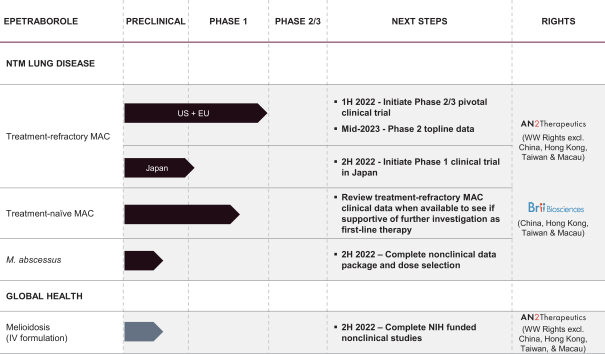
typically one-half the time between the effective date of a clinical investigation involving human beings is begun and the submission date of an application, plus the time between the submission date of an application and the ultimate approval date. Only one patent applicable to an approved product is eligible for patent term extension, and only those claims covering the approved product, a method for using it, or a method for manufacturing it may be extended. The application for patent term extension must be submitted prior to the expiration of the patent. The United States Patent and Trademark Office reviews and approves the application for any Patent Term Extension in consultation with the FDA.
As of December 31, 2021, we exclusively licensed three U.S. patents, 38 foreign patents, and approximately six pending foreign patent applications, covering our key programs and pipeline. We do not own any issued patents. We own two pending U.S. provisional patent applications, which are not eligible to become issued patents until, among other things, we file a non-provisional U.S. patent application within one year of filing of the U.S. provisional patent application with the USPTO.
Prosecution is a lengthy process, during which the scope of the claims initially submitted for examination by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and other patent offices may be significantly revised before issuance, if granted at all. The in-licensed patents and patent applications for epetraborole are detailed below.
Epetraborole Product Candidate
The patent portfolio for our epetraborole product candidate is based upon our in-licensed patent portfolio, which includes patents and patent applications directed generally to compositions of matter, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treatment. We have two granted patents in the United States, from the in-licensed patent portfolio, covering compositions of matter of a genus of molecules, and the epetraborole product candidate molecule specifically, pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of treating a bacterial-associated or fungal-associated disease. We have granted foreign patents from the in-licensed patent portfolio from Argentina, Armenia, Australia, Azerbaijan, Belgium, Canada, China, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Hong Kong, India, Indonesia, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kyrgyz Republic, Malaysia, Mexico, Moldovia, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Russian Federation, Singapore, South Africa, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Tajikistan, Turkey, United Kingdom, Uruguay, and Vietnam. Patent applications from the in-licensed patent portfolio are pending in Bangladesh, Brazil, Pakistan, South Africa, Thailand, and Venezuela. Patents and patent applications, if granted, in our in-licensed patent portfolio are expected to expire in 2028, without taking potential patent term extensions or patent term adjustment into account.
Trade Secrets
We also rely on trade secrets, know-how, confidential information and continuing technological innovation to develop, strengthen and maintain our proprietary position in our field and protect aspects of our business that are not amenable to, or that we do not consider appropriate for, patent protection. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. While we take measures to protect and preserve our trade secrets, such measures can be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any such breach. We seek to protect our proprietary information, in part, using confidentiality agreements and invention assignment agreements with our collaborators, employees and consultants. These agreements are designed to protect our proprietary information and, in the case of the invention assignment agreements, to grant us ownership of technologies that are developed through a relationship with a third party. We cannot guarantee, however, that we have executed such agreements with all applicable counterparties. Furthermore, these agreements may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors and other third parties, or misused by
128