
Fuze, Inc. Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020

Fuze, Inc. Index December 31, 2020 Page(s) Report of Independent Auditors ............................................................................................................... 1 Consolidated Financial Statements Consolidated Balance Sheet ....................................................................................................................... 2 Consolidated Statement of Operations ....................................................................................................... 3 Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Loss ...................................................................................… 4 Consolidated Statement of Redeemable Convertible and Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Deficit ………………………………………………………………………………...……. 5 Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows ..................................................................................................… 6 Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements ...................................................................................... 7 – 34

Report of Independent Auditors To the Board of Directors and Management of Fuze, Inc. We have audited the accompanying consolidated financial statements of Fuze, Inc. and its subsidiaries, which comprise the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2020 and the related consolidated statements of operations, of comprehensive loss, of redeemable convertible and convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ deficit, and of cash flows for the year then ended. Management's Responsibility for the Consolidated Financial Statements Management is responsible for the preparation and fair presentation of the consolidated financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America; this includes the design, implementation, and maintenance of internal control relevant to the preparation and fair presentation of consolidated financial statements that are free from material misstatement, whether due to fraud or error. Auditors’ Responsibility Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the consolidated financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in the United States of America. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free from material misstatement. An audit involves performing procedures to obtain audit evidence about the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. The procedures selected depend on our judgment, including the assessment of the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to fraud or error. In making those risk assessments, we consider internal control relevant to the Company's preparation and fair presentation of the consolidated financial statements in order to design audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes evaluating the appropriateness of accounting policies used and the reasonableness of significant accounting estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that the audit evidence we have obtained is sufficient and appropriate to provide a basis for our audit opinion. Opinion In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Fuze, Inc. and its subsidiaries as of December 31, 2020 and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the year then ended in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Emphasis of Matters The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring losses from operations and has a net capital deficiency and has stated that substantial doubt exists about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s evaluation of the events and conditions and management’s plans regarding these matters are also discussed in Note 1. The consolidated financial statement do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty. Our opinion is not modified with respect to this matter. As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it accounts for revenue from contracts with customers in 2020. Our opinion is not modified with respect to this matter. /s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP Boston, Massachusetts October 7, 2021, except for additional disclosures made in preparation for an SEC filing discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, as to which the date is November 30, 2021

Fuze, Inc. Consolidated Balance Sheet December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements. 2 December 31, 2020 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents $ 3,211 Accounts receivable 13,936 Inventory 514 Deferred commissions, current 4,700 Prepaid expenses and other current assets 3,031 Total current assets 25,392 Property and equipment, net 2,601 Goodwill 4,802 Acquired intangible assets, net 504 Restricted cash 868 Deferred commissions, non-current 8,030 Other assets 307 Total assets $ 42,504 Liabilities, Redeemable Convertible and Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders' Deficit Current liabilities: Accounts payable $ 11,105 Accrued expenses and other current liabilities 32,856 Long-term debt, current portion 90,161 Deferred revenue, current portion 6,329 Total current liabilities 140,451 Long-term debt, net of current portion 4,754 Deferred revenue, net of current portion 11,403 Deferred tax liabilities 261 Other long-term liabilities 14,493 Total liabilities 171,362 Commitments and contingencies (Note 14) Redeemable convertible preferred stock (Series B, C, D, E, F, G-1, G-2, G-3); $0.0001 par value; 233,413,623 shares authorized; 192,009,530 shares issued and outstanding; aggregate liquidation preference of $717,578 572,936 Convertible preferred stock (Series A); $0.0001 par value; 1,685,000 shares authorized, issued and outstanding; aggregate liquidation preference of $1,060 1,060 Stockholders’ deficit: Common stock; $0.0001 par value; 301,725,000 shares authorized; 28,113,069 shares issued and 25,844,880 shares outstanding 3 Treasury stock, at cost (2,268,189 shares) (2,259) Additional paid-in capital 14,047 Accumulated deficit (714,170) Accumulated other comprehensive loss (475) Total stockholders' deficit (702,854) Total liabilities, redeemable convertible and convertible preferred stock and stockholders' deficit $ 42,504

Fuze, Inc. Consolidated Statement of Operations Year Ended December 31, 2020 (in thousands) The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements. 3 Year Ended December 31, 2020 Revenue $ 129,746 Cost and expenses: Cost of revenue 59,207 Research and development 27,749 Sales and marketing 50,133 General and administrative 24,557 Total cost and expenses 161,646 Loss from operations (31,900) Other expense, net: Interest expense, net (8,660) Change in fair value of preferred stock warrants 3,776 Other expense, net (9,533) Total other expense, net (14,417) Loss before income tax expense (46,317) Income tax expense 1,036 Net loss $ (47,353)

Fuze, Inc. Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Loss Year Ended December 31, 2020 (in thousands) The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements. 4 Year Ended December 31, 2020 Net loss $ (47,353) Other comprehensive loss: Foreign currency translation adjustment (289) Comprehensive loss $ (47,642)

Fuze, Inc. Consolidated Statement of Redeemable Convertible and Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders' Deficit Year Ended December 31, 2020 (in thousands except share and per share data) The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements. 5 Series B, C, D, E, F, G-1, G-2, Accumulated and G-3 Redeemable Convertible Series A Convertible Additional Other Total Preferred Stock Preferred Stock Common Stock Treasury Paid-in Accumulated Comprehensive Stockholders' Shares Amount Shares Amount Shares Amount Stock Capital Deficit Income (loss) Deficit Balances at December 31, 2019 191,551,123 $ 547,350 1,685,000 $ 1,060 25,638,137 $ 3 $ (2,259) $ 37,111 $ (686,229) $ (186) $ (651,560) Cumulative adjustment from adoption of revenue recognition standard (Note 2) — — — — — — — — 19,412 — 19,412 Issuance of Series C Preferred Stock upon exercise of warrants 458,407 289 — — — — — — — — — Expiration of Series B and Series C Preferred Stock Warrants — — — — — — — 200 — — 200 Issuance costs related to issuance of Series A-1 Preferred Stock — — — — — — — (157) — — (157) Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options — — — — 206,743 — — 103 — — 103 Stock-based compensation expense — — — — — — — 2,087 — — 2,087 Accretion of redeemable convertible preferred stock to redemption value, net — 25,297 — — — — — (25,297) — — (25,297) Foreign currency translation adjustment — — — — — — — — — (289) (289) Net loss — — — — — — — — (47,353) — (47,353) Balances at December 31, 2020 192,009,530 $ 572,936 1,685,000 $ 1,060 25,844,880 $ 3 $ (2,259) $ 14,047 $ (714,170) $ (475) $ (702,854)
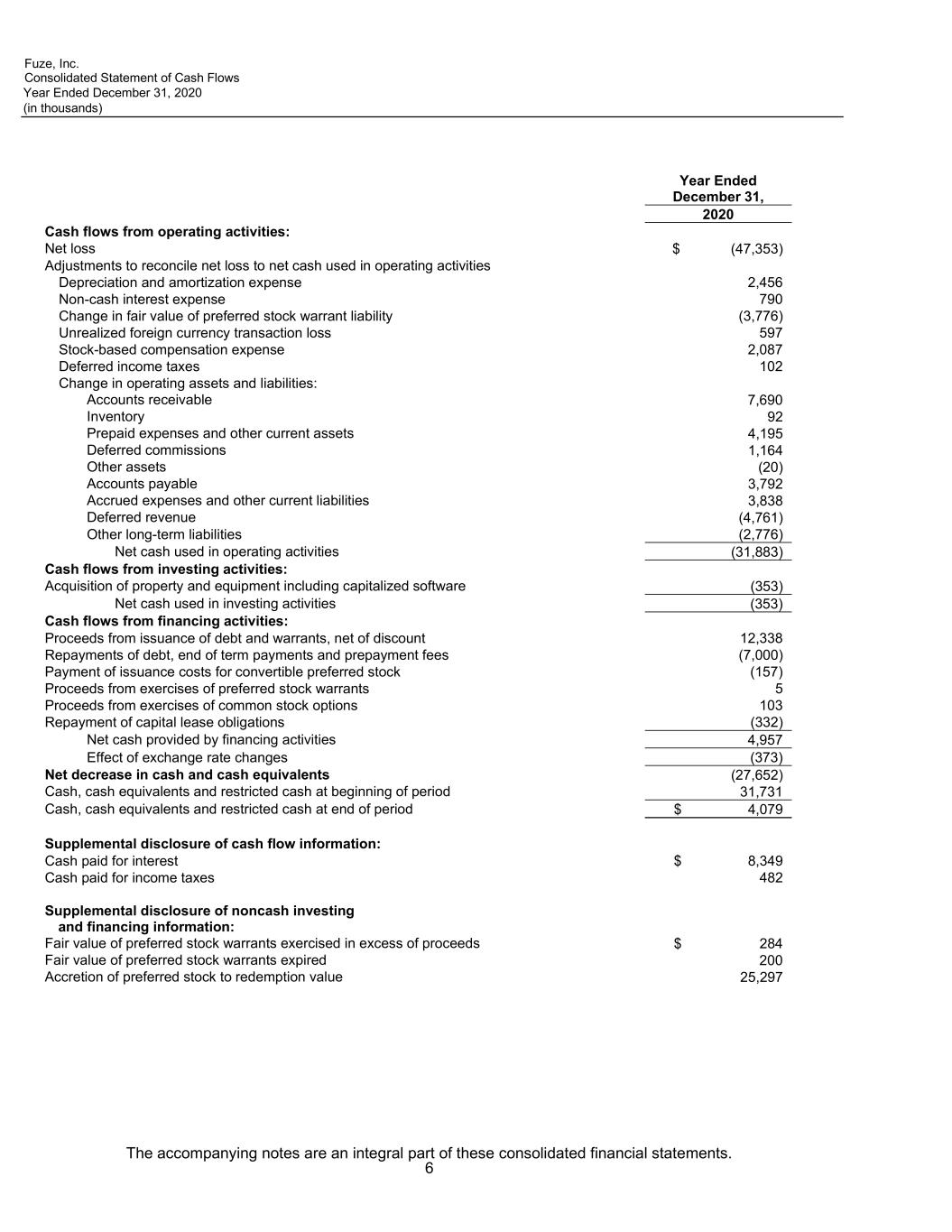
Fuze, Inc. Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows Year Ended December 31, 2020 (in thousands) The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements. 6 Year Ended December 31, 2020 Cash flows from operating activities: Net loss $ (47,353) Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities Depreciation and amortization expense 2,456 Non-cash interest expense 790 Change in fair value of preferred stock warrant liability (3,776) Unrealized foreign currency transaction loss 597 Stock-based compensation expense 2,087 Deferred income taxes 102 Change in operating assets and liabilities: Accounts receivable 7,690 Inventory 92 Prepaid expenses and other current assets 4,195 Deferred commissions 1,164 Other assets (20) Accounts payable 3,792 Accrued expenses and other current liabilities 3,838 Deferred revenue (4,761) Other long-term liabilities (2,776) Net cash used in operating activities (31,883) Cash flows from investing activities: Acquisition of property and equipment including capitalized software (353) Net cash used in investing activities (353) Cash flows from financing activities: Proceeds from issuance of debt and warrants, net of discount 12,338 Repayments of debt, end of term payments and prepayment fees (7,000) Payment of issuance costs for convertible preferred stock (157) Proceeds from exercises of preferred stock warrants 5 Proceeds from exercises of common stock options 103 Repayment of capital lease obligations (332) Net cash provided by financing activities 4,957 Effect of exchange rate changes (373) Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents (27,652) Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at beginning of period 31,731 Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at end of period $ 4,079 Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: Cash paid for interest $ 8,349 Cash paid for income taxes 482 Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing information: Fair value of preferred stock warrants exercised in excess of proceeds $ 284 Fair value of preferred stock warrants expired 200 Accretion of preferred stock to redemption value 25,297

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 7 1. Nature of Business Fuze, Inc. (the “Company” or “Fuze”) is a provider of cloud-based, unified communications and contact center services. The Company provides managed voice, video conferencing, instant messaging, application integration, contact center, and analytics to customers on a cloud-based software platform. The Company is subject to a number of risks similar to other companies in the industry, including but not limited to, competition from substitute products and larger companies, protection of proprietary technology and customer base, ongoing development and enhancement of its products, dependence on third parties and key members of its management team, and the need to obtain additional capital to fund the development of its products and network. Adverse effects arising from any of these situations could have a significant impact on the Company’s operations. With respect to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Company continues to be able to deliver its services to customers remotely and has not, to date, experienced significant project cancellations with any material negative impact to revenue in 2020. As new variants of COVID-19 emerge, the full extent to which the ongoing and continuing COVID-19 pandemic will directly or indirectly impact our business, future results of operations, and financial condition, including sales, expenses, reserves and allowances, and employee-related amounts, will depend on future developments that are uncertain. Such developments include the efficacy of new vaccines to treat these evolving variants of COVID-19, new government actions as a result of these changing conditions, as well as the economic impact on local, regional, national, and international customers and markets. The Company’s consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Although the Company has successfully completed financings in the past (Notes 8, 9, and 16), the Company may not be successful in raising additional capital to fund normal operations in future periods. In the event that the Company is unable to obtain financing on acceptable terms, or at all, it will likely be required to cease its operations, pursue a plan to sell its operating assets, or otherwise modify its business strategy, which could materially harm its future business prospects. These consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from this uncertainty. 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies Additional Disclosures Made in Preparation for an SEC Filing Subsequent to the original issuance of the consolidated financial statements and in connection with acquisition of the Company, which is discussed in Note 16 to the consolidated financial statements, certain footnote disclosures have been either updated or added in order to conform to the requirements for these consolidated financial statements to be included in an SEC filing. Specifically, the Company has expanded its disaggregation of revenue and contract liability disclosures within the ‘Revenue Recognition’ sub-section in Note 2, separately presented Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets in Note 4, separately presented Accrued Expenses and Other Current Liabilities in Note 7 and added an effective tax rate reconciliation in tabular format in Note 8. Finally, as discussed within the ‘Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements’ sub-section in Note 2, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2018-15, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other—Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350-40): Customer’s Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement That Is a Service Contract on January 1, 2020. Principles of Consolidation The consolidated financial statements reflect the accounts and operations of Fuze, Inc. and those of its subsidiaries. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Correction of Errors During the year, the Company identified certain prior period errors related to a regulatory tax liability (Note 14), accrued payroll expense, and deferred revenue. Specifically, the regulatory tax was under accrued in each of the years ended December 31, 2011 to 2019. Accrued payroll expense was overstated in the year ended December 31, 2018 and deferred revenue was not properly recognized into revenue in each of the years ended December 31, 2016 to 2019. The Company concluded that these errors were not material, individually or in the aggregate, to

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 8 any of the prior periods. The Company recorded an adjustment in the year ended December 31, 2020 to reflect the impact of these errors, which resulted in an increase in net loss of $2,010 and an increase in total liabilities of $2,010 as of December 31, 2020. Use of Estimates The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates and assumptions reflected in these consolidated financial statements include, but are not limited to, revenue recognition, allowance for doubtful accounts, inventory valuation and obsolescence, goodwill and intangible assets, the expensing and capitalization of software development costs, the valuations of common and preferred stock, preferred stock warrant liability and stock-based awards, and income taxes. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience, known trends, and other market-specific or other relevant factors that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. On an ongoing basis, management evaluates its estimates, as there are changes in circumstances, facts, and experience. Actual results may differ from these estimates. Cash Equivalents The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase to be cash equivalents. Financial instruments that potentially expose the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents and accounts receivable. The Company maintains its cash and cash equivalents with three accredited financial institutions that management believes to be of high-credit quality. The Company performs credit evaluations of its customers' financial condition and generally does not require collateral from its customers. As of and for the year ended December 31, 2020, no customer accounted for more than 10% of accounts receivable or revenue. Restricted Cash As of December 31, 2020, the Company maintained letters of credit totaling $868 for the benefit of the landlord of its leased properties. The Company was required to maintain a separate cash balance of that same amount to secure the letters of credit. Related to this separate cash balance, the Company classified $868 as restricted cash (non-current) on its consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2020. Property and Equipment Property and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from 3 to 7 years. Leasehold improvements are amortized using the straight-line method over the lesser of the lease term or the improvement’s estimated economic useful life. Lease terms are based upon the initial lease agreement and do not consider potential renewals or extensions until such time that the renewals or extensions are contracted. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred. The cost and accumulated depreciation and amortization applicable to assets sold or otherwise disposed of are removed from the asset accounts, and any resulting gain or loss is reflected in loss from operations. Software and Website Development Costs Research and development costs are expensed as incurred and primarily include salaries, fees to consultants, and other related costs. Relative to development costs of its products and website, the Company capitalizes certain direct costs to develop functionality as well as certain upgrades and enhancements that are probable to result in additional functionality. The costs incurred in the preliminary stages of development are expensed as incurred. Once an application has reached the development stage, internal and external costs, if direct and incremental, are capitalized as part of property and equipment until the software is substantially complete and ready for its intended use. Capitalized software is amortized over a three-year period in the expense category to which the software relates.

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 9 Business Combinations The Company accounts for business combinations using the acquisition method of accounting. Application of this method of accounting requires that (i) identifiable assets acquired (including identifiable intangible assets) and liabilities assumed generally be measured and recognized at fair value as of the acquisition date and (ii) the excess of the purchase price over the net fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed be recognized as goodwill, which is not amortized for accounting purposes but is subject to testing for impairment at least annually. Transaction costs related to business combinations are expensed as incurred. Determining the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed and the allocation of the purchase price requires management to use significant judgment and estimates, especially with respect to intangible assets. Critical estimates in valuing certain identifiable assets include, but are not limited to, the selection of valuation methodologies, estimates of future revenue and cash flows, expected long-term market growth, future expected operating expenses, costs of capital, and appropriate discount rates. Management's estimates of fair value are based upon assumptions believed to be reasonable, but which are inherently uncertain and unpredictable and, as a result, actual results may differ from estimates. During the measurement period, the Company may record certain adjustments to the carrying value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed with the corresponding offset to goodwill. After the measurement period, which could last up to one year after the transaction date, all adjustments are recorded in the consolidated statements of operations. Contingent payments that are dependent upon post-combination services, if any, are considered separate transactions outside of the business combination and are, therefore, included in the post-combination consolidated statements of operations. In addition, uncertain tax positions assumed and valuation allowances related to the net deferred tax assets acquired in connection with a business combination are estimated as of the acquisition date and recorded as part of the purchase. Thereafter, any changes to these uncertain tax positions and valuation allowances are recorded as part of the provision for income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations. Goodwill and Acquired Intangible Assets The Company records goodwill when consideration paid in a business acquisition exceeds the fair value of the net tangible assets and the identified intangible assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized, but rather is tested for impairment annually or more frequently if facts and circumstances warrant a review. If the Company determines that the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, an impairment charge would be required. The Company operates as a single operating segment with one reporting unit and consequently evaluates goodwill for impairment based on an evaluation of the fair value of the Company as a whole. The Company did not record any goodwill impairment losses during the year ended December 31, 2020. Intangible assets are recorded at their estimated fair values at the date of acquisition. The Company amortizes acquired intangible assets over their estimated useful lives based on the pattern of consumption of the economic benefits or, if that pattern cannot be readily determined, on a straight-line basis. Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Long-lived assets consist of property and equipment, deferred commissions, and acquired intangible assets. Long-lived assets to be held and used are tested for recoverability whenever events or changes in business circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be fully recoverable. Factors that the Company considers in deciding when to perform an impairment review include significant underperformance of the business in relation to expectations, significant negative industry or economic trends, and significant changes or planned changes in the use of the assets. If an impairment review is performed to evaluate a long-lived asset group for recoverability, the Company compares forecasts of undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the long-lived asset group to its carrying value. An impairment loss would be recognized when estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the use of an asset group are less than its carrying amount. The impairment loss would be based on the excess of the carrying value of the impaired asset group over its fair value, determined based on discounted cash flows. The Company did not record any impairment losses on long-lived assets during the year ended December 31, 2020. Fair Value Measurements Certain assets and liabilities are carried at fair value. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 10 the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value are to be classified and disclosed in one of the following three levels of the fair value hierarchy, of which the first two are considered observable and the last is considered unobservable: • Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. • Level 2—Observable inputs (other than Level 1 quoted prices), such as quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices in markets that are not active for identical or similar assets or liabilities, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data. • Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to determining the fair value of the assets or liabilities, including pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, and similar techniques. The carrying values of the Company’s accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued expenses, and other current liabilities approximate their fair values due to the short-term nature of these assets and liabilities. Classification of Preferred Stock and Accretion of Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock The Company has convertible preferred stock and redeemable convertible preferred stock that contain certain redemption features that are not solely within the control of the Company. Costs incurred in connection with the issuance of each series of preferred stock are recorded as a reduction of gross proceeds from issuance. The carrying values of the outstanding redeemable convertible preferred stock are accreted to their respective redemption values from the date of issuance through the earliest date of redemption. Revenue Recognition In accordance with ASC 606 (see Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements below), the Company recognizes revenue when a customer obtains control of promised goods or services. The amount of revenue recognized reflects the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled to receive in exchange for those goods or services. To achieve this core principle, the Company applies the following five steps: 1) Identify the contract(s) with a customer 2) Identify the performance obligations in the contract 3) Determine the transaction price 4) Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract 5) Recognize revenue when (or as) performance obligations are satisfied Nature of Products and Services The Company’s revenue includes fees billed in connection with subscriptions to the Company’s software- as-a-service (“SaaS”) applications. These fees include recurring fixed plan subscription fees, recurring circuit usage fees, recurring administrative cost recovery fees, variable usage-based fees for blocks of additional minutes, and other items systematically purchased in excess of plan limits. The Company’s software is delivered to the client via a hosting arrangement whereby the customer does not have the contractual right to take possession of the software. The Company’s revenue also includes professional services related to the implementation, installation, and configuration of the SaaS solution, sales of preconfigured office phones, cabling, and switches used in connection with the subscription, shipping and handling fees, and one-time upfront fees related to setup activities. The Company provides its subscriptions pursuant to contractual arrangements that range in duration from one month to three years. The Company’s subscription fees are generally billed in advance.

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 11 Revenue related to the Company’s SaaS subscription plans is recognized as services are rendered over the service period. Product revenues are billed at the time the order is received and recognized when the product has been shipped to the customer. Professional services revenue is recognized over time as the services are provided using an input measure based on expended level of effort incurred. Fees related to setup activities that do not represent promised services in the contract with the customer are accounted for as a part of the transaction price and allocated to the performance obligations in the contract. The Company has elected to treat shipping and handling activities related to contracts with customers as fulfillment costs, and not as separate performance obligations, and accrues the related costs when the related revenue is recognized. Total revenue recognized at a point in time and over time was as follows for the year ended December 31, 2020: Revenue recognized at a point in time $ 5,415 Revenue recognized over time 124,331 $ 129,746 Disaggregation of Revenue Year Ended December 31, 2020 United States $ 91,298 International 38,448 Total revenue $ 129,746 Remaining Performance Obligations The Company's subscription terms are typically three years and customers are billed on a monthly basis. Contract revenue from the remaining performance obligations that had not yet been recognized as of December 31, 2020 was approximately $49,500. The Company expects to recognize revenue on approximately $39,600 of the remaining performance obligation over the next 12 months and approximately $9,900 thereafter. Contracts with Multiple Performance Obligations When the Company’s contracts with customers contain multiple performance obligations, the transaction price is allocated on a relative standalone selling price basis to each performance obligation. The Company generally uses internal price lists that determine sales prices to external customers in determining standalone selling price. The Company’s internal price lists are based on multiple factors, including, but not limited to, market conditions, competitive landscape, internal costs, and gross margin objectives. Standalone selling price is typically established as a range, and the Company has more than one standalone selling price range for certain individual products and services due to the stratification of those products and services by customer class. In situations in which the stated contract price for a performance obligation is outside of the applicable standalone selling price range and has a different pattern of transfer to the customer than the other performance obligations in the contract, the Company will reallocate the total transaction price to each performance obligation based on the relative standalone selling price of each. Transaction Price The transaction price is the amount of consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for transferring goods and services to the customer. Revenue is recorded based on the transaction price, which includes fixed consideration and estimates of variable consideration. The Company determines the transaction price of each contract, which includes estimating the amount of variable consideration to be included in the transaction price, if any. This will involve updating the estimates of variable consideration, including any amounts that are constrained, to reflect revised

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 12 expectations about the amount of consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled considering uncertainties that are resolved or new information that is gained about remaining uncertainties. The amount of variable consideration included in the transaction price is limited to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur when the uncertainty associated with the variable consideration is subsequently resolved. Usage-based fees that meet the criteria to apply the allocation exception for variable consideration are recognized in the period of usage. The Company has service level agreements with customers warranting defined levels of uptime reliability and performance. Customers may get credits or refunds if the Company fails to meet such levels. If the services do not meet certain criteria, fees are subject to adjustment or refund representing a form of variable consideration. The Company historically has not experienced any significant incidents affecting the defined levels of reliability and performance as required by its subscription contracts. Accordingly, the amount of any estimated refunds related to these agreements in the consolidated financial statements is not material during the periods presented. The Company may impose minimum monthly recurring charges (“MRC”) on its customers at the inception of the contract. Thus, in estimating variable consideration the Company assesses both the probability of minimum MRC occurring and the collectability of the minimum MRC, both of which represent a form of variable consideration. Customer Renewal Options The Company’s contracts with customers may include renewal or other like options at fixed prices. Determining whether such options are considered distinct performance obligations that provide the customer with a material right and therefore should be accounted for separately requires significant judgment. Judgment is required to determine the standalone selling price for each renewal option to determine whether the renewal pricing is reflective of standalone selling price or is reflective of a discount that would provide the customer with a material right. Based on the Company’s assessment of standalone selling prices, the Company determined that there were no significant material rights provided to its customers requiring separate recognition. Contract Balances The timing of revenue recognition may not align with the right to invoice the customer. The Company records accounts receivable when it has the unconditional right to issue an invoice and receive payment, regardless of whether revenue has been recognized. Amounts billed in excess of revenue recognized for the period are reported as a contract liability (deferred revenue) on the consolidated balance sheets. The Company’s deferred revenue consists primarily of unearned revenue on annual and monthly subscription plans and professional services fees, and prepayments from customers that get applied against final month billings. Amounts not expected to be recognized as revenue within the next twelve months of the consolidated balance sheet date are classified as long-term deferred revenue. If revenue is recognized in advance of the right to invoice, a contract asset (unbilled receivable) is recorded. Opening balances as of January 1, 2020 and closing balances as of December 31, 2020 were as follows: Balance at January 1, 2020 Balance at December 31, 2020 Accounts receivable $ 21,390 $ 13,936 Deferred revenue, current portion (9,958) (6,329) Deferred revenue, net of current portion (12,021) (11,403) The net increase in deferred revenue was due to billings in advance of performance obligations being satisfied. During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company recognized revenues of approximately $11,290, which was included in the deferred revenue balance at the beginning of the period. In instances where the timing of revenue recognition differs from the timing of the right to invoice, the Company has determined that a significant financing component generally does not exist. The primary purpose of the Company’s invoicing terms is to provide customers with simplified and predictable ways of

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 13 purchasing the products and services and not to receive financing from or provide financing to the customer. Additionally, the Company has elected the practical expedient that permits an entity not to recognize a significant financing component if the time between the transfer of a good or service and payment is one year or less. Payment terms on invoiced amounts are typically due net 30 to net 45 days after invoice date. Other Considerations The Company does not offer rights of return for its products and services in the normal course of business, and contracts generally do not include service-type warranties that provide any incremental service to the customer beyond providing assurance that the goods and services conform to applicable specifications or customer-specific or subjective acceptance provisions. The Company also excludes from revenue government-assessed and imposed taxes on revenue-generating activities that are invoiced to customers. Costs to Obtain and Fulfill a Contract In accordance with ASC 340-40 (see Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements below), sales commissions paid to internal salespeople and other associated costs that are incremental to the acquisition of customer contracts are capitalized as deferred costs on the balance sheet when the period of benefit is determined to be greater than one year. The Company has elected to apply the practical expedient to expense sales commissions and associated costs as incurred when the expected amortization period is one year or less. The Company has determined the period of benefit for sales commissions paid to internal salespeople and external sales agents for the acquisition of the initial contract to be 60 months by taking into consideration the initial estimated customer life and the technological life of the Company’s products and services, as well as expectations about whether the renewal commission will be commensurate with the initial commission. Amortization is recognized on a straight-line basis commensurate with the pattern of revenue recognition. As of January 1, 2020 and in connection with the adoption of ASC 606, the Company had capitalized $13,894 in sales commissions. Amortization of deferred commissions is included in sales and marketing expenses in the consolidated statement of operations. For the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company recognized $4,071 of the beginning balance in commission expense. As of December 31, 2020, the Company has capitalized $12,730 in sales commissions. The Company periodically reviews these deferred commissions to determine whether events or changes in circumstances have occurred that could affect the recovery or period of benefit of these deferred contract acquisition costs. There were no impairment losses recorded during the year ended December 31, 2020. In accordance with ASC 340-40, the Company capitalizes incremental costs incurred to fulfill its contracts that (i) relate directly to the contract, (ii) are expected to generate resources that will be used to satisfy the Company’s performance obligation(s) under the contract, and (iii) are expected to be recovered through revenue generated under the contract. These costs have historically been immaterial. Accordingly, the Company has not capitalized any contract fulfillment costs as of January 1, 2020 or December 31, 2020. During periods prior to January 1, 2020, the Company recognized revenue in accordance with FASB ASC 605, Revenue Recognition. Revenue under service subscription plans was recognized as services were rendered. Product revenues were recognized when the product had been shipped to the customer. Professional services revenue related to products sold was recognized on completion of those services due to the short duration of the service period. One-time upfront fees were initially deferred and recognized on a straight-line basis over the estimated average customer life. In arrangements with multiple deliverables, the Company allocated the consideration to each deliverable based upon their relative selling prices. The Company determined the selling price using vendor-specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) for its subscription plans and best estimated selling price (“BESP”) for its product offerings. Reductions to revenue for customer credits were recorded at the time the related revenue was recognized.

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 14 Cost of Revenue Cost of revenue consists of services purchased from third-party telecommunications and cloud hyperscaler providers, network operations, costs to build-out and maintain data centers, including co- location fees for the right to place the Company’s servers in data centers owned by third parties, and depreciation of servers and equipment, along with related utilities and maintenance costs. In addition, personnel costs associated with non-administrative customer care and support of the Company’s platform and data center operations, including share-based compensation expenses and allocated costs of facilities and information technology, are included in costs of revenue. In addition, costs of revenue are comprised of the costs and expenses associated with purchased phones and equipment, as well as personnel costs for provisioning team and contractors and allocated costs of facilities and information technology related to the procurement, shipment and installation of phones and related services. These costs are expensed when the product is delivered to the customer. Accounts Receivable The Company provides credit to customers in the ordinary course of business and believes its credit policies are prudent and reflect industry practices and business risk. Management reviews accounts receivable on a periodic basis and reserves for receivables in its allowance for doubtful accounts on a specific identification basis when they are determined to be uncollectible. Inventory The Company’s inventory consists of certain hardware finished goods held for resale which complement the Company’s core unified communications software-based service solution. The Company’s policy for the valuation of inventory, including the determination of obsolete or excess inventory, requires management to estimate the future demand for the Company’s products held for resale, and considers actual sales experience for such products, among other factors. This determination is based on the inventory held at the balance sheet date and firm, non-cancellable commitments for the future purchase of inventory items. Inventory purchases and purchase commitments are based upon such forecasts of future demand, and anticipated customer demand for such products. The business environment in which the Company operates is subject to rapid changes in technology and customer demand. The Company performs an assessment of inventory during each reporting period, which includes a review of, among other factors, demand requirements, non-cancellable purchase commitments of the Company to certain key suppliers and other relevant factors. If actual sales experience and projected customer demand subsequently differs from the Company’s forecasts, requirements for additional inventory and other reserves that differ from the Company’s estimates could become necessary. If management believes that demand no longer allows the Company to sell inventories above cost or at all, such inventory is either reduced to its net realizable value or fully reserved if no future demand exists. During 2019, management determined that future demand for a certain third-party product held for resale, which is subject to future non-cancellable purchase commitments, had materially declined, primarily due to changes in the rapidly changing competitive environment in what the Company operates, and low enterprise customer demand for this hardware solution. In addition to considering the future sales projections, management also considered the low demand for such third-party product during 2019, and changes to market conditions which occurred during 2019. Based on consideration of all relevant factors, the Company recorded a one-time pre-tax charge of approximately $16,950 in cost of revenue related to this third-party product for the year ended December 31, 2019 for the future non-cancellable inventory purchase commitments that were determined to have no value. The remaining future minimum payments under this arrangement have been accrued and are included within Accrued expenses and other current liabilities ($3,284) and Other long-term liabilities ($13,750) in the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2020.

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 15 Future minimum payments under this purchase commitment as of December 31, 2020 are as follows: 2021 $ 3,284 2022 4,080 2023 3,672 2024 2,938 2025 2,040 Thereafter 1,020 $ 17,034 Advertising Advertising costs are included in sales and marketing expenses in the consolidated statement of operations and are expensed as incurred. Advertising expenses were $4,585 for the year ended December 31, 2020. Stock-Based Compensation The Company measures stock-based awards granted to employees and directors based on the fair value on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model for options and the fair value of its common stock for restricted stock awards. Compensation expense of those awards is recognized over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the respective award. Generally, the Company issues awards with only service-based vesting conditions and records the expense for these awards using the straight-line method. The Company has not recorded any compensation expense related to historically issued restricted stock awards and restricted stock units with both service-based and performance-based vesting conditions as the achievement of the related performance conditions has been deemed to be not probable. The Company classifies stock-based compensation expense in its statements of operations in the same manner in which the award recipient’s payroll costs are classified or in which the award recipient’s service payments are classified. Foreign Currency Translation In connection with foreign operations with functional currencies other than the U.S. dollar, assets and liabilities are translated at current exchange rates, while income and expenses are translated at the average exchange rates for the period. The resulting foreign currency translation adjustments are reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive loss. Foreign currency transaction losses are included in other expense, net, in the consolidated statement of operations and were $838 for the year ended December 31, 2020. Warrants The Company accounts for warrants for the purchase of shares that are redeemable, or contingently redeemable, as a liability at fair value with the change in fair value recorded in other expense, net, in the consolidated statement of operations. Comprehensive Loss Comprehensive loss includes net loss, as well as other changes in stockholders’ deficit that result from transactions and events other than those with stockholders. The Company’s only element of other comprehensive loss is foreign currency translation. Income Taxes The Company accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the consolidated financial statements or in the Company’s tax returns. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined on the basis of the differences between the consolidated financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities are recorded in the provision for income taxes. The Company assesses the likelihood that its deferred tax assets will be

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 16 recovered from future taxable income and, to the extent it believes, based upon the weight of available evidence, that it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized, a valuation allowance is established through a charge to income tax expense. The Company accounts for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in the consolidated financial statements by applying a two-step process to determine the amount of tax benefit to be recognized. First, the tax position must be evaluated to determine the likelihood that it will be sustained upon external examination by the taxing authorities. If the tax position is deemed more-likely-than-not to be sustained, the tax position is then assessed to determine the amount of benefit to recognize in the consolidated financial statements. The amount of the benefit that may be recognized is the largest amount that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. The provision for income taxes includes the effects of any resulting tax reserves, or unrecognized tax benefits, that are considered appropriate as well as the related net interest and penalties. Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, and has since issued several additional amendments thereto (collectively referred to herein as “ASC 606”). ASC 606 outlines a single comprehensive model for entities to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers and supersedes most current revenue recognition guidance, including industry-specific guidance. The new standards require entities to apportion consideration from contracts to performance obligations on a relative standalone selling price basis, based on a five-step model. Under ASC 606, revenue is recognized when a customer obtains control of a promised good or service and is recognized in an amount that reflects the consideration that the entity expects to receive in exchange for the good or service. In addition, ASC 606 provides guidance on accounting for certain revenue related costs including costs associated with obtaining and fulfilling a contract, as codified in ASC 340-40, Other Assets and Deferred Costs—Contracts with Customers. The Company adopted these new standards on January 1, 2020 using the modified retrospective method and applied the standard only to those contracts that were not completed as of January 1, 2020. Applying this method, the Company’s results for reporting periods beginning January 1, 2020 are presented under ASC 606, while prior period amounts are not adjusted and continue to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for the prior period. The Company elected to utilize the modified retrospective transition practical expedient, which allows the Company to not retrospectively restate contracts for contract modifications executed before the beginning of the earliest period presented and instead reflect the aggregate effect of those modifications when identifying the satisfied and unsatisfied performance obligations, determining the transaction price, and allocating the transaction price to the satisfied and unsatisfied performance obligations. The Company recorded a net decrease to beginning accumulated deficit of $19,412 as of January 1, 2020 due to the cumulative impact of adopting ASC 606 and ASC 340-40, with the impact primarily related to the acceleration of revenue related to nonrecurring, upfront professional services and the deferral of certain sales commissions paid to internal salespeople. Under ASC 605, one-time upfront fees were deferred and recognized on a straight-line basis over the estimated average customer life. Under ASC 606, these fees have been determined to relate to a distinct performance obligation and are recognized as the services are provided. Sales commissions paid to internal salespeople were previously expensed as incurred, but are now generally capitalized and amortized over the expected period of benefit under the amendments to ASC 340-40.

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 17 The cumulative effect of adopting ASC 606 effective January 1, 2020 on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet is as follows: As of January 1, 2020 As Previously Reported ASC 606 Adjustments As Adjusted Assets Deferred commissions, current $ — $ 4,071 $ 4,071 Deferred commissions, non-current $ — $ 9,823 $ 9,823 Liabilities Deferred revenue, current portion $ 12,308 $ (2,350) $ 9,958 Deferred revenue, net of current portion $ 15,189 $ (3,168) $ 12,021 Stockholders’ Deficit Accumulated deficit $ (686,229) $ 19,412 $ (666,817) In accordance with ASC 606, the impact from adoption of the standard to the Company’s financial statements in the current reporting period was as follows: Year Ended December 31, 2020 As Reported Balances Without Adoption of ASC 606 Effect of Change – Higher/(Lower) Revenue $ 129,746 $ 131,156 $ (1,410) Sales and marketing expenses 50,133 48,969 1,164 Net loss $ (47,353) $ (44,779) $ (2,574) As of December 31, 2020 As Reported Balances Without Adoption of ASC 606 Effect of Change – Higher/(Lower) Assets Deferred commissions, current $ 4,700 $ — $ 4,700 Deferred commissions, non-current $ 8,030 $ — $ 8,030 Liabilities Deferred revenue, current portion $ 6,329 $ 7,269 $ (940) Deferred revenue, net of current portion $ 11,403 $ 14,571 $ (3,168) Stockholders’ Deficit Accumulated deficit $ (714,170) $ (731,008) $ 16,838 Adoption of the new standard had no impact to cash provided by or used in operating, investing, or financing activities on the Company’s consolidated statements of cash flows. In June 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-07, Compensation—Stock Compensation (Topic 718), Improvements to Nonemployee Share-Based Payment Accounting (“ASU 2018-07”). This ASU is intended to simplify aspects of share-based compensation issued to non-employees by making the guidance consistent with the accounting for employee share-based compensation. For public entities, this

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 18 guidance is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. For nonpublic entities, this guidance is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019. The Company adopted the standard as of January 1, 2020. The adoption of ASU 2018-07 had no impact on the Company’s financial position, results of operations, or cash flows. In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-15, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other—Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350-40): Customer’s Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement That Is a Service Contract. ASU 2018-15 aligns the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract with the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred to develop or obtain internal-use software (and hosting arrangements that include an internal use software license). The accounting for the service element of a hosting arrangement that is a service contract is not affected by these amendments. For public entities, the standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years. For nonpublic entities, the standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2020. Early adoption is permitted for all entities. The Company adopted this guidance on a prospective basis effective January 1, 2020. The impact of the adoption was immaterial to the Company's consolidated financial statements. Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) (“ASU 2016-02”), which requires lessees to recognize most leases on their balance sheet as a right-of-use asset and a lease liability. In general, lease arrangements exceeding a twelve-month term must be recognized as assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. Under ASU 2016-02, a right-of-use asset and lease obligation is recorded for all leases, whether operating or financing, while the income statement reflects lease expense for operating leases and amortization/interest expense for financing leases. The FASB also issued ASU 2018-10, Codification Improvements to Topic 842 Leases, and ASU 2018-11, Targeted Improvements to Topic 842 Leases, which allows the new lease standard to be applied as of the adoption date with a cumulative effect adjustment to the opening balance of retained earnings rather than retroactive restatement of all periods presented. For nonpublic entities, the guidance is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2021 based on the FASB’s most recent extension of the effective date. Early adoption is permitted for all entities. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that the adoption of ASU 2016-02 will have on its consolidated financial statements. In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (Topic 326) (“ASU 2016-13”), which introduces a new methodology for accounting for credit losses on financial instruments, including available-for-sale debt securities. The guidance establishes a new “expected loss model” that requires entities to estimate current expected credit losses on financial instruments by using all practical and relevant information. Any expected credit losses are to be reflected as allowances rather than reductions in the amortized cost of available-for-sale debt securities. The FASB also issued ASU 2019-10, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326), Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815), and Leases (Topic 842), which changed the effective date of the amendment for nonpublic companies to annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2022. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact that ASU 2016-13 may have on its financial position and results of operations. In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment. The standard eliminates the second step in the goodwill impairment test which requires an entity to determine the implied fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill. The standard is effective for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests conducted in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect of the standard on its consolidated financial statements. In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-15, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other—Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350-40): Customer’s Accounting for Implementation Costs Incurred in a Cloud Computing Arrangement That Is a Service Contract. ASU 2018-15 aligns the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract with the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred to develop or obtain internal-use software (and hosting arrangements that include an internal use software license). The accounting for the service element of a

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 19 hosting arrangement that is a service contract is not affected by these amendments. For public entities, the standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years. For nonpublic entities, the standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2020. Early adoption is permitted for all entities. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that the adoption of ASU 2018-15 will have on its consolidated financial statements. In December 2019, the FASB issued ASU 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740). ASU 2019-12 is intended to simplify the accounting for income taxes by removing certain exceptions to the general principles in Topic 740 and improve consistent application of and simplify GAAP for other areas of Topic 740 by clarifying and amending existing guidance. For public entities, the standard is effective for annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2020, including interim periods within those fiscal years. For nonpublic entities, the standard is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2021. Early adoption is permitted for all entities. The Company is planning to adopt the standard in 2022 but does not expect it to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements. In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-06, Debt—Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40), which simplifies accounting for convertible instruments by eliminating two of the three accounting models available for convertible debt instruments and convertible preferred stock. The guidance also addresses how convertible instruments are accounted for in the diluted earnings per share calculation. The guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2023 and early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the impact of this pronouncement to its consolidated financial statements. 3. Fair Value Measurements The following tables set forth the Company’s financial assets and liabilities that were measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2020. The Company did not have any nonfinancial assets or liabilities that were measured or disclosed at fair value on a recurring basis at December 31, 2020. The Company did not have any transfers between levels for the year ended December 31, 2020. Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2020 Using: Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Total Cash equivalents: Money market funds $ 5 $ — $ — $ 5 Money market funds were valued by the Company based on quoted market prices, which represent a Level 1 measurement within the fair value hierarchy. The redeemable convertible preferred stock warrant liability in the tables above consists of the fair value of warrants to purchase Series B, Series C, Series D, Series F, and Series G-3 redeemable convertible preferred stock (Note 12) and was based on significant inputs not observable in the market, which represent a Level 3 measurement within the fair value hierarchy. The Company’s valuation of the redeemable convertible preferred stock warrants utilizes the Black-Scholes option pricing model, which incorporates assumptions and estimates to value the redeemable convertible preferred stock warrants. The Company assesses these assumptions and estimates on an annual basis as additional information impacting the assumptions was obtained. Changes in the fair value of the redeemable convertible preferred stock warrants are recognized as other expense, net, in the consolidated statements of operations. The quantitative elements associated with the Company’s Level 3 inputs impacting the fair value measurement of the redeemable convertible preferred stock warrant liability include the fair value per share of the underlying Series B, Series C, Series D, Series F, and Series G-3 redeemable convertible preferred stock, the remaining contractual term of the warrants, risk-free interest rate, expected dividend yield, and expected volatility of the price of the underlying preferred stock. The most significant assumption in the Black-Scholes option pricing model impacting the fair value of the redeemable convertible preferred stock warrants is the fair value of the Company’s convertible preferred

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 20 stock as of each remeasurement date. The Company determines the fair value per share of the underlying preferred stock by taking into consideration its most recent sales of its convertible preferred stock as well as additional factors that the Company deems relevant. As of December 31, 2020, the fair value per share of the Series B redeemable convertible preferred stock was $0.28, the fair value per share of the Series C redeemable convertible preferred stock was $0.49, the fair value per share of the Series D redeemable convertible preferred stock was $0.49, the fair value per share of the Series F redeemable convertible preferred stock was $0.97, and the fair value per share of the Series G-3 redeemable convertible preferred stock was $1.07. The Company historically has been a private company and lacks company-specific historical and implied volatility information of its stock. Therefore, it estimates its expected stock volatility based on the historical volatility of publicly traded peer companies for a term equal to the remaining contractual term of the warrants. The risk-free interest rate is determined by reference to the U.S. Treasury yield curve for time periods approximately equal to the remaining contractual term of the warrants. The Company has estimated a 0% dividend yield based on the expected dividend yield and the fact that the Company has never paid or declared dividends. The following table provides a roll-forward of the aggregate fair value of the Company’s redeemable convertible preferred stock warrants for which fair value is determined by Level 3 inputs: Preferred Stock Warrant Liability Balance at December 31, 2019 $ 4,260 Exercise of Series C Preferred Stock Warrants (284) Expiration of Series B and C Preferred Stock Warrants (200) Change in fair value of warrants (3,776) Balance at December 31, 2020 $ — 4. Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the following: December 31, 2020 Prepaid taxes $ 1,543 Prepaid expenses 1,251 Short-term deposits 237 $ 3,031 5. Property and Equipment Property and equipment consisted of the following: December 31, 2020 Computer equipment $ 7,908 Network operations equipment 4,789 Leasehold improvements 4,213 Software 2,343 Furniture and fixtures 1,708 20,961 Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization (18,360) $ 2,601

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 21 The Company did not capitalize any costs associated with the development of internal-use software and recorded related amortization expense of $355 during the year ended December 31, 2020, included in depreciation and amortization expense. The remaining net book value of capitalized software costs was $222 at December 31, 2020. As of December 31, 2020, the Company had $773 of assets purchased under capital leases and accumulated amortization related to assets under capital leases of $436 at December 31, 2020. Depreciation and amortization expense related to property and equipment for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $2,084. 6. Goodwill and Intangible Assets There was no change to goodwill during the year ended December 31, 2020. As of the balance sheet date, intangible assets consisted of the following: December 31, 2020 Weighted Average Life Gross Carrying Amount Accumulated Amortization Net Carrying Amount (years) Developed technology 5.2 $ 3,000 $ 2,568 $ 432 Customer relationships 2 1,070 1,070 — Trade name 6 520 448 72 $ 4,590 $ 4,086 $ 504 Amortization expense for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $372. Future estimated amortization expense for intangible assets is as follows: Year Ending December 31, 2021 $ 308 2022 196 Total $ 504 7. Accrued Expenses and Other Current Liabilities Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consisted of the following: December 31, 2020 Sales and other tax liabilities $ 15,661 Accrued commissions 5,550 Accrued compensation and benefits 4,482 Accrued expenses 3,372 Inventory purchase commitments (See Note 2) 3,240 Other accrued liabilities 551 $ 32,856

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 22 8. Financing Arrangements AB Private Credit Investors In September 2019, the Company entered into a credit agreement as amended with AB Private Credit Investors, LLC (“AB Credit Agreement”). The credit agreement provides for borrowings of up to $85,000 in initial term loans, up to $20,000 in delayed draw term loans, and $10,000 in revolving commitments. In September 2019, the Company borrowed $85,000 of initial term loans. The Company used $55,000 of these proceeds to repay amounts due under its outstanding debt agreements with other lenders. Upon extinguishment of the previously outstanding debt, the Company recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $1,959 within other income (expense) on its statement of operations during the year ended December 31, 2019. In December 2019, the Company borrowed $7,000 under the revolving commitments which was repaid in full in January 2020. In March 2020, the Company borrowed $6,000 in delayed draw term loans under the AB Credit Agreement at an interest rate equal to the greater of LIBOR or 2.0% plus the applicable margin percentage of 6.5%. Interest-only payments are due quarterly for the delayed draw term loans with a lump sum principal payment due in September 2024. Interest-only payments are due quarterly for the initial term loans through August 2022 at which time monthly principal payments are due from September 2022 through August 2024. The Company must pay a fee of 0.5% of the unused portions of both the delayed draw term loans and revolving commitments annually in addition to a one-time fee of 1.5% on borrowings under the delayed draw term loans. Borrowings under the initial term loans bear interest at a rate equal to the greater of LIBOR or 2.0% plus the applicable margin percentage of 6.5%. At December 31, 2020, the interest rate was 8.5% equal to 2.0% plus the margin percentage of 6.5%. Borrowings under the revolving commitments bear interest at a rate of 10.00%. The effective annual interest rate of the outstanding debt under the AB Credit Agreement is approximately 8.86%. Borrowings under the AB Credit Agreement are to mature on September 20, 2024 and are collateralized by substantially all of the Company’s personal property, including intellectual property. The AB Credit Agreement is subject to certain administrative and financial covenants including monthly, quarterly, and annual financial statement reporting and maintaining certain liquidity measures, leverage ratios, and quarterly EBITDA. There are negative covenants restricting the Company’s activities, including limitations on mergers or acquisitions, incurring indebtedness or liens, paying dividends, and certain other business transactions, and there are customary provisions regarding the occurrence of material adverse events and related rights available to AB if such an event were to occur. The obligations under the AB Credit Agreement are subject to acceleration upon the occurrence of specified events of default, including failing to make payments due or failing to meet the covenants related to the AB Credit Agreement, and upon the occurrence of material adverse events which remain uncured. As of December 31, 2020, the Company was not in compliance with certain administrative and financial covenants. As a result, the lender has the option to declare the borrowings under the AB Credit Agreement immediately due and payable. Therefore, the Company classified the balances associated with the AB Credit Agreement within current liabilities at December 31, 2020. In connection with the AB Credit Agreement, the lenders received warrants to purchase 1,425,003 shares of the Company’s Series G-3 convertible preferred stock with an exercise price of $2.00 per share and a 10-year term. The fair value of the warrants as of the issuance date of $2,176 was recorded as a preferred stock warrant liability and debt discount (Note 12). The debt discount is being amortized to interest expense using the effective-interest method from the date of the issuance through the maturity date. Paycheck Protection Program In June 2020, the Company issued a Promissory Note to Silicon Valley Bank, pursuant to which it received $6,338 provided under the Paycheck Protection Program established under the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (“CARES”) Act and guaranteed by the U.S. Small Business Administration (the “Paycheck Protection Program”). The loan is unsecured, is scheduled to mature in June 2022, has a fixed interest rate of 1.0% per annum and is subject to the standard terms and conditions applicable to loans administered under the Paycheck Protection Program. The loan may be forgiven to the extent

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 23 proceeds of the loan are used for eligible expenditures, such as payroll and other expenses described in the CARES Act. The Company applied for loan forgiveness and was notified that the U.S. Small Business Administration (“SBA”) had forgiven the loan in June 2021. Future minimum principal payment obligations under all of the Company’s outstanding debt as of December 31, 2020 are as follows: Year Ending December 31, 2021 $ 1,585 2022 16,559 2023 42,500 2024 36,695 Total outstanding principal balance 97,339 Unamortized deferred financing costs (2,424) 94,915 Current portion of long-term debt 90,161 Non-current portion of long-term debt $ 4,754 9. Redeemable Convertible and Convertible Preferred Stock The Company has issued Series A convertible preferred stock and Series B, Series C, Series D, Series E, Series F, Series G-1, Series G-2, and Series G-3 redeemable convertible preferred stock (collectively, the “Preferred Stock”). The Series G-1, Series G-2, and Series G-3 are collectively referred to as “Series G.” The holders of Preferred Stock have liquidation rights in the event of a deemed liquidation that, in certain situations, is not solely within the control of the Company. Therefore, the preferred stock is classified outside of stockholders’ deficit. The following provides a summary of these preferred stock issuances, with all such existing preferred stock as of December 31, 2020 converted to common stock in January 2021 (see Note 16). In February 2017, the Company issued 16,176,806 shares of its Series F redeemable convertible preferred stock (the “Series F”) at an issuance price of $6.44 per share for $104,200 in gross proceeds. In April 2017, the Company issued an additional 4,657,430 shares of its Series F for $30,000 in gross proceeds at an issuance price of $6.44 per share in a second closing. The Series F was recorded net of $211 of issuance costs. In May 2018, the Company issued 21,614,992 shares of its Series G-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock (the “Series G-1”) at an issuance price of $2.00 per share for $21,615 in gross proceeds and the exchange of 34,381 shares of Series C preferred stock (“Series C”), 1,549,266 shares of Series E preferred stock (“Series E”), and 1,791,950 shares of Series F. In addition, the Company issued 506,250 shares of Series G-2 redeemable convertible preferred stock (the “Series G-2”) at an issuance price of $2.00 per share for $1,012 in gross cash proceeds. In July 2018, the Company issued an additional 122,484,976 shares of Series G-1 at an issuance price of $2.00 per share for $122,485 in gross cash proceeds and the exchange of 194,823 shares of Series C, 2,522,023 shares of Series D preferred stock (“Series D”), 9,253,582 shares of Series E, and 8,407,823 shares of Series F. In addition, the Company issued 2,868,750 shares of Series G-2 at an issuance price of $2.00 per share for $5,738 in gross cash proceeds. The exchange of shares was accounted for as an extinguishment of existing shares and accordingly, the Company recorded a deemed contribution of capital related to the issuance of Series G-1 preferred stock of $12,231 and the deemed dividend related to the issuance of Series G-2 preferred stock of $709 to additional paid-in capital, representing the difference between the fair value of Series G and the carrying value of the exchanged shares. The Series G-1 was recorded net of $617 of issuance costs.
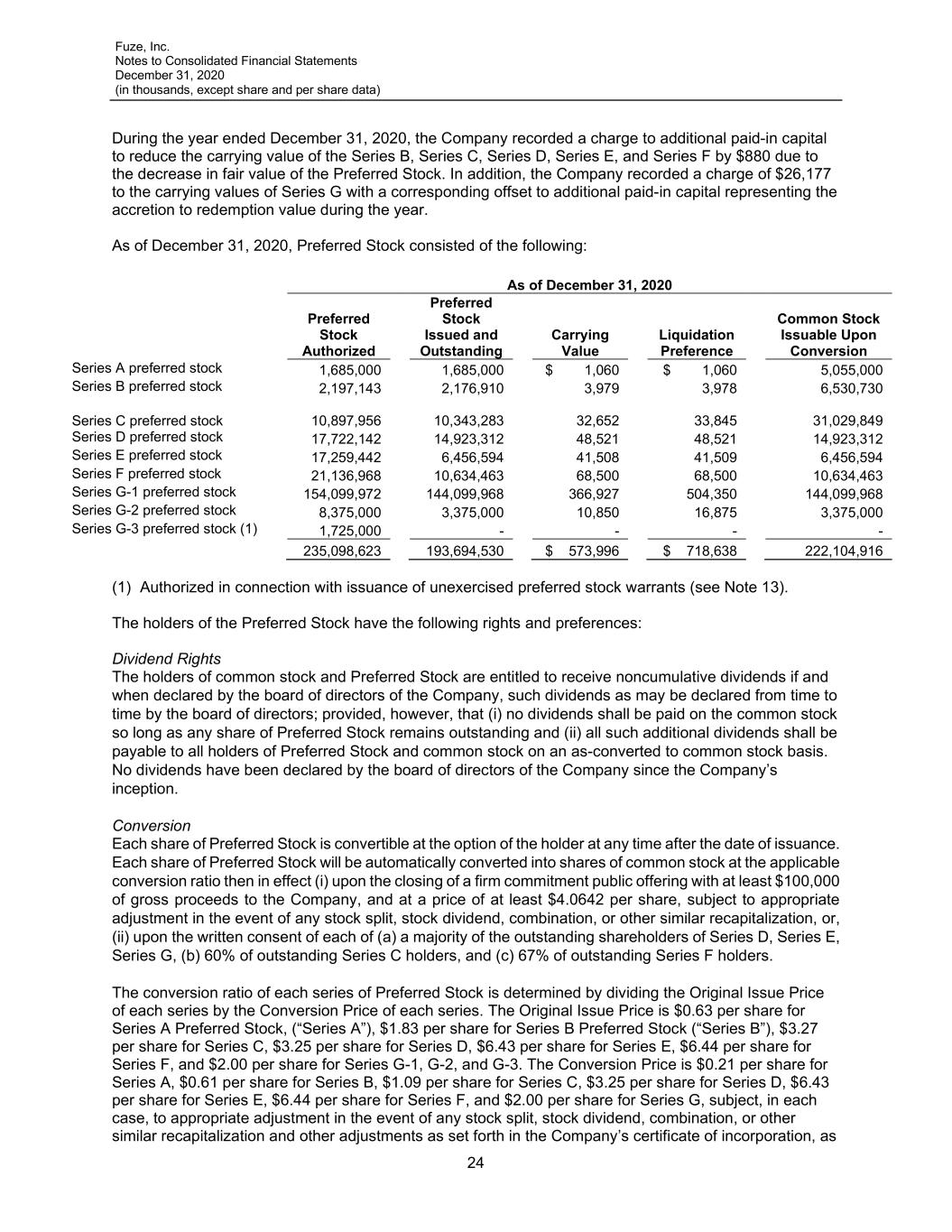
Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 24 During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company recorded a charge to additional paid-in capital to reduce the carrying value of the Series B, Series C, Series D, Series E, and Series F by $880 due to the decrease in fair value of the Preferred Stock. In addition, the Company recorded a charge of $26,177 to the carrying values of Series G with a corresponding offset to additional paid-in capital representing the accretion to redemption value during the year. As of December 31, 2020, Preferred Stock consisted of the following: As of December 31, 2020 Preferred Stock Authorized Preferred Stock Issued and Outstanding Carrying Value Liquidation Preference Common Stock Issuable Upon Conversion Series A preferred stock 1,685,000 1,685,000 $ 1,060 $ 1,060 5,055,000 Series B preferred stock 2,197,143 2,176,910 3,979 3,978 6,530,730 Series C preferred stock 10,897,956 10,343,283 32,652 33,845 31,029,849 Series D preferred stock 17,722,142 14,923,312 48,521 48,521 14,923,312 Series E preferred stock 17,259,442 6,456,594 41,508 41,509 6,456,594 Series F preferred stock 21,136,968 10,634,463 68,500 68,500 10,634,463 Series G-1 preferred stock 154,099,972 144,099,968 366,927 504,350 144,099,968 Series G-2 preferred stock 8,375,000 3,375,000 10,850 16,875 3,375,000 Series G-3 preferred stock (1) 1,725,000 - - - - 235,098,623 193,694,530 $ 573,996 $ 718,638 222,104,916 (1) Authorized in connection with issuance of unexercised preferred stock warrants (see Note 13). The holders of the Preferred Stock have the following rights and preferences: Dividend Rights The holders of common stock and Preferred Stock are entitled to receive noncumulative dividends if and when declared by the board of directors of the Company, such dividends as may be declared from time to time by the board of directors; provided, however, that (i) no dividends shall be paid on the common stock so long as any share of Preferred Stock remains outstanding and (ii) all such additional dividends shall be payable to all holders of Preferred Stock and common stock on an as-converted to common stock basis. No dividends have been declared by the board of directors of the Company since the Company’s inception. Conversion Each share of Preferred Stock is convertible at the option of the holder at any time after the date of issuance. Each share of Preferred Stock will be automatically converted into shares of common stock at the applicable conversion ratio then in effect (i) upon the closing of a firm commitment public offering with at least $100,000 of gross proceeds to the Company, and at a price of at least $4.0642 per share, subject to appropriate adjustment in the event of any stock split, stock dividend, combination, or other similar recapitalization, or, (ii) upon the written consent of each of (a) a majority of the outstanding shareholders of Series D, Series E, Series G, (b) 60% of outstanding Series C holders, and (c) 67% of outstanding Series F holders. The conversion ratio of each series of Preferred Stock is determined by dividing the Original Issue Price of each series by the Conversion Price of each series. The Original Issue Price is $0.63 per share for Series A Preferred Stock, (“Series A”), $1.83 per share for Series B Preferred Stock (“Series B”), $3.27 per share for Series C, $3.25 per share for Series D, $6.43 per share for Series E, $6.44 per share for Series F, and $2.00 per share for Series G-1, G-2, and G-3. The Conversion Price is $0.21 per share for Series A, $0.61 per share for Series B, $1.09 per share for Series C, $3.25 per share for Series D, $6.43 per share for Series E, $6.44 per share for Series F, and $2.00 per share for Series G, subject, in each case, to appropriate adjustment in the event of any stock split, stock dividend, combination, or other similar recapitalization and other adjustments as set forth in the Company’s certificate of incorporation, as

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 25 amended and restated. In the event of an initial public offering, if the offering price is less than certain per share amounts as defined in the articles of incorporation, as amended and restated, the Conversion Ratios of the Preferred Stock may be adjusted. Liquidation Upon a liquidation event, as defined in the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, any proceeds will be distributed to the holders of the Company’s shares in the following preferential order and amounts: (1) Holders of Series G will receive an amount equal to, in the case of Series G-1, the greater of (a) 1.75X the Series G-1 Original Issue Price, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon or (b) the amount per share as would have been payable had each such share been converted into common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event; in the case of Series G-2, the greater of (a) 2.5X the Series G-2 Original Issue Price, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon or (b) the amount per share as would have been payable had each such share been converted into common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event; and, in the case of Series G-3, the greater of (a) the Series G-3 Original Issue Price, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon or (b) the amount per share as would have been payable had each such share been converted into common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event; (2) Holders of Series C, D, E, and F will receive an amount equal to the greater of (a) the Original Issue Price of each series, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon or (b) the amount per share as would have been payable had each such share been converted into common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. If, upon any such liquidation, dissolution, or winding up, the assets of the Company shall be insufficient to make payment in full to all holders of Series C, Series D, Series E, and Series F of the liquidation preference, then such assets shall be distributed to the holders of Series C, Series D, Series E, and Series F ratably on a pari passu basis in proportion to the respective amounts to which they would otherwise be respectively entitled; (3) Holders of Series B will receive an amount equal to the greater of (a) the Series B Original Issue Price, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon or (b) amount per share as would have been payable had each such share been converted into common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. If, upon any such liquidation, dissolution, or winding up, the assets of the Company shall be insufficient to make payment in full to all holders of Series B of the liquidation preference, then such assets shall be distributed to the holders of Series B ratably in proportion to the respective amounts to which they would otherwise be respectively entitled; (4) Holders of Series A will receive an amount equal to the greater of (a) the Series A Original Issue Price, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon or (b) amount per share as would have been payable had each such share been converted into common stock immediately prior to the liquidation event. If, upon any such liquidation, dissolution, or winding up, the assets of the Company shall be insufficient to make payment in full to all holders of Series A of the liquidation preference, then such assets shall be distributed to the holders of Series A ratably in proportion to the respective amounts to which they would otherwise be respectively entitled; and (5) After the payment of the full liquidation preferences of the Preferred Stock, the assets of the Company legally available for distribution, if any, shall be distributed ratably to the holders of common stock, pro rated based on the number of shares held by each such holder. Redemption The Series A is not redeemable. The shares of Series G shall be redeemed on a pari passu basis in three equal annual installments commencing 90 days after receipt by the Corporation, at any time after March 20, 2025, of a written notice from a majority of the outstanding shares of Series G. The “Series G

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 26 Redemption Price” is the price per share equal to the greater of (i) the liquidation amount per share of Series G-1, G-2, or G-3 preferred stock and (ii) the Series G-1, G-2, or G-3 fair market value per share. At any time after redemption of the Series G, the shares of Series C, Series D, Series E, and Series F shall be redeemed on a pari passu basis in three equal annual installments commencing 90 days after receipt by the Corporation, of a written notice from a majority of the outstanding shares of Series C, Series D, Series E, and Series F together as a single class on an as-converted basis. The “Series C Redemption Price,” “Series D Redemption Price,” “Series E Redemption Price,” and “Series F Redemption Price” is the price per share equal to the greater of (i) the fair market value per share of Series C, Series D, Series E, or Series F, and (ii) the Series C Original Issue Price, Series D Original Issue Price, Series E Original Issue Price or Series F Original Issue Price, respectively, plus any dividends declared but unpaid. The shares of Series B shall be redeemed in three equal annual installments commencing 90 days after receipt by the Corporation, at any time on or after the Series C, Series D, Series E, Series F, and Series G redemption date with a written notice from at least a majority of the voting power of the then outstanding shares of Series B. The “Series B Redemption Price” is the price per share equal to the greater of (i) the fair market value per share of the Series B, and (ii) the Series B Original Issue Price plus any dividends declared but unpaid. Voting Rights The holder of each share of Series A, Series B, Series C, Series D, Series E, Series F, and Series G shall have the right to one vote for each share of common stock into which the Preferred Stock could then be converted. 10. Common Stock The voting, dividend and liquidation rights of the holders of common stock are subject to and qualified by the rights, powers, and preferences of the holders of Preferred Stock. The common stock has the following characteristics: Voting The holders of shares of common stock are entitled to one vote for each share of common stock held at all meetings of stockholders and written actions in lieu of meetings. Dividends The holders of shares of common stock are entitled to receive dividends, if and when declared by the board of directors of the Company. Cash dividends may not be declared or paid to holders of shares of common stock until all accrued unpaid dividends on Series A, Series B, Series C, Series D, Series E, Series F, Series G-1, Series G-2, and Series G-3 have been paid in accordance with their terms. No dividends have been declared or paid by the Company since its inception. Liquidation After payment to of their respective liquidation preferences to the holders of shares of Preferred Stock, the holders of shares of common stock are entitled to share ratably in the Company's remaining assets available for distribution to its stockholders in the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution, or winding up of the Company or upon occurrence of a deemed liquidation event. 11. Stock-based Compensation Equity Compensation Plan The Company has a 2006 Equity Compensation Plan (the “2006 Plan”), a 2012 Equity Compensation Plan (the “2012 Plan”), and a 2017 Equity Compensation Plan (the “2017 Plan”), which are administered by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors. The 2017 Plan became effective in July 2017, and upon effectiveness, the remaining shares available under the 2006 Plan and 2012 Plan became
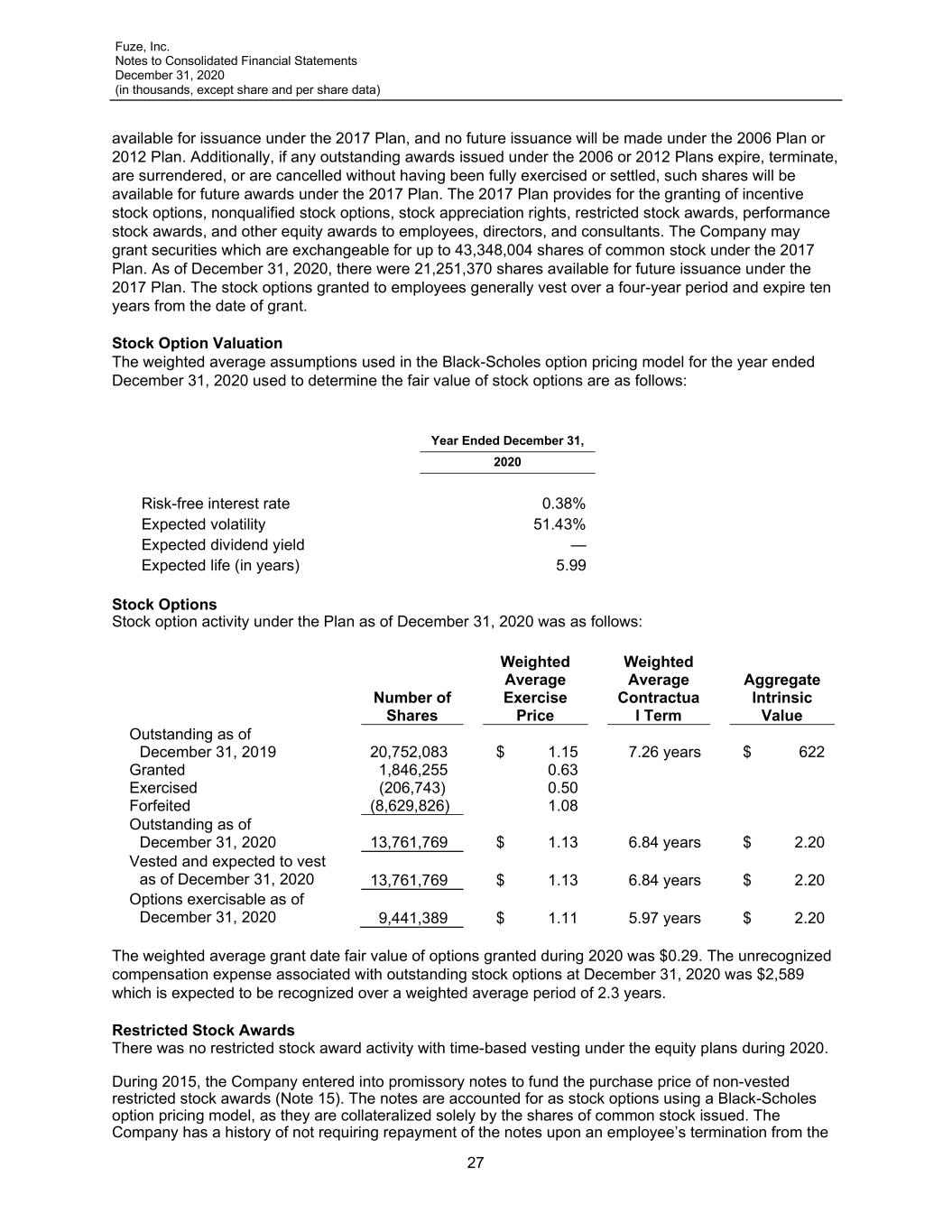
Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 27 available for issuance under the 2017 Plan, and no future issuance will be made under the 2006 Plan or 2012 Plan. Additionally, if any outstanding awards issued under the 2006 or 2012 Plans expire, terminate, are surrendered, or are cancelled without having been fully exercised or settled, such shares will be available for future awards under the 2017 Plan. The 2017 Plan provides for the granting of incentive stock options, nonqualified stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, performance stock awards, and other equity awards to employees, directors, and consultants. The Company may grant securities which are exchangeable for up to 43,348,004 shares of common stock under the 2017 Plan. As of December 31, 2020, there were 21,251,370 shares available for future issuance under the 2017 Plan. The stock options granted to employees generally vest over a four-year period and expire ten years from the date of grant. Stock Option Valuation The weighted average assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model for the year ended December 31, 2020 used to determine the fair value of stock options are as follows: Year Ended December 31, 2020 Risk-free interest rate 0.38% Expected volatility 51.43% Expected dividend yield — Expected life (in years) 5.99 Stock Options Stock option activity under the Plan as of December 31, 2020 was as follows: Number of Shares Weighted Average Exercise Price Weighted Average Contractua l Term Aggregate Intrinsic Value Outstanding as of December 31, 2019 20,752,083 $ 1.15 7.26 years $ 622 Granted 1,846,255 0.63 Exercised (206,743) 0.50 Forfeited (8,629,826) 1.08 Outstanding as of December 31, 2020 13,761,769 $ 1.13 6.84 years $ 2.20 Vested and expected to vest as of December 31, 2020 13,761,769 $ 1.13 6.84 years $ 2.20 Options exercisable as of December 31, 2020 9,441,389 $ 1.11 5.97 years $ 2.20 The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted during 2020 was $0.29. The unrecognized compensation expense associated with outstanding stock options at December 31, 2020 was $2,589 which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 2.3 years. Restricted Stock Awards There was no restricted stock award activity with time-based vesting under the equity plans during 2020. During 2015, the Company entered into promissory notes to fund the purchase price of non-vested restricted stock awards (Note 15). The notes are accounted for as stock options using a Black-Scholes option pricing model, as they are collateralized solely by the shares of common stock issued. The Company has a history of not requiring repayment of the notes upon an employee’s termination from the

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 28 Company. The weighted average assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model used to determine the fair value of the restricted stock awards are as follows: Risk-free interest rate 2.00% Expected volatility 54.91% Expected dividend yield — Expected life (in years) 7.00 Restricted Stock Awards with Service-Based and Performance-Based Vesting During 2018, the Company had restricted stock awards outstanding for 130,000 shares of common stock at a grant date fair value of $3.07. These restricted stock awards are subject to both service-based vesting conditions of 48 months and performance-based vesting conditions upon a liquidity event, defined as either a sale event or IPO. During 2020, no restricted stock awards subject to both service-based and performance-based vesting conditions were forfeited. The Company has not recorded any compensation expense related to these restricted stock awards during the year ended December 31, 2020, as the achievement of the performance condition has been deemed to be not probable. Restricted Stock Units with Service-Based and Performance-Based Vesting Restricted stock unit activity with service-based and performance-based vesting as of December 31, 2020 was as follows: Number of Shares Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value Unvested Restricted Common Stock as of December 31, 2019 8,994,361 $ 1.18 Granted 3,573,025 1.47 Vested — Forfeited (2,821,730) Unvested Restricted Common Stock as of December 31, 2020 9,745,656 These restricted stock units are subject to both service-based vesting conditions of 48 months and performance-based vesting conditions upon a liquidity event, defined as either change of control or IPO. The Company has not recorded any compensation expense related to these restricted stock units during the year ended December 31, 2020, as the achievement of the performance condition has been deemed to be not probable. Stock-Based Compensation Expense Stock-based compensation expense for all stock-based compensation awards was classified in the statement of operations as follows: Year Ended December 31, 2020 Cost of revenue $ 341 Research and development 644 Sales and marketing 352 General and administrative 750 Total $ 2,087 The Company did not capitalize any stock-based compensation expense related to the development of

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 29 internal-use software included in property and equipment during the year ended December 31, 2020. 12. Warrants The Company has outstanding warrants issued in connection with previous debt arrangements and funding received through preferred stock issuances. No warrants to purchase Series G-3 preferred stock were exercised in 2020. The Company is required to remeasure the fair value of outstanding warrants at each reporting date. Changes in the fair value of warrants to purchase Series B, Series C, Series D, Series F, and Series G-3 preferred stock are recorded in other income (expense) in the statement of operations. As a result of changes in the fair value of the preferred stock warrants, the Company recorded income associated with the change in fair value of warrants of $3,776 for the year ended December 31, 2020. The following tables summarize the Company’s outstanding warrants to purchase preferred stock as of December 31, 2020: As of December 31, 2020 Issue Date Expiration Date Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Exercise Price Number of Shares Outstanding Under Warrant Fair Value September 29, 2015 September 29, 2025 Series D 3.25 276,807 $ — December 19, 2016 December 19, 2026 Series F 6.44 46,574 — June 30, 2017 June 29, 2027 Series F 6.44 256,158 — September 20, 2019 September 20, 2029 Series G-3 2.00 1,425,003 — 2,004,542 $ — Warrants to purchase common stock During 2016, the Company issued a warrant to its primary bank to purchase 32,573 shares of common stock in connection with amendments made to previously outstanding debt. The warrant was issued with an exercise price of $3.07 per share, was immediately exercisable, and expires in 2026. 13. Income Taxes The domestic and foreign components of income (loss) before income tax expense are as follows: Year Ended December 31, 2020 Domestic $ (47,848) Foreign 1,531 Loss before income tax expense $ (46,317) Income tax expense consisted of the following: Year Ended December 31, 2020 Current $ 860 Deferred 176 $ 1,036
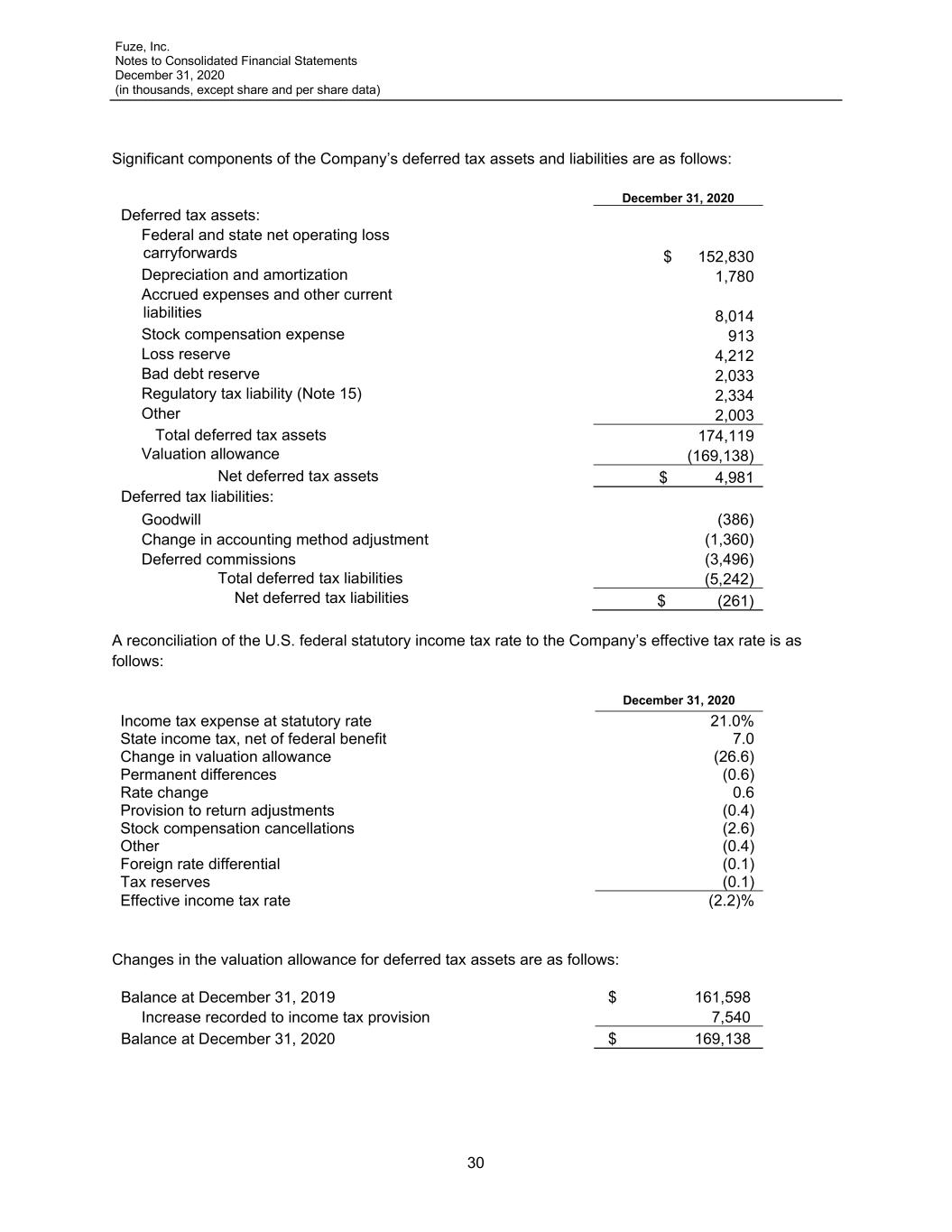
Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 30 Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows: December 31, 2020 Deferred tax assets: Federal and state net operating loss carryforwards $ 152,830 Depreciation and amortization 1,780 Accrued expenses and other current liabilities 8,014 Stock compensation expense 913 Loss reserve 4,212 Bad debt reserve 2,033 Regulatory tax liability (Note 15) 2,334 Other 2,003 Total deferred tax assets 174,119 Valuation allowance (169,138) Net deferred tax assets $ 4,981 Deferred tax liabilities: Goodwill (386) Change in accounting method adjustment (1,360) Deferred commissions (3,496) Total deferred tax liabilities (5,242) Net deferred tax liabilities $ (261) A reconciliation of the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate to the Company’s effective tax rate is as follows: December 31, 2020 Income tax expense at statutory rate 21.0% State income tax, net of federal benefit 7.0 Change in valuation allowance (26.6) Permanent differences (0.6) Rate change 0.6 Provision to return adjustments (0.4) Stock compensation cancellations (2.6) Other (0.4) Foreign rate differential (0.1) Tax reserves (0.1) Effective income tax rate (2.2)% Changes in the valuation allowance for deferred tax assets are as follows: Balance at December 31, 2019 $ 161,598 Increase recorded to income tax provision 7,540 Balance at December 31, 2020 $ 169,138

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 31 Changes in unrecognized tax benefits activity are as follows: December 31, 2020 Unrecognized tax benefits at the beginning of the year $ 1,022 Gross increases in tax benefits 38 Unrecognized tax benefits at the end of the year $ 1,060 At December 31, 2020, the Company had federal net operating loss carryforwards of $559 of which $366 will expire at various dates beginning in 2032 and $193 that has an indefinite life. At December 31, 2020, the Company had state net operating loss carryforwards of $596 of which $564 will expire at various dates beginning in 2032 and $32 that has an indefinite life. Utilization of the U.S. federal and state net operating loss carryforwards may be subject to a substantial annual limitation under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 due to ownership change limitations that have occurred previously or that could occur in the future. These ownership changes may limit the amount of net operating loss carryforwards that can be utilized annually to offset future taxable income and tax, respectively. Any limitation may result in expiration of a portion of the net operating loss carryforwards before utilization. Management of the Company has evaluated the positive and negative evidence bearing upon the realizability of its deferred tax assets, which are comprised principally of net operating loss carryforwards. The Company accounts for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in the financial statements by applying a two-step process to determine the amount of tax benefit to be recognized. First, the tax position must be evaluated to determine the likelihood that it will be sustained upon external examination by the taxing authorities. If the tax position is deemed more-likely-than-not to be sustained, the tax position is then assessed to determine the amount of benefit to recognize in the financial statements. The amount of the benefit that may be recognized is the largest amount that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. The provision for income taxes includes the effects of any resulting tax reserves, or unrecognized tax benefits, that are considered appropriate as well as the related net interest and penalties. After consideration of all evidence, both positive and negative, the Company determined that a valuation allowance was needed for a portion of its U.S. deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2020 because it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The previously recorded foreign valuation allowance was released in 2020 and the Company has determined that its foreign deferred tax assets are realizable as of December 31, 2020 and therefore has not recorded a valuation allowance against them. The Company establishes reserves for uncertain tax positions based on management’s assessment of exposures associated with tax positions taken on tax return filings. The tax reserves are analyzed periodically and adjustments are made as events occur to warrant adjustments to the reserve. At December 31, 2020, the Company reported an ending tax reserve balance for the U.S. entities of $384 for potential exposure for certain foreign and state tax return filings. For the foreign entities the Company reported an ending tax reserve balance of $677 for potential exposure for past foreign tax return filings. As of December 31, 2020, the unremitted earnings of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries are not material. The Company has not provided for U.S. income taxes or foreign withholding taxes on these earnings as it is the Company’s intention to permanently reinvest these earnings outside the U.S. The tax liabilities on these earnings are also not material. Events that could trigger a tax liability include, but are not limited to, distributions, reorganizations or restructurings and/or tax law changes. Interest and penalty charges, if any, related to unrecognized tax benefits would be classified as income tax expense in the accompanying statement of operations. As of December 31, 2020, the Company recorded for the U.S. entities $12 of income tax expense related to federal and state interest and penalties associated with certain foreign and state tax return filings. For the foreign entities the Company recorded $11 of income tax expense related to foreign jurisdictions interest and penalties associated with past foreign tax return filings. Since the Company is in a loss carry forward position, the Company is generally subject to examination by the U.S. federal, state, and local income tax authorities for all tax

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 32 years in which a loss carry forward is available. The Company is also subject to income taxes in several foreign jurisdictions that have various statutes of limitation but in general range between three to five years. 14. Commitments and Contingencies Operating and Capital Leases The Company leases office space in the United States, Canada, United Kingdom, Germany, Sweden, Switzerland, The Netherlands, France, Bulgaria, Denmark, Portugal, Australia, and Spain under operating agreements expiring through 2026. In addition to rental expense, the Company is obligated to pay costs of insurance, taxes, repairs, and maintenance pursuant to the terms of the leases. The rental payments include the minimum rentals plus common area maintenance charges. Rental expense for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $4,078. The Company also leases property and equipment under capital leases (see Note 5). Future minimum payments under operating and capital leases as of December 31, 2020 are as follows: Operating Leases Capital Lease Obligations 2021 $ 3,112 $ 317 2022 2,871 156 2023 1,353 — 2024 811 — 2025 751 — Thereafter 1,075 — Total minimum lease payments $ 9,973 473 Less: Amount representing interest 65 Present value of capital lease obligations 408 Less: Current portion 277 Capital lease obligation, net of current portion $ 131 Legal and Regulatory Proceedings The Company, from time to time, may be involved in proceedings relating to contractual disputes, employment matters, regulatory tax compliance matters, and other like matters relating to claims that arise in the normal course of business. The Company determines whether an estimated loss from any such matter should be accrued by evaluating the specific nature of the matter and its potential liability, based upon the facts and circumstances of the specific action or regulatory matter, using reasonably available information. The Company develops its views on estimated potential loss accruals in consultation with counsel, which involves a subjective analysis of potential outcomes. The Company recorded a charge in 2020 of $8,500 which is reflected as a component of other expense, net, in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations related to a regulatory matter. The Company intends on pursuing all cost-efficient settlement vehicles available to them to resolve this matter, including voluntary disclosure agreements (“VDA’s”). Actual claims could settle or be adjudicated against the Company in the future for materially different amounts than the Company has accrued, due to the inherently unpredictable nature of such matters, and also due to the generally favorable settlement conditions accorded those who voluntarily enter into the VDA process. Legal fees are expensed in the period in which they are incurred. 15. Related Party Transactions In November 2015, the Company loaned $1,472 to two employees of the Company to purchase shares of common stock pursuant to promissory notes and restricted stock agreements (Note 12). The promissory notes provide that the unpaid principal amount of the loans bear interest at 2.57% annually, and interest

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 33 is payable annually or is converted to principal and payable at the maturity date. The maturity date of the promissory notes occurs on the earliest of (i) seven years from the issuance date of the notes, (ii) 30 days following the date of termination of employment of the borrower, and (iii) immediately prior to an initial filing of a registration statement by the Company. The promissory notes are non-recourse and secured by a pledge of the shares of common stock purchased with the promissory notes. The promissory note for one employee was amended in 2018 to change the maturity date to the earlier of (i) 2023 or (ii) immediately prior to an initial filing of a registration statement by the Company. In the ordinary course of business, the Company had sales to Bessemer Venture Partners (“Bessemer”), a shareholder. Total revenue from Bessemer for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $71. 16. Subsequent Events The Company evaluated subsequent events through October 7, 2021, the date on which the consolidated financial statements were originally available to be issued. In January 2021, the Company raised approximately $13,600 of new equity capital by selling a new series of Series A-1 Preferred Stock to existing investors. As part of this January 2021 financing, all existing shares of preferred stock were converted to common stock. In February and August 2021, the Company entered into amendments to the AB Credit Agreement under which the lenders agreed to amend certain provisions of the AB Credit Agreement and waive certain defaults and events of default that have occurred and are continuing under the AB Credit Agreement. The lenders further waived their right to charge and receive interest at the default rate of interest as a result of the specified defaults. As of September 30, 2021, the Company did not meet certain covenants set forth in the AB Credit Agreement. Due to these breaches, AB Private Credit Investors (“AB”) is contractually entitled to request immediate repayment of the total outstanding amount. AB has not requested early payment of the loan as of the date when these financial statements were approved by the Board of Directors. In April 2021, the Company raised an additional $14,000 of term debt capital from AB, further amended the covenants of the AB Credit Agreement and extended the date of the first principal repayment to AB to September 2023, from September 2022. In connection with this April 2021 financing transaction, the Company issued warrants to purchase 4,734,189 shares of the Company’s Series A Prime Preferred Stock to the lenders under the AB Credit Agreement in replacement of the warrants to purchase the Company’s Series G-3 convertible preferred stock originally issued to the lenders in connection with the credit agreement in September 2019, cancelled the existing common warrants held by AB and agreed to new credit pricing terms and provisions. The new warrants have an exercise price of $0.19 per share and a 10-year term. The Company also raised an additional $2,500 of capital from the issuance of additional shares of Series A-1 Preferred Stock to existing investors coincident with this additional debt financing. In June 2021, the Company was notified that the SBA had forgiven the $6,338 loan issued to the Company under the Paycheck Protection Program in 2020. In August 2021, the Company raised an additional $12,000 of new equity capital from the issuance of additional shares of Series A-1 Preferred Stock to an independent new investor and certain existing investors. Events Subsequent to Original Issuance of the Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited) In connection with the reissuance of the consolidated financial statements, the Company has evaluated subsequent events through November 30, 2021, the date the consolidated financial statements were available to be reissued. On October 8, 2021, the Company amended its arrangement with a third-party provider of inventory held for resale subject to non-cancellable inventory

Fuze, Inc. Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements December 31, 2020 (in thousands, except share and per share data) 34 purchase commitments which resulted in a loss accrual in 2019, as disclosed in Note 2. Pursuant to this October 2021 amendment, the total obligations due to this vendor over the initial contractual life decreased to $7,650, in exchange for (i) an acceleration of remaining payments due under the contract, (ii) a change in the mix of the products available from the third-party vendor to fulfill the Company’s purchase commitment and (iii) a reduction in the support period and remaining term for these third-party products. The Company expects to record a non-operating gain in October 2021 based on the reduction in the total contractual payments due under this arrangement, as well as other elements of this amendment. On November 30, 2021, the Company entered into a Definitive Merger Agreement for the acquisition of 100% of the equity interests in the Company, on a cash-free, debt-free basis. This transaction is expected to close in early 2022, following shareholder and standard regulatory approvals, and fulfilment of customary closing conditions.



































