UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
☒ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2024
OR
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 1-8858
UNITIL CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| |
| |
New Hampshire | 02-0381573 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) |
|
|
6 Liberty Lane West, Hampton, New Hampshire | 03842-1720 |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (603) 772-0775
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | |
| | |
Title of each class
| Trading Symbol
| Name of each exchange of which registered
|
Common Stock, no par value | UTL | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: NONE
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer”, “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer ☒ Accelerated filer ☐ Non-accelerated filer ☐ Smaller reporting company ☐
Emerging growth company ☐
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 762(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
Based on the closing price of the registrant’s common stock on June 30, 2024, the aggregate market value of common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $819,534,612.
The number of shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding was 16,245,554 as of February 7, 2025.
Documents Incorporated by Reference:
Portions of the Proxy Statement relating to the 2025 Unitil Corporation Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held on April 30, 2025 are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Report.
UNITIL CORPORATION
FORM 10-K
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2024
Table of Contents
In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the “Company”, “Unitil”, “we”, “us”, “our” and similar terms refer to Unitil Corporation and its subsidiaries, unless the context requires otherwise.
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT
This report and the documents incorporated by reference into this report contain statements that may constitute “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), and the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, included or incorporated by reference into this report, including, without limitation, statements regarding the financial position, business strategy and other plans and objectives for the future operations of the Company (as such term is defined in Part I, Item I (Business)), are forward-looking statements.
These statements include declarations regarding the Company’s beliefs and current expectations. In some cases, forward-looking statements can be identified by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “expects,” “plans,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “predicts,” “potential” or “continue” or the negative of such terms or other comparable terminology. These forward-looking statements are subject to inherent risks and uncertainties in predicting future results and conditions that could cause the actual results to differ materially from those projected in these forward-looking statements. Some, but not all, of the risks and uncertainties include those described in Part I, Item 1A (Risk Factors) and the following:
•numerous hazards and operating risks relating to the Company’s electric and natural gas distribution activities, which could result in accidents and other operating risks and costs;
•fluctuations in the supply of, demand for, and the prices of, electric and gas energy commodities and transmission and transportation capacity and the Company’s ability to recover energy supply costs in its rates;
•cyber-attacks, acts of terrorism, acts of war, severe weather, a solar event, an electromagnetic event, a natural disaster, the age and condition of information technology assets, human error, or other factors could disrupt the Company’s operations and cause the Company to incur unanticipated losses and expense;
•outsourcing of services to third parties could expose us to substandard quality of service delivery or substandard deliverables, which may result in missed deadlines or other timeliness issues, non-compliance (including with applicable legal requirements and industry standards) or reputational harm, which could negatively affect the Company’s results of operations;
•unforeseen or changing circumstances, which could adversely affect the reduction of Company-wide direct greenhouse gas emissions;
•the Company’s regulatory and legislative environment (including laws and regulations relating to climate change, greenhouse gas emissions and other environmental matters) could affect the rates the Company is able to charge, the Company’s authorized rate of return, the Company’s ability to recover costs in its rates, the Company’s financial condition, results of operations and cash flows, and the scope of the Company’s regulated activities;
•general economic conditions, which could adversely affect (i) the Company’s customers and, consequently, the demand for the Company’s distribution services, (ii) the availability of credit and liquidity resources, and (iii) certain of the Company’s counterparty’s obligations (including those of its insurers and lenders);
•the Company’s ability to obtain debt or equity financing on acceptable terms;
•increases in interest rates, which could increase the Company’s interest expense;
•the Company’s payment of dividends in the future;
•declines in capital markets valuations, which could require the Company to make substantial cash contributions to cover its pension obligations, and the Company’s ability to recover pension obligation costs in its rates;
•the Company’s ability to consummate acquisitions or other strategic transactions, to successfully integrate any acquired assets or business, or derive value from strategic transactions and investment;
•restrictive covenants contained in the terms of the Company’s and its subsidiaries’ indebtedness, which restrict certain aspects of the Company’s business operations;
•customers’ preferred energy sources;
•severe storms and the Company’s ability to recover storm costs in its rates;
•variations in weather, which could decrease demand for the Company’s distribution services;
•long-term global climate change, which could adversely affect customer demand or cause extreme weather events that could disrupt the Company’s electric and natural gas distribution services;
•macroeconomic events, including the imposition of tariffs;
•employee workforce factors, including the ability to attract and retain key personnel;
•the Company’s ability to retain its existing customers and attract new customers;
•increased competition; and
•other presently unknown or unforeseen factors.
Many of these risks are beyond the Company’s control. Any forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this report, and the Company undertakes no obligation to update any forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which such statements are made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events, except as required by law. New factors emerge from time to time, and it is not possible for the Company to predict all such factors, nor can the Company assess the effect of any such factor on its business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements.
PART I
Item 1. Business
UNITIL CORPORATION
In this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the “Company”, “Unitil”, “we”, and “our” refer to Unitil Corporation and its subsidiaries, unless the context requires otherwise. Unitil is a public utility holding company incorporated under the laws of the State of New Hampshire in 1984. The following companies are wholly-owned subsidiaries of Unitil:
| | | | |
Company Name | | State and Year of
Organization | | Principal Business |
| |
| |
|
Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. (Unitil Energy) | | NH - 1901 | | Electric Distribution Utility |
| |
| |
|
Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company (Fitchburg) | | MA - 1852 | | Electric & Natural Gas Distribution Utility |
| |
| |
|
Northern Utilities, Inc. (Northern Utilities) | | NH - 1979 | | Natural Gas Distribution Utility |
| |
| |
|
Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. (Granite State) | | NH - 1955 | | Natural Gas Transmission Pipeline |
| |
| |
|
Unitil Power Corp. (Unitil Power) | | NH - 1984 | | Wholesale Electric Power Utility |
| |
| |
|
Unitil Service Corp. (Unitil Service) | | NH - 1984 | | Utility Service Company |
| |
| |
|
Unitil Realty Corp. (Unitil Realty) | | NH - 1986 | | Real Estate Management |
| |
| |
|
Unitil Resources, Inc. (Unitil Resources) | | NH - 1993 | | Non-regulated Energy Services |
Unitil and its subsidiaries are subject to regulation as a holding company system by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) under the Energy Policy Act of 2005.
Unitil’s principal business is the local distribution of electricity and natural gas to approximately 198,500 customers throughout its service territories in the states of New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Maine. Unitil is the parent company of three wholly-owned distribution utilities: i) Unitil Energy, which provides electric service in the southeastern seacoast and state capital regions of New Hampshire, including the capital city of Concord, ii) Fitchburg, which provides both electric and natural gas service in the greater Fitchburg area of north central Massachusetts, and iii) Northern Utilities, which provides natural gas service in southeastern New Hampshire and portions of southern and central Maine, including the city of Portland, which is the largest city in northern New England. In addition, Unitil is the parent company of Granite State, an interstate natural gas transmission pipeline company that provides interstate natural gas pipeline access and transportation services to Northern Utilities in its New Hampshire and Maine service territory. Together, Unitil’s three distribution utilities serve approximately 109,400 electric customers and 89,100 natural gas customers.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Customers Served as of December 31, 2024 | |
| | Residential | | | Commercial &
Industrial (C&I) | | | Total | |
Electric: | | | | | | | | | |
Unitil Energy | | | 67,428 | | | | 11,464 | | | | 78,892 | |
Fitchburg | | | 26,386 | | | | 4,166 | | | | 30,552 | |
Total Electric | | | 93,814 | | | | 15,630 | | | | 109,444 | |
Natural Gas: | | | | | | | | | |
Northern Utilities | | | 55,570 | | | | 17,124 | | | | 72,694 | |
Fitchburg | | | 14,685 | | | | 1,749 | | | | 16,434 | |
Total Natural Gas | | | 70,255 | | | | 18,873 | | | | 89,128 | |
Total Customers Served | | | 164,069 | | | | 34,503 | | | | 198,572 | |
Unitil had an investment in Net Utility Plant of $1,539.6 million at December 31, 2024. The Company’s total operating revenue was $494.8 million in 2024. Unitil’s operating revenue is substantially derived from regulated electric and natural gas distribution utility operations. A fifth utility subsidiary, Unitil Power, formerly functioned as the full requirements wholesale power supply provider for Unitil Energy, but ceased being the wholesale supplier of Unitil Energy with the implementation of industry restructuring and divested its long-term power supply contracts.
Unitil has three other wholly-owned non-utility subsidiaries: Unitil Service, Unitil Realty, and Unitil Resources. Unitil Service provides, at cost, a variety of administrative and professional services, including regulatory, financial, accounting, human resources, engineering, operations, technology and energy supply management services on a centralized basis to its affiliated Unitil companies. Unitil Realty owns and manages the Company’s corporate office in Hampton, New Hampshire and
land for future use in Kingston, New Hampshire. Unitil Resources is the Company’s wholly-owned non-regulated subsidiary which currently does not have any activity. For segment information relating to each segment’s revenue, earnings and assets, see Note 2 (Segment Information) to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8 (Financial Statements and Supplementary Data) of this report. All of the Company’s revenues are attributable to customers in the United States of America and all its long-lived assets are located in the United States of America.
On January 31, 2025, Unitil Corporation acquired Bangor Natural Gas Company, a natural gas distribution utility. Bangor Natural Gas Company was incorporated under the laws of the State of Maine in 1998.
OPERATIONS
Electric Distribution Utility Operations
Unitil’s electric distribution operations are conducted through two of the Company’s utilities, Unitil Energy and Fitchburg. Revenue from Unitil’s electric utility operations was $248.3 million in 2024, which represents about 50% of Unitil’s total operating revenue. The Company’s GAAP (as defined below) Electric Gross Margin was $78.0 million in 2024. The Company’s Electric Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $107.3 million in 2024, or 39% of Unitil’s total Adjusted Gross Margin. See “Results of Operations” in Part II, Item 7 (Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations) for a discussion of the non-GAAP financial measures presented in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including a reconciliation of the non-GAAP financial measures to the most comparable GAAP financial measures for the periods presented.
The primary business of Unitil’s electric utility operations is the local distribution of electricity to customers in its service territory in New Hampshire and Massachusetts. All of Unitil Energy’s and Fitchburg’s electric customers are entitled to purchase their supply of electricity from third-party competitive suppliers, while Unitil Energy and Fitchburg remain their electric distribution company. Both Unitil Energy and Fitchburg supply electricity to those customers who do not obtain their supply from third-party competitive suppliers, with the approved costs associated with electricity supply being recovered on a pass-through basis under regulated reconciling rate mechanisms that are periodically adjusted.
Unitil Energy distributes electricity to approximately 78,900 customers in New Hampshire in the capital city of Concord as well as parts of 12 surrounding towns, and all or part of 18 towns in the southeastern and seacoast regions of New Hampshire, including the towns of Hampton, Exeter, Atkinson and Plaistow. Unitil Energy’s service territory consists of approximately 408 square miles. Unitil Energy’s service territory encompasses retail and recreation centers for the central and southeastern parts of the state and includes the Hampton Beach recreational area. These areas serve diversified commercial and industrial businesses, including manufacturing firms engaged in the production of electronic components, wire and plastics, as well as firms engaged in the aviation, defense, healthcare and education sectors. Unitil Energy’s 2024 electric operating revenue was $164.7 million, of which approximately 57% was derived from residential sales and 43% from commercial and industrial (C&I) sales.
Fitchburg is engaged in the distribution of both electricity and natural gas in the greater Fitchburg area of north central Massachusetts. Fitchburg’s service territory encompasses approximately 170 square miles. Electricity is distributed by Fitchburg to approximately 30,500 customers in the communities of Fitchburg, Ashby, Townsend and Lunenburg. Fitchburg’s industrial customers include paper manufacturing and paper products companies, rubber and plastics manufacturers, precision machining and molding, non-lethal ballistics manufacturing, specialty chemicals compounding, cannabis growing and processing facilities, printing, and educational institutions. Fitchburg’s 2024 electric operating revenue was $83.6 million, of which approximately 58% was derived from residential sales and 42% from C&I sales.
Natural Gas Operations
Unitil’s natural gas operations include gas distribution utility operations and interstate gas transmission pipeline operations. Revenue from Unitil’s gas operations was $246.5 million in 2024, which represents about 50% of Unitil’s total operating revenue. The Company’s GAAP Gas Gross Margin was $120.1 million in 2024. The Company’s Gas Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $166.9 million in 2024, or 61% of Unitil’s total Adjusted Gross Margin. See “Results of Operations” in Part II, Item 7 (Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations) for a discussion of the non-GAAP financial measures presented in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including a reconciliation of the non-GAAP financial measures to the most comparable GAAP financial measures for the periods presented.
Natural Gas Distribution Utility Operations
Unitil’s natural gas distribution operations are conducted through two of the Company’s operating utilities, Northern Utilities and Fitchburg. The primary business of Unitil’s natural gas utility operations is the local distribution of natural gas to customers in its service territories in New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Maine. Northern Utilities’ C&I customers and Fitchburg’s residential and C&I customers are entitled to purchase their natural gas supply from third-party competitive suppliers, while Northern Utilities or Fitchburg remains their gas distribution company. Both Northern Utilities and Fitchburg supply gas to those customers who do not obtain their supply from third-party competitive suppliers, with the approved costs associated with this gas supply recovered on a pass-through basis under regulated reconciling rate mechanisms that are periodically adjusted.
Northern Utilities distributes natural gas to approximately 72,700 customers in 47 New Hampshire and southern Maine communities, from Plaistow, New Hampshire in the south to the city of Portland, Maine and then extending to Lewiston-Auburn, Maine to the north. Northern Utilities has a diversified customer base both in Maine and New Hampshire. Commercial businesses include healthcare, education, government and retail. Northern Utilities’ industrial base includes manufacturers in the auto, housing, paper, printing, textile, pharmaceutical, electronics, wire and food production industries as well as a military installation. Northern Utilities’ 2024 gas operating revenue was $188.7 million, of which approximately 38% was derived from residential firm sales and 62% from C&I firm sales.
Fitchburg distributes natural gas to approximately 16,400 customers in the communities of Fitchburg, Lunenburg, Townsend, Ashby, Gardner and Westminster, all located in Massachusetts. Fitchburg’s industrial customers include paper manufacturing and paper products companies, rubber and plastics manufacturers, cannabis growing and processing facilities, printing, educational institutions. Fitchburg’s 2024 gas operating revenue was $48.0 million, of which approximately 57% was derived from residential firm sales and 43% from C&I firm sales.
Gas Transmission Pipeline Operations
Granite State is an interstate natural gas transmission pipeline company, operating 85 miles of underground gas transmission pipeline primarily located in Maine and New Hampshire. Granite State provides Northern Utilities with interconnection to major natural gas pipelines and access to domestic natural gas supplies in the south and Canadian natural gas supplies in the north. Granite State had operating revenue of $9.8 million in 2024. Granite State derives its revenues principally from the transportation services provided to Northern Utilities and to third-party suppliers under FERC-approved rates.
Seasonality
The Company’s results of operations are expected to reflect the seasonal nature of the natural gas business. Annual gas revenues are substantially realized during the colder weather seasons of the year as a result of higher sales of natural gas used for heating-related purposes. Accordingly, the results of operations are historically most favorable in the first and fourth quarters. Fluctuations in seasonal weather conditions may have a significant effect on the result of operations. Sales of electricity are generally less sensitive to weather than natural gas sales, but may also be affected by weather conditions and the temperature in the winter and summer seasons.
Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Northern Utilities have a well-diversified customer mix and are not dependent on a single customer, or a few customers, for their electric and natural gas sales.
Revenue Decoupling
Revenue decoupling is the term given to the elimination of the dependency of a utility’s distribution revenue on the volume of electricity or gas sales. The difference between distribution revenue amounts billed to customers and the targeted revenue decoupling amounts is recognized as an increase or a decrease in Accrued Revenue, which forms the basis for resetting rates for future cash recoveries from, or credits to, customers. These revenue decoupling targets may be adjusted as a result of rate cases and other authorized adjustments that the Company files with the Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities (MDPU) and New Hampshire Public Utilities Commission (NHPUC). Fitchburg has been subject to revenue decoupling since 2011. Unitil Energy has been subject to revenue decoupling since June 1, 2022. As a result of Unitil Energy now being subject to revenue decoupling, as of June 1, 2022, revenue decoupling now applies to substantially all of Unitil’s total annual electric sales volumes. Substantially all of Northern Utilities’ gas sales volumes in New Hampshire have been subject to decoupling
since August 1, 2022. The Company's electric and gas sales in New Hampshire and Massachusetts are now largely decoupled. Northern Utilities’ gas sales volumes in Maine are not subject to revenue decoupling.
Non-Regulated and Other Non-Utility Operations
The results of Unitil’s other non-utility subsidiaries, Unitil Service, Unitil Resources, Unitil Realty, and the holding company, are included in the Company’s consolidated results of operations. The results of these non-utility operations are principally derived from income earned on short-term investments and real property owned for Unitil’s and its subsidiaries’ use and are reported, after intercompany eliminations, in Other segment income. For segment information, see Note 2 (Segment Information) to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8 (Financial Statements and Supplementary Data) of this report.
RATES AND REGULATION
Regulation
Unitil is subject to comprehensive regulation by federal and state regulatory authorities. Unitil and its subsidiaries are subject to regulation as a holding company system by the FERC under the Energy Policy Act of 2005 with regard to certain bookkeeping, accounting and reporting requirements. Unitil’s utility operations related to wholesale and interstate energy business activities also are regulated by the FERC. Unitil’s distribution utilities are subject to regulation by the applicable state public utility commissions, with regard to their rates, issuance of securities and other accounting and operational matters: Unitil Energy is subject to regulation by the NHPUC; Fitchburg is subject to regulation by the MDPU; and Northern Utilities is regulated by the NHPUC and Maine Public Utilities Commission (MPUC). Granite State, Unitil’s interstate natural gas transmission pipeline, is subject to regulation by the FERC with regard to its rates and operations. Because Unitil’s primary operations are subject to rate regulation, the regulatory treatment of various matters could significantly affect the Company’s operations and financial position.
Unitil’s distribution utilities deliver electricity and/or natural gas to all customers in their service territory, at rates established under cost of service regulation. Under this regulatory structure, Unitil’s distribution utilities are provided the opportunity to recover the cost of providing distribution service to their customers based on a test year, and to earn a reasonable return on their capital investment in utility assets. In addition, the Company’s distribution utilities and its natural gas transmission pipeline company may recover certain base rate costs, including capital project spending and enhanced reliability and vegetation management programs, through annual step adjustments and cost tracking rate mechanisms. The Company's electric and gas sales in New Hampshire and Massachusetts are now largely decoupled.
Also see Note 1 (Summary of Significant Accounting Policies), Note 6 (Energy Supply) and Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding rates and regulation.
EMPLOYEES
As of December 31, 2024, the Company and its subsidiaries had 544 employees. The Company considers its relationship with employees to be good and has not experienced any major labor disruptions.
The Company strives to be the employer of choice in the communities it serves—regardless of race, religion, color, gender, or sexual orientation. The Company works diligently to attract the best talent from a diverse range of sources to meet the current and future demands of the Company’s business.
To attract and retain a talented workforce, Unitil provides employee wages that are competitive and consistent with employee positions, skill levels, experience, knowledge and geographic location. All employees are eligible for health insurance, paid and unpaid leave, educational assistance, retirement plan and life and disability/accident coverage. Feedback from employees is collected annually in the Company’s employee opinion survey. This feedback helps create action plans to improve the engagement of employees consistent with the Company’s culture of continuous improvement.
As of December 31, 2024, a total of 172 employees of certain of the Company’s subsidiaries were represented by labor unions. The following table details by subsidiary the employees covered by a collective bargaining agreement (CBA) as of December 31, 2024:
| | | | | |
| | Employees Covered | | CBA Expiration |
Fitchburg | | 46 | | | 5/31/2027 |
Northern Utilities NH Division | | 36 | | | 06/07/2025 |
Northern Utilities ME Division | | 40 | | | 03/31/2026 |
Granite State | | 4 | | | 03/31/2026 |
Unitil Energy | | 41 | | | 5/31/2028 |
Unitil Service | | 5 | | | 5/31/2028 |
The CBAs provide discrete salary adjustments, established work practices and uniform benefit packages. The Company expects to negotiate new agreements prior to their expiration dates.
AVAILABLE INFORMATION
The Internet address for the Company’s website is unitil.com. On the Investors section of the Company’s website, the Company makes available, free of charge, its Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) reports, including annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and other reports, as well as amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practical after the Company electronically files such material with, or furnishes such material to, the SEC.
The Company’s current Code of Ethics was approved by Unitil’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) on January 15, 2004. This Code of Ethics, along with any amendments or waivers, is also available on Unitil’s website.
Unitil’s common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol “UTL”.
INVESTOR INFORMATION
Annual Meeting
The Company’s annual meeting of shareholders is scheduled to be held at the offices of the Company, 6 Liberty Lane West, Hampton, New Hampshire, on Wednesday, April 30, 2025, at 11:30 a.m. Eastern Time.
Transfer Agent
The Company’s transfer agent, Computershare Investor Services, is responsible for shareholder records, issuance of common stock, administration of the Dividend Reinvestment and Stock Purchase Plan, and the distribution of Unitil’s dividends and IRS Form 1099-DIV. Shareholders may contact Computershare at:
Computershare Investor Services
P.O. Box 43078
Providence, RI 02940-3078
Telephone: 800-736-3001
www.computershare.com/investor
Investor Relations
For information about the Company, you may call the Company directly, toll-free, at: 800-999-6501 and ask for the Investor Relations Representative; visit the Investors page at www.unitil.com; or contact the transfer agent, Computershare, at the number listed above.
Special Services & Shareholder Programs Available to Holders of Record
If a shareholder’s shares of the Company’s common stock are registered directly in the shareholder’s name with the Company’s transfer agent, the shareholder is considered a holder of record of the shares. The following services and programs are available to shareholders of record:
•Online Account Access is available at www.computershare.com/investor.
•Dividend Reinvestment and Stock Purchase Plan:
To enroll, please contact the Company’s Investor Relations Representative or Computershare.
•Dividend Direct Deposit Service:
To enroll, please contact the Company’s Investor Relations Representative or Computershare.
For information, please contact Computershare at 800-935-9330 or the Company’s Investor Relations Representative at 800-999-6501.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
When considering an investment in the Company’s securities, investors should consider the following risk factors, as well as the information contained under the caption “Cautionary Statement” immediately following the Table of Contents in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Additional risks not presently known to the Company or that the Company currently believes are immaterial may also impair business operations and financial results. If any of the following risks actually occur, the Company’s business, financial condition or results of operations could be adversely affected. In such case, the trading price of the Company’s common stock could decline and investors could lose all or part of their investment. The risk factors below are categorized by operational, regulatory, financial and general.
OPERATIONAL RISKS
A substantial disruption or lack of growth in interstate natural gas pipeline transmission and storage capacity and electric transmission capacity may impair the Company’s ability to meet customers’ existing and future requirements.
To meet existing and future customer demands for electricity and natural gas, the Company must acquire sufficient supplies of electricity and natural gas. In addition, the Company must contract for reliable and adequate upstream transmission and transportation capacity for its distribution systems while considering the dynamics of the natural gas interstate pipelines and storage, the electric transmission markets and its own on-system resources. The Company’s financial condition or results of operations may be adversely affected if the future availability of electric and natural gas supply were insufficient to meet future customer demands for electricity and natural gas.
The Company’s electric and natural gas distribution activities (including storing natural gas and supplemental gas supplies) involve numerous hazards and operating risks that may result in accidents and other operating risks and costs. Any such accident or costs could adversely affect the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
Inherent in the Company’s electric and natural gas distribution activities are a variety of hazards and operating risks, including leaks, explosions, electrocutions, mechanical problems and aging infrastructure. These hazards and risks could result in loss of human life, significant damage to property, environmental pollution, damage to natural resources and impairment of the Company’s operations, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
The Company maintains insurance against some, but not all, of these risks and losses in accordance with customary industry practice. The location of pipelines, storage facilities and electric distribution equipment near populated areas (including residential areas, commercial business centers and industrial sites) could increase the level of damages associated with these hazards and operating risks. The occurrence of any of these events could adversely affect the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
The Company’s operational and information systems on which it relies to conduct its business and serve customers could fail to function properly due to technological problems, a cyber-attack, acts of terrorism, severe weather, a solar event, an
electromagnetic event, a natural disaster, the age and condition of information technology assets, human error, or other reasons, that could disrupt the Company’s operations and cause the Company to incur unanticipated losses and expense.
The operation of the Company’s extensive electric and natural gas systems rely on evolving information and operating technology systems and network infrastructure that are likely to become more complex as new technologies and systems are developed. The Company’s business is highly dependent on its ability to process and monitor, on a daily basis, a very large number of transactions, many of which are highly complex. The failure of these systems and networks could significantly disrupt operations; result in outages and/or damages to the Company’s assets or operations or those of third parties on which it relies; and subject the Company to claims by customers or third parties, any of which could have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The Company’s information systems, including its financial information, operational systems, metering, and billing systems, require constant maintenance, modification, and updating, which can be costly and increases the risk of errors and malfunction. Any disruptions or deficiencies in existing information systems, or disruptions, delays or deficiencies in the modification or implementation of new information systems, could result in increased costs, the inability to track or collect revenues, the diversion of management’s and employees’ attention and resources, and could negatively affect the effectiveness of the Company’s control environment, and/or the Company’s ability to timely file required regulatory reports. Despite implementation of security and mitigation measures, all of the Company’s technology systems are vulnerable to impairment or failure due to cyber-attacks, computer viruses, human errors, acts of war or terrorism and other reasons. If the Company’s information technology systems were to fail or be materially impaired, the Company might be unable to fulfill critical business functions and serve its customers, which could have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
In the ordinary course of its business, the Company collects and retains sensitive electronic data including personal identification information about customers and employees, customer energy usage, and other confidential information. The theft, damage, or improper disclosure of sensitive electronic data through security breaches or other means could subject the Company to penalties for violation of applicable privacy laws or claims from third parties and could harm the Company’s reputation and adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, the Company’s electric and natural gas distribution and transmission delivery systems are part of an interconnected regional grid and pipeline system. If these neighboring interconnected systems were to be disrupted due to cyber-attacks, computer viruses, human errors, acts of war or terrorism or other reasons, the Company’s operations and its ability to serve its customers would be adversely affected, which could have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
We outsource certain business functions to third-party suppliers and service providers, and substandard performance by those third parties could harm the Company’s business, reputation and results of operations.
We outsource certain services to third parties in areas including information technology, telecommunications, networks, transaction processing, human resources, payroll and payroll processing and other areas. Outsourcing of services to third parties could expose us to substandard quality of service delivery or substandard deliverables, which may result in missed deadlines or other timeliness issues, non-compliance (including with applicable legal requirements and industry standards) or reputational harm, which could negatively affect the Company’s results of operations. We also continue to pursue enhancements to modernize the Company’s systems and processes. If any difficulties in the operation of these systems were to occur, they could adversely affect the Company’s results of operations, or adversely affect the Company’s ability to work with regulators, unions, customers or employees.
The inability to attract and retain a qualified workforce including, but not limited to, executive officers, key employees and employees with specialized skills, could have an adverse effect on the Company’s operations.
The success of the Company’s business depends on the leadership of the Company’s executive officers and other key employees to implement the Company’s business strategies. The inability to maintain a qualified workforce including, but not limited to, executive officers, key employees and employees with specialized skills, may negatively affect the Company’s ability to service the Company’s existing or new customers, or successfully manage the Company’s business or achieve the Company’s business objectives. There may not be sufficiently skilled employees available internally to replace employees when they retire or otherwise leave active employment. Shortages of certain highly skilled employees may also mean that qualified employees are not available externally to replace these employees when they are needed. In addition, shortages in highly skilled
employees coupled with competitive pressures may require the Company to incur additional employee recruiting and compensation expenses.
The Company may be adversely affected by work stoppages, labor disputes, and/or pandemic illness to which it may not be able to promptly respond.
Approximately one-third of the Company’s employees are represented by labor unions and are covered by collective bargaining agreements. Disputes with the unions over terms and conditions of the agreements could result in instability in the Company’s labor relationships and work stoppages that could affect the timely delivery of electricity and natural gas, which could strain relationships with customers and state regulators and cause a loss of revenues. The Company’s collective bargaining agreements also may increase the cost of employing its union workforce, affect its ability to continue offering market-based salaries and employee benefits, limit its flexibility in dealing with its workforce, and limit its ability to change work rules and practices and implement other efficiency-related improvements to successfully compete in today’s challenging marketplace, which may negatively affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
Additionally, pandemic illness could result in part, or all, of the Company’s workforce being unable to operate or maintain the Company’s infrastructure or perform other tasks necessary to conduct the Company’s business. A slow or inadequate response to this type of event may adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
REGULATORY RISKS
The Company is subject to comprehensive regulation, which could adversely affect the rates it is able to charge, its authorized rate of return and its ability to recover costs. In addition, certain regulatory authorities have the statutory authority to impose financial penalties and other sanctions on the Company, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The Company is subject to comprehensive regulation by federal regulatory authorities (including the FERC) and state regulatory authorities (including the NHPUC, MDPU and MPUC). These authorities regulate many aspects of the Company’s operations, including the rates that the Company can charge customers, the Company’s authorized rates of return, the Company’s ability to recover costs from its customers, construction and maintenance of the Company’s facilities, the Company’s safety protocols and procedures, including environmental compliance, the Company’s ability to issue securities, the Company’s accounting matters, and transactions between the Company and its affiliates. The Company is unable to predict the effect on its financial condition and results of operations from the regulatory activities of any of these regulatory authorities. Changes in regulations, the imposition of additional regulations, regulatory proceedings regarding fossil fuel use and system electrification, or regulatory decisions particular to the Company could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
The Company’s ability to obtain rate adjustments to maintain its current authorized rates of return depends upon action by regulatory authorities under applicable statutes, rules and regulations. These regulatory authorities are authorized to leave the Company’s rates unchanged, to grant increases in such rates, or to order decreases in such rates. The Company may be unable to obtain favorable rate adjustments or to maintain its current authorized rates of return, which could adversely affect its financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
Regulatory authorities also have authority with respect to the Company’s ability to recover its electricity and natural gas supply costs, as incurred by Unitil Energy, Fitchburg, Unitil Power, and Northern Utilities. If the Company is unable to recover a significant amount of these costs, or if the Company’s recovery of these costs is significantly delayed, the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows could be adversely affected.
In addition, certain regulatory authorities have the statutory authority to impose financial penalties and other sanctions on the Company if the Company is found to have violated statutes, rules or regulations governing its utility operations. Any such penalties or sanctions could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The Company’s business is subject to environmental regulation in all jurisdictions in which it operates and its costs of compliance are significant. New, or changes to existing, environmental regulation, including those related to climate change
or greenhouse gas emissions, and the incurrence of environmental liabilities could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The Company’s utility operations are generally subject to extensive federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations relating to air quality, water quality, waste management, natural resources, and the health and safety of the Company’s employees. The Company’s utility operations also may be subject to new and emerging federal, state and local legislative and regulatory initiatives related to climate change or greenhouse gas emissions including the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency’s mandatory greenhouse gas reporting rule. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations may result in the assessment of administrative, civil, and criminal penalties and other sanctions; imposition of remedial requirements; and issuance of injunctions to ensure future compliance. Liability under certain environmental laws and regulations is strict, joint and several in nature. Although the Company believes it is in material compliance with all applicable environmental and safety laws and regulations, there is no assurance that the Company will not incur significant costs and liabilities in the future. Moreover, it is possible that other developments, such as increasingly stringent federal, state or local environmental laws and regulations, including those related to climate change or greenhouse gas emissions, could result in increased environmental compliance costs. The Company has committed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from 2019 levels by at least 50% by 2030 and to achieve net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. Unforeseen or changing circumstances could adversely affect the Company's ability to achieve these greenhouse gas emissions goals and changes in the regulatory environment could result in the costs associated with efforts to achieve these goals not qualifying for recovery.
FINANCIAL RISKS
The Company may not be able to obtain financing, or may not be able to obtain financing on acceptable terms, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
The Company requires capital to fund utility plant additions, working capital and other utility expenditures. While the Company derives the capital necessary to meet these requirements primarily from internally generated funds, the Company supplements internally generated funds by incurring short-term and long-term debt, as needed. Additionally, from time to time the Company has accessed the public capital markets through public offerings of equity securities. A downgrade of the Company’s credit rating or events beyond the Company’s control, such as a disruption in global capital and credit markets, could increase the Company’s cost of borrowing and cost of capital or restrict the Company’s ability to access the capital markets and negatively affect the Company’s ability to maintain and to expand the Company’s businesses.
The Company’s short-term debt revolving credit facility typically has variable interest rates. Therefore, an increase or decrease in interest rates will increase or decrease the Company’s interest expense associated with its revolving credit facility. An increase in the Company’s interest expense could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. As of December 31, 2024, the Company had approximately $105.8 million in short-term debt outstanding under its revolving credit facility. If the lending counterparties under the Company’s current credit facility are unwilling or unable to meet their funding obligations, the Company may be unable to, or limited in its ability, to borrow under its credit facility. This situation could hinder or prevent the Company from meeting its current and future capital needs, which could correspondingly adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results or operations, and cash flows.
Also, from time to time the Company repays portions of its short-term debt with the proceeds it receives from long-term debt financings or equity financings. General economic conditions, conditions in the capital and credit markets and the Company’s operating and financial performance could negatively affect the Company’s ability to obtain such financings or the terms of such financings, which could correspondingly adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows. The Company’s long-term debt typically has fixed interest rates. Therefore, changes in interest rates will not affect the Company’s interest expense associated with its presently outstanding fixed rate long-term debt. However, an increase or decrease in interest rates may increase or decrease the Company’s interest expense associated with any new fixed rate long-term debt issued by the Company, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The Company may need to use a significant portion of its cash flow to repay its short-term debt and long-term debt, which would limit the amount of cash it has available for working capital, capital expenditures and other general corporate purposes and could adversely affect its financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
Changes in taxation and the ability to quantify such changes could adversely affect the Company’s financial results.
The Company is subject to taxation by the various taxing authorities at the federal, state and local levels where it does business. Legislation or regulation which could affect the Company’s tax burden could be enacted by any of these governmental authorities. The Company cannot predict the timing or extent of such tax-related developments which could have a negative effect on the financial results. The Company uses its best judgment in attempting to quantify and reserve for these tax obligations. However, a challenge by a taxing authority, the Company’s ability to utilize tax benefits such as carryforwards or tax credits, or a deviation from other tax-related assumptions may cause actual financial results to deviate from previous estimates.
Declines in capital market valuations could require the Company to make substantial cash contributions to cover its pension and other post-retirement benefit obligations. If the Company is unable to recover a significant amount of pension and other post-retirement benefit obligation costs in its rates, or if the Company’s recovery of these costs in its rates is significantly delayed, its financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
The amount of cash contributions the Company is required to make in respect of its pension and other post-retirement benefit obligations is dependent upon capital market valuations. Adverse changes in capital market valuations could result in the Company being required to make substantial cash contributions in respect to these obligations. These cash contributions could have an adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows if the Company is unable to recover such costs in rates or if such recovery is significantly delayed. See section titled Critical Accounting Policies—Retirement Benefit Obligations in Part II, Item 7 (Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations) and Note 9 (Retirement Benefit Plans) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements for a more detailed discussion of the Company’s pension obligations.
The terms of the Company’s and its subsidiaries’ indebtedness restrict the Company’s and its subsidiaries’ business operations (including their ability to incur material amounts of additional indebtedness), which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
The terms of the Company’s and its subsidiaries’ indebtedness impose various restrictions on the Company’s business operations, including the ability of the Company and its subsidiaries to incur additional indebtedness. These restrictions could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows. See sections titled Liquidity, Commitments and Capital Requirements in Part II, Item 7 (Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations) and Note 4 (Debt and Financing Arrangements) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements for a more detailed discussion of these restrictions.
Unitil is a public utility holding company and has no operating income of its own. The Company’s ability to pay dividends on its common stock is dependent on dividends and other payments received from its subsidiaries and on factors directly affecting Unitil, the parent corporation. The Company cannot assure that its current annual dividend will be paid in the future.
The ability of the Company’s subsidiaries to pay dividends or make distributions to Unitil depends on, among other things:
•the actual and projected earnings and cash flow, capital requirements and general financial condition of the Company’s subsidiaries;
•the prior rights of holders of existing and future preferred stock, mortgage bonds, long-term notes and other debt issued by the Company’s subsidiaries;
•the restrictions on the payment of dividends contained in the existing loan agreements of the Company’s subsidiaries and that may be contained in future debt agreements of the Company’s subsidiaries, if any; and
•limitations that may be imposed by New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Maine state regulatory authorities.
In addition, before the Company can pay dividends on its common stock, it must satisfy its debt obligations and comply with any statutory or contractual limitations.
As of February 10, 2025, the Company’s current effective annualized dividend is $1.80 per share of common stock, payable quarterly. The Board reviews Unitil’s dividend policy periodically in light of a number of business and financial
factors, including those referred to in this report, and the Company cannot assure the amount of dividends, if any, that may be paid in the future.
The Company has made and may make acquisitions and may pursue other strategic transactions, which could impact the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
As part of the Company’s business strategy, the Company has made and may make acquisitions to add complementary companies, assets, services or products, and from time to time may enter into other strategic transactions such as investments and joint ventures. For example, on July 8, 2024, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) among the Company, PHC Utilities, Inc., an Ohio corporation (the “Seller”), and Hearthstone Utilities, Inc., d/b/a Hope Companies, Inc., an Ohio corporation, pursuant to which the Company agreed to acquire all the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of Bangor Natural Gas Company, a Maine corporation, from the Seller, for $70.9 million in cash, subject to adjustment as set forth in the Purchase Agreement (the transaction, the “Bangor Transaction”). The acquisition closed on January 31, 2025.
In the future, the Company may not be able to find suitable acquisition candidates, and may not be able to complete acquisitions or other strategic transactions on favorable terms, or at all. In some cases, the costs of such acquisitions or other strategic transactions may be substantial, and there is no assurance that the Company will realize expected synergies and potential monetization opportunities for the Company’s acquisitions, or a favorable return on investment for strategic investments.
The Company may pay substantial amounts of cash, issue equity, or incur debt to pay for acquisitions or strategic transactions. The Company may also discover liabilities, deficiencies, or other claims associated with the companies or assets acquired that were not identified in advance, which may result in significant unanticipated costs. In addition, the Company may fail to accurately forecast the financial impact of an acquisition or other strategic transaction, including tax and accounting charges. Any of these factors may adversely affect the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
Potential tariffs could adversely affect the Company’s business and financial results.
The Company purchases natural gas from U.S. domestic and Canadian supply sources largely under contracts of one year or less. On occasion, the Company purchases natural gas from producers and marketers on the spot market. The U.S. presidential administration has proposed the implementation of a number of tariffs, including tariffs on energy imports from Canada, which could significantly increase the cost of natural gas in the U.S., potentially decreasing customer demand for natural gas. The Company may also need to obtain natural gas from other sources, when possible. Any of these factors may adversely affect the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
GENERAL RISKS
The Company’s electric and natural gas sales and revenues are highly correlated with the economy, and national, regional and local economic conditions may adversely affect the Company’s customers and correspondingly the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The Company’s business is influenced by the economic activity within its service territory. The level of economic activity in the Company’s electric and natural gas distribution service territories directly affects the Company’s business. As a result, adverse changes in the economy may adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results or operations, and cash flows. Economic downturns or periods of high electric and gas supply costs typically can lead to the development of legislative and regulatory policy designed to promote reductions in energy consumption and increased energy efficiency and self-generation by customers. This focus on conservation, energy efficiency and self-generation may result in a decline in electricity and gas sales in the Company’s service territories. If any such declines were to occur without corresponding adjustments in rates, the Company’s revenues would be reduced and the Company’s future growth prospects would be limited. In addition, a period of prolonged economic weakness could affect the Company’s customers’ ability to pay bills in a timely manner and increase customer bankruptcies, which may lead to increased bad debt expenses or other adverse effects on the Company’s financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
A significant amount of the Company’s sales are temperature sensitive. Because of this, mild winter and summer temperatures could decrease the Company’s sales, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and
results of operations. Also, the Company’s sales may vary from year to year depending on weather conditions, and the Company’s results of operations generally reflect seasonality.
A significant amount of the Company’s natural gas sales are temperature sensitive. Therefore, mild winter temperatures could decrease the amount of natural gas sold by the Company, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows. The Company’s electric sales also are temperature sensitive, but less so than its natural gas sales. The highest usage of electricity typically occurs in the summer months (due to air conditioning demand) and the winter months (due to heating-related and lighting requirements). Therefore, mild summer temperatures and mild winter temperatures could decrease the amount of electricity sold by the Company, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows. Also, because of this temperature sensitivity, sales by the Company’s distribution utilities vary from year to year, depending on weather conditions.
The Company’s results of operations are expected to reflect the seasonal nature of the natural gas business. Annual gas revenues are substantially realized during the colder weather seasons of the year as a result of higher sales of natural gas used for heating-related purposes. Accordingly, the results of operations are historically most favorable in the first and fourth quarters. Fluctuations in seasonal weather conditions may have a significant effect on the result of operations. Sales of electricity are generally less sensitive to weather than natural gas sales, but may also be affected by the weather conditions and the temperature in both the winter and summer seasons.
Catastrophic events could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations.
The electric and natural gas utility industries are from time to time affected by catastrophic events, such as unusually severe weather and significant and widespread failures of plant and equipment. Other catastrophic occurrences, such as terrorist attacks on utility facilities, may occur in the future. Such events could inhibit the Company’s ability to deliver electricity or natural gas to its customers for an extended period, which could affect customer satisfaction and adversely affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows. If customers, legislators, or regulators develop a negative opinion of the Company, this situation could result in increased regulatory oversight and could affect the equity returns that the Company is allowed to earn. Also, if the Company is unable to recover in its rates a significant amount of costs associated with catastrophic events, or if the Company’s recovery of such costs in its rates is significantly delayed, the Company’s financial condition, results or operations, or cash flows may be adversely affected.
The Company’s business could be adversely affected if it is unable to retain its existing customers or attract new customers, or if customers’ demand for its current products and services significantly decreases.
The success of the Company’s business depends, in part, on its ability to maintain and increase its customer base and the demand that those customers have for the Company’s products and services. The Company’s failure to maintain or increase its customer base and/or customer demand for its products and services could adversely affect its financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
The electricity and natural gas supply requirements of the Company’s customers are fulfilled by the Company or, in some instances and as allowed by state regulatory authorities, by third-party suppliers who contract directly with customers. In either scenario, significant increases in electricity and natural gas commodity prices may negatively affect the Company’s ability to attract new customers and grow its customer base.
Developments in distributed generation, energy conservation, power generation and energy storage could affect the Company’s revenues and the timing of the recovery of the Company’s costs. Advancements in power generation technology are improving the cost-effectiveness of customer self-supply of electricity. Improvements in energy storage technology, including batteries and fuel cells, could also better position customers to meet their around-the-clock electricity requirements. Such developments could reduce customer purchases of electricity, but may not necessarily reduce the Company’s investment and operating requirements due to the Company’s obligation to serve customers, including those self-supply customers whose equipment has failed for any reason, to provide the power they need. In addition, because a portion of the Company’s costs are recovered through charges based upon the volume of power delivered, reductions in electricity deliveries will affect the timing of the Company’s recovery of those costs and may require changes to the Company’s rate structures.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
For purposes of the following disclosure, the terms “cybersecurity incident” and “cybersecurity threat” have the meanings given to such terms in Item 106 of Regulation S-K promulgated under the Exchange Act.
Risk management and strategy
The Company has a Cybersecurity Plan for assessing, identifying, and managing material risks from cybersecurity threats. The intent of the Cybersecurity Plan is to provide a proactive and systemic approach to meet the evolving requirements for cybersecurity and related compliance in the utility industry. The Cybersecurity Plan’s objectives include:
•adopting and using established cybersecurity standards and industry best practices;
•protecting personally identifiable information;
•protecting infrastructure operations, including Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems at electric substations and natural gas plants;
•securing customers’, employees’, and the Company’s data;
•complying with North American Reliability Corporation Critical Infrastructure Protection Reliability Standards and standards for the protection of Bulk Electric System Cyber Systems; and
•continually assessing and, as necessary, enhancing the Company’s cybersecurity through a managed process integrated with the Company’s risk management principles.
The Cybersecurity Plan includes annual assessments using (i) the Department of Energy’s Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model, (ii) the National Institute of Standards and Technology Cybersecurity Framework, and (iii) the Center for Internet Security Controls. The Company uses the results of these assessments to benchmark the Company’s cybersecurity posture, to identify risks from cybersecurity threats, to prioritize any such risks that may have potential material effects on the Company, and to establish effective controls to manage, mitigate and remediate such risks.
The Cybersecurity Plan is part of the Company’s corporate Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) program. The Company’s ERM program includes an annual review of new or emerging risks (including risks from cybersecurity threats), the assessment of such risks and their potential effects on the Company, the velocity of potential cybersecurity incidents resulting from such risks, and risk mitigation strategies.
The Company maintains a Cybersecurity Employee Awareness Program, which provides targeted education and mandatory quarterly training to employees. The Cybersecurity Employee Awareness Program also conducts monthly phishing test exercises with employees, which includes an escalation procedure for repeated failures. Additionally, the Company performs an annual cyber knowledge assessment of all employees to address any identified knowledge gaps.
The Company engages or otherwise collaborates with cybersecurity consultants, cybersecurity experts, energy sector leaders, and other third parties in connection with the Cybersecurity Plan. Unitil Corporation also is a member of the cyber committees of both the American Gas Association and the Edison Electric Institute.
Third party entities that provide hardware, software or related support services to the Company or hold the Company’s customer data represent material cybersecurity risks to the Company. To help mitigate those risks, the Company has robust procurement processes and requirements for such third-parties (which include a formal assessment of the third-party’s cyber posture, cyber liability insurance, and breach reporting protocols) that help the Company to oversee and identify cybersecurity risks associated with its use of such third party entities.
During the fiscal year ended, and as of, December 31, 2024, there were no risks from cybersecurity threats (including as a result of previous cybersecurity incidents) that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect the Company (including its business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition).
Governance
The Board is responsible for oversight of the Company’s ERM program, including risks from cybersecurity threats. The Board has not assigned that responsibility to any committee or subcommittee of the Board. The Company’s management generally provides the Board with updates on and assessments of ongoing and emerging risks from cybersecurity threats at regularly scheduled Board meetings.
The Company’s cybersecurity management team is responsible for assessing and managing the Company’s material risks from cybersecurity threats, including implementing the Cybersecurity Plan. The team includes the Company’s Chief Technology Officer and Vice President of Information Technology (the “CTO”), the Director of Information Security and Cyber Operations, Manager of Cyber Security Operations and two Cyber Operations Engineers, all of whom have an educational background relevant to, professional experience in, or other expertise in cybersecurity. This team is supported by the Company’s Information Technology department. The CTO holds a Master of Business Administration and a Bachelor of Science in Electrical Engineering with over 30 years of professional experience in the utility industry with extensive management experience in engineering, operations and information technology. The CTO also assumes responsibilities as the Company’s Chief Information Security Officer and Chief Cyber Security Officer. The CTO has overall management responsibility for the Company’s cybersecurity. The CTO reports to the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. The Director of Information Security and Cyber Operations holds a Bachelor of Science in Computer Science and a Masters Certificate in Cyber Security with a concentration in Power Systems and has over 30 years of experience in the information technology field. The Director of Information Security and Cyber Operations has primary responsibility for the cyber security program including threat and vulnerability management, vendor security posture assessment, Industrial Control System (ICS) and SCADA infrastructure cyber security protection at electric substations and natural gas plants, as well as leading the Cyber Incident Response Team. The Manager of Cyber Security Operations has a Bachelor of Science in Information Technology and over 20 years of experience in various information technology and cyber roles.
The Company’s cybersecurity management team assesses and manages the Company’s material risks from cybersecurity threats through or by:
•active monitoring of cyber threat alerts, warnings, advisories, notices, vulnerability assessments, incident bulletins, security briefings, reports and white papers from industry and national organizations, including: downstream Natural Gas Information Sharing and Analysis Center; Electricity Information Sharing and Analysis Center; Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency; and Federal Bureau of Investigation;
•threat and vulnerability management;
•vendor security posture assessment;
•Industrial Control System and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition infrastructure cyber security protection at electric substations and natural gas plants; and
•leading the Company’s Cyber Incident Response Team.
In addition, the Company uses (i) a Security Operations Center vendor with 24x7 monitoring and response capabilities to identify any suspicious activity on the Company’s networks and (ii) a security consulting firm for assessments, penetration testing and incident response. In the event of a cybersecurity threat, the CTO and these parties would collaborate to assess and manage the risk with ultimate responsibility residing with the Board.
Also, in the event of a cybersecurity threat or cybersecurity incident, the Company’s cybersecurity management team will investigate and perform impact analysis and, as necessary, the CTO will activate the Company’s Cyber Incident Response Team. The Cyber Incident Response Team is a subset of the Company’s Crisis Response Team, which has responsibility for operational and business resilience, as well as tactical and strategic response. A foundational aspect of the Crisis Response Team is prompt and comprehensive communications to all concerned parties, both internal and external, including direction for management to inform the Board about risks from cybersecurity threats.
In the event that a cybersecurity incident occurs which results in damage to the Company’s data or infrastructure, the Cyber Incident Response Team would follow the Company’s Cyber Incident Response Plan. The Cyber Incident Response Plan was developed using the guidelines described in the National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 800-61 Revision 2 Computer Security Incident Handling Guide, has been reviewed and assessed by outside experts, is updated
annually, and is used to train for cybersecurity incidents. The Cyber Incident Response Plan details the identification, containment, eradication and recovery processes specific to the Company’s environment with prioritization of critical assets. The Cyber Incident Response Plan also details emergency actions required to isolate and protect industrial control system environments, should the incident pose a risk to electric or gas operations. The Company participates in annual industry drill exercises to test the Cyber Incident Response Plan.
The Company’s determination of the materiality of a cybersecurity incident would generally include an evaluation of the incident’s effect on the Company (including (i) its business strategy, results of operations, or financial condition, (ii) the integrity, confidentiality, resiliency, and security of the Company’s networks and systems, and (iii) the Company’s operations).
Item 2. Properties
As of December 31, 2024, Unitil owned through its natural gas and electric distribution utilities, five utility operating centers located in New Hampshire, Maine and Massachusetts. The Company’s real estate subsidiary, Unitil Realty, owns the Company’s corporate headquarters building and the land on which it is located in Hampton, New Hampshire. Unitil Realty also owns land for future use in Kingston, New Hampshire.
The following tables detail certain of the Company’s electric and natural gas operations properties.
Electric Operations
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Description | | Unitil Energy | | | Fitchburg | | | Total | |
Primary Transmission and Distribution Pole Miles—Overhead | | | 1,289 | | | | 452 | | | | 1,741 | |
Conduit Distribution Bank Miles—Underground | | | 241 | | | | 69 | | | | 310 | |
Transmission and Distribution Substations* | | | 26 | | | | 11 | | | | 37 | |
Transformer Capacity of Transmission and Distribution Substations** (MVA) | | | 458.1 | | | | 410.9 | | | | 869.0 | |
* Includes locations that are normally in-service sources of distribution circuits through the use of transformer(s).
** Does not include load served directly from sub-transmission.
Natural Gas Operations
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Northern Utilities | | | | | | | | | | |
Description | | NH | | | ME | | | Fitchburg | | | Granite
State | | | Total | |
Underground Natural Gas Mains—Miles | | | 585 | | | | 611 | | | | 268 | | | | — | | | | 1,464 | |
Natural Gas Transmission Pipeline—Miles | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 85 | | | | 85 | |
Service Pipes | | | 25,104 | | | | 24,285 | | | | 11,237 | | | | — | | | | 60,626 | |
Unitil Energy’s electric substations are located on land owned by Unitil Energy or land occupied by Unitil Energy pursuant to perpetual easements in the southeastern seacoast and state capital regions of New Hampshire. Unitil Energy’s electric distribution lines are located in, on or under public highways or private lands pursuant to lease, easement, permit, municipal consent, tariff conditions, agreement or license, expressed or implied through use by Unitil Energy without objection by the owners. In the case of certain distribution lines, Unitil Energy owns only a part interest in the poles upon which its wires are installed, the remaining interest being owned by telecommunication companies.
The physical utility properties of Unitil Energy, with certain exceptions, and its franchises are subject to its indenture of mortgage and deed of trust under which the respective series of first mortgage bonds of Unitil Energy are outstanding.
Fitchburg’s electric substations, with minor exceptions, are located in north central Massachusetts on land owned by Fitchburg or occupied by Fitchburg pursuant to perpetual easements. Fitchburg’s electric distribution lines and gas mains are located in, on, or under public highways or private lands pursuant to lease, easement, permit, municipal consent, tariff conditions, agreement or license, express or implied through use by Fitchburg without objection by the owners. Fitchburg owns full interest in the poles upon which its wires are installed.
The Company’s natural gas operations property includes two liquefied propane gas plants and two liquid natural gas plants. Northern Utilities also owns a propane air gas plant and an LNG storage and vaporization facility. Fitchburg owns a propane air gas plant and an LNG storage and vaporization facility, both of which are located on land owned by Fitchburg in north central Massachusetts.
Northern Utilities’ gas mains are primarily made up of polyethylene plastic (84.7%), coated and wrapped cathodically protected steel (15.3%), cast/wrought iron (0.0%), and unprotected bare and coated steel (0.0%). FG&E’s gas mains are primarily made up of polyethylene plastic (46.9%), coated steel (43.3%), cast iron (8.5%), bare steel (1.1%), and wrought and ductile iron (0.2%).
Granite State’s underground natural gas transmission pipeline, regulated by the FERC, is located primarily in Maine and New Hampshire.
The Company believes that its facilities are currently adequate for their intended uses.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
The Company is involved in legal and administrative proceedings and claims of various types, including those which arise in the ordinary course of business. The Company believes, based upon information furnished by counsel and others, that the ultimate resolution of these claims will not have a material effect on its financial position, operating results or cash flows.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Common Stock Information
The Company’s common stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “UTL.” As of December 31, 2024, there were 1,108 shareholders of record of the Company’s common stock.
Dividend Information
Information regarding dividend payments by the Company to the Company’s shareholders for the year ended December 31, 2024 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2023, is set forth in the following table.
| | | | | | | | |
Dividends per Common Share | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
1st Quarter | | $ | 0.425 | | | $ | 0.405 | |
2nd Quarter | | | 0.425 | | | $ | 0.405 | |
3rd Quarter | | | 0.425 | | | $ | 0.405 | |
4th Quarter | | | 0.425 | | | $ | 0.405 | |
Total for Year | | $ | 1.70 | | | $ | 1.62 | |
See “Dividends” in Part II, Item 7 (Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations).
Equity Compensation Plan Information
Information regarding securities authorized for issuance under the Company’s equity compensation plans, as of December 31, 2024, is set forth in the following table.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (a) | | | (b) | | | (c) | |
Plan Category | | Number of securities
to be issued upon exercise
of outstanding options,
warrants and rights | | | Weighted-average
exercise price of
outstanding options,
warrants and rights | | | Number of securities
remaining available for
future issuance under
equity compensation
plans (excluding
securities reflected in
column (a)) | |
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders(1) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 385,782 | |
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Total | | | — | | | | — | | | | 385,782 | |
NOTES: (also see Note 5 (Equity) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements)
(1)Consists of the Third Amended and Restated 2003 Stock Plan (as amended and restated, the “Plan”). On April 19, 2012, shareholders initially approved the Plan, and a total of 677,500 shares of the Company’s common stock were reserved for issuance pursuant to awards of restricted stock, restricted stock units and common stock under the Plan. On May 1, 2024, shareholders approved an additional 350,000 shares of the Company’s common stock to be reserved for issuance pursuant to awards of restricted stock, restricted stock units and common stock under the Plan. A total of 586,645 shares of restricted stock have been awarded and 58,272 restricted stock units have been settled and issued as shares of common stock by Plan participants through December 31, 2024. As of December 31, 2024, a total of 14,544 shares of restricted stock were forfeited and once again became available for issuance under the Plan.
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph compares Unitil Corporation’s cumulative stockholder return since December 31, 2019 with the Peer Group index, comprised of the S&P 500 Utilities Index, and the S&P 500 index. The graph assumes that the value of the investment in the Company’s common stock and each index (including reinvestment of dividends) was $100 on December 31, 2019.
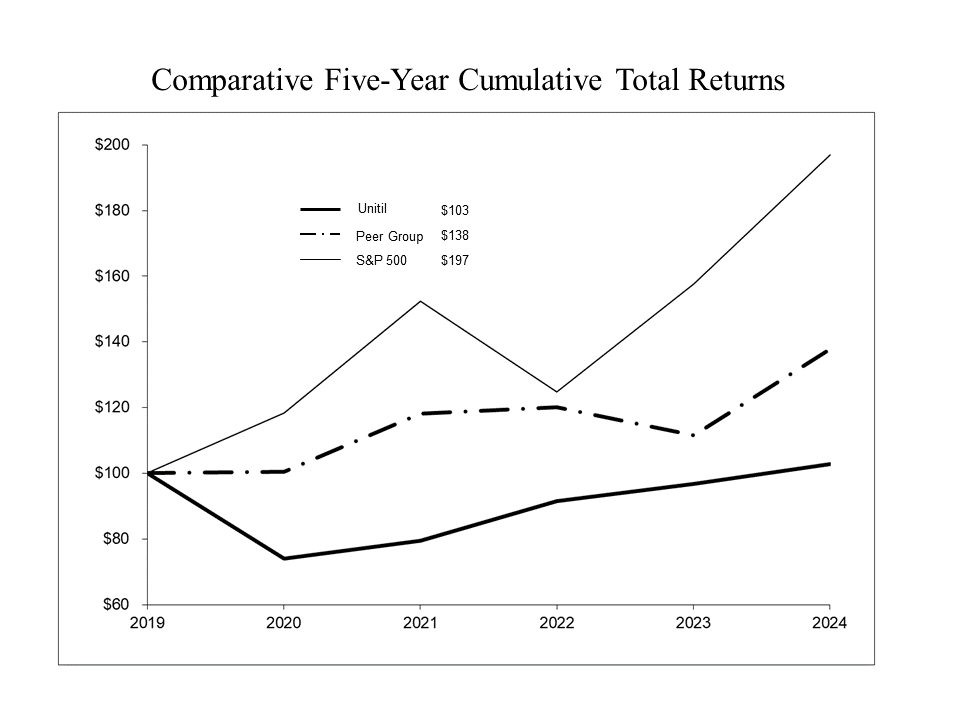
NOTE:
(1)The graph above assumes $100 invested on December 31, 2019, in each category and the reinvestment of all dividends during the five-year period. The Peer Group is comprised of the S&P 500 Utilities Index.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Uses of Proceeds
There were no sales of unregistered equity securities by the Company for the fiscal period ended December 31, 2024.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
On May 31, 2024, the Company’s 2023 10b5-1 written trading plan under Rule 10b5-1 under the Exchange Act terminated in accordance with its terms. The Company did not adopt a new written trading plan under Rule 10b5-1 in 2024.
The following table provides information regarding repurchases by or on behalf of the Company of shares of its common stock for each month in the quarter ended December 31, 2024.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Period | | Total
Number
of Shares
Purchased | | | Average
Price Paid
per Share | | | Total Number of
Shares Purchased as
Part of Publicly
Announced Plans or
Programs | | | Approximate Dollar
Value of Shares that
May Yet Be
Purchased Under the
Plans or Programs | |
10/1/24 – 10/31/24 | | | — | | | $ | — | | | | | | $ | — | |
11/1/24 – 11/30/24 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | — | |
12/1/24 – 12/31/24 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | — | |
Total | | | — | | | $ | — | | | | — | | | | |
Item 6. Reserved
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (MD&A) (Note references are to the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.)
You should read the following discussion and analysis together with the consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere herein.
OVERVIEW
Unitil is a public utility holding company headquartered in Hampton, New Hampshire. Unitil is subject to regulation as a holding company system by the FERC under the Energy Policy Act of 2005.
Unitil’s principal business is the local distribution of electricity and natural gas to approximately 198,500 customers throughout its service territory in the states of New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Maine. Unitil is the parent company of three wholly-owned distribution utilities:
i)Unitil Energy, which provides electric service in the southeastern seacoast and state capital regions of New Hampshire;
ii)Fitchburg, which provides both electric and natural gas service in the greater Fitchburg area of north central Massachusetts; and
iii)Northern Utilities, which provides natural gas service in southeastern New Hampshire and portions of southern and central Maine, including the city of Portland and the Lewiston-Auburn area.
Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Northern Utilities are collectively referred to as the “distribution utilities.” Together, the distribution utilities serve approximately 109,400 electric customers and 89,100 natural gas customers in their service territories. The distribution utilities are local “wires and pipes” operating companies.
In addition, Unitil is the parent company of Granite State, a natural gas transmission pipeline, regulated by the FERC, operating 85 miles of underground gas transmission pipeline primarily located in Maine and New Hampshire. Granite State provides Northern Utilities with interconnection to three major natural gas pipelines and access to North American pipeline supplies.
Unitil had an investment in Net Utility Plant of $1,539.6 million at December 31, 2024. Unitil’s total revenue was $494.8 million in 2024, which includes revenue to recover the approved cost of purchased electricity and natural gas in rates on a fully reconciling basis. As a result of this reconciling rate structure, the Company’s earnings are not affected by changes in the cost of purchased electricity and natural gas. Earnings from Unitil’s utility operations are derived from the return on investment in the three distribution utilities and Granite State.
The Company’s other subsidiaries include Unitil Service, which provides, at cost, a variety of administrative and professional services to Unitil’s affiliated companies, Unitil Resources, the Company’s non-regulated subsidiary, which currently does not have any activity, and Unitil Realty, which owns and manages the Company’s corporate office in Hampton, New Hampshire and land for future use in Kingston, New Hampshire. Unitil’s consolidated net income includes the earnings of the holding company and these subsidiaries.
Regulation
Unitil is subject to comprehensive regulation by federal and state regulatory authorities. Unitil and its subsidiaries are subject to regulation as a holding company system by the FERC under the Energy Policy Act of 2005 with regard to certain bookkeeping, accounting and reporting requirements. Unitil’s utility operations related to wholesale and interstate energy business activities are also regulated by the FERC. Unitil’s distribution utilities are subject to regulation by the applicable state public utility commissions, with regard to their rates, issuance of securities and other accounting and operational matters: Unitil Energy is subject to regulation by the NHPUC; Fitchburg is subject to regulation by the MDPU; and Northern Utilities is regulated by the NHPUC and MPUC. Granite State, Unitil’s interstate natural gas transmission pipeline, is subject to regulation by the FERC with regard to its rates and operations. Because Unitil’s primary operations are subject to rate regulation, the regulatory treatment of various matters could significantly affect the Company’s operations, financial position, and cash flows.
Unitil’s distribution utilities deliver electricity and/or natural gas to all customers in their service territories, at rates established under traditional cost of service regulation. Under this regulatory structure, Unitil’s distribution utilities are provided the opportunity to recover the cost of providing distribution service to their customers based on a historical test year, and earn a return on their capital investment in utility assets. In addition, the Company’s distribution utilities and its natural gas transmission pipeline company also may recover certain base rate costs, including capital project spending and enhanced reliability and vegetation management programs, through annual step adjustments and cost tracker rate mechanisms.
Most of Unitil’s customers have the opportunity to purchase their electricity or natural gas supplies from third-party energy suppliers. For customers that choose not to participate in the third-party energy supplier market, Unitil acts as a provider of last resort. Unitil’s distribution utilities purchase electricity or natural gas from unaffiliated wholesale energy suppliers and recover the actual approved costs of these supplies on a pass-through basis, through reconciling rate mechanisms that are periodically adjusted.
Revenue decoupling is the term given to the elimination of the dependency of a utility’s distribution revenue on the volume of electricity or gas sales. The difference between distribution revenue amounts billed to customers and the targeted revenue decoupling amounts is recognized as an increase or a decrease in Accrued Revenue, which forms the basis for resetting rates for future cash recoveries from, or credits to, customers. These revenue decoupling targets may be adjusted as a result of rate cases and other authorized adjustments that the Company files with the MDPU and NHPUC. Fitchburg has been subject to revenue decoupling since 2011. Unitil Energy has been subject to revenue decoupling since June 1, 2022. As a result of Unitil Energy now being subject to revenue decoupling, as of June 1, 2022, revenue decoupling now applies to substantially all of Unitil’s total annual electric sales volumes. Substantially all of Northern Utilities’ gas sales volumes in New Hampshire have been subject to decoupling since August 1, 2022. The Company's electric and gas sales in New Hampshire and Massachusetts are now largely decoupled. Northern Utilities’ gas sales volumes in Maine are not subject to decoupling.
Also see Regulatory Matters in this section and Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on rates and regulation.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion of the Company’s financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements and the accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this report.
The Company’s results of operations are expected to reflect the seasonal nature of the natural gas business. Annual gas revenues are substantially realized during the colder weather seasons of the year as a result of higher sales of natural gas used for heating-related purposes. Accordingly, the results of operations are historically most favorable in the first and fourth quarters. Fluctuations in seasonal weather conditions may have a significant effect on the result of operations. Sales of electricity are generally less sensitive to weather than natural gas sales, but may also be affected by weather conditions and the temperature in the winter and summer seasons.
Use of GAAP and Non-GAAP Financial Measures
The MD&A includes financial information prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (GAAP), as well as certain non-GAAP financial measures. The Company's management believes that the non-GAAP presentations of earnings and Earnings Per Share (EPS) and Electric and Gas Adjusted Gross Margins are a more meaningful representation of the Company's financial performance and provide additional and useful information to readers of this report in analyzing the historical and future performance of the business. The non-GAAP financial measures should be viewed as a supplement to, and not a substitute for, financial measures presented in accordance with GAAP. Non-GAAP measures as presented herein may not be comparable to similarly titled measures used by other companies.
The Company's earnings discussion includes Adjusted Net Income, a non-GAAP financial measure referencing the Company’s 2024 GAAP Net Income adjusted for certain transaction costs related to the Company's acquisition of Bangor Natural Gas Company (Bangor), which it disclosed previously in 2024. The Company's management believes that the transaction costs related to the acquisition of Bangor, which are included in Operation and Maintenance expense on the Consolidated Statements of Earnings, are
not indicative of the Company's ongoing costs and not directly related to the ongoing operations of the business and therefore are not an indicator of baseline operating performance.
In the following tables the Company has reconciled Adjusted Net Income to GAAP Net Income, which we believe to be the most comparable GAAP financial measure.
| | | |
(Millions, except per share data) | | |
| Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2024 |
| Amount | | Per Share |
GAAP Net Income | $ 47.1 | | $ 2.93 |
Transaction Costs | 0.7 | | 0.04 |
Adjusted Net Income | $ 47.8 | | $ 2.97 |
| | | |
| Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2023 |
| Amount | | Per Share |
GAAP Net Income | $ 45.2 | | $ 2.82 |
Transaction Costs | --- | | --- |
Adjusted Net Income | $ 45.2 | | $ 2.82 |
| | | |
| Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2022 |
| Amount | | Per Share |
GAAP Net Income | $ 41.4 | | $ 2.59 |
Transaction Costs | --- | | --- |
Adjusted Net Income | $ 41.4 | | $ 2.59 |
The Company analyzes operating results using Electric and Gas Adjusted Gross Margins, which are non-GAAP financial measures. Electric Adjusted Gross Margin is calculated as Total Electric Operating Revenue less Cost of Electric Sales. Gas Adjusted Gross Margin is calculated as Total Gas Operating Revenues less Cost of Gas Sales. The Company’s management believes Electric and Gas Adjusted Gross Margins provide useful information to investors regarding profitability. Also, the Company’s management believes Electric and Gas Adjusted Gross Margins are important financial measures to analyze revenue from the Company’s ongoing operations because the approved cost of electric and gas sales are tracked, reconciled and passed through directly to customers in electric and gas tariff rates, resulting in an equal and offsetting amount reflected in Total Electric and Gas Operating Revenue.
In the following tables the Company has reconciled Electric and Gas Adjusted Gross Margin to GAAP Gross Margin, which we believe to be the most comparable GAAP financial measure. GAAP Gross Margin is calculated as Revenue less Cost of Sales, and Depreciation and Amortization. The Company calculates Electric and Gas Adjusted Gross Margin as Revenue less Cost of Sales. The Company believes excluding Depreciation and Amortization, which are period costs and not related to volumetric sales, is a meaningful financial measure to inform investors of the Company’s profitability from electric and gas sales in the period.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2024 ($ millions) | |
| | Electric | | | Gas | | | Other | | | Total | |
Total Operating Revenue | | $ | 248.3 | | | $ | 246.5 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 494.8 | |
Less: Cost of Sales | | | (141.0 | ) | | | (79.6 | ) | | | — | | | | (220.6 | ) |
Less: Depreciation and Amortization | | | (29.3 | ) | | | (46.8 | ) | | | — | | | | (76.1 | ) |
GAAP Gross Margin | | | 78.0 | | | | 120.1 | | | | — | | | | 198.1 | |
Depreciation and Amortization | | | 29.3 | | | | 46.8 | | | | — | | | | 76.1 | |
Adjusted Gross Margin | | $ | 107.3 | | | $ | 166.9 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 274.2 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2023 ($ millions) | |
| | Electric | | | Gas | | | Other | | | Total | |
Total Operating Revenue | | $ | 306.5 | | | $ | 250.6 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 557.1 | |
Less: Cost of Sales | | | (202.4 | ) | | | (96.1 | ) | | | — | | | | (298.5 | ) |
Less: Depreciation and Amortization | | | (26.0 | ) | | | (40.4 | ) | | | (1.0 | ) | | | (67.4 | ) |
GAAP Gross Margin | | | 78.1 | | | | 114.1 | | | | (1.0 | ) | | | 191.2 | |
Depreciation and Amortization | | | 26.0 | | | | 40.4 | | | | 1.0 | | | | 67.4 | |
Adjusted Gross Margin | | $ | 104.1 | | | $ | 154.5 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 258.6 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Twelve Months Ended December 31, 2022 ($ millions) | |
| | Electric | | | Gas | | | Other | | | Total | |
Total Operating Revenue | | $ | 297.9 | | | $ | 265.3 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 563.2 | |
Less: Cost of Sales | | | (199.1 | ) | | | (121.4 | ) | | | — | | | | (320.5 | ) |
Less: Depreciation and Amortization | | | (25.4 | ) | | | (36.3 | ) | | | (0.9 | ) | | | (62.6 | ) |
GAAP Gross Margin | | | 73.4 | | | | 107.6 | | | | (0.9 | ) | | | 180.1 | |
Depreciation and Amortization | | | 25.4 | | | | 36.3 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 62.6 | |
Adjusted Gross Margin | | $ | 98.8 | | | $ | 143.9 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 242.7 | |
Electric GAAP Gross Margin was $78.0 million in 2024, a decrease of $0.1 million compared to 2023. The decrease was driven by higher depreciation and amortization expense of $3.3 million, largely offset by higher rates and customer growth of $3.2 million.
Electric GAAP Gross Margin was $78.1 million in 2023, an increase of $4.7 million compared to 2022. The increase was driven by higher rates and customer growth of $5.3 million, partially offset by higher depreciation and amortization expense of $0.6 million.
Gas GAAP Gross Margin was $120.1 million in 2024, an increase of $6.0 million compared to 2023. The increase was driven primarily by higher rates, and customer growth, of $12.4 million, partially offset by higher depreciation and amortization of $6.4 million.
Gas GAAP Gross Margin was $114.1 million in 2023, an increase of $6.5 million compared to 2022. The increase was driven by higher rates and customer growth of $14.1 million, partially offset by the unfavorable effects of warmer winter weather in 2023 of $1.1 million, higher depreciation and amortization of $4.1 million, and the recognition, in the second quarter of 2022, of $2.4 million in higher rates resulting from the Company’s base rate case in New Hampshire.
Net Income and EPS Overview
2024 Compared to 2023—The Company’s GAAP Net Income was $47.1 million, or $2.93 in Earnings Per Share (EPS), for the year ended December 31, 2024, an increase of $1.9 million in Net Income, or $0.11 in EPS, compared to 2023. The Company’s Adjusted Net Income (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $47.8 million, or $2.97 in EPS for the year ended December 31, 2024, an increase of $2.6 million, or $0.15 in EPS, compared to 2023. The Company’s earnings in 2024 reflect higher rates and customer growth.
Electric Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $107.3 million in 2024, an increase of $3.2 million compared with 2023. The increase was driven by higher rates and customer growth.
Gas Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $166.9 million in 2024, an increase of $12.4 million compared to 2023. The increase was driven primarily by higher rates, and customer growth.
Operation and Maintenance (O&M) expenses increased $2.0 million in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher labor costs of $2.5 million, partially offset by lower utility operating costs of $0.5 million.
Depreciation and Amortization expense increased $8.7 million in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher depreciation rates from recent base rate cases, additional depreciation associated with higher levels of utility plant in service and higher amortization of rate case and other deferred costs.
Taxes Other Than Income Taxes increased $1.4 million in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher local property taxes on higher utility plant in service and higher payroll taxes.
Interest Expense, Net increased $0.6 million in 2024 compared to 2023 primarily reflecting higher interest on higher levels of long-term debt and higher interest on short-term borrowings, partially offset by higher interest income on regulatory assets and other.
Other Expense (Income), Net increased $0.2 million in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher retirement benefit costs.
Federal and State Income Taxes increased $0.8 million in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher pre-tax earnings in 2024.
In 2024, Unitil’s annual common dividend was $1.70 per share, representing an unbroken record of quarterly dividend payments since trading began in Unitil’s common stock. At a January 2025 meeting of the Unitil Corporation Board of Directors (the “Board”), the Board declared a quarterly dividend on the Company’s common stock of $0.45 per share, an increase of $0.025 per share on a quarterly basis, resulting in an increase in the effective annualized dividend rate to $1.80 per share from $1.70 per share.
2023 Compared to 2022—The Company’s Net Income was $45.2 million, or $2.82 in Earnings Per Share (EPS), for the year ended December 31, 2023, an increase of $3.8 million in Net Income, or $0.23 in EPS, compared to 2022. The Company’s earnings in 2023 reflect higher Electric and Gas Adjusted Gross Margins (a non-GAAP financial measure), partially offset by higher operating expenses.
Electric Revenues, Adjusted Gross Margin and Sales
Electric Operating Revenues and Electric Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure)—The following table details Total Electric Operating Revenue and Electric Adjusted Gross Margin for the last three years by major customer class:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Change | |
Electric Operating Revenues and Electric Adjusted Gross Margin | | | | | | | | | | | 2024 vs. 2023 | | | 2023 vs. 2022 | |
(millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Electric Operating Revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | | $ | 140.6 | | | $ | 184.5 | | | $ | 174.8 | | | $ | (43.9 | ) | | | (23.8 | )% | | $ | 9.7 | | | | 5.5 | % |
Commercial & Industrial | | | 107.7 | | | | 122.0 | | | | 123.1 | | | | (14.3 | ) | | | (11.7 | )% | | | (1.1 | ) | | | (0.9 | )% |
Total Electric Operating Revenue | | $ | 248.3 | | | $ | 306.5 | | | $ | 297.9 | | | $ | (58.2 | ) | | | (19.0 | )% | | $ | 8.6 | | | | 2.9 | % |
Cost of Electric Sales | | $ | 141.0 | | | $ | 202.4 | | | $ | 199.1 | | | $ | (61.4 | ) | | | (30.3 | )% | | $ | 3.3 | | | | 1.7 | % |
Electric Adjusted Gross Margin | | $ | 107.3 | | | $ | 104.1 | | | $ | 98.8 | | | $ | 3.2 | | | | 3.1 | % | | $ | 5.3 | | | | 5.4 | % |
The decrease in Total Electric Operating Revenue of $58.2 million, or 19.0%, in 2024 compared to 2023 reflects lower costs of electric sales, which are tracked and reconciled costs as a pass-through to customers, partially offset by higher electric distribution rates and higher sales of electricity.
Electric GAAP Gross Margin is discussed above in the section entitled “Use of GAAP and Non-GAAP Financial Measures”.
Electric Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $107.3 million in 2024, an increase of $3.2 million compared with 2023. The increase was driven by higher rates and customer growth.
The increase in Total Electric Operating Revenue of $8.6 million, or 2.9%, in 2023 compared to 2022 reflects higher costs of electric sales, which are tracked and reconciled costs as a pass-through to customers, and higher electric distribution rates.
Electric Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $104.1 million in 2023, an increase of $5.3 million compared with 2022. The increase was driven by higher rates and customer growth.
Kilowatt-hour Sales—Unitil’s total electric kilowatt-hour (kWh) sales increased 1.3% in 2024 compared to 2023. Sales to Residential customers increased 1.6% and sales to C&I customers increased 1.1% in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting warmer weather for cooling purposes in the second quarter of 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, and customer growth. Based on weather data collected in the Company’s electric service areas, on average there were 12.2% more Cooling Degree Days in 2024 compared to 2023. As of December 31, 2024, the number of electric customers served increased by approximately 990 over the previous year. Sales margins derived from decoupled unit sales are not sensitive to changes in electric kWh sales, although those sales margins are sensitive to changes in the number of customers served. Substantially all of the Company's electric kWh sales volumes are decoupled.
Unitil’s total electric kWh sales decreased 3.2% in 2023 compared to 2022. Sales to Residential customers decreased 4.6% and sales to C&I customers decreased 2.1% in 2023 compared to 2022. The decreases in electric kWh sales reflect lower average usage, partially offset by customer growth. As of December 31, 2023, the number of electric customers served increased by approximately 350 over the previous year.
The following table details total kWh sales for the last three years by major customer class:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Change | |
| | | | | | | | | | | 2024 vs. 2023 | | | 2023 vs. 2022 | |
kWh Sales (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | kWh | | | % | | | kWh | | | % | |
Residential | | | 659.7 | | | | 649.3 | | | | 680.5 | | | | 10.4 | | | | 1.6 | % | | | (31.2 | ) | | | (4.6 | )% |
Commercial & Industrial | | | 924.6 | | | | 914.2 | | | | 933.9 | | | | 10.4 | | | | 1.1 | % | | | (19.7 | ) | | | (2.1 | )% |
Total kWh Sales | | | 1,584.3 | | | | 1,563.5 | | | | 1,614.4 | | | | 20.8 | | | | 1.3 | % | | | (50.9 | ) | | | (3.2 | )% |
Gas Revenues, Adjusted Gross Margin and Sales
Gas Operating Revenues and Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure)—The following table details total Gas Operating Revenue and Gas Adjusted Gross Margin for the last three years by major customer class:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Change | |
Gas Operating Revenues and Gas Adjusted Gross Margin | | | | | | | | | | | 2024 vs. 2023 | | | 2023 vs. 2022 | |
(millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | $ | | | % | | | $ | | | % | |
Gas Operating Revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | | $ | 101.0 | | | $ | 100.7 | | | $ | 103.4 | | | $ | 0.3 | | | | 0.3 | % | | $ | (2.7 | ) | | | (2.6 | )% |
Commercial & Industrial | | | 145.5 | | | | 149.9 | | | | 161.9 | | | | (4.4 | ) | | | (2.9 | )% | | | (12.0 | ) | | | (7.4 | )% |
Total Gas Operating Revenue | | $ | 246.5 | | | $ | 250.6 | | | $ | 265.3 | | | $ | (4.1 | ) | | | (1.6 | )% | | $ | (14.7 | ) | | | (5.5 | )% |
Cost of Gas Sales | | $ | 79.6 | | | $ | 96.1 | | | $ | 121.4 | | | $ | (16.5 | ) | | | (17.2 | )% | | $ | (25.3 | ) | | | (20.8 | )% |
Gas Adjusted Gross Margin | | $ | 166.9 | | | $ | 154.5 | | | $ | 143.9 | | | $ | 12.4 | | | | 8.0 | % | | $ | 10.6 | | | | 7.4 | % |
The decrease in Total Gas Operating Revenues of $4.1 million, or 1.6%, in 2024 compared to 2023 reflects lower costs of gas sales, which are tracked and reconciled as a pass-through to customers, and lower sales of gas, partially offset by higher gas distribution rates.
Gas GAAP Gross Margin is discussed above in the section entitled “Use of GAAP and Non-GAAP Financial Measures”.
Gas Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $166.9 million in 2024, an increase of $12.4 million compared to 2023. The increase was driven primarily by higher rates, and customer growth.
The decrease in Total Gas Operating Revenues of $14.7 million, or 5.50%, in 2023 compared to 2022 reflects lower costs of gas sales, which are tracked and reconciled as a pass-through to customers, partially offset by higher gas distribution rates.
Gas Adjusted Gross Margin (a non-GAAP financial measure) was $154.5 million in 2023, an increase of $10.6 million compared to 2022. The increase reflects higher rates and customer growth of $14.1 million, partially offset by the unfavorable effects of warmer winter weather in 2023 of $1.1 million and the recognition, in the second quarter of 2022, of $2.4 million in higher rates resulting from the Company’s base rate case in New Hampshire.
Therm Sales—Unitil’s total gas therm sales decreased 0.7% in 2024 compared to 2023. Sales to Residential customers decreased 1.4% and sales to C&I customers decreased 0.5% in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting lower average usage, partially offset by customer growth. As of December 31, 2024, the number of gas customers served increased by approximately 730 over the previous year. Sales margins derived from decoupled unit sales (currently representing approximately 43% of total annual therm sales volume) are not sensitive to changes in gas therm sales, although those sales margins are sensitive to changes in the number of customers served. In 2024 and 2023, there were 9.5% and 11.0% fewer Effective Degree Days (EDD) than normal, respectively.
Unitil’s total gas therm sales decreased 1.5% in 2023 compared to 2022. Sales to Residential customers decreased 3.8% and sales to C&I customers decreased 0.9% in 2023 compared to 2022. The decreases in gas therm sales reflect warmer winter weather in 2023 compared to 2022, partially offset by customer growth. Based on weather data collected in the Company’s gas service areas, on average there were 6.5% fewer EDD in 2023 compared to 2022. The Company estimates that weather-normalized gas therm sales for Northern Utilities’ Maine division, the Company’s only non-decoupled gas service area, increased 3.0% in 2023 compared to 2022. As of December 31, 2023, the number of gas customers served increased by approximately 950 over the previous year. Sales margins derived from decoupled unit sales (currently representing approximately 43% of total annual therm sales volume) are not sensitive to changes in gas therm sales, although those sales margins are sensitive to changes in the number of customers served.
The following table details total therm sales for the last three years, by major customer class:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Change | |
| | | | | | | | | | | 2024 vs. 2023 | | | 2023 vs. 2022 | |
Therm Sales (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | Therms | | | % | | | Therms | | | % | |
Residential | | | 42.3 | | | | 42.9 | | | | 44.6 | | | | (0.6 | ) | | | (1.4 | )% | | | (1.7 | ) | | | (3.8 | )% |
Commercial & Industrial | | | 177.7 | | | | 178.6 | | | | 180.2 | | | | (0.9 | ) | | | (0.5 | )% | | | (1.6 | ) | | | (0.9 | )% |
Total Therm Sales | | | 220.0 | | | | 221.5 | | | | 224.8 | | | | (1.5 | ) | | | (0.7 | )% | | | (3.3 | ) | | | (1.5 | )% |
Operating Expenses
Cost of Electric Sales—Cost of Electric Sales includes the cost of electric supply as well as other energy supply related restructuring costs, including power supply buyout costs, and spending on energy efficiency programs. Cost of Electric Sales decreased $61.4 million, or 30.3%, in 2024 compared to 2023. This decrease reflects lower wholesale electricity prices and an increase in the amount of electricity purchased by customers directly from third-party suppliers, partially offset by higher electric sales. The Company reconciles and recovers the approved Cost of Electric Sales in its rates at cost on a pass through basis and therefore changes in approved expenses do not affect earnings.
In 2023, Cost of Electric Sales increased $3.3 million, or 1.7%, compared to 2022. This increase reflects higher wholesale electricity prices, partially offset by lower electric sales and an increase in the amount of electricity purchased by customers directly from third-party suppliers.
Cost of Gas Sales—Cost of Gas Sales includes the cost of natural gas purchased to supply the Company’s total gas supply requirements and spending on energy efficiency programs. Cost of Gas Sales decreased $16.5 million, or 17.2%, in 2024 compared to 2023. This decrease reflects lower gas sales, lower wholesale gas commodity prices and an increase in the amount of gas purchased by customers directly from third-party suppliers. The Company reconciles and recovers the approved Cost of Gas Sales in its rates at cost on a pass through basis and therefore changes in approved expenses do not affect earnings.
In 2023, Cost of Gas Sales decreased $25.3 million, or 20.8%, compared to 2022. This decrease reflects lower gas sales, lower wholesale gas commodity prices, partially offset by a decrease in the amount of gas purchased by customers directly from third-party suppliers.
Operation and Maintenance—O&M expense includes electric and gas utility operating costs, and the operating costs of the Company’s other subsidiaries. Total O&M expenses increased $2.0 million, or 2.6%, in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher labor costs of $2.5 million, partially offset by lower utility operating costs of $0.5 million.
In 2023, total O&M expenses increased $1.9 million, or 2.6%, compared to 2022, reflecting higher utility operating costs of $1.2 million, higher professional fees of $0.4 million and higher labor costs of $0.3 million.
Depreciation and Amortization—Depreciation and Amortization expense increased $8.7 million, or 12.9%, in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher depreciation rates from recent base rate cases, additional depreciation associated with higher levels of utility plant in service and higher amortization of rate case and other deferred costs.
In 2023, Depreciation and Amortization expense increased $4.8 million, or 7.7%, compared to 2022, reflecting additional depreciation associated with higher levels of utility plant in service and higher amortization of rate case and other deferred costs.
Taxes Other Than Income Taxes—Taxes Other Than Income Taxes increased $1.4 million, or 4.9%, in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher local property taxes on higher utility plant in service and higher payroll taxes.
In 2023, Taxes Other Than Income Taxes increased $2.6 million, or 10.0%, compared to 2022, reflecting higher local property taxes on higher utility plant in service and higher payroll, excise and other taxes.
Interest Expense, Net
Interest expense is presented in the Consolidated Financial Statements net of interest income. Interest expense is mainly comprised of interest on long-term debt and short-term borrowings (See Note 4 (Debt and Financing Arrangements) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements). Certain reconciling rate mechanisms used by the Company’s distribution utilities give rise to regulatory assets and regulatory liabilities on which interest is calculated.
Interest Expense, Net increased $0.6 million, or 2.1%, in 2024 compared to 2023 primarily reflecting higher interest on higher levels of long-term debt and higher interest on short-term borrowings, partially offset by higher interest income on regulatory assets and other.
Interest Expense, Net increased $3.2 million, or 12.6%, in 2023 compared to 2022 primarily reflecting higher interest on short-term borrowings, partially offset by higher interest income on regulatory assets and other.
Other (Income) Expense, Net
Other Expense (Income), Net increased $0.2 million in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher retirement benefit costs.
Other Expense (Income), Net decreased $2.4 million in 2023 compared to 2022, reflecting lower retirement benefit costs.
Provision for Income Taxes
Federal and State Income Taxes increased $0.8 million in 2024 compared to 2023, reflecting higher pre-tax earnings in 2024.
Federal and State Income Taxes increased $2.0 million in 2023 compared to 2022, reflecting higher pre-tax earnings in 2023 and higher flow back, in 2022, of excess Accumulated Deferred Income Taxes per regulatory orders in New Hampshire.
LIQUIDITY, COMMITMENTS AND CAPITAL REQUIREMENTS
Sources of Capital
Unitil requires capital to fund utility plant additions, working capital and other utility expenditures recovered in subsequent periods through regulated rates. The capital necessary to meet these requirements is derived primarily from internally generated funds, which consist of cash flows from operating activities. The Company initially supplements internally generated funds through short-term bank borrowings, as needed, under its unsecured revolving Credit Facility. Periodically, the Company replaces portions of its short-term debt with long-term financings more closely matched to the long-term nature of its utility assets. Additionally, from time to time the Company has accessed the public capital markets through public offerings of equity securities. The Company’s utility operations are seasonal in nature and are therefore subject to seasonal fluctuations in cash flows. The amount, type and timing of any future financing will vary from year to year based on capital needs and maturity or redemptions of securities.
The Company and its subsidiaries are individually and collectively members of the Unitil Cash Pool (Cash Pool). The Cash Pool is the financing vehicle for day-to-day cash borrowing and investing. The Cash Pool allows for an efficient exchange of cash among the Company and its subsidiaries. The interest rates charged to the subsidiaries for borrowing from the Cash Pool are based on actual interest costs from lenders under the Company’s revolving Credit Facility. At December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company and all of its subsidiaries were in compliance with the regulatory requirements governing participation in the Cash Pool.
On September 29, 2022, the Company entered into a Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement with a syndicate of lenders (collectively, the “Credit Facility”), which amended and restated in its entirety the prior credit facility. On January 29, 2025, the Company entered into an amendment to the Credit Facility, which (among other things) increased the borrowing limit under the Credit Facility from $200 million to $275 million and extended the term of the Credit Facility from September 29, 2027 until September 29, 2028. Unitil may borrow under the Credit Facility until September 29, 2028, subject to two one-year extensions under certain circumstances.
The Credit Facility has a borrowing limit of $275 million ($200 million as of December 31, 2024), which includes a $25 million sublimit for the issuance of standby letters of credit. Unitil may increase the borrowing limit under the Credit Facility by up to $75 million under certain circumstances. The Credit Facility generally provides Unitil with the ability to elect that borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest under several options, including a daily fluctuating rate equal to (a) the forward-looking secured overnight financing rate (as administered by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York) term rate with a term equivalent to one month beginning on that date, plus (b) 0.1000%, plus (c) a margin of 1.125% to 1.375% (based on Unitil’s credit rating).
The Company utilizes the Credit Facility for cash management purposes related to its short-term operating activities. Total gross borrowings were $308.4 million and $327.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. Total gross repayments were $364.6 million and $281.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. The following table details the borrowing limits, amounts outstanding and amounts available under the revolving Credit Facility as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Revolving Credit Facility (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Limit | | $ | 200.0 | | | $ | 200.0 | |
Short-Term Borrowings Outstanding | | $ | 105.8 | | | $ | 162.0 | |
Available | | $ | 94.2 | | | $ | 38.0 | |
The Credit Facility contains customary terms and conditions for credit facilities of this type, including affirmative and negative covenants. There are restrictions on, among other things, Unitil’s and its subsidiaries’ ability to permit liens or incur indebtedness, and restrictions on Unitil’s ability to merge or consolidate with another entity or change its line of business. The affirmative and negative covenants under the Credit Facility shall apply to Unitil until the Credit Facility terminates and all amounts borrowed under the Credit Facility are paid in full (or with respect to letters of credit, they are cash collateralized).
The only financial covenant in the Credit Facility provides that Unitil’s Funded Debt to Capitalization (as each term is defined in the Credit Facility) cannot exceed 65%, tested on a quarterly basis. At December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company was in compliance with the covenants contained in the Credit Facility in effect on that date. (See also “Credit Arrangements” in Note 4 Debt and Financing Arrangements.)
Issuance of Long-Term Debt- On July 6, 2023, Fitchburg issued $12.0 million of Notes due July 2, 2033 at 5.70% and $13.0 million of Notes due July 2, 2053 at 5.96%. Fitchburg used the net proceeds from these offerings to refinance existing debt and for general corporate purposes. Approximately $0.2 million of costs associated with this issuance were recorded as a reduction of Long-Term Debt for presentation purposes on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in the third quarter of 2023.
On August 21, 2024, Unitil Corporation issued $20.0 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.99%. Fitchburg issued $12.5 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.54% and $12.5 million of Notes due 2044 at 5.99%. Unitil Energy issued $40.0 million of Bonds due 2054 at 5.69%. Northern Utilities issued $25.0 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.54% and $15.0 million of Notes due 2039 at 5.74%. Granite State issued $10.0 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.74%. The Company used the net proceeds from these
offerings to refinance existing debt and for general corporate purposes. Approximately $1.0 million of costs associated with this issuance were recorded as a reduction of Long-Term Debt for presentation purposes on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in the third quarter of 2024.
Unitil Corporation and its utility subsidiaries, Fitchburg, Unitil Energy, Northern Utilities, and Granite State are currently rated “BBB+” by Standard & Poor’s Ratings Services. Unitil Corporation and Granite State are currently rated “Baa2”, and Fitchburg, Unitil Energy and Northern Utilities are currently rated “Baa1” by Moody’s Investors Services.
The continued availability of various methods of financing, as well as the choice of a specific form of security for such financing, will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to: security market conditions; general economic climate; regulatory approvals; the ability to meet covenant issuance restrictions; the level of earnings, cash flows and financial position; and the competitive pricing offered by financing sources. The Company believes it has sufficient sources of working capital to fund its operations.
Contractual Obligations
The Company and its subsidiaries have material obligations for payment of principal and interest on its long-term debt as well as for operating and capital leases that are discussed in Note 4 (Debt and Financing Arrangements).
The Company and its subsidiaries have material energy supply commitments that are discussed in Note 6 (Energy Supply) and Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements. Cash outlays for the purchase of electricity and natural gas to serve customers are subject to reconciling recovery through periodic changes in rates, with carrying charges on deferred balances. From year to year, there are likely to be timing differences associated with the cash recovery of such costs, creating under- or over-recovery situations at any point in time. Rate recovery mechanisms are typically designed to collect the under-recovered cash or refund the over-collected cash over subsequent periods of less than one year.
The Company provides limited guarantees on certain energy and natural gas storage management contracts entered into by the distribution utilities. The Company’s policy is to limit the duration of these guarantees. As of December 31, 2024, there were no guarantees outstanding.
Northern Utilities enters into asset management agreements under which Northern Utilities releases certain natural gas pipeline and storage assets, resells the natural gas storage inventory to an asset manager and subsequently repurchases the inventory over the course of the natural gas heating season at the same price at which it sold the natural gas inventory to the asset manager. There was $7.8 million of natural gas storage inventory and corresponding obligations at December 31, 2024, related to these asset management agreements. The amount of natural gas inventory released in December 2024, which was payable in January 2025, was $1.8 million and was recorded in Accounts Payable at December 31, 2024.
Benefit Plan Funding
The Company, along with its subsidiaries, made cash contributions to its Pension Plan in the amounts of $3.8 million and $3.9 million in 2024 and 2023, respectively. The Company, along with its subsidiaries, contributed $2.5 million and $2.8 million to Voluntary Employee Benefit Trusts (VEBTs) in 2024 and 2023, respectively. The Company, along with its subsidiaries, expects to continue to make contributions to its Pension Plan and the VEBTs in 2025 and future years at least at minimum required amounts. See Note 9 (Retirement Benefit Plans) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
The Company and its subsidiaries do not currently use, and are not dependent on the use of, off-balance sheet financing arrangements such as securitization of receivables or obtaining access to assets or cash through special purpose entities or variable interest entities. As of December 31, 2024, there were no guarantees outstanding. See Note 4 (Debt and Financing Arrangements) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements.
Cash Flows
Unitil’s utility operations, taken as a whole, are seasonal in nature and subject to seasonal fluctuations in cash flows. The tables below summarize the major sources and uses of cash (in millions) for 2024 and 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Cash Provided by Operating Activities | | $ | 125.9 | | | $ | 107.0 | |
Cash Provided by Operating Activities - Cash Provided by Operating Activities was $125.9 million in 2024, an increase of $18.9 million compared to 2023.
Cash flow from Net Income, adjusted for the total of non-cash charges was $136.4 million in 2024 compared to $120.0 million in 2023, an increase of $16.4 million. The change to Net Income is primarily attributable to increases in electric and gas sales margin. The increase in depreciation and amortization of $8.7 million in 2024 compared to 2023 reflects higher rates and additional depreciation on higher utility plant in service. The increase in the deferred tax provision of $5.8 million in 2024 compared to 2023 is primarily driven by higher tax depreciation in 2024.
Changes in working capital items resulted in a ($1.6) million use of cash in 2024 compared to a ($4.6) million use of cash in 2023, representing an increase in sources of cash of $3.0 million. The change in working capital in 2024 compared to 2023 is primarily related to the net change in accrued revenue, accounts payable and exchange gas receivable and is reflective of the effect of the current macroeconomic environment and the timing of cash receipts and disbursements in the normal course of business.
Deferred Regulatory and Other Charges changed by $1.6 million in 2024 compared to 2023, primarily driven by changes in Regulatory Assets and Liabilities, and the change in Other, net in 2024 compared to 2023 was $2.1 million.
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Cash Used in Investing Activities | | $ | (169.9 | ) | | $ | (141.0 | ) |
Cash Used in Investing Activities - Cash Used in Investing Activities was ($169.9) million in 2024 compared to ($141.0) million in 2023, an increase of $28.9 million. The higher spending in 2024 is primarily related to normal utility capital expenditures for electric and gas utility system additions. The Company’s projected capital spending for 2025 is $176 million.
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Cash Provided by Financing Activities | | $ | 43.8 | | | $ | 31.5 | |
Cash Provided by Financing Activities - Cash Provided by Financing Activities was $43.8 million in 2024 compared to cash provided of $31.5 million in 2023. The higher cash provided from financing activities in 2024 compared to 2023 of $12.3 million is primarily attributable to, higher proceeds from the issuance of long-term debt of $110.0 million, lower repayment of long-term debt of $2.0 million, a change in exchange gas financing of $5.0 million, and higher repayment of short-term borrowings of ($102.2) million. Other changes in financing activities in 2024 total a use of ($2.5) million.
FINANCIAL COVENANTS AND RESTRICTIONS
The agreements under which the Company and its subsidiaries issue long-term debt contain various covenants and restrictions. These agreements do not contain any covenants or restrictions pertaining to the maintenance of financial ratios or the issuance of short-term debt. These agreements do contain covenants relating to, among other things, the issuance of additional long-term debt, cross-default provisions, business combinations and covenants restricting the ability to (i) pay dividends, (ii) incur indebtedness and liens, (iii) merge or consolidate with another entity or (iv) sell, lease or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all assets. See Note 4 (Debt and Financing Arrangements) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements.
Unitil’s Credit Facility contains customary terms and conditions for credit facilities of this type, including affirmative and negative covenants. There are restrictions on, among other things, Unitil’s and its subsidiaries’ ability to permit liens or incur indebtedness, and restrictions on Unitil’s ability to merge or consolidate with another entity or change its line of business. The affirmative and negative covenants under the Credit Facility apply to Unitil until the Credit Facility terminates and all
amounts borrowed under the Credit Facility are paid in full (or with respect to letters of credit, they are cash collateralized). The only financial covenant in the Credit Facility provides that Unitil’s Funded Debt to Capitalization (as each term is defined in the Credit Facility) cannot exceed 65%, tested on a quarterly basis. At December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company was in compliance with the covenants contained in the Credit Facility in effect on that date.
The Company and its subsidiaries are currently in compliance with all such covenants in these debt instruments.
DIVIDENDS
Unitil’s annual common dividend was $1.70 per common share in 2024, $1.62 per common share in 2023, and $1.56 per common share in 2022. Unitil’s dividend policy is reviewed periodically by the Board. Unitil has maintained an unbroken record of quarterly dividend payments since trading began in Unitil’s common stock. At a January 2025 meeting of the Board, the Board declared a quarterly dividend on the Company’s common stock of $0.45 per share, an increase of $0.025 per share on a quarterly basis, resulting in an increase in the effective annualized dividend rate to $1.80 from $1.70. The amount and timing of all dividend payments are subject to the discretion of the Board and will depend upon business conditions, results of operations, financial conditions and other factors. In addition, the ability of the Company’s subsidiaries to pay dividends or make distributions to Unitil, and, therefore, Unitil’s ability to pay dividends, depends on, among other things:
•the actual and projected earnings and cash flow, capital requirements and general financial condition of the Company’s subsidiaries;
•the prior rights of holders of existing and future preferred stock, mortgage bonds, long-term notes and other debt issued by the Company’s subsidiaries;
•the restrictions on the payment of dividends contained in the existing loan agreements of the Company’s subsidiaries and that may be contained in future debt agreements of the Company’s subsidiaries, if any; and
•limitations that may be imposed by New Hampshire, Massachusetts and Maine state regulatory agencies.
In addition, before the Company can pay dividends on its common stock, it must satisfy its debt obligations and comply with any statutory or contractual limitations. See Financial Covenants and Restrictions in this report, as well as Note 4 (Debt and Financing Arrangements) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements.
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
The Company is involved in legal and administrative proceedings and claims of various types, including those which arise in the ordinary course of business. The Company believes, based upon information furnished by counsel and others, that the ultimate resolution of these claims will not have a material effect on its financial position, operating results or cash flows. Refer to “Legal Proceedings” in Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies) of the Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of legal proceedings.
REGULATORY MATTERS
See Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies) to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The preparation of the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America requires the Company to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. In making those estimates and assumptions, the Company is sometimes required to make subjective and/or complex judgments about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain and for which different estimates that could reasonably have been used could have resulted in material differences in its financial statements. If actual results were to differ significantly from those estimates, assumptions and judgment, the financial position of the Company could be materially affected and the results of operations of the Company could be materially different than reported. The following is a summary of the Company’s most critical accounting policies, which are defined as those policies where judgments or uncertainties could materially affect the application of those policies. For a complete
discussion of the Company’s significant accounting policies, refer to the financial statements and Note 1 (Summary of Significant Accounting Policies).
Regulatory Accounting—The Company’s principal business is the distribution of electricity and natural gas by the three distribution utilities: Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Northern Utilities. Unitil Energy and Fitchburg are subject to regulation by the FERC. Fitchburg is also regulated by the MDPU, Unitil Energy is regulated by the NHPUC, and Northern Utilities is regulated by the MPUC and NHPUC. Granite State, the Company’s natural gas transmission pipeline, is regulated by the FERC. Accordingly, the Company uses the Regulated Operations guidance as set forth in the Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification (FASB Codification). In accordance with the FASB Codification, the Company has recorded Regulatory Assets and Regulatory Liabilities which will be recovered from customers, or applied for customer benefit, in accordance with rate provisions approved by the applicable public utility regulatory commission.
The FASB Codification specifies the economic effects that result from the cause and effect relationship of costs and revenues in the rate-regulated environment and the related accounting for a regulated enterprise. Revenues intended to cover certain costs may be recorded either before or after the costs are incurred. If regulation provides assurance that incurred costs will be recovered in the future, these costs would be recorded as deferred charges or “regulatory assets.” If revenues are recorded for costs that are expected to be incurred in the future, these revenues would be recorded as deferred credits or “regulatory liabilities.”
The Company’s principal regulatory assets and liabilities are included on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet and a summary of the Company’s Regulatory Assets is provided in Note 1 (Summary of Significant Accounting Policies) to the consolidated financial statements. Generally, the Company receives a return on investment on its regulated assets for which a cash outflow has been made. Regulatory commissions can reach different conclusions about the recovery of costs, which can have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
The Company believes it is probable that its regulated distribution and transmission utilities will recover their investments in long-lived assets, including regulatory assets. If the Company, or a portion of its assets or operations, were to cease meeting the criteria for application of these accounting rules, accounting standards for businesses in general would become applicable and immediate recognition of any previously deferred costs, or a portion of deferred costs, would be required in the year in which the criteria are no longer met, if such deferred costs were not recoverable in the portion of the business that continues to meet the criteria for application of the FASB Codification topic on Regulated Operations. If unable to continue to apply the FASB Codification provisions for Regulated Operations, the Company would be required to apply the provisions for the Discontinuation of Rate-Regulated Accounting included in the FASB Codification. In the Company’s opinion, its regulated operations will be subject to the FASB Codification provisions for Regulated Operations for the foreseeable future.
Retirement Benefit Obligations—The Company sponsors the Unitil Corporation Retirement Plan (Pension Plan), which is a defined benefit pension plan. Effective January 1, 2010, the Pension Plan was closed to new non-union employees. For union employees, the Pension Plan was closed on various dates between December 31, 2010 and June 1, 2013, depending on the various Collective Bargaining Agreements of each union. The Company also sponsors two non-qualified retirement plans, the Unitil Corporation Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (SERP), and the Unitil Corporation Deferred Compensation Plan, covering certain executives of the Company, and an employee 401(k) savings plan. Additionally, the Company sponsors the Unitil Employee Health and Welfare Benefits Plan (PBOP Plan), primarily to provide health care and life insurance benefits to retired employees.
The FASB Codification requires companies to record on their balance sheets as an asset or liability the overfunded or underfunded status of their retirement benefit obligations (RBO) based on the projected benefit obligation. The Company has recognized a corresponding Regulatory Asset, to recognize the future collection of these obligations in electric and gas rates. The Company’s RBO and reported costs of providing retirement benefits are dependent upon numerous factors resulting from actual plan experience and assumptions of future experience. The Company has made critical estimates related to actuarial assumptions, including assumptions of expected returns on plan assets, future compensation, health care cost trends, and appropriate discount rates. The Company’s RBO is affected by actual employee demographics, the level of contributions made to the plans, earnings on plan assets, and health care cost trends. Changes made to the provisions of these plans may also affect current and future costs. If these assumptions were changed, the resulting change in benefit obligations, fair values of plan assets, funded status and net periodic benefit costs could have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements. The discount rate assumptions used in determining retirement plan costs and retirement plan obligations are based on an assessment of current market conditions using high quality corporate bond interest rate indices and pension yield curves. For the year ended
December 31, 2024, a change in the discount rate of 0.25% would have resulted in an increase or decrease of approximately $450,800 in the Net Periodic Benefit Cost for the Pension Plan. Similarly, a change of 0.50% in the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets would have resulted in an increase or decrease of approximately $706,635 in the Net Periodic Benefit Cost for the Pension Plan. (See Note 9 (Retirement Benefit Plans) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements.)
Refer to “Recently Issued Pronouncements” in Note 1 of the Notes of Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding recently issued accounting standards.
For additional information regarding the foregoing matters, see Note 1 (Summary of Significant Accounting Policies), Note 6 (Energy Supply), and Note 9 (Retirement Benefit Plans) to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Please also refer to Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors”.
INTEREST RATE RISK
Unitil meets its external financing needs, in part, by issuing short-term and long-term debt. The majority of debt outstanding represents long-term notes bearing fixed rates of interest. Changes in market interest rates do not affect interest expense resulting from these outstanding long-term debt securities. However, the Company periodically repays its short-term debt borrowings through the issuance of new long-term debt securities. Changes in market interest rates may affect the interest rate and corresponding interest expense on any new issuances of long-term debt securities. In addition, short-term debt borrowings bear a variable rate of interest. As a result, changes in short-term interest rates will increase or decrease interest expense in future periods. For example, if the average amount of short-term debt outstanding was $25 million for the period of one year, a change in interest rates of 1% would result in a change in annual interest expense of approximately $250,000. The average interest rate on short-term borrowings and intercompany money pool transactions was 6.5%, 6.4%, and 3.3% during 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
COMMODITY PRICE RISK
Although Unitil’s three distribution utilities are subject to commodity price risk as part of their traditional operations, the current regulatory framework within which these companies operate allows for full collection of electric power and natural gas supply costs in rates on a pass-through basis. Consequently, there is limited commodity price risk after consideration of the related rate-making. Additionally, as discussed in the section entitled Rates and Regulation in Part I, Item 1 (Business) and in Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies) to the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements, the Company has divested its long-term power supply contracts and therefore, further reduced its exposure to commodity risk.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the shareholders and the Board of Directors of Unitil Corporation:
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Unitil Corporation and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of earnings, changes in common stock equity, and cash flows, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). We also have audited the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures to respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the
company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Impact of Rate-Regulation on Various Account Balances and Disclosures — Refer to Notes 1 and 7 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company’s principal business is the distribution of electricity and natural gas and is subject to regulation by the Massachusetts, New Hampshire and Maine Public Service Commissions as well as the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (collectively, the “Commissions”). Accordingly, the Company accounts for their regulated operations in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification Topic 980, Regulated Operations, and has recorded Regulatory Assets and Regulatory Liabilities which will be recovered from customers, or applied for customer benefit, in accordance with rate provisions approved by the applicable Commission. The Company believes it is probable that its regulated distribution and transmission utilities will recover their investments in long-lived assets, including regulatory assets. If the Company, or a portion of its assets or operations, were to cease meeting the criteria for application of these accounting rules, immediate recognition of any previously deferred costs, or a portion of deferred costs, would be required in the year in which the criteria are no longer met. In the Company’s opinion, its regulated operations will be subject to the FASB Codification provisions for Regulated Operations for the foreseeable future.
Accounting for the economics of rate regulation affects multiple financial statement line items, including property, plant, and equipment; regulatory assets and liabilities; operating revenues; and depreciation expense, and affects multiple disclosures in the Company’s financial statements. While the Company has indicated that it expects to recover costs and a return on its investments, there is a risk that the Commissions’ will not approve full recovery of the costs of providing utility service or recovery of all amounts invested in the utility business and a reasonable return on that investment. As a result, we identified the impact of rate regulation as a critical audit matter due to the high degree of subjectivity involved in assessing the impact of current and future regulatory orders on events that have occurred as of December 31, 2024, and the judgments made by management to support its assertions about impacted account balances and disclosures. Management judgments included assessing the likelihood of (1) recovery in future rates of incurred costs or (2) refunds to customers or future reduction in rates. Given that management’s accounting judgments are based on assumptions about the outcome of future decisions by the commissions, auditing these judgments require specialized knowledge of accounting for rate regulation and the rate setting process due to its inherent complexities.
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures related to the uncertainty of future decisions by the Commissions focused on the base rate proceedings for Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company and Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. and included the following, among others:
•We tested the effectiveness of controls over the relevant regulatory account balances and disclosures, including management’s controls over the monitoring and evaluation of regulatory developments that may affect the likelihood of recovering costs in future rates or of a future reduction in rates.
•We evaluated the Company’s disclosures related to the impacts of rate regulation, including the balances recorded and regulatory developments.
•We made inquiries of management and read relevant regulatory orders and settlements issued by the Commissions in Massachusetts, New Hampshire and Maine, regulatory statutes, interpretations, procedural memorandums, filings made by interveners or the Company, and other publicly available information to assess the likelihood of recovery in future rates or of a future reduction in rates based on precedents of the Commissions’ treatment of similar costs under similar circumstances. We evaluated this external information and compared to management’s recorded regulatory asset and liability balances and searched for any evidence that might contradict management’s assertions.
•We obtained an analysis from management describing the orders and filings that support management’s assertions regarding the probability of recovery for regulatory assets or refund or future reduction in rates for regulatory liabilities to assess management’s assertion that amounts are probable of recovery or a future reduction in rates.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Boston, MA
February 10, 2025
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2014.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EARNINGS
(Millions, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Operating Revenues: | | | | | | | | | |
Electric | | $ | 248.3 | | | $ | 306.5 | | | $ | 297.9 | |
Gas | | | 246.5 | | | | 250.6 | | | | 265.3 | |
Total Operating Revenues | | | 494.8 | | | | 557.1 | | | | 563.2 | |
Operating Expenses: | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of Electric Sales | | | 141.0 | | | | 202.4 | | | | 199.1 | |
Cost of Gas Sales | | | 79.6 | | | | 96.1 | | | | 121.4 | |
Operation and Maintenance | | | 77.6 | | | | 75.6 | | | | 73.7 | |
Depreciation and Amortization | | | 76.1 | | | | 67.4 | | | | 62.6 | |
Taxes Other Than Income Taxes | | | 29.9 | | | | 28.5 | | | | 25.9 | |
Total Operating Expenses | | | 404.2 | | | | 470.0 | | | | 482.7 | |
Operating Income | | | 90.6 | | | | 87.1 | | | | 80.5 | |
Interest Expense, Net | | | 29.3 | | | | 28.7 | | | | 25.5 | |
Other Expense (Income), Net | | | 0.2 | | | | — | | | | 2.4 | |
Income Before Income Taxes | | | 61.1 | | | | 58.4 | | | | 52.6 | |
Provision for Income Taxes | | | 14.0 | | | | 13.2 | | | | 11.2 | |
Net Income Applicable to Common Shares | | $ | 47.1 | | | $ | 45.2 | | | $ | 41.4 | |
Earnings per Common Share—Basic and Diluted | | $ | 2.93 | | | $ | 2.82 | | | $ | 2.59 | |
Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding - (Basic) | | | 16.1 | | | | 16.0 | | | | 16.0 | |
Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding - (Diluted) | | | 16.1 | | | | 16.1 | | | | 16.0 | |
(The accompanying Notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.)
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (Millions)
ASSETS
| | | | | | | | |
December 31, | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Current Assets: | | | | | | |
Cash and Cash Equivalents | | $ | 6.3 | | | $ | 6.5 | |
Accounts Receivable, Net | | | 75.0 | | | | 75.0 | |
Accrued Revenue | | | 77.4 | | | | 63.4 | |
Exchange Gas Receivable | | | 6.4 | | | | 9.4 | |
Gas Inventory | | | 1.1 | | | | 1.0 | |
Materials and Supplies | | | 14.2 | | | | 13.5 | |
Prepayments and Other | | | 8.4 | | | | 8.3 | |
Total Current Assets | | | 188.8 | | | | 177.1 | |
Utility Plant: | | | | | | |
Electric | | | 699.4 | | | | 654.9 | |
Gas | | | 1,189.9 | | | | 1,117.6 | |
Common | | | 69.0 | | | | 70.0 | |
Construction Work in Progress | | | 92.9 | | | | 65.3 | |
Utility Plant | | | 2,051.2 | | | | 1,907.8 | |
Less: Accumulated Depreciation | | | 511.6 | | | | 486.9 | |
Net Utility Plant | | | 1,539.6 | | | | 1,420.9 | |
Other Noncurrent Assets: | | | | | | |
Regulatory Assets | | | 41.9 | | | | 53.1 | |
Operating Lease Right of Use Assets | | | 6.7 | | | | 5.6 | |
Other Assets | | | 17.5 | | | | 13.7 | |
Total Other Noncurrent Assets | | | 66.1 | | | | 72.4 | |
TOTAL ASSETS | | $ | 1,794.5 | | | $ | 1,670.4 | |
(The accompanying Notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.)
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (cont.) (Millions, except number of shares)
LIABILITIES AND CAPITALIZATION
| | | | | | | | |
December 31, | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Current Liabilities: | | | | | | |
Accounts Payable | | $ | 49.7 | | | $ | 47.7 | |
Short-Term Debt | | | 105.8 | | | | 162.0 | |
Long-Term Debt, Current Portion | | | 4.9 | | | | 4.9 | |
Regulatory Liabilities | | | 17.2 | | | | 13.5 | |
Energy Supply Obligations | | | 10.0 | | | | 15.0 | |
Environmental Obligations | | | 0.7 | | | | 0.6 | |
Operating Lease Obligations | | | 1.8 | | | | 1.9 | |
Interest Payable | | | 8.4 | | | | 6.0 | |
Taxes Payable | | | — | | | | 1.9 | |
Other Current Liabilities | | | 30.2 | | | | 23.8 | |
Total Current Liabilities | | | 228.7 | | | | 277.3 | |
Noncurrent Liabilities: | | | | | | |
Retirement Benefit Obligations | | | 25.5 | | | | 45.6 | |
Deferred Income Taxes, Net | | | 186.1 | | | | 176.1 | |
Cost of Removal Obligations | | | 139.2 | | | | 126.3 | |
Regulatory Liabilities | | | 46.8 | | | | 34.4 | |
Environmental Obligations | | | 7.1 | | | | 4.0 | |
Operating Lease Obligations | | | 4.9 | | | | 3.7 | |
Other Noncurrent Liabilities | | | 5.3 | | | | 4.6 | |
Total Noncurrent Liabilities | | | 414.9 | | | | 394.7 | |
Capitalization: | | | | | | |
Long-Term Debt, Less Current Portion | | | 638.4 | | | | 509.1 | |
Stockholders’ Equity: | | | | | | |
Common Equity (No par value, Authorized 25,000,000 Shares; Outstanding 16,192,345 and 16,116,724 Shares as of respective dates) | | | 341.2 | | | | 337.6 | |
Retained Earnings | | | 171.1 | | | | 151.5 | |
Total Common Stock Equity | | | 512.3 | | | | 489.1 | |
Preferred Stock | | | 0.2 | | | | 0.2 | |
Total Stockholders’ Equity | | | 512.5 | | | | 489.3 | |
Total Capitalization | | | 1,150.9 | | | | 998.4 | |
Commitments and Contingencies (Note 7) | | | | | | |
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND CAPITALIZATION | | $ | 1,794.5 | | | $ | 1,670.4 | |
(The accompanying Notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (Millions)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31, | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Operating Activities: | | | | | | | | | |
Net Income | | $ | 47.1 | | | $ | 45.2 | | | $ | 41.4 | |
Adjustments to Reconcile Net Income to Cash Provided by Operating
Activities: | | | | | | | | | |
Depreciation and Amortization | | | 76.1 | | | | 67.4 | | | | 62.6 | |
Deferred Tax Provision | | | 13.2 | | | | 7.4 | | | | 11.0 | |
Changes in Working Capital Items: | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts Receivable | | | — | | | | (1.2 | ) | | | (6.9 | ) |
Accrued Revenue | | | (14.0 | ) | | | 9.4 | | | | (11.6 | ) |
Regulatory Liabilities | | | 3.7 | | | | (1.5 | ) | | | 5.5 | |
Exchange Gas Receivable | | | 3.0 | | | | 8.6 | | | | (10.6 | ) |
Accounts Payable | | | 2.0 | | | | (20.9 | ) | | | 16.2 | |
Other Changes in Working Capital Items | | | 3.7 | | | | 1.0 | | | | 1.4 | |
Deferred Regulatory and Other Charges | | | (6.9 | ) | | | (8.5 | ) | | | (6.5 | ) |
Other, net | | | (2.0 | ) | | | 0.1 | | | | (4.8 | ) |
Cash Provided by Operating Activities | | | 125.9 | | | | 107.0 | | | | 97.7 | |
Investing Activities: | | | | | | | | | |
Property, Plant and Equipment Additions | | | (169.9 | ) | | | (141.0 | ) | | | (122.1 | ) |
Cash Used In Investing Activities | | | (169.9 | ) | | | (141.0 | ) | | | (122.1 | ) |
Financing Activities: | | | | | | | | | |
(Repayment of) Proceeds from Short-Term Debt, net | | | (56.2 | ) | | | 46.0 | | | | 51.9 | |
Issuance of Long-Term Debt | | | 135.0 | | | | 25.0 | | | | — | |
Repayment of Long-Term Debt | | | (4.9 | ) | | | (6.9 | ) | | | (10.4 | ) |
Long-Term Debt Issuance Costs | | | (1.1 | ) | | | (0.2 | ) | | | — | |
Increase (Decrease) in Capital Lease Obligations | | | — | | | | 0.3 | | | | (0.1 | ) |
Net (Decrease) Increase in Exchange Gas Financing | | | (2.6 | ) | | | (7.6 | ) | | | 9.6 | |
Dividends Paid | | | (27.5 | ) | | | (26.2 | ) | | | (25.1 | ) |
Proceeds from Issuance of Common Stock | | | 1.1 | | | | 1.1 | | | | 1.0 | |
Cash Provided by Financing Activities | | | 43.8 | | | | 31.5 | | | | 26.9 | |
Net (Decrease) Increase in Cash and Cash Equivalents | | | (0.2 | ) | | | (2.5 | ) | | | 2.5 | |
Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Year | | | 6.5 | | | | 9.0 | | | | 6.5 | |
Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Year | | $ | 6.3 | | | $ | 6.5 | | | $ | 9.0 | |
Supplemental Information: | | | | | | | | | |
Interest Paid | | $ | 31.2 | | | $ | 30.9 | | | $ | 26.0 | |
Income Taxes Paid | | $ | 2.5 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1.2 | |
Payments on Capital Leases | | $ | 0.2 | | | $ | 0.2 | | | $ | 0.2 | |
Capital Expenditures Included in Accounts Payable | | $ | 11.7 | | | $ | 7.5 | | | $ | 7.3 | |
Right of Use Assets Obtained in Exchange for Lease Obligations | | $ | 2.6 | | | $ | 2.7 | | | $ | 1.1 | |
(The accompanying Notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.)
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF
CHANGES IN COMMON STOCK EQUITY (Millions, except shares data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Common
Equity | | | Retained
Earnings | | | Total | |
Balance at January 1, 2022 | | $ | 332.1 | | | $ | 116.2 | | | $ | 448.3 | |
Net Income for 2022 | | | | | | 41.4 | | | | 41.4 | |
Dividends ($1.56 per Common Share) | | | | | | (25.1 | ) | | | (25.1 | ) |
Shares Issued Under Stock Plans | | | 1.8 | | | | | | | 1.8 | |
Issuance of 18,853 Common Shares (See Note 5) | | | 1.0 | | | | | | | 1.0 | |
Balance at December 31, 2022 | | | 334.9 | | | | 132.5 | | | | 467.4 | |
Net Income for 2023 | | | | | | 45.2 | | | | 45.2 | |
Dividends ($1.62 per Common Share) | | | | | | (26.2 | ) | | | (26.2 | ) |
Shares Issued Under Stock Plans | | | 1.6 | | | | | | | 1.6 | |
Issuance of 21,321 Common Shares (See Note 5) | | | 1.1 | | | | | | | 1.1 | |
Balance at December 31, 2023 | | | 337.6 | | | | 151.5 | | | | 489.1 | |
Net Income for 2024 | | | | | | 47.1 | | | | 47.1 | |
Dividends ($1.70 per Common Share) | | | | | | (27.5 | ) | | | (27.5 | ) |
Shares Issued Under Stock Plans | | | 2.5 | | | | | | | 2.5 | |
Issuance of 19,510 Common Shares (See Note 5) | | | 1.1 | | | | | | | 1.1 | |
Balance at December 31, 2024 | | $ | 341.2 | | | $ | 171.1 | | | $ | 512.3 | |
(The accompanying Notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.)
Note 1: Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Nature of Operations - Unitil Corporation (Unitil or the Company) is a public utility holding company. Unitil and its subsidiaries are subject to regulation as a holding company system by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) under the Energy Policy Act of 2005. The following companies are wholly-owned subsidiaries of Unitil: Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. (Unitil Energy), Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company (Fitchburg), Northern Utilities, Inc. (Northern Utilities), Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. (Granite State), Unitil Power Corp. (Unitil Power), Unitil Realty Corp. (Unitil Realty), Unitil Service Corp. (Unitil Service) and Unitil Resources, Inc. (Unitil Resources).
The Company’s earnings are seasonal and are typically higher in the first and fourth quarters when customers use natural gas for heating purposes.
Unitil’s principal business is the local distribution of electricity in the southeastern seacoast and capital city areas of New Hampshire and the greater Fitchburg area of north central Massachusetts and the local distribution of natural gas in southeastern New Hampshire, portions of southern Maine to the Lewiston-Auburn area and in the greater Fitchburg area of north central Massachusetts. Unitil has three distribution utility subsidiaries, Unitil Energy, which operates in New Hampshire; Fitchburg, which operates in Massachusetts; and Northern Utilities, which operates in New Hampshire and Maine (collectively, the distribution utilities).
Granite State is an interstate natural gas transmission pipeline company, operating 85 miles of underground gas transmission pipeline primarily located in Maine and New Hampshire. Granite State provides Northern Utilities with interconnection to three major natural gas pipelines and access to domestic natural gas supplies in the south and Canadian natural gas supplies in the north. Granite State derives its revenues principally from the transportation services provided to Northern Utilities and, to a lesser extent, third-party marketers.
A fifth utility subsidiary, Unitil Power, formerly functioned as the full requirements wholesale power supply provider for Unitil Energy, but ceased being the wholesale supplier of Unitil Energy with the implementation of industry restructuring and divested its long-term power supply contracts.
Unitil also has three other wholly-owned subsidiaries: Unitil Service, Unitil Resources and Unitil Realty. Unitil Service provides, at cost, a variety of administrative and professional services, including regulatory, financial, accounting, human resources, engineering, operations, technology, energy management and management services on a centralized basis to its affiliated Unitil companies. Unitil Resources is the Company’s wholly-owned non-regulated subsidiary, which currently does not have any activity. Unitil Realty owns and manages the Company’s corporate office in Hampton, New Hampshire and leases this facility to Unitil Service under a long-term lease arrangement. Unitil Realty also owns land for future use in Kingston, New Hampshire.
On January 31, 2025, Unitil Corporation acquired Bangor Natural Gas Company, a natural gas distribution utility.
Basis of Presentation
Principles of Consolidation - The Company’s consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Unitil and all of its wholly-owned subsidiaries and all intercompany transactions are eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates - The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (GAAP) requires the Company to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, and requires disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Fair Value - The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Codification defines fair value, and establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). The three levels of the fair value hierarchy under the FASB Codification include:
| |
| |
Level 1 - | Inputs are quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the reporting entity has the ability to access at the measurement date. |
|
|
Level 2 - | Valuations based on quoted prices in markets that are not active or for which all significant inputs are observable, either directly or indirectly. |
|
|
Level 3 - | Prices or valuations that require inputs that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable. |
To the extent valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by the Company in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level 3. A financial instrument’s level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Fair value is a market-based measure considered from the perspective of a market participant rather than an entity-specific measure. Therefore, even when market assumptions are not readily available, the Company’s own assumptions are set to reflect those that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability at the measurement date. The Company uses prices and inputs that are current as of the measurement date, including during periods of market dislocation. In periods of market dislocation, the observability of prices and inputs may be reduced for many instruments. This condition could cause an instrument to be reclassified from Level 1 to Level 2 or from Level 2 to Level 3.
There have been no changes in the valuation techniques used during the current period.
Utility Revenue Recognition - Electric Operating Revenues and Gas Operating Revenues consist of billed and unbilled revenue and revenue from rate adjustment mechanisms. Billed and unbilled revenue includes delivery revenue and pass-through revenue, recognized according to tariffs approved by federal and state regulatory commissions which determine the amount of revenue the Company will record for these items. Revenue from rate adjustment mechanisms is accrued revenue, recognized in connection with rate adjustment mechanisms, and authorized by regulators for recognition in the current period for future cash recoveries from, or credits to, customers.
Billed and unbilled revenue is recorded when service is rendered or energy is delivered to customers. However, the determination of energy sales to individual customers is based on the reading of their meters, which occurs on a systematic basis throughout the month. At the end of each calendar month, amounts of energy delivered to customers since the date of the last meter reading are estimated and the corresponding unbilled revenues are calculated. These unbilled revenues are estimated each month based on estimated customer usage by class and applicable customer rates, taking into account current and historical weather data, assumptions pertaining to metering patterns, billing cycle statistics, and other estimates and assumptions, and are then reversed in the following month when billed to customers.
A majority of the Company’s revenue from contracts with customers continues to be recognized on a monthly basis based on applicable tariffs and customer monthly consumption. Such revenue is recognized using the invoice practical expedient which allows an entity to recognize revenue in the amount that directly corresponds to the value transferred to the customer.
The Company’s billed and unbilled revenue meets the definition of “revenues from contracts with customers” as defined in Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 606. Revenue recognized in connection with rate adjustment mechanisms is consistent with the definition of alternative revenue programs in ASC 980, as the Company has the ability to adjust rates in the future as a result of past activities or completed events. The rate adjustment mechanisms meet the criteria within ASC 980. In cases where allowable costs are greater than operating revenues billed in the current period for the individual rate adjustment mechanism additional operating revenue is recognized. In cases where allowable costs are less than operating revenues billed in the current period for the individual rate adjustment mechanism, operating revenue is reduced. ASC 606 requires the Company to disclose separately the amount of revenues from contracts with customers and alternative revenue program revenues.
In the following tables, revenue is classified by the types of goods/services rendered and market/customer type.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Twelve Months Ended | |
| | December 31, 2024 | |
Electric and Gas Operating Revenues (millions): | | Electric | | | Gas | | | Total | |
Billed and Unbilled Revenue: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | | $ | 135.0 | | | $ | 92.6 | | | $ | 227.6 | |
Commercial & Industrial | | | 103.4 | | | | 133.5 | | | | 236.9 | |
Other | | | 10.4 | | | | 9.7 | | | | 20.1 | |
Total Billed and Unbilled Revenue | | | 248.8 | | | | 235.8 | | | | 484.6 | |
Rate Adjustment Mechanism Revenue | | | (0.5 | ) | | | 10.7 | | | | 10.2 | |
Total Electric and Gas Operating Revenues | | $ | 248.3 | | | $ | 246.5 | | | $ | 494.8 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Twelve Months Ended | |
| | December 31, 2023 | |
Electric and Gas Operating Revenues (millions): | | Electric | | | Gas | | | Total | |
Billed and Unbilled Revenue: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | | $ | 181.6 | | | $ | 98.8 | | | $ | 280.4 | |
Commercial & Industrial | | | 120.1 | | | | 146.9 | | | | 267.0 | |
Other | | | 10.0 | | | | 8.1 | | | | 18.1 | |
Total Billed and Unbilled Revenue | | | 311.7 | | | | 253.8 | | | | 565.5 | |
Rate Adjustment Mechanism Revenue | | | (5.2 | ) | | | (3.2 | ) | | | (8.4 | ) |
Total Electric and Gas Operating Revenues | | $ | 306.5 | | | $ | 250.6 | | | $ | 557.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Twelve Months Ended | |
| | December 31, 2022 | |
Electric and Gas Operating Revenues (millions): | | Electric | | | Gas | | | Total | |
Billed and Unbilled Revenue: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | | $ | 159.9 | | | $ | 98.2 | | | $ | 258.1 | |
Commercial & Industrial | | | 112.6 | | | | 153.8 | | | | 266.4 | |
Other | | | 17.7 | | | | 11.3 | | | | 29.0 | |
Total Billed and Unbilled Revenue | | | 290.2 | | | | 263.3 | | | | 553.5 | |
Rate Adjustment Mechanism Revenue | | | 7.7 | | | | 2.0 | | | | 9.7 | |
Total Electric and Gas Operating Revenues | | $ | 297.9 | | | $ | 265.3 | | | $ | 563.2 | |
Revenue decoupling is the term given to the elimination of the dependency of a utility’s distribution revenue on the volume of electricity or gas sales. The difference between distribution revenue amounts billed to customers and the targeted revenue decoupling amounts is recognized as an increase or a decrease in Accrued Revenue, which forms the basis for resetting rates for future cash recoveries from, or credits to, customers. These revenue decoupling targets may be adjusted as a result of rate cases and other authorized adjustments that the Company files with the MDPU and NHPUC. Fitchburg has been subject to revenue decoupling since 2011. Unitil Energy has been subject to revenue decoupling since June 1, 2022. As a result of Unitil Energy now being subject to revenue decoupling, as of June 1, 2022, revenue decoupling now applies to substantially all of Unitil’s total annual electric sales volumes. Substantially all of Northern Utilities’ gas sales volumes in New Hampshire have been subject to decoupling since August 1, 2022. The Company's electric and gas sales in New Hampshire and Massachusetts are now largely decoupled. Northern Utilities’ gas sales volumes in Maine are not subject to revenue decoupling.
The Company bills its customers for sales tax in Massachusetts and Maine. These taxes are remitted to the appropriate departments of revenue in each state and are excluded from revenues on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Depreciation and Amortization - Depreciation expense is calculated on a group straight-line basis based on the useful lives of assets, and judgment is involved when estimating the useful lives of certain assets. The Company conducts independent depreciation studies on a periodic basis as part of the regulatory ratemaking process and considers the results presented in these studies in determining the useful lives of the Company’s fixed assets. A change in the estimated useful lives of these assets could have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Provisions for depreciation were equivalent to the following composite rates, based on the average depreciable property balances at the beginning and end of each year: 2024 - 3.49%, 2023 - 3.33% and 2022 - 3.26%.
Stock-based Employee Compensation - Unitil accounts for stock-based employee compensation using the fair value method (See Note 5 Equity).
Income Taxes - The Company is subject to Federal and State income taxes as well as various other business taxes. The Company’s process for determining income tax amounts involves estimating the Company’s current tax liabilities as well as assessing temporary and permanent differences resulting from the timing of the deductions of expenses and recognition of taxable income for tax and book accounting purposes. These temporary differences result in deferred tax assets and liabilities, which are included in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company accounts for income tax assets, liabilities and expenses in accordance with the FASB Codification guidance on Income Taxes. The Company classifies penalties and interest expense related to income tax liabilities as income tax expense and interest expense, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Provisions for income taxes are calculated in each of the jurisdictions in which the Company operates for each period for which a statement of earnings is presented. The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with the FASB Codification guidance on Income Taxes, which requires an asset and liability approach for the financial accounting and reporting of income taxes. Significant judgments and estimates are required in determining the current and deferred tax assets and liabilities. The Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities reflect its best assessment of estimated future taxes to be paid. In accordance with the FASB Codification, the Company periodically assesses the realization of its deferred tax assets and liabilities and adjusts the income tax provision, the current tax liability and deferred taxes in the period in which the facts and circumstances which gave rise to the revision become known.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes - Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures (ASU 2023-09). ASU 2023-09 establishes new income tax disclosure requirements in addition to modifying and eliminating certain existing requirements. The amendments in ASU 2023-09 are effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2024, with early adoption permitted. The Company does not expect this new guidance to have a material effect on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
Dividends - The Company’s dividend policy is reviewed periodically by the Board. The amount and timing of all dividend payments is subject to the discretion of the Board and will depend upon business conditions, results of operations, financial conditions and other factors. For the year ended December 31, 2024, the Company paid quarterly dividends of $0.425 per share, resulting in an annualized dividend rate of $1.70 per common share. For the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022, the Company paid quarterly dividends of $0.405 and $0.39 per common share, respectively, resulting in annualized dividend rates of $1.62 and $1.56 per common share, respectively. At a January 2025 meeting of the Board, the Board declared a quarterly dividend on the Company’s common stock of $0.45 per share, an increase of $0.025 per share on a quarterly basis, resulting in an increase in the effective annualized dividend rate to $1.80 per share from $1.70 per share.
Cash and Cash Equivalents - Cash and Cash Equivalents includes all cash and cash equivalents to which the Company has legal title. Cash equivalents include short-term investments with original maturities of three months or less and interest bearing deposits. The Company’s cash and cash equivalents are held at financial institutions and at times may exceed federally insured limits. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts. Under the Independent System Operator—New England (ISO-NE) Financial Assurance Policy (Policy), Unitil’s subsidiaries Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Unitil Power are required to provide assurance of their ability to satisfy their obligations to ISO-NE. Under this Policy, Unitil’s subsidiaries provide cash deposits covering approximately 2-1/2 months of outstanding obligations, less credit amounts that are based on the Company’s credit rating. On December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Unitil subsidiaries had deposited $5.0 million and $3.3 million, respectively, to satisfy their ISO-NE obligations.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts - The Company recognizes a provision for doubtful accounts that reflects the Company’s estimate of expected credit losses for electric and gas utility service accounts receivable. The allowance for doubtful accounts is calculated by applying a historical loss rate to customer account balances and management’s assessment of current and expected economic conditions, customer trends, or other factors. The Company also calculates the amount of written-off receivables that are recoverable through regulatory rate reconciling mechanisms. The Company’s distribution utilities are authorized by regulators to recover the costs of the energy commodity portion of bad debts through rate mechanisms. Also, the electric and gas divisions of Fitchburg are authorized to recover through rates past due amounts associated with protected hardship accounts. Evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts requires judgment about the assumptions used in the analysis. The Company’s experience has been that the assumptions used in evaluating the adequacy of the allowance for doubtful accounts have proven to be reasonably accurate. (See Note 3 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts).
Accounts Receivable, Net includes $2.3 million and $2.3 million of the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. Unbilled Revenues, net (a component of Accrued Revenue) includes $0.1 million and $0.1 million of the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively.
Accrued Revenue - Accrued Revenue includes the current portion of Regulatory Assets (see “Regulatory Accounting”) and unbilled revenues (see “Utility Revenue Recognition”). The following table shows the components of Accrued Revenue as of December 31, 2024 and 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Accrued Revenue (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Regulatory Assets—Current | | $ | 70.1 | | | $ | 56.5 | |
Unbilled Revenues | | | 7.3 | | | | 6.9 | |
Total Accrued Revenue | | $ | 77.4 | | | $ | 63.4 | |
Exchange Gas Receivable - Northern Utilities and Fitchburg have gas exchange and storage agreements whereby natural gas purchases during the months of April through October are delivered to a third party. The third party delivers natural gas back to the Company during the months of November through March. The exchange and storage gas volumes are recorded at weighted average cost. The following table shows the components of Exchange Gas Receivable as of December 31, 2024 and 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Exchange Gas Receivable (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Northern Utilities | | $ | 6.0 | | | $ | 8.6 | |
Fitchburg | | | 0.4 | | | | 0.8 | |
Total Exchange Gas Receivable | | $ | 6.4 | | | $ | 9.4 | |
Gas Inventory - The Company uses the weighted average cost methodology to value natural gas inventory. The following table shows the components of Gas Inventory as of December 31, 2024 and 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Gas Inventory (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Natural Gas | | $ | 0.2 | | | $ | 0.3 | |
Propane | | | 0.4 | | | | 0.3 | |
Liquefied Natural Gas & Other | | | 0.5 | | | | 0.4 | |
Total Gas Inventory | | $ | 1.1 | | | $ | 1.0 | |
The Company also has an inventory of Materials and Supplies in the amounts of $14.2 million and $13.5 million as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. These amounts are recorded at weighted average cost.
Utility Plant - The cost of additions to Utility Plant and the cost of renewals and betterments are capitalized. Cost of additions consists of labor, materials, services and certain indirect construction costs, including an allowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC). The average interest rates applied to AFUDC were 6.22%, 5.48% and 2.50% in 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The costs of current repairs and minor replacements are charged to appropriate operating expense accounts. The original cost of utility plant retired or otherwise disposed of is charged to the accumulated provision for depreciation. The Company includes in its mass asset depreciation rates, which are periodically reviewed as part of its ratemaking proceedings, cost of removal amounts to provide for future negative salvage value. At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company has recorded cost of removal amounts of $139.2 million and $126.3 million, respectively, that have been collected in depreciation rates but have not yet been expended, and which represent regulatory liabilities. These amounts are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets in Cost of Removal Obligations.
Regulatory Accounting - The Company’s principal business is the distribution of electricity and natural gas by the three distribution utilities: Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Northern Utilities. Unitil Energy and Fitchburg are subject to regulation by the FERC. Fitchburg is also regulated by the Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities (MDPU), Unitil Energy is regulated by the New Hampshire Public Utilities Commission (NHPUC) and Northern Utilities is regulated by the Maine Public Utilities Commission (MPUC) and NHPUC. Granite State, the Company’s natural gas transmission pipeline, is regulated by the FERC. Accordingly, the Company uses the Regulated Operations guidance as set forth in the FASB Codification. The Company has recorded Regulatory Assets and Regulatory Liabilities which will be recovered from customers, or applied for customer benefit,
in accordance with rate provisions approved by the applicable public utility regulatory commission. The electric and gas divisions of Fitchburg are authorized to recover through rates past due amounts associated with hardship accounts that are protected from shut-off. As of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company has recorded $7.9 million and $6.0 million, respectively, of hardship accounts in Regulatory Assets. These amounts are included in “Other Deferred Charges” in the following table. The Company currently receives recovery in rates or expects to receive recovery of these hardship accounts in future rate cases.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Regulatory Assets consist of the following (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Retirement Benefits | | $ | 14.4 | | | $ | 29.8 | |
Energy Supply & Other Rate Adjustment Mechanisms | | | 65.4 | | | | 52.4 | |
Deferred Storm Charges | | | 8.3 | | | | 9.2 | |
Environmental | | | 9.4 | | | | 6.1 | |
Income Taxes | | | 0.4 | | | | 1.1 | |
Other Deferred Charges | | | 14.1 | | | | 11.0 | |
Total Regulatory Assets | | | 112.0 | | | | 109.6 | |
Less: Current Portion of Regulatory Assets(1) | | | 70.1 | | | | 56.5 | |
Regulatory Assets—noncurrent | | $ | 41.9 | | | $ | 53.1 | |
(1)Reflects amounts included in Accrued Revenue on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Regulatory Liabilities consist of the following (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Rate Adjustment Mechanisms | | $ | 13.6 | | | $ | 9.3 | |
Income Taxes | | | 50.4 | | | | 38.6 | |
Total Regulatory Liabilities | | | 64.0 | | | | 47.9 | |
Less: Current Portion of Regulatory Liabilities | | | 17.2 | | | | 13.5 | |
Regulatory Liabilities—noncurrent | | $ | 46.8 | | | $ | 34.4 | |
Generally, the Company receives a return on investment on its regulated assets for which a cash outflow has been made. Included in Regulatory Assets as of December 31, 2024 are $7.1 million of environmental costs, rate case costs and other expenditures to be recovered over varying periods in the next seven years. Regulators have authorized recovery of these expenditures, but without a return. Regulatory commissions can reach different conclusions about the recovery of costs, which can have a material effect on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements. The Company believes it is probable that its regulated distribution and transmission utilities will recover their investments in long-lived assets, including regulatory assets. If the Company, or a portion of its assets or operations, were to cease meeting the criteria for application of these accounting rules, accounting standards for businesses in general would become applicable and immediate recognition of any previously deferred costs, or a portion of deferred costs, would be required in the year in which the criteria are no longer met, if such deferred costs were not recoverable in the portion of the business that continues to meet the criteria for application of the FASB Codification topic on Regulated Operations. If unable to continue to apply the FASB Codification provisions for Regulated Operations, the Company would be required to apply the provisions for the Discontinuation of Rate-Regulated Accounting included in the FASB Codification. In the Company’s opinion, its regulated operations will be subject to the FASB Codification provisions for Regulated Operations for the foreseeable future.
Leases - The Company records assets and liabilities on the balance sheet for all leases with terms longer than 12 months. Leases are classified as either finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern of expense recognition in the income statement. The Company has elected the practical expedient to not separate non-lease components from lease components and instead to account for both as a single lease component. The Company’s accounting policy election for leases with a lease term of 12 months or less is to recognize the lease payments as lease expense in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings on a straight-line basis over the lease term. See additional discussion in the “Leases” section of Note 4 (Debt and Financing Arrangements).
Derivatives - The Company’s regulated energy subsidiaries enter into energy supply contracts to serve their electric and gas customers. The Company follows a procedure for determining whether each contract qualifies as a derivative instrument under the guidance provided by the FASB Codification on Derivatives and Hedging. For each contract, the Company reviews and documents the key terms of the contract. Based on those terms and any additional relevant components of the contract, the Company determines and documents whether the contract qualifies as a derivative instrument as defined in the FASB Codification. The Company has determined that its energy supply contracts either do not qualify as a derivative instrument
under the guidance set forth in the FASB Codification, have been elected as normal purchase, or have contingencies that have not yet been met in order to establish a notional amount.
Fitchburg has entered into power purchase agreements for which contingencies exist (see “Fitchburg – Massachusetts RFP’s” section of Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies)). Until these contingencies are satisfied, these contracts will not qualify for derivative accounting. The Company believes that the power purchase obligations under these long-term contracts will have a material effect on the contractual obligations of Fitchburg.
Investments in Marketable Securities - The Company maintains a trust through which it invests in a money market fund and a fixed income fund. These funds are intended to satisfy obligations under the Company’s Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (SERP). See additional discussion of the SERP in Note 9 Retirement Benefit Plans.
At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the fair value of the Company’s investments in these trading securities, which are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets in Other Assets, were $6.3 million and $6.0 million, respectively, as shown in the following table. These investments are valued based on quoted prices from active markets and are categorized in Level 1 as they are actively traded and no valuation adjustments have been applied. Changes in the fair value of these investments are recorded in Other (Income) Expense, Net.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Fair Value of Marketable Securities (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Money Market Funds | | $ | 2.5 | | | $ | 2.0 | |
Fixed Income Funds | | | 3.8 | | | | 4.0 | |
Total Marketable Securities | | $ | 6.3 | | | $ | 6.0 | |
The Company also sponsors the Unitil Corporation Deferred Compensation Plan (the DC Plan). The DC Plan is a non-qualified deferred compensation plan that provides a vehicle for participants to accumulate tax-deferred savings to supplement retirement income. The DC Plan, which was effective January 1, 2019, is open to senior management or other highly compensated employees as determined by the Company’s Board of Directors, and may also be used for recruitment and retention purposes for newly hired senior executives. The DC Plan design mirrors the Company’s Tax Deferred Savings and Investment Plan formula, but provides for contributions on compensation above the IRS limit, which will allow participants to defer up to 85% of base salary, and up to 85% of any cash incentive for retirement. The Company may also elect to make discretionary contributions on behalf of any participant in an amount determined by the Company’s Board of Directors. A trust has been established to invest the funds associated with the DC Plan.
At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the fair value of the Company’s investments in these trading securities related to the DC Plan, which are recorded on the Consolidated Balance Sheets in Other Assets, were $2.2 million and $1.3 million, respectively. These investments are valued based on quoted prices from active markets and are categorized in Level 1 as they are actively traded and no valuation adjustments have been applied. Changes in the fair value of these investments are recorded in Other (Income) Expense, Net.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Fair Value of Marketable Securities (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Equity Funds | | $ | 2.0 | | | $ | 1.1 | |
Fixed Income Funds | | | 0.1 | | | | 0.1 | |
Money Market Funds | | | 0.1 | | | | 0.1 | |
Total Marketable Securities | | $ | 2.2 | | | $ | 1.3 | |
Energy Supply Obligations—The following discussion and table summarize the nature and amounts of the items recorded as Energy Supply Obligations on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Energy Supply Obligations consist of the following (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Renewable Energy Portfolio Standards | | $ | 4.0 | | | $ | 6.4 | |
Exchange Gas Obligation | | | 6.0 | | | | 8.6 | |
Total Energy Supply Obligations | | $ | 10.0 | | | $ | 15.0 | |
Renewable Energy Portfolio Standards - Renewable Energy Portfolio Standards (RPS) require retail electricity suppliers, including public utilities, to demonstrate that required percentages of their sales are met with power generated from certain types of resources or technologies. Compliance is demonstrated by purchasing and retiring Renewable Energy Certificates (REC) generated by facilities approved by the state as qualifying for REC treatment. Unitil Energy and Fitchburg purchase RECs in compliance with RPS legislation in New Hampshire and Massachusetts for supply provided to default service customers. RPS compliance costs are a supply cost that is recovered in customer default service rates. Unitil Energy and Fitchburg collect RPS compliance costs from customers throughout the year and demonstrate compliance for each calendar year on the following July 1. Due to timing differences between collection of revenue from customers and payment of REC costs to suppliers, Unitil Energy and Fitchburg typically defer costs for RPS compliance which are recorded within Accrued Revenue with a corresponding liability in Energy Supply Obligations on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Fitchburg has entered into long-term renewable contracts for the purchase of clean energy and/or RECs pursuant to Massachusetts legislation. The generating facilities associated with ten of these contracts have been constructed and are now operating. Three approved contracts are currently under development. These include long-term contracts filed with the MDPU in 2018, two for offshore wind generation (totaling 1,200 MW) and one for imported hydroelectric power and associated transmission, all three of which were approved in 2019. Four offshore wind contracts, totaling 2,400 MW, previously solicited for pursuant to the Green Communities Act and approved by the MDPU in 2021 and 2022, were subsequently terminated in 2023. In compliance with the Green Communities Act as amended by the Energy Diversity Act and the Act Driving Clean Energy and Offshore Wind in coordination with the other electric distribution companies (EDCs) in Massachusetts, on August 30, 2023 the Company issued a fourth offshore wind Request for Proposal seeking to procure at least 400 MW and up to the maximum amount remaining of the statutory requirement. The EDCs received bids for Offshore Wind Generation from three developers as part of a multi-state solicitation with Rhode Island and Connecticut and on September 6, 2024, the Department of Energy Resources selected a portfolio of projects totaling 2,678 MW from three projects. The EDCs have commenced contract negotiations which are scheduled to be completed in March 2025. Fitchburg recovers the costs associated with long-term renewable contracts on a fully reconciling basis through a MDPU-approved cost recovery mechanism, and has received remuneration for entering into them.
In December 2024, the Massachusetts Legislature approved “An Act promoting a clean energy grid, advancing equity, and protecting ratepayers” which among other provisions, extends the period for long-term renewable contracts up to 30 years and directs the EDCs to “jointly and competitively solicit proposals for energy storage systems and enter into cost-effective long-term contracts equal to, in the aggregate, approximately 5,000 megawatts of energy storage systems not later than July 31, 2030.” The first solicitation will be for approximately 1,500 megawatts of mid-duration storage to be procured by July 31, 2025.
Exchange Gas Obligation - Northern Utilities enters into gas exchange agreements under which Northern Utilities releases certain natural gas pipeline and storage assets, resells the natural gas storage inventory to an asset manager and subsequently repurchases the inventory over the course of the natural gas heating season at the same price at which it sold the natural gas inventory to the asset manager. The gas inventory related to these agreements is recorded in Exchange Gas Receivable on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets while the corresponding obligations are recorded in Energy Supply Obligations.
Retirement Benefit Obligations - The Company sponsors the Pension Plan, which is a defined benefit pension plan. Effective January 1, 2010, the Pension Plan was closed to new non-union employees. For union employees, the Pension Plan was closed on various dates between December 31, 2010 and June 1, 2013, depending on the various Collective Bargaining Agreements of each union. The Company also sponsors a non-qualified retirement plan, the SERP, covering certain executives of the Company, and an employee 401(k) savings plan. Additionally, the Company sponsors the PBOP Plan, primarily to provide health care and life insurance benefits to retired employees.
The Company records on its balance sheets as an asset or liability the overfunded or underfunded status of its retirement benefit obligations (RBO) based on the projected benefit obligations. The Company has recognized a corresponding Regulatory Asset, reflecting ultimate recovery from customers through rates. The regulatory asset (or regulatory liability) is amortized as the actuarial gains and losses and prior service cost are amortized to net periodic benefit cost for the Pension and PBOP plans. All amounts are remeasured annually. (See Note 9 Retirement Benefit Plans).
Commitments and Contingencies - The Company’s accounting policy is to record and/or disclose commitments and contingencies in accordance with the FASB Codification as it applies to an existing condition, situation, or set of circumstances involving uncertainty as to possible loss that will ultimately be resolved when one or more future events occur or fail to occur. As of December 31, 2024, the Company is not aware of any material commitments or contingencies other than those disclosed in Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies).
Environmental Matters - The Company’s past and present operations include activities that are generally subject to extensive federal and state environmental laws and regulations. The Company has recovered or will recover substantially all of the costs of the environmental remediation work performed to date from customers or from its insurance carriers. The Company believes it is in compliance with all applicable environmental and safety laws and regulations, and the Company believes that as of December 31, 2024, there are no material losses that would require additional liability reserves to be recorded other than those disclosed in Note 7 (Commitments and Contingencies). Changes in future environmental compliance regulations or in future cost estimates of environmental remediation costs could have a material effect on the Company’s financial position if those amounts are not recoverable in regulatory rate mechanisms.
Recently Issued Pronouncements - In November 2023, the FASB issued ASU 2023-07, Segment Reporting – Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures (ASU 2023-07). The amendments in ASU 2023-07 are intended to improve reportable segment disclosure requirements, primarily through enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses. The amendments in ASU 2023-07 are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023 and interim periods within fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024, with early adoption permitted. The Company adopted this new guidance for the year-ended December 31, 2024 and it did not have a material effect on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements (See Note 2: Segment Information).
Subsequent Events - The Company evaluates all events or transactions through the date of the related filing. During the period through the date of this filing, the Company did not have any material subsequent events that would result in adjustment to or disclosure in its Consolidated Financial Statements, except for the closing of the Company’s acquisition of Bangor Natural Gas Company (Bangor) and the amendment to the Company’s revolving credit facility. See below for the discussion on Bangor and see Note 4, Debt and Financing Arrangements for a discussion on the amendment to the Company’s revolving credit facility.
Acquisition of Bangor Natural Gas Company - On July 8, 2024, Unitil entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) among the Company, PHC Utilities, Inc. (the “Seller”), and, with respect to certain portions of the Purchase Agreement, Hearthstone Utilities, Inc., d/b/a Hope Companies, Inc. (the “Parent”). The Seller is a subsidiary of the Parent. Pursuant to, and subject to the terms and conditions of, the Purchase Agreement, the Company agreed to acquire all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of Bangor from the Seller (the “Acquisition”) for $70.9 million in cash, subject to certain adjustments as provided in the Purchase Agreement. The MPUC issued an order on December 18, 2024 approving the merger of Bangor into Unitil. The transaction closed on January 31, 2025.
Note 2: Segment Information
The Company’s Chief Operating Decision Maker (CODM), consists of the Company’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, President and Chief Administrative Officer, Chief Financial Officer, and Chief Accounting Officer. These individuals assess financial performance and make decisions, including the allocation of resources to the various operating segments, based on meeting with the managers of each segment and through their review of reports and analyses that are regularly provided to the CODM. The CODM uses Net Income Applicable to Common Shares for each segment predominantly in the annual budget and forecasting process. The CODM considers budget-to-actual variances on a quarterly basis when making decisions about the allocation of operating and capital resources to each segment. Unitil reports two operating and reportable segments: utility electric operations and utility gas operations.
Unitil’s principal business is the local distribution of electricity in the southeastern seacoast and state capital regions of New Hampshire and the greater Fitchburg area of north central Massachusetts and the local distribution of natural gas in southeastern New Hampshire, portions of southern Maine to the Lewiston-Auburn area and in the greater Fitchburg area of north central Massachusetts. Unitil has three distribution utility subsidiaries, Unitil Energy, which operates in New Hampshire, Fitchburg, which operates in Massachusetts and Northern Utilities, which operates in New Hampshire and Maine. Unitil Energy and the electric division of Fitchburg are included in the electric segment. Northern Utilities and the gas division of Fitchburg
are included in the gas segment. Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Northern Utilities have a well-diversified customer mix and are not dependent on a single customer, or a few customers, for their electric and natural gas sales. Granite State is an interstate natural gas transmission pipeline company, operating 85 miles of underground gas transmission pipeline primarily located in Maine and New Hampshire. Granite State provides Northern Utilities with interconnection to three major natural gas pipelines and access to domestic natural gas supplies in the south and Canadian natural gas supplies in the north. Granite State derives its revenues principally from the transmission services provided to Northern Utilities and, to a lesser extent, third-party marketers. Granite State is included in the utility gas operations segment.
Unitil Corp. (the holding company), and Unitil Resources are included in the “Other” category (ASC 280-10-50-15). The holding company has no operating income of its own. The earnings of the holding company are principally derived from income earned on short-term investments. Unitil Resources is the Company’s wholly-owned non-regulated subsidiary and currently does not have any activity. Unitil Service provides centralized management and administrative services, including information systems management and financial record keeping to support the affiliated Unitil companies. Unitil Realty owns certain real estate, principally the Company’s corporate headquarters in Hampton, New Hampshire and land for future use in Kingston, New Hampshire. Unitil Service’s and Unitil Realty’s costs are allocated to the Electric and Gas segments based on cost allocation factors.
The segments follow the same accounting policies as described in the Summary of Significant Accounting Policies. Intrasegment sales take place at cost and the effects of all intrasegment and/or intercompany transactions are eliminated in the consolidated financial statements. Segment profit or loss is based on Net Income Applicable to Common Shares. Expenses used to determine operating income before taxes are charged directly to each segment or are allocated based on cost allocation factors included in rate applications approved by the FERC, NHPUC, MDPU, and MPUC. Assets allocated to each segment are based upon specific identification of such assets provided by Company records.
The following tables provide significant segment financial data for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 (millions):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31, 2024 | | Electric | | | Gas | | | Total Reportable Segments | | | Other | | | Total | |
Total Operating Revenues | | $ | 248.3 | | | $ | 246.5 | | | $ | 494.8 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 494.8 | |
Energy Supply Costs | | | 141.0 | | | | 79.6 | | | | 220.6 | | | | — | | | | 220.6 | |
Operation and Maintenance | | | 34.9 | | | | 41.7 | | | | 76.6 | | | | 1.0 | | | | 77.6 | |
Depreciation and Amortization | | | 29.3 | | | | 46.8 | | | | 76.1 | | | | — | | | | 76.1 | |
Other Segment Expenses (Income) | | | 12.9 | | | | 17.3 | | | | 30.2 | | | | (0.1 | ) | | | 30.1 | |
Interest Income | | | (3.6 | ) | | | (4.6 | ) | | | (8.2 | ) | | | (0.2 | ) | | | (8.4 | ) |
Interest Expense | | | 13.4 | | | | 23.7 | | | | 37.1 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 37.7 | |
Provision for Income Taxes | | | 3.8 | | | | 11.2 | | | | 15.0 | | | | (1.0 | ) | | | 14.0 | |
Net Income Attributable to Commons Shares | | | 16.6 | | | | 30.8 | | | | 47.4 | | | | (0.3 | ) | | | 47.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Segment Assets | | | 647.2 | | | | 1,115.3 | | | | 1,762.5 | | | | 32.0 | | | | 1,794.5 | |
Capital Expenditures | | | 61.8 | | | | 103.9 | | | | 165.7 | | | | 4.2 | | | | 169.9 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Operating Revenues | | $ | 306.5 | | | $ | 250.6 | | | $ | 557.1 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 557.1 | |
Energy Supply Costs | | | 202.4 | | | | 96.1 | | | | 298.5 | | | | — | | | | 298.5 | |
Operation and Maintenance | | | 34.5 | | | | 40.7 | | | | 75.2 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 75.6 | |
Depreciation & Amortization Expense | | | 26.0 | | | | 40.4 | | | | 66.4 | | | | 1.0 | | | | 67.4 | |
Other Segment Expenses (Income) | | | 13.1 | | | | 16.9 | | | | 30.0 | | | | (1.5 | ) | | | 28.5 | |
Interest Income | | | (2.6 | ) | | | (2.4 | ) | | | (5.0 | ) | | | (1.2 | ) | | | (6.2 | ) |
Interest Expense | | | 11.2 | | | | 20.7 | | | | 31.9 | | | | 3.0 | | | | 34.9 | |
Provision for Income Taxes | | | 4.0 | | | | 9.4 | | | | 13.4 | | | | (0.2 | ) | | | 13.2 | |
Segment Profit (Loss) | | | 17.9 | | | | 28.8 | | | | 46.7 | | | | (1.5 | ) | | | 45.2 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Segment Assets | | | 612.6 | | | | 1,031.8 | | | | 1,644.4 | | | | 26.0 | | | | 1,670.4 | |
Capital Expenditures | | | 44.2 | | | | 92.7 | | | | 136.9 | | | | 4.1 | | | | 141.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Operating Revenues | | $ | 297.9 | | | $ | 265.3 | | | $ | 563.2 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 563.2 | |
Energy Supply Costs | | | 199.1 | | | | 121.4 | | | | 320.5 | | | | — | | | | 320.5 | |
Operation and Maintenance | | | 33.5 | | | | 40.1 | | | | 73.6 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 73.7 | |
Depreciation & Amortization Expense | | | 25.4 | | | | 36.3 | | | | 61.7 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 62.6 | |
Other Segment Expenses (Income) | | | 12.9 | | | | 17.0 | | | | 29.9 | | | | (1.6 | ) | | | 28.3 | |
Interest Income | | | (0.9 | ) | | | (1.0 | ) | | | (1.9 | ) | | | (0.9 | ) | | | (2.8 | ) |
Interest Expense | | | 9.1 | | | | 16.8 | | | | 25.9 | | | | 2.4 | | | | 28.3 | |
Provision for Income Taxes | | | 3.1 | | | | 8.2 | | | | 11.3 | | | | (0.1 | ) | | | 11.2 | |
Segment Profit (Loss) | | | 15.7 | | | | 26.5 | | | | 42.2 | | | | (0.8 | ) | | | 41.4 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Segment Assets | | | 580.9 | | | | 988.8 | | | | 1,569.7 | | | | 20.7 | | | | 1,590.4 | |
Capital Expenditures | | | 33.8 | | | | 87.6 | | | | 121.4 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 122.1 | |
Note 3: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Unitil’s distribution utilities are authorized by regulators to recover the costs of their energy commodity portion of bad debts through rate mechanisms. In 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company recorded provisions for the energy commodity portion of bad debts of $1.6 million, $3.8 million and $3.8 million, respectively. These provisions were recognized in Cost of Electric Sales and Cost of Gas Sales expense as the associated electric and gas utility revenues were billed. Cost of Electric Sales and Cost of Gas Sales costs are recovered from customers through periodic rate reconciling mechanisms. Also, the electric and gas divisions of Fitchburg are authorized to recover through rates past due amounts associated with hardship accounts that are protected from shut-off. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company has recorded $7.9 million and $6.0 million, respectively, of hardship accounts in Regulatory Assets. The Company currently receives recovery in rates or expects to receive recovery of these hardship accounts in future rate cases.
Accounts Receivable, Net includes $2.3 million and $2.3 million of the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. Unbilled Revenues, net (a component of Accrued Revenue) includes $0.1 million and $0.1 million of the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively.
The following table shows the balances and activity in the Company’s Allowance for Doubtful Accounts for 2024, 2023 and 2022 (millions):
ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Balance at
Beginning
of Period | | | Provision | | | Recoveries | | | Accounts
Written
Off | | | Regulatory
Deferrals | | | Balance at
End of
Period | |
Year Ended December 31, 2024 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Electric | | $ | 1.5 | | | $ | 2.0 | | | $ | 0.2 | | | $ | 2.3 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1.4 | |
Gas | | | 0.9 | | | | 2.3 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 2.5 | | | | — | | | | 1.0 | |
| | $ | 2.4 | | | $ | 4.3 | | | $ | 0.5 | | | $ | 4.8 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2.4 | |
Year Ended December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Electric | | $ | 1.6 | | | $ | 3.6 | | | $ | 0.2 | | | $ | 3.9 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1.5 | |
Gas | | | 1.0 | | | | 2.8 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 3.3 | | | | — | | | | 0.9 | |
| | $ | 2.6 | | | $ | 6.4 | | | $ | 0.6 | | | $ | 7.2 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2.4 | |
Year Ended December 31, 2022 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Electric | | $ | 2.0 | | | $ | 4.2 | | | $ | 0.3 | | | $ | 4.4 | | | $ | (0.5 | ) | | $ | 1.6 | |
Gas | | | 1.3 | | | | 2.5 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 3.2 | | | | (0.2 | ) | | | 1.0 | |
| | $ | 3.3 | | | $ | 6.7 | | | $ | 0.9 | | | $ | 7.6 | | | $ | (0.7 | ) | | $ | 2.6 | |
Note 4: Debt and Financing Arrangements
The Company funds a portion of its operations through the issuance of long-term debt, and short-term borrowings under its revolving Credit Facility. The Company’s subsidiaries conduct a portion of their operations in leased facilities and lease some of their machinery, vehicles and office equipment.
Long-Term Debt and Interest Expense
Long-Term Debt Structure and Covenants - The debt agreements for Unitil and its utility subsidiaries, Unitil Energy, Fitchburg, Northern Utilities, and Granite State, contain various covenants and restrictions. These agreements do not contain any covenants or restrictions pertaining to the maintenance of financial ratios or the issuance of short-term debt. These agreements do contain covenants relating to, among other things, the issuance of additional long-term debt, cross-default provisions and business combinations.
The long-term debt of Unitil is issued under Unsecured Promissory Notes with negative pledge provisions. The long-term debt’s negative pledge provisions contain restrictions which, among other things, limit the incursion of additional long-term debt. Accordingly, in order for Unitil to issue new long-term debt, the covenants of the existing long-term agreement(s) must be satisfied, including that Unitil has total funded indebtedness less than 70% of total capitalization, and earnings available for interest equal to at least two times the interest charges for funded indebtedness. Each future senior long-term debt issuance of Unitil will rank pari passu with all other senior unsecured long-term debt issuances. The Unitil long-term debt agreement requires that if Unitil defaults on any other future long-term debt agreement(s), it would constitute a default under Unitil’s present long-term debt agreement. Furthermore, the default provisions are triggered by the defaults of certain Unitil subsidiaries or certain other actions against Unitil subsidiaries.
Substantially all of the property of Unitil Energy is subject to liens of indenture under which First Mortgage Bonds (FMB) have been issued. In order to issue new FMB, the customary covenants of the existing Unitil Energy Indenture Agreement must be met, including that Unitil Energy have sufficient available net bondable plant to issue the securities and earnings available for interest charges equal to at least two times the annual interest requirement. The Unitil Energy agreements further require that if Unitil Energy defaults on any Unitil Energy FMB, it would constitute a default for all Unitil Energy FMB. The Unitil Energy default provisions are not triggered by the actions or defaults of Unitil or its other subsidiaries.
All of the long-term debt of Fitchburg, Northern Utilities and Granite State are issued under Unsecured Promissory Notes with negative pledge provisions. Each issue of long-term debt ranks pari passu with its other senior unsecured long-term debt within that subsidiary. The long-term debt’s negative pledge provisions contain restrictions which, among other things, limit the incursion of additional long-term debt. Accordingly, in order for Fitchburg, Northern Utilities or Granite State to issue new long-term debt, the covenants of the existing long-term agreements of that subsidiary must be satisfied, including that the subsidiary have total funded indebtedness less than 65% of total capitalization. Additionally, to issue new long-term debt, Fitchburg must maintain earnings available for interest equal to at least two times the interest charges for funded indebtedness. As with the Unitil Energy agreements, the Fitchburg, Northern Utilities and Granite State long-term debt agreements each require that if that subsidiary defaults on any of its own long-term debt agreements, it would constitute a default under all of that subsidiary’s long-term debt agreements. None of the Fitchburg, Northern Utilities and Granite State default provisions are triggered by the actions or defaults of Unitil or any of its other subsidiaries.
The Unitil, Unitil Energy, Fitchburg, Northern Utilities and Granite State long-term debt instruments and agreements contain covenants restricting the ability of each company to incur liens and to enter into sale and leaseback transactions, and restricting the ability of each company to consolidate with, to merge with or into, or to sell or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of its assets.
Unitil Energy, Fitchburg, Northern Utilities and Granite State pay common dividends to their sole common shareholder, Unitil Corporation and these common dividends are the primary source of cash for the payment of dividends to Unitil’s common shareholders. The long-term debt issued by the Company and its subsidiaries contains certain covenants that determine the amount that the Company and each of these subsidiary companies has available to pay for dividends. As of December 31, 2024, in accordance with the covenants, these subsidiary companies had a combined amount of $459.8 million available for the payment of dividends and Unitil Corporation had $250.6 million available for the payment of dividends. As of December 31, 2024, the Company’s balance in Retained Earnings was $171.1 million. Therefore, there were no restrictions on the Company’s Retained Earnings at December 31, 2024 for the payment of dividends.
Issuance of Long-Term Debt - On July 6, 2023, Fitchburg issued $12.0 million of Notes due July 2, 2033 at 5.70% and $13.0 million of Notes due July 2, 2053 at 5.96%. Fitchburg used the net proceeds from these offerings to refinance existing debt and for general corporate purposes. Approximately $0.2 million of costs associated with this issuance were recorded as a reduction of Long-Term Debt for presentation purposes on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in the third quarter of 2023.
On August 21, 2024, Unitil Corporation issued $20.0 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.99%. Fitchburg issued $12.5 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.54% and $12.5 million of Notes due 2044 at 5.99%. Unitil Energy issued $40.0 million of Bonds due 2054 at 5.69%. Northern Utilities issued $25.0 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.54% and $15.0 million of Notes due 2039 at 5.74%. Granite State issued $10.0 million of Notes due 2034 at 5.74%.
The Company used the net proceeds from these offerings to refinance existing debt and for general corporate purposes. Approximately $1.0 million of costs associated with this issuance were recorded as a reduction of Long-Term Debt for presentation purposes on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in the third quarter of 2024.
Debt Repayment -The total aggregate amount of debt repayments relating to bond issues and normal scheduled long-term debt repayments amounted to $4.9 million, $6.9 million and $10.4 million in 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
The aggregate amount of bond repayment requirements and normal scheduled long-term debt repayments for each of the five years following 2024 is: 2025 – $4.9 million; 2026 – $37.9 million; 2027 – $55.7 million; 2028 – $10.7 million; 2029 – $43.7 million and thereafter $494.2 million.
Fair Value of Long-Term Debt - Currently, the Company believes that there is no active market in the Company’s debt securities, which have all been sold through private placements. If there were an active market for the Company’s debt securities, the fair value of the Company’s long-term debt would be estimated based on the quoted market prices for the same or similar issues, or on the current rates offered to the Company for debt of the same remaining maturities. The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt is estimated using Level 2 inputs (valuations based on quoted prices available in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in inactive markets, inputs other than quoted prices that are directly observable, and inputs derived principally from market data). In estimating the fair value of the Company’s long-term debt, the assumed market yield reflects the Moody’s Baa Utility Bond Average Yield. Costs, including
prepayment costs, associated with the early settlement of long-term debt are not taken into consideration in determining fair value.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Estimated Fair Value of Long-Term Debt (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Estimated Fair Value of Long-Term Debt | | $ | 598.9 | | | $ | 470.5 | |
Details on long-term debt at December 31, 2024 and 2023 are shown below:
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Long-Term Debt (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Unitil Corporation: | | | | | | |
3.70% Senior Notes, Due August 1, 2026 | | $ | 30.0 | | | $ | 30.0 | |
3.43% Senior Notes, Due December 18, 2029 | | | 30.0 | | | | 30.0 | |
5.99% Senior Notes, Due August 21, 2034 | | | 20.0 | | | | — | |
Unitil Energy First Mortgage Bonds: | | | | | | |
6.96% Senior Secured Notes, Due September 1, 2028 | | | 8.0 | | | | 10.0 | |
8.00% Senior Secured Notes, Due May 1, 2031 | | | 10.5 | | | | 12.0 | |
6.32% Senior Secured Notes, Due September 15, 2036 | | | 15.0 | | | | 15.0 | |
3.58% Senior Secured Notes, Due September 15, 2040 | | | 27.5 | | | | 27.5 | |
4.18% Senior Secured Notes, Due November 30, 2048 | | | 30.0 | | | | 30.0 | |
5.69% Senior Secured Notes, Due August 21, 2054 | | | 40.0 | | | | — | |
Fitchburg: | | | | | | |
3.52% Senior Notes, Due November 1, 2027 | | | 10.0 | | | | 10.0 | |
7.37% Senior Notes, Due January 15, 2029 | | | 6.0 | | | | 7.2 | |
5.90% Senior Notes, Due December 15, 2030 | | | 15.0 | | | | 15.0 | |
7.98% Senior Notes, Due June 1, 2031 | | | 14.0 | | | | 14.0 | |
5.70% Senior Notes, Due July 2, 2033 | | | 12.0 | | | | 12.0 | |
5.54% Senior Notes, Due August 21, 2034 | | | 12.5 | | | | — | |
3.78% Senior Notes, Due September 15, 2040 | | | 27.5 | | | | 27.5 | |
5.99% Senior Notes, Due August 21, 2044 | | | 12.5 | | | | — | |
4.32% Senior Notes, Due November 1, 2047 | | | 15.0 | | | | 15.0 | |
5.96% Senior Notes, Due July 2, 2053 | | | 13.0 | | | | 13.0 | |
Northern Utilities: | | | | | | |
3.52% Senior Notes, Due November 1, 2027 | | | 20.0 | | | | 20.0 | |
5.54% Senior Notes, Due August 21, 2034 | | | 25.0 | | | | — | |
7.72% Senior Notes, Due December 3, 2038 | | | 50.0 | | | | 50.0 | |
5.74% Senior Notes, Due August 21, 2039 | | | 15.0 | | | | — | |
3.78% Senior Notes, Due September 15, 2040 | | | 40.0 | | | | 40.0 | |
4.42% Senior Notes, Due October 15, 2044 | | | 50.0 | | | | 50.0 | |
4.32% Senior Notes, Due November 1, 2047 | | | 30.0 | | | | 30.0 | |
4.04% Senior Notes, Due September 12, 2049 | | | 40.0 | | | | 40.0 | |
Granite State: | | | | | | |
3.72% Senior Notes, Due November 1, 2027 | | | 15.0 | | | | 15.0 | |
5.74% Senior Notes, Due August 21, 2034 | | | 10.0 | | | | — | |
Unitil Realty Corp.: | | | | | | |
2.64% Senior Secured Notes, Due December 18, 2030 | | | 3.8 | | | | 4.0 | |
Total Long-Term Debt | | | 647.3 | | | | 517.2 | |
Less: Unamortized Debt Issuance Costs | | | 4.0 | | | | 3.2 | |
Total Long-Term Debt, net of Unamortized Debt Issuance Costs | | | 643.3 | | | | 514.0 | |
Less: Current Portion(1) | | | 4.9 | | | | 4.9 | |
Total Long-Term Debt, Less Current Portion | | $ | 638.4 | | | $ | 509.1 | |
(1)The Current Portion of Long-Term Debt includes sinking fund payments.
Interest Expense, Net—Interest expense is presented in the financial statements net of interest income. Interest expense is mainly comprised of interest on long-term debt and short-term borrowings. In addition, certain reconciling rate mechanisms used by the Company’s distribution operating utilities give rise to regulatory assets and regulatory liabilities on which interest is calculated.
Unitil’s utility subsidiaries operate a number of reconciling rate mechanisms to recover specifically identified costs on a pass-through basis. These reconciling rate mechanisms track costs and revenue on a monthly basis. In any given month, this monthly tracking and reconciling process will produce either an under-collected or an over-collected balance of costs. In accordance with the distribution utilities’ rate tariffs, interest is accrued on these balances and will produce either interest income or interest expense.
Consistent with regulatory precedent, interest income is recorded on an under-collection of costs, which creates a regulatory asset to be recovered in future periods when rates are reset. Interest expense is recorded on an over-collection of costs, which creates a regulatory liability to be refunded in future periods when rates are reset. A summary of interest expense and interest income is provided in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest Expense, Net (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Interest Expense | | | | | | | | | |
Long-Term Debt | | $ | 27.8 | | | $ | 24.7 | | | $ | 24.7 | |
Short-Term Debt | | | 8.4 | | | | 9.2 | | | | 3.0 | |
Regulatory Liabilities & Other | | | 1.5 | | | | 1.0 | | | | 0.6 | |
Subtotal Interest Expense | | | 37.7 | | | | 34.9 | | | | 28.3 | |
Interest Income | | | | | | | | | |
Regulatory Assets | | | (4.1 | ) | | | (3.3 | ) | | | (1.0 | ) |
AFUDC(1) and Other | | | (4.3 | ) | | | (2.9 | ) | | | (1.8 | ) |
Subtotal Interest Income | | | (8.4 | ) | | | (6.2 | ) | | | (2.8 | ) |
Total Interest Expense, Net | | $ | 29.3 | | | $ | 28.7 | | | $ | 25.5 | |
(1)AFUDC—Allowance for Funds Used During Construction
Credit Arrangements
On September 29, 2022, the Company entered into a Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement with a syndicate of lenders (collectively, the “Credit Facility”), which amended and restated in its entirety the prior credit facility. On January 29, 2025, the Company entered into an amendment to the Credit Facility, which (among other things) increased the borrowing limit under the Credit Facility from $200 million to $275 million and extended the term of the Credit Facility from September 29, 2027 until September 29, 2028. Unitil may borrow under the Credit Facility until September 29, 2028, subject to two one-year extensions under certain circumstances.
The Credit Facility has a borrowing limit of $275 million ($200 million as of December 31, 2024), which includes a $25 million sublimit for the issuance of standby letters of credit. Unitil may increase the borrowing limit under the Credit Facility by up to $75 million under certain circumstances. The Credit Facility generally provides Unitil with the ability to elect that borrowings under the Credit Facility bear interest under several options, including a daily fluctuating rate equal to (a) the forward-looking secured overnight financing rate (as administered by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York) term rate with a term equivalent to one month beginning on that date, plus (b) 0.1000%, plus (c) a margin of 1.125% to 1.375% (based on Unitil’s credit rating).
The Company generally utilizes the Credit Facility for cash management purposes related to its short-term operating activities and may use the Credit Facility for certain acquisition financing. Total gross borrowings were $308.4 million and $327.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. Total gross repayments were $364.6 million and $281.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. The following table details the borrowing limits, amounts outstanding and amounts available under the revolving Credit Facility as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Revolving Credit Facility (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Limit | | $ | 200.0 | | | $ | 200.0 | |
Short-Term Borrowings Outstanding | | $ | 105.8 | | | $ | 162.0 | |
Available | | $ | 94.2 | | | $ | 38.0 | |
The Credit Facility contains customary terms and conditions for credit facilities of this type, including affirmative and negative covenants. There are restrictions on, among other things, Unitil’s and its subsidiaries’ ability to permit liens or incur
indebtedness, and restrictions on Unitil’s ability to merge or consolidate with another entity or change its line of business. The affirmative and negative covenants under the Credit Facility shall apply to Unitil until the Credit Facility terminates and all amounts borrowed under the Credit Facility are paid in full (or with respect to letters of credit, they are cash collateralized). The only financial covenant in the Credit Facility provides that Unitil’s Funded Debt to Capitalization (as each term is defined in the Credit Facility) cannot exceed 65%, tested on a quarterly basis. At December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company was in compliance with the covenants contained in the Credit Facility in effect on that date. The Company believes it has sufficient sources of working capital to fund its operations.
The weighted average interest rates on all short-term borrowings were 6.5%, 6.4%, and 3.3 % during 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
Unitil Corporation and its utility subsidiaries, Fitchburg, Unitil Energy, Northern Utilities, and Granite State are currently rated “BBB+” by Standard & Poor’s Ratings Services. Unitil Corporation and Granite State are currently rated “Baa2”, and Fitchburg, Unitil Energy and Northern Utilities are currently rated “Baa1” by Moody’s Investors Services.
Northern Utilities enters into asset management agreements under which Northern Utilities releases certain natural gas pipeline and storage assets, resells the natural gas storage inventory to an asset manager and subsequently repurchases the inventory over the course of the natural gas heating season at the same price at which it sold the natural gas inventory to the asset manager. There was $7.8 million of natural gas storage inventory and corresponding obligations at December 31, 2024, related to these asset management agreements. The amount of natural gas inventory released in December 2024, which was payable in January 2025, was $1.8 million and was recorded in Accounts Payable at December 31, 2024.
Contractual Obligations
The following table lists the Company’s contractual obligations for long-term debt as of December 31, 2024.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Payments Due by Period | |
Long-Term Debt
Contractual Obligations (millions) as of December 31, 2024 | | Total | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | | | 2029 | | | 2030 & Beyond | |
Long-Term Debt | | $ | 647.3 | | | $ | 4.9 | | | $ | 37.9 | | | $ | 55.7 | | | $ | 10.8 | | | $ | 43.8 | | | $ | 494.2 | |
Interest on Long-Term Debt | | | 452.0 | | | | 32.1 | | | | 31.8 | | | | 30.0 | | | | 27.6 | | | | 26.9 | | | | 303.6 | |
Total | | $ | 1,099.3 | | | $ | 37.0 | | | $ | 69.7 | | | $ | 85.7 | | | $ | 38.4 | | | $ | 70.7 | | | $ | 797.8 | |
Leases
Unitil’s subsidiaries lease some of their vehicles, machinery and office equipment under both capital and operating lease arrangements.
Total rental expense under operating leases charged to operations for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022 amounted to $2.2 million, $2.1 million and $1.8 million respectively. The balance sheet classification of the Company’s lease obligations was as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Lease Obligations (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Operating Lease Obligations: | | | | | | |
Operating Lease Obligations (current portion) | | $ | 1.8 | | | $ | 1.9 | |
Operating Lease Obligations (long-term portion) | | | 4.9 | | | | 3.7 | |
Total Operating Lease Obligations | | | 6.7 | | | | 5.6 | |
Capital Lease Obligations: | | | | | | |
Other Current Liabilities (current portion) | | | 0.1 | | | | 0.1 | |
Other Noncurrent Liabilities (long-term portion) | | | 0.4 | | | | 0.4 | |
Total Capital Lease Obligations | | | 0.5 | | | | 0.5 | |
Total Lease Obligations | | $ | 7.2 | | | $ | 6.1 | |
Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of operating lease obligations for the twelve months ended December 31, 2024 and 2023 was $2.2 million and $2.1 million, respectively and was included in Cash Provided by Operating Activities on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
Assets under capital leases amounted to approximately $0.6 million and $0.7 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, less accumulated amortization of $0.1 million and $0.2 million, respectively and are included in Net Utility Plant on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets.
The following table is a schedule of future operating lease payment obligations and future minimum lease payments under capital leases as of December 31, 2024. The payments for operating leases consist of $1.8 million of current operating lease obligations and $4.9 million of noncurrent operating lease obligations on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2024. The payments for capital leases consist of $0.1 million of current Capital Lease Obligations, which are included in Other Current Liabilities, and $0.4 million of noncurrent Capital Lease Obligations, which are included in Other Noncurrent Liabilities, on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2024.
| | | | | | | | |
Lease Payments ($000’s)
Year Ending December 31, | | Operating
Leases | | | Capital
Leases | |
2025 | | $ | 2,137 | | | $ | 154 | |
2026 | | | 1,819 | | | | 145 | |
2027 | | | 1,519 | | | | 131 | |
2028 | | | 958 | | | | 45 | |
2029 | | | 628 | | | | 22 | |
2030-2034 | | | 404 | | | | — | |
Total Payments | | | 7,465 | | | | 497 | |
Less: Interest | | | 788 | | | | 41 | |
Amount of Lease Obligations Recorded on Consolidated Balance Sheets | | $ | 6,677 | | | $ | 456 | |
Operating lease obligations are based on the net present value of the remaining lease payments over the remaining lease term. In determining the present value of lease payments, the Company used the interest rate stated in each lease agreement. As of December 31, 2024, the weighted average remaining lease term is 4.2 years and the weighted average operating discount rate used to determine the operating lease obligations was 5.1%. As of December 31, 2023, the weighted average remaining lease term was 3.7 years and the weighted average operating discount rate used to determine the operating lease obligations was 4.4%.
Guarantees
The Company provides limited guarantees on certain energy and natural gas storage management contracts entered into by the distribution utilities. The Company’s policy is to limit the duration of these guarantees. As of December 31, 2024, there were no guarantees outstanding.
Note 5: Equity
The Company has common stock outstanding and one of the Company’s subsidiaries has preferred stock outstanding.
Common Stock
The Company’s common stock trades on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “UTL”. The Company had 16,192,345 and 16,116,724 shares of common stock outstanding at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively. The Company has 25,000,000 shares of common stock authorized as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
Dividend Reinvestment and Stock Purchase Plan—During 2024, the Company sold 19,510 shares of its common stock, at an average price of $54.40 per share, in connection with its Dividend Reinvestment and Stock Purchase Plan (DRP) and its 401(k) plans resulting in net proceeds of $1.1 million. The DRP provides participants in the plan a method for investing cash dividends on the Company’s common stock and cash payments in additional shares of the Company’s common stock. During 2023 and 2022, the Company raised $1.1 million and $1.0 million, respectively, through the issuance of 21,321 and 18,853 shares, respectively, of its common stock in connection with its DRP and 401(k) plans.
Common Shares Repurchased, Cancelled and Retired—Pursuant to the written trading plan under Rule 10b5-1 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the Exchange Act), adopted by the Company on May 1, 2014 (trading plan), until October 3, 2023, the Company periodically repurchased shares of its common stock on the open market related to the
stock portion of the annual retainer for the members of the Company’s Board of Directors. Until December 1, 2018, the Company also periodically repurchased shares of its common stock on the open market related to Employee Length of Service Awards. On May 31, 2024, the Company’s 2023 trading plan terminated in accordance with its terms. The Company did not adopt a new written trading plan under Rule 10b5-1 and does not anticipate doing so in the near term. (See Part II, Item 5, for additional information). During 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company repurchased zero, 14,680 and 9,449 shares of its common stock, respectively, pursuant to the Rule 10b5-1 trading plan. The expense recognized by the Company for these repurchases was zero, $0.6 million, and $0.4 million in 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
During 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company did not cancel or retire any of its common stock.
Stock-Based Compensation Plans—Unitil maintains a stock-based compensation plan. The Company accounts for its stock-based compensation plan in accordance with the provisions of the FASB Codification and measures compensation costs at fair value at the grant date.
Stock Plan—The Company maintains the Unitil Corporation Third Amended and Restated 2003 Stock Plan (as amended, the “Stock Plan”). Participants in the Stock Plan are selected by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors to receive awards under the Stock Plan, including: (i) awards of restricted shares that vest based on time (Time Restricted Shares); (ii) awards of restricted shares that vest based on performance (Performance Restricted Shares), effective January 24, 2023; or (iii) awards of restricted stock units (Restricted Stock Units). The Compensation Committee has the authority to determine the sizes of awards; determine the terms and conditions of awards in a manner consistent with the Stock Plan; construe and interpret the Stock Plan and any agreement or instrument entered into under the Stock Plan as they apply to participants; establish, amend, or waive rules and regulations for the Stock Plan’s administration as they apply to participants; and, subject to the provisions of the Stock Plan, amend the terms and conditions of any outstanding award to the extent such terms and conditions are within the discretion of the Compensation Committee as provided for in the Stock Plan. On April 19, 2012 and May 1, 2024, the Company’s shareholders approved amendments to the Stock Plan to, among other things, increase the maximum number of shares of common stock available for awards to plan participants.
The maximum number of shares available for awards to participants under the Stock Plan was 677,500 as of March 31, 2024, and was increased on May 1, 2024 to 1,027,500. The maximum number of shares that may be awarded in any one calendar year to any one participant is 20,000. In the event of certain changes in capitalization of the Company, the Compensation Committee is authorized to make an equitable adjustment to the number and kind of shares of common stock that may be delivered under the Stock Plan and, in addition, may authorize and make an equitable adjustment to the Stock Plan’s annual individual award limit.
Time Restricted Shares
Outstanding awards of Time Restricted Shares fully vest over a period of four years at a rate of 25% each year. During the vesting period, dividends on Time Restricted Shares underlying the award may be credited to a participant’s account. The Company may deduct or withhold, or require a participant to remit to the Company, an amount sufficient to satisfy any taxes required by federal, state, or local law or regulation to be withheld with respect to any taxable event arising in connection with an award.
Prior to the end of the vesting period, the Time Restricted Shares are subject to forfeiture if the participant ceases to be employed by the Company other than due to the participant’s death, disability or retirement.
Time Restricted Shares issued in the years ended 2022, 2023, and 2024 in conjunction with the Stock Plan are presented in the following table:
| | | | |
Issuance Date | | Shares | | Aggregate
Market Value (millions) |
1/25/22 | | 36,770 | | $1.7 |
1/24/23 | | 18,770 | | $1.0 |
1/30/24 | | 22,680 | | $1.1 |
There were 34,417 and 36,483 non-vested Time Restricted Shares under the Stock Plan as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The weighted average grant date fair value of these shares was $48.84 per share and $46.94 per share, respectively. The compensation expense associated with the issuance of Time Restricted Shares under the Stock Plan is being
recorded over the vesting period and was $1.4 million, $1.4 million and $2.1 million in 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. At December 31, 2024, there was approximately $0.8 million of total unrecognized compensation cost for Time Restricted Shares under the Stock Plan which is expected to be recognized over approximately 2.4 years. During 2024, there were 354 Time Restricted Shares forfeited and zero Time Restricted Shares cancelled under the Stock Plan. On January 28, 2025, there were 26,430 Time Restricted Shares issued under the Stock Plan with an aggregate market value of $1.4 million.
Performance Restricted Shares
Outstanding awards of Performance Restricted Shares vest after a performance period of three years based on the attainment of certain goals set by the Compensation Committee at the beginning of the performance period. If goals are met, awards of Performance Restricted Shares may vest fully; if goals are exceeded, awards of Performance Restricted Shares may vest fully and additional shares of common stock may be awarded; if goals are not met, a portion of the Performance Restricted Shares may vest and/or all or a portion of the Performance Restricted Shares may be forfeited. During the performance period, dividends on Performance Restricted Shares underlying the award may be credited to a participant’s account. The Company may deduct or withhold, or require a participant to remit to the Company, an amount sufficient to satisfy any taxes required by federal, state, or local law or regulation to be withheld with respect to any taxable event arising in connection with an award.
Prior to the end of the performance period, the Performance Restricted Shares are subject to forfeiture if the participant ceases to be employed by the Company other than due to the participant’s death, disability or retirement.
Initial awards of Performance Restricted Shares were granted January 24, 2023. No Performance Restricted Shares were awarded in 2022. Performance Restricted Shares issued in the years ended 2023 and 2024 in conjunction with the Stock Plan are presented in the following table:
| | | | |
Issuance Date | | Shares | | Aggregate
Market Value (millions) |
1/24/23 | | 18,770 | | $1.0 |
1/30/24 | | 22,680 | | $1.1 |
There were 44,449 non-vested Performance Restricted Shares under the Stock Plan as of December 31, 2024. The weighted average grant date fair value of these shares was $50.26 per share. The compensation expense associated with the issuance of Performance Restricted Shares under the Stock Plan is being recognized over the vesting period and was $1.0 million and $0.5 million in 2024 and 2023, respectively. At December 31, 2024, there was approximately $1.5 million of total unrecognized compensation cost for Performance Restricted Shares under the Stock Plan which is expected to be recognized over approximately 1.7 years. During 2024, there were 250 Performance Restricted Shares forfeited and zero Performance Restricted Shares cancelled under the Stock Plan. On January 28, 2025, there were 26,430 Performance Restricted Shares issued under the Stock Plan with an aggregate market value of $1.4 million.
Restricted Stock Units
Restricted Stock Units, which are issued to members of the Company’s Board of Directors, earn dividend equivalents and will generally be settled by payment to each Director as soon as practicable following the Director’s separation from service to the Company. The Restricted Stock Units will be paid such that the Director will receive (i) 70% of the shares of the Company’s common stock underlying the restricted stock units and (ii) cash in an amount equal to the fair market value of 30% of the shares of the Company’s common stock underlying the Restricted Stock Units.
The equity portion of Restricted Stock Units activity during 2024 and 2023 in conjunction with the Stock Plan are presented in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Restricted Stock Units (Equity Portion) | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| | Units | | | Weighted
Average
Stock
Price | | | Units | | | Weighted
Average
Stock
Price | |
Beginning Restricted Stock Units | | | 33,375 | | | $ | 42.73 | | | | 43,799 | | | $ | 40.17 | |
Restricted Stock Units Granted | | | 2,215 | | | $ | 60.02 | | | | 2,646 | | | $ | 42.31 | |
Dividend Equivalents Earned | | | 1,046 | | | $ | 55.77 | | | | 1,442 | | | $ | 50.53 | |
Restricted Stock Units Settled | | | — | | | $ | — | | | | (14,512 | ) | | $ | 35.69 | |
Ending Restricted Stock Units | | | 36,636 | | | $ | 44.15 | | | | 33,375 | | | $ | 42.73 | |
Other Noncurrent Liabilities on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2024 and 2023 include $0.9 million and $0.8 million, respectively, representing the fair value of liabilities associated with the portion of fully vested RSUs that will be settled in cash.
Preferred Stock
There were $0.2 million, or 1,727 shares, of Unitil Energy’s 6.00% Series Preferred Stock outstanding as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023. There were less than $0.1 million of total dividends declared on Preferred Stock in each of the twelve month periods ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively.
Earnings Per Share
The following table reconciles basic and diluted earnings per share (EPS).
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Millions except shares and per share data) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Earnings Available to Common Shareholders | | $ | 47.1 | | | $ | 45.2 | | | $ | 41.4 | |
Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding—Basic (000’s) | | | 16,098 | | | | 16,045 | | | | 15,991 | |
Plus: Diluted Effect of Incremental Shares (000’s) | | | 11 | | | | 8 | | | | 5 | |
Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding—Diluted (000’s) | | | 16,109 | | | | 16,053 | | | | 15,996 | |
Earnings per Share—Basic and Diluted | | $ | 2.93 | | | $ | 2.82 | | | $ | 2.59 | |
The following table shows the number of weighted average non-vested restricted shares that were not included in the above computation of EPS because the effect would have been antidilutive.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Weighted Average Non-Vested Restricted Shares Not Included in EPS Computation | | | 6,675 | | | | 12,204 | | | | 12,086 | |
Note 6: Energy Supply
ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY
Fitchburg, Unitil Energy, and Unitil Power each are members of the New England Power Pool (NEPOOL) and participate in the Independent System Operator—New England (ISO-NE) markets for the purpose of facilitating wholesale electric power supply transactions, which are necessary to serve Unitil’s electric customers with their supply of electricity.
Unitil’s customers in both New Hampshire and Massachusetts are entitled to purchase their electric supply from competitive third-party suppliers. As of December 2024, 89% of Unitil’s largest New Hampshire customers, representing 25% of Unitil’s New Hampshire electric kilowatt-hour (kWh) sales, and 100% of Unitil’s largest Massachusetts customers, representing 30% of Unitil’s Massachusetts electric kWh sales, purchased their electric power supply in the competitive market. Additionally, cities and towns in Massachusetts may, with approval from the MDPU, implement municipal aggregations whereby the municipality purchases electric power on behalf of all citizens and businesses that do not opt out of the
aggregation. The Towns of Lunenburg, Townsend, Ashby, and the City of Fitchburg have active municipal aggregations. Customers in these four town’s represent 99.8% of Fitchburg’s customer base.
In New Hampshire, a majority of residential and small commercial customers purchase their electric supply through Community Choice Aggregations (CCA) and retail electric suppliers. As of December 2024, the percentage of residential customers purchasing electricity from a third-party supplier or CCA increased to 68% from nearly 22% in December 2023. There are currently 14 communities with active aggregations, representing 73% of Unitil’s customer base in New Hampshire. In Massachusetts, as of December 2024, 75% of Unitil’s residential customers in Massachusetts purchased their electricity from a CCA or third-party supplier which is up from 75% in 2023.
Regulated Electric Power Supply
To provide regulated electric supply service to their customers, Unitil’s electric distribution utilities enter into load-following wholesale electric power supply contracts to purchase electric supply from various wholesale suppliers.
Unitil Energy currently has power supply contracts with various wholesale suppliers for the provision of Default Service to its customers. Currently, with approval of the NHPUC, Unitil Energy purchases Default Service power supply contracts for small, medium and large customers every six months for 90% of the supply requirements. 10% of supply requirements are procured via direct market purchases from ISO-New England.
Fitchburg typically maintains power supply contracts with various wholesale suppliers for the provision of Basic Service electric supply. Pursuant to MDPU policy, Basic Service power supply contracts for residential and for small and medium general service customers are acquired every six months, are 12 months in duration and provide 50% of the supply requirements. On June 13, 2012, the MDPU approved Fitchburg’s request to discontinue the procurement process for Fitchburg’s large customers and become the load-serving entity for these customers. As such, Fitchburg procures electric power supply for large account customers directly through ISO-NE’s markets. The Company experienced a failed solicitation in its November 2024 solicitation, which results in Fitchburg self-supplying 50% of its load requirements for the February through July 2025 period. The failed solicitation was due to a combination of lack of bidders and excessively high-priced bids, which the Company rejected. The implications of the failed solicitation result in 50% of wholesale supply charges settling at the real-time energy price. The failed solicitation has no impact on the ability to provide default energy service to Fitchburg’s customers. The Company reconciles and recovers these supply expenses in its rates at cost on a pass through basis and therefore changes in approved expenses do not affect earnings.
The NHPUC and MDPU regularly review alternatives to their procurement policy for all electric distribution companies, and currently have open investigations in procurements processes, which may lead to future changes in this regulated power supply procurement structure.
Regional Electric Transmission and Power Markets
Fitchburg, Unitil Energy and Unitil Power, as well as virtually all New England electric utilities, are participants in the ISO-NE markets. ISO-NE is the Regional Transmission Organization (RTO) in New England. The purpose of ISO-NE is to assure reliable operation of the bulk power system in the most economical manner for the region. Substantially all operation and dispatching of electric generation and bulk transmission capacity in New England are performed on a regional basis. The ISO-NE tariff imposes generating capacity and reserve obligations, and provides for the use of major transmission facilities and associated support payments. The most notable benefits of the ISO-NE are coordinated, reliable power system operation and a supportive business environment for the development of competitive electric markets.
Electric Power Supply Divestiture
In connection with the implementation of retail choice, Unitil Power, which formerly functioned as the wholesale power supply provider for Unitil Energy, and Fitchburg divested their long-term power supply contracts through the sale of the entitlements to the electricity sold under those contracts. Unitil Energy and Fitchburg recover in their rates all the costs associated with the divestiture of their power supply portfolios and have secured regulatory approval from the NHPUC and MDPU, respectively, for the recovery of power supply-related stranded costs and other restructuring-related regulatory assets. The companies have a continuing obligation to submit regulatory filings that demonstrate their compliance with regulatory mandates and provide for timely recovery of costs in accordance with their approved restructuring plans.
NATURAL GAS SUPPLY
Unitil purchases and manages gas supply for customers served by Northern Utilities in Maine and New Hampshire, and by Fitchburg in Massachusetts.
Northern Utilities’ Commercial and Industrial (C&I) customers are entitled to purchase their natural gas supply from third-party gas suppliers. Many of Northern Utilities’ large, and some of its medium, C&I customers purchase their gas supply from third-party suppliers. Most small C&I customers, and all residential customers, purchase their gas supply from Northern Utilities under regulated rates and tariffs. As of December 2024, 74% of Unitil’s largest New Hampshire gas customers, representing 40% of Unitil’s New Hampshire gas therm sales, and 62% of Unitil’s largest Maine customers, representing 22% of Unitil’s Maine gas therm sales, purchased their gas supply from a third-party supplier.
Fitchburg’s residential and C&I business customers are entitled to purchase their natural gas supply from third-party gas suppliers. Many of Fitchburg’s large, and some of its medium, C&I customers, purchase their gas supply from third-party suppliers. Most of Fitchburg’s residential and small C&I customers continue to purchase their supplies at regulated rates from Fitchburg. As of December 2024, 78% of Unitil’s largest Massachusetts gas customers, representing 30% of Unitil’s Massachusetts gas therm sales, purchased their gas supply from third-party suppliers. The approved costs associated with natural gas supplied to customers who do not contract with third-party suppliers are recovered on a pass-through basis through periodically adjusted rates, and are included in Cost of Gas Sales in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Regulated Natural Gas Supply
Northern Utilities purchases the majority of its natural gas from U.S. domestic and Canadian suppliers largely under contracts of one year or less, and on occasion from producers and marketers on the spot market. Northern Utilities arranges for gas transportation and delivery to its system through its own long-term contracts with various interstate pipeline and storage facilities, through peaking supply contracts delivered to its system, or in the case of liquefied natural gas (LNG), via trucking of supplies to storage facilities within Northern Utilities’ service territory.
Northern Utilities has available under firm contract 85,500 million British Thermal Units (MMBtu) per day of year-round and an additional 44,000 MMBtu of winter seasonal transportation capacity to its distribution facilities, and 6.3 billion cubic feet (BCF) of underground storage. As a supplement to pipeline natural gas, Northern Utilities owns an LNG storage and vaporization facility. This plant is used principally during peak load periods to augment the supply of pipeline natural gas.
Fitchburg purchases natural gas under contracts from producers and marketers largely under contracts of one year or less, and occasionally on the spot market. Fitchburg arranges for gas transportation and delivery to its system through its own long-term contracts with Tennessee Gas Pipeline, through peaking supply contracts delivered to its system, or in the case of LNG or liquefied propane gas (LPG), via trucking of supplies to storage facilities within Fitchburg’s service territory.
Fitchburg has available under firm contract 14,439 MMBtu per day of year-round transportation and 0.4 BCF of underground storage capacity to its distribution facilities. As a supplement to pipeline natural gas, Fitchburg owns a propane air gas plant and an LNG storage and vaporization facility. These plants are used principally during peak load periods to augment the supply of pipeline natural gas.
Note 7: Commitments and Contingencies
Regulatory Matters
Overview—Unitil’s distribution utilities deliver electricity and/or natural gas to customers in the Company’s service territories at rates established under traditional cost of service regulation. Under this regulatory structure, Unitil Energy, Fitchburg, and Northern Utilities are provided the opportunity to recover the cost of providing distribution service to their customers based on a representative test year, in addition to earning a return on their capital investment in utility assets. Unitil Energy, Northern Utilities' New Hampshire division, and Fitchburg’s electric and gas divisions operate under revenue decoupling mechanisms.
Most of Unitil’s customers are entitled to purchase their electric or natural gas supplies from third-party suppliers. For Northern Utilities, only business customers are entitled to purchase their natural gas supplies from third-party suppliers at this time. Most small and medium-sized customers, however, continue to purchase such supplies through Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Northern Utilities as the providers of basic or default service energy supply. Unitil Energy, Fitchburg and Northern Utilities purchase electricity or natural gas for basic or default service from unaffiliated wholesale suppliers and recover the actual costs of these supplies, without profit or markup, through reconciling, pass-through rate mechanisms that are periodically adjusted. The MDPU, the NHPUC and the MPUC each have continued to approve these reconciling rate mechanisms which allow Fitchburg, Unitil Energy and Northern Utilities to recover their actual wholesale energy costs for electric power and natural gas.
Rate Case Activity
Northern Utilities - Base Rates - Maine - On September 20, 2023, the MPUC issued an order approving a Stipulation filed on August 31, 2023, between Northern Utilities and the Office of the Public Advocate which resolved all matters in the base rate filing made by Northern Utilities with the MPUC on May 1, 2023. The order approves an increase in distribution revenues of $7.6 million effective October 1, 2023. The order reflects a return on equity of 9.35%, an equity ratio of 52.01%, and a weighted average cost of capital of 7.22%.
Northern Utilities - Targeted Infrastructure Replacement Adjustment (TIRA) - Maine - The settlement in Northern Utilities’ Maine division’s 2013 rate case authorized the Company to implement a TIRA rate mechanism to adjust base distribution rates annually to recover the revenue requirements associated with targeted investments in gas distribution system infrastructure replacement and upgrade projects, including the Company’s Cast Iron Replacement Program (CIRP). In its Final Order issued on February 28, 2018 for Northern Utilities’ 2017 base rate case, the MPUC approved an extension of the TIRA mechanism for an additional eight-year period, which will allow for annual rate adjustments through the end of the CIRP program. The Company’s most recent request under the TIRA mechanism, to increase annual base rates by $2.4 million for 2023 eligible facilities, was filed with the MPUC on April 24, 2024. On April 30, 2024, the MPUC issued an order approving the filing, for rates effective May 1, 2024.
Northern Utilities - Base Rates - New Hampshire - On July 20, 2022, the NHPUC issued an Order in the distribution base rate case filed with the NHPUC on August 2, 2021 by Northern Utilities. The Order approved a comprehensive Settlement Agreement between the Company, the New Hampshire Department of Energy (DOE), and the Office of the Consumer Advocate (OCA). As provided in the Settlement Agreement, in addition to authorizing an increase to permanent distribution rates of $6.1 million, effective August 1, 2022, the Order (1) approved a revenue decoupling mechanism and (2) allowed for a step adjustment effective September 1, 2022 covering the additional revenue requirement resulting from changes in Net Plant in Service associated with non-growth investments for the period January 1, 2021, through December 31, 2021. This distribution base rate case reflected the Company’s operating costs and investments in utility plant for a test year ended December 31, 2020 as adjusted for known and measurable changes. The Order provided for a return on equity of 9.3% and a capital structure reflecting 52% equity and 48% long-term debt. The increase in permanent rates was reconciled back to October 1, 2021, the effective date of temporary rates previously approved in this docket. On June 8, 2022, the Company filed for its step increase of approximately $1.6 million of annual revenue, for rates effective as of September 1, 2022, to recover eligible 2021 capital investments. On August 31, 2022, the NHPUC approved the Company’s filing.
Unitil Energy - Base Rates - On May 3, 2022, the NHPUC issued an Order in the distribution base rate case filed with the NHPUC on April 2, 2021 by Unitil Energy. The Order approved, in part, a comprehensive Settlement Agreement between the Company, the New Hampshire DOE, the OCA, the New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services, Clean Energy New Hampshire, and ChargePoint, Inc. In addition to authorizing an increase to permanent distribution rates of $6.3 million, effective June 1, 2022, the Order approved the following components of the Settlement Agreement: (1) a multi-year rate plan, (2) a revenue decoupling mechanism, (3) time-of-use rates, (4) resiliency programs to support the Company’s commitment to reliability, and (5) other rate design and tariff changes. On May 10, 2022, the Company filed a request for clarification with the NHPUC to clarify that the authorized revenue requirement should exclude expenses related to the Company’s proposed Arrearage Management Program (AMP), which was not approved in the Order. On May 12, 2022, the Commission issued an Order, which clarified that because the Company will not incur the expenses associated with the AMP, those costs should be removed from the revenue requirement, and that the adjusted increase of $5.9 million will result in reasonable rates. The increase in permanent rates was reconciled back to June 1, 2021, the effective date of temporary rates previously approved in this docket. This distribution base rate case reflected the Company’s operating costs and investments in utility plant for a test year ended December 31, 2020 as adjusted for known and measurable changes. The Order provided for a return on equity of 9.2% and a capital structure reflecting 52% equity and 48% long-term debt. On July 28, 2022, the NHPUC approved the Company’s first step increase of approximately $1.3 million of annual revenue to recover eligible 2021 capital investments,
effective August 1, 2022. On May 31, 2023, the NHPUC approved the Company’s second and final step adjustment increase of approximately $1.2 million to recover eligible 2022 capital investments, effective June 1, 2023.
Fitchburg - Base Rates - Electric- Fitchburg’s base rates are decoupled and subject to an annual revenue decoupling adjustment mechanism, which includes a cap on the amount that rates may be increased in any year. In addition, Fitchburg has an annual capital cost recovery mechanism to recover the revenue requirement associated with certain capital additions. On July 26, 2023, the MDPU issued an Order approving the Company's cumulative revenue requirement of $3.1 million associated with its 2019-2021 capital expenditures. On September 11, 2024, the MDPU issued a final order approving the cumulative revenue requirement of $3.5 million associated with its 2019-2022 capital expenditures. On November 1, 2024, Fitchburg filed its cumulative revenue requirement of $0.5 million associated with its 2023 capital expenditures, which reflects the transfer of capital expenditures associated with its 2019-2023 year investments into base distribution rates effective July 1, 2024. On December 23, 2024, the MDPU approved recovery through its capital cost recovery mechanism effective January 1, 2025.
On August 17, 2023, Fitchburg filed a petition with the MDPU seeking approval for a $6.8 million increase to base distribution rates, with new rates to be effective July 1, 2024. Fitchburg also requested, among other things, approval for a performance-based ratemaking (PBR) plan for up to a five-year term and continuation of its revenue decoupling mechanism. On June 28, 2024, the MDPU issued an Order providing for a $4.7 million increase to base rates, effective July 1, 2024. This includes a transfer of $2.2 million in costs from certain reconciling mechanisms to base distribution rates. In addition to authorizing an increase to base rates, the Order approved a PBR plan for up to a five-year term and continuation of the Company’s revenue decoupling mechanism. The Order provided for a return on equity of 9.4% and a capital structure reflecting 52% equity and 48% long-term debt. On July 5, 2024, the Company filed its compliance tariff filing and made further revisions as directed by the MDPU on July 15, 2024. On July 16, 2024 the MDPU approved its revised compliance filing. Part of the transfer of revenues from reconciling mechanisms to base rates included $0.8 million of pension/PBOP revenues. In its Order, the MDPU found that allowing the Company to recover pension and PBOP expense through its Pension/PBOP Adjustment mechanism is no longer warranted. Instead, the MDPU concluded that these expenses should be recovered in base distribution rates, the mechanism should be discontinued and any unrecovered expenses existing as of the effective date of new rates will be recovered over two years. On July 18, 2024, the Company filed a Motion for Reconsideration and Recalculation in connection with this issue. The motion specifically requested that the MDPU reconsider its decision to require the Company to absorb $1.4 million in negative excess accumulated deferred income taxes (ADIT) because the effect of the Order was to inappropriately claw back amounts that were previously approved by the MDPU for recovery from customers. On November 26, 2024, the MDPU issued an Order on the Company’s motion holding, in part, that Pension/PBOP expenses shall be recovered in base distribution rates. On December 9, 2024 the Company filed an appeal with Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court requesting that it reverse and remand the final decision issued by the MDPU on June 28, 2024 along with the MDPU’s decision on reconsideration, issued November 26, 2024, unlawfully denying the Company’s recovery of approximately $1.4 million of negative, excess ADIT. The amount of $1.4 million is disaggregated between the Company’s gas division ($0.6 million) and the electric division ($0.8 million). This motion is pending. The ruling on November 26, 2024 approved certain other recalculations, resulting in an additional increase to electric base rates of $0.1 million effective December 1, 2024.
Fitchburg - Base Rates - Gas -On August 17, 2023, Fitchburg filed a petition with the MDPU seeking approval for a $10.9 million increase to base distribution rates, with new rates anticipated to be effective July 1, 2024. Fitchburg proposed to transfer $4.2 million in revenue requirements recovered through its Gas System Enhancement Program to base distribution rates. Net of these transfers, the proposed overall increase to distribution revenues is $6.7 million. As part of this filing, Fitchburg is requesting approval for a PBR plan for up to a five-year term and continuation of its revenue decoupling mechanism. On June 28, 2024, the MDPU issued an Order providing for a $10.1 million increase to base rates, effective July 1, 2024. This includes a transfer of $4.9 million in costs from certain reconciling mechanisms to base distribution rates. In addition to authorizing an increase to base rates, the Order approved a PBR plan for up to a five-year term. The order approves continuation of the Company’s revenue decoupling mechanism but changes the structure from a revenue per customer benchmark to a total revenue cap. The Order provided for a return on equity of 9.4% and a capital structure reflecting 52% equity and 48% long-term debt. On July 5, 2024, the Company filed its compliance tariff filing and made further revisions as directed by the MDPU on July 15, 2024. On July 16, 2024 the MDPU approved its revised compliance filing. Part of the transfer of revenues from reconciling mechanisms to base rates included $0.9 million of pension/PBOP revenues. In its order, the MDPU found that allowing the Company to recover pension and PBOP expense through its Pension/PBOP Adjustment mechanism is no longer warranted. Instead, the MDPU concluded that these expenses should be recovered in base distribution rates, the mechanism should be discontinued and any unrecovered expenses existing as of the effective date of new rates will be recovered over two years. On July 18, 2024, the Company filed a Motion for Reconsideration and Recalculation in connection with this issue. The motion specifically requested that the MDPU reconsider its decision to require the Company to absorb $1.4
million in negative excess accumulated deferred income taxes (ADIT) because the effect of the Order was to inappropriately claw back amounts that were previously approved by the MDPU for recovery from customers. On November 26, 2024, the MDPU issued an Order on the Company’s motion holding, in part, that Pension/PBOP expenses shall be recovered in base distribution rates. On December 9, 2024 the Company filed an appeal with Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court requesting that it reverse and remand the final decision issued by the MDPU on June 28, 2024 along with the MDPU’s decision on reconsideration, issued November 26, 2024, unlawfully denying the Company’s recovery of approximately $1.4 million of negative, excess ADIT. The amount of $1.4 million is disaggregated between the Company’s Gas Division ($0.6 million) and the Electric Division ($0.8 million). This motion is pending. The ruling on November 26, 2024 approved certain other recalculations, resulting in an additional increase to gas base rates of $0.1 million effective December 1, 2024.
Fitchburg - Gas System Enhancement Program- Pursuant to statute and MDPU order, Fitchburg has an approved Gas System Enhancement Plan tariff through which it may recover certain gas infrastructure replacement and safety related investment costs, subject to an annual cap. Under the plan, the Company is required to make two annual filings with the MDPU: a forward-looking filing for the subsequent construction year, to be filed on or before October 31; and a filing, submitted on or before May 1, of final project documentation for projects completed during the prior year, demonstrating substantial compliance with its plan in effect for that year and showing that project costs were reasonably and prudently incurred. Fitchburg’s forward-looking cumulative revenue requirement filing submitted on October 31, 2023 requested recovery of approximately $6.4 million, and received final approval on April 30, 2024, effective May 1, 2024. On July 15, 2024 the Company reduced the approved recovery of $6.4 million to $4.0 million to reflect the transfer of recovery of capital expenditures associated with its 2019-2022 year investments into base distribution rates effective July 1, 2024, as well as the impact of the base distribution rate case on forward looking revenue requirements. The MDPU approved the request on July 16, 2024. The Company’s most recent forward-looking cumulative revenue requirement filing, filed on October 31, 2024, requested recovery of approximately $3.5 million associated with 2023-2025 year investments. This matter remains pending.
Granite State - Base Rates - On August 24, 2021, the FERC accepted Granite State’s first limited Section 4 rate adjustment pursuant to the Settlement Agreement, for an annual revenue increase of $0.1 million, effective September 1, 2021. On August 19, 2022, the FERC accepted Granite State’s second limited Section 4 rate adjustment pursuant to the Settlement Agreement, for an annual revenue increase of $0.3 million, effective September 1, 2022. On July 27, 2023, Granite State filed its third and final limited Section 4 rate adjustment pursuant to the Settlement Agreement, for an annual revenue increase of $1.0 million, effective September 1, 2023. On August 22, 2023, the FERC approved this filing.
On October 4, 2024, Granite State filed an uncontested rate settlement with the FERC which provides for an increase in annual revenues of $3.0 million, effective November 1, 2024. The Settlement Agreement permits the filing of limited Section 4 rate adjustments for capital cost projects eligible for cost recovery in 2025, 2026, and 2027, and sets forth an overall cap of $29.9 million on the capital costs recoverable under such filings. Under the Settlement Agreement, Granite State may not file a new general rate case earlier than April 30, 2028 with rates to be effective no earlier than September 1, 2028 based on a test year ending no earlier than December 31, 2027. On November 25, 2024, the FERC approved Granite State’s filing.
Other Matters
Unitil Energy - Proposal to Construct Utility-Scale Solar Facility - On October 31, 2022, Unitil Energy submitted a petition to the NHPUC for review of Unitil Energy’s proposal to construct, own, and operate a 4.99 MW utility-scale photovoltaic generating facility, which was subsequently revised to a 4.88 MW facility. On May 1, 2023, the NHPUC issued an Order approving the Company's petition.
On February 5, 2024, the NH Department of Environmental Services (NHDES) issued an Alteration of Terrain Permit for the project. On February 9, 2024, NHDES issued a Wetland and Non-Site Specific Permit for the project. On February 14, 2024, the United States Army Corps of Engineers issued a NH General Permit for the project. The Company has commenced site work for the project.
Unitil Energy - Major Storm Cost Reserve Recovery - On April 26, 2024, Unitil Energy filed a request with the NHPUC to increase its Storm Reserve Adjustment Factor effective June 1, 2024. The increase would allow the Company to recover the under-collected Major Storm Cost Reserve (MSCR) balance as of December 31, 2023 of approximately $3.7 million plus $0.2 million of projected carrying costs over a three-year period. On May 31, 2024, the NHPUC approved the Company’s request, subject to further investigation and reconciliation. On November 14, 2024, the NHPUC granted final approval.
Fitchburg - Grid Modernization - On July 1, 2021, Fitchburg submitted its Grid Modernization Plan (GMP) to the MDPU. The GMP includes a five-year strategic plan, including a plan for the full deployment of advanced metering functionality, and a four-year short-term investment plan, which focuses on foundational investments to facilitate the interconnection and integration of distributed energy resources, optimizing system performance through command and control and self-healing measures, and optimizing system demand by facilitating consumer price-responsiveness. On October 7, 2022, the MDPU issued a “Track 1” Order approving a budget cap of $9.3 million through 2025 for previously deployed or preauthorized grid modernization investments. On November 30, 2022, the MDPU issued its “Track 2” Order addressing new technologies and Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) proposals. The MDPU preauthorizes a four-year $1.5 million budget for Fitchburg’s additional grid-facing investments. Any spending over the total budget cap is not eligible for targeted cost recovery through its Grid Modernization Factor (GMF), and instead, may be recovered by the Company in a base distribution rate proceeding subsequent to a prudency finding by the MDPU in a GMF filing or term review Order. The MDPU also preauthorized the Company’s AMI meter replacement investments, with a budget of $11.2 million through 2025. Additionally, the MDPU provided preliminary approval for the Company’s customer engagement and experience and data sharing platform investments, with a combined budget of $2.3 million through 2025. The Company may recover eligible costs incurred for preauthorized grid-facing investments and customer-facing investments that will be made during the 2022-2025 GMP term through the GMFs, subject to certain modifications to the Company’s GMF tariff and a final prudence review. On March 31, 2023, the Company submitted an AMI opt-out tariff with full support of proposed opt-out fees in compliance with the Track 2 Order. The MDPU approved the tariff on April 7, 2023.
On April 24, 2023, Fitchburg submitted its 2022 Grid Modernization Plan Annual Report to the MDPU. Among other things, the Company explained a modification to its implementation of the AMI plan that the MDPU preauthorized in D.P.U. 21-82. Due to a discontinuation of the meter technology upon which the Company’s initial AMI plan relied, the Company reported that it will need to replace its meters with a new meter technology and to implement a new communications system. On May 31, 2023, the MDPU issued an Order indicating its intent to explore the impact of the discontinuation and determine the appropriate next steps outside the GMF proceeding. On April 15, 2024, the Company submitted its annual Grid Modernization Filing seeking recovery of costs related to grid modernization investments placed into service in 2023. In connection with this filing, the Company submitted a request for preauthorization of communications systems and head end system investments that will be implemented in connection with the Company’s advanced metering infrastructure replacement project. The matter remains pending.
Fitchburg - Grid Modernization Cost Recovery Factor - On April 15, 2023, Fitchburg filed its GMF rate adjustment and reconciliation filing for recovery of the costs incurred as a result of implementing the Company’s 2022-2025 GMP, approved by the MDPU in Orders dated October 7, 2022 and November 30, 2022. On May 31, 2023, the MDPU approved, subject to further investigation and reconciliation, the cumulative recovery of $1.0 million associated with the Company’s 2022 GMP revenue requirement, effective June 1, 2023. The MDPU conducted a hearing on September 26, 2023 regarding the Company’s pending GMF filings and Grid Modernization Term Report. The matter remains pending. On April 15, 2024, Fitchburg filed its GMF rate adjustment and reconciliation filing for recovery of the costs incurred as a result of implementing the Company’s 2022-2025 GMP. On May 31, 2024, the MDPU approved, subject to further investigation and reconciliation, the cumulative recovery of $1.3 million associated with its 2023 revenue requirement, effective June 1, 2024. On June 28, 2024, the MDPU issued an Order in Fitchburg’s electric base rate case providing for the transfer of $1.6 million meter-related costs from base distribution rates to the GMF, effective July 1, 2024.
Fitchburg - Investigation into the role of gas LDCs to achieve Commonwealth 2050 climate goals - The MDPU has opened an investigation to examine the role of Massachusetts gas local distribution companies (LDCs) in helping the Commonwealth achieve its 2050 climate goal of net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. In its Order opening the inquiry, the MDPU stated it is required to consider new policies and structures as the Commonwealth reduces reliance on fossil fuels, including natural gas, which may require LDCs to make significant changes to their planning processes and business models. The LDCs, including Fitchburg, engaged an independent consultant to conduct a study and prepare a report (Consultant Report), including a detailed study of each LDC, that analyzes the feasibility of all identified pathways to help the Commonwealth achieve its net-zero GHG goal. The study includes an examination of the potential pathways identified in the 2050 Decarbonization Roadmap developed by the Massachusetts Executive Office of Energy and Environmental Affairs, in consultation with the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection and the Massachusetts Department of Energy Resources (DOER).
On December 6, 2023, the MDPU issued an Order announcing a regulatory framework intended to set forth its role and that of the LDCs in helping the Commonwealth achieve its target of net-zero GHG emissions by 2050. In this proceeding, the
MDPU reviewed eight potential decarbonization “pathways” and six regulatory design recommendations intended to facilitate the Commonwealth’s transition. The MDPU made no specific findings as to a preferred pathway or technology, but did make specific findings regarding regulatory design recommendations. The MDPU emphasized that the Order is not intended to jeopardize the rate recovery of existing investments in natural gas infrastructure by Fitchburg. As part of future cost recovery proposals, LDCs will bear the burden of demonstrating that non-gas pipeline alternatives (NPAs) were adequately considered and found to be non-viable or cost prohibitive to receive full cost recovery of investments. The MDPU further found that the “clean energy transition” will require coordinated planning between LDCs and electric distribution companies, monitoring progress through LDC reporting, and aligning existing MDPU practices with climate targets. To that end, the MDPU ordered the LDCs to submit individual Climate Compliance Plans (CCP) every five years beginning in 2025, and to propose climate compliance performance metrics in upcoming performance-based regulation filings, ensuring a proactive approach to achieving climate targets. The first CCP is due April 1, 2025.
On December 29, 2023, the LDCs filed a Joint Motion for Clarification and Extension of Judicial Appeal Period. The Joint Motion requests clarification of three issues: (1) the MDPU’s directive concerning the NPAs analysis; (2) the timetable for establishing ‘incentives and disincentives’ for progress toward compliance with Climate Act mandates as part of a PBR framework and achievement of approved Climate Compliance Plans; and (3) the methodology for emissions reduction accounting for Climate Compliance Plans, with particular attention to Scope 1 and Scope 3 emissions accounting. On April 2, 2024, the Commission issued an Order on the LDCs’ Joint Motion. In its Order, the MDPU clarified, among other things, that NPA analyses should be applied at the project level to all investment decisions going forward, and should be considered at project planning stage; that pending an approved NPA framework, LDCs should make all reasonable efforts to incorporate NPA analyses into investment decisions; and that LDCs will have the burden to demonstrate the prudence of implementing a traditional project instead of a NPA. The MDPU did not expressly exempt any category of project from the NPA analysis requirement.
Fitchburg - Electric Sector Modernization Plan- Pursuant to M.G.L. c. 164 § 92B, Fitchburg submitted a draft Electric Sector Modernization Plan (ESMP) to the statutorily created Massachusetts Grid Modernization Advisory Council (Council) for the Council’s review, input, and recommendations. The ESMP is a plan intended to upgrade the Company’s distribution system to enable and accommodate increased distributed energy resources (DERs) and electrification technologies, improve grid reliability and resiliency, and assist the Commonwealth in achieving climate goals, among other objectives. The Council provided recommendations on the ESMP in November 2023. The Company submitted its final ESMP to the MDPU on January 29, 2024. The Company concurrently submitted a proposal to recover, among other things, incremental costs associated with ESMP investments through an annual reconciling rate adjustment mechanism. On February 20, 2024, the MDPU issued an interlocutory order finding in part that “to the extent that the MDPU determines that accelerated cost recovery through annual reconciling mechanisms for proposed investments identified in the ESMPs is appropriate, we anticipate establishing the appropriate parameters for those mechanisms through a separate phase of these proceedings to be conducted after August 29, 2024.” On August 29, 2024, the MDPU issued a final order approving Fitchburg’s ESMP. Among other directives, the Order directs Fitchburg and other Massachusetts electric distribution companies (EDCs) to conduct a stakeholder process related to long term system planning related to forecasted DER interconnection and sets forth the criteria for biannual reports. The MDPU found it appropriate to allow Fitchburg and the other EDCs a short-term targeted cost recovery mechanism for ESMP costs. On December 18, 2024 Fitchburg filed a model ESMP tariff and a company-specific exemplar ESMP mechanism tariff, which describes the parameters of cost-recovery in the second phase of this proceeding. This matter remains pending.
Fitchburg - Electric Vehicle (EV) Proceeding - On December 30, 2022, the MDPU issued an order approving Fitchburg’s five-year EV program with a $1.0 million budget consisting of: (1) public infrastructure offering ($0.5 million); (2) Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) incentives for residential segment ($0.3 million); and (3) marketing and outreach ($0.2 million). The Company may shift spending between program segments and between years over the five-year term of its program, subject to a 15% cap. Any spending above the approved EV program budget or above the 15% cap for each program segment is not eligible for targeted cost recovery through the GMF and, instead, may be recovered in a base distribution rate proceeding subsequent to a prudency finding by the MDPU. The MDPU’s Order directs the Companies to submit annual reports that document their performance and these reports are due on or before May 15th of each year. The MDPU accepted the Company’s Demand Charge Alternative proposal and directed implementation within six months. The Demand Charge Alternative is offered for a ten-year period beginning July 1, 2023 with tiered rates to separately-metered EV general delivery service customers. The MDPU also accepted the Company’s proposed residential EV TOU rate, effective April 1, 2023.
In June 2023, the MDPU convened an EV stakeholder process to finalize EV program performance metrics. On April 3, 2023, the electric companies filed comments on the MDPU’s proposed metrics. On December 15, 2023, the MDPU approved
EV performance metrics. Following that approval, the MDPU required the electric companies to develop a joint state-wide program evaluation plan for MDPU approval and stakeholder input. On May 15, 2024, Fitchburg submitted its first annual report on the performance of its EV Program, and along with the other Massachusetts EDCs, a proposed statewide program evaluation plan for MDPU approval and stakeholder input. On September 30, 2024, the MDPU stamp approved the Joint Statewide Electric Vehicle Program Evaluation Plan. In addition, on October 1, 2024 the MDPU approved Fitchburg’s request for a supplemental budget increase to engage a consultant to assist with the Joint Statewide Electric Vehicle Program Evaluation Plan. On December 20, 2024, the Company submitted a request for approval to modify certain aspects of the public, residential, and income eligible offers of its EV program. Fitchburg does not anticipate any rate changes resulting from this filing, which is currently pending before the MDPU.
Fitchburg - Storm Cost Deferral Petition - On November 2, 2023, Fitchburg filed a request with the MDPU to increase its Storm Reserve Adjustment Factor effective January 1, 2024. The increase would allow the Company to recover approximately $4.8 million of costs of repairing damage to its electrical system plus $1.4 million of projected carrying costs resulting from the January and March 2023 winter storms over a five-year period. On December 19, 2023, the MDPU allowed the associated rate increase to become effective on January 1, 2024, subject to further investigation and reconciliation. This matter remains pending before the MDPU.
Fitchburg- Approval of Gas Supply Agreement with Constellation LNG- On February 16, 2024, Fitchburg filed a petition with the MDPU for approval of a six year agreement with Constellation LNG for the purchase of natural gas in the liquid or vapor form for the period June 1, 2024 through May 31, 2030 heating seasons. This request is for the approval of two contracts, the first for up to 3,400 Dth per day of natural gas peaking supply to the Company. This first contract will be broken out for 3,000 Dth per Day in the form of LNG for use at the Company’s Westminster LNG facility and 400 Dth per Day will be in the form of natural gas supply delivered to the city-gate connecting the Company’s system to the Tennessee Gas Pipeline. The second contract will provide up to 3,000 Dth per day of LNG trucking from the Everett Marine Terminal to the Company’s Westminster LNG facility.
This proposed agreement would ensure that the Everett Marine Terminal, which plays a critical role in both the Company’s and the New England energy market’s efficient and reliable operation, will continue to be available for the next six winter seasons. A six year agreement was also requested by Boston Gas Company, Eversource Gas Company, and NSTAR Gas Company. Fitchburg and the other LDCs received an Order on May 17, 2024 approving the agreements.
Northern Utilities / Granite State - Firm Capacity Contract - Northern Utilities relies on the transportation of gas supply over its affiliate Granite State pipeline to serve its customers in the Maine and New Hampshire service areas. Granite State facilitates critical upstream interconnections with interstate pipelines and third party suppliers essential to Northern Utilities’ service to its customers. Northern Utilities reserves firm capacity through a contract with Granite State, which is renewed annually. Pursuant to statutory requirements in Maine and orders of the MPUC, Northern Utilities submits an annual informational report requesting approval of a one-year extension of its 12-month contract for firm pipeline capacity reservation, with an evergreen provision and three-month termination notification requirement. On March 29, 2024, Northern Utilities submitted an annual informational report requesting approval on a one-year extension for the period of November 1, 2024 through October 31, 2025. The Company received an order approving the 2024-2025 contract on July 10, 2024.
Northern Utilities / Portland Natural Gas Transmission System (PNGTS) and TransCanada Pipelines Limited (TCPL) transportation from Empress, Alberta to Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. (GSGT) - On October 5, 2023, Northern Utilities filed with the NHPUC and the MPUC a request to approve agreements for the ability for Northern Utilities to increase supply portfolio capacity by 12,500 Dth per day in New Hampshire and Maine. This incremental capacity to Northern Utilities’ supply portfolio took effect April 1, 2024 for a thirty-year term. Northern Utilities was able to acquire this incremental supply of TCPL capacity through an open season process. On January 26, 2024 and January 30, 2024, the Company received orders from the NHPUC and MPUC, respectively, approving Northern Utilities’ proposal for Empress Agreements with PNGTS and TransCanada Pipelines. Conservation Law Foundation filed a motion for reconsideration of the Maine Commission’s decision on February 15, 2024. The Company objected to the motion, which remains pending before the Commission.
Reconciliation Filings - Fitchburg, Unitil Energy and Northern Utilities each have a number of regulatory reconciling accounts that require annual or semi-annual filings with the MDPU, NHPUC and MPUC, respectively, to reconcile revenues and costs, and to seek approval of any rate changes. These filings include: annual electric reconciliation filings by Fitchburg and Unitil Energy for a number of items, including default service, stranded cost changes and transmission charges; costs associated
with energy efficiency programs in New Hampshire and Massachusetts, as directed by the NHPUC and MDPU; recovery of the ongoing costs of storm repairs incurred by Unitil Energy and Fitchburg; and the actual wholesale energy costs for electric power and gas incurred by each of the three companies. Fitchburg, Unitil Energy and Northern Utilities have been, and remain in full compliance with all directives and orders regarding these filings. The Company considers these to be routine regulatory proceedings, and there are no material issues outstanding.
Fitchburg - Massachusetts Request for Proposals (RFPs) - Pursuant to Section 83C of “An Act to Promote Energy Diversity” (2016) (the Act), the Massachusetts EDCs, including Fitchburg, are required to jointly procure a total of 1,600 MW of offshore wind by June 30, 2027. Under Section 83D of the Act, the EDCs are required to jointly seek proposals for cost-effective clean energy (hydroelectric, solar and land-based wind) long-term contracts via one or more staggered solicitations for a total of 9,450,000 megawatt-hours (MWh) by December 31, 2022. Fitchburg’s pro rata share of these contracts is approximately 1%.
The EDCs issued the RFP for Section 83D Long-Term Contracts in March 2017, and power purchase agreements (PPAs) for 9,554,940 MWh of hydroelectric generation and associated environmental attributes from Hydro-Quebec Energy Services (U.S.), Inc. were filed in July 2018 for approval by the MDPU. On June 25, 2019, the MDPU approved the PPAs, including the EDCs’ proposal to sell the energy procured under the contract into the ISO-NE wholesale market and to credit or charge the difference between the contract costs and the ISO-NE market revenue to customers. The MDPU also approved the EDCs’ request for remuneration equal to 2.75% of the contract payments, as well as the EDCs’ proposal to recover costs associated with the contracts. On January 13, 2023, NECEC Transmission LLC (NECEC), the company with which Fitchburg and the other EDCs entered into transmission service agreements (TSAs) for the delivery of the Hydro-Quebec energy, provided a letter to the EDCs purporting to give notice of a “change in applicable law” related to a Maine ballot initiative and requesting a negotiated amendment to the TSAs including a price adjustment. On June 27, 2023, NECEC sent a letter to the EDCs seeking schedule relief also in accordance with their “change in law” determination. The EDCs are in the process of evaluating an amendment to the Transmission Service Agreement.
Section 83C of “An Act Relative to Green Communities,” St. 2008, c. 169, as amended by St. 2016, c. 188, § 12 (Section 83C) requires the EDCs to jointly and competitively solicit proposals for offshore wind energy generation not later than June 30, 2017. The EDCs issued an initial RFP pursuant to Section 83C in June 2017. On July 23, 2018, the EDCs, filed two long-term contracts with Vineyard Wind, each for 400 MW of offshore wind energy generation, for approval by the MDPU. On April 12, 2019, the MDPU approved the offshore wind energy generation PPAs, including the EDCs’ proposal to sell the energy procured under the contract into the ISO-NE wholesale market and to credit or charge the difference between the contract costs and the ISO-NE market revenue to customers. The EDCs issued a second RFP pursuant to Section 83C to procure an additional 800 MW of offshore wind energy generation in May 2019. The EDCs filed for approval of two PPAs with Mayflower Wind Energy LLC (now known as SouthCoast Wind), each for 400 MW of offshore wind energy generation, on February 10, 2020. On November 5, 2020, the MDPU approved the PPAs. In both cases, the MDPU approved the EDCs’ request for remuneration equal to 2.75% of the contract payments, as well as the EDCs’ proposal to recover costs associated with the contracts. In April 2023, SouthCoast Wind engaged with the EDCs to explore options to mitigate impacts of global resource constraints and pricing challenges associated with the PPAs from this procurement. They cited an inability to finance the project within the terms set out in the PPA. The EDCs negotiated a termination agreement with SouthCoast Wind which was filed with the MDPU for approval on August 28, 2023 and which received approval on September 30, 2023.
In accordance with “An Act to Advance Clean Energy” (2018) the DOER recommended that the EDCs solicit up to 1,600 MW in additional offshore wind in 2022 and 2024. On May 7, 2021, the EDCs issued a third RFP for up to an additional 1,600 MW of off shore wind generation. On May 25, 2022, the EDCs sought approval of PPAs with Commonwealth Wind for 1,200 MW and with SouthCoast Wind for 400 MW. On December 16, 2022, Commonwealth Wind filed a motion requesting that the MDPU dismiss proceedings related to the approval of its contract, arguing that, due to various economic conditions, its contracts with the EDCs would no longer facilitate the financing of offshore wind energy generation. On December 30, 2022, the MDPU denied Commonwealth’s motion and approved the PPAs. The MDPU also approved the EDCs’ request for remuneration equal to 2.25% as reasonable and in the public interest. On January 19, 2023, Commonwealth Wind filed a Petition for Appeal with the Massachusetts Supreme Judicial Court (SJC) seeking to set aside and vacate the MDPU’s Order approving the PPAs. In April 2023, SouthCoast Wind engaged with the EDCs to explore options to mitigate global resource constraints and pricing challenges associated with their PPAs from this procurement. SouthCoast Wind noted challenges around an inability to finance the projects under the current terms. The EDCs negotiated termination agreements with Commonwealth Wind and SouthCoast Wind and submitted the agreements to the MDPU for approval on July 13, 2023 and August 28, 2023, respectively. The MDPU approved both termination agreements on September 30, 2023.
In connection with the termination agreements from the second and third solicitations, the Company received termination payments from Commonwealth Wind and SouthCoast Wind totaling $1.1 million which is recorded as a regulatory liability on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets to be flowed back to customers. On October 12, 2023, Commonwealth Wind requested that the case with the SJC be entered as dismissed. Concurrently, Commonwealth Wind announced publicly they could not finance the project under the terms of the PPA.
The “Energy Diversity Act” (2021) and “An Act Driving Clean Energy and Offshore Wind” (2022) enacted by the Massachusetts legislature, increased the total solicitation target (including future solicitations) for offshore wind energy generation to 5,600 MW by June 30, 2027. On August 30, 2023, the EDCs issued a fourth offshore wind RFP seeking to procure at least 400 MW and up to the maximum amount remaining of the statutory requirement under Section 83C of 5,600 MW of Offshore Wind Energy Generation, and taking into account offshore wind generation under contract at the time when proposals are due. Bidders are allowed to offer proposals of at least 200 MW up to 2,400 MW of offshore wind generation. On January 18, 2024, the EDCs notified the MDPU that they are extending the bid submission date and subsequent solicitation schedule dates by an additional 56 days each to allow bidders the opportunity to gain more certainty around their eligibility for the investment tax credit and factor it into their proposals. The submission date was revised to March 27, 2024. The EDCs received bids for Offshore Wind Generation from three developers as part of a multi-state solicitation with Rhode Island and Connecticut and on September 6, 2024, the DOER selected a portfolio of projects totaling 2,678 MW from three projects. The EDCs have commenced contract negotiations which are scheduled to be completed in March 2025.
In December 2024, the Massachusetts Legislature approved “An Act promoting a clean energy grid, advancing equity, and protecting ratepayers” which among other provisions, extends the period for long-term renewable contracts up to 30 years and directs the EDCs to “jointly and competitively solicit proposals for energy storage systems and enter into cost-effective long-term contracts equal to, in the aggregate, approximately 5,000 megawatts of energy storage systems not later than July 31, 2030.” The first solicitation will be for approximately 1,500 megawatts of mid-duration storage to be procured by July 31, 2025.
Unitil Energy/Northern Utilities - 2024-2026 Triennial Energy Efficiency Plan - New Hampshire - On November 30, 2023, the NHPUC approved the changes to New Hampshire’s ratepayer-funded energy efficiency program offerings for the 2024–2026 period requested by New Hampshire’s electric and gas utilities. On July 1, 2024, the New Hampshire electric and gas utilities filed an interim update with the Commission, seeking approval to update the energy efficiency program models with benefit assumptions from the recently issued report of Avoided Energy Supply Components in New England: 2024 Report.
FERC Transmission Formula Rate Proceedings- Pursuant to Section 206 of the Federal Power Act, there are several pending proceedings before the FERC concerning the justness and reasonableness of the Return on Equity (ROE) component of the ISO-New England, Inc. Participating Transmission Owners’ (PTOs) Regional Network Service and Local Network Service formula rates. In August 2013, FERC had found that the Transmission Owners existing ROE was unlawful, and set a new ROE. On April 14, 2017, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the D.C. Circuit issued an opinion vacating and remanding FERC’s decision, finding that FERC had failed to articulate a satisfactory explanation for its orders. At this time, the ROE set in the vacated order will remain in place until further FERC action is taken. On November 21, 2019, the FERC issued an order in EL14-12, Midcontinent Independent System Operator ROE, in which FERC outlined a new methodology for calculating the ROE. The New England Transmission Owners (NETOs) thereafter filed a motion to reopen the record in their pending ROE dockets, which has been granted. This matter remains pending. The Company does not believe these proceedings will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition or results of operations.
On December 13, 2022, RENEW Northeast, Inc., a non-profit entity that advocates for the business interests of renewable power generators in New England filed a complaint with FERC against ISO-NE and the PTOs requesting a determination that certain open-access transmission tariff schedules are unjust and unreasonable to the extent they permit PTOs to directly assign to interconnection customers O&M costs associated with network upgrades. Fitchburg and Unitil Energy are PTOs, although Unitil Energy does not own transmission plant. The PTOs answered the complaint on January 23, 2023. This matter remains pending. The Company does not believe these proceedings will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition or results of operations.
Contractual Obligations
The following table lists the Company’s known specified gas and electric supply contractual obligations as of December 31, 2024.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Payments Due by Period | |
Gas and Electric Supply Contractual Obligations
(millions) as of December 31, 2024 | | Total | | | 2025 | | | 2026 | | | 2027 | | | 2028 | | | 2029 | | | 2030 & Beyond | |
Gas Supply Contracts | | $ | 742.4 | | | $ | 82.2 | | | $ | 71.9 | | | $ | 70.1 | | | $ | 65.2 | | | $ | 58.9 | | | $ | 394.1 | |
Electric Supply Contracts | | | 11.5 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 1.0 | | | | 5.0 | |
Total | | $ | 753.9 | | | $ | 83.6 | | | $ | 73.3 | | | $ | 71.5 | | | $ | 66.5 | | | $ | 59.9 | | | $ | 399.1 | |
The Company and its subsidiaries have material energy supply commitments (see Note 6 Energy Supply). Cash outlays for the purchase of electricity and natural gas to serve customers are subject to reconciling recovery through periodic changes in rates, with carrying charges on deferred balances. From year to year, there are likely to be timing differences associated with the cash recovery of such costs, creating under- or over-recovery situations at any point in time. Rate recovery mechanisms are typically designed to collect the under-recovered cash or refund the over-collected cash over subsequent periods of less than a year.
Legal Proceedings
The Company is involved in legal and administrative proceedings and claims of various types, including those which arise in the ordinary course of business. The Company believes, based upon information furnished by counsel and others, that the ultimate resolution of these claims will not have a material effect on its financial position, operating results or cash flows.
Environmental Matters
The Company’s past and present operations include activities that are generally subject to extensive and complex federal and state environmental laws and regulations. The Company is in material compliance with applicable environmental and safety laws and regulations and, as of December 31, 2024, has not identified any material losses reasonably likely to be incurred in excess of recorded amounts. However, the Company cannot assure that significant costs and liabilities will not be incurred in the future. It is possible that other developments, such as increasingly stringent federal, state or local environmental laws and regulations could result in increased environmental compliance costs. Based on its current assessment of its environmental responsibilities, existing legal requirements and regulatory policies, the Company does not believe that these environmental costs will have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position or results of operations.
Northern Utilities Manufactured Gas Plant Sites - Northern Utilities has an extensive program to identify, investigate and remediate former manufactured gas plant (MGP) sites, which were operated from the mid-1800s through the mid-1900s. In New Hampshire, MGP sites were identified in Dover, Exeter, Portsmouth, Rochester and Somersworth. In Maine, Northern Utilities has documented the presence of MGP sites in Lewiston and Portland, and a former MGP disposal site in Scarborough.
Northern Utilities has worked with the New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services (NH DES) and Maine Department of Environmental Protection to address environmental concerns with these sites. Northern Utilities or others have completed remediation activities at all sites; however, on site monitoring continues at several sites which may result in future remedial actions as directed by the applicable regulatory agency.
In May 2024, NH DES requested additional information in connection with the Company’s December 2022 remedial action plan (RAP), regarding groundwater contaminants at the Rochester site. In anticipation of the NH DES approval of one of the RAP alternatives and subsequent request for project design, the Company has accrued $5.6 million for estimated costs to complete the remediation at the Rochester site, which is included in Environmental Obligations on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets. Due to extended regulatory review time periods, Northern Utilities anticipates the commencement of remediation activities later in 2025.
The NHPUC and MPUC have approved regulatory mechanisms for the recovery of MGP environmental costs. For Northern Utilities’ New Hampshire division, the NHPUC has approved the recovery of MGP environmental costs over
succeeding seven-year periods. For Northern Utilities’ Maine division, the MPUC has authorized the recovery of environmental remediation costs over succeeding five-year periods.
The Environmental Obligations table includes amounts accrued for Northern Utilities related to estimated future cleanup costs associated with Northern Utilities’ environmental remediation obligations for former MGP sites. Corresponding Regulatory Assets were recorded to reflect that the future recovery of these environmental remediation costs is expected based on regulatory precedent and established practices.
Fitchburg’s Manufactured Gas Plant Site - Fitchburg has worked with the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection (Mass DEP) to address environmental concerns with the former MGP site at Sawyer Passway, and has substantially completed remediation activities, though on site monitoring continues. In April 2020, Fitchburg received notification from the Massachusetts Department of Transportation (Mass DOT) that a portion of the site may be incorporated into the proposed Twin City Rail Trail with an anticipated commencement date in 2025. Depending upon the final agreement between Fitchburg and Mass DOT, additional minor costs are expected prior to completion.
The Company is awaiting a decision regarding an Immediate Response Action (IRA) plan with three remediation alternatives, submitted to the MA DEP in October 2023 with an update in November 2024, regarding contaminants in the sediment and riverbank of an abutting watercourse, and observed river seep. In anticipation of the DEP accepting one of the remediation alternatives, Fitchburg has accrued $40,000 for estimated costs to complete the remediation at the Sawyer Passway site, which is included in Environmental Obligations on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets. The Company has determined that the high end of the range of reasonably possible remediation costs for the Sawyer Passway site could be $3.5 million based on remediation alternatives. Fitchburg anticipates the commencement of some remediation activities by the middle of 2025, while the river seep will likely be addressed in 2026.
Fitchburg recovers the environmental response costs incurred at this former MGP site in gas rates pursuant to the terms of a cost recovery agreement approved by the MDPU. Pursuant to this agreement, Fitchburg is authorized to amortize and recover environmental response costs from gas customers over succeeding seven-year periods.
Unitil Energy - Kensington Distribution Operations Center - Unitil Energy conducted a Phase I and II environmental site assessment (ESA) in the second quarter of 2021 at its former distribution operations center in Kensington, NH. The Company is awaiting a decision on a report, submitted to the NH DES in June 2023, as to whether there is a need to conduct further investigation or remedial actions regarding the impacts of soil and groundwater contaminants identified in the ESA. Unitil Energy anticipates the commencement of remediation activities in 2026, following work plan approval by the NH DES decision. The Company does not believe this investigation will have a material adverse effect on its financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
The following table sets forth a summary of changes in the Company’s liability for Environmental Obligations for the years-ended December 31, 2024 and 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | |
Environmental Obligations (millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Total Balance at Beginning of Period | | $ | 4.6 | | | $ | 4.4 | |
Additions | | | 3.6 | | | | 0.7 | |
Less: Payments / Reductions | | | 0.4 | | | | 0.5 | |
Total Balance at End of Period | | | 7.8 | | | | 4.6 | |
Less: Current Portion | | | 0.7 | | | | 0.6 | |
Noncurrent Balance at End of Period | | $ | 7.1 | | | $ | 4.0 | |
Note 8: Income Taxes
Provisions for Federal and State Income Taxes reflected as operating expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of earnings for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022 are shown in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (in millions) | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Current Income Tax Provision | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 0.4 | | | $ | 4.3 | | | $ | — | |
State | | | 0.4 | | | | 1.5 | | | | 0.2 | |
Total Current Income Taxes | | $ | 0.8 | | | $ | 5.8 | | | $ | 0.2 | |
Deferred Income Tax Provision | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 8.6 | | | $ | 4.8 | | | $ | 6.6 | |
State | | | 4.6 | | | | 2.6 | | | | 4.4 | |
Total Deferred Income Taxes | | | 13.2 | | | | 7.4 | | | | 11.0 | |
Total Income Tax Expense | | $ | 14.0 | | | $ | 13.2 | | | $ | 11.2 | |
The differences between the Company’s provisions for Income Taxes and the provisions calculated at the statutory federal tax rate, expressed in percentages, are shown in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Statutory Federal Income Tax Rate | | | 21 | % | | | 21 | % | | | 21 | % |
Income Tax Effects of: | | | | | | | | | |
State Income Taxes, net | | | 6 | % | | | 6 | % | | | 6 | % |
Utility Plant Differences | | | (5 | )% | | | (5 | )% | | | (6 | )% |
Other, net | | | 1 | % | | | 1 | % | | | — | % |
Effective Income Tax Rate | | | 23 | % | | | 23 | % | | | 21 | % |
Temporary differences which gave rise to deferred tax assets and liabilities in 2024 and 2023 are shown in the following table:
| | | | | | | | |
Temporary Differences (in millions) | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
Deferred Tax Assets | | | | | | |
Retirement Benefit Obligations | | $ | 6.1 | | | $ | 11.2 | |
Regulatory Assets & Liabilities | | | 5.6 | | | | — | |
Net Operating Loss Carryforwards | | | 2.3 | | | | 0.1 | |
Tax Credit Carryforwards | | | 2.0 | | | | 1.3 | |
Other, net | | | 2.5 | | | | 1.3 | |
Total Deferred Tax Assets | | $ | 18.5 | | | $ | 13.9 | |
Deferred Tax Liabilities | | | | | | |
Utility Plant Differences | | | 203.6 | | | $ | 180.3 | |
Regulatory Assets & Liabilities | | | — | | | | 8.9 | |
Other, net | | | 1.0 | | | | 0.8 | |
Total Deferred Tax Liabilities | | | 204.6 | | | | 190.0 | |
Net Deferred Tax Liabilities | | $ | 186.1 | | | $ | 176.1 | |
Under the Company’s Tax Sharing Agreement (the Agreement) which was approved upon the formation of Unitil as a public utility holding company, the Company files consolidated Federal and State tax returns and Unitil Corporation and each of its utility operating subsidiaries recognize the results of their operations in its tax returns as if it were a stand-alone taxpayer. The Agreement provides that the Company will account for income taxes in compliance with U.S. GAAP and regulatory accounting principles. The Company has evaluated its tax positions at December 31, 2024 in accordance with the FASB Codification, and has concluded that no adjustment for recognition, de-recognition, settlement or foreseeable future events to any tax liabilities or assets as defined by the FASB Codification is required. The Company remains subject to examination by Maine, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire tax authorities for the tax periods ended December 31, 2023; December 31, 2022; and December 31, 2021.
Income tax filings for the year ended December 31, 2023 have been filed with the IRS, Massachusetts Department of Revenue, the Maine Revenue Service, and the New Hampshire Department of Revenue Administration. In the Company’s federal tax returns for the year ended December 31, 2023 which were filed with the IRS in October 2024, the Company generated federal Net Operating Loss Carryforward (NOLC) assets of $2.9 million increasing the total amount of NOLC to $7.3 million to offset future years income. As of December 31, 2024, the Company recognized the utilization of approximately $6.6 million of the NOLC asset and $1.3 million of federal tax credits available to offset current taxes payable. In addition, at December 31, 2024, the Company had $1.6 million of cumulative state tax credit carryforwards to offset future income taxes payable. If unused, the Company’s state tax credit carryforwards will begin to expire in 2027.
On April 14, 2023, the IRS issued Revenue Procedure 2023-15 that provides a safe harbor method of accounting that taxpayers may use to determine whether to deduct or capitalize expenditures to repair, maintain, replace, or improve natural gas transmission and distribution property. Under the revenue procedure, the method of accounting will depend on the property’s classification as linear transmission property, linear distribution property, or non-linear property. The revenue procedure may be adopted in tax years ending after May 1, 2023. The Company elected a change in its tax accounting method on the 2023 consolidated tax return.
In August 2022, the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 (IRA) was signed into law. The IRA included new taxes on corporations, including the Corporate Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) and the Excise Tax on Repurchase of Corporate Stock. The AMT is equal to 15% of a corporation’s adjusted financial statement income (AFSI). The AMT applies to companies that have a three year average AFSI of greater than $1 billion. The IRA also extended and modified certain renewable energy related credits. The Company has evaluated the IRA provisions and determined that they do not have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements as of December 31, 2024.
In December 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), which included a reduction of the corporate federal income tax rate to 21% effective January 1, 2018, was signed into law. In accordance with FASB Codification Topic 740, the Company revalued its Accumulated Deferred Income Taxes (ADIT) and recorded a net liability in the amount of $48.9 million at December 31, 2017. The Company expects to flow through to customers $47.1 million of excess ADIT in utility base rates. The benefit of protected excess ADIT amounts will be subject to flow back to customers in utility rates according to the Average Rate Assumption Method (ARAM). The Company estimates the ARAM flow back period for protected and unprotected excess ADIT to be between fifteen and twenty years over the remaining life of the related utility plant. As of December 31, 2024, the Company flowed back $11.2 million to customers in its Massachusetts, Maine, New Hampshire and federal jurisdictions.
Note 9: Retirement Benefit Plans
The Company sponsors the following retirement benefit plans to provide certain pension and post-retirement benefits for its retirees and current employees as follows:
•The Unitil Corporation Retirement Plan (Pension Plan)—The Pension Plan is a defined benefit pension plan. Under the Pension Plan, retirement benefits are based upon an employee’s level of compensation and length of service. Effective January 1, 2010, the Pension Plan was closed to new non-union employees. For union employees, the Pension Plan was closed on various dates between December 31, 2010 and June 1, 2013, depending on the various Collective Bargaining Agreements of each union.
•The Unitil Retiree Health and Welfare Benefits Plan (PBOP Plan)—The PBOP Plan provides health care and life insurance benefits to retirees. The Company has established Voluntary Employee Benefit Trusts, into which it funds contributions to the PBOP Plan.
•The Unitil Corporation Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (SERP)—The SERP is a non-qualified retirement plan, with participation limited to executives selected by the Board of Directors.
The following table includes the key assumptions used in determining the Company’s benefit plan costs and obligations:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Used to Determine Plan costs for years ended December 31: | | | | | | | | | |
Discount Rate | | | 5.00 | % | | | 5.25 | % | | | 2.85 | % |
Rate of Compensation Increase | | | 3.00 | % | | | 3.00 | % | | | 3.00 | % |
Expected Long-term rate of return on plan assets | | | 7.50 | % | | | 7.50 | % | | | 7.50 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Used to Determine Benefit Obligations at December 31: | | | | | | | | | |
Discount Rate | | | 5.60 | % | | | 5.00 | % | | | 5.25 | % |
Rate of Compensation Increase | | | 3.00 | % | | | 3.00 | % | | | 3.00 | % |
The health care cost trend rate used to determine plan costs for 2024 for pre-65 retirees is 8.00%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2033, and for post-65 retirees, the health care cost trend rate is 6.00%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2033. The health care cost trend rate used to determine plan costs for 2023 for pre-65 retirees was 8.00%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2030, and for post-65 retirees, the health care cost trend rate was 6.25%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2030.The health care cost trend rate used to determine plan costs for 2022 for both pre-65 retirees and post-65 retirees was 6.20%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2029.
The health care cost trend rate used to determine benefit obligations at December 31, 2024 for pre-65 retirees is 8.50%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2034, and for post-65 retirees, the health care cost trend rate is 7.50%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2034. The health care cost trend rate used to determine benefit obligations at December 31, 2023 for pre-65 retirees was 8.00%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2033, and for post-65 retirees, the health care cost trend rate was 6.00%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2033. The health care cost trend rate used to determine benefit obligations at December 31, 2022 for pre-65 retirees was 8.00%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2030, and for post-65 retirees, the health care cost trend rate was 6.25%, with an ultimate rate of 4.50% in 2030.
The Discount Rate assumptions used in determining retirement plan costs and retirement plan obligations are based on an assessment of current market conditions using high quality corporate bond interest rate indices and pension yield curves. For 2024, a change in the discount rate of 0.25% would have resulted in an increase or decrease of approximately $450,800 in the Net Periodic Benefit Cost (NPBC). The Rate of Compensation Increase assumption used for 2024 was based on the expected long-term increase in compensation costs for personnel covered by the plans.
The following table provides the components of the Company’s Retirement plan costs (000’s):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Plan | | | PBOP Plan | | | SERP | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Service Cost | | $ | 1,990 | | | $ | 2,091 | | | $ | 3,165 | | | $ | 1,988 | | | $ | 1,493 | | | $ | 2,890 | | | $ | 216 | | | $ | 250 | | | $ | 273 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest Cost | | | 7,546 | | | | 7,480 | | | | 5,486 | | | | 3,269 | | | | 2,899 | | | | 3,194 | | | | 723 | | | | 754 | | | | 472 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expected Return on Plan Assets | | | (10,597 | ) | | | (10,689 | ) | | | (10,883 | ) | | | (3,877 | ) | | | (3,408 | ) | | | (3,415 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior Service Cost Amortization | | | 323 | | | | 356 | | | | 356 | | | | — | | | | 794 | | | | 1,092 | | | | 10 | | | | 55 | | | | 55 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Actuarial Loss Amortization | | | 1,446 | | | | — | | | | 5,507 | | | | (874 | ) | | | (1,464 | ) | | | 1,020 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 794 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sub-total | | | 708 | | | | (762 | ) | | | 3,631 | | | | 506 | | | | 314 | | | | 4,781 | | | | 949 | | | | 1,059 | | | | 1,594 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Amounts Capitalized or Deferred | | | 227 | | | | 1,598 | | | | (1,085 | ) | | | 191 | | | | 555 | | | | (2,388 | ) | | | (295 | ) | | | (327 | ) | | | (472 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
NPBC Recognized | | $ | 935 | | | $ | 836 | | | $ | 2,546 | | | $ | 697 | | | $ | 869 | | | $ | 2,393 | | | $ | 654 | | | $ | 732 | | | $ | 1,122 | |
The Company bases the actuarial determination of pension expense on a market-related valuation of assets, which reduces year-to-year volatility. This market-related valuation recognizes investment gains or losses over a three-year period from the year in which they occur. Investment gains or losses for this purpose are the difference between the expected return calculated using the market-related value of assets and the actual return based on the fair value of assets. Since the market-related value of assets recognizes gains or losses over a three-year period, the future value of the market-related assets will be affected as previously deferred gains or losses are recognized. Had the Company used the fair value of assets instead of the market-related value, pension expense for the years 2024, 2023 and 2022 would have been $1.8 million, $2.8 million and $2.4 million respectively, prior to amounts capitalized or deferred.
The following table represents information on the plans’ assets, projected benefit obligations (PBO), and funded status (000’s):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Plan | | | PBOP Plan | | | SERP | |
Change in Plan Assets: | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Plan Assets at Beginning of Year | | $ | 137,893 | | | $ | 126,098 | | | $ | 51,892 | | | $ | 44,770 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Actual Return on Plan Assets | | | 15,146 | | | | 16,822 | | | | 6,224 | | | | 6,865 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Employer Contributions | | | 3,758 | | | | 3,850 | | | | 2,552 | | | | 2,790 | | | | 679 | | | | 665 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Participant Contributions | | | — | | | | — | | | | 260 | | | | 234 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Benefits Paid | | | (7,823 | ) | | | (8,877 | ) | | | (2,526 | ) | | | (2,767 | ) | | | (679 | ) | | | (665 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Plan Assets at End of Year | | $ | 148,974 | | | $ | 137,893 | | | $ | 58,402 | | | $ | 51,892 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in PBO: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PBO at Beginning of Year | | $ | 154,567 | | | $ | 146,953 | | | $ | 66,691 | | | $ | 56,510 | | | $ | 14,854 | | | $ | 14,810 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Service Cost | | | 1,990 | | | | 2,091 | | | | 1,988 | | | | 1,493 | | | | 216 | | | | 250 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest Cost | | | 7,546 | | | | 7,480 | | | | 3,269 | | | | 2,899 | | | | 723 | | | | 754 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Participant Contributions | | | — | | | | — | | | | 260 | | | | 234 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Benefits Paid | | | (7,823 | ) | | | (8,877 | ) | | | (2,526 | ) | | | (2,767 | ) | | | (679 | ) | | | (665 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Actuarial (Gain) or Loss | | | (7,724 | ) | | | 6,920 | | | | 2,525 | | | | 8,322 | | | | (2,367 | ) | | | (295 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PBO at End of Year | | $ | 148,556 | | | $ | 154,567 | | | $ | 72,207 | | | $ | 66,691 | | | $ | 12,747 | | | $ | 14,854 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Funded Status: Assets vs PBO | | $ | 418 | | | $ | (16,674 | ) | | $ | (13,805 | ) | | $ | (14,799 | ) | | $ | (12,747 | ) | | $ | (14,854 | ) |
The decrease in the PBO for the Pension and SERP plans as of December 31, 2024 compared to December 31, 2023 primarily reflects an increase in the assumed discount rate as of December 31, 2024 and normal changes in service cost, interest cost and demographic data. The increase in the PBO for the PBOP plan as of December 31, 2024 compared to December 31, 2023 primarily reflects an increase in medical costs and normal changes in service cost, interest cost and demographic data, partially offset by an increase in the assumed discount rate as of December 31, 2024.
The funded status of the Pension, PBOP and SERP Plans is calculated based on the difference between the benefit obligation and the fair value of plan assets and is recorded on the balance sheets as an asset or a liability. Because the Company recovers the retiree benefit costs from customers through rates, regulatory assets are recorded in lieu of an adjustment to Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income/(Loss).
The Company has recorded on its consolidated balance sheets as a liability the underfunded status of its and its subsidiaries’ retirement benefit obligations based on the projected benefit obligation. The Company has recognized Regulatory Assets, net of deferred tax benefits, of $14.4 million and $29.8 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, to account for the future collection of these plan obligations in electric and gas rates. These amounts are recovered primarily over the average remaining service periods or life expectancies of employees covered by the benefit plans.
The Accumulated Benefit Obligation (ABO) is required to be disclosed for all plans where the ABO is in excess of plan assets. The difference between the PBO and the ABO is that the PBO includes projected compensation increases. The ABO for the Pension Plan was $141.6 million and $146.3 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The ABO for the
SERP was $12.4 million and $14.4 million as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. For the PBOP Plan, the ABO and PBO are the same. (See Note 1 (Summary of Significant Accounting Policies) for further discussion of SERP funding.)
The Company, along with its subsidiaries, expects to continue to make contributions to its Pension Plan in 2025 and future years at minimum required and discretionary funding levels consistent with the amounts recovered in the distribution utilities’ rates for these Pension Plan costs.
The following table represents employer contributions, participant contributions and benefit payments (000’s).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pension Plan | | | PBOP Plan | | | SERP | |
| | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Employer Contributions | | $ | 3,758 | | | $ | 3,850 | | | $ | 3,800 | | | $ | 2,552 | | | $ | 2,790 | | | $ | 12,153 | | | $ | 679 | | | $ | 665 | | | $ | 637 | |
Participant Contributions | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 260 | | | $ | 234 | | | $ | 279 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Benefit Payments | | $ | 7,823 | | | $ | 8,877 | | | $ | 9,724 | | | $ | 2,526 | | | $ | (2,767 | ) | | $ | 3,503 | | | $ | 679 | | | $ | 665 | | | $ | 637 | |
The following table represents estimated future benefit payments (000’s).
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Estimated Future Benefit Payments | |
| | Pension | | | PBOP | | | SERP | |
2025 | | $ | 8,701 | | | $ | 3,532 | | | $ | 678 | |
2026 | | | 9,214 | | | | 3,896 | | | | 677 | |
2027 | | | 10,259 | | | | 4,128 | | | | 676 | |
2028 | | | 10,388 | | | | 4,235 | | | | 1,168 | |
2029 | | | 10,759 | | | | 4,619 | | | | 1,160 | |
2030-2034 | | | 57,528 | | | | 23,650 | | | | 5,620 | |
The Expected Long-Term Rate of Return on Pension Plan assets assumption used by the Company is developed based on input from actuaries and investment managers. The Company’s Expected Long-Term Rate of Return on Pension Plan assets is based on target investment allocation of 54% in common stock equities, 42% in fixed income securities and 4% in real estate securities. The Company’s Expected Long-Term Rate of Return on PBOP Plan assets is based on target investment allocation of 55% in common stock equities and 45% in fixed income securities. The actual investment allocations are shown in the following tables.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pension Plan | | Target
Allocation | | | Actual Allocation at
December 31, | |
| | 2025 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Equity Funds | | | 54 | % | | | 53 | % | | | 57 | % | | | 53 | % |
Debt Funds | | | 42 | % | | | 41 | % | | | 36 | % | | | 38 | % |
Real Estate Fund | | | 4 | % | | | 5 | % | | | 6 | % | | | 7 | % |
Other(1) | | | — | | | | 1 | % | | | 1 | % | | | 2 | % |
Total | | | | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
(1)Represents investments being held in cash equivalents as of December 31, 2024, December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 pending payment of benefits.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PBOP Plan | | Target
Allocation | | | Actual Allocation at
December 31, | |
| | 2025 | | | 2024 | | | 2023 | | | 2022 | |
Equity Funds | | | 55 | % | | | 56 | % | | | 56 | % | | | 55 | % |
Debt Funds | | | 45 | % | | | 44 | % | | | 44 | % | | | 45 | % |
Total | | | | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % | | | 100 | % |
The combination of these target allocations and expected returns resulted in the overall assumed long-term rate of return of 7.50% for 2024. The Company evaluates the actuarial assumptions, including the expected rate of return, at least annually. The primary financial objective of the plans is to earn their expected long-term returns without assuming undue risks of funded status volatility. The target rate of return for the Plans has been based upon an analysis of historical returns supplemented with an economic and structural review for each asset class.
Following is a description of the valuation methodologies used for assets measured at fair value. There have been no changes in the methodologies used at December 31, 2024 and 2023. Please also see Note 1 (Summary of Significant Accounting Policies) for a discussion of the Company’s fair value accounting policy.
Equity, Fixed Income, Index and Asset Allocation Funds
These investments are valued based on quoted prices from active markets. These securities are categorized in Level 1 as they are actively traded and no valuation adjustments have been applied.
Cash Equivalents
These investments are valued at cost, which approximates fair value, and are categorized in Level 1.
Real Estate Fund
These investments are valued at net asset value per unit based on a combination of market- and income-based models utilizing market discount rates, projected cash flows and the estimated value into perpetuity. In accordance with FASB Codification Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurement”, these investments have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy. The fair value amounts presented in the tables below for the Real Estate Fund are intended to permit reconciliation of the fair value hierarchy to the “Plan Assets at End of Year” line item shown in the “Change in Plan Assets” table above.
Assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the Pension Plan as of December 31, 2024 and 2023 are as follows (000’s):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Fair Value Measurements at Reporting Date Using | |
Description | | Balance as of
December 31, | | | Quoted
Prices in
Active
Markets for
Identical
Assets
(Level 1) | | | Significant
Other
Observable
Inputs
(Level 2) | | | Significant
Unobservable
Inputs
(Level 3) | |
2024 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pension Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mutual Funds: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity Funds | | $ | 78,407 | | | $ | 78,407 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Fixed Income Funds | | | 61,741 | | | | 61,741 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Total Mutual Funds | | | 140,148 | | | | 140,148 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Cash Equivalents | | | 1,504 | | | | 1,504 | | | | | | | |
Total Assets in the Fair Value Hierarchy | | $ | 141,652 | | | $ | 141,652 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Real Estate Fund–Measured at Net Asset Value | | | 7,322 | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Assets | | $ | 148,974 | | | | | | | | | | |
2023 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Pension Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mutual Funds: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity Funds | | $ | 78,522 | | | $ | 78,522 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Fixed Income Funds | | | 49,359 | | | | 49,359 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Total Mutual Funds | | | 127,881 | | | | 127,881 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Cash Equivalents | | | 2,266 | | | | 2,266 | | | | | | | |
Total Assets in the Fair Value Hierarchy | | $ | 130,147 | | | $ | 130,147 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Real Estate Fund–Measured at Net Asset Value | | | 7,746 | | | | | | | | | | |
Total Assets | | $ | 137,893 | | | | | | | | | | |
Redemptions of the Real Estate Fund are subject to a sixty-five day notice period and the fund is valued quarterly. There are no unfunded commitments.
Assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis for the PBOP Plan as of December 31, 2024 and 2023 are as follows (000’s):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Fair Value Measurements at Reporting Date Using | |
Description | | Balance as of
December 31, | | | Quoted
Prices in
Active
Markets for
Identical
Assets
(Level 1) | | | Significant
Other
Observable
Inputs
(Level 2) | | | Significant
Unobservable
Inputs
(Level 3) | |
2024 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PBOP Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mutual Funds: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fixed Income Funds | | $ | 25,908 | | | $ | 25,908 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Equity Funds | | | 32,494 | | | | 32,494 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Total Assets | | $ | 58,402 | | | $ | 58,402 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
2023 | | | | | | | | | | | | |
PBOP Plan Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mutual Funds: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fixed Income Funds | | $ | 23,025 | | | $ | 23,025 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Equity Funds | | | 28,867 | | | | 28,867 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Total Assets | | $ | 51,892 | | | $ | 51,892 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Employee 401(k) Tax Deferred Savings Plan—The Company sponsors the Unitil Corporation Tax Deferred Savings and Investment Plan (the 401(k) Plan) under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code and covering substantially all of the Company’s employees. Participants may elect to defer current compensation by contributing to the plan. Employees may direct, at their sole discretion, the investment of their savings plan balances (both the employer and employee portions) into a variety of investment options, including a Company common stock fund.
The Company’s contributions to the 401(k) Plan were $4.5 million, $4.0 million and $3.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Management of the Company, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, and Chief Accounting Officer, conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2024. Based on this evaluation, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, and Chief Accounting Officer concluded as of December 31, 2024 that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) were effective.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f).
Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer, and Chief Accounting Officer, Unitil management has evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based upon criteria established in the “Internal Control–Integrated Framework” (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, Unitil management concluded that Unitil’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2024.
Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, as stated in their report which appears in Part II, Item 8 herein.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in Unitil’s internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f)) during the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2024 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, Unitil’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
(a) On February 10, 2025, the Company issued a press release announcing its results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2024. The press release is furnished with this Annual Report on Form 10-K as Exhibit 99.1.
(b) During the quarter ended December 31, 2024, no director or officer (as defined in Rule 16a-1(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act adopted or terminated a Rule10b5-1 trading arrangement (as defined in Item 408(a)(1)(i) of Regulation S-K promulgated under the Exchange Act) or any non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement (as defined in Item 408(c) of Regulation S-K promulgated under the Exchange Act).
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections.
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Information required by this Item is set forth in the “Proposal 1: Election of Directors” section and the “Description of Management” section of the Proxy Statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held April 30, 2025 (the “Proxy Statement”). Information regarding compliance with Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is set forth in the “Corporate Governance and Policies of the Board—Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” section of the Proxy Statement. Information regarding the Company’s Audit Committee is set forth in the “Committees of the Board—Audit Committee” section of the Proxy Statement. Information regarding the Company’s Code of Ethics is set forth in the “Corporate Governance and Policies of the Board—Code of Ethics” section of the Proxy Statement. Information regarding procedures by which shareholders may recommend nominees to the Company’s Board of Directors is set forth in the “Corporate Governance and Policies of the Board—Nominations” section of the Proxy Statement.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
Information required by this Item is set forth in the “Compensation Discussion and Analysis” and “Compensation of Named Executive Officers” sections of the Proxy Statement.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
Information required by this Item is set forth in the “Beneficial Ownership” section of the Proxy Statement, as well as the Equity Compensation Plan Information table in Part II, Item 5 of this Form 10-K.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
Information required by this Item is set forth in the “Corporate Governance and Policies of the Board—Transactions with Related Persons” and the “Corporate Governance and Policies of the Board—Director Independence” sections of the Proxy Statement.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
Information required by this Item is set forth in the “Audit Committee Report—Principal Accountant Fees and Services” and the “Audit Committee Report—Audit Committee Pre-Approval Policy” sections of the Proxy Statement.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) (1) and (2)—LIST OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
The following financial statements are included herein under Part II, Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data:
•Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (Deloitte & Touche LLP; PCAOB ID No. 34)
•Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022
•Consolidated Balance Sheets—December 31, 2024 and 2023
•Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022
•Consolidated Statements of Changes in Common Stock Equity for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022
•Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
All other schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulation of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instructions, are not applicable, or information required is included in the financial statements or notes thereto and, therefore, have been omitted.
(3)—LIST OF EXHIBITS
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
2.1 | Stock Purchase Agreement among Unitil Corporation, PHC Utilities, Inc., and Hearthstone Utilities, Inc. (d/b/a Hope Companies, Inc.) dated July 8, 2024 | | Exhibit 2.1 to Form 8-K for July 8, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
3.1 (P) | Articles of Incorporation of Unitil Corporation. | | Exhibit 3.1 to Form S-14 Registration Statement No. 2-93769 dated October 12, 1984 |
|
| |
|
3.2 (P) | Articles of Amendment to the Articles of Incorporation of Unitil Corporation filed on March 4, 1992. | | Exhibit 3.2 to Form 10-K for 1991 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
3.3 | Articles of Amendment to the Articles of Incorporation of Unitil Corporation filed on September 23, 2008. | | Exhibit 3.3 to Form S-3/A Registration Statement No. 333-152823 dated November 25, 2008 |
|
| |
|
3.4 | Articles of Amendment to the Articles of Incorporation of Unitil Corporation filed on April 27, 2011. | | Exhibit 4.4 to Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to Form S-3 Registration Statement No. 333-168394, dated January 28, 2014 |
|
| |
|
3.5 | Fourth Amended and Restated By-Laws of Unitil Corporation. | | Exhibit 3.1 to Form 8-K dated April 29, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.1 | Twelfth Supplemental Indenture of Unitil Energy Systems, Inc., successor to Concord Electric Company, dated as of December 2, 2002, amending and restating the Concord Electric Company Indenture of Mortgage and Deed of Trust dated as of July 15, 1958. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 10-K for 2002 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
4.2 | Fitchburg Note Agreement dated January 15, 1999 for the 7.37% Notes due January 15, 2029. | | Exhibit 4.25 to Form 10-K for 1999 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.3 | Fitchburg Note Agreement dated June 1, 2001 for the 7.98% Notes due June 1, 2031. | | Exhibit 4.6 to Form 10-Q for June 30, 2001 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.4 | Fitchburg Note Agreement dated December 21, 2005 for the 5.90% Notes due December 15, 2030. | | (2) |
|
| |
|
4.5 | Thirteenth Supplemental Indenture of Unitil Energy Systems, Inc., dated as of September 26, 2006. | | (2) |
|
| |
|
4.6 | Northern Utilities Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 3, 2008, for the 6.95% Senior Notes, Series A due December 3, 2018 and the 7.72% Senior Notes, Series B due December 3, 2038. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated December 3, 2008 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.7 | Fourteenth Supplemental Indenture of Unitil Energy Systems, Inc., dated as of March 2, 2010. | | Exhibit 4.4 to Form 8-K dated March 2, 2010 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.8 | Northern Utilities form of Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 15, 2014, for the 4.42% Senior Notes, due October 15, 2044. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated October 15, 2014 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.9 | Northern Utilities form of Note issued pursuant to the Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of October 15, 2014, for the 4.42% Senior Notes, due October 15, 2044. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated October 15, 2014 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.10 | Note Purchase Agreement dated August 1, 2016 by and among Unitil Corporation and the several purchasers named therein for the 3.70% Senior Notes, Series 2016, due August 1, 2026. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.11 | 3.70% Senior Note, Series 2016, dated as of August 1, 2016 purchased by Metropolitan Life Insurance Company in the principal amount of $11,200,000. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.12 | 3.70% Senior Note, Series 2016, dated as of August 1, 2016 purchased by Lincoln Benefit Life Company in the principal amount of $4,000,000. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.13 | 3.70% Senior Note, Series 2016, dated as of August 1, 2016 purchased by Lincoln Benefit Life Company in the principal amount of $3,800,000. | | Exhibit 4.4 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | |
|
4.14 | 3.70% Senior Note, Series 2016, dated as of August 1, 2016 purchased by Lincoln Benefit Life Company in the principal amount of $1,000,000. | | Exhibit 4.5 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.15 | 3.70% Senior Note, Series 2016, dated as of August 1, 2016 purchased by United of Omaha Life Insurance Company in the principal amount of $5,000,000. | | Exhibit 4.6 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
4.16 | 3.70% Senior Note, Series 2016, dated as of August 1, 2016 purchased by United of Omaha Life Insurance Company in the principal amount of $3,000,000. | | Exhibit 4.7 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.17 | 3.70% Senior Note, Series 2016, dated as of August 1, 2016 purchased by Companion Life Insurance Company in the principal amount of $2,000,000. | | Exhibit 4.8 to Form 8-K dated August 1, 2016 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.18 | Note Purchase Agreement dated July 14, 2017 by and among Northern Utilities, Inc. and the several purchasers named therein for the 3.52% Senior Notes, Series 2017A, due November 1, 2027 and the 4.32% Senior Notes, Series 2017B, due November 1, 2047. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated July 14, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.19 | Note Purchase Agreement dated July 14, 2017 by and among Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company and the several purchasers named therein for the 3.52% Senior Notes, Series 2017A, due November 1, 2027 and the 4.32% Senior Notes, Series 2017B, due November 1, 2047. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated July 14, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.20 | Note Purchase Agreement dated July 14, 2017 by and among Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. and the several purchasers named therein for the 3.72% Senior Notes, Series 2017A, due November 1, 2027. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated July 14, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.21 (4) | 3.52% Senior Note, Series 2017A, due November 1, 2027, issued by Northern Utilities, Inc. to Great-West Life & Annuity Insurance Company. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated November 1, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.22 (4) | 4.32% Senior Note, Series 2017B, due November 1, 2047, issued by Northern Utilities, Inc. to The Canada Life Insurance Company of Canada. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated November 1, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.23 (4) | 3.52% Senior Note, Series 2017A, due November 1, 2027, issued by Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company to Great-West Life & Annuity Insurance Company. | | Exhibit 4.5 to Form 8-K dated November 1, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.24 (4) | 4.32% Senior Note, Series 2017B, due November 1, 2047, issued by Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company to The Great-West Life Assurance Company. | | Exhibit 4.6 to Form 8-K dated November 1, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.25 (4) | 3.72% Senior Note, Series 2017A, due November 1, 2027, issued by Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. to Thrivent Financial for Lutherans. | | Exhibit 4.8 to Form 8-K dated November 1, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.26 | Bond Purchase Agreement dated November 30, 2018 by and among Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. and the several purchasers named therein for the $30,000,000 aggregate principal amount of first mortgage bonds, Series Q, due November 30, 2048. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated November 30, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.27 | Fifteenth Supplemental Indenture dated November 29, 2018 by and between Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association (as trustee). | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated November 30, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.28 (4) | First Mortgage Bond, Series Q, 4.18%, due November 30, 2048, issued by Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. to United of Omaha Life Insurance Company. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated November 30, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
4.29 | Note Purchase Agreement dated September 12, 2019 by and among Northern Utilities, Inc. and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated September 12, 2019 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.30 (4) | 4.04% Senior Note, Series 2019, due September 12, 2049, issued by Northern Utilities, Inc. to Pacific Life Insurance Company. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated September 12, 2019 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.31 | Note Purchase Agreement dated December 18, 2019 by and among Unitil Corporation and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated December 18, 2019 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.32 (4) | 3.43% Senior Note, Series 2019, due December 18, 2029, issued by Unitil Corporation to CHIMEFISH & CO, as nominee for American Equity Investment Life Insurance Company. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated December 18, 2019 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.33 | Note Purchase Agreement dated September 15, 2020 by and among Northern Utilities, Inc. and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated September 15, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.34 (4) | 3.78% Senior Note, Series 2020, due September 15, 2040, issued by Northern Utilities, Inc. to Metropolitan Life Insurance Company. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated September 15, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.35 | Note Purchase Agreement dated September 15, 2020 by and among Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated September 15, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.36 (4) | 3.78% Senior Note, Series 2020A, due September 15, 2040, issued by Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company to Brighthouse Life Insurance Company of NY. | | Exhibit 4.4 to Form 8-K dated September 15, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.37 | Bond Purchase Agreement dated September 15, 2020 by and among Unitil Energy Systems, Inc., U.S. Bank National Association (as trustee), and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.5 to Form 8-K dated September 15, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.38 | Sixteenth Supplemental Indenture dated September 15, 2020 by and between Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association (as trustee). | | Exhibit 4.6 to Form 8-K dated September 15, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.39 (4) | First Mortgage Bond, Series R, 3.58%, due September 15, 2040, issued by Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. to CUDD and CO (as nominee for Symetra Life Insurance Company). | | Exhibit 4.7 to Form 8-K dated September 15, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.40 (5) | Bond Purchase Agreement dated August 21, 2024 by and among Unitil Energy Systems, Inc., U.S. Bank Trust Company, National Association (as trustee) and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.11 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.41 | Seventeenth Supplemental Indenture dated August 21, 2024 by and between Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. and U.S. Bank Trust Company, National Association (as trustee) | | Exhibit 4.12 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
4.42 (4) | First Mortgage Bond, Series S, 5.69%, due August 21, 2054, issued by Unitil Energy Systems, Inc. to Metlife Reinsurance Company of Hamilton, Ltd. | | Exhibit 4.13 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.43 (5) | Note Purchase Agreement dated July 6, 2023 by and among Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated July 6, 2023 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.44 (4) | 5.70% Senior Note, Series 2023A, due July 2, 2033, issued by Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company to MetLife Reinsurance Company of Hamilton, Ltd. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated July 6, 2023 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.45 (4) | 5.96% Senior Note, Series 2023B, due July 2, 2053, issued by Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company to Mutual of Omaha Insurance Company | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated July 6, 2023 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.46 (5) | Note Purchase Agreement dated August 21, 2024 by and among Unitil Corporation and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.47 (4) | 5.99% Senior Note, Series 2024, due August 21, 2034, issued by Unitil Corporation to Metropolitan Tower Life Insurance Company | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.48 (5) | Note Purchase Agreement dated August 21, 2024 by and among Northern Utilities, Inc. and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.49 (4) | 5.54% Senior Note, Series 2024A, due August 21, 2034, issued by Northern Utilities, Inc. to Metropolitan Life Insurance Company | | Exhibit 4.4 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.50 (4) | 5.74% Senior Note, Series 2024B, due August 21, 2039, issued by Northern Utilities, Inc.to Modern Woodmen of America. | | Exhibit 4.5 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.51 (5) | Note Purchase Agreement dated August 21, 2024 by and among Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company and the several purchasers named therein | | Exhibit 4.6 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.52 (4) | 5.54% Senior Note, Series 2024A, due August 21, 2034, issued by Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company to Metlife Reinsurance Company of Hamilton, Ltd. | | Exhibit 4.7 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.53 (4) | 5.99% Senior Note, Series 2024B, due August 21, 2044, issued by Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company to Metlife Reinsurance Company of Hamilton, Ltd. | | Exhibit 4.8 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.54 (5) | Note Purchase Agreement dated August 21, 2024 by and among Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. and the several purchasers named therein. | | Exhibit 4.9 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.55 (4) | 5.74% Senior Note, Series 2024, due August 21, 2034, issued by Granite State Gas Transmission, Inc. to Metropolitan Life Insurance Company | | Exhibit 4.10 to Form 8-K for August 21, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
4.56 | Amended and Restated Note issued to Bank of America, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated July 25, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.57 | Loan Agreement dated December 18, 2020 between Unitil Realty Corp. and TD Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.48 to Form 10-K for 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.58 | Mortgage and Security Agreement dated December 18, 2020 between Unitil Realty Corp. and TD Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.49 to Form 10-K for 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.59 | Mortgage Loan Note dated December 18, 2020 issued to TD Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.50 to Form 10-K for 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.60 | Description of Registrant’s Securities | | Exhibit 4.50 to Form 10-K for 2021 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.61 (5) | Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated September 29, 2022 among Unitil Corporation, Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, and the Lenders | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated September 29, 2022 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.62 | First Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement between Unitil and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent, dated July 18, 2024 | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K for July 18, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.63 | Second Amended and Restated Note issued to Citizens Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated September 29, 2022 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
4.64 | Second Amended and Restated Note issued to TD Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated September 29, 2022 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.65 (5) | Second Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated January 29, 205 among Unitil Corporation; Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent; and Bank of America, N.A., Citizens Bank, N.A., and TD Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K dated January 29, 2025 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.66 | Third Amended and Restated Note issued to Citizens Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K dated January 29, 2025 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
4.67 | Third Amended and Restated Note issued to TD Bank, N.A. | | Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K dated January 29, 2025 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
10.1 (3) | Amended and Restated Form of Severance Agreement between the Company and the persons listed at the end of such Agreement. | | Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K dated June 19, 2008 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.2 (3) | Amended and Restated Form of Severance Agreement between the Company and the persons listed at the end of such Agreement. | | Exhibit 10.3 to Form 8-K dated June 19, 2008 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.3 (3) | Amended and Restated Form of Severance Agreement (Three-Year Term). | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K dated July 25, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
10.4 (3) | Amended and Restated Form of Severance Agreement (Two-Year Term). | | Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K dated July 25, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.5 (3) | Amended and Restated Form of Severance Agreement (Two-Year Term; Non Pension). | | Exhibit 10.3 to Form 8-K dated July 25, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.6 (3) | Severance Agreement dated March 23, 2020, between the Company and Daniel J. Hurstak. | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K dated March 19, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.7 (3) | Severance Agreement dated July 29, 2020, between the Company and Robert B. Hevert. | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K dated July 29, 2020 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.8 (3) | Amended and Restated Unitil Corporation Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan effective as of December 31, 2016. | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q for March 31, 2017 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.9 (3) | Amended and Restated Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan. | | Exhibit 10.5 to Form 8-K dated July 25, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.10 (3) | Unitil Corporation Deferred Compensation Plan. | | Exhibit 10.6 to Form 8-K dated July 25, 2018 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.11 (3) | Unitil Corporation Management Incentive Plan (amended and restated as of June 5, 2013). | | Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K dated June 5, 2013 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.12 (3) | Unitil Corporation Second Amended and Restated 2003 Stock Plan. | | Appendix 1 to the Proxy Statement filed on Schedule 14A dated March 13, 2012 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.13 (3) | Unitil Corporation Third Amended and Restated 2003 Stock Plan. | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q for March 31, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
10.14 (3) | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the Unitil Corporation Second Amended and Restated 2003 Stock Plan. | | Exhibit 4.7 to Form S-8 Registration Statement No. 333-184849 dated November 9, 2012 |
|
| |
|
10.15 (3) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement under the Unitil Corporation Second Amended and Restated 2003 Stock Plan. | | Exhibit 4.8 to Form S-8 Registration Statement No. 333-184849 dated November 9, 2012 |
|
| |
|
10.16 (3) | Unitil Corporation Tax Deferred Savings and Investment Plan, as amended and restated effective as of January 1, 2021. | | Exhibit 10.15 to Form 10-K for 2021 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
| | | |
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | | Reference (1) |
| | | |
10.17 (3) | Unitil Corporation Tax Deferred Savings and Investment Plan Trust Agreement. | | Exhibit 4.2 to Form S-8 Registration Statement No. 333-234391 dated October 31, 2019 |
|
| |
|
10.18 (3) | Unitil Corporation Incentive Plan (amended and restated as of January 26, 2015). | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q for March 31, 2015 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.19 (3) | Employment Agreement effective April 25, 2021 between Unitil Corporation and Thomas P. Meissner, Jr. | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K dated April 28, 2021 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
10.20 (3) | Employment Agreement between Unitil Corporation and Thomas P. Meissner, Jr. | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K for May 1, 2024 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.21 (3) | Unitil Corporation—Compensation of Directors effective as of January 1, 2022. | | Exhibit 10.21 to Form 10-K for 2021 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
10.22 (3) | Unitil Corporation - Compensation of Directors effective as of January 1, 2024 | | Exhibit 10.20 to Form 10-K for 2023 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
10.23 (3) | Unitil Corporation - Compensation of Directors effective as of January 1, 2025 | | Filed herewith |
| | | |
10.24 | Underwriting Agreement dated August 4, 2021 among Unitil Corporation, on the one hand, and RBC Capital Markets, LLC and BofA Securities, Inc., on the other hand, for themselves and as representatives of the several underwriters named therein. | | Exhibit 1.1 to Form 8-K dated August 3, 2021 (File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
10.25 (3) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Time Vesting) | | Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K dated January 24, 2023 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
10.26 (3) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Performance Vesting) | | Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K dated January 24, 2023 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
10.27 (5) | Transition Services Agreement dated January 31, 2025 between Bangor Natural Gas Company and Hearthstone Holdings, Inc. (d/b/a Hope Utilities, Inc.), acknowledged by Unitil Corporation | | Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K dated January 29, 2025 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
|
| |
|
19.1 | Unitil Corporation Corporate Governance Guidelines and Policies of the Board of Directors (includes the Registrant’s insider trading policies and procedures) | | Exhibit 19.1 to Form 10-K for 2023 (SEC File No. 1-8858) |
| | | |
19.2 | Unitil Corporation Insider Trading Policy | | Filed herewith |
| | | |
21.1 | Statement Re: Subsidiaries of Registrant. | | Filed herewith |
|
| |
|
23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | | Filed herewith |
|
| |
|
31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to Rule 13a-14 of the Exchange Act, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | | Filed herewith |
|
| |
|
(1) The exhibits referred to in this column by specific designations and dates have heretofore been filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission under such designations and are hereby incorporated by reference.
(2) In accordance with Item 601(b)(4)(iii)(A) of Regulation S-K, the instrument defining the debt of the Registrant and its subsidiary, described above, has been omitted but will be furnished to the Commission upon request.
(3) These exhibits represent a management contract or compensatory plan.
(4) This Note or Bond (each, an “Instrument”) is substantially identical in all material respects to other Instruments that are otherwise required to be filed as exhibits, except as to the registered payee of such Instrument, the identifying number of such Instrument, and the principal amount of such Instrument. In accordance with instruction no. 2 to Item 601 of Regulation S-K, the registrant has filed a copy of only one of such Instruments, with a schedule identifying the other Instruments omitted and setting forth the material details in which such Instruments differ from the Instrument that was filed. The registrant acknowledges that the Securities and Exchange Commission may at any time in its discretion require filing of copies of any Instruments so omitted.
(5) In accordance with Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K, this exhibit omits certain of its schedules and exhibits. This exhibit’s table of contents, or the cover page of its omitted schedules and exhibits, includes a brief description of the subject matter of all of its omitted schedules and exhibits. The Registrant acknowledges that it must provide a copy of any omitted schedules or exhibits to the Securities and Exchange Commission or its staff upon request.
(P) Paper exhibit.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
| | | |
|
| UNITIL CORPORATION |
|
|
|
|
Date February 10, 2025 |
| By | /S/ THOMAS P. MEISSNER, JR. |
|
|
| Thomas P. Meissner, Jr. |
|
|
| Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | |
Signature | | Capacity | | Date |
| | | | |
/s/ THOMAS P. MEISSNER, JR. | | Principal Executive Officer; Director | | February 10, 2025 |
Thomas P. Meissner, Jr. | | | | |
| | | | |
/S/ DANIEL J. HURSTAK Daniel J. Hurstak | | Principal Financial Officer | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ TODD R. DIGGINS Todd R. Diggins | | Principal Accounting Officer | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ MICHAEL B. GREEN Michael B. Green | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ EDWARD F. GODFREY Edward F. Godfrey | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ WINFIELD S. BROWN Winfield S. Brown | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ NEVEEN F. AWAD Neveen F. Awad | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ DAVID A. WHITELEY David A. Whiteley | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ SUZANNE FOSTER Suzanne Foster | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ JUSTINE VOGEL Justine Vogel | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| |
| |
|
/S/ MARK H. COLLIN Mark H. Collin | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
| | | | |
/s/ ANNE L. ALONZO | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
Anne L. Alonzo | | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ JANE LEWIS RAYMOND | | Director | | February 10, 2025 |
Jane Lewis-Raymond | | | | |
