SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009
Commission File Number 0-16211
DENTSPLY International Inc
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 39-1434669 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 221 West Philadelphia Street, York, PA | 17405-0872 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant's telephone number, including area code: (717) 845-7511
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| None | Not applicable |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
Common Stock, par value $.01 per share (Title of class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer. See definition of “accelerated filer and large accelerated filer” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | x | Accelerated filer | ¨ | Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | Smaller reporting company | ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
Yes o No x
The aggregate market value of the voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant computed by reference to the closing price as of the last business day of the registrants most recently completed second quarter June 30, 2009, was $4,762,176,900.
The number of shares of the registrant's Common Stock outstanding as of the close of business on February 16, 2010 was 147,173,059.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Certain portions of the definitive Proxy Statement of DENTSPLY International Inc (the “Proxy Statement”) to be used in connection with the 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K to the extent provided herein. Except as specifically incorporated by reference herein the Proxy Statement is not deemed to be filed as part of this Form 10-K.
PART I
Item 1. Business
The nature and geographic scope of DENTSPLY International Inc’s (“DENTSPLY” or the “Company”) business subjects it to changing economic, competitive, regulatory and technological risks and uncertainties. In accordance with the “Safe Harbor” provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, the Company provides the following cautionary remarks regarding important factors, which, among others, could cause future results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements, expectations and assumptions expressed or implied herein. All forward-looking statements made by the Company are subject to risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance. These forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause the Company’s actual results, performance and achievements, or industry results to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. These statements are identified by the use of such terms as “may,” “could,” “expect,” “intend,” “believe,” “plan,” “estimate,” “forecast,” “project,” “anticipate” or words of similar expression.
Investors are cautioned that forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties which may materially affect the Company's business and prospects, and should be read in conjunction with the risk factors and uncertainties discussed within Item 1A, Part I of this Form 10-K. Investors are further cautioned that the risk factors in Item 1A, Part I of this Form 10-K may not be exhaustive and that many of these factors are beyond the Company’s ability to control or predict. Accordingly, forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as a prediction of actual results. The Company undertakes no duty and has no obligation to update forward-looking statements.
History and Overview
DENTSPLY, a Delaware corporation, was created in 1899 as a manufacturer and distributor of artificial teeth, dental equipment and dental consumable products. Today, the Company continues to primarily focus on dental consumable products, dental laboratory products and dental specialty products.
DENTSPLY believes it is the world's largest designer, developer, manufacturer and marketer of a broad range of products for the dental market. The Company's worldwide headquarters and executive offices are located in York, Pennsylvania.
Sales of the Company's dental products accounted for approximately 97% of DENTSPLY's consolidated net sales, excluding precious metal content, for the year ended December 31, 2009. The remaining 3% of consolidated net sales, excluding precious metal content, are related to materials sold to the investment casting industry and various medical products. The presentation of net sales, excluding precious metal content, is considered a measure not calculated in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US GAAP”), and is therefore considered a non-US GAAP measure. This non-US GAAP measure is discussed further in “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and a reconciliation of net sales to net sales, excluding precious metal content, is provided.
Through the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company conducted its business through four operating segments, all of which were primarily engaged in the design, manufacture and distribution of dental products in three principal categories: 1) dental consumable products, 2) dental laboratory products and 3) dental specialty products.
In addition to the United States (“U.S.”), the Company conducts its business in over 120 foreign countries, principally through its foreign subsidiaries. DENTSPLY has a long-established presence in Canada and in the European market, particularly in Germany, Switzerland, France, Italy and the United Kingdom. The Company also has a significant market presence in Central and South America, South Africa and the Pacific Rim. DENTSPLY has also established marketing activities in Moscow, Russia to serve the countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States (“CIS”).
For 2009, 2008 and 2007, the Company's net sales, excluding precious metal content, to customers outside the U.S., including export sales, accounted for approximately 62%, 62% and 59%, respectively, of consolidated net sales, excluding precious metal content. Reference is made to the information about the Company's U.S. and foreign sales by shipment origin set forth in Note 4, Segment and Geographic Information, to the consolidated financial statements in this Form 10-K.
- 2 - -
Principal Products
The worldwide professional dental industry encompasses the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disease and ailments of the teeth, gums and supporting bone. DENTSPLY's principal dental product categories are dental consumable products, dental laboratory products and dental specialty products. These products are produced by the Company in the U.S. and internationally and are distributed throughout the world under some of the most well-established brand names and trademarks in the industry, including ANKYLOS®, AQUASIL, AQUASIL ULTRA, CALIBRA®, CAULK®, CAVITRON®, CERAMCO®, CERCON®, CITANEST®, DELTON®, DENTSPLY®, DETREY®, DYRACT®, ECLIPSE®, ELEPHANT®, ESTHET.X®, FRIADENT®, FRIALIT®, GENIE®, GOLDEN GATE®, IN-OVATION®, INTERACTIVE MYSTIQUE®, MAILLEFER®, MIDWEST®, NUPRO®, ORAQIX®, PEPGEN P-15®, POLOCAINE®, PORTRAIT®, PRIME & BOND®, PROFILE®, PROTAPER®, RINN®, R&R®, SANI-TIP®, SHADEPILOT™, STYLUS™, SULTAN®, SUREFIL®, THERMAFIL®, TRUBYTE®, XENO®, XIVE®, XYLOCAINE®, and ZHERMACK®.
Dental Consumable Products
Dental consumable products consist of dental sundries and small equipment used in dental offices for the treatment of patients. Sales of dental consumable products, excluding precious metal content, accounted for approximately 35%, 34% and 35% of the Company’s consolidated net sales, excluding precious metal content, for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
DENTSPLY’s dental sundry products in the dental consumable products category include dental anesthetics, prophylaxis paste, dental sealants, impression materials, restorative materials, tooth whiteners and topical fluoride. The Company manufactures thousands of different dental sundry consumable products marketed under more than one hundred brand names.
Small equipment products in the dental consumable products category consist of various durable goods used in dental offices for the treatment of patients. DENTSPLY’s small equipment products include high and low speed handpieces, intraoral curing light systems, dental diagnostic systems and ultrasonic scalers and polishers.
Dental Laboratory Products
Dental laboratory products are used in the preparation of dental appliances by dental laboratories. Net sales of dental laboratory products, excluding precious metal content, accounted for approximately 17%, 18% and 19% of the Company’s consolidated net sales, excluding precious metal content, for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
DENTSPLY’s products in the dental laboratory products category include dental prosthetics, including artificial teeth, precious metal dental alloys, dental ceramics and crown and bridge materials. Equipment in this category includes computer aided machining (CAM) ceramic systems and porcelain furnaces.
Dental Specialty Products
Dental specialty products are specialized treatment products used within the dental office and laboratory settings. Net sales of dental specialty products, excluding precious metal content, accounted for approximately 45%, 45% and 43% of the Company’s consolidated net sales, excluding precious metal content, for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. DENTSPLY’s products in this category include endodontic (root canal) instruments and materials, implants and related products, bone grafting materials, 3D digital implantology and orthodontic appliances and accessories.
Markets, Sales and Distribution
DENTSPLY distributes approximately 56% of its dental products through domestic and foreign distributors, dealers and importers. However, certain highly technical products such as precious metal dental alloys, dental ceramics, crown and bridge porcelain products, endodontic instruments and materials, orthodontic appliances, implants, and bone substitute and grafting materials are sold directly to the dental laboratory or dental professionals in some markets. During 2009, 2008 and 2007, one customer, Henry Schein Incorporated, a dental distributor, accounted for 11%, 11% and 12%, respectively, of DENTSPLY’s consolidated net sales. No other single customer represented ten percent or more of DENTSPLY’s consolidated net sales during 2009, 2008 or 2007.
Reference is made to the information about the Company's foreign and domestic operations and export sales set forth in Note 4, Segment and Geographic Information, to the consolidated financial statements in this Form 10-K.
Although many of its sales are made to distributors, dealers and importers, DENTSPLY focuses its marketing efforts on the dentists, dental hygienists, dental assistants, dental laboratories and dental schools who are the end users of its products. As part of this end-user “pull through” marketing approach, DENTSPLY employs approximately 2,700 highly trained, product-specific sales and technical staff to provide comprehensive marketing and service tailored to the particular sales and technical support requirements of the distributors, dealers and the end users. The Company conducts extensive distributor, dealer and end-user marketing programs. Additionally, the Company trains laboratory technicians, dental hygienists, dental assistants and dentists in the proper use of its products and introduces them to the latest technological developments at its educational courses located throughout the world. The Company also maintains ongoing relationships with various dental associations and recognized worldwide opinion leaders in the dental field, although there is no assurance that these influential dental professionals will continue to support the Company’s products.
- 3 - -
DENTSPLY believes that demand in a given geographic market for dental procedures and products vary according to the stage of social, economic and technical development of the particular market. Geographic markets for DENTSPLY's dental products can be categorized into the following two stages of development:
The U.S., Canada, Western Europe, Japan, Australia and certain other countries are highly developed markets that demand the most advanced dental procedures and products and have the highest level of expenditures for dental care. In these markets, the focus of dental care is increasingly upon preventive care and specialized dentistry. In addition to basic procedures, such as the excavation and filling of cavities, tooth extraction and denture replacement, dental professionals perform an increasing volume of preventive and cosmetic procedures. These markets require varied and complex dental products, utilize sophisticated diagnostic and imaging equipment, and demand high levels of attention to protect against infection and patient cross-contamination.
In certain countries in Central America, South America, Eastern Europe, Pacific Rim, Middle East and Africa, most dental care is often limited to the excavation and filling of cavities and other restorative techniques, reflecting more modest per capita expenditures for dental care. These markets demand diverse products, such as high and low speed handpieces, restorative compounds, finishing devices, custom restorative devices, basic surgical instruments, bridgework and artificial teeth for dentures. However, there is also a portion of the population in these markets that receive excellent dental care similar to that received in developed countries and expect to receive the best dental care available.
The Company offers products and equipment for use in markets at both of these stages of development. The Company believes that demand for more technically advanced products will increase as each of these markets develop. The Company also believes that its recognized brand names, high quality and innovative products, technical support services and strong international distribution capabilities position it well to take advantage of any opportunities for growth in all of the markets that it serves.
The Company believes that the market for its products will grow over the long-term based on the following factors:
| • | Increasing worldwide population. |
| • | Growth of the population 65 or older – The percentage of the U.S., European, Japanese and other regions population over age 65 is expected to nearly double by the year 2030. In addition to having significant needs for dental care, the elderly are well positioned to pay for the required procedures since they control sizable amounts of discretionary income. |
| • | Natural teeth are being retained longer – Individuals with natural teeth are much more likely to visit a dentist in a given year than those without any natural teeth remaining. |
| • | The changing dental practice in North America and Western Europe – Dentistry in North America and Western Europe has been transformed from a profession primarily dealing with pain, infections and tooth decay to one with increased emphasis on preventive care and cosmetic dentistry. |
| • | Per capita and discretionary incomes are increasing in emerging nations – As personal incomes continue to rise in the emerging nations of the Pacific Rim, CIS and Latin America, healthcare, including dental services, are a growing priority. |
| • | The Company’s business is less susceptible than other industries to general downturns in the economies in which it operates. Many of the products the Company offers relate to dental procedures that are considered necessary by patients regardless of the economic environment. Dental specialty products and products that support discretionary dental procedures are the most susceptible to recessionary conditions. |
Product Development
Technological innovation and successful product development are critical to strengthening the Company’s prominent position in worldwide dental markets, maintaining its leadership positions in product categories where it has a high market share and increasing market share in product categories where gains are possible. While many of DENTSPLY’s existing products undergo evolutionary improvements, the Company also continues to successfully launch innovative products that represent fundamental change.
- 4 - -
New advances in technology are also anticipated to have a significant influence on future products in dentistry. As a result, the Company pursues research and development initiatives to support this technological development, including collaborations with external research institutions and dental schools. Through its own internal research centers as well as through its collaborations with external research institutions and dental schools, the Company directly invested approximately $53.6 million, $52.3 million and $46.8 million for 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, in connection with the development of new products, improvement of existing products and advances in technology. The continued development of these areas is a critical step in meeting the Company's strategic goal as a leader in defining the future of dentistry.
In addition to the direct investment in product development and improvement, the Company also invests in these activities through acquisitions, by entering into licensing agreements and by purchasing technologies developed by third parties.
Acquisition Activities
DENTSPLY believes that the dental products industry continues to experience consolidation with respect to both product manufacturing and distribution, although it continues to be fragmented creating a number of acquisition opportunities. In 2009, the Company made an additional earn-out payment on an acquisition completed in 2007 and purchased a small sales and marketing organization of 3D digital implantology products. The Company made several acquisitions in 2008, including a 60% ownership in Zhermack S.p.A., a dental consumables manufacturer and sales and marketing organization; E.S. Holding N.V., a manufacturer and sales and marketing organization of dental laboratory products; Dental Depot Lomberg B.V., a sales and marketing organization of orthodontic products; and Apollonia & Fama Implant S.r.l., a sales and marketing organization of dental implant products. The Company also purchased an additional interest in Materialise Dental in 2008.
The Company continues to view acquisitions as a key part of its growth strategy. These acquisition activities are intended to supplement the Company's core growth and assure ongoing expansion of its business, including new technologies, additional products, and geographic breadth.
Operating and Technical Expertise
DENTSPLY believes that its manufacturing capabilities are important to its success. The manufacturing process of the Company's products requires substantial and varied technical expertise. Complex materials technology and processes are necessary to manufacture the Company's products. The Company continues to automate its global manufacturing operations in order to remain a low cost producer.
Financing
DENTSPLY’s cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments increased by $246.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 to $450.4 million. DENTSPLY's total long-term debt, including the current portion, at December 31, 2009 and 2008 was $453.7 million and $427.7 million, respectively, and the ratios of long-term debt, including the current portion, to total capitalization were 19.2% and 20.5%. DENTSPLY defines total capitalization as the sum of total long-term debt, including the current portion, plus total equity. The Company’s long-term borrowings increased by a net of $26.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2009. This net change included a net increase in borrowings of $30.2 million during the year ended 2009, less a decrease of $4.2 million due to exchange rate fluctuations on debt denominated in foreign currencies. The Company may incur additional debt in the future, including, but not limited to, the funding of additional acquisitions and capital expenditures.
Additional information about DENTSPLY's working capital, liquidity and capital resources is provided in “Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in this Form 10-K.
Competition
The Company conducts its operations, both domestic and foreign, under highly competitive market conditions. Competition in the dental products industry is based primarily upon product performance, quality, safety and ease of use, as well as price, customer service, innovation and acceptance by professionals and technicians. DENTSPLY believes that its principal strengths include its well-established brand names, its reputation for high quality and innovative products, its leadership in product development and manufacturing, its commitment to customer satisfaction and support of the Company’s products by dental professionals.
The size and number of the Company's competitors vary by product line and from region to region. There are many companies that produce some, but not all, of the same types of products as those produced by the Company.
- 5 - -
Regulation
The Company's products are subject to regulation by, among other governmental entities, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the “FDA”). In general, if a dental “device” is subject to FDA regulation, compliance with the FDA's requirements constitutes compliance with corresponding state regulations. In order to ensure that dental products distributed for human use in the U.S. are safe and effective, the FDA regulates the introduction, manufacture, advertising, labeling, packaging, marketing and distribution of, and record-keeping for, such products. The introduction and sale of dental products of the types produced by the Company are also subject to government regulation in the various foreign countries in which they are produced or sold. DENTSPLY believes that it is in substantial compliance with the FDA and foreign regulatory requirements that are applicable to its products and manufacturing operations.
Dental devices of the types sold by DENTSPLY are generally classified by the FDA into a category that renders them subject only to general controls that apply to all medical devices, including regulations regarding alteration, misbranding, notification, record-keeping and good manufacturing practices. In the European Union, DENTSPLY's products are subject to the medical devices laws of the various member states, which are based on a Directive of the European Commission. Such laws generally regulate the safety of the products in a similar way to the FDA regulations. DENTSPLY products in Europe bear the CE mark showing that such products adhere to the European regulations.
All dental amalgam filling materials, including those manufactured and sold by DENTSPLY, contain mercury. Various groups have alleged that dental amalgam containing mercury is harmful to human health and have actively lobbied state and federal lawmakers and regulators to pass laws or adopt regulatory changes restricting the use, or requiring a warning against alleged potential risks, of dental amalgams. The FDA's Dental Devices Classification Panel, the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Public Health Service have each indicated that no direct hazard to humans from exposure to dental amalgams has been demonstrated. In response to concerns raised by certain consumer groups regarding dental amalgam, the FDA formed an advisory committee in 2006 to review peer-reviewed scientific literature on the safety of dental amalgam. In July 2009, the FDA concluded its review of dental amalgam, confirming its use as a safe and effective restorative material. Also, as a result of this review, the FDA classified amalgam and its component parts, elemental mercury and powder alloy, as a Class II medical device. Previously there was no classification for encapsulated amalgam and dental mercury (Class I) and alloy (Class II) were classified separately. This new regulation places encapsulated amalgam in the same class of devices as most other restorative materials, including composite and gold fillings.
In Europe, particularly in Scandinavia and Germany, the contents of mercury in amalgam filling materials have been the subject of public discussion. As a consequence, in 1994 the German health authorities required suppliers of dental amalgam to amend the instructions for use for amalgam filling materials to include a precaution against the use of amalgam for children less than eighteen years of age and to women of childbearing age. Additionally, some groups have asserted that the use of dental amalgam should be prohibited because of concerns about environmental impact from the disposition of mercury within dental amalgam, which has resulted in the sale of mercury containing products being banned in Sweden and severely curtailed in Norway. DENTSPLY also manufactures and sells non-amalgam dental filling materials that do not contain mercury.
Sources and Supply of Raw Materials and Finished Goods
The Company manufactures the majority of the products sold by the Company. All of the raw materials used by the Company in the manufacture of its products are purchased from various suppliers and are typically available from numerous sources. No single supplier accounts for a significant percentage of DENTSPLY's raw material requirements. In addition to those products both manufactured and sold by the Company, some finished goods products sold by the Company are purchased from third party suppliers. Of these finished goods products purchased from third party suppliers, a significant portion of the Company’s injectable anesthetic products, orthodontic products and dental cutting instruments are purchased from a limited number of suppliers.
Intellectual Property
Products manufactured by DENTSPLY are sold primarily under its own trademarks and trade names. DENTSPLY also owns and maintains more than 2,000 patents throughout the world and is licensed under a small number of patents owned by others.
DENTSPLY's policy is to protect its products and technology through patents and trademark registrations in the U.S. and in significant international markets for its products. The Company carefully monitors trademark use worldwide and promotes enforcement of its patents and trademarks in a manner that is designed to balance the cost of such protection against obtaining the greatest value for the Company. DENTSPLY believes its patents and trademark properties are important and contribute to the Company's marketing position but it does not consider its overall business to be materially dependent upon any individual patent or trademark.
- 6 - -
Employees
As of December 31, 2009, the Company and its subsidiaries employed approximately 9,300 employees. A small percentage of the Company's U. S. employees are represented by labor unions. A facility in Des Plaines, Illinois is represented by the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers AFL-CIO, under a collective bargaining agreement that expires on May 31, 2012. Additionally, the Company’s Ransom & Randolph facility in Maumee, Ohio is represented by Local No. 12 of the International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agriculture Implement Workers of America under a collective bargaining agreement that expires on January 31, 2012. In Germany, approximately 45% of DeguDent employees, approximately 30% of Friadent employees, approximately 23% of VDW employees and approximately 30% of DeTrey employees are represented by labor unions. The Company provides pension and postretirement benefits to many of its employees (see Note 13, Benefits Plans, to the consolidated financial statements). The Company believes that its relationship with its employees is good.
Environmental Matters
DENTSPLY believes that its operations comply in all material respects with applicable environmental laws and regulations. Maintaining this level of compliance has not had, and is not expected to have, a material effect on the Company's capital expenditures or on its business.
Other Factors Affecting the Business
The Company’s business is subject to quarterly fluctuations of net sales and operating profits. The Company typically implements most of its price changes early in the fourth quarter or beginning of the year. Price changes, other marketing and promotional programs as well as the management of inventory levels by distributors and the implementation of strategic initiatives, may impact sales levels in a given period. Sales for the industry and the Company are generally strongest in the second and fourth calendar quarters and weaker in the first and third calendar quarters, due to the effects of the items noted above and due to the impact of summer holidays and vacations, particularly throughout Europe.
Securities and Exchange Act Reports
DENTSPLY makes available free of charge through its website at www.DENTSPLY.com its annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to these reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as soon as reasonably practicable after such materials are filed with or furnished to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
The public may read and copy any materials the Company files with the SEC at its Public Reference Room at the following address:
The Securities and Exchange Commission
100 F Street, NE
Washington, D.C. 20549
The public may obtain information on the operation of this Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. In addition, since the Company is an electronic filer, the public may access reports, the proxy and information statements and other information filed or furnished by the Company at the Internet site maintained by the SEC (http://www.sec.gov).
- 7 - -
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Following are the significant risk factors that could materially impact DENTSPLY’s business, financial condition or future results. The order in which these factors appear should not be construed to indicate its relative importance or priority.
Negative changes could occur in the dental markets, the general economic environments, or government reimbursement or regulatory programs of the regions in which the Company operates.
The success of the Company is largely dependent upon the continued strength of dental markets and is also somewhat dependent upon the general economic environments of the regions in which it operates. Negative changes to these markets and economies could materially impact the Company's results of operations and financial condition. In addition, many of the Company's markets are affected by government reimbursement and regulatory programs. In certain markets, particularly in the European Union, government and regulatory programs have a more significant impact than other markets. Changes to these programs could have a positive or negative impact on the Company's results.
Prolonged negative economic conditions in domestic and global markets may adversely affect the Company’s suppliers, customers and consumers, which could harm the Company’s financial position.
Prolonged negative changes in domestic and global economic conditions or disruptions of either or both of the financial and credit markets may affect the Company’s supply chain and the customers and consumers of the Company’s products and may have a material adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
Due to the Company’s international operations, the Company is exposed to the risk of changes in interest and foreign exchange rates.
DENTSPLY, with its significant international operations, is subject to fluctuations in exchange rates of various foreign currencies and other risks associated with foreign trade and the impact of currency fluctuations in any given period can be favorable or unfavorable. The Company’s balance sheet includes debt and net investment hedges that are sensitive to movements in interest and foreign exchange rates. Changes in interest rates and foreign exchange rates may have an adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
Volatility in the capital markets or investment vehicles could limit the Company’s ability to access capital or could raise the cost of capital.
Although the Company has had continued positive operating cash flow, a disruption in the credit markets may reduce sources of liquidity available to the Company. The Company relies on multiple financial institutions to provide funding pursuant to existing and/or future credit agreements, and those institutions may not be able to provide funding in a timely manner, or at all, when the Company requires it. The cost of or lack of available credit could impact the Company’s ability to develop sufficient liquidity to maintain or grow the Company, which in turn may adversely affect the Company’s businesses and results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
The Company also manages cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments through various institutions. There may be a risk of loss on investments based on the volatility of the underlying instruments that will not allow the Company to recover the full principal of its investments.
The market price for the Company’s common stock may be volatile.
DENTSPLY experiences fluctuations in quarterly sales and earnings. As a result, the Company may fail to meet or exceed the expectations of securities analysts and investors, which could cause its stock price to decline. The Company’s business is subject to quarterly fluctuations with net sales and operating profits historically being higher in the second and fourth quarters. The Company typically implements most of its price changes early in the fourth quarter or beginning of the year. These price changes, other marketing and promotional programs, which are offered to customers from time to time in the ordinary course of business, the management of inventory levels by distributors and the implementation of strategic initiatives, may impact sales levels in a given period. Net sales and operating profits generally have been lower in the first and third quarters, primarily due not only to increased sales in the quarters preceding the first and third quarters, but also due to the impact of summer holidays and vacations, particularly throughout Europe.
- 8 - -
In addition to fluctuations in quarterly earnings, a variety of other factors may have a significant impact on the market price of DENTSPLY’s common stock causing volatility. These factors include, but are not necessarily limited to, the publication of earnings estimates or other research reports and speculation in the press or investment community; changes in the Company’s industry and competitors; the Company’s financial condition and cash flows; any future issuances of DENTSPLY’s common stock, which may include primary offerings for cash, stock splits, issuances in connection with business acquisitions, restricted stock and the grant or exercise of stock options from time to time; general market and economic conditions; and any outbreak or escalation of hostilities in geographical areas the Company does business.
Also, the NASDAQ National Market can experience extreme price and volume fluctuations that can be unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of the companies listed on the NASDAQ. Broad market and industry factors may negatively affect the market price of the Company’s common stock, regardless of actual operating performance. In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against companies. This type of litigation, if instituted, could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources, which could harm the Company’s business.
The dental supplies market is highly competitive, and there is no guarantee that the Company can compete successfully.
The worldwide market for dental supplies is highly competitive. There can be no assurance that the Company will successfully identify new product opportunities and develop and market new products successfully, or that new products and technologies introduced by competitors will not render the Company's products obsolete or noncompetitive. Additionally, the size and number of the Company's competitors vary by product line and from region to region. There are many companies that produce some, but not all, of the same types of products as those produced by the Company. Certain of DENTSPLY's competitors may have greater resources than does the Company.
The Company may be unable to develop innovative products or obtain regulatory approval for new products.
DENTSPLY has identified new products as an important part of its growth opportunities. There can be no assurance that DENTSPLY will be able to continue to develop innovative products and that regulatory approval of any new products will be obtained, or that if such approvals are obtained, such products will be favorably accepted in the marketplace. Additionally, there is no assurance that entirely new technology or approaches to dental treatment or competitors’ new products will not be introduced that could render the Company's products obsolete.
The Company may fail to comply with regulations issued by the FDA and similar foreign regulatory agencies.
DENTSPLY's business is subject to periodic review and inspection by the FDA and similar foreign authorities to monitor DENTSPLY's compliance with the regulations administered by such authorities. There can be no assurance that these authorities will not raise compliance concerns. Failure to satisfy any such requirements can result in governmental enforcement actions, including possible product seizure, injunction and/or criminal or civil proceedings.
Challenges may be asserted against the Company’s dental amalgam product.
All dental amalgam filling materials, including those manufactured and sold by DENTSPLY, contain mercury. Some groups have asserted that amalgam should be discontinued because of its mercury content and/or that disposal of mercury containing products may be harmful to the environment. If governmental authorities elect to place restrictions or significant regulations on the sale and/or disposal of dental amalgam, that could have an adverse impact on the Company’s sales of dental amalgam.
The Company may be unable to obtain a supply for certain finished goods purchased from third parties.
A significant portion of the Company’s injectable anesthetic products, orthodontic products, dental cutting instruments and certain other products and raw materials are purchased from a limited number of suppliers. As there are a limited number of suppliers for these products, there can be no assurance that the Company will be able to obtain an adequate supply of these products and raw materials in the future.
- 9 - -
The Company’s expansion through acquisition involves risks and may not result in the expected benefits.
The Company continues to view acquisitions as a key part of its growth strategy. The Company continues to be active in evaluating potential acquisitions although there is no assurance that these efforts will result in completed transactions as there are many factors that affect the success of such activities. If the Company does succeed in acquiring a business or product, there can be no assurance that the Company will achieve any of the benefits that it might anticipate from such an acquisition and the attention and effort devoted to the integration of an acquired business could divert management’s attention from normal business operations. If the Company makes acquisitions, it may incur debt, assume contingent liabilities or create additional expenses, any of which might adversely affect its financial results. Any financing that the Company might need for acquisitions may only be available to it on terms that restrict its business or that impose additional costs that reduce its operating results.
Changes in, or interpretations of, accounting principles could result in unfavorable accounting charges.
The Company prepares its consolidated financial statements in accordance with US GAAP. These principles are subject to interpretation by the SEC and various bodies formed to interpret and create appropriate accounting principles. Market conditions have prompted accounting standard setters to issue new guidance which further interprets or seeks to revise accounting pronouncements related to financial instruments, structures or transactions as well as to issue new standards expanding disclosures. It is possible that future accounting standards the Company is required to adopt could change the current accounting treatment applied to the consolidated financial statements and that such changes could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
If the Company’s goodwill or amortizable intangible assets become impaired, the Company may be required to record a significant charge to earnings.
Under US GAAP, the Company reviews its goodwill and amortizable intangible assets for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. Additionally, goodwill is required to be tested for impairment at least annually. The valuations used to determine the fair values used to test goodwill or amortizable intangible assets are dependent upon various assumptions and reflect management’s best estimates. Net sales growth, discount rates, earnings multiples and future cash flows are critical assumptions used to determine these fair values. Slower net sales growth rates in the dental industry, an increase in discount rates, unfavorable changes in earnings multiples or a decline in future cash flows, among other factors, may cause a change in circumstances indicating that the carrying value of the Company’s goodwill or amortizable intangible assets may not be recoverable. The Company may be required to record a significant charge to earnings in the financial statements during the period in which any impairment of the Company’s goodwill or amortizable intangible assets is determined.
Changes in, or interpretations of, tax rules, structures, country profitability mix and regulations may adversely affect the Company’s effective tax rates.
The Company is a U.S. based multinational company subject to tax in multiple U.S. and foreign tax jurisdictions. Unanticipated changes in the Company’s tax rates could affect its future results of operations. The Company’s future effective tax rates could be unfavorably affected by changes in, or interpretation of, tax rules and regulations in the jurisdictions in which the Company does business, by structural changes in the Company’s businesses, by unanticipated decreases in the amount of revenue or earnings in countries with low statutory tax rates, by lapses of the availability of the U.S. research and development tax credit, or by changes in the valuation of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities.
The Company faces the inherent risk of litigation.
The Company’s business involves a risk of product liability and other types of claims, and from time to time the Company is named as a defendant in certain cases. The primary risks to which the Company is exposed are related to those products manufactured by the Company. The Company has insurance policies, including product liability insurance, covering these risks in amounts that are considered adequate; however, the Company cannot provide assurance that the maintained coverage is sufficient to cover future claims or that the coverage will be available in adequate amounts or at a reasonable cost. Also, other types of claims asserted against the Company may not be covered by insurance. A successful claim brought against the Company in excess of available insurance, or another type of claim which is uninsured or that results in significant adverse publicity against the Company, could harm its business and overall cash flows of the Company.
Various parties, including the Company, own and maintain patents and other intellectual property rights applicable to the dental field. Although the Company believes it operates in a manner that does not infringe upon any third party intellectual property rights, it is possible that a party could assert that one or more of the Company’s products infringe upon such party’s intellectual property and force the Company to pay damages and/or discontinue the sale of certain products.
The Company's success is dependent upon its management and employees.
The Company's success is dependent upon its management and employees. The loss of senior management employees or any failure to recruit and train needed managerial, sales and technical personnel, could have a material adverse effect on the Company.
- 10 - -
The Company may be unable to sustain the operational and technical expertise that is key to its success.
DENTSPLY believes that its manufacturing capabilities are important to its success. The manufacture of the Company's products requires substantial and varied technical expertise. Complex materials technology and processes are necessary to manufacture the Company's products. There can be no assurance that the Company will be able to maintain the necessary operational and technical expertise that is key to its success.
The Company may not generate sufficient cash flow to service its debt, pay its contractual obligations and operate the business.
DENTSPLY's ability to make payments on its indebtedness and contractual obligations, and to fund its operations depends on its future performance and financial results, which, to a certain extent, are subject to general economic, financial, competitive, regulatory and other factors and the interest rate environment that are beyond its control. Although Management believes that the Company has and will continue to have sufficient liquidity, there can be no assurance that DENTSPLY's business will generate sufficient cash flow from operations in the future to service its debt, pay its contractual obligations and operate its business.
The Company may not be able to repay its outstanding debt in the event that cross default provisions are triggered due to a breach of loan covenants.
DENTSPLY's existing borrowing documentation contains a number of covenants and financial ratios, which it is required to satisfy. The most restrictive of these covenants pertain to asset dispositions, maintenance of certain levels of net worth, and prescribed ratios of indebtedness to total capital and operating income excluding depreciation and amortization of interest expense. Any breach of any such covenants or restrictions would result in a default under the existing borrowing documentation that would permit the lenders to declare all borrowings under such documentation to be immediately due and payable and, through cross default provisions, would entitle DENTSPLY's other lenders to accelerate their loans. DENTSPLY may not be able to meet its obligations under its outstanding indebtedness in the event that any cross default provision is triggered.
Certain provisions in the Company’s governing documents may discourage third party offers to acquire DENTSPLY that might otherwise result in the Company’s stockholders receiving a premium over the market price of their shares.
Certain provisions of DENTSPLY's Certificate of Incorporation and By-laws and of Delaware law could have the effect of making it difficult for a third party to acquire control of DENTSPLY. Such provisions include the division of the Board of Directors of DENTSPLY into three classes, with the three-year term of a class expiring each year, a provision allowing the Board of Directors to issue preferred stock having rights senior to those of the common stock and certain procedural requirements which make it difficult for stockholders to amend DENTSPLY's By-laws and call special meetings of stockholders. In addition, members of DENTSPLY's management and participants in its Employee Stock Ownership Plan (“ESOP”) collectively own approximately 4% of the outstanding common stock of DENTSPLY.
Issues related to the quality and safety of the Company’s products, ingredients or packaging could cause a product recall resulting in harm to the Company’s reputation and negatively impacting the Company’s operating results.
The Company’s products generally maintain a good reputation with customers and end users. Issues related to quality and safety of products, ingredients or packaging, could jeopardize the Company’s image and reputation. Negative publicity related to these types of concerns, whether valid or not, might negatively impact demand for the Company’s products, or cause production and delivery disruptions. The Company may need to recall products if they become unfit for use. In addition, the Company could potentially be subject to litigation or government action, which could result in payment of fines or damages. Cost associated with these potential actions could negatively affect the Company’s operating results, financial condition and liquidity.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None
- 11 - -
Item 2. Properties
The following is a listing of DENTSPLY's principal manufacturing and distribution locations as of December 31, 2009:
Location | Function | Leased or Owned | ||
| United States: | ||||
| Milford, Delaware (1) | Manufacture of dental consumable products | Owned | ||
| Bradenton, Florida (3) | Manufacture of orthodontic accessory products | Leased | ||
| Baldwin, Georgia (3) | Manufacture of orthodontic accessory products | Leased | ||
| Des Plaines, Illinois (1) | Manufacture and assembly of dental handpieces | Leased | ||
| Elgin, Illinois (1) | Manufacture of dental x-ray film holders, film mounts and accessories | Owned/Leased | ||
| Bohemia, New York (3) | Manufacture and distribution of orthodontic products and materials | Leased | ||
| Maumee, Ohio (4) | Manufacture and distribution of investment casting products | Owned | ||
| Lancaster, Pennsylvania (5) | Distribution of dental products | Leased | ||
| York, Pennsylvania (4) | Manufacture and distribution of artificial teeth and other dental laboratory products | Owned | ||
| York, Pennsylvania (1) | Manufacture of small dental equipment, bone grafting products, and preventive dental products | Owned | ||
| Johnson City, Tennessee (3) | Manufacture and distribution of endodontic instruments and materials | Leased | ||
| Foreign: | ||||
| Beringen, Belgium (4) | Manufacture and distribution of dental products | Owned/Leased | ||
| Leuven, Belgium (4) | Manufacture and distribution of 3D digital implantology | Leased | ||
| Catanduva, Brazil (3) | Manufacture and distribution of dental anesthetic products | Owned | ||
| Petropolis, Brazil (3) | Manufacture and distribution of artificial teeth and dental consumable products | Owned | ||
| Shanghai, China (4) | Manufacture and distribution of dental products | Leased | ||
| Tianjin, China (2) | Manufacture and distribution of dental products | Leased | ||
| Ivry Sur-Seine, France (2) | Manufacture and distribution of investment casting products | Leased | ||
| Bohmte, Germany (4) | Manufacture and distribution of dental laboratory products | Owned |
- 12 - -
| Hanau, Germany (4) | Manufacture and distribution of precious metal dental | Owned | ||
| alloys, dental ceramics and dental implant products | ||||
| Konstanz, Germany (1) | Manufacture and distribution of dental consumable | Owned | ||
| products | ||||
| Mannheim, Germany (4) | Manufacture and distribution of dental | Owned/Leased | ||
| implant products | ||||
| Munich, Germany (3) | Manufacture and distribution of endodontic | Owned | ||
| instruments and materials | ||||
| Radolfzell, Germany (5) | Distribution of dental products | Leased | ||
| Rosbach, Germany (4) | Manufacture and distribution of dental ceramics | Owned | ||
| Badia Polesine, Italy (1) | Manufacture and distribution of dental consumable | Owned/Leased | ||
| products | ||||
| Nasu, Japan (2) | Manufacture and distribution of precious metal dental | Owned | ||
| alloys, dental consumable products and orthodontic | ||||
| products | ||||
| Hoorn, Netherlands (4) | Manufacture and distribution of precious metal | Owned | ||
| dental alloys and dental ceramics | ||||
| HA Soest, Netherlands (3) | Distribution of orthodontic products | Leased | ||
| Warsaw, Poland (1) | Manufacture and distribution of dental consumable | Owned | ||
| products | ||||
| Las Piedras, Puerto Rico (4) | Manufacture of crown and bridge materials | Owned | ||
| Ballaigues, Switzerland (3) | Manufacture and distribution of endodontic | Owned | ||
| instruments, plastic components and packaging material | ||||
Le Creux, Switzerland (3) | Manufacture and distribution of endodontic instruments | Owned |
| (1) | These properties are included in the U. S., Germany, and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses segment. |
| (2) | These properties are included in the France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses segment. |
| (3) | These properties are included in the Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/Orthodontics segment. |
| (4) | These properties are included in the Dental Laboratory Business/Implants/Non-Dental segment. |
| (5) | This property is a distribution warehouse not managed by named segments. |
- 13 - -
In addition, the Company maintains sales and distribution offices at certain of its foreign and domestic manufacturing facilities, as well as at various other U.S. and international locations. The Company maintains offices in Toronto, Mexico City, Paris, Rome, Weybridge, Hong Kong and Melbourne and other international locations. Most of these sites around the world that are used exclusively for sales and distribution are leased.
The Company also owns its corporate headquarters located in York, Pennsylvania.
DENTSPLY believes that its properties and facilities are well maintained and are generally suitable and adequate for the purposes for which they are used.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
Incorporated by reference to Part II, Item 8, Note 17, Commitments and Contingencies, to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Item 4. Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders
Not applicable.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the executive officers of the Company as of February 22, 2010.
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Bret W. Wise | 49 | Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Christopher T. Clark | 48 | President and Chief Operating Officer | ||
| William R. Jellison | 52 | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | ||
| James G. Mosch | 52 | Executive Vice President | ||
| Robert J. Size | 51 | Senior Vice President | ||
| Albert J. Sterkenburg | 46 | Senior Vice President | ||
| Brian M. Addison | 55 | Vice President, Secretary and General Counsel |
Bret W. Wise has served as Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of the Company since January 1, 2007 and also served as President in 2007 and 2008. Prior to that time, Mr. Wise served as President and Chief Operating Officer in 2006, as Executive Vice President in 2005 and Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from December 2002 through December 2004. Prior to that time, Mr. Wise was Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer with Ferro Corporation of Cleveland, OH (1999 - 2002), Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at WCI Steel, Inc., of Warren, OH, (1994 - 1999) and prior to that he was a partner with KPMG LLP. Mr. Wise is a Certified Public Accountant.
Christopher T. Clark has served as Chief Operating Officer of the Company since January 1, 2007, also serving as President since January 1, 2009 and as Executive Vice President in 2007 and 2008. Prior to that time, Mr. Clark served as Senior Vice President (2003 - 2005), as Vice President and General Manager of DENTSPLY’s global imaging business (1999 - 2002), as Vice President and General Manager of the Prosthetics Division (1996 - 1999), and as Director of Marketing of DENTSPLY’S Prosthetics Division (1992 - 1996). Prior to September 1992, Mr. Clark held various brand management positions with Proctor & Gamble.
William R. Jellison has served as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of the Company since January 2005, a position he also held from April 1998 until November 2002. From November 2002 until January 2005, Mr. Jellison served as a Senior Vice President with operating responsibilities. Prior to April 1998, Mr. Jellison held various financial management positions including Vice President of Finance, Treasurer and Corporate Controller for Donnelly Corporation of Holland, Michigan since 1980. Mr. Jellison is a Certified Management Accountant.
James G. Mosch has served as Executive Vice President since January 1, 2009, and prior to that as Senior Vice President since 2003. Prior to that, Mr. Mosch served as Vice President and General Manager of DENTSPLY’s Professional division, beginning in July 1994 when, he started with the Company. Prior to 1994, Mr. Mosch served in general management and marketing positions with Baxter International and American Hospital Supply Corporation.
- 14 - -
Robert J. Size has served as Senior Vice President since January 1, 2007. Prior to that, Mr. Size served as a Vice President (2006) and as Vice President and General Manager of DENTSPLY’s Caulk division beginning June 2003 through December 31, 2005. Prior to that time, he was the Chief Executive Officer and President of Superior MicroPowders and held various cross-functional and international leadership positions with The Cookson Group.
Albert J. Sterkenburg, D.D.S. has served as Senior Vice President since January 1, 2009. Prior to that, Dr. Sterkenburg served as Vice President (2006 - 2009), Vice President and General Manager of the DeguDent division (2003 - 2006) and Vice President and General Manger of the VDW division beginning in 2000. Prior to that time, he served in marketing and general management roles at Johnson & Johnson.
Brian M. Addison has served as Vice President, Secretary and General Counsel of the Company since January 1, 1998. Prior to that, he was Assistant Secretary and Corporate Counsel beginning in December 1994. Prior to that he was a Partner at the Harrisburg, Pennsylvania law firm of McNees, Wallace & Nurick, and prior to that he was Senior Counsel at Hershey Foods Corporation.
- 15 - -
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The information set forth under the caption “Supplemental Stock Information” is filed as part of this Form 10-K.
The Board of Directors has authorized the Company to repurchase shares under its stock repurchase program in an amount up to 17,000,000 shares of treasury stock. The table below contains certain information with respect to the repurchase of shares of the Company's common stock during the quarter ended December 31, 2009.
| Number of | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | Shares that | |||||||||||||||
| May be Purchased | ||||||||||||||||
| Total Number | Average Price | Total Cost | Under the Share | |||||||||||||
| of Shares | Paid Per | of Shares | Repurchase | |||||||||||||
| Period | Purchased | Share | Purchased | Program | ||||||||||||
| October 1-31, 2009 | 76.3 | $ | 33.01 | $ | 2,518.7 | 2,651.4 | ||||||||||
| November 1-30, 2009 | 1,652.9 | 33.24 | 54,946.6 | 1,329.4 | ||||||||||||
| December 1-31, 2009 | - | - | - | 1,185.6 | ||||||||||||
| 1,729.2 | $ | 33.23 | $ | 57,465.3 | ||||||||||||
- 16 - -
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the Company’s cumulative total stockholder return (Common Stock price appreciation plus dividends, on a reinvested basis) over the last five fiscal years with the NASDAQ Composite Index, the Standard & Poor’s S&P 500 Index and the Standard & Poor’s S&P Health Care Index.
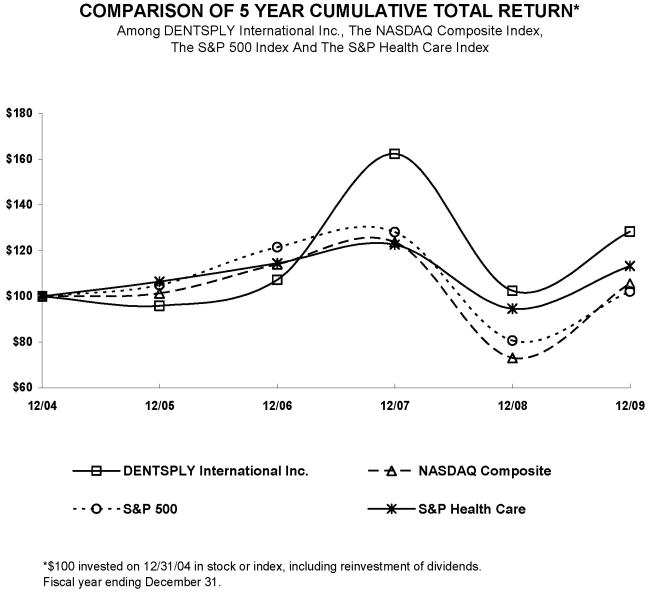
| 12/04 | 12/05 | 12/06 | 12/07 | 12/08 | 12/09 | |||||||||||||||||||
| DENTSPLY International Inc | 100.00 | 95.97 | 107.24 | 162.42 | 102.43 | 128.40 | ||||||||||||||||||
| NASDAQ Composite | 100.00 | 101.33 | 114.01 | 123.71 | 73.11 | 105.61 | ||||||||||||||||||
| S&P 500 | 100.00 | 104.91 | 121.48 | 128.16 | 80.74 | 102.11 | ||||||||||||||||||
| S&P Health Care | 100.00 | 106.46 | 114.48 | 122.67 | 94.69 | 113.34 |
- 17 - -
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The information set forth under the caption “Selected Financial Data” is filed as part of this Form 10-K.
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The information set forth under the caption “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” is filed as part of this Form 10-K.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk
The information set forth under the caption “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk” is filed as part of this Form 10-K.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The information set forth under the captions “Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting,” “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm,” “Consolidated Statements of Operations,” “Consolidated Balance Sheets,” “Consolidated Statements of Equity and Comprehensive Income,” “Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows,” and “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” is filed as part of this Form 10-K.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Not applicable.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
(a) Conclusion Regarding the Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company’s management, with the participation of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based on that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) as of the end of the period covered by this report were effective to provide reasonable assurance that the information required to be disclosed by the Company in reports filed under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and that it is accumulated and communicated to management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
(b) Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management’s report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is included under Item 15(a)(1) of this Form 10-K.
(c) Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2009 that have materially affected, or are likely to materially affect, its internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
Not applicable.
- 18 - -
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information (i) set forth under the caption “Executive Officers of the Registrant” in Part I of this Form 10-K and (ii) set forth under the captions “Election of Directors” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the 2010 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
Code of Ethics
The Company has adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that applies to the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer and substantially all of the Company's management level employees. A copy of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available upon request without charge by writing to DENTSPLY International Inc, Attention: Investor Relations Suite 60, 221 West Philadelphia Street, York, PA 17401.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information set forth under the caption “Executive Compensation” in the 2010 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information set forth under the caption “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans” in the 2010 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence
The information required under this item number is presented in the 2010 Proxy Statement, which is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information set forth under the caption “Relationship with Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in the 2010 Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
- 19 - -
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedule
| (a) | Documents filed as part of this Report |
| 1. | Financial Statements |
The following consolidated financial statements of the Company are filed as part of this Form 10-K:
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Statements of Operations - Years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
Consolidated Balance Sheets - December 31, 2009 and 2008
Consolidated Statements of Equity and Comprehensive Income - Years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - Years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| 2. | Financial Statement Schedule |
The following financial statement schedule is filed as part of this Form 10-K and is covered by the Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm:
Schedule II — Valuation and Qualifying Accounts.
All other schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required to be included herein under the related instructions or are inapplicable and, therefore, have been omitted.
| 3. | Exhibits |
The Exhibits listed below are filed or incorporated by reference as part of the Company’s Form 10-K.
| Exhibit | |||
| Number | Description | ||
| 3.1 | Restated Certificate of Incorporation (1) | ||
| 3.2 | By-Laws, as amended (8) | ||
| 4.1 | (a) | United States Commercial Paper Issuing and paying Agency Agreement dated as of August 12, 1999 between the Company and the Chase Manhattan Bank (2) | |
| (b) | United States Commercial Paper Dealer Agreement dated as of March 28, 2002 between the Company and Salomon Smith Barney Inc. (3) | ||
| (c) | Japanese Yen Term Loan Agreement, due March 28, 2012 dated as of July 31, 2008 (8) | ||
| 4.2 | (a) | Floating Rate Senior Notes Agreement, due March 13, 2010 dated as of March 13, 2007 (4) | |
| 4.3 | (a) | 5-Year Competitive Advance, Revolving Credit and Guaranty Agreements dated as of May 9, 2005 among the Company, the Initial Lenders named therein, the banks named therein, Citibank N.A. as Administrative Agent, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. as Syndication Agent, Harris Trust and Savings Bank, Manufacturers and Traders Trust Company, and Wachovia Bank, N.A. as Co-Documentation Agents, and Citigroup Global Markets, Inc. and J.P. Morgan Securities Inc. as Joint Lead Arrangers and Joint Bookrunners. (5) | |
| 4.4 | Private Placement Note Purchase Agreement, due February 19, 2016 dated as of October 16, 2009 | ||
| 10.1 | 1998 Stock Option Plan (6) | ||
| 10.2 | 2002 Amended and Restated Equity Incentive Plan (4) | ||
| 10.3 | Restricted Stock Unit Deferral Plan (4) | ||
| 10.4 | (a) | Trust Agreement for the Company's Employee Stock Ownership Plan between the Company and T. Rowe Price Trust Company dated as of November 1, 2000 (7) | |
| (b) | Plan Recordkeeping Agreement for the Company's Employee Stock Ownership Plan between the Company and T. Rowe Price Trust Company dated as of November 1, 2000 (7) | ||
| 10.5 | DENTSPLY Supplemental Saving Plan Agreement dated as of December 10, 2007 (4) | ||
| 10.6 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement entered February 19, 2008 between the Company and Bret W. Wise* (4) | ||
| 10.7 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement entered February 19, 2008 between the Company and Christopher T. Clark* (4) |
- 20 - -
| 10.8 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement entered February 19, 2008 between the Company and William R. Jellison* (4) | ||
| 10.9 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement entered February 19, 2008 between the Company and Brian M. Addison* (4) | ||
| 10.10 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement entered February 19, 2008 between the Company and James G. Mosch* (4) | ||
| 10.11 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement entered February 19, 2008 between the Company and Robert J. Size* (4) | ||
| 10.12 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement entered January 1, 2009 between the Company’s subsidiary, DeguDent GMBH and Albert Sterkenburg* (8) | ||
| 10.13 | DENTSPLY International Inc Directors' Deferred Compensation Plan effective January 1, 2008, as amended* (8) | ||
| 10.14 | Board Compensation Arrangement* | ||
| 10.15 | Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan effective January 1, 1999, as amended January 1, 2008* (8) | ||
| 10.16 | Written Description of the Amended and Restated Incentive Compensation Plan* (8) | ||
| 10.17 | AZ Trade Marks License Agreement, dated January 18, 2001 between AstraZeneca AB and Maillefer Instruments Holdings, S.A. (9) | ||
| 10.18 | (a) | Precious metal inventory Purchase and Sale Agreement dated November 30, 2001, as amended October 10, 2006 between Bank of Nova Scotia and the Company (10) | |
| (b) | Precious metal inventory Purchase and Sale Agreement dated December 20, 2001 between JPMorgan Chase Bank and the Company (9) | ||
| (c) | Precious metal inventory Purchase and Sale Agreement dated December 20, 2001 between Mitsui & Co., Precious Metals Inc. and the Company (9) | ||
| (d) | Precious metal inventory Purchase and Sale Agreement dated December 15, 2005 between ABN AMRO NV, Australian Branch and the Company (5) | ||
| (e) | Precious metal inventory Purchase and Sale Agreement dated January 30, 2002 between Dresdner Bank AG, Frankfurt, and the Company (4) | ||
| 10.19 | Executive Change in Control Plan for foreign executives, as amended December 31, 2008* | ||
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of the Company | ||
| 23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm - PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP | ||
| 31 | Section 302 Certification Statements | ||
| 32 | Section 906 Certification Statement | ||
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | ||
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | ||
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | ||
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | ||
| 101.LAB | XBRL Extension Labels Linkbase Document | ||
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
| * | Management contract or compensatory plan. |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (No. 333-101548). |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1999, File No. 0-16211. |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2002, File No. 0-16211. |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, File No. 0-16211. |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2005, File No. 0-16211. |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Registration Statement on Form S-8 (No. 333-56093). |
| (7) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2000, File No. 0-16211. |
| (8) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, File No. 0-16211. |
| (9) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2001, File No. 0-16211. |
| (10) | Incorporated by reference to exhibit included in the Company's Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2001, File No. 0-16211. |
- 21 - -
SCHEDULE II
VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
Additions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Charged | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at | (Credited) | Charged to | Write-offs | Balance | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beginning | To Costs | Other | Net of | Translation | at End | |||||||||||||||||||||
Description | of Period | And Expenses | Accounts | Recoveries | Adjustment | of Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | $ | 16,183 | $ | 2,854 | $ | (182 | ) | $ | (1,927 | ) | $ | 1,650 | $ | 18,578 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 18,578 | 3,674 | (348 | ) | (1,705 | ) | (1,350 | ) | 18,849 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 18,849 | (3,124 | ) | (a) | 17 | (4,253 | ) | 746 | 12,235 | |||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for trade discounts: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | $ | 457 | $ | (155 | ) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 5 | $ | 307 | |||||||||||||
| 2008 | 307 | 267 | 4 | - | (59 | ) | 519 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 519 | 505 | - | - | 79 | 1,103 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Inventory valuation reserves: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | $ | 26,305 | $ | 3,134 | $ | (449 | ) | $ | (4,525 | ) | $ | 1,725 | $ | 26,190 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 26,190 | 3,261 | 1,938 | (1,981 | ) | (1,019 | ) | 28,389 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 28,389 | 5,883 | 80 | (3,610 | ) | 1,190 | 31,932 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred tax asset valuation allowance: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | $ | 49,379 | $ | 7,076 | $ | - | $ | (11,124 | ) | (b) | $ | 4,919 | $ | 50,250 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | 50,250 | 603 | - | (13,203 | ) | (c) | (909 | ) | 36,741 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 36,741 | 13,419 | - | - | 1,649 | 51,809 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (a) | See Note 1, Significant Accounting Policies, to the consolidated financial statements, for further discussion. |
| (b) | The significant increase for write-offs during 2007 is the result of a global tax restructuring project, where-in net operating losses subject to a full valuation allowance are not available for future use. |
| (c) | The write-offs during 2008 are the result of a global tax restructuring project, tax audit closures, and expired tax losses. |
- 22 - -
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Statements of Operations Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 2,159,916 | $ | 2,193,723 | $ | 2,009,833 | $ | 1,810,496 | $ | 1,715,135 | ||||||||||||
| Net sales, excluding precious metal content | 1,991,204 | 1,993,800 | 1,819,899 | 1,623,074 | 1,542,711 | |||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit | 1,111,304 | 1,151,944 | 1,040,783 | 929,011 | 869,018 | |||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring, impairments and other costs | 6,890 | 32,355 | 10,527 | 7,807 | 232,755 | (a) | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating income | 381,187 | 380,421 | 354,891 | 314,794 | 72,922 | |||||||||||||||||
| Income before income taxes | 363,356 | 354,873 | 358,192 | 314,837 | 71,038 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net income attributable to | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| DENTSPLY International | $ | 274,258 | $ | 283,869 | $ | 259,654 | $ | 223,718 | $ | 45,413 | ||||||||||||
| Earnings per common share: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 1.85 | $ | 1.90 | $ | 1.71 | $ | 1.44 | $ | 0.29 | ||||||||||||
| Diluted | $ | 1.83 | $ | 1.87 | $ | 1.68 | $ | 1.41 | $ | 0.28 | ||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.200 | $ | 0.185 | $ | 0.165 | $ | 0.145 | $ | 0.125 | ||||||||||||
| Weighted Average Common Shares Outstanding: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic | 148,319 | 149,069 | 151,707 | 155,229 | 159,191 | |||||||||||||||||
| Diluted | 150,102 | 151,679 | 154,721 | 158,271 | 162,017 | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheets Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments | $ | 450,385 | $ | 204,249 | $ | 316,323 | $ | 65,143 | $ | 434,525 | ||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 439,619 | 432,276 | 371,409 | 329,616 | 316,218 | |||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill and other intangibles, net | 1,401,682 | 1,380,744 | 1,203,587 | 1,063,030 | 1,001,827 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total assets | 3,087,932 | 2,830,400 | 2,675,569 | 2,181,350 | 2,410,373 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total debt and notes payable | 469,325 | 449,474 | 483,307 | 370,156 | 682,316 | |||||||||||||||||
| Equity | 1,906,958 | 1,659,413 | 1,516,402 | 1,273,835 | 1,246,596 | |||||||||||||||||
| Return on average equity | 15.4 | % | 17.9 | % | 18.6 | % | 17.8 | % | 3.4 | % | ||||||||||||
| Long-term debt to total capitalization | 19.2 | % | 20.5 | % | 24.1 | % | 22.4 | % | 35.3 | % | ||||||||||||
| Other Data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | $ | 65,175 | $ | 56,929 | $ | 50,289 | $ | 47,434 | $ | 50,560 | ||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | 362,489 | 335,981 | 387,697 | 271,855 | 232,769 | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures | 56,481 | 76,440 | 64,163 | 50,616 | 45,293 | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense (income), net | 16,864 | 15,438 | (2,645 | ) | (1,683 | ) | 8,768 | |||||||||||||||
| Inventory days | 99 | 103 | 92 | 94 | 87 | |||||||||||||||||
| Receivable days | 55 | 54 | 51 | 57 | 53 | |||||||||||||||||
| Effective tax rate | 24.5 | % | 20.2 | % | 27.5 | % | 28.9 | % | 36.1 | % | ||||||||||||
| (a) | The Company recorded $230.8 million of impairment and restructuring charges related to the closing of the pharmaceutical manufacturing facility outside of Chicago. |
- 23 - -
Item 7.
MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The nature and geographic scope of the Company’s business subjects it to changing economic, competitive, regulatory and technological risks and uncertainties. In accordance with the “Safe Harbor” provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, the Company provides the following cautionary remarks regarding important factors, which, among others, could cause future results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements, expectations and assumptions expressed or implied herein. All forward-looking statements made by the Company are subject to risks and uncertainties and are not guarantees of future performance. These forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause the Company’s actual results, performance and achievements, or industry results to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. These statements are identified by the use of such terms as “may,” “could,” “expect,” “intend,” “believe,” “plan,” “estimate,” “forecast,” “project,” “anticipate” or words of similar expression.
Investors are cautioned that forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties which may materially affect the Company's business and prospects, and should be read in conjunction with the risk factors and uncertainties discussed within Item 1A, Part I of this Form 10-K. Investors are further cautioned that the risk factors in Item 1A, Part I of this Form 10-K may not be exhaustive and that many of these factors are beyond the Company’s ability to control or predict. Accordingly, forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as a prediction of actual results. The Company undertakes no duty and has no obligation to update forward-looking statements.
OVERVIEW
DENTSPLY International Inc believes it is the world's largest designer, developer, manufacturer and marketer of professional dental products. The Company is headquartered in the United States and operates in more than 120 other countries, principally through its foreign subsidiaries. The Company also has strategically located distribution centers to enable it to better serve its customers and increase its operating efficiency. While the United States and Europe are the Company's largest markets, the Company serves all of the major professional dental markets worldwide.
Key Measurements
The principal measurements used by the Company in evaluating its business are: (1) internal growth by geographic region; (2) constant currency growth by geographic region; (3) operating margins of each reportable segment; (4) the development, introduction and contribution of innovative new products; (5) growth through acquisition; and (6) continued focus on controlling costs and enhancing efficiency.
The Company defines “internal growth” as the increase or decrease in net sales from period to period, excluding (1) precious metal content; (2) the impact of changes in currency exchange rates; and (3) the net sales, for a period of twelve months following the transaction date, of businesses that have been acquired or divested. The Company defines “constant currency growth” as internal growth plus acquisition growth.
Management believes that an average internal growth rate of 4-6% is a long-term sustainable rate for the Company. The internal growth rate may vary outside of this range based on weaker or stronger economic conditions. Management expects the Company to operate below this range in the near future due to the current economic conditions; however, history shows that growth in the dental industry typically performs better than the overall economy. There can be no assurance that the Company’s assumptions concerning the growth rates in its markets or the dental market generally will continue in the future. If such rates are less than expected, the Company’s projected growth rates and results of operations may be adversely affected.
Product innovation is a key component of the Company's overall growth strategy. New advances in technology are anticipated to have a significant influence on future products in dentistry. As a result, the Company continues to pursue research and development initiatives to support this technological development, including collaborations with various research institutions and dental schools. In addition, the Company licenses and purchases technologies developed by third parties. Although the Company believes these activities will lead to new innovative dental products, they involve new technologies and there can be no assurance that commercialized products will be developed.
Although the professional dental market in which the Company operates has experienced consolidation, it is still a fragmented industry. The Company continues to focus on opportunities to expand the Company’s product offerings through acquisitions. Management believes that there will continue to be adequate opportunities to participate as a consolidator in the industry for the foreseeable future.
- 24 - -
Company’s Response to Economic Conditions
Price changes, other marketing and promotional programs offered to customers from time to time, the management of inventory levels by distributors and the implementation of strategic initiatives may impact sales and inventory levels in a given period. Due to the current economic conditions, the overall dental market has been negatively impacted by inventory reductions in its distribution channels, particularly in certain emerging market regions.
Additionally, the current conditions of the economy have negatively impacted the Company’s gross profit rate. Unfavorable product and geographic sales mix, unfavorable overhead absorption and movements in foreign currencies are the key factors that have recently affected the Company’s gross profits. The Company continues to manage these negative factors to help minimize their impact on the Company’s overall performance.
Due to the international nature of DENTSPLY’s business, movements in foreign exchange rates may impact the Consolidated Statements of Operations. With over 60% of the Company’s sales located in regions outside the U.S., the Company’s sales are significantly impacted by the strengthening or weakening of the U.S. dollar. As discussed further under the segment descriptions, the Company was negatively impacted by the movements in currencies in 2009.
The Company has always maintained its focus on minimizing costs and achieving operational efficiencies. In response to the recent credit crisis and the recessionary economic conditions, management is concentrating on cost containment that focuses the business on creating and maintaining operational and financial flexibility through controlling operating costs. Management will continue to evaluate the consolidation of operations or functions and reduce the cost of those operations and functions. In addition, the Company remains focused on enhancing efficiency through expanded use of technology and process improvement initiatives. The Company believes that the benefits from these initiatives will improve the cost structure and help offset areas of rising costs such as energy, employee benefits, and regulatory oversight and compliance.
In response to the recent economic conditions, the Company initiated several restructuring plans that included targeted headcount reductions and business consolidations and reorganizations in late 2008 through 2009. The Company began to realize the cost savings associated with these restructuring plans in 2009 and expects to realize incremental cost savings associated with these restructuring plans in 2010. (See Note 14, Restructuring, Impairments and Other Costs, to the consolidated financial statements).
Reclassification of Prior Year Amounts
Certain reclassifications have been made to prior years' data in order to conform to current year presentation.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
2009 Compared to 2008
Net Sales
The discussion below summarizes the Company’s sales growth, excluding precious metal content, into the following components: (1) constant currency, which includes internal growth and acquisition growth, and (2) foreign currency translation. These disclosures of net sales growth provide the reader with sales results on a comparable basis between periods.
Management believes that the presentation of net sales, excluding precious metal content, provides useful information to investors because a significant portion of DENTSPLY’s net sales is comprised of sales of precious metals generated through sales of the Company’s precious metal dental alloy products, which are used by third parties to construct crown and bridge materials. Due to the fluctuations of precious metal prices and because the precious metal content of the Company’s sales is largely a pass-through to customers and has minimal effect on earnings, DENTSPLY reports net sales both with and without precious metal content to show the Company’s performance independent of precious metal price volatility and to enhance comparability of performance between periods. The Company uses its cost of precious metal purchased as a proxy for the precious metal content of sales, as the precious metal content of sales is not separately tracked and invoiced to customers. The Company believes that it is reasonable to use the cost of precious metal content purchased in this manner since precious metal dental alloy sale prices are typically adjusted when the prices of underlying precious metals change.
The presentation of net sales, excluding precious metal content, is considered a measure not calculated in accordance with US GAAP, and is therefore considered a non-US GAAP measure. The Company provides the following reconciliation of net sales to net sales, excluding precious metal content. The Company’s definitions and calculations of net sales, excluding precious metal content, and other operating measures derived using net sales, excluding precious metal content, may not necessarily be the same as those used by other companies.
- 25 - -
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 2,159.9 | $ | 2,193.7 | $ | (33.8 | ) | (1.5 | )% | |||||||
| Less: Precious metal content of sales | 168.7 | 199.9 | (31.2 | ) | (15.6 | )% | ||||||||||
| Net sales, excluding precious metal content | $ | 1,991.2 | $ | 1,993.8 | $ | (2.6 | ) | (0.1 | )% | |||||||
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, for 2009 was $1,991.2 million, which remained relatively unchanged when compared to 2008. Net sales, excluding precious metal content, included constant currency growth of 2.3%, offset by currency translation, which reduced sales by 2.4%. The constant currency sales growth was comprised of acquisition growth of 4.5%, partially offset by internal growth of negative 2.2%. Sales for dental products grew on a constant currency basis by 3.0%, including internal growth of negative 1.3% and acquisition growth of 4.3%.
Internal Sales Growth
United States
In 2009, net sales, excluding precious metal content, decreased 0.9% in the United States on a constant currency basis, including 1.0% acquisition growth and internal growth of negative 1.9%. The negative internal growth was primarily driven by lower sales in dental laboratory and non-dental products, which was partially offset by internal growth in dental consumables products.
Europe
In 2009, net sales, excluding precious metal content, increased 4.0% in Europe on a constant currency basis, including 7.8% acquisition growth and internal growth of negative 3.8%. The negative internal growth was primarily driven by lower sales in dental consumables, dental laboratory products and non-dental products, which was partially offset by internal growth in dental specialty products.
All Other Regions
In 2009, net sales, excluding precious metal content, increased 4.6% across all other regions on a constant currency basis, including 4.3% acquisition growth and internal growth of 0.3%. The dental consumables and dental specialty products had positive internal growth, which was partially offset by negative internal growth in dental laboratory and non-dental products.
Gross Profit
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Gross profit | $ | 1,111.3 | $ | 1,151.9 | $ | (40.6 | ) | (3.5 | )% | |||||||
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales, including precious metal content | 51.5 | % | 52.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales, excluding precious metal content | 55.8 | % | 57.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales, excluding precious metal content, decreased 2.0 percentage points in 2009 compared to 2008. The decrease is the result of unfavorable product and geographic sales mix, unfavorable manufacturing overhead absorption and movements in foreign currencies. Additionally, acquisitions completed in 2008 negatively impacted gross profit as a percentage of net sales.
- 26 - -
Expenses
Selling, General and Administrative (“SG&A”) Expenses
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| SG&A expenses | $ | 723.2 | $ | 739.2 | $ | (16.0 | ) | (2.2 | )% | |||||||
SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales, including precious metal content | 33.5 | % | 33.7 | % | ||||||||||||
SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales, excluding precious metal content | 36.3 | % | 37.1 | % | ||||||||||||
The reduction in SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales, excluding precious metal content, was largely the result of the Company’s focus on cost containment in response to the recessionary economic conditions that occurred in late 2008 through 2009. In early 2009, the Company undertook action on discretionary expense categories, such as travel, and addressed non-discretionary expense categories where appropriate. Additionally, the Company executed several restructuring plans that focused on reductions in overhead spending. Although cost reductions were made across the Company, management continues to focus on controlling costs while creating and maintaining financial flexibility. These cost containment efforts were partially offset by a higher percentage of SG&A expenses in businesses acquired in 2008, costs related to the 2009 biennial International Dental Show and cost increases and higher investments in sales and marketing to support future growth in certain geographic areas.
Restructuring, Impairments and Other Costs
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Restructuring, impairments and other costs | $ | 6.9 | $ | 32.4 | $ | (25.5 | ) | NM | ||||||||
NM- not meaningful
The Company recorded net restructuring, impairments and other costs of $6.9 million in 2009 compared to $32.4 million in 2008. The Company incurred $5.9 million of costs in 2009 related to several restructuring plans in response to the worldwide economic crisis that began in late 2008. The restructuring plans related to the closure and/or consolidation of certain production and selling facilities in the United States, Europe and South America to better leverage the Company’s resources by reducing costs and obtaining operational efficiencies. Additionally, the Company executed targeted reductions in workforce both in the manufacturing and non-manufacturing business functions in certain locations. Also, the Company recorded certain other costs related to legal matters and an impairment of an intangible asset.
In 2008, the Company recorded costs of $24.2 million related to legal settlements and impairments of long-term assets. The legal settlements related to several legal matters with multiple plaintiffs. These cases included a patent dispute and cases relating to a prior distribution practice of the Company in connection with the sale of artificial teeth. The impairment charge was related to abandonment of patented technology purchased in 2005 and the impairment of a long-term note receivable recorded from a sale of a business in 2006. The impairment of the long-term note receivable occurred as the result of a change in payment terms on the non-interest bearing note receivable. Additionally, the Company initiated several restructuring plans primarily related to the closure and consolidation of certain production and selling facilities in the United States, Europe and Asia to better leverage the Company’s resources by reducing costs and obtaining operational efficiencies. These restructuring plans included charges of $5.9 million. Additionally, the Company expensed $2.3 million for the fair value of in-process research and development associated with acquired businesses (See Note 14, Restructuring, Impairments and Other Costs, to the consolidated financial statements).
Other Income and Expenses
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | |||||||||
| Net interest expense | $ | 16.9 | $ | 15.4 | $ | 1.5 | ||||||
| Other expense, net | 1.0 | 10.1 | (9.1 | ) | ||||||||
| Net interest and other expense | $ | 17.9 | $ | 25.5 | $ | (7.6 | ) | |||||
- 27 - -
Net Interest Expense
The change in net interest expense in 2009 compared to 2008 was primarily due to lower interest rates earned on invested cash balances offset by lower average debt and interest rates on the Company’s Euro net investment hedges. The impact of the Company’s net investment hedges typically move in the opposite direction of currency movements, reducing some of the volatility caused by movement in exchange rates on the Company’s income and equity.
Other Expense, Net
Other expense in the 2009 period included approximately $0.3 million of currency transaction losses and $0.7 million of other non-operating costs. The 2008 period included $8.9 million of currency transaction losses and $1.2 million of other non-operating costs. In the fourth quarter of 2008, currency exchange rate volatility was extremely high and global currencies weakened versus the U.S. Dollar. The Company incurred transaction losses, mostly in the fourth quarter of 2008, on settlement of intercompany and third party transactions.
Income Taxes and Net Income
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share amounts) | 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | |||||||||
| Effective income tax rate | 24.5 | % | 20.2 | % | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International | $ | 274.3 | $ | 283.9 | $ | (9.6 | ) | |||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 1.83 | $ | 1.87 | ||||||||
Income Taxes
The Company’s effective income tax rates for 2009 and 2008 were 24.5% and 20.2%, respectively. In 2009, the Company’s effective income tax rate included the impact of restructuring, impairments and other costs, acquisition related activity and various income tax adjustments, which impacted income before income taxes and the provision for income taxes by $11.0 million and $8.8 million, respectively. In 2008, the Company’s effective income tax rate included the impact of restructuring, impairments and other costs, acquisition related activity, provisions for the fair value measurement adjustment and various income tax adjustments, which impacted income before income taxes and the provision for income taxes by $30.5 million and $28.3 million, respectively. The various income tax adjustments included the impact of settlements with taxing authorities and statutes closures for both periods.
Net Income attributable to DENTSPLY International
Diluted earnings per common share during 2009 were $1.83 compared to $1.87 during the same period in 2008. Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International in 2009 includes restructuring, impairments and other costs of $5.1 million, or $0.03 per diluted share, net of tax and noncontrolling interests, and income tax related adjustments benefit of $5.4 million, or $0.03 per diluted share, net of tax and noncontrolling interests, and acquisition related activity expenses, net of tax and noncontrolling interests, of $1.8 million, or $0.01 per diluted share. Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International in 2008 includes an after tax impact from restructuring, impairments and other costs of $19.8 million, or $0.13 per diluted share and a net income tax benefit of $17.1 million, or $0.11 per diluted share due to income tax related adjustments, and provisions for the fair value measurement adjustment, net of tax of $1.1 million or $0.01 per diluted share.
Operating Segment Results
The Company’s operating businesses are combined into operating groups, which have overlapping product offerings, geographic presence, customer bases, distribution channels and regulatory oversight. These operating groups are considered the Company’s reportable segments as the Company’s chief operating decision-maker regularly reviews financial results at the operating group level and uses this information to manage the Company’s operations. Each of these operating groups covers a wide range of product categories and geographic regions. The product categories and geographic regions often overlap across the groups. Further information regarding the details of each group is presented in Note 4, Segment and Geographic Information, to the consolidated financial statements. The management of each group is evaluated for performance and incentive compensation purposes on net third party sales, excluding precious metal content, and segment operating income.
- 28 - -
In January 2009, the Company moved the reporting responsibility for several locations between segments which resulted in a change to the management structure and helped the Company gain operating efficiencies and effectiveness. The segment information below reflects this revised structure for all periods shown.
Net Sales, excluding precious metal content | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 526.7 | $ | 459.7 | $ | 67.0 | 14.6 | % | ||||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | $ | 419.4 | $ | 437.5 | $ | (18.1 | ) | (4.1 | )% | |||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | $ | 618.4 | $ | 628.9 | $ | (10.5 | ) | (1.7 | )% | |||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | $ | 429.6 | $ | 471.1 | $ | (41.5 | ) | (8.8 | )% | |||||||
Segment Operating Income | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 158.4 | $ | 162.7 | $ | (4.3 | ) | (2.6 | )% | |||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | $ | 18.7 | $ | 13.0 | $ | 5.7 | 43.8 | % | ||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | $ | 185.8 | $ | 200.1 | $ | (14.3 | ) | (7.1 | )% | |||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | $ | 93.6 | $ | 124.9 | $ | (31.3 | ) | (25.1 | )% | |||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, increased 14.6% during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008. On a constant currency basis, sales increased 15.7%, which was driven by acquisition growth.
Operating income decreased $4.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008. Operating income was negatively affected by lower sales in Europe, unfavorable product and geographic sales mix, and currency translation. In addition, the decrease was partially attributable to the roll-off of inventory step-up related to an acquisition completed in late 2008. The segment, excluding an acquisition completed in 2008, reduced operating expenses during 2009 when compared to the same period in 2008.
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, decreased 4.1% during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008, of which negative 2.7% was the result of currency translation. On a constant currency basis, sales were negative 1.4% primarily due to lower sales in the CIS partially offset by an acquisition and growth in the Pacific Rim.
Operating income increased $5.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008. The increase was driven primarily by higher profits in the Pacific Rim operations partially offset by lower profits, mainly in the CIS, due to lower sales.
- 29 - -
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/Orthodontics
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, decreased 1.7% during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008, of which negative 2.4% was the result of currency translation. On a constant currency basis, sales increased by 0.7% as a result of an acquisition completed in 2008.
Operating income decreased $14.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008. The decrease was driven primarily by lower sales in non-dental products, unfavorable absorption and the negative impact from foreign currency transactions.
Dental Laboratory Business/Implants/Non-Dental
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, decreased 8.8% during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008, of which negative 3.3% was the result of currency translation. On a constant currency basis, sales were negative 5.5%, primarily driven by the lower sales in dental laboratory products, dental implant products and non-dental products partially offset by acquisition growth.
Operating income decreased $31.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 compared to 2008 as a result of profitability being down across the segment primarily related to lower sales in the dental laboratory businesses, unfavorable product sales mix and currency translation.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
2008 Compared to 2007
Factors Impacting Comparability Between Years
Adoption of Fair Value Measurement
In 2008, the Company adopted the new accounting guidance for fair value measurement, which requires the Company to define fair value, establish a framework for measuring fair value in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“US GAAP”), and expand disclosures about fair value measurements. As part of the provisions, the Company is required to determine the impact of credit risk on its financial instruments recorded at fair value. As a result, the Company recognized pretax income of $1.8 million during 2008.
Net Sales
The discussion below summarizes the Company’s sales growth, excluding precious metal content, from internal growth and net acquisition growth and highlights the impact of foreign currency translation. These disclosures of net sales growth provide the reader with sales results on a comparable basis between periods.
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 2,193.7 | $ | 2,009.8 | $ | 183.9 | (9.2 | )% | ||||||||
| Less: Precious metal content of sales | 199.9 | 189.9 | 10.0 | (5.3 | )% | |||||||||||
| Net sales, excluding precious metal content | $ | 1,993.8 | $ | 1,819.9 | $ | 173.9 | (9.6 | )% | ||||||||
The net sales growth, excluding precious metal content, of 9.6% was comprised of 3.8% of internal growth, 3.7% of foreign currency translation and 2.1% related to acquisitions. The 3.8% internal growth was comprised of negative 0.9% in the United States, 7.0% in Europe and 7.0% for all other regions combined.
- 30 - -
Internal Sales Growth
United States
The internal sales growth of negative 0.9%, excluding precious metal content, in the United States was negatively impacted by the supply issues with injectable anesthetics and softness in dental consumables and in the dental specialty businesses in the fourth quarter, as the economy in the United States contracted.
Europe
In Europe, the internal sales growth of 7.0%, excluding precious metal content, was driven by strong performance in the dental specialty businesses and growth in the dental consumable businesses partially offset by softness in the dental laboratory businesses due to lower equipment and alloy product sales.
All Other Regions
During 2008, the internal growth of 7.0%, excluding precious metal content, was largely the result of strong growth in the dental specialty category. Asia, Australia, the Middle East and Latin America experienced strong growth.
Gross Profit
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Gross profit | $ | 1,151.9 | $ | 1,040.8 | $ | 111.1 | 10.7 | % | ||||||||
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales, including precious metal content | 52.5 | % | 51.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales, excluding precious metal content | 57.8 | % | 57.2 | % | ||||||||||||
The 2008 gross profit as a percentage of net sales, excluding precious metal content, was favorably impacted by product pricing, product mix and operational improvements.
Expenses
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| SG&A expenses | $ | 739.2 | $ | 675.4 | $ | 63.8 | 9.4 | % | ||||||||
SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales, including precious metal content | 33.7 | % | 33.6 | % | ||||||||||||
SG&A expenses as a percentage of net sales, excluding precious metal content | 37.1 | % | 37.1 | % | ||||||||||||
The 9.4% increase in SG&A expenses reflects additional SG&A expenses of $15.7 million from acquired companies and increases from currency translation of approximately $24.6 million. The remaining increase in SG&A expenses is primarily a result of increased expenditures to support growth in the dental specialty businesses and higher growth regions as well as continued investment in research and development.
- 31 - -
Restructuring, Impairments and Other Costs
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||
| Restructuring, impairments and other costs | $ | 32.4 | $ | 10.5 | $ | 21.9 | NM | |||||||||
| NM - Not Meaningful | ||||||||||||||||
In 2008, the Company recorded costs of $24.2 million related to legal settlements and impairments of long-term assets. The legal settlements related to several legal matters with multiple plaintiffs. These cases included a patent dispute and cases relating to a prior distribution practice of the Company in connection with the sale of artificial teeth. The impairment charge was related to abandonment of patented technology purchased in 2005 and the impairment of a long-term note receivable recorded from a sale of a business in 2006. The impairment of the long-term note receivable occurred as the result of a change in payment terms on the non-interest bearing note receivable. Additionally, the Company initiated several restructuring plans primarily related to the closure and consolidation of certain production and selling facilities in the United States, Europe and Asia to better leverage the Company’s resources by reducing costs and obtaining operational efficiencies. These restructuring plans included charges of $5.9 million. Additionally, the Company expensed $2.3 million for the fair value of in-process research and development associated with acquired businesses (See Note 14, Restructuring, Impairments and Other Costs, to the consolidated financial statements).
During 2007, the Company recorded net restructuring, impairment and other costs of $10.5 million. Several restructuring plans were initiated during 2007, primarily related to the closure and consolidation of certain production and selling facilities in the United States, Europe, Asia and South America in order to better leverage the Company’s resources by reducing costs and obtaining operational efficiencies. These restructuring plans included charges of $5.4 million. Additionally, the Company also recorded a total of $5.1 million in expenses related to several legal claims and impairments of long-term assets.
Other Income and Expenses
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | |||||||||
| Net interest expense (income) | $ | 15.4 | $ | (2.6 | ) | $ | 18.0 | |||||
| Other expense (income), net | 10.1 | (0.7 | ) | 10.8 | ||||||||
| Net interest and other expense (income) | $ | 25.5 | $ | (3.3 | ) | $ | 28.8 | |||||
Net Interest Expense (Income)
The change from net interest income in 2007 to net interest expense in 2008 was mainly the result of the sharp divergence of lower U.S. dollar interest rates versus increased Euro and Swiss franc interest rates, combined with weaker U.S. dollar average exchange rates against both currencies. This resulted in net interest expense in 2008 versus net interest income in 2007 on the Euro and Swiss franc net investment hedges executed in the form of cross currency swaps. The impact of the Company’s net investment hedges typically move in the opposite direction of currency movements, reducing some of the volatility caused by movement in exchange rates on the Company’s income and equity. Partially offsetting the net investment hedge impact was higher average investment balances in Euros and lower average interest rates on U.S. dollar debt.
Other Expense (Income), Net
Other expense (income) in the 2008 period included $8.9 million of currency transaction losses and $1.2 million of other non-operating losses. The 2007 period included $0.5 million of currency transaction gains and $0.2 million of other non-operating gains. Currency exchange rate volatility was extremely high, especially during the fourth quarter of 2008, and global currencies weakened versus the U.S. Dollar. The Company incurred transaction losses, mostly in the fourth quarter of 2008, on settlement of intercompany and third party transactions.
- 32 - -
Income Taxes and Net Income
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share amounts) | 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | |||||||||
| Effective income tax rate | 20.2 | % | 27.5 | % | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International | $ | 283.9 | $ | 259.7 | $ | 24.2 | ||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 1.87 | $ | 1.68 | ||||||||
Income Taxes
The Company’s effective income tax rates for 2008 and 2007 were 20.2% and 27.5%, respectively. In 2008, the Company’s effective income tax rate included the impact from restructuring, impairments and other costs, acquisition related activity, provisions for the fair value measurement adjustment and various income tax adjustments, which impacted income before income taxes and the provision for income taxes by $30.5 million and $28.3 million, respectively. In 2007, the Company’s effective income tax rate included the impact from restructuring, impairments and other costs and various income tax adjustments, which impacted income before income taxes and the provision for income taxes by $10.5 million and $13.7 million, respectively. The various income tax adjustments included the impact of settlements with taxing authorities and statutes closures for both periods.
Net Income attributable to DENTSPLY International
Diluted earnings per common share from during 2008 were $1.87 compared to $1.68 during the same period in 2007. Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International in 2008 includes an after tax impact from restructuring, impairments and other costs of $19.8 million, or $0.13 per diluted share and a net tax benefit of $17.1 million, or $0.11 per diluted share due to income tax related adjustments, and provisions for fair value measurement adjustment, net of tax of $1.1 million or $0.01 per diluted share. Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International for 2007 includes an after tax impact from restructuring, impairments and other costs of $6.7 million, or $0.04 per diluted share and a net tax benefit of $9.9 million, or $0.06 per diluted share due to income tax related adjustments.
Operating Segment Results
In January 2007, the Company reorganized its operating group structure expanding into four operating groups from the three groups under the prior management structure. These operating groups are considered the Company’s reportable segments as the Company’s chief operating decision-maker regularly reviews financial results at the operating group level and uses this information to manage the Company’s operations. Each of these operating groups covers a wide range of product categories and geographic regions. The product categories and geographic regions often overlap across the groups. Further information regarding the details of each group is presented in Note 4, Segment and Geographic Information, to the consolidated financial statements. The management of each group is evaluated for performance and incentive compensation purposes on net third party sales, excluding precious metal content, and segment operating income.
In January 2009, the Company moved the reporting responsibility for several locations between segments as a result of a change to the management structure. This change also helped the Company gain operating efficiencies and effectiveness. The segment information below reflects this revised structure for all periods shown.
- 33 - -
Net Sales, excluding precious metal content | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 459.7 | $ | 428.2 | $ | 31.5 | 7.4 | % | ||||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | $ | 437.5 | $ | 381.2 | $ | 56.3 | 14.8 | % | ||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | $ | 628.9 | $ | 583.9 | $ | 45.0 | 7.7 | % | ||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | $ | 471.1 | $ | 430.1 | $ | 41.0 | 9.5 | % | ||||||||
Segment Operating Income | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 162.7 | $ | 139.0 | $ | 23.7 | 17.1 | % | ||||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | $ | 13.0 | $ | 10.0 | $ | 3.0 | 30.0 | % | ||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | $ | 200.1 | $ | 180.9 | $ | 19.2 | 10.6 | % | ||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | $ | 124.9 | $ | 112.4 | $ | 12.5 | 11.1 | % | ||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, increased 7.4% during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. This increase was driven by acquisition related growth and positive currency translation. Supply issues with injectable anesthetics as well as softness in the United States dental consumable products in the fourth quarter due to a weakening economy hindered the growth within the segment.
Operating income increased $23.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. The increase was due to improved margins due to favorable product mix across most of the segment and acquisitions.
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, increased 14.8%, including the favorable impact of currency translation, during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. Strong growth occurred across many regions within the segment.
Operating income increased $3.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. The increase in income was related to sales growth and leveraging of expenses.
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/Orthodontics
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, increased 7.7%, including acquisition growth and favorable currency translation, during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. Strong growth occurred in the Orthodontic, Endodontic and Latin American businesses.
- 34 - -
Operating income increased $19.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. The increase in operating profits was driven primarily by sales growth and leveraging of expenses.
Dental Laboratory Business/Implants/Non-Dental
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, increased 9.5%, including favorable impact of currency translation, during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. Strong growth occurred in the dental implant products and from acquisition related activity.
Operating income increased $12.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. The increase in operating profits was driven primarily by sales growth in the dental implant products and leveraging of expenses in the dental laboratory products.
FOREIGN CURRENCY
Since approximately 63% of the Company's 2009 net sales, excluding precious metal content, were generated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar, the value of the U.S. dollar in relation to those currencies affects the results of operations of the Company. The impact of currency fluctuations in any given period can be favorable or unfavorable. The impact of foreign currency fluctuations of European currencies on operating income is partially offset by sales in the United States of products sourced from plants and third party suppliers located overseas, principally in Germany and Switzerland.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING JUDGMENTS AND POLICIES
The preparation of the Company’s consolidated financial statements in conformity with US GAAP requires the Company to make estimates and assumptions about future events that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Future events and their effects cannot be determined with absolute certainty. Therefore, the determination of estimates requires the exercise of judgment. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences may be material to the consolidated financial statements. The process of determining significant estimates is fact specific and takes into account factors such as historical experience, current and expected economic conditions, product mix and in some cases, actuarial techniques. The Company evaluates these significant factors as facts and circumstances dictate. Some events as described below have caused results to differ significantly from those determined using estimates. The Company has identified below the accounting estimates believed to be critical to its business and results of operations.
Accounts Receivable
The Company sells dental products both through a worldwide network of distributors and directly to end users. For customers on credit terms, the Company performs an ongoing credit evaluation of those customers' financial condition and generally does not require collateral from them. The Company establishes allowances for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the inability of its customers to make required payments. If the financial condition of the Company’s customers were to improve or deteriorate, their ability to make required payments may become less or more impaired and decreases or increases in these allowances may be required. In addition, a negative impact on sales to those customers may occur.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. The cost of inventories is determined primarily by the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) or average cost methods, with a small portion being determined by the last in, first-out (“LIFO”) method. The Company establishes reserves for inventory estimated to be obsolete or unmarketable equal to the difference between the cost of inventory and estimated market value based upon assumptions about future demand and market conditions. If actual market conditions are less favorable than those anticipated, additional inventory reserves may be required.
Goodwill and Other Long-Lived Assets
Goodwill
The Company follows the accounting standards for goodwill, which requires an annual test for impairment to goodwill using a fair value approach. In addition to minimum annual impairment tests, the Company also requires that impairment assessments be made more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the goodwill might be impaired. If impairment related to goodwill is identified as a result of impairment tests, the resulting charge is determined by recalculating goodwill through a hypothetical purchase price allocation of the fair value and reducing the current carrying value to the extent it exceeds the recalculated goodwill.
- 35 - -
Other Long-Lived Assets
Other long-lived assets, such as definite-lived intangible assets and fixed assets, are amortized or depreciated over their estimated useful lives. In accordance with US GAAP, these assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or circumstances provide evidence that suggest that the carrying amount of the asset may not be recoverable based upon an evaluation of the identifiable undiscounted cash flows. If impaired based on the identifiable undiscounted cash flows, the asset’s fair value is determined using the discounted cash flow and market participant assumptions. The resulting charge reflects the excess of the asset’s carrying cost over its fair value.
Impairment Assessment
Assessment of the potential impairment of goodwill and other long-lived assets is an integral part of the Company’s normal ongoing review of operations. Testing for potential impairment of these assets is significantly dependent on numerous assumptions and reflects management’s best estimates at a particular point in time. The dynamic economic environments in which the Company’s businesses operate and key economic and business assumptions with respect to projected selling prices, increased competition and introductions of new technologies can significantly affect the outcome of impairment tests. Estimates based on these assumptions may differ significantly from actual results. Changes in factors and assumptions used in assessing potential impairments can have a significant impact on the existence and magnitude of impairments, as well as the time at which such impairments are recognized. If there are unfavorable changes in these assumptions, particularly changes in the Company’s discount rates, earnings multiples and future cash flows, the Company may be required to recognize impairment charges. If the overall global economy continues to experience recessionary conditions, the economic outlook for the assets being evaluated could also result in additional impairment charges being recognized. Information with respect to the Company’s significant accounting policies on goodwill and other long-lived assets are included in Note 1, Significant Accounting Policies, to the consolidated financial statements.
Pension and Other Postretirement Benefits
Substantially all of the employees of the Company and its subsidiaries are covered by government or Company-sponsored defined benefit or defined contribution plans. Additionally, certain union and salaried employee groups in the U.S. are covered by postretirement healthcare plans. Costs for Company-sponsored plans are based on expected return on plan assets, discount rates, employee compensation increase rates and health care cost trends. Expected return on plan assets, discount rates and health care cost trend assumptions are particularly important when determining the Company’s benefit obligations and net periodic benefit costs associated with postretirement benefits. Changes in these assumptions can impact the Company’s pretax earnings. In determining the cost of postretirement benefits, certain assumptions are established annually to reflect market conditions and plan experience to appropriately reflect the expected costs as actuarially determined. These assumptions include medical inflation trend rates, discount rates, employee turnover and mortality rates. In establishing its discount rates, the Company predominantly uses observed indices of high-grade corporate bond yields with durations that are equivalent to the expected duration of the underlying liability. The discount rate for each plan is based on observed corporate bond yield indices in the respective economic region covered by the plan. The expected return on plan assets is the weighted average long-term expected return based upon asset allocations and historic average returns for the markets where the assets are invested, principally in foreign locations. Additional information related to the impact of changes in these assumptions is provided in Note 13, Benefit Plans, to the consolidated financial statements.
Litigation
The Company and its subsidiaries are from time to time parties to lawsuits arising out of their respective operations. The Company records liabilities when a loss is probable and can be reasonably estimated. These estimates are typically in the form of ranges, and the Company records the liabilities at the low point of the ranges. The ranges established by management are based on an analysis made by internal and external legal counsel who considers information known at the time. If the Company determines a liability to be only reasonably possible, it considers the same information to estimate the possible exposure and disclose any material potential liability. These loss contingencies are monitored regularly for a change in fact or circumstance that would require an accrual adjustment. The Company believes it has estimated liabilities for probable losses well in the past; however, the unpredictability of litigation and court decisions could cause a liability to be incurred in excess of estimates. Legal costs related to these lawsuits are expensed as incurred.
- 36 - -
Accruals for Product Returns, Customer Rebates and Product Warranties
The Company makes provisions for customer returns, customer rebates and for product warranties at the time of sale. These accruals are based on past history, projections of customer purchases and sales and expected product performance in the future. Because the actual results for product returns, rebates and warranties are dependent in part on future events, these matters require the use of estimates. The Company has a long history of product performance in the dental industry and thus has an extensive knowledge base from which to draw in measuring these estimates.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are determined using the liability method of accounting for income taxes. The Company’s tax expense includes the U.S. and international income taxes plus the provision for U.S. taxes on undistributed earnings of international subsidiaries not deemed to be permanently invested.
The Company applies a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company recognizes in the financial statements, the impact of a tax position, if that position is more likely than not of being sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the position.
Certain items of income and expense are not reported in tax returns and financial statements in the same year. The tax effect of such temporary differences is reported as deferred income taxes. Deferred tax assets are recognized if it is more likely than not that the assets will be realized in future years. The Company establishes a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets for which realization is not likely. As of December 31, 2009, the Company recorded a valuation allowance of $51.8 million against the benefit of certain deferred tax assets of foreign and domestic subsidiaries.
The Company operates within multiple taxing jurisdictions and in the normal course of business is examined in various jurisdictions. The reversal of the accruals is recorded when examinations are completed, statutes of limitation are closed or tax laws are changed.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Cash flows from operating activities during the year ended December 31, 2009 were $362.5 million compared to $336.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2008. The increase of $26.5 million was primarily the result of favorable working capital changes versus the prior year offset by lower earnings in the 2009 period compared to 2008. While net income decreased by $8.9 million to $274.4 million, the Company had lower working capital requirements. Improved inventory management in 2009 when compared to 2008 resulted in a $60.5 million generation of cash flow, which was partially offset by an increase in accounts receivable and a decrease in accounts payables and accrued liabilities. The Company’s cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments increased by $246.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 to $450.4 million.
For the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, the number of days for sales outstanding in accounts receivable was 55 days and 54 days, respectively. On a constant currency basis, the number of days in inventory was 99 days and 103 days for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Investing activities during 2009 include capital expenditures of $56.5 million. The Company expects that capital expenditures will be between $70.0 million and $80.0 million for the full year of 2010. Activity related to the acquisition of businesses, for the year ended December 31, 2009, was $3.0 million, which was primarily related to a final payment on an acquisition from a previous year. (See Note 3, Business Acquisitions, to the consolidated financial statements).
At December 31, 2009, the Company had authorization to maintain up to 17.0 million shares of treasury stock under its stock repurchase program as approved by the Board of Directors. Under this program, the Company purchased approximately 2.5 million shares during 2009 at an average price of $32.09. As of December 31, 2009 and 2008, the Company held 15.8 million and 14.2 million shares of treasury stock, respectively. The Company also received proceeds of $13.4 million primarily as a result of 0.9 million stock option exercises during the year ended December 31, 2009.
DENTSPLY's total long-term debt, including the current portion, at December 31, 2009 and 2008 was $453.7 million and $427.7 million, respectively. The Company’s long-term borrowings increased by a net of $26.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2009. This net change included net increase in borrowings of $30.2 million during the year ended 2009, less a decrease of $4.2 million due to exchange rate fluctuations on debt denominated in foreign currencies. During the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company’s ratio of long-term debt, including the current portion, to total capitalization decreased to 19.2% compared to 20.5% at December 31, 2008. DENTSPLY defines total capitalization as the sum of total long-term debt, including the current portion, plus total equity.
- 37 - -
Under its multi-currency revolving credit agreement, the Company is able to borrow up to $500.0 million through May 9, 2010. This facility is unsecured and contains certain affirmative and negative covenants relating to its operations and financial condition. The most restrictive of these covenants pertain to asset dispositions and prescribed ratios of indebtedness to total capital and operating income excluding depreciation and amortization to interest expense. At December 31, 2009, the Company was in compliance with these covenants. The Company also has available an aggregate $250.0 million under its U.S. commercial paper facility. The multi-currency revolving credit facility serves as a back-up to the commercial paper facility. The total available credit under the commercial paper facility and the multi-currency facility in the aggregate is $500.0 million with $62.8 million outstanding under the multi-currency facility and $85.2 million outstanding under the commercial paper facility at December 31, 2009. Management’s intent is to replace only a portion of the maturing facility, and expects to complete this in the second quarter of 2010.
The Company also has access to $72.5 million in uncommitted short-term financing under lines of credit from various financial institutions. The lines of credit have no major restrictions and are provided under demand notes between the Company and the lending institutions. At December 31, 2009, $15.6 million was outstanding under these short-term lines of credit. At December 31, 2009, the Company had total unused lines of credit related to the revolving credit agreement and the uncommitted short-term lines of credit of $404.9 million.
At December 31, 2009, the Company held $103.7 million of precious metals on consignment from several financial institutions. These consignment agreements allow the Company to acquire the precious metal at market rates at a point in time, which is approximately the same time, and for the same price as alloys are sold to the Company’s customers. In the event that the financial institutions would discontinue offering these consignment arrangements, and if the Company could not obtain other comparable arrangements, the Company may be required to obtain third party financing to fund an ownership position in the required precious metal inventory levels.
On October 16, 2009, the Company and a group of investors agreed to a new $250.0 million Private Placement Note (“PPN”) to be funded not later than February 19, 2010 with an average maturity of five years and a final maturity of six years at a fixed rate of 4.11%. The PPN is unsecured and contains certain affirmative and negative covenants relating to its operations and financial condition of the Company similar in substance to the existing $150.0 million U.S. Private Placement Note maturing March 15, 2010.
In accordance with the terms of PPN Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”), the Company received net proceeds of $250.0 million on February 19, 2010. The proceeds will be used to refinance the $150.0 million U.S. Private Placement Note due on March 15, 2010 with the remaining proceeds used to repay the commercial paper borrowing of $85.2 million and fund book overdrafts of $4.0 million. As of December 31, 2009, the Company has classified $239.2 million as long-term debt. The long-term debt classification is supported by the fact that the Company has demonstrated its intent and ability to fund existing short-term debt with the proceeds from the PPN. Additionally, the Agreement has an average maturity of five years, and the lenders are not permitted to cancel the Agreement or accelerate repayments. The Agreement does not contain a material adverse change clause subsequent to funding.
The following table presents the Company's scheduled contractual cash obligations at December 31, 2009:
Contractual Obligations | Greater | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Less Than | 1-3 | 3-5 | Than | ||||||||||||||||
1 Year | Years | Years | 5 Years | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-term borrowings (a) | $ | 66,580 | $ | 144,769 | $ | 76,897 | $ | 165,485 | $ | 453,731 | ||||||||||
| Operating leases | 26,688 | 31,021 | 12,088 | 12,423 | 82,220 | |||||||||||||||
Interest on long-term borrowings, net of interest rate swap agreements | 19,181 | 32,147 | 19,336 | 5,537 | 76,201 | |||||||||||||||
| Postretirement obligations | 8,619 | 18,283 | 21,233 | 62,229 | 110,364 | |||||||||||||||
| Cross currency swaps | 52,411 | 21,487 | 102,723 | - | 176,621 | |||||||||||||||
| Precious metal consignment agreements | 103,671 | - | - | - | 103,671 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 277,150 | $ | 247,707 | $ | 232,277 | $ | 245,674 | $ | 1,002,808 | |||||||||||
| (a) | Refer to Note 10, Financing Arrangements, to the consolidated financial statements for information on the Company’s classification of debt between short-term and long-term. |
Due to the uncertainty with respect to the timing of future cash flows associated with the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits at December 31, 2009, the Company is unable to make reasonably reliable estimates of the period of cash settlement with the respective taxing authority. Therefore, $18.4 million of the unrecognized tax benefit has been excluded from the contractual obligations table above (See Note 12, Income Taxes, to the consolidated financial statements).
- 38 - -
The Company expects on an ongoing basis to be able to finance cash requirements, including capital expenditures, stock repurchases, debt service, operating leases and potential future acquisitions, from the current cash, cash equivalents and short-term investment balances, funds generated from operations and amounts available under its existing credit facilities, which is further discussed in Note 10, Financing Arrangements, to the consolidated financial statements. As noted in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, the Company continues to generate strong cash flows from operations, which is used to finance the Company’s activities.
NEW ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
Refer to Note 1, Significant Accounting Policies, to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of recent accounting guidance and pronouncements.
Item 7A.
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURE ABOUT MARKET RISK
The Company's major market risk exposures are changing interest rates, movements in foreign currency exchange rates and potential price volatility of commodities used by the Company in its manufacturing processes. The Company's policy is to manage interest rates through the use of floating rate debt and interest rate swaps to adjust interest rate exposures when appropriate, based upon market conditions. The Company employs foreign currency denominated debt and currency swaps which serve to partially offset the Company's exposure on its net investments in subsidiaries denominated in foreign currencies. The Company's policy generally is to hedge major foreign currency transaction exposures through foreign exchange forward contracts. These contracts are entered into with major financial institutions thereby minimizing the risk of credit loss. In order to limit the unanticipated earnings fluctuations from volatility in commodity prices, the Company selectively enters into commodity swaps to convert variable raw material costs to fixed costs. The Company does not hold or issue derivative financial instruments for speculative or trading purposes. The Company is subject to other foreign exchange market risk exposure in addition to the risks on its financial instruments, such as possible impacts on its pricing and production costs, which are difficult to reasonably predict, and have therefore not been included in the table below. All items described are non-trading and are stated in U.S. dollars.
Financial Instruments
The fair value of financial instruments is determined by reference to various market data and other valuation techniques as appropriate. The Company believes the carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments, accounts receivable (net of allowance for doubtful accounts), prepaid expenses and other current assets, accounts payable, accrued liabilities, income taxes payable and notes payable approximate fair value due to the short-term nature of these instruments. The Company estimates the fair value and carrying value of its total debt, including the current portion of long-term debt, was $453.7 million and $427.7 million as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt equaled its carrying value as the Company’s debt is variable rate and reflects current market rates. The interest rates on private placement notes, revolving debt and commercial paper are variable and therefore the fair value of these instruments approximates carrying values. The following table shows the Company’s principal outstanding debt amounts and the associated weighted average interest rates as of December 31, 2009.
- 39 - -
EXPECTED MATURITY DATES
December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 and | Carrying | Fair | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | beyond | Value | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Financial Instruments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Notes Payable: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. dollar denominated | $ | 5,341 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 5,341 | $ | 5,341 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 3.04 | % | 3.04 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taiwan dollar denominated | 150 | - | - | - | - | - | 150 | 150 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Euro denominated | 9,721 | - | - | - | - | - | 9,721 | 9,721 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 2.53 | % | 2.53 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brazil Reais denominated | 382 | - | - | - | - | - | 382 | 382 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 13.43 | % | 13.43 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Notes Payable | $ | 15,594 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 15,594 | $ | 15,594 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2.95 | % | 2.95 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current Portion of Long-term Debt: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Swiss franc denominated | $ | 62,844 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 62,844 | $ | 62,844 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 0.60 | % | 0.60 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Euro denominated | 3,736 | - | - | - | - | - | 3,736 | 3,736 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 1.59 | % | 1.59 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total Current Portion of Long-Term Debt | $ | 66,580 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 66,580 | $ | 66,580 | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.66 | % | 0.66 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Long Term Debt: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. dollar denominated | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 75,015 | $ | 164,167 | $ | 239,182 | $ | 239,182 | ||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 0.56 | % | 0.41 | % | 0.46 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Japanese yen denominated | - | - | 134,776 | - | - | - | 134,776 | 134,776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 1.00 | % | 1.00 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Euro denominated | - | 5,299 | 4,694 | 1,215 | 667 | 1,318 | 13,193 | 13,193 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 2.06 | % | 3.59 | % | 2.21 | % | 2.93 | % | 2.71 | % | 2.73 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Long Term Debt, net current portion | $ | - | $ | 5,299 | $ | 139,470 | $ | 1,215 | $ | 75,682 | $ | 165,485 | $ | 387,151 | $ | 387,151 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2.06 | % | 1.09 | % | 2.21 | % | 0.58 | % | 0.43 | % | 0.72 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company employs derivative financial instruments to hedge certain anticipated transactions, firm commitments, or assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies. Additionally, the Company utilizes interest rate swaps to convert floating rate debt to fixed rate, cross currency basis swaps to convert debt denominated in one currency to another currency and commodity swaps to fix its variable raw materials.
Foreign Exchange Risk Management
The Company enters into forward foreign exchange contracts to selectively hedge assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies. Market value gains and losses are recognized in income currently and the resulting gains or losses offset foreign exchange gains or losses recognized on the foreign currency assets and liabilities hedged.
The Company selectively enters into forward foreign exchange contracts to hedge anticipated purchases of product to effectively fix certain variable costs. The forward foreign exchange contracts are used to stabilize the cost of certain of the Company's products. The Company generally accounts for the forward foreign exchange contracts as cash flow hedges. As a result, the Company records the fair value of the contract primarily through other comprehensive income based on the tested effectiveness of the forward foreign exchange contracts. Realized gains or losses in other comprehensive income are released and recorded to costs of products sold as the products associated with the forward foreign exchange contracts are sold. The Company measures the effectiveness of cash flow hedges of anticipated transactions on a spot to spot basis rather than on a forward to forward basis. Accordingly, any time value component of the hedge fair value is deemed ineffective and will be reported currently as interest expense in the period which it is applicable. The spot to spot change in the derivative fair value will be deferred in other comprehensive income and released and recorded to costs of products sold as the products associated with the forward foreign exchange contracts are sold. Any cash flows associated with these instruments are included in cash from operations in accordance with the Company’s policy of classifying the cash flows from these instruments in the same category as the cash flows from the items being hedged.
Determination of hedge activity is based upon market conditions, the magnitude of the foreign currency assets and liabilities and perceived risks. These foreign exchange contracts generally have maturities of less than twelve months and the counterparties to the transactions are typically large international financial institutions. The Company’s significant contracts outstanding as of December 31, 2009 are summarized in the table that follows.
- 40 - -
EXPECTED MATURITY DATES
(represents notional amounts for derivative financial instruments)
December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 and | Carrying | Fair | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | beyond | Value | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Derivative Financial Instruments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign Exchange Forward Contracts: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 13.3 million Australian dollars | $ | 11,268 | $ | 635 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (316 | ) | $ | (316 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Forward purchase, 6.2 million British pounds | (9,728 | ) | (298 | ) | - | - | - | - | 226 | 226 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 16.4 million Canadian dollars | 15,117 | 560 | - | - | - | - | (927 | ) | (927 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward purchase, 7.0 million Swiss francs | (6,804 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | (15 | ) | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 7.5 million Danish Krone | 1,454 | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward purchase, 0.1 million Euros | (18 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | 13 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 83.3 million Japanese yen | 895 | - | - | - | - | - | 628 | 628 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 96.7 million Mexican Pesos | 7,390 | - | - | - | - | - | 94 | 94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 1.2 billion South Korean won | 999 | - | - | - | - | - | 10 | 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 6.5 million Taiwanese dollars | 202 | - | - | - | - | - | (2 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Foreign Exchange Forward Contracts | $ | 20,775 | $ | 897 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (276 | ) | $ | (276 | ) | ||||||||||||||
The Company has numerous investments in foreign subsidiaries. The net assets of these subsidiaries are exposed to volatility in currency exchange rates. Currently, the Company uses both non-derivative financial instruments, including foreign currency denominated debt held at the parent company level and derivative financial instruments to hedge some of this exposure. Translation gains and losses related to the net assets of the foreign subsidiaries are offset by gains and losses in the non-derivative and derivative financial instruments designated as hedges of net investments, which are included in accumulated other comprehensive income.
In the first quarter of 2005, the Company entered into cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 457.5 million paying three month Swiss franc LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $384.4 million. In the first quarter of 2006, the Company entered into additional cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 55.5 million paying three month Swiss franc LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $42.0 million. In the fourth quarter of 2006, the Company entered into additional cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 80.4 million paying three month Swiss franc LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $64.4 million. In the first quarter of 2007, the Company entered into additional cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 56.6 million paying three month Swiss franc LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $46.3 million. Additionally, in the fourth quarter of 2005, the Company entered into cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Euro 358.0 million paying three month Euro LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $419.7 million. In the first quarter of 2009, the Company terminated Swiss francs 57.5 million cross currency swap at a fair value of zero. In the second and third quarters of 2009, the Company amended certain of its Swiss franc and Euro cross currency interest rate swaps to extend their maturity dates for an additional three years. Specifically, a total of Swiss francs 300.0 million have been extended to March and April of 2013 and a total of Euro 250.0 million have been extended to December 2013. The Swiss franc and Euro cross currency interest rate swaps are designated as net investment hedges of the Swiss and Euro denominated net assets. The interest rate differential is recognized in the earnings as interest income or interest expense as it is accrued. The foreign currency revaluation is recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax effects.
At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the Company had Euro-denominated, Swiss franc-denominated, and Japanese yen-denominated debt and cross currency interest rate swaps (at the parent company level) to hedge the currency exposure related to a designated portion of the net assets of its European, Swiss and Japanese subsidiaries. The fair value of the cross currency interest rate swap agreements is the estimated amount the Company would (pay) receive at the reporting date, taking into account the effective interest rates and foreign exchange rates. As of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the estimated net fair values of the cross currency interest rate swap agreements were negative $176.6 million and negative $148.9 million, respectively, which are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax effects. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the accumulated translation gains on investments in foreign subsidiaries, primarily denominated in Euros, Swiss francs and Japanese Yen, net of these net investment hedges, were $111.1 million and $77.6 million, respectively, which were included in accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax effects. The Company’s outstanding debt denominated in foreign currencies and the outstanding cross currency interest rate swaps as of December 31, 2009 are summarized in the table that follows.
- 41 - -
EXPECTED MATURITY DATES
(represents notional amounts for derivative financial instruments)
December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 and | Carrying | Fair | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | beyond | Value | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cross Currency Basis Swaps | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Swiss franc 592.5 million @ $1.21 | $ | 150,343 | $ | 77,734 | $ | 54,723 | $ | 290,051 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (83,979 | ) | $ | (83,979 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| pay CHF 3mo. LIBOR rec. USD 3mo. LIBOR | 0.02 | % | (0.02 | )% | (0.02 | )% | 0.02 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Euros 358.0 million @ $1.17 | 154,827 | - | - | 358,395 | - | - | (92,642 | ) | (92,642 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| pay EUR 3mo. LIBOR rec. USD 3mo. LIBOR | 0.46 | % | 0.56 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Cross Currency Basis Swaps | $ | 305,170 | $ | 77,734 | $ | 54,723 | $ | 648,446 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (176,621 | ) | $ | (176,621 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rate Risk Management
The Company uses interest rate swaps to convert a portion of its variable rate debt to fixed rate debt. As of December 31, 2009, the Company has three groups of significant variable rate to fixed rate interest rate swaps. One of the groups of swaps has notional amounts totaling 12.6 billion Japanese Yen, and effectively converts the underlying variable interest rates to an average fixed rate of 1.6% for a term of ten years, ending in March 2012. Another swap has a notional amount of 65.0 million Swiss francs, and effectively converts the underlying variable interest rates to a fixed rate of 4.2% for a term of seven years, ending in March 2012. A third group of swaps has a notional amount of $150.0 million, and effectively converts the underlying variable interest rates to a fixed rate of 3.9% for a term of two years, ending March 2010. The Company’s significant contracts outstanding as of December 31, 2009 are summarized in the table that follows.
EXPECTED MATURITY DATES
(represents notional amounts for derivative financial instruments)
December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 and | Carrying | Fair | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | beyond | Value | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest Rate Swaps | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps - Euro | $ | 2,056 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 3,046 | $ | (882 | ) | $ | (882 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 2.5 | % | 3.8 | % | 3.8 | % | 3.8 | % | 3.8 | % | 3.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps - Japanese yen | - | - | 134,776 | - | - | - | (3,351 | ) | (3,351 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 1.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps - Swiss francs | - | - | 62,844 | - | - | - | (4,470 | ) | (4,470 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 4.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps - U.S. dollars | 150,000 | - | - | - | - | - | (1,084 | ) | (1,084 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest rate | 3.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Interest Rate Swaps | $ | 152,056 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 198,974 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 3,046 | $ | (9,787 | ) | $ | (9,787 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Commodity Risk Management
The Company selectively enters into commodity swaps to effectively fix certain variable raw material costs. These swaps are used purely to stabilize the cost of components used in the production of certain of the Company's products. The Company generally accounts for the commodity swaps as cash flow hedges. As a result, the Company records the fair value of the swap primarily through other comprehensive income based on the tested effectiveness of the commodity swap. Realized gains or losses in other comprehensive income are released and recorded to costs of products sold as the products associated with the commodity swaps are sold. The Company measures the effectiveness of cash flow hedges of anticipated transactions on a spot to spot basis rather than on a forward to forward basis. Accordingly, any time value component of the hedge fair value is deemed ineffective and will be reported currently as interest expense in the period which it is applicable. The spot to spot change in the derivative fair value will be deferred in other comprehensive income and released and recorded to costs of products sold as the products associated with the forward foreign exchange contracts are sold. Any cash flows associated with these instruments are included in cash from operations in accordance with the Company’s policy of classifying the cash flows from these instruments in the same category as the cash flows from the items being hedged. The Company’s significant contracts outstanding as of December 31, 2009 are summarized in the table that follows.
EXPECTED MATURITY DATES
December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2015 and | Carrying | Fair | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | beyond | Value | Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodity Contracts: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Silver Swap - U.S. dollar | $ | (977 | ) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 129 | $ | 129 | |||||||||||||||
| Platinum Swap - U.S. dollar | (790 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | 164 | 164 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Commodity Contracts | $ | (1,767 | ) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 293 | $ | 293 | |||||||||||||||
- 42 - -
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
Consignment Arrangements
The Company consigns the precious metals used in the production of precious metal dental alloy products from various financial institutions. Under these consignment arrangements, the banks own the precious metal, and, accordingly, the Company does not report this consigned inventory as part of its inventory on its consolidated balance sheet. These agreements are cancelable by either party at the end of each consignment period, which typically run for a period of one to nine months; however, because the Company typically has access to numerous financial institutions with excess capacity, consignment needs created by cancellations can be shifted among the other institutions. The consignment agreements allow the Company to take ownership of the metal at approximately the same time customer orders are received and to closely match the price of the metal acquired to the price charged to the customer (i.e., the price charged to the customer is largely a pass through).
As precious metal prices fluctuate, the Company evaluates the impact of the precious metal price fluctuation on its target gross margins for precious metal dental alloy products and revises the prices customers are charged for precious metal dental alloy products accordingly, depending upon the magnitude of the fluctuation. While the Company does not separately invoice customers for the precious metal content of precious metal dental alloy products, the underlying precious metal content is the primary component of the cost and sales price of the precious metal dental alloy products. For practical purposes, if the precious metal prices go up or down by a small amount, the Company will not immediately modify prices, as long as the cost of precious metals embedded in the Company’s precious metal dental alloy price closely approximates the market price of the precious metal. If there is a significant change in the price of precious metals, the Company adjusts the price for the precious metal dental alloys, maintaining its margin on the products.
At December 31, 2009, the Company had 109,268 troy ounces of precious metal, primarily gold, platinum and palladium, on consignment for periods of less than one year with a market value of $103.7 million. Under the terms of the consignment agreements, the Company also makes compensatory payments to the consignor banks based on a percentage of the value of the consigned precious metals inventory. At December 31, 2009, the average annual rate charged by the consignor banks was 1.20%. These compensatory payments are considered to be a cost of the metals purchased and are recorded as part of the cost of products sold.
- 43 - -
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The Company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. A Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. In addition, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management of the Company has assessed the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009. In making its assessment, management used the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Based on its assessment management concluded that, as of December 31, 2009, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective based on the criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the COSO.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report, which appears herein.
| /s/ | Bret W. Wise | /s/ | William R. Jellison | |||
| Bret W. Wise | William R. Jellison | |||||
| Chairman of the Board and | Senior Vice President and | |||||
| Chief Executive Officer | Chief Financial Officer | |||||
| February 22, 2010 | February 22, 2010 |
- 44 - -
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
of DENTSPLY International Inc
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of DENTSPLY International Inc and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2) presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company's management is responsible for these financial statements and the financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in “Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting” appearing under Item 15(a)(1). Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, in 2009 the Company changed its method of presenting noncontrolling interests.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. In addition, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
| /s/ | PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP |
| PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP | |
| Philadelphia, Pennsylvania | |
| February 22, 2010 |
- 45 - -
DENTSPLY INTERNATIONAL INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 2,159,916 | $ | 2,193,723 | $ | 2,009,833 | ||||||
| Cost of products sold | 1,048,612 | 1,041,779 | 969,050 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | 1,111,304 | 1,151,944 | 1,040,783 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 723,227 | 739,168 | 675,365 | |||||||||
| Restructuring, impairments and other costs | 6,890 | 32,355 | 10,527 | |||||||||
| Operating income | 381,187 | 380,421 | 354,891 | |||||||||
| Other income and expenses: | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense | 21,896 | 32,527 | 23,783 | |||||||||
| Interest income | (5,032 | ) | (17,089 | ) | (26,428 | ) | ||||||
| Other expense (income), net | 967 | 10,110 | (656 | ) | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes | 363,356 | 354,873 | 358,192 | |||||||||
| Provision for income taxes | 88,944 | 71,603 | 98,481 | |||||||||
| Net income | 274,412 | 283,270 | 259,711 | |||||||||
| Less: Net income (loss) attributable | ||||||||||||
| to noncontrolling interests | 154 | (599 | ) | 57 | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to | ||||||||||||
| DENTSPLY International | $ | 274,258 | $ | 283,869 | $ | 259,654 | ||||||
| Earnings per common share: | ||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 1.85 | $ | 1.90 | $ | 1.71 | ||||||
| Diluted | 1.83 | 1.87 | 1.68 | |||||||||
| Cash dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.200 | $ | 0.185 | $ | 0.165 | ||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | ||||||||||||
| Basic | 148,319 | 149,069 | 151,707 | |||||||||
| Diluted | 150,102 | 151,679 | 154,721 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
- 46 - -
DENTSPLY INTERNATIONAL INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 450,348 | $ | 203,991 | ||||
| Short-term investments | 37 | 258 | ||||||
| Accounts and notes receivable-trade, net | 348,684 | 319,260 | ||||||
| Inventories, net | 291,640 | 306,125 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 127,087 | 120,228 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 1,217,796 | 949,862 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 439,619 | 432,276 | ||||||
| Identifiable intangible assets, net | 89,086 | 103,718 | ||||||
| Goodwill, net | 1,312,596 | 1,277,026 | ||||||
| Other noncurrent assets, net | 28,835 | 67,518 | ||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 3,087,932 | $ | 2,830,400 | ||||
| Liabilities and Equity | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 100,847 | $ | 104,329 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities | 249,169 | 193,660 | ||||||
| Income taxes payable | 12,366 | 36,178 | ||||||
| Notes payable and current portion | ||||||||
| of long-term debt | 82,174 | 25,795 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 444,556 | 359,962 | ||||||
| Long-term debt | 387,151 | 423,679 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 72,524 | 69,049 | ||||||
| Other noncurrent liabilities | 276,743 | 318,297 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 1,180,974 | 1,170,987 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
| Equity: | ||||||||
| Preferred stock, $.01 par value; .25 million shares authorized; no shares issued | - | - | ||||||
Common stock, $.01 par value; 200 million shares authorized; 162.8 million shares issued at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 | 1,628 | 1,628 | ||||||
| Capital in excess of par value | 195,495 | 187,154 | ||||||
| Retained earnings | 2,083,459 | 1,838,958 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | 83,542 | 39,612 | ||||||
Treasury stock, at cost, 15.8 million shares at December 31, 2009 and 14.2 million shares at December 31, 2008 | (532,019 | ) | (479,630 | ) | ||||
| Total DENTSPLY International Equity | 1,832,105 | 1,587,722 | ||||||
| Noncontrolling Interests | 74,853 | 71,691 | ||||||
| Total Equity | 1,906,958 | 1,659,413 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 3,087,932 | $ | 2,830,400 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
- 47 - -
DENTSPLY INTERNATIONAL INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(in thousands)
| Accumulated | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital in | Other | DENTSPLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common | Excess of | Retained | Comprehensive | Treasury | International | Noncontrolling | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock | Par Value | Earnings | Income (Loss) | Stock | Equity | Interests | Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2006 | $ | 1,628 | $ | 168,135 | $ | 1,352,342 | $ | 79,914 | $ | (328,184 | ) | $ | 1,273,835 | $ | 239 | $ | 1,274,074 | |||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | 259,654 | - | - | 259,654 | 57 | 259,711 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | 106,231 | - | 106,231 | - | 106,231 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities | - | - | - | (333 | ) | - | (333 | ) | - | (333 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss on derivative financial instruments | - | - | - | (53,790 | ) | - | (53,790 | ) | - | (53,790 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension liability adjustments | - | - | - | 13,797 | - | 13,797 | - | 13,797 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income | 325,559 | 57 | 325,616 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options | - | (20,592 | ) | - | - | 66,186 | 45,594 | - | 45,594 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from stock options exercised | - | 11,378 | - | - | - | 11,378 | - | 11,378 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share based compensation expense | - | 14,088 | - | - | - | 14,088 | - | 14,088 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding of Employee Stock Option Plan | - | 39 | - | - | 312 | 351 | - | 351 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury shares purchased | - | - | - | - | (125,422 | ) | (125,422 | ) | - | (125,422 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjustments to initially apply changes in US GAAP | - | - | (4,282 | ) | - | - | (4,282 | ) | - | (4,282 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| RSU dividends | - | 36 | (36 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends ($0.165 per share) | - | - | (24,995 | ) | - | - | (24,995 | ) | - | (24,995 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2007 | $ | 1,628 | $ | 173,084 | $ | 1,582,683 | $ | 145,819 | $ | (387,108 | ) | $ | 1,516,106 | $ | 296 | $ | 1,516,402 | |||||||||||||||
| Purchase of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interest | 71,931 | 71,931 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | 283,869 | - | - | 283,869 | (599 | ) | 283,270 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | (71,521 | ) | - | (71,521 | ) | 63 | (71,458 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss on derivative financial instruments | - | - | - | (13,986 | ) | - | (13,986 | ) | - | (13,986 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension liability adjustments | - | - | - | (20,700 | ) | - | (20,700 | ) | - | (20,700 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income | 177,662 | (536 | ) | 177,126 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options | - | (7,268 | ) | - | - | 19,994 | 12,726 | - | 12,726 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from stock options exercised | - | 3,910 | - | - | - | 3,910 | - | 3,910 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share based compensation expense | - | 17,290 | - | - | - | 17,290 | - | 17,290 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding of Employee Stock Option Plan | - | 62 | - | - | 118 | 180 | - | 180 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury shares purchased | - | - | - | - | (112,634 | ) | (112,634 | ) | - | (112,634 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| RSU dividends | - | 76 | (76 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends ($0.185 per share) | - | - | (27,518 | ) | - | - | (27,518 | ) | - | (27,518 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2008 | $ | 1,628 | $ | 187,154 | $ | 1,838,958 | $ | 39,612 | $ | (479,630 | ) | $ | 1,587,722 | $ | 71,691 | $ | 1,659,413 | |||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | 274,258 | - | - | 274,258 | 154 | 274,412 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | 50,566 | - | 50,566 | 3,008 | 53,574 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss on derivative financial instruments | - | - | - | (13,960 | ) | - | (13,960 | ) | - | (13,960 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension liability adjustments | - | - | - | 7,324 | - | 7,324 | - | 7,324 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive Income | 318,188 | 3,162 | 321,350 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options | - | (11,515 | ) | - | - | 24,921 | 13,406 | - | 13,406 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from stock options exercised | - | 3,505 | - | - | - | 3,505 | - | 3,505 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share based compensation expense | - | 16,276 | - | - | - | 16,276 | - | 16,276 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding of Employee Stock Option Plan | - | (63 | ) | - | - | 1,408 | 1,345 | - | 1,345 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury shares purchased | - | - | - | - | (78,718 | ) | (78,718 | ) | - | (78,718 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| RSU dividends | - | 138 | (138 | ) | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends ($0.200 per share) | - | - | (29,619 | ) | - | - | (29,619 | ) | - | (29,619 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2009 | $ | 1,628 | $ | 195,495 | $ | 2,083,459 | $ | 83,542 | $ | (532,019 | ) | $ | 1,832,105 | $ | 74,853 | $ | 1,906,958 | |||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
- 48 - -
| DENTSPLY INTERNATIONAL INC AND SUBSIDIARIES | ||||||||||||
| CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 274,412 | $ | 283,270 | $ | 259,711 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation | 54,087 | 47,887 | 42,628 | |||||||||
| Amortization | 11,088 | 9,042 | 7,661 | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 195 | 13,371 | 25,568 | |||||||||
| Share based compensation expense | 16,276 | 17,290 | 14,088 | |||||||||
| Restructuring, impairments and other costs - noncash | 369 | 8,303 | 190 | |||||||||
| Stock option income tax benefit | (3,505 | ) | (3,910 | ) | (11,414 | ) | ||||||
| Other non-cash income | (8,650 | ) | (19,654 | ) | (10,676 | ) | ||||||
| (Gain) loss on disposal of property, plant and equipment | (1,997 | ) | 1,373 | (1,904 | ) | |||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions: | ||||||||||||
| Accounts and notes receivable-trade, net | (16,942 | ) | (3,690 | ) | 9,029 | |||||||
| Inventories, net | 27,710 | (32,824 | ) | (716 | ) | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 6,996 | (1,220 | ) | 644 | ||||||||
| Other non current assets | (192 | ) | 390 | 1,253 | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | (4,947 | ) | 5,430 | (7,395 | ) | |||||||
| Accrued liabilities | (1,708 | ) | 5,748 | (396 | ) | |||||||
| Income taxes | 8,104 | 4,594 | 59,421 | |||||||||
| Other noncurrent liabilities | 1,193 | 581 | 5 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 362,489 | 335,981 | 387,697 | |||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||
| Cash paid for acquisitions of businesses and equity investments | (2,986 | ) | (117,300 | ) | (101,492 | ) | ||||||
| Capital expenditures | (56,481 | ) | (76,440 | ) | (64,163 | ) | ||||||
| Expenditures for identifiable intangible assets | (14 | ) | (2,477 | ) | (1,665 | ) | ||||||
| Purchases of short-term investments | - | (166,208 | ) | (138,471 | ) | |||||||
| Liquidations of short-term investments | 222 | 314,025 | 73 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property, plant and equipment | 5,860 | 596 | 6,327 | |||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (53,399 | ) | (47,804 | ) | (299,391 | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from long-term borrowings, net of deferred financing costs | 86,091 | 117,900 | 149,500 | |||||||||
| Payments on long-term borrowings | (58,403 | ) | (226,147 | ) | (50,543 | ) | ||||||
| (Decrease) increase in short-term borrowings | (7,465 | ) | 2,111 | (2,166 | ) | |||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 13,406 | 12,726 | 45,594 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefits from share based compensation | 3,505 | 3,910 | 11,378 | |||||||||
| Cash paid for treasury stock | (78,718 | ) | (112,634 | ) | (125,422 | ) | ||||||
| Cash dividends paid | (29,836 | ) | (26,952 | ) | (25,134 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (71,420 | ) | (229,086 | ) | 3,207 | |||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 8,687 | (24,484 | ) | 12,807 | ||||||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 246,357 | 34,607 | 104,320 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 203,991 | 169,384 | 65,064 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 450,348 | $ | 203,991 | $ | 169,384 | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | ||||||||||||
| Interest paid, net of amounts capitalized | $ | 23,231 | $ | 34,222 | $ | 21,926 | ||||||
| Income taxes paid | $ | 76,207 | $ | 66,696 | $ | 38,091 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
- 49 - -
DENTSPLY INTERNATIONAL INC AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 - SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Description of Business
DENTSPLY International Inc (“DENTSPLY” or the “Company”), designs, develops, manufactures and markets a broad range of products for the dental market. The Company believes that it is the world's leading manufacturer and distributor of dental prosthetics, endodontic instruments and materials, and ultrasonic scalers; the leading United States manufacturer and distributor of denture teeth, dental handpieces, dental x-ray film holders, film mounts and prophylaxis paste; and a leading worldwide manufacturer or distributor of dental injectable anesthetics, impression materials, orthodontic appliances, dental cutting instruments, dental implants, restorative dental materials, dental sealants, and crown and bridge materials. The Company distributes its dental products in over 120 countries under some of the most well established brand names in the industry.
DENTSPLY is committed to the development of innovative, high quality, cost effective products for the dental market.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“US GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expense during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates, if different assumptions are made or if different conditions exist.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company. The Company also consolidates all variable interest entities (“VIE”) where the Company has determined that it has the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance and shares in either the significant risks or rewards of the VIE. The Company continually reassess VIE to determine if consolidation is appropriate. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions are eliminated in consolidation.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include deposits with banks as well as highly liquid time deposits with maturities at the date of purchase of ninety days or less.
Short-term Investments
Short-term investments are highly liquid time deposits with original maturities at the date of purchase greater than ninety days and with remaining maturities of approximately one year or less.
Accounts and Notes Receivable-Trade
The Company sells dental products through a worldwide network of distributors and directly to end users. For customers on credit terms, the Company performs ongoing credit evaluation of those customers' financial condition and generally does not require collateral from them. The Company establishes allowances for doubtful accounts for estimated losses resulting from the inability of its customers to make required payments. The Company records a provision for doubtful accounts, which is included in “Selling, general and administrative expenses.”
Accounts receivable – trade is stated net of these allowances that were $12.2 million and $18.8 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. In 2009, the Company wrote-off $4.3 million of accounts receivable that were previously reserved. The tighter credit markets caused the Company to reassess and tighten its controls over customer credit terms, increase collection efforts and analyze accounts receivable activity. This, along with improved customer liquidity, enabled the Company to reduce the provision for doubtful accounts by $3.1 million in 2009. The Company recorded a provision for doubtful accounts of $3.7 million for 2008 and $2.9 million for 2007.
- 50 - -
Additionally, notes receivable – trade is stated net of these allowances that were $1.1 million and $0.5 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The Company recorded provisions for doubtful accounts on notes receivable – trade of approximately $0.5 million for 2009, $0.3 million for 2008, and negative $0.2 million for 2007.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the cost of $7.8 million, or 2.7%, and $9.6 million, or 3.1%, respectively, of inventories was determined by the last in, first-out (“LIFO”) method. The cost of other inventories was determined by the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) or average cost methods. The Company establishes reserves for inventory estimated to be obsolete or unmarketable equal to the difference between the cost of inventory and estimated market value based upon assumptions about future demand and market conditions.
If the FIFO method had been used to determine the cost of LIFO inventories, the amounts at which net inventories are stated would be higher than reported at December 31, 2009 and 2008 by $4.0 million and $3.5 million, respectively.
Valuation of Goodwill and Other Long-Lived Assets
Assessment of the potential impairment of goodwill and other long-lived assets is an integral part of the Company’s normal ongoing review of operations. Testing for potential impairment of these assets is significantly dependent on numerous assumptions and reflects management’s best estimates at a particular point in time. The dynamic economic environments in which the Company’s businesses operate and key economic and business assumptions with respect to projected selling prices, increased competition and introductions of new technologies can significantly affect the outcome of impairment tests. Estimates based on these assumptions may differ significantly from actual results. Changes in factors and assumptions used in assessing potential impairments can have a significant impact on the existence and magnitude of impairments, as well as the time at which such impairments are recognized. If there are unfavorable changes in these assumptions, the future cash flows, a key variable in assessing the impairment of these assets, may decrease and as a result the Company may be required to recognize impairment charges. Future changes in the environment and the economic outlook for the assets being evaluated could also result in additional impairment charges being recognized. Information with respect to the Company’s significant accounting policies on long-lived assets for each category of long-lived asset is discussed below.
Goodwill
US GAAP requires that at least an annual impairment test be applied to goodwill. The Company performs impairment tests using a fair value approach. If impairment is identified on goodwill, the resulting charge is determined by recalculating goodwill through a hypothetical purchase price allocation of the fair value and reducing the current carrying value to the extent it exceeds the recalculated goodwill.
The Company’s fair value approach involves using a discounted cash flow model with market-based support as its valuation technique to measure the fair value for its reporting units. The discounted cash flows model uses five year forecasted cash flows plus a terminal value based on a multiple of earnings. In addition, the Company applied gross margin and operating expense assumptions consistent with its historical trends. The total cash flows were discounted based on market participant data, which included the Company’s weighted-average cost of capital. The Company considered the current market conditions when determining its assumptions. Lastly, the Company reconciled the aggregate fair values of its reporting units to its market capitalization, which included a reasonable control premium based on market conditions. Additional information related to the testing for goodwill impairment is provided in Note 8, Goodwill and Intangible Assets.
Identifiable Definite-lived Intangible Assets
Identifiable definite-lived intangible assets, which primarily consist of patents, trademarks, brand names, non-compete agreements and licensing agreements, are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives. These assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or circumstances suggest that the carrying amount of the asset may not be recoverable. The Company closely monitors certain intangible assets related to new and existing technologies for indicators of impairment as these assets have more risk of becoming impaired. Impairment is based upon an initial evaluation of the identifiable undiscounted cash flows. If the initial evaluation identifies a potential impairment, a fair value is determined by using a discounted cash flows valuation. If impaired, the resulting charge reflects the excess of the asset’s carrying cost over its fair value.
- 51 - -
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Except for leasehold improvements, depreciation for financial reporting purposes is computed by the straight-line method over the following estimated useful lives: buildings - generally 40 years and machinery and equipment - 4 to 15 years. The cost of leasehold improvements is amortized over the shorter of the estimated useful life or the term of the lease. Maintenance and repairs are charged to operations; replacements and major improvements are capitalized. These assets groups are reviewed for impairment whenever events or circumstances suggest that the carrying amount of the asset group may not be recoverable. Impairment is based upon an evaluation of the identifiable undiscounted cash flows. If impaired, the resulting charge reflects the excess of the asset group’s carrying cost over its fair value.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company requires that all derivative instruments be recorded on the balance sheet at fair value and that changes in fair value be recorded each period in current earnings or accumulated other comprehensive income.
The Company employs derivative financial instruments to hedge certain anticipated transactions, firm commitments, and assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies. Additionally, the Company utilizes interest rate swaps to convert floating rate debt to fixed rate, fixed rate debt to floating rate, cross currency basis swaps to convert debt denominated in one currency to another currency, and commodity swaps to fix its variable raw materials costs.
On January 1, 2009, the Company adopted the new accounting guidance for expanded disclosures about derivative instruments and hedging activities. As a result, the Company has expanded its disclosures about its strategies, objectives and risks for using derivative instruments. In addition, the Company has disclosed the fair value of derivative instruments and their gains and losses in tabular format as required. The Company’s expanded disclosures regarding its derivative instruments can be found in Note 15, Financial Instruments and Derivatives.
Pension and Other Postretirement Benefits
Substantially all of the employees of the Company and its subsidiaries are covered by government or Company-sponsored defined benefit or defined contribution plans. Additionally, certain union and salaried employee groups in the United States are covered by postretirement healthcare plans. Costs for Company-sponsored plans are based on expected return on plan assets, discount rates, employee compensation increase rates and health care cost trends. Expected return on plan assets, discount rates and health care cost trend assumptions are particularly important when determining the Company’s benefit obligations and net periodic benefit costs associated with postretirement benefits. Changes in these assumptions can impact the Company’s pretax earnings. In determining the cost of postretirement benefits, certain assumptions are established annually to reflect market conditions and plan experience to appropriately reflect the expected costs as actuarially determined. These assumptions include medical inflation trend rates, discount rates, employee turnover and mortality rates. The Company predominantly uses liability durations in establishing its discount rates, which are observed from indices of high-grade corporate bond yields in the respective economic regions of the plans. The expected return on plan assets is the weighted average long-term expected return based upon asset allocations and historic average returns for the markets where the assets are invested, principally in foreign locations. The Company reports the funded status of its defined benefit pension and other postretirement benefit plans on its balance sheets as a net liability or asset. Additional information related to the impact of changes in these assumptions is provided in Note 13, Benefit Plans.
In December 2008, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued new guidance for disclosures about the Company’s postretirement benefit plans (“the Plans”). The objective of this new guidance is to provide financial statement users additional information concerning the Plans’ investment policies and strategies and how allocation decisions are made. Additionally, disclosures are to be made concerning categories of the Plans’ assets, the valuation technique used in regard to the fair value measurement of the Plans’ assets and concentrations of risk within the Plans’ assets. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2009 with early application permitted. The revised disclosures were not required to be applied to earlier periods that are presented for comparative periods. The Company’s expanded disclosures regarding its pension and postretirement benefits can be found in Note 13, Benefit Plans.
Accruals for Self-Insured Losses
The Company maintains insurance for certain risks, including workers’ compensation, general liability, product liability and vehicle liability, and is self-insured for employee related health care benefits. The Company accrues for the expected costs associated with these risks by considering historical claims experience, demographic factors, severity factors and other relevant information. Costs are recognized in the period the claim is incurred, and the financial statement accruals include an estimate of claims incurred but not yet reported. The Company has stop-loss coverage to limit its exposure to any significant exposure on a per claim basis.
- 52 - -
Litigation
The Company and its subsidiaries are from time to time parties to lawsuits arising out of their respective operations. The Company records liabilities when a loss is probable and can be reasonably estimated. These estimates are typically in the form of ranges, and the Company records the liabilities at the low point of the ranges. The ranges established by management are based on an analysis made by internal and external legal counsel who considers information known at the time. If the Company determines a liability to be only reasonably possible, it considers the same information to estimate the possible exposure and disclose any material potential liability. These loss contingencies are monitored regularly for a change in fact or circumstance that would require an accrual adjustment. The Company believes it has estimated liabilities for probable losses well in the past; however, the unpredictability of litigation and court decisions could cause a liability to be incurred in excess of estimates. Legal costs related to these lawsuits are expensed as incurred.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income
Accumulated other comprehensive income (“AOCI”) includes foreign currency translation adjustments related to the Company’s foreign subsidiaries, net of the related changes in certain financial instruments hedging these foreign currency investments. In addition, changes in the Company’s fair value of certain derivative financial instruments and changes in its unrecognized pension losses and prior service costs, net are recorded in AOCI. These changes are recorded in AOCI net of any related tax effects. For the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, these adjustments were net of tax effects of $143.0 million, $138.5 million and $111.3 million, respectively, primarily related to foreign currency translation adjustments.
The balances included in AOCI in the consolidated balance sheets are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | $ | 220,116 | $ | 169,550 | ||||
| Net loss on derivative financial instruments | (113,800 | ) | (99,840 | ) | ||||
| Pension liability adjustments | (22,774 | ) | (30,098 | ) | ||||
| $ | 83,542 | $ | 39,612 | |||||
The cumulative foreign currency translation adjustments included translation gains of $327.8 million and $278.1 million as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, offset by losses of $107.7 million and $108.5 million, respectively, on loans designated as hedges of net investments.
Foreign Currency Translation
The functional currency for foreign operations, except for those in highly inflationary economies, has been determined to be the local currency.
Assets and liabilities of foreign subsidiaries are translated at exchange rates on the balance sheet date; revenue and expenses are translated at the average year-to-date rates of exchange. The effects of these translation adjustments are reported in equity within AOCI. During the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company had gains of $0.9 million on its loans designated as hedges of net investments and translation gains of $49.7 million. During the year ended December 31, 2008, the Company had translation losses of $53.0 million, and losses of $18.5 million on its loans designated as hedges of net investments.
Exchange gains and losses arising from transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency of the entity involved and remeasurement adjustments in countries with highly inflationary economies are included in income. Net exchange gains of $0.3 million, exchange losses of $8.9 million, and exchange gains of $0.5 million in 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively, are included in “Other expense (income), net.”
Revenue Recognition
Revenue, net of related discounts and allowances, is recognized when the earnings process is complete. This occurs when products are shipped to or received by the customer in accordance with the terms of the agreement, title and risk of loss have been transferred, collectability is reasonably assured and pricing is fixed or determinable. Net sales include shipping and handling costs collected from customers in connection with the sale. Sales taxes, value added taxes and other similar types of taxes collected from customers in connection with the sale are recorded by the Company on a net basis and are not included in the statement of operations.
- 53 - -
Certain of the Company’s customers are offered cash rebates based on targeted sales increases. In accounting for these rebate programs, the Company records an accrual as a reduction of net sales for the estimated rebate as sales take place throughout the year.
A portion of the Company’s net sales is comprised of sales of precious metals generated through its precious metal dental alloy product offerings. As the precious metal content of the Company’s sales is largely a pass-through to customers, the Company uses its cost of precious metal purchased as a proxy for the precious metal content of sales, as the precious metal content of sales is not separately tracked and invoiced to customers. The Company believes that it is reasonable to use the cost of precious metal content purchased in this manner since precious metal alloy sale prices are typically adjusted when the prices of underlying precious metals change. The precious metals content of sales was $168.7 million, $199.9 million and $189.9 million for 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Cost of Products Sold
Cost of products sold represents costs directly related to the manufacture and distribution of the Company’s products. Primary costs include raw materials, packaging, direct labor, overhead, shipping and handling, warehousing and the depreciation of manufacturing, warehousing and distribution facilities. Overhead and related expenses include salaries, wages, employee benefits, utilities, lease costs, maintenance and property taxes.
Warranties
The Company provides warranties on certain equipment products. Estimated warranty costs are accrued when sales are made to customers. Estimates for warranty costs are based primarily on historical warranty claim experience. Warranty costs are included in “Cost of products sold.”
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses represent costs incurred in generating revenues and in managing the business of the Company. Such costs include advertising and other marketing expenses, salaries, employee benefits, incentive compensation, research and development, travel, office expenses, lease costs, amortization of capitalized software and depreciation of administrative facilities.
Research and Development Costs
Research and development (“R&D”) costs relate primarily to internal costs for salaries and direct overhead expenses. In addition, the Company contracts with outside vendors to conduct R&D activities. All such R&D costs are charged to expense when incurred. The Company capitalizes the costs of equipment that have general R&D uses and expenses such equipment that is solely for specific R&D projects. The depreciation expense related to this capitalized equipment is included in the Company’s R&D costs. R&D costs are included in “Selling, general and administrative expenses” and amounted to approximately $53.6 million, $52.3 million and $46.8 million for 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Stock Compensation
The Company recognizes the compensation cost relating to share-based payment transactions in the financial statements. The cost of share-based payment transactions is measured at the grant date, based on the calculated fair value of the award, and is recognized as an expense over the employee’s requisite service period (generally the vesting period of the equity awards). The compensation cost is only recognized for the portion of the awards that are expected to vest.
Income Taxes
The Company’s tax expense includes U.S. and international income taxes plus the provision for U.S. taxes on undistributed earnings of international subsidiaries not deemed to be permanently invested. Tax credits and other incentives reduce tax expense in the year the credits are claimed. Certain items of income and expense are not reported in tax returns and financial statements in the same year. The tax effect of such temporary differences is reported as deferred income taxes. Deferred tax assets are recognized if it is more likely than not that the assets will be realized in future years. The Company establishes a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets for which realization is not likely.
- 54 - -
The Company applies a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company recognizes in the financial statements, the impact of a tax position, if that position is more likely than not of being sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the position.
Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share are calculated by dividing net earnings by the weighted average number of shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per share is calculated by dividing net earnings by the weighted average number of shares outstanding for the period, adjusted for the effect of an assumed exercise of all dilutive options outstanding at the end of the period.
Business Acquisitions
During the first quarter of 2009, the Company adopted the new accounting guidance for business combinations. ��The new guidance establishes principles and requirements for transactions that represent business combinations to be accounted for under the acquisition method. It provides guidance regarding the recognition and measurement of assets acquired, liabilities assumed, goodwill, noncontrolling interest in the acquiree and financial statement disclosure requirements. Additionally, it provides guidance for identifying a business combination, measuring the acquisition date and defining the measurement period for adjusting provisional amounts recorded. The implementation of this standard did not impact the Company’s net income attributable to DENTSPLY International.
The Company purchases businesses and occasionally purchases partial interests in businesses. These acquisitions are accounted for as purchases and result in the recognition of goodwill in the Company’s financial statements. This goodwill arises because the purchase prices for these businesses reflect a number of factors including the future earnings and cash flow potential of these businesses; the multiple to earnings, cash flow and other factors at which similar businesses have been purchased by other acquirers; the competitive nature of the process by which the Company acquired the business; and because of the complementary strategic fit and expected synergies these businesses bring to existing operations.
The Company makes an allocation of the purchase price at the date of acquisition based upon the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The Company obtains this information during due diligence and through other sources. Examples of factors and information that the Company uses to determine the allocations include: tangible and intangible asset evaluations and appraisals; evaluations of existing contingencies and liabilities; product line integration information; and information systems compatibilities. If the initial accounting for an acquisition is incomplete by the end of the quarter in which the acquisition occurred, the Company will record a provisional estimate in the financial statements. The provisional estimate will be finalized as soon as information becomes available but will only occur up to one year from the acquisition date.
Noncontrolling Interests
On January 1, 2009, the Company adopted the new accounting guidance for reporting noncontrolling interest (“NCI”) in a subsidiary. As a result, the Company reported NCI as a separate component of Equity in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Additionally, the Company reported the portion of net income and comprehensive income (loss) attributed to the Company and NCI separately in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The Company also included a separate column for NCI in the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity and Comprehensive Income. All related disclosures have been adjusted accordingly. Prior year amounts associated with NCI in the financial statements and accompanied footnotes have been retrospectively adjusted to conform to the adoption.
Segment Reporting
The Company has numerous operating businesses covering a wide range of products and geographic regions, primarily serving the professional dental market. Professional dental products represented approximately 97% of sales in 2009, 2008 and 2007. The Company has four reportable segments and a description of the activities of these segments is included in Note 4, Segment and Geographic Information.
- 55 - -
Fair Value Measurement
Recurring Basis
The Company records certain financial assets and liabilities at fair value in accordance with the accounting guidance, which defines fair value as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. The accounting guidance establishes a hierarchal disclosure framework associated with the level of pricing observability utilized in measuring financial instruments at fair value. The three broad levels defined by the fair value hierarchy are as follows:
Level 1 – Quoted prices are available in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the reported date.
Level 2 – Pricing inputs are other than quoted prices in active markets, which are either directly or indirectly observable as of the reported date. The nature of these financial instruments include, derivative instruments whose fair value have been derived using a model where inputs to the model are directly observable in the market, or can be derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data.
Level 3 – Instruments that have little to no pricing observability as of the reported date. These financial instruments do not have two-way markets and are measured using management’s best estimate of fair value, where the inputs into the determination of fair value require significant management judgment or estimation.
The degree of judgment utilized in measuring the fair value of certain financial assets and liabilities generally correlates to the level of pricing observability. Pricing observability is impacted by a number of factors, including the type of financial instrument. Financial assets and liabilities with readily available active quoted prices or for which fair value can be measured from actively quoted prices generally will have a higher degree of pricing observability and a lesser degree of judgment utilized in measuring fair value. Conversely, financial assets and liabilities rarely traded or not quoted will generally have less, or no pricing observability and a higher degree of judgment utilized in measuring fair value.
The Company primarily applies the market approach for recurring fair value measurements and endeavors to utilize the best available information. Accordingly, the Company utilizes valuation techniques that maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Additionally, the Company considers its credit risks and its counterparties' credit risks when determining the fair values of its financial assets and liabilities. The Company has presented the required disclosures in Note 16, Fair Value Measurement.
Non-Recurring Basis
During the first quarter of 2009, the Company adopted the fair value measurement guidance for non-financial assets and liabilities. The new guidance changed the effective date for recognizing and disclosing the fair value for non-financial assets and liabilities except for items recognized or disclosed in the financial statements on a recurring basis. Additionally, the guidance also required additional disclosure about the fair value of financial instruments for interim reporting periods in addition to annual financial statements. The implementation of this new guidance did not impact the Company’s financial statements in the current or prior periods.
When events or circumstances require an asset or liability to be fair valued that otherwise is generally recorded based on another valuation method, such as, net realizable value, the Company will utilize the valuation techniques described above.
Subsequent Events
In May 2009, a new accounting guidance was issued for disclosures about subsequent events. The new guidance requires the Company to disclose the date through which it has evaluated subsequent events and whether the date represents the date the financial statements were issued or were available to be issued. The Company has evaluated subsequent events through February 22, 2010, which is the date the financial statements have been filed with the SEC.
- 56 - -
Codification
In June 2009, the FASB issued The FASB Accounting Standards Codification™ (the “Codification”) as the source of authoritative accounting principles recognized by the FASB to be applied by nongovernmental entities in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States. All guidance contained in the Codification carries an equal level of authority. On the effective date, the Codification superseded all then-existing non-SEC accounting and reporting standards. All other nongrandfathered non-SEC accounting literature not included in the Codification became nonauthoritative. The Codification is effective for financial statements issued for interim and annual periods ending after September 15, 2009. The Company has adopted this standard and updated all of its disclosures to be consistent with the Codification and has determined that the implementation of the Codification did not have a significant impact on its financial results.
Reclassification of Prior Year Amounts
Certain reclassifications have been made to prior years' data in order to conform to current year presentation.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2009, the FASB issued new accounting guidance for the transfer of financial assets and the effects of a transfer on its financial position, financial performance and cash flows. The new guidance eliminates the use of qualified special purpose entities, clarifies the derecognition criteria for a transfer accounted for as a sale, and expands the disclosure requirements among other things. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2009 and must be applied prospectively to new transfers of financial assets. The Company believes this new guidance will not have a material impact on its financial statements.
In June 2009, the FASB issued new accounting guidance for VIE. The new guidance includes: (1) the elimination of the exemption from consolidation for qualifying special purpose entities, (2) a new approach for determining the primary beneficiary of a VIE, which requires that the primary beneficiary have both (i) the power to control the most significant activities of the VIE and (ii) either the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that could potentially be significant to the VIE, and (3) the requirement to continually reassess who should consolidate a VIE. The new guidance is effective for annual reporting periods that begin after November 15, 2009 and applies to all existing and new VIE.
The Company will be adopting new accounting guidance for VIE during the first quarter of 2010. The Company believes this new guidance will not have a material impact on its financial statements. The Company continues to believe that it will be the primary beneficiary of Materialise and Zhermack under this new accounting guidance for VIE. The accounting for Materialise and Zhermack are discussed further in Note 3, Business Acquisitions.
- 57 - -
NOTE 2 - EARNINGS PER COMMON SHARE
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted earnings per common share:
| Net income | ||||||||||||
| attributable to | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except for share amounts) | DENTSPLY | Earnings per | ||||||||||
International | Shares | common share | ||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 274,258 | 148,319 | $ | 1.85 | |||||||
Incremental shares from assumed exercise of dilutive options | - | 1,783 | ||||||||||
| Diluted | $ | 274,258 | 150,102 | $ | 1.83 | |||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 283,869 | 149,069 | $ | 1.90 | |||||||
Incremental shares from assumed exercise of dilutive options | - | 2,610 | ||||||||||
| Diluted | $ | 283,869 | 151,679 | $ | 1.87 | |||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||||
| Basic | $ | 259,654 | 151,707 | $ | 1.71 | |||||||
Incremental shares from assumed exercise of dilutive options | - | 3,014 | ||||||||||
| Diluted | $ | 259,654 | 154,721 | $ | 1.68 | |||||||
Options to purchase 2.9 million, 1.6 million and 0.2 million shares of common stock that were outstanding during the years ended 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, were not included in the computation of diluted earnings per common share since the options' exercise prices were greater than the average market price of the common shares and, therefore, the effect would be antidilutive.
NOTE 3 - BUSINESS ACQUISITIONS
The Company accounts for all business combinations under the acquisition method of accounting; and accordingly, the results of the operations acquired are included in the accompanying financial statements for the periods subsequent to the respective dates of the acquisitions.
During 2009, the acquisition related activity was $3.0 million, net of cash. This activity was related to an additional earn-out payment on a prior acquisition from 2007 and acquisition of a small sales and marketing organization of 3D digital implantology products.
During 2008, the acquisition related activity was $117.3 million, net of cash and assumed debt. This activity was related to three business combinations, the acquisition and consolidation of two VIE, and three earn-out payments on acquisitions from prior years.
Business Combinations
The following list provides information about the companies acquired in 2008, excluding the VIE:
| · | In July 2008, the Company acquired Dental Depot Lomberg B.V. (“Lomberg”), which markets and sells various dental products, including but not limited to, orthodontic products and materials. Lomberg is included in the Canada/Latin America/ Endodontics/ Orthodontics segment and further strengthens the Company’s dental specialty business. |
- 58 - -
| · | In July 2008, the Company acquired E.S. Holding N.V. (“E.S. Holding”), which manufactures, markets and sells dental products, particularly dental laboratory products, and non-dental products. E.S. Holding is included in the Dental Laboratory Business/Implants/Non-Dental segment and further strengthens the Company’s dental specialty and laboratory businesses. |
| · | In December 2008, the Company acquired the assets of Apollonia & Fama Implant S.r.l. (“AFI”), which markets and sells dental implant products in Italy. AFI is included in the France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses segment and further strengthens the Company’s dental specialty business. |
Variable Interest Entities
During 2006, the Company acquired a 40% interest in Materialise Dental N.V. (“Materialise”), a simulation software company and a leading manufacturer of a variety of surgical guides to assist in the placement of dental implants. The transaction provides the opportunity for the Company to acquire the remaining interest over time. The Company accounted for the initial purchase of 40% interest under the equity method.
In 2007, Materialise received a $2.7 million uncollateralized loan of which the Company funded $1.1 million, which was equivalent to its ownership interest. The loan has a five year term and was issued to support Materialise’s working capital. If the Company purchases additional shares subsequent to December 31, 2009 under the provisions of the Sale and Purchase Agreement (“SPA”), the loan is repayable immediately.
In the fourth quarter of 2008, the Company purchased an additional 6% interest in Materialise. The purchase of additional interest increased the Company’s total ownership to 46%, and created a reconsideration event in determining if the Company is the primary beneficiary of Materialise. The Company determined it was the primary beneficiary based on the purchase of the additional 6% ownership interests, existing provisions in the Share Purchase Agreement, and increased business arrangements between Materialise and the Company. The results and final estimates of fair values of assets acquired and liabilities of Materialise have been included in the Company’s financial statements and included in the Dental Laboratory Business/Implants/Non-Dental segment. The consolidation of Materialise further strengthens the Company’s product offerings in the dental specialty business.
On December 31, 2008, the Company acquired a 60% interest in Zhermack S.p.A. (“Zhermack”), a manufacturer, designer, marketer, and seller of dental consumables products. The Company determined that Zhermack is considered a VIE due to disproportionate voting rights. The Company is considered the primary beneficiary based on its total ownership interest in Zhermack and its opportunity to acquire the remaining interest over time. The estimates of fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed of Zhermack have been included in the Company’s financial statements and included in the U.S., Germany, and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses segment. The consolidation of Zhermack further strengthens the Company’s product offerings in the dental consumables businesses.
The Company will be adopting new accounting guidance for VIE during the first quarter of 2010, which is discussed more fully in Note 1, Significant Accounting Policies. The Company continues to believe that it will be the primary beneficiary of Materialise and Zhermack under this new accounting guidance for VIE.
Additional Earn-out Payments
Several of the Company’s 2005 and 2007 acquisitions included provisions for possible additional payments based on the future performance of the individual businesses (generally for two to three years). During 2008, the Company paid $10.0 million in additional purchase price under these agreements. Several of the 2007 and 2008 acquisitions still have potential additional payments based on future operating performance of the businesses that could be paid out over the next five years.
Purchase Price Allocations for the Business Acquisitions, VIE, and Additional Earnout Payments
The purchase prices have been allocated on the basis of final estimates of fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed and have been included in the accompanying financial statements since the effective date of the respective transaction. As of December 31, 2009, the Company has recorded a total of $169.4 million in goodwill related to unallocated portions of the respective purchase prices for the three business combinations, two VIE, and additional earnout payments on acquisitions from prior years. None of this goodwill is expected to be deductible for tax purposes.
- 59 - -
The aggregate purchase price allocation for these acquisitions based on final estimates of fair value is as follows (in thousands):
| Current assets | $ | 58,390 | ||
| Property, plant and equipment | 41,375 | |||
| Identifiable intangible assets and goodwill | 200,788 | |||
| Other long-term assets | 885 | |||
| Total assets | $ | 301,438 | ||
| Current liabilities | (51,155 | ) | ||
| Long-term liabilities | (34,712 | ) | ||
| Total liabilities | $ | (85,867 | ) | |
| Noncontrolling Interests | $ | (67,962 | ) | |
| Net assets | $ | 147,609 |
As a result of the acquisition related activity in 2008, the Company expensed $2.3 million for the fair value of in-process research and development.
Also, as a result of the finalization of fair values assigned to assets acquired and liabilities assumed from 2008 acquisition related activity, the Company has recorded a total of $31.4 million in intangible assets. Of this total amount of intangible assets, $27.1 million was recorded as trademarks, brand names and patents with an average weighted life of 16.0 years, and $4.3 million was allocated to other intangible assets with an average weighted life of 6.4 years.
Goodwill was assigned to the following four segments:
| • | $77.6 million to U.S., Germany, and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses; |
| • | $2.8 million to France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses; |
| • | $16.2 million Canada/ Latin America/ Endodontics/ Orthodontics; and, |
| • | $72.8 million to Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental. |
NOTE 4 – SEGMENT AND GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION
The operating businesses are combined into operating groups, which have overlapping product offerings, geographical presence, customer bases, distribution channels and regulatory oversight. These operating groups are considered the Company’s reportable segments as the Company’s chief operating decision-maker regularly reviews financial results at the operating group level and uses this information to manage the Company’s operations. The accounting policies of the segments are consistent with those described for the consolidated financial statements in the summary of significant accounting policies (see Note 1, Significant Accounting Policies). The Company measures segment income for reporting purposes as net operating income before restructuring, impairments, and other costs, interest and taxes. Additionally, net operating income is derived from net third party sales, excluding precious metal content. A description of the services provided within each of the Company’s four reportable segments is provided below. The disclosure below reflects the Company’s segment reporting structure.
In January 2009, the Company moved the reporting responsibility for several locations between segments as a result of a change to the management structure. This change also helped the Company gain operating efficiencies and effectiveness. The segment information below reflects this revised structure for all periods shown.
- 60 - -
United States, Germany, and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses
This business group includes responsibility for the design, manufacture, sales and distribution for certain small equipment and chairside consumable products in the United States, Germany, and certain other European regions. It also has responsibility for the sales and distribution of certain Endodontic products in Germany.
France, United Kingdom, Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses
This business group includes responsibility for the sales and distribution for certain small equipment, chairside consumable products, certain laboratory products and certain Endodontic products in France, United Kingdom, Italy, the Commonwealth of Independent States (“CIS”), Middle East, Africa, Asia (excluding Japan), Japan and Australia, as well as the sale and distribution of implant products and bone substitute/grafting materials in Italy, Asia and Australia. This business group also includes the responsibility for sales and distribution for certain laboratory products, implants products and bone substitution/grafting materials for Austria. It also is responsible for sales and distribution for certain small equipment and chairside consumable products, certain laboratory products, implant products and bone substation/grafting materials in certain other European countries. In addition this business group also includes the manufacture and sale of Orthodontic products and certain laboratory products in Japan, and the manufacture of certain laboratory and certain Endodontic products in Asia.
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/Orthodontics
This business group includes responsibility for the design, manufacture, and/or sales and distribution of certain small equipment, chairside consumable products, certain laboratory products and Endodontic products in Brazil. It also has responsibility for the sales and distribution of most of the Company’s dental products sold in Latin America and Canada. This business group also includes the responsibility for the design and manufacture of Endodontic products in the United States, Switzerland and Germany and is responsible for the sales and distribution of the Company’s Endodontic products in the United States, Canada, Switzerland, Benelux, Scandinavia, Austria, Latin America and Eastern Europe, and for certain Endodontic products in Germany. This business group is also responsible for the world-wide sales and distribution, excluding Japan, as well as some manufacturing of the Company’s Orthodontic products. In addition, this business group is also responsible for sales and distribution in the United States for implant and bone substitute/grafting materials and the sales and distribution of implants in Brazil. This business group is also responsible for the manufacture and sale of certain products in the Company’s non-dental business.
Dental Laboratory Business/Implants/Non-Dental
This business group includes the responsibility for the design, manufacture, sales and distribution for most laboratory products, excluding certain countries mentioned previously, and the design, manufacture, and/or sales and distribution of the Company’s dental implant products and bone substitute/grafting materials, excluding sales and distribution of implants and bone substitute/grafting materials in the United States, Italy, Austria, and certain other Eastern European countries, Asia, and Australia. This business group is also responsible for most of the Company’s non-dental business.
Significant interdependencies exist among the Company’s operations in certain geographic areas. Inter-group sales are at prices intended to provide a reasonable profit to the manufacturing unit after recovery of all manufacturing costs and to provide a reasonable profit for purchasing locations after coverage of marketing, sales, distribution and general and administrative costs.
Generally, the Company evaluates performance of the operating groups based on the groups’ operating income, excluding restructuring, impairments and other costs, interest and taxes, and net third party sales, excluding precious metal content. The Company considers net third party sales, excluding precious metal content, as the appropriate sales measurement due to the fluctuations of precious metal prices and due to the fact that the precious metal content is largely a pass-through to customers and has a minimal effect on earnings.
- 61 - -
The following table sets forth information about the Company’s operating groups for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007.
Third Party Net Sales
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 526,668 | $ | 459,678 | $ | 428,236 | ||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 453,827 | 468,413 | 413,068 | |||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | 621,256 | 632,151 | 587,539 | |||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | 561,042 | 636,791 | 584,575 | |||||||||
| All Other (a) | (2,877 | ) | (3,310 | ) | (3,585 | ) | ||||||
| Total Net Sales | $ | 2,159,916 | $ | 2,193,723 | $ | 2,009,833 | ||||||
Third Party Net Sales, Excluding Precious Metal Content
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 526,668 | $ | 459,678 | $ | 428,237 | ||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 419,385 | 437,479 | 381,235 | |||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | 618,414 | 628,887 | 583,885 | |||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | 429,614 | 471,066 | 430,127 | |||||||||
| All Other (a) | (2,877 | ) | (3,310 | ) | (3,585 | ) | ||||||
| Total net sales, excluding precious metal content | $ | 1,991,204 | $ | 1,993,800 | $ | 1,819,899 | ||||||
| Precious metal content of sales | 168,712 | 199,923 | 189,934 | |||||||||
| Total net sales, including precious metal content | $ | 2,159,916 | $ | 2,193,723 | $ | 2,009,833 | ||||||
| (a) | Includes amounts recorded at Corporate headquarters |
- 62 - -
Intersegment Net Sales
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 104,328 | $ | 130,463 | $ | 100,964 | ||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 13,202 | 15,941 | 16,682 | |||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | 103,329 | 106,031 | 88,953 | |||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | 104,164 | 111,925 | 98,558 | |||||||||
| All Other (a) | 176,539 | 177,251 | 151,345 | |||||||||
| Eliminations | (501,562 | ) | (541,611 | ) | (456,502 | ) | ||||||
| Total | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
Depreciation and Amortization
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 14,945 | $ | 12,807 | $ | 10,977 | ||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 3,884 | 3,188 | 3,201 | |||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | 16,978 | 17,179 | 14,934 | |||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | 21,461 | 16,063 | 14,463 | |||||||||
| All Other (b) | 7,907 | 7,692 | 6,714 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 65,175 | $ | 56,929 | $ | 50,289 | ||||||
(a) Includes results of Corporate headquarters and one distribution warehouse not managed by named segments.
(b) Includes amounts recorded at Corporate headquarters.
- 63 - -
Segment Operating Income
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 158,389 | $ | 162,717 | $ | 139,001 | ||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 18,721 | 13,017 | 9,983 | |||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | 185,772 | 200,101 | 180,944 | |||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | 93,569 | 124,898 | 112,444 | |||||||||
| All Other (a) | (68,374 | ) | (87,957 | ) | (76,954 | ) | ||||||
| Segment Operating Income | $ | 388,077 | $ | 412,776 | $ | 365,418 | ||||||
| Reconciling Items: | ||||||||||||
| Restructuring and other costs | 6,890 | 32,355 | 10,527 | |||||||||
| Interest Expense | 21,896 | 32,527 | �� | 23,783 | ||||||||
| Interest Income | (5,032 | ) | (17,089 | ) | (26,428 | ) | ||||||
| Other expense (income), net | 967 | 10,110 | (656 | ) | ||||||||
| Income before income taxes | $ | 363,356 | $ | 354,873 | $ | 358,192 | ||||||
Capital Expenditures
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 8,333 | $ | 19,836 | $ | 10,538 | ||||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 2,506 | 3,839 | 2,286 | |||||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | 14,434 | 19,593 | 22,376 | |||||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | 25,546 | 24,510 | 23,896 | |||||||||
| All Other (b) | 5,662 | 8,662 | 5,067 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 56,481 | $ | 76,440 | $ | 64,163 | ||||||
| (a) | Includes results of Corporate headquarters, inter-segment eliminations and one distribution warehouse not managed by named segments |
| (b) | Includes capital expenditures of Corporate headquarters. |
- 64 - -
Assets
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
U.S., Germany and Certain Other European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 602,272 | $ | 556,125 | ||||
France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other European Countries, CIS, Middle East, Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 388,831 | 385,050 | ||||||
Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ Orthodontics | 809,924 | 763,479 | ||||||
Dental Laboratory Business/ Implants/Non-Dental | 973,764 | 942,504 | ||||||
| All Other (a) | 313,141 | 183,242 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 3,087,932 | $ | 2,830,400 | ||||
(a) Includes assets of Corporate headquarters, inter-segment eliminations and one distribution warehouse not managed by named segments.
Geographic Information
The following table sets forth information about the Company's operations in different geographic areas for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007. Net sales reported below represent revenues for shipments made by operating businesses located in the country or territory identified, including export sales. Assets reported represent those held by the operating businesses located in the respective geographic areas.
| United | Other | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | States | Germany | Foreign | Consolidated | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 843,349 | $ | 482,130 | $ | 834,437 | $ | 2,159,916 | ||||||||
| Long-lived assets | 167,574 | 143,469 | 232,691 | 543,734 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 865,743 | $ | 470,836 | $ | 857,144 | $ | 2,193,723 | ||||||||
| Long-lived assets | 175,360 | 137,871 | 233,668 | 546,899 | ||||||||||||
| 2007 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 844,162 | $ | 438,099 | $ | 727,572 | $ | 2,009,833 | ||||||||
| Long-lived assets | 172,204 | 144,340 | 157,207 | 473,751 | ||||||||||||
Product and Customer Information
The following table presents net sales information by product category:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
| Dental consumables products | $ | 710,606 | $ | 680,016 | $ | 634,480 | ||||||
| Dental laboratory products | 500,235 | 558,291 | 530,821 | |||||||||
| Dental specialty products | 895,357 | 888,484 | 782,808 | |||||||||
| Non-dental products | 53,718 | 66,932 | 61,724 | |||||||||
| Total net sales | $ | 2,159,916 | $ | 2,193,723 | $ | 2,009,833 | ||||||
- 65 - -
Dental consumable products consist of dental sundries and small equipment products used in dental offices for the treatment of patients. DENTSPLY’s products in this category include dental anesthetics, infection control products, prophylaxis paste, dental sealants, impression materials, restorative materials, bone grafting materials, tooth whiteners and topical fluoride. The Company manufactures thousands of different consumable products marketed under more than a hundred brand names. Small equipment products consist of various durable goods used in dental offices for treatment of patients. DENTSPLY’s small equipment products include high and low speed handpieces, intraoral curing light systems and ultrasonic scalers and polishers.
Dental laboratory products are used in dental laboratories in the preparation of dental appliances. DENTSPLY’s products in this category include dental prosthetics, including artificial teeth, precious metal dental alloys, dental ceramics, crown and bridge materials, and equipment products used in laboratories consisting of computer aided machining (CAM) ceramic systems and porcelain furnaces.
Dental specialty products are specialized treatment products used within the dental office and laboratory settings. DENTSPLY’s products in this category include endodontic (root canal) instruments and materials, implants and related products, bone grafting material, 3D digital implantology, and orthodontic appliances and accessories.
Non-dental products are comprised primarily of investment casting materials that are used in the production of jewelry, golf club heads and other casting products, as well as certain medical products.
One customer, Henry Schein, Incorporated, a dental distributor, accounted for more than ten percent of consolidated net sales in 2009, 2008 and 2007 accounting for 11%, 11% and 12% of all sales, respectively. Third party export sales from the U.S. are less than ten percent of consolidated net sales.
NOTE 5 – OTHER EXPENSE (INCOME)
Other expense (income), net, consists of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange transaction losses (gains) | $ | 336 | $ | 8,881 | $ | (452 | ) | |||||
| Other expense (income) | 631 | 1,229 | (204 | ) | ||||||||
| $ | 967 | $ | 10,110 | $ | (656 | ) | ||||||
NOTE 6 – INVENTORIES, NET
Inventories, net, consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Finished goods | $ | 178,721 | $ | 184,226 | ||||
| Work-in-process | 53,056 | 58,123 | ||||||
| Raw materials and supplies | 59,863 | 63,776 | ||||||
| $ | 291,640 | $ | 306,125 | |||||
The Company’s inventory valuation reserve was $31.9 million for 2009 and $28.4 million for 2008.
- 66 - -
NOTE 7- PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property, plant and equipment, net, consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Assets, at cost: | ||||||||
| Land | $ | 43,207 | $ | 40,702 | ||||
| Buildings and improvements | 295,297 | 256,172 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 546,806 | 511,618 | ||||||
| Construction in progress | 18,610 | 31,659 | ||||||
| 903,920 | 840,151 | |||||||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | 464,301 | 407,875 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 439,619 | $ | 432,276 | ||||
NOTE 8 – GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
The Company requires that impairment tests on goodwill or other indefinite-lived intangible assets be performed annually and are based upon a fair value approach rather than an evaluation of undiscounted cash flows. If goodwill impairment is identified, the resulting charge is determined by recalculating goodwill through a hypothetical purchase price allocation of the fair value and reducing the current carrying value to the extent it exceeds the recalculated goodwill. If impairment is identified on indefinite-lived intangibles, the resulting charge reflects the excess of the asset’s carrying cost over its fair value. Other intangible assets with finite lives are amortized over their useful lives and tested for impairment when events or changes in circumstances indicate that the finite-lived intangible assets may be impaired
In addition to minimum annual impairment tests, the Company also requires that impairment assessments be made more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the goodwill or indefinite-lived intangible assets might be impaired. As the Company learns of such changes in circumstances through periodic analysis of actual results or through the annual development of operating unit business plans in the fourth quarter of each year, for example, impairment assessments will be performed as necessary.
The Company performs its annual goodwill impairment test in the second quarter of each year. This impairment assessment includes an evaluation of various reporting units, which are generally an operating segment or one reporting level below the operating segment. The Company compares the fair value of each reporting unit to its carrying amount to determine if there is potential goodwill impairment. If the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an impairment loss is recorded to the extent that the fair value of the goodwill of the reporting unit is less than the carrying value of its goodwill.
The Company performed the required annual impairment tests of goodwill as of April 30, 2009 on seven reporting units. To determine the fair value of our reporting units, the Company uses a discounted cash flow model with market-based support as its valuation technique to measure the fair value for its reporting units. The discounted cash flow model uses five year forecasted cash flows plus a terminal value based on a multiple of earnings. In addition, the Company applied gross margin and operating expense assumptions consistent with historical trends. The total cash flows were discounted based on a range between 8% to 11%, which included assumptions regarding the Company’s weighted-average cost of capital. The Company considered the current market conditions when determining its assumptions as the U.S. economy, and to a certain extent, the global economy, were in a recession during 2009. Lastly, the Company reconciled the aggregated fair values of its reporting units to its market capitalization, which included a reasonable control premium based on market conditions. As a result of the annual impairment tests of goodwill, no impairment was identified.
As of December 31, 2009, the Company has assigned no value to indefinite-lived intangible assets. Impairments of finite-lived identifiable intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 were $0.3 million, $2.7 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
- 67 - -
The table below presents the net carrying values of goodwill and finite-lived identifiable intangible assets.
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Goodwill | $ | 1,312,596 | $ | 1,277,026 | ||||
| Finite-lived identifiable intangible assets, net | $ | 89,086 | $ | 103,718 | ||||
A reconciliation of changes in the Company’s goodwill is as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 1,277,026 | $ | 1,127,420 | ||||
| Acquisition activity | 3,572 | 164,200 | ||||||
| Changes to purchase price allocations | 5,245 | (175 | ) | |||||
| Effects of exchange rate changes | 26,753 | (14,419 | ) | |||||
| Balance, end of the year | $ | 1,312,596 | $ | 1,277,026 | ||||
The Company has not recorded impairments to goodwill for the year ended December 31, 2009.
The change in the net carrying value of goodwill from 2008 to 2009 was due to foreign currency translation adjustments, additional payments based on the performance of the previously acquired businesses and changes to purchase price allocations. The purchase price allocation changes were primarily related to the finalization of the purchase price allocation on 2008 acquisitions.
Goodwill by reportable segment is as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| U.S., Germany and Certain Other | ||||||||
| European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 252,538 | $ | 255,768 | ||||
| France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other | ||||||||
| European Countries, CIS, Middle East, | ||||||||
| Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 159,383 | 161,623 | ||||||
| Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ | ||||||||
| Orthodontics | 267,427 | 257,183 | ||||||
| Dental Laboratory Business/ | ||||||||
| Implants/Non-Dental | 633,248 | 602,452 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 1,312,596 | $ | 1,277,026 | ||||
- 68 - -
Finite-lived identifiable intangible assets consist of the following:
| December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Net | Gross | Net | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Carrying | Accumulated | Carrying | Carrying | Accumulated | Carrying | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Amount | Amortization | Amount | Amount | Amortization | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||
| Patents | $ | 38,840 | $ | (25,842 | ) | $ | 12,998 | $ | 41,353 | $ | (22,945 | ) | $ | 18,408 | ||||||||||
| Trademarks | 70,353 | (17,939 | ) | 52,414 | 75,310 | (14,472 | ) | 60,838 | ||||||||||||||||
| Licensing agreements | 28,880 | (14,138 | ) | 14,742 | 29,490 | (13,032 | ) | 16,458 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other | 15,364 | (6,432 | ) | 8,932 | 12,197 | (4,183 | ) | 8,014 | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | 153,437 | $ | (64,351 | ) | $ | 89,086 | $ | 158,350 | $ | (54,632 | ) | $ | 103,718 | |||||||||||
Amortization expense for finite-lived identifiable intangible assets for 2009, 2008 and 2007 was $10.6 million, $8.7 million and $7.7 million, respectively. The annual estimated amortization expense related to these intangible assets for each of the five succeeding fiscal years is $9.3 million, $8.6 million, $7.9 million, $6.6 million and $5.9 million for 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014, respectively.
NOTE 9 - ACCRUED LIABILITIES
Accrued liabilities consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Payroll, commissions, bonuses, other | ||||||||
| cash compensation and employee benefits | $ | 60,083 | $ | 68,602 | ||||
| General insurance | 13,222 | 14,130 | ||||||
| Sales and marketing programs | 28,468 | 27,441 | ||||||
| Professional and legal costs | 10,248 | 10,075 | ||||||
| Restructuring costs | 9,358 | 4,905 | ||||||
| Warranty liabilities | 4,141 | 4,260 | ||||||
| Deferred income | 3,385 | 2,613 | ||||||
| Accrued vacation and holidays | 13,425 | 12,391 | ||||||
| Third party royalties | 9,806 | 9,053 | ||||||
| Current portion of derivatives | 59,250 | 8,520 | ||||||
| Other | 37,783 | 31,670 | ||||||
| $ | 249,169 | $ | 193,660 | |||||
A reconciliation of changes in the Company's warranty liability for 2009 and 2008 is as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Balance, beginning of the year | $ | 4,260 | $ | 4,431 | ||||
| Accruals for warranties issued during the year | 1,129 | 859 | ||||||
| Accruals related to pre-existing warranties | - | (48 | ) | |||||
| Warranty settlements made during the year | (1,295 | ) | (875 | ) | ||||
| Effects of exchange rate changes | 47 | (107 | ) | |||||
| Balance, end of the year | $ | 4,141 | $ | 4,260 | ||||
- 69 - -
NOTE 10 - FINANCING ARRANGEMENTS
Recent Financing Activities
On October 16, 2009, the Company and a group of investors agreed to a new $250.0 million Private Placement Note (“PPN”) to be funded not later than February 19, 2010 with an average maturity of five years and a final maturity of six years at a fixed rate of 4.11%. The PPN is unsecured and contains certain affirmative and negative covenants relating to operations and financial condition of the Company similar in substance to the existing $150.0 million U.S. Private Placement Note maturing March 15, 2010.
In accordance with the terms of PPN Purchase Agreement (the “Agreement”), the Company received net proceeds of $250.0 million on February 19, 2010. The proceeds will be used to refinance the $150.0 million U.S. Private Placement Note due on March 15, 2010 with the remaining proceeds used to repay the commercial paper borrowing of $85.2 million and fund book overdrafts of $4.0 million. As of December 31, 2009, the Company has classified $239.2 million as long-term debt. The long-term debt classification is supported by the fact that the Company has demonstrated its intent and ability to fund existing short-term debt with the proceeds from the PPN. Additionally, the Agreement has an average maturity of five years, and the lenders are not permitted to cancel the Agreement or accelerate repayments. The Agreement does not contain a material adverse change clause subsequent to funding.
Short-Term Borrowings
Short-term bank borrowings amounted to $15.6 million and $21.8 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The weighted average interest rates of these borrowings were 3.0% and 5.3% at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Unused lines of credit for short-term financing at December 31, 2009 and 2008 were $56.9 million and $43.4 million, respectively. Substantially all other short-term borrowings were classified as long-term as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, reflecting the Company's intent and ability to refinance these obligations beyond one year and are included in the following table. The unused lines of credit have no major restrictions and are provided under demand notes between the Company and the lending institution. Interest is charged on borrowings under these lines of credit at various rates, generally below prime or equivalent money rates.
Long-Term Borrowings
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Multi-currency revolving credit agreement expiring May 2010: | ||||||||
| Swiss francs 65 million at 0.60% | $ | 62,844 | $ | 60,809 | ||||
| Swiss francs 57 million | - | 53,507 | ||||||
| Private placement notes: | ||||||||
| U.S. dollar denominated expiring March 2010 at 0.55% | 150,000 | 150,000 | ||||||
| Term Loan Agreement: | ||||||||
| Japanese yen denominated expiring March 2012 at 1.00% | 134,776 | 138,247 | ||||||
| U.S. dollar commercial paper: | ||||||||
| Facility rated A/2-P/2 U.S. dollar borrowings at 0.30% | 85,200 | - | ||||||
| Other borrowings, various currencies and rates | 20,911 | 25,096 | ||||||
| $ | 453,731 | $ | 427,659 | |||||
| Less: Current portion | ||||||||
| (included in notes payable and current portion of long-term debt) | 66,580 | 3,980 | ||||||
| Long term portion | $ | 387,151 | $ | 423,679 | ||||
- 70 - -
The table below reflects the contractual maturity dates of the various borrowings at December 31, 2009. The borrowings under the U.S. Private Placement Note and the commercial paper program are considered contractually due in 2014 and 2015 and beyond.
| (in thousands) | ||||
| 2010 | $ | 66,580 | ||
| 2011 | 5,299 | |||
| 2012 | 139,470 | |||
| 2013 | 1,215 | |||
| 2014 | 75,682 | |||
| 2015 and beyond | 165,485 | |||
| $ | 453,731 | |||
The Company utilizes interest rate swaps to convert the Swiss franc denominated debt under the revolving facility to fixed rate debt. The Company utilizes interest rate swaps to convert the variable rate Japanese yen and U.S. dollar denominated private placement notes to fixed rate debt. The Company's use of interest rate swaps is further described in Note 15, Financial Instruments and Derivatives.
The Company has a $500.0 million revolving credit agreement with participation from thirteen banks, which expires in May 2010. The revolving credit agreements contain a number of covenants and two financial ratios, which the Company is required to satisfy. The most restrictive of these covenants pertain to asset dispositions and prescribed ratios of indebtedness to total capital and operating income excluding depreciation and amortization to interest expense. Any breach of any such covenants or restrictions would result in a default under the existing borrowing documentation that would permit the lenders to declare all borrowings under such documentation to be immediately due and payable and, through cross default provisions, would entitle the Company's other lenders to accelerate their loans. At December 31, 2009, the Company was in compliance with these covenants. The Company pays a facility fee of 0.10% annually on the amount of the commitment under the $500.0 million five-year facility. The entire $500.0 million revolving credit agreement has a usage fee of 0.10% annually if utilization exceeds 50% of the total available facility. Interest rates on amounts borrowed under the facility will depend on the maturity of the borrowing, the currency borrowed, the interest rate option selected, and the Company’s long-term credit rating from Standard and Poor’s.
The Company has a U.S. dollar commercial paper facility totaling $250.0 million, which has utilization, dealer and annual appraisal fees which on average cost 0.11% annually. The $500.0 million revolving credit facility acts as back-up credit to this commercial paper facility. The total available credit under the commercial paper facility and the revolving credit facility is $500.0 million. As of December 31, 2009, the Company had $85.2 million outstanding in commercial paper and $62.8 million in revolving credit obligations.
At December 31, 2009, the Company had total unused lines of credit, including lines available under its short-term arrangements and revolving credit agreement, of $404.9 million.
NOTE 11 - EQUITY
At December 31, 2009, the Company had authorization to repurchase shares under its stock repurchase program in an amount up to 17,000,000 shares of treasury stock. Under its stock repurchase program, the Company purchased 2,452,903 shares and 2,971,155 shares during 2009 and 2008 at an average price of $32.09 and $37.91, respectively. As of December 31, 2009 and 2008, the Company held 15.8 million and 14.2 million shares of treasury stock, respectively. During 2009, the Company repurchased $78.7 million in treasury stock. The Company also received proceeds of $13.4 million primarily as a result of the exercise of 0.9 million stock options during the year ended December 31, 2009. It is the Company’s practice to issue shares from treasury stock when options are exercised. The tax benefit realized for the options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2009 is $3.9 million.
- 71 - -
The following table represents total outstanding shares for the years ended December 31:
| Common | Treasury | Outstanding | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Shares | Shares | Shares | |||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2006 | 162,776 | (10,985 | ) | 151,791 | ||||||||
| Shares Issued | - | 2,421 | 2,421 | |||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock at cost | - | (3,390 | ) | (3,390 | ) | |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2007 | 162,776 | (11,954 | ) | 150,822 | ||||||||
| Shares Issued | - | 677 | 677 | |||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock at cost | - | (2,971 | ) | (2,971 | ) | |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2008 | 162,776 | (14,248 | ) | 148,528 | ||||||||
| Shares Issued | - | 886 | 886 | |||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock at cost | - | (2,453 | ) | (2,453 | ) | |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2009 | 162,776 | (15,815 | ) | 146,961 | ||||||||
The Company maintains the 2002 Equity Incentive Plan (the “Plan”) under which it may grant non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units (“RSU”) and stock appreciation rights, collectively referred to as “Awards.” Awards are granted at exercise prices that approximate the fair market value of the common stock on the grant date. The Plan authorizes grants of 14,000,000 shares of common stock, plus any unexercised portion of canceled or terminated stock options granted under the DENTSPLY International Inc 1993 and 1998 Plans, subject to adjustment as follows: each January, if 7% of the total outstanding common shares of the Company exceed 14,000,000, the excess becomes available for grant under the Plan. No more than 2,000,000 shares may be awarded as restricted stock and restricted stock units, and no key employee may be granted restricted stock units in excess of 150,000 shares of common stock in any calendar year. The number of shares available for grant under the 2002 Plan as of December 31, 2009 is 1.0 million.
Stock options generally expire ten years after the date of grant under these plans and grants become exercisable over a period of three years after the date of grant at the rate of one-third per year, except when they become immediately exercisable upon death, disability or qualified retirement. RSU vest 100% on the third anniversary of the date of grant and are subject to a service condition, which requires grantees to remain employed by the Company during the three-year period following the date of grant. In addition to the service condition, certain key executives are subject to performance requirements. Similar to stock options, RSU become immediately exercisable upon death, disability or qualified retirement. The fair value of each RSU assumes that performance goals will be achieved. If such goals are not met, no compensation cost is recognized and any recognized compensation costs is reversed. Under the terms of the RSU, the three-year period is referred to as the restricted period. RSU and the rights under the award may not be sold, assigned, transferred, donated, pledged or otherwise disposed of during the three year restricted period prior to vesting. Upon the expiration of the applicable restricted period and the satisfaction of all conditions imposed, all restrictions imposed on RSU will lapse, and one share of common stock will be issued as payment for each vested RSU.
The following table represents total stock based compensation expense and the tax related benefit for the years ended:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
| Stock option expense | $ | 8.7 | $ | 11.7 | $ | 11.2 | ||||||
| RSU expense | 6.4 | 4.4 | 1.7 | |||||||||
| Total stock based compensation expense | $ | 15.1 | $ | 16.1 | $ | 12.9 | ||||||
| Related deferred income tax benefit | $ | 3.6 | $ | 3.9 | $ | 3.2 | ||||||
The stock option expense shown in the preceding table represents the aggregate fair value of shares vested during the year ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007. There were 3.4 million non-qualified stock options unvested as of December 31, 2009. The remaining unamortized compensation cost related to non-qualified stock options is $18.2 million, which will be expensed over the weighted average remaining vesting period of the options, or 1.8 years. The unamortized compensation cost related to RSU is $7.8 million, which will be expensed over the remaining weighted average restricted period of the RSU, or 1.5 years.
- 72 - -
The Company uses the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value of each option awarded. The following table sets forth the assumptions used to determine compensation cost for the Company’s non-qualified stock options issued during the years ended:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| Weighted average fair value per share | $ | 7.31 | $ | 5.23 | $ | 8.75 | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield | 0.60 | % | 0.69 | % | 0.41 | % | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 2.14 | % | 1.85 | % | 3.67 | % | ||||||
| Expected volatility | 22 | % | 21 | % | 21 | % | ||||||
| Expected life (years) | 4.84 | 4.66 | 4.66 | |||||||||
The total intrinsic value of options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 was $12.3 million, $13.7 million and $41.1 million, respectively.
The following table summarizes the non-qualified stock option transactions for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Outstanding | Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted | Weighted | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | Average | Aggregate | Average | Aggregate | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise | Intrinsic | Exercise | Intrinsic | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Price | Value | Shares | Price | Value | |||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | 11,285 | $ | 26.75 | $ | 41,428 | 8,185 | $ | 24.71 | $ | 37,796 | ||||||||||||||
| Granted | 1,805 | 33.33 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercised | (824 | ) | 16.26 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited | (228 | ) | 32.44 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | 12,038 | $ | 28.34 | $ | 94,148 | 8,682 | $ | 26.78 | $ | 80,839 | ||||||||||||||
The weighted average remaining contractual term of all outstanding options is 6.3 years and the weighted average remaining contractual term of exercisable options is 4.9 years.
The following table summarizes information about non-qualified stock options outstanding for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Outstanding | Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Average | Number | ||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding | Remaining | Weighted | Exercisable | Weighted | ||||||||||||||||
| at | Contractual | Average | at | Average | ||||||||||||||||
| Incremental Changes | December 31, | Life | Exercise | December 31, | Exercise | |||||||||||||||
| in Stock Price | 2009 | (in years) | Price | 2009 | Price | |||||||||||||||
| $5.00 - $10.00 | 5,200 | 0.2 | $ | 9.19 | 5,200 | $ | 9.19 | |||||||||||||
| 10.01 - 15.00 | 282,900 | 1.0 | 12.50 | 282,900 | 12.50 | |||||||||||||||
| 15.01 - 20.00 | 1,441,533 | 2.5 | 17.50 | 1,441,533 | 17.50 | |||||||||||||||
| 20.01 - 25.00 | 1,155,595 | 4.0 | 22.19 | 1,124,795 | 22.20 | |||||||||||||||
| 25.01 - 30.00 | 4,884,049 | 6.6 | 27.11 | 3,695,904 | 27.39 | |||||||||||||||
| 30.01 - 35.00 | 3,012,500 | 8.3 | 32.76 | 1,322,434 | 31.42 | |||||||||||||||
| 35.01 - 40.00 | 128,479 | 8.0 | 37.44 | 61,248 | 37.12 | |||||||||||||||
| 40.01 - 45.00 | 41,383 | 8.1 | 41.14 | 17,370 | 41.18 | |||||||||||||||
| 45.01 - 50.00 | 1,086,533 | 7.8 | 45.15 | 730,400 | 45.15 | |||||||||||||||
| 12,038,172 | 6.3 | $ | 28.34 | 8,681,784 | $ | 26.78 | ||||||||||||||
- 73 - -
The following table summarizes the unvested RSU and RSU dividend transactions for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Unvested Restricted Stock Units | ||||||||
| Weighted Average | ||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | Grant Date | |||||||
| Shares | Fair Value | |||||||
| Unvested at December 31, 2008 | 400 | $ | 36.11 | |||||
| Granted | 300 | 26.46 | ||||||
| Exercised | (1 | ) | 30.81 | |||||
| Vested | (10 | ) | 31.76 | |||||
| Forfeited | (27 | ) | 32.94 | |||||
| Unvested at December 31, 2009 | 662 | $ | 31.94 | |||||
NOTE 12 - INCOME TAXES
The components of income before income taxes from operations are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
| United States | $ | 99,009 | $ | 45,171 | $ | 100,740 | ||||||
| Foreign | 264,347 | 309,702 | 257,452 | |||||||||
| $ | 363,356 | $ | 354,873 | $ | 358,192 | |||||||
The components of the provision for income taxes from operations are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
| Current: | ||||||||||||
| U.S. federal | $ | 30,851 | $ | (9,913 | ) | $ | 14,395 | |||||
| U.S. state | 5,886 | 2,291 | 4,122 | |||||||||
| Foreign | 52,012 | 65,854 | 54,396 | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 88,749 | $ | 58,232 | $ | 72,913 | ||||||
| Deferred: | ||||||||||||
| U.S. federal | $ | (8,046 | ) | $ | 23,496 | $ | 28,131 | |||||
| U.S. state | (476 | ) | 3,283 | 1,627 | ||||||||
| Foreign | 8,717 | (13,408 | ) | (4,190 | ) | |||||||
| Total | $ | 195 | $ | 13,371 | $ | 25,568 | ||||||
| $ | 88,944 | $ | 71,603 | $ | 98,481 | |||||||
- 74 - -
The reconciliation of the U.S. federal statutory tax rate to the effective rate for the years ended is as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
| Statutory federal income tax rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| Effect of: | ||||||||||||
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |||||||||
| Federal benefit of R&D and foreign tax credits | (11.3 | ) | (15.8 | ) | (3.2 | ) | ||||||
| Tax effect of international operations | 0.7 | 5.3 | (2.4 | ) | ||||||||
| Net effect of tax audit activity | (1.3 | ) | (4.4 | ) | 1.0 | |||||||
| Tax effect of enacted statutory rate changes | - | 0.1 | (3.1 | ) | ||||||||
| Federal tax on unremitted earnings of certain | ||||||||||||
| foreign subsidiaries | 0.1 | (0.3 | ) | 0.1 | ||||||||
| Valuation allowance adjustments | - | (0.4 | ) | - | ||||||||
| Other | 0.3 | (0.3 | ) | (0.9 | ) | |||||||
| Effective income tax rate on operations | 24.5 | % | 20.2 | % | 27.5 | % | ||||||
The tax effect of temporary differences giving rise to deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
| December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||
| Current | Noncurrent | Current | Noncurrent | |||||||||||||
| Asset | Asset | Asset | Asset | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | (Liability) | (Liability) | (Liability) | (Liability) | ||||||||||||
| Employee benefit accruals | $ | 2,791 | $ | 25,085 | $ | 4,159 | $ | 20,832 | ||||||||
| Product warranty accruals | 980 | - | 1,065 | - | ||||||||||||
| Insurance premium accruals | 5,068 | - | 5,401 | - | ||||||||||||
| Commission and bonus accrual | 1,764 | - | 1,904 | - | ||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing accrual | 4,553 | - | 3,799 | - | ||||||||||||
| Restructuring and other cost accruals | 777 | - | 800 | 2,178 | ||||||||||||
| Differences in financial reporting and tax basis for: | ||||||||||||||||
| Inventory | 15,554 | - | 14,196 | - | ||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment | - | (38,663 | ) | - | (40,493 | ) | ||||||||||
| Identifiable intangible assets | - | (130,419 | ) | - | (109,278 | ) | ||||||||||
| Unrealized losses included in other comprehensive | ||||||||||||||||
| income | 22,249 | 33,296 | 2,347 | 82,641 | ||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous accruals | 7,072 | 1,457 | 10,108 | 1,073 | ||||||||||||
| Other | 974 | 11,853 | 1,673 | 1,594 | ||||||||||||
| Taxes on unremitted earnings of foreign subsidiaries | - | (1,486 | ) | - | (1,076 | ) | ||||||||||
| R&D and foreign tax credit carryforwards | 10,254 | 25,355 | 5,000 | 19,678 | ||||||||||||
| Tax loss carryforwards and other tax attributes | 3,979 | 66,031 | 11,833 | 46,869 | ||||||||||||
| Valuation allowance | (485 | ) | (51,324 | ) | (194 | ) | (36,547 | ) | ||||||||
| $ | 75,530 | $ | (58,815 | ) | $ | 62,091 | $ | (12,529 | ) | |||||||
Current and noncurrent deferred tax assets and liabilities are included in the following balance sheet captions:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | $ | 77,277 | $ | 63,952 | ||||
| Income taxes payable | 1,747 | 1,861 | ||||||
| Other noncurrent assets | 13,709 | 56,520 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 72,524 | 69,049 | ||||||
- 75 - -
The Company has $35.3 million of foreign tax credit carryforwards $7.9 million, $7.1 million, $9.9 million and $10.4 million will expire in 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2019 respectively.
Certain foreign and domestic subsidiaries of the Company have tax loss carryforwards of $536.3 million at December 31, 2009, of which $448.2 million expire through 2029 and $88.1 million may be carried forward indefinitely. The tax benefit of certain tax loss carryforwards and deferred tax assets has been offset by a valuation allowance as of December 31, 2009, because it is uncertain whether the benefits will be realized in the future. The valuation allowance at December 31, 2009 and 2008 was $51.8 million and $36.7 million, respectively.
The Company has provided federal income taxes on certain undistributed earnings of its foreign subsidiaries that the Company anticipates will be repatriated. Deferred federal income taxes have not been provided on $621.3 million of cumulative earnings of foreign subsidiaries that the Company has determined to be permanently reinvested. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of tax that might be payable on these permanently reinvested earnings.
Tax Contingencies
The Company applies a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company recognizes in the financial statements, the impact of a tax position, if that position is more likely than not of being sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the position.
The total amount of gross unrecognized tax benefits at December 31, 2009, is approximately $18.4 million, of this total, approximately $17.0 million represents the amount of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would affect the effective income tax rate. It is reasonably possible that certain amounts of unrecognized tax benefits will significantly increase or decrease within twelve months of the reporting date of the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Final settlement and resolution of outstanding tax matters in various jurisdictions during the next twelve months could include unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $1.1 million. In addition, expiration of statutes of limitation in various jurisdictions during the next twelve months could include unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $1.0 million.
The total amount of accrued interest and penalties were $5.6 million and $7.2 million as of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively. The Company has consistently classified interest and penalties recognized in its consolidated financial statements as income taxes based on the accounting policy election of the Company. During the year ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the Company recognized income tax benefits in the amount of $1.7 million and $5.5 million for interest and penalties. During the year ended December 31, 2007, the company recognized income tax expense of $2.6 million in interest and penalties.
The Company is subject to U.S. federal income tax as well as income tax of multiple state and foreign jurisdictions. The significant jurisdictions include the U.S., Germany and Switzerland. The Company has substantially concluded all U.S. federal income tax matters for years through 2005, resulting in the years 2006, 2007 and 2008 being subject to future potential tax audit adjustments while years prior to 2006 are settled. The Company has concluded audits in Germany through the tax year 2003 and is currently under audit for the years 2004 through 2008. The taxable years that remain open for Switzerland are 1999 through 2008.
The Company had the following activity recorded for unrecognized tax benefits:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits at beginning of period | $ | 17,285 | $ | 36,307 | $ | 36,862 | ||||||
| Gross change for prior period positions | (672 | ) | 2,939 | 1,619 | ||||||||
| Gross change for current year positions | 1,630 | 785 | 1,129 | |||||||||
| Decrease due to settlements and payments | (4,703 | ) | (15,677 | ) | - | |||||||
| Decrease due to statute expirations | (1,026 | ) | (5,752 | ) | (3,303 | ) | ||||||
| Increase due to effect of foreign currency translation | 350 | - | - | |||||||||
| Decrease due to effect from foreign currency translation | - | (1,317 | ) | - | ||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits at end of period | $ | 12,864 | $ | 17,285 | $ | 36,307 | ||||||
- 76 - -
NOTE 13 - BENEFIT PLANS
Substantially all of the employees of the Company and its subsidiaries are covered by government or Company-sponsored benefit plans. Total costs for Company-sponsored defined benefit, defined contribution and employee stock ownership plans amounted to $24.6 million, $21.2 million and $20.9 million in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Defined Contribution Plans
In December 2006, the Board of Directors amended the DENTSPLY Employee Stock Ownership Plan (“ESOP”) and 401(k) plans to redesign the future distribution of allocations of “Covered Compensation,” with a targeted 3% going into the ESOP in Company stock and a targeted 3% going into the 401(k) as a Non-Elective Contribution (“NEC”) in cash. The principal driver of this redesign is to provide quicker diversification opportunity to the participants as the investment of the NEC is participant directed. The Company sponsors an employee 401(k) savings plan for its U.S. workforce to which enrolled participants may contribute up to Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) defined limits. The annual expense and cash contribution to the 401(k) is expected to be $5.3 million for 2009 (to be contributed in the first quarter of 2010), and was $5.0 million and $4.6 million in 2008 and 2007, respectively.
The ESOP is a non-contributory defined contribution plan that covers substantially all of the U.S. based non-union employees of the Company. Contributions to the ESOP, net of forfeitures, are expected to be $1.4 million for 2009 (to be contributed in the first quarter of 2010), and were $1.3 million for 2008 (contributed in the first quarter of 2009), and were $0.2 million for 2007 (contributed in the first quarter of 2008).
All future ESOP allocations will come from a combination of forfeited shares and shares acquired in the open market. The Company has targeted future ESOP allocations at 3% of “Covered Compensation.” The share allocation will be accounted at fair value at the point of allocation, which is normally year-end.
Defined Benefit Plans
The Company maintains a number of separate contributory and non-contributory qualified defined benefit pension plans and other postretirement medical plans for certain union and salaried employee groups in the U.S. Pension benefits for salaried plans are based on salary and years of service; hourly plans are based on negotiated benefits and years of service. Annual contributions to the pension plans are sufficient to satisfy minimum funding requirements. Pension plan assets are held in trust and consist mainly of common stock and fixed income investments. The U.S. plans are funded in excess of the funding required by the U.S. Department of Labor.
The Company maintains defined benefit pension plans for its employees in Germany, Japan, the Netherlands, Switzerland and Taiwan. These plans provide benefits based upon age, years of service and remuneration. Substantially all of the German plans are unfunded book reserve plans. Other foreign plans are not significant individually or in the aggregate. Most employees and retirees outside the U.S. are covered by government health plans.
Defined Benefit Pension Plan Assets
The Company maintains defined benefit plans for it employees in the U.S., Germany, Japan, the Netherlands, Switzerland and Taiwan. The primary investment strategy is to ensure that the assets of the plans, along with anticipated future contributions, will be invested in order that the benefit entitlements of employees, pensioners and beneficiaries covered under the plan can be met when due with high probability. Pension plan assets consist mainly of common stock and fixed income investments. The target allocations for plan assets are 30% to 65% equity securities, 30% to 65% fixed income securities, 0% to 15% real estate, and 0% to 25% in all other types of investments. Equity securities include investments in companies located both in and outside the U.S. Equity securities do not include common stock of the Company. Fixed income securities include corporate bonds of companies from diversified industries, government bonds, mortgage notes and pledge letters. Other types of investments include investments in mutual funds, common trusts, insurance contracts, hedge funds and real estate. These plan assets are not recorded on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet as they are held in trust or other off-balance sheet investment vehicles.
The defined benefit pension plan assets in the U.S. are held in trust and the investment policies of the plans are generally to invest the plans assets in equities and fixed income investments. The objective is to achieve a long-term rate of return in excess of 5% while at the same time mitigating the impact of investment risk associated with investment categories that are expected to yield greater than average returns. In accordance with the investment policies of the U.S. plans, the plans assets were invested in the following investment categories: interest-bearing cash, registered investment companies (e.g. mutual funds), common/collective trusts, master trust investment accounts and insurance company general accounts. The investment objective is for assets to be invested in a manner consistent with the fiduciary standards of the Employee Retirement Security Act of 1974.
- 77 - -
The defined benefit pension plan assets maintained in Germany, Japan, the Netherlands, Switzerland and Taiwan all have separate investment policies but generally have an objective is to achieve a long-term rate of return in excess 5% while at the same time mitigating the impact of investment risk associated with investment categories that are expected to yield greater than average returns. In accordance with the investment policies for the plans outside the U.S., the plans assets were invested in the following investment categories: interest-bearing cash, U.S. and foreign equities, foreign fixed income securities (primarily corporate and government bonds), insurance company contracts, real estate, and hedge funds.
Postretirement Healthcare
The plans for postretirement healthcare have no plan assets. The postretirement healthcare plans cover certain union and salaried employee groups in the U.S. and is contributory, with retiree contributions adjusted annually to limit the Company’s contribution for participants who retired after June 1, 1985. The Company also sponsors unfunded non-contributory postretirement medical plans for a limited number of union employees and their spouses and retirees of a discontinued operation.
Reconciliations of changes in the defined benefit and postretirement healthcare plans’ benefit obligations, fair value of assets and statement of funded status are as follows:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||||
| Change in Benefit Obligation | ||||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 183,785 | $ | 176,634 | $ | 10,501 | $ | 10,420 | ||||||||
| Service cost | 8,375 | 6,980 | 50 | 50 | ||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 8,003 | 7,910 | 676 | 635 | ||||||||||||
| Participant contributions | 2,774 | 2,667 | 689 | 710 | ||||||||||||
| Actuarial (gains) losses | (7,202 | ) | 7,973 | 1,018 | 670 | |||||||||||
| Amendments | (29 | ) | - | - | - | |||||||||||
| Divestitures | 286 | 521 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Effects of exchange rate changes | 4,929 | 1,055 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Settlement gains | (808 | ) | (10,130 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||
| Benefits paid | (8,137 | ) | (9,825 | ) | (1,268 | ) | (1,984 | ) | ||||||||
| Benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 191,976 | $ | 183,785 | $ | 11,666 | $ | 10,501 | ||||||||
| Change in Plan Assets | ||||||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 75,986 | $ | 90,658 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| Actual return on assets | 5,687 | (11,200 | ) | - | - | |||||||||||
| Settlement gains | - | (10,130 | ) | - | - | |||||||||||
| Effects of exchange rate changes | 2,474 | 4,578 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Employer contributions | 10,082 | 9,238 | 579 | 1,274 | ||||||||||||
| Participant contributions | 2,774 | 2,667 | 689 | 710 | ||||||||||||
| Benefits paid | (8,137 | ) | (9,825 | ) | (1,268 | ) | (1,984 | ) | ||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 88,866 | $ | 75,986 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| Funded status at end of year | $ | (103,110 | ) | $ | (107,799 | ) | $ | (11,666 | ) | $ | (10,501 | ) | ||||
- 78 - -
The amounts recognized in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets, net of tax effects, are as follows:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||||
| Other noncurrent assets | $ | 1 | $ | 11 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| Deferred tax asset | 7,177 | 9,672 | 1,427 | 1,142 | ||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 7,178 | $ | 9,683 | $ | 1,427 | $ | 1,142 | ||||||||
| Current liabilities | (3,604 | ) | (3,290 | ) | (1,107 | ) | (1,084 | ) | ||||||||
| Long-term liabilities | (99,507 | ) | (104,521 | ) | (10,559 | ) | (9,416 | ) | ||||||||
| Deferred tax liability | (238 | ) | (452 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | (103,349 | ) | $ | (108,263 | ) | $ | (11,666 | ) | $ | (10,500 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated other | ||||||||||||||||
| comprehensive income | 20,504 | 28,282 | 2,270 | 1,816 | ||||||||||||
| Net amount recognized | $ | (75,667 | ) | $ | (70,298 | ) | $ | (7,969 | ) | $ | (7,542 | ) | ||||
Amounts recognized in AOCI consist of:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||||
| Net actuarial loss | $ | 27,056 | $ | 36,702 | $ | 3,697 | $ | 2,958 | ||||||||
| Net prior service cost | 262 | 437 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Net transition obligation | 125 | 364 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Pretax AOCI | $ | 27,443 | $ | 37,503 | $ | 3,697 | $ | 2,958 | ||||||||
| Less deferred taxes | 6,939 | 9,221 | 1,427 | 1,142 | ||||||||||||
| Post tax AOCI | $ | 20,504 | $ | 28,282 | $ | 2,270 | $ | 1,816 | ||||||||
The accumulated benefit obligation for all defined benefit pension plans was $182.8 million and $174.0 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Information for pension plans with an accumulated benefit obligation in excess of plan assets:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 191,785 | $ | 183,565 | ||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | 182,594 | 173,747 | ||||||
| Fair value of plan assets | 88,674 | 75,753 | ||||||
- 79 - -
Components of net periodic benefit cost:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Service cost | $ | 8,375 | $ | 6,980 | $ | 6,796 | $ | 50 | $ | 50 | $ | 42 | ||||||||||||
| Interest cost | 8,003 | 7,910 | 7,094 | 676 | 635 | 573 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Expected return on assets | (3,991 | ) | (4,458 | ) | (4,115 | ) | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial losses | 240 | 240 | 217 | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service | 138 | 141 | 148 | - | - | (386 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of net loss | 1,652 | 155 | 1,224 | 281 | 168 | 229 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Settlement gains | (1,148 | ) | (2,259 | ) | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||
| Net periodic benefit cost | $ | 13,269 | $ | 8,709 | $ | 11,364 | $ | 1,007 | $ | 853 | $ | 458 | ||||||||||||
Other changes in plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in AOCI:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net actuarial (gain) loss | $ | (7,994 | ) | $ | 26,214 | $ | (19,487 | ) | $ | 1,020 | $ | 670 | $ | 466 | ||||||||||
| Net prior service (credit) | (37 | ) | (3 | ) | (113 | ) | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Net transition obligation | 1 | 32 | (9 | ) | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||||
| Amortization | (2,030 | ) | (536 | ) | (1,589 | ) | (281 | ) | (168 | ) | 156 | |||||||||||||
| Total recognized in AOCI | $ | (10,060 | ) | $ | 25,707 | $ | (21,198 | ) | $ | 739 | $ | 502 | $ | 622 | ||||||||||
| Total recognized in net | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| periodic benefit cost and AOCI | $ | 3,209 | $ | 34,416 | $ | (9,834 | ) | $ | 1,746 | $ | 1,355 | $ | 1,080 | |||||||||||
The estimated net loss, prior service cost and transition obligation for the defined benefit plans that will be amortized from AOCI into net periodic benefit cost over the next fiscal year are $1.2 million. The estimated net loss and prior service credit for the other postretirement plans that will be amortized from AOCI into net periodic benefit cost over the next fiscal year is $0.3 million.
The weighted average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations for the Company's plans, principally in foreign locations, are as follows:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 4.7 | % | 4.5 | % | 5.0 | % | 5.5 | % | 6.3 | % | 6.3 | % | ||||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase | 2.7 | % | 2.7 | % | 2.8 | % | n/a | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||||
| Health care cost trend | n/a | n/a | n/a | 8.5 | % | 9.0 | % | 9.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Ultimate health care cost trend | n/a | n/a | n/a | 5.0 | % | 5.0 | % | 5.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Years until ultimate trend is reached | n/a | n/a | n/a | 8.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
- 80 - -
The weighted average assumptions used to determine net periodic benefit cost for the Company's plans, principally in foreign locations, are as follows:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefits | Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate | 4.5 | % | 5.0 | % | 4.1 | % | 6.3 | % | 6.3 | % | 5.8 | % | ||||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets | 5.2 | % | 5.4 | % | 5.3 | % | n/a | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increase | 2.7 | % | 2.8 | % | 2.7 | % | n/a | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||||
| Health care cost trend | n/a | n/a | n/a | 8.5 | % | 9.0 | % | 9.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Ultimate health care cost trend | n/a | n/a | n/a | 5.0 | % | 5.0 | % | 5.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Years until ultimate trend is reached | n/a | n/a | n/a | 8.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Measurement Date | 12/31/2009 | 12/31/2008 | 12/31/2007 | 12/31/2009 | 12/31/2008 | 12/31/2007 | ||||||||||||||||||
Assumed health care cost trend rates have an impact on the amounts reported for postretirement benefits. A one percentage point change in assumed healthcare cost trend rates would have the following effects for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Other Postretirement | ||||||||
| Benefits | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | 1% Increase | 1% Decrease | ||||||
| Effect on total of service and interest cost components | $ | 60 | $ | (51 | ) | |||
| Effect on postretirement benefit obligation | 948 | (818 | ) | |||||
Fair Value Measurements of Plan Assets
The fair value of the Company's pension plan assets at December 31, 2009 are presented in the table below by asset category. Over 80% of the total plan assets are categorized as Level 1, and therefore, the values assigned to these pension assets are based on quoted prices available in active markets. For the other category levels, a description of the valuation is provided in Note 1, Significant Accounting Policies, under the “fair value measurement” heading.
| December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| Assets Category | ||||||||||||||||
| Cash & equivalents | $ | 3,180 | $ | 3,038 | $ | 142 | $ | - | ||||||||
| Equity securities: | ||||||||||||||||
| U. S. | 954 | 954 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| International | 27,907 | 27,907 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Fixed income securities: | ||||||||||||||||
| Fixed rate bonds (a) | 35,350 | 35,350 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Other types of investments: | ||||||||||||||||
| Mutual funds (b) | 7,872 | - | 7,872 | - | ||||||||||||
| Common trusts (c) | 1,932 | 90 | - | 1,842 | ||||||||||||
| Insurance contracts | 4,567 | - | 2,825 | 1,742 | ||||||||||||
| Hedge funds | 1,672 | - | - | 1,672 | ||||||||||||
| Real estate | 5,432 | 5,107 | - | 325 | ||||||||||||
| Total | $ | 88,866 | $ | 72,446 | $ | 10,839 | $ | 5,581 | ||||||||
| (a) | This category includes fixed income securities invested primarily in Swiss bonds, foreign bonds in Swiss currency, foreign currency bonds, mortgage notes and pledged letters. |
| (b) | Mutual funds balanced between moderate-income generation and moderate capital appreciation with investments allocation of approximately 50% equities and 50% fixed income investments. |
| (c) | This category includes common/collective funds with investments in approximately 65% equities and 35% in fixed income investments. |
- 81 - -
The following tables provide a reconciliation from December 31, 2008 to December 31, 2009 for the plans assets categorized as Level 3. No assets were transferred in or out of the Level 3 category during the year ended December 31, 2009.
| Changes within Level 3 Category for | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Common | Insurance | Hedge | Real | |||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Trust | Contracts | Funds | Estate | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Beginning balance at December 31, 2008 | $ | 1,233 | $ | 1,578 | $ | 1,002 | $ | 314 | $ | 4,127 | ||||||||||
| Actual return on plan assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Relating to assets still held | ||||||||||||||||||||
| at the reporting date | 239 | 31 | (224 | ) | - | 46 | ||||||||||||||
| Relating to assets sold during | ||||||||||||||||||||
| the period | 16 | - | - | - | 16 | |||||||||||||||
| Purchases, sales and | ||||||||||||||||||||
| settlements | 354 | 89 | 832 | - | 1,275 | |||||||||||||||
| Effects of exchange rate changes | - | 44 | 62 | 11 | 117 | |||||||||||||||
| Ending balance at December 31, 2009 | $ | 1,842 | $ | 1,742 | $ | 1,672 | $ | 325 | $ | 5,581 | ||||||||||
Cash Flows
In 2010, the Company expects to contribute $8.0 million to its defined benefit pension plans and $1.1 million to its postretirement medical plans.
Estimated Future Benefit Payments
| (in thousands) | Pension Benefits | Other Post Retirement Benefits | ||||||
| 2010 | $ | 7,512 | $ | 1,107 | ||||
| 2011 | 7,825 | 1,138 | ||||||
| 2012 | 8,161 | 1,159 | ||||||
| 2013 | 9,287 | 1,100 | ||||||
| 2014 | 9,778 | 1,068 | ||||||
| 2015-2018 | 57,806 | 4,423 | ||||||
NOTE 14 – RESTRUCTURING, IMPAIRMENTS AND OTHER COSTS
Restructuring Costs
Restructuring costs of $5.9 million for 2009 are reflected in Restructuring, impairments and other costs in the statement of operations and the associated liabilities are recorded in accrued liabilities and other non-current liabilities in the consolidated balance sheet. These costs consist of employee severance benefits, payments due under operating contracts, and other restructuring costs.
During 2009, the Company initiated several restructuring plans primarily related to the closure and/or consolidation of certain production and selling facilities in the United States, Europe and South America to better leverage the Company’s resources by reducing costs and obtaining operational efficiencies. Additionally, the Company executed targeted reductions in workforce both in the manufacturing and non-manufacturing business functions in certain locations.
During 2008, the Company initiated several restructuring plans primarily related to the integration, reorganization, and closure or consolidation of certain production and selling facilities in order to better leverage the Company’s resources by minimizing costs and obtaining operational efficiencies.
- 82 - -
As of December 31, 2009, the Company’s restructuring accruals were as follows:
| Severances | ||||||||||||||||
| 2007 and | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Prior Plans | 2008 Plans | 2009 Plans | Total | ||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2008 | $ | 664 | $ | 2,806 | $ | - | $ | 3,470 | ||||||||
| Provisions and adjustments | (185 | ) | 3,165 | 4,389 | 7,369 | |||||||||||
| Amounts applied | (46 | ) | (1,102 | ) | (1,133 | ) | (2,281 | ) | ||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2009 | $ | 433 | $ | 4,869 | $ | 3,256 | $ | 8,558 | ||||||||
| Lease/contract terminations | ||||||||
| 2007 and | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | Prior Plans | Total | ||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2008 | $ | 1,271 | $ | 1,271 | ||||
| Provisions and adjustments | 50 | 50 | ||||||
| Amounts applied | (196 | ) | (196 | ) | ||||
| Balance, December 31, 2009 | $ | 1,125 | $ | 1,125 | ||||
| Other restructuring costs | ||||||||||||||||
| 2007 and | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Prior Plans | 2008 Plans | 2009 Plans | Total | ||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2008 | $ | 108 | $ | 56 | $ | - | $ | 164 | ||||||||
| Provisions and adjustments | 137 | 568 | (2,190 | ) | (1,485 | ) | ||||||||||
| Amounts applied | (133 | ) | (624 | ) | 2,190 | 1,433 | ||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2009 | $ | 112 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 112 | ||||||||
The following table provides the cumulative amounts for the provisions and adjustments and amounts applied for all the plans by segment:
| December 31, | Provisions | Amounts | December 31, | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2008 | and adjustments | applied | 2009 | ||||||||||||
| U.S., Germany and Certain Other | ||||||||||||||||
| European Regions Consumable Businesses | $ | 1,286 | $ | 338 | $ | (346 | ) | $ | 1,278 | |||||||
| France, U.K., Italy and Certain Other | ||||||||||||||||
| European Countries, CIS, Middle East, | ||||||||||||||||
| Africa, Pacific Rim Businesses | 190 | 285 | (391 | ) | 84 | |||||||||||
| Canada/Latin America/Endodontics/ | ||||||||||||||||
| Orthodontics | 178 | 924 | (463 | ) | 639 | |||||||||||
| Dental Laboratory Business/ | ||||||||||||||||
| Implants/Non-Dental | 3,251 | 4,147 | 396 | 7,794 | ||||||||||||
| All Other (a) | - | 240 | (240 | ) | - | |||||||||||
| Total Balance | $ | 4,905 | $ | 5,934 | $ | (1,044 | ) | $ | 9,795 | |||||||
| (a) | Includes amounts recorded at Corporate headquarters. |
Other Costs
In 2009, the Company recorded certain other costs of $0.9 million related to legal matters and an impairment of an intangible asset.
- 83 - -
Other costs of $26.5 million for 2008 included costs primarily related to settlements of legal matters and impairment of long-term assets. The legal settlements related to several legal matters with multiple plaintiffs. These cases included a patent dispute and cases relating to a prior distribution practice of the Company in connection with the sale of artificial teeth. The impairment charges were related to abandonment of patented technology purchased in 2005 and the impairment of a long-term note receivable recorded from a sale of a business in 2006. The impairment of the long-term note receivable occurred as the result of a change in payment terms on the non-interest bearing note receivable.
NOTE 15 – FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS AND DERIVATIVES
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
The Company's activities expose it to a variety of market risks, which primarily include the risks related to the effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates and commodity prices. These financial exposures are monitored and managed by the Company as part of its overall risk management program. The objective of this risk management program is to reduce the volatility that these market risks may have on the Company's operating results and equity.
Certain of the Company's inventory purchases are denominated in foreign currencies, which expose the Company to market risk associated with exchange rate movements. The Company's policy generally is to hedge major foreign currency transaction exposures through foreign exchange forward contracts. These contracts are entered into with major financial institutions thereby minimizing the risk of credit loss. In addition, the Company's investments in foreign subsidiaries are denominated in foreign currencies, which create exposures to changes in exchange rates. The Company uses debt and derivatives denominated in the applicable foreign currency as a means of hedging a portion of this risk.
With the Company’s significant level of variable interest rate long-term debt and net investment hedges, changes in the interest rate environment can have a major impact on the Company’s earnings, depending upon its interest rate exposure. As a result, the Company manages its interest rate exposure with the use of interest rate swaps, when appropriate, based upon market conditions.
The manufacturing of some of the Company’s products requires the use of commodities, which are subject to market fluctuations. In order to limit the unanticipated impact on earnings from such market fluctuations, the Company selectively enters into commodity swaps for certain materials used in the production of its products. Additionally, the Company uses non-derivative methods, such as the precious metal consignment agreements to effectively hedge commodity risks.
Cash Flow Hedges
The Company uses interest rate swaps to convert a portion of its variable interest rate debt to fixed interest rate debt. As of December 31, 2009, the Company has three groups of significant variable interest rate to fixed rate interest rate swaps. One of the groups of swaps has notional amounts totaling 12.6 billion Japanese yen, and effectively converts the underlying variable interest rates to an average fixed interest rate of 1.6% for a term of ten years, ending in September 2012. Another swap has a notional amount of 65.0 million Swiss francs, and effectively converts the underlying variable interest rates to a fixed interest rate of 4.2% for a term of seven years, ending in September 2012. A third group of swaps has a notional amount of $150.0 million, and effectively converts the underlying variable interest rates to a fixed interest rate of 3.9% for a term of two years, ending March 2010. The Company enters into interest rate swap contracts infrequently as they are only used to manage interest rate risk on long-term debt instruments and not for speculative purposes.
The Company selectively enters into commodity swaps to effectively fix certain variable raw material costs. At December 31, 2009, the Company had swaps in place to purchase 540 troy ounces of platinum bullion for use in the production of its impression material products. The average fixed rate of this agreement is $1,156 per troy ounce. In addition, the Company had swaps in place to purchase 57,372 troy ounces of silver bullion for use in the production of its amalgam products at an average fixed rate of $15 per troy ounce.
The Company enters into forward exchange contracts to hedge the foreign currency exposure of its anticipated purchases of certain inventory. In addition, exchange contracts are used by certain of the Company's subsidiaries to hedge intercompany inventory purchases, which are denominated in non-local currencies. The forward contracts that are used in these programs typically mature in twelve months or less. For these derivatives which qualify as hedges of future anticipated cash flows, the effective portion of changes in fair value is temporarily deferred in AOCI and then recognized in earnings when the hedged item affects earnings.
- 84 - -
Hedges of Net Investments in Foreign Operations
The Company has numerous investments in foreign subsidiaries. The net assets of these subsidiaries are exposed to volatility in currency exchange rates. Currently, the Company uses non-derivative financial instruments, including foreign currency denominated debt held at the parent company level and derivative financial instruments to hedge some of this exposure. Translation gains and losses related to the net assets of the foreign subsidiaries are offset by gains and losses in the non-derivative and derivative financial instruments designated as hedges of net investments.
In the first quarter of 2005, the Company entered into cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 457.5 million paying three month Swiss franc London Inter-Bank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $384.4 million. In the first quarter of 2006, the Company entered into additional cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 55.5 million paying three month Swiss franc LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $42.0 million. In the fourth quarter of 2006, the Company entered into additional cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 80.4 million paying three month Swiss franc LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $64.4 million. In the first quarter of 2007, the Company entered into additional cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Swiss francs 56.6 million paying three month Swiss franc LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $46.3 million. Additionally, in the fourth quarter of 2005, the Company entered into cross currency interest rate swaps with a notional principal value of Euro 358.0 million paying three month Euro LIBOR and receiving three month U.S. dollar LIBOR on $419.7 million. In the first quarter of 2009, the Company terminated Swiss francs 57.5 million cross currency swap at a fair value of zero. In the second and third quarters of 2009, the Company amended certain of its Swiss franc and Euro cross currency interest rate swaps to extend their maturity dates for an additional three years. Specifically, a total of Swiss francs 300.0 million have been extended to March and April of 2013 and a total of Euro 250.0 million have been extended to December 2013. ��The Swiss franc and Euro cross currency interest rate swaps are designated as net investment hedges of the Swiss and Euro denominated net assets. The interest rate differential is recognized in the earnings as interest income or interest expense as it is accrued, the foreign currency revaluation is recorded in AOCI, net of tax effects.
The fair value of these cross currency interest rate swap agreements is the estimated amount the Company would either pay or receive at the reporting date, taking into account the effective interest rates and foreign exchange rates. As of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the estimated net fair values of the swap agreements were negative $176.6 million and negative $148.9 million, respectively, which are recorded in AOCI, net of tax effects, and as other noncurrent liabilities and other noncurrent assets.
At December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, the Company had Euro-denominated, Swiss franc-denominated, and Japanese yen-denominated debt and cross currency interest rate swaps (at the parent company level) to hedge the currency exposure related to a designated portion of the net assets of its European, Swiss and Japanese subsidiaries. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the accumulated translation gains on investments in foreign subsidiaries, primarily denominated in Euros, Swiss francs and Japanese yen, net of these net investment hedges, were $111.1 million and $77.6 million, respectively, which are included in AOCI, net of tax effects.
The following tables summarize the fair value of the Company’s derivatives at December 31, 2009.
| Notional Amounts | Fair Value (Liability) Asset | |||||||||||
| Foreign Exchange Forward Contracts | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 | |||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Forward sale, 13.3 million Australian dollars | $ | 11,268 | $ | 635 | $ | (316 | ) | |||||
| Forward purchase, 6.2 million British pounds | (9,728 | ) | (298 | ) | 226 | |||||||
| Forward sale, 16.4 million Canadian dollars | 15,117 | 560 | (927 | ) | ||||||||
| Forward purchase, 7.0 million Swiss francs | (6,804 | ) | - | (15 | ) | |||||||
| Forward sale, 7.5 million Danish Krone | 1,454 | - | 13 | |||||||||
| Forward purchase, 0.01 million Euros | (18 | ) | - | 13 | ||||||||
| Forward sale, 83.3 million Japanese yen | 895 | - | 628 | |||||||||
| Forward sale, 96.7 million Mexican Pesos | 7,390 | - | 94 | |||||||||
| Forward sale, 1.2 billion South Korean won | 999 | - | 10 | |||||||||
| Forward sale, 6.5 million Taiwanese dollars | 202 | - | (2 | ) | ||||||||
| Total foreign exchange forward contracts | $ | 20,775 | $ | 897 | $ | (276 | ) | |||||
- 85 - -
| Notional Amount | Fair Value Liability | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest Rate Swaps | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 and Beyond | 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Euro | $ | 2,056 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 4,400 | $ | (882 | ) | |||||||||||
| Japanese yen | - | - | 134,776 | - | - | (3,351 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Swiss francs | - | - | 62,844 | - | - | (4,470 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| U.S. dollars | 150,000 | - | - | - | - | (1,084 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total interest rate swaps | $ | 152,056 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 198,974 | $ | 1,354 | $ | 4,400 | $ | (9,787 | ) | |||||||||||
| Notional Amount | Fair Value Liability | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross Currency Basis Swaps | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 and Beyond | 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Swiss franc 592.5 million @ $1.21 pay CHF 3mo. LIBOR rec. USD 3mo. LIBOR | $ | 150,343 | $ | 77,734 | $ | 54,723 | $ | 290,051 | $ | - | $ | (83,979 | ) | |||||||||||
| Euros 358.0 million @ $1.17 pay EUR 3mo. LIBOR rec. USD 3mo. LIBOR | 154,827 | - | - | 358,395 | - | (92,642 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total cross currency basis swaps | $ | 305,170 | $ | 77,734 | $ | 54,723 | $ | 648,446 | $ | - | $ | (176,621 | ) | |||||||||||
| Notional Amount | Fair Value Asset | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commodity Contracts | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 and Beyond | 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Silver swap - U.S. dollar | $ | (977 | ) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 129 | |||||||||||
| Platinum swap - U.S. dollar | (790 | ) | - | - | - | - | 164 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total commodity contracts | $ | (1,767 | ) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 293 | |||||||||||
As of December 31, 2009, $4.8 million of deferred net losses on derivative instruments recorded in AOCI are expected to be reclassified to current earnings during the next twelve months. This reclassification is primarily due to the sale of inventory that includes previously hedged purchases and interest rate swaps. The maximum term over which the Company is hedging exposures to variability of cash flows (for all forecasted transactions, excluding interest payments on variable interest rate debt) is eighteen months. Overall, the derivatives designated as cash flow hedges are highly effective. Any cash flows associated with these instruments are included in cash provided by operating activities in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows in accordance with the Company’s policy of classifying the cash flows from these instruments in the same category as the cash flows from the items being hedged.
The following tables summarize the fair value and location on the Consolidated Balance Sheets of the Company's derivatives at:
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | December 31, | |||||
| Asset Derivatives Designated as Hedging Instruments | Classification | 2009 | ||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Other current assets (a) | $ | 598 | |||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Other noncurrent assets, net | 5 | ||||
| Commodity contracts | Other current assets (a) | 293 | ||||
| Total asset derivatives designated as hedging instruments | $ | 896 | ||||
| Asset Derivatives Not Designated as Hedging Instruments | ||||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Other current assets (a) | $ | 556 | |||
| Total asset derivatives | $ | 1,452 | ||||
(a) Reported on the Consolidated Balance Sheets within "Prepaid expenses and other current assets."
- 86 - -
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | December 31, | |||||
| Liability Derivatives Designated as Hedging Instruments | Classification | 2009 | ||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||
| Interest rate contracts | Accrued liabilities | $ | 6,130 | |||
| Interest rate contracts | Other noncurrent liabilities | 2,775 | ||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Accrued liabilities | 1,010 | ||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Other noncurrent liabilities | 16 | ||||
| Cross currency interest rate swaps | Accrued liabilities | 52,411 | ||||
| Cross currency interest rate swaps | Other noncurrent liabilities | 124,210 | ||||
| Total liability derivatives designated as hedging instruments | $ | 186,552 | ||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | December 31, | |||||
| Liability Derivatives Not Designated as Hedging Instruments | Classification | 2009 | ||||
| Interest rate contracts | Other noncurrent liabilities | $ | 882 | |||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Accrued liabilities | 409 | ||||
| Total liability derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | $ | 1,291 | ||||
| Total liability derivatives | $ | 187,843 | ||||
The following table summarizes the statement of operations impact of the Company’s cash flow hedges for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Derivatives in Cash Flow | Gain (Loss) | ||||||||
| Hedging Relationships | Gain (Loss) | Consolidated Statements of Operations | Reclassified from | ||||||
| (in thousands) | in AOCI (a) | Classification | AOCI into Earnings (b) | ||||||
| Interest rate contracts | $ | (4,186 | ) | Interest expense | $ | (8,035 | ) | ||
| Foreign exchange contracts | (999 | ) | Cost of products sold | 905 | |||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | 660 | SG&A expenses | 459 | ||||||
| Commodity contracts | 1,655 | Cost of products sold | (1,149 | ) | |||||
| Total | $ | (2,870 | ) | $ | (7,820 | ) | |||
| Derivatives in Cash Flow | Loss | |||||
| Hedging Relationships | Consolidated Statements of Operations | Recognized | ||||
| (in thousands) | Classification | in Earnings (c) | ||||
| Interest rate contracts | Other expense, net | $ | (168 | ) | ||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Interest expense | (330 | ) | |||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Interest expense | (40 | ) | |||
| Commodity contracts | Interest expense | (48 | ) | |||
| Total | $ | (586 | ) | |||
The following table summarizes the statement of operations impact of the Company’s hedges of net investments for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Derivatives in Net Investment | Gain (Loss) | ||||||||
| Hedging Relationships | Loss in | Consolidated Statements of Operations | Recognized | ||||||
| (in thousands) | AOCI (a) | Classification | in Earnings (b) | ||||||
| Cross currency interest rate swaps | $ | (13,877 | ) | Interest Income | $ | 1,420 | |||
| Interest Expense | (85 | ) | |||||||
| Cross currency interest rate swaps | (13,868 | ) | Interest Expense | (4,098 | ) | ||||
| Total | $ | (27,745 | ) | $ | (2,763 | ) | |||
| (a) | Amount of (loss) reported in AOCI, effective portion. |
| (b) | Amount of gain or (loss) reclassed from AOCI into earnings, effective portion. |
| (c) | Amount of (loss) recognized in earnings, ineffective portion and amount excluded from effectiveness testing. |
- 87 - -
The following tables summarize the statement of operations impact of the Company’s hedges not designated as hedging for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Derivatives Not Designated as Hedging | ||||||
| Instruments under Hedging | Loss | |||||
| Relationships | Consolidated Statements of Operations | Recognized in | ||||
| (in thousands) | Classification | Earnings (a) | ||||
| Foreign exchange contracts | Other expense, net | $ | (14,984 | ) | ||
| Interest rate contracts | Other expense, net | (2 | ) | |||
| Interest rate contracts | Interest Expense | (514 | ) | |||
| $ | (15,500 | ) | ||||
(a) Amount of loss recognized in income, ineffective portion and amount excluded from effectiveness testing.
Amounts recorded in AOCI related to cash flow hedging instruments at:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands, net of tax) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | (7,874 | ) | $ | (1,573 | ) | ||
| Changes in fair value of derivatives | (1,627 | ) | (5,721 | ) | ||||
| Reclassifications to earnings from equity | 4,702 | (580 | ) | |||||
| Total activity | 3,075 | (6,301 | ) | |||||
| Ending balance | $ | (4,799 | ) | $ | (7,874 | ) | ||
Amounts recorded in AOCI related to hedges of net investments in foreign operations at:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in thousands, net of tax) | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 77,584 | $ | 156,790 | ||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | 49,685 | (52,983 | ) | |||||
| Changes in fair value of: | ||||||||
| foreign currency debt | 881 | (18,538 | ) | |||||
| derivative hedge instruments | (17,035 | ) | (7,685 | ) | ||||
| Total activity | 33,531 | (79,206 | ) | |||||
| Ending balance | $ | 111,115 | $ | 77,584 | ||||
NOTE 16 – FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENT
The Company records financial instruments at fair value with unrealized gains and losses related to certain financial instruments reflected in AOCI on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. In addition, the Company recognizes certain liabilities at fair value.
The fair value of financial instruments is determined by reference to various market data and other valuation techniques as appropriate. The Company believes the carrying amounts of accounts receivable (net of allowance for doubtful accounts), prepaid expenses and other current assets, accounts payable, accrued liabilities, income taxes payable and notes payable approximate fair value due to the short-term nature of these instruments. The Company estimates the fair value and carrying value of its total long term debt, including current portion of long-term debt, was $453.7 million and $427.7 million as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The fair value of the Company’s long-term debt equaled its carrying value as the Company’s debt is variable rate and reflects current market rates. The interest rates on private placement notes, revolving debt and commercial paper are variable and therefore the fair value of these instruments approximates their carrying values.
- 88 - -
The following tables set forth by level within the fair value hierarchy the Company’s financial assets and liabilities that were accounted for at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, which are classified as “Cash and cash equivalents,” “Prepaid expenses and other current assets,” “Other noncurrent assets, net,” “Accrued liabilities,” and “Other noncurrent liabilities.” Financial assets and liabilities that are recorded at fair value as of the balance sheet date are classified in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
| December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||||
| Money market funds | $ | 450,348 | $ | 450,348 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| Commodity forward purchase contracts | 293 | - | 293 | - | ||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | 1,159 | - | 1,159 | - | ||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 451,800 | $ | 450,348 | $ | 1,452 | $ | - | ||||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps | $ | 9,787 | $ | - | $ | 9,787 | $ | - | ||||||||
| Cross currency interest rate swaps | 176,621 | - | 176,621 | - | ||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | 1,435 | - | 1,435 | - | ||||||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 187,843 | $ | - | $ | 187,843 | $ | - | ||||||||
| December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||
| Assets | ||||||||||||||||
| Money market funds | $ | 203,991 | $ | 203,991 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| Interest rate swaps | 2 | - | 2 | - | ||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | 2,053 | - | 2,053 | - | ||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 206,046 | $ | 203,991 | $ | 2,055 | $ | - | ||||||||
| Liabilities | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps | $ | 12,529 | $ | - | $ | 12,529 | $ | - | ||||||||
| Commodity forward purchase contracts | 1,931 | - | 1,931 | - | ||||||||||||
| Cross currency interest rate swaps | 148,935 | - | 148,935 | - | ||||||||||||
| Total liabilities | $ | 163,395 | $ | - | $ | 163,395 | $ | - | ||||||||
Derivative valuations are based on observable inputs to the valuation model including interest rates, foreign currency exchange rates, future commodities prices and credit risks.
The commodity forward purchase contracts, interest rate swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts are considered cash flow hedges and cross currency interest rate swaps are considered hedge of net investments in foreign operations as discussed in Note 15, Financial Instruments and Derivatives.
NOTE 17 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Leases
The Company leases automobiles and machinery and equipment and certain office, warehouse and manufacturing facilities under non-cancellable operating leases. These leases generally require the Company to pay insurance, taxes and other expenses related to the leased property. Total rental expense for all operating leases was $32.2 million for 2009, $29.5 million for 2008 and $27.4 million for 2007.
- 89 - -
Rental commitments, principally for real estate (exclusive of taxes, insurance and maintenance), automobiles and office equipment are as follows:
| (in thousands) | ||||
| 2010 | $ | 26,688 | ||
| 2011 | 18,207 | |||
| 2012 | 12,814 | |||
| 2013 | 7,289 | |||
| 2014 | 4,799 | |||
| 2015 and thereafter | 12,423 | |||
| $ | 82,220 | |||
Litigation
On January 5, 1999, the Department of Justice filed a Complaint against the Company in the U.S. District Court in Wilmington, Delaware alleging that the Company’s tooth distribution practices violated the antitrust laws and seeking an order for the Company to discontinue its practices. This case has been concluded and the District Court, upon the direction of the Court of Appeals, issued an injunction in May 2006, preventing DENTSPLY from taking action to restrict its tooth dealers in the U.S. from adding new competitive teeth lines.
Subsequent to the filing of the Department of Justice Complaint in 1999, a private party putative class action was filed based on allegations similar to those in the Department of Justice case, on behalf of dental laboratories who purchased Trubyte® teeth or products containing Trubyte® teeth. The District Court granted the Company’s Motion on the lack of standing of the laboratory class action to pursue damage claims. The Plaintiffs appealed this decision to the Third Circuit and the Court largely upheld the decision of the District Court in dismissing the Plaintiffs’ damages claims against DENTSPLY, with the exception of allowing the Plaintiffs to pursue a damage claim based on a theory of resale price maintenance between the Company and its tooth dealers. The Plaintiffs then filed an amended complaint in the District Court asserting that DENTSPLY and its tooth dealers, and the dealers among themselves, engaged in a conspiracy to violate the antitrust laws. The District Court has granted the Motions filed by DENTSPLY and the dealers, to dismiss Plaintiffs’ claims, except for the resale price maintenance claims. The Plaintiffs have appealed the dismissal of these claims to the Third Circuit. The Third Circuit held oral arguments in January 2010 and we are awaiting a decision. Also pending is a case filed by a manufacturer of a competitive tooth line seeking damages alleged to have been incurred as a result of the Company’s tooth distribution practices, including the practice found to be a violation of the antitrust law. This case is currently scheduled for trial in May 2010 and the Plaintiffs have submitted their expert’s report, which claims single damages in the range of $1.6 million to $4.2 million.
On June 18, 2004, Marvin Weinstat, DDS and Richard Nathan, DDS filed a class action suit in San Francisco County, California alleging that the Company misrepresented that its Cavitron® ultrasonic scalers are suitable for use in oral surgical procedures. The Complaint seeks a recall of the product and refund of its purchase price to dentists who have purchased it for use in oral surgery. The Court certified the case as a class action in June 2006 with respect to the breach of warranty and unfair business practices claims. The class is defined as California dental professionals who purchased and used one or more Cavitron® ultrasonic scalers for the performance of oral surgical procedures. The Company filed a motion for decertification of the class and this motion was granted. Plaintiffs appealed the decertification of the class to the California Court of Appeals and the Court of Appeals has reversed the decertification decision of the trial Court. The Company is planning on filing a Petition for Review of the Court of Appeals decision with the California Supreme Court.
On December 12, 2006, a Complaint was filed by Carole Hildebrand, DDS and Robert Jaffin, DDS in the Eastern District of Pennsylvania (the Plaintiffs subsequently added Dr. Mitchell Goldman as a named class representative). The case was filed by the same law firm that filed the Weinstat case in California. The Complaint asserts putative class action claims on behalf of dentists located in New Jersey and Pennsylvania. The Complaint seeks damages and asserts that the Company’s Cavitron® ultrasonic scaler was negligently designed and sold in breach of contract and warranty arising from misrepresentations about the potential uses of the product because it cannot assure the delivery of potable or sterile water. Plaintiffs have filed their Motion for class certification to which the Company has filed its response. The Company also filed other motions, including a Motion to dismiss the claims of Drs. Hildebrand and Jaffin for lack of standing, which Motion was recently granted by the Court.
- 90 - -
As of December 31, 2009, a reasonable estimate of a range of loss related to the current litigation noted above cannot be made.
On November 21, 2008, Guidance Endodontics LLC filed a complaint in the U.S. District Court of New Mexico asserting claims against DENTSPLY arising principally out of a breach of a manufacturing and supply contract between the parties. Prior to trial, Guidance had claimed its damages were $1.2 million. The case went to trial in late September and early October 2009. On October 9, 2009, a jury returned a verdict against DENTSPLY, in the amount of approximately $4.0 million for compensatory and $40.0 million in punitive damages. The Company believes that this decision is not supported by the facts in the case or the applicable law and intends to vigorously pursue all available options to challenge it. The Company has filed separate motions to overturn the punitive damages verdict and the future damages verdict, or in the alternative to be granted a new trial, because of the inappropriateness of such verdicts. The Company plans to file additional motions. DENTSPLY does not believe the outcome of this matter will have a material adverse effect on its financial position.
Other
The Company has no material non-cancelable purchase commitments.
The Company has employment agreements with its executive officers. These agreements generally provide for salary continuation for a specified number of months under certain circumstances. If all of the employees under contract were to be terminated by the Company without cause, as defined in the agreements, the Company's liability would be approximately $12.6 million at December 31, 2009.
NOTE 18 – SUBSEQUENT EVENT
According to the terms of the Private Placement Note Purchase Agreement entered into on October 16, 2009 and further discussed in Note 10, Financing Arrangements, the Company received $250.0 million aggregate principal on February 19, 2010. The net proceeds after deducting fees and expenses of the loan are $250.0 million. The proceeds will be used to refinance the $150.0 million U.S. Private Placement Note and other short term obligations.
- 91 - -
NOTE 19 - QUARTERLY FINANCIAL INFORMATION (UNAUDITED)
DENTSPLY INTERNATIONAL INC
Quarterly Financial Information (Unaudited)
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter | Quarter | Quarter | Quarter | Rounding | Year | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 506,949 | $ | 553,216 | $ | 531,032 | $ | 568,719 | $ | - | $ | 2,159,916 | ||||||||||||
| Gross profit | 266,969 | 286,971 | 272,981 | 284,383 | - | 1,111,304 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income | 86,171 | 98,708 | 92,930 | 103,378 | - | 381,187 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International | 61,743 | 70,199 | 67,483 | 74,834 | (1 | ) | 274,258 | |||||||||||||||||
| Earnings per common share - basic | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.47 | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.51 | $ | - | $ | 1.85 | ||||||||||||
| Earnings per common share - diluted | $ | 0.41 | $ | 0.47 | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.50 | $ | - | $ | 1.83 | ||||||||||||
Cash dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.050 | $ | 0.050 | $ | 0.050 | $ | 0.050 | $ | - | $ | 0.200 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 560,782 | $ | 594,847 | $ | 529,953 | $ | 508,141 | $ | - | $ | 2,193,723 | ||||||||||||
| Gross profit | 285,243 | 315,486 | 280,183 | 271,032 | - | 1,151,944 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Operating income | 101,037 | 113,161 | 80,915 | 85,310 | (2 | ) | 380,421 | |||||||||||||||||
Net income attributable to DENTSPLY International | 68,180 | 78,648 | 66,047 | 70,995 | (1 | ) | 283,869 | |||||||||||||||||
| Earnings per common share - basic | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.48 | $ | - | $ | 1.90 | ||||||||||||
| Earnings per common share - diluted | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.52 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.47 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | 1.87 | |||||||||||
Cash dividends declared per common share | $ | 0.045 | $ | 0.045 | $ | 0.045 | $ | 0.050 | $ | - | $ | 0.185 | ||||||||||||
Net sales, excluding precious metal content, were $465.6 million, $511.9 million, $493.6 million and $520.1 million, respectively, for the first, second, third and fourth quarters of 2009. Net sales, excluding precious metal content, were $496.2 million, $542.3 million, $488.1 million and $467.2 million, respectively, for the first, second, third and fourth quarters of 2008. This measurement should be considered a non-US GAAP measure as discussed further in Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
- 92 - -
Supplemental Stock Information
The common stock of the Company is traded on the NASDAQ National Market under the symbol “XRAY.” The following table sets forth high, low and closing sale prices of the Company's common stock for the periods indicated as reported on the NASDAQ National Market:
| Market Range of Common Stock | Period-end | Cash | ||||||||||||||
| Closing | Dividend | |||||||||||||||
| High | Low | Price | Declared | |||||||||||||
| 2009 | ||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 29.19 | $ | 21.80 | $ | 26.85 | $ | 0.050 | ||||||||
| Second Quarter | 30.99 | 25.20 | 30.57 | 0.050 | ||||||||||||
| Third Quarter | 36.08 | 27.79 | 34.54 | 0.050 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 36.80 | 32.30 | 35.17 | 0.050 | ||||||||||||
| 2008 | ||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 47.06 | $ | 36.07 | $ | 38.60 | $ | 0.045 | ||||||||
| Second Quarter | 42.58 | 35.21 | 36.80 | 0.045 | ||||||||||||
| Third Quarter | 42.05 | 36.21 | 37.54 | 0.045 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 39.22 | 22.85 | 28.24 | 0.050 | ||||||||||||
| 2007 | ||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 33.35 | $ | 29.44 | $ | 32.75 | $ | 0.040 | ||||||||
| Second Quarter | 38.73 | 32.50 | 38.26 | 0.040 | ||||||||||||
| Third Quarter | 41.90 | 35.32 | 41.64 | 0.040 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 47.84 | 40.06 | 45.02 | 0.045 | ||||||||||||
The Company estimates, based on information supplied by its transfer agent, that there are 442 holders of record of the Company’s common stock. Approximately 92,300 holders of the Company’s common stock are “street name” or beneficial holders, whose shares are held of record by banks, brokers and other financial institutions.
- 93 - -
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| DENTSPLY INTERNATIONAL INC. | ||
| By: | /s/ | Bret W. Wise |
| Bret W. Wise | ||
| Chairman of the Board and | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| /s/ | Bret W. Wise | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Bret W. Wise | Date | |||
| Chairman of the Board and | ||||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||||
| (Principal Executive Officer) | ||||
| /s/ | William R. Jellison | February 22, 2010 | ||
| William R. Jellison | Date | |||
| Senior Vice President and | ||||
| Chief Financial Officer | ||||
| (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | ||||
| /s/ | John C. Miles II | February 22, 2010 | ||
| John C. Miles II | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | Dr. Michael C. Alfano | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Dr. Michael C. Alfano | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | Eric K. Brandt | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Eric K. Brandt | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | Paula H. Cholmondeley | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Paula H. Cholmondeley | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | Michael J. Coleman | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Michael J. Coleman | Date | |||
| Director |
- 94 - -
| /s/ | William F. Hecht | February 22, 2010 | ||
| William F. Hecht | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | Leslie A. Jones | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Leslie A. Jones | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | Wendy L. Dixon | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Wendy L. Dixon | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | Francis J. Lunger | February 22, 2010 | ||
| Francis J. Lunger | Date | |||
| Director | ||||
| /s/ | W. Keith Smith | February 22, 2010 | ||
| W. Keith Smith | Date | |||
| Director |
- 95 - -