factors that may be considered in determining the fair value of our investments include
non-binding
indicative bids and the number of trades (and the size and timing of each trade) in an investment. Valuation of certain investments is also based, in part, upon third party valuation models which take into account various market inputs. Investors should be aware that the models, information and/or underlying assumptions utilized by the Adviser or such models will not always correctly capture the fair value of an asset. Because such valuations, and particularly valuations of securities that are not publicly traded like those we hold, are inherently uncertain, they may fluctuate over short periods of time and may be based on estimates. The Adviser’s determinations of fair value may differ materially from the values that would have been used if an active public market for these securities existed. The Adviser’s determinations of the fair value of our investments have a material impact on our net earnings through the recording of unrealized appreciation or depreciation of investments and may cause our NAV on a given date to understate or overstate, possibly materially, the value that we may ultimately realize on one or more of our investments.
See
“
Determination of Net Asset Value
.”
Our financial condition and results of operations depend on the Adviser’s ability to effectively manage and deploy capital.
Our ability to achieve our investment objectives depends on the Adviser’s ability to effectively manage and deploy capital, which depends, in turn, on the Adviser’s ability to identify, evaluate and monitor, and our ability to acquire, investments that meet our investment criteria.
Accomplishing our investment objectives on a cost-effective basis is largely a function of the Adviser’s handling of the investment process, its ability to provide competent, attentive and efficient services and our access to investments offering acceptable terms, either in the primary or secondary markets. Even if we are able to grow and build upon our investment operations, any failure to manage our growth effectively could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. The results of our operations will depend on many factors, including the availability of opportunities for investment, readily accessible short and long-term funding alternatives in the financial markets and economic conditions. Furthermore, if we cannot successfully operate our business or implement our investment policies and strategies as described in this prospectus, it could adversely impact our ability to pay dividends or make distributions. In addition, because the trading methods employed by the Adviser on our behalf are proprietary, Shareholders will not be able to determine details of such methods or whether they are being followed.
We are reliant on CGCIM continuing to serve as the Adviser.
Since the Fund has no employees, it depends on the investment expertise, skill and network of business contacts of the Adviser. The Adviser evaluates, negotiates, structures, executes, monitors and services the Fund’s investments. The Fund’s future success depends to a significant extent on the continued service and coordination of the Adviser and its senior management team. The departure of any members of the Adviser’s senior management team could have a material adverse effect on the Fund’s ability to achieve its investment objective.
The Fund’s ability to achieve its investment objective depends on the Adviser’s ability to identify, analyze, invest in, finance and monitor companies that meet the Fund’s investment criteria. The Adviser’s capabilities in managing the investment process, providing competent, attentive and efficient services to the Fund, and facilitating access to financing on acceptable terms depend on the employment of investment professionals in an adequate number and of adequate sophistication to match the corresponding flow of transactions. To achieve the Fund’s investment objective, the Adviser may need to hire, train, supervise and manage new investment professionals to participate in the Fund’s investment selection and monitoring process. The Adviser may not be able to find investment professionals in a timely manner or at all. Failure to support the Fund’s investment process could have a material adverse effect on the Fund’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, the Investment Advisory Agreement has termination provisions that allow the parties to terminate the agreements without penalty. The Investment Advisory Agreement may be terminated at any time, without
penalty, by the Adviser upon 60 days’ notice to the Fund. If the Investment Advisory Agreement is terminated, it may adversely affect the quality of the Fund’s investment opportunities. In addition, in the event the Investment Advisory Agreement is terminated, it may be difficult for the Fund to replace the Adviser. Furthermore, the termination of the Investment Advisory Agreement may adversely impact the terms of the Fund’s or its subsidiaries’ financing facilities or any financing facility into which the Fund or its subsidiaries may enter in the future, which could have a material adverse effect on the Fund’s business and financial condition.
We are reliant on key personnel at CGCIM.
The Adviser depends on the diligence, skill and network of business contacts of certain professionals. The Adviser also depends, to a significant extent, on access to other investment professionals and the information and deal flow generated by these investment professionals in the course of their investment and portfolio management activities. The Fund’s success depends on the continued service of such personnel. The investment professionals associated with the Adviser are actively involved in other investment activities not concerning the Fund and will not be able to devote all of their time to the Fund’s business and affairs. The departure of any of the senior managers of the Adviser, or of a significant number of the investment professionals or partners of the Adviser’s affiliates, could have a material adverse effect on the Fund’s ability to achieve its investment objective. Individuals not currently associated with the Adviser may become associated with the Fund and the performance of the Fund may also depend on the experience and expertise of such individuals. In addition, there is no assurance that the Adviser will remain the Fund’s investment adviser or that the Adviser will continue to have access to the investment professionals and partners of its affiliates and the information and deal flow generated by the investment professionals of its affiliates.
We expect to rely to on Carlyle’s existing relationships to a significant extent.
The Fund expects that Carlyle will depend on its existing relationships with private equity sponsors, investment banks and commercial banks, and the Fund expects to rely to a significant extent upon these relationships for purposes of potential investment opportunities. If Carlyle fails to maintain its existing relationships or develop new relationships with other sources or sponsors of investment opportunities, the Fund may not be able to expand its investment portfolio. In addition, individuals with whom Carlyle has relationships are not obligated to provide the Fund with investment opportunities and, therefore, there is no assurance that such relationships will generate investment opportunities for the Fund.
The highly competitive market in which we operate may limit our investment opportunities.
The market for CLO securities is more limited than the market for other credit related investments. We can offer no assurances that sufficient investment opportunities for our capital be available.
The Fund competes for investments with other
closed-end
funds and investment funds, as well as traditional financial services companies such as commercial banks and other sources of funding. Moreover, alternative investment vehicles, such as hedge funds, have begun to invest in areas in which they have not traditionally invested. As a result of these new entrants, competition for investment opportunities may intensify. Many of the Fund’s competitors are substantially larger and may have considerably greater financial, technical and marketing resources than the Fund. For example, some competitors may have a lower cost of capital and access to funding sources that are not available to the Fund. In addition, some of the Fund’s competitors may have higher risk tolerances or different risk assessments than it has. These characteristics could allow the Fund’s competitors to consider a wider variety of investments, establish more relationships and pay more competitive prices for investments than it is able to do. The Fund may lose investment opportunities if it does not match its competitors’ pricing. If the Fund is forced to match its competitors’ pricing, it may not be able to achieve acceptable returns on its investments or may bear substantial risk of capital loss. A significant increase in the number and/or the size of the Fund’s competitors could force it to accept less attractive investment terms. Furthermore, many of the Fund’s competitors have greater experience operating under, or are not subject to, the regulatory restrictions that the 1940 Act imposes on it as a
closed-end
fund.
The risk of our investments may not be commensurate with the returns.
No assurance can be given that the returns on the Fund’s investments will be commensurate with the risk of investment in the Fund.
The Adviser, senior management and employees have certain conflicts of interest.
The Adviser is an entity in which the Fund’s Interested Trustees, officers and members of the investment committee of the Adviser may have indirect ownership and economic interests. Certain of the Fund’s Trustees and officers and members of the investment committee of the Adviser also serve as officers or principals of other investment managers affiliated with the Adviser that currently, and may in the future, manage investment funds with investment objectives similar to the Fund’s investment objective. In addition, certain of the Fund’s officers and Trustees and the members of the investment committee of the Adviser serve or may serve as officers, trustees or principals of entities that operate in the same or related line of business as the Fund does or of investment funds managed by the Fund’s affiliates. Accordingly, the Fund may not be made aware of and/or given the opportunity to participate in certain investments made by investment funds managed by advisers affiliated with the Adviser. However, the Adviser intends to allocate investment opportunities in a fair and equitable manner in accordance with the Adviser’s investment allocation policy, consistent with each fund’s or separate account’s investment objective and strategies and legal and regulatory requirements.
There may be conflicts of interest related to obligations that the Adviser has with respect to the allocation of investment opportunities.
The Adviser has adopted allocation procedures that are intended to treat each fund they advise in a manner that, over a period of time, is fair and equitable. The Adviser and its affiliates currently provide investment advisory and administration services and may provide in the future similar services to other entities (collectively, “
”). Certain existing Advised Funds have, and future Advised Funds may have, investment objectives similar to those of the Fund, and such Advised Funds will invest in asset classes similar to those targeted by the Fund. Certain other existing Advised Funds do not, and future Advised Funds may not, have similar investment objectives, but such funds may from time to time invest in asset classes similar to those targeted by the Fund. The Adviser will endeavor to allocate investment opportunities in a fair and equitable manner, and in any event consistent with any fiduciary duties owed to the Fund and other clients and in an effort to avoid favoring one client over another and taking into account all relevant facts and circumstances, including (without limitation): (i) differences with respect to available capital, size of client, and remaining life of a client; (ii) differences with respect to investment objectives or current investment strategies, including regarding: (a) current and total return requirements, (b) emphasizing or limiting exposure to the security or type of security in question, (c) diversification, including industry or company exposure, currency and jurisdiction, or (d) rating agency ratings; (iii) differences in risk profile at the time an opportunity becomes available; (iv) the potential transaction and other costs of allocating an opportunity among various clients; (v) potential conflicts of interest, including whether a client has an existing investment in the security in question or the issuer of such security; (vi) the nature of the security or the transaction, including minimum investment amounts and the source of the opportunity; (vii) current and anticipated market and general economic conditions; (viii) existing positions in a borrower/loan/security; and (ix) prior positions in a borrower/loan/security. Nevertheless, it is possible that the Fund may not be given the opportunity to participate in certain investments made by investment funds managed by investment managers affiliated with the Adviser.
In the event investment opportunities are allocated among the Fund and the other Advised Funds, the Fund may not be able to structure its investment portfolio in the manner desired. Furthermore, the Fund and the other Advised Funds may make investments in securities where the prevailing trading activity may make impossible the receipt of the same price or execution on the entire volume of securities purchased or sold by the Fund and the other Advised Funds. When this occurs, the various prices may be averaged, and the Fund will be charged or credited with the average price. Thus, the effect of the aggregation may operate on some occasions to the
disadvantage of the Fund. In addition, under certain circumstances, the Fund may not be charged the same commission or commission equivalent rates in connection with a bunched or aggregated order.
It is likely that the other Advised Funds may make investments in the same or similar securities at different times and on different terms than the Fund. The Fund and the other Advised Funds may make investments at different levels of a borrower’s capital structure or otherwise in different classes of a borrower’s securities, to the extent permitted by applicable law. Such investments may inherently give rise to conflicts of interest or perceived conflicts of interest between or among the various classes of securities that may be held by such entities. Conflicts may also arise because portfolio decisions regarding the Fund may benefit the other Advised Funds. For example, the sale of a long position or establishment of a short position by the Fund may impair the price of the same security sold short by (and therefore benefit) one or more Advised Funds, and the purchase of a security or covering of a short position in a security by the Fund may increase the price of the same security held by (and therefore benefit) one or more Advised Funds.
Applicable law, including the 1940 Act, may at times prevent the Fund from being able to participate in investments that it otherwise would participate in, and may require the Fund to dispose of investments at a time when it otherwise would not dispose of such investment, in each case, in order to comply with applicable law.
The 1940 Act contains prohibitions and restrictions relating to certain transactions between registered investment companies and certain affiliates (including any investment advisers or
sub-advisers),
principal underwriters and certain affiliates of those affiliates or underwriters. Because the Fund is a registered investment company, the Fund is not generally permitted to make loans to companies controlled by the Adviser or other funds managed by the Adviser or its affiliates, including Carlyle. The Fund is also not permitted to make any
co-investments
with Carlyle or its affiliates (including any fund managed by Carlyle or its affiliates) without exemptive relief from the SEC, subject to certain exceptions. The SEC has granted exemptive relief that permits the Fund and certain present and future funds advised by Carlyle-controlled investment advisers to
co-invest
in suitable negotiated investments.
Co-investments
made under the exemptive relief are subject to compliance with the conditions and other requirements contained in the exemptive relief, which could limit the Fund’s ability to participate in a
co-investment
transaction.
The Adviser, its affiliates and their clients may pursue or enforce rights with respect to a borrower in which the Fund has invested, and those activities may have an adverse effect on the Fund. As a result, prices, availability, liquidity and terms of the Fund’s investments may be negatively impacted by the activities of the Adviser and its affiliates or their clients, and transactions for the Fund may be impaired or effected at prices or terms that may be less favorable than would otherwise have been the case.
The Adviser may have a conflict of interest in deciding whether to cause the Fund to incur leverage or to invest in more speculative investments or financial instruments, thereby potentially increasing the management and incentive fee payable by the Fund and, accordingly, the fees received by the Adviser. Certain other Advised Funds pay the Adviser or its affiliates greater performance-based compensation, which could create an incentive for the Adviser or an affiliate to favor such investment fund or account over the Fund.
Certain personnel of the Adviser and their management may face conflicts in their time management and commitments.
The Fund’s executive officers and trustees, other current and future principals of the Adviser and certain members of the Adviser’s investment committee may serve as officers, trustees or principals of other entities and affiliates of the Adviser and funds managed by the Fund’s affiliates that operate in the same or a related line of business as the Fund does. Currently, the Fund’s executive officers, as well as the other principals of the Adviser, manage other funds affiliated with Carlyle, including other existing and future affiliated BDCs and registered
closed-end
funds, including Carlyle Secured Lending, Inc., Carlyle Credit Solutions, Inc. and Carlyle Tactical Private Credit Fund. In addition, the Adviser’s investment team has responsibilities for sourcing and managing
private debt investments for certain other investment funds and accounts. Accordingly, they have obligations to investors in those entities, the fulfillment of which may not be in the best interests of, or may be adverse to the interests of, the Fund and its Shareholders. Although the professional staff of the Adviser will devote as much time to management of the Fund as appropriate to enable the Adviser to perform its duties in accordance with the Investment Advisory Agreement, the investment professionals of the Adviser may have conflicts in allocating their time and services among the Fund, on the one hand, and investment vehicles managed by Carlyle or one or more of its affiliates on the other hand.
The Adviser and the Administrator each has the right to resign following a required notice period, and we may not be able to find a suitable replacement within that time, resulting in a disruption in our operations that could adversely affect our financial condition, business and results of operations.
The Adviser has the right, under the Investment Advisory Agreement, to resign at any time upon 60 days’ written notice, whether we have found a replacement or not. The Administrator has the right, under the Administration Agreement, to terminate the Administration Agreement upon 180 days’ written notice prior to the initial term expiration or renewal date. If the Adviser or the Administrator resigns, we may not be able to find a new investment adviser or hire internal management, or find a new administrator, as the case may be, with similar expertise and ability to provide the same or equivalent services on acceptable terms within the notice period, or at all. If we are unable to do so quickly, our operations are likely to experience a disruption, our financial condition, business and results of operations, as well as our ability to make distributions to our Shareholders and other payments to securityholders, are likely to be adversely affected and the market price of our securities may decline. In addition, the coordination of our internal management and investment activities is likely to suffer if we are unable to identify and reach an agreement with a single institution or group of executives having the expertise possessed by the Adviser and the Administrator and their affiliates. Even if we are able to retain comparable management and administration, whether internal or external, the integration of such management and their lack of familiarity with our investment objectives and operations would likely result in additional costs and time delays that may adversely affect our financial condition, business and results of operations.
Our success will depend on the ability of the Adviser to attract and retain qualified personnel in a competitive environment.
Our growth will require that the Adviser attract and retain new investment and administrative personnel in a competitive market. The Adviser’s ability to attract and retain personnel with the requisite credentials, experience and skills will depend on several factors including its ability to offer competitive compensation, benefits and professional growth opportunities. Many of the entities, including investment funds (such as private equity funds, mezzanine funds and business development companies) and traditional financial services companies, with which the Adviser will compete for experienced personnel have greater resources than the Adviser has.
Our incentive fee structure may incentivize the Adviser to pursue speculative investments, use leverage when it may be unwise to do so, or refrain from
de-levering
when it would otherwise be appropriate to do so.
The Investment Advisory Agreement entitles the Adviser to receive incentive compensation on income regardless of any capital losses. In such case, the Fund may be required to pay the Adviser incentive compensation for a fiscal quarter even if there is a decline in the value of the Fund’s portfolio or if the Fund incurs a net loss for that quarter. Any Incentive Fee payable by the Fund that relates to its net investment income may be computed and paid on income that may include interest that has been accrued but not yet received. If an investment defaults on a loan that is structured to provide accrued interest, it is possible that accrued interest previously included in the calculation of the Incentive Fee will become uncollectible.
The Adviser is not under any obligation to reimburse the Fund for any part of the Incentive Fee it received that was based on accrued income that the Fund never received as a result of a default by an entity on the obligation that resulted in the accrual of such income, and such circumstances would result in the Fund’s paying an Incentive Fee on income it never received. The Incentive Fee payable by the Fund to the Adviser may create an
incentive for it to make investments on the Fund’s behalf that are risky or more speculative than would be the case in the absence of such compensation arrangement. The way in which the Incentive Fee payable to the Adviser is determined may encourage it to use leverage to increase the return on the Fund’s investments. In addition, the fact that the Management Fee is payable based upon the Fund’s Managed Assets, which would include any borrowings for investment purposes, may encourage the Adviser to use leverage to make additional investments. Under certain circumstances, the use of leverage may increase the likelihood of default, which would disfavor Shareholders. Such a practice could result in the Fund’s investing in more speculative securities than would otherwise be in its best interests, which could result in higher investment losses, particularly during cyclical economic downturns.
Additionally, the incentive fee payable by us to the Adviser may create an incentive for the Adviser to pursue investments on our behalf that are riskier or more speculative than would be the case in the absence of such compensation arrangement. Such a practice could result in our investing in more speculative securities than would otherwise be the case, which could result in higher investment losses, particularly during economic downturns. The incentive fee payable to the Adviser is based on our
Pre-Incentive
Fee Net Investment Income, as calculated in accordance with our Investment Advisory Agreement. This may encourage the Adviser to use leverage to increase the return on our investments, even when it may not be appropriate to do so, and to refrain from
de-levering
when it would otherwise be appropriate to do so. Under certain circumstances, the use of leverage may increase the likelihood of default, which would impair the value of our securities. See “—
Risks Related to Our Investments — We may leverage our portfolio, which would magnify the potential for gain or loss on amounts invested and will increase the risk of investing in us
.”
We may be obligated to pay the Adviser incentive compensation even if we incur a loss or with respect to investment income that we have accrued but not received.
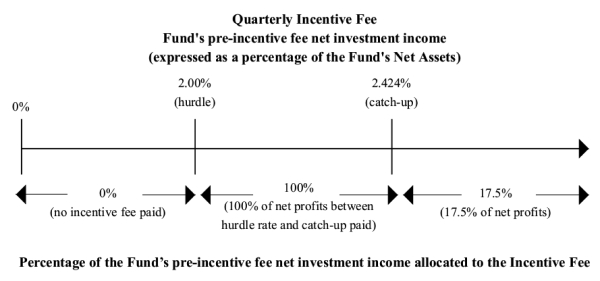
The Adviser is entitled to incentive compensation for each fiscal quarter based, in part, on our
Pre-Incentive
Fee Net Investment Income, if any, for the immediately preceding calendar quarter above a performance threshold for that quarter. Accordingly, since the performance threshold is based on a percentage of our NAV, decreases in our NAV make it easier to achieve the performance threshold. Our
Pre-Incentive
Fee Net Investment Income for incentive compensation purposes excludes realized and unrealized capital losses or depreciation that we may incur in the fiscal quarter, even if such capital losses or depreciation result in a net loss on our statement of operations for that quarter. Thus, we may be required to pay the Adviser incentive compensation for a fiscal quarter even if there is a decline in the value of our portfolio or we incur a net loss for that quarter. In addition, we accrue an incentive fee on accrued income that we have not yet received in cash. However, the portion of the incentive fee that is attributable to such income will be paid to the Adviser, without interest, only if and to the extent we actually receive such income in cash.
The Adviser’s liability is limited under the Investment Advisory Agreement, and we have agreed to indemnify the Adviser against certain liabilities, which may lead the Adviser to act in a riskier manner on our behalf than it would when acting for its own account.
Under the Investment Advisory Agreement, the Adviser does not assume any responsibility to us other `than to render the services called for under the agreement, and it is not responsible for any action of the Board in following or declining to follow the Adviser’s advice or recommendations. The Adviser maintains a contractual and fiduciary relationship with us. Under the terms of the Investment Advisory Agreement, the Adviser, its officers, managers, members, agents, employees and other affiliates are not liable to us for acts or omissions performed in accordance with and pursuant to the Investment Advisory Agreement, except those resulting from acts constituting willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence or reckless disregard of the Adviser’s duties under the Investment Advisory Agreement. In addition, we have agreed to indemnify the Adviser and each of its officers, managers, members, agents, employees and other affiliates from and against all damages, liabilities, costs and expenses (including reasonable legal fees and other amounts reasonably paid in settlement) incurred by such persons arising out of or based on performance by the Adviser of its obligations under the Investment
Advisory Agreement, except where attributable to willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence or reckless disregard of the Adviser’s duties under the Investment Advisory Agreement. These protections may lead the Adviser to act in a riskier manner when acting on our behalf than it would when acting for its own account.
The Adviser may not be able to achieve the same or similar returns as those achieved by other portfolios managed by the Senior Investment Team.
Although the Senior Investment Team manages other investment portfolios, including accounts using investment objectives, investment strategies and investment policies similar to ours, we cannot assure you that we will be able to achieve the results realized by such portfolios.
We may experience fluctuations in our NAV and quarterly operating results.
We could experience fluctuations in our NAV from month to month and in our quarterly operating results due to a number of factors, including the timing of distributions to our Shareholders, fluctuations in the value of the CLO securities that we hold, our ability or inability to make investments that meet our investment criteria, the interest and other income earned on our investments, the level of our expenses (including the interest or dividend rate payable on the debt securities or preferred shares we issue), variations in and the timing of the recognition of realized and unrealized gains or losses, the degree to which we encounter competition in our markets and general economic conditions. As a result of these factors, our NAV and results for any period should not be relied upon as being indicative of our NAV and results in future periods.
The Board may change our operating policies and strategies without Shareholder approval, the effects of which may be adverse.
The Board has the authority to modify or waive our current operating policies, investment criteria and strategies, other than those that we have deemed to be fundamental, without prior Shareholder approval. We cannot predict the effect any changes to our current operating policies, investment criteria and strategies would have on our business, NAV, operating results and value of our securities. However, the effects of any such changes could adversely impact our ability to pay dividends and cause you to lose all or part of your investment.
Our management’s estimates of certain metrics relating to our financial performance for a period are subject to revision based on our actual results for such period.
Our management makes and publishes unaudited estimates of certain metrics indicative of our financial performance, including the NAV per common share and the range of NAV per common share on a monthly basis, and the range of the net investment income and realized gain/loss per common share on a quarterly basis. While any such estimate will be made in good faith based on our most recently available records as of the date of the estimate, such estimates are subject to financial closing procedures, the Adviser’s final determination of the fair value of our applicable investments as of the end of the applicable quarter and other developments arising between the time such estimate is made and the time that we finalize our quarterly financial results and may differ materially from the results reported in the audited financial statements and/or the unaudited financial statements included in filings we make with the SEC. As a result, investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on any management estimates presented in this prospectus or any related amendment to this prospectus or related prospectus supplement and should view such information in the context of our full quarterly or annual results when such results are available.
We will be subject to corporate-level income tax if we are unable to maintain our RIC status for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
We can offer no assurance that we will be able to maintain our RIC status. To obtain and maintain RIC tax treatment under the Code, we must meet certain annual distribution, income source and asset diversification requirements.
The annual distribution requirement for a RIC will be satisfied if we distribute dividends to our shareholders each tax year of an amount generally at least equal to 90% of the sum of our net ordinary income, net
tax-exempt
interest income, if any, and realized net short-term capital gains in excess of realized net long-term capital losses, if any. Because we use debt financing, we are subject to certain asset coverage requirements under the 1940 Act and may be subject to financial covenants that could, under certain circumstances, restrict us from making distributions necessary to satisfy the distribution requirement. If we are unable to obtain cash from other sources, we could fail to qualify for RIC tax treatment and thus become subject to corporate-level income tax.
The income source requirement will be satisfied if we obtain at least 90% of our income for each tax year from dividends, interest, gains from the sale of our securities or similar sources.
The asset diversification requirement will be satisfied if we meet certain asset composition requirements at the end of each quarter of our tax year. Failure to meet those requirements may result in our having to dispose of certain investments quickly in order to prevent the loss of RIC status. Because most of our investments are expected to be in CLO securities for which there will likely be no active public market, any such dispositions could be made at disadvantageous prices and could result in substantial losses.
If we fail to qualify for RIC tax treatment for any reason and remain or become subject to corporate income tax, the resulting corporate taxes could substantially reduce our net assets and the amount of income available for distributions, and the amount of any such distributions, to our Shareholders and the holders of our other securities.
We may have difficulty paying our required distributions if we recognize income before or without receiving cash representing such income.
For federal income tax purposes, we will include in income certain amounts that we have not yet received in cash, such as original issue discount , or “OID,” or market discount, which may arise if we acquire a debt security at a significant discount to par, or
interest, which represents contractual interest added to the principal amount of a debt security and due at the maturity of the debt security. We also may be required to include in income certain other amounts that we have not yet, and may not ever, receive in cash. Our investments in debt securities that pay
interest may represent a higher credit risk than debt securities for which interest must be paid in full in cash on a regular basis. For example, even if the accounting conditions for income accrual are met, the issuer of the security could still default when our actual collection is scheduled to occur upon maturity of the obligation.
Since, in certain cases, we may recognize income before or without receiving cash representing such income, we may have difficulty meeting the annual distribution requirement necessary to maintain RIC tax treatment under the Code. In addition, since our incentive fee is payable on our income recognized, rather than cash received, we may be required to pay advisory fees on income before or without receiving cash representing such income. Accordingly, we may have to sell some of our investments at times and/or at prices we would not consider advantageous, raise additional debt or equity capital or forgo new investment opportunities for this purpose. If we are not able to obtain cash from other sources, we may fail to qualify for RIC tax treatment and thus become subject to corporate-level income tax.
Our cash distributions to Shareholders may change and a portion of our distributions to Shareholders may be a return of capital.
The amount of our cash distributions may increase or decrease at the discretion of the Board, based upon its assessment of the amount of cash available to us for this purpose and other factors. Unless we are able to generate sufficient cash through the successful implementation of our investment strategy, we may not be able to sustain a given level of distributions and may need to reduce the level of our cash distributions in the future. Further, to the extent that the portion of the cash generated from our investments that is recorded as interest
income for financial reporting purposes is less than the amount of our distributions, all or a portion of one or more of our future distributions, if declared, may comprise a return of capital. A return of capital distribution will generally not be taxable to our Shareholders. However, a return of capital distribution will reduce a Shareholder’s cost basis in our common shares on which the distribution was received, thereby potentially resulting in a higher reported capital gain or lower reported capital loss when those common shares are sold or otherwise disposed of. Accordingly, Shareholders should not assume that the sole source of any of our distributions is net investment income. Any reduction in the amount of our distributions would reduce the amount of cash received by our Shareholders and could have a material adverse effect on the market price of our common shares. See “
— Risks Related to Our Investments — Our investments are subject to prepayment risk
” and “
— Any unrealized losses we experience on our portfolio may be an indication of future realized losses, which could reduce our income available for distribution or to make payments on our other obligations
.”
Our Shareholders may receive our common shares as distributions, which could result in adverse tax consequences to them.
In order to satisfy certain annual distribution requirements to maintain RIC tax treatment under Subchapter M of the Code, we may declare a large portion of a distribution in our common shares instead of in cash even if a Shareholder has opted out of participation in the DRP. We do not intend to declare any portion of our distributions in our common shares. If, however, we do make such a declaration, as long as at least 20% of such distribution is paid in cash and certain requirements are met, the entire distribution will be treated as a dividend for U.S. federal income tax purposes. As a result, a Shareholder generally would be subject to tax on the distribution in the same manner as a cash distribution, even though most of the distribution was paid in our common shares.
We incur significant costs as a result of being a publicly traded company.
As a publicly traded company, we incur legal, accounting and other expenses, including costs associated with the periodic reporting requirements applicable to a company whose securities are registered under the Exchange Act as well as additional corporate governance requirements, including requirements under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and other rules implemented by the SEC.
Because we expect to distribute substantially all of our ordinary income and net realized capital gains to our shareholders, we may need additional capital to finance the acquisition of new investments and such capital may not be available on favorable terms, or at all.
In order to maintain our RIC tax treatment, we are required to distribute at least 90% of the sum of our net ordinary income, net
tax-exempt
interest income, if any, and realized net short-term capital gains in excess of realized net long-term capital losses, if any. As a result, these earnings will not be available to fund new investments, and we will need additional capital to fund growth in our investment portfolio. If we fail to obtain additional capital, we could be forced to curtail or cease new investment activities, which could adversely affect our business, operations and results. Even if available, if we are not able to obtain such capital on favorable terms, it could adversely affect our net investment income.
A disruption or downturn in the capital markets and the credit markets could impair our ability to raise capital and negatively affect our business.
We may be materially affected by market, economic and political conditions globally and in the jurisdictions and sectors in which we invest or operate, including conditions affecting interest rates and the availability of credit. Unexpected volatility, illiquidity, governmental action, currency devaluation or other events in the global markets in which we directly or indirectly hold positions could impair our ability to carry out our business and could cause us to incur substantial losses. These factors are outside our control and could adversely affect the liquidity and value of our investments, and may reduce our ability to make attractive new investments.
In particular, economic and financial market conditions significantly deteriorated for a significant part of the past decade as compared to prior periods. Global financial markets experienced considerable declines in the valuations of equity and debt securities, an acute contraction in the availability of credit and the failure of a number of leading financial institutions. As a result, certain government bodies and central banks worldwide, including the U.S. Treasury Department and the U.S. Federal Reserve, undertook unprecedented intervention programs, the effects of which remain uncertain. Although certain financial markets have improved, to the extent economic conditions experienced during the past decade recur, they may adversely impact our investments. Signs of deteriorating sovereign debt conditions in Europe and elsewhere and uncertainty regarding the U.S. economy more generally could lead to further disruption in the global markets. Trends and historical events do not imply, forecast or predict future events, and past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results. There can be no assurance that the assumptions made or the beliefs and expectations currently held by the Adviser will prove correct, and actual events and circumstances may vary significantly.
We may be subject to risk arising from a default by one of several large institutions that are dependent on one another to meet their liquidity or operational needs, so that a default by one institution may cause a series of defaults by the other institutions. This is sometimes referred to as “systemic risk” and may adversely affect financial intermediaries with which we interact in the conduct of our business.
We also may be subject to risk arising from a broad sell off or other shift in the credit markets, which may adversely impact our income and NAV. In addition, if the value of our assets declines substantially, we may fail to maintain the minimum asset coverage imposed upon us by the 1940 Act. Any such failure would affect our ability to issue preferred shares, debt securities and other senior securities, including borrowings, and may affect our ability to pay distributions on our capital stock, which could materially impair our business operations. Our liquidity could be impaired further by an inability to access the capital markets or to obtain additional debt financing. For example, we cannot be certain that we would be able to obtain debt financing on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. In previous market cycles, many lenders and institutional investors have previously reduced or ceased lending to borrowers. In the event of such type of market turmoil and tightening of credit, increased market volatility and widespread reduction of business activity could occur, thereby limiting our investment opportunities. Moreover, we are unable to predict when economic and market conditions may be favorable in future periods. Even if market conditions are broadly favorable over the long term, adverse conditions in particular sectors of the financial markets could adversely impact our business.
If we are unable to refinance and/or obtain debt capital or issue preferred shares, the Fund’s operations could be materially adversely affected.
We may obtain debt financing or issue preferred shares in order to obtain funds to make additional investments and grow our portfolio of investments. Such debt capital may take the form of a term credit facility with a fixed maturity date or other fixed term instruments, and we may be unable to extend, refinance or replace such debt financings prior to their maturity. If we are unable to issue preferred shares or refinance and/or obtain additional debt capital on commercially reasonable terms, our liquidity will be lower than it would have been with the benefit of such financings, which would limit our ability to grow our business. Any such limitations on our ability to grow and take advantage of leverage may decrease our earnings, if any, and distributions to Shareholders, which in turn may lower the trading price of our securities. In addition, in such event, we may need to liquidate certain of our investments, which may be difficult to sell if required, meaning that we may realize significantly less than the value at which we have recorded our investments. Furthermore, to the extent we are not able to raise capital and are at or near our targeted leverage ratios, we may receive smaller allocations, if any, on new investment opportunities under the Adviser’s allocation policy.
Debt capital that is available to us in the future, if any, including upon the refinancing of then-existing debt prior to its maturity, may be at a higher cost and on less favorable terms and conditions than costs and other terms and conditions at which we can currently obtain debt capital. In addition, if we are unable to repay amounts outstanding under any such debt financings and are declared in default or are unable to renew or refinance these
debt financings, we may not be able to make new investments or operate our business in the normal course. These situations may arise due to circumstances that we may be unable to control, such as lack of access to the credit markets, a severe decline in the value of the U.S. dollar, an economic downturn or an operational problem that affects third parties or us, and could materially damage our business.
We may be more susceptible than a diversified fund to being adversely affected by any single corporate, economic, political or regulatory occurrence.
The Fund is a
non-diversified
investment company under the 1940 Act and expects to hold a narrower range of investments than a diversified fund under the 1940 Act. Since the Fund will only participate in a limited number of investments, and since the Fund’s investments generally will involve a high degree of risk, poor performance by a few investments could severely affect the total returns to investors, which may be exacerbated by the use of leverage. See “
Risks Related to Our Investments — We may leverage our portfolio, which would magnify the potential for gain or loss on amounts invested and will increase the risk of investing in us
”
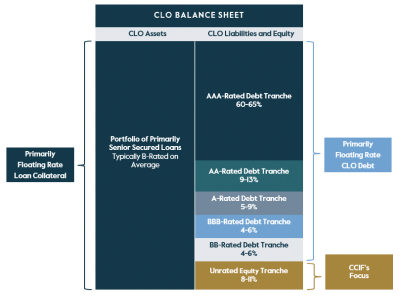
In addition, the Fund cannot provide assurance as to the degree of diversification of the Fund’s investments. To the extent the Fund concentrates investments in a particular asset, investors will be subject to concentration levels higher than currently targeted for the Fund, which concentration would result in the Fund being more susceptible to fluctuations in value resulting from adverse economic, business or market conditions. In particular, because our portfolio of investments may lack diversification among CLO securities and related investments, we are susceptible to a risk of significant loss if one or more of these CLO securities and related investments experience a high level of defaults on the collateral that they hold. Moreover, there is no guarantee that all of the Fund’s investments will perform well or provide a return capital. Therefore, if certain Investments perform unfavorably, for the Fund to achieve above-average returns, one or a few of its Investments must perform exceptionally well. There are no assurances that this will be the case.
Regulations governing our operation as a registered
closed-end
management investment company affect our ability to raise additional capital and the way in which we do so. The raising of debt capital or issuance of preferred shares may expose us to risks, including the typical risks associated with leverage.
Under the provisions of the 1940 Act, we are permitted, as a registered
closed-end
management investment company, to issue senior securities (including debt securities, preferred shares and/or borrowings from banks or other financial institutions); provided we meet certain asset coverage requirements (i.e., 300% for senior securities representing indebtedness and 200% in the case of the issuance of preferred shares under current law). See “
Risks Related to Our Investments — We may leverage our portfolio, which would magnify the potential for gain or loss on amounts invested and will increase the risk of investing in us
” for details concerning how asset coverage is calculated. If the value of our assets declines, we may be unable to satisfy this test. If that happens, we may be required to sell a portion of our investments and, depending on the nature of our leverage, repay a portion of our indebtedness (including by redeeming a portion of any series of preferred shares or debt that may be outstanding) at a time when such sales or redemptions may be disadvantageous. Also, any amounts that we use to service or repay our indebtedness would not be available for distributions to our Shareholders.
We are not generally able to issue and sell our common shares at a price below the then current NAV per common share (exclusive of any distributing commission or discount). We may, however, sell our common shares at a price below the then current NAV per share (1) in connection with a rights offering to our existing Shareholders, (2) with the consent of the majority of our Shareholders, (3) upon the conversion of a convertible security in accordance with its terms or (4) under such circumstances as the SEC may permit.
Significant Shareholders may control the outcome of matters submitted to our Shareholders or adversely impact the market price or liquidity of our securities.
To the extent any Shareholder, individually or acting together with other Shareholders, controls a significant number of our voting securities (as defined in the 1940 Act) or any class of voting securities, they may have the ability to control the outcome of matters submitted to our Shareholders for approval, including the election of trustees and any merger, consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets, and may cause actions to be taken that you may not agree with or that are not in your interests or those of other investors.
This concentration of beneficial ownership also might harm the market price of our securities by:
| | • | | delaying, deferring or preventing a change in corporate control; |
| | • | | impeding a merger, consolidation, takeover or other business combination involving us; or |
| | • | | discouraging a potential acquirer from making a tender offer or otherwise attempting to obtain control of us. |
The Fund is subject to the Control Share Statute, which may restrict the voting rights of certain Shareholders.
Because the Fund is organized as a Delaware statutory trust, it is subject to the Control Share Statute. With certain exceptions, the Control Share Statute provides that a holder of “control shares” of a Delaware statutory trust acquired in a “control share acquisition” has no voting rights with respect to those shares except to the extent approved by a vote of two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast on the matter, unless otherwise exempted by the Board. The Control Share Statute became automatically applicable to the Fund as of August 1, 2022. The Control Share Statute does not retroactively apply to acquisitions of shares that occurred prior to August 1, 2022. However, such shares will be aggregated with any shares acquired after August 1, 2022 for purposes of determining whether a voting power threshold is exceeded, resulting in the newly acquired shares constituting control shares. Shares of the Fund that are held by an affiliate of CGCIM were exempted from the provisions of the Control Share Statute by the Board. See “
Description of our Securities — Certain Aspects of the Delaware Control Share Statute
.”
We are subject to the risk of legislative and regulatory changes impacting our business or the markets in which we invest.
Legal and regulatory changes could occur and may adversely affect us and our ability to pursue our investment strategies and/or increase the costs of implementing such strategies. New or revised laws or regulations may be imposed by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission, or the “CFTC,” the SEC, the U.S. Federal Reserve, other banking regulators, other governmental regulatory authorities or self-regulatory organizations that supervise the financial markets that could adversely affect us. In particular, these agencies are empowered to promulgate a variety of new rules pursuant to recently enacted financial reform legislation in the United States. We also may be adversely affected by changes in the enforcement or interpretation of existing statutes and rules by these governmental regulatory authorities or self-regulatory organizations. Such changes, or uncertainty regarding any such changes, could adversely affect the strategies and plans set forth in this prospectus and may result in our investment focus shifting from the areas of expertise of the Senior Investment Team to other types of investments in which the investment team may have less expertise or little or no experience. Thus, any such changes, if they occur, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and the value of your investment.
. The derivative investments in which we may invest are subject to comprehensive statutes, regulations and margin requirements. In particular, certain provisions of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, or the “Dodd-Frank Act,” requires certain standardized derivatives to be executed on a regulated market and cleared through a central counterparty, which may result in increased margin requirements and costs for us. The Dodd-Frank Act also established minimum margin requirements on certain
uncleared derivatives which may result in us and our counterparties posting higher margin amounts for uncleared derivatives. In addition, we have claimed an exclusion from the definition of the term “commodity pool operator” pursuant to CFTC
No-Action
Letter
12-38
issued by the staff of the CFTC Division of Swap Dealer and Intermediary Oversight. For us to continue to qualify for this exclusion, (i) the aggregate initial margin and premiums required to establish our positions in derivative instruments subject to the jurisdiction of the U.S. Commodity Exchange Act, as amended, or the “CEA,” and (other than positions entered into for hedging purposes) may not exceed five percent of our liquidation value, (ii) the net notional value of our aggregate investments in
CEA-regulated
derivative instruments (other than positions entered into for hedging purposes) may not exceed 100% of our liquidation value, or (iii) we must meet an alternative test appropriate for a “fund of funds” as set forth in CFTC
No-Action
Letter
12-38.
In the event we fail to qualify for the exclusion and the Adviser is required to register as a “commodity pool operator” in connection with serving as our investment adviser and becomes subject to additional disclosure, recordkeeping and reporting requirements, our expenses may increase. The Adviser has claimed an exclusion from the definition of the term “commodity pool operator” under the CEA pursuant to CFTC Regulation 4.5 under the CEA promulgated by the CFTC with respect to us, and we currently intend to operate in a manner that would permit the Adviser to continue to claim such exclusion.
Under SEC Rule
18f-4,
related to the use of derivatives, short sales, reverse repurchase agreements and certain other transactions by registered investment companies, we are permitted to enter into derivatives and other transactions that create future payment or delivery obligations, including short sales, notwithstanding the senior security provisions of the 1940 Act if we comply with certain
leverage limits and derivatives risk management program and board oversight and reporting requirements or comply with a “limited derivatives users” exception. We have elected to rely on the limited derivatives users exception. We may change this election and comply with the other provisions of Rule
18f-4
related to derivatives transactions at any time and without notice. To satisfy the limited derivatives users exception, we have adopted and implemented written policies and procedures reasonably designed to manage our derivatives risk and limit our derivatives exposure in accordance with Rule
18f-4.
Rule
18f-4
also permits us to enter into reverse repurchase agreements or similar financing transactions notwithstanding the senior security provisions of the 1940 Act if we aggregate the amount of indebtedness associated with our reverse repurchase agreements or similar financing transactions with the aggregate amount of any other senior securities representing indebtedness when calculating our asset coverage ratios as discussed above or treat all such transactions as derivatives transactions for all purposes under Rule
18f-4.
In addition, we are permitted to invest in a security on a when-issued or forward-settling basis, or with a
non-standard
settlement cycle, and the transaction will be deemed not to involve a senior security under the 1940 Act, provided that (i) we intend to physically settle the transaction and (ii) the transaction will settle within 35 days of its trade date (the “
Delayed-Settlement Securities Provision
”). We may otherwise engage in such transactions that do not meet the conditions of the Delayed-Settlement Securities Provision so long as we treat any such transaction as a “derivatives transaction” for purposes of compliance with the rule. Furthermore, we are permitted to enter into an unfunded commitment agreement, and such unfunded commitment agreement will not be subject to the asset coverage requirements under the 1940 Act, if we reasonably believe, at the time we enter into such agreement, that we will have sufficient cash and cash equivalents to meet our obligations with respect to all such agreements as they come due. We cannot predict the effects of these requirements. The Adviser intends to monitor developments and seek to manage our assets in a manner consistent with achieving our investment objective, but there can be no assurance that it will be successful in doing so.
. Section 619 of the Dodd-Frank Act, commonly referred to as the “Volcker Rule,” generally prohibits, subject to certain exemptions, covered banking entities from engaging in proprietary trading or sponsoring, or acquiring or retaining an ownership interest in, a hedge fund or private equity fund, or “covered funds,” (which have been broadly defined in a way which could include many CLOs). Given the limitations on banking entities investing in CLOs that are covered funds, the Volcker Rule may adversely affect the market value or liquidity of any or all of the investments held by us. Although the Volcker Rule and the implementing rules exempt “loan securitizations” from the definition of covered fund, not all CLOs will qualify for this exemption.
In June 2020, the five federal agencies responsible for implementing the Volcker Rule adopted amendments to the Volcker Rule’s implementing regulations, including changes relevant to the treatment of securitizations (the “
”). Among other things, the Volcker Changes ease certain aspects of the “loan securitization” exclusion, and create additional exclusions from the “covered fund” definition, and narrow the definition of “ownership interest” to exclude certain “senior debt interests.” Also, under the Volcker Changes, a debt interest would no longer be considered an “ownership interest” solely because the holder has the right to remove or replace the manager following a cause-related default. The Volcker Changes were effective October 1, 2020. It is currently unclear how, or if, the Volcker Changes will affect the CLO securities in which the Fund invests.
. In October 2014, six federal agencies (the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, or the “FDIC,” the Comptroller of the Currency, the Federal Reserve Board, the SEC, the Department of Housing and Urban Development and the Federal Housing Finance Agency) adopted joint final rules implementing certain credit risk retention requirements contemplated in Section 941 of the Dodd-Frank Act, or the “Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules.” These rules were published in the Federal Register on December 24, 2014. With respect to the regulation of CLOs, the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules require that the “sponsor” or a “majority owned affiliate” thereof (in each case as defined in the rules), will retain an “eligible vertical interest” or an “eligible horizontal interest” (in each case as defined therein) or any combination thereof in the CLO in the manner required by the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules.
The Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules became fully effective on December 24, 2016, or the “Final U.S. Risk Retention Effective Date,” and to the extent applicable to CLOs, the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules contain provisions that may adversely affect the return of our investments. On February 9, 2018, a three judge panel of the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit, or the “DC Circuit Court,” rendered a decision in The Loan Syndications and Trading Association v. Securities and Exchange Commission and Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, No.
in which the DC Circuit Court held that open market CLO collateral managers are not “securitizers” subject to the requirements of the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules, or the “DC Circuit Ruling.” Thus, collateral managers of open market CLOs are no longer required to comply with the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules at this time. As such, it is possible that some collateral managers of open market CLOs will decide to dispose of the notes (or cause their majority owned affiliates to dispose of the notes) constituting the “eligible vertical interest” or “eligible horizontal interest” they were previously required to retain, or decide to take other action with respect to such notes that is not otherwise prohibited by the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules. To the extent either the underlying collateral manager or its majority-owned affiliate divests itself of such notes, this will reduce the degree to which the relevant collateral manager’s incentives are aligned with those of the noteholders of the CLO (which may include us as a CLO noteholder), and could influence the way in which the relevant collateral manager manages the CLO assets and/or makes other decisions under the transaction documents related to the CLO in a manner that is adverse to us.
There can be no assurance or representation that any of the transactions, structures or arrangements currently under consideration by or currently used by CLO market participants will comply with the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules to the extent such rules are reinstated or otherwise become applicable to open market CLOs. The ultimate impact of the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules on the loan securitization market and the leveraged loan market generally remains uncertain, and any negative impact on secondary market liquidity for securities comprising a CLO may be experienced due to the effects of the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules on market expectations or uncertainty, the relative appeal of other investments not impacted by the Final U.S. Risk Retention Rules and other factors.
. The securitization industry in both European Union (“
”) and the United Kingdom (“
”) has also undergone a number of significant changes in the past few years. Regulation (EU) 2017/2402 relating to a European framework for simple, transparent and standardized securitization (as amended by Regulation (EU) 2021/557 and as further amended from time to time, the “EU Securitization Regulation”) applies to certain specified EU investors, and Regulation (EU) 2017/2402 relating to a European framework for simple, transparent and standardized securitization in the form in effect on 31 December 2020 (which forms part
of UK domestic law by virtue of the European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018 (as amended, the “EUWA”)) (as amended by the Securitization (Amendment) (EU Exit) Regulations 2019 and as further amended from time to time, the “UK Securitization Regulation” and, together with the EU Securitization Regulation, the “Securitization Regulations”) applies to certain specified UK investors, in each case, who are investing in a “securitisation” (as such term is defined under each Securitization Regulation).
The due diligence requirements of Article 5 of the EU Securitization Regulation (the “
EU Due Diligence Requirements
”) apply to each investor that is an “institutional investor” (as such term is defined in the EU Securitization Regulation), being an investor which is one of the following: (a) an insurance undertaking as defined in Directive 2009/138/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2009 on the
taking-up
and pursuit of the business of Insurance and Reinsurance (Solvency II) (recast) (“
”); (b) a reinsurance undertaking as defined in Solvency II; (c) subject to certain conditions and exceptions, an institution for occupational retirement provision falling within the scope of Directive (EU) 2016/2341 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 December 2016 on the activities and supervision of institutions for occupational retirement provision (IORPs) (the “
”), or an investment manager or an authorized entity appointed by an institution for occupational retirement provision pursuant to the IORP Directive; (d) an alternative investment fund manager (“
”) as defined in Directive 2011/61/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 8 June 2011 on Alternative Investment Fund Managers that manages and/or markets alternative investment funds in the EU; (e) an undertaking for the collective investment in transferable securities (“
”) management company, as defined in Directive 2009/65/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 July 2009 on the coordination of laws, regulations and administrative provisions relating to undertakings for collective investment in transferable securities (UCITS) (the “
”); (f) an internally managed UCITS, which is an investment company authorised in accordance with the UCITS Directive and which has not designated a management company authorised under the UCITS Directive for its management; or (g) a credit institution as defined in Regulation (EU) No 575/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 26 June 2013 on prudential requirements for credit institutions and investment firms (the “
”) for the purposes of the CRR, or an investment firm as defined in the CRR, in each case, such investor an “EU Institutional Investor.”
The due diligence requirements of Article 5 of the UK Securitization Regulation (the “
UK Due Diligence Requirements
” and, together with the EU Due Diligence Requirements, the “
Due Diligence Requirements
”) apply to each investor that is an “institutional investor” (as such term is defined in the UK Securitization Regulation), being an investor which is one of the following: (a) an insurance undertaking as defined in the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (as amended, the “
”); (b) a reinsurance undertaking as defined in the FSMA; (c) an occupational pension scheme as defined in the Pension Schemes Act 1993 that has its main administration in the UK, or a fund manager of such a scheme appointed under the Pensions Act 1995 that, in respect of activity undertaken pursuant to that appointment, is authorised under the FSMA; (d) an AIFM (as defined in the Alternative Investment Fund Managers Regulations 2013 (the “
”)) which markets or manages AIFs (as defined in the AIFM Regulations) in the UK; (e) a management company as defined in the FSMA; (f) a UCITS as defined by the FSMA, which is an authorised open ended investment company as defined in the FSMA; (g) a FCA investment firm as defined by the CRR as it forms part of UK domestic law by virtue of EUWA (the “
”); or (h) a CRR investment firm as defined in the UK CRR, in each case, such investor a “UK Institutional Investor” and, such investors together with EU Institutional Investors, “Institutional Investors.”
Among other things, the applicable Due Diligence Requirements require that prior to holding a “securitization position” (as defined in each Securitization Regulation) an Institutional Investor (other than the originator, sponsor or original lender) has verified that:
| | (1) | the originator, sponsor or original lender will retain on an ongoing basis a material net economic interest which, in any event, shall be not less than five per cent. in the securitization, determined in accordance with Article 6 of the applicable Securitization Regulation, and has disclosed the risk retention to such Institutional Investor; |
| | (2) | (in the case of each EU Institutional Investor only) the originator, sponsor or securitization special purpose entity (“ ”) has, where applicable, made available the information required by Article 7 of the EU Securitization Regulation in accordance with the frequency and modalities provided for thereunder; |
| | (3) | (in the case of each UK Institutional Investor only) the originator, sponsor or SSPE: |
| | (i) | if established in the UK has, where applicable, made available the information required by Article 7 of the UK Securitization Regulation (the “ UK Transparency Requirements ”) in accordance with the frequency and modalities provided for thereunder; or |
| | (ii) | if established in a country other than the UK, where applicable, made available information which is substantially the same as that which it would have made available under the UK Transparency Requirements if it had been established in the UK, and has done so with such frequency and modalities as are substantially the same as those with which it would have made information available under the UK Transparency Requirements if it had been established in the UK; and |
| | (4) | in the case of each Institutional Investor, where the originator or original lender either (i) is not a credit institution or an investment firm (each as defined in the applicable Securitization Regulation) or (ii) is established in a third country (being (x) in respect of the EU Securitization Regulation, a country other than an EU member state, or (y) in respect of the UK Securitization Regulation, a country other than the UK), the originator or original lender grants all the credits giving rise to the underlying exposures on the basis of sound and well-defined criteria and clearly established processes for approving, amending, renewing and financing those credits and has effective systems in place to apply those criteria and processes in order to ensure that credit-granting is based on a thorough assessment of the obligor’s creditworthiness. |
The Due Diligence Requirements further require that prior to holding a securitisation position, an Institutional Investor, other than the originator, sponsor or original lender, carry out a due diligence assessment which enables it to assess the risks involved, including but not limited to (a) the risk characteristics of the individual securitisation position and the underlying exposures; and (b) all the structural features of the securitization that can materially impact the performance of the securitisation position, including the contractual priorities of payment and priority of payment-related triggers, credit enhancements, liquidity enhancements, market value triggers, and transaction-specific definitions of default.
In addition, pursuant to the applicable Due Diligence Requirements, while holding a securitization position, an Institutional Investor, other than the originator, sponsor or original lender, is subject to various ongoing monitoring obligations, including but not limited to: (a) establishing appropriate written procedures to monitor compliance with the Due Diligence Requirements and the performance of the securitisation position and of the underlying exposures; (b) performing stress tests on the cash flows and collateral values supporting the underlying exposures or, in the absence of sufficient data on cash flows and collateral values, stress tests on loss assumptions, having regard to the nature, scale and complexity of the risk of the securitisation position; (c) ensuring internal reporting to its management body so that the management body is aware of the material risks arising from the securitisation position and so that those risks are adequately managed; and (d) being able to demonstrate to its competent authorities, upon request, that it has a comprehensive and thorough understanding of the securitisation position and underlying exposures and that it has implemented written policies and procedures for the risk management of the securitisation position and for maintaining records of (i) the verifications and due diligence in accordance with the applicable Due Diligence Requirements and (ii) any other relevant information.
Any Institutional Investor that fails to comply with the applicable Due Diligence Requirements in respect of a securitization position which it holds may become subject to a range of regulatory sanctions including, in the case of a credit institution, investment firm, insurer or reinsurer, a punitive regulatory capital charge with respect to such securitization position, or, in certain other cases, a requirement to take corrective action.
CLOs issued in Europe are generally structured in compliance with the Securitization Regulations so that prospective investors subject to the Securitization Regulations can invest in compliance with such requirements. To the extent a CLO is structured in compliance with the Securitization Regulations, our ability to invest in the residual tranches of such CLOs could be limited, or we could be required to hold our investment for the life of the CLO. If a CLO has not been structured to comply with the Securitization Regulations, it will limit the ability of Institutional Investors to purchase CLO securities, which may adversely affect the price and liquidity of the securities (including the residual tranche) in the secondary market. Additionally, the Securitization Regulations and any regulatory uncertainty in relation thereto may reduce the issuance of new CLOs and reduce the liquidity provided by CLOs to the leveraged loan market generally. Reduced liquidity in the loan market could reduce investment opportunities for collateral managers, which could negatively affect the return of our investments. Any reduction in the volume and liquidity provided by CLOs to the leveraged loan market could also reduce opportunities to redeem or refinance the securities comprising a CLO in an optional redemption or refinancing and could negatively affect the ability of obligors to refinance of their collateral obligations, either of which developments could increase defaulted obligations above historic levels.
. The Japanese Financial Services Agency (the “
”) published a risk retention rule as part of the regulatory capital regulation of certain categories of Japanese investors seeking to invest in securitization transactions (the “
”). The JRR Rule mandates an “indirect” compliance requirement, meaning that certain categories of Japanese investors will be required to apply higher risk weighting to securitization exposures they hold unless the relevant originator commits to hold a retention interest equal to at least 5% of the exposure of the total underlying assets in the transaction (the “
Japanese Retention Requirement
”) or such investors determine that the underlying assets were not “inappropriately originated.” The Japanese investors to which the JRR Rule applies include banks, bank holding companies, credit unions (shinyo kinko), credit cooperatives (shinyo kumiai), labor credit unions (rodo kinko), agricultural credit cooperatives (nogyo kyodo kumiai), ultimate parent companies of large securities companies and certain other financial institutions regulated in Japan (such investors, “
Japanese Affected Investors
”). Such Japanese Affected Investors may be subject to punitive capital requirements and/or other regulatory penalties with respect to investments in securitizations that fail to comply with the Japanese Retention Requirement.