UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
FORM 10-K
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
(Mark One) | | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024
OR | | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO |
Commission File Number 001-37918
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
iRhythm Technologies, Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its Charter)
________________________________________________________________________________________________________ | | | | | |
| Delaware | 20-8149544 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
699 8th Street, Suite 600 San Francisco, California (Address of principal executive offices) | 94103 (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (415) 632-5700
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock, Par Value $.001 Per Share | IRTC | The Nasdaq Stock Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definition of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer”, “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☒ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Small reporting company | ☐ |
| | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the Registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the Registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the Registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant, based on the closing price of the shares of common stock on The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC on June 30, 2024, was approximately $3.3 billion.
The number of shares of Registrant’s Common Stock outstanding as of February 13, 2025, was 31,409,617.
______________________________________________________________________
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE:
Portions of the information called for by Part III of this Form 10-K is hereby incorporated by reference from the definitive Proxy Statement for our annual meeting of stockholders, which will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission not later than 120 days after December 31, 2024.
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). All statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K other than statements of historical fact, including statements concerning our plans, objectives, and expectations for our business, operations, and financial performance and condition, are forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “anticipate,” “assume,” “believe,” “contemplate,” “continue,” “could,” “due,” “estimate,” “expect,” “goal,” “intend,” “may,” “objective,” “plan,” “predict,” “potential,” “positioned,” “seek,” “should,” “target,” “will,” “would,” and other similar expressions that are predictions of or indicate future events and future trends, or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology. These forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements about:
•the expected impact of global business, political, and macroeconomic conditions, including inflation, interest rate volatility, cybersecurity events, potential instability in the global banking system, and volatile market conditions, and global events, including public health crises, and ongoing geopolitical conflicts, such as the war in Ukraine and conflict in the Middle East, on our business, operations, and financial results;
•the impact of supply chain disruptions on our operations and financial results;
•the impact of inflationary costs on our operations and financial results;
•plans to conduct further clinical studies, including any clinical trials initiated by third parties;
•our plans to modify our current systems and services, or identify and develop, or acquire, new products or services, to address additional indications;
•the expected growth of our business and our organization;
•our expectations regarding government and third-party payor coverage and reimbursement or other regulatory actions or decisions;
•our compliance with all applicable laws, rules, and regulations, including those of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration;
•our expectations regarding the size of our sales organization and expansion of our sales and marketing efforts, including in international geographies;
•our expectations regarding revenue, cost of revenue, cost of service per device, operating expenses, including research and development expense, sales and marketing expense, general and administrative expenses and gross margin;
•our ability to retain and recruit key personnel, including the continued development of a sales and marketing infrastructure;
•our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for our systems and services;
•our estimates of our expenses, ongoing losses, future revenue, capital requirements, and our needs for, or ability to obtain, additional financing;
•our financial performance; and
•developments and projections relating to our competitors or our industry.
We believe that it is important to communicate our future expectations to our investors. However, there may be events in the future that we are not able to accurately predict or control and that may cause our actual results to differ materially from the expectations we describe in our forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are based on management’s current expectations, estimates, forecasts, and projections about our business and the industry in which we operate and management’s beliefs and assumptions and are not guarantees of future performance or development and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that are in some cases beyond our control. As a result, any or all of our forward-looking statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K may turn out to be inaccurate. Factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from current expectations include, among other things, those listed under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Potential investors are urged to consider these factors carefully in evaluating the forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We assume no obligation to update or revise these forward-looking statements for any reason after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K to conform these statements to actual results or to changes in our expectations, even if new information becomes available in the future.
You should not rely upon forward-looking statements as predictions of future events. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee that the future results, levels of activity, performance or events and circumstances reflected in the forward-looking statements will be achieved or occur.
You should read this Annual Report on Form 10-K and the documents that we reference in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and have filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) as exhibits to the Annual Report on Form 10-K with the understanding that our actual future results, levels of activity, performance, and events and circumstances may be materially different from what we expect.
As used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the term “iRhythm,”, “the Company,” “we” or “us,” refers to iRhythm Technologies, Inc., a Delaware corporation, or iRhythm Technologies Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries, as the context requires.
Summary of Risk Factors
Our business is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including those risks more fully described below. These risks include, among others, the following, which we consider our most material risks:
•Reimbursement by Medicare is highly regulated and subject to change, and our failure to comply with applicable regulations, including regulations not designed for remote diagnostic tests like our Zio Services, could prevent us from receiving reimbursement under the Medicare program and some commercial payors, subject us to penalties, and adversely affect our reputation, business, and results of operations.
•If reimbursement or other payment for our Zio Services is reduced or modified in the United States or in our international markets, including through cost containment measures or changes to policies with respect to coding, coverage, and pricing, our business could suffer.
•If we are unable to expand the number of third-party commercial payors with which we contract or expand coverage for existing third-party commercial payors, our commercial success could be impacted.
•Our revenue relies on our Zio Services, which are currently our only offerings. If our Zio Services or future service offerings fail to gain, or lose, market acceptance, our business will suffer.
•The market for remote cardiac monitoring solutions is highly competitive. If our competitors are able to develop or market monitoring devices and services that are more effective, or gain greater acceptance in the marketplace, than any services and related devices we develop, our commercial opportunities will be reduced or eliminated.
•Billing for our Zio Services is complex and highly regulated, and we must dedicate substantial time and resources to the billing process. Failure to comply with legal, regulatory, or contractual requirements applicable to our billing and collection activities could subject us to penalties, and adversely affect our reputation, business and results of operations.
•Audits or denials of our claims by government agencies or payors could expose us to recoupment, regulatory scrutiny, and penalties.
•Although our current Zio Systems are comprised of medical devices that have received FDA marketing authorization (510(k) clearance) as well as, with respect to certain devices, regulatory certifications in the EU, Japan, Switzerland and the UK, we may regularly engage in exploring and implementing product enhancements and in iterative changes to existing products, as well as seek to develop new technology or use of technology for new indications for use. These medical device developments may trigger further regulatory reviews and the results of those reviews are unpredictable.
•We are subject to extensive compliance requirements for the quality, design, safety, performance, and post-market surveillance of the medical devices we manufacture for use in our Zio Services, and for vigilance on complaint-handling, escalation, assessment, and reporting of adverse events and malfunctions. A wide range of quality, risk, regulatory, or safety matters could trigger enforcement action by regulatory authorities, the need for a recall, a hold on the distribution of the marketed product, or other corrective actions to marketed product, and such matters have the potential to escalate to judicial actions that involve the DOJ.
•Because of the patient populations for which our services are provided and the complexity of the healthcare environment in which we operate, a high degree of medical and clinical input may be necessary to evaluate complaints and adverse events, and in some cases, there may be disagreement over whether our services or the medical devices used in our services may have caused or contributed to an adverse event.
•International expansion of our business exposes us to market, regulatory, political, operational, financial, and economic risks associated with doing business outside of the United States.
•We may face risks associated with acquisitions of companies, products, and technologies and our business could be harmed if we are unable to address these risks.
•Our use of third-party service providers or company resources located outside the United States to support certain customer care, clinical, and other operations of our IDTFs may present challenges, and if we are ineffective in limiting work performed by these service providers or company resources consistent with applicable regulations or our contractual agreements with commercial payors, we may be subject to penalties or experience loss of revenue.
•If we fail to comply with medical device, healthcare, and other governmental regulations, we could face substantial penalties and our business, results of operations, and financial condition could be adversely affected.
•Changes in applicable laws or regulations or the interpretation or enforcement policies of regulators governing our IDTFs and Zio Services may constrain or require us to restructure our operations or adapt certain business strategies, which may harm our revenue and operating results.
•Our business relies on orders from licensed healthcare providers, and the continuing clinical acceptance and adoption of our Zio Services depends upon strong working relationships with healthcare providers, including physicians. These relationships, interactions, and arrangements are subject to a high degree of scrutiny by government regulators and enforcement bodies.
•Our communications with healthcare stakeholders – physicians and other healthcare professionals, payors, and similar entities, as well as patients and lay caregivers – are subject to a high degree of scrutiny for compliance with a wide range of laws and regulations. Continuing or increasing our sales and marketing and other external communication efforts may expose us to additional risk of being alleged or deemed to be non-compliant by regulators, enforcement authorities, or competitors.
•In the future we may identify additional material weaknesses or otherwise fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, which may result in material misstatements of our consolidated financial statements or cause us to fail to meet our periodic reporting obligations.
•Our financial results may fluctuate significantly from quarter-to-quarter and may not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business.
•We are subject to legal proceedings and government investigations that could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
•We are subject to complex and evolving U.S. and foreign laws and regulations and other requirements regarding privacy, data protection, security, and other matters. Many of these laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretation, and could result in claims, changes to our business practices, monetary penalties, increased cost of operations, or declines in customer growth or engagement, or otherwise harm our business.
•If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, or if they issue an adverse or misleading opinion regarding our stock, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
•Our stock price is highly volatile and investing in our stock involves a high degree of risk, which could result in substantial losses for investors.
PART I
ITEM 1: BUSINESS
Company Background
iRhythm Technologies Inc.1 is a leading digital healthcare company that creates trusted solutions that detect, predict, and prevent disease. Our principal business is the design, development, and commercialization of device-based technology to provide ambulatory cardiac monitoring services that we believe allow clinicians to diagnose certain arrhythmias quicker and with greater efficiency than other services that rely on traditional technology.
Since first receiving clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) for our technology in 2009, we have supported physician and patient use of our technology and provided ambulatory cardiac monitoring services from our Medicare-enrolled independent diagnostic testing facilities (“IDTFs”) and with our qualified technicians. We have provided our Zio ambulatory cardiac monitoring services, including long-term continuous monitoring, short-term continuous monitoring, and mobile cardiac telemetry (“MCT”) monitoring services (collectively, the “Zio Services”), using our Zio Systems (as defined below).
Each Zio System combines an FDA-cleared and CE-marked, wire-free, patch-based, 14-day wearable biosensor that continuously records electrocardiogram (“ECG”) data with a proprietary, FDA-cleared, CE-marked cloud-based data analytic software to help physicians monitor patients and diagnose arrhythmias. Since receiving FDA clearance, we have provided the Zio Services to over eight million patients and have collected over 2 billion hours of curated heartbeat data.
The Company was incorporated in the state of Delaware in September 2006. Our principal executive offices are located at 699 8th Street, Suite 600, San Francisco, California 94103, and our telephone number is (415) 632-5700. Our common stock is listed on The Nasdaq Global Select Market under the symbol “IRTC”, and we employ approximately 2,000 regular full-time employees as of December 31, 2024.
Our website address is https://www.irhythmtech.com, and our investor relations website is located at https://investors.irhythmtech.com. Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and amendments to reports filed pursuant to Sections 13(a) and 15(d) of the Exchange Act are available free of charge on our investor relations website as soon as reasonably practicable after we file such material with the SEC.
iRhythm investors and others should note that we announce material information to the public about our company, products, and services, and other issues through a variety of means – including via our website, our investor relations website, press releases, SEC filings, and public conference calls – to achieve broad, non-exclusionary distribution of information to the public and to comply with our disclosure obligations under Regulation FD. We encourage our investors and others to review the information we make public in these locations as such information could be deemed material. Please note that this information may be updated from time to time.
Cardiac Arrhythmias and the Ambulatory Cardiac Monitoring Market
Cardiac Arrhythmias
Every year, millions of patients experience symptoms potentially associated with cardiac arrhythmias, a condition in which the electrical impulses that coordinate heartbeats do not occur properly, causing the heart to beat too quickly, too slowly, or irregularly. There are many different types of arrhythmias which are typically categorized based on where in the heart they originate - in either the atria or ventricles - and their speed - tachycardia for fast rhythms, bradycardia for slow rhythms. The causes of arrhythmias are diverse, and they can be triggered by conditions such as heart disease, high blood pressure, electrolyte imbalances, drug use, or stress. Some arrhythmias may not show symptoms, while others may lead to dizziness, shortness of breath, fainting, or chest pain.
The most common sustained type of arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation (“Afib”), a condition which causes the upper chambers of the heart to beat irregularly and blood not to flow properly to the lower chambers of the heart. It is estimated that more than 50 million patients worldwide have Afib with at least one-third of these patients presenting as asymptomatic at the time of their diagnosis, and the condition contributes to an estimated 350,000 deaths globally each year. The prevalence of Afib in the United States is estimated to increase from approximately 5.2 million in 2010 to 12.1 million in 2030, and more than 450,000 hospitalizations occur each year in the United States because of Afib. Since Afib is more common among people over the age of 60, these numbers are expected to increase as the U.S. population ages. In Europe, the prevalence of arrhythmias is also expected to continue to rise with atrial fibrillation affecting an estimated 7.6 million people over 65 in the EU in 2016 and projections indicating a surge to 9.5% of individuals over 65 by 2060.
1 As used throughout the text of Items 1 to 7, on Form 10-K, the term “iRhythm,”, “the Company,” “we” or “us,” refers to iRhythm Technologies, Inc., a Delaware corporation, or iRhythm Technologies Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries, as the context requires.
Atrial Fibrillation and Stroke
Early detection of heart rhythm disorders, such as Afib and other clinically relevant arrhythmias, supports appropriate medical intervention and can help avoid more serious downstream medical events, including stroke. In 2021, it was estimated that the age-adjusted US stroke death rate as an underlying cause of death was approximately 41.1 per 100,000, and there were approximately 7.4 million deaths attributable to stroke worldwide. Afib is the leading risk factor for stroke because Afib can cause blood to collect in the heart and potentially form a clot, which can then travel to the brain possibly resulting in an ischemic stroke. While individuals with Afib are approximately five times more likely to suffer a stroke, the American Stroke Association (“ASA”) estimated in 2022 that up to 80% of second clot-related strokes may be preventable. According to the AHA, stroke costs the United States an estimated $34.5 billion each year in healthcare costs and lost productivity and is a leading cause of serious long-term disability. Between 15% and 20% of people who have strokes also have Afib.
We believe early detection of Afib is critical to optimizing patient care, delivering earlier treatment to help avoid further adverse clinical events, managing symptoms caused by Afib, and reducing the total public health burden of treating stroke. The AHA and ASA have published treatment guidelines for patients diagnosed with Afib to manage heart rhythm and rate and to support stroke prevention. These early treatments include medications such as oral anticoagulants, treatment with anti-arrhythmic drugs, and interventions such as cardiac ablation therapy to help control heart rhythm and rate.
Afib burden, or the amount of time a patient spends in Afib during the period of time the patient is wearing a heart monitor, has been identified in the clinical community as a clinically relevant measure for helping to determine appropriate and effective therapeutic interventions to manage patients with Afib and for assessing stroke risk. We believe the calculated Afib burden is only as good as the data available for analysis during the monitoring period. Since the most common type of Afib occurs intermittently, we believe that long-term continuous monitoring with patch-based technology, such as with the Zio patch technology that is part of our Zio Systems, can more accurately measure Afib burden as it captures the patient’s heartbeat data is captured continuously through the wear period.
Ambulatory Cardiac Monitoring Overview
The ambulatory cardiac monitoring (“ACM”) market is well-established in the United States with an estimated 6.5 million diagnostic tests performed annually with meaningful expansion anticipated in the coming years due to an aging population, a rising number of heart-related disorders globally, and broader acceptance of innovative medical technologies. Traditional ambulatory cardiac monitoring devices used by physicians for diagnosing patients with suspected arrhythmias – such as traditional, 24-to-48-hour Holter and cardiac event monitors – are constrained by short-term monitoring times, non-continuous data collection and reporting, cumbersome equipment, and/or lower patient compliance. For example, patients often remove traditional monitors when sleeping, showering, or exercising, which can lead to a failure to capture critical data and result in incomplete diagnoses and repeat testing, which in turn can result in suboptimal patient care and higher costs to the health system.
Arrhythmia symptoms are generally monitored either in a physician’s office or healthcare facility, or with the ambulatory cardiac monitoring services. Typically, physicians will administer a resting ECG test in their offices to record and analyze the electrical impulses of patients’ hearts. If physicians determine that patients require monitoring for a longer wear period to generate a diagnosis, they have historically prescribed an ambulatory cardiac monitoring device such as a traditional Holter monitor, which is a non-invasive, battery powered device that typically records data continuously for 24 to 48 hours. For longer term (i.e., up to 30 days) event driven monitoring, physicians may prescribe ambulatory cardiac event monitoring services, including MCT services, which record ECG data upon auto-detection (i.e., asymptomatic events) and/or patient activation (i.e., symptomatic events) and may transmit such data wirelessly to a monitoring center like an IDTF. Physicians may also prescribe implantable loop recorders, which are implanted underneath the patient’s skin in a minimally invasive, hospital-based procedure and record ECG data similar to cardiac event monitors but are intended for monitoring up to 3 years.
If the diagnosis is not definitive following the first monitoring period, physicians may prescribe a repeat traditional, 24-to-48-hour Holter monitoring test or, alternatively, event monitoring services, MCT, or implantable loop recorders. Physicians use frequency and acuity of symptoms to determine which monitoring device to prescribe. Some physicians own their own ambulatory cardiac monitoring devices and provide ambulatory monitoring services directly to their patients, while others outsource these services to third-party providers, including IDTFs.
Our Products and Services
Zio Systems and Zio Services
The Zio Systems and Zio Services deliver a patient-friendly design that enables between 98%-99% patient compliance with minimal ECG data noise or artifact, thereby potentially delivering superior clinical accuracy to physicians diagnosing arrhythmias and reducing the cost of care for healthcare systems by avoiding costly downstream adverse events. We have developed a proprietary system that combines an FDA-cleared and CE-marked wire-free, patch-based, 14-day wearable biosensor that continuously records ECG data, with a proprietary FDA-cleared and CE-marked cloud-based data analytic platform to help physicians monitor patients and diagnose arrhythmias (collectively, the “Zio System”). We currently offer three Zio System options — the Zio Monitor System, the Zio XT System, and the Zio AT System.
Zio ECG monitors are designed to provide high-quality, accurate data with patient compliance for up to 14 days of wear time.1-6

1. Data on file. iRhythm Technologies; 2022-2023. 2. Data on file. iRhythm Technologies; 2019. 3. Data on file. iRhythm Technologies; 2022. 4. Zio XT Clinical Reference Manual, iRhythm Technologies; 2019. 5. Zio AT Clinical Reference Manual. iRhythm Technologies; 2022. 6. Zio Monitor Instructions for Use. iRhythm Technologies, 2023. 7. Data on file. iRhythm Technologies; 2023. 8. Continuous, uninterrupted refers to the recording of ECG data. Zio AT Gateway transmissions may be impacted by a variety of factors. See Product Labeling for more information. 9. Zio AT is contraindicated for critical care patients. 10. Do not use Zio AT for patients with symptomatic episodes where variations in cardiac performance could result in immediate danger to the patient or when real-time or in-patient monitoring should be prescribed. Refer to the Zio AT labeling and Clinical Reference Manual for full contraindications.
The Zio Service Monitoring Solutions
The Zio Monitor System is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that consists of a patch ECG monitor (the “Zio Monitor patch”) that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the Zio ECG Utilization Software (“ZEUS”) System, which supports the capture and analysis of ECG data recorded by the Zio Monitor patch at the end of the wear period, including specific arrhythmia events detected by the ZEUS System. The Zio XT System is the previous generation of the Zio Monitor System and is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that consists of a patch ECG monitor (the “Zio XT patch”) that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS System, which supports the capture and analysis of ECG data recorded by the Zio XT patch at the end of the wear period, including specific arrhythmia events detected by the ZEUS System.
The Zio Monitor patch is 72% smaller, 62% lighter, and 23% thinner than our Zio XT patch, attributes which have contributed to a positive impact on patient experience, including improved patient satisfaction, and associated improvement in device wear times. Furthermore, the Zio Monitor patch incorporates a breathable adhesive construct, which enhances the patient experience by removing moisture otherwise captured next to the patient’s skin, as well as Bluetooth communication capabilities and improved processing efficiency.
Zio Monitor Patch and Zio XT Patch
The Zio AT System is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that similarly consists of a patch ECG monitor (the “Zio AT patch”) that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS System, but which also incorporates the Zio AT wireless gateway that provides connectivity between the Zio AT patch and the ZEUS System during the patient wear period. The wireless gateway, slightly larger than a smart phone, is provided to the patient at the time of Zio AT patch application and collects and transmits data from the Zio AT patch to the cloud via a long-term evolution (“LTE”) cellular protocol.
Zio AT Patch and Wireless Gateway


We support physician and patient use of our Zio Systems through our Medicare-enrolled IDTF and qualified technicians, who perform the technical monitoring services associated with a physician’s order for long-term continuous monitoring or MCT monitoring services. Long-term continuous monitoring services (the “Zio LTCM Service”) and MCT services (the “Zio MCT Service”) are diagnostic medical procedures typically ordered by physicians for patients not suspected of having life-threatening arrhythmias, but who are suspected of having infrequent, difficult-to-detect, or asymptomatic arrhythmias. When physicians order long-term continuous monitoring services with our Zio System, our biosensor technology collects an uninterrupted, long-term continuous recording of ECG data for up to 14 days and delivers a comprehensive end-of-wear report, which includes specific arrhythmia events detected by the ZEUS algorithm upon return of the Zio Monitor patch or Zio XT patch (and with the Zio AT patch, each, a “Zio patch”) and analysis of the stored data by qualified technicians. A Zio patch typically collects approximately 1.5 million heartbeats of data for each patient during a single wear period of up to 14 consecutive days.
After we receive the Zio patch at our IDTF, the ECG data is uploaded to our secure cloud and preliminary findings are generated by our proprietary FDA-cleared deep learning algorithms. Each report is then validated by qualified technicians and sent to the patient’s prescribing physician who may access the Zio report on our proprietary, web-based portal, referred to as ZioSuite, and also through our Electronic Health Record (“EHR”) connections or ZioSuite mobile apps. Our technicians also notify physicians of potential urgent arrhythmias according to the ordering physician’s specified notification criteria.
ZioSuite web portal via desktop or mobile application
For the Zio MCT Services, the Zio AT patch and wireless gateway also offer the additional capability of providing actionable transmissions during the wear period to assist physicians in diagnosing and treating patients in situations where their physician has determined that there is a medical need to receive more timely, clinically actionable information. For the MCT services, physicians will receive daily reports, routine reports, and notifications from qualified technicians if there are significant events that meet predetermined and physician-specified notification criteria.
While wearing a Zio patch, patients can mark when symptoms occur by pressing a trigger button on the device and separately recording contextual data like activities and circumstances in a written symptom diary or digitally via the myZio application. This allows physicians to match symptoms and activity with ECG-based findings. The Zio patches are not available for sale outside of use with our Zio Services. The Zio patches include the following features:
•patented clear, flexible, lightweight, wire-free design;
•unobtrusive and inconspicuous profile;
•proprietary adhesive backing designed to keep the Zio patch securely in place for the duration of the prescribed wear period;
•water-resistant functionality, allowing patients to shower, sleep, and perform normal daily activities, including moderate exercise;
•hydrogel electrodes and a compliant mechanical design to deliver a clear ECG with minimal artifact from movement;
•large symptom button, or patient trigger, that is easy to find and press;
•indicated single application wear period of up to 14 days (for longer prescribed wear periods for MCT services, additional Zio AT patches and gateways can be provided); and
•sufficient battery power for the entire wear period, without the need to recharge or replace batteries.
The Zio Platform for Clinical-grade Wearables
We believe a clinical need and an opportunity exists to expand our Zio platform into clinical-grade wearables to detect and characterize arrhythmias while integrating with clinicians’ workflows. As part of this expansion strategy, we partnered with Verily Life Sciences LLC, an Alphabet Company (“VLS”) and Verity Ireland Limited (“VIL,” and together with VLS, “Verily”) to develop their Verily Study Watch wearable device into a clinical platform. We developed the Zio® Watch (Study Watch with Irregular Pulse Monitor) with our clinically integrated ZEUS System, a solution that is intended to be integrated into clinical care delivery and to assist healthcare providers in identifying and monitoring Afib.
We have what we believe to be the world’s largest repository of labelled ECG data, which we leveraged to develop our proprietary photoplethysmography (“PPG”) algorithms utilized in both the Zio Watch and the ZEUS System. In July 2022, we received FDA clearance on the clinically integrated ZEUS System, the AI algorithm and solution component of the Zio Watch. The Zio Watch has not been commercially launched. We are evaluating potential opportunities to leverage our PPG algorithms and ZEUS System with other PPG-based wearables, and we intend to further pursue development opportunities on a wearable platform in the future.
The iRhythm Difference
We believe there are strong benefits offered by our 14-day wear time, by the diagnostic yield possibly achieved through our technology, and by the clinical accuracy of our Zio report as enabled by our proprietary deep-learned artificial intelligence that can help to reduce inaccuracies in computerized ECG interpretations and improve the efficiency of expert human ECG interpretation. This is supported by more than 125 original scientific research manuscripts and a robust, growing body of clinical evidence by third-party researchers.
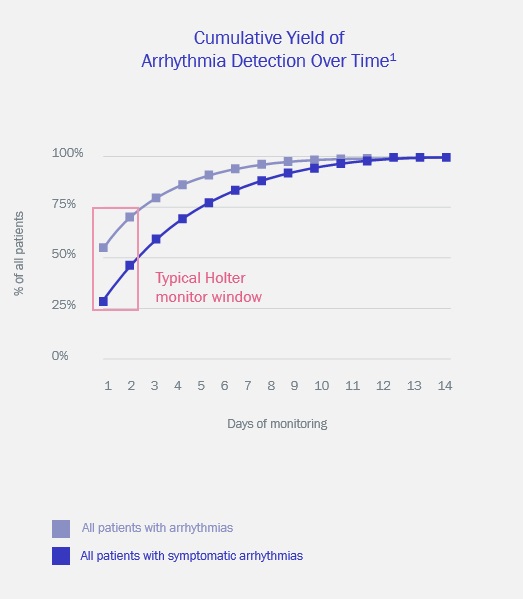
Among this compendium of clinical evidence are multiple studies which demonstrate significant increases in arrhythmia detection through a 14-day monitoring time such as with Zio LTCM Services, as compared to shorter-term 24- to 48-hour monitoring, such as performed as with standard Holter devices. Longer monitoring times with a consistent ECG signal of consistent quality permit detection of infrequent arrhythmias. Other publications illustrate high patient compliance with a 14-day prescribed wear time and low ECG signal artifact, with wear times routinely above 13 days and percent analyzable time above 95%. Additionally, data from the Zio LTCM Service has been used in development of proprietary artificial intelligence, including a deep-learned neural network model which has been shown to meet or exceed the performance of cardiologists in detection of 12 arrhythmia types. In clinical settings, we believe that this approach could reduce the number of misdiagnosed computerized ECG interpretations and improve the efficiency of expert human ECG interpretation by accurately triaging or prioritizing the most urgent conditions.
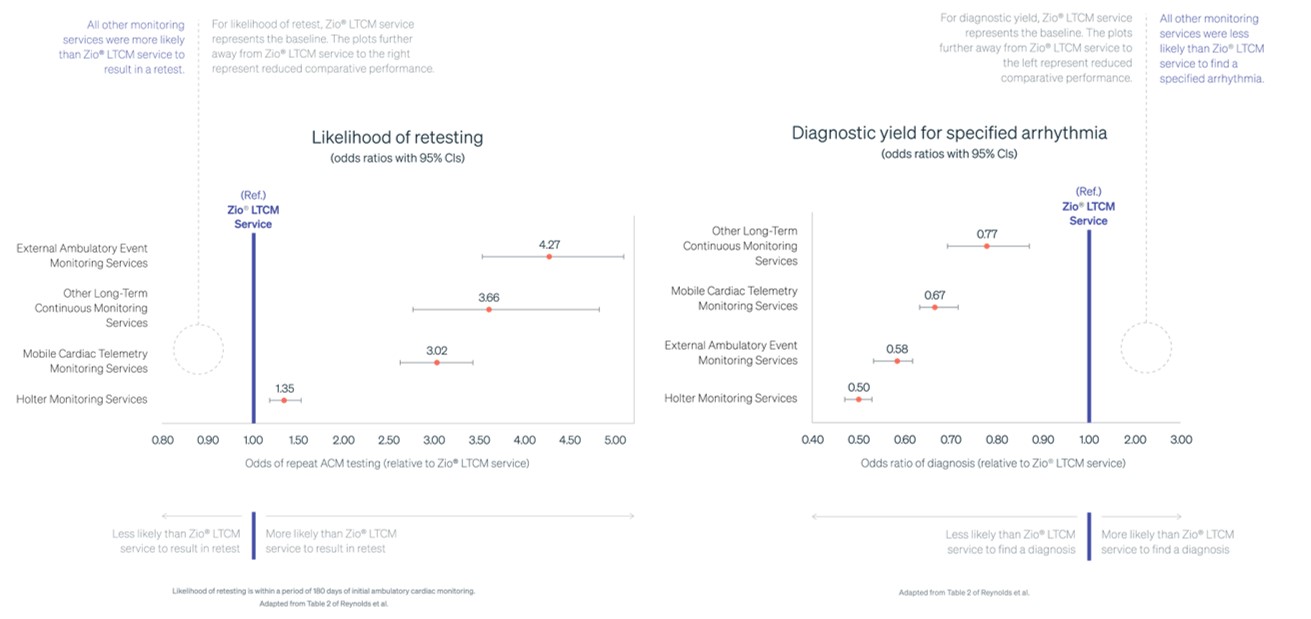
Long-term, continuous monitoring maximizes diagnostic yield1
1, Turakhia et al. Diagnostic Utility of a Novel Leadless Arrhythmia Monitoring Device. The American Journal of Cardiology, 2013.
Taken together, we believe that these elements are differentiators for the Zio Systems in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias and can lead to improved clinical outcomes, enhanced patient experience, high physician and healthcare staff satisfaction, and reduced cost of care to healthcare systems. This was demonstrated by the results from the Cardiac Ambulatory Monitor EvaLuation of Outcomes and Time to Events (“CAMELOT”) study that were published in the American Heart Journal in December 2023. The largest ever real-world evidence study of ambulatory cardiac monitoring, it revealed that the Zio LTCM Service using the Zio XT System was independently associated with the highest yield of clinical arrhythmia encounter diagnosis, lowest likelihood of retest, and the lowest incremental healthcare resource utilization of all strategies examined.
Results of the CAMELOT study1-4
1, Reynolds et al. Comparative effectiveness and healthcare utilization for ambulatory cardiac monitoring strategies in Medicare beneficiaries. Am Heart J. 2024;269:25–34. 2. A specified arrhythmia refers to an arrhythmia encounter diagnosis as per Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCC) 96. 3. Based on previous generation Zio XT device data. Zio Monitor utilizes the same operating principles and ECG algorithm. Additional data on file. 4. Zio LTCM service refers to Zio XT and Zio Monitor service.
Opportunities in Monitoring for Undiagnosed Arrhythmias
Currently, the Zio Services are generally ordered by physicians for patients that are experiencing symptoms, with limited provision of these services for the estimated one-third of the U.S. population that may be experiencing undiagnosed arrhythmias, including Afib. Because Afib is associated with increased risk of clinical outcomes such as stroke and heart failure, we see a future opportunity in supporting physicians in the proactive assessment of the approximately 12 million patients who are at high risk of undiagnosed Afib or other clinically actionable arrhythmias to identify those with the illness, enabling initiation of appropriate therapies which may reduce risks. To that end, iRhythm established the “Know Your Rhythm” program with the goal of enabling population health management strategies to identify undiagnosed arrhythmias in a defined patient population by using data-driven risk stratification, early disease identification, and targeted interventions.
What was initially conceived as our ‘Know Your Rhythm’ program for payor channels has been instead organically adopted by innovative, value-based care organizations to encapsulate proactive monitoring strategies. Early success of the Zio Services within this paradigm has been the culmination of several factors iRhythm has been driving over the past few years. The known increases in health care utilization and costs have been met with a focus on serving patients in lower cost settings of care. The ease of use for physicians and patients alike of our Zio Monitor System, together with iRhythm’s clinical evidence demonstrate the Zio Services' ability to identify undiagnosed arrhythmias and the cost-effectiveness of a proactive arrhythmia monitoring approach. To this end, we intend to utilize a precision artificial intelligence approach to better apply risk factor-based monitoring for atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias in targeted patient populations — many that would not be identified with conventional criteria.
In 2024, the European Society for Cardiology updated their practice guidelines for management of Afib to include recommended screening in all patients 75 years and older and for those 65 and older with additional risk factors. We have participated in multiple clinical studies, including SCREEN-AF, GUARD-AF, and mHealth Screening to Prevent Strokes ("mSToPS") which have demonstrated significant increases in Afib detection using Zio LTCM Services versus routine clinical care. During a three-year follow-up period in the mSToPS study, Afib screening with the Zio LTCM Service was associated with a reduction in the rate of the combined endpoint of stroke, death, systemic emboli, and myocardial infarction as compared to an observational cohort that did not participate in active screening.
In patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke, identification of the underlying cause is important in prevention of recurring strokes and to improve patient outcomes. The 2024 American College of Cardiology expert consensus decision statement on arrhythmia monitoring after stroke now recommends ambulatory cardiac monitoring of 14 or more days as the primary modality for use in detection of Afib in cases of stroke of unknown origin. The Zio LTCM Service was shown to be superior to Holter monitoring for detection of Afib in post-stroke patients as part of the Early Prolonged Ambulatory Cardiac Monitoring in StrokeTrial.
Utility of Zio Long-term Continuous Monitoring in Ventricular Rhythms
Recently published literature has also demonstrated the value of 14-day long-term continuous monitoring in assessment of ventricular rhythms, including ventricular tachycardia and premature ventricular contractions (“PVC”). Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (“HCM”) is among the most common genetic heart diseases and patients are at increased risk for ventricular tachycardia and sudden cardiac death. A 2024 study conducted by Rowin et al. assessed the incidence of ventricular tachycardia in 236 HCM patients and concluded that 14-day continuous monitoring with Zio LTCM Services identified three times as many patients with high-risk episodes as compared to Holter monitoring over 48 hours, the standard duration for Holter monitoring. Additionally, a 2024 study conducted by Krumerman et al. assessed 106,705 patients with elevated PVC burden and demonstrated reduced error in determining the burden of PVC with 14-day continuous monitoring as compared to short-term monitoring durations. This enabled improved classification of patients with respect to burden level, which is associated with increased risk for reduced ejection fraction and heart failure.
We believe that these studies together illustrate that 14-day continuous monitoring with the Zio Services may improve sensitivity for risk identification in ventricular rhythms and provides additional data valuable in clinical decision-making, such as determining the need for the implantable cardioverter defibrillator implant to reduce risk of sudden cardiac death in HCM patients, or the use of ablation procedures to reduce heart failure risks in patients with elevated PVC burden.
Our Strategy
Our mission is to boldly innovate to create trusted solutions that detect, predict, and prevent disease. The key elements of our strategy include:
•Further penetrating and expanding the U.S. ambulatory cardiac monitoring market. Our goal is to be the leading provider of ambulatory cardiac monitoring for patients at risk for arrhythmias. We intend to expand our market penetration by targeting the large existing ambulatory cardiac monitoring market in the United States and driving broader awareness of its advantages. We plan to leverage our portfolio of products, including the Zio Monitor System and Zio AT System, and position Zio Services as providing certainty in a single test due to high patient compliance and superior quality of uninterrupted data. The Zio Monitor System, which provides continuous long-term ECG monitoring, is designed to be appropriate for the majority of patients that require ambulatory cardiac monitoring while the Zio AT System, which includes near real-time monitoring, is intended for more acute patients that require timely notification. We estimate our current market penetration in the United States to be over 30%.
Marketing and education throughout the medical community are key to bringing awareness and communicating the strong clinical evidence backing Zio Services. In addition, we expect to continue developing and publishing clinical evidence to demonstrate the potential advantages of Zio Services relative to legacy and competitive monitoring technologies. Within existing accounts, we expect to continue to introduce our Zio Services beyond cardiology and electrophysiology into other departments, including primary care, neurology, and emergency room. To enable this broader adoption within a hospital system, we have successfully interfaced the Zio ordering and report posting processes into a number of large health systems’ electronic health record (“EHR”) systems. This seamless integration of Zio workflow processes has proven to be a key factor in spurring growth within existing and new accounts and is an important part of our ongoing market penetration strategy.
Furthermore, we believe there is potential to increase the core symptomatic total addressable market by moving further upstream in the care pathway to the primary care physician call point. We estimate that 15 million patients in the United States visit a primary care physician annually with palpitations due to suspected cardiac disease. In addition to approaching primary care physicians directly, we also are able to leverage virtual cardiology providers as key partners to deliver clinical decisions. By educating primary care physicians on the benefits of Zio Services for this patient population, we believe we can expand the market and reach more patients that are candidates for ambulatory cardiac monitoring.
•Pursuing international expansion opportunities. While our initial commercial focus is the U.S. market, we have initiated efforts that will allow for future expansion into international geographies. We have a presence in the UK with efforts underway to pursue national reimbursement. In September 2020, we were named a winner of the Artificial Intelligence in Health and Care Award run by the Accelerated Access Collaborate as part of the National Health Service (“NHS”) AI Lab. This funding brought Zio Services to selected NHS sites over a three-year program measuring clinical, pathway, and economic outcomes. We also received positive guidance from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (“NICE”) in December 2020 for the adoption of the Zio XT Service which may facilitate future support of Zio Services through the MedTech Funding Mandate.
We are also conducting diligence and prioritizing other geographies based on market size, regulatory pathway, and reimbursement opportunity. We initiated commercial launch of the Zio Monitor System and Zio Services in Austria, the Netherlands, Spain, and Switzerland in the third quarter of 2024 and were granted regulatory approval in Japan in September 2024. We estimate the total addressable market in our initial selected countries of the UK, Japan, and prioritized European countries to be at least 5 million existing ambulatory monitoring tests annually.
•Exploring adjacent market opportunities. We intend to continue assessing the potential pathways for expanding indications and clinical use cases for our Zio Services and developing new systems for patient populations with unmet needs. Leading with clinical and economical evidence, we are pursuing commercialization opportunities for proactive monitoring strategies that are focused on patients at risk for undiagnosed arrhythmias. With at least 12 million individuals in the United States estimated to be at risk for undiagnosed cardiac arrhythmias, we believe this could be a significant market opportunity for which we believe Zio Services are uniquely positioned to succeed. Initial efforts to proactively monitor this population with the Zio Monitor System were initiated in 2024 and will be continued into 2025.
In addition, we are actively exploring opportunities in adjacent markets beyond ambulatory cardiac monitoring. We have research and development efforts focused on exploring the use of our Zio Services or other new systems and services for the following patient populations:
•Obstructive sleep apnea patients, with an estimated prevalence of approximately 30 million in the United States. Approximately 50% to 80% of patients with Afib may also have sleep apnea compared with 30% to 60% in control groups, and there is a large prevalence of patients with undiagnosed sleep apnea.
•Heart failure patients, with an estimated prevalence of over 8 million in the United States by the year 2030. Atrial fibrillation and heart failure share many antecedent risk factors, and approximately 40% of people with either Afib or heart failure will develop the other condition. Total cost for heart failure in the U.S. are expected to reach $70 billion by 2030.
•Patients with hypertension, with an estimated prevalence of over 120 million in the United States. Up to 90% of patients with Afib may also have hypertension.
•Advancing our system portfolio and core technology offering. We continue to invest in building a unique, innovative system portfolio and digital platform that addresses unmet needs in the ACM market and adjacent markets. We will continue to invest in research and development efforts to further differentiate our biosensor, data analytics and reporting, our information system, and our digital platform. We intend to make improvements in Zio MCT Services during 2025, and we also intend to continue evaluating potential opportunities to leverage our PPG algorithms and ZEUS System with a PPG-based wearable platform in the future. Additionally, in 2024 we entered into an exclusive license agreement with BioIntelliSense, Inc., a continuous health monitoring and clinical intelligence company, to develop and commercialize their patented pulse oximetry, accelerometry and trending non-invasive blood pressure technologies for use within the ACM market. By incorporating medical grade, connected, multi-sensor capabilities, we believe iRhythm will be well positioned to deliver broad clinical insights within ACM that improve patient outcomes, enhance clinical and operational efficiency, and reduce costs to the healthcare system.
Sales and Marketing
We directly market our Zio Services in the United States to healthcare professional through our internal organization comprised of sales representatives, field billing specialists, and customer experience representatives. Our sales team focuses on initial introduction of the Zio Services to those participants that are instrumental to the decision-making process for ambulatory cardiac monitoring, which include physician practices and healthcare systems. We also focus on continuing efforts to ensure healthcare professionals are knowledgeable about the clinical benefits and economic value of the Zio Services. We continue to invest in our sales force and focus on ensuring we optimize the structure of our U.S. sales organization to expand the current customer account base and support adoption of the Zio Services.
We market our Zio Services to a variety of physician specialties including general cardiologists, electrophysiologists, primary care physicians, neurologists, and other physician specialists who diagnose and manage care for patients with arrhythmias. We have found success focusing on integrated delivery networks (“IDNs”), in which large networks of facilities and providers work together to offer a continuum of care to a specific geographic area or market, as well as with risk-bearing entities as our Zio Systems become a key tool in population health management. Focusing on sales to these customer programs gives us the opportunity to conduct a holistic sale for health systems interested in making value-based purchasing decisions.
In January 2021, we established a small direct sales and clinical infrastructure in Bagshot, Surrey in England to service the UK market. We have since focused efforts on the introduction of the Zio Services using the Zio XT System into new accounts and market access efforts, in particular through orders made by NHS Trusts and Hospitals. Additionally, we have built a small sales force covering Switzerland, Austria, and the Netherlands. In Japan and Spain, we intend to utilize distributor services.
We typically experience reduced revenue during the third quarter, as well as during the year-end holiday season. We believe this is the result of physicians and patients taking vacations and patients electing to delay our monitoring services during the summer months or holidays.
Competition
The market for remote cardiac monitoring is competitive, characterized by rapid change resulting from technological advances, scientific discoveries, and other market activities of industry participants.
In providing our Zio Services, we compete with BioTelemetry, Inc. (acquired by Royal Philips), Preventice Solutions, Inc. (acquired by Boston Scientific, Inc.), and Bardy Diagnostics, Inc. (acquired by Baxter International, Inc.) to offer remote cardiac monitoring technology and also function as diagnostic service providers. We also compete with companies that sell traditional, 24-to-48-hour Holter monitors, including GE Healthcare, Philips Healthcare, and Spacelabs Healthcare Inc., as well as Mortara Instrument, Inc. and Welch Allyn Holdings, Inc. (both acquired by Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. now part of Baxter International, Inc.).
Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, manufacturing, marketing, and technical resources than we do. Furthermore, many of our competitors have well-established brands, widespread distribution channels, broader product offerings, and an established customer base.
These competitors have also developed patch-based cardiac monitors that have received FDA and foreign regulatory clearances. We are also aware of small start-up companies entering the patch-based cardiac monitoring market. Large medical device companies may continue to acquire or form alliances with these smaller companies to diversify their product offering and participate in the digital health space. These competitors and potential competitors may introduce new products and services that more directly compete with our Zio Services and Zio Systems.
Future competition may also come from manufacturers of wearable fitness products or large information technology companies focused on general health and wellness. For example, in 2021 and 2022, Apple Inc. and Fitbit each respectively added capabilities on their watch platform to measure non-continuous ECG and to alert users to the potential presence of irregular heartbeats suggestive of asymptomatic Afib.
We believe the principal competitive factors in our market include:
•ease of use, comfort, and unobtrusiveness of the device for the patient;
•quality and clinical validation of the deep-learned algorithms used to detect arrhythmias;
•concise and comprehensive reports supporting efficient physician interpretation;
•ease of use of service workflow for physicians and supporting clinicians;
•digital tools for data management, including the myZio mobile app, website tools, and EHR integration;
•contracted rates with third-party payors;
•government reimbursement rates associated with our Zio Services and supporting Zio Systems;
•quality of clinical data and publications in peer-reviewed journals;
•size, experience, knowledge, and training of sales and marketing teams;
•availability and reliability of sales representatives and customer support services;
•workflow protocols for solution implementation in existing care pathways;
•reputation of existing device manufacturers and diagnostic service providers; and
•relationships with physicians, hospitals, administrators, and other third-party payors.
Manufacturing and Quality Assurance
We currently manufacture our Zio Systems, including the Zio Monitor System and Zio AT System, in our leased facility in Cypress, California. This manufacturing facility is approximately 34,000 square feet and provides space for our manufacturing and production operations, including inspection, assembly, testing, packaging, labeling, storage, and shipping. We believe this manufacturing facility has the capacity to meet our manufacturing needs for at least the next five years.
Outside suppliers are the source for components and sub-assemblies in the production of the Zio Systems. Any significant supplier of a critical component, such as the circuit boards for the Zio Systems provided by contract electronic manufacturers, is managed through our manufacturing team that is focused on reducing supply chain risk. These suppliers are evaluated, approved, and monitored by our quality team to ensure conformity with the specifications, policies, and procedures applicable to our devices.
Our manufacturing operations are subject to regulatory requirements of FDA’s Quality System Regulation (“QSR”), the Medical Devices Regulation 2017/745 of the European Parliament and of the Council (“EU MDR”), the UK Medical Device Regulations 2002 (“UK MDR”), and the Japanese medical device Quality Management System ("QMS"). We are also subject to applicable requirements relating to the environment, waste management, and health and safety matters, including measures relating to the release, use, storage, treatment, transportation, discharge, disposal, sale, labeling, collection, recycling, treatment, and remediation of hazardous substances.
We purchase certain components and materials used in manufacturing from single sources due to quality considerations, costs, or constraints resulting from regulatory or other requirements. As of December 31, 2024, those single sources include suppliers of application-specific integrated circuits used in our transmitters, seals used for the applicators, and certain polymers used to synthesize polymeric membranes for our sensors.
Our manufacturing facilities are also ISO certified (EN ISO 13485:2016). We have registered our device establishments with FDA and with the UK’s Medicines & Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (“MHRA”). Additional EU registrations may be sought in 2025 in EU member states by our EU authorized representative as appropriate.
Third-Party Reimbursement
We receive revenue for the Zio Services primarily from third-party payors, which include commercial payors and government agencies, such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (“CMS”). Third-party payors require us to identify the service for which we are seeking reimbursement by using a Current Procedural Terminology (“CPT”) code set maintained by the American Medical Association (“AMA”). These CPT codes are subject to periodic change and update, which will impact the reimbursement rates for our Zio Services.
For the year ended December 31, 2024, we received approximately 84% of our revenue through third-party payors, which includes approximately 24% of our total revenue from the Medicare program. As we continue to contract with more commercial payors and the patient population ages into eligibility for the Medicare Advantage program, we believe more of our revenue will convert to commercial payor billing.
Our clinical centers are enrolled in the Medicare program as IDTFs, which allows us to bill CMS directly for our Zio Services. To maintain enrollment, we must meet the CMS IDTF supplier standards, including having an independent medical director for oversight and qualified technicians who support the analysis of ECG data captured by the Zio patches as part of our Zio Services.
For additional information on third-party reimbursement, please see our Risk Factor titled “If reimbursement or other payment for our Zio Services is reduced or modified in the United States, including through cost containment measures or changes to policies with respect to coding, coverage, and pricing, our business could suffer.”
Research and Development
We focus our research and development efforts on improvement of our Zio System and Zio Services in alignment with our strategy. We employ engineering and research and development staff to focus on delivering future innovations and sustaining improvements. Our research and development activities are focused on:
•Continuous improvement and extensions to existing products and services. We are continuously working to improve the Zio Services to increase patient comfort, product quality, operational scalability, and security.
•International expansion. We are working on building our infrastructure and ensuring global compliance as we identify appropriate opportunities for international growth.
•Advancing our technology offering. Our product portfolio includes patch-based solutions (utilized in the Zio Monitor System, Zio AT System, and Zio XT System) and the FDA-cleared Zio Watch (not yet commercially available) that combine continuous monitoring for extended periods with accelerated notification of significant events through mobile transmission capabilities.
•Customer workflow optimization. We have initiatives that aim to increase customer productivity by optimizing workflow through easier patient enrollment, report access, and interpretation, in addition to integrating the reports from our Zio Services directly into EHRs.
•Data analytics. We are focused on improving and enhancing our back-end, deep-learning analytic platform, building on our core competency in data analytics.
•Developing clinical evidence. We frequently provide support to third parties conducting clinical studies that further support the benefits of the Zio System, including clinical research in areas such as obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, predictive features, and patient wearables.
•Continuing to solidify our footprint in digital healthcare. Using our repository of ambulatory ECG patient data, we will continue to look for ways to create value-driving opportunities in digital healthcare, such as expansion of indications for the Zio System, new therapeutic discoveries, development of an analytical engine for ambulatory consumers, other medical data and payor and provider decision support, and the potential for more complete system integration with large health systems.
We have supported clinical studies conducted by leading physicians and clinicians to explore and develop new techniques and applications for our Zio Systems, the clinically-integrated version of ZEUS for the Zio Watch, and other clinical and research activities, including healthcare economic outcomes research.
Our research and development activities consist of software development, algorithm and product development, regulatory affairs, and clinical research. Our research and development expenses (excluding in-process research and development) were $71.5 million, $60.2 million, and $46.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Technology License Agreement with BioIntelliSense, Inc.
On August 30, 2024, we entered into a Technology License Agreement (the “License Agreement”) with BioIntelliSense, Inc. (“BioIS”), pursuant to which (i) we will receive a perpetual fully paid up license to certain of BioIS’ intellectual property, technology and products for research, development and commercialization of potential next generation products and services in certain fields of use, including an exclusive license to develop and commercialize pulse oximetry, accelerometry, and trending non-invasive blood pressure technologies for use within our ambulatory cardiac monitoring products and services, and (ii) each party agreed to negotiate in good faith a supply agreement for pulse oximetry hardware.
Under the terms of the License Agreement, we paid BioIS an upfront fee of $15.0 million in cash consideration in acceptance of the initial transfer of certain licensed technologies and data following the execution of the License Agreement. In connection with the License Agreement, we also purchased an aggregate of $40.0 million of convertible promissory notes from BioIS (the “Convertible Notes”), of which $20.0 million (“Milestone Notes”) were designated for satisfaction of our regulatory milestone payment obligations. The Milestone Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, shall be cancelled, if outstanding, upon the achievement of the regulatory milestones up through December 31, 2026. Additionally, BioIS is eligible to receive low single digit royalty payments on annual net sales of certain products that include licensed rights in the home sleep testing field of use, subject to certain adjustments specified in the License Agreement.
Intellectual Property
To establish and protect our proprietary and other intellectual property rights, we rely on a combination of trademark, copyright, patent, trade secret, and other intellectual property laws, and employment, non-disclosure and invention assignment agreements, and other protective contractual provisions with our employees, contractors, consultants, suppliers, partners, outside scientific collaborators, and advisors, and other third parties. In addition, we have entered into licenses in the ordinary course of business relating to a wide array of technologies or other intellectual property rights or assets.
We hold patents and pending patent applications in the United States and other parts of the world which, in aggregate, we believe to be of importance in the operation of our business. As of December 31, 2024, we owned, or retained an exclusive license to, 46 issued patents from the U.S. Patent Office (“USPTO”), 13 issued patents from the Japanese Patent Office, 4 issued patents from the Australian Patent Office, 5 issued patents from the Canadian Patent Office, 7 issued patents from the European Patent Offices, 6 issued patents from the Korean Patent Office, two issued patents from the Chinese Patent Office, and 1 issued patent from the Indian Patent Office. Our U.S. issued patents as of December 31, 2024 are set to expire over a range of years, from November 2028 to August 2041, subject to any extensions. As of December 31, 2024, we had 50 pending patent applications globally, including 14 non-provisional applications and 2 design applications in the United States, 7 in the European Patent Office, 8 in Japan, 1 Patent Cooperation Treaty ("PCT") international application, 5 in Korea, 4 each in Australia and China, 3 in India, and 2 in Canada.
Our patents and patent applications seek to protect aspects of our core technologies and our product concepts for ambulatory cardiac monitoring. We believe that our patent position provides us with sufficient rights to protect our current and proposed commercial products and services. However, our patent applications may not result in issued patents, and any patents that have been issued or might be issued may not protect our intellectual property rights. We also rely on trade secrets, technical know-how, and continuing innovation to develop and maintain our competitive position.
As of December 31, 2024, our trademark portfolio contained U.S. trademark registrations for the marks MyZIO, ZIO, ZIO SUITE, ZIO AT, and IRHYTHM and pending U.S. trademark applications for the marks KNOW YOUR RHYTHM BY ZIO, KNOW YOUR RHYTHM, and ZIO MCT. It also contained registered trademarks for the mark IRHYTHM in Australia, the EU, Austria, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Japan, Italy, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland, and the UK. It further contained trademark registrations for the mark ZIO in Australia, Canada, China, the EU, Japan, Norway, Switzerland, and the UK. It also contained trademark registrations for the mark MYZIO in Canada, the UK, and the EU, trademark registrations for the mark ZIO MCT in the UK and the EU, and trademark registrations for the mark ZIOSUITE in the UK and the EU.
Regulation
Based on the nature of the services we provide, the medical devices used to deliver our services, and the ways in which payment is available for our services, we are subject to a complex spectrum of intersecting laws and regulatory frameworks.
Our facilities in Illinois, California, and Texas are enrolled in the Medicare program as IDTFs, defined by CMS as entities independent of a hospital or physician’s office in which diagnostic tests are performed by licensed or certified non-physician personnel under appropriate physician supervision. CMS has set certain performance standards that every IDTF must meet in order to obtain or maintain its billing privileges.
We are also regulated as a medical device manufacturer because of our role in the design, development, and manufacturing of the Zio Systems used in our Zio Services.
The United States has historically been the primary focus of the delivery of our services, but based on our operations we are subject to a range of laws and regulations outside the United States, and we expect the complexity of the global regulatory landscape to which we are subject to continue to increase.
U.S. Fraud and Abuse Laws and Other Healthcare Compliance Requirements
Medicare is a federal healthcare program administered by CMS that is available to individuals age 65 or over, and certain other individuals. The Medicare program provides, among other things, healthcare benefits that cover most medically necessary care for such individuals, subject to certain deductibles and co-payments. CMS has established guidelines for the coverage and reimbursement of certain products, supplies, and services, including ambulatory cardiac monitoring services. In general, Medicare will only reimburse ambulatory cardiac monitoring services, such as our Zio Services, that are reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of patients. CMS also administers the Medicaid program, a cooperative federal/state program that provides medical assistance benefits to qualifying low income and medically needy persons. State participation in Medicaid is optional, and each state is given discretion in developing and administering its own Medicaid program, subject to certain federal requirements. All CMS programs are subject to statutory and regulatory changes, retroactive and prospective rate adjustments, administrative rulings, interpretations of policy, intermediary determinations, and government funding restrictions, all of which may materially increase or decrease the rate of program payments to healthcare facilities and other healthcare providers, including those paid for our Zio Services.
Because of the significant federal funding involved, the government actively enforces a number of laws and regulations to eliminate fraud and abuse in federal healthcare programs. Our business is subject to compliance with these laws. The most significant of these laws for our business include the federal Anti-Kickback Statute (the “AKS”) and the federal False Claims Act (the “FCA”).
Anti-Kickback Laws
Under the AKS, it is a criminal offense to knowingly and willfully offer, pay, solicit, or receive any remuneration to induce, or in return for purchasing, ordering, or recommending, or arranging for, the purchase or order of items or services (or referrals of the same) reimbursable by a federal healthcare program. The AKS imposes criminal liability for both the party that provides or offers such remuneration and the party that receives or solicits such remuneration. Courts and enforcement agencies interpret the AKS broadly, such that it may be implicated whenever anything of value is provided to a party in a position to generate federal healthcare program business where any one purpose of an arrangement involving remuneration is to induce referrals. Penalties for violations include criminal penalties and civil sanctions such as fines, imprisonment, and possible exclusion from Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal healthcare programs. Many states have adopted laws similar to the AKS. Some of these state prohibitions apply to referral of recipients for healthcare products or services reimbursed by any source, not only CMS programs. The Physician Payments Sunshine Act requires transparency around certain transfers of value and ownership interests that may raise parallel scrutiny of the appropriateness of financial relationships. Notably, some kickback allegations are also interpreted as violations of the FCA.
False Claims Act
The FCA prohibits: (i) knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, a false or fraudulent claim for payment or approval and (ii) knowingly making, using, or causing to be made or used a false record or statement material to a false or fraudulent claim. Importantly, the FCA provides for “whistleblower” or qui tam actions, which allow a private individual to bring actions on behalf of the federal government alleging that the defendant has violated the FCA and to share in any monetary recovery. The federal government has used the FCA to assert liability on the basis of inadequate care, kickbacks, and other improper referrals, and improper use of CMS billing numbers, as well as allegations of off-label promotion of products, and activities relating to the reporting of discount and rebate information. The FCA is the federal government’s preferred enforcement vehicle for addressing a variety of alleged misconduct and provides for treble damages and civil money penalties ranging from $13,508 to approximately $27,018 per claim, as well as exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs and potential criminal penalties, including imprisonment and criminal fines. Additionally, as part of any settlement, the government will often require the entity to enter into a corporate integrity agreement, which imposes certain ongoing compliance, certification, and reporting obligations. In addition, various states have enacted false claims laws analogous to the FCA, and many of these state laws apply where a claim is submitted to any third-party payor and not only a federal healthcare program.
Healthcare Reform
Changes in healthcare policy could increase our costs and subject us to additional regulatory requirements that may interrupt commercialization of our current and future solutions. The Affordable Care Act (“ACA”) substantially changed the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and significantly impacts our industry. Any changes to, or repeal of, the ACA may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Additionally, for out-of-network or cash pay patients, we may be subject to state and federal surprise billing laws that impose limits on amounts that can be charged to such patients and/or the amount we can receive for out-of-network services from commercial payors. One such law, the federal No Surprises Act, requires covered providers to provide “good faith estimates” to patients and establishes a detailed and potentially costly independent dispute resolution process governing fee disputes with those patients. These laws and regulations may change, and additional implementation regulations are expected for the No Surprises Act, and we anticipate these requirements may apply to our business in the future.
We are subject to risks related to the U.S. fraud and abuse laws and other healthcare compliance requirements described above, as well as others that are or may be adopted in future. For further details on these risks, see “Risk Factors,” below.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Because we develop and manufacture the medical device technology used in the Zio Services (the hardware and software elements that FDA regulates as “devices”), we are subject to extensive and ongoing regulation by FDA under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (“FD&C Act”) and its implementing regulations, as well as other federal and state regulatory bodies in the United States. The laws and regulations govern, among other things, product design and development, preclinical and clinical testing, manufacturing, packaging, labeling, storage, recordkeeping and reporting, clearance or approval, marketing, distribution, promotion, import and export, and post-marketing surveillance and associated regulatory reporting.
Most Class II devices, including the Zio patches and the ZEUS System, require 510(k) clearance from FDA in order to be marketed in the United States. A 510(k) submission must demonstrate that the device is substantially equivalent to a device legally in commercial distribution in the United States. After clearance, changes made to devices must be evaluated on an ongoing basis and may trigger the need for additional 510(k) clearances or – depending on the nature of the change – might require a higher level of FDA review (through the de novo premarket approval or (“PMA”) process). To date, our product changes have been managed within the 510(k) framework.
After a device is placed on the market, numerous regulatory requirements continue to apply. These include:
•the FDA’s QSR, which requires manufacturers, including their suppliers, to follow stringent design, testing, control, documentation, and other quality assurance procedures during all aspects of the product lifecycle, including the manufacturing process;
•labeling regulations and FDA prohibitions against the promotion of products for uncleared, unapproved, or off-label uses, including parameters around manufacturer communications with payors and healthcare professionals;
•medical device reporting regulations, which require that manufacturers report to FDA if their device may have caused or contributed to a death or serious injury or malfunctioned in a way that would likely cause or contribute to a death or serious injury if the malfunction were to recur;
•medical device recalls, which require that manufacturers report to FDA any recall of a medical device, provided the recall was initiated to either reduce a risk to health posed by the device, or to remedy a violation of the FD&C Act caused by the device that may present a risk to health; and
•post-market surveillance regulations, which apply when necessary to protect the public health or to provide additional safety and effectiveness data for the device.
After a device receives 510(k) clearance or PMA, any modification that could significantly affect its safety or effectiveness, or that would constitute a major change in its intended use, performance, or functionality may require a new clearance or approval. FDA requires each manufacturer to make this determination initially, but FDA can review any such decision and can disagree with a manufacturer’s determination. If FDA disagrees with the determination not to seek a new 510(k) clearance or PMA approval, the FDA may retroactively require a new 510(k) clearance or PMA approval. FDA could also require a manufacturer to cease marketing and distribution and/or recall the modified device until 510(k) clearance or PMA approval is obtained. Also, in these circumstances, the manufacturer may be subject to significant regulatory fines, penalties, and other enforcement actions, such as warning letters.
We have registered appropriate facilities with FDA as a medical device specification developer, manufacturer, or designated complaint handling unit. We have also obtained a manufacturing license from the California Department of Public Health (“CDPH”). FDA and the CDPH have broad post-market and regulatory enforcement powers. We are subject to unannounced inspections by FDA and the Food and Drug Branch of CDPH to determine our compliance with the QSR and other regulations, and these inspections may include the manufacturing facilities of our suppliers.
Failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements can result in enforcement action by FDA, which may include any of the following sanctions:
•warning letters, fines, injunctions, consent decrees, and civil penalties;
•repair, replacement, refunds, recall, or seizure of our products;
•operating restrictions, partial suspension, or total shutdown of production;
•refusing our requests for 510(k) clearance or PMA approval of new products, new intended uses, or modifications to existing products;
•withdrawing 510(k) clearance or PMA approvals that have already been granted; and
•criminal prosecution.
For further details on these risks, see “Risk Factors” below.
Privacy and Security Regulation
Our business is subject to foreign, federal, and state privacy and security laws concerning the collection, use, analysis, retention, storage, protection, transfer, disclosure, and/or disposal of individually identifiable information including, without limitation, the General Data Protection Regulation (“GDPR”), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, as amended by the final regulations promulgated pursuant to the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (“HITECH”), found in the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (collectively, “HIPAA”), the Telephone Consumer Protection Act, the CAN-SPAM Act, and state privacy, consumer protection, and breach notification laws.
We are subject to risks related to privacy and security regulation. For further details on these risks, see “Risk Factors,” below.
European Union and United Kingdom
In the European Union, the system of regulating medical devices operates by way of a certification for each medical device. Each certified device is marked with the CE mark which shows that the device has a certificate of conformance under the EU MDR. Since May 2021, the EU MDR has been the relevant regulatory framework for devices in the EU, replacing the prior Medical Device Directive. The Zio Monitor System and the Zeus System are currently marked in the EU under our CE mark under the EU MDR issued by the British Standards Institution ("BSI") in December 2023.
National competent authorities in each member state of the EU oversee the implementation of the EU MDR within their jurisdiction, typically through so-called notified bodies which are certification organizations designated by a member state to conduct third-party conformity assessments (the “Notified Bodies”). The means for achieving the requirements for the CE mark vary according to the nature of the device. Devices are classified in accordance with their perceived risks, similarly to the U.S. system. The class of a product determines the conformity assessment required before the CE mark can be placed on a product. Conformity assessments for our products are carried out as required by Notified Bodies. If a Notified Body of one member state has issued a CE mark, the device can be distributed throughout the EU without further conformance tests being required in other member states, although certain member states may require in-country device registrations after the issuance of the CE mark. The CE mark is contingent upon continued compliance with the applicable regulations and the quality system requirements of the ISO 13485 standard.
Due to UK’s departure from the EU, the MHRA has issued requirements associated with the UK Conformity Assessed (“UKCA”) mark. The UKCA marking is a new UK product marking that is used for goods being placed on the market in Great Britain. It covers most goods which previously required the CE marking, including medical devices. The UKCA requirement became effective on January 1, 2021, and we have obtained a UKCA mark with the BSI, which also serves as our UK Approved Body, for the Zio XT System and the Zeus System. We are also registered with the UK’s Care Quality Commission to carry out diagnostic and screening procedures.
Additionally, the EU Notified Body and UK Approved Body regularly audit our manufacturing, design, and operational facilities to ensure ongoing ISO 13485 and EU MDR compliance and periodically audit technical design files in accordance with the EU MDR in order to maintain our CE mark or issue a CE mark or UKCA mark for new or updated devices.
Anti-Bribery and Anti-Corruption Laws
The U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”) and similar laws in foreign jurisdictions generally prohibit any U.S. corporations and their representatives from offering, promising, authorizing, or making payments, gifts, or transfers of value, directly or indirectly, to any foreign official, political party, or candidate for the purpose of influencing any act or decision of the foreign entity in order to obtain or retain business. The scope of the FCPA includes interactions with certain healthcare professionals and hospital administrators in many countries.
In addition, in Europe, various countries have adopted anti-bribery laws providing for severe consequences in the form of criminal penalties and significant fines for individuals or companies committing a bribery offense. Violations of these anti-bribery laws, or allegations of such violations, could have a negative impact on our business, results of operations, and reputation. For instance, in the UK, under the U.K. Bribery Act 2010, a bribery occurs when a person offers, gives, or promises to give a financial or other advantage to induce or reward another individual to improperly perform certain functions or activities, including any function of a public nature. Bribery of foreign public officials also falls within the scope of the U.K. Bribery Act 2010. An individual found in violation of the U.K. Bribery Act 2010 faces imprisonment of up to 10 years. In addition, the individual can be subject to an unlimited fine, as can commercial organizations for failure to prevent bribery.
Sustainability
To best serve our various stakeholders – including patients, caregivers, employees, investors, and communities – we believe in operating in a sustainable manner according to five core values. These principles guide how we accomplish our mission to drive the success of our business and enable long-term value creation.
•Lead with integrity. We believe that building trust, holding ourselves to the highest standards of ethics, acting with transparency, and being accountable forms the foundation of who we are as a company.
•Solve for the patient. Improving the lives of patients is our passion, so with everything we do, we put patients first, aim to deliver high-quality results, and consider customer needs.
•Think big, go fast. Achieving our vision requires bold action without compromising quality. This is why we strive to be open to new ideas, take intelligent risks, act with a sense of urgency, and learn from failure.
•Collaborate to win. Prioritizing collective success delivers astounding results, so we aim to think holistically and strategically, develop relationships proactively, and work as one team.
•Strive for better. We believe that immense possibility exists at iRhythm, so we are open to embracing change and pursuing opportunities for growth, and we seek diverse perspectives in that pursuit.
In accordance with these values, we believe that effectively managing environmental, social, and corporate governance (“ESG”) risks and opportunities drives business success and that, when fully integrated into the business, ESG can provide a competitive advantage. During 2024, we refreshed our ESG priority assessment to ensure we are aligning with the issues that matter most to our business and stakeholders. We made significant progress in many aspects of our ESG strategy, including:
•Expanded measurement of Greenhouse Gas Emissions to include Scope 3 in addition to Scope 1 and 2 measurements;
•Obtained ISO 14001:2015 Environmental Management System Certification for our manufacturing facility in Cypress, CA;
•Completed a Life Cycle Analysis to further assess the environmental impacts of our products;
•Published supplier code of conduct and conflict minerals policies on our website;
•Expanded patient access to Zio by launching commercially in Spain, Switzerland, Austria and The Netherlands;
•Added one new employee resource group for iRhythm employees to further build an inclusive culture that empowers and engages all employees.
Human Capital
As of December 31, 2024, we had approximately 2,000 employees globally. We believe in creating a flexible, productive, and globally connected dispersed workforce. Our work model is comprised of employees spanning remote, hybrid, and fully onsite work arrangements. Work arrangements are determined based on the needs of the role, nature of work, and regulatory requirements. Our approach is designed to empower our global workforce, fostering flexibility and productivity while maintaining a strong company culture.
The Compensation and Human Capital Management Committee of our Board of Directors has oversight of our culture and human capital management.
Inclusion and Belonging
We are committed to being an equal opportunity employer and we prohibit all forms of unlawful discrimination in accordance with applicable law. We believe in the richness and quality of a working environment that is informed by people from all walks of life and strive to create a genuinely inclusive environment. To build on our commitment to inclusion and belonging, we have various initiatives led by our Chief Risk Officer to foster a work environment where everyone feels valued, respected, and empowered to contribute.
Board and Management Oversight
The Compensation and Human Capital Management Committee of our Board of Directors has oversight of human capital management, including our approach to talent recruiting, development, progression and retention, culture, human health and safety, and total rewards. We are committed to nurturing our workforce and have also established a Global Leadership Forum that is led by our Executive Leadership Team to ensure broader alignment across our organization's leadership on key corporate initiatives, company culture, and transformation objectives.
Health and Safety
We believe that to date we have materially complied with applicable health, safety, and environmental laws as well as related company policies and procedures and provide necessary training as appropriate by role and location. During 2023, we published internally our Environmental, Health, and Safety Policy Statement demonstrating our ongoing commitment to the highest standards of environmental, health, and safety performance. We consistently track and evaluate recordable incident rates associated with our various facilities locations. We believe that by integrating sound environmental, health, and safety management practices into all elements of our business and operations, we will consistently deliver innovative and trusted solutions for the patients that we serve, as well as sustain higher standards of employee safety.
Total Rewards
We believe that we employ a fair and merit-based total compensation system, and we evaluate our compensation programs regularly to help ensure that our employees are compensated fairly for their work while fostering a pay-for-performance culture that is aligned with the interests of our stockholders.
We believe that we offer our employees competitive benefits that follow industry standards and support physical, mental, and financial wellness. We offer health benefits, a 401(k) plan with company match, paid time off and family leave, an Employee Stock Purchase Plan for employees in the United States, which allows them to purchase our stock at a discount, and an employee wellness program that is generally available to employees and their families globally with a variety of support services.
Workforce Development
The growth and success of our employees is one of our top priorities as it impacts our overall company performance. We are investing heavily to build in-house tools and resources to support managers and employees. Our core competencies are the foundation for programs and tools being developed to identify top talent, prepare future managers and leaders, and provide equal access to growth opportunities.
We offer a variety of training opportunities, whether focused on building vocational, management, or leadership skills. We facilitate sessions around our core competencies, interview skills, and coaching practices, and we offer a toolbox on our intranet with resources for employees and managers across the employee lifecycle.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
Our short and long-term success is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, many of which involve factors that are difficult to predict or beyond our control. Before making a decision to invest in, hold, or sell our common stock, stockholders and potential stockholders should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties described below, in addition to the other information contained in or incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K, as well as the other information we file with the SEC. If any of the following risks are realized, our business, financial condition, results of operations, and prospects could be materially and adversely affected. In that case, the value of our common stock could decline and stockholders may lose all or part of their investment. Furthermore, additional risks and uncertainties of which we are currently unaware, or which we currently consider to be immaterial, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations. Refer to our disclaimer regarding forward-looking statements at the beginning of “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Part II, Item 7 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Risks Related to Our Industry, Business and Operations
Reimbursement by Medicare is highly regulated and subject to change, and our failure to comply with applicable regulations, including regulations not designed for remote diagnostic tests like our Zio Services, could prevent us from receiving reimbursement under the Medicare program and some commercial payors, subject us to penalties, and adversely affect our reputation, business, and results of operations.
During the twelve months ended December 31, 2024, we received approximately 24% of our total revenue from the Medicare program (inclusive of Medicare Advantage). The Medicare program is administered by CMS, which imposes extensive and detailed requirements on diagnostic services providers, including IDTFs. These requirements include, but are not limited to, rules that govern how we structure our relationships with physicians, how we operate our IDTFs and market our Zio Services, when we may perform diagnostic tests, and how and when we submit reimbursement claims. Our failure to comply with the applicable Medicare rules and requirements could result in discontinuation of our reimbursement under the Medicare program, a requirement to return funds already paid to us, civil monetary penalties, criminal penalties, and/or exclusion from the Medicare program, which would have a material adverse impact on our reputation, business, and results of operations.
CMS has acknowledged that the IDTF regulations were designed for “traditional” IDTFs that administer tests to patients in-person, at a single point in time, and from a single location, and only recently has CMS initiated changes to the regulations to address IDTFs like ours that furnish “indirect tests” that do not require in-person interaction and involve technicians performing computer analyses offsite or at another location. The changes, however, do not address all gaps identified by CMS relating to IDTF operations and the Medicare billing requirements. For example, CMS has not addressed billing for remote diagnostic tests that are performed from one or more IDTF or other remote locations. Our failure to comply with the applicable Medicare regulations, or regulators’ disagreement with our interpretation of the regulations as applied to indirect tests, such as the Zio Services, could result in the discontinuation of our reimbursement under the Medicare program, a requirement to return funds already paid to us, civil monetary penalties, criminal penalties, and/or exclusion from the Medicare program.
In addition, many commercial payors require our IDTFs to maintain enrollment with the Medicare program as well as accreditation and certification with the Joint Commission. If we fail to obtain and maintain IDTF enrollment or accreditation and certification, our Zio Services may no longer be reimbursed by those commercial payors, which could have a material adverse impact on our reputation, business, and results of operations.
If reimbursement or other payment for our Zio Services is reduced or modified in the United States or in our international markets, including through cost containment measures or changes to policies with respect to coding, coverage, and pricing, our business could suffer.
We receive a substantial portion of our revenue from Medicare and third-party commercial payors with which we contract, and we cannot predict whether and to what extent existing reimbursement rates will continue to be available. If CMS or any of our key commercial payors reduce reimbursement rates for our Zio Services, our business, operating results, and prospects would be adversely affected.
CMS updates the reimbursement rates for diagnostic tests performed by IDTFs annually via the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule. Effective January 1, 2025, CMS updated the national payment rates for the CPT codes we use to report our cardiac monitoring services: CPT code 93247 (ECG recording conducted over a period of greater than 7 days and up to 15 days), CPT code 93243 (ECG recording conducted over a period of greater than 48 hours and up to 7 days), and CPT code 93229 (mobile cardiovascular telemetry). While the payment rates for CPT codes 93247 and 93243 saw a slight increase for calendar year 2025, the rate for CPT code 93229 experienced a decrease as compared to calendar year 2024.
Because remote cardiac monitoring technology, including the Zio System, is rapidly evolving, there is a continuing risk that relative value units assigned, and reimbursement rates set, by CMS may not adequately reflect the value and expense of this technology and associated monitoring services. Further, CMS may reduce the rates for the CPT codes assigned to our services in the future, which would adversely affect our financial results, particularly to the extent commercial payors with which we contract follow suit.
In addition, our agreements with commercial payors typically allow either party to terminate the contract at any time by providing prior written notice, in accordance with the agreement, to the other party, which means our commercial payors may elect to terminate their contracts with us for any reason. A commercial payor who terminates or does not renew their contract with us may, or may not, alter their coverage for the type of services we provide. In the event any of our key commercial payors terminate their agreements with us, elect not to renew or enter into new agreements with us upon expiration of their current agreements, or do not renew or establish new agreements on terms as favorable as are currently contracted, our business, operating results, and prospects would be adversely affected.
Finally, government and commercial payors have and may, in the future, consider healthcare policies and proposals intended to limit or reduce perceived increases in healthcare costs, including those that could significantly affect reimbursement for healthcare products such as our systems and services. These policies have included, and may in the future include: basing reimbursement policies and rates on clinical outcomes, the comparative effectiveness, and costs, of different treatment technologies and services, as well as other measures. Future significant changes in the healthcare systems in the United States or elsewhere could also have a negative impact on the demand for our current and future products and services. These include changes that may reduce reimbursement rates for our products and changes that may be proposed or implemented by the current or future laws or regulations.
If we are unable to expand the number of third-party commercial payors with which we contract or expand coverage for existing third-party commercial payors, our commercial success could be impacted.
There is significant uncertainty concerning third-party reimbursement of any new service until a contracted rate is established for that service with the commercial payor. Reimbursement by a commercial payor may depend on several factors, including, but not limited to, a payor’s determination that the ordered service is not experimental or investigational, medically necessary and appropriate for the specific patient, cost effective, supported by peer-reviewed publications, and accepted and used by physicians and other clinicians within their provider network.
Since each payor decides whether to establish a policy concerning reimbursement or to contract with us to set the price of reimbursement, seeking reimbursement on a payor-by-payor basis is a time-consuming and costly process to which we dedicate substantial resources. If we do not dedicate sufficient resources to establishing contracts with commercial payors and supporting payors’ reimbursement determinations by demonstrating the clinical value of our Zio Services through studies and physician adoption, we may encounter several adverse consequences that could compromise the commercial success of our business. Such adverse consequences may include an inability to secure additional contracts with commercial payors, reluctance by physicians to order our Zio Services due to concerns that patients may face significant out-of-pocket expenses associated with an out-of-network IDTF, a decline in the amount that we are reimbursed for our services, less predictable revenue, and an increase in the efforts and resources necessary to obtain reimbursement for our services on a claim-by-claim basis.
Additionally, for our out-of-network or cash pay patients, we may be subject to state and federal surprise billing laws that impose limits on amounts that can be charged to such patients and/or the amount we can receive for out-of-network services from commercial payors as well as penalties for noncompliance. One such law, the federal No Surprises Act, requires covered providers to provide “good faith estimates” to uninsured and self-pay patients of their out-of-pocket responsibility and establishes a detailed and potentially costly independent dispute resolution process governing fee disputes between our IDTFs and payors. These laws and regulations may change and we anticipate these evolving, highly technical requirements may apply to our business in the future and could necessitate the dedication of additional resources to ensure compliance.
We report to third party payors the technical components of the remote cardiac monitoring services that are performed with our Zio Monitor, Zio XT, and Zio AT Systems using CPT codes established by the American Medical Association. These CPT codes are manufacturer- and technology-agnostic but describe general technical features required to support the diagnostic medical procedures represented by these billing codes. Given the nature of CPT codes, there is always some degree of risk for an entity that bills for its services that regulators or other third parties could assert that the CPT codes utilized were not appropriate, and recent events have the potential to increase the risk of questions or inquiry regarding our use of a specific CPT code.
The CPT codes used to report remote cardiac monitoring services, including those used to report our Zio Services, were drafted by the American Medical Association (“AMA”) in a manufacturer- and specific technology-agnostic manner. Regulators or other third parties could assert that our technology does not support certain diagnostic procedures described by the CPT codes that we currently use to report our Zio Services. For example, a regulator or other third party could assert that the Zio AT System cannot support MCT services, which could jeopardize our ability to submit claims for reimbursement for services utilizing our Zio AT System and may require us to evaluate whether we have received any overpayments that must be reported and returned to third-party payors. Certain language in a warning letter we received from FDA on May 25, 2023 could increase the risk of inquiries regarding our historical or current use of CPT code 93229. Consistent with the AMA’s definition of MCT and the technology categorization in FDA’s outpatient cardiac telemetry product code, the Zio AT device is intended to capture and transmit symptomatic and asymptomatic cardiac events and record continuous ECG data for long-term monitoring on adult patients who may be asymptomatic or who may suffer from transient symptoms (e.g., palpitations, shortness of breath, dizziness, light-headedness, pre-syncope, syncope, fatigue, or anxiety), with escalation to the patient’s treating healthcare professional, consistent with the healthcare professional’s prescribed notification criteria, during the monitoring period.
Our revenue relies on our Zio Services, which are currently our only offerings. If our Zio Services or future service offerings fail to gain, or lose, market acceptance, our business will suffer.
Our current revenue is dependent on orders for our Zio Services, and we expect that reimbursement for our Zio Services will account for substantially all our revenue for the foreseeable future. We are in various stages of research and development for other diagnostic and/or screening solutions and new indications for our technology and our Zio Services; however, there can be no assurance that we will be able to successfully develop and commercialize any new services and related devices. Any new services may not be accepted by physicians or may merely replace revenue generated by our Zio Services and not generate additional revenue. If we have difficulty launching new services, our reputation may be harmed and our financial results adversely affected. In order to substantially increase our revenue, we will need to target physicians other than cardiologists, such as emergency room doctors, primary care physicians, and other physicians with whom we have had little contact and who may require a different type of marketing effort. If we are unable to increase orders for our Zio Services, expand reimbursement for our Zio Services, or successfully develop and commercialize new services and related devices, our revenue and our ability to achieve and sustain profitability would be impaired.
The market for remote cardiac monitoring solutions is highly competitive. If our competitors are able to develop or market monitoring devices and services that are more effective, or gain greater acceptance in the marketplace, than any services and related devices we develop, our commercial opportunities will be reduced or eliminated.
The market for remote cardiac monitoring products and services is competitive, characterized by rapid change resulting from technological advances, scientific discoveries, and other market activities of industry participants. Our Zio Services compete with a variety of products and services that provide alternatives for remote cardiac monitoring, including traditional, short-term Holter monitors and event monitors. Our industry is highly fragmented and characterized by a small number of large manufacturers and a large number of smaller regional service providers. These third parties compete with us in marketing to payors and ordering physicians, recruiting and retaining qualified personnel, acquiring technology, and developing products and services that compete with our Zio Services and related devices, and enhancing their product offerings with differentiating features. Our ability to compete effectively depends on our ability to distinguish our company and our Zio Services from our competitors and their products and services, and includes such factors as safety and effectiveness; acute and long-term outcomes; ease of use; price; physician, hospital, and clinic acceptance; and third-party reimbursement.
Our industry is subject to rapid change and is significantly affected by new product introductions, results of clinical research, corporate combinations, and other factors. Large competitors in the remote cardiac market include companies that sell standard Holter monitors including GE Healthcare, Philips Healthcare, Mortara Instrument, Inc., Spacelabs Healthcare Inc. and Welch Allyn Holdings, Inc. (acquired by Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. now part of Baxter International, Inc.). Additional competitors, such as BioTelemetry, Inc. (acquired by Royal Philips), Preventice Solutions, Inc. (acquired by Boston Scientific, Inc.), and Bardy Diagnostics, Inc. (acquired by Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. which was acquired by Baxter International, Inc.) manufacture remote cardiac monitoring devices and also offer monitoring services. These companies have also developed other patch-based cardiac monitors that have received FDA and foreign regulatory clearances. There are also several small start-up companies trying to compete in the patch-based cardiac monitoring space, as well as several entering the patch-based cardiac monitoring market.
We have also seen a trend in the market for large medical device companies to acquire, invest in, or form alliances with these smaller companies in order to diversify their product offerings and participate in the digital health space. Future competition could come from makers of wearable fitness products or large information technology companies focused on improving healthcare. For example, Apple Inc., Fitbit and Samsung, among others, have added capabilities on their platforms to measure non-continuous ECG and to alert customers to the potential presence of irregular heartbeats suggestive of asymptomatic Afib. These competitors and potential competitors may introduce new products and services that more directly compete with our Zio Services and related devices.
Billing for our Zio Services is complex and highly regulated, and we must dedicate substantial time and resources to the billing process. Failure to comply with legal, regulatory, or contractual requirements applicable to our billing and collection activities could subject us to penalties, and adversely affect our reputation, business and results of operations.
Billing for diagnostic services is complex, highly regulated, time-consuming, and expensive, and failure to comply with legal or contractual requirements applicable to our billing and collection activities could subject us to penalties, and adversely affect our reputation, business and results of operations. Depending on the billing arrangement and applicable law, we bill several types of entities and payors, including federal healthcare programs, third-party commercial payors, healthcare providers, and healthcare institutions, which may have different billing requirements, coverage criteria, procedures, or expectations. We also bill insured patients for co-payments, co-insurance, and deductible amounts, as well as bill self-pay patients directly.
Several factors make the billing and collection process uncertain, including differences between the submitted claim price for our Zio Services and the reimbursement rates of payors; compliance with complex federal and state regulations related to billing the Medicare and Medicaid programs and collecting co-payments, co-insurance, and deductible amounts from patients and other guarantors; the effect of patient co-payments, co-insurance, and deductible amounts, which may vary depending on the timing of the claim relative to the insured’s annual policy year; differences in coverage policies, criteria, and billing requirements among payors; and incorrect or missing patient history, indications, or billing information and delays in verifying and resolving the same. We also face risk in our collection efforts, including potential write-offs of doubtful accounts and long collection cycles, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations. We may also be adversely affected by the growth in patient responsibility accounts, as a result of increases in the adoption of plan structures, due to evolving health care policy and insurance landscapes, that shift greater responsibility for care to individuals through greater exclusions, prior authorizations, and co-payment and deductible amounts.
Additionally, our billing activities require us to implement compliance procedures and oversight, train and monitor our employees, subcontractors, and agents, and undertake internal review procedures to evaluate compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies. These activities require a tremendous dedication of resources and, as a result, we have engaged third-party vendors to undertake certain components of our billing and collections operations. While common in the healthcare industry, the outsourcing of billing and collections activities to third-party vendors requires diligent monitoring and oversight to ensure the completeness, accuracy, and propriety of the claims submitted to federal healthcare programs and other third-party commercial payors for our Zio Services. We may be held responsible by our regulators or payors for any acts, errors, or omissions by the third-party vendors engaged to perform billing and collections activities on our behalf.
The complexities we face related to billing for our Zio Services, and the related uncertainty in obtaining payment for our Zio Services, could negatively affect our revenue and cash flow, our ability to achieve profitability, and the consistency and comparability of our results of operations.
Audits or denials of our claims by government agencies or payors could expose us to recoupment, regulatory scrutiny, and penalties.
As an IDTF, we submit claims directly to, and receive reimbursement from, federal healthcare programs, including Medicare, as well as other third-party commercial payors for tests ordered by unaffiliated healthcare providers. These programs and payors, including contractors on their behalf, may conduct pre- and post-payment audits and reviews of claims submitted for reimbursement, including audits and reviews focused on the appropriateness of unaffiliated healthcare providers’ decisions to order a particular test furnished by our IDTF, which impact our claims. Further, the federal healthcare programs may impose suspensions on both payment and participation in response to allegations of fraud or other noncompliance.
Other controls imposed by CMS and commercial payors designed to reduce costs, commonly referred to as “utilization review,” may also affect our operations. Federal law contains numerous provisions designed to ensure that services rendered to CMS patients meet professionally recognized standards and are medically necessary, appropriate for the specific patient, and cost-effective. These provisions include a requirement that a quality improvement organization review a sampling of claims for Medicare beneficiaries to assess the quality of care and appropriateness of the services provided. These quality improvement organizations may deny payment for services or assess fines and have the authority to recommend to CMS that a provider in substantial noncompliance with applicable Medicare requirements and quality standards be excluded from participation in the Medicare program. CMS also engages Medicare Administrative Contractors, Comprehensive Error Rate Testing Contractors, Recovery Audit Contractors, and Unified Program Integrity Contractors to conduct a variety of pre- and post-payment reviews of healthcare providers’ claims, and any aberrant practices or findings from such reviews may result in referrals to the Office of Inspector General, Department of Justice (“DOJ”), or other law enforcement agencies for further investigation and follow-up. As a provider enrolled in federal healthcare programs, we expect to be subject to such audits and claims reviews in the future, which may result in suspensions or other restrictions on our ability to submit claims for our services, payment delays, overpayment recoupments, and claims denials, which would negatively impact our business, financial condition, and results of operations, and may jeopardize our participation in these federal healthcare programs.
We are transforming our revenue cycle management function and we may fail to realize the anticipated benefits of these efforts. These activities involve significant time and resources, and our failure to execute these activities efficiently and effectively may cause our revenue and accounts receivable to be delayed or reduced and could have an adverse effect on our business and cause reputational harm.
We are in the midst of a transformation of our revenue cycle management function, which transformation includes the utilization of third-party service providers to support certain activities. The success of this plan depends on our ability to complete the integration of these service providers in a timely manner to scale our operations to facilitate growth opportunities, without adversely affecting current revenues and accounts receivable. If we are not able to successfully achieve these objectives, the anticipated benefits of this transformation may not be realized fully or at all or may take longer to realize than expected. In addition, there is a significant degree of difficulty and management distraction inherent in the process of integrating with service providers. These difficulties include challenges supporting certain operations and activities with more than one service provider, integrating technologies (including IT systems and processes, procedures, policies and operations), and retaining key personnel. These activities are complex and time-consuming and involve delays or additional and unforeseen expenses. The process of transitioning to these service providers, the integration process, and other disruptions may also disrupt our ongoing businesses or cause inconsistencies in standards, controls, procedures, and policies that could adversely affect our relationships with payors, patients, employees, and others. Any failure to execute these activities effectively and efficiently may cause our revenue and accounts receivable to be delayed or reduced and could have an adverse effect on our business and cause reputational harm.
Although our current Zio Systems are comprised of medical devices that have received FDA marketing authorization (510(k) clearance) as well as, with respect to certain devices, regulatory certifications in the EU, Japan, Switzerland and the UK, we may regularly engage in exploring and implementing product enhancements and in iterative changes to existing products, as well as seek to develop new technology or use of technology for new indications for use. These medical device developments may trigger further regulatory reviews and the results of those reviews are unpredictable.
Before a new medical device or a new intended use for a medical device can be marketed in the United States, a company must first submit an application and receive either 510(k) clearance, De Novo marketing rights, or premarket approval from FDA, unless an exemption applies. All of these processes can be expensive, lengthy, and unpredictable. We may not be able to obtain the clearances or approvals we seek or may be unduly delayed in doing so, which could harm our business. Even if we are granted regulatory clearances or approvals, they may include significant limitations on the indicated uses for the product, which may limit the market for the product. Although we have obtained 510(k) clearances to market our Zio Systems, our clearances can be revoked if safety, efficacy, or significant regulatory compliance problems develop. Even planned changes and improvements to devices and their uses can trigger the need for a new submission. FDA requirements dictate that we must evaluate potential changes and document our decision-making regarding the need for additional submissions and clearances or approvals. Unless effectively planned for in advance, our desired commercial timeline may be impacted.
Significant changes or modifications in design, components, method of manufacture, or the intended use or technological characteristics of our Zio Systems may require new or modified FDA marketing authorization, CE Mark certification (EU), UKCA Mark certification (UK), Swiss Medical Devices Ordinance ("SMDO") marketing authorization or Japanese Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Agency (“PMDA”) marketing authorization. In some instances, we have identified a need for, and sought and obtained new, 510(k) clearances from FDA for these changes or modifications.
As permitted by applicable law, FDA allows device manufacturers to internally analyze and document a decision that a new clearance or approval is viewed by the manufacturer as unnecessary. Accordingly, we have made certain changes and modifications to our Zio Systems in the past that we believe did not require additional clearances or approvals by FDA.
Such internal decisions are, however, subject to review by FDA, and may require additional action in the event FDA questions earlier internal decision-making. For example, FDA raised questions in the warning letter issued on May 25, 2023 regarding certain changes and modifications to the Zio AT System for which we did not make 510(k) submissions, and rather documented our analysis in letters to file. We have recently (following, and in alignment with, discussion with FDA) submitted an updated 510(k) to address Zio AT Device modifications that were, prior to our receipt of the warning letter, previously documented in letters to file. In October 2024, following, and in alignment with, discussion with FDA, we received FDA 510(k) clearance for these design updates, as well as additional 510(k) clearance relating to further enhancements to our Zio AT Device.
In instances where FDA, an EU/UK Notified/Approved Body, the PMDA or the Swiss regulatory body disagrees with our internal analysis and decision that a new or additional approval or marketing authorization or certification is not needed for any such modifications, we may be required to recall and/or stop the distribution of the impacted Zio System and/or correct the labeling for such Zio System. We may be required to submit a new marketing application or certification, which could require additional testing or other supporting data, a redesign of a product, or otherwise impact the provision of services. In these circumstances, the process may require engagement with regulators to resolve concerns and reach a resolution for a product, and we may be subject to significant enforcement actions.
We may not be able to obtain additional marketing authorizations in a timely fashion, or at all, which could harm our ability to introduce new or enhanced products in a timely manner and to meet market expectations for the provision of the services, which in turn could harm our future growth.
We are subject to extensive compliance requirements for the quality, design, safety, performance, and post-market surveillance of the medical devices we manufacture for use in our Zio Services, and for vigilance on complaint-handling, escalation, assessment, and reporting of adverse events and malfunctions. A wide range of quality, risk, regulatory, or safety matters could trigger enforcement action by regulatory authorities, the need for a recall, a hold on the distribution of the marketed product, or other corrective actions to marketed product, and such matters have the potential to escalate to judicial actions that involve the DOJ.
As a manufacturer of medical devices, we are subject to extensive regulation and related compliance requirements. Noncompliance and even allegations of noncompliance with these wide-ranging requirements may subject us to high compliance costs to remediate or defend against allegations of noncompliance, as well as enforcement action from U.S. federal or state regulators and enforcement authorities. Regulators may interpret or apply reportability or field action requirements differently than a company, which can result in enforcement risk. Actions to which a company may be subject could include the issuance of warning letters, adverse publicity, seizures, prohibitions on product sales, recalls, and civil and criminal penalties, any one of which could significantly impact our manufacturing supply and provision of services and impair our financial results. Failure to maintain full compliance with the requirements of the Quality System Regulation (“QSR”), also known as 21 CFR Part 820, EU Standards (presently the Medical Devices Regulations (“EU MDR”)), UK Medical Device Regulations (“UK MDR”), Japanese medical device Quality Management System (“Japanese QMS”) and the SMDO could result in similar disruptions in these markets. Furthermore, even if we adhere to regulatory standards and expectations in our corrective actions, the public nature of such actions can result in broader negative publicity and perceptions, which could harm our reputation.
Our design and manufacturing facilities and processes and those of certain third-party suppliers are subject to FDA, state, EU/UK Notified/Approved Body, PMDA and Swiss regulatory inspections for compliance with various medical device regulations and standards, including EU MDR, UK MDR, Japanese QMS and SMDO requirements. Developing and maintaining a compliant quality system is time consuming and investment intensive. Requirements and standards may change and evolve over time, and we will need to adapt. For example, FDA has issued final regulations on updates to the QSR which will largely align with the ISO 13485 standard, and these are set to take effect February 2, 2026.
We are required to file various reports with FDA, as well as EU, UK, Japanese and Swiss regulators, including reports required by each jurisdiction’s adverse event, certain malfunctions, and field action reporting regulations. These reports are often required if our Zio System may have caused or contributed to a death or serious injury or malfunctioned in a way that would likely cause or contribute to a death or serious injury if the malfunction were to recur. They may also be reasonable, necessary, or prudent for a range of other reasons relating to the importance of gathering information in the post marketing setting and managing risk throughout the product lifecycle, or to address requests from regulators to increase or expand the scope of reporting. An increase in the reporting of events associated with the use of our products and services from us or others and any delays to the filing of reports may increase regulator and public scrutiny, especially given that these reports are typically publicly available information in most jurisdictions, including the United States, which could harm our business.
If we initiate a field action (whether a “correction” made relative to a device that remains in the field, which could be through a labeling or software update, or “removal” or “recall” and return of that device to us, or field advisory notices) to reduce a risk to health posed by our Zio System, we would be required to report the Correction or Removal to FDA and, in many cases, similar reports to other regulatory agencies.
Depending on the reason for the correction or removal and the potential severity of the impact to patient safety or the effectiveness of the device, FDA may require differing degrees of communication to alert those who may be in possession of an impacted device. We would generally be subject to similar requirements in jurisdictions outside the United States where the Zio products are used. Examples of the above include:
•Our receipt of Form 483 observations in August 2022 alleging certain quality system deficiencies, including in relation to our corrective and preventive action procedures, test validation, complaint handling and medical device reporting requirements. We submitted a response to FDA with further commitments to improve and remediate our Quality System. These activities, including dialogue with FDA, are ongoing.
•The Customer Advisory Notice we initiated September 28, 2022 to Zio AT customers, and our reports to FDA under 21 C.F.R. Part 806, regarding a Zio AT labeling correction involving additions and modifications to the Zio AT labeling precautions relating to the device’s maximum transmission limits during wear, and also to the need for healthcare providers to complete registration to initiate monitoring services. FDA classified this field action as a Class II Recall following our initial 806 report and although we believe we have completed the distribution of the Advisory Notice to our identified impacted customers, and we requested the closure of this field action in March 2023, the status remains open in the public FDA recall database. and FDA has not yet confirmed the termination or completion of this recall to us.
•Our May 25, 2023 receipt of a warning letter from FDA alleging non-conformities to regulations for medical devices, including medical device reporting requirements, relating to our Zio AT System and medical device quality system requirements. We submitted a timely response to FDA in June 2023 and are continuing to work with the agency to address the issues outlined in the warning letter, including specific dialogue on key topics and our planned path forward. As part of this dialogue we agreed to make two 510(k) submissions relating to the Zio AT, and on October 21, 2024, we were granted FDA clearance for one 510(k) encompassing design updates that had previously been documented through letters to file and on October 30, 2024 we were granted FDA clearance on a second 510(k) submission related to design modifications and labeling updates for the Zio AT device.
•In the fourth quarter of 2023, as part of our commitments following the FDA 483 observations and FDA warning letter issued on May 25, 2023, our retrospective submission of certain Medical Device Reports (“MDRs”) to FDA.
Our receipt of 483 observations following July 2024 FDA inspections of our Cypress and San Francisco FDA-registered facilities centered on complaint handling and medical device reporting, risk analysis regarding the involvement of the technicians to prepare the Zio ECG reports, the corrective and preventive action process, process controls and statistical techniques. We timely submitted our initial responses regarding the July 2024 483 observations to FDA on August 21, 2024, and provided supplemental information on September 6, 2024. In these responses we committed to a number of follow-up actions, and we intend to work with FDA to resolve the issues identified.
Executing on our follow-up actions, commitments to FDA, and remediation activities will require significant time, attention, and resources that might otherwise be applied to future product development activities and initiatives, and could result in delays or changes to these plans. Our commitments will also require a high degree of attention to design strategy and compliance going forward.
In addition, although we continue to fully cooperate and are in dialogue with FDA, there are ongoing enforcement risks, including escalation of further action by FDA, that remain given the inspection and enforcement activities of FDA over the past few years. FDA may determine that our remediation efforts to date or our responses to the 2024 483 observations are insufficient or unsatisfactory, or FDA may decide that it does not agree with the plans and commitments we have outlined in our previous communications. FDA could issue another warning letter, issue a consent decree in collaboration with the DOJ, and/or require recall or cessation of marketing and shipping our Zio device.
We cannot give any assurances that FDA will be satisfied with our response, the actions taken to resolve the concerns raised in the warning letter or the more recent 483 observations, or the expected date for the resolution of such matters. Until these issues are resolved to FDA’s satisfaction, additional legal or regulatory action may be taken with or without further notice. The warning letter and the 483 observations are publicly available on FDA’s website and have been the subject of a high degree of media and industry attention, which subjects us to additional scrutiny.
As we are already subject to an FDA warning letter associated with our Cypress facility, and in light of the 2024 inspection results, if we are unable to successfully execute follow-up actions consistent with our commitments to FDA, or if FDA determines that our follow-up commitments are insufficient or are not completed with sufficient promptness, we may face a greater risk of potential escalation, which could involve issuance of additional warning letters, or there is a possibility that FDA could initiate consent decree discussions. This may pose a considerable expense, divert management’s attention, and have a potentially negative impact on the public’s perception of us, all of which could negatively impact our financial position and results of operations. Further, should we be found out of compliance with any applicable laws, regulations, or programs, depending on the nature of the findings, our business, our financial position, and our results of operations could be negatively impacted.
Because of the patient populations for which our services are provided and the complexity of the healthcare environment in which we operate, a high degree of medical and clinical input may be necessary to evaluate complaints and adverse events, and in some cases, there may be disagreement over whether our services or the medical devices used in our services may have caused or contributed to an adverse event.
Our Zio Systems and Zio Services are not intended to be prescribed or ordered for use as an emergency system. They are not intended for critical care patients or patients suspected of life-threatening arrhythmias who require inpatient or emergency ECG monitoring. Given the nature of arrhythmias and the patient population for which our Zio Services are ordered by physicians, in which there may be several health conditions present, there are instances in which a patient may experience a medical event during the wear period of a Zio System. In some cases, it may be medically and logistically challenging to obtain information sufficient to definitively determine all contributing factors to an event. In some instances, we may receive initial reports of complaints from the qualified cardiac technicians or through our customer service representatives. The initial reports of these non-physicians are likely to contain information that requires verification and further investigation.
In addition, even though our services and their associated devices are not intended to recognize, detect, or initiate response to terminal end-of-life events, a patient may nevertheless be wearing a Zio device when they experience such an event. Given the functionality of our technology and our services, we may become aware of data reflecting a non-survivable, end-of-life cardiac event. We or others (such as healthcare professionals, patients, or family members) may report such events even where it does not appear to us that our device caused or could have prevented an end-of-life event. Given the structure of such reporting to FDA the full medical context is not generally available to the public, which may cause additional scrutiny, questions, or concerns regarding our products and services. For example, in the fourth quarter of 2023, as part of our commitments following the FDA Form 483 observations and warning letter issued on May 25, 2023, we retrospectively submitted certain MDRs to FDA, and the publicly available information in these reports may receive additional scrutiny.
We are subject to FDA requirements to investigate complaints about our Zio Systems. If we do not effectively manage and monitor our complaint-handling procedures, we may be subject to regulatory enforcement action, litigation risks, and risk of negative publicity.
If we are unable to keep up with demand for our Zio Services, our revenue could be impaired, market acceptance for our Zio Services could be harmed, and physicians may instead order our competitors’ services.
As demand for our Zio Services increases, we may encounter production or service delays or shortfalls. Such production or service delays or shortfalls may be caused by many factors, including the following:
•while we intend to continue to expand our manufacturing capacity, our production processes may have to change to accommodate this growth, potentially involving significant capital expenditures;
•we may experience technical challenges to increasing manufacturing capacity, including in connection with equipment design, automation, validation and installation, contractor issues and delays, licensing and permitting delays or rejections, materials procurement, manufacturing site expansion, problems with production yields, and quality control and assurance;
•key components of our Zio Systems are provided by a sole or single supplier or limited number of suppliers, and we do not maintain large inventory levels of these components; if we experience a shortage or quality issues in any of these components, we would need to identify and qualify new supply sources, which could increase our expenses and result in manufacturing delays;
•the extent to which we become dependent upon others for the manufacture of our Zio Systems which could adversely affect our future profit margins and our ability to market our Zio Services;
•global demand and supply factors concerning commodity components common to all electronic circuits, including Zio Systems, could result in shortages that manifest as extended lead times for circuit boards, which could limit our ability to sustain and/or grow our business;
•we may experience a delay in completing validation and verification testing for new production processes and/or equipment at our manufacturing facilities;
•to increase our manufacturing output significantly and scale our services, we will have to attract and retain qualified employees for our operations; and
•in response to unexpectedly rapid growth of our business, clinical operations capacity may not meet demand while new resources are being recruited and trained, which could negatively impact our volume capacity for our Zio Services.
If we were unable to successfully manufacture our Zio Systems in sufficient quantities, or to maintain sufficient capacity to provide our Zio Services, it would materially harm our business.
We depend on third-party vendors for the supply and manufacture of certain components of our Zio Systems, as well as for other aspects of our operations.
We rely on third-party vendors for components and sub-assemblies used in our Zio Systems and in connection with certain logistical aspects of our Zio Services. Our reliance on third-party vendors subjects us to a number of risks, including:
•inability to obtain adequate supply in a timely manner or on commercially reasonable terms, including due to our reliance on a single supplier for certain critical components and materials for which, in some cases, there are relatively few alternative sources of supply;
•modifications to, or discontinuation of, a vendor’s operations due to natural disasters, labor disruptions, human error, infrastructure failure, pandemics, military conflicts, or political or economic disruption, which may adversely impact our operations or otherwise lead to interruption of or shortage or delays in supply, including shortages impacting our printed circuit board assembly;
•production delays related to the evaluation and testing of products from alternative suppliers and corresponding regulatory qualifications;
•inability of the manufacturer or supplier to comply with our quality criteria and specifications and, where applicable, the QSR, state regulatory authorities, and, in some cases, the Notified Body audits;
•miscommunication of design specifications due to errors/omissions by either the vendor or our company, resulting in delayed delivery of acceptable materials or components for incorporation into our devices or recall of finished products;
•delays in device shipments resulting from quality issues or defects, reliability issues, or a supplier’s failure to consistently produce quality components;
•price fluctuations due to a lack of long-term supply arrangements with our suppliers for key components;
•inability to control the quality of products manufactured by third parties;
•delays in delivery by our suppliers due to changes in demand from us or their other customers; and
•delays in obtaining required materials and components that are in short supply within the time frames we require, at an affordable cost, or at all.
Further, we rely on single suppliers for the supply of components related to our adhesive sub-assembly, disposable plastic housings, instruments, and other materials that we use to manufacture and label our Zio patches. We have not qualified additional suppliers for some of these components and materials and we do not carry a significant inventory of these items. While we believe that alternative sources of supply may be available, we cannot be certain whether they will be available if and when we need them and that any alternative suppliers would be able to provide the quantity and quality of components and materials that we would need to manufacture our Zio patches if our existing suppliers were unable to satisfy our supply requirements.
Any significant delay or interruption in the supply of components or sub-assemblies, or our inability to obtain substitute components, sub-assemblies, or materials from alternate sources at acceptable prices and in a timely manner, could impair our ability to meet the demand for our Zio Services, significantly affect our future revenue, and harm our relations and reputation with physicians, hospitals, clinics, and patients.
We also rely on certain third-party vendors in connection with the analysis we perform to create diagnostic reports for our Zio Services, which is dependent upon a recording made by each Zio System. For long-term continuous monitoring utilizing our Zio XT System, for example, requires the physical return of the Zio XT patch to one of our clinical centers and we predominantly rely on the U.S. Postal Service (“USPS”) to perform this delivery service. Delivery of the Zio XT patch to one of our clinical centers may be subject to disruption to the USPS delivery infrastructure. Further, for the MCT monitoring services utilizing our Zio AT System, we rely on the provision of cellular communication services for the timely transmission of patient information and reportable events. The reliability of the electronic communication and cloud services required for these operations are subject to natural disasters, labor disruptions, human error, and infrastructure failure. Any of these disruptions may render it difficult or temporarily impossible for us to provide some or all our Zio Services and bill for those services, adversely affecting our operating results, causing significant distraction for management, and negatively impacting our business reputation. We also expect that our reliance on third-party vendors will increase as our business grows, exposing us to increased harm if such disruptions occur.
We have incorporated and continue to work to further incorporate AI into our products, services, and internal operations. Implementation of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies may result in legal and regulatory risks, reputational harm, or other adverse consequences to our business.
We have and are continuing to incorporate AI, including machine learning and independent algorithms, in certain of our products, services and internal operations, including in our MCT services with our Zio AT System, which is intended to enhance their operation and effectiveness internally and for physicians and patients. Our research and development of such technology remains ongoing. AI innovation presents risks and challenges that could impact our business. Issues relating to the use of new and evolving technologies such as AI that we integrate into our products, services and internal operations may cause us to experience brand or reputational harm, competitive harm, legal liability, new or enhanced governmental or regulatory scrutiny, and to incur additional costs to resolve such issues. As with many innovations, AI presents risks and challenges that could undermine or slow its adoption, and therefore harm our business to the extent we increase our reliance on AI in the future. Moreover, our competitors may introduce AI technologies and features into their products and services that achieve greater market acceptance that ours. Additionally, AI algorithms may be flawed or datasets may be insufficient or contain biased information resulting in perceived or actual negative outcomes. If the output that AI algorithms assist in producing are or are alleged to be inaccurate, deficient, or biased, our business, financial condition, and results of operations may be adversely affected. Developing, testing and deploying AI systems may also increase the costs of our product offerings due to the nature of the computing costs involved in such systems, which could impact our revenue and adversely affect our business and operating results.
Many countries and regions, including the EU, have proposed or passed new and evolving regulations related to the use of AI and machine learning technologies. The regulations may impose onerous obligations and may require us to unexpectedly rework or reevaluate improvements to be compliant. In particular, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act, which was adopted on June 13, 2024, will have a material impact on the way AI is regulated in the EU, may affect our use of AI technologies, and may require additional compliance measures and changes to our operations and processes. Use of AI technologies may expose us to an increased risk of regulatory enforcement and litigation. Furthermore, the integration of third-party AI models with our platform relies on certain safeguards implemented by the third-party developers of the underlying AI models, including those related to the accuracy, bias, and other variables of the data, and these safeguards may be insufficient. Moreover, some of the AI features involve the processing of personal data and may be subject to laws, policies, legal obligations, and codes of conduct related to privacy and data protection. AI development and deployment practices could subject us to competitive harm, regulatory enforcement, increased cyber risks, reputational harm, and legal liability.
Our ability to compete depends on our ability to innovate successfully.
The market for medical devices, including the remote cardiac monitoring segment, is competitive, dynamic, and marked by rapid and substantial technological development and product innovation. While there are barriers that would challenge new entrants or existing competitors from developing products that compete directly with the devices used in our Zio Services, these barriers can be overcome. Demand for our Zio Services and future related devices or services could be diminished by equivalent or superior products and technologies offered by competitors. If we are unable to innovate successfully, our services and related devices could become obsolete and our revenue would decline as our customers prescribe or purchase our competitors’ services.
In order to remain competitive, we must continue to develop new product offerings and enhancements to our Zio Services. We can provide no assurance that we will be successful in fully recognizing the strategic value of our ECG database, expanding the indications for our Zio Services, developing new services and related devices, or commercializing them in ways that achieve market acceptance. In addition, if we develop new services, sales of those services may reduce revenue generated from our existing services. Maintaining adequate research and development personnel and resources to meet the demands of the market is essential. If we are unable to develop new services and related devices, applications, or features, or improve our algorithms due to constraints, such as insufficient cash resources, high employee turnover, inability to hire personnel with sufficient technical skills, inability or delay to obtain FDA marketing authorization or regulatory clearances in the EU and the UK, or a lack of other research and development resources, we may not be able to maintain our competitive position compared
to other companies. Furthermore, many of our competitors devote a considerably greater amount of funds to their research and development programs than we do, and those that do not may be acquired by larger companies that would allocate greater resources to research and development programs. Our failure or inability to devote adequate research and development resources or compete effectively with the research and development programs of our competitors could harm our business.
We have entered into in the past, and may explore or enter into in the future, development or collaboration agreements with third parties. These development and collaboration agreements may not result in the development of commercially viable devices or the generation of significant future revenues.
We have entered into a development and collaboration agreement in the past to develop certain next-generation Afib screening, detection, or monitoring devices to enhance our Zio Services, which could involve combining our technology platforms and capabilities with those of a third party, and we intend to enter into similar development and collaboration agreements with third parties in the future. The success of our collaboration with third parties is highly dependent on the efforts provided to the collaboration by such third parties and us and the skill sets of our respective employees. Support of these efforts requires significant resources, including research and development, manufacturing, quality assurance, and clinical and regulatory personnel. Product testing, market research, and related activities may result in a delay to any device launch and additional expense associated with any commercialization efforts. Even if and when launched, the developed devices may also not be accepted in the marketplace, and there is no assurance that adequate coverage or reimbursement would be available, or that an alternative payment model can be developed.
Any collaboration with a third party may not result in the development of devices, and ultimately services, that achieve commercial success and could be terminated prior to developing any devices. In the event of any termination or expiration of any development or collaboration agreement, we may be required to devote additional resources to device development and we may face increased competition, including from our third party partner. A third party partner may use the experience and insights it develops in the course of any collaboration with us to initiate or accelerate their development of products that compete with our devices and services, which may create competitive disadvantages for us. Accordingly, we cannot provide assurance that our collaboration with any third party will result in the successful development of commercially viable devices and services or result in significant additional future revenues for our company.
We generally intend to continue assessing the potential pathways for expanding indications and use cases for our Zio Services, and developing potential new products and services, for patient populations with unmet needs in the remote cardiac monitoring market and adjacent markets. We intend to continue to invest in research and development efforts to further differentiate our biosensor, data analytics and reporting, information system, and digital platform and we may explore or enter into development or collaboration agreements with third parties to further these efforts. We cannot predict whether such efforts will be viable from a regulatory and commercial standpoint, and development or collaboration agreements may not result in the development of commercially viable products or services or the generation of significant future revenues. For example, enforcement action such as that conveyed through the FDA warning letter we received in 2023, as well as other digital health industry regulatory developments, may also impact the availability or viability of potential opportunities.
International expansion of our business exposes us to market, regulatory, political, operational, financial, and economic risks associated with doing business outside of the United States.
While we currently derive substantially all of our revenue and maintain substantially all of our assets in the United States, we intend to continue to pursue growth opportunities outside of the United States, especially in the Philippines, the EU, the UK, Switzerland and Japan, and we may increase our use of administrative and support functions from locations outside the United States, which could expose us to risks associated with international sales and operations. Additionally, our international expansion efforts may not be successful, we may experience difficulties in scaling these functions from locations outside the United States, and we may not experience the expected cost efficiencies.
Our international operations are, and will continue to be, subject to a number of risks, including:
•multiple, conflicting, and changing laws and regulations such as tax laws, privacy laws, export and import restrictions, employment laws, regulatory requirements, and other governmental approvals, permits, and licenses;
•obtaining and sustaining regulatory approvals, certifications, and regulatory compliance where required for the sale of our Zio Services in various countries or regions;
•requirements to maintain and secure data and the processing of that data on servers located within such countries or regions, which requirements may be subject to change;
•complexities associated with managing multiple payor reimbursement regimes, government payors, or patient self-pay systems, as well as with participating in public tenders or procurement processes run by national healthcare systems;
•logistics and regulations associated with shipping and returning our Zio patches following patient use;
•limits on our ability to penetrate international markets if we are required to process our Zio Services locally;
•financial risks, such as longer payment cycles, difficulty collecting accounts receivable, the effect of local and regional financial pressures on demand and payment for our services, fluctuations in trade policy and tariff regulations, changes in international tax regulations applicable to our business, and exposure to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations, which may reduce the reported value of our foreign currency denominated revenues, expenses, and cash flows;
•decreased emphasis or enforcement of intellectual property protections in some countries outside the United States in comparison to that in the United States;
•increased risk of litigation or administrative proceedings in connection with our relationships with international business partners, including litigation against persons whom we believe have infringed on our intellectual property, infringement litigation filed against us, litigation against a competitor, or litigation filed against us by distributors or service providers resulting from a breach of contract or other claim, as well as disputes regarding government and public tenders, any of which may result in substantial costs to us, adverse judgments, settlements, and diversion of our management’s attention;
•increased risk of litigation or administrative proceedings in connection with product liability claims, driven in part by a growing third-party litigation funding market in the EU as well as legal and regulatory reform across product safety and product liability such as the newly adopted EU Product Liability Directive of October 23, 2024, the proposed AI Liability Directive and further implementation of the collective redress regime which may lead to group claims in respect of medical devices;
•natural disasters, political and economic instability, including wars and other geopolitical conflicts, terrorism, political unrest, outbreak of disease, boycotts, curtailment of trade, and other market restrictions;
•risks associated with any shifts in economic relations between the UK and the EU, which could result in tariffs or quotas on imported goods or services moving between the UK and the EU;
•regulatory and compliance risks that relate to maintaining accurate information and control over activities subject to regulation under the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended (the “FCPA”), UK Bribery Act of 2010, and comparable laws and regulations in other countries;
•compliance risks associated with the General Data Protection Regulation (the “GDPR”) (including as it applies in the UK by virtue of the Data Protection Act 2018), enacted to protect the privacy of all individuals in the EU and the UK, and which places certain restrictions on the export of personally identifiable data outside of the EU or the UK, as applicable;
•compliance risks associated with the revised regulations in the EU MDR that outline the requirements for medical device CE marking;
•compliance risks associated with the UK MDR, which replaces the CE marking requirements for medical devices marketed and sold in the UK with a UKCA mark following the UK’s withdrawal from the EU, and the UK government’s announcement to amend the UK MDR, in particular to create a new access pathway to support innovation and create an innovative framework for regulating software and AI as medical devices;
•compliance risks associated with the Japanese PMDA;
•compliance risks associated with the SMDO;
•compliance risks associated with new or upcoming regulations associated with AI applicable to Software as a Medical Device, including compliance with the EU Artificial Intelligence Act; and
•compliance risks associated with new or upcoming requirements and expectations associated with medical device cybersecurity.
Any of these factors may require significant resources to address and could significantly harm our future international expansion and operations and, consequently, our revenue and results of operations.
Our success depends on our ability to attract and retain senior management and key personnel.
Our success depends on our ability to retain our senior management and to attract and retain qualified personnel in the future. Competition for senior management personnel, as well as salespersons, scientists, clinicians, and engineers, is intense and we may not be able to retain our personnel. The loss of key personnel, including key members of our senior management team or members of our board of directors, as well as certain of our key finance, legal, regulatory, research and development, quality, and clinical personnel, could disrupt our operations and have a material and adverse effect on our ability to grow our business. Each of our officers may terminate their employment at any time without notice and without cause or good reason. The loss of a member of our senior management team or our professional staff would require the remaining executive officers to divert immediate and substantial attention to seeking a replacement.
We have recently experienced significant changes in our executive leadership, for example the March 2023 resignation of Douglas Devine as Chief Operating Officer and the August 2024 resignation of Brice Bobzien as Chief Financial Officer and appointment of Daniel Wilson as Chief Financial Officer, and we may experience further changes in executive leadership in the future.
Changes to strategic or operating goals, which can often times occur with the appointment of new executives, can create uncertainty, may negatively impact our ability to execute quickly and effectively, and may ultimately be unsuccessful. If we do not integrate new executives successfully, we may be unable to manage and grow our business, and our financial condition and profitability may suffer as a result. In addition, to the extent we experience additional management turnover, competition for top management is high and it may take months to find a candidate that meets our requirements. If we are unable to attract and retain qualified management personnel, our business could suffer.
Further, we may undertake reorganizations of our workforce from time to time, which may result in a temporary reduction in the number of employees in certain locations. We would undertake a reorganization to reduce operating expenses or achieve other business objectives, though we cannot guarantee any specific amount of long-term cost savings. Further, the turnover in our employee base could result in operational and administrative inefficiencies, which could adversely impact the results of our operations, stock price, and customer relationships, could complicate our efforts to retain other valuable employees, and could make recruiting for future management and other positions more difficult.
Our continued rapid growth could strain our personnel resources and infrastructure, and if we are unable to manage the anticipated growth of our business, our future revenue and operating results may be harmed.
We have experienced rapid growth in our headcount and in our operations. Any growth that we experience in the future will provide challenges to our organization, requiring us to expand our sales personnel, manufacturing, clinical, customer care, and billing operations and general and administrative infrastructure. In addition to the need to scale our operational and service capacity, future growth will impose significant added responsibilities on management, including the need to identify, recruit, train, and integrate additional employees. Rapid expansion in personnel could impact our capacity to manufacture our Zio patches, market, sell, and support our Zio Services, and analyze the data to produce Zio reports, which could result in inefficiencies and unanticipated costs, impacts to our Zio Services, including our Zio patches, and disruptions to our service operations. Additionally, rapid expansion could require us to rely on overtime to increase capacity that could, in turn, result in greater employee attrition and/or a loss in productivity during the process of recruiting and training additional resources and add to our operating expenses. Further, a move toward automation to address, for example, staffing or scalability needs, could result in unintended consequences, such as increased scrap rate negatively impacting profitability.
As we seek to gain greater efficiency, we may look for ways to expand the automated portion of our Zio Services and require productivity improvements from our qualified cardiac technicians, within the framework of our wide-ranging regulatory obligations. Such improvements could impact the content of our Zio reports. In addition, rapid and significant growth may strain our administrative and operational infrastructure. Our ability to manage our business and growth will require us to continue to improve our operational, financial, and management controls, reporting systems, and procedures. If we are unable to manage our growth effectively, it may be difficult for us to execute our business strategy and our business could be harmed.
Failure to receive the Zio System patches used for the provision of the Zio Services we provide may result in a loss of capital as well as revenue where the receipt of returned devices and processing of data retrieved from returned devices is required to provide our Zio Services.
Our Zio System patches and gateways are provided to patients either (1) during in-office visits with a healthcare provider or (2) remotely via at-home hookup. We have also seen hybrid situations where accounts, in response to staffing shortages, provide in-clinic Zio device packages to patients for application at home. Although in all three scenarios there is the potential that a patient will not return the device(s) at the conclusion of the wear period, home hookups historically result in a higher likelihood that the patient will fail to return his or her device, which negatively impacts our financial condition when we are unable to provide the Zio Services. For example, when the patient returns the Zio Monitor patch to us at the end of the patient wear period, we provide the Zio Monitor services, which include the end of service report based on the data stored on the Zio Monitor patch, after which we submit a claim to the relevant payor or to the patient for the services rendered. If a patient fails to return a device, we experience financial losses, which include the cost of the device as well as the loss of potential revenue for the service that is contingent on the returned device for the submission of the associated claim.
Our strategic plans include a high degree of focus on the marketing of our services for proactive monitoring of undiagnosed arrhythmias, such as Afib screening. There are risks that the clinical or payor community will not identify, adopt or accept selection criteria to identify patients suitable for proactive monitoring of undiagnosed arrhythmias.
In January 2022, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (“USPSTF”) published a recommendation statement on the screening criteria for Afib screening, stating that current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harm of Afib screening, and thus found that it could neither recommend for or against screening of adults 50 years or older without a diagnosis or symptoms of Afib and without a history of transient ischemic attack or stroke. In its recommendation, the USPSTF also identified research needs and gaps, including for example assurance that future research involves randomized trials of diverse patient populations and conducting research to optimize the accuracy of screening for Afib. This USPSTF recommendation statement may deter some clinicians or payors from selecting patients for screening for Afib. We cannot predict whether or when the USPSTF’s recommendation on Afib screening will change or be modified based on findings from additional randomized trials, other research, or through the continued use of our products and services or other similarly situated products and services designed for remote cardiac monitoring.
We may face risks associated with acquisitions of companies, products, and technologies and our business could be harmed if we are unable to address these risks.
If we are presented with appropriate opportunities, we could acquire or make other investments in complementary companies, products, or technologies. We may not realize the anticipated benefit of our acquisitions, or the realization of the anticipated benefits may require greater expenditures than anticipated by us. For example, the License Agreement that we entered into with BioIS may not result in the development of commercially viable products or services or the generation of significant future revenues. The success of our efforts is highly dependent on the efforts and skill sets of our employees, and support of these efforts requires significant resources, including research and development, manufacturing, quality assurance, and clinical and regulatory personnel. Even if and when launched, the developed devices may also not be accepted in the marketplace, and there is no assurance that adequate coverage or reimbursement would be available, or that an alternative payment model can be developed.
In addition, we will likely face risks, uncertainties, and disruptions associated with the integration process, including difficulties in the integration of the operations and services of any acquired company, integration of acquired technology with our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, diversion of our management’s attention from other business concerns, the potential loss of key employees or suppliers of the acquired businesses, and impairment charges if future acquisitions are not as successful as we originally anticipated. If we fail to successfully integrate other companies, products, or technologies that we acquire, our business could be harmed. Furthermore, we may have to incur debt or issue equity or equity-linked securities to pay for any future acquisitions or investments, the issuance of which could be dilutive to our existing stockholders. In addition, our operating results may suffer because of acquisition-related costs, amortization expenses, investment required to address risks associated with the acquisition, or charges relating to acquired intangible assets.
The success of our collaboration with BioIS and the extent to which we realize a return on investment in the technology licensed from BioIS is dependent on our achievement of certain regulatory milestones. If those milestones are not met, or if any resulting products do not gain acceptance in the marketplace, our business and operating results may be negatively impacted.
Our License Agreement with BioIS grants us an exclusive license to develop and commercialize pulse oximetry, accelerometry, and trending non-invasive blood pressure technologies for use within our remote cardiac monitoring products and services. It is anticipated that BioIS’s multiparameter sensing technologies will position us to expand the capabilities of our product platform within the remote cardiac monitoring field of use and potentially into adjacent indications such as OSA over time. This will require that any new products developed undergo validation and achieve certain regulatory milestones. Should we fail to meet those milestones, or if there are material delays in doing so, this could impede our ability to commercialize any new products or solutions utilizing the technologies covered by the License Agreement and realize our return on investment.
We are currently in the early stages of exploring opportunities to expand into the market of sleep apnea screening and diagnostics, which carries unique regulatory requirements and represents an ongoing area of focus for government enforcement. Commercialization of new products and services in the sleep testing space will require a significant investment of time and resources. If we are unable to successfully execute on these opportunities, it could have an adverse affect on our reputation, business, and results of operations.
Our exploration of the sleep apnea screening and diagnostics market is in the early evaluation stages, and although we are devoting time and resources to this evaluation, we do not anticipate meaningful revenue from any such opportunities to expand into the sleep apnea screening and diagnostics market for the foreseeable future. If we fail to capitalize on these opportunities, we may face threats from our competitors should they be able to commercialize products and services in the home sleep testing (“HST”) space on a more expeditious timeline. Additionally, any new HST offering will be subject to specific requirements to qualify for reimbursement under Medicare and by third-party commercial payors. Improper billing activities related to HST services have been an area of significant government scrutiny in recent years. Failure to comply with the myriad, complex legal and regulatory requirements surrounding the provision of sleep apnea diagnostics could subject us to substantial civil or criminal penalties, exclusion from participation in the Medicare program, reputational harm, and other adverse consequences to our business and results of operations.
Risks Related to Healthcare Regulatory Matters
Our use of third-party service providers or company resources located outside the United States to support certain customer care, clinical, and other operations of our IDTFs may present challenges, and if we are ineffective in limiting work performed by these service providers or company resources consistent with applicable regulations or our contractual agreements with commercial payors, we may be subject to penalties or experience loss of revenue.
Beginning in the third quarter of 2022, we engaged Sutherland Healthcare Solutions, Inc. and Techindia Infoway Private Limited to support certain customer care and clinical operations of our IDTFs. We have developed operational and technical controls to limit the work performed by these vendors consistent with our interpretation of the Medicare coverage exclusion of services furnished outside the United States, other applicable laws and regulations, and any requirements imposed pursuant to our contracts with commercial payors. If these controls do not work as intended, or if regulators or commercial payors disagree with our interpretation of these requirements and their application to our operations, we may be subject to a requirement to return funds already paid to us, civil monetary penalties, other government enforcement, as highlighted by a recent enforcement action against our competitor, BioTelemetry, Inc., with respect to the support of certain clinical operations by vendors performing work outside the United States, and termination of contracts with commercial payors, as well as the loss of revenue associated with those contracts.
In addition, we are currently engaging with other third-party service providers that have resources located outside the United States, and we have established company resources in the Philippines to provide services in support of our IDTFs. These services include benefits verification, billing, collections, and customer service, which require complex oversight and monitoring for appropriate capture and escalation of complaint information that may be relevant to the quality, performance, and safety of our medical devices or the quality of our clinical services. If we are unable to effectively manage this oversight and monitoring, we may be subject to regulatory enforcement action or inquiries which may be expensive and time consuming to resolve. In addition, certain contracts with commercial payors include restrictions related to accessing patient data outside the United States and we have implemented reasonable controls intended to prohibit unauthorized use of patient data by service providers and company resources located outside the United States for these commercial payors, as appropriate. If these controls do not work as intended, or if the payor information we receive from ordering healthcare providers is delayed or inaccurate, we may encounter the suspension or termination of contracts with commercial payors, as well as any contractual remedies such payors might pursue. The suspension or loss of any of our key commercial payor agreements would have an adverse impact on our revenue and our results of operations.
If we fail to comply with medical device, healthcare, and other governmental regulations, we could face substantial penalties and our business, results of operations, and financial condition could be adversely affected.
The services and related devices we offer are highly regulated, and the regulatory environment in which we operate may change significantly and adversely in the future. Our arrangements with physicians, hospitals, clinics, and other stakeholders in the healthcare industry may expose us to broadly applicable medical device laws and healthcare fraud and abuse and other laws and regulations that may restrict the financial arrangements and relationships through which we market, sell, distribute, and provide our services and related devices. Our employees, consultants, and commercial partners and collaborators may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including non-compliance with regulatory standards and requirements. Federal, state and international healthcare laws and regulations that may affect our ability to conduct business, include, without limitation:
•state licensure laws applicable to the manufacture, marketing, distribution, and sale of medical devices;
•federal and state laws and regulations regarding billing, claims payment, and enrollment for participation in government healthcare programs, including regulations requiring the timely identification and refunding of overpayments to Medicare and other federally funded healthcare programs;
•the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, any person from knowingly and willfully offering, soliciting, receiving, or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in exchange for or to induce either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service for which payment may be made under federal healthcare programs, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs;
•the federal FCA, which prohibits, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, false claims, or knowingly using false statements, to obtain payment from the federal government;
•federal criminal laws that prohibit executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters;
•the FCPA, the UK Bribery Act of 2010, and other local anti-corruption, anti-kickback, and transparency laws that apply to our international activities;
•the federal Physician Payment Sunshine Act, or Open Payments, and its implementing regulations, which requires us to report payments or other transfers of value made to licensed physicians and certain mid-level health practitioners and teaching hospitals, as well as ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members;
•Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (“HIPAA”), as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, and its implementing regulations, which impose certain requirements relating to the privacy, security, and transmission of individually identifiable health information; HIPAA also created criminal liability for knowingly and willfully falsifying or concealing a material fact or making a materially false statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items, or services;
•the GDPR and the UK Data Protection Act 2018, which each provide legal requirements for the handling and disclosure (including across borders) of personal data collected in the EU and the UK, respectively;
•the FDA’s Code of Federal Regulations, including but not limited to, 21 CFR Parts 820, 803, 806, and 801, that outlines requirements for medical device design, testing, marketing authorization, manufacturing, labeling, distribution, and post-market surveillance requirements;
•the EU MDR that outline requirements for medical device CE marking;
•the UK MDR, which, post the UK’s withdrawal from the EU, replaces the CE marking requirement for medical devices sold in the UK with a UKCA mark;
•the Swiss Medical Devices Ordinance, which governs the approval and importation requirements of medical devices into Switzerland;
•the PMDA, which outlines comprehensive standards for the design, evaluation, marketing approval, production, labeling, distribution, and ongoing monitoring of medical devices in Japan; and
•state law equivalents of each of the above U.S. federal laws, such as anti-kickback and false claims laws which may apply to items or services reimbursed by any third-party payor, including commercial insurers, and state and foreign laws governing the privacy and security of individually identifiable information in certain circumstances (e.g., the Telephone Consumer Protection Act, the CAN-SPAM Act, and state privacy, consumer protection, and breach notification laws), many of which differ from each other in significant ways and often are not preempted by HIPAA, thus complicating compliance efforts.
These laws are broad in scope and available exceptions and exemptions are narrow; it is possible that some of our activities could be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. Any action brought against us for violations of these laws or regulations, even if successfully defended, could cause us to incur significant legal expenses and divert our management’s attention from the operation of our business. We may be subject to private “qui tam” actions brought by individual whistleblowers on behalf of the federal or state governments, with potential liability under the federal FCA including mandatory treble damages and significant per-claim penalties. If the government decides to intervene and prevails in the lawsuit, the individual will share in the proceeds from any fines or settlement funds. If the government declines to intervene, the individual may pursue the case alone. For violations assessed after January 15, 2025, the minimum FCA penalty increased from $13,946 to $14,308 per claim and the maximum penalty increased from $27,894 to $28,619 per claim. In addition, FCA lawsuits may expose defendants to follow-on claims by private payers based on fraudulent marketing practices. Recent growth in FCA litigation has increased the risk that companies will have to defend a false claim action, and pay settlements, fines or restitution, as well as criminal and civil penalties, agree to comply with burdensome reporting and compliance obligations, and/or be excluded from Medicare or other federal and state healthcare programs. For example, our industry has experienced recent FCA enforcement, including a December 2023 settlement by BioTelemetry, Inc. and its subsidiary LifeWatch Services Inc. involving allegations that these companies submitted claims to federal programs for a higher level of remote cardiac monitoring than physicians had intended to order or that was medically necessary, thus inflating the level of reimbursement paid, which highlights the importance of compliance with the rules and regulations governing claims submitted to federal healthcare programs.
Although we have adopted policies and procedures designed to comply with these laws and regulations and conduct internal reviews of our compliance with these laws, our compliance is also subject to governmental review. The growth of our business and sales organization and our expansion outside of the United States may increase the potential of violating these laws or our internal policies and procedures. The risk of our being found in violation of these or other laws and regulations is further increased by the fact that many have not been fully interpreted by the regulatory authorities or the courts, and their provisions are open to a variety of interpretations. Any action brought against us for violation of these or other laws or regulations, even if we successfully defend against it, could cause us to incur significant legal expenses and divert our management’s attention from the operation of our business. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the federal, state, or foreign laws described above or any other current or future fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including significant criminal, civil, and administrative penalties, damages, fines, imprisonment for individuals, exclusion from participation in government programs, such as Medicare, and we could be required to curtail or cease our operations. Any of the foregoing consequences could seriously harm our business and our financial results.
Further, in June 2024, the U.S. Supreme Court reversed its longstanding approach under the Chevron doctrine, which provided for judicial deference to regulatory agencies, including FDA. As a result of this decision, we cannot be sure whether there will be increased challenges to existing agency regulations or how lower courts will apply the decision in the context of other regulatory schemes without more specific guidance from the U.S. Supreme Court. For example, this decision may result in more companies bringing lawsuits against FDA to challenge longstanding decisions and policies of FDA, which could undermine FDA’s authority, lead to uncertainties in the industry, and disrupt FDA’s normal operations, which could impact the timely review of any regulatory filings or applications we submit to FDA.
Changes in applicable laws or regulations or the interpretation or enforcement policies of regulators governing our IDTFs and Zio Services may constrain or require us to restructure our operations or adapt certain business strategies which may harm our revenue and operating results.
Healthcare laws and regulations, and interpretations of the same, change frequently and may change significantly in the future. We may not be able to adapt our operations to address every new regulation or interpretation, and new regulations or interpretations may adversely affect our business. We also cannot assure that a review of our business by courts or regulatory authorities would not result in a determination that adversely affects our revenue and operating results.
Our business could be negatively impacted by changes in the United States political environment.
Any policy changes as a result of the new presidential administration and Congress could significantly affect our business as well as the markets in which we operate. Specific legislative and regulatory proposals discussed during election campaigns and more recently that might materially impact our business include, but are not limited to, promoting access to healthcare via market competition and pricing transparency, enhancing flexibility and choice in healthcare at the state and individual level, prioritizing domestic production and increasing tariffs on imports (which may complicate and increase costs associated with our supply chain), and rolling back regulatory initiatives adopted under the previous administration. We cannot predict whether industry initiatives to seek tariff carve-outs for devices or other life sciences goods and products will be successful. Additionally, the new administration is expected to evaluate potential budgetary cuts and reallocation of regulatory priorities by key federal agencies that oversee our products, services, and associated reimbursement, including FDA and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services more broadly. The new administration also has issued, and is expected to continue relying upon, executive orders to address a wide range of policy areas, some of which may impact our business. Examples of executive orders that have already been issued on public health and healthcare topics include orders seeking to withdraw the United States from the World Health Organization, rescind a 2022 order issued under the prior administration to lower the cost of prescription drugs, and address COVID-19 vaccination requirements. Such political developments may require us to allocate significant time, resources, and expense to modifying our policies and procedures, processes, systems, and practices to ensure compliance or adapt to the new regulatory climate, particularly to the extent such actions are subject to protracted and uncertain legal challenges. To the extent changes in the political environment have a negative impact on us or on our markets, our business, results of operation, and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected in the future.
Our business relies on orders from licensed healthcare providers, and the continuing clinical acceptance and adoption of our Zio Services depends upon strong working relationships with healthcare providers, including physicians. These relationships, interactions, and arrangements are subject to a high degree of scrutiny by government regulators and enforcement bodies.
As a CMS-enrolled IDTF, we may only provide our Zio Services upon receipt of a valid order from a licensed healthcare provider for use in the diagnosis and treatment of a patient’s medical condition. Accordingly, our revenue and the success of our business rely on the continued clinical acceptance and adoption of our Zio Services by healthcare providers whose patients require remote cardiac monitoring services. In addition to continuing to demonstrate the clinical value of our Zio Services, we also must support widespread clinical acceptance and adoption of our Zio Services by maintaining strong working relationships with these healthcare providers, including physicians. However, as we work to establish and maintain these relationships, we face significant scrutiny of these relationships, interactions, and arrangements by government regulators and enforcement agencies. Failure to structure and maintain these relationships, interactions, and arrangements in compliance with applicable laws and regulations, including those targeted at fraud and abuse like the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and the FCA, could expose us to significant legal and financial repercussions, including government civil and criminal investigations, civil monetary penalties, criminal penalties, and/or exclusion from federal healthcare programs.
Our communications with healthcare stakeholders – physicians and other healthcare professionals, payors, and similar entities, as well as patients and lay caregivers – are subject to a high degree of scrutiny for compliance with a wide range of laws and regulations. Continuing or increasing our sales and marketing and other external communication efforts may expose us to additional risk of being alleged or deemed to be non-compliant by regulators, enforcement authorities, or competitors.
Our sales and marketing efforts and initiatives, as well as other communications with healthcare professionals (“HCPs”), may subject us to a high degree of scrutiny for compliance with applicable laws and regulations and our practices of effective communication of risk information, benefits, or claims will be subject to oversight by FDA, the Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”) and others.
In addition, FDA applies a heightened level of scrutiny to comparative claims when applying its statutory standards for advertising and promotion, including with regard to its requirement that promotional labeling be truthful and not misleading. There is potential for differing interpretations of whether certain communications are consistent with a product’s FDA-required labeling, including with respect to communications that may reference or contemplate the use of the Zio devices with specified patient populations. FDA will evaluate communications, in context, on a fact-specific basis. This is a continued area of focus for regulators. In the fourth quarter of 2023, FDA issued final guidance focused on the presentation of quantitative risk and efficacy information to the consumer audience, with heightened focus on presenting such information in a manner that is accurate, understandable, and consumer-friendly. The FTC has also released updated guidance on health claims, with a high expectation for clinical data to support these claims.
In addition, making comparative claims may draw scrutiny from our competitors. Where a company makes a claim in advertising or promotion that its product is superior to the product of a competitor (or that the competitor’s product is inferior), this creates a risk of a lawsuit by the competitor under federal and state false advertising or unfair and deceptive trade practices law, and possibly also state libel law. Such a suit may seek injunctive relief against further advertising, a court order directing corrective advertising, and compensatory and punitive damages where permitted by law. If our compliance program and training and monitoring do not effectively keep pace with our sales and marketing growth, we may encounter increased risk in execution of activities by our personnel, potential enforcement and other exposure.
We may also seek to communicate certain information with physicians and scientists and their practices and health systems or with payors and similar entities, and may rely on a range of laws, regulations, regulatory guidance governing topics, including scientific exchange, and communication of healthcare economic information and product information under the Preapproval Information Exchange Act. Recent FDA final guidance on communication of scientific information on unapproved uses of cleared/approved medical products with HCPs further illustrates the agency’s focus on ensuring that such communications to those in a position to order or prescribe products are consistent with available scientific data and subject to organizational controls maintaining separation and distinction from promotional marketing.
For example, certain of our physicians may order the Zio Services for patients who are under 18, which is outside the cleared indications for use. While we do not intend for any personnel to promote our devices for pediatric use and we have policies addressing appropriate responses to unsolicited requests for information about pediatric use, our approach may be subject to ongoing scrutiny from FDA.
If FDA or other federal, state, or foreign enforcement authorities determine that our labeling, advertising, promotional materials, or user training materials, or representations made by our personnel include the promotion of an off-label use for the device, or that we have made false or misleading or inadequately substantiated promotional claims, or claims that could potentially change the regulatory status of the product, FDA or other authorities could take the position that these materials have misbranded our devices and request that we modify our labeling, advertising, or user training or promotional materials and/or subject us to regulatory or legal enforcement actions, including the issuance of an Untitled Letter or a Warning Letter, injunction, seizure, recall, adverse publicity, civil penalties, criminal penalties, including substantial fines, or other adverse actions. In that event, we would be subject to extensive fines and penalties and our reputation could be damaged and adoption of the products would be impaired. Although we intend to refrain from statements that could be considered off-label promotion of our products, FDA or another regulatory agency could disagree and conclude that we have engaged in off-label promotion.
Changes in laws and regulations governing our communications with patients or the interpretation or enforcement policies of regulators could subject us to regulatory scrutiny, damage awards, or fines.
As a Medicare-enrolled IDTF, we are prohibited from directly soliciting patients for diagnostic medical procedures. While we can engage in general marketing initiatives, consistent with applicable law, we cannot make telephone, computer, and in-person contacts for the purpose of soliciting business for our IDTF.
Regarding patients for whom we have received a valid order for our Zio Services, we may send or make text messages, emails, phone calls, and other communications for various informational, business purposes, including to confirm accurate demographic and payor information or to assist a patient via a home hookup. Communication-related laws require consent prior to certain communications and provide a specified monetary damage award or fine for each violation which could result in particularly significant damage awards or fines. For example, under the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (“TCPA”), plaintiffs may seek actual monetary loss or statutory damages of $500 per violation, whichever is greater, and courts may treble the damage award for willful or knowing violations. In the wake of a 2021 decision by the U.S. Supreme Court that limited the applicability of the TCPA, several states have enacted or introduced legislation that would regulate text messages and certain telephone calls to individuals. We may be subject to lawsuits (including class-action lawsuits) containing allegations that our business violated the TCPA or other communications laws. These lawsuits may seek damages (including statutory damages) and injunctive relief, among other remedies. A determination that there have been violations of the TCPA or other statutes regulating communications with patients could expose us to significant damage awards that could, individually or in the aggregate, materially harm our business.
While most of our revenue results from claims submitted to payors for diagnostic medical procedures, we offer, and are looking to expand, alternative payment and service delivery models. Piloting, evaluating, and implementing these alternative payment and service delivery models requires interactions with commercial payors, physicians, and patients; these interactions are subject to laws and regulations aimed at preventing healthcare fraud and abuse. If these models are unsuccessful, or if we are unable to fully comply with such laws as we pursue these strategies, our commercial success could be compromised and we could face substantial penalties.
Our operations may be directly or indirectly affected by various broad state and federal healthcare fraud and abuse laws, including the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, the FCA, the Anti-Mark Up Rule, and the Medicare Beneficiary Inducement Statute. For some of our services, we directly bill physicians or other healthcare entities, that, in turn, bill payors, and the amounts we bill may include a risk-based pricing component. We are also developing alternative service delivery models that include using our Zio Monitor System or Zio XT System to screen at-risk patient populations as part of a value-added service offered by managed care organizations, including Medicare Advantage Organizations, to qualifying participants. Although we have endeavored to properly design these billing and service models and structure our program development efforts, including related affiliations and relationships with physicians or other healthcare entities, to comply with applicable laws and regulations, these types of initiatives may draw a high degree of scrutiny and may subject us to assertions of non-compliance. If our past, present, or future operations are found to be in violation of fraud and abuse laws, we or our officers may be subject to civil or criminal penalties, including large monetary penalties, damages, fines, imprisonment, and exclusion from Medicare program participation. Furthermore, if we knowingly file, or “cause” the filing of, false claims for reimbursement with government programs such as Medicare, we may be subject to substantial civil penalties, including treble damages.
Risks Related to Financial and Accounting Matters
In the future we may identify additional material weaknesses or otherwise fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, which may result in material misstatements of our consolidated financial statements or cause us to fail to meet our periodic reporting obligations.
We previously identified material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of our annual or interim consolidated financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. As previously disclosed, in preparing our consolidated financial statements as of and for the years ended December 31, 2021 and 2020, our management concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures and our internal control over financial reporting were not effective at the reasonable assurance level due to a failure to maintain a sufficient number of professionals with an appropriate level of accounting and internal control knowledge, training, and experience to timely and accurately analyze, record, and disclose accounting matters. This material weakness contributed to additional material weaknesses, which have been previously disclosed and remediated. In aggregate, these material weaknesses (including the previously remediated material weaknesses) contributed to the misstatement of our revenues, revenue reserves, bad debt expense, property and equipment, research and development expense, and related financial disclosures, and in the revision of our consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2017, December 31, 2018, and each interim period therein as well as the quarters ended March 31, 2019, June 30, 2019, and September 30, 2019. Additionally, this material weakness could result in a misstatement of account balances or disclosures that would result in a material misstatement to the annual or interim consolidated financial statements that would not be prevented or detected.
To address this material weakness, we took actions designed to improve our internal control over financial reporting and remediate the control deficiencies that led to the material weakness, including hiring additional accounting and finance personnel with an appropriate level of expertise, providing for additional management oversight over financial reporting including through the establishment of a SOX Steering Committee within our internal audit function, and implementing new controls and processes. As of the year ended December 31, 2022, we concluded that our remediation efforts had been successful and that the previously identified material weakness in internal control over financial reporting had been remediated. However, while the material weakness has been remediated, we continue to seek improvements to enhance our control environment and to strengthen our internal controls to provide reasonable assurance that our financial statements continue to be fairly stated in all material respects.
If we discover additional weaknesses in our system of internal financial and accounting controls and procedures, our consolidated financial statements may contain material misstatements, and we could be required to restate our financial results. Our internal control over financial reporting will not prevent or detect all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control system’s objectives will be met. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that misstatements due to error or fraud will not occur or that all control issues and instances of fraud will be detected.
Any failure to implement and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting could cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial and other information, adversely impact our stock price, cause us to incur increased costs to remediate any deficiencies, and attract regulatory scrutiny or lawsuits that could be costly to resolve and distract management’s attention, limit our ability to access the capital markets, or cause our stock to be delisted from The Nasdaq Global Select Market or any other securities exchange on which it is then listed. Failure to remedy any material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting, or to implement or maintain other effective control systems required of public companies, could also restrict our future access to the capital markets.
Our financial results may fluctuate significantly from quarter-to-quarter and may not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business.
Our revenue and operating results may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter as a result of a variety of factors, a number of which are outside our control, and may therefore not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business. Such factors may include, for example, seasonal variations in prescription rates. We typically experience reduced revenue during the third quarter, as well as during the year-end holiday season. We believe this is the result of physicians and patients taking vacations, and patients electing to delay our monitoring services during the summer months and holidays. We believe that period-to-period comparisons of our operating results may not be meaningful and should not be relied on as an indication of our future performance. If quarterly revenues or operating results fall below the expectations of investors or public market analysts, the trading price of our common stock could decline substantially. Factors that might cause quarterly fluctuations in our operating results include:
•our inability to manufacture an adequate supply of our Zio Systems to support demand for our Zio Services at appropriate quality levels and acceptable costs;
•possible delays in our research and development programs or in the completion of any third-party clinical trials relating to our Zio Services;
•a lack of acceptance of our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, by physicians and potential patients;
•the inability of patients to receive reimbursements from third-party payors;
•the purchasing patterns of physicians and patients, including as a result of seasonality;
•failures to comply with regulatory requirements, which could lead to withdrawal of our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, from the market;
•our failure to continue the commercialization of our Zio Services;
•competition;
•inadequate financial and other resources; and
•global business, political, and economic conditions, including inflation, interest rate volatility, cybersecurity events, uncertainty with respect to the federal debt ceiling and budget and potential government shutdowns related thereto, potential instability in the global banking system, political instability, and military hostilities, including ongoing geopolitical conflicts, such as the war in Ukraine and conflict in the Middle East.
Further, we recognize a portion of our revenue from non-contracted third-party commercial payors. For example, during the year ended December 31, 2024, revenue from non-contracted third-party commercial payors accounted for approximately 7% of our total revenue. We have limited visibility as to when we will receive payment for our Zio Services with non-contracted payors and we or our third party billing vendors must appeal any negative payment decisions, which often delays collections further. Additionally, a portion of the revenue from non-contracted payors is received from patient co-pays, which we may not receive for several months following delivery of service or may not receive at all. For revenue related to non-contracted payors, we estimate an average collection rate based on factors including historical cash collections. Subsequent adjustments, if applicable, are recorded as an adjustment to revenue. Fluctuations in revenue may make it difficult for us, research analysts, and investors to accurately forecast our revenue and operating results or to assess our actual performance. If our revenue or operating results fall below expectations, the price of our common stock would likely decline.
We have a history of operating losses and may not achieve or sustain profitability in the future.
We have incurred net losses since our inception in September 2006. We generated net losses of $113.3 million and $123.4 million during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, we had an accumulated deficit of $758.9 million. We have financed our operations to date primarily through private and public offerings of equity securities and revenue generated by prescriptions of our Zio Services. We have and expect to continue to incur significant research and development, sales and marketing, regulatory, and other expenses as we expand our marketing efforts to increase the prescription of our Zio Services, expand existing relationships with physicians, obtain regulatory clearances or approvals for our current or future services and related devices, conduct clinical trials on our existing and future services, and develop new services or add new features to our existing Zio Services. We also expect that our general and administrative expenses will continue to increase due to, among other things, the operational and regulatory burdens applicable to medical service providers that are public companies. As a result, we expect to continue to incur operating losses in the future. These losses, among other things, may have an adverse effect on our stockholders’ equity and the value of our common stock.
We may require additional capital to support the growth of our business, and this capital might not be available on acceptable terms, if at all.
Our operations have consumed substantial amounts of cash since inception. We intend to continue to make investments to support our business, which may require us to engage in equity or debt financings to secure additional funds. Additional financing may not be available on a timely basis on terms acceptable to us, or at all. Any additional financing may be dilutive to stockholders or may require us to grant a lender a security interest in our assets. The amount of funding we may need will depend on many factors, including:
•the revenue generated by our Zio Services;
•the costs, timing, and risks of delay of additional regulatory approvals;
•the expenses we incur in manufacturing, developing, selling, and marketing our Zio Services;
•our ability to scale our manufacturing operations to meet demand for the Zio Systems used in our current and any future Zio Services or other offerings;
•the costs of filing, prosecuting, defending, and enforcing any patent claims and other intellectual property rights;
•the rate of progress and cost of our clinical trials and other development activities;
•the success of our research and development efforts;
•the emergence of competing or complementary technologies;
•the terms and timing of any collaborative, licensing, and other arrangements that we may establish;
•the cost of ongoing compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and third-party payors’ policies;
•the cost of obtaining and maintaining regulatory or payor clearance or approval for our current or future offerings including those integrated with other companies’ products; and
•the acquisition of business, products, and technologies.
If adequate funds are not available, we may not be able to commercialize our Zio Services at the rate we desire and/or we may have to delay the development or commercialization of our Zio Services or license to third parties the rights to commercialize services or technologies that we would otherwise seek to commercialize. We also may have to reduce sales, marketing, customer support, or other resources devoted to our Zio Services. Any of these factors could harm our business and financial condition.
Our ability to use our net operating losses to offset future taxable income may be subject to certain limitations which could subject our business to higher tax liability.
Our ability to use our net operating losses (“NOLs”) to offset future taxable income may be subject to certain limitations which could subject our business to higher tax liability. We may be limited in the portion of NOL carryforwards that we can use in the future to offset taxable income for U.S. federal and state income tax purposes, and federal tax credits to offset federal tax liabilities. Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), and similar state law provisions, limit the use of NOLs and tax credits after a cumulative change in corporate ownership of more than 50% occurs within a three-year period. Sections 382 and 383 of the Code place a formula limit on how much NOLs and tax credits a corporation can use in a tax year after a change in ownership. Avoiding an ownership change is generally beyond our control. We could experience an ownership change that might limit our use of NOLs and tax credits in the future. In addition, realization of deferred tax assets, including NOL carryforwards, depends upon our future earnings in the applicable tax jurisdictions. If we have insufficient future taxable income in the applicable tax jurisdiction for any reason, including as a result of any future corporate reorganization or restructuring activities, we may be limited in our ability to utilize some or all of our net operating losses to offset such income and reduce our tax liability in that jurisdiction. See Note 9, Income Taxes to the consolidated financial statements in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K (the “Consolidated Financial Statements”) for additional information.
There is also a risk that due to regulatory changes or changes to federal or state law, such as suspensions on the use of NOLs, or other unforeseen reasons, our existing NOLs could expire or otherwise be unavailable either in whole or in part to offset future income tax liabilities. For example, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“TCJA”), NOLs arising in taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 may offset no more than 80% of current taxable income (without regard for certain deductions). Therefore, we may be required to pay U.S. federal income taxes in future years despite the NOL carryforwards we have accumulated.
Risks Related to Other Legal and Regulatory Matters
We are subject to legal proceedings and government investigations that could adversely affect our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We are involved in legal proceedings related to securities litigation, patent litigation and other matters and may become involved in other legal proceedings that arise from time to time in the future. For example, as discussed further in Note 8, Commitments and Contingencies, to the Consolidated Financial Statements, a putative securities class action lawsuit has been filed against us and certain of our current officers or former officers alleging violations of Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Exchange Act and SEC Rule 10b-5 promulgated thereunder, and two patent lawsuits have been filed against us by companies affiliated with Baxter International.
Any claims against us, whether meritorious or not, can be time-consuming, result in costly litigation, be harmful to our reputation, require significant management attention, and divert significant resources. In addition, the expense of litigation and the timing of this expense from period to period are difficult to estimate and subject to change. Litigation and other claims are subject to inherent uncertainties and management’s view of these matters may change in the future. Given the uncertain nature of legal proceedings generally, we are not able in all cases to estimate the amount or range of loss that could result from an unfavorable outcome. We could incur judgments or enter into settlements of claims that could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations in any particular period.
In addition, healthcare companies are subject to numerous investigations and inquiries by various governmental agencies. For example, as discussed further in Note 8, Commitments and Contingencies, to the Consolidated Financial Statements, in March 2021, we received a grand jury subpoena from the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California requesting information related to communications with FDA and our Zio Systems, and, in September 2021, received a subpoena requesting additional information. On April 4, 2023, we received a Subpoena Duces Tecum from the Consumer Protection Branch, Civil Division of the DOJ, requesting production of various documents regarding our products and services. In addition, on May 25, 2023, we received a warning letter from FDA, which resulted from the inspection of our facility located in Cypress, California that concluded in August 2022. The warning letter alleges non-conformities to regulations for medical devices, including medical device reporting requirements, relating to our Zio AT System and medical device quality system requirements. On July 15, 2024, FDA initiated inspections of our Cypress and San Francisco facilities. We received 483 observations at the close of the inspection. We are cooperating fully in connection with these matters. Any future investigations of our executives, our managers, or our company could result in significant liabilities or penalties to us, as well as adverse publicity. Even if we are found to have complied with applicable law, the investigation or litigation may pose a considerable expense and would divert management’s attention, and have a potentially negative impact on the public’s perception of us, all of which could negatively impact our financial position and results of operations. Further, should we be found out of compliance with any of these laws, regulations, or programs, depending on the nature of the findings, our business, our financial position, and our results of operations could be negatively impacted.
Further, three decisions from the U.S. Supreme Court in July 2024 may lead to an increase in litigation against regulatory agencies that could create uncertainty and thus negatively impact our business. The first decision overturned established precedent that required courts to defer to regulatory agencies’ interpretations of ambiguous statutory language. The second decision overturned regulatory agencies’ ability to impose civil penalties in administrative proceedings. The third decision extended the statute of limitations within which entities may challenge agency actions. These cases may result in increased litigation by industry against regulatory agencies and impact how such agencies choose to pursue enforcement and compliance actions. However, the specific, lasting effects of these decisions, which may vary within different judicial districts and circuits, is unknown. We also cannot predict the extent to which FDA and SEC regulations, policies, and decisions may become subject to increasing legal challenges, delays, and changes.
Compliance with requirements of being a public company may strain our resources and divert management’s attention.
As a public company, we are subject to laws and regulations relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the rules and regulations implemented by the SEC, and The Nasdaq Stock Market listing rules. Compliance with these laws and regulations, including new laws and regulations or revisions to existing laws and regulations, has required and will continue to require, substantial management time and oversight and the incurrence of significant accounting and legal costs. These laws, regulations, and standards are subject to varying interpretations, in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. This could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices. We intend to continue to invest resources to comply with evolving laws, regulations, and standards, and this investment may result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management’s time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. If our efforts to comply with new laws, regulations, and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies due to ambiguities related to their application and practice, regulatory authorities may initiate legal proceedings against us and our business may be adversely affected.
We could be subject to changes in our tax rates, new U.S. or international tax legislation, or additional tax liabilities.
We are subject to taxes in the United States and numerous foreign jurisdictions, where certain of our subsidiaries are organized. The tax laws in the United States and in other countries in which we and our subsidiaries do business could change on a prospective or retroactive basis, and any such changes could adversely affect our business and financial condition. Our effective tax rates could be affected by numerous factors, including changes in the mix of earnings in countries with differing statutory tax rates, changes in the valuation of deferred tax assets and liabilities, and changes in tax laws or their interpretation, both in and outside the United States.
For example, in 2017, the U.S. government enacted the TCJA, which made significant changes to the taxation of business entities, including the requirement to capitalize research and development expenditures and amortize such expenditures over five years for domestic expenditures and fifteen years for foreign expenditures for taxable years beginning on or after January 1, 2022. While it is possible that Congress may modify or repeal this provision, we have no assurance that this provision will be modified or repealed and even if Congress makes any such decision, it may not be retroactive, and could still therefore result in an impact on cash from operating activities and on the balance of our deferred taxes. In addition, we have a presence in the UK, as well as sales in the UK, such that any changes in tax laws in the UK will impact our business. The overall impact of these changes is uncertain, and our business and financial condition could be adversely affected.
In addition, our tax obligations and effective tax rates could be adversely affected by changes in the relevant tax, accounting and other laws, regulations, principles and interpretations, including those relating to income tax nexus, by recognizing tax losses or lower than anticipated earnings in jurisdictions where we have lower statutory rates and higher than anticipated earnings in jurisdictions where we have higher statutory rates, by changes in foreign currency exchange rates, or by changes in the valuation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities. The TCJA introduced a Base Erosion and Anti-Abuse Tax (“BEAT”) which imposes a minimum tax on adjusted income of corporations with average applicable gross receipt of at least $500 million for the prior three tax years and that make certain payments to related foreign persons. In addition, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development has proposed a global minimum tax of 15% of reported profits (“Pillar 2”) that has been agreed upon in principle by over 140 countries. Many countries have taken steps to incorporate Pillar 2 into their domestic tax laws. While neither BEAT nor Pillar 2 impact our results of operations currently, if applicable in the future, they could have an impact on our financial results, the extent of which is uncertain.
Our tax returns and other tax matters also are subject to examination by the U.S. Internal Revenue Service and other tax authorities and governmental bodies. We regularly assess the likelihood of an adverse outcome resulting from these examinations to determine the adequacy of our provision for taxes. We cannot guarantee the outcome of these examinations. If our effective tax rates were to increase, particularly in the United States, or in other jurisdictions implementing legislation to reform existing tax legislation, including the UK, or if the ultimate determination of our taxes owed is for an amount in excess of amounts previously accrued, our financial condition, operating results, and cash flows could be adversely affected.
We may be liable for contamination or other harm caused by materials that we handle, and changes in environmental regulations could cause us to incur additional expense.
Our research and development and manufacturing operations may involve the use or handling of hazardous materials. We are subject to a variety of federal, state, local, and international laws, rules, and regulations governing the use, handling, storage, disposal and remediation of hazardous and biological materials, as well as the sale, labeling, collection, recycling, treatment, and disposal, of products containing such hazardous substances, and we incur expenses relating to compliance with these laws and regulations. If we violate environmental, health, and safety laws, including as a result of human error, equipment failure, or other cases, we could face substantial liabilities, fines, and penalties, personal injury and third-party property damage claims, and substantial investigation and remediation costs. These expenses or this liability could have a significant negative impact on our financial condition. Environmental laws could become more stringent over time, imposing greater compliance costs and increasing risks and penalties associated with violations. We are subject to potentially conflicting and changing regulatory agendas of political, business, and environmental groups. Changes to or restrictions on the procedures for hazardous or biological material storage or handling might require unplanned capital investment or relocation of our facilities. Failure to comply, or the cost of complying, with new or existing laws or regulations could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Risks Related to Intellectual Property
We may be subject to claims of infringement or misappropriation of the intellectual property rights of others, which could prohibit us from shipping affected devices, require us to obtain licenses from third parties or to develop non-infringing alternatives, and subject us to substantial monetary damages and injunctive relief.
We rely on a combination of patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secret laws, confidentiality and invention assignment agreements with employees and third parties, unfair competition, and other related laws to protect our intellectual property rights. Our patents and patent applications are directed to covering key aspects of the design, manufacture, and use of our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems.
Third parties may assert infringement or misappropriation claims against us with respect to our current or future Zio Services, including our Zio Systems. We are aware of numerous patents issued to third parties that may relate to aspects of our business, including the design and manufacture of the Zio Systems used in connection with our Zio Services. Whether a product infringes a patent involves complex legal and factual issues, the determination of which is often uncertain. Therefore, we cannot be certain that we have not infringed the intellectual property rights of such third parties or others. Our competitors may assert that our Zio Systems or the methods we employ to deliver our Zio Services are covered by U.S. or foreign patents held by them and we may be required to settle such allegations in the future. This risk is exacerbated by the fact that there are numerous issued patents and pending patent applications relating to remote cardiac monitoring services and the associated devices granted to third parties. There may be existing patents or patent applications now pending by third parties of which we are unaware that may later result in issued patents that our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, inadvertently infringe. As the number of competitors in the remote cardiac monitoring market grows, the possibility of patent infringement by us or a patent infringement claim against us increases. If we are unable to successfully defend any such claims as they may arise or enter into or extend settlement and license agreements on acceptable terms or at all, our business operations may be harmed.
Any infringement or misappropriation claim could cause us to incur significant costs, place significant strain on our financial resources, divert management’s attention from our business, and harm our reputation. In addition, if the relevant patents are upheld as valid and enforceable and we are found to infringe such patents, we could be prohibited from using any portion of our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, that is found to infringe such patent unless we could obtain licenses to use the technology covered by the patent or are able to design around the patent. We may be unable to obtain a license on terms acceptable to us, if at all, and we may not be able to redesign our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, to avoid infringement. We may be unable to maintain or renew licenses on terms acceptable to us, if at all, and we may be prohibited from selling any portion of our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, that required the technology covered by the relevant licensed patents. Although patent and intellectual property disputes in the healthcare and medical devices area have often been settled through licensing or similar arrangements, costs associated with such arrangements may be substantial and would likely include ongoing royalties. Even if we are able to redesign our Zio Services, including our Zio Systems, to avoid an infringement claim, we may not receive FDA approval for such changes in a timely manner or at all.
In addition, licensing technologies from third parties exposes us to increased risk of being the subject of intellectual property infringement and vulnerabilities due to, among other things, our lower level of visibility into the development process with respect to such technology and the care taken to safeguard against risks. We currently rely on or incorporate, and will in the future rely on or incorporate, technology that we license from third parties, including software, into our solutions. We cannot be certain that our licensors do not or will not infringe on the intellectual property rights of third parties or that our licensors have or will have sufficient rights to the licensed intellectual property in all jurisdictions in which we may sell our platform. Some of our agreements with our licensors may be terminated by them for convenience, or otherwise provide for a limited term. If we are unable to continue to license technology because of intellectual property infringement claims brought by third parties against our licensors or against us, or if we are unable to continue our license agreements or enter into new licenses on commercially reasonable terms, our ability to develop and sell solutions and services containing or dependent on that technology would be limited, and our business, including our financial conditions, cash flows and results of operations could be harmed. Additionally, if we are unable to license technology from third parties, we may be forced to acquire or develop alternative technology, which we may be unable to do in a commercially feasible manner, or at all, and may require us to use alternative technology of lower quality or performance standards. This could limit or delay our ability to offer new or competitive solutions and increase our costs. Third-party software we rely on may be updated infrequently, unsupported or subject to vulnerabilities that may not be resolved in a timely manner, any of which may expose our solutions to vulnerabilities. Any impairment of the technologies or of our relationship with these third parties could harm our business, operating results, and financial condition.
Further, if we are found to infringe third-party patents, a court could order us to pay damages to compensate the patent owner for the infringement, such as a reasonable royalty amount and/or profits lost by the patent owners, along with prejudgment and/or post-judgment interest. Furthermore, if we are found to willfully infringe third-party patents, we could, in addition to other penalties, be required to pay treble damages; and if the court finds the case to be exceptional, we may be required to pay attorneys’ fees for the prevailing party. If we are found to infringe third-party copyrights or trademarks or misappropriate third-party trade secrets, based on the intellectual property at issue, a court could order us to pay statutory damages, actual damages, or profits, such as reasonable royalty or lost profits of the owners, unjust enrichment, disgorgement of profits, and/or a reasonable royalty, and the court could potentially award attorneys’ fees or exemplary or enhanced damages. If litigation were to be initiated by intellectual property owners, there could significant legal fees and costs incurred in defending litigation (which may include filing administrative actions to attack the intellectual property) as well as a potential monetary settlement payment to the owners, even if the matter is resolved before going to trial. Moreover, the owners may take an overly aggressive approach and/or include multiple allegations in a single litigation.
Our inability to adequately protect our intellectual property could allow our competitors and others to produce devices and offer services based on our technology, which could substantially impair our ability to compete.
Our success and our ability to compete depend, in part, upon our ability to maintain the proprietary nature of our technologies. We rely on a combination of patent, copyright, and trademark law, and trade secrets, nondisclosure agreements, unfair competition laws, and other related laws, and contractual provisions to protect our intellectual property with our customers, third-party partners, and consultants. However, such methods may not be adequate to protect us or permit us to gain or maintain a competitive advantage.
For example, our patent applications may not issue as patents in a form that will be advantageous to us, or at all. Our issued patents, and those that may issue in the future, may be challenged, invalidated, or circumvented, which could limit our ability to stop competitors from marketing related devices and services. In addition, there are numerous recent changes to the patent laws and proposed changes to the rules of the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”), which may have a significant impact on our ability to protect our technology and enforce our intellectual property rights. We cannot be certain that we were the first to make the inventions claimed in our pending patent applications or that we were the first to file for patent protection. Additionally, the process of obtaining patent protection is expensive and time-consuming, and we may not be able to prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. In addition, recent changes to the patent laws in the U.S. may bring into question the validity of certain software patents and may make it more difficult and costly to prosecute patent applications. Such changes may lead to uncertainties or increased costs and risks surrounding the prosecution, validity, ownership, enforcement, and defense of our issued patents and patent applications and other intellectual property, the outcome of third-party claims of infringement, misappropriation, or other violation of intellectual property brought against us and the actual or enhanced damages (including treble damages) that may be awarded in connection with any such current or future claims, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results, and financial condition.
Despite our efforts to protect our proprietary rights, unauthorized parties may attempt to copy aspects of our platform or obtain and use information that we regard as proprietary. In particular, we are unable to predict or assure that:
•our intellectual property rights will not lapse or be invalidated, circumvented, challenged, or, in the case of third-party intellectual property rights licensed to us, be licensed to others;
•our intellectual property rights will provide competitive advantages to us;
•rights previously granted by third parties to intellectual property licensed or assigned to us, including portfolio cross-licenses, will not hamper our ability to assert our intellectual property rights or hinder the settlement of currently pending or future disputes;
•any of our pending or future patent, copyright, or trademark applications will be issued or have the coverage originally sought;
•we will be able to enforce our intellectual property rights in certain jurisdictions where competition is intense or where legal protection may be weak; or
•we have sufficient intellectual property rights to protect our products or our business.
We also may not be able to prevent the unauthorized disclosure or use of our technical knowledge or other trade secrets by consultants, vendors, or former or current employees, despite the existence generally of invention assignment and confidentiality agreements and other contractual restrictions we include in contracts with such parties. These agreements may not provide meaningful protection for our trade secrets, know-how, or other proprietary information in the event of any unauthorized use, misappropriation, or disclosure of such trade secrets, know-how, or other proprietary information. There can be no assurance that employees, consultants, vendors, and clients have executed such agreements or have not breached or will not breach their agreements with us, that we will have adequate remedies for any breach, or that our trade secrets will not otherwise become known or independently developed by competitors. Lastly, the measures we employ to limit the access and distribution of our proprietary information may not prevent unauthorized use or disclosure of our proprietary technology or intellectual property. As such, we cannot guarantee that the steps taken by us will prevent misappropriation of our technology.
In addition, we rely on trademarks, service marks, trade names, and brand names, such as our registered trademark “ZIO,” to distinguish our products from the products of our competitors, and have registered or applied to register these trademarks. We cannot assure you that our trademark applications will be approved. Further, during trademark registration proceedings, we may receive rejections. Although we are given an opportunity to respond to those rejections, we may be unable to overcome such rejections. In addition, in proceedings before the USPTO and in proceedings before comparable agencies in many foreign jurisdictions, third parties are given an opportunity to oppose pending trademark applications and to seek to cancel registered trademarks. Opposition or cancellation proceedings may be filed against our trademarks, and our trademarks may not survive such proceedings. Additionally, we are aware of at least one third party that has registered the “IRHYTHM” mark in the EU in connection with computer software for controlling and managing patient medical information, heart rate monitors, and heart rate monitors to be worn during moderate exercise, among other uses. However, despite that registration, we have successfully obtained a registration for the IRHYTHM mark in the EU in Classes 9 and 10 and we also own many national registrations for IRHYTHM in Europe.
To protect our proprietary rights, we may in the future need to assert claims of infringement against third parties. The outcome of litigation to enforce our intellectual property rights in patents, copyrights, trade secrets, or trademarks is highly unpredictable, could result in substantial costs and diversion of resources, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations regardless of the final outcome of such litigation. In the event of an adverse judgment, a court could hold that some or all of our asserted intellectual property rights are not infringed, or are invalid or unenforceable, and could award attorneys’ fees.
Despite our efforts to safeguard our unpatented and unregistered intellectual property rights, we may not succeed in doing so or the steps taken by us in this regard may not be adequate to detect or deter misappropriation of our technology or to prevent an unauthorized third party from copying or otherwise obtaining and using our devices, technology, or other information that we regard as proprietary. In addition, third parties may be able to design around our patents. Furthermore, the laws of foreign countries may not protect our proprietary rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States.
Risks Related to Privacy and Security
Cybersecurity risks, including those involving network security breaches, services interruptions and other incidents affecting the confidentiality, integrity or availability of our data and systems, could result in the compromise of confidential data or critical systems and give rise to potential harm to our patients, remediation costs and other expenses, expose us to liability under HIPAA, breach notification laws, consumer protection laws, or other common law theories, subject us to litigation and federal and state governmental inquiries, damage our reputation, and otherwise be disruptive to our business and operations.
Cybersecurity threats can come from a variety of sources, ranging in sophistication from an individual hacker to malfeasance by employees, consultants or service providers to criminal or other unauthorized threat actors, including state-sponsored attacks. Unauthorized parties may also attempt to gain access to our systems or facilities through fraud, trickery or other forms of deceiving our employees, and contractors. Cyber threats may be generic, or they may be custom-crafted against our information systems. Cyber incidents can result from deliberate attacks or unintentional events. Over the past several years, cyber-attacks and other cyber incidents have become more prevalent and much harder to detect and defend against. These cyber-attacks and other incidents include unauthorized access to our network, information technology and data, and that of our of contractors and service providers; compromise of employee credentials and accounts; transmission of computer viruses and other malware; phishing and spamming attacks; ransomware attacks and other acts of cyber extortion; and malicious actions by persons inside our organization and other insider threats. For example, during the first quarter of 2024, we experienced a temporary delay in the billing of our contracted and non-contracted payer customers, performed by our third-party claims processing vendor. The delay was due to a cybersecurity incident experienced by Change Healthcare, a division of UnitedHealth Group, which our third-party vendor engages for services relating to billing and collections. While we substantially cleared the billing backlog as of the end of the first quarter of 2024, the delay in billing resulted in a temporary delay in our cash collections. The increasing use of mobile devices for remote access to our systems and data also increases these vulnerabilities and risks.
Our internal technology systems and infrastructure, and those of our contractors, are vulnerable to damage from natural disasters, acts of terrorism, war and other acts of foreign governments and failures of telecommunication, electrical and other critical systems. In addition, hardware, software or applications we develop or procure from third parties may contain defects in design or manufacture or other problems that could unexpectedly compromise information security or other problems that unexpectedly could interfere with our business operations. Because the techniques used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service, or sabotage systems change frequently and may not immediately produce signs of intrusion, we may be unable to anticipate these incidents or techniques, timely discover them, or implement adequate preventative measures.
We have in the past been subject to cyber-attacks and data breaches and expect that we will be subject to additional cyber-attacks in the future and may experience future data breaches. Such incidents may impact the integrity, availability or confidentiality of the data we maintain or disrupt our information systems, devices or business, including our ability to deliver our services. As a result, cybersecurity, physical security and the continued development and enhancement of our controls, processes and practices designed to protect our enterprise, information systems and data from attack, damage or unauthorized access remain a priority for us. As cyber threats continue to evolve, we may be required to expend significant additional resources to continue to modify or enhance our protective measures or to investigate and remediate any cybersecurity vulnerabilities. If our Zio devices are subject to cybersecurity vulnerabilities leading to potential harm to patients or compromises data security and confidentiality, we may be required to initiate field actions, including device recalls, or subject to government inspections, investigations or enforcement actions.
The secure maintenance, processing, and transmission of data is critical to our business operations and we are dependent on sophisticated information technology systems to operate our business. System failures or outages, including any potential disruptions due to significantly increased global demand on certain cloud-based systems, or failures to adequately scale our data platforms and architectures to support patient care could compromise our ability to perform these functions in a timely manner, which could harm our ability to conduct business or delay our financial reporting. We have implemented multiple layers of security measures and monitoring to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of this data and the systems and devices that store and transmit such data. Despite our security measures and business controls, which undergo routine testing internally and by external parties, our information technology and infrastructure may still be vulnerable to attacks. Further, any resulting unauthorized access, disclosure, or other loss of information could result in legal claims or proceedings, and liability under laws that protect the privacy of personal information and regulatory penalties, increase in operating expenses, incurrence of expenses, including notification, mitigation, and remediation costs, disrupt our operations and the services we provide to our clients, or damage our reputation, any of which could adversely affect our profitability, revenue, and competitive position.
Cyber-attacks aimed at accessing our devices and services, or related devices and services, and modifying or using them in a way inconsistent with our FDA marketing authorizations and regulatory certifications in the EU and the UK, could create risks to patients.
Medical devices are increasingly connected to the Internet, hospital networks, and other medical devices to provide features that improve healthcare and increase the ability of healthcare providers to treat patients and of patients to manage their conditions and are subject to extensive oversight from FDA and foreign regulatory authorities with requirements designed to manage the risks of cyber-attacks with the potential to impact patient safety. As such, cyber-attacks aimed at accessing our devices and services, or related devices and services, and modifying or using them in a way inconsistent with our FDA marketing authorizations and regulatory certifications in the EU and the UK, may create risks to patients and potential exposure to our company.
We are required to comply with various laws and regulations with respect to implementing appropriate cybersecurity measures to ensure our devices and services are not compromised or disrupted, which could lead to potential risk of harm or injury to patients. FDA has issued guidance on cybersecurity management of medical devices during post market, and more recently finalized guidance on cybersecurity considerations for quality systems in device premarket submissions. These guidance documents serve as an indicator of agency expectations. If we do not implement the necessary quality measures to manage cybersecurity and minimize or avoid risks of a potential cyber-attack that impacts our devices and services, we could be subject to a range of FDA enforcement action, and such a situation could trigger the need for a recall, a hold on the distribution of our products, or require other corrective actions to our products.
In the EU, a number of interlocking rules regulate cybersecurity for medical devices. For example, the new Cybersecurity Directive (EU) 2022/2555 (also known as the NIS 2 Directive (Network and Information Security)) entered into force in January 2023. The EU NIS 2 Directive affects Critical National Infrastructure (CNI) providers, which includes the health sector and the manufacturers of medical devices considered to be critical during a public health emergency, as well as other covered entities. The requirements in the NIS 2 Directive will sit alongside the cybersecurity requirements addressed in the EU MDR, which are supplemented by specific guidance issued by the EU’s Medical Device Coordination Group. In addition, at this time, we cannot predict the impact on cybersecurity compliance that recent and forthcoming EU legislation such as the Artificial Intelligence Act and the European Health Data Space Regulation, may have. In addition, on January 15, 2024, the European Commission launched a European action plan to strengthen the cybersecurity of hospitals and healthcare providers. Several specific actions will be rolled out progressively in 2025 and 2026. At this time, it is not clear what these actions will entail. In the UK, the government announced as part of its consultations on the future regulation of medical devices, that it intends to develop legislation to impose cybersecurity requirements for software as a medical device, including for AI.
We are subject to complex and evolving U.S. and foreign laws and regulations and other requirements regarding privacy, data protection, security, and other matters. Many of these laws and regulations are subject to change and uncertain interpretation, and could result in claims, changes to our business practices, monetary penalties, increased cost of operations, or declines in customer growth or engagement, or otherwise harm our business.
In the ordinary course of our business, we collect, use and store, and transmit confidential and sensitive data, such as our proprietary business information and that of our suppliers, contractors, customers, vendors and others, as well as personal information, including health information, of these parties and of our patients. As a result, we are subject to several foreign, federal and state laws and regulations protecting the use, disclosure and confidentiality of certain personal information, namely individually identifiable information, and restricting the use and disclosure of that information. These laws include foreign, federal and state healthcare privacy laws, telehealth laws, breach notification laws and consumer protection laws. These frameworks impose stringent privacy and security standards and potentially significant non-compliance penalties and liability. U.S. and foreign legislators and regulators may make legal and regulatory changes, or interpret and apply existing laws, in ways that require us to incur substantial costs, expose us to unanticipated civil or criminal liability, or cause us to change our business practices. Further, if we fail to comply with applicable privacy laws, we could face civil and criminal penalties, or claims for breach of contract. In the United States, there are numerous federal and state patient and consumer, privacy and data security laws and regulations governing the collection, use, disclosure, protection and breach of personal information. HIPAA, for example, establishes privacy standards that limit the use and disclosure of individually identifiable health information (or “protected health information”); requires the implementation of reasonable administrative, physical and technological safeguards to protect the privacy and security of this information and ensure its confidentiality, integrity and availability; and sets forth notification standards in the event of a data breach. In addition, states have shown an increased interest in regulating personal information in general (for example, through state consumer privacy laws and data breach notification laws), and specifically with respect to consumer health data.
Foreign data protection, privacy, and related laws and regulations can be more restrictive than those in the United States. For example, data localization laws in some countries generally mandate that certain types of data collected in a particular country be stored and/or processed solely within that country. Other foreign laws, such as the GDPR, impose strict requirements for processing and cross-border transfers of personal data.
Determining how protected health information may be used, shared, or processed in compliance with applicable privacy standards and our contractual obligations can be complex and may be subject to changing interpretation. Both foreign and U.S. legislators and regulators may make legal and regulatory changes, or interpret and apply existing laws, in ways that require us to incur substantial costs, expose us to unanticipated civil or criminal liability, or cause us to change our business practices.As the regulatory guidance and enforcement landscape in relation to data transfers continue to develop, we could suffer additional costs, complaints and/or regulatory investigations or fines; we may have to stop using certain tools and vendors and make other operational changes; and/or it could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, or if they issue an adverse or misleading opinion regarding our stock, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts publish about us or our business. We do not have any control over the analysts, or the content and opinions included in their reports. If any of the analysts who cover us issues an adverse or misleading opinion regarding us, our business model, our intellectual property, or our stock performance, or if any third-party preclinical studies and clinical trials involving our Zio Services or our results of operations fail to meet the expectations of analysts, our stock price would likely decline. If one or more of such analysts cease coverage of us or fail to publish reports on us regularly, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause a decline in our stock price or trading volume.
Our stock price is highly volatile and investing in our stock involves a high degree of risk, which could result in substantial losses for investors.
Historically, the market price of our common stock, like the securities of many other medical service providers that are public companies, has fluctuated. It is likely that our stock price will continue to be volatile in the future. In addition, the trading prices for our common stock and the common stocks of other medical service providers been highly volatile as a result of macroeconomic conditions, including inflation, interest rate volatility and ongoing geopolitical conflicts, such as the war in Ukraine and conflict in the Middle East.
The market price of our common stock is influenced by many factors that are beyond our control, including the following:
•securities analyst coverage or lack of coverage of our common stock or changes in their estimates of our financial performance;
•variations in quarterly operating results;
•future sales of our common stock by our stockholders;
•investor perception of us and our industry;
•announcements by us or our competitors of significant agreements, acquisitions, or capital commitments or service or product launches or discontinuations;
•changes in market valuation or earnings of our competitors;
•negative business or financial announcements regarding our partners;
•regulatory actions;
•legislation and political conditions;
•cybersecurity events;
•global health pandemics, such as the COVID-19 pandemic;
•terrorist acts, acts of war, or periods of widespread civil unrest, including ongoing geopolitical conflicts, such as the war in Ukraine and conflict in the Middle East; and
•general economic, industry, and market conditions, including inflation, interest rate volatility, uncertainty with respect to the federal debt ceiling and budget and potential government shutdowns related thereto, potential instability in the global banking system, and fluctuating foreign currency exchange rates.
Please also refer to the factors described elsewhere in this “Risk Factors” section. In addition, the stock market in general has experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated and disproportionate to the operating performance of companies in our industry. These broad market and industry factors may materially reduce the market price of our common stock, regardless of our operating performance.
Securities class action litigation has often been brought against public companies that experience periods of volatility in the market prices of their securities. Securities class action litigation could result in substantial costs and a diversion of our management’s attention and resources.
Anti-takeover effects of our charter documents and Delaware law could make a merger, tender offer, or proxy contest difficult, thereby depressing the trading price of our common stock.
There are provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws, as well as provisions in the Delaware General Corporation Law (“DGCL”), that may discourage, delay, or prevent a change of control of our company that might otherwise be beneficial to stockholders. These provisions could also make it difficult for stockholders to elect directors who are not nominated by current members of our board of directors or take other corporate actions, including effecting changes in our management. For example:
•our board of directors may, without stockholder approval, issue shares of preferred stock with special voting or economic rights;
•our stockholders do not have cumulative voting rights and, therefore, each of our directors can only be elected by holders of a majority of our outstanding common stock;
•a special meeting of stockholders may only be called by a majority of our board of directors, the chairman of our board of directors, our chief executive officer, or our president (in the absence of a chief executive officer);
•our stockholders may not take action by written consent; and
•we require advance notice for nominations for election to the board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings.
Moreover, Section 203 of the DGCL may discourage, delay, or prevent a change of control of our company. Section 203 imposes certain restrictions on mergers, business combinations, and other transactions between us and holders of 15% or more of our common stock.
The exclusive forum provision in our organizational documents may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or any of our directors, officers, or other employees, or the underwriters of any offering giving rise to such claim, which may discourage lawsuits with respect to such claims.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation provides that, to the fullest extent permitted by law, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware is the exclusive forum for: any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf; any action asserting a claim of breach of fiduciary duty owed to us or our stockholders by any of our directors, officers, or other employees or agents; any action asserting a claim against us arising pursuant to any provision of the DGCL, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, or our amended and restated bylaws; any action to interpret, apply, enforce, or determine the validity of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, or our amended and restated bylaws; or any action asserting a claim against us that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. This exclusive forum provision does not apply to suits brought to enforce a duty or liability created by the Exchange Act.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, our stockholders will not be deemed to have waived our compliance with the federal securities laws and the regulations promulgated thereunder. Any person or entity purchasing or otherwise acquiring or holding any interest in any of our securities shall be deemed to have notice of and consented to our exclusive forum provisions. The exclusive forum provisions may limit a stockholder’s ability to bring a claim in a judicial forum that it finds favorable for disputes with us or any of our directors, officers, or other employees, which may discourage lawsuits with respect to such claims. Alternatively, if a court were to find the choice of forum provisions contained in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or amended and restated bylaws to be inapplicable or unenforceable in an action, we may incur additional costs associated with resolving such action in other jurisdictions, which could harm our business, operating results, and financial condition.
We do not intend to pay dividends for the foreseeable future.
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings to support operations and to finance the operation and expansion of our business, and we do not expect to declare or pay any dividends on our capital stock in the foreseeable future. As a result, stockholders must rely on sales of their common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any future gains on their investments.
Risks Related to Our Debt
Our indebtedness could adversely affect our financial health and our ability to respond to changes in our business.
As a result of our level of increased debt following the completion of the offering of our 1.50% Convertible Senior Notes due 2029 (the “2029 Notes”):
•our vulnerability to adverse general economic conditions and competitive pressures will be heightened;
•we will be required to dedicate a larger portion of our cash flow from operations to interest payments, limiting the availability of cash for other purposes;
•our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and industry may be more limited; and
•our ability to obtain additional financing in the future for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, general corporate purposes or other purposes may be impaired.
We cannot be sure that our leverage resulting from the level of increased debt will not materially and adversely affect our ability to finance our operations or capital needs or to engage in other business activities. In addition, we cannot be sure that additional financing will be available when required or, if available, will be on terms satisfactory to us. Further, even if we are able to obtain additional financing, we may be required to use such proceeds to repay a portion of our debt.
Furthermore, we will not be restricted under the terms of the indenture governing the 2029 Notes from incurring additional debt, securing future debt, recapitalizing our debt, repurchasing our stock, pledging our assets, making investments, paying dividends, guaranteeing debt or taking a number of other actions that could have the effect of diminishing our ability to make payments on the 2029 Notes when due.
Servicing our debt requires a significant amount of cash, and we may not have sufficient cash flow from our business to pay our indebtedness.
Our ability to repay the principal of, to pay interest on or to refinance our indebtedness, including the 2029 Notes, or to make cash payments in connection with any conversions of 2029 Notes, depends on our future performance, which is subject to economic, financial, competitive and other factors beyond our control. Our business may not generate cash flow from operations in the future sufficient to service our existing indebtedness and any future indebtedness we may incur and make necessary capital expenditures. If we are unable to generate such cash flow, we may be required to adopt one or more alternatives, such as reducing or delaying investments or capital expenditures, selling assets, restructuring debt or obtaining additional debt financing or equity capital on terms that may be onerous or highly dilutive. Our ability to refinance any current or future indebtedness will depend on the capital markets and our financial condition at such time. We may not be able to engage in any of these activities or engage in these activities on desirable terms or at all, which could result in a default on our debt obligations. In addition, any of our future current or future debt agreements may contain restrictive covenants that may prohibit us from adopting any of these alternatives. Our failure to comply with these covenants could result in an event of default which, if not cured or waived, could result in the acceleration of our debt.
In addition, we may be unable to repurchase the 2029 Notes upon a fundamental change when required by the holders or repay prior to maturity any accelerated amounts due under the 2029 Notes upon an event of default or redeem the 2029 Notes or pay cash upon conversion of the 2029 Notes, and our future debt may contain limitations on our ability to pay cash upon conversion, repurchase or repayment of the 2029 Notes.
The capped call transactions may affect the value of our common stock.
In connection with the pricing of the 2029 Notes, we entered into capped call transactions with the option counterparties. The 2029 Capped Calls are expected generally to reduce the potential dilution to our common stock upon conversion of the 2029 Notes and/or offset any cash payments we are required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted 2029 Notes, as the case may be, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap.
The option counterparties or their respective affiliates may modify their hedge positions by entering into or unwinding various derivatives with respect to our common stock and/or purchasing or selling our common stock or other securities of ours in secondary market transactions prior to the maturity of the 2029 Notes (and are likely to do so during any observation period related to a conversion of 2029 Notes or following any redemption or repurchase of 2029 Notes by us, in each case, if we elect to unwind a corresponding portion of the 2029 Capped Calls in connection with such conversion or such redemption or repurchase). This activity could also cause or avoid an increase or a decrease in the market price of our common stock.
We are subject to counterparty risk with respect to the capped call transactions.
The option counterparties are financial institutions or affiliates of financial institutions, and we are subject to the risk that one or more of such option counterparties may default under the 2029 Capped Calls. Our exposure to the credit risk of the option counterparties is not secured by any collateral. Past and current global economic conditions, including recent changes in prevailing interest rates, have resulted in the actual or perceived failure or financial difficulties of many financial institutions. If any option counterparty becomes subject to bankruptcy or other insolvency proceedings, we will become an unsecured creditor in those proceedings with a claim equal to our exposure at that time under the capped call transaction with such option counterparty. Our exposure will depend on many factors but, generally, an increase in our exposure will be positively correlated to an increase in our common stock market price and in the volatility of the market price of our common stock. In addition, upon a default by an option counterparty, we may suffer adverse tax consequences and dilution with respect to our common stock. We can provide no assurance as to the financial stability or viability of any option counterparty.
Conversion of the 2029 Notes will, to the extent we deliver shares upon conversion of such 2029 Notes, dilute the ownership interest of existing stockholders, including holders who had previously converted their 2029 Notes, or may otherwise depress our stock price.
The conversion of some or all of the 2029 Notes will dilute the ownership interests of existing stockholders to the extent we deliver shares upon conversion of any of such 2029 Notes. Any sales in the public market of the common stock issuable upon such conversion could adversely affect prevailing market prices of our common stock. In addition, the existence of the 2029 Notes may encourage short selling by market participants because the conversion of the 2029 Notes could be used to satisfy short positions, or anticipated conversion of the 2029 Notes into shares of our common stock could depress our stock price.
The conditional conversion feature of the 2029 Notes, if triggered, may adversely affect our financial condition and operating results.
In the event the conditional conversion feature of the 2029 Notes is triggered, holders of the 2029 Notes will be entitled to convert the 2029 Notes at any time during specified periods at their option. If one or more holders elect to convert their 2029 Notes, unless we elect to satisfy our conversion obligation by delivering solely shares of our common stock (other than cash in lieu of any fractional share), we would be required to settle a portion or all of our conversion obligation through the payment of cash, which could adversely affect our liquidity. In addition, even if holders of the 2029 Notes do not elect to convert their 2029 Notes, we could be required under applicable accounting rules to reclassify all or a portion of the outstanding principal of the 2029 Notes as a current rather than long-term liability, which would result in a material reduction of our net working capital.
The accounting method for convertible debt securities that may be settled in cash, such as the 2029 Notes, could have a material effect on our reported financial results.
Under current accounting principles, we do not expect to separately account for the liability and equity components of the 2029 Notes and will instead present the entire amount of the 2029 Notes as debt on the balance sheet. Additionally, under the “if-converted” method, diluted earnings per share is generally calculated assuming that all the debt securities were converted solely into shares of common stock at the beginning of the reporting period, unless the result would be anti-dilutive, which could adversely affect our diluted earnings per share. However, if we were to make an irrevocable election to settle the principal amount of the 2029 Notes in cash, the if-converted method for calculating diluted earnings per share will only take into consideration the number of shares that would be issuable based on the extent to which the conversion value of such 2029 Notes exceeds their principal amount, provided the effect were dilutive. Furthermore, if any of the conditions to the convertibility of the 2029 Notes is satisfied, then we may be required under applicable accounting standards to reclassify the liability carrying value of the 2029 Notes as a current, rather than a long-term, liability. This reclassification could be required even if no holders convert their 2029 Notes and could materially reduce our reported working capital.
General Risk Factors
We may be impacted by domestic and global economic and political conditions, as well as natural disasters, pandemics, and other catastrophic events, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
Our operations and performance may vary based on worldwide economic and political conditions, which have been adversely impacted by continued global economic uncertainty, political instability, and military hostilities in multiple geographies, including ongoing geopolitical conflicts such as the war in Ukraine and conflict in the Middle East, domestic and global inflationary trends, interest rate volatility, uncertainty with respect to the federal debt ceiling and budget and potential government shutdowns related thereto, potential instability in the global banking system, global supply shortages, and a tightening labor market. A severe or prolonged economic downturn or period of global political instability could drive hospitals and other healthcare professionals to tighten budgets and curtail spending, which could in turn negatively impact rates at which physicians prescribe our Zio Services. In addition, higher unemployment rates or reductions in employer-provided benefits plans could result in fewer commercially insured patients, resulting in a reduction in our margins and impairing the ability of uninsured patients to make timely payments. A weak or declining economy could also strain our suppliers, possibly resulting in supply delays and disruptions. There is also a risk that one or more of our current service providers, suppliers, or other partners may not survive such difficult economic times, which could directly affect our ability to attain our goals on schedule and on budget. If the current equity and credit markets deteriorate, it may make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult, more costly, and more dilutive. We cannot predict the timing, strength, or duration of an economic downturn, instability, or recovery, whether worldwide, in the United States, or within our industry.
In addition, legislation has been introduced in Congress to limit certain U.S. biotechnology companies from using equipment or services produced or provided by select Chinese biotechnology companies, including those affiliated with the manufacture of certain components of our Zio Monitor System, and others in Congress have advocated for the use of existing executive branch authorities to limit those Chinese service providers’ ability to engage in business in the U.S. We cannot predict what actions may ultimately be taken with respect to trade relations between the United States and China or other countries, what products and services may be subject to such actions or what actions may be taken by the other countries in retaliation.
Further, climate-related events, including the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, natural disasters, or other catastrophic events may cause damage or disruption to our operations, international commerce, and the global economy, and could have an adverse effect on our business, operating results, and financial condition. In the event of a natural disaster, including a major earthquake, blizzard, or hurricane, or a catastrophic event such as a fire, power loss, cyberattack, or telecommunications failure, we may be unable to continue our operations and may endure system and service interruptions, reputational harm, delays in development of our Zio Systems and Zio Services, breaches of data security, and loss of critical data, all of which could cause us to experience higher attrition, losses, and additional costs to maintain or resume operations, or otherwise have an adverse effect on our business and operating results. Further, we do not maintain insurance sufficient to compensate us for the potentially significant losses that could result from disruptions to our services. Additionally, all the aforementioned risks may be further increased if our or our partners’ disaster recovery plans are inadequate.
Environmental, social, and corporate governance (“ESG”) regulations, policies, and provisions may make our supply chain more complex and may adversely affect our relationships with customers.
There is an increasing focus from certain investors, physicians, patients, employees, and other stakeholders concerning corporate citizenship and sustainability matters and the governance of environmental and social risks. An increasing number of participants in the medical services industry are joining voluntary ESG groups or organizations, such as the Responsible Business Alliance. These ESG provisions and initiatives are subject to change, can be unpredictable, and may be difficult and expensive for us to comply with, given our reliance on our supply chain and the outsourced manufacturing of certain components and sub-assemblies of the Zio Systems used with our Zio Services.
At the same time, an increasing number of stakeholders, regulators and lawmakers have expressed or pursued contrary views, including the proposal or enactment of “anti-ESG” policies, legislation, executive orders or initiatives or issued related legal opinions. Conflicting regulations and a lack of harmonization of ESG legal and regulatory environments across the jurisdictions in which we operate may create enhanced compliance risks and costs. We may also face increasing scrutiny from our investors, physicians, patients, employees and other stakeholders relating to the appropriate role of ESG practices and disclosures.
Further, we have in the past and may continue to communicate certain initiatives, including goals, regarding environmental matters, responsible sourcing, and social investments. We could fail, or be perceived to fail, in our achievement of such initiatives or goals, or we could fail in fully and accurately reporting our progress on such initiatives and goals. In addition, we could be criticized for the scope of such initiatives or goals or perceived as not acting responsibly in connection with these matters.
If we are not effective in addressing ESG matters affecting our business, or setting and meeting relevant ESG goals, our reputation and financial results may suffer.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
Not applicable.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Strategy
Cybersecurity is an important part of our risk management at iRhythm. Our cybersecurity program includes mitigating risks for our company and for other companies that may have access to our data and systems. Our board of directors recognizes the critical importance of maintaining the trust and confidence of our customers, clients, business partners, and employees. The risk oversight responsibility of our board of directors and its committees is supported by our cybersecurity management reporting processes, which are designed to provide visibility to our board of directors and to our personnel that are responsible for risk assessment and information about the identification, assessment, and management of critical risks and management’s risk mitigation strategies. These areas of focus include risks from cybersecurity threats as well as competitive, economic, operational, financial, legal, regulatory, privacy, compliance, and reputational risks, among others. We understand that our customers, patients, and stakeholders entrust us with sensitive data, including Protected Health Information, and we take this responsibility seriously.
Our board of directors has an important role in the oversight of the Company’s cybersecurity risk management and strategy and has delegated certain components of such oversight related to the security of and risks related to computerized information and technology systems across the company, as well as by risk area (including privacy, data security, and cybersecurity matters), to the audit committee, which regularly interacts with our Chief Information Security Officer (“CISO") and Chief Risk Officer (“CRO”). We also regularly engage external parties to assist in the review of our cybersecurity risk oversight processes.
We have established policies to govern the security of our systems and the protection of customer and patient data, which include regular system updates and patches, employee training on cybersecurity and HIPAA best practices, incident reporting, and the use of encryption to secure sensitive information. Our Cybersecurity department, which reports to our CISO, is responsible for our cybersecurity program and our Global Risk & Integrity department, which reports to our CRO, is responsible for our privacy program as further discussed below. To identify, assess, and manage material cybersecurity risks, our Cybersecurity team uses a cybersecurity risk assessment process aligned with leading frameworks such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s (“NIST”) Cybersecurity Framework and HIPAA. To ensure appropriate and consistent risk evaluation and decision-making processes among our Cybersecurity and Global Risk & Integrity departments, we utilize an Adjusted Risk Rating (“ARR”) system that considers certain attributes that represent impact to the Company, and we prioritize our actions based on our ARR system. Our cybersecurity risk assessment program provides the underlying basis for the activities our Cybersecurity and Global Risk & Integrity departments take to identify and mitigate risks from, as well as develop risk management and response strategies for, evolving and emerging cybersecurity threats.
In addition, we also regularly perform phishing tests on our employees and review our training plan at least annually for appropriate updates to address results from this testing. Further, we are focused on building and maintaining a positive cybersecurity culture through a combination of trainings, educational tools, videos, and other cybersecurity awareness initiatives. On top of annual information security awareness training for our employees, we also provide focused training for certain departments. Our security training incorporates awareness of cyber threats (including malware, ransomware, and social engineering attacks), password hygiene, and incident reporting process, as well as physical security best practices.
We engage in the periodic assessment of our policies, standards, processes, and practices that are designed to address cybersecurity threats and incidents, internally and through assessments by external providers. These efforts include a wide range of activities, including audits, assessments, tabletop exercises, threat modeling, vulnerability testing, penetration testing, and other exercises focused on evaluating the effectiveness of our cybersecurity measures and planning. Assessments by external providers of our cybersecurity measures include information security maturity assessments, audits, and independent reviews of our information security control environment and operating effectiveness. The results of such internal and external assessments, audits, and reviews are reported to the audit committee and the board of directors, and we adjust our cybersecurity policies, standards, processes, and practices as necessary based on the information provided by these assessments, audits, and reviews.
In addition to the assessment of internal cybersecurity risks, we have implemented processes to oversee and identify risks from cybersecurity threats associated with our use of third-party service providers that have access to our data and systems, including payors and IDTFs. These processes include vetting of service providers for security, reliability, and availability; execution of a Business Associate Agreement with each provider for compliant management, storage, or processing of PHI; and confirmation by each service provider that its SOC-2 reports, or equivalent reports, are current and available, where applicable. In the event a service provider does not have a current and available SOC-2 or equivalent report, we complete a risk-based review of the service provider’s cybersecurity risk management and advise relevant business stakeholders of any significant identified risks.
Based on our board of directors’ and management’s review of risks associated with cybersecurity threats, we have concluded that, to date, there have been no cybersecurity threats which have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our company, including our business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition. If we were to experience a material cybersecurity incident in the future, such incident may have a material effect, including on our business strategy, operating results, or financial condition. For more information regarding cybersecurity risks that we face and potential impacts on our business related thereto, see the risk factor titled “Cybersecurity risks, including those involving network security breaches, services interruptions and other incidents affecting the confidentiality, integrity or availability of our data and systems, could result in the compromise of confidential data or critical data systems and give rise to potential harm to our patients, remediation and other expenses, expose us to liability under HIPAA, breach notification laws, consumer protection laws, or other common law theories, subject us to litigation and federal and state governmental inquiries, damage our reputation, and otherwise be disruptive to our business and operations.”
Governance
As described above, our board of directors has an important role in the oversight of the Company’s cybersecurity risk management and strategy, with certain components of such oversight, including matters related to the security of and risks related to computerized information and technology systems, delegated to the audit committee.
At the management level, our Cyber Security and Risk departments work together to monitor our cybersecurity and risk programs, reporting to our CISO and CRO, respectively. Our CISO currently leads a team of cybersecurity professionals, has held leadership roles in the Cybersecurity team since joining us in 2019, and has over fifteen years of management experience within cybersecurity teams. Our CRO has held leadership roles in internal audit and risk for over a decade, including most recently as CRO of another public company.
Individuals in our Cybersecurity and Global Risk & Integrity departments regularly monitor the prevention, detection, mitigation and remediation of cybersecurity incidents. We have implemented procedures by which any identified or potential cybersecurity risk is communicated to the CISO promptly and discussed in regular team meetings generally held several times per week. Risks are escalated to the CRO and other members of management in accordance with our incident response and reporting policy.
Our CISO reports cybersecurity-related matters twice annually to the audit committee, and promptly reports any significant cybersecurity developments or incidents to our management, who may similarly escalate to the audit committee. These periodic updates include updates on our cybersecurity risk posture, including material risk assessments, the status of any projects to improve our information security systems, and the emerging cybersecurity threat landscape. The audit committee’s reviews may also include presentations by members of senior management, as well as briefings with other internal and external subject-matter experts to help broaden the board of directors’ understanding of the latest cybersecurity issues and the latest regulatory and threat landscapes. Additionally, the audit committee monitors our progress to address cybersecurity risks and opportunities, as well as cybersecurity incident response and recovery metrics. Our management also periodically engages external service providers to conduct objective assessments of our cybersecurity program, and results of such assessments are directly reported to the audit committee. Finally, the audit committee reports out to the larger board of directors periodically on the company’s cybersecurity risks and posture.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
The following table summarizes the facilities leased as of December 31, 2024, including the location and size of each principal facility and their designated use. We believe that these facilities are sufficient to meet our current and anticipated future needs.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Location | | Primary Use | | Approximate Square Footage | | Lease Expiration Year |
| San Francisco, California | | Corporate Headquarters and Clinical Center | | 117,600 | | | 2031 | |
| Cypress, California | | Corporate Office and Manufacturing Facilities | | 68,900 | | | 2032 | |
| Deerfield, Illinois | | Corporate Office and Clinical Center | | 44,600 | | | 2033 | |
| Manila, Philippines | | Corporate Office | | 24,000 | | | 2028 | |
| Houston, Texas | | Clinical Center | | 20,300 | | | 2027 | |
| Solana Beach, California | | Corporate Office | | 16,800 | | | 2032 | |
| London, United Kingdom | | Corporate Office and Clinical Center | | 9,000 | | | 2029 | |
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
From time to time, we are involved in claims and legal proceedings or investigations, that arise in the ordinary course of business. Such matters could have an adverse impact on our reputation, business, and financial condition and divert the attention of our management from the operation of our business. These matters are subject to many uncertainties and outcomes that are not predictable.
On February 6, 2024, a putative class action lawsuit was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California alleging that we and our current Chief Executive Officer, Quentin Blackford, our former Chief Financial Officer, Brice Bobzien, and our former Chief Financial Officer and former Chief Operating Officer, Mr. Devine violated Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Exchange Act and SEC Rule 10b-5 promulgated thereunder, and seeks unspecified damages purportedly sustained by the class. On July 19, 2024, an amended complaint was filed, naming us, Mr. Blackford, Mr. Bobzien, Mr. Devine, our Chief Commercial Officer Chad Patterson, our former Chief Technology Officer Mark Day, and our Chief Medical Officer, Chief Scientific Officer, and Executive Vice President of Product Innovation Mintu Turakhia as defendants. On October 7, 2024, a second amended complaint was filed to include events from the recent FDA inspections, but otherwise included the same claims under the Exchange Act. On December 10, 2024, the defendants filed a motion to dismiss.
Our board members and certain of our current and former executives were named as defendants in two complaints filed as stockholder derivative actions in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware and the United States District Court for the Northern District of California, respectively. We are named as a nominal defendant in both complaints. The cases make similar allegations to those in the securities class action complaint described above and both cases have both been stayed pending the resolution of motion to dismiss briefing in the securities class action.
We believe the above securities class action and derivative lawsuits to be without merit and plan to continue to defend ourselves vigorously.
On March 26, 2021, we received a grand jury subpoena from the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California requesting information related to communications with the Food and Drug Administration and our products and services. On September 13, 2021, we received a second subpoena requesting additional information. On April 4, 2023, we received a Subpoena Duces Tecum from the Consumer Protection Branch, Civil Division of the U.S. Department of Justice (the “DOJ”), requesting production of various documents regarding our products and services. We are cooperating fully on these matters.
On July 1, 2024, the DOJ filed with the United States District Court for the Northern District of California a Petition for Order to Show Cause and Application for Enforcement with respect to the production of certain documentary materials which we assert are protected by legal privileges. We defended our privilege assertions over such materials in our response to the DOJ’s petition. The matter has been briefed, and oral argument is scheduled for March 6, 2025.
On February 20, 2024, Welch Allyn, Inc. (“Welch Allyn”), a subsidiary of Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. now part of Baxter International, Inc., filed a lawsuit against us in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware, alleging that our Zio devices infringe certain of its patents and that the Company’s infringement was willful. We filed a motion to dismiss Welch Allyn’s willful infringement claims on April 11, 2024. Welch Allyn filed an amended complaint on April 24, 2024 that continued to allege that our Zio devices infringe certain of its patents and that our infringement was willful. We filed a motion to dismiss Welch Allyn’s willful infringement allegations found in the amended complaint on May 22, 2024 and a hearing on the motion to dismiss was held on January 28, 2025. After hearing arguments, the Court granted our motion and the willful infringement claims in the amended complaint were dismissed without prejudice. Welch Allyn filed a second amended complaint adding additional patent claims on February 14, 2025. The Company is preparing to file a response to the allegations found in the second amended complaint no later than March 21, 2025. Welch Allyn seeks money damages and attorneys’ fees. We believe this lawsuit is without merit and plan to defend ourselves vigorously.
On December 10, 2024, Bardy Diagnostics, Inc. (“BardyDx”), a subsidiary of Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. now part of Baxter International, Inc., filed a lawsuit against us in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware, alleging that our Zio Monitor patch infringes one of its patents. On December 26, 2024, BardyDx filed an amended complaint alleging that the Company's Zio Monitor patch infringes two of its patents. We are preparing to file a response to the allegations found in the amended complaint no later than March 3, 2025. BardyDx seeks money damages and attorneys’ fees. We believe this lawsuit is without merit and plan to defend ourselves vigorously.
At this time, we are unable to predict the eventual scope, duration or outcome of the aforementioned proceedings. See also Part I, Item 1A “Risk Factors — Risks Related to Other Legal and Regulatory Matters” for more information on these matters.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Market Information for Common Stock
Our common stock is traded on The Nasdaq Global Select Market under the symbol “IRTC”.
As of February 13, 2025, there were 345 holders of record of our common stock. Certain shares are held in “street” name and, accordingly, the number of beneficial owners of such shares is not known or included in the foregoing number.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings, if any, to fund the development and expansion of our business and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination related to dividend policy will be made at the discretion of our board of directors.
Performance Graph
This graph is not “soliciting material,” is not deemed “filed” with the SEC and is not to be incorporated by reference into any filing of iRhythm Technologies, Inc. under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, whether made before or after the date hereof and irrespective of any general incorporation language in any such filing.
The following graph shows the total stockholder return of an investment of $100 in cash at market close on December 31, 2019, through December 31, 2024 for (i) our common stock, (ii) the NASDAQ Composite Index (U.S.), and (iii) the S&P Healthcare Equipment Select Industry. Pursuant to applicable SEC rules, all values assume reinvestment of the full amount of all dividends, however no dividends have been declared on our common stock to date. The stockholder return shown on the graph below is not necessarily indicative of future performance, and we do not make or endorse any predictions as to future stockholder returns.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 12/31/2019 | | 12/31/2020 | | 12/31/2021 | | 12/31/2022 | | 12/31/2023 | | 12/31/2024 |
| iRhythm Technologies, Inc. | | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 348.38 | | | $ | 172.84 | | | $ | 137.57 | | | $ | 157.20 | | | $ | 132.43 | |
| NASDAQ Composite | | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 144.92 | | | $ | 177.06 | | | $ | 119.45 | | | $ | 172.77 | | | $ | 223.87 | |
| S&P Healthcare Equipment Select Industry | | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 133.15 | | | $ | 137.80 | | | $ | 105.61 | | | $ | 99.63 | | | $ | 105.04 | |
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
Information regarding our equity compensation plans and the securities authorized for issuance thereunder is set forth in Part III, Item 12 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Equity Securities
None.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
None.
ITEM 6. [RESERVED]
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with the financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. This discussion and other parts of this Annual Report on Form 10-K contain forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties, such as statements of our plans, objectives, expectations and intentions. Our actual results could differ materially from those discussed in these forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, those discussed in the section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K entitled “Risk Factors.”
Overview
We are a leading digital healthcare company that creates trusted solutions that detect, predict, and prevent disease. Our principal business is the design, development, and commercialization of device-based technology to provide remote cardiac monitoring services that we believe allow clinicians to diagnose certain arrhythmias quicker and with greater efficiency than other services that rely on traditional technology.
Each Zio System combines an FDA-cleared, CE-marked and Japan PMDA-approved wire-free, patch-based, 14-day wearable biosensor that continuously records ECG data with a proprietary, FDA-cleared, CE-marked cloud-based data analytic software to help physicians monitor patients and diagnose arrhythmias. Since receiving FDA clearance, we have provided the Zio Services to over eight million patients and have collected over 2 billion hours of curated heartbeat data.
Since first receiving clearance from FDA for our technology in 2009, we have supported physician and patient use of our technology and provided ambulatory cardiac monitoring services from our Medicare-enrolled IDTFs and with our qualified technicians. We have provided our Zio Services using our Zio Systems.
We receive revenue for the Zio Services primarily from third-party payors, which include contracted third-party payors and CMS. The remainder of our revenue comes from healthcare institutions, which are typically hospitals or private physician practices, who purchase the Zio Services from us directly. We rely on third-party billing partners to submit patient claims and collect from commercial payors, certain government agencies, and patients.
The following are Zio Services shown as a percentage of revenue:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Contracted third-party payors | | 53 | % | | 54 | % | | 55 | % |
| Centers for Medicare and Medicaid | | 24 | % | | 25 | % | | 25 | % |
| Healthcare institutions | | 16 | % | | 14 | % | | 14 | % |
| Non-contracted third party payors | | 7 | % | | 7 | % | | 6 | % |
Key Business Metric
Non-GAAP Financial Measure
Adjusted EBITDA is a key measure we use to assess our financial performance and it is also used for internal planning and forecasting purposes. We believe Adjusted EBITDA is helpful to investors, analysts, and other interested parties because it can assist in providing a more consistent and comparable overview of our operational performance across our historical financial periods. In addition, this measure is frequently used by analysts, investors, and other interested parties to evaluate and assess performance.
We define Adjusted EBITDA for a particular period as net loss before income tax provision, depreciation and amortization, interest expense, interest income and as further adjusted for stock-based compensation expense, changes in fair value of strategic investments, impairment and restructuring charges, business transformation costs, and loss on extinguishment of debt. Business transformation costs include costs associated with professional services, employee termination and relocation, third-party merger and acquisition, integration, and other costs to augment and restructure the organization, inclusive of both outsourced and offshore resources.
Adjusted EBITDA is a non-GAAP financial measure and is presented for supplemental informational purposes only and should not be considered as an alternative or substitute to financial information presented in accordance with GAAP. This measure has certain limitations in that it does not include the impact of certain expenses that are reflected in our consolidated statements of operations that are necessary to run our business. We may identify additional charges and gains to exclude from Adjusted EBITDA that are significant in nature which may impact period to period comparability and do not represent the ongoing results of the business. Other companies, including other companies in our industry, may not use this measure or may calculate this measure differently, limiting its usefulness as a comparative measure.
The following table presents a reconciliation of Net loss, the most directly comparable financial measure calculated in accordance with GAAP, to Adjusted EBITDA (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | |
Net loss1 | | $ | (113,289) | | | $ | (123,406) | | | $ | (116,155) | | |
| Interest expense | | 12,821 | | | 3,650 | | | 4,138 | | |
| Interest income | | (21,938) | | | (6,353) | | | (2,350) | | |
| Changes in fair value of strategic investments | | (1,902) | | | — | | | — | | |
| Income tax provision | | 565 | | | 750 | | | 269 | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 20,715 | | | 16,348 | | | 13,405 | | |
| Stock-based compensation | | 75,978 | | | 77,204 | | | 57,740 | | |
| Impairment and restructuring charges | | 641 | | | 11,078 | | | 26,608 | | |
| Business transformation costs | | 11,072 | | | 15,866 | | | 5,082 | | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | | 7,589 | | | — | | | — | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | | $ | (7,748) | | | $ | (4,863) | | | $ | (11,263) | | |
1 Net loss for the year ended December 31, 2024 includes $32.4 million of acquired in-process research and development expense.
Macroeconomic Factors
Our future results of operations and liquidity could be materially adversely affected by macroeconomic factors contributing to delays in payments of outstanding receivables, supply chain disruptions, including shortages and inflationary pressure, uncertain or reduced demand, and the impact of any initiatives or programs that we may undertake to address financial and operational challenges faced by our customers.
The current macroeconomic environment is impacting our customers, both financially and operationally. Hospitals are experiencing staffing shortages and supply chain issues that could affect their ability to provide patient care. Additionally, hospitals are facing significant financial pressure as supply chain constraints and inflation drive up operating costs, interest rate volatility make access to credit more expensive, and unrealized losses decrease available cash reserves. As a consequence of the financial pressures and decreased profitability, some hospitals have indicated that they are lowering their capital investment plans and tightening their operational budgets. Climate-related events, including the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, natural disasters, or other catastrophic events may cause damage or disruption to our domestic or global customers or our operations, which could have an adverse effect on our business, operating results, and financial condition.
We have adapted our Zio Services to meet the immediate needs of physicians, customers, and patients and significantly increased the utilization of our home enrollment service, which allows patients to receive and wear the single-use Zio patch without going to a healthcare facility.
Our hybrid work arrangements and decision to pursue a sublease for our leased San Francisco headquarters resulted in an impairment of our right-of-use (“ROU”) asset and related leasehold improvements and furniture and fixtures during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. As we continue to evaluate our global real estate footprint, we may incur additional impairment charges related to real property lease agreements.
Revenue
The majority of our revenue is derived from provision of our Zio Services to customers in the United States. We earn revenue from the provision of our Zio Services primarily from contracted third-party payors, CMS, and healthcare institutions. A small percentage of our revenue is from non-contracted third-party payors.
We recognize revenue on an accrual basis based on estimates of the amount that will ultimately be realized, which considers the amount submitted for payment and the amount received. These estimates require significant judgment by management. In determining the amount to accrue for the Zio Services (including a delivered report), we consider factors such as claim payment history from both payors and patient, available reimbursement, including whether there is a contract between us and the payor or healthcare institution and historical amount received for the service, and any current developments or changes that could impact reimbursement and healthcare institution payments.
We typically experience reduced revenue during the third quarter, as well as during the year-end holiday season. We believe this is the result of physicians and patients taking vacations and patients electing to delay our monitoring services during the summer months or holidays. Revenue may be impacted by the outcome of adjudications with contracted and non-contracted payors, as well as changes in CMS reimbursement rates that are updated annually.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenue includes direct labor, material costs, equipment and infrastructure expenses, amortization of internal-use software, allocated overhead, royalties, and shipping and handling. Direct labor includes payroll-related costs including stock-based compensation involved in manufacturing, clinical data curation, and customer service. Material costs include both the disposable materials costs of the Zio patches and amortization of the re-usable printed circuit board assemblies (“PCBAs”). Each Zio XT patch and Zio Monitor patch includes a PCBA, and each Zio AT patch includes a PCBA and gateway board, the cost of which is amortized over the expected useful life of the board. We expect cost of revenue to increase in absolute dollars as our revenue increases due to increased direct labor, direct materials, and variable spending, as well as amortization of internal-use software, partially offset by economies of scale in relation to fixed costs such as overhead and facilities costs.
Our gross margin has been and will continue to be affected by a variety of factors, including increased contracting with third-party payors and institutional providers. We have in the past been able to increase our pricing as third-party payors become more familiar with the benefits of the Zio Services and move to contracted pricing arrangements. We expect increases to the cost of revenues due to increases to materials and electronics components pricing, labor rates, shipping rates, amortization of capitalized internal-use software, along with increases in the general level of inflation and potential tariffs on imports (which may complicate and increase costs associated with our supply chain). We expect to partially offset these increases by reduced costs from obtaining volume purchase discounts for our material costs, implementing scan-time algorithms and process improvements, automating manufacturing assembly and packaging, and through software-driven and other workflow enhancements to reduce labor costs. We experienced an improvement in gross margin from 2023 to 2024, and continue to focus on improving gross margins in the future, while navigating through the macroeconomic and supply chain headwinds discussed above that we expect to face.
Research and Development Expenses
We expense research and development costs as they are incurred. Research and development expenses include payroll-related costs, including stock-based compensation, consulting services, clinical studies, laboratory supplies, milestone payments and allocated facility overhead costs. We expect our research and development costs to increase in absolute dollars as we hire additional personnel to develop new product and service offerings, product enhancements, and clinical evidence.
Acquired In-Process Research and Development Expenses
Our in-process research and development acquired in an asset acquisition for use in research and development activities with no alternative future use is expensed in the consolidated statements of operations.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Our sales and marketing expenses consist of payroll-related costs, including stock-based compensation, sales commissions, travel expenses, consulting, public relations costs, direct marketing, tradeshow and promotional expenses, and allocated facility overhead costs.
Our general and administrative expenses consist primarily of payroll-related costs for executive, finance, legal and administrative personnel, including stock-based compensation. Other significant expenses include professional fees for legal and accounting services, consulting fees, recruiting fees, bad debt expense, third-party patient claims processing fees, business transformation, and travel expenses.
Interest Income
Interest income consists of interest income received on our cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities.
Interest Expense
Interest expense is attributable to borrowings under our loan agreements and 2029 Notes. See Note 9, Debt, in the notes to our consolidated financial statements in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K (the “Consolidated Financial Statements”) for further information on our loan agreements.
Other Income (Expense), Net
Other income (expense), net consists primarily of changes in fair value of our strategic loan and equity investments, as well as realized and unrealized foreign currency exchange gains or losses.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt
Loss on extinguishment of debt reflects the losses incurred in the early repayment of debt. See Note 9, Debt, in the notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on our loss on extinguishment of debt.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2023, and 2022
For discussion related to the results of operations and changes in financial condition for fiscal 2023 compared to fiscal 2022 refer to “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Part II, Item 7 of our 2023 Annual Report on Form 10-K, which was filed with the SEC on February 22, 2024.
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2024, and 2023
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | % Revenue | | 2023 | | % Revenue | | $ Change | | % Change |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (dollars in thousands, except percentages)* |
| Revenue, net | $ | 591,839 | | | 100 | % | | $ | 492,681 | | | 100 | % | | $ | 99,158 | | | 20 | % |
| Cost of revenue | 184,308 | | | 31 | % | | 160,875 | | | 33 | % | | 23,433 | | | 15 | % |
| Gross profit | 407,531 | | | 69 | % | | 331,806 | | | 67 | % | | 75,725 | | | 23 | % |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development | 71,459 | | | 12 | % | | 60,244 | | | 12 | % | | 11,215 | | | 19 | % |
| Acquired in-process research and development | 32,371 | | | 5 | % | | — | | | — | % | | 32,371 | | | N/M |
| Selling, general and administrative | 418,565 | | | 71 | % | | 385,645 | | | 78 | % | | 32,920 | | | 9 | % |
| Impairment and restructuring charges | 641 | | | — | % | | 11,078 | |
| 2 | % | | (10,437) | | | (94) | % |
| Total operating expenses | 523,036 | | | 88 | % | | 456,967 | | | 92 | % | | 66,069 | | | 14 | % |
| Loss from operations | (115,505) | | | (20) | % | | (125,161) | | | (25) | % | | 9,656 | | | (8) | % |
| Interest and other income (expense), net: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | 21,938 | | | 4 | % | | 6,353 | | | 1 | % | | 15,585 | | | 245 | % |
| Interest expense | (12,821) | | | (2) | % | | (3,650) | | | (1) | % | | (9,171) | | | 251 | % |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | (7,589) | | | (1) | % | | — | | | — | % | | (7,589) | | | N/M |
| Other income (expense), net | 1,253 | | | — | % | | (198) | | | — | % | | 1,451 | | | (733) | % |
| Total interest and other income (expense), net | 2,781 | | | — | % | | 2,505 | | | 1 | % | | 276 | | | 11 | % |
| Loss before income taxes | (112,724) | | | (19) | % | | (122,656) | | | (25) | % | | 9,932 | | | (8) | % |
| Income tax provision | 565 | | | — | % | | 750 | | | — | % | | (185) | | | (25) | % |
| Net loss | $ | (113,289) | | | (19) | % | | $ | (123,406) | | | (25) | % | | $ | 10,117 | | | (8) | % |
N/M - Not meaningful
* Certain numbers expressed may not sum due to rounding.
Revenue, net
Revenue increased by $99.2 million, or 20%, to $591.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to $492.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in revenue was primarily attributable to increases in the volume of Zio Services resulting from increased demand. Average selling price remained relatively stable period over period.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenue increased by $23.4 million, or 15%, to $184.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to $160.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in cost of revenue was primarily due to increases in headcount-related costs associated with the increase in volume of Zio Services. For the twelve months ended December 31, 2024, additional impacts to cost of revenue include an increase of approximately $4.0 million in amortization charges for Zio XT and Zio Monitor PCBAs in conjunction with the ongoing commercial launch of Zio Monitor, an increase of $3.4 million for freight-related charges in connection with our increased volume of Zio Services, and an increase of approximately $2.7 million in amortization charges for capitalized internal use software which support our revenue generation.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses increased by $11.2 million, or 19%, to $71.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to $60.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in research and development expenses during the twelve months ended December 31, 2024 was primarily due to higher headcount-related costs (including stock-based compensation), consulting costs to support regulatory affairs, product development, and legal matters, and further development, enhancement and functionality of our current and future product offerings.
Acquired In-Process Research and Development
Acquired IPR&D expense was $32.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2024. The expense was related to the Technology License Agreement (the “License Agreement”) we entered into with BioIntelliSense, Inc. (“BioIS”) during the third quarter of 2024. See Note 8, Commitments and Contingencies, in the notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further details.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased by $32.9 million, or 9%, to $418.6 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to $385.6 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in selling, general, and administrative expenses was primarily attributable to third-party patient claims processing fees and legal fees, offset by reductions in stock-based compensation and professional fees to support scaling the organization. During the twelve months ended December 31, 2024, we incurred $11.1 million of business transformation costs primarily related to severance, professional fees, and third-party merger and acquisition fees. During the twelve months ended December 31, 2023, we incurred $15.9 million of business transformation costs primarily related to severance and professional fees, to drive efficiencies and streamline our global operations.
Impairment and Restructuring Charges
Impairment and restructuring expenses decreased by $10.4 million, or 94%, to $0.6 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to $11.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. During the year ended December 31, 2024, we recorded an impairment charge of $0.6 million related to internal-use software in development not expected to be completed. During the fourth quarter of 2023, we recorded an impairment of our ROU asset and related property and equipment for our headquarters in San Francisco, California, due to real estate rental market conditions within San Francisco, California, of $11.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Interest Income
Interest income increased by $15.6 million to $21.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to $6.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase was attributable to higher market interest rates earned from our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities, as well as an increase in the average invested balances during the year ended December 31, 2024 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2023, primarily as a result of the borrowing under the 2029 Notes in March 2024.
Interest Expense
Interest expense increased by $9.2 million to $12.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to $3.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in interest expense was primarily attributable to the $75.0 million Braidwell Term Loan Facility (as defined below) borrowed and repaid during the first quarter of 2024, as well as the $661.3 million 2029 Notes borrowed in March 2024.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt
Loss on extinguishment of debt was $7.6 million during the year ended December 31, 2024. The increase was related to the early extinguishment of both the SVB Loan Agreement and the Braidwell Term Loan Facility during the first quarter of 2024. See Note 9, Debt, to our Consolidated Financial Statements for more information.
Other Income (Expense), Net
Other income (expense), net increased by $1.5 million to $1.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, as compared to other income (expense), net $(0.2) million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase was primarily attributable to the changes in the fair value of our strategic debt and equity investments recognized during the year ended December 31, 2024.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
As of December 31, 2024, we had cash and cash equivalents of $419.6 million, marketable securities of $116.0 million, and accounts receivable of $79.9 million. We continuously review our liquidity and anticipated capital requirements in light of the significant uncertainty created by the current macroeconomic environment, including inflation, interest rate volatility, and potential instability in the global banking system. We intend to continue to make investments to support our business, which may require us to engage in equity or debt financings to secure additional funds. During the first quarter of 2024, we experienced a temporary delay in the billing of our contracted and non-contracted payer customers, performed by our third-party claims processing vendor. The delay was due to a cybersecurity incident experienced by Change Healthcare, a division of UnitedHealth Group, which our third-party vendor engages for services relating to billing and collections. While we substantially cleared the billing backlog as of the end of the first quarter of 2024, the delay in billing resulted in a temporary delay in our cash collections. As of December 31, 2024, we have received a significant portion of our cash collections from the delayed billings. We believe that our current cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities balances, together with income to be derived from the sales of our Zio Services, will be sufficient to meet our liquidity requirements for at least the next 12 months.
On September 3, 2019, we entered into a Development Collaboration Agreement with Verily Life Sciences LLC, an Alphabet company (“VLS”) and Verily Ireland Limited (“VIL” and together with VLS, “Verily”) (such Development Collaboration Agreement, as amended, the “Development Agreement”). Under the terms of the Development Agreement, we agreed to make milestone payments to Verily up to an aggregate of $12.75 million upon achievement of various development and regulatory milestones. We have achieved milestones tied to payments totaling $11.0 million through December 31, 2024, and we are obligated to make additional milestone payments of $1.75 million, subject to the achievement of specified milestones.
On August 30, 2024, we entered into a License Agreement with BioIS, pursuant to which (i) we will receive a perpetual fully paid up license to certain of BioIS’ intellectual property, technology and products for research, development and commercialization of potential next generation products and services in certain fields of use, including an exclusive license to develop and commercialize pulse oximetry, accelerometry, and trending non-invasive blood pressure technologies for use within our ambulatory cardiac monitoring products and services, and (ii) the parties agreed to negotiate in good faith a supply agreement for pulse oximetry hardware.
Under the terms of the License Agreement, during the third quarter of 2024 we paid BioIS an upfront fee of $15.0 million in cash consideration in acceptance of the initial transfer of certain licensed technologies and data following the execution of the License Agreement. In connection with the License Agreement, we also purchased an aggregate of $40.0 million of convertible promissory notes from BioIS of which $20.0 million of the convertible promissory notes (“Milestone Notes”) were designated for satisfaction of our regulatory milestone payment obligations. The Milestone Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, shall be cancelled, if outstanding, upon the achievement of the regulatory milestones up through December 31, 2026.
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the years indicated (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | $ Change |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 3,390 | | | $ | (50,101) | | | $ | 53,491 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (122,983) | | | (1,209) | | | (121,774) | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 511,381 | | | 8,820 | | | 502,561 | |
Operating Activities
During the year ended December 31, 2024, cash provided by operating activities was $3.4 million, as compared to $50.1 million cash used in operating activities during the year ended December 31, 2023. Cash provided by operating activities increased by $53.5 million primarily attributable to a reduction in our loss from operations, favorable impacts from decreases in prepaid and other current assets, and favorable impacts from a reduction in other long-term assets, primarily from lower levels of purchases of PCBAs.
Investing Activities
During the year ended December 31, 2024, cash used in investing activities was $123.0 million, an increase of $121.8 million as compared to cash used in investing activities of $1.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in cash used in investing activities was primarily attributable to a net decrease in the change in marketable securities of $59.3 million, an increase of $54.0 million related to the purchase of strategic loan investments, and the acquisition of in-process research and development from BioIS of $15.0 million. Offsetting these increases in uses of cash was a decrease in property and equipment expenditures of $6.5 million.
Financing Activities
During the year ended December 31, 2024, cash provided by financing activities was $511.4 million, an increase of $502.6 million, as compared to $8.8 million provided by financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase was primarily attributed to $661.3 million in proceeds received from the issuance of our 2029 Notes. The increase was offset by $37.8 million associated with the payment of the SVB Loan Agreement and related termination costs, payment of $5.6 million associated with the Braidwell Term Loan Facility debt issuance and termination costs, payment of $17.4 million associated with debt issuance costs for our 2029 Notes, payment of $72.4 million for the purchase of the 2029 Capped Calls, and payment of $25.0 million for the repurchase of shares of our common stock.
1.50% Senior Convertible Notes due 2029
On March 7, 2024, we completed an offering of $661.3 million aggregate principal amount of unsecured senior convertible notes with a stated interest rate of 1.50% and a maturity date of September 1, 2029. The proceeds include the full exercise of the option granted by us to the initial purchasers of the 2029 Notes to purchase up to an additional $86.3 million aggregate principal amount of notes. Interest on the 2029 Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year, beginning on September 1, 2024. The net proceeds from the offering, after deducting initial purchasers’ discounts and costs directly related to the offering, were approximately $643.8 million. The initial conversion rate of the 2029 Notes is 6.7927 shares per $1,000 principal amount of notes, which is equivalent to a conversion price of approximately $147.22 per share, subject to adjustments. The 2029 Notes may be settled in cash, stock, or a combination thereof, solely at our discretion.
We used approximately $72.4 million of the net proceeds from the offering to pay the cost of the 2029 Capped Calls, as described below. In addition, we used approximately $80.2 million of the net proceeds from the offering for the repayment in full of the indebtedness outstanding from the Initial Loan of the Braidwell Term Loan Facility (as each such term is defined below). We also used approximately $25.0 million of the net proceeds from the offering to repurchase 229,252 shares of our common stock at a purchase price of $109.05 per share in privately negotiated transactions effected through one of the initial purchasers or its affiliate. These repurchases could increase (or reduce the size of any decrease in) the market price of our common stock, and could result in a higher effective conversion price for the 2029 Notes. We intend to use the remainder of the net proceeds from the offering for general corporate purposes.
No principal payments are due on the 2029 Notes prior to maturity. Other than restrictions relating to certain fundamental changes and consolidations, mergers or asset sales and customary anti-dilution adjustments, the indenture relating to the 2029 Notes includes customary terms and covenants, including certain events of default after which the 2029 Notes may be due and payable immediately.
In connection with the offering of the 2029 Notes, we entered into the privately negotiated capped call transactions (the “2029 Capped Calls”) with certain financial institutions. The 2029 Capped Calls will cover, subject to anti-dilution adjustments substantially similar to those applicable to the 2029 Notes, the number of shares of our common stock that will initially underlie the 2029 Notes. The 2029 Capped Calls are expected generally to reduce potential dilution to our common stock upon conversion of the 2029 Notes and/or offset any cash payments that we could be required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted 2029 Notes, as the case may be, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap. The 2029 Capped Calls have an initial cap price of $218.10 per share, subject to adjustments, which represents a premium of 100% over the closing price of our common stock of $109.05 per share on the Nasdaq Global Select Market on March 4, 2024. We completed the purchase of the 2029 Capped Calls on March 7, 2024, for the amount of $72.4 million.
Braidwell Debt
On January 3, 2024 (the “Closing Date”), we entered into the Credit, Security and Guaranty Agreement (the “Braidwell Credit Agreement”) with Braidwell Transactions Holdings LLC – Series 5 (“Braidwell”), which provided for a senior secured term loan in an aggregate principal amount of up to $150.0 million (the “Braidwell Term Loan Facility”). An initial tranche of $75.0 million (“Initial Loan”) was funded on the Closing Date. An additional tranche of $75.0 million was accessible through the one-year anniversary of the Closing Date, so long as we satisfied certain customary conditions.
Our net proceeds from the Initial Loan were approximately $35.0 million, after deducting costs, fees and expenses, and repayment of our existing term loan from Silicon Valley Bank, as discussed below.
On March 7, 2024, in conjunction with the issuance of the 2029 Notes, we used approximately $80.2 million of the net proceeds for the repayment in full of the $75.0 million outstanding Initial Loan and $5.2 million for interest, fees and expenses associated with terminating the Braidwell Credit Agreement.
SVB Term Loan
In October 2018, we entered into the Third Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement (“SVB Loan Agreement”) with Silicon Valley Bank (“SVB”). Under the SVB Loan Agreement, we had borrowed $35.0 million and had made repayments through March 2022, at which time the outstanding balance was $18.5 million.
On March 28, 2022, we entered into a Second Amendment (the “2022 Amendment”) to our SVB Loan Agreement which provided for a term loans facility in the aggregate principal amount of up to $75.0 million (the “2022 Term Loans”), of which $35.0 million was borrowed at closing and a portion of the proceeds was used to pay in full the outstanding balance of $18.5 million under the SVB Loan Agreement. The remaining $40.0 million of 2022 Term Loans was available to be borrowed from time to time at our option, in increments of at least $10.0 million, through December 31, 2023. The 2022 Amendment also amended the terms of the revolving credit line under the SVB Loan Agreement, which provided for an aggregate principal amount of $25.0 million.
On January 3, 2024, in connection with the entry into the Braidwell Credit Agreement, we used approximately $37.8 million of the net proceeds for the repayment in full of the $35.0 million outstanding principal balance as well as interest, fees and expenses associated with terminating the agreement. Upon termination of the SVB Loan Agreement, SVB’s security interest in our assets and property was released. We continue to hold $8.4 million in letters of credit with SVB, securing them with cash on deposit.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our Consolidated Financial Statements are prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“U.S. GAAP”), which requires us to make judgments, estimates, and assumptions. See Note 2, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, in the notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements, which describes our significant accounting policies and methods used in the preparation of our Consolidated Financial Statements. The methods, estimates, and judgments that we use in applying our accounting policies require us to make difficult and subjective judgments, often as a result of the need to make estimates regarding matters that are inherently uncertain. Our most critical accounting estimates include:
•Revenue recognition;
•Provision for credit losses and contractual allowances;
•PCBA valuation;
•Stock-based compensation;
•Lease impairment; and
•Contingent consideration.
Revenue Recognition
We have developed proprietary systems that combine a wire-free, patch-based, 14-day wearable biosensor that continuously records ECG data, with a proprietary cloud-based data analytic platform to help physicians monitor patients and diagnose arrhythmias. We currently offer three Zio System options—the Zio Monitor System, the Zio XT System, and the Zio AT System.
The Zio Monitor System is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that consists of the Zio Monitor patch that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS System, which supports the capture and analysis of ECG data recorded by the Zio Monitor patch at the end of the wear period, including specific arrhythmia events detected by the ZEUS algorithm. The final step in the Zio Services is the delivery of an electronic Zio report to the prescribing physician with a summary of preliminary findings. Our Zio Monitor services are generally billable when the Zio report is issued to the physician.
The Zio XT System is the previous generation of the Zio Monitor System and is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that consists of the Zio XT patch that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS System, which supports the capture and analysis of ECG data recorded by the Zio XT patch at the end of the wear period, including specific arrhythmia events detected by the ZEUS algorithm. Our Zio XT services are generally billable when the Zio report is issued to the physician.
The Zio AT System is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that similarly consists of the Zio AT patch that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS System, but which also incorporates
the Zio AT wireless gateway that provides connectivity between the patch and the ZEUS System during the patient wear period. The wireless gateway, slightly larger than a smart phone, is provided to the patient at the time of Zio AT patch application and collects and transmits data from the Zio AT patch to the cloud via a LTE protocol. The Zio AT service revenue is recognized under two performance obligations — the patient wear period and delivery of electronic Zio reports.
We recognize as revenue the amount of consideration to which we expect to be entitled in exchange for performing our service. The consideration we are entitled to varies by payor portfolio, as further described below, and includes estimates that require significant judgment by management. A unique aspect of healthcare is the involvement of multiple parties to the service transaction. In addition to the patient, often a third-party payor, for example a commercial or governmental payor or healthcare institution will pay us for some or all of the service on the patient’s behalf. Separate contractual arrangements exist between us and third-party payors that establish amounts the third-party payor will pay on behalf of a patient for covered services rendered.
A small portion of our transactions are covered by third-party payors with whom there is neither a contractual agreement nor an established amount that the third-party payor will pay. In determining the collectability and transaction price for our service, we consider factors such as insurance claims which are adjudicated as allowable under the applicable policy and payment history from both payors and patient out-of-pocket costs, payor coverage, whether there is a contract between the payor or healthcare institution and us, historical amount received for the service, and any current developments or changes that could impact reimbursement and healthcare institution payments. Certain of these factors are forms of variable consideration which are only included in the transaction price to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal of cumulative revenue will not occur when the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is subsequently resolved.
A summary of the payment arrangements with third-party payors and healthcare institutions is as follows:
•Contracted third-party payors – We have contracts with negotiated prices for services provided to patients with commercial healthcare insurance coverage.
•CMS - We have received IDTF approval from regional Medicare Administrative Contractors and will receive reimbursement per the relevant CPT code rates for the services rendered to the patient covered by CMS.
•Healthcare institutions – Healthcare institutions are typically hospitals or physician practices in which we have negotiated amounts for our monitoring services, including certain governmental agencies such as the Veterans Administration and U.S. Department of Defense.
•Non-contracted third-party payors – Non-contracted commercial and government payors often reimburse out-of-network rates provided under the relevant CPT codes on a case-by-case basis. The transaction price used for determining revenue recognition is based on factors including an average of our historical collection experience for our non-contracted services. This rate is reviewed at least quarterly.
We are utilizing the portfolio approach practical expedient under Accounting Standard Codification (“ASC”) 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, whereby services provided under each of the above payor types form a separate portfolio. We account for the contracts within each portfolio as a collective group, rather than individual contracts. Based on history with these portfolios and the similar nature and characteristics of the patients within each portfolio, we have concluded that the financial statement effects are not materially different than if accounting for revenue on a contract-by-contract basis.
For contracted and CMS portfolios, we recognize revenue, net of contractual allowances, and recognize a provision for credit losses for uncollectible patient accounts receivable. The transaction price is determined based on negotiated rates, and our historical experience of collecting substantially all of these contracted rates. These contracts also impose a number of obligations regarding billing and other matters, and our noncompliance with a material term of such contracts may result in a denial of the claim. We account for denied claims as a form of variable consideration that is included as a reduction to the transaction price recognized as revenue.
We make estimates around the amount of denied claims within a reporting period, a process that requires management judgment. The estimated denied claims are based on historical information, and judgement includes the historical period utilized. We monitor the estimated denied claims against the latest available information, and subsequent changes to the estimated denied claims are recorded as an adjustment to revenue in the periods during which such changes occur. Delays in claims submissions could lead to an increase in denials if we miss the payors’ filing deadlines, which could result in a reduction in our receipt of payments. Historical cash collection indicates that it is probable that substantially all of the transaction price, less the estimate of denied claims, will be received. Contracted payors may require that we bill patient co-payments and deductibles and from time to time we may not be able to collect such amounts due to credit risk. We provide for estimates of uncollectible patient accounts receivable, based upon historical experience where judgment includes the historical period utilized, at the time revenue is recognized, with such provisions presented as bad debt expense within the selling, general and administrative line item of the consolidated statements of operations. Adjustments to these estimates for actual experience are also recorded as an adjustment to bad debt expense.
For healthcare institutions, the transaction price is determined based on negotiated rates, and we have historical experience collecting substantially all of these contracted rates. Historical cash collections indicate that it is probable that substantially all of the transaction price will be received. As such, we are not providing an implicit price concession but, rather, has chosen to accept the risk of default, and any subsequent uncollected amounts are recorded as bad debt expense to selling, general and administrative expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
For non-contracted portfolios, we provide an implicit price concession due to the lack of a contracted rate with the underlying payor. As a result, we estimate the transaction price based on historical cash collections utilizing the expected value method. All subsequent changes to the transaction price are recorded as adjustments to revenue.
Provision for Credit Losses and Contractual Allowances
Accounts receivable include amounts due to us from healthcare institutions, third-party payors, government payors and our related patients as a result of our normal business activities. Accounts receivable is reported on the consolidated balance sheets net of an estimated provision for credit losses and contractual allowances.
We establish a provision for credit losses for estimated uncollectible receivables based on our assessment of the collectability of customer accounts and recognize the provision as a component of selling, general and administrative expenses. We record a provision for contractual allowances based on the estimated differences between contracted amounts and expected collection rates. Such provisions are based on our historical experience and are reported as a reduction of revenue.
We regularly review the allowances by considering factors such as historical experience, credit quality, the age of the accounts receivable balances, and current economic conditions that may affect a customer’s ability to pay.
PCBA Valuation
We reuse PCBAs in each wearable Zio Monitor patch, Zio XT patch, and Zio AT patch, as well as the wireless gateway used in conjunction with the Zio AT patch. As PCBAs are used in a wearable Zio Monitor patch, Zio XT patch, or Zio AT patch, a portion of the cost of the PCBA is recorded as a cost of revenue. We base our length of time estimates for charging a portion of the PCBAs cost through several considerations, including evaluation during product development, device loss rates, product launches and obsolescence, and the amount of time it takes the device to go through the manufacturing, shipping, customer shelf, and patient wear time and upload process. We periodically evaluate and update these estimates. PCBAs are included in other assets in our consolidated balance sheets.
Stock-Based Compensation
We measure the estimated fair values of our restricted stock units (“RSUs”) based on the closing price of our stock on the grant date. For performance-based restricted stock units (“PRSUs”), we estimate the fair value based on the closing price of our stock on the grant date and, if the award includes a market condition, a Monte Carlo simulation model. In addition, for PRSUs, we apply a probability assessment to determine the probable achievement of the performance-based metrics.
Stock-based compensation expense is recognized over the requisite service period using the straight-line method and is based on the value of the portion of stock-based payment awards that is ultimately expected to vest. As such, our stock-based compensation is reduced for the estimated forfeitures at the date of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. For restricted stock, the compensation cost for these awards is based on the closing price of our common stock on the date of grant, and is recognized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period.
We recognize compensation expense related to our 2016 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) based on the fair value at each enrollment date of the offering period using the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model value. The stock-based compensation is reduced by the estimated forfeiture and is expensed on a straight-line basis over the offering period.
Lease Impairment
We account for the impairment of long-lived assets in accordance with ASC 360, Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets. An impairment loss is recognized when estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition are less than its carrying value. If an asset is determined to be impaired, the impairment is measured by the amount that the carrying value of the asset exceeds its fair value.
We estimated undiscounted future cash flows from our vacant office lease based on our intent and ability to sub-lease the vacant office space which we had ceased using and estimated future sub-lease income considering the local real estate market conditions. We also factored into the estimate the amount of time to identify a tenant and to enter into an agreement. We estimated the fair value of the ROU asset related to the vacant office lease by discounting the estimated undiscounted future cash flows using the average lease capitalization rate, plus average inflation rate, for other lease transactions in the local area during the year.
Contingent Consideration
Certain agreements we entered into involve payments that are contingent upon the achievement of milestones. Contingent consideration obligations incurred in connection with acquired in-process research and development assets are recorded at fair value, with changes in fair value recorded to acquired in-process research and development expenses in the consolidated statements of operations.
As of December 31, 2024, we held $17.4 million of contingent consideration liabilities related to development milestones from the acquisition of licensed technologies from BioIS. The expected probability of achievement of those milestones has been estimated at 75% - 90% as of December 31, 2024. If the milestones are achieved by their due dates, we estimate an additional $4.8 million of additional contingent consideration. However, if the milestones are not achieved by their due dates, no contingent consideration may be due.
Material Cash Requirements
Our material cash requirements include the following contractual and other obligations.
•Purchase commitments - From time to time in the ordinary course of business, we enter into a variety of purchase arrangements including but not limited to, purchase arrangements related to components used in manufacturing our products. See Note 8, Commitments and Contingencies, to our Consolidated Financial Statements for more information.
•Operating leases - We lease our facilities under non-cancelable operating leases. See Note 8, Commitments and Contingencies, to our Consolidated Financial Statements for more information.
•Debt interest and principal payments - On March 28, 2022, we entered into the 2022 Amendment to our SVB Loan Agreement which provided for a term loans facility in the aggregate principal amount of up to $75.0 million, of which $35.0 million was borrowed at closing. On January 3, 2024, we repaid our outstanding indebtedness with SVB, and entered into the Braidwell Term Loan Facility. The Braidwell Term Loan Facility provides for an aggregate principal borrowing amount of up to $150.0 million, of which $75.0 million was borrowed at closing. On March 7, 2024, we repaid our outstanding indebtedness to Braidwell, and completed an offering of $661.3 million aggregate principal amount of our 2029 Notes. See Note 9, Debt, to our Consolidated Financial Statements for more information.
Recent Accounting Guidance
For a description of recently issued accounting guidance that is applicable to our financial statements, see Note 2, Significant Accounting Policies, to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risks in the ordinary course of our business. These risks primarily include risk related to interest rate sensitivities and foreign currency exchange rate sensitivity.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
We had cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities of $535.6 million and $133.8 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively; which consisted of bank deposits, money market funds and U.S. government securities. Such interest-earning instruments carry a degree of interest rate risk.
We do not enter into investments for trading or speculative purposes and have not used any derivative financial instruments to manage our interest rate risk exposure. We have not been exposed nor do we anticipate being exposed to material risks due to changes in interest rates. A hypothetical 10% change in interest rates would have had a $2.2 million and an $0.6 million impact to interest income for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
As of December 31, 2024 we had $661.3 million in outstanding aggregate principal amount of fixed rate debt relating to our 2029 Notes. Accordingly, we do not have economic interest rate exposure on the 2029 notes. However, changes in interest rates could impact the fair market value of the 2029 Notes. The estimated fair value of our 2029 Notes as of December 31, 2024 was $641.2 million.
As of December 31, 2023 we had total outstanding debt of $35.0 million, net of debt issuance costs relating to the 2022 Term Loans. The SVB Loan Agreement carried a variable interest rate based on the “Prime Rate” published by The Wall Street Journal. A hypothetical 10% change in interest rates during the year ended December 31, 2023 would have resulted in an immaterial impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Market Price Sensitive Instruments
The 2029 Capped Calls are expected generally to reduce potential dilution to our common stock upon conversion of the 2029 Notes and/or offset any cash payments that we could be required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted 2029 Notes, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap. See Note 9, Debt, in the notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on our debt.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Sensitivity
We face foreign exchange risk as a result of entering into transactions denominated in currencies other than U.S. dollars, particularly in British Pound Sterling, Philippine Pesos, Euros, and Swiss Francs. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, we do not consider this risk to be material. We do not utilize any forward foreign exchange contracts, although we may choose to do so in the future. All foreign transactions settle on the applicable spot exchange basis at the time such payments are made. The volatility of exchange rates depends on many factors that we cannot forecast with reliable accuracy. In the event our foreign currency denominated assets, liabilities, sales, or expenses increase, our operating results may be more greatly affected by fluctuations in the exchange rates of the currencies in which we do business.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.
IRHYTHM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of iRhythm Technologies, Inc.
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of iRhythm Technologies, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the related consolidated statements of operations, of comprehensive loss, of stockholders’ equity and of cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, including the related notes (collectively referred to as the "consolidated financial statements"). We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (i) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (ii) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Contractual Allowance – Contracted Third-Party Payors
As described in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, a large portion of the Company’s transactions are covered by third-party payors with whom there is a contractual agreement or established amount the third-party payor will pay (contracted third-party payors). These contracts impose a number of obligations regarding billing and other matters, and the Company’s noncompliance with a material term of such contracts may result in a denial of the claim. The Company recognizes revenue from contracted third-party payors, net of contractual allowances. As of December 31, 2024, the Company’s contractual allowance balance was $48 million, a significant portion of which relates to revenue from services provided to patients where contracted third-party payors pay for the service on the patient's behalf. As disclosed by management, management accounts for denied claims as a form of variable consideration that is included as a reduction to the transaction price and records as an adjustment to revenue as a contractual allowance. The contractual allowance requires judgment by management and is based on historical collections, review of specific outstanding claims and consideration of relevant qualitative factors.
The principal considerations for our determination that performing procedures relating to the contractual allowance for contracted third-party payors is a critical audit matter are (i) the significant judgment by management when developing the estimate of the contractual allowance; and (ii) a high degree of auditor judgment, subjectivity, and effort in performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence related to the contractual allowance based on historical collections, review of specific outstanding claims and consideration of relevant qualitative factors.
Addressing the matter involved performing procedures and evaluating audit evidence in connection with forming our overall opinion on the consolidated financial statements. These procedures included testing the effectiveness of controls relating to management’s estimate of the contractual allowance for contracted third party payors. These procedures also included, among others (i) testing management’s process for developing the estimate of the contractual allowance; (ii) testing the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data used in the estimate; (iii) testing, on a sample basis, the accuracy of revenue transactions and collections from the historical billing and collection data used in management’s analysis; and (iv) evaluating the reasonableness of adjustments made by management to contractual allowances.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
San Jose, California
February 20, 2025
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2009.
IRHYTHM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except par value)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Assets | | | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 419,597 | | | $ | 36,173 | |
| Marketable securities | 115,956 | | | 97,591 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 79,941 | | | 61,484 | |
| Inventory | 14,039 | | | 13,973 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 16,286 | | | 21,591 | |
| Total current assets | 645,819 | | | 230,812 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 125,092 | | | 104,114 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 47,564 | | | 49,317 | |
| Restricted cash | 8,358 | | | — | |
| Goodwill | 862 | | | 862 | |
| Long-term strategic investments | 61,902 | | | 3,000 | |
| Other assets | 41,852 | | | 45,039 | |
| Total assets | $ | 931,449 | | | $ | 433,144 | |
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 7,221 | | | $ | 5,543 | |
| Accrued liabilities | 84,900 | | | 83,362 | |
| Deferred revenue | 2,932 | | | 3,306 | |
| | | |
| Operating lease liabilities, current portion | 15,867 | | | 15,159 | |
| Total current liabilities | 110,920 | | | 107,370 | |
| Long-term senior convertible notes | 646,443 | | | — | |
| Debt, noncurrent portion | — | | | 34,950 | |
| Other noncurrent liabilities | 8,579 | | | 1,012 | |
| Operating lease liabilities, noncurrent portion | 74,599 | | | 79,715 | |
| Total liabilities | 840,541 | | | 223,047 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 8) | | | |
| Stockholders’ equity: | | | |
| Preferred stock, $0.001 par value – 5,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding at December 31, 2024 and 2023 | — | | | — | |
| Common stock, $0.001 par value – 100,000 shares authorized; 31,621 shares issued and 31,392 shares outstanding at December 31, 2024, respectively; and 30,954 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2023 | 31 | | | 31 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 874,607 | | | 855,784 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 165 | | | (112) | |
| Accumulated deficit | (758,895) | | | (645,606) | |
| Treasury stock, at cost; 229 and 0 shares at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively | (25,000) | | | — | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 90,908 | | | 210,097 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 931,449 | | | $ | 433,144 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
IRHYTHM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenue, net | $ | 591,839 | | | $ | 492,681 | | | $ | 410,921 | |
| Cost of revenue | 184,308 | | | 160,875 | | | 129,289 | |
| Gross profit | 407,531 | | | 331,806 | | | 281,632 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Research and development | 71,459 | | | 60,244 | | | 46,610 | |
| Acquired in-process research and development | 32,371 | | | — | | | — | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 418,565 | | | 385,645 | | | 322,198 | |
| Impairment and restructuring charges | 641 | | | 11,078 | | | 26,608 | |
| Total operating expenses | 523,036 | | | 456,967 | | | 395,416 | |
| Loss from operations | (115,505) | | | (125,161) | | | (113,784) | |
| Interest and other income (expense), net: | | | | | |
| Interest income | 21,938 | | | 6,353 | | | 2,350 | |
| Interest expense | (12,821) | | | (3,650) | | | (4,138) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | (7,589) | | | — | | | — | |
| Other income (expense), net | 1,253 | | | (198) | | | (314) | |
| Total interest and other income (expense), net | 2,781 | | | 2,505 | | | (2,102) | |
| Loss before income taxes | (112,724) | | | (122,656) | | | (115,886) | |
| Income tax provision | 565 | | | 750 | | | 269 | |
| Net loss | $ | (113,289) | | | $ | (123,406) | | | $ | (116,155) | |
| Net loss per common share, basic and diluted | $ | (3.63) | | | $ | (4.04) | | | $ | (3.88) | |
| Weighted-average shares, basic and diluted | 31,196 | | | 30,528 | | | 29,916 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
IRHYTHM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Loss
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net loss | $ | (113,289) | | | $ | (123,406) | | | $ | (116,155) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | |
| Net change in unrealized (losses) gains from marketable securities | (21) | | | 453 | | | (335) | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | 298 | | | (169) | | | — | |
| Comprehensive loss | $ | (113,012) | | | $ | (123,122) | | | $ | (116,490) | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
IRHYTHM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In
Capital | | Accumulated
Deficit | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income (Loss) | | Treasury Stock | | Total
Stockholders’
Equity |
| | Shares | | Amount | | |
| Balances at December 31, 2021 | | 29,494 | | | $ | 27 | | | $ | 685,594 | | | $ | (406,045) | | | $ | (61) | | | $ | — | | | $ | 279,515 | |
| Issuance of common stock in connection with employee equity incentive plans, net | | 699 | | | 1 | | | 13,182 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 13,183 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation | | — | | | — | | | 63,604 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 63,604 | |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (116,155) | | | — | | | — | | | (116,155) | |
| Net change in unrealized loss on marketable securities | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (335) | | | — | | | (335) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balances at December 31, 2022 | | 30,193 | | | $ | 28 | | | $ | 762,380 | | | $ | (522,200) | | | $ | (396) | | | $ | — | | | $ | 239,812 | |
| Issuance of common stock in connection with employee equity incentive plans, net | | 761 | | | 3 | | | 8,817 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 8,820 | |
| Stock-based compensation | | — | | | — | | | 84,587 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 84,587 | |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (123,406) | | | — | | | — | | | (123,406) | |
| Net change in unrealized gain on marketable securities | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 453 | | | — | | | 453 | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (169) | | | — | | | (169) | |
| Balances at December 31, 2023 | | 30,954 | | | $ | 31 | | | $ | 855,784 | | | $ | (645,606) | | | $ | (112) | | | $ | — | | | $ | 210,097 | |
| Issuance of common stock in connection with employee equity incentive plans, net | | 667 | | | — | | | 8,473 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 8,473 | |
| Purchase of capped call transactions | | — | | | — | | | (72,407) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (72,407) | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | | (229) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (25,000) | | | (25,000) | |
| Stock-based compensation | | — | | | — | | | 82,757 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 82,757 | |
| Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (113,289) | | | — | | | — | | | (113,289) | |
| Net change in unrealized loss on marketable securities | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (21) | | | — | | | (21) | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 298 | | | — | | | 298 | |
| Balances at December 31, 2024 | | 31,392 | | | $ | 31 | | | $ | 874,607 | | | $ | (758,895) | | | $ | 165 | | | $ | (25,000) | | | $ | 90,908 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
IRHYTHM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | |
| Net loss | $ | (113,289) | | | $ | (123,406) | | | $ | (116,155) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 20,715 | | | 16,348 | | | 13,405 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 75,978 | | | 77,204 | | | 57,740 | |
| Amortization of premium and accretion of discounts, net | (1,350) | | | (5,040) | | | (474) | |
| | | | | |
| Amortization of operating lease right-of-use assets | 5,062 | | | 5,796 | | | 6,204 | |
| Amortization of debt discount | 2,796 | | | 15 | | | 44 | |
| Change in fair value of strategic investments | (1,902) | | | — | | | — | |
| Provision for credit losses and contractual allowances | 73,463 | | | 69,628 | | | 58,349 | |
| Acquired in-process research and development | 32,371 | | | — | | | — | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 7,589 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Impairment charges | 641 | | | 11,078 | | | 23,164 | |
| Other | 432 | | | 322 | | | 220 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (91,920) | | | (81,193) | | | (61,837) | |
| Inventory | (224) | | | 979 | | | (5,108) | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 5,305 | | | (11,036) | | | (862) | |
| Other assets | 3,221 | | | (22,787) | | | (6,200) | |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | (7,408) | | | 17,325 | | | 11,480 | |
| | | | | |
| Deferred revenue | (374) | | | 255 | | | 2 | |
| Operating lease liabilities | (7,716) | | | (5,589) | | | (2,984) | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 3,390 | | | (50,101) | | | (23,012) | |
| Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | |
| Purchases of property and equipment | (33,942) | | | (40,424) | | | (29,830) | |
| Purchases of marketable securities | (118,241) | | | (164,285) | | | (188,569) | |
| Sales of marketable securities | — | | | — | | | 34,965 | |
| Maturities of marketable securities | 101,200 | | | 206,500 | | | 131,000 | |
| Purchases of strategic investments | (57,000) | | | (3,000) | | | — | |
| Purchase of acquired in-process research and development | (15,000) | | | — | | | — | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (122,983) | | | (1,209) | | | (52,434) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | |
| Payment of SVB term loan and termination costs | (37,751) | | | — | | | (21,466) | |
| Proceeds from SVB term loan | — | | | — | | | 35,000 | |
| Proceeds from Braidwell debt | 75,000 | | | — | | | — | |
| Payments of issuance costs for Braidwell debt | (2,100) | | | — | | | — | |
| Payment of Braidwell debt and termination costs | (78,660) | | | — | | | — | |
| Proceeds from issuance of 2029 notes | 661,250 | | | — | | | — | |
| Payments of issuance costs for 2029 notes | (17,424) | | | — | | | — | |
| Purchases of capped call transactions | (72,407) | | | — | | | — | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | (25,000) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
Proceeds from issuance of common stock in connection with employee
equity incentive plans | 8,473 | | | 8,820 | | | 13,182 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 511,381 | | | 8,820 | | | 26,716 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes | (6) | | | (169) | | | — | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 391,782 | | | (42,659) | | | (48,730) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 36,173 | | | 78,832 | | | 127,562 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | $ | 427,955 | | | $ | 36,173 | | | $ | 78,832 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Reconciliation of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 419,597 | | | $ | 36,173 | | | $ | 78,832 | |
| Restricted cash, long term | $ | 8,358 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Total cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | $ | 427,955 | | | $ | 36,173 | | | $ | 78,832 | |
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Interest paid | $ | 6,389 | | | $ | 2,960 | | | $ | 3,317 | |
| Cash taxes paid | $ | 923 | | | $ | 1,130 | | | $ | 287 | |
| Cash paid for operating lease liabilities | $ | 15,177 | | | $ | 14,105 | | | $ | 13,593 | |
| Cash received from tenant improvement allowances | $ | 736 | | | $ | 1,603 | | | $ | 3,279 | |
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | |
| Property and equipment costs included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | 275 | | | $ | 1,888 | | | $ | 160 | |
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for operating lease liabilities | $ | 4,009 | | | $ | 4,403 | | | $ | 7,686 | |
| Capitalized stock-based compensation in property and equipment | $ | 6,779 | | | $ | 7,383 | | | $ | 5,863 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
IRHYTHM TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1.ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
iRhythm Technologies, Inc. (the “Company”) was incorporated in the state of Delaware in September 2006. The Company is a leading digital healthcare company that creates trusted solutions that detect, predict, and prevent disease. The Company's principal business is the design, development, and commercialization of device-based technology to provide remote cardiac monitoring services that it believes allow clinicians to diagnose certain arrhythmias quicker and with greater efficiency than other services that rely on traditional technology.
Since first receiving clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) for the Company's technology in 2009, the Company has supported physician and patient use of its technology and provided remote cardiac monitoring services from its Medicare-enrolled independent diagnostic testing facilities (“IDTFs”) and its qualified technicians. The Company has provided the Zio remote cardiac monitoring services, including extended Holter, traditional Holter, and mobile cardiac telemetry (“MCT”) monitoring services (“Zio Services”), using the Zio Systems.
The Company is headquartered in San Francisco, California, which also serves as a clinical center. The Company has additional clinical centers in Deerfield, Illinois and Houston, Texas, a manufacturing facility in Cypress, California and corporate office space in Solana Beach, California.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”) and include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
Reclassification
Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation. These reclassifications have no impact on previously reported results of operations or financial position.
Risks and Uncertainties
Macroeconomic Factors and Supply Chain Constraints
The Company’s operations and performance may vary based on worldwide economic and political conditions, which have been adversely impacted by continued global economic uncertainty, political instability, and military hostilities in multiple geographies including ongoing geopolitical conflicts, such as the war in Ukraine and conflict in the Middle East, domestic and global inflationary trends, interest rate volatility, potential instability in the global banking system, global supply shortages, and a tightening labor market. A severe or prolonged economic downturn or period of global political instability could drive hospitals and other healthcare professionals to tighten budgets and curtail spending, which could in turn negatively impact rates at which physicians prescribe the Company’s Zio Services. In addition, higher unemployment rates or reductions in employer-provided benefits plans could result in fewer commercially insured patients, resulting in a reduction in the Company’s margins and impairing the ability of uninsured patients to make timely payments. A weak or declining economy could also strain the Company’s suppliers, possibly resulting in supply delays and disruptions. There is also a risk that one or more of the Company’s current service providers, suppliers, or other partners may not survive such difficult economic times, which could directly affect the Company’s ability to attain its goals on schedule and on budget. If the current equity and credit markets deteriorate, it may make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult, more costly, and more dilutive. The Company cannot predict the timing, strength, or duration of an economic downturn, instability, or recovery, whether worldwide, in the United States, or within its industry.
The Company’s hybrid work arrangements and decision to pursue a sublease for its leased San Francisco headquarters resulted in an impairment of its right-of-use (“ROU”) asset and related leasehold improvements and furniture and fixtures during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022. As the Company continues to evaluate its global real estate footprint, the Company may incur additional impairment charges related to real property lease agreements.
The Company is continuously reviewing its liquidity and anticipated capital requirements. The Company believes it has adequate liquidity over the next 12 months to operate its business and to meet its cash requirements. The Company is in compliance with its convertible debt requirements.
Reimbursement
The Company receives revenue for the Zio Services primarily from third-party payors, which include commercial payors and government agencies, such as the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (“CMS”). Third-party payors require the Company to identify the service for which it is seeking reimbursement by using a Current Procedural Terminology (“CPT”) code set maintained by the American Medical Association. These CPT codes are subject to periodic change and update, which will impact the reimbursement rates for the Company’s Zio Services.
Based on relative value units, CMS annually updates the reimbursement rates for diagnostic tests performed by IDTFs via the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule. CMS establishes national payment rates for the CPT codes the Company uses to report Zio Services performed by the Company. Because remote cardiac monitoring technology, including the Zio System, is rapidly evolving, there is a continuing risk that relative value units assigned, and reimbursement rates set, by CMS may not adequately reflect the value and expense of this technology and associated monitoring services, and CMS may reduce these rates in the future, which would adversely affect the Company’s financial results.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the periods presented. On an ongoing basis, management evaluates its estimates, including those related to revenue recognition, contractual allowances, provision for credit losses, the useful lives of property and equipment, the recoverability of long-lived assets, including the estimated usage of the printed circuit board assemblies (“PCBAs”), the incremental borrowing rate for operating leases, fair value of strategic loan investments, accounting for income taxes, impairment of ROU assets, contingent consideration liabilities, and various inputs used in estimating stock-based compensation. Actual results may differ from those estimates.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts of certain of the Company’s financial instruments, which include cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued liabilities, and debt, approximate fair value due to their short maturities.
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
Cash and cash equivalents consist of short-term, highly liquid investments with an original maturity from the date of purchase of three months or less.
Under the terms of certain facility operating lease agreements, the Company is required to maintain a letter of credit as collateral during the term of the lease. As of December 31, 2024, restricted cash of $8.4 million was pledged as collateral under the letter of credit with Silicon Valley Bank.
Fair Value Option
The Company elected the fair value option, Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 825-10, Financial Instruments - Overall, to account for its strategic loan investments. The Company recorded the strategic loan investments at fair value within long-term strategic investments in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets with changes in fair value recorded within other income (expense), net on the consolidated statements of operations. The primary reason for electing the fair value option was for simplification and cost-benefit considerations of accounting for the strategic loan investments at fair value versus bifurcation of the embedded derivatives. Refer to Note 5, Fair Value Measurements, for further details relating to the Company's strategic investments.
Contingent Consideration
Certain agreements the Company entered into involve payments that are contingent upon the achievement of milestones. Contingent consideration obligations incurred in connection with acquired in-process research and development assets are recorded at fair value, with changes in fair value recorded to acquired in-process research and development expenses in the consolidated statements of operations.
Marketable Securities
The Company's marketable security investments consist primarily of commercial paper, corporate bonds, U.S. agency obligations and U.S. treasury securities. The Company typically invests in highly-rated securities, and its investment policy generally limits the amount of credit exposure to any one issuer. The Company's policy generally requires investments to be investment grade, with the primary objective of minimizing the potential risk of principal loss. The Company classifies investments as available-for-sale at the time of purchase and re-evaluates such classification as of each balance sheet date. Available-for-sale debt securities with an amortized cost basis in excess of the estimated fair value are assessed to determine what amount of that difference, if any, is caused by expected credit losses. Allowance for credit losses on available-for-debt securities are recognized as a charge in other income (expense), net on the Company's consolidated statements of operations and any remaining unrealized gains or losses, net of taxes, are included in accumulated other comprehensive loss in accumulated deficit on the consolidated balance sheets. There were no impairment charges for any unrealized losses during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
Concentrations of Risk
Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to a concentration of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, investments and accounts receivable. Cash balances are deposited in financial institutions which, at times, may be in excess of federally insured limits. Cash equivalents are invested in highly rated money market funds. The Company invests in a variety of financial instruments, such as, but not limited to, U.S. government securities, corporate notes, commercial paper and, by policy, limits the amount of credit exposure with any one financial institution or commercial issuer. The Company has not experienced any material losses on its deposits of cash and cash equivalents or investments.
Concentrations of credit risk with respect to accounts receivable are limited due to the large number of customers comprising the Company’s customer base and their dispersion across many geographies. The Company does not require collateral. During the first quarter of 2024, the Company experienced a temporary delay in the billing of the Company's contracted and non-contracted payer customers, performed by the Company's third-party claims processing
vendor. The delay was due to a cybersecurity incident experienced by Change Healthcare, a division of UnitedHealth Group, which the Company's third-party vendor engages for services relating to billing and collections. While the Company substantially cleared the billing backlog as of the end of the first quarter of 2024, the delay in billing resulted in a temporary delay in the Company's cash collections. As of December 31, 2024, the Company has received the majority of its cash collections from the delayed billings.
The Company records a provision for credit losses based on the assessment of the collectability of customer accounts, considering factors such as historical experience, credit quality, the age of the accounts receivable balances, and current economic conditions that may affect a customer’s ability to pay. CMS accounted for approximately 15% and 25% of accounts receivable for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. One commercial customer accounted for approximately 13% of the Company's accounts receivable as of December 31, 2024. As presented in Note 3, CMS accounted for approximately 24%, 25% and 25% of the Company’s revenue for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Inflationary Risk
The Company continuously monitors the effects of inflationary factors, such as increases in cost of goods sold and selling and operating expenses, which may adversely affect its results of operations. Specifically, the Company may experience inflationary pressure affecting freight costs, the cost of the components for the Company’s Zio Services, overhead costs relating to maintenance of the Company’s facilities, and in the wages paid to its employees due to challenging labor market conditions. Competitive and regulatory conditions may restrict the Company’s ability to fully recover these costs through price increases. As a result, it may be difficult to fully offset the impact of persistent inflation. The Company’s inability or failure to do so could have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, and results of operations or cause the Company to need to obtain additional capital earlier than anticipated in the future.
Supply Risk
The Company relies on single-source vendors to supply some of its disposable housings, instruments and other materials used to manufacture the Zio patches and the adhesive that binds the Zio patch to a patient’s body. These components and materials are critical, and there could be a considerable delay in finding alternative sources of supply.
Inventory
Inventory owned by the Company is valued at cost, on the first in, first out (“FIFO”) basis, or the lower of cost or net realizable value. The Company records write-downs of inventory that is obsolete or in excess of anticipated demand. The Company also records market value-based write-downs in consideration of product lifecycle stage, technology trends, product development plans, and assumptions about future demand and market conditions. Actual demand may differ from forecasted demand, and such differences may have a material effect on recorded inventory values. Inventory write-downs are charged to cost of revenue and establish a new cost basis for the inventory.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from three to seven years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the lease term or the estimated useful lives of the assets. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred, and improvements and betterment are capitalized.
The Company classifies internal-use software in property and equipment. Internal-use software costs are capitalized during the application development stage. Costs related to planning and post implementation activities are expensed as incurred. Capitalized internal-use software is amortized, and recognized as cost of revenue or selling, general and administrative expenses, on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life generally ranging between three to seven years.
PCBAs
The Company reuses PCBAs in each wearable Zio Monitor patch, Zio XT patch, and Zio AT patch, as well as the wireless gateway used in conjunction with the Zio AT patch. As PCBAs are used in a wearable Zio Monitor patch, Zio XT patch, or Zio AT patch, a portion of the cost of the PCBA is recorded as a cost of revenue. The Company bases the length of time estimates for charging a portion of the PCBAs cost through several considerations, including evaluation during product development, device loss rates, product launches and obsolescence, and the amount of time it takes the device to go through the manufacturing, shipping, customer shelf, and patient wear time and upload process. The Company periodically evaluates and updates these estimates. PCBAs are included in other assets in the Company's consolidated balance sheets.
Implementation Costs in Cloud-Computing Arrangements
The Company capitalizes qualified implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract for which it is the customer in accordance with the requirements for cloud computing arrangements (“CCA”) to the extent it is incurred in the course of developing internal-use software. These capitalized implementation costs are generally amortized over the fixed, non-cancellable term of the associated hosting arrangement on a straight-line basis are recorded in prepaid expenses and other current assets or in other noncurrent assets. The Company amortizes capitalized implementation costs in a CCA on a straight-line basis over the terms of the associated hosting arrangement.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price of an acquired business over the fair value of the underlying net tangible and intangible assets. Goodwill amounts are not amortized, but rather tested for impairment at least annually, and more frequently when changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. The Company has determined that it operates its business as one reporting unit and the Company completes its annual impairment test in the fourth quarter. In the event that the Company determines that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than the reporting unit's carrying value, goodwill impairment charge will be incurred for the amount of the difference during the quarter in which the determination is made. The Company did not record any goodwill impairment charges in the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company reviews long-lived assets, inclusive of internal-use software, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability is measured by comparing the carrying amount to the future net cash flows that the assets are expected to generate. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured as the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the projected discounted future net cash flows arising from the asset.
Any impairments to ROU assets, leasehold improvements, or other assets as a result of a sublease or other similar action are initially recognized when a decision to take such action is made and recorded as an operating expense. Similar to other long-lived assets, management tests ROU assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances occur that could impact the recoverability of these assets. For ROU assets, such circumstances may include subleases that do not fully recover the costs of the associated leases or commitments to sublease a property. In addition, see Note 7, Impairment and Restructuring Charges, included in the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Comprehensive Loss
Comprehensive loss represents all changes in stockholders’ equity during the year from non-owner sources. The Company’s unrealized gains and losses on marketable securities represent the only component of other comprehensive loss that are excluded from the reported net loss and that are presented in the consolidated statements of comprehensive loss.
Revenue Recognition
The Company has developed proprietary systems that combine a wire-free, patch-based, 14-day wearable biosensor that continuously records ECG data, with a proprietary cloud-based data analytic platform to help physicians monitor patients and diagnose arrhythmias. The Company currently offers three Zio System options—the Zio Monitor System, the Zio XT System, and the Zio AT System.
The Zio Monitor System is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that consists of the Zio Monitor patch that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS algorithm, which supports the capture and analysis of ECG data recorded by the Zio Monitor patch at the end of the wear period, including specific arrhythmia events detected by the ZEUS System. The final step in the Zio Services is the delivery of an electronic Zio report to the prescribing physician with a summary of preliminary findings. The Company’s Zio Monitor services are generally billable when the Zio report is issued to the physician.
The Zio XT System is the previous generation of the Zio Monitor System and is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that consists of the Zio XT patch that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS System, which supports the capture and analysis of ECG data recorded by the Zio XT patch at the end of the wear period, including specific arrhythmia events detected by the ZEUS algorithm. The Company’s Zio XT services are generally billable when the Zio report is issued to the physician.
The Zio AT System is a prescription-only, remote ECG monitoring system that similarly consists of the Zio AT patch that records the electric signal from the heart continuously for up to 14 days and the ZEUS System, but which also incorporates the Zio AT wireless gateway that provides connectivity between the Zio AT patch and the ZEUS System during the patient wear period. The wireless gateway, slightly larger than a smart phone, is provided to the patient at the time of Zio AT patch application and collects and transmits data from the Zio AT patch to the cloud via a long- term evolution protocol. The Zio AT service revenue is recognized under two performance obligations — the patient wear period and delivery of electronic Zio reports.
The Company recognizes as revenue the amount of consideration to which it expects to be entitled in exchange for performing the service. The consideration the Company is entitled to varies by payor portfolio, as further described below, and includes estimates that require significant judgment by management. A unique aspect of healthcare is the involvement of multiple parties to the service transaction. In addition to the patient, often a third-party payor, for example a commercial or governmental payor or healthcare institution, will pay the Company for some or all of the service on the patient’s behalf. Separate contractual arrangements exist between the Company and third-party payors that establish amounts the third-party payor will pay on behalf of a patient for covered services rendered.
A small portion of the Company’s transactions are covered by third-party payors with whom there is neither a contractual agreement nor an established amount that the third-party payor will pay. In determining the collectability and transaction price for its service, the Company considers factors such as insurance claims which are adjudicated as allowable under the applicable policy and payment history from both payors and patient out-of-pocket costs, payor coverage, whether there is a contract between the payor or healthcare institution and the Company, historical amount received for the service, and any current developments or changes that could impact reimbursement and healthcare institution payments. Certain of these factors are forms of variable consideration which are only included in the transaction price to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal of cumulative revenue will not occur when the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is subsequently resolved.
A summary of the payment arrangements with third-party payors and healthcare institutions is as follows:
•Contracted third-party payors – The Company has contracts with negotiated prices for services provided to patients with commercial healthcare insurance coverage.
•CMS – The Company has received IDTF approval from regional Medicare Administrative Contractors and will receive reimbursement per the relevant CPT code rates for the services rendered to the patient covered by CMS.
•Healthcare institutions – Healthcare institutions are typically hospitals or physician practices in which the Company has negotiated amounts for its monitoring services, including certain governmental agencies such as the Veterans Administration and U.S. Department of Defense.
•Non-contracted third-party payors – Non-contracted commercial and government payors often reimburse out-of-network rates provided under the relevant CPT codes on a case-by-case basis. The transaction price used for determining revenue recognition is based on factors including an average of the Company’s historical collection experience for its non-contracted services. This rate is reviewed at least quarterly.
The Company is utilizing the portfolio approach practical expedient under Accounting Standard Codification (“ASC”) 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, whereby services provided under each of the above payor types form a separate portfolio. The Company accounts for the contracts within each portfolio as a collective group, rather than individual contracts. Based on history with these portfolios and the similar nature and characteristics of the patients within each portfolio, the Company has concluded that the financial statement effects are not materially different than if accounting for revenue on a contract-by-contract basis.
For contracted and CMS portfolios, the Company recognizes revenue, net of contractual allowances, and recognizes a provision for credit losses for uncollectible patient accounts receivable. The transaction price is determined based on negotiated rates, and the Company has historical experience of collecting substantially all of these contracted rates. These contracts also impose a number of obligations regarding billing and other matters, and the Company’s noncompliance with a material term of such contracts may result in a denial of the claim. The Company accounts for denied claims as a form of variable consideration that is included as a reduction to the transaction price recognized as revenue.
The Company makes estimates around the amount of denied claims within a reporting period, a process that requires management judgment. The estimated denied claims are based on historical information and judgement includes the historical period utilized. The Company monitors the estimated denied claims against the latest available information, and subsequent changes to the estimated denied claims are recorded as an adjustment to revenue in the periods during which such changes occur. Delays in claims submissions could lead to an increase in denials if the Company misses the payors’ filing deadlines, which could result in a reduction in the Company’s receipt of payments. Historical cash collection indicates that it is probable that substantially all of the transaction price, less the estimate of denied claims, will be received. Contracted payors may require that the Company bills patient co-payments and deductibles and from time to time the Company may not be able to collect such amounts due to credit risk. The Company provides for estimates of uncollectible patient accounts receivable, based upon historical experience where judgment includes the historical period utilized, at the time revenue is recognized, with such provisions presented as bad debt expense within the selling, general and administrative line item of the consolidated statements of operations. Adjustments to these estimates for actual experience are also recorded as an adjustment to bad debt expense.
For healthcare institutions, the transaction price is determined based on negotiated rates, and the Company has historical experience collecting substantially all of these contracted rates. Historical cash collections indicate that it is probable that substantially all of the transaction price will be received. As such, the Company is not providing an implicit price concession but, rather, has chosen to accept the risk of default, and any subsequent uncollected amounts are recorded as bad debt expense to selling, general and administrative expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
For non-contracted portfolios, the Company provides an implicit price concession due to the lack of a contracted rate with the underlying payor. As a result, the Company estimates the transaction price based on historical cash collections utilizing the expected value method. All subsequent changes to the transaction price are recorded as adjustments to revenue.
Leases
The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception. The Company's lease agreements generally contain lease and non-lease components. Payments under its lease arrangements are primarily fixed. Non-lease components primarily include payments for maintenance and utilities. The Company combines fixed payments for non-lease components with lease payments and accounts for them together as a single lease component which increases the amount of the Company’s ROU assets and lease liabilities.
Certain lease agreements contain variable payments, which are expensed as incurred and not included in the ROU assets and lease liabilities.
ROU assets and lease liabilities are recognized at the present value of the future lease payments at the lease commencement date. The interest rate used to determine the present value of the future lease payments is the Company's incremental borrowing rate, because the interest rate implicit in its leases is not readily determinable. The Company's incremental borrowing rate is estimated to approximate the interest rate on a collateralized basis with similar terms and payments, and in economic environments where the leased asset is located. The Company's lease terms include periods under options to extend or terminate the lease when it is reasonably certain that it will exercise that option. The Company generally uses the base, non-cancelable, lease term when determining the ROU assets and lease liabilities. ROU assets are adjusted for any prepaid lease payments and lease incentives.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenue includes direct labor, material costs, equipment and infrastructure expenses, amortization of internal-use software, allocated overhead, royalties, and shipping and handling. Direct labor includes payroll-related costs including stock-based compensation involved in manufacturing, clinical data curation, and customer service. Material costs include both the disposable materials costs of the Zio patches and amortization of the re-usable printed circuit board assemblies (“PCBAs”). Each Zio XT patch and Zio Monitor patch includes a PCBA, and each Zio AT patch includes a PCBA and gateway board, the cost of which is amortized over the expected useful life of the board.
Research and Development
The Company’s research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Research and development costs include payroll-related costs, including stock-based compensation, consulting services, clinical studies, laboratory supplies, milestone payments, and allocated facility overhead costs.
Acquired In-Process Research and Development Expenses
Acquired in-process research and development (“IPR&D”) assets, as a result of an asset acquisition, for use in research and development activities with no alternative future use are expensed in the consolidated statements of operations on the acquisition date. Accounting for acquisitions of IPR&D requires the Company to make certain judgements to determine if the transaction should be accounted for as an asset acquisition or a business combination, as well as assess if the IPR&D acquired has alternative future use in research and development activities.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
The Company's sales and marketing expenses consist of personnel costs, including stock-based compensation, and sales commissions. Other significant costs include travel expenses, consulting, public relations costs, direct marketing, tradeshow and promotional expenses and allocated facility overhead costs.
The Company incurred an immaterial amount of advertising expense during each of the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, which is included in selling, general and administrative expenses.
The Company’s general and administrative expenses consist primarily of payroll-related costs for executive, finance, legal and administrative personnel, including stock-based compensation. Other significant expenses include professional fees for legal and accounting services, consulting fees, recruiting fees, bad debt expense, third-party patient claims processing fees, business transformation, and travel expenses.
Income Taxes
The Company uses the asset and liability method to account for income taxes. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, and tax loss and credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates applied to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. A valuation allowance is established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. The Company records interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. To date, there have been no interest or penalties charged in relation to the unrecognized tax benefits.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company measures the estimated fair values of its restricted stock units (“RSUs”) based on the closing price of the Company's stock on the grant date. For performance-based restricted stock units (“PRSUs”), the Company estimates the fair value based on the closing price of its stock on the grant date and, if the award includes a market condition, a Monte Carlo simulation model. In addition, for PRSUs, the Company applies a probability assessment to determine the probable achievement of the performance-based metrics.
Stock-based compensation expense is recognized over the requisite service period using the straight-line method and is based on the value of the portion of stock-based payment awards that is ultimately expected to vest. As such, the Company's stock-based compensation is reduced for the estimated forfeitures at the date of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. For restricted stock, the compensation cost for these awards is based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant, and is recognized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period.
The Company recognizes compensation expense related to its 2016 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) based on the fair value at each enrollment date of the offering period using the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model value. The stock-based compensation is reduced by the estimated forfeiture and is expensed on a straight-line basis over the offering period.
Net Loss per Common Share
Basic net loss per common share is calculated by dividing the net loss by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period, without consideration of potentially dilutive securities. Diluted net loss per common share is the same as basic net loss per common share for all periods presented, since the effect of potentially dilutive securities are anti-dilutive.
Recently adopted accounting pronouncements
In November 2023, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2023-07 (“ASU 2023-07”), Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which updates reportable segment disclosure requirements primarily through enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses. The amendments are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023, and for interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The Company adopted ASU 2023-07 during the year ended December 31, 2024. See Note 3, Business Segment and Revenue, for disclosure within the notes to the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Recently issued accounting pronouncements not yet adopted
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU No. 2023-09 (“ASU 2023-09”), Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvement to Income Tax Disclosures to enhance the transparency and decision usefulness of income tax disclosures. Two primary enhancements related to this ASU include disaggregating existing income tax disclosures relating to the effective tax rate reconciliation and income taxes paid. ASU 2023-09 is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024 on a prospective basis. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating this ASU to determine its impact on the Company's financial statement disclosures.
On March 6, 2024, the SEC adopted SEC Release Nos. 33-11275; 34-99678, The Enhancement and Standardization of Climate-Related Disclosures for Investors, to require the disclosure of certain climate-related information in registration statements and annual reports, including Scope 1 and 2 emissions and information about climate-related risks that have materially impacted, or are reasonably likely to have a material impact on, a company’s business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition. In addition, under the final rules, certain disclosures related to severe weather events and other natural conditions will be required in audited financial statements. The disclosure requirements will begin phasing in for the Company's reports and registration statements including financial information in the fiscal year ending December 31, 2025. In April 2024, the SEC issued an order staying the final rules until the completion of judicial review. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this final rule on the Company's consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU 2024-03, Income Statement-Reporting Comprehensive Income-Expense Disaggregation Disclosures, which requires disclosure about the types of costs and expenses included in certain expense captions presented on the income statement. The new disclosure requirements are effective for the Company’s annual periods beginning after December 15, 2026, and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2027, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently in the process of evaluating the impact of this pronouncement on its related disclosures.
3. BUSINESS SEGMENT AND REVENUE
Reportable Segments
Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise where separate financial information is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker (“CODM”). The Company has one reportable and one operating segment, its global ambulatory cardiac monitoring business. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer, who is the Company’s CODM, reviews financial information presented on a consolidated basis for purposes of making operating decisions, allocating resources, and assessing financial performance.
The key measure of the Company's segment profit or loss is consolidated net loss, which is reported on the Company's consolidated statements of operations. Consolidated net loss is used to measure actual results versus expectations. The measure of segment assets is reported on the consolidated balance sheets as total assets.
Significant segment expenses within loss from operations, as well as within net loss, include cost of revenue, research and development, acquired in-process research and development, selling, general and administrative expenses, and impairment and restructuring charges which are each separately presented on the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. Other segment items within net loss include interest and other income (expense), net, and income tax provision.
Disaggregation of Revenue
The Company disaggregates revenue from contracts with customers by payor type. The Company believes these categories aggregate the payor types by nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of its revenue streams. Disaggregated revenue by payor type and major service line for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 were as follows (in thousands, except percentages):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Amount | % of Revenue | | Amount | % of Revenue | | Amount | % of Revenue |
| Contracted third-party payors | $ | 311,605 | | 53 | % | | $ | 267,195 | | 54 | % | | $ | 223,984 | | 55 | % |
| Centers for Medicare and Medicaid | 142,389 | | 24 | % | | 122,414 | | 25 | % | | 103,032 | | 25 | % |
| Healthcare institutions | 95,115 | | 16 | % | | 71,001 | | 14 | % | | 59,772 | | 14 | % |
| Non-contracted third-party payors | 42,730 | | 7 | % | | 32,071 | | 7 | % | | 24,133 | | 6 | % |
| Total | $ | 591,839 | | | | $ | 492,681 | | | | $ | 410,921 | | |
Revenue generated from the United States comprised substantially all of the Company's revenue. No other country comprised 10% or greater of the Company's revenue during each of the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
Accounts Receivable, Provision for Credit Losses, and Contractual Allowances
Accounts receivable includes amounts due to the Company from healthcare institutions, third-party payors, and government payors and their related patients, as a result of the Company's normal business activities. Accounts receivable is reported on the consolidated balance sheets net of an estimated provision for credit losses and contractual allowances.
The Company establishes a provision for credit losses for estimated uncollectible receivables based on its assessment of the collectability of customer accounts and recognizes the provision as a component of selling, general and administrative expenses. The Company records a provision for contractual allowances based on the estimated differences between contracted amounts and expected collection rates for services performed. Such provisions are based on the Company's historical experience and are reported as a reduction of revenue.
The Company regularly reviews the allowances by considering factors such as historical experience, credit quality, the age of the accounts receivable balances, and current economic conditions that may affect a customer’s ability to pay.
The following table presents the changes in the provision for credit losses (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 20,289 | | | $ | 18,475 | | | $ | 14,012 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 22,583 | | | 17,105 | | | 17,191 | |
| Write-offs | (26,624) | | | (15,291) | | | (12,728) | |
| Balance, end of year | $ | 16,248 | | | $ | 20,289 | | | $ | 18,475 | |
The following table presents the changes in the contractual allowance (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Balance, beginning of year | $ | 52,689 | | | $ | 41,389 | | | $ | 31,274 | |
| Add: provision for contractual adjustments | 50,880 | | | 52,523 | | | 41,158 | |
| Less: contractual adjustments | (52,608) | | | (41,223) | | | (31,043) | |
| Balance, end of year | $ | 50,961 | | | $ | 52,689 | | | $ | 41,389 | |
Contract Liabilities
ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, requires an entity to present a revenue contract as a contract liability when the Company has an obligation to transfer goods or services to a customer for which the Company has received consideration from the customer, or an amount of consideration from the customer is due and unconditional (whichever is earlier).
Certain of the Company’s customers pay the Company directly for the Zio XT service upon shipment of devices. Such advance payments are recognized as deferred revenue and are recorded as revenue when Zio reports are delivered to the healthcare provider. During the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, $3.1 million and $3.0 million related to the contract liability balance at the beginning of 2024 and 2023, was recognized as revenue. The deferred revenue liability was $2.9 million and $3.3 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Contract Costs
Under ASC 340, Other Assets and Deferred Costs (“ASC 340”), the incremental costs of obtaining a contract with a customer are recognized as an asset. Incremental costs of obtaining a contract are those costs that an entity incurs to obtain a contract with a customer that it would not have incurred if the contract had not been obtained.
The Company maintains short-term sales incentive compensation programs. As a practical expedient, ASC 340 permits the Company to immediately expense contract acquisition costs, because the asset that would have resulted from capitalizing these costs will be amortized in one year or less.
4. CASH EQUIVALENTS AND MARKETABLE SECURITIES
The fair value of cash equivalents and marketable securities at December 31, 2024 and 2023, were as follows (in thousands): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
| Amortized
Cost | | Gross Unrealized | |
Fair Value |
| | Gains | | Losses | |
| Money market funds | $ | 40,654 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 40,654 | |
| U.S. government securities | 276,467 | | | 57 | | | — | | | 276,524 | |
| Total cash equivalents and marketable securities | $ | 317,121 | | | $ | 57 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 317,178 | |
| Classified as: | | | | | | | |
| Cash equivalents | | | | | | | $ | 201,222 | |
| Marketable securities | | | | | | | 115,956 | |
| Total cash equivalents and marketable securities | | | | | | | $ | 317,178 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 |
| Amortized
Cost | | Gross Unrealized | |
Fair Value |
| | Gains | | Losses | |
| Money market funds | $ | 12,594 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 12,594 | |
| U.S. government securities | 97,534 | | | 59 | | | (2) | | | 97,591 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total cash equivalents and marketable securities | $ | 110,128 | | | $ | 59 | | | $ | (2) | | | $ | 110,185 | |
| Classified as: | | | | | | | |
| Cash equivalents | | | | | | | $ | 12,594 | |
| Marketable securities | | | | | | | 97,591 | |
| Total cash equivalents and marketable securities | | | | | | | $ | 110,185 | |
Unrealized gains (losses) during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 were not material. As of December 31, 2024, the weighted average maturity for the Company's marketable securities was 211 days.
5. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The Company discloses and recognizes the fair value of its assets and liabilities using a hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in an orderly transaction between market participants at the reporting date. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to valuations based upon unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to valuations based upon unobservable inputs that are significant to the valuation (Level 3 measurements). The guidance establishes three levels of the fair value hierarchy as follows:
Level 1—Inputs are unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities at the measurement date.
Level 2—Inputs (other than quoted market prices included in Level 1) are either directly or indirectly observable for the asset or liability through correlation with market data at the measurement date and for the duration of the instrument’s anticipated life.
Level 3—Inputs reflect management’s best estimate of what market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability at the measurement date. Consideration is given to the risk inherent in the valuation technique and the risk inherent in the inputs to the model.
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value are classified in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The Company’s assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires management to make judgments and consider factors specific to the asset or liability. The U.S. government securities are classified as Level 2 as they were valued based upon quoted market prices for similar instruments in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active and model-based valuation techniques for which all significant inputs are observable in the market or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets.
The Company had no transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy of its assets measured at fair value.
The following tables present the fair value of the Company’s financial assets determined using the inputs defined above (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
| Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Money market funds | $ | 40,654 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 40,654 | |
| U.S. government securities | — | | | 276,524 | | | — | | | 276,524 | |
| Strategic investments | — | | | — | | | 61,902 | | | 61,902 | |
| Total | $ | 40,654 | | | $ | 276,524 | | | $ | 61,902 | | | $ | 379,080 | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | |
| Contingent consideration | — | | | — | | | 17,371 | | | 17,371 | |
| Total | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 17,371 | | | $ | 17,371 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 |
| Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Money market funds | $ | 12,594 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 12,594 | |
| U.S. government securities | — | | | 97,591 | | | — | | | 97,591 | |
| Strategic investments | — | | | — | | | 3,000 | | | 3,000 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | $ | 12,594 | | | $ | 97,591 | | | $ | 3,000 | | | $ | 113,185 | |
Fair Value of Strategic Investments
The Company hold strategic investments upon which it measures the fair value on a recurring basis. The carrying value of these investments are $61.9 million and $3.0 million as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively.
The Company's strategic investments are with privately held companies, and as such, limited information is available. On a quarterly basis, the Company monitors information that becomes available and adjusts the carrying values of these investments if there are identified events or changes in circumstances that have a significant effect on their fair values. The strategic investments are categorized as Level 3 investments within the fair value hierarchy due to the uncertainty of the fair value measurement with respect to the use of significant unobservable inputs and included within long-term strategic investments in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company made an aggregate of $55.0 million in strategic loan investments in BioIntelliSense, Inc. (“BioIS”), a privately-held company. The loan investments have maturity dates ranging from April 2029 through August 2029. The loan investments can convert into preferred shares of BioIS based upon certain qualifying financing events. The aggregate fair value of the strategic loan investments is $56.4 million as of December 31, 2024. In accordance with ASC 820, Fair Value Measurement, the Company elected to apply the fair value option to these strategic loan investments, with changes in fair value reported within other income (expense), net in the Company's consolidated statements of operations at each reporting period. During the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company increased the fair value of the strategic loan investments by $1.4 million. The fair value of the loan investments in BioIS is determined by using a probability-weighted expected return model (“PWERM”) and a discounted cash flow valuation model with scenarios that correspond to the contractual settlement events. The determination of fair value involves significant assumptions such as discount rates, volatility rates, and expected years. These unobservable inputs represent a Level 3 measurement, as they are supported by little or no market activity and reflect the Company's own assumptions in measuring fair value.
The recurring Level 3 fair value measurements of the loan investment include the following significant unobservable inputs as of December 31, 2024:
| | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
| Discount rate | 12.0 | % |
| Equity volatility | 67.0 | % |
| Expected years (range) | 2025 - 2029 |
In November 2024, the Company made a $2.0 million strategic loan investment in a separate privately-held company. The fair value of the strategic loan investment was $2.0 million as of December 31, 2024.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company made a $3.0 million strategic equity investment in a separate privately-held company. During the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company increased the fair value of the strategic equity investment by $0.5 million. The carrying value of the strategic equity investment is $3.5 million as of December 31, 2024. The change in fair value is recorded within other income (expense), net in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations.
The following table sets forth the changes in the estimated fair value of the Company's strategic investments measured on a recurring basis (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended
December 31, 2024 | | Year Ended
December 31, 2023 |
| Balance, beginning of period | $ | 3,000 | | | $ | — | |
| Additions during the period | 57,000 | | | 3,000 | |
| Changes in estimated fair value | 1,902 | | | — | |
| Balance, end of period | $ | 61,902 | | | $ | 3,000 | |
Contingent Consideration Liabilities
The Company established contingent consideration liabilities in conjunction with the development milestones associated with the acquisition of certain technology from BioIS. The fair value of contingent consideration liabilities is determined using PWERM, with scenarios that correspond to the contractual settlement events. There are significant inputs of such model that are not observable in the market, such as probability of achievement of stated milestones and expected term. The unobservable inputs represent a Level 3 measurement. Fair value adjustments to contingent consideration liabilities are assessed quarterly and recorded through operating expenses within acquired in-process research and development in the consolidated statements of operations. Refer to Note 8, Commitments and Contingencies, for further details relating to the BioIS contingent consideration liabilities.
The recurring Level 3 fair value measurements of contingent consideration liabilities associated with the development agreement milestones include the following significant unobservable inputs as of December 31, 2024:
| | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
| Probability of achievement (range) | 75.0% - 90.0% |
| Expected years | 2025 - 2026 |
Contingent consideration liabilities for BioIS at the inception of acquisition of the licensed technology were $17.0 million. Contingent consideration liabilities were $17.4 million and nil as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, with the current portion included within accrued liabilities and the noncurrent portion included within other noncurrent liabilities in the Company’s consolidated balance sheet.
The following table sets forth the changes in the estimated fair value of the Company’s contingent consideration liabilities measured on a recurring basis (Level 3) (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Year Ended
December 31, 2024 |
| Balance, beginning of period | $ | — | |
| Addition during the period | 16,970 | |
Changes in estimated fair value | 401 | |
| Balance at end of period | $ | 17,371 | |
Fair Value of Senior Convertible Notes and SVB Term Loan
The fair value, based on a quoted market price (Level 1), of the Company’s senior convertible notes due 2029 (the “2029 Notes”) is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| Senior Convertible Notes due 2029 | $ | 641,214 | | | $ | — | |
The Company's SVB Term Loan debt obligation as of December 31, 2023 is classified as a Level 2 input. The fair value of the Company's outstanding interest-bearing obligation as of December 31, 2023 approximated the carrying value of $35.0 million.
6. BALANCE SHEET COMPONENTS
Inventory
Inventory consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Raw materials and work-in-progress | $ | 5,863 | | | $ | 6,299 | |
| Finished goods | 8,176 | | | 7,674 | |
| Total | $ | 14,039 | | | $ | 13,973 | |
Long-term Strategic Investments
Long-term strategic investments consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Strategic loan investments | $ | 58,407 | | | $ | — | |
| Strategic equity investments | 3,495 | | | 3,000 | |
| Total | $ | 61,902 | | | $ | 3,000 | |
Other Assets
Other assets consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| PCBAs | $ | 34,698 | | | $ | 38,987 | |
| Cloud computing arrangements | 5,230 | | | 4,959 | |
| Other | 1,924 | | | 1,093 | |
| Total | $ | 41,852 | | | $ | 45,039 | |
The Company reuses PCBAs in each wearable Zio Monitor patch, Zio XT patch, and Zio AT patch, as well as the wireless gateway used in conjunction with the Zio AT patch. As PCBAs are used in a wearable Zio Monitor patch, Zio XT patch, or Zio AT patch, a portion of the cost of the PCBA is recorded as a cost of revenue. Charges to cost of revenue were $13.7 million, $9.0 million, and $5.2 million as of December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2024, PCBAs decreased by $4.3 million primarily driven by accelerated Zio XT PCBA amortization in conjunction with the commercial launch of Zio Monitor.
The Company recorded $2.7 million, $1.4 million, and $0.6 million amortization expense during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively, related to capitalized implementation costs in a CCA.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, net consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| Useful Life | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Laboratory and manufacturing equipment | 2 to 7 | | $ | 9,687 | | | $ | 6,007 | |
| Computer equipment and software | 3 | | 4,227 | | | 3,905 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | 2 to 5 | | 4,181 | | | 4,020 | |
| Leasehold improvements | 3 to 12 | | 27,121 | | | 24,885 | |
| Internal-use software in service | 3 to 7 | | 79,660 | | | 61,980 | |
| Internal-use software in development | - | | 60,797 | | | 43,701 | |
| Construction in progress | - | | 10,638 | | | 10,119 | |
| Total property and equipment, gross | | | 196,311 | | | 154,617 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | (71,219) | | | (50,503) | |
| Total property and equipment, net | | | $ | 125,092 | | | $ | 104,114 | |
Depreciation and amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $20.7 million, $16.3 million and $13.4 million, respectively, of which amortization related to internal-use software, was $14.9 million, $12.2 million, and $9.8 million, for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Accrued Liabilities
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Accrued payroll and related expenses | $ | 42,293 | | | $ | 47,656 | |
| Accrued vacation | 6,914 | | | 8,608 | |
| Accrued expenses | 16,044 | | | 14,891 | |
| Claims payable | 2,011 | | | 4,578 | |
| Accrued employee share purchase plan contributions | 585 | | | 1,037 | |
| Accrued income and other taxes | 4,008 | | | 2,877 | |
| Accrued professional services fees | 3,345 | | | 3,715 | |
| Contingent consideration liabilities | 9,700 | | | — | |
| Total accrued liabilities | $ | 84,900 | | | $ | 83,362 | |
During the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company incurred expenses in connection with efforts to streamline and globalize its operations. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, globalization costs included within accrued payroll and related expenses were de minimis and $2.4 million, respectively.
7. IMPAIRMENT AND RESTRUCTURING CHARGES
The Company's restructuring and impairment charges consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Restructuring charges | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,444 | |
| Impairment charges | 641 | | | 11,078 | | | 23,164 | |
| Total | $ | 641 | | | $ | 11,078 | | | $ | 26,608 | |
Restructuring
The following table provides a summary of changes in the liability associated with the restructuring plan during 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Employee Severance |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | $ | 394 | |
| Charges | — | |
| Cash Payments | (394) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | $ | — | |
In February 2022, the Company's board of directors (the “Board”) approved a restructuring plan (”2022 Restructuring Plan”) to allow it to effectively and efficiently scale its business, which resulted in total severance and other employment related costs of $3.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2022.
Impairment
The Company's impairment charges consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| ROU asset | $ | — | | | $ | 9,912 | | | $ | 20,451 | |
| Leasehold improvements | — | | | 1,067 | | | 2,211 | |
| Furniture and fixtures | — | | | 99 | | | 502 | |
| Internal-use software | 641 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | $ | 641 | | | $ | 11,078 | | | $ | 23,164 | |
In February 2022, the Board approved a plan to reduce the Company’s leased space for its headquarters in San Francisco, California. The Company initiated an effort to pursue a sublease of one floor (approximately 50%) of its San Francisco, California facility. As a result, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $23.2 million, consisting of its ROU asset and property and equipment (inclusive of leasehold improvements and furniture and fixtures) of $20.5 million and $2.7 million, respectively. The impairment was recorded to impairment and restructuring charges within the consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2022.
At December 31, 2023, the Company recorded an additional impairment of its ROU asset and related property and equipment (inclusive of leasehold improvements and furniture and fixtures) for its headquarters in San Francisco, California. Due to continued declining real estate rental market conditions within San Francisco, California, the Company evaluated projected future cash flows related to the Company’s headquarters as compared to the remaining carrying value of the associated ROU asset and property and equipment. As a result, the Company recorded an additional impairment charge of $11.1 million, consisting of its ROU asset and property and equipment (inclusive of leasehold improvements and furniture and fixtures) of $9.9 million and $1.2 million, respectively. The impairment was recorded to impairment and restructuring charges within the consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023.
Significant judgment and estimates are required in assessing impairment of ROU assets, including identifying whether events or changes in circumstances require an impairment assessment, estimating future cash flows, and determining appropriate discount rates. The Company has engaged a leasing broker and has formalized a marketing plan for the San Francisco office market since the first quarter of 2022. The sublease market for commercial office space is currently very challenging in the San Francisco area due to lower demand for leased office space as most companies have adjusted to allowing their employees to work from home during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. The Company believes that it is likely to be able to sublease a portion of its existing office space, but at a rate below the amount that it is currently paying.
The Company estimated undiscounted future cash flows from its vacant office lease based on the Company’s intent and ability to sub-lease the vacant office space, based on the facts and circumstances discussed below, which it had ceased using and estimated future sub-lease income considering the local real estate market conditions. The Company also factored into its estimate the amount of time to identify a tenant, sublease rental market transactions within San Francisco business districts, entering into a sublease agreement, and expected rent concessions offered to future tenants. The Company estimated the fair value of the ROU asset related to the vacant office lease by discounting the estimated undiscounted future cash flows using the average lease capitalization rate, plus average inflation rate, for other lease transactions in the local area during the year. For further details on the Company's leases, refer to Note 8. Commitments and Contingencies.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $0.6 million within the Company’s consolidated statements of operations related to internal-use software in development not expected to be completed. No impairment charge related to internal-use software has been recognized for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022.
8. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Purchase Commitments
As of January 1, 2025, the Company's purchase commitments totaled $69.1 million, primarily related to inventory and revenue cycle front end service fees and expected to be due within a year.
Leases
The Company leases office, manufacturing, and clinical centers under non-cancelable operating leases which expire on various dates through 2033. These leases generally contain scheduled rent increases or escalation clauses and renewal options. Operating lease ROU assets and lease liabilities are recognized based on the present value of the future minimum lease payments over the lease term at commencement date. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made to the lessor at or before the commencement date as well as variable lease payments which are based on a consumer price index. The Company is also subject to variable lease payments related to janitorial services and electricity which are not included in the operating lease ROU asset as they are based on actual usage. The Company recognizes operating lease expenses, generally on a straight-line basis over the lease period.
In July 2023, the Company entered into an approximately seven-year facility lease in Solana Beach, California, as corporate office space (the “Solana Beach Lease”). In February 2024, the Company amended its lease to add additional space. The amended lease commenced in the fourth quarter of 2024, and extended the term of the entire facility lease by approximately one year. The amended lease provides an option to extend the term of the lease for one five-year period beyond the amended term, which the Company is not reasonably certain to exercise and therefore was not considered in determining the ROU assets and lease liabilities balance. The Company recognized $4.0 million in additional ROU assets and lease liabilities upon commencement of the amended lease. Total lease payments for the Solana Beach Lease approximate $9.6 million.
In August 2023, the Company entered into a five-year facility lease in Manila, Philippines, in order to further globalize the Company's operational footprint as a business service center. The lease provides an option to extend the term of the lease for two periods of five years beyond the initial term, which the Company is not reasonably certain to exercise and therefore was not considered in determining the ROU assets and lease liabilities balance. Total lease payments approximate $2.0 million as of the lease commencement date.
Contractual obligations under operating lease liabilities were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31: | |
| 2025 | $ | 15,103 | |
| 2026 | 16,679 | |
| 2027 | 17,093 | |
| 2028 | 17,012 | |
| 2029 | 17,130 | |
| Thereafter | 32,888 | |
| Total lease payments | 115,905 | |
| Less: imputed interest | (25,439) | |
| Total lease liabilities | $ | 90,466 | |
Other information related to the operating leases were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year Ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Operating lease expense (in thousands) | | $ | 11,831 | | $ | 12,861 | | $ | 13,524 |
| Weighted average remaining lease term (years) | | 6.8 | | 7.8 | | 8.8 |
| Weighted average discount rate (percentage) | | 7.3 | % | | 7.3 | % | | 7.3 | % |
Legal Proceedings
From time to time, the Company is involved in claims and legal proceedings or investigations, that arise in the ordinary course of business. Such matters could have an adverse impact on the Company's reputation, business, and financial condition and divert the attention of its management from the operation of the Company's business. These matters are subject to many uncertainties and outcomes that are not predictable.
On February 6, 2024, a putative class action lawsuit was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California alleging that the Company and its current Chief Executive Officer, Quentin Blackford, its former Chief Financial Officer, Brice Bobzien, and its former Chief Financial Officer and former Chief Operating Officer, Douglas Devine violated Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Exchange Act and SEC Rule 10b-5 promulgated thereunder, and seeks unspecified damages purportedly sustained by the class. On July 19, 2024, an amended complaint was filed, naming the Company, Mr. Blackford, Mr. Bobzien, Mr. Devine, its Chief Commercial Officer Chad Patterson, its former Chief Technology Officer Mark Day, and its Chief Medical Officer, Chief Scientific Officer, and Executive Vice President of Product Innovation Mintu Turakhia as defendants. On October 7, 2024, a second amended complaint was filed to include events from the recent FDA inspections, but otherwise included the same claims under the Exchange Act. On December 10, 2024, defendants filed a motion to dismiss.
The Company's board members and certain of its current and former executives were named as defendants in two complaints filed as stockholder derivative actions in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware and the United States District Court for the Northern District of California, respectively. iRhythm is named as a nominal defendant in both complaints. The cases make similar allegations to those in the securities class action complaint described above and both cases have both been stayed pending the resolution of motion to dismiss briefing in the securities class action.
The Company believes the above securities class action and derivative lawsuits to be without merit and plans to continue to defend itself vigorously.
On March 26, 2021, the Company received a grand jury subpoena from the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California requesting information related to communications with the FDA and its products and services. On September 13, 2021, the Company received a second subpoena requesting additional information. On April 4, 2023, the Company received a Subpoena Duces Tecum from the Consumer Protection Branch, Civil Division of the U.S. Department of Justice (the “DOJ”), requesting production of various documents regarding our products and services. The Company is cooperating fully on these matters.
On July 1, 2024, the DOJ filed with the United States District Court for the Northern District of California a Petition for Order to Show Cause and Application for Enforcement with respect to the production of certain documentary materials which the Company asserts are protected by legal privileges. The Company defended its privilege assertions over such materials in its response to the DOJ’s petition. The matter has been briefed, and oral argument is scheduled for March 6, 2025.
On February 20, 2024, Welch Allyn, a subsidiary of Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. now part of Baxter International, Inc., filed a lawsuit against the Company in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware, alleging that its Zio devices infringe certain of Welch Allyn's patents and that the Company's infringement was willful. The Company filed a motion to dismiss Welch Allyn’s willful infringement claims on April 11, 2024. Welch Allyn filed an amended complaint on April 24, 2024 that continued to allege that the Company's devices infringe certain of its patents and that the Company's infringement was willful. The Company filed a motion to dismiss Welch Allyn’s willful infringement allegations found in the amended complaint on May 22, 2024 and a hearing on the motion to dismiss was held on January 28, 2025. After hearing arguments, the Court granted the Company's motion and the willful infringement claims in the amended complaint were dismissed without prejudice. Welch Allyn filed a second amended complaint adding additional patent claims on February 14, 2025. The Company is preparing to file a response to the allegations found in the second amended complaint no later than March 21, 2025. Welch Allyn seeks money damages and attorneys’ fees. The Company believes this lawsuit is without merit and plans to defend itself vigorously.
On December 10, 2024, Bardy Diagnostics, Inc. (”BardyDx”), a subsidiary of Hill-Rom Holdings, Inc. now part of Baxter International, Inc., filed a lawsuit against the Company in the United States District Court for the District of Delaware, alleging that our Zio Monitor device infringes one of its patents. On December 26, 2024, BardyDx filed an amended complaint alleging that the Company's Zio Monitor device infringes two of BardyDx's patents. The Company is preparing to file a response to the allegations found in the amended complaint no later than March 3, 2025. BardyDx seeks money damages and attorneys’ fees. The Company believes this lawsuit is without merit and plans to defend itself vigorously.
Technology License Agreement
On August 30, 2024, the Company entered into a Technology License Agreement (the “License Agreement”) with BioIS, pursuant to which (i) the Company will receive a perpetual fully paid up license to certain of BioIS’ intellectual property, technology and products for research, development and commercialization of potential next generation products and services in certain fields of use, including an exclusive license to develop and commercialize pulse oximetry, accelerometry, and trending non-invasive blood pressure technologies for use within the Company’s ambulatory cardiac monitoring products and services, and (ii) the Company and BioIS agreed to negotiate in good faith a supply agreement for pulse oximetry hardware.
Under the terms of the License Agreement, during the third quarter of 2024 the Company paid BioIS an upfront fee of $15.0 million in cash consideration in acceptance of the initial transfer of certain licensed technologies and data following the execution of the License Agreement. In connection with the License Agreement, the Company also purchased an aggregate of $40.0 million of convertible promissory notes from BioIS (the “Convertible Notes”), of which $20.0 million of the convertible promissory notes (“Milestone Notes”) were designated for satisfaction of the Company's regulatory milestone payment obligations. The Milestone Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, shall be cancelled, if outstanding, upon the achievement of the regulatory milestones up through December 31, 2026. The Company has recorded a charge for $32.4 million for acquired IPR&D in the Company's consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2024, which includes the upfront fee of $15.0 million as well as contingent consideration of $17.4 million related to the regulatory milestones. Additionally, BioIS is eligible to receive low single digit royalty payments on annual net sales of certain products in the home sleep testing field, subject to certain adjustments specified in the License Agreement.
Development Agreement
On September 3, 2019, the Company entered into a Development Collaboration Agreement with Verily Life Sciences LLC, an Alphabet company (“VLS”) and Verily Ireland Limited (“VIL” and together with VLS, “Verily”) (such Development Collaboration Agreement, as amended, the “Development Agreement”). The Development Agreement involves joint development and production of intellectual property between the Company and Verily. Each participant has primary responsibility for certain aspects of development and approval, with all processes to be performed at each respective party’s own cost. Costs incurred by the Company in connection with the Development Agreement will be expensed as research and development expense in accordance with ASC 730, Research and Development.
Pursuant to the Development Agreement, the Company and Verily agreed to develop certain next-generation atrial fibrillation (“Afib”) screening, detection, or monitoring products, which products will involve combining Verily's and the Company’s technology platforms and capabilities. Under the terms of the Development Agreement, the Company paid Verily an upfront fee of $5.0 million in 2019. In addition, the Company agreed to make additional milestone payments to Verily up to an aggregate of $12.75 million upon achievement of various development and regulatory milestones over the term of the Development Agreement. The Company and Verily have achieved milestones tied to payments totaling $11.0 million to date and the Company is obligated to make additional payments over the term of the Development Agreement of $1.75 million, subject to the achievement of specified milestones.
The Development Agreement provides each party with licenses to use certain intellectual property of the other party for development activities in the field of Afib screening, detection, or monitoring. Ownership of developed intellectual property will be allocated to the Company or Verily depending on the subject matter of the underlying developed intellectual property, and, for certain subject matter, shall be jointly owned.
Indemnifications
In the ordinary course of business, the Company enters into agreements pursuant to which it agrees to indemnify customers, vendors, lessors, business partners, and other parties with respect to certain matters, including losses arising out of the breach of such agreements, services to be provided by the Company, or from intellectual property infringement claims made by third parties. Pursuant to such agreements, the Company may indemnify, hold harmless and defend an indemnified party for losses suffered or incurred by the indemnified party. Some of the provisions will limit losses to those arising from third-party actions. In some cases, the indemnification will continue after the termination of the agreement. The maximum potential amount of future payments the Company could be required to make under these provisions is not determinable. The Company has also entered into indemnification agreements with its directors and officers that may require the Company to indemnify its directors and officers against liabilities that may arise by reason of their status or service as directors or officers to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law. The Company currently has directors’ and officers’ insurance. The Company has never incurred material costs to defend lawsuits or settle claims related to these indemnification provisions, and believes that the estimated fair value of these indemnification obligations is not material and it has not accrued any amounts for these obligations.
9. DEBT
1.50% Senior Convertible Notes due 2029
The carrying amounts of the Company’s 2029 Notes were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Principal amount | $ | 661,250 | | | $ | — | |
| Unamortized debt issuance costs | (14,807) | | | — | |
| Carrying amount of senior convertible notes due 2029 | $ | 646,443 | | | $ | — | |
The following table summarizes the components of interest expense and the effective interest rate for the 2029 Notes for the periods shown (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Contractual coupon interest | $ | 8,266 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| Amortized debt issuance costs | 2,617 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total interest expense recognized on senior convertible notes due 2029 | $ | 10,883 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | |
| Effective interest rate | 2.0 | % | | — | % | | — | % |
On March 7, 2024, the Company completed an offering of $661.3 million aggregate principal amount of unsecured senior convertible notes with a stated interest rate of 1.50% and a maturity date of September 1, 2029. The proceeds include the full exercise of the option granted by the Company to the initial purchasers of the 2029 Notes to purchase up to an additional $86.3 million aggregate principal amount of notes. Interest on the 2029 Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year, beginning on September 1, 2024. The net proceeds from the offering, after deducting initial purchasers’ discounts and costs directly related to the offering, were approximately $643.8 million. The initial conversion rate of the 2029 Notes is 6.7927 shares per $1,000 principal amount of notes, which is equivalent to a conversion price of approximately $147.22 per share, subject to adjustments. The 2029 Notes may be settled in cash, stock, or a combination thereof, solely at the Company's discretion.
The Company used net proceeds from the offering to purchase capped calls, as well as repayment of the Company's outstanding debt which is described below. In addition, the Company also used net proceeds from the offering to repurchase shares of the Company's common stock. Refer to Note 11, Stockholders' Equity for further details relating to the Company's shares repurchase.
No principal payments are due on the 2029 Notes prior to maturity. Other than restrictions relating to certain fundamental changes and consolidations, mergers or asset sales and customary anti-dilution adjustments, the indenture relating to the 2029 Notes (the “Indenture”) includes customary terms and covenants, including certain events of default after which the 2029 Notes may be due and payable immediately. The Company uses the if-converted method for assumed conversion of the 2029 Notes to compute the weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding for diluted earnings per share, when applicable.
Conversion Rights at the Option of the Holders
Holders of the 2029 Notes who convert their notes in connection with a make-whole fundamental change (as defined in the Indenture) or convert their 2029 Notes called (or deemed called) for redemption in connection with any optional redemption are, under certain circumstances, entitled to an increase in the conversion rate. Additionally, in the event of a fundamental change (as defined in the Indenture), holders of the 2029 Notes may require the Company to repurchase for cash all or a portion of their notes at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount of notes, plus any accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the repurchase date.
Holders of the 2029 Notes may convert all or a portion of their notes prior to the close of business on the business day immediately preceding June 1, 2029, in multiples of $1,000 principal amount, only under the following circumstances:
(1) during any calendar quarter commencing after the calendar quarter ending on June 30, 2024 (and only during such calendar quarter), if the last reported sale price of the Company's common stock for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) during a period of 30 consecutive trading days ending on the last trading day of the immediately preceding calendar quarter is greater than or equal to 130% of the conversion price of the 2029 Notes on each applicable trading day;
(2) during the five business day period after any five consecutive trading day period (the “measurement period”) in which the trading price (as defined in the Indenture) per $1,000 principal amount of the 2029 Notes for each trading day of that measurement period was less than 98% of the product of the last reported sale price of the Company's common stock and the conversion rate of the 2029 Notes on such trading day;
(3) if the Company calls any or all 2029 Notes for redemption, at any time prior to the close of business on the scheduled trading day immediately preceding the redemption date, but only with respect to the 2029 Notes called (or deemed called) for redemption; or
(4) upon the occurrence of specified corporate events as specified in the Indenture.
On or after June 1, 2029, until 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on the second scheduled trading day immediately preceding September 1, 2029, holders of the notes may convert the 2029 Notes, in multiples of $1,000 principal amount, at their option regardless of the foregoing circumstances.
Conversion Rights at the Company's Option
The Company may not redeem the 2029 Notes prior to September 5, 2027. On or after September 5, 2027 and prior to June 1, 2029, the Company may redeem at its option for cash all or any portion of the 2029 Notes, at the redemption price, if the last reported sale price of the Company's common stock has been at least 130% of the conversion price then in effect for at least 20 trading days (whether or not consecutive) during any 30 consecutive trading day period ending on, and including, the trading day immediately preceding the date on which the Company provides the redemption notice. The redemption price will be equal to 100% of the principal amount of the 2029 Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to, but excluding, the redemption date.
2029 Capped Call Transactions
On March 4, 2024, in connection with the offering of the 2029 Notes, the Company entered into privately negotiated capped call transactions (the “2029 Capped Calls”) with certain financial institutions. The 2029 Capped Calls will cover, subject to anti-dilution adjustments substantially similar to those applicable to the 2029 Notes, the number of shares of the Company's common stock that will initially underlie the 2029 Notes. The 2029 Capped Calls are expected generally to reduce potential dilution to the Company's common stock upon conversion of the 2029 Notes and/or offset any cash payments that the Company could be required to make in excess of the principal amount of converted 2029 Notes, as the case may be, with such reduction and/or offset subject to a cap. The 2029 Capped Calls have an initial cap price of $218.10 per share, subject to adjustments, which represents a premium of 100% over the closing price of the Company's common stock of $109.05 per share on the Nasdaq Global Select Market on March 4, 2024. The Company completed the purchase of the 2029 Capped Calls on March 7, 2024, for the amount of $72.4 million. The cost to purchase the 2029 Capped Calls was recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital in the Company's consolidated balance sheets, as the 2029 Capped Calls met the criteria for classification within stockholders’ equity.
Braidwell Debt
On January 3, 2024 (the “Closing Date”), the Company entered into the Credit, Security and Guaranty Agreement (the “Braidwell Credit Agreement”) with Braidwell Transactions Holdings LLC – Series 5 (“Braidwell”), which provided for a senior secured term loan in an aggregate principal amount of up to $150.0 million (the “Braidwell Term Loan Facility”). An initial tranche of $75.0 million (“Initial Loan”) was funded on the Closing Date. In addition to the Initial Loan, the Braidwell Term Loan Facility included an additional tranche of $75.0 million, which was accessible by the Company through the one year anniversary of the Closing Date, so long as the Company satisfied certain customary conditions. The Braidwell Term Loan Facility had a maturity date of January 3, 2029 (the “Maturity Date”) and provided, at the Company’s election, for the option to have a portion of interest added to principal rather than paid in cash during the term of the loan, with principal and accrued interest due at the Maturity Date.
On March 7, 2024, in connection with the offering of the 2029 Notes, the Company used approximately $80.2 million of the net proceeds for the repayment in full of the $75.0 million outstanding Initial Loan, as well as interest, fees and expenses associated with terminating the agreement. Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2024 was $1.8 million. Interest expense for year ended December 31, 2024 consisted of contractual coupon interest and amortized debt issuance costs of $1.6 million and $0.2 million, respectively. The Company incurred $5.6 million of fees and expenses relating to the repayment of the Initial Loan and the termination of the Braidwell Credit Agreement, inclusive of unamortized debt origination costs, which has been recorded within loss on extinguishment of debt in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2024.
SVB Term Loan
In October 2018, the Company entered into the Third Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement (“SVB Loan Agreement”) with Silicon Valley Bank (“SVB”). Under the SVB Loan Agreement, the Company had borrowed $35.0 million and had made repayments through March 2022, at which time the outstanding balance was $18.5 million.
On March 28, 2022, the Company entered into a Second Amendment (“2022 Amendment”) to its SVB Loan Agreement which provided for a term loans facility in the aggregate principal amount of up to $75.0 million (the “2022 Term Loans”), of which $35.0 million was borrowed at closing and a portion of the proceeds was used to pay in full the outstanding balance of $18.5 million under the SVB Loan Agreement. The remaining $40.0 million of 2022 Term Loans may be borrowed from time to time at the Company’s option, in increments of at least $10.0 million, through December 31, 2023. The Company will pay interest only on the 2022 Term Loans until April 1, 2025, when it will commence repaying the 2022 Term Loans in 24 equal consecutive monthly installments, with all obligations under the 2022 Term Loans maturing on March 1, 2027. Interest charged on the 2022 Term Loans will accrue at a floating per annum rate equal to the greater of: (A) the Prime Rate plus 0.25%; and (B) 3.5%. The Company is also required to pay fees on any prepayment of the 2022 Term Loans, ranging from 1.0% to 3.0% depending on the date of prepayment, and a final payment equal to 5.0% of the principal amount of the 2022 Term Loans drawn. Once repaid or prepaid, the 2022 Term Loans may not be reborrowed. The Company accounted for the refinancing as an extinguishment of the original loans and paid a fee of $1.8 million, which was included in interest expense on the Consolidated Statement of Operations and recorded the 2022 Term Loans, net of issuance costs. The issuance costs on the new loans are amortized over the term of the loan.
The 2022 Amendment also amended the terms of the revolving credit line under the SVB Loan Agreement, which provided for an aggregate principal amount of $25.0 million, to: (i) extend the maturity date from August 1, 2023 to March 1, 2027, (ii) increase the letters of credit sublimit to $15.0 million and (iii) increase the cash management services sublimit to $15.0 million. Interest charged on the principal amount outstanding under the revolving credit line accrues at a floating per annum rate equal to the greater of (A) the Prime Rate plus 0.25% and (B) 3.5%. The Company is required to pay an annual fee equal to 0.15% of the revolving credit line.
The 2022 Amendment also amended the SVB Loan Agreement to require the Company to comply, as of the last day of each fiscal quarter, with a quick ratio of at least 1.0 to 1.15 or minimum adjusted EBITDA trailing 6 months of at least $15.0 million.
On January 3, 2024, in connection with the entry into the Braidwell Credit Agreement, the Company used approximately $37.8 million of the net proceeds for the repayment in full of the $35.0 million outstanding principal balance as well as interest, fees and expenses associated with terminating the agreement. Upon termination of the SVB Loan Agreement, SVB's security interest in the Company's assets and property was released. The Company continues to hold $8.4 million in letters of credit with SVB, securing them with cash on deposit.
Interest expense for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was nil, $3.4 million and $2.1 million, respectively. Contractual coupon interest for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was nil, $3.0 million and $1.7 million, respectively. Amortized debt issuance costs for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was nil, $0.4 million, and $0.4 million, respectively. The Company incurred $2.0 million of fees and expenses relating to the termination of the SVB Loan Agreement, which has been recorded within loss on extinguishment of debt in the Company's consolidated statement of operations during the year ended December 31, 2024.
10. INCOME TAXES
The components of income (loss) before provision for income taxes are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| United States | $ | (114,203) | | | $ | (122,974) | | | $ | (116,600) | |
| Foreign | 1,479 | | | 318 | | | 714 | |
| Loss before income taxes | $ | (112,724) | | | $ | (122,656) | | | $ | (115,886) | |
The provision for (benefit from) income taxes consists of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Current expense: | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| State | 218 | | | 401 | | | 160 | |
| Foreign | 474 | | | 349 | | | 111 | |
| Total current tax expense | 692 | | | 750 | | | 271 | |
| | | | | |
| Deferred tax benefit: | | | | | |
| Federal | — | | | — | | | — | |
| State | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Foreign | (127) | | | — | | | (2) | |
| Total deferred tax benefit | (127) | | | — | | | (2) | |
| | | | | |
| Total tax expense | $ | 565 | | | $ | 750 | | | $ | 269 | |
Income tax expense differs from the amount computed by applying the statutory federal income tax rate as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Tax at statutory federal rate | $ | (23,672) | | | $ | (25,758) | | | $ | (24,323) | |
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 307 | | | 371 | | | 160 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 727 | | | (820) | | | (3,492) | |
| Meals and entertainment | 174 | | | 361 | | | 348 | |
| Section 162(m) limitation - officers compensation | 5,093 | | | 5,217 | | | 2,498 | |
| Other | 425 | | | 823 | | | 526 | |
| Tax credits | (2,160) | | | (2,160) | | | (2,695) | |
| Foreign rate differential | 163 | | | 37 | | | (40) | |
| Change in valuation allowance | 19,508 | | | 22,679 | | | 27,287 | |
| Provision for income taxes | $ | 565 | | | $ | 750 | | | $ | 269 | |
The components of the net deferred tax assets are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
| Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 133,233 | | | $ | 127,503 | |
| Tax credit carryforwards | 19,460 | | | 16,401 | |
| Stock-based compensation | 11,810 | | | 10,801 | |
| Capital research expenditures | 24,280 | | | 18,849 | |
| Allowances and other | 38,938 | | | 31,952 | |
| Lease obligation | 23,011 | | | 23,817 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 4,288 | | | 519 | |
| Total deferred tax assets | 255,020 | | | 229,842 | |
| Less: Valuation allowance | (242,623) | | | (217,779) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | 12,397 | | | 12,063 | |
| | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
| | | |
| ROU assets | (12,094) | | | (12,005) | |
| Total deferred tax liabilities | (12,094) | | | (12,005) | |
| Total deferred tax assets | $ | 303 | | | $ | 58 | |
The realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of sufficient taxable income of the appropriate character in future periods. The Company establishes a valuation allowance if it is more-likely-than-not that some portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The Company weighs all available positive and negative evidence, including our earnings history and results of recent operations, scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, and tax planning strategies. Due to the uncertainties surrounding the realization of deferred tax assets through future taxable income, the Company has provided a full valuation allowance against its U.S. deferred tax assets, and, therefore, no benefit has been recognized for the net operating loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets. The U.S. valuation allowance increased by $24.8 million, $29.7 million and $33.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively. The current year change in the U.S. valuation allowance is primarily related to the increase in reserves and research and development not currently deductible. The Company recorded an immaterial deferred tax asset related to the Company’s foreign operations in the UK.
The valuation allowance for deferred tax assets consisted of the following activity for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at Beginning of Year | | Additions | | Deductions | | Balance at End of Year |
| Year Ended December 31, 2024 | $ | 217,779 | | | $ | 24,844 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 242,623 | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2023 | 188,070 | | | 29,709 | | | — | | | 217,779 | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2022 | 154,734 | | | 33,336 | | | — | | | 188,070 | |
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had approximately $525.5 million of federal and $368.8 million of state net operating loss carryforwards available to offset future taxable income which expires in varying amounts beginning in 2030 and 2025, respectively. Federal losses incurred from 2019 can be carried forward indefinitely.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had research tax credit carryforwards of approximately $16.1 million, and $12.0 million available to reduce future taxable income, if any, for both federal and state purposes, respectively. The federal tax credit carryforwards expire beginning in 2027 and the California tax credits can be carried forward indefinitely.
Federal and state tax laws impose restrictions on the utilization of net operating loss carryforwards in the event of a change in our ownership as defined by the Internal Revenue Code (the “Code”), Section 382. Under Section 382 of the Code, substantial changes in our ownership and the ownership of acquired companies may limit the amount of net operating loss carryforwards that are available to offset taxable income. The annual limitation would not automatically result in the loss of net operating loss carryforwards but may limit the amount available in any given future period.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending unrecognized tax benefit amount is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 5,774 | | | $ | 4,732 | | | $ | 3,310 | |
| Additions for tax positions taken in current year | 1,080 | | | 1,080 | | | 996 | |
| Increases in balance related to prior year tax positions | — | | | — | | | 426 | |
| Decreases in balance related to prior year tax positions | (55) | | | (38) | | | — | |
| Balance at end of year | $ | 6,799 | | | $ | 5,774 | | | $ | 4,732 | |
The Company’s policy is to include interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits within the provision for taxes. The Company determined that no accrual for interest or penalties was required as of December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022.
The Company files income tax returns in the U.S. and UK jurisdictions. All of the Company's tax years are open to examination by the U.S. federal and state tax authorities. The UK is open to examination for tax years starting 2017 and forward. The Company currently has no federal, state or foreign tax examinations in progress, nor has it had any federal or state examinations since inception.
11. STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
Common Stock
The Company’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation authorizes the Company to issue 100,000,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $0.001 per share and 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.001 per share. The holders of common stock are entitled to receive dividends whenever funds and assets are legally available and when declared by the Board, subject to the prior rights of holders of all series of convertible preferred stock outstanding. No dividends were declared through December 31, 2024.
Treasury Shares
On March 7, 2024, the Company used approximately $25.0 million of the net proceeds from the 2029 Notes offering to repurchase 229,252 shares of the Company's common stock at a purchase price of $109.05 per share via privately negotiated transactions effected through one of the initial purchasers or its affiliate. Repurchased shares of the Company's common stock are held as treasury shares until they are reissued or retired.
The Company had reserved shares of common stock for issuance as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| Options issued and outstanding | 283 | | | 307 | |
Unvested restricted stock units and performance-based restricted stock units1 | 2,289 | | | 2,438 | |
| Shares available for grant under future stock plans | 6,370 | | | 6,765 | |
| Shares available for future issuance | 8,942 | | | 9,510 | |
1 PRSUs are based on the maximum number of PRSUs in the key executive grant agreements. The actual number of PRSUs granted will be based on company performance criteria and relative Total Shareholder Return ("TSR"), as discussed in Note 13, Equity Incentive Plans
12. EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
401(k) Plan
The Company has a defined contribution 401(k) retirement plan (the “401(k) Plan”) covering substantially all employees in the United States. Employees who participate in the 401(k) Plan may contribute up to 90% of eligible compensation each year, subject to Internal Revenue Service limitations and the terms and conditions of the plan. Under the terms of the 401(k) Plan, the Company may elect to match a discretionary percentage of contributions. The Company matches contributions up to 50% and a maximum of $5,000 per year. Total matching contributions were $6.2 million, $5.6 million, and $5.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
13. EQUITY INCENTIVE PLANS
2016 Plan
In October 2016, the Company adopted the 2016 Equity Incentive Plan, (the “2016 Plan”). The 2016 Plan was approved by the Company’s stockholders and became effective on October 19, 2016. On the first day of each fiscal year starting from the 2017 fiscal year through the 2024 fiscal year, the 2016 Plan authorizes an annual increase in the number of shares available for issuance equal to the least of (i) 3,865,000 shares, (ii) 5% of the shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding on the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year or (iii) such number of shares determined by the Board. In November 2024, the Board of Directors approved an amendment to the 2016 Plan that removed the provision for annual increases. As of December 31, 2024, the Company has reserved approximately 6.4 million shares of common stock for issuance under the 2016 Plan.
A summary of awards available for grant under the Company's 2016 Equity Incentive Plan is as follows (in thousands): | | | | | |
| Shares Available
for Grant |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | 7,823 | |
| |
Awards granted1 | (1,373) | |
Awards forfeited1 | 315 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | 6,765 | |
| |
Awards granted1 | (869) | |
Awards forfeited1 | 474 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2024 | 6,370 | |
1 Awards granted and forfeited include PRSUs, which are based on the maximum number of PRSUs in the key executive grant agreements. The actual number of PRSUs granted will be based on company performance criteria and relative TSR, as described below.
Pursuant to the 2016 Plan, stock options, restricted stock, RSUs, performance units, performance shares, and stock appreciation rights may be granted to employees, consultants and directors of the Company. Stock options were not granted during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In October 2016, the Board and stockholders approved the 2016 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) which provides eligible employees of the Company with an opportunity to purchase shares of the Company's common stock at a discounted price through accumulated contributions not exceeding $25,000 in a given calendar year. On the first day of each fiscal year, the number of shares reserved for the ESPP increases by the least of (i) 966,062 shares, (ii) 1.5% of the shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding on the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year, or (iii) such number of shares determined by the Board. The ESPP allows eligible employees to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock at a discount through payroll deductions of up to 15% of their eligible compensation, subject to any plan limitations. The ESPP provides for 12-month offering periods that each contain two six-month purchase periods. At the end of each purchase period, employees purchase shares at 85% of the lower of the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the first trading day of the offering period or on the last day of the purchase period. If the stock price of the Company's common stock on any purchase date in an offering period is lower than the stock price on the first trading date of that offering period, the offering period will immediately reset after the purchase of shares on such purchase date and automatically roll into a new offering period.
Restricted Stock Units and Performance-Based Restricted Stock Units
The fair value of RSUs and PRSUs are based on the Company’s closing stock price on the date of grant. A summary is as follows (in thousands, except weighted average grant date fair value): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Restricted Stock Units | | Performance Based Restricted Stock Units and Market-Based Units |
| Shares
Underlying
RSUs | | Weighted
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value | | Shares Underlying PRSUs 1 | | Weighted
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | 1,465 | | | $ | 111.16 | | | 561 | | | $ | 120.22 | |
| Granted | 903 | | | 114.84 | | 470 | | | 124.17 |
| Vested | (622) | | | 96.54 | | (24) | | | 107.05 |
| Forfeited | (204) | | | 121.08 | | (111) | | | 127.07 |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | 1,542 | | | 117.90 | | 896 | | | 121.80 |
| Granted | 614 | | | 111.96 | | 254 | | | 132.66 |
| Vested | (483) | | | 115.33 | | (62) | | | 77.50 |
| Forfeited | (269) | | | 115.20 | | (203) | | | 110.03 |
| Balance as of December 31, 2024 | 1,404 | | | $ | 116.33 | | | 885 | | | $ | 130.44 | |
1Based on the maximum number of performance based restricted stock units in the key executive grant agreements, the actual number of units granted will be based on the annual unit volume compound annual growth rate ("CAGR") as described below.
As of December 31, 2024, there was total unamortized compensation costs of $100.4 million, net of estimated forfeitures, related to RSUs, which the Company expects to recognize over a weighted average period of 1.6 years. Aggregate intrinsic value of the RSUs was $126.6 million, $165.1 million, and $137.2 million as of December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
As of December 31, 2024, 1.3 million shares of RSUs were expected to vest with an aggregate intrinsic value of $116.1 million. Total grant date fair value of vested RSUs was $55.7 million, $60.0 million, and $33.4 million during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
As of December 31, 2024, there was total unamortized compensation costs of $24.9 million, net of estimated forfeitures, related to PRSUs, which the Company expects to recognize over a weighted average period of 1.2 years. Aggregate intrinsic value of the PRSUs was $79.8 million, $95.9 million, and $52.6 million as of December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
As of December 31, 2024, 0.9 million shares of PRSUs were expected to vest with an aggregate intrinsic value of $76.7 million. Total grant date fair value of vested PRSUs was $4.8 million, $2.6 million, and $12.1 million during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Market-based PRSUs
The Company grants PRSUs to its key executives. PRSUs can be earned in accordance with the performance equity program for each respective grant.
In February 2024, the Company granted market-based PRSUs to senior executive officers. These PRSUs to be earned will be based on the cumulative annual growth rate (“CAGR”) of annual unit volume calculated between fiscal years 2026's and 2023's annual unit volume growth and measuring a minimum performance threshold of 15% to earn 50% of target, and a maximum threshold of 25% achieved to earn 200% of target, as well as a relative comparison of the S&P Healthcare Equipment Select Industry Index to the Company's Total Shareholder Return (“TSR”). The fair value of market-based PRSUs were estimated at the date of grant using a Monte-Carlo simulation method. The grant date fair value of the TSR was based on the expected term of 2.8 years, interest risk free rate of 4.4%, implied volatility of 67.95% and no dividend yield. These February 2024 awards are subject to the recipient senior executive officer's continued employment through the vesting date of March 16, 2027.
In August 2023, the Company granted market-based retention PRSUs (“August 2023 awards”) to its Chief Executive Officer, other senior executive officers, and other members of the Company’s management team. The purpose of the performance-based awards was tied to several important long-term operational objectives, including to: (i) create stability among the leadership team, (ii) retain other critical talent and (iii) drive achievement of strategic objectives while the Company transforms and scales its business model. The performance period of the August 2023 awards will be measured between July 1, 2023 and June 30, 2026, with Company results subject to adjustment by the Company’s TSR as compared to the TSR of the S&P Healthcare Index. The fair value of market-based retention PRSUs were estimated at the date of grant using a Monte-Carlo simulation method. The grant date fair value of the TSR was based on the expected term of 2.9 years, interest risk free rate of 4.4%, implied volatility of 80.1% and no dividend yield. The August 2023 awards are subject to the respective continued employment of the recipients through the vesting date of August 7, 2026.
Options
The following table summarizes stock option activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options Outstanding |
Options Outstanding (in thousands) | | Weighted-
Average
Exercise
Price Per
Share | | Weighted-
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Life (years) | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(in thousands) |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | 328 | | | $ | 43.00 | | | 4.43 | | $ | 16,635 | |
| Options exercised | (21) | | | 52.56 | | | | | |
| Options forfeited | — | | | — | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | 307 | | | 42.34 | | | 3.29 | | 19,859 | |
| Options exercised | (22) | | | 52.69 | | | | | |
| Options forfeited | (2) | | | 67.55 | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | 283 | | | 41.32 | | | 2.38 | | 13,826 | |
| Options exercisable – December 31, 2024 | 283 | | | 41.32 | | | 2.38 | | 13,826 | |
| Options vested and expected to vest – December 31, 2024 | 283 | | | $ | 41.32 | | | 2.38 | | $ | 13,826 | |
| | | | | | | |
There have been no options granted since December 31, 2019. As of December 31, 2024, the options were fully vested. The total estimated grant date fair value of options vested during the period was nil, $0.1 million, and $2.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The Company issued approximately 99,000, 94,000, and 88,000 shares of common stock under the ESPP during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, approximately 2.0 million shares of the Company's common stock remained available for issuance under the ESPP.
The ESPP provides for 12-month offering periods that contain two six-month purchase periods. The Company determined the fair value of the stock purchase rights under the ESPP using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions for the specified periods.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Expected Term (years) | 0.5 - 1 | | 0.5 - 1 | | 0.5 - 1 |
| Expected Volatility | 46.5% - 64.1% | | 48.8% - 59.2% | | 68.1% - 96.3% |
| Dividend Yield | —% | | —% | | —% |
| Risk-Free Interest Rate | 4.3% - 5.4% | | 5.1% - 5.4% | | 1.6% - 4.7% |
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had $1.5 million of unrecognized compensation expense that will be recognized over a weighted average period of 0.5 years.
14. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
The following table summarizes the total stock-based compensation expense included in the statements of operations and comprehensive loss for all periods presented (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cost of revenue | $ | 3,092 | | | $ | 3,603 | | | $ | 2,153 | |
| Research and development | 13,932 | | | 11,391 | | | 6,976 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 58,954 | | | 62,210 | | | 48,611 | |
| Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 75,978 | | | $ | 77,204 | | | $ | 57,740 | |
Non-Employee Stock-Based Compensation
In March 2022, the former CEO retired from the Board and as a non-employee consultant. Vesting for all outstanding awards was accelerated upon his retirement. The Company recognized expense of $0.9 million related to the retirement of the former CEO during the year ended December 31, 2022.
On June 3, 2022, the Company’s former Chief Clinical Officer (the “former CCO”) retired and entered into a Consulting Agreement (“CA”) with the Company. Pursuant to the original terms of the awards, the former CCO will continue to vest in her outstanding awards as long as services are provided to the Company under the CA as a non-employee consultant. In accordance with ASC 718, Compensation - Stock Compensation (“ASC 718”), the Company recognized expense related to all awards vested over the duration of the CA in the current period as an equity-based severance cost because the consulting services are not substantive. The total expense related to the former CCO’s non-employee stock-based compensation recognized $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2022.
On July 25, 2022, the Company’s former Executive Vice President, Chief Commercial Officer (the “former EVP”) resigned and entered into a CA with the Company. Pursuant to the original terms of the agreement, the former EVP continues to vest in outstanding awards during the period of his CA services. In accordance with ASC 718, the Company recorded stock-based compensation expense related to the awards expected to vest over the duration of the CA, because the consulting services were substantive. The total expense related to the former EVP’s non-employee stock-based compensation recognized for each of the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 was $0.1 million.
On March 10, 2023, the Company’s former Chief Operating Officer (the “former COO”) resigned and entered into a CA with the Company through July 2024. Pursuant to the terms of the CA, the former COO vested in outstanding awards as long as services are provided to the Company under the CA as a non-employee consultant. In accordance with ASC 718, the Company recognized expense related to all awards vested over the duration of the CA in 2023 as an equity-severance cost because the consulting services were not substantive. The total expense related to the former COO’s non-employee stock-based compensation recognized for the year ended December 31, 2023 was $1.1 million.
On August 31, 2024, the Company’s former Chief Financial Officer (the “former CFO”) resigned and entered into a CA with the Company through March 15, 2025. Pursuant to the terms of the CA, the former CFO continues to vest in outstanding restricted stock unit awards during the period of his CA services. In accordance with ASC 718, the Company will continue to record stock-based compensation expense related to the awards expected to vest over the duration of the CA, because the consulting services are substantive. The total expense related to the former CFO’s non-employee stock-based compensation recognized for the year ended December 31, 2024 was $0.2 million.
15. NET LOSS PER COMMON SHARE
As the Company had net losses for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, all potential common shares were determined to be anti-dilutive. The following table sets forth the computation of the basic and diluted net loss per share during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 (in thousands, except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Numerator: | | | | | |
| Net loss | $ | (113,289) | | | $ | (123,406) | | | $ | (116,155) | |
| Denominator: | | | | | |
| Weighted-average shares used to compute net loss per common share, basic and diluted | 31,196 | | | 30,528 | | | 29,916 | |
| Net loss per common share, basic and diluted | $ | (3.63) | | | $ | (4.04) | | | $ | (3.88) | |
The following outstanding shares of potentially dilutive securities have been excluded from diluted net loss per common share for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 because their inclusion would be anti-dilutive (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Options to purchase common stock | 283 | | | 307 | | | 328 | |
RSUs and PRSUs1 | 2,289 | | | 2,438 | | | 2,026 | |
| Senior convertible notes | 4,492 | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | 7,064 | | | 2,745 | | | 2,354 | |
1PRSUs are based on the maximum number of PRSUs in the key executive grant agreements. The actual number of PRSUs granted will be based on company performance criteria and relative TSR, as discussed in Note 13, Equity Incentive Plan and Stock-Based Compensation.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
None
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) (principal executive officer) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”) (principal financial officer), as appropriate to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and management is required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
As required by Rule 13a under the Exchange Act, our management, including our CEO and CFO, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15e under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on that evaluation, our CEO and our CFO have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective at the reasonable assurance level as of December 31, 2024.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Our management has assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, using the criteria described in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on their evaluation, as of December 31, 2024, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective based on these criteria.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2024 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION.
Rule 10b5-1 Trading Plans
On November 14, 2024, Daniel Wilson, the Company's Chief Financial Officer, entered into a prearranged written stock sale plan in accordance with Rule 10b5-1 (the “Wilson 10b5-1 Plan”) under the Exchange Act for the sale of shares of the Company's common stock. The Wilson 10b5-1 Plan was entered into during an open trading window in accordance with the Company’s policies regarding transactions in the Company’s securities and is intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) under the Exchange Act. The Wilson 10b5-1 Plan provides for the potential sale of up to 18,000 shares of the Company's common stock, including upon the vesting and settlement of restricted stock units and performance restricted stock units for shares of the Company's common stock, so long as the market price of the Company's common stock is higher than a certain minimum threshold prices specified in Wilson 10b5-1 Plan, between March 3, 2025 and August 11, 2025.
On November 25, 2024, Chad Patterson, the Company's Chief Commercial Officer, entered into a prearranged written stock sale plan in accordance with Rule 10b5-1 (the “Patterson 10b5-1 Plan”) under the Exchange Act for the sale of shares of the Company's common stock. The Patterson 10b5-1 Plan was entered into during an open trading window in accordance with the Company’s policies regarding transactions in the Company’s securities and is intended to satisfy the affirmative defense of Rule 10b5-1(c) under the Exchange Act. The Patterson 10b5-1 Plan provides for the potential sale of up to 7,951 shares of the Company's common stock, including upon the vesting and settlement of restricted stock units and performance restricted stock units for shares of the Company's common stock, so long as the market price of the Company's common stock is higher than a certain minimum threshold prices specified in Patterson 10b5-1 Plan, between February 24, 2025 and December 2, 2025.
Each of the Wilson 10b5-1 Plan and the Patterson 10b5-1 Plan includes a representation from Mr. Wilson and Mr. Patterson, respectively, to the broker administering the plan that they were not in possession of any material nonpublic information regarding the Company or the securities subject to such Rule 10b5-1 Plan at the time it was entered into. A similar representation was made to the Company in connection with the adoption of such Rule 10b5-1 Plan under the Company’s policies regarding transactions in the Company’s securities. Those representations were made as of the date of adoption of the such Rule 10b5-1 Plan, and speak only as of such date. In making those representations, there is no assurance with respect to any material nonpublic information of which the insider was unaware, or with respect to any material nonpublic information acquired by the insider or the Company after the date of the representation.
ITEM 9C. DISCLOSURES REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS.
Not applicable.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
Certain information required by this item may be incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC in connection with our 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024, or alternatively, disclosed in an amendment to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Delinquent Section 16(a) Reports
Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act requires executive officers, directors, and persons who own more than 10% of a registered class of our equity securities to file reports of ownership with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Based solely on the copies of such forms received by us, we believe that during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024, all filing requirements were timely satisfied, except: (i) one Form 4 was filed one day late for one transaction by each of our outside directors (Cathleen Noel Bairey Merz, Bruce Bodaken, Karen Ling, Mark Rubash, Ralph Snyderman, Abhijit Talwalkar, Mojdeh Poul, and Brian Yoor) on June 3, 2024; and (ii) one Form 4 for one transaction was filed late by Daniel Wilson on December 27, 2024 and an amended Form 3 was filed by Daniel Wilson on February 14, 2025 to correct his aggregate holdings. The above identified late filings by our outside directors relate to the award of RSUs to such members of the Board of Directors as an automatic annual grant on May 29, 2024, the date of the Company's 2024 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, pursuant to the Company's Non-Employee Director Compensation Policy.
Insider Trading Policy
We have adopted an insider trading policy that governs the purchase, sale and/or other dispositions of our securities by directors, officers and employees. Our insider trading policy also provides that the Company will not transact in any of our own securities unless in compliance with U.S. securities laws. We believe that our insider trading policy is reasonably designed to promote compliance with insider trading laws, rules and regulations, and the Nasdaq listing standards applicable to us. A copy of our Insider Trading Policy is filed as Exhibit 19.1 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC in connection with our 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC in connection with our 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC in connection with our 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES.
Our independent registered public accounting firm is PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, San Jose, CA.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC in connection with our 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
(1)Financial Statements
The financial statements filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are listed in the “Index to Financial Statements” under Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(2)Financial Statement Schedules
Financial statement schedules have been omitted in this Annual Report on Form 10-K because they are not applicable, not required under the instructions, or the information requested is set forth in the financial statements or related notes thereto.
(3) Exhibits
The following is a list of exhibits filed with this Annual Report on Form 10-K incorporated herein by reference (numbered in accordance with Item 601 of Regulation S-K).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Index |
| | | | Incorporated by Reference | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Exhibit Title | | Form | | File No. | | Exhibit | | Filing Date | | Provided Herewith |
| 3.1 | | | | 10-Q | | 001-37918 | | 3.1 | | August 1, 2024 | | |
| 3.2 | | | | 8-K | | 001-37918 | | 3.1 | | November 16, 2023 | | |
| 4.1 | | | | S-1 | | 333-213773 | | 4.1 | | September 23, 2016 | | |
| 4.2 | | | | S-1/A | | 333-213773 | | 4.2 | | October 7, 2016 | | |
| 4.3 | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 4.3 | | March 2, 2020 | | |
| 4.4 | | | | 8-K | | 001-37918 | | 4.1 | | March 8, 2024 | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.1 | | | | 8-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.1 | | October 29, 2018 | | |
| 10.2 | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 4.4 | | March 2, 2020 | | |
| 10.3 | | | | 8-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.1 | | March 29, 2022 | | |
| 10.4 | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.8 | | February 22, 2024 | | |
| 10.5 | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.35 | | March 4, 2019 | | |
| 10.6 | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.10 | | February 22, 2024 | | |
| 10.7 | | | | 10-Q | | 001-37918 | | 10.42 | | May 10, 2021 | | |
| 10.8 | | | | 8-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.1 | | January 8, 2024 | | |
| 10.9+ | | | | 8-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.1 | | November 11, 2024 | | |
| 10.10+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-37918 | | 10.1 | | December 23, 2019 | | |
| 10.11+ | | | | S-1/A | | 333-213773 | | 10.5 | | October 7, 2016 | | |
| 10.12+ | | | | S-1 | | 333-213773 | | 10.1 | | September 23, 2016 | | |
| 10.13+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.2 | | February 22, 2024 | | |
| 10.14+ | | | | 10-Q | | 001-37918 | | 10.29 | | November 14, 2017 | | |
| 10.15+ | | | | 8-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.1 | | September 13, 2021 | | |
| 10.16+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.19 | | February 23, 2023 | | |
| 10.17+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.20 | | February 23, 2023 | | |
| 10.18+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.21 | | February 23, 2023 | | |
| 10.19+ | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 10.22 | | February 23, 2023 | | |
| 10.20+ | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.21+ | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
10.22± | | | | 10-Q | | 001-37918 | | 10.1 | | October 30, 2024 | | |
| 19.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 21.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 23.1 | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 31.1† | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 31.2† | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 32.1† | | | | | | | | | | | | X |
| 97.1 | | | | 10-K | | 001-37918 | | 97.1 | | February 22, 2024 | | |
| 101.INS | | Inline XBRL Instance Document | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.SCH | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.CAL | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.DEF | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.LAB | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | |
| 101.PRE | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | | | | | | | | | | |
________________________________________________________________________________________________
†The certification attached as 32.1 that accompanies this Annual Report on Form 10-K, is deemed furnished and not filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and is not to be incorporated by reference into any filing of iRhythm Technologies, Inc. under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, whether made before or after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, irrespective of any general incorporation language contained in such filing.
+ Indicates management contract or compensatory plan.
± Confidential treatment has been requested for portions of this exhibit. The Registrant agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of the omitted schedules and exhibits to the SEC upon request.
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY.
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the Registrant has duly caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | iRhythm Technologies, Inc. |
| | | |
| Date: February 20, 2025 | | By: | /s/ Quentin S. Blackford |
| | | Quentin S. Blackford
President and Chief Executive Officer
(Principal Executive Officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Name | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
| /s/ Quentin S. Blackford | | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | | February 20, 2025 |
| Quentin S. Blackford | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Daniel G. Wilson | | Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial Officer) | | February 20, 2025 |
| Daniel Wilson | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/Marc Rosenbaum | | Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting Officer) | | February 20, 2025 |
| Marc Rosenbaum | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Abhijit Y. Talwalkar | | Director and Chairman of the Board | | February 20, 2025 |
| Abhijit Y. Talwalkar | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Bruce Bodaken | | Director | | February 20, 2025 |
| Bruce G. Bodaken | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Ralph Snyderman | | Director | | February 20, 2025 |
| Ralph Snyderman M.D. | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ C. Noel Bairey Merz | | Director | | February 20, 2025 |
| C. Noel Bairey Merz, M.D. | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Mark Rubash | | Director | | February 20, 2025 |
| Mark J. Rubash | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Karen Ling | | Director | | February 20, 2025 |
| Karen Ling | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Brian Yoor | | Director | | February 20, 2025 |
| Brian Yoor | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Mojdeh Poul | | Director | | February 20, 2025 |
| Mojdeh Poul | | | | |
| | | | |