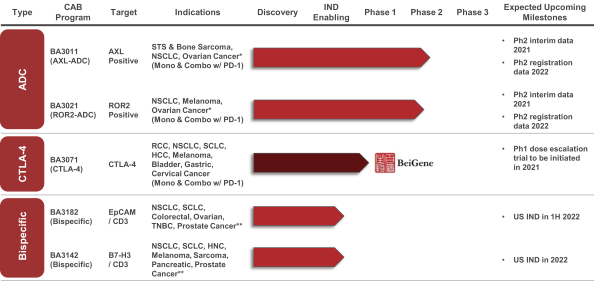
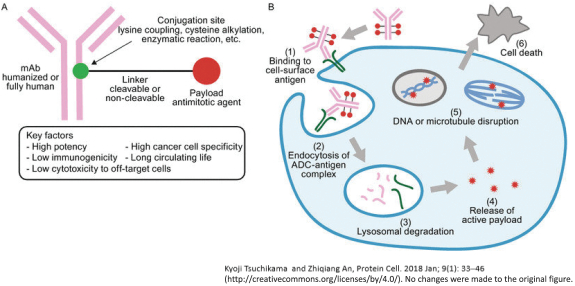
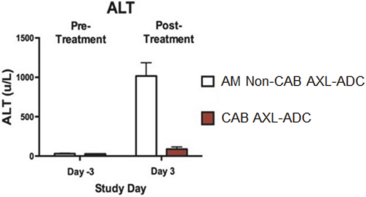
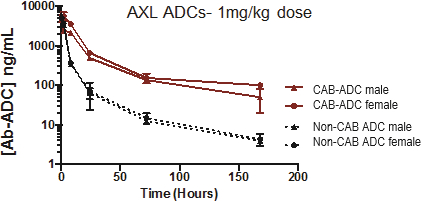
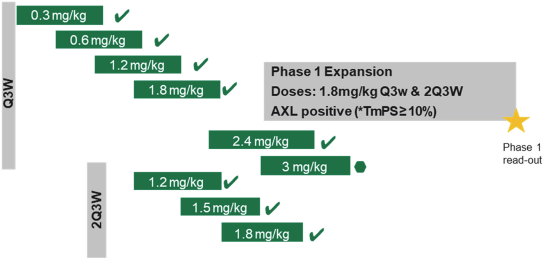
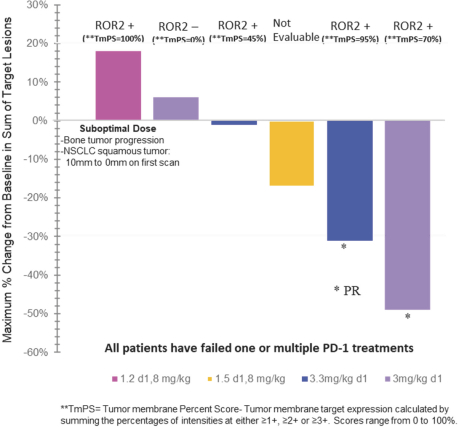
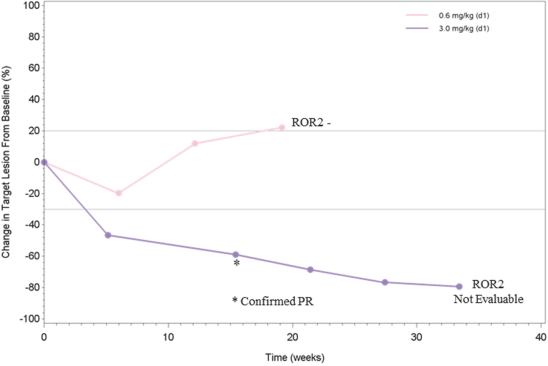
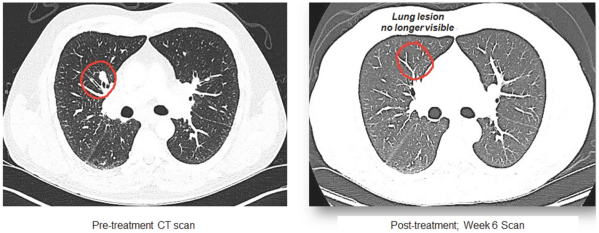
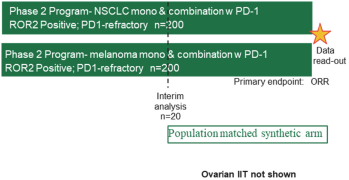
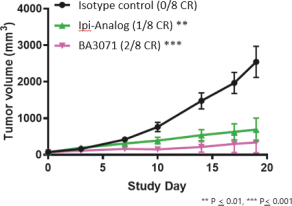
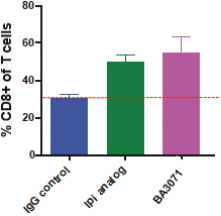
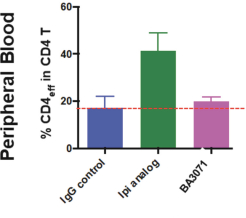
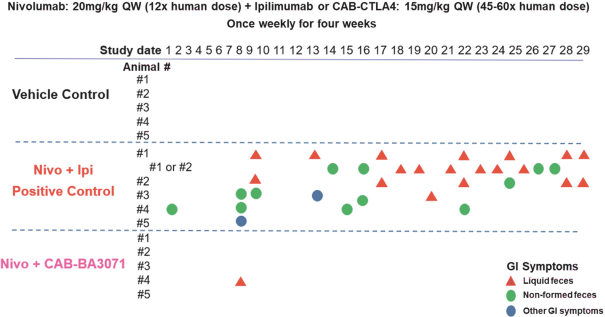
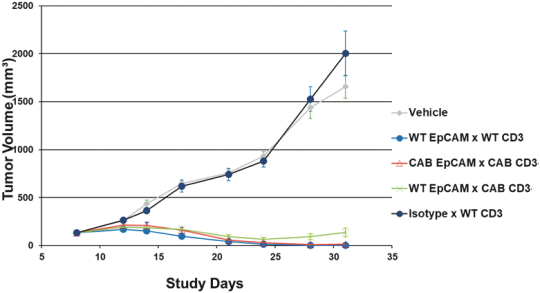
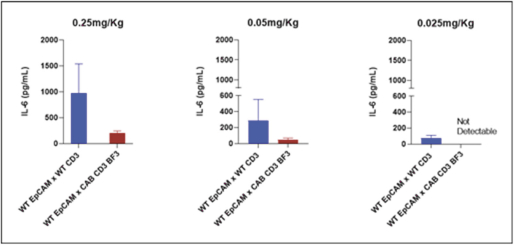
(Patent applications 201780023876X (China), and patent application 106112687 (Taiwan), both titled Anti-AXL antibodies and their immunoconjugates and uses thereof). Additionally, Himalaya Therapeutics SEZC has exclusive worldwide rights to patents/patent applications relating to IL-22 (Patent applications 108119613 and PCT/US19/35395, both titled Anti-IL-22 antibodies, antibody fragments and their immunoconjugates and uses thereof) and relating to HER2 (Patent application USP 62/964,747 titled Conditionally active anti-HER2 antibodies).
BioAtla Holdings, LLC has exclusive worldwide rights to all patents for the field of ACT (CAR-T), excluding the targets licensed to F1 Oncology, Inc.
Inversagen, LLC has exclusive worldwide rights to all patents solely in the field of diseases associated with aging (outside of cancer), diagnostics related thereto and an immuno-oncology antibody.
F1 Oncology, Inc. has an exclusive worldwide license to all patents solely to develop, make, have made, use, sell, have sold, offer for sale and import adoptive cell therapy (CAR-T) products to four named targets for the treatment of cancer. F1 Oncology, Inc.’s rights under the agreement exclude the right to grant sublicenses to third parties to discover, develop or manufacture any CAB ACT or any component of our CAB ACT technology, except as used in or incorporated into F1 Oncology, Inc.’s ACTs for cancer.
Government regulation and product approval
Government authorities in the United States, at the federal, state and local level and in other countries and jurisdictions, including the European Union, extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, quality control, import, export, safety, effectiveness, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, record keeping, approval, advertising, promotion, marketing, post-approval monitoring and post-approval reporting of biological product candidates such as those we are developing. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals and the subsequent compliance with appropriate federal, state, local and foreign statutes and regulations require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources and we may not be able to obtain the required regulatory approvals.
Licensure and regulation of biologics in the United States
In the United States, the FDA regulates biologic products under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or the FDCA, the Public Health Service Act, or the PHSA, and regulations and guidance implementing these laws. The FDCA, PHSA and their corresponding regulations govern, among other things, the testing, manufacturing, safety, purity, potency, labeling, packaging, storage, record keeping, distribution, reporting, advertising and other promotional practices involving biologic products. Biological products used for the prevention, treatment or cure of a disease or condition of a human being are subject to regulation under the FDCA, except the section of the FDCA that governs the approval of new drug applications, or NDAs. Biological products are approved for marketing under provisions of the PHSA, via a Biologic License Application, or BLA. However, the application process and requirements for approval of BLAs are very similar to those for NDAs, and biologics are associated with similar approval risks and costs as drugs. Failure to comply with applicable U.S. requirements may subject a company to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as clinical hold, FDA refusal to approve pending NDAs or BLAs, warning or untitled letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties and criminal prosecution.
164