UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| ☑ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | ||||
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2023
OR
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | ||||
Commission file number 001-11625

| Pentair plc | ||
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
| Ireland | 98-1141328 | |||||||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification number) | |||||||
| Regal House, 70 London Road, | Twickenham, | London, | TW13QS | United Kingdom | |||||||||||||||||||
| (Address of principal executive offices) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: 44-74-9421-6154
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered | ||||||
| Ordinary Shares, nominal value $0.01 per share | PNR | New York Stock Exchange | ||||||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☑
No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☑
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports) and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☑ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer”, “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☑ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☐ | Emerging growth company | ☐ | ||||||||||||||||||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management’s assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☑
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether the financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☑
Aggregate market value of voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant, based on the closing price of $64.60 per share as reported on the New York Stock Exchange on June 30, 2023 (the last business day of Registrant’s most recently completed second quarter): $10,553,275,633.
The number of shares outstanding of Registrant’s only class of common stock on December 31, 2023 was 165,334,513.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Parts of the Registrant’s definitive proxy statement for its annual general meeting to be held on May 7, 2024, are incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K in response to Part III, ITEM 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14.
Pentair plc
Annual Report on Form 10-K
For the Year Ended December 31, 2023
| Page | ||||||||||||||
| PART I | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 1. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 1A. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 1B. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 1C. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 2. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 3. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 4. | ||||||||||||||
| PART II | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 5. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 6. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 7. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 7A. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 8. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 9. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 9A. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 9B. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 9C. | ||||||||||||||
| PART III | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 10. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 11. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 12. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 13. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 14. | ||||||||||||||
| PART IV | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 15. | ||||||||||||||
| ITEM 16. | ||||||||||||||
PART I
ITEM 1. BUSINESS
Unless the context otherwise indicates, references herein to “Pentair,” the “Company,” and such words as “we,” “us,” and “our” include Pentair plc and its consolidated subsidiaries.
GENERAL
At Pentair, we help the world sustainably move, improve and enjoy water, life’s most essential resource. From our residential and commercial water solutions to industrial water management and everything in between, Pentair is focused on smart, sustainable water solutions that help people and the planet thrive.
Pentair strategy
Our vision is to be the world’s most valued sustainable water solutions company for our employees, customers and shareholders. As a company, we:
•Focus on growth in our core businesses and strategic initiatives;
•Accelerate digital, innovation, technology and environmental, social and governance (“ESG”) investments;
•Expedite growth and drive margin expansion through our Transformation Program; and
•Build a high performance growth culture and deliver on our commitments while living our Win Right values.
HISTORY AND DEVELOPMENT
We are an Irish public limited company that was formed in 2014. We are the successor to Pentair Ltd., a Swiss corporation formed in 2012, and Pentair, Inc., a Minnesota corporation formed in 1966 and our wholly-owned subsidiary, under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). Although our jurisdiction of organization is Ireland, we manage our affairs so that we are centrally managed and controlled in the United Kingdom (the “U.K.”) and therefore have our tax residency in the U.K.
In July 2022, as part of our Water Solutions reporting segment, we acquired the issued and outstanding equity securities of certain subsidiaries of Welbilt, Inc. (“Welbilt”) and certain other assets, rights, and properties, and assumed certain liabilities, comprising Welbilt’s Manitowoc Ice business (“Manitowoc Ice”), for approximately $1.6 billion in cash.
Our registered principal office is located at Regal House, 70 London Road, Twickenham, London, TW13QS United Kingdom. Our management office in the United States (“U.S.”) is located at 5500 Wayzata Boulevard, Suite 900, Golden Valley, Minnesota.
BUSINESS AND PRODUCTS
Pentair is comprised of three reportable business segments: Flow, Water Solutions and Pool. The following is a brief description of each of the Company’s reportable segments and business activities.
Flow
The Flow segment (formerly named the Industrial & Flow Technologies segment) delivers water where it is needed, when it is needed, more efficiently and transforms waste into value. This segment designs, manufactures and sells a variety of fluid treatment and pump products and systems, including pressure vessels, gas recovery solutions, membrane bioreactors, wastewater reuse systems and advanced membrane filtration, separation systems, water disposal pumps, water supply pumps, fluid transfer pumps, turbine pumps, solid handling pumps, and agricultural spray nozzles, while serving the global residential, commercial and industrial markets. These products and systems are used in a range of applications, including fluid delivery, ion exchange, desalination, food and beverage, separation technologies for the oil and gas industry, residential and municipal wells, water treatment, wastewater solids handling, pressure boosting, circulation and transfer, fire suppression, flood control, agricultural irrigation and crop spray.
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, our residential and irrigation flow businesses, which sell pumps focused on residential and agriculture, comprised approximately 39% of Flow sales. Another approximately 27% of Flow sales were from the commercial & infrastructure flow businesses, which sell larger pumps focused on fire suppression, wastewater and flood control. The remaining approximately 34% of Flow sales were from the industrial solutions business, comprised of applications focused on industrial process filtration and sustainable gas.
Flow brand names include Pentair Flow, Aurora, Berkeley, Codeline, Fairbanks-Nijhuis, Haffmans, Hydromatic, Hypro, Jung Pumpen, Myers, Sta-Rite, Shurflo, Südmo and X-Flow.
1
Customers
Flow customers include businesses engaged with end users, and wholesale and retail distribution in the residential, commercial, food and beverage, and industrial vertical markets.
Seasonality
We have historically experienced increased demand following warm weather trends for residential water supply and agricultural products. Such demand historically has been at seasonal highs from April to August. Seasonal effects may vary from year to year and are impacted by weather patterns, particularly by temperatures, heavy flooding and droughts.
Competition
Flow faces numerous domestic and international competitors, some of which have substantially greater resources directed to the vertical markets in which we compete. Competition focuses on brand names, product performance (including energy-efficient offerings and required specifications), quality, service and price. We compete by offering a wide variety of innovative and high-quality products, which are competitively priced.
Water Solutions
The Water Solutions segment provides great tasting, higher-quality water and ice while helping people use water more productively. This segment designs, manufactures and sells commercial and residential water treatment products and systems including pressure tanks, control valves, activated carbon products, commercial ice machines, conventional filtration products, and point-of-entry and point-of-use water treatment systems. These water treatment products and systems are used in residential whole home water filtration, drinking water filtration and water softening solutions in addition to commercial water management and filtration in foodservice operations. In addition, our water solutions business also provides installation and preventative services for water management solutions for commercial operators.
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2023, our commercial business, which products include pressure tanks, control valves, activated carbon products, commercial ice machines, conventional filtration products, and commercial point-of-entry and point-of-use water treatment systems, comprised approximately 67% of Water Solutions sales. In addition, our commercial business also provides installation and preventative services for water management solutions for commercial operators. The other approximately 33% of Water Solutions sales were associated with our residential business, which primarily focuses on products associated with residential point of entry and point of use filtration and softening systems.
Water Solutions brand names include Pentair Water Solutions, Everpure, Fleck, KBI, Manitowoc Ice, Pentek and RainSoft.
Customers
Water Solutions customers include businesses engaged in wholesale and retail distribution in the residential, commercial and food and beverage vertical markets. Customers also include end users, consumers, commercial operators and original equipment manufacturers.
Seasonality
We experience seasonal demand with several end customers and end users within Water Solutions. End-user demand for water solution products generally follows warm weather trends and is at seasonal highs from April to September.
Competition
Water Solutions faces numerous domestic and international competitors, some of which have substantially greater resources directed to the vertical markets in which we compete. Competition focuses on brand names, product performance (including required specifications), quality and price. We compete by offering a wide variety of innovative and high-quality products, which are competitively priced. We believe our distribution channels and reputation for quality also provide us a competitive advantage.
Pool
The Pool segment provides innovative, energy-efficient pool solutions to help people more sustainably enjoy water. This segment designs, manufactures and sells a complete line of energy-efficient residential and commercial pool equipment and accessories including pumps, filters, heaters, lights, automatic controls, automatic cleaners, maintenance equipment and pool accessories. Applications for our pool products include residential and commercial pool maintenance, pool repair, renovation, service and construction and aquaculture solutions.
The primary brand names associated with the Pool segment are Pentair Pool, Kreepy Krauly, Pleatco and Sta-Rite.
Customers
Pool customers include businesses engaged in wholesale and retail distribution in the residential and commercial vertical markets. Customers in the residential and commercial verticals also include end users and consumers.
2
One customer in the Pool business represented approximately 15% and 20% of our consolidated net sales in 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Seasonality
We have historically experienced seasonal demand with several end customers and end users. End-user demand for pool equipment follows warm weather trends and historically has been at seasonal highs from April to August. The magnitude of the sales spike has historically been partially mitigated by employing some advance sale “early buy” programs (generally including extended payment terms and/or additional discounts).
Competition
Pool faces numerous domestic and international competitors, some of which have substantially greater resources directed to the vertical markets in which we compete. Competition focuses on brand names, product performance (including energy-efficient offerings and required specifications), quality, service and price. We compete by offering a wide variety of innovative and high-quality products, which are competitively priced. We believe our distribution channels and reputation for quality also provide us a competitive advantage.
INFORMATION REGARDING ALL REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
Research and development
We conduct research and development activities primarily in our own facilities. These efforts consist mostly of the development of new products, product applications and manufacturing processes.
Raw materials
The principal materials we use in manufacturing our products are mild steel, stainless steel, electronic components (including drives and motors), plastics (resins, fiberglass, epoxies), metals and paint (powder and liquid). In addition to the purchase of raw materials, we purchase some finished goods for distribution for resale.
We purchase the materials we use in various manufacturing processes on the open market. We believe the majority of such materials are available through multiple sources and in adequate supply. We have certain long-term commitments, principally price commitments, for the purchase of various component parts and raw materials and continue to work with our suppliers to maintain delivery continuity. Alternate sources of supply are available for most materials and we believe that the termination of any of these commitments would not have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows. Global container transportation delays may also affect raw material availability and lead times.
Certain commodities, such as metals and resins, are subject to commodity market and duty-driven price fluctuations. We manage these fluctuations through several mechanisms, including long-term agreements with price adjustment clauses for significant commodity market movements in certain circumstances. Prices for raw materials, such as metals, may trend higher in the near future due to the volatile market trends.
Intellectual property
Patents, non-compete agreements, proprietary technologies, customer relationships, trademarks, trade names and brand names are important to our business. However, we do not regard our business as being materially dependent upon any single patent, non-compete agreement, proprietary technology, customer relationship, trademark, trade name or brand name.
Patents, patent applications and license agreements will expire or terminate over time by operation of law, in accordance with their terms or otherwise. We do not expect the termination of patents, patent applications or license agreements to have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Human capital resources
We believe our success depends on our ability to attract, develop and retain strong employees. We believe a deep-rooted culture energizes our employees to make a difference within and beyond the workplace. We strive to be the destination for top talent, and work hard to develop and retain high performers throughout their career. We also believe our Win Right values, positive culture and commitment to inclusion and diversity foster innovation and curiosity, which, in turn, contribute to us being an industry leader.
As of December 31, 2023, we had approximately 10,500 employees worldwide, of which approximately 49% are located in the U.S. A small portion of our U.S. employees are unionized, while outside the U.S., we have employees in certain countries, particularly in Europe, that are represented by an employee representative organization, such as a union, works council or employee association.
3
Employee engagement and development
Engaging our employees and developing their careers is important to our long-term success and ties directly to our Win Right culture and values. We support our Win Right culture by providing dedicated culture training to all our employees globally. We engage with our employees and gather feedback about our employee programs, practices and policies through various approaches that include town hall meetings where Pentair leaders share strategies and perspectives; quarterly leadership meetings to help ensure our results and expectations are clearly communicated; and an annual senior leadership meeting to help drive growth and productivity initiatives, share best practices, and invest in our leaders. In addition, we conduct employee engagement and pulse surveys multiple times a year to gauge the level of engagement and actions needed on culture, the business, employee experience and retention. We provide those insights transparently down to the manager level to drive quick insights, development and action planning to drive change.
Training and development
To support employees in their career journey, we have developed and shared, through our dedicated development site, a number of tools and resources. We recently rolled out career pathing and development resources for all functions throughout Pentair. We support development annually with a dedicated career week, individual development planning and targeted development experiences supported through live training sessions; on-demand eLearning and virtual classrooms; and downloadable materials. Additionally, our annual talent management process supports employees to set objectives, receive feedback and development, and build development plans with their leaders.
Our talent development efforts span across all levels of our organization, including our early career Leadership Development Program, a 36-month program in which future leaders participate in rotations intended to develop their capabilities through organization-wide exposure, and our Growth Manager development programs that prepare our new and experienced managers to be more effective and inclusive leaders at Pentair.
Inclusion and diversity
Our commitment to inclusion and diversity is part of living our Win Right values. Our success also depends on our ability to attract, engage and retain a diverse group of employees. We believe an inclusive and diverse workforce contributes different perspectives and innovative ideas that enable us to improve every day. We believe that every employee should be provided the same opportunity to be heard, respected, have a sense of belonging and contribute to our mission. Race, gender, ethnicity, country of origin, age, personal style, sexual orientation, physical ability, religion, life experiences and many more factors contribute to this diversity. Our Business Resource Groups have been put into place to help promote a culture of inclusion through employees providing feedback and sponsoring awareness, education and engagement.
Our statistics are a measure of our performance, and we are committed to advancing a diverse workplace. The following sets forth information regarding the diversity of our workforce as of December 31, 2023:
| Percent of workforce | Percent of leadership roles (3) | |||||||
Minorities (1) | 38% | 24% | ||||||
Women (2) | 31% | 31% | ||||||
(1) Inclusive of the following racial minority groups: Black/African American, Hispanic/Latino, American Indian/Alaskan Native, Asian, Native Hawaiian/Other Pacific Islander. Data for U.S. employee population only. | ||||||||
(2) Global data. | ||||||||
(3) Leadership roles are those of employees who are director level and above. | ||||||||
We take an integrated approach to supporting and promoting workplace inclusion and diversity including: ensuring leadership involvement and ownership; attracting and retaining diverse talent at all levels; fostering a globally aware, inclusive culture; and ensuring our practices are fair and nondiscriminatory. In addition, we promote an inclusive and diverse workplace through: a training called the “The Power of Inclusion”; Business Resource Groups led by employees; Pentair’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics; and an Inclusion and Diversity Hub on our company’s intranet.
Health, safety and wellness
We are committed to providing a safe workplace for all of our employees. We encourage employees to “Stop Work” anytime there is a potential concern regarding worker safety, and promote an open door policy so that all of our employees feel free to speak to their manager if there are any potential health, safety, compliance or sustainability concerns. Additionally, each site maintains a confidential reporting process, and we encourage the use of the Ethics Hotline for employees to report anonymously potential safety concerns. All locations, enterprise wide, must meet and/or exceed regulatory agency standards as applicable to each site’s location.
4
Compensation and benefits
In the U.S., all non-union full-time employees are eligible to receive the following benefits: short-term and long-term disability insurance; flexible and health savings accounts and wellness programs; health insurance (medical, pharmacy, dental); eight weeks paid parental leave for birth, adoptive and foster parents; two weeks paid caregiver leave; legal services; retirement benefits; stock ownership; tuition reimbursement; holidays; vacation and sick time. Union employee benefits vary by contract.
ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) Activities
As a leading provider of smart, sustainable water solutions and with a foundation of Win Right values, we recognize that the work we do and the products and services we provide help to improve lives and the environment around the world. Pentair strives to be a positive influence on the social and environmental issues of today. We are focused on building on our Win Right values and culture by further contributing to the development of a sustainable and responsible society that we believe will also drive our future growth. We are also focused on further integrating our sustainability goals throughout our business by creating accountability for our social responsibility strategy and shared commitments and targets. We have established a formal social responsibility program to further advance our social responsibility goals.
In 2020, Pentair completed a formal ESG assessment to identify ESG topics of importance to our shareholders, customers, suppliers, employees and communities. Through engagement with these stakeholders, internal business leaders and subject matter experts, we identified key ESG topic areas, which ultimately culminated in Pentair’s Social Responsibility Strategic Targets (“Strategic Targets”), which we announced in 2021. In 2023, Pentair completed a refreshed ESG assessment in alignment with the European Union’s Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (“CSRD”). This assessment supported the topics focused on for our Strategic Targets and they remain in effect. We expect to use the results of our updated ESG assessment for continued sustainability strategic planning and risk management, as well as to determine future disclosure requirements under CSRD.
Annually, we publish a corporate responsibility report on our ESG and social responsibility activities and accomplishments, which can be found on our corporate website, and which is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Environmental Matters
See ITEM 1A “Risk Factors – We are exposed to potential environmental laws, liabilities and litigation.”
Captive insurance subsidiary
A portion of our property and casualty insurance program is insured through our regulated wholly-owned captive insurance subsidiary, Penwald Insurance Company (“Penwald”). Reserves for policy claims are established based on actuarial projections of ultimate losses. Accruals with respect to liabilities insured by third parties, such as liabilities arising from acquired businesses, pre-Penwald liabilities and those of certain non-U.S. operations, are established.
Matters pertaining to Penwald are discussed in ITEM 8, Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements – Insurance subsidiary, included in this Form 10-K.
Available information
We make available free of charge (other than an investor’s own Internet access charges) through our Internet website (https://www.pentair.com) our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and if applicable, amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). Reports of beneficial ownership filed by our directors and executive officers pursuant to Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act are also available on our website. We are not including the information contained on our website as part of, or incorporating it by reference into, this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
In addition, the SEC maintains an internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC, and you may access any materials we file with the SEC through their website at www.sec.gov.
5
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
You should carefully consider all of the information in this document and the following risk factors before making an investment decision regarding our securities. Any of the following risks could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and the actual outcome of matters as to which forward-looking statements are made in this document.
Risks Relating to Our Business
General global economic and business conditions affect demand for our products.
We compete in various geographic regions and product markets around the world. Among these, the most significant are global industrial, commercial, and residential markets. We have experienced, and expect to continue to experience, fluctuations in revenues and results of operations due to economic and business cycles. In particular, during 2021, we had higher than anticipated demand in our pool business and certain parts of our residential and commercial businesses. However, such demand in our pool and other residential businesses declined during 2022 and 2023 as we saw inventory correcting within our residential distribution channels and may not be repeated in future periods. Important factors for our businesses and the businesses of our customers include the overall strength of the global economy and various regional economies and our customers’ confidence in these economies, industrial and governmental capital spending, the strength of residential and commercial real estate markets, residential housing markets, the commercial business climate, global supply chain stability, unemployment rates, availability of consumer and commercial financing, interest rates, inflation rates, and energy and commodity prices. Recessions, economic downturns, inflation, slowing economic growth and social and political instability in the industries and/or markets where we compete could negatively affect our revenues and financial performance in future periods, result in future restructuring charges, and adversely impact our ability to grow or sustain our business. For example, current macroeconomic and political instability caused by global supply chain disruptions, inflation and the strengthening of the U.S. dollar have and could continue to adversely impact our results of operations. In addition, military conflicts, such as those between Russia and Ukraine and Hamas and Israel, and their impact on economies may adversely impact our results of operations. The businesses of many of our industrial customers are to varying degrees cyclical and have experienced periodic downturns. While we attempt to minimize our exposure to economic or market fluctuations by serving a balanced mix of end markets and geographic regions, any of the above factors, individually or in the aggregate, or a significant or sustained downturn in a specific end market or geographic region could reduce demand for our products and services, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We compete in attractive markets with a high level of competition, which may result in pressure on our profit margins and limit our ability to maintain or increase the market share of our products.
The markets for our products and services are geographically diverse and highly competitive. We compete against large and well-established national and global companies, regional and local companies, diversified and pure-play companies, and lower cost manufacturers. Competition may also result from new entrants into the markets we serve offering products and/or services that compete with ours. We compete based on technical expertise, intellectual property, reputation for quality and reliability, timeliness of delivery, previous installation history, contractual terms, service offerings, customer experience and service, and price. Some of our competitors attempt to compete based primarily on price, localized expertise and local relationships, especially with respect to products and applications that do not require a great deal of engineering or technical expertise. In addition, during economic downturns, average selling prices tend to decrease as market participants compete more aggressively on price. Moreover, demand for our products, which impacts profit margins, is affected by changes in customer order patterns, such as changes in the levels of inventory maintained by customers and the timing of customer purchases, adoption of new technology and connected products, and changes in customers’ preferences for our products, including the success of products offered by our competitors. Customer purchasing behavior may also shift by product mix in the market or result in a shift to new distribution channels. If we are unable to continue to differentiate our products, services and solutions or adapt to changes in customer purchasing behavior or shifts in distribution channels, or if we are unable to maintain our desired pricing or forced to incur additional costs to remain competitive, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our future growth is dependent upon our ability to transform and adapt our products, services, solutions, and organization to meet the demands of local markets in both developed and emerging economies and by developing or acquiring new technologies that achieve market acceptance with acceptable margins.
We operate in global markets that are characterized by customer demand that is often global in scope but localized in delivery. We compete with thousands of smaller regional and local companies that may be positioned to offer products produced at lower cost than ours, or to capitalize on highly localized relationships and knowledge that are difficult for us to replicate. Also, in several emerging markets, potential customers prefer local suppliers, in some cases because of existing relationships and in other cases because of local legal restrictions or incentives that favor local businesses. In addition, we need to be flexible to adapt our products to ever changing customer preferences, including those relating to regulatory, climate change and social
6
responsibility matters. We have identified specific product and geographic market opportunities that we find attractive and continue to pursue, both within and outside the U.S. We expect to continue investing in our businesses to drive these opportunities through research and development and additional sales and marketing resources. Unless we successfully penetrate these markets, our core sales growth will likely be limited or may decline. Accordingly, our future success depends upon a number of factors, including our ability to transform and adapt our products, services, solutions, organization, workforce and sales strategies to fit localities throughout the world, particularly in high growth emerging markets; identify emerging technological and other trends in our target end markets; and develop or acquire competitive technologies, products, services, and solutions and bring them to market quickly and cost-effectively. We must also monitor disruptive technologies, such as artificial intelligence, and business models, and we may not be able to take advantage of such technologies, including if we are not able to attract and retain talent that would enable us to leverage such technologies. In addition, the markets for our products, services and solutions may not develop or grow as we anticipate. The failure of our products, services or solutions to gain market acceptance due to more attractive offerings by our competitors, the introduction of new competitors to the market with new or innovative product offerings or the failure to address any of the above factors could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We may not be able to identify, finance and complete suitable acquisitions and investments, and any completed acquisitions and investments may be unsuccessful or consume significant resources.
Our business strategy includes acquiring businesses and making investments that complement our existing businesses. We continue to analyze and evaluate the acquisition of strategic businesses or product lines with the potential to strengthen our industry position or enhance our existing set of product, service, and solution offerings. We may not be able to identify suitable acquisition candidates, obtain financing or have sufficient cash necessary for acquisitions or successfully complete acquisitions in the future. Acquisitions and investments may involve significant cash expenditures, debt incurrences, equity issuances, operating losses and expenses. Acquisitions involve numerous other risks, including:
•diversion of management time and attention from daily operations;
•difficulties integrating acquired businesses, technologies and personnel into our business;
•difficulties in obtaining and verifying the financial statements and other business information of acquired businesses;
•inability to obtain required regulatory approvals;
•potential loss of key employees, key contractual relationships or key customers of acquired companies or of ours;
•assumption of the liabilities and exposure to unforeseen liabilities of acquired companies; and
•dilution of interests of holders of our shares through the issuance of equity securities or equity-linked securities.
It may be difficult for us to integrate acquired businesses efficiently into our business operations. Any acquisitions or investments may not be successful or realize the intended benefits and may ultimately result in impairment charges or have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We may not achieve some or all of the expected benefits of our business initiatives.
During 2023 and 2022, we initiated and continued execution of certain business initiatives aimed at reducing our fixed cost structure and realigning our business. During 2021, we also launched and committed resources to a program designed to accelerate growth and drive margin expansion through transformation of our business model to drive operational excellence, reduce complexity and streamline our processes. As a result, we have incurred and expect to continue to incur in the future substantial expense, including transformation costs that include professional services, project management and related design and execution charges, as well as costs related to both labor and non-labor restructuring and IT investments, and restructuring charges. We may not be able to achieve accelerated growth and margin expansion or operating efficiencies to reduce costs or realize benefits that we anticipated in connection with these initiatives. If we are unable to execute these initiatives as planned, we may not realize all or any of the anticipated benefits, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
7
We may experience cost and other inflation.
In prior years, we experienced inflationary cost increases of raw materials, such as metals, resins, drives and motors, as well as increases in logistics, energy, insurance and labor costs (including wages, pensions and health care benefits), and due to the current volatile nature of the market, we expect inflationary cost increases to continue in 2024. We strive for productivity improvements and implement increases in selling prices to help mitigate cost increases. We continue to implement operational initiatives to mitigate the impacts of inflation and continuously reduce our costs. However, these actions may not be successful in managing our costs or increasing our productivity and we anticipate inflation to continue with respect to raw materials as well as labor and logistics. Continued cost inflation or failure of our initiatives to increase prices, generate cost savings or improve productivity could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Interruption of our supply chain could affect our ability to produce or deliver our products and could negatively impact our business and profitability.
During 2023, 2022 and 2021, we experienced supply chain challenges, including increased lead times for raw materials due to availability constraints and high demand for these materials. These disruptions or our failure to effectively respond to them have increased and may continue to increase product, logistics or labor costs, limit availability of raw materials or cause delays in delivering our backlog or may cause an inability to deliver products to our customers or meet customer demand. While we have elevated our engagement with our suppliers and used secondary suppliers and new methods of procurement where available to mitigate the supply chain pressures, supply chain challenges may continue in the future. In addition, as we execute on our ongoing Transformation Program, we may experience costs as a result of changing to new suppliers. Any material interruption in our supply chain, such as material interruption of the supply of raw materials and components due to the casualty loss of any of our manufacturing plants; interruptions in service by our third-party logistic service providers or common carriers that ship goods within our distribution channels; unexpected delays in shipping or processing through customs of goods; increased logistics costs, including air freight; lack of availability of marine cargo insurance for shipments in certain geographies due to hostilities; trade restrictions, such as increased tariffs or quotas, embargoes or customs restrictions or inspections; or other unexpected or uncontrollable events that cause a material interruption in our supply chain such as pandemics (including COVID-19); social or labor unrest; natural disasters; or political disputes, international hostilities and military conflicts; could negatively affect our ability to produce or deliver our products and have a negative material impact on our business and our profitability. Additionally, our raw materials and components are sourced from a wide variety of domestic and international business partners. We rely on these suppliers to provide high quality products and to comply with applicable laws. Our ability to find qualified suppliers who meet our standards and supply products in a timely and efficient manner may be a challenge, especially with respect to raw materials and components sourced from outside the U.S. and from countries or regions with diminished infrastructure, developing or failing economies or which are experiencing political instability or social unrest. For certain products, we may rely on one or very few suppliers. A supplier's failure to meet our standards, provide products in a timely and efficient manner, or comply with applicable laws is beyond our control. In addition, our competitors may be less reliant on third-party suppliers than we are, which may give such competitors more control over their supply chain and lead times for manufacturing products. These issues could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We are exposed to political, regulatory, economic, trade, and other risks that arise from operating a multinational business.
Sales outside of the U.S. for the year ended December 31, 2023 accounted for 31% of our net sales. Further, most of our businesses obtain some products, components and raw materials from non-U.S. suppliers. Accordingly, our business is subject to the political, regulatory, economic, trade, and other risks that are inherent in operating in, and purchasing from, numerous countries. These risks include:
•changes in general economic and political conditions in countries where we operate or purchase from, particularly in emerging markets;
•relatively more severe economic conditions in some international markets than in the U.S.;
•the imposition of sanctions, tariffs, duties, exchange controls, currency restrictions or other trade restrictions;
•changes in tax treaties, laws or rulings that could have a material adverse impact on our effective tax rate;
•the difficulty of enforcing agreements and collecting receivables through non-U.S. legal systems;
•the difficulty of communicating and monitoring evolving standards and directives across our product lines, services, and global facilities;
•the difficulty of ensuring that our products, services and supply chains meet ever-changing regional regulations and requirements;
8
•trade protection measures and import or export licensing requirements and restrictions;
•the possibility of military conflicts or terrorist action affecting us, our operations, supply chains, our end-markets or economies generally;
•the threat of nationalization and expropriation;
•changes due to nationalist consumer sentiment;
•the difficulty in staffing and managing widespread operations in non-U.S. labor markets;
•limitations on repatriation of earnings or other regionally-imposed capital requirements;
•the difficulty of protecting intellectual property in non-U.S. countries; and
•changes in and required compliance with a variety of non-U.S. laws and regulations, some of which may be incompatible with each other or U.S. laws and regulations.
Our success depends in part on our ability to anticipate and effectively manage these and other risks. We cannot assure that these and other factors will not have a material adverse effect on our international operations or on our business as a whole.
Changes in U.S. or foreign government administrative policy, including changes to existing trade agreements, could have a material adverse effect on us.
As a result of changes to U.S. or foreign government administrative policy, there may be changes to existing trade agreements; greater restrictions on free trade generally; significant increases in tariffs on goods including those imported into the U.S., particularly tariffs on products manufactured in Mexico, China, or other countries where we purchase, have operations or manufacture or sell products; prohibitions or restrictions on doing business with certain entities, including those with certain relationships with China; and adverse responses by foreign governments to U.S. trade policy, among other possible changes. It remains unclear what the U.S. administration or foreign governments, including China, will or will not do with respect to tariffs or international trade agreements and policies. A trade war; other governmental action related to tariffs or international trade agreements; changes in U.S. social, political, regulatory and economic conditions or in laws and policies governing foreign trade, manufacturing, development and investment in the territories and countries where we currently purchase, have operations or manufacture and sell products; and any resulting negative sentiments towards the U.S. as a result of such changes, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Intellectual property challenges may hinder our ability to develop, engineer and market our products.
Patents, non-compete agreements, proprietary technologies, customer relationships, trademarks, trade names and brand names are important to our business. Intellectual property protections, however, may not preclude competitors from developing products like ours, or from challenging our names or products. Our pending patent, copyright, and trademark registration applications may not be accepted, or competitors may challenge the validity or scope of our patents, copyrights or trademarks. In addition, our patents, copyrights, trademarks and other intellectual property rights may not provide us a significant competitive advantage. Furthermore, our business strategy also includes expanding our smart products and Internet of Things offerings and there are many other companies that hold patents in this space. Over the past few years, we have noticed an increasing tendency for participants in our markets, including competitors, to use challenges to intellectual property to compete. Patent and trademark challenges increase our costs to develop, engineer and market our products. We may need to spend significant resources monitoring, enforcing and defending, including through litigation, our intellectual property rights, and we may or may not be able to detect infringement by third parties. If we fail to successfully enforce our intellectual property rights or register new patents, our competitive position could suffer, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We have significant goodwill and intangible assets and future impairment of our goodwill and intangible assets could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We test goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment on at least an annual basis, and more frequently if circumstances warrant. As of December 31, 2023, our goodwill and intangible assets were $4,317.0 million and represented approximately 66% of our total assets. Declines in fair market value could result in future goodwill and intangible asset impairment charges.
A loss of, or material cancellation, reduction, or delay in purchases by or delivery of products to, one or more of our largest customers could harm our business.
Our net sales to our largest customer represented approximately 15% of our consolidated net sales in 2023. While we do not have any other customers that accounted for more than 10% of our consolidated net sales in 2023, we have other customers that are key to the success of our business. Our concentration of sales to a relatively small number of larger customers makes our
9
relationship with each of these customers important to our business. Our success is dependent on retaining these customers, which requires us to successfully manage relationships and anticipate the needs of our customers in the channels in which we sell our products. Our customers also may be impacted by economic conditions in the industries of those customers, which could result in reduced demand for or a delay in purchases of our products. In addition, our customers may cancel orders for purchases of our products or may not order products at rates consistent with past order levels, including due to inventory rebalancing or corrections in channels. In addition, we may not be able to timely deliver products to our largest customers due to supply chain interruptions or otherwise. We cannot provide assurance that we will be able to retain our largest customers. In addition, some of our customers may shift their purchases to our competitors in the future. The loss of one or more of our largest customers, any material cancellation, reduction, or delay in purchases by or delivery of products to these customers, or our inability to successfully develop relationships with additional customers could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Catastrophic and other events beyond our control may disrupt operations at our manufacturing facilities and those of our suppliers, which could cause us to be unable to meet customer demands or increase our costs, or reduce customer spending.
If operations at any of our manufacturing facilities or those of our suppliers were to be disrupted as a result of significant equipment failures, natural disasters, earthquakes, power outages, fires, explosions, terrorism, political disputes, international hostilities, military conflicts, cybersecurity incidents, adverse weather conditions, labor disputes, public health epidemics (including the COVID-19 pandemic) or other catastrophic events or disruptions outside of our control, we may be unable to fill customer orders and otherwise meet customer demand for our products. Some of our operations, including our pool business operations in North Carolina and California, are in areas that are more susceptible to natural disasters such as hurricanes, wildfires and earthquakes. These types of events may negatively impact residential, commercial and industrial spending in impacted regions or, depending on the severity, global spending. As a result, any of such events could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. We maintain property insurance that we believe to be adequate to provide for reconstruction of facilities and equipment, and to cover business interruption losses resulting from any production interruption or shutdown caused by an insured loss. However, any recovery under our insurance policies may not offset the lost sales or increased costs that may be experienced during the disruption of operations and may also affect the price and availability of insurance in the future, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Seasonality of sales and weather conditions could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
We experience seasonal demand with end customers and end users within each of our business segments. Demand for pool equipment in the Pool segment, water solution products in the Water Solutions segment, and residential water supply and agricultural products within the Flow segment follows warm weather trends, with seasonal highs from April to September. While historically we have attempted to mitigate the magnitude of the sales spikes in the Pool segment by employing some advance sale “early buy” programs (generally including extended payment terms and/or additional discounts), we cannot provide assurance that should we use such programs in the future they will be successful. In addition, seasonal effects associated with products within our Flow, Water Solutions and Pool segments may vary from year to year and be impacted by weather patterns, such as temperature, heavy flooding and droughts. Moreover, adverse weather conditions, such as cold or wet weather, may negatively impact demand for, and sales of products within our business segments.
Volatility in currency exchange rates could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Sales outside of the U.S. for the year ended December 31, 2023 accounted for approximately 31% of our net sales. Our financial statements reflect translation of items denominated in non-U.S. currencies to U.S. dollars. Therefore, if the U.S. dollar strengthens in relation to the principal non-U.S. currencies from which we derive revenue as compared to a prior period, our U.S. dollar reported revenue and income will effectively be decreased to the extent of the change in currency valuations, and vice-versa. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, most notably the strengthening of the U.S. dollar against the euro, could have a material adverse effect on our reported revenue in future periods. In addition, currency variations could have a material adverse effect on margins on sales of our products in countries outside of the U.S. and margins on sales of products that include components obtained from suppliers located outside of the U.S.
Our business may be adversely affected by matters associated with our labor force.
Certain of our employees are covered by collective bargaining agreements or represented by works councils. Although we believe that our relations with the labor unions and works councils that represent our employees are generally good and we have experienced no material work stoppages recently, no assurances can be made that we will not experience these and other types of conflicts with labor unions, works councils, other groups representing employees or our employees generally in the future, or that any future negotiations with these groups will not result in significant increases in our cost of labor. In addition, an important aspect of attracting and retaining qualified personnel is continuing to offer competitive wages, employee healthcare, retirement and other benefits. The expenses we record for our employee benefit plans depend on factors such as changes in market interest rates and healthcare cost inflation, and significant unfavorable changes in these factors could increase our
10
expenses and funding requirements. An inability to control costs and funding requirements related to employee benefits could negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition.
Complications with the design or implementation of our updated enterprise resource planning system could adversely impact our business and operations.
We rely extensively on information systems and technology to operate and manage our business and summarize operating results. We are in the process of a multi-year implementation of an updated global enterprise resource planning (“ERP”) system in connection with moving to digital processes under our Transformation Program. Ultimately, this ERP system will update our existing operating and transactional financial systems. The ERP system is designed to accurately maintain our financial records, enhance operational functionality and provide timely information to our management team related to the operation of the business. The ERP system implementation process has required, and will continue to require, the investment of significant personnel and financial resources. We may not be able to successfully implement the ERP system without experiencing delays, increased costs and other difficulties. If we are unable to successfully design and implement the updated ERP system as planned, our financial position, results of operations and cash flows could be negatively impacted. Additionally, if we do not effectively implement the ERP system as planned or the ERP system does not operate as intended, the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting could be adversely affected or our ability to assess those controls adequately could be further delayed.
Risks Relating to Our Debt and Financial Markets
Increased leverage may harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
As of December 31, 2023, we had $2,006.8 million of total debt outstanding on a consolidated basis. We and our subsidiaries may incur additional indebtedness in the future, including in connection with acquisitions, subject to restrictions in our debt agreements. Our increased level of indebtedness and any future increases in our level of indebtedness may have important effects on our future operations, including, without limitation:
•we will have additional cash requirements in order to support the payment of interest on our outstanding indebtedness;
•increases in our outstanding indebtedness and leverage may increase our vulnerability to adverse changes in general economic and industry conditions, as well as to competitive pressure;
•our ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, general corporate and other purposes may be reduced;
•our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and our industry may be reduced; and
•our flexibility to make acquisitions and develop technology may be limited.
Our ability to make payments of principal and interest on and to refinance our indebtedness, including our existing debt as well as any future debt that we may incur, will depend on our ability to generate cash in the future from operations, financings or asset sales. Our ability to generate cash is subject to general economic conditions and financial, business and other factors affecting our operations, many of which are beyond our control. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flow from operations in the future to service our debt and meet our other cash requirements, we may be required, among other things:
•to seek additional financing in the debt or equity markets;
•to refinance or restructure all or a portion of our indebtedness;
•to sell selected assets or businesses; or
•to reduce or delay planned capital or operating expenditures.
Such measures might not be sufficient to enable us to service our debt and meet our other cash requirements. In addition, any such financing, refinancing or sale of assets might not be available at all or on economically favorable terms.
Covenants in our debt instruments may adversely affect us.
Our credit agreements and indentures contain customary financial covenants, including those that limit the amount of our debt, which may restrict the operations of our business and our ability to incur additional debt to finance acquisitions. Our ability to meet the financial covenants may be affected by events beyond our control, and we cannot provide assurance that we will meet those tests. A breach of any of these covenants could result in a default under our credit agreements or indentures. Upon the occurrence of an event of default under any of our credit facilities or indentures, the lenders or trustees could elect to declare all amounts outstanding thereunder to be immediately due and payable and, in the case of credit facility lenders, terminate all
11
commitments to extend further credit. If the lenders or trustees accelerate the repayment of borrowings, we cannot provide assurance that we will have sufficient assets to repay our credit facilities and our other indebtedness. Furthermore, acceleration of any obligation under any of our material debt instruments will permit the holders of our other material debt to accelerate their obligations, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
We may increase our debt or raise additional capital, our credit ratings may be downgraded in the future, or our interest rates may increase, each of which could affect our financial condition, and may decrease our profitability.
As of December 31, 2023, we had $2,006.8 million of total debt outstanding on a consolidated basis. We may increase our debt or raise additional capital in the future, subject to restrictions in our debt agreements. If our cash flow from operations is less than we anticipate, if our cash requirements are more than we expect, or if we intend to finance acquisitions, we may require more financing. However, debt or equity financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If we incur additional debt or raise equity through the issuance of additional capital shares, the terms of the debt or capital shares issued may give the holders rights, preferences and privileges senior to those of holders of our ordinary shares, particularly in the event of liquidation. The terms of the debt may also impose additional and more stringent restrictions on our operations than we currently have. If we raise funds through the issuance of additional equity, the percentage ownership of existing shareholders in our company would decline. If we are unable to raise additional capital when needed, our financial condition could be adversely affected.
Unfavorable changes in the ratings that rating agencies assign to our debt may ultimately negatively impact our access to the debt capital markets and increase the costs we incur to borrow funds. If ratings for our debt fall below investment grade, our access to the debt capital markets may become restricted. Additionally, our credit agreements generally include an increase in interest rates if the ratings for our debt are downgraded. To the extent that our interest rates increase, our interest expense will increase, which could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Disruptions in the financial markets could adversely affect us, our customers and our suppliers by increasing funding costs or reducing availability of credit.
In the normal course of our business, we may access credit markets for general corporate purposes, which may include repayment of indebtedness, acquisitions, additions to working capital, repurchase of shares, capital expenditures and investments in our subsidiaries. Although we expect to have sufficient liquidity to meet our foreseeable needs, our access to and the cost of capital could be negatively impacted by disruptions in the credit markets, including due to failures of financial institutions, which have occurred in the past and made financing terms for borrowers unattractive or unavailable. These factors may make it more difficult or expensive for us to access credit markets if the need arises. In addition, these factors may make it more difficult for our suppliers to meet demand for products or for customers to purchase products or commence new projects, as suppliers and customers may experience increased costs of debt financing or difficulties in obtaining debt financing. Disruptions in the financial markets have had adverse effects on other areas of the economy and have led to a slowdown in general economic activity that may continue to adversely affect our businesses. One or more of these factors could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Risks Relating to Legal, Regulatory and Compliance Matters
Violations of the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, U.K. Bribery Act, and other anti-corruption laws outside the U.S. could have a material adverse effect on us.
The U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”), U.K. Bribery Act, and other anti-corruption laws in other jurisdictions generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to government officials or other persons for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. Recent years have seen a substantial increase in anti-bribery law enforcement activity, with more frequent and aggressive investigations and enforcement proceedings by both the U.S. Department of Justice and the SEC, increased enforcement activity by non-U.S. regulators and increases in criminal and civil proceedings brought against companies and individuals. Our policies mandate compliance with these anti-bribery laws. We operate in many parts of the world that are recognized as having governmental and commercial corruption and, in certain circumstances, strict compliance with anti-bribery laws may conflict with local customs and practices. We cannot assure that our internal control policies and procedures will always protect us from negligent, reckless or criminal acts committed by our employees or third-party intermediaries. In the event that we believe or have reason to believe that our employees, customers, or agents have or may have violated applicable anti-corruption laws, including the FCPA, we may be required to investigate the relevant facts and circumstances, which can be expensive and require significant time and attention from senior management. Violations of these laws may require self-disclosure to government agencies and result in criminal or civil sanctions, which could disrupt our business and result in a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
12
Our failure to satisfy international trade compliance regulations, and changes in U.S. government and other applicable sanctions, could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our global operations require importing and exporting goods and technology across international borders on a regular basis. Certain of the products we sell are “dual use” products, which are products that may have both civil and military applications, or may otherwise be involved in weapons proliferation, and are often subject to more stringent export controls. From time to time, we obtain or receive information alleging improper activity in connection with imports or exports. Our policies mandate strict compliance with U.S. and non-U.S. trade laws applicable to our products. However, even when we are in strict compliance with law and our policies, we may suffer reputational damage if certain of our products are sold through various intermediaries to sanctioned entities or to entities operating in sanctioned countries. When we receive information alleging improper activity, our policy is to investigate that information and respond appropriately, including, if warranted, reporting our findings to relevant governmental authorities. Nonetheless, our policies and procedures may not always protect us from actions that would violate U.S. and/or non-U.S. laws. Any improper actions could subject us to civil or criminal penalties, including material monetary fines, or other adverse actions including denial of import or export privileges, and could damage our reputation and business prospects.
We are exposed to environmental laws, liabilities and litigation.
We are subject to U.S. federal, state, local and non-U.S. laws and regulations governing protection of the environment and worker health and safety. Compliance with these environmental, health and safety regulations could require us to satisfy environmental liabilities, increase the cost of manufacturing our products or otherwise have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Any violations of these laws by us could cause us to incur unanticipated liabilities. We are also required to comply with various environmental laws and maintain permits, many of which are subject to renewal from time to time, for many of our businesses, and we could be adversely impacted if we are unable to renew existing permits or to obtain any additional permits that may be required. Compliance with environmental requirements also could require significant operating or capital expenditures or result in significant operational restrictions. We cannot provide assurance that we have been or will be at all times in compliance with environmental and health and safety laws. If we violate these laws, we could be fined, criminally charged or otherwise sanctioned by regulators.
We have been named as a defendant, target or a potentially responsible party (“PRP”) in a number of environmental matters relating to our current or former businesses. We have disposed of a number of businesses and in certain cases, we have retained responsibility and potential liability for certain environmental obligations. We have received claims for indemnification from certain purchasers of businesses from us. We may be named as a PRP at other sites in the future for existing business units, as well as both divested and acquired businesses. In addition to clean-up actions brought by governmental authorities, private parties could bring individual or class-action claims due to the presence of, or exposure to, hazardous substances, including at sites where we did not have operations but may have acquired liability through an acquisition of a business.
Certain environmental laws impose liability on current or previous owners or operators of real property for the cost of removal or remediation of hazardous substances at their properties or at properties at which they have disposed of hazardous substances. We have projects underway at several current and former manufacturing facilities to investigate and remediate environmental contamination resulting from our past operations or by the operations of divested or acquired businesses or other businesses that previously owned or used the properties. The cost of remediation and other environmental liabilities can be difficult to accurately predict and is typically excluded by insurance. In addition, environmental requirements change and tend to become more stringent over time. Our eventual environmental remediation costs and liabilities could exceed the amount of our current reserves.
Our subsidiaries are party to asbestos-related litigation that could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our subsidiaries, along with numerous other companies, are named as defendants in a substantial number of lawsuits based on alleged exposure to asbestos-containing materials, substantially all of which relate to our discontinued operations. These cases typically involve product liability claims based primarily on allegations of manufacture, sale or distribution of industrial products that either contained asbestos or were attached to or used with asbestos-containing components manufactured by third parties or to which asbestos insulation was applied after installation. In addition, some cases brought against us involve the presence of asbestos at facilities that we own or used to own. Each case typically names a large number of product manufacturers, service providers and premises owners. Historically, our subsidiaries have been identified as defendants in asbestos-related claims. Our strategy has been, and continues to be, to mount a vigorous defense aimed at having unsubstantiated suits dismissed, and settling claims before trial only where appropriate. As of December 31, 2023, there were approximately 590 claims pending against our subsidiaries, substantially all of which relate to our discontinued operations. We cannot predict with certainty the extent to which we will be successful in litigating or otherwise resolving lawsuits in the future, and we continue to evaluate different strategies related to asbestos claims filed against us including the possibility of entity restructuring. Unfavorable rulings, judgments or settlement terms could have a material adverse impact on our business and financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. In addition, while most of the asbestos claims against us are covered
13
by liability insurance policies from many years ago, not all claims are insured. As our insurers resolve claims relating to past policy periods, the aggregate coverage provided by those policies erodes. If we exhaust our coverage under those policies, we will be exposed to potential uninsured losses. Over time, the uninsured portion of our asbestos docket may increase, which may require us to set greater reserves to resolve future asbestos cases.
Failure to comply with the broad range of standards, laws and regulations in the jurisdictions in which we operate may result in exposure to substantial disruptions, costs and liabilities.
Our products, manufacturing facilities and business operations are subject to numerous federal, state and local statutory and regulatory requirements, both within and outside the U.S. These laws and regulations impose on us increasingly complex, stringent and costly monitoring and compliance activities, including but not limited to environmental, health, and safety protection standards and permitting, labeling and other requirements regarding (among other things) product efficiency and performance, material makeup, air quality and emissions, and wastewater discharges; the use, handling, and disposal of hazardous or toxic materials and substances, including perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances (“PFAS”) and other substances of concern; remediation of environmental contamination; and working conditions for and compensation of our employees. We may also be affected by future standards, laws or regulations, including those imposed in response to energy, climate change, product functionality, geopolitical, corporate social responsibility, or similar concerns. These standards, laws, or regulations may impact our costs of operation, the sourcing of raw materials, and the manufacture and distribution of our products and place restrictions and other requirements or impediments on the products and solutions we can sell in certain geographical locations or on the willingness of certain investors to own our shares.
We are exposed to certain regulatory, financial and other risks related to climate change and other sustainability matters.
Climate change is receiving ever increasing attention worldwide. Many scientists, legislators and others attribute global warming to increased levels of greenhouse gases, which has led to significant legislative and regulatory efforts to limit greenhouse gas emissions. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) has published findings that emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, and other greenhouse gases (“GHGs”) present an endangerment to public health and the environment because emissions of such gases are, according to the EPA, contributing to the warming of the earth’s atmosphere and other climate changes. Based on these findings, the EPA has implemented regulations that require reporting of GHG emissions, or that limit emissions of GHGs from certain mobile or stationary sources. In addition, the U.S. Congress and federal and state regulatory agencies have considered other legislation and regulatory proposals to reduce emissions of GHGs, and many states have already taken legal measures to reduce emissions of GHGs, primarily through the development of GHG inventories, GHG permitting and/or regional GHG cap-and-trade programs. It is uncertain whether, when and in what form a federal mandatory carbon dioxide emissions reduction program, or other state programs, may be adopted. Similarly, certain countries have adopted the Kyoto Protocol and, in 2021, the U.S. rejoined the Paris Accord. These and other existing or potential international initiatives and regulations could affect our international operations. To the extent our customers, particularly our energy and industrial customers, are subject to any of these or other similar proposed or newly enacted laws and regulations, we are exposed to risks that the additional costs by customers to comply with such laws and regulations could impact their ability or desire to continue to operate at similar levels in certain jurisdictions as historically seen or as currently anticipated, which could negatively impact their demand for our products and services. As customers become increasingly concerned about the environmental impact of their purchases, if we fail to keep up with changing regulations or innovate or operate in ways that minimize the energy use of our products or operations, customers may choose more energy efficient or sustainable alternatives. These actions could also increase costs associated with our operations, including costs for raw materials and transportation. We may also be subject to consumer lawsuits or enforcement actions by governmental authorities if our ESG claims relating to product marketing are inaccurate. It is uncertain what new laws will be enacted and therefore we cannot predict the potential impact of such laws on our future financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. The laws and regulations regarding ESG disclosures and requirements are rapidly evolving and could have an adverse effect on our operations and the costs of compliance with, and the other burdens imposed by, these and other laws or regulatory actions may increase our operational costs.
As part of our strategy regarding environmental, climate change and sustainability matters, we have set and may set additional targets aimed at reducing our impact on the environment and climate change and/or targets relating to other sustainability matters. In addition, as a leading provider of water treatment solutions, our business strategy includes positioning our products and services as sustainable solutions. Actions we take to achieve our targets or strategy could result in increased costs to our operations. We may not be able to achieve such targets or our desired impact, and any future investments we make in furtherance of achieving such targets and strategy may not meet investor expectations or standards regarding sustainability performance. Moreover, we may determine that it is in the best interest of our company and our shareholders to prioritize other business, social, governance or sustainable investments over the achievement of our current targets based on economic, regulatory and social factors, business strategy or pressure from investors or other stakeholders. In addition, investors and other stakeholders are increasingly focused on ESG matters, and as stakeholder ESG expectations and standards are evolving, we may not be able to sufficiently respond to these evolving standards and expectations or investors may not view our products and services as sustainable solutions. Furthermore, we could be criticized for the accuracy or completeness of the disclosure of our
14
ESG initiatives. If we are unable to meet our targets or successfully implement our strategy or our ESG reporting is inaccurate or incomplete, then we could suffer from reputational damage and incur adverse reaction from investors and other stakeholders, which could adversely impact the perception of our brand and our products and services by current and potential investors and customers, which could in turn adversely impact our business, results of operations, or financial condition.
Increased cybersecurity threats and computer crime pose a risk to our systems, networks, products and services, and we are exposed to potential regulatory, financial and reputational risks relating to the protection of our data.
We rely upon information technology systems and networks in connection with a variety of business activities, some of which are managed by third parties. As our business increasingly interfaces with employees, customers, dealers and suppliers using information technology systems and networks, we are subject to an increased risk to the secure operation of these systems and networks. Our evolution into smart products and Internet of Things subjects us to increased cyber and technology risks. The secure operation of our information technology systems and networks is critical to our business operations and strategy. Cybersecurity threats from user error to attacks designed to gain unauthorized access to our systems, networks and data are increasing in frequency and sophistication. These threats pose a risk to the security of our systems and networks and the confidentiality, availability and integrity of the data we process and maintain. Establishing systems and processes to address these threats may increase our costs. We have experienced cybersecurity incidents, and, although we have determined such cybersecurity incidents to be immaterial and such incidents have not had a material adverse effect on our business strategy, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows, there can be no assurance of similar results in the future. Should future attacks succeed, it could expose us and our employees, customers, dealers and suppliers to the theft of assets, misuse of information or systems, compromises of confidential information, manipulation and destruction of data, product failures, production downtimes and operations disruptions. The occurrence of any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. While we maintain cybersecurity insurance, the costs related to cybersecurity threats or incidents may not be fully insured, and future cybersecurity coverage may become more expensive if we experience a cybersecurity incident. In addition, such cybersecurity incidents could result in litigation, regulatory action and potential liability and the costs and operational consequences of implementing further data protection measures. For information on our cybersecurity risk management, strategy and governance, see ITEM 1C.- Cybersecurity.
Changes in data privacy laws and our ability to comply with them could have a material adverse effect on us.
We collect and store data that is sensitive to us and our employees, customers, dealers and suppliers. A variety of state, national, foreign and international laws and regulations apply to the collection, use, retention, protection, security, disclosure, transfer and other processing of personal and other data. Many foreign data privacy regulations, including the General Data Protection Regulation (the “GDPR”) in the European Union, are more stringent than federal regulations in the United States. Within the United States, many states are considering adopting, or have already adopted privacy regulations, including, for example, the California Consumer Privacy Act. These laws and regulations are rapidly evolving and changing, and could have an adverse effect on our operations. Companies’ obligations and requirements under these laws and regulations are subject to uncertainty in how they may be interpreted by courts and governmental authorities. The costs of compliance with, and the other burdens imposed by, these and other laws or regulatory actions may increase our operational costs, and/or result in interruptions or delays in the availability of systems. In the case of non-compliance with these laws, including the GDPR, regulators have the authority to levy significant fines. In addition, if there is a breach of privacy, we may be required to make notifications under data privacy laws or regulations, or could become subject to litigation. The occurrence of any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
We may be negatively impacted by litigation and other claims.
We are currently, and may in the future become, subject to litigation and other claims. These legal proceedings are typically claims that relate to our products or services or to the conduct of our business and include, without limitation, claims relating to commercial regulatory or contractual disputes with suppliers, authorities, customers or parties to acquisitions and divestitures; intellectual property matters; environmental, asbestos, safety and health matters; product quality and liability matters; matters arising from the use or installation of our products; consumer protection matters; and employment and labor matters. The outcome of such legal proceedings cannot be predicted with certainty and some may be disposed of unfavorably to us. Insurance coverage is not available for some of our claims and may be disputed by carriers in others. While we currently maintain what we believe to be suitable product liability insurance, we may not be able to maintain this insurance on our preferred terms or at an acceptable cost. Further, this insurance may not provide adequate protection against potential or previously existing liabilities. In addition, we self-insure a portion of product liability claims and must satisfy deductibles on other insured claims. Further, some of our business involves the sale of our products to customers that are constructing large and complex systems, facilities or other capital projects, and while we generally try to limit our exposure to liquidated damages, consequential damages and other potential damages in the contracts for these projects, we could be exposed to significant monetary damages and other liabilities in connection with the sale of our products for these projects for a variety of reasons. In addition, some of our businesses, customers, and dealers are subject to various laws and regulations regarding consumer
15
protection and advertising and sales practices, and we have been named, and may be named in the future, as a defendant in litigation, including class action complaints, arising from alleged violation of these laws and regulations. In addition, our indemnification obligations relating to the purchase or sale of businesses could result in litigation or claims of unknown amounts. Successful claims or litigation against us for significant amounts could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Risks Relating to Our Jurisdiction of Incorporation in Ireland and Tax Residency in the U.K.
We are subject to changes in law and other factors that may not allow us to maintain a worldwide effective corporate tax rate that is competitive in our industry.
While we believe that we should be able to maintain a worldwide effective corporate tax rate that is competitive in our industry, we cannot give any assurance as to what our effective tax rate will be in the future because of, among other things, uncertainty regarding tax policies of the jurisdictions where we operate. Also, the tax laws and treaties of the U.S., the U.K., Ireland and other jurisdictions could change in the future, and such changes could cause a material change in our worldwide effective corporate tax rate. For example, the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development Pillar Two Model Rules (“Pillar Two”) for a global 15.0% minimum tax, are in the process of being adopted by a number of jurisdictions in which we operate. In particular, the U.K. has completed passage of legislation to comply with the Pillar Two framework, which became effective at the start of 2024. We expect Pillar Two to have a negative 1.0% to 1.5% impact to our effective tax rate in 2024. That impact could change in the future as we continue to evaluate the enacted legislative changes and as new guidance becomes available. In addition, legislative action could be taken by the U.S., the U.K., Ireland or the European Union that could override tax treaties or modify tax statutes or regulations upon which we expect to rely and adversely affect our effective tax rate. We cannot predict the outcome of any specific legislative proposals. If proposals were enacted that had the effect of disregarding our incorporation in Ireland or limiting our ability as an Irish company to maintain tax residency in the U.K., we could be subject to increased taxation and/or be required to take action to maintain our effective tax rate, which could materially adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations, cash flows or our effective tax rate in future reporting periods.
A change in our tax residency could have a negative effect on our future profitability, and may trigger taxes on dividends or exit charges.
Under current Irish legislation, a company is regarded as resident for tax purposes in Ireland if it is incorporated in Ireland. Under current U.K. legislation, a company that is centrally managed and controlled in the U.K. is regarded as resident in the U.K. for taxation purposes unless it is treated as resident in another jurisdiction pursuant to any appropriate double tax treaty with the U.K. Other jurisdictions may also seek to assert taxing jurisdiction over us.
The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development proposed a number of measures relating to the tax treatment of multinationals, some of which are implemented by amending double tax treaties through the multilateral convention to implement tax treaty-related measures to prevent base erosion and profit shifting (the “MLI”). The MLI has now entered into force for a number of countries, including Ireland and the U.K. Under the Double Tax Convention between Ireland and the U.K., as amended by the MLI, the residency tie-breaker provides that a company will remain dual resident unless there is a determination otherwise by the tax authorities of the two contracting states.
In January 2021, we obtained a determination from the tax authorities in Ireland, the Irish Revenue Commissioners, and in the U.K., HM Revenue & Customs, which states that we are resident for tax purposes only in the U.K.
It is possible that in the future, whether as a result of a change in law or the practice of any relevant tax authority or as a result of any change in the conduct of our affairs, we could become, or be regarded as having become, resident in a jurisdiction other than the U.K. If we cease to be resident in the U.K. and become a resident in another jurisdiction, we may be subject to U.K. exit charges, and could become liable for additional tax charges in the other jurisdiction (including dividend withholding taxes or corporate income tax charges). If we were to be treated as resident in more than one jurisdiction, we could be subject to taxation in multiple jurisdictions. If, for example, we were considered to be a tax resident of Ireland, we could become liable for Irish corporation tax, and any dividends paid by us could be subject to Irish dividend withholding tax.
Irish law differs from the laws in effect in the United States and may afford less protection to holders of our securities.
It may not be possible to enforce court judgments obtained in the U.S. against us in Ireland based on the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal or state securities laws. In addition, there is some uncertainty as to whether the courts of Ireland would recognize or enforce judgments of U.S. courts obtained against us or our directors or officers based on the civil liabilities provisions of the U.S. federal or state securities laws or hear actions against us or those persons based on those laws. We have been advised that the U.S. currently does not have a treaty with Ireland providing for the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of judgments in civil and commercial matters. Therefore, a final judgment for the payment of money rendered by any U.S. federal or state court based on civil liability, whether or not based solely on U.S. federal or state securities laws, would not automatically be enforceable in Ireland.
16
As an Irish company, we are governed by the Irish Companies Act 2014, which differs in some material respects from laws generally applicable to U.S. corporations and shareholders, including, among others, differences relating to interested director and officer transactions and shareholder lawsuits. Further, the duties of directors and officers of an Irish company generally are owed to the company only. Shareholders of Irish companies generally do not have a personal right of action against directors or officers of the company and may exercise such rights of action on behalf of the company only in limited circumstances and require court permission to do so. Accordingly, holders of our securities may have more difficulty protecting their interests than would holders of securities of a corporation incorporated in a jurisdiction of the U.S.
Irish law differs from the laws in effect in the United States, which may negatively impact our ability to issue ordinary shares.
Under Irish law, we must have authority from our shareholders to issue any ordinary shares, including shares that are part of our authorized but unissued share capital. In addition, unless otherwise authorized by its shareholders or constitutional document, when an Irish company issues shares for cash to new shareholders, it is required first to offer those shares on the same or more favorable terms to existing shareholders on a pro-rata basis. If we are unable to obtain these authorizations from our shareholders, or are otherwise limited by the terms of our authorizations, our ability to issue ordinary shares under our equity compensation plans and, if applicable, to facilitate funding acquisitions or otherwise raise capital could be adversely affected.
Transfers of our ordinary shares may be subject to Irish stamp duty.
Transfers of our ordinary shares effected by means of the transfer of book entry interests in the Depository Trust Company (“DTC”) will not be subject to Irish stamp duty. However, if you hold your ordinary shares directly rather than beneficially through DTC, any transfer of your ordinary shares could be subject to Irish stamp duty (currently at the rate of 1% of the higher of the price paid or the market value of the shares acquired). Payment of Irish stamp duty is generally a legal obligation of the transferee.
We currently intend to pay, or cause one of our affiliates to pay, stamp duty in connection with share transfers made in the ordinary course of trading by a seller who holds shares directly to a buyer who holds the acquired shares beneficially. In other cases we may, in our absolute discretion, pay or cause one of our affiliates to pay any stamp duty. Our articles of association provide that, in the event of any such payment, we (i) may seek reimbursement from the buyer, (ii) will have a lien against the shares acquired by such buyer and any dividends paid on such shares and (iii) may set-off the amount of the stamp duty against future dividends on such shares. Parties to a share transfer may assume that any stamp duty arising in respect of a transaction in our shares has been paid unless one or both of such parties is otherwise notified by us.
Our ordinary shares, received by means of a gift or inheritance could be subject to Irish capital acquisitions tax.
Irish capital acquisitions tax (“CAT”) could apply to a gift or inheritance of our ordinary shares irrespective of the place of residence, ordinary residence or domicile of the parties. This is because our shares will be regarded as property situated in Ireland. The person who receives the gift or inheritance has primary liability for CAT. Gifts and inheritances passing between spouses are exempt from CAT. Children have a tax-free threshold of €335,000 per lifetime in respect of taxable gifts or inheritances received from their parents for periods on or after October 9, 2019. The standard rate of CAT for gifts and inheritances received above this threshold is 33%.
General Risk Factors
Our share price may fluctuate significantly.
We cannot predict the prices at which our shares may trade. The market price of our shares may fluctuate widely, depending on many factors, some of which may be beyond our control, including:
•actual or anticipated fluctuations in our results of operations due to factors related to our business;
•success or failure of our business strategy;
•our quarterly or annual earnings, or those of other companies in our industry;
•our ability to obtain third-party financing as needed;
•announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions or dispositions;
•changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations or principles;
•changes in earnings estimates or guidance by us or securities analysts or our ability to meet those estimates or guidance;
•the operating and share price performance of other comparable companies;
17
•investor perception of us;
•effect of certain events or occurrences on our reputation;
•overall market fluctuations;
•results from any material litigation or governmental investigation or environmental liabilities;
•natural or other environmental disasters;
•changes in laws and regulations affecting our business; and
•general economic conditions and other external factors.
Stock markets in general have experienced volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of a particular company. These broad market fluctuations could have a material adverse effect on our share price.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
ITEM 1C. CYBERSECURITY
Our management and Board of Directors (the “Board”) recognize the importance of maintaining the security and resiliency of our cybersecurity environment to deliver on the expectations of our customers, dealers, business partners, employees and investors. The Board is actively involved in our risk management practices, including oversight of our overall enterprise risk management (“ERM”) program, in which cybersecurity risk is included. Our cybersecurity program is aligned with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (“NIST”) Cybersecurity Framework (“CSF”) and leverages International Organization for Standardization and other applicable industry standards. Overall, the purpose of our information security program is to protect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of our systems and data, along with the safe operation of our connected products. This is supported by our security operating framework, roadmap and governance.
Cybersecurity Risk Management and Strategy
Our cybersecurity program is focused on the following areas:
Security governance
We have established processes to assess, identify and manage material risks from cybersecurity threats. Annual risk assessments are performed and incorporated as part of our ERM organizational process. Strategic and operational cybersecurity risks are assessed, identified and managed by our cybersecurity team, which is led by our Chief Information Security Officer (the “CISO”). Our cybersecurity team shares information regarding such risks with our Security Steering Committee, which consists of our Chief Financial Officer, General Counsel, Chief Human Resources Officer, Chief Technology Officer and Chief Supply Chain Officer, and our ERM function, both of which support the Board’s oversight of cybersecurity risk.
Technical safeguards
We deploy technical safeguards that are designed to protect our systems from cybersecurity threats, including firewalls, anti-malware software, and authentication and authorization controls. Ongoing enhancements are integrated into our security roadmap, as informed by our security audits and assessments.
Security and privacy incident response
We have in place an incident response plan to identify, protect, detect, respond to and recover from cybersecurity threats and incidents. The CISO, the Security Steering Committee, our Chief Executive Officer and the Board are notified of any material cybersecurity incidents through an established escalation process.
Our incident response team maintains a standard playbook to respond to any potential cybersecurity incidents. We test and evaluate our plans on a regular basis.
Third-party risk management
We maintain a risk-based third-party risk management process to identify, assess and manage risks presented by service providers, vendors and other third parties that access our systems or that process or store our data.
18
Security awareness and training
We provide ongoing security awareness and training to educate internal users on how to identify and report potential issues. Professional-level employees receive mandatory cybersecurity education and training. Employee phishing tests are conducted on a regular basis. Employees who do not follow protocol are redirected for additional training. We also provide periodic updates to employees on emerging cybersecurity trends and ways to protect themselves and our company.
Security audits and assessments
We perform periodic security audits and assessments to test our cybersecurity program. These efforts span across our cybersecurity program, including but not limited to audits, assessments, tabletop exercises, vulnerability scanning and penetration tests. We regularly engage third parties to assess our cybersecurity program, including cybersecurity maturity assessments, penetration testing, and independent review of our security control environment and operating effectiveness. The results of the assessments are included for review by the Security Steering Committee and the Audit and Finance Committee of the Board. We believe our cybersecurity program is enhanced with the results of the audits, assessments and reviews performed.
Governance
The Board is responsible for general oversight of our risk management, including cybersecurity risk. The Audit and Finance Committee of the Board is responsible for overseeing our risk exposure to information security, cybersecurity and data protection, as well as the steps management has taken to monitor and control such exposures. Cybersecurity reviews are conducted at least quarterly and reported to the Board or the Audit and Finance Committee by the CISO and/or Chief Financial Officer at least quarterly.
Our cybersecurity team, which assesses and manages our risks from cybersecurity threats, is led by the CISO, who reports to our Chief Financial Officer. Additional oversight for assessing and managing cybersecurity risk include the Security Steering Committee and as part of our ERM program.
The CISO has over 20 years of cybersecurity and technology experience and has previously held Chief Information Security Officer positions at a large public retail company, as well as at a public technology company and services organization. The CISO has an undergraduate degree in Management Information Systems. Members of our cybersecurity team have, combined, over 100 years of cybersecurity experience, have degrees including Bachelors in Information Systems, Management Information Systems and/or Masters in Security Technologies, and hold professional certifications including Certified Information Systems Security Professional, Global Information Assurance Certification Security Essentials, Certified Cloud Security Professional, Certified Information Systems Auditor, Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect Expert and/or Certified Digital Forensics Examiner. Our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and General Counsel each hold degrees in their respective fields, and each have over 25 years of experience managing risks at the Company and at similar companies, including risks arising from cybersecurity threats.
Impact of Cybersecurity Threats
Previous cybersecurity incidents have not materially affected us, including our business strategy, results of operations or financial condition. However, risks from cybersecurity threats, including but not limited to exploitation of vulnerabilities, ransomware, denial of service, supply chain attacks, or other similar threats may materially affect us, including our execution of business strategy, reputation, results of operations and/or financial condition. See ITEM 1A. “Risk Factors - Increased cybersecurity threats and computer crime pose a risk to our systems, networks, products and services, and we are exposed to potential regulatory, financial and reputational risks relating to the protection of our data” for a discussion of cybersecurity risks.
19
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES
Our principal office is located in leased premises in London, U.K., and our management office in the U.S. is located in leased premises in Golden Valley, Minnesota.
Our operations are conducted in sites throughout the world. These sites house manufacturing and distribution operations, as well as sales and marketing, engineering and administrative offices. The following is a summary of our principal properties as of December 31, 2023, including manufacturing, distribution, sales offices and service centers:
| No. of Sites | |||||||||||||||||
| Location | Manufacturing | Distribution | Sales and Corporate Offices | Service Centers | |||||||||||||
| Flow | U.S. and 15 foreign countries | 21 | 10 | 5 | 9 | ||||||||||||
| Water Solutions | U.S. and 6 foreign countries | 13 | 6 | 7 | 30 | ||||||||||||
| Pool | U.S. and 2 foreign countries | 7 | 11 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Corporate | U.S. and 3 foreign countries | — | — | 6 | — | ||||||||||||
| Total | 41 | 27 | 20 | 40 | |||||||||||||
We believe that our production sites, as well as the related machinery and equipment, are well maintained and suitable for their purpose and are adequate to support our businesses.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We have been, and in the future may be, made parties to a number of actions filed or have been, and in the future may be, given notice of potential claims relating to the conduct of our business, including those relating to commercial, regulatory or contractual disputes with suppliers, customers, authorities or parties to acquisitions and divestitures; intellectual property matters; environmental, asbestos, safety and health matters; product liability; the use or installation of our products; consumer matters; and employment and labor matters. Refer to “Legal proceedings” and “Environmental matters” within Note 15 “Commitments and Contingencies”, of the consolidated financial statements included in ITEM 8 of Part II of this Form 10-K for information regarding legal and regulatory proceedings we are involved in. In addition, see Item 1A “Risk Factors - Our subsidiaries are party to asbestos-related product litigation that could adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows” related to asbestos matters.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
20
INFORMATION ABOUT OUR EXECUTIVE OFFICERS
Current executive officers of Pentair plc, their ages, current position and their business experience during at least the past five years are as follows:
| Name | Age | Current Position and Business Experience | |||||||||
| John L. Stauch | 59 | President and Chief Executive Officer since 2018; Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer 2007 – 2018; Chief Financial Officer of the Automation and Control Systems unit of Honeywell International Inc. 2005 – 2007; Vice President, Finance and Chief Financial Officer of the Sensing and Controls unit of Honeywell International Inc. 2004 – 2005; Vice President, Finance and Chief Financial Officer of the Automation & Control Products unit of Honeywell International Inc. 2002 – 2004; Chief Financial Officer and IT Director of PerkinElmer Optoelectronics, a unit of PerkinElmer, Inc., 2000 – 2002. | |||||||||
| Adrian C. Chiu | 45 | Executive Vice President and President of the Water Solutions reporting segment since January 1, 2023; Executive Vice President, Chief Human Resources Officer and Chief Transformation Officer 2021 – 2022; Vice President of Total Rewards and Human Resources Information Systems 2018 – 2021; Vice President and Project Management Office Leader for the separation of nVent plc (Pentair’s former electrical business) 2017 – 2018; Vice President of Human Resources Technology, Operations, and Equity Compensation 2016 – 2018; Senior Director of Human Resources Technology and Services 2011 – 2016; Various consulting positions of increasing responsibility at IBM Global Business Services 2000 – 2011. | |||||||||
| Robert P. Fishman | 60 | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer since 2020; Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of NCR Corporation (a global provider of omni-channel technology solutions) 2016 – 2018; Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of NCR Corporation 2010 – 2016; Vice President and Corporate Controller of NCR Corporation 2007 – 2009. | |||||||||
| Tanya L. Hooper | 51 | Executive Vice President and Chief Human Resources Officer since January 1, 2023; Vice President of Global Talent and Corporate Human Resources of Honeywell International Inc. 2021 – 2022; Vice President and Chief Human Resources Officer of Collins Aerospace 2019 – 2021; Vice President of Talent of Collins Aerospace 2018 – 2019; Vice President of Human Resources of Collins Aerospace 2016 – 2018; Various positions of increasing responsibility at Shell 2000 – 2016. | |||||||||
| Jerome O. Pedretti | 53 | Executive Vice President and Chief Executive Officer of the Pool reporting segment since January 1, 2023; Executive Vice President and President of the Flow reporting segment 2020 – 2022; Senior Vice President of Pentair’s former Aquatic Systems reporting segment 2016 – 2019; Vice President of Pentair’s former Valves & Controls business 2014 – 2016; Vice President Growth Strategy 2010 – 2014; Various business leadership positions of Pentair 2005 – 2014; Consultant at Bain & Co 2002 – 2005. | |||||||||
| Stephen J. Pilla | 60 | Executive Vice President, Chief Supply Chain Officer and Chief Transformation Officer since January 1, 2023; Executive Vice President and Chief Supply Chain Officer 2020 – 2022; Vice President and Chief Supply Chain Officer of Red Wing Shoe Co. (a manufacturer of personal protection equipment and footwear) 2017 – 2020; Vice President and General Manager of Pentair’s former Enclosure Division 2015 – 2017; Vice President of Pentair’s Global Operations and Supply Chain 2014 – 2016; Vice President, Global Supply of Pentair 2009 – 2012; Various other business leadership positions of Pentair 2002 – 2009. | |||||||||
| Karla C. Robertson | 53 | Executive Vice President, General Counsel, Secretary and Chief Social Responsibility Officer since 2020; Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary 2018 – 2020; General Counsel, Water segment 2017 – 2018; Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary of SUPERVALU Inc. (a wholesaler and retailer of grocery products) 2013 – 2017; Vice President, Employment, Compensation and Benefits Law of SUPERVALU Inc. 2012 – 2013; Director, Employment Law of SUPERVALU Inc. 2011 – 2012; Senior Counsel, Employment Law of SUPERVALU Inc. 2009 – 2011; Senior Employee Relations Counsel of Target Corporation 2006 – 2008; Associate, Faegre & Benson LLP 2000 – 2005; Judicial Clerk, United States District Court for the Southern District of Iowa 1998 – 2000. | |||||||||
| Philip M. Rolchigo | 62 | Executive Vice President and Chief Technology Officer since 2018; Chief Technology Officer 2017 – 2018; Vice President of Technology 2015 – 2017; Vice President of Engineering 2007 – 2015; Business Development Director of Water Technologies business of GE Global Research Center 2006 – 2007; Director of Technology of GE Water & Process Technologies 2003 – 2006; Chief Technology Officer of Osmonics 2000 – 2003; Vice President of Research & Development of Osmonics 1998 – 2000. | |||||||||
| De’Mon L. Wiggins | 49 | Executive Vice President and President of the Flow reporting segment since January 1, 2023; Group President of Pentair’s Pool business 2021 – 2022; Vice President of Pentair’s Pool business 2017 – 2021; Vice President and Strategic Business Unit leader for Pentair’s Fluid Motion platform 2016 – 2017; Various other business leadership positions of Pentair 2010 – 2016. | |||||||||
21
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our ordinary shares are listed for trading on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol “PNR.” As of December 31, 2023, there were 12,363 shareholders of record.
Pentair has paid 192 consecutive quarterly cash dividends, including most recently a dividend of $0.22 per share in the fourth quarter of 2023. On December 11, 2023, Pentair’s Board of Directors approved a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.23 per share that was paid on February 2, 2024 to shareholders of record at the close of business on January 19, 2024. This dividend reflects a 5 percent increase in the Company’s regular cash dividend rate and marks the 48th consecutive year that Pentair has increased its dividend.
The timing, declaration and payment of future dividends to holders of our ordinary shares will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition and results of operations, the capital requirements of our businesses, industry practice and any other relevant factors.
Share Performance Graph
The following information under the caption “Share Performance Graph” in this ITEM 5 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K is not deemed to be “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC or subject to Regulation 14A or 14C under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), or to the liabilities of Section 18 of the Exchange Act and will not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Exchange Act, except to the extent we specifically incorporate it by reference into such a filing.
The following graph sets forth the cumulative total shareholder return on our ordinary shares for the last five years, assuming the investment of $100 on December 31, 2018 and the reinvestment of all dividends since that date to December 31, 2023. The graph also contains for comparison purposes the S&P 500 Index, the S&P 500 Industrials Index and the S&P Mid Cap 400 Index assuming the same investment level and reinvestment of dividends.
By virtue of our market capitalization, we are a component of the S&P 500 Index. On the basis of our size and diversity of businesses, we believe the S&P 500 Industrials Index and the S&P Mid Cap 400 Index are appropriate published industry indexes for comparison purposes.
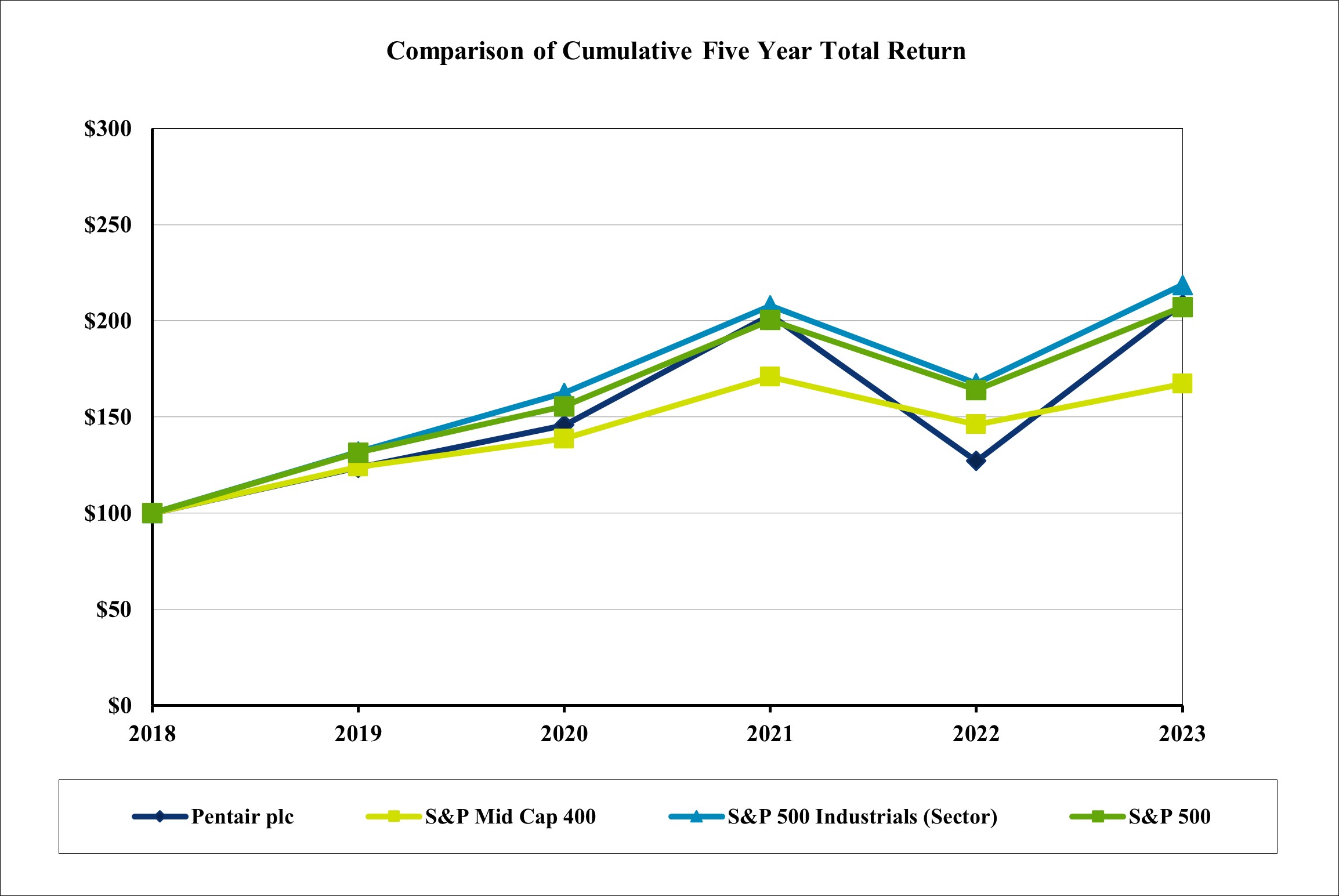
22
| Base Period December | INDEXED RETURNS Years ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Company / Index | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | |||||||||||||||||
| Pentair plc | $ | 100 | $ | 123.68 | $ | 145.80 | $ | 203.02 | $ | 127.14 | $ | 208.71 | |||||||||||
| S&P 500 Index | 100 | 131.49 | 155.68 | 200.37 | 164.08 | 207.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| S&P 500 Industrials Index | 100 | 131.97 | 162.55 | 207.89 | 167.55 | 218.55 | |||||||||||||||||
| S&P Mid Cap 400 Index | 100 | 124.05 | 138.70 | 170.89 | 146.14 | 167.26 | |||||||||||||||||
Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table provides information with respect to purchases we made of our ordinary shares during the fourth quarter of 2023:
| (a) | (b) | (c) | (d) | |||||||||||
| Total number of shares purchased | Average price paid per share | Total number of shares purchased as part of publicly announced plans or programs | Dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased under the plans or programs | |||||||||||
| October 1 – October 28 | 4,679 | $ | 63.56 | — | $ | 600,002,203 | ||||||||
| October 29 – November 25 | 594 | 60.99 | — | 600,002,203 | ||||||||||
| November 26 – December 31 | 1,283 | 65.23 | — | 600,002,203 | ||||||||||
| Total | 6,556 | — | ||||||||||||
(a)The purchases in this column include 4,679 shares for the period October 1 – October 28, 594 shares for the period October 29 – November 25, and 1,283 shares for the period November 26 – December 31 deemed surrendered to us by participants in our equity incentive plans to satisfy the exercise price or withholding of tax obligations related to the exercise of stock options and vesting of restricted and performance shares.
(b)The average price paid in this column includes shares repurchased as part of our publicly announced plans and shares deemed surrendered to us by participants in our equity incentive plans to satisfy the exercise price for the exercise price of stock options and withholding tax obligations due upon stock option exercises and vesting of restricted and performance shares.
(c)The number of shares in this column represents the number of shares repurchased as part of our publicly announced plans to repurchase our ordinary shares up to a maximum dollar limit authorized by the Board of Directors, discussed below.
(d)In December 2020, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of our ordinary shares up to a maximum dollar limit of $750.0 million. This authorization expires on December 31, 2025. As of December 31, 2023, we had $600.0 million remaining availability for repurchases under this authorization. From time to time, we may enter into a Rule 10b5-1 trading plan for the purpose of repurchasing shares under this authorization.
ITEM 6. [RESERVED]
23
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Forward-looking statements
This report contains statements that we believe to be “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, are forward-looking statements. Without limitation, any statements preceded or followed by or that include the words “targets,” “plans,” “believes,” “expects,” “intends,” “will,” “likely,” “may,” “anticipates,” “estimates,” “projects,” “should,” “would,” “could,” “positioned,” “strategy,” or “future” or words, phrases, or terms of similar substance or the negative thereof are forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and are subject to risks, uncertainties, assumptions and other factors, some of which are beyond our control, which could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. These factors include the overall global economic and business conditions impacting our business, including the strength of housing and related markets and conditions relating to international hostilities; supply, demand, logistics, competition and pricing pressures related to and in the markets we serve; the ability to achieve the benefits of our restructuring plans, cost reduction initiatives and Transformation Program; the impact of raw material, logistics and labor costs and other inflation; volatility in currency exchange rates and interest rates; failure of markets to accept new product introductions and enhancements; the ability to successfully identify, finance, complete and integrate acquisitions; risks associated with operating foreign businesses; the impact of seasonality of sales and weather conditions; our ability to comply with laws and regulations; the impact of changes in laws, regulations and administrative policy, including those that limit U.S. tax benefits or impact trade agreements and tariffs; the outcome of litigation and governmental proceedings; and the ability to achieve our long-term strategic operating and ESG goals. Additional information concerning these and other factors is contained in our filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), including this Annual Report on Form 10-K. All forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this report. Pentair assumes no obligation, and disclaims any obligation, to update the information contained in this report.
Overview
Pentair plc and its consolidated subsidiaries (“we,” “us,” “our,” “Pentair” or the “Company”) is a pure play water industrial manufacturing company comprised of three reporting segments: Flow (formerly named the Industrial & Flow Technologies segment), Water Solutions and Pool. We classify our operations into business segments based primarily on types of products offered and markets served. For the year ended December 31, 2023, the Flow, Water Solutions and Pool segments represented approximately 38%, 29% and 33% of total revenues, respectively.
Although our jurisdiction of organization is Ireland, we manage our affairs so that we are centrally managed and controlled in the United Kingdom (the “U.K.”) and therefore have our tax residency in the U.K.
In July 2022, as part of our Water Solutions reporting segment, we acquired the issued and outstanding equity securities of certain subsidiaries of Welbilt, Inc. (“Welbilt”) and certain other assets, rights, and properties, and assumed certain liabilities, comprising Welbilt’s Manitowoc Ice business (“Manitowoc Ice”), for approximately $1.6 billion in cash.
Key trends and uncertainties regarding our existing business
The following trends and uncertainties affected our financial performance in 2023, and are reasonably likely to impact our results in the future:
•In 2021, we created a transformation office and launched and committed resources to the Transformation Program designed to accelerate growth and drive margin expansion by driving operational excellence, reducing complexity and streamlining our processes. During 2023, we made strategic progress on our Transformation Program initiatives with a focus on our four key themes of pricing excellence, strategic sourcing, operations excellence and organizational effectiveness. We expect to continue to execute on our key Transformation Program initiatives to drive margin expansion and to continue to incur transformation costs in 2024 and beyond.
•In 2023, we executed certain business restructuring initiatives aimed at reducing our fixed cost structure and realigning our business. We expect these actions to continue into 2024 and to drive margin growth.
•The current volatile market for commodities has the potential to drive price increases in our supply chain. While we have taken pricing actions and implemented transformation initiatives that we expect to improve productivity and offset cost increases, we anticipate supply chain pressures and inflationary cost increases to continue into 2024.
24
•The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development Pillar Two Model Rules (“Pillar Two”), for a global 15.0% minimum tax, are in the process of being adopted by a number of jurisdictions in which we operate. In particular, the U.K. has completed passage of legislation to comply with the Pillar Two framework, which became effective at the start of 2024. We expect Pillar Two to have a negative 1.0% to 1.5% impact to our effective tax rate in 2024. That impact could change in the future as we continue to evaluate the enacted legislative changes and as new guidance becomes available.
•We have identified specific product and geographic market opportunities that we find attractive and continue to pursue, both within and outside the U.S. We expect to continue investing in our businesses to drive these opportunities through research and development and additional sales and marketing resources. Unless we successfully penetrate these markets, our core sales growth will likely be limited or may decline.
In 2024, our operating objectives focus on delivering our core and building our future. We expect to execute these objectives by:
•Delivering profitable revenue growth and productivity for customers and shareholders;
•Continuing to focus on capital allocation through:
◦Committing to maintain our investment grade rating;
◦Focusing on reducing our long-term debt;
◦Returning cash to shareholders through dividends and share repurchases; and
◦Accelerating our performance with strategically-aligned mergers and acquisitions;
•Focusing growth initiatives that accelerate our investments in digital, innovation, technology and ESG;
•Continuing to implement our Transformation Program initiatives that will drive operational excellence, reduce complexity and improve our organizational structure; and
•Building a high performance growth culture and delivering on our commitments while living our Win Right values.
25
CONSOLIDATED RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The consolidated results of operations were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | % / point change | |||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 4,104.5 | $ | 4,121.8 | $ | 3,764.8 | (0.4) | % | 9.5 | % | ||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 2,585.3 | 2,757.2 | 2,445.6 | (6.2) | % | 12.7 | % | |||||||||||||
| Gross profit | 1,519.2 | 1,364.6 | 1,319.2 | 11.3 | % | 3.4 | % | |||||||||||||
| % of net sales | 37.0 | % | 33.1 | % | 35.0 | % | 3.9 | pts | (1.9) | pts | ||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 680.2 | 677.1 | 596.4 | 0.5 | % | 13.5 | % | |||||||||||||
| % of net sales | 16.6 | % | 16.4 | % | 15.8 | % | 0.2 | pts | 0.6 | pts | ||||||||||
| Research and development | 99.8 | 92.2 | 85.9 | 8.2 | % | 7.3 | % | |||||||||||||
| % of net sales | 2.4 | % | 2.2 | % | 2.3 | % | 0.2 | pts | (0.1) | pts | ||||||||||
| Operating income | 739.2 | 595.3 | 636.9 | 24.2 | % | (6.5) | % | |||||||||||||
| % of net sales | 18.0 | % | 14.4 | % | 16.9 | % | 3.6 | pts | (2.5) | pts | ||||||||||
| Gain on sale of businesses | — | (0.2) | (1.4) | N.M. | N.M. | |||||||||||||||
| Net interest expense | 118.3 | 61.8 | 12.5 | N.M. | N.M. | |||||||||||||||
| Other expense (income) | 2.0 | (16.9) | (1.0) | N.M. | N.M. | |||||||||||||||
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 618.9 | 550.6 | 626.8 | 12.4 | % | (12.2) | % | |||||||||||||
| (Benefit) provision for income taxes | (4.0) | 67.4 | 70.8 | N.M. | (4.8) | % | ||||||||||||||
| Effective tax rate | (0.6) | % | 12.2 | % | 11.3 | % | (12.8) | pts | 0.9 | pts | ||||||||||
N.M. Not Meaningful
Net sales
The components of the consolidated net sales change were as follows:
| 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||
| Volume | (11.3) | % | (7.1) | % | ||||
| Price | 6.4 | 13.3 | ||||||
| Core growth | (4.9) | 6.2 | ||||||
| Acquisition/Divestiture | 4.4 | 5.5 | ||||||
| Currency | 0.1 | (2.2) | ||||||
| Total | (0.4) | % | 9.5 | % | ||||
The 0.4 percent decrease in consolidated net sales in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•decreased sales volume in our residential business within our Flow segment compared to the prior year;
•decreased sales volume in our residential business within our Water Solutions segment driven by lower demand compared to the prior year and certain business exits announced in the second half of 2022; and
•decreased sales volume in our Pool segment primarily due to higher channel inventory and lower demand compared to the prior year.
This decrease was partially offset by:
•increased selling prices to mitigate a rise in inflationary costs as well as lower rebates and incentives in our Pool segment;
26
•increased sales within our Water Solutions segment from the acquisition of Manitowoc Ice, which was completed in the third quarter of 2022;
•increased sales volume in our commercial business within our Water Solutions segment driven by demand and easing of supply chain pressures, which allowed increased productivity and delivery to market; and
•increased sales volume in our commercial and industrial solutions businesses within our Flow segment compared to the prior year.
Gross profit
The 3.9 percentage point increase in gross profit as a percentage of net sales in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•increased selling prices to mitigate impacts of inflation as well as lower rebates and incentives in our Pool segment;
•increased productivity within our Water Solutions segment as a result of certain transformation and restructuring initiatives;
•increased productivity in our Flow segment mainly driven by manufacturing leverage and transformation initiatives;
•inventory impairments and write-offs and certain accruals of $19.6 million, recorded in 2022 as part of exiting businesses in our Water Solutions segment; and
•amortization of inventory fair market value step-up of $5.8 million in 2022, as a result of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition.
This increase was partially offset by:
•inflationary cost increases related to labor costs and certain raw materials; and
•inventory impairments and write-offs of $7.0 million in 2023.
Selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”)
The 0.2 percentage point increase in SG&A expense as a percentage of net sales in 2023 from 2022 was driven by:
•higher employee compensation costs compared to the prior year; and
•transformation costs of $44.3 million in 2023, compared to $27.2 million in 2022.
This increase was partially offset by:
•no deal-related costs and expenses in 2023, compared to $22.2 million in 2022; and
•restructuring costs of $9.1 million in 2023, compared to $36.7 million in 2022.
Net interest expense
The increase in net interest expense in 2023 from 2022 was the result of:
•increased variable interest rates in 2023 compared to the prior year; and
•increased debt due to the acquisition of Manitowoc Ice in the third quarter of 2022.
This increase was partially offset by:
•the amortization of debt issuance costs of $9.0 million in 2022 related to financing commitments for a bridge loan facility established in connection with the acquisition of Manitowoc Ice that did not recur in 2023.
27
(Benefit) provision for income taxes
The 12.8 percentage point decrease in the effective tax rate in 2023 from 2022 was primarily due to:
•the favorable impact of worthless stock deductions related to exiting certain businesses in our Water Solutions segment;
•the favorable impact of discrete items primarily related to increases in tax basis in assets located in foreign jurisdictions; and
•the favorable mix of global earnings.
2022 Comparison with 2021
A discussion of changes in our consolidated results of operations, segment results of operations for the Flow (formerly named Industrial & Flow Technologies) segment and liquidity and capital resources from the year ended December 31, 2022 to December 31, 2021 can be found in Part II, ITEM 7, Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022, which was filed with the SEC on February 21, 2023. However, such discussion is not incorporated by reference into, and does not constitute a part of, this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
SEGMENT RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The summary that follows provides a discussion of the results of operations of our three reportable segments (Flow, Water Solutions and Pool). Each of these segments is comprised of various product offerings that serve multiple end users.
We evaluate performance based on net sales and segment income and use a variety of ratios to measure performance of our reporting segments. Segment income represents equity income of unconsolidated subsidiaries and operating income exclusive of intangible amortization, certain acquisition related expenses, costs of restructuring and transformation activities, impairments and other unusual non-operating items.
Flow
The net sales and segment income for Flow were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | % / point change | |||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 1,582.1 | $ | 1,500.8 | $ | 1,421.4 | 5.4 | % | 5.6 | % | ||||||||||
| Segment income | 282.3 | 242.3 | 213.3 | 16.5 | % | 13.6 | % | |||||||||||||
| % of net sales | 17.8 | % | 16.1 | % | 15.0 | % | 1.7 | pts | 1.1 | pts | ||||||||||
Net sales
The components of the change in Flow net sales were as follows:
| 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||
| Volume | (2.0) | % | (0.7) | % | ||||
| Price | 7.1 | 10.4 | ||||||
| Core growth | 5.1 | 9.7 | ||||||
| Currency | 0.3 | (4.1) | ||||||
| Total | 5.4 | % | 5.6 | % | ||||
The 5.4 percent increase in net sales for Flow in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•increased selling prices to mitigate inflationary cost increases;
•increased sales volume in our commercial and industrial solutions businesses in 2023 compared to the prior year; and
•favorable foreign currency effects in 2023 compared to the prior year.
The increase was partially offset by:
•decreased sales volume in our residential business in 2023 compared to the prior year.
28
Segment income
The components of the change in Flow segment income as a percentage of net sales from the prior period were as follows:
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Growth/Price/Acquisition | 5.6 | pts | 9.6 | pts | ||||
| Currency | (0.1) | (0.1) | ||||||
| Inflation | (5.6) | (7.4) | ||||||
| Productivity | 1.8 | (1.0) | ||||||
| Total | 1.7 | pts | 1.1 | pts | ||||
The 1.7 percentage point increase in segment income for Flow as a percentage of net sales in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•increased selling prices to mitigate impacts of inflation; and
•increased productivity mainly driven by manufacturing leverage and transformation initiatives.
This increase was partially offset by:
•inflationary cost increases related to labor costs and certain raw materials.
Water Solutions
The net sales and segment income for Water Solutions were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | % / point change | |||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 1,177.2 | $ | 986.8 | $ | 769.9 | 19.3 | % | 28.2 | % | ||||||||||
| Segment income | 247.6 | 149.0 | 101.7 | 66.2 | % | 46.5 | % | |||||||||||||
| % of net sales | 21.0 | % | 15.1 | % | 13.2 | % | 5.9 | pts | 1.9 | pts | ||||||||||
Net sales
The components of the change in Water Solutions net sales were as follows:
| 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||
| Volume | (2.0) | % | (6.2) | % | ||||
| Price | 3.1 | 15.1 | ||||||
| Core growth | 1.1 | 8.9 | ||||||
| Acquisition/Divestiture | 18.5 | 21.9 | ||||||
| Currency | (0.3) | (2.6) | ||||||
| Total | 19.3 | % | 28.2 | % | ||||
The 19.3 percent increase in net sales for Water Solutions in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•increased sales as a result of the acquisition of Manitowoc Ice, which was completed in the third quarter of 2022;
•higher sales volume in our commercial business driven by higher demand and easing of supply chain pressures, which allowed increased production and delivery to market; and
•increased selling prices to mitigate inflationary cost increases.
This increase was partially offset by:
•decreased sales volume in our residential business driven by lower demand in 2023 compared to the prior year and certain business exits announced in the second half of 2022; and
•unfavorable foreign currency effects.
29
The 28.2 percent increase in net sales for Water Solutions in 2022 from 2021 was primarily the result of:
•increased sales due to the acquisitions of Manitowoc Ice and Ken’s Beverage, Inc. completed in the third quarter of 2022 and the second quarter of 2021, respectively;
•increased selling prices to mitigate impacts of inflation; and
•increased sales volume in our commercial business in 2022 compared to the prior year.
This increase was partially offset by:
•decreased sales volume in our residential business in 2022 compared to the prior year; and
•unfavorable foreign currency effects.
Segment income
The components of the change in Water Solutions segment income as a percentage of net sales from the prior period were as follows:
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Growth/Price/Acquisition | 7.8 | pts | 14.6 | pts | ||||
| Currency | (0.5) | (0.3) | ||||||
| Inflation | (4.7) | (10.6) | ||||||
| Productivity | 3.3 | (1.8) | ||||||
| Total | 5.9 | pts | 1.9 | pts | ||||
The 5.9 percentage point increase in segment income for Water Solutions as a percentage of net sales in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•increased sales as a result of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition;
•increased selling prices to mitigate impacts of inflation; and
•increased productivity in the residential business as a result of certain transformation and restructuring initiatives.
This increase was partially offset by:
•inflationary cost increases related to labor costs and certain raw materials; and
•unfavorable foreign currency effects.
The 1.9 percentage point increase in segment income for Water Solutions as a percentage of net sales in 2022 from 2021 was primarily the result of:
•increased sales as a result of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition in the third quarter of 2022; and
•increased selling prices to mitigate impacts of inflation.
This increase was partially offset by:
•inflationary cost increases due to high demand and limited supply of raw materials such as metals, resins and electronics along with increased logistics and labor costs;
•decreased productivity in our residential business due to decreased sales volume; and
•unfavorable foreign currency effects.
30
Pool
The net sales and segment income for Pool were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | % / point change | |||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 1,343.6 | $ | 1,632.7 | $ | 1,572.0 | (17.7) | % | 3.9 | % | ||||||||||
| Segment income | 417.0 | 462.1 | 452.7 | (9.8) | % | 2.1 | % | |||||||||||||
| % of net sales | 31.0 | % | 28.3 | % | 28.8 | % | 2.7 | pts | (0.5) | pts | ||||||||||
Net sales
The components of the change in Pool net sales were as follows:
| 2023 vs 2022 | 2022 vs 2021 | |||||||
| Volume | (25.2) | % | (13.2) | % | ||||
| Price | 7.6 | 15.0 | ||||||
| Core growth | (17.6) | 1.8 | ||||||
| Acquisition/Divestiture | — | 2.4 | ||||||
| Currency | (0.1) | (0.3) | ||||||
| Total | (17.7) | % | 3.9 | % | ||||
The 17.7 percent decrease in net sales for Pool in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•sales volume decreases primarily due to higher channel inventory and lower demand compared to the prior year.
This decrease was partially offset by:
•increased selling prices to mitigate a rise in inflationary costs as well as lower rebates and incentives.
The 3.9 percent increase in net sales for Pool in 2022 from 2021 was primarily the result of:
•increased selling prices to mitigate impacts of inflation; and
•increased sales due to the acquisition of Pleatco Holdings, LLC completed in the fourth quarter of 2021.
This increase was partially offset by:
•decreased sales volume in 2022 compared to the prior year; and
•unfavorable foreign currency effects.
Segment income
The components of the change in Pool segment income as a percentage of net sales from the prior period were as follows:
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Growth/Price/Acquisition | 5.3 | pts | 10.1 | pts | ||||
| Currency | — | 0.1 | ||||||
| Inflation | (2.9) | (8.6) | ||||||
| Productivity | 0.3 | (2.1) | ||||||
| Total | 2.7 | pts | (0.5) | pts | ||||
The 2.7 percentage point increase in segment income for Pool as a percentage of net sales in 2023 from 2022 was primarily the result of:
•increased selling prices to mitigate impacts of inflation as well as lower rebates and incentives;
•increased productivity associated with benefits realized from our transformation initiatives; and
•cost management initiatives associated with decreased sales volume.
31
This increase was partially offset by:
•inflationary cost increases related to labor costs and certain raw materials.
The 0.5 percentage point decrease in segment income for Pool as a percentage of net sales in 2022 from 2021 was primarily the result of:
•inflationary cost increases due to high demand and limited supply of raw materials such as metals, resins and electronics along with increased logistics and labor costs; and
•decreased productivity due to decreased sales volume.
This decrease was partially offset by:
•increases in selling prices to mitigate the impacts of inflation; and
•increased sales as a result of the Pleatco Holdings, LLC acquisition in the fourth quarter of 2021.
BACKLOG OF ORDERS BY SEGMENT
| December 31 | ||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | $ change | % change | ||||||||||
| Flow | $ | 390.1 | $ | 512.1 | $ | (122.0) | (23.8) | % | ||||||
| Water Solutions | 108.5 | 193.5 | (85.0) | (43.9) | % | |||||||||
| Pool | 239.7 | 289.6 | (49.9) | (17.2) | % | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 738.3 | $ | 995.2 | $ | (256.9) | (25.8) | % | ||||||
The majority of our backlog is short cycle in nature with shipments within one year from when a customer places an order, and a substantial portion of our revenues has historically resulted from orders received and products delivered in the same month. A portion of our backlog, particularly from orders for major capital projects, can take more than one year from order to delivery depending on the size and type of order. We record, as part of our backlog, all orders from external customers, which represent firm commitments, and are supported by a purchase order or other legitimate contract. Our backlog of orders is dependent upon when customers place orders and is not necessarily an indicator of our expected results for our 2024 net sales. The decrease in our overall backlog from the prior year was primarily driven by our backlog trending down to more historical levels as a result of increased manufacturing capacity and improved lead times.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
We generally fund cash requirements for working capital, capital expenditures, equity investments, acquisitions, debt repayments, dividend payments and share repurchases from cash generated from operations, availability under existing committed revolving credit facilities and in certain instances, public and private debt and equity offerings. Our primary revolving credit facility has generally been adequate for these purposes, although we have negotiated additional credit facilities or completed debt and equity offerings as needed to allow us to complete acquisitions.
We experience seasonal cash flows primarily due to seasonal demand in a number of markets. Consistent with historical trends, we experienced seasonal cash usage in the first quarter of 2023 and drew on our revolving credit facility to fund our operations. This cash usage reversed in the second quarter of 2023 as the seasonality of our businesses peaked and generated significant cash to fund our operations. In the second half of 2023, we funded our operations using our strong cash flow and revolving credit facility.
End-user demand for pool equipment in the Pool segment, water solution products in the Water Solutions segment, and residential water supply and agricultural products within the Flow segment follows warm weather trends, with seasonal highs from April to September. The magnitude of the sales spike has historically been partially mitigated by employing some advance sale “early buy” programs (generally including extended payment terms and/or additional discounts). Demand for residential and agricultural water systems is also impacted by weather patterns, particularly by temperature, heavy flooding and droughts.
32
Summary of Cash Flows
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Cash provided by (used for): | |||||||||||
| Operating activities of continuing operations | $ | 620.8 | $ | 364.3 | $ | 613.6 | |||||
| Investing activities | (85.4) | (1,582.8) | (390.7) | ||||||||
| Financing activities | (468.1) | 1,232.7 | (222.2) | ||||||||
Operating activities
In 2023, net cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations primarily reflects net income from continuing operations, net of non-cash depreciation, definite-lived intangible amortization, asset impairment and deferred income taxes, of $653.1 million. Additionally, we had a cash outflow of $61.3 million as a result of changes in net working capital, primarily due to an increase in accounts receivable and decreases in accounts payable and other current liability balances, partially offset by lower inventory compared to December 31, 2022. Decreases in inventory and accounts payable were primarily related to supply chain efficiencies and improved lead times.
In 2022, net cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations primarily reflects net income from continuing operations, net of non-cash depreciation, definite-lived intangible amortization and asset impairment, of $615.4 million. Additionally, we had a cash outflow of $218.7 million as a result of changes in net working capital, primarily due to increased inventory balances compared to December 31, 2021. Inventory was higher due to inflationary impacts, continued supply chain inefficiencies and a rebalancing of inventory levels in the residential channel.
Investing activities
Net cash used for investing activities in 2023 primarily reflects capital expenditures of $76.0 million and cash paid upon the settlement of net investment hedges of $18.5 million, partially offset by proceeds from the sale of property and equipment of $5.6 million.
Net cash used for investing activities in 2022 primarily reflects the net cash paid of $1,579.5 million for the Manitowoc Ice acquisition and capital expenditures of $85.2 million, partially offset by cash received upon the settlement of net investment hedges of $78.9 million.
Financing activities
In 2023, net cash used for financing activities primarily relates to net repayments of revolving long-term debt of $320.0 million and dividend payments of $145.2 million.
In 2022, net cash provided by financing activities primarily relates to net borrowings of revolving long-term debt of $124.5 million, net proceeds received from the Term Loan Facility and issuance of the 2032 Senior Notes of $1,391.3 million used to finance the Manitowoc Ice acquisition and net cash receipts upon the settlement of cross currency swaps of $12.3 million, partially offset by dividend payments of $138.6 million, repayment of $88.3 million senior fixed notes, share repurchases of $50.0 million and payments of debt issuance costs of $15.8 million.
33
Free Cash Flow
In addition to measuring our cash flow generation or usage based upon operating, investing and financing classifications included in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, we also measure our free cash flow. We have a long-term goal to consistently generate free cash flow that is equal to 100 percent conversion of net income. Free cash flow is a non-U.S. GAAP financial measure that we use to assess our cash flow performance. We believe free cash flow is an important measure of liquidity because it provides us and our investors a measurement of cash generated from operations that is available to pay dividends, repurchase shares and repay debt. In addition, free cash flow is used as a criterion to measure and pay compensation-based incentives. Our measure of free cash flow may not be comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies.
The following table is a reconciliation of free cash flow:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations | $ | 620.8 | $ | 364.3 | $ | 613.6 | |||||
| Capital expenditures of continuing operations | (76.0) | (85.2) | (60.2) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property and equipment of continuing operations | 5.6 | 4.1 | 3.9 | ||||||||
| Free cash flow from continuing operations | $ | 550.4 | $ | 283.2 | $ | 557.3 | |||||
| Net cash used for operating activities of discontinued operations | (1.6) | (1.0) | (0.4) | ||||||||
| Free cash flow | $ | 548.8 | $ | 282.2 | $ | 556.9 | |||||
Debt and Capital
Pentair, Pentair Finance S.à r.l (“PFSA“) and Pentair, Inc. are parties to a credit agreement (the “Senior Credit Facility”), with Pentair as guarantor and PFSA and Pentair, Inc. as borrowers, providing for a $900.0 million senior unsecured revolving credit facility and a $200.0 million senior unsecured term loan facility. The revolving credit facility has a maturity date of December 16, 2026 and the term loan facility has a maturity date of December 16, 2024. Borrowings under the Senior Credit Facility bear interest at a rate equal to an alternate base rate, adjusted term secured overnight financing rate, adjusted euro interbank offered rate, adjusted daily simple secured overnight financing rate or central bank rate, plus, in each case, an applicable margin. The applicable margin is based on, at PFSA’s election, Pentair’s leverage level or PFSA’s public credit rating.
As of December 31, 2023, total availability under the Senior Credit Facility was $900.0 million. In addition, PFSA has the option to request to increase the revolving credit facility and/or to enter into one or more additional tranches of term loans in an aggregate amount of up to $300.0 million, subject to customary conditions, including the commitment of the participating lenders.
In 2022, Pentair and PFSA entered into a senior unsecured term loan facility (the “Term Loan Facility”), with PFSA, as borrower, Pentair, as guarantor, and the lenders and agents party thereto, providing for an aggregate principal amount of $1.0 billion. The Term Loan Facility has a maturity date of July 28, 2027, with required quarterly installment payments of $6.3 million which began on the last day of the third quarter of 2023 and increases to $12.5 million beginning with the last day of the third quarter of 2024. The Term Loan Facility bears interest at a rate equal to an alternate base rate, adjusted term secured overnight financing rate, or adjusted daily simple secured overnight financing rate, plus, in each case, an applicable margin. The applicable margin is based on, at PFSA’s election, Pentair’s leverage level or PFSA’s public credit rating.
In addition to the Term Loan Facility, Pentair, as guarantor, and PFSA, as issuer, completed a public offering in 2022 of $400.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.900% Senior Notes due 2032 (“2032 Senior Notes”). We used the net proceeds from the Term Loan Facility and the issuance of the 2032 Senior Notes to finance a portion of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition purchase price and to pay related fees and expenses.
Our debt agreements contain various financial covenants, but the most restrictive covenants are contained in the Senior Credit Facility and the Term Loan Facility. The Senior Credit Facility and the Term Loan Facility contain covenants requiring us not to permit (i) the ratio of our consolidated debt (net of our consolidated unrestricted cash and cash equivalents in excess of $5.0 million but not to exceed $250.0 million) to our consolidated net income (excluding, among other things, non-cash gains and losses) before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and non-cash share-based compensation expense (“EBITDA”) on the last day of any period of four consecutive fiscal quarters (each, a “testing period”) to exceed 3.75 to 1.00 (or, at PFSA’s election and subject to certain conditions, 4.25 to 1.00 for four testing periods in connection with certain material acquisitions) (the “Leverage Ratio”) and (ii) the ratio of our EBITDA to our consolidated interest expense, for the same period to be less than 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of each fiscal quarter. For purposes of the Leverage Ratio, the Senior Credit Facility and the Term
34
Loan Facility provide for the calculation of EBITDA giving pro forma effect to certain acquisitions, divestitures and liquidations during the period to which such calculation relates.
In addition to the Senior Credit Facility and the Term Loan Facility, we have various other credit facilities with an aggregate availability of $20.9 million, of which there were no outstanding borrowings at December 31, 2023. Borrowings under these credit facilities bear interest at variable rates.
We have $37.5 million of Term Loan Facility payments and $200.0 million of payments under the senior unsecured term loan facility, associated with the Senior Credit Facility, due in the next twelve months. We classified this debt as long-term as of December 31, 2023 as we have the intent and ability to refinance such obligations on a long-term basis under the revolving credit facility under the Senior Credit Facility.
As of December 31, 2023, we had $87.5 million of cash held in certain countries in which the ability to repatriate is limited due to local regulations or significant potential tax consequences.
Authorized shares
Our authorized share capital consists of 426.0 million ordinary shares with a par value of $0.01 per share.
Share repurchases
In December 2020, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of our ordinary shares up to a maximum dollar limit of $750.0 million. This authorization expires on December 31, 2025.
During the year ended December 31, 2022, we repurchased 1.0 million of our ordinary shares for $50.0 million. During the year ended December 31, 2023, no ordinary shares were repurchased. As of December 31, 2023, we had $600.0 million available for share repurchases under this authorization.
Dividends
On December 11, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.23 per share that was paid on February 2, 2024 to shareholders of record at the close of business on January 19, 2024. This dividend reflects a 5 percent increase in the Company’s regular cash dividend rate. The balance of dividends payable included in Other current liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets was $38.0 million at December 31, 2023. Dividends paid per ordinary share were $0.88, $0.84 and $0.80 for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Under Irish law, the payment of future cash dividends and repurchases of shares may be paid only out of Pentair plc’s “distributable reserves” on its statutory balance sheet. Pentair plc is not permitted to pay dividends out of share capital, which includes share premiums. Distributable reserves may be created through the earnings of the Irish parent company and through a reduction in share capital approved by the Irish High Court. Distributable reserves are not linked to a U.S. GAAP reported amount (e.g., retained earnings). Our distributable reserve balance was $6.9 billion and $7.1 billion as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Supplemental guarantor information
Pentair plc (the “Parent Company Guarantor”), fully and unconditionally, guarantees the senior notes of PFSA (the “Subsidiary Issuer”). The Subsidiary Issuer is a Luxembourg private limited liability company and 100 percent-owned subsidiary of the Parent Company Guarantor.
The Parent Company Guarantor is a holding company established to own directly and indirectly substantially all of its operating and other subsidiaries. The Subsidiary Issuer is a holding company formed to own directly and indirectly substantially all of its operating and other subsidiaries and to issue debt securities, including the senior notes. The Parent Company Guarantor’s principal source of cash flow, including cash flow to make payments on the senior notes pursuant to the guarantees, is dividends from its subsidiaries. The Subsidiary Issuer’s principal source of cash flow is interest income from its subsidiaries. None of the subsidiaries of the Parent Company Guarantor or the Subsidiary Issuer is under any direct obligation to pay or otherwise fund amounts due on the senior notes or the guarantees, whether in the form of dividends, distributions, loans or other payments. In addition, there may be statutory and regulatory limitations on the payment of dividends from certain subsidiaries of the Parent Company Guarantor or the Subsidiary Issuer. If such subsidiaries are unable to transfer funds to the Parent Company Guarantor or the Subsidiary Issuer and sufficient cash or liquidity is not otherwise available, the Parent Company Guarantor or the Subsidiary Issuer may not be able to make principal and interest payments on their outstanding debt, including the senior notes or the guarantees.
35
The following table presents summarized financial information as of December 31, 2023 for the Parent Company Guarantor and Subsidiary Issuer on a combined basis after elimination of (i) intercompany transactions and balances among the guarantors and issuer and (ii) equity in earnings from and investments in any subsidiary that is a non-Guarantor or issuer.
| In millions | December 31, 2023 | |||||||
Current assets (1) | $ | 71.7 | ||||||
Noncurrent assets (2) | 2,686.9 | |||||||
Current liabilities (3) | 1,659.0 | |||||||
Noncurrent liabilities (4) | 2,331.4 | |||||||
(1) No assets due from non-guarantor subsidiaries were included. | ||||||||
(2) Includes assets due from non-guarantor subsidiaries of $2,673.3 million. | ||||||||
(3) Includes liabilities due to non-guarantor subsidiaries of $1,583.6 million. | ||||||||
(4) Includes liabilities due to non-guarantor subsidiaries of $268.4 million. | ||||||||
The Parent Company Guarantor and Subsidiary Issuer do not have material results of operations on a combined basis.
Material Cash Requirements From Contractual Obligations and Commitments
We expect to continue to have sufficient cash and borrowing capacity to support working capital needs and capital expenditures, to pay interest and service debt and to pay dividends to shareholders quarterly. We believe we have the ability to meet our short-term and long-term cash requirements by using available cash and internally generated funds and to borrow under our committed and uncommitted credit facilities. The following summarizes our material cash requirements from significant contractual obligations and purchase commitments that impact our liquidity as of December 31, 2023:
| In millions | Next Twelve Months | Greater Than Twelve Months | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Debt obligations (Note 8) | $ | 237.5 | $ | 1,769.3 | $ | 2,006.8 | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest obligations on fixed-rate debt | 42.5 | 279.7 | 322.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations, net of sublease rentals (Note 15) | 31.4 | 97.8 | 129.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension and other post-retirement plan contributions (Note 11) | 9.5 | 79.9 | 89.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other purchase obligations | 42.4 | 24.2 | 66.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total contractual obligations, net | $ | 363.3 | $ | 2,250.9 | $ | 2,614.2 | |||||||||||||||||
Other purchase obligations primarily include service and marketing contracts as well as commitments for raw materials to be utilized in the normal course of business. For purposes of the above table, arrangements are considered purchase obligations if a contract specifies all significant terms, including fixed or minimum quantities to be purchased, a pricing structure and approximate timing of the transaction.
In addition to the significant contractual obligations described above, we will incur annual interest expense on outstanding variable rate debt. As of December 31, 2023, variable interest rate debt was $1,187.5 million at a weighted average interest rate of 6.84%. Inclusive of our interest rate swaps and collars, our weighted average interest rate on our variable rate debt was 6.29% as of December 31, 2023. Refer to ITEM 8, Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our interest rate swaps and collars.
The total gross liability for uncertain tax positions at December 31, 2023 was estimated to be $38.6 million. We record penalties and interest related to unrecognized tax benefits in (Benefit) provision for income taxes and Net interest expense, respectively, which is consistent with our past practices. As of December 31, 2023, we had recorded $0.3 million for the possible payment of penalties and $6.4 million related to the possible payment of interest.
36
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
We have been, and in the future may be, made parties to a number of actions filed or have been, and in the future may be, given notice of potential claims relating to the conduct of our business, including those relating to commercial, regulatory or contractual disputes with suppliers, authorities, customers or parties to acquisitions and divestitures, intellectual property matters, environmental, asbestos, safety and health matters, product liability, the use or installation of our products, consumer matters, and employment and labor matters.
While we believe that a material impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows from any such future claims or potential claims is unlikely, given the inherent uncertainty of litigation, a remote possibility exists that a future adverse ruling or unfavorable development could result in future charges that could have a material impact. We do and will continue to periodically reexamine our estimates of probable liabilities and any associated expenses and receivables and make appropriate adjustments to such estimates based on experience and developments in litigation and applicable accounting rules. As a result, the current estimates of the potential impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations and cash flows for the proceedings and claims described in ITEM 8, Note 15 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements could change in the future.
Product liability claims
We are subject to various product liability lawsuits and personal injury claims. A substantial number of these lawsuits and claims are insured and accrued for by Penwald, our captive insurance subsidiary. See discussion in ITEM 1 and ITEM 8, Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — Insurance subsidiary. Penwald records a liability for these claims based on actuarial projections of ultimate losses. For all other claims, accruals covering the claims are recorded, on an undiscounted basis, when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be reasonably estimated based on existing information. The accruals are adjusted periodically as additional information becomes available. We have not experienced significant unfavorable trends in either the severity or frequency of product liability lawsuits or personal injury claims.
Stand-by letters of credit, bank guarantees and bonds
In certain situations, Tyco International Ltd., Pentair Ltd.’s former parent company (“Tyco”), guaranteed performance by the flow control business of Pentair Ltd. (“Flow Control”) to third parties or provided financial guarantees for financial commitments of Flow Control. In situations where Flow Control and Tyco were unable to obtain a release from these guarantees in connection with the spin-off of Flow Control from Tyco, we will indemnify Tyco for any losses it suffers as a result of such guarantees.
In the ordinary course of business, we are required to commit to bonds, letters of credit and bank guarantees that require payments to our customers for any non-performance. The outstanding face value of these instruments fluctuates with the value of our projects in process and in our backlog. In addition, we issue financial stand-by letters of credit primarily to secure our performance to third parties under self-insurance programs.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the outstanding value of bonds, letters of credit and bank guarantees totaled $124.3 million and $99.7 million, respectively.
NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
See ITEM 8, Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, included in this Form 10-K, for information pertaining to accounting standards to be adopted in the future.
37
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
We have adopted various accounting policies to prepare the consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Our significant accounting policies are more fully described in ITEM 8, Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Certain accounting policies require the application of significant judgment by management in selecting the appropriate assumptions for calculating financial estimates. By their nature, these judgments are subject to an inherent degree of uncertainty. These judgments are based on our historical experience, terms of existing contracts, our observance of trends in the industry and information available from other outside sources, as appropriate. We consider an accounting estimate to be critical if:
•it requires us to make assumptions about matters that were uncertain at the time we were making the estimate; and
•changes in the estimate or different estimates that we could have selected which would have had a material impact on our financial condition or results of operations.
Our critical accounting estimates include the following:
Impairment of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangibles
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the cost of acquired businesses over the net of the fair value of identifiable tangible net assets and identifiable intangible assets purchased and liabilities assumed.
We test our goodwill for impairment at least annually during the fourth quarter or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. We perform our annual or interim goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of the relevant reporting unit with its carrying amount. We would recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value; however, the loss recognized would not exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit.
We have the option to perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is necessary to perform the quantitative goodwill impairment test. However, we may elect to perform the quantitative goodwill impairment test even if no indications of a potential impairment exist.
During 2023, a quantitative assessment was performed. The fair value of each reporting unit was determined using a discounted cash flow analysis and market approach. Projecting discounted future cash flows requires us to make significant estimates regarding future revenues and expenses, projected capital expenditures, changes in working capital and the appropriate discount rate. Use of the market approach consists of comparisons to comparable publicly-traded companies that are similar in size and industry. The non-recurring fair value measurement is a “Level 3” measurement under the fair value hierarchy. For the 2023 annual impairment test, the estimated fair value significantly exceeded the carrying value in each of our reporting units, therefore, no impairment charge was required.
During 2022, a qualitative assessment was performed. As a result, it was determined that it was more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting units exceeded their respective carrying values. Factors considered in the analysis included the 2020 discounted cash flow fair value assessment of the reporting units and the calculated excess fair value over carrying amount, financial performance, forecasts and trends, market capitalization, regulatory and environmental issues, macro-economic conditions, industry and market considerations, raw material costs and management stability. We also consider the extent to which each of the adverse events and circumstances identified affect the comparison of the respective reporting unit’s fair value with its carrying amount. We place more weight on the events and circumstances that most affect the respective reporting unit’s fair value or the carrying amount of its net assets. We consider positive and mitigating events and circumstances that may affect its determination of whether it is more likely than not that the fair value exceeds the carrying amount. The non-recurring fair value measurement is a “Level 3” measurement under the fair value hierarchy described in ITEM 8, Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
38
Identifiable intangible assets
Our primary identifiable intangible assets include: customer relationships, trade names, proprietary technology and patents. Identifiable intangibles with finite lives are amortized and those identifiable intangibles with indefinite lives are not amortized. Identifiable intangible assets that are subject to amortization are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. An impairment charge of $2.7 million was recorded in 2022 related to the write-off of a proprietary technology intangible asset as a result of restructuring initiatives implemented in the fourth quarter of 2022. The impairment charge was recorded in Selling, general and administrative in our Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income. No impairment charges associated with identifiable intangibles with finite lives were recognized in 2023.
Identifiable intangible assets not subject to amortization are tested for impairment annually or more frequently if events warrant. We complete our annual impairment test the first day of the fourth quarter each year for those identifiable assets not subject to amortization. The impairment test for trade names consists of a comparison of the fair value of the trade name with its carrying value. Fair value is measured using the relief-from-royalty method. This method assumes the trade name has value to the extent that the owner is relieved of the obligation to pay royalties for the benefits received from them. This method requires us to estimate the future revenue for the related brands, the appropriate royalty rate and the weighted average cost of capital. The non-recurring fair value measurement is a “Level 3” measurement under the fair value hierarchy. No impairment charges were recognized in 2023 or 2022 as a result of our annual impairment assessment.
Business combinations
Assets and liabilities acquired in a business combination are recorded at their estimated fair values at the acquisition date. Goodwill is recorded when the purchase price exceeds the estimated fair value of the net identifiable tangible and intangible assets acquired. Estimates of intangible asset fair value represent management’s best estimate of assumptions and about future events and uncertainties, including significant judgments related to future cash flows, discount rates, margin and revenue growth assumptions, royalty rates, customer attrition rates, useful lives and others. Inputs used are generally obtained from historical data supplemented by current and anticipated market conditions and growth rates. If the actual results differ from the estimates and judgments used in these fair values, the amounts recorded in the consolidated financial statements could result in a possible impairment of the intangible assets and goodwill or require acceleration of the amortization expense of finite-lived intangible assets.
Allocations of the purchase price for acquisitions are based on estimates of the fair value of the net assets acquired and are subject to adjustment upon finalization of the purchase price allocation. During this measurement period, we will adjust assets or liabilities if new information is obtained about facts and circumstances that existed as of the acquisition date that, if known, would have resulted in the recognition of those assets and liabilities as of that date. All changes that do not qualify as measurement period adjustments are included in current period earnings.
Pension and other post-retirement plans
We sponsor U.S. and non-U.S. defined-benefit pension and other post-retirement plans. The amounts recognized in our consolidated financial statements related to our defined-benefit pension and other post-retirement plans are determined from actuarial valuations. Inherent in these valuations are assumptions, including: expected return on plan assets, discount rates, rate of increase in future compensation levels and health care cost trend rates. These assumptions are updated annually and are disclosed in ITEM 8, Note 11 to the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Differences in actual experience or changes in assumptions may affect our pension and other post-retirement obligations and future expense.
We recognize changes in the fair value of plan assets and net actuarial gains or losses for pension and other post-retirement benefits annually in the fourth quarter each year (“mark-to-market adjustment”) and, if applicable, in any quarter in which an interim re-measurement is triggered. Net actuarial gains and losses occur when the actual experience differs from any of the various assumptions used to value our pension and other post-retirement plans or when assumptions change as they may each year. The primary factors contributing to actuarial gains and losses each year are (1) changes in the discount rate used to value pension and other post-retirement benefit obligations as of the measurement date and (2) differences between the expected and the actual return on plan assets. This accounting method also results in the potential for volatile and difficult to forecast mark-to-market adjustments. Mark-to-market adjustments resulted in a pre-tax loss of $6.1 million in 2023 and pre-tax gains of $17.5 million and $2.4 million in 2022 and 2021, respectively. The remaining components of pension expense, including service and interest costs and the expected return on plan assets, are recorded on a quarterly basis as ongoing pension expense.
Discount rates
The discount rate reflects the current rate at which the pension liabilities could be effectively settled at the end of the year based on our December 31 measurement date. The discount rate was determined by matching our expected benefit payments to payments from a stream of bonds rated AA or higher available in the marketplace. There are no known or anticipated changes in our discount rate assumptions that will impact our pension expense in 2024.
39
Expected rate of return
The expected rate of return is designed to be a long-term assumption that may be subject to considerable year-to-year variance from actual returns. In developing the expected long-term rate of return, we considered our historical returns, with consideration given to forecasted economic conditions, our asset allocations, input from external consultants and broader long-term market indices.
Sensitivity to changes in key assumptions
A 100 basis point increase or decrease in the discount rates used to measure our U.S. defined-benefit pension and other post-retirement plans would result in an approximately $7 million increase or $6 million decrease in our total projected benefit obligation. A 100 basis point increase or decrease in the assumed rate of return on pension assets or discount rates for our U.S. pension and other post-retirement benefit plans would result in an immaterial change in our ongoing pension expense. These estimates exclude any potential mark-to-market adjustments.
Loss contingencies
Accruals are recorded for various contingencies including legal proceedings, self-insurance and other claims that arise in the normal course of business. The accruals are based on judgment, the probability of losses and, where applicable, the consideration of opinions of internal and/or external legal counsel and actuarial estimates. Additionally, we record receivables from third party insurers when recovery has been determined to be probable.
Income taxes
In determining taxable income for financial statement purposes, we must make certain estimates and judgments. These estimates and judgments affect the calculation of certain tax liabilities and the determination of the recoverability of certain of the deferred tax assets, which arise from temporary differences between the tax and financial statement recognition of revenue and expense. In evaluating our ability to recover our deferred tax assets we consider all available positive and negative evidence including our past operating results, the existence of cumulative losses in the most recent years and our forecast of future taxable income. In estimating future taxable income, we develop assumptions including the amount of future pre-tax operating income, the reversal of temporary differences and the implementation of feasible and prudent tax planning strategies. These assumptions require significant judgment about the forecasts of future taxable income and are consistent with the plans and estimates we are using to manage the underlying businesses.
We currently have recorded valuation allowances that we will maintain until when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will be realized. Our income tax expense recorded in the future may be reduced to the extent of decreases in our valuation allowances. The realization of our remaining deferred tax assets is primarily dependent on future taxable income in the appropriate jurisdiction. Any reduction in future taxable income including but not limited to any future restructuring activities may require that we record an additional valuation allowance against our deferred tax assets. An increase in the valuation allowance could result in additional income tax expense in such period and could have a significant impact on our future earnings.
Changes in tax laws and rates could also affect recorded deferred tax assets and liabilities in the future. Management records the effect of a tax rate or law change on the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities in the period of enactment. Future tax rate or law changes could have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
In addition, the calculation of our tax liabilities involves dealing with uncertainties in the application of complex tax regulations in a multitude of jurisdictions across our global operations. We perform reviews of our income tax positions on a quarterly basis and accrue for uncertain tax positions. We recognize potential liabilities and record tax liabilities for anticipated tax audit issues in the tax jurisdictions in which we operate based on our estimate of whether, and the extent to which, additional taxes will be due. These tax liabilities are reflected net of related tax loss carryforwards. As events change or resolution occurs, these liabilities are adjusted, such as in the case of audit settlements with taxing authorities. The ultimate resolution may result in a payment that is materially different from our current estimate of the tax liabilities. If our estimate of tax liabilities proves to be less than the ultimate assessment, an additional charge to expense would result. If payment of these amounts ultimately proves to be less than the recorded amounts, the reversal of the liabilities would result in tax benefits being recognized in the period when we determine the liabilities are no longer necessary.
40
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Market risk is the potential economic loss that may result from adverse changes in the fair value of financial instruments. We are exposed to various market risks, including changes in interest rates and foreign currency rates. Periodically, we use derivative financial instruments to manage or reduce the impact of changes in interest rates and foreign currency rates. Counterparties to all derivative contracts are major financial institutions. All instruments are entered into for other than trading purposes. The major accounting policies and utilization of these instruments is described more fully in ITEM 8, Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Interest rate risk
Our debt portfolio as of December 31, 2023, was comprised of debt denominated in U.S. dollars. This debt portfolio is comprised of 41% fixed-rate debt and 59% variable-rate debt. Changes in interest rates have different impacts on the fixed and variable-rate portions of our debt portfolio. A change in interest rates on the fixed portion of the debt portfolio impacts the fair value, but has no impact on interest incurred or cash flows. A change in interest rates on the variable portion of the debt portfolio impacts the interest incurred and cash flows but does not impact the net financial instrument position.
Based on the fixed-rate debt included in our debt portfolio, as of December 31, 2023, a 100 basis point increase or decrease in interest rates would result in approximately a $48 million decrease or a $52 million increase in fair value of total fixed rate debt outstanding, respectively.
We manage our exposure to certain interest rate risks related to our variable rate debt through the use of interest rate swaps and collars. We enter into these agreements to hedge the variability of interest expense and cash flows attributable to changes in interest rates of our variable rate debt. As of December 31, 2023, we had an aggregate notional amount of $300.0 million and $200.0 million in interest rate swaps and collars, respectively, that are designated as cash flow hedges. Refer to ITEM 8, Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our interest rate swaps and collars.
A 100 basis point fluctuation in interest rates associated with our variable-rate debt as of December 31, 2023, inclusive of our interest rate swaps and collars, would result in an increase of approximately $7 million or decrease of approximately $8 million in interest incurred.
Foreign currency risk
We conduct business in various locations throughout the world and are subject to market risk due to changes in the value of foreign currencies in relation to our reporting currency, the U.S. dollar. Periodically, we use derivative financial instruments to manage these risks. The functional currencies of our foreign operating locations are generally the local currency in the country of domicile. We manage these operating activities at the local level and revenues, costs, assets and liabilities are generally denominated in local currencies, thereby mitigating the risk associated with changes in foreign exchange. However, our results of operations and assets and liabilities are reported in U.S. dollars and thus will fluctuate with changes in exchange rates between such local currencies and the U.S. dollar.
From time to time, we may enter into short duration foreign currency contracts to hedge foreign currency risks. As the majority of our foreign currency contracts have an original maturity date of less than one year, there is no material foreign currency risk. At December 31, 2023, we had outstanding foreign currency derivative contracts with gross notional U.S. dollar equivalent amounts of $23.9 million. Changes in the fair value of all derivatives are recognized immediately in income unless the derivative qualifies as a hedge of future cash flows. Gains and losses related to a hedge are deferred and recorded in the Consolidated Balance Sheets as a component of Accumulated other comprehensive loss and subsequently recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income when the hedged item affects earnings.
At December 31, 2023, we had outstanding cross currency swap agreements with a combined notional amount of $940.2 million. The cross currency swap agreements are accounted for as either cash flow hedges to hedge foreign currency fluctuations on certain intercompany debt, or as net investment hedges to manage our exposure to fluctuations in the Euro-U.S. Dollar exchange rate. The currency risk related to the cross currency swap agreements is measured by estimating the potential impact of a 10% change in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to the Euro. A 10% appreciation or a 10% depreciation of the U.S. dollar relative to the Euro would result in a change in accumulated other comprehensive income of approximately $73 million. However, the change in other comprehensive income would be offset by decreases or increases in the hedged items on our balance sheet.
41
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Management of Pentair plc and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of the financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023. In making this assessment, management used the criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting described in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this assessment, management believes that, as of December 31, 2023, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective based on those criteria.
Our independent registered public accounting firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP, has issued an attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023. That attestation report is set forth immediately following this management report.
| John L. Stauch | Robert P. Fishman | |||||||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer | |||||||
42
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the shareholders and the Board of Directors of Pentair plc
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Pentair plc and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2023, of the Company and our report dated February 20, 2024, expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Minneapolis, Minnesota
February 20, 2024
43
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the shareholders and the Board of Directors of Pentair plc
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Pentair plc and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income, cash flows and changes in equity, for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2023, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2023, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 20, 2024, expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current-period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
Income Taxes — Completeness of Uncertain Tax Positions — Refer to Notes 1 and 10 to the financial statements
Critical Audit Matter Description
The Company assesses uncertain tax positions (“UTPs”) based upon an evaluation of available information and records a liability when a position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return does not meet certain measurement or recognition criteria. A tax benefit is recognized only if management believes it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained upon examination by the relevant tax authority. Determining the completeness of UTPs is complex and significant judgment is involved in identifying which positions may not meet the required measurement or recognition criteria. As of December 31, 2023, the Company’s recorded UTP balance was $38.6 million.
The UTP analysis is complex as it includes numerous tax jurisdictions and varying applications of tax laws. Given the multiple jurisdictions in which the Company operates and the complexity of tax regulations, auditing the completeness of UTPs involved a high degree of auditor judgment, and an increased extent of audit effort, including the need to involve our tax specialists.
44
How the Critical Audit Matter Was Addressed in the Audit
Our audit procedures to evaluate the completeness of UTPs in material jurisdictions included the following, among others:
•We tested the effectiveness of controls over management’s determination of the existence of UTPs.
•With the assistance of our income tax specialists, we assessed the Company’s determination of the existence of UTPs. In particular, our procedures included:
–Evaluating the Company’s significant judgments related to completeness of UTPs in material jurisdictions:
•We performed inquiries of management to assess whether they are aware of any new items or significant changes to the business that would impact the UTP assessment or give rise to new UTPs.
•We evaluated the following: technical merits of existing UTPs, technical merits of potential UTPs, and significant transactions and their tax implications, including the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data supporting the transactions.
•We assessed the appropriateness and consistency of management’s methods and assumptions used in identifying UTPs.
•We evaluated former and ongoing tax audits by tax authorities.
•We considered changes in and assessed the Company’s interpretation of applicable tax laws.
•We inspected the Company’s summary of differences between the filed tax returns and the tax provision to obtain an understanding of significant differences. We assessed whether the appropriate UTPs were recorded as well as whether any additional UTPs needed to be considered.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Minneapolis, Minnesota
February 20, 2024
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1977.
45
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions, except per-share data | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 4,104.5 | $ | 4,121.8 | $ | 3,764.8 | |||||
| Cost of goods sold | 2,585.3 | 2,757.2 | 2,445.6 | ||||||||
| Gross profit | 1,519.2 | 1,364.6 | 1,319.2 | ||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 680.2 | 677.1 | 596.4 | ||||||||
| Research and development | 99.8 | 92.2 | 85.9 | ||||||||
| Operating income | 739.2 | 595.3 | 636.9 | ||||||||
| Other expense (income) | |||||||||||
| Gain on sale of businesses | — | (0.2) | (1.4) | ||||||||
| Net interest expense | 118.3 | 61.8 | 12.5 | ||||||||
| Other expense (income) | 2.0 | (16.9) | (1.0) | ||||||||
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 618.9 | 550.6 | 626.8 | ||||||||
| (Benefit) provision for income taxes | (4.0) | 67.4 | 70.8 | ||||||||
| Net income from continuing operations | 622.9 | 483.2 | 556.0 | ||||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | (0.2) | (2.3) | (3.0) | ||||||||
| Net income | $ | 622.7 | $ | 480.9 | $ | 553.0 | |||||
| Comprehensive income, net of tax | |||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 622.7 | $ | 480.9 | $ | 553.0 | |||||
| Changes in cumulative translation adjustment | 24.0 | (56.4) | (47.0) | ||||||||
| Changes in market value of derivative financial instruments, net of tax | (29.4) | 31.3 | 40.4 | ||||||||
| Comprehensive income | $ | 617.3 | $ | 455.8 | $ | 546.4 | |||||
| Earnings (loss) per ordinary share | |||||||||||
| Basic | |||||||||||
| Continuing operations | $ | 3.77 | $ | 2.93 | $ | 3.36 | |||||
| Discontinued operations | — | (0.01) | (0.02) | ||||||||
| Basic earnings per ordinary share | $ | 3.77 | $ | 2.92 | $ | 3.34 | |||||
| Diluted | |||||||||||
| Continuing operations | $ | 3.75 | $ | 2.92 | $ | 3.32 | |||||
| Discontinued operations | — | (0.02) | (0.02) | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings per ordinary share | $ | 3.75 | $ | 2.90 | $ | 3.30 | |||||
| Weighted average ordinary shares outstanding | |||||||||||
| Basic | 165.1 | 164.8 | 165.8 | ||||||||
| Diluted | 166.3 | 165.6 | 167.5 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
46
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| December 31 | ||||||||
| In millions, except per-share data | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current assets | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 170.3 | $ | 108.9 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net of allowances of $11.2 and $10.8, respectively | 561.7 | 531.5 | ||||||
| Inventories | 677.7 | 790.0 | ||||||
| Other current assets | 159.3 | 128.1 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 1,569.0 | 1,558.5 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 362.0 | 344.5 | ||||||
| Other assets | ||||||||
| Goodwill | 3,274.6 | 3,252.6 | ||||||
| Intangibles, net | 1,042.4 | 1,094.6 | ||||||
| Other non-current assets | 315.3 | 197.3 | ||||||
| Total other assets | 4,632.3 | 4,544.5 | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 6,563.3 | $ | 6,447.5 | ||||
| Liabilities and Equity | ||||||||
| Current liabilities | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 278.9 | $ | 355.0 | ||||
| Employee compensation and benefits | 125.4 | 106.0 | ||||||
| Other current liabilities | 545.3 | 602.1 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 949.6 | 1,063.1 | ||||||
| Other liabilities | ||||||||
| Long-term debt | 1,988.3 | 2,317.3 | ||||||
| Pension and other post-retirement compensation and benefits | 73.6 | 70.8 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | 40.0 | 43.3 | ||||||
| Other non-current liabilities | 294.7 | 244.9 | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 3,346.2 | 3,739.4 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 15) | ||||||||
| Equity | ||||||||
| Ordinary shares $0.01 par value, 426.0 authorized, 165.3 and 164.5 issued at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively | 1.7 | 1.7 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 1,593.6 | 1,554.9 | ||||||
| Retained earnings | 1,866.2 | 1,390.5 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (244.4) | (239.0) | ||||||
| Total equity | 3,217.1 | 2,708.1 | ||||||
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 6,563.3 | $ | 6,447.5 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
47
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Operating activities | |||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 622.7 | $ | 480.9 | $ | 553.0 | |||||
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | 0.2 | 2.3 | 3.0 | ||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income from continuing operations to net cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations | |||||||||||
| Equity income of unconsolidated subsidiaries | (2.8) | (1.8) | (0.3) | ||||||||
| Depreciation | 59.5 | 54.1 | 51.2 | ||||||||
| Amortization | 55.3 | 52.5 | 26.3 | ||||||||
| Gain on sale of businesses | — | (0.2) | (1.4) | ||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | (92.5) | (44.8) | (9.0) | ||||||||
| Share-based compensation | 29.1 | 24.9 | 29.8 | ||||||||
| Asset impairment and write-offs | 7.9 | 25.6 | — | ||||||||
| Amortization of bridge financing debt issuance costs | — | 9.0 | — | ||||||||
| Pension and other post-retirement expense (benefit) | 12.1 | (12.2) | 2.8 | ||||||||
| Pension and other post-retirement contributions | (8.7) | (8.8) | (9.4) | ||||||||
| (Gain) loss on sale of assets | (3.4) | (2.3) | 0.7 | ||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of business acquisitions | |||||||||||
| Accounts receivable | (24.4) | 30.4 | (142.0) | ||||||||
| Inventories | 109.6 | (187.0) | (121.4) | ||||||||
| Other current assets | (29.1) | (16.5) | (12.3) | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | (75.1) | (56.9) | 114.2 | ||||||||
| Employee compensation and benefits | 17.2 | (35.2) | 24.5 | ||||||||
| Other current liabilities | (59.5) | 46.5 | 116.2 | ||||||||
| Other non-current assets and liabilities | 2.7 | 3.8 | (12.3) | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations | 620.8 | 364.3 | 613.6 | ||||||||
| Net cash used for operating activities of discontinued operations | (1.6) | (1.0) | (0.4) | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 619.2 | 363.3 | 613.2 | ||||||||
| Investing activities | |||||||||||
| Capital expenditures | (76.0) | (85.2) | (60.2) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property and equipment | 5.6 | 4.1 | 3.9 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of businesses, net | — | — | 1.4 | ||||||||
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired | (0.6) | (1,580.9) | (338.5) | ||||||||
| (Payments) receipts upon the settlement of net investment hedges | (18.5) | 78.9 | — | ||||||||
| Other | 4.1 | 0.3 | 2.7 | ||||||||
| Net cash used for investing activities | (85.4) | (1,582.8) | (390.7) | ||||||||
| Financing activities | |||||||||||
| Net (repayments) borrowings of revolving long-term debt | (320.0) | 124.5 | 159.4 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from long-term debt | — | 1,391.3 | — | ||||||||
| Repayment of long-term debt | (12.5) | (88.3) | (103.8) | ||||||||
| Debt issuance costs | — | (15.8) | (2.3) | ||||||||
| Shares issued to employees, net of shares withheld | 9.6 | (2.7) | 22.2 | ||||||||
| Repurchases of ordinary shares | — | (50.0) | (150.0) | ||||||||
| Dividends paid | (145.2) | (138.6) | (133.0) | ||||||||
| Receipts (payments) upon the settlement of cross currency swaps | — | 12.3 | (14.7) | ||||||||
| Net cash (used for) provided by financing activities | (468.1) | 1,232.7 | (222.2) | ||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (4.3) | 1.2 | 12.1 | ||||||||
| Change in cash and cash equivalents | 61.4 | 14.4 | 12.4 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 108.9 | 94.5 | 82.1 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | $ | 170.3 | $ | 108.9 | $ | 94.5 | |||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | |||||||||||
| Cash paid for interest, net | $ | 146.4 | $ | 57.0 | $ | 29.9 | |||||
| Cash paid for income taxes, net | 120.0 | 122.6 | 71.8 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
48
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity
| In millions | Ordinary shares | Additional paid-in capital | Retained earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive loss | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Number | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2020 | 166.1 | $ | 1.7 | $ | 1,680.7 | $ | 631.2 | $ | (207.3) | $ | 2,106.3 | |||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 553.0 | — | 553.0 | ||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | — | (6.6) | (6.6) | ||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared | — | — | — | (132.8) | — | (132.8) | ||||||||||||||
| Share repurchases | (2.1) | — | (150.0) | — | — | (150.0) | ||||||||||||||
| Exercise of options, net of shares tendered for payment | 0.9 | — | 30.1 | — | — | 30.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted shares, net of cancellations | 0.3 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Shares surrendered by employees to pay taxes | (0.1) | — | (7.9) | — | — | (7.9) | ||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation | — | — | 29.8 | — | — | 29.8 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2021 | 165.1 | $ | 1.7 | $ | 1,582.7 | $ | 1,051.4 | $ | (213.9) | $ | 2,421.9 | |||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 480.9 | — | 480.9 | ||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | — | (25.1) | (25.1) | ||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared | — | — | — | (141.8) | — | (141.8) | ||||||||||||||
| Share repurchases | (1.0) | — | (50.0) | — | — | (50.0) | ||||||||||||||
| Exercise of options, net of shares tendered for payment | 0.1 | — | 3.6 | — | — | 3.6 | ||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted shares, net of cancellations | 0.4 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Shares surrendered by employees to pay taxes | (0.1) | — | (6.3) | — | — | (6.3) | ||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation | — | — | 24.9 | — | — | 24.9 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2022 | 164.5 | $ | 1.7 | $ | 1,554.9 | $ | 1,390.5 | $ | (239.0) | $ | 2,708.1 | |||||||||
| Net income | — | — | — | 622.7 | — | 622.7 | ||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | — | — | (5.4) | (5.4) | ||||||||||||||
| Dividends declared | — | — | — | (147.0) | — | (147.0) | ||||||||||||||
| Exercise of options, net of shares tendered for payment | 0.4 | — | 18.3 | — | — | 18.3 | ||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted shares, net of cancellations | 0.5 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Shares surrendered by employees to pay taxes | (0.1) | — | (8.7) | — | — | (8.7) | ||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation | — | — | 29.1 | — | — | 29.1 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2023 | 165.3 | $ | 1.7 | $ | 1,593.6 | $ | 1,866.2 | $ | (244.4) | $ | 3,217.1 | |||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
49
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
1.Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Business
Pentair plc and its consolidated subsidiaries (“we,” “us,” “our,” “Pentair” or the “Company”) is a water industrial manufacturing company comprised of three reporting segments: Flow (formerly named Industrial & Flow Technologies), Water Solutions and Pool.
Basis of presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Pentair plc, its wholly-owned subsidiaries and entities for which the Company has a controlling financial interest. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated. Investments in companies of which we own 20% to 50% of the voting stock or have the ability to exercise significant influence over operating and financial policies of the investee are accounted for using the equity method of accounting and as a result, our share of the earnings or losses of such equity affiliates is included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income.
The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in U.S. dollars (“USD”) and in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“U.S.”) (“U.S. GAAP”).
Fiscal year
Our fiscal year ends on December 31. We report our interim quarterly periods on a calendar quarter basis.
Use of estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in these consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes, disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. These estimates include our accounting for valuation of goodwill and indefinite lived intangible assets, estimated losses on accounts receivable, estimated realizable value on excess and obsolete inventory, over time revenue recognition, assets acquired and liabilities assumed in acquisitions, estimated selling proceeds from assets held for sale, contingent liabilities, income taxes and pension and other post-retirement benefits. Actual results could differ from our estimates.
Revenue recognition
Revenue is recognized when control of the promised goods or services is transferred to our customers, in an amount that reflects the consideration we expect to be entitled to in exchange for transferring those goods or providing services. We account for a contract when it has approval and commitment from both parties, the rights of the parties are identified, payment terms are identified, the contract has commercial substance and collectability of consideration is probable.
When determining whether the customer has obtained control of the goods or services, we consider any future performance obligations. Generally, there is no post-shipment obligation on product sold other than warranty obligations in the normal and ordinary course of business. In the event significant post-shipment obligations were to exist, revenue recognition would be deferred until Pentair has substantially accomplished what it must do to be entitled to the benefits represented by the revenue.
Performance obligations
A performance obligation is a promise in a contract to transfer a distinct good or service to the customer, and is the unit of account for purposes of revenue recognition. A contract’s transaction price is allocated to each distinct performance obligation and recognized as revenue when, or as, the performance obligation is satisfied. The majority of our contracts have a single performance obligation as the promise to transfer the individual goods or services is not separately identifiable from other promises in the contracts and, therefore, not distinct. For contracts with multiple performance obligations, standalone selling price is generally readily observable.
Our performance obligations are satisfied at a point in time or over time as work progresses. Revenue from goods and services transferred to customers at a point in time accounted for 90.6%, 91.7% and 91.9% of our revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. Revenue on these contracts is recognized when obligations under the terms of the contract with our customer are satisfied; generally, this occurs with the transfer of control upon shipment.
Revenue from products and services transferred to customers over time accounted for 9.4%, 8.3% and 8.1% of our revenue for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively. For the majority of our revenue recognized over time, we use an input measure to determine progress towards completion. Under this method, sales and gross profit are recognized as work is performed generally based on the relationship between the actual costs incurred and the total estimated costs at completion (“the cost-to-cost method”) or based on efforts for measuring progress towards completion in situations in which this approach is more representative of the progress on the contract than the cost-to-cost method. Contract costs include labor, material, overhead and, when appropriate, general and administrative expenses. Changes to the original estimates may be required during
50
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
the life of the contract, and such estimates are reviewed on a regular basis. Sales and gross profit are adjusted using the cumulative catch-up method for revisions in estimated total contract costs. These reviews have not resulted in adjustments that were significant to our results of operations. For performance obligations related to long term contracts, when estimates of total costs to be incurred on a performance obligation exceed total estimates of revenue to be earned, a provision for the entire loss on the performance obligation is recognized in the period the loss is determined.
On December 31, 2023, we had $113.9 million of remaining performance obligations on contracts with an original expected duration of one year or more. We expect to recognize the majority of our remaining performance obligations on these contracts within the next 12 to 18 months.
Sales returns
The right of return may exist explicitly or implicitly with our customers. Our return policy allows for customer returns only upon our authorization. Goods returned must be products we continue to market and must be in salable condition. When the right of return exists, we adjust the transaction price for the estimated effect of returns. We estimate the expected returns based on historical sales levels, the timing and magnitude of historical sales return levels as a percent of sales, type of product, type of customer and a projection of this experience into the future.
Pricing and sales incentives
Our contracts may give customers the option to purchase additional goods or services priced at a discount. Options to acquire additional goods or services at a discount can come in many forms, such as customer programs and incentive offerings including pricing arrangements, promotions and other volume-based incentives.
We reduce the transaction price for certain customer programs and incentive offerings including pricing arrangements, promotions and other volume-based incentives that represent variable consideration. Sales incentives given to our customers are recorded using either the expected value method or most likely amount approach for estimating the amount of consideration to which Pentair shall be entitled. The expected value is the sum of probability-weighted amounts in a range of possible consideration amounts. An expected value is an appropriate estimate of the amount of variable consideration when there are a large number of contracts with similar characteristics. The most likely amount is the single most likely amount in a range of possible consideration amounts (that is, the single most likely outcome of the contract). The most likely amount is an appropriate estimate of the amount of variable consideration if the contract has limited possible outcomes (for example, an entity either achieves a performance bonus or does not).
Pricing is established at or prior to the time of sale with our customers, and we record sales at the agreed-upon net selling price. However, one of our businesses allows customers to apply for a refund of a percentage of the original purchase price if they can demonstrate sales to a qualifying end customer. We use the expected value method to estimate the anticipated refund to be paid based on historical experience and reduce sales for the probable cost of the discount. The cost of these refunds is recorded as a reduction of the transaction price.
Volume-based incentives involve rebates that are negotiated at or prior to the time of sale with the customer and are redeemable only if the customer achieves a specified cumulative level of sales or sales increase. Under these incentive programs, at the time of sale, we determine the most likely amount of the rebate to be paid based on forecasted sales levels. These forecasts are updated at least quarterly for each customer, and the transaction price is reduced for the anticipated cost of the rebate. If the forecasted sales for a customer change, the accrual for rebates is adjusted to reflect the new amount of rebates expected to be earned by the customer.
Shipping and handling costs
Amounts billed to customers for shipping and handling activities after the customer obtains control are treated as a promised service performance obligation and recorded in Net sales in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income. Shipping and handling costs incurred by Pentair for the delivery of goods to customers are considered a cost to fulfill the contract and are included in Cost of goods sold in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income.
Contract assets and liabilities
Contract assets consist of unbilled amounts resulting from sales under long-term contracts when the cost-to-cost method of revenue recognition is utilized and revenue recognized exceeds the amount billed to the customer, such as when the customer retains a small portion of the contract price until completion of the contract. We typically receive interim payments on sales under long-term contracts as work progresses, although for some contracts, we may be entitled to receive an advance payment. Contract liabilities consist of advanced payments, billings in excess of costs incurred and deferred revenue.
Contract assets are recorded within Other current assets, and contract liabilities are recorded within Other current liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
51
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Contract assets and liabilities consisted of the following:
| December 31 | |||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
| Contract assets | $ | 70.8 | $ | 48.4 | $ | 22.4 | 46.3 | % | |||||||||
| Contract liabilities | 53.7 | 58.1 | (4.4) | (7.6) | % | ||||||||||||
| Net contract assets (liabilities) | $ | 17.1 | $ | (9.7) | $ | 26.8 | (276.3) | % | |||||||||
The $26.8 million increase in net contract assets from December 31, 2022 to December 31, 2023 was primarily the result of timing of milestone payments. Approximately 90% of our contract liabilities at December 31, 2022 were recognized in revenue during the twelve months ended December 31, 2023. There were no impairment losses recognized on our net contract assets for the twelve months ended December 31, 2023. For the twelve months ended December 31, 2022, there were $1.1 million of impairment losses recognized on our net contract liabilities as a result of our exit of business activity and sales in Russia.
Practical expedients and exemptions
We generally expense incremental costs of obtaining a contract when incurred because the amortization period would be less than one year. These costs primarily relate to sales commissions and are recorded in Selling, general and administrative expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income.
We do not disclose the value of unsatisfied performance obligations for contracts with an original expected length of one year or less. Further, we do not adjust the promised amount of consideration for the effects of a significant financing component if we expect, at contract inception, that the period between when we transfer a promised good or service to a customer and when the customer pays for that good or service will be one year or less.
Revenue by category
We disaggregate our revenue from contracts with customers by segment, geographic location and vertical market, as we believe these best depict how the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of our revenue and cash flows are affected by economic factors. Refer to Note 14 for revenue disaggregated by segment.
Geographic net sales information, based on geographic destination of the sale, was as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| U.S. | $ | 2,835.9 | $ | 2,913.2 | $ | 2,571.2 | |||||
| Western Europe | 471.9 | 439.2 | 460.4 | ||||||||
Developing (1) | 558.0 | 515.5 | 487.1 | ||||||||
Other Developed (2) | 238.7 | 253.9 | 246.1 | ||||||||
Consolidated net sales (3) | $ | 4,104.5 | $ | 4,121.8 | $ | 3,764.8 | |||||
(1) Developing includes China, Eastern Europe, Latin America, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. | |||||||||||
(2) Other Developed includes Australia, Canada and Japan. | |||||||||||
(3) Net sales in Ireland, for each of the years presented, were not material. | |||||||||||
Vertical market net sales information was as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Residential | $ | 2,134.0 | $ | 2,613.6 | $ | 2,437.6 | |||||
| Commercial | 1,177.2 | 809.1 | 665.9 | ||||||||
| Industrial | 793.3 | 699.1 | 661.3 | ||||||||
| Consolidated net sales | $ | 4,104.5 | $ | 4,121.8 | $ | 3,764.8 | |||||
Research and development
We conduct research and development (“R&D”) activities primarily in our own facilities, which mostly consist of development of new products, product applications and manufacturing processes. We expense R&D costs as incurred. R&D expenditures during 2023, 2022 and 2021 were $99.8 million, $92.2 million and $85.9 million, respectively.
52
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Cash equivalents
We consider highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less at the date of acquisition to be cash equivalents.
Trade receivables and concentration of credit risk
We record an allowance for credit losses, reducing our receivables balance to an amount we estimate is collectible from our customers. Estimates used in determining the allowance for credit losses are based on current trends, aging of accounts receivable, periodic credit evaluations of our customers’ financial condition, and historical collection experience as well as reasonable and supportable forecasts of future economic conditions. We generally do not require collateral.
The following table summarizes the activity in the allowance for credit losses:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 10.8 | $ | 9.1 | $ | 8.4 | |||||
| Bad debt expense | 0.7 | 3.6 | 1.1 | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | — | 0.3 | 1.0 | ||||||||
| Write-offs, net of recoveries | (0.7) | (1.4) | (0.9) | ||||||||
Other (1) | 0.4 | (0.8) | (0.5) | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 11.2 | $ | 10.8 | $ | 9.1 | |||||
(1) Other amounts are primarily the effects of changes in currency translations and the impact of allowance for credits. | |||||||||||
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value with substantially all inventories recorded using the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) cost method.
Property, plant and equipment, net
Property, plant and equipment is stated at historical cost. We compute depreciation by the straight-line method based on the following estimated useful lives:
| Years | |||||
| Land improvements | 5 to 20 | ||||
| Buildings and leasehold improvements | 5 to 50 | ||||
| Machinery and equipment | 3 to 15 | ||||
| Capitalized software | 3 to 10 | ||||
Significant improvements that add to productive capacity or extend the lives of properties are capitalized. Costs for repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred. We capitalize costs associated with software developed or obtained for internal use when both the preliminary project stage is completed, and it is probable the software being developed will be completed and placed in service. The costs of computer software developed or obtained for internal use are amortized on a straight-line basis unless another systematic and rational basis is more representative of the software’s use. When property or capitalized software is retired or otherwise disposed of, the recorded cost of the assets and their related accumulated depreciation are removed from the Consolidated Balance Sheets and any related gains or losses are included in income.
53
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
The following table presents geographic Property, plant and equipment, net by region as of December 31:
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | |||||||||
| U.S. | $ | 223.9 | $ | 213.3 | |||||||
| Western Europe | 77.4 | 74.4 | |||||||||
Developing (1) | 50.5 | 46.8 | |||||||||
Other Developed (2) | 10.2 | 10.0 | |||||||||
Consolidated (3) | $ | 362.0 | $ | 344.5 | |||||||
(1) Developing includes China, Eastern Europe, Latin America, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. | |||||||||||
(2) Other Developed includes Australia, Canada and Japan. | |||||||||||
(3) Property, plant and equipment, net in Ireland, for each of the years presented, were not material. | |||||||||||
We review the recoverability of long-lived assets to be held and used, such as property, plant and equipment, when events or changes in circumstances occur that indicate the carrying value of the asset or asset group may not be recoverable. The assessment of possible impairment is based on our ability to recover the carrying value of the asset or asset group from the expected future pre-tax cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) of the related operations. If these cash flows are less than the carrying value of such asset or asset group, an impairment loss is recognized for the difference between estimated fair value and carrying value. Impairment losses on long-lived assets held for sale are determined in a similar manner, except that fair values are reduced for the cost to dispose of the assets. The measurement of impairment requires us to estimate future cash flows and the fair value of long-lived assets. We recorded $9.2 million of long-lived asset impairment charges in 2022 comprised of long-lived assets which were primarily written off as a result of restructuring actions and certain business exits announced in the fourth quarter of 2022. No material long-lived asset impairment charges were recorded in 2023 or 2021.
Goodwill and identifiable intangible assets
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the cost of acquired businesses over the net of the fair value of identifiable tangible net assets and identifiable intangible assets purchased and liabilities assumed.
We test our goodwill for impairment at least annually during the fourth quarter or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. We perform our annual or interim goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of the relevant reporting unit with its carrying amount. We would recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value; however, the loss recognized would not exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit.
We have the option to perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is necessary to perform the quantitative goodwill impairment test. However, we may elect to perform the quantitative goodwill impairment test even if no indications of a potential impairment exist.
During 2023, a quantitative assessment was performed. The fair value of each reporting unit was determined using a discounted cash flow analysis and market approach. Projecting discounted future cash flows requires us to make significant estimates regarding future revenues and expenses, projected capital expenditures, changes in working capital and the appropriate discount rate. Use of the market approach consists of comparisons to comparable publicly-traded companies that are similar in size and industry. The non-recurring fair value measurement is a “Level 3” measurement under the fair value hierarchy. For the 2023 annual impairment test, the estimated fair value significantly exceeded the carrying value in each of our reporting units, therefore, no impairment charge was required.
During 2022, a qualitative assessment was performed. As a result, it was determined that it was more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting units exceeded their respective carrying values. Factors considered in the analysis included the 2020 discounted cash flow fair value assessment of the reporting units and the calculated excess fair value over carrying amount, financial performance, forecasts and trends, market capitalization, regulatory and environmental issues, macro-economic conditions, industry and market considerations, raw material costs and management stability. We also consider the extent to which each of the adverse events and circumstances identified affect the comparison of the respective reporting unit’s fair value with its carrying amount. We place more weight on the events and circumstances that most affect the respective reporting unit’s fair value or the carrying amount of its net assets. We consider positive and mitigating events and circumstances that may affect its determination of whether it is more likely than not that the fair value exceeds the carrying amount.
54
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Identifiable intangible assets
Our primary identifiable intangible assets include: customer relationships, trade names, proprietary technology and patents. Identifiable intangibles with finite lives are amortized and those identifiable intangibles with indefinite lives are not amortized. Identifiable intangible assets that are subject to amortization are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. An impairment charge of $2.7 million was recorded in 2022 related to the write-off of a proprietary technology intangible asset as a result of restructuring initiatives implemented in the fourth quarter of 2022. The impairment charge was recorded in Selling, general and administrative in our Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income. No impairment charges associated with identifiable intangibles with finite lives were recognized in 2023 or 2021.
Identifiable intangible assets not subject to amortization are tested for impairment annually or more frequently if events warrant. We complete our annual impairment test the first day of the fourth quarter each year for those identifiable assets not subject to amortization. The impairment test for trade names consists of a comparison of the fair value of the trade name with its carrying value. Fair value is measured using the relief-from-royalty method. This method assumes the trade name has value to the extent that the owner is relieved of the obligation to pay royalties for the benefits received from them. This method requires us to estimate the future revenue for the related brands, the appropriate royalty rate and the weighted average cost of capital. The non-recurring fair value measurement is a “Level 3” measurement under the fair value hierarchy described in Note 9. No impairment charges were recognized in 2023, 2022, or 2021 as a result of our annual impairment assessment.
Income taxes
We use the asset and liability approach to account for income taxes. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period when the change is enacted. We maintain valuation allowances unless it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will be realized. Changes in valuation allowances from period to period are included in our tax provision in the period of change. We recognize the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs.
Pension and other post-retirement plans
We sponsor U.S. and non-U.S. defined-benefit pension and other post-retirement plans. The pension and other post-retirement benefit costs for company-sponsored benefit plans are determined from actuarial assumptions and methodologies, including discount rates and expected returns on plan assets. These assumptions are updated annually and are disclosed in Note 11.
We recognize changes in the fair value of plan assets and net actuarial gains or losses for pension and other post-retirement benefits annually in the fourth quarter each year (“mark-to-market adjustment”) and, if applicable, in any quarter in which an interim re-measurement is triggered. Net actuarial gains and losses occur when the actual experience differs from any of the various assumptions used to value our pension and other post-retirement plans or when assumptions change, as they may each year. The remaining components of pension expense, including service and interest costs and estimated return on plan assets, are recorded on a quarterly basis. The service costs are recorded within Operating income and the interest costs, expected return on plan assets and net actuarial gain/loss components of net periodic pension and other post-retirement benefit costs are recorded within Other expense (income).
Insurance subsidiary
A portion of our property and casualty insurance program is insured through our regulated wholly-owned captive insurance subsidiary, Penwald Insurance Company (“Penwald”). Reserves for policy claims are established based on actuarial projections of ultimate losses. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, reserves for policy claims were $64.9 million, of which $13.0 million was included in Other current liabilities and $51.9 million was included in Other non-current liabilities, and $65.1 million, of which $13.0 million was included in Other current liabilities and $52.1 million was included in Other non-current liabilities, respectively.
Share-based compensation
We account for share-based compensation awards on a fair value basis. The estimated grant date fair value of each option award is recognized in income on an accelerated basis over the requisite service period (generally the vesting period). The estimated fair value of each option award is calculated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. From time to time, we have elected to modify the terms of the original grant. These modified grants are accounted for as a new award and measured using the fair value method, resulting in the inclusion of additional compensation expense in our Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income.
55
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Restricted share awards and units (“RSUs”) are recorded as compensation cost over the requisite service periods based on the market value on the date of grant.
Performance share units (“PSUs”) are stock awards where the ultimate number of shares issued will be contingent on the Company’s performance against certain performance goals. The Compensation Committee has the ability to adjust performance goals or modify the manner of measuring or evaluating a performance goal using its discretion. The fair value of each PSU is based on the market value on the date of grant. We recognize expense related to the estimated vesting of our PSUs granted. The estimated vesting of the PSUs is based on the probability of achieving certain performance metrics over the specified performance period.
Earnings per ordinary share
We present two calculations of earnings per ordinary share (“EPS”). Basic EPS equals net income divided by the weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding during the period. Diluted EPS is computed by dividing net income by the sum of weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding plus dilutive effects of ordinary share equivalents, calculated using the two-class method.
Derivative financial instruments
We recognize all derivatives, including those embedded in other contracts, as either assets or liabilities at fair value in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. If the derivative is designated and effective, the effective portion of changes in the fair value of the derivative is recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (“AOCI”) as a separate component of equity in the Consolidated Balance Sheets and is recognized in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income when the hedged item affects earnings. If the underlying hedged transaction ceases to exist or if the hedge becomes ineffective, all changes in fair value of the related derivatives that have not been settled are recognized in current earnings. For a derivative that is not designated as or does not qualify as a hedge, changes in fair value are reported in earnings immediately.
We use derivative instruments for the purpose of hedging interest rate and currency exposures, which exist as part of ongoing business operations. We do not hold or issue derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes. Our policy is not to enter into contracts with terms that cannot be designated as normal purchases or sales. From time to time, we may enter into short duration foreign currency contracts to hedge foreign currency risks.
Foreign currency translation
The financial statements of the Company’s non-U.S. dollar functional currency international subsidiaries are measured using the local currency as the functional currency. Assets and liabilities of these subsidiaries are translated at the rates of exchange at the balance sheet date. Income (loss) and expense items are translated at average monthly rates of exchange. The resultant translation adjustments are included in AOCI, a component of equity.
New accounting standards
In November 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2023-07, “Segment Reporting”, which expands annual and interim disclosure requirements for reportable segments, primarily through enhanced disclosures regarding significant expenses. We plan to adopt the standard retrospectively beginning with our annual reporting for the year ending December 31, 2024 and interim reporting beginning January 1, 2025. We are currently evaluating the potential effect that the updated standard will have on our financial statement disclosures.
In December 2023, the FASB issued ASU No. 2023-09, “Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures”, which requires new and enhanced disclosures primarily related to income taxes paid and the effective tax rate reconciliation. We will adopt the standard beginning with our annual reporting for the year ending December 31, 2025. We are currently evaluating the potential effect that the updated standard will have on our financial statement disclosures.
2. Acquisitions
In July 2022, as part of our Water Solutions reporting segment, we acquired the issued and outstanding equity securities of certain subsidiaries of Welbilt, Inc. (“Welbilt”) and certain other assets, rights, and properties, and assumed certain liabilities, comprising Welbilt’s Manitowoc Ice business (“Manitowoc Ice”), for approximately $1.6 billion in cash.
Manitowoc Ice is a designer, manufacturer and distributor of commercial ice machines. The acquisition of Manitowoc Ice allows us to enhance and deliver our total water management offerings to an expanded network of channel partners and customers.
The purchase price has been allocated based on the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition. The purchase price allocation was completed in the third quarter of 2023.
56
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
The following table summarizes the final allocation of the purchase price to the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the Manitowoc Ice acquisition:
| In millions | |||||||||||
| Cash | $ | 33.8 | |||||||||
| Accounts receivable | 36.7 | ||||||||||
| Inventories | 66.7 | ||||||||||
| Other current assets | 3.9 | ||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 21.6 | ||||||||||
| Identifiable intangible assets | 728.3 | ||||||||||
| Goodwill | 789.7 | ||||||||||
| Other assets | 0.7 | ||||||||||
| Current liabilities | (62.7) | ||||||||||
| Other liabilities | (4.8) | ||||||||||
| Purchase price | $ | 1,613.9 | |||||||||
The excess of purchase price over tangible net assets and identified intangible assets acquired has been allocated to goodwill in the amount of $789.7 million, all of which is deductible for income tax purposes. Goodwill recognized from the Manitowoc Ice acquisition primarily reflects the future economic benefit resulting from synergies of our combined operations.
Identifiable intangible assets acquired as part of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition include $78.4 million of indefinite-lived trade name intangible assets, $588.4 million of definite-lived customer relationships with a weighted-average estimated useful life of 20 years, $47.1 million of definite-lived proprietary technology intangible assets with a weighted-average estimated useful life of 10 years and $14.4 million of other definite-lived intangible assets with a weighted-average estimated useful life of four months. The fair values of trade names and proprietary technology acquired in the acquisition were determined using a relief-from-royalty method, and customer relationships and other definite-lived intangible assets acquired were determined using a multi-period excess earnings method. These methods utilize unobservable inputs that are significant to these fair value measurements and thus classified as Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy described in Note 9.
For the year ended December 31, 2022, non-recurring expense related to the fair value adjustment to acquisition-date inventory of $5.8 million, transaction-related charges of $19.9 million, and acquisition-related bridge financing costs of $9.0 million are reflected in Cost of goods sold, Selling, general and administrative and Net interest expense, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income. Manitowoc Ice’s net sales and operating income for the period from the acquisition date to December 31, 2022 were $156.3 million and $12.2 million, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2022, Manitowoc’s operating income includes $28.6 million of identifiable intangible asset amortization expense and $5.8 million of amortization of inventory fair market value step-up.
The following table presents unaudited pro forma financial information as if the Manitowoc Ice acquisition had occurred on January 1, 2021:
| Years Ended December 31 | ||||||||
| In millions, except per share data | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||
| Pro forma net sales | $ | 4,328.6 | $ | 4,072.1 | ||||
| Pro forma net income from continuing operations | 486.3 | 523.3 | ||||||
| Pro forma earnings per ordinary share - continuing operations | ||||||||
| Basic | $ | 2.95 | $ | 3.16 | ||||
| Diluted | 2.94 | 3.12 | ||||||
The unaudited pro forma net income from continuing operations includes Manitowoc Ice’s identifiable intangible asset amortization expense of $34.1 million and $48.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2022 and 2021, respectively. The unaudited pro forma net income from continuing operations for the year ended December 31, 2022 excludes the impact of $34.7 million of transaction-related charges, acquisition-related bridge financing costs and non-recurring expense related to the
57
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
fair value adjustment to acquisition-date inventory. The year ended December 31, 2021 was adjusted to include transaction-related charges and non-recurring expense related to the fair value adjustment to acquisition-date inventory.
The pro forma condensed consolidated financial information has been prepared for comparative purposes only and includes certain adjustments, as noted above. The adjustments are estimates based on currently available information and actual amounts may differ materially from these estimates. They do not reflect the effect of costs or synergies that would have been expected to result from the integration of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition. The pro forma information does not purport to be indicative of the results of operations that actually would have resulted had the Manitowoc Ice acquisition occurred on January 1, 2021.
In October 2021, as part of both of our Flow and Pool reporting segments, we completed the acquisition of Pleatco Holdings, LLC and related entities for $256.9 million in cash, net of cash acquired and working capital true-ups. The excess of purchase price over tangible net assets acquired has been allocated to goodwill in the amount of $140.6 million, $136.4 million of which is deductible for income tax purposes. Identifiable intangible assets acquired consisted of $97.9 million of definite-lived customer relationships with an estimated useful life of 17 years. The pro forma impact of this acquisition is not material.
In May 2021, as part of our Water Solutions reporting segment, we completed the acquisition of Ken’s Beverage, Inc. for $82.2 million in cash, net of cash acquired and working capital true-ups. The excess of purchase price over tangible net assets acquired has been allocated to goodwill in the amount of $28.3 million, all of which is deductible for income tax purposes. Identifiable intangible assets acquired consisted of $38.0 million of definite-lived customer relationships with an estimated useful life of 22 years. The pro forma impact of this acquisition is not material.
3. Earnings Per Share
Basic and diluted earnings per share were calculated as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions, except per share data | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Net income | $ | 622.7 | $ | 480.9 | $ | 553.0 | |||||
| Net income from continuing operations | $ | 622.9 | $ | 483.2 | $ | 556.0 | |||||
| Weighted average ordinary shares outstanding | |||||||||||
| Basic | 165.1 | 164.8 | 165.8 | ||||||||
| Dilutive impact of stock options and restricted stock awards | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.7 | ||||||||
| Diluted | 166.3 | 165.6 | 167.5 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per ordinary share | |||||||||||
| Basic | |||||||||||
| Continuing operations | $ | 3.77 | $ | 2.93 | $ | 3.36 | |||||
| Discontinued operations | — | (0.01) | (0.02) | ||||||||
| Basic earnings per ordinary share | $ | 3.77 | $ | 2.92 | $ | 3.34 | |||||
| Diluted | |||||||||||
| Continuing operations | $ | 3.75 | $ | 2.92 | $ | 3.32 | |||||
| Discontinued operations | — | (0.02) | (0.02) | ||||||||
| Diluted earnings per ordinary share | $ | 3.75 | $ | 2.90 | $ | 3.30 | |||||
| Anti-dilutive stock options excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.1 | ||||||||
58
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
4. Restructuring and Transformation Program
In 2021, we launched and committed resources to a program designed to accelerate growth and drive margin expansion through transformation of our business model to drive operational excellence, reduce complexity and streamline our processes (the “Transformation Program”). The Transformation Program is structured in multiple phases and is expected to empower us to work more efficiently and optimize our business to better serve our customers while meeting our financial objectives.
During 2023, 2022 and 2021, we initiated and continued execution of our Transformation Program as well as certain business restructuring initiatives aimed at reducing our fixed cost structure and realigning our business. Restructuring and Transformation Program initiatives during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 included a reduction in hourly and salaried headcount of approximately 475 employees, 625 employees and 75 employees, respectively.
Restructuring and transformation-related costs included within Cost of goods sold and Selling, general and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income included the following:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Restructuring Initiatives | |||||||||||
| Severance and related costs | $ | 8.2 | $ | 17.7 | $ | 7.0 | |||||
Asset impairment and write-offs (1) | 3.8 | 25.6 | — | ||||||||
Other restructuring costs and related adjustments (2) | (6.0) | 13.0 | 0.4 | ||||||||
| Total restructuring costs | 6.0 | 56.3 | 7.4 | ||||||||
| Transformation Program | |||||||||||
| Severance and related costs | 6.9 | 3.4 | — | ||||||||
Other transformation costs (3) | 37.8 | 23.8 | 11.7 | ||||||||
| Total transformation costs | 44.7 | 27.2 | 11.7 | ||||||||
| Total restructuring and transformation costs | $ | 50.7 | $ | 83.5 | $ | 19.1 | |||||
(1) Asset impairment and write-offs consist of inventory, long-lived assets and an identifiable intangible asset, which were impaired as a result of product line exits as well as certain business exits announced in the fourth quarter of 2022.
(2) Other restructuring costs and related adjustments primarily consist of certain accruals and related refinements as well as various contract termination costs associated with product line and business exits.
(3) Other transformation costs primarily consist of professional services, project management related costs and asset impairments, partially offset by gain on sale of assets.
Restructuring and transformation costs by reportable segment were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Flow | $ | 3.4 | $ | 2.2 | $ | 0.9 | |||||
| Water Solutions | (0.1) | 41.1 | 0.6 | ||||||||
| Pool | 9.1 | 14.3 | 0.3 | ||||||||
| Other | 38.3 | 25.9 | 17.3 | ||||||||
| Consolidated | $ | 50.7 | $ | 83.5 | $ | 19.1 | |||||
Activity related to accrued severance and related costs recorded in Other current liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets is summarized as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | ||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 23.2 | $ | 10.7 | ||||
| Costs incurred | 15.1 | 21.1 | ||||||
| Cash payments and other | (24.9) | (8.6) | ||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 13.4 | $ | 23.2 | ||||
59
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
5. Goodwill and Other Identifiable Intangible Assets
The changes in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 by reportable segment were as follows:
| In millions | December 31, 2022 | Purchase accounting adjustments | Foreign currency translation | December 31, 2023 | ||||||||||||||||
| Flow | $ | 747.6 | $ | — | $ | 19.5 | $ | 767.1 | ||||||||||||
| Water Solutions | 1,398.1 | (0.8) | 3.3 | 1,400.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Pool | 1,106.9 | — | — | 1,106.9 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total goodwill | $ | 3,252.6 | $ | (0.8) | $ | 22.8 | $ | 3,274.6 | ||||||||||||
| In millions | December 31, 2021 | Acquisitions | Purchase accounting adjustments | Foreign currency translation | December 31, 2022 | |||||||||||||||
| Flow | $ | 782.0 | $ | — | $ | 1.0 | $ | (35.4) | $ | 747.6 | ||||||||||
| Water Solutions | 618.0 | 790.5 | (0.9) | (9.5) | 1,398.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Pool | 1,104.5 | — | 2.3 | 0.1 | 1,106.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Total goodwill | $ | 2,504.5 | $ | 790.5 | $ | 2.4 | $ | (44.8) | $ | 3,252.6 | ||||||||||
There has been no impairment of goodwill for any of the years presented.
Identifiable intangible assets consisted of the following at December 31:
| 2023 | 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | Cost | Accumulated amortization | Net | Cost | Accumulated amortization | Net | |||||||||||||||||
| Definite-life intangibles | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Customer relationships | $ | 1,106.2 | $ | (361.8) | $ | 744.4 | $ | 1,100.9 | $ | (308.9) | $ | 792.0 | |||||||||||
| Proprietary technology and patents | 89.7 | (43.2) | 46.5 | 89.3 | (35.6) | 53.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other | — | — | — | 14.4 | (14.4) | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Total finite-life intangibles | 1,195.9 | (405.0) | 790.9 | 1,204.6 | (358.9) | 845.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Indefinite-life intangibles | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trade names | 251.5 | — | 251.5 | 248.9 | — | 248.9 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total intangibles | $ | 1,447.4 | $ | (405.0) | $ | 1,042.4 | $ | 1,453.5 | $ | (358.9) | $ | 1,094.6 | |||||||||||
Identifiable intangible asset amortization expense in 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $55.3 million, $52.5 million and $26.3 million, respectively.
An impairment charge of $2.7 million was recorded in 2022 related to the write-off of a proprietary technology intangible asset as a result of a business exit announced in the fourth quarter of 2022. No impairment charge was recorded for identifiable intangible assets in 2023 or 2021.
Estimated future amortization expense for identifiable intangible assets during the next five years is as follows:
| In millions | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Estimated amortization expense | $ | 54.2 | $ | 54.2 | $ | 52.9 | $ | 51.6 | $ | 49.0 | |||||||||||||
60
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
6. Supplemental Balance Sheet Information
| December 31 | ||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||
| Inventories | ||||||||
| Raw materials and supplies | $ | 369.1 | $ | 404.1 | ||||
| Work-in-process | 97.1 | 95.6 | ||||||
| Finished goods | 211.5 | 290.3 | ||||||
| Total inventories | $ | 677.7 | $ | 790.0 | ||||
| Other current assets | ||||||||
| Cost in excess of billings | $ | 70.8 | $ | 48.4 | ||||
| Prepaid expenses | 55.2 | 74.8 | ||||||
| Other current assets | 33.3 | 4.9 | ||||||
| Total other current assets | $ | 159.3 | $ | 128.1 | ||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | ||||||||
| Land and land improvements | $ | 32.3 | $ | 32.3 | ||||
| Buildings and leasehold improvements | 225.5 | 200.7 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 669.9 | 639.2 | ||||||
| Capitalized software | 70.5 | 68.8 | ||||||
| Construction in progress | 55.8 | 60.6 | ||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | 1,054.0 | 1,001.6 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation and amortization | 692.0 | 657.1 | ||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 362.0 | $ | 344.5 | ||||
| Other non-current assets | ||||||||
| Right-of-use lease assets | $ | 102.0 | $ | 78.6 | ||||
| Deferred income taxes | 113.2 | 26.0 | ||||||
| Deferred compensation plan assets | 26.1 | 21.7 | ||||||
| Other non-current assets | 74.0 | 71.0 | ||||||
| Total other non-current assets | $ | 315.3 | $ | 197.3 | ||||
| Other current liabilities | ||||||||
| Dividends payable | $ | 38.0 | $ | 36.2 | ||||
| Accrued warranty | 65.0 | 63.1 | ||||||
| Accrued rebates and incentives | 181.8 | 200.1 | ||||||
| Accrued freight | 20.4 | 39.4 | ||||||
| Billings in excess of cost | 46.9 | 43.8 | ||||||
| Current lease liability | 26.2 | 29.3 | ||||||
| Income taxes payable | 20.7 | 21.8 | ||||||
| Accrued restructuring | 13.4 | 23.2 | ||||||
| Interest payable | 29.7 | 32.9 | ||||||
| Other current liabilities | 103.2 | 112.3 | ||||||
| Total other current liabilities | $ | 545.3 | $ | 602.1 | ||||
| Other non-current liabilities | ||||||||
| Long-term lease liability | $ | 79.1 | $ | 52.4 | ||||
| Income taxes payable | 35.6 | 35.1 | ||||||
| Self-insurance liabilities | 51.9 | 52.1 | ||||||
| Deferred compensation plan liabilities | 26.1 | 21.7 | ||||||
| Foreign currency contract liabilities | 70.0 | 52.2 | ||||||
| Other non-current liabilities | 32.0 | 31.4 | ||||||
| Total other non-current liabilities | $ | 294.7 | $ | 244.9 | ||||
61
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
7. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss
Components of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss consist of the following:
| December 31 | ||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||
| Cumulative translation adjustments | $ | (256.5) | $ | (280.5) | ||||
| Market value of derivative financial instruments, net of tax | 12.1 | 41.5 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | $ | (244.4) | $ | (239.0) | ||||
8. Debt
Debt and the average interest rates on debt outstanding were as follows:
| In millions | Average interest rate at | Maturity Year | December 31 | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2023 | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||||||||
| Revolving credit facility (Senior Credit Facility) | 6.655% | 2026 | $ | — | $ | 320.0 | ||||||||
| Term Loan Facility | 6.891% | 2023 - 2027 | 987.5 | 1,000.0 | ||||||||||
| Term loans (Senior Credit Facility) | 6.610% | 2024 | 200.0 | 200.0 | ||||||||||
Senior notes - fixed rate (1) | 4.650% | 2025 | 19.3 | 19.3 | ||||||||||
Senior notes - fixed rate (1) | 4.500% | 2029 | 400.0 | 400.0 | ||||||||||
Senior notes - fixed rate (1) | 5.900% | 2032 | 400.0 | 400.0 | ||||||||||
| Unamortized debt issuance costs and discounts | N/A | N/A | (18.5) | (22.0) | ||||||||||
| Total debt | $ | 1,988.3 | $ | 2,317.3 | ||||||||||
(1) Senior notes are guaranteed as to payment by Pentair plc. | ||||||||||||||
Pentair, Pentair Finance S.à r.l (“PFSA“) and Pentair, Inc. are parties to a credit agreement (the “Senior Credit Facility”), with Pentair as guarantor and PFSA and Pentair, Inc. as borrowers, providing for a $900.0 million senior unsecured revolving credit facility and a $200.0 million senior unsecured term loan facility. The revolving credit facility has a maturity date of December 16, 2026 and the term loan facility has a maturity date of December 16, 2024. Borrowings under the Senior Credit Facility bear interest at a rate equal to an alternate base rate, adjusted term secured overnight financing rate, adjusted euro interbank offered rate, adjusted daily simple secured overnight financing rate or central bank rate, plus, in each case, an applicable margin. The applicable margin is based on, at PFSA’s election, Pentair’s leverage level or PFSA’s public credit rating.
As of December 31, 2023, total availability under the Senior Credit Facility was $900.0 million. In addition, PFSA has the option to request to increase the revolving credit facility and/or to enter into one or more additional tranches of term loans in an aggregate amount of up to $300.0 million, subject to customary conditions, including the commitment of the participating lenders.
In 2022, Pentair and PFSA entered into a senior unsecured term loan facility (the “Term Loan Facility”), with PFSA, as borrower, Pentair, as guarantor, and the lenders and agents party thereto, providing for an aggregate principal amount of $1.0 billion. The Term Loan Facility has a maturity date of July 28, 2027, with required quarterly installment payments of $6.3 million which began on the last day of the third quarter of 2023 and increases to $12.5 million beginning with the last day of the third quarter of 2024. The Term Loan Facility bears interest at a rate equal to an alternate base rate, adjusted term secured overnight financing rate, or adjusted daily simple secured overnight financing rate, plus, in each case, an applicable margin. The applicable margin is based on, at PFSA’s election, Pentair’s leverage level or PFSA’s public credit rating.
In addition to the Term Loan Facility, Pentair, as guarantor, and PFSA, as issuer, completed a public offering in 2022 of $400.0 million aggregate principal amount of 5.900% Senior Notes due 2032 (“2032 Senior Notes”). We used the net proceeds from the Term Loan Facility and the issuance of the 2032 Senior Notes to finance a portion of the Manitowoc Ice acquisition purchase price and to pay related fees and expenses.
62
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Our debt agreements contain various financial covenants, but the most restrictive covenants are contained in the Senior Credit Facility and the Term Loan Facility. The Senior Credit Facility and the Term Loan Facility contain covenants requiring us not to permit (i) the ratio of our consolidated debt (net of our consolidated unrestricted cash and cash equivalents in excess of $5.0 million but not to exceed $250.0 million) to our consolidated net income (excluding, among other things, non-cash gains and losses) before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and non-cash share-based compensation expense (“EBITDA”) on the last day of any period of four consecutive fiscal quarters (each, a “testing period”) to exceed 3.75 to 1.00 (or, at PFSA’s election and subject to certain conditions, 4.25 to 1.00 for four testing periods in connection with certain material acquisitions) (the “Leverage Ratio”) and (ii) the ratio of our EBITDA to our consolidated interest expense, for the same period to be less than 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of each fiscal quarter. For purposes of the Leverage Ratio, the Senior Credit Facility and the Term Loan Facility provide for the calculation of EBITDA giving pro forma effect to certain acquisitions, divestitures and liquidations during the period to which such calculation relates.
In addition to the Senior Credit Facility and the Term Loan Facility, we have various other credit facilities with an aggregate availability of $20.9 million, of which there were no outstanding borrowings at December 31, 2023. Borrowings under these credit facilities bear interest at variable rates.
We have $37.5 million of Term Loan Facility payments and $200.0 million of payments under the senior unsecured term loan facility, associated with the Senior Credit Facility, due in the next twelve months. We classified this debt as long-term as of December 31, 2023 as we have the intent and ability to refinance such obligations on a long-term basis under the revolving credit facility under the Senior Credit Facility.
Debt outstanding, excluding unamortized issuance costs and discounts, at December 31, 2023 matures on a calendar year basis as follows:
| In millions | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | Thereafter | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Contractual debt obligation maturities | $ | 237.5 | $ | 69.3 | $ | 50.0 | $ | 850.0 | $ | — | $ | 800.0 | $ | 2,006.8 | |||||||||
9. Derivatives and Financial Instruments
Derivative financial instruments
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates on our variable rate indebtedness. To manage the volatility related to these exposures, we periodically enter into a variety of derivative financial instruments. Our objective is to reduce, where it is deemed appropriate to do so, fluctuations in earnings and cash flows associated with changes in foreign currency rates or variable interest rates. The derivative contracts contain credit risk to the extent that our bank counterparties may be unable to meet the terms of the agreements. The amount of such credit risk is generally limited to the unrealized gains, if any, in such contracts. Such risk is minimized by limiting those counterparties to major financial institutions of high credit quality.
Foreign currency contracts
We conduct business in various locations throughout the world and are subject to market risk due to changes in the value of foreign currencies in relation to our reporting currency, the U.S. dollar. We manage our economic and transaction exposure to certain market-based risks through the use of foreign currency derivative financial instruments. Our objective in holding these derivatives is to reduce the volatility of net earnings and cash flows associated with changes in foreign currency exchange rates. The majority of our foreign currency contracts have an original maturity date of less than one year.
At December 31, 2023 and 2022, we had outstanding foreign currency derivative contracts with gross notional U.S. dollar equivalent amounts of $23.9 million and $9.4 million, respectively. The impact of these contracts on the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income was not material for any period presented.
Cross currency swaps
At December 31, 2023 and 2022, we had outstanding cross currency swap agreements with a combined notional amount of $940.2 million and $746.3 million, respectively. The agreements are accounted for as either cash flow hedges, to hedge foreign currency fluctuations on certain intercompany debt, or as net investment hedges to manage our exposure to fluctuations in the Euro-U.S. Dollar exchange rate. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, we had deferred foreign currency losses of $51.6 million and $40.3 million, respectively, recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive loss associated with our cross currency swap activity. The periodic interest settlements related to our cross currency swap agreements are classified as operating activities. The cash flows that relate to principal balances are classified as financing activities for the cash flow hedges on intercompany debt and investing activities for the net investment hedges.
63
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
In December 2023, we terminated a €150.0 million cross currency swap agreement, resulting in a net cash payment of $17.6 million, of which $18.5 million is included within investing activities and $0.9 million of interest income is included within operating activities on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows. Subsequent to the termination, we entered into new cross currency swaps with a combined notional amount of €300.0 million.
In October 2022, we entered into transactions to early terminate and cash settle €700.0 million of our cross currency swap agreements due to favorable market conditions. The termination of the cross currency swap agreements resulted in net cash receipts of $84.3 million, of which $2.1 million, $70.1 million and $12.1 million are included within operating activities, investing activities and financing activities, respectively, on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows. Subsequent to the termination, we entered into new cross currency swap agreements with euro notional amounts matching the original swap agreements.
In June 2022, we terminated €300.0 million of our cross currency swap agreements, resulting in total net cash received of $9.0 million, of which $8.8 million is included within investing activities and $0.2 million is included within financing activities on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows. Subsequent to the termination, we entered into new cross currency swaps with a combined notional amount of $320.0 million to replace the terminated cross currency swap agreements.
Hedging of variable interest rates
On March 31, 2023, we entered into floating-to-fixed interest rate swap agreements to hedge the interest rate movements related to a portion of our variable rate debt. The swaps have a combined notional amount of $300.0 million and an average fixed one-month U.S. Dollar secured overnight financing rate (“SOFR”) of 3.795%. They have an effective date of April 4, 2023 and settle monthly through April 2026.
On April 3, 2023, we entered into five-year interest rate collar agreements with a combined notional value of $200.0 million to hedge the cash flows related to the interest rate movements on our variable rate debt. In these collar agreements, the Company and counterparty financial institutions agreed to a one-month U.S. Dollar SOFR floor of 1.875% and a cap of 5.000%. The collars have an effective date of April 4, 2023 and settle monthly through April 2028.
The interest rate swaps and the collars were designated as cash flow hedges. Unrealized gains and losses related to the fair value of the interest rate swaps are recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive loss on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. We had an unrealized gain of $0.3 million at December 31, 2023 recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive loss associated with our interest rate swap and collar activity. The periodic interest settlements related to our interest rate swaps and collars are classified as operating activities.
Fair value measurements
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Assets and liabilities measured at fair value are classified using the following hierarchy, which is based upon the transparency of inputs to the valuation as of the measurement date:
| Level 1: | Valuation is based on observable inputs such as quoted market prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets. | |||||||
| Level 2: | Valuation is based on inputs such as quoted market prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets or other inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument. | |||||||
| Level 3: | Valuation is based upon other unobservable inputs that are significant to the fair value measurement. | |||||||
In making fair value measurements, observable market data must be used when available. When inputs used to measure fair value fall within different levels of the hierarchy, the level within which the fair value measurement is categorized is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
Fair value of financial instruments
The following methods were used to estimate the fair values of each class of financial instrument:
•short-term financial instruments (cash and cash equivalents, accounts and notes receivable, accounts payable and variable-rate debt) — recorded amount approximates fair value because of the short maturity period;
•long-term fixed-rate debt, including current maturities — fair value is based on market quotes available for issuance of debt with similar terms, which are inputs that are classified as Level 2 in the valuation hierarchy defined above;
64
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
•foreign currency contracts, interest rate swap and collar agreements — fair values are determined through the use of models that consider various assumptions, including time value, yield curves, as well as other relevant economic measures, which are inputs that are classified as Level 2 in the valuation hierarchy defined above; and
•deferred compensation plan assets (mutual funds, common/collective trusts and cash equivalents for payment of certain non-qualified benefits for retired, terminated and active employees) — fair value of mutual funds and cash equivalents are based on quoted market prices in active markets that are classified as Level 1 in the valuation hierarchy defined above; fair value of common/collective trusts are valued at net asset value (“NAV”), which is based on the fair value of the underlying securities owned by the fund and divided by the number of shares outstanding.
The recorded amounts and estimated fair values of total debt, excluding unamortized issuance costs and discounts, at December 31 were as follows:
| 2023 | 2022 | ||||||||||||||||
| In millions | Recorded Amount | Fair Value | Recorded Amount | Fair Value | |||||||||||||
| Variable rate debt | $ | 1,187.5 | $ | 1,187.5 | $ | 1,520.0 | $ | 1,520.0 | |||||||||
| Fixed rate debt | 819.3 | 824.5 | 819.3 | 789.3 | |||||||||||||
| Total debt | $ | 2,006.8 | $ | 2,012.0 | $ | 2,339.3 | $ | 2,309.3 | |||||||||
Financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring and nonrecurring basis were as follows:
| December 31, 2023 | |||||||||||||||||
| In millions | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | NAV | Total | ||||||||||||
| Recurring fair value measurements | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate contract assets | $ | — | $ | 0.3 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.3 | |||||||
| Foreign currency contract assets | — | 0.2 | — | — | 0.2 | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency contract liabilities | — | (70.0) | — | — | (70.0) | ||||||||||||
| Deferred compensation plan assets | 12.1 | — | — | 14.0 | 26.1 | ||||||||||||
| Total recurring fair value measurements | $ | 12.1 | $ | (69.5) | $ | — | $ | 14.0 | $ | (43.4) | |||||||
| December 31, 2022 | |||||||||||||||||
| In millions | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | NAV | Total | ||||||||||||
| Recurring fair value measurements | |||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency contract liabilities | $ | — | $ | (52.2) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (52.2) | |||||||
| Deferred compensation plan assets | 10.5 | — | — | 11.2 | 21.7 | ||||||||||||
| Total recurring fair value measurements | $ | 10.5 | $ | (52.2) | $ | — | $ | 11.2 | $ | (30.5) | |||||||
10. Income Taxes
Income from continuing operations before income taxes consisted of the following:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
Federal (1) | $ | (9.9) | $ | (10.1) | $ | (11.2) | |||||
International (2) | 628.8 | 560.7 | 638.0 | ||||||||
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | $ | 618.9 | $ | 550.6 | $ | 626.8 | |||||
(1) “Federal” reflects United Kingdom (“U.K.”) loss from continuing operations before income taxes, given U.K. tax residency.
(2) “International” reflects non-U.K. income from continuing operations before income taxes.
65
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
The (benefit) provision for income taxes consisted of the following:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Currently payable (receivable) | |||||||||||
International (1) | $ | 88.5 | $ | 112.2 | $ | 79.8 | |||||
| Total current taxes | 88.5 | 112.2 | 79.8 | ||||||||
| Deferred | |||||||||||
International (1) | (92.5) | (44.8) | (9.0) | ||||||||
| Total deferred taxes | (92.5) | (44.8) | (9.0) | ||||||||
| Total (benefit) provision for income taxes | $ | (4.0) | $ | 67.4 | $ | 70.8 | |||||
(1) “International” represents non-U.K. taxes.
Reconciliations of the federal statutory income tax rate to our effective tax rate were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| Percentages | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
U.K. federal statutory income tax rate (1) | 23.5 | % | 19.0 | % | 19.0 | % | |||||
Tax effect of international operations (2) | (13.2) | (7.6) | (5.1) | ||||||||
| Change in valuation allowances | 2.2 | 1.0 | (0.2) | ||||||||
| Excess tax benefits on stock-based compensation | (0.1) | (0.2) | (1.1) | ||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits | — | — | (1.3) | ||||||||
| Worthless stock deduction | (5.0) | — | — | ||||||||
Change in tax basis in foreign assets (3) | (8.0) | — | — | ||||||||
| Effective tax rate | (0.6) | % | 12.2 | % | 11.3 | % | |||||
(1) The U.K. Finance Act of 2021 increased the statutory tax rate from 19.0% to 25.0%, effective April 1, 2023. Given this change, a prorated U.K. federal statutory income tax rate was utilized for 2023.
(2) The tax effect of international operations consists of non-U.K. jurisdictions.
(3) The 2023 impact primarily represents the initial recognition of tax basis in intangible assets in foreign jurisdictions and the related valuation allowance.
Reconciliations of the beginning and ending gross unrecognized tax benefits were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 39.6 | $ | 37.3 | $ | 46.3 | |||||
| Gross increases for tax positions in prior periods | 0.6 | 3.6 | 2.5 | ||||||||
| Gross decreases for tax positions in prior periods | (0.2) | (0.9) | (0.7) | ||||||||
| Gross increases based on tax positions related to the current year | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.2 | ||||||||
| Gross decreases related to settlements with taxing authorities | (3.0) | (0.6) | (0.9) | ||||||||
| Reductions due to statute expiration | — | — | (10.1) | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 38.6 | $ | 39.6 | $ | 37.3 | |||||
We record gross unrecognized tax benefits in Other current liabilities and Other non-current liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Included in the $38.6 million of total gross unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2023 was $38.3 million of tax benefits that, if recognized, would impact the effective tax rate. It is reasonably possible that the gross unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2023 may decrease by a range of zero to $33.6 million during 2024, primarily as a result of the expiration of U.S. statute of limitations, and resolution of Germany and U.S. state examinations.
Based on the outcome of these examinations, or as a result of the expiration of statutes of limitations for specific jurisdictions, it is reasonably possible that certain unrecognized tax benefits for tax positions taken on previously filed tax returns will materially change from those recorded as liabilities in our financial statements. A number of tax periods from 2009 to present
66
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
are under audit by tax authorities in various jurisdictions, including Belgium, Germany and India. We anticipate that several of these audits may be concluded in the foreseeable future.
We record penalties and interest related to unrecognized tax benefits in (Benefit) provision for income taxes and Net interest expense, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income. At December 31, 2023 and 2022, we have liabilities of $0.3 million and $0.6 million, respectively, for the possible payment of penalties and $6.4 million and $4.9 million, respectively, for the possible payment of interest expense, which are recorded in Other current liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Deferred taxes arise because of different treatment between financial statement accounting and tax accounting, known as “temporary differences.” We record the tax effect of these temporary differences as “deferred tax assets” (generally items that can be used as a tax deduction or credit in future periods) and “deferred tax liabilities” (generally items for which we received a tax deduction but the tax impact has not yet been recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income).
Deferred taxes were recorded in the Consolidated Balance Sheets as follows:
| December 31 | ||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||
| Other non-current assets | $ | 113.2 | $ | 26.0 | ||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | 40.0 | 43.3 | ||||||
| Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) | $ | 73.2 | $ | (17.3) | ||||
The tax effects of the major items recorded as deferred tax assets and liabilities were as follows:
| December 31 | ||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets | ||||||||
| Accrued liabilities and reserves | $ | 58.8 | $ | 68.1 | ||||
| Pension and other post-retirement compensation and benefits | 20.1 | 19.4 | ||||||
| Employee compensation and benefits | 28.6 | 26.5 | ||||||
| Research and development costs | 28.4 | 18.1 | ||||||
| Tax loss and credit carryforwards | 769.4 | 752.4 | ||||||
| Interest limitations | 168.4 | 104.9 | ||||||
| Total deferred tax assets | 1,073.7 | 989.4 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | 816.6 | 756.9 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets, net of valuation allowance | 257.1 | 232.5 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | 17.9 | 18.1 | ||||||
| Goodwill and other intangibles | 149.7 | 213.0 | ||||||
| Other liabilities | 16.3 | 18.7 | ||||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities | 183.9 | 249.8 | ||||||
| Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) | $ | 73.2 | $ | (17.3) | ||||
Included in tax loss and credit carryforwards in the table above is a foreign tax credit deferred tax asset of $30.7 million as of December 31, 2023. The $30.7 million foreign tax credit carryover consists of $29.6 million from the tax period ended December 31, 2017 related to the transition tax and $1.1 million from the tax period ended December 31, 2023. The foreign tax credit carryover from the tax period ended December 31, 2017 will expire December 31, 2027, and the foreign tax credit carryover from the period ended December 31, 2023 will expire December 31, 2033. The entire amount of foreign tax credit carryovers generated from both periods are subject to a valuation allowance.
As of December 31, 2023, tax loss carryforwards of $3,044.4 million were available to offset future income. A valuation allowance of $732.5 million exists for deferred income tax benefits related to the tax loss carryforwards which may not be realized. We believe sufficient taxable income will be generated in the respective jurisdictions to allow us to fully recover the remainder of the tax losses. The tax losses primarily relate to non-U.S. carryforwards of $2,982.3 million of which
67
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
$1,857.1 million are located in jurisdictions with unlimited tax loss carryforward periods, while the remainder will begin to expire in 2024. In addition, there were $62.1 million of U.S. state tax loss carryforwards as of December 31, 2023. U.S. state tax losses of $8.6 million are in jurisdictions with unlimited tax loss carryforward periods, while the remainder will expire in future years through 2043.
Deferred taxes in the amount of $0.6 million have been provided on undistributed earnings of certain subsidiaries. Taxes have not been provided on undistributed earnings of subsidiaries where it is our intention to reinvest these earnings permanently or to repatriate the earnings only when it is tax effective to do so. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of tax that might be payable if such earnings were to be remitted.
11. Benefit Plans
Pension and other post-retirement plans
We sponsor U.S. and non-U.S. defined-benefit pension and other post-retirement plans. Pension benefits are based principally on an employee’s years of service and/or compensation levels near retirement. In addition, we provide certain post-retirement health care and life insurance benefits. Generally, the post-retirement health care and life insurance plans require contributions from retirees.
Obligations and funded status
The following tables present reconciliations of plan benefit obligations, fair value of plan assets and the funded status of pension plans and other post-retirement plans as of and for the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022:
| Pension plans | Other post-retirement plans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in benefit obligations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation beginning of year | $ | 90.5 | $ | 116.1 | $ | 9.0 | $ | 11.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Service cost | 1.7 | 2.4 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 4.1 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial loss (gain) | 7.4 | (22.6) | (0.8) | (1.3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | 1.1 | (0.2) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefits paid | (7.3) | (7.7) | (1.1) | (1.3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation end of year | $ | 97.5 | $ | 90.5 | $ | 7.6 | $ | 9.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Change in plan assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets beginning of year | $ | 28.4 | $ | 34.4 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Actual return on plan assets | 0.8 | (5.8) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Company contributions | 7.6 | 7.5 | 1.1 | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | 1.0 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefits paid | (7.3) | (7.7) | (1.1) | (1.3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets end of year | $ | 30.5 | $ | 28.4 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funded status | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligations in excess of the fair value of plan assets | $ | (67.0) | $ | (62.1) | $ | (7.6) | $ | (9.0) | ||||||||||||||||||
The actuarial loss in 2023 was primarily due to declines in the discount rates to reflect economic conditions at December 31, 2023. The actuarial gain in 2022 was primarily due to increases in the discount rates to reflect economic conditions at December 31, 2022.
Amounts recorded in the Consolidated Balance Sheets were as follows:
| Pension plans | Other post-retirement plans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current liabilities | $ | (6.5) | $ | (5.9) | $ | (1.1) | $ | (1.3) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-current liabilities | (60.5) | (56.2) | (6.5) | (7.7) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligations in excess of the fair value of plan assets | $ | (67.0) | $ | (62.1) | $ | (7.6) | $ | (9.0) | ||||||||||||||||||
68
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
The accumulated benefit obligation for our pension plans was $93.4 million and $88.7 million at December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Information for pension plans with an accumulated benefit obligation or projected benefit obligation in excess of plan assets as of December 31 was as follows:
| Projected benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of plan assets | Accumulated benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of plan assets | ||||||||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | |||||||||||||
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 97.5 | $ | 88.1 | $ | 83.5 | $ | 78.0 | |||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets | 30.5 | 25.9 | 18.8 | 16.5 | |||||||||||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | N/A | N/A | 81.9 | 77.7 | |||||||||||||
Components of net periodic benefit expense for our pension plans for the years ended December 31 were as follows:
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Service cost | $ | 1.7 | $ | 2.4 | $ | 2.8 | |||||
| Interest cost | 4.1 | 2.5 | 2.0 | ||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | (0.8) | (0.7) | (0.5) | ||||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) | 7.1 | (16.4) | (1.5) | ||||||||
| Net periodic benefit expense (income) | $ | 12.1 | $ | (12.2) | $ | 2.8 | |||||
Components of net periodic benefit expense and income for our other post-retirement plans for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, were not material.
Assumptions
The following table provides the weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations and net periodic benefit cost as they pertain to our pension and other post-retirement plans.
| Pension plans | Other post-retirement plans | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percentages | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation assumptions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 4.26 | % | 4.77 | % | 2.21 | % | 4.84 | % | 5.11 | % | 2.34 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase | 3.70 | % | 3.80 | % | 3.61 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net periodic benefit expense assumptions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 4.77 | % | 2.21 | % | 1.74 | % | 5.11 | % | 2.34 | % | 1.77 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expected long-term return on plan assets | 4.76 | % | 2.89 | % | 2.60 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase | 3.80 | % | 3.61 | % | 3.62 | % | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Discount rates
The discount rate reflects the current rate at which the pension liabilities could be effectively settled at the end of the year based on our December 31 measurement date. The discount rate was determined by matching our expected benefit payments to payments from a stream of bonds rated AA or higher available in the marketplace. There are no known or anticipated changes in our discount rate assumptions that will impact our pension expense in 2024.
Expected rates of return
The expected rate of return is designed to be a long-term assumption that may be subject to considerable year-to-year variance from actual returns. In developing the expected long-term rate of return, we considered our historical returns, with consideration given to forecasted economic conditions, our asset allocations, input from external consultants and broader long-term market indices. Pension plan assets yielded a gain of 2.82% in 2023 and losses of 16.86% and 0.89% in 2022 and 2021, respectively.
69
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Healthcare cost trend rates
The assumed healthcare cost trend rates for other post-retirement plans as of December 31 were as follows:
| 2023 | 2022 | |||||||
| Healthcare cost trend rate assumed for following year | 6.1 | % | 5.5 | % | ||||
| Rate to which the cost trend rate is assumed to decline (the ultimate trend rate) | 4.0 | % | 4.0 | % | ||||
| Year the cost trend rate reaches the ultimate trend rate | 2046 | 2043 | ||||||
Pension plans assets
Objective
The primary objective of our investment strategy is to meet the pension obligation to our employees at a reasonable cost to us. This is primarily accomplished through growth of capital and safety of the funds invested.
Asset allocation
Our actual overall asset allocation for our pension plans as compared to our investment policy goals as of December 31 was as follows:
| Actual | Target | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Percentages | 2023 | 2022 | 2023 | 2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fixed income | 53 | % | 58 | % | 53 | % | 58 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative | 47 | % | 42 | % | 47 | % | 42 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fair value measurement
The fair values of our pension plan assets and their respective levels in the fair value hierarchy as of December 31, 2023 and December 31, 2022 were as follows:
| December 31, 2023 | ||||||||||||||
| In millions | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 0.2 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.2 | ||||||
| Other investments | — | — | 14.2 | 14.2 | ||||||||||
| Total investments at fair value | $ | 0.2 | $ | — | $ | 14.2 | $ | 14.4 | ||||||
| Investments measured at NAV | 16.1 | |||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 30.5 | ||||||||||||
| December 31, 2022 | ||||||||||||||
| In millions | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||
| Other investments | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 11.9 | $ | 11.9 | ||||||
| Investments measured at NAV | 16.5 | |||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 28.4 | ||||||||||||
Valuation methodologies used for investments measured at fair value were as follows:
•Cash and cash equivalents — Cash consists of cash held in bank accounts and is considered a Level 1 investment.
•Other investments — Other investments include investments in commingled funds with diversified investment strategies. Investments in commingled funds that were valued based on unobservable inputs due to liquidation restrictions were classified as Level 3.
Activity for our Level 3 pension plan assets held during the years ended December 31, 2023 and 2022 was not material.
Cash flows
Contributions
Pension contributions totaled $7.6 million and $7.5 million in 2023 and 2022, respectively. We anticipate our 2024 pension contributions to be approximately $9.8 million. The 2024 expected contributions will equal or exceed our minimum funding requirements.
70
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Estimated future benefit payments
The following benefit payments, which reflect expected future service or payout from termination, as appropriate, are expected to be paid by the plans in each of the next five fiscal years and in the aggregate for the five fiscal years thereafter are as follows:
| In millions | Pension plans | Other post- retirement plans | |||||||||
| 2024 | $ | 8.4 | $ | 1.1 | |||||||
| 2025 | 8.3 | 1.0 | |||||||||
| 2026 | 8.1 | 0.9 | |||||||||
| 2027 | 9.1 | 0.9 | |||||||||
| 2028 | 9.0 | 0.8 | |||||||||
| 2029 - 2033 | 39.0 | 2.8 | |||||||||
Savings plan
We have a 401(k) plan (the “401(k) plan”) with an employee share ownership (“ESOP”) bonus component, which covers certain union and all non-union U.S. employees who met certain age requirements. Under the 401(k) plan, eligible U.S. employees may voluntarily contribute a percentage of their eligible compensation. We match contributions made by employees who met certain eligibility and service requirements. The 401(k) company match contribution is a dollar-for-dollar (100%) matching contribution on up to 5% of employee eligible earnings, contributed as before-tax contributions.
Our expense for the 401(k) plan, including the ESOP, was $19.5 million, $21.4 million and $19.0 million in 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Other retirement compensation
Total other accrued retirement compensation, primarily related to deferred compensation and supplemental retirement plans, was $32.7 million and $28.5 million as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, respectively, and is included in Pension and other post-retirement compensation and benefits and Other non-current liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
12. Shareholders’ Equity
Authorized shares
Our authorized share capital consists of 426.0 million ordinary shares with a par value of $0.01 per share.
Share repurchases
In December 2020, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of our ordinary shares up to a maximum dollar limit of $750.0 million. This authorization expires on December 31, 2025.
During the year ended December 31, 2022, we repurchased 1.0 million of our ordinary shares for $50.0 million. During the year ended December 31, 2023, no ordinary shares were repurchased. As of December 31, 2023, we had $600.0 million available for share repurchases under this authorization.
Dividends payable
On December 11, 2023, the Board of Directors approved a regular quarterly cash dividend of $0.23 per share that was paid on February 2, 2024 to shareholders of record at the close of business on January 19, 2024. This dividend reflects a 5 percent increase in the Company’s regular cash dividend rate. The balance of dividends payable included in Other current liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets was $38.0 million at December 31, 2023. Dividends paid per ordinary share were $0.88, $0.84 and $0.80 for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
71
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
13. Share Plans
Share-based compensation expense
Total share-based compensation expense for 2023, 2022 and 2021 was as follows:
| December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Restricted stock units | $ | 15.0 | $ | 14.6 | $ | 13.0 | |||||
| Stock options | 4.3 | 3.7 | 3.4 | ||||||||
| Performance share units | 9.8 | 6.6 | 13.4 | ||||||||
| Total share-based compensation expense | $ | 29.1 | $ | 24.9 | $ | 29.8 | |||||
Share incentive plans
In May 2020, the Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan (“2020 Share Plan”) was approved during the Annual General Meeting of Shareholders. The Pentair plc 2012 Stock and Incentive Plan (“2012 Stock Plan”) terminated upon the approval of the 2020 Share Plan, although awards outstanding under the 2012 Stock Plan continue in effect. Beginning May 5, 2020, all share-based compensation grants were made under the 2020 Share Plan.
The 2020 Share Plan authorizes the issuance of 3.3 million of our ordinary shares, plus the number of shares reserved under the 2012 Stock Plan that were not the subject of outstanding awards as of the date the 2020 Share Plan became effective, which was 2.5 million shares, plus certain shares that would become available under the 2012 Stock Plan if it had remained in effect. The shares may be issued as new shares or from shares held in treasury. Our practice is to settle equity-based awards by issuing new shares. The 2020 Share Plan terminates on the date all shares reserved for issuance have been issued. The 2020 Share Plan allows for the granting to our employees, consultants and directors of stock options, stock appreciation rights, performance share units, restricted shares, restricted stock units, deferred stock rights, incentive awards, dividend equivalent units and other equity-based awards.
The 2020 Share Plan is administered by our compensation committee (the “Committee”), which is made up of independent members of our Board of Directors. Employees eligible to receive awards under the 2020 Share Plan are managerial, administrative or professional employees. The Committee has the authority to select the recipients of awards, determine the type and size of awards, establish certain terms and conditions of award grants and take certain other actions as permitted under the 2020 Share Plan. The 2020 Share Plan prohibits the Committee from re-pricing awards or canceling and reissuing awards at lower prices.
Non-qualified and incentive stock options
Under the 2020 Share Plan, we may grant stock options to any eligible employee with an exercise price equal to the market value of the shares on the dates the options were granted. Options generally vest one-third each year over a period of three years commencing on the grant date and expire 10 years after the grant date.
Restricted shares and restricted stock units
Under the 2020 Share Plan, eligible employees may be awarded restricted shares or restricted stock units of our common stock. Restricted shares and restricted stock units generally vest one-third each year over a period of three years commencing on the grant date, subject to continuous employment and certain other conditions. Restricted shares and restricted stock units are valued at market value on the date of grant and are expensed over the vesting period.
Stock appreciation rights, performance shares and performance units
Under the 2020 Share Plan, the Committee is permitted to issue these awards which are generally contingent on the achievement of predetermined performance goals over a vesting period of three years. The Committee has the ability to adjust performance goals or modify the manner of measuring or evaluating a performance goal using its discretion. PSUs are granted to certain employees that vest based on the satisfaction of a service period of three years and the achievement of certain performance metrics over that same period. Upon vesting, PSU holders receive dividends that accumulate during the vesting period. The fair value of these PSUs is determined based on the closing market price of the Company’s ordinary shares at the date of grant. Compensation expense is recognized over the period an employee is required to provide service based on the estimated vesting of the PSUs granted. The estimated vesting of the PSUs is based on the probability of achieving certain performance metrics during the vesting period.
72
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Stock options
The following table summarizes stock option activity under all plans for the year ended December 31, 2023:
| Shares and intrinsic value in millions | Number of shares | Weighted- average exercise price | Weighted- average remaining contractual life (years) | Aggregate intrinsic value | ||||||||||
| Outstanding as of January 1, 2023 | 2.3 | $ | 45.16 | |||||||||||
| Granted | 0.3 | 47.34 | ||||||||||||
| Exercised | (0.3) | 47.35 | ||||||||||||
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 2.3 | $ | 45.07 | 4.9 | $ | 63.7 | ||||||||
| Options exercisable as of December 31, 2023 | 1.7 | $ | 42.39 | 3.7 | $ | 52.4 | ||||||||
| Options expected to vest as of December 31, 2023 | 0.6 | $ | 53.15 | 8.3 | $ | 10.9 | ||||||||
Fair value of options granted
The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted under Pentair plans in 2023, 2022 and 2021 was estimated to be $14.03, $17.88 and $12.88 per share, respectively. The total intrinsic value of options that were exercised during 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $5.3 million, $0.7 million and $29.0 million, respectively. At December 31, 2023, the total unrecognized compensation cost related to stock options was $4.0 million. This cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 1.7 years.
We estimated the fair value of each stock option award issued in the annual share-based compensation grant using a Black-Scholes option pricing model, modified for dividends and using the following assumptions:
| December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 4.00 | % | 1.18 | % | 0.37 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Expected dividend yield | 2.02 | % | 1.14 | % | 1.56 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Expected share price volatility | 30.40 | % | 29.60 | % | 29.60 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Expected term (years) | 6.1 | 6.4 | 6.5 | |||||||||||||||||
These estimates require us to make assumptions based on historical results, observance of trends in our share price, changes in option exercise behavior, future expectations and other relevant factors. If other assumptions had been used, share-based compensation expense, as calculated and recorded under the accounting guidance, could have been affected.
We based the expected life assumption on historical experience as well as the terms and vesting periods of the options granted. For purposes of determining expected volatility, we considered a rolling average of historical volatility measured over a period approximately equal to the expected option term. The risk-free rate for periods that coincide with the expected life of the options is based on the U.S. Treasury Department yield curve in effect at the time of grant.
Cash received from option exercises for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021 was $16.0 million, $2.5 million and $29.3 million, respectively. The tax benefit related to options exercised was $1.0 million, $0.1 million and $6.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Restricted stock units
The following table summarizes restricted stock unit activity under all plans for the year ended December 31, 2023:
| Shares in millions | Number of shares | Weighted average grant date fair value | ||||||
| Outstanding as of January 1, 2023 | 0.6 | $ | 53.10 | |||||
| Granted | 0.4 | 51.48 | ||||||
| Vested | (0.4) | 49.64 | ||||||
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 0.6 | $ | 53.88 | |||||
73
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
As of December 31, 2023, there was $23.9 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to restricted share compensation arrangements granted under the 2020 Plan and previous plans. That cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of one year. The total fair value of shares vested during the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, was $17.6 million, $11.7 million and $10.5 million, respectively. The tax benefit related to restricted stock units vested was $2.7 million, $2.1 million and $0.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
Performance share units
The following table summarizes performance share unit activity under all plans for the year ended December 31, 2023:
| Shares in millions | Number of shares | Weighted average grant date fair value | ||||||
| Outstanding as of January 1, 2023 | 0.4 | $ | 55.45 | |||||
| Granted | 0.2 | 46.34 | ||||||
| Vested | (0.2) | 45.33 | ||||||
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2023 | 0.4 | $ | 54.06 | |||||
The expense recognized each period is dependent upon our estimate of the number of shares that will ultimately be issued. As of December 31, 2023, there was $11.5 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to performance share compensation arrangements granted under the 2020 Plan and previous plans. That cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.3 years. The tax benefits related to performance share units were $0.9 million, $0.3 million and $0.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, respectively.
14. Segment Information
Effective January 1, 2023, we reorganized our reporting segments to reflect how we are managing our business and to help us accelerate our efforts to improve customer experience, differentiate our products and drive profitability for our shareholders. All prior period amounts related to the segment change have been retrospectively reclassified to conform to the new presentation. As part of this reorganization, the legacy Consumer Solutions segment was divided into a Pool segment and a Water Solutions segment. The Flow (formerly named the Industrial & Flow Technologies) segment remains the same. We classify our operations into the following reporting segments:
•Flow — The focus of this segment is to deliver water where it is needed, when it is needed, more efficiently and transforms waste into value. This segment designs, manufactures and sells a variety of fluid treatment and pump products and systems, including pressure vessels, gas recovery solutions, membrane bioreactors, wastewater reuse systems and advanced membrane filtration, separation systems, water disposal pumps, water supply pumps, fluid transfer pumps, turbine pumps, solid handling pumps, and agricultural spray nozzles, while serving the global residential, commercial and industrial markets. These products and systems are used in a range of applications, fluid delivery, ion exchange, desalination, food and beverage, separation technologies for the oil and gas industry, residential and municipal wells, water treatment, wastewater solids handling, pressure boosting, circulation and transfer, fire suppression, flood control, agricultural irrigation and crop spray.
•Water Solutions — The focus of this segment is to provide great tasting, higher-quality water and ice while helping people use water more productively. This segment designs, manufactures and sells commercial and residential water treatment products and systems including pressure tanks, control valves, activated carbon products, commercial ice machines, conventional filtration products, and point-of-entry and point-of-use water treatment systems. These water treatment products and systems are used in residential whole home water filtration, drinking water filtration and water softening solutions in addition to commercial total water management and filtration in foodservice operations. In addition, our water solutions business also provides installation and preventative services for water management solutions for commercial operators.
•Pool — The focus of this segment is to provide innovative, energy efficient pool solutions to help people more sustainably enjoy water. This segment designs, manufactures and sells a complete line of energy-efficient residential and commercial pool equipment and accessories including pumps, filters, heaters, lights, automatic controls, automatic cleaners, maintenance equipment and pool accessories. Applications for our pool products include residential and commercial pool maintenance, pool repair, renovation, service and construction and aquaculture solutions.
74
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
We evaluate performance based on net sales and segment income (loss) and use a variety of ratios to measure performance of our reporting segments. These results are not necessarily indicative of the results of operations that would have occurred had each segment been an independent, stand-alone entity during the periods presented. Segment income (loss) represents equity income of unconsolidated subsidiaries and operating income exclusive of intangible amortization, certain acquisition related expenses, costs of restructuring and transformation activities, impairments and other unusual non-operating items.
Financial information by reportable segment is as follows:
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | Net sales | Segment income (loss) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Flow | $ | 1,582.1 | $ | 1,500.8 | $ | 1,421.4 | $ | 282.3 | $ | 242.3 | $ | 213.3 | |||||||||||
| Water Solutions | 1,177.2 | 986.8 | 769.9 | 247.6 | 149.0 | 101.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Pool | 1,343.6 | 1,632.7 | 1,572.0 | 417.0 | 462.1 | 452.7 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.5 | (91.8) | (85.7) | (81.8) | |||||||||||||||||
Consolidated (1) | $ | 4,104.5 | $ | 4,121.8 | $ | 3,764.8 | $ | 855.1 | $ | 767.7 | $ | 685.9 | |||||||||||
(1) One customer in the Pool business represented approximately 15% of our consolidated net sales in 2023 and 20% of our consolidated net sales in both 2022 and 2021.
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In millions | Identifiable assets (1) | Capital expenditures | Depreciation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Flow | $ | 1,709.7 | $ | 1,722.4 | $ | 1,716.4 | $ | 19.6 | $ | 24.0 | $ | 23.0 | $ | 21.1 | $ | 19.5 | $ | 21.4 | |||||||||||||||||
| Water Solutions | 2,695.2 | 2,786.4 | 1,181.6 | 23.0 | 24.7 | 16.4 | 18.1 | 18.4 | 15.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pool | 1,679.8 | 1,710.3 | 1,641.4 | 17.3 | 28.8 | 16.1 | 11.4 | 8.9 | 7.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other | 478.6 | 228.4 | 214.2 | 16.1 | 7.7 | 4.7 | 8.9 | 7.3 | 6.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated | $ | 6,563.3 | $ | 6,447.5 | $ | 4,753.6 | $ | 76.0 | $ | 85.2 | $ | 60.2 | $ | 59.5 | $ | 54.1 | $ | 51.2 | |||||||||||||||||
(1) All cash and cash equivalents are included in “Other.”
The following table presents a reconciliation of consolidated segment income to consolidated income from continuing operations before income taxes:
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Segment income | $ | 855.1 | $ | 767.7 | $ | 685.9 | |||||
| Restructuring and other | (3.4) | (32.4) | (7.5) | ||||||||
| Transformation costs | (44.3) | (27.2) | (11.7) | ||||||||
| Inventory step-up | — | (5.8) | (2.3) | ||||||||
| Pension and other post-retirement mark-to-market (loss) gain | (6.1) | 17.5 | 2.4 | ||||||||
| Asset impairment and write-offs | (7.9) | (25.6) | — | ||||||||
| Gain on sale of businesses | — | 0.2 | 1.4 | ||||||||
| Russia business exit impact | — | (4.7) | — | ||||||||
| Deal-related costs and expenses | — | (22.2) | (7.9) | ||||||||
| Legal accrual adjustments and settlements | (2.2) | (0.2) | 7.6 | ||||||||
| Intangible amortization | (55.3) | (52.5) | (26.3) | ||||||||
| Interest expense, net | (118.3) | (61.8) | (12.5) | ||||||||
| Other income (expense) | 1.3 | (2.4) | (2.3) | ||||||||
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | $ | 618.9 | $ | 550.6 | $ | 626.8 | |||||
75
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
15. Commitments and Contingencies
Legal proceedings
We have been, and in the future may be, made parties to a number of actions filed or have been, and in the future may be, given notice of potential claims relating to the conduct of our business, including those relating to commercial, regulatory or contractual disputes with suppliers, authorities, customers or parties to acquisitions and divestitures, intellectual property matters, environmental, asbestos, safety and health matters, product liability, the use or installation of our products, consumer matters, and employment and labor matters.
While we believe that a material impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows from any such future claims or potential claims is unlikely, given the inherent uncertainty of litigation, a remote possibility exists that a future adverse ruling or unfavorable development could result in future charges that could have a material adverse impact. We do and will continue to periodically reexamine our estimates of probable liabilities and any associated expenses and receivables and make appropriate adjustments to such estimates based on experience and developments in litigation and applicable accounting rules. As a result, the current estimates of the potential impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations and cash flows for the proceedings and claims described in the notes to our consolidated financial statements could change in the future.
Environmental matters
We have been named as defendant, target or a potentially responsible party in a number of environmental clean-ups relating to our current or former business units. Accruals for environmental matters are recorded on a site-by-site basis when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be reasonably estimated, based on current law and existing technologies. It can be difficult to estimate reliably the final costs of investigation and remediation due to various factors. In our opinion, the amounts accrued are appropriate based on facts and circumstances as currently known. As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, our recorded reserves for environmental matters were not material.
Product liability claims
We are subject to various product liability lawsuits and personal injury claims. A substantial number of these lawsuits and claims are insured and accrued for by Penwald, our captive insurance subsidiary. Penwald records a liability for these claims based on actuarial projections of ultimate losses. For all other claims, accruals covering the claims are recorded, on an undiscounted basis, when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the liability can be reasonably estimated based on existing information. The accruals are adjusted periodically as additional information becomes available. We have not experienced significant unfavorable trends in either the severity or frequency of product liability lawsuits or personal injury claims.
Leases
Our lease portfolio principally consists of operating leases related to facilities, machinery, equipment and vehicles. Our accounting for lease terms does not include options to extend or terminate the lease until we are reasonably certain that we will exercise that option. Operating lease cost for lease payments is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term and principally consists of fixed payments for base rent.
These operating lease right-of-use (“ROU”) assets are included in Other non-current assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, and represent our right to use the underlying asset for the lease term. Our obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease are included in Other current liabilities and Other non-current liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. As we cannot readily determine the rate implicit in the lease, we use our incremental borrowing rate, determined by country of lease origin, based on the anticipated lease term at the commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments. The ROU asset also excludes any accrued lease payments and unamortized lease incentives.
For measurement and classification of lease agreements, we group lease and non-lease components into a single lease component for all underlying asset classes. Accordingly, all costs associated with a lease contract are accounted for as one lease cost.
The components of lease cost were as follows:
| In millions | December 31, 2023 | December 31, 2022 | ||||||
| Operating lease cost | $ | 49.7 | $ | 46.8 | ||||
| Sublease income | (0.9) | (0.9) | ||||||
| Total lease cost | $ | 48.8 | $ | 45.9 | ||||
76
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
Supplemental cash flow information related to leases was as follows:
| In millions | December 31, 2023 | December 31, 2022 | ||||||
| Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 35.5 | $ | 47.3 | ||||
| Right-of-use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations | $ | 14.0 | $ | 19.3 | ||||
Other information related to leases was as follows:
| December 31, 2023 | December 31, 2022 | |||||||
| Weighted-average remaining lease term of operating leases (years) | 6.2 | 3.7 | ||||||
| Weighted-average discount rate of operating leases | 5.7 | % | 4.4 | % | ||||
Future minimum lease commitments under non-cancelable operating leases as of December 31, 2023 were as follows:
| In millions | |||||
| 2024 | $ | 31.4 | |||
| 2025 | 21.5 | ||||
| 2026 | 17.9 | ||||
| 2027 | 13.3 | ||||
| 2028 | 9.6 | ||||
| Thereafter | 35.5 | ||||
| Total lease payments | 129.2 | ||||
| Less: imputed interest | (23.9) | ||||
| Total | $ | 105.3 | |||
Warranties and guarantees
In connection with the disposition of our businesses or product lines, we may agree to indemnify purchasers for various potential liabilities relating to the sold business, such as pre-closing tax, product liability, warranty, environmental, or other obligations. The subject matter, amounts and duration of any such indemnification obligations vary for each type of liability indemnified and may vary widely from transaction to transaction.
Generally, the maximum obligation under such indemnifications is not explicitly stated and as a result, the overall amount of these obligations cannot be reasonably estimated. Historically, we have not made significant payments for these indemnifications. We believe that if we were to incur a loss in any of these matters, the loss would not have a material effect on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
We recognize, at the inception of a guarantee, a liability for the fair value of the obligation undertaken in issuing the guarantee. In connection with the disposition of the Valves & Controls business, we agreed to indemnify Emerson Electric Co. for certain pre-closing tax liabilities. We have recorded a liability representing the fair value of our expected future obligation for this matter.
We provide service and warranty policies on our products. Liability under service and warranty policies is based upon a review of historical warranty and service claim experience. Adjustments are made to accruals as claim data and historical experience warrant.
77
Pentair plc and Subsidiaries
Notes to consolidated financial statements
The changes in the carrying amount of service and product warranties from continuing operations were as follows:
| Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| In millions | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 63.1 | $ | 40.5 | $ | 37.0 | |||||
| Service and product warranty provision | 90.0 | 85.3 | 55.3 | ||||||||
| Payments | (88.2) | (70.4) | (51.8) | ||||||||
| Acquisitions | — | 8.0 | 0.3 | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation | 0.1 | (0.3) | (0.3) | ||||||||
| Ending balance | $ | 65.0 | $ | 63.1 | $ | 40.5 | |||||
Stand-by letters of credit, bank guarantees and bonds
In certain situations, Tyco International Ltd., Pentair Ltd.’s former parent company (“Tyco”), guaranteed performance by the flow control business of Pentair Ltd. (“Flow Control”) to third parties or provided financial guarantees for financial commitments of Flow Control. In situations where Flow Control and Tyco were unable to obtain a release from these guarantees in connection with the spin-off of Flow Control from Tyco, we will indemnify Tyco for any losses it suffers as a result of such guarantees.
In the ordinary course of business, we are required to commit to bonds, letters of credit and bank guarantees that require payments to our customers for any non-performance. The outstanding face value of these instruments fluctuates with the value of our projects in process and in our backlog. In addition, we issue financial stand-by letters of credit primarily to secure our performance to third parties under self-insurance programs.
As of December 31, 2023 and 2022, the outstanding value of bonds, letters of credit and bank guarantees totaled $124.3 million and $99.7 million, respectively.
78
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the year ended December 31, 2023, pursuant to Rule 13a-15(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (“the Exchange Act”). Based upon their evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of the year ended December 31, 2023 to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms and to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The report of management required under this ITEM 9A is contained in ITEM 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the caption “Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting.”
Attestation Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The attestation report required under this ITEM 9A is contained in ITEM 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the caption “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.”
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2023 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
(b) During the fourth quarter of 2023, none of our directors or Section 16 officers adopted or terminated a “Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” or “non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement” (as each term is defined in Item 408(a) of Regulation S-K).
ITEM 9C. DISCLOSURE REGARDING FOREIGN JURISDICTIONS THAT PREVENT INSPECTIONS
Not applicable.
79
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Information required under this item with respect to directors is contained in our Proxy Statement for our 2024 annual general meeting of shareholders under the captions “Corporate Governance Matters” and “Proposal 1 Re-elect Director Nominees” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Information required under this item with respect to executive officers is contained in Part I of this Form 10-K under the caption “Information About Our Executive Officers.”
The information to be included in our Proxy Statement for our 2024 annual general meeting of shareholders under the caption “Delinquent Section 16(a) Reports” is incorporated herein by reference.
Our Board of Directors has adopted Pentair’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and designated it as the code of ethics for the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and senior financial officers. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics also applies to all employees and directors in accordance with New York Stock Exchange Listing Standards. We have posted a copy of Pentair’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics on our website at http://pentair.com/en/about-us/leadership/corporate-governance. We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirements under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding amendments to or waivers from, Pentair’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics by posting such information on our website at http://pentair.com/en/about-us/leadership/corporate-governance.
We are not including the information contained on our website as part of, or incorporating it by reference into, this report.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
Information required under this item is contained in our Proxy Statement for our 2024 annual general meeting of shareholders under the captions “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Compensation Committee Report,” “Executive Compensation Tables” and “Corporate Governance Matters - Director Compensation” and is incorporated herein by reference.
80
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
Information required under this item with respect to security ownership is contained in our Proxy Statement for our 2024 annual general meeting of shareholders under the caption “Security Ownership” and is incorporated herein by reference.
The following table summarizes, as of December 31, 2023, information about compensation plans under which our equity securities are authorized for issuance:
| Plan category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (a) | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (b) | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) (c) | |||||||||||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 Share and Incentive Plan | 1,834,455 | (1) | $ | 54.26 | (2) | 4,289,850 | (3) | |||||||||||||
| 2012 Stock and Incentive Plan | 1,569,863 | (4) | 39.91 | (2) | — | (5) | ||||||||||||||
| Total | 3,404,318 | $ | 44.85 | (2) | 4,289,850 | |||||||||||||||
(1)Consists of 820,709 shares subject to stock options, 570,685 shares subject to restricted stock units, and 443,061 shares subject to performance share awards.
(2)Represents the weighted average exercise price of outstanding stock options and does not take into account outstanding restricted stock units or performance share units.
(3)Represents securities remaining available for issuance under the 2020 Share and Incentive Plan.
(4)Consists of 1,563,198 shares subject to stock options, 6,665 shares subject to restricted stock units, and no shares subject to performance share awards.
(5)The 2012 Stock and Incentive Plan was terminated in 2020. Stock options and restricted stock units previously granted under the 2012 Stock and Incentive Plan remain outstanding, but no further options or shares may be granted under this plan.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Information required under this item is contained in our Proxy Statement for our 2024 annual general meeting of shareholders under the captions “Proposal 1 Re-elect Director Nominees - Director Independence” and “Corporate Governance Matters - The Board’s Role and Responsibilities - Policies and Procedures Regarding Related Person Transactions” and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
Information required under this item is contained in our Proxy Statement for our 2024 annual general meeting of shareholders under the caption “Proposal 3 Ratify, by Nonbinding, Advisory Vote, the Appointment of Deloitte & Touche LLP (PCAOB ID No. 34) as the Independent Auditor of Pentair plc and to Authorize, by Binding Vote, the Audit and Finance Committee of the Board of Directors to Set the Auditor’s Remuneration” and is incorporated herein by reference.
81
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) List of documents filed as part of this report:
(1) Financial Statements
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(2) Financial Statement Schedule
None.
All other schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission have been omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto.
(3) Exhibits
The exhibits of this Annual Report on Form 10-K included herein are set forth below.
| Exhibit Number | Exhibit | |||||||
| Amended and Restated Memorandum and Articles of Association of Pentair plc (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on May 9, 2017 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of December 16, 2021, among Pentair plc, Pentair Finance S.à r.l., Pentair, Inc. and the lenders and agents party thereto (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on December 20, 2021 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Amendment No. 1, dated as of December 23, 2022, to Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of December 16, 2021, among Pentair plc, Pentair Finance S.à r.l., Pentair, Inc. and the lenders and agents party thereto (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2022 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Indenture, dated as of September 16, 2015, among Pentair Finance S.A. (as Issuer), Pentair plc (as Parent and Guarantor), Pentair Investments Switzerland GmbH (as Guarantor) and U.S. Bank National Association (as Trustee) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on September 16, 2015 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Third Supplemental Indenture, dated as of September 16, 2015, among Pentair Finance S.A. (as Issuer), Pentair plc (as Parent and Guarantor), Pentair Investments Switzerland GmbH (as Guarantor) and U.S. Bank National Association (as Trustee) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on September 16, 2015 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Fifth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 26, 2017, among Pentair Finance S.A., Pentair plc, Pentair Investments Switzerland GmbH and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on May 31, 2017 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Sixth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 21, 2019, among Pentair Finance S.à r.l. (as Issuer), Pentair plc (as Parent and Guarantor), Pentair Investments Switzerland GmbH (as Guarantor) and U.S. Bank National Association (as Trustee) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 21, 2019 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
82
| Seventh Supplemental Indenture, dated as of June 22, 2020, among Pentair Finance S.à r.l. (as Issuer), Pentair plc (as Parent and Guarantor), Pentair Investments Switzerland GmbH (as Guarantor) and U.S. Bank National Association (as Trustee) (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on July 23, 2020 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Eighth Supplemental Indenture, dated as of July 8, 2022, among Pentair Finance S.à r.l., Pentair plc and U.S. Bank Trust Company, National Association, as trustee (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on July 8, 2022 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Loan Agreement, dated as of March 24, 2022, among Pentair plc, Pentair Finance S.à r.l., and the lenders and agents party thereto (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on March 25, 2022 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Amendment No. 1, dated as of June 30, 2022, to Loan Agreement, among Pentair plc, Pentair Finance S.à r.l., and the lenders and agents party thereto (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 30, 2022 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Description of Securities. | ||||||||
| Tax Matters Agreement, dated as of April 27, 2018, by and between Pentair plc and nVent Electric plc (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on April 30, 2018 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Pentair plc 2012 Stock and Incentive Plan, as amended and restated effective as of January 1, 2017. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2016 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Executive Officer Stock Option Grant Agreement for grants made prior to January 1, 2017 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 in the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 3, 2014 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Non-Employee Director Stock Option Grant Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 in the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 3, 2014 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Key Executive Employment and Severance Agreement for John L. Stauch (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 in the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Pentair plc for the quarter ended June 30, 2018 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Key Executive Employment and Severance Agreement for Karla C. Robertson, Philip M. Rolchigo, Robert P. Fishman, Jerome O. Pedretti and Stephen J. Pilla (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 in the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Pentair plc for the quarter ended June 30, 2018 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Amendment to Key Executive Employment and Severance Agreement, as of January 1, 2021, for John L. Stauch, Karla C. Robertson, Philip M. Rolchigo, Robert P. Fishman, Jerome O. Pedretti and Stephen J. Pilla.* | ||||||||
| Form of Key Executive Employment and Severance Agreement for Adrian C. Chiu, Tanya L. Hooper and De’Mon L. Wiggins (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2021 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Amendment to Key Executive Employment and Severance Agreement, as of November 30, 2023, for John L. Stauch, Karla C. Robertson, Philip M. Rolchigo, Robert P. Fishman, Jerome O. Pedretti, Stephen J. Pilla, Adrian C. Chiu, Tanya L. Hooper and De’Mon L. Wiggins.* | ||||||||
| Pentair plc Compensation Plan for Non-Employee Directors, as amended and restated (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 in the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 3, 2014 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Pentair plc Employee Stock Purchase and Bonus Plan, as amended and restated effective as of January 1, 2021. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2020 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Pentair, Inc. Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Plan, as amended and restated (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2018 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Trust Agreement for Pentair, Inc. Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Plan between Pentair, Inc. and Fidelity Management Trust Company (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 contained in the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair, Inc. for the year ended December 31, 1995 (File No. 000-04689)).* | ||||||||
| Pentair, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan effective January 1, 2009, as amended and restated (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 in the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 3, 2014 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
83
| Pentair, Inc. Restoration Plan effective January 1, 2009, as amended and restated (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 in the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 3, 2014 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Deed of Indemnification for directors and executive officers of Pentair plc (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 in the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 3, 2014 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Indemnification Agreement for directors and executive officers of Pentair plc (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 in the Current Report on Form 8-K of Pentair plc filed with the Commission on June 3, 2014 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Executive Officer Stock Option Grant Agreement for grants made on or after January 1, 2017 and prior to February 26, 2018 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2016 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Executive Officer Stock Option Award Agreement for grants made on or after February 26, 2018 and prior to May 5, 2020 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Pentair plc for the quarter ended March 31, 2018 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan, effective as of May 5, 2020 (Incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A of Pentair plc filed on March 20, 2020 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Employee Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement under the Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan.* | ||||||||
| Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement under the Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Registration Statement on Form S-8 of Pentair plc (Reg. No. 333-238544)).* | ||||||||
| Form of Key Talent Award Agreement under the Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan.* | ||||||||
| Form of Stock Option Award Agreement under the Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan.* | ||||||||
| Form of Performance Share Unit Award Agreement under the Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan.* | ||||||||
| Pentair plc Executive Officer Severance Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.30 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2020 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| Amendment No. 1 to the Pentair plc 2020 Share and Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Pentair plc for the year ended December 31, 2020 (File No. 001-11625)).* | ||||||||
| List of Pentair plc subsidiaries. | ||||||||
| List of Guarantors and Subsidiary Issuers of Guaranteed Securities. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 22 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q of Pentair plc for the quarter ended September 30, 2022 (File No. 001-11625)). | ||||||||
| Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm — Deloitte & Touche LLP. | ||||||||
| Power of attorney. | ||||||||
| Certification of Chief Executive Officer. | ||||||||
| Certification of Chief Financial Officer. | ||||||||
| Certification of Chief Executive Officer, Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||||||||
| Certification of Chief Financial Officer, Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||||||||
| Compensation Recovery Policy. | ||||||||
| 101 | The following materials from Pentair plc’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023 are filed herewith, formatted in iXBRL (Inline Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, (ii) the Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2023 and 2022, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for the years ended December 31, 2023, 2022 and 2021, (v) the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements, and (vi) the information included in Part II, Item 9B(b). The instance document does not appear in the interactive data file because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document. | |||||||
84
| 104 | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101). | |||||||
| * | Denotes a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. | ||||
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY
None.
85
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, on February 20, 2024.
| PENTAIR PLC | ||||||||
| By | /s/ Robert P. Fishman | |||||||
| Robert P. Fishman | ||||||||
| Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer | ||||||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities indicated, on February 20, 2024.
| Signature | Title | |||||||
| /s/ John L. Stauch | President and Chief Executive Officer, Director | |||||||
| John L. Stauch | ||||||||
| /s/ Robert P. Fishman | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer | |||||||
| Robert P. Fishman | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| Mona Abutaleb Stephenson | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| Melissa Barra | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| Tracey Doi | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| T. Michael Glenn | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| Theodore L. Harris | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| David A. Jones | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| Gregory E. Knight | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| Michael T. Speetzen | ||||||||
| * | Director | |||||||
| Billie I. Williamson | ||||||||
| *By | /s/ Karla C. Robertson | ||||||||||
| Karla C. Robertson | |||||||||||
| Attorney-in-fact | |||||||||||
86