UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
| |
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2012 |
| OR |
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number 001-07541
THE HERTZ CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
| | |
Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
| 13-1938568 (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
225 Brae Boulevard
Park Ridge, New Jersey 07656-0713
(201) 307-2000
(Address, including Zip Code, and telephone number,
including area code, of registrant's principal executive offices)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
The registrant meets the conditions as set forth in General Instructions I(1)(a) and (b) of Form 10-K and is therefore filing this Form with the reduced disclosure format as permitted.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
| | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | o | Non-accelerated filer | x | Smaller reporting company | o |
| | | | | (Do not check if a smaller
reporting company) | | | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No x
No voting or non-voting common equity of the registrant was held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2012. As of March 4, 2013, all of the common stock of the registrant was owned by its affiliate, Hertz Investors, Inc. As of March 4, 2013, 100 shares of the registrant's common stock (par value $0.01) were outstanding.
Documents incorporated by reference: None
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
| | |
| | | Page |
| |
| | |
| | |
| ITEM 1A. | | |
| ITEM 1B. | | |
| ITEM 2. | | |
| ITEM 3. | | |
| ITEM 4. | | |
| | |
| ITEM 5. | | |
| ITEM 6. | | |
| ITEM 7. | | |
| ITEM 7A. | | |
| ITEM 8. | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| ITEM 9. | | |
| ITEM 9A. | | |
| ITEM 9B. | | |
| | |
| ITEM 10. | | |
| ITEM 11. | | |
| ITEM 12. | | |
| ITEM 13. | | |
| ITEM 14. | | |
| | |
| ITEM 15. | | |
| |
| |
INTRODUCTORY NOTE
Unless the context otherwise requires, in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, or “Annual Report,” (i) “we,” “us,” “our,” “Hertz,” or the “Company,” mean The Hertz Corporation, Hertz Holdings' primary operating company and a direct wholly‑owned subsidiary of Hertz Investors, Inc., which is wholly‑owned by Hertz Holdings, and its consolidated subsidiaries, (ii) “Hertz Holdings” means Hertz Global Holdings, Inc., our top-level holding company, (iii) “HERC” means Hertz Equipment Rental Corporation, our wholly‑owned equipment rental subsidiary, together with our various other wholly‑owned international subsidiaries that conduct our industrial, construction and material handling equipment rental business, (iv) “cars” means cars, crossovers and light trucks (including sport utility vehicles and, outside North America, light commercial vehicles), (v) “program cars” means cars purchased by car rental companies under repurchase or guaranteed depreciation programs with car manufacturers, (vi) “non-program cars” means cars not purchased under repurchase or guaranteed depreciation programs for which the car rental company is exposed to residual risk and (vii) “equipment” means industrial, construction and material handling equipment.
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward‑Looking Statements
Certain statements contained or incorporated by reference in this Annual Report and in reports we subsequently file with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, or the “SEC,” on Forms 10-K, 10-Q and file or furnish on Form 8-K, and in related comments by our management, include “forward‑looking statements.” Forward‑looking statements include information concerning our liquidity and our possible or assumed future results of operations, including descriptions of our business strategies. These statements often include words such as “believe,” “expect,” “project,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “plan,” “estimate,” “seek,” “will,” “may,” “would,” “should,” “could,” “forecasts” or similar expressions. These statements are based on certain assumptions that we have made in light of our experience in the industry as well as our perceptions of historical trends, current conditions, expected future developments and other factors we believe are appropriate in these circumstances. We believe these judgments are reasonable, but you should understand that these statements are not guarantees of performance or results, and our actual results could differ materially from those expressed in the forward‑looking statements due to a variety of important factors, both positive and negative, that may be revised or supplemented in subsequent reports on SEC Forms 10-K, 10-Q and 8-K. Some important factors that could affect our actual results include, among others, those that may be disclosed from time to time in subsequent reports filed with the SEC, those described under “Risk Factors” set forth in Item 1A of this Annual Report, and the following, which were derived in part from the risks set forth in Item 1A of this Annual Report:
| |
| • | our ability to integrate the car rental operations of Dollar Thrifty and realize operational efficiencies from the acquisition; |
| |
| • | the operational and profitability impact of the Advantage divestiture and the divestiture of the Initial airport locations and the Secondary airport locations that we agreed to undertake in order to secure regulatory approval for the Dollar Thrifty acquisition; |
| |
| • | levels of travel demand, particularly with respect to airline passenger traffic in the United States and in global markets; |
| |
| • | the impact of pending and future U.S. governmental action to address budget deficits through reductions in spending and similar austerity measures, which could materially adversely affect unemployment rates and consumer spending levels; |
| |
| • | significant changes in the competitive environment, including as a result of industry consolidation, and the effect of competition in our markets, including on our pricing policies or use of incentives; |
| |
| • | occurrences that disrupt rental activity during our peak periods; |
| |
| • | our ability to achieve cost savings and efficiencies and realize opportunities to increase productivity and profitability; |
| |
| • | an increase in our fleet costs as a result of an increase in the cost of new vehicles and/or a decrease in the price at which we dispose of used vehicles either in the used vehicle market or under repurchase or guaranteed depreciation programs; |
| |
| • | our ability to accurately estimate future levels of rental activity and adjust the size and mix of our fleet accordingly; |
| |
| • | our ability to maintain sufficient liquidity and the availability to us of additional or continued sources of financing for our revenue earning equipment and to refinance our existing indebtedness; |
| |
| • | safety recalls by the manufacturers of our vehicles and equipment; |
| |
| • | a major disruption in our communication or centralized information networks; |
| |
| • | financial instability of the manufacturers of our vehicles and equipment; |
| |
| • | any impact on us from the actions of our licensees, franchisees, dealers and independent contractors; |
| |
| • | our ability to maintain profitability during adverse economic cycles and unfavorable external events (including war, terrorist acts, natural disasters and epidemic disease); |
| |
| • | shortages of fuel and increases or volatility in fuel costs; |
| |
| • | our ability to successfully integrate acquisitions and complete dispositions; |
| |
| • | our ability to maintain favorable brand recognition; |
| |
| • | costs and risks associated with litigation; |
| |
| • | risks related to our indebtedness, including our substantial amount of debt, our ability to incur substantially more debt and increases in interest rates or in our borrowing margins; |
| |
| • | our ability to meet the financial and other covenants contained in our Senior Credit Facilities, our outstanding unsecured Senior Notes and certain asset‑backed and asset‑based arrangements; |
| |
| • | changes in accounting principles, or their application or interpretation, and our ability to make accurate estimates and the assumptions underlying the estimates, which could have an effect on earnings; |
| |
| • | changes in the existing, or the adoption of new laws, regulations, policies or other activities of governments, agencies and similar organizations where such actions may affect our operations, the cost thereof or applicable tax rates; |
| |
| • | changes to our senior management team; |
| |
| • | the effect of tangible and intangible asset impairment charges; |
| |
| • | the impact of our derivative instruments, which can be affected by fluctuations in interest rates and commodity prices; |
| |
| • | our exposure to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates; and |
| |
| • | other risks described from time to time in periodic and current reports that we file with the SEC. |
You should not place undue reliance on forward‑looking statements. All forward‑looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the foregoing cautionary statements. All such statements speak only as of the date made, and we undertake no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward‑looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Our Company
Hertz operates its car rental business through the Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty brands from approximately 10,270 corporate, licensee and franchisee locations in North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia, Australia, Africa, the Middle East and New Zealand. Hertz is the largest worldwide airport general use car rental brand, operating from approximately 8,860 corporate and licensee locations in approximately 150 countries. Our Dollar and Thrifty brands have approximately 1,410 corporate and franchisee locations in 83 countries. Our Hertz brand name is one of the most recognized in the world, signifying leadership in quality rental services and products. We are one of the only car rental companies that has an extensive network of company‑operated rental locations both in the United States and in all major European markets. We believe that we maintain the leading airport car rental brand market share, by overall reported revenues, in the United States and at 120 major airports in Europe where we have company‑operated locations and where data regarding car rental concessionaire activity is available. We believe that we also maintain the second largest market share, by overall reported revenues, in the off-airport car rental market in the United States. In our equipment rental business segment, we rent equipment through approximately 340 branches in the United States, Canada, France, Spain, China and Saudi Arabia, as well as through our international licensees. We and our predecessors have been in the car rental business since 1918 and in the equipment rental business since 1965. We also own Donlen Corporation, or "Donlen," based in Northbrook, Illinois, which is a leader in providing fleet leasing and management services. We have a diversified revenue base and a highly variable cost structure and are able to dynamically manage fleet capacity, the most significant determinant of our costs. Our revenues have grown at a compound annual growth rate of 6.0% over the last 20 years, with year-over-year growth in 17 of those 20 years.
Corporate History
Hertz Holdings was incorporated in Delaware in 2005 to serve as the top-level holding company for the consolidated Hertz business. Hertz was incorporated in Delaware in 1967. Hertz is a successor to corporations that have been engaged in the car and truck rental and leasing business since 1918 and the equipment rental business since 1965. Ford Motor Company acquired an ownership interest in Hertz in 1987. Prior to this, Hertz was a subsidiary of United Continental Holdings, Inc. (formerly Allegis Corporation), which acquired Hertz's outstanding capital stock from RCA Corporation in 1985.
On December 21, 2005, investment funds associated with or designated by:
| |
| • | Clayton, Dubilier & Rice, Inc., which was succeeded by Clayton, Dubilier & Rice, LLC, or “CD&R,” |
| |
| • | The Carlyle Group, or “Carlyle,” and |
| |
| • | Merrill Lynch & Co., Inc., or "Merrill Lynch," |
or collectively the “Sponsors,” acquired all of Hertz's common stock from Ford Holdings LLC. We refer to the acquisition of all of Hertz's common stock by the Sponsors as the “Acquisition.”
In January 2009, Bank of America Corporation, or “Bank of America,” acquired Merrill Lynch. Accordingly, Bank of America is now an indirect beneficial owner of our common stock held by Merrill Lynch and certain other investment funds and affiliates of Merrill Lynch.
On September 1, 2011, Hertz completed the acquisition of Donlen Corporation, or "Donlen," a leading provider of fleet leasing and management services. See Note 4 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption "Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
In December 2011, Hertz purchased the noncontrolling interest of Navigation Solutions, L.L.C., thereby increasing its ownership interest from 65% to 100%.
On November 19, 2012, Hertz completed the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., or "Dollar Thrifty," a car and truck rental and leasing business. See Note 4 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption "Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
On December 12, 2012, Hertz completed the sale of Simply Wheelz LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Hertz that operated our Advantage Rent A Car business. See Note 4 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption "Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
In December 2012, the Sponsors sold 50,000,000 shares of their Hertz Holdings common stock to J.P. Morgan as the sole underwriter in the registered public offering of those shares.
As a result of our initial public offering in November 2006 and subsequent offerings in June 2007, May 2009, June 2009, March 2011 and December 2012, the Sponsors reduced their holdings to approximately 26% of the outstanding shares of common stock of Hertz Holdings.
Our Markets
We are engaged principally in the global car rental industry and in the equipment rental industry.
Worldwide Car Rental
We believe that the global car rental industry exceeds $37 billion in annual revenues. According to Auto Rental News, car rental industry revenues in the United States were estimated to be approximately $24 billion for 2012 and grew in 2012 by 3.9%. We believe car rental revenues in Europe account for over $13 billion in annual revenues, with the airport portion of the industry comprising approximately 37% of the total. Within Europe, the largest markets are Germany, France, Spain, Italy and the United Kingdom. We believe total rental revenues for the car rental industry in Europe in 2012 were approximately $10.8 billion in 10 countries-France, Italy, the United Kingdom, Germany, Spain, the Netherlands, Belgium, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Luxembourg-where we have company-operated rental locations and approximately $2.8 billion in 11 other countries-Ireland, Portugal, Sweden, Greece, Austria, Denmark, Poland, Finland, Hungary, Malta and Romania-where our Hertz brand is present through our licensees.
Rentals by airline travelers at or near airports, or “airport rentals,” are significantly influenced by developments in the travel industry and particularly in airline passenger traffic, or “enplanements,” as well as the Gross Domestic Product, or “GDP.” We believe domestic enplanements in 2012 approximated 2011 levels, however, we expect it to increase by 1.8% in 2013. Current data suggests that U.S. GDP decreased in the fourth quarter of 2012 at an annual rate of approximately 0.1%. The International Air Transport Association, or “IATA,” stated in December 2012 that annual global enplanements increased by 5.3% in 2012 and is expected to increase by 4.5% in 2013.
The off-airport portion of the industry has rental volume primarily driven by local business use, leisure travel and the replacement of cars being repaired. Because Europe has generally demonstrated a lower historical reliance on air travel, the European off-airport car rental market is significantly more developed than it is in the United States. However, we believe that in recent years, industry revenues from off-airport car rentals in the United States have grown faster than revenues from airport rentals.
We provide commercial fleet leasing and management services to national corporate customers throughout the United States and Canada through Donlen, a wholly owned subsidiary of Hertz. Donlen is a fully integrated fleet management services provider with a comprehensive suite of product offerings ranging from leasing and managing vehicle fleets to providing other fleet management services to reduce fleet operating costs.
Worldwide Equipment Rental
We estimate the size of the U.S. equipment rental industry, which is highly fragmented with few national competitors and many regional and local operators, increased to approximately $31 billion in annual revenues for 2012, but the part of the rental industry dealing with equipment of the type HERC rents is somewhat smaller than that. We believe that the industry is expected to grow at a 10.6% compound annual growth rate between 2013 and 2016. Other market data indicates that the equipment rental industries in China, France, Spain and Saudi Arabia generate approximately $5.1 billion, $4.5 billion, $2.5 billion and $0.5 billion in annual revenues, respectively, although the portions of those markets in which HERC competes are smaller.
The equipment rental industry serves a broad range of customers from small local contractors to large industrial national accounts and encompasses a wide range of rental equipment from small tools to heavy earthmoving equipment. We believe U.S. non-residential construction spending declined at an annual rate of approximately 7% in 2012 but is projected to increase at an annual rate of 6% in 2013. We also believe that rental equipment will account for approximately 50% of all equipment sold into the U.S. construction industry in 2012, up from approximately 5% in 1993. In addition, we believe that the trend toward rental instead of ownership of equipment in the U.S. construction industry will continue and that as much as 50% of the equipment used in the industry could be rental equipment by 2015.
Our Business Segments
Our business consists of two reportable segments: rental and leasing of cars, crossovers and light trucks, or “car rental,” and rental of industrial, construction and material handling equipment, or “equipment rental.” General corporate
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
expenses, certain interest expense (including net interest on corporate debt), as well as other business activities, such as fees and certain cost reimbursements from our licensees are included as “other reconciling items.”
Car Rental: Our “company‑operated” rental locations are those through which we, or an agent of ours, rent cars that we own or lease. We maintain a substantial network of company‑operated car rental locations both in the United States and internationally, and what we believe to be the largest number of company‑operated airport car rental locations in the world, enabling us to provide consistent quality and service worldwide. Our licensees and associates also operate rental locations in approximately 145 countries and jurisdictions, including most of the countries in which we have company‑operated rental locations.
Equipment Rental: We believe, based on an article in Rental Equipment Register published in May 2012, that HERC is one of the largest equipment rental companies in the United States and Canada combined. HERC rents a broad range of earthmoving equipment, material handling equipment, aerial and electrical equipment, air compressors, generators, pumps, small tools, compaction equipment and construction‑related trucks. HERC also derives revenues from the sale of new equipment and consumables as well as through its Hertz Entertainment Services division, which rents lighting and related aerial products used primarily in the U.S. entertainment industry.
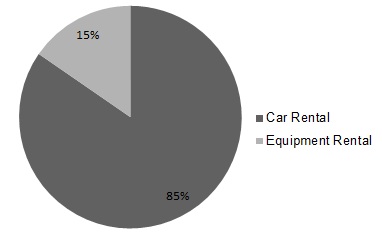
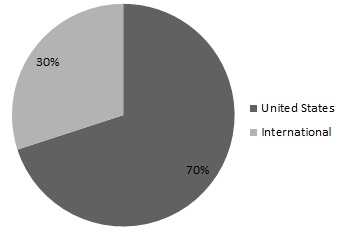
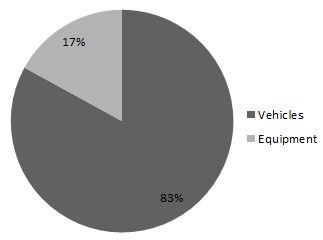
Set forth below are charts showing revenues by reportable segment, and revenues by geographic area, both for the year ended December 31, 2012 and revenue earning equipment at net book value as of December 31, 2012 (the majority of our international operations are in Europe).
|
| |
Revenues by Segment for Year Ended December 31, 2012(1)
$9.0 billion | Revenues by Geographic Area for Year Ended December 31, 2012
$9.0 billion |
| |
| |
Revenue Earning Equipment at net book value as of December 31, 2012
$12.9 billion |
|
| | |
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (1) | Car rental segment revenue includes fees and certain cost reimbursements from licensees. See Note 11 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” |
For further information on our business segments, including financial information for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, see Note 11 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
Worldwide Car Rental
Our worldwide car rental segment generated $7,633.0 million in revenues during the year ended December 31, 2012.
Our Brands
Our car rental business is primarily operated through three brands - Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty. Each of our brands generally maintains separate airport counters, reservations and reservation systems, marketing and all other customer contact activities, however a single management team manages all three brands. As we integrate the Dollar and Thrifty brands into our operations, we expect to eliminate many of the duplicative functions previously performed separately by Dollar Thrifty and identify synergies through combined fleet management, insurance, information technology functions, back office processing and procurement.
The Hertz brand is one of the most recognized brands in the world. Our customer surveys, in the United States, indicate that Hertz is the car rental brand most associated with the highest quality service. This is consistent with numerous published best-in class car rental awards that we have won, both in the United States and internationally, over many years. We have sought to support our reputation for quality and customer service in car rental through a variety of innovative service offerings, such as our customer loyalty program (Gold Plus Rewards), our global expedited rental program (Hertz #1 Club Gold), our one-way rental program (Rent-it-Here/Leave-it-There), our national‑scale luxury rental program (Prestige Collection), our sports car rental program (Adrenaline Collection), our environmentally friendly rental program (Green Traveler Collection), our car sharing service (Hertz On Demand) and our in-car navigational services (Hertz NeverLost). We intend to maintain our position as a premier provider of rental services through an intense focus on service, quality and product innovation.
Based on the latest available data, in the United States, the Hertz brand had the highest market share, by revenues, in 2010, 2011 and in the first eleven months of 2012 at approximately 200 of the largest airports where we have company‑operated locations. Out of the approximately 200 major European airports at which we have company‑operated rental locations, data regarding car rental concessionaire activity during 2012 was available at 120 of these airports. Based upon the latest available data, we believe that we were the largest airport car rental company, measured by aggregate airport rental revenues, at those 120 airports taken together. In the United States, we intend to maintain or expand our market share in the airport rental business. For a further description of our competitors, market share and competitive position see “—Competition” below.
Dollar and Thrifty are positioned as value car rental brands in the travel industry. The Dollar brand's main focus is serving the airport vehicle rental market, which is comprised of business and leisure travelers. The majority of its locations are on or near airport facilities. Dollar operates primarily through company-owned locations in the United States and Canada, and also licenses to independent franchisees which operate as a part of the Dollar brand system. Thrifty serves both the airport and local markets through company-owned locations and its franchisees which derive approximately 90% of their combined rental revenues from the airport market and approximately 10% from the local market.
In April 2009, we acquired certain assets of Advantage Rent A Car, or “Advantage” a brand focused on price‑oriented customers at key leisure travel destinations, and began operating the Advantage brand as part of our business. On November 19, 2012, we entered into an agreement with the Federal Trade Commission in connection with our acquisition of Dollar Thrifty to divest the Advantage brand and selected Dollar Thrifty airport concessions. On December 12, 2012, we divested the Simply Wheelz subsidiary, which owned and operated the Advantage brand, to Adreca Holdings Corp., a subsidiary of Macquarie Capital which is expected to be operated by Franchise Services of North America Inc. Immediately prior to the divestiture, Advantage was operating at 62 U.S. locations, including 35 on-airport locations where Advantage held concessions.
Operations
Locations
Airport Locations
As of December 31, 2012, we had approximately 3,210 staffed rental locations in the United States, of which approximately one-fifth were airport locations and four-fifths were off-airport locations, and we regularly rent cars from approximately 1,360 other locations that are not staffed. As of December 31, 2012, we had approximately 1,215 staffed rental locations internationally, of which approximately one-fourth were airport locations and three-fourths were off-airport locations, and we regularly rent cars from approximately 150 other locations that are not staffed. Our international car rental operations have company‑operated locations in France, Australia, Italy, the United Kingdom, Germany, Spain, Canada, Brazil, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Belgium, Puerto Rico, the Czech Republic, China, Luxembourg, Slovakia and the U.S. Virgin Islands. We believe that our extensive U.S. and international network of company‑operated
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
locations contributes to the consistency of our service, cost control, fleet utilization, yield management, competitive pricing and our ability to offer one-way rentals.
In order to operate airport rental locations, we have obtained concessions or similar leasing, licensing or permitting agreements or arrangements, or “concessions,” granting us the right to conduct a car rental business at all major, and many other airports in each country where we have company‑operated rental locations, except for airports where our licensees operate rental locations. Our concessions were obtained from the airports' operators, which are typically governmental bodies or authorities, following either negotiation or bidding for the right to operate a car rental business there. The terms of an airport concession typically require us to pay the airport's operator concession fees based upon a specified percentage of the revenues we generate at the airport, subject to a minimum annual guarantee. Under most concessions, we must also pay fixed rent for terminal counters or other leased properties and facilities. Most concessions are for a fixed length of time, while others create operating rights and payment obligations that are terminable at any time.
The terms of our concessions typically do not forbid us from seeking, and in a few instances actually require us to seek, reimbursement from customers of concession fees we pay; however, in certain jurisdictions the law limits or forbids our doing so. Where we are required or permitted to seek such reimbursement, it is our general practice to do so. The number of car rental concessions available at airports varies considerably, but, except at small, regional airports, it is rarely less than four. Certain of our concession agreements require the consent of the airport's operator in connection with material changes in our ownership. A growing number of larger airports are building consolidated airport rental car facilities to alleviate congestion at the airport. These consolidated rental facilities may eliminate certain competitive advantages among the brands as competitors operate out of one centralized facility for both customer rental and return operations, share consolidated bussing operations and maintain image standards mandated by the airports. See “Item 1A—Risk Factors” in this Annual Report.
Off-Airport Locations
In addition to our airport locations, we operate off-airport locations offering car rental services to a variety of customers. Our off-airport rental customers include people wishing to rent cars closer to home for business or leisure purposes, as well as those needing to travel to or from airports. Our off-airport customers also include people who have been referred by, or whose rental costs are being wholly or partially reimbursed by, insurance companies following accidents in which their cars were damaged, those expecting to lease cars that are not yet available from their leasing companies and those needing cars while their vehicle is being repaired or is temporarily unavailable for other reasons; we call these customers “replacement renters.” At many of our off-airport locations we will provide pick-up and delivery services in connection with rentals.
When compared to our airport rental locations, an off-airport rental location typically services the same variety of customers, uses smaller rental facilities with fewer employees, conducts pick-up and delivery services and deals with replacement renters using specialized systems and processes. In addition, on average, off-airport locations generate fewer transactions per period than airport locations. At the same time, though, our airport and off-airport rental locations employ common car fleets, are supervised by common country, regional and local area management, use many common systems and rely on common maintenance and administrative centers. Moreover, airport and off-airport locations, excluding replacement rentals, benefit from many common marketing activities and have many of the same customers. As a consequence, we regard both types of locations as aspects of a single, unitary, car rental business.
We believe that the off-airport portion of the car rental market offers opportunities for us on several levels. First, presence in the off-airport market can provide customers a more convenient and geographically extensive network of rental locations, thereby creating revenue opportunities from replacement renters, non-airline travel renters and airline travelers with local rental needs. Second, it can give us a more balanced revenue mix by reducing our reliance on airport travel and therefore limiting our exposure to external events that may disrupt airline travel trends. Third, it can produce higher fleet utilization as a result of the longer average rental periods associated with off-airport business, compared to those of airport rentals. Fourth, replacement rental volume is far less seasonal than that of other business and leisure rentals, which permits efficiencies in both fleet and labor planning. Finally, cross‑selling opportunities exist for us to promote off-airport rentals among frequent airport Hertz #1 Club Gold program renters and, conversely, to promote airport rentals to off-airport renters. In view of those benefits, along with our belief that our market share for off-airport rentals is generally smaller than our market share for airport rentals, we intend to seek profitable growth in the off-airport rental market, both in the United States and internationally.
Since January 1, 2009, we increased the number of our off-airport rental locations in the United States by 53% to approximately 2,520 locations. Our strategy includes selected openings of new off-airport locations, the disciplined evaluation of existing locations and the pursuit of same-store sales growth. We anticipate that same-store sales growth will be driven by our traditional leisure and business traveler customers and by increasing our market share in the
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
insurance replacement market, in which we currently have a relatively low market share. In the United States during the year ended December 31, 2012, approximately one-third of our rental revenues at off-airport locations were related to replacement rentals. We believe that if we successfully pursue our strategy of profitable off-airport growth, the proportion of replacement rental revenues will increase. As we move forward, our determination of whether to continue to expand our U.S. off-airport network will be based upon a combination of factors, including, commercial activity and potential profitability as well as the concentration of target insurance company policyholders, car dealerships and auto body shops. We also intend to increase the number of our staffed off-airport rental locations internationally based on similar criteria.
Rates
We rent a wide variety of makes and models of cars. We rent cars on an hourly (in select markets), daily, weekend, weekly, monthly or multi‑month basis, with rental charges computed on a limited or unlimited mileage rate, or on a time rate plus a mileage charge. Our rates vary at different locations depending on local market conditions and other competitive and cost factors. While cars are usually returned to the locations from which they are rented, we also allow one-way rentals from and to certain locations. In addition to car rentals and licensee fees, we generate revenues from reimbursements by customers of airport concession fees and vehicle licensing costs, fueling charges, and charges for ancillary customer products and services such as supplemental equipment (child seats and ski racks), loss or collision damage waiver, theft protection, liability and personal accident/effects insurance coverage, Hertz NeverLost navigation systems and satellite radio services.
Reservations
We accept reservations for our cars on a brand-by-brand basis, with each of our brands maintaining, and accepting reservations through, an independent Internet site. Our brands generally accept reservations only for a class of vehicles, although Hertz accepts reservations for specific makes and models of vehicles in our Prestige Collection, our Adrenaline Collection, our Green Traveler Collection and a limited number of models in high-volume, leisure‑oriented destinations. Beginning in December 2010, we made the next generation of electric vehicles available to the general public, initially through our Hertz On Demand car sharing service. Electric vehicles have been added to our fleet and are available at various cities across the U.S. such as New York, Washington D.C. and San Francisco, in Europe and in China. We plan continued deployment of electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles in both the U.S. and other countries throughout 2013.
When customers reserve cars for rental from us and our licensees, they may seek to do so through travel agents or third‑party travel websites. In many of those cases, the travel agent or website will utilize a third‑party operated computerized reservation system, also known as a Global Distribution System, or “GDS,” to contact us and make the reservation.
In major countries, including the United States and all other countries with company‑operated locations, customers may also reserve cars for rental from us and our licensees worldwide through local, national or toll-free telephone calls to our reservations center, directly through our rental locations or, in the case of replacement rentals, through proprietary automated systems serving the insurance industry. Additionally, we accept reservations for rentals worldwide through our websites, for us and our licensees. We also offer the ability to reserve cars through our smartphone apps for the Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty brands.
For the year ended December 31, 2012, approximately 32% of the worldwide reservations we accepted came through travel agents using GDSs, while 30% came through our websites, 17% through phone calls to our reservations center, 15% through third‑party websites and 6% through local booking sources and tour reservations. Our Dollar and Thrifty brands have historically used the Internet as their primary source of reservations. As a result, we expect the percent of our reservations that come through the Internet, particularly through our websites and third-party websites, to increase as a result of our acquisition of Dollar Thrifty.
Customer Service Offerings
At our major airport rental locations, as well as at some smaller airport and off-airport locations, customers participating in our Hertz #1 Club Gold program are able to rent vehicles in an expedited manner. In the United States, participants in our Hertz #1 Club Gold program often bypass the rental counter entirely and proceed directly to their vehicles upon arrival at our facility. Participants in our Hertz #1 Club Gold program are also eligible to earn Gold Plus Rewards points that may be redeemed for free rental days. For the year ended December 31, 2012, rentals by Hertz #1 Club Gold members accounted for approximately 37% of our worldwide rental transactions. We believe the Hertz #1 Club Gold program provides a significant competitive advantage to us, particularly among frequent travelers, and we have, through travel industry relationships, targeted such travelers for participation in the program.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
Hertz has introduced a number of customer service offerings in recent years in order to further differentiate itself from the competition. The most significant new offering was Gold Choice. Hertz Gold Choice now offers our customers an option to choose the car they drive. As is the case with participants in our Hertz #1 Club Gold program, Gold Choice offers customers a preassigned car, but also allows customers to choose a different model and color from those cars available at the new Gold Choice area. This service is free of charge to Hertz #1 Club Gold customers who book a midsize class or above. The Gold Choice program was launched during August 2011 and rolled out to 52 U.S. airport locations and 5 locations in Europe by December 2012. Additionally, in select locations customers can bypass the rental line to rent through our ExpressRent Kiosks.
Global Car-Sharing
In late 2008, we introduced a global car-sharing service, now referred to as Hertz On Demand, which rents cars by the hour and/or by the day, at various locations in the U.S., Canada and Europe. Hertz On Demand allows customers to sign up for free for the service and to rent cars by the hour or by the day. Members reserve vehicles online, then pick up the vehicles at various locations throughout a city, at a university or a corporate campus without the need to visit a Hertz rental office. Customers are charged an hourly or daily car-rental fee which includes fuel, insurance, 24/7 roadside assistance, in-car customer service and 180 miles per 24 hour period.
Fleet Leasing and Management Services
On September 1, 2011, Hertz acquired 100% of the equity of Donlen, a leading provider of fleet leasing and management services for corporate fleets. For the year ended December 31, 2012 and for the four months ended December 31, 2011 (period it was owned by Hertz), Donlen had an average of approximately 150,800 and 137,000 vehicles under lease and management, respectively. Donlen provides Hertz an immediate leadership position in long-term car, truck and equipment leasing and fleet management. Donlen's fleet management programs provide outsource solutions to reduce fleet operating costs and improve driver productivity. These programs include administration of preventive maintenance, advisory services, and fuel and accident management along with other complementary services. This transaction is part of the overall growth strategy of Hertz to provide the most flexible transportation programs for corporate and general consumers. Additionally, Donlen brings to Hertz a specialized consulting and technology expertise that will enable us to model, measure and manage fleet performance more effectively and efficiently.
Customers and Business Mix
We categorize our car rental business based on two primary criteria: the purpose for which customers rent from us (business or leisure) and the type of location from which they rent (airport or off-airport). The table below sets forth, for the year ended December 31, 2012, the percentages of rental revenues and rental transactions in our U.S. and international operations derived from business and leisure rentals and from airport and off-airport rentals. |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, 2012 |
| | U.S. | | International |
| | Revenues | | Transactions | | Revenues | | Transactions |
| Type of Car Rental | | | | | | | |
| By Customer: | | | | | | | |
| Business | 42 | % | | 44 | % | | 55 | % | | 58 | % |
| Leisure | 58 |
| | 56 |
| | 45 |
| | 42 |
|
| | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % |
| By Location: | | | | | | | |
| Airport | 70 | % | | 73 | % | | 49 | % | | 57 | % |
| Off-airport | 30 |
| | 27 |
| | 51 |
| | 43 |
|
| | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % |
Customers who rent from us for “business” purposes include those who require cars in connection with commercial activities, the activities of governments and other organizations or for temporary vehicle replacement purposes. Most business customers rent cars from us on terms that we have negotiated with their employers or other entities with which they are associated, and those terms can differ substantially from the terms on which we rent cars to the general public. We have negotiated arrangements relating to car rental with many large businesses, governments and other organizations, including most Fortune 500 companies.
Customers who rent from us for “leisure” purposes include not only individual travelers booking vacation travel rentals with us but also people renting to meet other personal needs. Leisure rentals, generally, are longer in duration and generate more revenue per transaction than do business rentals, although some types of business rentals, such as
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
rentals to replace temporarily unavailable cars, have a long average duration. Also included in leisure rentals are rentals by customers of U.S. and international tour operators, which are usually a part of tour packages that can also include air travel and hotel accommodations. Business rentals and leisure rentals have different characteristics and place different types of demands on our operations. We believe that maintaining an appropriate balance between business and leisure rentals is important to the profitability of our business and the consistency of our operations. Following our acquisition of Dollar Thrifty, we expect U.S. airport leisure business as a percentage of our worldwide car rental revenue to increase.
Our business and leisure customers rent from both our airport and off-airport locations. Demand for airport rentals is correlated with airline travel patterns, and transaction volumes generally follow enplanement and GDP trends on a global basis. Customers often make reservations for airport rentals when they book their flight plans, which make our strong relationships with travel agents, associations and other partners (e.g., airlines) a key competitive advantage in generating consistent and recurring revenue streams.
Off-airport rentals typically involve people wishing to rent cars closer to home for business or leisure purposes, as well as those needing to travel to or from airports. This category also includes people who have been referred by, or whose rental costs are being wholly or partially reimbursed by, insurance companies because their cars have been damaged. In order to attract these renters, we must establish agreements with the referring insurers establishing the relevant rental terms, including the arrangements made for billing and payment. While we estimate our share of the insurance replacement rental market was approximately 13% of the estimated insurance rental revenue volume for the year ended December 31, 2012, we have identified approximately 200 insurance companies, ranging from local or regional carriers to large, national companies, as our target insurance replacement market. As of December 31, 2012, we were a preferred or recognized supplier of 181 of these approximately 200 insurance companies and a co-primary at 39 of these approximately 200 insurance companies.
We conduct active sales and marketing programs to attract and retain customers. Our commercial and travel industry sales force calls on companies and other organizations whose employees and associates need to rent cars for business purposes. In addition, our sales force works with membership associations, tour operators, travel companies and other groups whose members, participants and customers rent cars for either business or leisure purposes. A specialized sales force calls on companies with replacement rental needs, including insurance and leasing companies and car dealers. We also advertise our car rental offerings through a variety of traditional media channels, such as television and newspapers, direct mail and the Internet. In addition to advertising, we also conduct a variety of other forms of marketing and promotion, including travel industry business partnerships and press and public relations activities.
In almost all cases, when we rent a car, we rent it directly to an individual who is identified in a written rental agreement that we prepare. Except when we are accommodating someone who cannot drive, the individual to whom we rent a car is required to have a valid driver's license and meet other rental criteria (including minimum age and creditworthiness requirements) that vary on the basis of location and type of rental. Our rental agreements permit only licensed individuals renting the car, people signing additional authorized operator forms and certain defined categories of other individuals (such as fellow employees, parking attendants and in some cases spouses or domestic partners) to operate the car.
With rare exceptions, individuals renting cars from us are personally obligated to pay all amounts due under their rental agreements. They typically pay us with a charge, credit or debit card issued by a third party, although certain customers use a Hertz charge account that we have established for them, usually as part of an agreement between us and their employer. For the year ended December 31, 2012, all amounts charged to Hertz charge accounts established in the United States and by our international subsidiaries, were billed directly to a company or other organization or were guaranteed by a company. We also issue rental vouchers and certificates that may be used to pay rental charges, mostly for prepaid and tour-related rentals. In addition, where the law requires us to do so, we rent cars on a cash basis. For the year ended December 31, 2012, no customer accounted for more than 7.5% of our car rental revenues.
In the United States for the year ended December 31, 2012, 83% of our car rental revenues came from customers who paid us with third‑party charge, credit or debit cards, while 8% came from customers using Hertz charge accounts or direct billing, 8% came from customers using rental vouchers or another method of payment and 1% came from cash transactions.
In our international operations for the year ended December 31, 2012, 48% of our car rental revenues came from customers who paid us with third‑party charge, credit or debit cards, while 29% came from customers using Hertz charge accounts, 22% came from customers using rental vouchers or another method of payment and 1% came from cash transactions. For the year ended December 31, 2012, bad debt expense represented 0.3% of car rental revenues for our U.S. operations and 0.3% of car rental revenues for our international operations.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
Fleet
We believe we are one of the largest private sector purchasers of new cars in the world. During the year ended December 31, 2012, we operated a peak rental fleet in the United States of approximately 490,700 cars and a combined peak rental fleet in our international operations of approximately 177,900 cars, and in each case exclusive of our licensees' fleet and Donlen's leasing fleet. During the year ended December 31, 2012, our approximate average holding period for a rental car was eighteen months in the United States and fourteen months in our international operations.
Under our repurchase programs, the manufacturers agree to repurchase cars at a specified price or guarantee the depreciation rate on the cars during established repurchase or auction periods, subject to, among other things, certain car condition, mileage and holding period requirements. Repurchase prices under repurchase programs are based on either a predetermined percentage of original car cost and the month in which the car is returned or the original capitalized cost less a set daily depreciation amount. Guaranteed depreciation programs guarantee on an aggregate basis the residual value of the cars covered by the programs upon sale according to certain parameters which include the holding period, mileage and condition of the cars. These repurchase and guaranteed depreciation programs limit our residual risk with respect to cars purchased under the programs and allow us to determine depreciation expense in advance, however, typically the acquisition cost is higher for these program cars.
Program cars as a percentage of all cars purchased by our U.S., International and worldwide operations were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 |
| U.S. | 19 | % | | 45 | % | | 54 | % | | 48 | % | | 55 | % |
| International | 53 | % | | 55 | % | | 56 | % | | 57 | % | | 59 | % |
| Worldwide | 30 | % | | 48 | % | | 55 | % | | 51 | % | | 57 | % |
Within our Donlen subsidiary, revenue earning equipment is under longer term lease agreements with our customers. These leases contain provisions whereby we have a contracted residual value guaranteed to us by the lessee, such that we do not experience any gains or losses on the disposal of these vehicles.
We have purchased a significant percentage of our car rental fleet from the following vehicle manufacturers:
|
| | | | | |
| | For the year ended December 31, 2012 |
| | U.S. | | International |
| General Motors Company | 25 | % | | 21 | % |
| Toyota Motor Company | 13 | % | | 12 | % |
| Ford Motor Company | 16 | % | | 26 | % |
| Nissan Motor Company | 16 | % | | 2 | % |
Purchases of cars are financed through cash from operations and by active and ongoing global borrowing programs. See “Item 7—Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources,” in this Annual Report.
We maintain automobile maintenance centers at certain airports and in certain urban and off-airport areas, which provide maintenance facilities for our car rental fleet. Many of these facilities, which include sophisticated car diagnostic and repair equipment, are accepted by automobile manufacturers as eligible to perform and receive reimbursement for warranty work. Collision damage and major repairs are generally performed by independent contractors.
We dispose of non-program cars, as well as program cars that become ineligible for manufacturer repurchase or guaranteed depreciation programs, through a variety of disposition channels, including auctions, brokered sales, sales to wholesalers and dealers and, to a lesser extent and primarily in the United States, sales at retail through a network of 26 company‑operated car sales locations dedicated exclusively to the sale of used cars from our rental fleet.
During 2009, we launched Rent2Buy, an innovative program designed to sell used rental cars. The program was licensed to operate in 32 states as of December 31, 2012. Customers have an opportunity for a three-day test rental of a competitively priced car from our rental fleet. If the customer purchases the car, he or she is credited with up to three days of rental charges, and the purchase transaction is completed through the internet and by mail in those states where permitted.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
During the year ended December 31, 2012, of the cars that were not repurchased by manufacturers, we sold approximately 33% at auction, 47% through dealer direct, 13% through our Rent2Buy program or at retail locations and approximately 7% through other channels.
Licensees Under Our Hertz Brand
We believe that our extensive worldwide ownership of car rental operations contributes to the consistency of our high-quality service, cost control, fleet utilization, yield management, competitive pricing and our ability to offer one-way rentals. However, in certain U.S. and international markets, we have found it more efficient to utilize independent licensees, which rent cars that they own. Our licensees operate locations in approximately 145 countries, including most of the countries where we have company‑operated locations. See “Item 1A—Risk Factors” in this Annual Report.
We believe that our licensee arrangements are important to our business because they enable us to offer expanded national and international service and a broader one-way rental program. Licenses are issued principally by our wholly‑owned subsidiaries, under franchise arrangements to independent licensees and affiliates who are engaged in the car rental business in the United States and in many other countries.
Licensees generally pay fees based on a percentage of their revenues or the number of cars they operate. The operations of all licensees, including the purchase and ownership of vehicles, are financed independently by the licensees, and we do not have any investment interest in the licensees or their fleets. Licensees in the U.S. share in the cost of our U.S. advertising program, reservations system, sales force and certain other services. Our European and other international licensees also share in the cost of our reservations system, sales force and certain other services. In return, licensees are provided the use of the Hertz brand name, management and administrative assistance and training, reservations through our reservations channels, the Gold Plus Rewards and #1 Club Gold programs, our “Rent-it-Here/Leave-it-There” one-way rental program and other services. In addition to car rental, certain licensees outside the United States engage in car leasing, chauffeur‑driven rentals and renting camper vans under the Hertz name.
U.S. licensees ordinarily are limited as to transferability without our consent and are terminable by us only for cause or after a fixed term. Licensees in the United States may generally terminate for any reason on 90 days' notice. In Europe and certain other international jurisdictions, licensees typically do not have early termination rights. Initial license fees or the price for the sale to a licensee of a company‑owned location may be payable over a term of several years. We continue to issue new licenses and, from time to time, purchase licensee businesses.
Franchisees Under Our Dollar Thrifty Brands
Both Dollar and Thrifty sell U.S. franchises on an exclusive basis for specific geographic areas, generally outside the top 75 U.S. airport markets. Most franchisees are located at or near airports that generate a lower volume of vehicle rentals than the airports served by company-owned locations. In Canada, Dollar and Thrifty sell franchises in markets generally outside the top eight airport markets. The typical length of a franchise is ten years with a renewal option for five years if certain conditions are met. The franchisee may terminate the franchise for convenience upon 120 days written notice and Dollar and Thrifty may terminate upon breach of the agreement or for cause as defined in the agreement.
Dollar and Thrifty offer franchisees the opportunity to dual franchise in smaller U.S. and Canadian markets. Under a dual franchise, one franchisee can operate both the Dollar and the Thrifty brand, thus allowing them to generate more business in their market while leveraging fixed costs.
Dollar and Thrifty license to franchisees the use of their respective brand service marks in the vehicle rental and leasing and parking businesses. Franchisees of Dollar and Thrifty pay an initial franchise fee generally based on the population, number of airline passengers, total airport vehicle rental revenues and the level of any other vehicle rental activity in the franchised territory, as well as other factors. Dollar and Thrifty offer their respective franchisees a wide range of products and services which may not be easily or cost effectively available from other sources.
System Fees in the U.S.
Dollar - In addition to an initial franchise fee, each Dollar U.S. franchisee generally pays a system fee as a percentage of rental revenue at airport locations and off-airport operations.
Thrifty - In addition to an initial franchise fee, each Thrifty U.S. franchisee generally pays a fee as a percentage of rental revenue.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
System Fees in Canada
All Dollar and Thrifty Canadian franchisees, whether operating a single-brand or co-brand location, pay a monthly fee generally based on a percentage of rental revenue.
Franchisee Services and Products
Dollar and Thrifty provide their U.S. and Canadian franchisees a wide range of products and services, including reservations, marketing programs and assistance, branded supplies, image and standards, rental rate management analysis and customer satisfaction programs. Additionally, Dollar and Thrifty offer their respective franchisees centralized corporate account and tour billing and travel agent commission payments.
International
Dollar and Thrifty offer master franchises outside the U.S. and Canada, generally on a countrywide basis. Each master franchisee is permitted to operate within its franchised territory directly or through subfranchisees. At December 31, 2012, exclusive of the U.S. and Canada, Dollar had franchised locations in 60 countries and Thrifty had franchised locations in 76 countries. These locations are in Latin America, Europe, the Middle East, Africa and the Asia-Pacific regions. The Company offers franchisees the opportunity to license the rights to operate either the Dollar or the Thrifty brand or both brands in certain markets on a dual franchise or co-brand basis.
Competition
In the United States, in addition to local and regional vehicle rental companies, our principal car rental industry competitors are Avis Budget Group, Inc., or “ABG,” which currently operates the Avis and Budget brands and Enterprise Holdings, which operates the Enterprise Rent-A-Car Company, or "Enterprise," National Car Rental and Alamo brands. In the United States, the Hertz brand had the highest market share, by revenues, in 2010, 2011 and in the first eleven months of 2012 at approximately 200 of the largest airports where we have company‑operated locations.
In Europe, in addition to us, the principal pan-European participants in the car rental industry are ABG, operating the Avis and Budget brands, and Europcar. Europcar also operates the National Car Rental and Alamo brands in the United Kingdom and Germany, and through franchises in Spain, Italy and France. In certain European countries, there are also other companies and brands with substantial market shares, including Sixt AG (operating the Sixt brand) in Germany, France, Spain, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, Belgium, Netherlands and Luxembourg; and Enterprise (operating the Enterprise brand) in the United Kingdom, Ireland and Germany. In every European country, there are also national, regional or other, smaller companies operating in the airport and off-airport rentals markets. Apart from Enterprise‑branded operations, all of which Enterprise owns, the other major car rental brands are present in European car rental markets through a combination of company‑operated and franchisee‑ or licensee‑operated locations.
Competition among car rental industry participants is intense and is primarily based on price, vehicle availability and quality, service, reliability, rental locations and product innovation. We believe, however, that the prominence and service reputation of the Hertz brand, our extensive worldwide ownership of car rental operations and our commitment to innovation and service provide us with a competitive advantage. Our acquisition of Dollar and Thrifty brands adds two popular value leisure brands enabling us to compete across multiple market segments.
Worldwide Equipment Rental
Our worldwide equipment rental segment generated $1,385.4 million in revenues during the year ended December 31, 2012.
Operations
Product Offerings
We, through HERC, operate an equipment rental business in the United States, Canada, France, Spain, China and Saudi Arabia. On the basis of total revenues, we believe HERC is one of the largest equipment rental companies in the United States and Canada combined. HERC has operated in the United States since 1965.
HERC's principal business is the rental of equipment. HERC offers a broad range of equipment for rental; major categories include earthmoving equipment, material handling equipment, aerial and electrical equipment, lighting, air compressors, pumps, generators, small tools, compaction equipment and construction‑related trucks.
Ancillary to its rental business, HERC is also a dealer of certain brands of new equipment in the United States and Canada, and sells consumables such as gloves and hardhats at many of its rental locations.
HERC's comprehensive line of equipment enables it to supply equipment to a wide variety of customers from local contractors to large industrial plants. The fact that many larger companies, particularly those with industrial plant
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
operations, now require single source vendors, not only for equipment rental, but also for management of their total equipment needs fits well with HERC's core competencies. Arrangements with such companies may include maintenance of the tools and equipment they own, supplies and rental tools for their labor force and custom management reports. HERC supports this through its dedicated in-plant operations, tool trailers and plant management systems.
Locations
As of December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, HERC had a total of approximately 340, 320 and 320 branches, respectively, in the U.S., Canada, France, Spain, China and Saudi Arabia.
HERC's rental locations generally are located in industrial or commercial zones. A growing number of locations have highway or major thoroughfare visibility. The typical location includes a customer service center, an equipment service area and storage facilities for equipment. The branches are built or conform to the specifications of the HERC prototype branch, which stresses efficiency, safety and environmental compliance. Most branches have stand‑alone maintenance and fueling facilities and showrooms.
HERC's broad equipment line in the United States and Canada also includes, equipment with an acquisition cost of under $10,000 per unit, ranging from air compressors and generators to small tools and accessories, in order to supply customers who are local contractors with a greater proportion of their overall equipment rental needs. As of December 31, 2012, these activities, referred to as “general rental activities,” were conducted at approximately 28% of HERC's U.S. and Canadian rental locations. Before it begins to conduct general rental activities at a location, HERC typically renovates the location to make it more appealing to walk-in customers and adds staff and equipment in anticipation of subsequent demand.
Business Initiatives
In early 2010, Hertz launched Hertz Entertainment Services, a division which provides single‑source car and equipment rental solutions to the entertainment and special events industries. Hertz Entertainment Services provides customized vehicle and equipment rental solutions to movie, film and television productions, live sports and entertainment events, and all-occasion special events, such as conventions, and fairs. Hertz Entertainment Services are tailored to fit the needs of large and small productions alike with competitive pricing and customized, monthly billing. Hertz delivers vehicles and equipment to production locations and a dedicated staff is available 24/7 to address specific client needs. Productions can also rent equipment for use at special events such as lighting, generators and other machinery.
In February 2010, HERC entered into a joint venture with Saudi Arabia based Dayim Holdings Company, Ltd. to set up equipment rental operations in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The joint venture entity rents and sells equipment and tools to construction and industrial markets throughout the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Customers
HERC's customers consist predominantly of commercial accounts and represent a wide variety of industries, such as construction, petrochemical, automobile manufacturing, railroad, power generation, shipbuilding and entertainment and special events. Serving a number of different industries enables HERC to reduce its dependence on a single or limited number of customers in the same business and somewhat reduces the seasonality of HERC's revenues and its dependence on construction cycles. HERC primarily targets customers in medium to large metropolitan markets. For the year ended December 31, 2012, no customer of HERC accounted for more than 1.5% of HERC's worldwide rental revenues. Of HERC's combined U.S. and Canadian rental revenues for the year ended December 31, 2012, approximately 37% were derived from customers operating in the construction industry (the majority of which were in the non-residential sector) and approximately 27% were derived from customers in the industrial business, while the remaining revenues were derived from rentals to governmental and other types of customers.
Unlike in our car rental business, where we enter into rental agreements with the end-user who will operate the cars being rented, HERC ordinarily enters into a rental agreement with the legal entity-typically a company, governmental body or other organization-seeking to rent HERC's equipment. Moreover, unlike in our car rental business, where our cars are normally picked up and dropped off by customers at our rental locations, HERC delivers much of its rental equipment to its customers' job sites and retrieves the equipment from the job sites when the rentals conclude. HERC extends credit terms to many of its customers to pay for rentals. Thus, for the year ended December 31, 2012, 95% of HERC's revenues came from customers who were invoiced by HERC for rental charges, while 5% came from customers paying with third‑party charge, credit or debit cards, cash or used another method of payment. For the year ended December 31, 2012, bad debt expense represented 0.4% of HERC's revenues.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
Fleet
HERC acquires its equipment from a variety of manufacturers. The equipment is typically new at the time of acquisition and is not subject to any repurchase program. The per-unit acquisition cost of units of rental equipment in HERC's fleet varies from over $200,000 to under $100. As of December 31, 2012, the average per-unit acquisition cost (excluding small equipment purchased for less than $5,000 per unit) for HERC's fleet in the United States was approximately $38,000. As of December 31, 2012, the average age of HERC's worldwide rental fleet was 43 months.
HERC disposes of its used equipment through a variety of channels, including private sales to customers and other third parties, sales to wholesalers, brokered sales and auctions.
Licensees
HERC licenses the Hertz name to equipment rental businesses in six countries in Europe, in Afghanistan and Chile. The terms of those licenses are broadly similar to those we grant to our international car rental licensees.
Competition
HERC's competitors in the equipment rental industry range from other large national companies to small regional and local businesses. In each of the six countries where HERC operates, the equipment rental industry is highly fragmented, with large numbers of companies operating on a regional or local scale. The number of industry participants operating on a national scale is, however, much smaller. HERC is one of the principal national‑scale industry participants in the U.S., Canada and France. HERC's operations in the United States represented approximately 70% of our worldwide equipment rental revenues during the year ended December 31, 2012. In the United States and Canada, the other top national‑scale industry participants are United Rentals, Inc., or “URI,” Sunbelt Rentals, Home Depot Rentals and Aggreko North America. A number of individual Caterpillar, Inc., or “CAT,” dealers also participate in the equipment rental market in the United States, Canada, France and Spain. In France, the other principal national‑scale industry participants are Loxam, Kiloutou and Laho. Aggreko also participates in the power generation rental markets in France and Spain. In China, the other principal national‑scale industry participants are Zicheng Corporation, Aggreko, Jin He Yuan, Lei Shing Hong and Far East Rental. In Saudi Arabia, the other principal national‑scale industry participants are Bin Quraya, Al Zahid Tractors (CAT), Rapid Access, Eastern Arabia and Rental Solutions & Services (RSS) Saudi Ltd.
Competition in the equipment rental industry is intense, and it often takes the form of price competition. HERC's competitors, some of which may have access to substantial capital, may seek to compete aggressively on the basis of pricing. To the extent that HERC matches downward competitor pricing without reducing our operating costs, it could have an adverse impact on our results of operations. We believe that HERC's competitive success has been primarily the product of its more than 40 years of experience in the equipment rental industry, its systems and procedures for monitoring, controlling and developing its branch network, its capacity to maintain a comprehensive rental fleet, the quality of its sales force and its established national accounts program.
Other Operations
Our wholly‑owned subsidiary, Hertz Claim Management Corporation, or “HCM,” provides claim administration services to us and, to a lesser extent, to third parties. These services include investigating, evaluating, negotiating and disposing of a wide variety of claims, including third‑party, first‑party, bodily injury, property damage, general liability and product liability, but not the underwriting of risks. HCM conducts business at five regional offices in the United States. Separate subsidiaries of ours conduct similar operations in six countries in Europe.
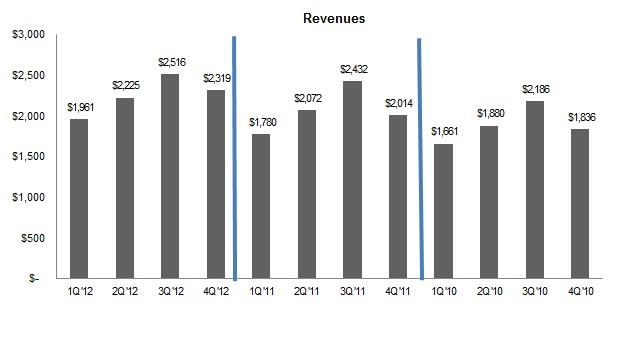
Seasonality
Generally, car rental and equipment rental are seasonal businesses, with decreased levels of business in the winter months and heightened activity during spring and summer. To accommodate increased demand, we increase our available fleet and staff during the second and third quarters of the year. As business demand declines, fleet and staff are decreased accordingly. However, certain operating expenses, including real estate taxes, rent, insurance, utilities, maintenance and other facility‑related expenses, the costs of operating our information technology systems and minimum staffing costs, remain fixed and cannot be adjusted for seasonal demand. Revenues related to our fleet management services are generally not seasonal. See “Item 1A—Risk Factors” in this Annual Report. The following tables set forth this seasonal effect by providing quarterly revenues for each of the quarters in the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 (in millions of dollars).
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
Employees
As of December 31, 2012, we employed approximately 30,200 persons, consisting of approximately 22,500 persons in our U.S. operations and 7,700 persons in our international operations. International employees are covered by a wide variety of union contracts and governmental regulations affecting, among other things, compensation, job retention rights and pensions. Labor contracts covering the terms of employment of approximately 5,740 employees in the United States (including those in the U.S. territories) are presently in effect under approximately 145 active contracts with local unions, affiliated primarily with the International Brotherhood of Teamsters and the International Association of Machinists. Labor contracts covering approximately 1,370 of these employees will expire during 2013. We have had no material work stoppage as a result of labor problems during the last ten years, and we believe our labor relations to be good. Nonetheless, we may be unable to negotiate new labor contracts on terms advantageous to us, or without labor interruptions.
In addition to the employees referred to above, we employ a substantial number of temporary workers, and engage outside services, as is customary in the industry, principally for the non-revenue movement of rental cars and equipment between rental locations and the movement of rental equipment to and from customers' job sites.
Risk Management
Three types of generally insurable risks arise in our operations:
| |
| • | legal liability arising from the operation of our cars and on-road equipment (vehicle liability); |
| |
| • | legal liability to members of the public and employees from other causes (general liability/workers' compensation); and |
| |
| • | risk of property damage and/or business interruption and/or increased cost of working as a consequence of property damage. |
In addition, we offer optional liability insurance and other products providing insurance coverage, which create additional risk exposures for us. Our risk of property damage is also increased when we waive the provisions in our rental contracts that hold a renter responsible for damage or loss under an optional loss or damage waiver that we offer. We bear these and other risks, except to the extent the risks are transferred through insurance or contractual arrangements.
In many cases we self-insure our risks or insure risks through wholly‑owned insurance subsidiaries. We mitigate our exposure to large liability losses by maintaining excess insurance coverage, subject to deductibles and caps, through unaffiliated carriers. For our international operations outside of Europe, and for our long-term fleet leasing operations, we maintain some liability insurance coverage with unaffiliated carriers.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
Third‑Party Liability
In our domestic operations, we are required by applicable financial responsibility laws to maintain insurance against legal liability for bodily injury (including death) or property damage to third parties arising from the operation of our cars and on-road equipment, sometimes called “vehicle liability,” in stipulated amounts. In most places, we satisfy those requirements by qualifying as a self-insurer, a process that typically involves governmental filings and demonstration of financial responsibility, which sometimes requires the posting of a bond or other security. In the remaining places, we obtain an insurance policy from an unaffiliated insurance carrier and indemnify the carrier for any amounts paid under the policy. As a result of such arrangements, we bear economic responsibility for domestic vehicle liability, except to the extent we successfully transfer such liability to others through insurance or contractual arrangements.
For our car and equipment rental operations in Europe, we have established a wholly‑owned insurance subsidiary, Probus Insurance Company Europe Limited, or “Probus,” a direct writer of insurance domiciled in Ireland. In European countries with company‑operated locations, we have purchased from Probus the vehicle liability insurance required by law, and Probus reinsured the risks under such insurance with Hertz International RE, a reinsurer organized in Ireland, or “HIRE,” and / or HIRE Bermuda Limited, a wholly‑owned reinsurance company domiciled in Bermuda. This coverage is purchased from unaffiliated carriers for Spain. We also insure a portion of our European property risk through Probus. Thus, as with our domestic operations, we bear economic responsibility for vehicle liability in our European car and equipment rental operations, except to the extent that we transfer such liability to others through insurance or contractual arrangements. For our international operations outside of Europe, we maintain some form of vehicle liability insurance coverage with unaffiliated carriers. The nature of such coverage, and our economic responsibility for covered losses, varies considerably. In all cases, though, we believe the amounts and nature of the coverage we obtain is adequate in light of the respective potential hazards.
Both domestically and in our international operations, from time to time in the course of our business we become legally responsible to members of the public for bodily injury (including death) or property damage arising from causes other than the operation of our cars and on-road equipment, sometimes known as “general liability.” As with vehicle liability, we bear economic responsibility for general liability losses, except to the extent we transfer such losses to others through insurance or contractual arrangements.
To mitigate these exposures, we maintain excess liability insurance coverage with unaffiliated insurance carriers at an aggregate of $200 million for policy periods ended December 21, 2013, 2012, 2011 and 2010. For our international car rental operations outside of Europe, we also maintain liability insurance coverage with unaffiliated carriers in such amounts as we deem adequate in light of the respective potential hazards, where such insurance is obtainable on commercially reasonable terms.
Our domestic rental contracts for both car and equipment rental as well as our domestic and international long-term fleet leasing contracts, typically provide that the renter will indemnify us for liability arising from the operation of the rented vehicle or equipment (for car rentals in certain places, though, only to the extent such liability exceeds the amount stipulated in the applicable financial responsibility law). In addition, many of HERC's domestic rental contracts require the renter to maintain liability insurance under which HERC is entitled to coverage. While such provisions are sometimes effective to transfer liability to renters, their value to us, particularly in cases of large losses, may be limited. The rental contracts used in our international operations sometimes contain provisions relating to insurance or indemnity, but they are typically more limited than those employed in our domestic operations.
In our domestic car rental operations, we offer an optional liability insurance product, Liability Insurance Supplement, or “LIS,” that provides vehicle liability insurance coverage substantially higher than state minimum levels to the renter and other authorized operators of a rented vehicle. LIS coverage is provided under excess liability insurance policies issued by an unaffiliated insurance carrier, the risks under which are reinsured with a subsidiary of ours, HIRE Bermuda Limited. As a consequence of those reinsurance arrangements, rental customers' purchases of LIS do not reduce our economic exposure to vehicle liability. Instead, our exposure to vehicle liability is potentially increased when LIS is purchased, because insured renters and other operators may have vehicle liability imposed on them in circumstances and in amounts where the applicable rental agreement or applicable law would not, absent the arrangements just described, impose vehicle liability on us.
In both our domestic car rental operations and our company‑operated international car rental operations in many countries, we offer optional products providing insurance coverage, or “PAI/PEC” coverage, to the renter and the renter's immediate family members traveling with the renter for accidental death or accidental medical expenses arising during the rental period or for damage or loss of their property during the rental period. PAI/PEC coverage is provided under insurance policies issued by unaffiliated carriers or, in Europe, by Probus, and the risks under such policies either are reinsured with HIRE or another subsidiary of ours or are the subject of indemnification arrangements between
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
us and the carriers. Rental customers' purchases of PAI/PEC coverage create additional risk exposures for us, since we would not typically be liable for the risks insured by PAI/PEC coverage if that coverage had not been purchased.
Our offering of LIS and PAI/PEC coverage in our domestic car rental operations is conducted pursuant to limited licenses or exemptions under state laws governing the licensing of insurance producers. In our international car rental operations, our offering of PAI/PEC coverage historically has not been regulated; however, in the countries of the European Union, the regulatory environment for insurance intermediaries is evolving, and we cannot assure you that we will be able to continue offering PAI/PEC coverage without substantial changes in its offering process or in the terms of the coverage or that such changes, if required, would not render uneconomic our continued offering of the coverage.
Provisions on our books for self-insured vehicle liability losses are made by charges to expense based upon evaluations of estimated ultimate liabilities on reported and unreported claims. As of December 31, 2012, this liability was estimated at $332.2 million for our combined domestic and international operations.
Damage to Our Property
We bear the risk of damage to our property, unless such risk is transferred through insurance or contractual arrangements.
To mitigate our risk of large, single-site property damage losses globally, we maintain property insurance with unaffiliated insurance carriers in such amounts as we deem adequate in light of the respective hazards, where such insurance is available on commercially reasonable terms.
Our rental contracts typically provide that the renter is responsible for damage to or loss (including loss through theft) of rented vehicles or equipment. We generally offer an optional rental product, known in various countries as “loss damage waiver,” “collision damage waiver,” “theft protection” or “accident excess reduction,” under which we waive or limit our right to make a claim for such damage or loss. This product is not regulated as insurance, but it is subject to specific laws in roughly half of the U.S. jurisdictions where we operate.
Collision damage costs and the costs of stolen or unaccounted-for vehicles and equipment, along with other damage to our property, are charged to expense as incurred.
Other Risks
To manage other risks associated with our businesses, or to comply with applicable law, we purchase other types of insurance carried by business organizations, such as worker's compensation and employer's liability, commercial crime and fidelity, performance bonds and directors' and officers' liability insurance from unaffiliated insurance companies in amounts deemed by us to be adequate in light of the respective hazards, where such coverage is obtainable on commercially reasonable terms.
Governmental Regulation and Environmental Matters
Throughout the world, we are subject to numerous types of governmental controls, including those relating to prices and advertising, privacy and data protection, currency controls, labor matters, charge card operations, insurance, environmental protection, used car sales and licensing.
Environmental
The environmental requirements applicable to our operations generally pertain to (i) the operation and maintenance of cars, trucks and other vehicles, such as heavy equipment, buses and vans; (ii) the ownership and operation of tanks for the storage of petroleum products, including gasoline, diesel fuel and oil; and (iii) the generation, storage, transportation and disposal of waste materials, including oil, vehicle wash sludge and waste water. We have made, and will continue to make, expenditures to comply with applicable environmental laws and regulations.
The use of cars and other vehicles is subject to various governmental requirements designed to limit environmental damage, including those caused by emissions and noise. Generally, these requirements are met by the manufacturer, except in the case of occasional equipment failure requiring repair by us. Measures are taken at certain locations in states that require the installation of Stage II Vapor Recovery equipment to reduce the loss of vapor during the fueling process.
As of December 31, 2012, we utilized approximately 485 tanks underground and approximately 1,700 tanks above-ground to store petroleum products, and we believe our tanks are maintained in material compliance with environmental regulations, including federal and state financial responsibility requirements for corrective action and third‑party claims due to releases. Our compliance program for our tanks is intended to ensure that (i) the tanks are properly registered
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
with the state or other jurisdiction in which the tanks are located and (ii) the tanks have been either replaced or upgraded to meet applicable secondary containment, leak detection and spill, overfill and corrosion protection requirements.
We are also incurring and providing for expenses for the investigation and cleanup of contamination from the discharge of petroleum substances at, or emanating from, currently and formerly owned and leased properties, as well as contamination at other locations at which our wastes have reportedly been identified. The amount of any such expenses or related natural resource damages for which we may be held responsible could be substantial. The probable losses that we expect to incur for such matters have been accrued, and those losses are reflected in our consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2012 and 2011, the aggregate amounts accrued for environmental liabilities reflected in our consolidated balance sheets in “Other accrued liabilities” were $2.6 million and $1.5 million, respectively. The accrual generally represents the estimated cost to study potential environmental issues at sites deemed to require investigation or clean-up activities, and the estimated cost to implement remediation actions, including ongoing maintenance, as required. Cost estimates are developed by site. Initial cost estimates are based on historical experience at similar sites and are refined over time on the basis of in-depth studies of the site. For many sites, the remediation costs and other damages for which we ultimately may be responsible cannot be reasonably estimated because of uncertainties with respect to factors such as our connection to the site, the nature of the contamination, the involvement of other potentially responsible parties, the application of laws and other standards or regulations, site conditions, and the nature and scope of investigations, studies, and remediation to be undertaken (including the technologies to be required and the extent, duration, and success of remediation).
With respect to cleanup expenditures for the discharge of petroleum substances at, or emanating from, currently and formerly owned or leased properties, we have received reimbursement, in whole or in part, from certain U.S. states that maintain underground storage tank petroleum cleanup reimbursement funds. Such funds have been established to assist tank owners in the payment of cleanup costs associated with releases from registered tanks. With respect to off-site U.S. locations at which our wastes have reportedly been identified, we have been and continue to be required to contribute to cleanup costs due to strict joint and several cleanup liability imposed by the federal Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 and comparable state superfund statutes.
Environmental legislation and regulations and related administrative policies have changed rapidly in recent years, both in the United States and in other countries. There is a risk that governmental environmental requirements, or enforcement thereof, may become more stringent in the future and that we may be subject to legal proceedings brought by government agencies or private parties with respect to environmental matters. In addition, with respect to the cleanup of contamination, additional locations at which waste generated by us or substances used by us may have been released or disposed, and of which we are currently unaware, may in the future become the subject of cleanup for which we may be liable, in whole or in part. Further, at airport‑leased properties, we may be subject to environmental requirements imposed by airports that are more restrictive than those obligations imposed by environmental regulatory agencies. Accordingly, while we believe that we are in substantial compliance with applicable requirements of environmental laws, we cannot offer assurance that our future environmental liabilities will not be material to our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Dealings with Renters
In the United States, car and equipment rental transactions are generally subject to Article 2A of the Uniform Commercial Code, which governs “leases” of tangible personal property. Car rental is also specifically regulated in more than half of the states of the United States. The subjects of state regulation include the methods by which we advertise, quote and charge prices, the consequences of failing to honor reservations, the terms on which we deal with vehicle loss or damage (including the protections we provide to renters purchasing loss or damage waivers) and the terms and method of sale of the optional insurance coverage that we offer. Some states (including California, New York, Nevada and Illinois) regulate the price at which we may sell loss or damage waivers, and many state insurance regulators have authority over the prices and terms of the optional insurance coverage we offer. See “-Risk Management” above for further discussion regarding the loss or damage waivers and optional insurance coverages that we offer renters. Internationally, regulatory regimes vary greatly by jurisdiction, but they do not generally prevent us from dealing with customers in a manner similar to that employed in the United States.
Both in the United States and internationally, we are subject to increasing regulation relating to customer privacy and data protection. In general, we are limited in the uses to which we may put data that we collect about renters, including the circumstances in which we may communicate with them. In addition, we are generally obligated to take reasonable steps to protect customer data while it is in our possession. Our failure to do so could subject us to substantial legal liability or seriously damage our reputation.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS (Continued)
Changes in Regulation
Changes in government regulation of our businesses have the potential to materially alter our business practices, or our profitability. Depending on the jurisdiction, those changes may come about through new legislation, the issuance of new laws and regulations or changes in the interpretation of existing laws and regulations by a court, regulatory body or governmental official. Sometimes those changes may have not just prospective but also retroactive effect; this is particularly true when a change is made through reinterpretation of laws or regulations that have been in effect for some time. Moreover, changes in regulation that may seem neutral on their face may have either more or less impact on us than on our competitors, depending on the circumstances. Several U.S. State Attorneys General have taken the position that car rental companies either may not pass through to customers, by means of separate charges, expenses such as vehicle licensing and concession fees or may do so only in certain limited circumstances. Recent or potential changes in law or regulation that affect us relate to insurance intermediaries, customer privacy and data security and rate regulation, each as described under “Item 1A—Risk Factors” in this Annual Report.
In addition, our operations, as well as those of our competitors, also could be affected by any limitation in the fuel supply or by any imposition of mandatory allocation or rationing regulations. We are not aware of any current proposal to impose such a regime in the United States or internationally. Such a regime could, however, be quickly imposed if there were a serious disruption in supply for any reason, including an act of war, terrorist incident or other problem affecting petroleum supply, refining, distribution or pricing.
Disclosure under Section 13(r) of the Exchange Act
Under Section 13(r) of the Exchange Act as added by the Iran Threat Reduction and Syrian Human Rights Act of 2012, we are required to include certain disclosures in our periodic reports if we or any of our "affiliates" (as defined in Rule 12b-2 thereunder) knowingly engage in certain activities specified in Section 13(r) during the period covered by the report. Hertz Holdings and Hertz do not conduct any business activities in Iran. But because the SEC defines the term "affiliate" broadly, it includes any entity that controls us or is under common control with us (“control” is also construed broadly by the SEC), which includes our Sponsors. Our affiliate, CD&R, has informed us that an indirect subsidiary of SPIE S.A., or "SPIE," an affiliate of CD&R based in France, maintained bank accounts during 2012 at Bank Melli, an Iranian bank designated under Executive Order No. 13382. We had no knowledge of or control over the activities of SPIE or its subsidiaries. CD&R has informed us that in 2012, an indirect subsidiary of SPIE received payments into the Bank Melli accounts for €2,497,732.83 from PetroIran Development Company, or “PEDCO,” and €11,062.58 from Iran Oil Pipelines & Telecommunication Group, or “IOPTC,” in partial payment of amounts that were owed to certain indirect subsidiaries of SPIE for goods and services delivered in prior years, indirectly transferred approximately €430,000 from the accounts to France through the use of an intermediary, indirectly transferred approximately €360,000 from the accounts to the U.A.E. through other intermediaries (part of which has not yet been received), and used the accounts to pay office rent, the salary of one employee and other administrative expenses. SPIE understands that PEDCO and IOPTC are companies owned or controlled by the Government of Iran. CD&R has informed us that the relevant SPIE entities received authorization from the French Ministry of the Economy, Finances and Industry for the receipt of the funds and the transfer to France, that SPIE and its subsidiaries obtained no revenue or profit from these transactions, apart from payment of the two receivables described above, that CD&R and SPIE have disclosed these matters to the Office of Foreign Assets Control in the U.S. Treasury Department, or “OFAC,” and that SPIE and its subsidiaries do not intend to conduct any transaction or dealing with Bank Melli, PEDCO or IOPTC in the future other than any transactions that may be authorized by the applicable French governmental authority and OFAC.
Available Information
We file annual, quarterly and current reports and other information with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, or the “SEC.” You may read and copy any documents that we file at the SEC's public reference room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You may call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 to obtain further information about the public reference room. In addition, the SEC maintains an Internet website (www.sec.gov) that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information about issuers that file electronically with the SEC, including Hertz Holdings. You may also access, free of charge, our reports filed with the SEC (for example, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and our Current Reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to those forms) indirectly through our Internet website (www.hertz.com). Reports filed with or furnished to the SEC will be available as soon as reasonably practicable after they are filed with or furnished to the SEC. The information found on our website is not part of this or any other report filed with or furnished to the SEC.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
Our business is subject to a number of important risks and uncertainties, some of which are described below. The risks and uncertainties described below, however, are not the only risks and uncertainties that we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently deem to be immaterial may also significantly impact us. Any of these risks and uncertainties may materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations, liquidity and cash flows. In such a case, you may lose all or part of your investment in our common stock. You should carefully consider each of the following risks and uncertainties. Any of the following risks and uncertainties could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results or cash flow and we believe that the following information identifies the material risks and uncertainties affecting our company; however, the following risks and uncertainties are not the only risks and uncertainties facing us and it is possible that other risks and uncertainties might significantly impact us.
Risks Related to Our Business
Our car rental business, which provides the majority of our revenues, is particularly sensitive to reductions in the levels of airline passenger travel, and reductions in air travel could materially adversely impact our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows.
The car rental industry is particularly affected by reductions in business and leisure travel, especially with respect to levels of airline passenger traffic. Reductions in levels of air travel, whether caused by general economic conditions, airfare increases (such as due to capacity reductions or increases in fuel costs borne by commercial airlines) or other events (such as work stoppages, military conflicts, terrorist incidents, natural disasters, epidemic diseases, or the response of governments to any of these events) could materially adversely affect us. Further, decreases in levels of airline passenger traffic in key leisure destinations, including Florida, Hawaii, California and Texas, could also materially adversely affect us.
We face intense competition that may lead to downward pricing or an inability to increase prices.
The markets in which we operate are highly competitive. We believe that price is one of the primary competitive factors in the car and equipment rental markets and that the Internet has enabled cost-conscious customers, including business travelers, to more easily compare rates available from rental companies. If we try to increase our pricing, our competitors, some of whom may have greater resources and better access to capital than us, may seek to compete aggressively on the basis of pricing. In addition, our competitors may reduce prices in order to attempt to gain a competitive or to compensate for declines in rental activity. To the extent we do not match or remain within a reasonable competitive margin of our competitors’ pricing, our revenues and results of operations could be materially adversely affected. If competitive pressures lead us to match any of our competitors’ downward pricing and we are not able to reduce our operating costs, then our margins, results of operations and cash flows could be materially adversely impacted. Additionally, we could be further affected if we are not able to adjust the size of our rental fleet in response to changes in demand, whether such changes are due to competition or otherwise. See the sections entitled ‘‘Business—Worldwide Car Rental—Competition’’ and ‘‘Business—Worldwide Equipment Rental—Competition’’ in this Annual Report.
Our business is highly seasonal and any occurrence that disrupts rental activity during our peak periods could materially adversely affect our liquidity, cash flows and results of operations.
Certain significant components of our expenses are fixed in the short-term, including minimum concession fees, real estate taxes, rent, insurance, utilities, maintenance and other facility-related expenses, the costs of operating our information technology systems and minimum staffing costs. Seasonal changes in our revenues do not alter those fixed expenses, typically resulting in higher profitability in periods when our revenues are higher. The second and third quarters of the year have historically been our strongest quarters due to their increased levels of leisure travel and construction activity. Any occurrence that disrupts rental activity during the second or third quarters could have a disproportionately material adverse effect on our liquidity, cash flows and results of operations. Following our acquisition of Dollar Thrifty, we expect this risk to increase, as the scale of our car rental business and the related fixed costs have increased.
A material downsizing of our rental car fleet could require us to make additional cash payments for tax liabilities, which could be material.
The Like-Kind Exchange Program, or “LKE Program,” allows tax gains on the disposition of vehicles in our car rental fleet to be deferred and has resulted in deferrals of federal and state income taxes for prior years. If a qualified replacement vehicle is not purchased within a specific time period after vehicle disposal, then taxable gain is recognized. A material reduction in the net book value of our car rental fleet, a material and extended reduction in vehicle purchases
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
and/or a material downsizing of our car rental fleet, for any reason, could result in reduced tax deferrals in the future, which in turn could require us to make material cash payments for U.S. federal and state income tax liabilities. In August 2010, we elected to temporarily suspend the U.S. car rental LKE Program. In October 2012, Hertz reinstated the program. See the section entitled “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Income Taxes” in this Annual Report
Dollar Thrifty similarly used an LKE Program prior to our acquisition of Dollar Thrifty, which allowed Dollar Thrifty to defer a material amount of federal and state income taxes beginning in 2002. Thus, our Dollar Thrifty subsidiary is subject to the similar risks described above related to material payments for U.S. federal and state tax liabilities in the event there is a material reduction in the net book value of its car rental fleet, a material and extended reduction in its vehicle purchases and/or a material downsizing of its car rental fleet, for any reason. Our ability to continue to defer the reversal of prior period tax deferrals by Dollar Thrifty will depend on a number of factors, including the net book value of its car rental fleet.
If we are unable to purchase adequate supplies of competitively priced cars or equipment and the cost of the cars or equipment we purchase increases, our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows may be materially adversely affected.
We are not a party to any long-term car supply arrangements with manufacturers. The price and other terms at which we can acquire cars thus varies based on market and other conditions. For example, certain car manufacturers have in the past, and may in the future, utilize strategies to de-emphasize sales to the car rental industry, which can negatively impact our ability to obtain cars on competitive terms and conditions. Consequently, there is no guarantee that we can purchase a sufficient number of vehicles at competitive prices and on competitive terms and conditions. Reduced or limited supplies of equipment together with increased prices are risks that we also face in our equipment rental business. If we are unable to obtain an adequate supply of cars or equipment, or if we obtain less favorable pricing and other terms when we acquire cars or equipment and are unable to pass on any increased costs to our customers, then our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows may be materially adversely affected.
Declines in the value of the non-program cars in our fleet and declines in the overall number of program cars in our fleet could materially adversely impact our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows.
Over the last few years the percentage of ‘‘program cars’’ in our car rental fleet (that is, cars that are subject to repurchase by car manufacturers under contractual repurchase or guaranteed depreciation programs) has decreased. For the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, 30% and 48%, respectively, of the vehicles purchased for our combined U.S. and international car rental fleets were program cars. We expect this percentage to continue to decrease in the future, particularly as we integrate the operations of Dollar Thrifty, which operated a lower percentage of program cars than Hertz immediately prior to our completion of the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty.
Manufacturers agree to repurchase program cars at a specified price or guarantee the depreciation rate on the cars during a specified time period. Therefore, with fewer program cars in our fleet, we have an increased risk that the market value of a car at the time of its disposition will be less than its estimated residual value at such time. Any decrease in residual values with respect to our non-program cars and equipment (prior to disposition) could also materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows.
The use of program cars enables us to determine our depreciation expense in advance and this is useful to us because depreciation is a significant cost factor in our operations. Using program cars is also useful in managing our seasonal peak demand for fleet, because in certain cases we can sell certain program cars shortly after having acquired them at a higher value than what we could for a similar non-program car at that time. With fewer program cars in our fleet, these benefits have diminished. Accordingly, we are now bearing increased risk relating to residual value and the related depreciation on our car rental fleet and our flexibility to reduce the size of our fleet by returning cars sooner than originally expected without the risk of loss in the event of an economic downturn or to respond to changes in rental demand has been reduced.
The failure of a manufacturer of our program cars to fulfill its obligations under a repurchase or guaranteed depreciation program could expose us to loss on those program cars and materially adversely affect certain of our financing arrangements, which could in turn materially adversely affect our liquidity, cash flows, financial condition and results of operations.
If any manufacturer of our program cars does not fulfill its obligations under its repurchase or guaranteed depreciation agreement with us, whether due to default, reorganization, bankruptcy or otherwise, then we would have to dispose of those program cars without receiving the benefits of the associated programs (we could be left with a substantial
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
unpaid claim against the manufacturer with respect to program cars that were sold and returned to the manufacturer but not paid for, or that were sold for less than their agreed repurchase price or guaranteed value) and we would also be exposed to residual risk with respect to these cars.
The failure by a manufacturer to pay such amounts could cause a credit enhancement deficiency with respect to our asset-backed and asset-based financing arrangements, requiring us to either reduce the outstanding principal amount of debt or provide more collateral (in the form of cash, vehicles and/or certain other contractual rights) to the creditors under any such affected arrangement.
If one or more manufacturers were to adversely modify or eliminate repurchase or guaranteed depreciation programs in the future, our access to and the terms of asset-backed and asset-based debt financing could be adversely affected, which could in turn have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, cash flows, financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be successful in implementing our strategy of further reducing operating costs and our cost reduction initiatives may have adverse consequences.
We are continuing to implement initiatives to reduce our operating expenses. These initiatives may include headcount reductions, business process outsourcing, business process re-engineering, internal reorganization and other expense controls. We cannot assure you that our cost reduction initiatives will achieve any further success. Whether or not successful, our cost reduction initiatives involve significant expenses and we expect to incur further expenses associated with these initiatives, some of which may be material in the period in which they are incurred.
Even if we achieve further success with our cost reduction initiatives, we face risks associated with our initiatives, including declines in employee morale or the level of customer service we provide, the efficiency of our operations or the effectiveness of our internal controls. Any of these risks could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition, liquidity and cash flows.
An impairment of our goodwill or our indefinite lived intangible assets could have a material non-cash adverse impact on our results of operations.
We review our goodwill and indefinite lived intangible assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of these assets may not be recoverable and at least annually. If economic deterioration occurs, then we may be required to record charges for goodwill or indefinite lived intangible asset impairments in the future, which could have a material adverse non-cash impact on our results of operations.
Significant increases in fuel prices or reduced supplies of fuel could harm our business.
Significant increases in fuel prices, reduced fuel supplies or the imposition of mandatory allocations or rationing of fuel could negatively impact our car rental business by discouraging consumers from renting cars, changing the types of cars our customers rent from us or the other services they purchase from us or disrupting air travel, on which a significant portion of our car rental business relies. In addition, significant increases in fuel prices or a reduction in fuel supplies could negatively impact our equipment rental business by increasing the cost of buying new equipment, since fuel is used in the manufacturing process and in delivering equipment to us, and by reducing the mobility of our fleet, due to higher costs of transporting equipment between facilities or regions. Accordingly, significant increases in fuel prices or reduced supplies of fuel could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our foreign operations expose us to risks that may materially adversely affect our results of operations, liquidity and cash flows.
A significant portion of our annual revenues are generated outside the United States, and we intend to pursue additional international growth opportunities. Operating in many different countries exposes us to varying risks, which include: (i) multiple, and sometimes conflicting, foreign regulatory requirements and laws that are subject to change and are often much different than the domestic laws in the United States, including laws relating to taxes, automobile-related liability, insurance rates, insurance products, consumer privacy, data security, employment matters, cost and fee recovery, and the protection of our trademarks and other intellectual property; (ii) the effect of foreign currency translation risk, as well as limitations on our ability to repatriate income; (iii) varying tax regimes, including consequences from changes in applicable tax laws; (iv) local ownership or investment requirements, as well as difficulties in obtaining financing in foreign countries for local operations; and (v) political and economic instability, natural calamities, war, and terrorism. The effects of these risks may, individually or in the aggregate, materially adversely affect our results of operations, liquidity, cash flows and ability to diversify internationally.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
Manufacturer safety recalls could create risks to our business.
Our cars may be subject to safety recalls by their manufacturers. A recall may cause us to retrieve cars from renters and decline to rent recalled cars until we can arrange for the steps described in the recall to be taken. We could also face liability claims if a recall affects cars that we have sold. If a large number of cars are the subject of a recall or if needed replacement parts are not in adequate supply, we may not be able to rent recalled cars for a significant period of time. Those types of disruptions could jeopardize our ability to fulfill existing contractual commitments or satisfy demand for our vehicles, and could also result in the loss of business to our competitors. Depending on the severity of any recall, it could materially adversely affect our revenues, create customer service problems, reduce the residual value of the recalled cars and harm our general reputation.
Our business is heavily reliant upon communications networks and centralized information technology systems and the concentration of our systems creates risks for us.
We rely heavily on communication networks and information technology systems to accept reservations, process rental and sales transactions, manage our fleets of cars and equipment, manage our financing arrangements, account for our activities and otherwise conduct our business. Our reliance on these networks and systems exposes us to various risks that could cause a loss of reservations, interfere with our ability to manage our fleet, slow rental and sales processes, comply with our financing arrangements and otherwise materially adversely affect our ability to manage our business effectively. We have centralized our reservations function for the United States in two facilities in Mobile, Alabama and Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, and we have concentrated our accounting functions for the United States in two facilities in Oklahoma City. Our reservations and accounting functions for our European operations are similarly centralized in a single facility near Dublin, Ireland. In addition, our major information technology systems are centralized in two facilities in Oklahoma City. Our Dollar and Thrifty brands' centralized information systems are located in Tulsa, Oklahoma and our Dollar and Thrifty brands rely on communication service providers to link their system with the business locations these systems serve. Any disruption, termination or substandard provision of these services, whether as the result of localized conditions (such as a fire or explosion) or as the result of events or circumstances of broader geographic impact (such as an earthquake, storm, flood, epidemic, strike, act of war, civil unrest or terrorist act), could materially adversely affect our business by disrupting normal reservations, customer service, accounting and information technology functions or by eliminating access to financing arrangements.
The misuse or theft of information we possess could harm our brand, reputation or competitive position and give rise to material liabilities.
Because we regularly possess, store and handle non-public information about millions of individuals and businesses, our failure to maintain the security of that data, whether as the result of our own error or the malfeasance or errors of others, could harm our reputation, result in governmental investigations and give rise to a host of civil or criminal liabilities. Any such failure could lead to lower revenues, increased remediation, prevention and other costs and other material adverse effects on our results of operations.
Maintaining favorable brand recognition is essential to our success, and failure to do so could materially adversely affect our results of operations.
While our ''Hertz'', “Dollar” and “Thrifty” brand names have substantial brand recognition in the markets in which they participate, factors affecting brand recognition are often outside our control, and our efforts to maintain or enhance favorable brand recognition, such as marketing and advertising campaigns, may not have their desired effects. In addition, although our licensing partners are subject to contractual requirements to protect our brands, it may be difficult to monitor or enforce such requirements, particularly in foreign jurisdictions. Any decline in perceived favorable recognition of our brands could materially adversely affect our results of operations.
Our business operations could be significantly disrupted if we were to lose the services of members of our senior management team.
Our senior management team has extensive industry experience, and our success significantly depends upon the continued contributions of that team. If we were to lose the services of any one or more members of our senior management team, whether due to death, disability or termination of employment, our ability to successfully implement our business strategy, financial plans, marketing and other objectives, could be significantly impaired.
We may pursue strategic transactions which could be difficult to implement, disrupt our business or change our business profile significantly.
Any future strategic acquisition or disposition of assets or a business could involve numerous risks, including: (i) potential disruption of our ongoing business and distraction of management; (ii) difficulty integrating the acquired
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
business or segregating assets to be disposed of; (iii) exposure to unknown, contingent or other liabilities, including litigation arising in connection with the acquisition or disposition or against any business we may acquire; (iv) changing our business profile in ways that could have unintended negative consequences; and (v) the failure to achieve anticipated synergies.
If we enter into significant strategic transactions, the related accounting charges may affect our financial condition and results of operations, particularly in the case of an acquisition. The financing of any significant acquisition may result in changes in our capital structure, including the incurrence of additional indebtedness. A material disposition could require the amendment or refinancing of our outstanding indebtedness or a portion thereof.
As a result of Hertz Holdings’ completion of the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty, we are subject to the risks and uncertainties associated with Dollar Thrifty’s business, and we have incurred a substantial amount of additional indebtedness. See ‘‘—Risks Related to Acquisition of Dollar Thrifty.’’
We face risks related to liabilities and insurance.
Our businesses expose us to claims for personal injury, death and property damage resulting from the use of the cars and equipment rented or sold by us, and for employment-related claims by our employees. Currently, we generally self-insure up to $10 million per occurrence in the United States and Europe for vehicle and general liability exposures, and we also maintain insurance with unaffiliated carriers in excess of such levels up to $200 million per occurrence for the current policy year, or in the case of international operations outside of Europe, in such lower amounts as we deem adequate given the risks. We cannot assure you that we will not be exposed to uninsured liability at levels in excess of our historical levels resulting from multiple payouts or otherwise, that liabilities in respect of existing or future claims will not exceed the level of our insurance, that we will have sufficient capital available to pay any uninsured claims or that insurance with unaffiliated carriers will continue to be available to us on economically reasonable terms or at all. See the sections entitled ‘‘Business—Risk Management’’ and ‘‘Legal Proceedings’’ in this Annual Report.
We could face a significant withdrawal liability if we withdraw from participation in one or more multiemployer pension plans in which we participate and at least one multiemployer plan in which we participate is reported to have underfunded liabilities.
We participate in various multiemployer pension plans. In the event that we withdraw from participation in one of these plans, then applicable law could require us to make an additional contribution to the plan, and we would have to reflect that as an expense in our consolidated statements of operations and as a liability on our consolidated balance sheet. The amount that we would be required to pay to the plan is referred to as a withdrawal liability. Our withdrawal liability for any multiemployer plan would depend on the extent of the plan's funding of vested benefits. One multiemployer plan in which we participated had significant underfunded liabilities and we withdrew from that plan in December 2012. Several of our remaining multiemployer plans have underfunded liabilities. Such underfunding may increase in the event other employers become insolvent or withdraw from the applicable plan or upon the inability or failure of withdrawing employers to pay their withdrawal liability. In addition, such underfunding may increase as a result of lower than expected returns on pension fund assets or other funding deficiencies. The occurrence of any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. See Note 6 to the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report.
Environmental laws and regulations and the costs of complying with them, or any liability or obligation imposed under them, could materially adversely affect our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
We are subject to federal, state, local and foreign environmental laws and regulations in connection with our operations, including with respect to the ownership and operation of tanks for the storage of petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel and motor and waste oils. We cannot assure you that our tanks will at all times remain free from leaks or that the use of these tanks will not result in significant spills or leakage. If leakage or a spill occurs, it is possible that the resulting costs of cleanup, investigation and remediation, as well as any resulting fines, could be significant. We cannot assure you that compliance with existing or future environmental laws and regulations will not require material expenditures by us or otherwise have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. See the section entitled ‘‘Business—Governmental Regulation and Environmental Matters’’ in this Annual Report.
The U.S. Congress and other legislative and regulatory authorities in the United States and internationally have considered, and will likely continue to consider, numerous measures related to climate change and greenhouse gas emissions. Should rules establishing limitations on greenhouse gas emissions or rules imposing fees on entities deemed to be responsible for greenhouse gas emissions become effective, demand for our services could be affected, our fleet and/or other costs could increase, and our business could be adversely affected.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
Changes in the U.S. legal and regulatory environment that affect our operations, including laws and regulations relating to taxes, automobile-related liability, insurance rates, insurance products, consumer privacy, data security, employment matters, cost and fee recovery and the banking and financing industry could disrupt our business, increase our expenses or otherwise have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We are subject to a wide variety of U.S. laws and regulations and changes in the level of government regulation of our business have the potential to materially alter our business practices and materially adversely affect our financial position and results of operations, including our profitability. Those changes may come about through new laws and regulations or changes in the interpretation of existing laws and regulations.
Any new, or change in existing, U.S. law and regulation with respect to optional insurance products or policies could increase our costs of compliance or make it uneconomical to offer such products, which would lead to a reduction in revenue and profitability. For further discussion regarding how changes in the regulation of insurance intermediaries may affect us, see the section entitled ‘‘Business—Risk Management’’ in this Annual Report. If customers decline to purchase supplemental liability insurance products from us as a result of any changes in these laws or otherwise, our results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Changes in the U.S. legal and regulatory environment in the areas of customer privacy, data security and cross-border data flow could have a material adverse effect on our business, primarily through the impairment of our marketing and transaction processing activities, and the resulting costs of complying with such legal and regulatory requirements. It is also possible that we could face significant liability for failing to comply with any such requirements.
In most places where we operate, we pass through various expenses, including the recovery of vehicle licensing costs and airport concession fees, to our rental customers as separate charges. We believe that our expense pass-throughs, where imposed, are properly disclosed and are lawful. However, we may in the future be subject to potential legislative, regulatory or administrative changes or actions which could limit, restrict or prohibit our ability to separately state, charge and recover vehicle licensing costs and airport concession fees, which could result in a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Certain new or proposed laws and regulations with respect to the banking and finance industries, including the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act and amendments to Regulation AB, could restrict our access to certain financing arrangements and increase our financing costs, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, liquidity and cash flows.
Investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors exercise significant control over Hertz Holdings’ and our Board of Directors, management, policies and significant transactions, and may have interests that differ from Hertz Holdings’ other stockholders.
Hertz Holdings is a party to an amended and restated stockholders’ agreement, or the "Stockholders’ Agreement," among it and investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors. Investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors currently beneficially own, in the aggregate, approximately 26% of the outstanding shares of Hertz Holdings’ common stock. Pursuant to the Stockholders’ Agreement, each of the funds has agreed to vote in favor of the other funds’ nominees to Hertz Holdings’ and our Board of Directors. The Sponsors currently exercise, and will continue to exercise, significant influence over Hertz Holdings’ and our Board of Directors, matters requiring stockholder approval and our management, policies and affairs for so long as the investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors continue to hold a significant amount of Hertz Holdings’ common stock. There can be no assurance that the interests of the Sponsors will not conflict with those of Hertz Holdings’ other stockholders. The Sponsors currently have the ability to significantly influence the vote on any transaction that requires the approval of stockholders, including many possible change in control transactions, and may discourage or prevent any such transaction regardless of whether or not Hertz Holdings’ other stockholders believe that such a transaction is in Hertz Holdings’ or their own best interests.
Additionally, the Sponsors may from time to time acquire and hold interests in businesses that compete directly with us. One or more of the Sponsors may also pursue acquisition opportunities and other corporate opportunities that may be complementary to our business and as a result, those opportunities may not be available to us.
Risks Related to Our Substantial Indebtedness
Our substantial level of indebtedness could materially adversely affect our results of operations, cash flows, liquidity and ability to compete in our industry.
As of December 31, 2012, we had debt outstanding of $15,014.5 million, which includes the indebtedness incurred in connection with the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty. Our substantial indebtedness could materially adversely affect us. For
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
example, it could: (i) make it more difficult for us to satisfy our obligations to the holders of our outstanding debt securities and to the lenders under our various credit facilities, resulting in possible defaults on, and acceleration of, such indebtedness; (ii) be difficult to refinance or borrow additional funds in the future; (iii) require us to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flows from operations and investing activities to make payments on our debt, which would reduce our ability to fund working capital, capital expenditures or other general corporate purposes; (iv) increase our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions (such as credit‑related disruptions), including interest rate fluctuations, because a portion of our borrowings are at floating rates of interest and are not hedged against rising interest rates, and the risk that one or more of the financial institutions providing commitments under our revolving credit facilities fails to fund an extension of credit under any such facility, due to insolvency or otherwise, leaving us with less liquidity than expected; (v) place us at a competitive disadvantage to our competitors that have proportionately less debt or comparable debt at more favorable interest rates or on better terms; and (vi) limit our ability to react to competitive pressures, or make it difficult for us to carry out capital spending that is necessary or important to our growth strategy and our efforts to improve operating margins. While the terms of the agreements and instruments governing our outstanding indebtedness contain certain restrictions upon our ability to incur additional indebtedness, they do not fully prohibit us from incurring substantial additional indebtedness and do not prevent us from incurring obligations that do not constitute indebtedness. If new debt or other obligations are added to our current liability levels without a corresponding refinancing or redemption of our existing indebtedness and obligations, these risks would increase. For a description of the amounts we have available under certain of our debt facilities, see “Item 7—Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations-Liquidity and Capital Resources—Credit Facilities” included in this annual report for the year ended December 31, 2012 and “Note 5—Debt” to the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report.
Our ability to manage these risks depends on financial market conditions as well as our financial and operating performance, which, in turn, is subject to a wide range of risks, including those described under “-Risks Related to Our Business” included in this Annual Report.
If our capital resources (including borrowings under our revolving credit facilities and access to other refinancing indebtedness) and operating cash flows are not sufficient to pay our obligations as they mature or to fund our liquidity needs, we may be forced to do, among other things, one or more of the following: (i) sell certain of our assets; (ii) reduce the size of our rental fleet; (iii) reduce the percentage of program cars in our rental fleet; (iv) reduce or delay capital expenditures; (v) obtain additional equity capital; (vi) forgo business opportunities, including acquisitions and joint ventures; or (vii) restructure or refinance all or a portion of our debt on or before maturity.
We cannot assure you that we would be able to accomplish any of these alternatives on a timely basis or on satisfactory terms, if at all. Furthermore, we cannot assure you that we will maintain financing activities and cash flows sufficient to permit us to pay the principal, premium, if any, and interest on our indebtedness. If we cannot refinance or otherwise pay our obligations as they mature and fund our liquidity needs, our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, liquidity, ability to obtain financing and ability to compete in our industry could be materially adversely affected.
Our reliance on asset‑backed and asset‑based financing arrangements to purchase cars subjects us to a number of risks, many of which are beyond our control.
We rely significantly on asset‑backed and asset‑based financing to purchase cars. If we are unable to refinance or replace our existing asset‑backed and asset‑based financing or continue to finance new car acquisitions through asset‑ backed or asset‑based financing on favorable terms, on a timely basis, or at all, then our costs of financing could increase significantly and have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, interest costs, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations.
Our asset‑backed and asset‑based financing capacity could be decreased, our financing costs and interest rates could be increased, or our future access to the financial markets could be limited, as a result of risks and contingencies, many of which are beyond our control, including: (i) the acceptance by credit markets of the structures and structural risks associated with our asset‑backed and asset‑based financing arrangements; (ii) the credit ratings provided by credit rating agencies for our asset‑backed indebtedness; (iii) third parties requiring changes in the terms and structure of our asset‑backed or asset‑based financing arrangements, including increased credit enhancement or required cash collateral and/or other liquid reserves; (iv) the insolvency or deterioration of the financial condition of one or more of our principal car manufacturers; or (v) changes in laws or regulations, including judicial review of issues of first impression, that negatively impact any of our asset‑ backed or asset‑based financing arrangements.
Any reduction in the value of certain cars in our fleet could effectively increase our car fleet costs, adversely impact our profitability and potentially lead to decreased borrowing base availability in our asset‑backed and certain
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
asset‑based vehicle financing facilities due to the credit enhancement requirements for such facilities, which could increase if market values for vehicles decrease below net book values for those vehicles. In addition, if disposal of vehicles in the used vehicle marketplace were to become severely limited at a time when required collateral levels were rising and as a result we failed to meet the minimum required collateral levels, the principal under our asset‑backed and certain asset‑based financing arrangements may be required to be repaid sooner than anticipated with vehicle disposition proceeds and lease payments we make to our special purpose financing subsidiaries. If that were to occur, the holders of our asset-backed and certain asset‑based debt may have the ability to exercise their right to direct the trustee or other secured party to foreclose on and sell vehicles to generate proceeds sufficient to repay such debt.
The occurrence of certain events, including those described in the paragraph above, could result in the occurrence of an amortization event pursuant to which the proceeds of sales of cars that collateralize the affected asset‑backed financing arrangement would be required to be applied to the payment of principal and interest on the affected facility or series, rather than being reinvested in our car rental fleet. In the case of our asset‑backed financing arrangements, certain other events, including defaults by us and our affiliates in the performance of covenants set forth in the agreements governing certain fleet debt, could result in the occurrence of a liquidation event with the passing of time or immediately pursuant to which the trustee or holders of the affected asset‑backed financing arrangement would be permitted to require the sale of the assets collateralizing that series. Any of these consequences could affect our liquidity and our ability to maintain sufficient fleet levels to meet customer demands and could trigger cross‑defaults under certain of our other financing arrangements.
Any reduction in the value of the equipment rental fleet of HERC (which could occur due to a reduction in the size of the fleet or the value of the assets within the fleet) could not only effectively increase our equipment rental fleet costs and adversely impact our profitability, but would result in decreased borrowing base availability under certain of our asset‑based financing arrangements, which would have a material adverse effect on our financial position, liquidity, cash flows and results of operations.
Substantially all of our consolidated assets secure certain of our outstanding indebtedness, which could materially adversely affect our debt and equity holders and our business.
Substantially all of our consolidated assets, including our car and equipment rental fleets and Donlen's lease portfolio, are subject to security interests or are otherwise encumbered for the lenders under our asset‑backed and asset‑based financing arrangements. As a result, the lenders under those facilities would have a prior claim on such assets in the event of our bankruptcy, insolvency, liquidation or reorganization, and we may not have sufficient funds to pay in full, or at all, all of our creditors or make any amount available to holders of our equity. The same is true with respect to structurally senior obligations: in general, all liabilities and other obligations of a subsidiary must be satisfied before the assets of such subsidiary can be made available to the creditors (or equity holders) of the parent entity.
Because substantially all of our assets are encumbered under financing arrangements, our ability to incur additional secured indebtedness or to sell or dispose of assets to raise capital may be impaired, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial flexibility and force us to attempt to incur additional unsecured indebtedness, which may not be available to us.
Restrictive covenants in certain of the agreements and instruments governing our indebtedness may materially adversely affect our financial flexibility or may have other material adverse effects on our business, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations.
Certain of our credit facilities and other asset‑based and asset‑backed financing arrangements contain covenants that, among other things, restrict Hertz and its subsidiaries' ability to: (i) dispose of assets; (ii) incur additional indebtedness; (iii) incur guarantee obligations; (iv) prepay other indebtedness or amend other financing arrangements; (v) pay dividends; (vi) create liens on assets; (vii) sell assets; (viii) make investments, loans, advances or capital expenditures; (ix) make acquisitions; (x) engage in mergers or consolidations; (xi) change the business conducted by us; and (xii) engage in certain transactions with affiliates.
Our Senior ABL Facility (as defined below in Note 5 to the Notes to the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data”) contains a financial covenant that obligates us to maintain a specified fixed charge coverage ratio if we fail to maintain a specified minimum level of liquidity. Our ability to comply with this covenant will depend on our ongoing financial and operating performance, which in turn are subject to, among other things, the risks identified in “—Risks Related to Our Business.”
The agreements governing our financing arrangements contain numerous covenants. The breach of any of these covenants or restrictions could result in a default under the relevant agreement, which could, in turn, cause cross‑ defaults under our other financing arrangements. In such event, we may be unable to borrow under the Senior ABL
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
Facility and certain of our other financing arrangements and may not be able to repay the amounts due under such arrangements. Therefore, we would need to raise refinancing indebtedness, which may not be available to us on favorable terms, on a timely basis or at all. This could have serious consequences to our financial condition and results of operations and could cause us to become bankrupt or insolvent. Additionally, such defaults could require us to sell assets, if possible, and otherwise curtail our operations in order to pay our creditors. Such alternative measures could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations.
An increase in interest rates or in our borrowing margin would increase the cost of servicing our debt and could reduce our profitability.
A significant portion of our outstanding debt bears interest at floating rates. As a result, to the extent we have not hedged against rising interest rates, an increase in the applicable benchmark interest rates would increase our cost of servicing our debt and could materially adversely affect our liquidity and results of operations.
In addition, we regularly refinance our indebtedness. If interest rates or our borrowing margins increase between the time an existing financing arrangement was consummated and the time such financing arrangement is refinanced, the cost of servicing our debt would increase and our liquidity and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
Risks Related to Acquisition of Dollar Thrifty
Combining the businesses of Hertz and Dollar Thrifty may be more difficult, costly or time-consuming than expected, which may adversely affect our results.
To realize the anticipated benefits and cost savings we contemplated as part of the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty, we must successfully combine and integrate our business with Dollar Thrifty's business in an efficient and effective manner. If we are not able to achieve these objectives within the anticipated time frame, or at all, the anticipated benefits and cost savings of the acquisition may not be realized fully, or at all, or may take longer to realize than expected. It is possible that the overall integration process could result in the loss of key employees, the disruption of each company's ongoing business or inconsistencies in standards, controls, procedures and policies that adversely affect our ability to maintain relationships with customers, employees, suppliers, lenders and franchisees or to achieve the anticipated benefits of the acquisition.
Specifically, issues that must be addressed in integrating the operations of Dollar Thrifty into our operations in order to realize the anticipated benefits of the acquisition include, among other things:
| |
| • | integrating and optimizing the utilization of the rental vehicle fleets and related financing of Hertz and Dollar Thrifty; |
| |
| • | integrating and consolidating the marketing, promotion, reservation and information technology systems of Hertz and Dollar Thrifty; |
| |
| • | conforming standards, controls, procedures and policies, business cultures and compensation structures between the companies; |
| |
| • | consolidating the automotive purchasing, maintenance and resale operations; |
| |
| • | consolidating corporate and administrative functions; and |
| |
| • | identifying and eliminating redundant and underperforming operations and assets. |
Integration efforts between the two companies will also divert management attention and resources. An inability to realize the full extent of the anticipated benefits of the acquisition, as well as any delays encountered in the integration process, could have an adverse effect upon the revenues, level of expenses and operating results of Hertz after the completion of the acquisition.
In addition, the actual integration may result in additional and unforeseen expenses, and the anticipated benefits of the integration plan may not be realized. Actual synergies, if achieved at all, may be lower than what we expect and may take longer to achieve than anticipated. If we are not able to adequately address these challenges, we may be unable to successfully integrate Dollar Thrifty.
We incurred significant transaction and acquisition-related costs in connection with the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty and expect to incur additional costs in connection with the integration of Dollar Thrifty's operations.
Hertz has incurred and expects to continue to incur a number of non-recurring costs associated with combining the operations of the two companies. Most of these costs have been and will be comprised of transaction costs related
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS (Continued)
to the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, facilities, fleet and systems consolidation costs and employment-related costs. We also incurred transaction fees and costs related to formulating integration plans. Although we expect that the elimination of duplicative costs, as well as the realization of other efficiencies related to the integration of the businesses, should allow us to offset the previously-incurred incremental transaction and acquisition-related costs over time, this net benefit may not be achieved in the near term, or at all.
Future results of the combined company may differ materially from the Unaudited Pro Forma Financial Information of Hertz and Dollar Thrifty presented in this annual report.
The future results of Hertz, as the combined company following the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, may be materially different from those shown in the pro forma financial information presented in Note 4 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" that reflect such results on a pro forma basis after giving effect only to: (i) the acquisition of Donlen by Hertz in September 2011, (ii) the Dollar Thrifty acquisition in November 2012, (iii) the divestiture of Advantage, (iv) the divestitures of the Initial airport locations and the Secondary airport locations (as defined herein), (v) the issuance of the 2020 Notes and the 2022 Notes and (vi) the incurrence of $750.0 million in Incremental Term Loans; in each case of (i) through (vi) above, as if they had occurred on January 1, 2011 for the pro forma financial information for the year ended December 31, 2011 and for the year ended December 31, 2012; and in each case (ii) through (vi) above, as if they had occurred on December 31, 2012 for the pro forma financial information as of December 31, 2012.
The pro forma financial information presented in this Annual Report reflects the acquisition method of accounting under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, and is subject to change and interpretation. Accordingly, the pro forma financial information presented in this Annual Report has been presented for informational purposes only. The pro forma financial information is not necessarily indicative of what the combined company's financial position or results of operations actually would have been had the applicable transactions been completed as of the dates indicated. In addition, the pro forma financial information does not purport to project the future financial position or operating results of the combined company.
Certain existing indebtedness of Dollar Thrifty and its subsidiaries, if not refinanced, amended or repaid, may decrease Hertz's business flexibility, reduce its ability to incur additional indebtedness, affect its existing debt covenants, increase its borrowing costs or result in repayment or collateralization obligations.
Certain of Dollar Thrifty's existing indebtedness remains outstanding after the closing of the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, including most of Dollar Thrifty's existing fleet financing. As of December 31, 2012, Dollar Thrifty's indebtedness was approximately $1.5 billion. For a description of Dollar Thrifty's indebtedness and other obligations as of December 31, 2012, see Note 5 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” See ''—Risks Related to Our Substantial Indebtedness-Our substantial level of indebtedness could adversely affect our results of operations, cash flows, liquidity and ability to compete in our industry.'' To service our indebtedness, we will require a significant amount of cash which we may not be able to raise or generate.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
We operate car rental locations at or near airports and in central business districts and suburban areas of major cities in the United States, including Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, the United Kingdom, Spain, The Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Australia, New Zealand, China and Brazil, as well as retail used car sales locations in the United States, France and Australia. We operate equipment rental locations in the United States, Canada, France, Spain and China. We also operate headquarters, sales offices and service facilities in the foregoing countries in support of our car rental and equipment rental operations, as well as small car rental sales offices and service facilities in a select number of other countries in Europe and Asia.
We own approximately 6% of the locations from which we operate our car and equipment rental businesses and in some cases own real property that we lease to franchisees or other third-parties. The remaining locations from which we operate our car and equipment rental businesses are leased or operated under concessions from governmental authorities and private entities. Those leases and concession agreements typically require the payment of minimum rents or minimum concession fees and often also require us to pay or reimburse operating expenses; to pay additional rent, or concession fees above guaranteed minimums, based on a percentage of revenues or sales arising at the
relevant premises; or to do both. See Note 10 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
In addition to the above operational locations, we own three major facilities in the vicinity of Oklahoma City, Oklahoma at which reservations for our car rental operations are processed, global information technology systems are serviced and major domestic and international accounting functions are performed. We also have a long-term lease for a reservation and financial center near Dublin, Ireland, at which we have centralized our European car rental reservation, customer relations, accounting and human resource functions. We maintain our executive offices in an owned facility in Park Ridge, New Jersey and lease a European headquarters office in Uxbridge, England. Dollar Thrifty has headquarters in Tulsa, Oklahoma. Donlen's headquarters is in Northbrook, Illinois. Donlen also leases office space in Darien, Illinois and Buffalo Grove, Illinois, for all of its fleet management services, consultation call center staff and certain financial systems functions. Donlen has other sales offices located throughout the United States.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
From time to time we are a party to various legal proceedings. Other than with respect to the aggregate claims for public liability and property damage pending against us, management does not believe that any of the matters resolved, or pending against us, during 2012 are material to us and our subsidiaries taken as a whole. While we have accrued a liability with respect to claims for public liability and property damage of $332.2 million at December 31, 2012, management, based on the advice of legal counsel, does not believe any of the other pending matters described below are material. We have summarized below, for purposes of providing background, various legal proceedings to which we were and/or are a party during 2012 or the period after December 31, 2012 but before the filing of this Annual Report. In addition to the following, various other legal actions, claims and governmental inquiries and proceedings are pending or may be instituted or asserted in the future against us and our subsidiaries. As previously disclosed, on June 15, 2011 we received a subpoena from the staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or "SEC," seeking production of documents related to our proposed business combination with Dollar Thrifty. On February 14, 2013, we were informed by the staff that the investigation has been completed and that no action was taken by the staff or the SEC.
| |
| 1. | Hertz Equipment Rental Corporation, or “HERC,” Loss Damage Waiver |
On August 15, 2006, Davis Landscape, Ltd., individually and on behalf of all others similarly situated, filed a complaint against HERC in the United States District Court for the District of New Jersey. In November 2006, the complaint was amended to add another plaintiff, Miguel V. Pro, and more claims. The Davis Landscape matter purports to be a nationwide class action on behalf of all persons and business entities who rented equipment from HERC and who paid a Loss Damage Waiver, or “LDW,” or an Environmental Recovery Fee, or “ERF.” The plaintiffs seek a declaratory judgment and injunction prohibiting HERC from engaging in acts with respect to the LDW and ERF charges that violate the New Jersey Consumer Fraud Act and claim that the charges violate the Uniform Commercial Code. The plaintiffs also seek an unspecified amount of compensatory damages with the return of all LDW and ERF charges paid, attorneys' fees and costs as well as other damages. The court has granted class certification, denied our motion for summary judgment and the case is in the discovery stages. In February 2012, we filed separate motions for partial summary judgment on the LDW and ERF claims and we filed a motion to decertify the class. In June 2012, the judge denied our motion for partial summary judgment on the LDW claim and, in July 2012, the judge granted our motion for partial summary judgment on the ERF claim. The court also entered an order referring the case to mediation by private consent of the parties. We have continued to work through the mediator and in direct discussions with plaintiffs’ counsel on an acceptable settlement of this litigation and have accrued our best estimate of the ultimate cost which is not material to our financial condition.
| |
| 2. | Concession Fee Recoveries |
On October 13, 2006, Janet Sobel, Daniel Dugan, PhD. and Lydia Lee, individually and on behalf of all others similarly situated v. The Hertz Corporation and Enterprise Rent-A-Car Company, or “Enterprise,” was filed in the United States District Court for the District of Nevada. The plaintiffs agreed to not pursue claims against Enterprise initially and the case only proceeded against Hertz. The Sobel case purports to be a nationwide class action on behalf of all persons who rented cars from Hertz at airports in Nevada and were separately charged airport concession recovery fees by Hertz as part of their rental charges. The plaintiffs seek an unspecified amount of compensatory damages, restitution of any charges found to be improper and an injunction prohibiting Hertz from quoting or charging those airport fees that are alleged not to be allowed by Nevada law. The complaint also seeks attorneys' fees and costs. Relevant documents were produced, depositions were taken and pre-trial motions were filed. After the court rendered a mixed
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS (Continued)
ruling on the parties' cross‑motions for summary judgment and after the Lydia Lee case was refiled against Enterprise, the parties engaged in mediation which resulted in a proposed settlement. Although the court tentatively approved the settlement in November 2010, the court denied the plaintiffs' motion for final approval of the proposed settlement in May 2011. Since that time, the plaintiffs filed a motion for class certification-which we opposed-and discovery has commenced again. A separate action is proceeding against Enterprise, National and Alamo. In May 2012, all briefing was completed on the two outstanding issues—unjust enrichment and damages. The briefing included expert reports as submitted by both sides. In October 2012, the court held a hearing on the plaintiffs’ motion for class certification. The court has since entered a stay order and the parties will again be engaging in mediation.
| |
| 3. | Telephone Consumer Protection Act |
On May 3, 2007, Fun Services of Kansas City, Inc., individually and as the representative of a class of similarly‑situated persons, v. Hertz Equipment Rental Corporation was commenced in the District Court of Wyandotte County, Kansas. The case was subsequently transferred to the District Court of Johnson County, Kansas. The Fun Services matter purports to be a class action on behalf of all persons in Kansas and throughout the United States who, on or after four years prior to the filing of the action, were sent facsimile messages of advertising materials relating to the availability of property, goods or services by HERC and who did not provide express permission for sending such faxes. The plaintiffs seek an unspecified amount of compensatory damages, attorney's fees and costs. In August 2009, the court issued an order that stayed all activity in this litigation pending a decision by the Kansas Supreme Court in Critchfield Physical Therapy, Inc. v. Taranto Group, Inc., another Telephone Consumer Protection Act case. The Kansas Supreme Court issued its decision in September 2011. Thereafter, the District Court of Johnson County lifted the stay in the Fun Services case and issued a scheduling order that addresses class certification discovery. In February 2012, HERC filed a Notice of Removal with the U.S. District Court for the District of Kansas seeking to remove the case to federal court based on federal question jurisdiction. In March 2012, the federal magistrate entered an order requiring the parties to engage in mediation and report back to her regarding their progress by June 2012. In June 2012, a mediation was held and as a result of the mediation, the parties reached an agreement in principle to settle this class action. A settlement that addresses compensation to class members, class counsel fees and the claims process was finalized by the parties’ counsel in January 2013. The court issued an order preliminarily approving the settlement in January 2013 and the final approval hearing is currently scheduled for April 2013. We have accrued our best estimate of the ultimate cost, which is not material to our financial condition.
| |
| 4. | California Tourism Assessments |
We are currently a defendant in a proceeding that purports to be a class action brought by Michael Shames and Gary Gramkow against The Hertz Corporation, Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., Avis Budget Group, Inc., Vanguard Car Rental USA, Inc., Enterprise Rent-A-Car Company, Fox Rent A Car, Inc., Coast Leasing Corp., The California Travel and Tourism Commission, and Caroline Beteta.
Originally filed in November of 2007, the action is pending in the United States District Court for the Southern District of California, and plaintiffs claim to represent a class of individuals or entities that purchased rental car services from a defendant at airports located in California after January 1, 2007. Plaintiffs allege that the defendants agreed to charge consumers a 2.5% tourism assessment and not to compete with respect to this assessment, while misrepresenting that this assessment is owed by consumers, rather than the rental car defendants, to the California Travel and Tourism Commission, or the “CTTC.” Plaintiffs also allege that defendants agreed to pass through to consumers a fee known as the Airport Concession Fee, which fee had previously been required to be included in the rental car defendants' individual base rates, without reducing their base rates. Based on these allegations, the amended complaint seeks treble damages, disgorgement, injunctive relief, interest, attorneys' fees and costs. Plaintiffs dropped their claims against Caroline Beteta. Plaintiffs' claims against the rental car defendants have been dismissed, except for the federal antitrust claim. In June 2010, the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit affirmed the dismissal of the plaintiffs' antitrust case against the CTTC as a state agency immune from antitrust complaint because the California Legislature foresaw the alleged price‑fixing conspiracy that was the subject of the complaint. The plaintiffs subsequently filed a petition with the Ninth Circuit seeking a rehearing and that petition was granted. In November 2010, the Ninth Circuit withdrew its June opinion and instead held that state action immunity was improperly invoked. The Ninth Circuit reinstated the plaintiffs' antitrust claims and remanded the case to the district court for further proceedings. In May 2012, the district court issued an order preliminarily approving the settlement
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS (Continued)
of this action; certifying a settlement class; certifying a class representative and lead counsel; and providing for class notice. In October 2012, the court held a final approval hearing. In November 2012, the court issued an order of final approval of the settlement of this action. One of the objectors to the settlement has filed a notice of appeal of this order with the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. We have accrued our best estimate of the ultimate cost which is not material to our financial condition.
| |
| 5. | Public Liability and Property Damage |
We are currently a defendant in numerous actions and have received numerous claims on which actions have not yet been commenced for public liability and property damage arising from the operation of motor vehicles and equipment rented from us. The obligation for public liability and property damage on self-insured U.S. and international vehicles and equipment, as stated on our balance sheet, represents an estimate for both reported accident claims not yet paid and claims incurred but not yet reported. The related liabilities are recorded on a non-discounted basis. Reserve requirements are based on actuarial evaluations of historical accident claim experience and trends, as well as future projections of ultimate losses, expenses, premiums and administrative costs. At December 31, 2012 and 2011, our liability recorded for public liability and property damage matters was $332.2 million and $281.5 million, respectively. We believe that our analysis is based on the most relevant information available, combined with reasonable assumptions, and that we may prudently rely on this information to determine the estimated liability. We note the liability is subject to significant uncertainties. The adequacy of the liability reserve is regularly monitored based on evolving accident claim history and insurance related state legislation changes. If our estimates change or if actual results differ from these assumptions, the amount of the recorded liability is adjusted to reflect these results.
We intend to assert that we have meritorious defenses in the foregoing matters and we intend to defend ourselves vigorously.
We have established reserves for matters where we believe that the losses are probable and reasonably estimated, including for various of the matters set forth above. Other than with respect to the aggregate reserves established for claims for public liability and property damage, none of those reserves are material. For matters, including those described above, where we have not established a reserve, the ultimate outcome or resolution cannot be predicted at this time, or the amount of ultimate loss, if any, cannot be reasonably estimated. Litigation is subject to many uncertainties and the outcome of the individual litigated matters is not predictable with assurance. It is possible that certain of the actions, claims, inquiries or proceedings, including those discussed above, could be decided unfavorably to us or any of our subsidiaries involved. Accordingly, it is possible that an adverse outcome from such a proceeding could exceed the amount accrued in an amount that could be material to our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows in any particular reporting period.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
There is no established public trading market for the common stock of Hertz. Hertz Investors, Inc., which is wholly‑owned by Hertz Holdings, owns all of the outstanding common stock of Hertz.
In 2012 and 2011, we paid $25.0 million and $22.95 million, respectively, in dividends to our stockholder. The agreements governing our indebtedness restrict our ability to pay dividends. See “Item 7—Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations-Liquidity and Capital Resources-Financing,” in this Annual Report.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following table presents selected consolidated financial information and other data for our business. The selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2012 and 2011 presented below were derived from our consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
You should read the following information in conjunction with the section of this Annual Report entitled “Item 7—Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| (In millions of dollars) | 2012(a) | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 |
| Statement of Operations Data | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 7,456.1 |
| | $ | 6,929.6 |
| | $ | 6,355.2 |
| | $ | 5,872.9 |
| | $ | 6,730.4 |
|
| Equipment rental | 1,383.2 |
| | 1,208.8 |
| | 1,069.8 |
| | 1,110.2 |
| | 1,657.3 |
|
Other(b) | 181.5 |
| | 160.0 |
| | 137.5 |
| | 118.4 |
| | 137.4 |
|
| Total revenues | 9,020.8 |
| | 8,298.4 |
| | 7,562.5 |
| | 7,101.5 |
| | 8,525.1 |
|
| Expenses: | | | | | | | | | |
| Direct operating | 4,795.8 |
| | 4,566.4 |
| | 4,283.4 |
| | 4,086.8 |
| | 4,935.3 |
|
Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges(c) | 2,148.2 |
| | 1,905.7 |
| | 1,868.1 |
| | 1,933.8 |
| | 2,196.9 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 945.5 |
| | 745.1 |
| | 664.5 |
| | 641.8 |
| | 768.8 |
|
| Interest expense | 597.8 |
| | 650.3 |
| | 726.5 |
| | 653.7 |
| | 870.5 |
|
| Interest income | (4.9 | ) | | (5.5 | ) | | (12.3 | ) | | (16.0 | ) | | (24.8 | ) |
| Other (income) expense, net | 35.5 |
| | 62.5 |
| | — |
| | (48.5 | ) | | — |
|
Impairment charges(d) | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,195.0 |
|
| Total expenses | 8,517.9 |
| | 7,924.5 |
| | 7,530.2 |
| | 7,251.6 |
| | 9,941.7 |
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 502.9 |
| | 373.9 |
| | 32.3 |
| | (150.1 | ) | | (1,416.6 | ) |
(Provision) benefit for taxes on income(e) | (227.1 | ) | | (143.8 | ) | | (33.3 | ) | | 50.8 |
| | 249.1 |
|
| Net income (loss) | 275.8 |
| | 230.1 |
| | (1.0 | ) | | (99.3 | ) | | (1,167.5 | ) |
| Noncontrolling interest | — |
| | (19.6 | ) | | (17.4 | ) | | (14.7 | ) | | (20.8 | ) |
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 275.8 |
| | $ | 210.5 |
| | $ | (18.4 | ) | | $ | (114.0 | ) | | $ | (1,188.3 | ) |
Item 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2012(a) | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | | 2008 |
| Balance Sheet Data | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 533.2 |
| | $ | 931.2 |
| | $ | 2,374.0 |
| | $ | 985.5 |
| | $ | 594.0 |
|
Total assets(f) | 23,290.2 |
| | 17,667.3 |
| | 17,336.9 |
| | 16,009.2 |
| | 16,464.1 |
|
| Total debt | 15,014.5 |
| | 10,907.8 |
| | 10,919.3 |
| | 9,997.0 |
| | 10,972.3 |
|
| Total equity | 2,917.5 |
| | 2,628.9 |
| | 2,502.4 |
| | 2,461.9 |
| | 1,450.7 |
|
| |
| (a) | The 2012 amounts reflect the inclusion of the Dollar Thrifty results from November 19, 2012 through December 31, 2012. See Note 4 to the notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data." |
| |
| (b) | Includes fees and certain cost reimbursements from our licensees and revenues from our car leasing operations and third‑party claim management services. |
| |
| (c) | The increases for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011 primarily reflect our acquisitions of Dollar Thrifty in November 2012 and Donlen in September 2011, respectively, as well as gains from disposal of revenue earning equipment, partly offset by a decrease due to changing depreciation rates. For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011, 2010, 2009 and 2008, depreciation of revenue earning equipment decreased by $130.1 million and $18.2 million and increased by $22.7 million, $19.3 million and $32.7 million, respectively, resulting from the net effects of changing depreciation rates to reflect changes in the estimated residual value of revenue earning equipment. For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011, 2010, 2009 and 2008, depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges includes net gains of $96.8 million and $112.2 million and net losses of $42.9 million, $72.0 million and $74.3 million, respectively, from the disposal of revenue earning equipment. |
| |
| (d) | For the year ended December 31, 2008, we recorded non-cash impairment charges related to our goodwill, other intangible assets and property and equipment. |
| |
| (e) | For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011, 2010, 2009 and 2008, tax valuation allowances increased by $35.8 million, decreased by $2.5 million and increased by $27.5 million, $39.7 million and $58.5 million, respectively, (excluding the effects of foreign currency translation) relating to the realization of deferred tax assets attributable to net operating losses, credits and other temporary differences in various jurisdictions. In 2011, we reversed a valuation allowance of $12.0 million relating to realization of deferred tax assets attributable to net operating losses and other temporary differences in Australia and China. Additionally, certain tax reserves were recorded and certain tax reserves were released due to settlement for various uncertain tax positions in Federal, state and foreign jurisdictions. |
| |
| (f) | Substantially all of our revenue earning equipment, as well as certain related assets, are owned by special purpose entities, or are subject to liens in favor of our lenders under our various credit facilities, other secured financings and asset-backed securities programs. None of such assets are available to satisfy the claims of our general creditors. For a description of those facilities, see “Item 7—Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” in this Annual Report. |
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations
The statements in this discussion and analysis regarding industry outlook, our expectations regarding the performance of our business and the other non-historical statements are forward‑looking statements. These forward‑looking statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the risks and uncertainties described in “Item 1A—Risk Factors.” The following discussion and analysis provides information that we believe to be relevant to an understanding of our consolidated financial condition and results of operations. Our actual results may differ materially from those contained in or implied by any forward‑looking statements. You should read the following discussion and analysis together with the sections entitled “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward‑Looking Statements,” “Item 1A—Risk Factors,” “Item 6—Selected Financial Data” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Overview of Our Business
We are engaged principally in the business of renting and leasing of cars and equipment.
Our revenues primarily are derived from rental and related charges and consist of:
| |
| • | Car rental revenues (revenues from all company-operated car rental and fleet leasing operations and management services, including charges to customers for the reimbursement of costs incurred relating to airport concession fees and vehicle license fees, the fueling of vehicles and the sale of loss or collision damage waivers, liability insurance coverage and other products); |
| |
| • | Equipment rental revenues (revenues from all company-operated equipment rental operations, including amounts charged to customers for the fueling and delivery of equipment and sale of loss damage waivers, as well as revenues from the sale of new equipment and consumables); and |
| |
| • | Other revenues (primarily relating to fees and certain cost reimbursements from our licensees). |
Our expenses primarily consist of:
| |
| • | Direct operating expenses (primarily wages and related benefits; commissions and concession fees paid to airport authorities, travel agents and others; facility, self-insurance and reservation costs; the cost of new equipment and consumables purchased for resale; and other costs relating to the operation and rental of revenue earning equipment, such as damage, maintenance and fuel costs); |
| |
| • | Depreciation expense and lease charges relating to revenue earning equipment (including net gains or losses on the disposal of such equipment). Revenue earning equipment includes cars and rental equipment; |
| |
| • | Selling, general and administrative expenses (including advertising); and |
Our profitability is primarily a function of the volume, mix and pricing of rental transactions and the utilization of cars and equipment. Significant changes in the purchase price or residual values of cars and equipment or interest rates can have a significant effect on our profitability depending on our ability to adjust pricing for these changes. We continue to balance our mix of non-program and program vehicles based on market conditions. Our business requires significant expenditures for cars and equipment, and consequently we require substantial liquidity to finance such expenditures. See "Liquidity and Capital Resources" below.
Car Rental
In the U.S., as of December 31, 2012, the percentage of non-program cars was 95% as compared to 83% as of December 31, 2011. Internationally, as of December 31, 2012, the percentage of non-program cars was 79%, compared to 75% as of December 31, 2011.
In recent periods we have decreased the percentage of program cars in our car rental fleet and we expect this percentage to continue to decrease in the future, particularly as we integrate the operations of Dollar Thrifty, which operated a lower percentage of program cars than Hertz immediately prior to our completion of the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty. Non-program cars typically have lower acquisition costs and lower depreciation rates than comparable program cars. With fewer program cars in our fleet, we have an increased risk that the market value of a car at the time of its disposition will be less than its estimated residual value. However, non-program cars allow us the opportunity for ancillary revenue,
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
such as warranty and financing, during disposition. Program cars generally provide us with flexibility to reduce the size of our fleet by returning cars sooner than originally expected without risk of loss in the event of an economic downturn or to respond to changes in rental demand. This flexibility is reduced as the percentage of non-program cars in our car rental fleet increases. Furthermore, it is expected that the average age of our fleet will increase since the average holding period for non-program vehicles is longer than program vehicles. However, the longer holding period does not necessarily equate to higher costs due to the stringent turnback requirements imposed by vehicle manufacturers for program cars.
In the year ended December 31, 2012, our monthly per vehicle depreciation costs decreased as compared to the prior year period due to improved residual values in the U.S., a continued move towards a greater proportion of non-program vehicles, mix optimization and improved procurement and remarketing efforts.
Depreciation rates are reviewed on a quarterly basis based on management's routine review of present and estimated future market conditions and their effect on residual values at the time of disposal. During 2012, 2011 and 2010, depreciation rates being used to compute the provision for depreciation of revenue earning equipment were adjusted on certain vehicles in our car rental operations to reflect changes in the estimated residual values to be realized when revenue earning equipment is sold. These depreciation rate changes resulted in net decreases of $130.6 million and $13.8 million and an increase of $19.1 million in depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. Depreciation rate changes in certain of our equipment rental operations resulted in increase of $0.5 million and decrease of $4.4 million and an increase of $3.6 million in depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, our worldwide car rental operations sold approximately 178,300, 164,100 and 161,200 non-program cars, respectively, an 8.7% increase in 2012 versus 2011. This increase was due to strong car sales during the first half of 2012. This increase was partially offset due to a stronger than normal car sales market in the third quarter of 2011, which came about as a result of a shortage of new and used vehicles available for sale, created primarily by the events in Japan in early 2011. In addition, rental demand was stronger compared with the same prior year period, which reduced required defleeting non-program car sales volume. We believe the residual values have remained fairly stronger primarily due to continued short supply of recent model year used vehicles and aided by strong new vehicle sales.
For the year ended December 31, 2012, we experienced a 12.6% increase in transaction days versus the prior year in the United States while rental rate revenue per transaction day, or "RPD," declined by 3.1%. During the year ended December 31, 2012, in our European operations, we experienced a 3.1% decline in transaction days and a 3.2% decline in RPD when compared to the year ended December 31, 2011.
Revenues from our U.S. off-airport operations represented $1,306.4 million, $1,198.6 million and $1,079.8 million of our total car rental revenues in the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. As of December 31, 2012, we have approximately 2,520 off-airport locations. Our strategy includes selected openings of new off-airport locations, the disciplined evaluation of existing locations and the pursuit of same-store sales growth. Our strategy also includes increasing penetration in the off-airport market and growing the online leisure market, particularly in the longer length weekly sector, which is characterized by lower vehicle costs and lower transaction costs at a lower RPD. Increasing our penetration in these sectors is consistent with our long-term strategy to generate profitable growth. When we open a new off-airport location, we incur a number of costs, including those relating to site selection, lease negotiation, recruitment of employees, selection and development of managers, initial sales activities and integration of our systems with those of the companies who will reimburse the location's replacement renters for their rentals. A new off-airport location, once opened, takes time to generate its full potential revenues and, as a result, revenues at new locations do not initially cover their start-up costs and often do not, for some time, cover the costs of their ongoing operations.
On September 1, 2011, Hertz acquired 100% of the equity of Donlen, a leading provider of fleet leasing and management services for corporate fleets. For the year ended December 31, 2012 and for the four months ended December 31, 2011 (period it was owned by Hertz), Donlen had an average of approximately 150,800 and 137,000 vehicles under lease and management, respectively. Donlen provides Hertz an immediate leadership position in long-term car, truck and equipment leasing and fleet management. Donlen's fleet management programs provide outsourced solutions to reduce fleet operating costs and improve driver productivity. These programs include administration of preventive maintenance, advisory services, and fuel and accident management along with other complementary services.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Additionally, Donlen brings to Hertz a specialized consulting and technology expertise that will enable us to model, measure and manage fleet performance more effectively and efficiently.
As of December 31, 2012, our worldwide car rental operations had a total of approximately 10,270 corporate and licensee locations in approximately 150 countries in North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia, Australia, Africa, the Middle East and New Zealand.
On November 19, 2012, Hertz acquired 100% of the equity of Dollar Thrifty, a car and truck rental and leasing business. Dollar Thrifty had approximately 290 corporate locations in the United States and Canada, with approximately 5,700 employees located mainly in North America. In addition to its corporate operations, Dollar Thrifty had approximately 1,120 franchise locations in 83 countries. Dollar Thrifty brings to Hertz an immediate leadership position in the value-priced rental vehicle market generally appealing to leisure customers, including domestic and foreign tourists, and to small businesses, government and independent business travelers.
Equipment Rental
HERC experienced higher rental volumes and pricing for the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to the prior year as the industry continued its recovery in North America. The recovery has been led by strong industrial performance, especially oil and gas related, and improvement in the construction sector in part reflecting higher rental penetration. We continued to see growth in our specialty services such as Pump & Power, Industrial Plant Services and Hertz Entertainment Services. Additionally, there continue to be opportunities for 2013 as the uncertain economic outlook makes rental solutions attractive to customers. Our European equipment rental business, which represents approximately 7% of our worldwide equipment rental revenues, saw a revenue decline of 12.4% for the year ended December 31, 2012 compared to the prior year period, due to the unfavorable industry conditions in Europe.
Seasonality
Our car rental and equipment rental operations are seasonal businesses, with decreased levels of business in the winter months and heightened activity during the spring and summer. We have the ability to dynamically manage fleet capacity, the most significant portion of our cost structure, to meet market demand. For instance, to accommodate increased demand, we increase our available fleet and staff during the second and third quarters of the year. As business demand declines, fleet and staff are decreased accordingly. A number of our other major operating costs, including airport concession fees, commissions and vehicle liability expenses, are directly related to revenues or transaction volumes. In addition, our management expects to utilize enhanced process improvements, including efficiency initiatives and the use of our information technology systems, to help manage our variable costs. Approximately three-fifths of our typical annual operating costs represent variable costs, while the remaining two-fifths are fixed or semi-fixed. We also maintain a flexible workforce, with a significant number of part time and seasonal workers. However, certain operating expenses, including rent, insurance, and administrative overhead, remain fixed and cannot be adjusted for seasonal demand. Revenues related to our fleet leasing and management services are generally not seasonal.
Restructuring
As part of our ongoing effort to implement our strategy of reducing operating costs, we have evaluated our workforce and operations and made adjustments, including headcount reductions and business process reengineering resulting in optimized work flow at rental locations and maintenance facilities as well as streamlined our back-office operations and evaluated potential outsourcing opportunities. When we made adjustments to our workforce and operations, we incurred incremental expenses that delay the benefit of a more efficient workforce and operating structure, but we believe that increased operating efficiency and reduced costs associated with the operation of our business are important to our long-term competitiveness.
During 2007 through 2012, we announced several initiatives to improve our competitiveness and industry leadership through targeted job reductions. These initiatives included, but were not limited to, job reductions at our corporate headquarters and back-office operations in the U.S. and Europe. As part of our re-engineering optimization we outsourced selected functions globally. In addition, we streamlined operations and reduced costs by initiating the closure of targeted car rental locations and equipment rental branches throughout the world. The largest of these closures occurred in 2008 which resulted in closures of approximately 250 off-airport locations and 22 branches in our U.S. equipment rental business. These initiatives impacted approximately 9,610 employees.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, our consolidated statement of operations includes restructuring charges relating to various initiatives of $38.0 million, $56.4 million and $54.7 million, respectively.
Additional efficiency and cost saving initiatives are being developed, however, we presently do not have firm plans or estimates of any related expenses.
See Note 13 of the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations are based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, or “GAAP.” The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts in our financial statements and accompanying notes.
We believe the following accounting policies may involve a higher degree of judgment and complexity in their application and represent the critical accounting policies used in the preparation of our financial statements. If different assumptions or conditions were to prevail, the results could be materially different from our reported results. For additional discussion of our accounting policies, see Note 2 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Acquisition Accounting
We account for business combinations using the acquisition method, which requires an allocation of the purchase price of an acquired entity to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values at the date of acquisition. Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the net tangible and intangible assets acquired.
Revenue Earning Equipment
Our principal assets are revenue earning equipment, which represented approximately 56% of our total assets as of December 31, 2012. Revenue earning equipment consists of vehicles utilized in our car rental operations and equipment utilized in our equipment rental operations. For the year ended December 31, 2012, 30% of the vehicles purchased for our combined U.S. and international car rental fleets were subject to repurchase by automobile manufacturers under contractual repurchase and guaranteed depreciation programs, subject to certain manufacturers' car condition and mileage requirements, at a specific price during a specified time period. These programs limit our residual risk with respect to vehicles purchased under these programs. For all other vehicles, as well as equipment acquired by our equipment rental business, we use historical experience and monitor market conditions to set depreciation rates. Generally, when revenue earning equipment is acquired, we estimate the period that we will hold the asset, primarily based on historical measures of the amount of rental activity (e.g., automobile mileage and equipment usage) and the targeted age of equipment at the time of disposal. We also estimate the residual value of the applicable revenue earning equipment at the expected time of disposal. The residual values for rental vehicles are affected by many factors, including make, model and options, age, physical condition, mileage, sale location, time of the year and channel of disposition (e.g., auction, retail, dealer direct). The residual value for rental equipment is affected by factors which include equipment age and amount of usage. Depreciation is recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated holding period. Depreciation rates are reviewed on a quarterly basis based on management's ongoing assessment of present and estimated future market conditions, their effect on residual values at the time of disposal and the estimated holding periods. Market conditions for used vehicle and equipment sales can also be affected by external factors such as the economy, natural disasters, fuel prices and incentives offered by manufacturers of new cars. These key factors are considered when estimating future residual values and assessing depreciation rates. As a result of this ongoing assessment, we make periodic adjustments to depreciation rates of revenue earning equipment in response to changing market conditions. Upon disposal of revenue earning equipment, depreciation expense is adjusted for any difference between the net proceeds received and the remaining net book value and a corresponding gain or loss is recorded.
Within our Donlen subsidiary, revenue earning equipment is under longer term lease agreements with our customers. These leases contain provisions whereby we have a contracted residual value guaranteed to us by the lessee, such that we do not experience any gains or losses on the disposal of these vehicles. Therefore depreciation rates on these vehicles are not adjusted at any point in time per the associated lease contract.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
See Note 8 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Public Liability and Property Damage
The obligation for public liability and property damage on self-insured U.S. and international vehicles and equipment represents an estimate for both reported accident claims not yet paid, and claims incurred but not yet reported. The related liabilities are recorded on a non-discounted basis. Reserve requirements are based on rental volume and actuarial evaluations of historical accident claim experience and trends, as well as future projections of ultimate losses, expenses, premiums and administrative costs. The adequacy of the liability is regularly monitored based on evolving accident claim history and insurance related state legislation changes. If our estimates change or if actual results differ from these assumptions, the amount of the recorded liability is adjusted to reflect these results. Our actual results as compared to our estimates have historically resulted in relatively minor adjustments to our recorded liability.
Pension Benefit Obligations
Our employee pension costs and obligations are dependent on our assumptions used by actuaries in calculating such amounts. These assumptions include discount rates, salary growth, long-term return on plan assets, retirement rates, mortality rates and other factors. Actual results that differ from our assumptions are accumulated and amortized over future periods and, therefore, generally affect our recognized expense in such future periods. While we believe that the assumptions used are appropriate, significant differences in actual experience or significant changes in assumptions would affect our pension costs and obligations. The various employee related actuarial assumptions (e.g., retirement rates, mortality rates, salary growth) used in determining pension costs and plan liabilities are reviewed periodically by management, assisted by the enrolled actuary, and updated as warranted. The discount rate used to value the pension liabilities and related expenses and the expected rate of return on plan assets are the two most significant assumptions impacting pension expense. The discount rate used is a market based spot rate as of the valuation date. For the expected return on assets assumption, we use a forward looking rate that is based on the expected return for each asset class (including the value added by active investment management), weighted by the target asset allocation. The past annualized long-term performance of the Plans' assets has generally been in line with the long-term rate of return assumption. See Note 6 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” For a discussion of the risks associated with our pension plans, see “Item 1A—Risk Factors” in this Annual Report.
Goodwill
We review goodwill for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the goodwill may not be recoverable, and also review goodwill annually. Goodwill impairment is deemed to exist if the carrying value of goodwill exceeds its fair value. Goodwill must be tested at least annually using a two-step process. The first step is to identify any potential impairment by comparing the carrying value of the reporting unit to its fair value. A reporting unit is an operating segment or a business one level below that operating segment (the component level) if discrete financial information is prepared and regularly reviewed by segment management. However, components are aggregated as a single reporting unit if they have similar economic characteristics. We estimate the fair value of our reporting units using a discounted cash flow methodology. The key assumptions used in the discounted cash flow valuation model for impairment testing include discount rates, growth rates, cash flow projections and terminal value rates. Discount rates are set by using the Weighted Average Cost of Capital, or “WACC,” methodology. The WACC methodology considers market and industry data as well as Company specific risk factors for each reporting unit in determining the appropriate discount rates to be used. The discount rate utilized for each reporting unit is indicative of the return an investor would expect to receive for investing in such a business. The cash flows represent management's most recent planning assumptions. These assumptions are based on a combination of industry outlooks, views on general economic conditions, our expected pricing plans and expected future savings generated by our past restructuring activities. Terminal value rate determination follows common methodology of capturing the present value of perpetual cash flow estimates beyond the last projected period assuming a constant WACC and low long-term growth rates. If a potential impairment is identified, the second step is to compare the implied fair value of goodwill with its carrying amount to measure the impairment loss. A significant decline in the projected cash flows or a change in the WACC used to determine fair value could result in a future goodwill impairment charge.
In the fourth quarter 2012, we performed our annual impairment analysis based upon market data as of October 1, 2012 and concluded that there was no impairment related to our goodwill and our other indefinite lived intangible
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
assets. At October 1, 2012, we had five reporting units: U.S. Car Rental, Europe Car Rental, Other International Car Rental, Donlen and Worldwide Equipment Rental.
We performed the impairment analyses for our reporting units, using our business and long-term strategic plans, revised to reflect the current economic conditions. Our weighted average cost of capital used in the discounted cash flow model was calculated based upon the fair value of our debt and our stock price with a debt to equity ratio comparable to our industry. The total fair value of our reporting units was then compared to our market capitalization to ensure their reasonableness.
See Note 3 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Intangible and Long-lived Assets
We re-evaluate the estimated useful lives of our intangible assets annually or as circumstances change. Those intangible assets considered to have indefinite useful lives, including our trade name, are evaluated for impairment on an annual basis, by comparing the fair value of the intangible assets to their carrying value. Intangible assets with finite useful lives are amortized over their respective estimated useful lives. In addition, whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of intangible assets might not be recoverable, we will perform an impairment review.
The valuation of our indefinite lived assets utilized the relief from royalty method, which incorporates cash flows and discount rates comparable to those discussed above. We also considered the excess earnings as a percentage of revenues to ensure their reasonableness. Our analysis supported our conclusion that an impairment did not exist.
Derivatives
We periodically enter into cash flow and other hedging transactions to specifically hedge exposure to various risks related to interest rates, fuel prices and foreign currency rates. Derivative financial instruments are viewed as risk management tools and have not been used for speculative or trading purposes. All derivatives are recorded on the balance sheet as either assets or liabilities measured at their fair value. The effective portion of changes in fair value of derivatives designated as cash flow hedging instruments is recorded as a component of other comprehensive income. The ineffective portion is recognized currently in earnings within the same line item as the hedged item, based upon the nature of the hedged item. For derivative instruments that are not part of a qualified hedging relationship, the changes in their fair value are recognized currently in earnings. The valuation methods used to mark these to market are either market quotes (for fuel swaps, interest rate caps and foreign exchange instruments) or a discounted cash flow method (for interest rate swaps). The key inputs for the discounted cash flow method are the current yield curve and the credit default swap spread. These valuations are subject to change based on movements in items such as the London inter-bank offered rate, or “LIBOR,” our credit worthiness and unleaded gasoline and diesel fuel prices.
Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect of a change in tax rates is recognized in the statement of operations in the period that includes the enactment date. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Subsequent changes to enacted tax rates and changes to the global mix of earnings will result in changes to the tax rates used to calculate deferred taxes and any related valuation allowances. Provisions are not made for income taxes on undistributed earnings of international subsidiaries that are intended to be indefinitely reinvested outside the United States or are expected to be remitted free of taxes. Future distributions, if any, from these international subsidiaries to the United States or changes in U.S. tax rules may require recording a tax on these amounts. We have recorded a deferred tax asset for unutilized net operating loss carryforwards in various tax jurisdictions. Upon utilization, the taxing authorities may examine the positions that led to the generations of those net operating losses. If the utilization of any of those losses are disallowed a deferred tax liability may have to be recorded.
See Note 9 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Stock Based Compensation
The cost of employee services received in exchange for an award of equity instruments is based on the grant date fair value of the award. That cost is recognized over the period during which the employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award. We estimated the fair value of options issued at the date of grant using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model, which includes assumptions related to volatility, expected term, dividend yield, risk-free interest rate and forfeiture rate. These factors combined with the stock price on the date of grant result in a fixed expense which is recorded on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. The key factors used in the valuation process, other than the forfeiture rate and volatility, remained unchanged from the date of grant. Because the stock of Hertz Holdings became publicly traded in November 2006 and had a short trading history, it was not practicable for us to estimate the expected volatility of our share price, or a peer company share price, because there was not sufficient historical information about past volatility prior to 2012. Therefore, prior to 2012 we used the calculated value method, substituting the historical volatility of an appropriate industry sector index for the expected volatility of Hertz Holdings' common stock price as an assumption in the valuation model. We selected the Dow Jones Specialized Consumer Services sub-sector within the consumer services industry, and we used the U.S. large capitalization component, which includes the top 70% of the index universe (by market value).
The calculation of the historical volatility of the index was made using the daily historical closing values of the index for the preceding 6.25 years, because that is the expected term of the options using the simplified approach.
Beginning in 2012, we have determined that there is now sufficient historical information available to estimate the expected volatility of Hertz Holdings' stock price. Therefore for equity awards made in 2012 the assumed volatility for Hertz Holdings' stock price is based on a weighted average combining implied volatility and the average of our peer’s most recent 5.79-year volatility and mean reversion volatility. The assumed dividend yield is zero. The risk-free interest rate is the implied zero-coupon yield for U.S. Treasury securities having a maturity approximately equal to the expected term of the options, as of the grant dates. The non-cash stock-based compensation expense associated with the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Stock Incentive Plan, or the “Stock Incentive Plan,” the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Director Stock Incentive Plan, or the “Director Plan,” and the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan, or the “Omnibus Plan,” are pushed down from Hertz Holdings and recorded on the books at the Hertz level. See Note 7 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
For a discussion of recent accounting pronouncements, see Note 2 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
In the following discussion, comparisons are made between the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010. The following table sets forth for each of the periods indicated, the percentage of total revenues represented by the various line items in our consolidated statements of operations (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | Percentage of Revenues |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 7,456.1 |
| | $ | 6,929.6 |
| | $ | 6,355.2 |
| | 82.7 | % | | 83.5 | % | | 84.0 | % |
| Equipment rental | 1,383.2 |
| | 1,208.8 |
| | 1,069.8 |
| | 15.3 |
| | 14.6 |
| | 14.2 |
|
| Other | 181.5 |
| | 160.0 |
| | 137.5 |
| | 2.0 |
| | 1.9 |
| | 1.8 |
|
| Total revenues | 9,020.8 |
| | 8,298.4 |
| | 7,562.5 |
| | 100.0 |
| | 100.0 |
| | 100.0 |
|
| Expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Direct operating | 4,795.8 |
| | 4,566.4 |
| | 4,283.4 |
| | 53.2 |
| | 55.0 |
| | 56.7 |
|
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 2,148.2 |
| | 1,905.7 |
| | 1,868.1 |
| | 23.8 |
| | 23.0 |
| | 24.7 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 945.5 |
| | 745.1 |
| | 664.5 |
| | 10.5 |
| | 9.0 |
| | 8.8 |
|
| Interest expense | 597.8 |
| | 650.3 |
| | 726.5 |
| | 6.6 |
| | 7.8 |
| | 9.6 |
|
| Interest income | (4.9 | ) | | (5.5 | ) | | (12.3 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| Other (income) expense, net | 35.5 |
| | 62.5 |
| | — |
| | 0.4 |
| | 0.8 |
| | — |
|
| Total expenses | 8,517.9 |
| | 7,924.5 |
| | 7,530.2 |
| | 94.4 |
| | 95.5 |
| | 99.6 |
|
| Income before income taxes | 502.9 |
| | 373.9 |
| | 32.3 |
| | 5.6 |
| | 4.5 |
| | 0.4 |
|
| Provision for taxes on income | (227.1 | ) | | (143.8 | ) | | (33.3 | ) | | (2.5 | ) | | (1.8 | ) | | (0.4 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | 275.8 |
| | 230.1 |
| | (1.0 | ) | | 3.1 |
| | 2.7 |
| | — |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | (19.6 | ) | | (17.4 | ) | | — |
| | (0.2 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| Net Income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 275.8 |
| | $ | 210.5 |
| | $ | (18.4 | ) | | 3.1 | % | | 2.5 | % | | (0.2 | )% |
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
The following table sets forth certain of our selected car rental, equipment rental and other operating data for each of the periods indicated:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended or as of December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Selected Car Rental Operating Data: | | | | | |
| Worldwide number of transactions (in thousands) | 29,127 |
| | 27,095 |
| | 25,970 |
|
| Domestic (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty) | 21,920 |
| | 19,903 |
| | 19,101 |
|
| International (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty) | 7,207 |
| | 7,192 |
| | 6,869 |
|
Worldwide transaction days (in thousands)(a) | 148,787 |
| | 137,301 |
| | 127,159 |
|
| Domestic (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty) | 105,539 |
| | 93,741 |
| | 86,422 |
|
| International (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty) | 43,248 |
| | 43,560 |
| | 40,737 |
|
Worldwide rental rate revenue per transaction day(b) | $ | 40.01 |
| | $ | 41.33 |
| | $ | 43.14 |
|
| Domestic (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty) | $ | 39.07 |
| | $ | 40.30 |
| | $ | 42.16 |
|
| International (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty) | $ | 42.30 |
| 44,470 |
| $ | 43.56 |
| | $ | 45.23 |
|
| Worldwide average number of cars during the period | 665,000 |
| | 615,600 |
| | 445,200 |
|
| Domestic (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty company-operated) | 359,100 |
| | 321,700 |
| | 297,900 |
|
| International (Hertz, Dollar and Thrifty company-operated) | 155,100 |
| | 156,900 |
| | 147,300 |
|
| Donlen (under lease and maintenance) | 150,800 |
| | 137,000 |
| | N/A |
|
Adjusted pre-tax income (in millions of dollars)(c) | $ | 1,020.1 |
| | $ | 850.2 |
| | $ | 641.9 |
|
| Worldwide revenue earning equipment, net (in millions of dollars) | $ | 10,710.1 |
| | $ | 8,318.7 |
| | $ | 7,220.1 |
|
| Selected Worldwide Equipment Rental Operating Data: | | | | | |
Rental and rental related revenue (in millions of dollars)(d) | $ | 1,257.9 |
| | $ | 1,094.4 |
| | $ | 976.1 |
|
Same-store revenue growth (decline), including growth initiatives(e) | 8.6 | % | | 9.3 | % | | (5.4 | )% |
| Average acquisition cost of rental equipment operated during the period (in millions of dollars) | $ | 3,069.0 |
| | $ | 2,804.8 |
| | $ | 2,732.6 |
|
Adjusted pre-tax income (in millions of dollars)(c) | $ | 227.0 |
| | $ | 161.6 |
| | $ | 78.0 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment, net (in millions of dollars) | $ | 2,198.2 |
| | $ | 1,786.7 |
| | $ | 1,703.7 |
|
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (a) | Transaction days represent the total number of days that vehicles were on rent in a given period. |
| |
| (b) | Car rental rate revenue consists of all revenue, net of discounts, associated with the rental of cars including charges for optional insurance products, but excluding revenue derived from fueling and concession and other expense pass-throughs, NeverLost units in the U.S. and certain ancillary revenue. Rental rate revenue per transaction day is calculated as total rental rate revenue, divided by the total number of transaction days, with all periods adjusted to eliminate the effect of fluctuations in foreign currency. Our management believes eliminating the effect of fluctuations in foreign currency is appropriate so as not to affect the comparability of underlying trends. This statistic is important to our management and investors as it represents the best measurement of the changes in underlying pricing in the car rental business and encompasses the elements in car rental pricing that management has the ability to control. The optional insurance products are packaged within certain negotiated corporate, government and membership programs and within certain retail rates being charged. Based upon these existing programs and rate packages, management believes that these optional insurance products should be consistently included in the daily pricing of car rental transactions. On the other hand, non-rental rate revenue items such as refueling and concession pass-through expense items are driven by factors beyond the control of management (i.e. the price of fuel and the concession fees charged by airports). Additionally, NeverLost units are an optional revenue product which management does not consider to be part of their daily pricing of car rental transactions. The following table reconciles our car rental segment revenues to our rental rate revenue and rental rate revenue per transaction day (based on December 31, 2011 foreign exchange rates) for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 (in millions of dollars, except as noted): |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Car rental segment revenues | $ | 7,633.0 |
| | $ | 7,083.5 |
| | $ | 6,486.2 |
|
| Non-rental rate revenue | (1,676.6 | ) | | (1,256.7 | ) | | (1,041.7 | ) |
| Foreign currency adjustment | (4.0 | ) | | (151.7 | ) | | 41.3 |
|
| Rental rate revenue | $ | 5,952.4 |
| | $ | 5,675.1 |
| | $ | 5,485.8 |
|
| Transaction days (in thousands) | 148,787 |
| | 137,301 |
| | 127,159 |
|
| Rental rate revenue per transaction day (in whole dollars) | $ | 40.01 |
| | $ | 41.33 |
| | $ | 43.14 |
|
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
| |
| (c) | Adjusted pre-tax income is calculated as income (loss) before income taxes plus non-cash purchase accounting charges, non-cash debt charges relating to the amortization and write-off of debt financing costs and debt discounts and certain one-time charges and non-operational items. Adjusted pre-tax income is important to management because it allows management to assess operational performance of our business, exclusive of the items mentioned above. It also allows management to assess the performance of the entire business on the same basis as the segment measure of profitability. Management believes that it is important to investors for the same reasons it is important to management and because it allows them to assess our operational performance on the same basis that management uses internally. The contribution of our reportable segments to adjusted pre-tax income and reconciliation to consolidated amounts are presented below (in millions of dollars): |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Adjusted pre-tax income: | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 1,020.1 |
| | $ | 850.2 |
| | $ | 641.9 |
|
| Equipment rental | 227.0 |
| | 161.6 |
| | 78.0 |
|
| Total reportable segments | 1,247.1 |
| | 1,011.8 |
| | 719.9 |
|
| Adjustments: | | | | | |
Other reconciling items(1) | (320.5 | ) | | (306.2 | ) | | (347.9 | ) |
Purchase accounting(2) | (109.6 | ) | | (87.6 | ) | | (90.3 | ) |
Non-cash debt charges(3) | (56.4 | ) | | (105.9 | ) | | (160.6 | ) |
| Restructuring charges | (38.0 | ) | | (56.4 | ) | | (54.7 | ) |
Restructuring related charges(4) | (11.1 | ) | | (9.8 | ) | | (13.2 | ) |
Derivative gains (losses)(5) | (0.9 | ) | | 0.1 |
| | (3.2 | ) |
Acquisition related costs and charges(6) | (163.7 | ) | | (18.8 | ) | | (17.7 | ) |
| Management transition costs | — |
| | (4.0 | ) | | — |
|
Pension adjustment(7) | — |
| | 13.1 |
| | — |
|
Premiums paid on debt(8) | — |
| | (62.4 | ) | | — |
|
Other(9) | (44.0 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Income before income taxes | $ | 502.9 |
| | $ | 373.9 |
| | $ | 32.3 |
|
| |
| (1) | Represents general corporate expenses, certain interest expense (including net interest on corporate debt), as well as other business activities. |
| |
| (2) | Represents the increase in amortization of other intangible assets, depreciation of property and equipment and accretion of revalued liabilities relating to purchase accounting. |
| |
| (3) | Represents non-cash debt charges relating to the amortization and write-off of deferred debt financing costs and debt discounts. |
| |
| (4) | Represents incremental costs incurred directly supporting our business transformation initiatives. Such costs include transition costs incurred in connection with our business process outsourcing arrangements and incremental costs incurred to facilitate business process re-engineering initiatives that involve significant organization redesign and extensive operational process changes. |
| |
| (5) | Represents the mark-to-market adjustment on our interest rate cap. |
| |
| (6) | Primarily represents Dollar Thrifty acquisition related expenses, change in control expenses, 'Day-1' compensation expenses and other adjustments related to the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, loss on the Advantage divestiture, expenses related to additional required divestitures and costs associated with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, pre-acquisition interest and commitment fee expenses for interim financing associated with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition and a gain on the investment in Dollar Thrifty stock. |
| |
| (7) | Represents a gain for the U.K. pension plan relating to unamortized prior service cost from a 2010 amendment that eliminated discretionary pension increases related to pre-1997 service primarily pertaining to inactive employees. |
| |
| (8) | Represents premiums paid to redeem our 10.5% Senior Subordinated Notes and a portion of our 8.875% Senior Notes. |
| |
| (9) | Primarily represents expenses related to the withdrawal from a multiemployer pension plan, litigation accrual and expenses associated with the impact of Hurricane Sandy. |
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
| |
| (d) | Equipment rental and rental related revenue consists of all revenue, net of discounts, associated with the rental of equipment including charges for delivery, loss damage waivers and fueling, but excluding revenue arising from the sale of equipment, parts and supplies and certain other ancillary revenue. Rental and rental related revenue is adjusted in all periods to eliminate the effect of fluctuations in foreign currency. Our management believes eliminating the effect of fluctuations in foreign currency is appropriate so as not to affect the comparability of underlying trends. This statistic is important to our management and investors as it is utilized in the measurement of rental revenue generated per dollar invested in fleet on an annualized basis and is comparable with the reporting of other industry participants. The following table reconciles our equipment rental segment revenues to our equipment rental and rental related revenue (based on December 31, 2011 foreign exchange rates) for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 (in millions of dollars): |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Equipment rental segment revenues | $ | 1,385.4 |
| | $ | 1,209.5 |
| | $ | 1,070.1 |
|
| Equipment sales and other revenue | (121.8 | ) | | (106.2 | ) | | (100.1 | ) |
| Foreign currency adjustment | (5.7 | ) | | (8.9 | ) | | 6.1 |
|
| Rental and rental related revenue | $ | 1,257.9 |
| | $ | 1,094.4 |
| | $ | 976.1 |
|
| |
| (e) | Same-store revenue growth (decline) is calculated as the year over year change in revenue for locations that are open at the end of the period reported and have been operating under our direction for more than twelve months. The same-store revenue amounts are adjusted in all periods to eliminate the effect of fluctuations in foreign currency. Our management believes eliminating the effect of fluctuations in foreign currency is appropriate so as not to affect the comparability of underlying trends. |
Year Ended December 31, 2012 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2011
REVENUES
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | | | |
| (in millions of dollars) | 2012 | | 2011 | | $ Change | | % Change |
| Revenues by Segment | | | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 7,633.0 |
| | $ | 7,083.5 |
| | $ | 549.5 |
| | 7.8 | % |
| Equipment rental | 1,385.4 |
| | 1,209.5 |
| | 175.9 |
| | 14.5 | % |
| Other reconciling items | 2.4 |
| | 5.4 |
| | (3.0 | ) | | (55.6 | )% |
| Total revenues | $ | 9,020.8 |
| | $ | 8,298.4 |
| | $ | 722.4 |
| | 8.7 | % |
Results from operations are discussed below and include comparisons to prior year periods. We acquired Donlen on September 1, 2011. Our results from operations include Donlen for the year ended December 31, 2012 and the post-acquisition period ended December 31, 2011, which is approximately four months in 2011. We acquired Dollar Thrifty on November 19, 2012. Our results from operations include Dollar Thrifty for the post-acquisition period ended December 31, 2012, which is approximately forty three days in 2012. The results of operations for Donlen and Dollar Thrifty are included within our car rental segment. The acquisitions of Donlen and Dollar Thrifty are referred to below as the "Recent Acquisitions." See Note 4 of the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Car Rental Segment
Revenues from our car rental segment increased 7.8%, primarily as a result of increases in car rental transaction days worldwide of 8.4%, incremental volume associated with the Recent Acquisitions and refueling fees of $34.9 million. These increases were partly offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $140.6 million and a decrease in worldwide RPD.
RPD for worldwide car rental for the year ended December 31, 2012 decreased 3.2% from 2011, due to decreases in U.S. and International RPD of 3.1% and 2.9%, respectively, and a proportionately higher amount attributable to the U.S. due to uncertain economic conditions in Europe. U.S. airport RPD decreased 3.1% and U.S. off-airport RPD declined by 2.7%. U.S. airport RPD was negatively impacted by a shift to longer life, lower RPD rentals (due to a proportionately higher amount attributable to off-airport). International RPD decreased primarily due to a decline in Europe's airport RPD which was due to the competitive pricing environment and uncertain economic conditions.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Equipment Rental Segment
Revenues from our equipment rental segment increased 14.5%, primarily due to increases of 12.3% and 3.6% in equipment rental volumes and pricing, respectively, partly offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $11.2 million. The increase in volumes were primarily due to strong industrial performance, especially oil and gas related, and improvement in the construction sector in part reflecting higher rental penetration. Additionally, Cinelease and other 2012 equipment rental segment acquisitions contributed to the increase in equipment rental revenues.
Other
Revenues from all other sources decreased $3.0 million, primarily due to a decrease in revenues from our third-party claim management services.
EXPENSES
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | | | |
| (in millions of dollars) | 2012 | | 2011 | | $ Change | | % Change |
| Expenses: | | | | | | | |
| Fleet related expenses | $ | 1,145.7 |
| | $ | 1,120.6 |
| | $ | 25.1 |
| | 2.2 | % |
| Personnel related expenses | 1,563.2 |
| | 1,478.0 |
| | 85.2 |
| | 5.8 | % |
| Other direct operating expenses | 2,086.9 |
| | 1,967.8 |
| | 119.1 |
| | 6.1 | % |
| Direct operating | 4,795.8 |
| | 4,566.4 |
| | 229.4 |
| | 5.0 | % |
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 2,148.2 |
| | 1,905.7 |
| | 242.5 |
| | 12.7 | % |
| Selling, general and administrative | 945.5 |
| | 745.1 |
| | 200.4 |
| | 26.9 | % |
| Interest expense | 597.8 |
| | 650.3 |
| | (52.5 | ) | | (8.1 | )% |
| Interest income | (4.9 | ) | | (5.5 | ) | | 0.6 |
| | (10.9 | )% |
| Other (income) expense, net | 35.5 |
| | 62.5 |
| | (27.0 | ) | | (43.2 | )% |
| Total expenses | $ | 8,517.9 |
| | $ | 7,924.5 |
| | $ | 593.4 |
| | 7.5 | % |
Total expenses increased 7.5%, but total expenses as a percentage of revenues decreased from 95.5% for the year ended December 31, 2011 to 94.4% for the year ended December 31, 2012.
Direct Operating Expenses
Car Rental Segment
Direct operating expenses for our car rental segment of $4,033.1 million for 2012 increased $192.8 million, or 5.0%, from $3,840.3 million for 2011 as a result of increases in fleet related expenses, personnel related expenses and other direct operating expenses.
Fleet related expenses for our car rental segment of $932.1 million for 2012 increased $5.4 million, or 0.6%, from 2011. On a comparable basis, the increase was primarily related to worldwide rental volume demand which resulted in increases in gasoline costs of $26.8 million, vehicle maintenance costs of $8.2 million and self insurance expenses of $4.7 million. The increase in gasoline costs reflect higher gasoline prices. These increases were partly offset by a decrease in vehicle damage costs of $20.6 million and the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $26.0 million. The remaining 2012 net increase was primarily attributable to the Recent Acquisitions.
Personnel related expenses for our car rental segment of $1,282.9 million for 2012 increased $64.9 million, or 5.3%, from 2011. On a comparable basis, the increase was primarily related to increases in salaries and related expenses associated with improved volume and compensation for employees at additional off-airport locations in 2012 as well as higher incentives. These increases were partly offset by the effects of foreign
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
currency translation of approximately $18.4 million. The remaining 2012 net increase was primarily attributable to the Recent Acquisitions.
Other direct operating expenses for our car rental segment of $1,818.1 million for 2012 increased $122.5 million, or 7.2%, from 2011. On a comparable basis, the increase was primarily related to increases in facilities expenses of $60.0 million due to 2011 property sales, commissions of $20.4 million, concession fees of $9.5 million, customer service costs of $10.7 million, field systems of $7.7 million and restructuring charges of $5.4 million. The increases were primarily a result of improved worldwide rental volume demand and off-airport expansions. The increases in other direct operating expenses were partly offset by decreases in computer costs of $4.9 million and charge card fees of $3.8 million as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $34.7 million. The remaining 2012 net increase was primarily attributable to the Recent Acquisitions.
Equipment Rental Segment
Direct operating expenses for our equipment rental segment of $769.7 million for 2012 increased $39.1 million, or 5.3% from $730.6 million for 2011 as a result of increases in personnel related expenses and fleet related expenses, partly offset by a decrease in other direct operating expenses.
Fleet related expenses for our equipment rental segment of $213.5 million for 2012 increased $19.7 million, or 10.1% from 2011. The increase was primarily related to increased rental volume resulting in increased freight expenses of $11.4 million, higher maintenance costs of $5.9 million and increased delivery costs of $4.3 million. Additionally, Cinelease and other 2012 equipment rental segment acquisitions added to the increase of fleet related expenses. These increases were partly offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $1.9 million.
Personnel related expenses for our equipment rental segment of $244.8 million for 2012 increased $22.5 million, or 10.1% from 2011. The increase was attributable to an increase in salaries and related expenses of $20.5 million and an increase in benefits of $4.8 million primarily related to increased volumes and new branch openings. Additionally, Cinelease and other 2012 equipment rental segment acquisitions added to the increase of personnel related expenses. These increases were partly offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $2.5 million.
Other direct operating expenses for our equipment rental segment of $311.4 million for 2012 decreased $3.1 million, or 1.0% from 2011. The decrease was primarily related to the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $2.6 million.
Depreciation of Revenue Earning Equipment and Lease Charges
Car Rental Segment
Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges for our car rental segment of $1,876.1 million for 2012 increased $224.7 million, or 13.6% from $1,651.4 million for 2011. The increase was primarily attributable to the increase in average fleet due to the Recent Acquisitions. The increase was partly offset by lower net depreciation per vehicle, higher vehicle residual values, a higher mix of non-program cars and the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $31.4 million.
Equipment Rental Segment
Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges in our equipment rental segment of $272.1 million for 2012 increased 7.0% from $254.3 million for 2011. The increase was primarily due to a 9.4% increase in the average acquisition cost of rental equipment operated during the period, partly offset by higher residual values on the disposal of used equipment and the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $2.5 million.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses of $945.5 million for 2012 increased $221.2 million due to increases in administrative, sales promotion and advertising expenses, partly offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $20.8 million.
Administrative expenses increased $192.9 million, or 42.3%. On a comparable basis, acquisition fees increased $26.0 million, expenses associated with the withdrawal from a multiemployer pension plan increased $23.2 million, contractor costs increased $5.5 million, legal expenses increased $6.4 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges increased by $8.1 million, which is in addition to litigation settlement expenses of $19.2 million. These increases were partly offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $14.2 million. The remaining 2012 net increase was primarily attributable to the Recent Acquisitions.
Sales promotion expenses increased $12.0 million, or 8.4%, primarily related to increases in sales salaries and commissions due to improved results, partially offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $2.4 million.
Advertising expenses increased $16.4 million, or 11.2%, primarily due to increased media and on-line advertising, higher airline miles expense associated with increased volume, costs related to our customer loyalty program, partly offset by the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $4.2 million. The remaining 2012 net increase was primarily attributable to the Recent Acquisitions.
Interest Expense
Car Rental Segment
Interest expense for our car rental segment of $316.3 million for 2012 decreased 5.0% from $333.1 million for 2011. The decrease was primarily due to debt refinancing activity, lower interest rates in 2012 and the effects of foreign currency translation of $8.5 million, partly offset by the higher levels of debt required to fund the Recent Acquisitions.
Equipment Rental Segment
Interest expense for our equipment rental segment of $52.0 million for 2012 increased 14.8% from $45.3 million for 2011. The increase was primarily due to increases in the weighted-average debt outstanding as a result of an increase in average fleet size.
Other
Other interest expense relating to interest on corporate debt of $229.5 million for 2012 decreased 15.6% from $271.9 million for 2011. The decrease was primarily due to larger write-offs last year of unamortized debt costs in connection with refinancing activity, lower rates achieved with the refinancing of our Senior Notes and Senior Subordinated Notes and a decrease in the weighted-average debt outstanding and interest rates.
Interest Income
Interest income decreased $0.6 million from the prior year.
Other (Income) Expense, Net
Other (income) expense, net of $35.5 million for 2012 decreased $27.0 million, or 43.2% from $62.5 million for 2011. Primarily included within 2012 other (income) expense, net is a loss on the Advantage divestiture of $31.4 million, expenses related to additional required divestitures and costs associated with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition of $24.2 million, partly offset by a gain from the sale of Switzerland operations of $10.3 million and a gain on the investment in Dollar Thrifty stock of $8.5 million. Other (income) expense, net for 2011 primarily includes premiums paid in connection with the redemption of our 10.5% Senior Subordinated Notes and a portion of our 8.875% Senior Notes.
ADJUSTED PRE-TAX INCOME (LOSS)
Car Rental Segment
Adjusted pre-tax income for our car rental segment of $1,020.1 million increased 20.0% from $850.2 million for 2011. The increase was primarily due to stronger volumes, lower net depreciation per vehicle, improved residual values and
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
disciplined cost management, partly offset by decreased pricing. Adjustments to our car rental segment income before income taxes for 2012 totaled $236.0 million (which consists of acquisition related costs and charges of $96.4 million, purchase accounting charges of $61.6 million, non-cash debt charges of $38.1 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $34.7 million, other of $5.0 million and loss on derivatives of $0.2 million). Adjustments to our car rental segment income before income taxes for 2011 totaled $94.5 million (which consists of non-cash debt charges of $43.9 million, purchase accounting of $39.5 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $23.6 million, pension adjustment of $(13.1) million and loss on derivatives of $0.6 million). See footnote (c) to the table under “Results of Operations” for a summary and description of these adjustments.
Equipment Rental Segment
Adjusted pre-tax income for our equipment rental segment of $227.0 million increased 40.5% from $161.6 million for 2011. The increase was primarily due to stronger volumes and pricing, strong cost management performance and higher residual values on the disposal of used equipment. Adjustments to our equipment rental segment income before income taxes for 2012 totaled $74.4 million (which consists of purchase accounting of $44.3 million, other of $15.8 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $9.3 million and non-cash debt charges of $5.0 million). Adjustments to our equipment rental loss before income taxes for 2011 totaled $92.3 million (which consists of purchase accounting of $44.4 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $42.4 million and non-cash debt charges of $5.5 million). See footnote (c) to the table under “Results of Operations” for a summary and description of these adjustments.
PROVISION FOR TAXES ON INCOME, NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO NONCONTROLLING INTEREST AND NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES' COMMON STOCKHOLDER
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | | | |
| (in millions of dollars) | 2012 | | 2011 | | $ Change | | % Change |
| Income before income taxes | $ | 502.9 |
| | $ | 373.9 |
| | $ | 129.0 |
| | 34.5 | % |
| Provision for taxes on income | (227.1 | ) | | (143.8 | ) | | (83.3 | ) | | 57.9 | % |
| Net income | 275.8 |
| | 230.1 |
| | 45.7 |
| | 19.9 | % |
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | (19.6 | ) | | 19.6 |
| | (100.0 | )% |
| Net income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 275.8 |
| | $ | 210.5 |
| | $ | 65.3 |
| | 31.0 | % |
Provision for Taxes on Income
The effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2012 was 45.2% as compared to 38.5% for the year ended December 31, 2011. The provision for taxes on income increased $83.3 million, primarily due to higher income before income taxes, changes in geographic earnings mix, changes in losses in certain non-U.S. jurisdictions for which tax benefits are not realized and non-deductible compensation payments under Internal Revenue Code Section 280(G) related to the Dollar Thrifty acquisition. See Note 9 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Net Income Attributable to Noncontrolling Interest
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest decreased $19.6 million due to Hertz's purchase of the noncontrolling interest of Navigation Solutions, L.L.C. on December 31, 2011, thereby increasing its ownership interest from 65% to 100%.
Net Income Attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' Common Stockholder
Net income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder increased 31.0% primarily due to higher rental volumes in our worldwide car and equipment rental operations, disciplined cost management, lower net depreciation per vehicle in our car rental operations, increased pricing in our equipment rental operations and improved residual values on the disposal of certain used equipment, partly offset by lower pricing in our worldwide car rental operations. Most revenue and expense transactions from operations outside of the United States are recorded in local currencies, which reduces the effect of changes in exchange rates on net income.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Year Ended December 31, 2011 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2010
REVENUES
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | | | |
| (in millions of dollars) | 2011 | | 2010 | | $ Change | | % Change |
| Revenues by Segment | | | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 7,083.5 |
| | $ | 6,486.2 |
| | $ | 597.3 |
| | 9.2 | % |
| Equipment rental | 1,209.5 |
| | 1,070.1 |
| | 139.4 |
| | 13.0 | % |
| Other reconciling items | 5.4 |
| | 6.2 |
| | (0.8 | ) | | (12.5 | )% |
| Total revenues | $ | 8,298.4 |
| | $ | 7,562.5 |
| | $ | 735.9 |
| | 9.7 | % |
Car Rental Segment
Revenues from our car rental segment increased 9.2%, primarily as a result of increases in car rental transaction days worldwide of 8.0%, refueling fees of $40.3 million and airport concession recovery fees of $30.8 million, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $157.9 million. The year ended December 31, 2011 also includes $142.7 million of revenues related to Donlen which was acquired on September 1, 2011. These increases were partly offset by a decrease in worldwide RPD.
RPD for worldwide car rental for the year ended December 31, 2011 decreased 3.7% from 2010, due to decreases in U.S. and International RPD of 4.4% and 2.3%, respectively. U.S. off-airport RPD declined by 2.7% and U.S. airport RPD decreased 4.7%. A mix shift to longer life, lower RPD rentals (including increased growth of off-airport and the Advantage brand); the competitive environment in the first half of the year, as well as a difficult year-over-year RPD comparison to last year, reduced U.S. RPD. International RPD decreased primarily due to a decrease in Europe's airport RPD which was due to the competitive pricing environment.
Equipment Rental Segment
Revenues from our equipment rental segment increased 13.0%, primarily due to increases of 10.5% and 2.4% in equipment rental volumes and pricing, respectively, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $17.3 million. The increase in volume was primarily due to strong industrial performance.
Other
Revenues from all other sources decreased 12.5%, primarily due to a decrease in revenues from our third-party claim management services.
EXPENSES
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | | | |
| (in millions of dollars) | 2011 | | 2010 | | $ Change | | % Change |
| Expenses: | | | | | | | |
| Fleet related expenses | $ | 1,120.6 |
| | $ | 1,003.2 |
| | $ | 117.4 |
| | 11.7 | % |
| Personnel related expenses | 1,478.0 |
| | 1,411.2 |
| | 66.8 |
| | 4.7 | % |
| Other direct operating expenses | 1,967.8 |
| | 1,869.0 |
| | 98.8 |
| | 5.3 | % |
| Direct operating | 4,566.4 |
| | 4,283.4 |
| | 283.0 |
| | 6.6 | % |
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 1,905.7 |
| | 1,868.1 |
| | 37.6 |
| | 2.0 | % |
| Selling, general and administrative | 745.1 |
| | 664.5 |
| | 80.6 |
| | 12.1 | % |
| Interest expense | 650.3 |
| | 726.5 |
| | (76.2 | ) | | (10.5 | )% |
| Interest income | (5.5 | ) | | (12.3 | ) | | 6.8 |
| | (54.9 | )% |
| Other (income) expense, net | 62.5 |
| | — |
| | 62.5 |
| | N/M |
|
| Total expenses | $ | 7,924.5 |
| | $ | 7,530.2 |
| | $ | 394.3 |
| | 5.2 | % |
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Total expenses increased 5.2%, but total expenses as a percentage of revenues decreased from 99.6% for the year ended December 31, 2010 to 95.5% for the year ended December 31, 2011.
Direct Operating Expenses
Car Rental Segment
Direct operating expenses for our car rental segment of $3,840.3 million for 2011 increased $235.6 million, or 6.5%, from 2010 as a result of increases in fleet related expenses, other direct operating expenses and personnel related expenses.
Fleet related expenses for our car rental segment of $926.8 million for 2011 increased $104.7 million, or 12.7% from 2010. The increase was primarily related to worldwide rental volume demand which resulted in increases in gasoline costs of $58.4 million, self insurance expenses of $10.1 million, vehicle license taxes of $7.4 million, vehicle maintenance costs of $6.2 million and vehicle registration fees of $5.4 million, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $29.4 million. The increase in gasoline costs also related to higher gasoline prices. These increases were partly offset by a decrease in vehicle damage costs of $11.5 million.
Other direct operating expenses for our car rental segment of $1,695.5 million for 2011 increased $74.9 million, or 4.6% from 2010. The increase was primarily related to increases in field administrative expenses of $23.0 million, customer service costs of $13.8 million, third‑party claim management expenses of $12.9 million, concession fees of $12.8 million, computer costs of $10.1 million, charge card fees of $4.7 million and reservation costs of $4.3 million, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $36.8 million. The increases were primarily a result of improved worldwide rental volume demand. The increase in field administrative expenses also related to a reimbursement received from a manufacturer in 2010. The increases in other direct operating expenses were partly offset by decreases in facilities expenses of $34.8 million, field systems of $4.7 million and restructuring and restructuring related charges of $2.8 million. The decrease in facilities expenses primarily related to gains recognized on the sale of certain properties in 2011.
Personnel related expenses for our car rental segment of $1,218.0 million for 2011 increased $56.0 million, or 4.8% from 2010. The increase was related to increases in salaries and related expenses of $34.0 million and outside services, including transporter wages of $14.8 million, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $20.6 million, partly offset by a decrease in benefits of $14.2 million. The expense increases were primarily related to improved results, as well as additional U.S. off-airport and Advantage locations in 2011. The decrease in benefits primarily related to the U.K. pension plan curtailment gain.
Equipment Rental Segment
Direct operating expenses for our equipment rental segment of $730.6 million for 2011 increased $53.3 million, or 7.9% from $677.3 million for 2010 as a result of increases in other direct operating expenses, fleet related expenses and personnel related expenses.
Other direct operating expenses for our equipment rental segment of $314.6 million for 2011 increased $27.8 million, or 9.7% from 2010. The increase was primarily related to increases in restructuring and restructuring related charges of $5.3 million, legal expenses of $3.6 million, re-rent expense of $3.5 million, amortization expense of $2.4 million, cost of sales of $2.2 million, field systems and administrative expenses of $1.9 million and credit and collections expense of $1.1 million, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $4.2 million. The increases in re-rent expense, costs of sales, field systems and administrative expenses and credit and collections expense primarily related to improved worldwide rental volume demand.
Fleet related expenses for our equipment rental segment of $193.8 million for 2011 increased $13.1 million, or 7.2% from 2010. The increase was primarily related to continued aging of the fleet which resulted in an increase in maintenance costs of $11.2 million and increased worldwide rental volume resulting in increased
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
freight and delivery costs of $6.5 million, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $2.6 million. These increases were partly offset by decreases in insurance and licenses of $3.8 million and personal property taxes of $2.6 million.
Personnel related expenses for our equipment rental segment of $222.2 million for 2011 increased $12.4 million, or 5.9% from 2010. The increase was related to increases in salaries and related expenses of $9.0 million primarily related to improved results, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $3.3 million.
Depreciation of Revenue Earning Equipment and Lease Charges
Car Rental Segment
Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges for our car rental segment of $1,651.4 million for 2011 increased 3.6% from $1,594.6 million for 2010. The increase was primarily due the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $34.8 million, a 7.5% increase in average fleet and an increase due to the acquisition of Donlen and its related depreciation expense of $117.0 million. The increase was partly offset by an improvement in certain vehicle residual values and a change in mix of vehicles.
Equipment Rental Segment
Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges in our equipment rental segment of $254.3 million for 2011 decreased 7.0% from $273.5 million for 2010. The decrease was primarily due to higher residual values on the disposal of used equipment, partly offset by a 2.6% increase in the average acquisition cost of rental equipment operated during the period and the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $3.1 million.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased 12.1%, due to increases in administrative, sales promotion and advertising expenses.
Administrative expenses increased $54.3 million, or 13.5%, primarily due to increases in salaries and related expenses of $34.0 million, consulting expenses of $8.8 million, travel and entertainment expenses of $3.5 million and legal expense of $2.5 million, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $8.4 million, partly offset by a decrease in unrealized loss on derivatives of $3.4 million.
Sales promotion expenses increased $14.3 million, or 11.1%, primarily related to increases in sales salaries and commissions due to improved results, as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $2.7 million.
Advertising expenses increased $12.0 million, or 9.0%, primarily due to increased media and production related to the new campaign (“Gas and Brake”), as well as the effects of foreign currency translation of approximately $4.3 million.
Interest Expense
Car Rental Segment
Interest expense for our car rental segment of $333.1 million for 2011 decreased 17.0% from $401.3 million for 2010. The decrease was primarily due to lower interest rates in 2011, partly offset by an increase in the weighted average debt outstanding as a result of an increased fleet size.
Equipment Rental Segment
Interest expense for our equipment rental segment of $45.3 million for 2011 increased 15.0% from $39.4 million for 2010. The increase was primarily due to a portion of the write-off of the unamortized debt costs in connection with the refinancing of our Senior ABL Facility which was allocated to our equipment rental segment in 2011.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Other
Other interest expense relating to interest on corporate debt of $271.9 million for 2011 decreased 4.9% from $285.8 million for 2010. The decrease was primarily due to lower rates in 2011, partly offset by increases due to the write-off of unamortized debt costs in connection with the refinancing of our Senior Term Facility and Senior ABL Facility, financing costs incurred in connection with the new Senior Term Facility and the write-off of unamortized debt costs in connection with the redemption of our 10.5% Senior Subordinated Notes and a portion of our 8.875% Senior Notes in 2011.
Interest Income
Interest income decreased $6.8 million primarily due to interest on a value added tax reclaim received in 2010.
Other (Income) Expense, Net
Other (income) expense, net increased $62.5 million primarily due to premiums paid in connection with the redemption of our 10.5% Senior Subordinated Notes and a portion of our 8.875% Senior Notes during 2011.
ADJUSTED PRE-TAX INCOME (LOSS)
Car Rental Segment
Adjusted pre-tax income for our car rental segment of $850.2 million increased 32.5% from $641.9 million for 2010. The increase was primarily due to stronger volumes, improved residual values and disciplined cost management, partly offset by decreased pricing. Adjustments to our car rental segment income before income taxes for 2011 totaled $94.5 million (which consists of non-cash debt charges of $43.9 million, purchase accounting of $39.5 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $23.6 million, pension adjustment of $(13.1) million and loss on derivatives of $0.6 million). Adjustments to our car rental segment income before income taxes for 2010 totaled $200.1 million (which consists of non-cash debt charges of $133.3 million, purchase accounting of $37.0 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $30.0 million and gain on derivatives of $(0.2) million). See footnote (c) to the table under “Results of Operations” for a summary and description of these adjustments.
Equipment Rental Segment
Adjusted pre-tax income for our equipment rental segment of $161.6 million increased 107.2% from $78.0 million for 2010. The increase was primarily due to stronger volumes and pricing, strong cost management performance and higher residual values on the disposal of used equipment. Adjustments to our equipment rental segment income before income taxes for 2011 totaled $92.3 million (which consists of purchase accounting of $44.4 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $42.4 million and non-cash debt charges of $5.5 million). Adjustments to our equipment rental loss before income taxes for 2010 totaled $92.6 million (which consists of purchase accounting of $50.1 million, restructuring and restructuring related charges of $35.0 million and non-cash debt charges of $7.5 million). See footnote (c) to the table under “Results of Operations” for a summary and description of these adjustments.
PROVISION FOR TAXES ON INCOME, NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO NONCONTROLLING INTEREST AND NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES' COMMON STOCKHOLDER
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | | | |
| (in millions of dollars) | 2011 | | 2010 | | $ Change | | % Change |
| Income before income taxes | $ | 373.9 |
| | $ | 32.3 |
| | $ | 341.6 |
| | N/M |
|
| Provision for taxes on income | (143.8 | ) | | (33.3 | ) | | (110.5 | ) | | 331.7 | % |
| Net income (loss) | 230.1 |
| | (1 | ) | | 231.1 |
| | N/M |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | (19.6 | ) | | (17.4 | ) | | (2.2 | ) | | 12.5 | % |
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 210.5 |
| | $ | (18.4 | ) | | $ | 228.9 |
| | N/M |
|
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Provision for Taxes on Income
The effective tax rate for 2011 was 38.5% as compared to 103.1% in 2010. The provision for taxes on income increased $110.5 million, primarily due to higher income before income taxes, changes in geographic earnings mix and changes in valuation allowances for losses in certain non-U.S. jurisdictions for which tax benefits cannot be realized. See Note 8 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8-Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Net Income Attributable to Noncontrolling Interest
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest increased 12.5% due to an increase in our formerly majority‑owned subsidiary Navigation Solutions, L.L.C.'s net income for 2011 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2010. In December 2011, Hertz purchased the noncontrolling interest of Navigation Solutions, L.L.C., thereby increasing its ownership interest from 65% to 100%.
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' Common Stockholder
The net income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder was $210.5 million in 2011 compared to a loss in 2010 of $18.4 million primarily due to higher rental volumes in our worldwide car and equipment rental operations, improved residual values on the disposal of certain vehicles and used equipment, disciplined cost management, lower interest expense and increased pricing in our equipment rental operations, partly offset by lower pricing in our worldwide car rental operations, costs incurred in connection with the refinancing of our Senior Term Facility and Senior ABL Facility and the write-off of unamortized debt costs and premiums paid in connection with the redemption of our 10.5% Senior Subordinated Notes and a portion of our 8.875% Senior Notes during 2011. The impact of changes in exchange rates on net income was mitigated by the fact that not only revenues but also most expenses outside of the United States were incurred in local currencies.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Our domestic and international operations are funded by cash provided by operating activities and by extensive financing arrangements maintained by us in the United States and internationally.
Cash Flows
As of December 31, 2012, we had cash and cash equivalents of $533.2 million, a decrease of $398.0 million from $931.2 million as of December 31, 2011. The following table summarizes such decrease:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, | | 2012 vs. 2011 | | 2011 vs. 2010 |
| (in millions of dollars) | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | $ Change | | $ Change |
| Cash provided by (used in): | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating activities | $ | 2,748.4 |
| | $ | 2,258.5 |
| | $ | 2,237.9 |
| | $ | 489.9 |
| | $ | 20.6 |
|
| Investing activities | (4,747.3 | ) | | (2,192.9 | ) | | (943.6 | ) | | (2,554.4 | ) | | (1,249.3 | ) |
| Financing activities | 1,595.2 |
| | (1,512.2 | ) | | 104.5 |
| | 3,107.4 |
| | (1,616.7 | ) |
| Effect of exchange rate changes | 5.7 |
| | 3.8 |
| | (10.3 | ) | | 1.9 |
| | 14.1 |
|
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | $ | (398.0 | ) | | $ | (1,442.8 | ) | | $ | 1,388.5 |
| | $ | 1,044.8 |
| | $ | (2,831.3 | ) |
During the year ended December 31, 2012, we generated $489.9 million more cash from operating activities compared with the same period in 2011. The increase was primarily a result of higher earnings before interest, depreciation and amortization and reduced interest expense as well as due to the timing of our payments.
Our primary use of cash in investing activities is for the acquisition of revenue earning equipment, which consists of cars and equipment. During the year ended December 31, 2012, we used $2,554.4 million more cash for investing activities compared with the same period in 2011. The increase in the use of funds was primarily due to the Dollar Thrifty acquisition along with other acquisitions during the year, decreases in proceeds from the disposal of revenue earning equipment, a decrease in the year-over-year change in restricted cash and cash equivalents and revenue earning equipment expenditures during the year. As of December 31, 2012 and 2011, we had $571.6 million and $308.0 million, respectively, of restricted cash and cash equivalents to be used for the purchase of revenue earning vehicles and other specified uses under our fleet financing facilities, our Like Kind Exchange Program, or "LKE Program," and to satisfy certain of our self-insurance regulatory reserve requirements. The increase in restricted cash and cash equivalents of $263.6 million from December 31, 2011 to December 31, 2012, primarily related to the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty.
During the year ended December 31, 2012, cash flows from financing activities increased by $3,107.4 million compared with the same period in 2011. The increase was primarily related to the 2012 issuance of incremental Senior Notes and incurrence of incremental Term Loans related to the Dollar Thrifty acquisition and higher payments of pre-funded debt associated with our Senior Note redemptions in the prior year.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
Capital Expenditures
The tables below set forth the revenue earning equipment and property and equipment capital expenditures and related disposal proceeds on a cash basis consistent with our consolidated statements of cash flows, by quarter for 2012, 2011 and 2010 (in millions of dollars).
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Revenue Earning Equipment | | Property and Equipment |
| | Capital Expenditures | | Disposal Proceeds | | Net Capital Expenditures (Disposal Proceeds) | | Capital Expenditures | | Disposal Proceeds | | Net Capital Expenditures |
| 2012 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| First Quarter | $ | 2,648.7 |
| | $ | (2,009.3 | ) | | $ | 639.4 |
| | $ | 74.2 |
| | $ | (47.6 | ) | | $ | 26.6 |
|
| Second Quarter | 3,050.2 |
| | (1,599.0 | ) | | 1,451.2 |
| | 63.0 |
| | (8.8 | ) | | 54.2 |
|
| Third Quarter | 1,982.1 |
| | (1,207.1 | ) | | 775.0 |
| | 92.2 |
| | (38.2 | ) | | 54.0 |
|
| Fourth Quarter | 1,932.2 |
| | (2,309.7 | ) | | (377.5 | ) | | 83.4 |
| | (43.1 | ) | | 40.3 |
|
| Total Year | $ | 9,613.2 |
| | $ | (7,125.1 | ) | | $ | 2,488.1 |
| | $ | 312.8 |
| | $ | (137.7 | ) | | $ | 175.1 |
|
| 2011 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| First Quarter | $ | 1,963.8 |
| | $ | (1,690.2 | ) | | $ | 273.6 |
| | $ | 56.8 |
| | $ | (14.5 | ) | | $ | 42.3 |
|
| Second Quarter | 3,503.0 |
| | (1,798.7 | ) | | 1,704.3 |
| | 68.6 |
| | (13.9 | ) | | 54.7 |
|
| Third Quarter | 2,397.8 |
| | (1,443.5 | ) | | 954.3 |
| | 76.9 |
| | (19.7 | ) | | 57.2 |
|
| Fourth Quarter | 1,589.7 |
| | (2,918.0 | ) | | (1,328.3 | ) | | 79.4 |
| | (5.7 | ) | | 73.7 |
|
| Total Year | $ | 9,454.3 |
| | $ | (7,850.4 | ) | | $ | 1,603.9 |
| | $ | 281.7 |
| | $ | (53.8 | ) | | $ | 227.9 |
|
| 2010 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| First Quarter | $ | 2,214.5 |
| | $ | (1,606.4 | ) | | $ | 608.1 |
| | $ | 51.3 |
| | $ | (6.7 | ) | | $ | 44.6 |
|
| Second Quarter | 3,102.8 |
| | (1,836.8 | ) | | 1,266.0 |
| | 40.7 |
| | (8.5 | ) | | 32.2 |
|
| Third Quarter | 1,796.4 |
| | (1,702.8 | ) | | 93.6 |
| | 42.3 |
| | (10.3 | ) | | 32.0 |
|
| Fourth Quarter | 1,327.2 |
| | (2,372.4 | ) | | (1,045.2 | ) | | 44.9 |
| | (13.4 | ) | | 31.5 |
|
| Total Year | $ | 8,440.9 |
| | $ | (7,518.4 | ) | | $ | 922.5 |
| | $ | 179.2 |
| | $ | (38.9 | ) | | $ | 140.3 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenue earning equipment expenditures | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 8,850.3 |
| | $ | 8,865.6 |
| | $ | 8,274.1 |
|
| Equipment rental | 762.9 |
| | 588.7 |
| | 166.8 |
|
| Total | $ | 9,613.2 |
| | $ | 9,454.3 |
| | $ | 8,440.9 |
|
Revenue earning equipment expenditures in our car rental operations for the year ended December 31, 2012 decreased by 0.2% compared to the year ended December 31, 2011 and revenue earning equipment expenditures in our equipment rental operations increased by 29.6% compared to the year ended December 31, 2011. The decrease in our car rental revenue earning equipment expenditures during the year ended December 31, 2012 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2011 was primarily due to the shift from the purchase of program cars to more non-program cars, which have much longer holding periods than program cars. The increase in our equipment rental operations revenue earning equipment expenditures is primarily due to increased volumes as well as continued improvement in the economic conditions during the year ended December 31, 2012.
Revenue earning equipment expenditures in our car rental and equipment rental operations for the year ended December 31, 2011 increased by 7.1% and 253.0%, respectively, compared to the year ended December 31, 2010. The increase in our car rental revenue earning equipment expenditures was primarily due to higher rental volumes during the year ended December 31, 2011 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2010, which required us to increase fleet levels. The increase in our equipment rental operations revenue earning equipment expenditures is primarily due to a continued improvement in the economic conditions as well as efforts to reduce the age of our fleet during the year ended December 31, 2011.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Property and equipment expenditures | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 268.1 |
| | $ | 244.3 |
| | $ | 156.0 |
|
| Equipment rental | 24.6 |
| | 28.8 |
| | 19.3 |
|
| Other | 20.1 |
| | 8.6 |
| | 3.9 |
|
| Total | $ | 312.8 |
| | $ | 281.7 |
| | $ | 179.2 |
|
Property and equipment expenditures in our car rental operations increased $23.8 million, equipment rental operations decreased $4.2 million, and other activities increased $11.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2012, compared to the year ended December 31, 2011. The increases in car rental operations are a result of increased locations in 2012. The decrease in equipment rental operations was primarily due to the timing of purchases and payments during the year ended December 31, 2012. The increase in other activities primarily relates to costs associated with an ERP system implementation in 2012.
Property and equipment expenditures in our car rental operations, equipment rental operations and for all other activities for the year ended December 31, 2011 increased by $88.3 million, $9.5 million and $4.7 million, respectively, compared to the year ended December 31, 2010. The car rental and equipment rental increases are a result of increased volumes, an improvement in the economic conditions during the year, as well as, in car rental due to the opening of new off-airport locations.
Financing
Our primary liquidity needs include servicing of corporate and fleet related debt, acquisitions, the payment of operating expenses and purchases of rental vehicles and equipment to be used in our operations. Our primary sources of funding are operating cash flows, cash received on the disposal of vehicles and equipment, borrowings under our asset-backed securitizations and our asset-based revolving credit facilities and access to the credit markets generally.
As of December 31, 2012, we had $15,014.5 million of total indebtedness outstanding. Cash paid for interest during the year ended December 31, 2012, was $535.1 million, net of amounts capitalized. Accordingly, we are highly leveraged and a substantial portion of our liquidity needs arise from debt service on our indebtedness and from the funding of our costs of operations, capital expenditures and acquisitions.
Our liquidity as of December 31, 2012 consisted of cash and cash equivalents, unused commitments under our Senior ABL Facility and unused commitments under our fleet debt. For a description of these amounts, see Note 5 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Maturities
The aggregate amounts of maturities of debt for each of the twelve-month periods ending December 31 (in millions of dollars) are as follows:
|
| | | | | |
| 2013 | $ | 5,744.1 |
| | (including $5,244.0 of other short-term borrowings*) |
| 2014 | $ | 1,122.1 |
| | |
| 2015 | $ | 1,894.1 |
| | |
| 2016 | $ | 267.1 |
| | |
| 2017 | $ | 219.2 |
| | |
| After 2017 | $ | 5,752.5 |
| | |
_______________________________________________________________________________
|
| |
| * | Our short-term borrowings as of December 31, 2012 include, among other items, the amounts outstanding under the Senior ABL Facility, HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes, U.S. Fleet Financing Facility, European Revolving Credit Facility, European Securitization, Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Australian Securitization, Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility and Capitalized Leases. These amounts are reflected as short-term borrowings, regardless of the facility maturity date, as these facilities are revolving in nature and/or the outstanding borrowings have maturities of three months or less. As of December 31, 2012, short-term borrowings had a weighted average interest rate of 1.8%. |
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
We believe that cash generated from operations and cash received on the disposal of vehicles and equipment, together with amounts available under various liquidity facilities will be adequate to permit us to meet our debt maturities over the next twelve months.
For subsequent events relating to our indebtedness, see Note 18 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report.
Registration Rights and Indentures for the Senior Notes
Hertz entered into exchange and registration rights agreements entered into in connection with (i) the issuance of $250 million in aggregate principal amount of the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019 in March 2012, and (ii) the release from escrow of the proceeds of $700 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Senior Notes due 2020 and $500 million aggregate principal amount of 6.250% Senior Notes due 2022. Pursuant to the terms of these agreements, Hertz agreed to file a registration statement under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, to permit either the exchange of such notes for registered notes or, in the alternative, the registered resale of such notes. Hertz's failure to meet its obligations under either exchange and registration rights agreement, including by failing to have the registration statement become effective by the date that is 365 days after the respective date of the exchange and registration rights agreement or failing to complete the exchange offer by the date that is 395 days after the date of the exchange and registration rights agreement, will result in Hertz incurring special interest on such notes at a per annum rate of 0.25% for the first 90 days of any period where a default has occurred and is continuing, which rate will be increased by an additional 0.25% during each subsequent 90 day period, up to a maximum of 0.50%. A registration statement on Form S-4 covering the exchange of such notes was declared effective by the SEC on February 1, 2013 and the exchange offer is scheduled to be completed on March 6, 2013, so we do not believe the special interest obligation is probable, and as such, we have not recorded any amounts for special interest with respect to these notes.
Hertz's obligations under the indentures for the Senior Notes are guaranteed by each of its direct and indirect domestic subsidiaries that is a guarantor under the Senior Term Facility. The guarantees of all of the subsidiary guarantors may be released to the extent such subsidiaries no longer guarantee our Senior Credit Facilities in the United States.
We refer to Hertz and its subsidiaries as the Hertz credit group. The indentures for the Senior Notes contain covenants that, among other things, limit or restrict the ability of the Hertz credit group to incur additional indebtedness, incur guarantee obligations, prepay certain indebtedness, make certain restricted payments (including paying dividends, redeeming stock or making other distributions to parent entities of Hertz and other persons outside of the Hertz credit group), make investments, create liens, transfer or sell assets, merge or consolidate, and enter into certain transactions with Hertz's affiliates that are not members of the Hertz credit group.
Other Financing Risks
A significant number of cars that we purchase are subject to repurchase by car manufacturers under contractual repurchase or guaranteed depreciation programs. Under these programs, car manufacturers agree to repurchase cars at a specified price or guarantee the depreciation rate on the cars during a specified time period, typically subject to certain car condition and mileage requirements. We use book values derived from this specified price or guaranteed depreciation rate to calculate financing capacity under certain asset-backed and asset-based financing arrangements.
In the event of a bankruptcy of a car manufacturer, our liquidity would be impacted by several factors including reductions in fleet residual values and the risk that we would be unable to collect outstanding receivables due to us from such bankrupt manufacturer. In addition, the program cars manufactured by any such company would need to be removed from our financing facilities or re-designated as non-program vehicles, which would require us to furnish additional credit enhancement associated with these program vehicles. For a discussion of the risks associated with a manufacturer's bankruptcy or our reliance on asset-backed and asset-based financing, see "Item 1A—Risk Factors" included in this Annual Report.
We rely significantly on asset-backed and asset-based financing arrangements to purchase cars for our domestic and international car rental fleet. The amount of financing available to us pursuant to these programs depends on a number of factors, many of which are outside our control, including recently adopted legislation, proposed SEC rules and regulations and other legislative and administrative developments. In this regard, there has been uncertainty regarding the potential impact of proposed SEC rules and regulations governing the issuance of asset-backed securities and additional requirements contained in the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act and the Basel III regulatory capital rules, a global regulatory standard on bank capital adequacy, stress testing and market liquidity
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
risk. While we will continue to monitor these developments and their impact on our ABS program, the SEC rules and regulations, once adopted and implemented, may impact our ability and/or desire to engage in asset-backed financings in the future. For further information concerning our asset-backed financing programs and our indebtedness, see Note 5 to the Notes to our audited annual consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption "Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data." For a discussion of the risks associated with our reliance on asset-backed and asset-based financing and the significant amount of indebtedness, see "Item 1A—Risk Factors" in this Annual Report.
For further information on our indebtedness, see Note 5 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report.
Covenants
Certain of our debt instruments and credit facilities contain a number of covenants that, among other things, limit or restrict the ability of the borrowers and the guarantors to dispose of assets, incur additional indebtedness, incur guarantee obligations, prepay certain indebtedness, make certain restricted payments (including paying dividends, redeeming stock or making other distributions), create liens, make investments, make acquisitions, engage in mergers, fundamentally change the nature of their business, make capital expenditures, or engage in certain transactions with certain affiliates.
Under the terms of our Senior Term Facility and Senior ABL Facility, we are not subject to ongoing financial maintenance covenants; however, under the Senior ABL Facility, failure to maintain certain levels of liquidity will subject the Hertz credit group to a contractually specified fixed charge coverage ratio of not less than 1:1 for the four quarters most recently ended. As of December 31, 2012, we were not subject to such contractually specified fixed charge coverage ratio.
In addition to borrowings under our Senior Credit Facilities, we have a significant amount of additional debt outstanding. For further information on the terms of our Senior Credit Facilities as well as our significant amount of other debt outstanding, see Note 5 to the Notes to our audited annual consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption "Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data." For a discussion of the risks associated with our significant indebtedness, see "Item 1A—Risk Factors" in this annual report.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
Borrowing Capacity and Availability
As of December 31, 2012, the following facilities were available for the use of Hertz and its subsidiaries (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Remaining Capacity | | Availability Under Borrowing Base Limitation |
| Corporate Debt | | | |
| Senior ABL Facility | $ | 1,183.7 |
| | $ | 1,146.0 |
|
| Total Corporate Debt | 1,183.7 |
| | 1,146.0 |
|
| Fleet Debt | | | |
| HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes | 88.8 |
| | — |
|
| RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes | 81.0 |
| | — |
|
| Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes | 105.0 |
| | — |
|
| U.S. Fleet Financing Facility | 24.0 |
| | — |
|
| European Revolving Credit Facility | 105.9 |
| | 7.9 |
|
| European Securitization | 287.2 |
| | — |
|
| Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization | 100.5 |
| | — |
|
| Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization | 95.5 |
| | — |
|
| Australian Securitization | 110.5 |
| | — |
|
| Capitalized Leases | 85.1 |
| | 27.5 |
|
| Total Fleet Debt | 1,083.5 |
| | 35.4 |
|
| Total | $ | 2,267.2 |
| | $ | 1,181.4 |
|
Our borrowing capacity and availability primarily comes from our "revolving credit facilities," which are a combination of asset-backed securitization facilities and asset-based revolving credit facilities. Creditors under each of our revolving credit facilities have a claim on a specific pool of assets as collateral. Our ability to borrow under each revolving credit facility is a function of, among other things, the value of the assets in the relevant collateral pool. We refer to the amount of debt we can borrow given a certain pool of assets as the "borrowing base."
We refer to "Remaining Capacity" as the maximum principal amount of debt permitted to be outstanding under the respective facility (i.e., the amount of debt we could borrow assuming we possessed sufficient assets as collateral) less the principal amount of debt then-outstanding under such facility.
We refer to "Availability Under Borrowing Base Limitation" as the lower of Remaining Capacity or the borrowing base less the principal amount of debt then-outstanding under such facility (i.e., the amount of debt we could borrow given the collateral we possess at such time).
As of December 31, 2012, the Senior Term Facility had approximately $8.0 million available under the letter of credit facility and the Senior ABL Facility had $1,010.4 million available under the letter of credit facility sublimit, subject to borrowing base restrictions.
Substantially all of our revenue earning equipment and certain related assets are owned by special purpose entities, or are encumbered in favor of our lenders under our various credit facilities.
Some of these special purpose entities are consolidated variable interest entities, of which we are the primary beneficiary, whose sole purpose is to provide commitments to lend in various currencies subject to borrowing bases comprised of rental vehicles and related assets of certain of Hertz International, Ltd.'s subsidiaries. As of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, our International Fleet Financing No. 1 B.V., International Fleet Financing No. 2 B.V. and HA Funding Pty, Ltd. variable interest entities had total assets primarily comprised of loans receivable and revenue earning equipment of $440.8 million and $456.3 million, respectively, and total liabilities primarily comprised of debt of $440.3 million and $455.8 million, respectively.
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
Contractual Obligations
The following table details the contractual cash obligations for debt and related interest payable, operating leases and concession agreements, tax liability for uncertain tax positions and related interest and other purchase obligations as of December 31, 2012 (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | Payments Due by Period | | |
| | Total | | 2013 | | 2014 to 2015 | | 2016 to 2017 | | After 2017 | | All Other |
Debt(1) | $ | 14,999.1 |
| | $ | 5,744.1 |
| | $ | 3,016.2 |
| | $ | 486.3 |
| | $ | 5,752.5 |
| | — |
|
Interest on debt(2) | 2,805.9 |
| | 614.4 |
| | 942.7 |
| | 672.6 |
| | 576.2 |
| | — |
|
Operating leases and concession agreements(3) | 2,400.1 |
| | 604.2 |
| | 732.2 |
| | 359.8 |
| | 703.9 |
| | — |
|
Uncertain tax positions liability and interest(4) | 20.5 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 20.5 |
|
Purchase obligations(5) | 5,837.5 |
| | 5,772.2 |
| | 60.2 |
| | 4.6 |
| | 0.5 |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 26,063.1 |
| | $ | 12,734.9 |
| | $ | 4,751.3 |
| | $ | 1,523.3 |
| | $ | 7,033.1 |
| | $ | 20.5 |
|
| |
| (1) | Amounts represent aggregate debt obligations included in “Debt” in our consolidated balance sheet and include $5,244.0 million of other short-term borrowings. See Note 5 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” |
Our short-term borrowings as of December 31, 2012 include, among other items, the amounts outstanding under the Senior ABL Facility, HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes, U.S. Fleet Financing Facility, European Revolving Credit Facility, European Securitization, Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Australian Securitization, Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility and Capitalized Leases. These amounts are reflected as short-term borrowings, regardless of the facility maturity date, as these facilities are revolving in nature and/or the outstanding borrowings have maturities of three months or less.
| |
| (2) | Amounts represent the estimated commitment fees and interest payments based on the principal amounts, minimum non-cancelable maturity dates and applicable interest rates on the debt at December 31, 2012. The minimum non-cancelable obligations under the HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, Senior ABL Facility, RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes, U.S. Fleet Financing Facility, European Revolving Credit Facility, European Securitization, Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Australian Securitization and Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility mature between June 2013 and March 2016. |
| |
| (3) | Includes obligations under various concession agreements, which provide for payment of rents and a percentage of revenue with a guaranteed minimum, and lease agreements for real estate, revenue earning equipment and office and computer equipment. Such obligations are reflected to the extent of their minimum non-cancelable terms. See Note 10 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” |
| |
| (4) | As of December 31, 2012, this represents our tax liability for uncertain tax positions and related net accrued interest and penalties of $16.3 million and $4.2 million, respectively. We are unable to reasonably estimate the timing of our uncertain tax positions liability and interest and penalty payments in individual years beyond twelve months due to uncertainties in the timing of the effective settlement of tax positions. See Note 9 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” |
| |
| (5) | Purchase obligations represent agreements to purchase goods or services that are legally binding on us and that specify all significant terms, including fixed or minimum quantities; fixed, minimum or variable price provisions; and the approximate timing of the transaction. Only the minimum non-cancelable portion of purchase agreements and related cancellation penalties are included as obligations. In the case of contracts, which state minimum quantities of goods or services, amounts reflect only the stipulated minimums; all other contracts reflect estimated amounts. Of the total purchase obligations as of December 31, 2012, $5,236.1 million represent fleet purchases where contracts have been signed or are pending with committed orders under the terms of such arrangements. We do not regard our employment relationships with our employees as “agreements to purchase services” for these purposes. |
The table excludes our pension and other postretirement benefit obligations. We contributed $38.4 million to our U.S. pension plan during 2012 and expect to contribute between $20 million and $30 million to our U.S. pension plan during 2013. The level of 2013 and future contributions will vary, and is dependent on a number of factors including investment
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (Continued)
returns, interest rate fluctuations, plan demographics, funding regulations and the results of the final actuarial valuation. See Note 6 of the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Off-Balance Sheet Commitments and Arrangements
As of December 31, 2012 and 2011, the following guarantees (including indemnification commitments) were issued and outstanding:
Indemnification Obligations
In the ordinary course of business, we execute contracts involving indemnification obligations customary in the relevant industry and indemnifications specific to a transaction such as the sale of a business. These indemnification obligations might include claims relating to the following: environmental matters; intellectual property rights; governmental regulations and employment-related matters; customer, supplier and other commercial contractual relationships; and financial matters. Performance under these indemnification obligations would generally be triggered by a breach of terms of the contract or by a third party claim. We regularly evaluate the probability of having to incur costs associated with these indemnification obligations and have accrued for expected losses that are probable and estimable. The types of indemnification obligations for which payments are possible include the following:
Sponsors; Directors
We have entered into customary indemnification agreements with Hertz Holdings, the Sponsors and Hertz Holdings' stockholders affiliated with the Sponsors, pursuant to which Hertz Holdings and Hertz will indemnify the Sponsors, Hertz Holdings' stockholders affiliated with the Sponsors and their respective affiliates, directors, officers, partners, members, employees, agents, representatives and controlling persons, against certain liabilities arising out of performance of a consulting agreement with Hertz Holdings and each of the Sponsors and certain other claims and liabilities, including liabilities arising out of financing arrangements or securities offerings. Hertz Holdings also entered into indemnification agreements with each of its directors. We do not believe that these indemnifications are reasonably likely to have a material impact on us.
Environmental
We have indemnified various parties for the costs associated with remediating numerous hazardous substance storage, recycling or disposal sites in many states and, in some instances, for natural resource damages. The amount of any such expenses or related natural resource damages for which we may be held responsible could be substantial. The probable expenses that we expect to incur for such matters have been accrued, and those expenses are reflected in our consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2012 and 2011, the aggregate amounts accrued for environmental liabilities including liability for environmental indemnities, reflected in our condensed consolidated balance sheets in "Other accrued liabilities" were $2.6 million and $1.5 million, respectively. The accrual generally represents the estimated cost to study potential environmental issues at sites deemed to require investigation or clean-up activities, and the estimated cost to implement remediation actions, including on-going maintenance, as required. Cost estimates are developed by site. Initial cost estimates are based on historical experience at similar sites and are refined over time on the basis of in-depth studies of the sites. For many sites, the remediation costs and other damages for which we ultimately may be responsible cannot be reasonably estimated because of uncertainties with respect to factors such as our connection to the site, the materials there, the involvement of other potentially responsible parties, the application of laws and other standards or regulations, site conditions, and the nature and scope of investigations, studies, and remediation to be undertaken (including the technologies to be required and the extent, duration, and success of remediation).
Risk Management
For a discussion of additional risks arising from our operations, including vehicle liability, general liability and property damage insurable risks, see “Item 1—Business—Risk Management” in this Annual Report.
Market Risks
We are exposed to a variety of market risks, including the effects of changes in interest rates (including credit spreads), foreign currency exchange rates and fluctuations in fuel prices. We manage our exposure to these market risks through our regular operating and financing activities and, when deemed appropriate, through the use of derivative financial
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
instruments. Derivative financial instruments are viewed as risk management tools and have not been used for speculative or trading purposes. In addition, derivative financial instruments are entered into with a diversified group of major financial institutions in order to manage our exposure to counterparty nonperformance on such instruments. For more information on these exposures, see Note 14 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Interest Rate Risk
From time to time, we may enter into interest rate swap agreements and/or interest rate cap agreements to manage interest rate risk. See Notes 4 and 13 to the Notes to our audited annual consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
We have a significant amount of debt with variable rates of interest based generally on LIBOR, Euro inter-bank offered rate, or “EURIBOR,” or their equivalents for local currencies or bank conduit commercial paper rates plus an applicable margin. Increases in interest rates could therefore significantly increase the associated interest payments that we are required to make on this debt. See Note 5 to the Notes to our audited annual consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
We have assessed our exposure to changes in interest rates by analyzing the sensitivity to our earnings assuming various changes in market interest rates. Assuming a hypothetical increase of one percentage point in interest rates on our debt portfolio as of December 31, 2012, our net income would decrease by an estimated $31.3 million over a twelve‑month period.
Consistent with the terms of the agreements governing the respective debt obligations, we may hedge a portion of the floating rate interest exposure under the various debt facilities to provide protection in respect of such exposure.
Foreign Currency Risk
We have foreign currency exposure to exchange rate fluctuations worldwide and primarily with respect to the Euro, Canadian dollar, Australian dollar and British pound.
We manage our foreign currency risk primarily by incurring, to the extent practicable, operating and financing expenses in the local currency in the countries in which we operate, including making fleet and equipment purchases and borrowing locally. Also, we have purchased foreign exchange options to manage exposure to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates for selected marketing programs. The effect of exchange rate changes on these financial instruments would not materially affect our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. Our risks with respect to foreign exchange options are limited to the premium paid for the right to exercise the option and the future performance of the option's counterparty.
We also manage exposure to fluctuations in currency risk on intercompany loans we make to certain of our subsidiaries by entering into foreign currency forward contracts at the time of the loans which are intended to offset the impact of foreign currency movements on the underlying intercompany loan obligations.
On October 1, 2006, we designated our 7.875% Senior Notes due 2014 as an effective net investment hedge of our Euro-denominated net investment in our international operations. Effective November 1, 2011, we de-designated the net investment hedge.
For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, our consolidated statement of operations contained realized and unrealized losses relating to the effects of foreign currency of $10.6 million, $6.7 million and $6.2 million, respectively.
See Note 14 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Other Risks
We purchase unleaded gasoline and diesel fuel at prevailing market rates. In January 2009, we began a program to manage our exposure to changes in fuel prices through the use of derivative commodity instruments. For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, we recognized gains of $0.7 million, $2.6 million and $2.8 million, respectively, in “Direct operating” on our consolidated statement of operations relating to our gasoline swaps. See Note 14 to the Notes to our consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
Inflation
The increased cost of vehicles is the primary inflationary factor affecting us. Many of our other operating expenses are also expected to increase with inflation, including health care costs and gasoline. Management does not expect that the effect of inflation on our overall operating costs will be greater for us than for our competitors.
Income Taxes
In January 2006, we implemented a LKE Program for our U.S. car rental business. Pursuant to the program, we dispose of vehicles and acquire replacement vehicles in a form intended to allow such dispositions and replacements to qualify as tax-deferred "like-kind exchanges" pursuant to section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code. The program has resulted in deferral of federal and state income taxes for fiscal years 2006, 2007, 2008 and 2009 and part of 2010 and 2012. A LKE Program for HERC has also been in place for several years. The program allows tax deferral if a qualified replacement asset is acquired within a specific time period after asset disposal. Accordingly, if a qualified replacement asset is not purchased within this limited time period, taxable gain is recognized. Over the last few years, for strategic purposes, such as cash management and fleet reduction, we have recognized some taxable gains in the program. In 2009, the bankruptcy filing of an original equipment manufacturer, or "OEM," also resulted in minimal gain recognition. We had sufficient net operating losses to fully offset the taxable gains recognized. We cannot offer assurance that the expected tax deferral will continue or that the relevant law concerning the programs will remain in its current form. An extended reduction in our car rental fleet could result in reduced deferrals in the future, which in turn could require us to make material cash payments for federal and state income tax liabilities. Our inability to obtain replacement financing as our fleet financing facilities mature would likely result in an extended reduction in the fleet. In the event of an extended fleet reduction, we believe the likelihood of making material cash tax payments in the near future is low because of our significant net operating losses. In August 2010, we elected to temporarily suspend the U.S. car rental LKE Program allowing cash proceeds from sales of vehicles to be utilized for various business purposes, including paying down existing debt obligations, future growth initiatives and for general operating purposes. From August 2010 through 2011, recognized tax gains on vehicle dispositions resulting from the LKE suspension were more than offset by 100% tax depreciation on newly acquired vehicles. During 2012 the allowable 50% bonus depreciation helped offset tax gains during the period of LKE suspension. The U.S. car rental LKE Program was reinstated on October 15, 2012.
On January 1, 2009, Bank of America acquired Merrill Lynch. Accordingly, Bank of America is now an indirect beneficial owner of our common stock held by Merrill Lynch and certain of its affiliates. For U.S. income tax purposes the transaction, when combined with other unrelated transactions during the previous 36 months, resulted in a change in control as that term is defined in Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. Consequently, utilization of all pre-2009 U.S. net operating losses is subject to an annual limitation. The limitation is not expected to result in a loss of net operating losses or have a material adverse impact on taxes.
Employee Retirement Benefits
Pension
We sponsor defined benefit pension plans worldwide. Pension obligations give rise to significant expenses that are dependent on assumptions discussed in Note 6 of the Notes to our audited annual consolidated financial statements included in this annual report under the caption "Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data." Our 2012 worldwide pre-tax pension expense is $34.7 million, which represents an increase of $13.4 million from 2011. The increase in expense compared to 2011 is primarily due to lower expected rates of return in 2012, lower discount rates at the end of 2011 compared to 2010 and a curtailment gain in the U.K. recorded in 2011.
The funded status (i.e., the dollar amount by which the projected benefit obligations exceeded the market value of pension plan assets) of our U.S. qualified plan, in which most domestic employees participate, improved as of December 31, 2012, compared with December 31, 2011 because asset values increased due to gains in the securities markets. We contributed $38.4 million to our U.S. pension plan during 2012. We expect to contribute between $20 million and $30 million to our U.S. plan during 2013. The level of 2013 and future contributions will vary, and is dependent on a number of factors including investment returns, interest rate fluctuations, plan demographics, funding regulations and the results of the final actuarial valuation.
We participate in various multiemployer pension plans. In the event that we withdraw from participation in one of these plans, then applicable law could require us to make an additional contribution to the plan, and we would have to reflect that as an expense in our consolidated statements of operations and as a liability on our consolidated balance sheet. The amount that we would be required to pay to the plan is referred to as a withdrawal liability. Our withdrawal liability
ITEM 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations (Continued)
for any multiemployer plan would depend on the extent of the plan's funding of vested benefits. One multiemployer plan in which we participated had significant underfunded liabilities and we withdrew from that plan in December 2012. Several of our remaining multiemployer plans have underfunded liabilities. Such underfunding may increase in the event other employers become insolvent or withdraw from the applicable plan or upon the inability or failure of withdrawing employers to pay their withdrawal liability. In addition, such underfunding may increase as a result of lower than expected returns on pension fund assets or other funding deficiencies. For a discussion of the risks associated with our pension plans, see “Item 1A—Risk Factors” in this Annual Report.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
See "Item 7—Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Market Risks" included elsewhere in this Annual Report.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholder
of The Hertz Corporation:
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2012 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedules listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2) present fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2012, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company's management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedules, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedules, and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As described in Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A, management has excluded Dollar Thrifty from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2012 because it was acquired by the Company in a purchase business acquisition during November 2012. We have also excluded Dollar Thrifty from our audit of internal control over financial reporting. Dollar Thrifty is a wholly‑owned subsidiary whose total assets and total revenues represent approximately 21% and 2%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2012.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Florham Park, New Jersey
March 4, 2013
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 533,235 |
| | $ | 931,208 |
|
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents | 571,634 |
| | 308,039 |
|
| Receivables, less allowance for doubtful accounts of $25,113 and $20,282 | 1,886,596 |
| | 1,616,382 |
|
| Due from Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | 12,809 |
| | — |
|
| Inventories, at lower of cost or market | 105,728 |
| | 83,978 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 461,502 |
| | 416,134 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment, at cost: | | | |
| Cars | 12,591,132 |
| | 9,678,765 |
|
| Less accumulated depreciation | (1,881,030 | ) | | (1,360,012 | ) |
| Other equipment | 3,240,095 |
| | 2,830,176 |
|
| Less accumulated depreciation | (1,041,861 | ) | | (1,043,520 | ) |
| Total revenue earning equipment | 12,908,336 |
| | 10,105,409 |
|
| Property and equipment, at cost: | | | |
| Land, buildings and leasehold improvements | 1,288,833 |
| | 1,146,112 |
|
| Service equipment and other | 1,261,049 |
| | 1,050,915 |
|
| | 2,549,882 |
| | 2,197,027 |
|
| Less accumulated depreciation | (1,113,496 | ) | | (945,173 | ) |
| Total property and equipment | 1,436,386 |
| | 1,251,854 |
|
| Other intangible assets, net | 4,032,111 |
| | 2,562,234 |
|
| Goodwill | 1,341,872 |
| | 392,094 |
|
| Total assets | $ | 23,290,209 |
| | $ | 17,667,332 |
|
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 999,061 |
| | $ | 897,489 |
|
| Due to Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | — |
| | 412 |
|
| Accrued salaries and other compensation | 440,936 |
| | 426,696 |
|
| Other accrued liabilities | 737,524 |
| | 699,642 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 167,314 |
| | 162,984 |
|
| Debt | 15,014,474 |
| | 10,907,849 |
|
| Public liability and property damage | 332,232 |
| | 281,534 |
|
| Deferred taxes on income | 2,681,140 |
| | 1,661,872 |
|
| Total liabilities | 20,372,681 |
| | 15,038,478 |
|
| Commitments and contingencies |
| |
|
| Equity: | | | |
| The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries stockholder's equity | | | |
| Common Stock, $0.01 par value, 3,000 shares authorized, 100 shares issued and outstanding | — |
| | — |
|
| Additional paid-in capital | 3,509,998 |
| | 3,473,625 |
|
| Accumulated deficit | (565,597 | ) | | (816,376 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (26,892 | ) | | (28,414 | ) |
| Total The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries stockholder's equity | 2,917,509 |
| | 2,628,835 |
|
| Noncontrolling interest | 19 |
| | 19 |
|
| Total equity | 2,917,528 |
| | 2,628,854 |
|
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 23,290,209 |
| | $ | 17,667,332 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 7,456,111 |
| | $ | 6,929,584 |
| | $ | 6,355,205 |
|
| Equipment rental | 1,383,196 |
| | 1,208,811 |
| | 1,069,820 |
|
| Other | 181,500 |
| | 159,985 |
| | 137,509 |
|
| Total revenues | 9,020,807 |
| | 8,298,380 |
| | 7,562,534 |
|
| Expenses: | | | | | |
| Direct operating | 4,795,788 |
| | 4,566,378 |
| | 4,283,394 |
|
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 2,148,158 |
| | 1,905,739 |
| | 1,868,147 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 945,581 |
| | 745,117 |
| | 664,442 |
|
| Interest expense | 597,788 |
| | 650,254 |
| | 726,539 |
|
| Interest income | (4,902 | ) | | (5,551 | ) | | (12,315 | ) |
| Other (income) expense, net | 35,542 |
| | 62,548 |
| | 5 |
|
| Total expenses | 8,517,955 |
| | 7,924,485 |
| | 7,530,212 |
|
| Income before income taxes | 502,852 |
| | 373,895 |
| | 32,322 |
|
| Provision for taxes on income | (227,073 | ) | | (143,846 | ) | | (33,322 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | 275,779 |
| | 230,049 |
| | (1,000 | ) |
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | (19,560 | ) | | (17,383 | ) |
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 275,779 |
| | $ | 210,489 |
| | $ | (18,383 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Net income (loss) | |
| | $ | 275,779 |
| | |
| | $ | 230,049 |
| | |
| | $ | (1,000 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Translation adjustment changes | $ | 11,358 |
| | |
| | $ | (23,545 | ) | | |
| | $ | (17,213 | ) | | |
|
| Unrealized holding gains (losses) on securities, (net of tax of 2012: $0; 2011: $125 and 2010: $0) | (318 | ) | | |
| | 226 |
| | |
| | 31 |
| | |
|
| Change in fair value of derivatives qualifying as cash flow hedges, (net of tax of 2012: $0; 2011: $0 and 2010: $31,885) | — |
| | | | — |
| | | | 49,759 |
| | |
| Other, (net of tax of 2012: $0; 2011: $(1,127) and 2010: $0) | 657 |
| | |
| | (984 | ) | | |
| | (19 | ) | | |
|
| Unrealized gain (loss) on Euro-denominated debt, (net of tax of 2012: $0; 2011: $(8,005) and 2010: $12,656) | — |
| | |
| | (12,573 | ) | | |
| | 12,358 |
| | |
|
| Defined benefit pension plans | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortization or settlement of net gain (loss) | 13,694 |
| | | | (4,021 | ) | | | | 4,073 |
| | |
| Net loss arising during the period | (30,932 | ) | | | | (40,895 | ) | | | | (8,629 | ) | | |
| Income tax related to defined pension plans | 7,063 |
| | |
| | 15,555 |
| | |
| | 794 |
| | |
|
| Defined benefit pension plans | (10,175 | ) | | |
| | (29,361 | ) | | |
| | (3,762 | ) | | |
|
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | |
| | 1,522 |
| | |
| | (66,237 | ) | | |
| | 41,154 |
|
| Comprehensive income | |
| | 277,301 |
| | |
| | 163,812 |
| | |
| | 40,154 |
|
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | |
| | — |
| | |
| | (19,560 | ) | | |
| | (17,383 | ) |
| Comprehensive income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | |
| | $ | 277,301 |
| | |
| | $ | 144,252 |
| | |
| | $ | 22,771 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY
(In Thousands of Dollars, except share data)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In Capital | | Accumulated
Deficit | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income (Loss) | | Non-
Controlling
Interest | | Total
Equity |
| Balance at: | Shares | | Amount | | | | | |
| December 31, 2009 | 100 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 3,410,518 |
| | $ | (962,532 | ) | | $ | (3,331 | ) | | $ | 17,293 |
| | $ | 2,461,948 |
|
| Net loss attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | | | | | | | (18,383 | ) | | | | | | (18,383 | ) |
| Dividends paid to Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | | | | | | | (23,000 | ) | | | | | | (23,000 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | 41,154 |
| | | | 41,154 |
|
| Dividend payment to noncontrolling interest | | | | | | | | | | | (18,200 | ) | | (18,200 | ) |
| Net income relating to noncontrolling interest | | | | | | | | | | | 17,409 |
| | 17,409 |
|
| Stock-based employee compensation charges, net of tax of $0 | | | | | 36,560 |
| | | | | | | | 36,560 |
|
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of stock options | | | | | (258 | ) | | | | | | | | (258 | ) |
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | | | | | 3,774 |
| | | | | | | | 3,774 |
|
| Hertz Holdings common and phantom shares issued to Directors | | | | | 1,425 |
| | | | | | | | 1,425 |
|
| December 31, 2010 | 100 |
| | — |
|
| 3,452,019 |
| | (1,003,915 | ) | | 37,823 |
| | 16,502 |
| | 2,502,429 |
|
| Net income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | | | | | | | 210,489 |
| | | | | | 210,489 |
|
| Dividends paid to Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | | | | | | | (22,950 | ) | | | | | | (22,950 | ) |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | (66,237 | ) | | | | (66,237 | ) |
| Dividend payment to noncontrolling interest | | | | | | | | | | | (23,100 | ) | | (23,100 | ) |
| Net income relating to noncontrolling interest | | | | | | | | | | | 19,560 |
| | 19,560 |
|
| Acquisition of remaining portion of non-controlling interest, net of tax of $9,798 | | | | | (15,287 | ) | | | | | | (12,943 | ) | | (28,230 | ) |
| Stock-based employee compensation charges, net of tax of $0 | | | | | 31,093 |
| | | | | | | | 31,093 |
|
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | | | | | 4,208 |
| | | | | | | | 4,208 |
|
| Hertz Holdings common and phantom shares issued to Directors | | | | | 1,592 |
| | | | | | | | 1,592 |
|
| December 31, 2011 | 100 |
| | — |
| | 3,473,625 |
| | (816,376 | ) | | (28,414 | ) | | 19 |
| | 2,628,854 |
|
| Net income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | |
| | |
| | |
| | 275,779 |
| | |
| | |
| | 275,779 |
|
| Dividends paid to Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | | | | | | | (25,000 | ) | | | | | | (25,000 | ) |
| Other comprehensive loss | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 1,522 |
| | |
| | 1,522 |
|
| Stock-based employee compensation charges, net of tax of tax of $399 | |
| | |
| | 29,855 |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 29,855 |
|
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | | | |
| | 5,030 |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 5,030 |
|
| Hertz Holdings common and phantom shares issued to Directors | |
| | |
| | 1,488 |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 1,488 |
|
| December 31, 2012 | 100 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 3,509,998 |
| | $ | (565,597 | ) | | $ | (26,892 | ) | | $ | 19 |
| | $ | 2,917,528 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 275,779 |
| | $ | 230,049 |
| | $ | (1,000 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment | 2,068,378 |
| | 1,809,609 |
| | 1,789,903 |
|
| Depreciation of property and equipment | 172,582 |
| | 158,009 |
| | 154,031 |
|
| Amortization of other intangible assets | 84,096 |
| | 70,039 |
| | 64,713 |
|
| Amortization and write-off of deferred financing costs | 51,835 |
| | 89,909 |
| | 70,825 |
|
| Amortization and write-off of debt discount | 3,987 |
| | 15,948 |
| | 20,968 |
|
| Stock-based compensation charges | 30,255 |
| | 31,093 |
| | 36,560 |
|
| (Gain) loss on derivatives | 4,326 |
| | (7,990 | ) | | 10,810 |
|
| Loss on disposal of business, net | 46,346 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| (Gain) loss on revaluation of foreign denominated debt | 2,498 |
| | (26,641 | ) | | — |
|
| Amortization and ineffectiveness of cash flow hedges | — |
| | — |
| | 68,815 |
|
| Provision for losses on doubtful accounts | 34,144 |
| | 28,164 |
| | 19,667 |
|
| Asset writedowns | — |
| | 23,174 |
| | 20,448 |
|
| Deferred taxes on income | 136,838 |
| | 73,720 |
| | (19,877 | ) |
| Gain on sale of property and equipment | (8,309 | ) | | (43,520 | ) | | (5,740 | ) |
| Gain on revaluation of investment | (8,470 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisition: | | | | | |
| Receivables | (157,732 | ) | | (79,851 | ) | | (3,145 | ) |
| Inventories, prepaid expenses and other assets | (25,514 | ) | | 543 |
| | (61,871 | ) |
| Accounts payable | 49,896 |
| | (1,139 | ) | | 119,054 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | (22,513 | ) | | (144,088 | ) | | (53,457 | ) |
| Accrued taxes | 14,331 |
| | 24,901 |
| | 10,281 |
|
| Public liability and property damage | (4,341 | ) | | 6,592 |
| | (3,058 | ) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 2,748,412 |
| | 2,258,521 |
| | 2,237,927 |
|
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Net change in restricted cash and cash equivalents | (261,605 | ) | | (101,766 | ) | | 160,516 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment expenditures | (9,613,239 | ) | | (9,454,311 | ) | | (8,440,872 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of revenue earning equipment | 7,125,096 |
| | 7,850,442 |
| | 7,518,446 |
|
| Property and equipment expenditures | (312,786 | ) | | (281,695 | ) | | (179,209 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment | 137,694 |
| | 53,814 |
| | 38,905 |
|
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (1,905,168 | ) | | (227,081 | ) | | (47,571 | ) |
| Purchase of short-term investments, net | — |
| | (32,891 | ) | | 3,491 |
|
| Proceeds from disposal of business | 84,497 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Other investing activities | (1,779 | ) | | 586 |
| | 2,726 |
|
| Net cash used in investing activities | $ | (4,747,290 | ) | | $ | (2,192,902 | ) | | $ | (943,568 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (Continued)
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | $ | 2,237,280 |
| | $ | 3,062,479 |
| | $ | 2,635,713 |
|
| Payment of long-term debt | (952,144 | ) | | (3,649,300 | ) | | (2,954,233 | ) |
| Short-term borrowings: | | | | | |
| Proceeds | 438,387 |
| | 460,890 |
| | 490,490 |
|
| Payments | (1,280,143 | ) | | (1,194,056 | ) | | (970,949 | ) |
| Proceeds (payments) under the revolving lines of credit, net | 1,273,164 |
| | (57,329 | ) | | 1,026,070 |
|
| Distributions to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | (23,100 | ) | | (18,200 | ) |
| Purchase of noncontrolling interest | (38,000 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | 4,275 |
| | 3,577 |
| | 3,208 |
|
| Loan with Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | (13,220 | ) | | (984 | ) | | (6,173 | ) |
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of stock options | — |
| | — |
| | (258 | ) |
| Payment of financing costs | (49,433 | ) | | (91,482 | ) | | (78,151 | ) |
| Dividends paid | (25,000 | ) | | (22,950 | ) | | (23,000 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 1,595,166 |
| | (1,512,255 | ) | | 104,517 |
|
| Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 5,739 |
| | 3,838 |
| | (10,337 | ) |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents during the period | (397,973 | ) | | (1,442,798 | ) | | 1,388,539 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 931,208 |
| | 2,374,006 |
| | 985,467 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 533,235 |
| | $ | 931,208 |
| | $ | 2,374,006 |
|
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Cash paid during the period for: | | | | | |
| Interest (net of amounts capitalized) | $ | 535,130 |
| | $ | 615,730 |
| | $ | 508,183 |
|
| Income taxes | 71,661 |
| | 49,557 |
| | 50,688 |
|
| Supplemental disclosures of non-cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Purchases of revenue earning equipment included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities | $ | 249,605 |
| | $ | 153,634 |
| | $ | 266,354 |
|
| Sales of revenue earning equipment included in receivables | 617,267 |
| | 620,724 |
| | 504,217 |
|
| Purchases of property and equipment included in accounts payable | 34,996 |
| | 53,263 |
| | 37,379 |
|
| Sales of property and equipment included in receivables | 895 |
| | 41,809 |
| | 11,071 |
|
| Purchase of noncontrolling interest included in accounts payable | — |
| | 38,000 |
| | — |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1—Background
The Hertz Corporation together with its subsidiaries are referred to herein as “we,” “our” and “us.” The Hertz Corporation is referred to herein as “Hertz,” 100% of Hertz outstanding capital stock is owned by Hertz Investors, Inc. (previously CCMG Corporation), and 100% of Hertz Investors, Inc.'s capital stock is owned by Hertz Holdings (previously known as CCMG Holdings, Inc.).
We are a successor to corporations that have been engaged in the car and truck rental and leasing business since 1918 and the equipment rental business since 1965. Hertz was incorporated in Delaware in 1967. Ford Motor Company acquired an ownership interest in Hertz in 1987. Prior to this, Hertz was a subsidiary of United Continental Holdings, Inc. (formerly Allegis Corporation), which acquired our outstanding capital stock from RCA Corporation in 1985.
On December 21, 2005, investment funds associated with or designated by:
| |
| • | Clayton, Dubilier & Rice, Inc., which was succeeded by Clayton, Dubilier & Rice, LLC, or “CD&R,” |
| |
| • | The Carlyle Group, or “Carlyle,” and |
| |
| • | Merrill Lynch & Co., Inc., or "Merrill Lynch," |
or collectively the “Sponsors,” acquired all of our common stock from Ford Holdings LLC. We refer to the acquisition of all of our common stock by the Sponsors as the “Acquisition.”
In January 2009, Bank of America Corporation, or “Bank of America,” acquired Merrill Lynch. Accordingly, Bank of America is now an indirect beneficial owner of Hertz Holdings' common stock held by Merrill Lynch and certain other investment funds and affiliates of Merrill Lynch.
On September 1, 2011, Hertz completed the acquisition of Donlen Corporation, or "Donlen," a leading provider of fleet leasing and management services. See Note 4—Business Combinations and Divestitures.
In December 2011, Hertz purchased the noncontrolling interest of Navigation Solutions, L.L.C., thereby increasing its ownership interest from 65% to 100%.
On November 19, 2012, Hertz completed the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., or "Dollar Thrifty," a car and truck rental and leasing business. See Note 4—Business Combinations and Divestitures.
On December 12, 2012, Hertz completed the sale of Simply Wheelz LLC, a wholly owned subsidiary of Hertz that operated our Advantage Rent A Car business. See Note 4—Business Combinations and Divestitures.
In December 2012, the Sponsors sold 50,000,000 shares of their Hertz Holdings common stock to J.P. Morgan as the sole underwriter in the registered public offering of those shares.
As a result of Hertz Holdings' initial public offering in November 2006 and subsequent offerings in June 2007, May 2009, June 2009, March 2011 and December 2012, the Sponsors reduced their holdings to approximately 26% of the outstanding shares of common stock of Hertz Holdings.
Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Hertz Holdings and our wholly owned and majority owned domestic and international subsidiaries. In the event that Hertz Holdings is a primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity, the assets, liabilities, and results of operations of the variable interest entity will be included in our consolidated financial statements. All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates and Assumptions
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America, or “GAAP,” requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and footnotes. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Significant estimates inherent in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements include depreciation of revenue earning equipment, reserves for litigation and other contingencies, accounting for income taxes and related uncertain tax positions, pension and postretirement benefit costs, the fair value of assets and liabilities acquired in business combinations, the recoverability of long-lived assets, useful lives and impairment of long-lived tangible and intangible assets including goodwill, valuation of stock based compensation, public liability and property damage reserves, reserves for restructuring, allowance for doubtful accounts, and fair value of derivatives, among others.
Reclassifications
Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform with current year presentation.
Acquisition Accounting
We account for business combinations using the acquisition method, which requires an allocation of the purchase price of an acquired entity to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values at the date of acquisition. Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the net tangible and intangible assets acquired.
Revenue Recognition
Rental and rental related revenue (including cost reimbursements from customers where we consider ourselves to be the principal versus an agent) are recognized over the period the revenue earning equipment is rented or leased based on the terms of the rental or leasing contract. Maintenance management administrative fees are recognized monthly and maintenance management service revenue is recognized when services are performed. Revenue related to new equipment sales and consumables is recognized at the time of delivery to, or pick-up by, the customer and when collectability is reasonably assured. Fees from our licensees are recognized over the period the underlying licensees' revenue is earned (over the period the licensees' revenue earning equipment is rented). Certain truck and equipment leases are originated with the intention of syndicating to banks, and upon the sale of rights to these direct financing leases, the net gain is recorded in revenue.
Sales tax amounts collected from customers have been recorded on a net basis.
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Other
We consider all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
In our consolidated statements of cash flows, we net cash flows from revolving borrowings in the line item “Proceeds (payments) under the revolving lines of credit, net.” The contractual maturities of such borrowings may exceed 90 days in certain cases.
Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents
Restricted cash and cash equivalents includes cash and cash equivalents that are not readily available for our normal disbursements. Restricted cash and cash equivalents are restricted for the purchase of revenue earning vehicles and other specified uses under our Fleet Debt facilities, for our Like-Kind Exchange Program, or “LKE Program,” and to satisfy certain of our self-insurance regulatory reserve requirements. These funds are primarily held in highly rated money market funds with investments primarily in government and corporate obligations. Restricted cash and cash equivalents are excluded from cash and cash equivalents.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Concentration of Credit Risk
Our cash and cash equivalents are invested in various investment grade institutional money market accounts and bank term deposits. Deposits held at banks may exceed the amount of insurance provided on such deposits. Generally, these deposits may be redeemed upon demand and are maintained with financial institutions with reputable credit and therefore bear minimal credit risk. We seek to mitigate such risks by spreading the risk across multiple counterparties and monitoring the risk profiles of these counterparties. In addition, we have credit risk from derivative financial instruments used in hedging activities. We limit our exposure relating to derivative financial instruments by diversifying the financial instruments among various counterparties, which consist of major financial institutions.
Receivables
Receivables are stated net of allowances for doubtful accounts and represent credit extended to manufacturers and customers that satisfy defined credit criteria. The estimate of the allowance for doubtful accounts is based on our historical experience and our judgment as to the likelihood of ultimate payment. Actual receivables are written-off against the allowance for doubtful accounts when we determine the balance will not be collected. Bad debt expense is reflected as a component of "Selling, general and administrative" in our consolidated statements of operations.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost and are depreciated utilizing the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the related assets. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the estimated useful lives of the related assets or leases, whichever is shorter. Useful lives are as follows:
|
| |
| Buildings | 3 to 50 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | 1 to 15 years |
| Capitalized internal use software | 1 to 15 years |
| Service cars and service equipment | 1 to 13 years |
| Other intangible assets | 3 to 20 years |
| Leasehold improvements | The shorter of their economic lives or the lease term |
We follow the practice of charging maintenance and repairs, including the cost of minor replacements, to maintenance expense accounts. Costs of major replacements of units of property are capitalized to property and equipment accounts and depreciated on the basis indicated above. Gains and losses on dispositions of property and equipment are included in income as realized. During the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, gains from the dispositions of property and equipment of $6.3 million and $43.1 million, respectively, were included in "Direct operating" in our consolidated statements of operations.
Revenue Earning Equipment
Revenue earning equipment is stated at cost, net of related discounts. Useful lives are as follows:
|
| |
| Cars | 4 to 28 months |
| Other equipment | 24 to 108 months |
Generally, when revenue earning equipment is acquired, we estimate the period that we will hold the asset, primarily based on historical measures of the amount of rental activity (e.g., automobile mileage and equipment usage) and the targeted age of equipment at the time of disposal. We also estimate the residual value of the applicable revenue earning equipment at the expected time of disposal. The residual values for rental vehicles are affected by many factors, including make, model and options, age, physical condition, mileage, sale location, time of the year and channel of disposition (e.g., auction, retail, dealer direct). The residual value for rental equipment is affected by factors which include equipment age and amount of usage. Depreciation is recorded on a straight-line basis over the estimated holding period. Depreciation rates are reviewed on a quarterly basis based on management's ongoing assessment of present and estimated future market conditions, their effect on residual values at the time of disposal and the estimated holding periods. Market conditions for used vehicle and equipment sales can also be affected by external factors such as the economy, natural disasters, fuel prices and incentives offered by manufacturers of new cars. These key factors are considered when estimating future residual values and assessing depreciation rates. As a result of this ongoing
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
assessment, we make periodic adjustments to depreciation rates of revenue earning equipment in response to changed market conditions. Upon disposal of revenue earning equipment, depreciation expense is adjusted for the difference between the net proceeds received and the remaining net book value.
Within Donlen, revenue earning equipment is under longer term lease agreements with our customers. These leases contain provisions whereby we have a contracted residual value guaranteed to us by the lessee, such that we do not experience any gains or losses on the disposal of these vehicles. Therefore depreciation rates on these vehicles are not adjusted at any point in time per the associated lease contract.
Environmental Liabilities
The use of automobiles and other vehicles is subject to various governmental controls designed to limit environmental damage, including that caused by emissions and noise. Generally, these controls are met by the manufacturer, except in the case of occasional equipment failure requiring repair by us. To comply with environmental regulations, measures are taken at certain locations to reduce the loss of vapor during the fueling process and to maintain, upgrade and replace underground fuel storage tanks. We also incur and provide for expenses for the cleanup of petroleum discharges and other alleged violations of environmental laws arising from the disposition of waste products. We do not believe that we will be required to make any material capital expenditures for environmental control facilities or to make any other material expenditures to meet the requirements of governmental authorities in this area. Liabilities for these expenditures are recorded at undiscounted amounts when it is probable that obligations have been incurred and the amounts can be reasonably estimated.
Public Liability and Property Damage
The obligation for public liability and property damage on self-insured U.S. and international vehicles and equipment represents an estimate for both reported accident claims not yet paid, and claims incurred but not yet reported. The related liabilities are recorded on a non-discounted basis. Reserve requirements are based on actuarial evaluations of historical accident claim experience and trends, as well as future projections of ultimate losses, expenses, premiums and administrative costs. The adequacy of the liability is regularly monitored based on evolving accident claim history and insurance-related state legislation changes. If our estimates change or if actual results differ from these assumptions, the amount of the recorded liability is adjusted to reflect these results.
Pension Benefit Obligations
Our employee pension costs and obligations are developed from actuarial valuations. Inherent in these valuations are key assumptions, including discount rates, salary growth, long-term return on plan assets, retirement rates, mortality rates and other factors. Actual results that differ from our assumptions are accumulated and amortized over future periods and, therefore, generally affect our recognized expense in such future periods. While we believe that the assumptions used are appropriate, significant differences in actual experience or significant changes in assumptions would affect our pension costs and obligations.
Foreign Currency Translation and Transactions
Assets and liabilities of international subsidiaries are translated at the rate of exchange in effect on the balance sheet date; income and expenses are translated at the average rate of exchange prevailing during the year. The related translation adjustments are reflected in “Accumulated other comprehensive loss” in the equity section of our consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2012 and 2011, the accumulated foreign currency translation gain was $102.7 million and $91.3 million, respectively. Foreign currency gains and losses resulting from transactions are included in earnings.
Derivative Instruments
We are exposed to a variety of market risks, including the effects of changes in interest rates, gasoline and diesel fuel prices and foreign currency exchange rates. We manage our exposure to these market risks through our regular operating and financing activities and, when deemed appropriate, through the use of derivative financial instruments. Derivative financial instruments are viewed as risk management tools and have not been used for speculative or trading purposes. In addition, derivative financial instruments are entered into with a diversified group of major financial institutions in order to manage our exposure to counterparty nonperformance on such instruments. We account for all
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
derivatives in accordance with GAAP, which requires that all derivatives be recorded on the balance sheet as either assets or liabilities measured at their fair value. The effective portion of changes in fair value of derivatives designated as cash flow hedging instruments is recorded as a component of other comprehensive income. The ineffective portion is recognized currently in earnings within the same line item as the hedged item, based upon the nature of the hedged item. For derivative instruments that are not part of a qualified hedging relationship, the changes in their fair value are recognized currently in earnings. See Note 14—Financial Instruments.
Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect of a change in tax rates is recognized in the statement of operations in the period that includes the enactment date. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will not be realized. Subsequent changes to enacted tax rates and changes to the global mix of earnings will result in changes to the tax rates used to calculate deferred taxes and any related valuation allowances. Provisions are not made for income taxes on undistributed earnings of international subsidiaries that are intended to be indefinitely reinvested outside of the United States or are expected to be remitted free of taxes. Future distributions, if any, from these international subsidiaries to the United States or changes in U.S. tax rules may require a change to reflect tax on these amounts. See Note 9—Taxes on Income.
Advertising
Advertising and sales promotion costs are expensed the first time the advertising or sales promotion takes place. Advertising costs are reflected as a component of “Selling, general and administrative” in our consolidated statements of operations and for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 were $158.0 million, $145.8 million and $133.8 million, respectively.
Goodwill
Goodwill is not amortized but is subject to periodic testing for impairment in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board, or "FASB," Accounting Standards Codification, or "ASC," Topic 350, “Intangibles—Goodwill and Other,” or “ASC 350,” at the reporting unit level which is one level below our operating segments. The assessment of goodwill impairment is conducted by estimating and comparing the fair value of our reporting units, as defined in ASC 350, to their carrying value as of that date. The fair value is estimated using an income approach whereby the fair value of the reporting unit is based on the future cash flows that each reporting unit's assets can be expected to generate. Future cash flows are based on forward-looking information regarding market share and costs for each reporting unit and are discounted using an appropriate discount rate. Future discounted cash flows can be affected by changes in industry or market conditions or the rate and extent to which anticipated synergies or cost savings are realized with newly acquired entities. The test for impairment is conducted annually each October 1st, and more frequently if events occur or circumstances change that indicate that the fair value of a reporting unit may be below its carrying amount.
Intangible and Long-lived Assets
Intangible assets include concession agreements, technology, customer relationships, trademarks and trade-names and other intangibles. Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized using the straight-line method over the estimated economic lives of the assets, which range from two to fifteen years. Long-lived assets, including intangible assets with finite lives, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 360, “Property, Plant, and Equipment,” or “ASC 360.” Determination of recoverability is based on an estimate of undiscounted future cash flows resulting from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. Measurement of an impairment loss for long-lived assets that management expects to hold and use is based on the estimated fair value of the asset. Long-lived assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of carrying amount or estimated fair value less costs to sell. Intangible assets determined to have indefinite useful lives are not amortized but are tested for impairment annually each October 1st and more frequently if events occur or circumstances change that indicate an asset may be impaired.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Stock‑Based Compensation
We measure the cost of employee services received in exchange for an award of equity instruments based on the grant date fair value of the award. That cost is to be recognized over the period during which the employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award. We have estimated the fair value of options issued at the date of grant using a Black‑Scholes option‑pricing model, which includes assumptions related to volatility, expected life, dividend yield and risk-free interest rate. See Note 7-Stock‑Based Compensation.
We are using equity accounting for restricted stock unit and performance stock unit awards. For restricted stock units the expense is based on the grant-date fair value of the stock and the number of shares that vest, recognized over the service period. For performance stock units the expense is based on the grant-date fair value of the stock, recognized over a two to four year service period depending upon a performance condition. For performance stock units, we re-assess the probability of achieving the applicable performance condition each reporting period and adjust the recognition of expense accordingly. The performance condition is not considered in determining the grant date fair value.
Franchise Revenues and Transactions
“Franchise revenues” includes franchise fees for use of our brands and services. Generally franchise fees from franchised locations are based on a percentage of net sales of the franchised business and are recognized as earned and when collectability is reasonably assured.
Initial franchise fees are recorded as deferred income when received and are recognized as revenue when all material services and conditions related to the franchise fee have been substantially performed.
Renewal franchise fees are recognized as revenue when the license agreements are effective and collectability is reasonably assured.
Other (income) expense, net includes the gains or losses from the sales of our operations or assets to new and existing franchisees. Such gains or losses are included in operating income because they are expected to be a recurring part of our business.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2011, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update, or "ASU," No. 2011-11, "Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities," or "ASU 2011-11" to amend the requirement for an entity to disclose information about offsetting and related arrangements to enable users of its financial statements to understand the effect of those arrangements on its financial position. An entity should provide the disclosures required by those amendments retrospectively for all comparative periods presented. ASU 2011-11 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. We plan to adopt ASU 2011-11 on January 1, 2013, as required, but do not believe this guidance will have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements or financial statement disclosures.
In July 2012, the FASB issued ASU No. 2012-02, "Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets for Impairment," or "ASU 2012-02" which states that an entity has the option first to assess qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events and circumstances indicates that it is more likely than not that an indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. If, after assessing the totality of events and circumstances, an entity concludes that it is not more likely than not that the indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired, then the entity is not required to take further action. However, if an entity concludes otherwise, then it is required to determine the fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset and perform the quantitative impairment test by comparing the fair value with the carrying amount. This provision is effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 15, 2012. This accounting guidance is not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements or financial statement disclosures.
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-02, "Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income," or "ASU 2013-02" which requires disclosure of significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component and their corresponding effect on the respective line items of net income. This guidance is effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2012 and is not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements or financial statement disclosures.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 3—Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
We account for our goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets under ASC 350. Under ASC 350, goodwill impairment is deemed to exist if the carrying value of goodwill exceeds its fair value. In addition, ASC 350 requires that goodwill be tested at least annually using a two-step process. The first step is to identify any potential impairment by comparing the carrying value of the reporting unit to its fair value. We estimate the fair value of our reporting units using a discounted cash flow methodology. The cash flows represent management’s most recent planning assumptions. These assumptions are based on a combination of industry outlooks, views on general economic conditions, our expected pricing plans and expected future savings generated by our ongoing restructuring activities. If a potential impairment is identified, the second step is to compare the implied fair value of goodwill with its carrying amount to measure the impairment loss. Those intangible assets considered to have indefinite useful lives, including our trade name, are evaluated for impairment on an annual basis, by comparing the fair value of the intangible assets to their carrying value. In addition, whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of intangible assets might not be recoverable, we will perform an impairment review. We estimate the fair value of our indefinite lived intangible assets using the relief from royalty method. Intangible assets with finite useful lives are amortized over their respective estimated useful lives and reviewed for impairment in accordance with ASC 360-10, "Impairment and Disposal of Long-Lived Assets."
At October 1, 2012, 2011 and 2010, we performed our annual goodwill impairment test and determined that the respective book values of our reporting units did not exceed their estimated fair values and therefore no impairment existed for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010.
The following summarizes the changes in our goodwill, by segment (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Car Rental | | Equipment Rental | | Total |
| Balance as of January 1, 2012 | | | | | |
| Goodwill | $ | 419.3 |
| | $ | 693.8 |
| | $ | 1,113.1 |
|
| Accumulated impairment losses | (46.1 | ) | | (674.9 | ) | | (721.0 | ) |
| | 373.2 |
| | 18.9 |
| | 392.1 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Goodwill acquired during the year | 884.9 |
| | 82.0 |
| | 966.9 |
|
Adjustments to previously recorded purchase price allocation(a) | (15.3 | ) | | — |
| | (15.3 | ) |
Other changes during the year(b) | (1.4 | ) | | (0.4 | ) | | (1.8 | ) |
| | 868.2 |
| | 81.6 |
| | 949.8 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | | | | | |
| Goodwill | 1,287.5 |
| | 775.4 |
| | 2,062.9 |
|
| Accumulated impairment losses | (46.1 | ) | | (674.9 | ) | | (721.0 | ) |
| | $ | 1,241.4 |
| | $ | 100.5 |
| | $ | 1,341.9 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Car Rental | | Equipment Rental | | Total |
| Balance as of January 1, 2011 | | | | | |
| Goodwill | $ | 367.9 |
| | $ | 681.7 |
| | $ | 1,049.6 |
|
| Accumulated impairment losses | (46.1 | ) | | (674.9 | ) | | (721.0 | ) |
| | 321.8 |
| | 6.8 |
| | 328.6 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Goodwill acquired during the year | 53.1 |
| | 12.3 |
| | 65.4 |
|
| Adjustments to previously recorded purchase price allocation | (0.9 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | (1.0 | ) |
Other changes during the year(b) | (0.8 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | (0.9 | ) |
| | 51.4 |
| | 12.1 |
| | 63.5 |
|
| | | | | | |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | | | | | |
| Goodwill | 419.3 |
| | 693.8 |
| | 1,113.1 |
|
| Accumulated impairment losses | (46.1 | ) | | (674.9 | ) | | (721.0 | ) |
| | $ | 373.2 |
| | $ | 18.9 |
| | $ | 392.1 |
|
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (a) | Consists of deferred tax adjustments recorded during 2012. |
| |
| (b) | Primarily consists of changes resulting from disposals and the translation of foreign currencies at different exchange rates from the beginning of the period to the end of the period. |
Other intangible assets, net, consisted of the following major classes (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2012 |
| | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value |
| Amortizable intangible assets: | | | | | |
| Customer-related | $ | 694.7 |
| | $ | (434.0 | ) | | $ | 260.7 |
|
Other(1) | 459.6 |
| | (33.8 | ) | | 425.8 |
|
| Total | 1,154.3 |
| | (467.8 | ) | | 686.5 |
|
| Indefinite-lived intangible assets: | | | | | |
| Trade name | 3,330.0 |
| | — |
| | 3,330.0 |
|
Other(3) | 15.6 |
| | — |
| | 15.6 |
|
| Total | 3,345.6 |
| | — |
| | 3,345.6 |
|
| Total other intangible assets, net | $ | 4,499.9 |
| | $ | (467.8 | ) | | $ | 4,032.1 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2011 |
| | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Net Carrying Value |
| Amortizable intangible assets: | | | | | |
| Customer-related | $ | 672.6 |
| | $ | (365.5 | ) | | $ | 307.1 |
|
Other(2) | 74.7 |
| | (27.8 | ) | | 46.9 |
|
| Total | 747.3 |
| | (393.3 | ) | | 354.0 |
|
| Indefinite-lived intangible assets: | | | | | |
| Trade name | 2,190.0 |
| | — |
| | 2,190.0 |
|
Other(3) | 18.2 |
| | — |
| | 18.2 |
|
| Total | 2,208.2 |
| | — |
| | 2,208.2 |
|
| Total other intangible assets, net | $ | 2,955.5 |
| | $ | (393.3 | ) | | $ | 2,562.2 |
|
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (1) | Other amortizable intangible assets primarily include Dollar Thrifty concession agreements, Donlen trade name, reacquired franchise rights, non-compete agreements and technology-related intangibles. |
| |
| (2) | Other amortizable intangible assets primarily consisted of our Advantage trade name and concession rights, Donlen trade name, reacquired franchise rights, non-compete agreements and technology-related intangibles. |
| |
| (3) | Other indefinite-lived intangible assets primarily consist of reacquired franchise rights. |
Long-lived assets, including intangible assets with finite lives, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable. Intangible assets determined to have indefinite useful lives are not amortized but are tested for impairment annually, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate the asset may be impaired.
Generally, our trademarks and trade names are expected to generate cash flows indefinitely. Consequently, these assets were classified as indefinite-lived intangibles and accordingly are not amortized but reviewed for impairment annually, or sooner under certain circumstances. Prior to the goodwill testing discussed above, we tested our intangible assets with indefinite lives. The test for impairment requires us to compare the fair value of our indefinite-lived intangible assets to the carrying value of those assets. In situations where the carrying value exceeds the fair value of the intangible asset, an impairment loss equal to the difference is recognized. We estimate the fair value of our indefinite-lived intangible assets using an income approach; specifically, based on discounted cash flows.
December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
At October 1, 2012, 2011 and 2010, we performed our annual test of recoverability of indefinite-lived intangible assets. We determined that the respective book values of our indefinite-lived intangible assets did not exceed their estimated fair values and therefore no impairment existed.
Amortization of other intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 was approximately $84.1 million, $70.0 million and $64.7 million, respectively. Based on our amortizable intangible assets as of December 31, 2012, we expect amortization expense to be approximately $120.5 million in 2013, $116.1 million in 2014, $113.7 million in 2015, $64.8 million in 2016 and $51.8 million in 2017.
Note 4—Business Combinations and Divestitures
Dollar Thrifty Acquisition
On November 19, 2012, Hertz Holdings completed the Dollar Thrifty acquisition pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement with Dollar Thrifty and Merger Sub, a wholly owned Hertz subsidiary. In accordance with the terms of the Merger Agreement, Merger Sub completed a tender offer in which it purchased a majority of the shares of Dollar Thrifty common stock then outstanding at a price equal to $87.50 per share in cash. Merger Sub subsequently acquired the remaining shares of Dollar Thrifty common stock by means of a short-form merger in which such shares were converted into the right to receive the same $87.50 per share in cash paid in the tender offer. The total purchase price was approximately $2,592.0 million, which comprised of $2,551.0 million of cash, including our use of approximately $404.0
million of cash and cash equivalents available from Dollar Thrifty, and the fair value of our previously held equity interest in Dollar Thrifty of $41.0 million. As a result of re-measuring to fair value our equity interest previously held in Dollar Thrifty immediately before the acquisition date, we recognized a gain of approximately $8.4 million in our consolidated statements of operations within "Other (income) expense, net." As a condition of the Merger Agreement, and pursuant to a divestiture agreement reached with the Federal Trade Commission, Hertz divested its Simply Wheelz subsidiary, which owned and operated the Advantage brand, and secured for the buyer of Advantage certain Dollar Thrifty on-airport car rental concessions. Dollar Thrifty is now a wholly-owned subsidiary of Hertz.
The purchase price of Dollar Thrifty was funded with (i) cash proceeds of $1,950.0 million received by Hertz from its issuance of $1,950.0 million in aggregate principal amount of Senior Notes and Term Loans, (ii) approximately $404.0 million of acquired cash and cash equivalents from Dollar Thrifty, and (iii) the balance funded by Hertz's existing cash.
The Dollar Thrifty acquisition has been accounted for utilizing the acquisition method, which requires an allocation of the purchase price of the acquired entity to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values from a market-participant perspective at the date of acquisition. The allocation of the purchase price as reflected within these consolidated financial statements is based on the best information available to management at the time these consolidated financial statements were issued and is preliminary pending the completion of the final valuation analysis of the Dollar Thrifty assets and liabilities. In particular, the valuation of income taxes, certain property and equipment and lease and other contracts acquired as of the acquisition date, have not been finalized. During the measurement period (which is not to exceed one year from the acquisition date), we will be required to retrospectively adjust the preliminary amounts recognized to reflect new information obtained about facts and circumstances that existed as of the acquisition date that, if known, would have affected the measurement of the amounts recognized as of that date. Further, during the measurement period, we are also required to recognize additional assets or liabilities if new information is obtained about facts and circumstances that existed as of the acquisition date that, if known, would have resulted in the recognition of those assets or liabilities as of that date.
The fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed were preliminarily determined using the income, cost and market approaches. The fair values of acquired trade names and concession agreements were estimated using the income approach which values the subject asset using the projected cash flows to be generated by the asset, discounted at a required rate of return that reflects the relative risk of achieving the cash flow and the time value of money. The cost approach was utilized in combination with the market approach to estimate the fair values of property, plant and equipment and reflects the estimated reproduction or replacement costs for the assets, less an allowance for loss in value due to depreciation. The cost approach was utilized in combination with the market approach to estimate the fair values of most working capital accounts.
The following summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the Dollar Thrifty acquisition date (in millions):
|
| | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 535.0 |
|
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents | 307.0 |
|
| Receivables | 170.0 |
|
| Inventories | 8.0 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 41.0 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment | 1,614.0 |
|
| Property and equipment | 119.0 |
|
| Other intangible assets | 1,546.0 |
|
| Other assets | 35.0 |
|
| Goodwill | 885.0 |
|
| Accounts payable | (43.0 | ) |
| Accrued liabilities | (277.0 | ) |
| Deferred taxes on income | (864.0 | ) |
| Debt | (1,484.0 | ) |
| Total | $ | 2,592.0 |
|
The identifiable intangible assets of $1,546.0 million consist of $1,140.0 million of trade names with an indefinite life and $406.0 million of concession agreements. The concession agreements will be amortized over their expected useful lives of nine years on a straight-line basis.
The excess of the purchase price over the net tangible and intangible assets acquired resulted in goodwill of $885.0 million which is attributable to the synergies and economies of scale provided to a market participant. The goodwill recorded in connection with this transaction is not deductible for income tax purposes. All such goodwill is reported in the car rental segment.
Donlen Acquisition
On September 1, 2011, Hertz acquired 100% of the equity of Donlen, a leading provider of fleet leasing and management services. Donlen provides Hertz an immediate leadership position in long-term car, truck and equipment leasing and fleet management, which enables us to present our customers a complete portfolio of transportation solutions and the enhanced ability to cross sell to each others' customer base. This transaction is part of the overall growth strategy of Hertz to provide the most flexible transportation programs for corporate and general consumers. Additionally, Donlen brings to Hertz a specialized consulting and technology expertise that will enable us to model, measure and manage fleet performance more effectively and efficiently. The combination of the strategic fit and expected fleet synergies described above are the primary drivers behind the excess purchase price paid over the fair value of the assets and liabilities acquired. All such goodwill recognized as part of this acquisition is reported in the car rental segment.
The Donlen equity valuation for the transaction was estimated at $250.0 million, subject to adjustment based on the net assets of Donlen at closing. The preliminary purchase price adjustment at closing resulted in a downward adjustment of $2.4 million. The final purchase price adjustment, based on the final Donlen closing date balance sheet, resulted in an upward adjustment of $2.4 million (resulting in a final closing cash payment of $250.0 million). None of the goodwill recognized as part of this acquisition is expected to be deductible for tax purposes.
The following summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the acquisition date (in millions):
|
| | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 35.6 |
|
| Receivables | 64.0 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 7.0 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment | 1,120.6 |
|
| Property and equipment | 13.5 |
|
| Other intangible assets | 75.0 |
|
| Goodwill | 51.1 |
|
| Accounts payable | (39.3 | ) |
| Accrued liabilities | (226.8 | ) |
| Deferred taxes on income | (121.9 | ) |
| Debt | (728.8 | ) |
| Total | $ | 250.0 |
|
Other intangible assets and their amortization periods are as follows: |
| | | | | |
| | Useful life (in years) | | Fair value (in millions) |
| Customer relationships | 16 | | $ | 65.0 |
|
| Trademark | 20 | | 7.0 |
|
| Non-compete agreement | 5 | | 3.0 |
|
| Total | | | $ | 75.0 |
|
This transaction has been accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with GAAP and operating results of Donlen from the date of acquisition are included in our consolidated statements of operations. The
allocation of the purchase price to the tangible and intangible net assets acquired is complete.
Actual and Pro forma Impact of Acquisitions
The pro forma information for December 31, 2012 and 2011 assumes that the Dollar Thrifty acquisition occurred on January 1, 2011.
The pro forma information for December 31, 2011 and 2010 assumes that the acquisition of Donlen occurred on January 1, 2010.
The unaudited pro forma financial information for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 was as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Revenue | | Earnings |
Actual from 09/01/11 - 12/31/11 (Donlen only)(1) | $ | 142.7 |
| | $ | 2.0 |
|
Actual from 11/19/12 - 12/31/12 (Dollar Thrifty only)(2) | 170.6 |
| | (25.9 | ) |
2012 supplemental pro forma from 1/1/12 - 12/31/12 (combined entity)(3) | 10,193.3 |
| | 441.8 |
|
2011 supplemental pro forma from 1/1/11 - 12/31/11 (combined entity)(4) | 9,920.3 |
| | 235.1 |
|
2010 supplemental pro forma from 1/1/10 - 12/31/10 (combined entity)(5) | 7,904.3 |
| | (48.6 | ) |
_______________________________________________
| |
| (1) | Donlen's actual earnings for the four months ended December 31, 2011 was impacted by certain charges related to the amortization expense associated with the acquired intangible assets and the fair value adjustment related to acquired software, as well as, the write-off of certain unamortized debt costs. |
| |
| (2) | Dollar Thrifty's actual earnings for the 43 days ended December 31, 2012 was impacted by certain charges related to the amortization expense associated with the acquired intangible assets and non-recurring compensation costs in connection with the merger. |
| |
| (3) | The unaudited pro forma financial information for the year ended December 31, 2012 combines the historical results of Hertz and Dollar Thrifty for the year ended December 31, 2012, and the effects of the pro forma adjustments listed below. |
| |
| (4) | The unaudited pro forma financial information for the year ended December 31, 2011 combines the historical results of Hertz, Donlen and Dollar Thrifty for the year ended December 31, 2011, and the effects of the pro forma adjustments listed below. |
| |
| (5) | The unaudited pro forma financial information for the year ended December 31, 2010 combines the historical results of Hertz and Donlen for the year ended December 31, 2010, and the effects of the pro forma adjustments listed below. |
The unaudited pro forma consolidated results do not purport to project the future results of operations of the combined entity nor do they reflect the expected realization of any cost savings associated with the acquisitions. The unaudited pro forma consolidated results reflect the historical financial information of Hertz Holdings, Donlen and Dollar Thrifty, adjusted for the following pre-tax amounts:
Pro forma adjustments - Dollar Thrifty acquisition
| |
| • | Additional amortization expense (approximately $38.9 million in 2012 and $44.4 million in 2011) related to the fair value of identifiable intangible assets acquired. |
| |
| • | Additional interest expense (approximately $72.7 million in 2012 and $79.1 million in 2011) associated with the new debt used to finance the Dollar Thrifty acquisition. |
| |
| • | Reclassifying merger related costs from 2012 to 2011 as though the Dollar Thrifty acquisition had been consummated as of January 1, 2011. |
| |
| • | Reclassifying non-recurring compensation costs incurred in connection with the merger and integration costs of approximately $46.7 million from 2012 to 2011 as though the Dollar Thrifty acquisition had been consummated as of January 1, 2011. |
| |
| • | Reclassifying the loss from the Advantage disposition from 2012 to 2011 as though the Dollar Thrifty acquisition had been consummated as of January 1, 2011. |
| |
| • | Reclassifying charges related to the impact of divesting Dollar Thrifty locations incurred in connection with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition from 2012 to 2011. |
| |
| • | Impact of fair value adjustment to revenue earning equipment. |
| |
| • | Adjustments to eliminate the results of operations of the Advantage business and locations to be divested where Dollar Thrifty operated at least one of its brands prior to the consummation of the Dollar Thrifty acquisition for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011. |
| |
| • | Including an estimated amount of leasing revenue to be earned by Hertz from leasing vehicles to the buyer of Advantage. The depreciation and other expenses associated with the vehicles being leased to the buyer of Advantage have not been eliminated from the pro forma financial statements, as their costs remain as part of Hertz's ongoing operations associated with owning such vehicles. |
All of the above adjustments were adjusted for the applicable tax impact. Hertz has generally assumed a 39% tax rate when estimating the tax impacts of the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, representing the statutory tax rate for Hertz. The effective tax rate of the combined company could be significantly different (either higher or lower) depending on post-Dollar Thrifty acquisition activities, cash needs and the geographical location of businesses.
Pro forma adjustments - Donlen acquisition
2011 supplemental pro forma revenue for the year ended December 31, 2011 excludes $3.2 million related to deferred revenue which was eliminated as part of acquisition accounting. 2011 supplemental pro forma earnings for the year ended December 31, 2011 excludes $2.0 million related to deferred income which was eliminated as part of acquisition accounting, and $6.1 million of acquisition related costs incurred in 2011.
2010 supplemental pro forma revenue for the year ended December 31, 2010 excludes $8.7 million related to deferred revenue which was eliminated as part of acquisition accounting. 2010 supplemental pro forma earnings for the year ended December 31, 2010 excludes $5.3 million related to deferred income which was eliminated as part of acquisition accounting, and includes $6.1 million of acquisition related costs incurred.
Other Acquisitions
During the year ended December 31, 2012, we added nineteen domestic equipment rental locations through external acquisitions. These acquisitions are not material to the consolidated amounts presented within our statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2012.
Divestitures
Potential Divestiture of Selected Dollar Thrifty Airport Locations
In order to obtain regulatory approval and clearance for the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, Hertz agreed to dispose of Advantage, to secure for the buyer of Advantage certain on-airport car rental concessions and related assets at 13 locations where Dollar Thrifty operated at least one of its brands prior to the consummation of the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, or the “Initial airport locations.” Additionally, Hertz agreed to secure for the buyer of Advantage or, in certain cases, one or more other Federal Trade Commission-approved buyers, on-airport car rental concessions at 13 additional locations where Dollar Thrifty operated prior to the consummation of the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, or the “Secondary airport locations.” The buyer of Advantage agreed to assume all of the Secondary airport locations. As of December 31, 2012, Hertz recorded a loss, including for estimated support payments of $24.1 million.
Advantage Divestiture
On December 12, 2012, Hertz completed the sale of Simply Wheelz LLC, or the “Advantage divestiture,” a wholly owned subsidiary of Hertz that operated our Advantage Rent A Car business, or “Advantage,” for approximately $16.0 million, plus the value of current assets as of the closing date, which was approximately $3.6 million. As part of the agreement to sell Advantage, Hertz agreed to provide financial support to the buyer of Advantage in the amount of $17.0 million over a period of three years from the closing date (with the present value of $15.6 million as of December 31, 2012). As a result of the Advantage divestiture, Hertz realized a loss (before income taxes) of approximately $31.4 million as of December 31, 2012.
To assist the buyer of Advantage in securing alternative fleet financing arrangements, Hertz entered into a senior note credit agreement, pursuant to which Hertz agreed, subject to certain conditions, to loan Simply Wheelz, on a senior unsecured basis, up to $45.0 million over 5 years (2.5 years weighted average life) at varied interest rates up to 13% over the life of the loan.
Further, Hertz agreed to sublease vehicles to the buyer of Advantage for use in continuing the operations of Advantage, for a period no longer than two years from the closing date. As such, Hertz will have significant continuing involvement
in the operations of the disposed Advantage business. Therefore, the operating results associated with the Advantage business will continue to be classified as part of our continuing operations in the consolidated statements of operations for all periods presented.
Note 5—Debt
Our debt consists of the following (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Facility | Average Interest Rate at December 31, 2012(1) | | Fixed or Floating Interest Rate | | Maturity | | December 31,
2012 | | December 31,
2011 |
| Corporate Debt | | | | | | | | | |
| Senior Term Facility | 3.75% | | Floating | | 3/2018 | | $ | 2,125.5 |
| | $ | 1,389.5 |
|
| Senior ABL Facility | 2.47% | | Floating | | 3/2016 | | 195.0 |
| | — |
|
Senior Notes(2) | 6.74% | | Fixed | | 10/2018–10/2022 | | 3,650.0 |
| | 2,638.6 |
|
| Promissory Notes | 6.96% | | Fixed | | 6/2012–1/2028 | | 48.7 |
| | 224.7 |
|
| Other Corporate Debt | 4.40% | | Floating | | Various | | 88.7 |
| | 49.6 |
|
| Unamortized Net (Discount) Premium (Corporate) | | | | | | | 3.3 |
| | (6.9 | ) |
| Total Corporate Debt | | | | | | | 6,111.2 |
| | 4,295.5 |
|
| Fleet Debt | | | | | | | | | |
| HVF U.S. ABS Program | | | | | | | | | |
| HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes: | | | | | | | | | |
HVF Series 2009-1(3) | 1.11% | | Floating | | 3/2014 | | 2,350.0 |
| | 1,000.0 |
|
HVF Series 2010-2(3) | N/A | | Floating | | 3/2013 | | — |
| | 170.0 |
|
HVF Series 2011-2(3) | N/A | | Floating | | 4/2012 | | — |
| | 175.0 |
|
| | | | | | | | 2,350.0 |
| | 1,345.0 |
|
| HVF U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes | | | | | | | | | |
HVF Series 2009-2(3) | 5.11% | | Fixed | | 3/2013–3/2015 | | 1,095.9 |
| | 1,384.3 |
|
HVF Series 2010-1(3) | 3.77% | | Fixed | | 2/2014–2/2018 | | 749.8 |
| | 749.8 |
|
HVF Series 2011-1(3) | 2.86% | | Fixed | | 3/2015–3/2017 | | 598.0 |
| | 598.0 |
|
| | | | | | | | 2,443.7 |
| | 2,732.1 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| RCFC U.S. ABS Program | | | | | | | | | |
| RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes | | | | | | | | | |
RCFC Series 2010-3 Notes(3)(4) | 1.06% | | Floating | | 12/2013 | | 519.0 |
| | — |
|
| RCFC U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes | | | | | | | | | |
RCFC Series 2011-1 Notes(3)(4) | 2.81% | | Fixed | | 2/2015 | | 500.0 |
| | — |
|
RCFC Series 2011-2 Notes(3)(4) | 3.21% | | Fixed | | 5/2015 | | 400.0 |
| | — |
|
| | | | | | | | 1,419.0 |
| | — |
|
| Donlen ABS Program | | | | | | | | | |
Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes(3) | 1.15% | | Floating | | 12/2013 | | 899.3 |
| | 811.2 |
|
| Other Fleet Debt | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Fleet Financing Facility | 3.27% | | Floating | | 9/2015 | | 166.0 |
| | 136.0 |
|
| European Revolving Credit Facility | 2.86% | | Floating | | 6/2015 | | 185.3 |
| | 200.6 |
|
| European Fleet Notes | 8.50% | | Fixed | | 7/2015 | | 529.4 |
| | 517.7 |
|
European Securitization(3) | 2.48% | | Floating | | 7/2014 | | 242.2 |
| | 256.2 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Facility | Average Interest Rate at December 31, 2012(1) | | Fixed or Floating Interest Rate | | Maturity | | December 31,
2012 | | December 31,
2011 |
Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization(3) | 2.16% | | Floating | | 6/2013 | | 100.5 |
| | 68.3 |
|
Dollar Thrifty Sponsored Canadian Securitization(3)(4) | 2.13% | | Floating | | 8/2014 | | 55.3 |
| | — |
|
Australian Securitization(3) | 4.61% | | Floating | | 12/2014 | | 148.9 |
| | 169.3 |
|
| Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility | 13.07% | | Floating | | 2/2013 | | 14.0 |
| | 23.1 |
|
| Capitalized Leases | 4.40% | | Floating | | Various | | 337.6 |
| | 363.7 |
|
| Unamortized Net (Discount) Premium (Fleet) | | | | | | | 12.1 |
| | (10.9 | ) |
| | | | | | | | 1,791.3 |
| | 1,724.0 |
|
| Total Fleet Debt | | | | | | | 8,903.3 |
| | 6,612.3 |
|
| Total Debt | | | | | | | $ | 15,014.5 |
| | $ | 10,907.8 |
|
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (1) | As applicable, reference is to the December 31, 2012 weighted average interest rate (weighted by principal balance). |
| |
| (2) | References to our "Senior Notes" include the series of Hertz's unsecured senior notes set forth in the table below. As of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, the outstanding principal amount for each such series of the Senior Notes is also specified below. |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Outstanding Principal (in millions) | | |
| Senior Notes | December 31, 2012 | | December 31, 2011 | | |
| 8.875% Senior Notes due January 2014 | $ | — |
| | $ | 162.3 |
| | |
| 7.875% Senior Notes due January 2014 | — |
| | 276.3 |
| | €(213.5) |
| 7.50% Senior Notes due October 2018 | 700.0 |
| | 700.0 |
| | |
| 6.75% Senior Notes due April 2019 | 1,250.0 |
| | 1,000.0 |
| | |
| 5.875% Senior Notes due October 2020 | 700.0 |
| | — |
| | |
| 7.375% Senior Notes due January 2021 | 500.0 |
| | 500.0 |
| | |
| 6.25% Senior Notes due October 2022 | 500.0 |
| | — |
| | |
| | $ | 3,650.0 |
| | $ | 2,638.6 |
| | |
| |
| (3) | Maturity reference is to the "expected final maturity date" as opposed to the subsequent "legal maturity date." The expected final maturity date is the date by which Hertz and investors in the relevant indebtedness expect the relevant indebtedness to be repaid. The legal final maturity date is the date on which the relevant indebtedness is legally due and payable. |
| |
| (4) | RCFC U.S. ABS Program and the Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization represent fleet debt acquired in connection with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition on November 19, 2012. |
Maturities
The aggregate amounts of maturities of debt for each of the twelve-month periods ending December 31 (in millions of dollars) are as follows:
|
| | | | | |
| 2013 | $ | 5,744.1 |
| | (including $5,244.0 of other short-term borrowings*) |
| 2014 | $ | 1,122.1 |
| | |
| 2015 | $ | 1,894.1 |
| | |
| 2016 | $ | 267.1 |
| | |
| 2017 | $ | 219.2 |
| | |
| After 2017 | $ | 5,752.5 |
| | |
_______________________________________________________________________________
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| |
| * | Our short-term borrowings as of December 31, 2012 include, among other items, the amounts outstanding under the Senior ABL Facility, HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes, Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes, U.S. Fleet Financing Facility, European Revolving Credit Facility, European Securitization, Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization, Australian Securitization, Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility and Capitalized Leases. These amounts are reflected as short-term borrowings, regardless of the facility maturity date, as these facilities are revolving in nature and/or the outstanding borrowings have maturities of three months or less. As of December 31, 2012, short-term borrowings had a weighted average interest rate of 1.8%. |
We are highly leveraged and a substantial portion of our liquidity needs arise from debt service on our indebtedness and from the funding of our costs of operations, acquisitions and capital expenditures. We believe that cash generated from operations and cash received on the disposal of vehicles and equipment, together with amounts available under various liquidity facilities will be adequate to permit us to meet our debt maturities over the next twelve months.
Letters of Credit
As of December 31, 2012, there were outstanding standby letters of credit totaling $681.4 million. Of this amount, $626.6 million was issued under the Senior Credit Facilities. As of December 31, 2012, none of these letters of credit have been drawn upon.
Acquisition Bridge Financing
In August 2012 in conjunction with signing of the merger agreement with Dollar Thrifty, Hertz obtained $1,950.0 million in financing commitments for use in acquiring Dollar Thrifty. In October 2012 after having secured permanent financing for the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, Hertz terminated these commitments having never drawn upon them.
CORPORATE DEBT
Senior Credit Facilities
Senior Term Facility: In March 2011, Hertz entered into a credit agreement that provides a $1,400.0 million term loan, or as amended, the ‘‘Senior Term Facility.’’ In addition, the Senior Term Facility includes a separate incremental pre-funded synthetic letter of credit facility in an aggregate principal amount of $200.0 million. Subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions and limitations, the Senior Term Facility allows for the incurrence of incremental term and/or revolving loans.
On October 9, 2012, Hertz entered into an Incremental Commitment Amendment to the Senior Term Facility which provided for commitments for the Incremental Term Loans of $750.0 million under the Senior Term Facility. Contemporaneously with the consummation of the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, the Incremental Term Loans were fully drawn and the proceeds therefrom were used to: (i) finance a portion of the consideration in connection with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, (ii) pay off obligations of Dollar Thrifty and its subsidiaries in connection with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition and (iii) pay fees and other transaction expenses in connection with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition and the related financing transactions.
The Incremental Term Loans are secured by the same collateral and guaranteed by the same guarantors as the previously existing term loans under the Senior Term Facility. The Incremental Term Loans will, like the previously existing term loans under the Senior Term Facility, mature on March 11, 2018 and the interest rate per annum applicable thereto will be the same as such previously existing term loans. The other terms of the Incremental Term Loans are also generally the same.
Senior ABL Facility: In March 2011, Hertz, HERC, and certain other of our subsidiaries entered into a credit agreement that provides for aggregate maximum borrowings of $1,800.0 million (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset‑based revolving credit facility. We refer to this facility, as amended, from time to time, as the “Senior ABL Facility.” Up to $1,500.0 million of the Senior ABL Facility is available for the issuance of letters of credit, subject to certain conditions including issuing lender participation. Subject to the satisfaction of certain conditions and limitations, the Senior ABL Facility allows for the addition of incremental revolving and/or term loan commitments. In addition, the Senior ABL Facility permits Hertz to increase the amount of commitments under the Senior ABL Facility with the consent of each lender providing an additional commitment, subject to satisfaction of certain conditions.
We refer to the Senior Term Facility and the Senior ABL Facility together as the “Senior Credit Facilities.” Hertz's obligations under the Senior Credit Facilities are guaranteed by its immediate parent (Hertz Investors, Inc.) and most of its direct and indirect domestic subsidiaries (subject to certain exceptions, including Hertz International Limited, which ultimately owns entities carrying on most of our international operations, and subsidiaries involved in the HVF U.S. Asset-Backed Securities, or "ABS," Program, the Donlen ABS Program and, the RCFC U.S. ABS Program). In
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
addition, the obligations of the “Canadian borrowers” under the Senior ABL Facility are guaranteed by their respective subsidiaries, subject to certain exceptions.
The lenders under the Senior Credit Facilities have been granted a security interest in substantially all of the tangible and intangible assets of the borrowers and guarantors under those facilities, including pledges of the stock of certain of their respective domestic subsidiaries (subject, in each case, to certain exceptions, including certain vehicles). Each of the Senior Credit Facilities permits the incurrence of future indebtedness secured on a basis either equal to or subordinated to the liens securing the applicable Senior Credit Facility or on an unsecured basis.
We refer to Hertz and its subsidiaries as the Hertz credit group. The Senior Credit Facilities contain a number of covenants that, among other things, limit or restrict the ability of the Hertz credit group to dispose of assets, incur additional indebtedness, incur guarantee obligations, prepay certain indebtedness, make dividends and other restricted payments (including to the parent entities of Hertz and other persons), create liens, make investments, make acquisitions, engage in mergers, change the nature of their business, engage in certain transactions with affiliates that are not within the Hertz credit group or enter into certain restrictive agreements limiting the ability to pledge assets.
Under the Senior ABL Facility, failure to maintain certain levels of liquidity will subject the Hertz credit group to a contractually specified fixed charge coverage ratio of not less than 1:1 for the four quarters most recently ended. As of December 31, 2012, we were not subject to such contractually specified fixed charge coverage ratio.
Covenants in the Senior Term Facility restrict payment of cash dividends to any parent of Hertz, including Hertz Holdings, with certain exceptions, including: (i) in an aggregate amount not to exceed 1.0% of the greater of a specified minimum amount and the consolidated tangible assets of the Hertz credit group (which payments are deducted in determining the amount available as described in the next clause (ii)), (ii) in additional amounts up to a specified available amount determined by reference to, among other things, an amount set forth in the Senior Term Facility plus 50% of net income from January 1, 2011 to the end of the most recent fiscal quarter for which financial statements of Hertz are available (less certain investments) and (iii) in additional amounts not to exceed the amount of certain equity contributions made to Hertz.
Covenants in the Senior ABL Facility restrict payment of cash dividends to any parent of Hertz, including Hertz Holdings, except in an aggregate amount, taken together with certain investments, acquisitions and optional prepayments, not to exceed $200 million. Hertz may also pay additional cash dividends under the Senior ABL Facility so long as, among other things, (a) no specified default then exists or would arise as a result of making such dividends, (b) there is at least $200 million of liquidity under the Senior ABL Facility after giving effect to the proposed dividend, and (c) either (i) if such liquidity is less than $400 million immediately after giving effect to the making of such dividends, Hertz is in compliance with a specified fixed charge coverage ratio, or (ii) the amount of the proposed dividend does not exceed the sum of (x) 1.0% of tangible assets plus (y) a specified available amount determined by reference to, among other things, 50% of net income from January 1, 2011 to the end of the most recent fiscal quarter for which financial statements of Hertz are available plus (z) a specified amount of certain equity contributions made to Hertz.
In November 2012, we amended the Senior ABL Facility to deem letters of credit issued under Dollar Thrifty's now-terminated senior revolving credit facility to have been issued under the Senior ABL Facility.
Senior Notes
In March 2012, Hertz issued an additional $250.0 million aggregate principal of the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019. The proceeds of this March 2012 offering were used in March 2012 in part to redeem $162.3 million principal amount of Hertz's outstanding 8.875% Senior Notes due 2014 which resulted in the write-off of unamortized debt costs of $1.2 million recorded in "Interest expense" on our consolidated statement of operations. The remainder of the proceeds of this March 2012 offering, along with cash on hand or drawings under the Senior ABL Facility were used to redeem €213.5 million ($286.0 million) of Hertz's outstanding 7.875% Senior Notes due 2014, which resulted in the write-off of unamortized debt costs of $2.0 million recorded in "Interest expense" on our consolidated statement of operations.
In October 2012, HDTFS, Inc., a newly-formed, wholly-owned subsidiary of Hertz issued and sold $700.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Senior Notes due 2020 and $500.0 million aggregate principal amount of 6.250% Senior Notes due 2022 in a private offering. The gross proceeds of the offering were held in an escrow account until the date of the completion of the acquisition of Dollar Thrifty, at which time the gross proceeds of the offering were released from escrow and HDTFS, Inc. was merged into Hertz.
Hertz's obligations under the indentures for the Senior Notes are guaranteed by each of its direct and indirect domestic subsidiaries that is a guarantor under the Senior Term Facility. The guarantees of all of the Subsidiary Guarantors may
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
be released to the extent such subsidiaries no longer guarantee our Senior Credit Facilities in the United States. HERC may also be released from its guarantee under the outstanding Senior Notes at any time at which no event of default under the related indenture has occurred and is continuing, notwithstanding that HERC may remain a subsidiary of Hertz.
The indentures for the Senior Notes contain covenants that, among other things, limit or restrict the ability of the Hertz credit group to incur additional indebtedness, incur guarantee obligations, prepay certain indebtedness, make certain restricted payments (including paying dividends, redeeming stock or making other distributions to parent entities of Hertz and other persons outside of the Hertz credit group), make investments, create liens, transfer or sell assets, merge or consolidate, and enter into certain transactions with Hertz's affiliates that are not members of the Hertz credit group.
The covenants in the indentures for the Senior Notes also restrict Hertz and other members of the Hertz credit group from redeeming stock or making loans, advances, dividends, distributions or other restricted payments to any entity that is not a member of the Hertz credit group, including Hertz Holdings, subject to certain exceptions.
Promissory Notes
References to our “Promissory Notes” relate to our promissory notes issued under three separate indentures prior to the Acquisition.
FLEET DEBT
The governing documents of certain of the fleet debt financing arrangements specified below contain covenants that, among other things, significantly limit or restrict (or upon certain circumstances may significantly restrict or prohibit) the ability of the borrowers, and the guarantors if applicable, to make certain restricted payments (including paying dividends, redeeming stock, making other distributions, loans or advances) to Hertz Holdings and Hertz, whether directly or indirectly.
HVF U.S. ABS Program
Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, an insolvency remote, direct, wholly‑owned, special purpose subsidiary of Hertz, or “HVF,” is the issuer under the HVF U.S. ABS Program. HVF has entered into a base indenture that permits it to issue term and revolving rental car asset‑backed securities, the collateral for which consists primarily of a substantial portion of the rental car fleet used in Hertz's (and through fleet sharing arrangements, a portion of the fleet used in Dollar Thrifty's) domestic car rental operations and contractual rights related to such vehicles.
References to the “HVF U.S. ABS Program” include HVF's U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes together with HVF's U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes.
HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes
References to the “HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes” include HVF's Series 2009-1 Variable Funding Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, as amended, or the “Series 2009-1 Notes,” Series 2010-2 Variable Funding Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, or the “Series 2010-2 Notes,” and Series 2011-2 Variable Funding Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, or the “Series 2011-2 Notes,” collectively. As of December 31, 2012, the only U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes committed or outstanding were the Series 2009-1 Notes, which, as of December 31, 2012, permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $2,438.8 million (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset‑backed variable funding note facility.
In April 2012, HVF paid the HVF Series 2011-2 notes in full and terminated the related asset-backed variable funding note facility.
In May 2012, HVF amended the HVF Series 2009-1 Notes to permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $2,188.0 million (subject to borrowing base availability).
In October 2012, HVF amended the HVF Series 2009-1 Notes to permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $2,238.8 million (subject to borrowing base availability) and extend the expected final maturity by one year to March 2014.
In December 2012, HVF paid the HVF Series 2010-2 Notes in full and terminated the related asset-backed variable funding note facility. At the same time, HVF amended the HVF Series 2009-1 Notes to permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $2,438.8 million (subject to borrowing base availability).
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
HVF U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes
References to the “HVF U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes” include HVF's Series 2009-2 Notes, Series 2010-1 Notes and Series 2011-1 Notes, collectively.
Series 2009-2 Notes: In October 2009, HVF issued the Series 2009-2 Rental Car Asset Back Notes, Class A, or the “HVF Series 2009-2 Class A Notes,” in an aggregate original principal amount of $1.2 billion. In June 2010, HVF issued the Subordinated Series 2009-2 Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, Class B, or the “HVF Series 2009-2 Class B Notes,” and together with the Series 2009-2 Class A, or the “HVF Series 2009-2 Notes,” in an aggregate original principal amount of $184.3 million.
Series 2010-1 Notes: In July 2010, HVF issued the Series 2010-1 Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, or the “HVF Series 2010-1 Notes,” in an aggregate original principal amount of $749.8 million.
Series 2011-1 Notes: In June 2011, HVF issued the Series 2011-1 Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, or the “HVF Series 2011-1 Notes,” in an aggregate original principal amount of $598.0 million.
See Note 18—Subsequent Events.
RCFC U.S. ABS Program
Rental Car Finance Corporation, or “RCFC,” became an insolvency remote, indirect, wholly‑owned, special purpose subsidiary of Hertz when Hertz acquired Dollar Thrifty. RCFC is the issuer under the RCFC U.S. ABS Program. RCFC has entered into a base indenture that permits it to issue term and revolving rental car asset-backed securities, the collateral for which consists primarily of a substantial portion of the rental car fleet used in Dollar Thrifty's (and through fleet sharing arrangements, a portion of the fleet used in Hertz's) domestic car rental operations and contractual rights related to such vehicles.
References to the “RCFC U.S. ABS Program” include RCFC's U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes together with RCFC's U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes.
RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes
References to the “RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes” are to the RCFC Series 2010-3 Variable Funding Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, as amended, or the “RCFC Series 2010-3 Notes,” which, as of December 31, 2012, permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $600.0 million (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset-backed variable funding note facility.
RCFC U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes
References to the “RCFC U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes” include RCFC's Series 2011-1 Notes and RCFC's Series 2011-2 Notes, collectively.
Series 2011-1 Notes: In July 2011, RCFC issued the Series 2011-1 Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, or the “RCFC Series 2011-1 Notes,” in an aggregate original principal amount of $500.0 million.
Series 2011-2 Notes: In October 2011, RCFC issued the Series 2011-2 Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, or the “RCFC Series 2011-2 Notes,” in an aggregate original principal amount of $400.0 million.
Donlen ABS Program
Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes
On September 1, 2011, in connection with our acquisition of Donlen, Donlen's GN II Variable Funding Notes, or the "GN II VFN," remained outstanding and lender commitments thereunder were increased to permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $850.0 million (subject to borrowing base availability).
In February 2012, Hertz's indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary GN Funding II L.L.C., or “GN II,” amended the GN II VFN to permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $900.0 million (subject to borrowing base availability).
In July 2012, GN II amended the GN II VFN to extend the expected maturity to December 2012 and to permit aggregate maximum borrowings of $1,000.0 million (subject to borrowing base availability).
In October 2012, GN II amended the GN II VFN to extend the expected final maturity to December 2013.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Fleet Debt-Other
U.S. Fleet Financing Facility
In September 2006, Hertz and Puerto Ricancars, Inc., a Puerto Rican corporation and wholly‑owned indirect subsidiary of Hertz, or “PR Cars,” entered into a credit agreement that provides for aggregate maximum borrowings of $165.0 million (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset‑based revolving credit facility, or the “U.S. Fleet Financing Facility.” The U.S. Fleet Financing Facility is the primary fleet financing for our car rental operations in Hawaii, Kansas, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
The obligations of each of Hertz and PR Cars under the U.S. Fleet Financing Facility are guaranteed by certain of Hertz's direct and indirect domestic subsidiaries. In addition, the obligations of PR Cars under the U.S. Fleet Financing Facility are guaranteed by Hertz. The lenders under the U.S. Fleet Financing Facility have been granted a security interest primarily in the owned rental car fleet used in our car rental operations in Hawaii, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands and certain contractual rights related to rental vehicles in Kansas, Hawaii, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands.
In September 2011, we extended the maturity of our U.S. Fleet Financing Facility to September 2015 and increased the facility size to $190.0 million. In connection with the extension, we made a number of modifications to the financing arrangement including decreasing the advance rate and increasing pricing.
European Revolving Credit Facility and European Fleet Notes
In June 2010, Hertz Holdings Netherlands B.V., an indirect wholly‑owned subsidiary of Hertz organized under the laws of The Netherlands, or “HHN BV,” entered into a credit agreement that provides for aggregate maximum borrowings of €220.0 million (the equivalent of $291.2 million as of December 31, 2012) (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset‑based revolving credit facility, or the “European Revolving Credit Facility,” and issued the 8.50% Senior Secured Notes due July 2015, or the “European Fleet Notes,” in an aggregate original principal amount of €400.0 million (the equivalent of $529.4 million as of December 31, 2012). References to the “European Fleet Debt” include HHN BV's European Revolving Credit Facility and the European Fleet Notes, collectively.
The European Fleet Debt is the primary fleet financing for our car rental operations in Germany, Italy, Spain, Belgium, New Zealand and Luxembourg, and can be expanded to provide fleet financing in Australia, Canada, France, The Netherlands, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.
The obligations of HHN BV under the European Fleet Debt are guaranteed by Hertz and certain of Hertz's domestic and foreign subsidiaries.
The agreements governing the European Revolving Credit Facility and the indenture governing the European Fleet Notes contain covenants that apply to the Hertz credit group similar to those for the Senior Notes. In addition, the agreements and indenture contain a combination of security arrangements, springing covenants and “no liens” covenants intended to give the lenders under the European Fleet Debt enhanced recourse to certain assets of HHN BV and certain foreign subsidiaries of Hertz. The terms of the European Fleet Debt permit HHN BV to incur additional indebtedness that would be pari passu with either the European Revolving Credit Facility or the European Fleet Notes.
In June 2012, HHN BV amended the European Revolving Credit Facility to extend the maturity date from June 2013 to June 2015.
European Securitization
In July 2010, certain foreign subsidiaries entered into a facility agreement that provides for aggregate maximum borrowings of €400.0 million (the equivalent of $529.4 million as of December 31, 2012) (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset‑backed securitization facility, or the “European Securitization.” The European Securitization is the primary fleet financing for our car rental operations in France and The Netherlands. The lenders under the European Securitization have been granted a security interest primarily in the owned rental car fleet used in our car rental operations in France and The Netherlands and certain contractual rights related to such vehicles.
In August 2011, certain foreign subsidiaries extended the expected maturity of our European Securitization Facility to July 2013. In connection with the extension, International Fleet Financing No. 2 B.V. made a number of modifications to the financing arrangement including increasing the advance rate and decreasing pricing.
In July 2012, International Fleet Financing No. 2 B.V. amended the European Securitization to extend the maturity from July 2013 to July 2014.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization
In May 2007, certain foreign subsidiaries entered into a facility agreement that provides for aggregate maximum borrowings of CAD$225.0 million (the equivalent of $226.1 million as of December 31, 2012) (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset‑backed securitization facility, or as amended, the “Canadian Securitization.” The Canadian Securitization is the primary fleet financing for our car rental operations in Canada. The lender under the Canadian Securitization has been granted an indirect security interest primarily in the owned rental car fleet used in our car rental operations in Canada and certain contractual rights related to such vehicles as well as certain other assets owned by entities connected to the financing.
In November 2011, Hertz's indirect wholly owned subsidiary HC Limited Partnership extended the maturity of the Canadian Securitization to January 2012 and reduced the facility size to CAD$200.0 million (equivalent to $201.0 million as of December 31, 2012). In connection with the extension, HC Limited Partnership made a number of modifications to the financing arrangement including decreasing the pricing.
In January 2012, HC Limited Partnership amended the Canadian Securitization to extend the maturity date from January 2012 to March 2012. In March 2012, HC Limited Partnership amended the Canadian Securitization to extend the maturity date from March 2012 to May 2012. In the second quarter of 2012, the maturity date was extended to June 2013.
Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization
In March 2012 certain foreign subsidiaries of Dollar Thrifty entered into a trust indenture that permits the issuance of term and revolving rental car asset-backed securities, the collateral for which consists primarily of the rental car fleet used in Dollar Thrifty’s Canadian car rental operations and contractual rights related to such vehicles. These subsidiaries became indirect wholly-owned subsidiaries of Hertz when Hertz acquired Dollar Thrifty.
In March 2012 these subsidiaries issued asset-backed variable funding notes that provide for aggregate maximum borrowings of CAD$150.0 million (the equivalent of $150.7 million as of December 31, 2012) (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis, or the “Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization.” The expected final maturity of the Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization is August 2014.
Australian Securitization
In November 2010, certain foreign subsidiaries entered into a facility agreement that provides for aggregate maximum borrowings of A$250.0 million (the equivalent of $259.4 million as of December 31, 2012) (subject to borrowing base availability) on a revolving basis under an asset‑backed securitization facility, or the “Australian Securitization.” The Australian Securitization is the primary fleet financing for Hertz's car rental operations in Australia. The lender under the Australian Securitization has been granted a security interest primarily in the owned rental car fleet used in our car rental operations in Australia and certain contractual rights related to such vehicles. In connection with the issuance of the Australian Securitization, an interest rate cap was purchased by a subsidiary, HA Fleet Pty Limited. Concurrently, Hertz sold an offsetting interest rate cap, thereby neutralizing the hedge on a consolidated basis and reducing the net cost of the hedge.
In October 2012, Hertz's indirect, wholly-owned subsidiary HA Fleet Pty Limited amended the Australian Securitization to extend the expected maturity date thereunder to December 2014 in connection with this transaction both HA Fleet Pty Limited and Hertz amended the existing interest rate caps, modifying and extending the amortization schedule to the new maturity date of the securitization.
See Note 14—Financial Instruments.
Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility
As of December 31, 2012, our Brazilian operating subsidiary is party to certain local financing arrangements, which are collateralized by certain of its assets, which we refer to as the "Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility."
In June 2012, Hertz caused its Brazilian operating subsidiary to amend the Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility to extend the maturity date from June 2012 to February 2013.
See Note 18—Subsequent Events.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Capitalized Leases
References to the “Capitalized Leases” include the capitalized lease financings outstanding in the United Kingdom, or the “U.K. Leveraged Financing,” Australia, The Netherlands and the United States. The amount available under the U.K. Leveraged Financing, which is the largest portion of the Capitalized Leases, as of December 31, 2012 was £195 million (the equivalent of $314.0 million as of December 31, 2012).
Restricted Net Assets
As a result of the contractual restrictions on Hertz's or its subsidiaries' ability to pay dividends (directly or indirectly) under various terms of our debt, as of December 31, 2012, the restricted net assets of our subsidiaries exceeded 25% of our total consolidated net assets.
Registration Rights
Hertz entered into exchange and registration rights agreements entered into in connection with (i) the issuance of $250 million in aggregate principal amount of the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019 in March 2012, and (ii) the release from escrow of the proceeds of $700 million aggregate principal amount of 5.875% Senior Notes due 2020 and $500 million aggregate principal amount of 6.250% Senior Notes due 2022. Pursuant to the terms of these agreements, Hertz agreed to file a registration statement under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, to permit either the exchange of such notes for registered notes or, in the alternative, the registered resale of such notes. Hertz's failure to meet its obligations under either exchange and registration rights agreement, including by failing to have the registration statement become effective by the date that is 365 days after the respective date of the exchange and registration rights agreement or failing to complete the exchange offer by the date that is 395 days after the date of the exchange and registration rights agreement, will result in Hertz incurring special interest on such notes at a per annum rate of 0.25% for the first 90 days of any period where a default has occurred and is continuing, which rate will be increased by an additional 0.25% during each subsequent 90 day period, up to a maximum of 0.50%. A registration statement on Form S-4 covering the exchange of such notes was declared effective by the SEC on February 1, 2013 and the exchange offer is scheduled to be completed on March 6, 2013, so we do not believe the special interest obligation is probable, and as such, we have not recorded any amounts for special interest with respect to these notes.
Financial Covenant Compliance
Under the terms of our Senior Term Facility and Senior ABL Facility, we are not subject to ongoing financial maintenance covenants; however, under the Senior ABL Facility, failure to maintain certain levels of liquidity will subject the Hertz credit group to a contractually specified fixed charge coverage ratio of not less than 1:1 for the four quarters most recently ended. As of December 31, 2012, we were not subject to such contractually specified fixed charge coverage ratio.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Borrowing Capacity and Availability
As of December 31, 2012, the following facilities were available for the use of Hertz and its subsidiaries (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Remaining Capacity | | Availability Under Borrowing Base Limitation |
| Corporate Debt | | | |
| Senior ABL Facility | $ | 1,183.7 |
| | $ | 1,146.0 |
|
| Total Corporate Debt | 1,183.7 |
| | 1,146.0 |
|
| Fleet Debt | | | |
| HVF U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes | 88.8 |
| | — |
|
| RCFC U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes | 81.0 |
| | — |
|
| Donlen GN II Variable Funding Notes | 105.0 |
| | — |
|
| U.S. Fleet Financing Facility | 24.0 |
| | — |
|
| European Revolving Credit Facility | 105.9 |
| | 7.9 |
|
| European Securitization | 287.2 |
| | — |
|
| Hertz-Sponsored Canadian Securitization | 100.5 |
| | — |
|
| Dollar Thrifty-Sponsored Canadian Securitization | 95.5 |
| | — |
|
| Australian Securitization | 110.5 |
| | — |
|
| Capitalized Leases | 85.1 |
| | 27.5 |
|
| Total Fleet Debt | 1,083.5 |
| | 35.4 |
|
| Total | $ | 2,267.2 |
| | $ | 1,181.4 |
|
Our borrowing capacity and availability primarily comes from our "revolving credit facilities," which are a combination of asset-backed securitization facilities and asset-based revolving credit facilities. Creditors under each of our revolving credit facilities have a claim on a specific pool of assets as collateral. Our ability to borrow under each revolving credit facility is a function of, among other things, the value of the assets in the relevant collateral pool. We refer to the amount of debt we can borrow given a certain pool of assets as the "borrowing base."
We refer to "Remaining Capacity" as the maximum principal amount of debt permitted to be outstanding under the respective facility (i.e., the amount of debt we could borrow assuming we possessed sufficient assets as collateral) less the principal amount of debt then-outstanding under such facility.
We refer to "Availability Under Borrowing Base Limitation" as the lower of Remaining Capacity or the borrowing base less the principal amount of debt then-outstanding under such facility (i.e., the amount of debt we could borrow given the collateral we possess at such time).
As of December 31, 2012, the Senior Term Facility had approximately $8.0 million available under the letter of credit facility and the Senior ABL Facility had $1,010.4 million available under the letter of credit facility sublimit, subject to borrowing base restrictions.
Substantially all of our revenue earning equipment and certain related assets are owned by special purpose entities, or are encumbered in favor of our lenders under our various credit facilities.
Some of these special purpose entities are consolidated variable interest entities, of which we are the primary beneficiary, whose sole purpose is to provide commitments to lend in various currencies subject to borrowing bases comprised of rental vehicles and related assets of certain of Hertz International, Ltd.'s subsidiaries. As of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, our International Fleet Financing No. 1 B.V., International Fleet Financing No. 2 B.V. and HA Funding Pty, Ltd. variable interest entities had total assets primarily comprised of loans receivable and revenue earning equipment of $440.8 million and $456.3 million, respectively, and total liabilities primarily comprised of debt of $440.3 million and $455.8 million, respectively.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Accrued Interest
As of December 31, 2012 and 2011, accrued interest was $86.4 million and $85.7 million, respectively, which is reflected in our consolidated balance sheet in “Other accrued liabilities.”
For subsequent events relating to our indebtedness, see Note 18—Subsequent Events.
Note 6—Employee Retirement Benefits
Qualified U.S. employees, after completion of specified periods of service, are eligible to participate in The Hertz Corporation Account Balance Defined Benefit Pension Plan, or the “Hertz Retirement Plan,” a cash balance plan. Under this qualified Hertz Retirement Plan, we pay the entire cost and employees are not required to contribute.
Most of our international subsidiaries have defined benefit retirement plans or participate in various insured or multiemployer plans. In certain countries, when the subsidiaries make the required funding payments, they have no further obligations under such plans.
Company plans are generally funded, except for certain nonqualified U.S. defined benefit plans and in Germany and France, where unfunded liabilities are recorded.
We sponsor defined contribution plans for certain eligible U.S. and non-U.S. employees. We match contributions of participating employees on the basis specified in the plans.
An amendment to the Hertz Corporation Account Balance Defined Benefit Plan took effect on January 1, 2012. A fixed interest rate of 3% will be applied to cash balance credits in 2012 and later years. Previously, it was the rate published by the Pension Benefit Guarantee Corporation, or “PGBC,” for the December prior to the year the credit was earned. Also effective January 1, 2012, service credit rates for each employee will be determined on the first day of the year.
We sponsored a defined benefit pension plan in the U.K. On June 30, 2011, we approved an agreement with the trustees of that plan to cease all future benefit accruals to existing members and to close the plan to new members. Effective July 1, 2011, we introduced a defined contribution plan with company matching contributions to replace the defined benefit pension plan. The company matching contributions are generally 100% of the employee contributions, up to 8% of pay, except that former members of the defined benefit plan receive an enhanced match for five years. This will result in lower contributions this year into the defined benefit plan, which will be offset by matching contributions to the new defined contribution plan. In the year ended December 31, 2011, we recognized a gain of $13.1 million for the U.K. plan that represented unamortized prior service cost from a 2010 amendment that eliminated discretionary pension increases related to pre-1997 service primarily related to inactive employees.
We also sponsor postretirement health care and life insurance benefits for a limited number of employees with hire dates prior to January 1, 1990. The postretirement health care plan is contributory with participants' contributions adjusted annually. An unfunded liability is recorded. We also have a key officer postretirement car benefit plan that provides the use of a vehicle for retired Senior Vice Presidents and above who have a minimum of 20 years of service and who retired at age 58 or above.
We use a December 31 measurement date for all of our plans.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following tables set forth the funded status and the net periodic pension cost of the Hertz Retirement Plan, other postretirement benefit plans (including health care and life insurance plans covering domestic (“U.S.”) employees and the retirement plans for international operations (“Non-U.S.”), together with amounts included in our consolidated balance sheets and statements of operations (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement |
| | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | Benefits (U.S.) |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Change in Benefit Obligation | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligation at January 1 | $ | 606.4 |
| | $ | 549.7 |
| | $ | 190.8 |
| | $ | 201.5 |
| | $ | 18.2 |
| | $ | 19.0 |
|
| Service cost | 24.8 |
| | 26.2 |
| | 1.9 |
| | 4.0 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
|
| Interest cost | 28.2 |
| | 27.5 |
| | 9.7 |
| | 11.0 |
| | 0.8 |
| | 0.9 |
|
| Employee contributions | — |
| | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | 0.7 |
| | 0.8 |
| | 0.9 |
|
| Plan amendments | — |
| | (10.2 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Plan curtailments | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (5.9 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Plan settlements | (5.4 | ) | | (7.4 | ) | | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Benefits paid | (29.9 | ) | | (18.4 | ) | | (5.5 | ) | | (4.0 | ) | | (2.2 | ) | | (2.2 | ) |
| Foreign exchange translation | — |
| | — |
| | 7.7 |
| | (1.0 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Actuarial loss (gain) | 54.8 |
| | 39.0 |
| | 9.4 |
| | (15.1 | ) | | 1.2 |
| | (0.6 | ) |
| Plan combination | — |
| | — |
| | 10.4 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Other | — |
| | — |
| | (0.1 | ) | | (0.5 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Benefit obligation at December 31 | $ | 678.9 |
| | $ | 606.4 |
| | $ | 224.4 |
| | $ | 190.8 |
| | $ | 19.0 |
| | $ | 18.2 |
|
| Change in Plan Assets | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at January 1 | $ | 423.2 |
| | $ | 365.9 |
| | $ | 157.0 |
| | $ | 152.8 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Actual return on plan assets | 64.2 |
| | 15.3 |
| | 15.6 |
| | (7.6 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Company contributions | 46.3 |
| | 67.8 |
| | 4.7 |
| | 16.0 |
| | 1.4 |
| | 1.3 |
|
| Employee contributions | — |
| | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | 0.7 |
| | 0.8 |
| | 0.9 |
|
| Plan settlements | (5.4 | ) | | (7.4 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Benefits paid | (29.9 | ) | | (18.4 | ) | | (5.5 | ) | | (4.0 | ) | | (2.2 | ) | | (2.2 | ) |
| Foreign exchange translation | — |
| | — |
| | 6.5 |
| | (0.7 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Other | — |
| | — |
| | (0.1 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Fair value of plan assets at December 31 | $ | 498.4 |
| | $ | 423.2 |
| | $ | 178.3 |
| | $ | 157.0 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Funded Status of the Plan | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Plan assets less than benefit obligation | $ | (180.5 | ) | | $ | (183.2 | ) | | $ | (46.1 | ) | | $ | (33.8 | ) | | $ | (19.0 | ) | | $ | (18.2 | ) |
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement |
| | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | | Benefits (U.S.) |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Amounts recognized in balance sheet: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Liabilities | $ | (180.5 | ) | | $ | (183.2 | ) | | $ | (46.1 | ) | | $ | (33.8 | ) | | $ | (19.0 | ) | | $ | (18.2 | ) |
| Net obligation recognized in the balance sheet | $ | (180.5 | ) | | $ | (183.2 | ) | | $ | (46.1 | ) | | $ | (33.8 | ) | | $ | (19.0 | ) | | $ | (18.2 | ) |
| Prior service credit (cost) | $ | 9.1 |
| | $ | 10.1 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Net gain (loss) | (167.6 | ) | | (160.3 | ) | | (17.5 | ) | | (10.7 | ) | | (2.3 | ) | | (1.2 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (158.5 | ) | | (150.2 | ) | | (17.5 | ) | | (10.7 | ) | | (2.3 | ) | | (1.2 | ) |
| Unfunded accrued pension or postretirement benefit | (22.0 | ) | | (33.0 | ) | | (28.6 | ) | | (23.1 | ) | | (16.7 | ) | | (17.0 | ) |
| Net obligation recognized in the balance sheet | $ | (180.5 | ) | | $ | (183.2 | ) | | $ | (46.1 | ) | | $ | (33.8 | ) | | $ | (19.0 | ) | | $ | (18.2 | ) |
| Total recognized in other comprehensive (income) loss | $ | 8.3 |
| | $ | 34.5 |
| | $ | 6.8 |
| | $ | 12.2 |
| | $ | 1.1 |
| | $ | (0.7 | ) |
| Total recognized in net periodic benefit cost and other comprehensive (income) loss | $ | 43.5 |
| | $ | 67.1 |
| | $ | 6.1 |
| | $ | 0.9 |
| | $ | 2.1 |
| | $ | 0.5 |
|
| Estimated amounts that will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss over the next fiscal year: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net gain (loss) | $ | (16.0 | ) | | $ | (11.1 | ) | | $ | (0.4 | ) | | $ | 0.1 |
| | $ | (0.1 | ) | | $ | (0.1 | ) |
| Accumulated Benefit Obligation at December 31 | $ | 619.2 |
| | $ | 537.0 |
| | $ | 216.8 |
| | $ | 187.6 |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
|
| Weighted‑average assumptions as of December 31 | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Discount rate | 4.0 | % | | 4.7 | % | | 4.3 | % | | 4.8 | % | | 3.6 | % | | 4.4 | % |
| Expected return on assets | 7.6 | % | | 8.0 | % | | 7.4 | % | | 7.4 | % | | N/A |
| | N/A |
|
| Average rate of increase in compensation | 4.6 | % | | 4.6 | % | | 2.0 | % | | 2.1 | % | | N/A |
| | N/A |
|
| Initial health care cost trend rate | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | 7.8 | % | | 8.1 | % |
| Ultimate health care cost trend rate | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | 4.5 | % | | 4.5 | % |
| Number of years to ultimate trend rate | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | 17 |
| | 18 |
|
The discount rate used to determine the December 31, 2012 benefit obligations for U.S. pension plans is based on the rate from the Mercer Pension Discount Curve-Above Mean Yield that is appropriate for the duration of our plan liabilities. For our plans outside the U.S., the discount rate reflects the market rates for an optimized subset of high-quality corporate bonds currently available. The discount rate in a country was determined based on a yield curve constructed from high quality corporate bonds in that country. The rate selected from the yield curve has a duration that matches our plan.
The expected return on plan assets for each funded plan is based on expected future investment returns considering the target investment mix of plan assets.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table sets forth the net periodic pension and postretirement (including health care, life insurance and auto) expense (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement Benefits (U.S.) |
| | U.S. | | Non-U.S. | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Components of Net Periodic Benefit Cost: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Service cost | $ | 24.8 |
| | $ | 26.2 |
| | $ | 24.0 |
| | $ | 1.9 |
| | $ | 4.0 |
| | $ | 5.2 |
| | $ | 0.2 |
| | $ | 0.2 |
| | $ | 0.3 |
|
| Interest cost | 28.2 |
| | 27.5 |
| | 26.1 |
| | 9.7 |
| | 11.0 |
| | 9.7 |
| | 0.8 |
| | 0.9 |
| | 0.9 |
|
| Expected return on plan assets | (31.5 | ) | | (30.5 | ) | | (26.6 | ) | | (12.1 | ) | | (12.8 | ) | | (10.0 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net amortizations | 11.8 |
| | 7.2 |
| | 4.6 |
| | (0.1 | ) | | (0.7 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | — |
|
| Settlement loss | 2.0 |
| | 2.2 |
| | 0.4 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Curtailment gain | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (12.9 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Special termination cost | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net pension and postretirement expense | $ | 35.3 |
| | $ | 32.6 |
| | $ | 28.5 |
| | $ | (0.6 | ) | | $ | (11.3 | ) | | $ | 3.7 |
| | $ | 1.0 |
| | $ | 1.2 |
| | $ | 1.2 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted‑average discount rate for expense (January 1) | 4.71 | % | | 5.12 | % | | 5.42 | % | | 4.78 | % | | 5.36 | % | | 5.71 | % | | 4.4 | % | | 4.9 | % | | 5.4 | % |
| Weighted‑average assumed long-term rate of return on assets (January 1) | 8.00 | % | | 8.40 | % | | 8.50 | % | | 7.44 | % | | 7.46 | % | | 7.46 | % | | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
|
| Initial health care cost trend rate | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | 8.1 | % | | 8.4 | % | | 8.7 | % |
| Ultimate health care cost trend rate | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | 4.5 | % | | 4.5 | % | | 4.5 | % |
| Number of years to ultimate trend rate | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | 17 |
| | 18 |
| | 19 |
|
The balance in “Accumulated other comprehensive loss” at December 31, 2012 and 2011 relating to pension benefits was $109.8 million and $99.6 million, respectively.
Changing the assumed health care cost trend rates by one percentage point is estimated to have the following effects (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | One Percentage Point |
| | Increase | | Decrease |
| Effect on total of service and interest cost components | — |
| | — |
|
| Effect on postretirement benefit obligation | $ | 0.5 |
| | $ | (0.4 | ) |
The provisions charged to income for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 for all other pension plans were approximately $8.9 million, $8.0 million and $8.8 million, respectively.
The provisions charged to income for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 for the defined contribution plans were approximately $18.6 million, $18.0 million and $14.8 million, respectively.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Plan Assets
We have a long-term investment outlook for the assets held in our Company sponsored plans, which is consistent with the long-term nature of each plan's respective liabilities. We have two major plans which reside in the U.S. and the U.K.
The U.S. Plan, or the “Plan,” currently has a target asset allocation of 65% equity and 35% fixed income. The equity portion of the Plan is invested in one passively managed S&P 500 index fund, one passively managed U.S. small/midcap fund and one actively managed international portfolio. The fixed income portion of the Plan is actively managed by a professional investment manager and is benchmarked to the Barclays Long Govt/Credit Index. The Plan assumes an 7.6% rate of return on assets, which represents the expected long-term annual weighted‑average return for the Plan in total.
The U.K. Plan currently invests in a professionally managed Balanced Consensus Index Fund, which has the investment objective of achieving a total return relatively equal to its benchmark. The benchmark is based upon the average asset weightings of a broad universe of U.K. pension funds invested in pooled investment vehicles and each of their relevant indices. The asset allocation as of December 31, 2012, was 79% equity, 9% fixed income and 12% cash and cash equivalents. The U.K. Plan currently assumes a rate of return on assets of 7.5%, which represents the expected long-term annual weighted‑average return.
The fair value measurements of our U.S. pension plan assets are based upon significant observable inputs (Level 2) and relate to common collective trusts and other pooled investment vehicles consisting of the following asset categories (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| Asset Category | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Short Term Investments | $ | 8.3 |
| | $ | 11.6 |
|
| Equity Securities: | | | |
| U.S. Large Cap | 135.9 |
| | 119.3 |
|
| U.S. Mid Cap | 42.0 |
| | 34.9 |
|
| U.S. Small Cap | 31.6 |
| | 27.5 |
|
| International Large Cap | 109.3 |
| | 89.0 |
|
| Fixed Income Securities: | | | |
| U.S. Treasuries | 67.5 |
| | 53.2 |
|
| Corporate Bonds | 83.8 |
| | 68.7 |
|
| Government Bonds | 4.4 |
| | 4.1 |
|
| Municipal Bonds | 9.1 |
| | 9.5 |
|
| Real Estate (REITs) | 6.5 |
| | 5.4 |
|
| Total fair value of pension plan assets | $ | 498.4 |
| | $ | 423.2 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Our U.K. Plan accounts for most of the $178.3 million in fair value of Non-U.S. plan assets. The fair value measurements of our U.K. pension plan assets are based upon significant observable inputs (Level 2) and relate to common collective trusts and other pooled investment vehicles consisting of the following asset categories (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| Asset Category | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Short Term Investments | $ | 12.9 |
| | $ | 11.6 |
|
| U.K. Equities | 66.1 |
| | 57.6 |
|
| Overseas Equities | 67.1 |
| | 60.5 |
|
| U.K. Conventional Gilts | 6.5 |
| | 6.6 |
|
| Corporate Bonds | 5.3 |
| | 5.0 |
|
| Global Treasury Bonds | 9.3 |
| | 6.5 |
|
| Index‑Linked Gilts‑Stocks | 1.8 |
| | 1.4 |
|
| Total fair value of pension plan assets | $ | 169.0 |
| | $ | 149.2 |
|
Contributions
Our policy for funded plans is to contribute annually, at a minimum, amounts required by applicable laws, regulations and union agreements. From time to time we make contributions beyond those legally required. In 2012, we made discretionary cash contributions to our U.S. qualified pension plan of $38.4 million. In 2011, we made discretionary cash contributions to our U.S. qualified pension plan of $58.9 million. We expect to contribute between $20.0 million and $30.0 million to our U.S. plan during 2013. The level of 2013 and future contributions will vary, and is dependent on a number of factors including investment returns, interest rate fluctuations, plan demographics, funding regulations and the results of the final actuarial valuation.
Estimated Future Benefit Payments
The following table presents estimated future benefit payments (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Pension Benefits | | Postretirement
Benefits (U.S.) |
| 2013 | $ | 31.1 |
| | $ | 1.3 |
|
| 2014 | 34.4 |
| | 1.4 |
|
| 2015 | 40.6 |
| | 1.5 |
|
| 2016 | 44.3 |
| | 1.4 |
|
| 2017 | 51.1 |
| | 1.3 |
|
| 2018-2022 | 314.1 |
| | 6.7 |
|
| | $ | 515.6 |
| | $ | 13.6 |
|
Multiemployer Pension Plans
We contribute to several multiemployer defined benefit pension plans under collective bargaining agreements that cover certain of our union‑represented employees. The risks of participating in such plans are different from the risks of single‑employer plans, in the following respects:
| |
| a) | Assets contributed to a multiemployer plan by one employer may be used to provide benefits to employees of other participating employers. |
| |
| b) | If a participating employer ceases to contribute to the plan, the unfunded obligations of the plan may be borne by the remaining participating employers. |
| |
| c) | If we cease to have an obligation to contribute to the multiemployer plan in which we had been a contributing employer, we may be required to pay to the plan an amount based on the underfunded status of the plan and on the history of our participation in the plan prior to the cessation of our obligation |
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
to contribute. The amount that an employer that has ceased to have an obligation to contribute to a multiemployer plan is required to pay to the plan is referred to as a withdrawal liability.
Our participation in multiemployer plans for the annual period ended December 31, 2012 is outlined in the table below. For each plan that is individually significant to us, the following information is provided:
The “EIN / Pension Plan Number” column provides the Employer Identification Number and the three‑digit plan number assigned to a plan by the Internal Revenue Service.
The most recent Pension Protection Act Zone Status available for 2011 and 2012 is for plan years that ended in 2011 and 2012, respectively. The zone status is based on information provided to us and other participating employers by each plan and is certified by the plan's actuary. A plan in the “red” zone has been determined to be in “critical status”, based on criteria established under the Internal Revenue Code, or the “Code,” and is generally less than 65% funded. A plan in the “yellow” zone has been determined to be in “endangered status”, based on criteria established under the Code, and is generally less than 80% funded. A plan in the “green” zone has been determined to be neither in “critical status” nor in “endangered status,” and is generally at least 80% funded.
The “FIP/RP Status Pending/Implemented” column indicates whether a Funding Improvement Plan, as required under the Code to be adopted by plans in the “yellow” zone, or a Rehabilitation Plan, as required under the Code to be adopted by plans in the “red” zone, is pending or has been implemented as of the end of the plan year that ended in 2012.
The “Surcharge Imposed” column indicates whether our contribution rate for 2012 included an amount in addition the contribution rate specified in the applicable collective bargaining agreement, as imposed by a plan in “critical status,” in accordance with the requirements of the Code.
The last column lists the expiration dates of the collective bargaining agreements pursuant to which we contribute to the plans.
For plans that are not individually significant to us, the total amount of contributions is presented in the aggregate. |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (In millions of dollars) | EIN /Pension
Plan | | Pension
Protection Act
Zone Status | | FIP /
RP Status
Pending / | | Contributions by
The Hertz Corporation | | Surcharge | | Expiration
Dates of
Collective
Bargaining | |
| Pension Fund | Number | | 2012 | | 2011 | | Implemented | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | Imposed | | Agreements | |
| Western Conference of Teamsters | 91-6145047 | | Green | | Green | | NA | | $ | 4.1 |
| | $ | 3.9 |
| | $ | 3.8 |
| | NA | | Various | |
| Teamsters Central States | 36-6044243 | | Critical | | Critical | | Implemented | | 1.2 |
| | 1.3 |
| | 1.2 |
| | No | | Various | |
| IAM National | 51-60321295 | | Green | | Green | | NA | | 0.7 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 0.6 |
| | NA | | Various | |
| Midwest Operating Engineers | 36-6140097 | | Green | | Green | | NA | | 0.5 |
| | 0.4 |
| | 0.2 |
| | NA | | 2/28/2014 | |
| Local 1034** | 13-6594795 | | Critical | | Critical | | Implemented | | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
| | Yes | | 5/2/2013 | |
| Operating Engineers Local 324 | 38-1900637 | | Critical | | Critical | | Implemented | | 0.1 |
| | 0.1 |
| | 0.1 |
| | No | | 6/30/2013 | |
| Western Pennsylvania Teamsters | 25-6029946 | | Critical | | Critical | | Implemented | | 0.1 |
| | 0.1 |
| | 0.1 |
| | No | | 11/4/2011 | * |
| | | | | | 7 Other Plans | | 0.6 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 0.5 |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | Total Contributions | | $ | 7.5 |
| | $ | 7.2 |
| | $ | 6.7 |
| | | | | |
* The parties are still attempting to negotiate a successor agreement.
| |
| ** | The amount contributed by Hertz to the Local 1034 Pension Fund was reported as being more than 5% of total contributions to the plan, on the fund's Form 5500 for the year ended 12/31/2011. |
During 2012, Hertz completely withdrew employees from an existing multi-employer pension plan with the Central States Pension Fund, or the “Pension Fund,” and entered into a new agreement with the Pension Fund, which adopted an alternative method for determining an employer's unfunded obligation that would limit Hertz funding obligations to the Pension Fund in the future. As part of the agreement, certain Pension Fund participants were effectively moved to the Hertz retirement plan and the remaining participants were moved to a new pension plan sponsored by the Pension Fund. In connection with the complete withdrawal from the Pension Fund, Hertz was subject to a withdrawal liability of approximately $23.2 million, which was paid in December 2012.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 7—Stock-Based Compensation
Plans
On February 28, 2008, the Board of Directors of Hertz and Hertz Holdings jointly adopted the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan, or the “Omnibus Plan,” which was approved by the stockholders of Hertz Holdings at the annual meeting of stockholders held on May 15, 2008 and amended and restated on May 27, 2010. A maximum of 32.7 million shares are reserved for issuance under the Omnibus Plan. The Omnibus Plan provides for grants of both equity and cash awards, including non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights, performance awards (shares and units), restricted stock, restricted stock units and deferred stock units to key executives, employees and non-management directors. We also granted awards under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Stock Incentive Plan, or the “Stock Incentive Plan,” and the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Director Stock Incentive Plan, or the “Director Plan”, or collectively the “Prior Plans.”
The Omnibus Plan provides that no further awards will be granted pursuant to the Prior Plans. However, awards that had been previously granted pursuant to the Prior Plans will continue to be subject to and governed by the terms of the Prior Plans. As of December 31, 2012, there were 8.0 million shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock underlying awards outstanding under the Prior Plans. In addition, as of December 31, 2012, there were 9.4 million shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock underlying awards outstanding under the Omnibus Plan.
In addition to the 17.4 million shares underlying outstanding awards as of December 31, 2012, we had 16.9 million shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock available for issuance under the Omnibus Plan. The shares of common stock to be delivered under the Omnibus Plan may consist, in whole or in part, of common stock held in treasury or authorized but unissued shares of common stock, not reserved for any other purpose.
Shares subject to any award granted under the Omnibus Plan that for any reason are canceled, terminated, forfeited, settled in cash or otherwise settled without the issuance of common stock after the effective date of the Omnibus Plan will generally be available for future grants under the Omnibus Plan.
In March 2012, Hertz Holdings granted 543,880 Restricted Stock Units, or "RSUs," to certain executives and employees at fair values ranging from $13.65 to $14.47, 747,423 Performance Stock Units, or "PSUs," at a fair value of $13.65, and 1,098,591 PSUs (referred to as Price Vesting Units, or "PVUs") at fair values ranging from $10.13 to $11.26 under the Omnibus Plan. The PSUs have a performance condition under which the number of units that will ultimately be awarded will vary from 0% to 150% of the original grant, based on 2012 and 2013 Hertz Holdings' Corporate EBITDA results. "EBITDA" means consolidated net income before net interest expense, consolidated income taxes and consolidated depreciation (which includes revenue earning equipment lease charges) and amortization. "Corporate EBITDA," represents EBITDA as adjusted for car rental fleet interest, car rental fleet depreciation and certain other items, as provided in the applicable award agreements. Of the PVUs granted, one half will fully vest after three years if Hertz Holdings' stock price appreciates 15% over the starting price established on March 2, 2012, and one half will fully vest after four years if Hertz Holdings' stock price appreciates 25% over the starting price established on March 2, 2012. The starting price for the PVU awards is the average of the 20 trading day closing stock price ending March 2, 2012. Partial attainment of Hertz Holdings' stock appreciation targets will result in partial vesting. The achievement of the market condition for the PVUs is determined based on the average closing stock price for the 20 trading day period ending March 6, 2015 and 2016, respectively. In May 2012, Hertz Holdings granted 146,301 RSUs at a fair value of $15.48, in August 2012, Hertz Holdings granted 59,480 RSUs at a fair value of $12.12, and in November 2012, we granted 24,713 RSUs at a fair value of $13.15. In November 2012, we granted 35,492 non-qualified options with a strike price of $0.17 in exchange for 6,000 Dollar Thrifty options with a strike price of $0.97.
The non-cash stock-based compensation expense associated with the Prior Plans (as defined below) and the Omnibus Plan is pushed down from Hertz Holdings and recorded on the books at the Hertz level.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
A summary of the total compensation expense and associated income tax benefits recognized under the Prior Plans and the Omnibus Plan, including the cost of stock options, RSUs, and PSUs, is as follows (in millions of dollars): |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Compensation expense | $ | 30.3 |
| | $ | 31.0 |
| | $ | 36.6 |
|
| Income tax benefit | (11.7 | ) | | (12.0 | ) | | (14.2 | ) |
| Total | $ | 18.6 |
| | $ | 19.0 |
| | $ | 22.4 |
|
As of December 31, 2012, there was approximately $38.0 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock options, RSUs and PSUs granted by Hertz Holdings under the Prior Plans and the Omnibus Plan. The total unrecognized compensation cost is expected to be recognized over the remaining 1.4 years, on a weighted average basis, of the requisite service period that began on the grant dates.
Stock Options and Stock Appreciation Rights
All stock options and stock appreciation rights granted under the Omnibus Plan will have a per-share exercise price of not less than the fair market value of one share of Hertz Holdings common stock on the grant date. Stock options and stock appreciation rights will vest based on a minimum period of service or the occurrence of events (such as a change in control, as defined in the Omnibus Plan) specified by the compensation committee of our Board of Directors. No stock options or stock appreciation rights will be exercisable after ten years from the grant date.
We have accounted for our employee stock‑based compensation awards in accordance with ASC 718, “Compensation-Stock Compensation.” The non-cash stock based compensation expense associated with the Stock Incentive Plan is pushed down from Hertz Holdings and recorded on the books at the Hertz level. The options are being accounted for as equity‑classified awards. We will recognize compensation cost on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. The value of each option award is estimated on the grant date using a Black‑Scholes option valuation model that incorporates the assumptions noted in the following table. Because the stock of Hertz Holdings became publicly traded in November 2006 and had a short trading history, it was not practicable for us to estimate the expected volatility of Hertz Holdings' share price, or a peer company share price, because there was insufficient historical information about past volatility prior to 2012. Therefore, prior to 2012 we used the calculated value method, substituting the historical volatility of an appropriate industry sector index for the expected volatility of Hertz Holdings' common stock price as an assumption in the valuation model. We selected the Dow Jones Specialized Consumer Services sub-sector within the consumer services industry, and we used the U.S. large capitalization component, which includes the top 70% of the index universe (by market value).
The calculation of the historical volatility of the index was made using the daily historical closing values of the index for the preceding 6.25 years, because that is the expected term of the options using the simplified approach.
For 2012, we have determined that there was sufficient historical information available to estimate the expected volatility of our share price. Therefore, for 2012 we calculated volatility for Hertz Holdings' stock price based on a weighted average combining implied volatility and the average of our peer’s most recent 5.79-year volatility and mean reversion volatility.
The risk-free interest rate is the implied zero-coupon yield for U.S. Treasury securities having a maturity approximately equal to the expected term, as of the grant dates. The assumed dividend yield is zero.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Assumption | 2012 Grants | | 2011 Grants | | 2010 Grants |
| Expected volatility | 81.5 | % | | 36.7 | % | | 36.1 | % |
| Expected dividend yield | — | % | | — | % | | — | % |
| Expected term (years) | 3 |
| | 6.25 |
| | 6.25 |
|
| Risk-free interest rate | 0.4 | % | | 2.56 | % | | 1.62%-2.96% |
|
| Weighted‑average grant date fair value | $ | 14.62 |
| | $ | 5.93 |
| | $ | 4.00 |
|
A summary of option activity under the Stock Incentive Plan and the Omnibus Plan as of December 31, 2012 is presented below.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options | Shares | | Weighted‑
Average
Exercise
Price | | Weighted‑
Average
Remaining
Contractual
Term (years) | | Aggregate Intrinsic
Value (In thousands
of dollars) |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2012 | 15,142,061 |
| | $ | 10.60 |
| | 6.3 | | $ | 41,110 |
|
| Granted | 35,492 |
| | 0.17 |
| | | | |
| Exercised | (1,740,447 | ) | | 5.75 |
| | | | |
| Forfeited or Expired | (248,431 | ) | | 14.66 |
| | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | 13,188,675 |
| | 11.13 |
| | 5.4 | | $ | 74,681 |
|
| Exercisable at December 31, 2012 | 10,321,945 |
| | 10.83 |
| | 4.7 | | $ | 63,086 |
|
A summary of non-vested options as of December 31, 2012, and changes during the year, is presented below.
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Non-vested
Shares | | Weighted‑
Average
Exercise Price | | Weighted‑
Average Grant-
Date Fair
Value |
| Non-vested as of January 1, 2012 | 4,915,825 |
| | $ | 12.04 |
| | $ | 4.86 |
|
| Granted | 35,492 |
| | 0.17 |
| | 0.17 |
|
| Vested | (1,959,032 | ) | | 11.56 |
| | 4.59 |
|
| Forfeited | (125,555 | ) | | 11.91 |
| | 4.84 |
|
| Non-vested as of December 31, 2012 | 2,866,730 |
| | $ | 12.23 |
| | $ | 4.98 |
|
Additional information pertaining to option activity under the plans is as follows (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended
December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Aggregate intrinsic value of stock options exercised | $ | 15.1 |
| | $ | 15.0 |
| | $ | 8.1 |
|
| Cash received from the exercise of stock options | 11.2 |
| | 13.1 |
| | 7.9 |
|
| Fair value of options that vested | 9.0 |
| | 17.4 |
| | 21.6 |
|
| Tax benefit realized on exercise of stock options | 0.9 |
| | 0.5 |
| | 0.3 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Performance Stock, Performance Stock Units, Restricted Stock and Restricted Stock Units
Performance stock, PSUs and performance units granted under the Omnibus Plan will vest based on the achievement of pre-determined performance goals over performance periods determined by the Compensation, Nominating and Governance Committee of the Board of Directors of Hertz Holdings. Each of the units granted under the Omnibus Plan represent the right to receive one share of Hertz Holdings' common stock on a specified future date. In the event of an employee's death or disability, a pro rata portion of the employee's performance stock, performance stock units and performance units will vest to the extent performance goals are achieved at the end of the performance period. Restricted Stock and RSUs granted under the Omnibus Plan will vest based on a minimum period of service or the occurrence of events (such as a change in control, as defined in the Omnibus Plan) specified by the Compensation, Nominating and Governance Committee of the Board of Directors of Hertz Holdings.
A summary of RSU and PSU activity under the Omnibus Plan as of December 31, 2012 is presented below.
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Weighted‑
Average
Fair Value | | Aggregate Intrinsic
Value (In thousands
of dollars) |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2012 | 4,327,461 |
| | $ | 6.46 |
| | $ | 50,718 |
|
| Granted | 869,894 |
| | 13.78 |
| | — |
|
| Vested | (3,198,219 | ) | | 4.58 |
| | — |
|
| Forfeited or Expired | (126,502 | ) | | 13.19 |
| | — |
|
| Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | 1,872,634 |
| | $ | 12.62 |
| | $ | 30,468 |
|
Additional information pertaining to RSU and PSU activity is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Total fair value of awards that vested ($ millions) | $ | 14.6 |
| | $ | 9.6 |
| | $ | 8.2 |
|
| Weighted average grant date fair value of awards | $ | 13.78 |
| | $ | 14.78 |
| | $ | 10.1 |
|
Compensation expense for RSUs and PSUs is based on the grant date fair value, and is recognized ratably over the vesting period. For grants in 2010, 2011 and 2012, the vesting period is three years (for grants in 2010 and 2011, 25% in the first year, 25% in the second year and 50% in the third year and for grants in 2012, 33 1/3% per year). In addition to the service vesting condition, the PSUs had an additional vesting condition which called for the number of units that will be awarded being based on achievement of a certain level of Corporate EBITDA over the applicable measurement period.
In March 2012, Hertz Holdings granted 1,846,014 PSUs that had a performance vesting condition under which the number of units that will ultimately be awarded will vary from 0% to 150% of the original grant, based on the sum of 2012 and 2013 Corporate EBITDA results, in addition to a service vesting condition. In March 2011 Hertz Holdings' granted 499,515 PSUs that had a performance vesting condition under which the number of units that will ultimately be awarded will vary from 0% to 150% of the original grant, based on the sum of 2011 and 2012 Corporate EBITDA results, in addition to a service vesting condition. An additional 193,798 PSUs granted in March 2011 contained a market condition whereby the 20 trading day average trailing Hertz Holdings' stock price must equal or exceed a certain price target at any time during the five year performance period, in addition to a service vesting condition. A summary of the PSU activity for this grant is presented below.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Weighted‑
Average
Fair Value | | Aggregate Intrinsic
Value (In thousands
of dollars) |
| Outstanding at January 1, 2012 | 677,971 |
| | $ | 13.34 |
| | $ | 7,946 |
|
| Granted | 1,846,014 |
| | 11.89 |
| | — |
|
| Vested | (124,874 | ) | | 14.60 |
| | — |
|
| Forfeited or Expired | (100,438 | ) | | 11.87 |
| | — |
|
| Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | 2,298,673 |
| | $ | 12.18 |
| | $ | 37,399 |
|
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
On February 28, 2008, upon recommendation of the compensation committee of the Board of Directors, or “Committee,” of Hertz Holdings, Hertz Holdings' Board of Directors adopted the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan, or the “ESPP,” and the plan was approved by the stockholders of Hertz Holdings on May 15, 2008. The ESPP is intended to be an “employee stock purchase plan” within the meaning of Section 423 of the Internal Revenue Code.
The maximum number of shares that may be purchased under the ESPP is 3,000,000 shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock, subject to adjustment in the case of any change in Hertz Holdings' shares, including by reason of a stock dividend, stock split, share combination, recapitalization, reorganization, merger, consolidation or change in corporate structure. An eligible employee may elect to participate in the ESPP each quarter (or other period established by the Committee) through a payroll deduction. The maximum and minimum contributions that an eligible employee may make under all of Hertz Holdings' qualified employee stock purchase plans will be determined by the Committee, provided that no employee may be permitted to purchase stock with an aggregate fair market value greater than $25,000 per year. At the end of the offering period, the total amount of each employee's payroll deduction will be used to purchase shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock. The purchase price per share will be not less than 85% of the market price of Hertz Holdings' common stock on the date of purchase; the exact percentage for each offering period will be set in advance by the Committee.
For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, we recognized compensation cost of approximately $0.8 million, $0.7 million and $0.6 million, respectively, for the amount of the discount on the stock purchased by our employees under the ESPP. Approximately 1,800 employees participated in the ESPP as of December 31, 2012.
Note 8—Depreciation of Revenue Earning Equipment and Lease Charges
Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges includes the following (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment | $ | 2,165.2 |
| | $ | 1,921.8 |
| | $ | 1,747.0 |
|
| Adjustment of depreciation upon disposal of revenue earning equipment | (96.8 | ) | | (112.2 | ) | | 42.9 |
|
| Rents paid for vehicles leased | 79.8 |
| | 96.1 |
| | 78.2 |
|
| Total | $ | 2,148.2 |
| | $ | 1,905.7 |
| | $ | 1,868.1 |
|
The adjustment of depreciation upon disposal of revenue earning equipment for the year ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, included net gains of $83.2 million and $98.9 million and net loss of $32.9 million, respectively, on the disposal of vehicles used in our car rental operations and net gains of $13.5 million and $13.3 million and net loss of $10.0 million, respectively, on the disposal of industrial and construction equipment used in our equipment rental operations.
Depreciation rates are reviewed on a quarterly basis based on management's routine review of present and estimated future market conditions and their effect on residual values at the time of disposal. During the year ended December
31, 2012, depreciation rates being used to compute the provision for depreciation of revenue earning equipment were adjusted on certain vehicles in our car rental operations to reflect changes in the estimated residual values to be realized when revenue earning equipment is sold. These depreciation rate changes resulted in net decreases of $130.6 million and $13.8 million and a net increase of $19.1 million in depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 respectively. The cumulative effect of the reduction in rates was indicative of the strong residual values experienced in the U.S. for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011. In 2012, 2011 and 2010, the depreciation rate changes in certain of our equipment rental operations resulted in an increase of $0.5 million, decrease of $4.4 million and increase of $3.6 million in depreciation expense, respectively.
Note 9—Taxes on Income
The components of income (loss) before income taxes for the periods were as follows (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years ended December 31, |
| | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Domestic | | $ | 407.7 |
| | $ | 235.9 |
| | $ | (81.2 | ) |
| Foreign | | 95.2 |
| | 138.0 |
| | 113.5 |
|
| Total | | $ | 502.9 |
| | $ | 373.9 |
| | $ | 32.3 |
|
The total provision (benefit) for taxes on income consists of the following (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Years ended December 31, |
| | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Current: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | $ | 20.1 |
| | $ | 10.3 |
| | $ | 10.2 |
|
| Foreign | | 32.3 |
| | 30.6 |
| | 41.5 |
|
| State and local | | 39.1 |
| | 28.5 |
| | 1.5 |
|
| Total current | | 91.5 |
| | 69.4 |
| | 53.2 |
|
| Deferred: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | 141.9 |
| | 82.4 |
| | (18.6 | ) |
| Foreign | | 11.9 |
| | (3.2 | ) | | 1.3 |
|
| State and local | | (18.2 | ) | | (4.8 | ) | | (2.6 | ) |
| Total deferred | | 135.6 |
| | 74.4 |
| | (19.9 | ) |
| Total provision (benefit) | | $ | 227.1 |
| | $ | 143.8 |
| | $ | 33.3 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The principal items of the U.S. and foreign net deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, 2012 and 2011 are as follows (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Deferred Tax Assets: | | | | |
| Employee benefit plans | | $ | 103.6 |
| | $ | 102.8 |
|
| Net operating loss carryforwards | | 1,610.9 |
| | 1,743.5 |
|
| Foreign tax credit carryforwards | | 20.8 |
| | 20.8 |
|
| Federal, state and foreign local tax credit carryforwards | | 26.8 |
| | 15.0 |
|
| Accrued and prepaid expenses | | 341.7 |
| | 327.4 |
|
| Total Deferred Tax Assets | | 2,103.8 |
| | 2,209.5 |
|
| Less: Valuation Allowance | | (226.4 | ) | | (186.7 | ) |
| Total Net Deferred Tax Assets | | 1,877.4 |
| | 2,022.8 |
|
| Deferred Tax Liabilities: | | | | |
| Depreciation on tangible assets | | (3,081.4 | ) | | (2,742.3 | ) |
| Intangible assets | | (1,477.1 | ) | | (942.4 | ) |
| Total Deferred Tax Liabilities | | (4,558.5 | ) | | (3,684.7 | ) |
| Net Deferred Tax Liability | | $ | (2,681.1 | ) | | $ | (1,661.9 | ) |
As of December 31, 2012, deferred tax assets of $1,294.3 million were recorded for unutilized U.S. Federal Net Operating Losses, or “NOL,” carry forwards of $3,697.9 million. The total Federal NOL carry forwards are $3,775.0 million of which $77.1 million relate to excess tax deductions associated with stock option plans which have yet to reduce taxes payable. Upon the utilization of these carry forwards, the associated tax benefits of approximately $27.0 million will be recorded to Additional paid-in capital. The Federal NOLs begin to expire in 2025. State NOLs exclusive of the effects of the excess tax deductions, have generated a deferred tax asset of $105.8 million. The state NOLs expire over various years beginning in 2013 depending upon particular jurisdiction.
On January 1, 2009, Bank of America acquired Merrill Lynch. For U.S. income tax purposes the transaction, when combined with other unrelated transactions during the previous 36 months, resulted in a change in control as that term is defined in Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. Consequently, utilization of all pre-2009 U.S. net operating losses is subject to an annual limitation. We have calculated the expected annual base limitation as well as additional limitations resulting from a net unrealized built in gain as of the acquisition date and other adjustments. Based on the calculations, the limitation is not expected to result in a loss of net operating losses or have a material adverse impact on taxes.
As of December 31, 2012, deferred tax assets of $248.5 million were recorded for foreign NOL carry forwards of $1,049.0 million. A valuation allowance of $200.6 million at December 31, 2012 was recorded against these deferred tax assets because those assets relate to jurisdictions that have historical losses and the likelihood exists that a portion of the NOL carry forwards may not be utilized in the future.
The foreign NOL carry forwards of $1,049.0 million include $775.5 million which have an indefinite carry forward period and associated deferred tax assets of $170.6 million. The remaining foreign NOLs of $273.5 million are subject to expiration beginning in 2015 and have associated deferred tax assets of $77.9 million.
As of December 31, 2012, deferred tax assets for U.S. Foreign Tax Credit carry forwards were $20.8 million which relate to credits generated as of December 31, 2007. The carry forwards will begin to expire in 2015. A valuation allowance of $13.5 million at December 31, 2012 was recorded against a portion of the U.S. foreign tax credit deferred tax assets in the likelihood that they may not be utilized in the future. A deferred tax asset was also recorded for various state tax credit carry forwards of $3.0 million, which will begin to expire in 2027.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
In determining the valuation allowance, an assessment of positive and negative evidence was performed regarding realization of the net deferred tax assets in accordance with ASC 740-10, “Accounting for Income Taxes,” or “ASC 740-10.” This assessment included the evaluation of scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, the availability of carry forwards and estimates of projected future taxable income. Based on the assessment, as of December 31, 2012, total valuation allowances of $226.4 million were recorded against deferred tax assets. Although realization is not assured, we have concluded that it is more likely than not the remaining deferred tax assets of $1,877.4 million will be realized and as such no valuation allowance has been provided on these assets.
The significant items in the reconciliation of the statutory and effective income tax rates consisted of the following:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Statutory Federal Tax Rate | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % | | 35.0 | % |
| Foreign tax differential | (3.2 | ) | | (3.3 | ) | | (32.1 | ) |
| State and local income taxes, net of federal income tax benefit | 2.9 |
| | 3.2 |
| | (5.2 | ) |
| Change in state statutory rates, net of federal income tax benefit | (1.0 | ) | | 0.5 |
| | 5.1 |
|
| Federal and foreign permanent differences | 2.3 |
| | (1.1 | ) | | (24.0 | ) |
| Withholding taxes | 1.7 |
| | 2.0 |
| | 26.2 |
|
| Uncertain tax positions | (0.6 | ) | | (0.8 | ) | | 11.2 |
|
| Change in valuation allowance | 7.9 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 85.1 |
|
| All other items, net | 0.2 |
| | 2.4 |
| | 1.8 |
|
| Effective Tax Rate | 45.2 | % | | 38.5 | % | | 103.1 | % |
The effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2012 was 45.2% as compared to 38.5% in the year ended December 31, 2011. The provision for taxes on income increased $83.3 million, primarily due to higher income before income taxes, changes in geographic earnings mix, changes in valuation allowances for losses in certain non-U.S. jurisdictions for which tax benefits cannot be realized and non-deductible compensation payments under Internal Revenue Code Section 280(G) related to the Dollar Thrifty acquisition.
The negative effective tax rate in 2010 is primarily due to a lower loss before income taxes in 2010, valuation allowances for losses in certain non-U.S. jurisdictions for which tax benefits cannot be realized and differences in foreign tax rates versus the U.S. Federal tax rate and the impact of the France law change in 2010.
As of December 31, 2012, our foreign subsidiaries have $270.3 million of undistributed earnings which would be subject to taxation if repatriated. Deferred tax liabilities have not been recorded for such earnings because it is management's current intention to permanently reinvest undistributed earnings offshore. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of such deferred tax liabilities. If, in the future, undistributed earnings are repatriated to the United States, or it is determined such earnings will be repatriated in the foreseeable future, deferred tax liabilities will be recorded.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
As of December 31, 2012, total unrecognized tax benefits were $17.2 million, all of which, if recognized, would favorably impact the effective tax rate in future periods. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Balance at January 1 | $ | 21.6 |
| | $ | 27.2 |
| | $ | 25.6 |
|
| Increase (decrease) attributable to tax positions taken during prior periods | (6.8 | ) | | (9.5 | ) | | 0.3 |
|
| Increase attributable to tax positions taken during the current year | 2.4 |
| | 3.9 |
| | 1.3 |
|
| Decrease attributable to settlements with taxing authorities | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Balance at December 31 | $ | 17.2 |
| | $ | 21.6 |
| | $ | 27.2 |
|
We conduct business globally and, as a result, file one or more income tax returns in the U.S. and non-U.S. jurisdictions. In the normal course of business we are subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world. The open tax years for these jurisdictions span from 2003 to 2012. We are currently under audit by the Internal Revenue Service for tax years 2006 to 2009. Several U.S. state and non-U.S. jurisdictions are under audit.
In many cases the uncertain tax positions are related to tax years that remain subject to examination by the relevant taxing authorities. It is reasonable that approximately $6.8 million of unrecognized tax benefits may reverse within the next twelve months due to settlement with the relevant taxing authorities and/or the filing of amended income tax returns.
Net, after-tax interest and penalties related to the liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits are classified as a component of “Provision for taxes on income” in the consolidated statement of operations. During the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, approximately $0.6 million, $1.9 million and $0.2 million, respectively, in net, after-tax interest and penalties were recognized. As of December 31, 2012 and 2011, approximately $4.2 million and $3.7 million, respectively, of net, after-tax interest and penalties was accrued in our consolidated balance sheet within "Accrued taxes."
Note 10—Lease and Concession Agreements
We have various concession agreements, which provide for payment of rents and a percentage of revenue with a guaranteed minimum, and real estate leases under which the following amounts were expensed (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Rents | $ | 135.9 |
| | $ | 130.6 |
| | $ | 133.9 |
|
| Concession fees: | | | | | |
| Minimum fixed obligations | 249.6 |
| | 248.7 |
| | 252.0 |
|
| Additional amounts, based on revenues | 329.4 |
| | 311.8 |
| | 278.7 |
|
| Total | $ | 714.9 |
| | $ | 691.1 |
| | $ | 664.6 |
|
For the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, sublease income reduced rent expense included in the above table by $5.0 million, $5.0 million and $4.5 million, respectively.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
As of December 31, 2012, minimum obligations under existing agreements referred to above are approximately as follows (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Rents | | Concessions |
| 2013 | $ | 157.3 |
| | $ | 390.3 |
|
| 2014 | 128.7 |
| | 279.4 |
|
| 2015 | 99.3 |
| | 192.8 |
|
| 2016 | 74.7 |
| | 141.4 |
|
| 2017 | 50.4 |
| | 91.3 |
|
| Years after 2017 | 194.1 |
| | 509.7 |
|
The future minimum rent payments in the above table have been reduced by minimum future sublease rental inflows in aggregate of $21.2 million.
Many of our concession agreements and real estate leases require us to pay or reimburse operating expenses, such as common area charges and real estate taxes, to pay concession fees above guaranteed minimums or additional rent based on a percentage of revenues or sales (as defined in those agreements) arising at the relevant premises, or both. Such obligations are not reflected in the table of minimum future obligations appearing immediately above. We operate from various leased premises under operating leases with terms up to 25 years. A number of our operating leases contain renewal options. These renewal options vary, but the majority include clauses for renewal for various term lengths at various rates, both fixed and market.
In addition to the above, we have various leases on revenue earning equipment and office and computer equipment under which the following amounts were expensed (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenue earning equipment | $ | 79.8 |
| | $ | 96.1 |
| | $ | 78.2 |
|
| Office and computer equipment | 12.2 |
| | 10.1 |
| | 10.4 |
|
| Total | $ | 92.0 |
| | $ | 106.2 |
| | $ | 88.6 |
|
As of December 31, 2012, minimum obligations under existing agreements referred to above that have a maturity of more than one year are as follows (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | |
| 2013 | $ | 56.6 |
|
| 2014 | $ | 25.2 |
|
| 2015 | $ | 6.7 |
|
| 2016 | $ | 2.1 |
|
| 2017 | $ | — |
|
| After 2017 | $ | — |
|
Commitments under capital leases within our vehicle rental programs have been reflected in Note 5—Debt.
Note 11—Segment Information
Our operating segments are aggregated into reportable business segments based primarily upon similar economic characteristics, products, services, customers, and delivery methods. We have identified two reportable segments: rental and leasing of cars, crossovers and light trucks, or “car rental,” and rental of industrial, construction and material handling equipment, or “equipment rental.” Other reconciling items includes general corporate assets and expenses,
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
certain interest expense (including net interest on corporate debt), as well as other business activities, such as our third party claim management services.
Adjusted pre-tax income (loss) is the measure utilized by management in making decisions about allocating resources to segments and measuring their performance. We believe this measure best reflects the financial results from ongoing operations. Adjusted pre-tax income (loss) is calculated as income (loss) before income taxes plus other reconciling items, non-cash purchase accounting charges, non-cash debt charges and certain one-time charges and non-operational items. The contribution of our reportable segments for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 is summarized below (in millions of dollars).
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenues | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 7,633.0 |
| | $ | 7,083.5 |
| | $ | 6,486.2 |
|
| Equipment rental | 1,385.4 |
| | 1,209.5 |
| | 1,070.1 |
|
| Other reconciling items | 2.4 |
| | 5.4 |
| | 6.2 |
|
| Total | $ | 9,020.8 |
| | $ | 8,298.4 |
| | $ | 7,562.5 |
|
| Adjusted pre-tax income(a) | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 1,020.1 |
| | $ | 850.2 |
| | $ | 641.9 |
|
| Equipment rental | $ | 227.0 |
| | $ | 161.6 |
| | $ | 78.0 |
|
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 1,876.1 |
| | $ | 1,651.4 |
| | $ | 1,594.6 |
|
| Equipment rental | 272.1 |
| | 254.3 |
| | 273.5 |
|
| Total | $ | 2,148.2 |
| | $ | 1,905.7 |
| | $ | 1,868.1 |
|
| Depreciation of property and equipment | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 126.9 |
| | $ | 116.1 |
| | $ | 112.3 |
|
| Equipment rental | 34.1 |
| | 33.7 |
| | 34.3 |
|
| Other reconciling items | 11.6 |
| | 8.2 |
| | 7.4 |
|
| Total | $ | 172.6 |
| | $ | 158.0 |
| | $ | 154.0 |
|
| Amortization of other intangible assets | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 41.7 |
| | $ | 32.7 |
| | $ | 30.2 |
|
| Equipment rental | 40.6 |
| | 35.8 |
| | 33.4 |
|
| Other reconciling items | 1.8 |
| | 1.5 |
| | 1.1 |
|
| Total | $ | 84.1 |
| | $ | 70.0 |
| | $ | 64.7 |
|
| Interest expense | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 316.3 |
| | $ | 333.1 |
| | $ | 401.3 |
|
| Equipment rental | 52.0 |
| | 45.3 |
| | 39.4 |
|
| Other reconciling items | 229.5 |
| | 271.9 |
| | 285.8 |
|
| Total | $ | 597.8 |
| | $ | 650.3 |
| | $ | 726.5 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenue earning equipment and property and equipment | | | | | |
| Car rental | | | | | |
| Expenditures | $ | 9,118.3 |
| | $ | 9,109.9 |
| | $ | 8,430.1 |
|
| Proceeds from disposals | (7,054.4 | ) | | (7,689.4 | ) | | (7,432.7 | ) |
| Net expenditures | $ | 2,063.9 |
| | $ | 1,420.5 |
| | $ | 997.4 |
|
| Equipment rental | | | | | |
| Expenditures | $ | 787.6 |
| | $ | 617.5 |
| | $ | 186.1 |
|
| Proceeds from disposals | (192.3 | ) | | (213.8 | ) | | (124.3 | ) |
| Net expenditures (proceeds) | $ | 595.3 |
| | $ | 403.7 |
| | $ | 61.8 |
|
| Other reconciling items | | | | | |
| Expenditures | $ | 20.1 |
| | $ | 8.6 |
| | $ | 3.9 |
|
| Proceeds from disposals | (16.1 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | | (0.3 | ) |
| Net expenditures | $ | 4.0 |
| | $ | 7.6 |
| | $ | 3.6 |
|
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Total assets at end of year | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 18,454.2 |
| | $ | 13,037.9 |
|
| Equipment rental | 3,623.0 |
| | 3,058.9 |
|
| Other reconciling items | 1,213.0 |
| | 1,570.5 |
|
| Total | $ | 23,290.2 |
| | $ | 17,667.3 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment, net, at end of year | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 10,710.1 |
| | $ | 8,318.7 |
|
| Equipment rental | 2,198.2 |
| | 1,786.7 |
|
| Total | $ | 12,908.3 |
| | $ | 10,105.4 |
|
| Property and equipment, net, at end of year | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 1,111.3 |
| | $ | 971.3 |
|
| Equipment rental | 235.9 |
| | 203.7 |
|
| Other reconciling items | 89.2 |
| | 76.9 |
|
| Total | $ | 1,436.4 |
| | $ | 1,251.9 |
|
We operate in the United States and in international countries. International operations are substantially in Europe. The operations within major geographic areas are summarized below (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenues | | | | | |
| United States | $ | 6,313.4 |
| | $ | 5,413.3 |
| | $ | 4,993.7 |
|
| International | 2,707.4 |
| | 2,885.1 |
| | 2,568.8 |
|
| Total | $ | 9,020.8 |
| | $ | 8,298.4 |
| | $ | 7,562.5 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | |
| | As of December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Total assets at end of year | | | |
| United States | $ | 18,140.9 |
| | $ | 12,724.4 |
|
| International | 5,149.3 |
| | 4,942.9 |
|
| Total | $ | 23,290.2 |
| | $ | 17,667.3 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment, net, at end of year | | | |
| United States | $ | 10,221.3 |
| | $ | 7,621.2 |
|
| International | 2,687.0 |
| | 2,484.2 |
|
| Total | $ | 12,908.3 |
| | $ | 10,105.4 |
|
| Property and equipment, net, at end of year | | | |
| United States | $ | 1,226.1 |
| | $ | 1,036.7 |
|
| International | 210.3 |
| | 215.2 |
|
| Total | $ | 1,436.4 |
| | $ | 1,251.9 |
|
| |
| (a) | The following table reconciles adjusted pre-tax income to income (loss) before income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 (in millions of dollars): |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| Adjusted pre-tax income | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Car rental | $ | 1,020.1 |
| | $ | 850.2 |
| | $ | 641.9 |
|
| Equipment rental | 227.0 |
| | 161.6 |
| | 78.0 |
|
| Total reportable segments | 1,247.1 |
| | 1,011.8 |
| | 719.9 |
|
| Adjustments: | | | | | |
Other reconciling items(1) | (320.5 | ) | | (306.2 | ) | | (347.9 | ) |
Purchase accounting(2) | (109.6 | ) | | (87.6 | ) | | (90.3 | ) |
Non-cash debt charges(3) | (56.4 | ) | | (105.9 | ) | | (160.6 | ) |
| Restructuring charges | (38.0 | ) | | (56.4 | ) | | (54.7 | ) |
Restructuring related charges(4) | (11.1 | ) | | (9.8 | ) | | (13.2 | ) |
Derivative gains (losses)(5) | (0.9 | ) | | 0.1 |
| | (3.2 | ) |
Acquisition related costs and charges(6) | (163.7 | ) | | (18.8 | ) | | (17.7 | ) |
| Management transition costs | — |
| | (4.0 | ) | | — |
|
Pension adjustment(7) | — |
| | 13.1 |
| | — |
|
Premiums paid on debt(8) | — |
| | (62.4 | ) | | — |
|
Other(9) | (44.0 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Income before income taxes | $ | 502.9 |
| | $ | 373.9 |
| | $ | 32.3 |
|
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (1) | Represents general corporate expenses, certain interest expense (including net interest on corporate debt), as well as other business activities. |
| |
| (2) | Represents the increase in amortization of other intangible assets, depreciation of property and equipment and accretion of revalued liabilities relating to purchase accounting. |
| |
| (3) | Represents non-cash debt charges relating to the amortization and write-off of deferred debt financing costs and debt discounts. |
| |
| (4) | Represents incremental costs incurred directly supporting our business transformation initiatives. Such costs include transition costs incurred in connection with our business process outsourcing arrangements and incremental costs incurred to facilitate business process re-engineering initiatives that involve significant organization redesign and extensive operational process changes. |
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| |
| (5) | Represents the mark-to-market adjustment on our interest rate cap. |
| |
| (6) | Primarily represents Dollar Thrifty acquisition related expenses, change in control expenses, 'Day-1' compensation expenses and other adjustments related to the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, loss on the Advantage divestiture, expenses related to additional required divestitures and costs associated with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, pre-acquisition interest and commitment fee expenses for interim financing associated with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition and a gain on the investment in Dollar Thrifty stock. |
| |
| (7) | Represents a gain for the U.K. pension plan relating to unamortized prior service cost from a 2010 amendment that eliminated discretionary pension increases related to pre-1997 service primarily pertaining to inactive employees. |
| |
| (8) | Represents premiums paid to redeem our 10.5% Senior Subordinated Notes and a portion of our 8.875% Senior Notes. |
| |
| (9) | Primarily represents expenses related to the withdrawal from a multiemployer pension plan, litigation accrual and expenses associated with the impact of Hurricane Sandy. |
Note 12—Contingencies and Off-Balance Sheet Commitments
Legal Proceedings
From time to time we are a party to various legal proceedings. Other than with respect to the aggregate claims for public liability and property damage pending against us, management does not believe that any of the matters resolved, or pending against us, during 2012 are material to us and our subsidiaries taken as a whole. While we have accrued a liability with respect to claims for public liability and property damage of $332.2 million at December 31, 2012, management, based on the advice of legal counsel, does not believe any of the other pending matters described below are material. We have summarized below, for purposes of providing background, various legal proceedings to which we were and/or are a party during 2012 or the period after December 31, 2012 but before the filing of this Annual Report. In addition to the following, various other legal actions, claims and governmental inquiries and proceedings are pending or may be instituted or asserted in the future against us and our subsidiaries. As previously disclosed, on June 15, 2011 we received a subpoena from the staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or "SEC," seeking production of documents related to our proposed business combination with Dollar Thrifty. On February 14, 2013, we were informed by the staff that the investigation has been completed and that no action was taken by the staff or the SEC.
| |
| 1. | Hertz Equipment Rental Corporation, or “HERC,” Loss Damage Waiver |
On August 15, 2006, Davis Landscape, Ltd., individually and on behalf of all others similarly situated, filed a complaint against HERC in the United States District Court for the District of New Jersey. In November 2006, the complaint was amended to add another plaintiff, Miguel V. Pro, and more claims. The Davis Landscape matter purports to be a nationwide class action on behalf of all persons and business entities who rented equipment from HERC and who paid a Loss Damage Waiver, or “LDW,” or an Environmental Recovery Fee, or “ERF.” The plaintiffs seek a declaratory judgment and injunction prohibiting HERC from engaging in acts with respect to the LDW and ERF charges that violate the New Jersey Consumer Fraud Act and claim that the charges violate the Uniform Commercial Code. The plaintiffs also seek an unspecified amount of compensatory damages with the return of all LDW and ERF charges paid, attorneys' fees and costs as well as other damages. The court has granted class certification, denied our motion for summary judgment and the case is in the discovery stages. In February 2012, we filed separate motions for partial summary judgment on the LDW and ERF claims and we filed a motion to decertify the class. In June 2012, the judge denied our motion for partial summary judgment on the LDW claim and, in July 2012, the judge granted our motion for partial summary judgment on the ERF claim. The court also entered an order referring the case to mediation by private consent of the parties. We have continued to work through the mediator and in direct discussions with plaintiffs’ counsel on an acceptable settlement of this litigation and have accrued our best estimate of the ultimate cost which is not material to our financial condition.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
| |
| 2. | Concession Fee Recoveries |
On October 13, 2006, Janet Sobel, Daniel Dugan, PhD. and Lydia Lee, individually and on behalf of all others similarly situated v. The Hertz Corporation and Enterprise Rent-A-Car Company, or “Enterprise,” was filed in the United States District Court for the District of Nevada. The plaintiffs agreed to not pursue claims against Enterprise initially and the case only proceeded against Hertz. The Sobel case purports to be a nationwide class action on behalf of all persons who rented cars from Hertz at airports in Nevada and were separately charged airport concession recovery fees by Hertz as part of their rental charges. The plaintiffs seek an unspecified amount of compensatory damages, restitution of any charges found to be improper and an injunction prohibiting Hertz from quoting or charging those airport fees that are alleged not to be allowed by Nevada law. The complaint also seeks attorneys' fees and costs. Relevant documents were produced, depositions were taken and pre-trial motions were filed. After the court rendered a mixed ruling on the parties' cross‑motions for summary judgment and after the Lydia Lee case was refiled against Enterprise, the parties engaged in mediation which resulted in a proposed settlement. Although the court tentatively approved the settlement in November 2010, the court denied the plaintiffs' motion for final approval of the proposed settlement in May 2011. Since that time, the plaintiffs filed a motion for class certification-which we opposed-and discovery has commenced again. A separate action is proceeding against Enterprise, National and Alamo. In May 2012, all briefing was completed on the two outstanding issues—unjust enrichment and damages. The briefing included expert reports as submitted by both sides. In October 2012, the court held a hearing on the plaintiffs’ motion for class certification. The court has since entered a stay order and the parties will again be engaging in mediation.
| |
| 3. | Telephone Consumer Protection Act |
On May 3, 2007, Fun Services of Kansas City, Inc., individually and as the representative of a class of similarly‑situated persons, v. Hertz Equipment Rental Corporation was commenced in the District Court of Wyandotte County, Kansas. The case was subsequently transferred to the District Court of Johnson County, Kansas. The Fun Services matter purports to be a class action on behalf of all persons in Kansas and throughout the United States who, on or after four years prior to the filing of the action, were sent facsimile messages of advertising materials relating to the availability of property, goods or services by HERC and who did not provide express permission for sending such faxes. The plaintiffs seek an unspecified amount of compensatory damages, attorney's fees and costs. In August 2009, the court issued an order that stayed all activity in this litigation pending a decision by the Kansas Supreme Court in Critchfield Physical Therapy, Inc. v. Taranto Group, Inc., another Telephone Consumer Protection Act case. The Kansas Supreme Court issued its decision in September 2011. Thereafter, the District Court of Johnson County lifted the stay in the Fun Services case and issued a scheduling order that addresses class certification discovery. In February 2012, HERC filed a Notice of Removal with the U.S. District Court for the District of Kansas seeking to remove the case to federal court based on federal question jurisdiction. In March 2012, the federal magistrate entered an order requiring the parties to engage in mediation and report back to her regarding their progress by June 2012. In June 2012, a mediation was held and as a result of the mediation, the parties reached an agreement in principle to settle this class action. A settlement that addresses compensation to class members, class counsel fees and the claims process was finalized by the parties’ counsel in January 2013. The court issued an order preliminarily approving the settlement in January 2013 and the final approval hearing is currently scheduled for April 2013. We have accrued our best estimate of the ultimate cost, which is not material to our financial condition.
| |
| 4. | California Tourism Assessments |
We are currently a defendant in a proceeding that purports to be a class action brought by Michael Shames and Gary Gramkow against The Hertz Corporation, Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., Avis Budget Group, Inc., Vanguard Car Rental USA, Inc., Enterprise Rent-A-Car Company, Fox Rent A Car, Inc., Coast Leasing Corp., The California Travel and Tourism Commission, and Caroline Beteta.
Originally filed in November of 2007, the action is pending in the United States District Court for the Southern District of California, and plaintiffs claim to represent a class of individuals or entities that purchased rental car services from a defendant at airports located in California after January 1, 2007. Plaintiffs allege that the defendants agreed to charge consumers a 2.5% tourism assessment and not to compete with respect
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
to this assessment, while misrepresenting that this assessment is owed by consumers, rather than the rental car defendants, to the California Travel and Tourism Commission, or the “CTTC.” Plaintiffs also allege that defendants agreed to pass through to consumers a fee known as the Airport Concession Fee, which fee had previously been required to be included in the rental car defendants' individual base rates, without reducing their base rates. Based on these allegations, the amended complaint seeks treble damages, disgorgement, injunctive relief, interest, attorneys' fees and costs. Plaintiffs dropped their claims against Caroline Beteta. Plaintiffs' claims against the rental car defendants have been dismissed, except for the federal antitrust claim. In June 2010, the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit affirmed the dismissal of the plaintiffs' antitrust case against the CTTC as a state agency immune from antitrust complaint because the California Legislature foresaw the alleged price‑fixing conspiracy that was the subject of the complaint. The plaintiffs subsequently filed a petition with the Ninth Circuit seeking a rehearing and that petition was granted. In November 2010, the Ninth Circuit withdrew its June opinion and instead held that state action immunity was improperly invoked. The Ninth Circuit reinstated the plaintiffs' antitrust claims and remanded the case to the district court for further proceedings. In May 2012, the district court issued an order preliminarily approving the settlement of this action; certifying a settlement class; certifying a class representative and lead counsel; and providing for class notice. In October 2012, the court held a final approval hearing. In November 2012, the court issued an order of final approval of the settlement of this action. One of the objectors to the settlement has filed a notice of appeal of this order with the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. We have accrued our best estimate of the ultimate cost which is not material to our financial condition.
| |
| 5. | Public Liability and Property Damage |
We are currently a defendant in numerous actions and have received numerous claims on which actions have not yet been commenced for public liability and property damage arising from the operation of motor vehicles and equipment rented from us. The obligation for public liability and property damage on self-insured U.S. and international vehicles and equipment, as stated on our balance sheet, represents an estimate for both reported accident claims not yet paid and claims incurred but not yet reported. The related liabilities are recorded on a non-discounted basis. Reserve requirements are based on actuarial evaluations of historical accident claim experience and trends, as well as future projections of ultimate losses, expenses, premiums and administrative costs. At December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011 our liability recorded for public liability and property damage matters was $332.2 million and $281.5 million, respectively. We believe that our analysis is based on the most relevant information available, combined with reasonable assumptions, and that we may prudently rely on this information to determine the estimated liability. We note the liability is subject to significant uncertainties. The adequacy of the liability reserve is regularly monitored based on evolving accident claim history and insurance related state legislation changes. If our estimates change or if actual results differ from these assumptions, the amount of the recorded liability is adjusted to reflect these results.
We intend to assert that we have meritorious defenses in the foregoing matters and we intend to defend ourselves vigorously.
We have established reserves for matters where we believe that the losses are probable and reasonably estimated, including for various of the matters set forth above. Other than with respect to the aggregate reserves established for claims for public liability and property damage, none of those reserves are material. For matters, including those described above, where we have not established a reserve, the ultimate outcome or resolution cannot be predicted at this time, or the amount of ultimate loss, if any, cannot be reasonably estimated. Litigation is subject to many uncertainties and the outcome of the individual litigated matters is not predictable with assurance. It is possible that certain of the actions, claims, inquiries or proceedings, including those discussed above, could be decided unfavorably to us or any of our subsidiaries involved. Accordingly, it is possible that an adverse outcome from such a proceeding could exceed the amount accrued in an amount that could be material to our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows in any particular reporting period.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Off-Balance Sheet Commitments
As of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, the following guarantees (including indemnification commitments) were issued and outstanding.
Indemnification Obligations
In the ordinary course of business, we execute contracts involving indemnification obligations customary in the relevant industry and indemnifications specific to a transaction such as the sale of a business. These indemnification obligations might include claims relating to the following: environmental matters; intellectual property rights; governmental regulations and employment-related matters; customer, supplier and other commercial contractual relationships; and financial matters. Performance under these indemnification obligations would generally be triggered by a breach of terms of the contract or by a third party claim. We regularly evaluate the probability of having to incur costs associated with these indemnification obligations and have accrued for expected losses that are probable and estimable. The types of indemnification obligations for which payments are possible include the following:
Sponsors; Directors
We have entered into customary indemnification agreements with Hertz Holdings, the Sponsors and Hertz Holdings' stockholders affiliated with the Sponsors, pursuant to which Hertz Holdings and Hertz will indemnify the Sponsors, Hertz Holdings' stockholders affiliated with the Sponsors and their respective affiliates, directors, officers, partners, members, employees, agents, representatives and controlling persons, against certain liabilities arising out of performance of a consulting agreement with Hertz Holdings and each of the Sponsors and certain other claims and liabilities, including liabilities arising out of financing arrangements or securities offerings. Hertz Holdings also entered into indemnification agreements with each of its directors. We do not believe that these indemnifications are reasonably likely to have a material impact on us.
Environmental
We have indemnified various parties for the costs associated with remediating numerous hazardous substance storage, recycling or disposal sites in many states and, in some instances, for natural resource damages. The amount of any such expenses or related natural resource damages for which we may be held responsible could be substantial. The probable expenses that we expect to incur for such matters have been accrued, and those expenses are reflected in our condensed consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, the aggregate amounts accrued for environmental liabilities including liability for environmental indemnities, reflected in our condensed consolidated balance sheets in "Accrued liabilities" were $2.6 million and $1.5 million, respectively. The accrual generally represents the estimated cost to study potential environmental issues at sites deemed to require investigation or clean-up activities, and the estimated cost to implement remediation actions, including on-going maintenance, as required. Cost estimates are developed by site. Initial cost estimates are based on historical experience at similar sites and are refined over time on the basis of in-depth studies of the sites. For many sites, the remediation costs and other damages for which we ultimately may be responsible cannot be reasonably estimated because of uncertainties with respect to factors such as our connection to the site, the materials there, the involvement of other potentially responsible parties, the application of laws and other standards or regulations, site conditions, and the nature and scope of investigations, studies, and remediation to be undertaken (including the technologies to be required and the extent, duration, and success of remediation).
Note 13—Restructuring
As part of our ongoing effort to implement our strategy of reducing operating costs, we have evaluated our workforce and operations and made adjustments, including headcount reductions and business process reengineering resulting in optimized work flow at rental locations and maintenance facilities as well as streamlined our back-office operations and evaluated potential outsourcing opportunities. When we made adjustments to our workforce and operations, we incurred incremental expenses that delay the benefit of a more efficient workforce and operating structure, but we believe that increased operating efficiency and reduced costs associated with the operation of our business are important to our long-term competitiveness.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
During 2007 through 2011, we announced several initiatives to improve our competitiveness and industry leadership through targeted job reductions. These initiatives included, but were not limited to, job reductions at our corporate headquarters and back-office operations in the U.S. and Europe. As part of our re-engineering optimization we outsourced selected functions globally. In addition, we streamlined operations and reduced costs by initiating the closure of targeted car rental locations and equipment rental branches throughout the world. The largest of these closures occurred in 2008 which resulted in closures of approximately 250 off-airport locations and 22 branches in our U.S. equipment rental business. These initiatives impacted approximately 8,960 employees.
During 2012, we continued to streamline operations and reduce costs with the closure of several car rental and equipment rental locations globally as well as a reduction in our workforce by approximately 650 employees.
From January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2012, we incurred $568.4 million ($282.7 million for our car rental segment, $230.3 million for our equipment rental segment and $55.4 million of other) of restructuring charges.
Additional efficiency and cost saving initiatives are being developed; however, we presently do not have firm plans or estimates of any related expenses.
Restructuring charges in our consolidated statement of operations can be summarized as follows (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| By Type: | | | | | |
| Termination benefits | $ | 26.2 |
| | $ | 14.4 |
| | $ | 12.2 |
|
| Pension and post retirement expense | 1.0 |
| | 0.4 |
| | 0.4 |
|
| Consultant costs | 1.2 |
| | 1.3 |
| | 1.1 |
|
| Asset writedowns | — |
| | 23.2 |
| | 20.4 |
|
| Facility closure and lease obligation costs | 8.9 |
| | 16.5 |
| | 14.3 |
|
| Relocation costs and temporary labor costs | 0.4 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 5.0 |
|
| Other | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | 1.3 |
|
| Total | $ | 38.0 |
| | $ | 56.4 |
| | $ | 54.7 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| By Caption: | | | | | |
| Direct operating | $ | 22.6 |
| | $ | 46.6 |
| | $ | 43.5 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 15.4 |
| | 9.8 |
| | 11.2 |
|
| Total | $ | 38.0 |
| | $ | 56.4 |
| | $ | 54.7 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| By Segment: | | | | | |
| Car rental | $ | 26.4 |
| | $ | 16.6 |
| | $ | 18.1 |
|
| Equipment rental | 8.8 |
| | 40.5 |
| | 34.7 |
|
| Other reconciling items | 2.8 |
| | (0.7 | ) | �� | 1.9 |
|
| Total | $ | 38.0 |
| | $ | 56.4 |
| | $ | 54.7 |
|
The following table sets forth the activity affecting the restructuring accrual during the year ended December 31, 2012 (in millions of dollars). We expect to pay the remaining restructuring obligations relating to termination benefits over
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
the next twelve months. The remainder of the restructuring accrual relates to future lease obligations which will be paid over the remaining term of the applicable leases.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Termination Benefits | | Pension and Post Retirement Expense | | Consultant Costs | | Other | | Total |
| Balance as of January 1, 2011 | $ | 6.3 |
| | $ | 0.2 |
| | $ | 0.1 |
| | $ | 10.9 |
| | $ | 17.5 |
|
| Charges incurred | 14.4 |
| | 0.4 |
| | 1.3 |
| | 40.3 |
| | 56.4 |
|
| Cash payments | (15.5 | ) | | — |
| | (0.6 | ) | | (2.3 | ) | | (18.4 | ) |
Other(1) | 3.9 |
| | (0.4 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (37.2 | ) | | (33.9 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2011 | $ | 9.1 |
| | $ | 0.2 |
| | $ | 0.6 |
| | $ | 11.7 |
| | $ | 21.6 |
|
| Charges incurred | 26.2 |
| | 1.0 |
| | 1.2 |
| | 9.6 |
| | 38.0 |
|
| Cash payments | (22.6 | ) | | — |
| | (0.9 | ) | | (3.3 | ) | | (26.8 | ) |
Other(2) | (0.3 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | (9.9 | ) | | (11.8 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, 2012 | $ | 12.4 |
| | $ | 0.2 |
| | $ | 0.3 |
| | $ | 8.1 |
| | $ | 21.0 |
|
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (1) | Consists of decreases of $23.2 million for asset writedowns, $13.9 million for facility closures, $0.4 million in ASC 715 pension adjustment and $0.2 million of consultant costs, partly offset by a $3.8 million increase for involuntary benefits. |
| |
| (2) | Primarily consists of decreases of $10.3 million for facility closures and $1.0 million in ASC 715 pension adjustment. |
Note 14—Financial Instruments
Gasoline Swap Contracts
We purchase unleaded gasoline and diesel fuel at prevailing market rates and maintain a program to manage our exposure to changes in fuel prices through the use of derivative commodity instruments. We currently have in place swaps to cover a portion of our fuel price exposure through March 2014. We presently hedge a portion of our overall unleaded gasoline and diesel fuel purchases with commodity swaps and have contracts in place that settle on a monthly basis. Gains and losses resulting from changes in the fair value of these commodity instruments are included in our results of operations in the periods incurred.
Interest Rate Cap Contracts
Hertz is exposed to market risks, such as changes in interest rates, and has purchased and sold interest rate cap agreements to manage that risk. Consequently, we manage the financial exposure as part of our risk management program by striving to reduce the potentially adverse effects that the volatility of the financial markets may have on our operating results. Gains and losses resulting from changes in the fair value of these interest rate caps are included in our results of operations in the periods incurred.
Foreign Currency Forward Contracts
We manage exposure to fluctuations in currency risk on intercompany loans we make to certain of our subsidiaries by entering into foreign currency forward contracts at the time of the loans which are intended to offset the impact of foreign currency movements on the underlying intercompany loan obligations.
Foreign Exchange Options
We manage our foreign currency risk primarily by incurring, to the extent practicable, operating and financing expenses in the local currency in the countries in which we operate, including making fleet and equipment purchases and borrowing for working capital needs. Also, we have purchased foreign exchange options to manage exposure to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates for selected marketing programs. The effect of exchange rate changes on these financial instruments would not materially affect our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. Our risks with respect to foreign exchange options are limited to the premium paid for the right to exercise the option and the future performance of the option's counterparty.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table summarizes the estimated fair value of derivatives (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Fair Value of Derivative Instruments(1) |
| | Asset Derivatives(2) | | | Liability Derivatives(2) |
| | December 31,
2012 | | December 31,
2011 | | | December 31,
2012 | | December 31,
2011 |
| Derivatives not designated as hedging | | | | | | | | |
| instruments under ASC 815: | | | | | | | | |
| Gasoline swaps | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | | $ | 0.1 |
| | $ | 0.4 |
|
| Interest rate caps | 0.9 |
| | 0.5 |
| | | 0.9 |
| | 0.4 |
|
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | 3.4 |
| | 4.4 |
| | | 4.5 |
| | 1.9 |
|
| Interest rate swaps | — |
| | — |
| | | — |
| | 0.2 |
|
| Foreign exchange options | 0.2 |
| | 0.1 |
| | | — |
| | — |
|
| Total derivatives not designated as hedging | | | | | | | | |
| instruments under ASC 815 | $ | 4.5 |
| | $ | 5.0 |
| | | $ | 5.5 |
| | $ | 2.9 |
|
_______________________________________________________________________________
| |
| (1) | All fair value measurements were primarily based upon significant observable (Level 2) inputs. |
| |
| (2) | All asset derivatives are recorded in "Prepaid expenses and other assets" and all liability derivatives are recorded in "Other accrued liabilities" on our consolidated balance sheets. |
The following table summarizes the (gains) and losses of derivatives (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Location of Gain or (Loss) Recognized on Derivatives | | Amount of Gain or (Loss) Recognized in Income on Derivatives |
| | | | Years Ended December 31, |
| | | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Derivatives not designated as hedging | | | | | |
| instruments under ASC 815: | | | | | |
| Gasoline swaps | Direct operating | | $ | 0.7 |
| | $ | 2.6 |
|
| Interest rate caps | Selling, general and administrative | | (0.8 | ) | | — |
|
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | Selling, general and administrative | | (15.4 | ) | | (11.0 | ) |
| Foreign exchange options | Selling, general and administrative | | — |
| | (0.2 | ) |
| Total | | | $ | (15.5 | ) | | $ | (8.6 | ) |
Fair value measures
Pursuant to the accounting guidance for fair value measurements and its subsequent updates, fair value is defined as the price that would be received from selling an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. When determining the fair value measurements for assets and liabilities required or permitted to be recorded at fair value, we consider the principal or most advantageous market in which we would transact and we consider assumptions that market participants would use when pricing the asset or liability.
Fair Value Hierarchy
The accounting guidance for fair value measurements also requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. A financial instrument's categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The inputs are prioritized into three levels that may be used to measure fair value:
Level 1: Inputs that reflect quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets that are observable.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Level 2: Inputs that reflect quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active; or model-derived valuations in which significant inputs are observable or can be derived principally from, or corroborated by, observable market data.
Level 3: Inputs that are unobservable to the extent that observable inputs are not available for the asset or liability at the measurement date.
Asset and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
Assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2012 and 2011 were as follows (in millions):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2012 |
| | Fair Value Measurements Using |
| | Total | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets
for Identical
Instruments
(Level 1) | | Significant
Other
Observable
Inputs
(Level 2) | | Significant
Unobservable
Inputs
(Level 3) |
| Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate caps | $ | 0.9 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 0.9 |
| | $ | — |
|
| Foreign currency forward contracts | 3.4 |
| | — |
| | 3.4 |
| | — |
|
| Foreign exchange options | 0.2 |
| | — |
| | 0.2 |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 4.5 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 4.5 |
| | $ | — |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Other Current Liabilities: | | | | | | | |
| Gasoline swaps | $ | 0.1 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 0.1 |
| | $ | — |
|
| Interest rate caps | 0.9 |
| | — |
| | 0.9 |
| | — |
|
| Foreign currency forward contracts | 4.5 |
| | — |
| | 4.5 |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 5.5 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 5.5 |
| | $ | — |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2011 |
| | Fair Value Measurements Using |
| | Total | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets
for Identical
Instruments
(Level 1) | | Significant
Other
Observable
Inputs
(Level 2) | | Significant
Unobservable
Inputs
(Level 3) |
| Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate caps | $ | 0.5 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 0.5 |
| | $ | — |
|
| Foreign currency forward contracts | 4.4 |
| | — |
| | 4.4 |
| | — |
|
| Foreign exchange options | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | — |
|
| Investment | 33.2 |
| | 33.2 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 38.2 |
| | $ | 33.2 |
| | $ | 5.0 |
| | $ | — |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Other Current Liabilities: | | | | | | | |
| Gasoline swaps | $ | 0.4 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 0.4 |
| | $ | — |
|
| Interest rate caps | 0.4 |
| | — |
| | 0.4 |
| | — |
|
| Foreign currency forward contracts | 1.9 |
| | — |
| | 1.9 |
| | — |
|
| Interest rate swaps | 0.2 |
| | | | 0.2 |
| | |
| Total | $ | 2.9 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 2.9 |
| | $ | — |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Gasoline swaps
Gasoline swaps classified as Level 2 assets and liabilities are priced using quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets.
Interest rate caps
Interest rate caps classified as Level 2 assets and liabilities are priced using quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets.
Foreign currency forward contracts
Foreign currency forward contracts classified as Level 2 assets and liabilities are priced using quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets.
Foreign exchange options
Foreign currency forward contracts classified as Level 2 assets and liabilities are priced using quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets.
Investments
Investments classified as Level 1 assets and liabilities are priced using quoted market prices for identical assets in active markets that are observable.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The fair values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued expenses, to the extent the underlying liability will be settled in cash, approximate carrying values because of the short-term nature of these instruments.
For borrowings with an initial maturity of 90 days or less, fair value approximates carrying value because of the short-term nature of these instruments. For all other debt, fair value is estimated based on quoted market rates as well as borrowing rates currently available to us for loans with similar terms and average maturities (Level 2 inputs). The aggregate fair value of all debt at December 31, 2012 was $15,529.4 million, compared to its aggregate unpaid principal balance of $14,999.1 million. The aggregate fair value of all debt at December 31, 2011 was $11,092.4 million, compared to its aggregate unpaid principal balance of $10,925.6 million.
Note 15—Related Party Transactions
Relationship with Hertz Investors, Inc. and the Sponsors
Stockholders Agreement
In connection with the Acquisition, Hertz Holdings entered into a stockholders agreement (as amended, the “Stockholders Agreement”) with investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors. Based on current share ownership of the Sponsors, the Stockholders Agreement contains agreements that entitle investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors to nominate two nominees of an investment fund associated with CD&R (one of whom shall serve as the chairman or, if the chief executive officer is the chairman, the lead director), one nominee of investment funds associated with Carlyle, and one nominee of an investment fund associated with Merrill Lynch. The Stockholders Agreement also provides that Hertz Holdings' chief executive officer shall be designated as a director, unless otherwise approved by a majority of the Sponsor Designees. In addition, the Stockholders Agreement provides that one of the nominees of an investment fund associated with CD&R shall serve as the chairman of the executive and governance committee of Hertz Holdings and, unless otherwise agreed by this fund, as Chairman of the Board of Directors of Hertz Holdings or lead director.
The Stockholders Agreement grants to the investment funds associated with CD&R or to the board, with the approval of the majority of the Sponsor Designees, the right to remove Hertz Holdings' chief executive officer. Any replacement chief executive officer requires the consent of the investment funds associated with CD&R as well as investment funds associated with at least one other Sponsor. It also contains restrictions on the transfer of Hertz Holdings' shares, and provides for tag-along and drag-along rights, in certain circumstances. The rights described above apply only for so long as the investment funds associated with the applicable Sponsor maintain certain specified minimum levels of shareholdings in Hertz Holdings.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The Stockholders Agreement limits the rights of the investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors that have invested in the common stock of Hertz Holdings and its affiliates, subject to several exceptions, to own, manage, operate or control any of our “competitors” (as defined in the Stockholders Agreement). The Stockholders Agreement may be amended from time to time in the future to eliminate or modify these restrictions without Hertz Holdings' consent.
Registration Rights Agreement
On December 21, 2005, Hertz Holdings entered into a registration rights agreement (as amended, the “Registration Rights Agreement”) with investment funds associated with or designated by the Sponsors. The Registration Rights Agreement grants to certain of these investment funds the right, to cause Hertz Holdings, at its own expense, to use its best efforts to register such securities held by the investment funds for public resale, subject to certain limitations. The exercise of this right is limited to three requests by the group of investment funds associated with each Sponsor, except for registrations effected pursuant to Form S-3, which are unlimited, subject to certain limitations, if Hertz Holdings is eligible to use Form S-3. The secondary offerings of the common stock of Hertz Holdings in June 2007, May 2009, June 2009, March 2011 and December 2012 were effected pursuant to this Registration Rights Agreement. In the event Hertz Holdings registers any of its common stock, these investment funds have the right to require us to use our best efforts to include shares of the common stock of Hertz Holdings held by them, subject to certain limitations, including as determined by the underwriters. The Registration Rights Agreement provides for Hertz Holdings to indemnify the investment funds party to that agreement and their affiliates in connection with the registration of Hertz Holdings' securities.
Director Compensation Policy
Our directors who are also members of the Board of Directors of Hertz Holdings receive no additional compensation for serving on our Board of Directors or any committee of our Board of Directors. Currently all members of our Board of Directors are also members of the Board of Directors of Hertz Holdings. The compensation expense of the Hertz Holdings' directors is pushed down from Hertz Holdings and recorded on the books at the Hertz level.
In November 2011, Hertz Holdings' Board of Directors amended and restated the Director Compensation Policy. Pursuant to the policy prior to November 2011 its directors who are not also employees each received a $170,000 annual retainer fee, of which $70,000 was payable in cash and $100,000 was payable in the form of shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock. Starting in November 2011, the policy now provides that Hertz Holdings' directors who are not also employees each receive a $210,000 annual retainer fee, of which $85,000 is payable in cash and $125,000 is payable in the form of equity. In May 2012, Hertz Holdings' Board of Directors further amended and restated the Director Compensation Policy to provide that the equity portion of the annual retainer fee would be paid annually following the annual meeting of shareholders (or the eligible director's date of election, if applicable) in the form of restricted stock units having an equivalent fair market value equal to the annual equity award amount on the date of grant. The restricted stock units will vest on the business day immediately preceding the next annual meeting of shareholders.
For 2013, the lead director of Hertz Holdings' is paid an additional annual cash fee of $100,000, the chairperson of Hertz Holdings' Audit Committee is paid an additional annual cash fee of $35,000 and each other member of its Audit Committee is paid an additional annual cash fee of $17,500. For 2013, the chairperson of Hertz Holdings' Compensation, Nominating and Governance Committee is paid an additional annual cash fee of $35,000 and each other member of its Compensation, Nominating and Governance Committee receives an additional annual cash fee of $17,500.
Financing Arrangements with Related Parties
Affiliates of Merrill Lynch (which is one of the Sponsors), including Bank of America and certain of its affiliates, have provided various investment and commercial banking and financial advisory services to us for which they have received customary fees and commissions. In addition, these parties have acted as agents, lenders, purchasers and/or underwriters to us under our respective financing arrangements, for which they have received customary fees, commissions, expenses and/or other compensation. More specifically, these parties have acted in the following capacities, or similar capacities, with respect to our financing arrangements: lenders and/or agents under the Senior Credit Facilities, the U.S. Fleet Financing Facility and certain of the U.S. Fleet Variable Funding Notes; purchasers and/or underwriters under the Senior Notes and certain of the U.S. Fleet Medium Term Notes; and structuring advisors and/or agents under the U.S. ABS Program.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
As of December 31, 2012 and December 31, 2011, approximately $189.8 million and $174.4 million, respectively, of our outstanding debt was with related parties.
For information on our total indebtedness, see Note 5—Debt.
On June 29, 2007, we entered into a master loan agreement with Hertz Holdings. The maximum amount which may be borrowed by us under this facility is $100 million. The facility expired June 29, 2012 and was renewed through June 28, 2013. The interest rate is based on the U.S. Dollar LIBOR rate plus a margin. As of December 31, 2012, there was a $12.8 million receivable from Hertz Holdings and as of December 31, 2012, there was $0.4 million in borrowings due to Hertz Holdings.
Other Sponsor Relationships
In May and June 2009, Merrill Lynch, one of the Sponsors, acted as an underwriter in the common stock follow-on public offering and in the public offering of Hertz Holdings' Convertible Senior Notes, for which they received customary fees and expenses.
In May 2009 Hertz Holdings entered into subscription agreements with investment funds affiliated with CD&R and Carlyle to purchase an additional 32,101,182 shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock at a price of $6.23 per share (the same price per share paid to Hertz Holdings by the underwriters in the common stock public offering) with proceeds to us of approximately $200.0 million. This closed on July 7, 2009 and the 32,101,182 shares of Hertz Holdings' common stock were issued to CD&R and Carlyle affiliated investment funds on the same date. In March 2011 and December 2012, the Sponsors sold 50,000,000 shares of their Hertz Holdings common stock to Goldman, Sachs & Co. and 50,000,000 shares of their Hertz Holdings common stock to J.P. Morgan, respectively, in each case as the sole underwriter in the registered public offering of those shares. Giving effect to these offerings, the Sponsors' ownership percentage in Hertz Holdings is approximately 26%.
Note 16—Quarterly Financial Information (Unaudited)
Provided below is a summary of the quarterly operating results during 2012 and 2011 (in millions of dollars).
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | First
Quarter
2012 | | Second
Quarter
2012 | | Third
Quarter
2012 | | Fourth
Quarter
2012 |
| Revenues | $ | 1,960.9 |
| | $ | 2,225.1 |
| | $ | 2,516.2 |
| | $ | 2,318.6 |
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes | (24.0 | ) | | 171.7 |
| | 382.1 |
| | (26.9 | ) |
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | (48.2 | ) | | 101.0 |
| | 251.3 |
| | (28.3 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | First
Quarter
2011 | | Second
Quarter
2011 | | Third
Quarter
2011 | | Fourth
Quarter
2011 |
| Revenues | $ | 1,780.0 |
| | $ | 2,072.3 |
| | $ | 2,432.3 |
| | $ | 2,013.8 |
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes | (146.7 | ) | | 107.0 |
| | 308.2 |
| | 105.4 |
|
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | (123.0 | ) | | 62.1 |
| | 212.6 |
| | 58.8 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 17—Guarantor and Non-Guarantor Condensed Consolidating Financial Statements
The following condensed consolidating financial information presents the Condensed Consolidating Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2012 and 2011 and the Condensed Consolidating Statements of Operations, Comprehensive Income (Loss) and Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, and Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, of (a) The Hertz Corporation, (“the Company” or “the Parent”); (b) the Parent's subsidiaries that guarantee the Parent's indebtedness, or the Guarantor Subsidiaries; (c) the Parent's subsidiaries that do not guarantee the Parent's indebtedness, or the Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries; (d) elimination entries necessary to consolidate the Parent with the Guarantor Subsidiaries and Non-Guarantor Subsidiaries; and of (e) the Company on a consolidated basis. The Guarantor Subsidiaries are consistent with those entities which guaranteed the Company's existing indebtedness as of December 31, 2011 and December 31, 2010, with the exception of the Company's Simply Wheelz subsidiary which was sold in connection with the Advantage divestiture, as more fully described below, and therefore is not included as a guarantor of the debt in this Form 10-K.
On December 12, 2012, pursuant to a consent agreement Hertz Holdings entered into with the Federal Trade Commission in connection with the Dollar Thrifty acquisition, we consummated the Advantage Divestiture. Prior to the Advantage Divestiture, Simply Wheelz, the legal entity associated with Advantage, had been included within these condensed consolidating financial statements as a Guarantor Subsidiary. The following condensed consolidating financial statements which include Simply Wheelz now reflects it as a Non-Guarantor Subsidiary for all periods presented.
Investments in subsidiaries are accounted for using the equity method for purposes of the consolidating presentation. The principal elimination entries relate to investments in subsidiaries and intercompany balances and transactions. Separate financial statements and other disclosures with respect to the Guarantor Subsidiaries have not been provided as management believes the following information is sufficient, as the Guarantor Subsidiaries are 100% owned by the Parent and all guarantees are full and unconditional and joint and several. Additionally, substantially all of the assets of the Guarantor Subsidiaries are pledged under the Senior Credit Facilities, and consequently will not be available to satisfy the claims of our general creditors.
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEET
December 31, 2012
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 24,602 |
| | $ | 2,578 |
| | $ | 506,055 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 533,235 |
|
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents | 32,681 |
| | 14,535 |
| | 524,418 |
| | — |
| | 571,634 |
|
| Receivables, less allowance for doubtful accounts | 544,454 |
| | 292,467 |
| | 1,049,675 |
| | — |
| | 1,886,596 |
|
| Due from Hertz affiliate | 1,047,986 |
| | 59,181 |
| | 2,199,247 |
| | (3,293,605 | ) | | 12,809 |
|
| Inventories, at lower cost or market | 24,422 |
| | 34,101 |
| | 47,205 |
| | — |
| | 105,728 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 2,570,539 |
| | 183,573 |
| | 203,678 |
| | (2,496,288 | ) | | 461,502 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment, net | 104,207 |
| | 1,734,325 |
| | 11,069,804 |
| | — |
| | 12,908,336 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | 865,694 |
| | 206,332 |
| | 364,360 |
| | — |
| | 1,436,386 |
|
| Investment in subsidiaries, net | 6,964,916 |
| | 506,123 |
| | — |
| | (7,471,039 | ) | | — |
|
| Other intangible assets, net | 74,606 |
| | 2,352,342 |
| | 1,605,163 |
| | — |
| | 4,032,111 |
|
| Goodwill | 106,210 |
| | 133,923 |
| | 1,101,739 |
| | — |
| | 1,341,872 |
|
| Total assets | $ | 12,360,317 |
| | $ | 5,519,480 |
| | $ | 18,671,344 |
| | $ | (13,260,932 | ) | | $ | 23,290,209 |
|
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
|
| Due to Hertz affiliate | $ | 2,254,223 |
| | $ | 628,275 |
| | $ | 411,107 |
| | $ | (3,293,605 | ) | | $ | — |
|
| Accounts payable | 239,247 |
| | 157,742 |
| | 602,072 |
| | — |
| | 999,061 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | 605,680 |
| | 84,992 |
| | 487,788 |
| | — |
| | 1,178,460 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 54,357 |
| | 11,511 |
| | 1,003,127 |
| | (901,681 | ) | | 167,314 |
|
| Debt | 6,190,040 |
| | 49,445 |
| | 8,774,989 |
| | — |
| | 15,014,474 |
|
| Public liability and property damage | 99,261 |
| | 10,390 |
| | 222,581 |
| | — |
| | 332,232 |
|
| Deferred taxes on income | — |
| | 1,776,199 |
| | 2,499,548 |
| | (1,594,607 | ) | | 2,681,140 |
|
| Total liabilities | 9,442,808 |
| | 2,718,554 |
| | 14,001,212 |
| | (5,789,893 | ) | | 20,372,681 |
|
| Equity: | | | | | | | | |
|
| The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries stockholder's equity | 2,917,509 |
| | 2,800,926 |
| | 4,670,113 |
| | (7,471,039 | ) | | 2,917,509 |
|
| Noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | 19 |
| | — |
| | 19 |
|
| Total equity | 2,917,509 |
| | 2,800,926 |
| | 4,670,132 |
| | (7,471,039 | ) | | 2,917,528 |
|
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 12,360,317 |
| | $ | 5,519,480 |
| | $ | 18,671,344 |
| | $ | (13,260,932 | ) | | $ | 23,290,209 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING BALANCE SHEET
December 31, 2011
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 565,002 |
| | $ | 7,385 |
| | $ | 358,821 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 931,208 |
|
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents | 44,663 |
| | 28,130 |
| | 235,246 |
| | — |
| | 308,039 |
|
| Receivables, less allowance for doubtful accounts | 297,292 |
| | 218,754 |
| | 1,100,336 |
| | — |
| | 1,616,382 |
|
| Due from Hertz affiliate | 655,411 |
| | 65,972 |
| | 1,194,041 |
| | (1,915,424 | ) | | — |
|
| Inventories, at lower cost or market | 22,440 |
| | 26,541 |
| | 34,997 |
| | — |
| | 83,978 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 2,088,579 |
| | 32,974 |
| | 137,189 |
| | (1,842,608 | ) | | 416,134 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment, net | 167,304 |
| | 1,505,867 |
| | 8,432,238 |
| | — |
| | 10,105,409 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | 824,381 |
| | 170,874 |
| | 256,599 |
| | — |
| | 1,251,854 |
|
| Investment in subsidiaries, net | 4,413,289 |
| | 460,201 |
| | — |
| | (4,873,490 | ) | | — |
|
| Other intangible assets, net | 94,682 |
| | 2,363,617 |
| | 103,935 |
| | — |
| | 2,562,234 |
|
| Goodwill | 100,221 |
| | 67,228 |
| | 224,645 |
| | — |
| | 392,094 |
|
| Total assets | $ | 9,273,264 |
| | $ | 4,947,543 |
| | $ | 12,078,047 |
| | $ | (8,631,522 | ) | | $ | 17,667,332 |
|
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
|
| Due to Hertz affiliate | $ | 1,251,347 |
| | $ | 266,604 |
| | $ | 397,885 |
| | $ | (1,915,424 | ) | | $ | 412 |
|
| Accounts payable | 188,695 |
| | 165,258 |
| | 543,536 |
| | — |
| | 897,489 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | 607,673 |
| | 209,263 |
| | 309,402 |
| | — |
| | 1,126,338 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 54,559 |
| | 134,186 |
| | (13,889 | ) | | (11,872 | ) | | 162,984 |
|
| Debt | 4,434,274 |
| | 4,237 |
| | 6,469,338 |
| | — |
| | 10,907,849 |
|
| Public liability and property damage | 107,881 |
| | 14,025 |
| | 159,628 |
| | — |
| | 281,534 |
|
| Deferred taxes on income | — |
| | 1,449,171 |
| | 2,043,437 |
| | (1,830,736 | ) | | 1,661,872 |
|
| Total liabilities | 6,644,429 |
| | 2,242,744 |
| | 9,909,337 |
| | (3,758,032 | ) | | 15,038,478 |
|
| Equity: | | | | | | | | |
|
| The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries stockholder's equity | 2,628,835 |
| | 2,704,799 |
| | 2,168,691 |
| | (4,873,490 | ) | | 2,628,835 |
|
| Noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | 19 |
| | — |
| | 19 |
|
| Total equity | 2,628,835 |
| | 2,704,799 |
| | 2,168,710 |
| | (4,873,490 | ) | | 2,628,854 |
|
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 9,273,264 |
| | $ | 4,947,543 |
| | $ | 12,078,047 |
| | $ | (8,631,522 | ) | | $ | 17,667,332 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2012
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Total revenues | $ | 4,259,049 |
| | $ | 975,500 |
| | $ | 6,255,039 |
| | $ | (2,468,781 | ) | | $ | 9,020,807 |
|
| Expenses: | | | | | | | | | |
| Direct operating | 2,384,829 |
| | 553,099 |
| | 1,857,860 |
| | — |
| | 4,795,788 |
|
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 2,402,032 |
| | 198,322 |
| | 2,016,585 |
| | (2,468,781 | ) | | 2,148,158 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 448,100 |
| | 123,300 |
| | 374,181 |
| | — |
| | 945,581 |
|
| Interest expense, net of interest income | 253,437 |
| | 39,679 |
| | 299,770 |
| | — |
| | 592,886 |
|
| Other (income) expense, net | (10,656 | ) | | (19 | ) | | 46,217 |
| | — |
| | 35,542 |
|
| Total expenses | 5,477,742 |
| | 914,381 |
| | 4,594,613 |
| | (2,468,781 | ) | | 8,517,955 |
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes and equity in earnings (losses) of subsidiaries | (1,218,693 | ) | | 61,119 |
| | 1,660,426 |
| | — |
| | 502,852 |
|
| (Provision) benefit for taxes on income | 476,444 |
| | (44,846 | ) | | (658,671 | ) | | — |
| | (227,073 | ) |
| Equity in earnings (losses) of subsidiaries (net of tax) | 1,018,028 |
| | 45,922 |
| | — |
| | (1,063,950 | ) | | — |
|
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 275,779 |
| | $ | 62,195 |
| | $ | 1,001,755 |
| | $ | (1,063,950 | ) | | $ | 275,779 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2011
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Total revenues | $ | 4,068,310 |
| | $ | 809,093 |
| | $ | 5,733,827 |
| | $ | (2,312,850 | ) | | $ | 8,298,380 |
|
| Expenses: | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| Direct operating | 2,262,371 |
| | 497,053 |
| | 1,806,954 |
| | — |
| | 4,566,378 |
|
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 1,996,733 |
| | 180,807 |
| | 2,041,049 |
| | (2,312,850 | ) | | 1,905,739 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 326,794 |
| | 85,414 |
| | 332,909 |
| | — |
| | 745,117 |
|
| Interest expense, net of interest income | 299,099 |
| | 27,226 |
| | 318,378 |
| | — |
| | 644,703 |
|
| Other (income) expense, net | 62,396 |
| | (18 | ) | | 170 |
| | — |
| | 62,548 |
|
| Total expenses | 4,947,393 |
| | 790,482 |
| | 4,499,460 |
| | (2,312,850 | ) | | 7,924,485 |
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes, noncontrolling interest and equity in earnings (losses) of subsidiaries | (879,083 | ) | | 18,611 |
| | 1,234,367 |
| | — |
| | 373,895 |
|
| (Provision) benefit for taxes on income (loss) | 342,469 |
| | (10,016 | ) | | (476,299 | ) | | — |
| | (143,846 | ) |
| Equity in earnings (losses) of subsidiaries (net of tax) | 747,103 |
| | 26,215 |
| | — |
| | (773,318 | ) | | — |
|
| Net income (loss) | 210,489 |
| | 34,810 |
| | 758,068 |
| | (773,318 | ) | | 230,049 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | (19,560 | ) | | — |
| | (19,560 | ) |
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 210,489 |
| | $ | 34,810 |
| | $ | 738,508 |
| | $ | (773,318 | ) | | $ | 210,489 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2010
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Total revenues | $ | 3,961,435 |
| | $ | 701,264 |
| | $ | 5,350,348 |
| | $ | (2,450,513 | ) | | $ | 7,562,534 |
|
| Expenses: | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| Direct operating | 2,217,864 |
| | 452,674 |
| | 1,612,856 |
| | — |
| | 4,283,394 |
|
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 1,938,416 |
| | 200,252 |
| | 2,179,992 |
| | (2,450,513 | ) | | 1,868,147 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 320,192 |
| | 67,739 |
| | 276,511 |
| | — |
| | 664,442 |
|
| Interest expense, net of interest income | 297,276 |
| | 20,068 |
| | 396,880 |
| | — |
| | 714,224 |
|
| Other (income) expense, net | 9,915 |
| | (3 | ) | | (9,907 | ) | | — |
| | 5 |
|
| Total expenses | 4,783,663 |
| | 740,730 |
| | 4,456,332 |
| | (2,450,513 | ) | | 7,530,212 |
|
| Income (loss) before income taxes, noncontrolling interest and equity in earnings (losses) of subsidiaries | (822,228 | ) | | (39,466 | ) | | 894,016 |
| | — |
| | 32,322 |
|
| (Provision) benefit for taxes on income (loss) | 314,692 |
| | 10,718 |
| | (358,732 | ) | | — |
| | (33,322 | ) |
| Equity in earnings (losses) of subsidiaries (net of tax) | 489,153 |
| | (5,268 | ) | | — |
| | (483,885 | ) | | — |
|
| Net income (loss) | (18,383 | ) | | (34,016 | ) | | 535,284 |
| | (483,885 | ) | | (1,000 | ) |
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | (17,383 | ) | | — |
| | (17,383 | ) |
| Net income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | (18,383 | ) | | $ | (34,016 | ) | | $ | 517,901 |
| | $ | (483,885 | ) | | $ | (18,383 | ) |
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
For the Year Ended December 31, 2012
(In Thousands of Dollars) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 275,779 |
| | $ | 62,195 |
| | $ | 1,001,755 |
| | $ | (1,063,950 | ) | | $ | 275,779 |
|
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax | 1,522 |
| | 121 |
| | 6,816 |
| | (6,937 | ) | | 1,522 |
|
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 277,301 |
| | $ | 62,316 |
| | $ | 1,008,571 |
| | $ | (1,070,887 | ) | | $ | 277,301 |
|
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
For the Year Ended December 31, 2011
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 210,489 |
| | $ | 34,810 |
| | $ | 758,068 |
| | $ | (773,318 | ) | | $ | 230,049 |
|
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax | (66,237 | ) | | — |
| | (34,619 | ) | | 34,619 |
| | (66,237 | ) |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 144,252 |
| | 34,810 |
| | 723,449 |
| | (738,699 | ) | | 163,812 |
|
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | (19,560 | ) | | — |
| | (19,560 | ) |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 144,252 |
| | $ | 34,810 |
| | $ | 703,889 |
| | $ | (738,699 | ) | | $ | 144,252 |
|
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
For the Year Ended December 31, 2010
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Net income (loss) | $ | (18,383 | ) | | $ | (34,016 | ) | | $ | 535,284 |
| | $ | (483,885 | ) | | $ | (1,000 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax | 41,154 |
| | — |
| | 28,427 |
| | (28,427 | ) | | 41,154 |
|
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 22,771 |
| | (34,016 | ) | | 563,711 |
| | (512,312 | ) | | 40,154 |
|
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | (17,383 | ) | | — |
| | (17,383 | ) |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | $ | 22,771 |
| | $ | (34,016 | ) | | $ | 546,328 |
| | $ | (512,312 | ) | | $ | 22,771 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2012
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 1,677,648 |
| | $ | 690,292 |
| | $ | 1,155,789 |
| | $ | (775,317 | ) | | $ | 2,748,412 |
|
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | |
| Net change in restricted cash and cash equivalents | 11,981 |
| | 13,596 |
| | (287,182 | ) | | — |
| | (261,605 | ) |
| Revenue earning equipment expenditures | (88,120 | ) | | (763,610 | ) | | (8,761,509 | ) | | — |
| | (9,613,239 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of revenue earning equipment | 79,390 |
| | 276,342 |
| | 6,769,364 |
| | — |
| | 7,125,096 |
|
| Property and equipment expenditures | (173,053 | ) | | (32,022 | ) | | (107,711 | ) | | — |
| | (312,786 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment | 67,370 |
| | 11,839 |
| | 58,485 |
| | — |
| | 137,694 |
|
| Capital contributions to subsidiaries | (4,267,118 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 4,267,118 |
| | — |
|
| Return of capital from subsidiaries | 1,829,256 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,829,256 | ) | | — |
|
| Loan to Parent From Non-Guarantor | — |
| | — |
| | (385,108 | ) | | 385,108 |
| | — |
|
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (1,708,520 | ) | | (196,648 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (1,905,168 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of business | — |
| | — |
| | 84,497 |
| | — |
| | 84,497 |
|
| Other investing activities | — |
| | — |
| | (1,779 | ) | | — |
| | (1,779 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (4,248,814 | ) | | (690,503 | ) | | (2,630,943 | ) | | 2,822,970 |
| | (4,747,290 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 2,210,000 |
| | — |
| | 27,280 |
| | — |
| | 2,237,280 |
|
| Payment of long-term debt | (650,407 | ) | | (18 | ) | | (301,719 | ) | | — |
| | (952,144 | ) |
| Short-term borrowings: | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| Proceeds | — |
| | — |
| | 438,387 |
| | — |
| | 438,387 |
|
| Payments | (26,775 | ) | | — |
| | (1,253,368 | ) | | — |
| | (1,280,143 | ) |
| Proceeds (payments) under the revolving lines of credit, net | 220,000 |
| | (1,262 | ) | | 1,054,426 |
| | — |
| | 1,273,164 |
|
| Capital contributions received from parent | — |
| | — |
| | 4,267,118 |
| | (4,267,118 | ) | | — |
|
| Loan to Parent From Non-Guarantor | 385,108 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (385,108 | ) | | — |
|
| Payment of dividends and return of capital | — |
| | — |
| | (2,604,573 | ) | | 2,604,573 |
| | — |
|
| Dividends paid | (25,000 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (25,000 | ) |
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | 4,275 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 4,275 |
|
| Loan with Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | (13,220 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (13,220 | ) |
| Purchase of noncontrolling interest | (38,000 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (38,000 | ) |
| Payment of financing costs | (35,215 | ) | | (3,316 | ) | | (10,902 | ) | | — |
| | (49,433 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 2,030,766 |
| | (4,596 | ) | | 1,616,649 |
| | (2,047,653 | ) | | 1,595,166 |
|
| Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | — |
| | — |
| | 5,739 |
| | — |
| | 5,739 |
|
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents during the period | (540,400 | ) | | (4,807 | ) | | 147,234 |
| | — |
| | (397,973 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 565,002 |
| | 7,385 |
| | 358,821 |
| | — |
| | 931,208 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 24,602 |
| | $ | 2,578 |
| | $ | 506,055 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 533,235 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2011
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 1,000,597 |
| | $ | 773,170 |
| | $ | 1,038,124 |
| | $ | (553,370 | ) | | $ | 2,258,521 |
|
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| Net change in restricted cash and cash equivalents | (28,570 | ) | | (2,662 | ) | | (70,534 | ) | | — |
| | (101,766 | ) |
| Revenue earning equipment expenditures | (142,134 | ) | | (670,056 | ) | | (8,642,121 | ) | | — |
| | (9,454,311 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of revenue earning equipment | 163,330 |
| | 170,522 |
| | 7,516,590 |
| | — |
| | 7,850,442 |
|
| Property and equipment expenditures | (189,562 | ) | | (29,696 | ) | | (62,437 | ) | | — |
| | (281,695 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment | 23,952 |
| | 9,263 |
| | 20,599 |
| | — |
| | 53,814 |
|
| Capital contributions to subsidiaries | (3,549,088 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 3,549,088 |
| | — |
|
| Return of capital from subsidiaries | 2,590,025 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,590,025 | ) | | — |
|
| Loan to Parent from Non-Guarantor | — |
| | — |
| | (490,273 | ) | | 490,273 |
| | — |
|
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (214,384 | ) | | (2,100 | ) | | (10,597 | ) | | — |
| | (227,081 | ) |
| Purchase of short-term investments, net | (32,891 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (32,891 | ) |
| Other investing activities | — |
| | (13,602 | ) | | 14,188 |
| | — |
| | 586 |
|
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (1,379,322 | ) | | (538,331 | ) | | (1,724,585 | ) | | 1,449,336 |
| | (2,192,902 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 2,455,309 |
| | — |
| | 607,170 |
| | — |
| | 3,062,479 |
|
| Payment of long-term debt | (3,596,295 | ) | | (17 | ) | | (52,988 | ) | | — |
| | (3,649,300 | ) |
| Short-term borrowings: | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| Proceeds | — |
| | — |
| | 460,890 |
| | — |
| | 460,890 |
|
| Payments | (29,224 | ) | | — |
| | (1,164,832 | ) | | — |
| | (1,194,056 | ) |
| Proceeds (payments) under the revolving lines of credit, net | (29,128 | ) | | (229,778 | ) | | 201,577 |
| | — |
| | (57,329 | ) |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | (23,100 | ) | | — |
| | (23,100 | ) |
| Capital contributions received from parent | — |
| | — |
| | 3,549,088 |
| | (3,549,088 | ) | | — |
|
| Payment of dividends and return of capital | (22,950 | ) | | — |
| | (3,143,395 | ) | | 3,143,395 |
| | (22,950 | ) |
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | 3,577 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3,577 |
|
| Loan to Parent from Non-Guarantor | 490,273 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (490,273 | ) | | — |
|
| Loan from Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | (984 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (984 | ) |
| Payment of financing costs | (81,229 | ) | | (2,817 | ) | | (7,436 | ) | | — |
| | (91,482 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | (810,651 | ) | | (232,612 | ) | | 426,974 |
| | (895,966 | ) | | (1,512,255 | ) |
| Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | — |
| | — |
| | 3,838 |
| | — |
| | 3,838 |
|
| Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents during the period | (1,189,376 | ) | | 2,227 |
| | (255,649 | ) | | — |
| | (1,442,798 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 1,754,378 |
| | 5,158 |
| | 614,470 |
| | — |
| | 2,374,006 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 565,002 |
| | $ | 7,385 |
| | $ | 358,821 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 931,208 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATING STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
For the Year Ended December 31, 2010
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Parent (The Hertz Corporation) | | Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | | Eliminations | | The Hertz Corporation & Subsidiaries |
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 337,055 |
| | $ | 88,941 |
| | $ | 2,193,486 |
| | $ | (381,555 | ) | | $ | 2,237,927 |
|
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | |
| Net change in restricted cash and cash equivalents | 19,932 |
| | (17,514 | ) | | 158,098 |
| | — |
| | 160,516 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment expenditures | (188,057 | ) | | (96,452 | ) | | (8,156,363 | ) | | — |
| | (8,440,872 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of revenue earning equipment | 169,451 |
| | 75,139 |
| | 7,273,856 |
| | — |
| | 7,518,446 |
|
| Property and equipment expenditures | (92,415 | ) | | (14,137 | ) | | (72,657 | ) | | — |
| | (179,209 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment | 4,311 |
| | 10,416 |
| | 24,178 |
| | — |
| | 38,905 |
|
| Capital contributions to subsidiaries | (1,544,332 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 1,544,332 |
| | — |
|
| Return of capital from subsidiaries | 1,877,095 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (1,877,095 | ) | | — |
|
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (35 | ) | | (43,789 | ) | | (3,747 | ) | | — |
| | (47,571 | ) |
| Purchase of short-term investments, net | 3,183 |
| | 94 |
| | 214 |
| | — |
| | 3,491 |
|
| Other investing activities | — |
| | — |
| | 2,726 |
| | — |
| | 2,726 |
|
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | 249,133 |
| | (86,243 | ) | | (773,695 | ) | | (332,763 | ) | | (943,568 | ) |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 1,209,866 |
| | — |
| | 1,425,847 |
| | — |
| | 2,635,713 |
|
| Payment of long-term debt | (73,342 | ) | | (68 | ) | | (2,880,823 | ) | | — |
| | (2,954,233 | ) |
| Short-term borrowings: | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds | — |
| | — |
| | 490,490 |
| | — |
| | 490,490 |
|
| Payments | (2,615 | ) | | — |
| | (968,334 | ) | | — |
| | (970,949 | ) |
| Proceeds (payments) under the revolving lines of credit, net | (18,907 | ) | | (3,515 | ) | | 1,048,492 |
| | — |
| | 1,026,070 |
|
| Distributions to noncontrolling interest | — |
| | — |
| | (18,200 | ) | | — |
| | (18,200 | ) |
| Capital contributions received from parent | — |
| | — |
| | 1,544,332 |
| | (1,544,332 | ) | | — |
|
| Payment of dividends and return of capital | (23,000 | ) | | — |
| | (2,258,650 | ) | | 2,258,650 |
| | (23,000 | ) |
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | 3,208 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3,208 |
|
| Loan from Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | (6,173 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (6,173 | ) |
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of stock | (258 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (258 | ) |
| Payment of financing costs | (29,111 | ) | | — |
| | (49,040 | ) | | — |
| | (78,151 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 1,059,668 |
| | (3,583 | ) | | (1,665,886 | ) | | 714,318 |
| | 104,517 |
|
| Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | — |
| | — |
| | (10,337 | ) | | — |
| | (10,337 | ) |
| Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents during the period | 1,645,856 |
| | (885 | ) | | (256,432 | ) | | — |
| | 1,388,539 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 108,522 |
| | 6,043 |
| | 870,902 |
| | — |
| | 985,467 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 1,754,378 |
| | $ | 5,158 |
| | $ | 614,470 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 2,374,006 |
|
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 18—Subsequent Events
On January 23, 2013, Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, or ‘‘HVF,’’ an insolvency remote, direct, wholly-owned, special purpose subsidiary of Hertz, completed the issuance of $950.0 million in aggregate principal amount of three year and five year Series 2013-1 Rental Car Asset Backed Notes, Class A and Class B. The $282.75 million of three year Class A notes carry a 1.12% coupon, the $42.25 million of three year Class B notes carry a 1.86% coupon, the $543.75 million of five year Class A notes carry a 1.83% coupon, and the $81.25 million of five year Class B notes carry a 2.48% coupon. The three year notes and five year notes have expected final payment dates in August 2016 and August 2018, respectively. The Class B notes are subordinated to the Class A notes.
The net proceeds from the sale of the notes will be, to the extent permitted by the applicable agreements, (i) used to pay the purchase price of vehicles acquired by HVF pursuant to HVF's U.S. ABS Program (as defined herein), (ii) used to pay the principal amount of other HVF U.S. ABS Program indebtedness that is then permitted or required to be paid or (iii) released to HVF to be distributed to Hertz or otherwise used by HVF for general purposes.
In February 2013, Hertz caused its Brazilian operating subsidiary to amend the Brazilian Fleet Financing Facility to extend the maturity date from February 2013 to October 2013.
SCHEDULE I
CONDENSED FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF REGISTRANT
THE HERTZ CORPORATION
PARENT COMPANY BALANCE SHEETS
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 24,602 |
| | $ | 565,002 |
|
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents | 32,681 |
| | 44,663 |
|
| Receivables, less allowance for doubtful accounts | 544,454 |
| | 297,292 |
|
| Due from Hertz affiliates | 1,047,986 |
| | 655,411 |
|
| Inventories, at lower of cost or market | 24,422 |
| | 22,440 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | 2,570,539 |
| | 2,088,579 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment, net | 104,207 |
| | 167,304 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | 865,694 |
| | 824,381 |
|
| Investments in subsidiaries, net | 6,964,916 |
| | 4,413,289 |
|
| Other intangible assets, net | 74,606 |
| | 94,682 |
|
| Goodwill | 106,210 |
| | 100,221 |
|
| Total assets | $ | 12,360,317 |
| | $ | 9,273,264 |
|
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | |
| Due to Hertz affiliates | $ | 2,254,223 |
| | $ | 1,251,347 |
|
| Accounts payable | 239,247 |
| | 188,695 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | 605,680 |
| | 607,673 |
|
| Accrued taxes | 54,357 |
| | 54,559 |
|
| Debt | 6,190,040 |
| | 4,434,274 |
|
| Public liability and property damage | 99,261 |
| | 107,881 |
|
| Total Liabilities | 9,442,808 |
| | 6,644,429 |
|
| Stockholder's equity: | | | |
| Common Stock, $0.01 par value, 3,000 shares authorized, 100 shares issued and outstanding | — |
| | — |
|
| Additional paid-in capital | 3,509,998 |
| | 3,473,625 |
|
| Accumulated deficit | (565,597 | ) | | (816,376 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (26,892 | ) | | (28,414 | ) |
| Total stockholder's equity | 2,917,509 |
| | 2,628,835 |
|
| Total liabilities and stockholder's equity | $ | 12,360,317 |
| | $ | 9,273,264 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SCHEDULE I (Continued)
THE HERTZ CORPORATION
PARENT COMPANY STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Revenues | $ | 4,259,049 |
| | $ | 4,068,310 |
| | $ | 3,961,435 |
|
| Expenses: | | | | | |
| Direct operating | 2,384,829 |
| | 2,262,371 |
| | 2,217,864 |
|
| Depreciation of revenue earning equipment and lease charges | 2,402,032 |
| | 1,996,733 |
| | 1,938,416 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | 448,100 |
| | 326,794 |
| | 320,192 |
|
| Interest expense, net of interest income | 253,437 |
| | 299,099 |
| | 297,276 |
|
| Other (income) expense, net | (10,656 | ) | | 62,396 |
| | 9,915 |
|
| Total expenses | 5,477,742 |
| | 4,947,393 |
| | 4,783,663 |
|
| Loss before income taxes | (1,218,693 | ) | | (879,083 | ) | | (822,228 | ) |
| Benefit for taxes on income | 476,444 |
| | 342,469 |
| | 314,692 |
|
| Equity in earnings of subsidiaries, net of tax | 1,018,028 |
| | 747,103 |
| | 489,153 |
|
| Net income (loss) | $ | 275,779 |
| | $ | 210,489 |
| | $ | (18,383 | ) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SCHEDULE I (Continued)
THE HERTZ CORPORATION
PARENT COMPANY STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years Ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 275,779 |
| | $ | 210,489 |
| | $ | (18,383 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | 1,522 |
| | (66,237 | ) | | 41,154 |
|
| Comprehensive income | $ | 277,301 |
| | $ | 144,252 |
| | $ | 22,771 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SCHEDULE I (Continued)
THE HERTZ CORPORATION
PARENT COMPANY STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
(In Thousands of Dollars, except share data)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In Capital | | Accumulated
Deficit | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Loss | | Total
Equity |
| Balance at: | Shares | | Amount | | | | |
| December 31, 2009 | 100 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 3,410,518 |
| | $ | (962,532 | ) | | $ | (3,331 | ) | | $ | 2,444,655 |
|
| Net loss attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | | | | | | | (18,383 | ) | | | | (18,383 | ) |
| Dividends paid to Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | | | | | | | (23,000 | ) | | | | (23,000 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | 41,154 |
| | 41,154 |
|
| Stock-based employee compensation charges, net of tax | | | | | 36,560 |
| | | | | | 36,560 |
|
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of stock options | | | | | (258 | ) | | | | | | (258 | ) |
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | | | | | 3,774 |
| | | | | | 3,774 |
|
| Hertz Holdings common and phantom shares issued to Directors | | | | | 1,425 |
| | | | | | 1,425 |
|
| December 31, 2010 | 100 |
| | — |
|
| 3,452,019 |
| | (1,003,915 | ) | | 37,823 |
| | 2,485,927 |
|
| Net income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | | | | | | | 210,489 |
| | | | 210,489 |
|
| Dividends paid to Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | | | | | | | (22,950 | ) | | | | (22,950 | ) |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | (66,237 | ) | | (66,237 | ) |
| Acquisition of remaining portion of non-controlling interest, net of tax of $9,798 | | | | | (15,287 | ) | | | | | | (15,287 | ) |
| Stock-based employee compensation charges, net of tax of $0 | | | | | 31,093 |
| | | | | | 31,093 |
|
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | | | | | 4,208 |
| | | | | | 4,208 |
|
| Hertz Holdings common and phantom shares issued to Directors | | | | | 1,592 |
| | | | | | 1,592 |
|
| December 31, 2011 | 100 |
| | — |
| | 3,473,625 |
| | (816,376 | ) | | (28,414 | ) | | 2,628,835 |
|
| Net income attributable to The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries' common stockholder | |
| | |
| | |
| | 275,779 |
| | |
| | 275,779 |
|
| Dividends paid to Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. | | | | | | | (25,000 | ) | | | | (25,000 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | 1,522 |
| | 1,522 |
|
| Stock-based employee compensation charges, net of tax of tax of $399 | |
| | |
| | 29,855 |
| | |
| | |
| | 29,855 |
|
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | | | |
| | 5,030 |
| | |
| | |
| | 5,030 |
|
| Hertz Holdings common and phantom shares issued to Directors | |
| | |
| | 1,488 |
| | |
| | |
| | 1,488 |
|
| December 31, 2012 | 100 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 3,509,998 |
| | $ | (565,597 | ) | | $ | (26,892 | ) | | $ | 2,917,509 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
SCHEDULE I (Continued)
THE HERTZ CORPORATION
PARENT COMPANY STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended December 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 275,779 |
| | $ | 210,489 |
| | $ | (18,383 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities | 1,401,869 |
| | 790,108 |
| | 355,438 |
|
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 1,677,648 |
| | 1,000,597 |
| | 337,055 |
|
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Net change in restricted cash and cash equivalents | 11,981 |
| | (28,570 | ) | ) | 19,932 |
|
| Revenue earning equipment expenditures | (88,120 | ) | | (142,134 | ) | ) | (188,057 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of revenue earning equipment | 79,390 |
| | 163,330 |
| | 169,451 |
|
| Property and equipment expenditures | (173,053 | ) | | (189,562 | ) | ) | (92,415 | ) |
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment | 67,370 |
| | 23,952 |
| | 4,311 |
|
| Capital contributions to subsidiaries | (4,267,118 | ) | | (3,549,088 | ) | ) | (1,544,332 | ) |
| Return of capital from subsidiaries | 1,829,256 |
| | 2,590,025 |
| | 1,877,095 |
|
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (1,708,520 | ) | | (214,384 | ) | ) | (35 | ) |
| Purchase of short-term investments, net | — |
| | (32,891 | ) | ) | 3,183 |
|
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | (4,248,814 | ) | | (1,379,322 | ) | ) | 249,133 |
|
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of long‑term debt | 2,210,000 |
| | 2,455,309 |
| | 1,209,866 |
|
| Payment of long‑term debt | (650,407 | ) | | (3,596,295 | ) | ) | (73,342 | ) |
| Short‑term borrowings: | | | | | |
| Payments | (26,775 | ) | | (29,224 | ) | ) | (2,615 | ) |
| Proceeds (payments) under the revolving lines of credit, net | 220,000 |
| | (29,128 | ) | ) | (18,907 | ) |
| Payment of dividends and return of capital | (25,000 | ) | | (22,950 | ) | ) | (23,000 | ) |
| Proceeds from employee stock purchase plan | 4,275 |
| | 3,577 |
| | 3,208 |
|
| Loan to parent from Non-Guarantor | 385,108 |
| | 490,273 |
| | — |
|
| Loan with Hertz affiliate | (13,220 | ) | | (984 | ) | ) | (6,173 | ) |
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of Stock options | — |
| | — |
| | (258 | ) |
| Purchase of noncontrolling interest | (38,000 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Payment of financing costs | (35,215 | ) | | (81,229 | ) | ) | (29,111 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 2,030,766 |
| | (810,651 | ) | ) | 1,059,668 |
|
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents during the period | (540,400 | ) | | (1,189,376 | ) | ) | 1,645,856 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 565,002 |
| | 1,754,378 |
| | 108,522 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 24,602 |
| | $ | 565,002 |
| | $ | 1,754,378 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
THE HERTS CORPORATION
NOTES TO PARENT COMPANY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1—Background and Basis of Presentation
The accompanying condensed financial statements include only the accounts of The Hertz Corporation, or the “Company.” Investments in the Company's subsidiaries are accounted for under the equity method. These parent company financial statements have been prepared in accordance with Rule 12‑04 of Regulation S-X, as restricted net assets of the Company's subsidiaries exceed 25% of the Company's consolidated net assets as of December 31, 2012.
Certain information and footnote disclosures normally included in financial statements prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America have been condensed or omitted since this information is included in the Company's annual consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report under the caption “Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
Note 2—Commitments and Contingencies
The following table details the contractual cash obligations of the Company for debt, related interest payable and tax liability for uncertain tax positions and related interest as of December 31, 2012 (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Total | | 2013 | | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2016 | | 2017 | | Thereafter |
| Debt | $ | 6,186.7 |
| | $ | 383.7 |
| | $ | 42.7 |
| | $ | 21.6 |
| | $ | 21.6 |
| | $ | 21.5 |
| | $ | 5,695.6 |
|
| Interest | 2,241.1 |
| | 341.4 |
| | 338.0 |
| | 334.9 |
| | 326.5 |
| | 324.4 |
| | 575.9 |
|
| Uncertain tax positions liability and interest | 1.2 |
| | 1.2 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 8,429.0 |
| | $ | 726.3 |
| | $ | 380.7 |
| | $ | 356.5 |
| | $ | 348.1 |
| | $ | 345.9 |
| | $ | 6,271.5 |
|
The following table details the contractual cash obligations of the Company for operating leases and purchase obligations as of December 31, 2012 (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Total | | Less than 1 Year | | 1-3 Years | | 3-5 Years | | More than 5 Years |
| Operating leases and concession agreements | $ | 1,309.1 |
| | $ | 295.3 |
| | $ | 367.6 |
| | $ | 180.6 |
| | $ | 465.6 |
|
| Purchase obligations | 4,129.1 |
| | 4,072.3 |
| | 52.9 |
| | 3.9 |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 5,438.2 |
| | $ | 4,367.6 |
| | $ | 420.5 |
| | $ | 184.5 |
| | $ | 465.6 |
|
Note 3—Distribution of Equity
The following table details distributions of equity received by the Company from its subsidiaries during 2012, 2011 and 2010 (in millions of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Distribution of Equity | $ | 2,604.6 |
| | $ | 3,143.4 |
| | $ | 2,256.7 |
|
SCHEDULE II
VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
THE HERTZ CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
(In Thousands of Dollars)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Balance at | | Additions | | | | |
| | Beginning of Period | | Charged to Expense | | Translation Adjustments | | Deductions | | Balance at End of Period |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts: | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2012 | $ | 20,282 |
| | $ | 34,144 |
| | $ | 28 |
| | $ | (29,341 | ) | (a) | $ | 25,113 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2011 | 19,708 |
| | 28,164 |
| | 68 |
| | (27,658 | ) | (a) | 20,282 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2010 | 21,268 |
| | 19,667 |
| | (695 | ) | | (20,532 | ) | (a) | 19,708 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Tax valuation allowances: | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2012 | $ | 186,710 |
| | $ | 35,805 |
| | $ | 3,930 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 226,445 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2011 | 185,807 |
| | (2,528 | ) | | 3,431 |
| | — |
| | 186,710 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2010 | 167,812 |
| | 27,473 |
| | (9,478 | ) | | — |
| | 185,807 |
|
_____________________________
| |
| (a) | Amounts written off, net of recoveries. |
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Disclosure controls and procedures are controls and other procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in company reports filed or submitted under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or the "Exchange Act," is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in company reports filed under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
An evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures was performed under the supervision of, and with the participation of, management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report. Based upon this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act, as amended. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2012. The assessment was based on criteria established in the framework Internal Control—Integrated Framework, issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. We have excluded from our evaluation the internal controls over financial reporting of Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., or "Dollar Thrifty," which was acquired on November 19, 2012. The total assets and total revenues of the excluded business represented 21% and 2%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2012. Based on this assessment, management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2012. PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, has issued an attestation report on our internal control over financial reporting. Their report is included in this Annual Report under the caption "Item 8—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
No changes in our internal control over financial reporting occurred during the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2012 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Omitted pursuant to General Instruction I to the Form 10-K.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Omitted pursuant to General Instruction I to the Form 10-K.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
Omitted pursuant to General Instruction I to the Form 10-K.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Omitted pursuant to General Instruction I to the Form 10-K.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Fees
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, or “PwC,” served as our independent registered public accounting firm, or “independent auditor” for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011. All fees and expenses for services rendered by PwC in 2012 and 2011 were approved by our Audit Committee. PwC's fees and expenses for services rendered to us for the past two fiscal years are set forth in the table below. We have determined that the provision of these services is compatible with maintaining the independence of our independent auditors. The aggregate fees billed by PwC to Hertz were as follows (in thousands of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Fees: | | | |
| Audit | $ | 8,043 |
| | $ | 6,499 |
|
| Audit‑related | 979 |
| | 678 |
|
| Tax | 560 |
| | 348 |
|
| All other | 3 |
| | 3 |
|
| Total | $ | 9,585 |
| | $ | 7,528 |
|
Audit fees were for services in connection with the audit of the consolidated financial statements included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K, reviews of the condensed consolidated financial statements included in our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, attestation of the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting, statutory audits and providing comfort letters in connection with our funding transactions. Audit‑related fees were for services in connection with due diligence, assurance services and employee benefit plan audits. Tax fees related to our Like Kind Exchange Program and tax audit assistance.
Our Audit Committee's charter requires the Audit Committee to pre-approve all audit and permitted non-audit services to be performed by the our independent registered public accounting firm; however, the Audit Committee is permitted to delegate pre-approval authority to a subcommittee consisting of one or more Audit Committee members who are independent directors, and who must then provide a report to the full Audit Committee at its next scheduled meeting. All audit and non-audit fees were pre-approved by the Audit Committee in 2012.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report:
|
| | | |
| | | | Page |
| (a) | 1. | Financial Statements: | |
| | | Our financial statements filed herewith are set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report as follows: | |
| | | The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries— | |
| | | Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
| | | Consolidated Balance Sheets | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Operations | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | |
| | | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
| | 2. | Financial Statement Schedules: | |
| | | Our financial statement schedules filed herewith are set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report as follows: | |
| | | The Hertz Corporation—Schedule I—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant | |
| | | The Hertz Corporation and Subsidiaries—Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts | |
| | 3. | Exhibits: | |
| | | The attached list of exhibits in the “Exhibit Index” immediately following the signature pages to this Annual Report is filed as part of this Annual Report and is incorporated herein by reference in response to this item. | |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the borough of Park Ridge, and state of New Jersey, on the 4th day of March, 2013.
|
| | |
| | THE HERTZ CORPORATION (Registrant) |
| | | |
| | By: | /s/ ELYSE DOUGLAS |
| | Name: | Elyse Douglas |
| | Title: | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on March 4, 2013:
|
| | | | | |
| | Signature | | | Title | |
| | |
| /s/ GEORGE W. TAMKE | Lead Director |
| George W. Tamke | |
| | |
| /s/ MARK P. FRISSORA | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors |
| Mark P. Frissora | |
| | |
| /s/ ELYSE DOUGLAS | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
| Elyse Douglas | |
| | |
| /s/ JATINDAR S. KAPUR | Senior Vice President, Finance and Corporate Controller |
| Jatindar S. Kapur | |
| | |
| /s/ BARRY H. BERACHA | Director |
| Barry H. Beracha | |
| | |
| /s/ BRIAN A. BERNASEK | Director |
| Brian A. Bernasek | |
| | |
| /s/ CARL T. BERQUIST | Director |
| Carl T. Berquist | |
| | |
| /s/ MICHAEL J. DURHAM | Director |
| Michael J. Durham | |
| | |
| /s/ MICHAEL F. KOEHLER | Director |
| Michael F. Koehler | |
| | |
| /s/ LINDA FAYNE LEVINSON | Director |
| Linda Fayne Levinson | |
| | |
| /s/ ANGEL L. MORALES | Director |
| Angel L. Morales | |
| | |
| /s/ DAVID H. WASSERMAN | Director |
| David H. Wasserman | |
| | |
| /s/ HENRY C. WOLF | Director |
| Henry C. Wolf | |
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
The registrant is an indirect wholly‑owned subsidiary of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. No annual report to security holders covering the registrant's last fiscal year or proxy statement, form of proxy or other proxy soliciting material has been sent to security holders.
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 2.1.1 | Agreement and Plan of Merger among The Hertz Corporation, DNL Merger Corp., Donlen Corporation, Gary Rappeport, as Shareholder Representative and Subsidiary Shareholder (solely with respect to Section 2.2, Section 3.3, Section 3.4, Section 6.5, Section 6.8, Section 6.9, Article IX and Article X) and Nancy Liace as Subsidiary Shareholder (solely with respect to Section 2.2 and Article X) dated July 12, 2011 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on July 18, 2011). |
| 2.1.2 | Amendment No. 1 to Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated August 25, 2011, among The Hertz Corporation, DNL Merger Corp., Donlen Corporation, Gary Rappeport, as Shareholder Representative and Subsidiary Shareholder and Nancy Liace as Subsidiary Shareholder dated July 12, 2011 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 7, 2011). |
| 2.2 | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of August 26, 2012, by and among Hertz Global Holdings, Inc., HDTMS, Inc. and Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 27, 2012). |
| 3.1 | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 30, 2007). |
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated By-Laws of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc., effective March 6, 2012 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 7, 2012). |
| 4.1.1 | Indenture, dated as of September 30, 2010, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors from time to time parties thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.50% Senior Notes Due 2018 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.21 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 9, 2010). |
| 4.1.2 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 11, 2011, among Hertz Entertainment Services Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.50% Senior Notes due 2018 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2.2 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-173023), as filed on March 23, 2011). |
| 4.1.3 | Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 21, 2011, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.50% Senior Notes due 2018 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2.3 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-173023), as filed on March 23, 2011). |
| 4.1.4 | Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of September 2, 2011, among Donlen Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.50% Senior Notes due 2018 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2.5 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 7, 2011). |
| 4.1.5 | Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of February 27, 2012, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.50% Senior Notes due 2018 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2.6 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 4, 2012). |
| 4.1.6 | Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 30, 2012, among Cinelease Holdings, Inc., Cinelease, Inc., Cinelease, LLC, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.50% Senior Notes due 2018 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 4, 2012). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 4.2.1 | Indenture, dated as of December 20, 2010, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors from time to time parties thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.375% Senior Notes Due 2021 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3.1 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 25, 2011). |
| 4.2.2 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 11, 2011, among Hertz Entertainment Services Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.375% Senior Notes due 2021 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3.2 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-173023), as filed on March 23, 2011). |
| 4.2.3 | Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 21, 2011, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.375% Senior Notes due 2021 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3.3 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-173023), as filed on March 23, 2011). |
| 4.2.4 | Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of September 2, 2011, among Donlen Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.375% Senior Notes due 2021 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3.5 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 7, 2011). |
| 4.2.5 | Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of February 27, 2012, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.375% Senior Notes due 2021 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3.6 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 4, 2012). |
| 4.2.6 | Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 30, 2012, among Cinelease Holdings, Inc., Cinelease, Inc., Cinelease, LLC, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 7.375% Senior Notes due 2021 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 4, 2012). |
| 4.3.1 | Indenture, dated as of February 8, 2011, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors from time to time parties thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 6.75% Senior Notes Due 2019 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.1 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 25, 2011). |
| 4.3.2 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 11, 2011, among Hertz Entertainment Services Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.2 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-173023), as filed on March 23, 2011). |
| 4.3.3 | Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of September 2, 2011, among Donlen Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.4 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 7, 2011). |
| 4.3.4 | Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of February 27, 2012, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.6 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 4, 2012). |
| 4.3.5 | Exchange and Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of March 13, 2012, among The Hertz Corporation, the Guarantors named therein, and Barclays Capital Inc., as the Initial Purchaser, relating to the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019 issued as additional notes (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 4, 2012). |
| 4.3.6 | Fourth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of March 30, 2012, among Cinelease Holdings, Inc., Cinelease, Inc., Cinelease, LLC, The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Existing Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 6.75% Senior Notes due 2019 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.8 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 4, 2012). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 4.4.1 | Indenture, dated as of October 16, 2012, between The Hertz Corporation (as successor-in-interest to HDTFS, Inc.), as Issuer, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, providing for the issuance of notes in series (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 2, 2012). |
| 4.4.2 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of October 16, 2012, between The Hertz Corporation (as successor-in-interest to HDTFS, Inc.), as Issuer, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 5.875% Senior Notes due 2020 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 2, 2012). |
| 4.4.3 | Second Supplemental Indenture, dated as of October 16, 2012, between The Hertz Corporation (as successor-in-interest to HDTFS, Inc.), as Issuer, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 6.250% Senior Notes due 2022 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.3 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 2, 2012). |
| 4.4.4 | Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 19, 2012, among The Hertz Corporation, as Issuer, the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 5.875% Senior Notes due 2020 and the 6.250% Senior Notes due 2022 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.4 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013). |
| 4.4.5 | Exchange and Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of November 19, 2012, among The Hertz Corporation, the Guarantors named therein, and Barclays Capital Inc., Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as representatives of the several Initial Purchasers, relating to the 5.875% Senior Notes due 2020 and the 6.250% Senior Notes due 2022 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4.5 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013). |
| 4.5.1 | Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, dated as of September 18, 2009, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee, relating to Rental Car Asset Backed Notes (Issuable in Series) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
| 4.5.2 | Supplemental Indenture No. 1, dated as of December 21, 2010, to the Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.2 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 25, 2011). |
| 4.5.3 | Supplemental Indenture No. 2, dated as of October 25, 2012, to the Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5.3 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013). |
| 4.5.4 | Third Amended and Restated Master Motor Vehicle Operating Lease and Servicing Agreement, dated as of September 18, 2009, between The Hertz Corporation, as Lessee and Servicer, and Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Lessor (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.7 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
| 4.5.5 | Amendment No. 1, dated as of December 21, 2010, to the Third Amended and Restated Master Motor Vehicle Operating Lease and Servicing Agreement, between The Hertz Corporation, as Lessee and Servicer, and Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Lessor (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.4 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 25, 2011). |
| 4.5.6 | Second Amended and Restated Participation, Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated as of September 18, 2009, among Hertz General Interest LLC, Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC and The Hertz Corporation, as Lessee and Servicer (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.8 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
| 4.5.7 | Amendment No. 1, dated as of December 21, 2010, to the Second Amended and Restated Purchase and Sale Agreement, among The Hertz Corporation, Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC and Hertz General Interest LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.6 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 25, 2011). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 4.5.8 | Third Amended and Restated Collateral Agency Agreement, dated as of September 18, 2009, among Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as a Grantor, Hertz General Interest LLC, as a Grantor, The Hertz Corporation, as Servicer, The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Collateral Agent, The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee and a Secured Party, and The Hertz Corporation, as a Secured Party (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.11 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
| 4.5.9 | Amendment No. 1, dated as of December 21, 2010, to the Third Amended and Restated Collateral Agency Agreement, among The Hertz Corporation, as a Secured Party and Servicer, Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as a Grantor, Hertz General Interest LLC, as a Grantor, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as a Secured Party, Trustee and Collateral Agent (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.8 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 25, 2011). |
| 4.5.10 | Second Amended and Restated Administration Agreement, dated as of September 18, 2009, among The Hertz Corporation, Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.12 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
| 4.5.11 | Second Amended and Restated Master Exchange Agreement, dated as of September 18, 2009, among The Hertz Corporation, Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, Hertz General Interest LLC, Hertz Car Exchange Inc., and DB Services Tennessee, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.13 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
| 4.5.12 | Second Amended and Restated Escrow Agreement, dated as of September 18, 2009, among The Hertz Corporation, Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, Hertz General Interest LLC, Hertz Car Exchange Inc., and J.P. Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.14 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
| 4.5.13 | Supplement to Second Amended and Restated Collateral Agency Agreement, dated as of January 26, 2007, among The Hertz Corporation, as Grantor, Gelco Corporation d/b/a GE Fleet Services, as Secured Party, and BNY Midwest Trust Company as Collateral Agent (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.25 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 30, 2007). |
| 4.6.1 | Second Amended and Restated Series 2009-1 Supplement, dated as of October 25, 2012, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee and Securities Intermediary, to the Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, dated as of September 18, 2009, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.1 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013). |
| 4.6.2 | Second Amended and Restated Series 2009-1 Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 25, 2012, among Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, The Hertz Corporation, as Administrator, Certain Conduit Investors, each as a Conduit Investor, Certain Financial Institutions, each as a Committed Note Purchaser, Certain Funding Agents, and Deutsche Bank AG, New York Branch, as Administrative Agent (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.6.2 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013). |
| 4.7 | Amended and Restated Series 2009-2 Supplement, dated as of June 18, 2010, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee and Securities Intermediary, to the Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, dated as of September 18, 2009, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC., as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.34 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 6, 2010). |
| 4.8 | Series 2010-1 Supplement, dated as of July 22, 2010, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee and Securities Intermediary, to the Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, dated as of September 18, 2009, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC., as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.9.35 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 6, 2010). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 4.9 | Series 2011-1 Supplement, dated as of June 16, 2011, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee and Securities Intermediary, to the Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, dated as of September 18, 2009, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC., as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.11 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 5, 2011). |
| 4.10 | Series 2013-1 Supplement, dated as of January 23, 2013, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC, as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee and Securities Intermediary, to the Third Amended and Restated Base Indenture, dated as of September 18, 2009, between Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC., as Issuer, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.10 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013). |
| 4.11.1 | Amended and Restated Base Indenture, dated as of February 14, 2007, between Rental Car Finance Corp. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.163 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2007, filed May 7, 2007 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.2 | Second Amended and Restated Master Collateral Agency Agreement, dated as of February 14, 2007, among Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., Rental Car Finance Corp., DTG Operations, Inc., various financing sources and beneficiaries party thereto and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as master collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.170 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2007, filed May 7, 2007 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.3 | Master Exchange and Trust Agreement, dated as of July 23, 2001, among Rental Car Finance Corp., Dollar Rent A Car Systems, Inc., Thrifty Rent-A-Car System, Inc., Chicago Deferred Exchange Corporation, VEXCO, LLC and The Chicago Trust Company (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.46 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2001, filed November 13, 2001 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.4 | Amendment No. 1 to Second Amended and Restated Master Collateral Agency Agreement, dated as of June 2, 2009, among Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., DTG Operations, Inc., Rental Car Finance Corp., the financing sources and beneficiaries named therein and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as master collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.210 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed June 8, 2009 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.5 | Amendment No. 1 to Master Exchange and Trust Agreement, dated as of April 23, 2010, among Rental Car Finance Corp., DTG Operations, Inc., Thrifty Rent-A-Car System, Inc., Chicago Deferred Exchange Company, LLC, VEXCO, LLC and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.224 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2010, filed August 3, 2010 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.6 | Collateral Assignment of Exchange Agreement, dated as of October 28, 2010, among Rental Car Finance Corp., DTG Operations, Inc. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as master collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.225 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2010, filed November 2, 2010 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.7 | Amended and Restated Master Motor Vehicle Lease and Servicing Agreement (Group VII), dated as of September 29, 2011, among Rental Car Finance Corp., as lessor, DTG Operations, Inc., as lessee and servicer, and those permitted lessees from time to time becoming lessees and servicers thereunder, and Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as guarantor and master servicer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.243 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed October 4, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.8 | Amendment No. 2 to Master Exchange and Trust Agreement, dated as of October 28, 2010, among Rental Car Finance Corp., DTG Operations, Inc., Thrifty Rent-A-Car System, Inc., DB Like-Kind Exchange Services Corp., VEXCO, LLC and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.229 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2010, filed November 2, 2010 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.9 | Collateral Assignment of Exchange Agreement, dated as of July 28, 2011, among Rental Car Finance Corp., DTG Operations, Inc. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as master collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.236 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed August 3, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 4.11.10 | Master Motor Vehicle Lease and Servicing Agreement (Group VIII), dated as of July 28, 2011, among Rental Car Finance Corp., as lessor, DTG Operations, Inc., as lessee and servicer, and those permitted lessees from time to time becoming lessees and servicers thereunder, and Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as guarantor and master servicer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.238 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed August 3, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.11 | Amendment No. 2 to Second Amended and Restated Master Collateral Agency Agreement, dated as of July 18, 2011, among Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., DTG Operations, Inc., Rental Car Finance Corp. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as master collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.240 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2011, filed August 8, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.12 | Amendment No. 1 to Amended and Restated Master Motor Vehicle Lease and Servicing Agreement (Group VII), dated as of May 18, 2012, among Rental Car Finance Corp., as lessor, DTG Operations, Inc., as lessee and servicer, and those permitted lessees from time to time becoming lessees and servicers thereunder, and Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as guarantor and master servicer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.265 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2012, filed August 2, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.13 | Amendment No. 1 to Master Motor Vehicle Lease and Servicing Agreement (Group VIII), dated as of May 18, 2012, among Rental Car Finance Corp., as lessor, DTG Operations, Inc., as lessee and servicer, and those permitted lessees from time to time becoming lessees and servicers thereunder, and Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as guarantor and master servicer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.266 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2012, filed August 2, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.14 | Amendment No. 2 to Amended and Restated Master Motor Vehicle Lease and Servicing Agreement (Group VII), dated as of June 15, 2012, among Rental Car Finance Corp., as lessor, DTG Operations, Inc., as lessee and servicer, and those permitted lessees from time to time becoming lessees and servicers thereunder, and Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as guarantor and master servicer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.267 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2012, filed August 2, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.11.15 | Amendment No. 2 to Master Motor Vehicle Lease and Servicing Agreement (Group VIII), dated as of June 15, 2012, among Rental Car Finance Corp., as lessor, DTG Operations, Inc., as lessee and servicer, and those permitted lessees from time to time becoming lessees and servicers thereunder, and Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as guarantor and master servicer (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.268 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2012, filed August 2, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.12.1 | Amended and Restated Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of September 29, 2011, among Rental Car Finance Corp., as seller, Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as master servicer, the conduit purchasers, committed purchasers and managing agents identified as such on Schedule III thereto and such other conduit purchasers, committed purchasers and managing agents from time to time party thereto, and Deutsche Bank AG, New York Branch, as administrative agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.241 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed October 4, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.12.2 | Amended and Restated Series 2010-3 Supplement, dated as of September 29, 2011, between Rental Car Finance Corp., as issuer, and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.242 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed October 4, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.12.3 | Amendment No. 1 to Amended and Restated Series 2010-3 Supplement, dated as of February 16, 2012, between Rental Car Finance Corp. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.255 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed February 21, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.13.1 | Note Purchase Agreement, dated July 21, 2011, among Rental Car Finance Corp., Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, RBS Securities Inc. and Scotia Capital (USA) Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.235 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed July 26, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.13.2 | Series 2011-1 Supplement, dated as of July 28, 2011, between Rental Car Finance Corp., as issuer, and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.237 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed August 3, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 4.13.3 | Amendment No. 1 to Series 2011-1 Supplement, dated as of February 16, 2012, between Rental Car Finance Corp. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.256 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed February 21, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.13.4 | Amendment No. 2 to Series 2011-1 Supplement, dated as of February 23, 2012, between Rental Car Finance Corp. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.258 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed February 28, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.14.1 | Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 26, 2011 among Rental Car Finance Corp., as seller, Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc., as master servicer, Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as initial note purchaser, and the note purchasers from time to time party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.245 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed October 31, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.14.2 | Series 2011-2 Supplement, dated as of October 26, 2011, between Rental Car Finance Corp., as issuer, and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.246 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed October 31, 2011 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.14.3 | Amendment No. 1 to Series 2011-2 Supplement, dated as of February 16, 2012, between Rental Car Finance Corp. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.257 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed February 21, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.14.4 | Amendment No. 2 to Series 2011-2 Supplement, dated as of February 23, 2012, between Rental Car Finance Corp. and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.259 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed February 28, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.15.1 | Series 2012-1 Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of March 9, 2012, among TCL Funding Limited Partnership, Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group Canada Inc., BNY Trust Company of Canada, in its capacity as trustee of Ridge Trust, and Computershare Trust Company of Canada, in its capacity as trustee of King Street Funding Trust (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.260 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed March 15, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.15.2 | Trust Indenture, dated as of March 9, 2012, among TCL Funding Limited Partnership, DTGC Car Rental Limited Partnership and BNY Trust Company of Canada, as indenture trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.261 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed March 15, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.15.3 | Series 2012-1 Indenture Supplement, dated as of March 9, 2012, among TCL Funding Limited Partnership, DTGC Car Rental Limited Partnership and BNY Trust Company of Canada, as indenture trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.262 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed March 15, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.15.4 | Parent Guarantee, dated as of March 9, 2012, of Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc. in favor of BNY Trust Company of Canada, as indenture trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.263 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed March 15, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.15.5 | DTAG Canada Guarantee, dated as of March 9, 2012, of Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group Canada Inc. in favor of DTGC Car Rental Limited Partnership (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.264 to Dollar Thrifty Automotive Group, Inc.'s Form 8-K, filed March 15, 2012 (File No. 001-13647)). |
| 4.16.1 | Indenture, dated as of May 27, 2009, between Hertz Global Holdings, Inc., as Issuer, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 5.25% Convertible Senior Notes due 2014 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 27, 2009). |
| 4.16.2 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of August 19, 2009, between Hertz Global Holdings, Inc., as Issuer, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee, relating to the 5.25% Convertible Senior Notes due 2014 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.19.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 6, 2009). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 10.1.1 | Credit Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2011, among The Hertz Corporation, the several lenders from time to time parties thereto, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch, as Administrative Agent and Collateral Agent, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Syndication Agent, Bank of America, N.A., Barclays Bank PLC, Citibank, N.A., Credit Agricole Corporate and Investment Bank and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Co-Documentation Agents, Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., Barclays Capital, Citigroup Global Markets Inc., Credit Agricole Corporate and Investment Bank, J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated and Wells Fargo Securities, LLC, as Joint Lead Arrangers and Joint Bookrunning Managers (referred to as the Senior Term Facility) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 17, 2011). |
| 10.1.2 | Guarantee and Collateral Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2011, between Hertz Investors, Inc., The Hertz Corporation, certain of its subsidiaries and Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch, as Administrative Agent and Collateral Agent, relating to the Senior Term Facility (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 17, 2011). |
| 10.1.3 | Incremental Commitment Amendment, dated as of October 9, 2012, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2011, among The Hertz Corporation, the several banks and financial institutions parties thereto that constitute Tranche B-1 Term Lenders, and Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch, as Administrative Agent (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on October 10, 2012). |
| 10.2.1 | Credit Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2011, among Hertz Equipment Rental Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, the Canadian Borrowers parties thereto, the several lenders from time to time parties thereto, Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch, as Administrative Agent and Collateral Agent, Deutsche Bank AG Canada Branch, as Canadian Agent and Canadian Collateral Agent, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Co-Collateral Agent, Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Syndication Agent, Bank of America, N.A., Barclays Bank PLC, Citibank, N.A., Credit Agricole Corporate and Investment Bank and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Co-Documentation Agents (referred to as the Senior ABL Facility) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 17, 2011). |
| 10.2.2 | U.S. Guarantee and Collateral Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2011, between Hertz Investors, Inc., The Hertz Corporation and certain of its subsidiaries and Deutsche Bank AG New York Branch, as Administrative Agent and Collateral Agent, relating to the Senior ABL Facility (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.4 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 17, 2011). |
| 10.2.3 | Canadian Guarantee and Collateral Agreement, dated as of March 11, 2011, among Matthews Equipment Limited, Western Shut-Down (1995) Limited, Hertz Canada Equipment Rental Partnership, 3222434 Nova Scotia Company and certain of their subsidiaries and Deutsche Bank AG Canada Branch, as Canadian Agent and Canadian Collateral Agent, relating to the Senior ABL Facility (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.5 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 17, 2011). |
| 10.3 | Credit Agreement, dated as of September 22, 2011, among The Hertz Corporation and Puerto Ricancars, Inc., as Borrowers, the several lenders from time to time parties thereto, Gelco Corporation d/b/a GE Fleet Services, as Administrative Agent, Domestic Collateral Agent and PRUSVI Collateral Agent, Bank of America, N.A., as Documentation Agent and Bank of America, N.A. and GE Capital Markets, Inc. as Joint Lead Arrangers and Bookrunning Managers (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 7, 2011). |
| 10.4.1 | Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Stock Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006).† |
| 10.4.2 | First Amendment to the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Stock Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1.1 to Amendment No. 4 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 333-135782), as filed on October 27, 2006).† |
| 10.4.3 | Form of Stock Subscription Agreement under Stock Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006).† |
| 10.4.4 | Form of Stock Option Agreement under Stock Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006).† |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 10.4.5 | Form of Management Stock Option Agreement under the Stock Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 16, 2007).† |
| 10.5.1 | Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Director Stock Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33 to Amendment No. 6 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 333-135782), as filed on November 8, 2006).† |
| 10.5.2 | Form of Director Stock Option Agreement under Director Stock Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.36 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 29, 2008).† |
| 10.6.1 | Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (as amended and restated, effective as of March 4, 2010) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on June 1, 2010).† |
| 10.6.2 | Form of Performance Stock Unit Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on June 1, 2010).† |
| 10.6.3 | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on June 1, 2010).† |
| 10.6.4 | Form of Employee Stock Option Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on June 1, 2010).† |
| 10.6.5 | Form of Director Stock Option Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on June 1, 2010).† |
| 10.6.6 | Form of Performance Stock Unit Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (form used for agreements entered into after January 1, 2011) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6.6 to the Registration Statement on Form S-4 (File No. 333-173023) of The Hertz Corporation, as filed on March 23, 2011).† |
| 10.6.7 | Form of Special Performance Stock Unit Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan approved for fiscal year 2011 grant to Mark P. Frissora (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6.7 to the Registration Statement on Form S-4 (File No. 333-173023) of The Hertz Corporation, as filed on March 23, 2011).† |
| 10.6.8 | Form of Price Vested Stock Unit Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7.8 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 3, 2012).† |
| 10.6.9 | Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7.9 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 3, 2012).† |
| 10.6.10 | Form of Director Designee Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7.10 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 3, 2012).† |
| 10.7.1 | The Hertz Corporation Supplemental Retirement and Savings Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-125764), as filed on August 30, 2005).† |
| 10.7.2 | Amendment of The Hertz Corporation Supplemental Retirement and Savings Plan (as amended and restated, effective as of December 31, 2008) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 3, 2009).† |
| 10.8 | The Hertz Corporation Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (as amended and restated, effective December 31, 2008) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 3, 2009).† |
| 10.9 | The Hertz Corporation Benefit Equalization Plan (as amended and restated, effective December 31, 2008) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 3, 2009).† |
| 10.10 | Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Senior Executive Bonus Plan (Incorporated by reference to 10.6 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on June 1, 2010).† |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 10.11.1 | Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Severance Plan for Senior Executives (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 7, 2008).† |
| 10.11.2 | Amendment to the Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. Severance Plan for Senior Executives, effective as of November 14, 2012 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11.2 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013).† |
| 10.12.1 | Form of Change in Control Severance Agreement among Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. and executive officers (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on November 7, 2008).† |
| 10.12.2 | Form of Change in Control Severance Agreement among Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. and executive officers (form used for agreements entered into after March 3, 2010) (Incorporated by reference to 10.7 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on June 1, 2010).† |
| 10.12.3 | Letter Agreement regarding revised Change in Control Severance Agreement from the Hertz Corporation to Michel Taride dated as of February 1, 2008 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13.3 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on February 27, 2012).† |
| 10.12.4 | Form of Amendment to Change in Control Severance Agreement for Executive Officers and Certain New Key Employees between Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. and executive officers (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12.4 of the Registration Statement on Form S-4 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-186328), as filed on January 31, 2013).† |
| 10.13 | The Hertz Corporation Key Officer Postretirement Assigned Car Benefit Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-125764), as filed on August 30, 2005).† |
| 10.14 | The Hertz Corporation Account Balance Defined Benefit Pension Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-125764), as filed on August 30, 2005).† |
| 10.15 | Form of Special Award Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Registration Statement on Form S-4 (File No. 333-173023) of The Hertz Corporation, as filed on March 23, 2011).† |
| 10.16 | The Hertz Corporation (UK) 1972 Pension Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-125764), as filed on August 30, 2005).† |
| 10.17 | The Hertz Corporation (UK) Supplementary Unapproved Pension Scheme (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-125764), as filed on August 30, 2005).† |
| 10.18 | Non-Compete Agreement, dated April 10, 2000, between Hertz Europe Limited and Michel Taride (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 333-125764), as filed on August 30, 2005).† |
| 10.19 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated as of December 31, 2008, between Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. and Mark P. Frissora (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.28 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 3, 2009).† |
| 10.20.1 | Form of Director Indemnification Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29 to Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 333-135782), as filed on October 23, 2006). |
| 10.20.2 | Amendment No. 1 to Form of Director Indemnification Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29.1 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 3, 2009). |
| 10.20.3 | Form of Director Indemnification Agreement (form used for agreements entered into after April 2009) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.51 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 6, 2010). |
| 10.21 | Amended and Restated Indemnification Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2005, between The Hertz Corporation, Hertz Vehicles LLC, Hertz Funding Corp., Hertz General Interest LLC, and Hertz Vehicle Financing LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006). |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 10.22 | Amended and Restated Indemnification Agreement, dated as of November 23, 2009, by and among Hertz Global Holdings, Inc., The Hertz Corporation, Clayton, Dubilier & Rice Fund VII, L.P., CDR CCMG Co-Investor L.P., Clayton, Dubilier & Rice, Inc., Clayton, Dubilier & Rice, LLC and Clayton Dubilier & Rice Holdings, L.P. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on August 5, 2011). |
| 10.23.1 | Indemnification Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2005, between CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), The Hertz Corporation, Carlyle Partners IV, L.P., CP IV Coinvestment L.P., CEP II U.S. Investments, L.P., CEP II Participations S.à r.l., and TC Group IV, L.L.C. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006). |
| 10.23.2 | Amendment No. 1 to the Indemnification Agreement, dated as of March 3, 2009, between CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), The Hertz Corporation, Carlyle Partners IV, L.P., CP IV Coinvestment L.P., CEP II U.S. Investments, L.P., CEP II Participations S.à r.l., and TC Group IV, L.L.C. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 8, 2009). |
| 10.24.1 | Indemnification Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2005, between CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), The Hertz Corporation, ML Global Private Equity Fund, L.P., Merrill Lynch Ventures L.P. 2001, CMC-Hertz Partners, L.P., ML Hertz Co-Investor, L.P., and Merrill Lynch Global Partners, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006). |
| 10.24.2 | Amendment No. 1 to the Indemnification Agreement, dated as of March 3, 2009, between CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), The Hertz Corporation, ML Global Private Equity Fund, L.P., Merrill Lynch Ventures L.P. 2001, CMC-Hertz Partners, L.P., ML Hertz Co-Investor, L.P., and Merrill Lynch Global Partners, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on May 8, 2009). |
| 10.25 | Tax Sharing Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2005, between CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), CCMG Corporation, The Hertz Corporation, and Hertz International, Ltd. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.25 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006). |
| 10.26 | Tax Sharing Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2005, between CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), CCMG Corporation, and The Hertz Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.26 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of The Hertz Corporation (File No. 001-07541), as filed on March 31, 2006). |
| 10.27.1 | Amended and Restated Stockholders Agreement, dated as of November 20, 2006, among Hertz Global Holdings, Inc., Clayton, Dubilier & Rice Fund VII, L.P., CDR CCMG Co-Investor L.P., CD&R Parallel Fund VII, L.P., Carlyle Partners IV, L.P., CP IV Coinvestment, L.P., CEP II U.S. Investments, L.P., CEP II Participations S.à r.l SICAR, ML Global Private Equity Fund, L.P., Merrill Lynch Ventures L.P. 2001, ML Hertz Co-Investor, L.P. and CMC-Hertz Partners, L.P. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.10 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 30, 2007). |
| 10.27.2 | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of December 21, 2005, among CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), Clayton, Dubilier & Rice Fund VII, L.P., CDR CCMG Co-Investor L.P., Carlyle Partners IV, L.P., CP IV Coinvestment, L.P., CEP II U.S. Investments, L.P., CEP II Participations S.à r.l, ML Global Private Equity Fund, L.P., Merrill Lynch Ventures L.P. 2001, ML Hertz Co-Investor, L.P. and CMC-Hertz Partners, L.P. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.11 to Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-135782), as filed on October 23, 2006). |
| 10.27.3 | Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of November 20, 2006, among CCMG Holdings, Inc. (now known as Hertz Global Holdings, Inc.), Clayton, Dubilier & Rice Fund VII, L.P., CDR CCMG Co-Investor L.P., CD&R Parallel Fund VII, L.P., Carlyle Partners IV, L.P., CP IV Coinvestment, L.P., CEP II U.S. Investments, L.P., CEP II Participations S.à r.l SICAR, ML Global Private Equity Fund, L.P., Merrill Lynch Ventures L.P. 2001, ML Hertz Co-Investor, L.P. and CMC-Hertz Partners, L.P. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.12 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on March 30, 2007). |
| 10.28 | Living accommodation and optional purchase agreement, dated as of July 7, 2011, between Michel Taride and Hertz Europe Ltd. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. (File No. 001-33139), as filed on July 8, 2011). |
| 12.1 | Computation of Consolidated Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges (Unaudited) for the years ended December 31, 2012, 2011, 2010, 2009 and 2008. |
|
| |
| Exhibit Number | Description |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of Hertz Global Holdings, Inc. |
| 31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a). |
| 31.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a). |
| 32.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350. |
| 32.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350. |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document* |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document* |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document* |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document* |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document* |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document* |
_______________________________________________________________________________
† Indicates management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
* Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, the Interactive Data Files on Exhibit 101 hereto are deemed not filed or part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, are deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and otherwise are not subject to liability under those sections.
As of December 31, 2011, we had various additional obligations which could be considered long-term debt, none of which exceeded 10% of our total assets on a consolidated basis. We agree to furnish to the SEC upon request a copy of any such instrument defining the rights of the holders of such long-term debt.
Schedules and exhibits not included above have been omitted because the information required has been included in the financial statements or notes thereto or are not applicable or not required.