and in the future may enter into, interest rate swaps that involve the exchange of floating for fixed rate interest payments to reduce interest rate volatility. However, we may not maintain interest rate swaps with respect to all of our variable rate indebtedness, and any swaps we enter into may not fully mitigate our interest rate risk.
General Risks
A financial crisis or deterioration in general economic, business or industry conditions could materially adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition and ability to pay dividends on our common stock.
Concerns over global economic conditions, stock market volatility, energy costs, geopolitical issues, inflation and U.S. Federal Reserve interest rate increases in response, the availability and cost of credit, and slowing of economic growth in the United States and fears of a recession have contributed and may continue to contribute to economic uncertainty and diminished expectations for the global economy.
Concerns about global economic growth can result in a significant adverse impact on global financial markets and commodity prices. In addition, any financial crisis may cause us to face limitations on our ability to borrow under our debt agreements, service our debt obligations, access the debt and equity capital markets and complete asset purchases or sales and may cause increased counterparty credit risk on our derivative instruments and such counterparties to cause us to post collateral guaranteeing performance.
Further, if there is a financial crisis or the economic climate in the United States or abroad deteriorates, worldwide demand for natural gas or oil could materially decrease, which would likely depress the level of production activity and result in a decline in the demand for our compression operations and ultimately materially adversely impact our results of operations and financial condition. If a material adverse change occurs in our business such that an event of default occurs under our debt agreements, the lenders under such agreements may be able to accelerate the maturity of our debt.
Events outside of our control, including an epidemic or outbreak of an infectious disease or the threat thereof, could have a material adverse effect on our business, liquidity, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay dividends on our common stock.
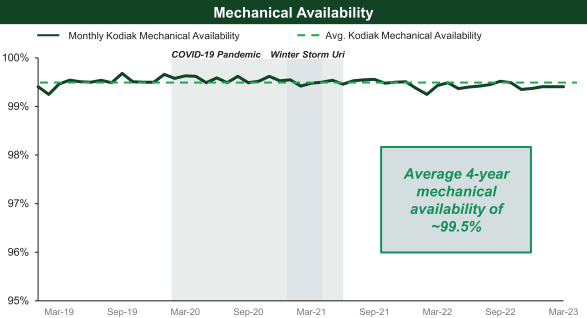
We face risks related to pandemics, epidemics, outbreaks or other public health events, or the threat thereof, that are outside of our control, and could significantly disrupt our business and operational plans and adversely affect our liquidity, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and ability to pay dividends on our common stock. The COVID-19 pandemic has adversely affected the global economy and has resulted in unprecedented governmental actions in the United States and countries around the world, including, among other things, social distancing guidelines, travel restrictions and stay-at-home orders, among other actions, which caused a significant decrease in activity in the global economy and the demand for oil, and to a lesser extent, natural gas.
The nature, scale and scope of the above-described events, combined with the uncertain duration and extent of governmental actions, prevent us from identifying all potential risks to our business.
Inflation may adversely affect us by increasing costs beyond what we can recover through price increases and limit our ability to enter into future traditional debt financing.
Inflation has adversely affected us by increasing costs of critical components, equipment, labor and other services we may rely on, and continued inflationary pressures could prevent us from operating at capacity, decreasing our revenues or having an adverse effect on our profitability. In addition, inflation is often accompanied by higher interest rates. Such higher interest rates may affect our ability to enter into future traditional debt financing, as high inflation may result in an increase in cost to borrow.
Although inflation in the United States had been relatively low for many years, there was a significant increase in inflation beginning in the second half of 2021, which has continued into 2022, due to a substantial increase in the
46