UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2015
or
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 0-30877
Marvell Technology Group Ltd.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | |
| Bermuda | | 77-0481679 |
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer
Identification No.) |
Canon’s Court, 22 Victoria Street, Hamilton HM 12, Bermuda
(Address of principal executive offices)
(441) 296-6395
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | |
Title of each class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
Common shares, $0.002 par value per share | | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of the registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer x | | Accelerated filer ¨ | | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
| | | | (Do not check if a smaller
reporting company) | | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common shares held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $4,926 million based upon the closing price of $13.39 per share on the NASDAQ Global Select Market on August 1, 2014 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second quarter). Common shares held by each director and executive officer of the registrant, as well as shares held by each holder of more than 5% of the common shares known to the registrant (based on Schedule 13G filings), have been excluded for purposes of the foregoing calculation.
As of March 19, 2015, there were 515.0 million common shares of the registrant outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of Part III of this Form 10-K are incorporated by reference from the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for its 2015 annual general meeting of shareholders, which proxy statement will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by thisForm 10-K.
TRADEMARKS
Marvell®, Alaska®, ARMADA® Avanta®, Avastar®, Kirkwood®, Link Street®, Prestera®, Xelerated® and Yukon® are registered trademarks of Marvell International Ltd. and/or its affiliates. Any other trademarks or trade names mentioned are the property of their respective owners.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), which are subject to the “safe harbor” created by those sections. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, which may cause our actual results to differ materially from those implied by the forward-looking statements. Words such as “anticipates,” “expects,” “intends,” “plans,” “believes,” “seeks,” “estimates,” “can,” “will” and similar expressions identify such forward-looking statements. Examples of forward-looking statements include statements regarding:
| | • | | our anticipation that the rate of new orders and shipments will vary significantly from quarter to quarter; |
| | • | | market acceptance of our products; |
| | • | | our expectations about industry trends; |
| | • | | future growth of our customer’s products, including the timing of any launches; |
| | • | | the pricing of our products; |
| | • | | future customer concentration; |
| | • | | net revenue, cost of goods sold as a percentage of revenue and operating expenses for future periods; |
| | • | | the impact of legal proceedings and claims, including the protection of our intellectual property; |
| | • | | our ability to meet our capital needs for at least the next 12 months; |
| | • | | our expectation that a significant percentage of our sales will continue to come from direct sales to key customers; |
| | • | | future growth opportunities; |
| | • | | our expectations regarding areas of revenue and operating income growth; |
| | • | | the effectiveness of our hedges of foreign currency exposures; |
| | • | | our plans regarding our investment portfolio; |
| | • | | our expectations that quarterly operating results will fluctuate from quarter to quarter; |
| | • | | general economic environment; |
| | • | | arrangements with suppliers; |
| | • | | our expectations regarding our facilities and the sufficiency of our facilities; |
| | • | | our ability to execute our business strategy; |
| | • | | our plan to strengthen and expand our relationship with customers; |
| | • | | our ability to anticipate the needs of our customers; |
| | • | | our expectations that average selling prices of our products will continue to be subject to significant pricing pressures; |
| | • | | our ability to develop and introduce new products and achieve market acceptance of our products; |
| | • | | our expectations regarding acquisitions and investments; |
| | • | | demand for our products and the impact of seasonality on demand; |
| | • | | gross margin and the events that may cause gross margin to fluctuate; |
1
| | • | | our operations and sales outside of the United States, including future sales in Asia; |
| | • | | our plans for our share repurchase program and dividends; |
| | • | | expected tax benefits we receive; and |
| | • | | the anticipated features and benefits of our technology solutions. |
These forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those indicated in the forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those predicted, include but are not limited to:
| | • | | our dependence upon the hard disk drive and mobile and wireless markets, which are highly cyclical and intensely competitive; |
| | • | | the outcome of pending or future litigation and legal proceedings, including our patent litigation action involving Carnegie Mellon University; |
| | • | | our dependence on a small number of customers; |
| | • | | our ability and the ability of our customers to successfully compete in the markets in which we serve; |
| | • | | our reliance on independent foundries and subcontractors for the manufacture, assembly and testing of our products; |
| | • | | our ability and our customers’ ability to develop new and enhanced products and the adoption of those products in the market; |
| | • | | decreases in our gross margin and results of operations in the future due to a number of factors; |
| | • | | our ability to estimate customer demand and future sales accurately, including the impact of lengthy and expensive product sales cycles; |
| | • | | our ability to scale our operations in response to changes in demand for existing or new products and services; |
| | • | | the impact of international conflict and continued economic volatility in either domestic or foreign markets; |
| | • | | the effects of transitioning to smaller geometry process technologies; |
| | • | | the risks associated with manufacturing and selling a majority of our products and our customers’ products outside of the United States; |
| | • | | the impact of any change in our application of the United States federal income tax laws and the loss of any beneficial tax treatment that we currently enjoy; |
| | • | | the effects of any potential acquisitions or investments; |
| | • | | our ability to protect our intellectual property; |
| | • | | the impact and costs associated with changes in international financial and regulatory conditions; and |
| | • | | our maintenance of an effective system of internal controls. |
Additional factors that could cause actual results to differ materially include the risks discussed in Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” and Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date hereof. Unless required by law, we undertake no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements.
2
PART I
Overview
We are a fabless semiconductor provider of high-performance application-specific standard products. Our core strength of expertise is the development of complex System-on-a-Chip (“SoC”) and System-in-a-Package (“SiP”) devices, leveraging our extensive technology portfolio of intellectual property in the areas of analog, mixed-signal, digital signal processing, and embedded and standalone integrated circuits. The majority of our product portfolio leverages the ARM technology portfolio. We also develop platforms that we define as integrated hardware along with software that incorporates digital computing technologies designed and configured to provide an optimized computing solution. Our broad product portfolio includes devices for data storage, enterprise-class Ethernet data switching, Ethernet physical-layer transceivers (“PHY”), mobile handsets, connectivity, Internet-of-Things (“IoT”) devices and other consumer electronics. We were incorporated in Bermuda in January 1995.
Our registered and mailing address is Canon’s Court, 22 Victoria Street, Hamilton HM 12, Bermuda, and our telephone number there is (441) 296-6395. The address of our U.S. operating subsidiary is Marvell Semiconductor, Inc., 5488 Marvell Lane, Santa Clara, California 95054, and our telephone number there is (408) 222-2500. We also have operations in many countries, including Canada, China, India, Israel, Italy, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and Taiwan. Our fiscal year ends on the Saturday nearest January 31. For example, the fiscal year ended January 31, 2015 is referred to as fiscal 2015.
Available Information
Our website address is located at www.marvell.com. The information contained in our website does not form any part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. However, we make available free of charge through our website our annual reports on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, our current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file this material with, or furnish it to, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
Our Markets and Products
Over the last several years, we have transitioned from a supplier of standalone semiconductor components to a supplier of fully integrated platform solutions. Our platform solutions contain multiple intellectual property components in integrated hardware along with software that incorporates digital, analog and mixed-signal computing and communication technologies, designed and configured to provide an optimized solution compared to individual components. Our solutions have become increasingly integrated, with more and more components resulting in an all-in-one solution for a given customer’s end product. The demand for such highly integrated platform solutions is generally driven by technological changes and anticipation of the future needs of device manufacturers and end users, as well as, to an increasing extent, service providers, including cellular network carriers and Internet based applications providers. For example, in order to provide a complete solution for a specific handheld consumer electronics device, a device manufacturer may require a solution that integrates a high-performance applications processor, along with seamless communications capability with a 3G/4G Long-Term Evolution (“LTE”) multi-band modem, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, radio frequency (“RF”), GPS and near field communication (“NFC”). In addition, a device manufacturer may require high-definition graphics processing, high-definition video and audio, and power management. These platforms will often cross multiple end markets, integrating components and technologies traditionally associated with one end market with components and technologies from another end market. For example, we may integrate an applications processor, traditionally associated with the mobile and wireless end market, with software and other components in an end user product targeting the home cloud. Therefore, it has become critical that our products across multiple end markets work together seamlessly.
3
The integration of these various technologies onto a single piece of silicon is referred to as SoC. The development of SoC’s became increasingly popular over the past decade, particularly within end markets such as mobile. We believe the development of SoC’s will continue to be popular for various end devices in the years to come.
In addition, software has become increasingly important to our business over the last several years and we expect software to become even more important in the years to come. On-chip software, which acts as the “driver” for the functionality of the chip, has always been a critical part of our business. However, the software that we deliver with our chip has become significantly more complex as the range of uses and the needs in application-level software have increased. For example, a chip that we develop for a smartphone may need to include software that is compatible with the latest version of a specific company’s operating system that enables 3D user interface and graphics, and that works seamlessly with a variety of popular end user applications. These demands require a significant amount of up-front software development, testing, and often, additional licensing.
The market for consumer electronics devices is becoming increasingly standards-based. These standards change rapidly and often several different standards may exist and overlap in a single market. Our platforms are typically designed to operate seamlessly with all relevant standards, which require us to design products in anticipation of these relevant standards. For example, we have communications processors and software designed to operate on several different cellular standards, including GSM/enhanced data for the GSM environment (“EDGE”) (2G), WCDMA (3G), TD-SCDMA (China 3G) and 4G LTE.
Our current product offerings are primarily in three broad end markets: mobile and wireless, storage, and networking. Our net revenue by end market for the last three fiscal years are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | | | | February 1,
2014 | | | | | | February 2,
2013 | | | | |
| | | (in millions, except for percentages) | |
Mobile and Wireless | | $ | 1,072 | | | | 29 | % | | $ | 839 | | | | 25 | % | | $ | 823 | | | | 26 | % |
Storage | | | 1,745 | | | | 47 | % | | | 1,682 | | | | 49 | % | | | 1,495 | | | | 47 | % |
Networking | | | 675 | | | | 18 | % | | | 670 | | | | 20 | % | | | 709 | | | | 22 | % |
Other | | | 215 | | | | 6 | % | | | 213 | | | | 6 | % | | | 142 | | | | 5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 3,707 | | | | | | | $ | 3,404 | | | | | | | $ | 3,169 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Mobile and Wireless
Communications and Applications Processors
Our communications processors are highly integrated cellular SoC devices that enable mobile handset developers to address GSM/EDGE (2G), WCDMA (3G), TD-SCDMA (China 3G) and 4G LTE mobile network standards. Our communication products include high-performance multi-band baseband thin modems and applications processors in highly integrated low-power platforms for voice, computation and multimedia-intensive mobile applications for smartphones and tablets. We also offer “thin modems,” highly optimized multi-mode baseband modem devices without an application processor.
Connectivity
We offer a variety of connectivity solutions, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, NFC and FM. These products are integrated into a wide variety of end-customer devices, such as mobile phones, gaming devices, printers, video dongles tablets, in-car infotainment and smart appliances. Our products are well positioned to deliver low-power and high-performance functionality with the latest technologies, such as Wi-Fi Certified Passpoint, Wi-Fi Certified Miracast, IEEE 802.11ac and Bluetooth Smart Ready. We have a broad wireless product portfolio that includes single stream 1x1, 2x2 MIMO and 4x4 MIMO devices, as well as Global Navigation Satellite System hybrid location products.
4
Mobile Computing
We offer high-performance applications processors that are designed to deliver advanced integration, excellent multimedia performance and superior power consumption savings for mobile computing products. These products have been incorporated into tablets, notebooks, eReaders, gaming devices, scanners and educational devices.
Other Technologies
We incorporate a variety of other technologies into our platforms, depending on the needs of our customers and their end products, including power management, GPS, memory, RF and memory.
Storage
Hard Disk Drive Controllers
Hard disk drive (“HDD”) controllers provide high-performance input/output (“I/O”) interface control between the HDD and the host system. We support a variety of host system interfaces, including SATA, SAS, PCIe and USB, which can support the complete range of enterprise, desktop and mobile HDDs. We are the leading HDD controller supplier and currently supply products to all of the major hard drive manufacturers. Our HDD controllers with advanced 500-gigabyte-per-platter technology for mobile HDDs provide a technological advantage that enables a higher level of data storage on a smaller form factor.
Solid-State Drive Controllers
Our solid-state drive (“SSD”) controller SoCs are targeted at the growing market for flash-based storage systems, for the enterprise, consumer and mobile computing markets, as well as for smartphones and tablets. We support a variety of host system interfaces, including PCIe, SATA, SAS and emerging mobile standards.
Networking
Ethernet Solutions
Ethernet connectivity is pervasive throughout networking infrastructures built for enterprise, small and medium business, home office, service provider and data centers. Our Ethernet solutions address a wide variety of end-customer products for those market spaces, from small, cost-effective appliances to large, high-performance modular solutions. Our Ethernet products include: a broad selection of Ethernet Switches with market optimized advanced features, such as audio video bridging and network traffic management, that make networks more effective at delivering content, and range from low-power five port switches to highly integrated, multi terabit Ethernet SoC devices that can be interconnected to form massive network solutions; a broad selection of Ethernet Transceivers for both fiber and copper interconnect with advanced power management, link security and time synchronization features that complement our Ethernet Switch and Embedded Communication Processors; and a family of single-chip network interface devices offered in ultra-small form factor with low-power consumption and targeted for client-server network interface cards.
Embedded Communication Processors
Our range of ARM-based SoC embedded communication processors provide multi-processor architectures optimized to consume low power while simultaneously delivering high-performance per watt. They provide a combination of I/O peripherals, including Ethernet, SATA, SAS, PCIe and USB and are ideally suited to a range of end-customer networking applications, such as home gateways, networked storage, point-of-service terminals, routers, switches and wireless application points and base stations.
Network Processors
Our family of Network Processors offer high-performance-per-watt programmable solutions ideally suited to applications where flexible functionality for differentiated, value-add solutions and enhanced quality of service
5
are essential, such as in carrier Ethernet access, aggregation, mobile backhaul, transport and mobile cloud platforms. They also offer 1G through 100G Ethernet connectivity into a multi-hundred gigabit Ethernet pipeline that has deterministic performance and ideally suited for software-defined networking.
Other Networking Technologies
Our Ethernet passive optical network and gigabit passive optical network products consist of a highly integrated Gateway-on-a-Chip solution, Ethernet and packet processing, voice processing, power management and applications processor. These products are designed for next generation networks and the significant increases in required bandwidth, including high-quality video, online gaming and conferencing. Our powerline connectivity solutions based on G.hn are designed for integration into a variety of consumer electronics products, enabling fast and convenient connectivity to any location in the home through the existing home electrical infrastructure.
Other Products
Printing Solutions
Our printer SoC products power many of today’s laser and ink printers and multi-function peripherals. These SoCs include a family of printer-specific standard products as well as full-custom printer ASICs. We continue to develop additional printing technologies including 3D printing and mobile printing.
Smart Home Products
Our smart home products are designed to enable the next generation of connected consumer platforms, and to enhance the eco-friendly “Connected Lifestyle” throughout the home, and include platforms for set-top boxes, video dongles such as Google Chromecast, smart lighting and smart appliances.
Financial Information about Segments and Geographic Areas
We have determined that we operate in one reportable business segment: the design, development and sale of integrated circuits. For information regarding our revenue by geographic area, and property and equipment by geographic area, please see “Note 13 — Segment and Geographic Information” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Customers, Sales and Marketing
As a fabless semiconductor company, our target customers are original equipment manufacturers (“OEM’s”) and original design manufacturers, both of which design and manufacture end market devices. Our sales force is strategically aligned along key customer lines in order to offer fully integrated platforms to our customers. In this way, we believe we can more effectively offer a broader set of content into our key customer’s end products, without having multiple product groups separately engage the same customer. We complement and support our direct sales force with manufacturers’ representatives for our products in North America, Europe and Asia. In addition, we have distributors who support our sales and marketing activities in the United States, Europe and Asia. We also use third-party logistics providers, who maintain warehouses in close proximity to our customer’s facilities. We expect a significant percentage of our sales will continue to come from direct sales to key customers. We use field application engineers to provide technical support and assistance to existing and potential customers in designing, testing and qualifying systems designs that incorporate our products. We believe that superior field applications engineering support plays a pivotal role in building long-term relationships with customers by improving our customers’ time-to-market, maintaining a high level of customer satisfaction and encouraging customers to use our next-generation products. Our marketing team works in conjunction with our field sales and application engineering force, and is organized around our product applications and end markets.
6
Historically, a relatively small number of customers have accounted for a significant portion of our net revenue. Net revenue attributable to significant customers is presented in the following table as a percentage of net revenue:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
End Customer: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Western Digital | | | 20 | % | | | 24 | % | | | 24 | % |
Seagate | | | 13 | % | | | 12 | % | | | 10 | % |
Toshiba | | | | * | | | | * | | | 10 | % |
Distributor: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Wintech | | | 11 | % | | | | * | | | 11 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| * | Less than 10% of net revenue |
A significant number of our products are being incorporated into consumer electronics products, including gaming devices and personal computers, which are subject to significant seasonality and fluctuations in demand. Holiday and back to school buying trends may at times negatively impact our results in the first and fourth quarter, and positively impact our results in the second and third quarter of our fiscal years. In addition, the timing of new product introductions by our customers may cause variations in our quarterly revenues, which may not be indicative of future trends.
Inventory and Working Capital
We place firm orders for products with our suppliers generally up to 16 weeks prior to the anticipated delivery date and typically prior to an order for the product. These lead times typically change based on the current capacity at the foundries. We often maintain substantial inventories of our products because the semiconductor industry is characterized by short lead time orders and quick delivery schedules. In addition, increased use of “hubs” managed by third-party logistics providers has resulted in a higher number of inventory locations and higher overall inventory levels.
Backlog
We do not believe that backlog is a meaningful or reliable indicator for future demand, due to the following:
| | • | | an industry practice that allows customers to cancel or change orders prior to the scheduled shipment dates; |
| | • | | an increasing portion of our revenue comes from products shipped to customers using third-party logistics providers, or “hubs” wherein the product can be pulled at any time by the customer and is therefore never reflected in backlog; and |
| | • | | scheduled future shipments include shipments to distributors for which we do not recognize revenue until the products are sold to end customers. |
Research and Development
We believe that our future success depends on our ability to introduce improvements to our existing products and to develop new products that deliver cost-effective solutions for both existing and new markets. Our research and development efforts are directed largely to the development of high-performance analog, mixed-signal, digital signal processing and embedded microprocessor integrated circuits with the smallest die size and lowest power. We devote a significant portion of our resources to expanding our product portfolio based on a broad intellectual property portfolio with designs that enable high-performance, reliable communications over a variety of physical transmission media. We are also focused on incorporating functions currently provided by stand alone integrated circuits into our integrated platform solutions to reduce our customers’ overall system costs.
7
We have assembled a core team of engineers who have extensive experience in the areas of mixed-signal circuit design, digital signal processing, embedded microprocessors, CMOS technology and system-level architectures. We have invested and will continue to invest significant funds for research and development. Our research and development expense was $1.2 billion, $1.2 billion and $1.1 billion in fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Manufacturing
Integrated Circuit Fabrication
The vast majority of our integrated circuits are fabricated using widely available CMOS processes, which provide greater flexibility to engage independent foundries to manufacture integrated circuits at lower costs. By outsourcing manufacturing, we are able to avoid the cost associated with owning and operating our own manufacturing facility. This allows us to focus our efforts on the design and marketing of our products. We currently outsource a large percentage of our integrated circuit manufacturing to Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company. We also utilize United Microelectronics Corporation, with the remaining manufacturing outsourced to other foundries primarily in Asia. We work closely with our foundry partners to forecast on a monthly basis our manufacturing capacity requirements. We closely monitor foundry production to ensure consistent overall quality, reliability and yield levels. Our integrated circuits are currently fabricated in several advanced manufacturing processes up to and including 28 nanometer. Because finer manufacturing processes lead to enhanced performance, smaller silicon chip size and lower power requirements, we continually evaluate the benefits and feasibility of migrating to smaller geometry process technology in order to reduce cost and improve performance.
Assembly and Test
We outsource all product packaging and testing requirements for our products in production to several assembly and test subcontractors, including STATS ChipPAC Ltd. in China, Korea and Singapore; Global Testing Corporation in Taiwan; Siliconware Precision Industries in China and Taiwan; and ASE Electronics in China, Singapore and Taiwan.
Environmental Management
We believe that our products are compliant with the current Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive, the European legislation that restricts the use of a number of substances, including lead, and the REACH (Regulation, Evaluation and Authorization of Chemicals) SVHC Substances Directive. In addition, each of our manufacturing subcontractors complies with ISO 14001:2004, the international standard related to environmental management. We are also working to establish a “conflict-free” supply chain, including ethical sourcing of certain minerals for our products.
Intellectual Property
Our future revenue growth and overall success depend in large part on our ability to protect our intellectual property. We rely on a combination of patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secret laws, contractual provisions, confidentiality agreements and licenses to protect our intellectual property. As of January 31, 2015, we have been issued and/or have acquired over 5,300 U.S. patents and over 1,400 foreign patents with expiration dates ranging from 2015 to 2035. We also have more than 3,800 U.S. and foreign pending patent applications on various aspects of our technology. See “Risk Factors” under Item 1A of this Report for a discussion of the risks associated with our patents and intellectual property, including the risk that our patents may be invalidated, the risk that third parties may copy or otherwise obtain and use our products and technology without authorization, and the risks involved with operating in foreign countries where the laws are not as protective of our intellectual property as in the United States. We have expended and will continue to expend considerable resources in establishing a patent position designed to protect our intellectual property. While our ability to compete is
8
enhanced by our ability to protect our intellectual property, we believe that in view of the rapid pace of technological change, the combination of the technical experience and innovative skills of our employees may be as important to our business as the legal protection of our patents and other proprietary information.
From time to time, we may desire or be required to renew or to obtain licenses from third parties in order to further develop and effectively market commercially viable products or in connection with a pending or future claim or action asserted against us. We cannot be sure that any necessary licenses will be available or will be available on commercially reasonable terms.
The integrated circuit industry is characterized by vigorous pursuit and protection of intellectual property rights, which has resulted in significant and often time consuming and expensive litigation. From time to time, we receive, and may continue to receive in the future, notices that claim we have infringed upon, misappropriated or misused the proprietary rights of other parties. In addition, we may be sued in the future by other parties who claim that we have infringed their patents or misappropriated or misused their trade secrets, or who may seek to invalidate one or more of our patents. Although we defend these claims vigorously, it is possible that we will not prevail in pending or future lawsuits. Furthermore, we may need to engage in litigation in the future to enforce our intellectual property rights or the rights of our customers, to protect our trade secrets or to determine the validity and scope of proprietary rights of others, including our customers. All such litigation, even if not valid or successfully asserted, could result in significant costs and a diversion of management and personnel resources, which could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. See “Risk Factors” under Item 1A of this Report on Form 10-K and “Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further discussion of the risks associated with patent litigation matters.
Competition
The markets for our products, particularly in the mobile and wireless end market, are intensely competitive, characterized by rapid technological change, evolving industry standards, frequent new product introductions, short product life cycles and pricing pressures imposed by high-volume customers and competitors, particularly in the product markets that we are targeting. Competition has intensified as a result of the increasing demand for higher levels of integration and smaller process geometries, and we expect competition to intensify as current competitors continue to strengthen their product offerings and new competitors enter our markets. In addition, we expect competitive pressure from our customers to increase as they may continue to increase the vertical nature of their business by developing their own in-house solutions.
We believe that our ability to compete successfully in the rapidly evolving markets for our products depends on a number of factors, including the:
| | • | | performance, features, quality and price of our products; |
| | • | | timing and success of new product introductions by us, our customers and our competitors; |
| | • | | emergence, and rate of adoption and acceptance of new industry standards; |
| | • | | ability to obtain adequate foundry capacity; and |
| | • | | number and nature of our competitors in a given market. |
By end market our major competitors are as follows:
| | | | |
Mobile and Wireless | | Storage | | Networking |
| | |
Broadcom Corporation | | Avago Technologies Ltd. | | Broadcom Corporation |
| | |
MediaTek, Inc. | | | | Cavium, Inc. |
| | |
QUALCOMM Incorporated | | | | Freescale Semiconductor, Ltd. |
| | |
Spreadtrum Communications, Inc. | | | | Intel Corporation |
9
We expect increased competition in the future from emerging or established companies, or alliances among competitors, customers or other third parties, any of which could acquire significant market share. Although we believe we will be able to successfully compete with existing and potential competitors, some of these current and potential competitors may have advantages over us that allow them to compete effectively against us. Our current or future competitors could also introduce products that are priced lower provide superior performance or are based on new or emerging technologies. Furthermore, some of our customers have already developed, or in the future may develop, technologies that could compete directly with our products. See “Risk Factors” under Item 1A of this Report for further discussion of competitive risks associated with our business.
Historically, average unit selling prices in the integrated circuit industry in general, and for our products in particular, have decreased over the life of a particular product. We expect that the average unit selling prices of our products will continue to be subject to significant pricing pressures. In order to offset expected declines in the selling prices of our products, we will need to continue to introduce innovative new products and reduce the cost of our products. To accomplish this, we intend to continue to implement design changes that lower the cost of manufacturing, and assembling and testing our products. We may also enter into long-term, strategic arrangements with foundry partners to secure wafer capacity at reduced prices, by negotiating reduced charges from our foundries. In addition, we plan to work with multiple foundry partners to ensure that our products are qualified and can be manufactured in multiple locations, which we believe will ensure favorable wafer pricing. Because we do not operate our own manufacturing, assembly or testing facilities, we may not be able to reduce our costs as rapidly as companies that operate their own facilities. See “Risk Factors” under Item 1A of this Report for further discussion of pricing risks.
Employees
As of January 31, 2015, we had a total of 7,163 employees.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The following table shows information about our executive officers as of March 19, 2015:
| | | | | | |
Name | | Age | | | Position(s) |
Dr. Sehat Sutardja | | | 53 | | | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board |
Weili Dai | | | 53 | | | President and Director |
Michael Rashkin | | | 70 | | | Chief Financial Officer |
Dr. Zining Wu | | | 43 | | | Chief Technology Officer |
Dr. Sehat Sutardja, one of our co-founders, has served as the Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of our Board of Directors since 1995 (from 1995 to 2003 he was Co-Chairman of the Board of Directors). While remaining deeply involved in the daily challenges of running a global growth company, Dr. Sutardja participates heavily in our engineering and marketing efforts across analog, video processor, and microprocessor design while offering input across all of our other product lines. Dr. Sutardja is widely regarded as one of the pioneers of the modern semiconductor age. His breakthrough designs and guiding vision have revolutionized numerous industry segments, from data storage to the high-performance, low-power chips now driving the growing global markets for mobile computing and telephony. For his relentless innovation, he has been awarded more than 360 patents and has been named a Fellow of IEEE. In 2006, Dr. Sutardja was recognized as the Inventor of the Year by the Silicon Valley Intellectual Property Law Association. Dr. Sutardja also served as President from 2003 to June 2013. Dr. Sutardja holds an M.S. and Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering and Computer Science from the University of California at Berkeley. Dr. Sutardja received a B.S. in Electrical Engineering from Iowa State University. Dr. Sutardja is the husband of Ms. Dai.
Ms. Weili Dai, one of our co-founders, has served as President of the Company since July 2013 and as a member of the Board of Directors of the Company since December 2014. Widely considered a technology
10
visionary, Ms. Dai is the only woman co-founder of a global semiconductor company. Her business acumen, strategic thinking, product leadership, endless passion and personal network have contributed greatly to Marvell’s success. Her close relationship with Marvell’s customers and the foundation of the trust shared with them have given her a strong reputation for professionalism and integrity throughout the technology industry. Prior to her appointment as President, Ms. Dai served as a Vice President of Marvell Semiconductor, Inc. (“MSI”) from 2008 to July 2013, including the position of General Manager of the Communications & Consumer Business of MSI since September 2011 and General Manager of the Communications and Computing Business Unit of MSI from March 2009 to September 2011. From 1995 to May 2007, Ms. Dai served as Chief Operating Officer, Executive Vice President and a member of the Board of Directors of the Company. Ms. Dai holds a B.S. degree in Computer Science from the University of California at Berkeley. Ms. Dai is the wife of Dr. Sutardja.
Michael Rashkinhas served as our Chief Financial Officer since February 2014 and served as our Interim Chief Financial Officer from December 2013 to February 2014. Mr. Rashkin served as President of the Marvell Charitable Fund from March 2011 to November 2013. From January 2008 to March 2011, Mr. Rashkin served as Vice President of Taxes and General Tax Counsel of MSI. From July 2007 to January 2008, Mr. Rashkin served as Interim Chief Financial Officer of the Company. In 2007, Mr. Rashkin was appointed Special Assistant to the CEO and Vice President of Strategic Development of MSI. Prior to 2007, Mr. Rashkin was Vice President and General Tax Counsel of MSI from 2005 to 2007. From 2000 to 2005, Mr. Rashkin served as Director of Taxes and General Tax Counsel of MSI and Director of Taxes and Tax Counsel of MSI from 1999 to 2000. Mr. Rashkin holds an LL.M. from the New York University Graduate School of Law, a J.D. from St. John’s University School of Law and a B.S. from Brooklyn College, City University of New York. Mr. Rashkin is a member of both the California and New York bars.
Dr. Zining Wu has served as our Chief Technology Officer since January 2014. From August 2008 to January 2014, Dr. Wu served as MSI’s Vice President, Data Storage Technology. Prior to August 2008, Dr. Wu worked as an engineer and in various managerial roles in MSI’s Storage group since July 1999. Dr. Wu holds a BS in Electronic Engineering from Tsinghua University in Beijing, China, and a M.S. and Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering from Stanford University. Dr. Wu holds over 230 U.S. patents and has published eight technical papers and a book related to data storage technology.
Investing in our common shares involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks and uncertainties described below, and all information contained in this report before you decide to purchase our common shares. Many of these risks and uncertainties are beyond our control, including business cycles and seasonal trends of the computing, semiconductor and related industries and end markets. If any of the possible adverse events described below actually occurs, we may be unable to conduct our business as currently planned and our financial condition and operating results could be harmed. In addition, the trading price of our common shares could decline due to the occurrence of any of these risks, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
Factors That May Affect Future Results
Our financial condition and results of operations may vary from quarter to quarter, which may cause the price of our common shares to decline.
Our quarterly results of operations have fluctuated in the past and could do so in the future. Because our results of operations are difficult to predict, you should not rely on quarterly comparisons of our results of operations as an indication of our future performance.
Fluctuations in our results of operations may be due to a number of factors, including, but not limited to, those listed below and those identified throughout this “Risk Factors” section:
| | • | | changes in general economic and political conditions and specific conditions in the end markets we address, including the continuing volatility in the technology sector and semiconductor industry; |
11
| | • | | the highly competitive nature of the end markets we serve, particularly within the semiconductor industry; |
| | • | | any current and future litigation that could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources that are needed to successfully maintain and grow our business; |
| | • | | our dependence on a few customers for a significant portion of our revenue; |
| | • | | our ability to maintain a competitive cost structure for our manufacturing and assembly and test processes and our reliance on third parties to produce our products; |
| | • | | cancellations, rescheduling or deferrals of significant customer orders or shipments, as well as the ability of our customers to manage inventory; |
| | • | | gain or loss of a design win or key customer; |
| | • | | seasonality in sales of consumer devices in which our products are incorporated; |
| | • | | failure to qualify our products or our suppliers’ manufacturing lines; |
| | • | | our ability to develop and introduce new and enhanced products in a timely and effective manner, as well as our ability to anticipate and adapt to changes in technology; |
| | • | | failure to protect our intellectual property; |
| | • | | impact of a significant natural disaster, including earthquakes, floods and tsunamis, particularly in certain regions in which we operate or own buildings, such as Santa Clara; and |
| | • | | our ability to attract and retain highly skilled managerial, engineering, sales and marketing personnel. |
Due to fluctuations in our quarterly results of operations and other factors, the price at which our common shares will trade is likely to continue to be highly volatile. From January 28, 2012 through January 31, 2015, our common shares traded as low as $6.98 and as high as $16.86 per share. Accordingly, you may not be able to resell your common shares at or above the price you paid. In future periods, our stock price could decline if, amongst other factors, our revenues or operating results are below our estimates or the estimates or expectations of securities analysts and investors. As a result of stock price volatility, we may be subject to securities class action litigation. Any litigation could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources that are needed to successfully maintain and grow our business.
We operate in intensely competitive markets, and our failure to compete effectively would harm our results of operations.
The semiconductor industry and specifically the mobile and wireless communications markets are extremely competitive, and we expect competition to intensify as current competitors expand their product offerings and new competitors enter the market. This has especially intensified as semiconductor companies have begun to offer more integrated platforms. We currently compete with a number of large domestic and international companies in the business of designing integrated circuits and related applications, some of which have greater financial, technical and management resources than us. Our efforts to introduce new products into markets with entrenched competitors will expose us to additional competitive pressures. For example, we are facing and expect we will continue to face significant competition in the LTE market. We expect competition to continue to increase as industry standards continue to evolve and become better known, and others realize the market potential of this trend to platform integration. Additionally, customer expectations and requirements in such areas as the need for turnkey solutions has been evolving rapidly and some of our competitors may be better situated to meet potential customer needs. As competition in the markets in which we operate continues to increase, our revenues and gross margins may decline. For example, competitors with greater financial resources may be able to offer lower prices than us, or they may offer additional products, services or other incentives that we may not be able to match. In addition, many of our competitors operate and maintain their own fabrication facilities and
12
have longer operating histories, greater name recognition, larger customer bases, and greater sales, marketing and distribution resources than we do. Furthermore, our current and potential competitors in the mobile and wireless markets have established or may establish financial and strategic relationships among themselves or with existing or potential customers or other third parties to increase the ability of their products to address the needs of customers. Accordingly, new competitors or alliances among these competitors may acquire significant market share, which would harm our business. While we continue to pursue similar strategic relationships, and currently have significant financial and technical resources, we cannot assure you that we will be able to continue to compete successfully against existing or new competitors, which would harm our results of operations.
In addition, semiconductor providers have experienced consolidation over the past several years. For example, Broadcom Corporation acquired NetLogic Microsystems in February 2011, Qualcomm Inc. acquired Atheros Communications Inc. in May 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated acquired National Semiconductor in September 2011 and Avago Technologies Limited (“Avago”) acquired LSI Corporation (“LSI”) in May 2014. Other pending transactions may further consolidate competition in our industry. Consolidation among our competitors could lead to a changing competitive landscape, capabilities and market share, which could harm our results of operations.
We are currently involved in a patent litigation action involving Carnegie Mellon University, and, if we do not prevail on appeal of the district court judgment, we could be liable for substantial damages.
On March 6, 2009, Carnegie Mellon University (“CMU”) filed a complaint in the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Pennsylvania naming Marvell Semiconductor, Inc. and us as defendants, and alleging patent infringement. CMU has asserted U.S. Patent Nos. 6,201,839 and 6,438,180 (collectively, the “CMU patents in suit”), which relate to read-channel integrated circuit devices and the HDD products incorporating such devices. A jury trial began on November 26, 2012. On December 26, 2012, a jury delivered a verdict that found the CMU patents in suit were literally and willfully infringed and valid, and awarded past damages in the amount of $1.17 billion. CMU sought in its post-trial motions enhanced damages up to three times the jury verdict, pre-judgment interest up to $322 million, post-judgment interest, supplemental damages, attorneys’ fees, and an injunction and/or ongoing royalties. Post-trial motions were heard on May 1 and 2, 2013. On June 26, 2013, the District Court denied CMU’s post-trial motion for attorney fees without prejudice. On August 23, 2013, the District Court denied our motion for mistrial. On September 23, 2013, the District Court denied our motion for judgment as a matter of law or a new trial on non-infringement, invalidity and other non-damages issues as well as our motion for reduced damages. On the same day, the District Court granted-in-part CMU’s motion for a finding of willful infringement and enhanced damages, reserving its further rulings on any enhancement of the verdict for a separate opinion. On January 14, 2014, the District Court denied our post-trial motion on laches. On March 31, 2014, the District Court rejected CMU’s motion for an injunction. The District Court also denied CMU’s request for pre-judgment interest, and substantially scaled back CMU’s request for enhanced damages. Based on these decisions, the Court calculated the damages including enhancement to total approximately $1.54 billion, and held that, under its decision, CMU is entitled to post judgment interest and an ongoing royalty. On May 7, 2014, the District Court entered final judgment, from which we filed a notice of appeal on May 14, 2014 to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit in Washington, D.C. We filed our opening appeal brief on August 4, 2014. CMU filed its opposition brief on October 20, 2014 and we filed our reply brief on November 20, 2014. We believe that there are strong grounds for appeal, which is set for oral argument in April 2015 before the U.S. Court of Appeals, but there is no guarantee that we will be successful on appeal. Please see “Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a more detailed description of a number of litigation matters we are currently engaged in. If we are required to pay most or all of the damages calculated by the District Court after all appeals have been exhausted, this could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
In order to stay the execution of the final judgment pending its appeal before the U.S. Court of Appeals, we filed a supersedeas bond for $1.54 billion with the District Court. The bond was issued by a consortium of sureties authorized by the U.S. Treasury. If the judgment is affirmed after the completion of all appellate
13
proceedings, and we do not thereafter fully satisfy the judgment within thirty days, the sureties are obligated under the bond to make payment to CMU. In support of the bond, we entered into separate indemnity agreements with each of the sureties to indemnify the sureties from all costs and payments made under the bond. The indemnity agreements did not require collateral to be posted at the time of the issuance of the bond. Therefore no cash is considered restricted as of the date of this filing. However, the indemnity agreements provide that each of the sureties have the right to demand to be placed in funds or call for collateral under pre-defined events. The indemnity agreements will remain outstanding for as long as the underlying bond remains outstanding.
The Court has required us to report ongoing royalties under the current judgment. Based on the royalty rate assessed by the District Court, such additional royalties for the period of time commencing on the date ordered by the District Court, January 15, 2013, through January 31, 2015 could be as much as $400 million. On November 14, 2014, we filed a second surety bond for $216 million and filed a commitment letter from the sureties to issue up to an additional $95 million in bonding under certain conditions. The second bond and commitment are secured by our campus located in Santa Clara, California, which has a carrying value of $139 million at January 31, 2015. We and CMU have agreed that the second bond and commitment satisfy the security for ongoing royalties while the appeal is pending.
A significant portion of our business is dependent on the HDD industry, which is highly cyclical, experiences rapid technological change, is subject to industry consolidation and is facing increased competition from alternative technologies.
The HDD industry is intensely competitive, and the technology changes rapidly. This industry has historically been cyclical, with periods of increased demand and rapid growth followed by periods of oversupply and subsequent contraction. These cycles may affect us because some of our largest customers are participants in this industry.
HDD manufacturers tend to order more components than they may need during growth periods, and sharply reduce orders for components during periods of contraction. Rapid technological changes in the HDD industry often result in shifts in market share among the industry’s participants. If the HDD manufacturers using our products do not retain or increase their market share, our sales may decrease.
In addition, the HDD industry has experienced consolidation over the past several years. For example, during fiscal 2010, Toshiba acquired the HDD operations of Fujitsu. In December 2011, Seagate Technology plc (“Seagate”) completed the acquisition of Samsung’s HDD unit. In March 2012, Western Digital completed the acquisition of Hitachi’s HDD unit. Consolidation among our customers could lead to changing demand for our products, replacement of our products by the merged entity with those of our competitors and cancellation of orders, each of which could harm our results of operations. On the other hand, this could lead to increased opportunities for our products within the combined company if we can leverage our technology and customer relationships.
Furthermore, future changes in the nature of information storage products could reduce demand for traditional HDDs. For example, products using alternative technologies, such as SSD and other storage technologies could become a source of competition to manufacturers of HDDs. Although we offer SSD controllers, leveraging our technology in hard drives, we cannot ensure we will be able to maintain significant market share if demand for traditional HDDs decreases. Additionally, we depend on a few customers for our SSD controllers and as such, the loss of any SSD controller customer or a significant reduction in sales we make to them (for example, as a result of a significant drop in market share) may harm our financial condition and results of operations.
We have been named as a party to several lawsuits and may be named in additional litigation in the future, including litigation involving our patents and other intellectual property, which could subject us to liability, require us to indemnify our customers, require us to obtain or renew licenses, stop selling our products or force us to redesign our products.
We have been named as a party to several lawsuits and we may be named in additional litigation in the future. Please see “Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies” of our Notes to the Consolidated Financial
14
Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a more detailed description of a number of the litigation matters we are currently engaged in. In particular, litigation involving patents and other intellectual property is widespread in the high-technology industry and is particularly prevalent in the semiconductor industry, where a number of companies and other entities aggressively bring numerous infringement claims to assert their patent portfolios. The amount of damages alleged in intellectual property infringement claims can often be very significant.
From time to time our subsidiaries and customers receive, and may continue to receive in the future, standards-based infringement claims, as well as claims against us and our subsidiaries’ proprietary technologies, particularly those related to storage technology, microprocessors and other circuit components. Our subsidiaries and customers could face claims of infringement for certain patent licenses that have not been renewed. These claims could result in litigation and/or claims for indemnification, which, in turn, could subject us to significant liability for damages, attorneys’ fees and costs. Any potential intellectual property litigation also could force us to do one or more of the following:
| | • | | stop selling, offering for sale, making, having made or exporting products or using technology that contains the allegedly infringing intellectual property; |
| | • | | limit or restrict the type of work that employees involved in such litigation may perform for us; |
| | • | | pay substantial damages and/or license fees and/or royalties to the party claiming infringement or other license violations that could adversely impact our liquidity or operating results; |
| | • | | attempt to obtain or renew licenses to the relevant intellectual property, which licenses may not be available on reasonable terms or at all; and |
| | • | | attempt to redesign those products that contain the allegedly infringing intellectual property. |
Under certain circumstances, we have contractual and other legal obligations to indemnify and to incur legal expenses for current and former directors and officers. Additionally, from time to time, we have agreed to indemnify select customers for claims made against our products, where such claims allege infringement of third-party intellectual property rights, including, but not limited to, patents, registered trademarks and/or copyrights. If we are required to make a significant payment under any of our indemnification obligations, our results of operations may be harmed.
In addition, due to the high volatility of our stock price, we may be vulnerable to securities class action litigation. Furthermore, as a result of a prior SEC settlement, we forfeited for three years our ability to invoke the “safe harbor” for forward-looking statements provided by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Because we could not benefit from the statutory safe harbor from June 2008 through June 2011, it may be more difficult for us to defend against any future claims based on any forward-looking statements issued during that timeframe.
The ultimate outcome of any litigation could have a material adverse effect on our business and our stock price. Litigation may be time-consuming, expensive, and disruptive to normal business operations, and the outcome of litigation is difficult to predict. The defense of these lawsuits may result in significant expenditures and the continued diversion of our management’s time and attention away from the operation of our business, which could impede our business. In the event we were to receive an unfavorable outcome in any lawsuit, our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows and our stock price may be materially and adversely affected.
Our sales are concentrated in a few customers, and if we lose or experience a significant reduction in sales to any of these key customers, or if any of these key customers experience a significant decline in market share, our revenues may decrease substantially.
We receive a significant amount of our revenues from a limited number of customers. Net revenue from our two largest customers represented 33% of our net revenue for the year ended January 31, 2015. Sales to our
15
largest customers have fluctuated significantly from period to period and year to year primarily due to the timing and number of design wins with each customer, natural disasters that may divert a customer’s operations, as well as the continued diversification of our customer base as we expand into new markets, and will likely continue to fluctuate in the future. The loss of any of our large customers or a significant reduction in sales we make to them would likely harm our financial condition and results of operations. Our operating results in the foreseeable future will continue to depend on sales to a relatively small number of customers, as well as the ability of these customers to sell products that incorporate our products. In the future, these customers may decide not to purchase our products at all, purchase fewer products than they did in the past, or alter their purchasing patterns in some other way, particularly because:
| | • | | a significant portion of our sales are made on a purchase order basis, which permits our customers to cancel, change or delay product purchase commitments with relatively short notice to us; |
| | • | | customers may purchase integrated circuits from our competitors; |
| | • | | customers may discontinue sales or lose market share in the markets for which they purchase our products (for example, a significant customer of our SSD products has recently seen a significant drop in its market share); |
| | • | | customers may develop their own solutions or acquire fully developed solutions from third-parties (for example, in September 2014, Seagate acquired the SSD business from Avago); or |
| | • | | customers may be subject to severe business disruptions. |
We rely on independent foundries and subcontractors for the manufacture, assembly and testing of our integrated circuit products, and the failure of any of these third-party vendors to deliver products or otherwise perform as requested could damage our relationships with our customers, decrease our sales and limit our ability to grow our business.
We do not have our own manufacturing or assembly facilities and have very limited in-house testing facilities. Therefore, we currently rely on several third-party foundries to produce our integrated circuit products. We also currently rely on several third-party assembly and test subcontractors to assemble, package and test our products. This exposes us to a variety of risks, including the following:
Regional Concentration
Substantially all of our products are manufactured by third-party foundries located in Taiwan, and other sources are located in China and Singapore. In addition, substantially all of our third-party assembly and testing facilities are located in Singapore, Taiwan, Malaysia and the Philippines. Because of the geographic concentration of these third-party foundries, as well as our assembly and test subcontractors, we are exposed to the risk that their operations may be disrupted by regional disasters including, for example, earthquakes (particularly in Taiwan and elsewhere in the Pacific Rim close to fault lines), tsunamis or typhoons, or by political, social or economic instability. In the case of such an event, our revenues, cost of goods sold and results of operations would be negatively impacted. In addition, if we were unable to quickly identify alternate manufacturing facilities, we could experience significant delays in product shipments, which could harm our results of operations.
No Guarantee of Capacity or Supply
The ability of each foundry to provide us with semiconductor devices is limited by its available capacity and existing obligations. When demand is strong, availability of foundry capacity may be constrained or not available, and with limited exceptions, our vendors are not obligated to perform services or supply products to us for any specific period, in any specific quantities, or at any specific price, except as may be provided in a particular purchase order. We place our orders on the basis of our customers’ purchase orders or our forecast of
16
customer demand, and the foundries can allocate capacity to the production of other companies’ products and reduce deliveries to us on short notice. It is possible that foundry customers that are larger and better financed than we are or that have long-term agreements with our main foundries may induce our foundries to reallocate capacity to those customers. This reallocation could impair our ability to secure the supply of components that we need. In particular, as the industry transitions to smaller geometries, our manufacturing partners may be supply constrained or may charge premiums, which may harm our business or results of operations. Moreover, if any of our third-party foundry suppliers are unable to secure necessary raw materials from their suppliers, lose benefits under material agreements, experience power outages, lack sufficient capacity to manufacture our products, encounter financial difficulties or suffer any other disruption or reduction in efficiency, we may encounter supply delays or disruptions, which could harm our business or results of operations.
Despite our strategy to move to multiple sources, most of our products are not manufactured at more than one foundry at any given time, and our products typically are designed to be manufactured in a specific process at only one of these foundries. Accordingly, if one of our foundries is unable to provide us with components as needed, it may be difficult for us to transition the manufacture of our products to other foundries, and we could experience significant delays in securing sufficient supplies of those components. This could result in a material decline in revenues, net income and cash flow.
In order to secure sufficient foundry capacity when demand is high and mitigate the risks described in the foregoing paragraph, we may enter into various arrangements with suppliers that could be costly and harm our results of operations, such as non-refundable deposits with or loans to foundries in exchange for capacity commitments, and contracts that commit us to purchase specified quantities of integrated circuits over extended periods. We may not be able to make any such arrangement in a timely fashion or at all, and any arrangements may be costly, reduce our financial flexibility, and not be on terms favorable to us. Moreover, if we are able to secure foundry capacity, we may be obligated to use all of that capacity or incur penalties. These penalties may be expensive and could harm our financial results.
Uncertain Yields and Quality
The fabrication of integrated circuits is a complex and technically demanding process. Our foundries have from time to time experienced manufacturing defects and reduced manufacturing yields, which are difficult to detect at an early stage of the manufacturing process and may be time consuming and expensive to correct. Changes in manufacturing processes or the inadvertent use of defective or contaminated materials by our foundries could result in lower than anticipated manufacturing yields or unacceptable performance. In addition, we may face lower manufacturing yields and reduced quality in the process of ramping up and diversifying our manufacturing partners. Poor yields from our foundries, or defects, integration issues or other performance problems in our products could cause us significant customer relations and business reputation problems, harm our financial results and result in financial or other damages to our customers. Our customers could also seek damages which could result in a product liability claim, which would likely be time consuming and costly to defend. In addition, defects could result in significant costs. See “Costs related to defective products could have a material adverse effect on us.”
To the extent that we rely on outside suppliers to manufacture or assemble and test our products, we may have a reduced ability to directly control product delivery schedules and quality assurance, which could result in product shortages or quality assurance problems that could delay shipments or increase costs.
Commodity Prices
We are also subject to risk from fluctuating market prices of certain commodity raw materials that are incorporated into our end products or used by our suppliers to manufacture our end products. Supplies for such commodities may from time to time become restricted, or general market factors and conditions may affect pricing of such commodities.
17
If we are unable to develop and introduce new and enhanced products that achieve market acceptance in a timely and cost-effective manner, our results of operations and competitive position will be harmed.
Our future success will depend on our ability, in a timely and cost-effective manner, to develop and introduce new products and enhancements to our existing products. We sell products in markets that are characterized by rapid technological change, evolving industry standards, frequent new product introductions, short product life cycles and increasing demand for higher levels of integration and smaller process geometries. In addition, the development of new silicon devices is highly complex, and due to supply chain cross-dependencies and other issues, we may experience delays in completing the development, production and introduction of our new products. Our ability to adapt to changes and to anticipate future standards, and the rate of adoption and acceptance of those standards, will be a significant factor in maintaining or improving our competitive position and prospects for growth. We may also have to incur substantial unanticipated costs to comply with these new standards. Our success will also depend on the ability of our customers to develop new products and enhance existing products for the markets they serve and to introduce and promote those products successfully in a timely manner. Even if new and enhanced products are introduced to the market, we and our customers may not be able to achieve market acceptance of them.
Our gross margin and results of operations may be adversely affected in the future by a number of factors, including decreases in average selling prices of products over time and shifts in our product mix.
The products we develop and sell are primarily used for high-volume applications. As a result, the prices of those products have historically decreased rapidly. In addition, more recently introduced products tend to have higher associated costs because of initial overall development and production ramp. Therefore, over time, we may not be able to maintain or improve our gross margins. Our financial results could suffer if we are unable to offset any reductions in our average selling prices by other means, including cost reductions through efficiencies, introduction of higher margin products and increased volume of sales.
To attract new customers or retain existing customers, we may offer certain customers certain price concessions, which could cause our average selling prices and gross margins to decline. In the past, we have reduced the average selling prices of our products in anticipation of future competitive pricing pressures, new product introductions by us or by our competitors and other factors. We expect that we will continue to have to reduce prices in the future. Moreover, because of the wide price differences across the markets we serve, the mix and types of performance capabilities of our products sold may affect the average selling prices of our products and have a substantial impact on our revenue and gross margin. We may enter new markets in which a significant amount of competition exists, and this may require us to sell our products with lower gross margins than our established businesses. In addition, these new markets may have lower standard gross margins than the traditional markets we have served. If we are successful in growing revenue in these markets, our overall gross margin may decline. Fluctuations in the mix and types of our products may also affect the extent to which we are able to recover the fixed costs and investments associated with a particular product, and as a result can harm our financial results.
Additionally, because we do not operate our own manufacturing, assembly or testing facilities, we may not be able to reduce our costs as rapidly as companies that operate their own facilities, and our costs may even increase, which could also reduce our gross margins.
We are subject to order and shipment uncertainties, and if we are unable to accurately predict customer demand, we may hold excess or obsolete inventory, which would reduce our gross margin; conversely, we may have insufficient inventory, which would result in lost revenue opportunities and potentially in loss of market share and damaged customer relationships.
We typically sell products pursuant to purchase orders rather than long-term purchase commitments. Customers can generally cancel or defer purchase orders on short notice without incurring a significant penalty.
18
Due to their inability to predict demand or other reasons, some of our customers may accumulate excess inventories and, as a consequence, defer purchase of our products. We cannot accurately predict what or how many products our customers will need in the future. Anticipating demand is difficult because our customers face unpredictable demand for their own products and are increasingly focused more on cash preservation and tighter inventory management. In addition, as an increasing number of our chips are being incorporated into consumer products, we anticipate greater fluctuations in demand for our products, which makes it more difficult to forecast customer demand. We place orders with our suppliers based on forecasts of customer demand and, in some instances, may establish buffer inventories to accommodate anticipated demand. Our forecasts are based on multiple assumptions, each of which may introduce error into our estimates. For example, our ability to accurately forecast customer demand may be impaired by the delays inherent in our lengthy sales cycle. The sales cycle for many of our products is long and requires us to invest significant resources with each potential customer without any assurance of sales to that customer. Our sales cycle typically begins with an extended evaluation and test period, also known as qualification, during which our products undergo rigorous reliability testing by our customers. Qualification is typically followed by an extended development period by our customers and an additional three to nine month period before a customer commences volume production of equipment incorporating our products. This lengthy sales cycle creates the risk that our customers will decide to cancel or change product plans for products incorporating our integrated circuits prior to completion, which makes it even more difficult to forecast customer demand.
Our products are incorporated into complex devices and systems, which may create supply chain cross-dependencies. For example, in fiscal 2012, many areas of Thailand sustained massive damage from flooding, which disrupted the global supply chain for HDDs. Due to cross dependencies, any supply chain disruptions could negatively impact the demand for our products in the short term. We have a limited ability to predict the timing of a supply chain correction. In addition, the market share of our customers could be adversely impacted on a long-term basis due to any continued supply chain disruption, which could negatively affect our results of operations.
If we overestimate customer demand, our excess or obsolete inventory may increase significantly, which would reduce our gross margin and adversely affect our financial results. The risk of obsolescence and/or excess inventory is heightened for devices designed for consumer electronics due to the rapidly changing market for these types of products. Conversely, if we underestimate customer demand or if insufficient manufacturing capacity is available, we would miss revenue opportunities and potentially lose market share and damage our customer relationships. In addition, any future significant cancellations or deferrals of product orders or the return of previously sold products could materially and adversely affect our profit margins, increase product obsolescence and restrict our ability to fund our operations.
If we fail to appropriately scale our operations in response to changes in demand for our existing products or to the demand for new products requested by our customers, our business and profitability could be materially and adversely affected.
To achieve our business objectives, it may be necessary from time to time for us to expand or contract our operations. In the future, we may not be able to scale our workforce and operations in a sufficiently timely manner to respond effectively to changes in demand for our existing products or to the demand for new products requested by our customers. In that event, we may be unable to meet competitive challenges or exploit potential market opportunities, and our current or future business could be materially and adversely affected. Conversely, if we expand our operations and workforce too rapidly in anticipation of increased demand for our products, and such demand does not materialize at the pace at which we expected, the rate of increase in our costs and operating expenses may exceed the rate of increase in our revenue, which would adversely affect our results of operations. In addition, if such demand does not materialize at the pace which we expect, we may be required to scale down our business through expense and headcount reductions as well as facility consolidations or closures that could result in restructuring charges that would materially and adversely affect our results of operations. Because many of our expenses are fixed in the short-term or are incurred in advance of anticipated sales, we may not be able to decrease
19
our expenses in a timely manner to offset any decrease in customer demand. If customer demand does not increase as anticipated, our profitability could be adversely affected due to our higher expense levels.
Our past growth has placed, and any future long-term growth is expected to continue to place, a significant strain on our management personnel, systems and resources. To implement our current business and product plans, we will need to continue to expand, train, manage and motivate our workforce. All of these endeavors will require substantial management effort. Although we have an enterprise resource planning system to help us improve our planning and management processes, we anticipate that we will also need to continue to implement and improve a variety of new and upgraded operational and financial systems, as well as additional procedures and other internal management systems. These systems can be time consuming and expensive to implement, increase management responsibilities and divert management attention. If we are unable to effectively manage our expanding operations, we may be unable to scale our business quickly enough to meet competitive challenges or exploit potential market opportunities, or conversely, we may scale our business too quickly and the rate of increase in our costs and expenses may exceed the rate of increase in our revenue, either of which would materially and adversely affect our results of operations.
Our business, financial condition and results of operations may be adversely impacted by global economic conditions, which may cause a decline in the market price of our common shares.
We operate in the semiconductor industry, which is cyclical and subject to rapid change and evolving industry standards. From time to time, this industry has experienced significant demand downturns. These downturns are characterized by decreases in product demand, excess customer inventories and sometimes accelerated erosion of prices, including as a result of volatile global economic conditions. These factors could cause substantial fluctuations in our net revenue, gross margin, cash flows and results of operations. In addition, during these downturns some competitors may become more aggressive in their pricing practices, which would adversely impact our gross margin. Any downturns in the current environment may be severe and prolonged, and any failure of the markets in which we operate to fully recover from downturns could seriously impact our revenue and harm our business, financial condition and results of operations. The semiconductor industry is also subject to periodic increases in demand and supply constraints, which may affect our ability to ship products. Accordingly, our results of operations may vary significantly as a result of the general conditions in the semiconductor industry, which could cause fluctuations in our stock price.
We cannot predict the timing, strength or duration of any economic slowdown or recovery or the impact of any such events on our vendors, customers or us. If the economy or markets in which we operate deteriorate from current levels, our business, financial condition and results of operations will likely be materially and adversely affected. Additionally, the combination of our lengthy sales cycle coupled with challenging macroeconomic conditions could adversely impact our results of operations.
We may experience reduced manufacturing yields, delays in product deliveries and increased expenses as a result of transitioning to smaller geometry process technologies.
In order to remain competitive, we expect to continue to transition our semiconductor products to increasingly smaller line width geometries. This transition requires us to modify the manufacturing processes for our products and to redesign some products. We periodically evaluate the benefits, on a product-by-product basis, of migrating to smaller geometry process technologies to reduce our costs. In the past, we have experienced some difficulties in shifting to smaller geometry process technologies or new manufacturing processes, which resulted in reduced manufacturing yields, delays in product deliveries and increased expenses. We may face similar difficulties, delays and expenses as we continue to transition our products to smaller geometry processes. We are dependent on our relationships with our foundry subcontractors to transition to smaller geometry processes successfully. We cannot assure you that the foundries that we use will be able to effectively manage the transition or that we will be able to maintain our existing foundry relationships or develop new ones. If we or any of our foundry subcontractors experience significant delays in this transition or fail to
20
efficiently implement this transition, we could experience reduced manufacturing yields, delays in product deliveries and increased expenses, all of which could harm our relationships with our customers and our results of operations. As smaller geometry processes become more prevalent, we expect to continue to integrate greater levels of functionality, as well as customer and third-party intellectual property, into our products. However, we may not be able to achieve higher levels of design integration or deliver new integrated products on a timely basis, if at all. Moreover, even if we are able to achieve higher levels of design integration, such integration may have a short-term adverse impact on our results of operations, as we may reduce our revenue by integrating the functionality of multiple chips into a single chip.
We are exposed to potential impairment charges on certain assets.
We had approximately $2.0 billion of goodwill and $30.7 million of acquired intangible assets, net on our balance sheet as of January 31, 2015. Under generally accepted accounting principles in the United States, we are required to review our intangible assets including goodwill for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable. We perform an assessment of goodwill for impairment annually or more frequently whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable. We have only one reporting unit, and the fair value of the reporting unit is determined by taking our market capitalization as determined through quoted market prices and as adjusted for a control premium and other relevant factors. If our fair value declines to below our carrying value, we could incur significant goodwill impairment charges, which could negatively impact our financial results.
In addition, from time to time, we have made investments in private companies. If the companies that we invest in are unable to execute their plans and succeed in their respective markets, we may not benefit from such investments, and we could potentially lose the amounts we invest. We evaluate our investment portfolio on a regular basis to determine if impairments have occurred. If the operations of any businesses that we have acquired declines significantly, we could incur significant intangible asset impairment charges. Impairment charges could have a material impact on our results of operations in any period.
We depend on key personnel to manage our business, and if we are unable to retain our current personnel or attract additional qualified personnel, our ability to develop and successfully market our products could be harmed.
We believe our future success will depend in large part upon our ability to attract and retain highly skilled managerial, engineering, sales and marketing personnel. The competition for qualified technical personnel with significant experience in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing and sales of integrated circuits is intense, and the inability to attract qualified personnel, including hardware and software engineers and sales and marketing personnel could delay the development and introduction of and harm our ability to sell our products. Additionally, we typically do not enter into employment agreements with any of our key technical personnel and the loss of such personnel could harm our business, as their knowledge of our business and industry would be extremely difficult to replace.
As a result of our global operations, we face additional risks, which may harm our results of operations, because a majority of our products and our customers’ products are manufactured and sold outside of the United States.
A substantial portion of our business is conducted outside of the United States and, as a result, we are subject to foreign business, political and economic risks. All of our products are manufactured outside of the United States. Our current qualified integrated circuit foundries are located in the same region within Taiwan, and our primary assembly and test subcontractors are located in the Pacific Rim region. In addition, many of our customers are located outside of the United States, primarily in Asia, which further exposes us to foreign risks. Sales to customers located in Asia represented approximately 96% of our net revenue in fiscal 2015, 95% of our net revenue in fiscal 2014 and 90% of our net revenue in fiscal 2013.
21
We also have substantial operations outside of the United States. These operations are directly influenced by the political and economic conditions of the region in which they are located, and with respect to Israel, possible military hostilities, such as the recent turmoil in the region, that could affect our operations there. We anticipate that our manufacturing, assembly, testing and sales outside of the United States will continue to account for a substantial portion of our operations and revenue in future periods. Accordingly, we are subject to risks associated with international operations, including:
| | • | | political, social and economic instability, including wars, terrorism, political unrest, boycotts, curtailment of trade and other business restrictions; |
| | • | | compliance with domestic and foreign export and import regulations, and difficulties in obtaining and complying with domestic and foreign export, import and other governmental approvals, permits and licenses; |
| | • | | local laws and practices that favor local companies, including business practices that we are prohibited from engaging in by the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and other anti-corruption laws and regulations; |
| | • | | difficulties in staffing and managing foreign operations; |
| | • | | natural disasters, including earthquakes, tsunamis and floods; |
| | • | | trade restrictions or higher tariffs; |
| | • | | difficulties of managing distributors; |
| | • | | less effective protection of intellectual property than is afforded to us in the United States or other developed countries; |
| | • | | inadequate local infrastructure; and |
| | • | | exposure to local banking, currency control and other financial-related risks. |
As a result of having global operations, the sudden disruption of the supply chain and/or the manufacture of our customer’s products caused by events outside of our control could impact our results of operations by impairing our ability to timely and efficiently deliver our products. For example, during fiscal 2012, the earthquake and tsunami that affected Japan disrupted the global supply chain for certain components important to our products and the flooding in Thailand affected the supply chain and manufacturing of the products for a number of our customers.
Moreover, the international nature of our business subjects us to risk associated with the fluctuation of the U.S. dollar versus foreign currencies. Decreases in the value of the U.S. dollar versus currencies in jurisdictions where we have large fixed costs or our third-party manufacturers have significant cost will increase the cost of such operations, which could harm our results of operations. For example, we have large fixed costs in Israel, which will become greater if the U.S. dollar declines in value versus the Israeli shekel. On the other hand, substantially all of our sales have been denominated in U.S. dollars.
Costs related to defective products could have a material adverse effect on us.
We have experienced, from time to time, hardware and software defects and bugs associated with the introduction of our highly complex products. Despite our testing procedures, we cannot assure you that errors will not be found in new products or releases after commencement of commercial shipments in the future, which could result in loss of or delay in market acceptance of our products, material recall and replacement costs, delay in revenue recognition or loss of revenues, writing down the inventory of defective products, the diversion of the attention of our engineering personnel from product development efforts, our having to defend against litigation related to defective products or related property damage or personal injury, and damage to our reputation in the
22
industry that could adversely affect our relationships with our customers. In addition, the process of identifying a recalled product in devices that have been widely distributed may be lengthy and require significant resources and we may have difficulty identifying the end customers of the defective products in the field, which may cause us to incur significant replacement costs, contract damage claims from our customers and further reputational harm. Any of these problems could materially adversely affect our results of operations.
Any potential future acquisitions, strategic investments, divestitures, mergers or joint ventures may subject us to significant risks, any of which could harm our business.
Our long-term strategy may include identifying and acquiring, investing in or merging with suitable candidates on acceptable terms, or divesting of certain business lines or activities. In particular, over time, we may acquire, make investments in, or merge with providers of product offerings that complement our business or may terminate such activities. Mergers, acquisitions and divestitures include a number of risks and present financial, managerial and operational challenges, including but not limited to:
| | • | | diversion of management attention from running our existing business; |
| | • | | possible material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting; |
| | • | | increased expenses including legal, administrative and compensation expenses related to newly hired or terminated employees; |
| | • | | increased costs to integrate the technology, personnel, customer base and business practices of the acquired company with us; |
| | • | | potential exposure to material liabilities not discovered in the due diligence process; |
| | • | | potential adverse effects on reported operating results due to possible write-down of goodwill and other intangible assets associated with acquisitions; and |
| | • | | unavailability of acquisition financing or unavailability of such financing on reasonable terms. |
Any acquired business, technology, service or product could significantly under-perform relative to our expectations, and may not achieve the benefits we expect from possible acquisitions. For all these reasons, our pursuit of an acquisition, investment, divestiture, merger or joint venture could cause its actual results to differ materially from those anticipated.
We rely on third-party distributors and manufacturers’ representatives and the failure of these distributors and manufacturers’ representatives to perform as expected could reduce our future sales.
From time to time, we enter into relationships with distributors and manufacturers’ representatives to sell our products, and we are unable to predict the extent to which these partners will be successful in marketing and selling our products. Moreover, many of our distributors and manufacturers’ representatives also market and sell competing products, and may terminate their relationships with us at any time. Our future performance will also depend, in part, on our ability to attract additional distributors or manufacturers’ representatives that will be able to market and support our products effectively, especially in markets in which we have not previously distributed our products. If we cannot retain or attract quality distributors or manufacturers’ representatives, our sales and results of operations will be harmed.
Changes in existing taxation benefits, rules or practices may adversely affect our financial results.
Changes in existing taxation benefits, rules or practices may also have a significant effect on our reported results. For example, both the U.S. Congress and the G-20 (Group of Twenty Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors) may consider legislation affecting the taxation of foreign corporations and such legislation if enacted might adversely affect our future tax liabilities and have a material impact on our results of operations.
23
Furthermore, in prior years, we have entered into agreements in certain foreign jurisdictions that if certain criteria are met, the foreign jurisdiction will provide a more favorable tax rate than their current statutory rate. For example, we have obtained an undertaking from the Minister of Finance of Bermuda that in the event Bermuda enacts legislation imposing tax computed on profits, income, or capital asset, gain or appreciation, then the imposition of any such taxes will not apply to us until March 31, 2035. Additionally, our Singapore subsidiary qualified for Pioneer status until it expired in June 2014. However, we re-negotiated with the Singapore government and in fiscal 2015, they extended the Development and Expansion Incentive (“DEI”) until June 2019. Furthermore, under the Israeli Encouragement law of “approved or benefited enterprise,” two branches of Marvell Israel (M.I.S.L) Ltd. are entitled to, and have certain existing programs that qualify as, approved and benefited tax programs that include reduced tax rates and exemption of certain income through fiscal 2027. Our subsidiary in Switzerland also has tax incentives on revenues from research and design and wafer supply trading activities that expire in fiscal 2016. If any of our tax agreements in any of these foreign jurisdictions were terminated, our results of our operations and profitability would be harmed.
We rely upon the performance of our information technology systems to process, transmit, store and protect electronic information, and the failure of any critical information technology system may result in serious harm to our reputation, business, results of operations and/or financial condition.
We are heavily dependent on our technology infrastructure and maintain and rely upon certain critical information systems for the effective operation of our business. These information technology systems are subject to damage or interruption from a number of potential sources including natural disasters, viruses, destructive or inadequate code, malware, power failures, cyber attacks, and other events. We have implemented processes for systems under our control to mitigate risks and while we believe these systems are appropriately controlled, processes for information systems cannot be guaranteed to be failsafe. We may incur significant costs in order to implement, maintain and/or update security systems that we feel are necessary to protect our information systems or we may miscalculate the level investment necessary to protect our systems adequately. To the extent that any system failure, accident or security breach results in disruptions or interruptions to our operations or the theft, loss or disclosure of, or damage to our data or confidential information, including our intellectual property, our reputation, business, results of operations and/or financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
We may be unable to protect our intellectual property, which would negatively affect our ability to compete.
We believe one of our key competitive advantages results from our collection of proprietary technologies that we have developed and acquired since our inception. If we fail to protect these intellectual property rights, competitors could sell products based on technology that we have developed that could harm our competitive position and decrease our revenues. We believe that the protection of our intellectual property rights is and will continue to be important to the success of our business. We rely on a combination of patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secret laws, contractual provisions, confidentiality agreements, licenses and other methods, to protect our proprietary technologies. We also enter into confidentiality or license agreements with our employees, consultants and business partners, and control access to and distribution of our documentation and other proprietary information. We have been issued a significant number of U.S. and foreign patents and have a significant number of pending U.S. and foreign patent applications. However, a patent may not be issued as a result of any applications or, if issued, claims allowed may not be sufficiently broad to protect our technology. In addition, it is possible that existing or future patents may be challenged, invalidated or circumvented. Despite our efforts, unauthorized parties may attempt to copy or otherwise obtain and use our products or proprietary technology. Monitoring unauthorized use of our technology is difficult, and the steps that we have taken may not prevent unauthorized use of our technology, particularly in foreign countries where the laws may not protect our proprietary rights as fully as in the United States. If our patents do not adequately protect our technology, our competitors may be able to offer products similar to ours, which would adversely impact our business and results of operations.
24
Certain of our software (as well as that of our customers) may be derived from so-called “open source” software that is generally made available to the public by its authors and/or other third parties. Open source software is made available under licenses that impose certain obligations on us in the event we were to distribute derivative works of the open source software. These obligations may require us to make source code for the derivative works available to the public, and/or license such derivative works under a particular type of license, rather than the forms of license customarily used to protect our intellectual property. While we believe we have complied with our obligations under the various applicable licenses for open source software, in the event that the copyright holder of any open source software were to successfully establish in court that we had not complied with the terms of a license for a particular work, we could be required to release the source code of that work to the public and/or stop distribution of that work if the license is terminated.
We must comply with a variety of existing and future laws and regulations that could impose substantial costs on us and may adversely affect our business.
We are subject to various state, federal and international laws and regulations governing the environment, including restricting the presence of certain substances in electronic products and making producers of those products financially responsible for the collection, treatment, recycling and disposal of those products. In addition, we are also subject to various industry requirements restricting the presence of certain substances in electronic products. Although our management systems are designed to maintain compliance, we cannot assure you that we have been or will be at all times in complete compliance with such laws and regulations. If we violate or fail to comply with any of them, a range of consequences could result, including fines, import/export restrictions, sales limitations, criminal and civil liabilities or other sanctions.
We and our customers are also subject to various import and export laws and regulations. Government export regulations apply to the encryption or other features contained in some of our products. If we fail to continue to receive licenses or otherwise comply with these regulations, we may be unable to manufacture the affected products at foreign foundries or ship these products to certain customers, or we may incur penalties or fines.
There is also regulation to improve the transparency and accountability concerning the supply of minerals coming from the conflict zones in and around the Democratic Republic of Congo. New U.S. legislation includes disclosure requirements regarding the use of conflict minerals mined from the Democratic Republic of Congo and adjoining countries and procedures regarding a manufacturer’s efforts to prevent the sourcing of such conflict minerals. The implementation of these requirements could affect the sourcing, availability and pricing of minerals used in the manufacture of semiconductor devices, including our products. As a result, there may only be a limited pool of suppliers who provide conflict-free metals, and we cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain products in sufficient quantities or at competitive prices, which could adversely affect our operations and product margins. Additionally, if we are unable to sufficiently source conflict-free metals, we may face difficulties in satisfying customers who may require that the products they purchase from us are conflict-free, which may harm our sales and operating results.
The costs of complying (including the costs of any investigations, auditing and monitoring) with these laws could adversely affect our current or future business. In addition, future regulations may become more stringent or costly and our compliance costs and potential liabilities could increase, which may harm our current or future business.
There can be no assurance that we will continue to declare cash dividends at all or in any particular amount, and statutory requirements under Bermuda Law, as well as ongoing litigation, may require us to defer payment of declared dividends.
In May 2012, we announced the declaration of our first quarterly cash dividend. Future payment of a regular quarterly cash dividend on our common shares will be subject to, among other things, the best interests of our
25
company, our results of operations, cash balances and future cash requirements, financial condition, statutory requirements under Bermuda law, developments in our ongoing litigation with CMU and other factors that the board of directors may deem relevant. Our dividend payments may change from time to time, and we cannot provide assurance that we will continue to declare dividends at all or in any particular amounts. In addition, developments in ongoing litigation could affect our ability to make a dividend payment on a declared payment date until such time as we can meet statutory requirements under Bermuda law. A reduction in, a delay of, or elimination of our dividend payments could have a negative effect on our share price.
If our internal control over financial reporting or disclosure controls and procedures are not effective, there may be errors in our financial statements that could require a restatement or our filings may not be filed on a timely basis and investors may lose confidence in our reported financial information, which could lead to a decline in our stock price.
We believe that effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports and effectively prevent fraud. However, a control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control system’s objectives will be met. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting will not necessarily prevent all error and all fraud. Controls can also be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the controls. In addition, we may modify the design and operating effectiveness of our internal controls, which could affect the overall effectiveness or evaluation of the control system in the future by us or our independent registered public accounting firm. Additionally, we cannot assure you that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions, as controls may become inadequate due to changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance. Any failure to maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting could limit our ability to provide reliance financial reports, or to detect and prevent fraud, which would harm our business.
Two of our officers own a large percentage of our voting stock and, together with another significant shareholder, are related by blood or marriage. These factors may allow the officers and directors as a group or the related individuals to influence the election of directors and the approval or disapproval of significant corporate actions.
Dr. Sehat Sutardja, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, and Weili Dai, who serves as our President, are husband and wife. Together, these two officers, along with a shareholder that is related to Dr. Sutardja, held approximately 20% of our outstanding common shares as of December 31, 2014. As a result, if these individuals act together, they may influence the election of our directors and the approval or disapproval of any significant corporate actions that require shareholder approval. This influence over our affairs might be adverse to the interests of other shareholders. For example, the voting power of these individuals could have the effect of delaying or preventing an acquisition of us on terms that other shareholders may desire.
Under Bermuda law, all of our officers, in exercising their powers and discharging their duties, must act honestly and in good faith with a view to our best interests and exercise the care, diligence and skill that a reasonably prudent person would exercise in comparable circumstances. Majority shareholders do not owe fiduciary duties to minority shareholders. As a result, the minority shareholders will not have a direct claim against the majority shareholders in the event the majority shareholders take actions that damage the interests of minority shareholders. Class actions are generally not available to shareholders under the laws of Bermuda, although there is some suggestion that their use may be gaining favor. Bermuda law permits, in exceptional circumstances, the bringing of derivative actions, i.e., for a shareholder to bring an action in our name, when it would otherwise be an action that the company would bring itself. In order to bring a derivative action, a shareholder would have to show (i) “fraud on the minority,” that is acts which amount to an unconscionable use of majority power resulting or likely to result in loss or unfair discriminatory treatment of the minority; and (ii) that the alleged wrongdoers have control of the company. In addition, a shareholder may be able to bring a claim when the shareholder alleges that the wrong has been done to the shareholder personally in his or her capacity as shareholder. Typically, shareholders’ personal claims arise from a breach or threatened breach of the bye-laws.
26
The Companies Act 1981 of Bermuda, as amended, provides that when one or more shareholders believes the affairs of a company are being conducted in a manner which is oppressive or prejudicial to the interest of some of such shareholders and others, a Bermuda court, upon petition, may make such order as it sees fit, including an order regulating the conduct of the company’s affairs in the future or ordering the purchase of the shares of any shareholders by other shareholders or by the company, and in the case of a purchase of the shares by the company, for the reduction accordingly of the company’s capital or otherwise.
We are subject to the risks of owning real property.
Our buildings in Santa Clara, California; Singapore; Etoy, Switzerland; and Shanghai, China subject us to the risks of owning real property, which include:
| | • | | the possibility of environmental contamination and the costs associated with fixing any environmental problems; |
| | • | | adverse changes in the value of these properties, due to interest rate changes, changes in the neighborhood in which the property is located, or other factors; |
| | • | | the possible need for structural improvements in order to comply with zoning, seismic and other legal or regulatory requirements; |
| | • | | the potential disruption of our business and operations arising from or connected with a relocation due to moving to or renovating the facility; |
| | • | | increased cash commitments for improvements to the buildings or the property or both; |
| | • | | increased operating expenses for the buildings or the property or both; |
| | • | | possible disputes with tenants or other third parties related to the buildings or the property or both; and |
| | • | | the risk of financial loss in excess of amounts covered by insurance, or uninsured risks, such as the loss caused by damage to the buildings as a result of earthquakes, floods and or other natural disasters. |
Additionally, the second surety bond and commitment from the sureties are secured by our campus located in Santa Clara, California. See “We are currently involved in a patent litigation action involving CMU and, if we do not prevail on appeal of the district court judgment, we could be liable for substantial damages.”
As we carry only limited insurance coverage, any incurred liability resulting from uncovered claims could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Our insurance policies may not be adequate to fully offset losses from covered incidents, and we do not have coverage for certain losses. For example, there is very limited coverage available with respect to the services provided by our third-party foundries and assembly and test subcontractors. In the event of a natural disaster (such as an earthquake or tsunami), political or military turmoil, widespread health issues or other significant disruptions to their operations, insurance may not adequately protect us from this exposure. We believe our existing insurance coverage is consistent with common practice, economic considerations and availability considerations. If our insurance coverage is insufficient to protect us against unforeseen catastrophic losses, any uncovered losses could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
We are incorporated in Bermuda, and, as a result, it may not be possible for our shareholders to enforce civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States. In addition, our Bye-Laws contain a waiver of claims or rights of action by our shareholders against our officers and directors, which will severely limit our shareholders’ right to assert a claim against our officers and directors under Bermuda law.
We are organized under the laws of Bermuda. As a result, it may not be possible for our shareholders to affect service of process within the United States upon us, or to enforce against us in U.S. courts judgments based on the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States. There is significant doubt as to whether the courts of Bermuda would recognize or enforce judgments of U.S. courts obtained against us or our directors
27
or officers based on the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state or hear actions brought in Bermuda against us or those persons based on those laws. The United States and Bermuda do not currently have a treaty providing for the reciprocal recognition and enforcement of judgments in civil and commercial matters. Therefore, a final judgment for the payment of money rendered by any federal or state court in the United States based on civil liability, whether or not based solely on U.S. federal or state securities laws, would not be automatically enforceable in Bermuda.
Our Bye-Laws contain a broad waiver by our shareholders of any claim or right of action, both individually and on our behalf, against any of our officers and directors. The waiver applies to any action taken by an officer or director, or the failure of an officer or director to take any action, in the performance of his or her duties with or for us, other than with respect to any matter involving any fraud or dishonesty on the part of the officer or director or to any matter arising under U.S. federal securities laws. This waiver will limit the rights of our shareholders to assert claims against our officers and directors unless the act complained of involves fraud or dishonesty or arises as a result of a breach of U.S. federal securities laws. Therefore, so long as acts of business judgment do not involve fraud or dishonesty or arise as a result of a breach of U.S. federal securities laws, they will not be subject to shareholder claims under Bermuda law. For example, shareholders will not have claims against officers and directors for a breach of trust, unless the breach rises to the level of fraud or dishonesty, or arises as a result of a breach of U.S. federal securities laws.
Our Bye-Laws contain provisions that could delay or prevent a change in corporate control, even if the change in corporate control would benefit our shareholders.
Our Bye-Laws contain change in corporate control provisions, which include:
| | • | | authorizing the issuance of preferred stock without shareholder approval; and |
| | • | | a shareholder vote requiring the approval of two-thirds of votes cast in person or by proxy to approve any business combination in the event the action is not approved by at least 662/3% of the directors holding office at the date of the Board meeting to approve the action. |
These foregoing provisions could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us, even if doing so would be a benefit to our shareholders.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None.
The following table presents the approximate square footage of our significant owned and leased facilities as of January 31, 2015:
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | (Square feet) | |
Locations | | Primary Use | | Owned Facilities | | | Leased Facilities (1) | |
United States | | Headquarters in Santa Clara, California: Research and design, sales and marketing, adminstration and operations | | | 993,000 | | | | 230,000 | |
China | | Research and design, and sales and marketing | | | 115,000 | | | | 227,000 | |
Singapore | | Operations, and research and design | | | 340,000 | | | | | |
Switzerland | | Research and design | | | 26,000 | | | | | |
Israel | | Research and design | | | | | | | 345,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Total | | | 1,474,000 | | | | 802,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | Lease terms expire in various years from 2015 through 2021. |
28
We also lease smaller facilities in India, Taiwan, Spain, Japan, Canada, South Korea, Sweden, Germany, Malaysia, and Italy which are occupied by administrative, sales, design and field application personnel. Based upon our estimates of future hiring, we believe that our current facilities in most locations will be adequate to meet our requirements at least through the next fiscal year.
The information set forth under “Note 10 – Commitments and Contingencies” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference. For additional discussion of certain risks associated with legal proceedings, please see Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” above.
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not Applicable.
29
PART II
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information
Our common shares are traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol “MRVL.” Our common shares began trading on June 27, 2000, upon completion of our initial public offering. For fiscal 2015 and fiscal 2014, the following table shows for the periods indicated the high and low sales prices for our common shares on the NASDAQ Global Select Market.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fiscal 2015 | | | Fiscal 2014 | |
| | | High | | | Low | | | High | | | Low | |
First Quarter | | $ | 16.65 | | | $ | 14.33 | | | $ | 10.99 | | | $ | 9.16 | |
Second Quarter | | $ | 16.09 | | | $ | 13.10 | | | $ | 13.18 | | | $ | 10.46 | |
Third Quarter | | $ | 14.25 | | | $ | 11.65 | | | $ | 13.51 | | | $ | 10.87 | |
Fourth Quarter | | $ | 16.19 | | | $ | 12.76 | | | $ | 15.82 | | | $ | 11.78 | |
As of March 19, 2015, the approximate number of record holders of our common shares was 138 (not including beneficial owners of stock held in street name).
30
Stock Price Performance Graph
This performance graph shall not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act or incorporated by reference into any filings under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except as shall be expressly set forth by specific reference in such filing.
The graph below compares the cumulative total shareholder return of our common shares with the cumulative total return of the S&P 500 Index and the Philadelphia Semiconductor Index since January 30, 2010 through January 31, 2015. The graph compares a $100 investment on January 30, 2010 in our common share with a $100 investment on January 30, 2010 in each index and assumes that any dividends were reinvested. Shareholder returns over the indicated periods should not be considered indicative of future stock prices or shareholder returns.
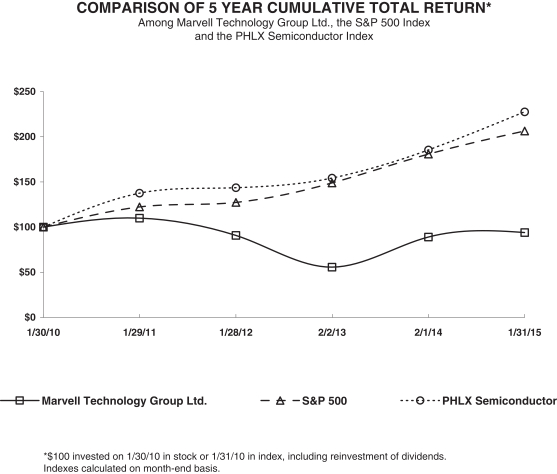
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 1/30/10 | | | 1/29/11 | | | 1/28/12 | | | 2/2/13 | | | 2/1/14 | | | 1/31/15 | |
Marvell Technology Group Ltd. | | | 100.00 | | | | 109.93 | | | | 90.59 | | | | 55.50 | | | | 88.97 | | | | 93.81 | |
S&P 500 | | | 100.00 | | | | 122.19 | | | | 127.34 | | | | 148.71 | | | | 180.70 | | | | 206.41 | |
PHLX Semiconductor | | | 100.00 | | | | 137.51 | | | | 143.45 | | | | 154.30 | | | | 185.27 | | | | 227.64 | |
31
Dividends
Our board of directors declared quarterly cash dividends of $0.06 per share payable to holders of our common shares in each quarter of fiscal 2015 and fiscal 2014. As a result, we paid total cash dividends of $122.8 million and $119.4 million in fiscal 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Future payment of a regular quarterly cash dividend on our common shares will be subject to, among other things, the best interests of the Company, our results of operations, cash balances and future cash requirements, financial condition, statutory requirements under Bermuda law and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. Our dividend payments may change from time to time, and we cannot provide assurance that we will continue to declare dividends at all or in any particular amounts. In addition, developments in ongoing litigation could affect our ability to make a dividend payment on a declared payment date until such time as we can meet statutory requirements under Bermuda law.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table presents details of our repurchases during the three months ended January 31, 2015 (in thousands, except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Period | | Total Number of
Shares
Purchased | | | Average
Price Paid
per Share | | | Total Number of
Shares Purchased as
Part of Publicly
Announced Plans or
Programs | | | Approximated Dollar
Value of Shares that
May Yet Be Purchased
Under the Plans or
Programs (1) | |
November 2 — November 29, 2014 | | | 108,300 | | | $ | 13.84 | | | | 108,300 | | | $ | 211,918 | |
November 30 — December 27, 2014 | | | 1,069,174 | | | $ | 14.25 | | | | 1,069,174 | | | $ | 446,671 | |
December 28 — January 31, 2015 | | | 225,900 | | | $ | 14.22 | | | | 225,900 | | | $ | 443,457 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | 1,403,374 | | | $ | 14.21 | | | | 1,403,374 | | | $ | 443,457 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | In August 2010, our board of directors initially authorized our current share repurchase program to repurchase up to $500 million of our outstanding common shares. Our board of directors authorized an additional $1.5 billion in fiscal 2012, $1.0 billion in fiscal 2013 and $250 million in fiscal 2015 to be used to repurchase our common shares under the share repurchase program for a total available under the program of $3.25 billion. We intend to effect share repurchases in accordance with the conditions of Rule 10b-18 under the Exchange Act, but may also make repurchases in the open market outside of Rule 10b-18 or in privately negotiated transactions. The share repurchase program will be subject to market conditions and other factors and does not obligate us to repurchase any dollar amount or number of our common shares and the repurchase program may be extended, modified, suspended or discontinued at any time. |
32
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The following selected consolidated financial data should be read together with Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and Part II, Item 8, “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” contained elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31, | | | February 1, | | | February 2, | | | January 28, | | | January 29, | |
| | | 2015 (1) | | | 2014 (2) | | | 2013 (3) | | | 2012 (4) | | | 2011 (5) | |
| | | (in thousands, except per share amounts and number of employees) | |
Consolidated Statements of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net revenue | | $ | 3,706,963 | | | $ | 3,404,400 | | | $ | 3,168,630 | | | $ | 3,393,040 | | | $ | 3,611,893 | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 1,843,706 | | | $ | 1,663,730 | | | $ | 1,493,497 | | | $ | 1,465,805 | | | $ | 1,473,274 | |
Research and development | | $ | 1,164,059 | | | $ | 1,156,885 | | | $ | 1,057,445 | | | $ | 1,013,678 | | | $ | 897,578 | |
Operating income | | $ | 408,819 | | | $ | 280,691 | | | $ | 294,657 | | | $ | 604,146 | | | $ | 901,192 | |
Net income | | $ | 435,346 | | | $ | 315,320 | | | $ | 306,585 | | | $ | 615,091 | | | $ | 904,129 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.85 | | | $ | 0.64 | | | $ | 0.55 | | | $ | 1.01 | | | $ | 1.39 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.84 | | | $ | 0.63 | | | $ | 0.54 | | | $ | 0.99 | | | $ | 1.34 | |
Weighted average shares: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 511,089 | | | | 496,518 | | | | 555,310 | | | | 607,857 | | | | 648,347 | |
Diluted | | | 520,760 | | | | 504,413 | | | | 563,123 | | | | 623,268 | | | | 676,878 | |
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments | | $ | 2,529,555 | | | $ | 1,969,405 | | | $ | 1,918,990 | | | $ | 2,246,498 | | | $ | 2,930,030 | |
Working capital | | $ | 2,706,644 | | | $ | 2,187,914 | | | $ | 1,977,458 | | | $ | 2,489,407 | | | $ | 3,071,961 | |
Total assets | | $ | 5,884,387 | | | $ | 5,451,010 | | | $ | 5,261,764 | | | $ | 5,767,619 | | | $ | 6,338,157 | |
Total shareholders’ equity | | $ | 5,146,089 | | | $ | 4,675,910 | | | $ | 4,484,595 | | | $ | 5,014,018 | | | $ | 5,521,869 | |
Other Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash dividends declared per share | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.18 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Number of employees | | | 7,163 | | | | 7,355 | | | | 7,259 | | | | 6,970 | | | | 5,893 | |
| (1) | Fiscal 2015 includes $13.8 million of restructuring and other exit-related costs that include $3.4 million for the write off of in-process research and development (“IPR&D”), and $3.2 million related to a loss from a contract termination, an $8.8 million gain from the sale of an investment, and a $7.3 million of costs associated with the surety bond to appeal the CMU judgment. |
| (2) | Fiscal 2014 includes $14.7 million for litigation settlements, an $8.1 million charge for the impairment of an intangible asset, a $7.0 million gain from the sale of a business, and $4.7 million of restructuring and other exit-related costs. The litigation settlements do not relate to our litigation with CMU. |
| (3) | Fiscal 2013 includes $5.7 million for an expense related to an ongoing litigation matter and $4.9 million for expenses related to acquisitions in prior fiscal years. |
| (4) | Fiscal 2012 includes $6.7 million for litigation settlements and assessments of payroll taxes on employee benefits in certain jurisdictions. |
| (5) | Fiscal 2011 includes $8.5 million for litigation settlements. |
33
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with the financial statements and related notes included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. This discussion may contain forward-looking statements based upon current expectations that involve risks and uncertainties including those discussed under Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors.” These risks and uncertainties may cause actual results to differ materially from those discussed in the forward-looking statements.
We are a fabless semiconductor provider of high-performance application-specific standard products. Our core strength of expertise is the development of complex SoC and SiP devices, leveraging our extensive technology portfolio of intellectual property in the areas of analog, mixed-signal, digital signal processing, and embedded and standalone integrated circuits. The majority of our product portfolio leverages the ARM technology portfolio. We also develop platforms that we define as integrated hardware along with software that incorporates digital computing technologies designed and configured to provide an optimized computing solution. Our broad product portfolio includes devices for data storage, enterprise-class Ethernet data switching, Ethernet PHY, mobile handsets, connectivity, IoT devices and other consumer electronics. Our products serve diverse applications used in carrier, metropolitan, enterprise and PC-client data communications and storage systems. Additionally, we serve the consumer electronics market for the convergence of voice, video and data applications. As a fabless integrated circuit company, we rely on independent, third-party contractors to perform manufacturing, assembly and test functions. This approach allows us to focus on designing, developing and marketing our products, and significantly reduces the amount of capital we need to invest in manufacturing products.
Overview
In fiscal 2015, we experienced growth in net revenue for the second consecutive year. Net revenue in fiscal 2015 reached a record high of $3.7 billion and was 9% higher than net revenue of $3.4 billion in fiscal 2014. The growth was led by a 28% increase in revenue from products for the mobile and wireless end markets, particularly in the first half of fiscal 2015, together with stable year over year growth in the storage market. Moreover, our operating income in fiscal 2015 accelerated more rapidly than revenue as we were able to effectively control our operating expenses. Going into fiscal 2016, we expect revenue growth to be driven by areas such as mobile handsets, tablets, connectivity and smart home devices along with a continued focus on operational execution.
| | • | | In the mobile market, competition and pricing remain fierce, and negatively affected our operating results in the second half of the year. However, we continue to make steady progress with our LTE solutions. Our focus was initially on the LTE market in China where we saw more OEM partners start new 4G LTE smartphone, tablet and mobile broadband device projects with our chipsets. We also expanded into multiple geographies and saw good expansion of our 4G LTE products outside of China with a leading OEM launching our LTE solution in the European market. Last fall, Samsung launched the new Galaxy Mini 4G smartphone and its multi-mode LTE mobile hotspot. We also introduced two new products, our quad-core 64-bit ARMANDA Mobile PXA 1908 platform and our octa-core 64-bit ARMADA Mobile PXA 1936. We expect many of our tier-1 customers in Korea and China to introduce smartphones using these solutions. Despite the positive steps, the ramp of open market smartphones as opposed to the initial “carrier driven” models was faster than anticipated. We are making solid progress in our turnkey LTE platforms including board layout and software to target the open market in China. With the expansion of our LTE solutions to markets outside of China, we will subsequently attempt to bring our turnkey platforms to those markets as well. |
| | • | | In the wireless connectivity market, we recently introduced the 4x4 11ac Wave-2 Wi-Fi and SoC platform for enterprise access point and smart home gateway solutions. Our 4x4 11ac devices have been growing our market share in carrier grade access point, supporting tier-1 customers like Cisco Systems, Inc. We believe we are well positioned to further expand into high-performance 4x4 MIMO product categories in both retail and service provider gateways with more devices in the pipeline for launch next year. Our wireless connectivity solutions are being used in game consoles at both |
34
| | Microsoft and Sony. We are seeing new opportunities for our connectivity solutions across multiple market segments. Our Wi-Fi and Zigbee devices are gaining strong adoption in the fast-growing IoT end market. Our EZ-Connect wireless microcontrollers have been well received and we have a strong design pipeline across a broad range of applications including lighting, appliances, home automation and other smart home and commercial IoT applications across China and North American regions. For example, Xiaomi launched a line of smart home products in late fall of 2014 based on our wireless microcontrollers. We are also an early partner in Apple’s HomeKit and we have several tier-1 customers designing HomeKit products using our EZ-Connect microcontrollers. In the video business, we saw strong volume shipments into Google Chromecast in European, South American and Asian markets. On the service provider side of the video business, a leading service provider in Korea launched their 4K platform using our ARMADA 1500 device and we expect several other service providers to start shipping their own version of Internet Protocol television and over-the-top hybrid set-top boxes using our ARMADA 1500 family of video SoC in the near future. For example, one of our leading service providers in France recently launched their set-top box based on the ARMDA 1500 PRO SoC. |
| | • | | In the storage market, we continued to execute well and the overall industry appears to have stabilized. Our HDD market remains strong as we continue to experience strong demand for our 500 gigabyte per platter products. We continued to see increased demand for our products used in enterprise drives at a top North America-based HDD customer. We are also continuing to accelerate our investment in next generation HDD technologies. Within the SSD market, our strategy of partnering with top tier OEMs has resulted in excellent traction for our advanced SSD solutions. Earlier this fiscal year, we announced multiple new products including our 5th generation SATA product with LDPC technology to support 3D NAND, as well as 15 nanometer 2D NAND, and a low-cost PCIe-based SSD solution priced similar to our SATA solution but with much higher performance. We continue to gain traction with our SATA SSD controller and are starting to see increased adoption of our PCIe SSD controller. We are also on track to introduce multiple embedded SSD products for the mobile market and expect to generate revenues from these products in fiscal 2016. Despite the drop in market share of one of our major customers, we are working to solidify our leadership position in the market over the next few years. |
| | • | | In the networking market, design win momentum continues with new programs that cover low-end fixed solutions to high-end modular platforms in the enterprise and service provider markets, driving new opportunities with our latest family of network processing solutions. We continue to gain traction with our recently introduced Questflo product line of network search engines that broadens our growing networking product portfolio. Today’s traditional TCAM-based solutions are unable to address future scaling requirements and multiple customers are actively engaged with us for next generation solutions. Our SRAM-based Questflo products are targeted for carrier customers and increase capacity using less power delivering better performance-power metrics compared to competitors. |
Our cost of goods sold as a percentage of net revenue for fiscal 2015 was higher compared to fiscal 2014. As we expand our presence in the mobile and wireless end markets, we expect our gross margin to face downward pressure, as these end markets generally have lower average gross margins than the rest of our business. However, we expect this growth will result in improvement to total gross margin dollars and operating profit. In addition, we are focused on efforts to improve both aspects of our gross profit, including through cost improvement and pricing.
We believe our financial position is strong and we remain committed to deliver shareholder value through our share repurchase and dividend programs.
| | • | | Our cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments were $2.5 billion at January 31, 2015. |
| | • | | We generated cash flow from operations of $728.9 million during fiscal 2015. |
35
| | • | | We paid cash dividends of $0.24 per share for a total of $122.8 million in fiscal 2015 and we recently announced a dividend of $0.06 per share to be paid in the first quarter of fiscal 2016. |
| | • | | We repurchased 5.1 million of our common shares for $65.0 million in fiscal 2015. |
We are currently involved in a patent litigation action with CMU (See “Risk Factors” under Part I, Item 1A of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and “Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies” in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a further discussion of the risks associated with this matter and other patent litigation matters). A jury has awarded past damages of $1.17 billion, and the Court calculated damages, including enhancement, to total approximately $1.54 billion, and held that, under its decision, CMU is entitled to post judgment interest and an ongoing royalty. Based on the royalty rate assessed by the District Court, such additional royalties for the period of time commencing on the date ordered by the District Court, January 15, 2013, through January 31, 2015 could be as much as $400 million. On May 7, 2014, the District Court entered final judgment and on May 14, 2014, we filed a notice of appeal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit in Washington, D.C., which is set for oral argument in April 2015. We have secured certain surety bonds for the duration of the appeal to stay execution of judgment pending the appeal. See “Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies — Surety Bonds” in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a further discussion of these surety bonds. We strongly believe that we do not infringe on the methods described in the CMU patents and that our products use our own internally developed patented read channel technology.
A significant number of our products are being incorporated into consumer electronics products, including gaming devices and personal computers, which are subject to significant seasonality and fluctuations in demand. Holiday and back to school buying trends may at times negatively impact our results in the first and fourth quarter, and positively impact our results in the second and third quarter of our fiscal years. In addition, consumer electronics sales are heavily dependent on new product launch timelines and product refreshes. For example, our sales of wireless connectivity products may increase significantly during a period when one of our consumers launches a new gaming console, and these sales may taper significantly after the initial launch period.
Historically, a relatively small number of customers have accounted for a significant portion of our net revenue. Net revenue from one customer was 20%, 24% and 24% for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Net revenue from a second customer was 13%, 12% and 10% for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. In fiscal 2013, net revenue from a third customer was 10%. We had net revenue from one distributor representing 11% and 11% for fiscal 2015 and 2013, respectively. No distributors accounted for 10% or greater of total net revenue in fiscal 2014.
Most of our sales are made to customers located outside of the United States, primarily in Asia. Sales to customers in Asia represented approximately 96%, 95% and 90% of our net revenue for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Because many manufacturers and manufacturing subcontractors of our customers are located in Asia, we expect that most of our net revenue will continue to be represented by sales to our customers in that region. Substantially all of our sales are denominated in U.S. dollars.
A relatively large portion of our sales have historically been made on the basis of purchase orders rather than long-term agreements. In addition, the sales cycle for our products is long, which may cause us to experience a delay between the time we incur expenses and the time revenue is generated from these expenditures. We anticipate that the rate of new orders may vary significantly from quarter to quarter. Consequently, if anticipated sales and shipments in any quarter do not occur when expected, expenses and inventory levels could be disproportionately high, and our operating results for that quarter and future quarters may be adversely affected.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates, judgments and assumptions
36
that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates, including those related to performance-based compensation, revenue recognition, provisions for sales returns and allowances, inventory excess and obsolescence, investment fair values, goodwill and other intangible assets, restructuring, income taxes, litigation and other contingencies. In addition, we use assumptions when employing the Monte Carlo simulation and Black-Scholes valuation models to calculate the fair value of share-based awards granted. We base our estimates of the carrying value of certain assets and liabilities on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances when these carrying values are not readily available from other sources. Actual results could differ from these estimates, and such differences could affect the results of operations reported in future periods. We believe the following critical accounting policies affect our more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Revenue Recognition. We recognize revenue when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, delivery has occurred, the fee is fixed or determinable, and collection is reasonably assured.
Product revenue is generally recognized upon shipment of product to customers, net of accruals for estimated sales returns and rebates. However, some of our sales are made through distributors under agreements allowing for price protection, shipped from stock pricing adjustment rights, and limited rights of stock rotation on product unsold by the distributors. Although title passes to the distributor upon shipment terms and payment by our distributors is not contingent on resale of the product, product revenue on sales made through distributors with price protection, shipped from stock pricing adjustment rights and stock rotation rights are deferred until the distributors sell the product to end customers. Deferred revenue less the related cost of the inventories is reported as deferred income. We do not believe that there is any significant exposure related to impairment of deferred cost of sales, as our historical returns have been minimal and inventory turnover for our distributors generally ranges from 60 to 90 days. Our sales to direct customers are made primarily pursuant to standard purchase orders for delivery of products.
A portion of our net revenue is derived from sales through third-party logistics providers, who maintain warehouses in close proximity to our customer’s facilities. Revenue from sales through these third-party logistics providers is not recognized until the product is pulled from stock by the customer.
The provision for estimated sales returns and allowances on product sales is recorded in the same period the related revenues are recorded. These estimates are based on historical sales returns, analysis of credit memo data and other known factors. In addition, payments to our customers, in cases where products with potential quality issues are not returned to us and the related quality issue can otherwise not be verified, or where the amount of the payment is not sufficiently supported by the fair value of the quality issue, may be recorded as a reduction of revenue. Actual returns could differ from these estimates. We account for rebates by recording reductions to revenue in the same period that the related revenue is recorded. The amount of these reductions is based upon the terms agreed to with the customers.
Share-based Compensation. We measure our share-based compensation at the grant date, based on the fair value of the award, and is recognized as expense over the requisite service period. We amortize share-based compensation expense for time-based and market-based awards under the straight-line attribution method over the vesting period, which is generally four years for annual grants to employees and five years for new hire grants. Performance-based awards are amortized using the accelerated method.
We estimate the fair value of time-based stock option awards on the date of grant using the Black Scholes option-pricing model. The fair value of market-based option awards is estimated on the date of grant using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The value of the portion of the awards that is ultimately expected to vest is recognized as expense over the requisite service periods. The Black-Scholes and Monte Carlo models incorporate various highly subjective assumptions including expected term of awards, expected future stock price volatility and expected forfeiture rates.
37
In developing estimates used to calculate assumptions, we establish the expected term for employee options, as well as expected forfeiture rates, based on the historical settlement experience and after giving consideration to vesting schedules. Assumptions for stock option exercises and pre-vesting terminations of stock options were stratified by employee groups with sufficiently distinct behavior patterns. Expected volatility was developed based on an equally weighted combination of historical stock price volatility and implied volatility derived from traded options on our stock in the marketplace. The expected dividend yield is calculated by dividing annualized dividend payments by the closing stock price on the grant date of the option.
Forfeitures are estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from initial estimates. Share-based compensation expense is recorded net of estimated forfeitures such that expense is recorded only for those share-based awards that are expected to vest. Previously recognized expense is reversed for the portion of awards forfeited prior to vesting as and when forfeitures occurred.
The fair value of each restricted stock unit is estimated based on the market price of the Company’s common shares on the date of grant less the expected dividend yield.
In addition, for both stock options and restricted stock units, we are required to estimate forfeiture rates, and true up these forfeiture rates when actual results are different from our estimates. Assumptions for forfeitures are stratified by employee groups with sufficiently distinct behavior patterns. Changes in the estimated forfeiture rate can have a significant effect on reported share-based compensation expense, as the effect of adjusting the rate for all expense amortization is recognized in the period the forfeiture estimate is changed. If the actual forfeiture rate is higher than the estimated forfeiture rate, then an adjustment will be made to increase the estimated forfeiture rate, which will result in a decrease to the expense recognized in the financial statements. If the actual forfeiture rate is lower than the estimated forfeiture rate, then an adjustment will be made to lower the estimated forfeiture rate, which will result in an increase to the expense recognized in the financial statements. The expense we recognize in future periods could be affected by changes in the estimated forfeiture rate and may differ significantly from amounts recognized in the current period and/or our forecasts.
Additionally, for certain of our performance-based awards, we must make subjective assumptions regarding the likelihood that the related performance metrics will be met. These assumptions are based on various revenue and operating performance criteria. Changes in our actual performance could cause a significant adjustment in future periods for these performance-based awards.
Accounting for Income Taxes. We estimate our income taxes in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. This process involves estimating our actual tax exposure together with assessing temporary differences resulting from the differing treatment of certain items for tax return and financial statement purposes. These differences result in deferred tax assets and liabilities, which are included within our consolidated balance sheets.
We recognize income taxes using an asset and liability approach. This approach requires the recognition of taxes payable or refundable for the current year, and deferred tax liabilities and assets for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in our consolidated financial statements or tax returns. The measurement of current and deferred taxes is based on provisions of the enacted tax law and the effects of future changes in tax laws or rates are not anticipated.
Evaluating the need for an amount of a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets often requires judgment and analysis of all the positive and negative evidence available to determine whether all or some portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. A valuation allowance must be established for deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that they will not be realized. Based on the available evidence and judgment, we have determined that it is more likely than not that our U.S. research credits, which we earn in excess of our current year tax liabilities, and certain acquired net operating losses will not be realized. Therefore, we have provided a full valuation allowance against these credits and a portion against the net operating losses. If there is a change in
38
our ability to realize our deferred tax assets, then our tax provision may decrease in the period in which we determine that realization is more likely than not.
As a multinational corporation, we conduct our business in many countries and are subject to taxation in many jurisdictions. The taxation of our business is subject to the application of various and sometimes conflicting tax laws and regulations as well as multinational tax conventions. Our effective tax rate is highly dependent upon the geographic distribution of our worldwide earnings or losses, the tax regulations and tax holidays in each geographic region, the availability of tax credits and carryforwards, and the effectiveness of our tax planning strategies. The application of tax laws and regulations is subject to legal and factual interpretation, judgment and uncertainty. Tax laws themselves are subject to change as a result of changes in fiscal policy, changes in legislation, and the evolution of regulations and court rulings. Consequently, taxing authorities may impose tax assessments or judgments against us that could materially impact our tax liability and/or our effective income tax rate.
We are subject to income tax audits by the respective tax authorities in all of the jurisdictions in which we operate. We recognize the effect of income tax positions only if these positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. We record interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. The calculation of our tax liabilities involves the inherent uncertainty associated with the application of GAAP and complex tax laws. We believe we have adequately provided for in our financial statements additional taxes that we estimate may be required to be paid as a result of such examinations. While we believe that we have adequately provided for all tax positions, amounts asserted by tax authorities could be greater or less than our accrued position. These tax liabilities, including the interest and penalties, are released pursuant to a settlement with tax authorities, completion of audit or expiration of various statutes of limitation. The material jurisdictions in which we may be subject to potential examination by tax authorities throughout the world include China, Israel, Singapore, Switzerland and the United States.
The recognition and measurement of current taxes payable or refundable, and deferred tax assets and liabilities require that we make certain estimates and judgments. Changes to these estimates or a change in judgment may have a material impact on our tax provision in a future period.
Inventories. We value our inventory at the lower of cost or market, cost being determined under the first-in, first-out method. We regularly review inventory quantities on hand and record a reduction to the total carrying value of our inventory for any difference between cost and estimated market value of inventory that is determined to be excess, obsolete or unsellable inventory based primarily on our estimated forecast of product demand and production requirements. The estimate of future demand is compared to our inventory levels, including open purchase commitments, to determine the amount, if any, of obsolete or excess inventory. Demand for our products can fluctuate significantly from period to period. A significant decrease in demand could result in an increase in the amount of excess inventory on hand. In addition, our industry is characterized by rapid technological change, frequent new product development and rapid product obsolescence that could result in an increase in the amount of obsolete inventory quantities on hand. Additionally, our estimates of future product demand may prove to be inaccurate, in which case we may have understated or overstated the reduction to the total carrying value of our inventory for excess and obsolete inventory. In the future, if our inventory is determined to be overvalued, we would be required to recognize such costs in our cost of goods sold at the time of such determination. Likewise, if our inventory is determined to be undervalued, we may have over-reported our cost of goods sold in previous periods and would be required to recognize additional gross margin at the time the related inventory is sold. Therefore, although we make every effort to ensure the accuracy of our forecasts of future product demand, any significant unanticipated changes in demand or technological developments could have a significant impact on the value of our inventory and our results of operations.
39
Long-lived Assets and Intangible Assets. We assess the impairment of long-lived assets and intangible assets whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable. Circumstances which could trigger a review include, but are not limited to the following:
| | • | | significant decreases in the market price of the asset; |
| | • | | significant adverse changes in the business climate or legal factors; |
| | • | | accumulation of costs significantly in excess of the amount originally expected for the acquisition or construction of the asset; |
| | • | | current period cash flow or operating losses combined with a history of losses or a forecast of continuing losses associated with the use of the asset; and |
| | • | | current expectation that the asset will more likely than not be sold or disposed of significantly before the end of its estimated useful life. |
Whenever events or changes in circumstances suggest that the carrying amount of long-lived assets and intangible assets may not be recoverable, we estimate the future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset from its use or eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected future cash flows is less than the carrying amount of those assets, we recognize an impairment loss based on the excess of the carrying amount over the fair value of the assets. Significant management judgment is required in the forecasts of future operating results that are used in the discounted cash flow method of valuation.
As of January 31, 2015, we had a total of $30.7 million in acquired intangible assets. In connection with our IPR&D, we performed a qualitative assessment in 2015 to determine whether it was more likely than not that our IPR&D was impaired. Based on our assessment we recorded a charge of $3.4 million in fiscal 2015 to write off IPR&D related to an abandoned project. In fiscal 2014, we recorded a charge of $8.1 million for the impairment of an acquired intangible asset as a result of our annual impairment evaluation.
Goodwill. We evaluate goodwill for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of such assets may not be recoverable. Factors we consider important which could trigger a goodwill impairment review include;
| | • | | significant underperformance relative to historical or projected future operating results; |
| | • | | significant changes in the manner of our use of the acquired assets or the strategy for our overall business; |
| | • | | significant negative industry or economic trends; |
| | • | | a significant decline in our stock price for a sustained period; and |
| | • | | a significant change in our market capitalization relative to our net book value. |
When performing our assessment, we include a control premium, in addition to our fair value to reflect the full value and amount that a buyer would be willing to pay for the company. Since our inception, we have not recognized any impairment of goodwill.
Litigation Costs. From time to time, we are involved in legal actions arising in the ordinary course of business. There can be no assurance these actions or other third-party assertions will be resolved without costly litigation, in a manner that does not adversely impact our financial position, results of operations or cash flows or without requiring royalty payments in the future, which may adversely impact gross margins. We are aggressively defending these litigation matters and believe no material adverse outcome will result. We record a liability when it is probable that a loss has been incurred and the amount can be reasonably estimated. In determining the probability of a loss and consequently, determining a reasonable estimate, management is required to use significant judgment. Given the uncertainties associated with any litigation, the actual outcome can be different than our estimates and could adversely affect our results of operations, financial position and cash flows.
40
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth information derived from our consolidated statements of operations expressed as a percentage of net revenue:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Net revenue | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % | | | 100.0 | % |
Operating costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | | 49.7 | | | | 48.9 | | | | 47.1 | |
Research and development | | | 31.4 | | | | 34.0 | | | | 33.4 | |
Selling and marketing | | | 3.9 | | | | 4.5 | | | | 5.1 | |
General and administrative | | | 3.5 | | | | 3.1 | | | | 3.4 | |
Amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets | | | 0.5 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 1.7 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating costs and expenses | | | 89.0 | | | | 91.8 | | | | 90.7 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | | 11.0 | | | | 8.2 | | | | 9.3 | |
Interest and other income, net | | | 0.6 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 0.5 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | | 11.6 | | | | 8.9 | | | | 9.8 | |
Provision (benefit) for income taxes | | | (0.1 | ) | | | (0.3 | ) | | | 0.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | 11.7 | % | | | 9.2 | % | | | 9.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Years Ended January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014
Net Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentage) | |
Net revenue | | $ | 3,706,963 | | | $ | 3,404,400 | | | | 8.9 | % |
Net revenue is gross revenue, net of accruals for estimated sales returns and rebates. Our net revenue for fiscal 2015 increased by $302.6 million compared to net revenue for fiscal 2014. The increase was led by sales of our mobile and wireless products, particularly in the first half of fiscal 2015, where we saw strong growth from multiple customers who launched their 4G LTE smartphones based on our solutions. In the storage market, we saw higher HDD revenue, which was mostly driven by continued growth for our 500 gigabyte per platter products and increased demand for our products used in enterprise drives at a top North America based HDD customer. Our networking revenue was up 1% in fiscal 2015 over fiscal 2014 due higher demand for enterprise switches and routers.
In the first quarter of fiscal 2016, we expect net revenue to decline, driven by a softening of demand in the PC end market, normal seasonality and slightly higher inventories in the supply chain at the end of the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015.
Cost of Goods Sold
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 1,843,706 | | | $ | 1,663,730 | | | | 10.8 | % |
% of net revenue | | | 49.7 | % | | | 48.9 | % | | | | |
41
Cost of goods sold as a percentage of net revenue was higher in fiscal 2015 due to a shift in the mix of our revenue, particularly in the first half of fiscal 2015, towards our mobile and wireless products which have a higher average cost of goods sold as a percentage of revenue. In addition, we also had higher inventory write downs and increased royalty expense in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. Our cost of goods sold as a percentage of net revenue may fluctuate in future periods due to, among other things, changes in the mix of products sold; the timing of production ramps of new products; increased pricing pressures from our customers and competitors, particularly in the consumer product markets that we are targeting; charges for obsolete or potentially excess inventory; changes in the costs charged by our foundry; assembly and test subcontractors; product warranty costs; changes in commodity prices such as gold; and the margin profiles of our new product introductions.
We currently expect that cost of goods sold as a percentage of net revenue in the first quarter of fiscal 2016 will be slightly higher than the amount in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015.
Share-Based Compensation Expense
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
| | | (in thousands) | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 7,972 | | | $ | 8,863 | |
Research and development | | | 94,432 | | | | 109,432 | |
Selling and marketing | | | 11,469 | | | | 13,940 | |
General and administrative | | | 23,373 | | | | 23,638 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 137,246 | | | $ | 155,873 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Share-based compensation expense decreased by $18.6 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. The decrease was primarily due to lower expense related to the employee stock purchase plan. In addition, the reversal of previously recognized expense associated with unvested equity awards that were cancelled as a result of the resignation in February 2014 of our former Chief Technology Officer reduced the fiscal 2015 share-based compensation expense. These decreases were partially offset by new grants of performance-based awards in fiscal 2015 to members of senior management and in April 2014 to our executive officers.
Research and Development
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Research and development | | $ | 1,164,059 | | | $ | 1,156,885 | | | | 0.6 | % |
% of net revenue | | | 31.4 | % | | | 34.0 | % | | | | |
Research and development expense increased by $7.2 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. The increase was primarily attributable to $27.5 million of higher personnel-related costs primarily associated with an increase in incentive compensation expense that were partially offset by lower share-based compensation. In addition, we had $3.8 million of higher depreciation and amortization expenses. These increases were offset by $26.5 million of lower costs primarily for non-recurring engineering services due to higher reimbursement from our customers combined with efforts to closely monitor research and development spending to improve efficiencies. In addition, there was $5.2 million of restructuring and other exit-related costs included in research and development expense in fiscal 2015 compared to $2.9 million in fiscal 2014, which is further described in the restructuring section of Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
42
Selling and Marketing
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Selling and marketing | | $ | 143,952 | | | $ | 152,698 | | | | (5.7 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | 3.9 | % | | | 4.5 | % | | | | |
Selling and marketing expense decreased by $8.7 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. The decrease was primarily attributable to lower personnel-related costs of $9.7 million due to lower headcount, which was partially offset by slightly higher marketing advertisement activities.
General and Administrative
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
General and administrative | | $ | 130,030 | | | $ | 106,471 | | | | 22.1 | % |
% of net revenue | | | 3.5 | % | | | 3.1 | % | | | | |
General and administrative expense increased by $23.6 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. The increase was primarily attributable to higher legal expenses of $8.3 million for ongoing litigation matters and costs of $7.2 million associated with the surety bond to appeal the CMU judgment. Higher incentive compensation expenses of $5.0 million in fiscal 2015 also contributed to the increase in general and administrative expense. In addition, there were $5.2 million of restructuring and other exit-related costs included in general and administrative expense in fiscal 2015 compared to $1.1 million in fiscal 2014.
We expect general and administrative expenses for the first quarter of fiscal 2016 to increase compared to the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015 due to a cash payment to our Chief Executive Officer. See “Note 15 — Subsequent Event” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of the Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information.
Amortization and Write-Off of Acquired Intangible Assets
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets | | $ | 16,397 | | | $ | 43,925 | | | | (62.7 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | 0.5 | % | | | 1.3 | % | | | | |
Amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets decreased by $27.5 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. The decrease was due to a reduction in amortization expense as certain intangible assets became fully amortized. In addition, fiscal 2015 included a $3.4 million write off of IPR&D upon our decision to discontinue the related project compared to a write-off of $8.1 million for the impairment of an acquired intangible asset in fiscal 2014.
43
Restructuring
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Research and development | | $ | 5,249 | | | $ | 2,886 | |
Selling and marketing | | | — | | | | 795 | |
General and administrative | | | 5,189 | | | | 1,051 | |
Write-off of acquired intangible assets | | | 3,386 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 13,824 | | | $ | 4,732 | |
| | | | | | | | |
We recorded a total $13.8 million restructuring charge in fiscal 2015, which included severance costs of $5.2 million and other exit-related costs of $2.0 million, primarily associated with facility closures. In addition, the charge included $3.4 million to write off an acquired intangible asset and a $3.2 million loss related to a lease agreement. The fiscal 2014 restructuring charge primarily related to the closure of two sites for a total cost of $4.2 million for severance and other exit-related costs. See “Note 8 — Restructuring” in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a more complete discussion of these restructuring charges.
Interest and Other Income, net
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Interest and other income, net | | $ | 23,334 | | | $ | 25,566 | | | | (8.7 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | 0.6 | % | | | 0.7 | % | | | | |
Interest and other income, net, decreased by $2.2 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. The decrease was primarily due to the recognition of foreign currency gains, which were $6.9 million lower in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. Although the U.S. dollar strengthened over certain foreign currencies in which we had exposures during fiscal 2015, most of our foreign currency gains arose from the revaluation of our foreign currency denominated tax liabilities that were lower in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. The decrease in foreign currency gains was partially offset by an increase in interest income from higher average cash and investment balances combined with an increase in other income. Other income included an $8.8 million gain from the sale of an investment in fiscal 2015 compared to a $7.0 million gain from the sale of a business in fiscal 2014.
Benefit for Income Taxes
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | % Change
in 2015 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Benefit for income taxes | | $ | (3,193 | ) | | $ | (9,063 | ) | | | (64.8 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | (0.1 | )% | | | (0.3 | )% | | | | |
We had income tax benefits of 0.7% in fiscal 2015 compared to 3.0% in fiscal 2014. The income tax benefit for fiscal 2015 included the current income tax liability of $17.4 million, plus a $7.4 million increase in current unrecognized tax benefits in non-U.S. jurisdictions. These charges were offset by a reduction in unrecognized tax benefits that arose from the release of $16.4 million due to the expiration of statutes of limitation and a $12.9 million increase in net deferred tax assets. The increase in net deferred tax assets was mostly due to an increase in the Singapore deferred tax assets since we re-negotiated with the Singapore government and in fiscal 2015, they extended the DEI until June 2019. See “Note 9 – Income Taxes” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of the Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information.
44
Years Ended February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013
Net Revenue
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
in 2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentage) | |
Net revenue | | $ | 3,404,400 | | | $ | 3,168,630 | | | | 7.4 | % |
The increase in net revenue of 235.8 million for fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013 was driven by an increase in sales of our storage products, as we continued to see growth for our 500-gigabyte-per-platter products and increased demand for enterprise drives at a top North America based HDD customer. In addition, revenue for SSD controllers increased significantly compared to the prior year, as these products continued to gain traction and popularity. We experienced growth in revenue for our mobile and wireless products in the second half of fiscal 2014 due to successful launches of our new multi-core 3G mobile devices with key OEM’s into mobile handsets and tablets. In addition, we saw increased demand for our wireless products driven by the holiday ramp up of new gaming platforms at two of our customers and the launch of new programs such as the Google Chromecast. However, mobile and wireless revenue was flat year over year as fiscal 2014 included significantly higher revenue from a North American handset customer. The increase in net revenue for fiscal 2014 was partially offset by slightly lower revenue for our networking products, primarily due to a weaker overall market and its effect on our networking customers.
Cost of Goods Sold
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
in 2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 1,663,730 | | | $ | 1,493,497 | | | | 11.4 | % |
% of net revenue | | | 48.9 | % | | | 47.1 | % | | | | |
Cost of goods sold as a percentage of net revenue was higher in fiscal 2014. Although we continued to benefit from lower commodity costs driven by our replacement of gold in our products with copper, manufacturing costs were higher in fiscal 2014 due to increased royalty expense and the ramp up of new product designs in consumer-oriented products.
Share-Based Compensation Expense
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
| | | (in thousands) | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 8,863 | | | $ | 8,142 | |
Research and development | | | 109,432 | | | | 87,149 | |
Selling and marketing | | | 13,940 | | | | 13,278 | |
General and administrative | | | 23,638 | | | | 18,711 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 155,873 | | | $ | 127,280 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Share-based compensation expense increased by $28.6 million in fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013. These increases were primarily due to increased headcount in fiscal 2014, combined with higher expense related to the employee stock purchase plan. The offering price of the employee stock purchase plan was reset in June 2012 and also in December 2012 due to the decline in our stock price. In addition, equity awards granted in fiscal 2014 contained shorter vesting periods, which accelerated the amount of share-based compensation expense.
45
Restructuring
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
| | | (in thousands) | |
Research and development | | $ | 2,886 | | | $ | 47 | |
Selling and marketing | | | 795 | | | | (3 | ) |
General and administrative | | | 1,051 | | | | 1,213 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 4,732 | | | $ | 1,257 | |
| | | | | | | | |
We recorded a $4.2 million charge primarily related to the closure of two sites in fiscal 2014. This amount included $2.8 million of severance costs, $1.3 million for other exit-related costs in connection with vacating three facilities and $0.1 million for the write off of equipment. All activities related to the closure of the two sites were substantially completed by the end of the fiscal year.
During fiscal 2014, we also continued to make payments and incur ongoing operating expenses related to vacated facilities under previous restructure actions.
Research and Development
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Research and development | | $ | 1,156,885 | | | $ | 1,057,445 | | | | 9.4 | % |
% of net revenue | | | 34.0 | % | | | 33.4 | % | | | | |
Research and development expense increased by $99.4 million in fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013, primarily attributable to higher personnel-related costs as a result of increased headcount in fiscal 2014 to support new designs, higher share-based compensation and higher average employee compensation. The increase in expense also reflected higher computer-aided design tool costs, and higher depreciation and amortization costs as we continued to invest in the development of innovative solutions.
Selling and Marketing
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
in 2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Selling and marketing | | $ | 152,698 | | | $ | 161,817 | | | | (5.6 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | 4.5 | % | | | 5.1 | % | | | | |
Selling and marketing expense decreased by $9.1 million in fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013. The decrease was primarily attributable to lower costs for marketing communication activities as a result of efforts to control discretionary spending and lower personnel-related costs caused by a decrease in headcount in fiscal 2014.
General and Administrative
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
in 2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
General and administrative | | $ | 106,471 | | | $ | 108,514 | | | | (1.9 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | 3.1 | % | | | 3.4 | % | | | | |
46
General and administrative expense decreased by $2.0 million in fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013. The decrease was primarily attributable to lower legal costs for ongoing litigation matters, partially offset by higher share-based compensation.
Amortization and Write-Off of Acquired Intangible Assets
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
in 2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets | | $ | 43,925 | | | $ | 52,700 | | | | (16.7 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | 1.3 | % | | | 1.7 | % | | | | |
Amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets decreased by $8.8 million in fiscal 2014 compared to fiscal 2013. The decrease was primarily due to certain intangible assets that became fully amortized. In addition, fiscal 2014 included a write-off of $8.1 million for the impairment of an acquired intangible asset compared to fiscal 2014, which included a $0.8 million write-off of IPR&D related to an abandoned project.
Interest and Other Income, net
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
in 2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Interest and other income, net | | $ | 25,566 | | | $ | 15,533 | | | | 64.6 | % |
% of net revenue | | | 0.7 | % | | | 0.5 | % | | | | |
Interest and other income, net, increased by $10.0 million in fiscal 2014 as compared to fiscal 2013, primarily due to a $7.0 million gain on the sale of a business (see “Note 2 — Divestiture” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of the Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information) and the impact of the strengthening of the U.S. dollar on our foreign currency denominated tax liabilities. This was partially offset by lower interest income from lower average cash and investment balances, lower realized investment gains, and higher imputed interest expense related to technology license obligations during fiscal 2014. We also had $1.5 million in write downs of equity investments in fiscal 2014.
Provision (benefit) for Income Taxes
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | | | | |
| | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | | | % Change
in 2014 | |
| | | (in thousands, except percentages) | |
Provision (benefit) for income taxes | | $ | (9,063 | ) | | $ | 3,605 | | | | (351.4 | )% |
% of net revenue | | | (0.3 | )% | | | 0.1 | % | | | | |
We had an income tax benefit of 3.0% in fiscal 2014 compared to an effective tax rate of 1.2% in fiscal 2013. The income tax benefit for fiscal 2014 included the current income tax liability of $13.2 million plus a $3.9 million reduction in net deferred tax assets that included $1.2 million charge for the settlement of an audit in a non-U.S. jurisdiction. These tax charges were offset by a net reduction in unrecognized tax benefits of $22.6 million combined with a $3.9 million tax benefit due to return-to-provision adjustments upon filing of tax returns in fiscal 2014 that included a $0.5 million benefit from the settlement of an audit in a non-U.S. jurisdiction. The reduction in net deferred tax assets was mostly due to an increase in the Singapore deferred tax liability since the Singapore government had not yet granted an extension of the tax incentive arrangement in Singapore which was then expected to expire in June 2014. See “Note 9 — Income Taxes” in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of the Annual Report on Form 10-K for further information. The net reduction in unrecognized tax benefits primarily arose from the expiration of statute of limitations in non-U.S. jurisdictions and from the settlement of two audits in non-U.S. jurisdictions less an increase in current unrecognized tax estimates.
47
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our principal source of liquidity as of January 31, 2015 consisted of approximately $2.5 billion of cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, of which approximately $900 million was held by foreign subsidiaries (outside Bermuda). Approximately $400 million of this amount held by foreign subsidiaries is related to undistributed earnings, which have been indefinitely reinvested outside of Bermuda. These funds are primarily held in China, Israel, Singapore, the United States and Switzerland. We have plans to use such amounts to fund various activities outside of Bermuda including working capital requirements, capital expenditures for expansion, funding of future acquisitions, or other financing activities. If such funds were needed by the parent company in Bermuda or if the amounts were otherwise no longer considered indefinitely reinvested, we would incur a tax expense of approximately $100 million. We believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, together with cash generated from operations, exercise of employee stock options and purchases under our employee stock purchase plan will be sufficient to cover our working capital needs, capital expenditures, investment requirements, any declared dividends and commitments for at least the next 12 months. Our capital requirements will depend on many factors, including our rate of sales growth, market acceptance of our products, costs of securing access to adequate manufacturing capacity, the timing and extent of research and development projects, and increases in operating expenses, which are all subject to uncertainty. In addition, we are named as defendants to several litigation actions and an unfavorable outcome in any current litigation could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, cash flows and results of operations. Specifically, with respect to the CMU litigation, a jury has awarded past damages of $1.17 billion plus enhancements. Based on a series of post-trial rulings, the District Court calculated the damages including enhancement to total approximately $1.54 billion, and held that, under its decision, CMU is entitled to post judgment interest and an ongoing royalty. Based on the royalty rate assessed by the District Court, such additional royalties for the period of time commencing on the date ordered by the District Court, January 15, 2013, through January 31, 2015 could be as much as $400 million. On May 7, 2014, the District Court entered final judgment and on May 14, 2014 we filed a notice of appeal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit in Washington, D.C., which is set for oral argument in April 2015. We have secured certain surety bonds for the duration of the appeal to stay execution of judgment pending the appeal. See “Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies — Surety Bonds” in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a further discussion of these surety bonds. We strongly believe that we do not infringe on the methods described in the CMU patents and that our products use our own internally developed patented read channel technology. See the section entitled “Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements” below for a discussion of the effects on liquidity from the CMU litigation.
To the extent that our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, and cash generated by operations are insufficient to fund our future activities, we may need to raise additional funds through public or private debt or equity financing. We may also enter into additional acquisitions of businesses, purchase assets or enter into other strategic arrangements in the future, which could also require us to seek debt or equity financing. Additional equity financing or convertible debt financing may be dilutive to our current shareholders. If we elect to raise additional funds, we may not be able to obtain such funds on a timely basis or on acceptable terms, if at all. If we raise additional funds by issuing additional equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership percentages of existing shareholders would be reduced. In addition, the equity or debt securities that we issue may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to our common shares.
On February 19, 2015, the Company announced that its board of directors declared a cash dividend of $0.06 per share to be paid on April 2, 2015 to shareholders of record as of March 12, 2015.
Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $728.9 million for fiscal 2015 compared to $448.0 million for fiscal 2014 and $729.0 million for fiscal 2013. The cash inflows from operations for fiscal 2015 were primarily due to $673.5 million of net income adjusted for non-cash items and positive working capital changes of $55.4 million. The positive impact on working capital was primarily driven by a decrease in accounts receivable
48
due to improved collections and a decrease in inventories, combined with an increase in accrued employee compensation as a result of higher incentive compensation. The positive effect on working capital was partially offset by decreases in accounts payable, and accrued liabilities and other non-current liabilities due the timing of payments.
The cash inflows from operations for fiscal 2014 were primarily due to $623.0 million of net income adjusted for non-cash items and positive working capital changes of $175.0 million. The negative change in working capital for fiscal 2014 was primarily driven by an increase in accounts receivable from higher revenue levels and higher inventories due to the ramp up of new products.
The cash inflows from operations for fiscal 2013 were primarily due to $592.0 million of net income adjusted for non-cash items and positive working capital changes of $137.0 million. The positive change in working capital for fiscal 2013 was primarily driven by a decrease in inventories due to increased shipment towards the end of the current year and a decrease in accounts receivable due to improved collections in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2013 compared to the fourth quarter of fiscal 2012.
Net Cash Provided by and (Used in) Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $368.9 million for fiscal 2015 compared to net cash provided by investing activities of $74.8 million for fiscal 2014 and $178.8 million for fiscal 2013. For fiscal 2015, net cash used in investing activities was primarily due to purchases of available-for-sale securities of $1.1 billion, offset by the sales and maturities of available-for-sale securities of $826.3 million. In addition, we paid $63.0 million for the purchase of property and equipment, and $16.4 million for the purchase of technology licenses.
For fiscal 2014, net cash provided by investing activities was primarily generated from the sale and maturities of available-for-sale securities of $995.0 million less purchases of available-for-sale securities of $837.9 million. The net cash inflow from available-for-sale securities in fiscal 2014 was partially offset by the purchases of $66.6 million of property and equipment, and $17.6 million of IP licenses.
For fiscal 2013, net cash provided by investing activities was primarily generated from the sale and maturities of available-for-sale securities of $1.8 billion less purchases of available-for-sale securities of $1.5 billion. The net cash inflow from available-for-sale securities in fiscal 2013 was partially offset by the purchases of $68.2 million of property and equipment, and $35.0 million of IP licenses.
Net Cash Used in Financing Activities
Net cash used in financing activities was $114.8 million for fiscal 2015 compared to $309.0 million for fiscal 2014 and $940.8 million for fiscal 2013. For fiscal 2015, net cash used in financing activities was primarily attributable to payments of our quarterly cash dividends of $122.8 million and repurchases under our share repurchase program of our common shares in the open market for $65.0 million. The cash outflow was partially offset by net proceeds of $85.9 million from the issuance of our common shares under our share-based plans less the minimum tax withholding on behalf of employees for net share settlements.
For fiscal 2014, net cash used in financing activities was primarily attributable to repurchases under our share repurchase program of $376.3 million and payment of our quarterly cash dividends of $119.4 million in fiscal 2014. The cash outflow was partially offset by net proceeds of $194.1 million from the issuance of our common shares under our share-based plans less the minimum tax withholding paid on behalf of employees for net share settlements.
For fiscal 2013, net cash used in financing activities was primarily attributable to repurchases under our share repurchase program of $959.1 million. Of this amount, $22.2 million was unpaid and included in accrued liabilities as of February 2, 2013. We also paid cash dividends of $98.8 million in fiscal 2013. The cash outflow was partially offset by net proceeds of $94.8 million from the issuance of our common shares under our share-based plans less the minimum tax withholding paid on behalf of employees for net share settlements.
49
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
On May 14, 2014, we filed a Notice of Appeal to appeal the final judgment issued by the District Court in the CMU litigation. In order to stay the execution of the final judgment pending its appeal, we filed a supersedeas bond for $1.54 billion with the District Court. The bond was issued by a consortium of sureties authorized by the U.S. Treasury. If the judgment is affirmed after the completion of all appellate proceedings, and we do not thereafter fully satisfy the judgment within thirty days, the sureties are obligated under the bond to make payment to CMU. In support of the bond, we entered into separate indemnity agreements with each of the sureties to indemnify the sureties from all costs and payments made under the bond. The indemnity agreements did not require collateral to be posted at the time of the issuance of the bond. Therefore no cash is considered restricted as of the date of this filing. However, the indemnity agreements provide that each of the sureties have the right to demand to be placed in funds or call for collateral under pre-defined events. The indemnity agreements will remain outstanding for as long as the underlying bond remains outstanding. See also “Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies” in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a further discussion of this matter.
The Court has required us to report ongoing royalties under the current judgment. Based on the royalty rate assessed by the District Court, such additional royalties for the period of time commencing on the date ordered by the District Court, January 15, 2013, through January 31, 2015 could be as much as $400 million. On November 14, 2014, we filed a second surety bond for $216 million and filed a commitment letter from the sureties to issue up to an additional $95 million in bonding under certain conditions. The second bond and commitment are secured by our campus located in Santa Clara, California, which has a carrying value of $139 million at January 31, 2015. We and CMU have agreed that the second bond and commitment satisfy the security for ongoing royalties while the appeal is pending.
As part of our ongoing business, we do not participate in transactions that generate relationships with unconsolidated entities of financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured finance or special purpose entities (“SPEs”), which would have been established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes. As of January 31, 2015, we were not involved in any unconsolidated SPE transactions.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
Under our manufacturing relationships with our foundry partners, cancellation of outstanding purchase orders is allowed but requires repayment of all expenses incurred through the date of cancellation. As of January 31, 2015, these foundries had incurred approximately $252.1 million of manufacturing costs and expenses relating to our outstanding purchase orders.
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations as of January 31, 2015 and the effect that such obligations are expected to have on our liquidity and cash flow in future periods (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Payment Obligations by Fiscal Year | |
| | | 2016 | | | 2017 | | | 2018 | | | 2019 | | | 2020 | | | Thereafter | | | Total | |
Contractual obligations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Facilities operating leases, net | | $ | 23,251 | | | $ | 11,885 | | | $ | 5,113 | | | $ | 1,622 | | | $ | 1,594 | | | $ | 3,542 | | | $ | 47,007 | |
CAD and other operating leases | | | 48,238 | | | | 30,435 | | | | 7,496 | | | | 1,078 | | | | 1,078 | | | | 180 | | | | 88,505 | |
Purchase commitments to foundries | | | 252,063 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 252,063 | |
Capital purchase obligations | | | 39,133 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 39,133 | |
Technology license obligations | | | 13,145 | | | | 7,869 | | | | 9,180 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 30,194 | |
Other non-current obligations (1) | | | — | | | | 6,346 | | | | 2,000 | | | | 2,000 | | | | 2,000 | | | | 2,784 | | | | 15,130 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total contractual cash obligations | | $ | 375,830 | | | $ | 56,535 | | | $ | 23,789 | | | $ | 4,700 | | | $ | 4,672 | | | $ | 6,506 | | | $ | 472,032 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | Amounts represent anticipated future cash payments, including anticipated interest payments not recorded in the consolidated balance sheet. |
50
In addition to the above commitments and contingencies, as of January 31, 2015, we have $38.5 million of unrecognized tax benefits as liabilities. We also have a liability for potential interest and penalties of $27.7 million as of January 31, 2015. During the next 12 months, it is reasonably possible that the amount of unrecognized tax benefits could increase or decrease significantly due to changes in tax law jurisdictions, new tax audits and changes in the U.S. dollar as compared to foreign currencies within the next 12 months. Excluding these factors, uncertain tax positions may decrease by as much as $20 million from the lapse of the statutes of limitation in various jurisdictions during the next 12 months.
Prospective Capital Needs
We believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, together with cash generated from operations, exercise of employee stock options and purchases under our employee stock purchase plan will be sufficient to cover our working capital needs, capital expenditures, investment requirements, any declared dividends and commitments for at least the next 12 months. Our capital requirements will depend on many factors, including our rate of sales growth, market acceptance of our products, costs of securing access to adequate manufacturing capacity, the timing and extent of research and development projects and increases in operating expenses, which are all subject to uncertainty. In addition, we are named as defendants to several litigation actions and an unfavorable outcome in any current litigation could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity, cash flows and results of operations. Specifically, with respect to the CMU litigation, a jury has awarded past damages of $1.17 billion plus enhancements. Based on a series of post-trial rulings, the District Court calculated the damages including enhancement to total approximately $1.54 billion, and held that, under its decision, CMU is entitled to post judgment interest and an ongoing royalty. Based on the royalty rate assessed by the District Court, such additional royalties for the period of time commencing on the date ordered by the District Court, January 15, 2013, through January 31, 2015 could be as much as $400 million. On May 7, 2014, the District Court entered final judgment and on May 14, 2014 we filed a notice of appeal to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit in Washington, D.C., which is set for oral argument in April 2015. We strongly believe that we do not infringe on the methods described in the CMU patents and that our products use our own internally developed patented read channel technology. See the sections entitled “Liquidity and Capital Resources” and “Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements” above for discussions of the effects on liquidity from the CMU litigation.
To the extent that our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, and cash generated by operations are insufficient to fund our future activities, we may need to raise additional funds through public or private debt or equity financing. We may also enter into additional acquisitions of businesses, purchase assets or enter into other strategic arrangements in the future, which could also require us to seek debt or equity financing. Additional equity financing or convertible debt financing may be dilutive to our current shareholders. If we elect to raise additional funds, we may not be able to obtain such funds on a timely basis or on acceptable terms, if at all. If we raise additional funds by issuing additional equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership percentages of existing shareholders would be reduced. In addition, the equity or debt securities that we issue may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to our common shares.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Please see “Note 1 — The Company and its Significant Accounting Policies — Recent Accounting Pronouncements” for further details in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
Related Party Transactions
Please see “Note 14 — Related Party Transactions” for further details in our Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
51
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
Interest Rate Risk. Our interest rate risk relates primarily to our fixed income short-term investment portfolio as we did not have any outstanding debt as of January 31, 2015. We maintain an investment policy that requires minimum credit ratings, diversification of credit risk and limits the long-term interest rate risk by requiring maturities of generally less than five years. We invest our excess cash primarily in highly liquid debt instruments of the U.S. government and agency debt, time deposits, money market funds, corporate debt securities and asset backed securities. These investments are classified as available-for-sale and, consequently, are recorded on our balance sheets at fair market value with their related unrealized gain or loss reflected as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders’ equity. Investments in both fixed rate and floating rate interest earning securities carry a degree of interest rate risk. Fixed rate securities may have their fair market value adversely impacted due to a rise in interest rates, while floating rate securities may produce less income than predicted if interest rates fall.
To provide an assessment of the interest rate risk associated with our investment portfolio, we performed a sensitivity analysis to determine the impact that an adverse change in interest rates would have on the value of the investment portfolio. Based on investment positions as of January 31, 2015, a hypothetical 100 basis point increase in interest rates across all maturities would result in a $18.8 million decline in the fair market value of the portfolio. Due to our positive cash flow from operations, the relatively short-term nature of our investment portfolio and our ability to hold investments to maturity, such change in fair market value would likely not result in any cash flow impact.
Investment Risk. We invest in equity instruments of privately-held companies for strategic purposes. We account for these investments under the cost method when we do not have the ability to exercise significant influence or control over the operations of these companies and under the equity method when we have the ability to exercise significant influence, but do not have control. Carrying value of these equity investments was $9.3 million at January 31, 2015, and was included in other non-current assets in our balance sheets. We monitor these investments for impairment and make appropriate reductions in carrying value when an impairment is deemed to be other-than-temporary.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk. Substantially all of our sales and the majority of our expenses are denominated in U.S. dollars. Since we operate in many countries, we pay certain payroll and other operating expenses in local currencies, and these expenses may be higher or lower in U.S. dollar terms. Furthermore, our operations in Israel and China represent a large portion of our total foreign currency exposure. We may also hold certain assets and liabilities, including potential tax liabilities in local currency on our balance sheet. These tax liabilities would be settled in local currency. Therefore, foreign exchange gains and losses from remeasuring the tax liabilities are recorded to interest and other income, net. The related effects of foreign exchange fluctuations on local currency expenses are recorded to operating expenses. Significant fluctuations in exchange rates in countries where we incur expenses or record assets or liabilities in local currency could affect our business and operating results in the future. There is also a risk that our customers may be negatively impacted in their ability to purchase our products priced in U.S. dollars when there has been significant volatility in foreign currency exchange rates.
We engage in hedging transactions to help mitigate some of the volatility to forecasted cash flows due to changes in foreign exchange rates, and in particular hedge a portion of the forecasted Israeli shekel and Chinese yuan expenses. We enter into certain short-term forward exchange contracts, typically less than 12 months in duration, to hedge exposures for expenses and purchases denominated in foreign currencies when the currency exposure is significant and there is a high certainty of the underlying cash flow. We do not enter into derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes. We may choose not to hedge certain foreign exchange exposures due to immateriality, offsetting exposures, prohibitive economic cost of hedging a particular currency, and limited availability of appropriate hedging instruments. To the extent our foreign currency hedges are effective, the results of the hedge activities offset the underlying expense within the operating expense. Financial
52
instruments not designated as hedges or hedges deemed ineffective are recorded in interest and other income, net. We do not hedge our tax liabilities denominated in local currency on our balance sheet as the timing of these tax liabilities becoming cash flows is not deemed to be certain.
To provide an assessment of the foreign currency exchange risk associated with our foreign currency exposures within operating expense, we performed a sensitivity analysis to determine the impact that an adverse change in exchange rates would have on our financial statements. If the U.S. dollar weakened by 10%, our operating expense could increase by 4.1%. We expect our hedges of foreign currency exposures to be highly effective and offset a significant portion of the short-term impact of changes in exchange rates.
53
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
INDEX
| | | | |
| | | Page | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | | | 55 | |
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014 | | | 56 | |
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended January 31, 2015, February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 | | | 57 | |
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended January 31, 2015, February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 | | | 58 | |
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the years ended January 31, 2015, February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 | | | 59 | |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended January 31, 2015, February 1, 2014 and February 2, 2013 | | | 60 | |
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | | | 61 | |
Supplementary Data (Unaudited) | | | 100 | |
54
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of Marvell Technology Group Ltd.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Marvell Technology Group Ltd. and its subsidiaries at January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2015 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2) presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2015, based on criteria established inInternal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
San Jose, California
March 26, 2015
55
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except par value per share)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 1,210,977 | | | $ | 965,750 | |
Short-term investments | | | 1,318,578 | | | | 1,003,655 | |
Accounts receivable, net of provision for sales returns and allowances of $2,112 and $2,294 in fiscal 2015 and 2014, respectively | | | 420,955 | | | | 453,496 | |
Inventories | | | 308,162 | | | | 347,861 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 68,140 | | | | 56,952 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 17,228 | | | | 11,506 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total current assets | | | 3,344,040 | | | | 2,839,220 | |
Property and equipment, net | | | 340,639 | | | | 356,165 | |
Long-term investments | | | 10,226 | | | | 16,279 | |
Goodwill | | | 2,029,945 | | | | 2,029,945 | |
Acquired intangible assets, net | | | 30,698 | | | | 49,035 | |
Other non-current assets | | | 128,839 | | | | 160,366 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 5,884,387 | | | $ | 5,451,010 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 282,899 | | | $ | 316,389 | |
Accrued liabilities | | | 131,388 | | | | 161,762 | |
Accrued employee compensation | | | 154,969 | | | | 111,408 | |
Deferred income | | | 68,120 | | | | 61,747 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total current liabilities | | | 637,376 | | | | 651,306 | |
Non-current income taxes payable | | | 68,729 | | | | 81,325 | |
Other non-current liabilities | | | 32,193 | | | | 42,469 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 738,298 | | | | 775,100 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | | | | | | | | |
Shareholders’ equity: | | | | | | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.002 par value; 8,000 shares authorized; no shares issued and outstanding | | | — | | | | — | |
Common stock, $0.002 par value; 992,000 shares authorized; 515,037 and 502,405 shares issued and outstanding in fiscal 2015 and 2014, respectively | | | 1,030 | | | | 1,005 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | | 3,099,548 | | | | 2,941,650 | |
Accumulated other comprehensive income | | | 308 | | | | 597 | |
Retained earnings | | | 2,045,203 | | | | 1,732,658 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total shareholders’ equity | | | 5,146,089 | | | | 4,675,910 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | | $ | 5,884,387 | | | $ | 5,451,010 | |
| | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
56
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(In thousands, except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Net revenue | | $ | 3,706,963 | | | $ | 3,404,400 | | | $ | 3,168,630 | |
Operating costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | | 1,843,706 | | | | 1,663,730 | | | | 1,493,497 | |
Research and development | | | 1,164,059 | | | | 1,156,885 | | | | 1,057,445 | |
Selling and marketing | | | 143,952 | | | | 152,698 | | | | 161,817 | |
General and administrative | | | 130,030 | | | | 106,471 | | | | 108,514 | |
Amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets | | | 16,397 | | | | 43,925 | | | | 52,700 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating costs and expenses | | | 3,298,144 | | | | 3,123,709 | | | | 2,873,973 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income | | | 408,819 | | | | 280,691 | | | | 294,657 | |
Interest and other income, net | | | 23,334 | | | | 25,566 | | | | 15,533 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income taxes | | | 432,153 | | | | 306,257 | | | | 310,190 | |
Provision (benefit) for income taxes | | | (3,193 | ) | | | (9,063 | ) | | | 3,605 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 435,346 | | | $ | 315,320 | | | $ | 306,585 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.85 | | | $ | 0.64 | | | $ | 0.55 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.84 | | | $ | 0.63 | | | $ | 0.54 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average shares: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 511,089 | | | | 496,518 | | | | 555,310 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted | | | 520,760 | | | | 504,413 | | | | 563,123 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash dividends declared per share | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.18 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
57
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Net income | | $ | 435,346 | | | $ | 315,320 | | | $ | 306,585 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net change in unrealized gain (loss) on marketable securities | | | 1,234 | | | | (208 | ) | | | (960 | ) |
Net change in unrealized gain (loss) on auction rate securities | | | 597 | | | | (190 | ) | | | (1,396 | ) |
Net change in unrealized gain (loss) on cash flow hedges | | | (2,120 | ) | | | (153 | ) | | | 2,728 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive income (loss), net | | | (289 | ) | | | (551 | ) | | | 372 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income | | $ | 435,057 | | | $ | 314,769 | | | $ | 306,957 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
58
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(In thousands except per share amounts)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Common Stock | | | Additional
Paid-in
Capital | | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income | | | Retained
Earnings | | | Total | |
| | | Shares | | | Amount | | | | | |
Balance at January 28, 2012 | | | 583,671 | | | | 1,167 | | | | 3,683,112 | | | | 776 | | | | 1,328,963 | | | | 5,014,018 | |
Shares issued pursuant to stock options and awards, net | | | 8,090 | | | | 17 | | | | 28,394 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 28,411 | |
Issuance of common stock under the employee stock purchase plan | | | 7,578 | | | | 15 | | | | 66,411 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 66,426 | |
Share-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | 126,683 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 126,683 | |
Tax deficiency from employee stock transactions | | | — | | | | — | | | | (52 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (52 | ) |
Repurchase of common stock | | | (91,001 | ) | | | (182 | ) | | | (958,905 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (959,087 | ) |
Cash dividends declared and paid (cumulatively $0.18 per share) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (98,761 | ) | | | (98,761 | ) |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 306,585 | | | | 306,585 | |
Other comprehensive income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 372 | | | | — | | | | 372 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 2, 2013 | | | 508,338 | | | | 1,017 | | | | 2,945,643 | | | | 1,148 | | | | 1,536,787 | | | | 4,484,595 | |
Shares issued pursuant to stock options and awards, net | | | 17,479 | | | | 35 | | | | 122,392 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 122,427 | |
Issuance of common stock under the employee stock purchase plan | | | 9,701 | | | | 19 | | | | 71,644 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 71,663 | |
Share-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | 156,126 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 156,126 | |
Tax deficiency from employee stock transactions | | | — | | | | — | | | | (88 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (88 | ) |
Repurchase of common stock | | | (33,113 | ) | | | (66 | ) | | | (354,067 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (354,133 | ) |
Cash dividends declared and paid (cumulatively $0.24 per share) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (119,449 | ) | | | (119,449 | ) |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 315,320 | | | | 315,320 | |
Other comprehensive loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (551 | ) | | | — | | | | (551 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 1, 2014 | | | 502,405 | | | | 1,005 | | | | 2,941,650 | | | | 597 | | | | 1,732,658 | | | | 4,675,910 | |
Shares issued pursuant to stock options and awards, net | | | 8,012 | | | | 16 | | | | 11,529 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 11,545 | |
Issuance of common stock under the employee stock purchase plan | | | 9,690 | | | | 19 | | | | 74,299 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 74,318 | |
Share-based compensation | | | — | | | | — | | | | 137,001 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 137,001 | |
Tax benefit from employee stock transactions | | | — | | | | — | | | | 21 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 21 | |
Repurchase of common stock | | | (5,070 | ) | | | (10 | ) | | | (64,952 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | (64,962 | ) |
Cash dividends declared and paid (cumulatively $0.24 per share) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (122,801 | ) | | | (122,801 | ) |
Net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 435,346 | | | | 435,346 | |
Other comprehensive loss | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (289 | ) | | | — | | | | (289 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at January 31, 2015 | | | 515,037 | | | $ | 1,030 | | | $ | 3,099,548 | | | $ | 308 | | | $ | 2,045,203 | | | $ | 5,146,089 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
59
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 435,346 | | | $ | 315,320 | | | $ | 306,585 | |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 106,248 | | | | 102,752 | | | | 91,028 | |
Share-based compensation | | | 137,246 | | | | 155,873 | | | | 127,280 | |
Amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets | | | 18,337 | | | | 44,006 | | | | 52,700 | |
Gain on sale of business | | | — | | | | (6,975 | ) | | | — | |
Other expense, net | | | (10,629 | ) | | | 8,178 | | | | 7,392 | |
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation | | | (145 | ) | | | (20 | ) | | | (58 | ) |
Deferred income tax | | | (12,913 | ) | | | 3,919 | | | | 7,026 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities, net of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in acquisitions: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts receivable | | | 34,165 | | | | (123,258 | ) | | | 77,025 | |
Inventories | | | 39,454 | | | | (97,188 | ) | | | 103,102 | |
Prepaid expenses and other assets | | | 5,788 | | | | 19,458 | | | | (6,894 | ) |
Accounts payable | | | (43,871 | ) | | | 39,791 | | | | (24,304 | ) |
Accrued liabilities and other non-current liabilities | | | (30,024 | ) | | | (9,627 | ) | | | 8,014 | |
Accrued employee compensation | | | 43,561 | | | | (5,787 | ) | | | (20,050 | ) |
Deferred income | | | 6,373 | | | | 1,597 | | | | 191 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 728,936 | | | | 448,039 | | | | 729,037 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Purchases of available-for-sale securities | | | (1,128,319 | ) | | | (837,892 | ) | | | (1,543,902 | ) |
Sales and maturities of available-for-sale securities | | | 826,310 | | | | 995,039 | | | | 1,835,655 | |
Investments in privately-held companies | | | (701 | ) | | | (1,869 | ) | | | (8,750 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of an investment in a privately-held company | | | 13,220 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Cash paid for acquisitions, net | | | — | | | | (2,551 | ) | | | (1,000 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of business | | | — | | | | 6,306 | | | | — | |
Purchases of technology licenses | | | (16,424 | ) | | | (17,647 | ) | | | (35,002 | ) |
Purchases of property and equipment | | | (63,030 | ) | | | (66,593 | ) | | | (68,186 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | | | (368,944 | ) | | | 74,793 | | | | 178,815 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Repurchase of common stock | | | (64,962 | ) | | | (376,285 | ) | | | (936,935 | ) |
Proceeds from employee stock plans | | | 112,357 | | | | 204,962 | | | | 104,936 | |
Minimum tax withholding paid on behalf of employees for net share settlement | | | (26,494 | ) | | | (10,872 | ) | | | (10,099 | ) |
Dividend payments to shareholders | | | (122,801 | ) | | | (119,449 | ) | | | (98,761 | ) |
Payments on technology license obligations | | | (13,010 | ) | | | (7,411 | ) | | | — | |
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation | | | 145 | | | | 20 | | | | 58 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in financing activities | | | (114,765 | ) | | | (309,035 | ) | | | (940,801 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | 245,227 | | | | 213,797 | | | | (32,949 | ) |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the year | | | 965,750 | | | | 751,953 | | | | 784,902 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of the year | | $ | 1,210,977 | | | $ | 965,750 | | | $ | 751,953 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid for interest | | $ | 1,167 | | | $ | 1,873 | | | $ | 563 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid for income taxes, net | | $ | 15,727 | | | $ | 9,385 | | | $ | 16,813 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Purchase of intellectual property under license obligations | | $ | — | | | $ | 8,900 | | | $ | 42,692 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
60
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 — The Company and its Significant Accounting Policies
The Company
Marvell Technology Group Ltd., a Bermuda company (the “Company”), is a leading global semiconductor provider of high-performance application-specific standard products. The Company’s core strength of expertise is the development of complex System-on-a-Chip and System-in-a-Package devices, leveraging its extensive technology portfolio of intellectual property in the areas of analog, mixed-signal, digital signal processing, and embedded and stand alone integrated circuits. The majority of the Company’s product portfolio leverages the ARM technology portfolio. The Company also develops platforms that it defines as integrated hardware along with software that incorporates digital computing technologies designed and configured to provide an optimized computing solution compared to individual components. The Company’s broad product portfolio includes devices for data storage, enterprise-class Ethernet data switching, Ethernet physical-layer transceivers, mobile handsets, connectivity, Internet-of-Things devices and other consumer electronics.
Basis of Presentation
The Company’s fiscal year is the 52- or 53-week period ending on the Saturday closest to January 31. In a 52-week year, each fiscal quarter consists of 13 weeks. The additional week in a 53-week year is added to the fourth quarter, making such quarter consist of 14 weeks. Fiscal 2015 and 2014 each had a 52-week period, and fiscal 2013 had a 53-week period.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an ongoing basis, the Company evaluates its estimates, including those related to performance-based compensation, revenue recognition, provisions for sales returns and allowances, inventory excess and obsolescence, investment fair values, goodwill and other intangible assets, restructuring, income taxes, litigation and other contingencies. In addition, the Company uses assumptions when employing the Monte Carlo simulation and Black-Scholes valuation models to calculate the fair value of share-based awards that are granted. Actual results could differ from these estimates, and such differences could affect the results of operations reported in future periods.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated. The functional currency of the Company and its subsidiaries is the U.S. dollar.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less from the date of purchase to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash on deposit with banks, time deposits, U.S. government and agency debt, municipal debt securities, corporate debt securities and money market funds.
Investments
The Company’s marketable investments are classified as available-for-sale and are reported at fair value. The Company determines any realized gains or losses on the sale of available-for-sale securities on a specific
61
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
identification method, and such gains and losses are recorded as a component of interest and other income, net. Unrealized gains and losses of the available-for-sale securities are excluded from earnings and reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income. The Company assesses whether an other-than-temporary impairment loss on its available-for-sale securities has occurred due to declines in fair value or other market conditions. Declines in fair value that are considered other-than-temporary are recorded as an impairment of investments in interest and other income, net in the consolidated statements of operations.
In general, investments with original maturities of greater than 90 days and remaining maturities of less than one year are classified as short-term investments. Investments with maturities beyond one year may also be classified as short-term based on their highly liquid nature and because such investments represent the investment of cash that is available for current operations.
The Company also has equity investments in privately-held companies. If the Company has the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee, but not control, or if the investee is a partnership type investment, the Company accounts for the investments under the equity method. If the Company does not have the ability to exercise significant influence over the operations of the investee, the Company accounts for the investment under the cost method. Investments in privately-held companies are included in other non-current assets.
Impairment of Investments
If a debt security’s market value is below amortized cost and the Company either intends to sell the security or it is more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the security before its anticipated recovery, the Company records an other-than-temporary impairment charge to interest and other income, net in the consolidated statements of operations.
Investments in privately-held companies are subject to a periodic impairment review. Investments are considered impaired when the fair value is below the investment’s cost basis and the decline in value is judged to be other-than-temporary. This assessment is based on a qualitative and quantitative analysis, including, but not limited to, the investee’s revenue and earnings trends, available cash and liquidity, and the status of the investee’s products and the related market for such products. During fiscal 2014, the Company recorded a charge of $1.5 million to write down equity investments that were considered to be impaired. There were no such charges recorded in fiscal 2015 and 2013.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company accounts for its derivative instruments as either assets or liabilities and carries them at fair value. For derivative instruments that hedge the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows and are designated as cash flow hedges, the effective portion of the gain or loss on the derivative instrument is reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders’ equity and reclassified into earnings in the same period or periods during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. The ineffective portion of the gain or loss on the derivative instrument is recognized in current earnings. To receive hedge accounting treatment, cash flow hedges must be highly effective in offsetting changes to expected future cash flows on hedged transactions. Derivatives that are not designated as hedges must be adjusted to fair value through earnings.
Concentration of Credit Risk and Significant Customers
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to a significant concentration of credit risk consist principally of cash equivalents, short-term investments and accounts receivable. Cash, cash equivalents
62
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
and short-term investments balances are maintained with high-quality financial institutions, the composition and maturities of which are regularly monitored by management. The Company believes that the concentration of credit risk in its trade receivables, which consists of a customer base located primarily in the Asia Pacific Region, is substantially mitigated by the Company’s credit evaluation process, relatively short collection terms and the high level of credit worthiness of its customers. The Company performs ongoing credit evaluations of its customers’ financial conditions and limits the amount of credit extended when deemed necessary based upon payment history and the customer’s current credit worthiness, but generally requires no collateral. The Company regularly reviews the allowance for bad debt and doubtful accounts by considering factors such as historical experience, credit quality, age of the accounts receivable balances and current economic conditions that may affect a customer’s ability to pay.
The Company’s accounts receivable was concentrated with two customers at January 31, 2015, representing 15% and 14% of gross accounts receivable, respectively, and with one customer at February 1, 2014, representing 13% of gross accounts receivable.
The allowance for doubtful accounts at January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014 was $1.2 million and $1.3 million, respectively. Please see “Note 1 – The Company and its Significant Accounting Policies – Revenue Recognition” for additional information on sales returns and allowances.
Historically, a relatively small number of customers have accounted for a significant portion of the Company’s net revenue. Net revenue from one customer was 20%, 24% and 24% for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Net revenue from a second customer was 13%, 12% and 10% for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. In fiscal 2013, net revenue from a third customer was 10%.
The Company also had net revenue from one distributor representing 11% and 11% for fiscal 2015 and 2013, respectively. No distributors accounted for 10% or greater of total net revenue in fiscal 2014. The Company continuously monitors the creditworthiness of its distributors and believes these distributors’ sales to diverse end customers and to diverse geographies further serve to mitigate the Company’s exposure to credit risk.
Inventories
Inventory is stated at the lower of cost or market, cost being determined under the first-in, first-out method. The total carrying value of the Company’s inventory is reduced for any difference between cost and estimated market value of inventory that is determined to be excess, obsolete or unsellable inventory based upon assumptions about future demand and market conditions. If actual future demand for the Company’s products is less than currently forecasted, the Company may be required to write inventory down below the current carrying value. Once the carrying value of inventory is reduced, it is maintained until the product to which it relates to is sold or otherwise disposed of. Shipping and handling costs are classified as a component of cost of goods sold in the consolidated statements of operations.
Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment, net, are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, which ranges from three to seven years for machinery and equipment, computer software, and furniture and fixtures. Buildings are depreciated over an estimated useful life of 30 years and building improvements are depreciated over estimated useful lives of 15 years. Leasehold improvements are depreciated using the shorter of the remaining lease term or the estimated useful life of the asset.
63
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Goodwill
Goodwill is recorded when the consideration paid for a business acquisition exceeds the fair value of net tangible and intangible assets acquired. Goodwill is measured and tested for impairment annually or more frequently if the Company believes indicators of impairment exist. The Company first assesses qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If the company concludes that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, then a two-step quantitative impairment test is performed. The first step requires comparing the fair value of the reporting unit to its net book value, including goodwill. As the Company has only one reporting unit, the fair value of the reporting unit is determined by taking the market capitalization of the Company as determined through quoted market prices and adjusted for control premiums and other relevant factors. A potential impairment exists if the fair value of the reporting unit is lower than its net book value. The second step of the process is only performed if a potential impairment exists, and it involves determining the difference between the fair value of the reporting unit’s net assets other than goodwill and the fair value of the reporting unit. If the difference is less than the net book value of goodwill, impairment exists and is recorded. In the event that the Company determines that the value of goodwill has become impaired, the Company will record a charge for the amount of impairment during the fiscal quarter in which the determination is made.
Long-Lived Assets and Intangible Assets
The Company assesses the impairment of long-lived assets and intangible assets whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of long-lived assets may not be recoverable. The Company estimates the future cash flows, undiscounted and without interest charges, expected to be generated by the assets from its use or eventual disposition. If the sum of the expected future cash flows is less than the carrying amount of those assets, the Company recognizes an impairment loss based on the excess of the carrying amount over the fair value of the assets. Please see “Note 7 – Goodwill and Acquired Intangible Assets” for further details regarding impairment of acquisition-related identified intangible assets.
Acquisition-related identified intangible assets are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated economic lives. In-process research and development (“IPR&D”) is not amortized until the completion of the related development.
Foreign Currency Transactions
The functional currency of all of the Company’s non-U.S. operations is the U.S. dollar. Monetary accounts maintained in currencies other than the U.S. dollar are re-measured using the foreign exchange rate at the balance sheet date. Operational accounts and nonmonetary balance sheet accounts are measured and recorded at the rate in effect at the date of the transaction. The effects of foreign currency re-measurement are reported in current operations.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, delivery has occurred, the fee is fixed or determinable, and collection is reasonably assured.
Product revenue is generally recognized upon shipment of product to customers, net of accruals for estimated sales returns and rebates. However, some of the Company’s sales are made through distributors under agreements allowing for price protection, shipped from stock pricing adjustment rights, and limited rights of stock rotation on products unsold by the distributors. Although title passes to the distributor upon shipment terms
64
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
and payment by the Company’s distributors is not contingent on resale of the product, product revenue on sales made through distributors with price protection, shipped from stock pricing adjustment rights and stock rotation rights are deferred until the distributors sell the product to end customers. Deferred revenue less the related cost of the inventories is reported as deferred income. The Company does not believe that there is any significant exposure related to impairment of deferred cost of sales, as its historical returns have been minimal and inventory turnover for its distributors generally ranges from 60 to 90 days. The Company’s sales to direct customers are made primarily pursuant to standard purchase orders for delivery of products.
A portion of the Company’s net revenue is derived from sales through third-party logistics providers, who maintain warehouses in close proximity to the customer’s facilities. Revenue from sales through these third-party logistics providers is not recognized until the product is pulled from stock by the end customer.
The provision for estimated sales returns on product sales is recorded in the same period the related revenues are recorded. These estimates are based on historical returns, analysis of credit memo data and other known factors. Actual returns could differ from these estimates. The Company accounts for rebates by recording reductions to revenue for rebates in the same period that the related revenue is recorded. The amount of these reductions is based upon the terms agreed to with the customer.
Advertising Expense
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred.
Share-Based Compensation
Share-based compensation is measured at the grant date, based on the fair value of the award, and is recognized as expense over the requisite service period. The Company amortizes share-based compensation expense for time-based and market-based awards under the straight-line attribution method over the vesting period, which is generally four years for annual grants to employees and five years for new hire grants. Performance-based awards are amortized using the accelerated method. For stock purchase rights under the stock purchase plan, the company amortized share-based compensation expense ratably over the two-year offering period.
The Company estimates the fair value of time-based stock option and stock purchase awards on the date of grant using the Black Scholes option-pricing model. The fair value of market-based stock option awards is estimated on the date of grant using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The value of the portion of the awards that is ultimately expected to vest is recognized as expense over the requisite service periods. The Black Scholes and Monte Carlo models incorporate various highly subjective assumptions including expected term of awards, expected future stock price volatility and expected forfeiture rates.
In developing estimates used to calculate assumptions, the Company establishes the expected term for employee stock options, as well as expected forfeiture rates, based on the historical settlement experience and after giving consideration to vesting schedules. Assumptions for stock option exercises and pre-vesting terminations of stock options were stratified by employee groups with sufficiently distinct behavior patterns. Expected volatility was developed based on equally weighted combination of historical stock price volatility and implied volatility derived from traded options on the Company’s stock in the marketplace. The expected dividend yield is calculated by dividing annualized dividend payments by the closing stock price on the grant date of the option.
65
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Forfeitures are estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from initial estimates. Share-based compensation expense is recorded net of estimated forfeitures such that expense is recorded only for those share-based awards that are expected to vest. Previously recognized expense is reversed for the portion of awards forfeited prior to vesting as and when forfeitures occurred.
The fair value of each restricted stock unit is estimated based on the market price of the Company’s common shares on the date of grant less the expected dividend yield.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is comprised of net income and unrealized gains and losses, net of tax, on available-for-sale securities, auction rate securities and cash flow hedges. Accumulated other comprehensive income, as presented on the accompanying balance sheets, consists of net unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities, auction rate securities and cash flow hedges, net of tax.
Accounting for Income Taxes
The Company recognizes income taxes using an asset and liability approach. This approach requires the recognition of taxes payable or refundable for the current year, and deferred tax liabilities and assets for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company’s consolidated financial statements or tax returns. The measurement of current and deferred taxes is based on provisions of the enacted tax law and the effects of future changes in tax laws or rates are not anticipated.
A valuation allowance must be established for deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that they will not be realized. Based on the available evidence and judgment, the Company has determined that it is more likely than not that U.S. research credits and certain acquired net operating losses will not be realized and therefore the Company has provided a full valuation allowance against these credits. If there is a change in the Company’s ability to realize its deferred tax assets, then the Company’s tax provision may decrease in the period in which it determines that realization is more likely than not.
The Company is subject to income tax audits by the respective tax authorities in each jurisdiction in which the Company operates. The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if these positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is more than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. The Company records interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
Warranty
The Company’s products are generally subject to warranty, which provides for the estimated future costs of repair, replacement or customer accommodation upon shipment of the product. The Company’s products carry a standard 90 day warranty, with certain exceptions in which the warranty period can extend to more than one year based on contractual agreements. The warranty accrual is primarily estimated based on historical claims compared to historical revenues and assumes that the Company will have to replace products subject to a claim. From time to time, the Company becomes aware of specific warranty situations, and it records specific accruals to cover these exposures.
66
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Accounting Pronouncements Recently Adopted
In July 2013, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued an amendment to the accounting guidance related to the financial statement presentation of an unrecognized tax benefit. The guidance requires an unrecognized tax benefit, or a portion of an unrecognized tax benefit, to be presented in the financial statements as a reduction to a deferred tax asset when a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss or a tax credit carryforward is available at the reporting date. The Company adopted this guidance in fiscal 2015 on a prospective basis and presented a portion of its unrecognized tax benefits as a reduction of its deferred tax assets on the face of the consolidated balance sheet as of January 31, 2015. See also “Note 9 — Income Taxes” in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.”
Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Effective
In April 2014, the FASB issued an amendment to its guidance regarding the reporting requirements of discontinued operations. Under this amended guidance, a discontinued operation is defined as a disposal of a component or group of components that is disposed of or is classified as held for sale and represents a strategic shift that has (or will have) a major effect on an entity’s operations and financial results. In addition, this amendment requires an entity to present, for each comparative period, the assets and liabilities of a disposal group that includes a discontinued operation separately in the asset and liability sections, respectively, of the statement of financial position and additional disclosures about discontinued operations. This amended guidance is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2014. The Company expects this guidance to have an impact on its financial statements only in the event of a future disposition which meets the criteria.
In May 2014, the FASB issued a new standard on the recognition of revenue from contracts with customers, which will supersede nearly all existing revenue recognition guidance under GAAP. The core principal of the standard is that an entity should recognize revenue when a customer has control of promised goods or services in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. It also requires additional disclosure about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from customer contracts, and assets recognized from costs incurred to obtain or fulfill a contract, including significant judgments and changes in judgments. This standard is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016 and will be effective for the Company’s first quarter of fiscal 2018. Early adoption is not permitted. The standard allows for either full retrospective or modified retrospective adoption. The Company is evaluating the transition method that will be elected and the potential effects of adoption on its financial statements.
Note 2 — Acquisitions and Divestitures
The Company had no acquisitions or divestitures in fiscal 2015.
Acquisitions
Fiscal 2014 and 2013. Acquisitions completed by the Company during fiscal 2014 or 2013 were not significant individually or in the aggregate.
Divestiture
Fiscal 2014. The Company exited one of its businesses and sold certain assets to an unrelated third party as part of cost reduction efforts related to related restructuring actions in fiscal 2014. See “Note 8 – Restructuring”
67
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
for further information. The transaction primarily included the sale of intellectual property and equipment with a carrying value of $0.1 million. The Company also wrote off $2.6 million of goodwill allocated to the business based on the relative fair values of the business and the Company’s remaining reporting unit. The buyer also hired the former employees of the business. As part of the transaction, the Company received a license to the intellectual property it sold. It also entered into a separate support services agreement with the buyer to cover an 18-month period. As a result of the sale of this business, the Company recorded a gain of $7.0 million, which is included in interest and other income, net, in the consolidated statement of operations.
Note 3 — Investments
The following tables summarize the Company’s investments (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of January 31, 2015 | |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Estimated
Fair Value | |
Short-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Corporate debt securities | | $ | 983,008 | | | $ | 3,872 | | | $ | (563 | ) | | $ | 986,317 | |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | 178,898 | | | | 265 | | | | (7 | ) | | | 179,156 | |
Asset backed securities | | | 91,432 | | | | 108 | | | | (9 | ) | | | 91,531 | |
Foreign government and agency debt | | | 28,051 | | | | 61 | | | | (2 | ) | | | 28,110 | |
Municipal debt securities | | | 33,421 | | | | 47 | | | | (4 | ) | | | 33,464 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total short-term investments | | | 1,314,810 | | | | 4,353 | | | | (585 | ) | | | 1,318,578 | |
Long-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Auction rate securities | | | 12,500 | | | | — | | | | (2,274 | ) | | | 10,226 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total long-term investments | | | 12,500 | | | | — | | | | (2,274 | ) | | | 10,226 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total investments | | $ | 1,327,310 | | | $ | 4,353 | | | $ | (2,859 | ) | | $ | 1,328,804 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of February 1, 2014 | |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Estimated
Fair Value | |
Short-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Corporate debt securities | | $ | 587,095 | | | $ | 2,789 | | | $ | (370 | ) | | $ | 589,514 | |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | 301,423 | | | | 128 | | | | (72 | ) | | | 301,479 | |
Asset backed securities | | | 76,220 | | | | 89 | | | | (38 | ) | | | 76,271 | |
Foreign government and agency debt | | | 20,324 | | | | 12 | | | | (44 | ) | | | 20,292 | |
Municipal debt securities | | | 16,059 | | | | 44 | | | | (4 | ) | | | 16,099 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total short-term investments | | | 1,001,121 | | | | 3,062 | | | | (528 | ) | | | 1,003,655 | |
Long-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Auction rate securities | | | 19,150 | | | | — | | | | (2,871 | ) | | | 16,279 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total long-term investments | | | 19,150 | | | | — | | | | (2,871 | ) | | | 16,279 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total investments | | $ | 1,020,271 | | | $ | 3,062 | | | $ | (3,399 | ) | | $ | 1,019,934 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
68
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
As of January 31, 2015, the Company’s investment portfolio included auction rate securities with an aggregate par value of $12.5 million. Although these securities have continued to pay interest and show an improvement in the underlying collateralization, there is currently limited trading volume. To estimate the fair value of the auction rate securities, the Company uses a discounted cash flow model based on estimated timing and amount of future interest and principal payments. In developing the cash flow model, the Company considers the credit quality and liquidity of the underlying securities and related issuer, the collateralization of underlying security investments and other considerations. The fair value of the auction rate securities as of January 31, 2015 was $2.3 million less than the par value and was recorded in long-term investments. Based on the Company’s balance of approximately $2.5 billion in cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, and the fact that the Company continues to generate positive cash flow from operations on a quarterly basis, the Company does not anticipate having to sell these securities below par value and does not have the intent to sell these auction rate securities until recovery. Since the Company considers the impairment to be temporary, the Company recorded the unrealized loss to accumulated other comprehensive income, a component of shareholders’ equity.
Gross realized gains and gross realized losses on sales of available-for-sales securities are presented in the following table (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Gross realized gains | | $ | 1,618 | | | $ | 1,567 | | | $ | 3,557 | |
Gross realized losses | | | (169 | ) | | | (268 | ) | | | (319 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total net realized gains | | $ | 1,449 | | | $ | 1,299 | | | $ | 3,238 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
The contractual maturities of available-for-sale securities are presented in the following table (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31, 2015 | | | February 1, 2014 | |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | | Estimated
Fair Value | | | Amortized
Cost | | | Estimated
Fair Value | |
Due in one year or less | | $ | 361,108 | | | $ | 361,396 | | | $ | 309,543 | | | $ | 309,861 | |
Due between one and five years | | | 950,702 | | | | 954,151 | | | | 686,062 | | | | 688,280 | |
Due over five years | | | 15,500 | | | | 13,257 | | | | 24,666 | | | | 21,793 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 1,327,310 | | | $ | 1,328,804 | | | $ | 1,020,271 | | | $ | 1,019,934 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
For individual securities that have been in a continuous unrealized loss position, the fair value and gross unrealized loss for these securities aggregated by investment category and length of time in an unrealized position are presented in the following tables (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31, 2015 | |
| | | Less than 12 months | | | 12 months or more | | | Total | |
| | | Fair
Value | | | Unrealized
Loss | | | Fair
Value | | | Unrealized
Loss | | | Fair
Value | | | Unrealized
Loss | |
Corporate debt securities | | $ | 243,699 | | | $ | (558 | ) | | $ | 2,005 | | | $ | (5 | ) | | $ | 245,704 | | | $ | (563 | ) |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | 32,165 | | | | (7 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 32,165 | | | | (7 | ) |
Asset backed securities | | | 25,053 | | | | (9 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 25,053 | | | | (9 | ) |
Foreign government and agency debt | | | 2,999 | | | | (2 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,999 | | | | (2 | ) |
Municipal debt securities | | | 2,845 | | | | (4 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,845 | | | | (4 | ) |
Auction rate securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 10,226 | | | | (2,274 | ) | | | 10,226 | | | | (2,274 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total securities | | $ | 306,761 | | | $ | (580 | ) | | $ | 12,231 | | | $ | (2,279 | ) | | $ | 318,992 | | | $ | (2,859 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
69
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | February 1, 2014 | |
| | | Less than 12 months | | | 12 months or more | | | Total | |
| | | Fair
Value | | | Unrealized
Loss | | | Fair
Value | | | Unrealized
Loss | | | Fair
Value | | | Unrealized
Loss | |
Corporate debt securities | | $ | 110,903 | | | $ | (366 | ) | | $ | 2,105 | | | $ | (4 | ) | | $ | 113,008 | | | $ | (370 | ) |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | 93,118 | | | | (72 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 93,118 | | | | (72 | ) |
Asset backed securities | | | 18,865 | | | | (19 | ) | | | 1,912 | | | | (19 | ) | | | 20,777 | | | | (38 | ) |
Foreign government and agency debt | | | 14,299 | | | | (44 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 14,299 | | | | (44 | ) |
Municipal debt securities | | | 723 | | | | (4 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | 723 | | | | (4 | ) |
Auction rate securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 16,279 | | | | (2,871 | ) | | | 16,279 | | | | (2,871 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total securities | | $ | 237,908 | | | $ | (505 | ) | | $ | 20,296 | | | $ | (2,894 | ) | | $ | 258,204 | | | $ | (3,399 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Note 4 — Supplemental Financial Information (in thousands)
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Cash and cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | |
Cash | | $ | 864,680 | | | $ | 694,789 | |
Cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | |
Time deposits | | | 213,012 | | | | 247,958 | |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | — | | | | 11,999 | |
Municipal debt securities | | | — | | | | 4,800 | |
Corporate debt securities | | | 21,999 | | | | 3,400 | |
Money market funds | | | 111,286 | | | | 2,804 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 1,210,977 | | | $ | 965,750 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Inventories: | | | | | | | | |
Work-in-process | | $ | 183,869 | | | $ | 195,495 | |
Finished goods | | | 124,293 | | | | 152,366 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Inventories | | $ | 308,162 | | | $ | 347,861 | |
| | | | | | | | |
70
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Property and equipment, net: | | | | | | | | |
Machinery and equipment | | $ | 601,961 | | | $ | 562,038 | |
Buildings | | | 144,320 | | | | 144,320 | |
Computer software | | | 99,312 | | | | 96,096 | |
Land | | | 53,373 | | | | 53,373 | |
Building improvements | | | 49,753 | | | | 49,645 | |
Leasehold improvements | | | 51,434 | | | | 49,060 | |
Furniture and fixtures | | | 27,883 | | | | 27,621 | |
Construction in progress | | | 6,167 | | | | 2,911 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 1,034,203 | | | | 985,064 | |
Less: Accumulated depreciation | | | (693,564 | ) | | | (628,899 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment, net | | $ | 340,639 | | | $ | 356,165 | |
| | | | | | | | |
The Company recorded depreciation expense of $78.3 million, $77.2 million and $70.7 million for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Other non-current assets: | | | | | | | | |
Technology and other licenses | | $ | 61,217 | | | $ | 83,521 | |
Deferred tax assets | | | 22,273 | | | | 19,282 | |
Investments in privately-held companies | | | 9,267 | | | | 14,565 | |
Prepaid land use rights | | | 13,432 | | | | 13,744 | |
Deposits | | | 7,903 | | | | 12,433 | |
Other | | | 14,747 | | | | 16,821 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Other non-current assets | | $ | 128,839 | | | $ | 160,366 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Amortization of technology and other licenses was $27.9 million, $25.6 million and $20.3 million in fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Accrued liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Accrued rebates | | $ | 39,105 | | | $ | 61,616 | |
Accrued royalties | | | 24,680 | | | | 36,568 | |
Technology license obligations | | | 14,428 | | | | 18,482 | |
Accrued legal expense | | | 10,027 | | | | 14,589 | |
Other | | | 43,148 | | | | 30,507 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Accrued liabilities | | $ | 131,388 | | | $ | 161,762 | |
| | | | | | | | |
71
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Other non-current liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Technology license obligations | | $ | 16,468 | | | $ | 28,959 | |
Long-term accrued employee compensation | | | 4,610 | | | | 4,370 | |
Other | | | 11,115 | | | | 9,140 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Other non-current liabilities | | $ | 32,193 | | | $ | 42,469 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Accumulated other comprehensive income:
The changes in accumulated other comprehensive income by components are presented in the following tables (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Unrealized
Gain
(Loss) on
Marketable
Securities | | | Unrealized
Loss on
Auction
Rate
Securities | | | Unrealized
Gain
(Loss) on
Cash Flow
Hedges | | | Total | |
Balance at February 1, 2014 | | $ | 2,534 | | | $ | (2,871 | ) | | $ | 934 | | | $ | 597 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | | 2,479 | | | | 85 | | | | (2,338 | ) | | | 226 | |
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income | | | (1,245 | ) | | | 512 | | | | 218 | | | | (515 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net current-period other comprehensive income (loss) | | | 1,234 | | | | 597 | | | | (2,120 | ) | | | (289 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at January 31, 2015 | | $ | 3,768 | | | $ | (2,274 | ) | | $ | (1,186 | ) | | $ | 308 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Unrealized
Gain
(Loss) on
Marketable
Securities | | | Unrealized
Loss on
Auction
Rate
Securities | | | Unrealized
Gain
(Loss) on
Cash Flow
Hedges | | | Total | |
Balance at February 2, 2013 | | $ | 2,742 | | | $ | (2,681 | ) | | $ | 1,087 | | | $ | 1,148 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | | | 931 | | | | (190 | ) | | | 3,466 | | | | 4,207 | |
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income | | | (1,139 | ) | | | — | | | | (3,619 | ) | | | (4,758 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net current-period other comprehensive loss | | | (208 | ) | | | (190 | ) | | | (153 | ) | | | (551 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 1, 2014 | | $ | 2,534 | | | $ | (2,871 | ) | | $ | 934 | | | $ | 597 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
72
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income by components are presented in the following table (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
Affected Line Item in the Statement of Operations | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Interest and other income, net: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Marketable securities | | $ | 1,245 | | | $ | 1,139 | | | $ | 3,101 | |
Auction rate securities | | | (512 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
Cash flow hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Research and development | | | (198 | ) | | | 3,329 | | | | (2,283 | ) |
Selling and marketing | | | (8 | ) | | | 266 | | | | (135 | ) |
General and administrative | | | (12 | ) | | | 24 | | | | (77 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 515 | | | $ | 4,758 | | | $ | 606 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Consolidated Statement of Operations
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Interest and other income, net: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest income | | $ | 11,370 | | | | 9,379 | | | | 12,357 | |
Realized gain on investments | | | 1,449 | | | | 1,299 | | | | 3,238 | |
Currency translation gain (loss) | | | 1,871 | | | | 8,739 | | | | (1,908 | ) |
Other income | | | 9,811 | | | | 8,025 | | | | 2,409 | |
Interest expense | | | (1,167 | ) | | | (1,876 | ) | | | (563 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 23,334 | | | $ | 25,566 | | | $ | 15,533 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per share
The Company reports both basic net income per share, which is based on the weighted average number of shares outstanding, and diluted net income per share, which is based on the weighted average number of shares
73
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
outstanding and potentially dilutive shares. The computations of basic and diluted net income per share are presented in the following table (in thousands, except per share amounts):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Numerator: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 435,346 | | | $ | 315,320 | | | $ | 306,585 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Denominator: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average shares — basic | | | 511,089 | | | | 496,518 | | | | 555,310 | |
Effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Share-based awards | | | 9,671 | | | | 7,895 | | | | 7,813 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average shares — diluted | | | 520,760 | | | | 504,413 | | | | 563,123 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.85 | | | $ | 0.64 | | | $ | 0.55 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.84 | | | $ | 0.63 | | | $ | 0.54 | |
Anti-dilutive potential shares are presented in the following table (in thousands, except per share amounts):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Weighted average shares outstanding from stock options: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Time-based options | | | 22,485 | | | | 36,882 | | | | 25,133 | |
Market-based options | | | 2,288 | | | | 2,711 | | | | 2,991 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 24,773 | | | | 39,593 | | | | 28,124 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average exercise price: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Time-based options | | $ | 17.58 | | | $ | 15.12 | | | $ | 17.72 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Market-based options | | $ | 15.43 | | | $ | 15.43 | | | $ | 15.43 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 17.38 | | | $ | 15.14 | | | $ | 17.48 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Anti-dilutive potential shares for stock options are excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share for the periods reported above because either their exercise price exceeded the average market price during the period or certain stock options with exercise prices less than the average market price were determined to be anti-dilutive based on applying the treasury stock method.
Note 5 — Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company manages some of its foreign currency exchange rate risk through the purchase of foreign currency exchange contracts that hedge against the short-term effect of currency fluctuations. The Company’s policy is to enter into foreign currency forward contracts with maturities less than 12 months that mitigate the effect of rate fluctuations on certain local currency denominated operating expenses. All derivative instruments are recorded at fair value in either prepaid expenses and other current assets or accrued liabilities. The Company reports cash flows from derivative instruments in cash flows from operating activities. The Company uses quoted prices to value its derivative instruments.
74
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The notional amounts of outstanding forward contracts were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Buy Contracts | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Israeli shekel | | $ | 51,326 | | | $ | 39,670 | |
Euro | | | — | | | | 5,718 | |
Swedish krona | | | — | | | | 3,709 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 51,326 | | | $ | 49,097 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Cash Flow Hedges. The Company designates and documents its foreign currency forward exchange contracts as cash flow hedges for certain operating expenses. The Company evaluates and calculates the effectiveness of each hedge at least quarterly. The effective change is recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income and is subsequently reclassified to operating expense when the hedged expense is recognized. Ineffectiveness is recorded in interest and other income, net.
Other Foreign Currency Forward Contracts. The Company may enter into foreign currency forward exchange contracts to hedge certain assets and liabilities denominated in various foreign currencies that it does not designate as hedges for accounting purposes. The maturities of these contracts are generally less than 12 months. Gains or losses arising from the remeasurement of these contracts to fair value each period are recorded in interest and other income, net.
The fair value of foreign currency exchange contracts was not significant as of any period presented.
The following table provides information about gains (losses) associated with our derivative financial instruments (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Location of
Gains (Losses)
Location of Gains (Losses)
in Statement of Operations | | Amount of Gains (Losses) in Statement
of Operations for the year ended | |
| | | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Derivatives designated as cash flow hedges: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Forward contracts: | | Research and development | | $ | (1,930 | ) | | $ | 3,099 | | | $ | (1,909 | ) |
| | Selling and marketing | | | (24 | ) | | | 23 | | | | (13 | ) |
| | General and administrative | | | (157 | ) | | | 246 | | | | (155 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | $ | (2,111 | ) | | $ | 3,368 | | | $ | (2,077 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The portion of gains excluded from the assessment of hedge effectiveness are included in interest and other income, net, and these amounts were $0.2 million, $0.5 million and $0.4 million in fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. In addition, realized losses from forward contracts that are not designated as hedging instruments that are included in interest and other income, net, were not material in fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013. The Company also reports hedge ineffectiveness from derivative financial instruments in current earnings, which were not material in fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013. No cash flow hedges were terminated as a result of forecasted transactions that did not occur.
75
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Note 6 — Fair Value Measurements
Fair value is an exit price representing the amount that would be received in the sale of an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or a liability. As a basis for considering such assumptions, the accounting guidance establishes a three-tier value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in the valuation methodologies in measuring fair value:
Level 1 — Observable inputs that reflect quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2 — Include other inputs that are directly or indirectly observable in the marketplace.
Level 3 — Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity.
The fair value hierarchy also requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value.
The Company’s Level 1 assets include institutional money-market funds that are classified as cash equivalents and marketable investments in U.S. government and agency debt, which are valued primarily using quoted market prices. The Company’s Level 2 assets and liabilities include its marketable investments in time deposits, corporate debt securities, foreign government and agency debt, municipal debt securities and asset back securities as the market inputs to value these instruments consist of market yields, reported trades and broker/dealer quotes, which are corroborated with observable market data. In addition, foreign currency forward contracts and the severance pay fund are classified within Level 2 as the valuation inputs are based on quoted prices and market observable data of similar instruments. The Company’s Level 3 assets include its investments in auction rate securities, which are classified within Level 3 because there are currently no active markets for the auction rate securities and consequently the Company is unable to obtain independent valuations from market sources. Therefore, the auction rate securities are valued using a discounted cash flow model. Some of the inputs to the cash flow model are unobservable in the market. The total amount of assets measured using Level 3 valuation methodologies represented 0.2% of total assets as of January 31, 2015.
76
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The tables below set forth, by level, the Company’s financial assets that were accounted for at fair value as of January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014. The tables do not include assets and liabilities that are measured at historical cost or any basis other than fair value (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fair Value Measurements at January 31, 2015 | |
| | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
Items measured at fair value on a recurring basis: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Money market funds | | $ | 111,286 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 111,286 | |
Time deposits | | | — | | | | 213,012 | | | | — | | | | 213,012 | |
Corporate debt securities | | | — | | | | 21,999 | | | | — | | | | 21,999 | |
Short-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | 179,156 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 179,156 | |
Corporate debt securities | | | — | | | | 986,317 | | | | — | | | | 986,317 | |
Asset backed securities | | | — | | | | 91,531 | | | | — | | | | 91,531 | |
Foreign government and agency debt | | | — | | | | 28,110 | | | | — | | | | 28,110 | |
Municipal debt securities | | | — | | | | 33,464 | | | | — | | | | 33,464 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency forward contracts | | | — | | | | 124 | | | | — | | | | 124 | |
Long-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Auction rate securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 10,226 | | | | 10,226 | |
Other non-current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Severance pay fund | | | — | | | | 1,758 | | | | — | | | | 1,758 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 290,442 | | | $ | 1,376,315 | | | $ | 10,226 | | | $ | 1,676,983 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accrued liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency forward contracts | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,379 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,379 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
77
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fair Value Measurements at February 1, 2014 | |
| | | Level 1 | | | Level 2 | | | Level 3 | | | Total | |
Items measured at fair value on a recurring basis: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash equivalents: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Money market funds | | $ | 2,804 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,804 | |
Time deposits | | | — | | | | 247,958 | | | | — | | | | 247,958 | |
Municipal debt securities | | | — | | | | 4,800 | | | | — | | | | 4,800 | |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | 11,999 | | | | | | | | — | | | | 11,999 | |
Corporate debt securities | | | — | | | | 3,400 | | | | — | | | | 3,400 | |
Short-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government and agency debt | | | 301,479 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 301,479 | |
Corporate debt securities | | | — | | | | 589,514 | | | | — | | | | 589,514 | |
Asset backed securities | | | — | | | | 76,271 | | | | — | | | | 76,271 | |
Foreign government and agency debt | | | — | | | | 20,292 | | | | — | | | | 20,292 | |
Municipal debt securities | | | — | | | | 16,099 | | | | — | | | | 16,099 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency forward contracts | | | — | | | | 1,012 | | | | — | | | | 1,012 | |
Long-term investments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Auction rate securities | | | — | | | | — | | | | 16,279 | | | | 16,279 | |
Other non-current assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Severance pay fund | | | — | | | | 2,193 | | | | — | | | | 2,193 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 316,282 | | | $ | 961,539 | | | $ | 16,279 | | | $ | 1,294,100 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accrued liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency forward contracts | | $ | — | | | $ | 26 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 26 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The following table summarizes the change in fair values for Level 3 assets for the year ended January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014 (in thousands):
| | | | |
| | | Level 3 | |
Changes in fair value during the year (pre-tax): | | | | |
Ending balance at February 2, 2013 | | $ | 16,769 | |
Sales, redemption and settlement | | | (300 | ) |
Unrealized loss included in accumulated other comprehensive income | | | (190 | ) |
| | | | |
Ending balance at February 1, 2014 | | | 16,279 | |
Sales, redemption and settlement | | | (3,650 | ) |
Transfer Out | | | (3,000 | ) |
Unrealized loss included in accumulated other comprehensive income | | | 597 | |
| | | | |
Ending balance at January 31, 2015 | | $ | 10,226 | |
| | | | |
The Company received notification by the issuer of a mandatory full call on November 6, 2014 of an auction rate security and as a result, the security was classified within Level 2 based on the issuer’s quoted price. By the end of fiscal 2015, the auction rate security was subsequently fully redeemed at par value.
78
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Note 7 — Goodwill and Acquired Intangible Assets
Goodwill
The Company had no additions to goodwill in fiscal 2015 due to business combinations. In addition, the Company concluded there was no impairment of goodwill in fiscal 2015 based on its qualitative assessment that it was more likely than not the fair value of the reporting unit was greater than its carrying value.
The following table summarizes the activity related to the carrying value of goodwill (in thousands):
| | | | |
Balance at February 2, 2013 | | $ | 2,032,138 | |
Additions due to business combinations | | | 400 | |
Sale of a business | | | (2,593 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance at February 1, 2014 | | $ | 2,029,945 | |
| | | | |
Balance at January 31, 2015 | | $ | 2,029,945 | |
| | | | |
Acquired Intangible Assets
The carrying amounts of acquired intangible assets are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | January 31, 2015 | | | February 1, 2014 | |
| | | Range of
Useful Lives | | | Gross
Carrying
Amounts | | | Accumulated
Amortization
and
Write-Offs | | | Net
Carrying
Amounts | | | Gross
Carrying
Amounts | | | Accumulated
Amortization
and
Write-Offs | | | Net
Carrying
Amounts | |
Purchased technology | | | 4 - 7 years | | | $ | 35,498 | | | $ | (15,684 | ) | | $ | 19,814 | | | $ | 49,240 | | | $ | (20,634 | ) | | $ | 28,606 | |
Core technology | | | 5 - 8 years | | | | 850 | | | | (423 | ) | | | 427 | | | | 2,350 | | | | (1,583 | ) | | | 767 | |
Trade names | | | 5 years | | | | 1,300 | | | | (828 | ) | | | 472 | | | | 1,300 | | | | (568 | ) | | | 732 | |
Customer intangibles | | | 5 - 7 years | | | | 28,600 | | | | (18,615 | ) | | | 9,985 | | | | 28,600 | | | | (13,056 | ) | | | 15,544 | |
IPR&D | | | * | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,386 | | | | — | | | | 3,386 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total acquired intangible assets, net | | | | | | $ | 66,248 | | | $ | (35,550 | ) | | $ | 30,698 | | | $ | 84,876 | | | $ | (35,841 | ) | | $ | 49,035 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Intangible assets, along with the related accumulated amortization, are removed from the table above at the end of the fiscal year they become fully amortized. The Company recorded a charge to write-off $3.4 million of IPR&D in fiscal 2015, upon the Company’s decision to discontinue the related project. The Company also recorded charges of $8.1 million in fiscal 2014 for the impairment of an acquired intangible asset and $0.8 million in fiscal 2013 to write-off IPR&D related to an abandoned project. These impairment charges are included in amortization and write-off of acquired intangible assets in the consolidated statement of operations.
Based on the identified intangible assets recorded at January 31, 2015, the future amortization expense of identified intangibles excluding IPR&D for the next five fiscal years is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | |
Fiscal Year | | | |
2016 | | $ | 12,212 | |
2017 | | | 11,027 | |
2018 | | | 5,599 | |
2019 | | | 1,860 | |
2020 | | | — | |
| | | | |
| | $ | 30,698 | |
| | | | |
79
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Note 8 —Restructuring
Fiscal 2015. In connection with ongoing evaluations of its business, the Company decided to streamline its operations, primarily in Israel to align with its overall strategic plan, and to discontinue the development of a product it originally acquired from a business that it previously purchased. These actions were substantially completed by the end of fiscal 2015. In addition, the Company decided to exercise an early buy out option to acquire an asset under an existing operating lease agreement, which will result in a loss from the termination of the agreement.
Fiscal 2014. The Company closed two sites for which it incurred severance and exit-related costs in connection with vacating the facilities, in addition to the write-off of equipment. All activities were substantially completed by the end of fiscal 2014.
Fiscal 2013. The Company incurred restructuring costs when the sublease of one of its previously vacated facilities was terminated in fiscal 2013.
The following table presents detail of the related restructuring charges recorded by the Company (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Severance and related costs | | $ | 5,181 | | | $ | 2,786 | | | $ | — | |
Facilities and related costs | | | 1,924 | | | | 1,672 | | | | 1,257 | |
Loss on early contract termination | | | 3,230 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Other exit-related costs | | | 86 | | | | 213 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 10,421 | | | | 4,671 | | | | 1,257 | |
Write-off of assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equipment | | | 17 | | | | 61 | | | | — | |
Acquired intangible asset | | | 3,386 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 13,824 | | | $ | 4,732 | | | $ | 1,257 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Facilities and related costs include a charge for a portion of the lease obligation related to vacating the floors the Company no longer planned to occupy in one of its Israel facilities. The write-off of an acquired intangible asset in fiscal 2015 was due to the Company’s decision to discontinue the related project. Other exit-related costs are primarily associated with ongoing operating expenses related to vacated facilities under restructure actions in previous fiscal years.
The following table presents details of restructuring charges by functional line item (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Research and development | | $ | 5,249 | | | $ | 2,886 | | | $ | 47 | |
Selling and marketing | | | — | | | | 795 | | | | (3 | ) |
General and administrative | | | 5,189 | | | | 1,051 | | | | 1,213 | |
Write-off of acquired intangible assets | | | 3,386 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 13,824 | | | $ | 4,732 | | | $ | 1,257 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
80
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following table sets forth a reconciliation of the beginning and ending restructuring liability balances by each major type of costs associated with the restructuring charges (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Severance
and Related
Costs | | | Facilities
and Related
Costs | | | Other
Exit-Related
Costs | | | Total | |
Balance at February 2, 2013 | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,855 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,855 | |
Restructuring charges | | | 2,786 | | | | 1,672 | | | | 213 | | | | 4,671 | |
Net cash payments | | | (2,735 | ) | | | (2,144 | ) | | | (194 | ) | | | (5,073 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 1, 2014 | | | 51 | | | | 2,383 | | | | 19 | | | | 2,453 | |
Restructuring charges | | | 5,181 | | | | 1,924 | | | | 3,316 | | | | 10,421 | |
Net cash payments | | | (5,232 | ) | | | (2,968 | ) | | | (105 | ) | | | (8,305 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at January 31, 2015 | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,339 | | | $ | 3,230 | | | $ | 4,569 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The balance at January 31, 2015 for facility and related costs includes remaining payments under lease obligations related to vacated space that are expected to be paid through fiscal 2018. Other exit-related costs include payment related to the exercise of the early buy out option for an asset under an existing operating lease agreement, which is expected to be paid in the first quarter of fiscal 2016.
Note 9 — Income Taxes
The U.S. and non-U.S. components of income before income taxes consist of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
U.S. operations | | $ | 31,942 | | | $ | 31,339 | | | $ | 34,900 | |
Non-U.S. operations | | | 400,211 | | | | 274,918 | | | | 275,290 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 432,153 | | | $ | 306,257 | | | $ | 310,190 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
The provision (benefit) for income taxes consists of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Current income tax provision (benefit): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 9,096 | | | $ | 5,774 | | | $ | 4,461 | |
State | | | (161 | ) | | | 73 | | | | 407 | |
Foreign | | | 785 | | | | (18,829 | ) | | | (8,289 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total current income tax provision (benefit) | | | 9,720 | | | | (12,982 | ) | | | (3,421 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred income tax provision (benefit): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | | (1,775 | ) | | | 317 | | | | 6,306 | |
State | | | 16 | | | | 32 | | | | 90 | |
Foreign | | | (11,154 | ) | | | 3,570 | | | | 630 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total deferred income tax provision (benefit) | | | (12,913 | ) | | | 3,919 | | | | 7,026 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total provision (benefit) for income taxes | | $ | (3,193 | ) | | $ | (9,063 | ) | | $ | 3,605 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
81
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The income tax benefit for fiscal 2015 includes the current income tax liability of $17.4 million plus a $7.4 million increase in current unrecognized tax benefit. These charges were offset by a reduction in unrecognized tax benefits that arose from the release of $16.4 million due to the expiration of statute of limitations in non-U.S. jurisdictions and a $12.9 million increase in net deferred tax assets. The income tax benefit for fiscal 2014 included the current income tax liability of $13.2 million plus a $9.1 million increase in current unrecognized tax benefit which were offset by a reduction in unrecognized tax benefits that arose from the release of $31.8 million due to the expiration of statute of limitations and the settlement of an audit in non-U.S. jurisdictions. The provision for income taxes for fiscal 2013 consisted of the current income tax liability of $20.1 million plus a $8.0 million increase in current unrecognized tax benefit which were offset by a reduction in unrecognized tax benefits that arose from the release of $26.8 million due to the expiration of statute of limitations in non-U.S. jurisdictions.
Deferred tax assets consist of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | | | |
Federal and California research and other tax credits | | $ | 382,726 | | | $ | 335,894 | |
Reserves and accruals | | | 35,538 | | | | 25,833 | |
Share-based compensation | | | 4,502 | | | | 4,067 | |
Net operating losses | | | 14,940 | | | | 18,470 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Gross deferred tax assets | | | 437,706 | | | | 384,264 | |
Valuation allowance | | | (382,796 | ) | | | (335,890 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Total deferred tax assets | | | 54,910 | | | | 48,374 | |
Total deferred tax liabilities | | | (11,209 | ) | | | (17,586 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net deferred tax assets | | $ | 43,701 | | | $ | 30,788 | |
| | | | | | | | |
As presented in the consolidated balance sheet as of January 31, 2015, deferred tax assets for certain net operating losses that are available to be used included in the table above have been offset by unrecognized tax benefits.
The non-current portion of the deferred tax assets as of January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014 was $22.3 million and $19.3 million, respectively, and is included in other non-current assets. During fiscal 2015, deferred tax assets, net of a corresponding valuation allowance increased $12.9 million from the end of fiscal 2014, mostly due to an increase in the Singapore deferred tax asset since the Company re-negotiated with the Singapore government and in fiscal 2015, they extended the Development and Expansion Incentive (“DEI”) until June 2019.
As of January 31, 2015, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards available to offset future taxable income of approximately $58.2 million, $1.8 million and $7.4 million for foreign, U.S. federal and state of California purposes, respectively. The federal carryforwards will expire in various fiscal years between 2020 and 2024, and the California carryforwards will expire at various fiscal years between 2018 and 2033, if not utilized before these years. The losses in non-U.S. companies vary; some countries allows the loss be carried forward indefinitely while another allows only 15 years. For U.S. federal income tax return purposes, the Company had research tax credit carryforwards of approximately $233.2 million that expire through fiscal 2035. As of January 31, 2015, the Company had unused California research and tax credit carryforwards of approximately $239.1 million, which can be carryforward indefinitely. Included in the U.S. federal and California carryforward amounts are $56.8 million and $55.0 million, respectively, that are attributable to excess tax benefits from stock
82
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
options. Upon realization, the benefit associated with these credits will increase additional paid-in capital. The Company also has research and investment tax credit carryforwards of approximately $20.8 million in other U.S. states that expire through fiscal 2030 due to the statute of limitation.
At the end of fiscal 2015, the Company has provided a full valuation allowance against its federal and various state research credits which it earns in excess of its current year tax liabilities, as well as a portion against its net operating loss carryforwards. Based on the available objective positive and negative evidence, the Company has determined that it is more likely than not that these research credits and acquired net operating losses will not be realized. Therefore, the Company has recorded a valuation allowance of $382.8 million, an increase of $46.9 million from fiscal 2014.
Reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax to the Company’s effective tax:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Provision at U.S. notional statutory rate | | | 35.0 | % | | | 35.0 | % | | | 35.0 | % |
Non-deductible share-based compensation | | | 11.2 | | | | 19.4 | | | | 15.4 | |
Difference in U.S. and non-U.S. tax rates | | | (46.0 | ) | | | (55.8 | ) | | | (48.8 | ) |
Benefits from utilization of general business credits | | | (12.0 | ) | | | (14.1 | ) | | | (13.8 | ) |
Change in valuation allowance | | | 10.5 | | | | 11.9 | | | | 12.9 | |
Other | | | 0.6 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 0.5 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Effective tax rate | | | (0.7 | )% | | | (3.0 | )% | | | 1.2 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
The following table reflects changes in the unrecognized tax benefits (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Unrecognized tax benefits as the beginning of the period | | $ | 51,682 | | | $ | 79,031 | | | $ | 96,294 | |
Increases related to prior year tax positions | | | 976 | | | | 499 | | | | 1,106 | |
Decreases related to prior year tax positions | | | (386 | ) | | | (111 | ) | | | — | |
Increases related to current year tax positions | | | 5,356 | | | | 2,666 | | | | 1,139 | |
Settlements | | | — | | | | (7,423 | ) | | | (3,956 | ) |
Lapse in the statute of limitations | | | (10,691 | ) | | | (13,969 | ) | | | (15,543 | ) |
Foreign exchange gain | | | (1,740 | ) | | | (9,011 | ) | | | (9 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gross amounts of unrecognized tax benefits as of the end of the period | | $ | 45,197 | | | $ | 51,682 | | | $ | 79,031 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Included in the balances as of January 31, 2015 is $38.5 million of unrecognized tax benefit that would affect the effective income tax rate if recognized. Also, a portion of the gross unrecognized tax benefits presented in the table above are offset in the consolidated balance sheet as of January 31, 2015 against deferred tax assets.
The amounts in the table above do not include the related interest and penalties. The amount of interest and penalties accrued as of January 31, 2015 was approximately $27.7 million, as of February 1, 2014 was approximately $29.6 million and as of February 2, 2013 was approximately $33.8 million. The consolidated statements of operations for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013 included $3.8 million, $6.2 million and $5.8 million, respectively, of interest and penalties related to the unrecognized tax benefits.
83
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The Company is subject to income tax audits by the respective tax authorities in all of the jurisdictions in which it operates. The examination of tax liabilities in each of these jurisdictions requires the interpretation and application of complex and sometimes uncertain tax laws and regulations. As of January 31, 2015, the material jurisdictions that are subject to examination include China, Israel, Singapore, Switzerland and the United States for the Company’s fiscal years 2004 through 2014. As of January 31, 2015, several of the Company’s non-U.S. entities are under examination for fiscal years encompassing 2004 through 2013.
For fiscal 2015, the Company will continue to review its tax positions and provide for or reverse unrecognized tax benefits as issues arise. During the next 12 months, it is reasonably possible that the amount of unrecognized tax benefits could increase or decrease significantly due to changes in tax law in various jurisdictions, new tax audits and changes in the U.S. dollar as compared to foreign currencies within the next 12 months. Excluding these factors, uncertain tax positions may decrease by as much as $20 million from the lapse of the statutes of limitation in various jurisdictions during the next 12 months.
The Singapore Economic Development Board (“EDB”) initially granted a 10-year Pioneer Status in July 1999 to Company’s Singapore subsidiary. In October 2004, the Company’s subsidiary in Singapore was granted a second incentive known as the DEI, and in June 2006, the EDB agreed to extend the Pioneer status for 15 years to June 2014. The Company re-negotiated with the Singapore government and in fiscal 2015, they extended the DEI until June 2019. In fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013 tax savings associated with these tax holidays were approximately $0.1��million, $3.7 million and $13.6 million, respectively, which if paid would impact the Company’s earnings per share less than $0.01 per share in fiscal 2015, $0.01 per share in fiscal 2014 and $0.02 per share in fiscal 2013.
Under the Israeli Encouragement law of “approved or benefited enterprise,” two branches of Marvell Israel (M.I.S.L) Ltd., the GTL branch and the cellular branch (formerly Marvell DSPC), are entitled to approved and benefited tax programs that include reduced tax rates and exemption of certain income. Income from the approved or benefited enterprises is eligible for fiscal years 2008 through fiscal 2027. For fiscal 2014 and 2013, the benefit associated with these approved or benefited enterprise programs was $2.2 million and $13.8 million, respectively, which provided earnings per share of $0.01 per share in fiscal 2014 and $0.02 per share in fiscal 2013. There was no such benefit in fiscal 2015.
During fiscal 2007, each of the Swiss Federal Department of Economy and the Vaud Cantonal Tax Administration granted the Company’s subsidiary in Switzerland a 10 year tax holiday on revenues from research and design wafer supply trading activities commencing with its fiscal 2007 and ending in fiscal 2016. The fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013 tax savings associated with this tax holiday is approximately $4.5 million, $5.1 million and $4.6 million, respectively, which provided earnings per share of $0.01 per share in 2015, $0.01 per share in 2014 and less than $0.01 per share in fiscal 2013.
Our principal source of liquidity as of January 31, 2015 consisted of approximately $2.5 billion of cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, of which approximately $900 million was held by foreign subsidiaries (outside Bermuda). Approximately $400 million of this amount held by foreign subsidiaries is related to undistributed earnings, which have been indefinitely reinvested outside of Bermuda. These funds are primarily held in China, Israel, Singapore, the United States and Switzerland. We have plans to use such amounts to fund various activities outside of Bermuda including working capital requirements, capital expenditures for expansion, funding of future acquisitions, or other financing activities. If such funds were needed by the parent company in Bermuda or if the amounts were otherwise no longer considered indefinitely reinvested, we would incur a tax expense of approximately $100 million.
84
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Note 10 — Commitments and Contingencies
Warranty Obligations
The Company’s products carry a standard 90 day warranty with certain exceptions in which the warranty period can extend to more than one year based on contractual agreements. The Company’s warranty expense has not been significant in the periods presented.
Lease Commitments
The Company leases some of its facilities, equipment and computer aided design software under non-cancelable operating leases. Rent expense, net of sublease income for fiscal 2015, 2014, and 2013 was approximately $26.1 million, $25.8 million and $23.7 million, respectively. The Company also purchases certain intellectual property under technology license obligations. Future minimum lease payments, net of estimated sublease, and payments under technology license obligations as of January 31, 2015, are presented in the following tables (in thousands):
| | | | |
Fiscal Year: | | Minimum
Operating
Leases
Payments | |
2016 | | $ | 71,489 | |
2017 | | | 42,320 | |
2018 | | | 12,609 | |
2019 | | | 2,700 | |
2020 | | | 2,672 | |
Thereafter | | | 3,722 | |
| | | | |
Total future minimum lease payments | | $ | 135,512 | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
Fiscal Year: | | Technology
License
Obligations | |
2016 | | $ | 13,145 | |
2017 | | | 7,869 | |
2018 | | | 9,180 | |
2019 | | | — | |
2020 | | | — | |
Thereafter | | | — | |
| | | | |
Total future minimum lease payments | | $ | 30,194 | |
Less: amount representing interest | | | (1,236 | ) |
| | | | |
Present value of future minimum payments | | | 28,958 | |
Less: current portion | | | (12,490 | ) |
| | | | |
Non-current portion | | $ | 16,468 | |
| | | | |
Technology license obligations include the liabilities under the subscription agreements for technology licenses between the Company and various vendors.
85
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Purchase Commitments
Under the Company’s manufacturing relationships with its foundry partners, cancellation of all outstanding purchase orders are allowed but require payment of all costs and expenses incurred through the date of cancellation. As of January 31, 2015, these foundries had incurred approximately $252.1 million of manufacturing costs and expenses relating to the Company’s outstanding purchase orders.
Intellectual Property Indemnification
The Company has agreed to indemnify certain customers for claims made against the Company’s products, where such claims allege infringement of third-party intellectual property rights, including, but not limited to, patents, registered trademarks, and/or copyrights. Under the aforementioned indemnification clauses, the Company may be obligated to defend the customer and pay for the damages awarded against the customer under an infringement claim as well as the customer’s attorneys’ fees and costs. The Company’s indemnification obligations generally do not expire after termination or expiration of the agreement containing the indemnification obligation. Generally, there are limits on and exceptions to the Company’s potential liability for indemnification. Although historically the Company has not made significant payments under these indemnification obligations, the Company cannot estimate the amount of potential future payments, if any, that it might be required to make as a result of these agreements. The maximum potential amount of any future payments that the Company could be required to make under these indemnification obligations could be significant.
Contingencies
The Company and certain of its subsidiaries are currently parties to various legal proceedings, including those noted in this section. The legal proceedings and claims described below could result in substantial costs and could divert the attention and resources of the Company’s management. The Company is also engaged in other legal proceedings and claims not described below, which arise in the ordinary course of its business. Litigation is subject to inherent uncertainties and unfavorable rulings could occur. An unfavorable ruling in litigation could require the Company to pay damages, one-time license fees or ongoing royalty payments, and could prevent the Company from manufacturing or selling some of its products or limit or restrict the type of work that employees involved in such litigation may perform for the Company, any of which could adversely affect financial results in future periods. The Company believes that its products do not infringe valid and enforceable claims and it will continue to conduct a vigorous defense in these proceedings. However, there can be no assurance that these matters will be resolved in a manner that is not adverse to the Company’s business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
As of January 31, 2015, the Company has a $3.2 million accrued liability related to certain legal proceedings described below in this section. The amount recorded does not relate to the litigation with Carnegie Mellon University (“CMU”). Other than for the matters that the Company has recognized in the consolidated financial statements, it has not recorded any amounts for contingent losses associated with the matters described below based on its belief that losses, while reasonably possible, are not probable. Unless otherwise stated, the Company is currently unable to predict the final outcome of these lawsuits and therefore cannot determine the likelihood of loss nor estimate a range of possible loss.
Carnegie Mellon University Litigation. On March 6, 2009, CMU filed a complaint in the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Pennsylvania naming Marvell Semiconductor, Inc. (“MSI”) and the Company as defendants and alleging patent infringement. CMU has asserted U.S. Patent Nos. 6,201,839 and 6,438,180 (collectively, the “CMU patents in suit”), which relate to read-channel integrated circuit devices and the hard disk drive (“HDD”) incorporating such devices. A jury trial began on November 26, 2012. On December 26, 2012, a jury delivered a verdict that found the CMU patents in suit were literally and willfully infringed and valid, and
86
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
awarded past damages in the amount of $1.17 billion. CMU sought in its post-trial motions enhanced damages up to three times the jury verdict, pre-judgment interest up to $322 million, post-judgment interest, supplemental damages, attorneys’ fees, and an injunction and/or ongoing royalties. Post-trial motions were heard on May 1 and 2, 2013. On June 26, 2013, the District Court denied CMU’s post-trial motion for attorney fees without prejudice. On August 23, 2013, the District Court denied the Company’s motion for mistrial. On September 23, 2013, the District Court denied the Company’s motion for judgment as a matter of law or a new trial on non-infringement, invalidity and other non-damages issue as well as the Company’s motion for reduced damages. On the same day, the District Court granted-in-part CMU’s motion for a finding of willful infringement and enhanced damages, reserving its further rulings on any enhancement of the verdict for a separate opinion. On December 6, 2013, CMU filed a motion to permit registration of judgment and a motion for supplemental relief including a request to enjoin future share repurchases, any leveraged buyout or similar asset leveraging transaction, and dividends, in the absence of a court approved bond or other security. On December 23, 2013, the District Court denied the motions. On January 8, 2014, CMU filed a motion for telephonic status conference, which was denied on January 28, 2014. On January 14, 2014, the District Court denied the Company’s post-trial motion on laches. On March 31, 2014, the District Court rejected CMU’s motion for an injunction. The District Court also denied CMU’s request for pre-judgment interest, and substantially scaled back CMU’s request for enhanced damages. Based on these decisions, the District Court calculated the damages including enhancement to total approximately $1.54 billion, and held that, under its decision, CMU is entitled to post judgment interest and an ongoing royalty. On May 7, 2014, the District Court entered final judgment, from which the Company filed a notice of appeal on May 14, 2014. The Company filed its opening appeal brief on August 4, 2014. CMU filed its opposition brief on October 20, 2014 and the Company filed its reply brief on November 20, 2014. The District Court has required the Company to report ongoing royalties under the current judgment. Based on the royalty rate assessed by the District Court, such additional royalties for the period of time commencing on the date ordered by the District Court, January 15, 2013, through January 31, 2015 could be as much as $400 million. The Company has secured certain surety bonds for the duration of the appeal to stay execution of judgment pending the appeal. See “—Surety Bond.”
The Company and MSI believe that the evidence and the law do not support the jury’s findings of infringement, validity and the award of damages and do not believe a material loss is probable. The Company believes that there are strong grounds for appeal and the Company and MSI are currently pursuing an appeal before the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit in Washington, D.C. which is set for oral argument in April 2015. The Company believes the low end of the possible range of loss is zero, but it cannot reasonably estimate the upper range of the possible loss, as a number of factors could significantly change the assessment of damages.
USEI Litigation. On October 9, 2009, U.S. Ethernet Innovations, LLC (“USEI”) filed a complaint in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas, in which USEI has accused a number of system manufacturers, including the Company’s customers, of patent infringement (the “USEI litigation”). Specifically, USEI has asserted that these customers infringe U.S. Patent Nos. 5,307,459, 5,434,872, 5,732,094 and 5,299,313, which relate to Ethernet technologies. The complaint seeks unspecified damages and an injunction.
On May 4, 2010, MSI filed a motion to intervene in the USEI litigation, which was granted on May 19, 2010. On July 13, 2010, the District Court issued an order granting the defendants’ motion to transfer the action to the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California; the case was formally transferred on August 23, 2010. On September 14, 2011, USEI withdrew its allegations against MSI for the ‘459 patent. The District Court issued a first claim construction ruling on January 31, 2012 and a supplemental claim construction ruling on August 29, 2012. On August 16, 2013, the District Court granted defendants’ summary judgment motion to preclude the plaintiff from recovering certain pre-suit damages. On November 7, 2014, on summary judgment, the District Court found that all the patents-in-suit were either invalid or not infringed. On December 1, 2014, the District Court entered a judgment in favor of defendants and awarded defendants’ costs. On December 29, 2014,
87
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
USEI filed a motion to alter or amend the District Court’s summary judgment order. The District Court has set a hearing date in March 2015.
Lake Cherokee Patent Litigation. On June 30, 2010, September 5, 2013 and September 25, 2013, Lake Cherokee Hard Drive Technologies, L.L.C. filed three separate complaints, which were consolidated into one case in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas. All the parties involved in the three cases reached settlement in August 2014 and the three cases were dismissed with prejudice. The settlement did not have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Azure Networks Litigation. On March 22, 2011, Azure Networks, LLC (“Azure”) and Tri-County Excelsior Foundation filed suit in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas against MSI and eight other companies. The Complaint asserts U.S. Patent No. 7,756,129 against MSI’s Bluetooth products. MSI filed its answer and counterclaims on July 20, 2011. On November 2, 2012, MSI and the other defendants filed a motion for summary judgment of invalidity, which was denied. A claim construction hearing was held on December 20, 2012. On January 15, 2013, the magistrate judge issued a claim construction ruling. On May 20, 2013, the District Court issued an order denying plaintiff’s motion for reconsideration and adopted the magistrate judge’s claim construction ruling. On May 30, 2013, the District Court entered a judgment of non-infringement. On June 24, 2013, Azure appealed, and the appeal has been briefed. Oral argument before a Federal Circuit panel was held on April 11, 2014. On November 6, 2014, the Federal Circuit issued an order vacating the judgment of non-infringement and remanding for further proceedings. On January 7, 2015, the District Court issued a supplemental claim construction order in light of the Federal Circuit remand and issued a scheduling order. The Company filed a petition for writ of certiorari to the United States Supreme Court on February 4, 2015. On February 10, 2015, the District Court stayed all proceedings pending the Supreme Court’s ruling on the Company’s petition.
On January 13, 2015, Azure filed a second suit in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas, alleging infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 8,582,570; 8,582,571; 8,588,196; 8,588,231; 8,589,599; 8,675,590; 8,683,092; 8,700,815; 8,732,347; and 8,732,361, purportedly related to certain Wi-Fi and NFC technologies. The complaint seeks unspecified damages.
Power Management Systems Litigation. On August 22, 2011, Power Management Systems LLC (“PMS”), a subsidiary of Acacia Research Corp., filed a complaint against the Company’s subsidiary Marvell Semiconductor, Ltd. (“MSL”) and other defendants, in the U.S. District Court for the District of Delaware. On June 14, 2013, the District Court entered a judgment of non-infringement. The Federal Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed the District Court’s rulings on January 14, 2014. The deadline for PMS to appeal to the United States Supreme Court passed in mid-April 2014 without PMS taking any further action.
France Telecom Litigation. On June 26, 2012, France Telecom S.A. filed a complaint against MSI in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. The complaint asserts U.S. Patent No.5,446,747 against MSI’s communications processors and thin modems. The complaint seeks unspecified damages as well as injunctive relief. MSI answered the complaint on July 18, 2012 and August 1, 2012. On July 30, 2012, MSI filed a motion to transfer the lawsuit to the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California. On September 17, 2012, the Court granted MSI’s motion and transferred the case to the Northern District of California. A claim construction hearing was held on December 13, 2013. On April 14, 2014, the Court denied MSI’s motion for summary judgment of invalidity, and granted MSI’s summary judgment motion concerning certain damages preclusion. A jury trial began on September 17, 2014. On September 30, 2014, a jury delivered a verdict that found the patent in suit was literally, but not willfully, infringed and valid, and awarded damages. The award did not have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements. A hearing for post-trial motions and non-jury issues took place on January 14, 2015. On March 2, 2015, the District Court issued an order on post-trial briefs finding no direct infringement by Marvell as a matter of law and entered judgment in favor of Marvell.
88
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Freescale Litigation. On July 6, 2012, Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. (“Freescale”) filed a complaint against MSI in the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Texas. On January 4, 2013, three of the Company’s subsidiaries, MSI, Marvell International Ltd. and Marvell World Trade Ltd., filed a complaint against Freescale in the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Texas. On April 11, 2014, the Court dismissed both of the above two cases with prejudice pursuant to a settlement and patent license agreement. The settlement did not have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Progressive Semiconductor Solutions Patent Litigation. On September 30, 2013, Progressive Semiconductor Solutions LLC (“PSS”) filed a complaint in the Central District of California against MSI and another defendant. On March 3, 2014, the District Court dismissed MSI without prejudice. On March 4, 2014, PSS filed a new complaint against MSI. The parties reached settlement in August 2014 and the case was dismissed with prejudice on August 21, 2014. The settlement did not have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements.
Vantage Point Technology Patent Litigation. On November 21, 2013, Vantage Point Technology, Inc. (“VPT”) filed suit against a third-party defendant in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas for patent infringement relating to processor technology. On February 3, 2014, VPT filed an amended complaint against the third party and added MSI as an additional defendant. The complaint seeks unspecified damages. On December 8, 2014, the case was transferred to the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California. The case was dismissed with prejudice in March 2015.
Voss Litigation and Consolidated Cases. On April 7, 2014, Lee Voss (“Voss”) filed an action asserting putative class action claims on behalf of the Company’s shareholders and derivative claims ostensibly on behalf of the Company in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California, San Jose Division. This action was consolidated with two additional, nearly identical complaints from Sebastiano D’Arrigo and James and Marie DiBiase. The complaint alleged that certain officers and directors of the Company breached their fiduciary duties by causing or allowing the Company to engage in the purported willful infringement of certain patents asserted against it in litigation by CMU and by failing to institute adequate internal controls, resulting in an adverse verdict, and alleged unjust enrichment and a breach of the duty of honest services by three of the Company’s officers. The Company was named as a nominal defendant. The complaint requested damages and restitution in unspecified amounts, equitable and/or injunctive relief, and the costs and fees of bringing the action. The Company and the defendant officers and directors filed a motion to dismiss the amended consolidated complaint on September 4, 2014. On January 26, 2015, the District Court granted the Company’s motion to dismiss with leave to amend and on February 24, 2015, the District Court granted the plaintiffs’ motion to dismiss without prejudice.
Bandspeed Litigation. On May 9, 2014, Bandspeed, Inc. filed suit against MSI in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of Texas, alleging infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 7,027,418; 7,570,614; 7,477,624; 7,903,608; and 8,542,643, purportedly related to certain Bluetooth technology. The complaint seeks unspecified damages. On February 13, 2015, Bandspeed amended its complaint and added allegations of infringement of U.S. Patent No. 8,873,500. A claim construction hearing is currently scheduled for October 2, 2015.
SOTA Litigation. On October 24, 2014, SOTA Semiconductor LLC (“SOTA”) filed suit against MSI, alleging infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 5,991,545 and 6,643,713, purportedly related to certain processor technology. The complaint sought unspecified damages. The parties reached settlement and the case was dismissed with prejudice on January 20, 2015. The settlement did not have a significant impact on the Company’s financial statements.
NXP Litigation. On January 22, 2015, NXP Semiconductors N.V. filed suit against MSI in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of California, alleging infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 5,939,791; 7,039,133; 8,185,050; and 8,203,432, purportedly related to certain NFC technology. The complaint seeks unspecified damages. MSI filed its response and counterclaims on February 26, 2015. Marvell International
89
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Limited (“MIL”) also filed counterclaims against NXP Semiconductors U.S.A. (“NXP USA”), alleging infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 7,047,393; 7,555,065; and 7,302,600. On February 2, 2015, MIL filed suit against NXP USA in the U.S. District Court for the Central District of California, alleging patent infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 8,171,309; 7,957,777; 7,454,634; and 6,903,448, related to certain NFC and automotive technologies.
Paone Litigation. On February 6, 2015, Luciano F. Paone filed suit against MSI in the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of New York, alleging infringement of U.S. Patent No. 6,259,789, purportedly related to certain encryption technology. The complaint seeks unspecified damages.
Innovatio Litigation. On March 16, 2015, Innovatio IP Ventures, LLC filed suit against MSI in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Illinois, alleging infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 6,697,415; 5,844,893; 5,740,366; 7,916,747; 6,665,536; 7,013,138; 7,107,052; 5,546,397; 7,710,907; 7,710,935; 6,714,559; 7,457,646; and 6,374,311, purportedly related to certain wireless technology. The complaint seeks unspecified damages.
Surety Bond
On May 14, 2014, the Company filed a Notice of Appeal to appeal the final judgment issued by the District Court in the CMU litigation. In order to stay the execution of the final judgment pending its appeal, the Company filed a supersedeas bond for $1.54 billion with the District Court. The bond was issued by a consortium of sureties authorized by the U.S. Treasury. If the judgment is affirmed after the completion of all appellate proceedings, and the Company does not thereafter fully satisfy the judgment within thirty days, the sureties are obligated under the bond to make payment to CMU. In support of the bond, the Company entered into separate indemnity agreements with each of the sureties to indemnify the sureties from all costs and payments made under the bond. The indemnity agreements did not require collateral to be posted at the time of the issuance of the bond. Therefore no cash is considered restricted as of the date of this filing. However, the indemnity agreements provide that each of the sureties have the right to demand to be placed in funds or call for collateral under pre-defined events. The indemnity agreements will remain outstanding for as long as the underlying bond remains outstanding.
The Court has required us to report ongoing royalties under the current judgment. Based on the royalty rate assessed by the District Court, such additional royalties for the period of time commencing on the date ordered by the District Court, January 15, 2013, through January 31, 2015 could be as much as $400 million. On November 14, 2014, the Company filed a second surety bond for $216 million and filed a commitment letter from the sureties to issue up to an additional $95 million in bonding under certain conditions. The second bond and commitment are secured by the Company’s campus located in Santa Clara, California, which has a carrying value of $139 million at January 31, 2015. The Company and CMU have agreed that the second bond and commitment satisfy the security for ongoing royalties while the appeal is pending.
Indemnities, Commitments and Guarantees
During its normal course of business, the Company has made certain indemnities, commitments and guarantees under which it may be required to make payments in relation to certain transactions. These indemnities may include intellectual property indemnities to the Company’s customers in connection with the sales of its products, indemnities for liabilities associated with the infringement of other parties’ technology based upon the Company’s products, indemnities for general commercial obligations, indemnities to various lessors in connection with facility leases for certain claims arising from such facility or lease, and indemnities to directors and officers of the Company to the maximum extent permitted under the laws of Bermuda. In addition, the Company has contractual commitments to various customers, which could require the Company to incur
90
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
costs to repair an epidemic defect with respect to its products outside of the normal warranty period if such defect were to occur. The duration of these indemnities, commitments and guarantees varies, and in certain cases, is indefinite. Some of these indemnities, commitments and guarantees do not provide for any limitation of the maximum potential future payments that the Company could be obligated to make. In general, the Company does not record any liability for these indemnities, commitments and guarantees in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as the amounts cannot be reasonably estimated and are not considered probable. The Company does, however, accrue for losses for any known contingent liability, including those that may arise from indemnification provisions, when future payment is probable.
Note 11 — Benefit Plans
The Company sponsors a 401(k) savings and investment plan that allows eligible U.S. employees to participate by making pre-tax contributions to the 401(k) plan ranging from 1% to 50% of eligible earnings subject to a required annual limit. The Company matches 100% of the employee contribution up to $500 per eligible employee on a quarterly basis. The participant must be employed by the Company on the last day of the calendar quarter to qualify for the match. At the end of the calendar year, the eligible employees receive a true-up match equal to the accumulated employee contribution for the calendar year up to $2,000. The Company made matching contributions to employees of $5.1 million during each of fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013. As of January 31, 2015, the 401(k) plan offers a variety of investment alternatives, representing different asset classes. Employees may not invest in the Company’s common shares through the 401(k) plan.
The Company also has voluntary defined contribution plans in various non-U.S. locations. The Company made contributions on behalf of employees totaling $18.6 million, $20.6 million and $17.2 million during fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The Company also maintains a limited number of defined benefit plans for certain non-U.S. locations. Total costs under these plans were not significant.
Note 12 — Shareholders’ Equity
Common and Preferred Stock
As of January 31, 2015, the Company is authorized to issue 992.0 million shares of $0.002 par value common stock and 8.0 million shares of $0.002 par value preferred stock. As of January 31, 2015 and February 1, 2014, no shares of preferred stock were outstanding.
1995 Stock Option Plan
In April 1995, the Company adopted the 1995 Stock Option Plan (the “Option Plan”). The Option Plan, as amended from time to time, had 383.4 million common shares reserved for issuance thereunder as of January 31, 2015. Options granted under the Option Plan generally have a term of 10 years and generally must be issued at prices equal to the fair market value of the stock on the date of grant. Incentive stock options granted to shareholders who own greater than 10% of the outstanding stock at the time of the grant may not have a term exceeding five years and these options must be issued at prices of at least 110% of the fair market value of the stock on the date of grant.
The Company can also grant stock awards, which may be subject to vesting. Further, the Company can grant restricted stock unit awards. Restricted stock unit awards are denominated in shares of stock, but may be settled in cash or shares upon vesting, as determined by the Company at the time of grant.
Equity awards to new hires under the Option Plan generally vest 20% one year after the vesting commencement date and the remaining shares vest one-sixtieth per month over the remaining 48 months. Other equity awards generally vest annually in four equal installments.
91
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
In fiscal 2015, the Company granted performance-based restricted stock units (“PSUs”) to certain members of senior management. Pursuant to the PSUs, each eligible employee is entitled to vest in a certain number of shares based on such employee’s achievement of individual financial and strategic performance goals for fiscal 2015, including, for example, net revenue and operating expense targets, and other individual strategic milestones. The actual number of shares that vest for each eligible employee is based on the achievement of such performance goals determined at the end of fiscal 2015 and vest over two years, with 50% vesting on April 1, 2015 and 50% vesting on April 1, 2016. The Company recognizes expenses associated with the PSUs when it becomes probable that the performance conditions will be met. Once it becomes probable that a PSU will vest, the Company recognizes compensation expense equal to the number of shares multiplied by the fair value of the related shares measured at the grant date.
In fiscal 2015, the Company also granted performance-based equity awards to each of our executive officers which are based on their achievement of certain performance goals in fiscal 2015 and 2016. These equity awards include restricted stock units which vest based on financial performance criteria (“Financial Performance RSU”) and restricted stock units which vest based on both financial performance criteria and individual strategic goals (“Strategic Performance Award”). The Financial Performance RSUs will be earned based on the achievement of revenue and modified non-GAAP operating income that have been established at “threshold,” “target” and “maximum” levels. Each Financial Performance RSU will vest 50% on the first anniversary of the commencement date based on achievement of fiscal 2015 financial performance criteria and 50% on the second anniversary of the vesting commencement date based on the achievement of fiscal 2016 financial performance criteria. The Strategic Performance Awards will vest based on achievement at the threshold level of either the revenue or modified non-GAAP operating income objective established for the Financial Performance RSU, in addition to the achievement of additional individual strategic goals. Each Strategic Performance Award will vest 50% on the first anniversary of the commencement date based on achievement of fiscal 2015 individual strategic goals and 50% on second anniversary date based on the achievement of the fiscal 2016 individual strategic goals.
In March 2015, the Executive Compensation Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors completed its evaluation of the number of shares to be issued to the Company’s executive officers based on their achievement of the fiscal 2015 performance goals and determined that 478,001 shares would vest on April 1, 2015. As a result, there was no material adjustment to the related share-based compensation expense in fiscal 2015.
As of January 31, 2015, approximately 90.0 million shares remained available for future issuance under the Option Plan.
1997 Directors’ Stock Option Plan
In August 1997, the Company adopted the 1997 Directors’ Stock Option Plan (the “1997 Directors’ Plan”). Under the 1997 Directors’ Plan, an outside director was granted an option to purchase 30,000 common shares upon appointment to the Company’s Board of Directors. These options vested 20% one year after the vesting commencement date and remaining shares vest one-sixtieth per month over the remaining 48 months. An outside director was also granted an option to purchase 6,000 common shares on the date of each annual meeting of the shareholders. These options vested one-twelfth per month over 12 months after the fourth anniversary of the vesting commencement date. Options granted under the 1997 Directors’ Plan could be exercised prior to vesting and had a term of 10 years. The 1997 Directors’ Plan was terminated in October 2007. There are two outstanding grants remaining under the 1997 Directors’ Plan.
2007 Directors’ Stock Incentive Plan
In October 2007, the Company adopted the 2007 Directors’ Stock Incentive Plan, for which shareholders approved a total of 750,000 common shares that could be issued under the plan to all eligible outside directors.
92
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Each outside director was granted an option to purchase 50,000 common shares upon his or her initial appointment to the Company’s Board of Directors. These options, which have a term of 10 years, vested one-third of the total shares on the one-year anniversary of the date of grant and one-third of the total shares on each one-year anniversary thereafter. From time to time, the Board has the authority to approve the amendment and restatement of the plan to revise the size of automatic annual awards granted under the plan.
In fiscal 2012, each outside director who had been serving on the Company’s Board of Directors for the prior six months and was re-elected by the shareholders at the annual general meeting was granted an option to purchase 9,000 common shares. These options, which have a term of 10 years, vested 100% on the earlier of the date of the next annual general meeting of shareholders or the one-year anniversary of the date of grant. In addition, each outside director was also granted a restricted stock unit (“RSU”) award for a number of shares with an aggregate fair market value equal to $70,000 immediately following the annual general meeting of shareholders. These RSU awards vested 100% on the earlier of the date of the next annual general meeting of shareholders or the one-year anniversary of the date of grant.
In fiscal 2013 and 2014, each outside director who was appointed at the annual general meeting of shareholders was granted an option to purchase a number of common shares with an aggregate grant date fair value equal to $110,000 immediately following the annual general meeting of shareholders. In addition, each outside director who was elected or appointed at the annual general meeting of shareholders was granted an RSU award for a number of shares with an aggregate fair market value equal to $110,000 immediately following each annual general meeting. The option awards, which have a term of 10 years, and the RSU awards vest 100% on the earlier of the date of the next annual general meeting of shareholders or the one-year anniversary of the date of grant. An outside director elected or appointed after an annual general meeting of shareholders would receive a pro rata stock option award and RSU award based on the number of quarters completed since the previous annual general meeting of shareholders. In no event would any outside director be awarded in any calendar year an annual option award or annual RSU award under the 2007 Director Plan for more than 25,000 shares and 10,000 shares, respectively.
Beginning in fiscal 2015, each outside director who is first elected or appointed at the annual general meeting of shareholders will be granted an RSU award for a number of shares with an aggregate fair market value equal to $220,000 immediately following each annual general meeting of shareholders. The RSU award vests as to 100% of the shares on the earlier of the date of the next annual general meeting of shareholders or the one-year anniversary of the date of grant. An outside director who is elected or appointed after an annual general meeting of shareholders will receive a pro rata RSU award based on the number of quarters completed since the prior annual general meeting of shareholders. In no event shall any outside director be awarded in any calendar year an annual RSU award under the 2007 Director Plan for more than 20,000 shares, respectively.
As of January 31, 2015, approximately 144,692 shares remained available for future issuance under the 2007 Directors’ Plan.
2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
Under the 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended and restated on October 31, 2011 (the “ESPP”), participants purchase the Company’s stock using payroll deductions, which may not exceed 15% of their total cash compensation. Pursuant to the terms of the current ESPP, the “look-back” period for the stock purchase price is 24 months. Offering and purchase periods begin on December 8 and June 8 of each year. Participants enrolled in a 24-month offering period will continue in that offering period until the earlier of the end of the offering period or the reset of the offering period. A reset occurs if the fair market value of the Company’s common shares on any purchase date is less than it was on the first day of the offering period. Participants in a 24-month offering period will be granted the right to purchase common shares at a price per
93
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
share that is 85% of the lesser of the fair market value of the shares at (i) the participant’s entry date into the two-year offering period or (ii) the end of each six-month purchase period within the offering period.
During fiscal 2015, a total of 9.7 million shares were issued under the ESPP at a weighted-average price of $7.67. During fiscal 2014, a total of 9.7 million shares were issued under the ESPP at a weighted-average price of $7.39. During fiscal 2013, a total of 7.6 million shares were issued under the ESPP at a weighted-average price of $8.77. As of January 31, 2015, there was $39.7 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to the ESPP.
As of January 31, 2015, approximately 14.8 million shares remained available for future issuance under the ESPP.
Option Plan and Stock Award Activity
Stock option activity under the Company’s stock option and stock incentive plans is included in the following table (in thousands, except for per share amounts):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Time-Based Options | | | Market-Based Options | | | Total | |
| | | Options
Outstanding | | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | | Options
Outstanding | | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | | Options
Outstanding | | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | |
Balance at January 28, 2012 | | | 52,467 | | | $ | 12.53 | | | | 3,124 | | | $ | 15.43 | | | | 55,591 | | | $ | 12.70 | |
Granted | | | 7,041 | | | $ | 14.59 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7,041 | | | $ | 14.59 | |
Exercised | | | (5,977 | ) | | $ | 6.44 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,977 | ) | | $ | 6.44 | |
Canceled/Forfeited | | | (3,894 | ) | | $ | 16.10 | | | | (365 | ) | | $ | 15.43 | | | | (4,259 | ) | | $ | 16.04 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 2, 2013 | | | 49,637 | | | $ | 13.28 | | | | 2,759 | | | $ | 15.43 | | | | 52,396 | | | $ | 13.39 | |
Granted | | | 18,922 | | | $ | 10.82 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18,922 | | | $ | 10.82 | |
Exercised | | | (15,482 | ) | | $ | 9.40 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (15,482 | ) | | $ | 9.40 | |
Canceled/Forfeited | | | (3,921 | ) | | $ | 15.15 | | | | (136 | ) | | $ | 15.43 | | | | (4,057 | ) | | $ | 15.16 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 1, 2014 | | | 49,156 | | | $ | 13.40 | | | | 2,623 | | | $ | 15.43 | | | | 51,779 | | | $ | 13.51 | |
Granted | | | 6,365 | | | $ | 15.33 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 6,365 | | | $ | 15.33 | |
Exercised | | | (3,732 | ) | | $ | 10.19 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (3,732 | ) | | $ | 10.19 | |
Canceled/Forfeited | | | (4,649 | ) | | $ | 14.66 | | | | (391 | ) | | $ | 15.43 | | | | (5,040 | ) | | $ | 14.72 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at January 31, 2015 | | | 47,140 | | | $ | 13.79 | | | | 2,232 | | | $ | 15.43 | | | | 49,372 | | | $ | 13.88 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Vested or expected to vest at January 31, 2015 | | | 44,470 | | | $ | 13.84 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercisable at January 31, 2015 | | | 22,457 | | | $ | 15.31 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
For time-based stock options vested and expected to vest at January 31, 2015, the aggregate intrinsic value was $122.1 million and the weighted average remaining contractual term was 5.9 years. For time-based stock options exercisable at January 31, 2015, the aggregate intrinsic value was $51.9 million and the weighted average remaining contractual term was 3.5 years. The aggregate intrinsic value of stock options exercised during fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $19.3 million, $51.1 million and $33.6 million, respectively. There was no aggregate intrinsic value for market-based stock options at January 31, 2015 and the weighted average remaining contractual term of market-based stock options vested and expected to reach the end of the vesting period at January 31, 2015 was 6.2 years. The Company’s closing stock price of $15.49 as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market as of January 30, 2015 was used to calculate the aggregate intrinsic value for all in-the-money options.
94
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
As of January 31, 2015, the unamortized compensation expense for time-based stock options was $53.3 million and market-based stock options were fully amortized in fiscal 2014. The unamortized compensation expense for time-based options will be amortized on a straight-line basis and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.3 years.
Activity related to the non-vested portion of the restricted stock units is included in the following table (in thousands, except for share prices):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Time-Based | | | Performance-Based | | | Total | |
| | | Number of
Shares | | | Weighted
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value | | | Number of
Shares | | | Weighted
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value | | | Number of
Shares | | | Weighted
Average
Grant Date
Fair Value | |
Balance at January 28, 2012 | | | 9,646 | | | $ | 17.38 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 7,370 | | | $ | 14.64 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Vested | | | (2,796 | ) | | $ | 17.78 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Canceled/Forfeited | | | (1,481 | ) | | $ | 17.16 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 2, 2013 | | | 12,739 | | | $ | 15.78 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 3,728 | | | $ | 10.79 | | | | 100 | | | $ | 10.52 | | | | 3,828 | | | $ | 10.78 | |
Vested | | | (3,925 | ) | | $ | 16.19 | | | | — | | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | — | |
Canceled/Forfeited | | | (1,288 | ) | | $ | 14.39 | | | | — | | | $ | — | | | | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at February 1, 2014 | | | 11,254 | | | $ | 14.14 | | | | 100 | | | $ | 10.52 | | | | 11,354 | | | $ | 14.11 | |
Granted | | | 5,534 | | | $ | 15.20 | | | | 1,277 | * | | $ | 14.98 | * | | | 6,811 | | | $ | 15.16 | |
Vested | | | (5,938 | ) | | $ | 13.96 | | | | (3 | ) | | $ | 10.52 | | | | (5,941 | ) | | $ | 13.96 | |
Canceled/Forfeited | | | (1,102 | ) | | $ | 14.32 | | | | (120 | ) | | $ | 11.23 | | | | (1,222 | ) | | $ | 14.02 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at January 31, 2015 | | | 9,748 | | | $ | 14.84 | | | | 1,254 | | | $ | 14.99 | | | | 11,002 | | | $ | 14.85 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| * | Amounts represent the target number of restricted stock units at grant date. For awards granted to our executive officers, up to 200% of the target restricted stock units may vest if the maximum level for financial and strategic goals is achieved. |
The aggregate intrinsic value of restricted stock units expected to vest as of January 31, 2015 was $160.3 million. The number of restricted stock units that are expected to vest is 10.4 million shares.
As of January 31, 2015, unamortized compensation expense related to restricted stock units was $87.5 million. The unamortized compensation expense for restricted stock units will be amortized on a straight-line basis and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.3 years.
Share-Based Compensation
The following table presents details of share-based compensation expenses by functional line item (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 7,972 | | | $ | 8,863 | | | $ | 8,142 | |
Research and development | | | 94,432 | | | | 109,432 | | | | 87,149 | |
Selling and marketing | | | 11,469 | | | | 13,940 | | | | 13,278 | |
General and administrative | | | 23,373 | | | | 23,638 | | | | 18,711 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 137,246 | | | $ | 155,873 | | | $ | 127,280 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
95
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Share-based compensation capitalized in inventory was $1.5 million at January 31, 2015, $1.7 million at February 1, 2014, and $1.5 million at February 2, 2013.
Valuation Assumptions
The expected volatility for awards granted during fiscal 2015, 2014, and 2013 was based on an equally weighted combination of historical stock price volatility and implied volatility derived from traded options on the Company’s stock in the marketplace. The Company believes that the combination of historical volatility and implied volatility provides a better estimate of future stock price volatility.
The expected dividend yield is calculated by dividing the current annualized dividend by the closing stock price on the date of grant of the option.
The following weighted average assumptions were used for each respective period to calculate the fair value of each time-based equity award on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and of each market-based equity award using a Monte Carlo simulation model:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Time-based Stock Options: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average fair value | | $ | 4.35 | | | $ | 3.43 | | | $ | 5.52 | |
Expected volatility | | | 35 | % | | | 45 | % | | | 44 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | | 5.0 | | | | 5.0 | | | | 4.8 | |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 1.6 | % | | | 0.8 | % | | | 0.9 | % |
Expected dividend yield | | | 1.6 | % | | | 2.4 | % | | | 0.3 | |
There were no market-based stock options granted during fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013. In fiscal 2012, the Company issued 3.1 million stock options with a market-based condition for a group of senior employees. If the market price condition is not met within five years from the date of grant, the options automatically expire. The fair value of each market-based stock option award was estimated on the date of grant using a Monte Carlo simulation model that uses the assumptions noted in the above table, including the same volatility applied to the Company’s time-based options. Because a Monte Carlo simulation model incorporates ranges of assumptions for inputs, those ranges are disclosed where applicable. The Company uses historical data to estimate employee termination within the valuation model. The expected term was 2.66 years for market-based stock options granted in fiscal 2012 and was derived from the output of the valuation model and represents the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Employee Stock Purchase Plan: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Estimated fair value | | $ | 4.10 | | | $ | 3.65 | | | $ | 3.13 | |
Expected volatility | | | 30 | % | | | 37 | % | | | 40 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | | 1.3 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 1.2 | |
Risk-free interest rate | | | 0.3 | % | | | 0.2 | % | | | 0.2 | % |
Expected dividend yield | | | 1.6 | % | | | 2.0 | % | | | 2.4 | |
96
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Share Repurchase Program
The Company’s board of directors initially authorized its current share repurchase program to repurchase up to $500 million of its outstanding common shares in August 2010. Since then, the Company’s board of directors have authorized an additional $2.8 billion for a total available under the program of $3.3 billion to be used to repurchase its common shares. The Company intends to effect share repurchases in accordance with the conditions of Rule 10b-18 under the Exchange Act but may also make repurchases in the open market outside of Rule 10b-18 or in privately negotiated transactions. The share repurchase program will be subject to market conditions and other factors, and does not obligate the Company to repurchase any dollar amount or number of its common shares and the repurchase program may be extended, modified, suspended or discontinued at any time.
The Company repurchased 5.1 million of its common shares for $65.0 million in cash during fiscal 2015, 33.1 million of its common shares for $354.1 million in cash during fiscal 2014 and 91.0 million of its common shares for $959.1 million in cash during fiscal 2013. All of the repurchased shares were retired immediately after the repurchases were completed. The Company records all repurchases, as well as investment purchases and sales, based on trade date. As of January 31, 2015, a total of 222.0 million cumulative shares have been repurchased under the Company’s share repurchase program for a total $2.8 billion in cash and there was $443.5 million remaining available for future share repurchases.
Dividends
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
| | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Cash dividend per share | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.24 | | | $ | 0.18 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total payment to shareholders (in thousands) | | $ | 122,801 | | | $ | 119,449 | | | $ | 98,761 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Future payment of a regular quarterly cash dividend on the Company’s common shares will be subject to, among other things, the best interests of the Company, the Company’s results of operations, cash balances and future cash requirements, financial condition, statutory requirements under Bermuda law and other factors that the Company’s board of directors may deem relevant. The Company’s dividend payments may change from time to time, and the Company cannot provide assurance that it will continue to declare dividends at all or in any particular amounts. In addition, developments in ongoing litigation could affect the Company’s ability to make a dividend payment on a declared payment date until such time as the Company can meet statutory requirements under Bermuda law.
On February 19, 2015, the Company announced that its board of directors declared a cash dividend of $0.06 per share to be paid on April 2, 2015 to shareholders of record as of March 12, 2015.
Note 13 — Segment and Geographic Information
The Company operates in one reportable segment — the design, development and sale of integrated circuits. The chief executive officer has been identified as the chief operating decision maker (“CODM”). The Company’s CODM is ultimately responsible and actively involved in the allocation of resources and the assessment of the Company’s operational and financial performance. The fact that the Company operates in only one reportable segment is based on the following:
| | • | | The Company uses a highly integrated approach in developing its products in that discrete technologies developed by the Company are frequently integrated across many of its products. Substantially all of the Company’s integrated circuits are manufactured under similar manufacturing processes. |
97
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
| | • | | The Company’s organizational structure is based along functional lines. Each of the functional department heads reports directly to the CODM. Shared resources in the Company also report directly to the CODM or to a direct report of the CODM. |
| | • | | The assessments of performance across the Company, including assessment of the Company’s incentive compensation plan, are based largely on operational performance and consolidated financial performance. |
| | • | | The decisions on allocation of resources and other operational decisions are made by the CODM based on his hands-on involvement with the Company’s operations and product development. |
The following tables present net revenue and long-lived asset information based on geographic region. Net revenue is based on the destination of the shipments and long-lived assets are based on the physical location of the assets (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
Net Revenue: | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
United States | | $ | 62,333 | | | $ | 68,321 | | | $ | 176,581 | |
China | | | 2,214,876 | | | | 1,869,381 | | | | 1,599,681 | |
Thailand | | | 294,706 | | | | 353,363 | | | | 369,855 | |
Malaysia | | | 377,903 | | | | 352,756 | | | | 351,401 | |
Philippines | | | 254,381 | | | | 257,899 | | | | 246,269 | |
Others | | | 502,764 | | | | 502,680 | | | | 424,843 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 3,706,963 | | | $ | 3,404,400 | | | $ | 3,168,630 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment, net: | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | |
Bermuda | | $ | 3,358 | | | $ | 4,453 | |
China | | | 25,910 | | | | 29,146 | |
Israel | | | 26,728 | | | | 33,758 | |
Singapore | | | 79,216 | | | | 76,367 | |
United States | | | 186,321 | | | | 195,253 | |
Others | | | 19,106 | | | | 17,188 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 340,639 | | | $ | 356,165 | |
| | | | | | | | |
The following table presents net revenue by end market (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended | |
Net Revenue by End Market | | January 31,
2015 | | | February 1,
2014 | | | February 2,
2013 | |
Storage | | $ | 1,744,656 | | | $ | 1,681,953 | | | $ | 1,494,959 | |
Mobile and Wireless | | | 1,071,777 | | | | 839,407 | | | | 822,533 | |
Networking | | | 674,701 | | | | 670,249 | | | | 708,821 | |
Other | | | 215,829 | | | | 212,791 | �� | | | 142,317 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 3,706,963 | | | $ | 3,404,400 | | | $ | 3,168,630 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
98
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Note 14 — Related Party Transactions
MIL is party to a technology license agreement with VeriSilicon Holdings Co., Ltd. (“VeriSilicon”). MIL assumed the technology license agreement between VeriSilicon and UTStarcom, Inc. after the Company’s acquisition of the semiconductor business of UTStarcom in December 2005. MIL has subsequently entered into various addenda to the agreement for additional technology beyond the scope of the original agreement. In addition, in September 2010, MIL entered into a services agreement with VeriSilicon, pursuant to which VeriSilicon has agreed to provide design support services to MIL. Under the services agreement, VeriSilicon helped on three projects for MIL during fiscal 2013. In connection with all of its transactions with VeriSilicon, MIL paid $3.7 million, $2.0 million and $2.8 million to VeriSilicon during fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. As of January 31, 2015, the Company had $0.8 million of liability to VeriSilicon. Weili Dai’s brother (and Dr. Sehat Sutardja’s brother-in-law) is the Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer of VeriSilicon. Ms. Dai is also a shareholder of VeriSilicon. Ms. Dai is President of the Company and Dr. Sehat Sutardja is the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. Dr. Sehat Sutardja and Ms. Dai are husband and wife.
In December 2009, MIL entered into a technology license agreement with Vivante Corporation (“Vivante”) that provides for the license of graphics technology and associated services. This agreement restates, expands and succeeds previous agreements between the parties for the same technology. In December 2012, the parties renewed this technology license agreement for another three years. The total amount of the license fee was approximately $13.0 million (to be paid over three years) and ten percent for support fees (to be paid over three years). In February 2012, the parties entered into a services agreement, pursuant to which Vivante agreed to provide support services to MIL. In connection with all of its transactions with Vivante, MIL paid $9.1 million, $6.9 million and $8.6 million to Vivante during fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. As of January 31, 2015, the Company had $3.7 million of liability to Vivante. Dr. Sehat Sutardja and Ms. Dai, through their ownership and control of Estopia LLC, are indirect shareholders of Vivante. In addition, Dr. Sehat Sutardja is also a direct shareholder and Chairman of the board of directors of Vivante. Ms. Dai’s brother (and Dr. Sehat Sutardja’s brother-in-law) is the Chief Executive Officer of Vivante.
Note 15 — Subsequent Events
On February 25, 2015, the Executive Compensation Committee (“Committee”) of the Company’s Board of Directors approved a cash payment of approximately $15.4 million to Dr. Sehat Sutardja, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. The U.S. Court of Federal Claims ruled against Dr. Sutardja in his legal challenge with the Internal Revenue Service and the California Franchise Tax Board related to the tax treatment of several stock options granted in fiscal 2004. After discussing and evaluating the alternatives to a continuing legal challenge of the court’s determination, the likelihood of success of further appeal by Dr. Sutardja and the potential negative impact on the Company of a continuation of the case regardless of the outcome, on February 25, 2015, the Committee determined to provide Dr. Sutardja with relief from the financial effects of the penalty taxes. Accordingly, the Committee approved the cash payment to Dr. Sutardja equal to the amount of his penalty taxes owed under the Tax Codes, plus accrued interest owed with respect to such liabilities, all grossed-up for income taxes that will be owed by Dr. Sutardja on receipt of such cash payment. The Company will record the payment in general and administrative expense in the first quarter of fiscal 2016.
99
MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
(Unaudited)
The following table presents the unaudited consolidated statements of operations data for each of the eight quarters in the period ended January 31, 2015. In management’s opinion, this information has been presented on the same basis as the audited consolidated financial statements included in a separate section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and all necessary adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, have been included in the amounts below to fairly state the unaudited quarterly results when read in conjunction with the audited consolidated financial statements and related notes. The operating results for any period should not be considered indicative of results to be expected in any future period. The Company expects the quarterly operating results to fluctuate in future periods due to a variety of reasons, including those discussed in Part I, Item 1A “Risk Factors.”
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fiscal 2015 | |
| | | First
Quarter (1) | | | Second
Quarter (2) | | | Third
Quarter (3) | | | Fourth
Quarter (4) | |
| | | (In thousands, except per share amounts) | |
Net revenue | | $ | 957,830 | | | $ | 961,545 | | | $ | 930,136 | | | $ | 857,452 | |
Gross profit | | $ | 463,970 | | | $ | 483,804 | | | $ | 475,162 | | | $ | 440,321 | |
Net income | | $ | 99,479 | | | $ | 138,870 | | | $ | 115,304 | | | $ | 81,693 | |
Net income per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.20 | | | $ | 0.27 | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | 0.16 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.19 | | | $ | 0.27 | | | $ | 0.22 | | | $ | 0.16 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Fiscal 2014 | |
| | | First
Quarter | | | Second
Quarter (5) | | | Third
Quarter (6) | | | Fourth
Quarter (7) | |
| | | (In thousands, except per share amounts) | |
Net revenue | | $ | 734,369 | | | $ | 807,056 | | | $ | 931,226 | | | $ | 931,749 | |
Gross profit | | $ | 398,931 | | | $ | 420,997 | | | $ | 466,245 | | | $ | 454,497 | |
Net income | | $ | 53,209 | | | $ | 61,826 | | | $ | 103,156 | | | $ | 97,129 | |
Net income per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | $ | 0.11 | | | $ | 0.13 | | | $ | 0.21 | | | $ | 0.20 | |
Diluted | | $ | 0.11 | | | $ | 0.12 | | | $ | 0.21 | | | $ | 0.19 | |
| (1) | The first quarter of fiscal 2015 includes $8.5 million of restructuring and other exit-related cost that includes a $3.4 million write off of IPR&D. |
| (2) | The second quarter of fiscal 2015 includes an $8.8 million gain from the sale of an investment and $2.2 million of costs associated with the surety bond to appeal the CMU judgment. |
| (3) | The third quarter of fiscal 2015 includes $2.3 million of costs associated with the surety bond to appeal the CMU judgment. |
| (4) | The fourth quarter of fiscal 2015 includes $3.4 million of restructuring and other exit-related cost, and $2.8 million of costs associated with the surety bond to appeal the CMU judgment. |
| (5) | The second quarter of fiscal 2014 includes $5.2 million for litigation settlements that do not relate to the litigation with CMU. |
| (6) | The third quarter of fiscal 2014 includes $4.2 million of restructuring and other exit-related costs. |
| (7) | The fourth quarter of fiscal 2014 includes $9.5 million for anticipated litigation settlements that do not relate to the litigation with CMU, $8.1 million charge for the impairment of an intangible asset and a $7.0 million gain from the sale of a business. |
100
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Management’s Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) of the Exchange Act) as of January 31, 2015. Disclosure controls and procedures are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the SEC and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Based on this evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of January 31, 2015, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Our internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management has evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2015 using the criteria set forth in theInternal Control — Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). Based on our evaluation, management has concluded that we maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2015 based on the COSO criteria.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2015 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) of the Exchange Act) during the three months ended January 31, 2015 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations on Effectiveness of Controls
Our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, does not expect that our disclosure controls or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent or detect all error and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control system’s objectives will be met. The design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Further, because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute
101
assurance that misstatements due to error or fraud will not occur or that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected. The design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of controls to future periods are subject to risks. Over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance with policies or procedures.
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
None
102
PART III
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
The information required by Items 401 and 407(c)(3) of Regulation S-K with respect to our directors, director nominees, executive officers and corporate governance is incorporated by reference herein to the information set forth under the caption “Board of Directors and Committees of the Board” in our definitive proxy statement in connection with our 2015 annual general meeting of shareholders (the “2015 Proxy Statement”), which will be filed with the SEC no later than 120 days after January 31, 2015, and to the information set forth in Part I, Item 1 hereof under the caption “Executive Officers of the Registrant.”
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
The information required by Item 405 of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference herein to the information set forth under the caption “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a Code of Ethics and Business Conduct for Employees, Officers and Directors that applies to all of our directors, officers (including our Chief Executive Officer (our principal executive officer), Chief Financial Officer (our principal financial and accounting officer), Corporate Controller and any person performing similar functions) and employees. This Code of Ethics was most recently amended as of August 29, 2013. We will disclose future amendments to or waivers from our Code of Ethics and Business Conduct for Employees, Officers and Directors on our website or in a report on Form 8-K within four business days following the date of such amendment or waiver. Our Code of Ethics and Business Conduct for Employees, Officers and Directors is available on our websitewww.marvell.com. None of the material on our website is part of our Annual Report on Form 10-K or is incorporated by reference herein.
Committees of the Board of Directors
The information required by Items 407(d)(4) and (d)(5) of Regulation S-K concerning our Audit Committee and audit committee financial expert is incorporated by reference herein to the information set forth under the caption “Board of Directors and Committees of the Board — Committees of our Board of Directors” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The information required by Items 402, 407(e)(4) and 407(e)(5) of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference herein to the information set forth under the caption “Board of Directors and Committees of the Board — Director Compensation Table,” “Executive Compensation” and “Executive Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters |
The information required by Item 403 of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference herein to the information set forth under the caption “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
103
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table provides certain information with respect to all of our equity compensation plans in effect as of January 31, 2015:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Plan Category | | (a)
Number of
Securities
to Be Issued
Upon Exercise
of Outstanding
Options, Warrants
and Rights (1) | | | (b)
Weighted
Average
Exercise Price
of Outstanding
Options,
Warrants, and
Rights (2) | | | (c)
Number of
Securities Remaining
Available for Future
Issuance under Equity
Compensation Plans
(Excluding Securities
Reflected in Column (a)) | |
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders (3)(4) | | | 60,373,845 | | | $ | 14.06 | | | | 104,934,514 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | Includes only options and restricted stock units (outstanding under our equity compensation plans, as no stock warrants or other rights were outstanding as of January 31, 2015). |
| (2) | The weighted average exercise price calculation does not take into account any restricted stock units as those units vest, without any cash consideration or other payment required for such shares. |
| (3) | Includes our Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, our 1997 Directors’ Stock Option Plan, our Amended 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2000 ESPP”) and our 2007 Directors’ Stock Incentive Plan. |
| (4) | The number of shares reserved for issuance under our 2000 ESPP includes an annual increase in shares reserved for issuance equal to the lesser of (i) 8,000,000 shares of Common Stock, or (ii) 1.5% of the outstanding shares of capital stock on such date, or (iii) an amount determined by the Board (provided that the amount approved by the Board shall not be greater than (i) or (ii)). |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information required by Item 404 of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference herein to the information set forth under the caption “Related Party Transactions” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
The information required by Item 407(a) of Regulation S-K is incorporated by reference herein to the information set forth under the caption “Board of Directors and Committees of the Board” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
| Item 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services |
The information required by Item 9(e) of Schedule 14A is incorporated by reference to the information set forth under the caption “Information Concerning Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
104
PART IV
| Item 15. | Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules |
| | (a) | The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K: |
| | See | the “Index to Consolidated Financial Statements” on page 54 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
| | 2. | Financial Statement Schedule: |
| | See | “Schedule II – Valuation and Qualifying Accounts” on page 107 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K: |
All other schedules not listed above have been omitted because they are not applicable or required, or the information required to be set forth therein is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements or Notes thereto.
See the “Index to Exhibits” immediately following the signature page of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
105
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | |
| | | MARVELL TECHNOLOGY GROUP LTD. |
| | |
| Dated: March 26, 2015 | | By: | | /S/ DR. SEHAT SUTARDJA |
| | | | Dr. Sehat Sutardja Chief Executive Officer |
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Dr. Sehat Sutardja and Michael Rashkin, and each of them individually, as his attorney-in-fact, each with full power of substitution, for him in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with exhibits thereto and all other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorney-in-fact, or his substitute or substitutes, may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | |
Name and Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | |
/S/ SEHAT SUTARDJA Dr. Sehat Sutardja | | Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | | March 26, 2015 |
| | |
/S/ MICHAEL RASHKIN Michael Rashkin | | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | March 26, 2015 |
| | |
/S/ WEILI DAI Weili Dai | | President and Director | | March 26, 2015 |
| | |
/S/ JUERGEN GROMER Dr. Juergen Gromer | | Director | | March 26, 2015 |
| | |
/S/ JOHN G. KASSAKIAN Dr. John G. Kassakian | | Director | | March 26, 2015 |
| | |
/S/ ARTURO KRUEGER Arturo Krueger | | Director | | March 26, 2015 |
| | |
/S/ RANDHIR THAKUR Dr. Randhir Thakur | | Director | | March 26, 2015 |
106
SCHEDULE II
VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
(in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at
Beginning
of Year | | | Additions | | | Deductions | | | Balance at
End of
Year | |
Fiscal year ended January 31, 2015 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for doubtful accounts and sales return reserve | | $ | 2,294 | | | $ | 3,041 | | | $ | (3,223 | ) | | $ | 2,112 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax valuation allowance | | $ | 335,890 | | | $ | 46,906 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 382,796 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fiscal year ended February 1, 2014 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for doubtful accounts and sales return reserve | | $ | 7,921 | | | $ | 3,808 | | | $ | (9,435 | ) | | $ | 2,294 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax valuation allowance | | $ | 299,449 | | | $ | 36,441 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 335,890 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fiscal year ended February 2, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for doubtful accounts and sales return reserve | | $ | 2,663 | | | $ | 9,024 | | | $ | (3,766 | ) | | $ | 7,921 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred tax valuation allowance | | $ | 259,316 | | | $ | 40,133 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 299,449 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
107
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
| | |
Exhibit
No. | | Description |
| |
| 3.1 | | Memorandum of Association of Marvell Technology Group Ltd., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 of the registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (file no. 333-33086) as filed on March 23, 2000 |
| |
| 3.2 | | Third Amended and Restated Bye-Laws of Marvell Technology Group Ltd., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on July 13, 2010 |
| |
| 3.3 | | Memorandum of Increase of Share Capital of Marvell Technology Group Ltd., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on July 6, 2006 |
| |
| 10.1# | | 1997 Directors’ Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (file no. 333-33086) as filed on March 23, 2000 |
| |
| 10.2# | | Form of Notice of Stock Option Grants, Nonstatutory Stock Option Agreement, Exercise Notice and Restricted Stock Purchase Agreement for use under the 1997 Directors’ Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 of the registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (file no. 333-148621) as filed on January 11, 2008 |
| |
| 10.3# | | 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (as amended and restated as of October 31, 2011), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended October 29, 2011 as filed on December 2, 2011 |
| |
| 10.4# | | 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan Form of Subscription Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of the registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 2, 2013 as filed on March 29, 2013 |
| |
| 10.5# | | Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q as filed on June 5, 2014 |
| |
| 10.6# | | Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan Restricted Stock Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 of the registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2006 as filed on April 13, 2006 |
| |
| 10.7# | | Form of Option Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 of the registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 28, 2006 as filed on April 13, 2006 (for options granted prior to December 4, 2008) |
| |
| 10.7.1# | | Form of Stock Option Agreement and Notice of Grant of Stock Options and Option Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on December 17, 2008 (for options granted on or after December 4, 2008) |
| |
| 10.7.2# | | Form of Stock Option Agreement and Notice of Grant of Stock Options and Option Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the registrant’s quarterly report on 10-Q for the period ended July 31, 2010 as filed on September 3, 2010 (for options granted on or after August 2, 2010) |
| |
| 10.7.3# | | Form of Stock Option Agreement and Notice of Grant of Stock Options and Option Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan (for options granted on or after September 20, 2013), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on September 26, 2013 |
108
| | |
Exhibit
No. | | Description |
| |
| 10.8# | | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 of the registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 27, 2007 as filed on July 2, 2007 (for RSUs granted prior to December 4, 2008) |
| |
| 10.8.1# | | Form of Stock Unit Agreement and Notice of Grant of Award and Award Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on December 17, 2008 (for RSUs granted on or after December 4, 2008) |
| |
| 10.8.2# | | Form of Stock Unit Agreement and Notice of Grant of Award and Award Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 of the registrant’s quarterly report on 10-Q for the period ended July 31, 2010 as filed on September 3, 2010 (for RSUs granted on or after August 2, 2010) |
| |
| 10.9# | | Form of Notice of Grant of Stock Options – Performance-Based, for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on December 19, 2008 |
| |
| 10.10# | | Reformation of Stock Option Agreement dated December 27, 2006 by and between Sehat Sutardja and Marvell Technology Group Ltd., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on January 4, 2007 |
| |
| 10.11# | | Reformation of Stock Option Agreement dated December 27, 2006 by and between Weili Dai and Marvell Technology Group Ltd., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K for the period dated December 27, 2006 as filed on January 4, 2007 |
| |
| 10.12# | | Reformation of Stock Option Agreement dated May 6, 2007 between Marvell Technology Group Ltd. and Dr. Sehat Sutardja, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on May 8, 2007 |
| |
| 10.13# | | Amendment of Stock Option Agreement dated May 6, 2007 between Marvell Technology Group Ltd. and Weili Dai, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the registrant’s current report on Form 8-K for the period dated May 2, 2007 as filed on May 8, 2007 |
| |
| 10.14# | | Form of Performance Award Agreement and Notice of Grant of Performance Award and Award Agreement for use with the Amended and Restated 1995 Stock Option Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on June 5, 2014 |
| |
| 10.15# | | Marvell Technology Group Ltd. Executive Performance Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on July 13, 2010 |
| |
| 10.16# | | 2007 Director Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated effective March 11, 2014, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 of the registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended February 1, 2014 as filed on March 27, 2014 |
| |
| 10.17.1# | | Form of Stock Option Agreement for use with the 2007 Director Stock Incentive Plan — Initial Award, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on October 25, 2007 |
| |
| 10.17.2# | | Form of Stock Option Agreement for use with the 2007 Director Stock Incentive Plan — Annual Award, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on October 25, 2007 |
| |
| 10.17.3# | | Form of Stock Unit Agreement and Notice of Grant of Award and Award Agreement for use with the 2007 Director Stock Incentive Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 of our Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on July 1, 2011 |
109
| | |
Exhibit
No. | | Description |
| |
| 10.18# | | Policy for Non-Business Use of Corporate Aircraft, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on May 23, 2008 |
| |
| 10.19# | | Description of Indemnification Rights for certain current and former directors, officers and employees, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.37 of the registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended July 28, 2007 as filed on September 6, 2007 |
| |
| 10.20# | | Form of Indemnification Agreement with Directors and Executive Officers, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on October 10, 2008 |
| |
| 10.21# | | Indemnification Arrangement with Dr. Sehat Sutardja, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of our Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on March 7, 2011 |
| |
| 21.1 | | Subsidiaries of the registrant |
| |
| 23.1 | | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
| |
| 24.1 | | Power of Attorney (contained in the signature page to this Annual Report) |
| |
| 31.1 | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer as required pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act |
| |
| 31.2 | | Certification of Chief Financial Officer as required pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act |
| |
| 32.1~ | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer as required pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act |
| |
| 32.2~ | | Certification of Chief Financial Officer as required pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act |
| |
| 101.INS | | XBRL Instance Document |
| |
| 101.SCH | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| |
| 101.CAL | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| |
| 101.DEF | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition |
| |
| 101.LAB | | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
| |
| 101.PRE | | XBRL Taxonomy Presentation Linkbase Document |
| # | Management contracts or compensation plans or arrangements in which directors or executive officers are eligible to participate. |
| ~ | In accordance with Item 601(b)(32)(ii) of Regulation S-K and SEC Release No. 33-8238 and 34-47986, Final Rule: Management’s Reports on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting and Certification of Disclosure in Exchange Act Periodic Reports, the certifications furnished in Exhibits 32.1 and 32.2 hereto are deemed to accompany this Form 10-K and will not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act. Such certifications will not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filings under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except to the extent that the registrant specifically incorporates it by reference. |
110
