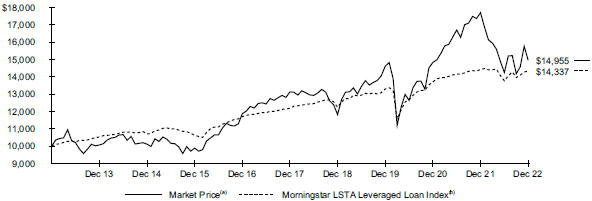
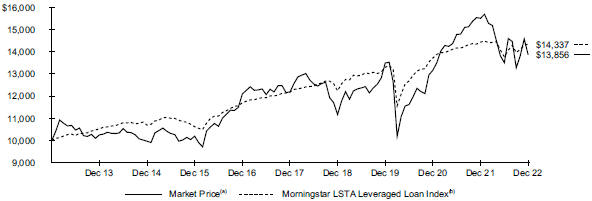
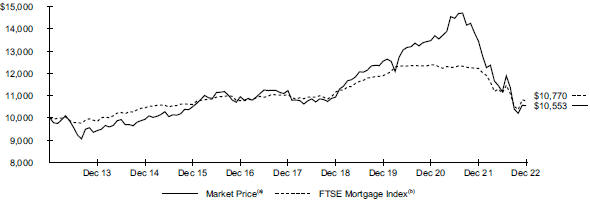
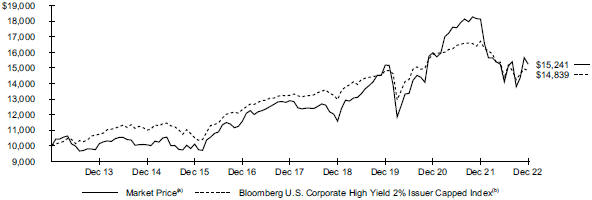
| | |
| 140 | | 2 0 2 2 B L A C K R O C K A N N U A L R E P O R T T O S H A R E H O L D E R S |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
The following information is a summary of certain changes since December 31, 2021.This information may not reflect all of the changes that have occurred since you purchased the relevant Fund.
During each Fund’s most recent fiscal year, there were no material changes in the Fund’s investment objectives or policies that have not been approved by shareholders or in the principal risk factors associated with investment in the Fund.
Investment Objectives and Policies
BlackRock Debt Strategies Fund, Inc. (DSU)
The Fund’s primary investment objective is to seek to provide current income by investing primarily in a diversified portfolio of U.S. companies’ debt instruments, including Corporate Loans (as defined below), which are rated in the lower rating categories of the established rating services (Baa or lower by Moody’s Investor’s Service (“Moody’s”) or BBB or lower by S&P Global Ratings (“S&P”)) or unrated debt instruments which are in the judgment of BlackRock Advisors, LLC (the “Manager”) of equivalent quality. Such investments generally involve greater volatility of price and risks to principal and income than securities in the higher rating categories. As a secondary objective, the Fund will seek to provide capital appreciation. The Fund’s investment objectives are fundamental policies and may not be changed without the approval of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Fund (as defined in the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “1940 Act”)).
Under normal market conditions, at least 80% of the Fund’s total assets will be invested in debt instruments. The Fund may invest directly in debt instruments or synthetically through the use of derivatives. The Fund has no restrictions on portfolio maturity or duration of the debt securities in which it may invest.
The Fund’s investment policies permit investment in the following asset classes which are described in greater detail below: (i) senior and subordinated corporate loans, both secured and unsecured (“Corporate Loans”), issued either directly by the borrower or in the form of participation interests in Corporate Loans made by banks and other financial institutions; (ii) publicly offered and privately placed high-yield debt securities, senior and subordinated, both secured and unsecured; and (iii) convertible debt instruments and preferred stock, each of which may be converted into common stock or other securities of the same or a different issuer, and nonconvertible preferred stock. The debt securities and Corporate Loans in which the Fund invests may pay interest at fixed rates or at rates that float at a margin above a generally recognized base lending rate such as the prime rate of a designated U.S. bank, or that adjust periodically at a margin above the CD rate or LIBOR.
In connection with its investments in corporate debt securities, or restructuring of investments owned by the Fund, the Fund may receive warrants or other non-income producing debt or equity securities. The Fund may retain such securities until the Manager determines it is appropriate in light of current market conditions to effect a disposition of such securities.
The Fund will not invest in Corporate Loans that would require the Fund to make any additional investments in connection with its obligation to make future advances to a borrower in connection with revolving credit facilities if such commitments would exceed 20% of the Fund’s total assets or would cause the Fund to fail to meet the diversification requirements described herein.
The Fund may invest in high-yield corporate debt securities, including Corporate Loans, which are rated in the lower rating categories of the established rating services (Baa or lower by Moody’s and BBB or lower by S&P Global Ratings), or in unrated securities considered by the Manager to be of comparable quality. Securities rated below Baa or lower by Moody’s or BBB or lower by S&P and unrated securities of comparable quality, are commonly known as “junk bonds.” Securities which subsequently are downgraded may continue to be held by the Fund and will be sold only if, in the judgment of the Manager, it is advantageous to do so.
Up to 20% of the Fund’s total assets may be invested in Distressed Securities (defined below), which includes publicly offered or privately placed debt securities and Corporate Loans which, at the time of investment, are the subject of bankruptcy proceedings or otherwise in default as to the repayment of principal and/or payment of interest or are rated in the lowest rating categories (Ca or lower by Moody’s and CC or lower by S&P) or which, if unrated, are in the judgment of the Manager of equivalent quality (“Distressed Securities”). Although the Fund will invest primarily in lower-rated securities, other than with respect to Distressed Securities (which are discussed below) it will not invest in securities in the lowest rating categories (Ca or below by Moody’s and CC or below by S&P) unless the Manager believes that the financial condition of the issuer or the protection afforded to the particular securities is stronger than would otherwise be indicated by such low ratings. Securities which subsequently are downgraded may continue to be held by the Fund and will be sold only if, in the judgment of the Manager, it is advantageous to do so.
Up to 20% of the Fund’s total assets may be invested in financial instruments of issuers domiciled outside the United States or that are denominated in various foreign currencies and multinational foreign currency units, provided that the foreign issuers of any non-U.S. dollar denominated instruments purchased by the Fund are domiciled in a country that is a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
Up to 20% of the Fund’s total assets can be invested in convertible debt instruments and preferred stock, each of which may be converted into common stock or other securities of the same or a different issuer, and non-convertible preferred stock. The types of preferred securities in which the Fund may invest include trust preferred securities.
As a result of conversions of convertible securities or upon an exchange offer or bankruptcy plan of reorganization, a significant portion of the Fund’s total assets may be invested in common stock at certain points in time.
The Fund may engage in various portfolio strategies to seek to increase its return and to hedge its portfolio against movements in interest rates or foreign currencies through the use of interest rate or foreign currency swap transactions, the purchase of call and put options on securities, the sale of covered call and put options on its portfolio securities and transactions in financial futures and related options on such futures. There can be no assurance that the Fund will employ these strategies or that, if employed, they will be effective.
| | |
I N V E S T M E N T O B J E C T I V E S , P O L I C I E S A N D R I S K S | | 141 |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
Investment Objectives and Policies
(continued)
The Fund may make short sales of securities, provided that the market value of all securities sold short does not exceed 10% of its total assets. The Fund may make short sales both as a form of hedging to offset potential declines in long positions in similar securities and in order to seek to enhance return. The Fund’s obligation to replace the borrowed security will be secured by collateral deposited with the broker dealer, usually cash, U.S. government securities or other liquid securities similar to those borrowed. The Fund also will be required to segregate similar collateral with its custodian or designate such collateral on its books and records to the extent, if any, necessary so that the value of both collateral amounts in the aggregate is at all times equal to at least 100% of the current market value of the security sold short. The Fund also may make short sales “against the box.” Short sales “against the box” are not subject to the foregoing 10% limitation.
Subject to other investment restrictions applicable to the Fund, up to 10% of the Fund’s assets may be invested in debt instruments, including Corporate Loans, of investment companies (which may or may not be registered under the 1940 Act) whose portfolio securities consist entirely of (i) corporate debt or equity securities acceptable to the Manager or (ii) money market instruments.
The Fund has no limitation on the amount of its investments that are not readily marketable or are subject to restrictions on resale.
The Fund currently utilizes leverage for investment purposes in the form of a bank credit facility. The Fund generally will not utilize leverage if it anticipates that the Fund’s leveraged capital structure would result in a lower return to common stockholders than that obtainable if the common stock were unleveraged for any significant amount of time. At times, the Fund could utilize leverage through borrowings, including the issuance of short term debt securities, the issuance of shares of preferred stock or a combination thereof. The Fund also has the ability to utilize leverage through the issuance of shares of preferred stock. The Fund may also utilize leverage through the use of reverse repurchase agreements.
The Fund may also borrow money as a temporary measure for extraordinary or emergency purposes, including the payment of dividends and the settlement of securities transactions which may otherwise require untimely dispositions of Fund securities. The Fund at times may borrow from affiliates of the Manager, provided that the terms of such borrowings are no less favorable than those available from comparable sources of funds in the marketplace.
There can be no assurance that the Fund will borrow in order to leverage its assets or, if it does, what percentage of the Fund’s assets such borrowings will represent. The Fund does not currently anticipate issuing any preferred stock.
BlackRock Floating Rate Income Strategies Fund, Inc. (FRA)
The Fund’s investment objective is to provide stockholders with high current income and such preservation of capital as is consistent with investment in a diversified, leveraged portfolio consisting primarily of floating rate debt securities and instruments (“floating rate debt securities”). The Fund’s investment objective is a fundamental policy and may not be changed without stockholder approval.
The Fund seeks to achieve its investment objective by investing, under normal market conditions, at least 80% of its Managed Assets in floating rate debt securities, including floating or variable rate debt securities that pay interest at rates that adjust whenever a specified interest rate changes and/or which reset on predetermined dates (such as the last day of a month or calendar quarter). “Managed Assets” means the total assets of the Fund (including any assets attributable to money borrowed for investment purposes) minus the sum of the Fund’s accrued liabilities (other than money borrowed for investment purposes). The Fund invests a substantial portion of its investments in floating rate debt securities consisting of secured or unsecured senior floating rate loans that are rated below investment grade at the time of investment or, if unrated, are considered by BlackRock Advisors, LLC (the “Manager”) or BlackRock International Limited (“BIL” and together with the Manager, the “Advisors”), the Fund’s sub-advisor, to be of comparable quality. Secured loans may be either wholly or partially secured at the time of investment. In addition to senior loans, floating rate debt securities may include, without limitation, instruments such as catastrophe and other event linked bonds, bank capital securities, corporate bonds, notes, money market instruments and certain types of mortgage related and other asset backed securities. Due to their floating or variable rate features, these instruments will generally pay higher levels of income in a rising interest rate environment and lower levels of income as interest rates decline. For the same reason, the market value of a floating rate debt security is generally expected to have less sensitivity to fluctuations in market interest rates than a fixed rate debt instrument, although the value of a floating rate debt security may nonetheless decline as interest rates rise and due to other factors, such as real or perceived changes in credit quality or financial condition of the issuer or borrower, volatility in the capital markets or other adverse market conditions.
The Fund may invest directly in floating rate debt securities or synthetically through the use of derivatives.
The Fund’s policy to invest, under normal market conditions, at least 80% of its Managed Assets in floating rate debt securities, as described above, is a non-fundamental policy and may be changed by the Board of Directors of the Fund provided that stockholders are provided with at least 60 days’ prior notice of any change, unless such change was previously approved by shareholders, as required by the rules under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “1940 Act”).
The Fund may invest up to 20% of its total assets in securities other than floating rate debt securities, including, but not limited to, fixed rate debt securities such as convertible securities, bonds, notes, fixed rate loans and mortgage related and other asset backed securities issued on a public or private basis, collateralized debt obligations, preferred securities, commercial paper, U.S. government securities, structured notes, credit linked notes, credit linked trust certificates and other hybrid instruments.
To a limited extent, incidental to and in connection with its investment activities or pursuant to a convertible feature in a security, the Fund may acquire warrants and other debt and equity securities. The Fund may also acquire other debt and equity securities of a borrower or issuer in connection with an amendment, waiver, conversion or exchange of a senior loan or other debt security or in connection with a bankruptcy or workout of the borrower or issuer.
The Fund may invest without limit, and generally intends to invest a substantial portion of its assets, in high yield securities, including senior loans and other floating or fixed rate debt securities, that are rated below investment grade by the established rating services (Ba or lower by Moody’s Investor’s Service (“Moody’s”) or BB or lower by S&P Global Ratings (“S&P”)) or, if unrated, are considered by the Advisors to be of comparable quality. High yield bonds commonly are referred to as “junk” bonds. The high yield securities in which the Fund invests may include credit linked notes, structured notes, credit linked trust certificates or other instruments evidencing interests in special purpose vehicles
| | |
| 142 | | 2 0 2 2 B L A C K R O C K A N N U A L R E P O R T T O S H A R E H O L D E R S |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
Investment Objectives and Policies
(continued)
or trusts that hold interests in high yield securities. Other than with respect to Distressed Securities (which are discussed below), the high yield securities in which the Fund may invest do not include securities which, at the time of investment, are in default or the issuers of which are in bankruptcy. The Fund may also invest in investment grade securities, which are securities rated at least BBB– as determined by S&P, Baa3 as determined by Moody’s or, if unrated, determined to be of comparable quality by the Advisors.
The Fund may not invest more than 10% of its total assets (at the time of investment) in securities that are rated Caa1 or lower (if rated by Moody’s) or CCC+ or lower (if rated by S&P) by each agency rating such security or, if unrated, are considered by the Advisors to be of comparable quality or are otherwise considered to be distressed securities (“Distressed Securities”).
The Fund may invest without limitation in debt securities of issuers domiciled outside the United States. The Fund, however, will not invest more than 10% of its total assets in debt securities of issuers located in emerging market countries. Emerging market countries generally include every nation in the world (including countries that may be considered “frontier” markets) except the United States, Canada, Japan, Australia, New Zealand and most countries located in Western Europe. The Fund will invest primarily in U.S. dollar denominated debt securities. The Fund will not invest more than 10% of its total assets in debt securities denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar or that do not provide for payment to the Fund in U.S. dollars, including obligations of non-U.S. governments and their respective subdivisions, agencies and government sponsored enterprises.
The Fund may invest in bonds of varying maturities issued by U.S. and non-U.S. corporations and other business or governmental entities. Bonds can be variable or fixed rate debt obligations, including bills, notes, debentures, money market instruments and similar instruments and securities. The Fund may also invest in catastrophe or other “event linked” bonds. The Fund may invest in securities of any maturity.
The Fund may invest in preferred securities, including preferred securities that may be converted into common stock or other securities of the same or a different issuer. The types of preferred securities in which the Fund may invest include trust preferred securities.
The Fund may invest in convertible securities. A convertible security is a bond, debenture, note, preferred security or other security that may be converted into or exchanged for a prescribed amount of common stock or other equity security of the same or a different issuer within a particular period of time at a specified price or formula.
The Fund may invest without limit in illiquid securities, which are floating rate debt securities, senior loans, high yield securities and other securities that lack a secondary trading market or are otherwise considered illiquid.
The Fund currently utilizes leverage for investment purposes in the form of a bank credit facility. At times, the Fund could utilize leverage through borrowings, the issuance of short term debt securities, the issuance of shares of preferred stock or a combination thereof. The Fund also has the ability to utilize leverage through the issuance of shares of preferred stock. The Fund may also leverage through the use of reverse repurchase agreements. There can be no assurance that the Fund will borrow in order to leverage its assets or, if it does, what percentage of the Fund’s assets such borrowings will represent. The Fund does not currently anticipate issuing any preferred stock.
BlackRock Income Trust, Inc. (BKT)
The Fund’s investment objective is to manage a portfolio of high-quality securities to achieve both preservation of capital and high monthly income. The Fund will seek to distribute monthly income that is greater than that obtainable on an annualized basis by investment in United States government securities having the same maturity as the weighted average maturity of the Fund’s investments. The Fund’s portfolio is expected to consist primarily of mortgage-backed securities and, to a lesser extent, asset-backed securities.
Mortgage-backed securities are securities that directly or indirectly represent a participation in, or are secured by and payable from, mortgage loans secured by real property. There are three basic types of mortgage-backed securities: (i) those issued or guaranteed by the United States government or one of its agencies or instrumentalities, such as the Government National Mortgage Association (“GNMA”), the Federal National Mortgage Association (“Fannie Mae”) and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (“Freddie Mac”); (ii) those issued by private issuers that are collateralized by securities issued or guaranteed by the United States government or one of its agencies or instrumentalities; and (iii) those issued by private issuers and collateralized by securities without a government guarantee but usually with some form of private credit enhancement.
The Fund will invest at least 65% of its assets in mortgage-backed securities. The balance of the Fund’s assets generally will be invested in asset-backed securities, which have structural characteristics similar to mortgage-backed securities but have underlying assets that are not mortgage loans or interests in mortgage loans. The Fund may also invest in various derivative mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities, such as collateralized mortgage obligations and asset-backed security residual interests and stripped mortgage-backed securities. The Fund may invest directly in such securities or synthetically through the use of derivatives. In addition, for hedging purposes, the Fund may utilize a portion of its assets for certain options, futures, interest rate swaps and related transactions. For purposes of enhancing liquidity and/or preserving capital, the Fund may invest without limit in securities issued by the United States government and its agencies and instrumentalities, or repurchase agreements collateralized by such securities, certificates of deposit, time deposits or bankers’ acceptances of similar quality.
At least 80% of the Fund’s assets will be invested in securities that are (i) issued or guaranteed by the United States government or one of its agencies or instrumentalities or (ii) rated at the time of investment either AAA by S&P Global Ratings (“S&P”) or Aaa by Moody’s Investors Service (“Moody’s”). Securities issued or guaranteed by the United States government or its agencies or instrumentalities are generally considered to be of the same or higher quality than privately issued securities rated AAA or Aaa. No more than 20% of the Fund’s assets will be invested in other securities, all of which will have been determined by BlackRock Advisors, LLC (the “Manager”) or BlackRock International Limited (“BIL” and together with the Manager, the “Advisors”), the Fund’s sub-advisor, to be of comparable credit quality.
The yield characteristics of mortgage-backed and asset-backed securities differ from traditional debt securities. Among the major differences are that interest and principal payments are made more frequently, usually monthly, and that principal may be prepaid at any time because the underlying mortgage loans or other assets generally may be
| | |
I N V E S T M E N T O B J E C T I V E S , P O L I C I E S A N D R I S K S | | 143 |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
Investment Objectives and Policies
(continued)
prepaid at any time. As a result, if the Fund purchases such a security at a premium, a prepayment rate that is faster than expected will reduce yield to maturity, while a prepayment rate that is slower than expected will have the opposite effect of increasing yield to maturity. Conversely, if the Fund purchases these securities at a discount, faster than expected prepayments will increase, while slower than expected prepayments will reduce, yield to maturity. The Fund may also invest in derivative securities such as stripped mortgage-backed securities or residual interests, which generally are more sensitive to changes in prepayment and interest rates. The Advisors will seek to manage these risks (and potential benefits) by investing in a variety of such securities and through hedging techniques.
Prepayments on a pool of mortgage loans are influenced by a variety of economic, geographic, social and other factors, including changes in mortgagors’ housing needs, job transfers, unemployment, mortgagors’ net equity in the mortgaged properties and servicing decisions. Generally, however, prepayments on fixed rate mortgage loans will increase during a period of falling interest rates and decrease during a period of rising interest rates. The same factors apply to prepayments on asset-backed securities but the predominant factor in a particular case may be different than in the case of mortgage-backed securities. Accordingly, amounts available for reinvestment by the Fund are likely to be greater during a period of declining interest rates than during a period of rising interest rates.
The Fund’s yield will also be affected by the interest rates on instruments in which the Fund is able to reinvest the proceeds of payments and prepayments. Accelerated prepayments on securities purchased by the Fund at a premium also impose a risk of loss of principal because the premium may not have been fully amortized at the time the principal is repaid in full.
The Fund may borrow from time to time, at the Advisors’ discretion, for purposes of investment leverage when yields on available investments exceed interest rates and other expenses of related borrowing, or when, in the Advisors’ opinion, unusual market conditions otherwise make it advantageous for the Fund to increase its investment capacity.
The Fund may also borrow for emergency purposes, for the payment of dividends or for the clearance of transactions.
The Fund may enter into reverse repurchase agreements.
BlackRock Limited Duration Income Trust (BLW)
The Fund’s investment objective is to provide current income and capital appreciation. The Fund pursues its objective by investing primarily in three distinct asset classes:
| | • | | intermediate duration, investment grade corporate bonds, mortgage related securities and asset-backed securities and U.S. government and agency securities; |
| | • | | senior, secured floating rate loans made to corporate and other business entities; and |
| | • | | U.S. dollar-denominated securities of U.S. and non-U.S. issuers rated below investment grade and, to a limited extent, non-U.S. dollar denominated securities of non-U.S. issuers rated below investment grade. |
The Fund may invest directly in such securities or synthetically through the use of derivatives.
BlackRock Advisors, LLC (the “Manager”) and the Fund’s sub-advisers, BlackRock International Limited (“BIL”) and BlackRock (Singapore) Limited (“BSL” and collectively with BIL and the Manager, the “Advisors”), have broad discretion to allocate the Fund’s assets among these three principal asset classes.
The Fund’s investment objective may be changed by the Board of Trustees of the Fund without prior shareholder approval.
The Fund’s portfolio normally has an average portfolio duration of less than five years (including the effect of anticipated leverage), although it may be longer from time to time depending on market conditions. In comparison to maturity (which is the date on which the issuer of a debt instrument is obligated to repay the principal amount), duration is a measure of the price volatility of a debt instrument as a result in changes in market rates of interest, based on the weighted average timing of the instrument’s expected principal and interest payments. Specifically, duration measures the anticipated percentage change in net asset value that is expected for every percentage point change in interest rates. The two have an inverse relationship. Duration differs from maturity in that it takes into account a security’s yield, coupon payments and its principal payments in addition to the amount of time until the security finally matures. As the value of a security changes over time, so will its duration. Prices of securities with longer durations tend to be more sensitive to interest rate changes than securities with shorter durations. In general, a portfolio of securities with a longer duration can be expected to be more sensitive to interest rate changes than a portfolio with a shorter duration.
The Fund is intended to have a relatively low level of interest rate risk compared to investment portfolios of similar credit quality but with longer durations. Certain of the Fund’s other strategies, however, may result in an above average amount of risk and volatility or loss of principal.
The Fund may invest in corporate bonds.
The Fund anticipates that, under normal market conditions, a significant portion of its Managed Assets will be invested in securities rated below investment grade, such as those rated (Ba or lower by Moody’s Investor’s Service (“Moody’s”) or BB or lower by S&P Global Ratings (“S&P”)) or securities comparably rated by other rating agencies or in unrated securities determined by the Advisors to be of comparable quality. High yield securities commonly are referred to as “junk” bonds. The Fund may invest in individual securities of any credit quality. “Managed Assets” means the total assets of the Fund (including any assets attributable to money borrowed for investment purposes) minus the sum of the Fund’s accrued liabilities (other than money borrowed for investment purposes).
The Fund may also invest in investment grade securities, which are securities rated at least BBB– as determined by S&P, Baa3 as determined by Moody’s or, if unrated, determined to be of comparable quality by the Advisors. When the Advisors believe it to be in the best interests of the Fund’s shareholders, the Fund will reduce its investment in lower grade securities and, in certain market conditions, the Fund may invest none of its assets in lower grade securities.
| | |
| 144 | | 2 0 2 2 B L A C K R O C K A N N U A L R E P O R T T O S H A R E H O L D E R S |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
Investment Objectives and Policies
(continued)
The Fund may invest without limitation in U.S. dollar denominated securities of non-U.S. issuers and, to a limited extent, non-U.S. dollar-denominated securities of non-U.S. issuers (“Non-U.S. Securities”), including up to 20% of its Managed Assets in issuers located in emerging market countries. The Fund can hold no more than 10% of its Managed Assets in non-U.S. dollar-denominated Non-U.S. Securities.
Non-U.S. Securities may include debt securities issued by foreign governments and other sovereign entities and debt securities issued by foreign corporations or supranational entities and securities denominated in U.S. dollars or, to a limited extent (as described above), in foreign currencies or multinational currency units. The Fund may invest in Brady Bonds and other sovereign debt of countries that have restructured their debt pursuant to the Brady Plan, which are viewed as speculative investments. The Fund may also purchase debt securities of supranational organizations such as the European Coal and Steel Community, the European Economic Community and theWorld Bank, which are chartered to promote economic development.
The Fund may invest in debt securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. government, its agencies or instrumentalities including but not limited to: (1) U.S. Treasury obligations, which differ in their interest rates, maturities and times of issuance, such as U.S. Treasury bills (maturity of one year or less), U.S. Treasury notes (maturity of one to ten years), and U.S. Treasury bonds (generally maturities of greater than ten years), including the principal components or the interest components issued by the U.S. government under the separate trading of registered interest and principal securities program (i.e., “STRIPS”), all of which are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States; and (2) obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. government agencies or instrumentalities, including government guaranteed mortgage-related securities, some of which are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury, some of which are supported by the right of the issuer to borrow from the U.S. government and some of which are backed only by the credit of the issuer itself.
The Fund may invest in mortgage-related securities, which include collateralized mortgage obligations, stripped mortgage-backed securities, mortgage pass-through securities, interests in real estate mortgage investment conduits, real estate investment trusts (“REITs”), including debt and preferred stock issued by REITs, as well as other real estate-related securities. The mortgage-related securities in which the Fund may invest include those with fixed, floating or variable interest rates, those with interest rates that change based on multiples of changes in a specified index of interest rates and those with interest rates that change inversely to changes in interest rates, as well as those that do not bear interest. The Fund may invest in residential and commercial mortgage-related securities issued by governmental entities and private issuers, including subordinated mortgage-related securities. The Fund will not invest more than 15% of its Managed Assets in commercial mortgage-related securities.
Asset-backed securities are a form of structured debt obligations. The securitization techniques used for asset-backed securities are similar to those used for mortgage-related securities. The collateral for these securities may include home equity loans, automobile and credit card receivables, boat loans, computer leases, airplane leases, mobile home loans, recreational vehicle loans and hospital account receivables. The Fund may invest in these and other types of asset-backed securities that may be developed in the future.
In addition to senior, secured floating rate loans made to corporate and other business entities, the Fund may also purchase unsecured loans, other floating rate debt securities, and credit-linked notes.
A senior loan is typically originated, negotiated and structured by a U.S. or foreign commercial bank, insurance company, finance company or other financial institution (the “Agent”) for a group of loan investors (“Loan Investors”). The Fund may purchase “Assignments” from the Agent or other Loan Investors. The Fund also may invest in “Participations.” Participations by the Fund in a Loan Investor’s portion of a senior loan typically will result in the Fund having a contractual relationship only with such Loan Investor, not with the borrower, whereas the Fund, as a purchaser of an Assignment, would typically succeed to all the rights and obligations under the loan agreement of the assigning Loan Investor and become a Loan Investor under the loan agreement with the same rights and obligations as the assigning Loan Investor. The Fund will only acquire Participations if the Loan Investor selling the Participation, and any other persons interpositioned between the Fund and the Loan Investor, are believed by the Advisors to be creditworthy at the time they enter into such transactions.
The Fund may also acquire equity securities or debt securities (including non-dollar denominated debt securities) issued in exchange for a senior loan or issued in connection with the debt restructuring or reorganization of a borrower, or if such acquisition, in the judgment of the Advisors, may enhance the value of a senior loan or would otherwise be consistent with the Fund’s investment policies.
The Fund may invest in collateralized bond obligations (“CBOs”), which are structured securities backed by a diversified pool of high yield, public or private fixed income securities. Under normal market conditions, the Fund expects to invest in the lower tranches of CBOs.
The Fund may purchase and sell futures contracts, enter into various interest rate transactions such as swaps, caps, floors or collars, currency transactions such as currency forward contracts, currency futures contracts, currency swaps or options on currency or currency futures and swap contracts (including, but not limited to, credit default swaps) and may purchase and sell exchange-listed and over-the-counter put and call options on securities and swap contracts, financial indices and futures contracts and use other derivative instruments or management techniques. The Fund also may purchase derivative instruments that combine features of these instruments.
The Fund may invest up to 10% of its Managed Assets in securities of other open- or closed-end investment companies that invest primarily in bonds of the types in which the Fund may invest directly. The Fund generally expects to invest in other investment companies either during periods when it has large amounts of uninvested cash, such as the period shortly after the Fund receives the proceeds of the offering of its common shares, or during periods when there is a shortage of attractive opportunities in the fixed income market.
The Fund currently utilizes leverage for investment purposes in the form of reverse repurchase agreements. The Fund may borrow from banks and other financial institutions and may also borrow additional funds using such investment techniques as the Advisors may from time to time determine. Of these investment techniques, the Fund expects primarily to use reverse repurchase agreements and dollar rolls.
The Fund also has the ability to utilize leverage through the issuance of preferred shares. The Fund does not currently anticipate issuing any preferred shares.
| | |
I N V E S T M E N T O B J E C T I V E S , P O L I C I E S A N D R I S K S | | 145 |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
Investment Objectives and Policies
(continued)
The Fund generally will not utilize leverage if it anticipates that the Fund’s leveraged capital structure would result in a lower return to shareholders than that obtainable over time with an unleveraged capital structure. There can be no assurance that the Fund will borrow in order to leverage its assets or, if it does, what percentage of the Fund’s assets such borrowings will represent.
This section contains a discussion of the general risks of investing in each Fund. The net asset value and market price of, and dividends paid on, the common shares will fluctuate with and be affected by, among other things, the risks more fully described below. As with any fund, there can be no guarantee that a Fund will meet its investment objective or that the Fund’s performance will be positive for any period of time. Each risk noted below is applicable to each Fund unless the specific Fund or Funds are noted in a parenthetical. The order of the below risk factors does not indicate the significance of any particular risk.
Investment and Market Discount Risk:
An investment in the Fund’s common shares is subject to investment risk, including the possible loss of the entire amount that you invest. As with any stock, the price of the Fund’s common shares will fluctuate with market conditions and other factors. If shares are sold, the price received may be more or less than the original investment. Common shares are designed for long-term investors and the Fund should not be treated as a trading vehicle. Shares of closed-end management investment companies frequently trade at a discount from their net asset value. This risk is separate and distinct from the risk that the Fund’s net asset value could decrease as a result of its investment activities. At any point in time an investment in the Fund’s common shares may be worth less than the original amount invested, even after taking into account distributions paid by the Fund. During periods in which the Fund may use leverage, the Fund’s investment, market discount and certain other risks will be magnified.
Debt securities, such as bonds, involve interest rate risk, credit risk, extension risk, and prepayment risk, among other things.
| | • | | Interest Rate Risk — The market value of bonds and other fixed-income securities changes in response to interest rate changes and other factors. Interest rate risk is the risk that prices of bonds and other fixed-income securities will increase as interest rates fall and decrease as interest rates rise. |
The Fund may be subject to a greater risk of rising interest rates due to the recent period of historically low interest rates. For example, if interest rates increase by 1%, assuming a current portfolio duration of ten years, and all other factors being equal, the value of the Fund’s investments would be expected to decrease by 10%. (Duration is a measure of the price sensitivity of a debt security or portfolio of debt securities to relative changes in interest rates.) The magnitude of these fluctuations in the market price of bonds and other fixed-income securities is generally greater for those securities with longer maturities. Fluctuations in the market price of the Fund’s investments will not affect interest income derived from instruments already owned by the Fund, but will be reflected in the Fund’s net asset value. The Fund may lose money if short-term or long-term interest rates rise sharply in a manner not anticipated by Fund management.
To the extent the Fund invests in debt securities that may be prepaid at the option of the obligor (such as mortgage-backed securities), the sensitivity of such securities to changes in interest rates may increase (to the detriment of the Fund) when interest rates rise. Moreover, because rates on certain floating rate debt securities typically reset only periodically, changes in prevailing interest rates (and particularly sudden and significant changes) can be expected to cause some fluctuations in the net asset value of the Fund to the extent that it invests in floating rate debt securities.
These basic principles of bond prices also apply to U.S. Government securities. Asecurity backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. Government is guaranteed only as to its stated interest rate and face value at maturity, not its current market price. Just like other fixed-income securities, government-guaranteed securities will fluctuate in value when interest rates change.
A general rise in interest rates has the potential to cause investors to move out of fixed-income securities on a large scale, which may increase redemptions from funds that hold large amounts of fixed-income securities. Heavy redemptions could cause the Fund to sell assets at inopportune times or at a loss or depressed value and could hurt the Fund’s performance.
| | • | | Credit Risk — Credit risk refers to the possibility that the issuer of a debt security (i.e., the borrower) will not be able to make payments of interest and principal when due. Changes in an issuer’s credit rating or the market’s perception of an issuer’s creditworthiness may also affect the value of the Fund’s investment in that issuer. The degree of credit risk depends on both the financial condition of the issuer and the terms of the obligation. |
| | • | | Extension Risk — When interest rates rise, certain obligations will be paid off by the obligor more slowly than anticipated, causing the value of these obligations to fall. |
| | • | | Prepayment Risk — When interest rates fall, certain obligations will be paid off by the obligor more quickly than originally anticipated, and the Fund may have to invest the proceeds in securities with lower yields. |
U.S. Government Obligations Risk:
Certain securities in which the Fund may invest, including securities issued by certain U.S. Government agencies and U.S. Government sponsored enterprises, are not guaranteed by the U.S. Government or supported by the full faith and credit of the United States.
U.S. Government Mortgage-Related Securities Risk (FRA, BKT and BLW):
There are a number of important differences among the agencies and instrumentalities of the U.S. Government that issue mortgage-related securities and among the securities that they issue. Mortgage-related securities guaranteed by the Government National Mortgage Association (“GNMA” or “Ginnie Mae”) are guaranteed as to the timely payment of principal and interest by GNMAand such guarantee is backed by the full faith and credit of the United States. GNMA securities also are supported by the right of GNMA to borrow funds from the U.S. Treasury to make payments under its guarantee. Mortgage-related securities issued by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac are solely the obligations of Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac, as the case may be, and are not backed by or entitled to the full faith and credit of the United States but are supported by the right of the issuer to borrow from the Treasury.
| | |
| 146 | | 2 0 2 2 B L A C K R O C K A N N U A L R E P O R T T O S H A R E H O L D E R S |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
Mortgage- and Asset-Backed Securities Risks (FRA, BKT and BLW):
Mortgage- and asset-backed securities represent interests in “pools” of mortgages or other assets, including consumer loans or receivables held in trust. Mortgage- and asset-backed securities are subject to credit, interest rate, prepayment and extension risks. These securities also are subject to risk of default on the underlying mortgage or asset, particularly during periods of economic downturn. Small movements in interest rates (both increases and decreases) may quickly and significantly reduce the value of certain mortgage-backed securities.
Senior Loans Risk (DSU, FRA and BLW):
There is less readily available, reliable information about most senior loans than is the case for many other types of securities. An economic downturn generally leads to a higher non-payment rate, and a senior loan may lose significant value before a default occurs. Moreover, any specific collateral used to secure a senior loan may decline in value or become illiquid, which would adversely affect the senior loan’s value. No active trading market may exist for certain senior loans, which may impair the ability of the Fund to realize full value in the event of the need to sell a senior loan and which may make it difficult to value senior loans. Although senior loans in which the Fund will invest generally will be secured by specific collateral, there can be no assurance that liquidation of such collateral would satisfy the borrower’s obligation in the event of non-payment of scheduled interest or principal or that such collateral could be readily liquidated. To the extent that a senior loan is collateralized by stock in the borrower or its subsidiaries, such stock may lose all of its value in the event of the bankruptcy of the borrower. Uncollateralized senior loans involve a greater risk of loss.
Risks of Loan Assignments and Participations (BLW):
As the purchaser of an assignment, the Fund typically succeeds to all the rights and obligations of the assigning institution and becomes a lender under the credit agreement with respect to the debt obligation; however, the Fund may not be able unilaterally to enforce all rights and remedies under the loan and with regard to any associated collateral. Because assignments may be arranged through private negotiations between potential assignees and potential assignors, the rights and obligations acquired by the Fund as the purchaser of an assignment may differ from, and be more limited than, those held by the assigning lender. In addition, if the loan is foreclosed, the Fund could become part owner of any collateral and could bear the costs and liabilities of owning and disposing of the collateral. The Fund may be required to pass along to a purchaser that buys a loan from the Fund by way of assignment a portion of any fees to which the Fund is entitled under the loan. In connection with purchasing participations, the Fund generally will have no right to enforce compliance by the borrower with the terms of the loan agreement relating to the loan, nor any rights of set-off against the borrower, and the Fund may not directly benefit from any collateral supporting the loan in which it has purchased the participation. As a result, the Fund will be subject to the credit risk of both the borrower and the lender that is selling the participation. In the event of the insolvency of the lender selling a participation, the Fund may be treated as a general creditor of the lender and may not benefit from any set-off between the lender and the borrower.
Corporate Loans Risk (DSU):
Commercial banks and other financial institutions or institutional investors make corporate loans to companies that need capital to grow or restructure. Borrowers generally pay interest on corporate loans at rates that change in response to changes in market interest rates such as the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) or the prime rates of U.S. banks. As a result, the value of corporate loan investments is generally less exposed to the adverse effects of shifts in market interest rates than investments that pay a fixed rate of interest. The market for corporate loans may be subject to irregular trading activity and wide bid/ask spreads. In addition, transactions in corporate loans may settle on a delayed basis. As a result, the proceeds from the sale of corporate loans may not be readily available to make additional investments or to meet the Fund’s redemption obligations. To the extent the extended settlement process gives rise to short-term liquidity needs, the Fund may hold additional cash, sell investments or temporarily borrow from banks and other lenders. The corporate loans in which the Fund invests are usually rated below investment grade.
Variable and Floating Rate Instrument Risk (DSU, FRA and BLW):
Variable and floating rate securities provide for periodic adjustment in the interest rate paid on the securities. These securities may be subject to greater illiquidity risk than other fixed income securities, meaning the absence of an active market for these securities could make it difficult for the Fund to dispose of them at any given time.
Junk Bonds Risk (DSU, FRA and BLW):
Although junk bonds generally pay higher rates of interest than investment grade bonds, junk bonds are high risk investments that are considered speculative and may cause income and principal losses for the Fund.
Distressed Securities Risk (DSU and FRA):
Distressed securities are speculative and involve substantial risks in addition to the risks of investing in junk bonds. The Fund will generally not receive interest payments on the distressed securities and may incur costs to protect its investment. In addition, distressed securities involve the substantial risk that principal will not be repaid. These securities may present a substantial risk of default or may be in default at the time of investment. The Fund may incur additional expenses to the extent it is required to seek recovery upon a default in the payment of principal of or interest on its portfolio holdings. In any reorganization or liquidation proceeding relating to a portfolio company, the Fund may lose its entire investment or may be required to accept cash or securities with a value less than its original investment. Distressed securities and any securities received in an exchange for such securities may be subject to restrictions on resale.
Collateralized Bond Obligations Risk (BLW):
The pool of high yield securities underlying collateralized bond obligations is typically separated into groupings called tranches representing different degrees of credit quality. The higher quality tranches have greater degrees of protection and pay lower interest rates. The lower tranches, with greater risk, pay higher interest rates.
Collateralized Debt Obligations Risk (FRA):
In addition to the typical risks associated with fixed-income securities and asset-backed securities, collateralized debt obligations (“CDOs”), including collateralized loan obligations, carry additional risks including, but not limited to: (i) the possibility that distributions from collateral securities will not be adequate to make interest or other payments; (ii) the risk that the collateral may default or decline in value or be downgraded, if rated by a nationally recognized statistical rating organization; (iii) the Fund may invest in tranches of CDOs that are subordinate to other tranches; (iv) the structure and complexity of the transaction and the legal documents could lead to disputes among investors regarding the characterization of proceeds; (v) the investment return achieved by the Fund could be significantly different than those predicted by financial models; (vi) the lack of a readily available secondary market for CDOs; (vii) the risk of forced “fire sale” liquidation due to technical defaults such as coverage test failures; and (viii) the CDO’s manager may perform poorly.
Sovereign Debt Risk (FRA and BLW):
Sovereign debt instruments are subject to the risk that a governmental entity may delay or refuse to pay interest or repay principal on its sovereign debt, due, for example, to cash flow problems, insufficient foreign currency reserves, political considerations, the relative size of the governmental entity’s debt position in relation to the economy or the failure to put in place economic reforms required by the International Monetary Fund or other multilateral agencies.
| | |
I N V E S T M E N T O B J E C T I V E S , P O L I C I E S A N D R I S K S | | 147 |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
Brady Bonds involve various risk factors described above associated with investing in non-U.S. securities, including the history of defaults with respect to commercial bank loans by public and private entities of countries issuing Brady Bonds.
Supranational Entities Risk (BLW):
The Fund may invest in obligations issued or guaranteed by the World Bank. The government members, or “stockholders,” usually make initial capital contributions to the World Bank and in many cases are committed to make additional capital contributions if the World Bank is unable to repay its borrowings. There is no guarantee that one or more stockholders of the World Bank will continue to make any necessary additional capital contributions. If such contributions are not made, the entity may be unable to pay interest or repay principal on its debt securities, and the Fund may lose money on such investments.
Yield and Ratings Risk (BKT):
The yields on debt obligations are dependent on a variety of factors, including general market conditions, conditions in the particular market for the obligation, the financial condition of the issuer, the size of the offering, the maturity of the obligation and the ratings of the issue. The ratings of Moody’s, S&P and Fitch, represent their respective opinions as to the quality of the obligations they undertake to rate. Ratings, however, are general and are not absolute standards of quality. Consequently, obligations with the same rating, maturity and interest rate may have different market prices. Subsequent to its purchase by the Fund, a rated security may cease to be rated. The Manager will consider such an event in determining whether the Fund should continue to hold the security.
Repurchase Agreements and Purchase and Sale Contracts Risk (BKT):
If the other party to a repurchase agreement or purchase and sale contract defaults on its obligation under the agreement, the Fund may suffer delays and incur costs or lose money in exercising its rights under the agreement. If the seller fails to repurchase the security in either situation and the market value of the security declines, the Fund may lose money.
Foreign Securities Risk (DSU, FRA and BLW):
Foreign investments often involve special risks not present in U.S. investments that can increase the chances that the Fund will lose money. These risks include:
| | • | | The Fund generally holds its foreign securities and cash in foreign banks and securities depositories, which may be recently organized or new to the foreign custody business and may be subject to only limited or no regulatory oversight. |
| | • | | Changes in foreign currency exchange rates can affect the value of the Fund’s portfolio. |
| | • | | The economies of certain foreign markets may not compare favorably with the economy of the United States with respect to such issues as growth of gross national product, reinvestment of capital, resources and balance of payments position. |
| | • | | The governments of certain countries, or the U.S. Government with respect to certain countries, may prohibit or impose substantial restrictions through capital controls and/or sanctions on foreign investments in the capital markets or certain industries in those countries, which may prohibit or restrict the ability to own or transfer currency, securities, derivatives or other assets. |
| | • | | Many foreign governments do not supervise and regulate stock exchanges, brokers and the sale of securities to the same extent as does the United States and may not have laws to protect investors that are comparable to U.S. securities laws. |
| | • | | Settlement and clearance procedures in certain foreign markets may result in delays in payment for or delivery of securities not typically associated with settlement and clearance of U.S. investments. |
| | • | | The Fund’s claims to recover foreign withholding taxes may not be successful, and if the likelihood of recovery of foreign withholding taxes materially decreases, due to, for example, a change in tax regulation or approach in the foreign country, accruals in the Fund’s net asset value for such refunds may be written down partially or in full, which will adversely affect the Fund’s net asset value. |
| | • | | The European financial markets have recently experienced volatility and adverse trends due to concerns about economic downturns in, or rising government debt levels of, several European countries as well as acts of war in the region. These events may spread to other countries in Europe and may affect the value and liquidity of certain of the Fund’s investments. |
Emerging Markets Risk (FRA and BLW):
Emerging markets are riskier than more developed markets because they tend to develop unevenly and may never fully develop. Investments in emerging markets may be considered speculative. Emerging markets are more likely to experience hyperinflation and currency devaluations, which adversely affect returns to U.S. investors. In addition, many emerging securities markets have far lower trading volumes and less liquidity than developed markets.
Equity Securities Risk (DSU, FRA and BLW):
Stock markets are volatile. The price of equity securities fluctuates based on changes in a company’s financial condition and overall market and economic conditions.
Preferred Securities Risk (DSU, FRA and BLW):
Preferred securities may pay fixed or adjustable rates of return. Preferred securities are subject to issuer-specific and market risks applicable generally to equity securities. In addition, a company’s preferred securities generally pay dividends only after the company makes required payments to holders of its bonds and other debt. For this reason, the value of preferred securities will usually react more strongly than bonds and other debt to actual or perceived changes in the company’s financial condition or prospects. Preferred securities of smaller companies may be more vulnerable to adverse developments than preferred securities of larger companies.
Convertible Securities Risk (DSU and FRA):
The market value of a convertible security performs like that of a regular debt security; that is, if market interest rates rise, the value of a convertible security usually falls. In addition, convertible securities are subject to the risk that the issuer will not be able to pay interest or dividends when due, and
| | |
| 148 | | 2 0 2 2 B L A C K R O C K A N N U A L R E P O R T T O S H A R E H O L D E R S |
Investment Objectives, Policies and Risks
(continued)
their market value may change based on changes in the issuer’s credit rating or the market’s perception of the issuer’s creditworthiness. Since it derives a portion of its value from the common stock into which it may be converted, a convertible security is also subject to the same types of market and issuer risks that apply to the underlying common stock.
Warrants Risk (DSU and FRA):
If the price of the underlying stock does not rise above the exercise price before the warrant expires, the warrant generally expires without any value and the Fund will lose any amount it paid for the warrant. Thus, investments in warrants may involve substantially more risk than investments in common stock. Warrants may trade in the same markets as their underlying stock; however, the price of the warrant does not necessarily move with the price of the underlying stock.
Real Estate-Related Securities Risk (BLW):
The main risk of real estate-related securities is that the value of the underlying real estate may go down. Many factors may affect real estate values. These factors include both the general and local economies, vacancy rates, tenant bankruptcies, the ability to re-lease space under expiring leases on attractive terms, the amount of new construction in a particular area, the laws and regulations (including zoning, environmental and tax laws) affecting real estate and the costs of owning, maintaining and improving real estate. The availability of mortgage financing and changes in interest rates may also affect real estate values. If the Fund’s real estate-related investments are concentrated in one geographic area or in one property type, the Fund will be particularly subject to the risks associated with that area or property type. Many issuers of real estate-related securities are highly leveraged, which increases the risk to holders of such securities. The value of the securities the Fund buys will not necessarily track the value of the underlying investments of the issuers of such securities.
REIT Investment Risk (BLW):
Investments in REITs involve unique risks. REITs may have limited financial resources, may trade less frequently and in limited volume, may engage in dilutive offerings of securities and may be more volatile than other securities. REIT issuers may also fail to maintain their exemptions from investment company registration or fail to qualify for the “dividends paid deduction” under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, which allows REITs to reduce their corporate taxable income for dividends paid to their shareholders.
The Fund’s use of derivatives may increase its costs, reduce the Fund’s returns and/or increase volatility. Derivatives involve significant risks, including:
| | • | | Leverage Risk — The Fund’s use of derivatives can magnify the Fund’s gains and losses. Relatively small market movements may result in large changes in the value of a derivatives position and can result in losses that greatly exceed the amount originally invested. |
| | • | | Market Risk — Some derivatives are more sensitive to interest rate changes and market price fluctuations than other securities. The Fund could also suffer losses related to its derivatives positions as a result of unanticipated market movements, which losses are potentially unlimited. Finally, the Manager may not be able to predict correctly the direction of securities prices, interest rates and other economic factors, which could cause the Fund’s derivatives positions to lose value. |
| | • | | Counterparty Risk — Derivatives are also subject to counterparty risk, which is the risk that the other party in the transaction will be unable or unwilling to fulfill its contractual obligation, and the related risks of having concentrated exposure to such a counterparty. |
| | • | | Illiquidity Risk — The possible lack of a liquid secondary market for derivatives and the resulting inability of the Fund to sell or otherwise close a derivatives position could expose the Fund to losses and could make derivatives more difficult for the Fund to value accurately. |
| | • | | Operational Risk — The use of derivatives includes the risk of potential operational issues, including documentation issues, settlement issues, systems failures, inadequate controls and human error. |