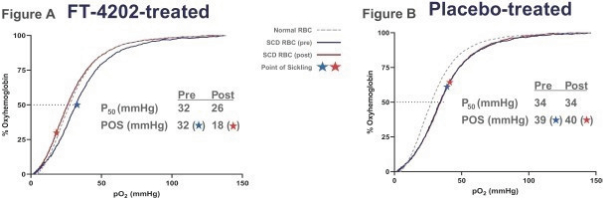
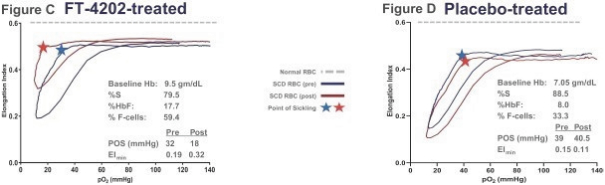
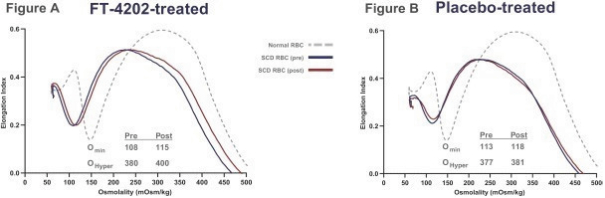
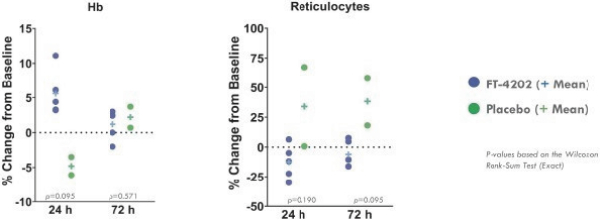
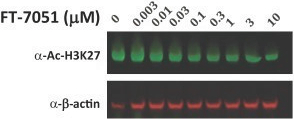
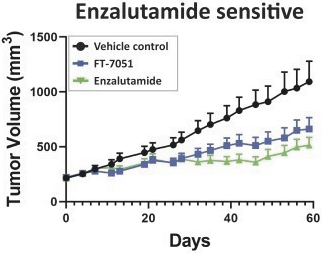
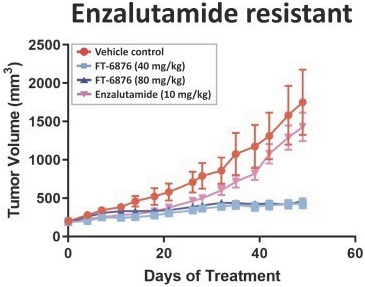
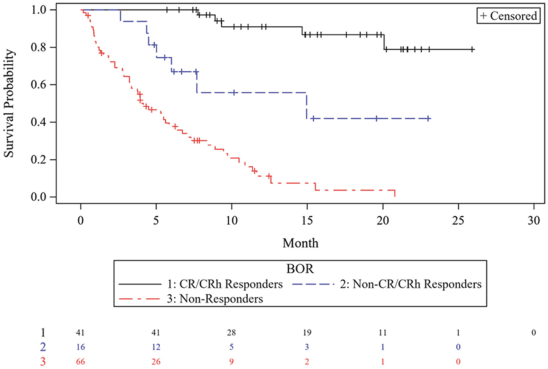
While we intend to timely file non-provisional patent applications relating to our provisional patent applications, we cannot predict whether any such patent applications will result in the issuance of patents that provide us with any competitive advantage. Moreover, the patent application and approval process is expensive and time-consuming. We may not be able to file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner.
We may not receive an extension if we fail to exercise due diligence during the testing phase or regulatory review process, fail to apply within applicable deadlines, fail to apply prior to expiration of relevant patents or otherwise fail to satisfy applicable requirements. Moreover, the length of the extension could be less than we request.
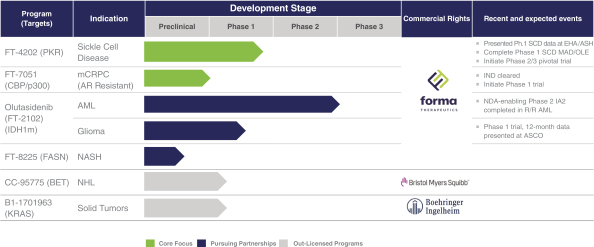
For more information, see the section entitled “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Intellectual Property”.
Other IP Rights
In addition to patents, we rely upon unpatented trade secrets and know-how and continuing technological innovation to develop and maintain our competitive position. However, trade secrets and know-how can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary information, in part, by executing confidentiality agreements with our collaborators and scientific advisors, and non-competition, non-solicitation, confidentiality, and invention assignment agreements with our employees and consultants. We have also executed agreements requiring assignment of inventions with selected scientific advisors and collaborators. The confidentiality agreements we enter into are designed to protect our proprietary information and the agreements or clauses requiring assignment of inventions to us are designed to grant us ownership of technologies that are developed through our relationship with the respective counterparty. We cannot guarantee, however, that we have executed such agreements with all applicable counterparties, that such agreements will not be breached, or that these agreements will afford us adequate protection of our intellectual property and proprietary rights. For more information, see the section entitled “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Intellectual Property”.
Government Regulation
The FDA and other regulatory authorities at federal, state and local levels, as well as in foreign countries, extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, quality control, import, export, safety, effectiveness, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, record keeping, approval, advertising, promotion, marketing, post-approval monitoring and post-approval reporting of drugs. We, along with our vendors, contract research organizations and contract manufacturers, will be required to navigate the various preclinical, clinical, manufacturing and commercial approval requirements of the governing regulatory agencies of the countries in which we wish to conduct studies or seek approval of our product candidates. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals of drugs and ensuring subsequent compliance with appropriate federal, state, local and foreign statutes and regulations requires the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources.
In the U.S., the FDA regulates drug products under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or FD&C Act, as amended, its implementing regulations and other laws. If we fail to comply with applicable FDA or other requirements at any time with respect to product development, clinical testing, approval or any other legal requirements relating to product manufacture, processing, handling, storage, quality control, safety, marketing, advertising, promotion, packaging, labeling, export, import, distribution, or sale, we may become subject to administrative or judicial sanctions or other legal consequences. These sanctions or consequences could include, among other things, the FDA’s refusal to approve pending applications, issuance of clinical holds for ongoing studies, withdrawal of approvals, warning or untitled letters, product withdrawals or recalls, product seizures, relabeling or repackaging, total or partial suspensions of manufacturing or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties or criminal prosecution.
148