously our trademarks against infringement, misappropriation or dilution by others. A third-party, however, could attempt to misappropriate our intellectual property or claim that our intellectual property infringes or otherwise violates third-party trademarks in the future. Any litigation or claims relating to our intellectual property brought by or against us, whether with or without merit, or whether successful or not, could result in substantial costs and diversion of our resources, which could have a material adverse effect on us.
Failure to protect the security of our customers’, employees’ or suppliers’ information or failure to comply with data privacy and protection laws could expose us to litigation, compromise the integrity of our products, damage our reputation and materially adversely affect us. Our business regularly captures, collects, handles, processes, transmits and stores significant amounts of sensitive information about our customers, employees, suppliers and others, including financial records, credit and business information, and certain other personally identifiable or other sensitive personal information. A number of other retailers have experienced security breaches, including a number of highly publicized incidents involving well-known retailers. To our knowledge, we have not suffered a significant security breach. While we have implemented systems and processes to protect against unauthorized access to or use of secured data and to prevent data loss and theft, there is no guarantee that these procedures are adequate to safeguard against all data security breaches or misuse of data. In addition, we rely on the secure operation of our website and other third-party systems generally to assist us in the collection and transmission of the sensitive data we collect. Our information systems are vulnerable to damage or interruption from power outages, computer and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, security breaches (including credit card information breaches), vandalism, catastrophic events and human error or malfeasance. A compromise of our information security controls or of those businesses with which we interact, which results in confidential information being accessed, obtained, damaged, or used by unauthorized or improper persons, could harm our reputation and expose us to regulatory actions and claims from customers, employees, financial institutions, payment card associations and other persons, any of which could materially adversely affect us. Moreover, a data security breach could require that we expend significant resources related to our information systems and infrastructure, and could distract management and other key personnel from performing their primary operational duties. If our information systems are damaged, fail to work properly or otherwise become unavailable, we may incur substantial costs to repair or replace them, and may experience loss of critical information, customer disruption and interruptions or delays in our ability to perform essential functions and implement new and innovative services. In addition, compliance with changes in privacy and information security laws and standards may result in considerable expense due to increased investment in technology and the development of new operational processes.
We maintain data breach and network security liability insurance, but we cannot be certain that our coverage will be adequate for any liabilities actually incurred or that insurance will continue to be available to us on economically reasonable terms or at
all. We may need to devote significant resources to protect against security breaches or to address problems caused by breaches, which would divert resources from the growth and expansion of our business.
Our tax liabilities could be materially impacted by any changes in the tax laws of the jurisdictions in which we operate, beginning operations in new states, and assessments as a result of tax audits. Legislation could be introduced at any time that changes our tax liabilities in a way that has a material adverse effect on us. In particular, because of the extent of our operations in Texas, the Texas margin tax, which is based on gross profit rather than earnings, can create significant volatility in our effective tax rate. In addition, our significant expansion in Florida and Georgia in connection with our acquisition of Badcock and entry into new states in the future, could subject us to additional tax rate volatility, dependent upon the tax laws in place in those states. Moreover, we periodically review our indirect tax audit reserve based on recent assessments of prior year periods. In the event that actual results differ from our estimate, we may revise our estimate of post-audit periods, which could materially impact our financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to sales, income and other taxes, which can be difficult and complex to calculate due to the nature of our business. A failure to correctly calculate and pay such taxes could result in substantial tax liabilities and have a material adverse effect on us. The application of indirect taxes, such as sales tax, is a complex and evolving issue and we may not have accrued or remitted required amounts to various jurisdictions. Many of the fundamental statutes and regulations that impose these taxes were established before the growth of e-commerce and, therefore, in many cases it is not clear how existing statutes apply to certain aspects of our business and we rely on advice from our third-party tax advisors. In addition, governments are increasingly looking for ways to increase revenues, which has resulted in discussions about tax reform and other legislative action to increase tax revenues, including through indirect taxes. This also could result in other adverse changes in or interpretations of existing sales, income and other tax regulations, the exact nature or effect of which cannot be reasonably calculated, but which could have a material adverse effect on us.
Failure to successfully utilize and manage e-commerce, and to compete effectively with the growing e-commerce sector, could materially adversely affect our business and prospects. Our websites provide new and existing customers with the ability to review our product offerings and prices, apply for credit, and make payments on their credit accounts. Customers may apply for credit, be approved for credit, and complete a transaction to purchase merchandise on our websites. Customers may also purchase certain products on our websites using a credit card. Our websites are a significant component of our advertising strategy. We believe our websites represent a possible source for future sales and growth in our credit sales. In order to promote our products and services, allow our customers to complete credit applications in the privacy of their homes and on their mobile devices and make payments on their accounts, and drive traffic to our stores, we must effectively create, design, publish and distribute content over the internet. We currently offer certain credit-qualified customers the ability to complete an entire purchase transaction financed online. We are monitoring and adjusting the availability of our online sales channels for credit performance and profitability. There can be no assurance that we will be able to design and publish web content with a high level of effectiveness or grow our e-commerce business in a profitable manner. Certain of our competitors, and a number of e-commerce retailers, have established e-commerce operations against which we compete for customers. It is possible that the increasing competition from the e-commerce sector may reduce our market share, gross margin or operating margin, and may have a material adverse effect on us.
If we fail to maintain adequate systems and processes to detect and prevent fraudulent activity, including in our e-commerce business, our business could be materially adversely impacted. Criminals are using increasingly sophisticated methods to engage in illegal activities such as paper instrument counterfeiting, fraudulent payment or refund schemes and identity theft. As we make more of our services available over the internet and other media, and as we expand into new geographic regions without an established customer base, we subject ourselves to increased consumer fraud risk. While we believe past incidents of fraudulent activity have been relatively isolated, we cannot be certain that our systems and processes will always be adequate in the face of increasingly sophisticated and ever-changing fraud schemes. We use a variety of tools to protect against fraud, but these tools may not always be successful at preventing such fraud. Instances of fraud may result in increased costs, including possible settlement and litigation expenses, and could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our reputation, ability to do business and operating results may be impaired by improper conduct by any of our employees, agents or business partners. Our employees, agents or business partners may violate the policies and procedures we have implemented to ensure compliance with applicable laws. Improper actions by any of the foregoing could subject us to civil, criminal or administrative investigations, could lead to substantial civil and criminal, monetary and non-monetary penalties, and related stockholder lawsuits, could cause us to incur significant legal fees, and could damage our reputation.
Because we maintain a significant supply of cash and inventories in our stores, we may be subject to employee and third-party robberies, burglaries, thefts, riots and looting, and may be subject to liability as a result of crimes at our stores. Our business requires us to maintain a significant supply of cash, loan collateral and inventories in most of our stores. As a result, we are subject to the risk of robberies, burglaries, thefts, riots and looting. Although we have implemented various programs in an effort to reduce these risks, maintain insurance coverage for robberies, burglaries and thefts and utilize various security measures at our facilities, there can be no assurance that robberies, burglaries, thefts, riots and looting will not occur. The
extent of our cash, loan collateral and inventory, losses or shortages could increase as we expand the nature and scope of our products and services. Robberies, burglaries, thefts, riots and looting could lead to losses and shortages and could have a material adverse effect on us. It is also possible that violent crimes such as armed robberies may be committed at our stores. We could experience liability or adverse publicity arising from such crimes. For example, we may be liable if an employee, customer, guard or bystander suffers bodily injury or other harm. Any such event may have a material adverse effect on us.
We are subject to risks associated with leasing substantial amounts of space, including future increases in occupancy costs. We lease almost all of our store locations, our corporate headquarters and our distribution centers. Our success depends in part on our ability to locate property for new stores and renew leases for existing locations. There is no assurance that we will be able to locate real estate and negotiate leases for new stores, or renegotiate leases for existing locations, on the same or similar terms, or on favorable terms at all, and we could be forced to move or exit a market as a result. Furthermore, a significant rise in real estate prices or real property taxes could result in an increase in store lease expense as we open new locations and renew leases for existing locations, thereby negatively impacting our results of operations. Our inability to enter into new leases or renew existing leases on terms acceptable to us, or be released from our obligations under leases for stores that we close, could materially adversely affect us.
We depend primarily on cash flow from operations to pay our lease expenses. If our business does not generate sufficient cash flow from operating activities to fund these expenses, we may not be able to service our lease expenses, which could materially adversely affect us. If an existing or future store is not profitable, and we decide to close it, we may be nonetheless committed to perform our obligations under the applicable lease including, among other things, paying the base rent for the balance of the lease term. Moreover, even if a lease has an early cancellation clause, we might not satisfy the contractual requirements for early cancellation under that lease.
Failure to maintain positive brand perception and recognition could have a negative impact on our business. Maintaining a good reputation is critical to the success of our business. The considerable expansion of the use of social media by our customers (including, but not only, as a result of our technological outreach), has increased the risk that our reputation could be negatively impacted in a short amount of time. If we are unable to quickly and effectively respond to criticism of our brand or reputation (on any basis), we may suffer declines in customer loyalty and traffic, vendor relationship issues, and other consequences, all of which could have a material adverse effect on us.
We face risks with respect to product liability claims and product recalls, which could materially adversely affect our reputation, our business, and our consolidated results of operations. We purchase merchandise from third-parties and offer this merchandise to customers for sale. This merchandise could be subject to recalls and other actions by regulatory authorities. Changes in laws and regulations could also impact the type of merchandise we offer to customers. We have experienced, and may in the future experience, recalls of merchandise. In addition, individuals may in the future assert claims that they have sustained injuries from third-party merchandise offered by us, and we may be subject to future lawsuits relating to these claims. These claims or liabilities may exceed, or fall outside the scope of, our insurance coverage. Any of the issues mentioned above could result in damage to our reputation, diversion of management resources, or reduced sales and increased costs, any of which could have a material adverse effect on us.
If we fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, our ability to product accurate and timely financial statements could be impaired, which could harm our business and have a material adverse effect on the price of our common stock. I
We are required to comply with a variety of reporting, accounting and other rules and regulations. As a result, we maintain a system of internal control over financial reporting, but there are limitations inherent in internal control systems and significant deficiencies or material weaknesses are possible. A control system can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. In addition, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints and the benefit of controls must be appropriate relative to their costs. Furthermore, compliance with existing requirements is expensive and we may need to implement additional finance and accounting and other systems, procedures and controls to satisfy our reporting requirements. If our internal control over financial reporting is determined to be ineffective, or if we are unable to appropriately or timely remediate any such effectiveness, such failure could cause us to restate financial results that have been made public, cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, negatively affect the market price of our common stock, subject us to regulatory investigations and penalties, require us to expend significant resources to remediate the deficiencies, impair our access to capital and otherwise materially adversely impact us.
Our governance documents and Delaware law provide certain anti-takeover measures which could discourage, delay or prevent a change in control of the Company, even if such changes would be beneficial to our stockholders. Provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws, as well as provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”) could discourage, delay or prevent a merger, acquisition or other change in control of the Company, even if such change in control would be beneficial to our stockholders. These provisions include:
•A prohibition on stockholder action without a meeting, unless such action has been approved in advance by our Board of Directors;
•A prohibition on stockholders’ ability to call special meetings of stockholders;
•Express powers to adjourn, postpone, reschedule or cancel meetings of stockholders, and rules regarding presiding, and conduct, at such meetings;
•Significant advance notice requirements for nominations for election to the Board of Directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings; and
•Authorization of the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock that could be issued by our Board of Directors to increase the number of outstanding shares and thwart a takeover attempt.
Further, we are subject to Section 203 of the DGCL, which limits certain transactions and business combinations between a corporation and a stockholder owning 15% or more of the corporation’s outstanding voting stock for a period of three years from the date the stockholder becomes a 15% stockholder. These provisions and our stockholders’ rights plan, either alone or in combination with each other, could delay, deter or prevent a change of control, whether or not it is desired by, or beneficial to, our stockholders.
Our corporate actions may be substantially controlled by our principal stockholders and affiliated entities. A large proportion of our outstanding common stock is beneficially owned by a small group of principal stockholders and their affiliates. Large holders, such as these, may be able to affect matters requiring approval by Company stockholders, including the election of directors and the approval of mergers or other business combination transactions. The concentration of ownership of our shares of common stock by the relatively small number of investors and hedge funds may:
•Have significant influence in determining the outcome of any matter submitted to stockholders for approval, including the election of directors, mergers, consolidations, and the sale of all or substantially of our assets or other significant corporate actions;
•Delay or deter a change of control of the Company;
•Deprive stockholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their shares as part of a sale of the Company; and
•Affect the market price volatility and liquidity of our shares of common stock.
The interests of these investors and their respective affiliates may differ from or be adverse to the interests of our other stockholders. If any of these investors sells a substantial number of shares in the public market, the market price of our shares could fall. The perception among the public that these sales will occur could also contribute to a decline in the market price of our shares.
Risks Associated with the Badcock Acquisition
We may not be able to successfully integrate the Badcock business and our failure to do so could negatively impact our business and financial results. The acquisition of Badcock involves numerous operational, strategic, financial, accounting, legal and other functions that must be integrated. Difficulties in integrating Badcock may result in the combined company performing differently than expected, in operational challenges or in the failure to realize anticipated expense-related efficiencies. Potential difficulties that may be encountered in the integration process include, among other factors:
•the inability to successfully integrate the businesses of Badcock into Conn’s in a manner that permits Conn’s to achieve the anticipated benefits and cost savings from the acquisition;
•challenges associated with managing the larger, more complex, integrated business;
•not realizing anticipated operating synergies or incurring unexpected costs to realize such synergies;
•integrating personnel from the two companies while maintaining focus on performance;
•potential unknown liabilities and unforeseen expenses, delays or other conditions associated with the acquisition;
•loss of key employees;
•integrating relationships with customers, vendors and business partners;
•performance shortfalls at one or both of the companies as a result of the diversion of management’s attention caused by completing the acquisition and integrating Badcock’s operations into Conn’s; and
•the disruption of, or the loss of momentum in, each company’s ongoing business or inconsistencies in standards, controls, procedures and policies.
Conn’s success will depend, in part, on its ability to manage its expansion, which poses numerous risks and uncertainties, including the need to integrate the operations and business of Badcock into its existing business in an efficient and timely manner including the combination of systems and management controls.
We may fail to realize all of the anticipated benefits of the acquisition. The success of the transaction will depend, in part, on our ability to realize the anticipated benefits and cost savings from combining Conn’s and Badcock’s businesses. The anticipated benefits and cost savings of the acquisition may not be realized fully or at all, may take longer to realize than expected, may require more non-recurring costs and expenditures to realize than expected or could have other adverse effects that we do not currently foresee. For example, the integration process may result in the loss of key employees, the disruption of ongoing businesses or inconsistencies in standards, controls, procedures and policies and there could be potential unknown liabilities and unforeseen expenses associated with the acquisition that were not discovered in the course of performing due diligence.
We have incurred substantial transaction fees and costs in connection with the acquisition. We have incurred and expect to incur a number of non-recurring transaction-related costs associated with the acquisition, combining our operations with Badcock’s and achieving desired synergies. These fees and costs may be substantial. Non-recurring transaction costs include, but are not limited to, fees paid to legal, financial and accounting advisors, filing fees and printing costs.
We may not be able to retain key personnel following the acquisition. Our success after the acquisition will depend in part upon our ability to retain management personnel and other employees. Current and prospective employees of Conn’s and Badcock may experience uncertainty about their roles within the combined company following the acquisition, which may have an adverse effect on our ability to attract or retain management and other personnel. Accordingly, no assurance can be given that the combined company will be able to attract or retain management personnel and other employees to the same extent that they have previously been able to attract or retain their employees which could have an adverse result on our business and results of operations.
The market price of our common stock after the acquisition may be affected by factors different from those affecting the shares of our common stock historically. Conn’s business differs from that of Badcock. Accordingly, the results of operations of the combined company and the market price of Conn’s common stock after the completion of the acquisition may be affected by factors different from those currently affecting the independent results of operations of each company.
Conn’s preferred shares and any to-be-created shares of non-voting common stock into which the preferred stock will convert, have, or will have, if applicable, different rights from the Conn’s common stock. In the acquisition, holders of the W.S. Badcock LLC interests received preferred shares of Conn’s that are convertible into non-voting common stock to be created and issued upon stockholder approval. The rights associated with the preferred and any non-voting common stock, if applicable, are different from, and may be adverse in some respects to, the rights associated with Conn’s common stock.
We may fail to receive sufficient stockholder support for establishing the class of non-voting common stock or the related conversion of the preferred shares into such new class which could result in us paying a dividend on the preferred shares. In the acquisition, holders of the W.S. Badcock LLC interests received preferred shares of Conn’s that are convertible into non-voting common stock to be created and issued upon stockholder approval. If the stockholders do not approve the class of non-voting common stock or the related conversion, the preferred shares will require our payment of a dividend beginning on September 4, 2024. The dividend is initially 8% per annum but it may grow to as much as 16% per annum.
Risk Related to Laws and Regulations
We may expand our retail, credit, or lease-to-own offerings and become subject to different operating, regulatory or legal requirements. In addition to the retail, consumer finance and lease-to-own products we currently offer, we may offer other products and services in the future, including new financing or leasing products and services. These products and services may require additional or different operating and compliance systems or have additional or different legal or regulatory requirements than the products and services we currently offer.
To the extent we undertake expansion into additional states that allow for direct consumer lending, and do not have the proper legal and regulatory compliance infrastructure, consumer lending licenses or personnel, or otherwise do not successfully execute such an expansion, or our customers do not positively respond to such an expansion, it could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our business could be materially adversely affected by changes in consumer protection laws and regulations. Federal and state consumer protection laws, regulations and agencies, such as the FCRA and the CFPB, heavily regulate the way we conduct business and could limit the manner in which we may offer and extend credit or leases and collect on our accounts. Because a substantial portion of our sales are financed or leased any adverse change in related regulation could have a material adverse effect on us.
New laws or regulations, or new interpretations of existing laws or regulations, could limit the amount of interest or fees that may be charged to our consumer, or impose limitations on our ability to collect on account balances, which could have a material adverse effect on us. Compliance with existing and future laws or regulations, including regulations that may be applicable to us under the Dodd-Frank Act, could require the expenditure of substantial resources. Failure to comply with these
laws or regulations, even if inadvertent, could result in negative publicity, fines or additional licensing expenses, any of which could result in a material adverse effect on us.
We have procedures and controls in place that we believe are reasonable to monitor compliance with the numerous federal and state laws and regulations and believe we are in compliance with such laws and regulations. However, these laws and regulations are complex, differ between jurisdictions and are often subject to interpretation. As we expand into additional jurisdictions and offer credit products such as our direct consumer loans and lease-to-own offerings, the complexities grow. Compliance with these laws and regulations is expensive and requires the time and attention of management. If we do not successfully comply with laws, regulations, or policies, we could incur fines or penalties, lose existing or new customers, or suffer damage to our reputation. Changes in these laws and regulations can significantly alter our business environment, limit business operations, and increase costs of doing business, and we may not be able to predict the impact such changes would have on our profitability.
Regulatory agencies may reshape consumer financial laws and there continues to be uncertainty as to how such actions will impact our business. The Dodd-Frank Act comprehensively overhauled the financial services industry within the U.S. and established the CFPB. The CFPB has enforcement and rulemaking authority under certain federal consumer financial laws, including, but not limited to, the TILA, ECOA, FCRA, FDCPA, and GLBA. This means, for example, that the CFPB has the ability to adopt rules that interpret provisions of the FDCPA, potentially affecting all facets of debt collection. The CFPB published a revised final rule under the FDCPA that would, among other things, limit the timing and number of calls that can be made to a consumer debtor by a third-party collection agency. This rule could impact our ability to contact our consumers and collect amounts owed. In addition, the CFPB has issued guidance in the form of bulletins on debt collection and credit furnishing activities generally, including bulletins that address furnisher requirements and the application of the CFPB’s prohibition on “unfair, deceptive, or abusive” acts or practices with respect to debt collection.
In addition, the CFPB maintains an online complaint system that allows consumers to log complaints with respect to the products we offer. The system could inform future agency decisions with respect to regulatory, enforcement, or examination focus. The CFPB is authorized to collect fines and provide consumer restitution in the event of violations of certain consumer financial service laws, engage in consumer financial education, request data, and promote the availability of financial services to under-served consumers and communities. There continues to be uncertainty as to how, or if, the CFPB and its strategies and priorities will impact our businesses and our results of operations going forward and could result in new regulatory requirements and regulatory costs for us.
Although we have committed substantial resources to enhancing our compliance programs, changes in regulatory expectations, interpretations or practices could increase the risk of enforcement actions, fines and penalties. Actions by the CFPB, FTC and various state agencies could result in requirements to alter our products and services that would make our products less attractive to consumers or impair our ability to offer them profitably. Future actions by regulators that discourage the use of products we offer or steer consumers to other products or services could result in reputational harm and a loss of customers.
We expect the CFPB, FTC and various state agencies will continue their focus on alternative consumer financial services products, and, as a result, businesses transacting with subprime consumers, may be held to higher standards of monitoring, disclosure and reporting, regardless of whether new laws or regulations governing our industry are adopted. This increased attention may increase our compliance costs significantly, result in fines or monetary penalties or settlements due to future government investigations, and materially and adversely impact the manner in which we operate, which may be materially adverse to our business and financial results. In recent years, state regulatory authorities have been increasingly focused on the subprime financial marketplace, including the lease-to-own industry.
Certain aspects of our business, such as the content of our advertising and other disclosures to customers about transactions, our data collection practices, the manner in which we contact customers, the decisioning process regarding whether we enter into a transaction with a potential customer, our credit reporting practices, and the manner in which we process and store certain customer, employee and other information are all subject to federal and state laws and regulatory oversight.
We have incurred and will continue to incur substantial costs to comply with federal, state and local laws and regulations, including rapidly evolving consumer protection standards. In addition to compliance costs, we may incur substantial expenses to respond to regulatory and third-party investigations and enforcement actions, proposed fines and penalties, sanctions, and private litigation, as well as potential "headline risks" that may negatively impact our business. Consumer complaints with respect to our industry have resulted in, and may in the future result in, state, federal and local regulatory and other investigations. In addition, while we are not aware of any whistleblower claims regarding our specific business practices, such claims are on the rise generally. We believe these claims will likely continue and could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial results.
Judicial or administrative decisions, CFPB rule-making or amendments to the Federal Arbitration Act could render the arbitration agreements we use illegal or unenforceable. Dispute arbitration provisions are commonplace in our customer credit arrangements. These provisions are designed to allow us to resolve customer disputes through individual arbitration
rather than in court. Our arbitration provisions explicitly provide that all arbitrations will be conducted on an individual and not on a class basis. In the past, various courts and administrative authorities have concluded that arbitration agreements with class action waivers are unenforceable, particularly where a small dollar amount is in controversy on an individual basis.
Any judicial or administrative decisions, federal legislation or final CFPB or other administrative rule that would impair our ability to enter into and enforce consumer dispute arbitration agreements with class action waivers could significantly increase our exposure to class action litigation as well as litigation in plaintiff-friendly jurisdictions. Such litigation could have a material adverse effect on us.
We are required to comply with laws and regulations regulating extensions of credit, lease-to-own transactions and other dealings with customers and our failure to comply with applicable laws and regulations, or any adverse change in those laws or regulations, could have a negative impact on our business. A substantial portion of our customers finance purchases through our credit offerings or enter into lease-to-own transactions. The extension of credit to consumers, leasing and related collection efforts is a highly regulated area of our business. Numerous federal and state laws impose disclosure and other requirements on the origination, servicing and enforcement of credit accounts. These laws include, but are not limited to, TILA, ECOA, the Dodd-Frank Act, FCRA, GLBA, FTCA, FDCPA, MLA, SCRA, the Texas Debt Collection Act, the Florida Consumer Collection Practices Act and the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (“TCPA”). Our business practices, marketing and advertising terms, procedures and practices for credit and lease applications and underwriting, terms of credit extensions, leases and related disclosures, data privacy and protection practices, and collection practices, may be subject to periodic or special reviews by regulatory and enforcement authorities under the foregoing laws. These reviews could range from investigations of specific consumer complaints or concerns to broader inquiries into our practices generally. If, as part of these reviews, the regulatory authorities conclude that we are not complying with applicable laws or regulations, they could request or impose a wide range of sanctions and remedies including requiring changes in advertising and collection practices, changes in our credit application and underwriting practices, changes in our data privacy or protection practices, changes in the terms of our credit or other financial products (such as decreases in interest rates or fees), the imposition of fines or penalties, or the paying of restitution or the taking of other remedial action with respect to affected customers. They also could require us to stop offering some of our credit or other financial products within one or more states, or nationwide.
Negative publicity relating to any specific inquiry or investigation, regardless of whether we have violated any applicable law or regulation or the extent of any such violation, could negatively affect our reputation, our brand and our stock price, which could have a material adverse effect on us. If any deficiencies or violations of law or regulations are identified by us or asserted by any regulator or other person, or if any regulatory or enforcement authority or court requires us to change any of our practices, the correction of such deficiencies or violations, or the making of such changes, could have a material adverse effect on us. We face the risk that restrictions or limitations resulting from the enactment, change, or interpretation of federal or state laws and regulations, such as the Dodd-Frank Act, could negatively affect our business activities, require us to make significant expenditures or effectively eliminate credit products or other financial products currently offered to customers.
Any failure on our part to comply with legal requirements in connection with credit or other financial products, or in connection with servicing or collecting our accounts or otherwise dealing with consumers, could significantly impair our ability to collect the full amount of the account balances and could subject us to substantial liability for damages or penalties. The institution of any litigation of this nature, or the rendering of any judgment against us in any litigation of this nature, could have a material adverse effect on us.
We may also expand into additional jurisdictions or offer new credit products in existing jurisdictions. We must comply with the laws of each jurisdiction we operate in, which are not uniform. New or different laws in new jurisdictions into which we expand, or changes to the laws in those jurisdictions or the ones in which we currently operate, could increase our compliance costs, expose us to litigation risk or otherwise have a material adverse effect on us.
We face the risk of litigation resulting from calls and text messages in violation of the TCPA. Contacting current and prospective customers in connection with delinquent accounts and marketing efforts are parts of our business. The TCPA restricts certain calling and the use of automated SMS text messages without proper consent. This has resulted and may in the future result in civil claims against us. The scope and interpretation of the TCPA applicable to calling and texting are continuously evolving and developing, and there are differing interpretations of the TCPA among the jurisdictions in which we operate. In some cases, violations of the TCPA may be enforced by individual customers through class actions, and statutory penalties for TCPA violations range from $500 to $1,500 per violation. If we do not comply with the TCPA or if we become liable under the TCPA, we could face direct liability and our business and financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
A large number of our stores are located in the State of Texas and the State of Florida, which subjects us to concentrated regulatory risks. Negative or unexpected legislative or regulatory changes in Texas or Florida could have a material adverse effect on us. We currently have 75 retail stores in Texas and 138 stores in Florida. In Texas, the Office of the Consumer Credit Commissioner (“OCCC”) issues the consumer loan licenses that permit us to offer direct consumer loans. The OCCC also
regulates us as a licensee. If we fail to establish or implement a proper regulatory infrastructure to comply with Texas’ regulatory requirements, the OCCC could restrict or rescind our consumer loan licenses. Similar regulation applies in Florida under the Florida Office of Financial Regulation ("FLOFR"). A restriction on or a loss of such licenses issued could have a material adverse effect on our financial performance and cause reputational harm. Failure on our part to comply with applicable consumer lending laws of the State of Texas or the State of Florida could also expose us to consumer litigation and regulatory enforcement action, possibly resulting in substantial penalties and claims for damages and, in certain circumstances, may subject us to injunctions, require us to refund finance charges already paid, forgo finance charges not yet paid under credit accounts, change our credit extension, servicing, collection, and marketing practices or a combination of the foregoing. Should Texas, Florida, the OCCC or FLOFR change laws, regulations or codes related to consumer loans, or modify past regulatory guidance, our compliance costs and litigation exposure could increase. We believe that we are in substantial compliance with the applicable consumer credit laws in the State of Texas and the State of Florida.
Our inability to maintain our insurance licenses requirements in the states in which we operate and changes in premium and commission rates on the insurance products we sell could have a material adverse effect on us. We derive a significant portion of our revenues and operating income from the commissions we earn from the sale of various insurance products of third-party insurers to our customers. These products include credit insurance, repair service agreements and product replacement policies. Most states and many local jurisdictions in which we operate require registration and licenses to sell these products or otherwise conduct our business. These states and local jurisdictions have, in many cases, established criteria we must satisfy in order to obtain, maintain and renew these licenses. For example, certain states or other jurisdictions require us to meet or exceed certain operational, advertising, disclosure, collection and recordkeeping requirements and to maintain a minimum amount of net worth or equity. From time to time, we are subject to audits in these jurisdictions to ensure we are satisfying the applicable requirements in order to maintain these necessary licenses. If, for any reason, we are unable to satisfy these requirements, we might be unable to maintain our insurance licenses in the states and other jurisdictions in which we operate, we might be subject to various fines and penalties or store closures, or our requests for new or renewed licenses may be denied, any of which consequences could have a material adverse effect on us. In addition, any material claims or future material litigation involving our credit insurance agreements, repair service agreements or product replacement policies, or any decline in the commissions we retain from our sales of these insurance products, may have a material adverse effect on us. Commissions earned on our credit insurance, repair service agreement or product replacement agreement products could also be materially adversely affected by changes in statutory premium rates, commission rates, adverse claims experience and other factors.
General Risk Factors
Stock market volatility may materially adversely affect the market price of our common stock. Our common stock price has been and is likely to continue to be subject to significant volatility. A variety of factors could cause the price of our common stock to fluctuate substantially, including:
•General market fluctuations resulting from factors not directly related to our operations or the inherent value of our common stock;
•State or federal legislative or regulatory proposals, initiatives, actions or changes that are, or are perceived to be, adverse to our operations;
•Our ability to integrate Badcock and realize anticipated synergies;
•Announcements of developments related to our business or our competitors;
•Fluctuations in our operating results and the provision for bad debts;
•General conditions in the consumer financial service industry, the domestic or global economy or the domestic or global credit or capital markets;
•Changes in financial estimates by securities analysts;
•Our failure to meet the expectations of securities analysts or investors;
•Negative commentary regarding us and corresponding short-selling market behavior;
•Adverse developments in our relationships with our customers or vendors;
•Legal proceedings brought against us or our officers and directors; and
•Changes in our senior management team.
Due to the volatility of our stock price, we are and may be in the future the target of securities litigation. Such lawsuits generally result in the diversion of management’s time and attention away from business operations, which could materially
adversely affect us. In addition, the costs of defense and any damages resulting from such litigation, a ruling against us, or a settlement of any such litigation could materially adversely affect our financial results.
We may incur property, casualty or other losses not covered by insurance. We maintain a program of insurance coverage for various types of property, casualty and other risks. The types and amounts of insurance that we obtain vary from time to time, depending on availability, cost and our decisions with respect to risk retention. The insurance policies are subject to deductibles and exclusions that result in our retention of a level of risk on a self-insurance basis. Losses not covered by insurance could be substantial and may increase our expenses, which could harm our results of operations and financial condition.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS.
None.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY.
Leadership and Governance
Our organization is guided by our Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) who leads our enterprise-wide cybersecurity strategy, compliance, policy, standards, architecture, cyber operations, risk management, governance, and processes. With over 25 years of experience in Information Security, including 14 years as a CISO for several multi-billion-dollar organizations, our CISO brings unparalleled expertise to our security initiatives.
Executive Reporting
Our CISO provides periodic security and risk management updates to executive leadership, the board of directors, and audit committee, ensuring comprehensive awareness and oversight of our security posture. Updates are delivered during quarterly meetings with executive leadership and bi-annual meetings with the audit committee. Topics related to cybersecurity risk, control maturity, incident management, compliance posture, and security improvement initiatives are addressed during these meetings.
Standards and Frameworks
Our cybersecurity program aligns with leading industry standards, including the National Institute of Standards and Technology ("NIST") Cybersecurity Framework. The NIST CSF provides a structured and flexible approach to managing cybersecurity risk, enabling us to effectively identify, protect, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats. By adhering to NIST standards, we enhance our resilience and ensure alignment with recognized best practices.
Thought Leadership and Collaboration
We leverage thought leadership from key vendors, business partners, and industry intelligence sources to stay abreast of emerging threats and align with best practices. This collaborative approach enables us to proactively respond to evolving cyber risks while effectively managing risk in line with our organizational risk appetite.
Continuous Monitoring and Response
Our security operations include 24/7 monitoring conducted by a third-party provider in collaboration with internal teams. Conn's has implemented vendor management controls that ensure our service providers practice due diligence and due care when providing professional services to Conn's or managing our data. Additionally, Conn's has implemented risk management processes to monitor for cybersecurity threats associated with vendors who have access to our systems, applications, or data. This proactive approach ensures timely detection and response to cybersecurity threats, minimizing the potential impact on our business operations and financial condition.
Incident Management
As of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, there are no known security threats or incidents that are likely to materially affect our business strategy, operations, or financial condition. We maintain robust incident management processes to swiftly address any security incidents that may arise, mitigating their impact and preserving the integrity of our operations.
In conclusion, our information security program is underpinned by strong leadership, adherence to industry standards, proactive monitoring, and collaboration with internal and external stakeholders. By prioritizing cybersecurity and risk management, we uphold our commitment to safeguarding our assets, maintaining operational resilience, and protecting the interests of our stockholders.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES.
The number of stores, distribution centers/cross-dock facilities, and corporate offices we operate, together with location and square footage information, are disclosed in Part I, Item 1., Business, under the caption “Store Operations,” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS.
The information set forth in Part II, Item 8., in Note 13, Contingencies, of the Consolidated Financial Statements of this Annual Report on Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES.
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Market Information and Holders
As of April 10, 2024, we had approximately 514 common stockholders of record and an estimated 4,610 beneficial owners of our common stock. The principal market for our common stock is the NASDAQ Global Select Market, where it is traded under the symbol “CONN.”
Dividends
No cash dividends were declared or paid in fiscal year 2024 or fiscal year 2023. We do not anticipate paying dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future payment of dividends will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements and other factors deemed relevant by the Board of Directors, including the terms of our indebtedness. Provisions in agreements governing our long-term indebtedness restrict the amount of dividends that we may pay to our stockholders. See Item 7., Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, under the heading “Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table summarizes information as of January 31, 2024, relating to our equity compensation plans to which grants of options, restricted stock units or other rights to acquire shares of our common stock may be granted from time to time:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Number of Securities to be Issued upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights (a) (1) | | Weighted-Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights (b) (2) | | Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans (Excluding Securities Reflected in Column (a)) |
| Plan Category: | | | | | |
| Equity compensation plans approved by stockholders | 2,890,589 | | | $ | 6.25 | | | 1,295,451 | |
| Equity compensation plans not approved by stockholders | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | 2,890,589 | | | $ | 6.25 | | | 1,295,451 | |
(1)Inclusive of 600,000 stock options, 1,910,349 restricted stock units (“RSUs”) and 380,240 performance-based RSUs (“PSUs”).
(2)The $6.25 is inclusive of the 1,910,349 shares related to RSUs which only have a service requirement and the 380,240 PSUs that have a service, performance and/or market requirement. Neither the RSUs nor PSUs have an exercise price. The weighted-average exercise price of the 600,000 outstanding stock options is $30.12.
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock for the last five fiscal years with the cumulative total returns of the NASDAQ U.S. Stock Market Index and a customized peer group index comprised of First Cash, Aaron’s, Upbound Group (formerly Rent-a-Center), La-Z-Boy, Sleep Number, Ethan Allen, EZCORP, Haverty Furniture, Hooker Furniture, Kirkland's, Encore Capital, Enova International, PRA Group and PROG Holdings (the “Peer Group”). The peer group index reflects comparable companies across our two operating segments and removes one entity that is no longer publicly traded. The graph assumes an investment of $100 at the close of trading on January 31, 2019, and reinvestment of any dividends. The stock performance shown below is based solely on historical data and is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
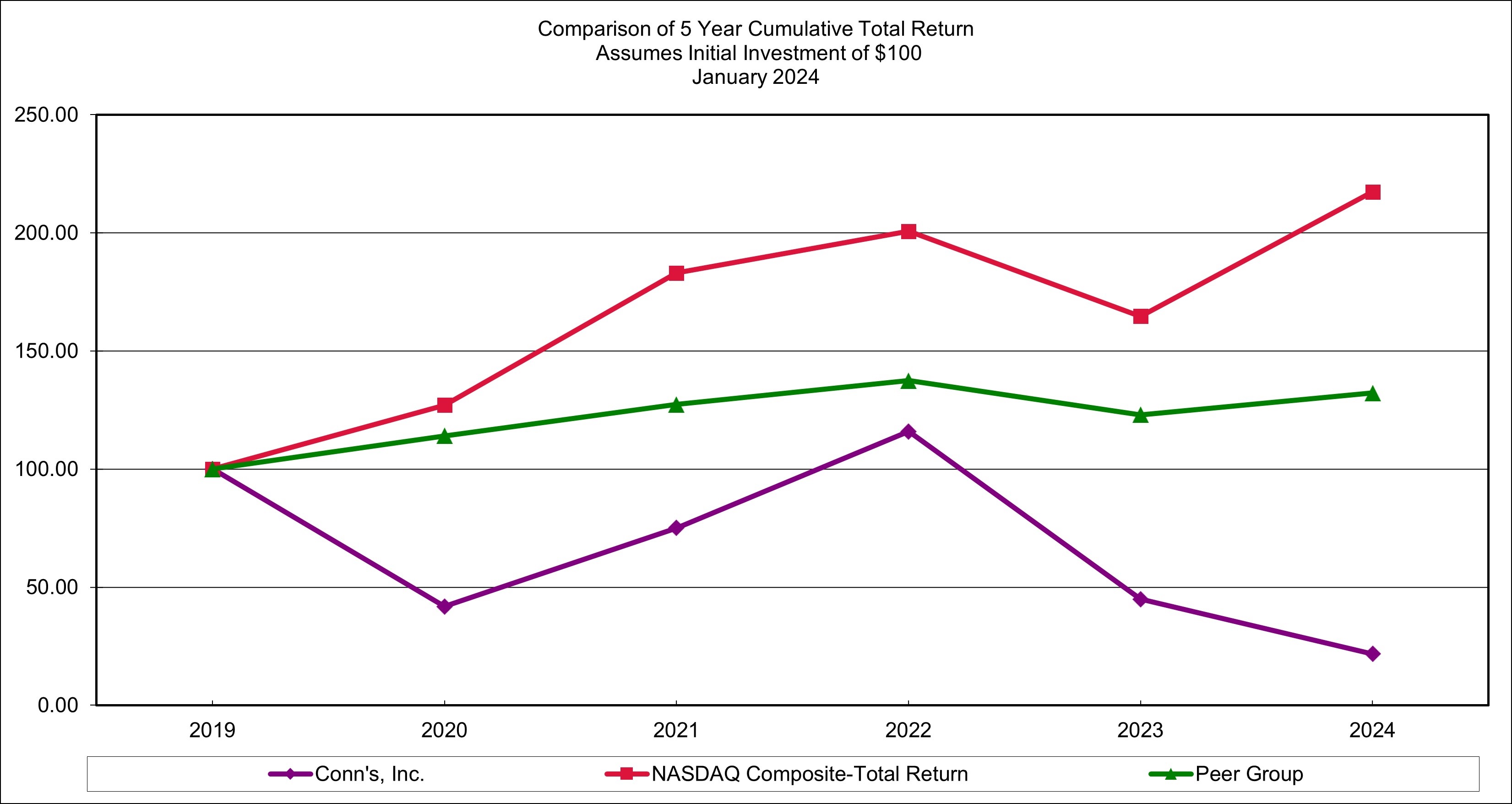
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Base Period | | Value for the Fiscal Years Ended January 31, |
| January 31, 2019 | | 2020 | | 2021 | | 2022 | | 2023 | | 2024 |
| Company/Index: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Conn’s, Inc. | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 41.83 | | | $ | 75.12 | | | $ | 115.90 | | | $ | 44.93 | | | $ | 21.72 | |
| NASDAQ U.S. Stock Market Index | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 127.03 | | | $ | 183.04 | | | $ | 200.70 | | | $ | 164.68 | | | $ | 217.36 | |
| Peer Group | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 114.11 | | | $ | 127.34 | | | $ | 137.40 | | | $ | 122.97 | | | $ | 132.16 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The information set forth under the heading “Performance Graph” is not deemed to be “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC or subject to the SEC’s proxy rules or to the liabilities of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, and the graph shall not be deemed to be incorporated into any of our prior or subsequent filings under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (“Securities Act”), or the Exchange Act.
ITEM 6. [Reserved]
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
Overview
This section provides a discussion of our historical financial condition, cash flows and results of operations for the periods indicated herein. We encourage you to read this Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and related notes included herein and the discussion in Item 1. Business of this annual report on Form 10-K. This discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve numerous risks and uncertainties. The forward-looking statements are subject to a number of important factors, including those factors discussed in Item 1A. Risk Factors and Part I Forward-Looking Statements that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described or implied by such forward-looking statements.
Discussion and analysis of matters pertaining to the year ended January 31, 2022 and year-to-year comparisons between the years ended January 31, 2023 and 2022 are not included in this Form 10-K, but can be found under Part II, Item 7 of our annual report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 31, 2023 that was filed on March 29, 2023.
Our fiscal year ends on January 31. References to a fiscal year refer to the calendar year in which the fiscal year ends.
Executive Summary
Total revenues were $1.2 billion for fiscal year 2024 compared to $1.3 billion for fiscal year 2023, a decrease of $104.8 million or 7.8%. Retail revenues were $1.0 billion for fiscal year 2024 compared to $1.1 billion for fiscal year 2023, a decrease of $89.1 million or 8.3%. The decrease in retail revenue was primarily driven by a decrease in same store sales of 16.2%. The decrease in same store sales was primarily driven by lower discretionary spending for home-related products following several periods of excess consumer liquidity resulting in the acceleration of sales. The decrease in same store sales was partially offset by new store growth and the acquisition of W.S. Badcock in December 2023. Credit revenues were $257.2 million for fiscal year 2024 compared to $264.8 million for fiscal year 2023, a decrease of $7.6 million or 2.9%. The decrease in credit revenue was primarily due to a decrease of 6.1% in the average outstanding balance of the customer accounts receivable portfolio, a decrease in our yield rate and a decrease in late fee revenues. The yield rate for the year ended January 31, 2024 was 22.7% compared to 23.1% for the year ended January 31, 2023.
Retail gross margin for fiscal year 2024 was 35.9%, an increase of 190 basis points from the 34.0% reported in fiscal year 2023. The year-over-year increase in retail gross margin was primarily driven by pricing and assortment changes, a more profitable product mix and normalizing freight costs. The increase was partially offset by the deleveraging of fixed distribution costs.
SG&A for fiscal year 2024 was $561.6 million compared to $526.2 million for fiscal year 2023, an increase of $35.4 million, or 6.7%, over the prior year. The SG&A increase was primarily due to an increase in occupancy from new stores, advertising costs, labor costs, and other general operating costs from the acquisition of Badcock in December 2023.
Provision for bad debts increased to $154.1 million for the year ended January 31, 2024 from $121.2 million for the year ended January 31, 2023, an increase of $32.9 million. The year-over-year increase was primarily driven by a smaller decrease in the allowance charge for bad debts during the year ended January 31, 2024 of $1.5 million, compared to the decrease during the year ended January 31, 2023 of $26.9 million. The increase was also due to an increase in net charge-offs of $7.0 million. Finally, Badcock added $5.6 million in total provision expense. During the year ended January 31, 2023, the decrease in allowance for bad debts was primarily driven by an improvement in the forecasted unemployment rate that drove a $31.5 million decrease in the economic reserve and a decline in the customer portfolio receivable balance, partially offset by an increase in loss rates.
Interest expense increased to $81.7 million for fiscal year 2024 compared to $36.9 million for fiscal year 2023, an increase of $44.8 million, or 121.4%. The increase was driven by a higher average outstanding balance of debt and higher effective interest rates.
Net loss for fiscal year 2024 was $76.9 million, or $3.17 per diluted share, compared to a net loss of $59.3 million, or $2.46 per diluted share, for fiscal year 2023.
How We Evaluate Our Operations
Senior management focuses on certain key indicators to monitor our performance including:
•Same store sales - Our management considers same store sales, which consists of both brick and mortar and eCommerce sales, to be an important indicator of our performance because they reflect our attempts to leverage our SG&A costs, which include rent and other store expenses, and they have a direct impact on our total net sales, net income, cash and working capital. Same store sales is calculated by comparing the reported sales for all stores that were open during both comparative fiscal years, starting in the first period in which the store has been open for a full quarter. Sales from closed stores, if any, are removed from each period. Sales from relocated stores have been included in each period if each such store was relocated within the same general geographic market. Sales from expanded stores have also been included in each period.
•Retail gross margin - Our management views retail gross margin as a key indicator of our performance because it reflects our pricing power relative to the prices we pay for our products. Retail gross margin is calculated by comparing retail total net sales to the cost of goods sold.
•60+ Day Delinquencies - Our management views customer account delinquencies as a key indicator of our performance because it reflects the quality of our credit portfolio, drives future credit performance and credit offerings, and impacts the interest rates we pay on our asset-backed securitizations. Delinquencies are measured as the percentage of balances that are 60+ days past due.
•Net yield - Our management considers yield to be a key performance metric because it drives future credit decisions and credit offerings and directly impacts our net income. Yield reflects the amount of interest we receive from our portfolio of customer receivables.
Company Initiatives
We delivered the following financial and operational results in fiscal year 2024 as compared to the prior fiscal year period (unless otherwise noted):
•Total consolidated revenue declined 7.8% to $1.2 billion, due to a 9.1% decline in total net sales, and a 3.6% reduction reduction in finance charges and other revenues;
•Badcock, which was acquired on December 18, 2023, contributed $68.4 million to total consolidated revenue;
•Net loss per diluted share was $3.17 and included $16.3 million of one-time transaction expenses.
Strategic Update
In response to challenging macroeconomic pressures, the Company has updated its near-term strategic priorities which include:
•Integration of Badcock. We intend to focus our efforts on a successful integration of the Badcock business. We have created an Integration Management Office, an Integration Steering Committee and regularly update our Board of Directors as to our progress. We are implementing identified synergies within merchandising, inventory and logistics management, integrating ERP systems and intend to extend our traditional installment loan financing options to all Badcock stores by early summer.
•Refocus on core customer. We continue to refocus our efforts on serving core credit-constrained customers as we continue to face the impacts of macroeconomic headwinds and changes in consumer behavior. Providing multiple financing options is our key differentiator. We are pursuing profitable growth strategies aimed at enhancing the payment options we provide to our large and established customer base.
•eCommerce enhancement. We completed the final phase of the eCommerce platform conversion, which further enhanced our digital capabilities and produced record fiscal year eCommerce sales.
Outlook
The broad appeal of our value proposition to our geographically diverse core demographic and the unit economics of our business should provide the stability necessary to maintain and grow our business. We expect our brand recognition and long history in our core markets to give us the opportunity to further penetrate our existing footprint, particularly as we leverage existing marketing spend, logistics infrastructure, and service footprint. We plan to improve our operating results by leveraging our existing infrastructure and seeking to continually optimize the efficiency of our marketing, merchandising, distribution and credit operations and by realizing on synergies associated with our acquisition of Badcock. As we expand in existing markets, including in connection with the integration of Badcock, we expect to increase our purchase volumes, achieve distribution efficiencies and strengthen our relationships with our key vendors. Over time, we also expect our increased store base and the resulting higher net sales to further leverage our existing corporate and regional infrastructure.
Results of Operations
The following tables present certain financial and other information, on a consolidated basis:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consolidated: | Year Ended January 31, | |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Total net sales | $ | 978,331 | | | $ | 1,076,590 | | | $ | (98,259) | |
| Finance charges and other revenues | 259,352 | | | 265,937 | | | (6,585) | |
| Total revenues | 1,237,683 | | | 1,342,527 | | | (104,844) | |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | 629,688 | | | 710,234 | | | (80,546) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | 561,628 | | | 526,212 | | | 35,416 | |
| Provision for bad debts | 154,080 | | | 121,193 | | | 32,887 | |
| Charges and credits | 17,565 | | | 14,360 | | | 3,205 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 1,362,961 | | | 1,371,999 | | | (9,038) | |
| Operating loss | (125,278) | | | (29,472) | | | (95,806) | |
| Interest expense | 81,707 | | | 36,891 | | | 44,816 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 14,221 | | | — | | | 14,221 | |
| Bargain purchase gain, net of deferred taxes | (104,857) | | | — | | | (104,857) | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | (116,349) | | | (66,363) | | | (49,986) | |
| Benefit for income taxes | (39,456) | | | (7,071) | | | (32,385) | |
| Net loss | $ | (76,893) | | | $ | (59,292) | | | $ | (17,601) | |
Supplementary Operating Segment Information
Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise that engage in business activities and for which discrete financial information is available that is evaluated on a regular basis by the chief operating decision maker to make decisions about how to allocate resources and assess performance. We are a leading specialty retailer and offer a broad selection of quality, branded durable consumer goods and related services in addition to a proprietary credit solution for our core consumers. We have two operating segments: (i) retail and (ii) credit. Our operating segments complement one another. The retail segment operates primarily through our stores and website and its product offerings include furniture and mattresses, home appliances, consumer electronics and home office products from leading global brands across a wide range of price points. Our credit segment offers affordable financing solutions to a large, under-served population of consumers who typically have limited credit alternatives. Our operating segments provide customers the opportunity to comparison shop across brands with confidence in our competitive prices as well as affordable monthly payment options, fast delivery and installation in the majority of our markets, and product repair service. We believe our large, attractively merchandised retail stores and credit solutions offer a distinctive value proposition compared to other retailers that target our core customer demographic. The operating segments follow the same accounting policies used in our consolidated financial statements.
We evaluate a segment’s performance based upon operating income (loss). SG&A includes the direct expenses of the retail and credit operations, allocated corporate overhead expenses, and a charge to the credit segment to reimburse the retail segment for expenses it incurs related to occupancy, personnel, advertising and other direct costs of the retail segment which benefit the credit operations by sourcing credit customers and collecting payments. The reimbursement received by the retail segment from the credit segment is calculated using an annual rate of 2.5% multiplied by the average outstanding portfolio balance for each applicable period.
The following table represents total revenues, costs and expenses, operating income (loss) and income (loss) before taxes attributable to these operating segments for the periods indicated:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Retail Segment: | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Product sales | $ | 903,658 | | | $ | 986,600 | | | $ | (82,942) | |
| Repair service agreement commissions | 72,738 | | | 80,446 | | | (7,708) | |
| Service revenues | 8,763 | | | 9,544 | | | (781) | |
| Total net sales | 985,159 | | | 1,076,590 | | | (91,431) | |
| Finance charges and other | 3,409 | | | 1,119 | | | 2,290 | |
| Total revenues | 988,568 | | | 1,077,709 | | | (89,141) | |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | 631,604 | | | 710,234 | | | (78,630) | |
Selling, general and administrative expense (1) | 431,887 | | | 391,393 | | | 40,494 | |
| Provision for bad debts | 540 | | | 896 | | | (356) | |
| Charges and credits | 17,565 | | | 14,360 | | | 3,205 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 1,081,596 | | | 1,116,883 | | | (35,287) | |
| Operating loss | (93,028) | | | (39,174) | | | (53,854) | |
| Interest expense | 46 | | | — | | | 46 | |
| Bargain purchase gain, net of deferred taxes | (104,857) | | | — | | | (104,857) | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | $ | 11,783 | | | $ | (39,174) | | | $ | 50,957 | |
| Number of stores: | | | | | |
| Beginning of fiscal year | 168 | | | 158 | | | |
| Acquired | 376 | | | — | | | |
| Opened | 9 | | | 11 | | | |
| Closed | (1) | | | (1) | | | |
| End of fiscal year | 552 | | | 168 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Credit Segment: | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Finance charges and other revenues | $ | 257,193 | | | $ | 264,818 | | | $ | (7,625) | |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | 4,377 | | | — | | | 4,377 | |
Selling, general and administrative expense (1) | 130,741 | | | 134,819 | | | (4,078) | |
| Provision for bad debts | 153,540 | | | 120,297 | | | 33,243 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 288,658 | | | 255,116 | | | 33,542 | |
| Operating (loss) income | (31,465) | | | 9,702 | | | (41,167) | |
| Interest expense | 81,662 | | | 36,891 | | | 44,771 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 14,221 | | | — | | | 14,221 | |
| Loss before income taxes | $ | (127,348) | | | $ | (27,189) | | | $ | (100,159) | |
(1)For the years ended January 31, 2024 and January 31, 2023, the amount of overhead allocated to each segment reflected in SG&A was $32.5 million and $31.7 million, respectively. For the years ended January 31, 2024 and January 31, 2023, the amount of reimbursement made to the retail segment by the credit segment was $25.0 million and $26.3 million, respectively.
Year ended January 31, 2024 compared to the year ended January 31, 2023
Revenues. The following table provides an analysis of retail net sales by product category in each period, including repair service agreement commissions and service revenues, expressed both in dollar amounts and as a percent of total net sales:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | | | % | | Same Store |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | % of Total | | 2023 | | % of Total | | Change | | Change | | % Change |
| Furniture and mattress | $ | 352,375 | | | 35.8 | % | | $ | 340,325 | | | 31.6 | % | | $ | 12,050 | | | 3.5 | % | | (10.9) | % |
| Home appliance | 338,725 | | | 34.4 | | | 430,250 | | | 40.0 | | | (91,525) | | | (21.3) | | | (24.6) | |
| Consumer electronics | 110,571 | | | 11.2 | | | 139,868 | | | 13.0 | | | (29,297) | | | (20.9) | | | (24.0) | |
| Home office | 37,737 | | | 3.8 | | | 37,547 | | | 3.5 | | | 190 | | | 0.5 | | | (2.7) | |
| Other | 64,250 | | | 6.5 | | | 38,610 | | | 3.6 | | | 25,640 | | | 66.4 | | | 55.3 | |
| Product sales | 903,658 | | | 91.7 | | | 986,600 | | | 91.7 | | | (82,942) | | | (8.4) | | | (16.4) | |
Repair service agreement commissions (1) | 72,738 | | | 7.4 | | | 80,446 | | | 7.5 | | | (7,708) | | | (9.6) | | | (14.6) | |
| Service revenues | 8,763 | | | 0.9 | | | 9,544 | | | 0.8 | | | (781) | | | (8.2) | | | |
| Total net sales | $ | 985,159 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | 1,076,590 | | | 100.0 | % | | $ | (91,431) | | | (8.5) | % | | (16.2) | % |
(1) The total change in sales of repair service agreement commissions includes retrospective commissions, which are not reflected in the change in same store sales.
The decrease in product sales for the year ended January 31, 2024 was primarily driven by a decrease in same store sales of 16.4%. The decrease in same store sales was primarily driven by lower discretionary spending for home-related products following several periods of excess consumer liquidity resulting in the acceleration of sales. The decrease in same store sales was partially offset by new store growth and the acquisition of Badcock in December 2023.
The following table provides the change of the components of finance charges and other revenues:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Interest income and fees | $ | 229,170 | | | $ | 244,137 | | | $ | (14,967) | |
| Insurance income | 23,614 | | | 20,681 | | | 2,933 | |
| Other revenues | 6,568 | | | 1,119 | | | 5,449 | |
| Finance charges and other revenues | $ | 259,352 | | | $ | 265,937 | | | $ | (6,585) | |
The decrease in finance charges and other revenues was primarily due to a decrease of 6.1% in the average outstanding balance of the customer accounts receivable portfolio coupled with a slight decrease in the effective yield which decreased from 23.1% for the year ended January 31, 2023 to 22.7% for the year ended January 31, 2024. This decrease was partially offset by the revenue contributed by Badcock.
The following table provides key portfolio performance information for our installment loan portfolio:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Interest income and fees | $ | 224,631 | | | $ | 244,137 | | | $ | (19,506) | |
| Net charge-offs | (150,295) | | | (148,138) | | | (2,157) | |
| Net portfolio income | $ | 74,336 | | | $ | 95,999 | | | $ | (21,663) | |
| Average outstanding portfolio balance | $ | 991,149 | | | $ | 1,055,600 | | | $ | (64,451) | |
| Interest income and fee yield | 22.7 | % | | 23.1 | % | | |
| Net charge-off % | 15.2 | % | | 14.0 | % | | |
Retail Gross Margin
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Retail total net sales | $ | 985,159 | | | $ | 1,076,590 | | | $ | (91,431) | |
| Cost of goods sold | 631,604 | | | 710,234 | | | (78,630) | |
| Retail gross margin | $ | 353,555 | | | $ | 366,356 | | | $ | (12,801) | |
| Retail gross margin percentage | 35.9 | % | | 34.0 | % | | |
The year-over-year increase in retail gross margin percentage was primarily driven by pricing and assortment changes, a more profitable product mix and normalizing freight costs. The increase was partially offset by the deleveraging of fixed distribution costs.
Selling, General and Administrative Expense
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Retail segment | $ | 431,887 | | | $ | 391,393 | | | $ | 40,494 | |
| Credit segment | 130,741 | | | 134,819 | | | (4,078) | |
| Eliminations | (1,000) | | | — | | | (1,000) | |
| Selling, general and administrative expense - Consolidated | $ | 561,628 | | | $ | 526,212 | | | $ | 35,416 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expense as a percent of total revenues | 45.4 | % | | 39.2 | % | | |
The SG&A increase in the retail segment was primarily due to an increase in labor costs, occupancy and operational costs associated with new store growth and the acquisition of Badcock. These increases were partially offset by a decline in delivery and transportation costs.
As a percent of average total customer portfolio balance, SG&A for the credit segment for the year ended January 31, 2024 was 13.2%, as compared to 12.8% for the year ended January 31, 2023. The SG&A increase in the credit segment was primarily due to an increase in occupancy costs which were partially offset by a decrease in labor costs and other operating expenses.
Provision for Bad Debts
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Retail segment | $ | 540 | | | $ | 896 | | | $ | (356) | |
| Credit segment | 153,540 | | | 120,297 | | | 33,243 | |
| Provision for bad debts - Consolidated | $ | 154,080 | | | $ | 121,193 | | | $ | 32,887 | |
| Provision for bad debts - Credit segment, as a percent of average outstanding portfolio balance | 15.5 | % | | 11.4 | % | | |
The provision for bad debts increased to $154.1 million for the year ended January 31, 2024 from $121.2 million for the year ended January 31, 2023, an increase of $32.9 million. The year-over-year increase was primarily driven by an increased allowance charge of $25.2 million due to the portfolio mix coupled with increased loss rates. In addition, net charge-offs increased $7.7 million.
Charges and Credits
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Store lease termination and closure costs | $ | 2,340 | | | $ | (896) | | | $ | 3,236 | |
| Professional Fees | 18,372 | | | — | | | 18,372 | |
| Employee severance | — | | | 8,006 | | | (8,006) | |
| Gain from asset sale | (3,147) | | | — | | | (3,147) | |
| Loss on asset disposal | — | | | 7,250 | | | (7,250) | |
| $ | 17,565 | | | $ | 14,360 | | | $ | 3,205 | |
During the year ended January 31, 2024, we recognized $18.4 million in professional fees related to corporate transactions, primarily related to the acquisition of Badcock. In addition, we recognized a $3.1 million gain related to the sale of a single store location net of asset disposal costs and a loss of $2.3 million in store closure costs related to the impairment of assets associated with the decision to end the store-within-a-store test with Belk, Inc. During the year ended January 31, 2023, we recognized $8.0 million in severance costs related to a change in the executive management team. In addition, we recognized a $0.9 million gain related to the termination of a lease for a single store location net of store closure costs. Furthermore, we recognized $7.3 million in asset disposal costs related to a change in the e-commerce platform.
Bargain Purchase Gain
During the year ended January 31, 2024, we recognized $104.9 million bargain purchase gain which represents the fair value of net assets acquired over the consideration transferred, net of tax, for the acquisition of Badcock.
Interest Expense
Interest expense increased to $81.7 million for the year ended January 31, 2024 from $36.9 million for the year ended January 31, 2023, an increase of $44.8 million. The increase was driven by a higher average outstanding balance of debt and a higher effective interest rate.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Revolving Credit Facility | $ | 23,374 | | | $ | 12,513 | | | $ | 10,861 | |
Term loans(1) | 13,984 | | | — | | | 13,984 | |
| Asset-backed notes | 39,583 | | | 25,236 | | | 14,347 | |
| Delayed Draw Term Loan | 1,640 | | | — | | | 1,640 | |
| Secured borrowings | 3,498 | | | — | | | 3,498 | |
| Other | (372) | | | (861) | | | 489 | |
| Total interest expense | $ | 81,707 | | | $ | 36,888 | | | $ | 44,819 | |
(1) Includes interest associated with the Pathlight Term Loan and BRF Term Loan.
Benefit for Income Taxes
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | Change |
| Benefit for income taxes | $ | (39,456) | | | $ | (7,071) | | | $ | (32,385) | |
| Effective tax rate | 33.9 | % | | 10.7 | % | | |
The decrease in income tax expense for the year ended January 31, 2024 compared to the year ended January 31, 2023 was primarily driven by a $22.0 million decrease from the bargain purchase gain of $104.9 million, net of deferred taxes of $31.1 million as bargain purchase gains are treated as a permanent difference. Income tax expense also decreased due to a $50.0 million decrease of pre-tax book income at the statutory rate of 21%, offset by a net increase of $12.1 million in the valuation allowance against our U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets. Our income tax for the year ended January 31, 2024 includes the benefit from derecognition of $6.9 million, including interest, resulting from the lapse of statute of limitations of an uncertain tax position.
Impact of Inflation and Changing Prices
We continue to monitor the impact the current rise in inflation may have on our customers and our business. Moreover, further significant inflation could adversely affect our customers’ shopping decisions and payment patterns. We rely heavily on our distribution system and our fast delivery policy to satisfy our customers’ needs and desires, and increases in transportation and gasoline prices could result in increased distribution costs and delivery charges. If we are unable to effectively pass increased transportation costs on to the consumer, either by increased delivery costs or higher prices, such costs could adversely affect our results of operations. In addition, the cost of items we purchase may increase or shortages of these items may arise as a result of changes in trade regulations, currency fluctuations, border taxes, import tariffs, or other factors beyond our control.
Seasonality
Our business is seasonal which typically means that a higher portion of sales and operating profit are realized during the fourth quarter due primarily to the holiday shopping season. In addition, during the first quarter, our portfolio performance benefits from the timing of personal income tax refunds received by our customers, which typically results in higher cash collection rates.
Quarterly Results of Operations
Our quarterly results may fluctuate materially depending on factors such as the following:
•timing of new product introductions, new store openings and store relocations;
•sales contributed by new stores;
•changes in our merchandise mix;
•increases or decreases in comparable store sales;
•changes in delinquency rates and amount of charge-offs with respect to customer accounts receivable;
•the pace of growth or decline in the customer accounts receivable balance;
•adverse weather conditions;
•shifts in the timing of certain holidays and promotions; and
•charges incurred in connection with store closures or other non-routine events.
Results for any quarter are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be achieved for any other quarter or for a full fiscal year.
Customer Accounts Receivable Portfolio
We provide in-house financing to individual consumers on a short-term and medium-term basis (contractual terms generally range from 12 to 36 months for our installment loans) for the purchase of durable products for the home. A significant portion of our customer credit portfolio is due from customers that are considered higher-risk, subprime borrowers. Our financing is executed using contracts that require fixed monthly payments over fixed terms. We maintain a secured interest in the product financed. If a payment is delayed, missed or paid only in part, the account becomes delinquent. Our collection personnel attempt to contact a customer once their account becomes delinquent. Our installment loan contracts generally reflect an interest rate of between 18% and 36%. Where we offer our installment loan product, we have implemented our direct consumer loan program across all Texas, Louisiana, Tennessee and Oklahoma locations and recently offer these types of loans in some parts of Georgia. For Conn's, the states of Texas, Louisiana, Tennessee and Oklahoma represented approximately 66% of our fiscal year 2024 originations, with maximum equivalent interest rates of up to 37% in Oklahoma, up to 30% in Texas and Tennessee, and up to 36% in Louisiana. In states where regulations do not generally limit the interest rate charged, our loan contracts generally reflect an interest rate between 29.99% and 35.99%. These states represented 16% of our fiscal year 2024 originations.
We offer qualified customers a 12-month no-interest option finance program. If the customer is delinquent in making a scheduled monthly payment or does not repay the principal in full by the end of the no-interest option program period (grace periods are provided), the account does not qualify for the no-interest provision and none of the interest earned is waived.
We regularly extend or “re-age” a portion of our delinquent customer accounts as a part of our normal collection procedures to protect our investment. Generally, extensions are granted to customers who have experienced a financial difficulty (such as the temporary loss of employment), which is subsequently resolved, and when the customer indicates a willingness and ability to resume making monthly payments. These re-ages involve modifying the payment terms to defer a portion of the cash payments currently required of the debtor to help the debtor improve his or her financial condition and eventually be able to pay the account balance. Our re-aging of customer accounts does not change the interest rate or the total principal amount due from the
customer and typically does not reduce the monthly contractual payments. We may also charge the customer an extension fee, which approximates the interest owed for the time period the contract was past due. Our re-age programs consist of extensions and two payment updates, which include unilateral extensions to customers who make two full payments in three calendar months in certain states. During the second quarter of fiscal year 2021, we changed our re-age policy to increase the number of days required for a customer to qualify for a unilateral re-age. Re-ages are not granted to debtors who demonstrate a lack of intent or ability to service the obligation or have reached our limits for account re-aging. To a much lesser extent, we may provide the customer the ability to re-age their obligation by refinancing the account, which typically does not change the interest rate or the total principal amount due from the customer but does reduce the monthly contractual payments and extends the term. Under these options, as with extensions, the customer must resolve the reason for delinquency and show a willingness and ability to resume making contractual monthly payments.
In conjunction with our Badcock acquisition, we acquired and continue to originate revolving credit accounts with no defined expiration date or amortization schedule. Like our installment loans, we contact customers when they become delinquent and work with our customers to bring their account current. If a delinquent account makes a payment, we reset the account to a current status. When revolving accounts reach 360 days past due they are charged off. For Badcock, the states of Florida, Georgia and North Carolina represent approximately 73% of our fiscal year 2024 originations. We expect to cease originating revolving accounts and begin offering our installment loan products in all Badcock stores during 2024. The revolving accounts are accounted for under the fair value option of accounting.
The following tables present, for comparison purposes, information about our managed portfolio of (information reflects on a combined basis the securitized receivables transferred to the VIEs and receivables not transferred to the VIEs):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | January 31, |
| Conn's Inc. | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
Weighted average credit score of outstanding balances (1) | 615 | | | 613 | | | 606 | |
| Average outstanding customer balance | $ | 2,682 | | | $ | 2,597 | | | $ | 2,498 | |
Balances 60+ days past due as a percentage of total customer portfolio carrying value (2)(3) | 12.2 | % | | 12.7 | % | | 10.4 | % |
Re-aged balance as a percentage of total customer portfolio carrying value (2)(3) | 18.8 | % | | 16.5 | % | | 16.8 | % |
Carrying value of account balances re-aged more than six months (in thousands) (3) | $ | 35,341 | | | $ | 29,511 | | | $ | 50,282 | |
| Allowance for bad debts and uncollectible interest as a percentage of total customer accounts receivable portfolio balance | 18.1 | % | | 18.0 | % | | 18.5 | % |
| Percent of total customer accounts receivable portfolio balance represented by no-interest option receivables | 36.1 | % | | 34.1 | % | | 33.7 | % |
| | | | | |
| Badcock | Period from December 18, 2023 through January 31, 2024 |
| Average outstanding customer balance | $ | 2,049 | |
| Balances 60+ days past due as a percentage of total customer portfolio carrying value (2)(3) | 5.4 | % |
| Fair value adjustment as a percentage of total customer accounts receivable portfolio balance under the fair value option | 24.2 | % |
| Percent of total customer accounts receivable portfolio balance represented by no-interest option receivables | 7.4 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended January 31, |
| Conn's Inc. | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Total applications processed | 1,278,520 | | | 1,034,860 | | | 1,297,025 | |
Weighted average origination credit score of sales financed (1) | 622 | | | 620 | | | 616 | |
| Percent of total applications approved and utilized | 20.5 | % | | 22.5 | % | | 21.8 | % |
| Average income of credit customer at origination | $ | 52,900 | | | $ | 51,500 | | | $ | 49,100 | |
| Percent of retail sales paid for by: | | | | | |
| In-house financing, including down payments received | 61.3 | % | | 53.2 | % | | 51.0 | % |
| Third-party financing | 14.6 | % | | 17.7 | % | | 17.7 | % |
| Third-party lease-to-own option | 8.5 | % | | 7.3 | % | | 10.4 | % |
| | 84.4 | % | | 78.2 | % | | 79.1 | % |
| | | | | |
| Badcock | Period from December 18, 2023 through January 31, 2024 |
| Total applications processed | 18,757 | |
| Percent of total applications approved and utilized | 43.3 | % |
| Percent of retail sales paid for by: | |
| In-house financing, including down payments received | 57.6 | % |
| Third-party financing | 7.1 | % |
| Third-party lease-to-own option | 2.6 | % |
| | 67.3 | % |
(1)Credit scores exclude non-scored accounts.
(2)Accounts that become delinquent after being re-aged are included in both the delinquency and re-aged amounts.
(3)Carrying value reflects the total customer accounts receivable portfolio balance, net of deferred fees and origination costs, the allowance for no-interest option credit programs and the allowance for uncollectible interest.
Our customer portfolio balance and related allowance for uncollectible accounts are segregated between customer accounts receivable and restructured accounts. Customer accounts receivable include all accounts for which payment term has not been cumulatively extended over three months or refinanced. Restructured accounts includes all accounts for which payment term has been re-aged in excess of three months or refinanced.
For customer accounts receivable (excluding restructured accounts), the allowance for uncollectible accounts as a percentage of the total customer accounts receivable portfolio balance decreased to 15.8% as of January 31, 2024 from 16.0% as of January 31, 2023.
The percentage of the carrying value of non-restructured accounts greater than 60 days past due decreased 80 basis points over the prior year period to 10.6% as of January 31, 2024 from 11.4% as of January 31, 2023. The decrease is primarily due to an overall improvement in 60+ delinquency within restructured accounts.
For restructured accounts, the allowance for uncollectible accounts as a percentage of the restructured portfolio balance was 41.1% as of January 31, 2024 as compared to 40.8% as of January 31, 2023.
The percent of bad debt charge-offs, net of recoveries, to average outstanding portfolio balance was 15.2% for fiscal year 2024 compared to 14.0% for fiscal year 2023. The increase is primarily related to greater gross charge offs in the current quarter when compared to the prior period.
As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, balances under no-interest programs included within customer receivables were $358.7 million and $350.0 million, respectively.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We require liquidity and capital resources to finance our operations and future growth as we add new stores to our operations, which in turn requires additional working capital for increased customer receivables and inventory. We generally finance our operations through a combination of cash flow generated from operations, the use of our Revolving Credit Facility, and through periodic securitizations of originated customer receivables. We plan to execute periodic securitizations of future originated customer receivables.
We believe, based on our current projections, that we have sufficient sources of liquidity to fund our operations and capital expenditures for at least the next 12 months.
Operating cash flows. For the year ended January 31, 2024, net cash used in operating activities was $51.2 million compared to $60.4 million provided by operating activities for the year ended January 31, 2023. The change in net cash used in operating activities was primarily driven by lower cash collections compared to the prior year due to a lower average customer accounts receivable portfolio balance, an increased net loss of $17.6 million and other changes in operating assets and liabilities.
For the year ended January 31, 2023, net cash provided by operating activities was $60.4 million compared to $176.4 million for the year ended January 31, 2022. The decrease in net cash provided by operating activities was primarily driven by an increase in inventory in comparison to the prior year period when we were preserving liquidity in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, higher prior year collections due to a higher customer accounts receivable balance compared to the current year period and a decrease in net income when adjusted for non-cash activity.
Investing cash flows. For the year ended January 31, 2024, net cash used in investing activities was $47.3 million compared to $73.0 million for the year ended January 31, 2023. The cash used during the year ended January 31, 2024 was primarily for investments in new stores and technology investments, including the acquisition and build out of a lease-to-own technology platform. This use of cash was offset by the acquisition of Badcock which included cash acquired of $3.7 million.
For the year ended January 31, 2023, net cash used in investing activities was $73.0 million compared to $44.9 million for the year ended January 31, 2022. The cash used during the year ended January 31, 2023 was primarily for investments in new stores and technology investments. The cash used during the year ended January 31, 2022 was primarily for investments in new stores, two new distribution centers and technology investments.
Financing cash flows. For the year ended January 31, 2024, net cash provided by financing activities was $109.0 million compared to net provided by financing activities of $33.3 million for the year ended January 31, 2023.
During the year ended January 31, 2024, we issued the 2024-A and 2023-A VIE asset-backed notes resulting in net proceeds to us of approximately $518.8 million, net of transaction costs. The proceeds from both offerings were used to pay down the balance of the Company's Revolving Credit Facility and for other general corporate purposes. In addition, we entered into the BRF Term Loan which provided cash of $108.0 million which was used to terminate the Pathlight Term Loan. Cash collections from the securitized receivables were used to make payments on the asset-backed notes of approximately $393.5 million during the year ended January 31, 2024 compared to approximately $410.0 million during the year ended January 31, 2023. During the year ended January 31, 2024, net borrowings under our Revolving Credit Facility were $146.7 million compared to net borrowings of $72.0 million during the year ended January 31, 2023.
During the year ended January 31, 2023, we issued the 2022-A Class A, Class B, and Class C VIE asset-backed notes resulting in net proceeds to us of approximately $273.7 million, $129.1 million, and $43.7 million, net of transaction costs, respectively. The proceeds were used to pay down the balance of the Company's Revolving Credit Facility and for other general corporate purposes.
During the year ended January 31, 2022, we issued 2020-A Class C VIE asset backed notes and 2021-A VIE asset-backed notes resulting in net proceeds to us of approximately $62.5 million and $375.2 million, net of transaction costs, respectively. The proceeds from the asset-backed notes were used to pay down the balance of the Company’s Revolving Credit Facility and for other general corporate purposes. During the year ended January 31, 2022, we retired the remaining $141.2 million aggregate principal amount of our Senior Notes outstanding.
Share Repurchase Program. For the year ended January 31, 2024, the Company had no share repurchases. For the year ended January 31, 2023, we settled the repurchase of 3,462,848 shares of our common stock at an average weighted cost per share of $20.70 for an aggregate amount of $71.7 million.
Asset-backed Notes. From time to time, we securitize customer accounts receivables by transferring the receivables to various bankruptcy-remote VIEs. In turn, the VIEs issue asset-backed notes secured by the transferred customer accounts receivables and restricted cash held by the VIEs.
Under the terms of the securitization transactions, all cash collections and other cash proceeds of the customer receivables go first to the servicer and the holders of issued notes, and then to us as the holder of non-issued notes, if any, and residual equity. We retain the servicing of the securitized portfolios and receive a monthly fee of 4.75% (annualized) based on the outstanding balance of the securitized receivables. In addition, we, rather than the VIEs, retain all credit insurance income together with certain recoveries related to credit insurance and repair service agreements on charge-offs of the securitized receivables, which are reflected as a reduction to net charge-offs on a consolidated basis.
The asset-backed notes were offered and sold to qualified institutional buyers pursuant to the exemptions from registration provided by Rule 144A under the Securities Act. If an event of default were to occur under the indenture that governs the respective asset-backed notes, the payment of the outstanding amounts may be accelerated, in which event the cash proceeds of
the receivables that otherwise might be released to the residual equity holder would instead be directed entirely toward repayment of the asset-backed notes, or if the receivables are liquidated, all liquidation proceeds could be directed solely to repayment of the asset-backed notes as governed by the respective terms of the asset-backed notes. The holders of the asset-backed notes have no recourse to assets outside of the VIEs. Events of default include, but are not limited to, failure to make required payments on the asset-backed notes or specified bankruptcy-related events.
The asset-backed notes outstanding as of January 31, 2024 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Asset-Backed Notes | | Original Principal Amount | | Original Net Proceeds (1) | | Current Principal Amount | | Issuance Date | | Maturity Date | | Contractual Interest Rate | | Effective Interest Rate (2) |
| 2021-A Class C Notes | | $ | 63,890 | | | $ | 63,450 | | | $ | 16,815 | | | 11/23/2021 | | 5/15/2026 | | 4.59% | | 5.14% |
| 2022-A Class B Notes | | 132,090 | | | 129,050 | | | 51,238 | | | 7/21/2022 | | 12/15/2026 | | 9.52% | | 10.67% |
| 2022-A Class C Notes | | 63,090 | | | 43,737 | | | 63,090 | | | 11/30/2022 | | 12/15/2026 | | 0.00% | | 19.20% |
| 2023-A Class A Notes | | 160,690 | | | 159,603 | | | 67,673 | | | 8/17/2023 | | 01/17/2028 | | 8.01% | | 15.87% |
| 2023-A Class B Notes | | 82,430 | | | 79,958 | | | 82,430 | | | 8/17/2023 | | 01/17/2028 | | 10.00% | | 12.57% |
| 2023-A Class C Notes | | 30,550 | | | 26,665 | | | 30,550 | | | 8/17/2023 | | 01/17/2028 | | 11.00% | | 12.78% |
| 2024-A Class A Notes | | 133,490 | | | 132,587 | | | 133,490 | | | 1/26/2024 | | 1/16/2029 | | 7.05% | | 13.86% |
| 2024-A Class B Notes | | 98,120 | | | 96,279 | | | 98,120 | | | 1/26/2024 | | 1/16/2029 | | 9.80% | | 8.28% |
| 2024-A Class C Notes | | 27,760 | | | 23,689 | | | 27,760 | | | 1/26/2024 | | 1/16/2029 | | 10.34% | | 7.73% |
| Total | | $ | 792,110 | | | $ | 755,018 | | | $ | 571,166 | | | | | | | | | |
(1)After giving effect to debt issuance costs and discount on debt.
(2)For the year ended January 31, 2024, and inclusive of the impact of changes in timing of actual and expected cash flows.
On August 7, 2023, Conn’s, Inc., Conn’s Receivables Funding 2023-A, LLC, a newly formed special purpose entity that is indirectly owned by the Company (the “2023-A Issuer”), Conn Appliances Receivables Funding, LLC, an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (the “Depositor”), and Conn Appliances, Inc., a direct and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Conn Appliances”), entered into a Note Purchase Agreement (the “2023-A Note Purchase Agreement”) with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., MUFG Securities Americas Inc., Citizens JMP Securities, LLC and Regions Securities LLC (collectively, the “2023-A Initial Purchasers”), for the sale of the Issuer’s 8.01% $160.7 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class A, Series 2023-A (the “Class A Notes”), 10.00% $82.4 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class B, Series 2023-A (the “Class B Notes”) and 11.00% $30.6 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class C, Series 2023-A (the “Class C Notes” and, together with the Class A Notes and the Class B Notes, the “2023-A Purchased Notes”). The 2023-A Issuer also issued the Asset Backed Notes, Class R, Series 2023-A (the “Class R Notes” and, collectively with the Purchased Notes, the “Series 2023-A Notes”). The Class R Notes do not have a principal amount or interest rate and were transferred to the Depositor on August 17, 2023 to satisfy the risk retention obligations of Conn Appliances. The Series 2023-A Notes were issued on August 17, 2023 (the “Closing Date”). The Series 2023-A Notes have not been and will not be registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) or the securities laws of any jurisdiction. The 2023-A Purchased Series Notes were sold initially to the 2023-A Initial Purchasers and then reoffered and resold only (i) to “Qualified Institutional Buyers” as defined in Rule 144A under the Securities Act (“Rule 144A”) in transactions meeting the requirements of Rule 144A or (2) solely with respect to the Class A Notes, outside the United States to non-U.S. Persons in transactions in compliance with Regulation S under the Securities Act.
On January 26, 2024, Conn’s, Inc., Conn’s Receivables Funding 2024-A, LLC, a newly formed special purpose entity that is indirectly owned by the Company (the “2024-A Issuer”), the Depositor, and Conn Appliances, entered into a Note Purchase Agreement (the “2024-A Note Purchase Agreement”) with MUFG Securities Americas Inc., Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., J.P. Morgan Securities LLC and Regions Securities LLC (collectively, the “2024-A Initial Purchasers”), for the sale of the 2024-A Issuer’s 7.05% $133.5 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class A, Series 2024-A (the “Class A Notes”), 9.80% $98.1 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class B, Series 2024-A (the “Class B Notes”) and 10.34% $27.8 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class C, Series 2024-A (the “Class C Notes” and, together with the Class A Notes and the Class B Notes, the “2024-A Purchased Notes”). The 2024-A Issuer will also issue the Asset Backed Notes, Class R, Series 2024-A (the “Class R Notes” and, collectively with the Purchased Notes, the “Series 2024-A Notes”). The Class R Notes will be retained by the Depositor on the Closing Date. The Class R Notes will not have a principal amount or interest rate and will be transferred to the Depositor on the Closing Date to satisfy the risk retention obligations of Conn Appliances. The Series 2024-A Notes were issued on January 26, 2024 (the “Closing Date”). The Series 2024-A Notes have not been and will not be registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) or the securities laws of any jurisdiction. The Purchased Series 2024-A Notes are being sold initially to the 2024-A Initial Purchasers and then reoffered and resold only (i) to “Qualified Institutional Buyers” as defined in Rule 144A under the Securities Act (“Rule 144A”) in transactions meeting the requirements of Rule 144A or (2) solely with respect to the Class A Notes, outside the United States to non-U.S. Persons in transactions in compliance with Regulation S under the Securities Act.
Revolving Credit Facility. On March 29, 2021, Conn’s, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries (the “Borrowers”) entered into the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement (the “Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement”), with certain lenders, which provides for a $555.0 million asset-based revolving credit facility (as amended, the “Revolving Credit Facility”) under which credit availability is subject to a borrowing base and a maturity date of December 31, 2026.
The Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, among other things, permits borrowings under the Letter of Credit Subline (as defined in the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement) that exceed the cap of $40 million to $100 million, solely at the discretion of the lenders for such amounts in excess of $40 million. The obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are secured by substantially all assets of the Company, excluding the assets of the VIEs. As of January 31, 2024, we had available borrowing capacity of $155.3 million under our Revolving Credit Facility, net of standby letters of credit issued of $25.2 million.
On November 21, 2022, we entered into Amendment No. 1 (the "Amendment") to the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement. Under the Amendment, loans under the Revolving Credit Facility bear interest, at our option, at a rate of SOFR plus a margin ranging from 2.50% to 3.25% per annum (depending on a pricing grid determined by our total leverage ratio) or the alternate base rate plus a margin ranging from 1.50% to 2.25% per annum (depending on a pricing grid determined by our total leverage ratio). The alternate base rate is a rate per annum equal to the greatest of the prime rate, the federal funds effective rate plus 0.5%, or SOFR for a 30-day interest period plus 1.0%. We also pay an unused fee on the portion of the commitments that is available for future borrowings or letters of credit at a rate ranging from 0.25% to 0.50% per annum, depending on the average outstanding balance and letters of credit of the Revolving Credit Facility in the immediately preceding quarter. The Amendment also waived testing of the interest coverage covenants beginning with the third quarter of fiscal year 2023 and continuing until the date on which the Company delivers financial statements and a compliance certificate for the fiscal quarter ending April 30, 2024 (unless earlier terminated pursuant to the terms of the Amendment). After giving effect to the foregoing amendment, as of January 31, 2024, we were in compliance with the covenants in our Revolving Credit Facility.
On February 21, 2023, the Company, the Borrowers, the guarantors party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the required lenders party thereto entered into the second amendment (the “Second Amendment”) to the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement. The Second Amendment, among other things, permits the Company and the Borrowers to enter into the Term Loan (as defined below) and made certain changes conforming to the Term Loan.
On December 18, 2023, the Company entered into an Amendment No. 3 (the “Third Amendment”) to the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2021 (the “Revolving Credit Agreement”), by and among the Company, as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as existing borrowers (the “Existing Borrowers”), and substantially concurrently with the closing of the Revolving Credit Agreement Amendment, Badcock, pursuant to a joinder, as new borrower (“New Borrower”, and together with the Existing Borrowers, collectively, “Borrowers”), certain banks and financial institutions named therein, as lenders, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent for the Lenders. The Third Amendment, among other things: (a) consents to the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Investment Agreement; (b) extends the maturity date of the Revolving Credit Agreement to December 31, 2026; (c) provides for certain adjustments to the representations, warranties and covenants to incorporate the New Borrower into the Revolving Credit Agreement; (d) increases the existing interest rate margins by 0.50%, resulting in possible interest rate margins between (i) 3.00% and 3.75% for SOFR Rate Loans and (ii) 2.00% and 2.75% for Base Rate Loans, in each case based on the total net leverage ratio; (e) extends the termination date of the covenant relief period, which removes testing of the interest coverage covenant, to April 30, 2025; (f) provides for certain amendments to the borrowing base, including (i) modifying the inventory advance rate by removing the cap of 33.3% of revolving commitments and (ii) modifying the contract advance rate to equal the lesser of (x) 80% of net eligible contract payments and (y) 80% of the net fair market value of the owned contract portfolio; (g) provides for increased reporting requirements; (h) amends the minimum excess availability covenant to require, at all times during the term of the Revolving Credit Agreement, availability under the revolver of no less than the greater of (i) 17.5% of the borrowing base and (ii) $100.0 million; (i) replaces the minimum liquidity covenant with a springing, minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of 1.00:1.00, which shall only be tested to the extent availability under the Revolving Credit Agreement is less than 20% of the borrowing base, and testing of such covenant shall continue until the occurrence of the first fiscal-quarter end where availability as of such date has been in excess of 20% of the borrowing base for 30 consecutive days; (j) added a minimum EBITDA financial covenant; (k) increased the cap on revolver borrowings at any one time outstanding to $400.0 million with step downs beginning September 1, 2025 thereafter to $300.0 million; and (l) reduced revolver borrowing base to a $555.0 million asset-based revolving credit facility. The weighted-average interest rate on borrowings outstanding and including unused line fees under the Revolving Credit Facility was 8.8% for the year ended January 31, 2024.
The Revolving Credit Facility places restrictions on our ability to incur additional indebtedness, grant liens on assets, make distributions on equity interests, dispose of assets, make loans, pay other indebtedness, engage in mergers, and other matters. The Revolving Credit Facility restricts our ability to make dividends and distributions unless no event of default exists and a liquidity test is satisfied. Subsidiaries of the Company may pay dividends and make distributions to the Company and other obligors under the Revolving Credit Facility without restriction. We are restricted from making distributions as a result of the Revolving Credit Facility distribution and payment restrictions. The Revolving Credit Facility contains customary default provisions, which, if triggered, could result in acceleration of all amounts outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility.
Debt Covenants. The Third Amendment waived testing of the interest coverage covenants until the date on which the Company delivers financial statements and a compliance certificate for the fiscal quarter ending April 30, 2025 (unless earlier terminated pursuant to the terms of the Amendment). After giving effect to the foregoing amendment, as of January 31, 2024, we were in compliance with the covenants in our Revolving Credit Facility.
A summary of the significant financial covenants that govern our Revolving Credit Facility compared to our actual compliance status as of January 31, 2024 is presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Actual | | Required
Minimum/
Maximum |
| Interest Coverage Ratio for the quarter must equal or exceed minimum | Not Tested | | 1.00:1.00 |
| Interest Coverage Ratio for the trailing two quarters must equal or exceed minimum | Not Tested | | 1.50:1.00 |
| Leverage Ratio must not exceed maximum | 3.21:1.00 | | 4.50:1.00 |
| ABS Excluded Leverage Ratio must not exceed maximum | 1.63:1.00 | | 2.50:1.00 |
| Capital Expenditures, net, must not exceed maximum | $70.1 million | | $100.0 million |
All capitalized terms in the above table are defined by the Revolving Credit Facility and may or may not agree directly to the financial statement captions in this document. The covenants are calculated quarterly, except for capital expenditures, which is calculated for a period of four consecutive fiscal quarters, as of the end of each fiscal quarter.
Pathlight Term Loan and Security Agreement. On February 21, 2023, Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers (the “Borrowers”), entered into a second-lien term loan and security agreement (the “Pathlight Term Loan,” and together with the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, the “Senior Loan Agreements”) with Pathlight Capital LP, as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the financial institutions
party thereto, as lenders (the “Lenders”). The Pathlight Term Loan provides for an aggregate commitment of $100.0 million to the Borrowers pursuant to a three-year secured term loan credit facility, which was fully drawn on February 21, 2023.
This loan was paid in full on December 18, 2023 with the proceeds from the BRF Term Loan (described below). When this loan was paid in full, we recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of $14.2 million which included the prepayment penalty of $8.9 million and the write-off of debt issuance costs of $5.3 million.
BRF Term Loan and Security Agreement. On December 18, 2023, the Company, as parent and guarantor, and the Borrowers, entered into a second-lien term loan and security agreement with BRF Finance Co., LLC, (the “BRF Term Loan”), as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the financial institutions party thereto, as lenders. The BRF Term Loan provides for an aggregate commitment of $108.0 million to the Borrowers pursuant to a secured term loan credit facility maturing on February 20, 2027, which was fully drawn on December 18, 2023. Outstanding amounts under the BRF Term Loan will bear interest at an aggregate rate per annum equal to the Term SOFR Rate (as defined in the Term Loan), subject to a 4.80% floor, plus a margin of 8.00%. The obligations of the Borrowers under the BRF Term Loan are guaranteed by the Company and certain of the Borrowers’ subsidiaries. The Borrowers are required to make quarterly scheduled amortization payments of the BRF Term Loan prior to the maturity thereof in an amount equal to $1.35 million beginning January 2025. The BRF Term Loan is secured by liens (subject, in the case of priority, to the liens under the Revolving Credit Agreement) on substantially all of the assets of the Borrowers and their subsidiaries, subject to customary exceptions.
The Borrowers may elect to prepay all or any portion of the amounts owed under the BRF Term Loan, without a premium or penalty. The Borrowers are required to make mandatory prepayments of amounts owed under the BRF Term Loan in an amount equal to 100% of the proceeds received as a result of any of the following events, subject to certain adjustments: (i) the issuance of any equity securities by the Company that the Company contributes as additional common equity contributions to any Borrower; and (ii) the receipt by the Company, the Borrowers or any of their affiliates of any portion of the CARES Act Tax Refund Proceeds (as defined in the BRF Term Loan), subject to a cap. Voluntary and mandatory prepayments will be applied to the remaining scheduled installments of principal due in respect of the BRF Term Loan in the inverse order of maturity.
The BRF Term Loan contains customary covenants regarding the Borrowers and their subsidiaries that are generally based upon and are comparable to those contained in the Revolving Credit Agreement including, without limitation: financial covenants, such as the maintenance of a minimum interest coverage ratio, subject to a covenant relief period through the fiscal quarter ending April 30, 2025, a maximum leverage ratio, a minimum excess availability covenant and a springing, minimum fixed charge coverage ratio; and negative covenants, such as limitations on indebtedness, liens, mergers, asset transfers, certain investing activities and other matters customarily restricted in such agreements. Most of these restrictions are subject to certain minimum thresholds and exceptions. The BRF Term Loan also contains customary events of default, including, without limitation, payment defaults, material inaccuracy of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, bankruptcy and insolvency proceedings, cross-defaults to certain other agreements, and change of control.
Delayed Draw Term Loan and Security Agreement. On July 31, 2023, Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers (the “Borrowers”), entered into a delayed draw term loan and security agreement (the “Delayed Draw Term Loan”) with Stephens Investments Holdings LLC (“Stephens Investments”) and Stephens Group, LLC and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (the “Lenders”), and Stephens Investments, as administrative agent. The Delayed Draw Term Loan provides for an aggregate commitment of $50.0 million, of which the total commitment is available to be funded in one or a series of borrowings until February 20, 2026, with the Delayed Draw Term Loan to mature on May 22, 2026.
Outstanding amounts under the Delayed Draw Term Loan will bear interest at an aggregate rate per annum equal to the Term SOFR Rate (as defined in the Delayed Draw Term Loan), subject to a 5.00% floor, plus a margin of 10.00%, which shall be payable monthly in arrears in cash except to the extent such payment in cash would result in a default or event of default under any of the Senior Loan Agreements, in which case such portion may be paid-in-kind and added to the outstanding principal amount of the term loans. Amounts under the Delayed Draw Term Loan that remain undrawn are subject to a commitment fee payable monthly based on the undrawn portion of the Delayed Draw Term Loan at a rate of 5.00% per annum. Furthermore, in connection with the funding of each draw under the Delayed Draw Term Loan and on the terms and subject to the conditions of the Delayed Draw Term Loan, including the Share Cap (which equals 19.99% of the shares of common stock in the Company issued and outstanding as of the date of the Delayed Draw Term Loan), the Company will issue to or as directed by the Lenders warrants to purchase a number of shares of common stock of the Company equal to 20% of the aggregate principal amount of such delayed draw term loan funded by a such Lender divided by the exercise price (as defined by the loan agreement). The obligations of the Borrowers under the Delayed Draw Term Loan are guaranteed by the Company and certain of the Borrowers’ subsidiaries. The Borrowers are not required to make any amortization or other payments (whether voluntary or mandatory) of principal under the Delayed Draw Term Loan until the maturity date. The Delayed Draw Term Loan is secured by liens
(subject, in the case of priority, to the liens under the Fifth Amendment and Restated Loan) on substantially all of the assets of the Borrowers and their subsidiaries, subject to customary exceptions.
Proceeds from borrowings made under the Delayed Draw Term Loan may be used by the Borrowers for working capital and other lawful corporate purposes. The Borrowers may elect to prepay all or any portion of the amounts owed under the Delayed Draw Term Loan, without a premium or penalty, subject to certain conditions, including pro forma compliance with a fixed charge coverage ratio test and reduction of the outstanding principal amount under the Second-Lien Loan Agreement to an amount equal to $40.0 million.
The Delayed Draw Term Loan contains customary covenants regarding the Borrowers and their subsidiaries that are generally based upon and are comparable to those contained in the Senior Loan Agreements including, without limitation: financial covenants, such as a maximum leverage ratio; and negative covenants, such as limitations on indebtedness, liens, mergers, asset transfers, certain investing activities and other matters customarily restricted in such agreements. Most of these restrictions are subject to certain minimum thresholds and exceptions and, where applicable, cushions to the Senior Loan Agreements. The Delayed Draw Term Loan also contains customary events of default, including, without limitation, payment defaults, material inaccuracy of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, bankruptcy and insolvency proceedings, cross-acceleration to the Senior Loan Agreements, cross-defaults to the warrants and certain other agreements (other than the Senior Loan Agreements as defined in the indenture), and change of control.
On December 18, 2023, the Company, entered into Amendment No. 1 (the “DDTL Amendment”) to the Delayed Draw Term Loan, by and among the Company, as parent and guarantor, the Existing Borrowers and substantially concurrently with the closing of the DDTL Amendment, Badcock, pursuant to a joinder, as new borrower, Stephens Investments Holdings LLC (“Stephens Investments”) and Stephens Group, LLC and the other lenders party thereto from time to time, and Stephens Investments, as administrative agent. The DDTL Amendment, among other things: (a) consents to the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Investment Agreement; (b) extends the maturity date of the Term Loan Agreement to May 22, 2027; (c) provides for certain adjustments to the representations, warranties and covenants to incorporate the New Borrower into the Delayed Draw Term Loan; (d) added a minimum EBITDA financial covenant; and (e) provides for the ability of Borrowers to prepay all or any portion of the amounts owed under the Delayed Draw Term Loan, without a premium or penalty, subject to certain conditions, including demonstrating a trailing twelve-month EBITDA (on a pro forma basis) of the Company and its subsidiaries of no less than $185.0 million and a trailing six-month liquidity (on a pro forma basis) of the Company and its subsidiaries of no less than $100.0 million. In addition, the DDTL Amendment (i) obligates the Company to solicit stockholder approval to issue the maximum amount of Non-Voting Common Stock upon exercise of the maximum number of warrants thereunder, (ii) if stockholder approval is received, obligates the Company to issue warrants under the Delayed Draw Term Loan exercisable for Non-Voting Common Stock and (iii) if stockholder approval is received, clarifies that the provision of the Delayed Draw Term Loan limiting the number of shares underlying warrants issued thereunder to no more than 19.99% of the outstanding shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding as of the date of the Delayed Draw Term Loan does not apply to limit the number of shares of Non-Voting Common Stock issuable upon exercise of warrants.
Stephens Inc, and its affiliates, and The Stephens Group LLC, and its affiliates, are significant stockholders of the Company. Bob L. Martin, a member of the Company’s Board of Directors and Lead Independent Director, is an Operating Partner of The Stephens Group LLC, one of the Lenders under the Delayed Draw Term Loan; and Douglas H. Martin, a member of the Company’s Board of Directors, is a Senior Executive Vice President of Stephens Inc., an affiliate of Stephens Investments Holdings LLC, one of the Lenders under the Delayed Draw Term Loan.
Secured Borrowings. Prior to our acquisition Badcock's strategy had been to securitize the majority of the customer accounts receivable by transferring them into separate special purpose entities. As these transfers failed sale accounting, the Company accounts for the transfers as secured borrowings. The cash collections on the receivables will amortize the borrowing until the third party debt held by the securitization vehicle is paid in full, at which time, the Company will receive cash flows related to certain residual balances. These secured borrowings are accounted for under the fair value option which are valued using Level 3 inputs. The valuation was conducted using the income approach which incorporates an estimate of projected future cash flows associated with the related customer receivables and applying a discount rate which incorporates the relevant risks associated with the related assets and the time value of money.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of January 31, |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Current installments of debt secured by accounts receivable | $ | 146,009 | | | $ | — | |
| Non-current installments of debt secured by accounts receivable | 20,801 | | | — | |
| Total debt secured by accounts receivable, net | $ | 166,810 | | | $ | — | |
During the year ended January 31, 2024, the Company recognized interest expense related to the secured borrowings of $3.5 million. The Company had no secured borrowings during or for the year ended January 31, 2023.
Capital Expenditures. We lease the majority of our stores under operating leases, and our plans for future store locations anticipate operating leases, but do not exclude store ownership. Our capital expenditures for future new store projects should primarily be for our tenant improvements to the property leased (including any new distribution centers and cross-dock facilities), the cost of which is estimated to be between $1.5 million and $2.0 million per store (before tenant improvement allowances) depending on store size. In the event we purchase existing properties, our capital expenditures will depend on the particular property and whether it is improved when purchased. We are continuously reviewing new relationships and funding sources and alternatives for new stores, which may include “sale-leaseback” or direct “purchase-lease” programs, as well as other funding sources for our purchase and construction of those projects. If we do not purchase the real property for new stores, our direct cash needs should include only our capital expenditures for tenant improvements to leased properties and our remodel programs for existing stores. We opened 9 new stores during fiscal year 2024, and currently plan to open 1 new store during fiscal year 2025. Our anticipated capital expenditures for fiscal year 2025 are between $20.0 and $30.0 million, which is primarily related to synergy-driving integration activities and technology investments.
Cash Flow. We periodically evaluate our liquidity requirements, capital needs and availability of resources in view of inventory levels, expansion plans, debt service requirements and other operating cash needs. To meet our short- and long-term liquidity requirements, including payment of operating expenses, funding of capital expenditures and repayment of debt, we rely primarily on cash from operations. As of January 31, 2024, beyond cash generated from operations we had (i) available borrowing capacity of $155.3 million under our Revolving Credit Facility and (ii) $18.7 million of cash on hand. However, we have, in the past, sought to raise additional capital.
We expect that for the next 12 months and the foreseeable future, cash generated from operations, proceeds from potential accounts receivable securitizations and our Revolving Credit Facility will be sufficient to provide us the ability to fund our operations, provide the increased working capital necessary to support our strategy and fund capital expenditures as discussed above in Capital Expenditures.
We may repurchase or otherwise retire our debt and take other steps to reduce our debt or otherwise improve our financial position. These actions could include open market debt repurchases, negotiated repurchases, other retirements of outstanding debt and opportunistic refinancing of debt. The amount of debt that may be repurchased or otherwise retired, if any, will depend on market conditions, the Company’s cash position, compliance with debt covenant and restrictions and other considerations.
Off-Balance Sheet Liabilities and Other Contractual Obligations
We do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements as defined by Item 303(a)(4) of Regulation S-K. The following table presents a summary of our minimum contractual commitments and obligations as of January 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Payments due by period |
| (in thousands) | Total | | Less Than 1
Year | | 1-3
Years | | 3-5
Years | | More Than 5 Years |
| Debt, including estimated interest payments: | | | | | | | | | |
Revolving Credit Facility (1) | $ | 202,531 | | | $ | 14,417 | | | $ | 188,114 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Term Loan(4) | 152,054 | | | 16,226 | | | 38,878 | | | 96,950 | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
2021-A Class C Notes (2) | 18,581 | | | 772 | | | 17,809 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | |
2022-A Class B Notes (2) | 65,257 | | | 4,878 | | | 60,379 | | | — | | | — | |
2022-A Class C Notes (2) | 63,090 | | | — | | | 63,090 | | | — | | | — | |
2023-A Class A Notes (2) | 89,162 | | | 5,421 | | | 10,841 | | | 72,900 | | | — | |
2023-A Class B Notes (2) | 115,108 | | | 8,243 | | | 16,486 | | | 90,379 | | | — | |
2023-A Class C Notes (2) | 43,873 | | | 3,361 | | | 6,721 | | | 33,791 | | | — | |
2024-A Class A Notes (2) | 322,776 | | | 9,411 | | | 18,822 | | | 151,977 | | | 142,566 | |
2024-A Class B Notes (2) | 253,250 | | | 9,616 | | | 19,232 | | | 117,009 | | | 107,393 | |
2024-A Class C Notes (2) | 72,538 | | | 2,870 | | | 5,741 | | | 33,399 | | | 30,528 | |
| Financing lease obligations | 6,510 | | | 1,338 | | | 1,805 | | | 987 | | | 2,380 | |
| Operating leases: | | | | | | | | | |
| Real estate | 607,851 | | | 101,157 | | | 178,032 | | | 145,931 | | | 182,731 | |
| Equipment | 25 | | | 15 | | | 10 | | | — | | | — | |
Contractual commitments (3) | 78,889 | | | 62,076 | | | 11,455 | | | 5,358 | | | — | |
| Total | $ | 2,091,495 | | | $ | 239,801 | | | $ | 637,415 | | | $ | 748,681 | | | $ | 465,598 | |
(1)Estimated interest payments are based on the outstanding balance as of January 31, 2024 and the interest rate in effect at that time.
(2)The payments due by period for the asset-backed notes were based on their respective maturity dates at their respective fixed annual interest rate. Actual principal and interest payments on the asset-backed notes will reflect actual proceeds from the securitized customer accounts receivables.
(3)Contractual commitments primarily include commitments to purchase inventory of $50.0 million.
(4)We applied the tax refund of $15.0 million in March 2024.
Issuer and Guarantor Subsidiary Summarized Financial Information
Conn’s, Inc. is a holding company with no independent assets or operations other than its investments in its subsidiaries. As of January 31, 2024, the direct or indirect subsidiaries of Conn’s, Inc. that were not Guarantors (the “Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries”) were the VIEs and minor subsidiaries. There are no restrictions under the Indenture on the ability of any of the Guarantors to transfer funds to Conn’s, Inc. in the form of dividends or distributions.
The following tables present on a combined basis for the Issuer and the Guarantor Subsidiaries, a summarized Balance Sheet as of January 31, 2024 and a summarized Statement of Operations on a consolidated basis for the twelve months ended January 31, 2024. The information presented below excludes eliminations necessary to arrive at the information on a consolidated basis. Investments in subsidiaries are accounted for by the parent company using the equity method for purposes of this presentation. Amounts provided do not represent our total consolidated amounts, as of January 31, 2024 and for the twelve months ended January 31, 2024:
| | | | | |
| January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 |
| Assets | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 20,812 | |
| Customer accounts receivable, net of allowances | 67,181 | |
| Inventories | 333,962 | |
| Other current assets | 113,590 | |
| Total current assets | 535,545 | |
| Long-term portion of customer accounts receivable, net of allowances | 88,296 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 250,468 | |
| Right of use assets, net | 556,416 | |
| Other assets | 30,701 | |
| Total assets | $ | 1,461,426 | |
| |
| Liabilities | |
| Current portion of debt | $ | 1,923 | |
| Lease liability operating - current | 82,153 | |
| Net due to non-guarantor subsidiary | 44,103 |
| Other liabilities | 230,145 | |
| Total current liabilities | 358,324 | |
| Lease liability operating - non current | 598,712 | |
| Long-term debt | 273,149 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 5,859 | |
| Total liabilities | $ | 1,236,044 | |
| | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Year Ended
January 31, 2023 |
| Revenues: | |
| Net sales and finances charges | $ | 1,144,381 | |
| Servicing fee revenue from non-guarantor subsidiary | 31,601 | |
| Total revenues | 1,175,982 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 1,273,194 | |
| Net loss | $ | (97,212) | |
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of financial statements and related disclosures in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires us to make estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Certain accounting policies, as described below, are considered “critical accounting policies” because they are particularly dependent on estimates made by us about matters that are inherently uncertain and could have a material impact to our consolidated financial statements. We base our estimates on historical experience and on other assumptions that we believe are reasonable. As a result, actual results could differ because of the use of estimates. A summary of all of our significant accounting policies is included in Note 1, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, of the Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II, Item 8., of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Allowance for credit losses. The determination of the amount of the allowance for credit losses is, by nature, highly complex and subjective. Future events that are inherently uncertain could result in material changes to the level of the allowance for credit losses. General economic conditions, changes to state or federal regulations and a variety of other factors that affect the ability of borrowers to service their debts or our ability to collect will impact the future performance of the portfolio.
We establish an allowance for credit losses, including estimated uncollectible interest, to cover expected credit losses on our customer accounts receivable resulting from the failure of customers to make contractual payments. Our customer accounts receivable portfolio balance consists of a large number of relatively small, homogeneous accounts. None of our accounts are large enough to warrant individual evaluation for impairment.
On February 1, 2021, we adopted ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments (“ASC 326”). The allowance for credit losses is measured on a collective (pool) basis where similar risk characteristics exist. The allowance for credit losses is determined for each pool and added to the pool’s carrying amount to establish a new amortized cost basis. We apply the requirements of ASC 326 to our installment loan portfolio only.
We have elected to use a risk-based, pool-level segmentation framework to calculate the expected loss rate. This framework is based on our historical gross charge-off history. In addition to adjusted historical gross charge-off rates, estimates of post-charge-off recoveries, including cash payments from customers, sales tax recoveries from taxing jurisdictions, and payments received under credit insurance and repair service agreement (“RSA”) policies are also considered. We also consider forward-looking economic forecasts based on a statistical analysis of economic factors (specifically, forecast of unemployment rates over the reasonable and supportable forecast period). To the extent that situations and trends arise which are not captured in our model, management will layer on additional qualitative adjustments.
We use a 24-month reasonable and supportable forecast period for the Customer Accounts Receivable portfolio. We estimate losses beyond the 24-month forecast period based on historic loss rates experienced over the life of our historic loan portfolio by loan pool type. We revisit our measurement methodology and assumption annually, or more frequently if circumstances warrant.
As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, the balance of allowance for credit losses and uncollectible interest for non-significantly modified customer receivables was $142.2 million and $150.6 million, respectively. As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, the amount included in the allowance for credit losses associated with principal and interest on significantly modified accounts was $37.1 million and $33.6 million, respectively. A 100 basis point increase in our estimated gross charge-off rate would increase our allowance for credit losses on our customer accounts receivable by $6.1 million based on the balance outstanding at January 31, 2024.
Interest income on customer accounts receivable. Interest income, which includes interest income and amortization of deferred fees and origination costs, is recorded using the interest method and is reflected in finance charges and other revenues. Typically, interest income is recorded until the customer account is paid off or charged-off, and we provide an allowance for estimated uncollectible interest. Any contractual interest income received from customers in excess of the interest income calculated using the interest method is recorded as deferred revenue on our balance sheets. At January 31, 2024 and 2023, there were $7.8 million and $8.1 million, respectively, of deferred interest included in deferred revenues and other credits and other long-term liabilities. The deferred interest will ultimately be brought into income as the accounts pay off or charge-off.
We offer a 12-month no-interest option program. If the customer is delinquent in making a scheduled monthly payment or does not repay the principal in full by the end of the no-interest option program period (grace periods are provided), the account does not qualify for the no-interest provision and none of the interest earned is waived. Interest income is recognized based on estimated accrued interest earned to date on all no-interest option finance programs with an offsetting reserve for those customers expected to satisfy the requirements of the program based on our historical experience.
We recognize interest income on significantly modified accounts using the interest income method, which requires reporting interest income equal to the increase in the net carrying amount of the loan attributable to the passage of time. Cash proceeds and other adjustments are applied to the net carrying amount such that it equals the present value of expected future cash flows.
We place accounts in non-accrual status when legally required. Payments received on non-accrual loans will be applied to principal and reduce the amount of the loan. At January 31, 2024 and 2023, the carrying value of customer accounts receivable in non-accrual status was $8.9 million and $7.9 million. At January 31, 2024 and 2023, the carrying value of customer accounts receivable that were past due 90 days or more and still accruing interest totaled $81.7 million and $92.2 million, respectively. At January 31, 2024 and 2023, the carrying value of customer accounts receivable in a bankruptcy status that were less than 60 days past due of $8.1 million and $7.1 million, respectively, were included within the customer receivables balance carried in non-accrual status.
Fair value option. In conjunction with the acquisition of Badcock and its customer accounts receivable, we adopted ASC 820, Fair Value Option. The fair value option requires the input of various assumptions about the receivables including cash flow forecasts, interest rates, discount rates and macro environment conditions. The inputs are used to determine the value of the receivables using a discounted cash flow approach. Each reporting period, we adjust the balance of the receivables with an adjustment in earnings which is include in Other Revenue. In addition, we apply the fair value option to the related securitized borrowings which reflect the amount of cash flows remaining on the external debt held by the third party securitized vehicle.
Inventories. Inventories consist of merchandise purchased for resale and service parts and are recorded at the lower of cost or net realizable value. The carrying value of the inventory is reduced to its net realizable value for any product lines with excess of carrying amount, typically weighted-average cost, over the amount we expect to realize from the ultimate sale or other disposition of the inventory, with a corresponding charge to cost of sales. The write-down of inventory to net realizable value is estimated based on assumptions regarding inventory aging and historical product sales. A 10% difference in our actual inventory reserve at January 31, 2024, would have affected our cost of goods sold by $1.5 million.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets. Long-lived assets are evaluated for impairment, primarily at the asset group level. The asset group is defined as stores and cross-docks within a distribution center’s service area. We monitor asset group performance in order to assess if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be recoverable. The most likely condition that would necessitate an assessment would be an adverse change in historical and estimated future results of an asset group's performance. For property and equipment held and used, we measure an impairment loss if the carrying amount is not recoverable through its undiscounted cash flows and measure the impairment loss based on the difference between the carrying amount and estimated fair value. For the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 we recorded impairments of $2.3 million, $0 and $0 which is included in Charges and Credits.
Vendor allowances. We receive funds from vendors for price protection, product rebates (earned upon purchase or sale of product), marketing, and promotion programs, collectively referred to as vendor allowances, which are recorded on an accrual basis. We estimate the vendor allowances to accrue based on the progress of satisfying the terms of the programs based on actual and projected sales or purchase of qualifying products. If the programs are related to product purchases, the vendor allowances are recorded as a reduction of product cost in inventory still on hand with any remaining amounts recorded as a reduction of cost of goods sold. During the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, we recorded $128.7 million, $129.0 million and $118.1 million, respectively, as reductions in cost of goods sold from vendor allowances.
Income Taxes. We are subject to U.S. federal income tax as well as income tax in multiple state jurisdictions. We follow the liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on temporary differences between GAAP and tax bases of assets and liabilities and for operating loss and tax credit carryforwards, as measured using the enacted tax rates expected to be in effect when the temporary differences are expected to be realized or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period in which the enactment occurs. A valuation allowance is provided when it is more-likely-than-not that some portion or all of a deferred tax asset will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become realizable. To the extent penalties and interest are incurred, we record these charges as a component of our provision for income taxes.
During the year ended January 31, 2024, we concluded that, based on our evaluation of available objective positive and negative evidence, it is not more likely than not that our net U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets are recoverable. As of January 31, 2024, the total valuation allowance relative to U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets was $25.2 million as compared to $6.6 million as of January 31, 2023. The net change during the year ended January 31, 2024 and 2023 in the valuation allowance was $18.6 million and $6.6 million, respectively.
We review and update our tax positions as necessary to add any new uncertain tax positions taken, or to remove previously identified uncertain positions that have been adequately resolved. Additionally, uncertain positions may be remeasured as warranted by changes in facts or law. Accounting for uncertain tax positions requires estimating the amount, timing and likelihood of ultimate settlement.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
The information related to recent accounting pronouncements as set forth in Note 1, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, of the Consolidated Financial Statements in Part II, Item 8., of this Annual Report on Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK.
The market risk inherent in our financial instruments represents the potential loss arising from adverse changes in interest rates. We have not been materially impacted by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, as substantially all of our business is transacted in, and is expected to continue to be transacted in, U.S. dollars or U.S. dollar-based currencies. Our asset-backed notes bear interest at a fixed rate and would not be affected by interest rate changes.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Conn’s, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Conn’s, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of January 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at January 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2024, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated April 18, 2024, expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
| | | | | |
| Allowance for Credit Losses |
| |
| Description of the Matter | As of January 31, 2024 the Company’s balance of customer accounts receivable was $992.3 million and the related allowance for credit losses was $179.3 million. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company recognizes an allowance for expected credit losses over the life of customer accounts receivable. Management measures expected losses on a pool basis where similar risk characteristics exist using historical charge-off experience to estimate an allowance. In addition to historical gross charge-off rates, estimates of post-charge-off recoveries as well as forward-looking macro-economic forecasts are also considered. To the extent that situations and trends arise which are not captured in management’s model, management will layer on additional qualitative adjustments. Auditing management’s estimate of the allowance for credit losses for customer accounts receivable involves a high degree of complexity in testing the model and modeling assumptions used to derive the segmentation level loss estimates utilized in the allowance calculation. Additionally, in light of the current economic environment, auditing the estimate is complex due to the judgments necessary to evaluate management’s qualitative adjustments, as well as the macro-economic forecast used to estimate current expected credit losses over the life of the customer accounts receivable portfolio.
|
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design, and tested the operating effectiveness of the Company’s controls over the allowance for credit losses process, including management’s review and approval of models used to calculate the estimate and the evaluation of the completeness and accuracy of data inputs, assumptions, and outputs of those models. We also evaluated the Company’s controls over the identification and measurement of qualitative adjustments, review of portfolio trends, and overall evaluation of the recorded allowance estimate. With the assistance of our specialists, we tested the quantitative model methodology, modeling assumptions, model calculation and clerical accuracy of the segmentation level loss estimates. We tested the completeness and accuracy of historical data. We evaluated management’s identification of historical loss periods used in the models. We also assessed management’s adjustments to historical loss data and evaluated whether those adjustments were reflective of management’s current expected loss estimates, and consistent with the underlying supporting documentation for any such quantitative adjustments. We evaluated the inputs used by management in determining the qualitative adjustments for consistency with management’s evaluation framework. We tested the completeness and accuracy of underlying portfolio and macro-economic data considered by management in determining the qualitative adjustments. We also inspected management’s documentation of the evaluation of adjustments considered for consistency with the underlying data and evaluated the reasonableness of the qualitative adjustments recorded. We evaluated the reasonableness of the overall allowance estimate, inclusive of the adjustments for qualitative factors, through comparison of historical estimation results to actual recorded losses. We also reviewed subsequent events and transactions and considered whether they corroborated or contradicted the Company’s estimation conclusion.
|
| | | | | |
| Accounting for Acquisitions |
| |
| Description of the Matter | The Company completed its acquisition of W.S. Badcock LLC, on December 18, 2023 for total consideration transferred of $69.3 million. As discussed further in Note 1 and Note 17 to the financial statements, the transaction was accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting and, accordingly, assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and consideration exchanged were recorded at estimated fair values on the acquisition date. The assets acquired included $306.7 million of customer accounts receivable, the fair value of which was determined with the assistance of management's specialist. Fair value was estimated using a discounted cash flow approach and included assumptions regarding default rates, cash flow estimates and discount rates. For valuation purposes, the acquired receivables were aggregated into pools based on predominate risk characteristics. Auditing management’s estimate of the fair value of acquired receivables was complex due to the judgmental nature and sensitivity of the fair value measurement to assumptions used including, among others, the discount rate and default rate assumptions.
|
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design, and tested the operating effectiveness of the Company’s controls over the measurement and valuation of the acquired receivables. To test the estimated fair value of acquired receivables, our audit procedures included, among others, involving valuation specialists to assist us in testing the value derived by management value and evaluating the significant assumptions used in measuring the fair value of the acquired accounts receivable portfolio. For example, we compared the significant assumptions used by management to third party market sources, where available, and compared our independently calculated fair value to management’s estimate. We also tested the completeness and accuracy of the underlying loan data that was used to derive the fair value estimate.
|
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2001.
Houston, Texas
April 18, 2024
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(amounts in thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | January 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Assets | | | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 18,703 | | | $ | 19,534 | |
| Restricted cash (includes VIE balances of $49,940 and $38,727, respectively) | 52,050 | | | 40,837 | |
| Customer accounts receivable, net of allowance (includes VIE balances of $351,825 and $251,689, respectively) | 419,005 | | | 421,683 | |
| Customer accounts receivable under fair value option | 266,786 | | | — | |
| Other accounts receivable | 50,559 | | | 56,887 | |
| Inventories | 333,962 | | | 240,783 | |
| Income taxes receivable | 44,352 | | | 38,436 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 18,679 | | | 12,937 | |
| Total current assets | 1,204,096 | | | 831,097 | |
| Long-term portion of customer accounts receivable, net of allowances (includes VIE balances of $276,700 and $181,575, respectively) | 364,996 | | | 389,054 | |
| Customer accounts receivable under fair value option, non-current | 37,365 | | | — | |
| Property and equipment, net | 250,468 | | | 218,956 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 556,416 | | | 262,104 | |
| Other assets | 30,701 | | | 15,004 | |
| Total assets | $ | 2,444,042 | | | $ | 1,716,215 | |
| Liabilities, Mezzanine Equity and Stockholders’ Equity | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Short-term debt and finance lease obligations | $ | 1,923 | | | $ | 937 | |
| | | |
| Accounts payable | 98,567 | | | 71,685 | |
| Accrued compensation and related expenses | 19,309 | | | 13,285 | |
| Accrued expenses | 97,775 | | | 69,334 | |
| Operating lease liability | 82,153 | | | 53,208 | |
| Secured borrowing | 147,815 | | | — | |
| Income taxes payable | 2,693 | | | 2,869 | |
| Deferred revenues and other credits | 16,288 | | | 11,043 | |
| Total current liabilities | 466,523 | | | 222,361 | |
| Operating lease liability - non current | 598,712 | | | 331,109 | |
| Long-term debt and finance lease obligations (includes VIE balances of $571,166 and $410,790 respectively) | 820,787 | | | 636,079 | |
| Secured borrowings, non current | 20,841 | | | — | |
| Deferred tax liability | 5,603 | | | 2,041 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 34,078 | | | 22,215 | |
| Total liabilities | 1,946,544 | | | 1,213,805 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 13) | | | |
| Mezzanine equity: | | | |
| Redeemable preferred shares, $0.01 par value, 1,000 shares issued, authorized, and outstanding at January 31, 2024 and 1,000 shares authorized at January 31, 2023 | 62,246 | | | — | |
| Stockholders’ equity: | | | |
| Common stock ($0.01 par value, 100,000 shares authorized; 33,992 and 33,379 shares issued, respectively) | 340 | | | 334 | |
| Treasury stock (at cost; 9,405 shares and 9,405 shares, respectively) | (193,370) | | | (193,370) | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 164,966 | | | 155,523 | |
| Retained earnings | 463,316 | | | 539,923 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 435,252 | | | 502,410 | |
| Total liabilities, mezzanine equity, and stockholders’ equity | $ | 2,444,042 | | | $ | 1,716,215 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Product sales | $ | 896,830 | | | $ | 986,600 | | | $ | 1,205,545 | |
| Repair service agreement commissions | 72,738 | | | 80,446 | | | 89,101 | |
| Service revenues | 8,763 | | | 9,544 | | | 10,743 | |
| Total net sales | 978,331 | | | 1,076,590 | | | 1,305,389 | |
| Finance charges and other revenues | 259,352 | | | 265,937 | | | 284,642 | |
| Total revenues | 1,237,683 | | | 1,342,527 | | | 1,590,031 | |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | 629,688 | | | 710,234 | | | 825,987 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | 561,628 | | | 526,212 | | | 544,490 | |
| Provision for bad debts | 154,080 | | | 121,193 | | | 48,184 | |
| Charges and credits | 17,565 | | | 14,360 | | | 2,677 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 1,362,961 | | | 1,371,999 | | | 1,421,338 | |
| Operating (loss) income | (125,278) | | | (29,472) | | | 168,693 | |
| Interest expense | 81,707 | | | 36,891 | | | 25,758 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 14,221 | | | — | | | 1,218 | |
| Bargain purchase gain, net of deferred taxes | (104,857) | | | — | | | — | |
| (Loss) income before income taxes | (116,349) | | | (66,363) | | | 141,717 | |
| (Benefit) provision for income taxes | (39,456) | | | (7,071) | | | 33,512 | |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (76,893) | | | $ | (59,292) | | | $ | 108,205 | |
| Earnings (loss) per share: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | (3.17) | | | $ | (2.46) | | | $ | 3.70 | |
| Diluted | $ | (3.17) | | | $ | (2.46) | | | $ | 3.61 | |
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | | | | | |
| Basic | 24,250 | | | 24,117 | | | 29,268 | |
| Diluted | 24,250 | | | 24,117 | | | 30,001 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Additional | | | | | | | | |
| Common Stock | | Paid-in | | Retained | | Treasury Stock | | |
| | Shares | | Amount | | Capital | | Earnings | | Shares | | Amount | | Total |
| Balance January 31, 2021 | 32,712 | | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 132,108 | | | $ | 491,010 | | | (3,485) | | | $ | (66,290) | | | $ | 557,155 | |
| Exercise of options and vesting of restricted stock, net of withholding tax | 252 | | | 2 | | | (1,412) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (1,410) | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 51 | | | 1 | | | 808 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 809 | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | | — | | | 8,915 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 8,915 | |
| Common stock repurchase | | | | | | | | | (2,604) | | | (58,855) | | | (58,855) | |
| Net income | — | | | — | | | — | | | 108,205 | | | — | | | — | | | 108,205 | |
| Balance January 31, 2022 | 33,015 | | | $ | 330 | | | $ | 140,419 | | | $ | 599,215 | | | (6,089) | | | $ | (125,145) | | | $ | 614,819 | |
| Exercise of options and vesting of restricted stock, net of withholding tax | 258 | | | 3 | | | (2,381) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,378) | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 106 | | | 1 | | | 777 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 778 | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | | — | | | 16,708 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 16,708 | |
| Common stock repurchase | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (3,316) | | | (68,225) | | | (68,225) | |
| Net loss | — | | | — | | | — | | | (59,292) | | | — | | | — | | | (59,292) | |
| Balance January 31, 2023 | 33,379 | | | $ | 334 | | | $ | 155,523 | | | $ | 539,923 | | | (9,405) | | | $ | (193,370) | | | $ | 502,410 | |
| Adoption of ASU 2022-02 | — | | | — | | | — | | | 286 | | | — | | | — | | | 286 | |
| Exercise of options and vesting of restricted stock, net of withholding tax | 455 | | | 3 | | | (1,373) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (1,370) | |
| Issuance of common stock under Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 158 | | | 3 | | | 559 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 562 | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | | — | | | 10,257 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 10,257 | |
| Net loss | — | | | — | | | — | | | (76,893) | | | — | | | — | | | (76,893) | |
| Balance January 31, 2024 | 33,992 | | | $ | 340 | | | $ | 164,966 | | | $ | 463,316 | | | (9,405) | | | $ | (193,370) | | | $ | 435,252 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (76,893) | | | $ | (59,292) | | | $ | 108,205 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation | 50,416 | | | 46,276 | | | 45,450 | |
| Impairment of long-lived assets | 3,500 | | | — | | | — | |
| Amortization of right-of-use asset | 39,517 | | | 39,860 | | | 35,186 | |
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 21,790 | | | 8,980 | | | 5,485 | |
| Provision for bad debts and uncollectible interest | 191,122 | | | 168,842 | | | 84,286 | |
| Change in fair value of accounts receivable | 4,773 | | | — | | | — | |
| Amortization of securitized financing costs | 784 | | | — | | | — | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 10,258 | | | 10,972 | | | 8,915 | |
| Charges, net of credits | 3,952 | | | 14,360 | | | 2,677 | |
| Deferred income taxes | (27,596) | | | (5,309) | | | 16,799 | |
| Loss on early termination of debt | 14,221 | | | — | | | 1,218 | |
| Gain from bargain purchase | (104,857) | | | — | | | — | |
| Loss from disposal of property and equipment | — | | | 859 | | | 258 | |
| Tenant improvement allowances received from landlords | 23,698 | | | 11,560 | | | 14,143 | |
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Customer accounts receivable | (165,587) | | | (90,465) | | | (62,543) | |
| Other accounts receivables | 5,724 | | | 5,273 | | | (1,818) | |
| Inventories | 36,569 | | | 6,043 | | | (50,363) | |
| Other assets | 9,006 | | | (4,317) | | | 1,081 | |
| Accounts payable | (16,789) | | | (3,020) | | | 5,338 | |
| Accrued expenses | 15,130 | | | (35,905) | | | 19,325 | |
| Operating leases | (64,741) | | | (56,430) | | | (53,435) | |
| Income taxes | (11,254) | | | 6,788 | | | (4,687) | |
| Deferred revenues and other credits | (1,289) | | | (4,627) | | | 882 | |
| Other liabilities | (12,688) | | | — | | | — | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities | (51,234) | | | 60,448 | | | 176,402 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Purchases of property and equipment | (51,054) | | | (72,966) | | | (44,859) | |
| Acquisitions, net of cash | 3,714 | | | — | | | — | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (47,340) | | | (72,966) | | | (44,859) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of asset-backed notes | 533,040 | | | 451,853 | | | 440,710 | |
| Payments on asset-backed notes | (393,476) | | | (409,973) | | | (483,904) | |
| Borrowings under revolving credit facility | 819,659 | | | 1,070,795 | | | 1,530,376 | |
| Payments on revolving credit facility | (672,931) | | | (998,795) | | | (1,433,376) | |
| Payment of securitized financings | (33,541) | | | — | | | — | |
| Payment for share repurchases | — | | | (71,696) | | | (55,384) | |
| Payment of debt issuance costs and amendment fees | (35,096) | | | (6,413) | | | (7,658) | |
| Proceeds from stock issued under employee stock purchase plan | 561 | | | 777 | | | 809 | |
| Tax payments associated with equity-based compensation transactions | (1,238) | | | (2,378) | | | (1,410) | |
| Payment for extinguishment of debt | (108,175) | | | — | | | (141,279) | |
| Other | 153 | | | (918) | | | (1,050) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 108,956 | | | 33,252 | | | (152,166) | |
| Net change in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | 10,382 | | | 20,734 | | | (20,623) | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, beginning of period | 60,371 | | | 39,637 | | | 60,260 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, end of period | $ | 70,753 | | | $ | 60,371 | | | $ | 39,637 | |
(continued on next page)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | |
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new operating lease liabilities | $ | 111,487 | | | $ | 65,397 | | | $ | 34,847 | |
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for new financing lease liabilities | — | | | 1 | | | 1,160 | |
| Property and equipment purchases not yet paid | 14,425 | | | 17,258 | | | 9,059 | |
| Fair value of net assets acquired in business combination | 174,124 | | | — | | | — | |
| Preferred stock issued in exchange for Badcock capital stock | 62,246 | | | — | | | — | |
| Supplemental cash flow data: | | | | | |
| Cash interest paid | 60,019 | | | 26,001 | | | 18,252 | |
| Cash income taxes paid (refunded), net | 1,453 | | | (8,508) | | | 21,525 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Business. Conn’s, Inc., a Delaware corporation, is a holding company with no independent assets or operations other than its investments in its subsidiaries. References to “we,” “our,” “us,” “the Company,” “Conn’s” or “CONN” refer to Conn’s, Inc. and its subsidiaries. Conn’s is a leading specialty retailer that offers a broad selection of quality, branded durable consumer goods and related services in addition to proprietary credit solutions for its core consumers. We operate an integrated and scalable business through our retail stores and website. Our complementary product offerings include furniture and mattresses, home appliances, consumer electronics and home office products from leading global brands across a wide range of price points. Our credit offering provides financing solutions to a large, under-served population of consumers who typically have limited credit alternatives.
On December 18, 2023, the Company acquired 100% of the outstanding stock units of W.S. Badcock, LLC in exchange for 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock which is convertible into an aggregate of 24,540,295 non-voting common shares, subject to stockholder approval. The non-voting common shares represent 49.99% of the issued and outstanding shares of common stock immediately available after conversion.
We operate two reportable segments: retail and credit. Our retail stores bear the “Conn’s HomePlus” or "Badcock and more" name with all of our stores providing the same products and services to a common customer group. Our stores follow the same procedures and methods in managing their operations. Our retail business and credit business are operated independently from each other. The credit segment is dedicated to providing short- and medium-term financing to our retail customers. The retail segment is not involved in credit approval decisions or collection efforts. Our management evaluates performance and allocates resources based on the operating results of the retail and credit segments.
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and prevailing industry practices.
Fiscal Year. Our fiscal year ends on January 31. References to a fiscal year refer to the calendar year in which the fiscal year ends.
Principles of Consolidation. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Conn’s, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All material intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Variable Interest Entities. Variable Interest Entities (“VIEs”) are consolidated if the Company is the primary beneficiary. The primary beneficiary of a VIE is the party that has (i) the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the performance of the VIE and (ii) the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that could potentially be significant to the VIE.
We securitize customer accounts receivables by transferring the receivables to various bankruptcy-remote VIEs. We retain the servicing of the securitized portfolio and have a variable interest in each corresponding VIE by holding the residual equity. We have determined that we are the primary beneficiary of each respective VIE because (i) our servicing responsibilities for the securitized portfolio give us the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the performance of the VIE and (ii) our variable interest in the VIE gives us the obligation to absorb losses and the right to receive residual returns that potentially could be significant. As a result, we consolidate the respective VIEs within our consolidated financial statements.
Refer to Note 7, Debt and Financing Lease Obligations, and Note 14, Variable Interest Entities, for additional information.
Use of Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make informed judgments and estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Changes in facts and circumstances or additional information may result in revised estimates, and actual results may differ, even significantly, from these estimates. Management evaluates its estimates and related assumptions regularly, including those related to the allowance for credit losses and allowances for no-interest option credit programs, which are particularly sensitive given the size of our customer portfolio balance.
Cash and Cash Equivalents. As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, cash and cash equivalents included cash and credit card deposits in transit. Credit card deposits in transit included in cash and cash equivalents were $2.5 million and $5.2 million as of January 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Restricted Cash. The restricted cash balance as of January 31, 2024 and 2023 includes $41.2 million and $33.6 million, respectively, of cash we collected as servicer on the securitized receivables that was subsequently remitted to the VIEs and $8.8 million and $5.2 million, respectively, of cash held by the VIEs as additional collateral for the asset-backed notes.
Customer Accounts Receivable. Customer accounts receivable reported in the Consolidated Balance Sheet includes total receivables managed. The Company has two types of lending products including installment loans from the legacy Conn’s
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
business and in conjunction with the acquisition of Badcock revolving credit accounts.
Installment Loans. Customer accounts receivable are recognized at the time the customer takes possession of the product. Customer accounts receivable include installment loans that are both transferred to a VIE and those not transferred to a VIE. The expected lifetime losses on installment loans are recognized upon origination through an allowance for credit losses account that is deducted from the customer account receivable balance and presented net thereof. Customer accounts receivable include the net of unamortized deferred fees charged to customers and origination costs. Customer receivables are considered delinquent if a payment has not been received on the scheduled due date. Installment loans that are delinquent more than 209 days as of the end of a month are charged-off against the allowance for doubtful accounts along with interest accrued subsequent to the last payment.
In an effort to mitigate losses on our installment loans, we may make loan modifications to a borrower experiencing financial difficulty. The loan modifications are intended to maximize net cash flow after expenses and avoid the need to exercise legal remedies available to us. We may extend or “re-age” a portion of our customer accounts, which involves modifying the payment terms to defer a portion of the cash payments due. Our re-aging of customer accounts does not change the interest rate or the total principal amount due from the customer and typically does not reduce the monthly contractual payments. To a much lesser extent, we may provide the customer the ability to refinance their account, which typically does not change the interest rate or the total principal amount due from the customer but does reduce the monthly contractual payments and extend the term. We consider accounts that have been re-aged in excess of three months, refinanced or with significant concessions as "restructured accounts".
Interest Income on Customer Accounts Receivable. Interest income, which includes interest income and amortization of deferred fees and origination costs, is recorded using the interest method and is reflected in finance charges and other revenues. Typically, interest income is recorded until the customer account is paid off or charged-off, and we provide an allowance for estimated uncollectible interest. We reserve for interest that is more than 60 days past due. Any contractual interest income received from customers in excess of the interest income calculated using the interest method is recorded as deferred revenue on our balance sheets. At January 31, 2024 and 2023, there were $7.8 million and $8.1 million, respectively, of deferred interest included in deferred revenues and other credits and other long-term liabilities. The deferred interest will ultimately be brought into income as the accounts pay off or charge-off.
We offer a 12-month no-interest option program. If the customer is delinquent in making a scheduled monthly payment or does not repay the principal in full by the end of the no-interest option program period (grace periods are provided), the account does not qualify for the no-interest provision and none of the interest earned is waived. Interest income is recognized based on estimated accrued interest earned to date on all no-interest option finance programs with an offsetting reserve for those customers expected to satisfy the requirements of the program based on our historical experience.
We recognize interest income on significantly modified accounts using the interest income method, which requires reporting interest income equal to the increase in the net carrying amount of the loan attributable to the passage of time. Cash proceeds and other adjustments are applied to the net carrying amount such that it equals the present value of expected future cash flows.
We place accounts in non-accrual status when legally required. Payments received on non-accrual loans will be applied to principal and reduce the balance of the loan. At January 31, 2024 and 2023, the carrying value of customer accounts receivable in non-accrual status was $8.9 million and $7.9 million, respectively. At January 31, 2024 and 2023, the carrying value of customer accounts receivable that were past due 90 days or more and still accruing interest totaled $81.7 million and $92.2 million, respectively. At January 31, 2024 and January 31, 2023, the carrying value of customer accounts receivable in a bankruptcy status that were less than 60 days past due of $8.1 million and $7.1 million, respectively, were included within the customer receivables balance carried in non-accrual status.
Allowance for Credit Losses. The allowance for credit losses is measured on a collective (pool) basis where similar risk characteristics exist and is only applied to our installment loan portfolio. Upon adoption of ASC 326, the Company elected to maintain the pools of customer accounts receivable that were previously accounted for under ASC 310 (Non-Modified, Modified and Significantly Modified which were previously referred to as Non-TDR Non-Re-aged, Non-TDR Re-aged, and TDR, respectively). These pools are further segmented based on shared risk attributes, which include the borrower’s Vantage score, product class, length of customer relationship and delinquency status. The allowance for credit losses is determined for each pool and reduces the pool’s carrying amount to establish a new amortized cost basis. Changes to the allowance for credit losses after adoption are recorded through provision expense.
We have elected to use a risk-based, pool-level segmentation framework to calculate the expected loss rate. This framework is based on our historical gross charge-off history. In addition to adjusted historical gross charge-off rates, estimates of post-charge-off recoveries, including cash payments from customers, sales tax recoveries from taxing jurisdictions, and payments received under credit insurance and repair service agreement (“RSA”) policies are also considered. We also consider forward-
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
looking economic forecasts based on a statistical analysis of economic factors (specifically, forecast of unemployment rates over the reasonable and supportable forecasting period). To the extent that situations and trends exist and are not captured in our model, management will layer on additional qualitative adjustments. Qualitative factors can include both external and internal information and consider management’s view on available facts and circumstances at each reporting period. More specifically, external factors that may have an impact on the application of qualitative factors would include new laws or regulations relating to collections or originations, new interpretations of existing laws or regulations, and the overall condition of the economy. Internal factors that may have an impact on the application of qualitative factors would include necessary revisions to modeling estimates and operational activities.
The Company uses a 24-month reasonable and supportable forecast period for the installment loan portfolio. We estimate losses beyond the 24-month forecast period based on historic loss rates experienced over the life of our historic loan portfolio by loan pool type. We revisit our measurement methodology and assumption annually, or more frequently if circumstances warrant.
Revolving Accounts. As of December 18, 2023, the Company elected the fair value option to account for all revolving accounts acquired through the Badcock acquisition as well as future originations of revolving accounts. Instead of recording an allowance to estimate expected lifetime losses, we apply fair value methods to estimate the current value of the revolving accounts. This election is non-revocable and will remain in place until the accounts pay or charge off or another event occurs requiring consideration of the fair value option. Typically, we use a discounted cash flow approach which relies on assumptions regarding default rates, cash flow estimates of both duration and volume, and the discount rate among other factors. Of the $304.2 million of Badcock accounts on the balance sheet at January 31, 2024, $173.6 million were included in non-consolidated securitization vehicles. These accounts failed the requirements for sale accounting per ASC 860, “Transfers of Financial Assets and Liabilities”, and therefore the related debt is accounted for as secured borrowings in the liability section reflective of the underlying debt of the securitization vehicle. The fair value adjustment for both the revolving accounts and related secured borrowings are included in the income statement under the caption, “Finance charges and other revenues” as a component of revenue.
Inventories. Inventories consist of merchandise purchased for resale and service parts and are recorded at the lower of cost or net realizable value. The carrying value of the inventory is reduced to its net realizable value for any product lines with excess of carrying amount, typically weighted-average cost, over the amount we expect to realize from the ultimate sale or other disposition of the inventory, with a corresponding charge to cost of sales. The write-down of inventory to net realizable value is estimated based on assumptions regarding inventory aging and historical product sales.
Vendor Allowances. We receive funds from vendors for price protection, product rebates (earned upon purchase or sale of product), marketing, and promotion programs, collectively referred to as vendor allowances, which are recorded on an accrual basis. We estimate the vendor allowances to accrue based on the progress of satisfying the terms of the programs based on actual and projected sales or purchase of qualifying products. If the programs are related to product purchases, the vendor allowances are recorded as a reduction of product cost in inventory still on hand with any remaining amounts recorded as a reduction of cost of goods sold. During the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, we recorded $128.7 million, $129.0 million and $118.1 million, respectively, as reductions in cost of goods sold from vendor allowances.
Property and Equipment. Property and equipment, including any major additions and improvements to property and equipment, are recorded at cost. Normal repairs and maintenance that do not materially extend the life of property and equipment are expensed as incurred. Depreciation, which includes amortization of financed leases, is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, or in the case of leasehold improvements, over the shorter of the estimated useful lives or the remaining terms of the leases.
Internal-Use Software Costs. Costs related to software developed or obtained for internal use and cloud-based computing arrangements are expensed as incurred until the application development stage has been reached. Once the application development stage has been reached, certain qualifying costs are capitalized until the software is ready for its intended use. Costs incurred during the post implementation stage are expensed as incurred. Once placed into service, capitalized costs are amortized over periods of up to 10 years. For the year ended January 31, 2024, no software costs were written-off. For the year ended January 31, 2023, we incurred a $7.3 million loss from the write-off of previously capitalized costs related to a change in the e-commerce platform. No software costs were written-off in the years ended January 31, 2022. Refer to Note 5, Charges and Credits, for additional information.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets. Long-lived assets are evaluated for impairment, primarily at the asset group level. The asset group is defined as stores and cross-docks within a distribution center’s service area. We monitor asset group performance in order to assess if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be recoverable. The most likely condition that would necessitate an assessment would be an adverse change in historical and estimated future results of an asset group's performance. For property and equipment held and used, we measure an impairment loss if the
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
carrying amount is not recoverable through its undiscounted cash flows and measure the impairment loss based on the difference between the carrying amount and estimated fair value. For the years ended January 31, 2024, we recorded an impairment loss of $2.3 million which is included in "Charges and Credits". For the years ended January 31, 2023 and 2022, there were no impairments.
Leases. We determine if an arrangement is a lease at inception. Operating lease right-of-use assets and liabilities are recognized at the commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of our leases do not provide an implicit rate, we use our estimated incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at the commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. If the estimate of our incremental borrowing rate was changed, our operating lease assets and liabilities could differ materially.
We record lease incentives as a reduction to the operating lease right-of-use assets upon commencement of the lease and amortize the balance on a straight-line basis over the life of the lease. Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the balance sheet. Lease terms may include options to extend or terminate the lease when it is reasonably certain that we will exercise the option. Lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
We have made a policy election for all classifications of leases to combine lease and non-lease components and to account for them as a single lease component.
Debt Issuance Costs. Costs that are direct and incremental to debt issuance are deferred and amortized to interest expense using the effective interest method over the expected life of the debt. All other costs related to debt issuance are expensed as incurred. We present debt issuance costs associated with long-term debt as a reduction of the carrying amount of the debt. Unamortized costs related to the Revolving Credit Facility, as defined in Note 7, Debt and Financing Lease Obligations, are included in other assets on our Consolidated Balance Sheet and were $8.6 million and $5.4 million as of January 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Revenue Recognition. The Company accounts for revenue under ASC 606 and has the following material revenue streams: the sale of products (e.g. appliances, electronics) including delivery; the sale of third party warranty and insurance programs, including retrospective income; service income; interest income generated from the financing of point of sale transactions; and volume rebate incentives received from a third party financier.
Sale of Products Including Delivery: The Company has a single performance obligation associated with these contracts: the delivery of the product to the customer, at which point control transfers. Revenue for the sale of products is recognized at the time of delivery, net of any adjustments for sales incentives such as discounts, coupons, rebates or other free products or services. Sales financed through third-party no-interest option programs typically require us to pay a fee to the third party on each completed sale, which is recorded as a reduction of net sales in the retail segment.
Sale of Third Party Warranty and Insurance Programs, Including Retrospective Income: We sell repair service agreements (“RSA”) and credit insurance contracts on behalf of unrelated third-parties. The Company has a single performance obligation associated with these contracts: the delivery of the product to the customer, at which point control transfers. Commissions related to these contracts are recognized in revenue upon delivery of the product. We also may serve as the administrator of the RSAs sold and defer 5% of the revenue received from the sale of RSAs as compensation for this performance obligation as 5% represents the estimated stand-alone sales price to serve as the administrator. The deferred RSA administration fee is recorded in income ratably over the life of the RSA contract sold. Retrospective income on RSA contracts is recognized upon delivery of the product based on an estimate of claims and is adjusted throughout the life of the contracts as actual claims materialize. Retrospective income on insurance contracts is recognized when earned as that is the point at which we no longer believe a significant reversal of income is probable as the consideration is highly susceptible to factors outside of our influence.
Service Income: The Company has a single performance obligation associated with these contracts: the servicing of the RSA claims. Service revenues are recognized at the time service is provided to the consumer.
Volume Rebate Incentive: As part of our agreement with our third-party provider of no-interest option programs, we may receive a volume rebate incentive based on the total dollar value of sales made under our third-party provider program. The Company has a single performance obligation associated with this contract: the delivery of the product to the customer, at which point control transfers. Revenue for the volume rebate incentive is recognized upon delivery of the product to the customer based on the projected total annual dollar value of sales to be made under our third-party provider.
Deferred Revenue. Deferred revenue related to contracts with customers consists of deferred customer deposits and deferred RSA administration fees. During the twelve months ended January 31, 2024, we recognized $3.8 million of revenue for customer deposits deferred as of the beginning of the period compared to $6.9 million recognized during the twelve months ended January 31, 2023. During the twelve months ended January 31, 2024, we recognized $2.8 million of revenue for RSA
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
administrative fees deferred as of the beginning of the period compared to $3.1 million recognized during the twelve months ended January 31, 2023.
Expense Classifications. We record as cost of goods sold, the direct cost of products and parts sold and related costs for delivery, transportation and handling, inbound freight, receiving, inspection, and other costs associated with the operations of our distribution system, including occupancy related to our warehousing operations. The costs associated with our merchandising, advertising, sales commissions, and all store occupancy costs, are included in selling, general and administrative expense (“SG&A”).
Advertising Costs. Advertising costs are expensed as incurred. For fiscal years 2024, 2023 and 2022, advertising expense was $94.3 million, $86.7 million and $90.4 million, respectively.
Stock-based Compensation. Stock-based compensation expense is recorded for share-based compensation awards, net of actual forfeitures, over the requisite service period using the straight-line method. For equity-classified share-based compensation awards, expense is recognized based on the grant-date fair value. For stock option grants, we use the Black-Scholes model to determine fair value. For grants of restricted stock units, the fair value of the grant is the market value of our stock at the date of issuance. For grants of performance-based restricted stock units, the fair value of the grant is the market value of our stock at the date of issuance adjusted for any market conditions.
Self-insurance. We are self-insured for certain losses relating to group health, workers’ compensation, automobile, general and product liability claims. We have stop-loss coverage to limit the exposure arising from these claims. Self-insurance losses for claims filed and claims incurred, but not reported, are accrued based upon our estimates of the net aggregate liability for claims incurred using development factors based on historical experience.
Income Taxes. We are subject to U.S. federal income tax as well as income tax in multiple state jurisdictions. We follow the liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on temporary differences between GAAP and tax bases of assets and liabilities and for operating loss and tax credit carryforwards, as measured using the enacted tax rates expected to be in effect when the temporary differences are expected to be realized or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period in which the enactment occurs. A valuation allowance is provided when it is more-likely-than-not that some portion or all of a deferred tax asset will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become realizable. To the extent penalties and interest are incurred, we record these charges as a component of our provision for income taxes.
During the years ended January 31, 2024 and 2023, we concluded that, based on our evaluation of available objective positive and negative evidence, it is not more likely than not that our net U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets are recoverable. As of January 31, 2024, the total valuation allowance relative to U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets was $25.2 million as compared to $6.6 million as of January 31, 2023. The net change during the year ended January 31, 2024 and 2023 in the valuation allowance was $18.6 million and $6.6 million, respectively.
We review and update our tax positions as necessary to add any new uncertain tax positions taken, or to remove previously identified uncertain positions that have been adequately resolved. Additionally, uncertain positions may be remeasured as warranted by changes in facts or law. Accounting for uncertain tax positions requires estimating the amount, timing and likelihood of ultimate settlement.
Contingencies. An estimated loss from a contingency is recorded if it is probable that an asset has been impaired or a liability has been incurred at the date of the financial statements and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. Gain contingencies are not recorded until realization is assured beyond a reasonable doubt. Legal costs related to loss contingencies are expensed as incurred.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments. Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Assets and liabilities recorded at fair value are categorized using defined hierarchical levels related to subjectivity associated with the inputs to fair value measurements as follows:
•Level 1 – Inputs represent unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
•Level 2 – Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly (for example, quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets or quoted market prices for identical assets or liabilities in markets not considered to be active, inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability, or market-corroborated inputs).
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
•Level 3 – Inputs that are not observable from objective sources such as our internally developed assumptions used in pricing an asset or liability (for example, an estimate of future cash flows used in our internally developed present value of future cash flows model that underlies the fair-value measurement).
In determining fair value, we use observable market data when available, or models that incorporate observable market data. When we are required to measure fair value and there is not a market-observable price for the asset or liability or for a similar asset or liability, we use the cost or income approach depending on the quality of information available to support management’s assumptions. The cost approach is based on management’s best estimate of the current asset replacement cost. The income approach is based on management’s best assumptions regarding expectations of future net cash flows and discounts the expected cash flows using a commensurate risk-adjusted discount rate. Such evaluations involve significant judgment, and the results are based on expected future events or conditions such as sales prices, economic and regulatory climates, and other factors, most of which are often outside of management’s control. However, we believe assumptions used reflect a market participant’s view of long-term prices, costs, and other factors and are consistent with assumptions used in our business plans and investment decisions.
In arriving at fair-value estimates, we use relevant observable inputs available for the valuation technique employed. If a fair-value measurement reflects inputs at multiple levels within the hierarchy, the fair-value measurement is characterized based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair-value measurement.
The fair value of cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and accounts payable approximate their carrying amounts because of the short nature of these instruments. The fair value of the installment loans included in customer accounts receivable, approximates their carrying value, net of the allowance for credit losses. The fair value of revolving accounts included in customer accounts receivable are recorded at fair value which was determined using Level 3 inputs to develop a discounted cash flow forecast as further described in Note 3. The fair value of our Revolving Credit Facility approximates carrying value based on the current borrowing rate for similar types of borrowing arrangements. At January 31, 2024, the fair value of the asset-backed notes was $536.3 million, compared to the carrying value of $571.2 million, which was determined using Level 2 inputs based on inactive trading activity.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements Adopted.
Financial Instruments - Troubled Debt Restructurings and Vintage Disclosures. In March 2022, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2022-02 ("ASU 2022-02"), Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326): Troubled Debt Restructurings and Vintage Disclosures, an update that eliminates the accounting guidance for troubled debt restructurings ("TDR") by creditors in Accounting Standard Codification 310 - Receivables ("ASC 310-40") while enhancing disclosure requirements for certain loan refinancings and restructurings by creditors when a borrower is experiencing financial difficulty. Under ASU 2022-02, the use of a discounted cash flow method is no longer required when measuring expected credit losses on modified loans. The ASU also refines existing credit-related disclosures by requiring disclosure of current-period gross charge-offs of receivables by year of origination. The amendments in the ASU are to be applied prospectively to modifications and disclosures of gross charge-offs, and, as such, there will be no comparative disclosures to prior periods until such time as both periods disclosed are subject to the new guidelines. However, adoption on a modified retrospective basis is permitted for the effect on the allowance for credit losses related to the elimination of the TDR recognition and measurement guidance. The ASU became effective for the Company on February 1, 2023. Upon adoption, the Company recorded an adjustment to reduce the beginning balance of its allowance for credit losses by $0.4 million to reflect the elimination of the measurement guidance related to TDRs with an offsetting increase, net of tax, to beginning retained earnings.
Liabilities - Supplier Finance Programs ASU 2022-04. In September 2022, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2022-04 ("ASU 2022-04"), Liabilities - Supplier Finance Programs (Subtopic 405-50): Disclosure of Supplier Finance Program Obligations, an update that requires that a buyer in a supplier finance program disclose sufficient information about the program to allow a user of financial statements to understand the program's nature, activity during the period, changes from period to period, and potential magnitude. The ASU became effective for the Company in the second quarter of fiscal year 2024. The adoption did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements Yet To Be Adopted.
Segment Reporting - Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures ASU 2023-07. In November 2023, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2023-07 ("ASU 2023-07"), Segment Reporting: Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, that improves disclosures about a public entity's reportable segments and addresses requests from investors and other allocators of capital for additional, more detailed information about a reportable segment's expenses. We expect to adopt ASU 2023-07 during the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2025. The adoption of ASU 2023-07 will require additional disclosures related to our segment reporting but will likely not have a material impact on our financial statements.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Income Taxes - Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures ASU 2023-09. In December 2023, the FASB issued an Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2023-09 ("ASU 2023-09"), Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, to enhance the transparency and decision usefulness of income tax disclosures. The ASU is intended to address investor requests for more transparency about income tax information through improvements to income tax disclosures primarily related to the rate reconciliation and income taxes paid information. We expect to adopt ASU 2023-09 during fiscal year 2026. The adoption of ASU 2023-09 will require additional disclosures related to our income tax reporting but will likely not have a material impact on our financial statements.
2. Customer Accounts Receivable
Customer accounts receivable consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | January 31,
2024 | | January 31,
2023 |
Customer accounts receivable (1)(2) | $ | 992,346 | | | $ | 1,025,364 | |
| Deferred fees and origination costs, net | (11,283) | | | (11,699) | |
| Allowance for no-interest option credit programs | (18,224) | | | (18,753) | |
| Allowance for uncollectible interest and fees | (18,488) | | | (20,007) | |
| Carrying value of customer accounts receivable | 944,351 | | | 974,905 | |
Allowance for credit losses (3) | (160,825) | | | (164,168) | |
| Other net customer receivables | 475 | | | — | |
| Carrying value of customer accounts receivable, net of allowance | 784,001 | | | 810,737 | |
| Short-term portion of customer accounts receivable, net | (419,005) | | | (421,683) | |
| Long-term customer accounts receivable, net | $ | 364,996 | | | $ | 389,054 | |
(1)As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, the customer accounts receivable balance included $27.1 million and $27.5 million, respectively, in interest and fees receivable. Net of the allowance for uncollectible interest and fees, the outstanding receivable as of January 31, 2024 and 2023 was $8.6 million and $7.5 million, respectively.
(2)As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, the carrying value of customer accounts receivable past due one day or greater was $304.9 million and $290.4 million, respectively. Further, the carrying amount of customer accounts receivable which received a re-age at least once during the lifetime of the loan was $177.5 million and $160.9 million as of January 31, 2024 and January 31, 2023, respectively.
(3)As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, the allowance for credit losses is presented net of recovery receivables of $48.1 million and $47.4 million, respectively.
The allowance for credit losses included in the current and long-term portion of customer accounts receivable, net as shown in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | January 31, 2024 | | January 31, 2023 |
| Customer accounts receivable - current | $ | 509,975 | | | $ | 517,611 | |
| Allowance for credit losses for customer accounts receivable - current | (90,970) | | | (95,928) | |
| Customer accounts receivable, net of allowances | 419,005 | | | 421,683 | |
| Customer accounts receivable - non current | 453,339 | | | 477,301 | |
| Allowance for credit losses for customer accounts receivable - non current | (88,343) | | | (88,247) | |
| Long-term portion of customer accounts receivable, net of allowances | 364,996 | | | 389,054 | |
| Total customer accounts receivable, net | $ | 784,001 | | | $ | 810,737 | |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The following presents the activity in our allowance for credit losses and uncollectible interest for customer accounts receivable:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | January 31, 2024 |
| (in thousands) | Customer Accounts Receivable | | Restructured Accounts | | Total |
| Allowance at beginning of period | $ | 150,579 | | | $ | 33,596 | | | $ | 184,175 | |
| ASU 2022-02 adoption | — | | | (372) | | | (372) | |
| Adjusted allowance at beginning of period | 150,579 | | | 33,224 | | | 183,803 | |
Provision for credit loss expense (1) | 148,522 | | | 42,302 | | | 190,824 | |
Principal charge-offs (2) | (148,884) | | | (36,496) | | | (185,380) | |
| Interest charge-offs | (36,156) | | | (8,863) | | | (45,019) | |
Recoveries (2) | 28,178 | | | 6,907 | | | 35,085 | |
| Allowance at end of period | $ | 142,239 | | | $ | 37,074 | | | $ | 179,313 | |
| Average total installment loan portfolio | $ | 905,610 | | | $ | 85,539 | | | $ | 991,149 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | January 31, 2023 |
| (in thousands) | Customer Accounts Receivable | | Restructured Accounts | | Total |
| Allowance at beginning of period | $ | 165,044 | | | $ | 43,976 | | | $ | 209,020 | |
| | | | | |
Provision for credit loss expense(1) | 132,150 | | | 35,797 | | | 167,947 | |
Principal charge-offs (2) | (142,442) | | | (44,863) | | | (187,305) | |
| Interest charge-offs | (33,959) | | | (10,695) | | | (44,654) | |
Recoveries (2) | 29,786 | | | 9,381 | | | 39,167 | |
| Allowance at end of period | $ | 150,579 | | | $ | 33,596 | | | $ | 184,175 | |
| Average total installment loan portfolio | $ | 968,085 | | | $ | 87,515 | | | $ | 1,055,600 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | January 31, 2022 |
| (in thousands) | Customer Accounts Receivable | | Restructured Accounts | | Total |
| Allowance at beginning of period | $ | 219,739 | | | $ | 78,298 | | | $ | 298,037 | |
| | | | | |
Provision for credit loss expense(1) | 52,872 | | | 30,936 | | | 83,808 | |
Principal charge-offs (2) | (105,889) | | | (64,239) | | | (170,128) | |
| Interest charge-offs | (28,972) | | | (17,576) | | | (46,548) | |
Recoveries (2) | 27,294 | | | 16,557 | | | 43,851 | |
| Allowance at end of period | $ | 165,044 | | | $ | 43,976 | | | $ | 209,020 | |
| Average total installment loan portfolio | $ | 995,373 | | | $ | 140,618 | | | $ | 1,135,991 | |
(1)Includes provision for uncollectible interest, which is included in finance charges and other revenues, and changes in expected future recoveries.
(2)Charge-offs include the principal amount of losses (excluding accrued and unpaid interest). Recoveries include the principal amount collected during the period for previously charged-off balances. Net charge-offs are calculated as the net of principal charge-offs and recoveries.
We manage our Customer Accounts Receivable portfolio using delinquency as a key credit quality indicator. The following table presents the delinquency distribution of the carrying value of customer accounts receivable by calendar year of origination as of January 31, 2024:
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | | | | | |
| Delinquency Bucket | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | Prior | Total | % of Total |
| Current | $38,592 | $404,424 | $148,846 | $44,528 | $3,076 | $639,466 | 67.7% |
| 1-30 | — | 73,894 | 46,019 | 19,466 | 2,931 | 142,310 | 15.1% |
| 31-60 | — | 23,401 | 15,426 | 7,132 | 1,341 | 47,300 | 5.0% |
| 61-90 | — | 15,846 | 11,045 | 5,251 | 1,000 | 33,142 | 3.5% |
| 91+ | — | 34,855 | 29,100 | 14,518 | 3,660 | 82,133 | 8.7% |
| Total | $38,592 | $552,420 | $250,436 | $90,895 | $12,008 | $944,351 | 100.0% |
| Gross Charge-offs for the year ended January 31, 2024 | $ — | $18,198 | $82,335 | $61,629 | $23,217 | $185,379 | |
Loan Modifications Made to Borrowers Experiencing Financial Difficulty
In an effort to mitigate losses on our accounts receivable, we may modify a loan to a borrower experiencing financial difficulty. The loan modifications are intended to maximize net cash flow after expenses and avoid the need to exercise legal remedies available to us. We may extend or “re-age” a portion of our customer accounts, which involves modifying the payment terms to defer a portion of the cash payments due. Our re-aging of customer accounts does not change the interest rate or the total principal amount due from the customer and typically does not reduce the monthly contractual payments. We may provide concessions in the form of balance forgiveness to customers experiencing financial difficulty. Balance forgiveness is primarily comprised of reductions in the principal balance of the loan but may also include reductions in uncollected fees or interest balances. We may also provide the customer the ability to refinance their account, which includes reducing the interest rate and extending the term of the loan, and generally includes waiving certain uncollected fees. We consider accounts that have been re-aged in excess of three months (“significantly re-aged”), refinanced, or with significant concessions as “restructured accounts”.
The following tables show the amortized cost basis of loans modified during the twelve months ended January 31, 2024 (since the adoption of ASU 2022-02) to borrowers experiencing financial difficulty disaggregated by modification type:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | Year ended January 31, 2024 |
| Modification Type | Carrying Value | | % of Carrying Value of Customer Accounts Receivable |
| Significantly re-aged | $ | 59,218 | | | 6.0 | % |
| Balance forgiveness | 182 | | | — | % |
| Combination - significantly re-aged & balance forgiveness | 610 | | | 0.1 | % |
| Refinance | 462 | | | — | % |
| Total modifications | $ | 60,472 | | | 6.1 | % |
Loan receivables that have been modified are subject to the same requirements for the accrual of expected credit losses over their expected remaining lives as are unmodified loan receivables. The allowance for credit losses incorporates modeling of historical loss data and thereby captures the higher risk associated with modified loans to borrowers experiencing financial difficulty based on their account attributes.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company monitors the performance of modified loans to borrowers experiencing financial difficulty. The following table depicts the delinquency distribution of loans that were modified on or after February 1, 2023, the date we adopted ASU 2022-02:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | As of January 31, 2024 |
| Current | 1 - 30 | 31 - 60 | 61 - 90 | 91+ | Total |
| Significantly re-aged | $ | 19,532 | | $ | 13,451 | | $ | 7,866 | | $ | 5,740 | | $ | 12,629 | | $ | 59,218 | |
| Balance forgiveness | 48 | | 20 | | 22 | | 12 | | 80 | | 182 | |
| Combination - significantly re-aged & balance forgiveness | 205 | | 152 | | 58 | | 56 | | 139 | | 610 | |
| Refinance | 220 | | 82 | | 43 | | 37 | | 80 | | 462 | |
| Total | $ | 20,005 | | $ | 13,705 | | $ | 7,989 | | $ | 5,845 | | $ | 12,928 | | $ | 60,472 | |
During the twelve months ended January 31, 2024, the Company charged off $10.0 million of balances on loans that were significantly re-aged or received balance forgiveness.
The following tables describe the financial effect of the modifications made to customers experiencing financial difficulty:
| | | | | |
| Twelve Months Ended January 31, 2024 |
| Significantly re-aged | |
| Payment delay duration (in months) | 4 to 12 |
| Balance forgiveness | |
| Balance forgiven (in thousands) | $ | 18 | |
| Combination - significantly re-aged & balance forgiveness | |
| Payment delay duration (in months) | 4 to 12 |
| Balance forgiven (in thousands) | $ | 66 | |
| Refinance | |
| Weighted-average interest rate reduction | 6.95 | % |
| Term extension duration (in months) | 28 |
| Balance forgiven (in thousands) | $ | 40 | |
Troubled Debt Restructurings Prior to the Adoption of ASU 2022-02
Prior to the adoption of ASU 2022-02, loans were classified as TDRs based on modifications made over the lifetime of the loan. The amortized cost basis of loans categorized as TDRs as of January 31, 2023 was $76.8 million. Conversely, ASU 2022-02 only requires disclosures of loans modified during the most recent 12 months and the subsequent performance of such loans, which the Company is applying on a prospective basis.
Further, the Company previously utilized the discounted cash flow method when measuring the expected credit losses of certain restructured accounts as prescribed under ASC 310: Receivables. Through the adoption of ASU 2022-02, this recognition and measurement guidance was eliminated, and the measurement is now performed in accordance with ASC 326: Financial Instruments - Credit Losses. Upon adoption of ASU 2022-02, the allowance for credit losses was reduced by $0.4 million due to the change in guidance.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
3. Customer Accounts Receivable under Fair Value Option
Upon the acquisition of Badcock, the Company acquired customer accounts receivable which are unsecured revolving accounts. Concurrently with the acquisition, the Company adopted ASC 820, "Fair Value Measurements" ("ASC 820") to account for the acquired accounts receivable. The Company elected this option for these customer accounts receivable due to the short-term nature of the accounts as we plan to cease originating revolving accounts and instead begin originating our installment loan product as described in Note 2. Under the fair value option, the Company performs a valuation each reporting period to determine the fair value of the receivables and liability. In order to perform the valuation, the Company stratifies the portfolio into four buckets based on credit score at origination. The accounts are then grouped into pools with varying assumptions. The key assumptions used to develop the valuation include discount rate, prepayment rate, and default rate. Changes in the assumptions could impact the future valuation of the assets.
As of January 31, 2024 and December 18, 2023, the range of values and the weighted average of these key inputs were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| January 31, 2024 | December 18, 2023 |
| Range | | Weighted Average | | Range | | Weighted Average |
| Discount rate | 34.0 - 40.0% | | 35.59 | % | | 34.0 - 40.0% | | 35.73 | % |
| Default rate | 1.04 - 100.0% | | 17.42 | % | | 1.04 - 100.0% | | 16.41 | % |
| Prepayment rate | 0.0% - 8.0% | | 5.12 | % | | 0.0 - 8.0% | | 4.93 | % |
The Company recognizes interest income on the customer receivables and the change in fair value in the line item in the Statement of Operations under the caption "Finance Charges and Other Revenue". For the year ended January 31, 2024, the change in fair value related to the customer accounts receivable was a decrease of $4.8 million. The Company recognizes charge-offs, net of recoveries in the line item, Provision for Bad Debts which for the year ended January 31, 2024 was $5.8 million.
In order to monetize its customer accounts receivable portfolio, Badcock transferred the majority of its customer receivables to securitization vehicles. The securitizations did not qualify as a sale under ASC 860, "Transfers and Servicing", even though the underlying receivables are deemed to be legally sold. In connection with the securitization of the receivables, Badcock has entered into a receivables servicing agreement with securitization vehicles pursuant to which Badcock will provide certain customary servicing and account management services.
The components of customer accounts receivable under fair value option at January 31, 2024 and 2023 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | January 31, |
| (in thousands) | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Current customer accounts receivable under fair value option | | $ | 357,776 | | | $ | — | |
| Fair value adjustment | | (90,954) | | | — | |
| Current customer accounts receivable under fair value option, net | | 266,822 | | | — | |
| Non-current customer accounts receivable under fair value option | | 50,322 | | | — | |
| Fair value adjustment | | (12,958) | | | — | |
| Non-current customer accounts receivable under fair value option, net | | 37,364 | | | — | |
Total customer accounts receivable under fair value option, net (1) | | $ | 304,186 | | | $ | — | |
(1) As of January 31, 2024, the balance of customer accounts receivable under fair value option that are not securitized was $124.6 million
When customer receivables under fair value option are delinquent for approximately one year, the estimated uncollectible amount from the customer is written off and the corresponding accounts receivable is reduced. For the period December 18, 2023 through January 31, 2024, the Company charged-off $5.8 million in receivables. Since the Company accounts for these assets at fair value, there is no allowance for credit losses.
The changes in the balance of customer accounts receivable under the fair value option for the year ended January 31, 2024 at par and fair value were as follows:
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| January 31, 2024 |
| (in thousands) | Par Value | | Fair Value |
| Balance at December 18, 2023 | $ | 405,875 | | | $ | 306,737 | |
| Originations | 35,207 | | | 35,207 | |
| Finance charges | 12,165 | | | 12,165 | |
| Cash collections | (39,387) | | | (39,611) | |
| Charge-offs | (5,762) | | | (5,539) | |
| Fair value adjustment | — | | | (4,773) | |
| Balance at end of year | $ | 408,098 | | | $ | 304,186 | |
The components of finance charges and other revenue generated from customer accounts receivable under the fair value option for the years ended January 31, 2024 and 2023 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Interest income | $ | 12,165 | | | $ | — | |
| Fair value adjustment | (4,773) | | | — | |
| Total finance revenue from customer accounts receivable under the fair value option | $ | 7,392 | | | $ | — | |
4. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Estimated | | January 31, |
| (dollars in thousands) | Useful Lives | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Land | Indefinite | | $ | 1,057 | | | $ | 1,644 | |
| Buildings | 30 years | | 4,482 | | | 4,176 | |
| Leasehold improvements | 5 to 15 years | | 404,680 | | | 365,312 | |
| Equipment and fixtures | 3 to 5 years | | 199,728 | | | 122,456 | |
| Finance leases | 3 to 20 years | | 9,481 | | | 9,481 | |
| Construction in progress | — | | 10,622 | | | 46,390 | |
| | | 630,050 | | | 549,459 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation | | | (379,582) | | | (330,503) | |
| Property and equipment, net | | | $ | 250,468 | | | $ | 218,956 | |
Depreciation expense was approximately $50.4 million, $46.3 million and $45.5 million for the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Construction in progress is comprised primarily of the construction of leasehold improvements related to unopened retail stores and internal-use software under development. Finance lease assets primarily include retail locations.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
5. Charges and Credits
Charges and credits consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Store lease termination and closure costs | $ | 2,340 | | | $ | (896) | | | $ | — | |
| Professional Fees | 18,372 | | | — | | | — | |
| Employee severance | — | | | 8,006 | | | — | |
| Gain from asset sale | (3,147) | | | — | | | — | |
| Excess import freight costs | — | | | — | | | 2,677 | |
| Loss on asset disposal | — | | | 7,250 | | | — | |
| $ | 17,565 | | | $ | 14,360 | | | $ | 2,677 | |
During the year ended January 31, 2024, we recognized $18.4 million in professional fees related to corporate transactions primarily related to the acquisition of Badcock and debt modifications. In addition, we recognized a $3.1 million gain related to the sale of a single store location net of asset disposal costs and $2.3 million in store closure costs related to the impairment of assets associated with the decision to end the store-within-a-store test with Belk, Inc. During the year ended January 31, 2023, we recognized $8.0 million in severance costs related to a change in the executive management team. In addition, we recognized a $0.9 million gain related to the termination of a lease for a single store location net of store closure costs. Furthermore, we recognized $7.3 million in write-offs of previously capitalized costs related to a change in the eCommerce platform. During the year ended January 31, 2022, we recognized $2.7 million of non-recurring domestic transportation costs incurred due to unprecedented congestion in U.S. ports.
6. Finance Charges and Other Revenues
Finance charges and other revenues consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Interest income and fees | $ | 229,170 | | | $ | 244,137 | | | $ | 259,422 | |
| Insurance income | 23,614 | | | 20,681 | | | 24,270 | |
| Other revenues | 6,568 | | | 1,119 | | | 950 | |
| Total finance charges and other revenues | $ | 259,352 | | | $ | 265,937 | | | $ | 284,642 | |
Interest income and fees and insurance income are derived from the credit segment operations, whereas other revenues are derived from the retail segment operations. Insurance income is comprised of sales commissions from third-party insurance companies that are recognized when coverage is sold and retrospective income paid by the insurance carrier if insurance claims are less than earned premiums.
For the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, interest income and fees reflected provisions for uncollectible interest of $45.0 million, $43.8 million and $36.1 million, respectively. The amount included in interest income and fees related to restructured accounts for the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 is $15.7 million, $15.3 million and $24.9 million, respectively.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
7. Debt and Financing Lease Obligations
Debt and financing lease obligations outstanding consist of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Revolving Credit Facility | $ | 160,978 | | | $ | 221,000 | |
| Term Loan | 108,000 | | | — | |
| | | |
| Secured Borrowings | 168,587 | | | — | |
| 2021-A VIE Asset-backed Class B Notes | — | | | 54,597 | |
| 2021-A VIE Asset-backed Class C Notes | 16,815 | | | 63,890 | |
| 2022-A VIE Asset-backed Class A Notes | — | | | 117,935 | |
| 2022-A VIE Asset-backed Class B Notes | 51,238 | | | 132,090 | |
| 2022-A VIE Asset-backed Class C Notes | 63,090 | | | 63,090 | |
| 2023-A VIE Asset-backed Class A Notes | 67,673 | | | — | |
| 2023-A VIE Asset-backed Class B Notes | 82,430 | | | — | |
| 2023-A VIE Asset-backed Class C Notes | 30,550 | | | — | |
| 2024-A VIE Asset-backed Class A Notes | 133,490 | | | — | |
| 2024-A VIE Asset-backed Class B Notes | 98,120 | | | — | |
| 2024-A VIE Asset-backed Class C Notes | 27,760 | | | — | |
| Financing lease obligations | 5,315 | | | 5,226 | |
| Total debt and financing lease obligations | 1,014,046 | | | 657,828 | |
| Less: | | | |
| Deferred debt issuance costs and discount on debt | (23,623) | | | (20,812) | |
| Current Secured Borrowing | (147,815) | | | — | |
| Current finance lease obligations | (980) | | | (937) | |
| Secured borrowings, non current | (20,841) | | | — | |
| Long-term debt and financing lease obligations | $ | 820,787 | | | $ | 636,079 | |
Future maturities of debt, excluding financing lease obligations, as of January 31, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | |
| (in thousands) | |
| Year Ended January 31, | |
| 2025 | $ | — | |
| 2026 | — | |
| 2027 | 292,121 | |
| 2028 | 288,653 | |
| 2029 | 259,370 | |
| Total | $ | 840,144 | |
Asset-backed Notes. From time to time, we securitize customer accounts receivables by transferring the receivables to various bankruptcy-remote VIEs. In turn, the VIEs issue asset-backed notes secured by the transferred customer accounts receivables and restricted cash held by the VIEs.
Under the terms of the securitization transactions, all cash collections and other cash proceeds of the customer receivables go first to the servicer and the holders of issued notes, and then to us as the holder of non-issued notes, if any, and residual equity. We retain the servicing of the securitized portfolios and receive a monthly fee of 4.75% (annualized) based on the outstanding balance of the securitized receivables. In addition, we, rather than the VIEs, retain all credit insurance income together with certain recoveries related to credit insurance and repair service agreements on charge-offs of the securitized receivables, which are reflected as a reduction to net charge-offs on a consolidated basis.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The asset-backed notes were offered and sold to qualified institutional buyers pursuant to the exemptions from registration provided by Rule 144A under the Securities Act. If an event of default were to occur under the indenture that governs the respective asset-backed notes, the payment of the outstanding amounts may be accelerated, in which event the cash proceeds of the receivables that otherwise might be released to the residual equity holder would instead be directed entirely toward repayment of the asset-backed notes, or if the receivables are liquidated, all liquidation proceeds could be directed solely to repayment of the asset-backed notes as governed by the respective terms of the asset-backed notes. The holders of the asset-backed notes have no recourse to assets outside of the VIEs. Events of default include, but are not limited to, failure to make required payments on the asset-backed notes or specified bankruptcy-related events.
The asset-backed notes outstanding as of January 31, 2024 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Asset-Backed Notes | | Original Principal Amount | | Original Net Proceeds (1) | | Current Principal Amount | | Issuance Date | | Maturity Date | | Contractual Interest Rate | | Effective Interest Rate (2) |
| 2021-A Class C Notes | | $ | 63,890 | | | $ | 63,450 | | | $ | 16,815 | | | 11/23/2021 | | 5/15/2026 | | 4.59% | | 5.14% |
| 2022-A Class B Notes | | 132,090 | | | 129,050 | | | 51,238 | | | 7/21/2022 | | 12/15/2026 | | 9.52% | | 10.67% |
| 2022-A Class C Notes | | 63,090 | | | 43,737 | | | 63,090 | | | 11/30/2022 | | 12/15/2026 | | 0.00% | | 19.20% |
| 2023-A Class A Notes | | 160,690 | | | 159,603 | | | 67,673 | | | 8/17/2023 | | 01/17/2028 | | 8.01% | | 15.87% |
| 2023-A Class B Notes | | 82,430 | | | 79,958 | | | 82,430 | | | 8/17/2023 | | 01/17/2028 | | 10.00% | | 12.57% |
| 2023-A Class C Notes | | 30,550 | | | 26,665 | | | 30,550 | | | 8/17/2023 | | 01/17/2028 | | 11.00% | | 12.78% |
| 2024-A Class A Notes | | 133,490 | | | 132,587 | | | 133,490 | | | 1/26/2024 | | 1/16/2029 | | 7.05% | | 13.86% |
| 2024-A Class B Notes | | 98,120 | | | 96,279 | | | 98,120 | | | 1/26/2024 | | 1/16/2029 | | 9.80% | | 8.28% |
| 2024-A Class C Notes | | 27,760 | | | 23,689 | | | 27,760 | | | 1/26/2024 | | 1/16/2029 | | 10.34% | | 7.73% |
| Total | | $ | 792,110 | | | $ | 755,018 | | | $ | 571,166 | | | | | | | | | |
(1)After giving effect to debt issuance costs and discount on debt.
(2)For the year ended January 31, 2024, and inclusive of the impact of changes in timing of actual and expected cash flows.
On August 7, 2023, Conn’s, Inc., Conn’s Receivables Funding 2023-A, LLC, a newly formed special purpose entity that is indirectly owned by the Company (the “2023-A Issuer”), Conn Appliances Receivables Funding, LLC, an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (the “Depositor”), and Conn Appliances, Inc., a direct and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“Conn Appliances”), entered into a Note Purchase Agreement (the “2023-A Note Purchase Agreement”) with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., MUFG Securities Americas Inc., Citizens JMP Securities, LLC and Regions Securities LLC (collectively, the “2023-A Initial Purchasers”), for the sale of the Issuer’s 8.01% $160.7 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class A, Series 2023-A (the “Class A Notes”), 10.00% $82.4 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class B, Series 2023-A (the “Class B Notes”) and 11.00% $30.6 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class C, Series 2023-A (the “Class C Notes” and, together with the Class A Notes and the Class B Notes, the “2023-A Purchased Notes”). The 2023-A Issuer also issued the Asset Backed Notes, Class R, Series 2023-A (the “Class R Notes” and, collectively with the Purchased Notes, the “Series 2023-A Notes”). The Class R Notes do not have a principal amount or interest rate and were transferred to the Depositor on August 17, 2023 to satisfy the risk retention obligations of Conn Appliances. The Series 2023-A Notes were issued on August 17, 2023 (the “Closing Date”). The Series 2023-A Notes have not been and will not be registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) or the securities laws of any jurisdiction. The 2023-A Purchased Series Notes were sold initially to the 2023-A Initial Purchasers and then reoffered and resold only (i) to “Qualified Institutional Buyers” as defined in Rule 144A under the Securities Act (“Rule 144A”) in transactions meeting the requirements of Rule 144A or (2) solely with respect to the Class A Notes, outside the United States to non-U.S. Persons in transactions in compliance with Regulation S under the Securities Act.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
On January 26, 2024, Conn’s, Inc., Conn’s Receivables Funding 2024-A, LLC, a newly formed special purpose entity that is indirectly owned by the Company (the “2024-A Issuer”), the Depositor, and Conn Appliances, entered into a Note Purchase Agreement (the “2024-A Note Purchase Agreement”) with MUFG Securities Americas Inc., Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., J.P. Morgan Securities LLC and Regions Securities LLC (collectively, the “2024-A Initial Purchasers”), for the sale of the 2024-A Issuer’s 7.05% $133.5 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class A, Series 2024-A (the “Class A Notes”), 9.80% $98.1 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class B, Series 2024-A (the “Class B Notes”) and 10.34% $27.8 million Asset Backed Fixed Rate Notes, Class C, Series 2024-A (the “Class C Notes” and, together with the Class A Notes and the Class B Notes, the “2024-A Purchased Notes”). The 2024-A Issuer will also issue the Asset Backed Notes, Class R, Series 2024-A (the “Class R Notes” and, collectively with the Purchased Notes, the “Series 2024-A Notes”). The Class R Notes will be retained by the Depositor on the Closing Date. The Class R Notes will not have a principal amount or interest rate and will be transferred to the Depositor on the Closing Date to satisfy the risk retention obligations of Conn Appliances. The Series 2024-A Notes were issued on January 26, 2024 (the “Closing Date”). The Series 2024-A Notes have not been and will not be registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) or the securities laws of any jurisdiction. The Purchased Series 2024-A Notes are being sold initially to the 2024-A Initial Purchasers and then reoffered and resold only (i) to “Qualified Institutional Buyers” as defined in Rule 144A under the Securities Act (“Rule 144A”) in transactions meeting the requirements of Rule 144A or (2) solely with respect to the Class A Notes, outside the United States to non-U.S. Persons in transactions in compliance with Regulation S under the Securities Act.
Revolving Credit Facility. On March 29, 2021, Conn’s, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries (the “Borrowers”) entered into the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement (the “Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement”), with certain lenders, which provides for a $555.0 million asset-based revolving credit facility (as amended, the “Revolving Credit Facility”) under which credit availability is subject to a borrowing base and a maturity date of December 31, 2026.
The Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, among other things, permits borrowings under the Letter of Credit Subline (as defined in the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement) that exceed the cap of $40 million to $100 million, solely at the discretion of the lenders for such amounts in excess of $40 million. The obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are secured by substantially all assets of the Company, excluding the assets of the VIEs. As of January 31, 2024, we had available borrowing capacity of $155.3 million under our Revolving Credit Facility, net of standby letters of credit issued of $25.2 million.
On November 21, 2022, we entered into Amendment No. 1 (the "Amendment") to the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement. Under the Amendment, loans under the Revolving Credit Facility bear interest, at our option, at a rate of Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR") plus a margin ranging from 2.50% to 3.25% per annum (depending on a pricing grid determined by our total leverage ratio) or the alternate base rate plus a margin ranging from 1.50% to 2.25% per annum (depending on a pricing grid determined by our total leverage ratio). The alternate base rate is a rate per annum equal to the greatest of the prime rate, the federal funds effective rate plus 0.5%, or SOFR for a 30-day interest period plus 1.0%. We also pay an unused fee on the portion of the commitments that is available for future borrowings or letters of credit at a rate ranging from 0.25% to 0.50% per annum, depending on the average outstanding balance and letters of credit of the Revolving Credit Facility in the immediately preceding quarter. The Amendment also waived testing of the interest coverage covenants beginning with the third quarter of fiscal year 2023 and continuing until the date on which the Company delivers financial statements and a compliance certificate for the fiscal quarter ending April 30, 2024 (unless earlier terminated pursuant to the terms of the Amendment).
On February 21, 2023, the Company, the Borrowers, the guarantors party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the required lenders party thereto entered into the second amendment (the “Second Amendment”) to the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement. The Second Amendment, among other things, permits the Company and the Borrowers to enter into the Pathlight Term Loan (as defined below) and made certain changes conforming to the Term Loan.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
On December 18, 2023, the Company entered into Amendment No. 3 (the “Third Amendment”) to the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2021 (the “Revolving Credit Agreement”), by and among the Company, as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as existing borrowers (the “Existing Borrowers”), and substantially concurrently with the closing of the Revolving Credit Agreement Amendment, Badcock, pursuant to a joinder, as new borrower (“New Borrower”, and together with the Existing Borrowers, collectively, “Borrowers”), certain banks and financial institutions named therein, as lenders, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent for the Lenders. The Third Amendment, among other things: (a) consents to the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Investment Agreement; (b) extends the maturity date of the Revolving Credit Agreement to December 31, 2026; (c) provides for certain adjustments to the representations, warranties and covenants to incorporate the New Borrower into the Revolving Credit Agreement; (d) increases the existing interest rate margins by 0.50%, resulting in possible interest rate margins between (i) 3.00% and 3.75% for SOFR Rate Loans and (ii) 2.00% and 2.75% for Base Rate Loans, in each case based on the total net leverage ratio; (e) extends the termination date of the covenant relief period, which removes testing of the interest coverage covenant, to April 30, 2025; (f) provides for certain amendments to the borrowing base, including (i) modifying the inventory advance rate by removing the cap of 33.3% of revolving commitments and (ii) modifying the contract advance rate to equal the lesser of (x) 80% of net eligible contract payments and (y) 80% of the net fair market value of the owned contract portfolio; (g) provides for increased reporting requirements; (h) amends the minimum excess availability covenant to require, at all times during the term of the Revolving Credit Agreement, availability under the revolver of no less than the greater of (i) 17.5% of the borrowing base and (ii) $100.0 million; (i) replaces the minimum liquidity covenant with a springing, minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of 1.00:1.00, which shall only be tested to the extent availability under the Revolving Credit Agreement is less than 20% of the borrowing base, and testing of such covenant shall continue until the occurrence of the first fiscal-quarter end where availability as of such date has been in excess of 20% of the borrowing base for 30 consecutive days; (j) added a minimum EBITDA financial covenant; (k) increased the cap on revolver borrowings at any one time outstanding to $400.0 million with step downs beginning September 1, 2025 thereafter to $300.0 million; and (l) reduced revolver borrowing base to a $555.0 million asset-based revolving credit facility. The weighted-average interest rate on borrowings outstanding and including unused line fees under the Revolving Credit Facility was 8.8% for the year ended January 31, 2024.
The Revolving Credit Facility places restrictions on our ability to incur additional indebtedness, grant liens on assets, make distributions on equity interests, dispose of assets, make loans, pay other indebtedness, engage in mergers, and other matters. The Revolving Credit Facility restricts our ability to make dividends and distributions unless no event of default exists and a liquidity test is satisfied. Subsidiaries of the Company may pay dividends and make distributions to the Company and other obligors under the Revolving Credit Facility without restriction. We are restricted from making distributions as a result of the Revolving Credit Facility distribution and payment restrictions. The Revolving Credit Facility contains customary default provisions, which, if triggered, could result in acceleration of all amounts outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility.
Debt Covenants. The Third Amendment waived testing of the interest coverage covenants until the date on which the Company delivers financial statements and a compliance certificate for the fiscal quarter ending April 30, 2025 (unless earlier terminated pursuant to the terms of the Amendment). After giving effect to the foregoing amendment, as of January 31, 2024, we were in compliance with the covenants in our Revolving Credit Facility.
A summary of the significant financial covenants that govern our Revolving Credit Facility compared to our actual compliance status as of January 31, 2024 is presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Actual | | Required
Minimum/
Maximum |
| Interest Coverage Ratio for the quarter must equal or exceed minimum | Not Tested | | 1.00:1.00 |
| Interest Coverage Ratio for the trailing two quarters must equal or exceed minimum | Not Tested | | 1.50:1.00 |
| Leverage Ratio must not exceed maximum | 3.21:1.00 | | 4.50:1.00 |
| ABS Excluded Leverage Ratio must not exceed maximum | 1.63:1.00 | | 2.50:1.00 |
| Capital Expenditures, net, must not exceed maximum | $70.1 million | | $100.0 million |
All capitalized terms in the above table are defined by the Revolving Credit Facility and may or may not agree directly to the financial statement captions in this document. The covenants are calculated quarterly, except for capital expenditures, which is calculated for a period of four consecutive fiscal quarters, as of the end of each fiscal quarter.
Pathlight Term Loan and Security Agreement. On February 21, 2023, Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers (the “Borrowers”), entered into a second-lien term loan and security agreement (the “Pathlight Term Loan,” and together with the Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, the
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
“Senior Loan Agreements”) with Pathlight Capital LP, as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the financial institutions party thereto, as lenders (the “Lenders”). The Pathlight Term Loan provides for an aggregate commitment of $100.0 million to the Borrowers pursuant to a three-year secured term loan credit facility, which was fully drawn on February 21, 2023.
This loan was paid in full on December 18, 2023 with the proceeds from the BRF Term Loan (described below). When this loan was paid in full, we recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of $14.2 million which included the prepayment penalty of $8.9 million and the write-off of debt issuance costs of $5.3 million.
BRF Term Loan and Security Agreement. On December 18, 2023, the Company, as parent and guarantor, and the Borrowers, entered into a second-lien term loan and security agreement with BRF Finance Co., LLC, (the “BRF Term Loan”), as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the financial institutions party thereto, as lenders. The BRF Term Loan provides for an aggregate commitment of $108.0 million to the Borrowers pursuant to a secured term loan credit facility maturing on February 20, 2027, which was fully drawn on December 18, 2023. Outstanding amounts under the BRF Term Loan will bear interest at an aggregate rate per annum equal to the Term SOFR Rate (as defined in the Term Loan), subject to a 4.80% floor, plus a margin of 8.00%. The obligations of the Borrowers under the BRF Term Loan are guaranteed by the Company and certain of the Borrowers’ subsidiaries. The Borrowers are required to make quarterly scheduled amortization payments of the BRF Term Loan prior to the maturity thereof in an amount equal to $1.35 million beginning January 2025. The BRF Term Loan is secured by liens (subject, in the case of priority, to the liens under the Revolving Credit Agreement) on substantially all of the assets of the Borrowers and their subsidiaries, subject to customary exceptions.
The Borrowers may elect to prepay all or any portion of the amounts owed under the BRF Term Loan, without a premium or penalty. The Borrowers are required to make mandatory prepayments of amounts owed under the BRF Term Loan in an amount equal to 100% of the proceeds received as a result of any of the following events, subject to certain adjustments: (i) the issuance of any equity securities by the Company that the Company contributes as additional common equity contributions to any Borrower; and (ii) the receipt by the Company, the Borrowers or any of their affiliates of any portion of the CARES Act Tax Refund Proceeds (as defined in the BRF Term Loan), subject to a cap. Voluntary and mandatory prepayments will be applied to the remaining scheduled installments of principal due in respect of the BRF Term Loan in the inverse order of maturity.
The BRF Term Loan contains customary covenants regarding the Borrowers and their subsidiaries that are generally based upon and are comparable to those contained in the Revolving Credit Agreement including, without limitation: financial covenants, such as the maintenance of a minimum interest coverage ratio, subject to a covenant relief period through the fiscal quarter ending April 30, 2025, a maximum leverage ratio, a minimum excess availability covenant and a springing, minimum fixed charge coverage ratio; and negative covenants, such as limitations on indebtedness, liens, mergers, asset transfers, certain investing activities and other matters customarily restricted in such agreements. Most of these restrictions are subject to certain minimum thresholds and exceptions. The BRF Term Loan also contains customary events of default, including, without limitation, payment defaults, material inaccuracy of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, bankruptcy and insolvency proceedings, cross-defaults to certain other agreements, and change of control.
Delayed Draw Term Loan and Security Agreement. On July 31, 2023, Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers (the “Borrowers”), entered into a delayed draw term loan and security agreement (the “Delayed Draw Term Loan”) with Stephens Investments Holdings LLC (“Stephens Investments”) and Stephens Group, LLC and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (the “Lenders”), and Stephens Investments, as administrative agent. The Delayed Draw Term Loan provides for an aggregate commitment of $50.0 million, of which the total commitment is available to be funded in one or a series of borrowings until February 20, 2026, with the Delayed Draw Term Loan to mature on May 22, 2026.
Outstanding amounts under the Delayed Draw Term Loan will bear interest at an aggregate rate per annum equal to the Term SOFR Rate (as defined in the Delayed Draw Term Loan), subject to a 5.00% floor, plus a margin of 10.00%, which shall be payable monthly in arrears in cash except to the extent such payment in cash would result in a default or event of default under any of the Senior Loan Agreements, in which case such portion may be paid-in-kind and added to the outstanding principal amount of the term loans. Amounts under the Delayed Draw Term Loan that remain undrawn are subject to a commitment fee payable monthly based on the undrawn portion of the Delayed Draw Term Loan at a rate of 5.00% per annum. Furthermore, in connection with the funding of each draw under the Delayed Draw Term Loan and on the terms and subject to the conditions of the Delayed Draw Term Loan, including the Share Cap (which equals 19.99% of the shares of common stock in the Company issued and outstanding as of the date of the Delayed Draw Term Loan), the Company will issue to or as directed by the Lenders warrants to purchase a number of shares of common stock of the Company equal to 20% of the aggregate principal amount of such delayed draw term loan funded by a such Lender divided by the exercise price (as defined by the loan agreement). The obligations of the Borrowers under the Delayed Draw Term Loan are guaranteed by the Company and certain of the Borrowers’ subsidiaries. The Borrowers are not required to make any amortization or other payments (whether voluntary or mandatory) of principal under the Delayed Draw Term Loan until the maturity date. The Delayed Draw Term Loan is secured by liens
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(subject, in the case of priority, to the liens under the Fifth Amendment and Restated Loan) on substantially all of the assets of the Borrowers and their subsidiaries, subject to customary exceptions.
Proceeds from borrowings made under the Delayed Draw Term Loan may be used by the Borrowers for working capital and other lawful corporate purposes. The Borrowers may elect to prepay all or any portion of the amounts owed under the Delayed Draw Term Loan, without a premium or penalty, subject to certain conditions, including pro forma compliance with a fixed charge coverage ratio test and reduction of the outstanding principal amount under the Second-Lien Loan Agreement to an amount equal to $40.0 million.
The Delayed Draw Term Loan contains customary covenants regarding the Borrowers and their subsidiaries that are generally based upon and are comparable to those contained in the Senior Loan Agreements including, without limitation: financial covenants, such as a maximum leverage ratio; and negative covenants, such as limitations on indebtedness, liens, mergers, asset transfers, certain investing activities and other matters customarily restricted in such agreements. Most of these restrictions are subject to certain minimum thresholds and exceptions and, where applicable, cushions to the Senior Loan Agreements. The Delayed Draw Term Loan also contains customary events of default, including, without limitation, payment defaults, material inaccuracy of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, bankruptcy and insolvency proceedings, cross-acceleration to the Senior Loan Agreements, cross-defaults to the warrants and certain other agreements (other than the Senior Loan Agreements as defined in the indenture), and change of control.
On December 18, 2023, the Company, entered into Amendment No. 1 (the “DDTL Amendment”) to the Delayed Draw Term Loan, by and among the Company, as parent and guarantor, the Existing Borrowers and substantially concurrently with the closing of the DDTL Amendment, Badcock, pursuant to a joinder, as new borrower, Stephens Investments Holdings LLC (“Stephens Investments”) and Stephens Group, LLC and the other lenders party thereto from time to time, and Stephens Investments, as administrative agent. The DDTL Amendment, among other things: (a) consents to the consummation of the transactions contemplated by the Investment Agreement; (b) extends the maturity date of the Term Loan Agreement to May 22, 2027; (c) provides for certain adjustments to the representations, warranties and covenants to incorporate the New Borrower into the Delayed Draw Term Loan; (d) added a minimum EBITDA financial covenant; and (e) provides for the ability of Borrowers to prepay all or any portion of the amounts owed under the Delayed Draw Term Loan, without a premium or penalty, subject to certain conditions, including demonstrating a trailing twelve-month EBITDA (on a pro forma basis) of the Company and its subsidiaries of no less than $185.0 million and a trailing six-month liquidity (on a pro forma basis) of the Company and its subsidiaries of no less than $100.0 million. In addition, the DDTL Amendment (i) obligates the Company to solicit stockholder approval to issue the maximum amount of Non-Voting Common Stock upon exercise of the maximum number of warrants thereunder, (ii) if stockholder approval is received, obligates the Company to issue warrants under the Delayed Draw Term Loan exercisable for Non-Voting Common Stock and (iii) if stockholder approval is received, clarifies that the provision of the Delayed Draw Term Loan limiting the number of shares underlying warrants issued thereunder to no more than 19.99% of the outstanding shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding as of the date of the Delayed Draw Term Loan does not apply to limit the number of shares of Non-Voting Common Stock issuable upon exercise of warrants.
Stephens Inc, and its affiliates, and The Stephens Group LLC, and its affiliates, are significant stockholders of the Company. Bob L. Martin, a member of the Company’s Board of Directors and Lead Independent Director, is an Operating Partner of The Stephens Group LLC, one of the Lenders under the Delayed Draw Term Loan; and Douglas H. Martin, a member of the Company’s Board of Directors, is a Senior Executive Vice President of Stephens Inc., an affiliate of Stephens Investments Holdings LLC, one of the Lenders under the Delayed Draw Term Loan.
Secured Borrowings. Prior to our acquisition, Badcock's strategy had been to securitize the majority of the customer accounts receivable by transferring them into separate special purpose entities. As these transfers failed sale accounting, the Company accounts for the transfers as secured borrowings. The cash collections on the receivables will amortize the borrowing until the third party debt held by the securitization vehicle is paid in full, at which time, the Company will receive cash flows related to certain residual balances. These secured borrowings are accounted for under the fair value option which are valued using Level 3 inputs. The valuation was conducted using the income approach which incorporates an estimate of projected future cash flows associated with the related customer receivables and applying a discount rate which incorporates the relevant risks associated with the related assets and the time value of money.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Current installments of debt secured by accounts receivable | $ | 147,815 | | | $ | — | |
| Non-current installments of debt secured by accounts receivable | 20,772 | | | — | |
| Total debt secured by accounts receivable, net | $ | 168,587 | | | $ | — | |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
During the year ended January 31, 2024, the Company recognized interest expense related to the secured borrowings of $3.5 million. The Company had no secured borrowings during or for the year ended January 31, 2023.
8. Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
| Deferred revenue | $ | — | | | $ | 579 | |
| Capitalized costs | 1,771 | | | — | |
| Customer accounts receivable | 23,583 | | | — | |
| | | |
| Indirect tax reserve | 4,935 | | | 3,393 | |
| Inventories | — | | | 2,354 | |
| Lease liability | 153,494 | | | 70,869 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 4,118 | | | 4,009 | |
| Net operating loss carryforwards | 8,670 | | | 11,122 | |
| Other | 5,242 | | | 3,030 | |
| Total deferred tax assets | 201,813 | | | 95,356 | |
| Valuation allowance | (25,219) | | | (6,584) | |
| Total deferred tax assets, net of allowance | 176,594 | | | 88,772 | |
| | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
| Allowance for credit losses | — | | | (13,217) | |
| Inventory | (18,824) | | | — | |
| Right-of-use asset | (125,441) | | | (58,895) | |
| Vendor prepayments | (3,088) | | | (1,961) | |
| Sales tax receivable | (3,445) | | | (3,718) | |
| Property and equipment | (30,845) | | | (12,985) | |
| Other | (554) | | | (37) | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | (182,197) | | | (90,813) | |
| Net deferred tax liability | $ | (5,603) | | | $ | (2,041) | |
As of January 31, 2024, the Company had tax-effected federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of $8.7 million. Our federal net operating loss may be carried forward indefinitely, while our state net operating loss carryforwards begin to expire starting with fiscal year 2030. During the period, an ownership change occurred for tax purposes whereby future utilization of a significant portion of our current net operating loss carryforwards and net unrealized built-in losses are expected to be limited to $2.7 million a year.
In assessing the recoverability of its deferred tax assets, the Company evaluates the available objective positive and negative evidence to estimate whether it is more likely than not that sufficient future taxable income will be generated to permit use of existing deferred tax assets in each taxpaying jurisdiction. For any deferred tax asset in excess of the amount for which it is more likely than not that the Company will realize a benefit, the Company establishes a valuation allowance. A valuation allowance is a non-cash charge and does not limit the Company's ability to utilize its deferred tax assets, including its ability to utilize tax loss and credit carryforward amounts, against future taxable income.
The Company assessed all available positive and negative evidence to estimate whether sufficient future taxable income will be generated to permit use of existing deferred tax assets in each taxpaying jurisdiction. On the basis of this evaluation, as of January 31, 2024, a valuation allowance of $25.2 million was recorded against the Company's net federal and state deferred tax assets as it is not more likely than not that these assets would be realized. A valuation allowance of $6.6 million was recorded as of January 31, 2023.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Provision (benefit) for income taxes consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Current: | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | (12,702) | | | $ | (2,607) | | | $ | 13,428 | |
| State | 842 | | | 845 | | | 3,285 | |
| Total current | (11,860) | | | (1,762) | | | 16,713 | |
| Deferred: | | | | | |
| Federal | (25,009) | | | (5,974) | | | 14,726 | |
| State | (2,587) | | | 665 | | | 2,073 | |
| Total deferred | (27,596) | | | (5,309) | | | 16,799 | |
| (Benefit) provision for income taxes | $ | (39,456) | | | $ | (7,071) | | | $ | 33,512 | |
A reconciliation of the provision (benefit) for income taxes at the U.S. federal statutory tax rate and the total tax provision for each of the periods presented in the statements of operations follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Income tax (benefit) provision at U.S. federal statutory rate | $ | (24,434) | | | $ | (13,936) | | | $ | 29,761 | |
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit | (2,121) | | | 396 | | | 3,782 | |
| Bargain purchase gain | (22,020) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Provision to return adjustments | (1,841) | | | (1,401) | | | — | |
| Recognition of uncertain tax benefit | (6,100) | | | — | | | — | |
| Interest on tax | (3,342) | | | — | | | — | |
| Employee benefits | 1,737 | | | 2,193 | | | 419 | |
| Change in valuation allowance | 18,635 | | | 6,584 | | | — | |
| Other tax | 30 | | | (907) | | | (450) | |
| (Benefit) provision for income taxes | $ | (39,456) | | | $ | (7,071) | | | $ | 33,512 | |
Federal tax returns for fiscal years subsequent to January 31, 2020, remain subject to examination. Generally, state tax returns for fiscal years subsequent to January 31, 2020 remain subject to examination.
Changes in the balance of unrecognized tax benefits, excluding interest and penalties on uncertain tax positions, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Balance at February 1 | $ | (10,642) | | | $ | (9,323) | | | $ | (9,853) | |
| Increases related to prior year tax positions | (1,701) | | | — | | | — | |
| Decreases related to prior year tax positions | 1,210 | | | — | | | 982 | |
| Increases related to current year tax positions | — | | | (1,319) | | | (452) | |
| Lapse of statute | 4,581 | | | — | | | — | |
| Balance at January 31 | $ | (6,552) | | | $ | (10,642) | | | $ | (9,323) | |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As of January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 there are $1.7 million, $4.6 million, and $4.6 million, respectively of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would favorably affect the Company’s annual effective tax rate.
The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in its provision for income taxes. During the years ended January 31, 2024, the Company recognized a net benefit of $1.5 million related to interest and penalties. For the year ended January 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company recognized a net provision related to interest and penalties of approximately $0.3 million and $0.6 million, respectively.
It is reasonably possible that the Company may recognize a tax benefit of approximately $0.8 million within the next 12 months regarding the deductibility of compensation due to the lapse of the applicable statute of limitations. That recognition would result in a decrease of the Company's unrecognized tax benefit of $0.8 million.
9. Leases
We lease most of our corporate store locations and our facilities and operating equipment under operating leases. In some cases we hold the lease for our dealer locations and lease back to the dealer. The fixed, non-cancelable terms of our real estate leases are generally five to fifteen years and generally include renewal options that allow us to extend the term beyond the initial non-cancelable term. However, prior to the expiration of the existing contract, the Company will typically renegotiate any lease contracts as opposed to continuing in the current lease under the renewal terms. As such, the lease renewal options are not recognized as part of the right-of-use assets and liabilities. Most of the real estate leases require payment of real estate taxes, insurance and certain common area maintenance costs in addition to future minimum lease payments. Equipment leases generally provide for initial lease terms of three to five years and provide for a purchase right at the end of the lease term at the then fair market value of the equipment.
Certain operating leases contain tenant allowance provisions, which obligate the landlord to remit cash to us as an incentive to enter into the lease agreement. We record the full amount to be remitted by the landlord as a reduction to the operating lease right-of-use assets upon commencement of the lease and amortize the balance on a straight-line basis over the life of the lease.
Supplemental lease information is summarized below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Assets | | January 31, |
| (in thousands) | Balance sheet classification | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Operating lease assets | Operating lease right-of-use assets | $ | 556,416 | | | $ | 262,104 | |
| Finance lease assets | Property and equipment, net | 3,821 | | | 4,900 | |
| Total leased assets | | $ | 560,237 | | | $ | 267,004 | |
| Liabilities | | | | |
Operating (1) | Operating lease liability | $ | 82,153 | | | $ | 66,204 | |
| Finance | Short-term debt and finance lease obligations | 980 | | | 937 | |
| Operating | Operating lease liability - non current | 598,712 | | | 331,109 | |
| Finance | Long-term debt and finance lease obligations | 4,335 | | | 4,289 | |
| Total lease liabilities | | $ | 686,180 | | | $ | 402,539 | |
(1)Represents the gross operating lease liability before tenant improvement allowances. As of January 31, 2024 and 2023, we had $6.7 million and $13.0 million of tenant improvement allowances to be remitted by the landlord.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease Cost | | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | Income statement classification | 2024 | | 2023 |
Operating lease costs (1) | Selling, general and administrative expense | $ | 77,463 | | | $ | 69,135 | |
| Total operating lease cost | | $ | 77,463 | | | $ | 69,135 | |
(1)Includes short-term and variable lease costs, which are not significant.
Operating lease right-of-use assets (“ROU Assets”) and liabilities are recognized at the commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As most of our leases do not provide an implicit rate, we use our estimated incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at lease commencement in determining the present value of lease payments.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Operating lease ROU Assets are regularly reviewed for impairment under the long-lived assets impairment guidance in ASC Subtopic 360-10, Property, Plant, and Equipment - Overall. No impairment was recognized for the year ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022.
Additional details regarding the Company’s leasing activities as a lessee are presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other Information | Year Ended January 31, |
| (dollars in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | |
| Operating cash flows for operating leases | $ | 98,956 | | | $ | 87,304 | |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (in years) | | | |
| Finance leases | 8.3 | | 8.4 |
| Operating leases | 8.9 | | 6.5 |
| Weighted-average discount rate | | | |
| Finance leases | 5.6 | % | | 5.1 | % |
| Operating leases | 7.8 | % | | 7.3 | % |
For the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, total rent expense was $81.3 million, $69.8 million and $65.8 million, respectively.
The following table presents a summary of our minimum contractual lease commitments and obligations as of January 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Operating Leases | | Finance Leases | | Total |
| Year ending January 31, | | | | | |
| 2025 | $ | 122,034 | | | $ | 1,338 | | | $ | 123,372 | |
| 2026 | 123,467 | | | 1,041 | | | 124,508 | |
| 2027 | 113,106 | | | 764 | | | 113,870 | |
| 2028 | 103,456 | | | 707 | | | 104,163 | |
| 2029 | 91,722 | | | 280 | | | 92,002 | |
| Thereafter | 383,971 | | | 2,380 | | | 386,351 | |
| Total undiscounted cash flows | 937,756 | | | 6,510 | | | 944,266 | |
| Less: Interest | 256,891 | | | 1,195 | | | 258,086 | |
| Total lease liabilities | $ | 680,865 | | | $ | 5,315 | | | $ | 686,180 | |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Company as Lessor
The Company subleases some of its leased locations to certain dealers for operation as Badcock stores. The terms of these leases generally match those of the lease the Company has with the lessor.
The following table illustrates the Company’s expectation of lease payments to be received for non-cancelable subleases as of January 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | Operating Leases |
| Fiscal Year | | Subleases |
| 2025 | | $ | 8,801 | |
| 2026 | | 7,838 | |
| 2027 | | 6,829 | |
| 2028 | | 5,503 | |
| 2029 | | 3,509 | |
| Thereafter | | 7,704 | |
| Total future minimum receipts | | $ | 40,184 | |
10. Stock-Based Compensation
On May 28, 2020, our stockholders approved the Conn’s, Inc. 2020 Omnibus Incentive Plan (“2020 Plan”). Upon the effectiveness of the 2020 Plan, no further awards were, or may in the future, be granted under any of our prior plans, which include the 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan (“2016 Plan”), 2011 Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Plan (“2011 Director Plan”) and the 2003 Non-Employee Director Stock Option Plan (“2003 Director Plan”). The 2020 plan provides for the issuance of 1,800,000 shares of Company common stock plus such number of shares as were, and may become, available under our prior plans. As such, shares subject to an award under the 2020 Plan, the 2016 Plan, the 2011 Plan, the 2011 Director Plan, the 2003 Director Plan or our Amended and Restated 2003 Incentive Stock Option Plan (“2003 Plan”) that lapse, expire, are forfeited or terminated, or are settled in cash will again become available for future grant under the 2020 Plan. During fiscal year 2024, a total of 1,465,784 shares were transferred to the 2020 Plan which all derived from the 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan. During fiscal year 2023, a total of 261,935 shares were transferred to the 2020 Plan which all derived from the 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan.
Our 2020 Plan is an equity-based compensation plan that allows for the grant of a variety of awards, including stock options, restricted stock awards, RSUs, PSUs, stock appreciation rights and performance and cash awards. Awards are generally granted once per year, with the amount and type of awards determined by the Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors. Stock options, RSUs and PSUs are subject to early termination provisions but generally vest over a period of three years or four years from the date of grant. Stock options under the various plans are issued with exercise prices equal to the market value on the date of the grant and, typically, expire ten years after the date of grant.
In the event of a change in control of the Company, as defined in the 2020 Plan, the Board of Directors of the Company (“Board of Directors”) may cause some or all outstanding awards to fully or partially vest, either upon the change in control or upon a subsequent termination of employment or service, and may provide that any applicable performance criteria be deemed satisfied at the target or any other level. The Board of Directors may also cause outstanding awards to terminate in exchange for a cash or stock payment or to be substituted or assumed by the surviving corporation.
As of January 31, 2024, shares authorized for future issuance were 1,032,934 under the 2020 Plan.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense. Total stock-based compensation expense, recognized primarily in SG&A, from stock-based compensation consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Stock options | $ | — | | | $ | 208 | | | $ | 1,608 | |
| RSUs and PSUs | 10,028 | | | 10,392 | | | 7,038 | |
| Employee stock purchase plan | 230 | | | 372 | | | 269 | |
| Accelerated RSU expense charged to severance | — | | | 5,736 | | | — | |
| Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 10,258 | | | $ | 16,708 | | | $ | 8,915 | |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
During the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, we recognized tax benefits related to stock-based compensation of $2.4 million, $2.5 million and $1.8 million, respectively. As of January 31, 2024, the total unrecognized compensation cost related to all unvested stock-based compensation awards was $9.2 million and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.4 years. The total fair value of RSUs, PSUs and stock options vested during fiscal years 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $4.0 million, $13.6 million and $14.0 million, respectively, based on the market price at the vesting date.
Stock Options.
The following table summarizes the activity for outstanding stock options:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Shares
Under
Option | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life |
| Outstanding, January 31, 2023 | 600,000 | | | $ | 30.12 | | | |
| Granted | — | | | $ | — | | | |
| Exercised | — | | | $ | — | | | |
| Forfeited and expired | — | | | $ | — | | | |
| Outstanding, January 31, 2024 | 600,000 | | | $ | 30.12 | | | 4.0 |
| Vested and expected to vest, January 31, 2024 | 600,000 | | | $ | 30.12 | | | 4.0 |
| Exercisable, January 31, 2024 | 600,000 | | | $ | 30.12 | | | 4.0 |
No stock options were granted, exercised, or forfeited during the years ended January 31, 2024 and January 31, 2022. During the year ended January 31, 2023, 120,166 stock options were forfeited at a weighted average exercise price of $32.35. The aggregate intrinsic value of stock options outstanding, vested and expected to vest and exercisable at January 31, 2024 was approximately $0.0 million. The total fair value of common stock options vested during fiscal years 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $0.0 million, $6.3 million and $7.5 million, respectively, based on the market price at the vesting date.
Restricted Stock Units. The restricted stock unit program consists of a combination of PSUs and RSUs. RSUs vest on a straight-line basis over their term, which is generally three years to four years.
As of January 31, 2024 there are three PSU awards outstanding. Under each PSU award, the number of PSUs issued is dependent upon attainment of an annualized Total Shareholder Return (“TSR”) target for the period identified in the award, which is three fiscal years. In the event TSR exceeds the respective defined target, shares will be awarded in excess of the target amount. For the first award, this is up to a maximum of 150% of the target award, and for the second and third awards, this is up to 200% of the target award. In the event TSR falls below the respective predefined target, a reduced number of shares will be awarded. If TSR falls below the respective threshold level, no shares will be awarded. PSUs vest on predetermined schedules, which occur over three years.
For grants of PSUs, the fair value is the market value of our stock at the date of issuance adjusted for the market condition using a Monte Carlo model. No dividend yield was included in the weighted average assumptions for the PSUs granted during fiscal years 2024 or 2023. The weighted average fair value per grant issued is $13.49 and $30.39 for fiscal years 2024 and 2023, respectively. The weighted-average assumptions used in the Monte Carlo valuations are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended January 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Expected stock price volatility | 73.0% | | 78.0%-80.0% |
| Risk-free interest rate | 3.75% | | 1.39%-2.58% |
| Expected life (in years) | 3.0 | | 2.8 - 3.0 |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The following table summarizes the activity for RSUs and PSUs:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Time-Based RSUs | | Performance-Based RSUs | | |
| Number of Units | | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Number of Units | | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Total Number of Units |
| Balance, January 31, 2023 | 1,233,640 | | | $ | 14.94 | | | 504,718 | | | $ | 20.68 | | | 1,738,358 | |
| Granted | 1,624,518 | | | $ | 6.29 | | | 174,290 | | | $ | 13.49 | | | 1,798,808 | |
| Vested and converted to common stock | (675,299) | | | $ | 13.53 | | | — | | | $ | — | | | (675,299) | |
| Forfeited | (272,510) | | | $ | 11.24 | | | (298,768) | | | $ | 12.47 | | | (571,278) | |
| Balance, January 31, 2024 | 1,910,349 | | | $ | 8.61 | | | 380,240 | | | $ | 23.83 | | | 2,290,589 | |
The total fair value of restricted and performance shares vested during fiscal years 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $4.0 million, $7.2 million, and $6.4 million, respectively, based on the market price at the vesting date. The total fair value of restricted and performance shares granted during fiscal years 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $12.6 million, $19.9 million and $17.9 million, respectively.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan. Our Employee Stock Purchase Plan is available to our employees, subject to minimum employment conditions and maximum compensation limitations. At the end of each calendar quarter, employee contributions are used to acquire shares of common stock at 85% of the lower of the fair market value of the common stock on the first or last day of the calendar quarter. During the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, we issued 157,555, 106,257 and 51,262 shares of common stock, respectively, to employees participating in the plan, leaving 262,517 shares remaining reserved for future issuance under the plan as of January 31, 2024.
11. Significant Vendors
As shown in the table below, a significant portion of our merchandise purchases were made from six vendors:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Vendor A | 31.3 | % | | 31.6 | % | | 31.5 | % |
| Vendor B | 18.5 | | | 17.4 | | | 21.1 | |
| Vendor C | 11.1 | | | 11.0 | | | 11.0 | |
| Vendor D | 2.6 | | | 4.2 | | | 5.0 | |
| Vendor E | 2.3 | | | 2.7 | | | 2.5 | |
| Vendor F | 2.1 | | | 2.5 | | | 2.2 | |
| Top six vendors combined | 67.9 | % | | 69.4 | % | | 73.3 | % |
The vendors shown above represent the top six vendors with the highest dollar volume in each period shown. The same vendor may not necessarily be represented in all periods presented.
12. Defined Contribution Plan
We have established a defined contribution 401(k) plan for eligible employees. Employees may contribute up to 50% of their eligible pretax compensation to the plan and we match 100% of the first 3% of the employees’ contributions and an additional 50% of the next 2% of the employees’ contributions. At our option, we may make supplemental contributions to the plan, but have not made such supplemental contributions in the past four years. The matching contributions made by us totaled $2.1 million, $1.6 million and $2.2 million during the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
13. Commitments and Contingencies
We are involved in routine litigation and claims, incidental to our business from time to time which, individually or in the aggregate, are not expected to have a material adverse effect on us. As required, we accrue estimates of the probable costs for the resolution of these matters. These estimates have been developed in consultation with counsel and are based upon an analysis of potential results, assuming a combination of litigation and settlement strategies. However, the results of these proceedings cannot be predicted with certainty, and changes in facts and circumstances could impact our estimate of reserves for litigation. The Company believes that any probable and reasonably estimable loss associated with the foregoing has been adequately reflected in the accompanying financial statements.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
14. Variable Interest Entities
From time to time, we securitize customer accounts receivables by transferring the receivables to various bankruptcy-remote VIEs. Under the terms of the respective securitization transactions, all cash collections and other cash proceeds of the customer receivables go first to the servicer and the holders of the asset-backed notes, and then to the residual equity holder. We retain the servicing of the securitized portfolio and receive a monthly fee of 4.75% (annualized) based on the outstanding balance of the securitized receivables, and we currently hold all of the residual equity. In addition, we, rather than the VIEs, will retain certain credit insurance income together with certain recoveries related to credit insurance and RSAs on charge-offs of the securitized receivables, which will continue to be reflected as a reduction of net charge-offs on a consolidated basis for as long as we consolidate the VIEs.
We consolidate VIEs when we determine that we are the primary beneficiary of these VIEs, we have the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the performance of the VIEs and our obligation to absorb losses and the right to receive residual returns are significant.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The following table presents the assets and liabilities held by the VIEs (for legal purposes, the assets and liabilities of the VIEs will remain distinct from Conn’s, Inc.):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | January 31,
2024 | | January 31,
2023 |
| Assets: | | | |
| Restricted cash | $ | 49,940 | | | $ | 38,727 | |
| Customer accounts receivable: | | | |
| Customer accounts receivable | 715,176 | | | 506,811 | |
| Restructured accounts | 73,205 | | | 46,626 | |
| Allowance for credit losses | (136,821) | | | (105,982) | |
| Allowance for no-interest option credit programs | (15,505) | | | (9,340) | |
| Deferred fees and origination costs | (7,530) | | | (4,851) | |
| Total customer accounts receivable, net | 628,525 | | | 433,264 | |
| Customer accounts receivable under fair value option | 173,631 | | | — | |
| Due from Conn's, Inc., net | 44,103 | | | — | |
| Total assets | $ | 852,096 | | | $ | 471,991 | |
| Liabilities: | | | |
| Accrued expenses | $ | 1,155 | | | $ | 3,475 | |
| Other liabilities | 5,995 | | | 4,578 | |
| Due to Conn’s, Inc., net | — | | | 2,249 | |
| Secured borrowings - current | 147,815 | | | — | |
| | | |
| Long-term debt: | | | |
| Secured borrowings - non-current | 20,841 | | | — | |
| 2021-A Class B Notes | — | | | 54,597 | |
| 2021-A Class C Notes | 16,815 | | | 63,890 | |
| 2022-A Class A Notes | — | | | 117,935 | |
| 2022-A Class B Notes | 51,238 | | | 132,090 | |
| 2022-A Class C Notes | 63,090 | | | 63,090 | |
| 2023-A Class A Notes | 67,673 | | | — | |
| 2023-A Class B Notes | 82,430 | | | — | |
| 2023-A Class C Notes | 30,550 | | | — | |
| 2024-A Class A Notes | 133,490 | | | — | |
| 2024-A Class B Notes | 98,120 | | | — | |
| 2024-A Class C Notes | 27,760 | | | — | |
| 739,822 | | | 431,602 | |
| Less deferred debt issuance costs | (23,623) | | | (20,812) | |
| Total debt | 716,199 | | | 410,790 | |
| Total liabilities | $ | 723,349 | | | $ | 421,092 | |
The assets of the VIEs serve as collateral for the obligations of the VIEs. The holders of asset-backed notes have no recourse to assets outside of the respective VIEs.
15. Segment Information
Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise that engage in business activities and for which discrete financial information is available that is evaluated on a regular basis by the chief operating decision maker to make decisions about how to allocate resources and assess performance. We are a leading specialty retailer and offer a broad selection of quality, branded durable consumer goods and related services in addition to a proprietary credit solution for our core
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
consumers. We have two operating segments: (i) retail and (ii) credit. Our operating segments complement one another. The retail segment operates primarily through our stores and website. Our retail segment product offerings include furniture and mattresses, home appliances, consumer electronics and home office products from leading global brands across a wide range of price points. Our credit segment offers affordable financing solutions to a large, under-served population of consumers who typically have limited credit alternatives. Our operating segments provide customers the opportunity to comparison shop across brands with confidence in our competitive prices as well as affordable monthly payment options, fast delivery and installation in the majority of our markets, and product repair service. The operating segments follow the same accounting policies used in our consolidated financial statements.
With the acquisition of Badcock, we evaluated our segments and determined we continue to have two operating and reportable segments. We made this determination based on the following facts and circumstances: our chief operating decision maker remains the same, Badcock historically operated a retail and credit business, and the overall similarity of the legacy Conn's and Badcock businesses.
We evaluate a segment’s performance based upon operating income before taxes. SG&A includes the direct expenses of the retail and credit operations, allocated overhead expenses, and a charge to the credit segment to reimburse the retail segment for expenses it incurs related to occupancy, personnel, advertising and other direct costs of the retail segment which benefit the credit operations by sourcing credit customers and collecting payments. The reimbursement received by the retail segment from the credit segment is calculated using an annual rate of 2.5% times the average outstanding portfolio balance for each applicable period. The eliminations column comprises intercompany transactions between the credit and retail segment for our in-house lease-to-own business which began operations during the fiscal year ended 2024.
As of January 31, 2024, we operated retail stores in 15 states with no operations outside of the United States. No single customer accounts for more than 10% of our total revenues.
Financial information by segment is presented in the following tables:
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, 2024 |
| (in thousands) | Retail | | Credit | | Eliminations | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | |
| Furniture and mattress | $ | 352,375 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (2,054) | | | $ | 350,321 | |
| Home appliance | 338,725 | | | — | | | (2,105) | | | 336,620 | |
| Consumer electronics | 110,571 | | | — | | | (1,580) | | | 108,991 | |
| Computers | 37,737 | | | — | | | (1,027) | | | 36,710 | |
| Other | 64,250 | | | — | | | (62) | | | 64,188 | |
| Product sales | 903,658 | | | — | | | (6,828) | | | 896,830 | |
| Repair service agreement commissions | 72,738 | | | — | | | — | | | 72,738 | |
| Service revenues | 8,763 | | | — | | | — | | | 8,763 | |
| Total net sales | 985,159 | | | — | | | (6,828) | | | 978,331 | |
| Finance charges and other revenues | 3,409 | | | 257,193 | | | (1,250) | | | 259,352 | |
| Total revenues | 988,568 | | | 257,193 | | | (8,078) | | | 1,237,683 | |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | 631,604 | | | 4,377 | | | (6,293) | | | 629,688 | |
Selling, general and administrative expense (1) | 431,887 | | | 130,741 | | | (1,000) | | | 561,628 | |
| Provision for bad debts | 540 | | | 153,540 | | | — | | | 154,080 | |
| Charges and credits | 17,565 | | | — | | | — | | | 17,565 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 1,081,596 | | | 288,658 | | | (7,293) | | | 1,362,961 | |
| Operating loss | (93,028) | | | (31,465) | | | (785) | | | (125,278) | |
| Interest expense | 45 | | | 81,662 | | | — | | | 81,707 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | 14,221 | | | — | | | 14,221 | |
| Bargain purchase gain, net of deferred taxes | (104,857) | | | — | | | — | | | (104,857) | |
| (Loss) income before income taxes | $ | 11,784 | | | $ | (127,348) | | | $ | (785) | | | $ | (116,349) | |
| Additional Disclosures: | | | | | | | |
| Property and equipment additions | $ | 38,698 | | | $ | 3,078 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 41,776 | |
| Depreciation expense | $ | 46,309 | | | $ | 4,108 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 50,417 | |
| | January 31, 2024 |
| (in thousands) | Retail | | Credit | | Eliminations | | Total |
| Total assets | $ | 594,865 | | | $ | 1,849,177 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,444,042 | |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, 2023 |
| (in thousands) | Retail | | Credit | | | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | |
| Furniture and mattress | $ | 340,325 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | 340,325 | |
| Home appliance | 430,250 | | | — | | | | | 430,250 | |
| Consumer electronics | 139,868 | | | — | | | | | 139,868 | |
| Computers | 37,547 | | | — | | | | | 37,547 | |
| Other | 38,610 | | | — | | | | | 38,610 | |
| Product sales | 986,600 | | | — | | | | | 986,600 | |
| Repair service agreement commissions | 80,446 | | | — | | | | | 80,446 | |
| Service revenues | 9,544 | | | — | | | | | 9,544 | |
| Total net sales | 1,076,590 | | | — | | | | | 1,076,590 | |
| Finance charges and other revenues | 1,119 | | | 264,818 | | | | | 265,937 | |
| Total revenues | 1,077,709 | | | 264,818 | | | | | 1,342,527 | |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | 710,234 | | | — | | | | | 710,234 | |
Selling, general and administrative expense (1) | 391,393 | | | 134,819 | | | | | 526,212 | |
| Provision for bad debts | 896 | | | 120,297 | | | | | 121,193 | |
| Charges and credits | 14,360 | | | — | | | | | 14,360 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 1,116,883 | | | 255,116 | | | | | 1,371,999 | |
| Operating (loss) income | (39,174) | | | 9,702 | | | | | (29,472) | |
| Interest expense | — | | | 36,891 | | | | | 36,891 | |
| Loss before income taxes | $ | (39,174) | | | $ | (27,189) | | | | | $ | (66,363) | |
| Additional Disclosures: | | | | | | | |
| Property and equipment additions | $ | 80,942 | | | $ | 939 | | | | | $ | 81,881 | |
| Depreciation expense | $ | 44,304 | | | $ | 1,971 | | | | | $ | 46,275 | |
| | January 31, 2023 |
| (in thousands) | Retail | | Credit | | | | Total |
| Total assets | $ | 537,332 | | | $ | 1,178,883 | | | | | $ | 1,716,215 | |
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, 2022 |
| (in thousands) | Retail | | Credit | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Furniture and mattress | $ | 411,167 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 411,167 | |
| Home appliance | 500,051 | | | — | | | 500,051 | |
| Consumer electronics | 191,234 | | | — | | | 191,234 | |
| Computers | 66,707 | | | — | | | 66,707 | |
| Other | 36,386 | | | — | | | 36,386 | |
| Product sales | 1,205,545 | | | — | | | 1,205,545 | |
| Repair service agreement commissions | 89,101 | | | — | | | 89,101 | |
| Service revenues | 10,743 | | | — | | | 10,743 | |
| Total net sales | 1,305,389 | | | — | | | 1,305,389 | |
| Finance charges and other revenues | 949 | | | 283,693 | | | 284,642 | |
| Total revenues | 1,306,338 | | | 283,693 | | | 1,590,031 | |
| Costs and expenses: | | | | | |
| Cost of goods sold | 825,987 | | | — | | | 825,987 | |
Selling, general and administrative expense (1) | 399,393 | | | 145,097 | | | 544,490 | |
| Provision for bad debts | 479 | | | 47,705 | | | 48,184 | |
| Charges and credits | 2,677 | | | — | | | 2,677 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 1,228,536 | | | 192,802 | | | 1,421,338 | |
| Operating income | 77,802 | | | 90,891 | | | 168,693 | |
| Interest expense | — | | | 25,758 | | | 25,758 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | 1,218 | | | 1,218 | |
| (Loss) income before income taxes | $ | 77,802 | | | $ | 63,915 | | | $ | 141,717 | |
| Additional Disclosures: | | | | | |
| Property and equipment additions | $ | 44,618 | | | $ | 1,392 | | | $ | 46,010 | |
| Depreciation expense | $ | 43,728 | | | $ | 1,721 | | | $ | 45,449 | |
| | January 31, 2022 |
| (in thousands) | Retail | | Credit | | Total |
| Total assets | $ | 671,920 | | | $ | 1,082,546 | | | $ | 1,754,466 | |
(1)For the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the amount of overhead allocated to each segment reflected in SG&A was $32.5 million, $31.7 million and $40.6 million, respectively. For the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the amount of reimbursement made to the retail segment by the credit segment was $25.0 million, $26.3 million and $28.3 million, respectively.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
16. Stockholder's Equity
Earnings per Share. Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share includes the dilutive effects of any stock options, restricted stock unit awards (“RSUs”) and performance stock awards (“PSUs”), which are calculated using the treasury-stock method. The following table sets forth the shares outstanding for the earnings per share calculations:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding - Basic | 24,250 | | | 24,117 | | | 29,268 | |
| Dilutive effect of stock options, RSUs and PSUs | — | | | — | | | 733 | |
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding - Diluted | 24,250 | | | 24,117 | | | 30,001 | |
For the years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the weighted-average number of stock options, RSUs, and PSUs not included in the calculation due to their anti-dilutive effect, was 1,730,025, 1,446,168 and 704,582, respectively.
Preferred Stock. In conjunction with the acquisition of Badcock, the Company issued 1,000,000 shares of its preferred stock. The shares are convertible into an aggregate of 24,540,295 shares of Non-Voting Common Stock, which represents 49.99% of the issued and outstanding shares of common stock. Effective immediately upon the receipt of stockholder approval, all Preferred Stock will automatically be converted into a number of shares of Non-Voting Common Stock. Except as otherwise required by law, the Preferred Stock does not have voting rights. Preferred stock is separately stated in the Mezzanine Equity section of the Consolidated Balance Sheet and stated at fair value upon issuance. If stockholder approval occurs, the shares immediately convert to non-voting common shares and the current amount of $62.2 million will be reclassified to Additional Paid In Capital.
Under the guidance of FASB Accounting Standards Codification Topic 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity ("ASC 480"), we determined that the preferred stock issued in connection with our acquisition of Badcock is participating due to their priority over common shareholders and accrue dividends which are payable until they convert to non-voting common shares. The preferred shares are contained within mezzanine equity, between Total Liabilities and Stockholder's Equity on the Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Stock Repurchase Plan. On December 14, 2021, our board of directors approved a stock repurchase program pursuant to which the Company is authorized to repurchase up to $150.0 million of our outstanding common stock. The stock repurchase program expired on December 14, 2022. During the year ended January 31, 2024, we did not repurchase any shares of our common stock. For the year ended January 31, 2023, we repurchased 3,316,000 shares of our common stock at an average weighted cost per share of $20.57 for an aggregate amount of $68.2 million.
17. Business Acquisition
On December 18, 2023, the Company acquired 100% of the outstanding stock units of W.S. Badcock, LLC (Badcock) in exchange for 1,000,000 shares of Conn's preferred stock which is convertible into an aggregate of 24,540,295 non-voting common shares, subject to stockholder approval. The non-voting common shares represent 49.99% of the issued and outstanding shares of Conn's common stock immediately available after conversion. The fair value of the consideration transferred at the acquisition date was $69.3 million which includes $7.1 million of expenses paid on behalf of the seller. The primary driver for this acquisition was to accelerate growth opportunities by combining two complementary businesses with similar product categories, payment solutions and customer profiles.
The Company incurred transaction costs of approximately $16.3 million during the year ended January 31, 2024. These costs are included in the line item "Charges and Credits" on the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
The Company accounted for this purchase in accordance with ASC Topic 805, “Business Combinations.” Under this guidance, an entity is required to recognize the assets acquired, liabilities assumed and the consideration given at their fair value on the acquisition date. The following table summarizes the preliminary allocation of the fair values of the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the Badcock acquisition, all of which are considered level 3 assets. We engaged an outside valuation firm to assist in the fair value determination of acquired assets and liabilities. We may adjust the preliminary purchase price allocation, after the acquisition closing date and through the end of the measurement period of one year or less, as we finalize the valuation of acquired assets and liabilities.
CONN’S, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Recognized amounts of identifiable assets and liabilities are as follows:
| | | | | |
| (in thousands) | December 18,
2023 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 3,714 | |
| Inventories | 129,748 | |
| Customer accounts receivable | 90,603 | |
| Securitized customer accounts receivable, current | 189,191 | |
| Other current assets | 8,901 | |
| Securitized customer accounts receivable, non-current | 26,953 | |
| Property, plant, and equipment | 50,430 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use-assets | 222,342 | |
| Other assets | 4,306 | |
| Total assets | 726,188 | |
| Current operating lease liabilities | 23,982 | |
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 77,175 | |
| Other current liabilities | 8,216 | |
| Secured borrowings | 204,867 | |
| Deferred tax liability | 31,074 | |
| Non-current operating lease liabilities | 202,122 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 4,628 | |
| Total liabilities | 552,064 | |
| Net assets acquired | 174,124 | |
| Consideration transferred | 69,267 | |
| Bargain purchase gain | $ | 104,857 | |
The accounts receivables acquired consists of consumer receivables owned by Badcock as well as receivables that are beneficially owned by a securitization trust. The original transfer of these receivables did not meet the requirements of sale accounting under ASC 860 and therefore are reflected as assets on the balance sheet with the corresponding amounts payable to the securitization trust as a secured borrowing.
Operating lease right-of-use assets of $222.3 million and operating lease liabilities of $202.1 million, consist of leases for retail store locations, warehouses and office equipment.
Property, plant and equipment consists of fixtures and equipment of $27.8 million, buildings and building improvements of $2.0 million, land and land improvements of $1.4 million, leasehold improvements of $8.5 million, assets held for sale of $9.6 million, and construction in progress of $1.1 million.
As of December 18, 2023, the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed exceeded the fair value of the consideration given and as such, we recorded a bargain purchase gain net of deferred taxes of $104.9 million. The amount is classified as “Bargain purchase gain, net of deferred taxes” on the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company determined the bargain purchase is appropriate as a result of a few factors. The Badcock business will require substantial liquidity in future periods which the Company is in a unique position to offer. With the current macro economic circumstances of high inflation and interest rates, Badcock has experienced a combination of reduced sales and increased liquidity requirements which motivated the seller to dispose of this business.
Badcock Results
The Company's results for the year ended January 31, 2024 include the operations of Badcock from the acquisition date of December 18, 2023 through January 31, 2024.
The table below presents the estimated impact of the Badcock acquisition on our revenue and loss from continuing operations, net of tax for the year ended January 31, 2024. The table also includes unaudited pro forma information on our combined results of operations as they may have appeared assuming the Badcock acquisition had been completed on February 1, 2023.
These amounts include certain corporate expenses, transaction costs or merger related expenses that resulted from the acquisition and are therefore not representative of the actual results of the operations of these businesses on a stand-alone basis.
Included in the unaudited combined pro forma results are adjustments to reflect the impact of certain purchase accounting adjustments, including adjustments to Customer accounts receivable; Inventory; Leases; Charges and Credits; Depreciation and amortization; and Interest expense.
The unaudited pro forma combined financial information is presented for illustrative purposes only and does not indicate the actual combined financial results had the closing of the Badcock acquisition been completed on February 1, 2023 nor does it reflect the benefits obtained through the integration of business operations realized since acquisition. Furthermore, the information is not indicative of the results of operations in future periods. The unaudited pro forma combined financial information does not reflect the impact of possible business model changes nor does it consider any potential impacts of market conditions, expense efficiencies or other factors.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Badcock Impact
(Unaudited) | | Combined Pro Forma Results (Unaudited) |
| | | Year Ended January 31, |
| (in thousands) | From December 18, 2023 through January 31, 2024 | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Revenues | $ | 68,428 | | | $ | 1,868,976 | | | $ | 2,261,583 | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to Conn's, Inc. | $ | (4,426) | | | $ | (80,862) | | | $ | 31,486 | |
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
In connection with the preparation of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, our management conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting as of the end of the period covered by this report (under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”)). Based on that assessment, our CEO and CFO have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) are effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms, and is accumulated and communicated to management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in our internal controls over financial reporting that occurred in the quarter ended January 31, 2024 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal controls over financial reporting. However, we completed the Badcock acquisition during the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2024. We have begun the process of assessing Badcock's controls for design and operating effectiveness, and intend to include the results of that work in our fiscal year 2025 annual evaluation of internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) or Rule 15(d)-15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
Our management (under the supervision and with the participation of our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer) assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2024. In making this assessment, management used the criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). Based on our assessment and those criteria, management believes that, as of January 31, 2024, our internal controls over financial reporting are effective.
We have excluded Badcock in fiscal year 2024 from our evaluation of our internal controls over financial reporting. Badcock represented 28% of the Company’s consolidated Total assets at January 31, 2024, while its Revenues comprised 6% of the Company’s consolidated revenues for the year ended January 31, 2024.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2024 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included elsewhere herein.
Conn’s, Inc.
The Woodlands, Texas
April 18, 2024
| | |
| /s/ Timothy Santo |
| Timothy Santo |
| Chief Financial Officer |
|
| /s/ Norman L. Miller |
| Norman L. Miller |
| President and Chief Executive Officer |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Conn’s, Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Conn’s, Inc. and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Conn’s, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2024, based on the COSO criteria.
As indicated in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of W.S. Badcock LLC (“Badcock”), which is included in the 2024 consolidated financial statements of the Company and constituted 28% of total assets as of January 31, 2024 and 6% of revenues for the year then ended. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting of the Company also did not include an evaluation of the internal control over financial reporting of Badcock.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of January 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2024, and the related notes and our report dated April 18, 2024 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Houston, Texas
April 18, 2024
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION.
None.
ITEM 9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS.
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive Proxy Statement in connection with the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive Proxy Statement in connection with the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive Proxy Statement in connection with the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive Proxy Statement in connection with the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES.
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive Proxy Statement in connection with the 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
(a)The following documents are filed as a part of this report:
(1)Financial statements:
See listing of financial statements included in Item 8. of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(2)Financial Statement Schedules:
Financial statement schedules are omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
(3)Exhibits:
| | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Description of Document |
| 2.1 | | Investment Agreement, dated as of December 18, 2023, among Conn’s, Inc., Franchise Group Newco BHF, LLC, W.S. Badcock LLC, Freedom VCM Interco Holdings, Inc. and Franchise Group, Inc. (incorporated by reference to exhibit 2.1 to Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 20, 2023)
|
| 3.1 | | |
| 3.1.1 | | |
| 3.1.2 | | |
| 3.1.3 | | |
| 3.1.4 | | |
| 3.2 | | |
| 3.3 | |
|
| 4.1 | | |
| 4.2 | | |
| 4.3 | | |
| 4.4 | | |
| 4.5 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 4.6 | | |
| 4.7 | |
|
| 4.8 | |
|
| 4.9 | |
|
| 4.10 | | |
| 4.11 | | |
| * 10.1 | | |
| * 10.1.1 | | |
| * 10.1.2 | | |
| * 10.2 | | |
| * 10.2.1 | | |
| * 10.3 | | |
| * 10.3.1 | | |
| * 10.4 | | |
| *10.4.1 | | |
| *10.4.2 | | |
| *10.4.3 | | |
| *10.4.4 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| *10.4.5 | | |
| *10.4.6 | | |
| * 10.5 | | |
| *10.5.1 | | |
| *10.5.2 | | |
| *10.5.3 | | |
| *10.5.4 | | |
| *10.5.5 | | |
| *10.6 | | |
| * 10.7 | | |
| * 10.8 | | |
| * 10.9 | | |
| * 10.10 | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| *10.11 | | |
| *10.12 | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| *10.13 | | |
| 10.14 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| **10.15 | | Fifth Amended and Restated Loan Agreement, dated March 29, 2021, by and among the Company, as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers, certain banks and financial institutions named therein, as lenders, and Bank of America N.A., in its capacity as agent for lenders (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to Form 10-K for the annual period ended January 2021 (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 31, 2021) |
| **10.16 | | Amendment No. 1 to Fifth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated November 21, 2022, among the Company, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., certain banks and financial institutions named therein, as lenders, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent for the lenders (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 22, 2022 |
| 10.17 | | Amendment No. 2 to Fifth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of February 21, 2023, among Conn's Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers, the guarantors party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the lenders party thereto, as lenders (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K (File No. 00-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 24, 2023 |
| 10.18 | | |
| 10.19 | | Note Purchase Agreement, dated November 17, 2021, by and among Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn’s Receivables Funding 2021-A, LLC, Conn Appliances Receivables Funding, LLC, Conn’s, Inc. and the Initial Purchasers (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 1.1 to Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 18, 2021) |
| 10.20 | | |
| 10.21 | | |
| 10.22 | | |
| 10.23 | | |
| 10.24 | | Note Purchase Agreement, dated July 14, 2022, by and among Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn’s Receivables Funding 2022-A, LLC, Conn Appliances Receivables Funding, LLC, Conn’s, Inc. and the Initial Purchasers (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 1.1 to Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 18, 2022) |
| 10.25 | |
|
| 10.26 | | |
| 10.27 | | |
| 10.28 | | |
| | |
| 10.31 | | |
| 10.32 | | |
| 10.33 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 10.34 | | |
| 10.35 | | |
| 10.36 | | |
| 10.37 | | |
| 10.38 | | |
| 10.39 | |
|
| 10.40 | |
|
| 10.41 | |
|
| 10.42 | |
Amendment No. 3 to Fifth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of December 18, 2023, among Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers, the guarantors party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the lenders party thereto, as lenders (incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.4 to Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 20, 2023)
|
| 10.43 | | Term Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of December 18, 2023, among Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP, Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., and W.S. Badcock LLC, as borrowers, BRF Finance Co., LLC, as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the financial institutions party thereto, as lenders (incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.5 to Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 20, 2023) |
| 10.44 | |
Amendment No. 1 to Delayed Draw Term Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of December 18, 2023, among Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers, certain financial institutions, as lenders, and Stephens Investments Holdings LLC, as administrative agent (incorporated by reference to exhibit 10.6 to Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 20, 2023)
|
| 10.45 | | Delayed Draw Term Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of July 31, 2023, among Conn's Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP and Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., as borrowers, certain financial institutions, as lenders, and Stephens Investments Holdings LLC, as administrative agent (incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Conn's, Inc.'s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-34956) as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 31, 2023) |
| 10.46 | | Amendment No. 1 to Term Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of January 22, 2024, among Conn’s, Inc., as parent and guarantor, Conn Appliances, Inc., Conn Credit I, LP, Conn Credit Corporation, Inc., and W.S. Badcock LLC, as borrowers, BRF Finance Co., LLC, as administrative agent and collateral agent, and the financial institutions party thereto, as lenders. |
| 10.47* | | |
| 10.48* | | |
| 21 | | |
| 23.1 | | |
| 31.1 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 31.2 | | |
| 32.1 | | |
| 97 | | |
| 101 | | The following financial information from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the annual period ended January 31, 2024, filed with the SEC on April 18, 2024, formatted in Inline Extensible Business Reporting Language (iXBRL): (i) consolidated balance sheets as of January 31, 2024 and 2023, (ii) consolidated statements of operations for the fiscal years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, (iii) consolidated statements of comprehensive income for the fiscal years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, (iv) consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity for the fiscal years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, (v) consolidated statements of cash flows for the fiscal years ended January 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, and (vi) notes to consolidated financial statements |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (embedded within the Inline XBRL Document and included in Exhibit 101) |
* Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
** Schedules and exhibits to this Exhibit have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K. The Company hereby undertakes to furnish supplemental copies of any of the omitted schedules and exhibits upon request by the SEC.
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY.
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | |
| | CONN’S, INC. |
| | (Registrant) |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Norman L. Miller |
| Date: | | Norman L. Miller |
| April 18, 2024 | | President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
| /s/ Norman L. Miller | | | | |
| Norman L. Miller | | President and Chief Executive Officer | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Timothy Santo | | | | |
| Timothy Santo | | Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Bob L. Martin | | | | |
| Bob L. Martin | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ William E. Saunders Jr. | | | | |
| William E. Saunders Jr. | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Douglas H. Martin | | | | |
| Douglas H. Martin | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ David Schofman | | | | |
| David Schofman | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Oded Shein | | | | |
| Oded Shein | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ James H. Haworth | | | | |
| James H. Haworth | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Ann B. Gugino | | | | |
| Ann B. Gugino | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| /s/ Karen Hartje | | | | |
| Karen Hartje | | Director | | April 18, 2024 |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
