UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One) | | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024
or | | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number 001-36243
Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) | | | | | | | | |
| Delaware | | 27-4384691 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| | |
| 7930 Jones Branch Drive, Suite 1100, McLean, VA | | 22102 |
| (Address of Principal Executive Offices) | | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (703) 883-1000
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | | Trading symbol(s) | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock, $0.01 par value per share | | HLT | | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer," "smaller reporting company" and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer ☒ Accelerated filer ☐
Non-accelerated filer ☐ Smaller reporting company ☐
Emerging growth company ☐
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management's assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to § 240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of June 30, 2024, the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter, the aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $53,020 million (based upon the closing sale price of the common stock on that date on the New York Stock Exchange). The number of shares of common stock outstanding on January 31, 2025 was 240,596,519.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 of Part III incorporate information by reference from the registrant's definitive proxy statement relating to its 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the close of the registrant's fiscal year.
HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC.
FORM 10-K TABLE OF CONTENTS
YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2024
| | | | | | | | |
| | Page No. |
| PART I | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| Item 1. | | |
| Item 1A. | | |
| Item 1B. | | |
| Item 1C. | Cybersecurity | |
| Item 2. | | |
| Item 3. | | |
| Item 4. | | |
| | |
| PART II | | |
| Item 5. | | |
| | |
| Item 6. | | |
| Item 7. | | |
| Item 7A. | | |
| Item 8. | | |
| Item 9. | | |
| Item 9A. | | |
| Item 9B. | | |
| Item 9C. | | |
| | |
| PART III | |
|
| Item 10. | | |
| Item 11. | | |
| Item 12. | | |
| | |
| Item 13. | | |
| Item 14. | | |
| | |
| PART IV | | |
| Item 15. | | |
| Item 16. | | |
| | |
PART I
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the "Securities Act") and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"). These statements include, but are not limited to, statements related to our expectations regarding the performance of our business, future financial results, liquidity and capital resources and other non-historical statements. In some cases, you can identify these forward-looking statements by the use of words such as "outlook," "believes," "expects," "forecasts," "potential," "continues," "may," "will," "should," "could," "seeks," "projects," "predicts," "intends," "plans," "estimates," "anticipates" or the negative version of these words or other comparable words. Such forward-looking statements are subject to various risks and uncertainties that could cause actual outcomes or results to differ materially from those indicated in these statements, including, among others, those described under "Part I—Item 1A. Risk Factors" and under "Summary of Risk Factors" below. These factors should not be construed as exhaustive and should be read in conjunction with the other cautionary statements that are included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or review any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise, except as required by law.
Summary of Risk Factors
In addition to the other information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the following risk factors should be considered carefully in evaluating our company and our business. A summary of the principal factors that create risk in investing in our securities and might cause actual results to differ from expectations is set forth below:
•We are subject to the business, financial and operating risks inherent to the hospitality industry, any of which could reduce our revenues and limit opportunities for growth;
•Macroeconomic conditions, public health concerns, geopolitical activity and other factors beyond our control can adversely affect and reduce demand for our products and services;
•Because we operate in a highly competitive industry, our revenues or profits could be harmed if we are unable to compete effectively;
•Our business is subject to risks related to doing business with third-party property owners that could adversely affect our reputation, operational results or prospects for growth;
•Failure to keep pace with developments in technology could adversely affect our operations or competitive position;
•Failures in, material damage to or interruptions in our information technology systems, software or websites, including as a result of cyber-attacks on our systems or systems operated by third parties that provide operational and technical services to us, costs associated with protecting the integrity and security of personal data and other sensitive information and difficulties in updating our existing software or developing or implementing new software could have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations;
•The growth of internet reservation channels could adversely affect our business and profitability;
•Because we derive a portion of our revenues from operations outside the United States ("U.S."), the risks of doing business internationally could lower our revenues, increase our costs, reduce our profits or disrupt our business;
•The loss of key senior management personnel or labor shortages could restrict our ability to grow our business or operate our properties or result in increased labor costs that could adversely affect our results of operations;
•Our business is subject to evolving corporate governance and public disclosure regulations and expectations, including with respect to sustainability matters, that could increase costs or expose us to reputational and other risks; and
•Our substantial indebtedness and other contractual obligations could adversely affect our financial condition, our ability to raise additional capital to fund our operations, our ability to operate our business, our ability to react to changes in the economy or our industry and our ability to pay our debts, and could require us to divert our cash flows from operations to make required debt or interest payments.
These risk factors do not identify all risks that we face, and our business, financial condition and results of operations could also be affected by factors, events or uncertainties that are not presently known to us or that we currently do not consider to present material risks.
Terms Used and Basis of Presentation in this Annual Report on Form 10-K
Except where the context requires otherwise, references in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to "Hilton," "the Company," "we," "us" and "our" refer to Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., together with all of its consolidated subsidiaries. Except where the context requires otherwise, references to our "properties" refer to the hotels, resorts and timeshare properties that are managed, franchised, owned or leased by us, as well as third-party hotels we do not manage or franchise but that use our booking channels and related programs ("strategic partner hotels"), while references to "hotels" exclude timeshare properties.
Refer to "Part II—Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Key Business and Financial Metrics Used by Management" for additional information on our financial and performance metrics.
Social Media
We use our website at stories.hilton.com, our Facebook page at facebook.com/hiltonnewsroom, our LinkedIn page at linkedin.com/company/hilton and our corporate X account at x.com/hiltonnewsroom as channels of distribution of company information. We also use our website at cr.hilton.com to communicate our Travel with Purpose strategy. The information we post through these channels may be deemed material. Accordingly, investors should monitor these channels, in addition to following our press releases, our filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC") and our webcasts. The contents of our website and social media channels are not, however, part of this report.
Item 1. Business
Overview
Hilton is one of the largest global hospitality companies, with 8,447 properties comprising 1,268,206 rooms in 140 countries and territories as of December 31, 2024. Founded in 1919, Hilton has been an innovator in the industry for over 105 years, driven by the vision of founder Conrad Hilton "to fill the earth with the light and warmth of hospitality." Our premier brand portfolio includes luxury, lifestyle, full service, focused service and all-suites hotel brands, as well as timeshare brands. As of December 31, 2024, we had 211 million members in our award-winning guest loyalty program, Hilton Honors, an increase of 17 percent from December 31, 2023; refer to "—Our Brand Portfolio" and "—Our Guest Loyalty Program" below for additional information on our brands, including Hilton Honors.
We operate our business through: (i) a management and franchise segment and (ii) an ownership segment, each of which is reported as a segment based on (a) delivering a similar set of products and services and (b) being managed separately given its distinct economic characteristics. The management and franchise segment includes all of the hotels we manage for third-party owners, as well as all properties that license our intellectual property ("IP") and/or use our booking channels and related programs, and where we provide other contracted services, but the day-to-day services of the hotels are operated or managed by someone other than us. Revenues from this segment include: (i) management and franchise fees charged to third-party hotel owners; (ii) licensing fees from our strategic partners, including co-branded credit card providers, strategic partner hotels and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. ("HGV"); and (iii) fees for managing hotels in our ownership segment. The ownership segment primarily derives revenues from nightly hotel room sales, food and beverage sales and other services at our consolidated owned and leased hotels. For more information regarding our segments, refer to "—Our Business—Management and Franchise" and "—Our Business—Ownership" below.
In addition to our current hotel portfolio, we are focused on the growth of our business by expanding our global hotel network through our development pipeline, which represents hotels that we expect to add to our system in the future. The following table summarizes our development activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of or for the Year Ended December 31, 2024 |
| Hotels | | Rooms(1) |
| Hotel system | | | |
Openings(2) | 973 | | | 98,400 | |
Net additions(3) | 904 | | | 83,000 | |
| | | |
| Development pipeline | | | |
Additions(4) | 1,432 | | | 154,200 | |
Count as of period end(5) | 3,578 | | | 498,600 | |
____________
(1)Rounded to the nearest hundred.
(2)Openings include 411 hotels and approximately 19,500 rooms from strategic partner hotels.
(3)Represents room additions, net of rooms removed from our system. During 2024, 409 hotels and approximately 19,400 rooms added were from strategic partner hotels. Net unit growth for the year ended December 31, 2024 was 7.3 percent.
(4)Additions include 423 hotels and approximately 20,100 rooms from strategic partner hotels.
(5)The hotels in our development pipeline were under development throughout 118 countries and territories, including 25 countries and territories where we had no existing hotels, with nearly half of the rooms under construction and more than half of the rooms located outside of the U.S. Rooms under construction include rooms for hotels under construction or operating hotels that are in the process of conversion to our system. Nearly all of the rooms in our development pipeline will be in our management and franchise segment upon opening. We do not consider any individual development project to be material to us.
We continue to drive customer loyalty, including participation in our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program, through: (i) our experience in the hospitality industry, which spans more than a century of customer service and entrepreneurship, and continues to evolve to meet the tastes, preferences and demands of our guests; (ii) our strong, well-defined brands that operate throughout the hospitality industry chain scales; (iii) our dedicated and collaborative workforce, built to focus on providing exceptional customer experiences; and (iv) our commercial service offerings. We believe that satisfied customers will generate additional business at our properties, yielding strong overall hotel performance for us and our hotel owners. Strong results at our existing properties will encourage further development of additional hotels under our brands and conversions of existing hotels to our brands with both (i) owners who currently have properties in our system and (ii) new owners who sign management or franchise contracts with us in the future, which further supports our growth and future financial performance. We believe that our existing hotel system and development pipeline, which will require minimal capital investment from us, positions us to further improve and grow our business, allocate capital effectively and meet our customers' demands and preferences in the future.
Our Brand Portfolio
The goal of each of our brands is to deliver exceptional customer experiences and superior operating performance. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024(1) | | |
Brand(1) | | Countries/ Territories | | Properties | | Rooms | | Percentage of Total Rooms | | Selected Competitors(2) |
| | 17 | | 34 | | 8,796 | | 0.7% | | Four Seasons, Mandarin Oriental, Peninsula, Ritz-Carlton,
Rosewood Hotels & Resorts, St. Regis |
| | 24 | | 49 | | 17,195 | | 1.4% | |
JW Marriott, Intercontinental, Sofitel, Grand Hyatt, Shangri-La, Fairmont |
| | 7 | | 15 | | 2,619 | | 0.2% | | Leading Hotels of the World, Legend Preferred Hotels & Resorts, Belmond, The Luxury Collection |
| | 1 | | 1 | | 91 | | —% | | Firmdale Hotels, EDITION Hotels, Rosewood Hotels, One Aldwych |
| | 2 | | 4 | | 2,797 | | 0.2% | | JW Marriott, Grand Hyatt, Fairmont, Intercontinental, Omni |
| | 13 | | 43 | | 7,581 | | 0.6% | | Kimpton, Thompson Hotels, W Hotels, Virgin Hotels, The Hoxton, SO/ |
| | 98 | | 617 | | 227,467 | | 17.9% | | Hyatt Regency, Marriott,
Omni, Sheraton, Westin |
| | 44 | | 180 | | 33,734 | | 2.7% | | Autograph Collection, The Unbound Collection, Independent Hotels, MGallery, Kimpton |
| | 2 | | 34 | | 5,788 | | 0.5% | | Le Meridien, Hyatt Centric, 25h, Hotel Indigo |
| | 59 | | 695 | | 156,943 | | 12.4% | | Marriott, Crowne Plaza, Delta, Holiday Inn, Radisson, Sheraton, Wyndham |
| | 21 | | 151 | | 17,768 | | 1.4% | | Joie de Vivre, Tribute Portfolio, Kimpton, Hotel Indigo, Ascend, Trademark |
| | 8 | | 269 | | 61,974 | | 4.9% | | Hyatt Regency, Marriott, Sheraton, Westin |
| | 1 | | 4 | | 1,224 | | 0.1% | | AC Hotels, Aloft Hotels, Cambria, Hotel Indigo, Hyatt Centric |
| | 4 | | 8 | | 1,727 | | 0.1% | | MAMA Shelter, CitizenM, Ace Hotels, Yotel, Freehand |
| | 64 | | 1,060 | | 156,471 | | 12.3% | | Aloft, Courtyard by Marriott, Four Points, Holiday Inn, Hyatt Place |
| | 43 | | 3,072 | | 342,737 | | 27.0% | | Comfort Suites, Courtyard by Marriott,
Fairfield Inn, Holiday Inn Express, Springhill Suites |
| | 5 | | 283 | | 27,605 | | 2.2% | | Best Western, Comfort Inn, La Quinta, Sleep Inn, Wingate, Avid |
| | 4 | | 96 | | 8,710 | | 0.7% | | Quality Inn, Baymont, Travelodge, Howard Johnson, Super 8, Days Inn |
| | 4 | | 544 | | 62,319 | | 4.9% | | Element, Hyatt House, Residence Inn, Staybridge Suites |
| | 3 | | 757 | | 82,515 | | 6.5% | | TownePlace Suites, Staybridge Suites, Hyatt Studios |
| | — | | — | | — | | —% | | StudioRes, Candlewood Suites, Stay Apt Suites, ECHO Suites, Extended Stay America Premiere Suites |
| | 8 | | 105 | | 18,392 | | 1.5% | | Disney Vacation Club, Holiday Inn Club Vacations,
Marriott Vacations Worldwide,
Travel & Leisure Co. |
____________ (1)Excludes 17 unbranded properties with 4,392 rooms, representing approximately 0.3% of total rooms and 409 strategic partner hotels with 19,361 rooms, representing approximately 1.5% of total rooms. Hilton Grand Vacations is inclusive of Hilton Club, Hilton Grand Vacations Club and Hilton Vacation Club.
(2)These selected competitors exclude lesser-known regional competitors.
Waldorf Astoria Hotels & Resorts: Waldorf Astoria Hotels & Resorts is a luxury brand with an award-winning portfolio of iconic properties with a relentless commitment to elegant service, one-of-a-kind experiences and culinary expertise in landmark destinations around the world. Waldorf Astoria hotels deliver an effortless experience seamlessly, creating a true sense of place for guests through stunning architecture and design, the signature Peacock Alley restaurant, refined art collections, Michelin-starred dining restaurants and chef partnerships and elevated in-room amenities.
Conrad Hotels & Resorts: Conrad Hotels & Resorts is a luxury brand that connects bold design, impactful experiences and curated contemporary art to inspire the conscientious traveler. Found in major urban centers and resort destinations, Conrad is a place where guests are empowered to explore through intuitive service and experiences that authentically connect them with local culture.
LXR Hotels & Resorts: LXR Hotels & Resorts is a hand-picked collection of independent and spirited luxury properties celebrating the timeless pursuit of personal adventure. Found in alluring destinations, LXR connects legendary properties into an exclusive network of hotels that are set apart by individual design, an unrivaled commitment to personalized service and elegant, yet locally immersive, experiences for guests.
NoMad Hotels: NoMad Hotels is a luxury brand that brings guests sophisticated offerings in some of the world's most sought-after locations. NoMad Hotels are both grand and intimate, creating a unique blend of luxury and lifestyle experiences throughout the stay with special touches like unique local art collections featured in each property.
Signia by Hilton: Signia by Hilton is a luxury brand with a portfolio of exceptional hotels in gateway cities and resort destinations around the world. Each Signia by Hilton property infuses sophistication into every stay, offering top-tier meetings and event spaces, a vibrant atmosphere, exceptional amenities and personalized service catered to the needs of today's global traveler.
Canopy by Hilton: Canopy by Hilton is an upper upscale brand that delivers elevated, boutique hotel experiences that celebrate the best of the locale. Inviting, sophisticated design, bespoke food and beverage and crafted touchpoints deliver a locally inspired, high-end and welcoming stay.
Hilton Hotels & Resorts: As Hilton’s flagship brand, Hilton Hotels & Resorts is the trusted global leader in hospitality. An upper upscale brand with more than 600 hotels and resorts in nearly 100 countries and territories, Hilton Hotels & Resorts continues to set the standard for the industry and upholds Conrad Hilton’s vision to fill the earth with the light and warmth of hospitality by elevating every celebration and event, creating real human connections, and immersing guests in the best of global and local cultures in the world’s most desired destinations.
Curio Collection by Hilton: Curio Collection by Hilton is an upper upscale brand with a global portfolio of individually remarkable hotels hand-picked to immerse guests in one-of-a-kind moments in sought-after destinations. Each hotel in the Curio Collection evokes a bespoke story through distinctive architecture and design, world-class food and beverage and curated experiences.
Graduate by Hilton: Graduate by Hilton is an upper upscale lifestyle brand of handcrafted hotels in dynamic, university-anchored towns. Each Graduate hotel brings stories and traditions to life and offers the perfect setting for game days, reunions, graduations, campus visits and more.
DoubleTree by Hilton: DoubleTree by Hilton is a fast-growing global upscale brand that continues to be a symbol of comfort for business and leisure travelers around the world, offering contemporary accommodations and amenities. DoubleTree by Hilton is renowned for its warm, caring service, beginning with its signature welcome that includes the hotel’s famous original chocolate chip cookie, now available in an allergy-friendly option. The inclusive service experience offers upscale food and beverage experiences and features a variety of flexible meeting spaces for events of all sizes.
Tapestry Collection by Hilton: Tapestry Collection by Hilton is an upper upscale brand with a portfolio of original hotels that offer guests unique style and vibrant personality, encouraging travelers to connect to their destination and enjoy authentic off-the-beaten-path experiences. While each property is unique, every Tapestry Collection by Hilton property is united by the reliability that comes with the Hilton name.
Embassy Suites by Hilton: Embassy Suites by Hilton offers both leisure and business travelers an approachable, upper upscale experience. As a full-service hotel, every Embassy Suites provides spacious two-room suites with separate bedroom
and living room spaces, free made-to-order breakfast each morning, complimentary drinks and snacks during evening reception every night, flexible meetings and events spaces and 24-hour fitness centers.
Tempo by Hilton: Tempo by Hilton is an upscale, stylish and contemporary lifestyle hotel brand designed for the ambitious traveler looking to maintain a sense of balance and momentum. Tempo by Hilton offers re-imagined guest rooms designed with well-being in mind, dynamic communal spaces for collaboration or focused work, healthy cafe-style dining, a leading-edge beverage program and next-level fitness facilities.
Motto by Hilton: Motto by Hilton is an upper midscale brand with an urban, lifestyle feel designed to connect guests to the center of it all – buzz-worthy spaces and the pulse of the community. Through its efficient guest rooms, lively common spaces and locally inspired food and beverage options catering to guests and locals alike, Motto is a launchpad to destinations around the globe and delivers a flexible and innovative hospitality experience through elements like first-of-its-kind connecting rooms for up to nine rooms.
Hilton Garden Inn: Hilton Garden Inn is an award-winning, upscale brand where guests find an open, inviting atmosphere with warm, glowing service and simple, thoughtful touches that allow them to socialize and unwind. As a recognized leader in food and beverage offerings, Hilton Garden Inn caters to guests' dining needs by serving cooked-to-order breakfast and offering handcrafted cocktails, shareable small plates and full meals at its on-site restaurants and bars. Flexible meeting space, free Wi-Fi, wireless printing and fitness centers are offered to help guests stay productive.
Hampton by Hilton: Hampton by Hilton is our largest brand and includes both Hampton Inn and Hampton Inn & Suites hotels, with properties located on five continents. Recognized as a leading upper midscale brand in the lodging industry, Hampton has been ranked the #1 lodging brand to franchise by Entrepreneur for 16 consecutive years. Hampton by Hilton hotels around the world provide guests high-quality and thoughtfully designed accommodations, friendly and authentic service and value-added amenities, like complimentary hot breakfast and free Wi-Fi, all backed by the 100% Hampton Guarantee.
Tru by Hilton: Tru by Hilton is a game-changing, midscale hotel brand where guests don't have to compromise between a consistent, fun and affordable hotel stay. Spirited, simplified and grounded in value, Tru by Hilton is designed for cross-generational appeal, with a large, reimagined public space where guests can work, play, lounge and eat. Intuitively designed modern guest rooms feature a rolling desk, oversized windows for natural light and bright, spacious bathrooms. Guests can enjoy complimentary amenities, including the build-your-own "Top It" breakfast bar featuring our tasty pancakes, a multifunctional fitness center and fast Wi-Fi. Premium snacks, light meal options and single-serve wine and beer are available for purchase at the 24/7 Eat. & Sip. market.
Spark by Hilton: Spark by Hilton is a premium economy hotel brand at the intersection of value and consistency. Spark by Hilton provides a reliable and comfortable stay at a hotel with friendly service for every guest, all at an accessible price. Offering simple design with splashes of color and cheer, Spark by Hilton hotels provide a welcoming sense of arrival with colorful exterior statement walls and inspiring artwork. The public spaces provide multi-functional seating, from communal tables to rocking chairs, and guest rooms are comfortable and relaxing with simple, streamlined furniture. Travelers can enjoy complimentary breakfast with premium coffee and a signature bagel bar.
Homewood Suites by Hilton: Homewood Suites by Hilton is an upscale, award-winning, all-suites, extended-stay hotel brand that delivers the comforts of home. This brand offers home-like accommodations for guests and their pets traveling for an extended stay or quick overnight trip. Guests enjoy inviting, generous-sized suites featuring separate living and sleeping areas and fully equipped kitchens with full-size refrigerators as well as value-driven amenities including free breakfast and complimentary evening receptions every week.
Home2 Suites by Hilton: Home2 Suites by Hilton is an upper midscale, all-suites, award-winning extended-stay hotel brand offering stylish accommodations with flexible guest room configurations and home-like amenities. With a focus on environmentally friendly products and hotel operations, Home2 Suites by Hilton offers laundry and fitness areas, outdoor spaces, pet-friendly environments and complimentary breakfast.
LivSmart Studios by Hilton: LivSmart Studios by Hilton is a midscale, long-stay hotel brand for guests looking for comfortable apartment-style accommodations for 10 nights or more. Offering simplicity, consistency and convenience, LivSmart Studios by Hilton will create a space where guests can seamlessly maintain their daily routines while also immersing themselves in the local community. In addition to studio suites with ample storage space and fully equipped kitchens, the hotel will feature a streamlined public area filled with natural light that includes a retail market, a large guest laundry room and a state-of-the-art fitness center. There will also be a spacious outdoor gathering area and comfortable seating for guests looking to
connect. LivSmart Studios' pioneering vision for transforming the extended-stay segment is credited with Hilton’s recognition as one of Fast Company’s 2024 Most Innovative Companies. We expect to open our first LivSmart hotel in 2025 and as of December 31, 2024 had over 75 hotels in our development pipeline.
Hilton Grand Vacations: Our timeshare brands, including Hilton Club, Hilton Grand Vacations Club and Hilton Vacation Club, are premier vacation ownership brands known for delivering a consistently exceptional standard of service, maximum flexibility for members and guests and elegant, family-friendly resorts in desirable locations around the world. Signature elements include spacious, well-appointed accommodations and resorts with extensive on-site amenities. A special points-based reservation system gives owners the flexibility to vacation when, where and how they prefer. HGV has the exclusive right to use our timeshare brands, subject to the terms of a long-term license agreement with us.
Our Guest Loyalty Program
Hilton Honors is our award-winning guest loyalty program that supports our portfolio of brands. The program generates significant repeat business by rewarding guests with points for each stay at our owned, leased, managed, franchised and timeshare properties, as well as each stay at strategic partner hotels when the stay is reserved through our booking channels, which are then redeemable for free or discounted room nights at our properties and other goods and services. Hilton Honors members can also use points earned to transact with strategic partner hotels as well as many strategic partners, including credit card providers, such as American Express, airlines, rail and car rental companies, Amazon, Lyft and others. Hilton Honors members who book through preferred Hilton channels also have access to instant benefits, including a flexible payment slider that allows members to choose nearly any combination of points and money to book a stay, an exclusive member discount and free standard Wi-Fi. Members also have access to contactless technology exclusively through the Hilton Honors app, where members can check in, choose their room and access their room using Digital Key. The program provides targeted marketing, promotions and customized guest experiences to 211 million members. Affiliation with our loyalty program encourages members to allocate more of their travel spend to our hotels. The percentage of travel spend we capture from loyalty members increases as they move up the tiers of our program. The program is funded by contributions from eligible revenues generated by Hilton Honors members and collected from properties in our system, as well as our strategic partnerships. The funds collected by the Hilton Honors program are subsequently applied to reimburse properties and strategic partners for Hilton Honors points redemptions by loyalty members and to pay for administrative expenses and marketing initiatives that support the program.
Our Business
As of December 31, 2024, our existing system included the following properties and rooms, by type, brand and region:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owned / Leased(1) | | Managed | | Franchised / Licensed | | Total |
| Properties | | Rooms | | Properties | | Rooms | | Properties | | Rooms | | Properties | | Rooms |
| Waldorf Astoria Hotels & Resorts | 2 | | | 463 | | | 32 | | | 8,333 | | | — | | | — | | | 34 | | | 8,796 | |
| Conrad Hotels & Resorts | 2 | | | 779 | | | 43 | | | 13,920 | | | 4 | | | 2,496 | | | 49 | | | 17,195 | |
| LXR Hotels & Resorts | — | | | — | | | 7 | | | 1,155 | | | 8 | | | 1,464 | | | 15 | | | 2,619 | |
| NoMad | — | | | — | | | 1 | | | 91 | | | — | | | — | | | 1 | | | 91 | |
| Signia by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 4 | | | 2,797 | | | — | | | — | | | 4 | | | 2,797 | |
| Canopy by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 11 | | | 1,850 | | | 32 | | | 5,731 | | | 43 | | | 7,581 | |
| Hilton Hotels & Resorts | 46 | | | 15,896 | | | 298 | | | 127,317 | | | 273 | | | 84,254 | | | 617 | | | 227,467 | |
| Curio Collection by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 27 | | | 6,055 | | | 153 | | | 27,679 | | | 180 | | | 33,734 | |
| Graduate by Hilton | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 34 | | | 5,788 | | | 34 | | | 5,788 | |
| DoubleTree by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 170 | | | 46,265 | | | 525 | | | 110,678 | | | 695 | | | 156,943 | |
| Tapestry Collection by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 5 | | | 694 | | | 146 | | | 17,074 | | | 151 | | | 17,768 | |
| Embassy Suites by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 40 | | | 10,551 | | | 229 | | | 51,423 | | | 269 | | | 61,974 | |
| Tempo by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 1 | | | 661 | | | 3 | | | 563 | | | 4 | | | 1,224 | |
| Motto by Hilton | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 8 | | | 1,727 | | | 8 | | | 1,727 | |
| Hilton Garden Inn | — | | | — | | | 126 | | | 24,736 | | | 934 | | | 131,735 | | | 1,060 | | | 156,471 | |
| Hampton by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 53 | | | 8,549 | | | 3,019 | | | 334,188 | | | 3,072 | | | 342,737 | |
| Tru by Hilton | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 283 | | | 27,605 | | | 283 | | | 27,605 | |
| Spark by Hilton | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 96 | | | 8,710 | | | 96 | | | 8,710 | |
| Homewood Suites by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 8 | | | 1,020 | | | 536 | | | 61,299 | | | 544 | | | 62,319 | |
| Home2 Suites by Hilton | — | | | — | | | 2 | | | 210 | | | 755 | | | 82,305 | | | 757 | | | 82,515 | |
Strategic partner hotels(2) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 409 | | | 19,361 | | | 409 | | | 19,361 | |
Other(3) | — | | | — | | | 3 | | | 1,087 | | | 14 | | | 3,305 | | | 17 | | | 4,392 | |
| Total hotels | 50 | | | 17,138 | | | 831 | | | 255,291 | | | 7,461 | | | 977,385 | | | 8,342 | | | 1,249,814 | |
Hilton Grand Vacations(4) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 105 | | | 18,392 | | | 105 | | | 18,392 | |
| Total system | 50 | | | 17,138 | | | 831 | | | 255,291 | | | 7,566 | | | 995,777 | | | 8,447 | | | 1,268,206 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Owned / Leased(1) | | Managed | | Franchised / Licensed | | Total |
| Properties | | Rooms | | Properties | | Rooms | | Properties | | Rooms | | Properties | | Rooms |
| U.S. | — | | | — | | | 187 | | | 81,173 | | | 5,700 | | | 735,705 | | | 5,887 | | | 816,878 | |
| Americas (excluding U.S.) | 1 | | | 405 | | | 70 | | | 17,819 | | | 393 | | | 54,446 | | | 464 | | | 72,670 | |
| Europe | 39 | | | 11,579 | | | 111 | | | 27,920 | | | 665 | | | 83,727 | | | 815 | | | 123,226 | |
| Middle East & Africa | 4 | | | 1,991 | | | 112 | | | 31,153 | | | 36 | | | 5,796 | | | 152 | | | 38,940 | |
| Asia Pacific | 6 | | | 3,163 | | | 351 | | | 97,226 | | | 667 | | | 97,711 | | | 1,024 | | | 198,100 | |
| Total hotels | 50 | | | 17,138 | | | 831 | | | 255,291 | | | 7,461 | | | 977,385 | | | 8,342 | | | 1,249,814 | |
Hilton Grand Vacations(4) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 105 | | | 18,392 | | | 105 | | | 18,392 | |
| Total system | 50 | | | 17,138 | | | 831 | | | 255,291 | | | 7,566 | | | 995,777 | | | 8,447 | | | 1,268,206 | |
____________
(1)Includes hotels owned or leased by entities in which we own a noncontrolling financial interest.
(2)Includes hotels that are included in our booking channels and participate in the Hilton Honors guest loyalty program through strategic partnership arrangements.
(3)Includes other hotels in our system that are not distinguished by a specific Hilton brand.
(4)Includes properties under timeshare brands including Hilton Club, Hilton Grand Vacations Club and Hilton Vacation Club.
Management and Franchise
We manage hotels and license our brands through our management and franchise segment. This segment generates its revenue primarily from fees charged to hotel owners under management and franchise contracts, as well as from fees associated with license agreements, which include arrangements with strategic partner hotels. We grow our management and franchise business by attracting owners to become a part of our system and participate in our commercial services to support their properties. Our management and franchise contracts provide significant return on investment for us as we earn and collect fees.
Hotel Management
Our core management services consist of operating hotels under management contracts for the benefit of third parties who either own or lease the hotels and the associated personal property. Often, particularly in the U.S., we employ the individuals working at these locations. Terms of our management contracts vary, but our fees generally consist of a base management fee, which is generally based on a percentage of the hotel’s monthly gross operating revenue, and, when applicable, an incentive management fee, which is generally based on a percentage of the hotel's operating profits, normally over a one calendar year period, and, in some cases, may be subject to a stated return threshold to the hotel owner. In general, the owner pays all operating and other expenses and reimburses any of our out-of-pocket expenses. In turn, our managerial discretion is subject to approval by the owner in certain major areas, including the approval of annual operating and capital expenditure budgets and, in most instances, the appointment of certain key personnel. Additionally, the owners generally pay monthly program fees based on the underlying hotel's sales or usage, as reimbursement for the costs related to our: (i) advertising and marketing programs; (ii) internet, technology and reservation systems; and (iii) quality assurance programs. Owners are also responsible for various other fees and charges, including payments for participation in our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program, training, consultation and procurement of certain goods and services. As of December 31, 2024, we managed 831 hotels with 255,291 rooms, which does not include hotels in our ownership segment.
The initial terms of our management contracts are typically 20 to 30 years. In certain cases, we are both the franchisor and manager of the hotel, when we enter into a franchise contract in addition to the management contract, and, in these cases, we classify the hotel as managed in our system. Extension options for our management contracts are negotiated and vary, but typically are more prevalent in full service hotels. Generally, these contracts contain one or two extension options that are for either five or 10 years and can be exercised at our or the hotel owner's option or by mutual agreement, as specified by the contract.
Some of our management contracts provide early termination rights to hotel owners upon certain events, including the failure to meet certain financial or performance criteria. Performance test measures typically are based upon the hotel’s performance individually and/or in comparison to specified competitive hotels. We often have an optional cure right to pay an amount equal to the performance shortfall over a specified period, although in some cases our cure rights are limited.
Franchising
We license our IP, including our brand names, trademarks and service marks, and our operating systems to hotel owners under franchise contracts. We do not own, manage or operate franchised properties, do not employ the individuals working at these properties and do not have any legal responsibility for the employees or the liabilities associated with operating these properties. We conduct periodic inspections of our franchised hotels to ensure that brand standards that we establish are maintained. For newly franchised hotels, including both new construction and conversions of existing hotels outside of our system, we approve the location, as well as the plans for the facilities, to ensure the hotels meet our brand standards. For existing franchised hotels, we provide franchisees with property improvement plans that must be completed to keep the hotels in compliance with our brand standards, so that they can remain in our hotel system.
Each franchisee pays us an application, initiation or other fee in conjunction with the inception of a franchise contract. Franchisees also pay a royalty fee, generally based on a percentage of the hotel’s monthly gross room revenue and, in some cases, may also include a percentage of gross food and beverage revenues and other revenues, as applicable. Additionally, franchised properties generally pay monthly program fees based on the underlying property's sales or usage, as reimbursement for the costs related to our: (i) advertising and marketing programs; (ii) internet, technology and reservation systems; and (iii) quality assurance programs. They are also responsible for various other fees and charges, including payments for participation in our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program, training, consultation and procurement of certain goods and services. We also earn license fees from license agreements with strategic partners, including co-branded credit card providers and strategic partner hotels, and HGV. As of December 31, 2024, including timeshare properties and strategic partner hotels, we franchised or licensed 7,566 hotels and resorts with 995,777 rooms.
Our franchise contracts typically have initial terms of approximately 20 years for new hotels and approximately 10 to 20 years for hotels converting from hotels outside of our system. At the expiration of the initial term, we may relicense the hotel to the franchisee, at our or the hotel owner's option or by mutual agreement, for an additional term generally ranging from 10 to 15 years. We have the right to terminate a franchise contract upon specified events of default, including nonpayment of fees or noncompliance with brand standards. If a franchise contract is terminated by us because of a franchisee’s default, the franchisee is contractually required to pay us liquidated damages.
Ownership
As a hotel owner and lessee, we focus on maximizing cost efficiency and profitability of the portfolio by, among other things, maximizing hotel revenues, implementing cost-effective labor management practices and systems and reducing fixed costs. Through our disciplined approach to hotel and asset management, we develop and execute on strategic plans for each of our hotels to enhance their competitive position and we invest in renovating guest rooms and public spaces and adding or enhancing meeting and retail space for properties where we believe such investments will improve profitability. As of December 31, 2024, the ownership segment included 50 hotels totaling 17,138 rooms, comprising 43 hotels that we leased, two hotels that were each leased by a consolidated variable interest entity ("VIE") and five hotels owned or leased by unconsolidated affiliates.
Corporate Responsibility
Hilton strives to create long-term value for all our stakeholders and strengthen the resilience of our business while also advancing responsible travel and tourism globally through our Travel with Purpose strategy. As one of the world’s largest hospitality companies, Hilton recognizes its responsibility to create positive environmental and social impacts across our operations, supply chain and communities to ensure our properties and surrounding communities remain vibrant and resilient for generations of travelers to come. We have established and maintain a governance structure that supports our strategy by overseeing the management of the business in a manner consistent with the best interests of Hilton and our stakeholders.
We continue to make progress towards our Travel with Purpose goals, including: (i) building a more sustainable future through destination stewardship and well-defined targets for emissions, water and waste; (ii) supporting positive social impact by advancing careers, communities and responsible conduct; and (iii) advancing and measuring our goals with integrity and transparency through our company policies and reporting mechanisms.
Our efforts are supported by a governance structure that is designed to ensure the objectives are an important part of our business and strategic priorities. Our executive committee receives at least quarterly updates on our Travel with Purpose programs and progress, and one of the three standing committees of Hilton's board of directors also receives quarterly reports on this progress, reviews and assesses our related strategy and makes recommendations to the board and management as appropriate. The board of directors also receives annual updates on our Travel with Purpose strategy and impact.
LightStay is our proprietary system for measuring and reporting our progress toward our Travel with Purpose goals. Our properties track energy, water, waste and associated utility cost reduction projects under way, as well as community volunteerism and charitable donations. Robust reports inform our properties of their progress on a regular basis.
The Hilton Global Foundation supports nonprofits and local community organizations that serve as partners to amplify our positive environmental and social impact around the world. The Hilton Global Foundation, created in 2019, is our primary international philanthropic arm and is registered as a U.S.-based 501(c)(3) charitable organization. In 2024, the Hilton Global Foundation announced $5.3 million in grants to support environmental sustainability, hospitality career development, and community resilience.
More details about our Travel with Purpose goals and our progress toward them are reported annually in our Travel with Purpose Report, available at cr.hilton.com.
Environmental Impact
We remain focused on our goal of reducing emissions, water and waste intensity at the hotels we operate. These efforts are supported by utility cost savings measures including HVAC controls, building automation system technologies and turnkey LED lighting, fueled by utility incentives wherever possible, to strengthen the return on investment and deliver cost savings to owners and enhance the guest experience. We also continued to create resources that will help facilitate the efficient operation of our hotels and take steps to increase our sourcing of renewable electricity at our hotels around the world. Additionally, through our Meet with Purpose offering, we partner with our corporate customers to quantify and plan sustainable meetings by providing them, upon request, with reporting that estimates emissions for their event, as well as options to reduce those estimated emissions.
Social Impact
With a presence in 140 countries and territories, we use our global scale to be an engine of opportunity by positively impacting our communities through local support and volunteering, creating learning and career growth opportunities, disaster relief and other economic support initiatives.
During 2024, Hilton and the Hilton Global Foundation supported our hotel teams and surrounding communities through disasters and crises, including the floods in Brazil and Hurricanes Helene and Milton that devastated parts of the southeastern U.S. This included making a series of contributions to World Central Kitchen, supporting the delivery of meals to those in need.
Hilton also remains committed to combating human trafficking, and we require all hotel-based employees to complete an annual training on identifying signs of trafficking. We partner with PACT, an organization dedicated to reducing trafficking and exploitation, to help prevent trafficking, and similarly collaborate on human rights initiatives through the World Sustainable Hospitality Alliance, World Travel and Tourism Council, American Hotel & Lodging Association ("AHLA") and United Kingdom ("U.K.") Stop Slavery Hotel Industry Network. The Hilton Global Foundation continues to support the AHLA Foundation's No Room for Trafficking Survivor Fund, which aims to equip community-based organizations to engage and support trafficking survivors.
At Hilton, we prioritize responsible sourcing by requiring suppliers to comply with the standards in our Hilton Responsible Sourcing Policy, which include integrity and fair dealing, human rights, protecting personal and business information, commitment to the environment and providing a safe and healthy work environment.
See "—Human Capital Management—Career Opportunities, Development and Training" below for information on learning and career growth opportunities.
Human Capital Management
As of December 31, 2024, we employed or managed approximately 181,000 individuals at our owned, leased and managed hotels and corporate offices. There were approximately 311,000 additional individuals employed by third-party owners working at our franchised properties.
Our human capital management strategy focuses on attracting, developing and retaining the best talent in the industry, and our executive committee reviews talent strategy and succession plans on a quarterly basis to assess current and future talent needs. We want to build a strong employee-centered culture that creates connectivity, camaraderie and trust among all employees, which then supports our employees to deliver positive experiences to guests at our hotels. Hilton's commitment to building strong culture focuses on creating a workplace that offers strong growth opportunities and is driven by purpose and earned Hilton recognition by Fortune magazine and Great Place to Work as the 2024 #2 World's Best Workplace and top hospitality company in the world for the eighth consecutive year.
During the year ended December 31, 2024 we saw improvements in workforce stability, with both hiring and retention volumes normalizing in comparison to pre-pandemic levels. We continue to review our benefits and programmatic offerings to ensure we remain competitive, are investing in our employees' development and well-being and are enhancing our recruiting strategies to tap into new pools of talent.
Compensation and Benefits
Hilton offers competitive pay and benefits to its employees, including a variety of compensation programs and comprehensive benefit programs. We regularly review pay parity across various workforce segments as part of our ongoing talent processes. Through our employee stock purchase plan, eligible employees can purchase Hilton stock through after-tax payroll deductions at a 15 percent discount from the market stock price.
As of December 31, 2024, approximately 25 percent of people employed or managed by us globally and approximately 40 percent of people working in the U.S. were covered by various collective bargaining agreements that generally address pay rates, working hours, other terms and conditions of employment, certain employee benefits and orderly settlement of labor disputes.
Our benefits and programs include paid time off, parental leave, adoption assistance, subsidized health insurance, education assistance, flexible work arrangements and Go Hilton travel programs, which make discounted rooms available to hotel and corporate employees, as well as their families and friends.
Our medical and mental health care programs include a global platform focused on caregiving that provides resources for employee self-care, as well as enabling employees to care for others, including sick, disabled or elderly family members, children and pets; a concierge service supporting eligible employees with logistical and administrative tasks related to caregiving; education, training and resources on substance use disorders to eligible employees; an Employee Assistance Program; and parental and bereavement leave and education resources for expecting and new parents.
We regularly survey our employees to monitor levels of engagement, trust, and management effectiveness, among other targeted topics, and use their feedback to inspire program enhancements and new offerings. We strive to maximize employee retention and minimize attrition with these and other measures. Approximately 32 percent of our U.S. employees have been with Hilton for at least 10 years.
Career Opportunities, Development and Training
We take a broad, long-term and business-aligned approach to develop a dedicated and collaborative workforce to better serve our guests. Our Pathway Programs help foster economic mobility in the communities in which we operate and create a more robust talent pipeline for our business drawing from underrepresented groups including veterans, which consists of individuals who have served in the military and the caregivers and spouses of those who have served in the military, as well as people with disabilities and displaced persons.
The advancement of our employees is important to us and we provide them with robust learning and development opportunities, as well as mentorship opportunities to corporate employees at all levels. We are focused on providing opportunities for the internal movement of our employees and the promotion from entry level positions into management positions at our hotels or corporate offices across the organization. Our career development approach emphasizes customized experiences so that employees can follow a training and career path best suited to their goals including a wide array of general business, industry or function-specific technical skills and leadership development courses and programs.
Our leadership development programs aim to build leadership skills through structured levels of self-paced learning and live facilitated sessions with focus areas of leading self, leading individuals and leading teams. Additionally, our People Leader Essential training offers a self-paced curriculum to employees, with content on key leadership topics, including effective communication, delegation, prioritization, coaching and talent development to support current, new and future people leaders at Hilton. One of our targeted programs for developing General Managers (“GMs”), GM Academy, is centered on nine core GM business capabilities, some of which include leadership and people management, asset management, customer engagement and commercial performance. Additionally, Hilton's global Signature Leadership Development programs and mentorship programs focus on building effective leaders across the enterprise to grow our leadership bench strength. These programs provide opportunities for participants to develop key competencies, network with and learn from senior leaders and enhance business acumen.
Governance, Ethics and Regulatory Compliance
As a core underpinning of our entire organization, our board of directors oversees our ethics and compliance program, which requires all Hilton employees to conduct themselves at the highest standards with respect to all ethics and compliance matters. Our Code of Conduct establishes a set of global business principles, with our compliance organization, training, risk
management and monitoring activities tailored to address unique risks by geography, business line, function and level. Our Code of Conduct is supported by robust compliance policies addressing risk areas such as corruption, trade sanctions, insider trading, privacy, confidential information, antitrust and escalation of concerns. Our legal and compliance training program, which is an annual requirement for all of our employees, conveys consistent compliance standards across the organization in formats designed to target different knowledge levels, learning styles and functional needs. Our annual training calendar includes mandatory training and supplemental training that is supported by periodic company-wide awareness campaigns highlighting Hilton-specific risks and scenarios.
In governing the physical safety of our properties and teams, to help ensure the safety and security of our employees and guests, we constantly monitor threats and incidents around the world through online tools and external networks and partnerships; support our properties globally with crisis alert communications, crisis plans and area crisis teams; provide employees with safety and security training resources; and conduct safety and security audits annually using a risk-based approach.
Our legal compliance team administers a third-party risk management program so that we understand the qualifications, reputation and associations of third parties with whom we transact, particularly third parties who interface with government officials and third parties who act in Hilton’s name, such as owners of our hotels. The third-party risk management program includes due diligence, education materials for third parties, ongoing monitoring of relationships and appropriate contract audit and termination rights. Our legal compliance team also monitors a comprehensive and confidential reporting tool to assist management and employees in addressing fraud, abuse and other misconduct in the workplace. The Audit Committee of our board of directors receives regular updates from our legal compliance team on third-party risk and information from our confidential reporting tool.
Competition
We encounter active and robust competition as a hotel and resort manager, franchisor, owner and lessee. Competition in the hospitality industry is based on several criteria, generally including: the attractiveness of the facility; location; level of service; quality of accommodations; amenities; food and beverage options and outlets; public and meeting spaces and other guest services; consistency of service; room rate; brand reputation; and the ability to earn and redeem loyalty program points through a global system. Our properties and brands compete with other hotels, resorts, motels, inns and other accommodation rental services in their respective geographic markets or customer segments, including facilities owned by local interests, individuals, national and international chains, institutions, investment and pension funds and real estate investment trusts ("REITs"). We believe that our capabilities as a multi-branded manager, franchisor, owner and lessee of hotels with an associated global, system-wide guest loyalty program and commercial platform help us continue to maintain our position as one of the largest and most geographically diverse hospitality companies in the world.
Our principal competitors include other branded and independent hotel operating companies, national and international hotel brands and ownership companies. While local and independent brand competitors vary, on a global scale, our primary competitors are Accor S.A., Choice Hotels International, Hongkong and Shanghai Hotels, Hyatt Hotels Corporation, Intercontinental Hotel Group, Marriott International, Radisson Hotel Group and Wyndham Hotels & Resorts.
Seasonality
The hospitality industry is seasonal in nature. The periods during which our properties experience higher or lower levels of demand vary from property to property, depending principally upon their location, type of property and competitive mix within the specific location. Based on historical results, we generally expect our revenues to be lower in the first quarter of each year than in each of the three subsequent quarters.
Cyclicality
The hospitality industry is cyclical, and demand generally follows, on a lagged basis, key macroeconomic indicators. There is a history of increases and decreases in the development and supply of and demand for hotel rooms, occupancy levels and room rates realized by hotel owners through economic cycles. The combination of changes in economic conditions and in the supply of hotel rooms can result in significant volatility in results for owners and managers of hotel properties. The costs of running a hotel, including personnel costs, rent, property taxes, insurance and utilities, tend to be more fixed than variable. As a result of such fixed costs, in a negative economic environment, the rate of decline in earnings can be higher than the rate of decline in revenues.
Intellectual Property
In the highly competitive hospitality industry in which we operate, trademarks, service marks, trade names, logos and patents are very important to the success of our business. We have a significant number of trademarks, service marks, trade names, logos, patents and pending registrations and expend significant resources each year on surveillance, registration and protection of our IP, which we believe has become synonymous in the hospitality industry with a reputation for excellence in service and authentic hospitality.
Government Regulation
Our business is subject to various foreign and U.S. federal and state laws and regulations, including laws and regulations that govern the offer and sale of franchises, many of which impose substantive requirements on franchise contracts and require that certain materials be registered before franchises can be offered or sold in a particular jurisdiction.
In addition, a number of states regulate the activities of hospitality properties and restaurants, including safety and health standards, as well as the sale of liquor at such properties, by requiring licensing, registration, disclosure statements and compliance with specific standards of conduct. Operators of hospitality properties also are subject to laws governing their relationship with employees, including minimum wage requirements, overtime, working conditions and work permit requirements. Our franchisees are responsible for their own compliance with laws, including with respect to their employees, minimum wage requirements, overtime, working conditions and work permit requirements. Compliance with, or changes in, these laws could reduce the revenue and profitability of our properties and could otherwise adversely affect our operations.
We also manage hotels with casino gaming operations as part of or adjacent to the hotels, which are typically managed and operated by third parties. If we manage and operate the casinos, we employ third-party compliance consultants and service providers and hold and maintain the casino gaming license. As a result, our business operations at such facilities are subject to the licensing and regulatory control of the local regulatory agency responsible for gaming licenses and operations in those jurisdictions.
For additional information on government regulation, including environmental regulations and requirements, refer to "Part I—Item 1A. Risk Factors."
Insurance
U.S. managed hotels and foreign managed and franchised hotels are permitted to participate in certain of our insurance programs by mutual agreement with the hotel owners; however, if they do not participate in our insurance programs, the hotel owners must purchase insurance programs consistent with our requirements. Generally, U.S. franchised hotels are not permitted to participate in our insurance programs, but rather the hotel owners must purchase insurance programs consistent with our requirements. In addition, our management and franchise contracts typically include provisions requiring the hotel owner to indemnify us against losses arising from the design, development and operation of such hotel.
Most of our insurance policies are written with self-insured retentions or deductibles that are common in the insurance market for similar risks, and we believe such risks are prudent for us to assume. Our third-party insurance policies provide coverage for claim amounts that exceed our self-insurance retentions or deductible obligations. We maintain insurance coverage for general liability, property, business interruption, terrorism and other risks with respect to our business for all of our owned and leased hotels, and we maintain workers' compensation or equivalent coverage for all of our employees. We also are self-insured for health coverages for some of our U.S. and Puerto Rico employees, which include those working at our corporate operations and managed hotels, with third-party insurance protection for costs over specified thresholds.
Where You Can Find More Information
We file annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. Our SEC filings are available to the public over the internet at the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. Our SEC filings are also available free of charge on our website at ir.hilton.com as soon as reasonably practicable after they are filed with or furnished to the SEC. Our website and the information contained on or connected to that site are not incorporated into this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
In addition to the other information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the following risk factors should be considered carefully in evaluating our company and our business.
Risks Related to Our Industry
We are subject to the business, financial and operating risks inherent to the hospitality industry, any of which could reduce our revenues and limit opportunities for growth.
Our business is subject to a number of business, financial and operating risks inherent to the hospitality industry, including:
•significant competition from multiple hospitality providers in all parts of the world;
•changes in the supply and demand for hotel services, including rooms, food and beverage and other products and services;
•the financial condition of and relationships with third-party property owners, developers and joint venture and strategic partners, including the risk that owners may terminate or fail to comply with our management, franchise, joint venture or strategic partner contracts;
•decreases in the frequency of business travel that may result from alternatives to in-person meetings, including virtual meetings hosted online or over private teleconferencing networks;
•decreases in the availability and/or increases in the cost of capital necessary for us and third-party hotel owners to fund investments, capital expenditures and service debt obligations;
•increases in operating costs, including employee compensation and benefits, energy, insurance, food and beverage and other supplies;
•significant increases in cost for health care coverage for employees and potential government regulation with respect to health care coverage;
•increases in costs due to inflation or other factors that may not be fully offset by increases in revenues in our business, as well as increases in overall consumer prices, including the prices of our offerings, due to inflation, which could weaken consumer demand for travel and the other products we offer and adversely affect our revenues;
•changes in taxes and governmental regulations that influence or set wages, prices, interest rates or construction and maintenance procedures and costs;
•the costs and administrative burdens associated with complying with applicable laws and regulations;
•the costs or desirability of complying with local practices and customs;
•shortages of labor or labor disruptions;
•the ability of third-party internet and other travel intermediaries who sell our hotel rooms to guests to attract and retain customers;
•the quality of services provided by franchisees, as well as their ability to comply with relevant regulations and contractual requirements relating to a variety of issues including environment, human rights and labor;
•delays in or cancellations of planned or future development or refurbishment projects at hotels in our system;
•cyclical over-building in the hospitality industry;
•changes in desirability of geographic regions of the hotels in our business, geographic concentration of our operations and customers and shortages of desirable locations for development; and
•the costs required for environmental initiatives, including those resulting from regulatory changes or stakeholder or customer expectations.
Any of these factors could (i) increase our costs or (ii) limit or reduce the prices we are able to charge (a) third-party hotel owners for providing management and franchise services or (b) hotel customers for hospitality products and services, or (iii) otherwise affect our ability to maintain existing properties or develop new properties. As a result, any of these factors can reduce our revenues and limit opportunities for growth.
Macroeconomic conditions, public health concerns, geopolitical activity and other factors beyond our control can adversely affect and reduce demand for our products and services.
Macroeconomic conditions, geopolitical activity, public health concerns and other factors beyond our control can reduce demand for hospitality products and services, including demand for rooms at our hotels. These factors include, but are not limited to:
•changes in general economic conditions, including inflation, interest rates, supply chain disruptions, low consumer confidence, increases in unemployment levels and depressed real estate prices resulting from the severity and duration of any downturn in the U.S. or global economy and financial markets;
•conditions that negatively shape public perception of travel or result in temporary closures or other disruption at our hotel properties, including travel-related accidents, outbreaks of pandemic or contagious diseases, such as COVID-19, Ebola, Zika, avian flu, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), H1N1 (swine flu) and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS);
•geopolitical activity, political and social unrest and governmental action and uncertainty resulting from U.S. and global political and social trends and policies, including potential barriers to travel, trade and immigration;
•wars, such as Russia's invasion of Ukraine and the escalation of conflict in the Middle East, political instability or civil unrest, terrorist activities or threats and resulting heightened travel security measures, any of which may foreclose travel to certain locales or decrease the appeal of travel among the general population;
•the impact of U.S. Federal government shutdowns and other similar governmental budgetary impasses or reductions;
•decreased corporate or government travel-related budgets and spending, as well as cancellations, deferrals or renegotiations of group business, such as industry conventions;
•statements, actions or interventions by governmental officials related to travel and corporate travel-related activities and the resulting negative public perception of such travel and activities;
•the financial and general business condition of the airline, automotive and other transportation-related industries and its effect on travel, including decreased airline capacity and routes and increased travel costs;
•perceived negative impacts of tourism on local cultures, human rights and the environment;
•cyber-attacks;
•the impact of climate change or availability of natural resources;
•natural, climate-related or man-made disasters and extreme weather conditions, including earthquakes, tsunamis, tornadoes, hurricanes, typhoons, floods, wildfires, volcanic eruptions, oil spills and nuclear incidents;
•labor shortages, which could restrict our ability to efficiently operate or grow our business and/or increase our costs;
•organized labor activities, which could cause a diversion of business from hotels involved in labor negotiations and loss of business for our hotels generally as a result of certain labor tactics; and
•other changes in the overall demand for what we offer, including the desirability of particular locations or travel patterns of customers.
Any one or more of these factors could limit or reduce overall demand for our products and services or could negatively affect our revenue sources, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Contraction in the global economy or low levels of economic growth could adversely affect our revenues and profitability, as well as limit or slow our future growth.
Consumer demand for our services is closely linked to the performance of the general economy and is sensitive to business and personal discretionary spending levels. Decreased global or regional demand for hospitality products and services can be especially pronounced during periods of economic contraction or low levels of economic growth, and the recovery period in our industry may lag overall economic improvement. Declines in demand for our products and services due to general economic conditions could negatively affect our business by limiting the amount of fee revenues we are able to generate from our managed and franchised properties and decreasing the revenues and profitability of our owned and leased properties. In addition, many of the expenses associated with our services, including personnel costs, interest, rent, property taxes, insurance and utilities, are relatively fixed. During a period of overall economic weakness, if we are unable to meaningfully decrease these costs as demand for our services decreases, our business operations, financial performance, results and prospects for future growth may be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Operating Our Business
Because we operate in a highly competitive industry, our revenues or profits could be harmed if we are unable to compete effectively.
The segments of the hospitality industry in which we operate are subject to intense competition. Our principal competitors are other operators of luxury, full-service and focused-service hotels, including other major hospitality chains with well-established and recognized brands. We also compete against smaller hotel chains, independent and local hotel owners and operators, home and apartment sharing services and timeshare operators. If we are unable to compete successfully, our revenues or profits may decline.
Competition for hotel guests
We face competition for individual guests, group reservations and conference business at our hotels. We compete for these customers based primarily on brand name recognition and reputation, as well as location, rates for hotel rooms, food and beverage and other services, property size and availability of guest rooms and conference and meeting space, quality of the accommodations and technology provided, previous customer experience and satisfaction, amenities and the ability to earn and redeem loyalty program points. Our competitors may have greater commercial, financial and marketing resources and more efficient technology platforms, which could allow them to improve their properties and expand and improve their marketing efforts in ways that could affect our ability to compete for guests effectively, or they could offer a type of lodging product that customers find attractive but that we do not offer.
Competition for management and franchise contracts
We compete to enter into management and franchise contracts. Our ability to compete effectively is based primarily on the value and quality of our management services, brand name recognition and reputation, our access to and willingness to invest capital or provide other incentives or inducements, availability of suitable properties to maintain brand variety across geographic areas, the overall economic terms of our contracts and the economic advantages to the third-party hotel owner of retaining our management services and/or using our brands. If the properties that we manage or franchise perform less successfully than those of our competitors, if we are unable to offer terms as favorable as those offered by our competitors or if the availability of suitable properties is limited, we may not be able to compete effectively for new management or franchise contracts.
Any deterioration in the quality or reputation of our brands could have an adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our brands are among our most important assets. Our ability to attract and retain guests depends, in part, on the public recognition of our brands and their associated reputation. In addition, the success of our hotel owners’ businesses and the amount of payments to us for the assets and services we provide them may depend on the strength and reputation of our brands. If our brands become obsolete or consumers view them as unfashionable, unsustainable or lacking in consistency and quality, we may be unable to attract guests to our hotels and may further be unable to attract or retain our hotel owners to use our management and franchise services.
Changes in ownership or management practices, perceptions of our corporate responsibility practices, perception of guest or employee health or safety, the occurrence of accidents or injuries, cyber-attacks, security breaches, natural disasters, crime, failure of suppliers, franchisees or business partners to comply with relevant regulations and contractual requirements relating to a variety of issues including environmental, human rights and labor, individual guest, owner or employee notoriety or similar events at our hotels and resorts can harm our reputation, create adverse publicity and cause a loss of consumer confidence in our business. Because of the global nature of our brands and the broad expanse of our business and hotel locations, events occurring in one location could negatively affect the reputation and operations of otherwise successful individual locations. In addition, the expansion of social media has compounded the potential scope of negative publicity by increasing the speed and expanse of information dissemination. Many social media platforms publish content immediately and without filtering or verifying the accuracy of that content. A negative incident or the perception of occurrence of a negative incident at one hotel could have far-reaching effects, including lost sales, customer boycotts, loss of development opportunities and employee difficulties. Such incidents have in the past and could in the future subject us to legal actions, including litigation, governmental investigations or penalties, along with the resulting additional adverse publicity. A perceived decline in the quality of our brands or damage to our reputation could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our business is subject to risks related to doing business with third-party property owners that could adversely affect our reputation, operational results or prospects for growth.
Unless we maintain good relationships with third-party hotel owners and renew or enter into new management and franchise contracts, we may be unable to maintain or expand our presence and our business, financial condition and results of operations may suffer.
Our business depends on our ability to: (i) establish and maintain long-term, positive relationships with third-party hotel owners; and (ii) enter into new, and renew, management and franchise contracts. Although our management and franchise contracts are typically long-term arrangements, hotel owners may be able to terminate the contracts under certain circumstances, including the failure to meet specified financial or performance criteria. Our ability to meet these financial and performance criteria is subject to, among other things, risks common to the overall hospitality industry, including factors outside of our control. In addition, negative pricing trends in the industry for management and franchise and related fees more broadly could adversely affect our ability to negotiate with hotel owners. If we fail to maintain and renew existing management and franchise contracts or enter into new contracts on favorable terms, we may be unable to expand our presence and our business, and our financial condition and results of operations may suffer.
Our business is subject to real estate investment risks for third-party hotel owners that could adversely affect our operational results and our prospects for growth.
Growth of our business is affected, and may potentially be limited, by factors influencing real estate development generally, including site availability, financing availability and cost, planning, zoning and other local approvals. In addition, market factors such as projected room occupancy, changes in growth in demand for customers compared to projected supply, geographic area restrictions in management and franchise contracts, costs and availability of construction labor and materials and anticipated room rate structure, if not managed effectively by our third-party hotel owners could adversely affect the growth of our management and franchise business.
If our third-party hotel owners are unable to repay or refinance loans secured by properties, or to obtain financing adequate to fund current operations or growth plans, our revenues, profits and capital resources could be reduced and our business could be harmed.
Many of our third-party hotel owners pledge their properties as collateral for loans entered into at the time of development, purchase or refinancing. If our third-party hotel owners are unable to repay or refinance maturing indebtedness on favorable terms or at all, which could be more difficult in the current interest rate environment, their lenders could declare a default, accelerate the related debt and repossess the property. We have been required and may, in the future, be required to make cash payments for any debt that we have guaranteed or letters of credit that we have extended. While we maintain certain contractual protections, repossession could result in the termination of our management or franchise contract or eliminate revenues and cash flows from the property. In addition, the owners of managed and franchised hotels depend on financing to develop or buy and improve hotels and, in some cases, fund operations during down cycles. Our hotel owners’ inability to obtain adequate funding or to do so at interest rates that they are willing to accept could materially adversely affect the operation, maintenance and improvement plans of existing hotels, result in the delay or stoppage of the development of our existing development pipeline and limit additional development to further expand our hotel portfolio.
Hotel owners with financial difficulties have been and may continue to be unable or unwilling to pay us amounts that we are entitled to under our existing contracts on a timely basis or at all. Likewise, if we or our hotel owners or franchisees are unable to access capital to make physical improvements to our hotels, the quality of our hotels may suffer, which may negatively impact our reputation and guest loyalty, and our performance may suffer as a result.
If our third-party property owners fail to make investments necessary to maintain or improve their properties, guest preference for Hilton brands, Hilton's reputation and performance results could suffer.
Substantially all of our management and franchise contracts, as well as our license agreement with HGV, require third-party property owners to comply with quality and reputation standards of our brands, which include requirements related to the physical condition, use of technology, safety standards and appearance of the properties, as well as the service levels provided by hotel employees. These standards may evolve with customer preference, or we may introduce new requirements over time. If our property owners fail to make investments necessary to maintain or improve the properties and related operations in accordance with our standards, or based on customer demand more broadly, guest preference for our brands could diminish. In addition, if third-party property owners fail to observe standards or meet their contractual requirements, we may elect to
exercise our termination rights, which would eliminate revenues from these properties and cause us to incur expenses related to terminating these contracts. We may be unable to find suitable or offsetting replacements for any individually terminated hotels or broader third-party owner relationships.
Contractual and other disagreements with third-party property owners could make us liable to them or result in litigation costs or other expenses or termination of existing management or franchise contracts.
Our management and franchise contracts require us and our hotel owners to comply with operational and performance conditions that are subject to interpretation and could result in disagreements. Any dispute with a property owner could increase our costs even if the outcome is ultimately in our favor. We cannot predict the outcome of any arbitration or litigation, the effect of any negative judgment against us or the amount of any settlement that we may enter into with any third party. Furthermore, specific to our industry, some courts have applied principles of agency law and related fiduciary standards to managers of third-party hotel properties, which means that property owners may assert the right to terminate contracts even where the contracts do not expressly provide for termination. Our fees from any property permitted to be terminated would be eliminated, and accordingly, may negatively affect our results of operations.
Some of our existing development pipeline may not be developed into new hotels, which could materially adversely affect our growth prospects.
As of December 31, 2024, we had 3,578 hotels in our development pipeline under one of our brands or a strategic partner hotel brand, of which 225,100 rooms are under construction, which includes operating hotels that are in the process of conversion into our system. The commitments of owners and developers with whom we have contracts are subject to conditions, and the eventual development and construction of our development pipeline, in particular for hotels not currently under construction, is subject to risks, including, in certain cases, the owner's or developer's ability to obtain adequate financing and governmental or regulatory approvals. Unfavorable economic conditions also could affect our ability to enter into management and franchise contracts with potential third-party owners of our hotels, who may be unable to obtain financing or face other delays or cost pressures in developing hotel projects. As a result, at times new hotels have entered our pipeline at a slower rate than anticipated, some properties in our development pipeline have entered our system later than we anticipated and some hotels under development never enter our system at all, thereby negatively affecting our overall growth.
New hotel brands or non-hotel branded concepts that we launch in the future may not be as successful as we anticipate, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
We have launched and acquired and may continue to launch and acquire new hotel products, brands and/or concepts or execute brand expansions into new markets, including international markets. These products may not be accepted by hotel owners, franchisees or customers and we cannot guarantee the level of acceptance any new or acquired brand will have in the development and consumer marketplaces. If new or acquired branded hotel products, non-hotel branded concepts or brand expansions are not as successful as we anticipate, we may not recover the costs we incurred in their development, acquisition or expansion, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The risks resulting from investments in owned and leased real estate could increase our costs, reduce our profits and limit our ability to respond to market conditions.
Our investments in owned and leased real property (including through joint ventures) subject us to various risks that may not be applicable to managed or franchised properties, including:
•governmental regulations relating to real estate ownership or operations, including tax, environmental, zoning and eminent domain laws;
•fluctuations or loss in value of real estate or potential impairments in the value of our assets due to changes in market conditions and expectations of future hotels revenues and costs of operations in the area in which real estate or assets are located;
•increased potential civil liability for accidents or other occurrences on owned or leased properties;
•the ongoing need for capital improvements and expenditures funded by us to maintain or upgrade properties, some of which were constructed many years ago, and contractual requirements to deliver properties back to landlords in a particular state of repair and condition at the end of a lease term;
•construction delays, lack of availability of required construction materials or cost overruns (including labor and materials) related to necessary capital improvements of owned and leased properties;
•periodic total or partial closures due to renovations and facility improvements;
•risks associated with any mortgage debt, including the possibility of default, interest rate levels, particularly in the current interest rate environment, and uncertainties in the availability of replacement financing;
•the inability to rebuild a property that has been damaged or destroyed by casualty, including a climate-related weather event, as a result of governmental regulations or other restrictions;
•the inability to renew our leases on favorable terms or at all;
•our limited ability to influence the decisions and operations of joint ventures in which we have a minority interest;
•force majeure events, including earthquakes, tornadoes, hurricanes, wildfires, floods, tsunamis, climate-related weather events, outbreaks of pandemic or contagious diseases or acts of terrorism;
•contingent liabilities that exist after we have exited a property;
•costs linked to the employment and management of staff to run and operate an owned or leased property;
•increased operating costs including energy, insurance, food and beverage, supplies and other operating costs; and
•the relative illiquidity of real estate compared to some other assets.
The negative effect on profitability and cash flow from declines in revenues is more pronounced in owned and leased properties because we, as the owner or lessee, bear the risk of the costs required to own and operate a hotel. Further, during times of economic distress, declining demand and declining earnings often result in declining asset values, and we or our joint ventures may not be able to sell properties or exit leasing arrangements on favorable terms or at all. Accordingly, we may not be able to adjust our owned and leased property portfolio promptly in response to changes in economic or other conditions.
Failure to keep pace with developments in technology could adversely affect our operations or competitive position.
The hospitality industry demands the use of sophisticated technology and systems for property management, brand assurance and compliance, procurement, finance, human resources, reservation systems, distribution of hotel resources to current and future customers and guest amenities and the operation of the Hilton Honors guest loyalty program. These technologies may require refinements and upgrades, and third parties may cease support of systems that are currently in use. The development and maintenance of these technologies has required and may further require significant investment by us. As various systems and technologies become outdated or new technology is required, we may not be able to replace or introduce them as quickly as needed or in a cost-effective and timely manner. In some cases, hotel owners may refuse to upgrade systems or deploy new technology to replace aging or end-of-life software and/or hardware. As a result, our business operations could be disrupted and our competitive position could decline, adversely affecting our financial performance, or we may not achieve the benefits we may have been anticipating from any new technology or system.
Failures in, material damage to or interruptions in our information technology systems, software or websites, including as a result of cyber-attacks on our systems or systems operated by third parties that provide operational and technical services to us, costs associated with protecting the integrity and security of personal data and other sensitive information and difficulties in updating our existing software or developing or implementing new software could have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
We depend heavily upon our information technology systems in the conduct of our business. We develop, own and license or otherwise contract for sophisticated technology systems and services for property management, brand assurance and compliance, procurement, finance, human resources, reservation systems, distribution of hotel resources to current and future customers and guest amenities and the operation of the Hilton Honors guest loyalty program. Such systems are subject to, among other things, damage or interruption from power outages, computer and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, third-party criminal activity including "ransomware" or other malware and natural and man-made disasters. Although we have a cold disaster recovery site in a separate location and cloud backup processes to provide continuous resilience of our core reservation, property management, distribution and financial systems, certain of our data center operations are currently located in a single facility or with a single cloud-based provider. Although we continue to renovate and migrate portions of our operations to cloud-based providers while simultaneously building and operating new applications and services with those cloud-based providers, any loss or damage to our primary physical or cloud-based facilities could result in operational disruption and data loss as we transfer production operations to our disaster recovery site or cloud providers. Damage or interruption to our information systems may require a significant investment to update, remediate or replace with alternate systems, and we may suffer interruptions in our operations as a result. In addition, costs and potential problems or interruptions associated with the implementation of new or upgraded systems and technology or with maintenance or support of existing systems could also disrupt or reduce the efficiency of our operations. Any material interruptions or failures in our systems, including those that may result from our failure to adequately develop, implement and maintain a robust disaster recovery plan and backup systems could severely affect our ability to conduct normal business operations and, as a result, have a material adverse effect on our business operations and financial performance.
We rely on third parties for the performance of a significant portion of our information technology functions worldwide. In particular, our loyalty platform, property management, reservation and distribution systems rely on data communications networks and systems operated by unaffiliated third parties and cloud providers. The success of our business depends in part on maintaining our relationships with these third parties and their continuing ability to perform these functions and services in a timely and satisfactory manner. If we experience a loss or disruption in the provision of any of these functions or services, or they are not performed in a satisfactory manner, we may have difficulty in finding alternate providers on terms favorable to us, in a timely manner or at all, and our business could be adversely affected.
We rely on certain vendors for traditional software and cloud/software-as-a-service operations to maintain and periodically upgrade many of these systems and applications so that they can continue to support our business. The software programs supporting many of our systems were licensed to us by independent software developers. The inability of these developers or us to continue to maintain and upgrade these information systems and software programs has impacted, and in the future could, disrupt or reduce, the efficiency of our operations if we were unable to convert to alternate systems in an efficient and timely manner. For example, in July 2024 a software update by CrowdStrike Holdings, Inc., a cybersecurity technology company, caused a global information technology outage. Although the outage did not have a material impact to our business, we were temporarily impacted by the outage, and similar software outages in the future could harm our operations and be material to us.
We are vulnerable to various risks and uncertainties associated with our websites and mobile applications, including changes in required technology interfaces, website and mobile application downtime and other technical failures, unexpected costs and changes and issues as we upgrade our website software and mobile applications. Additional risks include computer malware, changes in applicable federal, state and international regulations, security breaches, legal claims related to our website operations, e-commerce fulfillment and other consumer privacy concerns. Our failure to successfully respond to these risks and uncertainties could reduce website and mobile application sales and have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
Cyber-attacks could have a disruptive effect on our business.
From time to time we and our third-party service providers experience cyber-attacks, attempted and actual breaches of our or their information technology systems and networks or similar events, which could result in a loss of sensitive business or customer information, systems interruption or the disruption of our operations. The techniques that are used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service or sabotage systems change frequently and may be difficult to detect for long periods of time, and despite our deployment of cyber-attack prevention and detection techniques, we are accordingly unable to anticipate and prevent all data security incidents. We have in the past been subject to cyber-attacks and expect that we will be subject to additional cyber-attacks in the future and may experience data breaches, especially as the pace, scale and sophistication of cyber-attacks continue to increase across all industry sectors, including hospitality.
Even if we are fully compliant with legal standards and contractual or other requirements, we still may not be able to prevent security breaches involving sensitive data. The sophistication of efforts by hackers to gain unauthorized access to information systems has continued to increase in recent years and may continue to do so at an accelerating pace as criminals leverage generative artificial intelligence-based technologies and services. Breaches, thefts, losses or fraudulent uses of customer, employee or company data could cause consumers to lose confidence in the security of our websites, mobile applications, point of sale systems and other information technology systems and, as a result of this loss in confidence, choose not to purchase from us. Such security breaches also could expose us to risks of data loss, business disruption, litigation, fines, regulatory charges and other costs or liabilities, any of which could adversely affect our business.
We are incorporating artificial intelligence technologies into our processes. These technologies may present business, compliance and reputational risks.
If we fail to keep pace with rapidly evolving technological developments in artificial intelligence, our competitive position and business results may suffer. The introduction of these technologies, particularly generative AI, into new or existing offerings may also result in new or expanded risks and liabilities, including due to enhanced governmental or regulatory scrutiny, litigation, copyright infringement, compliance issues, ethical concerns, security risks relating to private and/or confidential information, as well as other factors that could adversely affect our business, reputation, and financial results. In addition, it is possible that artificial intelligence and machine learning-technology could, unbeknownst to us, be improperly utilized by employees while carrying out their responsibilities. The use of artificial intelligence can lead to unintended consequences, including generating content that appears correct but is factually inaccurate, misleading or otherwise flawed, or that results in unintended biases and discriminatory outcomes, which could harm our reputation and business and expose us to risks related to inaccuracies or errors in the output of such technologies.
We are exposed to risks and costs associated with protecting the integrity and security of personal data and other sensitive information.
We are subject to various risks and costs associated with the collection, handling, storage and transmission of personally identifiable information and commercial information, including costs related to compliance with U.S. and foreign data collection and privacy laws and other contractual obligations, as well as risks associated with the compromise of our systems collecting such information. Many jurisdictions, including the European Union ("E.U."), the U.K., China and certain states within the U.S., have passed laws that require companies to meet specific requirements regarding the handling of personally identifiable information. We collect internal and customer data, including credit card numbers and other personally identifiable information for a variety of important business purposes, including managing our workforce, providing requested products and services and maintaining guest preferences to enhance customer service and for marketing and promotion purposes. In some cases, we share personal customer and payment data with select third party partners to enable fulfillment of customer reservations and other requested or related services and we are dependent on those third-party partners to protect the integrity and safety of that data from unauthorized exposure. We could be exposed to fines, penalties, restrictions, litigation, reputational harm or other expenses, or other adverse effects on our business, due to failure to protect personally identifiable information and commercial sensitive information or failure to maintain compliance with the various U.S. and foreign data collection and privacy laws or with credit card industry standards or other applicable data security standards.
In addition, U.S. states and the federal government have enacted additional laws and regulations to protect consumers against identity theft. These laws and similar laws in other jurisdictions have increased the costs of doing business, and failure on our part to implement appropriate safeguards or to detect and provide prompt notice of unauthorized access as required by some of these laws could subject us to potential claims for damages and other remedies. If we were required to pay any significant amounts in satisfaction of claims under these laws, or if we were forced to cease our business operations for any length of time as a result of our inability to comply fully with any such law, our business, operating results and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Because third parties provide us with a number of operational and technical services, third-party security incidents could expose us to liability, harm our reputation, damage our competitiveness and adversely affect our financial performance.
Third parties provide us with certain operational and technical services. These third parties may have access to our systems, provide hosting services, or otherwise process data about us or our guests, employees or partners. Any third-party security incident could compromise the integrity or availability of or result in the theft of confidential or otherwise sensitive data, which could negatively impact our operations. Unauthorized access to data and other confidential or proprietary information may be obtained through break-ins, network breaches by unauthorized parties, employee theft or misuse or other misconduct. We rely on the internal processes and controls of third-party software and application vendors to maintain the security of all software code, systems and data provided to or used by Hilton. Should those vendors fail to secure their products then we would be at risk of unintentionally injecting malware into our systems via compromised software code they provide and/or losing important data. The occurrence of any of the foregoing could negatively affect our reputation, our competitive position and our financial performance, and we could face lawsuits and potential liability.
Delays in service from third-party service providers could expose us to liability, harm our reputation, damage our competitiveness and adversely affect our financial performance.
From time to time, we may rely on a single or limited number of suppliers for the provision of various goods or services that we use in the operation of our business. The inability of such third parties to satisfy our requirements or our guests' expectations or provide such goods and services in a safe and secure manner could disrupt our business operations or make it more difficult for us to implement our business strategy. If any of these situations were to occur, our reputation could be harmed, we could be subject to third-party liability, including under data protection and privacy laws in certain jurisdictions, the physical safety of our properties could be impaired and our financial performance could be negatively affected.
We have expanded and may continue to seek to expand through acquisitions of and investments in other businesses and properties, or through alliances and strategic partner arrangements, and we may also seek to divest some of our properties and other assets. These acquisition and disposition activities may be unsuccessful or divert management’s attention.
We may consider strategic and complementary acquisitions of and investments in other hotel or hospitality brands, businesses, properties or other assets. For example, in 2024 we acquired the Graduate hotel brand, invested in the NoMad hotel brand and partnered with Small Luxury Hotels of the World and AutoCamp. Acquisitions or investments in brands, businesses, properties or assets as well as third-party partnerships and alliances are subject to risks that could affect our business, including risks related to:
•using cash balances and incurring debt;
•issuing shares of stock that could dilute the interests of our existing stockholders;
•assuming contingent liabilities; or
•creating additional expenses.
We may not actually realize any anticipated benefits from such acquisitions, investments or third-party partnerships and alliances. We may also experience challenges from regulatory authorities in connection with our acquisitions, investments or partnerships, including from antitrust authorities who are increasingly scrutinizing such transactions, and which may lead to unforeseen expenditures or which may block, delay or impose undesirable conditions on our acquisitions, investments or partnerships. In addition, the success of any acquisition, investment or partnership also will depend, in part, on our ability to integrate the acquisition or investment with our existing operations. We also may divest certain properties or assets, and any such divestments may yield lower than expected returns or otherwise fail to achieve the benefits we expect. In some circumstances, sales of properties or other assets may result in losses. Upon sales of properties or assets, we may become subject to contractual indemnity obligations, incur material tax liabilities or, as a result of required debt repayment, face a shortage of liquidity. Finally, any acquisitions, investments, partnerships, dispositions or arrangements with strategic partners could demand significant attention from management that would otherwise be available for business operations, which could harm our business.
Failure to comply with marketing and advertising laws, including with regard to direct marketing, could result in fines or place restrictions on our business.
We rely on a variety of direct marketing techniques, including telemarketing, email and social media marketing and postal mailings, and we are subject to various laws and regulations in the U.S. and internationally that govern marketing and advertising practices. Any further restrictions in laws and court or agency interpretations of such laws, such as the Telephone Consumer Protection Act of 1991, the Telemarketing Sales Rule, the CAN-SPAM Act of 2003, various U.S. state laws, such as the California Privacy Rights Act, international data protection laws, such as the E.U. General Data Protection Regulation ("GDPR"), and laws limiting the cross-border transfer of data that govern these activities or new laws that become effective in the future could adversely affect current or planned marketing activities and cause us to change our marketing strategy. If this occurs, we may not be able to develop adequate alternative marketing strategies, which could affect our ability to maintain relationships with our customers and acquire new customers. We also obtain access to names of potential customers from travel service providers or other companies, and we market to some individuals on these lists directly or through other companies’ marketing materials. If access to these lists were prohibited or otherwise restricted, our ability to develop new customers and introduce them to products could be impaired.
The growth of internet reservation channels could adversely affect our business and profitability.
A significant percentage of hotel rooms for individual guests are booked through internet travel intermediaries, to whom we commit to pay various commissions and transaction fees for sales of our rooms through their systems. Search engines and peer-to-peer inventory sources also provide online travel services that compete with our direct channels. If these bookings increase, these hospitality intermediaries may be able to obtain higher commissions or other significant concessions from us or our franchisees. These hospitality intermediaries also may reduce bookings at our hotel properties by de-ranking our hotels in search results on their platforms, and other online providers may divert business away from our hotels. Although our contracts with many hospitality intermediaries limit transaction fees for hotels, there can be no assurance that we will be able to renegotiate these contracts upon their expiration with terms as favorable as the provisions that existed before the expiration, replacement or renegotiation. Moreover, hospitality intermediaries generally employ aggressive marketing strategies, including expending significant resources for online and television advertising campaigns to drive consumers to their websites. As a result, consumers may develop brand loyalties to the intermediaries’ brands due to their websites, reservations systems and loyalty programs rather than to the Hilton brands. If this happens, our business and profitability may be significantly affected
over time as shifting customer loyalties divert bookings away from our websites, which increases costs to hotels in our system. Internet travel intermediaries also have been subject to regulatory scrutiny, particularly in Europe. The outcome of this regulatory activity may affect our ability to compete for direct bookings through our own internet channels.
In addition, although internet travel intermediaries have traditionally competed to attract individual leisure consumers or transient business rather than group business for meetings and events, in recent years they have expanded their business to include marketing to group business and also to corporate transient business. If that growth continues, it could both divert group and corporate transient business away from our hotels and also increase our cost of sales for group and corporate transient business. Consolidation of internet travel intermediaries, or the entry of major internet companies into the internet travel bookings business, also could divert bookings away from our direct channels and increase our hotels' cost of sales.
Our reservation system is an important component of our business operations and a disruption to its functioning could have an adverse effect on our performance and results.
We manage a global reservation system that communicates reservations to our branded and strategic partner hotels when made by individuals directly, either online, by telephone to our call centers, through devices via our mobile application, or through intermediaries like travel agents, internet travel websites and other distribution channels. The cost, speed, efficacy and efficiency of the reservation system are important aspects of our business and are important considerations of hotel owners in choosing to affiliate with our brands. Any disruption to the continuity of our reservation system, including any failure to maintain or upgrade such system, may adversely affect our ability to serve customers effectively and support reservations at our hotels.
The cessation, reduction or taxation of program benefits of our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program could adversely affect the Hilton brands and guest loyalty.
We manage the Hilton Honors guest loyalty program for the benefit of all the brands that we operate and our strategic partners. Program members accumulate points primarily based on eligible stays and hotel charges and redeem the points for a range of benefits including free rooms and other items of value. The program is an important aspect of our business and of the affiliation value for hotel owners under management and franchise contracts as well as for our strategic partner arrangements. System hotels, including, without limitation, third-party hotels under management and franchise contracts and strategic partner hotels, contribute a percentage of the charges incurred by members of the loyalty program for each stay of a program member. In addition to the accumulation of points for future hotel stays at our brands and strategic partner hotels, Hilton Honors arranges with third parties, such as airlines, other transportation services, online vendors, retailers and credit card companies, to sell Hilton Honors points for the use of their customers and/or to allow Hilton Honors members to use or exchange points for products or services made available to loyalty program members by those third parties. Currently, the program benefits are not taxed as income to members. If the program awards and benefits are materially altered, curtailed or taxed such that a material number of Hilton Honors members choose to no longer participate in the program, our business could be adversely affected.
Because we derive a portion of our revenues from operations outside the U.S., the risks of doing business internationally could lower our revenues, increase our costs, reduce our profits or disrupt our business.
We currently manage, franchise, own or lease or have a strategic partnership arrangement with hotels and resorts in 140 countries and territories around the world. Our rooms outside the U.S. represented approximately 35 percent, 33 percent and 31 percent of our system-wide hotel rooms for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. We expect that our international operations will continue to account for a material portion of our results. As a result, we are subject to the risks of doing business outside the U.S., including:
•rapid changes in governmental, economic or political policy, wars, political or civil unrest, acts of terrorism or the threat of international boycotts or U.S. anti-boycott legislation;
•increases in anti-American sentiment and the identification of our licensed brands as an American brand;
•recessionary trends or economic instability in international markets;
•changes in foreign currency exchange rates or currency restructurings and hyperinflation or deflation in the countries and territories in which we operate;
•the effect of disruptions, including the temporary closure of hotel properties, caused by severe weather or climate-related events, natural disasters (including as a result of climate change), outbreak of disease, or other events that make travel to a particular region less attractive or more difficult;
•the presence and acceptance of varying levels of business corruption in international markets and the effect of various anti-corruption and other laws;
•the imposition of restrictions on currency conversion or the transfer of funds or limitations on our ability to repatriate non-U.S. earnings in a tax-efficient manner;
•the ability to comply with or the effect of complying with complex and changing laws, sanctions, regulations and policies of foreign governments that may affect investments or operations, including foreign ownership restrictions, import and export controls, tariffs, embargoes, increases in taxes paid and other changes in applicable tax laws;
•the ability to comply with or the effect of complying with developing laws, regulations and policies of foreign governments with respect to human rights, including in the supply chain;
•instability or changes in a country's or region's economic, regulatory or political conditions, including inflation, recession, interest rates and actual or anticipated military or political conflicts or any other change;
•uncertainties as to local laws regarding, and enforcement of, contract and IP rights;
•forced nationalization of our properties by local, state or national governments; and
•the difficulties involved in managing an organization doing business in many different countries and territories.
These factors may adversely affect the revenues earned from our hotels and resorts (as well as the market value of properties that we own or lease) located in international markets. While these factors and the effect of these factors are difficult to predict, any one or more of them could lower our revenues, increase our costs, reduce our profits or disrupt our business operations.
Failure to comply with laws and regulations applicable to our international operations may increase costs, reduce profits, limit growth or subject us to broader liability.
Our business operations in countries and territories outside the U.S. are subject to a number of laws and regulations, including restrictions imposed by the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act ("FCPA"), as well as trade sanctions administered by the Office of Foreign Assets Control ("OFAC"). Although we have policies in place designed to comply with applicable sanctions, rules and regulations, it is possible that hotels we manage, own or lease in the countries and territories in which we operate may provide services to or receive funds from persons subject to sanctions. Where we have identified potential violations in the past, we have taken appropriate remedial action including filing voluntary disclosures to OFAC. In addition, some of our operations may be subject to the laws and regulations of non-U.S. jurisdictions, including the U.K.’s Bribery Act 2010, which contains significant prohibitions on bribery and other corrupt business activities, and other local anti-corruption laws in the countries and territories in which we conduct operations.
If we fail to comply with these laws and regulations, we could be exposed to claims for damages, financial penalties, reputational harm and incarceration of employees or restrictions on our operation or ownership of hotels and other properties, including the termination of management, franchising and ownership rights. In addition, in certain circumstances, the actions of parties affiliated with us (including our owners, joint venture partners, employees and agents) may expose us to liability under the FCPA, U.S. sanctions or other laws. These restrictions could increase costs of operations, reduce profits or cause us to forgo development opportunities that would otherwise support growth.
In addition, we are subject to a number of modern slavery, human trafficking and forced labor reporting, training and mandatory due diligence laws in various jurisdictions and expect additional statutory regimes to combat these crimes to be enacted in the future. The impact of these laws, such as the U.K.'s Modern Slavery Act 2015 and the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act, and similar legislation on hotel operations could increase costs of operations and reduce our profits.
Collective bargaining activity could disrupt our operations, increase our labor costs or interfere with the ability of our management to focus on executing our business strategies.
A significant number of our employees and employees of our hotel owners are covered by collective bargaining agreements and similar agreements, including approximately 25 percent of people employed or managed by us globally and approximately 40 percent of people working in the U.S. as of December 31, 2024. If relationships with our employees or employees of our hotel owners or the unions that represent them become adverse, the properties we manage, franchise, own or lease have in the past and could in the future experience labor disruptions such as strikes, lockouts, boycotts and public demonstrations. A number of our collective bargaining agreements are in the process of being renegotiated, and, if more employees become unionized, we may be required to negotiate additional collective bargaining agreements in the future. Labor disputes, which may be more likely when collective bargaining agreements are being negotiated, could harm our relationship with our employees or employees of our hotel owners, result in increased regulatory inquiries and enforcement by governmental authorities and deter guests. Further, adverse publicity related to a labor dispute could harm our reputation and reduce customer demand for our services. During 2024, certain of our managed hotels in the U.S. experienced labor disruptions while these agreements were being negotiated that negatively affected operations at those hotels. Labor regulation and the
negotiation of new or existing collective bargaining agreements could lead to higher wage and benefit costs, changes in work rules that raise operating expenses, legal costs and limitations on our ability or the ability of our third-party property owners to take cost saving measures during economic downturns. We do not have the ability to influence the negotiations of collective bargaining agreements covering unionized labor employed by third-party property owners or third-party operators. Increased unionization of our workforce, new labor legislation or changes in regulations could disrupt our operations and our ability to promote services expected by customers, reduce our profitability or interfere with the ability of our management to focus on executing our business strategies.
The loss of key senior management personnel or labor shortages could restrict our ability to grow our business or operate our properties or result in increased labor costs that could adversely affect our results of operations.
Our success depends in large part on our ability to attract, retain, train, manage and engage employees. As of December 31, 2024, we employed or managed approximately 181,000 individuals at our owned, leased and managed hotels and corporate offices around the world. If we are unable to attract, retain, train, manage and engage skilled individuals, our ability to staff and operate the hotels that we manage, own and lease could be diminished, which could reduce customer satisfaction, and our ability to manage our corporate business could be adversely affected. In addition, the inability of our franchisees to attract, retain, train, manage and engage skilled employees for the franchised hotels could adversely affect the reputation of our brands. Staffing shortages in various parts of the world also could hinder our ability to grow and expand our businesses. Because payroll costs are a major component of the operating expenses at our owned, leased and managed hotels, as well as our franchised hotels, a shortage of skilled labor could also require higher wages that would increase labor costs, which could adversely affect our results of operations and the results of hotels that we manage on behalf of third-party owners. Additionally, an increase in minimum wage rates could increase costs and reduce profits for us and our franchisees, which could, in turn, lower demand from third-party owners to add hotels to our system. We also face challenges with respect to retaining corporate employees. If we lost the services of one or more senior executives, this could adversely affect strategic relationships, including relationships with third-party hotel owners, significant customers, joint venture partners and vendors, and limit our ability to execute our business strategies.
Any failure to protect our trademarks and other IP could reduce the value of the Hilton brands and harm our business.
The recognition and reputation of our brands are important to our success. We have a significant number of trademark registrations in jurisdictions around the world for use in connection with our services, plus at any given time, a number of pending applications for trademarks and other IP. However, those trademark or other IP registrations may not be granted or the steps we take to use, control or protect our trademarks or other IP in the U.S. and other jurisdictions may not always be adequate to prevent third parties from copying or using the trademarks or other IP without authorization. We may also fail to obtain and maintain trademark protection for all of our brands in all jurisdictions. For example, in certain jurisdictions, third parties have registered or otherwise have the right to use certain trademarks that are the same as or similar to our trademarks, which could prevent us from registering trademarks and opening hotels in those jurisdictions. Third parties may also challenge our rights to certain trademarks or oppose our trademark applications. Defending against any such proceedings may be costly, and if unsuccessful, could result in the loss of important IP rights. Obtaining and maintaining trademark protection for multiple brands in multiple jurisdictions is also expensive, and we may therefore elect not to apply for or to maintain certain trademarks.
Our IP is also vulnerable to unauthorized copying or use where local law, or lax enforcement of law, may not provide adequate protection. If our trademarks or other IP are improperly used, the value and reputation of the Hilton brands could be harmed. There are times where we may need to resort to litigation to enforce our IP rights. Litigation of this type could be unsuccessful, costly, force us to divert our resources, lead to counterclaims or other claims against us or otherwise harm our business or reputation. In addition, we license certain of our trademarks to third parties. For example, we have granted HGV the right to use certain of our IP in its timeshare business and we grant our franchisees a right to use certain of our IP in connection with their operation of the licensed hotel property. If HGV, a franchisee or other licensee fails to maintain the quality of the goods and services used in connection with the licensed trademarks, our rights to, and the value of, our trademarks could be harmed. Failure to maintain, control and protect our trademarks and other IP could likely adversely affect our ability to attract guests or third-party owners, and could adversely affect our results.
In addition, we license the right to use certain IP from unaffiliated third parties, including the right to grant sublicenses to franchisees. If we are unable to use this IP, our ability to generate revenue from such properties may be diminished.
Third-party claims that we infringe IP rights of others could subject us to damages and other costs and expenses.
Third parties may make claims against us for infringing their patent, trademark, copyright or other IP rights or for misappropriating their trade secrets. We have been and are currently party to a number of such claims and may receive additional claims in the future. Any such claims, even those without merit, could:
•be expensive and time consuming to defend, and result in significant damages;
•force us to stop using the IP that is being challenged or to stop providing products or services that use the challenged IP;
•force us to redesign or rebrand our products or services;
•require us to enter into royalty, licensing, co-existence agreements or other contracts to obtain the right to use a third party’s IP;
•limit our ability to develop new IP; and
•limit the use or the scope of our IP or other rights.
In addition, we may be required to indemnify third-party owners of the hotels that we manage for any losses they incur as a result of any infringement claims against them. All necessary royalty, licensing or other contracts may not be available to us on acceptable terms. Any adverse results associated with third-party IP claims could negatively affect our business.
Exchange rate fluctuations and foreign exchange hedging arrangements could result in significant foreign currency gains and losses that affect our business results.
Conducting business in currencies other than the U.S. dollar ("USD") subjects us to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates that could have a negative effect on our financial results. We earn revenues and incur expenses in foreign currencies as part of our operations outside of the U.S. As a result, fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates may significantly increase the amount of USD required for foreign currency denominated expenses or significantly decrease the USD received from foreign currency denominated revenues. We also have exposure to currency translation risk for the results of our business outside of the U.S. that are reported in local currencies and then translated to USD for inclusion in our consolidated financial statements. As a result, changes between the foreign currency exchange rates and the USD will affect the recorded amounts of our foreign assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and could have a negative effect on our financial results. Our exposure to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations will grow if the relative contribution of our operations outside the U.S. increases.
To mitigate foreign currency exposure, we enter into foreign exchange derivatives with financial institutions. However, these derivatives may not eliminate foreign currency exchange rate risk entirely and involve costs and risks of their own in the form of transaction costs, credit requirements, interest rate differentials and counterparty risk.
If the insurance that we or our property owners carry does not sufficiently cover damage or other potential losses or liabilities to third parties involving properties that we manage, franchise, own or lease, our profits could be reduced.
We operate in certain areas where the risk of natural or climate-related disaster or other catastrophic losses exists, and the occasional incidence of such an event could cause substantial damage to us, our property owners or the surrounding area. We carry, and/or we require our property owners to carry, insurance from solvent insurance carriers that we believe is adequate for foreseeable first-party and third-party losses and with terms and conditions that are reasonable and customary. Nevertheless, market forces beyond our control, such as the natural, climate-related and man-made disasters, geopolitical events that occurred in recent years or are occurring, social claims, inflation and cyber or data security incidents could limit the scope of the insurance coverage that we and our property owners can obtain or may otherwise restrict our or our property owners' ability to buy insurance coverage at reasonable rates. We anticipate increased costs of property, general liability and excess liability insurance across the portfolio in 2025 due to the significant losses that insurers suffered globally in recent years. In the event of a substantial loss, the insurance coverage that we and/or our property owners carry may not be sufficient to pay the full value of our financial obligations, our liabilities or the replacement cost of any lost investment or property. Additionally, certain types of losses may be uninsurable or prohibitively expensive to insure. In addition, other types of losses or risks that we may face could fall outside of the general coverage terms and limits of our policies.
While Hilton procures a standalone terrorism property damage policy that covers owned and leased hotels and other hotels that choose to participate, the U.S. Terrorism Risk Insurance Program (the "Program") also provides insurance capacity for terrorist acts and is currently authorized through December 31, 2027. If the Program is not extended or renewed upon its expiration in 2027, or if there are changes to the Program that would negatively affect insurance carriers, premiums for
terrorism insurance coverage will likely increase and/or the terms of such insurance may be materially amended to increase stated exclusions or to otherwise effectively decrease the scope of coverage available, perhaps to the point where it is effectively unavailable.
In some cases, these factors could result in certain losses being partially or completely uninsured. As a result, we or the owners of properties that we manage or franchise could lose some or all of the capital we or they have invested in a property, as well as the anticipated future revenues, profits, management fees or franchise fees from the property.
Climate change could adversely affect our business.
As one of the world's largest global hospitality companies, with hotels and resorts in 140 countries and territories, we are subject to the physical effects of climate change, including sea level rise, droughts and intensified storms and other weather events. Damage to our hotels resulting from the physical effects of climate change could lower demand for travel to certain locales and affect the performance of certain of our hotels, which could in turn have a negative impact on our results of operations.
Our business is subject to evolving corporate governance and public disclosure regulations and expectations, including with respect to sustainability matters, that could increase costs or expose us to reputational and other risks.
We are subject to the evolving rules and regulations with respect to sustainability matters of a number of governmental and self-regulatory bodies and organizations, including the SEC, the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE"), the Financial Accounting Standards Board, the state of California, and the European Union, that could make compliance more difficult and uncertain. In addition, regulators, guests, investors, employees and other stakeholders are increasingly focused on sustainability matters and related disclosures. These changing rules, regulations and stakeholder expectations have resulted in, and are likely to continue to result in, increased general and administrative expenses and increased management time and attention to comply with or meet those regulations and expectations. Developing and acting on sustainability initiatives and collecting, measuring and reporting sustainability related information and metrics can be costly, difficult and time consuming. Further, sustainability related information is subject to evolving reporting standards that continue to be introduced in various states and jurisdictions, such as the European Union's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive, and complying with evolving global sustainability reporting regulations may be costly and complex. Our sustainability initiatives and goals could be difficult and expensive to implement, and we could be criticized for the accuracy, adequacy or completeness of our sustainability disclosures. Further, statements about our sustainability related initiatives and goals, and progress against those goals, may be based on standards for measuring progress that are still developing, internal controls and processes that continue to evolve and assumptions that are subject to change in the future. In addition, we could be criticized for the scope or nature of such initiatives or goals, or for revisions to these goals and, our competitors may have sustainability initiatives or programs that resonate more with guests and property owners than our initiatives do, which may cause reduced consumer demand at our hotel properties in favor of other brands. If our sustainability data, processes and reporting are incomplete or inaccurate, or if we fail to achieve progress with respect to our sustainability goals on a timely basis, or at all, our reputation and financial results could be adversely affected.
Legal and Regulatory Risks
Governmental regulation may adversely affect the operation of our properties.
In many jurisdictions, the hospitality industry is subject to extensive foreign or U.S. federal, state and local governmental regulations, including those relating to the service of alcoholic beverages, the preparation and sale of food, building and zoning requirements, and data protection, cybersecurity and privacy. We and our third-party owners are also subject to licensing and regulation by foreign or U.S. state and local departments relating to health, sanitation, fire and safety standards, and to laws governing our relationships with employees, including minimum wage requirements, overtime, working conditions and citizenship requirements. These requirements are complex and subject to frequent revision, with changes at the U.S. federal level often accompanying new U.S. presidential administrations. We or our third-party owners may be required to expend funds to meet foreign or U.S. federal, state and local regulations in connection with the construction, continued operation or remodeling of certain of our properties. The failure to meet the requirements of applicable regulations and licensing requirements, or publicity resulting from actual or alleged failures, could have an adverse effect on our results of operations. For instance, in 2010, we entered into a settlement with the U.S. Department of Justice related to compliance with the Americans with Disabilities Act ("ADA"). Although the bulk of our obligations under this settlement expired in 2015, certain managed and franchised hotels remain under an obligation to remove architectural barriers at their facilities. We have an obligation to have an independent consultant to monitor those barrier removal efforts. If we fail to comply with any of the requirements of the ADA, we could be subject to fines, penalties, injunctive action, reputational harm, guest, advocacy group or
employee lawsuits, and other business effects that could materially and negatively affect our performance and results of operations.
Changes in U.S. federal, state and local or foreign tax law, interpretations of existing tax law or adverse determinations by tax authorities, could increase our tax burden or otherwise adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations.
We are subject to taxation at the federal, state or provincial and local levels in the U.S. and various other countries and jurisdictions. Our future effective tax rate could be affected by changes in the composition of earnings in jurisdictions with differing tax rates, changes in statutory rates and other legislative changes, changes in the valuation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities, or changes in determinations regarding the jurisdictions in which we are subject to tax. From time to time, the U.S. federal, state and local and foreign governments make substantive changes to tax rules and their application, which could result in materially higher corporate taxes than would be incurred under existing tax law and could adversely affect our financial condition or results of operations.
We are subject to ongoing and periodic tax audits and disputes in U.S. federal and various state, local and foreign jurisdictions. In particular, our consolidated U.S. federal income tax returns for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2011 through December 31, 2020 are actively under audit by the Internal Revenue Service ("IRS"). We have had a dispute regarding the federal taxation of the Hilton Honors guest loyalty program, which has been effectively settled through the tax year ended December 31, 2018. However, the Hilton Honors guest loyalty program is still subject to audit for subsequent years, which may result in material increases to our income tax liability. An unfavorable outcome from any tax audit could result in higher tax costs, penalties and interest, thereby adversely affecting our financial condition or results of operations.
Foreign or U.S. environmental laws and regulations may cause us to incur substantial costs or subject us to potential liabilities.
We are subject to certain compliance costs and potential liabilities under various foreign and U.S. federal, state and local environmental, health and safety laws and regulations. These laws and regulations govern actions including air emissions, the use, storage and disposal of hazardous and toxic substances and wastewater disposal. Our failure to comply with such laws, including obtaining and maintaining any required permits or licenses, could result in substantial fines, penalties, litigation or possible revocation of our authority to conduct some of our operations. We could also be liable under such laws for the costs of investigation, removal or remediation of hazardous or toxic substances at our currently or formerly owned, leased or operated real property (including managed and franchised properties) or at third-party locations in connection with our waste disposal operations, regardless of whether or not we knew of, or caused, the presence or release of such substances. From time to time, we may be required to remediate such substances or remove, abate or manage asbestos, mold, radon gas, lead or other hazardous conditions at our properties. The presence or release of such toxic or hazardous substances could result in third-party claims for personal injury, property or natural resource damages, business interruption or other losses. Such claims and the need to investigate, remediate or otherwise address hazardous, toxic or unsafe conditions could adversely affect our operations, the value of any affected real property, or our ability to sell, lease or assign our rights in any such property, or could otherwise harm our business or reputation. Environmental, health and safety requirements have also become increasingly stringent, and our costs to comply with such requirements may increase as a result. New or revised laws and regulations or new interpretations of existing laws and regulations, such as those intended to lessen the impact of climate change, could affect the operation of our properties or result in significant additional expense and operating restrictions on us.
Risks Related to Our Indebtedness
Our substantial indebtedness and other contractual obligations could adversely affect our financial condition, our ability to raise additional capital to fund our operations, our ability to operate our business, our ability to react to changes in the economy or our industry and our ability to pay our debts, and could require us to divert our cash flows from operations to make required debt or interest payments.
We have a significant amount of indebtedness. As of December 31, 2024, our total indebtedness, excluding the deduction for unamortized deferred financing costs and discounts, was approximately $11.2 billion, and our contractual debt maturities of our long-term debt for the years ending December 31, 2025, 2026 and 2027 are $535 million, $31 million and $616 million, respectively. Our substantial debt and other contractual obligations could have important consequences, including:
•requiring a substantial portion of cash flow from operations to be dedicated to the payment of principal and interest on our indebtedness, thereby reducing our ability to use our cash flow to fund our operations, capital expenditures or dividends to stockholders and to pursue future business opportunities;
•increasing our vulnerability to adverse economic, industry or competitive developments;
•exposing us to increased interest expense, as our degree of leverage may cause the interest rates of any future indebtedness (whether fixed or floating rate interest) to be higher than they would be otherwise;
•exposing us to the risk of increased interest rates because certain of our indebtedness is at variable rates of interest;
•making it more difficult for us to satisfy our obligations with respect to our indebtedness, and any failure to comply with the obligations of any of our debt instruments, including restrictive covenants, could result in an event of default that accelerates our obligation to repay indebtedness;
•restricting us from making strategic acquisitions or causing us to make non-strategic divestitures;
•limiting our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, product development, satisfaction of debt service requirements, acquisitions and general corporate or other purposes; and
•limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business or market conditions and placing us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors who may be better positioned to take advantage of opportunities that our leverage prevents us from exploiting.
Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. is a holding company, and substantially all of its consolidated assets are owned by, and most of its business is conducted through, its subsidiaries. Revenues from these subsidiaries are our primary source of funds for debt payments and operating expenses. If our subsidiaries are restricted from making distributions to us, that may impair our ability to meet our debt service obligations or otherwise fund our operations. Moreover, there may be restrictions on payments by subsidiaries to their parent companies under applicable laws, including laws that require companies to maintain minimum amounts of capital and to make payments to stockholders only from profits. As a result, although a subsidiary of ours may have cash, we may not be able to obtain that cash to satisfy our obligation to service our outstanding debt or fund our operations.
Servicing our indebtedness will require a significant amount of cash. Our ability to generate sufficient cash depends on many factors, some of which are not within our control.
Our ability to make payments on our indebtedness, to fund planned capital expenditures, to pay future dividends, if any, to our stockholders and repurchase our common stock will depend on our ability to generate cash in the future. To a certain extent, this is subject to general economic, financial, competitive, legislative, regulatory and other factors that are beyond our control. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flow to service our debt and meet our other commitments, we may need to restructure or refinance all or a portion of our debt, sell material assets or operations or raise additional debt or equity capital. We may not be able to effect any of these actions on a timely basis, on commercially reasonable terms or at all, and these actions may not be sufficient to meet our capital requirements. In addition, the terms of our existing or future debt arrangements may restrict us from effecting any of these alternatives.
Certain of our debt agreements impose operating and financial restrictions on us and our subsidiaries, which may prevent us from capitalizing on business opportunities.
The indentures that govern our senior notes and the credit agreement that governs our senior secured credit facilities impose operating and financial restrictions on us. The restrictions under certain of these agreements limit our ability and/or the ability of our subsidiaries to, among other things:
•incur or guarantee additional debt or issue disqualified stock or preferred stock;
•make certain investments;
•pay dividends, including our subsidiaries paying dividends to us, and make other distributions on, or redeem or repurchase, capital stock;
•incur certain liens;
•enter into transactions with affiliates;
•merge or consolidate;
•enter into agreements that restrict the ability of restricted subsidiaries to make dividends or other payments to us;
•designate restricted subsidiaries as unrestricted subsidiaries;
•transfer or sell assets; and
•enter into sale and lease-back transactions.
In addition, the credit agreement requires us to maintain a consolidated secured net leverage ratio not to exceed 5.0 to 1.0 as of the last day of any period of four consecutive quarters.
As a result of these restrictions, we are limited as to how we conduct our business and we may be unable to raise additional debt or equity financing to compete effectively or to take advantage of new business opportunities. The terms of any future
indebtedness we may incur could include more restrictive covenants. We may not be able to maintain compliance with these covenants in the future and, if we fail to do so, we may not be able to obtain waivers from the lenders and/or amend the covenants.
Our failure to comply with the restrictive covenants described above, as well as other terms of our other indebtedness and/or the terms of any future indebtedness from time to time, could result in an event of default, which, if not cured or waived, could result in our being required to repay these borrowings before their due date. If we are forced to refinance these borrowings on less favorable terms or are unable to refinance these borrowings, our results of operations and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Despite our current level of indebtedness, we may be able to incur substantially more debt and enter into other transactions, which could further exacerbate the risks to our financial condition described above.
We may be able to incur significant additional indebtedness, including secured debt, in the future. Although the credit agreements and indentures that govern the majority of our indebtedness contain restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness and entering into certain types of other transactions, these restrictions are subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions. Additional indebtedness incurred in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial. These restrictions also do not prevent us from incurring obligations, such as trade payables, that do not constitute indebtedness as defined under our debt instruments. To the extent new debt is added to our current debt levels, the substantial leverage risks described in the preceding three risk factors would increase.
Risks Related to Ownership of Our Common Stock
Although we currently pay a quarterly cash dividend to holders of our common stock, we may change our dividend policy at any time.
Our dividend policy may change at any time without notice to our stockholders. For example, we suspended payment of our quarterly cash dividend to holders of our common stock beginning in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and did not resume quarterly dividend payments until June 2022. The declaration and payment of any future dividends is at the discretion of our board of directors in accordance with applicable law after taking into account various factors, including our financial condition, operating results, current and anticipated cash needs, limitations imposed by our indebtedness, legal requirements and other factors that our board of directors deems relevant. If we were to cease dividend payments, you may not receive any return on an investment in our common stock unless you sell your common stock for a price greater than that which you paid for it.
Anti-takeover provisions in our organizational documents and Delaware law might discourage or delay acquisition attempts for us that stockholders might consider favorable.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated by-laws contain provisions that may make the merger or acquisition of our company more difficult without the approval of our board of directors. Among other things:
•although we do not have a stockholder rights plan, and would either submit any such plan to stockholders for ratification or cause such plan to expire within a year, these provisions would allow us to authorize the issuance of undesignated preferred stock in connection with a stockholder rights plan or otherwise, the terms of which may be established and the shares of which may be issued without stockholder approval, and which may include super voting, special approval, dividend or other rights or preferences superior to the rights of the holders of common stock;
•these provisions prohibit stockholder action by written consent unless such action is recommended by all directors then in office;
•these provisions provide that our board of directors is expressly authorized to make, alter or repeal our by-laws and that our stockholders may only amend our by-laws with the approval of 80 percent or more of all the outstanding shares of our capital stock entitled to vote; and
•these provisions establish advance notice requirements for nominations for elections to our board or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings.
Further, as a Delaware corporation, we are subject to provisions of Delaware law, which may impair a takeover attempt that our stockholders may find beneficial. These anti-takeover provisions and other provisions under Delaware law could discourage, delay or prevent a transaction involving a change in control of our company, including actions that our stockholders may deem advantageous, or negatively affect the trading price of our common stock. These provisions could also discourage
proxy contests and make it more difficult for our stockholders to elect directors of their choosing and to cause us to take other corporate actions they desire.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity Governance
Hilton has a dedicated Global Information Security team (collectively, the "GIS team") led by our Chief Information Security Officer ("CISO") that is responsible for identifying, assessing, monitoring, managing and communicating the Company's cybersecurity risks. The GIS team is organized into five functional areas: (i) cloud, network and infrastructure architecture security; (ii) application security; (iii) incident response; (iv) endpoint security and vulnerability management; and (v) governance, risk and compliance ("GRC"). Collectively, the GIS team has decades of dedicated cybersecurity experience with personnel certified in various disciplines, including data privacy, enterprise risk management, cloud security and ethical hacking.
While the full board of directors has overall responsibility for risk oversight, for cyber security matters, it is supported by its Audit Committee, which regularly reports to the full board of directors. The Audit Committee assists the board of directors in monitoring cybersecurity risk by receiving quarterly reports and as needed updates from the Chief Information Officer and the CISO, that cover, among other things, our information security framework, threat assessment, response readiness and training efforts.
Hilton has adopted a Cybersecurity Policy that requires all employees to immediately report a potential cybersecurity incident to the GIS team, and all employees are required to certify their understanding of the Cybersecurity Policy on an annual basis. Our Global Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan ("CIRP") includes the criteria for determining if a cybersecurity incident is considered a qualifying cybersecurity incident ("QCI"), which requires management escalation and review, identifies the first response team and the leadership team responsible for supervising the response and provides guidelines for when and how to communicate such incident to the appropriate members of management and the Audit Committee.
Cybersecurity Strategy and Risk Management
The GIS team leverages several mechanisms to continuously identify and assess cybersecurity risks across the Company and utilizes a GRC platform to monitor identified risks and mitigation and remediation activities. The GIS team uses defined industry accepted risk management and controls frameworks to determine the potential likelihood and impact of each risk. Monitoring activities are designed and executed based on the materiality of the assessed likelihood and magnitude of impact of the risks that are identified. The GIS team, with the assistance of third-party consultants, performs application security reviews, penetration tests and gap assessments against certain cybersecurity frameworks. Management reviews any assessments performed by the third-party consultants and determines the final evaluations and communication plan, which the GIS team executes.
In the event of a reported potential cybersecurity incident, a first response team, which includes leaders of the GIS team, other members of management and the legal team, determines without undue delay whether it is a QCI as defined in the CIRP. If an incident is determined to be a QCI, the process included in the CIRP is initiated and such incident is communicated to the designated leadership team, including Hilton's general counsel. Further, appointed leaders collaborate on determining if the incident is material, as well as the resulting response, including any legal and financial reporting obligations of the Company. Information also is provided to additional members of senior management as appropriate. The remediation plan for the QCI is entered within Hilton's GRC platform and monitored and reviewed at least monthly to ensure effective implementation; depending upon the type of incident, additional reporting may be produced and monitored by the GIS team to ensure the effectiveness of the remediation plan. All cybersecurity incidents are tracked within our incident response platform, regardless of the potential materiality of the impact.
We also have a process in place to manage cybersecurity risks associated with third-party service providers. However, we rely on the third parties we use to implement security programs commensurate with their risk, and we cannot ensure in all circumstances that their efforts will be successful.
As of the date of this report, we are not aware of any cybersecurity threats that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect the Company, including our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition. However, as discussed under "Part I—Item 1A. Risk Factors," specifically the risks titled "Failures in, material damage to or interruptions in our information technology systems, software or websites, including as a result of cyber-attacks on our systems or systems operated by third parties that provide operational and technical services to us, costs associated with protecting the integrity and security of personal data and other sensitive information and difficulties in updating our existing software or developing or implementing new software could have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations" and "Cyber-attacks could have a disruptive effect on our business," the sophistication of cyber threats continues to increase, and the preventative actions we take to reduce the risk of cyber incidents and protect our systems and information may be insufficient. Accordingly, no matter how well designed or implemented our controls are, we will not be able to anticipate all security breaches, and we may not be able to implement effective preventive measures against such security breaches in a timely manner.
Item 2. Properties
Hotel Properties
Joint Venture Hotels
As of December 31, 2024, we had a minority or noncontrolling financial interest in the entities that own or lease the following 5 properties, representing 2,245 rooms, and we manage each of the hotels for these entities. We have a right of first refusal to purchase additional equity interests in certain of these joint ventures.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property | | Location | | Ownership Percentage | | Rooms |
| Conrad Hotels & Resorts | | | | | | |
| Conrad Cairo | | Cairo, Egypt | | 10% | | 615 |
| Hilton Hotels & Resorts | | | | | | |
| Hilton Tokyo Bay | | Urayasu-shi, Japan | | 24% | | 828 |
| Hilton Nagoya | | Nagoya, Japan | | 24% | | 460 |
| Hilton Mauritius Resort & Spa | | Flic-en-Flac, Mauritius | | 20% | | 193 |
| Hilton Imperial Dubrovnik | | Dubrovnik, Croatia | | 18% | | 149 |
Leased Hotels
As of December 31, 2024, we leased the following 45 hotels, representing 14,893 rooms.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property | | Location | | Rooms |
| Waldorf Astoria Hotels & Resorts | | | | |
| Rome Cavalieri, Waldorf Astoria Hotels & Resorts | | Rome, Italy | | 370 |
| Waldorf Astoria Amsterdam | | Amsterdam, Netherlands | | 93 |
| Conrad Hotels & Resorts | | | | |
| Conrad Osaka | | Osaka, Japan | | 164 |
| Hilton Hotels & Resorts | | | | |
Hilton Tokyo(1) | | (Shinjuku-ku) Tokyo, Japan | | 830 |
| Ramses Hilton | | Cairo, Egypt | | 811 |
| Hilton Vienna | | Vienna, Austria | | 663 |
| Hilton London Kensington | | London, United Kingdom | | 601 |
Hilton Osaka(1) | | Osaka, Japan | | 562 |
| Hilton Tel Aviv | | Tel Aviv, Israel | | 560 |
| Hilton Munich Park | | Munich, Germany | | 484 |
| Hilton Munich City | | Munich, Germany | | 483 |
| Hilton Istanbul Bosphorus | | Istanbul, Turkiye | | 475 |
| London Hilton on Park Lane | | London, United Kingdom | | 453 |
| Hilton Diagonal Mar Barcelona | | Barcelona, Spain | | 433 |
| Hilton Mainz | | Mainz, Germany | | 431 |
| Hilton Trinidad & Conference Centre | | Port of Spain, Trinidad | | 405 |
| Hilton London Heathrow Airport | | London, United Kingdom | | 398 |
| Hilton Addis Ababa | | Addis Ababa, Ethiopia | | 372 |
| Hilton Vienna Danube Waterfront | | Vienna, Austria | | 368 |
| Hilton Frankfurt City Centre | | Frankfurt, Germany | | 342 |
| Hilton Glasgow | | Glasgow, United Kingdom | | 322 |
| Hilton Milan | | Milan, Italy | | 320 |
| Hilton Brisbane | | Brisbane, Australia | | 319 |
| The Waldorf Hilton, London | | London, United Kingdom | | 298 |
| Hilton Cologne | | Cologne, Germany | | 296 |
(continued on next page)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Property | | Location | | Rooms |
| Hilton Stockholm Slussen | | Stockholm, Sweden | | 289 |
| Hilton Madrid Airport | | Madrid, Spain | | 284 |
| Hilton London Canary Wharf | | London, United Kingdom | | 282 |
| Hilton Amsterdam | | Amsterdam, Netherlands | | 271 |
| Hilton Newcastle Gateshead | | Newcastle Upon Tyne, United Kingdom | | 254 |
| Hilton Vienna Plaza | | Vienna, Austria | | 254 |
| Hilton London Tower Bridge | | London, United Kingdom | | 248 |
| Hilton Antwerp Old Town | | Antwerp, Belgium | | 210 |
| Hilton Reading | | Reading, United Kingdom | | 210 |
| Hilton Leeds City | | Leeds, United Kingdom | | 208 |
| Hilton Watford | | Watford, United Kingdom | | 200 |
| Hilton Nottingham | | Nottingham, United Kingdom | | 176 |
| Hilton London Croydon | | Croydon, United Kingdom | | 168 |
| Hilton Cobham | | Cobham, United Kingdom | | 158 |
| Hilton Paris La Défense | | Paris, France | | 153 |
| Hilton East Midlands Airport | | Derby, United Kingdom | | 152 |
| Hilton Northampton | | Northampton, United Kingdom | | 144 |
| Hilton London Hyde Park | | London, United Kingdom | | 136 |
| Hilton York | | York, United Kingdom | | 131 |
| Hilton Puckrup Hall, Tewkesbury | | Tewkesbury, United Kingdom | | 112 |
____________
(1)We own a controlling financial interest, but less than a 100 percent interest, in the entity that leases the property.
Corporate Headquarters and Regional Offices
Our corporate headquarters is located at 7930 Jones Branch Drive, McLean, Virginia 22102, which is under a lease agreement that expires in April 2037. We also own or lease corporate offices or centralized operations centers in Memphis, Tennessee; Glasgow, Scotland (Europe); Watford, England (Europe); Dubai, United Arab Emirates (Middle East and Africa); Singapore (Asia Pacific); Tokyo, Japan; Shanghai, China; and Mexico City, Mexico. Additionally, we have support operations and other commercial services at a leased office in Addison, Texas. We believe that our existing office properties are in good condition and are sufficient and suitable for the conduct of our business. In the event we need to expand our operations, or upon expiration of our current leases, we believe that suitable space will be available on commercially reasonable terms.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
We are involved in various claims and lawsuits arising in the ordinary course of business, some of which include claims for substantial sums, including proceedings involving tort and other general liability claims, employee claims, consumer protection claims and claims related to our management of certain hotels. We recognize a liability when we believe the loss is probable and can be reasonably estimated. Most occurrences involving liability, claims of negligence and employees are covered by indemnification from third-party hotel owners and/or policies that we hold with solvent insurance carriers. The ultimate results of claims and litigation cannot be predicted with certainty. We believe we have adequate reserves against such matters. We currently believe that the ultimate outcome of such lawsuits and proceedings will not, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. However, depending on the amount and timing, an unfavorable resolution of some or all of these matters could materially affect our future results of operations in a particular period.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity
Securities
Market Information and Dividends
Our common stock is listed for trading on the NYSE under the symbol "HLT." As of December 31, 2024, there were 12 holders of record of our common stock, which does not include a substantially greater number of beneficial holders whose shares are held of record by banks, brokers and other financial institutions.
We currently pay regular quarterly cash dividends and expect to continue paying regular cash dividends on a quarterly basis. Any decision to declare and pay dividends in the future will be made at the sole discretion of our board of directors, whose decision will depend on, among other things, our results of operations, cash requirements, financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. Because we are a holding company and have no direct operations, we will only be able to pay dividends from funds we receive from our subsidiaries.
Performance Graph
The following graph compares Hilton's cumulative total stockholder return since December 31, 2019 with the Standard and Poor's ("S&P") 500 Index ("S&P 500") and the S&P Hotels, Resorts & Cruise Lines Index ("S&P Hotel"). The graph assumes that the value of the investment in our common stock and each index was $100 on December 31, 2019. The comparisons in the graph below are based on historical data and are not indicative of, or intended to forecast, future performance of our common stock.
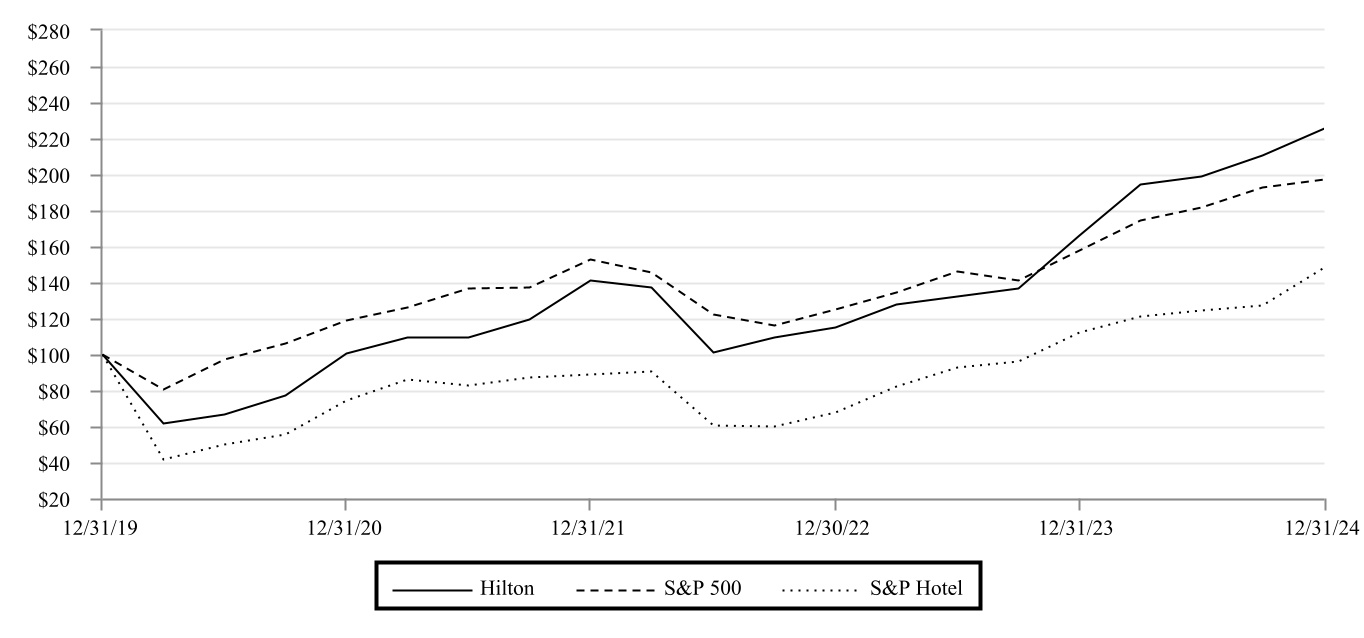
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 12/31/2019 | | 12/31/2020 | | 12/31/2021 | | 12/31/2022 | | 12/31/2023 | | 12/31/2024 |
| Hilton | $ | 100.00 | | | $ | 100.47 | | | $ | 140.87 | | | $ | 114.49 | | | $ | 165.64 | | | $ | 225.46 | |
| S&P 500 | 100.00 | | | 118.39 | | | 152.34 | | | 124.73 | | | 157.48 | | | 196.85 | |
| S&P Hotel | 100.00 | | | 74.12 | | | 88.83 | | | 67.29 | | | 111.92 | | | 147.93 | |
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table sets forth information regarding our purchases of shares of our common stock during the three months ended December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Number of Shares Purchased | | Average Price Paid per Share(1) | | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Program(2) | | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Program(2) (in millions) |
| October 1, 2024 to October 31, 2024 | 1,123,811 | | | $ | 235.63 | | | 1,123,811 | | | $ | 1,404 | |
| November 1, 2024 to November 30, 2024 | 927,020 | | | 248.12 | | | 927,020 | | | 4,674 | |
| December 1, 2024 to December 31, 2024 | 988,434 | | | 251.93 | | | 988,434 | | | 4,425 | |
| Total | 3,039,265 | | | 244.74 | | | 3,039,265 | | | |
____________
(1)Includes commissions paid.
(2)In November 2024, our board of directors authorized the repurchase of an additional $3.5 billion of our common stock under our stock repurchase program, which was initially announced in February 2017 and subsequently increased in November 2017, February 2019, March 2020, November 2022 and November 2023. As such, our stock repurchase program allows for the repurchase of up to a total of $14.5 billion of our common stock. Under this publicly announced program, we are authorized to repurchase shares through open market purchases, privately-negotiated transactions or otherwise in accordance with applicable federal securities laws, including through Rule 10b5-1 trading plans and under Rule 10b-18 of the Exchange Act. The repurchase program does not have an expiration date and may be suspended or discontinued at any time.
Item 6. [Reserved]
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
For the discussion of the financial condition and results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023 compared to the year ended December 31, 2022, refer to "Part II—Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023 filed with the SEC on February 7, 2024, which is incorporated herein by reference.
Overview
Our Business
Hilton is one of the largest global hospitality companies, with 8,447 properties comprising 1,268,206 rooms in 140 countries and territories as of December 31, 2024. Our premier brand portfolio includes luxury, lifestyle, full service, focused service and all-suites hotel brands, as well as timeshare brands. As of December 31, 2024, we had 211 million members in our award-winning guest loyalty program, Hilton Honors, an increase of 17 percent from December 31, 2023.
Segments and Regions
We analyze our operations and business by both operating segments and geographic regions. Our operations consist of two reportable segments that are based on similar products and services: (i) management and franchise and (ii) ownership. The management and franchise segment provides services, including hotel management and licensing of our IP and/or the use of our booking channels and related programs. Revenues from this segment include: (i) management and franchise fees charged to third-party hotel owners; (ii) licensing fees from our strategic partners, including co-branded credit card providers and strategic partner hotels, and HGV; and (iii) fees for managing the hotels in our ownership segment. As a manager of hotels, we typically are responsible for supervising or operating the hotel in exchange for management fees. As a franchisor of hotels, we charge franchise fees in exchange for the use of one of our brand names and/or related commercial services, such as our reservations system, marketing and information technology services, while a third party manages or operates such franchised hotels. The ownership segment primarily derives revenues from nightly hotel room sales, food and beverage sales and other services at our consolidated owned and leased hotels.
We conduct business in three distinct geographic regions: (i) the Americas; (ii) EMEA; and (iii) Asia Pacific. The Americas region includes North America, South America and Central America, including all Caribbean nations. Although the U.S., which represented 65 percent of our system-wide hotel rooms as of December 31, 2024, is included in the Americas region, it is often analyzed separately and apart from the Americas region and, as such, it is presented separately within our hotel operating statistics in "—Results of Operations." The EMEA region includes Europe, which represents the western-most peninsula of Eurasia stretching from Iceland in the west to Russia in the east, and the Middle East and Africa ("MEA"), which represents the Middle East region and all African nations, including the Indian Ocean island nations. Europe and MEA are often analyzed separately and, as such, are presented separately within our hotel operating statistics in "—Results of Operations." The Asia Pacific region includes the eastern and southeastern nations of Asia, as well as India, Australia, New Zealand and the Pacific Island nations.
System Growth and Development Pipeline
Our strategic objectives include the continued expansion of our global hotel network, in particular our fee-based business. As we enter into new management and franchise contracts and enter into strategic agreements to complement our hotel portfolio, we expand our business with limited or no capital investment by us as the manager, franchisor or licensor, since the capital required to build, renovate and maintain hotels is typically provided by the third-party owners with whom we contract to provide management services, license our IP or provide access to our booking channels and related programs. Prior to approving the addition of new hotels to our management and franchise development pipeline, we evaluate the economic viability of the hotel based on its geographic location, the credit quality of the third-party owner and other factors. By increasing the number of management and franchise contracts with third-party owners, over time we expect to increase revenues, overall return on invested capital and free cash flow. See further discussion on our cash management policy in "—Liquidity and Capital Resources." The current economic environment, including elevated levels of inflation and interest rates, has posed certain challenges to the execution of our growth strategy, which in some cases have included and may continue to include delays in openings and new development.
In addition to our current hotel portfolio, we are focused on the growth of our business by expanding our global hotel network through our development pipeline, which represents hotels that we expect to add to our system in the future. The following table summarizes our development activity:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of or for the Year Ended December 31, 2024 |
| Hotels | | Rooms(1) |
| Hotel system | | | |
Openings(2) | 973 | | | 98,400 | |
Net additions(3) | 904 | | | 83,000 | |
| | | |
| Development pipeline | | | |
Additions(4) | 1,432 | | | 154,200 | |
Count as of period end(5) | 3,578 | | | 498,600 | |
____________
(1)Rounded to the nearest hundred.
(2)Openings include 411 hotels and approximately 19,500 rooms from strategic partner hotels.
(3)Represents room additions, net of rooms removed from our system. During 2024, 409 hotels and approximately 19,400 rooms added were from strategic partner hotels. Net unit growth for the year ended December 31, 2024 was 7.3 percent.
(4)Additions include 423 hotels and approximately 20,100 rooms from strategic partner hotels.
(5)The hotels in our development pipeline were under development throughout 118 countries and territories, including 25 countries and territories where we had no existing hotels, with nearly half of the rooms under construction and more than half of the rooms located outside of the U.S. Rooms under construction include rooms for hotels under construction or operating hotels that are in the process of conversion to our system. Nearly all of the rooms in our development pipeline will be in our management and franchise segment upon opening. We do not consider any individual development project to be material to us.
Principal Components and Factors Affecting our Results of Operations
Revenues
Principal Components
We primarily derive our revenues from the following sources:
•Franchise and licensing fees. Represents fees earned in connection with licensing our IP, including our brands and/or the use of our booking channels and related programs. Under our long-term franchise contracts with hotel owners, franchisees typically pay us franchise fees that include: (i) monthly royalty fees, generally based on a percentage of the hotel's monthly gross room revenue, and, in some cases, may also include a percentage of gross food and beverage revenues and other revenues, as applicable; and (ii) application, initiation and other fees for when new hotels enter the system, when there is a change of ownership of a hotel or when contracts with hotels already in our system are extended. Consideration provided to incentivize hotel owners to enter into franchise contracts with us is amortized over the life of the applicable contract as a reduction to franchise and licensing fees. Our license agreements, for which we receive licensing fees for the use of our IP and/or the use of our booking channels and related programs, are predominantly with strategic partners, including co-branded credit card providers, strategic partner hotels and HGV.
•Base and incentive management fees. Represents fees earned in connection with the management of hotels. Terms of our management contracts vary, but our fees typically consist of a base management fee, which is generally based on a percentage of the hotel's monthly gross operating revenue and, when applicable, an incentive management fee, which is generally based on a percentage of the hotel's operating profits, normally over a one calendar year period, and, in some cases, may be subject to a stated return threshold to the hotel owner. Outside of the U.S., our fees are often more dependent on hotel profitability measures, either because of a single management fee structure where the entire fee is an incentive management fee, or because our two-tier fee structure is more heavily weighted toward the incentive management fee than the base management fee. Consideration provided to incentivize hotel owners to enter into management contracts with us is amortized over the life of the applicable contract as a reduction to base and other management fees.
•Owned and leased hotels. Represents revenues derived from the operations of our consolidated owned and leased hotels, including hotel room sales, accommodations sold in conjunction with other services, food and beverage sales and other ancillary goods and services. These revenues are primarily derived from two categories of customers:
transient and group. Transient guests are individual travelers who are traveling for business or leisure. Group guests are travelers who are traveling for group events that reserve rooms for meetings, conferences or social functions, and may be sponsored by corporate, social, military, educational, religious or other organizations or associations. Group business usually includes a block of room accommodations, as well as other ancillary services, such as meeting facilities and catering and banquet services. A majority of our food and beverage sales and other ancillary goods and services are provided to customers who are also occupying rooms at our hotels. As a result, occupancy affects all components of our owned and leased hotels revenues.
•Other revenues. Represents revenues primarily generated by our purchasing operations.
•Other revenues from managed and franchised properties. Represents amounts that are contractually reimbursed to us by property owners, either directly as costs are incurred or indirectly through monthly program fees related to certain costs and expenses supporting the operations of the related properties. The direct reimbursements by property owners are primarily for payroll and related costs if the managed hotel employees are legally employed by us. We have no legal responsibility for the employee liabilities related to certain of our managed properties, predominately those located outside of the U.S., where we are not the legal employer, as well as the employees or the liabilities associated with operating franchised properties or strategic partner hotels. Revenues and expenses for these direct reimbursements have no net effect on operating income (loss) or net income (loss). For the indirect reimbursements, Hilton collects monthly program fees from our managed and franchised properties, which are based on the underlying hotel's sales or usage. The program fees serve as reimbursement for the costs related to the operation of our marketing, sales and brand programs and shared services. Hilton collects program fees from strategic partner hotels when a stay that was reserved using our booking channels is completed. Indirect reimbursements also include revenues related to our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program, which are primarily derived from payments from hotel franchisees and third-party owners of hotels we manage that participate in the program, as well as strategic partners, including strategic partner hotels. We are contractually required to use these fees that we collect solely for these programs.
Factors Affecting our Revenues
The following factors affect the revenues we derive from our operations:
•Consumer demand and global economic conditions. Consumer demand for our products and services, as well as the products and services of the third parties from which we earn licensing fees, is closely linked to the performance of the general economy and is sensitive to business and personal discretionary spending levels. Among other factors, declines in consumer demand due to adverse general economic conditions, risks reducing or otherwise negatively affecting travel patterns, lower consumer confidence and adverse geopolitical conditions can reduce the amount of management and franchise fees we are able to generate and/or reduce the revenues and profitability of the operations of our owned and leased hotels. Further, competition for hotel guests and the supply of hotel services affect our ability to sustain or increase rates charged to customers of our hotels. Also, declines in hotel profitability during an economic downturn directly affect the incentive portion of our management fees, which is based on hotel profitability measures. As a result, changes in consumer demand and general business cycles have historically subjected and could in the future subject our revenues to significant volatility.
•Contracts with third-party hotel owners and franchisees and relationships with developers. We depend on our long-term management and franchise contracts with third-party hotel owners and hotel franchisees for our management and franchise fee revenues. The success and sustainability of our management and franchise business depends on our ability to perform under our management and franchise contracts and maintain good relationships with third-party hotel owners and franchisees. Our relationships with these third parties allow us to maintain our current presence as contracts mature and also generate new incremental opportunities for property development that can support our growth. Growth and maintenance of our hotel system and earning fees related to hotels in development are dependent on the ability of developers and owners to access capital for the development, maintenance and renovation of properties. We believe that we generally have good relationships with our third-party hotel owners, franchisees and developers and are committed to the continued growth and development of these relationships. These relationships exist with a diverse group of owners, franchisees and developers and are not significantly concentrated with any one particular third party.
Expenses
Principal Components
We primarily incur the following expenses:
•Owned and leased hotels. Reflects the operating expenses of our consolidated owned and leased hotels, including room expenses, food and beverage costs, other support costs and property expenses. Room expenses include compensation costs for housekeeping, laundry and front desk staff, as well as supply costs for guest room amenities and laundry. Food and beverage costs include costs for wait and kitchen staff and food and beverage inventory. Other support expenses include costs associated with property-level management, utilities, sales and marketing, operating hotel spas, operating telephones, parking and other guest recreation, entertainment and other services. Property expenses include property taxes, repairs and maintenance, rent and insurance.
•Depreciation and amortization. These are non-cash expenses that primarily consist of: (i) amortization of capitalized software costs; (ii) depreciation and amortization of property and equipment, including our finance lease right-of-use ("ROU") assets, such as buildings and furniture and equipment that are used in corporate operations or at our consolidated owned and leased hotels; (iii) amortization of management and franchise contracts acquired from third parties and (iv) amortization of intangible assets that were recorded at their fair value at the time of the 2007 transaction whereby we became a wholly owned subsidiary of affiliates of Blackstone Inc. (the "Merger"). As of January 1, 2022, the only remaining finite-lived intangible assets resulting from the Merger related to leases, international management contracts and our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program. The assets related to the international management contracts and Hilton Honors, which both had useful lives of 16 years, were fully amortized during the year ended December 31, 2023.
•General and administrative. Consists primarily of compensation costs for our corporate employees, including share-based compensation; professional fees, including consulting, audit and legal fees; travel and entertainment expenses; credit losses for estimated uncollectible management, franchise and other fees; and administrative and related expenses.
•Other expenses. Primarily consists of expenses incurred by our purchasing operations.
•Other expenses from managed and franchised properties. Represents certain costs and expenses that are contractually reimbursed to us by property owners, primarily for (i) payroll and related costs for hotels that we manage where the employees are legally employed by us and (ii) expenses related to our marketing, sales, brands and shared services programs. We are contractually required to use these fees solely for these programs. We have no legal responsibility for the employees or the liabilities associated with operating franchised properties, strategic partner hotels or certain of our managed hotels, predominately those located outside of the U.S. Other expenses from managed and franchised properties also includes expenses for the operation of our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program as well as credit losses for estimated uncollectible Hilton Honors and program fees.
Factors Affecting our Costs and Expenses
The following are principal factors that affect the costs and expenses we incur in the course of our operations:
•Fixed expenses. Many of the expenses associated with owning and leasing hotels are relatively fixed. These expenses include personnel costs, rent, property taxes, insurance and utilities. If we are unable to decrease these costs significantly or rapidly when demand for our hotels decreases, the resulting decline in our revenues can have an adverse effect on our net cash flows and profits. This effect can be especially pronounced during periods of economic contraction or slow economic growth. Economic downturns generally affect the results of our ownership segment more significantly than the results of our management and franchise segment due to the high fixed costs associated with operating an owned or leased hotel. Employees at some of our owned and leased hotels are parties to collective bargaining agreements that may also limit our ability to make timely staffing or labor changes in response to declining revenues. In addition, any efforts to reduce costs, including the deferral or cancellation of capital improvements, could adversely affect the economic value of our hotels and brands. Additionally, the general and administrative expenses of operating a global business also include fixed personnel costs, rent, property taxes, insurance and utilities. The effectiveness of any cost-cutting efforts related to owning and leasing hotels or corporate operations is limited by the amount of inherent fixed costs. However, we have taken steps to manage our fixed costs to levels we believe are
appropriate to maximize profitability and respond to market conditions, while continuing to optimize value for the experiences of our customers, owners and Hilton employees, which supports the long-term sustainability of our brands and business.
•Changes in depreciation and amortization expenses. We capitalize costs associated with certain software development projects and, as those projects are completed and placed into service, amortization expense will increase. As the finite-lived intangible assets that were recorded at the Merger become fully amortized, amortization expense will decrease. As of December 31, 2024, the only remaining finite-lived intangible assets that resulted from the Merger were those related to leases, as included in other intangible assets. We capitalize management and franchise contract intangibles acquired from third parties and amortize the amounts over their useful lives. Additionally, changes in depreciation expense may be driven by renovations of existing hotels, acquisition or development of new hotels, the disposition of existing hotels or corporate facilities through sale, closure or lease termination, lease renewals, expenditures related to our corporate facilities or changes in estimates of the useful lives of our assets. As we place new assets into service, we will be required to recognize additional depreciation expense on those assets. If we are required to recognize impairment losses related to our depreciable assets or finite-lived intangible assets, the related depreciation or amortization expense, respectively, will decrease.
Other Items
Effect of foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations
Significant portions of our operations are conducted in functional currencies other than our reporting currency, which is USD, and we have assets and liabilities, including those that are payable or receivable by consolidated subsidiaries, denominated in a variety of foreign currencies. As a result, we are required to translate the results of those operations, assets and liabilities from their functional currency into USD at market-based foreign currency exchange rates for each reporting period. When comparing our results of operations between reporting periods, there may be material portions of the changes in our revenues or expenses that are derived from fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates experienced between those periods. We hedge foreign currency exchange-based cash flow variability of certain of our fees using foreign currency forward contracts designated as hedging instruments. We also hold short-term foreign currency forward contracts to offset exposure to fluctuations in certain of our foreign currency denominated cash balances and intercompany financing arrangements, and we have not currently elected to designate these forward contracts as hedging instruments.
Seasonality
The hospitality industry is seasonal in nature. The periods during which our properties experience higher or lower levels of demand vary from property to property, depending principally upon their location, type of property and competitive mix within the specific location. Based on historical results, we generally expect our revenues to be lower in the first quarter of each year than in each of the three subsequent quarters.
Key Business and Financial Metrics Used by Management
Comparable Hotels
We define our comparable hotels as those that: (i) were active and operating in our system for at least one full calendar year, have not undergone a change in brand or ownership type during the current or comparable periods and were open January 1st of the previous year; and (ii) have not undergone large-scale capital projects, sustained substantial property damage, encountered business interruption or for which comparable results were not available. We exclude strategic partner hotels from our comparable hotels. Of the 8,342 hotels in our system as of December 31, 2024, 409 hotels were strategic partner hotels and 6,050 hotels were classified as comparable hotels. Our 1,883 non-comparable hotels as of December 31, 2024 included (i) 1,005 hotels that were added to our system after January 1, 2023 or that have undergone a change in brand or ownership type during the current or comparable periods reported and (ii) 878 hotels that were removed from the comparable group for the current or comparable periods reported because they underwent or are undergoing large-scale capital projects, sustained substantial property damage, encountered business interruption or comparable results were otherwise not available.
Occupancy
Occupancy represents the total number of room nights sold divided by the total number of room nights available at a hotel or group of hotels for a given period. Occupancy measures the utilization of available capacity at a hotel or group of hotels.
Management uses occupancy to gauge demand at a specific hotel or group of hotels in a given period. Occupancy levels also help management determine achievable Average Daily Rate ("ADR") pricing levels as demand for hotel rooms increases or decreases.
ADR
ADR represents hotel room revenue divided by the total number of room nights sold for a given period. ADR measures the average room price attained by a hotel, and ADR trends provide useful information concerning the pricing environment and the nature of the customer base of a hotel or group of hotels. ADR is a commonly used performance measure in the industry, and we use ADR to assess pricing levels that we are able to generate by type of customer, as changes in rates charged to customers have different effects on overall revenues and incremental profitability than changes in occupancy, as described above.
Revenue per Available Room ("RevPAR")
RevPAR is calculated by dividing hotel room revenue by the total number of room nights available to guests for a given period. We consider RevPAR to be a meaningful indicator of our performance as it provides a metric correlated to two primary and key drivers of operations at a hotel or group of hotels, as previously described: occupancy and ADR. RevPAR is also a useful indicator in measuring performance over comparable periods for comparable hotels.
References to occupancy, ADR and RevPAR are presented on a comparable basis, based on the comparable hotels as of December 31, 2024, and references to ADR and RevPAR are presented on a currency neutral basis, unless otherwise noted. As such, comparisons of these hotel operating statistics for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 use the foreign currency exchange rates used to translate the results of the Company's foreign operations within its consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2024.
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA
EBITDA reflects net income (loss), excluding interest expense, a provision for income tax benefit (expense) and depreciation and amortization expenses. Adjusted EBITDA is calculated as EBITDA, as previously defined, further adjusted to exclude certain items, including gains, losses, revenues and expenses in connection with: (i) asset dispositions for both consolidated and unconsolidated investments; (ii) foreign currency transactions; (iii) debt restructurings and retirements; (iv) furniture, fixtures and equipment ("FF&E") replacement reserves required under certain lease agreements; (v) share-based compensation; (vi) reorganization, severance, relocation and other expenses; (vii) non-cash impairment; (viii) amortization of contract acquisition costs; (ix) other revenues from managed and franchised properties and other expenses from managed and franchised properties; and (x) other items.
We believe that EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA provide useful information to investors about us and our financial condition and results of operations for the following reasons: (i) these measures are among the measures used by our management team to evaluate our operating performance and make day-to-day operating decisions and (ii) these measures are frequently used by securities analysts, investors and other interested parties as a common performance measure to compare results or estimate valuations across companies in our industry. Additionally, these measures exclude certain items that can vary widely across different industries and among competitors within our industry. For instance, interest expense and income taxes are dependent on company specifics, including, among other things, capital structure and operating jurisdictions, respectively, and, therefore, could vary significantly across companies. Depreciation and amortization expenses, as well as amortization of contract acquisition costs, are dependent upon company policies, including the method of acquiring and depreciating assets and the useful lives that are assigned to those depreciating or amortizing assets for accounting purposes. For Adjusted EBITDA, we also exclude items such as: (i) FF&E replacement reserves for leased hotels to be consistent with the treatment of capital expenditures for property and equipment, where depreciation of such capitalized assets is reported within depreciation and amortization expenses; (ii) share-based compensation, as this could vary widely among companies due to the different plans in place and the usage of them; and (iii) other items that are not reflective of our operating performance, such as amounts related to debt restructurings and debt retirements and reorganization and related severance costs, to enhance period-over-period comparisons of our ongoing operations. Further, Adjusted EBITDA excludes both other revenues from managed and franchised properties and other expenses from managed and franchised properties as we contractually do not operate the related programs to generate a profit and have the contractual rights to adjust future collections to recover prior period expenditures. The direct reimbursements from property owners are billable and reimbursable as the costs are incurred and have no net effect on net income (loss) in the reporting period. The indirect reimbursements from property owners are typically billed and collected monthly, based on the underlying hotel's sales or usage (e.g., gross room revenue or number of reservations processed), while the associated costs are recognized as incurred by Hilton, creating timing differences, with the net effect impacting net income
(loss) in the reporting period. These timing differences are due to our discretion to spend in excess of revenues earned or less than revenues earned in a single period to ensure that the programs are operated in the best long-term interests of our property owners. However, over the life of the operation of these programs, the expenses incurred related to the indirect reimbursements are designed to equal the revenues earned from the indirect reimbursements over time such that, in the long term, the programs will not earn a profit or generate a loss and do not impact our economics, either positively or negatively. Therefore, the net effect of our cost reimbursement revenues and expenses is not used by management to evaluate our operating performance, determine executive compensation or make other operating decisions, and we exclude their impact when evaluating period over period performance results.
EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA are not recognized terms under U.S. generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") and should not be considered as alternatives, either in isolation or as a substitute, for net income (loss) or other measures of financial performance or liquidity, including cash flows, derived in accordance with GAAP. Further, EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA have limitations as analytical tools, including:
•EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect changes in, or cash requirements for, our working capital needs;
•EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect our interest expense, or the cash requirements necessary to service interest or principal payments, on our indebtedness;
•EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect income tax expenses or the cash requirements to pay our taxes;
•EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect historical cash expenditures or future requirements for capital expenditures or contractual commitments;
•EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect the effect on earnings or changes resulting from matters that we consider not to be indicative of our future operations;
•although depreciation and amortization are non-cash charges, the assets being depreciated and amortized will often have to be replaced in the future, and EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA do not reflect any cash requirements for such replacements; and
•other companies in our industry may calculate EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA differently, limiting their usefulness as comparative measures.
Because of these limitations, EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA should not be considered as discretionary cash available to us to reinvest in the growth of our business, return to our stockholders through share repurchases and dividends or as measures of cash that will be available to us to meet our obligations.
Results of Operations
The hotel operating statistics by region for our system-wide comparable hotels were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended | | Change |
| December 31, 2024 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| System-wide | | | | |
| Occupancy | 72.1 | % | | 0.8 | % | pts. |
| ADR | $ | 159.55 | | 1.6 | % | |
| RevPAR | $ | 115.09 | | 2.7 | % | |
| | | | |
| U.S. | | | | |
| Occupancy | 72.5 | % | | 0.5 | % | pts. |
| ADR | $ | 167.27 | | 1.0 | % | |
| RevPAR | $ | 121.34 | | 1.8 | % | |
| | | | |
| Americas (excluding U.S.) | | | | |
| Occupancy | 69.0 | % | | 0.8 | % | pts. |
| ADR | $ | 155.88 | | 5.2 | % | |
| RevPAR | $ | 107.50 | | 6.5 | % | |
| | | | |
| Europe | | | | |
| Occupancy | 74.6 | % | | 2.5 | % | pts. |
| ADR | $ | 165.69 | | 3.8 | % | |
| RevPAR | $ | 123.62 | | 7.4 | % | |
| | | | |
| MEA | | | | |
| Occupancy | 73.0 | % | | 2.9 | % | pts. |
| ADR | $ | 180.77 | | 5.3 | % | |
| RevPAR | $ | 131.88 | | 9.6 | % | |
| | | | |
| Asia Pacific | | | | |
| Occupancy | 69.5 | % | | 0.5 | % | pts. |
| ADR | $ | 110.03 | | 0.8 | % | |
| RevPAR | $ | 76.49 | | 1.6 | % | |
System-wide RevPAR increased during the year ended December 31, 2024 supported by improvements in system-wide ADR, which included the impact of inflation, and an increase in occupancy in all regions, which was driven by an increase in group demand, with leisure and business demand also improving modestly. The increase in RevPAR in the U.S. was driven by an increase in bookings due to an increase in weekday travel, primarily for groups, with consistent growth in business demand. The Americas region, excluding the U.S., continued to see improvement resulting from an increase in inbound leisure travel to Mexico and the Caribbean and Latin America. The RevPAR increase in Europe was driven by continued growth in inbound international leisure travel, which increased in several major cities that held large popular sporting events, as well as steady business demand. The RevPAR improvement in MEA was driven by increased demand from special regional events as well as more relaxed travel policies. The increase in Asia Pacific was due to growth in countries and territories outside of China across the region, driven by increased holiday travel, less restrictive tourism policies and special events in the region, partially offset by tougher year-over-year comparisons in China, after the reacceleration in the prior year as a result of the removal of cross-border travel restrictions.
The table below provides a reconciliation of net income to EBITDA and Adjusted EBITDA:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Net income | $ | 1,539 | | | $ | 1,151 | |
| Interest expense | 569 | | | 464 | |
| Income tax expense | 244 | | | 541 | |
| Depreciation and amortization expenses | 146 | | | 147 | |
| EBITDA | 2,498 | | | 2,303 | |
| Gain on sales of assets, net | (5) | | | — | |
| Loss on foreign currency transactions | 12 | | | 16 | |
Loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate(1) | — | | | 92 | |
Loss on debt guarantees(2) | 50 | | | — | |
| FF&E replacement reserves | 57 | | | 63 | |
| Share-based compensation expense | 176 | | | 169 | |
| Impairment losses | — | | | 38 | |
| Amortization of contract acquisition costs | 50 | | | 43 | |
Other revenues from managed and franchised properties(3) | (6,428) | | | (5,827) | |
Other expenses from managed and franchised properties(3) | 6,985 | | | 6,164 | |
Other adjustments(4) | 34 | | | 28 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 3,429 | | | $ | 3,089 | |
____________
(1)Amount includes losses recognized related to equity and debt financing that we had previously provided to an unconsolidated affiliate with underlying investments in certain hotels that we manage or franchise; refer to Note 6: "Loss on Investments in Unconsolidated Affiliate" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information.
(2)Amount includes losses on debt guarantees for certain hotels that we manage; refer to Note 20: "Commitments and Contingencies" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information.
(3)Amounts include results from the operation of programs conducted for the benefit of property owners and exclude cash receipts recorded as deferred revenues on our consolidated balance sheets related to these programs. Under the terms of the related contracts, we do not operate these programs to generate a profit and have the contractual rights to adjust future collections to recover prior period expenditures.
(4)Amount for the year ended December 31, 2024 includes losses for the full or partial settlement of certain pension plans and restructuring costs related to one of our leased properties as well as transaction costs incurred for acquisitions. Amounts for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 include transaction costs resulting from the amendments of our credit agreement governing the senior secured term loan facilities ("Term Loans") in June 2024 and November 2023, respectively. Amounts for both periods also include net losses (gains) related to certain of our investments in unconsolidated affiliates, other than the loss included separately in "loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate," severance and other items.
Revenues
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Percent Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| (in millions) | | |
| Franchise and licensing fees | $ | 2,600 | | | $ | 2,370 | | | 9.7 |
| | | | | |
| Base and other management fees | $ | 369 | | | $ | 342 | | | 7.9 |
| Incentive management fees | 290 | | | 274 | | | 5.8 |
| Total management fees | $ | 659 | | | $ | 616 | | | 7.0 |
The increase in both franchise fees and management fees were largely attributable to increases in RevPAR at our comparable franchised and managed hotels. During the year ended December 31, 2024, RevPAR at our comparable franchised and managed hotels increased 1.8 percent and 5.2 percent, respectively, contributing to currency neutral increases in franchise and management fees of $61 million and $37 million, respectively, as a result of increased occupancy of 0.4 percentage points and 2.1 percentage points, respectively, and increased ADR of 1.3 percent and 2.1 percent, respectively.
Further, franchise and management fees included net increases of $57 million and $10 million, respectively, during the year ended December 31, 2024 as a result of net hotel additions and increases of $9 million and $12 million, respectively, in termination fees.
Licensing fees increased $98 million as a result of an increase in fees from our strategic partnerships, primarily resulting from activity under our co-branded credit card arrangements, HGV and branded residential fees. Increased fees from HGV resulted from increased timeshare revenues earned by HGV, inclusive of the impact of adding new timeshare properties to our system during the period, including those acquired by HGV from third parties.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Percent Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| (in millions) | | |
| Owned and leased hotels revenues | $ | 1,255 | | | $ | 1,244 | | | 0.9 |
The $11 million increase in owned and leased hotel revenues included a currency neutral increase of $23 million, partially offset by a $12 million decrease resulting from unfavorable fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates.
Revenues from our comparable owned and leased hotels increased $59 million, on a currency neutral basis, due to the increase in RevPAR at our comparable owned and leased hotels of 8.1 percent. The increase in RevPAR was due to increases in occupancy of 2.5 percentage points and ADR of 4.7 percent. Revenues from our non-comparable owned and leased hotels decreased $36 million, on a currency neutral basis, primarily due to hotels undergoing renovations, offset by hotels that underwent renovations in the prior year, hotels that exited our system between the periods and the business disruption, caused by military conflict, that occurred at our leased hotel in Israel.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Percent Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| (in millions) | | |
| Other revenues | $ | 232 | | | $ | 178 | | | 30.3 |
The increase in other revenues was primarily due to increased procurement volume and associated vendor rebates for purchases made by properties, including properties outside of our system, that participate in our purchasing programs.
Operating Expenses
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Percent Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| (in millions) | | |
| Owned and leased hotels expenses | $ | 1,126 | | | $ | 1,141 | | | (1.3) |
The $15 million decrease in owned and leased hotels expenses included a decrease of $10 million on a currency neutral basis and a $5 million decrease resulting from favorable fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates.
Expenses from our comparable owned and leased hotels increased $37 million, on a currency neutral basis, as a result of increased occupancy and cost inflation, primarily due to increases in payroll and other compensation costs, as well as rent expense and expenses related to FF&E replacement reserves. Operating expenses from our non-comparable owned and leased hotels decreased $47 million, on a currency neutral basis, primarily due to hotels undergoing renovations, hotels that exited our system and the business disruption, caused by military conflict, that occurred at our leased hotel in Israel.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Percent Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| (in millions) | | |
| Depreciation and amortization expenses | $ | 146 | | | $ | 147 | | | (0.7) |
| General and administrative expenses | 415 | | | 408 | | | 1.7 |
| Impairment losses | — | | | 38 | | | NM(1) |
| Other expenses | 137 | | | 112 | | | 22.3 |
____________
(1)Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful.
The decrease in depreciation and amortization expenses was primarily driven by a decrease of $32 million for certain intangible assets that became fully amortized during the year ended December 31, 2023. The decrease was mostly offset by an increase related to software and corporate and leased hotel assets placed in service between the periods.
The increase in general and administrative expenses was primarily due to an increase in costs related to payroll and other compensation costs.
We recognized $38 million of impairment losses during the year ended December 31, 2023 on assets associated with certain leased hotels; see Note 12: "Fair Value Measurements" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information.
The increase in other expenses was primarily due to costs associated with higher procurement volume from our purchasing operations.
Non-operating Income and Expenses
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Percent Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| (in millions) | | |
| Interest expense | $ | (569) | | | $ | (464) | | | 22.6 |
| Loss on foreign currency transactions | (12) | | | (16) | | | (25.0) |
| Loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate | — | | | (92) | | | NM(1) |
| Other non-operating income (loss), net | (6) | | | 39 | | | NM(1) |
| Income tax expense | (244) | | | (541) | | | (54.9) |
____________
(1)Fluctuation in terms of percentage change is not meaningful.
In November 2023, we amended the credit agreement governing the Term Loans and increased borrowings by $500 million (the "November 2023 Amendment"). In addition, in both March 2024 and in September 2024 we issued $1.0 billion Senior Notes (collectively, the "March and September Senior Notes issuances") for a total aggregate principal amount of $2.0 billion for the year. See Note 10: "Debt" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information.
The increase in interest expense was primarily attributable to (i) an increase related to the Term Loans of $31 million as a result of the increase in the outstanding borrowings resulting from the November 2023 Amendment and (ii) an increase of $66 million due to the March and September Senior Notes issuances.
The net gains and losses on foreign currency transactions are a result of changes in foreign currency exchange rates, including on certain intercompany financing arrangements, such as short-term cross-currency intercompany loans, as well as transactions denominated in foreign currencies.
The loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate included: (i) a $44 million other-than-temporary impairment loss on our investment in one of our third-party unconsolidated affiliates (the "Fund"), which has underlying investments in certain hotels that we manage or franchise, and (ii) $48 million of credit losses on financing receivables provided to the Fund. See Note 6: "Loss on Investments in Unconsolidated Affiliate" and Note 12: "Fair Value Measurements" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information.
The net change in other non-operating income (loss), net during the year ended December 31, 2024 was primarily driven by an increase in losses on debt guarantees for certain hotels that Hilton manages. See Note 20: "Commitments and Contingencies" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information.
The decrease in income tax expense was primarily attributable to the $270 million benefit for the tax claim for increased foreign tax basis for certain brand assets, as well as an increase of $64 million in uncertain tax position reserves related to our guest loyalty program in 2023 that did not recur in 2024, partially offset by a $23 million increase to income tax expense attributable to the increase in income before income taxes. For additional information, see Note 14: “Income Taxes” in our consolidated financial statements.
Segment Results
As of December 31, 2024, our management and franchise segment included 831 managed and 7,566 franchised and licensed properties, which included 105 timeshare and 409 strategic partner hotels, consisting of 1,251,068 total rooms, and our ownership segment included 50 hotels consisting of 17,138 total rooms. Refer to Note 19: "Business Segments" in our consolidated financial statements for reconciliations of revenues for our reportable segments to consolidated total revenues and of segment Adjusted EBITDA to consolidated income before income taxes.
Franchise and licensing fees and total management fees including fees charged to our ownership segment and excluding amortization of contract acquisition costs reflects our management and franchise segment revenues and segment Adjusted EBITDA. For the year ended December 31, 2024, refer to "—Revenues" for further discussion of the increase in our franchise and licensing fees and total management fees. For the year ended December 31, 2024, refer to "—Revenues" for further discussion of the primary changes in revenues from our owned and leased hotels, which reflect our ownership segment revenues. Our ownership segment Adjusted EBITDA reflects owned and leased hotels revenues, less (i) owned and leased hotels expenses, excluding FF&E replacement reserves expenses, share-based compensation expenses and certain other items, less (ii) fees charged by our management and franchise segment to our ownership segment, plus (iii) income (losses) from hotels owned or leased by entities in which we own a noncontrolling financial interest. Refer to "—Operating Expenses" for further discussion of the changes in owned and leased hotels expenses.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
As of December 31, 2024, we had total cash and cash equivalents of $1,376 million, including $75 million of restricted cash and cash equivalents. The majority of our restricted cash and cash equivalents is related to cash collateral and cash held for FF&E reserves.
Our known short-term liquidity requirements primarily consist of funds necessary to pay for operating and other expenditures, including:
•costs associated with the management and franchising of hotels;
•corporate expenses;
•payroll and compensation costs;
•taxes and compliance costs;
•scheduled debt maturities and interest payments on our outstanding indebtedness, which, excluding finance lease liabilities, are estimated to be approximately $1.1 billion in 2025;
•lease payments under our finance and operating leases, which include minimum lease payments that are estimated to be approximately $42 million and $152 million, respectively, in 2025;
•costs, other than compensation and lease payments that are noted separately, associated with the operations of owned and leased hotels, including, but not limited to, utilities and operating supplies;
•committed contract acquisition costs;
•capital and maintenance expenditures for required renovations and maintenance at the hotels within our ownership segment;
•corporate capital and information technology expenditures;
•dividends as declared; and
•share repurchases.
Our known long-term liquidity requirements primarily consist of funds necessary to pay for:
•scheduled debt maturities and interest payments on our outstanding indebtedness, which, excluding finance lease liabilities, are estimated to total an aggregate of $13.3 billion after December 31, 2025;
•lease payments under our finance and operating leases, which include minimum lease payments that are estimated to total an aggregate of $92 million and $924 million, respectively, after December 31, 2025;
•committed contract acquisition costs;
•capital improvements to the hotels within our ownership segment;
•corporate capital and information technology expenditures;
•dividends as declared;
•share repurchases; and
•commitments to owners in our management and franchise segment made in the normal course of business for which we are reimbursed by these owners through Hilton Honors and program fees to operate our Hilton Honors program, marketing, sales and brand programs and shared services.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, we repurchased approximately 13.3 million shares of our common stock for $2.9 billion. As of December 31, 2024, approximately $4.4 billion remained available for share repurchases under our stock repurchase program.
In circumstances where we have the opportunity to support our strategic objectives, we may provide guarantees or other commitments, as necessary, to owners of hotels that we currently or in the future will manage or franchise or other third parties. See Note 20: "Commitments and Contingencies" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information on our commitments that were outstanding as of December 31, 2024.
We have a long-term investment policy that is focused on the preservation of capital and maximizing the return on new and existing investments and returning available capital to stockholders through dividends and share repurchases. Within the framework of our investment policy, we intend to finance our business activities primarily with cash on our balance sheet as of December 31, 2024, cash generated from our operations and, as needed, the use of the available capacity of our senior secured revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Credit Facility"). Additionally, we have continued access to debt markets and expect to be able to obtain financing as a source of liquidity as required and to extend maturities of existing borrowings, if necessary.
After considering our approach to liquidity and our available sources of cash, we believe that our cash position and sources of liquidity will meet anticipated requirements for operating and other expenditures, including corporate expenses, payroll and other compensation costs, taxes and compliance costs, current maturities of long-term debt and other commitments for the foreseeable future based on current conditions. The objectives of our cash management policy are maintaining the availability of liquidity and minimizing operational costs.
We may from time to time issue or incur or increase our capacity to incur new debt and/or purchase our outstanding debt through underwritten offerings, open market transactions, privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. Issuances or incurrence of new debt (or an increase in our capacity to incur new debt) and/or purchases or retirements of outstanding debt, if
any, will depend on prevailing market conditions, liquidity requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors. The amounts involved may be material.
Sources and Uses of Our Cash and Cash Equivalents
The following table summarizes our net cash flows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, | | Percent Change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 vs. 2023 |
| (in millions) | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 2,013 | | | $ | 1,946 | | | 3.4 |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (446) | | | (305) | | | 46.2 |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (1,045) | | | (2,040) | | | (48.8) |
Operating Activities
Cash flows from operating activities were primarily generated from management, franchise and licensing fee revenue and operating income from our owned and leased hotels. The increase in net cash inflows during the period was primarily due to the increase in cash inflows generated from our management and franchise segment, discussed in "—Revenues," largely as a result of an increase in RevPAR at our comparable managed and franchised hotels as well as revenues from net hotel additions and a $128 million decrease in payments of contract acquisition costs due to the timing of certain strategic hotel developments supporting our growth during the year ended December 31, 2023. The increase in cash provided by operating activities was partially offset by an outflow of $77 million for debt guarantee payments and an increase in cash paid for interest of $70 million.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities primarily included cash flows related to: (i) the acquisitions of (a) the Graduate brand and the associated franchise contracts and (b) a controlling financial interest in Sydell Hotels & Resorts, LLC and Sydell Holding Company UK Ltd, both completed during the year ended December 31, 2024, (ii) capitalized software costs that were related to various systems initiatives for the benefit of both our property owners and our overall corporate operations, and (iii) capital expenditures for property and equipment related to corporate property and the renovation of certain hotels in our ownership segment, which decreased between the periods due to the timing of certain corporate and hotel capital expenditure projects. Additionally, our investing activities include the net cash inflows and outflows related to our undesignated derivative financial instruments that we have in place to hedge against the impact of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates on certain of our intercompany loan and cash balances, which were primarily the result of changes in the exchange rates for the Euro for the year ended December 31, 2024 and the Pound Sterling to the U.S. dollar for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023.
Financing Activities
The decrease in net cash used in financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2024 was primarily attributable to a $2.0 billion increase in cash inflows from the March and September Senior Notes issuances. This increase in cash inflows was partially offset by a $555 million increase in cash outflows for share repurchases and payment of the related excise taxes and additional borrowings on the Term Loans of $500 million during the year ended December 31, 2023 as part of the November 2023 Amendment.
Debt and Borrowing Capacity
As of December 31, 2024, our total indebtedness, excluding the deduction for unamortized deferred financing costs and discounts, was approximately $11.2 billion. No debt amounts were outstanding under our Revolving Credit Facility as of December 31, 2024, which had an available borrowing capacity of $1,910 million after considering $90 million of outstanding letters of credit. For additional information on our total indebtedness and guarantees on our debt, refer to Note 10: "Debt" in our consolidated financial statements.
If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flow from operations in the future to service our debt, we may be required to reduce capital expenditures or issue additional equity securities. We have $500 million of 5.375% Senior Notes due in May
2025 ("May 2025 Senior Notes") and have no other material indebtedness that matures prior to April 2027. We believe that we have sufficient sources of liquidity and access to debt financing to address the repayment of the May 2025 Senior Notes at or prior to their maturity date as well as all indebtedness that becomes due thereafter. Our ability to make scheduled principal payments and to pay interest on our debt depends on our future operating performance, which is subject to general conditions in or affecting the hospitality industry that may be beyond our control.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities as of the date of the consolidated financial statements, the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods and the related disclosures in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying footnotes. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate these estimates and judgments based on historical experiences and various other factors that we believe reflect the current circumstances. While we believe our estimates, assumptions and judgments are reasonable, they are based on information available when they are made. Actual results may differ significantly from these estimates due to changes in judgments, assumptions and conditions as a result of unforeseen events or otherwise, which could have a material effect on our financial position or results of operations.
We believe that the following estimates, which are used in conjunction with our significant accounting policies, are critical because they involve a higher degree of judgment and are based on information that is inherently uncertain; refer to Note 2: "Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" in our consolidated financial statements for information on our significant accounting policies. Management has discussed the development and selection of the following critical accounting estimates with the Audit Committee of the board of directors:
Impairment of Goodwill and Brands Intangible Assets
We evaluate goodwill and brands intangible assets for potential impairment on an annual basis or at other times during the year if indicators of impairment exist. Our reporting units are the same as our operating segments as described in Note 19: "Business Segments" in our consolidated financial statements.
As part of the evaluation of goodwill and brands intangible assets for potential impairment, we exercise judgment to:
•perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit or brand intangible asset is less than its carrying value. Factors we consider when making this determination include assessing historical trends and the overall effect of current trends in and future expectations of the hospitality industry and the general economy and regional performance;
•decide whether to bypass the qualitative assessment and perform a quantitative assessment. Factors we consider when making this determination include negative changes in the Company or general economic conditions since the previous quantitative assessment was performed, the amount by which the fair value exceeded the carrying value at the time of the previous assessment and the period of time that has passed since such quantitative assessment; and
•perform a quantitative analysis to identify both the existence and the amount of an impairment loss. The estimated fair value is based on internal projections of expected future cash flows and operating plans, discount rates and market conditions relative to the operations of the reporting unit or brand, as applicable.
Changes in the estimates and assumptions used in our impairment analysis, or changes in the factors that we consider that would affect these estimates and assumptions, such as those described above, could result in impairment losses, which could be material.
Impairment of Certain Finite-Lived Assets
We evaluate the carrying value of our specifically identifiable lease intangible assets, operating and finance lease ROU assets and property and equipment for indicators of impairment. As part of the process, we exercise judgment to:
•determine if there are indicators of impairment present. Factors we consider when making this determination include assessing historical trends and the overall effect of current trends in and future expectations of the hospitality industry and the general economy and regional performance, capital costs and other asset-specific information;
•determine the projected undiscounted future cash flows when indicators of impairment are present to determine whether an asset group is recoverable by comparing the expected undiscounted future cash flows to the net carrying value of that asset group. Judgment is required when developing projections of future revenues and expenses to determine the undiscounted cash flows, which are based on estimated performance over the expected useful life of the asset group. Forward-looking estimates of performance are based on historical operating results, adjusted for current and expected future market conditions, as well as various internal projections and external sources; and
•determine the asset group fair value when an asset group is determined not to be recoverable. In determining the fair value, we often use internally-developed discounted cash flow models, appraisals, recent similar transactions in the market and, if appropriate and available for a specific asset group, current estimated net sales proceeds from pending offers. The discounted cash flow models include the undiscounted cash flows, as discussed above, which may require us to adjust for specific market conditions, and a discount rate to determine the present value of those cash flows. The discount rate applied to forward-looking projections takes into account market-specific considerations.
Changes in the estimates and assumptions used in our impairment analysis, or changes in the factors that we consider that would affect these estimates and assumptions, such as those described above, could result in impairment losses, which could be material.
Hilton Honors
We record a point redemption liability for amounts received from properties participating in our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program and from strategic partners affiliated with the loyalty program, in an amount equal to the estimated cost per point of the future redemption obligation. We engage third-party actuaries annually to assist in determining the fair value of the future reward redemption obligation using a discount rate and statistical formulas that project future point redemptions based on factors that require judgment, including: (i) an estimate of the number of points that will eventually be redeemed, which includes an estimate of breakage (i.e., points that will never be redeemed); (ii) an estimate of when such points will be redeemed; and (iii) an estimate of the cost of reimbursing managed and franchised properties and other third parties for redemptions. The cost of the points expected to be redeemed includes further estimates of available room nights, occupancy rates, room rates and any changes to the Hilton Honors program, including devaluation or appreciation of points based on changes in the number of points required to redeem a reward. Any amounts received related to the issuance of points that are in excess of the cost per point, as determined with assistance from an actuary, are recorded as deferred revenue in our consolidated balance sheet and recognized as revenue upon point redemption. We recognize revenue for point redemptions in the amount we expect to retain in excess of the cost per point, inclusive of estimated breakage, and limit the revenue recognized to an amount that is probable to not result in a significant reversal in the cumulative revenue recognized when breakage occurs.
In addition to the Hilton Honors fees we receive from property owners to operate the program, we earn fees from strategic partnerships, including co-branded credit card arrangements, for a license to use our IP and the issuance of points. The allocation of the overall fees from the strategic partnerships between the IP license and the points is based on their estimated standalone selling prices. The estimated standalone selling price of the IP license is determined using a relief-from-royalty valuation method incorporating statistical formulas based on factors that require significant judgment, including estimates of the usage of the strategic partner's goods or services, an appropriate royalty rate and a discount rate applied to the projected cash flows. The estimated standalone selling price of the future reward redemptions of points under the strategic partnerships is calculated using a discounted cash flow analysis with the same assumptions as the point redemption liability discussed above, adjusted for an appropriate margin.
Changes in our estimates and assumptions that are used to determine our estimated cost per point and the allocation of fees from strategic partnerships between the IP license fee and the points could result in material changes in the balances of our liability for guest loyalty program and deferred revenues in our consolidated balance sheet. Further, the estimates and assumptions used for the allocation of fees could result in material changes to our licensing fees and other revenues from managed and franchised properties recognized in our consolidated statement of operations.
Income Taxes
We regularly review our deferred tax assets to assess their potential realization and establish valuation allowances for portions of such assets that we believe will not be ultimately realized. In performing this review, we consider all positive and negative evidence available, including, but not limited to, estimates and assumptions regarding projected future taxable income, the expected timing of reversals of existing temporary differences and the implementation of tax planning strategies, all of which require significant use of judgment. A change in these assumptions may increase or decrease our valuation allowances
resulting in an increase or decrease in our effective tax rate, respectively, which could materially affect our consolidated financial statements. Refer to Note 14: "Income Taxes" for information on the balances of our deferred tax assets and respective valuation allowances as of December 31, 2024.
We record the benefits of income tax positions by recognizing the largest amount of income tax benefit more-likely-than-not to be realized upon resolution. Estimating this benefit involves, but is not limited to, interpreting complex tax laws in the multiple jurisdictions where we operate, evaluating the technical merits of each tax position and assessing amounts we would ultimately accept in a negotiated settlement with the tax authorities, if applicable. The complexities and judgment involved in estimating the Company's income tax positions could result in payments materially different than the liabilities previously recognized for such expected payments. Additionally, as new information becomes available (e.g., legislative changes or administrative rulings) changes in the Company's judgment and assumptions could result in adjustments to our existing income tax position recognition. Changes to these assumptions and estimates may increase or decrease our existing liabilities, resulting in additional income tax expense or benefit, respectively, which could materially affect our consolidated financial statements.
Legal Contingencies
We are subject to various legal proceedings and claims, the outcomes of which are subject to significant uncertainty. An estimated loss from a loss contingency will be accrued as a charge to income if it is probable and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. Significant judgment is required when we evaluate, among other factors, the degree of probability of an unfavorable outcome and the ability to make a reasonable estimate of the amount of loss in determining whether an accrual of an estimated loss is appropriate. Changes in these factors could materially affect our consolidated financial statements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are exposed to market risk primarily from changes in the one-month Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR"), the benchmark rate for which the interest rate of the majority of our variable-rate indebtedness is based on, and foreign currency exchange rates. These rate changes may affect future income, cash flows and the fair value of the Company, its assets and its liabilities. In certain situations, we may seek to reduce volatility associated with changes in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates by entering into derivative financial instruments intended to provide a hedge against a portion of the risks associated with such volatility. We continue to have exposure to such risks to the extent they are not hedged. We enter into derivative financial instruments to the extent they meet our objectives to reduce volatility in our results of operations and cash flows, and we do not use derivatives for speculative purposes.
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to interest rate risk on our variable-rate indebtedness. Our primary sensitivity in 2024 was to changes in one-month SOFR, as the interest rates on our Term Loans, which represent the majority of our variable-rate indebtedness, were based on this benchmark rate. We use an interest rate swap in order to maintain what we believe to be an appropriate level of exposure to interest rate variability. As of December 31, 2024, we held an interest rate swap for a portion of the Term Loans, through which we receive one-month term SOFR and pay a fixed rate. For our fixed-rate indebtedness, a change in interest rates impacts the fair value but generally does not have an impact on our future results of operations and cash flows.
The following table sets forth the current carrying values of our contractual maturities, total fair values and interest rates as of December 31, 2024 for our financial instruments that are materially affected by interest rate risk, including long-term debt and our interest rate swap:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Maturities by Period | | | | |
| 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 | | 2028 | | 2029 | | Thereafter | | Carrying Value | | Fair Value |
| (dollars in millions) |
Long-term debt(1): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fixed-rate long-term debt | $ | 500 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 600 | | | $ | 500 | | | $ | 1,350 | | | $ | 5,050 | | | $ | 8,000 | | | $ | 7,560 | |
Weighted average fixed interest rate(2) | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4.76 | % | | |
| Variable-rate long-term debt | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,119 | | | $ | 3,119 | | | $ | 3,140 | |
Variable interest rate(2)(3) | | | | | | | | | | | | | 6.09 | % | | |
Interest rate swap(4): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Variable to fixed | $ | — | | | $ | 1,600 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,600 | | | $ | 45 | |
Variable interest rate receivable(3) | | | | | | | | | | | | | 4.34 | % | | |
| Fixed interest rate payable | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1.76 | % | | |
____________
(1)The carrying values exclude the deduction for unamortized deferred financing costs and any applicable discounts, as well as all finance lease liabilities totaling $117 million as of December 31, 2024.
(2)The weighted average fixed interest rate is the weighted average of the actual rates and the variable interest rate is based on the market rate that was applicable as of December 31, 2024.
(3)The variable interest rate receivable on the interest rate swap excludes the fixed component of the variable interest rate on the long-term debt.
(4)The carrying value reflects the notional amount and the variable interest rate receivable is based on the market rate prevailing as of December 31, 2024. We measure our derivative instruments at fair value and, as of December 31, 2024, our interest rate swap was in an asset position.
Refer to Note 12: "Fair Value Measurements" in our consolidated financial statements for additional information on the fair value measurements of our long-term debt and interest rate swap.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
We conduct business in various currencies and are exposed to earnings and cash flow volatility associated with changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Our principal exposure results from management and franchise fees earned in foreign currencies, as well as revenues and expenses from our international leased hotels. The value of these revenues and expenses could change materially in relation to the functional currencies of the exposed entities and to our reporting currency, USD. We also have exposure from our international financial assets and liabilities, including certain intercompany financing arrangements not deemed to be permanently invested, the value of which could change materially in relation to the functional currencies of the exposed entities.
We use foreign currency forward contracts designated as cash flow hedges to offset exposure from foreign currency exchange rate risks associated with certain of our management, franchise and other fees denominated in certain foreign currencies. We use foreign currency forward contracts not designated as hedging instruments to offset exposure to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations in certain cash and intercompany loan balances. We do not consider the fair value or earnings effect of these foreign currency forward contracts to be material to our consolidated financial statements.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| | | | | |
| Page No. |
| |
| |
| |
| Consolidated Financial Statements: | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. (the "Company") is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP"). The Company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that: (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of the Company’s management and directors; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of assets of the Company that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management has assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024. In making this assessment, management used the criteria established in the Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework). Based on this assessment, management determined that the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024.
Ernst & Young LLP (PCAOB ID: 42), the independent registered public accounting firm that has audited the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024. The report is included herein.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of
Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, cash flows and noncontrolling interests and stockholders' equity (deficit) for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes and our report dated February 6, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Tysons, Virginia
February 6, 2025
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of
Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, cash flows and noncontrolling interests and stockholders’ equity (deficit) for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "consolidated financial statements"). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 6, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
| | | | | | | | |
| | Accounting for the Loyalty Program |
| Description of the Matter | | The Company had deferred revenues of $1,032 million and a liability for guest loyalty program of $2,974 million as of December 31, 2024 associated with the Hilton Honors guest loyalty and marketing program (the “Loyalty Program”). As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has a performance obligation to provide or arrange for the provision of goods or services, for free or at a discount, to Hilton Honors members in exchange for the redemption of points earned through participation in the Loyalty Program. The consideration for the Loyalty Program is received from hotel properties or other program partners at the time points are earned by Hilton Honors members. Such amounts are recognized as revenue when the related point obligation is satisfied based upon the estimated standalone selling price per point in excess of the related cost per point.
Auditing the Loyalty Program is complex due to the complexity of models and high volume of data used to monitor and account for the Loyalty Program results. |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s process of accounting for the Loyalty Program during the year. For example, we tested controls over the accounting model and data used in recording revenue when Hilton Honors points are redeemed.
To test the recognition of revenue associated with the Loyalty Program, we performed audit procedures that included, among others, testing the clerical accuracy and consistency with US generally accepted accounting principles of the accounting model developed by the Company to recognize revenue associated with the Loyalty Program and testing significant inputs into the accounting model. |
| | |
| | Accounting for Income Taxes |
| Description of the Matter | | The Company recognized income tax expense of $244 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, and unrecognized tax benefits of $849 million as of December 31, 2024. As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, for all tax positions taken in a tax return, the Company will first determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination. If the Company determines that a position meets the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold, the benefit recognized in the financial statements is measured as the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement.
Auditing the accounting for income taxes is complex as a result of: (1) the judgment and estimation associated with both the identification and measurement of the Company's unrecognized tax benefits, including its evaluation of the technical merits related to matters for which no reserves or partial reserves have been recorded, and (2) the significant estimation associated with the measurement of unrecognized tax benefits outstanding as of the balance sheet date.
|
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of controls over the Company’s process of accounting for income taxes, including unrecognized tax benefits, during the year. For example, we tested management’s controls over the review of tax positions taken by the Company to determine whether they met the threshold for recognition within the consolidated financial statements.
To test the recognition of the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits and measurement of unrecognized tax benefits, we involved tax professionals with specialized skills and knowledge to assess the technical merits of the Company’s tax positions and performed audit procedures that included, among others, evaluation of communications with relevant taxing authorities, evaluation of whether management appropriately considered new information that could significantly change the recognition, measurement or disclosure of the unrecognized tax benefits, and testing the assumptions used by management in estimating the valuation of any associated liability.
|
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2002.
Tysons, Virginia
February 6, 2025
HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in millions, except share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| Current Assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,301 | | | $ | 800 | |
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents | 75 | | | 75 | |
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for credit losses of $145 and $131 | 1,583 | | | 1,487 | |
| Prepaid expenses | 193 | | | 131 | |
| Other | 120 | | | 121 | |
Total current assets (variable interest entities – $71 and $65) | 3,272 | | | 2,614 | |
| Intangibles and Other Assets: | | | |
| Goodwill | 5,035 | | | 5,052 | |
| Brands | 4,990 | | | 4,846 | |
| Management and franchise contracts, net | 1,235 | | | 1,064 | |
| Other intangible assets, net | 194 | | | 173 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 567 | | | 618 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 411 | | | 382 | |
| Deferred income tax assets | 318 | | | 140 | |
| Other | 500 | | | 512 | |
Total intangibles and other assets (variable interest entities – $100 and $112) | 13,250 | | | 12,787 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 16,522 | | | $ | 15,401 | |
| LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS AND EQUITY (DEFICIT) | | | |
| Current Liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | $ | 2,124 | | | $ | 1,979 | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | 535 | | | 39 | |
| Current portion of deferred revenues | 664 | | | 502 | |
| Current portion of liability for guest loyalty program | 1,377 | | | 1,202 | |
Total current liabilities (variable interest entities – $51 and $50) | 4,700 | | | 3,722 | |
| Long-term debt | 10,616 | | | 9,157 | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 735 | | | 808 | |
| Deferred revenues | 1,300 | | | 1,132 | |
| Deferred income tax liabilities | 322 | | | 401 | |
| Liability for guest loyalty program | 1,597 | | | 1,530 | |
| Other | 941 | | | 998 | |
Total liabilities (variable interest entities – $110 and $137) | 20,211 | | | 17,748 | |
Commitments and contingencies – see Note 20 | | | |
| Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 17 | | | — | |
| Equity (Deficit): | | | |
| Common stock, $0.01 par value; 10,000,000,000 authorized shares, 241,806,421 outstanding as of December 31, 2024 and 253,488,288 outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 3 | | | 3 | |
| Treasury stock, at cost; 94,087,917 shares as of December 31, 2024 and 80,807,049 shares as of December 31, 2023 | (11,256) | | | (8,393) | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 11,130 | | | 10,968 | |
| Accumulated deficit | (2,822) | | | (4,207) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (782) | | | (731) | |
| Total Hilton stockholders' deficit | (3,727) | | | (2,360) | |
| Noncontrolling interests | 21 | | | 13 | |
| Total deficit | (3,706) | | | (2,347) | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS AND EQUITY (DEFICIT) | $ | 16,522 | | | $ | 15,401 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in millions, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Revenues | | | | | |
| Franchise and licensing fees | $ | 2,600 | | | $ | 2,370 | | | $ | 2,068 | |
| Base and other management fees | 369 | | | 342 | | | 294 | |
| Incentive management fees | 290 | | | 274 | | | 196 | |
| Owned and leased hotels | 1,255 | | | 1,244 | | | 1,076 | |
| Other revenues | 232 | | | 178 | | | 102 | |
| 4,746 | | | 4,408 | | | 3,736 | |
| Other revenues from managed and franchised properties | 6,428 | | | 5,827 | | | 5,037 | |
| Total revenues | 11,174 | | | 10,235 | | | 8,773 | |
| | | | | |
| Expenses | | | | | |
| Owned and leased hotels | 1,126 | | | 1,141 | | | 999 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 146 | | | 147 | | | 162 | |
| General and administrative | 415 | | | 408 | | | 382 | |
| Impairment losses | — | | | 38 | | | — | |
| Other expenses | 137 | | | 112 | | | 60 | |
| 1,824 | | | 1,846 | | | 1,603 | |
| Other expenses from managed and franchised properties | 6,985 | | | 6,164 | | | 5,076 | |
| Total expenses | 8,809 | | | 8,010 | | | 6,679 | |
| | | | | |
| Gain on sales of assets, net | 5 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Operating income | 2,370 | | | 2,225 | | | 2,094 | |
| | | | | |
| Interest expense | (569) | | | (464) | | | (415) | |
| Gain (loss) on foreign currency transactions | (12) | | | (16) | | | 5 | |
| Loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate | — | | | (92) | | | — | |
| Other non-operating income (loss), net | (6) | | | 39 | | | 50 | |
| | | | | |
| Income before income taxes | 1,783 | | | 1,692 | | | 1,734 | |
| | | | | |
| Income tax expense | (244) | | | (541) | | | (477) | |
| | | | | |
| Net income | 1,539 | | | 1,151 | | | 1,257 | |
| Net income attributable to redeemable and nonredeemable noncontrolling interests | (4) | | | (10) | | | (2) | |
| Net income attributable to Hilton stockholders | $ | 1,535 | | | $ | 1,141 | | | $ | 1,255 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings per share: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 6.20 | | | $ | 4.36 | | | $ | 4.56 | |
| Diluted | $ | 6.14 | | | $ | 4.33 | | | $ | 4.53 | |
| | | | | |
| Cash dividends declared per share | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.60 | | | $ | 0.45 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(in millions)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net income | $ | 1,539 | | | $ | 1,151 | | | $ | 1,257 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax benefit (expense): | | | | | |
| Currency translation adjustment, net of tax of $13, $(4) and $22 | (53) | | | 8 | | | (8) | |
| Pension liability adjustment, net of tax of $(6), $1 and $18 | 22 | | | (3) | | | (49) | |
| Cash flow hedge adjustment, net of tax of $7, $10 and $(44) | (21) | | | (31) | | | 130 | |
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | (52) | | | (26) | | | 73 | |
| | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | 1,487 | | | 1,125 | | | 1,330 | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to redeemable and nonredeemable noncontrolling interests | (3) | | | (9) | | | (2) | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to Hilton stockholders | $ | 1,484 | | | $ | 1,116 | | | $ | 1,328 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in millions)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Operating Activities: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 1,539 | | | $ | 1,151 | | | $ | 1,257 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Amortization of contract acquisition costs | 50 | | | 43 | | | 38 | |
| Depreciation and amortization expenses | 146 | | | 147 | | | 162 | |
| Impairment losses | — | | | 38 | | | — | |
| Gain on sales of assets, net | (5) | | | — | | | — | |
| Loss (gain) on foreign currency transactions | 12 | | | 16 | | | (5) | |
| Loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate | — | | | 92 | | | — | |
| Share-based compensation expense | 176 | | | 169 | | | 162 | |
| Amortization of deferred financing costs and discounts | 17 | | | 16 | | | 16 | |
| Deferred income taxes | (247) | | | (264) | | | 34 | |
| Contract acquisition costs, net of refunds | (105) | | | (233) | | | (81) | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable, net | (103) | | | (126) | | | (270) | |
| Prepaid expenses | (67) | | | (27) | | | (21) | |
| Other current assets | 5 | | | 16 | | | 78 | |
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | 155 | | | 181 | | | 198 | |
| Change in deferred revenues | 330 | | | 215 | | | 174 | |
| Change in liability for guest loyalty program | 242 | | | 337 | | | 31 | |
| Change in other liabilities | (58) | | | 284 | | | (11) | |
| Other | (74) | | | (109) | | | (81) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 2,013 | | | 1,946 | | | 1,681 | |
| Investing Activities: | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures for property and equipment | (96) | | | (151) | | | (39) | |
| Cash paid for acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (236) | | | — | | | — | |
| Issuance of financing receivables | (15) | | | (22) | | | (46) | |
| Payments received on financing receivables | 7 | | | — | | | 2 | |
| Settlements of undesignated derivative financial instruments | (7) | | | (26) | | | 79 | |
| Proceeds from asset dispositions | 8 | | | 5 | | | — | |
| Capitalized software costs | (102) | | | (96) | | | (63) | |
| Investments in unconsolidated affiliates | (5) | | | (15) | | | (53) | |
| Other | — | | | — | | | (3) | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (446) | | | (305) | | | (123) | |
| Financing Activities: | | | | | |
| Borrowings | 2,283 | | | 609 | | | 23 | |
| Repayment of debt | (330) | | | (183) | | | (48) | |
| Debt issuance costs | (32) | | | (20) | | | — | |
| Dividends paid | (150) | | | (158) | | | (123) | |
| Repurchases of common stock, including excise tax payments | (2,893) | | | (2,338) | | | (1,590) | |
| Share-based compensation tax withholdings | (72) | | | (54) | | | (58) | |
| Proceeds from share-based compensation | 93 | | | 51 | | | 29 | |
| Settlements of interest rate swap with financing component | 56 | | | 53 | | | 2 | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (1,045) | | | (2,040) | | | (1,765) | |
| | | | | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash, restricted cash and cash equivalents | (21) | | | (12) | | | (19) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, restricted cash and cash equivalents | 501 | | | (411) | | | (226) | |
| Cash, restricted cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | 875 | | | 1,286 | | | 1,512 | |
| Cash, restricted cash and cash equivalents, end of period | $ | 1,376 | | | $ | 875 | | | $ | 1,286 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements. For supplemental disclosures, see Note 21: "Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information."
HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(in millions)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | | | | | Additional
Paid-in
Capital | | | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Loss | | | | |
| Common Stock | | Treasury Stock | | | Accumulated Deficit | | | Noncontrolling
Interests | | Total |
| Shares | | Amount | | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | $ | — | | 279.1 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | (4,443) | | | $ | 10,720 | | | $ | (6,322) | | | $ | (779) | | | $ | 2 | | | $ | (819) | |
| Net income | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,255 | | | — | | | 2 | | | 1,257 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of taxes: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency translation adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (8) | | | — | | | (8) | |
| Pension liability adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (49) | | | — | | | (49) | |
| Cash flow hedge adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 130 | | | — | | | 130 | |
| Other comprehensive income | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 73 | | | — | | | 73 | |
| Dividends | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (123) | | | — | | | — | | | (123) | |
| Repurchases of common stock | — | | (12.3) | | | — | | | (1,608) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (1,608) | |
| Share-based compensation | — | | 1.1 | | | — | | | 11 | | | 111 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 122 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | — | | 267.9 | | | 3 | | | (6,040) | | | 10,831 | | | (5,190) | | | (706) | | | 4 | | | (1,098) | |
| Net income | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,141 | | | — | | | 10 | | | 1,151 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of taxes: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency translation adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 9 | | | (1) | | | 8 | |
| Pension liability adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (3) | | | — | | | (3) | |
| Cash flow hedge adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (31) | | | — | | | (31) | |
| Other comprehensive loss | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (25) | | | (1) | | | (26) | |
| Dividends | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (158) | | | — | | | — | | | (158) | |
Repurchases of common stock(1) | — | | (15.6) | | | — | | | (2,369) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,369) | |
| Share-based compensation | — | | 1.2 | | | — | | | 16 | | | 137 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 153 | |
Balance as of December 31, 2023(2) | — | | 253.5 | | | 3 | | | (8,393) | | | 10,968 | | | (4,207) | | | (731) | | | 13 | | | (2,347) | |
| Acquisition date fair value of redeemable noncontrolling interests | 22 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Net income (loss) | (5) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,535 | | | — | | | 9 | | | 1,544 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of taxes: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency translation adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (52) | | | (1) | | | (53) | |
| Pension liability adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 22 | | | — | | | 22 | |
| Cash flow hedge adjustment | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (21) | | | — | | | (21) | |
| Other comprehensive loss | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (51) | | | (1) | | | (52) | |
| Dividends | — | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (150) | | | — | | | — | | | (150) | |
Repurchases of common stock(1) | — | | (13.3) | | | — | | | (2,882) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (2,882) | |
| Share-based compensation | — | | 1.6 | | | — | | | 19 | | | 162 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 181 | |
Balance as of December 31, 2024(2) | $ | 17 | | 241.8 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | (11,256) | | | $ | 11,130 | | | $ | (2,822) | | | $ | (782) | | | $ | 21 | | | $ | (3,706) | |
____________
(1) Amounts include excise tax of $25 million and $22 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, as imposed by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022.
(2) As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, 3.0 billion shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.01 were authorized with no such shares issued.
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1: Organization
Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. (the "Parent," or together with its subsidiaries, "Hilton," "we," "us," "our" or the "Company"), a Delaware corporation, is one of the largest global hospitality companies and is engaged in managing, franchising, owning and leasing hotels and resorts, and licensing its intellectual property ("IP"), including brand names, trademarks and service marks.
Note 2: Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
These consolidated financial statements present the consolidated financial position of Hilton as of December 31, 2024 and 2023 and the results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022.
Principles of Consolidation
Our consolidated financial statements include the accounts of our wholly owned subsidiaries and other non-wholly owned entities in which we have a controlling financial interest, including variable interest entities ("VIEs") for which we are the primary beneficiary. Non-wholly owned entities in which we have a controlling financial interest primarily comprise majority owned entities that own or lease real estate.
The determination of a controlling financial interest is based upon the terms of the governing agreements of the respective entities, including the evaluation of rights held by third-party ownership interests. If the entity is considered to be a VIE, we evaluate whether we are the primary beneficiary and then consolidate those VIEs for which we have determined we are the primary beneficiary. If the entity in which we hold an interest does not meet the definition of a VIE, we evaluate whether we have a controlling financial interest through our voting interest in the entity, and, if we do, we consolidate the entity.
We hold interests in VIEs, for which we are not the primary beneficiary, that may provide us with the option to acquire an additional interest in such an entity at a predetermined amount, if certain contingent events occur. In a circumstance that we exercise or have the ability to exercise our option to acquire an additional interest in a VIE, we would reassess whether we are the primary beneficiary of the VIE. If we determine that we are the primary beneficiary of the VIE, we would be required to consolidate the total assets, liabilities and results of operations of the VIE on the date that we became the primary beneficiary. If such consolidation is required, the amounts may be material.
All material intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation. References in these financial statements to net income (loss) attributable to Hilton stockholders and Hilton stockholders' equity (deficit) do not include redeemable and nonredeemable noncontrolling interests, which represent the third-party ownership interests of our consolidated, non-wholly owned entities and are reported separately.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with United States ("U.S.") generally accepted accounting principles ("GAAP") requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported and, accordingly, ultimate results could differ from those estimates.
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Revenue Recognition
Revenues are primarily derived from: (i) fees earned from management and franchise contracts with third-party hotel owners; (ii) fees earned from license agreements with strategic partners, including co-branded credit card providers, third-party hotels we do not manage or franchise but that use our booking channels and related programs ("strategic partner hotels"), and Hilton Grand Vacations Inc. ("HGV"); and (iii) our owned and leased hotels. The majority of our performance obligations are promises to provide a series of distinct goods or services, for which we receive variable consideration through our management and franchise and licensing fees or fixed consideration through our owned and leased hotels. We allocate the variable fees to the
distinct services to which they relate applying the prescribed variable consideration allocation guidance, and we allocate fixed consideration to the related performance obligations based on their estimated standalone selling prices.
We do not adjust the promised amount of consideration for the effects of a significant financing component when it is our expectation, at contract inception, that the period between our transfer of a promised good or service to a customer and when the customer pays for that good or service will be twelve months or less, which it is in substantially all cases. Additionally, we do not typically include extended payment terms in our contracts with customers.
Management and franchise revenues
We identified the following performance obligations in connection with our management and franchise contracts:
•IP licenses grant the licensee the right to access our IP, including brand IP, reservations systems and property management systems.
•Hotel management services include providing day-to-day management services in the operation of the hotels for the hotel owners.
•Development services include providing consultative services (e.g., design assistance and contractor selection) to the third-party hotel owner to assist with the construction of the hotel prior to the hotel opening.
•Pre-opening services include providing services (e.g., advertising, budgeting, e-commerce strategies and food and beverage testing) to the third-party hotel owner to assist in preparing for the hotel opening.
•Rewards from Hilton Honors, our guest loyalty program, provide substantive rights for free or discounted goods or services to Hilton Honors members.
Each of the identified performance obligations is considered to be a series of distinct services transferred over time, except for the performance obligation related to rewards from Hilton Honors, which is satisfied at the point in time when a Hilton Honors point is redeemed by a Hilton Honors member. For the performance obligations other than rewards from Hilton Honors, while the underlying activities may vary from day to day, the nature of the commitments are the same each day, and the property owner can independently benefit from each day's services. Management and franchise fees are typically based on the sales or usage of the underlying hotel, with the exception of fixed upfront fees, which usually represent an insignificant portion of the transaction price.
Franchise and licensing fees represent fees earned in connection with the licensing of one of our brands, usually under a long-term contract with a hotel owner, as well as fees from license agreements for the use of our IP and/or booking channels and related programs, and include the following:
•Royalty fees are generally based on a percentage of the hotel's monthly gross room revenue and, in some cases, may also include a percentage of gross food and beverage revenues and other revenues, as applicable. These fees are typically billed and collected monthly, and revenue is generally recognized as services are provided.
•Application, initiation and other fees are charged when: (i) new hotels enter our system; (ii) there is a change of ownership of a hotel; or (iii) contracts with hotels already in our system are extended. These fees are typically fixed and collected upfront and are recognized as revenue over the term of the franchise contract. We do not consider this advance consideration to include a significant financing component, since it is used to protect us from the hotel owner failing to adequately complete some or all of its obligations under the contract, including establishing and maintaining the hotel in accordance with our standards.
•Licensing fees for the use of our IP and/or booking channels and related programs are earned from: (i) strategic partnerships, including from co-branded credit card arrangements, which are recognized as revenue when points for Hilton Honors are issued, generally as spend with the strategic partner or co-branded credit card provider occurs (see "—Hilton Honors" below for further discussion); (ii) strategic partner hotels, which are recognized as revenue in the period when the room stay occurs; and (iii) a license agreement with HGV for its timeshare business, which are typically billed monthly and recognized as revenue at the same time the fees are billed.
Management fees represent fees earned from hotels that we manage, usually under a long-term contract with a hotel owner, and include the following:
•Base management fees are generally based on a percentage of the hotel's monthly gross operating revenue. Base management fees are typically billed and collected monthly, and revenue is generally recognized as services are provided.
•Incentive management fees are generally based on a percentage of the hotel's operating profits, normally over a one-calendar year period (the "incentive period"), and, in some cases, may be subject to a stated return threshold to the hotel owner. Incentive management fee revenue is recognized on a monthly basis, but only to the extent the cumulative fee earned does not exceed the probable fee for the incentive period. Incentive management fee payment terms vary, but they are generally billed and collected monthly or annually upon completion of the incentive period.
Consideration paid or anticipated to be paid to incentivize hotel owners to enter into management and franchise contracts with us is amortized over the life of the applicable contract, generally including any extension periods that are at our sole option, as a reduction to base and other management fees and franchise and licensing fees, respectively.
We do not estimate revenues expected to be recognized related to our unsatisfied performance obligations for our:
(i) royalty fees, since they are considered sales-based royalty fees recognized as hotel room sales occur in exchange for licenses of our IP over the terms of the franchise contracts and (ii) other licensing fees, base management fees and incentive management fees since they are allocated entirely to the wholly unsatisfied promise to transfer IP or provide management services, respectively, which form part of a single performance obligation in a series, over the term of the individual contract.
Other revenues from managed and franchised properties represent amounts that are contractually reimbursed to us by property owners, either directly as costs are incurred or indirectly through monthly program fees related to certain costs and expenses supporting the operations of the related properties, and include the following:
•Direct reimbursements primarily include reimbursements received by us for payroll and related costs of managed hotels, if the managed hotel employees are legally employed by us. Direct reimbursements are contractually reimbursed to us by the property owners as expenses are incurred. We have no legal responsibility for the employee liabilities related to certain of our managed properties, predominately those located outside of the U.S., where we are not the legal employer, as well as the employees or the liabilities associated with operating franchised properties or strategic partner hotels. Revenue is recognized based on the amount of expenses incurred by Hilton, which are presented as other expenses from managed and franchised properties in our consolidated statement of operations, and results in no net effect on operating income (loss) or net income (loss). These amounts are reimbursed to us by the property owner at least on a monthly basis.
•Indirect reimbursements include reimbursements received by us for marketing and sales expenses and other expenses associated with our brand programs and shared services, which are reimbursed by program fees billed and collected from our managed and franchised properties and strategic partner hotels. Indirect reimbursements also include reimbursements for expenses incurred to operate the Hilton Honors program (see the "—Hilton Honors" below for additional information). Indirect reimbursements are typically billed and collected monthly, based on the underlying hotel's sales or usage (e.g., gross room revenue or number of reservations processed), and revenue is generally recognized as services are provided. System implementation fees charged to property owners are deferred and recognized as revenue over the term of the management or franchise contract. The expenses incurred by Hilton to operate the marketing, sales and brand programs and shared services as well as the Hilton Honors program are recognized as incurred and are presented as other expenses from managed and franchised properties in our consolidated statement of operations. If we collect amounts in excess of amounts expended, we have a commitment to spend these amounts on the related programs. Additionally, if we expend in excess of amounts collected, we have a contractual right to adjust future collections to recover prior period expenditures.
The management and franchise fees and reimbursements from third-party property owners are allocated to the performance obligations and the distinct services to which they relate using their estimated standalone selling prices. The terms of the fees earned under the contract relate to a specific outcome of providing the services (e.g., hotel room sales) or to Hilton's efforts (e.g., costs) to satisfy the performance obligations. Using time as the measure of progress, excluding revenue recognized for point redemptions, we recognize fee revenue and indirect reimbursements in the period earned per the terms of the contract and revenue related to direct reimbursements in the period in which the cost is incurred. For discussion on revenue recognition for point redemptions, refer to the "—Hilton Honors" below.
Owned and leased hotels revenues
We identified the following performance obligations in connection with our owned and leased hotels revenues, with such revenues recognized as the respective performance obligations are satisfied, which results in recognizing the amount we expect to be entitled to for providing the goods or services:
•Cancellable room reservations or ancillary services are typically satisfied as the good or service is transferred to the hotel guest, which is generally when the room stay occurs.
•Noncancellable room reservations and banquet or conference reservations represent a series of distinct goods or services provided over time and satisfied as each distinct good or service is provided, which is reflected by the duration of the reservation.
•Substantive rights for free or discounted goods or services are satisfied when the underlying free or discounted good or service is provided to the hotel guest.
•Other ancillary goods and services are purchased independently of the room reservation at standalone selling prices and are considered separate performance obligations, which are satisfied when the related good or service is provided to the hotel guest.
•Components of package reservations for which each component could be sold separately to other hotel guests are considered separate performance obligations and are satisfied as set forth above.
Owned and leased hotels revenues primarily consist of hotel room sales, revenues from accommodations sold in conjunction with other services (e.g., package reservations), food and beverage sales and sales of other ancillary goods and services (e.g., parking) related to consolidated owned and leased hotels. Revenue is recognized when a room stay occurs or goods and services have been provided. Payment terms typically align with when the goods and services are provided. A portion of owned and leased hotels revenues are deferred upon issuance of Hilton Honors points for Hilton Honors members' paid stay transactions, and revenue is recognized when Hilton Honors points are redeemed for a free or discounted stay at an owned or leased hotel (see "—Hilton Honors" below for additional information).
Although the transaction prices of hotel room sales, goods and other services are generally fixed and based on the respective room reservation or other agreement, an estimate to reduce the transaction price is required if a discount is expected to be provided to the customer. For package reservations, the transaction price is allocated to the performance obligations within the package based on the estimated standalone selling prices of each component. On occasion, the hotel may also provide the customer with a substantive right to a free or discounted good or service in conjunction with a room reservation or banquet contract (e.g., free breakfast or free room night for every four room nights reserved). This substantive right is considered a separate performance obligation to which a portion of the transaction price is allocated based on the estimated standalone selling price of the good or service, adjusted for the likelihood the hotel guest will exercise such right. Revenue is recognized when the substantive right to a free or discounted good or service is redeemed.
Other revenues
Other revenues primarily includes revenues generated by our purchasing operations for our owned, leased, managed and franchised hotels, as well as from properties outside of our system that participate in our purchasing programs. Purchasing revenues include any amounts we expect to retain for vendor rebate arrangements related to purchases made directly by managed and franchised properties, as well as properties outside of our system, through our purchasing programs.
Taxes and fees collected on behalf of governmental agencies
We are required to collect certain taxes and fees from customers on behalf of governmental agencies and remit these back to the applicable governmental agencies on a periodic basis. We have a legal obligation to act as a collection agent. We do not retain these taxes and fees, and, therefore, they are not included in our measurement of transaction prices. We have elected to present revenue net of sales taxes and other similar taxes. We record a liability when the amounts are collected and relieve the liability when payments are made to the applicable taxing authority or other appropriate governmental agency.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include all highly liquid investments with maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase.
Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents
Restricted cash and cash equivalents include cash balances established as collateral for certain guarantees and insurance, including self-insurance and furniture, fixtures and equipment replacement ("FF&E") reserves required under certain lease agreements.
Accounts Receivable
Our accounts receivable primarily consist of amounts due from the property owners with whom we have management and franchise contracts, including the reimbursements due to us for amounts that we have incurred on behalf of our managed and franchised properties.
Allowance for Credit Losses
An allowance for credit losses is provided on our financial instruments, primarily accounts receivable and notes receivable, which are included in other current assets and other assets in our consolidated balance sheet. Expected credit losses on off-balance-sheet commitments, such as guarantees, letters of credit and financing commitments are typically included in other long-term liabilities in our consolidated balance sheet. Our expected credit losses are based on historical collection activity, the nature of the financial instrument, geographic considerations, current and forecasted business conditions and, in the case of off-balance-sheet commitments, the probability that funding will be required.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the future economic benefits arising from assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized. In connection with the 2007 transaction whereby we became a wholly owned subsidiary of affiliates of Blackstone Inc. (the "Merger"), we recorded goodwill representing the excess purchase price over the fair value of the identified assets and liabilities.
We do not amortize goodwill, but rather evaluate goodwill for potential impairment on an annual basis or at other times during the year if indicators of impairment exist. Our reporting units are the same as our operating segments as described in Note 19: "Business Segments." When we evaluate goodwill for potential impairment, generally, we first perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value. If we determine qualitatively that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, or if we decide to bypass the qualitative assessment, we perform a quantitative analysis. The quantitative analysis is used to identify both the existence of impairment and the amount of the impairment loss by comparing the estimated fair value of a reporting unit to its carrying value, including goodwill. The estimated fair value is based on forward-looking estimates of performance and cash flows of our reporting units, which are based on historical operating results, adjusted for current and expected future market conditions, as well as various internal projections and external sources. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its estimated fair value, an impairment loss would be recognized in our consolidated statement of operations in an amount equal to the excess of the carrying value over the estimated fair value, limited to the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit.
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, our goodwill balance was only attributable to our management and franchise reporting unit, which had no accumulated impairment losses as of either date. The changes in our goodwill balances during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 were due to foreign currency translation.
Brands
Brands intangible assets were initially recorded at their fair value at the time of the Merger for the portfolio of brands that existed at the time of the Merger, using the relief-from-royalty valuation approach for owned and leased hotels and the multi-period excess earnings method for managed and franchised hotels. During the year ended December 31, 2024, we recorded brands intangible assets related to the acquisition of the Graduate brand and NoMad brand (refer to Note 3: "Acquisitions" for additional information). The fair value of the Graduate brand intangible asset was determined on a relative fair value basis and
the fair value of the NoMad brand intangible asset was determined using the multi-period excess earnings method. There are no legal, regulatory, contractual, competitive, economic or other factors that limit the useful lives of these brands, and, accordingly, the useful lives of these brands are considered to be indefinite. A portion of our brands intangible assets are denominated in foreign currencies and, as such, a period over period change in these assets is attributable to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates.
We evaluate our indefinite-lived brands intangible assets for impairment on an annual basis or at other times during the year if indicators of impairment exist. When we evaluate our brands intangible assets for potential impairment, generally, we first perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of the asset is less than its carrying value. If we determine qualitatively that the fair value of the asset is more likely than not less than its carrying value, or if we decide to bypass the qualitative assessment, we perform a quantitative analysis. The estimated fair value of the brands intangible assets are based on forward-looking estimates of performance and cash flows of each respective brand, which are based on historical operating results, adjusted for current and expected future market conditions as well as various internal projections and external sources. If the carrying value of a brand intangible asset exceeds its estimated fair value, an impairment loss would be recognized in our consolidated statement of operations in an amount equal to the excess of the carrying value over the estimated fair value.
Intangible Assets with Finite Useful Lives
We capitalize consideration paid to incentivize hotel owners to enter into management and franchise contracts with us as contract acquisition costs and the incremental costs to obtain the contracts as development commissions and other, both of which are generally fixed. We also capitalize costs incurred to develop internal-use computer software and costs to acquire software licenses, as well as internal and external costs incurred in connection with the development of upgrades or enhancements that result in additional information technology functionality. During the year ended December 31, 2024, we recorded franchise contract intangible assets and management contract intangible assets related to the acquisitions of the Graduate brand and NoMad brand, respectively (refer to Note 3: "Acquisitions" for additional information). Additionally, certain finite-lived intangible assets were initially recorded at their fair value at the time of the Merger. As of January 1, 2022, the only remaining finite-lived intangible assets resulting from the Merger related to leases, international management contracts and our Hilton Honors guest loyalty program. The assets related to the international management contracts and Hilton Honors, which both had useful lives of 16 years, were fully amortized during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Intangible assets with finite useful lives are amortized using the straight-line method over their respective estimated useful lives, which for contract acquisition costs and development commissions and other is the contract term, generally including any extension periods that are at our sole option. The estimated useful lives of our finite-lived intangible assets are generally as follows: (i) management contract acquisition costs and development commissions and other (20 to 30 years); (ii) franchise contract acquisition costs and development commissions and other (10 to 20 years); (iii) leases (17 to 35 years); (iv) Graduate brand franchise contract intangible assets and NoMad brand management contract intangible assets acquired in 2024 (9 to 15 years); and (v) capitalized software costs (3 years). In our consolidated statement of operations, the amortization of these intangible assets, excluding contract acquisition costs, is included in depreciation and amortization expenses and the amortization of contract acquisition costs is recognized as a reduction to franchise and licensing fees or base and other management fees, depending on the contract type. Costs incurred prior to the acquisition of a contract, such as external legal costs, are expensed as incurred and included in general and administrative expenses in our consolidated statement of operations. Cash flows for contract acquisition costs and development commissions and other are included as operating activities in our consolidated statement of cash flows, and cash flows for capitalized software costs and management and franchise contract intangible assets acquired are included as investing activities.
We evaluate the carrying value of all finite-lived intangible assets for indicators of impairment, and, if such indicators exist, we perform an analysis to determine the recoverability of the asset group by comparing the expected undiscounted future cash flows to the net carrying value of the asset group. If the carrying value of the asset group is not recoverable and it exceeds the estimated fair value of the asset group, we recognize an impairment loss in our consolidated statement of operations for the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value. We allocate the impairment loss related to the asset group among the various assets within the asset group pro rata based on the relative carrying values of the respective assets.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are recorded at cost. Costs of improvements that extend the economic life or improve service potential are also capitalized. Capitalized costs are depreciated over their estimated useful lives. Costs for normal repairs and
maintenance are expensed as incurred. Right-of-use ("ROU") assets of finance leases are included in property and equipment, net in our consolidated balance sheet; see "—Leases" below for additional information.
Depreciation is recorded using the straight-line method over the assets’ estimated useful lives, which are generally: (i) 8 to 40 years for buildings and improvements; (ii) 3 to 8 years for furniture and equipment; and (iii) 3 to 5 years for computer equipment. Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the shorter of the estimated useful life, based on the estimates above, or the remaining lease term.
We evaluate the carrying value of our property and equipment for indicators of impairment, and, if such indicators exist, we perform an analysis to determine the recoverability of the asset group by comparing the estimated undiscounted future cash flows to the net carrying value of the asset group. If the carrying value of the asset group is not recoverable and it exceeds the estimated fair value of the asset group, we recognize an impairment loss in our consolidated statement of operations for the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value. We allocate the impairment loss related to the asset group among the various assets within the asset group pro rata based on the relative carrying values of the respective assets.
Leases
We determine if a contract is or contains a lease at the inception of the contract, and we classify that lease as a finance lease if it meets certain criteria or as an operating lease when it does not. We reassess if a contract is or contains a lease upon modification of the contract. For contracts in which we are the lessee that contain fixed payments for both lease and non-lease components, we have elected to account for these components as a single lease component.
At the commencement date of a lease, we recognize a lease liability for future fixed lease payments and a ROU asset representing our right to use the underlying asset during the lease term. The lease liability is initially measured as the present value of the future fixed lease payments that will be made over the lease term. The lease term includes lessor options to renew the lease within the lessor's control and lessee options to extend the lease and periods occurring after a lessee early termination option, only to the extent it is reasonably certain that we will exercise such extension options and not exercise such early termination options, respectively. The future fixed lease payments are discounted using the rate implicit in the lease, if available, or our incremental borrowing rate. Current and long-term portions of operating lease liabilities are classified as accounts payable, accrued expenses and other and operating lease liabilities, respectively, and current and long-term portions of finance lease liabilities are classified as current maturities of long-term debt and long-term debt, respectively, in our consolidated balance sheet.
The ROU asset is measured as the amount of the lease liability with adjustments, if applicable, for lease prepayments made prior to or at lease commencement, initial direct costs incurred by us, deferred rent and lease incentives. In our consolidated balance sheet, ROU assets of operating leases are included in operating lease right-of-use assets and ROU assets of finance leases are included in property and equipment, net. We evaluate the carrying value of our ROU assets for indicators of impairment, and, if such indicators exist, we perform an analysis to determine the recoverability of the asset group by comparing the estimated undiscounted future cash flows to the net carrying value of the asset group. If the carrying value of the asset group is not recoverable and it exceeds the estimated fair value of the asset group, we recognize an impairment loss in our consolidated statement of operations for the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value. We allocate the impairment loss related to an asset group among the various assets within the asset group pro rata based on the relative carrying values of the respective assets.
Depending on the individual agreement, our operating leases may require: (i) fixed lease payments as contractually stated in the lease agreement; (ii) variable lease payments, which, for our hotels, are generally based on a percentage of the hotel's revenues or profits or result from changes in inflationary indices; or (iii) lease payments equal to the greater of the fixed or variable lease payments. In addition, during the term of our hotel leases, we may be required to pay some, or all, of the capital costs for FF&E and leasehold improvements in the hotel property. For operating leases, lease expense relating to fixed payments is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term, and lease expense related to variable payments is expensed as incurred, with amounts recognized in owned and leased hotels expenses, general and administrative expenses and other expenses from managed and franchised properties in our consolidated statement of operations. For operating leases for which the ROU asset has been impaired, the periodic lease expense is determined as the sum of (i) the amortization of any remaining ROU asset on a straight-line basis over the remaining term of the lease and (ii) the accretion of the lease liability based on the discount rate applied to the lease liability. For finance leases, the amortization of the ROU asset is recognized over the shorter of the lease term or useful life of the underlying asset within depreciation and amortization expenses and other expenses from managed and franchised properties in our consolidated statement of operations. The interest expense related to finance leases, including any variable lease payments, is recognized in interest expense in our consolidated statement of operations.
Contract Liabilities
Contract liabilities primarily relate to: (i) amounts received when points are issued for the Hilton Honors program, but for which revenue is not yet recognized, since the related points are not yet redeemed; and (ii) advance consideration received from hotel owners for services considered to be part of the contract's performance obligations, such as application, initiation and other fees and system implementation fees. Contract liabilities related to amounts received for points issued for the Hilton Honors program are recognized as revenue when the points are redeemed for a free or discounted good or service by the Hilton Honors member. Contract liabilities related to advance consideration received from hotel owners are recognized ratably as revenue over the term of the related contract. Contract liabilities are included in current and long-term deferred revenues in our consolidated balance sheet, with the current portion based on our estimates of the amounts that will be recognized in the next twelve months.
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests
Noncontrolling interests with redemption features that are not solely within our control are considered redeemable noncontrolling interests. The redeemable noncontrolling interests are a component of temporary equity and are reported between liabilities and equity (deficit) in our consolidated balance sheet. At each reporting period, the redeemable noncontrolling interests are recognized at the higher of (i) the initial carrying amount, adjusted for accumulated earnings (losses), contributions and distributions, or (ii) the redemption value as of the balance sheet date. We include both the earnings (losses) for the period attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests and any adjustment to the carrying value of redeemable noncontrolling interests as a result of a change in the redemption value in net income attributable to redeemable and nonredeemable noncontrolling interests in our consolidated statement of operations.
Hilton Honors
Hilton Honors is our guest loyalty program, and substantially all of our properties participate in the program. Hilton Honors members earn points based on their spend at our participating properties and through participation in affiliated strategic partner programs, including co-branded credit card arrangements. When points are earned by Hilton Honors members, they are provided with a substantive right to free or discounted goods or services in the future upon accumulation of the required number of points. Points may be redeemed for a stay at participating properties, as well as for other goods and services from third parties, including, but not limited to, airlines, car rentals, cruises, vacation packages, shopping and dining.
As points are issued to a Hilton Honors member, the property or strategic partner pays Hilton based on the member's spend at the property or with the strategic partner. The amounts charged are equal to the estimated cost of operating the program, which includes marketing, promotion, communication and administrative expenses, as well as the estimated cost of reward redemptions. When we receive payments related to the issuance of points, we record amounts equal to the estimated cost per point of the future redemption obligation within liability for guest loyalty program and any amounts received in excess of the estimated cost per point within deferred revenues in our consolidated balance sheet. For the Hilton Honors fees that are charged to the participating properties, we allocate such fees to the substantive right created by the points that are issued using the variable consideration allocation guidance, since the fees are directly related to the issuance of points to the Hilton Honors member and Hilton's efforts to satisfy the future redemption of those points. We engage third-party actuaries annually to assist in determining the estimated cost per point of the future reward redemption obligation using a discount rate and statistical formulas that project future point redemptions based on our historical experience and future expectations. Factors used in the estimate include: (i) an estimate of points that will eventually be redeemed, which includes an estimate of breakage (i.e., points that will never be redeemed), (ii) an estimate of when such points will be redeemed and (iii) an estimate of the cost of reimbursing managed and franchised properties and other third parties for redemptions. When a Hilton Honors member stays and earns points at an owned or leased hotel, we recognize a portion of the revenues associated with that stay in owned and leased hotels revenues, with the remaining portion recorded in liability for guest loyalty program and deferred revenues until the points are redeemed. We estimate the current portions of our liability for guest loyalty program and Hilton Honors deferred revenues based on the total point redemptions and, for the liability for guest loyalty program, also breakage that is expected to occur within the next 12 months; these amounts are presented as current portion of liability for guest loyalty program and current portion of deferred revenues in our consolidated balance sheet.
The transaction prices for the Hilton Honors points issued are reduced by the expected payments to the managed and franchised properties and other third parties that will provide the free or discounted good or service using the actuarial projection of the cost per point. The remaining transaction price is then further allocated to the points that are expected to be redeemed, which is determined by adjusting the points that are issued for estimated breakage, and recognized when those points are redeemed. While the points are outstanding, both the estimate of the expected payments to third parties (i.e., cost per point
redeemed) and the estimated breakage are reevaluated. The combined estimate yields the amount of revenue that will be recognized when our point obligation is satisfied and is adjusted so that the final amount allocated to the substantive right of the Hilton Honors member to redeem their points for free or discounted goods and services is reflective of the amount retained by Hilton after the cost of providing the free or discounted goods and services.
We also earn licensing fees from strategic partnerships, including co-branded credit card arrangements (see "—Management and franchise revenues" within "—Revenue Recognition" above). The consideration received is allocated based on the estimated standalone selling prices between two performance obligations: (i) an IP license using the relief-from-royalty valuation method; and (ii) substantive rights for free or discounted goods or services to the Hilton Honors members using a discounted cash flow analysis adjusted for an appropriate margin.
We satisfy our performance obligation related to the IP license over time as the strategic partner simultaneously receives and consumes the benefits of the goods or services provided, and we satisfy our performance obligation related to points issued under the Hilton Honors program when points are redeemed for a free or discounted good or service by the Hilton Honors members. Hilton reimburses managed and franchised properties and other third parties when points are redeemed by Hilton Honors members for stays at the participating properties or for other goods or services from the third-party providers, respectively, at which time the redemption obligation is reduced and the related deferred revenue is recognized in other revenues from managed and franchised properties in our consolidated statement of operations. Additionally, when Hilton Honors members redeem points for a free or discounted stay at our owned and leased hotels, we recognize room revenue, included in owned and leased hotels revenues in our consolidated statement of operations.
Fair Value Measurements – Valuation Hierarchy
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date (i.e., an exit price). We use the three-level valuation hierarchy for classification of fair value measurements. The valuation hierarchy is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation of an asset or liability as of the measurement date. Inputs refer broadly to the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. Inputs may be observable or unobservable. Observable inputs are inputs that reflect the assumptions market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on market data obtained from independent sources. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect our own assumptions about the data market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability developed based on the best information available to us in the specific circumstances. The three-tier hierarchy of inputs is summarized below:
•Level 1 – Valuation is based upon quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
•Level 2 – Valuation is based upon quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, or other inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the instrument.
•Level 3 – Valuation is based upon other unobservable inputs that are significant to the fair value measurement.
The classification of assets and liabilities within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. Proper classification of fair value measurements within the valuation hierarchy is considered each reporting period. The use of different market assumptions or estimation methods may have a material effect on the estimated fair value amounts.
Estimates of the fair values of our financial instruments and nonfinancial assets are determined using available market information and appropriate valuation methods. Considerable judgment is necessary to interpret market data and develop the estimated fair values and the classification within the valuation hierarchy. We have not elected the fair value measurement option for any of our financial assets or liabilities.
Derivative Instruments
We use derivative instruments as part of our overall strategy to manage our exposure to market risks associated with fluctuations in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates. We regularly monitor the financial stability and credit standing of the counterparties to our derivatives. We do not enter into derivatives for speculative purposes.
We record all derivatives at fair value. On the date the derivative contract is entered into, we may designate the derivative as a hedging instrument, and, if so, we formally document all relationships between hedging activities, including the risk
management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions. We generally enter into cash flow hedges (i.e., a hedge of a specific forecasted transaction or the variability of cash flows to be paid), and, in the past, we also entered into net investment hedges (i.e., a hedge of an investment in a foreign operation). Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is qualified and designated as a cash flow hedge or net investment hedge are recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) in our consolidated statement of comprehensive income (loss) until they are reclassified into earnings in the same period or periods during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. If we do not specifically designate a derivative as a cash flow hedge or another type of hedging instrument, changes in the fair value of the undesignated derivative are reported in current period earnings. Cash flows from designated derivatives are classified within the same category as the item being hedged in the consolidated statement of cash flows, while cash flows from undesignated derivatives are included as an investing activity.
We perform an initial prospective assessment of hedge effectiveness on a quantitative basis between the inception date and the earlier of the first quarterly hedge effectiveness date or the issuance of the financial statements that include the hedged transaction. On a quarterly basis, we assess the effectiveness of our designated derivatives in offsetting the variability in the cash flows using a statistical method. This method compares the cumulative change in fair value of each designated derivative to the cumulative change in fair value of a hypothetical derivative, which has terms that identically match the critical terms of the respective hedged transactions, and therefore is presumed to perfectly offset the hedged cash flows. Ineffectiveness results when the cumulative change in the fair value of the designated derivative exceeds the cumulative change in the fair value of the hypothetical derivative. We would discontinue hedge accounting prospectively when the derivative is no longer highly effective as a hedge, the underlying hedged transaction is no longer probable, the hedging instrument expires, is sold, terminated or exercised or if we voluntarily choose to do so.
Currency Translation
The U.S. dollar ("USD") is our reporting currency and is the functional currency of our entities operating in the U.S. The functional currency for our entities operating outside of the U.S. is the currency of the primary economic environment in which the respective entity operates, unless it is considered a highly inflationary economy in which case the functional currency of that entity is the reporting currency of its immediate parent. Assets and liabilities measured in foreign currencies are translated into USD at the prevailing foreign currency exchange rates in effect as of the financial statement date and the related gains and losses, net of applicable deferred income taxes, are reflected in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in our consolidated balance sheet. Income and expense accounts are translated at the average foreign currency exchange rate for the period. Gains and losses from foreign currency exchange rate changes related to transactions denominated in a currency other than an entity's functional currency or intercompany receivables and payables denominated in a currency other than an entity’s functional currency that are not of a long-term investment nature are recognized within gain (loss) on foreign currency transactions in our consolidated statement of operations. Where certain specific evidence indicates intercompany receivables and payables will not be settled in the foreseeable future and are of a long-term nature, gains and losses from foreign currency exchange rate changes are recognized as currency translation adjustment within other comprehensive income (loss) in our consolidated statement of comprehensive income (loss).
Insurance
We are self-insured for losses up to our third-party insurance deductibles for domestic general liability, auto liability, workers' compensation, employment practices liability and crime insurance at our owned, leased and managed hotels that participate in our insurance programs, in addition to other corporate related coverages. We are also self-insured for health coverages for some of our U.S. and Puerto Rico employees, which include those working at our corporate operations and managed hotels, with purchased insurance protection for costs over specified thresholds. In addition, through our captive insurance subsidiary, we participate in reinsurance arrangements that provide coverage and/or act as a financial intermediary for claim payments on our self-insurance program. These obligations and reinsurance arrangements can cause timing differences in the recognition of assets, liabilities, gains and losses between reporting periods, although we expect these amounts to ultimately offset when the related claims are settled. Our insurance reserves are accrued based on the estimated ultimate cost to us of claims that occurred during the covered period, which includes claims incurred but not reported, for which we will be responsible. These estimates are prepared with the assistance of third-party actuaries and consultants. The ultimate cost of claims for a covered period are reviewed at least annually, or more frequently as circumstances dictate, and are adjusted based on the latest information available to us, which may differ from our original estimates.
Share-Based Compensation
Our share-based compensation primarily consists of awards that we grant to eligible employees under the Hilton 2017 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the "2017 Plan") and includes time-vesting restricted stock units ("RSUs"), nonqualified stock options ("options") and performance-vesting RSUs ("performance shares") to our eligible employees:
•RSUs vest in equal annual installments over two or three years from the date of grant. Vested RSUs generally will be settled for the Company's common stock, with the exception of certain awards that will be settled in cash. The grant date fair value per share is equal to the closing stock price on the date of grant.
•Options vest in equal annual installments over three years from the date of grant and terminate 10 years from the date of grant or earlier if the individual’s service terminates under certain circumstances. The grant date fair value per share is estimated using the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model. The exercise price is equal to the closing stock price on the date of grant. Upon the exercise of stock options, new shares of our common stock are issued.
•Performance shares vest three years from the date of grant based on a set of specified performance measures over a defined performance period. Vested performance shares generally will be settled for the Company's common stock, with the exception of certain awards that will be settled in cash. The grant date fair value is equal to the closing stock price on the date of grant. The total number of performance shares that vest related to each performance measure is based on an achievement factor that ranges from zero percent to 200 percent, with 100 percent being the target.
We recognize these share-based payment transactions when services from the employees are rendered and recognize either a corresponding increase in additional paid-in capital or accounts payable, accrued expenses and other in our consolidated balance sheet, depending on whether the instruments granted satisfy the equity or liability classification criteria, respectively. The measurement objective for these equity awards is the estimated fair value at the date of grant of the equity instruments that we are obligated to issue when employees have rendered the requisite service and satisfied any other conditions necessary to earn the right to benefit from the instruments. The compensation expense for an award classified as an equity instrument is recognized ratably over the requisite service period, which is the period during which an employee is required to provide service in exchange for an award. Liability awards are measured based on the award’s estimated fair value, and the fair value is remeasured at each reporting date until the date of settlement. For such liability awards, compensation expense for each period until settlement is based on the change (or a portion of the change, depending on the percentage of the requisite service that has been rendered as of the reporting date) in the fair value of the instrument for each reporting period. Compensation expense for awards with a performance condition is dependent on the expected achievement percentage of such awards, which is reassessed each reporting period from the date of grant through the vesting date of such performance awards, and is recognized over the requisite service period if it is probable that the performance condition will be satisfied. If such performance conditions are not or are no longer considered probable to be satisfied, no compensation expense for these awards is recognized, and any previously recognized expense related to awards that are determined to be improbable of achievement is reversed. Additionally, we have a retirement provision whereby the vesting date for eligible participants is accelerated based on certain criteria, and we recognize total compensation expense for these awards through the accelerated vesting date. We recognize forfeitures of share-based compensation awards as they occur. Share-based compensation expense is recognized in owned and leased hotels expenses, general and administrative expenses and other expenses from managed and franchised properties in our consolidated statement of operations.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes using the asset and liability method. The objectives of accounting for income taxes are to recognize the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the current year and to recognize the deferred tax assets and liabilities that relate to tax consequences in future years, which result from differences between the respective tax basis of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting amounts and tax attribute carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using the enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the respective temporary differences or tax attribute carryforwards are expected to be recovered or settled. The realization of deferred tax assets is contingent upon the generation of future taxable income and other restrictions that may exist under the tax laws of the jurisdiction in which a deferred tax asset exists. Valuation allowances are provided to reduce such deferred tax assets to amounts more likely than not to be ultimately realized.
We are taxed on global intangible low-tax income ("GILTI") earned by certain foreign subsidiaries. We recognize the current tax on GILTI as an expense in the period the tax is incurred.
We use a prescribed more-likely-than-not recognition threshold for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return if there is uncertainty in income taxes recognized in the consolidated financial statements. For all income tax positions, we first determine whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination, including resolution of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of each evaluated tax position and the amounts we would ultimately accept in a negotiated settlement with tax authorities. If it is determined that a position meets the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold, the benefit recognized in the financial statements is measured as the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement.
Loss Contingencies
We are involved in various claims and lawsuits arising in the ordinary course of business, the outcomes of which are subject to significant uncertainty. An estimated loss from a loss contingency will be accrued as a charge to income if it is probable a loss has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated.
Acquisitions
We make certain judgments to determine whether a transaction should be accounted for as a business combination or an asset acquisition. These judgments include the assessment of the inputs, processes and outputs associated with an acquired set of activities and whether the fair value of total assets acquired is concentrated to a single identifiable asset or group of similar assets. We account for a transaction as a business combination when the assets acquired include inputs and one or more substantive processes that, together, significantly contribute to the ability to create outputs and substantially all of the total fair value of the assets acquired is not concentrated to a single identifiable asset or group of similar assets. Otherwise, we account for the transaction as an asset acquisition.
We account for acquisitions that meet the definition of a business combination using the acquisition method of accounting whereby the identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as well as any noncontrolling interests in the acquired business, are recorded at their estimated fair values at the acquisition date, with any excess purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired recorded as goodwill. In business combinations, the purchase price allocations may be based on preliminary estimates and assumptions and, accordingly, during the measurement period, which is up to one year from the acquisition date, we may record adjustments to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed. Any such measurement period adjustments are recognized during the period in which the amount of the adjustment is determined generally with a corresponding offset to goodwill or gain on bargain purchase. We recognize any adjustments subsequent to the measurement period in our consolidated statement of operations. We expense transaction costs related to business combinations as incurred. We record the net assets and results of operations of an acquired entity in our consolidated financial statements from the acquisition date.
In determining the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination, we use various recognized valuation methods including present value modeling and referenced market values, where available. Further, we make assumptions within certain valuation methods including discount rates and timing of future cash flows. Valuations are performed by external valuation professionals with skills and qualifications under management's supervision. We believe the estimated fair values assigned to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed are based on assumptions that market participants would use. However, such assumptions are inherently uncertain and actual results may differ from those estimates.
Acquisitions that do not meet the definition of a business combination are accounted for as asset acquisitions. We allocate the cost of the acquisition, including direct and incremental transaction costs, to the individual assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their relative fair values. We do not recognize any goodwill in an asset acquisition.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
Adopted Accounting Standards
In November 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2023-07 ("ASU 2023-07"), Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which requires, among other things, the following: (i) enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses that are regularly provided to the chief operating decision maker ("CODM") and included in a segment's reported measure of profit or loss; (ii) disclosure of the amount and description of the composition of other segment items, as defined in ASU 2023-07, by reportable segment; (iii) disclosure about how the CODM uses segment profitability measures to make resource allocation decisions; and (iv) reporting the disclosures about each reportable segment's profit or loss and assets on an annual and interim basis. We
adopted the provisions of ASU 2023-07 as of January 1, 2024, which resulted in additional disclosures in the notes to our consolidated financial statements that we applied retrospectively to all prior periods presented.
Accounting Standards Not Yet Adopted
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU No. 2023-09 ("ASU 2023-09"), Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which requires, among other things, the following for public business entities: (i) enhanced disclosures of specific categories of reconciling items included in the rate reconciliation, as well as additional information for any of these items meeting certain qualitative and quantitative thresholds; (ii) disclosure of the nature, effect and underlying causes of each individual reconciling item disclosed in the rate reconciliation and the judgment used in categorizing them if not otherwise evident; and (iii) enhanced disclosures for income taxes paid, which includes federal, state, and foreign taxes, as well as for individual jurisdictions over a certain quantitative threshold. The amendments in ASU 2023-09 eliminate the requirement to disclose the nature and estimate of the range of the reasonably possible change in unrecognized tax benefits for the 12 months after the balance sheet date. The provisions of ASU 2023-09 are effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024; early adoption is permitted. We expect ASU 2023-09 to require additional disclosures in the notes to our consolidated financial statements.
In November 2024, the FASB issued ASU No. 2024-03 ("ASU 2024-03"), Income Statement - Reporting Comprehensive Income - Expense Disaggregation Disclosures (Subtopic 220-40): Disaggregation of Income Statement Expenses, which requires, among other things, the following for public business entities: (i) tabular disclosure of amounts for the following categories that are included in each expense caption within continuing operations on the statement of operations, with each expense caption that includes one of these expense categories deemed a relevant expense caption: (a) purchases of inventory, (b) employee compensation, (c) depreciation, (d) intangible asset amortization and (e) depreciation, depletion, and amortization recognized as part of oil-and gas-producing activities; (ii) disclosure of certain amounts that are already required to be disclosed under current GAAP in the same disclosure as the other disaggregation requirements; (iii) qualitative description of the amount remaining in relevant expense captions that are not separately disaggregated quantitatively; and (iv) disclosure of the total amount of selling expenses and, in annual reporting periods, an entity's definition of selling expenses. The provisions of ASU 2024-03 are effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2026 and interim periods within annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2027; early adoption is permitted. Entities must apply the updates in ASU 2024-03 prospectively and are permitted to apply the updates retrospectively. We expect ASU 2024-03 to require additional disclosures in the notes to our consolidated financial statements.
Note 3: Acquisitions
Graduate by Hilton
In May 2024, we completed the acquisition of the Graduate brand for a total purchase price of $210 million, $200 million of which we paid in cash upon closing. The remaining amount was included in accounts payable, accrued expenses and other in our consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2024 and will be paid upon the satisfaction of certain conditions by the seller, which are expected to occur within the next 12 months. We accounted for the transaction as an asset acquisition. On the date of the acquisition, we added 32 existing properties located in the U.S. and United Kingdom ("U.K.") to our franchise portfolio.
We allocated the cost of the acquisition, including transaction costs, to the assets acquired on a relative fair value basis. As a result, we recorded an indefinite-lived brand intangible asset of approximately $122 million and franchise contract intangible assets of approximately $91 million. The franchise contract intangible assets will be amortized over an estimated useful life of 15 years to depreciation and amortization expenses in our consolidated statements of operations.
The results of operations related to the Graduate brand, which did not have a material impact on our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2024, were included in the consolidated financial statements for the period from the date of acquisition to December 31, 2024.
NoMad
In April 2024, we acquired a controlling financial interest in both Sydell Hotels & Resorts, LLC and Sydell Holding Company UK Ltd (collectively, the "Sydell Group"), which owns the NoMad brand. We accounted for the transaction as a business combination and recognized the fair value, which included measurement period adjustments made subsequent to the acquisition date, of an indefinite-lived brand intangible asset of approximately $48 million and management contract intangible
assets, with an aggregate fair value of approximately $8 million. The management contract intangible assets will be amortized over a weighted average estimated useful life of approximately 14 years to depreciation and amortization expenses in our consolidated statements of operations.
We measured the net assets acquired at fair value as of the date of acquisition. The fair values of the respective net assets acquired were determined by management with assistance from external valuation specialists. We developed our estimate of the fair value of the brand intangible asset and contract intangible assets by applying the multi-period excess earnings method. The multi-period excess earnings method uses unobservable inputs for projected cash flows, including projected financial results and a discount rate, which are considered Level 3 inputs within the fair value measurement valuation hierarchy.
Our redeemable noncontrolling interests relate to our interest in the Sydell Group. The Sydell Group's governing documents contain put options that give the noncontrolling interest holders the right to sell their equity interests to us beginning in the second quarter of 2030, as well as call options that give us the right to purchase the remaining equity interests beginning in the second quarter of 2032. The exercise price of the put and call options is based on a multiple of the Sydell Group's earnings as of the date that such option would be exercised. The redeemable noncontrolling interests were recorded at a fair value of $22 million as of the acquisition date.
The results of operations of the Sydell Group were included in the consolidated financial statements for the period from the date of acquisition to December 31, 2024. The acquisition of a controlling financial interest in the Sydell Group did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2024, and, as such, historical and pro forma results are not disclosed.
Note 4: Revenues from Contracts with Customers
Contract Liabilities
The following table summarizes the activity of our contract liabilities during the year ended December 31, 2024:
| | | | | |
| (in millions) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | $ | 1,521 | |
| Cash received in advance and not recognized as revenue | 767 | |
Revenue recognized(1) | (418) | |
Other(2) | (41) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2024 | $ | 1,829 | |
____________
(1)Primarily related to Hilton Honors, including co-branded credit card arrangements.
(2)Primarily represents the changes in estimated transaction prices for our performance obligations related to the issuance of Hilton Honors points, which had no effect on revenues.
Performance Obligations
As of December 31, 2024, deferred revenues for unsatisfied performance obligations consisted of: (i) $1,032 million related to Hilton Honors that will be recognized as revenue over approximately the next two years; (ii) $780 million related to advance consideration received from hotel owners for application, initiation and other fees and system implementation fees; and (iii) $17 million related to other obligations.
Note 5: Consolidated Variable Interest Entities
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, we consolidated two VIEs that each lease one hotel property, both of which are located in Japan, and for which the assets are only available to settle the obligations of the respective entities and the liabilities of the respective entities are non-recourse to us. We consolidated these VIEs since we are the primary beneficiary, having the power to direct the activities that most significantly affect their economic performance. Additionally, we have the obligation to absorb losses and the right to receive benefits that could be significant to each of the VIEs individually.
Our consolidated balance sheets include the assets and liabilities of these entities, including the effect of foreign currency translation, which primarily comprised the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 53 | | | $ | 46 | |
| Accounts receivable, net | 16 | | | 17 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 40 | | | 37 | |
| Deferred income tax assets | 21 | | | 32 | |
| Other non-current assets | 39 | | | 43 | |
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | 36 | | | 29 | |
Long-term debt(1)(2) | 65 | | | 95 | |
____________
(1)Represents and includes finance lease liabilities of $65 million and $86 million, respectively, as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
(2)Includes current maturities of $13 million and $19 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Note 6: Loss on Investments in Unconsolidated Affiliate
We provide equity and debt financing to certain unconsolidated affiliates with an objective of supporting the growth of our network. The assets relating to these investments are classified as other current assets or other non-current assets in our consolidated balance sheet based on the expected maturity date of the respective investment, if applicable.
In March 2023, as a result of the rise in market-based interest rates, one of our third-party unconsolidated affiliates (the "Fund"), which has underlying investments in certain hotels that we manage or franchise, failed to comply with certain requirements of its debt agreements. As a result, we determined that: (i) our investment in the Fund was fully impaired and (ii) short-term subordinated financing receivables due to us from the Fund were uncollectible. As such, we recognized an other-than-temporary impairment loss on our investment of $44 million and credit losses of $48 million to fully reserve the financing receivables, such that their net carrying values were zero. These losses were recognized in loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023. See Note 12: "Fair Value Measurements" for additional information.
Note 7: Intangible Assets
Finite-lived intangible assets were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
| Gross Carrying Value | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value |
| (in millions) |
| Management and franchise contracts: | | | | | |
| Contract acquisition costs | $ | 1,289 | | | $ | (289) | | | $ | 1,000 | |
Other(1) | 281 | | | (46) | | | 235 | |
| $ | 1,570 | | | $ | (335) | | | $ | 1,235 | |
| Other intangible assets: | | | | | |
| Capitalized software costs | $ | 754 | | | $ | (590) | | | $ | 164 | |
Leases(2) | 88 | | | (58) | | | 30 | |
| $ | 842 | | | $ | (648) | | | $ | 194 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 |
| Gross Carrying Value | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value |
| (in millions) |
| Management and franchise contracts: | | | | | |
| Contract acquisition costs | $ | 1,183 | | | $ | (244) | | | $ | 939 | |
Other(1) | 162 | | | (37) | | | 125 | |
| $ | 1,345 | | | $ | (281) | | | $ | 1,064 | |
| Other intangible assets: | | | | | |
| Capitalized software costs | $ | 712 | | | $ | (576) | | | $ | 136 | |
Leases(2)(3) | 126 | | | (89) | | | 37 | |
| $ | 838 | | | $ | (665) | | | $ | 173 | |
____________
(1)Includes development commissions and other intangible assets. Amount for the year ended December 31, 2024 also includes management and franchise contract intangible assets acquired from third parties.
(2)Represents intangible assets that were initially recorded at fair value at the time of the Merger.
(3)During the year ended December 31, 2023, we recognized $4 million of impairment losses related to our leases intangible assets in our consolidated statement of operations; see Note 12: "Fair Value Measurements" for additional information.
Amortization of our finite-lived intangible assets was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
Recognized in depreciation and amortization expenses(1) | $ | 91 | | | $ | 104 | | | $ | 116 | |
| Recognized as a reduction of franchise and licensing fees and base and other management fees | 50 | | | 43 | | | 38 | |
____________
(1)Includes amortization expense of $5 million, $37 million and $45 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, associated with assets that were initially recorded at fair value at the time of the Merger, some of which fully amortized during the year ended December 31, 2023.
As of December 31, 2024, we estimate future amortization expense of our finite-lived intangible assets that will be recognized in depreciation and amortization expenses to be as follows:
| | | | | |
| Year | (in millions) |
| 2025 | $ | 96 | |
| 2026 | 74 | |
| 2027 | 43 | |
| 2028 | 21 | |
| 2029 | 17 | |
| Thereafter | 178 | |
| $ | 429 | |
Note 8: Property and Equipment
Property and equipment were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Land | $ | 8 | | | $ | 8 | |
| Buildings and leasehold improvements | 368 | | | 364 | |
| Furniture and equipment | 375 | | | 407 | |
| Construction-in-progress | 65 | | | 37 | |
| Finance lease ROU assets | 94 | | | 86 | |
| 910 | | | 902 | |
Accumulated depreciation and amortization(1) | (499) | | | (520) | |
| $ | 411 | | | $ | 382 | |
____________
(1)During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, depreciation and amortization expenses on property and equipment was $55 million, $43 million and $46 million, respectively.
Property and equipment, net attributed to U.S. operations was $208 million and $183 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, and to operations outside the U.S. was $203 million and $199 million, respectively, most significantly in the U.K. and Japan.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, we recognized $1 million of impairment losses in our consolidated statement of operations related to property and equipment, net; see Note 12: "Fair Value Measurements" for additional information.
Note 9: Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other
Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Accrued employee compensation and benefits | $ | 637 | | | $ | 592 | |
| Accounts payable | 409 | | | 457 | |
| Operating lease liabilities, current | 117 | | | 116 | |
| Insurance reserves, current | 114 | | | 99 | |
Other current liabilities and accrued expenses(1) | 847 | | | 715 | |
| $ | 2,124 | | | $ | 1,979 | |
____________
(1)Includes deposit liabilities related to hotel operations and application fees, promotional liabilities, contract acquisition costs payable and income taxes payable, as well as accrued expenses related to taxes, interest, advertising, rent and other.
Note 10: Debt
Long-term Debt
Long-term debt balances, including obligations for finance leases, and associated interest rates and maturities as of December 31, 2024, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Senior secured term loan facility due 2028 | $ | — | | | $ | 1,000 | |
| Senior secured term loan facility with a rate of 6.09%, due 2030 | 3,119 | | | 2,119 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 5.375%, due 2025(1) | 500 | | | 500 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 4.875%, due 2027(1) | 600 | | | 600 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 5.750%, due 2028(1) | 500 | | | 500 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 5.875%, due 2029(1) | 550 | | | — | |
Senior notes with a rate of 3.750%, due 2029(1) | 800 | | | 800 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 4.875%, due 2030(1) | 1,000 | | | 1,000 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 4.000%, due 2031(1) | 1,100 | | | 1,100 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 3.625%, due 2032(1) | 1,500 | | | 1,500 | |
Senior notes with a rate of 6.125%, due 2032(1) | 450 | | | — | |
Senior notes with a rate of 5.875%, due 2033(1) | 1,000 | | | — | |
Finance lease liabilities with a weighted average rate of 6.03%, due 2025 to 2030(2) | 117 | | | 139 | |
Other debt of consolidated VIEs(2) | — | | | 9 | |
| 11,236 | | | 9,267 | |
| Less: unamortized deferred financing costs and discounts | (85) | | | (71) | |
Less: current maturities of long-term debt(3) | (535) | | | (39) | |
| $ | 10,616 | | | $ | 9,157 | |
____________
(1)These notes are collectively referred to as the Senior Notes and are jointly and severally guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by the Parent and substantially all of its direct and indirect wholly owned domestic restricted subsidiaries, other than Hilton Domestic Operating Company Inc. ("HOC"), an indirect wholly owned subsidiary of the Parent and the issuer of all of the series of Senior Notes.
(2)Long-term debt of our consolidated VIEs is included in finance lease liabilities and other debt of consolidated VIEs as applicable. Refer to Note 5: "Consolidated Variable Interest Entities" for additional information.
(3)Represents current maturities of finance lease liabilities and the 5.375% Senior Notes due 2025 as of December 31, 2024 and current maturities of finance lease liabilities and borrowings of consolidated VIEs as of December 31, 2023. We believe that we have sufficient sources of liquidity and access to debt financing to address the current maturities of long-term debt at or prior to the respective maturity dates.
Senior Secured Credit Facilities
Our senior secured credit facilities consist of a senior secured revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Credit Facility") and senior secured term loan facilities (the "Term Loans"). The obligations under our senior secured credit facilities are unconditionally and irrevocably guaranteed by the Parent and substantially all of its direct and indirect wholly owned domestic restricted subsidiaries, other than HOC, the named borrower of the senior secured credit facilities.
In June 2024, we amended the credit agreement governing our Term Loans pursuant to which $1.0 billion of outstanding Term Loans due June 2028 were replaced with $1.0 billion of incremental Term Loans due November 2030, aligning their maturity with the outstanding $2.1 billion tranche of Term Loans due November 2030. Additionally, the entire balance of the Term Loans was repriced with an interest rate of the Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR") plus 1.75% (collectively, the "June 2024 Amendment"). In connection with the June 2024 Amendment, we incurred $3 million of debt issuance costs, which were recognized in other non-operating loss, net in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2024.
In March 2024, we borrowed and subsequently repaid $200 million under the Revolving Credit Facility.
In November 2023, we amended the credit agreement governing our Term Loans pursuant to which $1.0 billion of outstanding Term Loans were converted into a new tranche of Term Loans due June 2028 with an interest rate of SOFR plus 1.85% and $1.6 billion of outstanding Term Loans were converted into a new tranche, which was also increased by $500 million of aggregate principal amount, due November 2030 with an interest rate of SOFR plus 2.10%. In connection with
the amendment of the Term Loans, we incurred $21 million of original issue discounts and fees, of which $11 million was recognized as a reduction to the outstanding debt balance in our consolidated balance sheet to be amortized to interest expense through the respective maturity dates of the Term Loans. The remaining $10 million was recognized in other non-operating income, net in our consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2023.
In January 2023, we amended the credit agreement governing our Revolving Credit Facility to increase the borrowing capacity from $1.75 billion to $2.0 billion, $250 million of which is available in the form of letters of credit, and extended the maturity date to January 2028. In connection with this amendment, we incurred approximately $9 million of debt issuance costs, which were recognized in other non-current assets in our consolidated balance sheet and will be amortized to interest expense through the maturity date of the Revolving Credit Facility.
No borrowings were outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility as of December 31, 2024, which had an available borrowing capacity of $1,910 million after considering $90 million of outstanding letters of credit.
Senior Notes
In September 2024, we issued $1.0 billion aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Senior Notes due 2033 (the "2033 Senior Notes") and incurred an aggregate $15 million of debt issuance costs which were recognized as a reduction to the outstanding debt balance in our consolidated balance sheet and will be amortized to interest expense through the maturity date of the 2033 Senior Notes. Interest on the 2033 Senior Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on March 15 and September 15 of each year, beginning March 15, 2025.
In March 2024, we issued $550 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Senior Notes due 2029 (the "5.875% 2029 Senior Notes") and $450 million aggregate principal amount of 6.125% Senior Notes due 2032 (the "6.125% 2032 Senior Notes") (collectively, the "March Senior Notes issuance") and incurred an aggregate $15 million of debt issuance costs which were recognized as a reduction to the outstanding debt balance in our consolidated balance sheet and will be amortized to interest expense through the respective maturity dates of the 5.875% 2029 Senior Notes and the 6.125% 2032 Senior Notes. Interest on the 5.875% 2029 Senior Notes and the 6.125% 2032 Senior Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on April 1 and October 1 of each year, beginning October 1, 2024. We used a portion of the net proceeds from the March Senior Notes issuance to repay $200 million borrowed under our Revolving Credit Facility earlier in March 2024.
Debt Maturities
The contractual maturities of our long-term debt as of December 31, 2024 were as follows:
| | | | | |
| Year | (in millions) |
| 2025 | $ | 535 | |
| 2026 | 31 | |
| 2027 | 616 | |
| 2028 | 512 | |
| 2029 | 1,362 | |
| Thereafter | 8,180 | |
| $ | 11,236 | |
Note 11: Other Liabilities
Other long-term liabilities were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Other long-term tax liabilities | $ | 618 | | | $ | 645 | |
| Insurance reserves | 158 | | | 154 | |
| Deferred employee compensation and benefits | 89 | | | 86 | |
| Pension obligations | 17 | | | 34 | |
| Other | 59 | | | 79 | |
| $ | 941 | | | $ | 998 | |
Note 12: Fair Value Measurements
The fair values of certain financial instruments and the hierarchy level we used to estimate the fair values are shown below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 |
| | | Hierarchy Level |
| Carrying Value(1) | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| (in millions) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate swap | $ | 45 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 45 | | | $ | — | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Long-term debt(2) | 11,119 | | | 7,560 | | | — | | | 3,140 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2023 |
| | | Hierarchy Level |
| Carrying Value(1) | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| (in millions) |
| Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate swaps | $ | 75 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 75 | | | $ | — | |
| Liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Long-term debt(2) | 9,119 | | | 5,631 | | | — | | | 3,129 | |
____________
(1)The fair values of cash equivalents and restricted cash equivalents approximate their carrying values due to their short-term maturities. The fair values of all other financial instruments not included in these tables are estimated to be equal to their carrying values.
(2)The carrying values and fair values exclude the deduction for unamortized deferred financing costs and any applicable discounts, as well as all finance lease liabilities and other debt of consolidated VIEs; refer to Note 10: "Debt" for additional information.
We measured our interest rate swaps at fair value, which was determined using a discounted cash flow analysis that reflects the contractual terms of the interest rate swaps, including the period to maturity, and uses observable market-based inputs of similar instruments, including interest rate curves, as applicable.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, we measured the net assets acquired in the acquisition of the Sydell Group at fair value on a non-recurring basis; see Note 3: "Acquisitions" for additional information.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, we measured a financial asset at fair value on a non-recurring basis and recognized an other-than-temporary impairment loss of $44 million in loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate in our consolidated statement of operations. In March 2023, the financial asset, an equity method investment in the Fund, which derives its market value from the underlying hotel assets it owns, failed to comply with its debt agreements, as discussed in Note 6: "Loss on Investments in Unconsolidated Affiliate." Given the lack of an active market or observable inputs for the fair value of the Fund, we determined that at March 31, 2023 our investment had a fair value of zero using Level 3 valuation inputs.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the forecasted operating results of certain leased hotels caused us to evaluate the carrying value of the affected properties for impairment. We estimated the fair value of the related assets using discounted cash flow analyses and Level 3 valuation inputs including growth rates and discount rates that reflected the risk profile of the underlying cash flows and the individual markets where the assets are located. Estimations of the stabilized growth rates approximated 1.8 percent and the discount rates ranged from 8.0 percent to 11.3 percent, with the weighted average, based on relative impairment losses, being at the lower end of the range. As a result of these non-recurring fair value measurements, we recognized impairment losses on these assets, all of which are in our ownership segment, of $38 million during the year ended December 31, 2023. The fair values of these assets as of December 31, 2023, the date of measurement, were as follows:
| | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | (in millions) |
| Other intangible assets, net | | | $ | 3 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | | | 69 | |
| Property and equipment, net | | | 1 | |
Note 13: Leases
We lease hotel properties, land, corporate office space and equipment used at hotels and corporate offices, with our most significant lease liabilities relating to hotel properties. As of December 31, 2024, we leased 40 hotels under operating leases and five hotels under finance leases, two of which were the liabilities of consolidated VIEs, which are non-recourse to us. Our hotel leases expire at various dates, with varying renewal and termination options.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, we recognized $33 million of impairment losses in our consolidated statement of operations related to certain operating lease ROU assets; see Note 12: "Fair Value Measurements" for additional information.
Supplemental balance sheet information related to leases was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Operating leases: | | | |
Operating lease right-of-use assets(1) | $ | 567 | | | $ | 618 | |
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other | 117 | | | 116 | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 735 | | | 808 | |
| | | |
| Finance leases: | | | |
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 37 | | | $ | 36 | |
| Current maturities of long-term debt | 35 | | | 34 | |
| Long-term debt | 82 | | | 105 | |
| | | |
| Weighted average remaining lease term: | | | |
| Operating leases | 10.0 years | | 10.6 years |
| Finance leases | 4.3 years | | 5.1 years |
| | | |
| Weighted average discount rate: | | | |
| Operating leases | 4.49 | % | | 4.33 | % |
| Finance leases | 6.03 | % | | 6.01 | % |
____________
(1)Includes $77 million and $73 million attributable to U.S. operations as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, and $490 million and $545 million to operations outside the U.S., respectively, most significantly in the U.K. and Germany for both years.
The components of lease expense were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| Operating lease expense for fixed payments | $ | 109 | | | $ | 118 | | | $ | 113 | |
| Finance lease expense: | | | | | |
| Amortization of ROU assets | 22 | | | 21 | | | 21 | |
| Fixed interest on lease liabilities | 8 | | | 9 | | | 10 | |
Variable lease expense(1) | 189 | | | 179 | | | 139 | |
____________
(1)Includes amounts related to both operating leases and finance leases.
Supplemental cash flow information related to leases was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities: | | | | | |
| Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 138 | | | $ | 137 | | | $ | 157 | |
| Financing cash flows from finance leases | 38 | | | 40 | | | 42 | |
| ROU assets obtained in exchange for lease liabilities in non-cash transactions: | | | | | |
| Operating leases | 44 | | | 39 | | | 135 | |
| Finance leases | 24 | | | 24 | | | 21 | |
Our future minimum lease payments as of December 31, 2024 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating
Leases | | Finance
Leases |
| Year | (in millions) |
| 2025 | $ | 152 | | | $ | 42 | |
| 2026 | 128 | | | 33 | |
| 2027 | 117 | | | 19 | |
| 2028 | 115 | | | 15 | |
| 2029 | 109 | | | 15 | |
| Thereafter | 455 | | | 10 | |
| Total minimum lease payments | 1,076 | | | 134 | |
| Less: imputed interest | (224) | | | (17) | |
| Total lease liabilities | $ | 852 | | | $ | 117 | |
Note 14: Income Taxes
Income Tax Provision
The domestic and foreign components of income before income taxes were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| U.S. income before income taxes | $ | 1,237 | | | $ | 1,301 | | | $ | 1,320 | |
| Foreign income before income taxes | 546 | | | 391 | | | 414 | |
| Income before income taxes | $ | 1,783 | | | $ | 1,692 | | | $ | 1,734 | |
The components of our provision for income taxes were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| Current: | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | 357 | | | $ | 586 | | | $ | 306 | |
| State | 82 | | | 136 | | | 81 | |
| Foreign | 52 | | | 83 | | | 56 | |
| Total current | 491 | | | 805 | | | 443 | |
| Deferred: | | | | | |
| Federal | (51) | | | (250) | | | 16 | |
| State | (15) | | | (83) | | | 6 | |
Foreign(1) | (181) | | | 69 | | | 12 | |
| Total deferred | (247) | | | (264) | | | 34 | |
| Total provision for income taxes | $ | 244 | | | $ | 541 | | | $ | 477 | |
____________
(1)Includes a $29 million tax benefit from the release of valuation allowances as the Company concluded it is more likely than not to realize the benefit of certain foreign deferred tax assets.
Reconciliations of the provision for income taxes at the U.S. statutory rate to the provision for income taxes were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| Statutory U.S. federal income tax provision | $ | 375 | | | $ | 355 | | | $ | 364 | |
| State income taxes, net of U.S. federal income tax benefit | 55 | | | 45 | | | 65 | |
| Impact of foreign operations | 90 | | | 33 | | | 35 | |
| Changes in deferred tax asset valuation allowances | (24) | | | 40 | | | (5) | |
| Income tax rate changes | — | | | (9) | | | — | |
| Provision for uncertain tax positions | 26 | | | 69 | | | 14 | |
Claim for increased foreign tax basis(1) | (270) | | | — | | | — | |
| Excess tax benefits related to share-based compensation | (22) | | | (6) | | | (8) | |
| Other, net | 14 | | | 14 | | | 12 | |
| Provision for income taxes | $ | 244 | | | $ | 541 | | | $ | 477 | |
____________
(1)Includes tax benefit for claim for increased foreign tax basis, net of $547 million tax expense for related valuation allowance increase as of December 31, 2024.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, we filed an affirmative claim with a foreign taxing authority to increase the tax basis of certain brand assets that were part of a prior-year intercompany transfer that is subject to ongoing tax audits in relevant jurisdictions. We have evaluated this claim in accordance with the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold for the financial statement recognition and measurement of this tax position and have recognized a deferred tax asset representing the greatest amount of benefit that is more than 50 percent likely to be realized upon settlement. We also increased our valuation allowances related to the portion of this deferred tax asset that we believe will ultimately not be realized.
Deferred Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes represent the tax effect of the differences between the book and tax bases of assets and liabilities plus carryforward items. The tax effects of the temporary differences and carryforwards that give rise to our net deferred taxes were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | |
| Net tax loss carryforwards and carrybacks | $ | 525 | | | $ | 604 | |
| Foreign brands | 763 | | | — | |
| Compensation | 118 | | | 124 | |
| Reserves | 57 | | | 81 | |
| Operating and finance lease liabilities | 282 | | | 290 | |
| Deferred income | 659 | | | 558 | |
| Foreign tax credit carryforwards | 70 | | | 63 | |
| Other | 127 | | | 114 | |
| Total gross deferred tax assets | 2,601 | | | 1,834 | |
| Less: valuation allowance | (1,200) | | | (698) | |
| Deferred tax assets | 1,401 | | | 1,136 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
| U.S. brands | (1,124) | | | (1,123) | |
| Foreign brands | — | | | (20) | |
| Operating and finance lease ROU assets | (200) | | | (195) | |
| Other | (81) | | | (59) | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | (1,405) | | | (1,397) | |
| Net deferred taxes | $ | (4) | | | $ | (261) | |
As of December 31, 2024, we had gross U.S. separate return limitation year loss carryforwards and foreign operating loss carryforwards of $2.2 billion, resulting in deferred tax assets of $525 million. Approximately $27 million of our deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2024 related to loss carryforwards that will expire between 2025 and 2044 with less than $1 million of that amount expiring in 2025. Approximately $498 million of our deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2024 related to loss carryforwards that are not subject to expiration. We believe that it is more likely than not that the benefit from certain U.S. and foreign loss carryforwards will not be realized. In recognition of this assessment, we provided valuation allowances totaling $462 million as of December 31, 2024 on the deferred tax assets relating to these loss carryforwards. As of December 31, 2024, we also had deferred tax assets for U.S. tax credit carryforwards of $70 million that will expire between 2029 and 2034, for which we have provided full valuation allowances.
Tax Uncertainties
We file income tax returns, including returns for our subsidiaries, with federal, state, local and foreign tax jurisdictions. We are under regular and recurring audit by the Internal Revenue Service ("IRS") and other taxing authorities on open tax positions. The timing of the resolution of tax audits is highly uncertain, as are the amounts, if any, that may ultimately be paid upon such resolution. Changes may result from the conclusion of ongoing audits, appeals or litigation in federal, state, local and foreign tax jurisdictions or from the resolution of various proceedings between the U.S. and foreign tax authorities. As of December 31, 2024, the Company's federal income tax returns remain subject to examination by the IRS for tax years from 2011 through 2024. Various income tax returns filed with state, local and foreign jurisdictions remain subject to examination by the applicable taxing authorities.
Reconciliations of the beginning and ending amounts of unrecognized tax benefits were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 555 | | | $ | 337 | | | $ | 375 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 288 | | | 268 | | | 1 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to the current year | 19 | | | 4 | | | 3 | |
| Reductions for tax positions related to prior years | (4) | | | (2) | | | (32) | |
| Settlements | (1) | | | (48) | | | — | |
| Lapse of statute of limitations | (4) | | | (4) | | | (5) | |
| Currency translation adjustment | (4) | | | — | | | (5) | |
| Balance at end of year | $ | 849 | | | $ | 555 | | | $ | 337 | |
We recognize interest and penalties accrued related to uncertain tax positions in income tax benefit (expense) in our consolidated statement of operations. During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, we recognized income tax expense related to interest and penalties of $35 million, $72 million and $17 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, we had accrued approximately $182 million and $150 million, respectively, for interest and penalties related to our unrecognized tax benefits in our consolidated balance sheets. Included in the balances of unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2024 and 2023 were $597 million and $314 million, respectively, associated with positions that, if favorably resolved, would provide a benefit to our effective income tax rate. We believe resolutions of examinations with tax authorities are reasonably possible within the next 12 months. We are unable to estimate the amount of unrecognized tax benefits that will increase or decrease during the next 12 months, as this estimate could change depending on the nature and timing of settlements.
Note 15: Employee Benefit Plans
We sponsor multiple domestic and international employee benefit plans (the "pension plans"), and the benefits are based upon years of service and compensation.
The employee benefit plan in the U.S. (the "Domestic Plan") covers certain employees not earning union benefits. This plan was frozen for participant benefit accruals in 1996; therefore, the projected benefit obligation is equal to the accumulated benefit obligation. The plan assets will be used to pay benefits due to employees for service through December 31, 1996. Since employees have not accrued additional benefits from that time, we do not utilize salary or pension inflation assumptions in calculating our benefit obligation for the Domestic Plan.
The employee benefit plans covering certain of our international employees include: (i) a plan that covers employees in the U.K. (the "U.K. Plan"), which was frozen to further service accruals in 2013 and (ii) a number of smaller plans that cover employees in various countries around the world (the "International Plans"). We do not consider the International Plans to be material to our consolidated financial statements.
The annual measurement date for all of our plans is December 31. We are required to recognize the funded status of our pension plans, which is the difference between the fair value of plan assets and the projected benefit obligations, in our consolidated balance sheet and make corresponding adjustments for changes in the difference between the fair value of plan assets and the projected benefit obligations through accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of taxes.
The following table presents the projected benefit obligation, fair value of plan assets, funded status and accumulated benefit obligation for the Domestic Plan and the U.K. Plan:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic Plan | | U.K. Plan |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Change in projected benefit obligation | | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 281 | | | $ | 284 | | | $ | 309 | | | $ | 286 | |
| Service cost | — | | | — | | | 2 | | | 2 | |
| Interest cost | 14 | | | 15 | | | 14 | | | 14 | |
| Actuarial loss (gain), net of expenses | (8) | | | 5 | | | (32) | | | 4 | |
Settlements(1) | (41) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Effect of foreign currency exchange rates | — | | | — | | | (2) | | | 16 | |
| Benefits paid | (23) | | | (23) | | | (16) | | | (13) | |
| Benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 223 | | | $ | 281 | | | $ | 275 | | | $ | 309 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Change in plan assets | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 278 | | | $ | 271 | | | $ | 298 | | | $ | 277 | |
| Actual return on plan assets, net of expenses | 13 | | | 25 | | | (14) | | | 10 | |
| Employer contributions | 4 | | | 5 | | | 9 | | | 9 | |
Settlements(1) | (41) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Effect of foreign currency exchange rates | — | | | — | | | (2) | | | 15 | |
| Benefits paid | (23) | | | (23) | | | (16) | | | (13) | |
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year | 231 | | | 278 | | | 275 | | | 298 | |
Funded status at end of year (underfunded)(2) | 8 | | | (3) | | | — | | | (11) | |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 223 | | | $ | 281 | | | $ | 275 | | | $ | 309 | |
____________
(1)During the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company purchased a group annuity contract (the "annuity purchase") and transferred $41 million of its pension plan assets and related benefit obligations related to its Domestic Plan to a third-party insurer.
(2)Funded amounts are recognized in other long-term assets and underfunded amounts are recognized in other long-term liabilities in our consolidated balance sheets, as applicable.
Changes in amounts recorded in accumulated other comprehensive loss consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic Plan | | U.K. Plan |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
Net actuarial loss (gain)(1) | $ | (3) | | | $ | (3) | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 27 | | | $ | 39 | |
| Amortization of prior service cost | (4) | | | (4) | | | (4) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Amortization of net loss | (1) | | | — | | | (3) | | | (8) | | | (6) | | | (3) | |
Settlement losses(2) | (10) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Net amount recognized | $ | (18) | | | $ | (7) | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | (5) | | | $ | 21 | | | $ | 36 | |
____________
(1)Amounts for the U.K. Plan include the impact of foreign currency exchange.
(2)Amount for the year ended December 31, 2024 includes a loss for a settlement related to the Company's Domestic Plan as a result of the annuity purchase, which was recognized in other non-operating loss, net in our consolidated statement of operations.
The net periodic pension cost (credit) was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic Plan | | U.K. Plan |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
Service cost(1) | $ | — | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 3 | | | $ | 2 | | | $ | 2 | | | $ | 2 | |
Interest cost(2) | 14 | | | 15 | | | 8 | | | 14 | | | 14 | | | 8 | |
Expected return on plan assets(2) | (18) | | | (20) | | | (20) | | | (23) | | | (22) | | | (23) | |
Amortization of prior service cost(2) | 4 | | | 4 | | | 4 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Amortization of net loss(2) | 1 | | | — | | | 3 | | | 8 | | | 6 | | | 3 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Settlement losses(3) | 10 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Net periodic pension cost (credit) | $ | 11 | | | $ | 2 | | | $ | (2) | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (10) | |
____________
(1)Recognized in owned and leased hotels expenses and general and administrative expenses, as applicable, in our consolidated statements of operations.
(2)Recognized in other non-operating income (loss), net in our consolidated statements of operations.
(3)During the year ended December 31, 2024, as a result of the annuity purchase, we recognized a non-cash pension settlement loss in other non-operating loss, net in our consolidated statement of operations.
The weighted average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic Plan | | U.K. Plan |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Discount rate | 5.6 | % | | 5.2 | % | | 5.5 | % | | 4.5 | % |
| Salary inflation | N/A | | N/A | | 2.5 | | | 2.4 | |
| Pension inflation | N/A | | N/A | | 2.9 | | | 2.8 | |
The weighted average assumptions used to determine net periodic pension cost (credit) were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic Plan | | U.K. Plan |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Discount rate | 5.2 | % | | 5.6 | % | | 2.9 | % | | 4.5 | % | | 4.8 | % | | 1.9 | % |
| Expected return on plan assets | 7.0 | | | 6.8 | | | 6.3 | | | 7.5 | | | 7.3 | | | 5.0 | |
| Salary inflation | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | 2.4 | | | 2.6 | | | 2.6 | |
| Pension inflation | N/A | | N/A | | N/A | | 2.8 | | | 3.1 | | | 3.1 | |
The investment objectives for the various plans are preservation of capital, current income and long-term growth of capital. All plan assets are managed by third-party investment managers and do not include investments in Hilton stock. Asset allocations are reviewed periodically by the investment managers.
Expected long-term returns on plan assets are determined using historical performance for return-seeking assets and liability-driven investments held by our plans, actual performance of plan assets and current and expected market conditions. Expected returns are formulated based on the target asset allocation. As of December 31, 2024 the target asset allocations for the Domestic Plan and U.K. Plan were 70 percent and 65 percent, respectively, in return-seeking assets, and 30 percent and 35 percent, respectively, in liability-driven investments and cash.
The following tables present the fair value hierarchy of total plan assets measured at fair value by asset category:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic Plan | | U.K. Plan |
| December 31, | | December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| (in millions) |
| Level 1 | | | | | | | |
| Cash | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2 | | | $ | 1 | |
| Bond funds | 7 | | | 12 | | | — | | | — | |
| Level 2 | | | | | | | |
| Bond funds | — | | | — | | | 36 | | | 37 | |
Net asset value(1) | | | | | | | |
| Cash equivalents | — | | | — | | | 6 | | | 7 | |
| Bond funds | — | | | — | | | 72 | | | 82 | |
| Common collective trusts | 224 | | | 266 | | | — | | | — | |
| Alternative investments | — | | | — | | | 110 | | | 121 | |
| Other | — | | | — | | | 49 | | | 50 | |
| $ | 231 | | | $ | 278 | | | $ | 275 | | | $ | 298 | |
____________
(1)Certain investments are measured at net asset value per share as a practical expedient and, therefore, have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy.
As of December 31, 2024, the benefits expected to be paid in the next five years and in the aggregate for the five years thereafter were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Domestic Plan | | U.K. Plan |
| Year | (in millions) |
| 2025 | $ | 22 | | | $ | 16 | |
| 2026 | 21 | | | 17 | |
| 2027 | 21 | | | 17 | |
| 2028 | 20 | | | 17 | |
| 2029 | 20 | | | 18 | |
| 2030-2034 | 89 | | | 94 | |
| $ | 193 | | | $ | 179 | |
In 2007, the Domestic Plan and plans maintained for certain domestic hotels currently or formerly managed by us were merged into a multiple employer plan. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the multiple employer plan had combined plan assets of $240 million and $303 million, respectively, and a projected benefit obligation of $230 million and $301 million, respectively.
Note 16: Share-Based Compensation
We recognized share-based compensation expense of $176 million, $169 million and $162 million during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, which included amounts reimbursed by hotel owners, and the related tax benefit recognized was $72 million, $48 million and $48 million, respectively. In December 2020, we modified our then-outstanding performance shares in response to the COVID-19 pandemic to reward for results achieved prior to the pandemic and incentivize our recovery efforts, with a portion of the awards modified to vest based on continued service and the remaining portion of the awards to vest based on new performance measures. As a result of this modification, our share-based compensation expense for the year ended December 31, 2022 includes incremental share-based compensation expense of $25 million.
As of December 31, 2024, unrecognized compensation costs for unvested awards under the 2017 Plan were approximately $132 million, which are expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.7 years on a straight-line basis. As of December 31, 2024, there were 9.7 million remaining shares authorized for awards under the 2017 Plan, including any shares subject to awards outstanding under the 2013 Omnibus Incentive Plan that will become available for issuance under the 2017 Plan if such outstanding awards expire or are terminated or are canceled or forfeited.
RSUs
The following table provides information about our RSU grants:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Number of shares granted (in thousands) | 473 | | | 604 | | | 507 | |
| Weighted average grant date fair value per share | $ | 203.98 | | | $ | 146.19 | | | $ | 150.58 | |
| Aggregate fair value of shares vested (in millions) | $ | 107 | | | $ | 84 | | | $ | 97 | |
The following table summarizes the activity of our RSUs during the year ended December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value per Share |
| (in thousands) | | |
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 1,012 | | | $ | 144.49 | |
| Granted | 473 | | | 203.98 | |
| Vested | (521) | | | 142.12 | |
| Forfeited | (42) | | | 165.89 | |
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2024 | 922 | | | 175.37 | |
Options
The following table provides information about our option grants:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Number of options granted (in thousands) | 264 | | | 341 | | | 318 | |
| Weighted average exercise price per share | $ | 203.95 | | | $ | 146.18 | | | $ | 150.67 | |
| Weighted average grant date fair value per share | $ | 71.25 | | | $ | 52.27 | | | $ | 51.15 | |
| Aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised (in millions) | $ | 90 | | | $ | 18 | | | $ | 9 | |
The weighted average grant date fair value per share of the option grants for each year was determined using the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
Expected volatility(1) | 27.94 | % | | 30.16 | % | | 33.28 | % |
Dividend yield(2) | 0.33 | % | | 0.43 | % | | 0.41 | % |
Risk-free rate(3) | 4.17 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 1.93 | % |
Expected term (in years)(4) | 6.0 | | 6.0 | | 6.0 |
____________
(1)Estimated using a blended approach of historical and implied volatility. Historical volatility is based on the historical movement of Hilton's stock price for a period that corresponds to the expected terms of the options.
(2)Estimated based on the expected quarterly dividend and the three-month average stock price at the date of each grant.
(3)Based on the yields of U.S. Department of Treasury instruments with similar expected terms of the options at the date of each grant.
(4)Estimated using the midpoint of the vesting periods and the contractual terms of the options as we do not have sufficient historical share option exercise data to estimate the terms of our option grants.
The following table summarizes the activity of our options during the year ended December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Exercise Price per Share |
| (in thousands) | | |
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 3,102 | | | $ | 94.50 | |
| Granted | 264 | | | 203.95 | |
| Exercised | (648) | | | 73.99 | |
| Forfeited | (7) | | | 144.93 | |
Outstanding as of December 31, 2024(1) | 2,711 | | | 109.94 | |
Exercisable as of December 31, 2024(2) | 2,122 | | | 92.49 | |
____________
(1)The aggregate intrinsic value was $372 million and the weighted average remaining contractual term was 5.3 years.
(2)The aggregate intrinsic value was $328 million and the weighted average remaining contractual term was 4.4 years.
Performance Shares
As of December 31, 2024, we determined that all of the performance measures for the outstanding performance shares granted in 2022, 2023, and 2024 were probable of achievement, with the average of the applicable achievement factors estimated to be between the target and maximum achievement percentages for performance shares granted in each year.
The following table provides information about our performance share grants for the last three years:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Number of shares granted (in thousands) | 187 | | | 244 | | | 216 | |
| Weighted average grant date fair value per share | $ | 204.31 | | | $ | 146.18 | | | $ | 150.67 | |
| Aggregate fair value of shares vested (in millions) | $ | 47 | | | $ | 42 | | | $ | 42 | |
The following table summarizes the activity of our performance shares in aggregate for all of our performance measures during the year ended December 31, 2024, with the performance shares reflected at the target achievement percentage until completion of the performance period:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value per Share |
| (in thousands) | | |
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 679 | | | $ | 139.74 | |
| Granted | 187 | | | 204.31 | |
Performance achievement share adjustments(1) | 231 | | | 123.13 | |
| Vested | (462) | | | 123.13 | |
| Forfeited | (14) | | | 148.56 | |
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2024 | 621 | | | 165.12 | |
____________
(1)Reflects the number of shares achieved above target, based on actual performance as determined at the completion of the respective three-year performance period.
Note 17: Earnings Per Share
The following table presents the calculation of basic and diluted earnings per share ("EPS"):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions, except per share amounts) |
| Basic EPS: | | | | | |
| Numerator: | | | | | |
| Net income attributable to Hilton stockholders | $ | 1,535 | | | $ | 1,141 | | | $ | 1,255 | |
| Denominator: | | | | | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding | 248 | | | 262 | | | 275 | |
| Basic EPS | $ | 6.20 | | | $ | 4.36 | | | $ | 4.56 | |
| | | | | |
| Diluted EPS: | | | | | |
| Numerator: | | | | | |
| Net income attributable to Hilton stockholders | $ | 1,535 | | | $ | 1,141 | | | $ | 1,255 | |
| Denominator: | | | | | |
Weighted average shares outstanding(1) | 250 | | | 264 | | | 277 | |
Diluted EPS(1) | $ | 6.14 | | | $ | 4.33 | | | $ | 4.53 | |
____________
(1)Amounts for all periods include less than 1 million shares related to share-based compensation that were excluded from the calculations of diluted EPS because their effect would have been anti-dilutive under the treasury stock method.
Note 18: Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss
The changes in the components of accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of taxes, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency Translation Adjustment(1) | | Pension Liability Adjustment(2) | | Cash Flow Hedge Adjustment(3) | | Total |
| (in millions) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2021 | $ | (540) | | | $ | (210) | | | $ | (29) | | | $ | (779) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | (9) | | | (57) | | | 114 | | | 48 | |
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss | 1 | | | 8 | | | 16 | | | 25 | |
| Net other comprehensive income (loss) for the period | (8) | | | (49) | | | 130 | | | 73 | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2022 | (548) | | | (259) | | | 101 | | | (706) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | 9 | | | (11) | | | 9 | | | 7 | |
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss | — | | | 8 | | | (40) | | | (32) | |
| Net other comprehensive income (loss) for the period | 9 | | | (3) | | | (31) | | | (25) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2023 | (539) | | | (262) | | | 70 | | | (731) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | (54) | | | 4 | | | 30 | | | (20) | |
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss | 2 | | | 18 | | | (51) | | | (31) | |
| Net other comprehensive income (loss) for the period | (52) | | | 22 | | | (21) | | | (51) | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2024 | $ | (591) | | | $ | (240) | | | $ | 49 | | | $ | (782) | |
____________
(1)Includes net investment hedge gains and intra-entity foreign currency transactions that are of a long-term investment nature. Amounts reclassified relate to the liquidation of investments in foreign entities which were recognized in gain (loss) on foreign currency transactions in our consolidated statements of operations during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2022.
(2)Amount reclassified for the year ended December 31, 2024 includes losses for the full or partial settlement of certain pension plans and were recognized in other non-operating loss, net in our consolidated statement of operations. Amounts reclassified for all periods relate to the amortization of prior service cost and amortization of net loss and were recognized in other non-operating income (loss), net in our consolidated statements of operations.
(3)Amounts reclassified were the result of hedging instruments, primarily comprising interest rate swaps, inclusive of interest rate swaps that were dedesignated in prior periods, with related amounts recognized in interest expense in our consolidated statements of operations. Amounts reclassified also related to foreign currency forward contracts that hedge our foreign currency denominated fees, with related amounts recognized in various revenue line items, as applicable, in our consolidated statements of operations.
Note 19: Business Segments
We are a hospitality company with operations organized in two distinct operating segments: (i) management and franchise and (ii) ownership, each of which is reported as a segment based on (a) delivering a similar set of products and services and (b) being managed separately given its distinct economic characteristics.
The management and franchise segment includes all of the hotels we manage for third-party owners, as well as all properties that license our IP, and/or use our booking channels and related programs, and where we provide other contracted services, but the day-to-day services of the hotels are operated or managed by someone other than us. Revenues from this segment include: (i) management and franchise fees charged to third-party hotel owners; (ii) licensing fees from our strategic partners, including co-branded credit card providers, strategic partner hotels and HGV; and (iii) fees for managing hotels in our ownership segment. The ownership segment primarily derives revenues from nightly hotel room sales, food and beverage sales and other services at our consolidated owned and leased hotels.
Our President and Chief Executive Officer is our CODM. Our CODM uses Adjusted EBITDA to evaluate the performance of our operating segments. Adjusted EBITDA is calculated as EBITDA, which reflects net income (loss), excluding interest expense, a provision for income tax benefit (expense) and depreciation and amortization expenses, further adjusted to exclude certain items, including gains, losses, revenues and expenses in connection with: (i) asset dispositions for both consolidated and unconsolidated investments; (ii) foreign currency transactions; (iii) debt restructurings and retirements; (iv) FF&E replacement reserves required under certain lease agreements; (v) share-based compensation; (vi) reorganization, severance, relocation and other expenses; (vii) non-cash impairment; (viii) amortization of contract acquisition costs; (ix) other revenues from managed and franchised properties and other expenses from managed and franchised properties; and (x) other items. Our CODM uses Adjusted EBITDA to evaluate the trends of our segments over time and monitor the segments in light of the performance of our industry and competitors to determine how to allocate capital resources, including contract acquisition costs and capital expenditures. Our CODM does not use assets by operating segment when assessing performance or making operating segment resource allocations. We previously were required to report segment profitability based on segment operating income (loss) as such measure was also regularly provided to our CODM. Beginning in the fourth quarter of 2024, segment operating income (loss) was no longer included in regular reporting provided to the CODM, and, as a result, our reported measure of segment profit changed to Adjusted EBITDA. The change in our reported measure of segment profit did not change the identification of our reportable segments from prior periods. Prior period amounts presented are measured on the same basis as amounts for the year ended December 31, 2024.
The following table presents revenues for our reportable segments, reconciled to consolidated amounts:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| Franchise and licensing fees | $ | 2,622 | | | $ | 2,388 | | | $ | 2,085 | |
Base and other management fees(1) | 427 | | | 393 | | | 338 | |
| Incentive management fees | 290 | | | 274 | | | 196 | |
| Management and franchise | 3,339 | | | 3,055 | | | 2,619 | |
| Ownership | 1,255 | | | 1,244 | | | 1,076 | |
| Segment revenues | 4,594 | | | 4,299 | | | 3,695 | |
| Amortization of contract acquisition costs | (50) | | | (43) | | | (38) | |
| Other revenues | 232 | | | 178 | | | 102 | |
| Other revenues from managed and franchised properties | 6,428 | | | 5,827 | | | 5,037 | |
Intersegment fees elimination(1) | (30) | | | (26) | | | (23) | |
| Total revenues | $ | 11,174 | | | $ | 10,235 | | | $ | 8,773 | |
____________
(1)Includes management, royalty and IP fees charged to consolidated hotels in our ownership segment by our management and franchise segment, which were eliminated in our consolidated statements of operations.
The following table presents Adjusted EBITDA for each of our reportable segments, reconciled to consolidated income before income taxes:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
Management and franchise(1)(2) | $ | 3,339 | | | $ | 3,055 | | | $ | 2,619 | |
Ownership(1)(2) | 172 | | | 150 | | | 110 | |
| Segment Adjusted EBITDA | 3,511 | | | 3,205 | | | 2,729 | |
Corporate and other(3) | (82) | | | (116) | | | (130) | |
| Interest expense | (569) | | | (464) | | | (415) | |
| | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization expenses | (146) | | | (147) | | | (162) | |
| Gain on sales of assets, net | 5 | | | — | | | — | |
| Gain (loss) on foreign currency transactions | (12) | | | (16) | | | 5 | |
| Loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate | — | | | (92) | | | — | |
Loss on debt guarantees(4) | (50) | | | — | | | — | |
| FF&E replacement reserves | (57) | | | (63) | | | (54) | |
| Share-based compensation expense | (176) | | | (169) | | | (162) | |
| Impairment losses | — | | | (38) | | | — | |
| Amortization of contract acquisition costs | (50) | | | (43) | | | (38) | |
Other revenues from managed and franchised properties(5) | 6,428 | | | 5,827 | | | 5,037 | |
Other expenses from managed and franchised properties(5) | (6,985) | | | (6,164) | | | (5,076) | |
Other adjustment items(6) | (34) | | | (28) | | | — | |
| Income before income taxes | $ | 1,783 | | | $ | 1,692 | | | $ | 1,734 | |
____________
(1)Includes management, royalty and IP fees charged to consolidated hotels in our ownership segment by our management and franchise segment, which were eliminated in our consolidated statements of operations.
(2)No expenses are allocated to the management and franchise segment. For the ownership segment, rent expense is a significant expense regularly provided to the CODM; rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $224 million, $233 million and $213 million, respectively, and total other expenses were $868 million, $870 million and $753 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, comprising (i) room expenses; (ii) food and beverage costs; (iii) property expenses; and (iv) other support costs. Ownership segment Adjusted EBITDA also includes income (losses) from hotels owned or leased by entities in which we own a noncontrolling financial interest.
(3)Amounts primarily include activity related to general and administrative expenses, excluding share-based compensation expense, and our purchasing operations.
(4)Amount includes losses on debt guarantees for certain hotels that we manage; refer to Note 20: Commitments and Contingencies for additional information.
(5)Amounts include results from the operation of programs conducted for the benefit of property owners and exclude cash receipts recorded as deferred revenues on our consolidated balance sheets related to these programs. Under the terms of the related contracts, we do not operate these programs to generate a profit and have the contractual rights to adjust future collections to recover prior period expenditures.
(6)Amount for the year ended December 31, 2022 was less than $1 million. Amount for the year ended December 31, 2024 relates to losses for the full or partial settlement of certain pension plans, restructuring costs related to one of our leased properties as well as transaction costs incurred for acquisitions. Amounts for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 include transaction costs resulting from the amendments of our Term Loans in June 2024 and November 2023, respectively. Amounts for all periods include net losses (gains) related to certain of our investments in unconsolidated affiliates, other than the loss included separately in "loss on investments in unconsolidated affiliate," severance and other items.
Total revenues by country were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| (in millions) |
| U.S. | $ | 8,779 | | | $ | 7,986 | | | $ | 6,947 | |
All other(1) | 2,395 | | | 2,249 | | | 1,826 | |
| $ | 11,174 | | | $ | 10,235 | | | $ | 8,773 | |
____________
(1)There are no countries included in these amounts that individually represented more than 10 percent of total revenues for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022.
Note 20: Commitments and Contingencies
Although we include performance clauses in certain of our management contracts, most of these clauses do not require us to fund shortfalls but instead allow the owner to terminate the contract if specified operating performance levels are not
achieved. In limited cases, we are obligated to fund performance shortfalls and our obligations under these guarantees in future periods are dependent on the operating performance level of the related hotel over the remaining term of the performance guarantee for that particular hotel. As of December 31, 2024, we had performance guarantees with expirations ranging from 2025 to 2043 and possible cash outlays totaling $20 million.
We also have extended debt guarantees and provided letters of credit to owners of certain hotels that we currently or in the future will manage or franchise. During the year ended December 31, 2024, we recognized losses of $50 million in other non-operating loss, net in our consolidated statement of operations for debt guarantees extended to certain hotels that we manage that have failed to comply with the requirements of their respective debt agreements. We paid $77 million during the year ended December 31, 2024 related to debt guarantees. Our debt guarantees and letters of credit as of December 31, 2024 had expirations ranging from 2025 to 2033 and remaining possible cash outlays totaling $49 million.
The performance and debt guarantees create variable interests in the ownership entities of the related hotels, of which we are not the primary beneficiary.
We receive Hilton Honors and program fees from managed and franchised properties that we are contractually required to use to operate our Hilton Honors program, marketing, sales and brand programs and other shared services on behalf of property owners. If we collect amounts in excess of amounts expended, we have a commitment to spend these amounts on the related programs.
We are involved in various claims and lawsuits arising in the ordinary course of business, some of which include claims for substantial sums. While the ultimate results of claims and litigation cannot be predicted with certainty, we expect that the ultimate resolution of all pending or threatened claims and litigation as of December 31, 2024 will not have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Note 21: Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information
Cash interest paid included within operating activities in our consolidated statements of cash flows was $562 million, $492 million and $385 million during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. These amounts exclude $56 million, $53 million and $2 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, of cash receipts related to settlements of our interest rate swap with a financing component, which are separately disclosed within financing activities in our consolidated statements of cash flows.
Income tax payments, net of refunds received, were $492 million, $478 million and $389 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company maintains a set of disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to the Company's management, including its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures. The design of any disclosure controls and procedures is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance of achieving the desired control objectives. In accordance with Rule 13a-15(b) of the Exchange Act, as of the end of the period covered by this annual report, an evaluation was carried out under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including its Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of its disclosure controls and procedures. Based on that evaluation, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures, as of the end of the period covered by this annual report, were effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by the Company in reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms and is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have set forth management's report on internal control over financial reporting and the attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Management's report on internal control over financial reporting is incorporated in this Item 9A by reference.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There has been no change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting during the Company’s most recent fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
During the three months ended December 31, 2024, no director or officer (as defined in Rule 16a-1(f) of the Exchange Act) of the Company adopted, modified or terminated a “Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” or “non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement,” as each term is defined in Item 408 of Regulation S-K.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to our definitive proxy statement for the 2025 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
The following documents are filed as part of this report:
(a)Financial Statements
We include this portion of Item 15 under Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(b)Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules are omitted as the required information is either not present, not present in material amounts or presented within the consolidated financial statements or related notes.
(c)Exhibits:
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 2.1 | | |
| 3.1 | | |
| 3.2 | | |
| 3.3 | | |
| 4.1 | | |
| 4.2 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 4.3 | | |
| 4.4 | | |
| 4.5 | | |
| 4.6 | | |
| 4.7 | | |
| 4.8 | | |
| 4.9 | | |
| 4.10 | | |
| 4.11 | | |
| 4.12 | | |
| 4.13 | | |
| 4.14 | | |
| 4.15 | | |
| 4.16 | | |
| 4.17 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 4.18 | | |
| 4.19 | | |
| 4.20 | | |
| 4.21 | | |
| 4.22 | | |
| 4.23 | | |
| 4.24 | | |
| 4.25 | | |
| 4.26 | | |
| 4.27 | | |
| 4.28 | | |
| 4.29 | | |
| 4.30 | | |
| 4.31 | | |
| 4.32 | | |
| 4.33 | | |
| 4.34 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 4.35 | | |
| 4.36 | | |
| 4.37 | | |
| 4.38 | | |
| 4.39 | | |
| 4.40 | | |
| 4.41 | | |
| 10.1 | | Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013, among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., as parent, Hilton Worldwide Finance LLC, as borrower, the other guarantors from time to time party thereto, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch, as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer, and the other lenders from time to time party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on November 8, 2013). |
| 10.2 | | Amendment No. 1, dated as of August 18, 2016, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013, by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Finance LLC, the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 18, 2016). |
| 10.3 | | Amendment No. 2, dated as of November 21, 2016, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Finance LLC, the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 23, 2016). |
| 10.4 | | Amendment No. 3, dated as of March 16, 2017, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Worldwide Finance LLC, the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 22, 2017). |
| 10.5 | | Amendment No. 4, dated as of April 19, 2018, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Worldwide Finance LLC, the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 19, 2018). |
| 10.6 | | Amendment No. 5, dated as of June 5, 2019, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Credit Agreement dated as of August 18, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 2 to the Credit Agreement dated as of November 21, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 3 to the Credit Agreement dated as of March 16, 2017 and as further amended by Amendment No. 4 to the Credit Agreement dated as of April 19, 2018), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Worldwide Finance LLC, the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 7, 2019). |
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 10.7 | | Amendment No. 6, dated as of June 21, 2019, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Credit Agreement dated as of August 18, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 2 to the Credit Agreement dated as of November 21, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 3 to the Credit Agreement dated as of March 16, 2017, as further amended by Amendment No. 4 to the Credit Agreement dated as of April 19, 2018 and as further amended by Amendment No. 5 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 5, 2019), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Worldwide Finance LLC, the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 24, 2019). |
| 10.8 | | |
| 10.9 | | Loan Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013, among the subsidiaries party thereto, collectively, as borrower and JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, German American Capital Corporation, Bank of America, N.A., GS Commercial Real Estate LP and Morgan Stanley Mortgage Capital Holdings LLC, collectively, as lender (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on November 8, 2013). |
| 10.10 | | Guaranty Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013, among the guarantors named therein and JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, German American Capital Corporation, Bank of America, N.A., GS Commercial Real Estate LP and Morgan Stanley Mortgage Capital Holdings LLC, collectively, as lender (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on November 8, 2013). |
| 10.11 | | |
| 10.12 | | |
| 10.13 | | |
| 10.14 | | |
| 10.15 | | |
| 10.16 | | |
| 10.17 | | |
| 10.18 | | |
| 10.19 | | |
| 10.20 | | |
| 10.21 | | |
| 10.22 | | |
| 10.23 | | |
| 10.24 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 10.25 | | |
| 10.26 | | |
| 10.27 | | |
| 10.28 | | |
| 10.29 | | |
| 10.30 | | Amendment No. 7, dated as of October 21, 2021, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Credit Agreement dated as of August 18, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 2 to the Credit Agreement dated as of November 21, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 3 to the Credit Agreement dated as of March 16, 2017, as further amended by Amendment No. 4 to the Credit Agreement dated as of April 19, 2018, as further amended by Amendment No. 5 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 5, 2019, and as further amended by Amendment No. 6 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 21, 2019), between Hilton Domestic Operating Company Inc. and Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.43 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021). |
| 10.31 | | |
| 10.32 | | |
| 10.33 | | |
| 10.34 | | |
| 10.35 | | Amendment No. 8, dated as of December 9, 2022, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Credit Agreement dated as of August 18, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 2 to the Credit Agreement dated as of November 21, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 3 to the Credit Agreement dated as of March 16, 2017, as further amended by Amendment No. 4 to the Credit Agreement dated as of April 19, 2018, as further amended by Amendment No. 5 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 5, 2019, as further amended by Amendment No. 6 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 21, 2019, and as further amended by Amendment No. 7 to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 21, 2021, by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Domestic Operating Company, Inc., the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.47 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022). |
| 10.36 | | Amendment No. 9, dated as of January 5, 2023, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Credit Agreement dated as of August 18, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 2 to the Credit Agreement dated as of November 21, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 3 to the Credit Agreement dated as of March 16, 2017, as further amended by Amendment No. 4 to the Credit Agreement dated as of April 19, 2018, as further amended by Amendment No. 5 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 5, 2019, as further amended by Amendment No. 6 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 21, 2019, as further amended by Amendment No. 7 to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 21, 2021 and as further amended by Amendment No. 8 to the Credit Agreement dated as of December 9, 2022), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Domestic Operating Company, Inc., the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent, collateral agent, swing line lender and L/C issuer and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 5, 2023). |
| 10.37 | | |
| 10.38 | | |
| 10.39 | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 10.40 | | |
| 10.41 | | Amendment No. 10, dated as of November 8, 2023, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Credit Agreement dated as of August 18, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 2 to the Credit Agreement dated as of November 21, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 3 to the Credit Agreement dated as of March 16, 2017, as further amended by Amendment No. 4 to the Credit Agreement dated as of April 19, 2018, as further amended by Amendment No. 5 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 5, 2019, as further amended by Amendment No. 6 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 21, 2019, as further amended by Amendment No. 7 to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 21, 2021, as further amended by Amendment No. 8 to the Credit Agreement dated as of December 9, 2022 and as further amended by Amendment No. 9 to the Credit Agreement dated as of January 5, 2023), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Domestic Operating Company, Inc., the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent and collateral agent and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 8, 2023). |
| 10.42 | | |
| 10.43 | | |
| 10.44 | | |
| 10.45 | | Amendment No. 11, dated as of June 14, 2024, to the Credit Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 to the Credit Agreement dated as of August 18, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 2 to the Credit Agreement dated as of November 21, 2016, as further amended by Amendment No. 3 to the Credit Agreement dated as of March 16, 2017, as further amended by Amendment No. 4 to the Credit Agreement dated as of April 19, 2018, as further amended by Amendment No. 5 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 5, 2019, as further amended by Amendment No. 6 to the Credit Agreement dated as of June 21, 2019, as further amended by Amendment No. 7 to the Credit Agreement dated as of October 21, 2021, as further amended by Amendment No. 8 to the Credit Agreement dated as of December 9, 2022, as further amended by Amendment No. 9 to the Credit Agreement dated as of January 5, 2023 and as further amended by Amendment No. 10, dated as of November 8, 2023), by and among Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc., Hilton Worldwide Parent LLC, Hilton Domestic Operating Company Inc., the other guarantors party thereto from time to time, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch as administrative agent and collateral agent and the other lenders party thereto from time to time (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 14, 2024). |
| 19 | | |
| 21.1 | | |
| 23.1 | | |
| 31.1 | | |
| 31.2 | | |
| 32.1 | | |
| 32.2 | | |
| 97 | | |
| 101.INS | | Inline XBRL Instance Document - this instance document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. |
| 101.SCH | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| 101.CAL | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| 101.DEF | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
| 101.LAB | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
| | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit Number | | Exhibit Description |
| 101.PRE | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (embedded within the Inline XBRL document). |
____________
*This document has been identified as a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
The agreements and other documents filed as exhibits to this report are not intended to provide factual information or other disclosure other than with respect to the terms of the agreements or other documents themselves, and you should not rely on them for that purpose. In particular, any representations and warranties made by us in these agreements or other documents were made solely within the specific context of the relevant agreement or document and may not describe the actual state of affairs as of the date they were made or at any other time.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, on the 6th day of February 2025.
| | | | | | | | |
| HILTON WORLDWIDE HOLDINGS INC. |
| | |
| By: | | /s/ Christopher J. Nassetta |
| Name: | | Christopher J. Nassetta |
| Title: | | President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed by the following persons in the capacities indicated on the 6th day of February 2025. | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title |
| /s/ Christopher J. Nassetta | | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director |
| Christopher J. Nassetta | | (principal executive officer) |
| | |
| /s/ Jonathan D. Gray | | Chairman of the Board of Directors |
| Jonathan D. Gray | | |
| | |
| /s/ Charlene T. Begley | | Director |
| Charlene T. Begley | | |
| | |
| /s/ Chris Carr | | Director |
| Chris Carr | | |
| | |
| /s/ Melanie L. Healey | | Director |
| Melanie L. Healey | | |
| | |
| /s/ Raymond E. Mabus, Jr. | | Director |
| Raymond E. Mabus, Jr. | | |
| | |
| /s/ Judith A. McHale | | Director |
| Judith A. McHale | | |
| | |
| /s/ Elizabeth A. Smith | | Director |
| Elizabeth A. Smith | | |
| | |
| /s/ Douglas M. Steenland | | Director |
| Douglas M. Steenland | | |
| | |
| /s/ Kevin J. Jacobs | | Chief Financial Officer and President, Global Development |
| Kevin J. Jacobs | | (principal financial officer) |
| | |
| /s/ Michael W. Duffy | | Senior Vice President, Chief Accounting and Risk Officer |
| Michael W. Duffy | | (principal accounting officer) |




















![HGV_Primary_Color_RGB[1].jpg](https://capedge.com/proxy/10-K/0001585689-25-000008/hlt-20241231_g22.jpg)
