Exhibit 99.1
Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited and The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited take no responsibility for the contents of this announcement, make no representation as to its accuracy or completeness and expressly disclaim any liability whatsoever for any loss howsoever arising from or in reliance upon the whole or any part of the contents of this announcement.

(a joint stock limited company incorporated in the People’s Republic of China)
(Stock Code: 00525)
2016 ANNUAL RESULT ANNOUNCEMENT
The Board of Directors of Guangshen Railway Company Limited (the “Company”) is pleased to announce the audited results of the Company and its subsidiaries for the year ended 31 December 2016. This announcement, containing the full text of the 2016 Annual Report of the Company, complies with the relevant requirements of the Rules Governing the Listing of Securities on The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited in relation to information to accompany preliminary announcement of annual results. Printed version of the Company’s 2016 Annual Report will be available on the websites of the HKExnews of The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited at www.hkexnews.hk and of the Company at www.gsrc.com on 29 March 2017 and will be despatched to holders of H shares of the Company as soon as practicable. |

Chapter 1 Definitions In this report, unless the context otherwise requires, the expressions stated below will have the following meanings: The Company, Company, Guangshen Railway Reporting period, this period, this year Guangshen Railway Company Limited 12 months from January 1 to December 31, 2016 Same period last year, last year 12 months from January 1 to December 31, 2015 A Share Renminbi-denominated ordinary shares of the Company with a par value of RMB1.00 issued in the PRC and listed on the SSE for subscription in Renminbi H Share Overseas listed foreign shares of the Company with a par value of RMB1.00 issued in Hong Kong and listed on the SEHK for subscription in Hong Kong dollars ADS U.S. dollar-denominated American Depositary Shares representing ownership of 50 H shares issued by trustees in the United States under the authorization of the Company CSRC The China Securities Regulatory Commission SSRB The Shenzhen Securities Regulatory Bureau of the China Securities Regulatory Commission HKSFC The Securities and Futures Commission of Hong Kong SSE The Shanghai Stock Exchange SEHKThe Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited NYSE The New York Stock Exchange SFO The Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571 of the Laws of Hong Kong) Listing Rules The listing rules of SEHK and/or the listing rules of SSE (as the case may be) Articles The articles of associations of the Company Company Law The Company Law of the People’s Republic of China Securities Law The Securities Law of the People’s Republic of China CRC China Railway Corporation GRGC, largest shareholder Guangzhou Railway (Group) Company GZIR Guangdong Guangzhou Intercity Rail Transportation Company Limited WGPR Wuhan-Guangzhou Passenger Railway Line Co., Ltd.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 016 017 GSHER Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link Company Limited GZR Guangzhou-Zhuhai Railway Company Limited XSR Xiamen-Shenzhen Railway Company Limited GSR Ganzhou-Shaoguan Railway Company Limited GGR Guiyang-Guangzhou Railway Company Limited NGR Nanning-Guangzhou Railway Company Limited GMSR Guangmeishan Railway Limited Company SR Guangdong Sanmao Railway Limited Company PRDIR Guangdong Pearl River Delta Inter-city Railway Traffic Company Limited

Chapter 2 Company Profile and Major Financial Indicators I. GENERAL INFORMATION OF THE COMPANY (1) Company Information Chinese name Chinese name abbreviation English name Guangshen Railway Company Limited Legal representative of the Company Wu Yong (2) Contact Person and Contact Information Company Secretary Representative of Securities Affairs Name Guo Xiangdong Deng Yanxia Address No. 1052 Heping Road, Luohu District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province No. 1052 Heping Road, Luohu District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province Tel. (86) 755-25588150 (86) 755-25588150 Fax. (86) 755-25591480 (86) 755-25591480 E-mail ir@gsrc.com ir@gsrc.com (3) Basic Information Registered Address No. 1052 Heping Road, Luohu District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province Postal Code of Registered Address 518010 Place of Business No. 1052 Heping Road, Luohu District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province Postal Code of the Place of Business 518010 Company Website http://www.gsrc.com E-mail ir@gsrc.com (4) Places for Information Disclosure and Reserve Address Newspapers for information disclosure of the Company Websites specified by CSRC to publish the annual report China Securities Journal, Securities Times, Shanghai Securities News, Securities Daily http://www.sse.com.cn http://www.hkexnews.hk http://www.gsrc.com Reserve address of annual report No. 1052 Heping Road, Luohu District, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 018 019 (5) Share information of the Company Share information of the Company Type of the Shares Stock Exchange Stock Short Name Stock Code A Share SSE 601333 H Share SEHK 00525 ADS NYSE — GSH (6) Other Relevant Information Auditor Engaged by the Company (Domestic) Name PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP Office Address 11/F PricewaterhouseCoopers Center, 2 Corporate Avenue, 202 Hu Bin Road, Huangpu District, Shanghai, China Name of signing auditors Zhou Weiran, Hua Jun Auditor Engaged by the Company (International) Legal advisor as to PRC law Legal advisor as to Hong Kong law Legal advisor as to United States law Name PricewaterhouseCoopers Office Address 22nd Floor, Prince’s Building, Central, Hong Kong Name Beijing Grandway Law Office Office Address 12/F, Block C, Skyworth Building, 8 South One Street, Hi-Tech Zone, Nanshan District, Shenzhen, China Name Cleary Gottlieb Steen & Hamilton (Hong Kong) Office Address 37th Floor, Hysan Place, 500 Hennessy Road, Causeway Bay, Hong Kong Name Shearman & Sterling LLP Office Address 12th Floor, Gloucester Tower, The Landmark, 15 Queen’s Road Central, Central, Hong Kong Registrar for A Share Name China Securities Depository and Clearing Corporation Limited Shanghai Branch Office Address 36th Floor, China Insurance Building, No. 166, Lujiazui East Road, Pudong New District, Shanghai, China Registrar for H Share Name Computershare Hong Kong Investor Services Limited Office Address Rooms 1712-1716, 17th Floor, Hopewell Centre, 183 Queen’s Road East, Wan Chai, Hong Kong Depository Name JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. Office Address 13th Floor, No. 4 New York Plaza, New York, USA Principal banker Name Construction Bank of China Shenzhen Branch Jiabin Road Sub-branch Office Address 1st to 4th Floors, Jinwei Building, Jiabin Road, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, China

II. COMPANY PROFILE On March 6, 1996, the Company was registered and established in Shenzhen, the PRC in accordance with the Company Law. In May 1996, H shares and American Depositary Shares issued by the Company were listed on the SEHK and the NYSE respectively. In December 2006, the A Share issued by the Company were listed on the SSE. In January 2007, the Company used the proceeds from the issue of A shares to acquire the railway of Guangzhou-Pingshi section, taking the coverage of the Company’s operations into the national trunk line networks. Currently, the Company is the only PRC railway enterprise with its shares listed in Shanghai, Hong Kong and New York. The Company is mainly engaged in railway passenger and freight transportation businesses, the Hong Kong Through Train passenger services in cooperation with MTR Corporation Limited, and management services for commissioned transportation for other railway companies in the PRC. The Company is also engaged in the provision of integrated services in relation to railway facilities and technology, commercial trading and other industrial businesses that are consistent with the Company’s objectives. The Shenzhen-Guangzhou-Pingshi Railway, which is operated solely and independently by the Company, runs 481.2 kilometers long in operation and connects the entire Guangdong Province vertically. Of which, Guangzhou-Pingshi Railway is the southern part of Beijing-Guangzhou railway, forming an aorta connecting north and south China, whereas Guangzhou-Shenzhen Railway is the only railway passway from mainland China to Hong Kong, and links with the Beijing-Guangzhou, Beijing-Kowloon, Sanshui-Maoming, Pinghu- Nantou, and Pinghu-Yantian lines, as well as to the Xiamen-Shenzhen Railway and the East Rail Line in Hong Kong, forming an important integral part of the railway transportation network in the PRC. Passenger transportation is the principal business of the Company. As at December 31, 2016, the Company operated 253 pairs of passenger trains each day, including 102 pairs of intercity high-speed passenger trains between Guangzhou and Shenzhen (including 94 pairs of inter-city trains between Guangzhou East to Shenzhen (including 20 stand-by pairs), 8 pairs of Guangzhou East to the Chaozhou-Shantou cross-network EMU trains), 13 pairs of Hong Kong Through Trains (including 11 pairs of Canton-Kowloon Through Trains, 1 pair of Zhaoqing-Kowloon Through Trains and 1 pair of Beijing/Shanghai-Kowloon Through Trains) and 138 pairs of long-distance trains (including 10 pairs of Guangzhou-Foshan-Zhaoqing intercity trains, 3 pairs of Guangzhou to Guilin North, Nanning East and Guiyang North cross-network EMU trains). The Company adopts an ‘As-frequent-as-buses’ operation for Guangzhou-Shenzhen inter-city trains, one pair of China Railway High- speed trains (the ‘CRHs’) is dispatched every 10 minutes on average during peak hours between Guangzhou and Shenzhen. The through-trains passing Hong Kong jointly operated by the Company and MTR Corporation Limited are one of the important transportation means going between Guangzhou and Hong Kong. The Company organized and operated a number of long-distance trains running from and to Guangzhou and Shenzhen that linked with most of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipals across the nation. Freight transportation is an important business of the Company. The Company is well-equipped with comprehensive freight facilities and is able to efficiently transport full load cargo, single load cargo, containers, bulky and overweight cargo, dangerous cargo, fresh and live cargo, and oversized cargo, and the rail lines operated are closely knitted with the major ports in Guangzhou and Shenzhen and are connected to several large industrial zones, logistics zones and plants and mines in the Pearl River Delta region via the railroad sidings. The major market of the Company’s freight transportation business is domestic mid- to long- distance transportation, and the Company enjoys competitive advantages in domestic mid- to long-distance freight transportation. Railway operation service is an extended business of passenger and freight transportation expanded by the Company since the commencement of operation of WGPR in December 2009. So far, the Company has provided such service to WGPR, GZIR, GSHER, GZR, XSR, GSR, NGR, GGR and PRDIR. With the completion and commencement of operation of a series of high-speed railways and inter-city railways in ‘Pan Pearl River Delta’ successively, the geographical coverage of railway operation service provided by the Company will be more extensive. Railway operation service will also become a new business growth point of the Company.

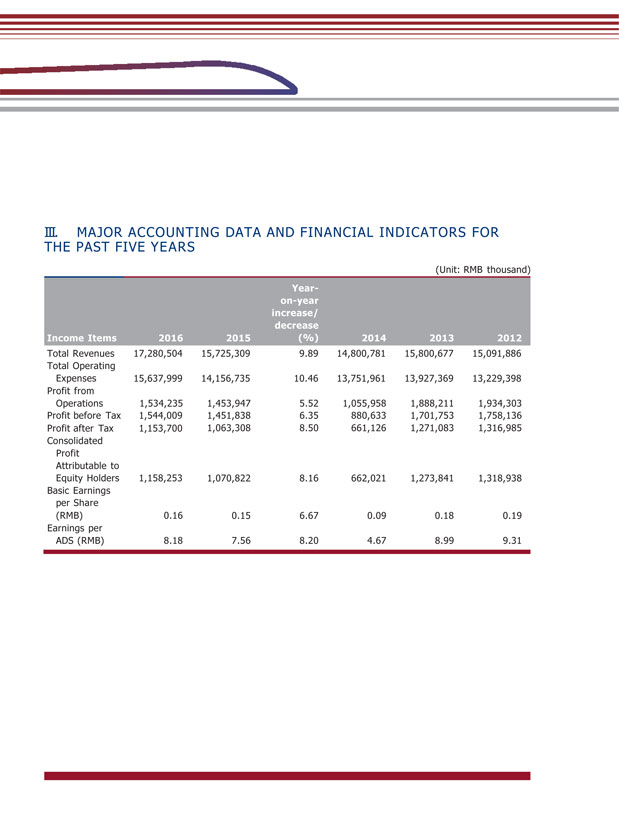
III. MAJOR ACCOUNTING DATA AND FINANCIAL INDICATORS FOR THE PAST FIVE YEARS (Unit: RMB thousand) Income Items 2016 2015 Year- on-year increase/ decrease (%) 2014 2013 2012 Total Revenues Total Operating Expenses 17,280,504 15,637,999 15,725,309 14,156,735 9.89 10.46 14,800,781 13,751,961 15,800,677 13,927,369 15,091,886 13,229,398 Profit from Operations 1,534,235 1,453,947 5.52 1,055,958 1,888,211 1,934,303 Profit before Tax 1,544,009 1,451,838 6.35 880,633 1,701,753 1,758,136 Profit after Tax 1,153,700 Consolidated 1,063,308 8.50 661,126 1,271,083 1,316,985 Attributable to Equity Holders 1,158,253 Basic Earnings 1,070,822 8.16 662,021 1,273,841 1,318,938 per Share (RMB) 0.16 0.15 6.67 0.09 0.18 0.19 ADS (RMB) 8.18 7.56 8.20 4.67 8.99 9.31
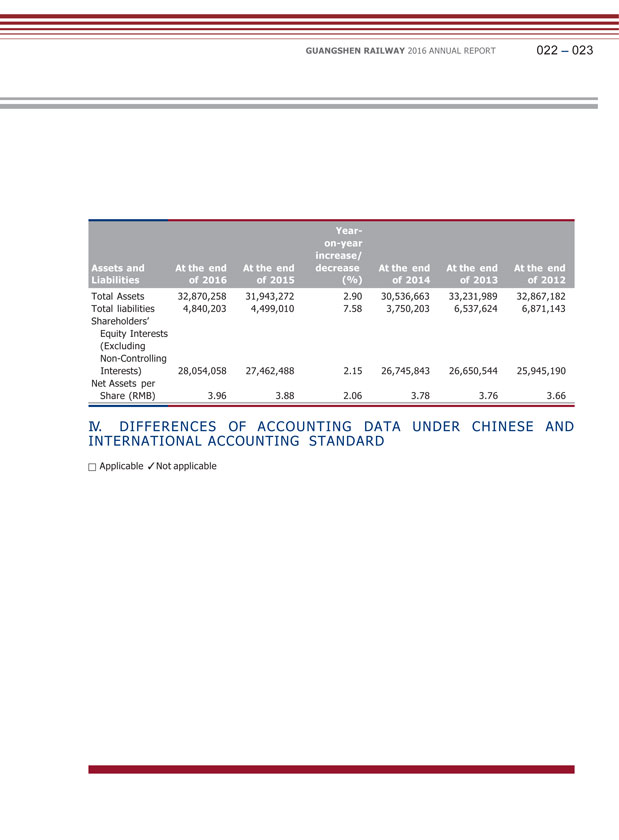
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 022 023 Total Assets 32,870,258 31,943,272 2.90 30,536,663 33,231,989 32,867,182 Total liabilities 4,840,203 4,499,010 7.58 3,750,203 6,537,624 6,871,143 Shareholders’ Equity Interests (Excluding Non-Controlling Interests) 28,054,058 27,462,488 2.15 26,745,843 26,650,544 25,945,190 Net Assets per Share (RMB) 3.96 3.88 2.06 3.78 3.76 3.66 IV. DIFFERENCES OF ACCOUNTING DATA UNDER CHINESE AND INTERNATIONAL ACCOUNTING STANDARD Applicable Not applicable

Chapter 3 Summary of the Company’s Business PRINCIPAL ACTIVITIES, BUSINESS MODEL AND INDUSTRY FACT SHEET DURING THE REPORTING PERIOD Principal Activities and Business Model During the reporting period, as a railway transport enterprise, the Company has been operating the passenger and freight transportation businesses of the Shenzhen-Guangzhou-Pingshi Railway independently, operating the Hong Kong Through Train passenger services in cooperation with MTR Corporation Limited, and providing railway operation services for commissioned transportation for other railway companies such as WGPR, GZIR, GSHER, GZR ,XSR ,GSR, NGR, GGR and PRDIR. Industry Fact Sheet Being the aorta of the nation’s economy, the key important infrastructure and an significant project for people’s livelihood, as well as the backbone of integrated transportation system and one of the main transportation, railway is of crucial importance for nation’s economic and social development. Since the approval for implementation of Medium to Long Term Plan for Railway Network Development by the State Council in 2004, the railway in China developed rapidly. With the completion and commencement of a series of high-speed railways and inter-city railways in recent years, currently on the whole, the tight capacity of railway in China has been alleviated, the bottle-neck restriction has been eliminated and the economic and social development needs have been met in general. By the end of 2016, the national railway reached 124,000 kilometers in operation; while the high-speed railway ran over 22,000 kilometers in operation. In 2016, the national railway achieved a passenger delivery volume of 2,770 million persons, achieving a year- on-year increase of 11.2% of which, locomotives achieved a passenger delivery volume of 1,443 million persons, representing more than 52% of the total passenger delivery volume; the freight transportation of national railway stopped falling and stabilized, reaching a tonnage of freight of 2,650 million tonnes for the year, of which, the tonnage of container, commodity automobile and scattered cargo each recorded historical highs, with an increase of 40%, 53% and 25% respectively.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 024 025 II. EXPLANATION OF THE SIGNIFICANT CHANGE IN THE MAJOR ASSETS OF THE COMPANY DURING THE REPORTING PERIOD For the explanation of the significant change in the major assets of the Company during the reporting period, please read ‘Analysis of assets and liabilities’ in the chapter ‘Report of Directors (Including Management’s Discussion and Analysis)’ in this annual report for details.







Chapter 4 Report of Directors (Including Management’s Discussion and Analysis) Chairman I. CHAIRMAN’S STATEMENT Dear Shareholders, I, on behalf of the Board, am hereby pleased to present the audited operating results of the Company for the year 2016 for the shareholders to review. In 2016, the Company achieved operating revenues of RMB17,281 million, representing a year-on-year increase of 9.89%; consolidated profits attributable to shareholders of RMB1,158 million, representing a year-on-year increase of 8.16%, and basic earnings per share of RMB0.16. The Company has been committed to enhancing corporate values and upholding long-term and stable cash dividend policy, which is in long-term and short-term interest of investors, to provide good and sustainable return for shareholders. The Board recommended the payment of final cash dividend of RMB0.08 per share for 2016, representing 50.00% of the basic earnings per share of this year. The proposal above shall be subject to approval at the 2016 annual general meeting. (1) Business Review 2016 is the first year for China to implement “The Thirteenth Five-Year Plan”, during which China’s economy operated at a slower pace and trended stably and positively. GDP growth rate remained within a reasonable range and the quality and efficiency of economic development were enhanced, providing strong and solid protection for the long-term and stable development of the Company. Nevertheless, with the still complicated and evolving domestic and international economic environment, the operation of the economy still faced greater downward pressure, which suppressed the demand growth of passenger and freight transportation. Meanwhile, the continuous enhancement of high-speed railways networks brought diversion-effect to passenger delivery volume of existing railway sections. All these brought challenges to the Company’s operation. In 2016, the Company achieved a passenger delivery volume of 84.8957 million persons, representing a year-on-year decrease of 0.55%, and a tonnage of freight of 15.3563 million tonnes, representing a year-on-year decrease of 9.03%.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 032 033 Under the above-mentioned operating environment, the Board, which lead the Company’s operation, has upheld stable and sound operation approach during the past year. All dedicated and proactive staff adopted a range of “increasing volume and income, reducing cost and consumption” measures. In regards of increasing income, the Company explored the market potential of passenger and freight transportation, added 5 pairs of cross-network EMU trains between Guangzhou East and Chaozhou-Shantou and 1 pair of long-distance trains between Shenzhen to Urumqi, commenced inter-city passenger transportation business at Pinghu Railway Station, fully pressed ahead with railway supply-side structural reform measures, increased the frequency of southern express lines for freight transportation, continuously expanded service scope of railway operation. In regards of cost reduction, general and non-productive expenses were reduced substantially under strengthened cost management, as a result, cost and expenses were under effective control. Upon the above efforts, the Company has overcome various difficulties and achieved better operating results, generally realized the annual operating objectives determined by the Board. In 2016, the Board has duly performed their duties under the Company’s Articles of Association. With their meticulous and conscientious effort, the Directors strived to enhance the corporate governance and operation management of the Company. The Company has convened 2 general meetings, 5 board meetings and 6 audit committee meetings during the year, in which sound decisions in relation to the Company’s profit distribution, financial budget, production and operation, connected transactions, system establishments as well as recruitment of senior management were made to enhance the Company’s continuous development. (2) Prospects Shareholders are reminded that the Company has made certain forward-looking statements in relation to domestic and international economic conditions and railway transportation market, as well as the work plans of the Company in 2017 and in the future in this annual report. These forward-looking statements are subject to the influences of various uncertainties and risks, and the actual outcome may be greatly different from the forward-looking statements. These statements do not constitute any commitment to the future operating results of the Company. Please be advised to consider the investment risks. In 2017, domestic and international economic conditions are not positive and the Chinese economy is still faced with greater downward pressure. Nevertheless, with the implementation of a range of “stabilizing growth, adjusting structure” policies and measures by the government, it is expected the Chinese economy will retain the pace of “progress with stability”, and GDP growth rate may slow down but remain within a reasonable range. In respect of industry developments, being the aorta of the nation’s economy and an important infrastructure of the nation, investments in railway has been intensified by the State in recent years. Various high-speed railways and inter-city railways will be completed and commence operation in 2017, and the capacity of railway transportation, especially passenger delivery capacity will continue to grow at a steady pace. Consequently, under the combined effect of the above factors, market demand of railway passenger transportation will grow at a faster pace in 2017.

In 2017, facing complicated and evolving business environment, with the railway spirit of “Safety, Quality, Development of Railway and Prosperity of Country” in the new era, the Company will uphold the operating objectives of the Company, adapt to the new normal of economic development proactively, adhere to market-oriented approach, focus on economic efficiency, preserve the main theme of scientific and harmonious development, enhance coordination in workplace safety, explore operational potentials, enhance service quality, improve assets management, strengthen cost control, standardize operation management, coordinate and control work in the areas of safety, transportation, operation, construction and stability. In 2017, the Company will meticulously materialize the spirit of the Central Economic Work Conference and CRC’s annual work conference through expediting the pace of reformation of the investment and financing system and proactively explore the reformative model of mixed ownership with diversified equity investment, in an effort to grow and prosper the Company and generate solid operating results. I, together with the members of the Board, believe that in the forthcoming year, the Company is going to attain new achievements in different aspects, create new values for our shareholders and make new contributions to the development of society under the strong support of all shareholders and various sectors of the society, along with the joint efforts of the Board, supervisory committee, management and all staff. By order of the Board Wu Yong Chairman of the Board Shenzhen, China 29 March 2017
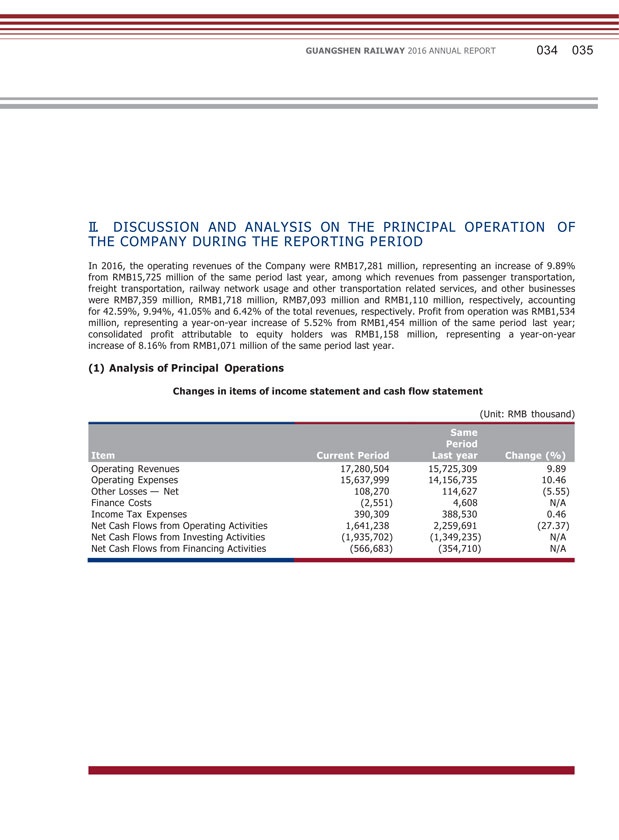
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 034 035 II. DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS ON THE PRINCIPAL OPERATION OF THE COMPANY DURING THE REPORTING PERIOD In 2016, the operating revenues of the Company were RMB17,281 million, representing an increase of 9.89% from RMB15,725 million of the same period last year, among which revenues from passenger transportation, freight transportation, railway network usage and other transportation related services, and other businesses were RMB7,359 million, RMB1,718 million, RMB7,093 million and RMB1,110 million, respectively, accounting for 42.59%, 9.94%, 41.05% and 6.42% of the total revenues, respectively. Profit from operation was RMB1,534 million, representing a year-on-year increase of 5.52% from RMB1,454 million of the same period last year; consolidated profit attributable to equity holders was RMB1,158 million, representing a year-on-year increase of 8.16% from RMB1,071 million of the same period last year. (1) Analysis of Principal Operations Changes in items of income statement and cash flow statement (Unit: RMB thousand) Item Current Period Same Period Last year Change (%) Operating Revenues 17,280,504 15,725,309 9.89 Operating Expenses 15,637,999 14,156,735 10.46 Other Losses — Net 108,270 114,627 (5.55) Finance Costs (2,551) 4,608 N/A Income Tax Expenses 390,309 388,530 0.46 Net Cash Flows from Operating Activities 1,641,238 2,259,691 (27.37) Net Cash Flows from Investing Activities (1,935,702) (1,349,235) N/A Net Cash Flows from Financing Activities (566,683) (354,710) N/A
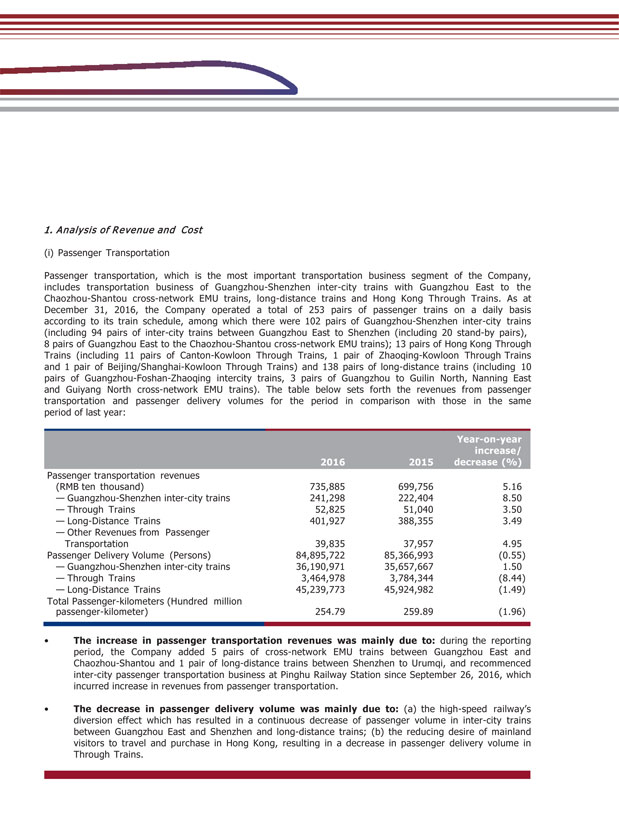
1. Analysis of Revenue and Cost (i) Passenger Transportation Passenger transportation, which is the most important transportation business segment of the Company, includes transportation business of Guangzhou-Shenzhen inter-city trains with Guangzhou East to the Chaozhou-Shantou cross-network EMU trains, long-distance trains and Hong Kong Through Trains. As at December 31, 2016, the Company operated a total of 253 pairs of passenger trains on a daily basis according to its train schedule, among which there were 102 pairs of Guangzhou-Shenzhen inter-city trains (including 94 pairs of inter-city trains between Guangzhou East to Shenzhen (including 20 stand-by pairs), 8 pairs of Guangzhou East to the Chaozhou-Shantou cross-network EMU trains); 13 pairs of Hong Kong Through Trains (including 11 pairs of Canton-Kowloon Through Trains, 1 pair of Zhaoqing-Kowloon Through Trains and 1 pair of Beijing/Shanghai-Kowloon Through Trains) and 138 pairs of long-distance trains (including 10 pairs of Guangzhou-Foshan-Zhaoqing intercity trains, 3 pairs of Guangzhou to Guilin North, Nanning East and Guiyang North cross-network EMU trains). The table below sets forth the revenues from passenger transportation and passenger delivery volumes for the period in comparison with those in the same period of last year: 2016 2015 Year-on-year increase/ decrease (%) Passenger transportation revenues (RMB ten thousand) 735,885 699,756 5.16 — Guangzhou-Shenzhen inter-city trains 241,298 222,404 8.50 — Through Trains 52,825 51,040 3.50 — Long-Distance Trains 401,927 388,355 3.49 — Other Revenues from Passenger Transportation 39,835 37,957 4.95 Passenger Delivery Volume (Persons) 84,895,722 85,366,993 (0.55) — Guangzhou-Shenzhen inter-city trains 36,190,971 35,657,667 1.50 — Through Trains 3,464,978 3,784,344 (8.44) — Long-Distance Trains 45,239,773 45,924,982 (1.49) Total Passenger-kilometers (Hundred million passenger-kilometer) 254.79 259.89 (1.96) • The increase in passenger transportation revenues was mainly due to: during the reporting period, the Company added 5 pairs of cross-network EMU trains between Guangzhou East and Chaozhou-Shantou and 1 pair of long-distance trains between Shenzhen to Urumqi, and recommenced inter-city passenger transportation business at Pinghu Railway Station since September 26, 2016, which incurred increase in revenues from passenger transportation. • The decrease in passenger delivery volume was mainly due to: (a) the high-speed railway’s diversion effect which has resulted in a continuous decrease of passenger volume in inter-city trains between Guangzhou East and Shenzhen and long-distance trains; (b) the reducing desire of mainland visitors to travel and purchase in Hong Kong, resulting in a decrease in passenger delivery volume in Through Trains.
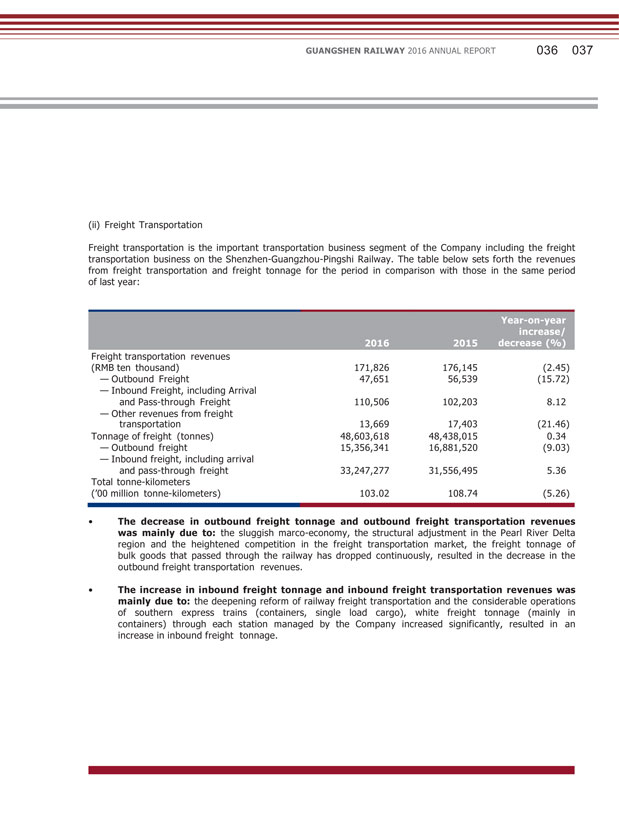
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 036 037 (ii) Freight Transportation Freight transportation is the important transportation business segment of the Company including the freight transportation business on the Shenzhen-Guangzhou-Pingshi Railway. The table below sets forth the revenues from freight transportation and freight tonnage for the period in comparison with those in the same period of last year: 2016 2015 Year-on-year increase/ decrease (%) Freight transportation revenues (RMB ten thousand) 171,826 176,145 (2.45) — Outbound Freight 47,651 56,539 (15.72) — Inbound Freight, including Arrival and Pass-through Freight 110,506 102,203 8.12 — Other revenues from freight transportation 13,669 17,403 (21.46) Tonnage of freight (tonnes) 48,603,618 48,438,015 0.34 — Outbound freight 15,356,341 16,881,520 (9.03) — Inbound freight, including arrival and pass-through freight 33,247,277 31,556,495 5.36 Total tonne-kilometers (‘00 million tonne-kilometers) 103.02 108.74 (5.26) • The decrease in outbound freight tonnage and outbound freight transportation revenues was mainly due to: the sluggish marco-economy, the structural adjustment in the Pearl River Delta region and the heightened competition in the freight transportation market, the freight tonnage of bulk goods that passed through the railway has dropped continuously, resulted in the decrease in the outbound freight transportation revenues. • The increase in inbound freight tonnage and inbound freight transportation revenues was mainly due to: the deepening reform of railway freight transportation and the considerable operations of southern express trains (containers, single load cargo), white freight tonnage (mainly in containers) through each station managed by the Company increased significantly, resulted in an increase in inbound freight tonnage.
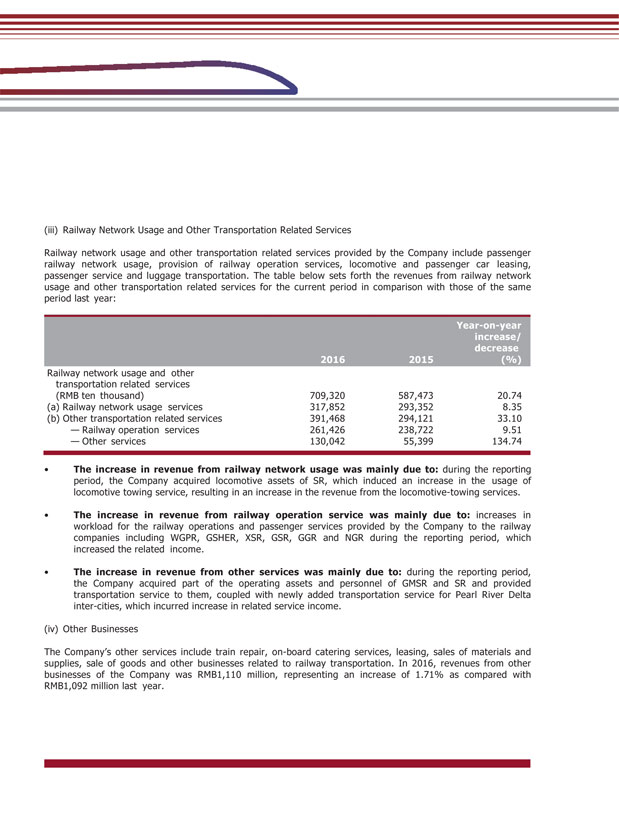
(iii) Railway Network Usage and Other Transportation Related Services Railway network usage and other transportation related services provided by the Company include passenger railway network usage, provision of railway operation services, locomotive and passenger car leasing, passenger service and luggage transportation. The table below sets forth the revenues from railway network usage and other transportation related services for the current period in comparison with those of the same period last year: 2016 2015 Year-on-year increase/ decrease (%) Railway network usage and other transportation related services (RMB ten thousand) 709,320 587,473 20.74 (a) Railway network usage services 317,852 293,352 8.35 (b) Other transportation related services 391,468 294,121 33.10 — Railway operation services 261,426 238,722 9.51 — Other services 130,042 55,399 134.74 • The increase in revenue from railway network usage was mainly due to: during the reporting period, the Company acquired locomotive assets of SR, which induced an increase in the usage of locomotive towing service, resulting in an increase in the revenue from the locomotive-towing services. • The increase in revenue from railway operation service was mainly due to: increases in workload for the railway operations and passenger services provided by the Company to the railway companies including WGPR, GSHER, XSR, GSR, GGR and NGR during the reporting period, which increased the related income. • The increase in revenue from other services was mainly due to: during the reporting period, the Company acquired part of the operating assets and personnel of GMSR and SR and provided transportation service to them, coupled with newly added transportation service for Pearl River Delta inter-cities, which incurred increase in related service income. (iv) Other Businesses The Company’s other services include train repair, on-board catering services, leasing, sales of materials and supplies, sale of goods and other businesses related to railway transportation. In 2016, revenues from other businesses of the Company was RMB1,110 million, representing an increase of 1.71% as compared with RMB1,092 million last year.
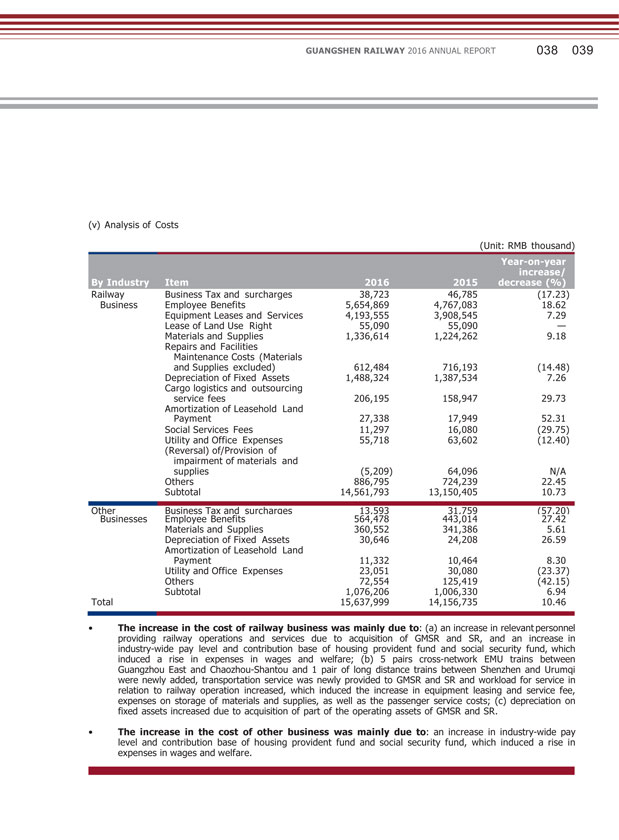
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 038 039 (v) Analysis of Costs (Unit: RMB thousand) By Industry Item 2016 2015 Year-on-year increase/ decrease (%) Railway Business Tax and surcharges 38,723 46,785 (17.23) Business Employee Benefits 5,654,869 4,767,083 18.62 Equipment Leases and Services 4,193,555 3,908,545 7.29 Lease of Land Use Right 55,090 55,090 — Materials and Supplies 1,336,614 1,224,262 9.18 Repairs and Facilities Maintenance Costs (Materials and Supplies excluded) 612,484 716,193 (14.48) Depreciation of Fixed Assets 1,488,324 1,387,534 7.26 Cargo logistics and outsourcing service fees 206,195 158,947 29.73 Amortization of Leasehold Land Payment 27,338 17,949 52.31 Social Services Fees 11,297 16,080 (29.75) Utility and Office Expenses 55,718 63,602 (12.40) (Reversal) of/Provision of impairment of materials and supplies (5,209) 64,096 N/A Others 886,795 724,239 22.45 Subtotal 14,561,793 13,150,405 10.73 Other Business Tax and surcharges 13,593 31,759 (57.20) Businesses Employee Benefits 564,478 443,014 27.42 Materials and Supplies 360,552 341,386 5.61 Depreciation of Fixed Assets 30,646 24,208 26.59 Amortization of Leasehold Land Payment 11,332 10,464 8.30 Utility and Office Expenses 23,051 30,080 (23.37) Others 72,554 125,419 (42.15) Subtotal 1,076,206 1,006,330 6.94 Total 15,637,999 14,156,735 10.46 • The increase in the cost of railway business was mainly due to: (a) an increase in relevant personnel providing railway operations and services due to acquisition of GMSR and SR, and an increase in industry-wide pay level and contribution base of housing provident fund and social security fund, which induced a rise in expenses in wages and welfare; (b) 5 pairs cross-network EMU trains between Guangzhou East and Chaozhou-Shantou and 1 pair of long distance trains between Shenzhen and Urumqi were newly added, transportation service was newly provided to GMSR and SR and workload for service in relation to railway operation increased, which induced the increase in equipment leasing and service fee, expenses on storage of materials and supplies, as well as the passenger service costs; (c) depreciation on fixed assets increased due to acquisition of part of the operating assets of GMSR and SR. • The increase in the cost of other business was mainly due to: an increase in industry-wide pay level and contribution base of housing provident fund and social security fund, which induced a rise in expenses in wages and welfare.
(vi) Major Sales Customers and Suppliers During the reporting period, the sales from top five customers amounted to RMB2,742.72 million, accounting for 15.87% of the annual total sales; of which the sales from related parties amounted to RMB2,392.27 million, accounting for 13.84% of the annual total sales. During the reporting period, the purchase from top five suppliers amounted to RMB2,011.39 million, accounting for 12.84% of annual total procurement; of which purchase from related parties amounted to RMB2,011.39 million, accounting for 12.84% of annual total procurement. 2. Expenses (Unit: RMB thousand) Item 2016 2015 decrease (%) Major reason for the changes Other losses — 108,270 114,627 (5.55) Increase in loss arising from retirement of fixed net assets, while decrease in impairment loss of fixed assets and loss arising from business combination. Finance costs (2,551) 4,608 N/A — Income tax 390,309 388,530 0.46 — expenses 3. Cash Flow In 2016, the principal capital sources of the Company were revenues generated from operating activities. The Company’s capital was mainly used for operating and capital expenses, payment of taxes and dividends. The Company has sufficient cash flow and it believes it has sufficient working capital, bank loans and other capital sources to meet its operation and development needs. (Unit: RMB thousand) Net cash flows from operating activities Net cash flows from investment activities Net cash flows from financing activities 1,641,238 2,259,691 (27.37) Increase in operating cash outflows. (1,935,702) (1,349,235) N/A Increase in expenses on investment of fixed assets. (566,683) (354,710) N/A Increase in allocation of cash dividends.
(2) Explanation of significant change in profit caused by non-principal activities Applicable Not applicable (3) Analysis of assets and liabilities (Unit: RMB thousand) Changes in amount from the end of Amount at the Amount at the previous period end of current end of previous to current Item period period period (%) Fixed Assets 24,278,032 24,073,759 0.85 Construction-in-Progress 790,308 569,573 38.75 Leasehold land payments 1,624,859 948,526 71.30 Trade Receivables 3,364,366 2,886,066 16.57 Prepayments and other receivables 330,491 142,613 131.74 Cash and Cash Equivalents 1,359,656 2,220,803 (38.78) Payables for Fixed Assets and Construction-in-Progress 1,765,185 1,425,998 23.79 Income Tax payable 121,513 313,656 (61.26) The increase in fixed assets was mainly due to: transfer of completed construction-in-progress into fixed assets and acquisition of part of the operating assets of GMSR and SR. The increase in construction-in-progress was mainly due to: the increase in investment projects of construction-in-progress. The increase in leasehold land payments was mainly due to: settlement of completion of constructions temporarily transferred into fixed assets in previous years, which reclassified part of the costs that could be classified as land use right into intangible assets in the year. The increase in account receivables was mainly due to: the increase in receivable service fee from the provision of railway operation service and increase in flow of funds from operational connected transactions.
The increase in prepayments and other receivables was mainly due to: the increase in input tax credit. The decrease in cash and cash equivalents was mainly due to: the increase in operating cash expenses and fixed assets investment expense. Increase in payables for fixed assets and construction-in-progress was mainly due to: the increase of payments for construction works and equipment payable. The decrease in income tax payables was mainly due to: the decrease in corporate income tax payable. As at the end of the reporting period, the gearing ratio (calculated by total liabilities divided by total assets as at the end of the reporting period) of the Company was 14.73%. As at the end of the reporting period, the Company had no charge on any of its assets and had not provided any guarantees, and had no entrusted deposits. (4) Analysis on investment position 1. General analysis on investments in external equity interests During the reporting period, the Company had not made investment in securities such as stock, warrants or convertible bonds, and had not held or dealt in equity interests of other listed companies and non-listed financial enterprises. Details of investments on external equity interests of the Company at the end of the reporting period are set out in Notes 10, 11 and 15 to the financial statements. (i) Significant investments in equity interests During the reporting period, the Company had no significant investments in equity interests. (ii) Significant non-equity investments During the reporting period, the significant non-equity investment project of the Company mainly included: (Unit: RMB ten thousand) (Unit: RMB ten thousand) Reconstruction of automatic inter-locking equipment from Guangzhou to Pingshi section 72,651 17% 12,667 12,667 Newly acquired 4 pairs of section from Guangzhou

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 042 043 (iii) Financial assets at fair value During the reporting period, the Company had no financial assets at fair value. (5) Major assets and disposal of equity interests During the reporting period, the Company had no major assets and disposal of equity interests. III. DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS ON THE FUTURE DEVELOPMENT OF THE COMPANY (1) Industry competition scenario and development trend Industry development trend: Being the aorta of the nation’s economy, an important infrastructure of the nation and a popular form of transportation, railway is of crucial importance for nation’s economic and social development. Since the implementation of Medium to Long Term Plan for Railway Network Development in 2004, the railway in China developed rapidly. Currently on the whole, the tight capacity of railway in China has been alleviated, the bottle-neck restriction has been eliminated and the economic and social development needs have been met in in general. However, when benchmarking with the new general requirements of economic development, other transportation forms and the level of developed countries, China’s railway still faces deficiencies such as incomplete layout, low operational efficiency and severe structural conflicts. To expedite the establishment of a modern railway network with reasonable layout, wide coverage, high efficiency and convenience, safety and economic efficiencies, Medium to Long Term Plan for Railway Network Development (2016-2025) was jointly modified by National Development and Reform Commission, Ministry of Transport and China Railway Corporation in July 2016, highlighting a more ambitious “Eight East-West Lines and Eight South-North Lines” high-speed railway network for a new era. Consequently, it is estimated that in the long run in the future, development of railway transportation industry will remain at a high rate, and passenger and freight transportation capacity and market competitive position of railway will be gradually elevated. Industry competition scenario: The national railway is highly concentrated with a unified transportation management system. Competition mainly comes from other transportation industries such as highway, aviation and water transportation, and is expected to exist in the long run. However, as the marketization reform of the railway industry (including the reformation of the investment and financing system, the transportation management system and the pricing system) gradually deepens, the entry barrier to the industry will decrease, investors of the industry will become more diversified and the State’s high-speed railway network with Four East-West Lines and Four South-North Lines and numerous inter-city railways will complete construction and commence operation, the competition structure of the railway transportation industry is expected to experience substantial changes in the future, with more intense competition not only externally from the highway, aviation and water transportation industries but also within the industry itself. (2) Development strategies of the Company Under the sound leadership scientific decision-making by the Board, the Company will capitalize the historic opportunity of extensive railway construction, proactively adapt to the policy direction of railway system reform in order to establish a steadfast foothold in the Pan Pearl River Delta, perfect and enhance its business portfolio centered on railway passenger and freight transportation and complemented by the railway-related businesses. Striving to become a top-notch railway transportation services enterprise in the PRC and actualize its development objective of scaling up and consolidating its strengths, the Company will also focus on the improvement of quality of service in the continued efforts for the advancement of management innovation, service innovation and technology innovation.

Operating plans in 2017 At the fifteenth meeting of the seventh session of the Board held on March 29, 2017, the financial budget for 2017 were passed upon consideration. The Company plans to achieve passenger delivery volume of 85.10 million persons (excluding commissioned transportation), outbound freight tonnes of 16.10 million tonnes. To actualize the aforesaid objectives, the Company will focus on the following tasks: Production safety: based upon construction of route with illustrative standards on safety and quality; consistently adopt the approach of “safely first, prevention-led, integrated governance” to optimize safety management system, reinforce control over safe production process and intensify rectification of safety problems and investment in safety facilities and equipment and enhance the capability of safety protection. Passenger transportation: Firstly, enhance the passenger traffic volume analysis on Guangzhou- Shenzhen inter-city trains and cross-network EMU trains between Guangzhou East and Chaozhou-Shantou to timely adjust transportation coordination and improve the train routes and schedules, with a view to increase revenues; secondly, strengthen integrated research on railway passenger transportation market to proactively apply to competent authorities of the industry for adding long-distance trains from various stations managed by the Company to areas currently not covered by high-speed trains; thirdly, speed up large scale construction projects, including the reconstruction of the section from Guangzhou East to Xintang of Guangshen line III and IV, as well as the Xintang District public transport interchange in East Guangzhou, striving to complete and commence operation as soon as possible, stepping efforts in exploring new growth points for passenger transportation; fourthly, further improve service environment of passenger transportation, enhance customers’ service experience, aiming to enhance quality and increase efficiencies of passenger transportation. Freight transportation: Firstly, step up the efforts in implementing railway supply-side reform measures, fully leverage on relaxation policy on transportation fees and charges of coal and steel by China Raily Corporation, and actively visit large-scale enterprises of steel and electricity companies to stabilize and expand freight transportation volume of bulk goods; secondly, weigh on the advantage of scale transportation of railway, boost the development of trains schedule and network of “white freight” express trains, and on the basis of restoration of freight transportation for suspended trains during spring season, actively realize the addition of new trains from Guotang to Wulabo, Tangxi to Gaolan, with the focus on pressing ahead the coordination of container tonnage of “white freight” express trains for Dongguan Hsu Fu Chi Foods Co., Ltd.. Operational management: Firstly, enhance awareness of operation efficiencies and process management, stringently exert control on the cost budget, uplift management level of budget; secondly, strengthen budget management of funds and carried out centralized management to secure source, reduce cost and increase efficiency of funds; thirdly, enhance tax management and planning to promote risk prevention of value-added tax sales invoices and management of input tax credit invoices to strictly control tax risks.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 044 045 (3) Potential risks Macro-economic risk Railway transportation industry is highly related to macro-economic development condition and greatly affected by macro- economic atmosphere. If the macro- economic atmosphere becomes depressing, the Company’s operation results and financial condition may be adversely affected. Policy and regulatory risk Railway transportation industry is greatly affected by policy and regulations. With changes in domestic and international economic environment, and reform and development of railway transportation industry, corresponding adjustment may be required for relative laws and regulations and industrial policies. These changes incur uncertainties to the Company’s business development and operation results in the future. Transportation safety risk Transportation safety is the prerequisite and foundation for normal operation and good reputation of railway transportation industry. Bad weather, mechanical failures, human error and other force majeure may impose adverse impact on the transportation safety of the Company. Market competition risk Competition exists in certain markets between aviation, road and water transportation and railway transportation. In addition, with the development in railway transportation industry, a range of high- speed railways and inter-city railways completed and commenced operation. Internal competition within railway transportation industry also intensifies. The Company may be subject to greater competitive pressure in the future, which in turn constitutes impact on the operation results of the Company. Financial risk The operating activities of the Company are subject to various financial risks, such as exchange risk, interest risk, credit risk and liquidity risk. The Company will pay close attention to the changes in international and domestic macro-economic conditions, to strengthen analysis and study on factors affecting railway transportation industry and be committed to achieve stability in the Company’s production and operation. The Company will proactively engage in different seminars for improvement of industrial polices and regulations development, study the latest changes in policy and regulations, capture the development opportunities brought by amendments of policy and regulations and adopt a prudent approach in addressing uncertainties caused by changes in policy and regulations. The Company proactively participate in transportation safely meetings held by competent authorities of the industry to understand the transportation safety condition of the Company, deploy resources in transportation safety management, establish and optimize safety risk management and control and intensify the training of safety knowledge and capability of transportation personnel. The Company will take proactive actions in addressing market competition by leveraging the advantages of “safe, comfortable, convenience, on time” of railway transportation, improving service facilities and enhancing service quality. In respect of freight transportation, the Company is committed to increase the efficiencies, turnover rate and frequency of freight trains. In addition, the Company will strengthen the analysis and research on railway transportation market, and proactively apply to competent authorities of the industry for adding new long-distance trains in area not covered by high-speed railways. The Company has established a set of managerial procedures for financial risk with the focus on the uncertainties of financial market, designated to minimize the potential adverse impact on financial performance of the Company. For more detailed analysis, please refer to “Note 3 to the financial statements”.

IV. EXPLANATION OF CONDITIONS AND REASONS NOT DISCLOSED BY THE COMPANY IN ACCORDANCE WITH STANDARDS DUE TO NON- APPLICABLE STANDARDS AND REGULATIONS OR SPECIAL REASONS SUCH AS NATIONAL SECRETS, COMMERCIAL SECRETS Applicable Not applicable V. OTHER DISCLOSURES (1) Taxation Details of income tax applicable to the Company during the reporting period are set out in Note 31 to the financial statements. (2) Interest Capitalized During the reporting period, no interest was capitalized in the fixed assets or construction-in-progress of the Company. (3) Properties and Fixed Assets During the reporting period, all properties held by the Company were all for the purpose of development, and their percentage ratio (as defined by Rule 14.04(9) of the Listing Rules) did not exceed 5%. Movements in the properties and fixed assets held by the Company during the reporting period are set out in Note 6 to the financial statements. (4) Undistributed Profit Details of movements in the undistributed profit of the Company during the reporting period are set out in the Statements of Changes in Equity.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 046 047 (5) Surplus Reserve Details of movements in the surplus reserve of the Company during the reporting period are set out in the Statements of Changes in Equity and Note 22 to the financial statements. (6) Subsidiaries Details of the principal subsidiaries of the Company as at the end of the reporting period are set out in Note 10 to the financial statements. (7) Material investments held, material acquisitions and disposals of subsidiaries and associates, and future plans of material investments or acquisition of capital assets Except as disclosed in this annual report, during the reporting period, the Company had no material investment held, had not carried out any material acquisition or disposal of subsidiaries and associates, and had no definite plan for material investment or acquisition of capital assets. (8) Contingent liabilities At the end of the reporting period, the Company had no contingent liability. (9) Fixed Interest Rate At the end of the reporting period, the Company has no loan bearing fixed interest rates.

(10) Laws and Regulations During the reporting period, the Company has complied with all relevant laws and regulations that have significant impact on the Company. (11) Directors of Subsidiaries At the end of the reporting period, save for Dongguan Changsheng Enterprise Company Limited, Shenzhen Nantie Construction Supervision Company Limited and Zengcheng Lihua Stock Company Limited, no other subsidiaries of the Company had set up their board of directors. The members of the boards of directors for the above three subsidiaries are as follows: Dongguan Changsheng Enterprise Company Limited Mu Anyun, Li Yingtang, Deng Hui, Lin Wensheng, Li Pingwen, Li Jianping, Zhou Xiaomei Shenzhen Nantie Construction Supervision Company Limited Mu Anyun, Wu Yuefang, Jin Rong, Fang Lei, Deng Rongjun Zengcheng Lihua Stock Company Limited Mu Anyun, Deng Hui, Lin Wensheng, Huang Jian, Zhu Xiaoqiang (12) Persons of Significant Relationship with the Company During the reporting period, save as disclosed in this annual report, the Company has no other relationship with its employees, customers and suppliers apart from the relationship of employees, customers and suppliers, and there was no person who had a significant impact on the business of the Company. (13) Assessment of Property Interests or Tangible Assets During the reporting period, the Company has not valued its property interests or other tangible assets in accordance with Chapter 5 of the Listing Rules. (14) Management Contracts During the reporting period, the Company has not entered into any contract containing the following term: the counterparty of the contract undertakes the management and administration of the whole or any substantial part of any business of the Company pursuant to the contract; and the contract was not a service contract entered into with any Director or full-time employee of the Company.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 048 049 (15) Loans to Entities During the reporting period, the Company has not provided any loan to any entity. (16) Permitted Compensation Provisions At the end of the reporting period, the Company did not have any compensation provision for the benefit which had been enjoyed or being enjoyed by any one of the Directors (including former directors) of the Company, or any of the affiliated companies.

Chapter 5 Matters of Importance Chairman of the Supervisory Committee I. PLANS FOR PROFIT DISTRIBUTION OF ORDINARY SHARES OR COMMON RESERVE CAPITALIZATION (1) Formulation, implementation, adjustment of cash dividend distribution policy Pursuant to the related requirements of the ‘Notice on Further Implementing Issues concerning Cash Dividends Distribution of Listed Companies’ by CSRC and SSRB, the Company amended provisions related to profit distribution in the Articles in 2012. The amended Articles clearly stipulate the standards, percentages and related decision-making procedures for cash dividend distribution by the Company, the detailed conditions, decision-making procedures and mechanisms for adjustments to the profit distribution policy by the Company, which will provide systematic guarantee of the due diligence of the Independent Directors and the full expression of the minority shareholders’ requests and fully protect the legal interests of minority shareholders. Since its listing in 1996, the Company has consistently adhered to a sustained and stable profit distribution policy, emphasized on reasonable return to investors, and at the same time strived for the sustainable development of the Company. During the reporting period, the Company implemented the profit distribution plan of 2015 and distributed a cash dividend of RMB0.80 (tax inclusive) per 10 shares to all shareholders of the Company, totaling RMB566,682,960 on the basis of the total share capital at the end of 2015.
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 050 051 (2) Plans or budgets for profit distribution of ordinary shares or common reserve capitalization of the Company for the past three years (including the reporting period) (Unit: RMB thousand) Net profit attributable to the ordinary Percentage shareholders of net profit of the attributable Company to the ordinary in the shareholders consolidated of the Amount of financial Company in the Dividend per Amount of statements consolidated 10 shares cash dividend for the year of financial Year of Distribution (incl. tax) (incl. tax) distribution statements (%) 2016 0.80 566,683 1,158,253 48.93 2015 0.80 566,683 1,070,822 52.92 2014 0.50 354,177 662,021 53.50 Explanation of the profit distribution plan 2016: The Board recommended the payment of a final cash dividend of RMB0.08 per share (including tax) for 2016 to all shareholders of the Company, based on the total share capital of 7,083,537,000 shares as at December 31, 2016, totaling RMB566,682,960. The above proposal is subject to approval at the 2016 annual general meeting. The Company will complete the profit distribution within two months after the proposal has been approved. Holders of A Shares are reminded to timely and carefully read the announcement to be issued by the Company on distribution of dividends for 2016 which contains details of the distribution of the final cash dividends for 2016. Holders of H Shares are reminded to timely and carefully read the notice of the 2016 annual general meeting and the announcement of poll results of the 2016 annual general meeting to be issued by the Company on the HKEXnews website of SEHK (http://www.hkexnews.hk) on the date of the annual general meeting, respectively, which contain details of the distribution of the final cash dividends for 2016. The expected payment date of a final cash dividend for 2016 is on or around August 18, 2017. To the best knowledge of the Company, as at the date of publication of this annual report, there were no any arrangements of shareholders waiving or agreeing to waive the proposed distribution of final dividend for 2016. (3) Repurchase offer by cash included in cash dividend Applicable Not applicable
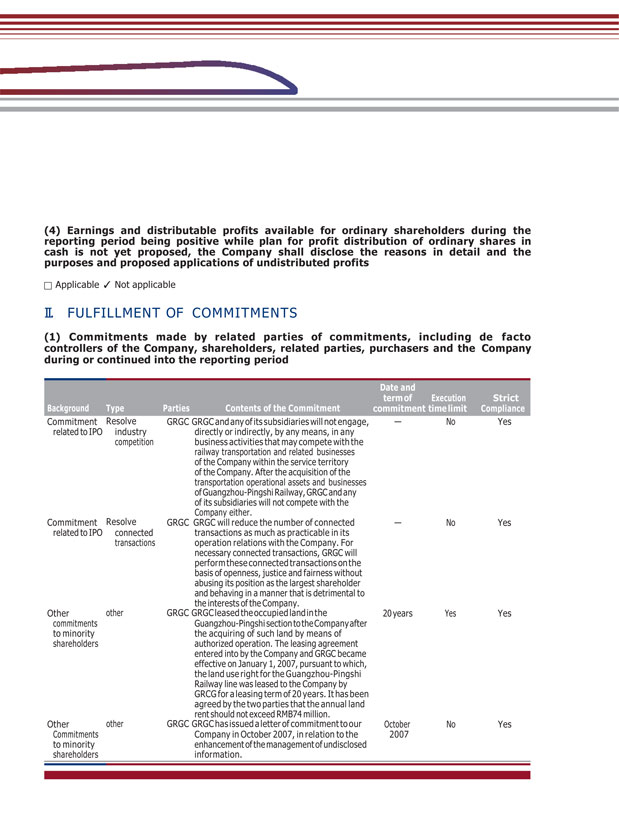
(4) Earnings and distributable profits available for ordinary shareholders during the reporting period being positive while plan for profit distribution of ordinary shares in cash is not yet proposed, the Company shall disclose the reasons in detail and the purposes and proposed applications of undistributed profits Applicable Not applicable II. FULFILLMENT OF COMMITMENTS (1) Commitments made by related parties of commitments, including de facto controllers of the Company, shareholders, related parties, purchasers and the Company during or continued into the reporting period during or continued into the reporting period Commitment related to IPO Commitment related to IPO Resolve industry competition Resolve connected transactions GRGC GRGC and any of its subsidiaries will not engage, directly or indirectly, by any means, in any business activities that may compete with the railway transportation and related businesses of the Company within the service territory of the Company. After the acquisition of the transportation operational assets and businesses of Guangzhou-Pingshi Railway, GRGC and any of its subsidiaries will not compete with the Company either. GRGC GRGC will reduce the number of connected transactions as much as practicable in its operation relations with the Company. For necessary connected transactions, GRGC will perform these connected transactions on the basis of openness, justice and fairness without abusing its position as the largest shareholder and behaving in a manner that is detrimental to the interests of the Company. — No Yes — No Yes Other commitments to minority shareholders other GRGC GRGC leased the occupied land in the Guangzhou-Pingshi section to the Company after the acquiring of such land by means of authorized operation. The leasing agreement entered into by the Company and GRGC became effective on January 1, 2007, pursuant to which, the land use right for the Guangzhou-Pingshi Railway line was leased to the Company by GRCG for a leasing term of 20 years. It has been agreed by the two parties that the annual land rent should not exceed RMB74 million. 20 years Yes Yes Other Commitments to minority shareholders other GRGC GRGC has issued a letter of commitment to our Company in October 2007, in relation to the enhancement of the management of undisclosed information. October 2007 No Yes

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 052 053 (2) THE COMPANY’S EXPLANATION ON WHETHER ORIGINAL PROFIT FORECAST HAS BEEN MET IN RESPECT OF ASSETS OR PROJECTS AND THE RELATED REASONS FOR PROFIT FORECAST OF ASSETS OR PROJECTS AND IN THE EVENT OF REPORTING PERIOD BEING WITH THE PROFIT FORECAST PERIOD Achieved Not achieved Not applicable III. APPROPRIATION OF FUND AND PROGRESS OF DEBT CLEARANCE LISTING IN THE REPORTING PERIOD Applicable Not applicable IV. EXPLANATION ON ACCOUNTANT’S “NON-STANDARD AUDIT REPORT” BY THE COMPANY Applicable Not applicable V. THE COMPANY’S ANALYSIS AND EXPLANATION ON ACCOUNTING POLICIES, CHANGES IN ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES OR REASONS AND IMPACT OF RECTIFICATION ON SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING ERRORS (1) The Company’s explanation on accounting policies, reasons and impacts of changes in accounting estimate Applicable Not applicable (2) The Company’s explanations on reasons and impact of rectification on significant accounting errors Applicable Not applicable (3) The communication between predecessor accountant Applicable Not applicable
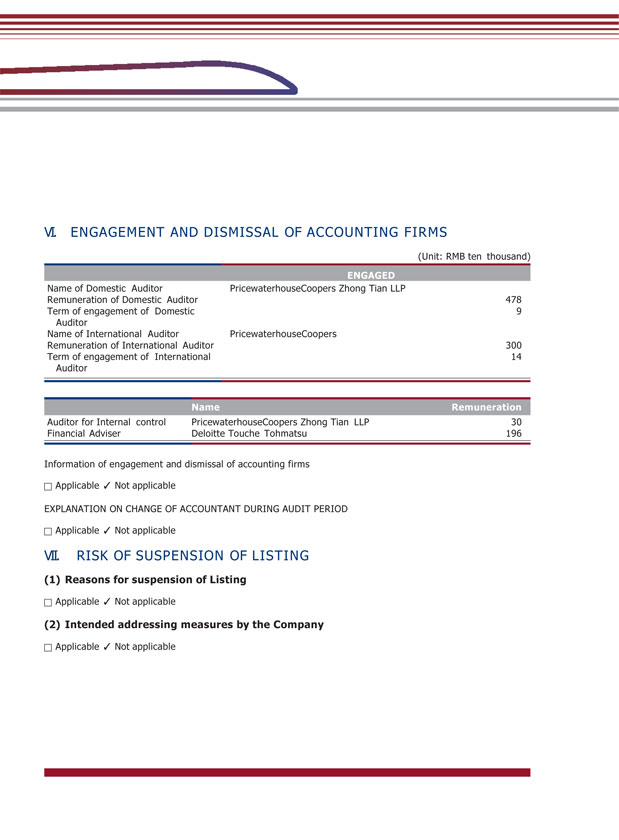
VI. ENGAGEMENT AND DISMISSAL OF ACCOUNTING FIRMS (Unit: RMB ten thousand) Name of Domestic Auditor PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP Remuneration of Domestic Auditor 478 Term of engagement of Domestic 9 Auditor Name of International Auditor PricewaterhouseCoopers Remuneration of International Auditor 300 Term of engagement of International 14 Auditor Auditor for Internal control PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP 30 Financial Adviser Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu 196 Information of engagement and dismissal of accounting firms Applicable Not applicable EXPLANATION ON CHANGE OF ACCOUNTANT DURING AUDIT PERIOD Applicable Not applicable VII. RISK OF SUSPENSION OF LISTING (1) Reasons for suspension of Listing Applicable Not applicable (2) Intended addressing measures by the Company Applicable Not applicable

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 054 055 VIII. INFORMATION AND REASON FOR DELISTING Applicable Not applicable IX. BANKRUPTCY AND RESTRUCTURING Applicable Not applicable X. MATERIAL LITIGATION AND ARBITRATION The Company had material litigation and arbitration during the year The Company did not have material litigation and arbitration during the year XI. PUNISHMENT ON THE COMPANY, ITS DIRECTORS, SUPERVISORS, SENIOR MANAGEMENT, CONTROLLING SHAREHOLDERS, DE FACTO CONTROLLER, PURCHASER AND THE RECTIFICATION THEREOF Applicable Not applicable XII. EXPLANATION ON INTEGRITY OF THE COMPANY, ITS CONTROLLING SHAREHOLDERS AND DE FACTO CONTROLLER DURING THE REPORTING PERIOD During the reporting period, there is no explanation on integrity of the Company, its shareholders and de facto controller. XIII. THE COMPANY’S SHARE INCENTIVE SCHEME, EMPLOYEE STOCK OWNERSHIP PLAN, OR OTHER EMPLOYEES’ INCENTIVE MEASURES AND THEIR IMPACT Applicable Not applicable
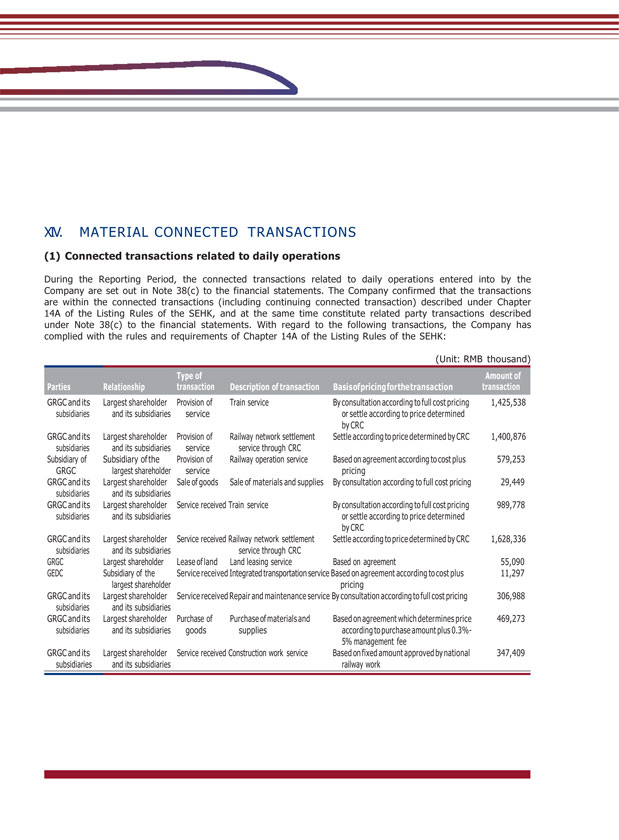
XIV. MATERIAL CONNECTED TRANSACTIONS (1) Connected transactions related to daily operations During the Reporting Period, the connected transactions related to daily operations entered into by the Company are set out in Note 38(c) to the financial statements. The Company confirmed that the transactions are within the connected transactions (including continuing connected transaction) described under Chapter 14A of the Listing Rules of the SEHK, and at the same time constitute related party transactions described under Note 38(c) to the financial statements. With regard to the following transactions, the Company has complied with the rules and requirements of Chapter 14A of the Listing Rules of the SEHK: (Unit: RMB thousand) GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Provision of service Train service By consultation according to full cost pricing or settle according to price determined by CRC 1,425,538 GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Provision of service Railway network settlement service through CRC Settle according to price determined by CRC 1,400,876 Subsidiary of GRGC Subsidiary of the largest shareholder Provision of service Railway operation service Based on agreement according to cost plus pricing 579,253 GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Sale of goods Sale of materials and supplies By consultation according to full cost pricing 29,449 GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Service received Train service By consultation according to full cost pricing or settle according to price determined by CRC 989,778 GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Service received Railway network settlement service through CRC Settle according to price determined by CRC 1,628,336 GRGC Largest shareholder Lease of land Land leasing service Based on agreement 55,090 GEDC Subsidiary of the largest shareholder Service received Integrated transportation service Based on agreement according to cost plus pricing 11,297 GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Service received Repair and maintenance service By consultation according to full cost pricing 306,988 GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Purchase of goods Purchase of materials and supplies Based on agreement which determines price according to purchase amount plus 0.3%- 5% management fee 469,273 GRGC and its subsidiaries Largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Service received Construction work service Based on fixed amount approved by national railway work 347,409
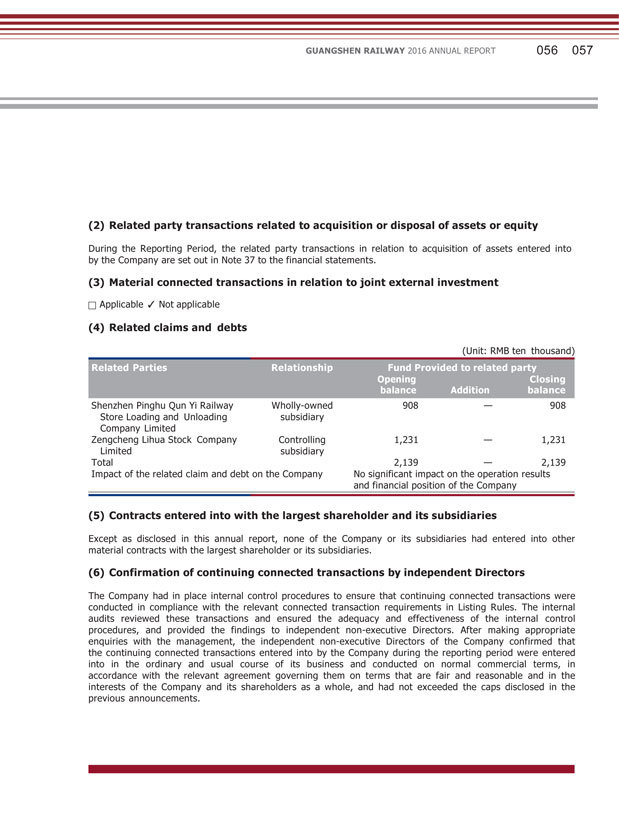
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 056 057 (2) Related party transactions related to acquisition or disposal of assets or equity During the Reporting Period, the related party transactions in relation to acquisition of assets entered into by the Company are set out in Note 37 to the financial statements. (3) Material connected transactions in relation to joint external investment Applicable Not applicable (4) Related claims and debts (Unit: RMB ten thousand) Shenzhen Pinghu Qun Yi Railway Store Loading and Unloading Company Limited Zengcheng Lihua Stock Company Limited Wholly-owned subsidiary Controlling subsidiary 908 — 908 1,231 — 1,231 Total 2,139 — 2,139 Impact of the related claim and debt on the Company No significant impact on the operation results and financial position of the Company (5) Contracts entered into with the largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Except as disclosed in this annual report, none of the Company or its subsidiaries had entered into other material contracts with the largest shareholder or its subsidiaries. (6) Confirmation of continuing connected transactions by independent Directors The Company had in place internal control procedures to ensure that continuing connected transactions were conducted in compliance with the relevant connected transaction requirements in Listing Rules. The internal audits reviewed these transactions and ensured the adequacy and effectiveness of the internal control procedures, and provided the findings to independent non-executive Directors. After making appropriate enquiries with the management, the independent non-executive Directors of the Company confirmed that the continuing connected transactions entered into by the Company during the reporting period were entered into in the ordinary and usual course of its business and conducted on normal commercial terms, in accordance with the relevant agreement governing them on terms that are fair and reasonable and in the interests of the Company and its shareholders as a whole, and had not exceeded the caps disclosed in the previous announcements.

(7) Confirmation of continuing connected transactions by the auditor The auditors of the Company have carried out procedures on the above connected transactions for the year ended at the end of the reporting period in accordance with the Hong Kong Standard on Assurance Engagements 3000 ‘Assurance Engagement Other Than Audits or Reviews of Historical Financial Information’ and with reference to Practice Note 740 ‘Auditor’s Letter on Continuing Connected Transactions under the Hong Kong Listing Rules’ issued by the Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants and reported that, in respect of the above connected transactions: (i) nothing has come to the Company’s auditors’ attention that would cause them to believe that the disclosed continuing connected transactions had not been approved by the Board; (ii) for transactions involving the provision of goods or services by the Company, nothing has come to the Company’s auditors’ attention that would cause them to believe that such transactions were not, in all material respects, in accordance with the pricing policies of the Company; (iii) nothing has come to the Company’s auditors’ attention that would cause them to believe that such transactions were not entered into, in all material respects, in accordance with the terms of agreements governing such transactions; (iv) with respect to the aggregate amount of each of the continuing connected transactions, nothing has come to the Company’s auditors’ attention that would cause them to believe that the value of such continuing connected transactions have exceeded the maximum aggregate annual caps disclosed in the previous announcements.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 058 059 XV. MATERIAL CONTRACTS AND THE IMPLEMENTATION THEREOF (1) Trust, contracted businesses and leasing affairs 1. Trusted business Applicable Not applicable 2. Contracted business Applicable Not applicable 3. Leased affairs Applicable Not applicable (2) Guarantees or financial assistance Applicable Not applicable

(3) Entrusted cash asset management carried out by other person 1. Entrusted investment Applicable Not applicable 2. Entrusted loans Applicable Not applicable 3. Other investment and derivatives investment Applicable Not applicable (4) Pledges During the reporting period, the largest shareholder of the Company and its de facto controller have not pledged the interests in all or part of the shares of the Company held as support for the Company’s indebtedness, guarantees or other liabilities. (5) Loan agreements and their performances During the reporting period, the Company and its subsidiaries have not entered into any loan agreements nor violated any terms of loan agreements which had significant impact to its operation. (6) Other material contracts During the reporting period, save as disclosed in this annual report, the Company did not enter into any other material contracts.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 060 061 XVI. EXPLANATION OF OTHER MATERIAL EVENTS Applicable Not applicable XVII. ACTIVE FULFILLMENT OF SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY (1) Poverty alleviation by listed companies Applicable Not applicable (2) Efforts of social responsibilities During the reporting period, the Company did not have significant environmental protection or other significant social safety issues. For Details of the fulfillment of social responsibilities in the areas of transportation safety, environmental protection and social welfare by the Company in the reporting period, please read the Social Responsibility Report 2016 disclosed on the website of SSE (http://www.sse.com.cn), the HKEXnews website of SEHK (http://www.hkexnews.hk) and the website of the Company (http://www. gsrc.com). (3) Explanation of environmental protection efforts by companies and its subsidiaries which are a key discharging units announced by environmental protection department Applicable Not applicable XVIII. CONVERTIBLE COMPANY BONDS Applicable Not applicable

Chapter 6 Changes in Ordinary Share Capital and Particulars of Shareholders General Manager I. PARTICULARS OF CHANGES IN ORDINARY SHARE CAPITAL (1) Changes in ordinary share capital During the reporting period, there was no change in the Company’s total number of ordinary shares and structure of share capital. (2) Changes in shares with selling restrictions Applicable Not applicable

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 062 063 II. PARTICULARS OF SECURITIES ISSUE AND LISTING (1) Particulars of securities issue up to the reporting period The Company had not issued any securities for the 3 years prior to the end of the reporting period. Particulars of securities issue up to the reporting period (particulars of bonds with different interest rates during existing period shall be provided separately): Applicable Not applicable (2) Changes in the Company’s total number of ordinary shares and structure of shareholder and changes in structure of asset and liability of the Company During the reporting period, there was no change in the total number of ordinary shares and structure of shareholder, asset and liability of the Company as a result of bonus issue, increase in share capital, placing, allotment of new shares or other reasons. (3) Existing employee shares The Company had not issued shares to any of its employees. III. PARTICULARS OF SHAREHOLDERS AND DE FACTO CONTROLLERS (1) Number of Shareholders Number of ordinary shareholders as at the end of the reporting period (Number) Number of ordinary shareholders as at the end of the previous month before the date of disclosure of the annual report (Number) 253,828 264,107
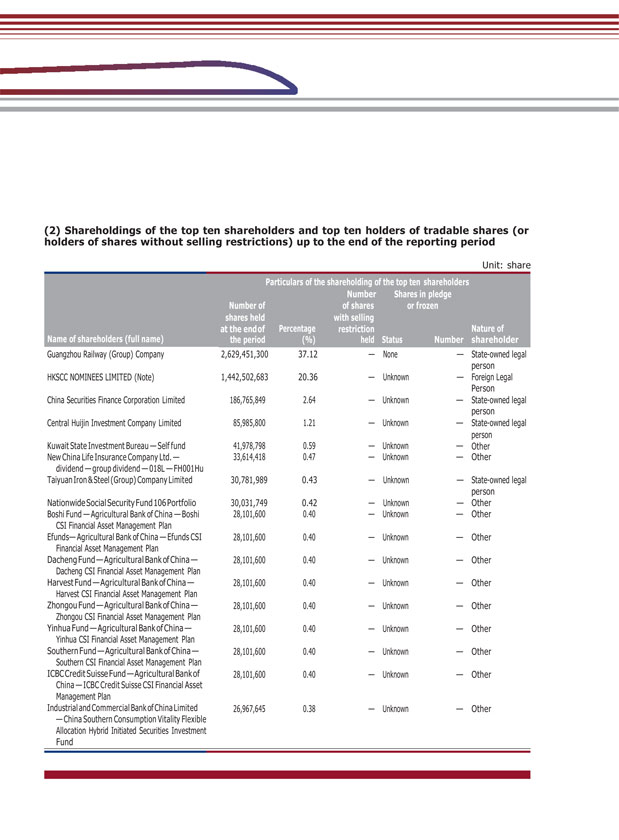
(2) Shareholdings of the top ten shareholders and top ten holders of tradable shares (or holders of shares without selling restrictions) up to the end of the reporting period Unit: share Particulars of the shareholding of the top ten shareholders Number Shares in pledge Number of of shares or frozen shares held with selling at the endof Percentage restriction Nature of Name of shareholders (full name) the period (%) held Status Number shareholder Guangzhou Railway (Group) Company 2,629,451,300 37.12 — None — State-owned legal person HKSCC NOMINEES LIMITED (Note) 1,442,502,683 20.36 — Unknown — Foreign Legal Person China Securities Finance Corporation Limited 186,765,849 2.64 — Unknown — State-owned legal person Central Huijin Investment Company Limited 85,985,800 1.21 — Unknown — State-owned legal person Kuwait State Investment Bureau — Self fund 41,978,798 0.59 — Unknown — Other New China Life Insurance Company Ltd. — 33,614,418 0.47 — Unknown — Other dividend — group dividend — 018L — FH001Hu Taiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Company Limited 30,781,989 0.43 — Unknown — State-owned legal person NationwideSocial Security Fund 106 Portfolio 30,031,749 0.42 — Unknown — Other Boshi Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — Boshi 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other CSI Financial Asset Management Plan Efunds— Agricultural Bank of China — Efunds CSI 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other Financial Asset Management Plan Dacheng Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other Dacheng CSI Financial Asset Management Plan Harvest Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other Harvest CSI Financial Asset Management Plan Zhongou Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other Zhongou CSI Financial Asset Management Plan Yinhua Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other Yinhua CSI Financial Asset Management Plan Southern Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other Southern CSI Financial Asset Management Plan ICBC Credit Suisse Fund —Agricultural Bank of 28,101,600 0.40 — Unknown — Other China — ICBC Credit Suisse CSI Financial Asset Management Plan Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Limited 26,967,645 0.38 — Unknown — Other — China Southern Consumption Vitality Flexible Allocation Hybrid Initiated Securities Investment Fund
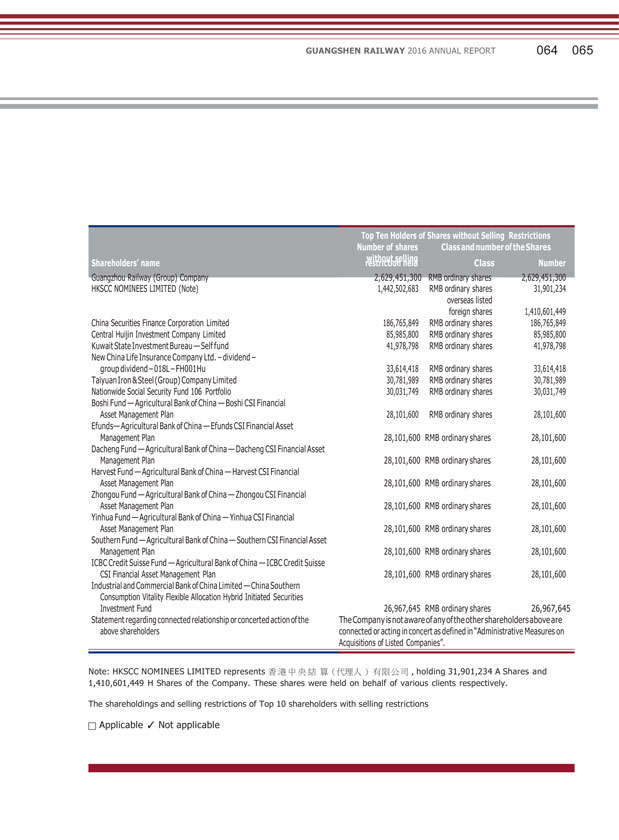
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Top Ten Holders of Shares without Selling Restrictions Number of shares Class and number of the Shares without selling Shareholders’ name restriction held Class Number Guangzhou Railway (Group) Company 2,629,451,300 RMB ordinary shares 2,629,451,300 HKSCC NOMINEES LIMITED (Note) 1,442,502,683 RMB ordinary shares 31,901,234 overseas listed foreign shares 1,410,601,449 China Securities Finance Corporation Limited 186,765,849 RMB ordinary shares 186,765,849 Central Huijin Investment Company Limited 85,985,800 RMB ordinary shares 85,985,800 Kuwait State Investment Bureau — Self fund 41,978,798 RMB ordinary shares 41,978,798 New China Life Insurance Company Ltd. – dividend – group dividend – 018L – FH001Hu 33,614,418 RMB ordinary shares 33,614,418 Taiyuan Iron & Steel (Group) Company Limited 30,781,989 RMB ordinary shares 30,781,989 Nationwide Social Security Fund 106 Portfolio 30,031,749 RMB ordinary shares 30,031,749 Boshi Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — Boshi CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 Efunds— Agricultural Bank of China — Efunds CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 Dacheng Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — Dacheng CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 Harvest Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — Harvest CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 Zhongou Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — Zhongou CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 Yinhua Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — Yinhua CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 Southern Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — Southern CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 ICBC Credit Suisse Fund — Agricultural Bank of China — ICBC Credit Suisse CSI Financial Asset Management Plan 28,101,600 RMB ordinary shares 28,101,600 Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Limited — China Southern Consumption Vitality Flexible Allocation Hybrid Initiated Securities Investment Fund 26,967,645 RMB ordinary shares 26,967,645 Statement regarding connected relationship or concerted action of the TheCompany isnot aware of any of theother shareholders above are above shareholders connected or acting in concert as defined in “Administrative Measures on Acquisitions of Listed Companies”. Note: HKSCC NOMINEES LIMITED represents , holding 31,901,234 A Shares and 1,410,601,449 H Shares of the Company. These shares were held on behalf of various clients respectively. The shareholdings and selling restrictions of Top 10 shareholders with selling restrictions Applicable Not applicable
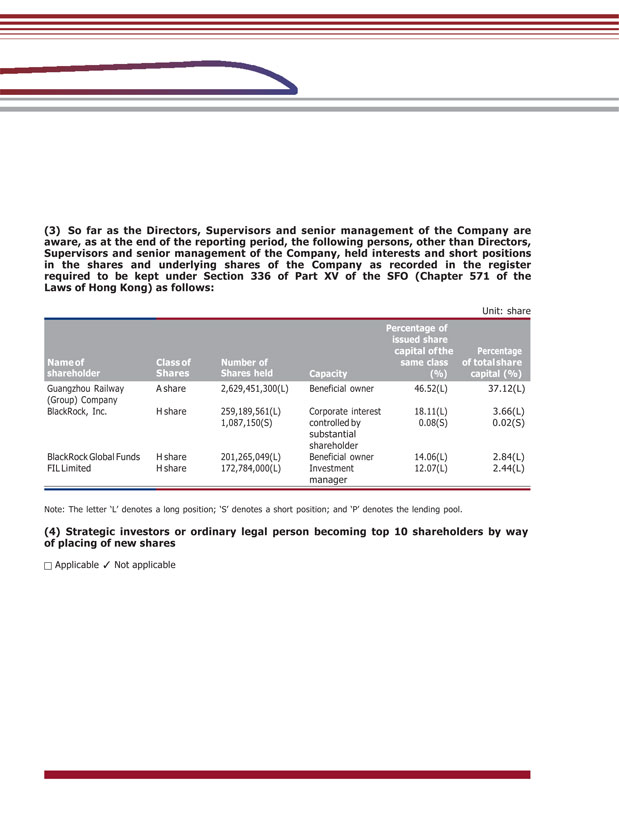
(3) So far as the Directors, Supervisors and senior management of the Company are aware, as at the end of the reporting period, the following persons, other than Directors, Supervisors and senior management of the Company, held interests and short positions in the shares and underlying shares of the Company as recorded in the register required to be kept under Section 336 of Part XV of the SFO (Chapter 571 of the Laws of Hong Kong) as follows: Unit: share Percentage of issued share capital ofthe Percentage Name of Class of Number of same class of total share shareholder Shares Shares held Capacity (%) capital (%) Guangzhou Railway A share 2,629,451,300(L) Beneficial owner 46.52(L) 37.12(L) (Group) Company BlackRock, Inc. H share 259,189,561(L) Corporate interest 18.11(L) 3.66(L) 1,087,150(S) controlled by 0.08(S) 0.02(S) substantial shareholder BlackRock Global Funds H share 201,265,049(L) Beneficial owner 14.06(L) 2.84(L) FIL Limited H share 172,784,000(L) Investment 12.07(L) 2.44(L) manager Note: The letter ‘L’ denotes a long position; ‘S’ denotes a short position; and ‘P’ denotes the lending pool. (4) Strategic investors or ordinary legal person becoming top 10 shareholders by way of placing of new shares Applicable Not applicable

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT IV. INFOR MAT ION ON THE LARGEST SHAREHOLDER AND ITS DE FACTO CONTROLLER (1) Information on the Largest Shareholder 1. Legal person Name GRGC Person in charge or legal representative Wu Yong Date of incorporation 1992-12-05 Principal operations Organization and management of railway passenger and freight transportation, technologies and other industrial development etc. Equity interests in other domestic and Nil overseas listed controlling and invested companies during the reporting period 2. Chart on the property rights and controlling relationship between the Company and the largest shareholder 37.12% GRGC The Company

(2) Information on the de facto controller of the Largest Shareholder 1. Legal person Name CRC Person in charge or legal Lu Dongfu representative Principal Date of incorporation operations Diversified 2013-03-14 operations with railway transportation services of passengers and goods as its main business Equity interests in other CRC is the de facto controller of Daqin Railway Co. Ltd. and China Railway domestic and overseas listed Tielong Container Logistics Co. Ltd. (listed companies on the SSE). controlling and invested companies during the reporting period Explanation on other On March 14, 2013, the de facto controller of GRGC, namely the former information Ministry of Railways of the People’s Republic of China (the “former MOR”), was dissolved in accordance with the proposal in relation to the institutional reform and functional transformation of the State Council and the “Reply of the State Council to Issues concerning the Establishment of China Railway Corporation”. The administrative functions of the former MOR were transferred to the Ministry of Transport and its subordinate body, the newly established State Railway Administration, whereas its commercial functions were transferred to the newly incorporated CRC. GRGC was a railway corporation directly under the former MOR, and its interests were transferred to the CRC (the “Reform”). Upon completion of the Reform, the de facto controller of the largest shareholder of the Company was changed to CRC. 2. Chart on the property rights and controlling relationship amongst the Company, the largest shareholder and its de facto controller 100% 37.12% CRC GRGC The Company (3) Other information of the largest shareholder and its de facto controller Applicable Not applicable

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT V. OTHER CORPORATE SHAREHOLDERS WITH A SHAREHOLDING OF 10% OR ABOVE As at the end of the reporting period, apart from the aforesaid largest shareholder, there was no other corporate shareholder with a shareholding of 10% or above in the Company (except for HKSCC NOMINEES LIMITED). VI. EXPLANATION ON REDUCED SHAREHOLDING Applicable Not applicable VII. PUBLIC FLOAT As at the end of the reporting period, the public float of the Company was 4,454,085,700 shares, representing 62.88% of the total share capital of the Company. Calculated at HK$4.68 per share, the closing price of the Company’s H shares as at 30 December 2016, the market capitalization of the public float was approximately HK$20.845 billion. The public float of the Company was in compliance with the requirements of the relevant rules on the sufficiency of public float. VIII. DUBLICATION During the reporting period, Directors, chief executives or such other persons did not have duplicated interests. IX. REPURCHASE, SALE OR REDEMPTION OF THE LISTED SHARES OF THE COMPANY As of the end of the reporting period, there was no repurchase, sale or redemption by the Company, or any of its subsidiaries, of the listed shares of the Company.

X. PRE-EMPTIVE RIGHT Under the memorandum and articles of association of the Company and the PRC Laws, there is no pre- emptive right, which requires the Company to offer new shares to its existing shareholders on a pro rata basis. XI. TRANSACTIONS INVOLVING ITS OWN SECURITIES As at the end of the reporting period, none of the Company and its subsidiaries has issued or granted any convertible securities, options, warrants or other similar rights, and redeemable securities and share option schemes. XII. TAX DEDUCTION FOR HOLDERS OF LISTED SECURITIES As at the end of the reporting period, holders of listed securities of the Company were not entitled to obtain any relief from taxation by reason of their holding of such securities pursuant to the laws of the PRC.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Chapter 7 Information of Preference Shares Information of Preference Shares Applicable Not applicable




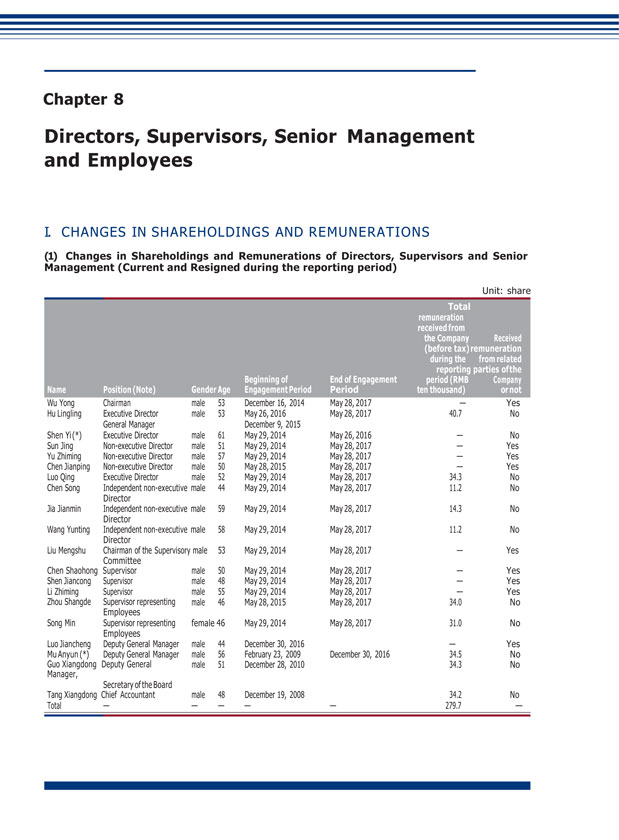
Chapter 8 Directors, Supervisors, Senior Management and Employees I. CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDINGS AND REMUNERATIONS (1) Changes in Shareholdings and Remunerations of Directors, Supervisors and Senior Management (Current and Resigned during the reporting period) Unit: share Total remuneration received from the Company Received (before tax) remuneration during the from related reporting parties of the Gender Age Beginning Engagement of Period Period End of Engagement tenperiod thousand) (RMB Company or not Name Position (Note) Wu Yong Chairman male 53 December 16, 2014 May 28, 2017 — Yes Hu Lingling Executive Director male 53 May 26, 2016 May 28, 2017 40.7 No General Manager December 9, 2015 Shen Yi (*) Executive Director male 61 May 29, 2014 May 26, 2016 — No Sun Jing Non-executive Director male 51 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 — Yes Yu Zhiming Non-executive Director male 57 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 — Yes Chen Jianping Non-executive Director male 50 May 28, 2015 May 28, 2017 — Yes Luo Qing Executive Director male 52 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 34.3 No Chen Song Independent non-executive male 44 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 11.2 No Director Jia Jianmin Independent non-executive male 59 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 14.3 No Director Wang Yunting Independent non-executive male 58 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 11.2 No Director Liu Mengshu Chairman of the Supervisory male 53 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 — Yes Committee Chen Shen Jiancong Shaohong Supervisor Supervisor male male 50 48 May May 29, 29, 2014 2014 May May 28, 28, 2017 2017 — — Yes Yes Li Zhou Zhiming Shangde Supervisor Supervisor representing male 55 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 — Yes Employees male 46 May 28, 2015 May 28, 2017 34.0 No Song Min Supervisor representing female 46 May 29, 2014 May 28, 2017 31.0 No Employees Luo Jiancheng Deputy General Manager male 44 December 30, 2016 — Yes Mu Anyun (*) Deputy General Manager male 56 February 23, 2009 December 30, 2016 34.5 No Guo Manager, Xiangdong Deputy General male 51 December 28, 2010 34.3 No Tang Xiangdong Chief Secretary Accountant of the Board male 48 December 19, 2008 34.2 No Total — — — — — 279.7 —

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Note: (1) During the reporting period, none of the Directors, Supervisors or senior management of the Company has held or dealt in the shares of the Company, or has held the Company’s share option or has been granted any shares with selling restrictions. (2) Those marked with asterisk (*) in the table represents that the person has resigned during the reporting period, of which: Mr. Shen Yi ceased to serve as the executive Director of the Company for the reason of age and Mr. Mu Anyun ceased to serve as the Deputy General Manager of the Company due to change of position. (3) Mr. Luo Jiancheng confirmed, except as disclosed in this annual report, they had no relationship with other Directors, supervisors, senior management, substantial shareholders or controlling shareholders of the Company. Name Biographies Wu Yong Male, born in June 1963, is the current chairman of the Board of the Company. Mr. Wu is a graduate with a bachelor degree and a senior engineer with advanced remuneration. Started his career in July 1986, Mr. Wu served successively as chief of the track divisions of Suxian, Huaibei, Fuyang and Suzhou of Bengbu Sub-bureau of Shanghai Railway Bureau, the bureau chief assistant (from September 2003) and deputy bureau chief (from November 2004) of Benghu Sub-bureau of Shanghai Railway Bureau, commander chief (from March 2005) of Hefei-Wuhan Railway Engineering Construction Headquarters of Shanghai Railway Bureau, the bureau chief assistant (from April 2005), deputy bureau chief (from April 2006) and executive deputy bureau chief (from August 2008) of Wuhan Railway Bureau, and the bureau chief and deputy party secretary (from March 2009) of Chengdu Railway Bureau. Since August 2014, he has been the chairman and general manager of Guangzhou Railway (Corporation) Company (GRGC) and deputy secretary of the party committee. Hu Lingling Male, born in November 1963, is an executive Director and a general manager of the Company. Mr. Hu is a graduate with a bachelor degree and is an engineer. Mr. Hu has been working in this industry since 1985 and has obtained 30 years’ experience in the railway transportation industry. He had served successively as the deputy chief engineer and the deputy station master of Shaoguan Station (now, Shaoguan East Station) of former Yangcheng Company of GRGC, the deputy chief engineer and the deputy general manager of former Yangcheng Company of GRGC and the director of the transportation department of GRGC between 1985 and 2003. Mr. Hu was the deputy general manager of GRGC and the Director of the Company from July 2003 to March 2006. He had worked in the global business department in the headquarters of International Union of Railways in Paris, France from March 2006 to February 2012 and served as the deputy general manager of Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong Express Rail Link Company Limited from February 2012 to December 2015 and he served as the general manager of the Company since December 2015. Sun Jing Male, born in July 1965, is a non-executive Director of the Company. He is a graduate with a bachelor degree, an engineering master degree holder and also a senior engineer. Before June 2004, Mr. Sun has successively worked at the northern locomotive section of Zhengzhou Sub-bureau of Zhengzhou Railway Bureau, locomotive department of Zhengzhou Railway Bureau and Yueshan locomotive section of Zhengzhou Sub-bureau of Zhengzhou Railway Bureau. From June 2004 to March 2007, he has served as division chief of locomotive department of Zhengzhou Railway Bureau. He was an assistant to the director of Zhengzhou Railway Bureau from April 2007. He has served as deputy general manager of GRGC since May 2007. Yu Zhiming Male, born in April 1959, is a non-executive Director of the Company. Mr. Yu is a graduate with a bachelor degree, obtained a master degree of engineering and is a senior accountant. He has many years of experience in the financial field. Before April 2008, he had successively served as director of the Sub-division of Finance of Wuhan Railway Sub- bureau of Zhengzhou Railway Bureau, the director of the finance department of Wuhan Railway Bureau, director of capital settlement center of Wuhan Railway Bureau, and the standing vice-director of capital settlement center of MOR. Since April 2008, he has been chief accountant of GRGC.

Name Biographies Chen Male, born in November 1966, is a non-executive Director of the Company. Mr. Chen used to work at the First High School Jianping of Guangzhou Railway, Locomotive Sports Association of GRGC and at GRGC and the Company. Mr. Chen served as the office secretary of the trade union of GRGC, director of the logistic department of the Company, deputy secretary of the party committee and concurrently the secretary of committee for disciplinary inspection of the passenger transportation business unit of the Company, deputy office manager of the Company, chairman of the trade union of the mechanized line center of GRGC. From 2007 to October 2012, he has served as the section chief of Guangzhou Passenger Transportation Division, and from November 2012 to October 2013, he has been the general manager of diversified operation and development center, deputy secretary of the party committee and director of various operation and management offices of GRGC. From November 2013 to September 2014, he has been the stationmaster of Shenzhen North station and deputy secretary of the Party Committee of the Company. Since October 2014, he has been chief of the passenger transport department of GRGC. Mr. Chen was a Supervisor representing employees of the Company from May 2014 to May 2015. Luo Qing Male, born in September 1964, is an executive Director of the Company. Mr. Luo graduated from the Correspondence College of the Party School of CPC, majoring in economic management with a master’s degree and is a political engineer. Before April 2006, he had served as sportsman, coach and secretary-general of Guangdong Physical Culture and Sports Team, labor union of Guangzhou Railway Sub-bureau of Guangzhou Railway Bureau, labor union of YangCheng Railway Company of GRGC, Locomotive Sports Association of YangCheng Railway Company of GRGC and Locomotive Sports Association of GRGC. From April 2006 to October 2008, he was the chief of the organization department of trade union of GRGC. From November 2008 to April 2010, he served as the chairman of the trade union of the Company. Since May 2010, he has been the deputy secretary of the party and working committee and secretary of the discipline inspection and working commission of the Company and also the chairman of the trade union of the Company. Chen Song Male, born in January 1973, is currently an independent non-executive Director of our Company. Mr. Chen has a Doctorate degree majoring in finance and investment from Management School of Sun Yat-sen University, a certified public accountant of China, a certified internal auditor registered in the US. Mr. Chen was the teacher in higher mathematics and pharmaceutical machinery in Guangdong Food and Drug Vocational College, the tutor for MBA and EMBA in Management School of Sun Yat-sen University, managerial trainee in P&G (China) Investment Limited Company, financial analysis manager in Crest Oral Department, financial supervisor of business department, CFO, executive director of Heinz (China) Investment Co., Ltd., the chief financial officer of Ren Coty (China) and a director and general manager of its cosmetics division, financial supervisor of Greater China Region in Boer Cmc Markets Asia Pacific Pty Ltd., the deputy general manager and CFO of Chongqing Brewery Co., Ltd. He currently serves as general manager of Chongqing Brewery Co., Ltd. Jia Jianmin Male, born in August 1957, is an independent non-executive Director of our Company. Mr. Jia has master degree and he has a doctorate degree in Business School of the University of Texas at Austin. He was a member of advisory committee of experts of department of management of The National Natural Science Foundation, the member of China National MBA Education Supervisory Committee, the Scholar Director of MSI USA. He has rich experiences in consulting and training, he served for companies including Hutchison Whampoa, China Telecom, China Mobile, Citic Bank, IBM, China Rail, CSR and CNR etc. Now He is a professor and chairman of the Department of Marketing of Faculty of Business Administration of The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Changjiang Scholar Professor of the Ministry of Education of PRC. Wang Male, born in July 1958, is an independent non-executive Director of the Company. Mr. Wang graduated from Medical Yunting School of Xi’an Jiaotong University with a bachelor’s degree and obtained an EMBA degree from Guanghua School of Management, Peking University. Mr. Wang was the vice general manager of China Commercial Foreign Trade Corporation, Ltd. (Shenzhen), vice general manager of Beijing Capital Huayin Group, now he is the director of Shaanxi Fortune Investment Limited.
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Name Biographies Liu Male, born in July 1963, is currently the chairman of the Company’s supervisory committee. Mr. Liu holds a bachelor Mengshu degree and is an engineer. He had successively served in Huaihua sub-bureau of Guangzhou Railway Bureau and GRGC Changsha headquarters before November 2004. He served in GRGC as the head of director of organization department of party committee of GRGC from November 2004 to April 2006, as head of GRGC party committee’s propaganda department from April 2006 to September 2008, as GRGC’s office director from September 2008 to December 2013. Since December 2013, he has been the deputy secretary of CPC and the secretary of Committee for Discipline Inspection of GRGC. Chen Male, born in January 1967, is a supervisor of the Company. Mr. Chen holds a bachelor degree and is an economist. Mr. Shaohong Chen has been engaged in the research and practice of enterprise management for a long time. Before April 2006, he has been vice section chief and section chief of mechanism reform section of corporate management office, vice-director of corporate management office and vice-director of corporate management and legal affairs department of GRGC. From April 2006 to May 2008, he served as director of corporate management and legal affairs department of GRGC and from June 2008 to July 2015, he was the vice-chief economist and director of corporate and legal affairs department of GRGC. Since August 2015, he has been the director of corporate and legal affairs department of GRGC. Shen Male, born in September 1968, is a Supervisor of the Company. He is a graduate with a bachelor degree and an economist. Jiancong Before March 2011, Mr. Shen had worked as secretary of Chinese Youth League of the Guangzhou mechanical refrigerator car depot of Guangzhou Sub-bureau of Guangzhou Railway Bureau, deputy director and director of division of personnel of GRGC, deputy director of division of human resources of GRGC, concurrently as deputy director of organization department of Party Committee of GRGC, and secretary of CPC committee and vice stationmaster of Shenzhen station of the Company. He has been the director of division of human resources and director of organization department of party committee of GRGC since March 2011. Li Zhiming Male, born in May 1961, is a Supervisor of the Company. Mr. Li graduated from the Party School of CPC, with a bachelor’s degree majoring in economics and management and is an accountant. Before 1996, Mr. Li had served in various managerial positions in Hengyang Railway Sub-bureau of Guangzhou Railway Bureau and Changsha Railway Company of GRGC. From 1996 to March 2005, he was chief of finance sub-division of Changsha Railway Company of GRGC. Since April 2005, Mr. Li has been deputy chief and chief of the audit department of GRGC. Zhou Male, born in December 1970, is the Company’s Supervisor representing employees. Mr. Zhou graduated from Central Shangde Party School of Central Committee of the CPC with a master degree and holds a political officer title. Mr. Zhou served in the Company from June 1994 to July 2007 successively as the secretary of the Communist Youth League of the then Shenzhen North Station (Now Sungang Station), deputy chief of the organization and human resources department, director of the Party committee office, chairman of the trade union of the integrated service center of the Company, etc. Between July 2007 and March 2011, Mr. Zhou was transferred to the GRGC and served successively as deputy head of the human resource office, deputy office manager and concurrently director of the reception office, chief party secretary of office administration, etc. In March 2011, Mr. Zhou was transferred back to the Company and served successively as party secretary and station master of Shenzhen station, etc. Since December 2014, he has been the station master of the Shenzhen North Station. Song Min Female, born in November 1970, is Supervisor representing employees of the Company. Ms. Song graduated from Lanzhou University, holds a bachelor degree in accounting, and is an accountant. Ms. Song joined the Railway industry in 1991 and has served in many railway companies. She has successively served as the deputy manager of the operating finance office, department of finance of Qinghai-Tibet Railway Company, deputy office director and finance director of Qinghai- Tibet Railway Public Security Bureau, vice office supervisor of Qinghai-Tibet Railway Company Annuity Council, the vice consultant of department of financial management of the State Taxation Bureau of Qinghai Province, the senior manager of Petrol China Guangdong Sales Company Shenzhen Branch, etc. Since November 2012, she has been the chief of Department of Audit of our Company.

Name Biographies Luo Male, born in January 1973, is a deputy general manager of the Company. Mr. Lou is a graduate with a bachelor degree Jiancheng and is a senior engineer. Mr. Luo served sucessively as the chief of Investigation & Inspection Division of the General Office of GRGC, Shiweitang station master of SR, deputy chief of Transportation Department of GRGC, the assistant of the general manager of the Company, the general manager of Guangzhou Tiecheng Industrial Company and the deputy general manager of GMSR. Since December 2016, he has been the deputy general manager of our Company. Guo Male, born in November 1965, is the deputy general manager and secretary of the Board. Mr. Guo graduated from Central Xiangdong China Normal University and is a graduate with a bachelor degree and holds an MBA degree, and is an economist. Before January 2004, he has been deputy section chief, deputy head and head of secretariat of the Board. From January 2004 to November 2010, he has been appointed as the secretary of the Board and since December 2010, Mr. Guo has been appointed as the deputy general manager and secretary of the Board. Tang Male, born in September 1968, is chief accountant of the Company. Mr. Tang graduated from Jinan University majoring in Xiangdong business administration and is a graduate with a bachelor degree and holds an MBA degree, and is a senior accountant. Before March 2006, he has served in various professional management positions in the Labor and Capital Department, Diversified Business Department and Revenue Settlement Center of the Company. From March 2006 to November 2008, he was director of Finance Department of the Company. Since December 2008, Mr. Tang has been the Chief Accountant of the Company. (2) Share incentives granted to the Directors, Supervisors and Senior Management during the reporting period Applicable Not applicable
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT II. ENGAGEM ENTS OF D IR ECTOR S, SUP ERVISOR S AND SENIOR MANAGEMENT (CURRENT AND RESIGNED DURING THE REPORTING PERIOD) (1) Engagements in shareholders Name Name of Position at Shareholder Beginning of End of Shareholder Engagement Engagement Wu Yong GRGC Chairman, General Manager, Deputy August 2014 Sun Jing GRGC Secretary Deputy General of Party Manager Committee May 2007 Chen Yu Zhiming Jianping GRGC GRGC Chief Chief of Accountant the Passenger Transport April 2008 October 2014 Department Liu Mengshu GRGC Deputy Secretary of Party Committee, December 2013 Secretary of Committee for Discipline Inspection Chen Shaohong GRGC Chief of the Corporate Management August 2015 Department, Chief of Legal Affairs Department Shen Jiancong GRGC Chief of the HR department, Director March 2011 of Organization Department of Party Committee Li Zhiming GRGC Chief of the Audit Department April 2006 (2) Engagements in other companies Name Name of other companies Position at other companies Wu Yong GMSR, SR, Shichang Railway Company Limited and Yuehai Railway Company Limited Chairman Sun Jing Guangzhou Electric Locomotive Co., Ltd. Director Yu Zhiming China Railway (HK) Holdings Ltd. Chairman Yuehai Railway Company Limited, GZIR, MaoZhan Railway Company Limited and Chairman of the supervisory Guangdong Pearl River Delta Inter-city Railway Traffic Co., Ltd. committee GMSR, SR, Shichang Railway Company Limited, Hukun Passenger Railway Line Director (Hunan) Company Limited, Hainan Eastern Ring Railway Company Limited, GSR, China Railway Container Transportation Limited and China Railway Special Goods Transportation Limited Guangzhou–Zhuhai Railway Company Limited and China Railway Express Co., Ltd. Supervisor
Name Name of other companies Position at other companies Chen Jianping Hainan Railway Economic Technology Development Co., Ltd. Director China Railway Commemorative Ticket Company Supervisor Chen Song Chongqing Brewery Co., Ltd. General manager Jia Jianmin The Chinese University of Hong Kong Professor and chairman of the Department of Marketing of Faculty of Business Administration and Changjiang Scholar Professor of the Ministry of Education Wang Yunting Shaanxi Fortune Investment Limited Chairman Liu Mengshu GMSR andSR Chairman of the supervisory committee Chen Shaohong GMSR, Yuehai Railway Company Limited, XSR, Jingyue Railway Company Limited, Director Guangdong Shenmao Railway Company Limited and Guangdong Meishan Passenger Railway Line Company Limited Shichang Railway Company Limited, Hukun Passenger Railway Line (Hunan) Company Chairman of the supervisory Limitedand Hainan Railway Economic and Technological Development Co., Ltd. committee SR, Hunan Inter-city Railway Company Limited, Gaungdong Pearl River Delta Inter- Supervisor city Railway Traffic Co., Ltd., Hainan Eastern Ring Railway Company Limited, GSR, China Railway Express Co., Ltd. and Guangzhou Electric Locomotive Co., Ltd. Li Zhiming Hong Kong Qiwen Limited and Hainan Railway Economic and Technological Director Development Co., Ltd. Guangdong Shenmao Railway Company Limited, Guangzhou Tiecheng Enterprise Chairman of the supervisory Company Limited and Xingguangji Trade Company Limited in Beijing committee GMSR, SR, Shichang Railway Company Limited, Yuehai Railway Company Limited, Supervisor Hukun Passenger Railway Line (Hunan) Co., Ltd., XSR, GSR, GGR, NGR, Jingyue Railway Company Limited and GZR, Guangdong Meishan Passenger Railway Line Company Limited, Guangzhou Northeastern Cargo Outer Ring Railway Company Limited and Guangzhou Nanshagang Railway Company Limited Tang Xiangdong Guangzhou Tiecheng Enterprise Company Limited and Shenzhen Guangshen Railway Director Civil Engineering Company

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT III. RE MUNER AT ION OF DIRECTORS, SUPERVISORS AND SENIOR MANAGEMENT Decision-making procedure of Remuneration or allowance standards of the Directors and Supervisors of the Company the remuneration of Directors, should be submitted for approval at the general shareholder meeting of the Company after Supervisors and senior consideration and discussion by the Board. management Basis for determination of the Determined with reference to the level of remuneration in Shenzhen, where the Company is remuneration of Directors, located, the job nature of individual staff, as well as the annual objective of the Company, the Supervisors and senior completion status of work targets and the operating results of the Company. management Payment of remuneration of During the reporting period, none of the following Directors, namely Mr. Wu Yong, Mr. Sun Jing, Directors, Supervisors and senior Mr. Yu Zhiming and Mr. Chen Jianping and the following Supervisors Mr. Liu Mengshu, Mr. Chen management Shaohong, Mr. Shen Jiancong and Mr. Li Zhiming has received remuneration from the Company. As far as the Company is aware, as at the date of disclosure of this report, the Company had no arrangements of Directors, Supervisors and senior management having waived or agreed to waive any plans of remuneration. For details of the payment of remuneration to the Directors, Supervisors and senior management and details of remuneration by level of remuneration, please see the section “Changes in shareholdings and remunerations of Directors, Supervisors and senior management (current and resigned during the reporting period)” above and the relevant contents of Note 42 to the financial statements of the Company prepared in accordance with the International Financial Reporting Standards. Actual total amount of During the reporting period, the Directors, Supervisors and senior management received a total remuneration received by remuneration in the amount of RMB2.797 million. Directors, Supervisors and senior management at the end of the reporting period IV. C H A N G E S IN D I R E C T O R S , S U P E R V I S O R S AND S E N I O R MANAGEMENT Name Position Changes Reasons of Change Hu Lingling Executive director, member of Election Being Elected Remuneration Committee Shen Yi Executive director, member of Dismissal Reached the age of Remuneration Committee retirement Luo Jiancheng Deputy General Manager Appointment Being Elected Mu Anyun Deputy General Manager Dismissal Change of position V. EXPLANATION ON PUNISHMENT BY SECURITIES REGULATORY BODIES FOR THE PAST THREE YEARS Applicable Not applicable

VI. OTHER INFORMATION ON DIRECTORS AND SUPERVISORS AND SENIOR MANAGEMENT (1) Equity interests of Directors, Supervisors or Chief Executives As at the end of the reporting period, there was no record of interests or short positions (including the interests and short positions which were taken or deemed to have under the provisions of the SFO) of the Directors, Supervisors or chief executives of the Company in the shares, underlying shares and debentures of the Company or any associated corporation (within the meaning of the SFO) in the register required to be kept under section 352 of the SFO. The Company had not received notification of such interests or short positions from any Director, Supervisor or chief executives of the Company as required to be made to the Company and the SEHK pursuant to the Model Code for Securities Transactions by Directors of Listed Companies (the ‘Model Code’) in Appendix 10 to the Rules Governing the Listing of Securities on The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited (the ‘Listing Rules’). During the reporting period, none of the Company or the subsidiaries of the Company had entered into any arrangement such that Company’s Directors, Supervisors or chief executives or their respective spouses or children under the age of 18 could obtain any right to subscribe for any shares or debentures of the Company and any other legal entities. Other companies in which Directors and Supervisors of the Company were directors or employees did not have interests in shares and underlying shares of the Company required to be disclosed to the Company under Sections 2 and 3 of Part XV of the SFO. (2) Service contracts of Directors and Supervisors Each of the Directors and Supervisors of the Company has entered into a service contract with the Company, and the Company and its subsidiaries had no director’s or supervisor’s service contract that was entered into before January 31, 2004 and was waived from complying with the requirements of shareholders’ approval under Rule 13.68 of the Listing Rules. None of the Directors or Supervisors has entered into any service contract with the Company which is not terminable by the Company within one year without payment of compensation (other than statutory compensation). (3) Interests of Directors and Supervisors in contracts None of the Directors or Supervisors of the Company had any direct or indirect interests in any transaction, contract or arrangement of significance subsisting during the year to which the Company or any of its subsidiaries was a party.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT VII. INFORMATION OF EMPLOYEES (1) Information of employees Total Number of Current Employees 44,609 Number of disengaged and retired employees for whom the parent company 115 and major subsidiaries shall be liable to expenses Professional Constitution Category of Professional Constitution Number of Professionals Passenger and freight transportation and transit operation personnel 19,989 Engineering personnel 5,418 Driving personnel 4,428 Public works personnel 4,510 Electricity personnel 2,042 Electricity and water supplies personnel 2,376 Building construction personnel 1,067 Various operations and other employees of subsidiaries 69 Technical and administrative personnel 4,710 Total 44,609 Level of Education Category of Education Level Number of Person Postgraduate or above 154 University graduate 3,708 College for professional training 14,439 Others (secondary vocational school, high school and vocational technical school, etc) 26,308 Total 44,609

(2) Remuneration policy The Company implements salary budget management, under which an annual salary budget is formulated at the beginning of each year jointly by the budget department and labor department of the Company. Budget is first discussed and approved at the meeting of the general manager’s office, and then is organized for implementation by the labor department of the Company after being considered and approved by the Board of the Company. Salary of the Company’s staff is mainly comprised of basic salary, performance-based salary and benefit plans. Basic salary includes post salaries, skill salaries and various allowances and subsidies accounted for under salaries payable as required. Performance-based salary refers to salaries calculated on the basis of economic benefits and social benefits, or piece rates calculated on the basis of workload, or performance based salary calculated on the basis of the performance of the staff at the position. Benefit plans include various social insurance and housing funds paid as required by the relevant policies. Please refer to Note 28 to the financial statements for the total wages and benefits paid by the Company to its employees in the reporting period. In the process of staff salary allocation, the Company always adheres to the principles of allocation based on labor, efficiency-orientation and fairness. It follows that allocation of staff salary is determined on the premises of macro-control, on the basis of post labor assessment, and on the foundation of staff performance assessment, which fully bring out the importance of allocation arrangement in the incentive system of the Company and motivate the staff’s initiative. (3) Training Plan During the reporting period, the Company had a total of 116 occupational education management personnel and a total of 798,803 persons participated in trainings, which mainly includes training on post standardization, adaptability, qualification and continuing education. The annual training plan of the Company for the year was completed 100% and the training expense amounted to approximately RMB34.63 million.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT (4) Employee insurance and benefits plan Pursuant to applicable national policies and industrial regulations, the Company provides the employees with a series of insurance and benefits plan that mainly include: housing fund, retirement pension (basic medical insurance, supplemental retirement pension), medical insurance (basic medical insurance, supplemental medical insurance, birth medical insurance), work-related injury insurance and unemployment insurance. (5) Retirement plan As at the end of the reporting period, the Company has not implemented any retirement plan.

Chapter 9 Corporate Governance I. INFORMATION OF CORPORATE GOVERNANCE Since the listing of the Company on the SEHK and the NYSE in 1996 and on the SSE in 2006, the Company has been continuously improving its corporate governance structure, perfecting the internal control and management systems, enhancing information disclosures and regulating its operation in accordance with the relevant domestic and overseas listing rules and regulatory requirements, after taking into account the actual status of affairs of the Company. General meeting, the Board and the Supervisory Committee of the Company have clearly defined powers and duties, each assuming and performing its specific responsibilities and making its own decisions in an independent, efficient and transparent manner. Currently, there is no material difference between the status quo of the Company’s corporate governance structure and the regulatory documents of the regulatory authorities of the place of listing of the Company’s stocks related to corporate governance of listed company. During the reporting period, according to the regulatory requirements in relation to the internal control of listed companies from domestic and overseas securities regulatory bodies, the Company has completed the self-assessment on internal control and relevant auditing for the year 2015, and made amendment to the Articles of Association and Management Method of Information Disclosure, taking a further step to improve the Company’s corporate governance and internal control, promoting the Company’s sound and sustainable development. During the reporting period, in view of the highly centralized systematic transportation management on the nationwide railway network, it is necessary for the Company’s largest shareholder, GRGC, to obtain the Company’s financial information, the Company’s monthly financial data summaries during the reporting period provided by the Company to the GRGC, in order to exercise its administrative function as an industry’s leader granted by the law and administrative regulations. In view of this, the Company duly followed the regulations set out on the System for the Management of Inside Information and Insiders, enhanced the management on unrevealed information, remind shareholders of their obligation in confidentiality and prevention of insiders’ trade in due course. Improvement of corporate governance is a long-term systematic project, which needs continuous improvement and enhancement. The Company will, as it has always had, continue to promptly update and improve its internal systems according to the relevant regulations, timely discover and solve problems, strengthen its management basis and enhance its awareness of standardized operation and level of governance to promote the regulated, healthy and sustainable development of the Company. Is there any significant difference between corporate governance and requirements of related regulations of CSRCM? If there is significant difference, explanations shall be made. Applicable Not applicable

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT II. SUMMARY OF GENERAL MEETINGS (1) General meetings held during the reporting period Media in which resolutions Date of Session of meeting Date were Disclosed disclosure Annual General May 26, 2016 Website of SSE (www.sse.com.cn) 27 May, 2016 Meeting of 2015 HKExnews Website of SEHK 26 May, 2016 (www.hkexnews.hk) Extraordinary General December 30, 2016 Website of SSE (www.sse.com.cn) 31 December, 2016 Meeting of 2016 HKExnews Website of SEHK 30 December, 2016 (www.hkexnews.hk) (2) Important event for the attention of Shareholders in the coming year The Company plans to convene the annual general meeting of 2016, during which voting will be conducted and resolutions will be made on issues including profit distribution plan. With respect to the specific arrangements of the annual general meeting for the year 2016, investors please note in a timely manner and carefully read the “Notice of 2016 Annual General Meeting” which will be published on the website of the SSE (http://www.sse.com.cn), the HKExnews website of the SEHK (http://www.hkexnews.hk) and the Company’s website (http://www.gsrc.com) in due course.
III. PERFORMANCE OF DUTIES BY DIRECTORS (1) Attendance at Board meetings and general meetings by Directors Attendance at Attendance at Boardmeetings general meetings Number of No. of No. of Number of Twoconsecutive Board meetings meetings meetings Attended meetings Board meetings No. of Independent to be attended attended by way of attended Number of not attended general meetings Name Director or not this year in person telecommunication by Proxy Absence or not attended Wu Yong No 5 5 4 0 0 No 1 Hu Lingling No 3 3 3 0 0 No 1 Shen Yi (*) No 2 1 1 1 0 No 0 Sun Jing No 5 4 4 1 0 No 0 Yu Zhiming No 5 5 4 0 0 No 1 Chen Jianping No 5 5 4 0 0 No 0 Luo Qing No 5 5 4 0 0 No 2 Chen Song Yes 5 4 4 1 0 No 1 Jia Jianmin Yes 5 4 4 1 0 No 1 Wang Yunting Yes 5 5 4 0 0 No 1 Note: Asterisk(*) indicates that the person has resigned during the reporting period. During the reporting period, there was no incident of non-attendance in person by Directors at two consecutive Board meetings. Number of Board meetings held during the year 5 Including: Number of on-site meetings 1 Number of meetings held by way of telecommunication 4 Number of meetings held in a mixed model 0

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT (2) Performance of duties by independent Directors 1. Attendance at Meetings During the reporting period, the Company has held 2 general meetings, 5 board meetings and 6 audit committee meetings. The Company has not held remuneration committee meeting. All independent Directors attended all the meetings either in person or by proxy. Please read the relevant part of ‘Attendance at Board meetings and general meetings by Directors’ and ‘Audit committee’ of this chapter for details. 2. Objection to related matters of the Company by Independent Directors During the reporting period, no objection to the proposals raised at the meetings of the Board or other matters which were not the proposals of the Board meetings of the Company was lodged by the independent Directors. 3. Recommendations for the Company and approval During the reporting period, the Company’s all independent Directors faithfully performed their responsibilities and obligations stipulated by laws, regulations, the memorandum and articles of association and Working Rules of Independent Directors with an attitude of responsibility towards all the shareholders. They showed solicitude for the Company’s operation and compliance with laws, proactively attended Board meetings and other related meetings, carefully reviewed proposals of the meetings, made valuable suggestions and opinions on important project investments, operation and management of the Company with their professional knowledge. They also raised independent opinions, according to relevant rules and facts to their knowledge, on material affairs of the Company, such as external guarantees, change of Directors and connected transactions. During the preparation and disclosure process of the annual report, independent Directors of the Company fulfilled their duties required by the security regulatory authorities and the Annual Report Working Rules of the Audit Committee and Independent Directors. They communicated with the Company, finance and auditing firms adequately and carefully and raised useful suggestions. The independent Directors exerted their independent functions adequately and ensured the legitimate rights and interests of the shareholders, especially minority shareholders, of the Company. Firstly, they recommended the Company to cooperate with the external auditor in relation to the auditing of the 2015 annual report in accordance with the agreed audit arrangements. The Company timely provided the accounting information and other relevant information required for the audit to ensure the audit quality of the 2015 annual report. Secondly, they recommended the re-appointment of PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP as the domestic auditor and PricewaterhouseCoopers as the international auditor of the Company for 2016. The above resolutions for the re-appointment of domestic and international auditors were passed upon consideration at the tenth meeting of the seventh session of the Board and the 2015 annual general meeting of the Company.
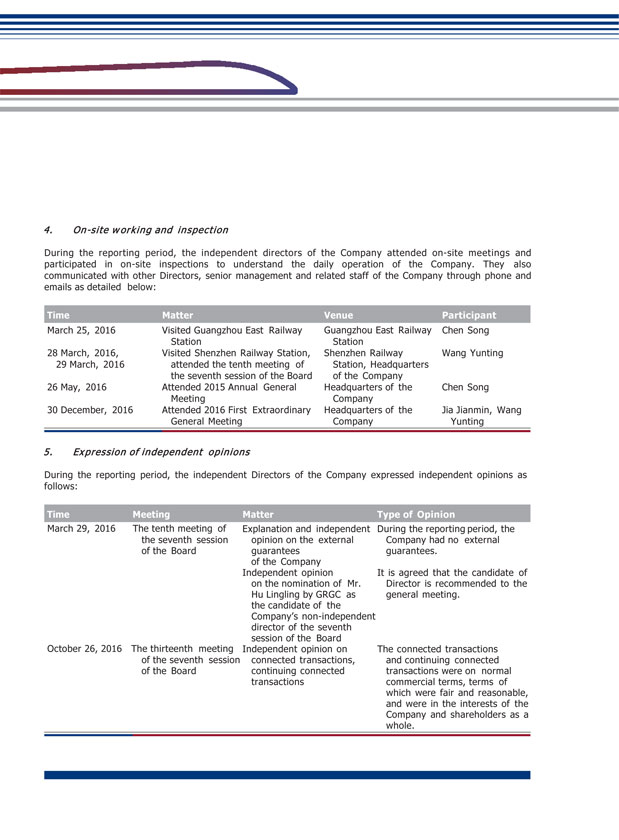
4. On-site working and inspection During the reporting period, the independent directors of the Company attended on-site meetings and participated in on-site inspections to understand the daily operation of the Company. They also communicated with other Directors, senior management and related staff of the Company through phone and emails as detailed below: Time Matter Venue Participant March 25, 2016 Visited Guangzhou East Railway Guangzhou East Railway Chen Song Station Station 28 March, 2016, Visited Shenzhen Railway Station, Shenzhen Railway Wang Yunting 29 March, 2016 attended the tenth meeting of Station, Headquarters the seventh session of the Board of the Company 26 May, 2016 Attended 2015 Annual General Headquarters of the Chen Song Meeting Company 30 December, 2016 Attended 2016 First Extraordinary Headquarters of the Jia Jianmin, Wang General Meeting Company Yunting 5. Expression of independent opinions During the reporting period, the independent Directors of the Company expressed independent opinions as follows: Time Meeting Matter Type of Opinion March 29, 2016 The tenth meeting of Explanation and independent During the reporting period, the the seventh session opinion on the external Company had no external of the Board guarantees guarantees. of the Company Independent opinion It is agreed that the candidate of on the nomination of Mr. Director is recommended to the Hu Lingling by GRGC as general meeting. the candidate of the Company’s non-independent director of the seventh session of the Board October 26, 2016 The thirteenth meeting Independent opinion on The connected transactions of the seventh session connected transactions, and continuing connected of the Board continuing connected transactions were on normal transactions commercial terms, terms of which were fair and reasonable, and were in the interests of the Company and shareholders as a whole.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT IV. S P E C I A L C O M M I T T E E S U N D E R T HE B O A R D HAD M A D E IMPORTANT OPINIONS AND SUGGESTIONS IN THE PERFORMANCE OF T H E I R D U T I E S D U R I N G T HE R E P O R T I N G P E R I O D , AND DISCLOSURES OF DETAILS SHALL BE MADE IN THE EVENT OF THE MATTER OF OBJECTION During the reporting period, special committees under the Board did not make important opinions and suggestions in the performance of their duties and there was not matter of objection. V. EXPLANATION ON EXISTENCE OF RISKS BY THE SUPERVISORY COMMITTEE During the reporting period, the supervisory committee has no objection to the matters of supervision. VI. I N A B I L I T Y OF T H E C O M P A N Y A N D IT S C O N T R O L L I N G SHAREHOLDERS TO ENSURE INDEPENDENCE AND MAINTAIN THEIR CAPACITY OF INDEPENDENT OPERATION IN TERMS OF BUSINESS, PERSONNEL, ASSETS, ORGANISATION AND FINANCE During the reporting period, the Company maintained autonomy in operation and finance, and maintained independence from the largest shareholder, GRGC, in such respects as business, staff, assets, organization and finance. During the reporting period, there was no peer competition due to factors including partial restructuring, characteristics of the industry, national policies or mergers and acquisitions for the Company. The Company’s largest shareholder, GRGC, also committed to avoid peer competition and minimize connected transactions. Details of the related commitments and their implementation are set out in the chapter ‘Matters of Importance’ of this annual report.

VII. ESTABLISHMENT AND IMPLEMENTATION OF THE COMPANY’S APPRAISAL MECHANISM AND INCENTIVE MECHANISM FOR SENIOR MANAGEMENT DURING THE REPORTING PERIOD To strengthen the incentive and restriction of senior management, motivate the senior management to enhance their management capability and level, and to review and evaluate the work and performance of the individual senior management, the Company implements the objective responsibility assessment mechanism on senior management, under which the Board and the senior management of the Company and its subsidiaries enter into target assessment responsibility letters at the beginning of every year in relation to indicators including passenger and freight transportation volume, revenues from transportation, safety, costs, profit and management, etc After the assessment period, the Company realizes its incentive commitments on an individual basis based on the completion of targets and tasks by individual senior management and their assessment results. VIII. WHET HER OR NOT TO D ISCL OSE THE REP ORT OF SELF - ASSESSMENT ON INTERNAL CONTROL During the reporting period, the Board has complied with the relevant domestic and overseas requirements and carried out self assessment of the effectiveness of internal control. For details of the assessment report, please read the Report on Internal Control 2016 disclosed on the website of SSE (http://www.sse.com.cn), the HKExnews website of SEHK (http://www.hkexnews.hk) and the website of the Company (http://www. gsrc.com). Explanation on significant deficiencies in internal control during the reporting period Applicable Not applicable IX. INFORMATION OF AUDIT REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP has assessed the efficacy of the internal control system related to the financial reporting by the Board, and has issued an unqualified audit report. For details of the audit report, please refer to the Audit Report of Internal Control disclosed on the website of SSE (http://www.sse. com.cn), the HKExnews website of SEHK (http://www.hkexnews.hk) and the website of the Company (http:// www.gsrc.com). Whether or not to disclose the audit report on internal control: Yes

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT X. CORPORATE GOVERNANCE REPORT (1) Compliance with the Corporate Governance Code During the reporting period, apart from the provision of the Corporate Governance Code on the establishment of a nomination committee, as far as the Company and its Directors are aware, the Company has complied with the relevant code provisions set out in the Corporate Governance Code in Appendix 14 to the Listing Rules of the SEHK. Meanwhile, the Company has applied the principles set out in the Corporate Governance Report in its corporate governance structure and practices. As at the end of the reporting period, the Board of the Company decided not to set up a nomination committee after prudent consideration of the policy environment and background of the industry to which the Company belongs as well as the corporate governance structure over a long time. According to the requirements of the memorandum and articles of association and the Procedures for Shareholders to Propose a Person for Election as Director, upon expiration of the term of a Director or there is a vacancy for Director, shareholders individually or collectively holding three percent or above of the issued shares of the Company may nominate a candidate for non-independent Director by way of written proposal to the Company; shareholders individually or collectively holding one percent or above of the issued shares of the Company may nominate a candidate for an independent Director by way of written proposal to the Company. Directors of the Company shall be elected at general meetings for a term of office of three years. Upon expiration of his term, Director shall be entitled to be re-elected. (2) Securities transactions by Directors, Supervisors and senior management and Interests on competitive business The Company has adopted the Model Code for Securities Transactions by Directors of Listed Issuers as set out in Appendix 10 to the Listing Rules of the SEHK and the Administrative Rules on Shares Held by the Directors, Supervisors and Senior Management Officers of Listed Companies and the Changes Thereof (Zheng Jian Gong Si Zi [2007] No. 56) of CSRC as its own code of conduct regarding securities transactions of the Directors. The Company formulated the Administrative Rules on Shares Held by the Directors, Supervisors and Senior Management Officers of Guangshen Railway Company Limited and the Changes Thereof, which was approved at the twenty second meeting of the fourth session of the Board. After making specific enquiries with all the Directors, Supervisors and senior management, the Company confirms that during the reporting period, all the Directors, Supervisors and senior management have complied with the required standard set out in the above-mentioned code, rules and regulations and system requirements. After making specific enquiries with all the executive Directors, non-executive Directors and Supervisors, the Company confirms that during the reporting period, none of the Directors, non-executive Directors and Supervisors has held any interests in businesses that compete or may compete with the businesses of the Company directly or indirectly.

(3) Board The Board leads the Company in a responsible attitude and effective manner. The Board is responsible for devising and reviewing the Company’s development strategies and planning, reviewing and approving the annual budget and business plans, recommending the dividend proposal, ensuring the implementation of effective internal control system and supervising the performance of the management in accordance with the memorandum and articles of association, the rules of procedure of the general meetings and the rules of procedure of the Board meetings. The management of the Company is led by the general manager, who is responsible for the daily operation of the Company. The general manager supervises the daily business operations, development planning and implementation under the assistance of the deputy general manager, and is liable for all businesses of the Company to the Board. The Board comprises nine members, including three independent non-executive Directors. Members of the Board are diversified as reflecting their having different cultural and education background and extensive experience in various industries, possessing the appropriate qualifications related to the businesses of the Company, ranging from 40 to 60 in age, and therefore are able to provide recommendations to the management from multiple angles with diversified modes of thinking. The names, biographical details and occupations of the Directors are set out in the relevant part of the chapter ‘Directors, Supervisors, Senior Management and Employees’ of this annual report. The Company provides information on business development of the Company to all Directors, including statements of various forms, documents and minutes of meetings. The independent Directors timely obtain in-depth knowledge of operating situation of the Company through hearing reports of the management of the Company regarding production and operation and on-the-spot investigation. The Company undertakes to provide independent Directors with working conditions necessary for the performance of duties. The secretary to the Board actively assists independent Directors in performing their duties and other relevant persons of the Company cooperate with the independent Directors in their work performance of their duties. The fees required for the engagement of intermediaries and discharge of other duties by the independent Directors shall be borne by the Company so that independent Directors can effectively perform their duties. During the reporting period, the Board held 5 meetings. For details of the attendance of the Directors at the Board meetings, please read the relevant parts of ‘Performance of Duties by Directors’ of this chapter. There is no financial, business, family or other material/connected relationship between members of the Board and between the chairman of the Board and the general manager. The Board has established the audit committee and the remuneration committee to supervise relevant affairs of the Company. Each committee has specific responsibilities, reports to and gives advice to the Board on a regular basis.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT (4) Chairman of the Board and general manager Mr. Wu Yong and Mr. Hu Lingling are the chairman of the Board and the general manager of the Company, respectively. The chairman of the Board is responsible for the leadership and effective running of the Board and ensuring that all key and appropriate issues are discussed by the Board in a timely manner. The Company does not have a chief executive officer and the relevant duties of a chief executive officer (including the implementation of annual business plan and investment proposal of the Company and decision-making on production, operation and management, etc.) are performed by the general manager of the Company. (5) Tenure of non-executive Directors and independence confirmation of independent non-executive Directors For the tenure of the existing non-executive Directors of the Company, please refer to the relevant part of the section ‘Directors, Supervisors, Senior Management and Employees’ of this annual report. The Company has received annual confirmation letters for this year from all independent non-executive Directors, in respect of their independence pursuant to Rule 3.13 of the Listing Rules of the SEHK. The Company concurs with their independence.

(6) Remuneration committee and remuneration of Directors Members of the remuneration committee are appointed by the Board. It consists of three independent non-executive Directors and two executive Directors, namely, Mr. Chen Song (chairman of remuneration committee), Mr. Jia Jianmin, Mr. Wang Yunting, Mr. Wu Yong and Mr. Hu Lingling. According to the requirements of the Terms of Reference of the Remuneration Committee of the Company, the principal duties of the remuneration committee include reviewing and making recommendations to the Board for the remuneration packages for the Directors and the Supervisors of the Company, as well as approving the terms and conditions of the executive Directors’ service contracts. The remuneration policy of the Company seeks to provide, in accordance with the Company’s business development strategy, reasonable remuneration to attract and retain high caliber executives. The remuneration committee shall obtain the benchmark information from internal and external sources in relation to market remuneration standard, packages offered in the industry and consider the overall performance of the Company when determining the Directors’ and the Supervisors’ emoluments and recommending the Directors’ and the Supervisors’ emoluments to the Board. The remuneration committee is provided with adequate resources from the Company to perform its duties. During the reporting period, the remuneration committee of the Company did not convene any meeting. At the annual general meeting of 2013 held by the Company on May 29, 2014, it was considered and approved that the remuneration of each of domestic independent non-executive Directors was RMB100,000 per year and the remuneration of each of overseas independent non-executive Directors was HK$150,000 per year. For details of remuneration of Directors during 2016, please refer to the relevant parts of the section ‘Directors, Supervisors, Senior Management and Employees’ of this annual report. (7) Audit committee Members of the audit committee are appointed by the Board. It consists of three independent non-executive Directors, namely, Mr. Chen Song (chairman of audit committee), Mr. Jia Jianmin and Mr. Wang Yunting. They possess appropriate academic and professional qualifications or related financial management expertise. The secretary to the Board of the Company, Mr. Guo Xiangdong is the secretary of the audit committee. According to the requirements of the Working Rules of the Audit Committee of the Company, the principal duties of the audit committee include but are not limited to reviewing the financial performance of the Company and its subsidiaries, confirming the nature and scope of audit as well as supervising the establishment of the internal control and compliance with the relevant laws and regulations. It shall also discuss matters raised by the internal auditors, external auditors and regulatory authorities to ensure that appropriate recommendations are implemented. The audit committee has been provided with adequate resources to perform its duties. The Board has no disagreement in relation to the audit committee’s advice on the selection, appointment, resignation or removal of auditors.
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT During the reporting period, the audit committee held 6 meetings to examine, review and supervise the Company’s internal control performance related to financial reporting, review the Company’s financial statements and auditing results of the auditors, and recommend the appointment of external auditors to the Board. Attendance of each member of the audit committee is set out as below: Number of Number of meetings Meetings to be attended Attendance Name of Member attended in person Rate Chen Song 6 6 100% Jia Jianmin 6 6 100% Wang Yunting 6 6 100% The Audit Committee discussed with external auditors on the audit plan of the annual report and urged the external auditors to submit the auditing report timely. The Audit Committee reviewed the Company’s financial and accounting statements before external auditors commenced their work and made written suggestions. When the external auditor’s made initial opinion, the Audit Committee reviewed the statements and made written suggestions again. The Company’s 2016 quarterly financial statements, 2016 interim financial statements, and 2016 annual financial statements and results announcements have been reviewed by the Audit Committee. (8) Auditors remuneration and related professional fee The Company has appointed PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP as its domestic auditor and PricewaterhouseCoopers as its international auditor for 2016. As at the end of the reporting period, the Company’s domestic auditor has served for a consecutive term of 9 years and its international auditor has served for a consecutive term of 14 years. The rotation of persons in charge of auditing affairs and endorsing CPA is in compliance with the Requirements on the Regular Rotation of the Endorsing Accountants for Securities and Futures Auditing Services of the CSRC and the Ministry of Finance of the PRC. During the reporting period, the Company paid a remuneration of RMB5.08 million (including RMB300,000 as audit fee for internal control) and RMB3 million to PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP and PricewaterhouseCoopers for their annual auditing services of 2016 respectively. In addition, the Company paid a fee of RMB190,000 to PricewaterhouseCoopers Consultants (Shanghai) Limited Beijing Branch for its non-audit service.

(9) Training of Directors and company secretary The Company places high importance on the continuing training of the Directors, Supervisors and senior management. Each Director receives materials on training of directors upon joining the Board, which contains guide on conduct and other important matters related to governance. Apart from this, the Company provides the latest directors’ responsibilities handbook to all Directors to inform them about the latest requirements and amendments of the Listing Rules, and at the same time encourages all Directors to participate in related training courses and documents the training record of the Directors. During the reporting period, Mr. Guo Xiangdong, deputy general manager and secretary of the Board, has participated in a series of professional trainings jointly organized by the SSE, SEHK and HK Institute of Chartered Secretaries, and has participated in no less than 15 hours of relevant professional training. (10) Corporate governance functions The Board is responsible for the fulfillment of the following corporate governance responsibilities: 1. developing and reviewing the Company’s corporate governance policies and practices; 2. reviewing and monitoring the training and continuing professional developments for the Company’s directors and senior management; 3. reviewing and monitoring the Company’s policies and regulations with respect to its compliance with the laws and regulatory requirements, which include the Listing Rules, applicable laws, other regulatory requirements, and any policies and practices pertaining to the requirements, guidelines and regulations of applicable organizational governance standards; 4. developing, reviewing and monitoring the code of conduct and compliance manual (if any) for the Company’s employees and directors; 5. reviewing the Company’s compliance with the corporate governance code as adopted by the Company from time to time, and the disclosure in the corporate governance report in the Company’s annual report.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT (11) Shareholders’ rights In accordance with the requirements of the Articles, two or more shareholders holding in aggregate 10% or more of the shares carrying the right to vote at the proposed general meeting shall have the right, by delivery of one or more written requests signed in counterparts through mail or electronic mail to the Board or the company secretary to require an extraordinary general meeting or a class meeting to be called by the Board for the business specified in such request. The Board shall as soon as possible proceed to convene the extraordinary general meeting or a class meeting after receiving such request; shareholder or shareholders individually or collectively holding 3% or more of the shares carrying the right to vote at the proposed general meeting shall have the right, by delivery of one or more written requests signed in counterparts through mail or electronic mail to the Board or the company secretary to require the proposal set forth in the written request to be considered at the proposed general meeting. Shareholders shall attend the general meetings to raise questions or opinions in relation to the results, operation, strategies and/or management of the Company. The chairman or deputy chairman of the Board, appropriate management and administrative personnel and the external auditors shall attend the general meetings to answer questions from the shareholders. Each general meeting shall make reasonable arrangements for a questioning session for the shareholders. Shareholders may raise enquiries to the Board based on the contact information provided by the Company and make proposals at the general meetings. For contact information, please read ‘Company Profile and major Financial Indicators’ of this annual report. (12) Investor relations The secretary to the Board of the Company is in charge of information disclosure and investor relations of the Company. The Company has formulated Working Rules of Secretary to the Board, Management Method of Information Disclosure and Management System for Investor Relations. The Company has strictly fulfilled the obligation of information disclosure and commenced management of investor relations in accordance with the relevant requirements. The Company advocates a corporate culture that respects investors and holds itself accountable for investors. The Company establishes a smooth communication channel with investors and enhances mutual trust and interaction based on good information disclosure and initiating various investor relations activities, and respects investors’ rights of knowledge and option, while asserting to reward its shareholders.

1. Information Disclosure Credible information disclosure can effectively build a bridge of communication and understanding between investors, regulatory authorities, the public and the Company. This can facilitate a broader and more thorough understanding of the Company’s values. For years, according to the basic principles of openness, impartiality and fairness, the Company has been striving to comply with the requirements of the relevant laws and listing rules, and fulfilling the information disclosure obligations in a timely and accurate manner. The Company takes the initiative to understand investors’ concerns and voluntarily discloses information in response to these concerns so as to increase its transparency. In 2016, the Company timely completed the preparation and disclosure of its annual, interim and quarterly reports and released various announcements and other shareholders’ document and information disclosing in detail the following information of the Company: operations of the Board, the Supervisory Committee and general meetings, operating conditions, investment, dividends and distribution, corporate governance and so forth. Moreover, the Company consistently maintained to provide in-depth and comprehensive analyses on its operating and financial positions as well as the major factors affecting its business performance in its annual reports and interim reports with a view to strengthening investors’ understanding about the operation, management, and development trends of the Company. 2. Ongoing Communication On the basis of a competent disclosure of information, the Company maintains an effective two-way communication with investors through various channels and convey information which investors are concerned with, so as to boost their confidence in the Company’s future development. Meanwhile, the Company extensively collects feedback from the market to elevate the standards of the Company’s governance and operations management. (i) Making the public known the investor hotline, investor relations e-mail box, and the Investors’ Message section on the Company’s website, and promptly responding to investors’ enquiries. (ii) Properly arranging request of visits and researches from the investors, communicate with the investors with an open-minded attitude, and has built up a direct communication mechanism between investors and the Company. (iii) Investors and the public may check out information such as the Group’s basic information, rules for the Company’s corporate governance, information disclosure documents and profiles of directors, supervisors and the senior management at any time on the Company’s website. (iv) The Company timely handled and replied investors’ messages through the “e-interaction” platform developed by the SSE for listed companies and investors.
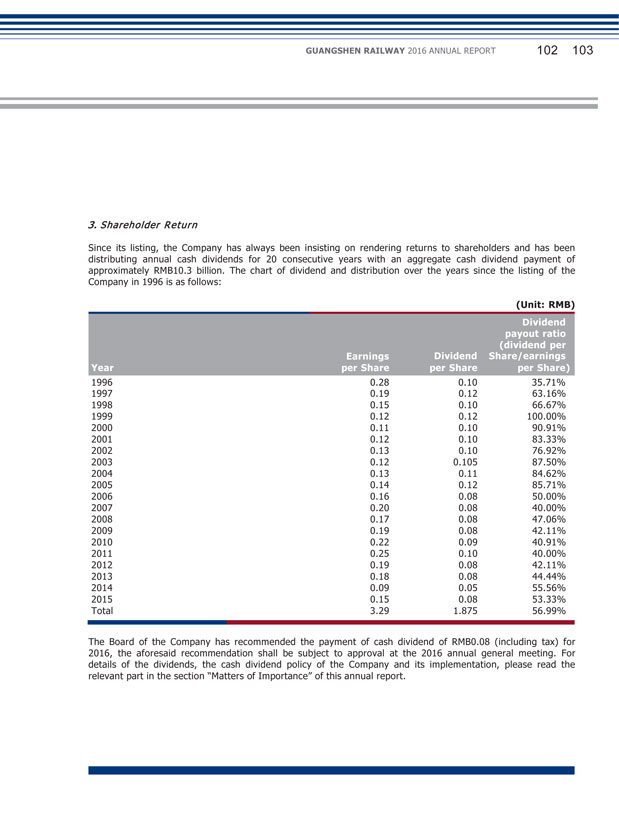
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 3. Shareholder Return Since its listing, the Company has always been insisting on rendering returns to shareholders and has been distributing annual cash dividends for 20 consecutive years with an aggregate cash dividend payment of approximately RMB10.3 billion. The chart of dividend and distribution over the years since the listing of the Company in 1996 is as follows: (Unit: RMB) Dividend payout ratio (dividend per Earnings Dividend Share/earnings Year per Share per Share per Share) 1996 0.28 0.10 35.71% 1997 0.19 0.12 63.16% 1998 0.15 0.10 66.67% 1999 0.12 0.12 100.00% 2000 0.11 0.10 90.91% 2001 0.12 0.10 83.33% 2002 0.13 0.10 76.92% 2003 0.12 0.105 87.50% 2004 0.13 0.11 84.62% 2005 0.14 0.12 85.71% 2006 0.16 0.08 50.00% 2007 0.20 0.08 40.00% 2008 0.17 0.08 47.06% 2009 0.19 0.08 42.11% 2010 0.22 0.09 40.91% 2011 0.25 0.10 40.00% 2012 0.19 0.08 42.11% 2013 0.18 0.08 44.44% 2014 0.09 0.05 55.56% 2015 0.15 0.08 53.33% Total 3.29 1.875 56.99% The Board of the Company has recommended the payment of cash dividend of RMB0.08 (including tax) for 2016, the aforesaid recommendation shall be subject to approval at the 2016 annual general meeting. For details of the dividends, the cash dividend policy of the Company and its implementation, please read the relevant part in the section “Matters of Importance” of this annual report.

(13) Accountability and auditing The Directors of the Company acknowledge their responsibility for preparing the accounts and supervising the preparation of the accounts for each financial period, so that the accounts can truly and fairly reflect the business position, results and cash flow of the Company during the period. During the preparation of the accounts for the year ended December 31, 2016, the Directors adopted and consistently applied appropriate accounting policies, made scrupulous judgments and estimates, and prepared the accounts on a going concern basis. The Company announced its annual and interim reports in a timely manner within the limits of 4 months and 2 months, respectively after the end of the relevant period in accordance with the Listing Rules of the SEHK. The Company also announced its annual, interim and quarter reports timely in accordance with the Rules Governing the Listing of Stocks of SSE. The responsibility statements of the Directors and the auditors as to the preparation of the financial statements of the Company are set out in the “Audit Report” in Chapter 11 — Financial Statements of this annual report. (14) Risk Management and Internal Controls Optimized and practicable risk management and internal control system is the foundation of sound corporate governance. The Board is responsible for the establishment of sound and effective of internal controls, assessment of its effectiveness and true disclosures of internal control assessment report. In accordance with the requirements of laws and regulations such as Company Law, Securities Law, the Basic Regulations on Enterprise Internal Control and its related guidelines, Guidelines for Internal Control of Listed Companies, the United States Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Board established and enhanced risk control measures of each part of the operation and management of the Company on the basis of risk-oriented approach, i.e. the internal control management system of risk management. Such system aims at managing instead of eliminating the risk of failure in achieving business objectives, and the Board shall only give reasonable but not absolute assurance against material misstatements or loss. In respect of the establishment of internal control system under risk management oriented approach, the Company has strived to establish an internal control system in compliance of international standards and regulatory requirements. Since 2006, the Company has started to commence the establishment and assessment of the efficacy of internal control related to financial reporting in accordance with the requirements of the United States Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Since 2011, the Company has started to consistently apply the Basic Regulations on Enterprise Internal Control and Implementation Guidelines for Enterprise Internal Control jointly promulgated by five departments of the PRC, and has formed an internal control system that centers around the different departments and units under the group companies and encompasses finance management, information disclosure, budget management, fund management, contract management, project management, procurement and payment, sales and payment collection, costs and expenses, personnel management and preparation of financial reports. The Company has basically built up an internal control system that strings up decision-making, implementation and supervision, an equalizing system that separates different positions, and a management regulation and workflow that adapts to the operation characteristics of the Company to form a relatively comprehensive assessment system for internal control.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT The Board is responsible for continuous supervision over the Company’s risk management and internal control system, review of the efficiencies of the Company and its subsidiaries, internal control system (including aspects such as finance, operation, compliance, risk management) as least once a year, and assurance of the adequacy of resources, qualification and experience of the staff of the accounting, internal audit and financial reporting functions), as well as the training sessions received by staff and related budgets. Such systems aim at managing instead of eliminating the risk of failure in achieving business objectives, and only reasonable but not absolute assurance against material misstatements or loss shall be given. The audit committee is established under the Board with the responsibilities of inspecting and supervising the financial reporting and internal control of the Company, inspecting and assessing the overall risk management of the Company, particularly risk management and control system of decision-markings, events and business of significance, as well as supervising implementation thereof. During 2016, the audit committee held 6 meetings, each with the attendance of senior management, external auditor and internal auditor. The audit committee shall examine report results of external auditor and internal auditors, the compliance of the accounting policies and internal controls adopted by the Company with requirements of Listing Rules, as well as review of the audits, internal control, risk management and financial statements. The Company’s 2016 first quarterly results, interim results, the third quarterly results and annual results will be recommended to the Board for approval after the meeting and discussion of the audit committee. The audit department has been established by the Company to operate independence internal audit system. Under the leadership of the Board and the supervision of the audit committee, the audit department of the Company is responsible for supervision, examination and evaluation of implementation of internal controls against risk management by the Company and its controlling subsidiaries coordination of internal control and audit, as well as independent audit over the adequacy and effectiveness of the Company’s operating and managing activities and internal control system. Audit plans of each year shall be discussed and determined by the audit committee, and key auditing results shall be discussed with the audit committee each time. The principal reporting process of the audit department is to report to the general manager and may report to the Chairman of the audit committee directly. All internal audit reports shall be submitted to the Chairman of the Board, general manager, CFO, audited departments and related management of such departments. The Board and the audit committee of the Company will actively monitor the quantity and significance of inspection results submitted by internal audit department, and remedial actions adopted by relative departments. The Company has established internal control system of material information, process and internal control measures for addressing and disseminating price-sensitive information. The Company has established systems relating to information disclosure, registration and management system of inside information and prevention of misuse and dissemination of sensitive information. The Company has established comprehensive procedures and internal control measures covering from report, identification, audit and disclosures to the final announcement of inside information, for the purpose of inside information processing and dissemination. The secretary of the Board assists the Board in managing relative information in relation to inside information. Meanwhile, the Company carried out information disclosure in a true, accurate, complete, and timely manner pursuant to the laws and regulations and requirements under the Listing Rules, the Articles, and Administrative Measures for the Disclosure of Information of Listed Companies, so as to ensure equal opportunities of all investors to timely access relevant information of the Company.

In 2016, the Company continued to implement the coordination and corporation of the three lines of defense: “the self-evaluation of the effectiveness of internal controls of business and functional departments, the independent evaluation of the audit department, the internal audit conducted by the appointed auditors” in accordance with the requirements of laws and regulations of the State and various regulatory institutions, coupled with its own management needs. Meanwhile, the Company provided trainings and carried out tests for the staff as a whole regarding risk management and internal control system, so as to enhance risk management awareness of the staff as a whole, strengthen the business departments’ ability to directly assume the responsibilities of risk management and control and achieve a daily operation system for internal control relating to risk management of “risk control awareness for all, internal control participation for all, and compliance responsibility for all”, safeguarding the smooth operation of internal control system as a whole. During the reporting period, the Board confirmed the Company has developed sufficient and adequate identification, management and reporting systems and procedures for the material risks it is subjects to in achieving it strategic objectives. The Board continued to monitor risks and be supported by various professional committee and senior management. (15) Material change in the Articles of Association On May 26, 2016, the Company convened its 2015 annual general meeting, in which the proposal for amendments to the Articles of Association were approved. For details of the amendments, please read “2015 Annual General Meeting Information” disclosed on the website of the SSE (http://www.sse.com.cn) on April 9, 2016, “Proposed changes in directors, proposed amendment to the articles of association and notice of 2015 Annual Meeting” on the HKExnews website of the SEHK (http://www.hkexnews.hk) on April 8, 2016.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Chapter 10 Information of Corporate Bonds Information of Corporate Bonds Applicable Not applicable

Chapter 11 Financial Statements INDEPENDENT AUDITOR’S REPORT To the Shareholders of Guangshen Railway Company Limited (incorporated in the People’s Republic of China with limited liability) OPINION What we have audited The consolidated financial statements of Guangshen Railway Company Limited (the “Company”) and its subsidiaries (the “Group”) set out on pages 114 to 202, which comprise: • the consolidated balance sheet as at 31 December 2016; • the consolidated comprehensive income statement for the year then ended; • the consolidated statement of changes in equity for the year then ended; • the consolidated cash flow statement for the year then ended; and • the notes to the consolidated financial statements, which include a summary of significant accounting policies. Our opinion In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements give a true and fair view of the consolidated financial position of the Group as at 31 December 2016, and of its consolidated financial performance and its consolidated cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRSs”) and have been properly prepared in compliance with the disclosure requirements of the Hong Kong Companies Ordinance. PricewaterhouseCoopers, 22/F Prince’s Building, Central, Hong Kong T: +852 2289 8888, F: +852 2810 9888, www.pwchk.com

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT BASIS FOR OPINION We conducted our audit in accordance with International Standards on Auditing (“ISAs”). Our responsibilities under those standards are further described in the Auditor’s Responsibilities for the Audit of the Consolidated Financial Statements section of our report. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our opinion. Independence We are independent of the Group in accordance with the International Ethics Standards Board for Accountants’ Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants (“IESBA Code”), and we have fulfilled our other ethical responsibilities in accordance with the IESBA Code. KEY AUDIT MATTERS Key audit matters are those matters that, in our professional judgment, were of most significance in our audit of the consolidated financial statements of the current period. These matters were addressed in the context of our audit of the consolidated financial statements as a whole, and in forming our opinion thereon, and we do not provide a separate opinion on these matters.

A Key audit matter is identified in our audit and our audit procedures performed to address this key audit matter are set out as below: Key Audit Matter How our audit addressed the Key Audit Matter Provision for impairment of trade receivables We have performed the following procedures to address this key audit matter: Refer to notes 4 and 18 to the consolidated financial statements. (i) We understood, evaluated and validated the key controls relating to management assessment performed on of the recoverability of the trade As at 31 December 2016, the gross trade receivables of the receivables, including aging analysis review and Group were approximately RMB3,369 million including regular assessment performed on collectability of the balances aged more than one year of approximately receivable balances; RMB847 million, which were assessed by the management of the Company as past due but not yet impaired. The majority (i) We sent audit confirmation on major balances and of the trade receivables were due from related parties of the also on certain small balances outstanding at year Group, other state-owned railroad companies or companies end. in the transportation industry. A provision for impairment of trade receivables amounting to RMB5 million had been (i) We tested the accuracy of aging analysis of receivable balances prepared by management on a recorded thereon. sample basis; Impairment provision of trade receivables is made based on (iv) We obtained management’s assessment on the an assessment of the recoverability of the amounts. collectability of individual significant outstanding Provision for impairment of trade receivables involves balances, focusing on those aged more than one management judgement and the actual outcome may be year. We corroborated management’s assessment different from original estimation. against available evidence, including searching c us t o m er s ‘ b ac k g r o u nd , r e vi ew i ng c ur r ent We focused on this area because of the significance of the operational and cash flow status; and their historical transactions enacted with the Group and the gross trade receivables to the consolidated financial respective collection pattern etc.; statements and the estimation and judgement involved in the determination of the recoverability of these trade (v) For those items with impairment provision being receivables. made, we corroborated management’s assessment against evidence of significant financial difficulties encountered by the customers and we checked the mathematical accuracy of the impairment charge calculations. We also verified the third party evidence which demonstrates the Group no longer possess the right to recover the outstanding balance to corroborate the trade receivables being written off. Ba s e d on t he w o r k p e r f o r m e d , we c o n s i d e r e d management’s judgements made in relation to the impairment assessment of trade receivables were supported by the evidence we obtained.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT OTHER INFORMATION The directors of the Company are responsible for the other information set out in the Company’s 2016 Annual Report. The other information comprises all of the information included in the annual report other than the consolidated financial statements and our auditor’s report thereon. Our opinion on the consolidated financial statements does not cover the other information and we do not express any form of assurance conclusion thereon. In connection with our audit of the consolidated financial statements, our responsibility is to read the other information and, in doing so, consider whether the other information is materially inconsistent with the consolidated financial statements or our knowledge obtained in the audit or otherwise appears to be materially misstated. If, based on the work we have performed, we conclude that there is a material misstatement of this other information, we are required to report that fact. We have nothing to report in this regard. RESPONSIBILITIES OF DIRECTORS AND AUDIT COMMITTEE FOR THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS The directors of the Company are responsible for the preparation of the consolidated financial statements that give a true and fair view in accordance with IFRSs and the disclosure requirements of the Hong Kong Companies Ordinance, and for such internal control as the directors determine is necessary to enable the preparation of consolidated financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error. In preparing the consolidated financial statements, the directors are responsible for assessing the Group’s ability to continue as a going concern, disclosing, as applicable, matters related to going concern and using the going concern basis of accounting unless the directors either intend to liquidate the Group or to cease operations, or have no realistic alternative but to do so. The audit committee is responsible for overseeing the Group’s financial reporting process.

A U D I T O R ‘ S R E S P O N S I B I L I T I E S F O R T H E A U D I T OF T H E CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS Our objectives are to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements as a whole are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error, and to issue an auditor’s report that includes our opinion. We report our opinion solely to you, as a body, and for no other purpose. We do not assume responsibility towards or accept liability to any other person for the contents of this report. Reasonable assurance is a high level of assurance, but is not a guarantee that an audit conducted in accordance with ISAs will always detect a material misstatement when it exists. Misstatements can arise from fraud or error and are considered material if, individually or in the aggregate, they could reasonably be expected to influence the economic decisions of users taken on the basis of these consolidated financial statements. As part of an audit in accordance with ISAs, we exercise professional judgment and maintain professional scepticism throughout the audit. We also: • Identify and assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to fraud or error, design and perform audit procedures responsive to those risks, and obtain audit evidence that is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our opinion. The risk of not detecting a material misstatement resulting from fraud is higher than for one resulting from error, as fraud may involve collusion, forgery, intentional omissions, misrepresentations, or the override of internal control. • Obtain an understanding of internal control relevant to the audit in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Group’s internal control. • Evaluate the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of accounting estimates and related disclosures made by the directors. • Conclude on the appropriateness of the directors’ use of the going concern basis of accounting and, based on the audit evidence obtained, whether a material uncertainty exists related to events or conditions that may cast significant doubt on the Group’s ability to continue as a going concern. If we conclude that a material uncertainty exists, we are required to draw attention in our auditor’s report to the related disclosures in the consolidated financial statements or, if such disclosures are inadequate, to modify our opinion. Our conclusions are based on the audit evidence obtained up to the date of our auditor’s report. However, future events or conditions may cause the Group to cease to continue as a going concern.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT • Evaluate the overall presentation, structure and content of the consolidated financial statements, including the disclosures, and whether the consolidated financial statements represent the underlying transactions and events in a manner that achieves fair presentation. • Obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding the financial information of the entities or business activities within the Group to express an opinion on the consolidated financial statements. We are responsible for the direction, supervision and performance of the group audit. We remain solely responsible for our audit opinion. We communicate with the audit committee regarding, among other matters, the planned scope and timing of the audit and significant audit findings, including any significant deficiencies in internal control that we identify during our audit. We also provide the audit committee with a statement that we have complied with relevant ethical requirements regarding independence, and to communicate with them all relationships and other matters that may reasonably be thought to bear on our independence, and where applicable, related safeguards. From the matters communicated with the audit committee, we determine those matters that were of most significance in the audit of the consolidated financial statements of the current period and are therefore the key audit matters. We describe these matters in our auditor’s report unless law or regulation precludes public disclosure about the matter or when, in extremely rare circumstances, we determine that a matter should not be communicated in our report because the adverse consequences of doing so would reasonably be expected to outweigh the public interest benefits of such communication. The engagement partner on the audit resulting in this independent auditor’s report is Wilson W.Y. Chow. PricewaterhouseCoopers Certified Public Accountants Hong Kong, 29 March 2017
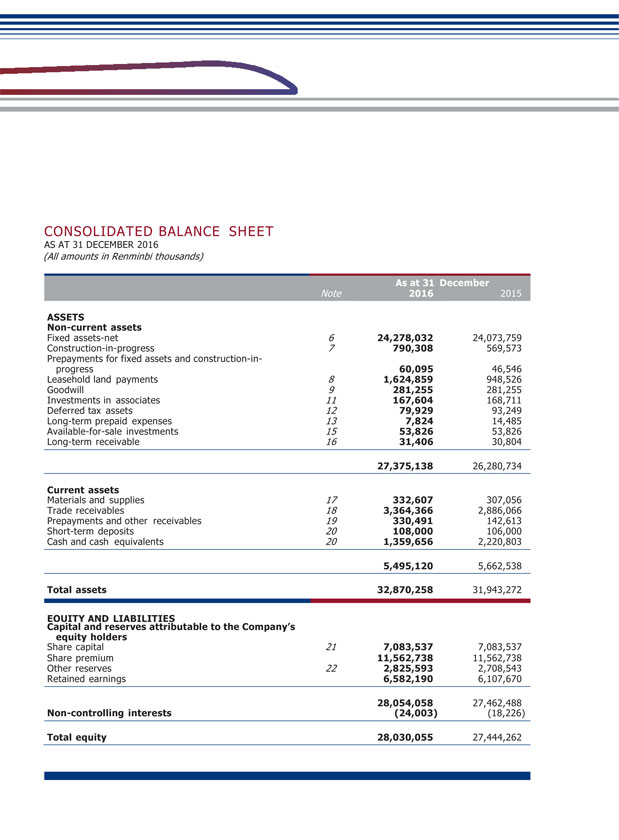
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET AS AT 31 DECEMBER 2016 (All amounts in Renminbi thousands) As at 31 December Note 2016 2015 ASSETS Non-current assets Fixed assets-net 6 24,278,032 24,073,759 Construction-in-progress 7 790,308 569,573 Prepayments for fixed assets and construction-in- progress 60,095 46,546 Leasehold land payments 8 1,624,859 948,526 Goodwill 9 281,255 281,255 Investments in associates 11 167,604 168,711 Deferred tax assets 12 79,929 93,249 Long-term prepaid expenses 13 7,824 14,485 Available-for-sale investments 15 53,826 53,826 Long-term receivable 16 31,406 30,804 27,375,138 26,280,734 Current Materials assets and supplies 17 332,607 307,056 Trade receivables 18 3,364,366 2,886,066 Prepayments and other receivables 19 330,491 142,613 Short-term deposits 20 108,000 106,000 Cash and cash equivalents 20 1,359,656 2,220,803 5,495,120 5,662,538 Total assets 32,870,258 31,943,272 EQUITY AND LIABILITIES Capital and reserves attributable to the Company’s Share equity capital holders 21 7,083,537 7,083,537 Share premium 11,562,738 11,562,738 Other reserves 22 2,825,593 2,708,543 Retained earnings 6,582,190 6,107,670 Non-controlling interests 28,054,058 (24,003) 27,462,488 (18,226) Total equity 28,030,055 27,444,262
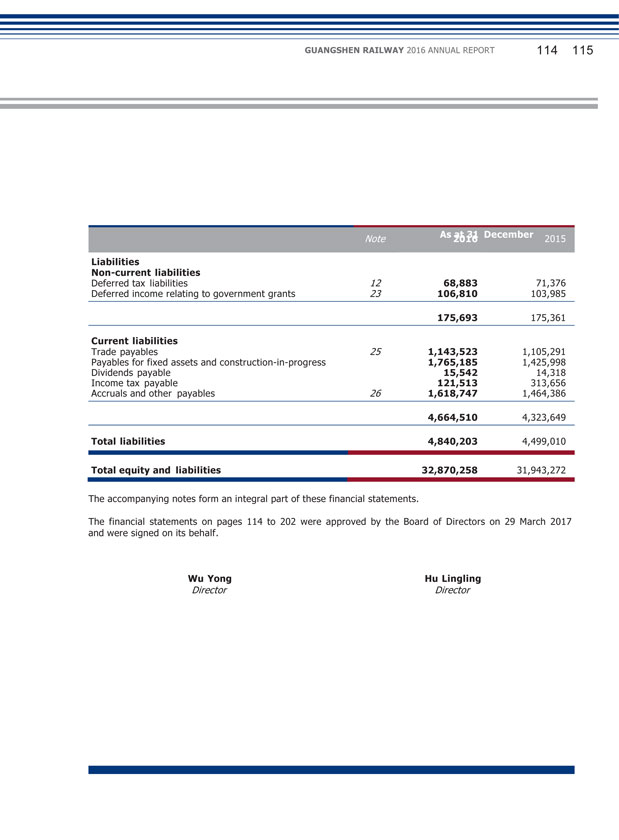
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Note As 2016 at 31 December 2015 Liabilities Non-current liabilities Deferred tax liabilities 12 68,883 71,376 Deferred income relating to government grants 23 106,810 103,985 175,693 175,361 Current liabilities Trade payables 25 1,143,523 1,105,291 Payables for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 1,765,185 1,425,998 Dividends payable 15,542 14,318 Income tax payable 121,513 313,656 Accruals and other payables 26 1,618,747 1,464,386 4,664,510 4,323,649 Total liabilities 4,840,203 4,499,010 Total equity and liabilities 32,870,258 31,943,272 The accompanying notes form an integral part of these financial statements. The financial statements on pages 114 to 202 were approved by the Board of Directors on 29 March 2017 and were signed on its behalf. Wu Yong Hu Lingling Director Director
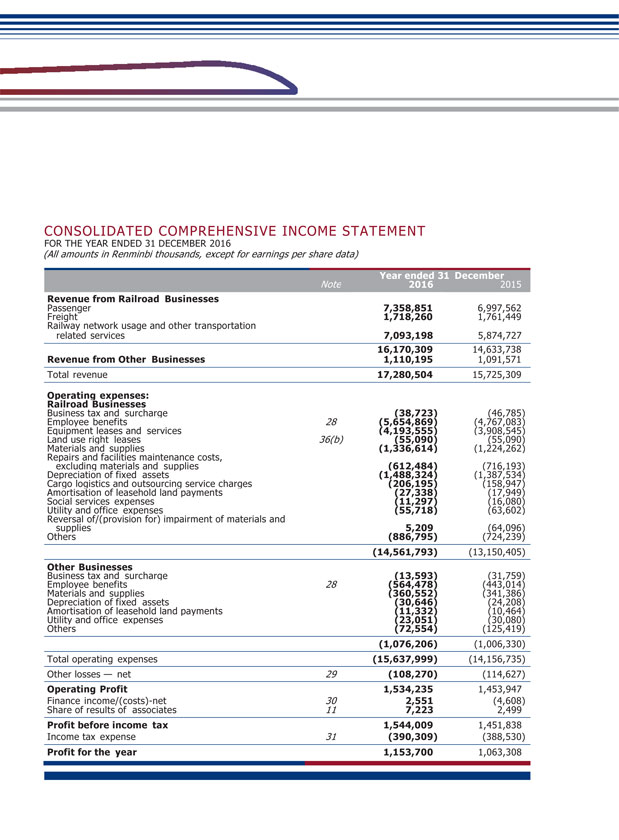
CONSOLIDATED COMPREHENSIVE INCOME STATEMENT FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2016 (All amounts in Renminbi thousands, except for earnings per share data) Year ended 31 December Note 2016 2015 Passenger Revenue from Railroad Businesses 7,358,851 6,997,562 Freight Railway network usage and other transportation 1,718,260 1,761,449 related services 7,093,198 5,874,727 16,170,309 14,633,738 Revenue from Other Businesses 1,110,195 1,091,571 Total revenue 17,280,504 15,725,309 Operating expenses: Railroad Businesses Employee Business tax benefits and surcharge 28 (5,654,869) (38,723) (4,767,083) (46,785) Land Equipment use right leases leases and services 36(b) (4,193,555) (55,090) (3,908,545) (55,090) Materials and supplies (1,336,614) (1,224,262) Repairs and facilities maintenance costs, Depreciation excluding materials of fixed and assets supplies (1,488,324) (612,484) (1,387,534) (716,193) Amortisation Cargo logistics of and leasehold outsourcing land payments service charges (206,195) (27,338) (158,947) (17,949) Social services expenses (11,297) (16,080) Reversal Utility and of/(provision office expenses for) impairment of materials and (55,718) (63,602) Others supplies (886,795) 5,209 (724,239) (64,096) (14,561,793) (13,150,405) Other Businesses Employee Business tax benefits and surcharge 28 (564,478) (13,593) (443,014) (31,759) Materials and supplies (360,552) (341,386) Depreciation of fixed assets (30,646) (24,208) Utility Amortisation and office of leasehold expenses land payments (11,332) (23,051) (10,464) (30,080) Others (72,554) (125,419) (1,076,206) (1,006,330) Total operating expenses (15,637,999) (14,156,735) Other losses — net 29 (108,270) (114,627) Operating Profit 1,534,235 1,453,947 Finance Share of income/(costs) results of associates -net 30 11 2,551 7,223 (4,608) 2,499 Profit before income tax 1,544,009 1,451,838 Income tax expense 31 (390,309) (388,530) Profit for the year 1,153,700 1,063,308
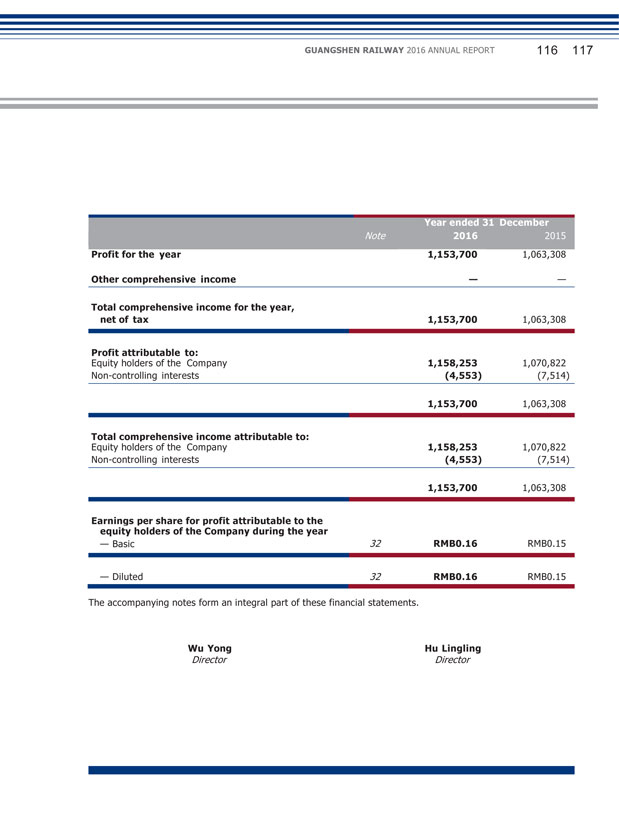
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Year ended 31 December Note 2016 2015 Profit for the year 1,153,700 1,063,308 Other comprehensive income — — Total comprehensive income for the year, net of tax 1,153,700 1,063,308 Profit attributable to: Equity holders of the Company 1,158,253 1,070,822 Non-controlling interests (4,553) (7,514) 1,153,700 1,063,308 Total comprehensive income attributable to: Equity holders of the Company 1,158,253 1,070,822 Non-controlling interests (4,553) (7,514) 1,153,700 1,063,308 Earnings per share for profit attributable to the equity holders of the Company during the year — Basic 32 RMB0.16 RMB0.15 — Diluted 32 RMB0.16 RMB0.15 The accompanying notes form an integral part of these financial statements. Wu Yong Hu Lingling Director Director
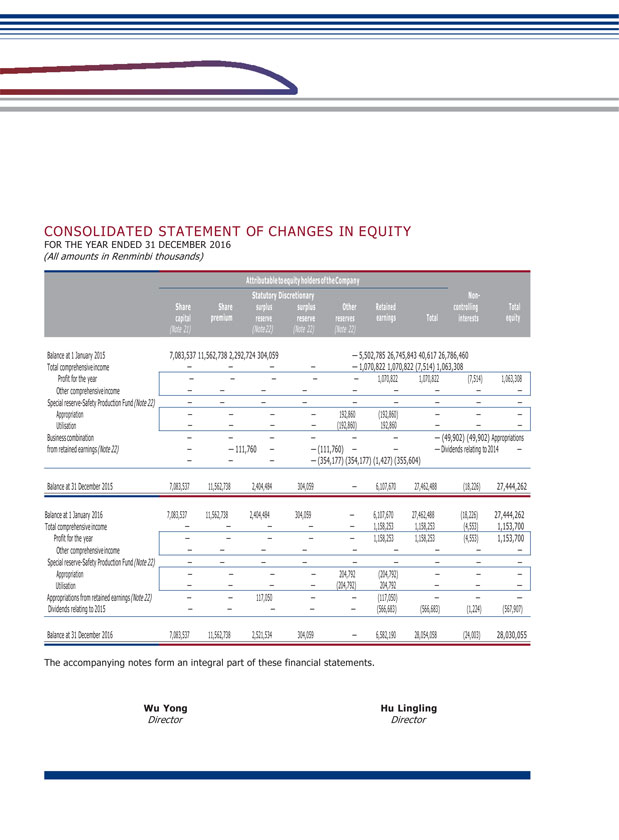
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN EQUITY FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2016 (All amounts in Renminbi thousands) Attributable to equity holders of the Company Statutory Discretionary Non- Share Share surplus surplus Other Retained controlling Total capital premium reserve reserve reserves earnings Total interests equity (Note 21) (Note22) (Note 22) (Note 22) Balance at 1 January 2015 7,083,537 11,562,738 2,292,724 304,059 — 5,502,785 26,745,843 40,617 26,786,460 Total comprehensive income — — — — — 1,070,822 1,070,822 (7,514) 1,063,308 Profit for the year — — — — — 1,070,822 1,070,822 (7,514) 1,063,308 Other comprehensive income — — — — — — — — — Special reserve-Safety Production Fund (Note 22) — — — — — — — — — Appropriation — — — — 192,860 (192,860) — — — Utilisation — — — — (192,860) 192,860 — — — Business combination — — — — — — — (49,902) (49,902) Appropriations from retained earnings (Note 22) — — 111,760 — — (111,760) — — — Dividends relating to 2014 — — — — — (354,177) (354,177) (1,427) (355,604) Balance at 31 December 2015 7,083,537 11,562,738 2,404,484 304,059 — 6,107,670 27,462,488 (18,226) 27,444,262 Balance at 1 January 2016 7,083,537 11,562,738 2,404,484 304,059 — 6,107,670 27,462,488 (18,226) 27,444,262 Total comprehensive income — — — — — 1,158,253 1,158,253 (4,553) 1,153,700 Profit for the year — — — — — 1,158,253 1,158,253 (4,553) 1,153,700 Other comprehensive income — — — — — — — — — Special reserve-Safety Production Fund (Note 22) — — — — — — — — — Appropriation — — — — 204,792 (204,792) — — — Utilisation — — — — (204,792) 204,792 — — — Appropriations from retained earnings (Note 22) — — 117,050 — — (117,050) — — — Dividends relating to 2015 — — — — — (566,683) (566,683) (1,224) (567,907) Balance at 31 December 2016 7,083,537 11,562,738 2,521,534 304,059 — 6,582,190 28,054,058 (24,003) 28,030,055 The accompanying notes form an integral part of these financial statements. Wu Yong Hu Lingling Director Director
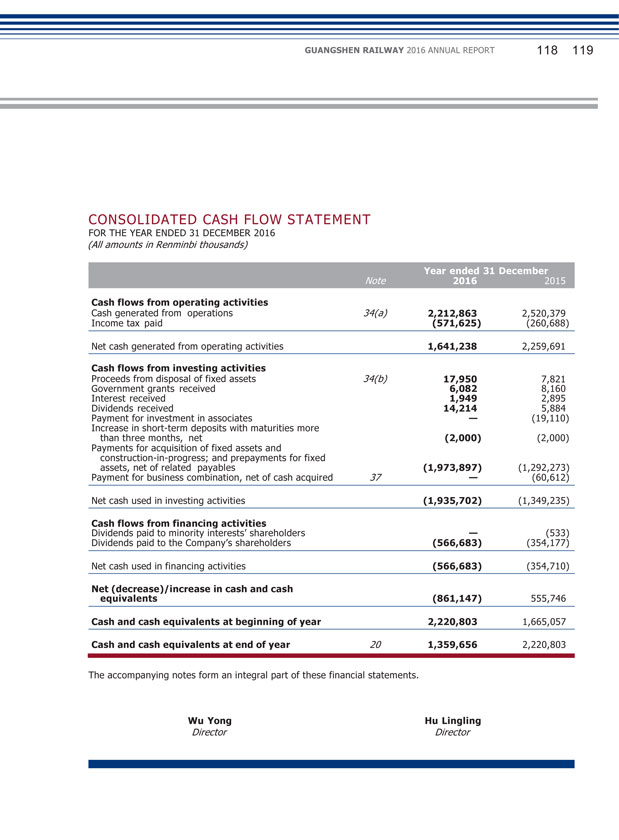
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOW STATEMENT FOR THE YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2016 (All amounts in Renminbi thousands) Year ended 31 December Note 2016 2015 Cash flows from operating activities Cash Income generated tax paid from operations 34(a) 2,212,863 (571,625) 2,520,379 (260,688) Net cash generated from operating activities 1,641,238 2,259,691 Cash flows from investing activities Proceeds Government from grants disposal received of fixed assets 34(b) 17,950 6,082 7,821 8,160 Interest Dividends received received 14,214 1,949 5,884 2,895 Payment Increase in for short-term investment deposits in associates with maturities more — (19,110) Payments than three for months, acquisition net of fixed assets and (2,000) (2,000) construction-in-progress; and prepayments for fixed Payment assets, for net business of related combination, payables net of cash acquired 37 (1,973,897) — (1,292,273) (60,612) Net cash used in investing activities (1,935,702) (1,349,235) Cash Dividends flows paid from to minority financing interests’ activities shareholders — (533) Dividends paid to the Company’s shareholders (566,683) (354,177) Net cash used in financing activities (566,683) (354,710) Net equivalents (decrease)/increase in cash and cash (861,147) 555,746 Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year 2,220,803 1,665,057 Cash and cash equivalents at end of year 20 1,359,656 2,220,803 The accompanying notes form an integral part of these financial statements. Wu Yong Hu Lingling Director Director

NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS For the year ended 31 December 2016 (All amounts expressed in Renminbi unless otherwise stated) 1. GENERAL INFORMATION Guangshen Railway Company Limited (the “Company”) was established as a joint stock limited company in the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC”) on 6 March 1996. On the same date, the Company assumed the business operations of certain railroad and other related businesses (collectively the “Businesses”) that had been undertaken previously by its predecessor, Guangshen Railway Company (the “Predecessor”), certain subsidiaries of the Predecessor; and Guangzhou Railway (Group) Company (the “Guangzhou Railway Group”) and certain of its subsidiaries prior to the formation of the Company. The Predecessor was controlled by and was under the administration of the Guangzhou Railway Group. Pursuant to a restructuring agreement entered into between the Guangzhou Railway Group, the Predecessor and the Company in 1996, the Company issued to the Guangzhou Railway Group 100% of its equity interest in the form of 2,904,250,000 ordinary shares (the “State-owned Domestic Shares”) for the exchange of assets and liabilities associated with the operations of the Businesses (the “Restructuring”). After the Restructuring, the Predecessor changed its name to Guangzhou Railway (Group) Guangshen Railway Enterprise Development Company (the “GEDC”). In May 1996, the Company issued 1,431,300,000 shares, representing 217,812,000 H Shares (“H Shares”) and 24,269,760 American Depositary Shares (“ADSs”, one ADS represents 50 H Shares) in a global public offering for cash of approximately RMB4,214,000,000 in order to finance the capital expenditure and working capital requirements of the Company and its subsidiaries (collectively defined as the “Group”). In December 2006, the Company issued 2,747,987,000 A Shares on the Shanghai Stock Exchange through an initial public offering of shares in order to finance the acquisition of the business and related assets and liabilities associated with the railway transportation business (“Yangcheng Railway Business”) of Guangzhou Railway Group Yangcheng Railway Enterprise Development Company (“Yangcheng Railway”), a wholly owned subsidiary of Guangzhou Railway Group which operates a railway line between the cities of Guangzhou and Pingshi in the Southern region of the PRC. Before March 2013, the Ministry of Railway of the PRC (“MOR”) was the controlling entity of the Company’s single largest shareholder (i.e. Guangzhou Railway Group). In addition, it was the government authority which governed and monitored the railway business centrally within the PRC.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 1. GENERAL INFORMATION (continued) On 14 March 2013, pursuant to the approved plan on State Council Institutional Reform and Transformation of Government Functions and Approval On Setting Up China Railway Company by the State Council, the previous controlling entity of Guangzhou Railway Group, MOR, was dissolved. The administrative functions of MOR were transferred to the Ministry of Transport and a newly established National Railway Bureau. The business functions were transferred to the China Railway Corporation (“CRC”). Accordingly, the equity interests of Guangzhou Railway Group which was wholly controlled by MOR previously were also transferred to the CRC (“Reform”). The Reform was completed and CRC became the controlling entity of the Company’s principal shareholder, Guangzhou Railway Group. Upon the completion of necessary procedures and approval, CRC became the controlling entity of the Company’s principal shareholder, Guangzhou Railway Group since 1 January 2017. CRC, together with subsidiaries which were wholly controlled by MOR previously became related parties (hereinafter collectively as “CRC Group”). The principal activities of the Group are the provision of passenger and freight transportation on railroads. The Group also operates certain other businesses, which principally include services offered in railway stations; and sales of food, beverages and merchandises on board the trains and in the railway stations. The registered address of the Company is No. 1052 Heping Road, Shenzhen, Guangdong Province, the People’s Republic of China. The business license for the Company will expire in 2056. The financial statements were authorised for issue by the board of directors of the Company on 29 March 2017. The English names of all companies listed in the financial statements are direct translations of their registered names in Chinese.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES The principal accounting policies applied in the preparation of these consolidated financial statements are set out below. These policies have been consistently applied to all the years presented, unless otherwise stated. 2.1 Basis of preparation The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with all applicable International Financial Reporting Standards (“IFRS”) as issued by International Accounting Standards Board (“IASB”) and the disclosure requirements of the Hong Kong Companies Ordinance Cap. 622. The consolidated financial statements have been prepared under the historical cost convention. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires the use of certain critical accounting estimates. It also requires management to exercise its judgement in the process of applying the Group’s accounting policies. The areas involving a higher degree of judgement or complexity, or areas where assumptions and estimates are significant to the consolidated financial statements are disclosed in Note 4. 2.1.1 Changes in accounting policy and disclosures (a) New and amended standards adopted by the Group The following amendments to standards have been adopted by the Group for the first time for the financial year beginning on 1 January 2016: • Accounting for acquisitions of interests in joint operations – Amendments to IFRS 11 • Clarification of acceptable methods of depreciation and amortisation – Amendments to IAS 16 and IAS 38 • Annual improvements to IFRSs 2012 – 2014 cycle, and • Disclosure initiative – amendments to IAS 1. The directors of the Company consider that the adoption of the amendments to standards have no material impact on the Group’s operating results and financial position.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.1 Basis of preparation (continued) 2.1.1 Changes in accounting policy and disclosures (continued) (b) The following new standards, amendments and interpretations have been issued as at 31 December 2016 but are not effective for IFRS financial statements for the year ended 31 December 2016: • Amendments to IFRS 10 and IAS 28 “Sale or contribution of assets between an investor and its associate or joint venture”. The amendments address an inconsistency between IFRS 10 and IAS 28 in the sale and contribution of assets between an investor and its associate or joint venture. A full gain or loss is recognised when a transaction involves a business. A partial gain or loss is recognised when a transaction involves assets that do not constitute a business, even if those assets are in a subsidiary. These amendments were originally intended to be effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2016. The effective date is unknown. • Amendments to IAS 7 “Disclosure Initiative”. The amendments are part of the IASB’s disclosure initiative project and introduce additional disclosure requirements intended to address investors’ concerns that financial statements do not currently enable them to understand the entity’s cash flows; particularly in respect to the management of financing activities. These amendments will be effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2017. • Amendments to IAS 12 “Recognition of Deferred Tax Assets for Unrealised Losses”. The amendments clarify the recognition of deferred tax assets for unrealised losses related to debt instruments measured at fair value. These amendments will be effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2017. • Amendments to IFRS 2 “ Classification and Measurement of Share-based Payment Transactions”. The amendments relate to the following areas: (1) The accounting for the effects of vesting conditions on cash-settled share- based payment transactions; (2) The classification of share-based payment transactions with net settlement features for withholding tax obligations; (3) The accounting for a modification to the terms and conditions of a share- based payment that changes the transaction from cash-settled to equity- settled. These amendments will be effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2018.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.1 Basis of preparation (continued) 2.1.1 Changes in accounting policy and disclosures (continued) (b) The following new standards, amendments and interpretations have been issued as at 31 December 2016 but are not effective for IFRS financial statements for the year ended 31 December 2016 (continued) : • IFRS 9, “Financial instruments”. IFRS 9 (2014), “Financial instruments” replaces the whole of IAS 39. IFRS 9 has three financial asset classification categories for investments in debt instruments: amortised cost, fair value through other comprehensive income (“OCI”) and fair value through profit or loss. Classification is driven by the entity’s business model for managing the debt instruments and their contractual cash flow characteristics. Investments in equity instruments are always measured at fair value. However, management can make an irrevocable election to present changes in fair value in OCI, provided the instrument is not held for trading. If the equity instrument is held for trading, changes in fair value are presented in profit or loss. For financial liabilities there are two classification categories: amortised cost and fair value through profit or loss. Where non- derivative financial liabilities are designated at fair value through profit or loss, the changes in the fair value due to changes in the liability’s own credit risk are recognised in OCI, unless such changes in fair value would create an accounting mismatch in profit or loss, in which case, all fair value movements are recognised in profit or loss. There is no subsequent recycling of the amounts in OCI to profit or loss. For financial liabilities held for trading (including derivative financial liabilities), all changes in fair value are presented in profit or loss. IFRS 9 introduces a new model for the recognition of impairment losses — the expected credit losses (ECL) model, which constitutes a change from the incurred loss model in IAS 39. IFRS 9 contains a ‘three stage’ approach, which is based on the change in credit quality of financial assets since initial recognition. IFRS 9 applies to all hedging relationships, with the exception of portfolio fair value hedges of interest rate risk. The new guidance better aligns hedge accounting with the risk management activities of an entity and provides relief from the more “rule-based” approach of IAS39. This standard will be effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2018.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.1 Basis of preparation (continued) 2.1.1 Changes in accounting policy and disclosures (continued) (b) The following new standards, amendments and interpretations have been issued as at 31 December 2016 but are not effective for IFRS financial statements for the year ended 31 December 2016 (continued) : • IFRS 15 “Revenue from Contracts with Customers”. IFRS 15 establishes a how comprehensive much revenue framework to recognize for determining through a 5-step when approach: to recognize (1) revenue Identify and the contract(s) with customer; (2) Identify separate performance obligations in a contract (3) Determine the transaction price (4) Allocate transaction price to performance obligations and (5) recognize revenue when performance obligation is satisfied. The core principle is that a company should recognize customer in revenue an amount to depict that the reflects transfer the of consideration promised goods to which or services the company to the expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. It moves away from a revenue recognition model based on an ‘earnings processes to an ‘asset-liability’ approach based on transfer of control. IFRS 15 provides specific guidance on capitalization of contract cost and license arrangements. It amount, also includes timing and a cohesive uncertainty set of of disclosure revenue and requirements cash flows about arising the from nature, the entity’s contracts with customers. IFRS 15 replaces the previous revenue standards: IAS 18 Revenue and IAS 11 Construction Contracts, and the related Interpretations on revenue recognition: IFRIC 13 Customer Loyalty Programmes, IFRIC 15 Agreements for the Construction of Real Estate, IFRIC 31 18 Transfers Revenue of — Assets Barter from Transactions Customers and Involving SIC- Advertising Services. This standard will be effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2018. • IFRS16 “Leases”. IFRS 16 provides updated guidance on the definition of Under leases, IFRS and the 16, a guidance contract on is, the or combination contains, a lease and separation if the contract of contracts. conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration. IFRS 16 requires lessees to recognise lease liability reflecting future lease payments and a ‘right-of-use-asset’ for almost all lease contracts, with an exemption for certain short-term leases and as under leases of IAS low-value 17. However, assets. The the lessors new accounting accounting model stays almost for lessees the same is expected to impact negotiations between lessors and lessees. This standard will be effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2019. The Group has already commenced an assessment of the impact of these new or revised standards which are relevant to the Group’s operation. According to the preliminary assessment made by the directors of the Company, no significant impact on the financial performance and positions of the Group is expected when adopting IFRS 9, IFRS 15 and IFRS16. At this stage, the Group does not intend to adopt the standard before its effective date.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.2 Subsidiaries 2.2.1 Consolidation A subsidiary is an entity (including a structured entity) over which the Group has control. The Group controls an entity when the Group is exposed to, or has rights to, variable returns from its involvement with the entity and has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the entity. Subsidiaries are consolidated from the date on which control is transferred to the Group. They are deconsolidated from the date that control ceases. (a) Business combinations The Group applies the acquisition method to account for business combinations. The consideration transferred for the acquisition of a subsidiary is the fair values of the assets transferred, the liabilities incurred to the former owners of the acquiree and the equity interests issued by the Group. The consideration transferred includes the fair value of any asset or liability resulting from a contingent consideration arrangement. Identifiable assets acquired and liabilities and contingent liabilities assumed in a business combination are measured initially at their fair values at the acquisition date. The Group recognises any non-controlling interest in the acquiree on an acquisition-by-acquisition basis. Non-controlling interests in the acquiree that are present ownership interests and entitle their holders to a proportionate share of the entity’s net assets in the event of liquidation are measured at either fair value or the present ownership interests’ proportionate share in the recognised amounts of the acquiree’s identifiable net assets. All other components of non-controlling interests are measured at their acquisition date fair value, unless another measurement basis is required by IFRS. Acquisition-related costs are expensed as incurred. If the business combination is achieved in stages, the acquirer shall remeasure its previously held equity interest in the acquiree at its acquisition-date fair value and recognise the resulting gain or loss, if any, in profit or loss. Any contingent consideration to be transferred by the Group is recognised at fair value at the acquisition date. Subsequent changes to the fair value of the contingent consideration that is deemed to be an asset or liability is recognised in accordance with IAS 39 either in profit or loss. Contingent consideration that is classified as equity is not remeasured, and its subsequent settlement is accounted for within equity.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.2 Subsidiaries (continued) 2.2.1 Consolidation (continued) (a) Business combinations (continued) The excess of the consideration transferred, the amount of any non-controlling interest in the acquiree and the acquisition-date fair value of any previous equity interest in the acquiree over the fair value of the identifiable net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. If the total of consideration transferred, non- controlling interest recognised and previously held interest measured is less than the fair value of the net assets of the subsidiary acquired in the case of a bargain purchase, the difference is recognised directly in the income statement (Note 2.9). Intra-group transactions, balances and unrealised gains on transactions between group companies are eliminated. Unrealised losses are also eliminated. When necessary, amounts reported by subsidiaries have been adjusted to conform with the Group’s accounting policies. (b) Changes in ownership interests in subsidiaries without change of control Transactions with non-controlling interests that do not result in loss of control are accounted for as equity transactions – that is, as transactions with the owners in their capacity as owners. The difference between fair value of any consideration paid and the relevant share acquired of the carrying value of net assets of the subsidiary is recorded in equity. Gains or losses on disposals to non-controlling interests are also recorded in equity. (c) Disposal of subsidiaries When the Group ceases to have control, any retained interest in the entity is re- measured to its fair value at the date when control is lost, with the change in carrying amount recognised in profit or loss. The fair value is the initial carrying amount for the purposes of subsequently accounting for the retained interest as an associate, joint venture or financial asset. In addition, any amounts previously recognised in other comprehensive income in respect of that entity are accounted for as if the Group had directly disposed of the related assets or liabilities. This may mean that amounts previously recognised in other comprehensive income are reclassified to profit or loss.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.2 Subsidiaries (continued) 2.2.2 Separate financial statements Investments in subsidiaries are accounted for at cost less impairment. Cost also includes direct attributable costs of investment. The results of subsidiaries are accounted for by the Company on the basis of dividend received and receivable. Impairment testing of the investments in subsidiaries is required upon receiving a dividend from these investments if the dividend exceeds the total comprehensive income of the subsidiary in the period the dividend is declared or if the carrying amount of the investment in the separate financial statements exceeds the carrying amount in the consolidated financial statements of the investee’s net assets including goodwill. 2.3 Associates An associate is an entity over which the Group has significant influence but not control, generally accompanying a shareholding of between 20% and 50% of the voting rights. Investments in associates are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. Under the equity method, the investment is initially recognised at cost, and the carrying amount is increased or decreased to recognise the investor’s share of the profit or loss of the investee after the date of acquisition. The Group’s investments in associates include goodwill identified on acquisition. Upon the acquisition of the ownership interest in an associate, any difference between the cost of the associate and the Group’s share of the net fair value of the associate’s identifiable assets and liabilities is accounted for as goodwill. If the ownership interest in an associate is reduced but significant influence is retained, only a proportionate share of the amounts previously recognised in other comprehensive income is reclassified to profit or loss where appropriate. The Group’s share of post-acquisition profit or loss is recognised in the comprehensive income statement, and its share of post-acquisition movements in other comprehensive income is recognised in other comprehensive income with a corresponding adjustment to the carrying amount of the investment. When the Group’s share of losses in an associate equals or exceeds its interest in the associate, including any other unsecured receivables, the Group does not recognise further losses, unless it has incurred legal or constructive obligations or made payments on behalf of the associate. The Group determines at each reporting date whether there is any objective evidence that the investment in the associate is impaired. If this is the case, the Group calculates the amount of impairment as the difference between the recoverable amount of the associate and its carrying value and recognises the amount adjacent to ‘share of result of associates’ in the comprehensive income statement.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.3 Associates (continued) Profits or losses and other comprehensive income resulting from upstream and downstream transactions between the Group and its associate are recognised in the Group’s financial statements only to the extent of unrelated investor’s interests in the associates. Unrealised losses are eliminated unless the transaction provides evidence of an impairment of the asset transferred. Accounting policies of associates have been changed where necessary to ensure consistency with the policies adopted by the Group. In the Company’s balance sheet, investments in associates are accounted for at cost less provision for impairment losses. Cost also includes direct attributable costs of investment. The results of associates are accounted for by the Company on the basis of dividend received and receivable. 2.4 Segment reporting Operating segments are reported in a manner consistent with the internal reporting provided to the chief operating decision-maker. The chief operating decision-maker, who is responsible for allocating resources and assessing performance of the operating segments, has been identified as the senior executives that make strategic decisions. 2.5 Foreign currency transaction (a) Functional and presentation currency Items included in the financial statements of each of the Group’s entities are measured using the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates (“the functional currency”). The consolidated financial statements are presented in Renminbi (“RMB”), which is the Company’s functional and the Group’s presentation currency. (b) Transactions and balances Foreign currency transactions are translated into the functional currency using the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transactions or valuation where items are remeasured. Foreign exchange gains and losses resulting from the settlement of such transactions and from the translation at year-end exchange rates of monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are recognised in the comprehensive income statement. Foreign exchange gains and losses are presented in the consolidated comprehensive income statement within “Finance income/(costs)-net”.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.6 Fixed assets Fixed assets are stated at historical cost less depreciation and impairment losses. Historical cost includes expenditure that is directly attributable to the acquisition of the items (for the case of fixed assets acquired by the Company from Predecessor during the Restructuring, the revaluated amount in the Restructuring was deemed costs). Subsequent costs are included in the asset’s carrying amount or recognised as a separate asset, as appropriate, only when it is probable that future economic benefits associated with the item will flow to the Group and the cost of the item can be measured reliably. The carrying amount of the replaced part is derecognised. All other repairs and maintenance are charged to the comprehensive income statement during the financial period in which they are incurred. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method to allocate the cost amount, after taking into account the estimated residual value of not more than 4% of cost, of each asset over its estimated useful life. The estimated useful lives are as follows: Buildings (Note a) 20 to 40 years Tracks, bridges and service roads (Note a) 16 to 100 years Locomotives and rolling stock 20 years Communications and signalling systems 8 to 20 years Other machinery and equipment 4 to 25 years Note a: The estimated useful lives of some buildings, tracks, bridges and service roads exceed the initial lease periods of the land use rights from operation lease (details contained in Note 36(b)); and the initial period of certain land use right acquired (Note 2.8), on which these assets are located. The Group will renew the term of extend land use right upon its expiry in strict compliance with requirements of relevant laws and regulations. There is no substantive impediment for the renewal except public interests. In addition, based on the provision of the land use right operating lease agreement entered into with the single largest shareholder (Note 36(b)), the Company can renew the lease at its own discretion upon expiry of the operating lease term. Based on the above consideration, the directors consider the current estimated useful lives of those assets to be reasonable. The assets’ residual values and estimated useful lives are reviewed, and adjusted if appropriate, at the end of each year. An asset’s carrying amount is written down immediately to its recoverable amount if the asset’s carrying amount is greater than its estimated recoverable amount (Note 2.10). Gains and losses on disposals are determined by comparing the proceeds with the carrying amount and are recognised within “other losses — net”, included in the comprehensive income statement.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.7 Construction-in-progress Construction-in-progress represents buildings, tracks, bridges and service roads, mainly includes the construction related costs for the associated facilities of the existing railway line of the Group. Construction-in-progress is stated at cost, which includes all expenditures and other direct costs, site restoration costs, prepayments attributable to the construction and interest charges arising from borrowings used to finance the construction during the construction period, less impairment loss. Construction-in-progress is not depreciated until such assets are completed and ready for their intended use. 2.8 Leasehold land payments The Group acquired the right to use certain parcels of land for certain of its rail lines, stations and other businesses. The payment paid for such land represents pre-paid lease payments, which are amortised over the lease terms of 36.5 to 50 years using the straight-line method. 2.9 Goodwill Goodwill represents the excess of the consideration transferred, the amount of any non- controlling interest in the acquiree and the acquisition-date fair value of any previous equity interest in the acquiree over the fair value of the Group’s share of identifiable net assets acquired. Goodwill arising from acquisitions of subsidiaries’ business is disclosed separately on the balance sheet. For the purpose of impairment testing, goodwill acquired in a business combination is allocated to each of the cash-generating units (“CGUs”), or groups of CGUs, that is expected to benefit from the synergies of the combination. Each unit or group of units to which the goodwill is allocated represents the lowest level within the entity at which the goodwill is monitored for internal management purposes. Goodwill is monitored at the operating segment level. Goodwill impairment reviews are undertaken annually or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate a potential impairment. The carrying value of goodwill is compared to the recoverable amount, which is the higher of value in use and the fair value less costs to sell. Any impairment is recognised immediately as an expense and is not subsequently reversed.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.10 Impairment of investment in subsidiaries and non-financial assets other than goodwill Impairment testing of the investments in subsidiaries is required upon receiving dividends from these investments if the dividend exceeds the total comprehensive income of the subsidiary or associate in the period the dividend is declared or if the carrying amount of the investment in the separate financial statements exceeds the carrying amount in the consolidated financial statements of the investee’s net assets including goodwill. Assets that subjected to amortisation are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may not be recoverable. An impairment loss is recognised for the amount by which the asset’s carrying amount exceeds its recoverable amount. The recoverable amount is the higher of an asset’s fair value less costs to sell and value in use. For the purposes of assessing impairment, assets are grouped at the lowest levels for which there are separately identifiable cash flows (CGUs). Non-financial assets other than goodwill that suffered impairment are reviewed for possible reversal of the impairment at each reporting date. 2.11 Financial assets 2.11.1 Classification The Group classifies its financial assets in the following categories: at fair value through profit or loss, loans and receivables, available-for-sale financial assets and held to maturity investment. The classification depends on the purpose for which the financial assets were acquired. Management determines the classification of its financial assets at initial recognition. In current year, the Group held loan and receivables and available-for- sale financial assets. (a) Loans and receivables Loans and receivables are non-derivative financial assets with fixed or determinable payments that are not quoted in an active market. They are included in current assets except for the amounts that are settled or expected to be settled more than 12 months after the end of the reporting period. These are classified as non-current assets. The Group’s loans and receivables comprise “long-term receivables”, “trade and other receivables”, “short-term deposits” and “cash and cash equivalents” in the balance sheet (Notes 2.16 and 2.17).

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.11 Financial assets (continued) 2.11.1 Classification (continued) (b) Available-for-sale financial assets Available-for-sale financial assets are non-derivatives that are either designated in this category or not classified in any of the other categories. They are included in non-current assets unless the investment matures or management intends to dispose of it within 12 months of the end of the reporting period. 2.11.2 Recognition and measurement Regular way purchases and sales of financial assets are recognised on the trade-date — the date on which the Group commits to purchase or sell the asset. Investments are initially recognised at fair value plus transaction costs for all financial assets not carried at fair value through profit or loss. Available-for-sale financial assets are subsequently carried at fair value, except for those investments in equity instruments that do not have a quoted market price in an active market and whose fair value cannot be reliably measured, which shall be measured at cost. Financial assets are derecognised when the rights to receive cash flows from the investments have expired or have been transferred and the Group has transferred substantially all risks and rewards of ownership. Loans and receivables are subsequently carried at amortised cost using the effective interest method. Changes in the fair value of monetary and non-monetary securities classified as available-for-sale are recognised in other comprehensive income. When securities classified as available-for-sale are sold or impaired, the accumulated fair value adjustments recognised in equity are included in the comprehensive income statement as “other losses — net”. Dividends on available-for-sale equity instruments are recognised in the comprehensive income statement as part of other income when the Group’s right to receive payments is established.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.11 Financial assets (continued) 2.11.2 Recognition and measurement (continued) The fair values of quoted investments are based on current bid prices. If the market for a financial asset is not active (and for unlisted securities), the Group established fair value by using valuation techniques. These include the use of recent arm’s length transactions, reference to other instruments that are substantially the same, discounted cash flow analysis, and option pricing models, making maximum use of market inputs and relying as little as possible on entity-specific inputs. In case of unlisted equity instruments that do not have a quoted market price in an active market and whose fair value cannot be reliably determined via valuation techniques, they are measured at cost, subject to impairment review. 2.12 Offsetting financial instruments Financial assets and liabilities are offset and the net amount reported in the balance sheet when there is a legally enforceable right to offset the recognised amounts and there is an intention to settle on a net basis, or realise the asset and settle the liability simultaneously. The legally enforceable right must not be contingent on future events and must be enforceable in the normal course of business and in the event of default, insolvency or bankruptcy of the Company or the counterparty. 2.13 Impairment of financial assets (a) Assets carried at amortised cost The Group assesses at the end of each reporting period whether there is objective evidence that a financial asset or group of financial assets is impaired. A financial asset or a group of financial assets is impaired and impairment losses are incurred only if there is objective evidence of impairment as a result of one or more events that occurred after the initial recognition of the asset (a “loss event”) and that loss event (or events) has an impact on the estimated future cash flows of the financial asset or group of financial assets that can be reliably estimated.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.13 Impairment of financial assets (continued) (a) Assets carried at amortised cost (continued) The criteria that the Group uses to determine that there is objective evidence of an impairment loss include: • Significant financial difficulty of the issuer or obligor; • A breach of contract, such as a default or delinquency in interest or principal payments; • The Group, for economic or legal reasons relating to the borrower’s financial difficulty, granting to the borrower a concession that the lender would not otherwise consider; • It becomes probable that the borrower will enter bankruptcy or other financial reorganisation; • The disappearance of an active market for that financial asset because of financial difficulties; or • Observable data indicating that there is a measurable decrease in the estimated future cash flows from a portfolio of financial assets since the initial recognition of those assets, although the decrease cannot yet be identified with the individual financial assets in the portfolio, including: (i) adverse changes in the payment status of borrowers in the portfolio; (ii) national or local economic conditions that correlate with defaults on the assets in the portfolio. The Group first assesses whether objective evidence of impairment exists. For loans and receivables category, the amount of the loss is measured as the difference between the asset’s carrying amount and the present value of estimated future cash flows (excluding future credit losses that have not been incurred) discounted at the financial asset’s original effective interest rate. The carrying amount of the asset is reduced and the amount of the loss is recognised in the comprehensive income statement. If a loan has a variable interest rate, the discount rate for measuring any impairment loss is the current effective interest rate determined under the contract. As a practical expedient, the Group may measure impairment on the basis of an instrument’s fair value using an observable market price.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.13 Impairment of financial assets (continued) (a) Assets carried at amortised cost (continued) If, in a subsequent period, the amount of the impairment loss decreases and the decrease can be related objectively to an event occurring after the impairment was recognised (such as an improvement in the debtor’s credit rating), the reversal of the previously recognised impairment loss is recognised in the comprehensive income statement. (b) Assets classified as available for sale The Group assesses at the end of each reporting period whether there is objective evidence that a financial asset or a group of financial assets is impaired. For equity investments, a significant or prolonged decline in the fair value of the security below its cost is also evidence that the assets are impaired. If any such evidence exists the cumulative loss, which is measured as the difference between the acquisition cost and the current fair value, less any impairment loss on that financial asset previously recognised in profit or loss, is removed from equity and recognised in profit or loss. Impairment losses recognised in the consolidated comprehensive income statement on equity instruments are not reversed through the consolidated comprehensive income statement. 2.14 Long-term prepaid expenses Long-term prepaid expenses include the various expenditures that have been incurred but should be recognised as expenses over more than one year in the current and subsequent periods. Long-term prepaid expenses are amortised on the straight-line basis over the expected beneficial period and are presented at actual expenditure net of accumulated amortisation. 2.15 Materials and supplies Materials and supplies are stated at the lower of cost and net realisable value. Cost is determined using the weighted average method. Materials and supplies are charged as fuel costs and repair and maintenance expenses when consumed, or capitalised to fixed assets when the items are installed with the related fixed assets, whichever is appropriate. The cost of materials and supplies may not be recoverable if they are damaged, if they have become wholly or partially obsolete, or if their selling prices have declined due to various reasons. When such circumstances happen, cost of materials and supplies is written to net realisable value, which is the estimated selling price less applicable variable expenses.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.16 Trade and other receivables Trade receivables are amounts due from customers for merchandise sold or services performed in the ordinary course of business. If collection of trade and other receivables is expected in one year or less (or in the normal operating cycle of the business if longer), they are classified as current assets. If not, they are presented as non-current assets. Trade and other receivables are recognised initially at fair value and subsequently measured at amortised cost using the effective interest method, less provision for impairment. 2.17 Cash and cash equivalents Cash and cash equivalents include cash in hand; deposits held at call with banks; and other short-term highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less. 2.18 Share capital Ordinary shares are classified as equity. Incremental costs directly attributable to the issue of new shares or options are shown in equity as a deduction, net of tax, from the proceeds. 2.19 Trade payables Trade payables are obligations to pay for goods or services that have been acquired in the ordinary course of business from suppliers. Accounts payable are classified as current liabilities if payment is due within one year or less (or in the normal operating cycle of the business if longer). If not, they are presented as non-current liabilities. Trade payables are recognised initially at fair value and subsequently measured at amortised cost using the effective interest method. The Group derecognises financial liability when, and only when, the Group’s obligations are discharged, cancelled or expired. The difference between the carrying amount of the financial liability derecognised and the consideration paid and payable is recognised in profit or loss.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.20 Borrowings Borrowings are recognised initially at fair value, net of transaction costs incurred. They are subsequently carried at amortised cost; and any difference between proceeds (net of transaction costs) and the redemption value is recognised in the comprehensive income statement over the period of the borrowings using the effective interest method. Fees paid on the establishment of loan facilities are recognised as transaction costs of the loan to the extent that it is probable that some or all of the facility will be drawn down. In this case, the fee is deferred until the draw-down occurs. To the extent there is no evidence that it is probable that some or all of the facility will be drawn down, the fee is capitalised as a prepayment for liquidity services and amortised over the period of the facility to which it relates. Borrowings are classified as current liabilities unless the Group has an unconditional right to defer settlement of the liability for at least 12 months after the end of the reporting period. 2.21 Borrowing costs General and specific borrowing costs directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of qualifying assets, which are assets that necessarily take a substantial period of time to get ready for their intended use or sale, are added to the cost of those assets, until such time as the assets are substantially ready for their intended use or sale. Investment income earned on the temporary investment of specific borrowings pending their expenditure on qualifying assets is deducted from the borrowing costs eligible for capitalisation. All other borrowing costs are recognised in profit or loss in the period in which they are incurred.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.22 Current and deferred income tax The tax expense for the period comprises current and deferred tax. Tax is recognised in the consolidated comprehensive income statement, except to the extent that it relates to items recognised in other comprehensive income or directly in equity. In this case, the tax is also recognised in other comprehensive income or directly in equity, respectively. (a) Current income tax The current income tax charge is calculated on the basis of the tax laws enacted or substantively enacted at the balance sheet date in PRC where the Company’s subsidiaries and associates operate and generate taxable income. Management periodically evaluates positions taken in tax returns with respect to situations in which applicable tax regulation is subject to interpretation and establishes provisions where appropriate on the basis of amounts expected to be paid to the tax authorities. (b) Deferred income tax Inside basis differences Deferred income tax is recognised, using the liability method, on temporary differences arising between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts in the consolidated financial statements. However, the deferred income tax is not accounted for if it arises from initial recognition of an asset or liability in a transaction other than a business combination that at the time of the transaction affects neither accounting nor taxable profit nor loss. Deferred income tax is determined using tax rates (and laws) that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance sheet date and are expected to apply when the related deferred income tax asset is realised or the deferred income tax liability is settled. Deferred income tax assets are recognised only to the extent that it is probable that future taxable profit will be available against which the temporary differences can be utilised.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.22 Current and deferred income tax (continued) (b) Deferred income tax (continued) Outside basis differences Deferred income tax liabilities are provided on taxable temporary differences arising from investments in subsidiaries, and associates and joint arrangements, except for deferred income tax liability where the timing of the reversal of the temporary difference is controlled by the Group and it is probable that the temporary difference will not reverse in the foreseeable future. Generally the Group is unable to control the reversal of the temporary difference for associates. Only when there is an agreement in place that gives the Group the ability to control the reversal of the temporary difference in the foreseeable future, deferred tax liability in relation to taxable temporary differences arising from the associate’s undistributed profits is not recognised. Deferred income tax assets are recognised on deductible temporary differences arising from investments in subsidiaries, and associates and joint arrangements only to the extent that it is probable the temporary difference will reverse in the future and there is sufficient taxable profit available against which the temporary difference can be utilised. (c) Offsetting Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are offset when there is a legally enforceable right to offset current tax assets against current tax liabilities and when the deferred income taxes assets and liabilities relate to income taxes levied by the same taxation authority on either the taxable entity or different taxable entities where there is an intention to settle the balances on a net basis. 2.23 Employee benefits (a) Defined contribution plan The Group pays contributions to defined contribution schemes operated by the local government for employee benefits in respect of pension and unemployment. The Group also pays contribution to defined contribution schemes operated by Guangzhou Railway Group for employee supplementary pension benefit. The Group has no further payment obligations once the contributions have been paid. The contributions to the defined contribution schemes are recognised as staff costs when they are due.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.23 Employee benefits (continued) (b) Termination benefits Termination benefits are payable when employment is terminated by the Group before the normal retirement date, or whenever an employee accepts voluntary redundancy in exchange for these benefits. The Group recognises termination benefits at the earlier of the following dates: (a) when the Group can no longer withdraw the offer of those benefits; and (b) when the entity recognises costs for a restructuring that is within the scope of IAS 37 and involves the payment of termination benefits. In the case of an offer made to encourage voluntary redundancy, the termination benefits are measured based on the number of employees expected to accept the offer. Benefits falling due more than 12 months after the end of the reporting period are discounted to their present value. 2.24 Provisions Provisions for environmental restoration, restructuring costs and legal claims are recognised when: the Group has a present legal or constructive obligation as a result of past events; it is probable that an outflow of resources will be required to settle the obligation; and the amount has been reliably estimated. Restructuring provisions comprise lease termination penalties and employee termination payments. Provisions are not recognised for future operating losses. Where there are a number of similar obligations, the likelihood that an outflow will be required in settlement is determined by considering the class of obligations as a whole. A provision is recognised even if the likelihood of an outflow with respect to any one item included in the same class of obligations may be small. Provisions are measured at the present value of the expenditures expected to be required to settle the obligation using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects current market assessments of the time value of money and the risks specific to the obligation. The increase in the provision due to passage of time is recognised as interest expense. 2.25 Revenue recognition Revenue comprises the fair value of the consideration received or receivable for the sale of goods and services in the ordinary course of the Group’s activities. Revenue is shown net of value-added tax, rebates and discounts and after eliminating sales within the Group. The Group recognises revenue when the services are rendered and the amount of revenue can be reliable measured, future economic benefits will probably flow to the entity with reasonably certainty, and specific criteria have been met for each of the Group’s activities as described below. The recognition also involves use of estimates exercised by management based on historical results, takes into consideration the different type of customers, transactions and the specifics of each arrangement.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.25 Revenue recognition (continued) (a) Revenue from railroad and related business Revenue from passenger transportation The passenger transportation is generally classified by transportation business of Guangzhou-Shenzhen inter-city express trains, long-distance trains and Guangzhou-Hong Kong city through trains. These services are provided in cooperation with other railway companies in PRC and the corresponding revenue information is captured and processed by CRC through a central clearance system. Revenues are recognized on a monthly basis when the train transportation services are rendered within the month, i.e. upon the passenger tickets with fixed prices and dates of travel, which are non-refundable and non-reschedulable, are sold and the respective trains have reached the prescribed destinations within that particular month; as well as upon approval and notification is made by CRC on a monthly basis (the “CRC Monthly Statement”) for transactions completed within that month and when the amounts of revenue can be reliably measured and collectability is certain. The revenue is presented net of value-added tax but before deduction of any sales handling commissions. Revenue from freight transportation The Group also operates with other railway companies in PRC for the provision of freight transportation services. Service information and computation of the attributable revenues entitled by the Group are processed by the central clearance system of CRC on a monthly basis. Revenue from outbound and inbound freight transportation with ports of loading and discharge located at railway lines owned and operated by the Group; pass-through transportation with freight trains passing through railway lines owned and operated by the Group; as well as goods loading and discharge services rendered at ports located at railway lines owned by the Group, are recognized, on a monthly basis, when the goods are delivered to the ports of discharge within a month, or when the loading/discharge services are rendered, and when the amounts are approved and notified in the CRC Monthly Statement, upon which the amounts can be reliably measured and collectability is certain. The revenues are presented at the gross amounts of the attributable freight charges computed from the standard freight charges imposed by CRC.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.25 Revenue recognition (continued) (a) Revenue from railroad and related business (continued) Revenue from railway network usage and other transportation related services Revenue from railway network usage and other transportation related services, mainly consist of network usage services (locomotive traction, track usage and electric catenaries service, etc.) and railway operation services and other services, are rendered by the Group together with other railway companies in PRC. The information relating to network usage service is captured and processed by the central clearance system of CRC. The revenue from network usage services are recognized on a monthly basis, when the services are rendered within that month and revenue can be reliably measured, i.e. upon approval and notification made in the CRC Monthly Statement, for the transactions completed within that month, when the respective revenue amounts can be reliably measured and when collectability is certain. Railway operation services and other services are rendered solely by the Group and they are recognized when the services are rendered and revenue can be reliably measured. All proceeds are collected by the Group directly. The operations of the railway business of the Group form part of the nationwide railway system in PRC and they are supervised and governed by CRC. The Group render the passenger transportation and freight transportation services in cooperation with other railway companies and the related service fees and charges are collected either by the Group itself or by other railway companies. In addition, the Group also receives service fees and charges for on behalf of other railway companies. The respective fares and charges of the services, fee sharing basis, and processing of the respective revenue sharing among different railway companies are done centrally by a central clearance system operated by CRC. The Group records revenues based on the amounts of attributable revenue approved and notified in the CRC Monthly Statement for services undertaken by the Group completed within the specific month, upon then the revenues can be reliably measured and collectability is certain. The respective share of revenues, in excess of amount collected by the Group itself, are credited by CRC to bank accounts maintained by the Group. In the case that the attributable amount is less than the amount collected by the Group, the Group remits the surplus to CRC. (b) Revenue from other businesses Revenue from other business mainly consist of on-board catering services, leasing, sales of materials, sale of goods and other businesses related to railway transportation. Revenues from on-board catering services are recognized when the related services are rendered. Revenues from sales of materials and supplies and sale of goods are recognized when the respective materials and goods are delivered to customers. Revenue from operating lease arrangements on certain properties and locomotives is recognized on a straight-line basis over the period of the respective leases.

2. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued) 2.26 Interest income Interest income is recognised using the effective interest method. When a loan and receivable is impaired, the Group reduces the carrying amount to its recoverable amount, being the estimated future cash flow discounted at original effective interest rate of the instrument, and continues unwinding the discount as interest income. Interest income on impaired receivables is recognised using the original effective interest rate. 2.27 Dividend income Dividend income is recognised when the right to receive payment is established. 2.28 Government grants Grants from the government are recognised at their fair value where there is a reasonable assurance that the grant will be received and the Group will comply with all attached conditions. Government grants relating to costs are deferred and recognised in the comprehensive income statement over the period necessary to match them with the costs that they are intended to compensate. Government grants relating to fixed assets are included in non-current liabilities as deferred government grants and are credited to the comprehensive income statement on a straight-line basis over the expected lives of the related assets. 2.29 Operating leases Leases in which a significant portion of the risks and rewards of ownership are retained by the lessor are classified as operating leases. Payments made under operating leases (net of any incentives received from the lessor) are charged to the comprehensive income statement on a straight-line basis over the period of the lease. 2.30 Dividend distribution Dividend distribution to the shareholders is recognised as a liability in the Group’s and the Company’s financial statements in the period in which the dividends are approved by the shareholders.
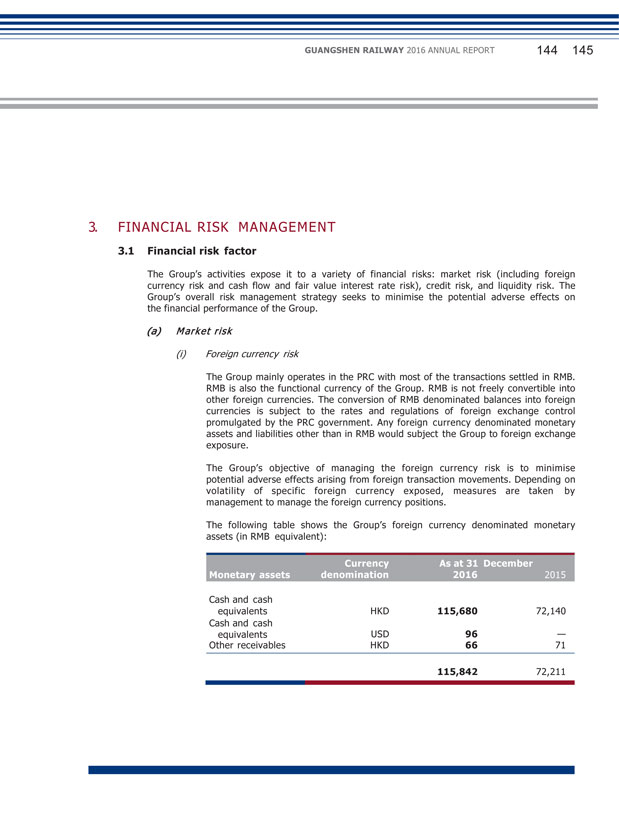
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 3. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT 3.1 Financial risk factor The Group’s activities expose it to a variety of financial risks: market risk (including foreign currency risk and cash flow and fair value interest rate risk), credit risk, and liquidity risk. The Group’s overall risk management strategy seeks to minimise the potential adverse effects on the financial performance of the Group. (a) Market risk (i) Foreign currency risk The Group mainly operates in the PRC with most of the transactions settled in RMB. RMB is also the functional currency of the Group. RMB is not freely convertible into other foreign currencies. The conversion of RMB denominated balances into foreign currencies is subject to the rates and regulations of foreign exchange control promulgated by the PRC government. Any foreign currency denominated monetary assets and liabilities other than in RMB would subject the Group to foreign exchange exposure. The Group’s objective of managing the foreign currency risk is to minimise potential adverse effects arising from foreign transaction movements. Depending on volatility of specific foreign currency exposed, measures are taken by management to manage the foreign currency positions. The following table shows the Group’s foreign currency denominated monetary assets (in RMB equivalent): Currency As at 31 December Monetary assets denomination 2016 2015 Cash and cash equivalents HKD 115,680 72,140 Cash and cash equivalents USD 96 — Other receivables HKD 66 71 115,842 72,211

3. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT (continued) 3.1 Financial risk factor (continued) (a) Market risk (continued) (i) Foreign currency risk (continued) The Group may experience a loss as a result of any foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations in connection with monetary assets shown above. The Group has not used any means to hedge the exposure. As at 31 December 2016, if RMB had weakened/strengthened by 5% against the HKD with all other variables held constant, profit after tax for the year would have been RMB4,340,000 (2015: RMB2,708,000 ) higher/lower, mainly as a result of foreign exchange gains/losses on translation of HKD-denominated cash in banks. The impact of exchange fluctuations of USD is not significant. (ii) Cash flow and fair value interest rate risk Other than deposits held in banks, the Group does not have significant interest- bearing assets. The average interest rate of deposits held in banks in the PRC throughout the year was approximately 1.38% (2015: 1.71%). Any change in the interest rate promulgated by the People’s Bank of China from time to time is not considered to have a significant impact to the Group. As at 31 December 2016 and 2015, the Group had no interest bearing debts, which may expose the Group to any interest rate risk.
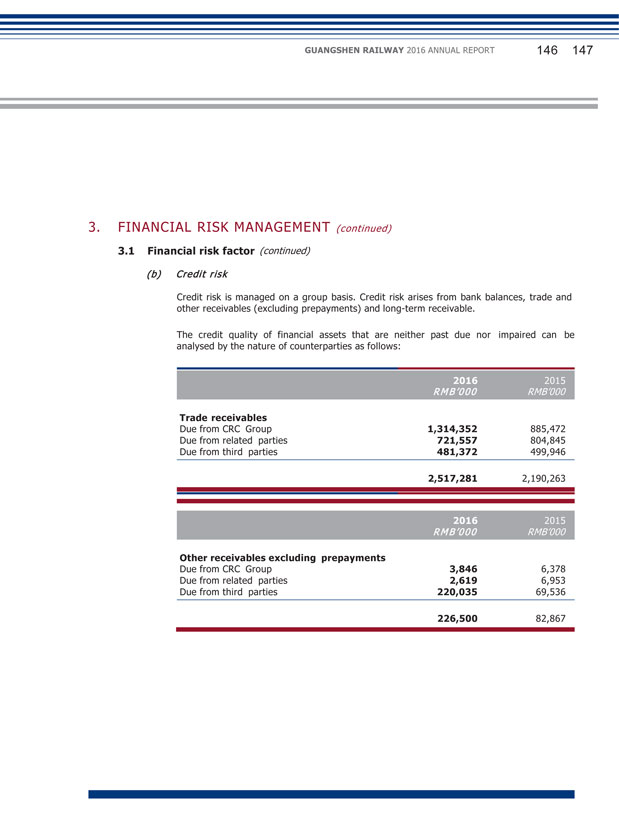
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 3. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT (continued) 3.1 Financial risk factor (continued) (b) Credit risk Credit risk is managed on a group basis. Credit risk arises from bank balances, trade and other receivables (excluding prepayments) and long-term receivable. The credit quality of financial assets that are neither past due nor impaired can be analysed by the nature of counterparties as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Trade receivables Due from CRC Group 1,314,352 885,472 Due from related parties 721,557 804,845 Due from third parties 481,372 499,946 2,517,281 2,190,263 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Other receivables excluding prepayments Due from CRC Group 3,846 6,378 Due from related parties 2,619 6,953 Due from third parties 220,035 69,536 226,500 82,867
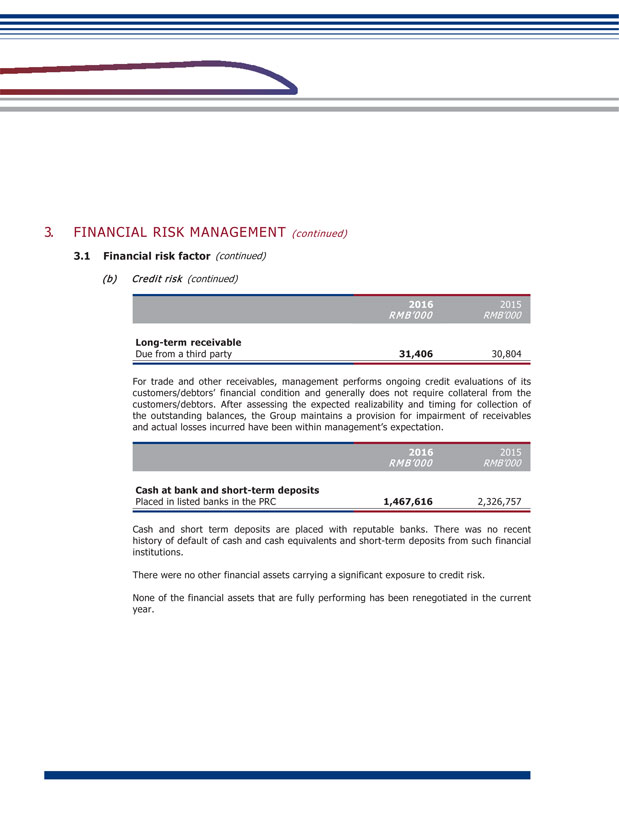
3. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT (continued) 3.1 Financial risk factor (continued) (b) Credit risk (continued) 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Long-term receivable Due from a third party 31,406 30,804 For trade and other receivables, management performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers/debtors’ financial condition and generally does not require collateral from the customers/debtors. After assessing the expected realizability and timing for collection of the outstanding balances, the Group maintains a provision for impairment of receivables and actual losses incurred have been within management’s expectation. 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Cash at bank and short-term deposits Placed in listed banks in the PRC 1,467,616 2,326,757 Cash and short term deposits are placed with reputable banks. There was no recent history of default of cash and cash equivalents and short-term deposits from such financial institutions. There were no other financial assets carrying a significant exposure to credit risk. None of the financial assets that are fully performing has been renegotiated in the current year.
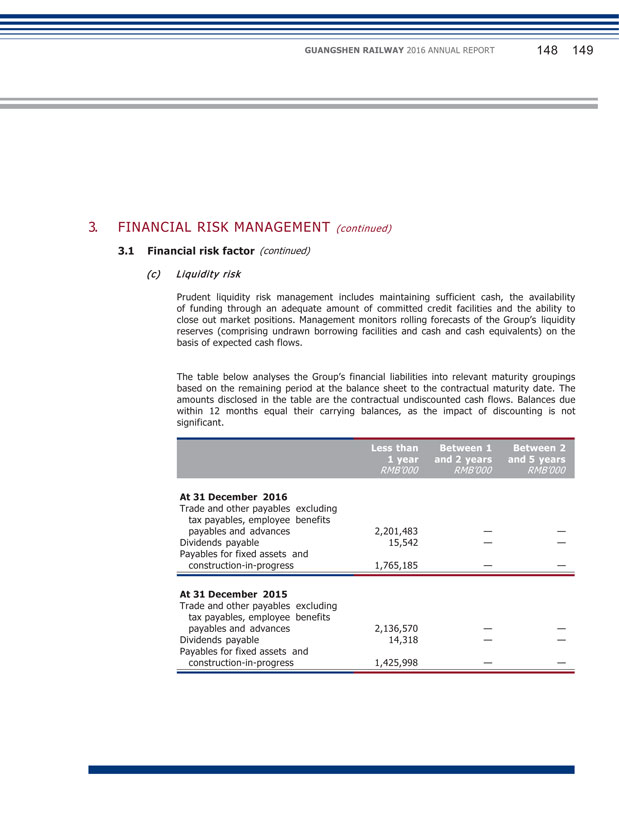
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 3. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT (continued) 3.1 Financial risk factor (continued) (c) Liquidity risk Prudent liquidity risk management includes maintaining sufficient cash, the availability of funding through an adequate amount of committed credit facilities and the ability to close out market positions. Management monitors rolling forecasts of the Group’s liquidity reserves (comprising undrawn borrowing facilities and cash and cash equivalents) on the basis of expected cash flows. The table below analyses the Group’s financial liabilities into relevant maturity groupings based on the remaining period at the balance sheet to the contractual maturity date. The amounts disclosed in the table are the contractual undiscounted cash flows. Balances due within 12 months equal their carrying balances, as the impact of discounting is not significant. Less than Between 1 Between 2 1 year and 2 years and 5 years RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 At 31 December 2016 Trade and other payables excluding tax payables, employee benefits payables and advances 2,201,483 — — Dividends payable 15,542 — — Payables for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 1,765,185 — — At 31 December 2015 Trade and other payables excluding tax payables, employee benefits payables and advances 2,136,570 — — Dividends payable 14,318 — — Payables for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 1,425,998 — —

3. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT (continued) 3.2 Capital risk management The Group’s objectives of managing capital are to safeguard the Group’s ability to continue as a going concern in order to provide returns for shareholders and benefits for other stakeholders and to maintain an optimal capital structure to reduce the cost of capital. As at December 2016 and 2015, the Group did not have borrowings and bonds. The directors are of the opinion that the Group’s capital risk is low. 3.3 Fair value estimation According to amendment to IFRS 7 for financial instruments that are measured in the balance sheet at fair value, it requires disclosure of fair value measurements by level of following fair value measurement hierarchy: • Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (level 1). • Inputs other than quoted prices included within level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (that is, as prices) or indirectly (that is, derived from prices) (level 2). • Inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (that is, unobservable inputs) (level 3). As at 31 December 2016, the Group did not have any financial instruments that were measured at fair value. As at 31 December 2016, the fair values of other financial instruments approximated their carrying values.

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 4. CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES AND JUDGEMENTS Estimates and judgements are continually evaluated and are based on historical experience and other factors, including expectations of future events that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. The Group makes estimates and assumptions concerning the future. The resulting accounting estimates will, by definition, seldom equal the related actual results. The estimates and assumptions that have a significant risk of causing a material adjustment to the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities within the next financial year are addressed below. Impairment of receivables The Group makes provision for impairment of receivables based on an assessment of the recoverability of trade and other receivables with reference to the extent and duration that the amount will be recovered. Provisions are applied where events or changes in circumstances indicate that the balances may not be collectible. The identification of impairment requires the use of judgment and estimates. Where the expectation is different from the original estimate, such difference will impact the carrying amount of trade and other receivables and the impairment charge in the period in which such estimate has been changed.
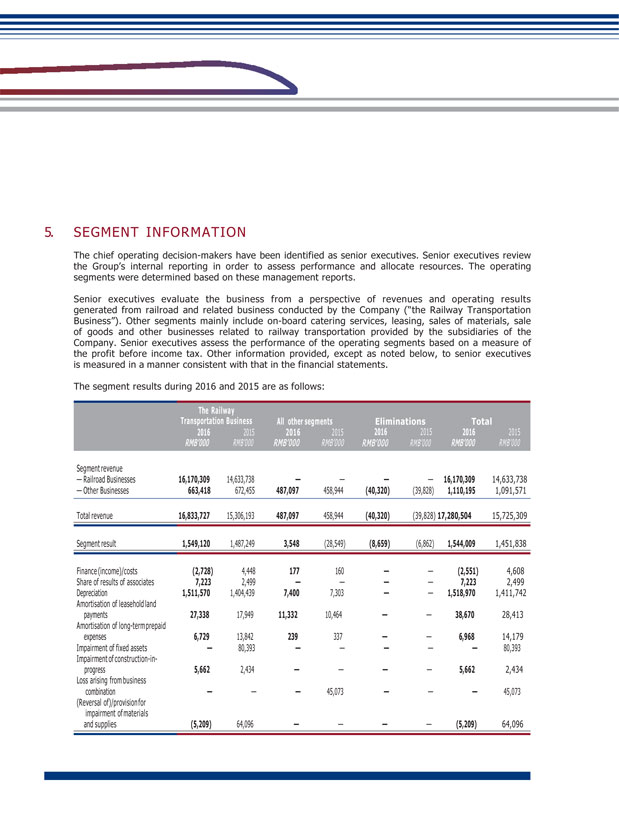
5. SEGMENT INFORMATION The chief operating decision-makers have been identified as senior executives. Senior executives review the Group’s internal reporting in order to assess performance and allocate resources. The operating segments were determined based on these management reports. Senior executives evaluate the business from a perspective of revenues and operating results generated from railroad and related business conducted by the Company (“the Railway Transportation Business”). Other segments mainly include on-board catering services, leasing, sales of materials, sale of goods and other businesses related to railway transportation provided by the subsidiaries of the Company. Senior executives assess the performance of the operating segments based on a measure of the profit before income tax. Other information provided, except as noted below, to senior executives is measured in a manner consistent with that in the financial statements. The segment results during 2016 and 2015 are as follows: The Railway Transportation Business All other segments Eliminations Total 2016 2015 2016 2015 2016 2015 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Segment revenue — Railroad Businesses 16,170,309 14,633,738 — — — — 16,170,309 14,633,738 — Other Businesses 663,418 672,455 487,097 458,944 (40,320) (39,828) 1,110,195 1,091,571 Total revenue 16,833,727 15,306,193 487,097 458,944 (40,320) (39,828) 17,280,504 15,725,309 Segment result 1,549,120 1,487,249 3,548 (28,549) (8,659) (6,862) 1,544,009 1,451,838 Finance (income)/costs (2,728) 4,448 177 160 — — (2,551) 4,608 Share of results of associates 7,223 2,499 — — — — 7,223 2,499 Depreciation 1,511,570 1,404,439 7,400 7,303 — — 1,518,970 1,411,742 Amortisation of leasehold land payments 27,338 17,949 11,332 10,464 — — 38,670 28,413 Amortisation of long-termprepaid expenses 6,729 13,842 239 337 — — 6,968 14,179 Impairment of fixed assets — 80,393 — — — — — 80,393 Impairment of construction-in- progress 5,662 2,434 — — — — 5,662 2,434 Loss arising from business combination — — — 45,073 — — — 45,073 (Reversal of)/provision for impairment of materials and supplies (5,209) 64,096 — — — — (5,209) 64,096
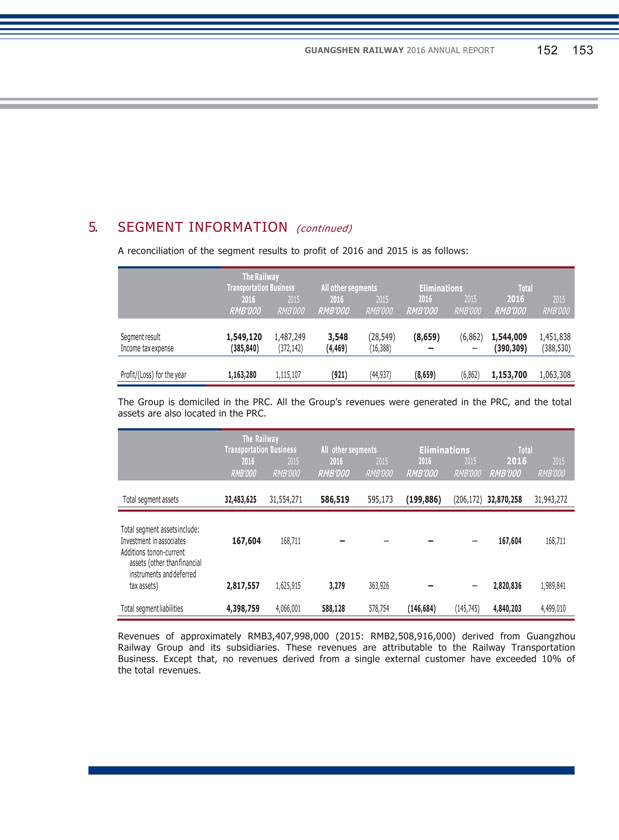
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 5. SEGMENT INFORMATION (continued) A reconciliation of the segment results to profit of 2016 and 2015 is as follows: The Railway Transportation Business All other segments Eliminations Total 2016 2015 2016 2015 2016 2015 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Segment result 1,549,120 1,487,249 3,548 (28,549) (8,659) (6,862) 1,544,009 1,451,838 Income tax expense (385,840) (372,142) (4,469) (16,388) — — (390,309) (388,530) Profit/(Loss) for the year 1,163,280 1,115,107 (921) (44,937) (8,659) (6,862) 1,153,700 1,063,308 The Group is domiciled in the PRC. All the Group’s revenues were generated in the PRC, and the total assets are also located in the PRC. The Railway Transportation Business All other segments Eliminations Total 2016 2015 2016 2015 2016 2015 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Total segment assets 32,483,625 31,554,271 586,519 595,173 (199,886) (206,172) 32,870,258 31,943,272 Total segment assetsinclude: Investment in associates 167,604 168,711 — — — — 167,604 168,711 Additions to non-current assets (other than financial instruments and deferred tax assets) 2,817,557 1,625,915 3,279 363,926 — — 2,820,836 1,989,841 Total segment liabilities 4,398,759 4,066,001 588,128 578,754 (146,684) (145,745) 4,840,203 4,499,010 Revenues of approximately RMB3,407,998,000 (2015: RMB2,508,916,000) derived from Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries. These revenues are attributable to the Railway Transportation Business. Except that, no revenues derived from a single external customer have exceeded 10% of the total revenues.
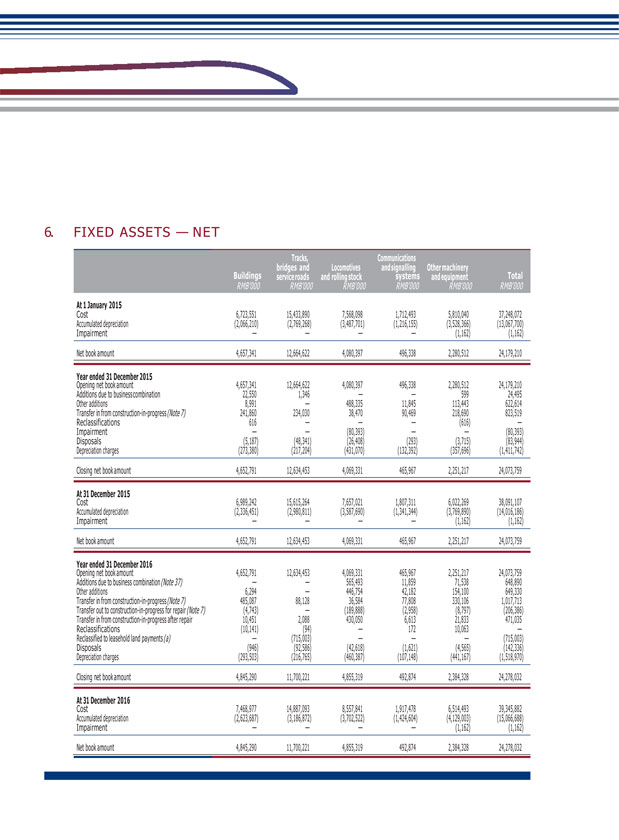
6. FIXED ASSETS — NET Tracks, Communications Buildings bridges and Locomotives and signalling Other machinery Total RMB’000 service RMB’000 roads and rolling RMB’000 stock systems RMB’000 and equipment RMB’000 RMB’000 At 1 January 2015 Accumulated Cost depreciation (2,066,210) 6,723,551 15,433,890 (2,769,268) (3,487,701) 7,568,098 (1,216,155) 1,712,493 (3,528,366) 5,810,040 (13,067,700) 37,248,072 Impairment — — — — (1,162) (1,162) Net book amount 4,657,341 12,664,622 4,080,397 496,338 2,280,512 24,179,210 Year ended 31 December 2015 Additions Opening net due book to business amount combination 4,657,341 22,550 12,664,622 1,346 4,080,397 — 496,338 — 2,280,512 599 24,179,210 24,495 Transfer Other additions in from construction-in-progress (Note 7) 241,860 8,991 234,030 — 488,335 38,470 11,845 90,469 218,690 113,443 622,614 823,519 Reclassifications Impairment 616 — — — (80,393) — — — (616) — (80,393) — Depreciation Disposals charges (273,380) (5,187) (217,204) (48,341) (431,070) (26,408) (132,392) (293) (357,696) (3,715) (1,411,742) (83,944) Closing net book amount 4,652,791 12,634,453 4,069,331 465,967 2,251,217 24,073,759 At 31 December 2015 Accumulated Cost depreciation (2,336,451) 6,989,242 15,615,264 (2,980,811) (3,587,690) 7,657,021 (1,341,344) 1,807,311 (3,769,890) 6,022,269 (14,016,186) 38,091,107 Impairment — — — — (1,162) (1,162) Net book amount 4,652,791 12,634,453 4,069,331 465,967 2,251,217 24,073,759 Year ended 31 December 2016 Opening Additions net due book to business amount combination (Note 37) 4,652,791 — 12,634,453 — 4,069,331 565,493 465,967 11,859 2,251,217 71,538 24,073,759 648,890 Transfer Other additions in from construction-in-progress (Note 7) 485,087 6,294 88,128 — 446,754 36,584 42,182 77,808 330,106 154,100 1,017,713 649,330 Transfer Transfer in out from to construction-in-progress construction-in-progress for after repair repair (Note 7) 10,451 (4,743) 2,088 — (189,888) 430,050 (2,958) 6,613 21,833 (8,797) (206,386) 471,035 Reclassified Reclassifications to leasehold land payments (a) (10,141) — (715,003) (94) — — 172 — 10,063 — (715,003) — Depreciation Disposals charges (293,503) (946) (216,765) (92,586) (460,387) (42,618) (107,148) (1,621) (441,167) (4,565) (1,518,970) (142,336) Closing net book amount 4,845,290 11,700,221 4,855,319 492,874 2,384,328 24,278,032 At 31 December 2016 Accumulated Cost depreciation (2,623,687) 7,468,977 14,887,093 (3,186,872) (3,702,522) 8,557,841 (1,424,604) 1,917,478 (4,129,003) 6,514,493 (15,066,688) 39,345,882 Impairment — — — — (1,162) (1,162) Net book amount 4,845,290 11,700,221 4,855,319 492,874 2,384,328 24,278,032
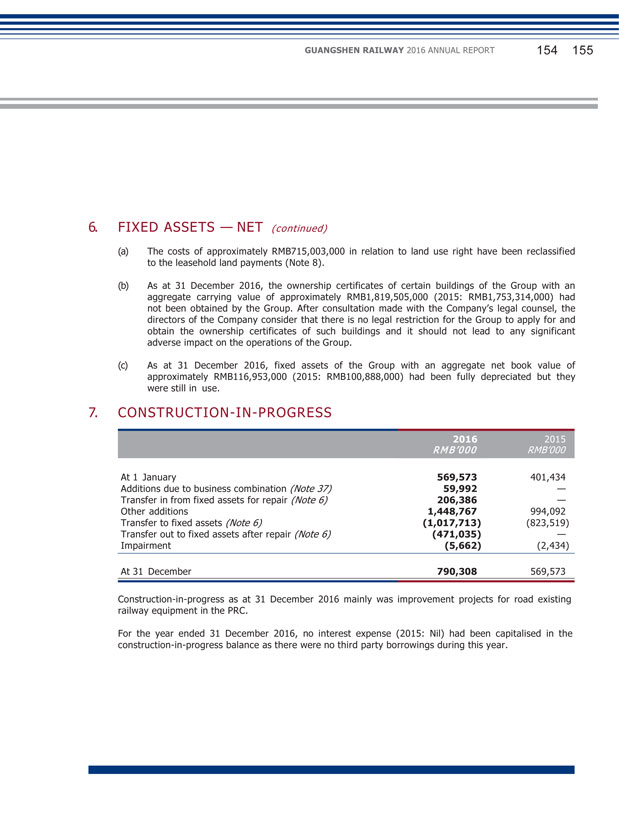
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 6. FIXED ASSETS — NET (continued) (a) The costs of approximately RMB715,003,000 in relation to land use right have been reclassified to the leasehold land payments (Note 8). (b) As at 31 December 2016, the ownership certificates of certain buildings of the Group with an aggregate carrying value of approximately RMB1,819,505,000 (2015: RMB1,753,314,000) had not been obtained by the Group. After consultation made with the Company’s legal counsel, the directors of the Company consider that there is no legal restriction for the Group to apply for and obtain the ownership certificates of such buildings and it should not lead to any significant adverse impact on the operations of the Group. (c) As at 31 December 2016, fixed assets of the Group with an aggregate net book value of approximately RMB116,953,000 (2015: RMB100,888,000) had been fully depreciated but they were still in use. 7. CONSTRUCTION-IN-PROGRESS 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 At 1 January 569,573 401,434 Additions due to business combination (Note 37) 59,992 — Transfer in from fixed assets for repair (Note 6) 206,386 — Other additions 1,448,767 994,092 Transfer to fixed assets (Note 6) (1,017,713) (823,519) Transfer out to fixed assets after repair (Note 6) (471,035) — Impairment (5,662) (2,434) At 31 December 790,308 569,573 Construction-in-progress as at 31 December 2016 mainly was improvement projects for road existing railway equipment in the PRC. For the year ended 31 December 2016, no interest expense (2015: Nil) had been capitalised in the construction-in-progress balance as there were no third party borrowings during this year.

8. LEASEHOLD LAND PAYMENTS The Group’s interests in leasehold land represent prepaid operating lease payments in the PRC and its net book value are analysed as follows: RMB’000 At 1 January 2015 Cost 965,148 Accumulated amortisation (297,143) Net book amount 668,005 Opening Year ended net book 31 December amount 2015 668,005 Additions 308,934 Amortisation charges (28,413) Closing net book amount 948,526 At Cost 31 December 2015 1,274,082 Accumulated amortisation (325,556) Net book amount 948,526 Opening Year ended net book 31 December amount 2016 948,526 Transfer from fix assets (Note 6) 715,003 Amortisation charges (38,670) Closing net book amount 1,624,859 At Cost 31 December 2016 1,989,085 Accumulated amortisation (364,226) Net book amount 1,624,859
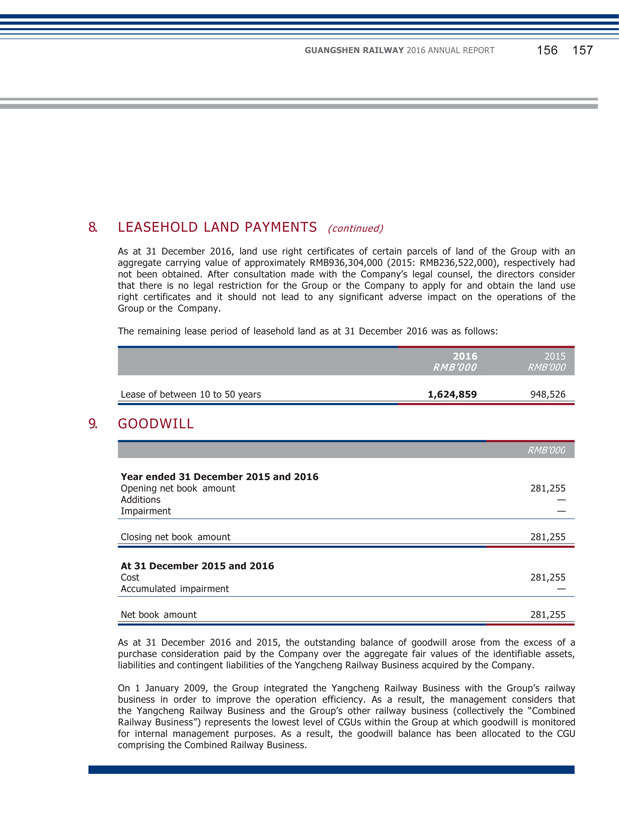
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 8. LEASEHOLD LAND PAYMENTS (continued) As at 31 December 2016, land use right certificates of certain parcels of land of the Group with an aggregate carrying value of approximately RMB936,304,000 (2015: RMB236,522,000), respectively had not been obtained. After consultation made with the Company’s legal counsel, the directors consider that there is no legal restriction for the Group or the Company to apply for and obtain the land use right certificates and it should not lead to any significant adverse impact on the operations of the Group or the Company. The remaining lease period of leasehold land as at 31 December 2016 was as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Lease of between 10 to 50 years 1,624,859 948,526 9. GOODWILL RMB’000 Year ended 31 December 2015 and 2016 Opening net book amount 281,255 Additions — Impairment — Closing net book amount 281,255 At 31 December 2015 and 2016 Cost 281,255 Accumulated impairment — Net book amount 281,255 As at 31 December 2016 and 2015, the outstanding balance of goodwill arose from the excess of a purchase consideration paid by the Company over the aggregate fair values of the identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities of the Yangcheng Railway Business acquired by the Company. On 1 January 2009, the Group integrated the Yangcheng Railway Business with the Group’s railway business in order to improve the operation efficiency. As a result, the management considers that the Yangcheng Railway Business and the Group’s other railway business (collectively the “Combined Railway Business”) represents the lowest level of CGUs within the Group at which goodwill is monitored for internal management purposes. As a result, the goodwill balance has been allocated to the CGU comprising the Combined Railway Business.
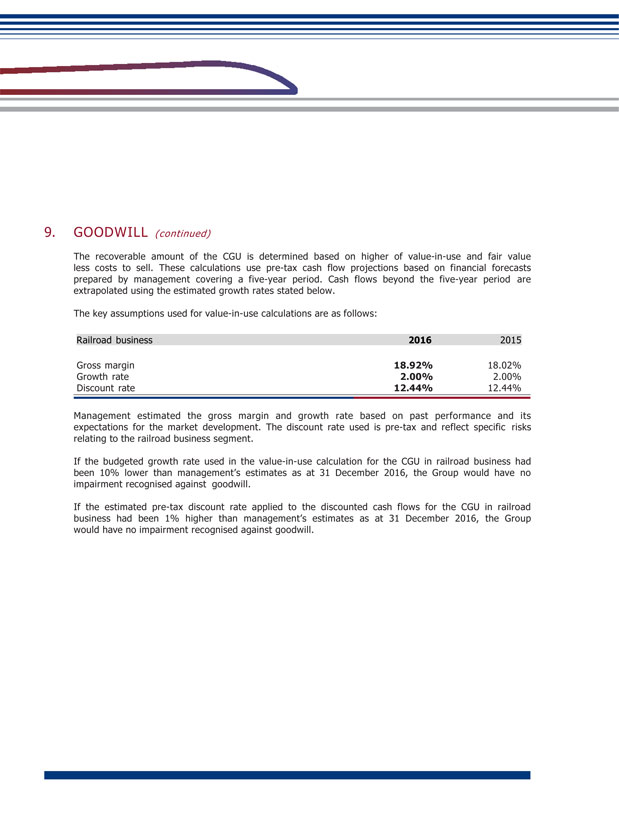
9. GOODWILL (continued) The recoverable amount of the CGU is determined based on higher of value-in-use and fair value less costs to sell. These calculations use pre-tax cash flow projections based on financial forecasts prepared by management covering a five-year period. Cash flows beyond the five-year period are extrapolated using the estimated growth rates stated below. The key assumptions used for value-in-use calculations are as follows: Railroad business 2016 2015 Gross margin 18.92% 18.02% Growth rate 2.00% 2.00% Discount rate 12.44% 12.44% Management estimated the gross margin and growth rate based on past performance and its expectations for the market development. The discount rate used is pre-tax and reflect specific risks relating to the railroad business segment. If the budgeted growth rate used in the value-in-use calculation for the CGU in railroad business had been 10% lower than management’s estimates as at 31 December 2016, the Group would have no impairment recognised against goodwill. If the estimated pre-tax discount rate applied to the discounted cash flows for the CGU in railroad business had been 1% higher than management’s estimates as at 31 December 2016, the Group would have no impairment recognised against goodwill.
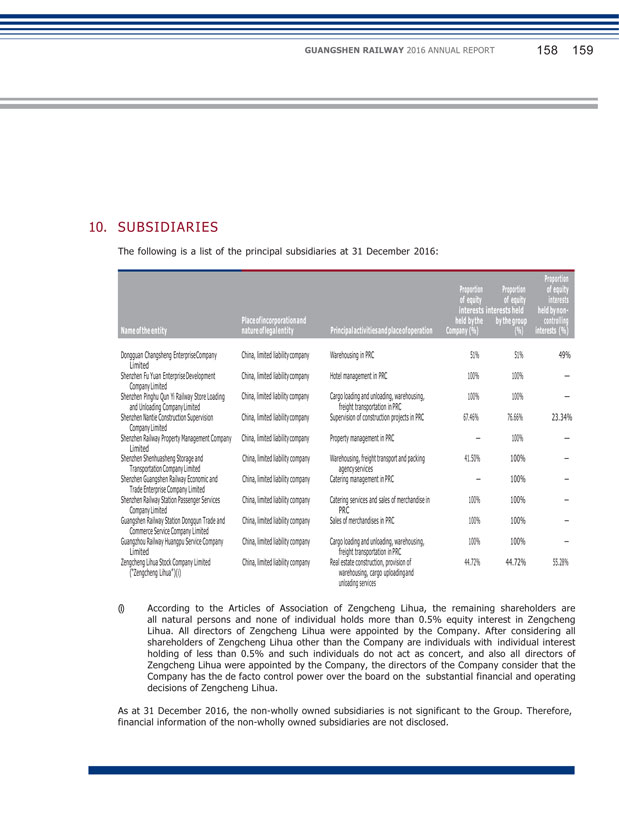
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 10. SUBSIDIARIES The following is a list of the principal subsidiaries at 31 December 2016: Proportion Proportion Proportion of equity of equity of equity interests interests interests held held by non-Place nature of of incorporationand legal entity held by the by the group controlling Name of the entity Principalactivitiesand placeof operation Company (%) (%) interests (%) Dongguan Changsheng Enterprise Company China, limited liability company Warehousing in PRC 51% 51% 49% Limited Shenzhen Fu Yuan Enterprise Development China, limited liability company Hotel management in PRC 100% 100% — Company Limited Shenzhen Pinghu Qun Yi Railway Store Loading China, limited liability company Cargo loading and unloading, warehousing, 100% 100% — and Unloading Company Limited freight transportation in PRC Shenzhen Nantie Construction Supervision China, limited liability company Supervision of construction projects in PRC 67.46% 76.66% 23.34% Company Limited Shenzhen Railway Property Management Company China, limited liability company Property management in PRC — 100% — Limited Shenzhen Transportation Shenhuasheng Company Storage Limited and China, limited liability company Warehousing, agency services freight transport and packing 41.50% 100% — Shenzhen Guangshen Railway Economic and China, limited liability company Catering management in PRC — 100% — Trade Enterprise Company Limited Shenzhen Railway Station Passenger Services China, limited liability company Catering services and sales of merchandise in 100% 100% — Company Limited PRC Guangshen Railway Station Dongqun Trade and China, limited liability company Sales of merchandises in PRC 100% 100% — Commerce Service Company Limited Guangzhou Railway Huangpu Service Company China, limited liability company Cargo loading and unloading, warehousing, 100% 100% — Limited freight transportation in PRC Zengcheng Lihua Stock Company Limited China, limited liability company Real estate construction, provision of 44.72% 44.72% 55.28% (“Zengcheng Lihua” )(i) warehousing, cargo uploading and unloading services (i) According to the Articles of Association of Zengcheng Lihua, the remaining shareholders are all natural persons and none of individual holds more than 0.5% equity interest in Zengcheng Lihua. All directors of Zengcheng Lihua were appointed by the Company. After considering all shareholders of Zengcheng Lihua other than the Company are individuals with individual interest holding of less than 0.5% and such individuals do not act as concert, and also all directors of Zengcheng Lihua were appointed by the Company, the directors of the Company consider that the Company has the de facto control power over the board on the substantial financial and operating decisions of Zengcheng Lihua. As at 31 December 2016, the non-wholly owned subsidiaries is not significant to the Group. Therefore, financial information of the non-wholly owned subsidiaries are not disclosed.
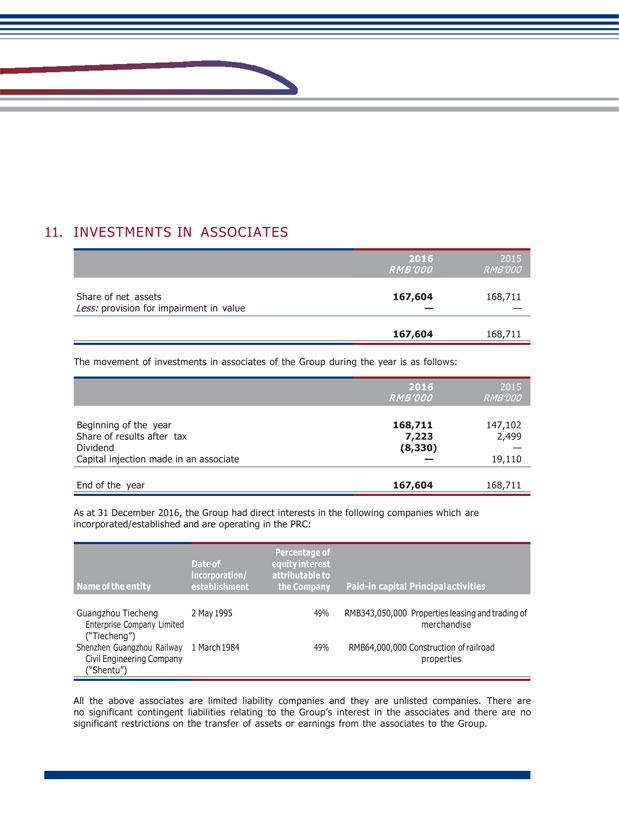
11. INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Share of net assets 167,604 168,711 Less: provision for impairment in value — — 167,604 168,711 The movement of investments in associates of the Group during the year is as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Beginning of the year 168,711 147,102 Share of results after tax 7,223 2,499 Dividend (8,330) — Capital injection made in an associate — 19,110 End of the year 167,604 168,711 As at 31 December 2016, the Group had direct interests in the following companies which are incorporated/established and are operating in the PRC: Percentage of Date of equity interest incorporation/ attributable to Name of the entity establishment the Company Paid-in capital Principal activities Guangzhou Tiecheng 2 May 1995 49% RMB343,050,000 Properties leasing and trading of Enterprise Company Limited merchandise (“Tiecheng”) Shenzhen Guangzhou Railway 1 March 1984 49% RMB64,000,000 Construction of railroad Civil Engineering Company properties (“Shentu”) All the above associates are limited liability companies and they are unlisted companies. There are no significant contingent liabilities relating to the Group’s interest in the associates and there are no significant restrictions on the transfer of assets or earnings from the associates to the Group.
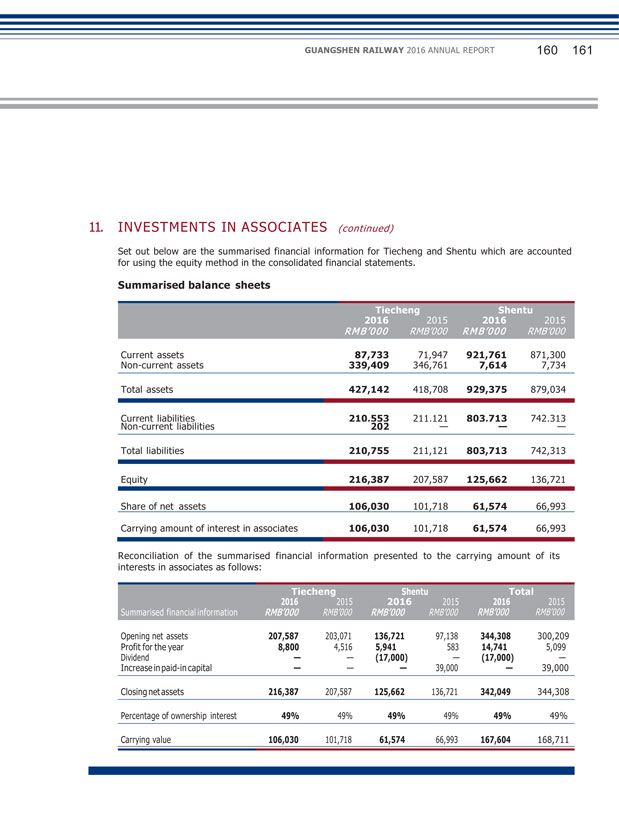
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 11. INVESTMENTS IN ASSOCIATES (continued) Set out below are the summarised financial information for Tiecheng and Shentu which are accounted for using the equity method in the consolidated financial statements. Summarised balance sheets 2016 Tiecheng 2015 2016 Shentu 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Current assets 87,733 71,947 921,761 871,300 Non-current assets 339,409 346,761 7,614 7,734 Total assets 427,142 418,708 929,375 879,034 Current liabilities 210,553 211,121 803,713 742,313 Non-current liabilities 202 — — — Total liabilities 210,755 211,121 803,713 742,313 Equity 216,387 207,587 125,662 136,721 Share of net assets 106,030 101,718 61,574 66,993 Carrying amount of interest in associates 106,030 101,718 61,574 66,993 Reconciliation of the summarised financial information presented to the carrying amount of its interests in associates as follows: 2016 Tiecheng 2015 2016 Shentu 2016Total 2015 2015 Summarised financial information RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Opening net assets 207,587 203,071 136,721 97,138 344,308 300,209 Profit for the year 8,800 4,516 5,941 583 14,741 5,099 Dividend — — (17,000) — (17,000) — Increase in paid-in capital — — — 39,000 — 39,000 Closing net assets 216,387 207,587 125,662 136,721 342,049 344,308 Percentage of ownership interest 49% 49% 49% 49% 49% 49% Carrying value 106,030 101,718 61,574 66,993 167,604 168,711
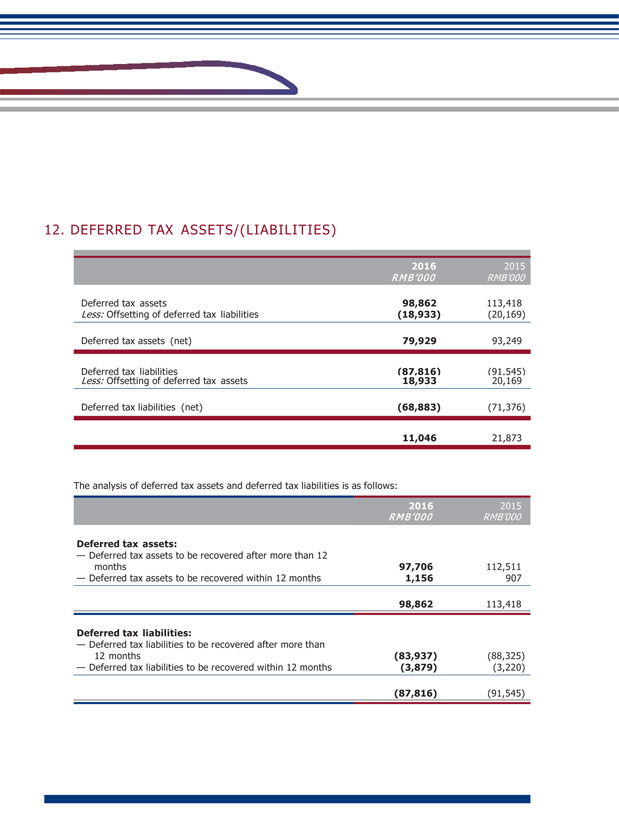
2. DEFERRED TAX ASSETS/(LIABILITIES) 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Deferred tax assets 98,862 113,418 Less: Offsetting of deferred tax liabilities (18,933) (20,169) Deferred tax assets (net) 79,929 93,249 Deferred Less: Offsetting tax liabilities of deferred tax assets (87,816) 18,933 (91,545) 20,169 Deferred tax liabilities (net) (68,883) (71,376) 11,046 21,873 The analysis of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities is as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Deferred tax assets: — Deferred tax assets to be recovered after more than 12 months 97,706 112,511 — Deferred tax assets to be recovered within 12 months 1,156 907 98,862 113,418 Deferred tax liabilities: — Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered after more than 12 months (83,937) (88,325) — Deferred tax liabilities to be recovered within 12 months (3,879) (3,220) (87,816) (91,545)
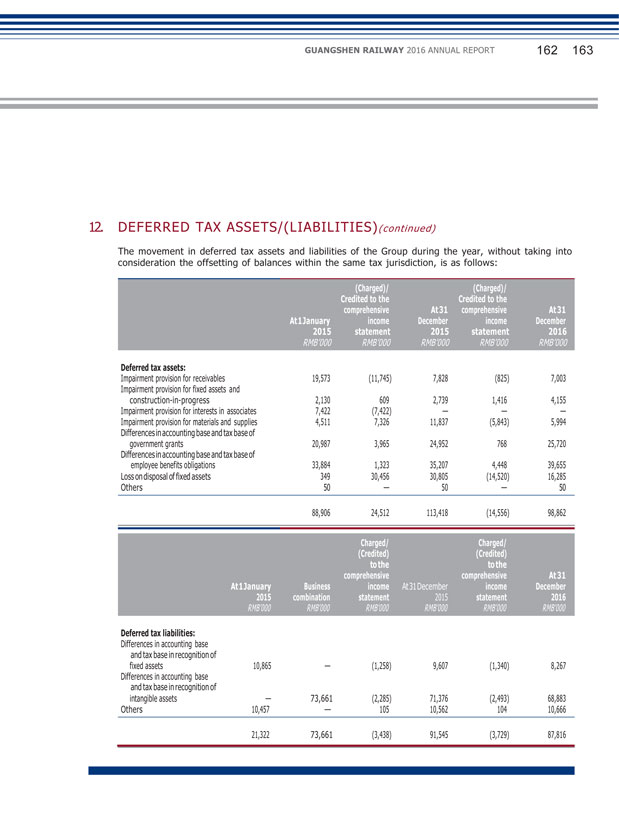
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 12. DEFERRED TAX ASSETS/(LIABILITIES)(cont inued) The movement in deferred tax assets and liabilities of the Group during the year, without taking into consideration the offsetting of balances within the same tax jurisdiction, is as follows: (Charged)/ (Charged)/ Credited to the Credited to the comprehensive At 31 comprehensive At 31 At 1 January income December income December 2015 statement 2015 statement 2016 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Deferred tax assets: Impairment provision for receivables 19,573 (11,745) 7,828 (825) 7,003 Impairment provision for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 2,130 609 2,739 1,416 4,155 Impairment provision for interests in associates 7,422 (7,422) — — — Impairment provision for materials and supplies 4,511 7,326 11,837 (5,843) 5,994 Differences in accounting base and tax base of government grants 20,987 3,965 24,952 768 25,720 Differences in accounting base and tax base of employee benefits obligations 33,884 1,323 35,207 4,448 39,655 Loss on disposal of fixed assets 349 30,456 30,805 (14,520) 16,285 Others 50 — 50 — 50 88,906 24,512 113,418 (14,556) 98,862 Charged/ Charged/ (Credited) (Credited) to the to the comprehensive comprehensive At 31 At 1 January Business income At 31 December income December 2015 combination statement 2015 statement 2016 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Deferred tax liabilities: Differences in accounting base and tax base in recognition of fixed assets 10,865 — (1,258) 9,607 (1,340) 8,267 Differences in accounting base and tax base in recognition of intangible assets — 73,661 (2,285) 71,376 (2,493) 68,883 Others 10,457 — 105 10,562 104 10,666 21,322 73,661 (3,438) 91,545 (3,729) 87,816
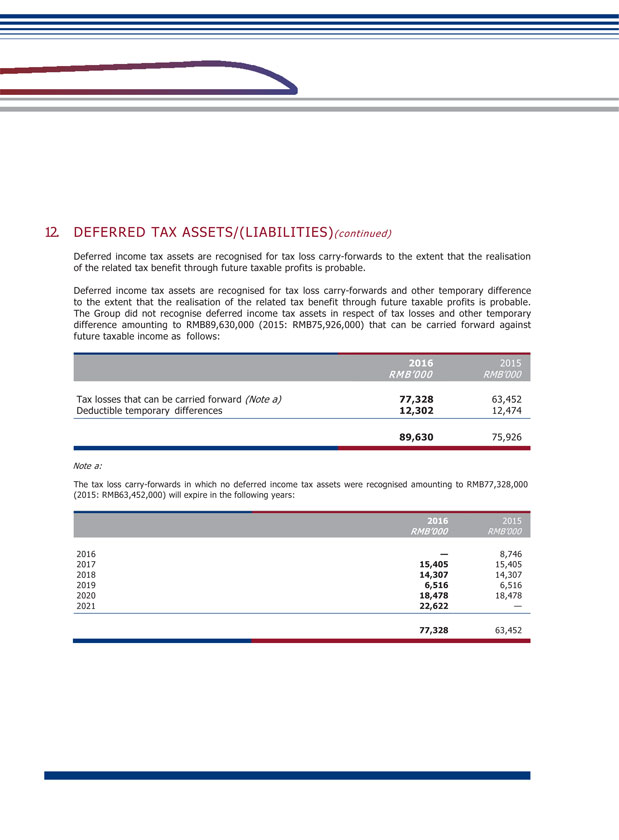
12. DEFERRED TAX ASSETS/(LIABILITIES)(cont inued) Deferred income tax assets are recognised for tax loss carry-forwards to the extent that the realisation of the related tax benefit through future taxable profits is probable. Deferred income tax assets are recognised for tax loss carry-forwards and other temporary difference to the extent that the realisation of the related tax benefit through future taxable profits is probable. The Group did not recognise deferred income tax assets in respect of tax losses and other temporary difference amounting to RMB89,630,000 (2015: RMB75,926,000) that can be carried forward against future taxable income as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Tax losses that can be carried forward (Note a) 77,328 63,452 Deductible temporary differences 12,302 12,474 89,630 75,926 Note a: The tax loss carry-forwards in which no deferred income tax assets were recognised amounting to RMB77,328,000 (2015: RMB63,452,000) will expire in the following years: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 2016 — 8,746 2017 15,405 15,405 2018 14,307 14,307 2019 6,516 6,516 2020 18,478 18,478 2021 22,622 — 77,328 63,452
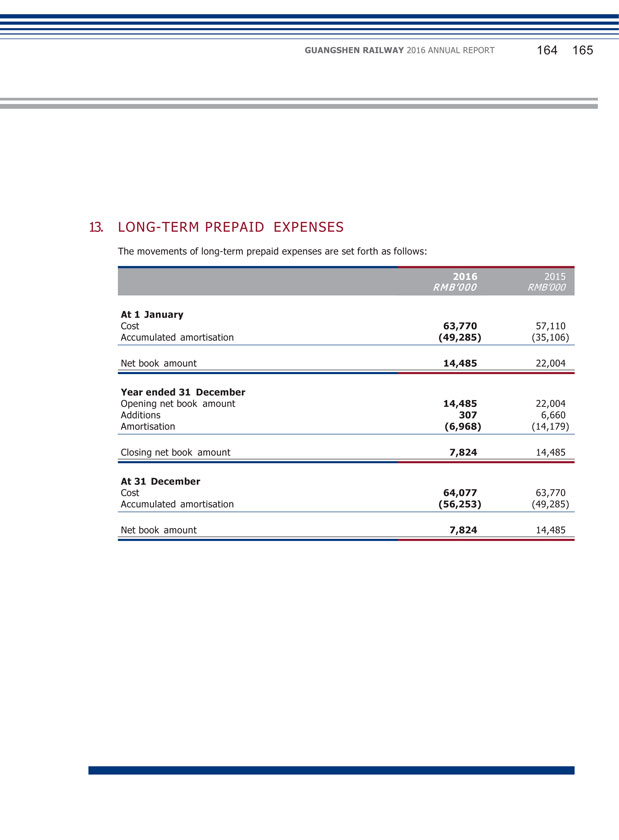
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 13. LONG-TERM PREPAID EXPENSES The movements of long-term prepaid expenses are set forth as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 At 1 January Cost 63,770 57,110 Accumulated amortisation (49,285) (35,106) Net book amount 14,485 22,004 Year ended 31 December Opening net book amount 14,485 22,004 Additions 307 6,660 Amortisation (6,968) (14,179) Closing net book amount 7,824 14,485 At 31 December Cost 64,077 63,770 Accumulated amortisation (56,253) (49,285) Net book amount 7,824 14,485
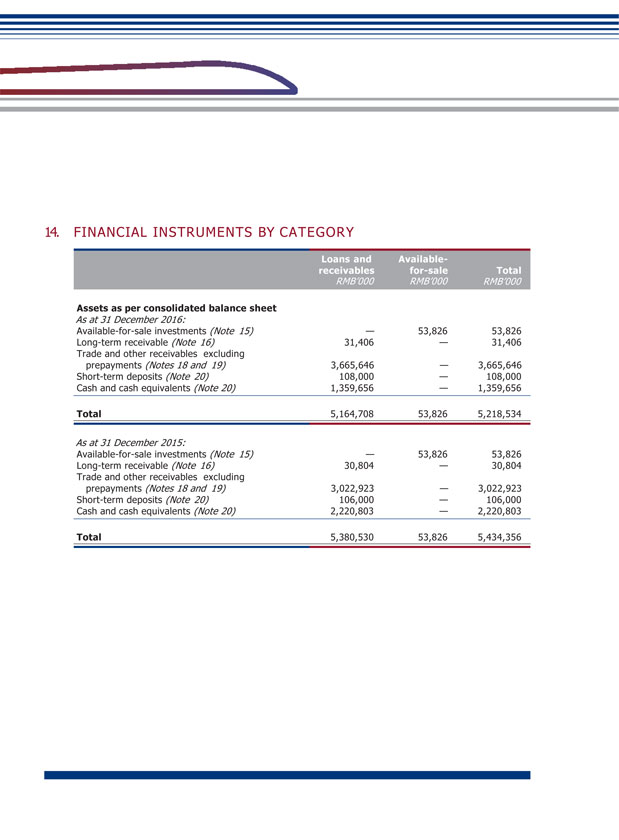
14. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS BY CATEGORY Loans and Available-receivables for-sale Total RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Assets as per consolidated balance sheet As at 31 December 2016: Available-for-sale investments (Note 15) — 53,826 53,826 Long-term receivable (Note 16) 31,406 — 31,406 Trade and other receivables excluding prepayments (Notes 18 and 19) 3,665,646 — 3,665,646 Short-term deposits (Note 20) 108,000 — 108,000 Cash and cash equivalents (Note 20) 1,359,656 — 1,359,656 Total 5,164,708 53,826 5,218,534 As at 31 December 2015: Available-for-sale investments (Note 15) — 53,826 53,826 Long-term receivable (Note 16) 30,804 — 30,804 Trade and other receivables excluding prepayments (Notes 18 and 19) 3,022,923 — 3,022,923 Short-term deposits (Note 20) 106,000 — 106,000 Cash and cash equivalents (Note 20) 2,220,803 — 2,220,803 Total 5,380,530 53,826 5,434,356
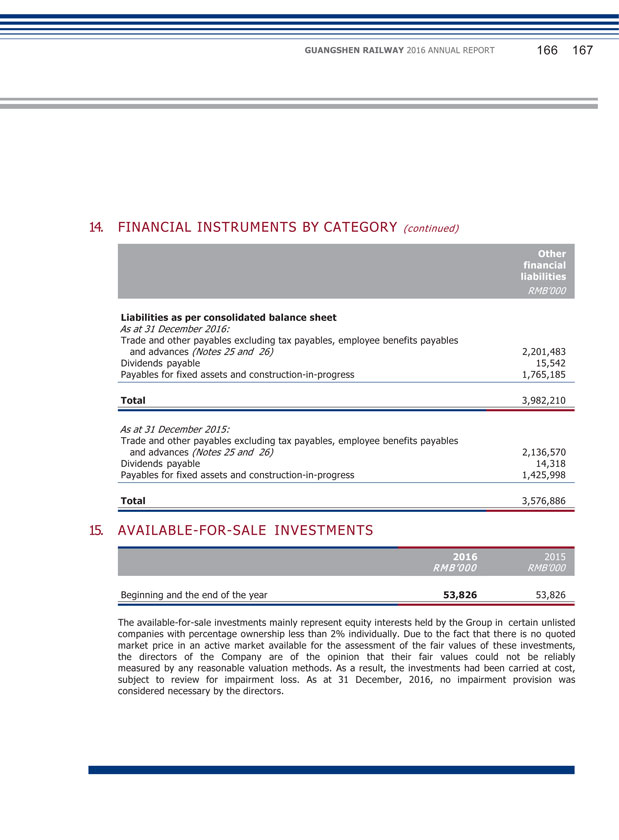
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 14. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS BY CATEGORY (continued) Other financial liabilities RMB’000 Liabilities as per consolidated balance sheet As at 31 December 2016: Trade and other payables excluding tax payables, employee benefits payables and advances (Notes 25 and 26) 2,201,483 Dividends payable 15,542 Payables for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 1,765,185 Total 3,982,210 As at 31 December 2015: Trade and other payables excluding tax payables, employee benefits payables and advances (Notes 25 and 26) 2,136,570 Dividends payable 14,318 Payables for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 1,425,998 Total 3,576,886 15. AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE INVESTMENTS 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Beginning and the end of the year 53,826 53,826 The available-for-sale investments mainly represent equity interests held by the Group in certain unlisted companies with percentage ownership less than 2% individually. Due to the fact that there is no quoted market price in an active market available for the assessment of the fair values of these investments, the directors of the Company are of the opinion that their fair values could not be reliably measured by any reasonable valuation methods. As a result, the investments had been carried at cost, subject to review for impairment loss. As at 31 December, 2016, no impairment provision was considered necessary by the directors.
16. LONG-TERM RECEIVABLE The long-term receivable balance represents freight service fees receivable from a third party customer which was acquired from Yangcheng Railway Business. On the acquisition date of Yangcheng Railway Business, it was remeasured at its then fair value, which was assessed by the discounted cash flow method by making reference to the repayment schedule agreed by both parties. The balance is subsequently carried at amortised cost using an average effective interest rate of 6.54%. The balance approximated its fair value as at 31 December 2016. 17. MATERIALS AND SUPPLIES 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Raw materials 184,520 156,441 Reusable rail-line track materials 79,311 93,134 Accessories 67,236 55,264 Retailing consumables 1,540 2,217 332,607 307,056 The costs of materials and supplies consumed by the Group during the year were recognised as “operating expenses” in the amount of RMB1,697,166,000 (2015: RMB1,565,648,000). As at 31 December 2016, the balance of the provision for writing down the materials and supplies to their net realizable values was approximately RMB23,976,000 (2015: RMB47,348,000). During the year, no additional provision had been made and RMB18,163,000 was written off due to the reusable rail-line track materials disposal (2015: RMB34,792,000).
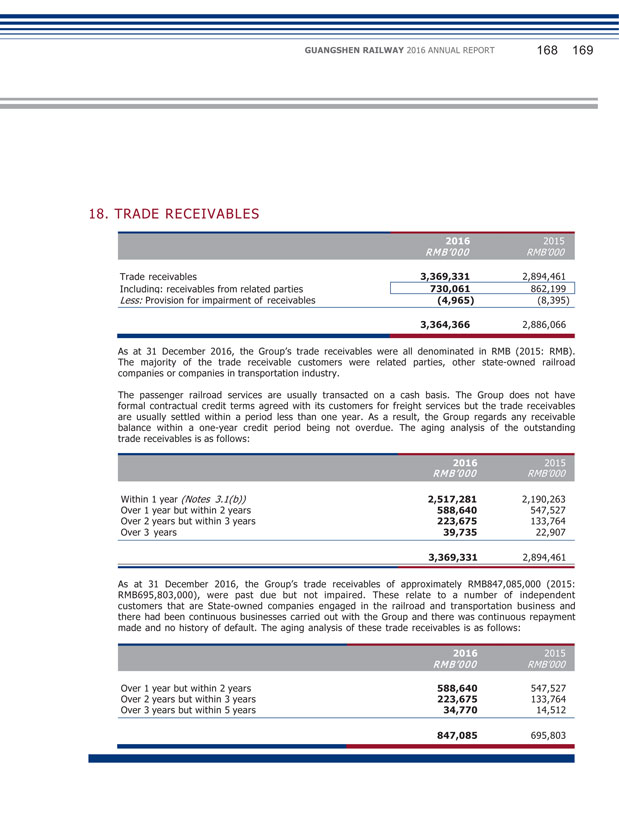
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 18. TRADE RECEIVABLES 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Trade receivables 3,369,331 2,894,461 Including: receivables from related parties 730,061 862,199 Less: Provision for impairment of receivables (4,965) (8,395) 3,364,366 2,886,066 As at 31 December 2016, the Group’s trade receivables were all denominated in RMB (2015: RMB). The majority of the trade receivable customers were related parties, other state-owned railroad companies or companies in transportation industry. The passenger railroad services are usually transacted on a cash basis. The Group does not have formal contractual credit terms agreed with its customers for freight services but the trade receivables are usually settled within a period less than one year. As a result, the Group regards any receivable balance within a one-year credit period being not overdue. The aging analysis of the outstanding trade receivables is as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Within 1 year (Notes 3.1(b)) 2,517,281 2,190,263 Over 1 year but within 2 years 588,640 547,527 Over 2 years but within 3 years 223,675 133,764 Over 3 years 39,735 22,907 3,369,331 2,894,461 As at 31 December 2016, the Group’s trade receivables of approximately RMB847,085,000 (2015: RMB695,803,000), were past due but not impaired. These relate to a number of independent customers that are State-owned companies engaged in the railroad and transportation business and there had been continuous businesses carried out with the Group and there was continuous repayment made and no history of default. The aging analysis of these trade receivables is as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Over 1 year but within 2 years 588,640 547,527 Over 2 years but within 3 years 223,675 133,764 Over 3 years but within 5 years 34,770 14,512 847,085 695,803

18. TRADE RECEIVABLES (continued) As at 31 December 2016, the Group’s trade receivables of approximately RMB4,965,000 (2015: RMB8,395,000), had been impaired and provided for. The impaired receivable balances were mainly related to the provision of freight transportation services. The related customers were in significant financial difficulties. The aging analysis of these receivables is as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Over 5 years 4,965 8,395 Movements on the provision for impairment of trade receivables are as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 At 1 January 8,395 7,003 Provision for impairment loss 6 3,305 Reversal — (127) Written-off (3,436) (1,786) At 31 December 4,965 8,395 The creation and release of provision for impaired receivables have been included in operating expenses in the comprehensive income statement. Amounts charged to the allowance account are generally written off against the gross accounts receivable balances when there is no expectation of recovering additional cash. The maximum exposure to credit risk at the reporting date is the carrying value mentioned above. The Group does not hold any collateral as security.
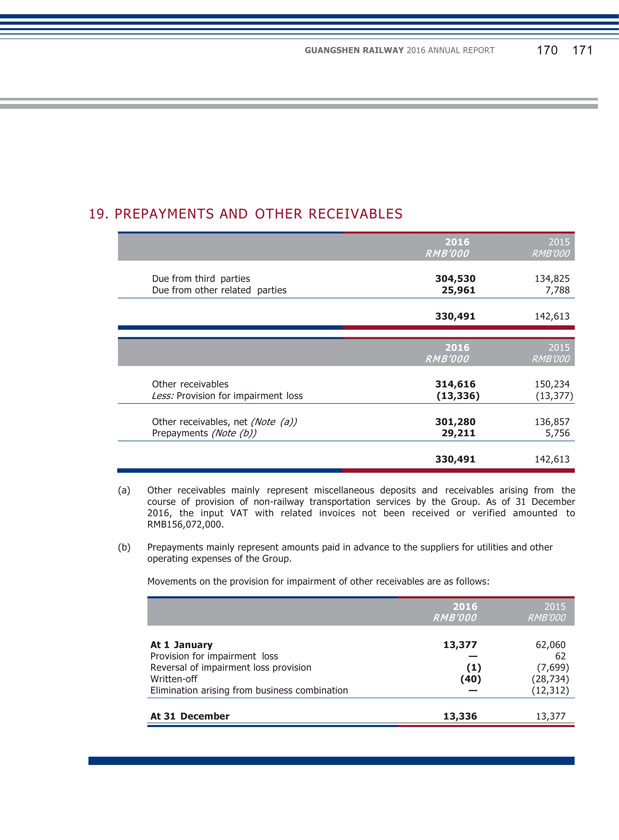
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 19. PREPAYMENTS AND OTHER RECEIVABLES 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Due from third parties 304,530 134,825 Due from other related parties 25,961 7,788 330,491 142,613 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Other receivables 314,616 150,234 Less: Provision for impairment loss (13,336) (13,377) Other receivables, net (Note (a)) 301,280 136,857 Prepayments (Note (b)) 29,211 5,756 330,491 142,613 (a) Other receivables mainly represent miscellaneous deposits and receivables arising from the course of provision of non-railway transportation services by the Group. As of 31 December 2016, the input VAT with related invoices not been received or verified amounted to RMB156,072,000. (b) Prepayments mainly represent amounts paid in advance to the suppliers for utilities and other operating expenses of the Group. Movements on the provision for impairment of other receivables are as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 At 1 January 13,377 62,060 Provision for impairment loss — 62 Reversal of impairment loss provision (1) (7,699) Written-off (40) (28,734) Elimination arising from business combination — (12,312) At 31 December 13,336 13,377
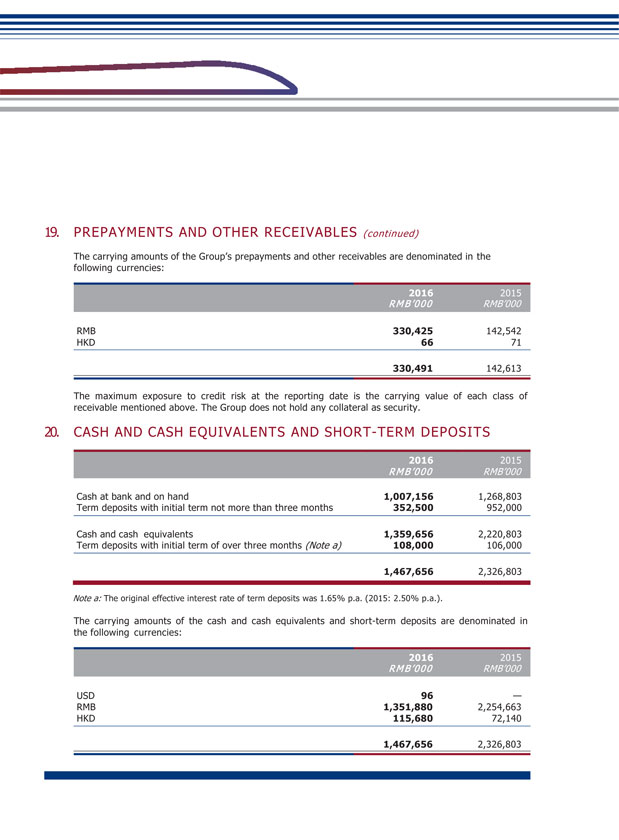
19. PREPAYMENTS AND OTHER RECEIVABLES (continued) The carrying amounts of the Group’s prepayments and other receivables are denominated in the following currencies: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB 330,425 142,542 HKD 66 71 330,491 142,613 The maximum exposure to credit risk at the reporting date is the carrying value of each class of receivable mentioned above. The Group does not hold any collateral as security. 20. CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS AND SHORT-TERM DEPOSITS 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Cash at bank and on hand 1,007,156 1,268,803 Term deposits with initial term not more than three months 352,500 952,000 Cash and cash equivalents 1,359,656 2,220,803 Term deposits with initial term of over three months (Note a) 108,000 106,000 1,467,656 2,326,803 Note a: The original effective interest rate of term deposits was 1.65% p.a. (2015: 2.50% p.a.). The carrying amounts of the cash and cash equivalents and short-term deposits are denominated in the following currencies: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 USD 96 — RMB 1,351,880 2,254,663 HKD 115,680 72,140 1,467,656 2,326,803
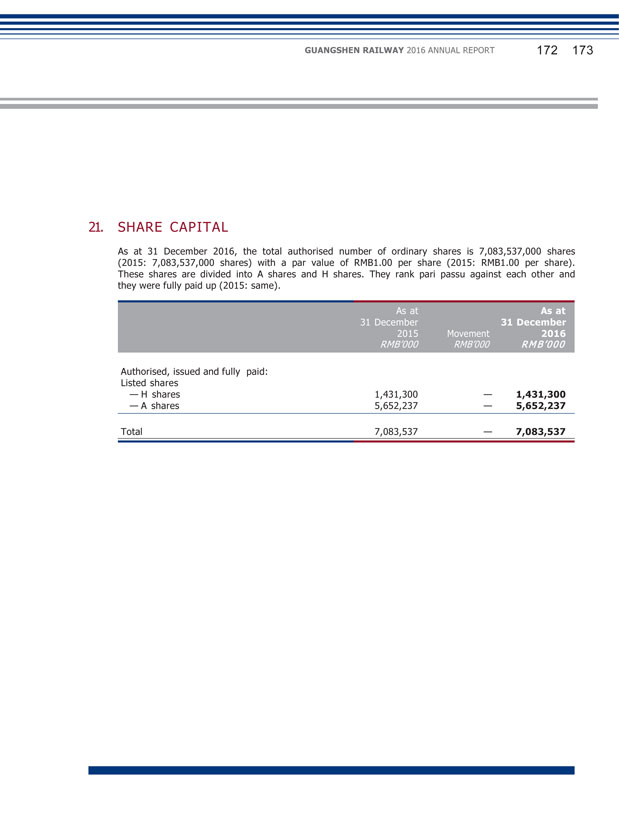
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 21. SHARE CAPITAL As at 31 December 2016, the total authorised number of ordinary shares is 7,083,537,000 shares (2015: 7,083,537,000 shares) with a par value of RMB1.00 per share (2015: RMB1.00 per share). These shares are divided into A shares and H shares. They rank pari passu against each other and they were fully paid up (2015: same). As at As at 31 December 31 December 2015 Movement 2016 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Authorised, issued and fully paid: Listed shares — H shares 1,431,300 — 1,431,300 — A shares 5,652,237 — 5,652,237 Total 7,083,537 — 7,083,537

22. RESERVES According to the provisions of the articles of association of the Company, the Company shall first set aside 10% of its profit after tax attributable to shareholders as indicated in the Company’s statutory financial statements for the statutory surplus reserve (except where the reserve has reached 50% of the Company’s registered share capital) in each year. The Company may also make appropriations from its profit attributable to shareholders to a discretionary surplus reserve, provided that it is approved by a resolution passed in a shareholders’ general meeting. These reserves cannot be used for purposes other than those for which they are created and are not distributable as cash dividends without the prior approval obtained from the shareholders in a shareholders’ general meeting under specific circumstances. When the statutory surplus reserve is not sufficient to make good for any losses of the Company in previous years, the current year profit attributable to shareholders shall be used to make good the losses before any allocations are set aside for the statutory surplus reserve. The statutory surplus reserve, the discretionary surplus reserve and the share premium account could be converted into share capital of the Company provided it is approved by a resolution passed in a shareholders’ general meeting with the provision that the ending balance of the statutory surplus reserve does not fall below 25% of the registered share capital amount. The Company may either allot newly created shares to the shareholders at the same proportion of the existing number of shares held by these shareholders, or it may increase the par value of each share. For the year ended 31 December 2016 and 2015, the directors proposed the following appropriations to reserves of the Company: 2016 2016 2015 2015 Percentage RMB’000 Percentage RMB’000 Statutory surplus reserve 10% 117,050 10% 111,760 In accordance with the provisions of the articles of association of the Company, the profit after appropriation to reserves and available for distribution to shareholders shall be the lower of the retained earnings determined under (a) PRC GAAP or (b) IFRS. Due to the fact that the statutory financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with PRC GAAP, the retained earnings so reported may be different from those reported in the statement of changes in shareholders’ equity prepared under IFRS contained in these financial statements. The main difference between the retained earnings of the Company determined under PRC GAAP and those determined under IFRS was relating to accounting policies in respect of investment in associates adopted under PRC GAAP and IFRS.
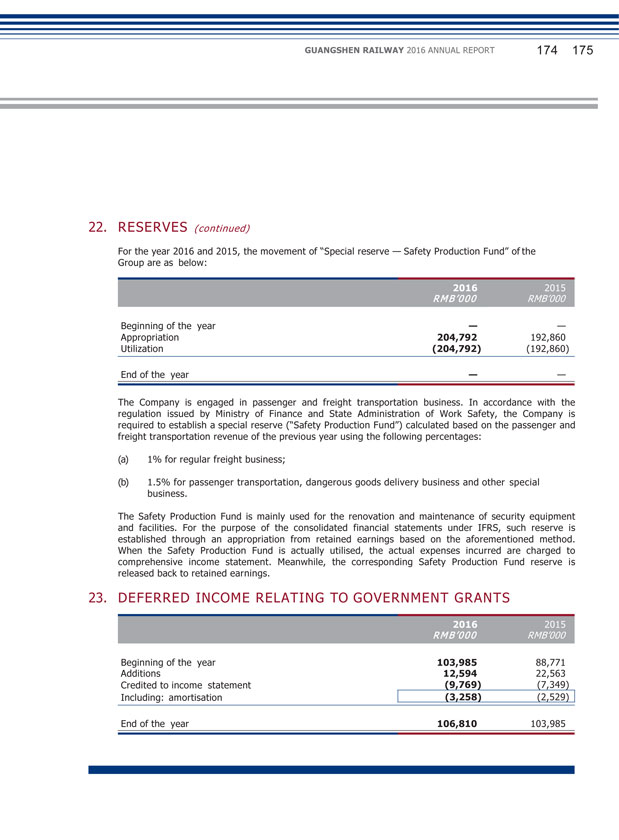
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 22. RESERVES (continued) For the year 2016 and 2015, the movement of “Special reserve — Safety Production Fund” of the Group are as below: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Beginning of the year — — Appropriation 204,792 192,860 Utilization (204,792) (192,860) End of the year — — The Company is engaged in passenger and freight transportation business. In accordance with the regulation issued by Ministry of Finance and State Administration of Work Safety, the Company is required to establish a special reserve (“Safety Production Fund”) calculated based on the passenger and freight transportation revenue of the previous year using the following percentages: (a) 1% for regular freight business; (b) 1.5% for passenger transportation, dangerous goods delivery business and other special business. The Safety Production Fund is mainly used for the renovation and maintenance of security equipment and facilities. For the purpose of the consolidated financial statements under IFRS, such reserve is established through an appropriation from retained earnings based on the aforementioned method. When the Safety Production Fund is actually utilised, the actual expenses incurred are charged to comprehensive income statement. Meanwhile, the corresponding Safety Production Fund reserve is released back to retained earnings. 23. DEFERRED INCOME RELATING TO GOVERNMENT GRANTS 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Beginning of the year 103,985 88,771 Additions 12,594 22,563 Credited to income statement (9,769) (7,349) Including: amortisation (3,258) (2,529) End of the year 106,810 103,985
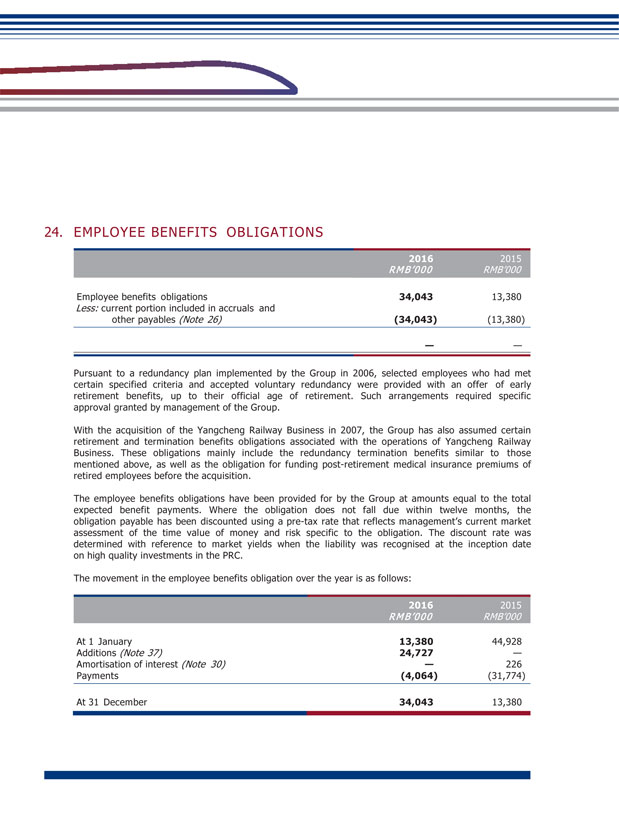
24. EMPLOYEE BENEFITS OBLIGATIONS 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Employee benefits obligations 34,043 13,380 Less: current portion included in accruals and other payables (Note 26) (34,043) (13,380) — — Pursuant to a redundancy plan implemented by the Group in 2006, selected employees who had met certain specified criteria and accepted voluntary redundancy were provided with an offer of early retirement benefits, up to their official age of retirement. Such arrangements required specific approval granted by management of the Group. With the acquisition of the Yangcheng Railway Business in 2007, the Group has also assumed certain retirement and termination benefits obligations associated with the operations of Yangcheng Railway Business. These obligations mainly include the redundancy termination benefits similar to those mentioned above, as well as the obligation for funding post-retirement medical insurance premiums of retired employees before the acquisition. The employee benefits obligations have been provided for by the Group at amounts equal to the total expected benefit payments. Where the obligation does not fall due within twelve months, the obligation payable has been discounted using a pre-tax rate that reflects management’s current market assessment of the time value of money and risk specific to the obligation. The discount rate was determined with reference to market yields when the liability was recognised at the inception date on high quality investments in the PRC. The movement in the employee benefits obligation over the year is as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 At 1 January 13,380 44,928 Additions (Note 37) 24,727 — Amortisation of interest (Note 30) — 226 Payments (4,064) (31,774) At 31 December 34,043 13,380
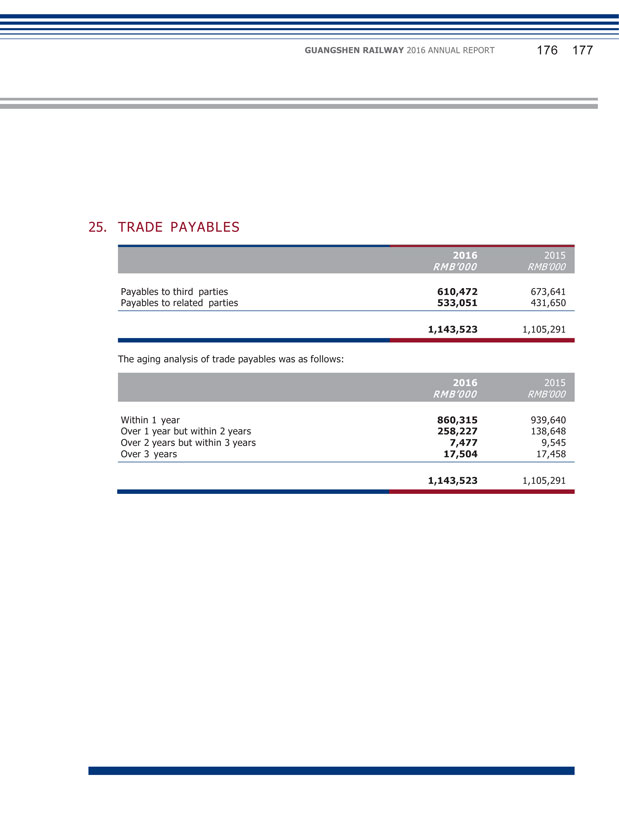
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 25. TRADE PAYABLES 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Payables to third parties 610,472 673,641 Payables to related parties 533,051 431,650 1,143,523 1,105,291 The aging analysis of trade payables was as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Within 1 year 860,315 939,640 Over 1 year but within 2 years 258,227 138,648 Over 2 years but within 3 years 7,477 9,545 Over 3 years 17,504 17,458 1,143,523 1,105,291
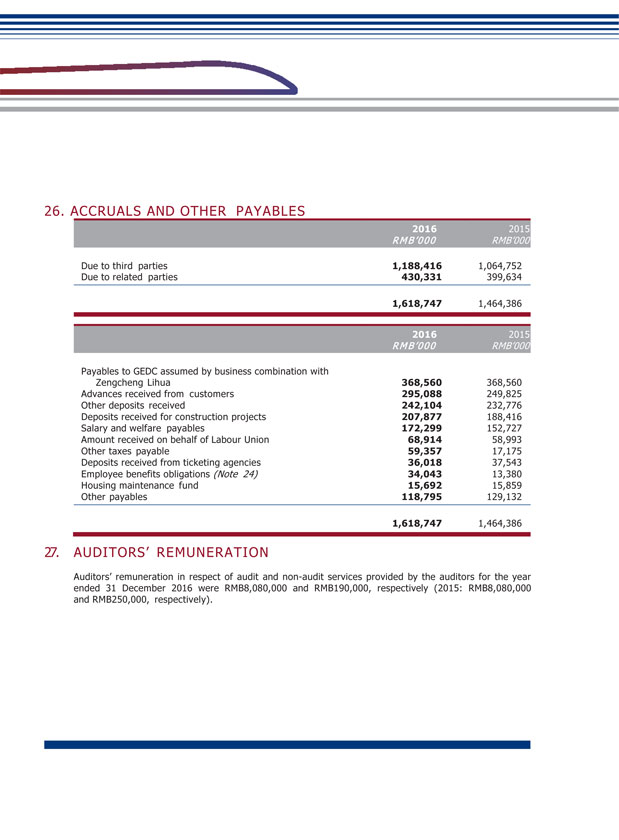
26. ACCRUALS AND OTHER PAYABLES 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Due to third parties 1,188,416 1,064,752 Due to related parties 430,331 399,634 1,618,747 1,464,386 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Payables to GEDC assumed by business combination with Zengcheng Lihua 368,560 368,560 Advances received from customers 295,088 249,825 Other deposits received 242,104 232,776 Deposits received for construction projects 207,877 188,416 Salary and welfare payables 172,299 152,727 Amount received on behalf of Labour Union 68,914 58,993 Other taxes payable 59,357 17,175 Deposits received from ticketing agencies 36,018 37,543 Employee benefits obligations (Note 24) 34,043 13,380 Housing maintenance fund 15,692 15,859 Other payables 118,795 129,132 1,618,747 1,464,386 27. AUDITORS’ REMUNERATION Auditors’ remuneration in respect of audit and non-audit services provided by the auditors for the year ended 31 December 2016 were RMB8,080,000 and RMB190,000, respectively (2015: RMB8,080,000 and RMB250,000, respectively).
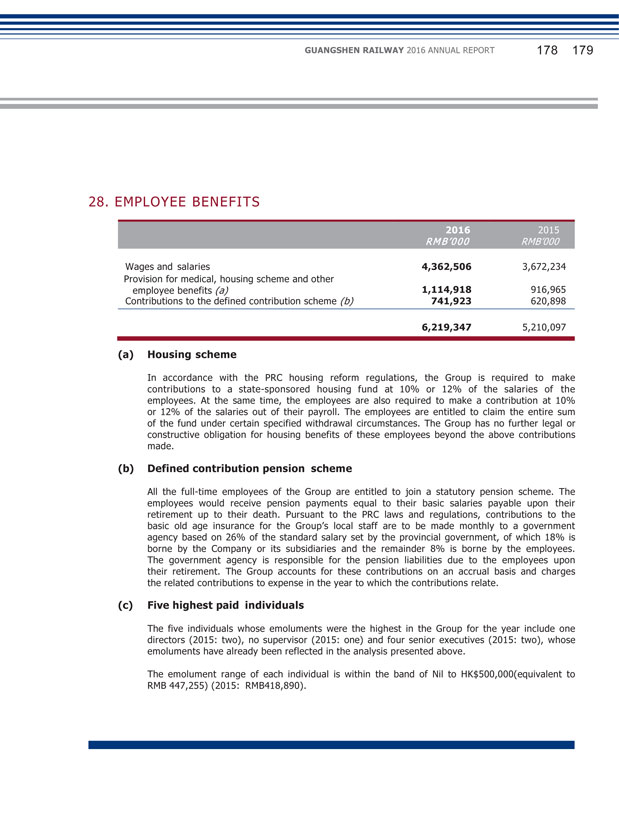
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 28. EMPLOYEE BENEFITS 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Wages and salaries 4,362,506 3,672,234 Provision for medical, housing scheme and other employee benefits (a) 1,114,918 916,965 Contributions to the defined contribution scheme (b) 741,923 620,898 6,219,347 5,210,097 (a) Housing scheme In accordance with the PRC housing reform regulations, the Group is required to make contributions to a state-sponsored housing fund at 10% or 12% of the salaries of the employees. At the same time, the employees are also required to make a contribution at 10% or 12% of the salaries out of their payroll. The employees are entitled to claim the entire sum of the fund under certain specified withdrawal circumstances. The Group has no further legal or constructive obligation for housing benefits of these employees beyond the above contributions made. (b) Defined contribution pension scheme All the full-time employees of the Group are entitled to join a statutory pension scheme. The employees would receive pension payments equal to their basic salaries payable upon their retirement up to their death. Pursuant to the PRC laws and regulations, contributions to the basic old age insurance for the Group’s local staff are to be made monthly to a government agency based on 26% of the standard salary set by the provincial government, of which 18% is borne by the Company or its subsidiaries and the remainder 8% is borne by the employees. The government agency is responsible for the pension liabilities due to the employees upon their retirement. The Group accounts for these contributions on an accrual basis and charges the related contributions to expense in the year to which the contributions relate. (c) Five highest paid individuals The five individuals whose emoluments were the highest in the Group for the year include one directors (2015: two), no supervisor (2015: one) and four senior executives (2015: two), whose emoluments have already been reflected in the analysis presented above. The emolument range of each individual is within the band of Nil to HK$500,000(equivalent to RMB 447,255) (2015: RMB418,890).
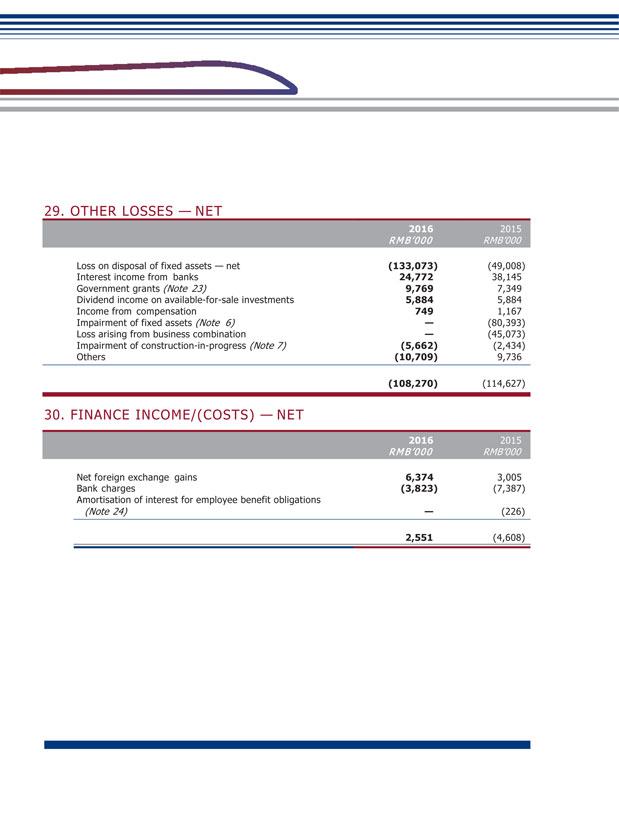
29. OTHER LOSSES — NET 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Loss on disposal of fixed assets — net (133,073) (49,008) Interest income from banks 24,772 38,145 Government grants (Note 23) 9,769 7,349 Dividend income on available-for-sale investments 5,884 5,884 Income from compensation 749 1,167 Impairment of fixed assets (Note 6) — (80,393) Loss arising from business combination — (45,073) Impairment of construction-in-progress (Note 7) (5,662) (2,434) Others (10,709) 9,736 (108,270) (114,627) 30. FINANCE INCOME/(COSTS) — NET 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Net foreign exchange gains 6,374 3,005 Bank charges (3,823) (7,387) Amortisation of interest for employee benefit obligations (Note 24) — (226) 2,551 (4,608)
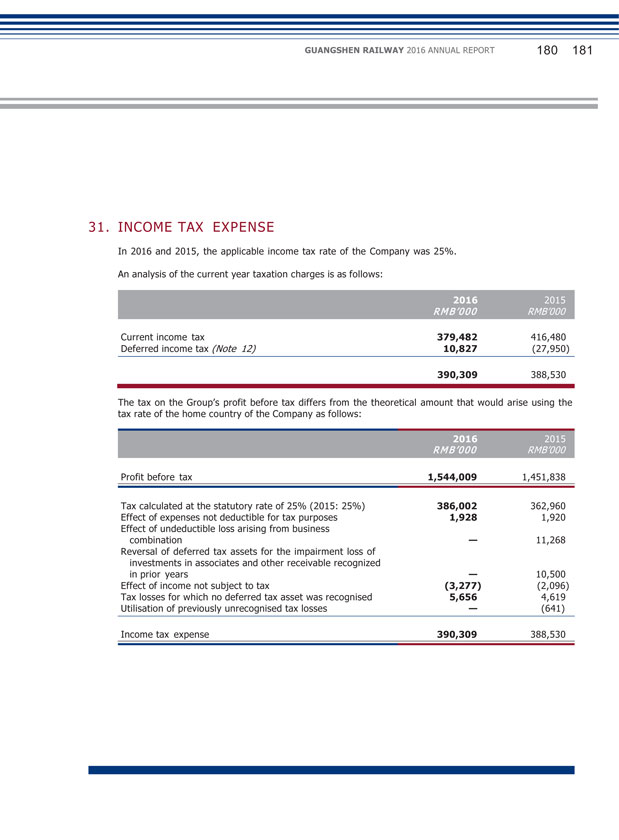
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 31. INCOME TAX EXPENSE In 2016 and 2015, the applicable income tax rate of the Company was 25%. An analysis of the current year taxation charges is as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Current income tax 379,482 416,480 Deferred income tax (Note 12) 10,827 (27,950) 390,309 388,530 The tax on the Group’s profit before tax differs from the theoretical amount that would arise using the tax rate of the home country of the Company as follows: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Profit before tax 1,544,009 1,451,838 Tax calculated at the statutory rate of 25% (2015: 25%) 386,002 362,960 Effect of expenses not deductible for tax purposes 1,928 1,920 Effect of undeductible loss arising from business combination — 11,268 Reversal of deferred tax assets for the impairment loss of investments in associates and other receivable recognized in prior years — 10,500 Effect of income not subject to tax (3,277) (2,096) Tax losses for which no deferred tax asset was recognised 5,656 4,619 Utilisation of previously unrecognised tax losses — (641) Income tax expense 390,309 388,530
32. EARNINGS PER SHARE The calculation of basic earnings per share is based on the net profit for the year attributable to equity holders of approximately RMB1,158,253,000 (2015: RMB1,070,822,000), divided by the weighted average number of ordinary shares outstanding during the year of 7,083,537,000 shares (2015: 7,083,537,000 shares). There were no dilutive potential ordinary shares during both years. 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Profit attributable to owners of the Company 1,158,253 1,070,822 Weighted average number of ordinary shares in issue 7,083,537 7,083,537 Basic and diluted earnings per share RMB 0.16 RMB0.15 33. DIVIDENDS 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Final, proposed, of RMB0.08 (2015: RMB0.08) per ordinary share 566,683 566,683 At the meeting of the directors held on 29 March 2017, the directors proposed a final dividend of RMB0.08per ordinary share for the year ended 31 December 2016, which is subject to the approval by the shareholders in general meeting. This proposed dividend was not reflected as a dividend payable in the financial statements as at 31 December 2016.
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 34. CASH FLOW GENERATED FROM OPERATIONS (a) Reconciliation from profit before income tax to cash generated from operations: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Profit before income tax: 1,544,009 1,451,838 Adjustments for: Depreciation of fixed assets (Note 6) 1,518,970 1,411,742 Impairment of fixed assets (Note 6) — 80,393 Impairment of construction-in-progress (Note 7) 5,662 2,434 Loss arising from business combination — 45,073 (Reversal) of/Provision of impairment of materials and supplies (Note 17) (5,209) 64,096 Amortisation of leasehold land payments (Note 8) 38,670 28,413 Loss on disposal of fixed assets (Note 29) 133,073 49,008 Amortisation of long-term prepaid expenses (Note 13) 6,968 14,179 Amortisation of interest for employee benefit obligations (Note 24) — 226 Share of results of associates (Note 11) (7,223) (2,499) Dividends income on available-for-sale investments (Note 29) (5,884) (5,884) Provision for/(reversal of) impairment of receivables 5 (4,459) Amortisation of government grants related to fixed assets (Note 23) (3,258) (2,529) Interest income (4,353) (5,502) Operating profit before working capital changes 3,221,430 3,126,529 Increase in trade receivables (1,034,064) (553,980) Decrease in materials and supplies 14,432 34,843 (Increase)/decrease in prepayments and other receivables (47,594) 83,553 Decrease in long-term receivable 2,000 2,000 Increase/(decrease) in trade payables 34,178 (270,151) Increase in accrued and other payables 22,481 97,585 Cash generated from operations 2,212,863 2,520,379
34. CASH FLOW GENERATED FROM OPERATIONS (continued) (b) In the cash flow statement, proceeds from disposal of fixed assets comprise: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Net book amount (Note 6) 142,336 83,944 Receivable arising from disposal of fixed assets 20,349 (21,627) Transfer to inventories (11,662) (5,488) Loss on disposal of fixed assets (Note 29) (133,073) (49,008) Proceeds from disposal of fixed assets 17,950 7,821 (c) Except the business combination as set out in note 37, no non-cash investing or financing activities incurred in the year ended 31 December 2016 (2015: Nil). 35. CONTINGENCY There were no significant contingent liabilities as at the date of approval of these financial statements.
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 36. COMMITMENTS (a) Capital commitments As at 31 December 2016, the Group had the following capital commitments which are authorised but not contracted for, and contracted but not provided for: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Contracted but not provided for 769,013 304,199 Authorised but not contracted for 1,165,237 1,967,894 A substantial amount of these commitments is related to the reform of stations or facilities relating to the existing railway line of the Company, which would be financed by self-generated operating cash flow. (b) Operating lease commitments In connection with the acquisition of Yangcheng Railway Business, the Company signed an agreement on 15 November 2004 with Guangzhou Railway Group for leasing the land use rights associated with the land on which the acquired assets of Yangcheng Railway Business are located. The agreement became effective upon the completion of the acquisition on 1 January 2007 and the remaining lease term is 20 years, renewable at the discretion of the Company. According to the terms of the agreement, the rental for such lease would be agreed by both parties every year with a maximum amount not exceeding RMB74,000,000 per year. During the year ended 31 December 2016, the related lease rental paid and payable was approximately RMB55,090,000 (2015: RMB55,090,000).
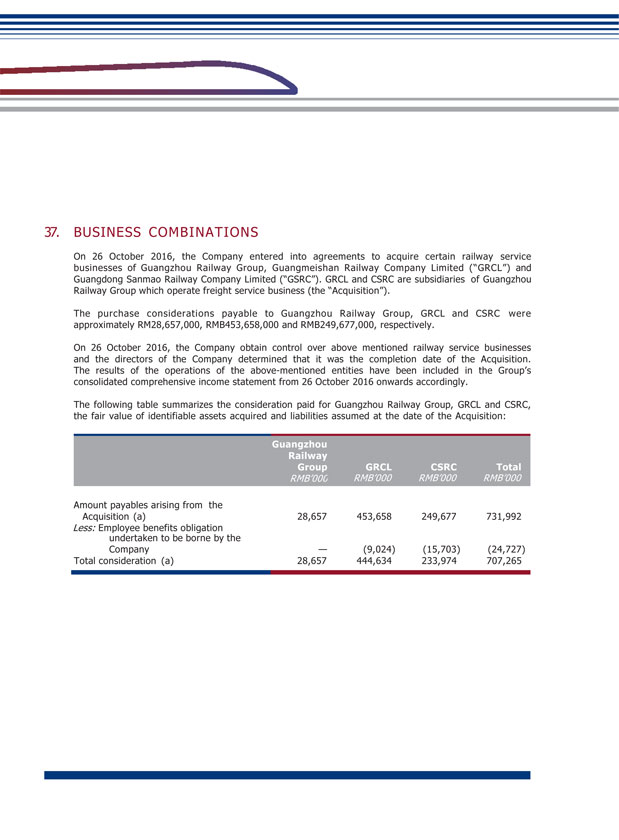
37. BUSINESS COMBINATIONS On 26 October 2016, the Company entered into agreements to acquire certain railway service businesses of Guangzhou Railway Group, Guangmeishan Railway Company Limited (“GRCL”) and Guangdong Sanmao Railway Company Limited (“GSRC”). GRCL and CSRC are subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group which operate freight service business (the “Acquisition”). The purchase considerations payable to Guangzhou Railway Group, GRCL and CSRC were approximately RM28,657,000, RMB453,658,000 and RMB249,677,000, respectively. On 26 October 2016, the Company obtain control over above mentioned railway service businesses and the directors of the Company determined that it was the completion date of the Acquisition. The results of the operations of the above-mentioned entities have been included in the Group’s consolidated comprehensive income statement from 26 October 2016 onwards accordingly. The following table summarizes the consideration paid for Guangzhou Railway Group, GRCL and CSRC, the fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of the Acquisition: Guangzhou Railway Group GRCL CSRC Total RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Amount payables arising from the Acquisition (a) 28,657 453,658 249,677 731,992 Less: Employee benefits obligation undertaken to be borne by the Company — (9,024) (15,703) (24,727) Total consideration (a) 28,657 444,634 233,974 707,265
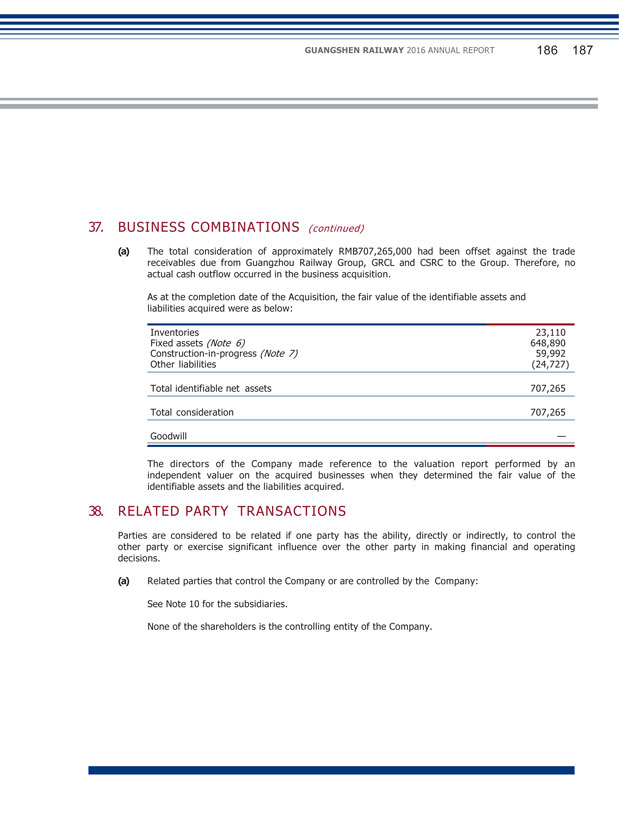
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 37. BUSINESS COMBINATIONS (continued) (a) The total consideration of approximately RMB707,265,000 had been offset against the trade receivables due from Guangzhou Railway Group, GRCL and CSRC to the Group. Therefore, no actual cash outflow occurred in the business acquisition. As at the completion date of the Acquisition, the fair value of the identifiable assets and liabilities acquired were as below: Inventories 23,110 Fixed assets (Note 6) 648,890 Construction-in-progress (Note 7) 59,992 Other liabilities (24,727) Total identifiable net assets 707,265 Total consideration 707,265 Goodwill — The directors of the Company made reference to the valuation report performed by an independent valuer on the acquired businesses when they determined the fair value of the identifiable assets and the liabilities acquired. 38. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS Parties are considered to be related if one party has the ability, directly or indirectly, to control the other party or exercise significant influence over the other party in making financial and operating decisions. (a) Related parties that control the Company or are controlled by the Company: See Note 10 for the subsidiaries. None of the shareholders is the controlling entity of the Company.

38. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (continued) (b) Nature of the principal related parties that do not control/are not controlled by the Company: Name of related parties Relationship with the Company Single largest shareholder and its subsidiaries Guangzhou Railway Group Single largest shareholder Guangzhou Railway Group YangCheng Railway Enterprise Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Development Company GRCL GEDC Subsidiary Subsidiary of of the the single single largest largest shareholder shareholder Guangzhou Railway Material Supply Company Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Railway Engineer Construction Enterprise Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Development Company Yangcheng Construction Company of YangCheng Railway Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Enterprise Development Company Guangzhou Railway Real Estate Construction Company Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Yuehai Railway Company Limited Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Shichang Railway Company Limited Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Railway Station Service Centre Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Changsha Railway Construction Company Limited Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder GSRC Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Qingda Transportation Company Limited Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Yuetie Operational Development Company Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Railway Rolling Stock Works Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Foreign Economic & Trade Development Corporation of Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Railway Group Shenzhen Guangshen Railway Living Service Centre Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Yangcheng Living Service Centre Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Pajiangkou Stone Pit of YangCheng Railway Enterprise Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Development Company Guangdong Tieqing International Travel Agency Company Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Limited Guangdong Sanmao Enterprise Development Company Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Limited Huaihua Railway Engineer Construction Company Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Lechang Anjie Railway Sleeper Company Limited Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Xiashen Railway Guangdong Company Limited Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Ganshao Railway Company Limited Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Guangzhou Railway Economic Technology Development Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Corporation Hunan Changtie Industrial Development Co. Ltd. Subsidiary of the single largest shareholder Associates of the Group Tiecheng Associate of the Group Shentu Associate of the Group
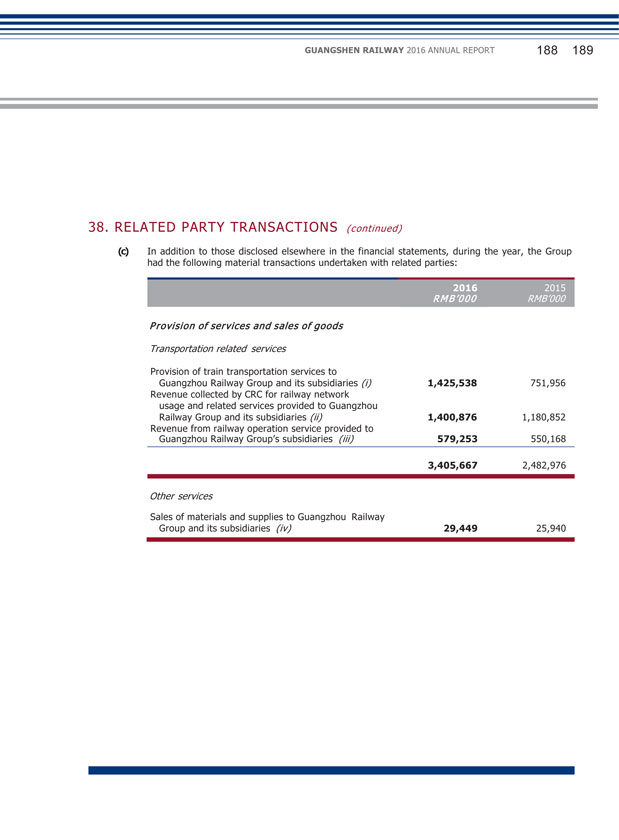
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 38. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (continued) (c) In addition to those disclosed elsewhere in the financial statements, during the year, the Group had the following material transactions undertaken with related parties: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Provision of services and sales of goods Transportation related services Provision of train transportation services to Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (i) 1,425,538 751,956 Revenue collected by CRC for railway network usage and related services provided to Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (ii) 1,400,876 1,180,852 Revenue from railway operation service provided to Guangzhou Railway Group’s subsidiaries (iii) 579,253 550,168 3,405,667 2,482,976 Other services Sales of materials and supplies to Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (iv) 29,449 25,940
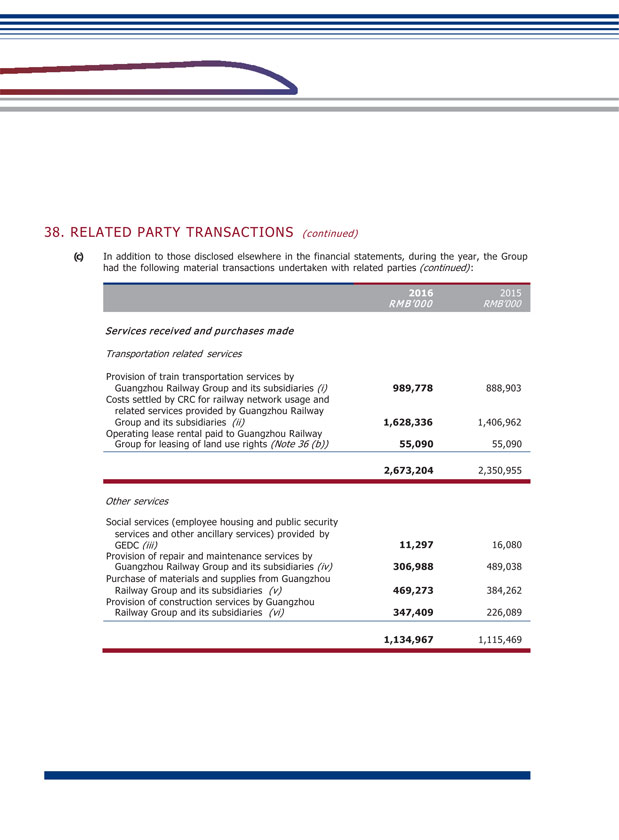
38. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (continued) (c) In addition to those disclosed elsewhere in the financial statements, during the year, the Group had the following material transactions undertaken with related parties (continued) : 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Services received and purchases made Transportation related services Provision of train transportation services by Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (i) 989,778 888,903 Costs settled by CRC for railway network usage and related services provided by Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (ii) 1,628,336 1,406,962 Operating lease rental paid to Guangzhou Railway Group for leasing of land use rights (Note 36 (b)) 55,090 55,090 2,673,204 2,350,955 Other services Social services (employee housing and public security services and other ancillary services) provided by GEDC (iii) 11,297 16,080 Provision of repair and maintenance services by Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (iv) 306,988 489,038 Purchase of materials and supplies from Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (v) 469,273 384,262 Provision of construction services by Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries (vi) 347,409 226,089 1,134,967 1,115,469

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 38. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (continued) (c) (i) The service charges are determined based on a pricing scheme set by the CRC or based on negotiation between the contracting parties with reference to actual costs incurred. (ii) Such revenues/charges are determined by the CRC based on its standard charges applied on a nationwide basis. (iii) The service charges are levied based on contract prices determined based on a “cost plus a profit margin” and explicitly agreed between both contracting parties. (iv) The prices are determined based on mutual negotiation between the contracting parties with reference to actual costs incurred. (v) The prices are determined based on mutual negotiation between the contracting parties with reference to procurement costs incurred plus a management fee ranged from 0.3% to 5% on the costs. (vi) Based on construction amount determined under national railway engineering guidelines. (d) Key management compensation The compensation paid or payable to key management for employee services is shown in Note 28(c).
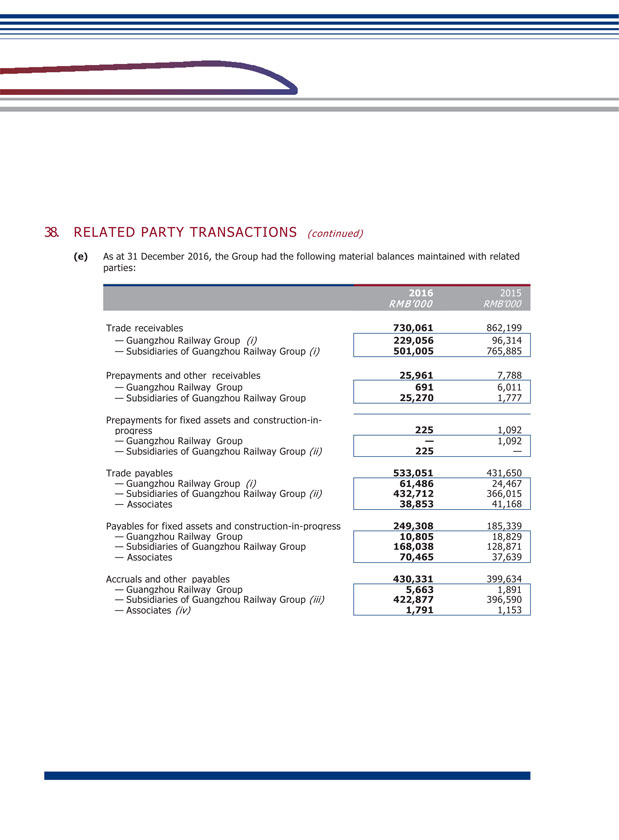
38. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (continued) (e) As at 31 December 2016, the Group had the following material balances maintained with related parties: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Trade receivables 730,061 862,199 — Guangzhou Railway Group (i) 229,056 96,314 — Subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group (i) 501,005 765,885 Prepayments and other receivables 25,961 7,788 — Guangzhou Railway Group 691 6,011 — Subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group 25,270 1,777 Prepayments for fixed assets and construction-in- progress 225 1,092 — Guangzhou Railway Group 225 — 1,092 — — Subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group (ii) Trade payables 533,051 431,650 — — Subsidiaries Guangzhou Railway of Guangzhou Group Railway (i) Group (ii) 432,712 61,486 366,015 24,467 — Associates 38,853 41,168 Payables for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 249,308 185,339 — Guangzhou Railway Group 10,805 18,829 — Subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group 168,038 128,871 — Associates 70,465 37,639 Accruals and other payables 430,331 399,634 — — Subsidiaries Guangzhou Railway of Guangzhou Group Railway Group (iii) 422,877 5,663 396,590 1,891 — Associates (iv) 1,791 1,153

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 38. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (continued) (e) As at 31 December 2016, the Group had the following material balances maintained with related parties (continued) : (i) The trade balances due from/to Guangzhou Railway Group, subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group mainly represent service fees and charges payable and receivable balances arising from the provision of passenger transportation and cargo forwarding businesses jointly with these related parties within the PRC. (ii) The trade payables due to subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group mainly represent payables arising from unsettled fees for purchase of materials and provision of other services according to various service agreements entered into between the Group and the related parties. (iii) The other payables due to subsidiaries of Guangzhou Railway Group mainly represent the performance deposits received for construction projects and deposits received from ticketing agencies. (iv) The other payables due to associates mainly represent the performance deposits received for construction projects operated by associates. As at 31 December 2016, all the balances maintained with related parties were unsecured, non- interest bearing and were repayable on demand. 39. TRANSACTIONS WITH CRC AND OTHER RAILWAY COMPANIES On 14 March 2013, pursuant to the Approval, the previous controlling entity of Guangzhou Railway Group, MOR, had been dismantled. The administrative function of MOR were transferred to the Ministry of Transport and the newly established National Railway Bureau, and its business functions were transferred to the CRC. Accordingly, the equity interests of Guangzhou Railway Group which was wholly controlled by MOR previously were transferred to the CRC (“Reform”). The Reform was completed since 1 January 2017. In order to facilitate user’s comprehensive understanding of the Company’s business transactions, the Company disclosed these transactions with CRC Group for 2016 and 2015. Unless otherwise specified, the transactions disclosed below have excluded the transactions undertaken with Guangzhou Railway Group and its subsidiaries disclosed in Note 38. The Company works in cooperation with the CRC and other railway companies owned and controlled by the CRC for the operation of certain long distance passenger train and freight transportation businesses within the PRC. The revenues generated from these long-distance passenger and freight transportation businesses are collected and settled by the CRC according to its settlement systems. The charges for the use of the rail lines and services provided by other railway companies are also instructed by the CRC and settled by the CRC based on its systems. Since March 2013, the collecting, processing and distribution functions of revenues which were executed by MOR previously had been transferred to CRC. As at 31 December 2016, the cooperation mode and pricing model had not been subject to any material changes.
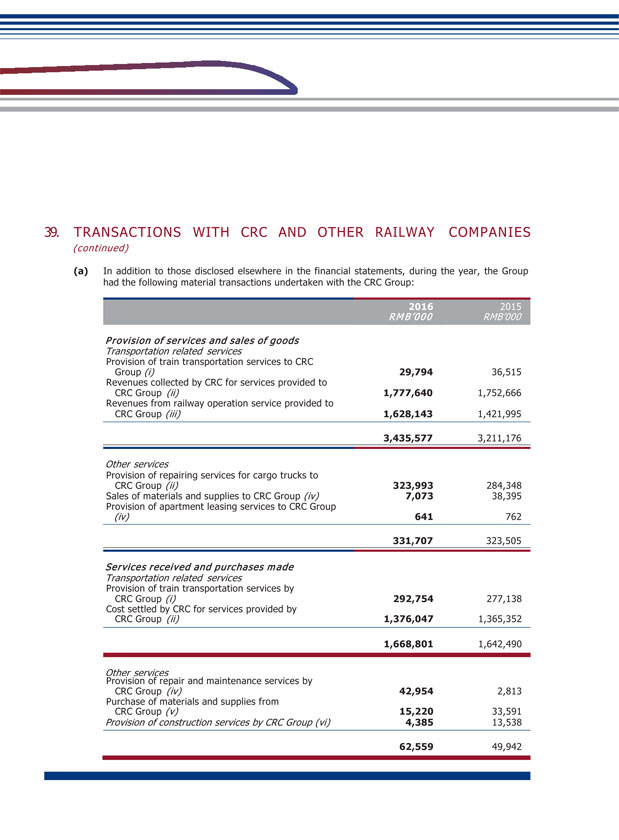
39. TRANSACTIONS WITH CRC AND OTHER RAILWAY COMPANIES (continued) (a) In addition to those disclosed elsewhere in the financial statements, during the year, the Group had the following material transactions undertaken with the CRC Group: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Provision of services and sales of goods Transportation related services Provision of train transportation services to CRC Group (i) 29,794 36,515 Revenues collected by CRC for services provided to CRC Group (ii) 1,777,640 1,752,666 Revenues from railway operation service provided to CRC Group (iii) 1,628,143 1,421,995 3,435,577 3,211,176 Other services Provision of repairing services for cargo trucks to CRC Group (ii) 323,993 284,348 Sales of materials and supplies to CRC Group (iv) 7,073 38,395 Provision of apartment leasing services to CRC Group (iv) 641 762 331,707 323,505 Services received and purchases made Transportation related services Provision of train transportation services by CRC Group (i) 292,754 277,138 Cost CRC settled Group by (ii) CRC for services provided by 1,376,047 1,365,352 1,668,801 1,642,490 Other services Provision of repair and maintenance services by CRC Group (iv) 42,954 2,813 Purchase CRC Group of materials (v) and supplies from 15,220 33,591 Provision of construction services by CRC Group (vi) 4,385 13,538 62,559 49,942
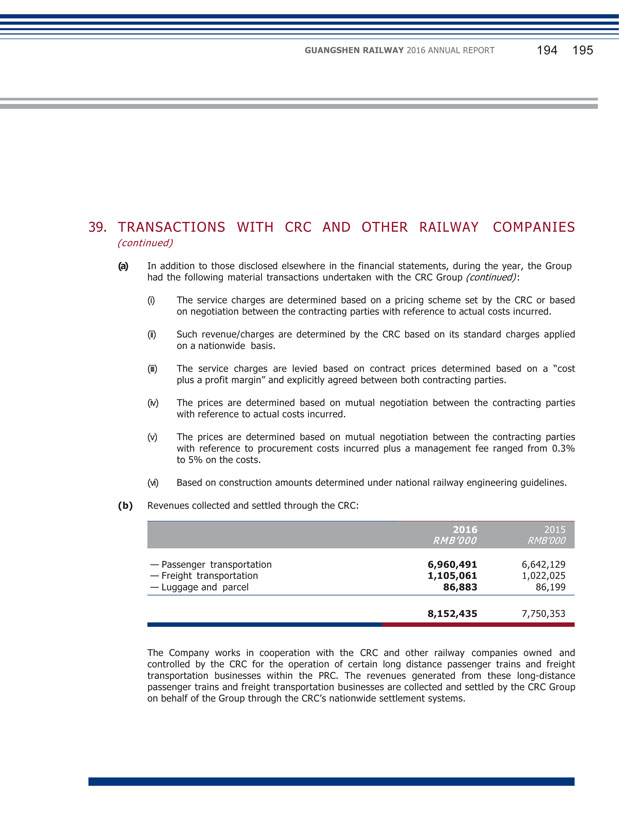
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 39. TRANSACTIONS WITH CRC AND OTHER RAILWAY COMPANIES (continued) (a) In addition to those disclosed elsewhere in the financial statements, during the year, the Group had the following material transactions undertaken with the CRC Group (continued) : (i) The service charges are determined based on a pricing scheme set by the CRC or based on negotiation between the contracting parties with reference to actual costs incurred. (ii) Such revenue/charges are determined by the CRC based on its standard charges applied on a nationwide basis. (iii) The service charges are levied based on contract prices determined based on a “cost plus a profit margin” and explicitly agreed between both contracting parties. (iv) The prices are determined based on mutual negotiation between the contracting parties with reference to actual costs incurred. (v) The prices are determined based on mutual negotiation between the contracting parties with reference to procurement costs incurred plus a management fee ranged from 0.3% to 5% on the costs. (vi) Based on construction amounts determined under national railway engineering guidelines. (b) Revenues collected and settled through the CRC: 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 — Passenger transportation 6,960,491 6,642,129 — Freight transportation 1,105,061 1,022,025 — Luggage and parcel 86,883 86,199 8,152,435 7,750,353 The Company works in cooperation with the CRC and other railway companies owned and controlled by the CRC for the operation of certain long distance passenger trains and freight transportation businesses within the PRC. The revenues generated from these long-distance passenger trains and freight transportation businesses are collected and settled by the CRC Group on behalf of the Group through the CRC’s nationwide settlement systems.
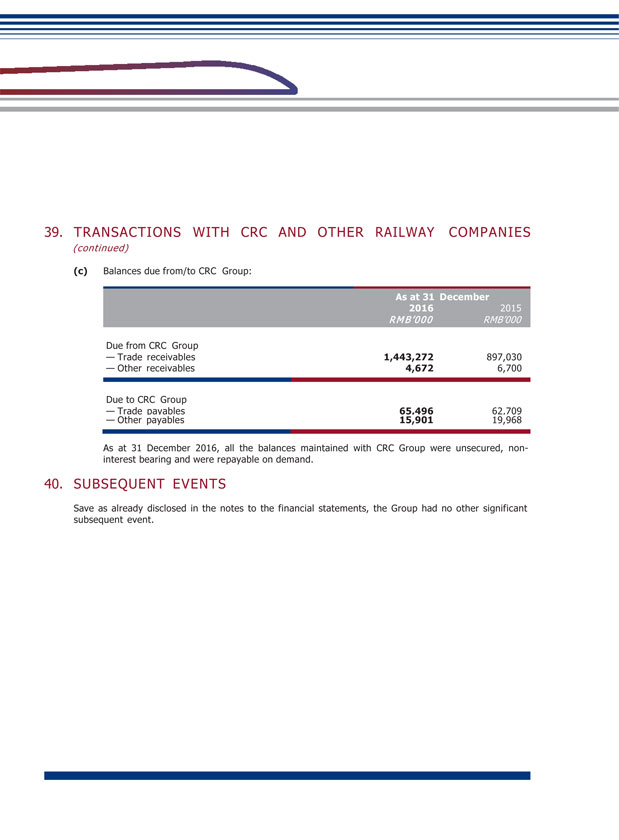
39. TRANSACTIONS WITH CRC AND OTHER RAILWAY COMPANIES (continued) (c) Balances due from/to CRC Group: As at 31 December 2016 2015 RMB’000 RMB’000 Due from CRC Group — Trade receivables 1,443,272 897,030 — Other receivables 4,672 6,700 Due to CRC Group — — Other Trade payables payables 65,496 15,901 19,968 62,709 As at 31 December 2016, all the balances maintained with CRC Group were unsecured, non- interest bearing and were repayable on demand. 40. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS Save as already disclosed in the notes to the financial statements, the Group had no other significant subsequent event.
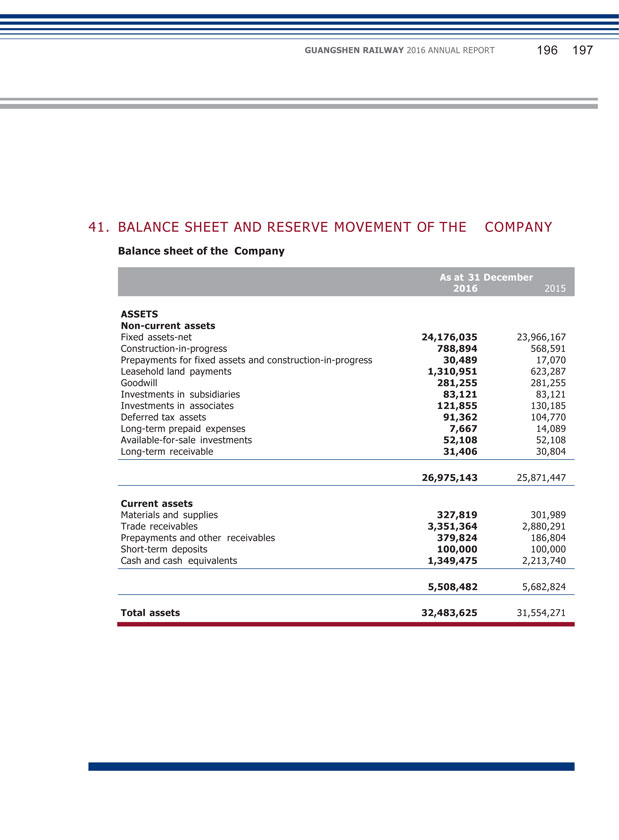
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 41. BALANCE SHEET AND RESERVE MOVEMENT OF THE COMPANY Balance sheet of the Company As at 31 December 2016 2015 ASSETS Non-current assets Fixed assets-net 24,176,035 23,966,167 Construction-in-progress 788,894 568,591 Prepayments for fixed assets and construction-in-progress 30,489 17,070 Leasehold land payments 1,310,951 623,287 Goodwill 281,255 281,255 Investments in subsidiaries 83,121 83,121 Investments in associates 121,855 130,185 Deferred tax assets 91,362 104,770 Long-term prepaid expenses 7,667 14,089 Available-for-sale investments 52,108 52,108 Long-term receivable 31,406 30,804 26,975,143 25,871,447 Current assets Materials and supplies 327,819 301,989 Trade receivables 3,351,364 2,880,291 Prepayments and other receivables 379,824 186,804 Short-term deposits 100,000 100,000 Cash and cash equivalents 1,349,475 2,213,740 5,508,482 5,682,824 Total assets 32,483,625 31,554,271
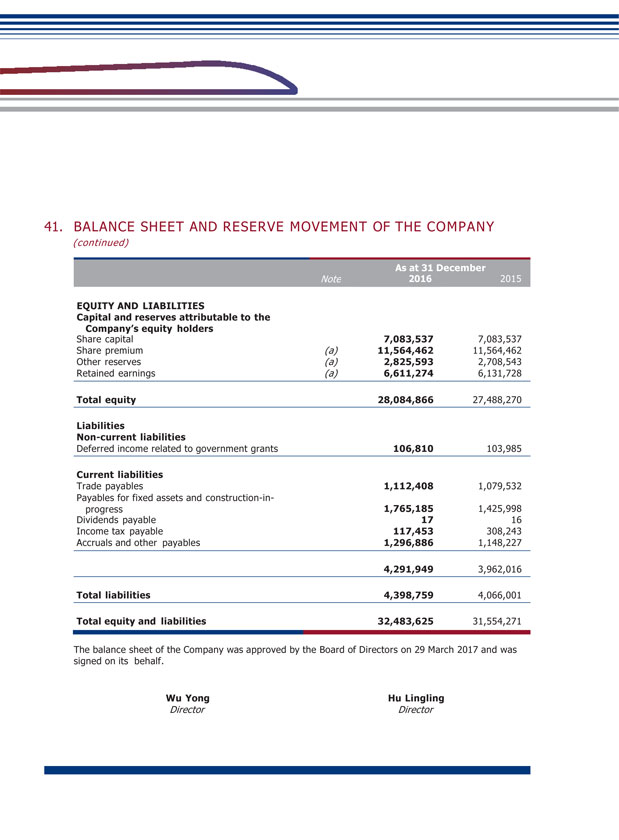
41. BALANCE SHEET AND RESERVE MOVEMENT OF THE COMPANY (continued) As at 31 December Note 2016 2015 EQUITY AND LIABILITIES Capital and reserves attributable to the Company’s equity holders Share capital 7,083,537 7,083,537 Share premium (a) 11,564,462 11,564,462 Other reserves (a) 2,825,593 2,708,543 Retained earnings (a) 6,611,274 6,131,728 Total equity 28,084,866 27,488,270 Liabilities Non-current liabilities Deferred income related to government grants 106,810 103,985 Current liabilities Trade payables 1,112,408 1,079,532 Payables for fixed assets and construction-in- progress 1,765,185 1,425,998 Dividends payable 17 16 Income tax payable 117,453 308,243 Accruals and other payables 1,296,886 1,148,227 4,291,949 3,962,016 Total liabilities 4,398,759 4,066,001 Total equity and liabilities 32,483,625 31,554,271 The balance sheet of the Company was approved by the Board of Directors on 29 March 2017 and was signed on its behalf. Wu Yong Hu Lingling Director Director
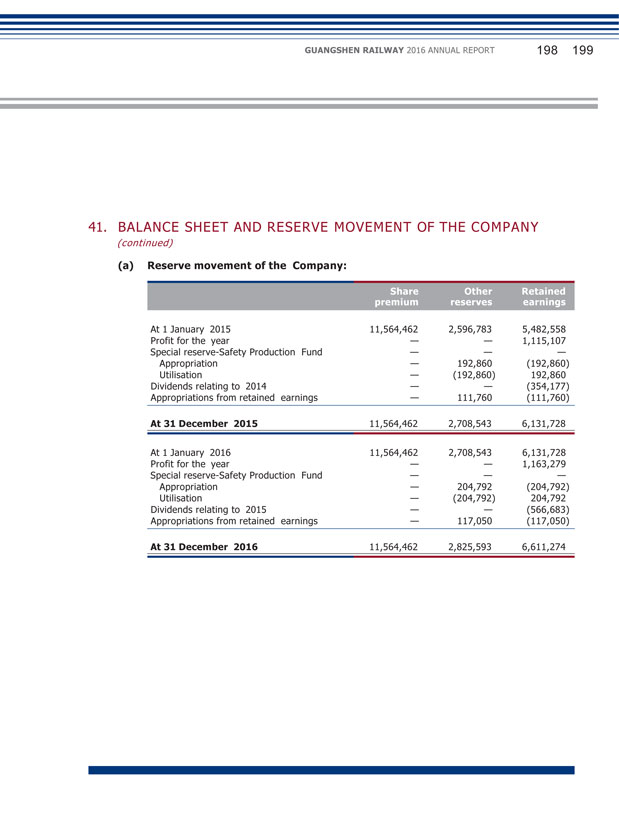
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 41. BALANCE SHEET AND RESERVE MOVEMENT OF THE COMPANY (continued) (a) Reserve movement of the Company: Share Other Retained premium reserves earnings At 1 January 2015 11,564,462 2,596,783 5,482,558 Profit for the year — — 1,115,107 Special reserve-Safety Production Fund — — — Appropriation — 192,860 (192,860) Utilisation — (192,860) 192,860 Dividends relating to 2014 — — (354,177) Appropriations from retained earnings — 111,760 (111,760) At 31 December 2015 11,564,462 2,708,543 6,131,728 At 1 January 2016 11,564,462 2,708,543 6,131,728 Profit for the year — — 1,163,279 Special reserve-Safety Production Fund — — — Appropriation — 204,792 (204,792) Utilisation — (204,792) 204,792 Dividends relating to 2015 — — (566,683) Appropriations from retained earnings — 117,050 (117,050) At 31 December 2016 11,564,462 2,825,593 6,611,274
42. BENEFITS AND INTERESTS OF DIRECTORS (a) Directors’, supervisors’ and senior executives’ emoluments For the year ended 31 December 2016 Emoluments paid or receivable in respect of a person’s services as a director, whether of the Company or its subsidiary undertaking Remunerations paid or Employer’s receivable in Discretionary Housing Allowances contribution a respect of Name Fee Salary bonuses allowance and benefits retirement accepting office Total in kind benefit scheme as director RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 Directors Wu, Yong — — — — — — — — Luo, Shen, Qing Yi (i) — — 124 — — 144 29 — — 11 — 35 — — —343 Yu, Sun, Zhiming Jing — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — Chen, Jia, Jianmin Song 112 143 — — — — — — — — — — — — 112 143 Wang, Yunting 112 — — — — — — 112 Chen, Jianping — — — — — — — — Supervisors Liu, Mengshu — — — — — — — — Chen, Shaohong — — — — — — — — Shen, Jiancong — — — — — — — — Li, Song, Zhiming Min — — — 118 120 — 29 — — 9 34 — — — —310 Zhou, Shangde — 198 — 29 80 33 — 340 Chief Executives Hu, Lingling (ii) — 127 206 29 9 36 — 407 Senior Mu, Anyun Executives (iii) — 125 144 29 10 37 — 345 Luo, Tang, Jiancheng Xiangdong (iv) — — — 123 148 — 29 — 8 — 34 — — — —342 Guo, Xiangdong — 124 146 29 9 35 — 343 (i) Resigned from the position in May 2016. (ii) Appointed the position of director in May 2016 and continue to serve as a chief executive of the Company. (iii) Resigned from the position in December 2016. (iv) Appointed in December 2016.
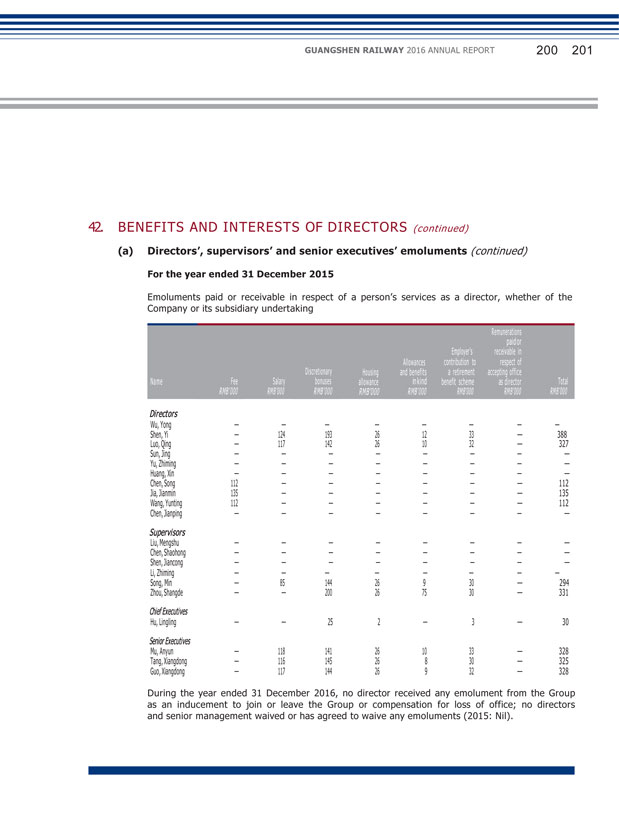
GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT 42. BENEFITS AND INTERESTS OF DIRECTORS (continued) (a) Directors’, supervisors’ and senior executives’ emoluments (continued) For the year ended 31 December 2015 Emoluments paid or receivable in respect of a person’s services as a director, whether of the Company or its subsidiary undertaking Remunerations paid or Employer’s receivable in Discretionary Allowances contribution to respect of Fee Salary bonuses Housing and benefits in kind a retirement accepting office Total Name RMB’000 RMB’000 RMB’000 allowance RMB’000 benefit RMB’000 scheme as RMB’000 director RMB’000 RMB’000 Directors Wu, Shen, Yong Yi — — 124 — 193 — — 26 — 12 — 33 — — — 388 Sun, Luo, Qing Jing — — 117 — 142 — 26 — 10 — 32 — — — 327 — Yu, Huang, Zhiming Xin — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — Chen, Jia, Jianmin Song 135 112 — — — — — — — — — — — — 112 135 Wang, Yunting 112 — — — — — — 112 Chen, Jianping — — — — — — — — Supervisors Liu, Mengshu — — — — — — — — Shen, Chen, Jiancong Shaohong — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — Li, Song, Zhiming Min — — 85 — — 144 — 26 — 9 30 — — — — 294 Zhou, Shangde — — 200 26 75 30 — 331 Chief Executives Hu, Lingling — — 25 2 — 3 — 30 Senior Mu, Anyun Executives — 118 141 26 10 33 — 328 Tang, Xiangdong — 116 145 26 8 30 — 325 Guo, Xiangdong — 117 144 26 9 32 — 328 During the year ended 31 December 2016, no director received any emolument from the Group as an inducement to join or leave the Group or compensation for loss of office; no directors and senior management waived or has agreed to waive any emoluments (2015: Nil).

42. BENEFITS AND INTERESTS OF DIRECTORS (continued) (b) Director’s retirement benefits The retirement benefits paid to Shen Yi and Luo Qing during the year end of 2016 by a defined benefit pension plan operated by the Group in respect of their services as directors of the Company and its subsidiaries are RMB0 and RMB35,000 (2015: RMB33,000 and RMB32,000). No other retirement benefits were paid to them in respect of their other services in connection with the management of the affairs of the Company or its subsidiary undertaking (2015: Nil). (c) Directors’ termination benefits During the year ended 31 December 2016, no payments to the directors of the Company as compensation for the early termination of the appointment (2015: Nil). (d) Consideration provided to third parties for making available directors’ services During the year ended 31 December 2016, the Company didn’t provide to third any party for making available director’s services (2015: Nil). (e) Information about loans, quasi-loans and other dealings in favour of directors, controlled bodies corporate by and connected entities with such directors During the year ended 31 December 2016, no loans, quasi-loans or other dealings in favour of directors of the Company, controlled bodies corporate by and connected entities with such directors (2015: Nil). (f) Directors’ material interests in transactions, arrangements or contracts No significant transactions, arrangements and contracts in relation to the Group’s business to which the Company was a party and in which a director of the Company had a material interest, whether directly or indirectly, subsisted at the end of the year or at any time during the year (2015: Nil).

GUANGSHEN RAILWAY 2016 ANNUAL REPORT Chapter 12 Documents Available for Inspection DOCUMENTS AVAILABLE FOR INSPECTION 1. Accounting statements signed and stamped by the legal representative, person in charge of accounting affairs and responsible person of accounting firm; 2. The original audit report signed and stamped by PricewaterhouseCoopers Zhong Tian LLP and the financial Statements prepared in accordance with China accounting standards, and the original audit report signed and stamped by PricewaterhouseCoopers and the financial Statements prepared in accordance with IFRS; 3. All the original of files and announcements disclosed in China Securities Journal, Securities Times, Shanghai Securities News and Securities Daily during the reporting period; 4. The annual report published on Hong Kong’s security market and the annual report published in the security market in United States (Form 20-F). The documents are placed at the Secretariat to the Board. Chairman of the Board: Wu Yong Date of Approval from the Board: 29 March 2017 Amendments to Information Applicable Not applicable