UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington D.C. 20549
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Form 10-K |
| | |
| (Mark One) | | |
| x | | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015 |
| Or |
| o | | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 or 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the transition period from to |
Commission file number 001-10716
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
TRIMAS CORPORATION
(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
|
| | |
Delaware (State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | | 38-2687639 (IRS Employer Identification No.) |
39400 Woodward Avenue, Suite 130
Bloomfield Hills, Michigan 48304
(Address of Principal Executive Offices, Including Zip Code)
(248) 631-5450
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
| | |
| Title of Each Class: | | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered: |
| Common stock, $0.01 par value | | NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 and Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See definition of "accelerated filer," "large accelerated filer," and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
| | | | | | |
Large Accelerated Filer x | | Accelerated Filer o | | Non-accelerated Filer o (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | | Smaller Reporting Company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes o No x
The aggregate market value of the voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant as of June 30, 2015 was approximately $1.3 billion, based upon the closing sales price of the Registrant's common stock, $0.01 par value, reported for such date on the NASDAQ Global Select Market. For purposes of this calculation only, directors, executive officers and the principal controlling shareholder or entities controlled by such controlling shareholder are deemed to be affiliates of the Registrant.
As of February 19, 2016, the number of outstanding shares of the Registrant's common stock, $0.01 par value, was 45,332,516 shares.
Portions of the Registrant's Proxy Statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated herein by reference in Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K to the extent stated herein.
TRIMAS CORPORATION INDEX
Forward-Looking Statements
This report may contain forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 about our financial condition, results of operations and business. These forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of forward-looking words, such as “may,” “could,” “should,” “estimate,” “project,” “forecast,” “intend,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “target,” “plan” or other comparable words, or by discussions of strategy that may involve risks and uncertainties.
These forward-looking statements are subject to numerous assumptions, risks and uncertainties which could materially affect our business, financial condition or future results including, but not limited to, risks and uncertainties with respect to: the Company's leverage; liabilities imposed by the Company's debt instruments; market demand; competitive factors; supply constraints; material and energy costs; risks and uncertainties associated with intangible assets, including goodwill or other intangible asset impairment charges; technology factors; litigation; government and regulatory actions; the Company's accounting policies; future trends; general economic and currency conditions; various conditions specific to the Company's business and industry; the Company’s ability to integrate Allfast and attain the expected synergies, including that the acquisition is accretive; the Company’s ability to attain targeted savings and free cash flow amounts under its Financial Improvement Plan; future prospects of the Company; and other risks that are discussed in Part I, Item 1A, "Risk Factors." The risks described in this report are not the only risks facing our Company. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently deemed to be immaterial also may materially adversely affect our business, financial position and results of operations or cash flows.
The cautionary statements set forth above should be considered in connection with any subsequent written or oral forward-looking statements that we or persons acting on our behalf may issue. We caution readers not to place undue reliance on the statements, which speak only as of the date of this report. We do not undertake any obligation to review or confirm analysts' expectations or estimates or to release publicly any revisions to any forward-looking statement to reflect events or circumstances after the date of this report or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
We disclose important factors that could cause our actual results to differ materially from our expectations implied by our forward-looking statements under Part II, Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and elsewhere in this report. These cautionary statements qualify all forward-looking statements attributed to us or persons acting on our behalf. When we indicate that an event, condition or circumstance could or would have an adverse effect on us, we mean to include effects upon our business, financial and other conditions, results of operations, prospects and ability to service our debt.
PART I
Item 1. Business
We are a global designer, manufacturer and distributor of engineered and applied products for commercial, industrial and consumer markets. Most of our businesses share important characteristics, including leading market positions, strong brand names, broad product offerings in focused markets, established distribution networks, relatively high operating margins, relatively low capital investment requirements and both organic and acquisition growth opportunities. We use a common operating model across our businesses. The TriMas Operating Model is the framework that provides, wherever possible given the diverse nature of our businesses, commonality and consistency across TriMas, and drives how we plan, budget, measure, review, incent and reward our people. It provides the foundation for determining our priorities, executing our growth and productivity initiatives and allocating capital and resources. We believe that a majority of our 2015 net sales were in markets in which our products enjoy the number one or number two market position within their respective product categories.
Our Reportable Segments
We operate through four reportable segments which had net sales and operating profit for the year ended December 31, 2015 as follows: Packaging (net sales: $334.3 million; operating profit: $78.5 million), Aerospace (net sales: $176.5 million; operating profit: $28.3 million), Energy (net sales: $193.4 million; operating loss: $97.2 million) and Engineered Components (net sales: $159.8 million; operating profit: $18.2 million). For information pertaining to the net sales and operating profit attributed to our reportable segments, refer to Note 19, "Segment Information," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
Due to a significant decline in current and expected profitability levels in our Energy reportable segment and our Arrow Engine business within our Engineered Components reportable segment during 2015, and a decline in our stock price and resulting market capitalization, we recorded pre-tax goodwill impairment charges in the fourth quarter of 2015 of approximately $70.9 million and $3.2 million, respectively. For information pertaining to these impairment charges, refer to Note 8, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
In addition to our reportable segments as presented, we have discontinued certain lines of businesses over the past three years as follows, the results of which are presented as discontinued operations for all periods presented in the financial statements attached hereto:
| |
| • | On June 30, 2015, we completed the spin-off of our Cequent businesses, comprised of the former Cequent Americas and Cequent Asia Pacific Europe Africa ("Cequent APEA") reportable segments, creating a new independent publicly traded company, Horizon Global Corporation ("Horizon"), through the distribution of 100% of the Company's interest in Horizon to holders of the Company's common stock. |
| |
| • | During the third quarter of 2014, we ceased operations of our NI Industries business. NI Industries manufactured cartridge cases for the defense industry and was party to a U.S. Government facility maintenance contract. We received approximately $6.7 million for the sale of certain intellectual property and related inventory and tooling. As a result of discontinuing operations of NI Industries, we renamed the "Aerospace & Defense" reportable segment "Aerospace." |
Each reportable segment has distinct products, distribution channels, strengths and strategies, which are described below.
Packaging
We believe Packaging is a leading designer, manufacturer and distributor of specialty, highly-engineered closure and dispensing systems for a range of end markets, including steel and plastic industrial and consumer packaging applications. We believe that Packaging is one of the largest manufacturers of steel and plastic industrial container closures and dispensing products in North America, with a significant presence in Europe, Asia and other geographic markets. Packaging manufactures high-performance, value-added products that are designed to enhance its customers' ability to store, transport, process and dispense various products for the industrial, food and beverage, and health, beauty and home markets. Packaging's products include steel and plastic closure caps, drum enclosures, and specialty plastic closure and dispensing systems, such as foamers, pumps and specialty sprayers.
Packaging is dual headquartered in the United Kingdom and Indiana. We believe our Packaging brands, which include Rieke®, Arminak & Associates®, Englass®, Innovative Molding™ and Stolz®, are well established and recognized in their respective markets.
Packaging's specialty closure portion of the business designs and manufactures industrial closure products under the Rieke and Stolz brands in North America, Europe and Asia. We believe Rieke has significant market share for many of its key products, such as steel drum enclosures, plastic drum closures, plastic pail dispensers and plugs and plastic enclosures for sub-20 liter-sized containers.
The specialty dispensing portion of the business designs and manufactures products sold as Rieke, Arminak & Associates, Englass and Innovative Molding brands serving two primary markets:
| |
| • | In the health, beauty and home market segments, the products include foamers, pumps, fine mist sprayers and other packaging solutions for the cosmetic, personal care and household product markets in North America, Europe, Asia, Latin America, Middle East, Australia and Africa, and pharmaceutical and personal care dispensers sold primarily in Europe. |
| |
| • | In the food and beverage markets, the products include specialty plastic closures for bottles and jars, and dispensing pumps for North America, Europe, Asia and Australia. |
In the third quarter of 2013, we sold our packaging business in Italy which manufactured ring and lever closures for steel drums and pails and served the industrial market in Europe.
Competitive Strengths
We believe Packaging benefits from the following competitive strengths:
| |
| • | Strong Product Innovation. We believe that Packaging's research and development capability and new product focus is a competitive advantage. For more than 90 years, Packaging's product development programs have provided innovative and proprietary product solutions, such as the Visegrip® steel flange and plug closure, and the all-plastic, environmentally safe, self-venting FlexSpout® flexible pouring spout. Recent examples of innovation within specialty dispensing include hands-free foamer applications for soap, potable water dispenser systems for two-to-five gallon water containers and improved airless high-viscosity liquid dispensing systems to meet thick characteristics in personal care creamers. Packaging’s recent developments of child resistant dispensers for the medical field and several specialty solutions for dispensing, closure and trigger applications for our customers are further examples of our technical advancements. During 2015, Packaging added to this capability by opening a Global Innovation Center in Asia. Based outside Delhi, India, this center houses a cross-functional team of product development, sales, marketing, customer service and supply chain experts. This team is focused on driving innovation across Packaging's broad range of packaging solutions for its customers in the industrial, food & beverage, and health, beauty and home care markets. Packaging's emphasis upon highly-engineered packaging solutions and research and development has yielded numerous issued and enforceable patents, with many other patent applications pending. We believe that Packaging's innovative product solutions have enabled this segment to evolve our products to meet existing customers' needs, as well as attract new customers in a variety of consumer end markets such as beverage, cosmetic, food, medical, nutraceutical, personal care and pharmaceutical. |
| |
| • | Customized Solutions that Enhance Customer Loyalty and Relationships. A significant portion of Packaging's products are customized for end-users, as Packaging's products are often developed and engineered to address specific customer needs, providing solutions for issues or problems. Packaging provides extensive in-house design, development and technical staff to provide solutions to customer requirements for closures and dispensing applications. For example, the customization of specialty plastic caps and closures including unique colors, collar sizes, lining, venting and branding at short-lead times provides substantial customer loyalty. The continual investment in flexible manufacturing cells allows Packaging to offer both short lead times for high volume products and extensive customization for low order volumes, which provides significant advantages to our consumer goods customer base. In addition, Packaging provides customized dispensing solutions including unique pump design, precision metering, unique colors and special collar sizes to fit the bottles. Packaging has also been successful in promoting the sale of complementary products in an effort to create preferred supplier status. |
| |
| • | Leading Market Positions and Global Presence. We believe that Packaging is a leading designer and manufacturer of plastic closure caps, drum enclosures, and dispensing systems, such as pumps, foamers and specialty sprayers. Packaging maintains a global network of manufacturing and distribution sites, reflecting its global opportunities and increasing global customer base. Packaging's global customers often want supply chain capability and a flexible manufacturing footprint close to their end market consumers. To better serve our customers in Asia, we added to this global footprint by acquiring Lion Holdings Pvt. Ltd. ("Lion Holdings") in July 2014. Lion Holdings has increased our manufacturing capacity for highly engineered dispensing solutions through locations in India and Vietnam, and increased our Asian market coverage. Also during 2014, we added manufacturing capacity in China to better serve the domestic Chinese market. The majority of Packaging's manufacturing facilities around the world have technologically advanced injection molding machines required to manufacture engineered dispensing and closure solutions, as well as automated, high-speed agile assembly equipment for multiple component products. |
Strategies
We believe Packaging has significant opportunities to grow, including:
| |
| • | Innovate New Products and New Applications. Packaging has focused its research and development capabilities on consumer applications requiring special packaging forms, stylized containers and dispenser systems requiring a high degree of functionality and engineering, as well as continuously evolving its industrial applications. Many new product innovations take years to develop. Packaging has a consistent pipeline of new products ready for launch. For example, 39 new patent filings were filed in 2015, with 22 new patents issued. Other recent examples include a dual component dispensing device for the application of pre-operation surgical sterilization, as well as various foamers, pumps and sprayers. |
| |
| • | Globalize Product Opportunities. Packaging successfully globalizes its products by localizing its expertise in product customization to meet regional market requirements. Our network of manufacturing and distribution sites ensures customers have a global product standard manufactured locally providing the shortest lead-time, to provide products and support where our customers need them. All salespeople in the organization are trained at successfully selling all products in the Packaging group. We believe that, as compared with our competitors, Packaging is able to offer a wider variety of products to our long-term North American customers with enhanced service and tooling support. We have entered into supply agreements with many of these customers based on our broad product offering. |
| |
| • | Increase Global Presence. Over the past few years, Packaging has increased its international manufacturing and sales presence, with advanced manufacturing capabilities in China, India and Vietnam, as well as an increased sales presence in that region. We have also increased our sales coverage in China and India. By maintaining a presence in international locations, Packaging hopes to continue to discover new markets and new applications and to capitalize on lower-cost production opportunities. |
Marketing, Customers and Distribution
Packaging employs an internal sales force in North America, Europe and Asia. Packaging also uses third-party agents and distributors in key geographic markets, including Europe, South America and Asia. Packaging's agents and distributors primarily sell directly to container manufacturers and to users or fillers of containers. While the point of sale may be to a container manufacturer or bottle filling business, Packaging, via a "pull through" strategy, calls on the container user or filler and suggests that it specify that our product be used on its container.
To support its "pull-through" strategy, Packaging offers more attractive pricing on products purchased directly from us and on products in which the container users or fillers specify Packaging. Users or fillers that utilize or specify our products include agricultural chemical, food, industrial chemical, paint, personal care, petroleum, pharmaceutical and sanitary supply chemical companies such as BASF, Gechem Gmbh, McDonald's, Pennzoil Quaker State, Reckitt Benckiser (UK) Healthcare, Sherwin-Williams and Wings Food Products, among others.
Packaging's primary end customers include Colgate, ConAgra Foods, Dial Corporation, Ecolab, L’Oreal, Mast Global (Bath & Body Works and Victoria Secret), Method, Nestle, Purna Pharmaceuticals, RB (formerly known as Reckitt Benckiser), Starbucks, Thornton & Ross and Unilever. We also supply major container manufacturers around the world such as Berenfield, Berlin Packaging, BWAY, Cleveland Steel Container, Greif, North Coast Container and Tricorbraun. Packaging maintains a customer service center that provides technical support as well as other technical assistance to customers to reduce overall production costs.
Competition
Since Packaging has a broad range of products in both closures and dispensing systems, there are competitors in each of our product offerings. We do not believe that there is a single competitor that matches our entire product offering.
Depending on the product and customers served, Packaging's competitors include Aptar, Albea, Bericap, West Rock, Berry Plastics, Greif, and Phoenix Closures.
Aerospace
We believe Aerospace is a leading designer and manufacturer of a diverse range of products for use in focused markets within the aerospace industry. In general, Aerospace's products are highly-engineered, customer-specific items that are sold into focused markets with few competitors.
Aerospace's brands include Monogram Aerospace Fasteners™, Allfast Fastening Systems®, Mac Fasteners™ and Martinic Engineering™, which we believe are well established and recognized in their markets.
| |
| • | Monogram Aerospace Fasteners. We believe Monogram Aerospace Fasteners ("Monogram") is a leading manufacturer of permanent blind bolts and temporary fasteners used in commercial, business and military aircraft construction and assembly. Certain Monogram products contain patent protection, with additional patents pending. We believe Monogram is a leader in the development of blind bolt fastener technology for the aerospace industry, specifically in high-strength, rotary-actuated blind bolts that allow sections of aircraft to be joined together when access is limited to only one side of the airframe, providing certain cost efficiencies over conventional two piece fastening devices. |
| |
| • | Allfast Fastening Systems. Acquired in October 2014, Allfast Fastening Systems ("Allfast") is a leading global manufacturer of solid and blind rivets, blind bolts, temporary fasteners and installation tools for the aerospace industry with content on substantially all commercial, defense and general aviation platforms in production and in service. Certain Allfast products contain patent protection. |
| |
| • | Mac Fasteners. Acquired in October 2013, Mac Fasteners manufactures alloy and stainless steel aerospace fasteners, globally utilized by original equipment manufacturers ("OEMs"), aftermarket repair companies, and commercial and military aircraft producers. |
| |
| • | Martinic Engineering. Acquired in January 2013, Martinic Engineering ("Martinic") manufactures highly-engineered, precision machined, complex parts for commercial and military aerospace applications, including auxiliary power units, as well as electrical hydraulic and pneumatic systems. In November 2015, we added to this product capability by acquiring certain assets and personnel related to Parker Hannifin's Tolleson, Arizona facility, which also manufactures complex machined parts for the aerospace industry. |
Competitive Strengths
We believe Aerospace benefits from the following competitive strengths:
| |
| • | Broad Product Portfolio of Established Brands. We believe that Aerospace is a leading designer and manufacturer of fasteners and other complex, machined components for the aerospace industry. The combination of the Monogram, Allfast and Mac Fasteners brands enables Aerospace to offer a broad range of fastener products covering a broad scope of complexity and price ranges, as well as providing scale to customers who continue to rationalize their supply base and prefer to deal with fewer, broader-ranged suppliers. In several of the product categories, including rotary actuated blind bolts and blind and solid rivets, Aerospace has a meaningful market share with well-known and established brands. |
| |
| • | Strong Product Innovation. We believe that Aerospace's engineering, research and development capability and new product focus is a competitive advantage. For many years, Aerospace’s product development programs have provided innovative and proprietary product solutions. Recent innovations already brought to market include collars, extended range blind bolts and titanium screws. During 2015, Aerospace created a focused Engineering, Research and Technology team across the brands that incorporates sales, marketing and engineering disciplines into one group. We believe this is a unique approach which will provide quick technical solutions for our customers, drive the development of new products and create new opportunities for additional revenue. |
| |
| • | Leading Manufacturing Capabilities and Processes. We believe that Aerospace is a leading manufacturer of precision engineered components for the aerospace industry. As a result regulations and customer requirements for Aerospace, products need to be manufactured within tight tolerances and specifications, often out of hard to work with materials including titanium, inconel and specialty steels. Many of this businesses' products, facilities and manufacturing processes are required to be qualified and/or certified. Key certifications in Aerospace include : AS9100:2009 Revision C; ISO9001:2008; ISO14001:2004; TSO; and NADCAP for non-destructive testing, heat treatment, wet processes and materials testing. While proprietary products and patents are important, having proprietary manufacturing processes and capabilities makes Aerospace's products difficult to replicate. We believe Aerospace's manufacturing processes, capabilities and quality focus create a competitive strength for the business. |
Strategies
We believe the Aerospace segment has significant opportunities to grow and improve margins, based on the following strategies:
| |
| • | Leverage Strengths and Integrate Across the Aerospace Brands. The combined product sets of Monogram, Allfast and Mac Fasteners uniquely position us to benefit from platform-wide supply opportunities and grow at a level in excess of industry aircraft build rates. In addition, our aerospace platform will benefit from expected synergistic cost savings, including leveraging combined purchasing activities and indirect labor, joint commercial and product development efforts, and sharing of better practices between previously separate businesses. Aerospace customers will benefit from a combined product portfolio of proprietary products and product development efforts. The addition of Allfast, Martinic and Mac Fasteners products to the portfolio enables this segment to reach additional customers, including tier one suppliers to airframe OEMs and aftermarket repair companies, respectively. Monogram and Allfast can also cross-sell products into each other's legacy set of customers. |
| |
| • | Develop New Products. The Aerospace segment has a history of successfully creating and introducing new products and there are currently several significant product initiatives underway. We focus on expanding our current products into new applications on the aircraft, as well as securing qualified products onto new programs. Aerospace products contain patent protection, with additional patents pending, as well as proprietary manufacturing processes and "know-how." Monogram has developed the next generation Composi-Lok® 3, offering a flush break upon installation, a new Composi-Lite™ derivative affording significant installed weight savings in concert with fuel efficient aircraft designs, and is developing and testing other fasteners to offer improved clamping characteristics on composite structures. Aerospace also continues to expand its fastener offerings to include existing aerospace fastening products, including a suite of collar families used in traditional two-sided assembly. Our close working relationship between our new Engineering, Research and Technology team and our customers' engineering teams is key to developing future products desired and required by our customers. |
| |
| • | Increase Margins. The Aerospace segment is focused on expanding its margins through a variety of initiatives, including, but not limited to, executing on profitable growth strategies, leveraging one aerospace platform and implementing programs to improve manufacturing efficiencies. Increasing sales over the existing fixed cost structure, implementing price improvement strategies, and adding higher margin products to the product portfolio will all improve margins. In addition, by implementing the TriMas Operating System at all Aerospace locations, productivity, cycle times and on time delivery should improve, while reducing costs and spend. |
Marketing, Customers and Distribution
Aerospace's customers operate primarily in the aerospace industry, serving both OE and aftermarket customers on a wide variety of platforms. Given the focused nature of many of our products, the Aerospace segment relies upon a combination of direct sales forces and established networks of independent distributors with familiarity of the end-users. Although the markets for fasteners and complex machine components are highly competitive, we provide products and services primarily for specialized markets, and compete principally as technology, quality and service-oriented suppliers in their respective markets. Aerospace's products are sold to manufacturers and distributors within the commercial, business and military aerospace industry, both domestic and foreign. While products are sold to manufacturers, distributors, tier one suppliers and aftermarket repair companies, Aerospace works directly with aircraft manufacturers to develop and test new products and improve existing products. Aerospace's OEM, distribution, tier one supplier and other customers include Airbus, Boeing, Embraer, Hamilton Sunstrand (United Technologies Corp.), KLX, Inc., Parker Hannifin, Peerless Aerospace Fasteners, Spirit Aero Systems, TPS Aviation, Wesco Aircraft Hardware, and the United States government.
Competition
This segment's primary competitors include Ateliers de la Haute Garonne (AHG), Alcoa Fastening Systems, Cherry Aerospace (Precision Castparts Corp.) and LISI Aerospace. We believe that we are a leader in the blind bolt market with significant market share in all blind fastener product categories in which we compete. Aerospace companies supply highly engineered, non-commodity, customer-specific products that principally have large shares of small markets supplied by a limited number of competitors.
Energy
We believe Energy is a leading manufacturer and distributor of metallic and non-metallic gaskets, bolts, industrial fasteners and specialty products for the petroleum refining, petrochemical, oil field and industrial markets. With operations principally in North America and newer locations in Europe and Asia, Energy supplies gaskets and complementary fasteners to both maintenance repair operations ("MRO") and industrial OEMs. Our brands which comprise this segment include Lamons® and Basrur Uniseal Private Limited™ (Basrur).
Competitive Strengths
We believe Energy benefits from the following competitive strengths:
| |
| • | Comprehensive Product Offering. We offer a full suite of gasket and bolt products to the petroleum refining, petrochemical, oil field and industrial markets. Over the years, Energy has expanded its product offering to include custom-manufactured, specialty bolts of various sizes and made-to-order configurations and other CNC-machined components in Europe, as well as isolation kits, capabilities to produce high quality sheet jointing used in the manufacture of soft gaskets, and PTFE for its chemical customers. While many of the competitors manufacture and distribute either gaskets or bolts, supplying both provides us with an advantage to customers who prefer to deal with fewer suppliers. |
| |
| • | Established and Extensive Distribution Channels. Our business utilizes an established hub-and-spoke distribution system whereby our primary manufacturing facilities supply products to our own branches and highly knowledgeable network of worldwide distributors and licensees, which are located in close proximity to our primary customers. Our primary manufacturing facilities are in Houston, Texas; Faridabad and Bangalore, India; Wolverhampton, United Kingdom; and the newly opened facility in Reynosa, Mexico; with company-owned branches strategically located around the world to serve our global customer base. Enabled by its branch network and close proximity to its customers, Energy's ability to provide quick turn-around and customized solutions for its customers is also a competitive strength. This established network of branches, enhanced by third-party distributors, allows us to add new customers in various locations and to increase distribution to existing customers. Our experienced in-house sales support teams work with our global network of distributors and licensees to create a strong market presence in all aspects of the oil, gas and petrochemical refining industries. |
| |
| • | Leading Market Positions and Strong Brand Name. We believe we are one of the largest gasket and bolt suppliers to the global energy market. We believe that Lamons is known as a quality brand and offers premium service to the industry. We also believe that our facilities have the latest proprietary technology and equipment to be able to produce urgent requirement gaskets and bolts locally to meet its customers' demands. |
Strategies
The Energy segment has been faced with several external challenges related to the reduction of its upstream business as a result of the decline in oil prices, as well as downstream business postponement of refinery shutdowns and customer capital expenditures. We believe Energy has opportunities to improve its margins, while maintaining its market leadership, including:
| |
| • | Reconfiguring its Footprint to Drive Lower-Costs. Over the past year, we have been in the process, and continue to work through, reducing the cost structures through ongoing manufacturing, overhead and administrative productivity initiatives, global sourcing and selectively shifting manufacturing capabilities to countries with lower costs. We have performed a comprehensive review of our physical footprint and have closed and or consolidated locations to reduce our fixed cost structure. We have also moved a portion of our gasket and fastener operations from our Houston facility to a new facility in Reynosa, Mexico. The move to Mexico is expected to improve our global operating model and enhance the competitiveness of the business, while increasing customer service, as we move our higher-volume, longer lead-time products to this facility. In addition to our core domestic manufacturing facility in Houston, we have advanced manufacturing facilities and sourcing capabilities in China and India. Multi-country manufacturing capabilities provide flexibility to move specific manufacturing requirements amongst facilities to leverage lower cost opportunities and better serve our customers. We believe expanding our new Matrix® product and capacity in India will further increase profitability, as we manufacture our own sheet product compared to reliance for comparable product from our competitors. |
| |
| • | Improve Operational Efficiency at all Locations. We believe that there are additional opportunities to improve our operational efficiency at all of our locations by continuing the implementation of the lean-based TriMas Operating System. Through improved planning, inventory management, pricing and processes, Energy should improve its margins, while reducing its product lead-times and increase customer fill-rates. |
| |
| • | Expand Engineered and Specialty Product Offering. Over the past couple of years, we have launched several new highly-engineered and specialty products and have broadened our specialty bolt offering. Examples of new products include: WRI-LP gaskets, a hydrofluoric acid gasket solution; inhibitor gaskets designed to prevent corrosion in offshore platform flanges; IsoTekTM Gaskets, an engineered sealing solution for flanged pipe connections; and intelligent bolts which provide more reliable load indication. Most recently, Energy was the first in Europe approved to manufacture the API 20E fasteners used in subsea critical applications, and the first in the world approved to manufacture to API 6A, 17D, 20E and Q1 quality systems. In addition to providing revenue growth opportunities, specialty products tend to have higher margins than their standard counterparts. |
Marketing, Customers and Distribution
Energy relies upon a combination of direct sales forces and established networks of independent distributors and licensees with familiarity of the end users. Gaskets and bolts are supplied directly to major customers through our sales and service facilities in major regional markets, or through a large network of independent distributors/licensees. The sales and distribution network's close proximity to the customer makes it possible for Energy to respond to customer-specific engineered applications and provide a high degree of customer service. Our overseas sales are made either through newer sales and service facilities in Belgium, India, Singapore, Spain, Thailand and the United Kingdom, licensees or through our many distributors. Significant Energy customers include Dow Chemical, ExxonMobil, Bechtel, DNOW, LyondellBasell, MRC and Valero.
Competition
Energy's primary competitors include ERIKS, Flexitallic Group, Garlock (EnPro), Klinger, Lone Star and Teadit. Most of Energy's competitors supply either gaskets or bolts. We believe that providing both gaskets and bolts, as well as our hub-and-spoke distribution model, gives us a competitive advantage with many customers. We believe that our broader product portfolio and strong brand name enables us to maintain our market leadership position as one of the largest gasket and bolt suppliers to the energy market.
Engineered Components
We believe Engineered Components is a leading designer, manufacturer and distributor of high-pressure and acetylene cylinders for the transportation, storage and dispensing of compressed gases, as well as a variety of natural gas powered engines and parts, gas compressors, gas production equipment, meter runs, engine electronics and chemical pumps all engineered for use in oil and natural gas production. In general, these products are highly-engineered, customer-specific items that are sold into focused markets with few competitors.
Engineered Components' brands include Arrow® Engine and Norris Cylinder™ which we believe are well established and recognized in their respective markets.
| |
| • | Arrow Engine. We believe that Arrow Engine is a market leading provider of natural gas powered engines and parts. Arrow Engine also provides gas compressors, gas production, meter runs, engine electronics and chemical pumps, all engineered for use in oil and natural gas production and other industrial and commercial markets. Arrow Engine distributes its products through a worldwide distribution network with a particularly strong presence in the United States and Canada. Arrow Engine owns the original equipment manufacturing rights to distribute engines and replacement parts for four main OEM engine lines and offers a wide variety of spare parts for an additional six engine lines, which are widely used in the energy industry and other industrial applications. Arrow Engine has developed a new line of products in the area of industrial engine spare parts for various industrial engines not manufactured by Arrow Engine, including selected engines manufactured and sold under the Caterpillar®, Waukesha®, Ajax® and Gemini® brands. Arrow Engine has expanded its product line to include compressors and compressor packaging, gas production equipment, meter runs and other electronic products. |
| |
| • | Norris Cylinder. Norris Cylinder is a leading provider of a complete line of large and intermediate/small size, high-pressure and acetylene steel cylinders for the transportation, storage and dispensing of compressed gases. Norris Cylinder's large high-pressure seamless compressed gas cylinders are used principally for shipping, storing and dispensing oxygen, nitrogen, argon, helium and other gases for industrial and health care markets. In addition, Norris Cylinder offers a complete line of acetylene steel cylinders used to contain and dispense acetylene gas for the welding and cutting industries. Norris Cylinder markets cylinders primarily to major domestic and international industrial gas producers and distributors, welding equipment distributors and buying groups, as well as equipment manufacturers. |
Strategies
We believe the businesses within the Engineered Components segment have opportunities to grow, based on the following:
| |
| • | Strong Product Innovation. The Engineered Components segment has a history of successfully creating and introducing new products and there are currently several significant product initiatives underway. Arrow Engine continues to introduce new products in the area of industrial engine spare parts for various industrial engines not manufactured by Arrow Engine, including selected engines manufactured and sold under the Caterpillar®, Waukesha®, Ajax® and Gemini® brands. Arrow Engine has also launched an offering of customizable compressors and gas production and meter run equipment, which are used by existing end customers in the oil and natural gas extraction markets, as well as development of a natural gas compressor used for compressed natural gas (CNG) filling stations. Norris Cylinder developed a process for manufacturing ISO cylinders capable of holding higher pressure gases and has been awarded a United Nations certification for its ISO cylinders, making Norris Cylinder the first manufacturer approved to distribute ISO cylinders domestically. Norris Cylinder has also created new designs for seamless acetylene applications in marine and international markets. |
| |
| • | Entry into New Markets and Development of New Customers. Engineered Components has opportunities to grow its businesses by offering its products to new customers, markets and geographies. In November 2013, Norris Cylinder acquired the assets of Worthington Cylinder's Tilbury, Ontario and Jefferson, Ohio facilities, making Norris Cylinder the only manufacturer of steel high-pressure and acetylene cylinders in North America. Norris Cylinder is selling its cylinders internationally into Europe, South Africa, and South and Central America, as well as pursuing new end markets such as cylinders for use at cell towers (hydrogen fuel cells), in mine safety (breathing air and rescue chambers) and in fire suppression. Arrow Engine continues to expand its product portfolio to serve new customers and new applications for oil and natural gas production in all areas of the industry, including shale drilling. Arrow Engine is also expanding international sales, particularly in Mexico, Indonesia and Venezuela. |
| |
| • | Reconfigure Capacity to Reflect Expected Demand Levels. Norris Cylinder is in the process of deploying previously acquired assets in both its Huntsville, Alabama and Longview, Texas facilities to support its future expected growth, increasing its capacity for both large and small high pressure cylinders. Norris Cylinder is in process of installing equipment obtained during previous acquisitions in an effort to produce higher volume cylinders more efficiently, while allowing higher technology products to be produced on the current forge asset. At the same time, Arrow Engine, has been unfavorably impacted by reductions in drilling activity driven by the decline in oil prices. In response, Arrow Engine has been focused on right-sizing its business to reflect the current demand levels by lowering costs and maximizing resources until the end market recovers. Where possible, Arrow Engine is variablizing the cost structure to respond quickly to end market changes and enhance flexibility, driving low cost sourcing efforts, and focusing on additional productivity and Lean initiatives. |
Marketing, Customers and Distribution
Engineered Components' customers operate in the oil, gas, industrial and commercial industries. Given the focused nature of many of our products, the Engineered Components segment relies upon a combination of direct sales forces and established networks of independent distributors with familiarity of the end-users. In many of the markets this segment serves, its companies' brand names are virtually synonymous with product applications. The narrow end-user base of many of these products makes it possible for this segment to respond to customer-specific engineered applications and provide a high degree of customer service. Engineered Components' OEM and aftermarket customers include Airgas, Air Liquide, Chesapeake, Kidde-Fenwal, Midcon Compression, Praxair and Total Operations and Production Services (TOPS). In years with higher levels of drilling activity, DNOW and Weatherford would also be larger customers of engines, parts and compressor products.
Competition
Arrow Engine tends to compete against natural gas powered, lower horsepower, multi-cylinder engines from manufacturers such as Caterpillar, Chevy, Cummins and Ford industrial engines and electric motors. Norris Cylinder competes against Worthington, Beijing Tianhai Industry Co., Faber and Vitkovice Cylinders. In May 2012, the U.S. International Trade Commission made a unanimous final determination that Norris Cylinder had been materially injured by imports of DOT high pressure steel cylinders that were being subsidized by the Government of China, as well as being dumped in the U.S. market by producers in China, and as a result, imposed antidumping and countervailing duties on the subject imports to create a fairer competitive environment in the United States. Engineered Components' companies supply highly engineered, non-commodity, customer-specific products with large shares of small markets supplied by a limited number of competitors.
Acquisition Strategy
We believe that our businesses have significant opportunities to grow through disciplined, strategic acquisitions that enhance the strengths of our core businesses. We typically seek "bolt-on" acquisitions, in which we acquire another industry participant or adjacent product lines that expand our existing product offerings, gain access to new customers, end markets and distribution channels, expand our geographic footprint and/or capitalize on scale and cost efficiencies. Strategically, our primary focus is on acquisition targets in the Packaging and Aerospace segments, as these segments have higher growth and margin profiles. This is evidenced by our 2014 acquisitions of Allfast Fastening Systems in Aerospace and Lion Holdings and the remaining 30% interest in Arminak & Associates in Packaging, and our 2015 acquisition of certain assets and personnel related to Parker Hannifin’s Tolleson, Arizona facility, which manufactures complex machined parts for the aerospace industry. We will also consider opportunistic bolt-on acquisitions in our other segments, although such transactions are likely to be more modest in terms of target size and transaction value.
Materials and Supply Arrangements
Our largest raw material purchases are for steel, aluminum, titanium, cast iron, polyethylene and other resins. Raw materials and other supplies used in our operations are normally available from a variety of competing suppliers. In addition to raw materials, we purchase a variety of components and finished products from low-cost sources in China, India, Mexico, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam.
Steel is purchased primarily from steel mills and service centers with pricing contracts principally in the three-to-six month time frame. Changing global dynamics for steel production and supply will continue to present a challenge to our business. Polyethylene is generally a commodity resin with multiple suppliers capable of providing product globally. While both steel and polyethylene are readily available from a variety of competing suppliers, our business has experienced, and we believe will continue to experience, volatility in the costs of these raw materials.
Employees and Labor Relations
As of December 31, 2015, we employed approximately 4,200 people, of which approximately 49% were located outside the United States and 19% were unionized. We currently have collective bargaining agreements covering seven facilities worldwide, two of which are in the United States. Employee relations have generally been satisfactory.
On January 5, 2015, we finalized the decision to move a portion of the gasket and fastener operations from our Energy facility in Houston, Texas to a new facility in Reynosa, Mexico. This announcement impacts approximately 10% of facility's current unionized work force. The decision to move a portion of the manufacturing is the result of our effort to improve our Energy global operating model and enhance the competitiveness of the business. This transition is expected to be completed over the next 12 to 18 months.
In August 2015, we concluded, without a work stoppage or strike, a three year extension of our labor agreement with the United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America at our aerospace facility in California.
Seasonality and Backlog
None of our reportable segments experience significant seasonal fluctuations. However, our fourth quarter tends to be our lowest revenue quarter as a result of holiday slowdowns at certain of our significant customers.
We do not consider sales order backlog to be a material factor in our businesses. Our Aerospace customers often provide a forward view of build rates and needs for products, but firm orders do not extend for more than a few months, and often times are not guaranteed and could change.
Environmental Matters
We are subject to increasingly stringent environmental laws and regulations, including those relating to air emissions, wastewater discharges and chemical and hazardous waste management and disposal. Some of these environmental laws hold owners or operators of land or businesses liable for their own and for previous owners' or operators' releases of hazardous or toxic substances or wastes. Other environmental laws and regulations require the obtainment and compliance with environmental permits. To date, costs of complying with environmental, health and safety requirements have not been material. However, the nature of our operations and our long history of industrial activities at certain of our current or former facilities, as well as those acquired, could potentially result in material environmental liabilities.
Current laws and regulations have not had a material impact on our business, capital expenditures or financial position, while we must comply with existing and pending climate change legislation, regulation and international treaties or accords. Future events, including those relating to climate change or greenhouse gas regulation could require us to incur expenses related to the modification or curtailment of operations, installation of pollution control equipment or investigation and cleanup of contaminated sites.
Intangible Assets
Our identified intangible assets, consisting of customer relationships, trademarks and trade names and technology, are recorded at approximately $273.9 million at December 31, 2015, net of accumulated amortization. The valuation of each of the identified intangibles was performed using broadly accepted valuation methodologies and techniques.
Customer Relationships. We have developed and maintained stable, long-term selling relationships with customer groups for specific branded products and/or focused market product offerings within each of our businesses. Useful lives assigned to customer relationship intangibles range from five to 25 years and have been estimated using historic customer retention and turnover data. Other factors considered in evaluating estimated useful lives include the diverse nature of focused markets and products of which we have significant share, how customers in these markets make purchases and these customers' position in the supply chain. We also monitor and evaluate the impact of other evolving risks including the threat of lower cost competitors and evolving technology.
Trademarks and Trade Names. Each of our operating groups designs and manufactures products for focused markets under various trade names and trademarks (see discussion above by reportable segment). Our trademark/trade name intangibles are well-established and considered long-lived assets that require maintenance through advertising and promotion expenditures. Because it is our practice and intent to maintain and to continue to support, develop and market these trademarks/trade names for the foreseeable future, we consider our rights in these trademarks/trade names to have an indefinite life, except as otherwise dictated by applicable law.
Technology. We hold a number of United States and foreign patents, patent applications, and proprietary product and process-oriented technologies within all four of our reportable segments. We have, and will continue to dedicate, technical resources toward the further development of our products and processes in order to maintain our competitive position in the industrial, commercial and consumer end markets that we serve. Estimated useful lives for our technology intangibles range from one to 30 years and are determined in part by any legal, regulatory or contractual provisions that limit useful life. For example, patent rights have a maximum limit of 20 years in the United States. Other factors considered include the expected use of the technology by the operating groups, the expected useful life of the product and/or product programs to which the technology relates, and the rate of technology adoption by the industry.
International Operations
Approximately 13.7% of our net sales for the year ended December 31, 2015 were derived from sales by our subsidiaries located outside of the United States, and we may significantly expand our international operations through organic growth actions and acquisitions. In addition, approximately 15.0% of our operating net assets as of December 31, 2015 were located outside of the United States. We operate manufacturing facilities in Belgium, Canada, China, Germany, India, Mexico, Singapore, Spain, Thailand, the United Kingdom and Vietnam. In addition to the net sales derived from sales by our subsidiaries located outside of the United States, we also generated approximately $82.7 million of export sales from the United States. For information pertaining to the net sales and operating net assets attributed to our international operations, refer to Note 19, "Segment Information," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
Website Access to Company Reports
We use our corporate website, www.trimascorp.com/Investor Relations, as a channel for routine distribution of important information, including news releases, analyst presentations and financial information. We post filings as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed with, or furnished to, the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC"), including our annual, quarterly, and current reports on Forms 10-K, 10-Q, and 8-K, our proxy statements and any amendments to those reports or statements. All such postings and filings are available on our Investor Relations section of the website free of charge. The SEC also maintains a website, www.sec.gov, that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. The content on any website referred to in this Annual Report on Form 10-K is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K unless expressly noted.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
You should carefully consider each of the risks described below, together with information included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and other documents we file with the SEC. The risks and uncertainties described below are those that we have identified as material, but are not the only risks and uncertainties facing us. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently believe are immaterial may also impact our business operations, financial results and liquidity.
Risks Relating to our Business
Our businesses depend upon general economic conditions and we serve some customers in highly cyclical industries; as such, we may be subject to the loss of sales and margins due to an economic downturn or recession.
Our financial performance depends, in large part, on conditions in the markets that we serve in both the U.S. and global economies. Some of the industries that we serve are highly cyclical, such as the industrial equipment, energy and aerospace industries. When combined with ongoing customer consolidation activity and periodic manufacturing and inventory initiatives, an uncertain macro-economic and political climate could lead to reduced demand from our customers and increased price competition for our products, increased risk of excess and obsolete inventories and uncollectible receivables, and higher overhead costs as a percentage of revenue all of which would impact our operating margins.
Many of the markets we serve are highly competitive, which could limit the volume of products that we sell and reduce our operating margins.
Many of our products are sold in competitive markets. We believe that the principal points of competition in our markets are product quality and price, design and engineering capabilities, product development, conformity to customer specifications, reliability and timeliness of delivery, customer service and effectiveness of distribution. Maintaining and improving our competitive position will require continued investment by us in manufacturing, engineering, quality standards, marketing, customer service and support of our distribution networks. We may have insufficient resources in the future to continue to make such investments and, even if we make such investments, we may not be able to maintain or improve our competitive position. We also face the risk of lower-cost foreign manufacturers located in China, Southeast Asia, India and other regions competing in the markets for our products and we may be driven as a consequence of this competition to increase our investment overseas. Making overseas investments can be highly complicated and we may not always realize the advantages we anticipate from any such investments. Competitive pressure may limit the volume of products that we sell and reduce our operating margins.
Trends in oil and natural gas prices may affect the demand for, and profitability of, our energy products and services, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, consolidated results of operations, and consolidated financial condition.
The oil and gas industry historically has experienced periodic downturns. Demand for our energy-related products, such as engines, gaskets and fasteners, is sensitive to the level of drilling and production activity of, and the corresponding capital spending by, oil and natural gas companies. The level of drilling and production activity is directly affected by trends in oil and natural gas prices, which have been recently volatile and may continue to be volatile.
Prices for oil and natural gas are subject to large fluctuations in response to changes in the supply of and demand for oil and natural gas, market uncertainty, geopolitical developments and a variety of other factors that are beyond our control. Even the perception of longer-term lower oil and natural gas prices can reduce or defer major capital expenditures by our customers in the oil and gas industry. Given the long-term nature of many large-scale development projects, a significant downturn in the oil and gas industry could result in the reduction in demand for our energy-related products, and could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Our growth strategy includes the impact of acquisitions. If we are unable to identify attractive acquisition candidates, successfully integrate acquired operations or realize the intended benefits of our acquisitions, we may be adversely affected.
One of our principal growth strategies is to pursue strategic acquisition opportunities. We have completed 16 acquisitions over the past five years (excluding ones completed in our former Cequent businesses), primarily bolt-on businesses to our existing platforms. Each of these acquisitions required integration expense and actions that negatively impacted our results of operations and that could not have been fully anticipated beforehand. In addition, attractive acquisition candidates may not be identified and acquired in the future, financing for acquisitions may be unavailable on satisfactory terms and we may be unable to accomplish our strategic objectives in effecting a particular acquisition. We may encounter various risks in acquiring other companies, including the possible inability to integrate an acquired business into our operations, diversion of management's attention and unanticipated problems or liabilities, some or all of which could materially and adversely affect our business strategy and financial condition and results of operations.
We have significant goodwill and intangible assets, and future impairment of our goodwill and intangible assets could have a material negative impact on our financial results.
At December 31, 2015, our goodwill and intangible assets were approximately $652.8 million and represented approximately 55.8% of our total assets. Due to a significant decline in profitability levels in our Energy and engine products reporting units, we recorded pre-tax goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment charges in the fourth quarter of 2015 of approximately $75.7 million. If we experience declines in sales and operating profit or do not meet our current and forecasted operating budget, we may be subject to additional goodwill and/or other intangible asset impairments in the future. Historically, included within our net losses were pre-tax, non-cash goodwill and indefinite-lived impairment charges of approximately $62.5 million (excluding discontinued operations primarily relating to our former Cequent businesses) which were recorded during the year ended December 31, 2008. While the fair value of our remaining goodwill exceeds its carrying value, significantly worse financial performance of our businesses, significantly different assumptions regarding future performance of our businesses or significant declines in our stock price could result in future impairment losses. Because of the significance of our goodwill and intangible assets, and based on the magnitude of historical impairment charges, any future impairment of these assets could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
We may be unable to successfully implement our business strategies. Our ability to realize our business strategies may be limited.
Our businesses operate in relatively mature industries and it may be difficult to successfully pursue our growth strategies and realize material benefits therefrom. Even if we are successful, other risks attendant to our businesses and the economy generally may substantially or entirely eliminate the benefits. While we have successfully utilized some of these strategies in the past, our growth has principally come through acquisitions.
Our ability to deliver products that satisfy customer requirements is dependent on the performance of our subcontractors and suppliers, as well as on the availability of raw materials and other components.
We rely on other companies, including subcontractors and suppliers, to provide and produce raw materials, integrated components and sub-assemblies and production commodities included in, or used in the production of, our products. If one or more of our suppliers or subcontractors experiences delivery delays or other performance problems, we may be unable to meet commitments to our customers or incur additional costs. In some instances, we depend upon a single source of supply. Any service disruption from one of these suppliers, either due to circumstances beyond the supplier’s control, such as geo-political developments, or as a result of performance problems or financial difficulties, could have a material adverse effect on our ability to meet commitments to our customers or increase our operating costs.
Increases in our raw material or energy costs or the loss of critical suppliers could adversely affect our profitability and other financial results.
We are sensitive to price movements in our raw materials supply base. Our largest material purchases are for steel, copper, aluminum, titanium, polyethylene and other resins. Prices for these products fluctuate with market conditions, and have generally increased over time. We may be unable to completely offset the impact with price increases on a timely basis due to outstanding commitments to our customers, competitive considerations or our customers’ resistance to accepting such price increases and our financial performance may be adversely impacted by further price increases. A failure by our suppliers to continue to supply us with certain raw materials or component parts on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, could have a material adverse effect on us. To the extent there are energy supply disruptions or material fluctuations in energy costs, our margins could be materially adversely impacted.
Our products are typically highly engineered or customer-driven and we are subject to risks associated with changing technology and manufacturing techniques that could place us at a competitive disadvantage.
We believe that our customers rigorously evaluate their suppliers on the basis of product quality, price competitiveness, technical expertise and development capability, new product innovation, reliability and timeliness of delivery, product design capability, manufacturing expertise, operational flexibility, customer service and overall management. Our success depends on our ability to continue to meet our customers’ changing expectations with respect to these criteria. We anticipate that we will remain committed to product research and development, advanced manufacturing techniques and service to remain competitive, which entails significant costs. We may be unable to address technological advances, implement new and more cost-effective manufacturing techniques, or introduce new or improved products, whether in existing or new markets, so as to maintain our businesses’ competitive positions or to grow our businesses as desired.
We depend on the services of key individuals and relationships, the loss of which could materially harm us.
Our success will depend, in part, on the efforts of our senior management, including our chief executive officer. Our future success will also depend on, among other factors, our ability to attract and retain other qualified personnel. The loss of the services of any of our key employees or the failure to attract or retain employees could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our reputation, ability to do business, and results of operations may be impaired by improper conduct by any of our employees, agents, or business partners.
While we strive to maintain high standards, we cannot provide assurance that our internal controls and compliance systems will always protect us from acts committed by our employees, agents, or business partners that would violate U.S. and/or non-U.S. laws or fail to protect our confidential information, including the laws governing payments to government officials, bribery, fraud, anti-kickback and false claims rules, competition, export and import compliance, money laundering, and data privacy laws, as well as the improper use of proprietary information or social media. Any such allegations, violations of law or improper actions could subject us to civil or criminal investigations in the U.S. and in other jurisdictions, could lead to substantial civil or criminal, monetary and non-monetary penalties, and related shareholder lawsuits, could lead to increased costs of compliance, could damage our reputation and could have a material effect on our financial statements.
We have debt principal and interest payment requirements that may restrict our future operations and impair our ability to meet our obligations.
As of December 31, 2015, we have approximately $419.6 million of outstanding debt. After consideration of our interest rate swap agreement (see Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for additional information), approximately 66% of our debt bears interest at variable rates. We may experience increases in our interest expense as a result of general increases in interest rate levels. Our debt service payment obligations in 2015 were approximately $30.2 million, and based on amounts outstanding as of December 31, 2015, a 1% increase in the per annum interest rate for our variable rate debt would increase our interest expense by approximately $2.8 million annually.
Our degree of leverage and level of interest expense may have important consequences, including:
| |
| • | our leverage may place us at a competitive disadvantage as compared with our less leveraged competitors and make us more vulnerable in the event of a downturn in general economic conditions or in any of our businesses; |
| |
| • | our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our businesses and the industries in which we operate may be limited; |
| |
| • | a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations will be dedicated to the payment of interest and principal on our indebtedness, thereby reducing the funds available to us for operations, capital expenditures, acquisitions, future business opportunities or obligations to pay rent in respect of our operating leases; and |
| |
| • | our operations are restricted by our debt instruments, which contain certain financial and operating covenants, and those restrictions may limit, among other things, our ability to borrow money in the future for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, rent expense or other purposes. |
Our ability to service our debt and other obligations will depend on our future operating performance, which will be affected by prevailing economic conditions and financial, business and other factors, many of which are beyond our control. Our business may not generate sufficient cash flow, and future financings may not be available to provide sufficient net proceeds, to meet these obligations or to successfully execute our business strategies. See "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources."
Restrictions in our debt instruments and accounts receivable facility limit our ability to take certain actions and breaches thereof could impair our liquidity.
Our credit agreement contains covenants that restrict our ability to:
| |
| • | pay dividends or redeem or repurchase capital stock; |
| |
| • | incur additional indebtedness and grant liens; |
| |
| • | make acquisitions and joint venture investments; |
| |
| • | make capital expenditures. |
Our credit agreement also requires us to comply with financial covenants relating to, among other things, interest coverage and leverage. Our accounts receivable facility contains covenants similar to those in our credit agreement and includes additional requirements regarding our receivables. We may not be able to satisfy these covenants in the future or be able to pursue our strategies within the constraints of these covenants. Substantially all of the assets of our domestic subsidiaries (other than our special purpose receivables subsidiary) are pledged as collateral pursuant to the terms of our credit agreement. Borrowings under the foreign currency sub limit are secured by a pledge of the assets of the foreign subsidiary borrowers that are party to our credit agreement. A breach of a covenant contained in our debt instruments could result in an event of default under one or more of our debt instruments, our accounts receivable facility and our lease financing arrangements. Such breaches would permit the lenders under our credit agreement to declare all amounts borrowed thereunder to be due and payable, and the commitments of such lenders to make further extensions of credit could be terminated. In addition, such breach may cause a termination of our accounts receivable facility. Each of these circumstances could materially and adversely impair our liquidity.
We may face liability associated with the use of products for which patent ownership or other intellectual property rights are claimed.
We may be subject to claims or inquiries regarding alleged unauthorized use of a third party's intellectual property. An adverse outcome in any intellectual property litigation could subject us to significant liabilities to third parties, require us to license technology or other intellectual property rights from others, require us to comply with injunctions to cease marketing or using certain products or brands, or require us to redesign, re-engineer, or re-brand certain products or packaging, any of which could affect our business, financial condition and operating results. If we are required to seek licenses under patents or other intellectual property rights of others, we may not be able to acquire these licenses on acceptable terms, if at all. In addition, the cost of responding to an intellectual property infringement claim, in terms of legal fees and expenses and the diversion of management resources, whether or not the claim is valid, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may be unable to adequately protect our intellectual property.
While we believe that our patents, trademarks and other intellectual property have significant value, it is uncertain that this intellectual property or any intellectual property acquired or developed by us in the future, will provide a meaningful competitive advantage. Our patents or pending applications may be challenged, invalidated or circumvented by competitors or rights granted thereunder may not provide meaningful proprietary protection. Moreover, competitors may infringe on our patents or successfully avoid them through design innovation. Policing unauthorized use of our intellectual property is difficult and expensive, and we may not be able to, or have the resources to, prevent misappropriation of our proprietary rights, particularly in countries where the laws may not protect such rights as fully as in the U.S. The cost of protecting our intellectual property may be significant and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and future results of operations.
We may incur material losses and costs as a result of product liability, recall and warranty claims that may be brought against us.
We are subject to a variety of litigation incidental to our businesses, including claims for damages arising out of use of our products, claims relating to intellectual property matters and claims involving employment matters and commercial disputes.
We currently carry insurance and maintain reserves for potential product liability claims. However, our insurance coverage may be inadequate if such claims do arise and any liability not covered by insurance could have a material adverse effect on our business. Although we have been able to obtain insurance in amounts we believe to be appropriate to cover such liability to date, our insurance premiums may increase in the future as a consequence of conditions in the insurance business generally or our situation in particular. Any such increase could result in lower net income or cause the need to reduce our insurance coverage. In addition, a future claim may be brought against us that could have a material adverse effect on us. Any product liability claim may also include the imposition of punitive damages, the award of which, pursuant to certain state laws, may not be covered by insurance. Our product liability insurance policies have limits that, if exceeded, may result in material costs that could have an adverse effect on our future profitability. In addition, warranty claims are generally not covered by our product liability insurance. Further, any product liability or warranty issues may adversely affect our reputation as a manufacturer of high-quality, safe products, divert management's attention, and could have a material adverse effect on our business.
In addition, the Lamons business within our Energy reportable segment is a party to lawsuits related to asbestos contained in gaskets formerly manufactured by it or its predecessors. Some of this litigation includes claims for punitive and consequential as well as compensatory damages. We are not able to predict the outcome of these matters given that, among other things, claims may be initially made in jurisdictions without specifying the amount sought or by simply stating the minimum or maximum permissible monetary relief, and may be amended to alter the amount sought. Of the 6,242 claims pending at December 31, 2015, 120 set forth specific amounts of damages (other than those stating the statutory minimum or maximum). See Note 15, "Commitments and Contingencies," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for additional information.
Total settlement costs (exclusive of defense costs) for all such cases, some of which were filed over 20 years ago, have been approximately $7.8 million. All relief sought in the asbestos cases is monetary in nature. To date, approximately 40% of our costs related to settlement and defense of asbestos litigation have been covered by our primary insurance. Effective February 14, 2006, we entered into a coverage-in-place agreement with our first level excess carriers regarding the coverage to be provided to us for asbestos-related claims when the primary insurance is exhausted. The coverage-in-place agreement makes asbestos defense costs and indemnity insurance coverage available to us that might otherwise be disputed by the carriers and provides a methodology for the administration of such expenses. Nonetheless, we believe it is likely that there will be a period within the next 12 to 18 months, prior to the commencement of coverage under this agreement and following exhaustion of our primary insurance coverage, during which we likely will be solely responsible for defense costs and indemnity payments, the duration of which would be subject to the scope of damage awards and settlements paid. We also may incur significant litigation costs in defending these matters in the future. We may be required to incur additional defense costs and pay damage awards or settlements or become subject to equitable remedies that could adversely affect our businesses.
Our business may be materially and adversely affected by compliance obligations and liabilities under environmental laws and regulations.
We are subject to increasingly stringent environmental laws and regulations, including those relating to air emissions, wastewater discharges and chemical and hazardous waste management and disposal. Some of these environmental laws hold owners or operators of land or businesses liable for their own and for previous owners' or operators' releases of hazardous or toxic substances or wastes. Other environmental laws and regulations require the obtainment and compliance with environmental permits. To date, costs of complying with environmental, health and safety requirements have not been material. However, the nature of our operations and our long history of industrial activities at certain of our current or former facilities, as well as those acquired, could potentially result in material environmental liabilities.
While we must comply with existing and pending climate change legislation, regulation and international treaties or accords, current laws and regulations have not had a material impact on our business, capital expenditures or financial position. Future events, including those relating to climate change or greenhouse gas regulation, could require us to incur expenses related to the modification or curtailment of operations, installation of pollution control equipment or investigation and cleanup of contaminated sites.
Our borrowing costs may be impacted by our credit ratings developed by various rating agencies.
Two major ratings agencies, Standard & Poor's and Moody's, evaluate our credit profile on an ongoing basis and have each assigned ratings for our long-term debt. If our credit ratings were to decline, our ability to access certain financial markets may become limited, the perception of us in the view of our customers, suppliers and security holders may worsen and as a result, we may be adversely affected.
We have significant operating lease obligations and our failure to meet those obligations could adversely affect our financial condition.
We lease many of our manufacturing facilities and certain capital equipment. Our rental expense in 2015 under these operating leases was approximately $17.2 million. A failure to pay our rental obligations would constitute a default allowing the applicable landlord to pursue any remedy available to it under applicable law, which would include taking possession of our property and, in the case of real property, evicting us. These leases are categorized as operating leases and are not considered indebtedness for purposes of our debt instruments.
We may be subject to further unionization and work stoppages at our facilities or our customers may be subject to work stoppages, which could seriously impact the profitability of our business.
As of December 31, 2015, approximately 19% of our work force was unionized under several different unions and bargaining agreements. We currently have collective bargaining agreements covering seven facilities worldwide, two of which are in the United States.
On January 5, 2015, we finalized the decision to move a portion of the gasket and fastener operations from our Energy facility in Houston to a new facility in Mexico. This announcement impacts approximately 10% of facility's current unionized work force. The decision to move a portion of the manufacturing is the result of our effort to improve our Energy global operating model and enhance the competitiveness of the business. This transition is expected to be completed over the next 12 to 18 months.
In August 2015, we concluded, without a work stoppage or strike, a three year extension of our labor agreement with the United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America at our aerospace facility in California.
We are not aware of any present active union organizing drives at any of our other facilities. We cannot predict the impact of any further unionization of our workplace.
Many of our direct or indirect customers have unionized work forces. Strikes, work stoppages or slowdowns experienced by these customers or their suppliers could result in slowdowns or closures of assembly plants where our products are included. In addition, organizations responsible for shipping our customers' products may be impacted by occasional strikes or other activity. Any interruption in the delivery of our customers' products could reduce demand for our products and could have a material adverse effect on us.
Our healthcare costs for active employees and future retirees may exceed our projections and may negatively affect our financial results.
We maintain a range of healthcare benefits for our active employees and a limited number of retired employees pursuant to labor contracts and otherwise. Healthcare benefits for active employees and certain retirees are provided through comprehensive hospital, surgical and major medical benefit provisions or through health maintenance organizations, all of which are subject to various cost-sharing features. Some of these benefits are provided for in fixed amounts negotiated in labor contracts with the respective unions. If our costs under our benefit programs for active employees and retirees exceed our projections, our business and financial results could be materially adversely affected. Additionally, foreign competitors and many domestic competitors provide fewer benefits to their employees and retirees, and this difference in cost could adversely impact our competitive position.
A growing portion of our sales may be derived from international sources, which exposes us to certain risks which may adversely affect our financial results and impact our ability to service debt.
We have operations outside of the United States. Approximately 13.7% of our net sales for the year ended December 31, 2015 were derived from sales by our subsidiaries located outside of the U.S. In addition, we may significantly expand our international operations through internal growth and acquisitions. International operations, particularly sales to emerging markets and manufacturing in non-U.S. countries, are subject to risks which are not present within U.S. markets, which include, but are not limited to, the following:
| |
| • | volatility of currency exchange between the U.S. dollar and currencies in international markets; |
| |
| • | changes in local government regulations and policies including, but not limited to, foreign currency exchange controls or monetary policy, governmental embargoes, repatriation of earnings, expropriation of property, duty or tariff restrictions, investment limitations and tax policies; |
| |
| • | political and economic instability and disruptions, including labor unrest, civil strife, acts of war, guerrilla activities, insurrection and terrorism; |
| |
| • | legislation that regulates the use of chemicals; |
| |
| • | disadvantages of competing against companies from countries that are not subject to U.S. laws and regulations, including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act ("FCPA"); |
| |
| • | compliance with international trade laws and regulations, including export control and economic sanctions, such as anti-dumping duties; |
| |
| • | difficulties in staffing and managing multi-national operations; |
| |
| • | limitations on our ability to enforce legal rights and remedies; |
| |
| • | tax inefficiencies in repatriating cash flow from non-U.S. subsidiaries that could affect our financial results and reduce our ability to service debt; |
| |
| • | reduced protection of intellectual property rights; and |
| |
| • | other risks arising out of foreign sovereignty over the areas where our operations are conducted. |
In addition, we could be adversely affected by violations of the FCPA and similar worldwide anti-bribery laws as well as export controls and economic sanction laws. The FCPA and similar anti-bribery laws in other jurisdictions generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to non-U.S. officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business.
Our acquisition and disposition agreements by which we have acquired or sold companies, include indemnification provisions that may not fully protect us and may result in unexpected liabilities.
Certain of the agreements related to the acquisition and disposition of businesses require indemnification against certain liabilities related to the operations of the company for the previous owner. We cannot be assured that any of these indemnification provisions will fully protect us, and as a result we may incur unexpected liabilities that adversely affect our profitability and financial position.
Increased IT security threats and more sophisticated and targeted computer crime could pose a risk to our systems, networks, and products.
Increased global IT security threats and more sophisticated and targeted computer crime pose a risk to the security of our systems and networks and the confidentiality, availability and integrity of our data and communications. While we attempt to mitigate these risks by employing a number of measures, including employee training, comprehensive monitoring of our networks and systems, and maintenance of backup and protective systems, our networks and systems remain potentially vulnerable to advanced persistent threats. Depending on their nature and scope, such threats could potentially lead to the compromising of confidential information and communications, improper use of our systems and networks, manipulation and destruction of data, defective products, production downtimes and operational disruptions, which in turn could adversely affect our reputation, competitiveness and results of operations.
A major failure of our information systems could harm our business.
We depend on integrated information systems to conduct our business. We may experience operating problems with our information systems as a result of system failures, viruses, computer hackers or other causes. Any significant disruption or slowdown of our systems could cause customers to cancel orders or cause standard business processes to become inefficient or ineffective.
Our stock price may be subject to significant volatility due to our own results or market trends.
If our revenue, earnings or cash flows in any quarter fail to meet the investment community's expectations, there could be an immediate negative impact on our stock price. Our stock price could also be impacted by broader market trends and world events unrelated to our performance.
Risks Relating to the Spin-off of our former Cequent Businesses
We may be unable to achieve some or all of the benefits that we expected to achieve from the spin-off.
Although we believe that the separation of our former Cequent businesses from TriMas will provide financial, operational, managerial and other benefits to us and our shareholders, the spin-off may not provide such results on the scope or scale we anticipate, and we may not realize the assumed benefits of the spin-off. If we do not realize these assumed benefits, we could suffer a material adverse effect on our financial condition.
If the spin-off does not qualify as a tax-free transaction, the Company and its shareholders could be subject to substantial tax liabilities.
The spin-off was conditioned on our receipt of an opinion from our tax advisors, in form and substance satisfactory to us, that the distribution of shares of our Cequent businesses in the spin-off qualifies as tax-free to the Cequent businesses, the Company and our shareholders for U.S. federal income tax purposes under Sections 355 and 368(a)(1)(D) and related provisions of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the "Code"), the Company and other members of our consolidated tax reporting group. The opinion relied on, among other things, various assumptions and representations as to factual matters made by the Company and the Cequent businesses which, if inaccurate or incomplete in any material respect, could jeopardize the conclusions reached by our advisor in its opinion. The opinion is not binding on the Internal Revenue Service ("IRS"), or the courts, and there is no assurance that the IRS or the courts will not challenge the qualification of the spin-off as a transaction under Sections 355 and 368(a) of the Code or that any such challenge would not prevail.
If the spin-off were determined not to qualify under Section 355 of the Code, each U.S. holder of our common shares who received shares of the Cequent businesses in connection with the spin-off would generally be treated as having received a taxable distribution of property in an amount equal to the fair market value of the shares of the Cequent businesses that were received. That distribution would be taxable to each such shareholder as a dividend to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits. For each such shareholder, any amount that exceeded our earnings and profits would be treated first as a non-taxable return of capital to the extent of such shareholder’s tax basis in his or her common shares of the Company with any remaining amount being taxed as a capital gain. We would be subject to tax as if we had sold common shares in a taxable sale for their fair market value and we would recognize taxable gain in an amount equal to the excess of the fair market value of such common shares over our tax basis in such common shares, which could have a material adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Certain members of our board of directors and management may have actual or potential conflicts of interest because of their ownership of shares of the Cequent businesses or their relationships with the Cequent businesses following the spin-off.
Certain members of our board of directors and management are expected to own shares of the Cequent businesses and/or options to purchase shares of the Cequent businesses, which could create, or appear to create, potential conflicts of interest when our directors and executive officers are faced with decisions that could have different implications for the Company and the Cequent businesses. It is possible that some of our directors might also be directors of the Cequent businesses following the spin-off. This may create, or appear to create, potential conflicts of interest if these directors are faced with decisions that could have different implications for the Cequent businesses then the decisions have for the Company.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
Item 2. Properties
Properties
Our principal manufacturing facilities range in size from approximately 10,000 square feet to approximately 255,000 square feet. Except as set forth in the table below, all of our manufacturing facilities are owned. The leases for our manufacturing facilities have initial terms that expire from 2016 through 2026 and are all renewable, at our option, for various terms, provided that we are not in default under the lease agreements. Substantially all of our owned U.S. real properties are subject to liens in connection with our credit facility. Our executive offices are located in Bloomfield Hills, Michigan under a lease through June 2017. Our buildings have been generally well maintained, are in good operating condition and are adequate for current production requirements.
The following list sets forth the location of our principal owned and leased manufacturing and other facilities used in continuing operations and identifies the principal reportable segment utilizing such facilities as of December 31, 2015:
|
| | | | | | |
| Packaging | | Energy | | Aerospace | | Engineered Components |
United States: Arkansas:
Atkins(1) California: Azusa(1) Rohnert Park(1) Indiana:
Auburn
Hamilton(1) Ohio: New Albany(1) International: Germany:
Neunkirchen
Mexico:
Mexico City
United Kingdom:
Leicester China:
Hangzhou(1) Haining City(1) India: Greater Noida Baddi Vietnam: Thu Dau Mot(1) | | United States: Texas:
Houston(1) International: Belgium:
Geel, Antwerp(1) Canada:
Sarnia, Ontario(1) India:
Faridabad(1) Bangalore(1) Mexico: Reynosa(1) Thailand: Muang Rayong(1) United Kingdom: Wolverhampton(1) | | United States: California: Commerce(1) Stanton(1) City of Industry Kansas: Ottawa(1) Arkansas: Paris(1) Arizona: Tolleson | | United States: Alabama: Huntsville
Oklahoma:
Tulsa Texas:
Longview |
| | | |
__________________________
| |
(1) | Represents a leased facility. All such leases are operating leases. |
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
See Note 15, "Commitments and Contingencies" included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Supplementary Item. Executive Officers of the Company
As of December 31, 2015, the following were executive officers of the Company:
David M. Wathen. Mr. Wathen, age 63, has served as president and chief executive officer of the Company since 2009. He served as president and chief executive officer of Balfour Beatty, Inc. (U.S. operations), an engineering, construction and building management services company, from 2003 until 2007. Prior to his Balfour Beatty appointment, he was a principal member of Questor, a private equity firm, from 2000 to 2002. Mr. Wathen held management positions from 1977 to 2000 with General Electric, a diversified technology and financial services company, Emerson Electric, a global manufacturing and technology company, Allied Signal, an automotive parts manufacturer, and Eaton Corporation, a diversified power management company.
Robert J. Zalupski. Mr. Zalupski, age 56, was appointed chief financial officer of the Company in January 2015. Prior to his appointment as chief financial officer, he served as vice president, finance and treasurer for the Company since 2003 and assumed responsibility for corporate development in March 2010. He joined the Company as director of finance and treasury in 2002, prior to which he worked in the Detroit office of Arthur Andersen. From 1996 through 2001, Mr. Zalupski was a partner in the audit and business advisory services practice of Arthur Andersen providing audit, business consulting, and risk management services to both public and privately held companies in the manufacturing, defense and automotive industries. Prior to 1996, Mr. Zalupski held various positions of increasing responsibility within the audit practice of Arthur Andersen serving public and privately held clients in a variety of industries.
Joshua A. Sherbin. Mr. Sherbin, age 52, was appointed the Company’s general counsel and corporate secretary in 2005, and vice president and chief compliance officer in May 2008, prior to which he was employed as the North American corporate counsel and corporate secretary for Valeo, a diversified Tier 1 international automotive supplier headquartered in Europe. Prior to joining Valeo in 1997, Mr. Sherbin was senior counsel, assistant corporate secretary for Kelly Services, Inc., an employment staffing company, from 1995 to 1997. From 1988 until 1995, he was an associate with the law firm Butzel Long in its general business practice.
Colin E. Hindman. Mr. Hindman, age 41, has been with the Company since 2002 and was appointed vice president of human resources in February 2010. In August 2008, Mr. Hindman was appointed group HR director and from 2002 to 2007, Mr. Hindman served in a variety of management positions within the Company's human resource departments. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Hindman held various human resource management positions from 1996 to 2002 with Dana Corporation, a manufacturer of automotive product solutions, and Wabash Technologies, a manufacturer of sensors, actuators and assemblies.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our common stock, par value $0.01 per share, is listed for trading on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol "TRS." As of February 19, 2016, there were 302 holders of record of our common stock.
Our credit agreement restricts the payment of dividends on common stock, as such we did not pay dividends in 2015 or 2014. Our current policy is to retain earnings to repay debt and finance our operations and acquisitions. See the discussion under Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources" and Note 12 to the Company's financial statements captioned "Long-term Debt," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
The high and low sales prices per share of our common stock by quarter, as reported on the NASDAQ through December 31, 2015, are shown below:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Price range of common stock |
| | | High Price | | Low Price |
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | | | | |
| 4th Quarter | | $ | 22.02 |
| | $ | 15.29 |
|
| 3rd Quarter | | $ | 25.35 |
| | $ | 15.32 |
|
| 2nd Quarter | | $ | 32.54 |
| | $ | 27.74 |
|
| 1st Quarter | | $ | 31.85 |
| | $ | 26.59 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | | | | |
| 4th Quarter | | $ | 33.23 |
| | $ | 23.68 |
|
| 3rd Quarter | | $ | 39.16 |
| | $ | 24.32 |
|
| 2nd Quarter | | $ | 38.51 |
| | $ | 30.80 |
|
| 1st Quarter | | $ | 39.92 |
| | $ | 30.73 |
|
At the close of business on June 30, 2015, our shareholders received two common shares of Horizon common stock for every five shares of the Company they held as of the close of business on June 25, 2015. On June 30, 2015, the last trading day before the spin-off became effective, the closing price of our common shares, trading "regular way" (that is with an entitlement to common shares of Horizon distributed in the spin-off) was $29.60. On July 1, 2015, the first trading day after the spin-off, the opening price of our common shares was $24.99 per share and the opening price of Horizon common shares was $15.50 per share. These stock prices for our common stock and Horizon common stock were as quoted on the NASDAQ Global Select Market and the New York Stock Exchange, respectively.
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative total stockholder return from December 31, 2007 through December 31, 2015 for TriMas common stock, the Russell 2000 Index and a peer group(1) of companies we have selected for purposes of this comparison. We have assumed that dividends have been reinvested (and taking into account the value of Horizon Global shares distributed in the spin-off) and returns have been weighted-averaged based on market capitalization. The graph assumes that $100 was invested on December 31, 2007 in each of TriMas common stock, the stocks comprising the Russell 2000 Index and the stocks comprising the peer group.
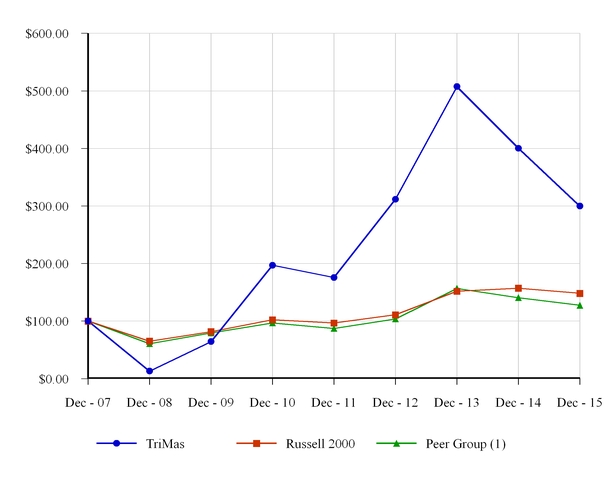 ______________
______________ | |
(1) | Includes Actuant Corporation, Carlisle Companies Inc., Crane Co., Dover Corporation, IDEX Corporation, Illinois Tool Works, Inc., SPX Corporation, Teleflex, Inc. and Kaydon Corp (included in peer group 2007-2012, due to being acquired during 2013). |
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following table sets forth our selected historical financial data from continuing operations for the five years ended December 31, 2015. The financial data for each of the five years presented has been derived from our financial statements and notes to those financial statements, for which the years ended December 31, 2011 and December 31, 2012 were audited by KPMG LLP and the years ended December 31, 2013 through December 31, 2015 have been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP. The following data should be read in conjunction with Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and our audited financial statements included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | | (dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data) |
| Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net sales | | $ | 863,980 |
| | $ | 887,300 |
| | $ | 799,700 |
| | $ | 738,550 |
| | $ | 590,800 |
|
| Gross profit | | 236,110 |
| | 237,010 |
| | 226,040 |
| | 211,750 |
| | 185,360 |
|
Operating profit (loss) (a) | | (4,250 | ) | | 86,650 |
| | 97,210 |
| | 88,400 |
| | 83,390 |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations (a), (b) | | (28,660 | ) | | 46,890 |
| | 59,240 |
| | 13,750 |
| | 26,850 |
|
| Per Share Data: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic: | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations (a) | | $ | (0.64 | ) | | $ | 1.03 |
| | $ | 1.34 |
| | $ | 0.30 |
| | $ | 0.78 |
|
| Weighted average shares | | 45,124 |
| | 44,882 |
| | 40,926 |
| | 37,521 |
| | 34,246 |
|
| Diluted: | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations (a) | | $ | (0.64 | ) | | $ | 1.02 |
| | $ | 1.32 |
| | $ | 0.30 |
| | $ | 0.77 |
|
| Weighted average shares | | 45,124 |
| | 45,269 |
| | 41,396 |
| | 37,949 |
| | 34,780 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets (c), (d), (e), (f) | | $ | 1,170,300 |
| | $ | 1,625,430 |
| | $ | 1,268,990 |
| | $ | 1,101,570 |
| | $ | 959,940 |
|
Total debt (d), (e) | | 419,630 |
| | 630,810 |
| | 294,620 |
| | 407,950 |
| | 458,040 |
|
Goodwill and other intangibles (a), (d) | | 652,790 |
| | 757,500 |
| | 445,840 |
| | 401,370 |
| | 301,160 |
|
__________________________
(a) During the fourth quarter of 2015, we recorded a goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment charge of approximately $75.7 million. See Note 8, "Goodwill and Other Intangibles Assets," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for further information.
(b) During 2012, we incurred debt extinguishment costs of approximately $46.8 million related to the redemption of our former senior notes and the refinance of our previous credit agreement.
(c) On June 30, 2015, we completed the spin-off of our Cequent businesses, thereby reducing the amount of our total assets as compared to prior periods. See Note 6, "Discontinued Operations" included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for further information.
(d) On October 17, 2014, we acquired 100% of the equity interest in Allfast Fastening Systems, thereby increasing the amount of our total assets, total debt and goodwill and other intangibles as of December 31, 2014. See Note 5, "Acquisitions" and Note 12, "Long-term Debt" included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for further information.
(e) Due to the adoption of Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2015-03, "Interest - Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30): Simplifying the Presentation of Debt Issuance Costs," in 2015, unamortized debt issuance costs of $7.8 million, $9.2 million, $9.7 million and $11.8 million as of December 31, 2014, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, which were previously presented in total assets have been reclassified to total debt. See Note 2, "New Accounting Pronouncements" and Note 12, "Long-term Debt" included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for further information.
(f) Due to the adoption of ASU 2015-17, "Income Taxes (Topic 740): Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes", during the fourth quarter of 2015, deferred tax assets of $28.6 million, $22.6 million, $19.7 million and $20.1 million as of December 31, 2014, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, which were previously presented in total assets have been reclassified to noncurrent deferred tax liabilities. See Note 2, "New Accounting Pronouncements" included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for further information.
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The statements in the discussion and analysis regarding industry outlook, our expectations regarding the performance of our business and the other non-historical statements in the discussion and analysis are forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the risks and uncertainties described in Item 1A "Risk Factors." Our actual results may differ materially from those contained in or implied by any forward-looking statements. You should read the following discussion together with Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
Introduction
We are a global manufacturer and distributor of products for commercial, industrial and consumer markets. We are principally engaged in four reportable segments: Packaging, Aerospace, Energy and Engineered Components.
On June 30, 2015, we completed the spin-off of our Cequent businesses, creating a new independent publicly-traded company, Horizon Global Corporation ("Horizon"). On June 30, 2015, our stockholders received two shares of Horizon common stock for every five shares of TriMas common stock that they held as of the close of business on June 25, 2015. The financial position, results of operations and cash flows of Horizon are reflected as discontinued operations for all periods presented through the date of the spin-off.
Key Factors and Risks Affecting Our Reported Results. Our businesses and results of operations depend upon general economic conditions and we serve some customers in cyclical industries that are highly competitive and themselves significantly impacted by changes in economic conditions. There has been little or no economic growth, particularly in the United States, although global economic conditions appear to have been relatively stable over the past couple of years. The most significant external factor impacting us in 2015 was the impact of lower oil prices, which directly impacted our Arrow Engine business (which serves the upstream oil and natural gas market at the well site) and our Energy business, which primarily serves petrochemical and other refineries in the downstream oil and gas markets. Our Arrow Engine business revenue declined more than 50% during 2015, primarily due to fewer orders for new engines and well-site content as a result of the reduction in oil prices and drilling activity. The Arrow Engine business reacted aggressively in cutting costs and structuring its business to the lower demand levels, and was essentially able to break-even in profit during 2015 despite the significant top line reduction.
In addition to oil prices, our 2015 results were also significantly impacted by a stronger U.S. dollar and a slowing of industrial production and related customer demand during the back half of 2015. While we experienced some organic growth in certain of our businesses in 2015 as compared to 2014, the majority of our growth was generated by sales from acquisitions. Our 2015 sales decreased as compared to 2014, as the aforementioned sales growth was more than offset by reductions in sales, primarily as a result of the impact of lower oil prices.
During 2014 and 2015, we undertook significant actions in our Energy reportable segment to reassess, restructure and optimize our manufacturing and sales footprints, as demand levels had been less consistent and lower than historical levels. Starting in the second half of 2013, both in the United States and abroad, petrochemical plants and refinery customers deferred shutdown activity, plus we experienced decreases in engineering and construction ("E&C") customer activity. We were able to gain market share and additional product content during 2014 and the first three quarters of 2015, primarily consisting of standard and highly-engineered bolts, which essentially offset the reduction in upstream channel business impacted by lower oil prices. Thus, we held total sales at consistent levels at around $50 million each quarter, but with significantly less favorable product sales mix primarily due to the lower E&C and shutdown activity, which would typically be a higher-margin business. Given these factors, during 2014, we announced the closure of a sales branch in China, a manufacturing facility in Brazil and the move of certain longer lead-time standard products from our Houston, Texas manufacturing facility to a new facility in Mexico, which began production in the fourth quarter of 2015. In 2015, we also announced the consolidation and/or closure of several of our facilities, including manufacturing facilities in Hangzhou, China, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil and Houston, Texas (former South Texas Bolt and Fitting facility).
During the third quarter of 2015, given the impact of lower oil prices on net sales and profitability, the uncertain macroeconomic environment and a recent slowing of industrial production and related demand, we announced a financial improvement plan ("FIP") to improve our profitability, cash flow conversion and operational efficiency. As part of the FIP, we originally targeted cost actions to yield approximately $15 million of annual savings, accelerating approximately $5 million of savings initiatives in the Energy reportable segment, with the remaining $10 million of savings initiatives spread relatively evenly across the remainder of the Company. The FIP consisted of headcount reductions, manufacturing and administrative cost reduction and facility closures or consolidations, for which we estimate one-time cash and non-cash charges to implement of approximately $6 million to $7 million. We expect the majority of the actions to be completed by the end of the first quarter of 2016. We believe the FIP will help to mitigate the external factors pressuring our top-line, and position the Company for improved profitability and operating leverage across a lower fixed cost structure in the future when demand levels recover. We continue to evaluate further actions as merited based on business performance, considering additional cost reductions or facility closures should sales and profitability levels continue below historical levels.
Due to a significant decline in profitability levels in our Energy and engine products reporting units during 2015 and a decline in our stock price and resulting market capitalization, we determined there were indicators that the fair value of the Energy and engine products reporting units, and/or other units, may be less than the carrying value. As such, we performed an impairment analysis of each of our reporting units and indefinite-lived trademarks/trade names, along with a comparison of the estimated aggregate fair value of all reporting units to our market capitalization, all as required by the authoritative accounting literature. Based on the results of the goodwill impairment test, we recorded pre-tax goodwill impairment charges in the fourth quarter of 2015 of approximately $70.9 million in our Energy reporting unit and approximately $3.2 million in our engine products reporting unit. As of December 31, 2015, there is no goodwill recorded in the Energy and engine products reporting units.
Over the past few years, we have executed on our growth strategies via bolt-on acquisitions, new products and geographic expansion within our existing platforms in each of our reportable segments. We have also proceeded with the aforementioned cost savings activities in our Energy reportable segment, moving toward more efficient facilities and lower cost country production. While our growth strategies have significantly contributed to increased net sales levels over this time period, our earnings margins over the period of execution have declined from historical levels, primarily due to costs incurred to move, close or consolidate existing facilities, the incurrence of acquisition diligence and integration costs, the margin impact of acquiring businesses with historically lower margins than our legacy businesses and due to increasing business in new markets to TriMas, where we make pricing decisions to penetrate new markets and do not yet have volume leverage. In addition to the energy end-market challenges, we have also incurred significant costs related to manufacturing inefficiencies associated with changes in aerospace customer demand with some distribution customer consolidation, a trend toward smaller lot order sizes and less consistent order patterns over the past few quarters. While these challenges and endeavors have significantly impacted margins, we believe that the margins in these businesses will migrate to historical levels over time (and have in Packaging, for example, where the acquisitions in the past few years have been integrated) as we integrate our acquisitions into our businesses, right-size our facilities and staffing levels to current and expected demand levels and patterns and capitalize on productivity initiatives and volume efficiencies.
Critical factors affecting our ability to succeed include: our ability to create organic growth through product development, cross selling and extending product-line offerings, and our ability to quickly and cost-effectively introduce new products; our ability to acquire and integrate companies or products that supplement existing product lines, add new distribution channels, expand our geographic coverage or enable better absorption of overhead costs; our ability to manage our cost structure more efficiently via supply base management, internal sourcing and/or purchasing of materials, selective outsourcing and/or purchasing of support functions, working capital management, and greater leverage of our administrative functions. If we are unable to do any of the foregoing successfully, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely impacted.
Our businesses do not experience significant seasonal fluctuation. We do not consider sales order backlog to be a material factor in our business. We expect sales growth to be derived from international sources, which exposes us to certain risks, including currency risks.
We are sensitive to price movements in our raw materials supply base. Our largest material purchases are for steel, aluminum, polyethylene and other resins and utility-related inputs. Historically, we have experienced volatility in costs of steel and resin and have worked with our suppliers to manage costs and disruptions in supply. We also utilize pricing programs to pass increased steel, aluminum and resin costs to customers. Although we may experience delays in our ability to implement price increases, we have been generally able to recover such increased costs. We may experience disruptions in supply in the future and may not be able to pass along higher costs associated with such disruptions to our customers in the form of price increases.
In addition to the aforementioned price movements in significant raw materials, certain of our businesses are sensitive to oil price movements. Our Arrow Engine business is most directly impacted by significant volatility in oil prices. Arrow's pumpjack and other engine sales and related parts, which comprise a significant portion of the business, are impacted by oil drilling levels, rig counts and commodity pricing. The decline of oil prices in late fourth quarter 2014 and through 2015 has significantly impacted demand levels in this business, with sales levels dropping more than 50% from 2014. Our other businesses may be impacted by volatile oil prices, but not as directly. For example, a portion of our Energy reportable segment serves upstream customers at oil well sites that have been impacted by changes in oil prices, while the majority of the segment provides parts for refineries and chemical plants, which may or may not choose to defer capital expenditures or changeover production stock, both of which would require retooling with our gaskets and bolts, in times of fluctuations in oil prices. Our Packaging reportable segment may be impacted by oil prices, as it is a significant driver of resin pricing, although we generally are able to maintain profit levels when oil prices change due to escalator/de-escalator clauses in contracts with many of our customers.
Segment Information and Supplemental Analysis
The following table summarizes financial information for our four reportable segments: |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | As a Percentage of Net Sales | | 2014 | | As a Percentage of Net Sales | | 2013 | | As a Percentage of Net Sales |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Net Sales | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 334,270 |
| | 38.7 | % | | $ | 337,710 |
| | 38.1 | % | | $ | 313,220 |
| | 39.2 | % |
| Aerospace | | 176,480 |
| | 20.4 | % | | 121,510 |
| | 13.7 | % | | 95,530 |
| | 11.9 | % |
| Energy | | 193,390 |
| | 22.4 | % | | 206,720 |
| | 23.3 | % | | 205,580 |
| | 25.7 | % |
| Engineered Components | | 159,840 |
| | 18.5 | % | | 221,360 |
| | 24.9 | % | | 185,370 |
| | 23.2 | % |
| Total | | $ | 863,980 |
| | 100.0 | % | | $ | 887,300 |
| | 100.0 | % | | $ | 799,700 |
| | 100.0 | % |
| Gross Profit | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 120,610 |
| | 36.1 | % | | $ | 118,210 |
| | 35.0 | % | | $ | 111,930 |
| | 35.7 | % |
| Aerospace | | 58,580 |
| | 33.2 | % | | 34,710 |
| | 28.6 | % | | 34,640 |
| | 36.3 | % |
| Energy | | 23,720 |
| | 12.3 | % | | 35,660 |
| | 17.3 | % | | 46,170 |
| | 22.5 | % |
| Engineered Components | | 33,200 |
| | 20.8 | % | | 48,430 |
| | 21.9 | % | | 33,300 |
| | 18.0 | % |
| Total | | $ | 236,110 |
| | 27.3 | % | | $ | 237,010 |
| | 26.7 | % | | $ | 226,040 |
| | 28.3 | % |
| Selling, General and Administrative | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 41,990 |
| | 12.6 | % | | $ | 38,490 |
| | 11.4 | % | | $ | 38,540 |
| | 12.3 | % |
| Aerospace | | 29,700 |
| | 16.8 | % | | 16,860 |
| | 13.9 | % | | 11,790 |
| | 12.3 | % |
| Energy | | 46,790 |
| | 24.2 | % | | 40,600 |
| | 19.6 | % | | 37,150 |
| | 18.1 | % |
| Engineered Components | | 11,750 |
| | 7.4 | % | | 14,190 |
| | 6.4 | % | | 13,600 |
| | 7.3 | % |
| Corporate expenses | | 32,120 |
| | N/A |
| | 36,450 |
| | N/A |
| | 37,460 |
| | N/A |
|
| Total | | $ | 162,350 |
| | 18.8 | % | | $ | 146,590 |
| | 16.5 | % | | $ | 138,540 |
| | 17.3 | % |
| Operating Profit (Loss) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 78,470 |
| | 23.5 | % | | $ | 77,850 |
| | 23.1 | % | | $ | 83,770 |
| | 26.7 | % |
| Aerospace | | 28,320 |
| | 16.0 | % | | 17,830 |
| | 14.7 | % | | 22,830 |
| | 23.9 | % |
| Energy | | (97,160 | ) | | (50.2 | )% | | (6,660 | ) | | (3.2 | )% | | 8,620 |
| | 4.2 | % |
| Engineered Components | | 18,240 |
| | 11.4 | % | | 34,080 |
| | 15.4 | % | | 19,450 |
| | 10.5 | % |
| Corporate | | (32,120 | ) | | N/A |
| | (36,450 | ) | | N/A |
| | (37,460 | ) | | N/A |
|
| Total | | $ | (4,250 | ) | | (0.5 | )% | | $ | 86,650 |
| | 9.8 | % | | $ | 97,210 |
| | 12.2 | % |
| Capital Expenditures | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 13,670 |
| | 4.1 | % | | $ | 13,730 |
| | 4.1 | % | | $ | 11,010 |
| | 3.5 | % |
| Aerospace | | 5,010 |
| | 2.8 | % | | 4,430 |
| | 3.6 | % | | 4,810 |
| | 5.0 | % |
| Energy | | 7,610 |
| | 3.9 | % | | 2,690 |
| | 1.3 | % | | 5,250 |
| | 2.6 | % |
| Engineered Components | | 2,320 |
| | 1.5 | % | | 1,690 |
| | 0.8 | % | | 2,190 |
| | 1.2 | % |
| Corporate | | 50 |
| | N/A |
| | 460 |
| | N/A |
| | 970 |
| | N/A |
|
| Total | | $ | 28,660 |
| | 3.3 | % | | $ | 23,000 |
| | 2.6 | % | | $ | 24,230 |
| | 3.0 | % |
| Depreciation and Amortization | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 20,920 |
| | 6.3 | % | | $ | 20,410 |
| | 6.0 | % | | $ | 18,960 |
| | 6.1 | % |
| Aerospace | | 13,290 |
| | 7.5 | % | | 7,630 |
| | 6.3 | % | | 3,790 |
| | 4.0 | % |
| Energy | | 4,790 |
| | 2.5 | % | | 4,600 |
| | 2.2 | % | | 3,820 |
| | 1.9 | % |
| Engineered Components | | 4,200 |
| | 2.6 | % | | 4,460 |
| | 2.0 | % | | 4,270 |
| | 2.3 | % |
| Corporate | | 340 |
| | N/A |
| | 340 |
| | N/A |
| | 260 |
| | N/A |
|
| Total | | $ | 43,540 |
| | 5.0 | % | | $ | 37,440 |
| | 4.2 | % | | $ | 31,100 |
| | 3.9 | % |
Results of Operations
Year Ended December 31, 2015 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2014
The principal factors impacting us during the year ended December 31, 2015, compared with the year ended December 31, 2014 were:
| |
| • | the spin-off of the Cequent businesses, including costs incurred to affect and reclassifying to discontinued operations for all periods presented, and amending our credit agreement ("Credit Agreement"); |
| |
| • | the impact of lower oil prices, primarily in our Engineered Components and Energy reportable segments; |
| |
| • | the impact of acquisitions (see below for the impact by reportable segment); |
| |
| • | cash and non-cash costs incurred related to facility closures and consolidations, primarily within our Energy reportable segment; |
| |
| • | an approximate $74.1 million goodwill impairment charge between our Energy and Engineered Components reportable segments; |
| |
| • | the impact of the stronger U.S. dollar, primarily in our Packaging and Energy reportable segments; and |
| |
| • | the impact of industrial slowing demand in the back half of 2015, primarily in our Packaging and Engineered Components reportable segments; |
Overall, net sales decreased approximately $23.3 million, or approximately 2.6%, to $864.0 million in 2015, as compared to $887.3 million in 2014. The impact of lower oil prices and the strong U.S. dollar significantly pressured the top-line during 2015, more than offsetting additional sales from organic sales growth and acquisitions in our Aerospace reportable segment. As a result of lower oil prices and related activity, sales of engine and compression-related products declined approximately $52.9 million during 2015 within our Engineered Components reportable segment. Sales further declined in our Engineered Components reportable segment by approximately $8.6 million, primarily due to a reduction of sales of our acetylene cylinders and lower export sales due to the impact of the stronger U.S. dollar. In addition, sales declined approximately $8.8 million (constant currency) in our Energy reportable segment, primarily from lower North American upstream gasket and bolt sales into oil and natural gas fields. Sales were further impacted by approximately $13.1 million of net unfavorable currency exchange, as our reported results in U.S. dollars were negatively impacted as a result of the stronger U.S. dollar relative to foreign currencies. These decreases were partially offset by an increase in sales during 2015 of approximately $57.5 million due to our recent acquisitions and by approximately $7.9 million of higher demand from our OEM and other customers in our Aerospace reportable segment.
Gross profit margin (gross profit as a percentage of sales) approximated 27.3% and 26.7% in 2015 and 2014, respectively. The primary driver of the increase in gross profit was our Aerospace reportable segment, due to both higher profit and margin associated with the Allfast Fastening Systems ("Allfast") acquisition and improved manufacturing efficiencies in 2015 in our legacy Aerospace business. Lower material costs also benefited profit margins in our Packaging and Engineered Components reportable segments. Gross profit margin also increased in our Packaging reportable segment due to productivity initiatives and a more favorable product sales mix. While gross profit margin declined within our Engineered Components reportable segment due to lower fixed cost absorption, this segment was able to substantially offset the impact of an approximate 28% sales reduction to only a 110 basis point reduction in gross profit margin due to cost reductions and aligning its structure with current demand levels. Gross profit margin declined in our Energy reportable segment due to higher costs related to our restructuring and footprint optimization efforts as well as costs related to U.S. West Coast port delays. In addition, gross profit was negatively impacted by approximately $4.8 million of unfavorable currency exchange, as our reported results in U.S. dollars were negatively impacted as a result of the stronger U.S. dollar relative to foreign currencies.
Operating profit (loss) margin (operating profit (loss) as a percentage of sales) approximated (0.5)% and 9.8% in 2015 and 2014, respectively. Operating profit decreased $91.0 million, or 104.9%, to an operating loss of $4.3 million in 2015 as compared to operating profit of $86.7 million in 2014, primarily due to approximately $74.1 million in goodwill impairment charges in our Energy and Engineered Components reportable segments. Increases in operating profit margin in our Packaging and Aerospace reportable segments due to productivity and manufacturing efficiencies, plus the favorable product sales mix impact of the Allfast acquisition, and a reduction in corporate costs and expenses were more than offset by reductions in profit margin in Energy and Engineered Components reportable segments. The decline in the Energy reportable segment, after consideration of the goodwill impairment, was due to costs related to our restructuring and footprint optimization efforts, higher legal expenses and costs related to U.S. West Coast port delays. The decline in operating profit margin within Engineered Components is primarily due to lower fixed cost absorption related to our engine and compression-related products, while costs were reduced year-over-year, net sales of such products were down more than 50% from 2014 levels.
Interest expense increased approximately $4.5 million, to $14.1 million in 2015, as compared to $9.6 million in 2014. The increase in interest expense was primarily due to an increase in our weighted-average variable rate borrowings to approximately $631.8 million in 2015, from approximately $512.3 million in 2014, primarily due to incremental net borrowings associated with funding the Allfast acquisition in October 2014 and the distribution received from the Cequent spin-off in June 2015. The effective weighted average interest rate on our outstanding variable rate borrowings, including our Credit Agreement and accounts receivable facilities, was approximately 1.9% for 2015 and 2014, respectively. Historically, a portion of our interest expense was allocated to the Cequent businesses and was recorded as discontinued operations.
We incurred debt financing and extinguishment costs of approximately $2.0 million in 2015 related to the amendment of our Credit Agreement in conjunction with the spin-off of the Cequent businesses during the second quarter of 2015. During 2014, we incurred debt financing expenses of approximately $3.4 million related to our former incremental term loan A facility used to fund the Allfast acquisition.
Other expense, net decreased approximately $2.3 million to $1.8 million in 2015, from $4.1 million in 2014. The decrease was primarily due to costs attributed to a reduction of certain indemnification assets related to uncertain tax liabilities during 2014 that did not recur.
The effective income tax rate for 2015 was (29.6)%, compared to 32.6% for 2014. During 2015, we reported domestic and foreign pre-tax losses of approximately $3.2 million and $19.0 million, respectively, and recognized tax benefits of approximately $3.1 million due to a change in an uncertain tax position for which the statute of limitations expired and research and manufacturing tax incentives. In addition, we were unable to record tax benefit of approximately $11.4 million related to pre-tax goodwill impairment charges in the U.S. and certain other jurisdictions. We also incurred tax charges of approximately $3.8 million directly attributable to increases in valuation allowances on certain deferred tax assets including foreign tax operating loss carryforwards. In 2014, we reported domestic and foreign pre-tax income of approximately $67.3 million and $2.3 million, respectively, and recognized tax benefits of approximately $4.4 million due to a change in an uncertain tax position for which the statute of limitations expired and research and manufacturing tax incentives. In addition, we incurred tax charges of approximately $3.3 million during 2014 directly attributable to increases in valuation allowances on certain deferred tax assets including foreign tax operating loss carryforwards.
Income (loss) from continuing operations decreased approximately $75.6 million to a loss of $28.7 million in 2015, from income of $46.9 million in 2014. The decrease was primarily the result of an approximately $91.0 million decrease in operating profit, which includes approximately $74.1 million in goodwill impairment charges in 2015, and increased interest expense of approximately $4.5 million, partially offset by a decrease in income tax expense of approximately $16.2 million, decreases in other expenses of approximately $2.3 million, and decreased debt financing and extinguishment costs of approximately $1.4 million.
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest was $0.8 million in 2014. The income was related to our 70% acquisition in Arminak & Associates LLC ("Arminak") in February 2012, and represented the 30% interest not attributed to TriMas Corporation. We acquired the remaining 30% interest in Arminak on March 11, 2014. See Note 5, "Acquisitions," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
See below for a discussion of operating results by reportable segment.
Packaging. Net sales decreased approximately $3.4 million, or 1.0%, to $334.3 million in 2015, as compared to $337.7 million in 2014, primarily as a result of approximately $8.5 million of unfavorable currency exchange, as our reported results in U.S. dollars were negatively impacted as a result of the stronger U.S. dollar relative to foreign currencies. Sales of our industrial closures also decreased approximately $2.4 million, primarily as a result of lower demand in North America. These decreases were partially offset by incremental net sales of approximately $7.0 million related to the acquisition of Lion Holdings Pvt. Ltd. ("Lion Holdings") in the third quarter of 2014 and an increase of approximately $0.4 million related to our specialty systems products, primarily due to increased demand from customers in North America.
Packaging's gross profit increased approximately $2.4 million to $120.6 million, or 36.1% of sales in 2015, as compared to $118.2 million, or 35.0% of sales in 2014. Gross profit increased primarily due to profit derived from the acquisition of Lion Holdings, as well as a $1.2 million reduction of an estimated acquisition related liability, a more favorable product mix and continued productivity initiatives. These increases were partially offset by approximately $3.9 million of unfavorable currency exchange as a result of the stronger U.S. dollar relative to foreign currencies.
Packaging's selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $3.5 million to $42.0 million, or 12.6% of sales in 2015, as compared to $38.5 million, or 11.4% of sales in 2014, primarily as a result of approximately $1.8 million of incremental selling, general and administrative costs associated with our Lion Holdings acquisition and a $0.9 million charge associated with the closure of a distribution center in Europe. Additionally, during 2015 we recognized a $1.1 million reduction in the Arminak contingent liability to the estimated fair value, as compared to a $2.0 million reduction in the Arminak contingent liability recognized during 2014.
Packaging's operating profit increased approximately $0.6 million to $78.5 million, or 23.5% of sales in 2015, as compared to $77.9 million, or 23.1% of sales, in 2014, primarily due to an approximate $1.7 million charge in 2014 associated with the disposal of equipment which was rendered obsolete as part of the Lion Holdings acquisition that did not repeat in 2015. Although sales levels decreased and selling general and administrative expenses increased, operating profit and margin increased due to a more favorable product mix and continued productivity initiatives.
Aerospace. Net sales increased approximately $55.0 million, or 45.2%, to $176.5 million in 2015, as compared to $121.5 million in 2014. Sales increased approximately $50.5 million due to the acquisition of Allfast in October 2014 and Parker-Hannifin Corporation's Tolleson, Arizona facility in November 2015. In addition, sales increased by approximately $7.9 million due to higher demand from our OEM and other customers. These increases were partially offset by lower demand from our two largest distribution customers, as they have communicated they are reducing their on-hand inventory levels of certain of our fastener products.
Gross profit within Aerospace increased approximately $23.9 million to $58.6 million, or 33.2% of sales, in 2015, from $34.7 million, or 28.6% of sales, in 2014, primarily due to additional profit and the favorable product sales mix associated with the acquisition of Allfast. In addition, the additional sales levels from our legacy business and improved manufacturing and labor efficiencies in 2015 lifted profit dollars and margin slightly, as this segment improved its manufacturing throughput and operating effectiveness following inefficiencies in 2014 resulting from increased change-over and processing related to smaller customer order quantities and less predictable than expected order patterns associated with our large OE and distribution customers.
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $12.8 million to $29.7 million, or 16.8% of sales, in 2015, as compared to $16.9 million, or 13.9% of sales, in 2014, primarily due to higher ongoing selling, general and administrative costs of approximately $8.5 million related to our Allfast acquisition. In addition, we incurred approximately $2.1 million in incremental costs related to a warehouse consolidation and other sales-related reorganizations. The remaining increase is primarily due to costs incurred to affect future synergies associated with combining four previously separate businesses and processes into one Aerospace platform.
Operating profit within Aerospace increased approximately $10.5 million to $28.3 million, or 16.0% of sales, in 2015, as compared to $17.8 million, or 14.7% of sales, in 2014. Operating profit increased due to higher sales levels, while operating profit margin increased due to increases in gross margin due to profit derived from Allfast and improved manufacturing efficiencies in 2015, which were partially offset by increased selling, general and administrative costs primarily related to the ongoing cost of acquisitions.
Energy. Net sales in 2015 decreased approximately $13.3 million, or 6.4%, to $193.4 million, as compared to $206.7 million in 2014. Through the first three quarters of 2015, this segment, after consideration of foreign currency exchange, increased sales levels compared to 2014 by approximately $1.2 million, as market share gains and higher E&C sales more than offset weaker upstream sales at well sites due to the lower oil prices and lower sales as a result of closure of locations in China and Brazil. However, in the fourth quarter of 2015, sales declined approximately 20% from the level in the first three quarters of 2015, due primarily to lower demand from large refinery and petrochemical customers, partially due to the lower oil prices and partially due to deferring planned fourth quarter capital spending projects. Despite this significant change in late 2015, overall 2015 sales still increased by approximately $1.9 million from 2014 levels in our international branches due to continued geographic market expansion and new product introductions. However, the international branch sales increase was more than offset by an approximate $5.9 million sales decline in North America due to the lower petrochemical and refinery customer demand levels and approximately $4.8 million of lower sales in China and Brazil due to our restructuring activities in those regions. In addition, this segment was impacted by approximately $4.5 million of net unfavorable currency exchange, as our reported results in U.S. dollars were negatively impacted as a result of the stronger U.S. dollar relative to foreign currencies.
Gross profit within Energy decreased approximately $12.0 million to $23.7 million, or 12.3% of sales, in 2015, as compared to $35.7 million, or 17.3% of sales, in 2014. Gross profit decreased primarily due to the decrease in sales and the resulting reduction in fixed costs absorption. In addition, we incurred approximately $4.0 million due to higher material sourcing costs, related to U.S. West Coast port delays, where we moved certain production to higher cost facilities to meet current orders. Gross profit continues to be impacted by our restructuring efforts, including facility closures and footprint optimization costs and severance, as this effort was also underway during 2014, the year over year impact on gross profit was approximately $3.1 million.
Selling, general and administrative expenses within Energy increased approximately $6.2 million to $46.8 million, or 24.2% of net sales, in 2015, as compared to $40.6 million or 19.6% of net sales, in 2014. During 2015, we incurred incremental costs of approximately $6.0 million associated with our restructuring efforts, including facility closures and footprint optimization costs, consulting fees and severance costs. Additionally, we incurred higher legal costs of approximately $0.6 million primarily due to the resolution of a previous legal claim, net of insurance recoveries.
Operating profit within Energy decreased approximately $90.5 million to a $97.2 million loss, or 50.2% of sales, in 2015, as compared to a $6.7 million loss, or 3.2% of sales, in 2014. Operating profit and related margin decreased primarily as a result of a $72.5 million goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets impairment charge during the fourth quarter of 2015, an approximate $1.4 million charge in 2015 associated with the disposal of equipment in conjunction with our facility closures and consolidation efforts, higher restructuring related costs and higher sourcing costs resulting from port delays.
Engineered Components. Net sales in 2015 decreased approximately $61.5 million, or 27.8%, to $159.8 million, as compared to $221.4 million in 2014. Sales of our slow speed and compressor engine and related products declined approximately $35.2 million, and sales of our gas compression products declined approximately $17.7 million, both primarily as a result of reduced levels of oil and gas drilling and well completions in the U.S. and Canada in response to lower oil prices. Sales further declined as a result of a one-time sale of our compressor packages by a significant customer in 2014 for approximately $5.6 million that did not recur. In addition, sales of our industrial cylinder products decreased approximately $8.6 million, primarily due to a reduction of sales of our acetylene cylinders and lower export sales due to the impact of the stronger U.S. dollar.
Gross profit within Engineered Components decreased approximately $15.2 million to $33.2 million, or 20.8% of sales, in 2015, from $48.4 million, or 21.9% of sales, in 2014. Gross profit declined as a result of the decreased sales levels in our engine and compression-related products due to lower oil prices. Gross profit margin for engine and compression-related products further declined due to lower fixed cost absorption, despite cost reductions to better align our cost structure with current demand levels. These decreases were partially offset by increased gross profit and gross profit margin from sales of our industrial cylinders as a result of continued productivity initiatives, as we continue to gain efficiencies from our previous asset acquisition.
Selling, general and administrative expenses decreased approximately $2.4 million to $11.8 million, or 7.4% of sales, in 2015, as compared to $14.2 million, or 6.4% of sales, in 2014, substantially all due to cost reductions in our engine and compression-related products, as we reduced costs given the low oil-related activity to better align our cost structure with current demand levels.
Operating profit within Engineered Components decreased approximately $15.8 million to $18.2 million, or 11.4% of sales, in 2015, as compared to $34.1 million, or 15.4% of sales, in 2014, primarily due to the reduced sales levels. Operating profit also decreased as a result of a $3.2 million goodwill impairment charge during the fourth quarter of 2015 as a result of the significant decline in current and forecasted sales of engine and engine-related products. Operating profit margin decreased as a result of lower fixed cost absorption related to our engine and compression-related products, which was partially offset by increased productivity initiatives and additional fixed cost absorption for our industrial cylinder products.
Corporate Expenses. Corporate expenses included in operating profit consist of the following:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2015 | | 2014 |
| | (in millions) |
| Corporate operating expenses | $ | 12.4 |
| | $ | 15.3 |
|
| Employee costs and related benefits | 19.7 |
| | 21.2 |
|
| Corporate expenses | $ | 32.1 |
| | $ | 36.5 |
|
Corporate expenses included in operating profit decreased approximately $4.4 million to $32.1 million in 2015, from $36.5 million in 2014. The decrease between years is primarily attributed to $1.4 million lower acquisition due diligence costs incurred in 2015 than in 2014 , a decrease in expense due to the timing and estimated attainment of our short and long-term incentive compensation and a reduction in employee costs and related benefits due to headcount reductions as part of the FIP.
Discontinued Operations. The results of discontinued operations consists of our former Cequent businesses, which were spun-off on June 30, 2015, and our former NI Industries business, which ceased operation in September 2014. Loss from discontinued operations, net of income tax expenses, was $4.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to income from discontinued operations, net of income tax expenses of $22.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. See Note 6, "Discontinued Operations," to our consolidated financial statements attached herein.
Year Ended December 31, 2014 Compared with Year Ended December 31, 2013
The principal factors impacting us during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared with the year ended December 31, 2013 were:
| |
| • | the impact of our various acquisitions during 2014 and 2013 (see below for the impact by reportable segment); |
| |
| • | business unit restructuring within our Energy reportable segment, under which we incurred approximately $13.2 million of costs during 2014; |
| |
| • | continued economic strength in certain of the markets our businesses serve in 2014 compared to 2013, contributing to increased net sales in all four of our reportable segments; |
| |
| • | the sale of our business in Italy within the Packaging reportable segment, for which we recorded a pre-tax gain of approximately $10.5 million; |
| |
| • | our equity offering during 2013, where we issued 5,175,000 shares of common stock for net proceeds of approximately $174.7 million; and |
| |
| • | our fourth quarter 2014 amendment to our Credit Agreement to add a $275.0 million incremental senior secured term loan A facility, and our amendment of our new credit agreement in 2013, which allowed us to reduce interest costs. |
Overall, net sales increased approximately $87.6 million, or approximately 11.0%, to $887.3 million in 2014, as compared to $799.7 million in 2013. During 2014, net sales increased in all four of our reportable segments. Of the sales increase, approximately $54.9 million was due to our recent acquisitions. The remainder of the increase in sales levels between years was due to the impact of continued economic strength in certain of our end markets, primarily in our Packaging and Engineered Components reportable segments, our expansion in international markets, primarily in our Packaging reportable segment and our new product introductions and related growth, primarily in our Engineered Components reportable segment.
Gross profit margin (gross profit as a percentage of sales) approximated 26.7% and 28.3% in 2014 and 2013, respectively. Gross profit increased due to continued productivity, cost reductions and automation efforts primarily in our Engineered Components and Packaging reportable segments. The increases in gross profit margin were partially offset by a less favorable product sales mix, primarily in our Energy, Aerospace and Packaging reportable segments, manufacturing inefficiencies in our Aerospace reportable segment and the impact of the restructuring in our Energy reportable segment. In addition, we continue to experience an overall less favorable product sales mix in the reportable segments with recent acquisitions, as the acquired businesses tend to have lower margins than our historical businesses, plus we incur purchase accounting charges and integration costs in the first several quarters of ownership.
Operating profit margin (operating profit as a percentage of sales) approximated 9.8% and 12.2% in 2014 and 2013, respectively. Operating profit decreased $10.5 million, or 10.9%, to $86.7 million in 2014 as compared to $97.2 million in 2013, primarily as a result of higher sales levels. Operating profit margin decreased primarily due the impact of the restructuring in our Energy reportable segment, a less favorable product sales mix, primarily in our Energy, Aerospace and Packaging reportable segments and as a result of the newly acquired companies comprising a larger percentage of sales and having lower margins than our legacy businesses and manufacturing inefficiencies in our Aerospace reportable segment. In addition, our operating profit margin decreased due to a $10.5 million gain recognized within our Packaging reportable segment on the sale of the Italian business, including $7.9 million related to the release of historical currency translation adjustments into net income during 2013, that did not recur in 2014. Partially offsetting the decreases in operating profit margin were continued productivity, cost reductions and automation efforts primarily in our Packaging and Engineered Components reportable segments as well as operating leverage gained on the higher sales levels primarily in our Packaging and Engineered Components reportable segments.
Interest expense decreased approximately $5.7 million, to $9.6 million in 2014, as compared to $15.3 million in 2013. The decrease in interest expense was primarily due to a reduction in our overall interest rates due to the refinancing of our Credit Agreement at lower interest rates in the fourth quarter of 2013. Interest expense further declined due to a decrease in our effective weighted average interest rate on variable rate borrowings, including our Credit Agreement and accounts receivable facilities, to approximately 1.9% for 2014, from 2.7% for 2013, and a decrease in our weighted-average variable rate borrowings to approximately $512.3 million in 2014, from approximately $514.2 million in 2013.
We incurred debt financing expenses of approximately $3.4 million in 2014 related to our incremental term loan A facility used to fund the Allfast acquisition. During 2013, we incurred debt extinguishment costs of approximately $2.5 million related to the refinance of our U.S. bank debt.
Other expense, net increased approximately $0.8 million to $4.1 million in 2014, from $3.3 million in 2013. The change was primarily related to higher losses on transactions denominated in foreign currencies.
The effective income tax rate was 32.6% for 2014, as compared to 22.2% for 2013. During 2014, we reported domestic and foreign pre-tax income of approximately $67.3 million and $2.3 million, respectively, and recognized tax benefits of approximately $4.4 million primarily due to a change in an uncertain tax position for which the statute of limitations expired and research and manufacturing tax incentives. In addition, we incurred tax charges of approximately $3.3 million during 2014 directly attributable to increases in valuation allowances on certain deferred tax assets including foreign tax operating loss carryforwards. In 2013, we reported domestic and foreign pre-tax income of approximately $47.8 million and $28.4 million, respectively, and recognized tax benefits of approximately $9.0 million primarily attributable to certain gains not subject to tax, a change in an uncertain tax position for which the statute of limitations expired and research and manufacturing tax incentives. We also incurred tax charges of approximately $3.0 million during 2013 directly attributable to increases in valuation allowances on certain deferred tax assets including foreign tax operating loss carryforwards and international restructuring events.
Income from continuing operations decreased approximately $12.3 million to $46.9 million in 2014, from $59.2 million in 2013. The decrease was primarily the result of a $10.5 million gain recognized within our Packaging reportable segment on the sale of the Italian business in 2013 that did not recur in 2014, a $5.8 million increase in income tax expense, plus a a $0.9 million increase in debt financing and extinguishment costs and a $0.8 million increase in other expenses, partially offset by a $5.7 million reduction in interest expense.
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest was $0.8 million in 2014, compared to $4.5 million in 2013. The income relates to our 70% acquisition in Arminak & Associates LLC ("Arminak") in February 2012, which represents the 30% interest not attributed to TriMas Corporation. On March 11, 2014, we acquired the remaining 30% interest in Arminak. See Note 5, "Acquisitions," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
See below for a discussion of operating results by reportable segment.
Packaging. Net sales increased approximately $24.5 million, or 7.8%, to $337.7 million in 2014, as compared to $313.2 million in 2013. Sales of our specialty systems products increased by approximately $22.0 million, primarily due to increases in demand from our major customers in North America and Europe, as well as continued growth in our revenue base in Asia. Sales further increased approximately $4.8 million as a result of the acquisition of Lion Holdings Pvt. Ltd. ("Lion Holdings") in the third quarter of 2014. Sales of our industrial closures declined by approximately $3.9 million, primarily as a result of the loss of approximately $10.2 million of sales associated with our Italian rings and levers business sold in the third quarter of 2013, which was partially offset by increased sales of our other industrial closures, primarily in our U.S. markets. In addition, sales also increased by approximately $1.6 million as a result of a net favorable currency exchange, as our reported results in U.S. dollars were positively impacted as a result of a weaker U.S. dollar relative to foreign currencies.
Packaging's gross profit increased approximately $6.3 million to $118.2 million, or 35.0% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $111.9 million, or 35.7% of sales, in 2013, primarily due to the higher sales levels. Gross profit margin decreased from the prior year as ongoing productivity and automation initiatives and increased sales in certain higher-margin industrial products were more than offset by a less favorable product mix shift, with sales of our lower margin specialty products comprising a larger percentage of overall sales, as well as cost incurred in Asia as we add capacity to meet expected demand.
Packaging's selling, general and administrative expenses decreased approximately $0.1 million to $38.5 million, or 11.4% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $38.5 million, or 12.3% of sales, in 2013. Selling, general and administrative expenses decreased as a percent of sales, as a $2.0 million reduction in the Arminak & Associates contingent liability to estimated fair value was offset by increased selling, general and administrative costs associated with the continued investment in growth initiatives, including costs associated with the Lion Holdings acquisition.
Packaging's operating profit decreased approximately $5.9 million to $77.9 million, or 23.1% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $83.8 million, or 26.7% of sales, in 2013. Operating profit decreased primarily due an approximately $10.5 million gain recognized on the sale of the Italian business in the third quarter of 2013, which included approximately $7.9 million related to the release of historical currency translation adjustments into net income. In addition to the impact of the Italian business gain in 2013, operating profit margin decreased further as ongoing productivity initiatives and operating leverage gained were more than offset by a less favorable product sales mix and costs associated with the Lion Holdings acquisition, including approximately $1.7 million of charges associated with the disposal of equipment which was rendered obsolete as part of our recent acquisitions.
Aerospace. Net sales increased approximately $26.0 million, or 27.2%, to $121.5 million in 2014, as compared to $95.5 million in 2013. Sales increased approximately $27.0 million due to the acquisition of Allfast in the fourth quarter of 2014, Mac Fasteners, Inc. ("Mac") in the fourth quarter of 2013, and Martinic Engineering, Inc. ("Martinic") in the first quarter of 2013. These increases were partially offset by a decrease in sales in our legacy aerospace business.
Gross profit within Aerospace remained flat at $34.7 million, or 28.6% of sales, in 2014, from $34.6 million, or 36.3% of sales, in 2013. Gross profit margins declined due to approximately $1.2 million of incremental inventory step-up costs and approximately $0.5 million of incremental ongoing intangible asset amortization costs related to our recent acquisitions. Gross profit margins also declined due to manufacturing and labor inefficiencies resulting from increased change-over and processing related to smaller customer order quantities, less predictable than expected order patterns associated with our large OE and distribution customers and a less favorable product sales mix. Additionally, gross profit margin declined due to our Mac and Martinic acquisitions, which have lower gross margin than our legacy aerospace business.
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $5.1 million to $16.9 million, or 13.9% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $11.8 million, or 12.3% of sales, in 2013, primarily due to higher ongoing selling, general and administrative costs of approximately $2.1 million associated with our Allfast, Mac and Martinic acquisitions, and approximately $1.6 million of incremental intangible asset amortization costs and legal and professional fees associated with consummating the acquisitions. Selling, general and administrative costs increased in our legacy aerospace business, primarily due to an approximately $1.1 million charge for resolution of a customer claim. In addition, we incurred approximately $0.7 million in additional employee related costs in 2014 associated with changes in leadership.
Operating profit within Aerospace decreased approximately $5.0 million to $17.8 million, or 14.7% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $22.8 million, or 23.9% of sales, in 2013, primarily due to manufacturing and labor inefficiencies, a less favorable product sales mix, lower profit margins associated with our recent acquisitions and higher selling, general and administrative expenses in support of our growth initiatives, which more than offset the impact of higher sales levels.
Energy. Net sales for 2014 increased approximately $1.1 million, or 0.6%, to $206.7 million, as compared to $205.6 million in 2013. Sales increased by approximately $6.1 million due to our acquisitions in 2013, including Wulfrun Specialised Fasteners ("Wulfrun") and substantially all the business assets of Tat Lee (Thailand) Ltd. ("Tat Lee"), as well as growth in our U.S. markets as a result of increased sales of standard gaskets and bolts, particularly in the fourth quarter of 2014. These increases were partially offset by decreased sales of approximately $4.5 million in China and Brazil as a result of our facility closure and restructuring activities in those regions in the second quarter of 2014, approximately $1.1 million as a result of lower branch sales in Europe and lower demand in certain Canadian markets.
Gross profit within Energy decreased approximately $10.5 million to $35.7 million, or 17.3% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $46.2 million, or 22.5% of sales in 2013, primarily due to approximately $6.7 million of charges associated with the closure of our China sales branch and Brazilian manufacturing facility, including a charge of approximately $3.9 million for the estimated future unrecoverable lease obligation on our Brazilian manufacturing facility. In addition, gross profit margin declined as a result of a less favorable product sales mix, with a higher percentage of sales being generated by lower margin standard gaskets and bolts, as well as labor inefficiencies associated with our footprint, restructuring and optimization efforts and additional sales being generated by our recent acquisitions, which have lower margins than the historical business.
Selling, general and administrative expenses within Energy increased approximately $3.4 million to $40.6 million, or 19.6% of net sales, in 2014, as compared to $37.2 million, or 18.1% of net sales, in 2013, as we continued to invest in our growth initiatives, including approximately $1.3 million for the normal operating selling, general and administrative costs of our recent acquisitions. In addition, we incurred approximately $4.9 million of expense in the current year related to both the remaining operating charges and exit costs associated with the facility closure and restructuring activities, including approximately $1.9 million as a result of the reduction in value of certain intangible assets, offset by reduced spending the back half of 2014 due to the closure of the facilities.
Operating profit within Energy decreased approximately $15.3 million to $6.7 million, or 3.2% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $8.6 million, or 4.2% of sales, in 2013. Operating profit and profit margin decreased primarily due to approximately $13.2 million of charges associated with our China sales branch and Brazil manufacturing facility restructuring activity, including an approximately $1.3 million loss related to the release of historical currency translation adjustments into net income, a higher percentage of our sales being generated by our recent acquisitions, which have lower margins than our historical business and increased normal selling, general and administrative costs.
Engineered Components. Net sales in 2014 increased approximately $36.0 million, or 19.4%, to $221.4 million, as compared to $185.4 million in 2013. Sales in our industrial cylinder business increased by approximately $26.0 million, due primarily to approximately $17.0 million in sales being generated from our November 2013 cylinder asset acquisition, as well as continued growth projects related to both new product sales of fire suppressant and aviation cylinders, and growth in our Mexico and South America markets. Sales in our engine business increased approximately $10.0 million, with approximately $5.6 million of the increase related to a large order for compressor packages by a significant customer in the first quarter of 2014. In addition, sales increased in our gas compression products by approximately $7.2 million resulting from both growth in our existing customer base and new customers. These increases were partially offset by an approximate $2.9 million decrease in our slow speed and compressor engine and related products business, primarily due to a reduced demand of our single cylinder engines and the impact of falling oil prices in late 2014.
Gross profit within Engineered Components increased approximately $15.1 million to $48.4 million, or 21.9% of sales, in 2014, from $33.3 million, or 18.0% of sales, in 2013, primarily due to margin improvement, as well as higher sales levels in both of our industrial cylinder and engine businesses. Gross profit margin in our engine business increased, as the lower fixed cost absorption we experienced during the third quarter of 2013, primarily a result of lower production and procurement levels, did not recur in 2014, and as a result of a more favorable product sales mix and continued productivity initiatives. Gross profit margin in our industrial cylinder business remained flat, as increased gross profit margin due to continued productivity initiatives and operating leverage gained on the recent cylinder asset acquisition was offset by a less favorable product sales mix.
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $0.6 million to $14.2 million, or 6.4% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $13.6 million, or 7.3% of sales, in 2013, as a result of the increased sales in both our engine and industrial cylinder businesses, with lower selling, general and administrative expenses as a percent of sales as a result of additional operating leverage gained on the higher sales levels, primarily in our engine business, as well as reduced legal fees in our industrial cylinder business, which was partially offset by increased amortization of the intangible assets associated with the fourth quarter 2013 cylinder asset acquisition.
Operating profit within Engineered Components increased approximately $14.6 million to $34.1 million, or 15.4% of sales, in 2014, as compared to $19.5 million, or 10.5% of sales, in 2013, primarily due to the increased sales levels, with margin improvement resulting from improved fixed cost absorption in our engine business, continued productivity and cost reduction initiatives, as well as the additional operating leverage gained on selling, general and administrative expenses.
Corporate Expenses. Corporate expenses included in operating profit consist of the following:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (in millions) |
| Corporate operating expenses | | $ | 15.3 |
| | $ | 14.7 |
|
| Employee costs and related benefits | | 21.2 |
| | 22.8 |
|
| Corporate expenses | | $ | 36.5 |
| | $ | 37.5 |
|
Corporate expenses included in operating profit decreased approximately $1.0 million to $36.5 million in 2014, from $37.5 million in 2013. The decrease between years is primarily attributed to a reduction in costs associated with our long-term incentive programs due to year-over-year reductions in estimated attainment for certain of our performance awards, which was partially offset by an increase in costs related to acquisition due diligence.
Discontinued Operations. The results of discontinued operations consists of our former Cequent businesses, which were spun-off on June 30, 2015, our former NI Industries business, which ceased operation in September 2014, and our precision tool cutting and specialty fitting lines of business, which were sold in December 2011. Income from discontinued operations, net of income tax expense, was $22.4 million and $20.8 million in 2014 and 2013, respectively. See Note 6, "Discontinued Operations," to our consolidated financial statements attached herein.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Cash Flows
Cash flows provided by operating activities of continuing operations in 2015 were approximately $76.6 million, as compared to $92.5 million in 2014. Significant changes in cash flows provided by operating activities of continuing operations and the reasons for such changes are as follows:
| |
| • | In 2015, the Company generated $92.8 million in cash flows, based on the reported net loss from continuing operations of $28.7 million and after considering the effects of non-cash items related to impairment of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets, losses on dispositions of businesses and other assets, depreciation, amortization, stock compensation and related changes in excess tax benefits, changes in deferred income taxes, debt financing and extinguishment costs and other, net. In 2014, the Company generated $91.2 million based on the reported net income from continuing operations of $46.9 million and after considering the effects of similar non-cash items. |
| |
| • | Decreases in accounts receivable resulted in a source of cash of approximately $5.3 million in 2015, while increases in receivables resulted in a use of cash of approximately $9.8 million in 2014. The primary driver of the change in each year was the year-over-year change in net sales, given sales in the last quarter of each year, based on historical turnover, are likely collected in the quarter following the sale. Fourth quarter 2015 net sales was approximately 14% lower than fourth quarter 2014 sales, and fourth quarter 2014 sales was approximately 17% higher than fourth quarter 2013. Partially offsetting the cash source in 2015 was an increase in days sales outstanding of receivables to approximately 58 days, as compared to approximately 55 days in 2014. |
| |
| • | For the year ended December 31, 2015, we reduced our investment in inventory by approximately $3.3 million, primarily as a result of lower sales levels. For the year ended December 31, 2014, we used approximately $6.0 million of cash for investment in our inventories. While our gross inventory levels decreased in 2015, our days sales in inventory increased by approximately 14 days, primarily due to higher material sourcing costs and increased purchases related to U.S. West Coast port delays, mainly in our Energy reportable segment. |
| |
| • | Decreases in accounts payable and accrued liabilities resulted in a cash use of approximately $29.5 million in 2015, as compared to a cash source of $11.8 million in 2014. The decrease in accounts payable and accrued liabilities is primarily driven by the decrease in purchases in the second half of 2015 as a result of the decrease in sales, the timing of payments made to suppliers and mix of vendors and related terms. In addition, accrued liabilities decreased in 2015 due to the settlement of various liabilities related to the October 2014 Allfast acquisition. Our days accounts payable on hand at year end remained essentially flat at 55 days in both 2015 and 2014. |
Net cash used for investing activities in 2015 was approximately $37.0 million, as compared to $405.7 million in 2014. During 2015, we paid approximately $10.0 million for two acquisitions, the largest of which was the acquired business assets of Parker Hannifin in our Aerospace reportable segment. We also incurred approximately $28.7 million in capital expenditures in 2015, as we have continued our investment in growth, capacity and productivity-related capital projects. Cash received from the disposition of assets was approximately $1.7 million in 2015. During 2014, we paid approximately $382.9 million for the acquisition of Allfast in our Aerospace reportable segment and Lion Holdings in our Packaging reportable segment. We also invested approximately $23.0 million in capital expenditures and received cash from the disposition of assets of approximately $0.2 million.
Net cash used for financing activities in 2015 was approximately $236.4 million, as compared to net cash provided by financing activities of $284.5 million in 2014. In conjunction with the spin-off, Horizon made a cash distribution to us of $214.5 million, we used the distribution received from Horizon to amend and pay down our term loan facilities. During 2015, we had net additional repayments of approximately $169.9 million on our term loan facilities and $39.5 million on our receivables and revolving credit facilities. We transferred cash of approximately $17.1 million during the period to Horizon, as a result of the spin-off of our former Cequent businesses. We also made deferred purchase price payments related to our previous acquisitions of approximately $6.4 million, we used approximately $1.9 million related to debt financing fees, and used a net cash amount of approximately $1.7 million net, related to our stock compensation arrangements. During 2014, we had net additional borrowings of approximately $266.1 million on our term loan facilities and $74.9 million on our receivables and revolving credit facilities, of which a significant portion was used to fund the Allfast acquisition. In addition, we purchased the remaining 30% noncontrolling interest of Arminak for a cash purchase price of $51.0 million. We also had cash uses of approximately $3.8 million related to debt financing costs and $1.1 million net, related to our stock compensation arrangements.
Our Debt and Other Commitments
During the second quarter of 2015, we amended our Credit Agreement, pursuant to which we were able to extend maturities and resize our credit facilities following the spin-off of the Cequent businesses. The cash distribution to the Company from Horizon was used to reduce the outstanding borrowings under the previous credit agreement. The Credit Agreement consists of a $500.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility, which permits revolving borrowings denominated in specific foreign currencies ("Foreign Currency Loans"), subject to a $75.0 million sub limit, and a $275.0 million senior secured term loan A facility ("Term Loan A Facility").
Below is a summary of the key terms under the Credit Agreement as of December 31, 2015, and the key terms of the previous credit agreement in place immediately prior to entering into the amended Credit Agreement on June 30, 2015, with term loans showing the face amount of borrowings upon issuance and revolving credit facilities showing gross availability at each date:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Instrument | | Amount
($ in millions) | | Maturity Date | | Interest Rate |
| Credit Agreement | | | | | | |
| Senior secured revolving credit facility | | $ | 500.0 |
| | 6/30/2020 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.750%(b) |
| Senior secured term loan A facility | | 275.0 |
| | 6/30/2020 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.750%(b) |
| | | | | | | |
| Previous Credit Agreement | | | | | | |
| Senior secured revolving credit facility | | 575.0 |
| | 10/16/2018 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.625%(b) |
| Senior secured term loan A facility | | 450.0 |
| | 10/16/2018 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.625%(b) |
__________________________
(a) London Interbank Offered Rate ("LIBOR")
(b) The interest rate spread is based upon the leverage ratio, as defined, as of the most recent determination date.
The Credit Agreement also provides incremental term loan facility commitments and/or incremental revolving credit facility commitments in an amount not to exceed the greater of $300 million and an amount such that, after giving effect to such incremental commitments and the incurrence of any other indebtedness substantially simultaneously with the making of such incremental commitments, the senior secured net leverage ratio, as defined in the Credit Agreement, is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00. The terms and conditions of any incremental term loan facility and/or incremental revolving credit facility commitments must be no more favorable than the existing credit facilities under the Credit Agreement.
We may be required to prepay a portion of the loans under the Term Loan A Facility in an amount equal to a percentage of our excess cash flow, as defined, with such percentage based on our leverage ratio, as defined. As of December 31, 2015, no amounts are due under this provision.
Amounts drawn under our revolving credit facility fluctuate daily based upon our working capital and other ordinary course needs. Availability under our revolving credit facility depends upon, among other things, compliance with the Credit Agreement's financial covenants. Our Credit Agreement contains various negative and affirmative covenants and other requirements affecting us and our subsidiaries that are comparable to the previous credit agreement, including restrictions on incurrence of debt, liens, mergers, investments, loans, advances, guarantee obligations, acquisitions, asset dispositions, sale-leaseback transactions, hedging agreements, dividends and other restricted payments, transactions with affiliates, restrictive agreements and amendments to charters, bylaws, and other material documents. The terms of the Credit Agreement also require us and our subsidiaries to meet certain restrictive financial covenants and ratios computed quarterly, including a maximum leverage ratio (total consolidated indebtedness plus outstanding amounts under the accounts receivable securitization facility over consolidated EBITDA, as defined) and a minimum interest expense coverage ratio (consolidated EBITDA, as defined, over cash interest expense, as defined). Our permitted leverage ratio under the Credit Agreement is 3.50 to 1.00 as of December 31, 2015. If we were to complete an acquisition which qualifies for a Covenant Holiday Period, as defined in our Credit Agreement, then our permitted leverage ratio cannot exceed 4.00 to 1.00 during that period. Our actual leverage ratio was 2.80 to 1.00 as of December 31, 2015. Our permitted interest expense coverage ratio under the Credit Agreement is 3.00 to 1.00 and, our actual interest expense coverage ratio was 12.77 to 1.00 as of December 31, 2015. At December 31, 2015, we were in compliance with our financial and other covenants contained in the Credit Agreement.
The following is a reconciliation of net income (loss), as reported, which is a GAAP measure of our operating results, to Consolidated Bank EBITDA, as defined in our Credit Agreement, for the year ended December 31, 2015. We present Consolidated Bank EBITDA to show our performance under our financial covenants.
|
| | | | |
| | | Year ended
December 31, 2015 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (33,400 | ) |
| Bank stipulated adjustments: | | |
| Interest expense, net (as defined) | | 14,060 |
|
| Income tax expense | | 6,540 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | | 43,540 |
|
| Extraordinary non-cash charges | | 75,680 |
|
Non-cash compensation expense(1) | | 6,340 |
|
| Other non-cash expenses or losses | | 17,830 |
|
Non-recurring expenses or costs(2) | | 15,000 |
|
Acquisition integration costs(3) | | 1,880 |
|
Debt financing and extinguishment costs(4) | | 1,970 |
|
Permitted dispositions(5) | | 4,740 |
|
| Consolidated Bank EBITDA, as defined | | $ | 154,180 |
|
|
| | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2015 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
Total Consolidated Indebtedness, as defined(6) | | $ | 432,230 |
| |
| Consolidated Bank EBITDA, as defined | | 154,180 |
| |
| Actual leverage ratio | | 2.80 |
| x |
| Covenant requirement | | 3.50 |
| x |
|
| | | | |
| | | December 31, 2015 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Interest expense, as defined | | $ | 14,060 |
|
| Interest income | | (420 | ) |
| Non-cash amounts attributable to amortization of financing costs | | (1,700 | ) |
| Pro forma adjustment for acquisitions and dispositions | | 130 |
|
| Total consolidated cash interest expense, as defined | | $ | 12,070 |
|
|
| | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2015 | |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | |
| Consolidated Bank EBITDA, as defined | | $ | 154,180 |
| |
| Total consolidated cash interest expense, as defined | | 12,070 |
| |
| Actual interest expense coverage ratio | | 12.77 |
| x |
| Covenant requirement | | 3.00 |
| x |
________________________________________
(1)Non-cash compensation expenses resulting from the grant of restricted shares of common stock and common stock options.
(2)Non-recurring costs and expenses related to cost savings projects, including restructuring and severance expenses, not to exceed $15 million in any fiscal year and $40.0 million in aggregate, subsequent to January 1, 2013.
(3)Costs and expenses arising from the integration of any business acquired not to exceed $15 million in any fiscal year and $40 million in the aggregate.
(4)Costs incurred with refinancing our credit facilities.
(5)EBITDA from permitted dispositions, as defined.
(6)Includes $6.6 million of acquisition related deferred purchase price and contingent consideration as of December 31, 2015.
Another important source of liquidity is our $75.0 million accounts receivable facility, under which we have the ability to sell eligible accounts receivable to a third-party multi-seller receivables funding company. During the second quarter of 2015, we amended the facility to remove the former Cequent businesses and to reduce the committed funding from $105.0 million to $75.0 million, with no other significant changes to the facility. In December 2015, the Company further amended the facility to extend the maturity date from October 16, 2018 to June 30, 2020.
Our available liquidity under our accounts receivable facility ranges from $60 million to $96 million, depending on the level of receivables outstanding at a given point in time during the year. We had $53.6 million and $78.7 million outstanding under the facility as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and $7.1 million and $1.6 million available but not utilized as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. At December 31, 2015, we had $100.3 million outstanding under our revolving credit facility and had $378.1 million potentially available after giving effect to approximately $21.6 million of letters of credit issued and outstanding. At December 31, 2014, we had $118.1 million outstanding under our revolving credit facility and had $435.0 million potentially available after giving effect to approximately $21.9 million of letters of credit issued and outstanding. The letters of credit are used for a variety of purposes, including support of certain operating lease agreements, vendor payment terms and other subsidiary operating activities, and to meet various states' requirements to self-insure workers' compensation claims, including incurred but not reported claims. Including availability under our accounts receivable facility and after consideration of leverage restrictions contained in the Credit Agreement, as of December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, we had $107.4 million and $192.0 million, respectively, of borrowing capacity available for general corporate purposes.
We rely upon our cash flow from operations and available liquidity under our revolving credit and accounts receivable facilities to fund our debt service obligations and other contractual commitments, working capital and capital expenditure requirements. At the end of each quarter, we use cash on hand from our domestic and certain foreign subsidiaries to pay down amounts outstanding under our revolving credit and accounts receivable facilities. Generally, excluding the impact and timing of acquisitions, we use available liquidity under these facilities to fund capital expenditures and daily working capital requirements.
Our combined weighted average monthly amounts outstanding on our Credit Agreement and our accounts receivable facility approximated $631.8 million and $512.3 million during 2015 and 2014, respectively. The overall increase is due primarily to the incremental term loan and additional borrowings under our existing senior secured revolving credit facility to fund the Allfast acquisition during the fourth quarter of 2014.
Cash management related to our revolving credit and accounts receivable facilities is centralized. We monitor our cash position and available liquidity on a daily basis and forecast our cash needs on a weekly basis within the current quarter and on a monthly basis outside the current quarter over the remainder of the year. Our business and related cash forecasts are updated monthly. Given aggregate available funding under our revolving credit and accounts receivable facilities of $107.4 million at December 31, 2015, after consideration of the aforementioned leverage restrictions, and based on forecasted cash sources and requirements inherent in our business plans, we believe that our liquidity and capital resources, including anticipated cash flows from operations, will be sufficient to meet our debt service, capital expenditure and other short-term and long-term obligation needs for the foreseeable future.
Our exposure to interest rate risk results primarily from the variable rates under our Credit Agreement. Borrowings under the Credit Agreement bear interest, at various rates, as more fully described in Note 12, "Long-term Debt," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K. We use interest rate swap agreements to fix the LIBOR-based variable portion of the interest rates on our term loan facility. As of December 31, 2015, we had interest rate swap agreements in place that hedge a notional amount of debt from approximately $251.5 million to approximately $192.7 million, with established fixed interest rates in a range of 0.74% to 2.68% with various expiration terms extending to June 30, 2020.
We are subject to variable interest rates on our term loan and revolving credit facility. At December 31, 2015, one-Month LIBOR and three-Month LIBOR approximated 0.43% and 0.61%, respectively. Based on our variable rate-based borrowings outstanding at December 31, 2015, and after consideration of the interest rate swap agreement associated with our $275.0 million term loan A, a 1% increase in the per annum interest rate would increase our interest expense by approximately $2.8 million annually.
Principal payments required under the Credit Agreement for the term loan A facility are $3.4 million due each fiscal quarter beginning December 2015 through September 2018 and approximately $5.2 million due each fiscal quarter from December 2018 through March 2020, with final payment of $202.8 million due on June 30, 2020.
In addition to our long-term debt, we have other cash commitments related to leases. We account for these lease transactions primarily as operating leases, and incurred expense from continuing operations related thereto of approximately $17.2 million in 2015. We expect to continue to utilize leasing as a financing strategy in the future to meet capital expenditure needs and to reduce debt levels.
In addition to lease expense from continuing operations, we also have approximately $2.4 million in annual future lease obligations related to businesses that have been discontinued, of which, approximately 64% relate to the facility for the former specialty laminates, jacketings and insulation tapes line of business (which extends through 2024) and 36% relates to the facility for the former industrial fastening business (which extends through 2022).
Market Risk
We conduct business in various locations throughout the world and are subject to market risk due to changes in the value of foreign currencies. The functional currencies of our foreign subsidiaries are primarily the local currency in the country of domicile. We manage these operating activities at the local level and revenues and costs are generally denominated in local currencies; however, results of operations and assets and liabilities reported in U.S. dollars will fluctuate with changes in exchange rates between such local currencies and the U.S. dollar.
We have historically used derivative financial instruments to manage currency risks, albeit in immaterial notional contracts, as we explored the predictability of our procurement activities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of our subsidiaries and the impact of currency rate volatility on our earnings.
We are also subject to interest risk as it relates to our long-term debt. We use interest rate swap agreements to fix the variable portion of our debt to manage this risk. See Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for additional information.
Common Stock
TriMas is listed in the NASDAQ Global Select MarketSM. Our stock trades under the symbol "TRS."
Commitments and Contingencies
Under various agreements, we are obligated to make future cash payments in fixed amounts. These include payments under our long-term debt agreements, rent payments required under operating and capital lease agreements, certain benefit obligations and interest obligations on our credit agreement.
The following table summarizes our expected fixed cash obligations over various future periods related to these items as of December 31, 2015.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Payments Due by Periods |
| | | Total | | Less than One Year | | 1 - 3 Years | | 3 - 5 Years | | More than 5 Years |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Contractual cash obligations: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term debt and receivables facilities | | $ | 425,680 |
| | $ | 13,850 |
| | $ | 29,380 |
| | $ | 382,450 |
| | $ | — |
|
| Lease obligations | | 91,810 |
| | 17,400 |
| | 30,450 |
| | 21,090 |
| | 22,870 |
|
| Benefit obligations | | 20,980 |
| | 880 |
| | 3,600 |
| | 4,740 |
| | 11,760 |
|
Interest obligations (a) | | 36,670 |
| | 8,720 |
| | 16,530 |
| | 11,420 |
| | — |
|
| Deferred purchase price and contingent consideration | | 6,550 |
| | 6,550 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Total contractual obligations | | $ | 581,690 |
| | $ | 47,400 |
| | $ | 79,960 |
| | $ | 419,700 |
| | $ | 34,630 |
|
__________________________
(a)Interest on our both our senior secured revolving credit facility and term loan A facility is based on LIBOR plus 175.0 basis points, which equaled approximately 2.2% at December 31, 2015. Interest on our receivables facility is based on LIBOR plus 100.0 basis points, which equaled 1.4% at December 31, 2015. These rates were used to estimate our future interest obligations with respect to the long-term debt.
As of December 31, 2015, we had a $500.0 million revolving credit facility and a $75.0 million accounts receivable facility. We had $100.3 million outstanding under our revolving credit facility, and $53.6 million outstanding under the accounts receivable facility as of December 31, 2015.
We may be required to prepay a portion of our term loan A facility in an amount equal to a percentage of our excess cash flow, as defined, which such percentage based on our leverage ratio, as defined. No amounts have been included in the contractual obligations table as a reasonable estimate cannot be determined.
As of December 31, 2015, we are contingently liable for standby letters of credit totaling $21.6 million issued on our behalf by financial institutions under the Credit Agreement. These letters of credit are used for a variety of purposes, including to support certain operating lease agreements, vendor payment terms and other subsidiary operating activities, and to meet various states' requirements to self-insure workers' compensation claims, including incurred but not reported claims.
The liability related to unrecognized tax benefits has been excluded from the contractual obligations table because a reasonable estimate of the timing and amount of cash flows from future tax settlements cannot be determined. For additional information, refer to Note 20, "Income Taxes," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
Credit Rating
We and certain of our outstanding debt obligations are rated by Standard & Poor's and Moody's. On June 3, 2015, Moody's assigned a rating of Ba3 to our new senior secured credit facilities, as presented in Note 12, "Long-term Debt" included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" within this Form 10-K. Moody's downgraded our Corporate Family Rating to Ba3 from Ba2 and maintained our outlook as stable. On June 1, 2015, Standard & Poor's affirmed a BB- corporate credit rating to our amended credit facilities and maintained our outlook as stable. If our credit ratings were to decline, our ability to access certain financial markets may become limited, our cost of borrowings may increase, the perception of us in the view of our customers, suppliers and security holders may worsen and as a result, we may be adversely affected.
Outlook
Over the past two years, we have significantly reshaped our portfolio with the spin-off of Cequent and the acquisitions of Allfast and Lion Holdings, to where we are heavily-weighted toward the Packaging and Aerospace sectors. We believe these two businesses offer higher-growth and higher-margin profiles and potential, and are the two strategic platforms that we plan to invest more heavily in and would like to grow more quickly than our other segments to increase our overall profitability and improve other financial metrics.
We believe that the current macroeconomic environment will continue into 2016, with many headwinds continuing to pressure our results of operations - most notably lower oil prices, the strong U.S. dollar and a general industrial weakness, all with little or no economic growth. Our sales were essentially flat in the first nine months of 2015, as organic and acquisition-related sales increases essentially offset the impact of lower oil prices and the strong U.S. dollar. However, our sales sharply declined in the fourth quarter as economic conditions worsened and customer demand across our businesses slowed. In response, we increased our previously announced FIP by 50%, to an expected annual full run-rate cost savings level of $22 million, with actions taking place across all of our businesses and within our corporate office. We plan to execute on internal initiatives which we believe will enable us to navigate through the current environment until demand levels and activity increase, and position us for improved profitability and ability to leverage our lower fixed cost structure with higher sales levels.
While the tactics we employ may differ between years, our strategic priorities remain consistent: generating profitable growth, enhancing profit margins, optimizing capital and resource allocation and striving to be a workplace of choice for great people.
Impact of New Accounting Standards
See Note 2, "New Accounting Pronouncements," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K.
Critical Accounting Policies
The following discussion of accounting policies is intended to supplement the accounting policies presented in Note 3, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K. Certain of our accounting policies require the application of significant judgment by management in selecting the appropriate assumptions for calculating financial estimates. By their nature, these judgments are subject to an inherent degree of uncertainty. These judgments are based on our historical experience, our evaluation of business and macroeconomic trends, and information from other outside sources, as appropriate.
Receivables. Receivables are presented net of allowances for doubtful accounts of approximately $3.7 million and $2.2 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. We monitor our exposure for credit losses and maintain adequate allowances for doubtful accounts. We determine these allowances based on our historical write-off experience and/or specific customer circumstances and provide such allowances when amounts are reasonably estimable and it is probable a loss has been incurred. We do not have concentrations of accounts receivable with a single customer or group of customers and do not believe that significant credit risk exists due to our diverse customer base. Trade accounts receivable of substantially all domestic business operations may be sold, on an ongoing basis, to TSPC, but remain included in our consolidated balance sheet.
Depreciation and Amortization. Depreciation is computed principally using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Annual depreciation rates are as follows: land and land improvements/buildings, 10 to 40 years, and machinery and equipment, three to 15 years. Capitalized debt issuance costs are amortized over the underlying terms of the related debt securities. Customer relationship intangibles are amortized over periods ranging from five to 25 years, while technology and other intangibles are amortized over periods ranging from one to 30 years.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets and Definite-Lived Intangible Assets. We review, on at least a quarterly basis, the financial performance of each business unit for indicators of impairment. In reviewing for impairment indicators, we also consider events or changes in circumstances such as business prospects, customer retention, market trends, potential product obsolescence, competitive activities and other economic factors. An impairment loss is recognized when the carrying value of an asset group exceeds the future net undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by that asset group. The impairment loss recognized is the amount by which the carrying value of the asset group exceeds its fair value.
Goodwill and Indefinite-Lived Intangibles. We assess goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment at the reporting unit level on an annual basis as of October 1, by reviewing relevant qualitative and quantitative factors. More frequent evaluations may be required if we experience changes in our business climate or as a result of other triggering events that take place. If carrying value exceeds fair value, a possible impairment exists and further evaluation is performed.
We determine our reporting units at the individual operating segment level, or one level below, when there is discrete financial information available that is regularly reviewed by segment management for evaluating operating results. For purposes of our 2015 goodwill impairment test, we had 10 reporting units within our four reportable segments, all of which had goodwill.
We first perform a qualitative assessment for our annual goodwill impairment test and for our indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment test, which involves significant use of management's judgment and assumptions to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit or indefinite-lived intangible asset is less than its carrying amount. In conducting the qualitative assessment, we consider macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, overall financial performance, entity and reporting unit specific events, capital markets pricing, recent fair value estimates and carrying amounts, as well as legal, regulatory, and contractual factors. These factors are all considered in reaching a conclusion about whether it is more likely than not that the fair values of the intangible assets are less than the carrying values. If we conclude that further testing is required, we would perform a quantitative valuation to estimate the fair value of our intangible assets.
Due to a significant decline in profitability levels in our Energy and engine products reporting units during 2015 and a decline in our stock price and resulting market capitalization, we determined there were indicators that the fair value of the Energy and engine products reporting units, and/or other units, may be less than the carrying value. As such, we performed a Step I quantitative goodwill impairment test for nine out of 10 of our reporting units. For the Allfast reporting unit, we performed a Step Zero qualitative analysis. In conducting the Step I quantitative analysis, we determined the estimated fair value of the reporting units utilizing both income and market-based approaches. The income approach relies on the present value of estimated future cash flows of the business, discounted using a rate appropriately reflecting the risks inherent in the cash flows. The market approach relies on market data of other public companies that we deem comparable in operations to our reporting units. Upon completion of the goodwill impairment test, we determined that the Energy and engine products reporting units failed Step I, requiring a Step II test to determine the amount, if any, of an impairment charge. All other reporting units passed the Step I test, with estimated fair value of goodwill exceeding the carrying value by more than 25%, and thus there was no goodwill impairment. In addition, a 1% reduction in residual growth rate combined with a 1% increase in the weighted average cost of capital would not have changed the conclusions reached under the Step I impairment test. In performing Step II of the quantitative goodwill impairment test, we determined the implied fair value of the Energy and engine reporting unit goodwill in the same manner as if the reporting units were being acquired in a business combination and compared the implied fair value of the reporting unit's goodwill to the respective carrying value of the goodwill. Based on our analysis, the implied fair value of goodwill for our Energy and engine products reporting units were less than the respective carrying values, therefore we recorded pre-tax goodwill impairment charges of appropriately $74.1 million during the fourth quarter of 2015.
Additionally, because of the factors previously mentioned, during the fourth quarter of 2015 we performed a quantitative assessment for all of our indefinite-lived intangibles assets except for the Allfast trade name, using a relief-from-royalty method. For the Allfast trade name we performed a Step Zero qualitative analysis. The relief-from-royalty method involves the estimation of appropriate market royalty rates for our indefinite-lived intangible assets and the application of these royalty rates to forecasted net sales attributable to the intangible assets. The resulting cash flows are then discounted to present value, using a rate appropriately reflecting the risks inherent in the cash flows, which is compared to the carrying value of the assets. Upon completion of the quantitative impairment test, we determined that the fair value of our indefinite-lived intangible assets exceeded the carrying value, and thus there was no impairment. Although our indefinite-lived intangible assets passed the quantitative testing, we noted a trademark/trade name within our Aerospace reportable segment that had excess fair value over its carrying value of less than 10%.
Future declines in sales and/or operating profit, declines in our stock price, or other changes in our business or the markets for our products could result in further impairments of our goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets.
Pension and Postretirement Benefits. Annual net periodic expense and accrued benefit obligations recorded with respect to our defined benefit plans are determined on an actuarial basis. We determine assumptions used in the actuarial calculations which impact reported plan obligations and expense, considering trends and changes in the current economic environment in determining the most appropriate assumptions to utilize as of our measurement date. Annually, we review the actual experience compared to the most significant assumptions used and make adjustments to the assumptions, if warranted. The healthcare trend rates are reviewed based upon actual claims experience. Discount rates are based upon an expected benefit payments duration analysis and the equivalent average yield rate for high-quality fixed-income investments. Pension benefits are funded through deposits with trustees and the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is based upon actual historical returns modified for known changes in the market and any expected change in investment policy. Postretirement benefits are not funded and our policy is to pay these benefits as they become due. Certain accounting guidance, including the guidance applicable to pensions, does not require immediate recognition of the effects of a deviation between actual and assumed experience or the revision of an estimate. This approach allows the favorable and unfavorable effects that fall within an acceptable range to be netted.
Income Taxes. We compute income taxes using the asset and liability method, whereby deferred income taxes using current enacted tax rates are provided for the temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities and for operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. We determine valuation allowances based on an assessment of positive and negative evidence on a jurisdiction-by-jurisdiction basis and record a valuation allowance to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount more likely than not to be realized. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. We record interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
Other Loss Reserves. We have other loss exposures related to environmental claims, asbestos claims and litigation. Establishing loss reserves for these matters requires the use of estimates and judgment in regard to risk exposure and ultimate liability. We are generally self-insured for losses and liabilities related principally to workers' compensation, health and welfare claims and comprehensive general, product and vehicle liability. Generally, we are responsible for up to $0.5 million per occurrence under our retention program for workers' compensation, between $0.3 million and $2.0 million per occurrence under our retention programs for comprehensive general, product and vehicle liability, and have a $0.3 million per occurrence stop-loss limit with respect to our self-insured group medical plan. We accrue loss reserves up to our retention amounts based upon our estimates of the ultimate liability for claims incurred, including an estimate of related litigation defense costs, and an estimate of claims incurred but not reported using actuarial assumptions about future events. We accrue for such items when such amounts are reasonably estimable and probable. We utilize known facts and historical trends, as well as actuarial valuations in determining estimated required reserves. Changes in assumptions for factors such as medical costs and actual experience could cause these estimates to change significantly.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
In the normal course of business, we are exposed to market risk associated with fluctuations in commodity prices, insurable risks due to property damage, employee and liability claims, and other uncertainties in the financial and credit markets, which may impact demand for our products.
We conduct business in various locations throughout the world and are subject to market risk due to changes in the value of foreign currencies. The functional currencies of our foreign subsidiaries are primarily the local currency in the country of domicile. We manage these operating activities at the local level and revenues and costs are generally denominated in local currencies; however, results of operations and assets and liabilities reported in U.S. dollars will fluctuate with changes in exchange rates between such local currencies and the U.S. dollar. We are also subject to interest risk as it relates to long-term debt, for which we have historically and may prospectively employ derivative instruments such as interest rate swaps to mitigate the risk of variable interest rates. See Item 7 "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" for details about our primary market risks, and the objectives and strategies used to manage these risks. Also see Note 12, "Long-term Debt," and Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," included in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," within this Form 10-K for additional information.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
TriMas Corporation
Bloomfield Hills, Michigan
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of TriMas Corporation and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, cash flows, and shareholders’ equity for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of TriMas Corporation and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
As discussed in Notes 1 and 6 to the consolidated financial statements, on June 30, 2015, the Company completed the spin-off of its Cequent businesses. As a result of the spin-off, the financial position and the results of operations and cash flows related to the Cequent businesses have been presented as discontinued operations for all periods presented.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 26, 2016 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Detroit, Michigan
February 26, 2016
TriMas Corporation
Consolidated Balance Sheet
(Dollars in thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 |
| Assets | | | | |
| Current assets: | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 19,450 |
| | $ | 24,420 |
|
| Receivables, net | | 121,990 |
| | 132,800 |
|
| Inventories | | 167,370 |
| | 171,260 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 17,810 |
| | 8,690 |
|
| Current assets, discontinued operations | | — |
| | 192,580 |
|
| Total current assets | | 326,620 |
| | 529,750 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | | 181,130 |
| | 177,470 |
|
| Goodwill | | 378,920 |
| | 460,080 |
|
| Other intangibles, net | | 273,870 |
| | 297,420 |
|
| Other assets | | 9,760 |
| | 20,030 |
|
| Non-current assets, discontinued operations | | — |
| | 140,680 |
|
| Total assets | | $ | 1,170,300 |
| | $ | 1,625,430 |
|
| Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | |
| Current maturities, long-term debt | | $ | 13,850 |
| | $ | 23,400 |
|
| Accounts payable | | 88,420 |
| | 103,510 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | | 50,480 |
| | 60,150 |
|
| Current liabilities, discontinued operations | | — |
| | 119,900 |
|
| Total current liabilities | | 152,750 |
| | 306,960 |
|
| Long-term debt, net | | 405,780 |
| | 607,410 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | | 11,260 |
| | 22,120 |
|
| Other long-term liabilities | | 53,320 |
| | 67,410 |
|
| Non-current liabilities, discontinued operations | | — |
| | 30,900 |
|
| Total liabilities | | 623,110 |
| | 1,034,800 |
|
Preferred stock $0.01 par: Authorized 100,000,000 shares;
Issued and outstanding: None | | — |
| | — |
|
Common stock, $0.01 par: Authorized 400,000,000 shares;
Issued and outstanding: 45,322,527 shares at December 31, 2015 and 45,280,385 shares at December 31, 2014 | | 450 |
| | 450 |
|
| Paid-in capital | | 812,160 |
| | 806,810 |
|
| Accumulated deficit | | (254,120 | ) | | (226,850 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | (11,300 | ) | | 10,220 |
|
| Total shareholders' equity | | 547,190 |
| | 590,630 |
|
| Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | | $ | 1,170,300 |
| | $ | 1,625,430 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
TriMas Corporation
Consolidated Statement of Operations
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| Net sales | | $ | 863,980 |
| | $ | 887,300 |
| | $ | 799,700 |
|
| Cost of sales | | (627,870 | ) | | (650,290 | ) | | (573,660 | ) |
| Gross profit | | 236,110 |
| | 237,010 |
| | 226,040 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | (162,350 | ) | | (146,590 | ) | | (138,540 | ) |
| Net gain (loss) on dispositions of property and equipment | | (2,330 | ) | | (3,770 | ) | | 9,710 |
|
| Impairment of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets | | (75,680 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Operating profit (loss) | | (4,250 | ) | | 86,650 |
| | 97,210 |
|
| Other expense, net: | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | | (14,060 | ) | | (9,590 | ) | | (15,270 | ) |
| Debt financing and extinguishment expenses | | (1,970 | ) | | (3,360 | ) | | (2,460 | ) |
| Other expense, net | | (1,840 | ) | | (4,100 | ) | | (3,330 | ) |
| Other expense, net | | (17,870 | ) | | (17,050 | ) | | (21,060 | ) |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations before income tax expense | | (22,120 | ) | | 69,600 |
| | 76,150 |
|
| Income tax expense | | (6,540 | ) | | (22,710 | ) | | (16,910 | ) |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | | (28,660 | ) | | 46,890 |
| | 59,240 |
|
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | | (4,740 | ) | | 22,390 |
| | 20,830 |
|
| Net income (loss) | | (33,400 | ) | | 69,280 |
| | 80,070 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | — |
| | 810 |
| | 4,520 |
|
| Net income (loss) attributable to TriMas Corporation | | $ | (33,400 | ) | | $ | 68,470 |
| | $ | 75,550 |
|
| Basic earnings (loss) per share attributable to TriMas Corporation: | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | (0.64 | ) | | $ | 1.03 |
| | $ | 1.34 |
|
| Discontinued operations | | (0.10 | ) | | 0.50 |
| | 0.51 |
|
| Net income (loss) per share | | $ | (0.74 | ) | | $ | 1.53 |
| | $ | 1.85 |
|
| Weighted average common shares - basic | | 45,123,626 |
| | 44,881,925 |
| | 40,926,257 |
|
| Diluted earnings (loss) per share attributable to TriMas Corporation: | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | (0.64 | ) | | $ | 1.02 |
| | $ | 1.32 |
|
| Discontinued operations | | (0.10 | ) | | 0.49 |
| | 0.51 |
|
| Net income (loss) per share | | $ | (0.74 | ) | | $ | 1.51 |
| | $ | 1.83 |
|
| Weighted average common shares - diluted | | 45,123,626 |
| | 45,269,409 |
| | 41,395,706 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
TriMas Corporation
Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income
(Dollars in thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (33,400 | ) | | $ | 69,280 |
| | $ | 80,070 |
|
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | |
| Defined pension and postretirement pension plans (Note 16) | | 1,810 |
| | (3,340 | ) | | 1,600 |
|
| Foreign currency translation | | (12,370 | ) | | (13,820 | ) | | (15,770 | ) |
| Derivative instruments (Note 13) | | (2,650 | ) | | (450 | ) | | 2,740 |
|
| Total other comprehensive loss | | (13,210 | ) | | (17,610 | ) | | (11,430 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) | | (46,610 | ) | | 51,670 |
| | 68,640 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | — |
| | 810 |
| | 4,520 |
|
| Total comprehensive income (loss) attributable to TriMas Corporation | | $ | (46,610 | ) | | $ | 50,860 |
| | $ | 64,120 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
TriMas Corporation
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows
(Dollars in thousands) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | (33,400 | ) | | $ | 69,280 |
| | $ | 80,070 |
|
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | (4,740 | ) | | 22,390 |
| | 20,830 |
|
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | | (28,660 | ) | | 46,890 |
| | 59,240 |
|
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities, net of acquisition impact: | | | | | | |
| Impairment of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets | | 75,680 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| (Gain) loss on dispositions of businesses and other assets | | 2,330 |
| | 3,770 |
| | (9,710 | ) |
| Depreciation | | 22,570 |
| | 21,380 |
| | 18,810 |
|
| Amortization of intangible assets | | 20,970 |
| | 16,060 |
| | 12,290 |
|
| Amortization of debt issue costs | | 1,710 |
| | 1,940 |
| | 1,780 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | | (8,750 | ) | | (6,530 | ) | | (4,540 | ) |
| Non-cash compensation expense | | 6,340 |
| | 7,110 |
| | 8,800 |
|
| Excess tax benefits from stock based compensation | | (590 | ) | | (1,180 | ) | | (1,550 | ) |
| Debt financing and extinguishment expenses | | 1,970 |
| | 3,360 |
| | 2,460 |
|
| (Increase) decrease in receivables | | 5,300 |
| | (9,790 | ) | | (11,380 | ) |
| (Increase) decrease in inventories | | 3,250 |
| | (6,010 | ) | | (5,750 | ) |
| (Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses and other assets | | 4,730 |
| | 5,250 |
| | (6,380 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | (29,530 | ) | | 11,830 |
| | 2,860 |
|
| Other, net | | (750 | ) | | (1,560 | ) | | 1,290 |
|
| Net cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations, net of acquisition impact | | 76,570 |
| | 92,520 |
| | 68,220 |
|
| Net cash provided by (used for) operating activities of discontinued operations | | (14,030 | ) | | 30,880 |
| | 19,390 |
|
| Net cash provided by operating activities, net of acquisition impact | | 62,540 |
| | 123,400 |
| | 87,610 |
|
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities: | | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | | (28,660 | ) | | (23,000 | ) | | (24,230 | ) |
| Acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | | (10,000 | ) | | (382,880 | ) | | (84,790 | ) |
| Net proceeds from disposition of businesses and other assets | | 1,700 |
| | 200 |
| | 10,560 |
|
| Net cash used for investing activities of continuing operations | | (36,960 | ) | | (405,680 | ) | | (98,460 | ) |
| Net cash used for investing activities of discontinued operations | | (2,510 | ) | | (4,410 | ) | | (31,880 | ) |
| Net cash used for investing activities | | (39,470 | ) | | (410,090 | ) | | (130,340 | ) |
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities: | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from sale of common stock in connection with the Company's equity offering, net of issuance costs | | — |
| | — |
| | 174,670 |
|
| Proceeds from borrowings on term loan facilities | | 275,000 |
| | 275,000 |
| | 175,040 |
|
| Repayments of borrowings on term loan facilities | | (444,890 | ) | | (8,910 | ) | | (400,780 | ) |
| Proceeds from borrowings on revolving credit and accounts receivable facilities | | 1,129,840 |
| | 1,063,960 |
| | 1,222,980 |
|
| Repayments of borrowings on revolving credit and accounts receivable facilities | | (1,169,370 | ) | | (989,090 | ) | | (1,113,910 | ) |
| Payments for deferred purchase price | | (6,440 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Debt financing fees | | (1,850 | ) | | (3,840 | ) | | (3,610 | ) |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | — |
| | (580 | ) | | (2,710 | ) |
| Payment for noncontrolling interests | | — |
| | (51,000 | ) | | — |
|
| Shares surrendered upon vesting of options and restricted stock awards to cover tax obligations | | (2,770 | ) | | (2,910 | ) | | (4,440 | ) |
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | | 500 |
| | 640 |
| | 1,620 |
|
| Excess tax benefits from stock based compensation | | 590 |
| | 1,180 |
| | 1,550 |
|
| Cash transferred to the Cequent businesses | | (17,050 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities of continuing operations | | (236,440 | ) | | 284,450 |
| | 50,410 |
|
| Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities of discontinued operations | | 208,400 |
| | (340 | ) | | (1,260 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used for) financing activities | | (28,040 | ) | | 284,110 |
| | 49,150 |
|
| Cash and Cash Equivalents: | | | | | | |
| Increase (decrease) for the year | | (4,970 | ) | | (2,580 | ) | | 6,420 |
|
| At beginning of year | | 24,420 |
| | 27,000 |
| | 20,580 |
|
| At end of year | | $ | 19,450 |
| | $ | 24,420 |
| | $ | 27,000 |
|
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | | |
| Cash paid for interest | | $ | 15,170 |
| | $ | 10,870 |
| | $ | 16,750 |
|
| Cash paid for income taxes | | $ | 30,580 |
| | $ | 41,110 |
| | $ | 37,700 |
|
TriMas Corporation
Consolidated Statement of Shareholders' Equity
Years Ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013
(Dollars in thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Common Stock | | Paid-In Capital | | Accumulated Deficit | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | | Total |
| Balances at December 31, 2012 | | $ | 390 |
| | $ | 634,800 |
| | $ | (370,870 | ) | | $ | 39,260 |
| | $ | 303,580 |
|
| Net income attributable to TriMas Corporation | | — |
| | — |
| | 75,550 |
| | — |
| | 75,550 |
|
| Other comprehensive loss | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (11,430 | ) | | (11,430 | ) |
| Net proceeds from equity offering of common stock (Note 4) | | 50 |
| | 174,620 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 174,670 |
|
| Shares surrendered upon vesting of options and restricted stock awards to cover tax obligations | | — |
| | (4,440 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (4,440 | ) |
| Stock option exercises and restricted stock vestings | | 10 |
| | 1,610 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,620 |
|
| Excess tax benefits from stock based compensation | | — |
| | 1,550 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,550 |
|
| Non-cash compensation expense | | — |
| | 9,200 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,200 |
|
| Redemption value adjustment for noncontrolling interests (Note 5) | | — |
| | (890 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (890 | ) |
| Balances at December 31, 2013 | | $ | 450 |
| | $ | 816,450 |
| | $ | (295,320 | ) | | $ | 27,830 |
| | $ | 549,410 |
|
| Net income attributable to TriMas Corporation | | — |
| | — |
| | 68,470 |
| | — |
| | 68,470 |
|
| Other comprehensive loss | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (17,610 | ) | | (17,610 | ) |
| Shares surrendered upon vesting of options and restricted stock awards to cover tax obligations | | — |
| | (2,910 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,910 | ) |
| Stock option exercises and restricted stock vestings | | — |
| | 640 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 640 |
|
| Excess tax benefits from stock based compensation | | — |
| | 1,180 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,180 |
|
| Non-cash compensation expense | | — |
| | 7,440 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,440 |
|
Acquisition of remaining 30% interest in Arminak & Associates, LLC (net of tax of $8.4 million) (Note 5)
| | — |
| | (15,990 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (15,990 | ) |
| Balances at December 31, 2014 | | $ | 450 |
| | $ | 806,810 |
| | $ | (226,850 | ) | | $ | 10,220 |
| | $ | 590,630 |
|
| Net loss attributable to TriMas Corporation | | — |
| | — |
| | (33,400 | ) | | — |
| | (33,400 | ) |
| Other comprehensive loss | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (13,210 | ) | | (13,210 | ) |
| Shares surrendered upon vesting of options and restricted stock awards to cover tax obligations | | — |
| | (2,770 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,770 | ) |
| Stock option exercises and restricted stock vestings | | — |
| | 500 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 500 |
|
| Excess tax benefits from stock based compensation | | — |
| | 590 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 590 |
|
| Non-cash compensation expense | | — |
| | 7,030 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,030 |
|
| Distribution of the Cequent businesses | | — |
| | — |
| | 6,130 |
| | (8,310 | ) | | (2,180 | ) |
| Balances at December 31, 2015 | | $ | 450 |
| | $ | 812,160 |
| | $ | (254,120 | ) | | $ | (11,300 | ) | | $ | 547,190 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Basis of Presentation
TriMas Corporation ("TriMas" or the "Company"), and its consolidated subsidiaries, is a global manufacturer and distributor of products for commercial, industrial and consumer markets. The Company is principally engaged in the following reportable segments with diverse products and market channels: Packaging, Aerospace, Energy and Engineered Components. See Note 19, "Segment Information," for further information on each of the Company's reportable segments.
On June 30, 2015, the Company completed the previously announced spin-off of its Cequent businesses, creating a new independent publicly traded company, Horizon Global Corporation ("Horizon"). In addition, on June 30, 2015, immediately prior to the effective time of the spin-off, Horizon paid a cash distribution to the Company of $214.5 million using the proceeds of its new debt financing arrangement and cash on hand.
The Company incurred approximately $30 million of one-time, pre-tax costs associated with the spin-off, of which approximately $29 million was incurred during 2015. These costs primarily related to financing, legal, tax and accounting services rendered by third parties. Of the $30 million in costs, approximately $18 million was included in income (loss) from discontinued operations, $9 million was capitalized as deferred financing fees associated with Horizon's debt issuance coincident with the spin-off and was included in the balance sheet of the discontinued operations and approximately $3 million relates to fees associated with the Company's refinancing of long-term debt, of which approximately $2 million was included in income from continuing operations as debt financing and extinguishment costs and approximately $1 million was capitalized as deferred financing fees in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet.
The financial position, results of operations and cash flows of the Cequent businesses are reflected as discontinued operations for all periods presented through the date of the spin-off. See Note 6, "Discontinued Operations," for further details regarding the spin-off.
2. New Accounting Pronouncements
In September 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2015-17, "Income Taxes (Topic 740): Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes" ("ASU 2015-17"). ASU 2015-17 eliminates the current requirement to present deferred tax liabilities and assets as current and noncurrent in a classified balance sheet and instead requires that deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent in a classified balance sheet. ASU 2015-17 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2016, with early adoption permitted. Additionally, the guidance may be applied either prospectively to all deferred tax liabilities and assets or retrospectively to all periods presented. During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company early adopted the provisions of ASU 2015-17, with all deferred tax liabilities and assets presented as noncurrent on its balance sheet, and applied retrospectively to all periods presented.
In September 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-16, "Business Combinations (Topic 805): Simplifying the Accounting for Measurement - Period Adjustments" ("ASU 2015-16"). ASU 2015-16 requires that an acquirer recognize adjustments to provisional amounts that are identified during the measurement period in the reporting period in which the adjustment amounts are determined. The effect on earnings of changes in depreciation, amortization or other income effects, if any, as a result of the change to the provisional amounts, calculated as if the accounting had been completed at the acquisition date, must be recorded in the reporting period in which the adjustment amounts are determined rather than retrospectively. Additionally, an entity is required to present separately on the face of the income statement or disclose in the notes to the financial statements the portion of the amount recorded in current-period earnings by line item that would have been recorded in previous reporting periods if the adjustment to the provisional amounts had been recognized as of the acquisition date. ASU 2015-16 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company early adopted the provisions of ASU 2015-16. See Note 5, "Acquisitions," and Note 8, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets," for further details.
In July 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-11, "Inventory (Topic 330): Simplifying the Measurement of Inventory" ("ASU 2015-11"). ASU 2015-11 requires an entity to measure inventory at the lower of cost and net realizable value, thereby simplifying the current guidance under which an entity must measure inventory at the lower of cost or market. The ASU defines net realizable value as the estimated selling prices in the ordinary course of business, less reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal and transportation. ASU 2015-11 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2016 and is to be applied prospectively with early adoption permitted. The Company is in the process of assessing the impact of adoption of ASU 2015-11 on its consolidated financial statements.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-03, "Interest - Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30): Simplifying the Presentation of Debt Issuance Costs" ("ASU 2015-03"). ASU 2015-03 requires that debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of that debt liability. Given the absence of authoritative guidance within ASU 2015-03 for debt issuance costs related to line-of-credit arrangements, in August 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-15, "Interest - Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30) - Presentation and Subsequent Measurement of Debt Issuance Costs Associated with Line-of-Credit Arrangements," which clarifies ASU 2015-03 by stating that the staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission would not object to an entity deferring and presenting debt issuance costs associated with line-of-credit arrangements as an asset and subsequently amortizing the deferred debt issuance costs ratably over the term of the arrangement, regardless of whether there are any outstanding borrowings on the line-of-credit arrangement. ASU 2015-03 is currently effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company early adopted the provisions of ASU 2015-03, with long-term debt shown net of all debt issuance costs for all periods presented. See Note 12, "Long-term Debt," for further details.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)" ("ASU 2014-09"). ASU 2014-09 requires that an entity recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. ASU 2014-09 was originally effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after December 15, 2016. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-14, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date", which defers ASU 2014-09 by one year, making it effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after December 15, 2017, while also providing for early adoption, but not before the original effective date. The Company is in the process of assessing the impact of the adoption of ASU 2014-09 on its consolidated financial statements.
3. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation. The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts and transactions of TriMas and its subsidiaries. Intercompany transactions have been eliminated.
The Company records the initial carrying amount of redeemable noncontrolling interests at fair value. In the event a redeemable noncontrolling interest is present at the end of a reporting period, the Company adjusts the carrying amount to the greater of (1) the initial carrying amount, increased or decreased for the redeemable noncontrolling interests' share of net income or loss, their share of comprehensive income or loss and dividends and (2) the redemption value as determined by a specified multiple of earnings, as defined. This method views the end of the reporting period as if it were also the redemption date for the redeemable noncontrolling interests. The Company conducts a quarterly review to determine if the fair value of the redeemable noncontrolling interests is less than the redemption value. If the fair value of the redeemable noncontrolling interests is less than the redemption value, there may be a charge to earnings per share attributable to TriMas Corporation.
Use of Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management of the Company to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements. Such estimates and assumptions also affect the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Significant items subject to such estimates and assumptions include the carrying amount of property and equipment, goodwill and other intangibles, valuation allowances for receivables, inventories and deferred income tax assets, valuation of derivatives, estimated future unrecoverable lease costs, estimated unrecognized tax benefits, reserves for asbestos and ordinary course litigation, assets and obligations related to employee benefits and valuation of redeemable non-controlling interests. Actual results may differ from such estimates and assumptions.
Cash and Cash Equivalents. The Company considers cash on hand and on deposit and investments in all highly liquid debt instruments with initial maturities of three months or less to be cash and cash equivalents.
Receivables. Receivables are presented net of allowances for doubtful accounts of approximately $3.7 million and $2.2 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Company monitors its exposure for credit losses and maintains allowances for doubtful accounts based upon the Company's best estimate of probable losses inherent in the accounts receivable balances. The Company does not believe that significant credit risk exists due to its diverse customer base.
Sales of Receivables. The Company may, from time to time, sell certain of its receivables to third parties. Sales of receivables are recognized at the point in which the receivables sold are transferred beyond the reach of the Company and its creditors, the purchaser has the right to pledge or exchange the receivables and the Company has surrendered control over the transferred receivables.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Inventories. Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value, with cost determined using the first-in, first-out method. Direct materials, direct labor and allocations of variable and fixed manufacturing-related overhead are included in inventory cost.
Property and Equipment. Property and equipment additions, including significant improvements, are recorded at cost. Upon retirement or disposal of property and equipment, the cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts, and any gain or loss is included in the accompanying statement of operations. Repair and maintenance costs are charged to expense as incurred.
Depreciation and Amortization. Depreciation is computed principally using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Annual depreciation rates are as follows: building and land/building improvements three to 40 years, and machinery and equipment, three to 15 years. Capitalized debt issuance costs are amortized over the underlying terms of the related debt securities. Customer relationship intangibles are amortized over periods ranging from five to 25 years, while technology and other intangibles are amortized over periods ranging from one to 30 years.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets and Definite-Lived Intangible Assets. The Company reviews, on at least a quarterly basis, the financial performance of its businesses for indicators of impairment. In reviewing for impairment indicators, the Company also considers events or changes in circumstances such as business prospects, customer retention, market trends, potential product obsolescence, competitive activities and other economic factors. An impairment loss is recognized when the carrying value of an asset group exceeds the future net undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by that asset group. The impairment loss recognized is the amount by which the carrying value of the asset group exceeds its fair value.
Goodwill. The Company assesses goodwill for impairment on an annual basis by reviewing relevant qualitative and quantitative factors. More frequent evaluations may be required if the Company experiences changes in its business climate or as a result of other triggering events that take place. If carrying value exceeds fair value, a possible impairment exists and further evaluation is performed.
The Company determines its reporting units at the individual operating segment level, or one level below, when there is discrete financial information available that is regularly reviewed by segment management for evaluating operating results. For purposes of the Company's 2015 goodwill impairment test, the Company had 10 reporting units within its four reportable segments, all of which had goodwill. See Note 8, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets," for further details regarding the Company's 2015 goodwill impairment testing.
In conducting a qualitative assessment, the Company considers relevant events and circumstances that affect the fair value or carrying amount of a reporting unit. Such events and circumstances can include macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, overall financial performance, entity and reporting unit specific events, and capital markets pricing. The Company considers the extent to which each of the adverse events and circumstances identified affect the comparison of a reporting unit's fair value with its carrying amount. The Company places more weight on the events and circumstances that most affect a reporting unit's fair value or the carrying amount of its net assets. The Company considers positive and mitigating events and circumstances that may affect its determination of whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. The Company also considers recent valuations of its reporting units, including the difference between the most recent fair value estimate and the carrying amount. These factors are all considered by management in reaching its conclusion about whether to perform the first step of the quantitative goodwill impairment test. If management concludes that further testing is required, the Company performs a quantitative valuation to estimate the fair value of its reporting units.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
If the Company concludes that conducting a quantitative assessment is required, it performs the first step of a two-step goodwill impairment test. For the first step ("Step I"), the Company estimates the fair value of the reporting unit being evaluated utilizing a combination of three valuation techniques: discounted cash flow (income approach), market comparable method (market approach) and market capitalization (direct market data method). The income approach is based on management's operating plan and internal five-year forecast and utilizes forward-looking assumptions and projections, but considers factors unique to each reporting unit and related long-range plans that may not be comparable to other companies and that are not yet public. The market approach considers potentially comparable companies and transactions within the industries where the Company's reporting units participate, and applies their trading multiples to the Company's reporting units. This approach utilizes data from actual marketplace transactions, but reliance on its results is limited by difficulty in identifying companies that are specifically comparable to the Company's reporting units, considering the diversity of the Company's businesses, the relative sizes and levels of complexity. The Company also uses the direct market data method by comparing its book value and the estimates of fair value of the reporting units to the Company's market capitalization as of and at dates near the annual testing date. Management uses this comparison as additional evidence of the fair value of the Company, as its market capitalization may be suppressed by other factors such as the control premium associated with a controlling shareholder, the Company's degree of leverage and the float of the Company's common stock. Management evaluates and weights the results based on a combination of the income and market approaches, and, in situations where the income approach results differ significantly from the market and direct data approaches, management re-evaluates and adjusts, if necessary, its assumptions.
Based on the Step I test, if it is determined that the carrying value of the reporting unit is higher than its fair value, there is an indication that an impairment may exist and the second step ("Step II") must be performed to measure the amount of impairment loss, if any. In Step II, the Company determines the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill in the same manner as if the reporting unit was being acquired in a business combination and compares the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill to the carrying value of the goodwill. If the implied fair value of the goodwill is less than the carrying value, goodwill is impaired and is written down to the implied fair value amount.
Indefinite-Lived Intangibles. The Company assesses indefinite-lived intangible assets (primarily trademark/trade names) for impairment on an annual basis by reviewing relevant qualitative and quantitative factors. More frequent evaluations may be required if the Company experiences changes in its business climate or as a result of other triggering events that take place. If carrying value exceeds fair value, a possible impairment exists and further evaluation is performed.
In conducting a qualitative assessment, the Company considers relevant events and circumstances to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair values of the indefinite-lived intangible assets are less than the carrying values. In addition to the events and circumstances that the Company considers above in its qualitative analysis for potential goodwill impairment, the Company also considers legal, regulatory and contractual factors that could affect the fair value or carrying amount of the Company's indefinite-lived intangible assets. The Company also considers recent valuations of its indefinite-lived intangible assets, including the difference between the most recent fair value estimates and the carrying amounts. These factors are all considered by management in reaching its conclusion about whether it is more likely than not that the fair values of the indefinite-lived intangible assets are less than the carrying values. If management concludes that further testing is required, the Company performs a quantitative valuation to estimate the fair value of its indefinite-lived intangible assets. In conducting the quantitative impairment analysis, the Company determines the fair value of its indefinite-lived intangible assets using the relief-from-royalty method. The relief-from-royalty method involves the estimation of appropriate market royalty rates for the indefinite-lived intangible assets and the application of these royalty rates to forecasted net sales attributable to the intangible assets. The resulting cash flows are then discounted to present value, using a rate appropriately reflecting the risks inherent in the cash flows, which is compared to the carrying value of the assets. If the carrying value exceeds fair value, an impairment is recorded. See Note 8, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets," for further details regarding the Company's 2015 indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment testing.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
High Deductible Insurance. The Company generally, has a high deductible insurance plan for losses and liabilities related to workers' compensation, health and welfare claims and comprehensive general, product and vehicle liability. The Company is generally responsible for up to $0.5 million per occurrence under its retention program for workers' compensation, between $0.3 million and $2.0 million per occurrence under its retention programs for comprehensive general, product and vehicle liability, and has a $0.3 million per occurrence stop-loss limit with respect to its group medical plan. Total insurance limits under these retention programs vary by year for comprehensive general, product and vehicle liability and extend to the applicable statutory limits for workers' compensation. Reserves for claims losses, including an estimate of related litigation defense costs, are recorded based upon the Company's estimates of the aggregate liability for claims incurred using actuarial assumptions about future events. Changes in assumptions for factors such as medical costs and actual experience could cause these estimates to change.
Pension Plans and Postretirement Benefits Other Than Pensions. Annual net periodic pension expense and benefit liabilities under defined benefit pension plans are determined on an actuarial basis. Assumptions used in the actuarial calculations could have a significant impact on plan obligations, and a lesser impact on current period expense. Annually, the Company reviews the actual experience compared to the more significant assumptions used and makes adjustments to the assumptions, if warranted. The healthcare trend rates are reviewed based upon actual claims experience. Discount rates are based upon an expected benefit payments duration analysis and the equivalent average yield rate for high-quality fixed-income investments. Pension benefits are funded through deposits with trustees and the expected long-term rate of return on fund assets is based upon actual historical returns and a review of other public company pension asset return data, modified for known changes in the market and any expected change in investment policy. Postretirement benefits are not funded and it is the Company's policy to pay these benefits as they become due.
Revenue Recognition. Revenues are recognized when products are shipped or services are provided to customers, the customer takes ownership and assumes risk of loss, the sales price is fixed and determinable and collectability is reasonably assured. Net sales is comprised of gross revenues less estimates of expected returns, trade discounts and customer allowances, which include incentives such as volume discounts and other supply agreements in connection with various programs. Such deductions are recorded during the period the related revenue is recognized.
Cost of Sales. Cost of sales includes material, labor and overhead costs incurred in the manufacture of products sold in the period. Material costs include raw material, purchased components, outside processing and inbound freight costs. Overhead costs consist of variable and fixed manufacturing costs, wages and fringe benefits, and purchasing, receiving and inspection costs.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses. Selling, general and administrative expenses include the following: costs related to the advertising, sale, marketing and distribution of the Company's products, shipping and handling costs, amortization of customer intangible assets, costs of finance, human resources, legal functions, executive management costs and other administrative expenses.
Research and Development Costs. Research and development ("R&D") costs are expensed as incurred. R&D expenses were approximately $0.6 million, $0.8 million and $0.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and are included in cost of sales in the accompanying statement of operations.
Advertising and Sales Promotion Costs. Advertising and sales promotion costs are expensed as incurred. Advertising costs were approximately $0.7 million, $0.9 million and $0.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and are included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying statement of operations.
Income Taxes. The Company computes income taxes using the asset and liability method, whereby deferred income taxes using current enacted tax rates are provided for the temporary differences between the financial reporting basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities and for operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. The Company determines valuation allowances based on an assessment of positive and negative evidence on a jurisdiction-by-jurisdiction basis and records a valuation allowance to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount more likely than not to be realized. The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. The Company records interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Foreign Currency Translation. The financial statements of subsidiaries located outside of the United States are measured using the currency of the primary economic environment in which they operate as the functional currency. When translating into U.S. dollars, income and expense items are translated at average monthly exchange rates and assets and liabilities are translated at exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet date. Translation adjustments resulting from translating the functional currency into U.S. dollars are deferred as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in the statement of shareholders' equity. Net foreign currency transaction losses were approximately $0.2 million, $1.3 million and $0.9 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and are included in other expense, net in the accompanying statement of operations.
Derivative Financial Instruments. The Company records all derivative financial instruments at fair value on the balance sheet as either assets or liabilities, and changes in their fair values are immediately recognized in earnings if the derivatives do not qualify as effective hedges. If a derivative is designated as a fair value hedge, then changes in the fair value of the derivative are offset against the changes in the fair value of the underlying hedged item. If a derivative is designated as a cash flow hedge, then the effective portion of the changes in the fair value of the derivative is recognized as a component of other comprehensive income until the underlying hedged item is recognized in earnings or the forecasted transaction is no longer probable of occurring. The Company formally documents hedging relationships for all derivative transactions and the underlying hedged items, as well as its risk management objectives and strategies for undertaking the hedge transactions. See Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," for further information on the Company's financial instruments.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments. In accounting for and disclosing the fair value of these instruments, the Company uses the following hierarchy:
| |
| • | Level 1 inputs are quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the Company has the ability to access at the measurement date; |
| |
| • | Level 2 inputs are inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly; and |
| |
| • | Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. |
Valuation of the Company's interest rate swaps are based on the income approach, which uses observable inputs such as interest rate yield curves.
The carrying value of financial instruments reported in the balance sheet for current assets and current liabilities approximates fair value due to the short maturity of these instruments. The Company's term loan A traded at 99.6% and 99.5% of par value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Company's revolving credit facility traded at 99.3% and 99.2% of par value as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The valuations of the term loan A and credit facility were determined based on Level 2 inputs under the fair value hierarchy, as defined.
Business Combinations. The Company records assets acquired and liabilities assumed from acquisitions at fair value. The fair value of working capital accounts generally approximate book value. The valuation of inventory, property, plant and equipment, and intangible assets require significant assumptions. Inventory is recorded at fair value based on the estimated selling price less costs to sell, including completion, disposal and holding period costs with a reasonable profit margin. Property, plant and equipment is recorded at fair value using a combination of both the cost and market approaches for both the real and personal property acquired. Under the cost approach, consideration is given to the amount required to construct or purchase a new asset of equal value at current prices, with adjustments in value for physical deterioration, as well as functional and economic obsolescence. Under the market approach, recent transactions for similar types of assets are used as the basis for estimating fair value. For trademark/trade names and technology and other intangible assets, the estimated fair value is based on projected discounted future net cash flows using the relief-from-royalty method. For customer relationship intangible assets, the estimated fair value is based on projected discounted future cash flows using the excess earnings method. The relief-from-royalty and excess earnings method are both income approaches that utilize key assumptions such as forecasts of revenue and expenses over an extended period of time, royalty rate percentages, tax rates, and estimated costs of debt and equity capital to discount the projected cash flows.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Earnings Per Share. Net earnings are divided by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the year to calculate basic earnings per share. Diluted earnings per share are calculated to give effect to stock options and other stock-based awards. For the year ended December 31, 2015, no restricted shares were included in the computation of net income (loss) per share because to do so would be anti-dilutive. The calculation of diluted earnings per share included 245,828 and 293,021 restricted shares for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Options to purchase 206,123, 251,667 and 342,448 shares of common stock were outstanding at December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2015, no options to purchase shares of common stock were included in the computation of net income (loss) per share because to do so would have been anti-dilutive. The calculation of dilutive earnings per share included 141,656 and 176,428 options to purchase shares of common stock for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Stock-based Compensation. The Company recognizes compensation expense related to equity awards based on their fair values as of the grant date. In addition, the Company periodically updates its estimate of attainment for each restricted share with a performance factor based on current and forecasted results, reflecting the change from prior estimate, if any, in current period compensation expense. The disclosed number of shares granted considers only the targeted number of shares until such time that the performance condition has been satisfied. If the performance conditions are not achieved, no award is earned.
Other Comprehensive Income. The Company refers to other comprehensive income as revenues, expenses, gains and losses that under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America are included in comprehensive income but are excluded from net earnings as these amounts are recorded directly as an adjustment to stockholders' equity. Other comprehensive income is comprised of foreign currency translation adjustments, amortization of prior service costs and unrecognized gains and losses in actuarial assumptions for pension and postretirement plans and changes in unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
Reclassifications. Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform with the current year presentation.
4. Equity Offering
In September 2013, the Company issued 5,175,000 shares of its common stock via a public offering at a price of $35.40 per share. Net proceeds from the offering, after deducting underwriting discounts, commissions and offering expenses of $8.5 million, totaled approximately $174.7 million. The Company used the net offering proceeds for general corporate purposes, including retirement of debt in connection with the Company's October 2013 refinancing, acquisitions, capital expenditures and working capital requirements.
5. Acquisitions
2015 Acquisitions
During 2015, the Company completed two acquisitions for an aggregate amount of approximately $10.0 million, net of cash acquired. The largest acquisition was the November 2015 acquisition of certain business assets of Parker-Hannifin Corporation ("Parker Hannifin"), located in Tolleson, AZ, within the Company's Aerospace reportable segment.
2014 Acquisitions
Allfast Fastening Systems
On October 17, 2014, the Company acquired 100% of the equity interest in Allfast Fastening Systems, Inc. ("Allfast") for the purchase price of approximately $351.2 million, net of cash acquired, with an additional $15.7 million of deferred purchase price related to certain tax related and other reimbursements in accordance with the purchase agreement. Allfast is a global manufacturer of solid and blind rivets, blind bolts, temporary fasteners and installation tools for the aerospace industry. The acquisition strengthens the Company's specialty product offering and is strategically aligned with its growing aerospace businesses. Allfast is included in the Company's Aerospace segment.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table summarizes the fair value of consideration paid for Allfast, and the assets acquired and liabilities assumed:
|
| | | | |
| | | October 17, 2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Consideration | | |
| Cash paid, net of cash acquired | | $ | 351,220 |
|
Deferred purchase price(a) | | 15,730 |
|
| Total consideration | | $ | 366,950 |
|
| Recognized amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed | | |
| Receivables | | $ | 8,950 |
|
| Inventories | | 19,850 |
|
Intangible assets other than goodwill(b) | | 165,000 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | | 340 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | | 26,490 |
|
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | (2,620 | ) |
| Total identifiable net assets | | 218,010 |
|
Goodwill(c) | | 148,940 |
|
| | | $ | 366,950 |
|
___________________________
(a) Of the deferred purchase price, approximately $8.7 million, represents the Company's best estimate of the underlying obligations for certain tax amounts the Company has agreed to reimburse the previous owner in order to acquire additional tax attributes. During 2015, the Company paid $5.2 million of such amount and the remaining $3.5 million liability was removed, with a corresponding reduction to goodwill, due to the finalization of the Seller's tax liability. In addition, deferred purchase price includes approximately $7.0 million of other liabilities which the Company has agreed to pay on behalf of the previous owner, of which approximately $4.9 million was paid through December 31, 2015.
(b) Consists of approximately $83.0 million of customer relationships with an estimated useful life of 18 years, $33.0 million of technology and other intangible assets with an estimated useful life of 15 years and $49.0 million of trademark/trade name with an indefinite useful life.
(c) All of the goodwill was assigned to the Company's Aerospace reportable segment and is expected to be deductible for tax purposes.
The results of operations of Allfast are included in the Company's results beginning October 17, 2014. The actual amounts of net sales and operating profit of Allfast included in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2014 are $9.1 million and $1.3 million, respectively.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table summarizes the supplemental pro forma results of the combined entity as if the acquisition had occurred on January 1, 2013. The supplemental pro forma information presented below is for informational purposes and is not necessarily indicative of either future results of operations or results that might have been achieved had the acquisition been consummated on January 1, 2013:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Pro forma Combined (a) |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Net sales | | $ | 936,440 |
| | $ | 853,590 |
|
| Net income attributable to TriMas Corporation | | $ | 49,590 |
| | $ | 56,550 |
|
___________________________
(a) The supplemental pro forma results reflect certain material adjustments, as follows:
| |
| 1. | Pre-tax pro forma adjustments for amortization expense of $6.0 million and $6.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 on the intangible assets associated with the acquisition. |
| |
| 2. | Pre-tax pro forma adjustments of $4.9 million and $7.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, respectively, to reflect interest expense incurred on the incremental term loan A and revolver borrowings incurred in order to fund the acquisition. |
Total acquisition costs incurred by the Company in connection with its purchase of Allfast, primarily related to third party legal, accounting and tax diligence fees, were approximately $2.2 million, all of which were incurred during 2014. These costs are recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
Other Acquisitions
In July 2014, the Company completed the acquisition of Lion Holdings PVT. Ltd. ("Lion Holdings") within the Company's Packaging reportable segment for the amount of approximately $27.5 million, net of cash acquired. Located in both India and Vietnam, Lion Holdings specializes in the manufacture of highly engineered dispensing solutions and generated approximately $10 million in revenue for the twelve months ended June 30, 2014.
2013 Acquisitions
During 2013, the Company completed various 100%-owned acquisitions for an aggregate amount of approximately $84.8 million, net of cash acquired, with an additional $4.3 million of deferred purchase price and contingent consideration, based primarily on a fixed date and payment schedule over the next five years. Of these acquisitions, the most significant, in chronological order of acquisition date, are as follows:
| |
| • | Martinic Engineering, Inc. ("Martinic"), acquired in January, located in the United States and included in the Company's Aerospace reportable segment, is a manufacturer of highly-engineered, precision machined, complex parts for commercial and military aerospace applications, including auxiliary power units, as well as electrical, hydraulic and pneumatic systems and generated approximately $13 million in revenue for the 12 months ended December 31, 2012. |
| |
| • | Wulfrun Specialised Fasteners Limited ("Wulfrun"), acquired in March, located in the United Kingdom and included in the Company's Energy reportable segment, is a manufacturer and distributor of specialty bolting and CNC machined components for use in critical oil and gas, pipeline and power generation applications, and generated approximately $10 million in revenue for the 12 months ended December 31, 2012. |
| |
| • | Mac Fasteners, Inc. ("Mac Fasteners"), acquired in October, located in the United States and included in the Company's Aerospace reportable segment, is in the business of manufacturing and distribution of stainless steel aerospace fasteners, globally utilized by OEMs, aftermarket repair companies, and commercial and military aircraft producers, and generated approximately $17 million in revenue for the 12 months ended September 30, 2013. |
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
While the individual and aggregate historical and current year revenue and earnings associated with the Company's 2013 acquisitions is not significant compared to the Company's total results of operations, the following information has been provided to summarize the aggregate fair value of consideration paid for the acquisitions, the assets acquired and liabilities assumed.
|
| | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Consideration | | |
| Initial cash paid net of cash acquired | | $ | 84,790 |
|
Deferred/contingent consideration(a) | | 4,280 |
|
| Total consideration | | $ | 89,070 |
|
| Recognized amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed | | |
| Receivables | | $ | 7,240 |
|
| Inventories | | 16,630 |
|
Intangible assets other than goodwill(b) | | 29,020 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | | 8,420 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | | 10,080 |
|
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | (6,950 | ) |
| Deferred income taxes | | (4,260 | ) |
| Other long-term liabilities | | (8,410 | ) |
| Total identifiable net assets | | 51,770 |
|
| Goodwill | | 37,300 |
|
| | | $ | 89,070 |
|
__________________________
(a) Deferred/contingent consideration included approximately $2.6 million of both short-term and long-term deferred purchase price, based on set amounts and fixed payment schedules per the purchase agreement, and an additional $1.7 million of contingent consideration to be paid, if earned, based on a multiple of future earnings, as defined.
(b) Consists of approximately $23.1 million of customer relationships with an estimated weighted average useful life of 10 years, $1.4 million of technology and other intangible assets with an estimated weighted average useful life of four years and $4.5 million of trademark/trade names with an indefinite useful life.
Arminak & Associates
During the first quarter of 2012, the Company acquired 70% of the membership interests of Arminak & Associates, LLC ("Arminak") for the purchase price of approximately $67.7 million, which is included in the Company's Packaging reportable segment. The original purchase agreement provided the Company an option to purchase, and Arminak's previous owners an option to sell, the remaining 30% noncontrolling interest at specified dates in the future based on a multiple of earnings, as defined in the purchase agreement. The original combination of a noncontrolling interest and a redemption feature resulted in a redeemable noncontrolling interest, which was classified outside of permanent equity on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet. In order to estimate the fair value of the redeemable noncontrolling interest in Arminak upon acquisition, the Company utilized the Monte Carlo valuation method, using variations of estimated future discounted cash flows given certain significant assumptions including expected revenue growth, minimum and maximum estimated levels of gross profit margin, future expected cash flows, amounts transferred during each call and put exercise period and appropriate discount rates. As these assumptions are not observable in the market, the calculation represents a Level 3 fair value measurement. The Company recorded the redeemable noncontrolling interest at fair value at the date of acquisition.
On March 11, 2014, in lieu of the put call option in the original purchase agreement, the Company entered into a new agreement to purchase the entire 30% noncontrolling interest in Arminak for a cash purchase price of $51.0 million. The purchase agreement also included additional contingent consideration of up to $7.0 million, with the amount to be earned based on the achievement of certain levels of 2015 financial performance. As of December 31, 2015, there is no estimated liability for the payout of contingent consideration as no amounts were earned.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
As part of purchasing the remaining membership interest, the Company finalized the calculation of the redeemable noncontrolling interest as of March 11, 2014. Changes in the carrying amount of redeemable noncontrolling interest are summarized as follows:
|
| | | | |
| | | Redeemable Noncontrolling interest |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Balance, December 31, 2012 | | $ | 26,780 |
|
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | (2,710 | ) |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | 4,520 |
|
| Redemption value adjustments for noncontrolling interests | | 890 |
|
| Balance, December 31, 2013 | | $ | 29,480 |
|
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | (580 | ) |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | 810 |
|
| Balance, March 11, 2014 | | $ | 29,710 |
|
The difference between the cash purchase price and final redeemable noncontrolling interest as of March 11, 2014 was recorded as a reduction in paid in capital, net of tax, as included in the accompanying consolidated statement of shareholders' equity.
6. Discontinued Operations
Spin-off of the Cequent businesses
On June 30, 2015, the Company completed the spin-off of its Cequent businesses (comprised of the former Cequent Americas and Cequent Asia Pacific Europe Africa ("Cequent APEA") reportable segments), creating a new independent publicly traded company, Horizon, through the distribution of 100% of the Company's interest in Horizon to holders of the Company's common stock. On June 30, 2015, each of the Company's shareholders of record as of the close of business on the record date of June 25, 2015, received two shares of Horizon common stock for every five shares of TriMas common stock held. In addition, on June 30, 2015, immediately prior to the effective time of the spin-off, Horizon entered into a new debt financing arrangement and used the proceeds to make a cash distribution of $214.5 million to the Company.
The Cequent businesses are presented as discontinued operations in the Company's consolidated balance sheet, the consolidated statements of operations and cash flows for all periods presented.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The carrying value of the assets and liabilities immediately preceding the spin-off of the Cequent businesses on June 30, 2015, and as of December 31, 2014 were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Immediately preceding the spin-off on June 30, 2015 | | December 31,
2014 |
| Assets | | | | |
| Current assets: | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 17,050 |
| | $ | — |
|
| Receivables, net | | 92,750 |
| | 63,520 |
|
| Inventories | | 125,750 |
| | 123,370 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | 6,520 |
| | 5,690 |
|
| Total current assets | | 242,070 |
| | 192,580 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | | 48,870 |
| | 55,180 |
|
| Goodwill | | 5,630 |
| | 6,580 |
|
| Other intangibles, net | | 61,400 |
| | 66,510 |
|
| Other assets | | 16,390 |
| | 12,410 |
|
| Total assets | | $ | 374,360 |
| | $ | 333,260 |
|
| Liabilities | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | |
| Current maturities, long-term debt | | $ | 17,940 |
| | $ | 460 |
|
| Accounts payable | | 81,830 |
| | 81,500 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | | 44,190 |
| | 37,940 |
|
| Total current liabilities | | 143,960 |
| | 119,900 |
|
| Long-term debt | | 195,460 |
| | 300 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | | 4,860 |
| | 4,610 |
|
| Other long-term liabilities | | 27,900 |
| | 25,990 |
|
| Total liabilities | | $ | 372,180 |
| | $ | 150,800 |
|
Following the spin-off, there were no assets or liabilities remaining from the Cequent operations.
Results of discontinued operations, including the discontinued Cequent businesses and NI Industries, are summarized as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Net sales | | $ | 300,900 |
| | $ | 615,260 |
| | $ | 595,160 |
|
| Cost of sales | | (227,860 | ) | | (468,060 | ) | | (467,800 | ) |
| Gross profit | | 73,040 |
| | 147,200 |
| | 127,360 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | | (72,360 | ) | | (111,900 | ) | | (104,040 | ) |
| Operating profit | | 680 |
| | 35,300 |
| | 23,320 |
|
| Interest expense | | (2,540 | ) | | (5,430 | ) | | (3,060 | ) |
| Other expense, net | | (1,970 | ) | | 4,170 |
| | 2,370 |
|
| Other expense, net | | (4,510 | ) | | (1,260 | ) | | (690 | ) |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, before income taxes | | (3,830 | ) | | 34,040 |
| | 22,630 |
|
| Income tax expense | | (910 | ) | | (11,650 | ) | | (1,800 | ) |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of tax | | $ | (4,740 | ) | | $ | 22,390 |
| | $ | 20,830 |
|
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Other Discontinued Operations
During the third quarter of 2014, the Company ceased operations of its former NI Industries business. NI Industries manufactured cartridge cases for the defense industry and was party to a U.S. Government facility maintenance contract. The Company received approximately $6.7 million for the sale of certain intellectual property and related inventory and tooling. This amount is included in income from discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
During the fourth quarter of 2011, the Company sold its precision tool cutting and specialty fittings lines of business, both of which were part of the Engineered Components reportable segment. The purchase agreement included up to $2.5 million of contingent consideration, based on achievement of certain levels of financial performance in 2012 and 2013. During the second quarter of 2013, the Company received approximately $1.0 million of a possible $1.3 million as payout for the 2012 financial performance criteria. This amount is included in income from discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations. No payout was received in 2014, as the 2013 financial performance criteria were not met.
During the first quarter of 2009, the Company completed the sale of certain assets within its specialty laminates, jacketings and insulation tapes line of business, which was part of the Packaging reportable segment. The Company's manufacturing facility is subject to a lease agreement expiring in 2024 that was not assumed by the purchaser of the business. During the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company re-evaluated its estimate of unrecoverable future obligations initially recorded in 2009 and recorded an additional charge of approximately $1.8 million, based on further deterioration of real estate values and market comparables for this facility.
The results of the aforementioned businesses are reported as discontinued operations for all periods presented.
7. Facility Closures, Consolidations and Sale of Business
During 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company closed and consolidated several facilities, and also sold a business. The majority of the costs to implement the facility actions were incurred within the Company’s Energy reportable segment. See below for details of the most significant actions.
2015 Facility Closures and Consolidations
During 2015, the Company closed and consolidated certain manufacturing facilities, branches, warehouses and sales offices, the largest of which were the closure of the Hangzhou, China, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil and Houston, Texas (former South Texas Bolt and Fitting) manufacturing facilities within the Energy reportable segment. As a part of the closure and consolidation actions, the Company recorded non-cash charges of approximately $1.4 million, primarily related to write-down of property to its salvage value. As a part of these facility closures and other cost savings actions within the Energy reportable segment, the Company recorded charges of approximately $3.0 million related to severance benefits for its approximately 240 employees that were involuntarily terminated.
The Company did not fully exit certain of the closed and consolidated facilities during 2015. As such the Company did not record significant unrecoverable lease obligations. The Company will assess the potential recoverability of its future lease obligations for its closed facilities upon the cease-use date, and at that time will record any estimate for unrecoverable amounts, if any.
2014 Facility Closures and Consolidations
In June 2014, the Company announced the restructuring of its Brazilian business within the Energy reportable segment, including plans to close its manufacturing facility in São Paulo, Brazil by the end of 2014. In connection with this action, the Company recorded charges of approximately $0.5 million, primarily related to severance benefits, which is included in cost of sales in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations, for its approximately 60 employees involuntarily terminated as a result of this closure. During the fourth quarter of 2014, upon the cease use date of the facility, the Company recorded a pre-tax charge within in its Energy reportable segment of approximately $3.9 million for estimated future unrecoverable lease obligation, net of estimated sublease recoveries, for the lease agreement that expires in 2022. Additionally, the Company recorded a $1.3 million charge related to the release of historical currency translation adjustments, which is included in dispositions of property and equipment in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company re-evaluated its estimate of unrecoverable future obligations initially recorded for its Brazilian business during 2014 and reduced its estimate by approximately $1.7 million following entry into a sublease agreement for the facility.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2013 Sale of Business
On August 5, 2013, the Company announced the sale of its business in Italy within the Packaging reportable segment for cash of approximately $10.3 million. As a result, the Company recorded a pre-tax gain of approximately $10.5 million, of which $7.9 million related to the release of historical currency translation adjustments into income, which is included in dispositions of property and equipment in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
8. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
Goodwill
The Company conducts its annual goodwill impairment test as of October 1, and as of interim dates whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. Due to a significant decline in profitability levels in the Company's Energy and engine products reporting units during 2015 and a decline in the Company's stock price and resulting market capitalization which management believes is partially due to the decline in profitability of the aforementioned two reporting units, the Company determined there were indicators that the fair value of the Energy and engine products reporting units, and/or other units, may be less than the carrying value. As such, the Company performed a Step I quantitative goodwill impairment test for nine out of 10 of its reporting units. For the Allfast reporting unit, the Company performed a Step Zero qualitative analysis, as it was acquired in October 2014 and generated profit levels consistent with those expected in the purchase price valuation completed less than one year prior.
In preparing the Step I quantitative analysis, the Company utilized both income and market-based approaches, placing a 75% and 25% weighting on each, respectively. Significant management assumptions used under the income approach were weighted average costs of capital ranging from 11% to 14.5% and an estimated residual growth rate of 3%. In considering the weighted average cost of capital for the reporting units under the income approach, management considered the level of risk inherent in the cash flow projections based on historical attainment of its projections and current market conditions. The use of these unobservable inputs resulted in the fair value estimate being classified as a Level 3 measurement within the fair value hierarchy.
Upon completion of the Step I goodwill impairment test, the Company determined that the Energy and engine products reporting units required a Step II test to determine the amount, if any, of an impairment charge. All other reporting units passed the Step I test.
Based on the results of the Step II goodwill impairment test, the Company recorded pre-tax goodwill impairment charges in the fourth quarter of 2015 of approximately $70.9 million in its Energy reporting unit and approximately $3.2 million in its engine products reporting unit. As of December 31, 2015, there is no goodwill remaining for the Company's Energy and engine products reporting units.
For the Company's 2015 goodwill impairment testing of its Allfast reporting unit, and for purposes of its 2014 and 2013 goodwill impairment tests, the Company performed a Step Zero qualitative assessment of potential goodwill impairment. In performing the Step Zero assessment, the Company considered relevant events and circumstances that could affect the fair value or carrying amount of the Company's reporting units, such as macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, overall financial performance, entity and reporting unit specific events and capital markets pricing. Based on the analysis performed, the Company did not believe that it was more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount; therefore, the Company determined that the Step I and Step II tests were not required.
Additionally, during the third quarter of 2014, based on a few consecutive quarters of revenue and earnings declines compared to historical levels within the Company's Energy reporting unit, the Company determined that there were indicators of a decline in fair value of the Energy reporting unit, and as such, the Company conducted a Step I quantitative goodwill impairment analysis. Upon completion of the goodwill impairment test, the Company determined that the fair value of the Energy reporting unit exceeded the carrying value, and thus there was no goodwill impairment.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| |
| |
| | Engineered | |
|
| Packaging | | Aerospace | | Energy | | Components | | Total |
| (dollars in thousands) |
| Balance, December 31, 2013 | $ | 158,060 |
| | $ | 61,080 |
| | $ | 75,920 |
| | $ | 7,420 |
| | $ | 302,480 |
|
| Goodwill from acquisitions | 15,810 |
| | 149,050 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 164,860 |
|
| Foreign currency translation and other | (4,520 | ) | | — |
| | (2,740 | ) | | — |
| | (7,260 | ) |
| Balance, December 31, 2014 | $ | 169,350 |
| | $ | 210,130 |
| | $ | 73,180 |
| | $ | 7,420 |
| | $ | 460,080 |
|
| Goodwill from acquisitions | — |
| | (3,500 | ) | | — |
| | 2,320 |
| | (1,180 | ) |
| Impairment charge | — |
| | — |
| | (70,930 | ) | | (3,180 | ) | | (74,110 | ) |
| Foreign currency translation and other | (3,620 | ) | | — |
| | (2,250 | ) | | — |
| | (5,870 | ) |
| Balance, December 31, 2015 | $ | 165,730 |
| | $ | 206,630 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 6,560 |
| | $ | 378,920 |
|
During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company's estimate of the underlying obligation for certain tax amounts related to the acquisition of Allfast was adjusted due to the finalization of the Seller's tax liability, resulting in a $3.5 million decrease to the deferred purchase price liability and goodwill. This measurement period adjustment has been reflected as a current period adjustment to these balances during the year ended December 31, 2015, in accordance with the guidance in ASU 2015-16. See Note 2, "New Accounting Pronouncements," for further details.
Other Intangible Assets
During the fourth quarter of 2015, as part of the broadly focused restructuring initiative within the Company's Energy reportable segment, it was determined that the Company would discontinue use and wrote-off all of the approximately $1.6 million of carrying value of certain of its Energy-related trade names.
Additionally, the Company conducted its annual indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment test as of October 1, 2015. For the purposes of the Company's 2015 indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment tests, the Company performed a quantitative assessment for all of its indefinite-lived intangibles assets except for the Allfast trade name, using a relief-from-royalty method. The Company performed a Step Zero qualitative analysis for the Allfast trade name as it was acquired less than one year prior and has long-term sales projections consistent with those expected in the purchase price valuation. Significant management assumptions used under the relief-from-royalty method were discount rates ranging from 14% to 17.5% and an estimated residual growth rate of 3%. The use of these unobservable inputs resulted in the fair value estimates being classified as a Level 3 measurement within the fair value hierarchy. Upon completion of the quantitative impairment test, the Company determined that the fair value of the Company's indefinite-lived intangible assets exceeded the carrying value, and thus there was no impairment.
For the purposes of the Company's 2015 indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment testing of the Allfast trade name, and for purposes of its 2014 and 2013 indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment tests, the Company performed a qualitative assessment to determine whether it was more likely than not that the fair values of the indefinite-lived intangible assets are less than the carrying values. In performing the qualitative assessment, the Company considered similar events and circumstances to those considered in the Step Zero analysis for goodwill impairment testing and also considered legal, regulatory and contractual factors that could affect the fair value or carrying amount of the Company's indefinite-lived intangible assets. Based on the qualitative assessment performed, the Company did not believe that it was more likely than not that the fair values of each of its indefinite-lived intangible assets were less than the carrying values; therefore, a quantitative assessment was not required.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The gross carrying amounts and accumulated amortization of the Company's other intangibles as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are summarized below. The Company amortizes these assets over periods ranging from one to 30 years.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, 2015 | | As of December 31, 2014 |
| Intangible Category by Useful Life | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization | | Gross Carrying Amount | | Accumulated Amortization |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Finite-lived intangible assets: | | | | | | | | |
| Customer relationships, 5 - 12 years | | $ | 74,890 |
| | $ | (25,960 | ) | | $ | 75,300 |
| | $ | (18,180 | ) |
| Customer relationships, 15 - 25 years | | 132,230 |
| | (38,060 | ) | | 132,230 |
| | (31,140 | ) |
| Total customer relationships | | 207,120 |
| | (64,020 | ) | | 207,530 |
| | (49,320 | ) |
| Technology and other, 1 - 15 years | | 57,860 |
| | (22,770 | ) | | 58,040 |
| | (18,750 | ) |
| Technology and other, 17 - 30 years | | 43,300 |
| | (29,250 | ) | | 43,300 |
| | (27,150 | ) |
| Total technology and other | | 101,160 |
| | (52,020 | ) | | 101,340 |
| | (45,900 | ) |
| Indefinite-lived intangible assets: | |
| |
| |
| |
|
| Trademark/Trade names | | 81,630 |
| | — |
| | 83,770 |
| | — |
|
| Total other intangible assets | | $ | 389,910 |
| | $ | (116,040 | ) | | $ | 392,640 |
| | $ | (95,220 | ) |
Amortization expense related to intangible assets as included in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations is summarized as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Technology and other, included in cost of sales | | $ | 6,010 |
| | $ | 5,030 |
| | $ | 4,460 |
|
| Customer relationships, included in selling, general and administrative expenses | | 14,960 |
| | 11,030 |
| | 7,830 |
|
| Total amortization expense | | $ | 20,970 |
| | $ | 16,060 |
| | $ | 12,290 |
|
Estimated amortization expense for the next five fiscal years beginning after December 31, 2015 is as follows:
|
| | |
| Year ended December 31, | Estimated Amortization Expense |
| | (dollars in thousands) |
| 2016 | | $20,340 |
| 2017 | | $20,090 |
| 2018 | | $19,660 |
| 2019 | | $19,240 |
| 2020 | | $18,310 |
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
9. Inventories
Inventories consist of the following components:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
2015 | | December 31,
2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Finished goods | | $ | 101,480 |
| | $ | 104,760 |
|
| Work in process | | 23,620 |
| | 24,300 |
|
| Raw materials | | 42,270 |
| | 42,200 |
|
| Total inventories | | $ | 167,370 |
| | $ | 171,260 |
|
10. Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment consists of the following components:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
2015 | | December 31,
2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Land and land improvements | | $ | 14,820 |
| | $ | 14,710 |
|
| Building and building improvements | | 67,790 |
| | 60,570 |
|
| Machinery and equipment | | 274,650 |
| | 262,670 |
|
| | | 357,260 |
| | 337,950 |
|
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | | 176,130 |
| | 160,480 |
|
| Property and equipment, net | | $ | 181,130 |
| | $ | 177,470 |
|
Depreciation expense as included in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Depreciation expense, included in cost of sales | | $ | 19,730 |
| | $ | 18,450 |
| | $ | 16,210 |
|
| Depreciation expense, included in selling, general and administrative expense | | 2,840 |
| | 2,930 |
| | 2,600 |
|
| Total depreciation expense | | $ | 22,570 |
| | $ | 21,380 |
| | $ | 18,810 |
|
11. Accrued Liabilities
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
2015 | | December 31,
2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| High deductible insurance | | $ | 6,580 |
| | $ | 7,960 |
|
| Wages and bonus | | 16,820 |
| | 13,670 |
|
| Other | | 27,080 |
| | 38,520 |
|
| Total accrued liabilities | | $ | 50,480 |
| | $ | 60,150 |
|
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
12. Long-term Debt
The Company's long-term debt consists of the following:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31,
2015 | | December 31,
2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Credit Agreement | | $ | 371,820 |
| | $ | 559,530 |
|
| Receivables facility and other | | 53,860 |
| | 79,040 |
|
| Debt issuance costs | | (6,050 | ) | | (7,760 | ) |
| | | 419,630 |
| | 630,810 |
|
| Less: Current maturities, long-term debt | | 13,850 |
| | 23,400 |
|
| Long-term debt, net | | $ | 405,780 |
| | $ | 607,410 |
|
Credit Agreement
During the second quarter of 2015, the Company amended its credit agreement (the "Credit Agreement"), pursuant to which the Company was able to extend maturities and resize its credit facilities following the spin-off of the Cequent businesses. The Credit Agreement consists of a $500.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility, which permits borrowings denominated in specific foreign currencies ("Foreign Currency Loans"), subject to a $75.0 million sub limit, and a $275.0 million senior secured term loan A facility ("Term Loan A Facility"). The cash distribution to the Company from Horizon was used to reduce the outstanding borrowings under the previous credit agreement.
Below is a summary of key terms under the Credit Agreement as of December 31, 2015, and the key terms of the previous credit agreement in place immediately prior to entering into the amended Credit Agreement on June 30, 2015, with term loans showing the face amount of borrowings upon issuance and revolving credit facilities showing gross availability at each date:
|
| | | | | | |
| Instrument | | Amount
($ in millions) | | Maturity Date | | Interest Rate |
| Credit Agreement | | | | | | |
| Senior secured revolving credit facility | | $500.0 | | 6/30/2020 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.750%(b) |
| Senior secured term loan A facility | | $275.0 | | 6/30/2020 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.750%(b) |
| | | | | | | |
| Previous Credit Agreement | | | | | | |
| Senior secured revolving credit facility | | $575.0 | | 10/16/2018 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.625%(b) |
| Senior secured term loan A facility | | $450.0 | | 10/16/2018 | | LIBOR(a) plus 1.625%(b) |
__________________________
(a) London Interbank Offered Rate ("LIBOR")
(b) The interest rate spread is based upon the leverage ratio, as defined, as of the most recent determination date.
The Credit Agreement also provides incremental term loan facility commitments and/or incremental revolving credit facility commitments in an amount not to exceed the greater of $300.0 million and an amount such that, after giving effect to such incremental commitments and the incurrence of any other indebtedness substantially simultaneously with the making of such incremental commitments, the senior secured net leverage ratio, as defined in the Credit Agreement, is no greater than 2.50 to 1.00. The terms and conditions of any incremental term loan facility and/or incremental revolving credit facility commitments must be no more favorable than the existing credit facilities under the Credit Agreement.
The Company may be required to prepay a portion of the loans under the Term Loan A Facility in an amount equal to a percentage of the Company's excess cash flow, as defined, with such percentage based on the Company's leverage ratio, as defined. As of December 31, 2015, no amounts are due under this provision.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The Company is also able to issue letters of credit, not to exceed $40.0 million in aggregate, against its revolving credit facility commitments. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had letters of credit of approximately $21.6 million and $21.9 million, respectively, issued and outstanding.
At December 31, 2015, the Company had $100.3 million outstanding under its revolving credit facility and had $378.1 million potentially available after giving effect to approximately $21.6 million of letters of credit issued and outstanding. At December 31, 2014, the Company had $118.1 million outstanding under its revolving credit facility and had $435.0 million potentially available after giving effect to approximately $21.9 million of letters of credit issued and outstanding. However, including availability under its accounts receivable facility and after consideration of leverage restrictions contained in the Credit Agreement, at December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had $107.4 million and $192.0 million, respectively, of borrowing capacity available for general corporate purposes.
Principal payments required under the Credit Agreement for the Term Loan A Facility are approximately $3.4 million due each fiscal quarter from December 2015 through September 2018 and approximately $5.2 million due each fiscal quarter from December 2018 through March 2020, with final payment of $202.8 million due on June 30, 2020.
The debt under the Credit Agreement is an obligation of the Company and certain of its domestic subsidiaries and is secured by substantially all of the assets of such parties. Borrowings under the $75.0 million foreign currency sub limit of the $500.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility are secured by a pledge of the assets of the foreign subsidiary borrowers that are a party to the agreement. The Credit Agreement also contains various negative and affirmative covenants and other requirements affecting the Company and its subsidiaries, including restrictions on incurrence of debt, liens, mergers, investments, loans, advances, guarantee obligations, acquisitions, asset dispositions, sale-leaseback transactions, hedging agreements, dividends and other restricted payments, transactions with affiliates, restrictive agreements and amendments to charters, bylaws, and other material documents. The terms of the Credit Agreement also require the Company and its subsidiaries to meet certain restrictive financial covenants and ratios computed quarterly, including a maximum leverage ratio (total consolidated indebtedness plus outstanding amounts under the accounts receivable securitization facility over consolidated EBITDA, as defined) and a minimum interest expense coverage ratio (consolidated EBITDA, as defined, over cash interest expense, as defined). At December 31, 2015, the Company was in compliance with its financial covenants contained in the Credit Agreement.
The Company incurred approximately $1.8 million in fees during 2015 to amend the Credit Agreement, of which approximately $1.4 million was capitalized as deferred financing fees and $0.4 million was recorded as debt financing fees in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2015. The Company also recorded non-cash debt extinguishment costs of $1.5 million related to the write-off of deferred financing fees associated with the previous credit facilities.
In 2014 and 2013, the Company incurred approximately $3.8 million and $3.6 million, respectively, in fees to amend the previous credit agreements, of which $0.4 million and $3.1 million was capitalized as deferred financing fees, respectively, and $3.4 million and $0.5 million was recorded as debt extinguishment costs in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations, respectively. The Company also recorded non-cash debt extinguishment costs of $1.9 million related to the write-off of deferred financing fees associated with the previous credit agreement for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Receivables Facility
The Company is a party to an accounts receivable facility through TSPC, Inc. ("TSPC"), a wholly-owned subsidiary, to sell trade accounts receivable of substantially all of the Company's domestic business operations. In June 2015, the Company amended the facility to remove the Cequent businesses and to reduce the committed funding from $105.0 million to $75.0 million, with no other significant changes to the facility. In December 2015, the Company further amended the facility to extend the maturity date from October 16, 2018 to June 30, 2020.
Under this facility, TSPC, from time to time, may sell an undivided fractional ownership interest in the pool of receivables up to approximately $75.0 million to a third party multi-seller receivables funding company. The net amount financed under the facility is less than the face amount of accounts receivable by an amount that approximates the purchaser's financing costs. The cost of funds under this facility consisted of a 1-month LIBOR plus a usage fee of 1.00% and a fee on the unused portion of the facility of 0.35% as of December 31, 2015, and a 3-month LIBOR plus a usage fee of 1.00% and a fee on the unused portion of the facility of 0.35% as of December 31, 2014.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The Company had $53.6 million and $78.7 million outstanding under the facility as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and $7.1 million and $1.6 million available but not utilized as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Aggregate costs incurred under the facility were $1.0 million, $1.3 million and $1.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, and are included in interest expense in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
The cost of funds fees incurred are determined by calculating the estimated present value of the receivables sold compared to their carrying amount. The estimated present value factor is based on historical collection experience and a discount rate based on a 1-month LIBOR-based rate plus the usage fee discussed above and is computed in accordance with the terms of the securitization agreement. As of December 31, 2015, the cost of funds under the facility was based on an average liquidation period of the portfolio of approximately 1.8 months and an average discount rate of 1.8%.
Long-term Debt Maturities
Future maturities of the face value of long-term debt at December 31, 2015 are as follows:
|
| | | | |
| Year Ending December 31: | | (dollars in thousands) |
| 2016 | | $ | 13,850 |
|
| 2017 | | 13,850 |
|
| 2018 | | 15,530 |
|
| 2019 | | 20,630 |
|
| 2020 | | 361,820 |
|
| Total | | $ | 425,680 |
|
Debt Issuance Costs
The Company's unamortized debt issuance costs approximated $6.1 million and $7.8 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, and are included as a direct reduction from the related debt liability in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet. These amounts consist primarily of legal, accounting and other transaction advisory fees as well as facility fees paid to the lenders. Debt issuance costs for the current and previous term loan facilities and the previous discount on the senior notes are amortized using the interest method over the terms of the underlying debt instruments to which these amounts relate. The debt issuance costs for the current and previous revolving credit facilities and the receivables facility are amortized on a straight line basis over the term of the facilities. Amortization expense for these items was approximately $1.7 million, $1.9 million and $1.8 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and is included in interest expense in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
13. Derivative Instruments
The Company utilizes interest rate swap agreements to fix the LIBOR-based variable portion of the interest rate on its long term debt. Terms of the interest rate swap agreements require the Company to receive a variable interest rate and pay a fixed interest rate. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had interest rate swap agreements in place that hedge a notional value of debt ranging from approximately $251.5 million to approximately $192.7 million and amortize consistent with future debt principal payments. The interest rate swap agreements establish fixed interest rates in a range of 0.74% to 2.68% with various expiration terms extending to June 30, 2020. At inception, the interest rate swaps were and continue to be designated as cash flow hedges.
In December 2012, the Company entered into interest rate swap agreements to fix the LIBOR-based variable portion of the interest rates on its term loan facilities. At inception, the Company designated the swap agreements as cash flow hedges and utilized hedge accounting. However, the Company entered into a new credit agreement in 2013 and, as a result, the swap agreement was no longer expected to be an effective economic hedge. The Company terminated the interest rate swap and received cash of $3.3 million upon completion of the new credit agreement. At the date of the credit agreement, the Company de-designated this swap, which had $2.0 million (net of tax of $1.3 million) of unrealized gain remaining in accumulated other comprehensive income in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet, which was reclassified into earnings in 2013.
In March 2012, the Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement to fix the LIBOR-based variable portion of the interest rate on its previous term loan B facility. At inception, the Company formally designated this swap agreement as a cash flow hedge and utilized hedge accounting. Upon the Company's amendment and restatement of its credit agreement during the fourth quarter
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
of 2012, the Company determined that the interest rate swap was no longer expected to be an effective economic hedge. The Company terminated the interest rate swap and repaid the obligation upon completion of the previous credit agreement. After that date, the Company de-designated this swap, which had $1.0 million (net of tax of $0.6 million) of unrealized loss remaining in accumulated other comprehensive income, which was being amortized into earnings during the period in which the originally hedged transactions would have affected earnings. However, when the Company entered into a new credit agreement in 2013, the Company reclassified the remaining $0.6 million (net of tax of $0.4 million) of unrealized loss remaining in accumulated other comprehensive income into earnings.
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, the fair value carrying amount of the Company's derivatives designated as hedging instruments are recorded as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Asset / (Liability) Derivatives |
| | | Balance Sheet Caption | | December 31, 2015 | | December 31, 2014 |
| | | | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments | | | | | | |
| Interest rate swaps | | Other assets | | $ | 430 |
| | $ | 1,270 |
|
| Interest rate swaps | | Accrued liabilities | | (150 | ) | | (180 | ) |
| Interest rate swaps | | Other long-term liabilities | | (3,180 | ) | | — |
|
| Total derivatives designated as hedging instruments | | | | $ | (2,900 | ) | | $ | 1,090 |
|
The following tables summarize the income (loss) recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income ("AOCI"), the amounts reclassified from AOCI into earnings and the amounts recognized directly into earnings as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 and for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Amount of Income (Loss) Recognized
in AOCI on Derivative
(Effective Portion, net of tax) | | Location of Income (Loss) Reclassified from AOCI into Earnings
(Effective Portion) | | Amount of Income (Loss) Reclassified from
AOCI into Earnings |
| | | As of December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) | | | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate swaps | | $ | (1,790 | ) | | $ | 680 |
| | Interest expense | | $ | (420 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| | | | | | | Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | $ | (440 | ) | | $ | (970 | ) | | $ | 2,510 |
|
Over the next 12 months, the Company expects to reclassify approximately $0.2 million of pre-tax deferred losses from AOCI to interest expense as the related interest payments for the designated interest rate swap are funded.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Amount of Loss Recognized in Earnings on Derivatives |
| | | | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | Location of Loss Recognized in Earnings on Derivatives | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate swaps | | Interest expense | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | (1,480 | ) |
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The fair value of the Company's derivatives are estimated using an income approach based on valuation techniques to convert future amounts to a single, discounted amount. Estimates of the fair value of the Company's interest rate swaps use observable inputs such as interest rate yield curves. Fair value measurements and the fair value hierarchy level for the Company's assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 are shown below.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Description | | Frequency | | Asset / (Liability) | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets
(Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs
(Level 2) | | Significant Unobservable Inputs
(Level 3) |
| | | | | | (dollars in thousands) |
| December 31, 2015 | Interest rate swaps | | Recurring | | $ | (2,900 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | (2,900 | ) | | $ | — |
|
| December 31, 2014 | Interest rate swaps | | Recurring | | $ | 1,090 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 1,090 |
| | $ | — |
|
14. Leases
The Company leases certain equipment and facilities under non-cancelable operating leases. Rental expense for the Company totaled approximately $17.2 million in 2015, $16.8 million in 2014 and $14.7 million in 2013.
Minimum payments for operating leases having initial or remaining non-cancelable lease terms in excess of one year at December 31, 2015, including approximately $2.4 million annually related to discontinued operations, are summarized below:
|
| | | | |
| Year ended December 31, | | (dollars in thousands) |
| 2016 | | $ | 17,400 |
|
| 2017 | | 16,320 |
|
| 2018 | | 14,130 |
|
| 2019 | | 11,380 |
|
| 2020 | | 9,710 |
|
| Thereafter | | 22,870 |
|
| Total | | $ | 91,810 |
|
15. Commitments and Contingencies
Environmental
The Company is subject to increasingly stringent environmental laws and regulations, including those relating to air emissions, wastewater discharges and chemical and hazardous waste management and disposal. Some of these environmental laws hold owners or operators of land or businesses liable for their own and for previous owners' or operators' releases of hazardous or toxic substances or wastes. Other environmental laws and regulations require the obtainment and compliance with environmental permits. To date, costs of complying with environmental, health and safety requirements have not been material. However, the nature of the Company's operations and the long history of industrial activities at certain of the Company's current or former facilities, as well as those acquired, could potentially result in material environmental liabilities.
While the Company must comply with existing and pending climate change legislation, regulation and international treaties or accords, current laws and regulations have not had a material impact on the Company's business, capital expenditures or financial position. Future events, including those relating to climate change or greenhouse gas regulation, could require the Company to incur expenses related to the modification or curtailment of operations, installation of pollution control equipment or investigation and cleanup of contaminated sites.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Asbestos
As of December 31, 2015, the Company was a party to 1,035 pending cases involving an aggregate of 6,242 claimants primarily alleging personal injury from exposure to asbestos containing materials formerly used in gaskets (both encapsulated and otherwise) manufactured or distributed by certain of its subsidiaries for use primarily in the petrochemical refining and exploration industries. The following chart summarizes the number of claimants, number of claims filed, number of claims dismissed, number of claims settled, the average settlement amount per claim and the total defense costs, excluding amounts reimbursed under the Company's primary insurance, at the applicable date and for the applicable periods:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Claims pending at beginning of period | | Claims filed during period | | Claims dismissed during period | | Claims settled during period | | Average settlement amount per claim during period | | Total defense costs during period |
| Fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 | | 7,880 |
| | 360 |
| | 226 |
| | 39 |
| | $ | 8,294 |
| | $ | 2,620,000 |
|
| Fiscal year ended December 31, 2014 | | 7,975 |
| | 210 |
| | 155 |
| | 38 |
| | $ | 18,734 |
| | $ | 2,800,000 |
|
| Fiscal year ended December 31, 2015 | | 7,992 |
| | 266 |
| | 1,990 |
| | 26 |
| | $ | 16,963 |
| | $ | 3,160,000 |
|
The Company acquired various companies to distribute its products that had distributed gaskets of other manufacturers prior to acquisition. The Company believes that many of the pending cases relate to locations at which none of its gaskets were distributed or used.
The Company may be subjected to significant additional asbestos-related claims in the future, the cost of settling cases in which product identification can be made may increase, and the Company may be subjected to further claims in respect of the former activities of its acquired gasket distributors. The Company is unable to make a meaningful statement concerning the monetary claims made in the asbestos cases given that, among other things, claims may be initially made in some jurisdictions without specifying the amount sought or by simply stating the requisite or maximum permissible monetary relief, and may be amended to alter the amount sought. The large majority of claims do not specify the amount sought. Of the 6,242 claims pending at December 31, 2015, 120 set forth specific amounts of damages (other than those stating the statutory minimum or maximum).
Below is a breakdown of the amount sought for those claims seeking specific amounts:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Compensatory & Punitive | | Compensatory Only | | Punitive Only |
| Range of damages sought (in millions) | $0.0 to $5.0 | | $5.0 to $10.0 | | $10.0+ | | $0.0 to $0.6 | | $0.6 to $5.0 | | $5.0+ | | $0.0 to $2.5 |
| Number of claims | 57 | | 38 | | 25 | | 12 | | 45 | | 63 | | 120 |
In addition, relatively few of the claims have reached the discovery stage and even fewer claims have gone past the discovery stage.
Total settlement costs (exclusive of defense costs) for all such cases, some of which were filed over 20 years ago, have been approximately $7.8 million. All relief sought in the asbestos cases is monetary in nature. To date, approximately 40% of the Company's costs related to settlement and defense of asbestos litigation have been covered by its primary insurance. Effective February 14, 2006, the Company entered into a coverage-in-place agreement with its first level excess carriers regarding the coverage to be provided to the Company for asbestos-related claims when the primary insurance is exhausted. The coverage-in-place agreement makes asbestos defense costs and indemnity insurance coverage available to the Company that might otherwise be disputed by the carriers and provides a methodology for the administration of such expenses. Nonetheless, the Company believes it is likely that there will be a period within the next 12 to 18 months, prior to the commencement of coverage under this agreement and following exhaustion of the Company's primary insurance coverage, during which the Company likely will be solely responsible for defense costs and indemnity payments, the duration of which would be subject to the scope of damage awards and settlements paid.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Based on the settlements made to date and the number of claims dismissed or withdrawn for lack of product identification, the Company believes that the relief sought (when specified) does not bear a reasonable relationship to its potential liability. Based upon the Company's experience to date, including the trend in annual defense and settlement costs incurred to date, and other available information (including the availability of excess insurance), the Company does not believe that these cases will have a material adverse effect on its financial position and results of operations or cash flows.
Metaldyne Corporation
Prior to June 6, 2002, the Company was wholly-owned by Metaldyne Corporation ("Metaldyne"). In connection with the reorganization between TriMas and Metaldyne in June 2002, TriMas assumed certain liabilities and obligations of Metaldyne, mainly comprised of contractual obligations to former TriMas employees, tax related matters, benefit plan liabilities and reimbursements to Metaldyne of normal course payments to be made on TriMas' behalf.
On January 11, 2007, Metaldyne merged into a subsidiary of Asahi Tec Corporation (“Asahi”) whereby Metaldyne became a wholly-owned subsidiary of Asahi. In connection with the consummation of the merger, Metaldyne dividended the 4,825,587 shares of the Company's common stock that it owned on a pro rata basis to the holders of Metaldyne's common stock at the time of such dividend. As a result of the merger, Metaldyne and the Company were no longer related parties. In addition, as a result of the merger, it has been asserted that Metaldyne may be obligated to accelerate funding and payment of actuarially determined amounts owing to seven former Metaldyne executives under a supplemental executive retirement plan (“SERP”). Under the stock purchase agreement between Metaldyne and Heartland Industrial Partners (“Heartland”), TriMas is required to reimburse Metaldyne, when billed, for its allocated portion of the amounts due to certain Metaldyne SERP participants, as defined.
Subject to certain limited exceptions, Metaldyne and TriMas retained separate liabilities associated with the respective businesses following the reorganization in June 2002. Accordingly, the Company will indemnify and hold Metaldyne harmless from all liabilities associated with TriMas and its subsidiaries and the respective operations and assets, whenever conducted, and Metaldyne will indemnify and hold harmless Heartland and TriMas from all liabilities associated with Metaldyne and its subsidiaries (excluding TriMas and its subsidiaries) and their respective operations and assets, whenever conducted. In addition, TriMas agreed with Metaldyne to indemnify one another for its allocated share (42.01% with respect to TriMas and 57.99% with respect to Metaldyne) of liabilities not readily associated with either business, or otherwise addressed including certain costs related to other matters intended to effectuate other provisions of the agreement. These indemnification provisions survive indefinitely and are subject to a $50,000 deductible.
On May 28, 2009, Metaldyne and its U.S. subsidiaries filed voluntary petitions in the United States Bankruptcy Court under Chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code. On February 23, 2010, the U.S. Bankruptcy Court confirmed the reorganization plan of Metaldyne and its U.S. subsidiaries.
The Company continues to evaluate the impact of Metaldyne's reorganization plans on its estimated obligations to Metaldyne. At December 31, 2015, TriMas has accrued an estimated liability to Metaldyne on its reported balance sheet of approximately $7.2 million. However, if Metaldyne is required to accelerate funding of these liabilities, TriMas may be obligated to reimburse Metaldyne up to approximately $9.6 million, which could result in future charges to the Company's statement of operations of up to $2.4 million. The Metaldyne bankruptcy distribution trust is expected to terminate in the third quarter of 2016, at which time a final assessment of the liabilities will be determined.
Claims and Litigation
The Company is subject to other claims and litigation in the ordinary course of business which the Company does not believe are material. In addition, a claim was recently made against the Company by a competitor alleging false advertising where, although no formal demand was made, the Company believed the competitor may be seeking in excess of $10 million. During the second quarter of 2015, the Company resolved the matter for approximately $2.8 million, inclusive of attorney fees and expenses. During the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company recorded an insurance reimbursement of $1.5 million related to this matter.
The Company does not believe claims and litigation will have a material adverse effect on its financial position and results of operations or cash flows.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
16. Employee Benefit Plans
Pension and Profit-Sharing Benefits
The Company provides a defined contribution profit sharing plan for the benefit of substantially all the Company's domestic salaried and non-union hourly employees. The plan contains both contributory and noncontributory profit sharing arrangements, as defined. Aggregate charges included in the accompanying statement of operations under this plan for both continuing and discontinued operations were approximately $5.2 million, $5.8 million and $5.6 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Certain of the Company's foreign and union hourly employees participate in defined benefit pension plans.
Postretirement Benefits
The Company provides postretirement medical and life insurance benefits, none of which are pre-funded, for certain of its retired employees.
Plan Assets, Expenses and Obligations
Plan assets, expenses and obligations for pension and postretirement benefit plans disclosed herein include both continuing and discontinued operations.
Net periodic pension and postretirement benefit expense (income) recorded in the Company's statement of operations for defined benefit pension plans and postretirement benefit plans include the following components:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefit | | Postretirement Benefit |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Service cost | | $ | 890 |
| | $ | 760 |
| | $ | 680 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Interest cost | | 1,580 |
| | 1,760 |
| | 1,610 |
| | 20 |
| | 30 |
| | 40 |
|
| Expected return on plan assets | | (1,840 | ) | | (2,070 | ) | | (1,810 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Settlement/curtailment | | 2,750 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Amortization of net (gain)/loss | | 1,340 |
| | 1,120 |
| | 1,280 |
| | (30 | ) | | (90 | ) | | (80 | ) |
| Net periodic benefit expense (income) | | $ | 4,720 |
| | $ | 1,570 |
| | $ | 1,760 |
| | $ | (10 | ) | | $ | (60 | ) | | $ | (40 | ) |
During the second quarter of 2015, the Company recognized a one-time settlement charge associated with annuitizing the defined benefit obligations for certain current and former Cequent employees. The settlement charge of approximately $2.8 million is included in the income (loss) from discontinued operations in the accompanying consolidated statement of operations.
The estimated net actuarial loss and prior service cost for the defined benefit pension and postretirement benefit plans that is expected to be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) into net periodic benefit cost in 2016 is approximately $0.9 million.
Actuarial valuations of the Company's defined benefit pension and postretirement plans were prepared as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013. Weighted-average assumptions used in accounting for the U.S. defined benefit pension plans and postretirement benefit plans are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefit | | Postretirement Benefit |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| Discount rate for obligations | | 4.62 | % | | 4.17 | % | | 5.01 | % | | 4.21 | % | | 3.89 | % | | 4.48 | % |
| Discount rate for benefit costs | | 4.17 | % | | 5.01 | % | | 4.24 | % | | 3.89 | % | | 4.48 | % | | 3.69 | % |
| Rate of increase in compensation levels | | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
|
| Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets | | 7.50 | % | | 7.50 | % | | 7.50 | % | | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | N/A |
|
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The Company utilizes a high-quality (Aa) corporate bond yield curve as the basis for its domestic discount rate for its pension and postretirement benefit plans. Management believes this yield curve removes the impact of including additional required corporate bond yields (potentially considered in the above-median curve) resulting from the uncertain economic climate that does not necessarily reflect the general trend in high-quality interest rates.
Actuarial valuations of the Company's non-U.S. defined benefit pension plans were prepared as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013. Weighted-average assumptions used in accounting for the non-U.S. defined benefit pension plans are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefit |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| Discount rate for obligations | | 3.80 | % | | 3.70 | % | | 4.50 | % |
| Discount rate for benefit costs | | 3.70 | % | | 4.50 | % | | 4.50 | % |
| Rate of increase in compensation levels | | 3.90 | % | | 3.80 | % | | 4.10 | % |
| Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets | | 4.90 | % | | 5.60 | % | | 5.40 | % |
The Company reviews the employee demographic assumptions annually and updates these assumptions as necessary. During 2014, the mortality assumptions were updated to incorporate a new set of mortality tables. This resulted in an increase in the projected benefit obligation of the Company's defined benefit pension and postretirement benefit plans.
The following provides a reconciliation of the changes in the Company's defined benefit pension and postretirement benefit plans' projected benefit obligations and fair value of assets for each of the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 and the funded status as of December 31, 2015 and 2014:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefit | | Postretirement Benefit |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Changes in Projected Benefit Obligations | | | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligations at January 1 | | $ | (43,730 | ) | | $ | (38,230 | ) | | $ | (660 | ) | | $ | (810 | ) |
| Service cost | | (890 | ) | | (760 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Interest cost | | (1,580 | ) | | (1,760 | ) | | (20 | ) | | (30 | ) |
| Participant contributions | | (60 | ) | | (60 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Actuarial gain (loss) | | (150 | ) | | (6,470 | ) | | 200 |
| | 100 |
|
| Benefit payments | | 1,640 |
| | 2,230 |
| | 70 |
| | 80 |
|
| Settlement payments | | 5,210 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Change in foreign currency | | 1,320 |
| | 1,320 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Projected benefit obligations at December 31 | | $ | (38,240 | ) | | $ | (43,730 | ) | | $ | (410 | ) | | $ | (660 | ) |
| Changes in Plan Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Fair value of plan assets at January 1 | | $ | 32,610 |
| | $ | 31,780 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Actual return on plan assets | | 50 |
| | 1,830 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Employer contributions | | 3,640 |
| | 2,340 |
| | 70 |
| | 80 |
|
| Participant contributions | | 60 |
| | 60 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Benefit payments | | (1,640 | ) | | (2,230 | ) | | (70 | ) | | (80 | ) |
| Settlement payment | | (5,210 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Change in foreign currency | | (1,240 | ) | | (1,170 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Fair value of plan assets at December 31 | | $ | 28,270 |
| | $ | 32,610 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Funded status at December 31 | | $ | (9,970 | ) | | $ | (11,120 | ) | | $ | (410 | ) | | $ | (660 | ) |
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefit | | Postretirement Benefit |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Amounts Recognized in Balance Sheet | | | | | | | | |
| Prepaid benefit cost | | $ | 590 |
| | $ | 790 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Current liabilities | | (320 | ) | | (320 | ) | | (50 | ) | | (70 | ) |
| Noncurrent liabilities | | (10,240 | ) | | (11,590 | ) | | (360 | ) | | (590 | ) |
| Net liability recognized at December 31 | | $ | (9,970 | ) | | $ | (11,120 | ) | | $ | (410 | ) | | $ | (660 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefit | | Postretirement Benefit |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Amounts Recognized in Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Income) Loss | | | | | | | | |
| Unrecognized prior-service cost | | $ | 80 |
| | $ | 90 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Unrecognized net loss/(gain) | | 18,570 |
| | 21,420 |
| | (840 | ) | | (670 | ) |
| Total accumulated other comprehensive (income) loss recognized at December 31 | | $ | 18,650 |
| | $ | 21,510 |
| | $ | (840 | ) | | $ | (670 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Accumulated Benefit Obligations | | Projected Benefit Obligations |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2015 | | 2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Benefit Obligations at December 31, | | | | | | | | |
| Total benefit obligations | | $ | (35,890 | ) | | $ | (41,450 | ) | | $ | (38,240 | ) | | $ | (43,730 | ) |
| Plans with benefit obligations exceeding plan assets | | | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligations | | $ | (17,940 | ) | | $ | (40,630 | ) | | $ | (37,560 | ) | | $ | (42,910 | ) |
| Plan assets | | 9,200 |
| | 31,000 |
| | 27,000 |
| | 31,000 |
|
The assumptions regarding discount rates and expected return on plan assets can have a significant impact on amounts reported for benefit plans. A 25 basis point change in benefit obligation discount rates or 50 basis point change in expected return on plan assets would have the following affect:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2015
Benefit Obligation | | 2015 Expense |
| | | Pension | | Postretirement Benefit | | Pension | | Postretirement Benefit |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Discount rate | | | | | | | | |
| 25 basis point increase | | $ | (1,370 | ) | | $ | (10 | ) | | $ | (90 | ) | | $ | — |
|
| 25 basis point decrease | | $ | 1,420 |
| | $ | 10 |
| | $ | 100 |
| | — |
|
| Expected return on assets | | | | | | | | |
| 50 basis point increase | | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | $ | (150 | ) | | N/A |
|
| 50 basis point decrease | | N/A |
| | N/A |
| | $ | 150 |
| | N/A |
|
The Company expects to make contributions of approximately $2.0 million to fund its pension plans during 2016.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Plan Assets
The Company's overall investment goal is to provide for capital growth with a moderate level of volatility by investing assets in targeted allocation ranges. Specific long term investment goals include total investment return, diversity to reduce volatility and risk, and to achieve an asset allocation profile that reflects the general nature and sensitivity of the plans' liabilities. Investment goals are established after a comprehensive review of current and projected financial statement requirements, plan assets and liability structure, market returns and risks as well as special requirements of the plans. The Company reviews investment goals and actual results annually to determine whether stated objectives are still relevant and the continued feasibility of achieving the objectives.
The actual weighted average asset allocation of the Company's domestic and foreign pension plans' assets at December 31, 2015 and 2014 and target allocations by class, were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Domestic Pension | | Foreign Pension |
| | | | | Actual | | | | Actual |
| | | Target | | 2015 | | 2014 | | Target | | 2015 | | 2014 |
| Equity securities | | 50%-70% |
| | 62 | % | | 63 | % | | 55 | % | | 40 | % | | 52 | % |
| Fixed income securities | | 30%-50% |
| | 36 | % | | 35 | % | | 45 | % | | 46 | % | | 48 | % |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | — |
| | 2 | % | | 2 | % | | — |
| | 14 | % | | — | % |
| Total | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % | | 100 | % |
Actual allocations to each asset vary from target allocations due to periodic investment strategy changes, market value fluctuations and the timing of benefit payments and contributions. The expected long-term rate of return for both the domestic and foreign plans' total assets is based on the expected return of each of the above categories, weighted based on the target allocation for each class. Actual allocation is reviewed regularly and rebalancing investments to their targeted allocation range is performed when deemed appropriate. During 2015, the Company made higher than expected contributions to one of its foreign defined benefit plans as part of a recovery plan to reduce the plan's net funding deficit. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had not yet completed its investment allocation strategy with respect to the incremental contributions, with the funds remaining in a cash account and causing a deviation from the targeted asset allocation.
In managing the plan assets, the Company reviews and manages risk associated with the funded status risk, interest rate risk, market risk, liquidity risk and operational risk. Investment policies reflect the unique circumstances of the respective plans and include requirements designed to mitigate these risks by including quality and diversification standards.
The following table summarizes the level under the fair value hierarchy (see Note 3, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies") that the Company's pension plan assets are measured on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2015:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| Equity Securities | | | | | | | | |
| Investment funds | | $ | 13,980 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 13,980 |
| | $ | — |
|
| Fixed Income Securities | | | | | | | | |
| Investment funds | | 7,920 |
| | — |
| | 7,920 |
| | — |
|
| Corporate bonds | | 3,540 |
| | — |
| | 3,540 |
| | — |
|
Other (a) | | 110 |
| | — |
| | 110 |
| | — |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | | |
| Short term investment funds | | 2,720 |
| | 2,550 |
| | 170 |
| | — |
|
| Total | | $ | 28,270 |
| | $ | 2,550 |
| | $ | 25,720 |
| | $ | — |
|
________________________________________
(a) Comprised of mortgage-backed, asset backed securities and non-government backed c.m.o.s.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, as appropriate, are expected to be paid:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Pension Benefit | | Postretirement Benefit |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| December 31, 2016 | | $ | 1,490 |
| | $ | 50 |
|
| December 31, 2017 | | 1,510 |
| | 40 |
|
| December 31, 2018 | | 1,580 |
| | 40 |
|
| December 31, 2019 | | 1,640 |
| | 40 |
|
| December 31, 2020 | | 1,680 |
| | 30 |
|
| Years 2021-2025 | | 9,420 |
| | 130 |
|
The assumed health care cost trend rate used for purposes of calculating the Company's postretirement benefit obligation in 2015 was 7.5% for pre-65 plan participants, decreasing to an ultimate rate of 5.0% in 2022 and 7.0% for post-65 plan participants, decreasing to an ultimate rate of 5.0% in 2020. A one-percentage point change in the assumed health care cost trend would have the following effects:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | One Percentage-Point Increase | | One Percentage-Point Decrease |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Effect on total service and interest cost | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| Effect on postretirement benefit obligation | | 30 |
| | (30 | ) |
17. Equity Awards
The Company maintains the following long-term equity incentive plans (collectively, the "Plans"):
|
| | | | | |
| Plan Names | | Shares Approved for Issuance | | Fungible Ratio |
| TriMas Corporation Director Retainer Share Election Program | | 100,000 |
| | N/A |
| 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan | | 3,246,588 |
| | 1.75:1 |
| 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan | | 2,870,221 |
| | 2:1 |
| 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan | | 2,111,567 |
| | 1:1 |
The fungible ratio presented above applies to restricted shares of common stock. Stock options and stock appreciation rights have a fungible ratio of 1:1 (one granted option/appreciation right counts as one share against the aggregate available to issue) under each Plan, if applicable. In addition, the 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan expired in 2012, such that, while existing grants remain outstanding until exercised, vested or cancelled, no new shares may be issued under the plan.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Spin-off of the Cequent businesses
On June 30, 2015, due to the spin-off of the Cequent businesses, stock options and restricted shares previously granted to Cequent participants were cancelled and transferred to Horizon. On July 1, 2015, the Company adjusted the number of shares outstanding, and the exercise price of stock options, as required by the anti-dilution provisions of the Plans, to maintain the intrinsic value of the outstanding equity awards immediately post spin-off.
Stock Options
The Company did not grant any stock options during 2015, 2014 and 2013.
Information related to stock options at December 31, 2015 is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Number of Stock Options | | Weighted Average Option Price | | Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
Outstanding at January 1, 2015 (a) | | 298,095 |
| | $ | 5.40 |
| | | | |
| Exercised | | (83,242 | ) | | 6.26 |
| | | | |
| Cancelled | | (5,769 | ) | | 5.95 |
| | | | |
| Expired | | (2,961 | ) | | 19.42 |
| | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | | 206,123 |
| | $ | 4.84 |
| | 2.6 | | $ | 2,880,112 |
|
__________________________
(a) Beginning balance and weighted average option price have been retrospectively adjusted to give effect to the distribution ratio as required per the anti-dilution provisions of the Plans, resulting in 46,428 additional shares.
As of December 31, 2015, all 206,123 stock options outstanding were exercisable under the Plans. The fair value of options which vested during each of the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $0.1 million, respectively.
The Company did not incur significant stock-based compensation expense related to stock options during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013.
Restricted Shares
The Company awarded 1,760 and 2,200 restricted stock grants to certain employees during 2015 and 2014, respectively. These shares are subject only to a service condition and vest on the first anniversary date of the award so long as the employee remains with the Company.
During 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company issued 209,825, 23,226 and 29,498 shares, respectively, of its common stock to certain employees which are subject only to a service condition and vest ratably over three years so long as the employee remains with the Company.
The Company awarded 42,937, 40,837 and 41,480 restricted shares of common stock to certain employees during 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. These shares are subject only to a service condition and vest on the first anniversary date of the award. The awards were made to participants in the Company's Short-Term Incentive Compensation Plan ("STI"), where all STI participants whose target STI annual award exceeds $20 thousand receive 80% of the value earned in cash and 20% in the form of a restricted stock award upon finalization of the award amount in the first quarter each year following the previous plan year.
During 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company granted 32,040, 20,832 and 17,240 shares, respectively, of its common stock to its non-employee independent directors, which vest one year from date of grant so long as the director and/or Company does not terminate their service prior to the vesting date.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
During the third quarter of 2015, the Company awarded 192,348 performance-based shares of common stock to certain Company key employees which vest on March 1, 2018, so long as the employee remains with the Company. The performance criteria for these awards is based on the Company's total shareholder return ("TSR") relative to the TSR of the common stock of a pre-defined industry peer-group, measured over a period beginning September 10, 2015 and ending December 31, 2017. TSR is calculated as the Company's average closing stock price for the 20-trading days at the end of the performance period plus Company dividends, divided by the Company's average closing stock price for the 20-trading days prior to the start of the performance period. Depending on the performance achieved, the amount of shares earned can vary from 0% of the target award to a maximum of 200% of the target award. The Company estimated the grant-date fair value and term of the awards subject to a market condition using a Monte Carlo simulation model, using the following weighted-average assumptions: risk-free interest rate of 0.85% and annualized volatility of 35.8%.
The Company awarded 243,124 restricted shares of common stock to certain Company key employees during the first quarter of 2014. Half of the restricted shares granted are service-based restricted stock units. These awards vest ratably over three years. The other half of the shares awarded were performance-based shares of common stock to certain Company key employees which were earned based upon the achievement of the Company's pre-spin earnings per share ("EPS") cumulative average growth rate ("EPS CAGR") and average return on invested capital performance metrics over a period of three calendar years, beginning January 1, 2014 and ending on December 31, 2016. In the third quarter of 2015, this award was modified due to the Company's spin-off of the Cequent businesses. At the time of the spin-off, the performance period was 50% complete; thus, the Company measured attainment for the half completed, and cancelled the remaining performance shares. The Company determined that the original performance metrics resulted in a 30% attainment of the target on a weighted average basis, resulting in a reduction of 35,096 shares during the third quarter of 2015. The Company awarded new performance-based grants of 86,924 restricted shares to these key employees, with the performance criteria based upon the Company's total TSR relative to the TSR of the common stock of a pre-defined industry peer-group and measured over the period beginning September 10, 2015 and ending December 31, 2016. Depending on the performance achieved, the amount of shares earned can vary from 0% of the target award to a maximum of 200% of the target award. These awards vest on March 5, 2017, so long as the employee remains with the Company. The Company estimated the grant-date fair value and term of the awards subject to a market condition using a Monte Carlo simulation model, using the following weighted-average assumptions: risk-free interest rate of 0.50% and annualized volatility of 38.8%.
The Company awarded 238,808 restricted shares to certain Company key employees during 2013. Half of the restricted shares granted are service-based restricted stock units. These awards vest ratably over three years. The other half of the shares awarded were performance-based shares of common stock to certain Company key employees which were earned based upon the achievement of EPS CAGR and cash generation performance metrics over a period of three calendar years, beginning January 1, 2013 and ending on December 31, 2015. In the third quarter of 2015, this award was modified due to the spin-off of the Cequent businesses. Due to the timing of the spin-off, the Company considered the performance measurement period complete for certain employees, resulting in an attainment of 50% of the target on a weighted average basis, resulting in a reduction of 14,331 shares during the third quarter of 2015.
During 2012, the Company awarded performance-based shares of common stock to certain Company key employees which were earned based upon the achievement of EPS CAGR and cash generation performance metrics over a period of three calendar years, beginning January 1, 2012 and ending on December 31, 2014. The Company attained 70.25% of the target on a weighted average basis, resulting in a reduction of 28,205 shares during the first quarter of 2015.
The Company allows for its non-employee independent directors to make an annual election to defer all or a portion of their director fees and to receive the deferred amount in cash or equity. Certain of the Company's directors have elected to defer all or a portion of their director fees and to receive the amount in Company common stock at a future date. The Company issued 11,026, 10,140 and 5,215 shares in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, related to director fee deferrals.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Information related to restricted shares at December 31, 2015 is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Number of Unvested Restricted Shares | | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | | Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
Outstanding at January 1, 2015 (a) | | 867,236 |
| | $ | 24.66 |
| | | | |
| Granted | | 576,860 |
| | 23.49 |
| | | | |
| Vested | | (340,493 | ) | | 23.74 |
| | | | |
| Cancelled | | (338,289 | ) | | 25.68 |
| | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | | 765,314 |
| | $ | 23.73 |
| | 1.0 | | $ | 14,273,106 |
|
__________________________
(a) Beginning balance and weighted average grant date fair value have been retrospectively adjusted to give effect to the distribution ratio as required per the anti-dilution provisions of the Plans, resulting in 141,777 additional shares.
As of December 31, 2015, there was approximately $8.1 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested restricted shares that is expected to be recorded over a weighted-average period of 1.9 years.
The Company recognized stock-based compensation expense related to restricted shares of approximately $6.3 million, $7.1 million and $8.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. The stock-based compensation expense is included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the accompanying statement of operations.
18. Other Comprehensive Income
Changes in AOCI by component for the year ended December 31, 2015 are summarized as follows, net of tax:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Defined Benefit Plans | | Derivative Instruments | | Foreign Currency Translation | | Total |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Balance, December 31, 2014 | | $ | (14,180 | ) | | $ | 610 |
| | $ | 23,790 |
| | $ | 10,220 |
|
Net unrealized losses arising during the period (a) | | (1,320 | ) | | (3,610 | ) | | (12,370 | ) | | (17,300 | ) |
Less: Net realized losses reclassified to net income (b) | | (3,130 | ) | | (960 | ) | | — |
| | (4,090 | ) |
| Net current-period other comprehensive income (loss) | | 1,810 |
| | (2,650 | ) | | (12,370 | ) | | (13,210 | ) |
| Less: Distribution of the Cequent businesses | | — |
| | 250 |
| | (8,560 | ) | | (8,310 | ) |
| Balance, December 31, 2015 | | $ | (12,370 | ) | | $ | (1,790 | ) | | $ | 2,860 |
| | $ | (11,300 | ) |
__________________________
(a) Defined benefit plans, net of income tax expense of $0.4 million. See Note 16, "Employee Benefit Plans," for additional details. Derivative instruments, net of income tax expense of $1.9 million. See Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," for further details.
(b) Defined benefit plans, net of income tax expense of $1.8 million. See Note 16, "Employee Benefit Plans," for additional details. Derivative instruments, net of income tax expense of $0.3 million. See Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," for further details.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Changes in AOCI by component for the year ended December 31, 2014 are summarized as follows, net of tax:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Defined Benefit Plans | | Derivative Instruments | | Foreign Currency Translation | | Total |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Balance, December 31, 2013 | | $ | (10,840 | ) | | $ | 1,060 |
| | $ | 37,610 |
| | $ | 27,830 |
|
Net unrealized losses arising during the period (a) | | (4,040 | ) | | (900 | ) | | (15,090 | ) | | (20,030 | ) |
Less: Net realized losses reclassified to net income (b) | | (700 | ) | | (450 | ) | | (1,270 | ) | | (2,420 | ) |
Net current-period other comprehensive loss
| | (3,340 | ) | | (450 | ) | | (13,820 | ) | | (17,610 | ) |
| Balance, December 31, 2014 | | $ | (14,180 | ) | | $ | 610 |
| | $ | 23,790 |
| | $ | 10,220 |
|
__________________________
(a) Defined benefit plans, net of income tax expense of $2.0 million. See Note 16, "Employee Benefit Plans," for additional details. Derivative instruments, net of income tax expense of $0.6 million. See Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," for further details.
(b) Defined benefit plans, net of income tax expense of $0.3 million. See Note 16, "Employee Benefit Plans," for additional details. Derivative instruments, net of income tax expense of $0.3 million. See Note 13, "Derivative Instruments," for further details.
The Company reclassified approximately $1.3 million of foreign currency translation losses from AOCI into net income related to the restructuring of business during the year ended December 31, 2014. See Note 7, "Facility Closures and Sale of Business," for additional details.
19. Segment Information
TriMas groups its operating segments into reportable segments that provide similar products and services. Each operating segment has discrete financial information evaluated regularly by the Company's chief operating decision maker in determining resource allocation and assessing performance. Within these reportable segments, there are no individual products or product families for which reported net sales accounted for more than 10% of the Company's consolidated net sales. For purposes of this Note, the Company defines operating net assets as total assets less current liabilities. See below for more information regarding the types of products and services provided within each reportable segment:
Packaging-Highly engineered closure and dispensing systems for a range of end markets, including steel and plastic industrial and consumer packaging applications.
Aerospace-Permanent blind bolts, temporary fasteners, highly engineered specialty fasteners and other precision machined parts used in the commercial, business and military aerospace industries.
Energy-Metallic and non-metallic industrial sealant products and fasteners for the petroleum refining, petrochemical and other industrial markets.
Engineered Components-High-pressure and low-pressure cylinders for the transportation, storage and dispensing of compressed gases, and natural gas engines, compressors, gas production equipment and chemical pumps engineered at well sites for the oil and gas industry.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Segment activity is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Net Sales | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 334,270 |
| | $ | 337,710 |
| | $ | 313,220 |
|
| Aerospace | | 176,480 |
| | 121,510 |
| | 95,530 |
|
| Energy | | 193,390 |
| | 206,720 |
| | 205,580 |
|
| Engineered Components | | 159,840 |
| | 221,360 |
| | 185,370 |
|
| Total | | $ | 863,980 |
| | $ | 887,300 |
| | $ | 799,700 |
|
| Operating Profit (Loss) | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 78,470 |
| | $ | 77,850 |
| | $ | 83,770 |
|
| Aerospace | | 28,320 |
| | 17,830 |
| | 22,830 |
|
| Energy | | (97,160 | ) | | (6,660 | ) | | 8,620 |
|
| Engineered Components | | 18,240 |
| | 34,080 |
| | 19,450 |
|
| Corporate | | (32,120 | ) | | (36,450 | ) | | (37,460 | ) |
| Total | | $ | (4,250 | ) | | $ | 86,650 |
| | $ | 97,210 |
|
| Capital Expenditures | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 13,670 |
| | $ | 13,730 |
| | $ | 11,010 |
|
| Aerospace | | 5,010 |
| | 4,430 |
| | 4,810 |
|
| Energy | | 7,610 |
| | 2,690 |
| | 5,250 |
|
| Engineered Components | | 2,320 |
| | 1,690 |
| | 2,190 |
|
| Corporate | | 50 |
| | 460 |
| | 970 |
|
| Total | | $ | 28,660 |
| | $ | 23,000 |
| | $ | 24,230 |
|
| Depreciation and Amortization | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 20,920 |
| | $ | 20,410 |
| | $ | 18,960 |
|
| Aerospace | | 13,290 |
| | 7,630 |
| | 3,790 |
|
| Energy | | 4,790 |
| | 4,600 |
| | 3,820 |
|
| Engineered Components | | 4,200 |
| | 4,460 |
| | 4,270 |
|
| Corporate | | 340 |
| | 340 |
| | 260 |
|
| Total | | $ | 43,540 |
| | $ | 37,440 |
| | $ | 31,100 |
|
| Operating Net Assets | | | | | | |
| Packaging | | $ | 380,630 |
| | $ | 398,530 |
| | $ | 377,480 |
|
| Aerospace | | 494,570 |
| | 498,560 |
| | 150,750 |
|
| Energy | | 90,880 |
| | 170,430 |
| | 180,410 |
|
| Engineered Components | | 67,460 |
| | 65,910 |
| | 73,780 |
|
| Corporate | | (15,990 | ) | | (28,320 | ) | | (15,630 | ) |
| Subtotal from continuing operations | | 1,017,550 |
| | 1,105,110 |
| | 766,790 |
|
| Discontinued operations | | — |
| | 213,360 |
| | 240,690 |
|
| Total operating net assets | | 1,017,550 |
| | 1,318,470 |
| | 1,007,480 |
|
| Current liabilities | | 152,750 |
| | 306,960 |
| | 261,510 |
|
| Consolidated total assets | | $ | 1,170,300 |
| | $ | 1,625,430 |
| | $ | 1,268,990 |
|
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table presents the Company's net sales for each of the years ended December 31 and operating net assets at each year ended December 31, attributed to each subsidiary's continent of domicile. There was no single non-U.S. country for which net sales and net assets were significant to the combined net sales and net assets of the Company taken as a whole.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | Net Sales | | Operating Net Assets | | Net Sales | | Operating
Net Assets(a) | | Net Sales | | Operating
Net Assets(a) |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Non-U.S. | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Europe | | $ | 70,760 |
| | $ | 61,050 |
| | $ | 75,350 |
| | $ | 74,350 |
| | $ | 74,760 |
| | $ | 110,570 |
|
| Australia | | 1,480 |
| | 250 |
| | 1,810 |
| | 1,790 |
| | 2,260 |
| | 1,960 |
|
| Asia | | 28,800 |
| | 79,400 |
| | 22,850 |
| | 80,840 |
| | 14,620 |
| | 41,340 |
|
| Other Americas | | 17,000 |
| | 12,130 |
| | 23,370 |
| | 20,300 |
| | 28,910 |
| | 43,960 |
|
| Total non-U.S | | 118,040 |
| | 152,830 |
| | 123,380 |
| | 177,280 |
| | 120,550 |
| | 197,830 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total U.S. | | 745,940 |
| | 864,720 |
| | 763,920 |
| | 927,830 |
| | 679,150 |
| | 568,960 |
|
| Total | | $ | 863,980 |
| | $ | 1,017,550 |
| | $ | 887,300 |
| | $ | 1,105,110 |
| | $ | 799,700 |
| | $ | 766,790 |
|
________________________________________
(a) Excludes discontinued operations. See Note 6, "Discontinued Operations".
The Company's export sales from the U.S. approximated $82.7 million, $95.3 million and $85.8 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
20. Income Taxes
The Company's income (loss) before income taxes and income tax expense for continuing operations, each by tax jurisdiction, consisted of the following:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Income (loss) before income taxes: | | | | | | |
| Domestic | | $ | (3,150 | ) | | $ | 67,300 |
| | $ | 47,760 |
|
| Foreign | | (18,970 | ) | | 2,300 |
| | 28,390 |
|
| Total income (loss) before income taxes | | $ | (22,120 | ) | | $ | 69,600 |
| | $ | 76,150 |
|
| Current income tax expense: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | $ | 12,150 |
| | $ | 24,630 |
| | $ | 13,020 |
|
| State and local | | 1,080 |
| | 3,440 |
| | 1,740 |
|
| Foreign | | 2,060 |
| | 1,170 |
| | 6,690 |
|
| Total current income tax expense | | 15,290 |
| | 29,240 |
| | 21,450 |
|
| Deferred income tax expense (benefit): | | | | | | |
| Federal | | (1,980 | ) | | (9,370 | ) | | (2,420 | ) |
| State and local | | (1,530 | ) | | (40 | ) | | (1,280 | ) |
| Foreign | | (5,240 | ) | | 2,880 |
| | (840 | ) |
| Total deferred income tax expense | | (8,750 | ) | | (6,530 | ) | | (4,540 | ) |
| Income tax expense | | $ | 6,540 |
| | $ | 22,710 |
| | $ | 16,910 |
|
The components of deferred taxes at December 31, 2015 and 2014 are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | | $ | 550 |
| | $ | 350 |
|
| Inventories | | 5,680 |
| | 5,680 |
|
| Accrued liabilities and other long-term liabilities | | 27,550 |
| | 34,430 |
|
| Tax loss and credit carryforwards | | 4,660 |
| | 12,420 |
|
| Gross deferred tax asset | | 38,440 |
| | 52,880 |
|
| Valuation allowances | | (3,060 | ) | | (5,980 | ) |
| Net deferred tax asset | | 35,380 |
| | 46,900 |
|
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | |
| Property and equipment | | (16,340 | ) | | (19,290 | ) |
| Goodwill and other intangible assets | | (26,600 | ) | | (44,570 | ) |
| Other, principally deferred income | | (3,450 | ) | | (5,020 | ) |
| Gross deferred tax liability | | (46,390 | ) | | (68,880 | ) |
| Net deferred tax liability | | $ | (11,010 | ) | | $ | (21,980 | ) |
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following is a reconciliation of income tax expense computed at the U.S. federal statutory rate to income tax expense allocated to income from continuing operations before income taxes:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2015 | | 2014 | | 2013 |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| U.S. federal statutory rate | | 35 | % | | 35 | % | | 35 | % |
| Tax at U.S. federal statutory rate | | $ | (7,740 | ) | | $ | 24,360 |
| | $ | 26,650 |
|
| State and local taxes, net of federal tax benefit | | (520 | ) | | 2,520 |
| | 280 |
|
| Differences in statutory foreign tax rates | | 110 |
| | (200 | ) | | (4,330 | ) |
| Change in recognized tax benefits | | (460 | ) | | (2,490 | ) | | (1,900 | ) |
| Goodwill impairment | | 11,430 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Nontaxable gains | | (980 | ) | | — |
| | (5,460 | ) |
| Restructuring (benefits)/charges | | — |
| | — |
| | 2,230 |
|
| Noncontrolling interest | | — |
| | (280 | ) | | (1,410 | ) |
| Research and manufacturing incentives | | (1,680 | ) | | (1,920 | ) | | (1,680 | ) |
| Tax on undistributed foreign earnings | | 610 |
| | 50 |
| | 290 |
|
| Net change in valuation allowance | | 3,770 |
| | 3,270 |
| | 820 |
|
| Other, net | | 2,000 |
| | (2,600 | ) | | 1,420 |
|
| Income tax expense | | $ | 6,540 |
| | $ | 22,710 |
| | $ | 16,910 |
|
The Company has recorded deferred tax assets on $29.9 million of various state operating loss carryforwards and $9.5 million of various foreign operating loss carryforwards. The majority of the state tax loss carryforwards expire between 2024 and 2027 and the majority of the foreign losses have indefinite carryforward periods.
In general, it is the practice and intention of the Company to reinvest the earnings of its non-U.S. subsidiaries in those operations. As of December 31, 2015, the Company has not made a provision for U.S. or additional non-U.S. withholding taxes on approximately $87.2 million of undistributed earnings of non-U.S. subsidiaries that are considered to be permanently reinvested. Generally, such amounts become subject to U.S. taxation upon remittance of dividends and under certain other circumstances. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of deferred tax liability related to investments in these non-U.S. subsidiaries.
Unrecognized tax benefits
The Company has approximately $4.6 million and $5.3 million of unrecognized tax benefits ("UTBs") as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. If the unrecognized tax benefits were recognized, the impact to the Company's effective tax rate would be to reduce reported income tax expense for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 approximately $4.1 million and $4.8 million, respectively.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
A reconciliation of the change in the UTBs and related accrued interest and penalties for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 is as follows:
|
| | | | |
| | | Unrecognized Tax Benefits |
| | | (dollars in thousands) |
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | | $ | 8,470 |
|
| Tax positions related to current year: | | |
| Additions | | 390 |
|
| Tax positions related to prior years: | | |
| Additions | | 270 |
|
| Reductions | | (1,280 | ) |
| Settlements | | — |
|
| Lapses in the statutes of limitations | | (2,580 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2014 | | $ | 5,270 |
|
| Tax positions related to current year: | | |
| Additions | | 240 |
|
| Tax positions related to prior years: | |
|
|
| Additions | | 1,570 |
|
| Reductions | | (360 | ) |
| Settlements | | (390 | ) |
| Lapses in the statutes of limitations | | (1,720 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2015 | | $ | 4,610 |
|
In addition to the UTBs summarized above, the Company has recorded approximately $2.2 million in potential interest and penalties associated with uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2015 and 2014.
The Company is subject to U.S. federal, state and local, and certain non-U.S. income tax examinations for tax years 2010 through 2014. The Company is currently under audit by the Internal Revenue Service for tax year 2013. In addition, there are currently several state examinations and one foreign income tax examination in process. The Company does not believe that the results of these examinations will have a significant impact on the Company's tax position or its effective tax rate. During 2015, the Company concluded its 2011 U.S. examination as well as settled two foreign income tax examinations. The examination results did not have a significant impact on the Company's tax position or its effective tax rate.
Management monitors changes in tax statutes and regulations and the issuance of judicial decisions to determine the potential impact to UTBs and is not aware of, nor does it anticipate, any material subsequent events that could have a significant impact on the Company's financial position during the next twelve months.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
21. Summary Quarterly Financial Data
On June 30, 2015, the Company completed the spin-off of its Cequent businesses. The results of its operations have been presented as discontinued operations below for all periods presented.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, 2015 |
| | | First Quarter | | Second Quarter | | Third Quarter | | Fourth Quarter |
| | | (unaudited, dollars in thousands, except for per share data) |
| Net sales | | $ | 224,130 |
| | $ | 224,900 |
| | $ | 222,190 |
| | $ | 192,760 |
|
| Gross profit | | 62,920 |
| | 61,720 |
| | 62,470 |
| | 49,000 |
|
Income (loss) from continuing operations(a) | | 11,940 |
| | 8,490 |
| | 11,710 |
| | (60,800 | ) |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | | 2,040 |
| | (6,780 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Net income (loss) | | 13,980 |
| | 1,710 |
| | 11,710 |
| | (60,800 | ) |
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to TriMas Corporation—basic: | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | 0.19 |
| | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | (1.35 | ) |
| Discontinued operations | | 0.05 |
| | (0.15 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Net income (loss) per share | | $ | 0.31 |
| | $ | 0.04 |
| | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | (1.35 | ) |
| Weighted average shares—basic | | 44,997,961 |
| | 45,150,827 |
| | 45,157,412 |
| | 45,188,303 |
|
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to TriMas Corporation—diluted: | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | 0.19 |
| | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | (1.35 | ) |
| Discontinued operations | | 0.05 |
| | (0.15 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Net income (loss) per share | | $ | 0.31 |
| | $ | 0.04 |
| | $ | 0.26 |
| | $ | (1.35 | ) |
| Weighted average shares—diluted | | 45,400,843 |
| | 45,418,907 |
| | 45,499,104 |
| | 45,188,303 |
|
________________________________________
(a) Loss from continuing operations for the fourth quarter of 2015 includes pre-tax goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible asset impairment charges of $75.7 million. See Note 8, "Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets", for further details.
TRIMAS CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, 2014 |
| | | First Quarter | | Second Quarter | | Third Quarter | | Fourth Quarter |
| | | (unaudited, dollars in thousands, except for per share data) |
| Net sales | | $ | 216,830 |
| | $ | 224,710 |
| | $ | 222,330 |
| | $ | 223,430 |
|
| Gross profit | | 60,440 |
| | 62,760 |
| | 59,870 |
| | 53,940 |
|
| Income from continuing operations | | 13,690 |
| | 14,440 |
| | 11,090 |
| | 7,670 |
|
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | | 5,690 |
| | 11,760 |
| | 11,140 |
| | (6,200 | ) |
| Net income | | 19,380 |
| | 26,200 |
| | 22,230 |
| | 1,470 |
|
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | | 810 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net income attributable to TriMas Corporation | | 18,570 |
| | 26,200 |
| | 22,230 |
| | 1,470 |
|
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to TriMas Corporation—basic: | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | 0.29 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
| | $ | 0.24 |
| | $ | 0.17 |
|
| Discontinued operations | | 0.12 |
| | 0.26 |
| | 0.25 |
| | (0.14 | ) |
| Net income per share | | $ | 0.41 |
| | $ | 0.58 |
| | $ | 0.49 |
| | $ | 0.03 |
|
| Weighted average shares—basic | | 44,768,594 |
| | 44,901,090 |
| | 44,919,340 |
| | 44,938,675 |
|
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to TriMas Corporation—diluted: | | | | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | | $ | 0.29 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
| | $ | 0.24 |
| | $ | 0.17 |
|
| Discontinued operations | | 0.12 |
| | 0.26 |
| | 0.25 |
| | (0.14 | ) |
| Net income per share | | $ | 0.41 |
| | $ | 0.58 |
| | $ | 0.49 |
| | $ | 0.03 |
|
| Weighted average shares—diluted | | 45,186,114 |
| | 45,230,862 |
| | 45,276,199 |
| | 45,384,460 |
|
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Not applicable.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures
As of December 31, 2015, an evaluation was carried out by management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and Rule 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the "Exchange Act")), pursuant to Rule 13a-15 of the Exchange Act. Our disclosure controls and procedures are designed only to provide reasonable assurance that they will meet their objectives. Based upon that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that as of December 31, 2015, the Company's disclosure controls and procedures were effective to provide reasonable assurance that they would meet their objectives.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of the consolidated financial statements included in this annual report. The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with United States generally accepted accounting principles and reflect management's judgments and estimates concerning events and transactions that are accounted for or disclosed.
Management is also responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting. The Company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that pertain to the Company's ability to record, process, summarize, and report reliable financial data. Management recognizes that there are inherent limitations in the effectiveness of any internal control and effective internal control over financial reporting can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation. Additionally, because of changes in conditions, the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting may vary over time.
In order to ensure that the Company's internal control over financial reporting is effective, management regularly assesses such controls and did so most recently for its financial reporting as of December 31, 2015. Management's assessment was based on criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting described in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this assessment, management asserts that the Company has maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015.
Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, who audited the Company's consolidated financial statements, has also audited the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, as stated in their report below.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
TriMas Corporation
Bloomfield Hills, Michigan
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of TriMas Corporation and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2015, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company's management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company's principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company's board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule as of and for the year ended December 31, 2015, of the Company and our report dated February 26, 2016 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and financial statement schedule and included an explanatory paragraph regarding the presentation of the Cequent businesses, prior to the spin-off from TriMas Corporation, as discontinued operations for all periods presented.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Detroit, Michigan
February 26, 2016
Changes in disclosure controls and procedures
There have been no changes in the Company's internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2015 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Information regarding our executive officers is included in Part I of this Form 10-K under the heading “Executive Officers of the Company.”
The Company's Code of Ethics and Business Conduct is applicable to its directors, officers and employees. The Code of Ethics and Business Conduct is available on the "investors" portion of the Company's website under the "Corporate Governance" link. The Company's website address is www.trimascorp.com.
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive proxy statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive proxy statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive proxy statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive proxy statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference from our definitive proxy statement for the 2016 Annual Meeting of Shareholders.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) Listing of Documents
(1) Financial Statements
The Company's Financial Statements included in Item 8 hereof, as required at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, and for the periods ended December 31, 2015, December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, consist of the following:
Balance Sheet
Statement of Operations
Statement of Comprehensive Income
Statement of Cash Flows
Statement of Shareholders' Equity
Notes to Financial Statements
(2) Financial Statement Schedules
Financial Statement Schedule of the Company appended hereto, as required for the periods ended December 31, 2015, December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, consists of the following:
Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
All other schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, not required, or the information is otherwise included in the financial statements or the notes thereto.
(3) Exhibits
See the Exhibits Index at the end of this Form 10-K, which is incorporated by reference.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
| | | | | |
| | | | TRIMAS CORPORATION (Registrant) |
| | | | | | |
| | | | BY: | | /s/ DAVID M. WATHEN |
| DATE: | February 26, 2016 | | | | Name: David M. Wathen Title: President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
| | | | |
| Name | | Title | | Date |
| | | | | |
| /s/ DAVID M. WATHEN | | President and Chief Executive Officer | | February 26, 2016 |
| David M. Wathen | | (Principal Executive Officer) and Director | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ ROBERT J. ZALUPSKI | | Chief Financial Officer | | February 26, 2016 |
| Robert J. Zalupski | | (Principal Financial Officer) | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ PAUL A. SWART | | Vice President Business Planning, Controller and Chief Accounting Officer | | February 26, 2016 |
| Paul A. Swart | | (Principal Accounting Officer) | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ SAMUEL VALENTI III | | Chairman of the Board of Directors | | February 26, 2016 |
| Samuel Valenti III | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ MARSHALL A. COHEN | | Director | | February 26, 2016 |
| Marshall A. Cohen | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ RICHARD M. GABRYS | | Director | | February 26, 2016 |
| Richard M. Gabrys | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ NANCY S. GOUGARTY | | Director | | February 26, 2016 |
| Nancy S. Gougarty | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ EUGENE A. MILLER | | Director | | February 26, 2016 |
| Eugene A. Miller | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ HERBERT K. PARKER | | Director | | February 26, 2016 |
| Herbert K. Parker | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ NICK L. STANAGE | | Director | | February 26, 2016 |
| Nick L. Stanage | | | | |
| | | | | |
| /s/ DANIEL P. TREDWELL | | Director | | February 26, 2016 |
| Daniel P. Tredwell | | | | |
SCHEDULE II
PURSUANT TO ITEM 15(a)(2)
OF FORM 10-K VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS FOR THE YEARS ENDED
December 31, 2015, 2014 AND 2013
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | ADDITIONS | | | | |
| DESCRIPTION | | BALANCE AT BEGINNING OF PERIOD | | CHARGED TO COSTS AND EXPENSES | | CHARGED (CREDITED) TO OTHER ACCOUNTS(A) | | DEDUCTIONS(B) | | BALANCE AT END OF PERIOD |
| Allowance for doubtful accounts deducted from accounts receivable in the balance sheet | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2015 | | $ | 2,220,000 |
| | $ | 2,380,000 |
| | $ | (40,000 | ) | | $ | 850,000 |
| | $ | 3,710,000 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | | $ | 1,300,000 |
| | $ | 2,200,000 |
| | $ | 80,000 |
| | $ | 1,360,000 |
| | $ | 2,220,000 |
|
| Year ended December 31, 2013 | | $ | 1,260,000 |
| | $ | 160,000 |
| | $ | 70,000 |
| | $ | 190,000 |
| | $ | 1,300,000 |
|
________________________________________
| |
(A) | Allowance of companies acquired, and other adjustments, net. |
| |
(B) | Deductions, representing uncollectible accounts written-off, less recoveries of amounts written-off in prior years. |
Item 15. Exhibits.
Exhibits Index:
|
| |
| 2.1(p) | Purchase Agreement dated as of February 24, 2012, among Rieke-Arminak Corp., HRA Holding Corporation, NC Holding, LLC, Helga Arminak, Armin Arminak, Roger Abadjian and Arminak & Associates, LLC.** |
| 2.2(x) | Purchase Agreement dated as of March 11, 2014, among Rieke-Arminak Corp., HRA Holding Corporation, NC Holding, LLC, Helga Arminak, Armin Arminak, Roger Abadjian, and Arminak & Associates, LLC.** |
| 2.3(ab) | Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of September 19, 2014, among TriMas UK Aerospace Holdings Limited, TriMas Corporation, Allfast Fastening Systems, Inc., The James and Eleanor Randall Trust dated June 1, 1993 and James H. Randall.** |
| 2.4(ac) | Separation and Distribution Agreement, dated as of June 30, 2015, by and between Horizon Global Corporation and TriMas Corporation.** |
| 3.1(e) | Fourth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of TriMas Corporation. |
| 3.2(l) | Third Amended and Restated By‑laws of TriMas Corporation. |
| 10.1(a) | Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of May 17, 2002, among Heartland Industrial Partners, L.P., TriMas Corporation and Metaldyne Company LLC. |
| 10.2(d) | Amendment No. 1 to Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of August 31, 2006, among Heartland Industrial Partners, L.P., TriMas Corporation and Metaldyne Corporation. |
| 10.3(f) | Amendment No. 2 to Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of November 27, 2006, among Heartland Industrial Partners, L.P., TriMas Corporation and Metaldyne Corporation. |
| 10.4(b) | Asset Purchase Agreement dated as of May 9, 2003, among TriMas Corporation, Metaldyne Corporation and Metaldyne Company LLC. |
| 10.5(v) | Credit Agreement, dated October 16, 2013, by and among TriMas Corporation, TriMas Company LLC and JPMorgan Chase bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent and Collateral Agent, and the various lenders from time to time thereto. |
| 10.6(ab) | Incremental Facility Agreement and Amendment dated as of October 17, 2014, among TriMas Company LLC, the other Loan Parties party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, the Incremental Tranche A Term Lenders and the other Lenders party thereto. |
| 10.7(ac) | Replacement Facility Amendment, dated as of June 30, 2015, among TriMas Company LLC, the other Loan Parties party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the Lenders party thereto. |
| 10.8(j) | Amended and Restated Receivables Purchase Agreement dated as of December 29, 2009, among TriMas Corporation, the Sellers named therein and TSPC, Inc. as Purchaser. |
| 10.9(n) | Amendment No. 1 dated as of September 15, 2011 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Purchase Agreement. |
| 10.10(q) | Amendment No. 2 dated as of December 21, 2011 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Purchase Agreement. |
| 10.11(q) | Amendment No. 3 dated as of June 29, 2012 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Purchase Agreement. |
| 10.12(y) | Amendment No. 4 dated as of April 17, 2014 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Purchase Agreement. |
| 10.13(ad) | Amendment No. 5, effective as of February 28, 2015, to the Amended and Restated Receivables Purchase Agreement. |
| 10.14(af) | Amendment No. 6, effective as of June 29, 2015, to the Amended and Restated Receivables Purchase Agreement. |
| 10.15(n) | Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement dated as of September 15, 2011, among TSPC, Inc., as Transferor, TriMas Corporation, as Collection Agent, TriMas Company LLC, as Guarantor, the persons party thereto from time to time as Purchasers and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as LC Issuer and Administrative Agent. |
| 10.16(q) | Amendment No. 1 dated as of June 29, 2012 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement. |
|
| |
| 10.17(r) | Amendment No. 2 dated as of December 17, 2012 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement. |
| 10.18(y) | Amendment No. 3 dated as of April 17, 2014 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement. |
| 10.19(ah) | Amendment No. 4 dated as of November 26, 2014 to the Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement. |
| 10.20(ad) | Amendment No. 5, effective as of February 28, 2015, to the Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement. |
| 10.21(af) | Amendment No. 6, effective as of June 29, 2015, to the Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement. |
| 10.22 | Amendment No. 7, effective as of December 16, 2015, to the Amended and Restated Receivables Transfer Agreement. |
| 10.23(y) | Second Amended and Restated Fee Letter dated as of April 17, 2014, among Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, TSPC, Inc., as Transferor, TriMas Corporation, as Collection Agent, TriMas Company LLC, as Guarantor, and the persons from time to time party thereto as Purchasers. |
| 10.24(ah) | Third Amended and Restated Fee Letter dated as of November 26, 2014, among Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, TSPC, Inc., as Transferor, TriMas Corporation, as Collection Agent, TriMas Company LLC, as Guarantor, and the persons from time to time party thereto as Purchasers. |
| 10.25 | Fourth Amended and Restated Fee Letter dated as of June 29, 2015, among Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, TSPC, Inc., as Transferor, TriMas Corporation, as Collection Agent, TriMas Company LLC, as Guarantor, and the persons from time to time party thereto as Purchasers. |
| 10.26 | Fifth Amended and Restated Fee Letter dated as of December 16, 2015, among Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, TSPC, Inc., as Transferor, TriMas Corporation, as Collection Agent, TriMas Company LLC, as Guarantor, and the persons from time to time party thereto as Purchasers. |
| 10.27(a) | TriMas Corporation 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.28(g) | First Amendment to the TriMas Corporation 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.29(g) | Second Amendment to the TriMas Corporation 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.30(g) | Third Amendment to the TriMas Corporation 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.31(g) | Fourth Amendment to the TriMas Corporation 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.32(c) | 2004 Form of Indemnification Agreement.* |
| 10.33(k) | TriMas Corporation 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan Composite Plan Document.* |
| 10.34(h) | TriMas Corporation Long Term Equity Incentive Plan Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement.* |
| 10.35(i) | Flexible Cash Allowance Policy.* |
| 10.36(m) | 2011 TriMas Corporation Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.37(t) | Amendment No. 1 to the TriMas Corporation 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.38(o) | Form of Performance Unit Agreement - 2012 LTI - under the 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.39(o) | Form of Performance Unit Agreement - 2012 LTI - under the 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.40(o) | Form of Performance Stock Unit Agreement - 2012 LTI - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.41(o) | Form of Restricted Share Agreement - 2012 LTI - under the 2002 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.42(o) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2012 LTI - under the 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.43(o) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2012 LTI - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.44(s) | Form of Performance Stock Unit Agreement - 2013 LTI - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.45(s) | Form of Performance Unit Agreement - 2013 LTI - under the 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.46(s) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2013 LTI - under the 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.47(s) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2013 LTI - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
|
| |
| 10.48(s) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2013 LTI (Board of Directors) - under the 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.49(z) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2014 LTI (One-Year Vest) - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.50(z) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2014 LTI - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.51(z) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement - 2014 LTI (Board of Directors) - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.52(z) | Form of Performance Stock Unit Agreement - 2014 LTI - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.53(ad) | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement - 2015 (One-Year Vest) - under the 2006 Long Term Equity Incentive Plan.* |
| 10.54(ad) | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement - 2015 (Board of Directors) - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.55(ad) | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement - 2015 (One-Year Vest) - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.56(ad) | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement - 2015 (Three-Year Vest) - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.57(ag) | Form of Performance Stock Unit Award - 2014 LTI (Second Half) - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.58(ag) | Form of Performance Stock Unit Award - 2015 LTI - under the 2011 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan.* |
| 10.59(u) | Executive Severance / Change of Control Policy.* |
| 10.60(aa) | Letter Agreement dated as of August 12, 2014, between TriMas Corporation and Lynn Brooks.* |
| 10.61(w) | 2013 Form of Indemnification Agreement.* |
| 10.62(ae) | Settlement Agreement, dated as of February 24, 2015, by and among TriMas Corporation and Engaged Capital Master Feeder I, LP, Engaged Capital Master Feeder II, LP, Engaged Capital I, LP, Engaged Capital I Offshore, Ltd., Engaged Capital II, LP, Engaged Capital, LLC, Engaged Capital Holdings, LLC, Glenn Welling and Herbert Parker. |
| 10.63(ac) | Tax Sharing Agreement, dated as of June 30, 2015, by and between Horizon Global Corporation and TriMas Corporation. |
| 10.64(ac) | Employee Matters Agreement, dated as of June 30, 2015, by and between Horizon Global Corporation and TriMas Corporation. |
| 10.65(ac) | Transition Services Agreement, dated as of June 30, 2015, by and between Horizon Global Corporation and TriMas Corporation. |
| 10.66(ac) | Noncompetition and Nonsolicitation Agreement, dated as of June 30, 2015, by and between Horizon Global Corporation and TriMas Corporation. |
| 10.67(af) | Consultant Services Agreement dated as of May 1, 2015 by and between Cequent Performance Products, Inc. and Velocity Consulting, LLC. |
| 21.1 | TriMas Corporation Subsidiary List. |
| 23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
| 31.1 | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act of 2002. |
| 31.2 | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act of 2002. |
| 32.1 | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act of 2002. |
| 32.2 | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes‑Oxley Act of 2002. |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document. |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
|
| |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
*Management contracts and compensatory plans or arrangements required to be filed as an exhibit pursuant to Item 15(b) of Form 10-K.
** Certain exhibits and schedules have been omitted and the Company agrees to furnish supplementally to the Securities and Exchange Commission a copy of any omitted exhibits and schedules upon request.
|
| | |
| (a) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed on October 4, 2002 (File No. 333-100351). |
| (b) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Registration Statement on Form S-4 filed June 9, 2003 (File No. 333-105950). |
| (c) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with Amendment No. 3 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1/A filed on June 29, 2004 (File No. 333-113917). |
| (d) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with Amendment No. 1 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on September 19, 2006 (File No. 333-136263). |
| (e) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on August 3, 2007 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (f) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on August 7, 2008 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (g) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 10, 2008 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (h) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on March 6, 2009 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (i) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on December 10, 2009 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (j) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on January 15, 2010 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (k) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on March 26, 2010 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (l) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on December 18, 2015 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (m) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on April 4, 2011 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (n) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on September 21, 2011 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (o) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on February 22, 2012 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (p) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on February 28, 2012 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (q) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on July 30, 2012 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (r) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on December 20, 2012 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (s) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on February 25, 2013 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (t) | | Incorporated by reference to Appendix A filed with our Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed on April 5, 2013 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (u) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on August 23, 2013 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (v) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on October 21, 2013 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (w) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Report on Form 8-K filed on November 13, 2013 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (x) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 17, 2014 (File No. 001-10716). |
|
| | |
| (y) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 22, 2014 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (z) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on April 29, 2014 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (aa) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 18, 2014 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (ab) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on October 20, 2014 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (ac) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 6, 2015 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (ad) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on April 28, 2015 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (ae) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 25, 2015 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (af) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on August 4, 2015 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (ag) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on October 29, 2015 (File No. 001-10716). |
| (ah) | | Incorporated by reference to the Exhibits filed with our Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on February 26, 2014 (File No. 001-10716). |
 ______________
______________