UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
Annual Report Pursuant To Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
For the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2014
Commission File No. 001-32632
UROPLASTY, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its Charter)
| Minnesota | 41-1719250 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
5420 Feltl Road
Minnetonka, Minnesota 55343
(Address of principal executive offices)
(952) 426-6140
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered under Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act:
| Title of class | Name of Exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, $.01 par value | NASDAQ |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
YES o NO x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act.
YES o NO x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. YES x NO o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 229.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
YES x NO o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large Accelerated Filer o | Accelerated Filer x | Non-Accelerated Filer o | Smaller Reporting Company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
YES o NO x
The aggregate market value of the voting stock and nonvoting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked prices of such common equity, as of September 30, 2013 was $64,961,799.
As of May 30, 2014, the registrant had 22,013,835 shares of common stock outstanding.
Documents Incorporated By Reference: Portions of our Proxy Statement for our 2014 Annual Meeting of Shareholders (the “Proxy Statement”), are incorporated by reference in Part III.
| Item | Description | Page | ||
| PART I | ||||
| 1. | 3 | |||
| 1A. | 14 | |||
| 1B. | 21 | |||
| 2. | 22 | |||
| 3. | 22 | |||
| 4. | 22 | |||
| PART II | ||||
| 5. | 22 | |||
| 6. | 24 | |||
| 7. | 24 | |||
| 7A. | 32 | |||
| 8. | 32 | |||
| 9. | 32 | |||
| 9A. | 32 | |||
| 9B. | 34 | |||
| PART III | ||||
| 10. | 35 | |||
| 11. | 35 | |||
| 12. | 35 | |||
| 13. | 35 | |||
| 14. | 35 | |||
| PART IV | ||||
| 15. | 35 |
References to “Uroplasty,” “Company,” “we,” “our” or “us” in this report refer to Uroplasty, Inc. and its subsidiaries.
This report contains references to among others, our trademarks Urgent PC® Neuromodulation System and Urgent® for our neuromodulation product, Macroplastique® Implants for our urological tissue bulking products, VOX® for our otolaryngology tissue bulking products, PTQ® for our colorectal tissue bulking and Uroplasty® for our company. All other trademarks or trade names referred to in this report are the property of their respective owners.
Our fiscal year-end always ends March 31. References in this report to a particular year generally refer to the applicable fiscal year. For example, references to “2014,” “Fiscal 2014” or “the year ended March 31, 2014” mean the fiscal year ended March 31, 2014.
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains “forward-looking statements” relating to projections, plans, objectives, estimates, and other statements of future performance. These forward-looking statements are subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties relating to our future performance that may cause our actual results, performance, achievements, or industry results, to differ materially from those expressed or implied in any such forward-looking statements. Our business operates in highly competitive markets and our operating results and the achievement of the forward-looking statements may be impacted by changes in general economic conditions, competition, reimbursement levels, customer and market preferences, government regulation, tax regulation, foreign exchange rate fluctuations, the degree of market acceptance of products, the uncertainties of potential litigation, and other matters detailed in the “Risk Factors” contained in Item IA of this report.
We do not undertake nor assume any obligation to update any forward-looking statements that we may make from time to time.
We are a medical device company that develops, manufactures and markets innovative, proprietary products for the treatment of voiding dysfunctions. You can access, free of charge, our filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including our annual report on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and any other amendments to those reports, at our website www.uroplasty.com, or at the Commission’s website at www.sec.gov.
Our primary focus is on two products: the Urgent PC® Neuromodulation System (“Urgent PC System”), which we believe is the only commercially available Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) cleared, minimally-invasive, neuromodulation system that delivers percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (“PTNS”) for office-based treatment of overactive bladder (“OAB”) and the associated symptoms of urinary urgency, urinary frequency, and urge incontinence; and Macroplastique® Implants (“Macroplastique”), an injectable, urethral bulking agent for the treatment of adult female stress urinary incontinence primarily due to intrinsic sphincter deficiency (“ISD”). Our Urgent PC System has CE Mark for the treatment of OAB as well as the treatment of fecal incontinence. Macroplastique also has CE Mark for the treatment of adult female stress urinary incontinence as well as male stress incontinence, fecal incontinence, vocal cord rehabilitation and vesicoureteral reflux. While our focus is on commercializing our Urgent PC System and Macroplastique in the United States and Europe, each of these products has market clearance in approximately 15 countries outside of this focus area.
Our primary focus is on growth in the U.S. market, which we entered in 2005 with our Urgent PC System. Prior to that time, essentially all of our business involved the sale of Macroplastique and other products outside of the U.S. We believe the U.S. market presents a significant opportunity for growth in sales of our products.
Our Urgent PC System uses a percutaneous stimulation method to deliver electrical pulses to the tibial nerve which has an effect on the sacral nerve plexus, a control center for bladder function. We have received regulatory clearances for sale of our Urgent PC System in the United States, Canada and Europe. We have intellectual property rights relating to key aspects of our neuromodulation therapy.
We have sold Macroplastique for urological indications in over 40 countries outside the United States since 1991. In October 2006, we received from the FDA pre-market approval for the use of Macroplastique to treat adult female stress urinary incontinence. We began marketing Macroplastique in the United States in 2007.
We believe physicians prefer our products because they offer effective therapies for patients that can be administered in office or outpatient surgical-based settings and, to the extent reimbursement is available, provide the physicians a profitable revenue stream. We believe patients prefer our products because they are minimally invasive treatment alternatives that do not have the side effects associated with pharmaceutical treatment options nor the morbidity associated with surgery.
Our sales are and have been significantly influenced by the availability of third-party reimbursement for PTNS treatments. Effective January 2011, the American Medical Association (“AMA”) granted a Category 1 Current Procedural Terminology (“CPT”) code for PTNS treatments. As a result, we expanded our U.S. field sales and support organization from 15 employed sales representatives and six independent manufacturer’s representatives on April 1, 2010 to 43 employed sales representatives on March 31, 2014, and sales of our Urgent PC System have begun to increase. As of March 31, 2014, we also employed 6 field based clinical support specialists and 5 Regional Sales Directors.
We have focused our efforts on expanding reimbursement coverage with Medicare carriers and private payers by instituting a comprehensive program to educate their medical directors regarding the clinical effectiveness, cost effectiveness and patient benefits of PTNS treatments using our Urgent PC System. As of May 1, 2014, regional Medicare carriers covering 40 states and the District of Columbia, with approximately 40 million covered lives, provide coverage for PTNS treatments. In addition, we estimate that private payers insuring approximately 119 million lives provide coverage for PTNS treatments. As of May 1, 2014, only one regional Medicare carrier representing 10 states, with approximately 10 million covered lives, continued to decline reimbursement coverage for PTNS treatments. Increasing coverage from private payers, as well as obtaining reimbursement from the sole regional Medicare carrier not to provide coverage for PTNS, is a key element of our strategy.
During Fiscal 2014, significant management changes occurred. In April, our Chief Executive Officer resigned, and we appointed Robert Kill as our interim Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”). Mr. Kill became our President and CEO in July 2013. We also have new leaders in sales, marketing, finance, research and development, clinical affairs and healthcare affairs. This team has expertise in medical devices and in urology, as well as experience in growing businesses.
We expect to continue to emphasize sales of our Urgent PC System in the United States and internationally. In fiscal 2014, we implemented new sales strategies and refocused the sales organization. We will continue to emphasize generating greater patient and physician awareness of our Urgent PC system, and on training physicians in the proper use and clinical benefits of our Urgent PC System for overactive bladder. As part of this process, we intend to hire additional clinical support specialists in some of our markets during fiscal 2015 and plan to expand our call point beyond our historical focus on urologists. Specifically, we plan to expand our call point to include gynecologists, urogynecologists and a highly targeted group for primary care physicians who are high prescribers of OAB medications as we look to accelerate the growth of our Urgent PC System. We do not expect to see significant growth in our Macroplastique business, because we believe it is a small, mature market that is more competitively penetrated than the market for OAB treatment using PTNS.
Another key focus in fiscal 2015 will be investments in research and development to build our product pipeline. Our pilot clinical trial for fecal incontinence in the United States using our Urgent PC System is well underway, and we plan to investigate other potential indication expansions in the pelvic health area. We will also seek to expand our product portfolio through business development activities. Our focus will be on capitalizing upon our leverage at the call point created by our strong distribution channel.
Both of our products are targeted at the market for treatment of voiding dysfunctions and address overlapping submarkets. Voiding dysfunctions affect urinary or bowel control and can result in uncontrolled bladder or bowel sensations (overactive bladder or bowel urgency) or unwanted leakage (urinary or fecal incontinence).
We believe that over the next several years a number of key demographic and technological factors will accelerate growth in the market for medical devices to treat OAB symptoms and other urinary and bowel voiding dysfunctions. These factors include the following:
Symptoms. For individuals with overactive bladder symptoms, the nervous system control for bladder filling and urinary voiding is incompetent. For OAB patients, signals to indicate a full bladder are sent early and frequently, triggers to allow the bladder to relax for filling are ineffective, and nervous controls of the urethral sphincter to keep the bladder closed until an appropriate time are inadequate. An individual with OAB may exhibit one or all of the symptoms that characterize overactive bladder: urinary urgency, urinary frequency and urge incontinence. Urgency is the strong, compelling need to urinate and frequency is a repetitive need to void. For most individuals, normal urinary voiding is approximately eight times per day while individuals with OAB may seek to void over 20 times per day and more than two times during the night. Urge incontinence refers to the involuntary loss of urine associated with an abrupt, strong desire to urinate that typically results in an accident before the individual can reach a restroom.
Treatment of Symptoms. When patients seek treatment for OAB, physicians normally start with conservative therapies such as biofeedback and behavioral modification. When, as is often the case, these therapies are not entirely successful, the next treatment of choice is drug therapy. If, as is the case with a majority of the patients, the drug therapy is ineffective or cannot be tolerated by the patient, the physicians suggest other treatments. For those patients, we believe the minimally invasive Urgent PC treatments offer an alternative to the more invasive treatments such as surgery, implantation of a sacral nerve stimulation device, or injection of OnabotulinumtoxinA into the bladder.
Biofeedback and Behavioral Modification. Bladder training, scheduled voiding techniques and pelvic floor training, often accompanied by the use of voiding diaries, are non-invasive approaches to managing OAB. These techniques are seldom completely effective because they rely on the diligence of and compliance by the individual. In addition, these techniques may not affect the underlying cause of the condition.
Drug Therapy. The most common treatment for OAB is drug therapy using an anticholinergic agent. However, for many patients, drugs are ineffective or the side effects are so bothersome that they discontinue the medications. Common side effects include dry mouth, dry eyes, constipation, cognitive changes and blurred vision.
Neuromodulation. Normal urinary control is dependent upon properly functioning neural pathways and coordination among the central and peripheral nervous systems, the nerve pathways, the bladder and the sphincter. Unwanted, uncoordinated or disrupted signals along these pathways can lead to OAB symptoms. Therapy using neuromodulation incorporates electrical stimulation to target specific neural tissue and modulate the generation of unwanted signals. To alter bladder function, neuromodulation must affect the sacral nerve plexus, which innervates the bladder and pelvic floor. This type of neuromodulation to treat OAB may be provided by a surgically implanted sacral nerve stimulation device by the non-surgical PTNS procedure delivered by our Urgent PC System in a physician’s office.
OnabotulinumtoxinA. OnabotulinumtoxinA, marketed under the name of BOTOX, is a prescription medicine that is injected into the bladder. One BOTOX treatment can last up to six months before the effects wear off, with the need then to repeat the procedure. However, BOTOX may cause serious side effects that can be life threatening. In addition, due to the risk of urinary retention (not being able to empty the bladder), only patients who are willing and able to initiate self-catheterization post-treatment, if required, are considered for treatment. We believe many patients may be more inclined to elect a treatment for OAB with less significant potential adverse events.
The Uroplasty Solution: The Urgent PC System. Our Urgent PC System is a minimally invasive nerve stimulation device designed for office-based treatment of OAB and the associated symptoms of urge incontinence, urinary urgency and urinary frequency. Using a small-gauge needle electrode inserted above the ankle, our Urgent PC System delivers electrical impulses to the tibial nerve that affect the sacral nerve plexus, a control center for pelvic floor and bladder function.
We believe that our Urgent PC System is the only commercially available FDA-cleared PTNS device in the United States market for treatment of OAB. Components of our Urgent PC System include a hair-width needle electrode, a lead set and an external, handheld, battery-powered stimulator. For each 30-minute office-based therapy session, the physician or other qualified health care provider inserts the needle electrode above the ankle and connects the electrode to the stimulator. Typically, a patient undergoes a course of 12 consecutive weekly treatments, and, subsequently, a personal treatment plan of single treatments at lesser frequency to sustain the therapeutic effect.
Symptoms and Prevalence. Urinary incontinence is defined as the involuntary loss of urine, and is the result of either bladder or urethral dysfunction. In 2007, the US Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases reported that, depending on the definition of urinary incontinence used, 5% to 50% of the adult U.S. population suffers from some form of urinary incontinence. The prevalence of urinary incontinence increases with advancing age, and the prevalence of the U.S. population with urinary incontinence is expected to grow over the next decades as the U.S. population ages. Urinary incontinence often results in social isolation, depression, and poor self-rated health and quality of life, and is a significant medical condition with considerable public health impact.
Causes of Urinary Incontinence. The mechanisms of urinary continence are complex and involve the interaction among several anatomical structures. Urinary continence is controlled by the urinary sphincteric mechanism, the pelvic floor support structures and the nervous system. The sphincter muscle surrounds the urethra and provides constrictive pressure to prevent urine from flowing out of the bladder, especially with increased intra-abdominal pressure. In healthy individuals, urination occurs when the nervous system signals the sphincter to relax as the bladder contracts, allowing urine to flow through the urethra. Incontinence may result when one or more parts of this complex mechanism fails to function as intended. Incontinence may be caused by tissue damage during childbirth, pelvic trauma, pelvic surgery, pelvic organ prolapse, spinal cord injuries, neurological diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis and poliomyelitis), birth defects (e.g., spina bifida) and degenerative changes associated with aging.
Types of Urinary Incontinence. Per the American Urological Association (“AUA”), there are three types of urinary incontinence:
| · | Overflow Incontinence — Overflow incontinence is associated with an over-distention of the bladder. This can be the result of an under-active bladder or an obstruction in the bladder or urethra. |
Per the AUA, stress and urge incontinence often coexist resulting in mixed incontinence.
Treatments. There are two general approaches to dealing with urinary incontinence. One approach is to manage symptoms, such as through absorbent products, catheters, behavior modification and drug therapy. The other approach is to undergo curative treatments in an attempt to restore continence, such as injection of urethral bulking agents or surgery, or a combination of the two. We believe that patients prefer less invasive treatments that provide the most benefit and have little or no side effects.
Injectable Bulking Agents. Urethral bulking agents (“UBAs”) are injected into the area around the urethra, to augment the surrounding tissue for increased capacity to control the release of urine for patients with SUI. Hence, these materials are often called “bulking agents” or “injectables” and are an attractive alternative to surgery because they are considerably less invasive, offer a quick recovery, and do not require the use of an operating room for placement; UBAs can be implanted in an office or out-patient facility. Additionally, the use of a UBA does not preclude the subsequent use of more invasive treatments if required. Furthermore, UBAs may be used to resolve lingering symptoms for patients who have undergone certain more invasive treatments, such as mid-urethral slings, which failed to completely resolve the stress urinary incontinence conditions.
Surgery. In women, SUI may be corrected through surgery with a mid-urethral sling which provides a hammock-type support for the urethra to prevent its downward movement and the associated leakage of urine.
The Uroplasty Solution: Macroplastique Implants. Macroplastique is used to treat adult female stress urinary incontinence due to ISD. It is designed to restore the patient’s urinary continence immediately following treatment. Macroplastique is a soft-textured, permanent implant injected, under endoscopic visualization, around the urethra distal to the bladder neck. It is a proprietary composition of heat vulcanized, solid, soft, irregularly shaped polydimethylsiloxane (solid silicone elastomer) implants suspended in a biocompatible excretable carrier gel. We believe our compound is better than other commercially available bulking agents because, with its unique composition, shape and size, it does not degrade, is not absorbed into surrounding tissues and does not migrate from the implant site.
We have sold Macroplastique for several urological indications in over 40 countries outside the United States since 1991. In October 2006, we received FDA pre-market approval for the use of Macroplastique to treat adult female SUI due to ISD. We began marketing Macroplastique in the United States in early 2007.
Macroplastique® for Vesicoureteral Reflux. Outside the U.S., we market our Macroplastique products for treatment of vesicoureteral reflux: the abnormal backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureters or kidneys that is most prevalent in infants and children where the ureters did not fully develop. In this application, a bolus of the elastomer implant is injected around the orifice or valve where the ureter enters the bladder.
PTQ® Implants. We also market our silicone elastomer implants under the name PTQ® Implants outside of the U.S. as a minimally invasive product to address fecal incontinence (sometimes referred to as bowel incontinence). Our PTQ Implants offer minimally-invasive, soft-textured permanent implant for treatment of fecal incontinence. PTQ is implanted circumferentially into the submucosa of the anal canal, creating a “bulking” and supportive effect around the anal sphincter. PTQ is CE marked and currently sold outside the United States in various international markets.
Urgent PC for Fecal Incontinence. Our Urgent PC System is CE marked and sold outside of the United States for the treatment of fecal incontinence. We also intend to explore the commercialization of our Urgent PC System for this application in the U.S. and started on a multiyear pilot clinical trial in fiscal 2013 as a prelude to a full clinical study for FDA clearance.
VOX® Implants. In addition to urological applications, we market our silicone elastomer bulking material outside the United States to help improve speech and swallowing function in patients with unilateral vocal cord paralysis. The implants are sold for vocal cord rehabilitation applications under the trade name VOX® Implants.
Distributed Products. In The Netherlands and United Kingdom only, we distribute certain wound care products in accordance with a distributor agreement. Under the terms of the distributor agreement, we are not obligated to purchase any minimum level of wound care products.
Our goal is to become the leading provider of minimally invasive, office and outpatient surgical-based solutions to treat and improve the quality of life for patients suffering from the physical and emotional stress resulting from voiding dysfunction problems. We believe that with our Urgent PC System and Macroplastique products we can increasingly garner the attention of key physicians and distributors to grow our revenue. The key elements of our strategy are to:
| · | Educate physicians and third-party insurance carriers about the benefits of our Urgent PC System. We believe education of physicians and third-party insurance carriers regarding the benefits of our Urgent PC System is critical to the successful adoption of this System, and to reimbursement for treatments by third-party carriers. To this end, we have conducted clinical studies which we believe will help us with our sales and marketing efforts. |
We are focusing our sales and marketing efforts primarily on urologists, urogynecologists and gynecologists with significant office-based and outpatient surgery-based patient volume.
To support our business in the United States, we have a sales organization, consisting primarily of 43 direct field sales representatives, 5 Regional Sales Directors, 6 clinical specialists, a marketing organization to market our products directly to our customers and a reimbursement department. We anticipate further increasing our sales and marketing organization in the United States, as needed, to support our sales growth.
Outside of the United States, we sell our products primarily through a direct sales organization in the United Kingdom, The Netherlands, Switzerland and the Nordic countries, and in all other markets primarily through distributors. Each of our distributors has a territory-specific distribution agreement, including requirements indicating they may not sell products that compete directly with ours. Collectively, distributors accounted for approximately 13%, 14% and 17% of our total net sales for fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
We use clinical studies and worldwide scientific community awareness programs to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our products. This data is important to obtain regulatory approval and to support our sales staff and distributors in securing product reimbursement in their territories. Publications of clinical data in peer-reviewed journals and presentations at professional society meetings by clinical researchers add to the scientific community awareness of our products, including patient indications, treatment technique and expected outcomes. We provide a range of activities designed to support physicians in their clinical research.
In the United States as well as in foreign countries, sales of our products depend in significant part on the availability of reimbursement from third-party payers. In the United States, third-party payers consist of government programs such as Medicare, private health insurance plans, managed care organizations and other similar programs. For any product, three factors are critical to reimbursement:
| • | coding, which ensures uniform descriptions of procedures, diagnoses and medical products; |
| • | coverage, which is the payer’s policy describing the clinical circumstances under which it will pay for a given treatment; and |
| • | payment processes and amounts. |
We believe the availability of a Category 1 CPT code for PTNS treatments has encouraged, and will continue to encourage, broader coverage and subsequent use of our Urgent PC System in the U.S. However, each governmental and private payer makes its own coverage decision.
We have focused our efforts on expanding reimbursement coverage with Medicare carriers and private payers by instituting a comprehensive program to educate their medical directors regarding the clinical effectiveness, cost effectiveness and patient benefits of PTNS treatments using our Urgent PC System. As of May 1, 2014, regional Medicare carriers (“MACs”) covering 40 states and the District of Columbia, with approximately 40 million covered lives, provide coverage for PTNS treatments. In addition, we estimate that private payers insuring approximately 119 million lives provide coverage for PTNS treatments. As of May 1, 2014, only one regional Medicare carrier representing 10 states with approximately 10 million covered lives, continued to decline reimbursement coverage for PTNS treatments. This regional Medicare carrier had jurisdiction over two states at April 1, 2013, but due to consolidation of certain MACs, now has jurisdiction over ten states. In May 2014, National Government Services (“NGS”) re-affirmed its non-coverage policy for PTNS. We plan to continue to educate NGS Medical Directors about the benefits and positive outcomes of PTNS therapy.
The code under which PTNS is reimbursed was one of several hundred codes that the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (“CMS”) noted as a potentially misvalued code earlier this year. In November 2013, CMS indicated further review of PTNS is warranted, and as a result, CMS will be gathering additional feedback before a final decision is made. The final decision could result in an increase, a decrease or no change in the reimbursement rate for PTNS. Any change to the reimbursement rate due to this review is not expected to be published until November 2014 and will become effective beginning in January 2015.
In December 2013, the Blue Cross and Blue Shield (“BCBS”)Association Medical Advisory Panel concluded that use of PTNS for the treatment of voiding dysfunction meets their Technology Evaluation Center criteria. This panel is responsible for assessing medical technologies through a comprehensive review of clinical evidence. This positive assessment concluded that PTNS improves net health outcomes as much as, or more than, other established therapies and is strong validation of the acceptance of Urgent PC as an important treatment option for OAB. Currently, there are approximately 100 million lives covered by the 37 BCBS companies across the United States, with approximately 30 million lives as of May 1, 2014 having access to PTNS through positive coverage from their local plan. This decision can now be used by the remaining BCBS companies as an important tool in assessing positive coverage for PTNS for the treatment of overactive bladder.
Outside of the U.S., our Urgent PC System treatments are reimbursed under an available reimbursement code in the Netherlands. In other countries in Europe there are no specific reimbursement codes for Urgent PC System treatments and generally reimbursement is from fund-holder trusts or global hospital budgets.
We believe there are appropriate CPT codes available to describe the use of Macroplastique to treat adult female SUI due to ISD in the United States. Outside of the United States, government managed health care systems and private insurance control reimbursement for devices and procedures. Reimbursement systems in international markets vary significantly by country. In the European Union, reimbursement decision-making is neither regulated nor integrated at the European Union level. Each country has its own system, often closely protected by its corresponding national government. Reimbursement for Macroplastique has been successful in multiple international markets where hospitals and physicians have budgets approved by fund-holder trusts or global hospital budgets.
We subcontract the manufacturing of our Urgent PC System and its related components, and have a U.S. FDA-registered manufacturing facility in Minnetonka, Minnesota, where we manufacture all of our tissue bulking products. Our facility uses dedicated heating, cooling, ventilation and high efficiency particulate air filtration systems to provide cleanroom and other controlled working environments. Our trained technicians perform all critical manufacturing processes in qualified environments according to validated written procedures. We use qualified vendors to sterilize our products using validated methods.
Our U.S. manufacturing facility and systems are periodically audited by regulatory agencies and other authorities to ensure compliance with ISO 13485 (medical device quality management systems), applicable European and Canadian medical device requirements, as well as FDA’s Quality Systems Regulations. We also are subject to additional state, local, and federal government regulations applicable to the manufacture of our products. While we believe we are compliant with all applicable regulations, we cannot guarantee that we will pass each regulatory audit.
We purchase several medical grade materials and other components for use in our finished products from single source suppliers meeting our quality and other requirements. Although we believe our sources of supply could be replaced if necessary without undue disruption, it is possible that the process of qualifying new suppliers could cause an interruption in our ability to manufacture our products, which could have a negative impact on sales.
The market for voiding dysfunction products is intensely competitive. Competitors offer management and curative treatments, pharmaceutical products such as anticholinergic drugs, injectable drugs, implantables including neuromodulation devices, urethral injectables and urethral sling products. We believe the principal decision factors among treatment methods include severity of patient symptoms and procedure risk, physician and patient acceptance of the treatment method, cost, availability of third-party reimbursement, and marketing and sales coverage. In addition to adequately addressing the decision factors, our ability to compete in this market will also depend on the consistency of our product quality as well as delivery and product pricing. Other factors affecting our success include our product development and innovation capabilities, clinical study results, ability to obtain required regulatory approvals, ability to protect our proprietary technology, manufacturing and marketing capabilities and ability to attract and retain skilled employees.
PTNS. We believe our Urgent PC System offers a minimally invasive, office-based treatment alternative in the continuum of care for OAB patients. Conservative therapies such as dietary restrictions, pelvic floor exercises, bladder retraining, biofeedback, and anticholinergic drugs usually precede our Urgent PC System treatments. Anticholinergic medications that could be seen as competing with PTNS include Detrol® and Toviaz® (both by Pfizer Inc.); Ditropan® (Johnson & Johnson); Enablex® (Novartis AG); Sanctura® (Allergan, Inc.) and Vesicare® (GlaxoSmithKline plc). These medications treat symptoms of OAB, some by preventing unwanted bladder contractions and others by tightening the bladder or urethra muscles or by relaxing bladder muscles. We believe our Urgent PC System normally is prescribed after these drugs are used but discontinued because they were ineffective or had unwanted side effects. In the case of anticholinergic medications, the side effects often include dry eyes, dry mouth, constipation, cognitive changes and blurred vision.
Allergan, Inc. recently began to commercialize Botulinum toxin A (Botox®) for OAB treatments, and this treatment is a direct competitor for our Urgent PC System following unsuccessful drug therapy. In this procedure, Botox is injected in and around the urethra, often with approximately twenty individual injection sites, to numb and mask the symptoms of urgency and frequency. Nevertheless, although we believe that marketing campaigns by Allergan, Inc. will increase awareness of OAB, we also believe that the side effects of Botox injections for this application, which can include urinary retention and urinary tract infection, will lead many patients to choose our less invasive solution.
The Medtronic InterStim neuromodulation device, which stimulates the sacral nerve, requires surgical implantation of a lead near the patient’s spine in addition to a battery powered stimulator in the buttocks. In contrast, our Urgent PC System allows minimally invasive stimulation of the sacral nerve plexus in an office-based setting without any surgical intervention. Other companies may also enter the U.S. market with neuromodulation or other products for the treatment of OAB.
Bulking. Injectable urethral bulking agents for SUI competing directly with Macroplastique in the United States include: Durasphere® manufactured by Carbon Medical Technologies, Inc. and distributed by Coloplast Corp; and Coaptite® manufactured by Merz Aesthetics, Inc. and distributed by Boston Scientific Corporation. We believe Macroplastique competes favorably against these products because it will not degrade, resorb or migrate, has no special preparation or storage requirements, and is safe and effective for treating adult female stress urinary incontinence.
Outside of the United States, Deflux® (manufactured by Q-Med AB, a wholly owned subsidiary of Galderma S.A., and distributed by Salix Pharmaceuticals, Ltd.) and Bulkamid® (manufactured by Contura, Inc., Denmark and distributed by Johnson & Johnson) compete with Macroplastique for vesicoureteral reflux and SUI, respectively.
Many of our competitors and potential competitors have significantly greater financial, manufacturing, marketing and distribution resources than us. In addition, many of our competitors offer broader product lines within the urology market, which may give these competitors the ability to negotiate exclusive, long-term supply contracts and to offer comprehensive pricing for their products. It is possible other large health care and consumer products companies may enter this industry in the future. Furthermore, smaller companies, academic institutions, governmental agencies and other public and private research organizations will continue to conduct research, seek patent protection and establish arrangements for commercializing products. These products may compete directly with any products that we may offer in the future.
The testing, manufacturing, promotion, marketing and distribution of our products in the United States, Europe and other parts of the world are subject to regulation by numerous governmental authorities, including the FDA, the European Union and other analogous agencies.
Our products are regulated in the United States as medical devices by the FDA under the Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act (FDC Act). Noncompliance with applicable requirements can result in, among other things:
Depending on the degree of risk posed by the medical device and the extent of controls needed to ensure safety and effectiveness, there are two pathways for FDA marketing clearance of medical devices. For devices deemed by FDA to pose relatively less risk (Class I or Class II devices), manufacturers, in most instances, must submit a pre-market notification requesting permission for commercial distribution, known as 510(k) clearance. Devices deemed by FDA to pose the greatest risk (Class III devices), such as life-sustaining, life-supporting or implantable devices, or a device deemed not to be substantially equivalent to a previously cleared 510(k) device, require the submission of a pre-market approval (PMA) application. The FDA can also impose restrictions on the sale, distribution or use of devices at the time of their clearance or approval, or subsequent to marketing.
In October 2005, our initial version of the Urgent PC System received 510(k) clearance for sale within the United States. In July 2006, our second generation Urgent PC System received 510(k) clearance for sale within the United States.
In October 2006, we received FDA pre-market approval for the use of Macroplastique to treat female stress urinary incontinence in the United States. As part of the FDA-approval process, we are conducting a customary post-market study.
| · | Quality System Regulations, which require manufacturers to follow design, testing, control, documentation and other quality assurance procedures during the manufacturing process; |
The FDC Act requires that medical devices be manufactured in accordance with FDA’s current Quality System Regulations, which require, among other things, that we:
| · | allow the FDA to inspect our manufacturing facilities on a periodic basis to monitor our compliance with Quality System Regulations. |
Our U.S. manufacturing facility and processes have been inspected and certified in compliance with ISO 13485, applicable European medical device directives and Canadian Medical Device Requirements.
The European Union has adopted rules that require that medical products receive the right to affix the CE mark, which stands for Conformité Européenne. The CE mark demonstrates adherence to quality standards and compliance with relevant European medical device directives. Products that bear the CE mark can be imported to, sold or distributed within the European Union.
Our initial version of the Urgent PC System received CE marking in November 2005. Our second generation Urgent PC System received CE mark approval and approval from the Canadian Therapeutic Products Directorate of Health in June 2006.
We received the CE mark approval for Macroplastique in 1996 for the treatment of male and female stress urinary incontinence and vesicoureteral reflux; for VOX in 2000 for vocal cord rehabilitation and; for PTQ in 2002 for the treatment of fecal incontinence. Our manufacturing facilities and processes have been inspected and certified by AMTAC Certification Services, a recognized Notified Body, a testing and certification firm based in the United Kingdom.
We currently sell our products in approximately 40 foreign countries, including those within the European Union. Requirements pertaining to medical devices vary widely from country to country, ranging from no health regulations to detailed submissions such as those required by the FDA. We have obtained regulatory approvals in countries where required of us to sell our products. We believe the extent and complexity of regulations for medical devices such as those produced by us are increasing worldwide. We anticipate that this trend will continue and that the cost and time required to obtain approval to market in any given country will increase.
We seek to establish and protect our proprietary technology using a combination of patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade secrets, and nondisclosure and non-competition agreements. We file patent applications for patentable technologies we consider important to the development of our business based on an analysis of the cost of obtaining a patent, the likely scope of protection, and the relative benefits of patent protection compared to trade secret protection, among other considerations.
We have obtained, by filing and by acquisition, various issued U.S. and foreign patents and pending patent applications related to electro-nerve stimulation. In addition, we hold U.S. and foreign patents covering soft-tissue bulking materials, processes and applications. While we believe that our patents adequately protect our technologies, there can be no assurance that any of our issued patents are of sufficient scope or strength to provide meaningful protection and that any of our pending patent applications will result in patents being issued to us. In addition, there can be no assurance that any of our current or future patents will not be challenged, narrowed, invalidated or circumvented by others, or that our patents will provide us with any competitive advantage. Any legal proceedings to maintain, defend or enforce our patent rights could be lengthy and costly, with no guarantee of success. Third parties could also hold patents that may require us to negotiate licenses to conduct our business, and there can be no assurance that the required licenses would be available on reasonable terms, or at all.
We also seek to protect our trade secrets by requiring employees, consultants, and other parties to sign confidentiality agreements and noncompetition agreements, and by limiting access by outside parties to confidential information. There can be no assurance that these measures will prevent the unauthorized disclosure or use of this information or that others will not be able to independently develop this information.
In the U.S. and throughout the European Union, we have registered “Uroplasty” as our Company name, “Urgent” for our neuromodulation product, “Macroplastique” for our urological tissue bulking products, “VOX” for our otolaryngology tissue bulking products, and “PTQ” for our colorectal tissue bulking products.
We have certain royalty agreements under which we pay royalties on sales of Macroplastique and the Macroplastique implantation needle-positioning device.
We have research and development projects and activities to develop, enhance and evaluate potential new products for which we incur costs for regulatory submissions, regulatory compliance and clinical research. Our expenditures for clinical research include studies for new applications or indications for existing products, post-approval regulatory compliance and marketing and reimbursement approval by third-party payers. Our expenditures for research and development totaled approximately $2.2 million, $2.4 million and $1.9 million for fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The medical device industry is subject to substantial litigation. We face an inherent risk of liability for claims alleging adverse effects to the patient. We currently carry $10 million of worldwide product liability insurance. However, we cannot assure you that our existing insurance coverage limits are adequate to protect us from liabilities we might incur. Product liability insurance is expensive and in the future may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. Furthermore, we do not expect to be able to obtain insurance covering our costs and losses as a result of any product recall. A successful claim in excess of our insurance coverage could materially deplete our assets. Moreover, any claim against us could generate negative publicity, which could decrease the demand for our products and our ability to generate revenues.
Compliance with Environmental Laws
Compliance by us with applicable environmental requirements during fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively has not had a material effect upon our capital expenditures, earnings or competitive position.
During fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, none of our customers individually accounted for 10% or more of our net sales.
We did not have significant backlog at fiscal year-end 2014, 2013 or 2012. We process customer orders generally within one or two days of receipt of the order.
As of March 31, 2014, we had 118 employees, of which 113 were full-time and 5 were part-time. No employee was subject to a collective bargaining agreement. We believe we maintain good relations with our employees.
We were incorporated in January 1992 as a Minnesota corporation and a wholly owned subsidiary of our original parent. In February 1995, we became a stand-alone, privately held company pursuant to a Plan of Reorganization confirmed by the U.S. Bankruptcy Court. We became a reporting company pursuant to a registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission in July 1996.
| Uroplasty BV | Incorporated in The Netherlands, distributes the Urgent PC Neuromodulation System, Macroplastique Implants, VOX Implants, PTQ Implants, all of their accessories, and wound care products. Products are sold primarily through our direct sales force in the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Switzerland and the Nordic countries, and through distributors in all other markets. |
| Uroplasty LTD | Incorporated in the United Kingdom and acts as the sole distributor of the Urgent PC Neuromodulation System, Macroplastique Implants, PTQ Implants, all of their accessories, and wound care products in the United Kingdom and Ireland. Products are sold primarily through a direct sales organization. |
Available Information
Our principal executive offices are located at 5420 Feltl Road, Minnetonka, Minnesota 55343. Our telephone number at this address is (952) 426-6140. Our website is located at www.uroplasty.com. The information contained on our website or connected to our website is not incorporated by reference into and should not be considered part of this report.
We make available, free of charge and through our Internet web site, our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments to any such reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Our operations are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties that may affect our financial results, our accounting, and the accuracy of the statements we make in this Form 10-K. For example, we make statements about our belief in the efficacy of our product, the impact of regulatory and reimbursement approvals on our products and revenues, trends in international regulation, the attributes of our products versus those of our competitors, the adequacy of our resources, including cash, available to us, and other matters all of which represent our expectations or beliefs about future events. Our actual results may vary from these expectations because of a number of factors that affect our business, the most important of which include the following:
We have incurred net losses in each of the last five fiscal years. As of March 31, 2014, we had an accumulated deficit of approximately $44 million primarily because of costs relating to the development, including seeking regulatory approvals, and commercialization of our products. We expect our operating expenses relating to sales and marketing activities, product development and clinical trials, including an FDA-mandated post-market clinical study for our Macroplastique product, will continue during the foreseeable future. To achieve profitability, we must generate substantially more revenue than we have in prior years. Our ability to achieve significant revenue growth will depend, in large part, on our ability to achieve widespread market acceptance and third-party reimbursement for our products and successfully expand our business in the U.S. We may never achieve substantial market acceptance, realize significant revenue from the sale of our products or be profitable.
The use and acceptance of our products is heavily dependent upon the availability of third-party reimbursement for the procedures in which our products are used.
In the United States, healthcare providers that purchase medical devices, including our products, generally rely on third-party payers, including Medicare, Medicaid, private health insurance carriers and managed care organizations, to reimburse all or part of the cost and fees associated with the procedures performed using these devices. The commercial success of our products will depend on the ability of healthcare providers to obtain adequate reimbursement from third-party payers for the procedures in which our products are used. Third-party payers are increasingly challenging the coverage and pricing of medical products and procedures.
Even if a procedure is eligible for reimbursement, the level of reimbursement may not be adequate to justify the use of our products. In addition, third-party payers may deny reimbursement if they determine that the device used in the treatment was not cost-effective or was used for a non-approved indication, particularly if there is not a published CPT code for reimbursement. For example, in 2009, the AMA advised the medical community that the previously recommended Category 1 CPT code for PTNS treatments should be replaced with an unlisted code. As a result, many third-party insurers delayed or denied reimbursement for PTNS treatments, significantly impacting the sales of our Urgent PC System, until a new code was effective in January 2011.
The availability of the Category 1 CPT code for PTNS treatments has encouraged broader use of our Urgent PC System, but it has not resulted in universal coverage and there can be no assurance that additional payers will agree to create coverage policies or that the policies, if they are created, will provide adequate reimbursement, that existing coverage will not again be challenged (as it was in fiscal 2009), or that government actions will not decrease the level of reimbursement.
Reimbursement and healthcare payment systems in international markets vary significantly by country, with some countries offering government-sponsored healthcare or private insurance, or both. In many countries where there is government-sponsored healthcare reimbursement, decisions are made by individual hospitals with the government setting an upper limit of reimbursement. In most foreign countries, there are also insurance systems that may offer payments for alternative procedures. We cannot be certain that we, or in countries in which we work with our distributors, will successfully and cost-effectively manage all of these payment systems.
All third-party reimbursement programs, whether government-funded or insured commercially, inside the United States or outside, are developing increasingly sophisticated methods of controlling health care costs through prospective reimbursement and capitation programs, group purchasing, redesign of benefits, second opinions, careful review of bills, encouragement of healthier lifestyles and exploration of more cost-effective methods of delivering healthcare. These types of programs can potentially limit the amount that healthcare providers may be willing to pay for medical devices and could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
In addition to the availability of third-party reimbursement, market acceptance of our products will depend on our ability to demonstrate the safety, clinical efficacy, perceived benefits, and cost-effectiveness of our products compared to products or treatment options of our competitors. We cannot assure you that we will be successful in educating the marketplace about the benefits of our products. Our Urgent PC System requires a new treatment protocol for the physicians and their staff to implement repeatedly. Even if customers accept our products, this acceptance may not translate into repeat sales if our customers do not fully adopt the new treatment protocol in their practice.
We are subject to changing federal and state regulations that could increase the cost of doing business or impose requirements with which we cannot comply
In response to perceived increases in health care costs in recent years, there have been and continue to be proposals by the federal government, state governments, regulators and third-party payers to control these costs and, more generally, to reform the U.S. healthcare system. Certain of these proposals could limit the prices we are able to charge for our products or the amounts of reimbursement available for our products and could limit the acceptance and availability of our products, adversely affecting our financial position and results of operations.
The 2010 Healthcare Reform Legislation imposes an excise tax on us that we may be unable to recoup, and requires cost controls that may impact the rate of reimbursement for our products.
Significant U.S. healthcare reform legislation, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as reconciled by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (collectively, the “PPACA”), was enacted into law in March 2010. Commencing January 1, 2013, the PPACA imposed on manufacturers or producers making sales of medical devices in the U.S., other than sales at retail for individual use, an excise tax. Our U.S. net sales, all subject to the excise tax, represented approximately 73% of our worldwide consolidated net sales in fiscal 2014 and we expect U.S. sales to continue to grow and become a greater proportion of our worldwide consolidated net sales. To the extent the clinics and physicians will not absorb increased costs represented by the tax because of reimbursement limitations, we likely will not be able to offset the tax with increased revenue. Accordingly, the new tax will adversely affect our business, cash flows and results of operations. Although several bills have been proposed in U.S. Congress to eliminate the tax, including a bill passed by the U.S. Senate, most of these bills are tied to corresponding increases in taxes from other sources, and therefore face substantial opposition.
The PPACA also contains provisions aimed at improving the quality and decreasing the costs of healthcare. The Medicare provisions include value-based payment programs, increased funding of comparative effectiveness research, reduced hospital payments for avoidable readmissions and hospital acquired conditions, and pilot programs to evaluate alternative payment methodologies that promote care coordination (such as bundled physician and hospital payments). Additionally, the PPACA includes a reduction in the annual rate of reimbursement growth for hospitals that began in 2011 and provides for the establishment of an independent payment advisory board to recommend ways of reducing the rate of growth in Medicare spending beginning in 2014. Many of these provisions will not be effective for a number of years and there are many programs and requirements for which the details have not yet been fully established. Accordingly, although it remains impossible to predict the extent of the regulation and the full impact of the PPACA, any changes that lower reimbursement for our products or reduce medical procedure volumes could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
The FDA has increased significantly the scrutiny applied to 510(k) submissions, and it may also focus more scrutiny on other regulation within its purview. Both the FDA and the United States Congress are influenced by high profile events, injuries and cases that generate publicity and public attention, and new legislation is often generated as a result of those events. There can be no assurance that new products we introduce will not be delayed by the current level of scrutiny applied to applications at the FDA or that new laws and regulations will not be adopted that impact the cost of production and marketing of our existing products.
If we are not able to attract, retain and motivate our sales force and expand our distribution channels, our sales and revenues will suffer.
In the U.S., we have a sales organization consisting primarily of direct sales representatives, and a marketing organization to market our products directly and support our distributor organizations. We expect to expand our sales and marketing organization, as needed, to support our growth. We have and will continue to incur significant additional expenses to support this organization. We cannot be certain that our sales organization will be able to generate sales of our Urgent PC System at levels that justify its expense, or even if it can, that we will be able to recruit, train, motivate or retain qualified sales and marketing personnel. Except for our direct sales organization in the United States, United Kingdom, The Netherlands, Switzerland and the Nordic countries, for other countries we sell our products through a network of independent distributors. Our ability to increase product sales in foreign markets will largely depend on our ability to develop and maintain relationships with our distributors and on their ability to successfully market and sell our products. We may not be able to retain distributors who are willing to commit the necessary resources to market and sell our products to the level of our expectations. Failure to maintain or expand our distribution channels or to recruit, retain and motivate qualified personnel could have a material adverse effect on our product sales and revenues.
The size and resources of our competitors may render it difficult for us to successfully compete in the marketplace.
Our products compete against similar medical devices and other treatment methods, including drugs, for treating voiding dysfunctions. Many of our competitors, which include some of the largest medical products and pharmaceutical companies in the world, have significantly greater financial, research and development, manufacturing and marketing resources than we have. Our competitors could use these resources to develop or acquire products that are safer, more effective, less invasive, less expensive or more readily accepted than our products. Their products could make our technology and products obsolete or noncompetitive. Our competitors could also devote greater resources to the marketing and sale of their products and adopt more aggressive pricing policies than we can.
We are primarily dependent on sales of two product lines and our business would suffer if sales of either of these product lines decline.
Currently, we are dependent on sales of our Urgent PC System and Macroplastique products. In fiscal 2014, net sales of our Urgent PC System and Macroplastique accounted for approximately 61% and 34%, respectively, of our total net sales. If demand for any or both of the product lines declines, our revenues and business prospects may suffer.
We may require additional financing and may find it difficult to obtain the financing on favorable terms, or at all.
Our future liquidity and capital requirements will depend on numerous factors, including: the timing and cost required to expand our sales, marketing and distribution capabilities in the United States markets; the cost and effectiveness of our marketing and sales efforts of our products in international markets; the effect of competing technologies and market, reimbursement and regulatory developments; the cost of research and development programs; and the cost involved in protecting our proprietary rights. Although we currently have an adequate cash balance, we may need to raise additional financing to support our operations and planned growth activities in the future because we have yet to achieve profitability and generate positive cash flows. Any equity financing could substantially dilute your equity interests in our company and any debt financing could impose significant financial and operational restrictions on us. We cannot assure you that we will obtain additional financing on acceptable terms, or at all.
We could be subject to fines and penalties, or required to temporarily or permanently cease offering products, if we fail to comply with the extensive regulations applicable to the sale and manufacture of medical products.
The production and marketing of our products and our ongoing research and development, preclinical testing and clinical trial activities are subject to extensive regulation and review by numerous governmental authorities both in the United States and abroad. U.S. and foreign regulations applicable to medical devices are wide-ranging and govern, among other things, the testing, marketing and pre-market review of new medical devices, and the manufacturing practices, reporting, advertising, exporting, labeling and record keeping procedures. We are required to obtain regulatory approval or clearance before we can market our products in the United States and certain foreign countries. The regulatory process requires significant time, effort and expenditures to bring our products to market, and we cannot assure you that the regulatory authority we currently possess to market our products will remain available, or that we will be able to obtain authority to sell new or existing products in new markets. Further, the manufacture and manufacturing facilities of medical products are subject to periodic reviews and inspection by the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities. Our failure to comply with regulatory requirements could result in governmental agencies:
Even if we receive regulatory approval or clearance of a product, the approval or clearance could limit the uses for which we may label and promote the product, which may limit the market for our products.
We often rely on our distributors in countries outside the United States in seeking regulatory approval to market our products in particular countries. To the extent we do so, we are dependent on persons outside of our direct control to make regulatory submissions and secure approvals, and we do or will not have direct access to health care agencies in those markets to ensure timely regulatory approvals or prompt resolution of regulatory or compliance matters. If our distributors fail to obtain the required approvals or do not do so in a timely manner, our sales from our international operations and our results of operations may be adversely affected.
We may not have the resources to successfully market our products, which would adversely affect our business and results of operations.
The marketing of our products requires a significant amount of time and expense in order to identify the physicians who would use our products and to train a sales force that is large enough to interact with the targeted physicians. The ease and predictability of third-party reimbursement significantly impacts the success of our marketing activities. We may not have adequate resources to market our products successfully against larger competitors who have more resources than we do. If we cannot market our products successfully, our business and results of operations would be adversely affected.
If we cannot attract and retain our key personnel and management team, we may not be able to manage and operate successfully, and we may not be able to meet our strategic objectives.
Our future success depends, in large part, upon our ability to attract and retain and motivate our management team and key managerial, scientific, sales and technical personnel. Key personnel may depart because of difficulties with change or a desire not to remain with our company. We are highly dependent on our President and CEO and other senior management, and any unanticipated loss or interruption of their services could significantly reduce our ability to meet our strategic objectives because, given the intense competition for senior management and other key personnel, it may not be possible for us to find appropriate replacement personnel should the need arise. The loss of a member of our senior management or our professional staff would require the remaining senior executive officers to divert immediate and substantial attention to seeking a replacement. There is no guarantee that we will be successful in retaining our current personnel or in hiring or retaining qualified personnel in the future. Loss of key personnel or the inability to hire or retain qualified personnel in the future could have a material adverse effect on our ability to operate successfully. Further, any inability on our part to enforce non-compete arrangements related to key personnel who have left the company could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If third parties claim that we infringe upon their intellectual property rights, we may incur liabilities and costs and may have to redesign or discontinue selling the affected product.
The medical device industry is litigious with respect to patents and other intellectual property rights. Companies operating in our industry routinely seek patent protection for their product designs, and many of our principal competitors have large patent portfolios. Companies in the medical device industry have used intellectual property litigation to gain a competitive advantage. Whether a product infringes a patent involves complex legal and factual issues, the determination of which is often uncertain. We face the risk of claims that we have infringed on third parties’ intellectual property rights. Our efforts to identify and avoid infringing on third parties’ intellectual property rights may not always be successful. Any claims of patent or other intellectual property infringement, even those without merit, could:
| · | cause us to cease making or selling products that incorporate the challenged intellectual property; |
| · | result in our customers or potential customers deferring or limiting their purchases or use of the affected products until resolution of the litigation. |
In addition, new patents obtained by our competitors could threaten our product’s continued life in the market even after it has already been introduced.
If we are unable to adequately protect our intellectual property rights, we may not be able to compete effectively.
Our success depends in part on our ability to protect the proprietary rights to the technologies used in our products. We rely on patent protection, as well as a combination of trademark laws and confidentiality, noncompetition and other contractual arrangements to protect our proprietary technology. However, these legal means afford only limited protection and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep a competitive advantage. Our patents and patent applications, if issued, may not be broad enough to prevent competitors from introducing similar products into the market. Our patents, if challenged or if we attempt to enforce them, may not necessarily be upheld by the courts. In addition, patent protection in foreign countries may be different from patent protection under U.S. laws and may not be favorable to us.
We also rely on unpatented proprietary technology. We cannot assure you that we can meaningfully protect all of our rights in our unpatented proprietary technology or that others will not independently develop substantially equivalent products or processes or otherwise gain access to our unpatented proprietary technology. We attempt to protect our trade secrets and other unpatented proprietary technology through the use of confidentiality and noncompetition agreements with our current key employees and with other parties to whom we have divulged trade secrets. However, these agreements may not be enforceable or may not provide meaningful protection for our proprietary information in the event of unauthorized use or disclosure or other breaches of the agreements or in the event competitors discover or independently develop similar proprietary information.
Efforts on our part to enforce any of our proprietary rights could be time-consuming and expensive, which could adversely affect our business and prospects and divert our management’s attention.
The manufacture and sale of medical devices exposes us to significant risk of product liability claims, some of which may have a negative impact on our business. Any defects or risks that we have not yet identified with our products may give rise to product liability claims. Our existing $10 million of worldwide product liability insurance coverage may be inadequate to protect us from liabilities we may incur or we may not be able to maintain adequate product liability insurance at acceptable rates. If a product liability claim or series of claims is brought against us for uninsured liabilities or in excess of our insurance coverage and it is ultimately determined that we are liable, our business could suffer. Additionally, we could experience a material design or manufacturing failure in our products, a quality system failure, other safety issues or heightened regulatory scrutiny that would warrant a recall of some of our products. A recall of any of our products likely would be costly, would be uninsured and could also result in increased product liability claims. Further, while we train our physician customers in the proper use of our products, we cannot be certain that they will implement our instructions accurately. If our products are used incorrectly by our customers, injury may result and this could give rise to product liability claims against us.
Security breaches and other disruptions could compromise our information and expose us to liability, which would cause our business and reputation to suffer.
In the ordinary course of our business, we use our networks to collect and store sensitive data, including intellectual property, our proprietary business information and that of our customers, suppliers and business partners, personally identifiable information of our customers and employees, and data relating to patients who use our products. The secure processing, maintenance and transmission of this information is critical to our operations. Despite our security measures, our information technology and infrastructure may be vulnerable to attacks by hackers or breached due to employee error, malfeasance or other disruptions. Any such breach could compromise our networks and the information stored there could be accessed, publicly disclosed, lost or stolen. Any such access, disclosure or other loss of information could result in legal claims or proceedings, liability under laws that protect the privacy of personal information, and regulatory penalties, disrupt our operations and the services we provide to customers, damage our reputation, and cause a loss of confidence in our products and services, which could adversely affect our operating margins, revenues and competitive position.
The loss or interruption of materials from any of our key suppliers could delay the manufacture of our products, which would limit our ability to generate sales and revenues.
We currently purchase several key materials used in our products from single source suppliers, including the finished products for our Urgent PC System. If one of these suppliers delayed or curtailed shipments to us, our ability to manufacture and deliver product would be impaired, our sales would decline or be curtailed for that product, and we would be forced to quickly locate an alternative source of supply. We cannot be sure that acceptable alternative arrangements could be made on a timely basis. Further, our reliance on such suppliers and the cost and difficulty we would encounter in qualifying an alternative subjects us to increased risk of price increase by single source suppliers. Additionally, the qualification of materials and processes as a result of a supplier change could be deemed as unacceptable to regulatory authorities and cause delays and increased costs due to additional test requirements. A significant interruption in the supply of materials, for any reason, could delay the manufacture and sale of our products, which would limit our ability to generate revenues.
If we are not able to maintain sufficient quality controls, regulatory approvals of our products by the European Union, Canada, the FDA or other relevant authorities could be delayed or denied and our sales and revenues will suffer.
The FDA, European Union, Canada or other related authorities could stop or delay approval of production of products if our manufacturing facilities do not comply with applicable manufacturing requirements. The FDA’s Quality System Regulations impose extensive testing, control, documentation and other quality assurance requirements. Canada and the European Union also impose requirements on quality systems of manufacturers, who are inspected and certified on a periodic basis and may be subject to additional unannounced inspections. Further, our suppliers are also subject to these regulatory requirements. Failure by any of our suppliers or us to comply with these requirements could prevent us from obtaining or retaining approval for and marketing of our products.
If we are not able to acquire or license other products, our business and future growth prospects could suffer.
As part of our growth strategy, we intend to acquire or license additional products and technologies for development and commercialization. The success of this strategy depends upon our ability to identify, select and acquire the right products and technologies.
Products and technologies that we license or acquire may require additional development prior to sale, including clinical testing and approval by the FDA and other regulatory bodies, and we may encounter difficulty or delays in completing the development or receiving the necessary approvals. We may find that the product or technology cannot be manufactured economically or commercialized successfully. We may not be able to acquire or license the right to products on terms that we find acceptable, or at all.
Even if we complete future acquisitions, our business, financial condition and the results of operations could be negatively affected because:
| · | we may be unable to integrate the acquired business or products successfully and realize anticipated economic, operational and other benefits in a timely manner; and |
| · | the acquisition may disrupt our ongoing business, distract our management team and divert our resources. |
Our business strategy relies on assumptions about the market for our products, which, if incorrect, would adversely affect our business prospects and profitability.
We are focused on the market for minimally invasive therapies used to treat voiding dysfunctions. We believe that the aging of the general population will continue and that these trends will increase the need for our products. However, the projected demand for our products could materially differ from actual demand if our assumptions regarding these trends and acceptance of our products by the medical community prove to be incorrect or do not materialize. Actual demand for our products could also be affected if drug therapies gain more widespread acceptance as a viable alternative treatment, which in each case would adversely affect our business prospects and profitability.
We derive a significant portion of our sales from outside of the United States and are subject to the risks of international operations.
We derived approximately 27% of our net sales in fiscal 2014 from customers and operations in international markets. The sale and shipping of our products and services across international borders, as well as the purchase of components and products from international sources, subject us to a number of risks, including:
| · | difficulties in recruiting and maintaining distributors and staff in remote locations, including sales people; |
| · | the imposition of restrictions on the activities of foreign agents, representatives and distributors; |
| · | difficulties in enforcing agreements and collecting receivables through certain foreign legal systems; and |
Failure to comply with the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act could subject us to, among other things, penalties and legal expenses that could harm our reputation and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and operating results.
We are required to comply with the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, or FCPA, which generally prohibits covered entities and their intermediaries from engaging in bribery or making other prohibited payments to foreign officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business or other benefits. In addition, the FCPA imposes accounting standards and requirements on publicly traded U.S. corporations and their foreign affiliates, which are intended to prevent the diversion of corporate funds to the payment of bribes and other improper payments, and to prevent the establishment of “off books” slush funds from which such improper payments can be made. We also are subject to similar anticorruption legislation implemented in Europe under the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development’s Convention on Combating Bribery of Foreign Public Officials in International Business Transactions. We either operate or plan to operate in a number of jurisdictions that pose a high risk of potential violations of the FCPA and other anticorruption laws, and we utilize a number of distributors for whose actions we could be held liable under the FCPA. We inform our personnel, distributors and agents of the requirements of the FCPA and other anticorruption laws, including, but not limited to their reporting requirements. We also have developed and will continue to develop and implement systems for formalizing contracting processes, performing due diligence on personnel, distributors and agents and improving our recordkeeping and auditing practices regarding these regulations. However, there is no guarantee that our personnel, distributors or agents have not or will not engage in conduct undetected by our processes and for which we might be held responsible under the FCPA or other anticorruption laws.
If our personnel, distributors or agents are found to have engaged in such practices, we could suffer severe penalties, including criminal and civil penalties, disgorgement and other remedial measures, including further changes or enhancements to our procedures, policies and controls, as well as potential personnel changes and disciplinary actions. During the past few years, the SEC has increased its enforcement of violations of the FCPA against companies, including several medical device companies. Although we do not believe we are currently a target, any investigation of any potential violations of the FCPA or other anticorruption laws by U.S. or foreign authorities also could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and operating results.
Certain foreign companies, including some of our competitors, are not subject to prohibitions as strict as those under the FCPA or, even if subjected to strict prohibitions, such prohibitions may be laxly enforced in practice. If our competitors engage in corruption, extortion, bribery, pay-offs, theft or other fraudulent practices, they may receive preferential treatment from personnel of some companies, giving our competitors an advantage in securing business, or from government officials, who might give them priority in obtaining new licenses, which would put us at a disadvantage.
Our stock is thinly traded and you may find it difficult to sell your investment in our stock at quoted prices.
There is only a limited trading market for our common stock, which is quoted on the NASDAQ. Transactions in our common stock may lack the volume and liquidity necessary to maintain an orderly trading market and this could result in both depressed and highly variable trading prices.
The market price of our common stock may be subject to significant fluctuations due to the following factors, among others:
| · | general economic conditions. |
The stock market in recent years has experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of affected companies. These broad market fluctuations may cause the price of our common stock to fall abruptly or remain significantly depressed.
The market price of our common stock could decline due to sales by our existing shareholders of a large number of shares of our common stock or the perception that these sales could occur. These sales could also make it more difficult for us to raise capital through the sale of common stock at a time and price we deem appropriate.
Our corporate documents and Minnesota law contain provisions that could discourage, delay or prevent a change in control of our company.
Provisions in our articles of incorporation may discourage, delay or prevent a merger or acquisition, even if our stockholders consider the terms favorable. Our articles of incorporation provide for a staggered board of directors, requiring our directors to serve for three-year terms, with approximately one third of the directors standing for reelection each year. A staggered board could make it more difficult for a third party to obtain control of our board of directors through a proxy contest, which may be a necessary step in an acquisition of us that is not favored by our board of directors.
We are also subject to the anti-takeover provisions of Section 302A.673 of the Minnesota Business Corporation Act. Under these provisions, if anyone becomes an “interested shareholder” in a transaction not approved by a committee consisting of disinterested members of our board of directors, we may not enter into a “business combination” with that person for four years, which could discourage a third party from making a takeover offer and could delay or prevent a change of control. For purposes of Section 302A.673, “interested shareholder” generally means someone owning 10% or more of our outstanding voting stock or an affiliate of ours that owned 10% or more of our outstanding voting stock during the past four years, subject to certain exceptions.
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our common stock. We currently intend to retain all future earnings, if any, for the operation and expansion of our business and, therefore, do not anticipate declaring or paying cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Any payment of cash dividends on our common stock will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon our results of operations, earnings, capital requirements, financial condition, future prospects, contractual restrictions and other factors deemed relevant by our board of directors. Therefore, you should not expect to receive dividend income from shares of our common stock.
We lease an 18,258 square-foot office, warehouse and manufacturing facility in Minnetonka, Minnesota for our corporate headquarters pursuant to a lease agreement with Liberty Property Limited Partnership expiring in June 2019, with average minimum rent payments of approximately $154,000. We also own 9,774 square feet of office and warehouse space in Geleen, The Netherlands. We believe that these facilities are suitable and adequate for our operations for the foreseeable future
We are not involved in any material active legal actions, however, from time to time may be subject to various pending or threatened legal actions and proceedings, including those that arise in the ordinary course of its business. Such matters are subject to many uncertainties and to outcomes that are not predictable with assurance and that may not be known for extended periods of time.
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
The following table sets forth the high and low closing prices for our common stock for our fiscal years ended March 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 as reported on the NASDAQ Capital Markets.
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2014 | Low | High | ||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 2.00 | $ | 2.67 | ||||
| Second Quarter | 1.72 | 3.83 | ||||||
| Third Quarter | 2.58 | 3.58 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 2.75 | 4.58 | ||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2013 | Low | High | ||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 2.75 | $ | 4.64 | ||||
| Second Quarter | 3.76 | 4.78 | ||||||
| Third Quarter | 3.10 | 3.81 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 2.44 | 3.43 | ||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2012 | Low | High | ||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 6.33 | $ | 8.32 | ||||
| Second Quarter | 4.50 | 9.00 | ||||||
| Third Quarter | 3.87 | 5.85 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 2.66 | 4.45 | ||||||
As of March 31, 2014, we had approximately 305 holders of record of our common stock. Registered ownership includes nominees who may hold securities on behalf of multiple beneficial owners. We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our common stock. We currently intend to retain all future earnings, if any, for the operation and expansion of our business and, therefore, do not anticipate declaring or paying cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future.
The following table provides particular information regarding our equity compensation plans as of March 31, 2014.
Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | Weighted-Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans (Excluding Securities Reflected in the First Column) | ||||||||||
| Equity Compensation Plans Approved by Security Holders (1) | 1,428,043 | $ | 2.97 | 821,496 | ||||||||
| Equity Compensation Plans Not Approved by Security Holders (2) | 900,000 | $ | 4.05 | - | ||||||||
| Total | 2,328,043 | $ | 3.39 | 821,496 | ||||||||
The following graph compares the 5-year cumulative total shareholder return of our common stock to the NASDAQ U.S. index and to the NASDAQ Surgical and Medical Instruments and Supplies Index, assuming an initial investment of $100 and reinvestment of all dividends.
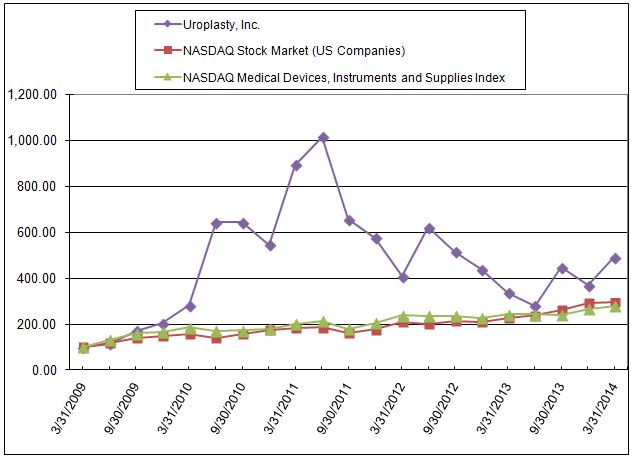
| 3/31/2009 | 3/31/2010 | 3/31/2011 | 3/31/2012 | 3/31/2013 | 3/31/2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Uroplasty, Inc. | $ | 100.00 | $ | 281.08 | $ | 893.24 | $ | 406.76 | $ | 336.49 | $ | 490.54 | ||||||||||||
| NASDAQ Stock Market (US Companies) | $ | 100.00 | $ | 156.85 | $ | 184.26 | $ | 210.46 | $ | 227.07 | $ | 294.04 | ||||||||||||
| NASDAQ Medical Devices, Instruments and Supplies Index | $ | 100.00 | $ | 185.65 | $ | 202.10 | $ | 237.96 | $ | 241.39 | $ | 277.62 | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 24,577 | $ | 22,418 | $ | 20,562 | $ | 13,787 | $ | 11,863 | ||||||||||
| Gross profit | 21,527 | 19,403 | 17,525 | 11,401 | 9,804 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating loss | (5,299 | ) | (3,301 | ) | (4,266 | ) | (4,698 | ) | (3,203 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net loss | (5,353 | ) | (3,305 | ) | (4,250 | ) | (4,648 | ) | (3,204 | ) | ||||||||||
| Basic and diluted loss per share | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (0.16 | ) | $ | (0.21 | ) | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (0.21 | ) | |||||
| Basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding | 21,118 | 20,777 | 20,690 | 18,874 | 14,944 | |||||||||||||||
| Other data | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based expense and depreciation and amortization | $ | 1,790 | $ | 1,965 | $ | 1,803 | $ | 1,553 | $ | 1,553 | ||||||||||
There were no outstanding long-term obligations and no cash dividends declared for all periods presented.
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Working capital | $ | 12,623 | $ | 12,621 | $ | 13,081 | $ | 14,650 | $ | 6,056 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | 17,301 | 20,041 | 22,291 | 25,727 | 11,574 | |||||||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity | 13,214 | 16,686 | 19,235 | 22,629 | 9,215 | |||||||||||||||
You should read this discussion of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with, and we qualify our discussion in its entirety by, the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included elsewhere within this report, the material contained under Part 1, Item 1. “Description of Business” and Part I, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” of this report, and the cautionary disclosure about forward-looking statements at the front of Part I of this report.
We are a medical device company that develops, manufactures and markets innovative, proprietary products for the treatment of voiding dysfunctions. Our primary focus is on two products: our Urgent PC® System, which we believe is the only FDA-cleared minimally invasive, office-based neuromodulation therapy for the treatment of OAB and associated symptoms of urinary urgency, urinary frequency, and urge incontinence; and Macroplastique® a urethral bulking agent for the treatment of adult female stress urinary incontinence primarily due to ISD. Outside of the U.S., our Urgent PC System is also approved for treatment of fecal incontinence, and Macroplastique is also approved for treatment of male stress incontinence, vocal cord rehabilitation and vesicoureteral reflux.
Our sales have been significantly influenced by the availability of third-party reimbursement for PTNS treatments. Sales of our Urgent PC System in the U.S. grew rapidly during fiscal 2007 and 2008 with rapid market acceptance of PTNS treatments that were reimbursed under a Category 1 CPT code. Sales declined from the first quarter of fiscal 2009 through the third quarter of fiscal 2011, because of lower or unavailable reimbursement when the AMA advised the providers that reimbursement for PTNS treatments should be requested under an unlisted CPT code.
We responded by sponsoring several clinical studies over the following two years that were published in U.S. peer-review journals. With favorable results from these studies, we applied for, and effective January 2011 the AMA granted, a new Category 1 CPT code for PTNS treatments. As a result, we expanded our U.S. field sales and support organization from 15 employed sales representatives and six independent manufacturer’s representatives on April 1, 2010 to 43 employed sales representatives on March 31, 2014, and sales of our Urgent PC System began to increase. As of March 31, 2014, we also employed 6 field based clinical support specialists and 5 Regional Sales Directors.
We have focused our efforts on expanding reimbursement coverage with Medicare carriers and private payers by instituting a comprehensive program to educate their medical directors regarding the clinical effectiveness, cost effectiveness and patient benefits of PTNS treatments using our Urgent PC System. As of May 1, 2014, regional Medicare carriers covering 40 states and the District of Columbia, with approximately 40 million covered lives, provide coverage for PTNS treatments. In addition, we estimate that private payers insuring approximately 119 million lives provide coverage for PTNS treatments. As of May 1, 2014, one regional Medicare carrier representing 10 states, with approximately 10 million covered lives, continued to decline reimbursement coverage for PTNS treatments. Increasing coverage from private payers, as well as obtaining reimbursement from the sole regional Medicare carrier not to provide coverage for PTNS, is a key element of our strategy.
We expect to continue to emphasize sales of our Urgent PC System in the United States and internationally. In fiscal 2014, we implemented new sales strategies and refocused the sales organization. We will continue to emphasize generating greater patient and physician awareness of our Urgent PC system, and on training physicians in the proper use and clinical benefits of our Urgent PC System for OAB. As part of this process, we intend to hire additional clinical support specialists in some of our markets during fiscal 2015 and plan to expand our call point beyond our historical focus on urologists. Specifically, we will expand our call point to include gynecologists, urogynecologists and a highly targeted group for primary care physicians who are high prescribers of OAB medications as we look to accelerate the growth of our Urgent PC System. We do not expect to see significant growth in our Macroplastique business, because we believe it is a small, mature market that is more competitively penetrated than the market for OAB treatment using PTNS.
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, which require us to make estimates and assumptions in certain circumstances that affect amounts reported. In preparing these consolidated financial statements, we have made our best estimates and judgments of certain amounts, giving due consideration to materiality. We believe that of our significant accounting policies, the following can be characterized as “critical accounting policies” and are particularly important to the portrayal of our results of operations and financial position. These critical policies may require the application of a higher level of judgment by us, and as a result are subject to an inherent degree of uncertainty.
Reclassifications: Certain amounts in the fiscal 2013 consolidated financial statements have been reclassified to conform with the fiscal 2014 presentation. These reclassifications had no effect on net income or stockholder’s equity as previously reported.
Revenue Recognition. We recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, title and risk of ownership have passed, the sales price is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably assured. Generally, these criteria are met at the time the product is shipped to the customer. We include shipping and handling charges billed to customers in net sales, and include such costs incurred by us in cost of goods sold. Typically our agreements contain no customer acceptance provisions or clauses. We sell our products to end users and to distributors. Payment terms range from prepayment to 120 days. The distributor payment terms are not contingent on the distributor selling the product to end users. Customers do not have the right to return products except for warranty claims. We offer customary product warranties. We present our sales in our statement of operations net of taxes, such as sales, use, value-added and certain excise taxes, collected from the customers and remitted to governmental authorities.
Accounts Receivable. We grant credit to our customers in the normal course of business and, generally, do not require collateral or any other security to support amounts due. If necessary, we have an outside party assist us with performing credit and reference checks and establishing credit limits for the customer. Accounts outstanding longer than the contractual payment terms, are considered past due. We carry our accounts receivable at the original invoice amount less an estimated allowance for doubtful receivables based on a periodic review of all outstanding amounts, and less an estimated sales return allowance. We determine the allowance for doubtful accounts based on the customer’s financial health, and both historical and expected credit loss experience. We write off our accounts receivable when we deem them uncollectible. We record recoveries of accounts receivable previously written off when received. We are not always able to timely anticipate changes in the financial condition of our customers and if circumstances related to these customers deteriorate, our estimates of the recoverability of accounts receivable could be materially affected and we may be required to record additional allowances. Alternatively, if more allowances are provided than are ultimately required, we may reverse a portion of such provisions in future periods based on the actual collection experience. We determine the sales return allowance based on historical experience. Historically, the accounts receivable balances we have written off and the sales returns have generally been within our expectations.
Inventories. We state inventories at the lower of cost or market using the first-in, first-out method. We value at lower of cost or market the slow moving and obsolete inventories based upon current and expected future product sales and the expected impact of product transitions or modifications. Historically, the inventory write-offs have generally been within our expectations.
Foreign Currency Translation/Transactions. The financial statements of our foreign subsidiaries are translated in accordance with the provisions of ASC 830, “Foreign Currency Matters.” We translate all assets and liabilities using period-end exchange rates, and we translate statements of operations items using average exchange rates for the period. We record the resulting translation adjustment within accumulated other comprehensive loss, a separate component of shareholders’ equity. We recognize foreign currency transaction gains and losses in the statement of operations, including unrealized gains and losses on short-term intercompany obligations using period-end exchange rates, resulting in an increase in the volatility of our consolidated statements of operations.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets. Our long-lived assets consist of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets. We review our long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or business circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. We measure the recoverability of assets to be held and used by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted net cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. We use judgment to forecast future cash flows including forecasting revenues and margins, and working capital needs. If we consider such assets impaired, we measure the impairment to be recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. We did not record any impairment charge in fiscal years 2014, 2013 or 2012.
Share-Based Compensation. We account for share-based compensation costs under ASC 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation.” ASC 718 covers a wide range of share-based compensation arrangements including stock options, restricted share plans, performance-based awards, share appreciation rights, and employee share purchase plans. We recognize the compensation cost relating to share-based payment transactions, including grants of employee stock options and restricted shares, in our financial statements. We measure that cost based on the fair value of the equity or liability instruments issued.
Defined Benefit Pension Plans. We have a liability attributed to defined benefit pension plans we offered to certain former and current employees of our subsidiaries in the UK and the Netherlands. The liability is dependent upon numerous factors, assumptions and estimates, and the continued benefit costs we incur may be significantly affected by changes in key actuarial assumptions such as the discount rate, mortality, compensation rates, or retirement dates used to determine the projected benefit obligation. Additionally, changes made to the provisions of the plans may impact current and future benefit costs. In accordance with the provisions of ASC 715, “Compensation – Retirement Benefits,” changes in benefit obligations associated with these factors may not be immediately recognized as costs in the statement of operations, but are recognized in future years over the expected average future service of the active employees or the average remaining life expectancies of inactive employees.
Income Taxes. We recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. We measure deferred tax assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates we expect to apply to taxable income in the years in which we expect to recover or settle those temporary differences. As of March 31, 2014, we have generated approximately $36 million in U.S. net operating loss (“NOL”) carry forwards that we cannot use to offset taxable income in foreign jurisdictions. We recognize a valuation allowance when we determine it is more likely than not that we will not realize a portion of the deferred tax asset. We have established a valuation allowance for U.S. and certain foreign deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty that we will generate enough income in those taxing jurisdictions to utilize the assets.
In addition, future utilization of NOL carry forwards is subject to certain limitations under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. This section generally relates to a 50 percent change in ownership of a company over a three-year period. We believe that the issuance of our common stock in the December 2006 follow-on public offering resulted in an "ownership change" under Section 382. Accordingly, our ability to use NOL tax attributes generated prior to December 2006 is limited to approximately $750,000 per year. Additionally, we believe there was an ownership change in December 2012. Accordingly, our ability to use NOL tax attributes generated after December 2006 and before December 2012 is limited to approximately $2,000,000 per year.
See Note 5 to our consolidated financial statements for further discussion.
Results of Operations
Net Sales. In fiscal 2014, consolidated net sales of $24.6 million represented a $2.2 million, or a 10% increase, over net sales of $22.4 million in fiscal 2013. In fiscal 2013, consolidated net sales of $22.4 million represented a $1.9 million, or a 9% increase, over net sales of $20.6 million in fiscal 2012. The increase in consolidated net sales is mainly attributed to the sales growth of our Urgent PC System.
Net sales to customers in the U.S. of $18.0 million in fiscal 2014, represented an increase of $1.6 million, or 10%, over net sales of $16.4 million in fiscal 2013. Net sales to customers in the U.S. of $16.4 million in fiscal 2013, represented an increase of $2.5 million, or 18%, over net sales of $13.9 million in fiscal 2012.
Net sales in the U.S. of our Urgent PC System increased 17% to $12.3 million in fiscal 2014, from $10.5 million last year. Net sales in the U.S. of our Urgent PC System of $10.5 million in fiscal 2013 increased 35% from $7.8 million in fiscal 2012. Net sales increased as a result of improved sales execution of our Urgent PC System within the U.S. in addition to new account conversions and improved customer retention rates.
Net sales in the U.S. of our Macroplastique product decreased 2%, or $121,000, to $5.6 million in fiscal 2014, compared to fiscal 2013. Net sales in the U.S. of our Macroplastique product decreased 2%, or $138,000 to $5.7 million in fiscal 2013, compared to fiscal 2012.
Net sales to customers outside the U.S. in fiscal 2014 increased 9% to $6.5 million, compared to $6.0 million in fiscal 2013. The increase in sales is attributed to the increase in adoption of our Urgent PC System by our customers, primarily in the United Kingdom. Net sales to customers outside the U.S. in fiscal 2013 decreased 10% to $6.0 million compared to $6.7 million in fiscal 2012.
Urgent PC System sales to customers outside of the U.S. of $2.7 million in fiscal 2014 increased 29% from $2.1 million in fiscal 2013. The increase in sales is attributed to the increase in adoption of the product by our customers, primarily in the United Kingdom. Urgent PC System sales to customers outside of the U.S. of $2.1 million in fiscal 2013 increased 5% from $2.0 million in fiscal 2012.
Macroplastique sales to customers outside of the U.S. decreased 2% to $2.8 million in fiscal 2014 over fiscal 2013 and Macroplastique sales to customers outside of the U.S. decreased 18% to $2.8 million in fiscal 2013 over fiscal 2012. The decrease in fiscal 2013 in Macroplastique sales was mainly due to budget cuts for hospitals in several European countries.
Gross Profit: Gross profit was $21.5 million, or 87.6% of net sales in fiscal 2014, $19.4 million, or 86.6% in fiscal 2013, and $17.5 million, or 85.2% in fiscal 2012.
The 1.0% increase in the gross profit percentage in fiscal 2014 is attributed primarily to a 0.2% impact of a favorable product mix, a 0.2% impact from an increase in capacity absorption, and a 0.3% impact from reduced royalty payments. Starting with fiscal 2014, we no longer pay royalties on sales of our bulking agent products in markets outside of the U.S.
The 1.4% increase in gross profit percentage in fiscal 2013 was attributed primarily to a 1% impact of a favorable product mix, and a 0.2% impact from an increase in capacity absorption.
General and Administrative Expenses (G&A): G&A expenses of $6.5 million during fiscal 2014 increased $2.3 million from $4.2 million during fiscal 2013. Changes in executive management attributed to $1.0 million of this increase, of which $696,000 is non-cash, share based compensation expense. Further, we incurred $1.1 million in legal and accounting fees pertaining to the review of certain internal control issues in the first and second quarter of fiscal 2014.
G&A expenses of $4.2 million during fiscal 2013 increased $455,000 from $3.7 million during fiscal 2012. Included in fiscal 2013 is a charge of $473,000 for non-cash, share-based compensation expense, compared with $412,000 in fiscal 2012. Excluding share-based compensation charges, G&A expenses increased by $394,000 in 2013, primarily due to an $182,000 increase in personnel costs primarily from an increase in headcount, and a $127,000 increase in professional fees for legal, audit, tax and consulting.
Research and Development Expenses (“R&D”): R&D expenses of $2.2 million during fiscal 2014, decreased $0.2 million from $2.4 million in fiscal 2013. The decrease is attributed primarily to a $389,000 expense in the prior fiscal year for product testing and validation of the planned replacement of components for one of our products, offset by a $189,000 increase in costs attributed to clinical studies.
R&D expenses of $2.4 million during fiscal 2013 increased $0.5 million from $1.9 million in fiscal 2012. The increase is attributed primarily to a $389,000 charge for product testing and validation of the planned replacement of components for one of our products, a $253,000 increase in new product development costs, a $35,000 increase in cost for the U.S. fecal incontinence study, and a $121,000 increase in compensation costs due to increased headcount, increased bonuses, and promotions, offset by a $170,000 decrease in human clinical study costs and a $112,000 charge in the prior fiscal year for costs incurred for utilizing a third-party for tooling development.
Selling and Marketing Expenses (“S&M”): S&M expenses of $18.1 million in fiscal 2014 increased $2.9 million from $15.2 million in fiscal 2013. The increase is attributed primarily to a $2.2 million increase in personnel and travel costs due to the expansion and reorganization of our selling and marketing team, $234,000 for the Medical Device Tax, and a $189,000 increase in marketing costs related to product promotion and education, advertising, trade shows and conventions.
S&M expenses of $15.2 million in fiscal 2013 decreased $57,000 from $15.3 million in fiscal 2012. S&M expenses decreased primarily because of a $863,000 decrease in bonus and incentive costs, offset by a $54,000 increase in salary primarily due to increase in head count, a $308,000 increase in commission costs primarily due to an increase in sales, and a $310,000 increase in travel related expenses. Also, included in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2013 is a charge of $68,000 for the medical device excise tax on U.S. sales that went into effect on January 1, 2013.
Amortization of Intangibles: Amortization of intangibles was $30,000 in fiscal 2014, $863,000 in fiscal 2013, and $857,000 in fiscal 2012. In April 2007, we acquired from CystoMedix, Inc., certain intellectual property assets related to the Urgent PC system for $4.7 million, which became fully amortized in fiscal 2013.
Other Income (Expense): Other income (expense) includes interest income, interest expense, foreign currency exchange and other non-operating costs when incurred. Net other income was $17,000, $47,000 and $64,000 for fiscal 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Other income decreased primarily as the result of a decrease in interest income on lower cash and investment balances and interest rates.
We recognize exchange gains and losses primarily as a result of fluctuations in currency rates between the U.S. dollar (the functional reporting currency) and the Euro and British pound (currencies of our subsidiaries), as well as their effect on the dollar denominated short-term intercompany obligations between us and our foreign subsidiaries. In fiscal 2014, fiscal 2013, and fiscal 2012 we recorded foreign currency exchange (losses) gains of $(5,000), $2,000, and $4,000 respectively.
Income Tax Expense: In fiscal 2014, fiscal 2013, and fiscal 2012, we recorded income tax expense of $72,000, $51,000 and $48,000, respectively. Income tax expense is attributed to our foreign subsidiaries and to the payment of minimum State taxes in the U.S. We cannot use our U.S. net operating loss carry forwards to offset taxable income in foreign jurisdictions. Our actual income tax expense differs from the statutory federal income tax benefit largely due to the recording of valuation allowances in all three periods presented.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures: The following table reconciles our operating loss calculated in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. (“GAAP”) to non-GAAP financial measures that exclude non-cash charges for share-based compensation, and depreciation and amortization from gross profit, operating expenses and operating loss. The non-GAAP financial measures used by management and disclosed by us are not a substitute for, or superior to, financial measures and consolidated financial results calculated in accordance with GAAP, and you should carefully evaluate our reconciliations to non-GAAP. We may calculate our non-GAAP financial measures differently from similarly titled measures used by other companies. Therefore, our non-GAAP financial measures may not be comparable to those used by other companies. We have described the reconciliations of each of our non-GAAP financial measures described above to the most directly comparable GAAP financial measures.
We use these non-GAAP financial measures, and in particular non-GAAP operating loss, for internal managerial purposes and incentive compensation for senior management because we believe such measures are one important indicator of the strength and the operating performance of our business. Analysts and investors frequently ask us for this information. We believe that they use these measures to evaluate the overall operating performance of companies in our industry, including as a means of comparing period-to-period results and as a means of evaluating our results with those of other companies.
Our non-GAAP operating loss for fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012 was approximately $3.5 million, $1.3 million and $2.5 million, respectively. The fiscal 2014 increase in non-GAAP operating loss is attributed to the increase in operating spending (including $1.4 million of cash costs related to our review of internal control over financial reporting and executive management changes), offset partially by the increase in net sales and gross profit percent. The fiscal 2013 decrease in non-GAAP operating loss compared to the same prior year period is attributed primarily to an increase in net sales which more than offset the increase in non-GAAP spending.
| Expense Adjustments | ||||||||||||||||||||
| GAAP | Share-based Expense | Depreciation | Amortization of Intangibles | Non-GAAP | ||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended March 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Profit | $ | 21,527,000 | $ | 27,000 | $ | 33,000 | $ | - | $ | 21,587,000 | ||||||||||
| % of Net sales | 87.6 | % | 87.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating Expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| General & administrative | 6,522,000 | (1,117,000 | ) | (200,000 | ) | - | 5,205,000 | |||||||||||||
| Research and development | 2,151,000 | (51,000 | ) | (4,000 | ) | - | 2,096,000 | |||||||||||||
| Selling and marketing | 18,123,000 | (241,000 | ) | (86,000 | ) | - | 17,796,000 | |||||||||||||
| Amortization | 30,000 | - | - | (30,000 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| 26,826,000 | (1,409,000 | ) | (290,000 | ) | (30,000 | ) | 25,097,000 | |||||||||||||
| Operating Loss | $ | (5,299,000 | ) | $ | 1,436,000 | $ | 323,000 | $ | 30,000 | $ | (3,510,000 | ) | ||||||||
| Year Ended March 31, 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Profit | $ | 19,403,000 | $ | 31,000 | $ | 34,000 | $ | - | $ | 19,468,000 | ||||||||||
| % of Net sales | 86.6 | % | 86.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating Expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| General & administrative | 4,188,000 | (473,000 | ) | (196,000 | ) | - | 3,519,000 | |||||||||||||
| Research and development | 2,415,000 | (54,000 | ) | (3,000 | ) | - | 2,358,000 | |||||||||||||
| Selling and marketing | 15,238,000 | (254,000 | ) | (57,000 | ) | - | 14,927,000 | |||||||||||||
| Amortization | 863,000 | - | - | (863,000 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| 22,704,000 | (781,000 | ) | (256,000 | ) | (863,000 | ) | 20,804,000 | |||||||||||||
| Operating Loss | $ | (3,301,000 | ) | $ | 812,000 | $ | 290,000 | $ | 863,000 | $ | (1,336,000 | ) | ||||||||
| Year Ended March 31, 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Profit | $ | 17,525,000 | $ | 22,000 | $ | 34,000 | $ | - | $ | 17,581,000 | ||||||||||
| % of Net sales | 85.2 | % | 85.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating Expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| General & administrative | 3,733,000 | (412,000 | ) | (163,000 | ) | - | 3,158,000 | |||||||||||||
| Research and development | 1,905,000 | (39,000 | ) | (9,000 | ) | - | 1,857,000 | |||||||||||||
| Selling and marketing | 15,296,000 | (212,000 | ) | (55,000 | ) | - | 15,029,000 | |||||||||||||
| Amortization | 857,000 | - | - | $ | (857,000 | ) | - | |||||||||||||
| 21,791,000 | (663,000 | ) | (227,000 | ) | (857,000 | ) | 20,044,000 | |||||||||||||
| Operating Loss | $ | (4,266,000 | ) | $ | 685,000 | $ | 261,000 | $ | 857,000 | $ | (2,463,000 | ) | ||||||||
Liquidity and Capital Resources
At March 31, 2014, our cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments balances totaled $12.1 million. At March 31, 2014, we had working capital of approximately $12.6 million.
Cash used in operating activities was $2.9 million in fiscal 2014, $1.2 million in fiscal 2013 and $3.1 million in fiscal 2012. We used this cash primarily to fund the operating loss, net of non-cash charges for depreciation, amortization of intangibles and equity compensation, of $3.6 million, $1.3 million, and $2.4 million in the respective years. We have continued to show an operating loss because we have continued to invest, primarily in selling and marketing, to grow our U.S. business. The fiscal 2014 net loss includes nonrecurring cash expenses of $696,000 attributed to changes in executive management and $1.1 million for legal and audit fees pertaining to the review of certain internal control issues.
In fiscal 2014 we generated $7.9 million of net cash from the sale of marketable securities compared with $195,000 of net cash generated in fiscal 2013, and $1.9 million of net cash generated in fiscal 2012.
In fiscal 2014, we used $248,000 to purchase property, plant and equipment compared with approximately $190,000 in fiscal 2013, and approximately $268,000 in fiscal 2012. The increase in fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013 is related to the purchase of new computer equipment for our sales force.
In fiscal 2014, we generated proceeds from financing activities of $360,000 from the exercise of stock options, $150,000 in fiscal 2013, and $209,000 in fiscal 2012.
We believe the $12.1 million of cash and short-term investments we maintained at March 31, 2014, is adequate to meet our needs for the next twelve months, and depending upon our profitability, substantially longer. Although we have historically not generated cash from operations because we have yet to achieve profitability, we anticipate that we will become profitable and generate excess cash from operations prior to the full use of the current available cash and investments. To achieve this however, we must generate substantially more revenue than we have this year or in prior years.
Our ability to achieve significant revenue growth will depend, in large part, on our ability to achieve widespread market acceptance for our products and successfully expand our business in the U.S. We cannot guarantee that we will be entirely successful at this. If we fail to meet our projections of profitability and cash flow, or determine to use cash for matters we have not currently projected, we may need to again seek financing to meet our cash needs. We cannot assure you that such financing, if needed, will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
We expect to continue to incur costs for clinical studies to support our ongoing marketing efforts and to meet regulatory requirements. We also expect to continue to incur significant expenses to support our U.S. sales and marketing organization, and for regulatory activities.
Future payments under our contractual obligations as of March 31, 2014, consisting of royalties, purchase commitments, and operating leases, are summarized below:
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less Than 1 Year | 1 – 3 Years | 3 – 5 Years | More Than 5 Years | ||||||||||||||||
| Minimum royalty payments (a) | $ | 117,000 | $ | 54,000 | $ | 63,000 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||||
| Minimum purchase agreement (b) | 283,000 | 283,000 | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Operating lease commitments (c) | 1,004,000 | 252,000 | 584,000 | 168,000 | - | |||||||||||||||
| Total contractual obligations | $ | 1,404,000 | $ | 589,000 | $ | 647,000 | $ | 168,000 | $ | - | ||||||||||
We have a defined benefit pension plan covering seven current and nineteen former employees in The Netherlands. We pay premiums to an insurance company to fund annuities for the current employees. We are responsible for funding additional annuities based on continued service and future salary increases. We closed this defined benefit plan for new employees in April 2005. As of that date, The Netherlands subsidiary established a defined contribution plan that now covers new employees. We also have a defined benefit pension plan for six former employees of our U.K. subsidiary. We closed this plan to further accrual for all employees effective December 31, 2004, and, effective March 2005, established a defined contribution plan that now covers new employees.
The following table presents the sensitivity of our funded status as of March 31, 2014, and expected fiscal 2015 pension expense to the following changes in key assumptions:
Increase/(Decrease) Funded Status at March 31, 2014 | Increase/(Decrease) Fiscal 2015 Pension Expense | |||||||
| Assumption: | ||||||||
| Increase in discount rate by 1 percentage point | $ | 295,000 | $ | (16,000 | ) | |||
| Decrease in discount rate by 1 percentage point | (390,000 | ) | 25,000 | |||||
| Increase in estimated return on assets by 1 percentage point | n/ | a | (8,000 | ) | ||||
| Decrease of estimated return on assets by 1 percentage point | n/ | a | 8,000 | |||||
| Increase in inflation rate by 1 percentage point | (460,000 | ) | 57,000 | |||||
| Decrease in inflation rate by 1 percentage point | 396,000 | (45,000 | ) | |||||
| Increase in compensation by 1 percentage point | (420,000 | ) | 51,000 | |||||
| Decrease in compensation by 1 percentage point | 6,000 | (1,000 | ) | |||||
Regarding the Netherlands defined benefit plan, the market value of the assets is determined as the discounted stream of guaranteed benefit payments. Given the valuation method of the assets, the expected long-term rate of return on assets equals the discount rate. As such the Netherlands defined benefit plan is not included in the sensitivity analysis for the estimated return on assets, because the sensitivity on the estimated return on assets is implicitly already included in the sensitivity analysis for the discount rate.
New Accounting Pronouncements.
In February 2013, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2013-02, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income.” ASU 2013-02 requires an entity to provide information about the amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. In addition, an entity is required to present, either on the face of the statement where net income is presented or in the notes, significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by the respective line items of net income but only if the amount reclassified is required under GAAP to be reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period. For other amounts that are not required under GAAP to be reclassified in their entirety to net income, an entity is required to cross-reference to other disclosures required under GAAP that provide additional detail about those amounts. The guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2012. The adoption of ASU 2013-02 did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or liquidity.
In July 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-11, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carry forward, a Similar Tax Loss, or a Tax Credit Carry forward Exists.” ASU No. 2013-11 provides financial statement presentation guidance on whether an unrecognized tax benefit must be presented as either a reduction to a deferred tax asset or separately as a liability. ASU No. 2013-11 will be effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2013. We do not believe the adoption of this update will have a material impact on our financial statements.
In April 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-08, “Presentation of Financial Statements (Topic 205) and Property, Plant, and Equipment (Topic 360): Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Disposals of Components of an Entity.” The amendments in the ASU change the criteria for reporting discontinued operations while enhancing disclosures in this area. It also addresses sources of confusion and inconsistent application related to financial reporting of discontinued operations guidance in GAAP. Under the new guidance, only disposals representing a strategic shift in operations should be presented as discontinued operations. In addition, the new guidance requires expanded disclosures about discontinued operations that will provide financial statement users with more information about the assets, liabilities, income, and expenses of discontinued operations.
The new guidance also requires disclosure of the pre-tax income attributable to a disposal of a significant part of an organization that does not qualify for discontinued operations reporting. This disclosure will provide users with information about the ongoing trends in a reporting organization’s results from continuing operations. The amendments in the ASU are effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2014. We do not believe the adoption of this update will have a material impact on our financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB has issued ASU No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)”. The guidance in this update supersedes the revenue recognition requirements in Topic 605, “Revenue Recognition.” In addition, the existing requirements for the recognition of a gain or loss on the transfer of nonfinancial assets that are not in a contract with a customer (for example, assets within the scope of Topic 360, Property, Plant, and Equipment, and intangible assets within the scope of Topic 350, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other) are amended to be consistent with the guidance on recognition and measurement (including the constraint on revenue) in this Update. Under the new guidance, an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The amendments in ASU No, 2014-09 are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within that reporting period. Early application is not permitted. We do not believe the adoption of this update will have a material impact on our financial statements.
Cash Investments – The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve our capital for the purpose of funding operations while at the same time maximizing the income we receive from our investments without significantly increasing risk or availability. To achieve these objectives, our investment policy allows us to maintain a portfolio of cash equivalents and investments in a variety of marketable securities, including money market funds, U.S. government securities, and certain bank obligations. Our cash and cash equivalents as of March 31, 2014 include liquid money market accounts. Due to the relative short-term nature of these investments, we believe that there is no material exposure to interest rate risk.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk – We are subject to exposures resulting from foreign currency exchange fluctuations in the normal course of business because of the global nature of our operations. Our primary exchange rate exposures are with the Euro and the British pound. The direct financial impact of foreign currency exchange includes the effect of translating profits from local currencies to U.S. dollars, the impact of currency fluctuations on the transfer of goods between our operations in the United States and abroad and transaction gains and losses. A stronger dollar generally has a negative impact on results from operations outside the United States, while a weaker dollar generally has a positive effect because our products are currently manufactured or sourced primarily from the United States.
In addition to the direct financial impact, foreign currency exchange has an indirect financial impact on our results, including the effect on sales volumes within local economies and the impact of any pricing actions we may take as a result of foreign exchange rate fluctuations. When the U.S. dollar weakens against foreign currencies, the dollar value of sales denominated in foreign currencies increases. When the U.S. dollar strengthens against foreign currencies, the dollar value of sales denominated in foreign currencies decreases. A hypothetical 10% change in the value of the U.S. dollar in relation to our foreign currency exposures would have had an impact of approximately $653,000 on our fiscal 2014 sales. This amount is not indicative of the hypothetical net earnings impact due to the partially offsetting impacts on the related cost of goods sold and operating expenses in the applicable foreign currencies.
The information is contained immediately after the signature page to this Form 10-K under the headings “Consolidated Statements of Operations,” “Consolidated Balance Sheets,” “Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Loss,” “Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity,” “Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows,” “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” and “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firms” and is incorporated herein by reference.
Disclosure controls and procedures are defined by Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"), as controls and other procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in applicable rules and forms and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including our CEO and CFO, in a manner that allows timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
As of March 31, 2014, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our President and CEO (principal executive officer) and our Senior Vice President and CFO (principal financial officer), of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act). Based upon that evaluation, we have concluded that as of March 31, 2014, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Other than such actions noted below under the heading “Remediation Steps to Address Material Weakness in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting,” there have been no changes to our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended March 31, 2014 that have materially affected, or are likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as that term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Our internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to our management and Board of Directors regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in conformity withGAAP, and includes those policies and procedures that:
| · | pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
| · | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations from our management and directors; and |
| · | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2014, based upon the framework in “1992 Internal Control — Integrated Framework” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on this assessment and those criteria, management has determined that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of March 31, 2014.
Remediation of Material Weakness Previously Reported
Our management and Board of Directors previously assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2013. The assessment was provided in our “Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” as set forth in Part II, Item 9A in our Annual Report Form 10-K, for the year ended March 31, 2013 (“2013 Form 10-K”). The assessment identified we did not have adequate internal controls to address the risk of management override of our internal controls. Although we did not experience any material errors in the amounts that we had previously reported in our financial statements, we believe that we had a material weakness in our internal controls such that a material error in our financial statements could have occurred.
Because of the material weakness that was identified, we performed an additional review of internal control over financial reporting for the periods covered by the financial statements included in the 2013 Form 10-K to ensure that the consolidated financial statements included in the 2013 Form 10-K were prepared in accordance with GAAP. No material misstatements of our financial results or financial condition were detected during these additional procedures that caused us to believe that a revision of our previously released earnings report for Fiscal 2013, or restatement of our previously filed financial statements, was required. Nevertheless, the control deficiencies caused us to conclude that there was a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of financial results would not be timely detected if the control deficiencies were not corrected.
Our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, concluded that as of March 31, 2014, the changes described below in “Remediation Steps to Address Material Weakness in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” have successfully remediated the aforementioned material weakness.
Remediation Steps to Address Material Weakness in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
With the oversight of our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, and the Audit Committee of our Board of Directors, we have implemented additional measures to remediate the underlying causes of the material weakness described above. In addition to the management changes we have experienced, these additional measures include updating our internal attestation procedures and additional education of personnel relative to their responsibility for internal control, including sales, accounting, customer service and shipping personnel. With the implementation of these corrective actions, and validation of the operating effectiveness of these corrective actions through testing, management has concluded the remediation measures undertaken by us are operating effectively and the material weakness identified in the 2013 Form 10-K was remediated as of March 31, 2014.
Our operating lease with Liberty Property Limited Partnership for an 18,258 square foot headquarters facility in Minnetonka, Minnesota was amended on January 24, 2014. The amended lease agreement has a term of 62 months and requires average annual minimum rent payments of approximately $154,000. The amended lease also contains the option to extend the lease term for five additional years. The foregoing description of the amendment to the operating lease is a summary of the material terms of the amendment to the lease, does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the complete text of the amendment to the lease, a copy of which is included as Exhibit 10.21 to this Form 10-K.
PART III
The information contained under the headings “Election of Directors,” “Executive Officers” and “Section 16 Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
The information contained under the heading “Executive Compensation” and “Director Compensation” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information contained under the heading “Principal Shareholders” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
The information contained under the heading “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions,” if any, in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
This information contained under the headings Auditing Matters “--Fees,” “--All Other Fees” and “--Pre-Approval Process” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated herein by reference.
| PAGE | |
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | 39 - 40 |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | 41 |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations | 43 |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Loss | 44 |
| Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity | 45 |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | 46 |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | 47 |
Balance at beginning of fiscal year | Additions charged to expenses | Written off, less recoveries | Effects of foreign currency fluctuations | Balance at end of fiscal year | ||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts | ||||||||||||||||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2014 | $ | 21,000 | $ | 8,000 | $ | (5,000 | ) | $ | 1,000 | $ | 25,000 | |||||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2013 | 31,000 | 17,000 | (27,000 | ) | - | 21,000 | ||||||||||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2012 | 11,000 | 30,000 | (9,000 | ) | (1,000 | ) | 31,000 | |||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of fiscal year | Additions charged against revenues | Returns written off | Effects of foreign currency fluctuations | Balance at end of fiscal year | ||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for sales returns | ||||||||||||||||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2014 | $ | 53,000 | $ | 43,000 | $ | (76,000 | ) | $ | 0.00 | $ | 20,000 | |||||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2013 | 62,000 | 26,000 | (35,000 | ) | - | 53,000 | ||||||||||||||
Fiscal year ended March 31, 2012 | 59,000 | 82,000 | (79,000 | ) | - | 62,000 | ||||||||||||||
| Number | Description | |
| Amended & Restated By Laws of Uroplasty, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Registrant’s Form 8-K filed November 20, 2009) | ||
| Restated Articles of Incorporation of Uroplasty, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form SB-2 filed October 18, 2007 (File No. 333-146787)) | ||
| Settlement Agreement and Release dated November 30, 1993 by and between Bioplasty, Inc., Bio-Manufacturing, Inc., Uroplasty, Inc., Arthur A. Beisang, Arthur A. Beisang III, MD and Robert A. Ersek, MD (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 6.1 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form 10SB filed July 10, 1996) | ||
| Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Susan Holman dated December 7, 1999. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to Registrant’s Form 10-KSB for the year ended March 31, 2000 filed June 26, 2000) | ||
| Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Larry Heinemann dated December 7, 1999. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to Registrant’s Form 10-KSB for the year ended March 31, 2000, filed June 26, 2000) | ||
| Agreement, dated October 14, 1998, by and between Uroplasty, Inc. and Samir M. Henalla (pertaining to Macroplastique Implantation System). (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to Registrant’s Form 10-KSB/A for the year ended March 31, 2001, filed March 27, 2002) | ||
| 2002 Employee Stock Option Plan (Incorporated by reference to the copy filed as Appendix B to the Proxy Statement filed with the SEC on August 1, 2002) |
| 10.6* | Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Mr. Marc Herregraven dated November 15, 2002. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to Registrant’s Form 10-KSB for the year ended March 31, 2003, filed May 20, 2003) | |
| 10.7* | Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Mahedi A. Jiwani dated November 14, 2005 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to Registrant’s Form 10-QSB filed November 14, 2005) | |
| 10.8* | Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and David B. Kaysen dated May 17, 2006 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.30 to Registrant’s Form 10-KSB filed June 29, 2006) | |
| 10.9* | 2006 Amended Stock and Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to the copy attached as Appendix A to the Company’s Definitive Proxy Statement filed on July 25, 2008) | |
| 10.10* | Amendment to the Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Mr. David B. Kaysen. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Form 8-K dated April 26, 2011) | |
| 10.11 | Lease Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Liberty Property Limited Partnership dated January 20, 2006 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.25 to Registrant’s Form 8-K filed January 24, 2006) | |
| 10.12 | Form of Purchase Agreement, dated as of March 15, 2007, by and between Uroplasty, Inc. and CystoMedix, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.36 to Registrant’s Form 8-K filed March 20, 2007 | |
| 10.13* | Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Nancy Kolb dated May 22, 2012 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to Registrant’s Form 10-K filed May 24, 2012) | |
| 10.14* | Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Darin Hammers dated February 11, 2013 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to Registrant’s Form 10-K filed July 23, 2013) | |
| 10.15* | Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Robert C. Kill dated July 19, 2013 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to Registrant’s Form 10-K filed July 23, 2013) | |
| 10.16* | Separation Agreement dated April 5, 2013, as amended by Addendum to Settlement Agreement dated July 22, 2013, between Uroplasty, Inc. and David B. Kaysen (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to Registrant’s Form 10-K filed July 23, 2013) | |
| 10.17* | Separation Agreement dated July 19, 2013 between Uroplasty and Mahedi Jiwani (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to Registrant’s Form 10-K filed July 23, 2013) | |
| 10.18* | Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Brett Reynolds dated July 25, 2013 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Form 8-K filed August 12, 2013) | |
| 10.19* | Separation Agreement dated April 28, 2014, between Uroplasty and Nancy Kolb (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Form 8-K dated May 21, 2014) | |
| 10.20* | Amendment to the Employment Agreement between Uroplasty, Inc. and Robert C. Kill dated May 29, 2014 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Form 8-K dated June 3, 2014) | |
| 14.1 | Revised Code of Ethics titled Code of Business Conduct and Ethics for Directors, Officers and Employees (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 14.1 to Registrant’s Form 8-K filed April 12, 2007) |
| Number | Description | |
| First Amendment to Lease by and between Liberty Property Limited Partnership and Uroplasty, Inc. dated January 24, 2014 | ||
| List of Subsidiaries | ||
| Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm – Grant Thornton LLP | ||
| Power of Attorney | ||
| Certification by the CEO and CFO pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | ||
| Certification by the CEO and CFO pursuant to 18 USC Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | ||
| Press Release dated May 15, 2014. | ||
| 101 | Financial statements from the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2014, formatted in Extensible Business Reporting Language: (i) Financial Statement Schedules, (ii) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Loss, (v) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows and (vi) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
| * Management contract, compensation plan or arrangement |
In accordance with Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| Dated: June 9, 2014 | UROPLASTY, INC. | ||
| By | /s/ Robert Kill | ||
| Robert Kill | |||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | |||
In accordance with the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Name | Title / Capacity | Date | |
| /s/ Robert Kill | President, Chief Executive Officer and | June 9, 2014 | |
| Robert Kill | Chairman of the Board of Directors (Principal Executive Officer) | ||
| /s/ Brett Reynolds | Senior Vice President, Chief Financial | June 9, 2014 | |
| Brett Reynolds | Officer and Corporate Secretary (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | ||
| /s/ Thomas E. Jamison* | Director | June 9, 2014 | |
| Thomas E. Jamison | |||
| /s/ Lee A. Jones* | Director | June 9, 2014 | |
| Lee A. Jones | |||
| /s/ R. Patrick Maxwell* | Director | June 9, 2014 | |
| R. Patrick Maxwell | |||
| /s/ Kevin H. Roche* | Director | June 9, 2014 | |
| Kevin H. Roche | |||
| /s/ James P. Stauner* | Lead Director | June 9, 2014 | |
| James P. Stauner | |||
| /s/ Sven A. Wehrwein* | Director | June 9, 2014 | |
| Sven A. Wehrwein |
*Robert Kill, by signing his name hereto, does hereby sign this document on behalf of each of the above named directors of the registrant pursuant to powers of attorney duly executed by such persons.
| Page(s) | |
| Consolidated Financial Statements: | |
| 42 | |
| 44 | |
| 45 | |
| 46 | |
| 47 | |
| 48 |
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Uroplasty, Inc. (a Minnesota corporation) and subsidiaries (together the “Company”) as of March 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive loss, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2014. Our audits of the basic consolidated financial statements included the financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2). These financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Uroplasty, Inc. and subsidiaries as of March 31, 2014 and 2013, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended March 31, 2014, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2014, based on criteria established in 1992 Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated June 9, 2014, expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Grant Thornton LLP
Minneapolis, Minnesota
June 9, 2014
Uroplasty, Inc.
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Uroplasty, Inc. (a Minnesota corporation) and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of March 31, 2014, based on criteria established in 1992 Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of March 31, 2014, based on criteria established in 1992 Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by COSO.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements of the Company as of and for the year ended March 31, 2014, and our report dated June 9, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements and financial statement schedule.
/s/ Grant Thornton LLP
Minneapolis, Minnesota
June 9, 2014
UROPLASTY, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
March 31,
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 8,681,609 | $ | 3,533,864 | ||||
| Short-term investments | 3,451,086 | 7,936,605 | ||||||
| Accounts receivable, net | 2,875,275 | 2,553,447 | ||||||
| Inventories | 517,217 | 718,933 | ||||||
| Other | 507,299 | 566,536 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 16,032,486 | 15,309,385 | ||||||
| Property, plant, and equipment, net | 997,609 | 1,033,085 | ||||||
| Intangible assets, net | 119,980 | 100,502 | ||||||
| Long-term investments | - | 3,451,711 | ||||||
| Prepaid pension assets | 855 | - | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets | 150,116 | 146,052 | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 17,301,046 | $ | 20,040,735 | ||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
UROPLASTY, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
March 31,
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 904,879 | $ | 618,916 | ||||
| Current portion - deferred rent | 2,917 | 35,000 | ||||||
| Income tax payable | 21,922 | 7,729 | ||||||
| Accrued liabilities: | ||||||||
| Compensation | 1,999,966 | 1,550,846 | ||||||
| Other | 479,373 | 476,287 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 3,409,057 | 2,688,778 | ||||||
| Deferred rent – less current portion | 171 | 5,141 | ||||||
| Accrued pension liability | 678,118 | 660,580 | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 4,087,346 | 3,354,499 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity: | ||||||||
Common stock $.01 par value; 40,000,000 shares authorized, 21,653,835 and 21,005,582 shares issued and outstanding at March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. | 216,538 | 210,056 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 57,655,628 | 55,866,338 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (44,174,071 | ) | (38,820,981 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (484,395 | ) | (569,177 | ) | ||||
| Total shareholders’ equity | 13,213,700 | 16,686,236 | ||||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 17,301,046 | $ | 20,040,735 | ||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Years ended March 31,
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net sales | $ | 24,577,126 | $ | 22,417,980 | $ | 20,561,714 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 3,049,811 | 3,014,886 | 3,036,967 | |||||||||
| Gross profit | 21,527,315 | 19,403,094 | 17,524,747 | |||||||||
| Operating expenses | ||||||||||||
| General and administrative | 6,522,388 | 4,187,819 | 3,732,623 | |||||||||
| Research and development | 2,151,257 | 2,415,123 | 1,905,366 | |||||||||
| Selling and marketing | 18,121,732 | 15,238,600 | 15,296,217 | |||||||||
| Amortization | 30,462 | 862,833 | 856,995 | |||||||||
| 26,825,839 | 22,704,375 | 21,791,201 | ||||||||||
| Operating loss | (5,298,524 | ) | (3,301,281 | ) | (4,266,454 | ) | ||||||
| Other income (expense) | ||||||||||||
| Interest income | 22,095 | 46,039 | 60,072 | |||||||||
| Interest expense | - | (707 | ) | (57 | ) | |||||||
Foreign currency exchange gain | (4,762 | ) | 1,573 | 3,780 | ||||||||
| $ | 17,333 | 46,905 | 63,795 | |||||||||
| Loss before income taxes | (5,281,191 | ) | (3,254,376 | ) | (4,202,659 | ) | ||||||
| Income tax expense | 71,899 | 50,770 | 47,712 | |||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (5,353,090 | ) | $ | (3,305,146 | ) | $ | (4,250,371 | ) | |||
| Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (0.25 | ) | $ | (0.16 | ) | $ | (0.21 | ) | |||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: | ||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted | 21,118,258 | 20,777,238 | 20,689,819 | |||||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
UROPLASTY, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Years ended March 31,
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (5,353,090 | ) | $ | (3,305,146 | ) | $ | (4,250,371 | ) | |||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | ||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | 133,810 | (85,264 | ) | (79,555 | ) | |||||||
| Unrealized gain on available-for-sale investments | 1,111 | 800 | 8,022 | |||||||||
| Pension adjustments | (50,139 | ) | (120,548 | ) | 34,266 | |||||||
| Total other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | 84,782 | (205,012 | ) | (37,267 | ) | |||||||
| Comprehensive loss | $ | (5,268,308 | ) | $ | (3,510,158 | ) | $ | (4,287,638 | ) | |||
UROPLASTY, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Years ended March 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012
| Common Stock | Additional Paid-in | Accumulated | Accumulated Other Comprehensive | Total Shareholders’ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Deficit | Income (Loss) | Equity | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2011 | 20,664,332 | $ | 206,643 | $ | 54,014,368 | $ | (31,265,464 | ) | $ | (326,898 | ) | $ | 22,628,649 | |||||||||||
| Share-based consulting and compensation expense | 50,200 | 502 | 684,417 | - | - | 684,919 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 94,000 | 940 | 207,885 | - | - | 208,825 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss | - | - | - | (4,250,371 | ) | (37,267 | ) | (4,287,638 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2012 | 20,808,532 | 208,085 | 54,906,670 | (35,515,835 | ) | (364,165 | ) | 19,234,755 | ||||||||||||||||
| Share-based consulting and compensation expense | 157,050 | 1,571 | 810,068 | - | - | 811,639 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 40,000 | 400 | 149,600 | - | - | 150,000 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss | - | - | - | (3,305,146 | ) | (205,012 | ) | (3,510,158 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2013 | 21,005,582 | 210,056 | 55,866,338 | (38,820,981 | ) | (569,177 | ) | 16,686,236 | ||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense | 319,620 | 3,196 | 1,433,074 | - | - | 1,436,270 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 328,633 | 3,286 | 356,216 | - | - | 359,502 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss | - | - | - | (5,353,090 | ) | 84,782 | (5,268,308 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2014 | 21,653,835 | $ | 216,538 | $ | 57,655,628 | $ | (44,174,071 | ) | $ | (484,395 | ) | $ | 13,213,700 | |||||||||||
UROPLASTY, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Years ended March 31,
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (5,353,090 | ) | $ | (3,305,146 | ) | $ | (4,250,371 | ) | |||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 353,238 | 1,152,929 | 1,118,243 | |||||||||
| Gain (loss) on disposal of equipment | (2,872 | ) | 7,617 | 8,447 | ||||||||
| Amortization of premium on marketable securities | 8,341 | 47,559 | 35,277 | |||||||||
| Share-based consulting expense | - | 1,623 | 5,448 | |||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense | 1,436,270 | 810,016 | 679,471 | |||||||||
| Deferred income tax expense | 6,498 | (29,053 | ) | (40,116 | ) | |||||||
| Deferred rent | (37,053 | ) | (36,902 | ) | (35,228 | ) | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net | (257,794 | ) | 108,495 | (653,110 | ) | |||||||
| Inventories | 207,050 | (25,370 | ) | (29.719 | ) | |||||||
| Other current assets | 63,899 | (205,778 | ) | (17,510 | ) | |||||||
| Accounts payable | 281,104 | 30,925 | (59,025 | ) | ||||||||
| Accrued compensation | 436,765 | (25,301 | ) | (21,510 | ) | |||||||
| Accrued liabilities. other | 6,472 | 164,176 | 85,491 | |||||||||
| Accrued pension liability, net | (51,000 | ) | 79,598 | 45,843 | ||||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (2,902,172 | ) | (1,224,612 | ) | (3,128,369 | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from maturity of available-for-sale marketable investments | 7,930,000 | 4,200,000 | 10,018,252 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from maturity of held-to-maturity marketable investments | - | 6,920,000 | 3,740,000 | |||||||||
| Purchases of available-for-sale marketable investments | - | (8,425,034 | ) | (3,046,270 | ) | |||||||
| Purchases of held-to-maturity marketable investments | - | (2,500,000 | ) | (8,840,000 | ) | |||||||
| Purchases of property, plant and equipment | (248,105 | ) | (189.929 | ) | (267,944 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property, plant and equipment | 6,773 | 5,591 | - | |||||||||
| Payments for intangible assets | (49,940 | ) | (17,455 | ) | (77,738 | ) | ||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | 7,638,728 | (6,827 | ) | 1,526,300 | ||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 359,502 | 150,000 | 208,825 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 359,502 | 150,000 | 208,825 | |||||||||
| Effect of exchange rates on cash and cash equivalents | 51,687 | (37,923 | ) | (17,103 | ) | |||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 5,147,745 | (1,119,362 | ) | (1,410,347 | ) | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 3,533,864 | 4,653,226 | 6,063,573 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 8,681,609 | $ | 3,533,864 | $ | 4,653,226 | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | ||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for interest | $ | - | $ | 707 | $ | 57 | ||||||
| Cash paid during the year for income tax | $ | 71,899 | $ | 57,288 | $ | 39,005 | ||||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Nature of Business. We are a medical device company that develops, manufactures and markets innovative, proprietary products for the treatment of voiding dysfunctions. Our primary focus is on two products: our Urgent PC® Neuromodulation System (“Urgent PC System”), which we believe is the only FDA-cleared minimally invasive, office-based neuromodulation therapy for the treatment of overactive bladder (“OAB”) and associated symptoms of urinary urgency, urinary frequency, and urge incontinence; and Macroplastique® Implants, a urethral bulking agent for the treatment of adult female stress urinary incontinence primarily due to intrinsic sphincter deficiency (“ISD”). Outside of the U.S., our Urgent PC System is also approved for treatment of fecal incontinence, and Macroplastique is also approved for treatment of male stress incontinence and vesicoureteral reflux.
Our primary focus is on growth in the U.S. market, which we entered in 2005. Prior to that, essentially all of our business was outside of the U.S. We believe the U.S. market presents a significant opportunity for growth in sales of our products.
Our Urgent PC System uses percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (“PTNS”) to deliver to the tibial nerve an electrical pulse that travels to the sacral nerve plexus, a control center for pelvic floor and bladder function. We have received regulatory clearances for sale of our Urgent PC System in the United States, Canada and Europe. We launched sales of our second generation Urgent PC System in late 2006. We have intellectual property rights relating to key aspects of our neurostimulation therapy, and we believe our intellectual property portfolio provides us a competitive advantage.
We have sold Macroplastique for urological indications in over 40 countries outside the United States since 1991. In October 2006, we received from the FDA pre-market approval for the use of Macroplastique to treat adult female stress urinary incontinence. We began marketing Macroplastique in the United States in 2007.
Principles of Consolidation. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Uroplasty, Inc. and its wholly owned foreign subsidiaries. We have eliminated all significant intercompany accounts and transactions in consolidation.
Revenue Recognition. We recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, title and risk of ownership have passed, the sales price is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably assured. Generally, these criteria are met at the time the product is shipped to the customer. We include shipping and handling charges billed to customers in net sales, and include such costs incurred by us in cost of goods sold. Typically our agreements contain no customer acceptance provisions or clauses. We sell our products to end users and to distributors. Payment terms range from prepayment to 120 days. The distributor payment terms are not contingent on the distributor selling the product to end users. Customers do not have the right to return products except for warranty claims. We offer customary product warranties. During fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, none of our customers individually accounted for 10% or more of our consolidated net sales. We present our sales in our statement of operations net of taxes, such as sales, use, value-added and certain excise taxes, collected from the customers and remitted to governmental authorities.
Use of Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from these estimates. Our significant accounting policies and estimates include revenue recognition, accounts receivable, valuation of inventory, foreign currency translation/transactions, the determination of recoverability of long-lived and intangible assets, share-based compensation, defined benefit pension plans, and income taxes.
Share-Based Compensation. We account for share-based compensation costs under ASC 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation”. ASC 718 covers a wide range of share-based compensation arrangements including stock options, restricted share plans, performance-based awards, share appreciation rights, and employee share purchase plans. We recognize the compensation cost relating to share-based payment transactions, including grants of employee stock options and restricted shares, in our financial statements. We measure that cost based on the fair value of the equity or liability instruments issued.
Defined Benefit Pension Plans. We have a liability attributed to defined benefit pension plans we offered to certain former and current employees of our subsidiaries in the UK and the Netherlands. The liability is dependent upon numerous factors, assumptions and estimates, and the continued benefit costs we incur may be significantly affected by changes in key actuarial assumptions such as the discount rate, mortality, compensation rates, or retirement dates used to determine the projected benefit obligation. Additionally, changes made to the provisions of the plans may impact current and future benefit costs. In accordance with the provisions of ASC 715, “Compensation – Retirement Benefits”, changes in benefit obligations associated with these factors may not be immediately recognized as costs in the statement of operations, but are recognized in future years over the expected average future service of the active employees or the average remaining life expectancies of inactive employees.
Disclosures About Fair Value of Financial Instruments. Estimates of fair value for financial assets and liabilities are based on the framework established in the accounting guidance for fair value measurements. The framework defines fair value, provides guidance for measuring fair value and requires certain disclosures. The framework prioritizes a fair value hierarchy that requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. The following three broad levels of inputs may be used to measure fair value under the fair value hierarchy:
| · | Level 1: Observable inputs such as quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
If the inputs used to measure the financial assets and liabilities fall within more than one of the different levels described above, the categorization is based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement of the instrument.
The following table provides the assets carried at fair value measured on a recurring basis at March 31:
| Asset Class | Fair Value | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Short-term investments: | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government and Agency debt securities | $ | 3,451,000 | $ | - | $ | 3,451,000 | $ | - | ||||||||
| 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Short-term investments: | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government and Agency debt securities | $ | 3,757,000 | $ | - | $ | 3,757,000 | $ | - | ||||||||
| Long-term investments: | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government and Agency debt securities | 3,452,000 | - | 3,452,000 | - | ||||||||||||
U.S. Government and U.S. Government Agency debt securities. Our debt securities consist of bonds, notes and treasury bills with risk ratings of AAA/Aaa and maturity dates within two years from date of purchase. The estimated fair value of these securities is based on valuations provided by external investment managers.
Remeasurements to fair value on a nonrecurring basis relate primarily to our property, plant and equipment and intangible assets and occur when the derived fair value is below their carrying value on our Consolidated Balance Sheet. As of March 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 we had no remeasurements of such assets to fair value.
The carrying amounts reported in the Consolidated Balance Sheets for Long-term investments include certificates of deposit of $4,180,000 at March 31, 2013, for which, due to the negligible risk of changes in value resulting from changes in interest rates of these investments, cost approximates fair market value.
The carrying amounts reported in the Consolidated Balance Sheets for cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, inventories, other current assets, accounts payable and accrued liabilities approximate fair market value.
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Marketable Securities. We consider all cash on-hand and highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. We classify marketable securities having original maturities of more than three months when purchased and remaining maturities of one year or less as short-term investments and marketable securities with remaining maturities of more than one year as long-term investments. We further classify marketable securities as either held-to-maturity or available-for-sale. We classify marketable securities as held-to-maturity when we believe we have the ability and intent to hold such securities to their scheduled maturity dates. All other marketable securities are classified as available-for-sale. We have not designated any of our marketable securities as trading securities.
We carry held-to-maturity marketable securities at their amortized cost and available-for-sale marketable securities at their fair value and report any unrealized appreciation or depreciation in the fair value of available-for-sale marketable securities in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). We monitor our investment portfolio for any decline in fair value that is other-than-temporary and record any such impairment as an impairment loss. We recorded no impairment losses for other-than-temporary declines in the fair value of marketable securities in fiscal 2014, 2013, and 2012.
Cash and cash equivalents include highly liquid money market funds and debt securities with original maturities of three months or less of $6.7 million and $2.2 million at March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Money market funds present negligible risk of changes in value due to changes in interest rates, and their cost approximates their fair market value. We maintain cash in bank accounts, which, at times, may exceed federally insured limits. We have not experienced any losses in such accounts. Cash and cash equivalents held in foreign bank accounts totaled $991,000 and $639,000 at March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
The amortized cost and fair value of our marketable securities classified as available-for-sale at March 31 are summarized as follows:
Amortized Cost | Unrealized Gains | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | |||||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Short-term investments: | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government and Agency debt securities | $ | 3,450,000 | $ | 1,000 | $ | - | $ | 3,451,000 | ||||||||
| Total | $ | 3,450,000 | $ | 1,000 | $ | $ | 3,451,000 | |||||||||
| 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Short-term investments: | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government and Agency debt securities | $ | 3,756,000 | $ | 1,000 | $ | - | $ | 3,757,000 | ||||||||
| Long-term investments: | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Government and Agency debt securities | 3,453,000 | - | (1,000 | ) | 3,452,000 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | 7,209,000 | $ | 1,000 | $ | (1,000 | ) | $ | 7,209,000 | |||||||
Short-term investments include held-to-maturity certificates of deposit of $0.0 million and $4.2 million at March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Long-term investments at March 31, 2013 include $0.0 million of held-to-maturity certificates of deposit that mature within two years from the date of purchase. There were no long-term, held-to-maturity investments at March 31, 2014. Due to the negligible risk of changes in value due to changes in interest rates of these investments, their cost approximates their fair market value.
Accounts Receivable. We grant credit to our customers in the normal course of business and, generally, do not require collateral or any other security to support amounts due. If necessary, we have an outside party assist us with performing credit and reference checks and establishing credit limits for the customer. Accounts outstanding longer than the contractual payment terms, are considered past due. We carry our accounts receivable at the original invoice amount less an estimated allowance for doubtful receivables based on a periodic review of all outstanding amounts, and less an estimated sales return allowance. We determine the allowance for doubtful accounts based on the customer’s financial health, and both historical and expected credit loss experience. We write off our accounts receivable when we deem them uncollectible. We record recoveries of accounts receivable previously written off when received. We are not always able to timely anticipate changes in the financial condition of our customers and if circumstances related to these customers deteriorate, our estimates of the recoverability of accounts receivable could be materially affected and we may be required to record additional allowances. Alternatively, if more allowances are provided than are ultimately required, we may reverse a portion of such provisions in future periods based on the actual collection experience. We determine the sales return allowance based on historical experience. Historically, the accounts receivable balances we have written off and the sales returns have generally been within our expectations. The allowance for doubtful accounts and sales returns was $45,000 and $74,000 at March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Inventories. We state inventories at the lower of cost or market using the first-in, first-out method. We value at lower of cost or market the slow moving and obsolete inventories based upon current and expected future product sales and the expected impact of product transitions or modifications. Historically, the inventory write-offs have generally been within our expectations. Inventories consist of the following at March 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Raw materials | $ | 136,000 | $ | 219,000 | ||||
| Work-in-process | 25,000 | 21,000 | ||||||
| Finished goods | 356,000 | 479,000 | ||||||
| $ | 517,000 | $ | 719,000 | |||||
Property, Plant, and Equipment. We carry property, plant, and equipment, including leasehold improvements, at cost, less accumulated depreciation which consist of the following at March 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Land | $ | 169,000 | $ | 157,000 | ||||
| Building | 768,000 | 716,000 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements | 383,000 | 383,000 | ||||||
| Internal use software | 568,000 | 543,000 | ||||||
| Equipment | 1,573,000 | 1,374,000 | ||||||
| 3,461,000 | 3,173,000 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (2,463,000 | ) | (2,140,000 | ) | ||||
| $ | 998,000 | $ | 1,033,000 | |||||
We provide for depreciation using the straight-line method over useful lives of three to seven years for equipment and 40 years for the building. We charge maintenance and repairs to expense as incurred. We capitalize improvements and amortize them over the shorter of their estimated useful service lives or the remaining lease term. We recognized depreciation expense of approximately $323,000, $290,000 and $261,000 in fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. We capitalized internal use software and web site development costs of $25,000, $75,000, and $109,000 in fiscal 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. These costs are amortized over a three-year period. The net book value of our capitalized software for internal use was $67,000 and $123,000 at March 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Intangible Assets. Our intangible assets are comprised of patents which we amortize on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives of six years.
Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Net value | ||||||||||
| March 31, 2014 | $ | 5,653,000 | $ | 5,533,000 | $ | 120,000 | ||||||
| March 31, 2013 | 5,603,000 | 5,502,000 | 101,000 | |||||||||
At March 31, 2014, we estimate the following annual amortization for these assets in subsequent fiscal years:
| 2015 | $ | 42,000 | ||
| 2016 | 39,000 | |||
| 2017 | 29,000 | |||
| 2018 | 5,000 | |||
| 2019 and beyond | 5,000 | |||
| $ | 120,000 |
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets. Long-lived assets at March 31, 2014 consisted of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets. We review our long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or business circumstances indicate that we may not recover the carrying amount of an asset. We measure recoverability of assets held and used by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future undiscounted net cash flows we expect to generate by the asset. If we consider such assets impaired, we measure the impairment recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. We completed our impairment analysis and concluded there were no impairments in fiscal 2014, 2013, and 2012.
Product Warranty. We warrant our products to be free from defects in material and workmanship under normal use and service for a period of twelve months after the date of sale. Under the terms of these warranties, we repair or replace products we deem defective due to material or workmanship. We recognized warranty expense of $3,000, $11,000 and $37,000 for the years ended March 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Foreign Currency Translation. We translate all assets and liabilities using period-end exchange rates. We translate statements of operations items using average exchange rates for the period. We record the resulting translation adjustment within accumulated other comprehensive loss, a separate component of shareholders’ equity. We recognize foreign currency transaction gains and losses in our consolidated statements of operations, including unrealized gains and losses on short-term intercompany obligations using period-end exchange rates.
We recognize exchange gains and losses primarily as a result of fluctuations in currency rates between the U.S. dollar (the functional reporting currency) and the Euro and British pound (currencies of our subsidiaries), as well as their effect on the dollar denominated intercompany obligations between us and our foreign subsidiaries. All intercompany balances are revolving in nature and we do not deem any portion of them to be long-term. We recognized foreign currency exchange gains and losses of approximately $(5,000), $2,000 and $4,000 for the years ended March 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Income Taxes. We account for income taxes using the asset and liability method. The asset and liability method provides that deferred tax assets and liabilities be recorded based on the differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts for financial reporting purposes. We reduce deferred tax assets by a valuation allowance, when we believe it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
ASC 740, “Accounting for Income Taxes”, prescribes a recognition threshold and a measurement attribute for financial statement recognition of tax positions we take or expect to take in a tax return. It is management’s responsibility to determine whether it is “more-likely-than-not” that a taxing authority will sustain a tax position upon examination, including resolution of any related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of the position.
Under our accounting policies we recognize interest and penalties accrued on unrecognized tax benefits as well as interest received from favorable tax settlements within income tax expense.
As of March 31, 2014, we have generated approximately $36 million in U.S. net operating loss carry forwards that we cannot use to offset taxable income in foreign jurisdictions. We recognize a valuation allowance when we determine it is more likely than not that we will not realize a portion of the deferred tax asset. We have established a valuation allowance for all U.S. deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty that we will generate enough income in those taxing jurisdictions to utilize the assets.
In addition, future utilization of net operating loss (“NOL”) carry forwards is subject to certain limitations under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. This section generally relates to a 50 percent change in ownership of a company over a three-year period. We believe that the issuance of our common stock in the December 2006 follow-on public offering resulted in an “ownership change” under Section 382. Accordingly, our ability to use NOL attributes generated prior to December 2006 is limited to approximately $750,000 per year. Additionally, we believe there was an ownership change in December 2012. Accordingly, our ability to use NOL tax attributes generated after December 2006 and before December 2012 is limited to approximately $2,000,000 per year.
Basic and Diluted Net Loss per Share. We calculate basic per common share amounts by dividing net loss by the weighted-average common shares outstanding, excluding outstanding shares contingently subject to forfeiture. For calculating diluted per common share amounts, we add additional shares to the weighted-average common shares outstanding for the assumed exercise of stock options and vesting of restricted shares, if dilutive. Because we had a net loss in fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, the following options outstanding and unvested restricted stock to purchase shares of our common stock were excluded from diluted net loss per common share because of their anti-dilutive effect, and therefore, basic net loss per common share equals dilutive net loss per common share:
Number of options and unvested restricted stock | Range of exercise prices | |||||||
| Years ended: | ||||||||
| March 31, 2014 | 741,000 | $ | 0.77 - $2.75 | |||||
| March 31, 2013 | 545,000 | $ | 0.77 - $2.06 | |||||
| March 31, 2012 | 909,000 | $ | 0.77 - $3.00 | |||||
Advertising Expenses. Advertising costs are expensed as incurred. We expensed $595,000, $519,000 and $571,000 in fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-02, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income.” ASU 2013-02 requires an entity to provide information about the amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. In addition, an entity is required to present, either on the face of the statement where net income is presented or in the notes, significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by the respective line items of net income but only if the amount reclassified is required under GAAP to be reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period. For other amounts that are not required under GAAP to be reclassified in their entirety to net income, an entity is required to cross-reference to other disclosures required under GAAP that provide additional detail about those amounts. The guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2012. The adoption of ASU 2013-02 did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or liquidity.
In July 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-11, “Income Taxes (Topic 740): Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carry forward, a Similar Tax Loss, or a Tax Credit Carry forward Exists.” ASU No. 2013-11 provides financial statement presentation guidance on whether an unrecognized tax benefit must be presented as either a reduction to a deferred tax asset or separately as a liability. ASU No. 2013-11 will be effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2013. We do not believe the adoption of this update will have a material impact on our financial statements.
In April 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-08, “Presentation of Financial Statements (Topic 205) and Property, Plant, and Equipment (Topic 360): Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Disposals of Components of an Entity.” The amendments in the ASU change the criteria for reporting discontinued operations while enhancing disclosures in this area. It also addresses sources of confusion and inconsistent application related to financial reporting of discontinued operations guidance in GAAP. Under the new guidance, only disposals representing a strategic shift in operations should be presented as discontinued operations. In addition, the new guidance requires expanded disclosures about discontinued operations that will provide financial statement users with more information about the assets, liabilities, income, and expenses of discontinued operations.
The new guidance also requires disclosure of the pre-tax income attributable to a disposal of a significant part of an organization that does not qualify for discontinued operations reporting. This disclosure will provide users with information about the ongoing trends in a reporting organization’s results from continuing operations. The amendments in the ASU are effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2014. We do not believe the adoption of this update will have a material impact on our financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB has issued ASU No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)”. The guidance in this update supersedes the revenue recognition requirements in Topic 605, “Revenue Recognition.” In addition, the existing requirements for the recognition of a gain or loss on the transfer of nonfinancial assets that are not in a contract with a customer (for example, assets within the scope of Topic 360, Property, Plant, and Equipment, and intangible assets within the scope of Topic 350, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other) are amended to be consistent with the guidance on recognition and measurement (including the constraint on revenue) in this Update. Under the new guidance, an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The amendments in ASU No, 2014-09 are effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within that reporting period. Early application is not permitted. We do not believe the adoption of this update will have a material impact on our financial statements.
Share-based Compensation. At March 31, 2014, we had one active plan for share-based compensation grants (“2006 Plan”). Under the 2006 plan, if we have a change in control, all outstanding grants, including those subject to vesting or other performance targets, fully vest immediately. Under the 2006 Plan, we reserved 3,450,000 shares of our common stock for share-based grants, which includes an additional 750,000 shares as approved by the shareholders at our annual meeting on September 12, 2013, and 821,496 shares remain available for grant at March 31, 2014.
On July 23, 2013, and in connection with the commencement of his employment, Robert Kill received a stock grant of 300,000 shares under the 2006 Plan that did not carry vesting restrictions.
We grant option awards with an exercise price equal to the closing market price of our stock at the date of the grant. We have options outstanding to purchase 1,428,043 shares of common stock granted under the 2006 Plan. Options granted under the 2006 Plan generally expire over a period ranging from five to seven years from date of grant and vest at varying rates ranging up to three years.
We have fully vested options outstanding to purchase 900,000 shares of common stock, not granted under a plan, which expire up to ten years from date of grant.
We grant options at the discretion of our directors. The options granted under the 2006 Plan generally provide for the exercise of options during a limited period following termination of employment, death or disability.
We recognize share-based compensation expense in the statement of operations based on the fair value at the time of grant of the share-based payment over the requisite service period. We incurred a total of approximately $1,436,000, $812,000 and $685,000 in share-based compensation expense (inclusive of $0, $2,000 and $5,000, respectively, for grants to consultants) in fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
We determine the fair value of the option awards using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. We used the following weighted-average assumptions to value the options granted during the years ended March 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Expected life, in years | 4.51 | 6.00 | 5.32 | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.36 | % | 1.15 | % | 1.57 | % | ||||||
| Expected volatility | 89.1 | % | 89.03 | % | 90.08 | % | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
The expected life selected for options granted represents the period of time we expect options to be outstanding based on historical data of option holder exercise and termination behavior for similar grants. The risk-free interest rate for periods within the contractual life of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury rate over the expected life at the time of grant. Expected volatility is based upon historical volatility of our stock. We estimate the forfeiture rate for stock awards to be approximately 1.6% for executive employees and directors and approximately 18% for non-executive employees for fiscal 2014 based on our historical experience.
The following table summarizes the activity related to our stock options in fiscal 2012, 2013 and 2014:
Number of shares | Weighted average exercise price | Weighted average grant date fair value | Aggregate intrinsic value | Weighted average remaining life in years | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2011 | 2,066,000 | $ | 3.39 | |||||||||||||||||
| Options granted | 140,000 | 6.66 | $ | 4.70 | ||||||||||||||||
| Options exercised | (94,000 | ) | 2.22 | $ | 430,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Options surrendered | (29,000 | ) | 5.36 | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2012 | 2,083,000 | $ | 3.64 | $ | 968,000 | 2.96 | ||||||||||||||
| Options granted | 188,000 | 3.09 | $ | 2.26 | ||||||||||||||||
| Options exercised | (40,000 | ) | 3.75 | 18,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Options surrendered | (215,000 | ) | 4.36 | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2013 | 2,016,000 | $ | 3.51 | $ | 598,000 | 2.64 | ||||||||||||||
| Options granted | 939,000 | 2.57 | $ | 1.71 | ||||||||||||||||
| Options exercised | (346,000 | ) | 1.21 | 792,000 | ||||||||||||||||
| Options surrendered | (280,000 | ) | 4.22 | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2014 | 2,329,000 | 3.39 | $ | 1,781,000 | 3.85 | |||||||||||||||
| Options exercisable at March 31, 2014 | 1,279,340 | $ | 3.98 | $ | 684,236 | 1.87 | ||||||||||||||
The total fair value of stock options vested during fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $435,000, $490,000 and $398,000, respectively.
We received net proceeds of $360,000 in fiscal 2014, $150,000 in fiscal 2013 and $209,000 in fiscal 2012 from the exercise of stock options.
We grant restricted shares at the discretion of our directors with vesting terms ranging from six months to four years. The following table summarizes the activity related to our restricted stock in fiscal 2012, 2013 and 2014:
Number of Shares | Weighted average grant date fair value | Weighted average remaining life in years | Aggregate intrinsic value | |||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2011 | 55,000 | $ | 4.96 | |||||||||||||
| Shares granted | 50,000 | 6.80 | ||||||||||||||
| Shares vested | (35,000 | ) | $ | 4.91 | $ | 170,000 | ||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2012 | 70,000 | $ | 6.30 | 0.95 | 443,000 | |||||||||||
| Shares granted | 167,000 | 3.61 | ||||||||||||||
| Shares vested | (47,000 | ) | 4.76 | 225,000 | ||||||||||||
| Shares surrendered | (10,000 | ) | $ | 3.21 | ||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2013 | 180,000 | $ | 4.39 | 1.50 | $ | 790,000 | ||||||||||
| Shares granted | 122,000 | 3.06 | ||||||||||||||
| Shares vested | (53,000 | ) | 4.13 | 221,000 | ||||||||||||
| Shares surrendered | (102,000 | ) | 4.38 | |||||||||||||
| Balance at March 31, 2014 | 147,000 | $ | 3.38 | 2.23 | $ | 540,000 | ||||||||||
The aggregate intrinsic value shown above for the restricted shares represents the total pre-tax value based on the closing price of our common stock on the grant date.
At March 31, 2014, we had approximately $1,750,460 of unrecognized share-based compensation cost, net of estimated forfeitures, related to stock options and restricted shares that we expect to recognize over a weighted-average requisite service period of approximately two years.
Royalties. We received an absolute assignment of a patent relating to the Macroplastique Implantation System, in return for a royalty of 10 British Pounds for each unit sold during the life of the patent. Under the terms of an agreement with some former officers and directors of our company, we pay royalties equal to five percent of the net sales of certain Macroplastique products, subject to a specified monthly minimum of $4,500. The royalties payable under this agreement will continue until certain patents referenced in the agreement expire in 2015. We recognized an aggregate of $353,000, $353,000 and $383,000 of royalty expense under these agreements in fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Purchase Requirements. In our normal course of business we have commitments, generally for periods of less than one year, to purchase from various vendors finished goods and manufacturing components under issued purchase orders. As of March 31, 2014 payments of our contractual obligations for purchase commitments within the next twelve months are $283,000.
Operating Lease Commitments. We lease office, warehouse, and production space under operating lease agreements, which include escalating lease payments, and lease various automobiles for our European employees. These leases expire at various times through June 2019. At March 31, 2014, the approximate future minimum lease payments in subsequent fiscal years under noncancelable operating leases with an initial term in excess of one year are as follows:
| 2015 | $ | 252,000 | ||
| 2016 | 225,000 | |||
| 2017 | 184,000 | |||
| 2018 | 175,000 | |||
| 2019 | 168,000 | |||
| Thereafter | 42,000 | |||
| $ | 1,046,000 |
Total operating lease expenses were $294,000, $252,000 and $271,000 in fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Employment Agreements. We have entered into employment agreements with certain officers, the terms of which, among other things, specify a base salary subject to annual adjustments by mutual agreement of the parties, and a severance payment to the employee upon employment termination without cause. We provide for various severance amounts payable under the agreements after employment termination. Contemporaneously with the execution of their employment agreement, all of the officers executed an “Employee Confidentiality, Inventions, Non-Solicitation, and Non-Compete Agreement.” This agreement prohibits the employee from disclosing confidential information, requires the employee to assign to us without charge all intellectual property relating to our business which is created or conceived during the term of employment, prohibits the employee from encouraging employees to leave our employment for any reason and prohibits competition with us during the term of employment and for a specified term thereafter.
Product Liability. The manufacture and sale of medical devices exposes us to significant risk of product liability claims, some of which may have a negative impact on our business. Any defects or risks that we have not yet identified with our products may give rise to product liability claims. Our existing $10 million of worldwide product liability insurance coverage may be inadequate to protect us from liabilities we may incur or we may not be able to maintain adequate product liability insurance at acceptable rates. If a product liability claim or series of claims is brought against us for uninsured liabilities or in excess of our insurance coverage and it is ultimately determined that we are liable, our business could suffer.
We sponsor various plans for eligible employees in the United States, the United Kingdom (“U.K.”), and The Netherlands. Our retirement savings plan in the United States conforms to Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code and participation is available to substantially all employees. We may also make discretionary contributions ratably to all eligible employees. We made discretionary contributions to the U.S. plan of $224,000, $228,000 and $218,000 for fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Our international subsidiaries in the U.K. and The Netherlands have defined benefit retirement plans for eligible employees. These plans provide benefits based on the employee’s years of service and compensation during the years immediately preceding retirement, termination, disability, or death, as defined in the plans. We froze the U.K. subsidiary’s defined benefit plan on December 31, 2004. On March 10, 2005, we established a defined contribution plan for the U.K. subsidiary. As of April 1, 2005, we closed The Netherlands subsidiary’s defined benefit retirement plan for new employees and established a defined contribution plan for them. The total contribution expense associated with the defined contribution plans in The Netherlands and the U.K. was $22,000, $16,000 and $12,000 for fiscal 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The amortization of actuarial gains or losses is included as a component of the annual expense for a year if, as of the beginning of the year, the cumulative net gain or loss exceeds 10% of the greater of the projected benefit obligation or plan assets. If amortization is required, the amortization is that excess divided by the expected average future service of the active employees participating in the plans or the average remaining life expectancies of inactive employees.
The Netherlands defined benefit pension plan is funded through a guaranteed insurance contract with Swiss Life, an insurance company. Our contract with Swiss Life requires us to make annual premium payments which are sufficient to satisfy the Vested Benefit Obligation (“VBO”). Swiss Life does not hold separate investment assets for our contract, but rather is obligated to provide the stream of future benefits for the annual premium payments we make. We calculate the market value of the pension plan assets, held in Swiss Life insured assets, as the stream, based on mortality, of the earned guaranteed benefit payments discounted at market interest rate. The benefit obligation is calculated based on the same assumptions as well. Accordingly, the impact on pension plan assets of a change in assumption for discount rate and mortality would equally offset the change in VBO.
| 2015 | $ | 4,000 | ||
| 2016 | 23,000 | |||
| 2017 | 23,000 | |||
| 2018 | 24,000 | |||
| 2019 | 24,000 | |||
| 2020 to 2024 | 172,000 | |||
| $ | 270,000 |
We contributed $216,000 in fiscal 2014, $122,000 in fiscal 2013, $154,000 in fiscal 2012, and expect to contribute approximately $150,000 in fiscal 2015.
The following table summarizes the change in benefit obligations and the change in plan assets for the years ended March 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Changes in benefit obligations: | ||||||||
| Projected benefit obligation, beginning of year | $ | 2,624,000 | $ | 1,572,000 | ||||
| Service cost | 126,000 | 74,000 | ||||||
| Interest cost | 108,000 | 88,000 | ||||||
| Benefits paid | (1,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Value transfers | (57,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Plan Amendment | (46,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Actuarial result | 384,000 | 956,000 | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation | 205,000 | (66,000 | ) | |||||
| Projected benefit obligation, end of year | $ | 3,343,000 | $ | 2,624,000 | ||||
Changes in plan assets: | ||||||||
| Plan assets, beginning of year | $ | 1,993,000 | $ | 1,217,000 | ||||
| Contributions to plan | 216,000 | 122,000 | ||||||
| Management cost | (15,000 | ) | (11,000 | ) | ||||
| Actual return on assets | 370,000 | 716,000 | ||||||
| Benefits paid | (1,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Value transfers | (57,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Foreign currency translation | 159,000 | (51,000 | ) | |||||
| Plan assets, end of year | $ | 2,665,000 | $ | 1,993,000 | ||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Unrecognized net prior service benefit | $ | (348,000 | ) | $ | (313,000 | ) | ||
| Unrecognized net losses | 711,000 | 612,000 | ||||||
| Additional other comprehensive loss (gross of deferred taxes) | $ | 363,000 | $ | 299,000 | ||||
The projected benefit obligation, accumulated benefit obligations and the fair value plan assets at March 31 were as follows:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 3,343,000 | $ | 2,624,000 | ||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | 2,704,000 | 2,083,000 | ||||||
| Fair value of plan assets | 2,665,000 | 1,993,000 | ||||||
We have recorded the excess of the projected benefit obligation over the fair value of the plan assets on March 31, 2014 and 2013, of $678,000 and $631,000, respectively, as accrued pension liability.
The cost of our defined benefit retirement plan includes the following components for the years ended March 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Gross service cost, net of employee contribution | $ | 113,000 | �� | $ | 60,000 | $ | 58,000 | |||||
| Interest cost | 108,000 | 88,000 | 86,000 | |||||||||
| Management cost | 11,000 | 11,000 | 14,000 | |||||||||
| Expected return on assets | (72,000 | ) | 2,000 | 9,000 | ||||||||
| Amortization | - | (11,000 | ) | (6,000 | ) | |||||||
| Net periodic retirement cost | $ | 160,000 | $ | 150,000 | $ | 161,000 | ||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Discount rate | 3.40 | % | 3.90 | % | ||||
| Expected return on assets | 3.40 | % | 3.90 | % | ||||
| Expected rate of increase in future compensation: | ||||||||
| General | 2.5 | % | 2.5 | % | ||||
| Individual | 0-3 | % | 0-3 | % | ||||
The discount rate used is based upon the yields available on high quality corporate bonds with a term that matches the liabilities. The impact of the decrease in discount rate used for March 31, 2014 over 2013 was an increase in the projected benefit obligation and actual return on assets. The market value of the assets is determined as the discounted stream of guaranteed benefit payments. Given the valuation method of the assets, the expected long-term rate of return on assets equals the discount rate.
As of March 31, 2014 and 2013, we held all the assets of the U.K. defined benefit pension plan in a Deposit Administration Contract with Phoenix Life Limited.
| 2015 | $ | - | ||
| 2016 | - | |||
| 2017 | 119,000 | |||
| 2018 | - | |||
| 2019 | 184,000 | |||
| 2020 to 2024 | 816,000 | |||
| $ | 1,119,000 |
We contributed $43,000 in fiscal 2014, $34,000 in fiscal 2013, $35,000 in fiscal 2012, and expect to contribute approximately $47,000 in fiscal 2015.
The following table summarizes the change in benefit obligations and the change in plan assets for the years ended March 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Changes in benefit obligations: | ||||||||
| Projected benefit obligation, beginning of year | $ | 665,000 | $ | 733,000 | ||||
| Service cost | 5,000 | 5,000 | ||||||
| Interest cost | 33,000 | 35,000 | ||||||
| Other | (5,000 | ) | (5,000 | ) | ||||
| Actuarial result | (7,000 | ) | (69,000 | ) | ||||
| Foreign currency translation | 64,000 | (34,000 | ) | |||||
| Projected benefit obligation, end of year | $ | 755,000 | $ | 665,000 | ||||
| Changes in plan assets: | ||||||||
| Plan assets, beginning of year | $ | 636,000 | $ | 614,000 | ||||
| Contributions to plan | 43,000 | 34,000 | ||||||
| Management cost | (5,000 | ) | (5,000 | ) | ||||
| Actual return on assets | 19,000 | 24,000 | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation | 63,000 | (31,000 | ) | |||||
| Plan assets, end of year | $ | 756,000 | $ | 636,000 | ||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Unrecognized net losses (gross of deferred taxes) | $ | 130,000 | $ | 130,000 | ||||
The projected benefit obligation, accumulated benefit obligation and the fair value plan assets at March 31 were as follows:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 755,000 | $ | 665,000 | ||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation | 755,000 | 665,000 | ||||||
| Fair value of plan assets | 756,000 | 636,000 | ||||||
We have recorded the excess of the fair value of the plan assets over the projected benefit obligation of $1,000, as of March 31, 2014, as prepaid pension asset. We have recorded the excess of the projected benefit obligation over the fair value of the plan assets of $29,000, as of March 31, 2013, as accrued pension liability.
The cost of our defined benefit retirement plan includes the following components for the years ended March 31:
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Gross service cost, net of employee contribution | $ | 5,000 | $ | 5,000 | $ | 5,000 | ||||||
| Interest cost | 33,000 | 35,000 | 36,000 | |||||||||
| Expected return on assets | (21,000 | ) | (21,000 | ) | (29,000 | ) | ||||||
| Amortization | 7,000 | 15,000 | 12,000 | |||||||||
| Net periodic retirement cost | $ | 24,000 | $ | 34,000 | $ | 24,000 | ||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Discount rate | 4.60 | % | 4.80 | % | ||||
| Expected return on assets | 3.70 | % | 3.10 | % | ||||
The discount rate used is based upon the yields available on high quality corporate bonds with a term that matches the liabilities. The expected return on assets assumption on the investment portfolio for the defined benefit plan is based on the long-term expected returns for the assets currently in the portfolio. Management uses historic return trends of the asset portfolio combined with recent market conditions to estimate the future rate of return.
The primary objective of the Netherlands pension plan is to meet retirement income commitments to plan participants at a reasonable cost. In The Netherlands, consistent with typical practice, the pension plan is funded through a guaranteed insurance contract with Swiss Life, an insurance company. Swiss Life is responsible for the investment strategy of the insurance premiums we make. We have characterized the assets of the pension plan as an “other contract.”
The primary objective of the U.K. pension plan is to meet retirement income commitments to plan participants at a reasonable cost. The objective is achieved through growth of capital and safety of funds invested. The pension plan assets are invested in a Deposit Administration Contract with Phoenix Life Limited, an insurance company, with underlying investments primarily in fixed interest U.K. government bonds.
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
Target Allocation | Actual Allocation | Target Allocation | Actual Allocation | |||||||||||||
| Other Contract (Netherlands Plan) | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||||
| Deposit Administration Contract (U.K. Plan) | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||||
We calculate the market value of the pension plan assets, held in Swiss Life insured assets, as the stream, based on mortality (an unobservable input), of the earned guaranteed benefit payments discounted at market interest rate. Accordingly, we have classified the Netherlands pension plan assets as Level 3 assets. The market value of the U.K. pension plan reflects the value of our contributions to the plan and the credited accrued interest at the rate specified in the Deposit Administration Contract. Accordingly, we have classified the U.K. plan assets as Level 2 assets.
The fair value of the pension plan assets at March 31 by asset class is as follows:
| Asset Class | Total | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | Significant Observable Inputs (Level 2) | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other Contract (Netherlands Plan) | $ | 2,665,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 2,665,000 | ||||||||
| Deposit Administration Contract (U.K. Plan) | 756,000 | - | 756,000 | - | ||||||||||||
| 2013 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other Contract (Netherlands Plan) | $ | 1,993,000 | $ | (3,000 | ) | $ | - | $ | 1,996,000 | |||||||
| Deposit Administration Contract (U.K. Plan) | 636,000 | - | 636,000 | - | ||||||||||||
Other Contract (Netherlands Pension Plan Assets) | ||||
| Beginning balance as at April 1, 2013 | $ | 1,996,000 | ||
| Loss recognized in earnings | 57,000 | |||
| Unrealized actuarial gain recognized in other comprehensive loss | 296,000 | |||
| Purchases | 215,000 | |||
| Sales | (1,000 | ) | ||
| Transfers | (57,000 | ) | ||
| Unrealized foreign currency translation loss recognized in other comprehensive loss | 159,000 | |||
| Ending balance as at March 31, 2014 | $ | 2,665,000 | ||
The unrealized actuarial gain of $296,000, recognized in other comprehensive loss, is equally offset by an unrealized actuarial loss, recognized in other comprehensive income, in the Vested Benefit Obligation.
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Income tax provision: | ||||||||||||
| Current: | ||||||||||||
| U.S. and State | $ | 13,000 | $ | 15,000 | $ | 16,000 | ||||||
| Foreign | 45,000 | 31,000 | 35,000 | |||||||||
| Deferred: | ||||||||||||
| Foreign | 14,000 | 5,000 | (3,000 | ) | ||||||||
| Total income tax expense | $ | 72,000 | $ | 51,000 | $ | 48,000 | ||||||
Actual income tax expense differs from statutory federal income tax benefit for the years ended March 31 as follows:
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Statutory federal income tax benefit | $ | (1,799,000 | ) | $ | (1,111,000 | ) | $ | (1,429,000 | ) | |||
| State tax benefit, net of federal taxes | (125,000 | ) | (82,000 | ) | (91,000 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign tax | (39,000 | ) | (27,000 | ) | (35,000 | ) | ||||||
| Nondeductible expenses | 122,000 | 111,000 | 75,000 | |||||||||
| Stock compensation tax shortfall | 267,000 | (155,000 | ) | - | ||||||||
| Subpart F income | 35,000 | 33,000 | 35,000 | |||||||||
| Undistributed foreign earnings | - | - | 9,000 | |||||||||
| NOL expiration | 307,000 | - | - | |||||||||
| Valuation allowance increase | 1,007,000 | 1,035,000 | 1,210,000 | |||||||||
| Other | 297,000 | 247,000 | 274,000 | |||||||||
| Total income tax expense | $ | 72,000 | $ | 51,000 | $ | 48,000 | ||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets (liabilities): | ||||||||
| Depreciation | $ | 126,000 | $ | 88,000 | ||||
| Amortization | 21,000 | 121,000 | ||||||
| Pension liability | 150,000 | 140,000 | ||||||
| Stock based compensation | 691,000 | 981,000 | ||||||
| Other reserves and accruals | 141,000 | 169,000 | ||||||
| Undistributed foreign earnings | (345,000 | ) | (288,000 | ) | ||||
| Foreign tax credits | 68,000 | 68,000 | ||||||
| Net operating losses | 12,487,000 | 11,050,000 | ||||||
| $ | 13,339,000 | $ | 12,329,000 | |||||
| Less valuation allowance | (13,189,000 | ) | (12,183,000 | ) | ||||
| $ | 150,000 | $ | 146,000 | |||||
At March 31, 2014, we had U.S. NOL carry forwards of approximately $36 million for U.S. income tax purposes, which expire in 2018 through 2033. U.S. net operating loss carry forwards cannot be used to offset taxable income in foreign jurisdictions. In addition, future utilization of NOL carry forwards is subject to certain limitations under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. This section generally relates to a 50 percent change in ownership of a company over a three-year period. We believe that the issuance of our common stock in the December of 2006 follow-on public offering resulted in an "ownership change" under Section 382. Accordingly, our ability to use NOL tax attributes generated prior to December 2006 is limited to approximately $750,000 per year. Additionally, we believe there was an ownership change in December of 2012. Our ability to use NOL tax attributes generated after December 2006 and before December 2012 is limited to approximately $2,000,000 per year.
Certain stock option exercises resulted in tax deductions in excess of previously recorded tax benefits. Our NOL carry forwards of $36 million referenced above include approximately $1.8 million of income tax deductions in excess of previously recorded tax benefits. Although these additional tax deductions are reflected in NOL carry forwards referenced above, the related tax benefit will not be recognized until the deductions reduce taxes payable. Accordingly, since the tax benefit does not reduce our current taxes payable in 2014, these tax benefits are not reflected in our deferred tax assets presented above. The tax benefit of these excess deductions will be reflected as a credit to additional paid-in-capital when and if recognized.
We provide for a valuation allowance when it is more likely than not that we will not realize a portion of the deferred tax assets. We have established a valuation allowance for U.S. and certain foreign deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty that enough taxable income will be generated in those taxing jurisdictions to utilize the assets. Therefore, we have not reflected any benefit of such deferred tax assets in the accompanying financial statements. The deferred tax asset increased by $1,010,227 and $1,058,315, respectively, in fiscal 2014 and 2013. The related valuation allowance increased by $1,006,586 and $1,035,135, respectively, in fiscal 2014 and 2013.
We reviewed all income tax positions taken or that we expect to be taken for all open years and determined that our income tax positions are appropriately stated and supported for all open years.
Under our accounting policies, we recognize interest and penalties on unrecognized tax benefits as well as interest received from favorable tax settlements within income tax expense. As of March 31, 2014 and 2013, we recorded no accrued interest or penalties related to uncertain tax positions.
We have provided for U.S. deferred income taxes as of March 31, 2014 and 2013 for the undistributed earnings from our non-U.S. subsidiaries.
The fiscal tax years 2010 through 2014 remain open to examination by the Internal Revenue Service and various state taxing jurisdictions to which we are subject. In addition, we are subject to examination by certain foreign taxing authorities for which the fiscal years 2011 through 2014 remain open for examination.
ASC 280, “Segment Reporting,” establishes disclosure standards for segments of a company based on management’s approach to defining operating segments. Reportable segments are defined primarily by the nature of products and services, the nature of the production processes, and the type of customers for our products and services. In accordance with the objective and basic principles of the standard we aggregate our operating segments into one reportable segment: voiding dysfunctions.
Information regarding geographic area net sales to customers for the years ended March 31 is as follows:
United States | United Kingdom | All Other Foreign Countries (1) | Consolidated | |||||||||||||
| 2014 | $ | 18,042,000 | $ | 2,485,000 | $ | 4,050,000 | $ | 24,577,000 | ||||||||
| 2013 | 16,401,000 | 2,189,000 | 3,828,000 | 22,418,000 | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 13,854,000 | 1,929,000 | 4,779,000 | 20,562,000 | ||||||||||||
United States | United Kingdom | The Netherlands | Consolidated | |||||||||||||
| 2014 | $ | 379,000 | $ | 4,000 | $ | 615,000 | $ | 998,000 | ||||||||
| 2013 | 434,000 | 5,000 | 594,000 | 1,033,000 | ||||||||||||
Accounting policies of the operations in the various geographic areas are the same as those described in Note 1. Sales attributed to each geographic area are net of intercompany sales and are attributed to countries based on location of customers. No single customer represents 10% or more of our consolidated net sales. Long-lived assets consist of property, plant and equipment.
The following table presents selected unaudited consolidated financial data for each of the eight quarters in the two-year period ended March 31, 2014. In our opinion, this unaudited information is prepared on the same basis as the audited information and includes all adjustments (consisting of only normal recurring adjustments) necessary for a fair statement of the financial information for the period presented. The summation of quarterly data may not equate to the calculation for the full fiscal year as quarterly calculations are performed on a discrete basis.
| 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | ||||||||||||||||
| Net Sales | $ | 5,840,841 | $ | 5,976,875 | $ | 6,398,675 | $ | 6,360,735 | $ | 24,577,126 | ||||||||||
| Gross Profit | 5,092,794 | 5,235,033 | 5,620,408 | 5,579,080 | 21,527,315 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (1,609,292 | ) | (1,927,480 | ) | (670,832 | ) | (1,145,486 | ) | (5,353,090 | ) | ||||||||||
| Basic and Diluted Net Loss per Share | $ | (0.08 | ) | $ | (0.09 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | (0.25 | ) | |||||
| 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | ||||||||||||||||
| Net Sales | $ | 5,577,000 | $ | 5,710,000 | $ | 5,590,000 | $ | 5,541,000 | $ | 22,418,000 | ||||||||||
| Gross Profit | 4,822,000 | 4,935,000 | 4,856,000 | 4,790,000 | 19,403,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Loss | (1,019,000 | ) | (640,000 | ) | (677,000 | ) | (969,000 | ) | (3,305,000 | ) | ||||||||||
| Basic and Diluted Net Loss per Share | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | (0.16 | ) | |||||
64