Table of Contents
Filed Pursuant to Rule 424(b)(3)
Registration No. 333-248598
Prospectus
Lamar Media Corp.
Offer to Exchange
Up to $600,000,000
outstanding 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 issued on February 6, 2020, for
a Like Principal Amount of 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028,
which have been registered under the Securities Act of 1933
Offer to Exchange
Up to $400,000,000
outstanding 4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029 issued on May 13, 2020, for
a Like Principal Amount of 4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029,
which have been registered under the Securities Act of 1933
Offer to Exchange
Up to $550,000,000
outstanding 4% Senior Notes due 2030 issued on February 6, 2020 and August 19, 2020, for
a Like Principal Amount of 4% Senior Notes due 2030,
which have been registered under the Securities Act of 1933
The Exchange Offer
| • | We will exchange all outstanding notes that are validly tendered and not validly withdrawn for an equal principal amount of exchange notes that are freely tradable. |
| • | You may withdraw tenders of outstanding notes at any time prior to the expiration date of the exchange offer. |
| • | The exchange offer expires at 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on October 15, 2020 unless we extend the offer. We do not currently intend to extend the expiration date. |
| • | The exchange of outstanding notes for exchange notes in the exchange offer generally will not be a taxable event to a holder for United States federal income tax purposes. |
| • | We will not receive any proceeds from the exchange offer. |
| • | The exchange offer is subject to customary conditions, including the condition that the exchange offer not violate applicable law or any applicable interpretation of the staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
The Exchange Notes
| • | The exchange notes are being offered in order to satisfy certain of our obligations under the registration rights agreements entered into in connection with the private offerings of the outstanding notes. |
| • | The terms of the exchange notes to be issued in the exchange offer are substantially identical to the terms of the outstanding notes, except that the exchange notes will be freely tradable. |
| • | The exchange notes will be our unsecured senior obligations and will rank senior to all of our existing and future debt that is expressly subordinated to the exchange notes. The exchange notes will rank equally with all of our existing and future senior debt and will be effectively subordinated to all of our secured debt (to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such debt), including our senior credit facility, and structurally subordinated to all of the liabilities of our subsidiaries that do not guarantee the exchange notes. |
| • | The outstanding notes are, and the exchange notes will be, unconditionally guaranteed on a joint and several basis by substantially all of our existing and future domestic subsidiaries, with certain exceptions. |
| • | We do not intend to apply for listing of the exchange notes on any securities exchange or to arrange for them to be quoted on any quotation system. |
Broker-Dealers
| • | Each broker-dealer that receives exchange notes for its own account pursuant to the exchange offer must acknowledge that it will deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of such exchange notes. The letter of transmittal states that by so acknowledging and delivering a prospectus, a broker-dealer will not be deemed to admit that it is an “underwriter” within the meaning of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. |
| • | This prospectus, as it may be amended or supplemented from time to time, may be used by a broker-dealer in connection with resales of exchange notes received in exchange for outstanding notes where such outstanding notes were acquired by such broker-dealer as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities. |
| • | We and the guarantors have agreed that, for a period of 180 days after consummation of the exchange offer, we will make this prospectus available to any broker-dealer for use in connection with any such resale. See “Plan of Distribution.” |
See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 19 for a discussion of certain risks that you should consider before participating in the exchange offer.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities or passed upon the adequacy or accuracy of this prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The date of this prospectus is September 16, 2020
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 19 | ||||
| 33 | ||||
| 34 | ||||
| 36 | ||||
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 37 | |||
| 62 | ||||
| 73 | ||||
| 77 | ||||
| 79 | ||||
| Page | ||||
| 91 | ||||
| 92 | ||||
| 95 | ||||
| 96 | ||||
| 105 | ||||
| 112 | ||||
| 143 | ||||
| 144 | ||||
| 146 | ||||
| 165 | ||||
| 166 | ||||
| 166 | ||||
| 166 | ||||
| F-1 | ||||
No dealer, salesperson or other person is authorized to give any information or to represent anything not contained in this prospectus. You should not rely on any unauthorized information or representations. This prospectus is an offer to exchange only the notes offered by this prospectus, and only under the circumstances and in those jurisdictions where it is lawful to do so. The information contained in this prospectus is current only as of its date.
Lamar Media Corp. is a Delaware corporation. Our principal executive offices are located at 5321 Corporate Blvd., Baton Rouge, LA 70808 and our telephone number at that address is (225) 926-1000. Lamar Media Corp. is a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising Company. Our parent’s website is located at http://www.lamar.com. The information on or linked to from the website is not part of this prospectus.
In this prospectus, except as the context otherwise requires or as otherwise noted, “Lamar Media,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to Lamar Media Corp. and its subsidiaries, except with respect to the notes, in which case such terms refer only to Lamar Media Corp. Lamar Advertising Company is referred to herein as “Lamar Advertising.”
Table of Contents
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”) a registration statement on Form S-4 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) with respect to the exchange notes offered hereby. As permitted by the rules and regulations of the Commission, this prospectus incorporates important information about us that is not included in or delivered with this prospectus but that is included in the registration statement. For further information with respect to us and the exchange notes offered hereby, we refer you to the registration statement, including the exhibits and schedules filed therewith.
We and our parent, Lamar Advertising, file annual, quarterly, and current reports and other information with the Commission. The Commission maintains a website on the Internet that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding registrants that file electronically with the Commission, and such website is located at http://www.sec.gov.
You may request a copy of these filings at no cost, by writing or calling us at the following address: 5321 Corporate Boulevard, Baton Rouge, LA 70808, Tel: (225) 926-1000, Attention: Chief Financial Officer.
To obtain timely delivery of any of these documents, you must request them no later than five business days before the date you must make your investment decision. Accordingly, if you would like to request any documents, you should do so no later than October 7, 2020 in order to receive them before the expiration of the exchange offer.
Pursuant to the indentures under which the exchange notes will be issued (and the outstanding notes were issued), we have agreed that, whether or not we are required to do so by the rules and regulations of the Commission, for so long as any of the notes remain outstanding, we (not including our subsidiaries) will furnish to the holders of the notes copies of all quarterly and annual financial information that would be required to be contained in a filing with the Commission on Forms 10-Q and 10-K if we were required to file such forms and all current reports that would be required to be filed with the Commission on Form 8-K if we were required to file such reports, in each case within the time periods specified in the Commission’s rules and regulations. In addition, following the consummation of this exchange offer, whether or not required by the rules and regulations of the Commission, we will file a copy of all such information and reports with the Commission for public availability within the time periods specified in the Commission’s rules and regulations (unless the Commission will not accept such a filing) and make such information available to securities analysts and prospective investors upon request. See “Description of Exchange Notes—Material Covenants—Reports to Holders.”
1
Table of Contents
The market data and other statistical information used throughout this prospectus are based on independent industry publications, government publications, reports by market research firms or other published independent sources. Some data are also based on our good faith estimates, which are derived from our review of internal surveys, as well as the independent sources listed above. Although we believe these sources are reliable, we have not independently verified the information and cannot guarantee its accuracy and completeness. As a result, you should be aware that any such market, industry and other similar data may not be reliable. While we are not aware of any misstatements regarding any industry data presented in this prospectus, our estimates involve risks and uncertainties and are subject to change based on various factors, including those discussed under the section entitled “Risk Factors” below.
2
Table of Contents
STATEMENTS REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). These are statements that relate to future periods and include statements about:
| • | our future financial performance and condition; |
| • | our business plans, objectives, prospects, growth and operating strategies; |
| • | our anticipated capital expenditures and level of acquisition activity; |
| • | our ability to integrate acquired assets and realize operating efficiency from acquisitions; |
| • | market opportunities and our competitive positions; |
| • | our future cash flows and expected cash requirements; |
| • | estimated risks; |
| • | our ability to maintain compliance with applicable covenants and restrictions included in Lamar Media’s senior credit facility, the indentures relating to its outstanding notes and its Accounts Receivables Securitization Program (as defined below); and |
| • | Lamar Advertising’s ability to remain qualified as a real estate investment trust (“REIT”). |
Generally, the words “may,” “will,” “should,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “expects,” “intends,” “estimates,” “projects,” “plans” and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that could cause our actual results, performance or achievements or industry results, to differ materially from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by these forward-looking statements. These risks, uncertainties and other important factors include, among others:
| • | the state of the economy and financial markets generally and their effects on the markets in which we operate and the broader demand for advertising; |
| • | the magnitude of the impact of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) on our operations and on general economic conditions; |
| • | the levels of expenditures on advertising in general and outdoor advertising in particular; |
| • | risks and uncertainties relating to our significant indebtedness; |
| • | the demand for outdoor advertising and its continued popularity as an advertising medium; |
| • | our need for, and ability to obtain, additional funding for acquisitions, operations and debt refinancing; |
| • | increased competition within the outdoor advertising industry; |
| • | the regulation of the outdoor advertising industry by federal, state and local governments; |
| • | our ability to renew expiring contracts at favorable rates; |
| • | the integration of businesses and assets that we acquire and our ability to recognize cost savings and operating efficiencies as a result of these acquisitions; |
| • | our ability to successfully implement our digital deployment strategy; |
| • | changes in accounting principles, policies or guidelines; |
| • | our ability to effectively mitigate the threat of and damages caused by hurricanes and other kinds of severe weather; |
| • | Lamar Advertising’s ability to qualify as a REIT and maintain its status as a REIT; |
3
Table of Contents
| • | changes in tax laws applicable to REITs or in the interpretation of those laws; and |
| • | the other factors under “Risk Factors.” |
Although we believe that the statements contained in this prospectus are based upon reasonable assumptions, we can give no assurance that our goals will be achieved. Given these uncertainties, prospective investors are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are made as of the date of this prospectus. We assume no obligation to update or revise them or provide reasons why actual results may differ.
4
Table of Contents
This summary highlights the information contained elsewhere in this prospectus. Because this is only a summary, it does not contain all of the information that may be important to you. For a more complete understanding of this exchange offer, we encourage you to read this entire prospectus. You should read the following summary together with the more detailed information and consolidated financial statements and the notes to those statements included in this prospectus. Unless otherwise indicated, financial information included in this prospectus is presented on a historical basis.
Lamar Media Corp.
We are one of the largest outdoor advertising companies in the United States based on number of displays and have operated under the Lamar name since 1902. We operate in a single operating and reporting segment, advertising. We lease space for advertising on billboards, buses, shelters, benches, logo plates and in airport terminals. We offer our tenants a fully integrated service, satisfying all aspects of their billboard display requirements from ad copy production to placement and maintenance.
Our Business
We operate three types of outdoor advertising displays: billboards, logo signs and transit advertising displays.
Billboards. As of June 30, 2020, we owned and operated over 155,800 billboard advertising displays in 45 states and Canada. We lease most of our advertising space on two types of billboards: bulletins and posters.
| • | Bulletins are generally large, illuminated advertising structures that are located on major highways and target vehicular traffic. |
| • | Posters are generally smaller advertising structures that are located on major traffic arteries and city streets and target vehicular and pedestrian traffic. |
In addition to these traditional billboards, we also lease advertising space on digital billboards, which are generally located on major traffic arteries and city streets. As of June 30, 2020, we owned and operated over 3,600 digital billboard advertising displays in 43 states and Canada.
Logo signs. We lease advertising space on logo signs located near highway exits.
| • | Logo signs generally advertise nearby gas, food, camping, lodging and other attractions. |
We are the largest provider of logo signs in the United States, currently operating 23 of the 26 privatized state logo sign contracts. As of June 30, 2020, we operated over 150,000 logo sign advertising displays in 24 states and Canada.
Transit advertising displays. We also lease advertising space on the exterior and interior of public transportation vehicles, in airport terminals, and on transit shelters and benches in over 75 markets. We operated over 51,000 transit advertising displays in 22 states and Canada as of June 30, 2020.
Operating strategies
We strive to be a leading provider of outdoor advertising services in each of the markets that we serve, and our operating strategies for achieving that goal include:
Continuing to provide high quality local sales and service. We seek to identify and closely monitor the needs of our tenants and to provide them with a full complement of high quality advertising services. Local advertising
5
Table of Contents
constituted approximately 81% of our net revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2020, which management believes is higher than the industry average. We believe that the experience of our regional, territory and local managers has contributed greatly to our success. For example, our regional managers have been with us for an average of 34 years. In an effort to provide high quality sales and service at the local level, we employed over 1,000 local account executives as of June 30, 2020. Local account executives are typically supported by additional local staff and have the ability to draw upon the resources of our central office, as well as our offices in other markets, in the event business opportunities or tenants’ needs support such an allocation of resources.
Continuing a centralized control and decentralized management structure. Our management believes that, for our particular business, centralized control and a decentralized organization provide for greater economies of scale and are more responsive to local market demands. Therefore, we maintain centralized accounting and financial control over our local operations, but our local managers are responsible for the day-to-day operations in each local market and are compensated according to that market’s financial performance.
Continuing to focus on internal growth. Within our existing markets, we seek to increase our revenue and improve cash flow by employing highly-targeted local marketing efforts to improve our display occupancy rates and by increasing advertising rates where and when demand can absorb rate increases. Our local offices spearhead this effort and respond to local tenant demands quickly.
In addition, we routinely invest in upgrading our existing displays and constructing new displays. Since January 1, 2010, we invested approximately $1.1 billion in capitalized expenditures, which include improvements to our existing real estate portfolio and the construction of new locations. Our regular improvement and expansion of our advertising display inventory allows us to provide high quality service to our current tenants and to attract new tenants.
Continuing to pursue other outdoor advertising opportunities. We plan to renew existing logo sign contracts and pursue additional logo sign contracts. Logo sign opportunities arise periodically, both from states initiating new logo sign programs and states converting from government-owned and operated programs to privately-owned and operated programs. Furthermore, we plan to pursue additional tourist oriented directional sign programs in both the United States and Canada and also other motorist information signing programs as opportunities present themselves. In addition, in an effort to maintain market share, we continue to pursue attractive transit advertising opportunities as they become available.
Investing in capital expenditures including digital technology. We invested approximately $141.0 million in capital expenditures in fiscal 2019, of which approximately $57.5 million was spent on digital technology. We expect our 2020 capitalized expenditures to be approximately $58.0 million, as we have sharply curtailed spending on capital projects in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. See “Recent developments—Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic”.
Recent developments
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The unprecedented and rapid spread of COVID-19 and the related government-imposed restrictions and social distancing measures implemented throughout the world have reduced demand for out-of-home advertising. Beginning in late March, large public events were cancelled, and governments began imposing restrictions on non-essential activities, which in turn lead to advertisers suspending, delaying or cancelling their advertising campaigns. The government-imposed restrictions have had an adverse impact on the volume of vehicles on roadways (particularly in larger markets), pedestrians in airports and riders on public transit and numerous advertising customer segments including, but not limited to, entertainment, retail, restaurant and automotive advertisers.
6
Table of Contents
As a result, demand for billboard, transit and airport advertising declined, which has had an adverse impact on our revenues and financial position. The decrease in outdoor advertising demand during the three months ended June 30, 2020 resulted in a 22.5% decrease in our consolidated net revenues as compared to the same period in 2019. As revenues declined, we responded through a variety of cost saving and liquidity measures as discussed below.
While we cannot predict the length and severity of the reduction in demand due to the pandemic, we observed an improvement in customer activity in June and July as the government-imposed restrictions on travel were eased.
However, the exact timing and pace of the recovery remain uncertain given the continued impact of the pandemic on the overall U.S. and global economy, and new or renewed government-imposed restrictions on travel may be enacted in the future. Our liquidity measures and expense management initiatives may be modified as we monitor the timing of economic recovery.
In response to the ongoing pandemic, we have implemented measures to mitigate the impact on our financial position and operations. These measures include, but are not limited to, the following:
| • | reducing our consolidated operating costs (exclusive of depreciation and amortization and gain on disposition of assets) by $25.3 million or 10.4% for the three months ended June 30, 2020 over the same period in 2019 which included: |
| • | reductions in our transit and airport franchise costs and billboard lease costs; and |
| • | reducing our workforce by approximately 5% through attrition and selected layoffs; |
| • | sharply curtailing spending on capital projects, including new digital displays; |
| • | limiting acquisition activity; and |
| • | utilizing portions of the CARES Act for deferral of employer portions of social security taxes through the end of 2020, with 50% of the deferral due December 31, 2021 and the remaining 50% due December 31, 2022. |
Redemption of 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023
On July 30, 2020, we announced the redemption of $267.5 million aggregate principal amount of the total $535.0 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of our 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (“5% Subordinated Notes”) on August 31, 2020 (the “Partial 5% Notes Redemption”). On August 17, 2020, we announced the redemption of the remaining $267.5 million aggregate principal amount of the 5% Subordinated Notes on September 16, 2020 (the “Remaining 5% Notes Redemption”).
We funded the Partial 5% Notes Redemption with new borrowings under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, net of deferred financing costs, of $121.8 million and the remainder with cash on hand. We intend to use the proceeds from the offering and sale of the additional 2030 outstanding notes (as defined below), plus cash on hand and borrowings under our revolving credit facility to fund the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption.
Both the Partial 5% Notes Redemption occurred and the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption will occur at a redemption price equal to 100.833% of the principal amount of outstanding notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the applicable redemption date.
Additional 4% Senior Notes due 2030
On August 19, 2020, we offered and sold an additional $150.0 million in aggregate principal amount of our 4% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “additional 2030 outstanding notes”), which were issued as additional notes to the
7
Table of Contents
$400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of our 4% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “original 2030 outstanding notes”).
Organization
The following summary organization chart sets forth the basic corporate structure of Lamar.
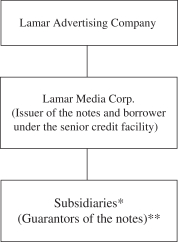
| * | All but one of our domestic subsidiaries (Missouri Logos, a partnership) are wholly owned. |
| ** | All of our domestic subsidiaries (except Lamar QRS Receivables, LLC and Lamar TRS Receivables, LLC (the “Special Purpose Subsidiaries”) and Missouri Logos, a partnership) will unconditionally guarantee the notes. Our foreign subsidiaries will not guarantee the notes. |
Our History
Lamar Media Corp. has been in operation since 1902. We completed a reorganization on July 20, 1999 to create our current holding company structure. At that time, Lamar Advertising Company was renamed Lamar Media Corp. and all its stockholders became stockholders in a new holding company. The new holding company then took the Lamar Advertising Company name and Lamar Media Corp. became a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising Company.
During 2014, we completed a reorganization in order for Lamar Advertising to qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. As part of the plan to reorganize our business operations so that Lamar Advertising could elect to qualify as a REIT for the taxable year ended December 31, 2014 and each taxable year thereafter, Lamar Advertising completed a merger with its predecessor that was approved by its stockholders on November 17, 2014. At the time of the merger, the surviving corporation took the Lamar Advertising Company name. We hold and operate certain assets through one or more taxable REIT subsidiaries (“TRSs”). The non-REIT qualified businesses that we hold through TRSs include most of our transit and foreign operations.
8
Table of Contents
Summary of the Exchange Offer
In this prospectus, the term “outstanding notes” refers, collectively, to the outstanding 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 issued on February 6, 2020 (“2028 outstanding notes”), the outstanding 4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029 issued on May 13, 2020 (“2029 outstanding notes”) and the outstanding 4% Senior Notes due 2030 issued on February 6, 2020 and August 19, 2020 (“2030 outstanding notes”); the term “exchange notes” refers, collectively, to the 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 registered under the Securities Act (“2028 exchange notes”), the 4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029 registered under the Securities Act (“2029 exchange notes”) and the 4% Senior Notes due 2030 registered under the Securities Act (“2030 exchange notes”); and the term “notes” refers to both the outstanding notes and the exchange notes. The 2028 outstanding notes and the 2028 exchange notes are referred to herein as the “2028 notes”, the 2029 outstanding notes and the 2029 exchange notes are referred to herein as the “2029 notes” and the 2030 outstanding notes and the 2030 exchange notes are referred to herein as the “2030 notes”.
General | In connection with the private offerings of the outstanding notes, we entered into registration rights agreements with the initial purchasers of the respective outstanding notes in which we agreed, among other things, to deliver this prospectus to you and to use our reasonable best efforts to complete an exchange offer for the outstanding notes. |
Exchange Offer | We are offering to exchange: (i) $600,000,000 principal amount of 2028 exchange notes, which have been registered under the Securities Act, for $600,000,000 principal amount of 2028 outstanding notes; (ii) $400,000,000 principal amount of 2029 exchange notes, which have been registered under the Securities Act, for $400,000,000 principal amount of 2029 outstanding notes; and (iii) $550,000,000 principal amount of 2030 exchange notes, which have been registered under the Securities Act, for $550,000,000 principal amount of 2030 outstanding notes. |
| The outstanding notes may be exchanged only in denominations of $2,000 and integral multiples of $1,000. |
Resale of the Exchange Notes | Based on the position of the staff of the Division of Corporation Finance of the Commission in certain interpretive letters issued to third parties in other transactions, we believe that the exchange notes acquired in this exchange offer may be freely traded without compliance with the provisions of the Securities Act, if: |
| • | you are acquiring the exchange notes in the ordinary course of your business, |
| • | you have not engaged in, do not intend to engage in, and have no arrangement or understanding with any person to participate in, a distribution of the exchange notes, and |
| • | you are not our affiliate as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. |
| If you fail to satisfy any of these conditions, you must comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with the resale of the exchange notes. |
9
Table of Contents
| Broker-dealers that acquired outstanding notes directly from us, but not as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities, must comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with a resale of the exchange notes. See “Plan of Distribution.” |
| Each broker-dealer that receives exchange notes for its own account pursuant to the exchange offer in exchange for outstanding notes that it acquired as a result of market-making or other trading activities must deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of the exchange notes and provide us with a signed acknowledgement of this obligation. |
Expiration Date | This exchange offer will expire at 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on October 15, 2020, unless we extend the offer. |
Conditions to the Exchange Offer | The exchange offer is subject to limited, customary conditions, which we may waive. |
Procedures for Tendering Outstanding Notes | If you wish to accept the exchange offer, you must deliver to the exchange agent, before the expiration of the exchange offer: |
| • | either a completed and signed letter of transmittal or, for outstanding notes tendered electronically, an agent’s message from The Depository Trust Company (“DTC”), Euroclear or Clearstream stating that the tendering participant agrees to be bound by the letter of transmittal and the terms of the exchange offer, |
| • | your outstanding notes, either by tendering them in physical form or by timely confirmation of book-entry transfer through DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream, and |
| • | all other documents required by the letter of transmittal. |
| If you hold outstanding notes through DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream, you must comply with their standard procedures for electronic tenders, by which you will agree to be bound by the letter of transmittal. |
| By signing, or by agreeing to be bound by, the letter of transmittal, you will be representing to us that: |
| • | you will be acquiring the exchange notes in the ordinary course of your business, |
| • | you have no arrangement or understanding with any person to participate in the distribution of the exchange notes, and |
| • | you are not our affiliate as defined under Rule 405 of the Securities Act. |
| See “The Exchange Offer—Procedures for Tendering.” |
10
Table of Contents
Guaranteed Delivery Procedures for Tendering Outstanding Notes | If you cannot meet the expiration deadline or you cannot deliver your outstanding notes, the letter of transmittal or any other documentation to comply with the applicable procedures under DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream standard operating procedures for electronic tenders in a timely fashion, you may tender your notes according to the guaranteed delivery procedures set forth under “The Exchange Offer—Guaranteed Delivery Procedures.” |
Special Procedures for Beneficial Holders | If you beneficially own outstanding notes that are registered in the name of a broker, dealer, commercial bank, trust company or other nominee and you wish to tender in the exchange offer, you should contact that registered holder promptly and instruct that person to tender on your behalf. If you wish to tender in the exchange offer on your own behalf, you must, prior to completing and executing the letter of transmittal and delivering your outstanding notes, either arrange to have the outstanding notes registered in your name or obtain a properly completed bond power from the registered holder. The transfer of registered ownership may take considerable time. |
Acceptance of Outstanding Notes and Delivery of Exchange Notes | We will accept any outstanding notes that are properly tendered for exchange before 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on the day this exchange offer expires. The exchange notes will be delivered promptly after expiration of this exchange offer. |
Exchange Date | We will notify the exchange agent of the date of acceptance of the outstanding notes for exchange. |
Withdrawal Rights | If you tender your outstanding notes for exchange in this exchange offer and later wish to withdraw them, you may do so at any time before 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on the day this exchange offer expires. |
Consequences if You Do Not Exchange Your Outstanding Notes | Outstanding notes that are not tendered in the exchange offer or are not accepted for exchange will continue to bear legends restricting their transfer. You will not be able to sell the outstanding notes unless: |
| • | an exemption from the requirements of the Securities Act is available to you, |
| • | we register the resale of outstanding notes under the Securities Act, or |
| • | the transaction requires neither an exemption from nor registration under the requirements of the Securities Act. |
| After the completion of the exchange offer, we will no longer have any obligation to register the outstanding notes, except in limited circumstances. |
11
Table of Contents
Accrued Interest on the Outstanding Notes | Any interest that has accrued on an outstanding note before its exchange in this exchange offer will be payable on the exchange note on the first interest payment date after the completion of this exchange offer. |
United States Federal Income Tax Considerations | The exchange of the outstanding notes for the exchange notes generally will not be a taxable event for United States federal income tax purposes. See “Material United States Federal Income Tax Considerations.” |
Exchange Agent | The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. is serving as the exchange agent. Its address and telephone number are provided in this prospectus under the heading “The Exchange Offer—Exchange Agent.” |
Use of Proceeds | We will not receive any cash proceeds from this exchange offer. See “Use of Proceeds.” |
Registration Rights Agreement | When we issued the outstanding notes, we and the guarantors entered into registration rights agreements with the respective initial purchasers of the outstanding notes. Under the terms of the registration rights agreements, we agreed to use our reasonable best efforts to cause to become effective a registration statement with respect to an offer to exchange the outstanding notes for other freely tradable notes issued by us and that are registered with the Commission and that have substantially identical terms as the outstanding notes. If we fail to effect the exchange offer, we will use our reasonable best efforts to file and cause to become effective a shelf registration statement related to resales of the outstanding notes. We will be obligated to pay additional interest on the outstanding notes if we do not complete the exchange offer by November 2, 2020 with respect to the 2028 outstanding notes and 2030 outstanding notes and February 7, 2021 with respect to the 2029 outstanding notes, or, if required, the shelf registration statement is not declared effective by November 2, 2020 or February 7, 2021, respectively. See “Registration Rights Agreements.” |
Accounting Treatment | We will not recognize any gain or loss for accounting purposes upon the completion of the exchange offer in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. See “The Exchange Offer—Accounting Treatment.” |
12
Table of Contents
Summary of the Terms of the Exchange Notes
Each series of the exchange notes will be identical to the respective series of the outstanding notes except that:
| • | the exchange notes will be registered under the Securities Act and therefore will not bear legends restricting their transfer; and |
| • | specified rights under the registration rights agreement, including the provisions providing for registration rights and the payment of additional interest in specified circumstances, will be limited or eliminated. |
Each series of the exchange notes will evidence the same debt as the respective series of the outstanding notes and the same indentures will govern both the outstanding notes and the exchange notes of each respective series. For a more complete understanding of the exchange notes, please refer to the section of this prospectus entitled “Description of Exchange Notes.”
Issuer | Lamar Media Corp. |
Securities Offered | An aggregate principal amount of $1,550,000,000 of senior notes, consisting of: |
| i. $600,000,000 aggregate principal amount of 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028; |
| ii. $400,000,000 aggregate principal amount of 4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029; and |
| iii. $550,000,000 aggregate principal amount of 4% Senior Notes due 2030. |
2028 Exchange Notes Maturity Date | February 15, 2028 |
2028 Exchange Notes Interest Rate | 3.750% per year |
2029 Exchange Notes Maturity Date | January 15, 2029 |
2029 Exchange Notes Interest Rate | 4.875% per year |
2030 Exchange Notes Maturity Date | February 15, 2030 |
2030 Exchange Notes Interest Rate | 4.000% per year |
2028 Exchange Notes Optional Redemption | We may redeem some or all of the 2028 exchange notes at any time on or after February 15, 2023. We may also redeem some or all of the 2028 exchange notes before February 15, 2023 at a redemption price of 100% of the principal amount, plus accrued, unpaid, and special interest, if any, to the redemption date, plus a “make-whole” premium. We may also redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2028 exchange notes using the proceeds from certain public equity offerings completed before February 15, 2023 so long as at least 60% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2028 notes remains outstanding. The redemption prices are described under “Description of Exchange Notes—Optional Redemption.” |
13
Table of Contents
2029 Exchange Notes Optional Redemption | We may redeem some or all of the 2029 exchange notes at any time on or after January 15, 2024. We may also redeem some or all of the 2029 exchange notes before January 15, 2024 at a redemption price of 100% of the principal amount, plus accrued, unpaid, and special interest, if any, to the redemption date, plus a “make-whole” premium. We may also redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2029 exchange notes using the proceeds from certain public equity offerings completed before May 15, 2023 so long as at least 60% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2029 notes remains outstanding. The redemption prices are described under “Description of Exchange Notes—Optional Redemption.” |
2030 Exchange Notes Optional Redemption | We may redeem some or all of the 2030 exchange notes at any time on or after February 15, 2025. We may also redeem some or all of the 2030 exchange notes before February 15, 2025 at a redemption price of 100% of the principal amount, plus accrued, unpaid, and special interest, if any, to the redemption date, plus a “make-whole” premium. We may also redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2030 exchange notes using the proceeds from certain public equity offerings completed before February 15, 2023 so long as at least 60% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2030 notes remains outstanding. The redemption prices are described under “Description of Exchange Notes—Optional Redemption.” |
2028 Exchange Notes Interest Payment Date | January 15 and July 15 of each year, beginning on January 15, 2021. Interest will accrue from July 15, 2020. |
2029 Exchange Notes Interest Payment Date | March 15 and September 15 of each year, beginning on September 15, 2020. Interest will accrue from May 13, 2020 or the date of the last periodic payment of interest on the 2029 outstanding notes, whichever is later. |
2030 Exchange Notes Interest Payment Date | June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning on December 15, 2020. Interest will accrue from June 15, 2020. |
Guarantees | Substantially all of our existing and certain of our future domestic subsidiaries will unconditionally guarantee the notes. |
Ranking | The exchange notes will be our general unsecured obligations and will rank senior to all of our existing and future debt that is expressly subordinated to the exchange notes, including our 5% Subordinated Notes which were partially redeemed on August 31, 2020 and will be fully redeemed on September 16, 2020. The exchange notes will rank equally with all of our existing and future senior debt, including all of the outstanding notes, and will be effectively subordinated to all of our secured debt (to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such debt), including our senior credit facility and our Accounts |
14
Table of Contents
Receivables Securitization Program, and structurally subordinated to all of the liabilities of any of our subsidiaries that do not guarantee the exchange notes (including, without limitation, the liabilities of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program). |
| The guarantees will be generally unsecured obligations of the subsidiary guarantors and will rank senior to all their existing and future debt that is expressly subordinated to the guarantees. The guarantees will rank equally with all existing and future senior debt of such subsidiary guarantors and will be effectively subordinated to all of such subsidiary guarantors’ secured debt (to the extent of the collateral securing such debt), including their guarantees of our senior credit facility. |
| As of June 30, 2020, on an as adjusted basis after giving effect to the Partial 5% Notes Redemption, the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption and the issuance of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, the exchange notes and the subsidiary guarantees would have been effectively subordinated to approximately $689.2 million in secured debt, net of deferred issuance costs, excluding approximately $633.7 million of additional borrowing capacity under our senior credit facility, and would rank equally with $2.2 billion in various series of senior notes, net of deferred issuance costs, including the notes. As of June 30, 2020, on an as adjusted basis after giving effect to the Partial 5% Notes Redemption, the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption and the issuance of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, our non-guarantor subsidiaries had approximately $0.3 million in trade payables and $121.8 million of borrowings under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, net of deferred issuance costs. |
Change of Control and Asset Sales | If we or Lamar Advertising experience specific kinds of changes of control or we sell assets under certain circumstances, we will be required to make an offer to purchase the notes at the prices listed in “Description of Exchange Notes—Material Covenants—Change of Control” and “Description of Exchange Notes—Material Covenants—Limitations on Certain Asset Sales.” We may not have sufficient funds available at the time of any change of control to effect the purchase. |
Material Covenants | The indentures governing the notes restrict our ability and the ability of our restricted subsidiaries to, among other things: |
| • | incur additional debt and issue preferred stock; |
| • | make certain distributions, investments and other restricted payments; |
| • | create certain liens; |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
15
Table of Contents
| • | agree to any restrictions on the ability of restricted subsidiaries to make payments to us; |
| • | merge, consolidate or sell substantially all of our assets; and |
| • | sell assets. |
| These covenants are subject to important exceptions and qualifications, and certain of these covenants will not be applicable during any period of time if the exchange notes have an investment grade rating. See “Description of Exchange Notes” in this prospectus. |
Risk Factors
See “Risk Factors” for a discussion of certain factors that you should carefully consider before participating in the exchange offer.
16
Table of Contents
Summary Consolidated Historical Financial Data
The following table contains our summary consolidated historical information and other operating data for the five years ended December 31, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019 and the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020. We have prepared this information from audited financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2015 through December 31, 2019 and the unaudited financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020. This information is only a summary. You should read it in conjunction with our historical financial statements and related notes thereto included in this prospectus.
In our opinion, the information for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020 reflects all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, necessary to fairly present our results of operations and financial condition. Results from interim periods should not be considered indicative of results for any other periods or for the year.
This information is only a summary. You should read it in conjunction with our historical financial statements and related notes included in this prospectus, as well as “Selected Historical Consolidated Financial Data” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
| Year ended December 31, | Six months ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Statement of operations data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,353,396 | $ | 1,500,294 | $ | 1,541,260 | $ | 1,627,222 | $ | 1,753,644 | $ | 833,199 | $ | 754,221 | ||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses | 473,760 | 525,597 | 540,880 | 561,848 | 590,078 | 286,860 | 283,553 | |||||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 242,182 | 269,423 | 276,229 | 289,428 | 318,380 | 157,709 | 149,612 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses | 71,426 | 75,994 | 61,962 | 82,497 | 84,229 | 35,505 | 35,012 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 191,433 | 204,958 | 211,104 | 225,261 | 250,028 | 123,199 | 126,311 | |||||||||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | (8,765 | ) | (15,095 | ) | (4,664 | ) | 7,233 | (7,241 | ) | (5,161 | ) | (3,519 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Total operating expenses | 970,036 | 1,060,877 | 1,085,511 | 1,166,267 | 1,235,474 | 598,112 | 590,969 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Operating income | 383,360 | 439,417 | 455,749 | 460,955 | 518,170 | 235,087 | 163,252 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 98,399 | 123,682 | 128,390 | 129,198 | 149,852 | 75,532 | 71,621 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment | — | 3,198 | 71 | 15,429 | — | — | 18,184 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 284,961 | 312,537 | 327,288 | 316,328 | 368,318 | 159,555 | 73,447 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | 22,058 | 13,356 | 9,230 | 10,697 | (4,222 | ) | (10,292 | ) | 1,296 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 262,903 | $ | 299,181 | $ | 318,058 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 372,540 | $ | 169,847 | $ | 72,151 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Other financial data (unaudited): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA(1) | $ | 591,918 | $ | 657,840 | $ | 671,788 | $ | 722,892 | $ | 785,312 | $ | 354,257 | $ | 293,242 | ||||||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA margin(2) | 44 | % | 44 | % | 44 | % | 44 | % | 45 | % | 43 | % | 39 | % | ||||||||||||||
Ratio of Adjusted EBITDA to interest expense, net(3) | 6.0x | 5.3x | 5.2x | 5.6x | 5.2x | 4.7x | 4.1x | |||||||||||||||||||||
Ratio of total debt to Adjusted EBITDA(4) | 3.2x | 3.6x | 3.8x | 4.0x | 3.8x | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | $ | 110,425 | $ | 107,612 | $ | 109,329 | $ | 117,638 | $ | 140,956 | $ | 60,560 | $ | 36,274 | ||||||||||||||
Other data (as of end of period)(unaudited): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total billboard displays | 143,732 | 148,828 | 149,827 | 156,919 | 157,790 | 156,868 | 155,821 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total logo displays | 134,172 | 143,722 | 145,061 | 148,909 | 151,216 | 150,253 | 150,464 | |||||||||||||||||||||
17
Table of Contents
| As of December 31, | As of June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance sheet data(5): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 21,827 | $ | 35,030 | $ | 114,971 | $ | 20,994 | $ | 25,688 | $ | 16,754 | $ | 176,593 | ||||||||||||||
Working capital (deficit) | 48,882 | 39,691 | 98,033 | (86,699 | ) | (357,180 | ) | (297,269 | ) | 56,245 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | 3,347,340 | 3,882,480 | 4,197,942 | 4,527,886 | 5,924,421 | 5,782,411 | 5,964,847 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs (including current maturities) | 1,893,404 | 2,349,183 | 2,556,690 | 2,888,688 | 2,980,118 | 2,972,502 | 3,155,899 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholder’s equity | 1,007,181 | 1,056,386 | 1,091,098 | 1,120,196 | 1,169,531 | 1,128,088 | 1,113,007 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Adjusted EBITDA is defined as net income (loss) before stock-based compensation, the impact of Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 842 adoption, capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net, interest expense (income), income tax expense (benefit), depreciation and amortization, (gain) loss on disposition of assets and investments and (gain) loss on extinguishment of debt and investments. Adjusted EBITDA represents a measure that we believe is customarily used by investors and analysts to evaluate the financial performance of companies in the media industry. Our management also believes that Adjusted EBITDA is useful in evaluating our core operating results. However, Adjusted EBITDA is not a measure of financial performance under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and should not be considered an alternative to operating income or net income as an indicator of our operating performance or to net cash provided by operating activities as a measure of our liquidity. Because Adjusted EBITDA is not calculated identically by all companies, the presentation in this offering memorandum may not be comparable to those disclosed by other companies. In addition, the definition of Adjusted EBITDA differs from the definition of EBITDA applicable to the covenants for the notes. |
Below is a table that reconciles net income to Adjusted EBITDA:
| Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Statement of operations data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 262,903 | $ | 299,181 | $ | 318,058 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 372,540 | $ | 169,847 | $ | 72,151 | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 25,890 | 28,560 | 9,599 | 29,443 | 29,647 | 7,506 | 6,162 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Impact of ASC 842 adoption | — | — | — | — | 3,894 | 1,930 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net | — | — | — | — | (9,186 | ) | (8,304 | ) | 1,036 | |||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 191,433 | 204,958 | 211,104 | 225,261 | 250,028 | 123,199 | 126,311 | |||||||||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets and investments | (8,765 | ) | (15,095 | ) | (4,664 | ) | 7,233 | (7,241 | ) | (5,161 | ) | (3,519 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 98,399 | 123,682 | 128,390 | 129,198 | 149,852 | 75,532 | 71,621 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment | — | 3,198 | 71 | 15,429 | — | — | 18,184 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense | 22,058 | 13,356 | 9,230 | 10,697 | (4,222 | ) | (10,292 | ) | 1,296 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA (unaudited) | $ | 591,918 | $ | 657,840 | $ | 671,788 | $ | 722,892 | $ | 785,312 | $ | 354,257 | $ | 293,242 | ||||||||||||||
| (2) | Adjusted EBITDA margin is defined as Adjusted EBITDA divided by net revenues. |
| (3) | Ratio of Adjusted EBITDA to interest expense is defined as Adjusted EBITDA divided by net interest expense. |
| (4) | Ratio of total debt to Adjusted EBITDA is defined as total debt divided by Adjusted EBITDA. |
| (5) | Certain balance sheet reclassifications were made in order to be comparable to the current year presentation. |
18
Table of Contents
In deciding whether to participate in the exchange offer, you should carefully consider the risks described below, which could cause our operating results and financial condition to be materially adversely affected, as well as other information and data included in this prospectus.
Risks Related to the Exchange Offer
Holders who fail to exchange their outstanding notes will continue to be subject to restrictions on transfer and may have reduced liquidity after the exchange offer.
If you do not exchange your outstanding notes in the exchange offer, you will continue to be subject to the restrictions on transfer applicable to the outstanding notes. The restrictions on transfer of your outstanding notes arise because we issued the outstanding notes under exemptions from, or in transactions not subject to, the registration requirements of the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws. In general, you may only offer or sell the outstanding notes if they are registered under the Securities Act and applicable state securities laws, or are offered and sold under an exemption from these requirements. We do not plan to register the outstanding notes under the Securities Act.
Furthermore, we have not conditioned the exchange offer on receipt of any minimum or maximum principal amount of outstanding notes. As outstanding notes are tendered and accepted in the exchange offer, the principal amount of remaining outstanding notes will decrease. This decrease could reduce the liquidity of the trading market for the outstanding notes. We cannot assure you of the liquidity, or even the continuation, of the trading market for the outstanding notes following the exchange offer.
For further information regarding the consequences of not tendering your outstanding notes in the exchange offer, see the discussions below under the captions “The Exchange Offer—Consequences of Failure to Properly Tender Outstanding Notes in the Exchange” and “Material United States Federal Income Tax Considerations.”
You must comply with the exchange offer procedures to receive exchange notes.
Delivery of exchange notes in exchange for outstanding notes tendered and accepted for exchange pursuant to the exchange offer will be made only after timely receipt by the exchange agent of the following:
| • | certificates for outstanding notes or a book-entry confirmation of a book-entry transfer of outstanding notes into the exchange agent’s account at DTC, New York, New York as a depository, including an agent’s message, as defined in this prospectus, if the tendering holder does not deliver a letter of transmittal; |
| • | a complete and signed letter of transmittal, or facsimile copy, with any required signature guarantees, or, in the case of a book-entry transfer, an agent’s message in place of the letter of transmittal; and |
| • | any other documents required by the letter of transmittal. |
Therefore, holders of outstanding notes who would like to tender outstanding notes in exchange for exchange notes should be sure to allow enough time for the necessary documents to be timely received by the exchange agent. We are not required to notify you of defects or irregularities in tenders of outstanding notes for exchange. Outstanding notes that are not tendered or that are tendered but we do not accept for exchange will, following consummation of the exchange offer, continue to be subject to the existing transfer restrictions under the Securities Act and will no longer have the registration and other rights under the registration rights agreement. See “The Exchange Offer—Procedures for Tendering” and “The Exchange Offer—Consequences of Failures to Properly Tender Outstanding Notes in the Exchange.”
Some holders who exchange their outstanding notes may be deemed to be underwriters, and these holders will be required to comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements in connection with any resale transaction.
19
Table of Contents
If you exchange your outstanding notes in the exchange offer for the purpose of participating in a distribution of the exchange notes, you may be deemed to have received restricted securities. If you are deemed to have received restricted securities, you will be required to comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with any resale transaction.
An active trading market may not develop for the exchange notes.
The exchange notes have no established trading market and will not be listed on any securities exchange. The initial purchasers have informed us that they currently intend to make a market in the exchange notes. However, the initial purchasers are not obligated to do so and may discontinue any such market making at any time without notice. The liquidity of any market for the exchange notes will depend upon various factors, including:
| • | the number of holders of the exchange notes; |
| • | the interest of securities dealers in making a market for the exchange notes; |
| • | the overall market for high yield securities; |
| • | our financial performance or prospects; and |
| • | the prospects for companies in our industry generally. |
Accordingly, we cannot assure you that a market or liquidity will develop for the exchange notes. Historically, the market for non-investment grade debt has been subject to disruptions that have caused substantial volatility in the prices of securities similar to the exchange notes. We cannot assure you that the market for the exchange notes, if any, will not be subject to similar disruptions. Any such disruptions may adversely affect you as a holder of the exchange notes.
Risks Related to the Exchange Notes
Our substantial debt may adversely affect our business, financial condition and financial results and prevent us from fulfilling our obligations under the exchange notes.
At June 30, 2020, we had approximately $3.2 billion of total debt outstanding, net of deferred financing costs, consisting of approximately $585.6 million in debt outstanding under our senior credit facility, $2.0 billion in various series of senior notes, $532.2 million in senior subordinated notes and $11.7 million in other seller notes. Despite the level of debt presently outstanding, the terms of the indentures governing our senior and senior subordinated notes and the terms of our senior credit facility and Accounts Receivable Securitization Program allow us to incur substantially more debt, including approximately $737.2 million and $171.8 million available for borrowing as of June 30, 2020 under our revolving senior credit facility and Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, respectively. As adjusted for the Partial 5% Notes Redemption, the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption and the issuance of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, we would have had approximately $3.0 billion of total debt outstanding, net of deferred financing costs, as of June 30, 2020, including $689.2 million in debt outstanding under our senior credit facility, $2.2 billion in various series of senior notes (including the outstanding notes and the notes offered hereby), $121.8 million in debt outstanding under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program and $11.7 million in other seller notes, and we would have had approximately $633.7 million and $49.3 million available for borrowing under our revolving senior credit facility and Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, respectively.
Our substantial debt and our use of cash flow from operations to make principal and interest payments on our debt may, among other things:
| • | make it more difficult for us to comply with the financial covenants in our senior credit facility and in our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, which could result in a default and an acceleration of all amounts outstanding under the facility or under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program; |
20
Table of Contents
| • | limit the cash flow available to fund our working capital, capital expenditures or other general corporate requirements; |
| • | limit our ability to obtain additional financing to fund future working capital, capital expenditures or other general corporate requirements; |
| • | place us at a competitive disadvantage relative to those of our competitors that have less debt; |
| • | force us to seek and obtain alternate or additional sources of funding, which may be unavailable, or may be on less favorable terms, or may require the consent of lenders under our senior credit facility or the holders of our other debt; |
| • | limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and industry; and |
| • | increase our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions. |
Any of these problems could adversely affect our business, financial condition and financial results.
We may be unable to generate sufficient cash flow to satisfy our significant debt service obligations, including our obligations under the exchange notes.
Our ability to generate cash flow from operations to make principal and interest payments on our debt, including the exchange notes, will depend on our future performance, which will be affected by a range of economic, competitive and business factors. We cannot control many of these factors, including general economic conditions, our tenants’ allocation of advertising expenditures among available media and the amount spent on advertising in general, and our business would be negatively impacted if the general economy were to deteriorate in the future. If our operations do not generate sufficient cash flow from operations to satisfy our debt service obligations, we may need to borrow additional funds to make these payments or undertake alternative financing plans, such as refinancing or restructuring our debt, or reducing or delaying capital investments and acquisitions. We cannot guarantee that such additional funds or alternative financing will be available on favorable terms, if at all. Our inability to generate sufficient cash flow from operations or obtain additional funds or alternative financing on acceptable terms could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Restrictions in our debt agreements reduce operating flexibility and contain covenants and restrictions that create the potential for defaults, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and financial results.
The terms of our senior credit facility and the indentures relating to our existing notes, including the outstanding notes, restrict our and Lamar Advertising’s ability to, among other things:
| • | incur or repay debt; |
| • | dispose of assets; |
| • | create liens; |
| • | make investments; |
| • | enter into affiliate transactions; and |
| • | pay dividends and make inter-company distributions. |
The terms of our senior credit facility and of our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program also restrict us from exceeding a secured debt ratio of 4.50 to 1.00. Please see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Conditions and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” for a description of the specific financial ratio requirements under our senior credit facility.
21
Table of Contents
Our ability to comply with the financial covenant in the senior credit facility and in the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program and the indentures governing our existing notes, including the outstanding notes, (and to comply with similar covenants in future agreements) and the exchange notes offered hereby depends on our operating performance, which in turn depends significantly on prevailing economic, financial and business conditions and other factors that are beyond our control. Therefore, despite our best efforts and execution of our strategic plan, we may be unable to comply with these financial covenants in the future.
We and Lamar Advertising are currently in compliance with the financial covenant in our senior credit facility and in the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. However, if there are adverse changes in the economic environment in the future, these changes may negatively affect our financial results and, in turn, our ability to meet these financial covenant requirements. If we fail to comply with our financial covenant, we could be in default under our senior credit facility and under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program (which could result in an event of default under the indentures governing our existing notes, including the outstanding notes, and the exchange notes offered hereby). In the event of such a default under the senior credit facility, the lenders under the senior credit facility could accelerate all of the debt outstanding, could elect to institute foreclosure proceedings against our assets, and we could be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation. Any of these events could adversely affect our business, financial condition and financial results. In the event of such a default under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, the lenders under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program could accelerate all of the debt outstanding, could elect to institute foreclosure proceedings against the assets of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries, and the Special Purpose Subsidiaries could be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation. Any of these events could adversely affect our business, financial condition and financial results.
In addition, these restrictions reduce our operating flexibility and could prevent us from exploiting investment, acquisition, marketing, or other time-sensitive business opportunities.
The exchange notes and the subsidiary guarantees will be unsecured and are effectively subordinated to all of our and our subsidiary guarantors’ secured indebtedness.
The exchange notes will not be secured. The lenders under our senior credit facility are currently secured by a pledge of the stock of all of the subsidiary guarantors, a pledge of our stock, and a substantial portion of our and the guarantors’ other property (excluding accounts receivable balances and related assets that secure the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program).
If we or any of the subsidiary guarantors declare bankruptcy, liquidate or dissolve, or if payment under our senior credit facility or any of our other secured indebtedness is accelerated, our secured lenders would be entitled to exercise the remedies available to a secured lender under applicable law and will have a claim on those assets before the holders of the exchange notes. As a result, the exchange notes are effectively subordinated to our and our subsidiaries’ secured indebtedness to the extent of the value of the assets securing that indebtedness and the holders of the exchange notes would in all likelihood recover ratably less than the lenders of our and our subsidiaries’ secured indebtedness in the event of our bankruptcy, liquidation or dissolution. As of June 30, 2020, we had approximately $585.6 million of secured indebtedness outstanding, net of deferred financing costs, and $737.2 million of additional secured indebtedness was available for borrowing under our revolving senior credit facility. As adjusted for the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption, we would have had approximately $689.2 million of secured indebtedness outstanding, net of deferred financing costs, and $633.7 million of additional secured indebtedness available for borrowing under our revolving senior credit facility.
Claims of noteholders will be structurally subordinate to claims of creditors of our non-guarantor subsidiaries
As of the date of this prospectus, the exchange notes will not be guaranteed by any of our foreign or less than wholly owned subsidiaries who do not guarantee our senior credit facility or by the Special Purpose Subsidiaries. Claims of holders of the exchange notes will be structurally subordinated to all of the liabilities of our subsidiaries that do not guarantee the exchange notes. In the event of a bankruptcy, liquidation or dissolution of
22
Table of Contents
any of the non-guarantor subsidiaries, holders of their indebtedness, their trade creditors and holders of their preferred equity will generally be entitled to payment on their claims from assets of those subsidiaries before any assets are made available for distribution to us. However, under some circumstances, the terms of the exchange notes will permit our non-guarantor subsidiaries to incur additional specified indebtedness. As of June 30, 2020, our non-guarantor subsidiaries had approximately $0.2 million in trade payables. The lenders under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program are currently secured by the accounts receivable balances and certain related assets transferred by certain of our subsidiaries to the Special Purpose Subsidiaries pursuant to the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. As adjusted for the Partial 5% Notes Redemption, the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption and the offering of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, we would have had approximately $121.8 million of indebtedness outstanding under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, net of deferred financing costs.
Upon a change of control, we may not have the funds necessary to finance the change of control offer required by the indentures governing the notes, which would violate the terms of the exchange notes.
Upon the occurrence of a change of control, holders of the exchange notes will have the right to require us to purchase all or any part of the exchange notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of purchase. The indentures governing our existing notes, including the outstanding notes, contain similar requirements. We may not have sufficient financial resources available to satisfy all of the obligations under the exchange notes and our existing notes, including the outstanding notes, in the event of a change of control. Further, we will be contractually restricted under the terms of our senior credit facility from repurchasing all of the exchange notes tendered upon a change of control. Accordingly, we may be unable to satisfy our obligations to purchase the exchange notes unless we are able to refinance or obtain waivers under our senior credit facility. Our failure to purchase the exchange notes as required under the indentures would result in a default under the indentures and a cross-default under our senior credit facility, each of which could have material adverse consequences for us and the holders of the exchange notes. In addition, each of the senior credit facility and our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program provides that a change of control is a default that permits lenders to accelerate the maturity of borrowings under it. See “Description of Exchange Notes—Material Covenants—Change of Control.”
Certain covenants contained in the indentures governing the notes will not be applicable during any period in which the exchange notes are rated investment grade.
The indentures governing the notes provide that certain covenants will not apply to us if the exchange notes are rated investment grade by Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s and no default has otherwise occurred and is continuing under the indentures and so long as such notes retain an investment grade rating by both of these rating agencies. The covenants that would be suspended include, among others, limitations on our and our restricted subsidiaries’ ability to pay dividends, incur indebtedness, sell assets, make restricted payments and enter into certain other transactions. Any actions that we take while these covenants are not in force will not result in an event of default with respect to the exchange notes even if the exchange notes are subsequently downgraded below investment grade and such covenants are subsequently reinstated. There can be no assurance that the exchange notes will ever be rated investment grade, or that if they are rated investment grade, the exchange notes will maintain such ratings. See “Description of Exchange Notes—Material Covenants—Effectiveness of Covenants.”
Certain exceptions contained in the indentures governing the notes permit Lamar Advertising to make distributions to maintain its REIT status even when Lamar Advertising could not otherwise make restricted payments under the indentures.
Under the indentures governing the notes, subject to certain exceptions, we are allowed to make restricted payments only if, among other things, we have a ratio of consolidated indebtedness to EBITDA of less than 7.00 to 1.00 on a pro forma basis. However, even when we do not meet such leverage ratio, subject to certain
23
Table of Contents
conditions, the indentures permit Lamar Advertising to declare or pay any dividend or make any distribution to its equity holders to fund a dividend or distribution so long as Lamar Advertising believes in good faith that Lamar Advertising qualifies as a REIT and the declaration or payment of any such dividend or the making of any such distribution is necessary to maintain its status as a REIT for any calendar year. For a more complete discussion of the restricted payment and debt incurrence covenants of the indentures applicable to the notes, see “Description of Exchange Notes—Material Covenants—Limitation on Restricted Payments” and “—Limitation on Additional Indebtedness and Preferred Stock of Restricted Securities.”
Federal and state statutes allow courts, under specific circumstances, to void the guarantees of the exchange notes by our subsidiaries and require the holders of the exchange notes to return payments received from the subsidiary guarantors.
Under the federal bankruptcy law and comparable provisions of state fraudulent transfer laws, the subsidiary guarantees could be voided, or claims in respect of the subsidiary guarantees could be subordinated to all other debts of a subsidiary guarantor if, either, the subsidiary guarantee was incurred with the intent to hinder, delay or defraud any present or future creditors of the subsidiary guarantor or the subsidiary guarantors, at the time it incurred the indebtedness evidenced by its subsidiary guarantee, received less than reasonably equivalent value or fair consideration for the incurrence of such indebtedness and the subsidiary guarantor either:
| • | was insolvent or rendered insolvent by reason of such incurrence; |
| • | was engaged in a business or transaction for which such subsidiary guarantor’s remaining assets constituted unreasonably small capital; or |
| • | intended to incur, or believed that it would incur, debts beyond its ability to pay such debts as they mature. |
If a subsidiary guarantee is voided, you will be unable to rely on the applicable subsidiary guarantor to satisfy your claim in the event that we fail to make one or more required payments due on the exchange notes. In addition, any payment by such subsidiary guarantor pursuant to its subsidiary guarantee could be voided and required to be returned to such subsidiary guarantor, or to a fund for the benefit of creditors of such subsidiary guarantor.
The measures of insolvency for purposes of these fraudulent transfer laws will vary depending upon the law applied in any proceeding to determine whether a fraudulent transfer has occurred. Generally, however, a subsidiary guarantor would be considered insolvent if:
| • | the sum of its debts, including contingent liabilities, were greater than the fair saleable value of all of its assets; |
| • | the present fair saleable value of its assets were less than the amount that would be required to pay its probable liability on its existing debts, including contingent liabilities, as they become absolute and mature; or |
| • | it could not pay its debts as they become due. |
On the basis of historical financial information, recent operating history and other factors, we and each subsidiary guarantor believe that, after giving effect to the indebtedness incurred in connection with this offering, no subsidiary guarantor will be insolvent, will have unreasonably small capital for the business in which it is engaged or will have incurred debts beyond its ability to pay such debts as they mature. There can be no assurance, however, as to what standard a court would apply in making such determinations or that a court would agree with our or the subsidiary guarantors’ conclusions in this regard.
24
Table of Contents
Risks Related to Our Business and Operations
Pandemics or disease outbreaks, such as COVID-19, have and are expected to continue to materially affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Any outbreaks of contagious diseases and other adverse public health developments could have a significant adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. The recent outbreak of COVID-19 has resulted in the implementation of significant governmental measures to control the spread of the virus, including quarantines, travel restrictions, business shutdowns and restrictions on non-essential activities in the United States and abroad. Such restrictions have had an adverse impact on the volume of vehicles on roadways (particularly in larger markets), pedestrians in airports and riders on public transit, which has temporarily reduced the size of the audience for our advertising in certain jurisdictions. The restrictions have also negatively affected the financial condition of numerous advertising customer segments including, but not limited to, entertainment, retail, restaurant and automotive advertisers, which have temporarily closed or limited their operations, and caused certain of our advertisers to decrease or eliminate the amount they spend on advertising with us on a temporary basis.
Our business has been affected adversely due to decreased demand for its advertising in jurisdictions that have imposed such restrictions. In the United States, state and local governments have begun to lift certain of these restrictions in many locations, however, the extension of existing measures or implementation of new similar measures may further adversely affect our business in the future. Even if such measures are further relaxed, the perceived risk of infection may continue to alter the behavior of the audience for our advertising, which may continue to negatively affect our business. Such risks are also expected to continue to affect the financial condition of certain of our advertising customers, which may have a negative effect on our business if advertising customers continue to reduce advertising expenditures generally or for outdoor advertising specifically.
In addition to the above, the general market volatility resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic has caused a decline in Lamar Advertising’s stock price.
These and other potential impacts of COVID-19 (or other epidemics, pandemics or other health crises) have and are expected to continue to adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. The ultimate extent of the impact of COVID-19 or any epidemic, pandemic or other health crisis on our business, financial condition and results of operations will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted, including new information that may emerge concerning the severity of COVID-19 and the actions taken to contain COVID-19 and address its impact, among others. To the extent the COVID-19 pandemic adversely affects our business and financial results, it may also have the effect of heightening many of the other risks described in this “Risk factors” section.
Our revenues are sensitive to the state of the economy and financial markets generally and other external events beyond our control.
We lease advertising space on outdoor structures to generate revenues. Advertising spending is particularly sensitive to changes in economic conditions.
Additionally, the occurrence of any of the following external events could depress our revenues:
| • | a widespread reallocation of advertising expenditures to other available media by significant renters of our displays; and |
| • | a decline in the amount spent on advertising in general or outdoor advertising in particular. |
25
Table of Contents
If we are unable to continue to grow through acquisitions, it could adversely affect our future financial performance. In addition, if we are unable to successfully integrate any completed acquisitions our financial performance would also be adversely affected.
We have historically grown through acquisitions. During the six months ended June 30, 2020, we paid approximately $26.2 million in purchase price for acquisitions. As described under “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic”, we have limited acquisition activity as a means to conserve liquidity.
The future success of our acquisition strategy could be adversely affected by many factors, including the following:
| • | the pool of suitable acquisition candidates is dwindling, and we may have a more difficult time negotiating acquisitions on favorable terms; |
| • | we may face increased competition for acquisition candidates from other outdoor advertising companies, some of which have greater financial resources than we do, which may result in higher prices for those businesses and assets; |
| • | we may not have access to the capital needed to finance potential acquisitions and may be unable to obtain any required consents from our current lenders to obtain alternate financing; |
| • | Lamar Advertising’s compliance with REIT requirements may hinder our ability to make certain investments and may limit our acquisition opportunities; |
| • | we may be unable to integrate acquired businesses and assets effectively with our existing operations and systems as a result of unforeseen difficulties that could divert significant time, attention and effort from management that could otherwise be directed at developing existing business; |
| • | we may be unable to retain key personnel of acquired businesses; |
| • | we may not realize the benefits and cost savings anticipated in our acquisitions; and |
| • | as the industry consolidates further, larger mergers and acquisitions may face substantial scrutiny under antitrust laws. |
These obstacles to our opportunistic acquisition strategy may have an adverse effect on our future financial results
We could suffer losses due to asset impairment charges for goodwill and other intangible assets.
We tested goodwill for impairment on December 31, 2019. Based on our review at December 31, 2019, no impairment charge was required. We continue to assess whether factors or indicators become apparent that would require an interim impairment test between our annual impairment test dates. For instance, if our market capitalization is below our equity book value for a period of time without recovery, we believe there is a strong presumption that would indicate a triggering event has occurred and it is more likely than not that the fair value of one or both of our reporting units (logo operations and billboard operations) are below their carrying amount. This would require us to test the reporting units for impairment of goodwill. If this presumption cannot be overcome, a reporting unit could be impaired under ASC 350 “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” and a non-cash charge would be required. Any such charge could have a material adverse effect on our net income.
We face competition from larger and more diversified outdoor advertisers and other forms of advertising that could hurt our performance.
While we enjoy a significant market share in many of our small and medium-sized markets, we face competition from other outdoor advertisers and other media in all of our markets. Although we are one of the largest
26
Table of Contents
companies focusing exclusively on outdoor advertising in a relatively fragmented industry, we compete against larger companies with diversified operations, such as television, radio and other broadcast media. These diversified competitors have the advantage of cross-selling complementary advertising products to advertisers.
We also compete against an increasing variety of out-of-home advertising media, such as advertising displays in shopping centers, malls, airports, stadiums, movie theaters and supermarkets, and on taxis, trains and buses. To a lesser extent, we also face competition from other forms of media, including radio, newspapers, direct mail advertising, telephone directories and the Internet. The industry competes for advertising revenue along the following dimensions: exposure (the number of “impressions” an advertisement makes), advertising rates (generally measured in cost-per-thousand impressions), ability to target specific demographic groups or geographies, effectiveness, quality of related services (such as advertising copy design and layout) and customer service. We may be unable to compete successfully along these dimensions in the future, and the competitive pressures that we face could adversely affect our profitability or financial performance.
Federal, state and local regulation impact our operations, financial condition and financial results.
Outdoor advertising is subject to governmental regulation at the federal, state and local levels. Regulations generally restrict the size, spacing, lighting and other aspects of advertising structures and pose a significant barrier to entry and expansion in many markets.
Federal law, principally the Highway Beautification Act of 1965, or the HBA, regulates outdoor advertising on Federal—Aid Primary, Interstate and National Highway Systems roads. The HBA requires states, through the adoption of individual Federal/State Agreements, to “effectively control” outdoor advertising along these roads, and mandates a state compliance program and state standards regarding size, spacing and lighting. These state standards, or their local and municipal equivalents, may be modified over time in response to legal challenges or otherwise, which may have an adverse effect on our business. The HBA requires any state or political subdivision that compels the removal of a lawful billboard along a Federal—Aid Primary or Interstate highway to pay just compensation to the billboard owner.
All states have passed billboard control statutes and regulations at least as restrictive as the federal requirements, including laws requiring the removal of illegal signs at the owner’s expense (and without compensation from the state). Although we believe that the number of our billboards that may be subject to removal as illegal is immaterial, and no state in which we operate has banned billboards entirely, from time to time governments have required us to remove signs and billboards legally erected in accordance with federal, state and local permit requirements and laws. Municipal and county governments generally also have sign controls as part of their zoning laws and building codes. We contest laws and regulations that we believe unlawfully restrict our constitutional or other legal rights and may adversely impact the growth of our outdoor advertising business.
Using federal funding for transportation enhancement programs, state governments have purchased and removed billboards for beautification, and may do so again in the future. Under the power of eminent domain, state or municipal governments have laid claim to property and forced the removal of billboards. Under a concept called amortization by which a governmental body asserts that a billboard operator has earned compensation by continued operation over time, local governments have attempted to force removal of legal but nonconforming billboards (i.e., billboards that conformed to applicable zoning regulations when built but which do not conform to current zoning regulations). Although the legality of amortization is questionable, it has been upheld in some instances. Often, municipal and county governments also have sign controls as part of their zoning laws, with some local governments prohibiting construction of new billboards or allowing new construction only to replace existing structures. Although we have generally been able to obtain satisfactory compensation for those of our billboards purchased or removed as a result of governmental action, there is no assurance that this will continue to be the case in the future.
We have also introduced and intend to expand the deployment of digital billboards that display static digital advertising copy from various advertisers that change every 6 to 8 seconds. We have encountered some existing
27
Table of Contents
regulations that restrict or prohibit these types of digital displays but it has not yet materially impacted our digital deployment. Since digital billboards have been developed and introduced relatively recently into the market on a large scale, however, existing regulations that currently do not apply to them by their terms could be revised or new regulations could be enacted to impose greater restrictions. These regulations may impose greater restrictions on digital billboards due to alleged concerns over aesthetics or driver safety.
Relatively few large scale studies have been conducted to date regarding driver safety issues, if any, related to digital billboards. On December 30, 2013, the results of a study conducted by the U.S. Department of Transportation and the Federal Highway Administration that looked at the effect of digital billboards and conventional billboards on driver visual behavior were issued. The conclusions of the report indicated that the presence of digital billboards did not appear to be related to a decrease in looking toward the road ahead and were generally within acceptable thresholds. The report cautioned, however, that it adds to the knowledge base but does not present definitive answers to the research questions investigated. Accordingly, the results of future studies may result in regulations at the federal or state level that impose greater restrictions on digital billboards. Any new restrictions on digital billboards could have a material adverse effect on both our existing inventory of digital billboards and our plans to expand our digital deployment, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our logo sign contracts are subject to state award and renewal.
In the six months ended June 30, 2020, we generated approximately 6% of our revenues from state-awarded logo sign contracts. In bidding for these contracts, we compete against other national logo sign providers, as well as numerous smaller, local logo sign providers. As a logo sign provider, we incur significant start-up costs upon being awarded a new contract. These contracts generally have a term of five to ten years, with additional renewal periods. Some states reserve the right to terminate a contract early, and most contracts require the state to pay compensation to us as a logo sign provider for early termination. At the end of the contract term, we, as the logo sign provider, transfer ownership of the logo sign structures to the state. Depending on the contract, we may or may not be entitled to compensation for the structures at the end of the contract term.
Of our 24 logo sign contracts in place at June 30, 2020, four are subject to renewal or expiration in the next twelve months. We may be unable to renew these expiring contracts. We may also lose the bidding on new contracts.
We are a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising, which is controlled by significant stockholders who have the power to determine the outcome of all matters submitted to Lamar Advertising’s stockholders for approval and whose interests may be different than yours.
As of June 30, 2020, members of the Reilly family, including Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Lamar Advertising’s Executive Chairman, and Sean Reilly, Lamar Advertising’s and our Chief Executive Officer and President, owned in the aggregate approximately 15% of Lamar Advertising’s common stock, assuming the conversion of all Class B common stock to Class A common stock. As of that date, their combined holdings represented approximately 63% of the voting power of Lamar Advertising’s outstanding capital stock, which would give the Reilly family the power to:
| • | elect Lamar Advertising’s entire board of directors; |
| • | control Lamar Advertising’s management and policies; and |
| • | determine the outcome of any corporate transaction or other matter requiring the approval of Lamar Advertising’s stockholders, including charter amendments, mergers, consolidations, financings and asset sales. |
The Reilly family may have interests that are different than yours as holders of the exchange notes in making these decisions.
28
Table of Contents
If our contingency plans relating to hurricanes and other natural disasters fail, the resulting losses could hurt our business.
We have determined that it is not economical to insure against losses resulting from hurricanes and other natural disasters. Although we have developed contingency plans designed to mitigate the threat posed by hurricanes and other forms of inclement weather to our real estate portfolio (e.g., removing advertising faces at the onset of a storm, when possible, which better permits the structures to withstand high winds during the storm), these plans could fail and significant losses could result.
If our parent, Lamar Advertising, fails to remain qualified as a REIT, both Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media would be taxed as regular C corporations and would not be able to deduct distributions to the stockholders of Lamar Advertising when computing their taxable income.
Our parent, Lamar Advertising, elected to qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes starting with its taxable year ended December 31, 2014 and for each subsequent taxable year thereafter. REIT qualification involves the application of highly technical and complex provisions of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”) to Lamar Advertising’s assets and operations as well as various factual determinations concerning matters and circumstances not entirely within its control. There are limited judicial or administrative interpretations of these provisions. Although Lamar Advertising plans to operate in a manner consistent with the REIT qualification rules, we cannot assure you that it will so qualify or remain so qualified. Lamar Media is treated as a qualified REIT subsidiary of Lamar Advertising that is disregarded as separate from its parent REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
If, in any taxable year, Lamar Advertising fails to qualify for taxation as a REIT, and is not entitled to relief under the Code:
| • | it will not be allowed a deduction for distributions to its stockholders in computing its taxable income; |
| • | it and its subsidiaries, including Lamar Media, will be subject to applicable federal and state income tax, including any applicable state-level alternative minimum tax, on its taxable income at regular corporate rates; and |
| • | it would be disqualified from REIT tax treatment for the four taxable years following the year during which it was so disqualified. |
Any such corporate tax liability could be substantial and would reduce the amount of cash available for distributions to Lamar Advertising’s stockholders, may require Lamar Advertising to borrow funds (under Lamar Media’s senior credit facility or otherwise) or liquidate some investments to pay any such additional tax liability which may affect Lamar Media’s ability to service debt, including the exchange notes offered hereby. This adverse impact could last for five or more years because, unless it is entitled to relief under certain statutory provisions, it will be taxable as a corporation, beginning in the year in which the failure occurs, and it will not be allowed to re-elect to be taxed as a REIT for the following four years.
Even if it qualifies as a REIT, certain of Lamar Advertising’s and its subsidiaries’ business activities, including those of Lamar Media, will be subject to U.S. and foreign taxes, which will continue to reduce its cash flows, and it will have potential deferred and contingent tax liabilities.
Even if it qualifies as a REIT, Lamar Advertising may be subject to certain U.S. federal, state and local taxes and foreign taxes on its income and assets, including any applicable state-level alternative minimum taxes, taxes on any undistributed income, and state, local or foreign income, franchise, property and transfer taxes. In addition, Lamar Advertising could in certain circumstances be required to pay an excise or penalty tax, which could be significant in amount, in order to utilize one or more relief provisions under the Code to maintain qualification for taxation as a REIT which may affect Lamar Media’s ability to service debt, including the exchange notes offered hereby.
29
Table of Contents
In order to maintain its qualification as a REIT, Lamar Advertising holds certain of its non-qualifying REIT assets and receives certain non-qualifying items of income through one or more TRSs. These non-qualifying REIT assets consist principally of our advertising services business and transit advertising business. Those TRS assets and operations will continue to be subject, as applicable, to U.S. federal and state corporate income taxes. Furthermore, our assets and operations outside the United States are subject to foreign taxes in the jurisdictions in which those assets and operations are located. In addition, we may incur a 100% excise tax on transactions with a TRS if they are not conducted on an arm’s-length basis. Any of these taxes would decrease Lamar Media’s and Lamar Advertising’s earnings and the cash available for payments on the exchange notes.
Lamar Advertising was subject to a U.S. federal income tax at the highest regular corporate rate (currently 21%) on all or a portion of the gain recognized from a sale of assets occurring within five years after the effective date of its REIT conversion, to the extent of the built-in gain based on the fair market value of those assets held by Lamar Advertising on the effective date of REIT conversion in excess of its then tax basis in those assets. Such five-year period has expired with respect to Lamar Advertising but certain tax years for which this rule applied remain open such that additional taxes could be assessed with respect to sales in those tax years. The same rules apply to any assets it acquires from a “C” corporation in a carry-over basis transaction with built-in gain at the time of the acquisition by it. Gain from a sale of an asset occurring after the specified period ends will not be subject to this corporate level tax.
Failure to make sufficient distributions would jeopardize Lamar Advertising’s qualification as a REIT and/or would subject it to U.S. federal income and excise taxes.
As a REIT, Lamar Advertising is required to distribute to its stockholders with respect to each taxable year at least 90% of its REIT taxable income (excluding capital gains and net of any available net operating loss carry forwards) in order to qualify as a REIT, and 100% of its REIT taxable income (excluding capital gains and net of any available net operating loss carry forwards) in order to avoid U.S. federal income and excise taxes. For these purposes, Lamar Advertising’s subsidiaries that are not TRSs, including Lamar Media, will be treated as part of the REIT and therefore Lamar Advertising also will be required to distribute out their taxable income.
Because the REIT distribution requirements will prevent us from retaining earnings, we may be required to refinance debt, including the exchange notes offered hereby, at maturity with additional debt or equity, which may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all.
Covenants specified in our existing and future debt instruments may limit Lamar Advertising’s ability to make required REIT distributions.
Our senior credit facility and the indentures governing our existing notes, including the outstanding notes, and the exchange notes being offered hereby contain certain covenants that could limit Lamar Advertising’s distributions to its stockholders. If these limits prevent Lamar Advertising from satisfying its REIT distribution requirements, it could fail to qualify for taxation as a REIT. If these limits do not jeopardize its qualification for taxation as a REIT but do nevertheless prevent it from distributing 100% of its REIT taxable income, it will be subject to U.S. federal corporate income tax, and potentially a nondeductible excise tax, on the retained amounts.
Lamar Advertising and its subsidiaries may be required to borrow funds, sell assets, or raise equity to satisfy its REIT distribution requirements or maintain the asset tests.
In order to meet the REIT distribution requirements and maintain its qualification and taxation as a REIT and avoid corporate income taxes, Lamar Advertising and/or its subsidiaries, including Lamar Media, may need to borrow funds, sell assets or raise equity, even if the then prevailing market conditions are not favorable for these borrowings, sales or offerings. Any insufficiency of its cash flows to cover Lamar Advertising’s REIT distribution requirements could require it to raise short- and long-term debt, to sell assets, or to offer equity securities in order to fund distributions required to maintain its qualification and taxation as a REIT and avoid
30
Table of Contents
corporate income taxes. Furthermore, the REIT distribution requirements may increase the financing Lamar Advertising needs to fund capital expenditures, future growth and expansion initiatives. This would increase its total leverage.
In addition, if Lamar Advertising fails to comply with certain asset tests at the end of any calendar quarter, it must correct the failure within 30 days after the end of the calendar quarter or qualify for certain statutory relief provisions to avoid losing its REIT qualification. As a result, it may be required to liquidate otherwise attractive investments. These actions may reduce its income and amounts available for distribution to its stockholders which may affect Lamar Media’s ability to service debt, including the exchange notes offered hereby.
Complying with REIT requirements may cause Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media to forego otherwise attractive opportunities.
To qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, Lamar Advertising must continually satisfy tests concerning, among other things, the sources of its income, the nature and diversification of its assets, the amounts it distributes to its stockholders and the ownership of Lamar Advertising common stock. For these purposes, Lamar Advertising is treated as owning the assets of and receiving or accruing the income of Lamar Media. Thus, compliance with these tests will require Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media to refrain from certain activities and may hinder their ability to make certain attractive investments, including investments in the businesses to be conducted by TRSs, and to that extent limit their opportunities. Furthermore, acquisition opportunities in domestic and international markets may be adversely affected if Lamar Advertising needs or requires the target company to comply with certain REIT requirements prior to closing.
Prospective investors should consult with their tax advisors regarding the effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act and the CARES Act.
On December 22, 2017, President Trump signed into law H.R. 1, informally titled the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “TCJA”). The TCJA made major changes to the Code, including a number of provisions of the Code that affect the taxation of REITs and their stockholders. Among the changes made by the TCJA are permanently reducing the generally applicable corporate tax rate, generally reducing the tax rate applicable to individuals and other non-corporate taxpayers for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2026, eliminating or modifying certain previously allowed deductions (including substantially limiting interest deductibility and, for individuals, the deduction for non-business state and local taxes). On March 27, 2020, legislation intended to support the economy during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (the “CARES Act”), was signed into law. The CARES Act made technical corrections, or temporary modifications, to certain of the provisions of the TJCA, including, without limitation, the provisions of the TCJA concerning net operating losses (“NOLs”) and interest expense deductions. Certain CARES Act related interest expense deduction changes are discussed in the following subsection. With respect to NOLs, effective for taxable years beginning on or after January 1, 2018, the TCJA limited the deduction for NOL carryforwards to 80% of taxable income (before the deduction) and eliminated NOL carrybacks for individuals and non-REIT corporations (NOL carrybacks did not apply to REITs under prior law), but allows for indefinite NOL carryforwards. The CARES Act repealed such 80% limitation for carryforwards to taxable years beginning before January 1, 2021. The CARES Act also allows a five-year carryback for NOLs arising in 2018, 2019, or 2020. The TCJA’s NOL limitations (even as modified by the CARES Act) may result in Lamar Advertising having to make additional distributions in order to comply with REIT distribution requirements or avoid taxes on retained income and gains.
The individual and collective impact of the changes made by the TCJA and the CARES Act on REITs and their security holders are uncertain and may not become evident for some period of time. The effect of any technical corrections with respect to the TCJA and CARES Act could have an adverse effect on us, Lamar Advertising, its subsidiaries, and holders of our notes. It is also possible additional legislation could be enacted in the future as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic which may affect the holders of our securities. Investors should consult their
31
Table of Contents
tax advisors regarding the implications of the TCJA and the CARES Act on their investment in the exchange notes being offered hereby.
Lamar Advertising may potentially be unable to deduct the full amount of its interest expense pursuant to the TCJA and the CARES Act.
For taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017, interest deductions for businesses with average annual gross receipts of over $25 million are capped at 30% of the business’ “adjusted taxable income” plus business interest income pursuant to the TCJA. For these purposes, for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2022, “adjusted taxable income” is computed without regard to deductions allowable for depreciation, amortization, or depletion. The CARES Act increased the aforementioned 30% limitation to 50% for taxable years beginning in 2019 or 2020 and permitted an entity to elect to use its 2019 adjusted taxable income to calculate the applicable limitation for its 2020 taxable year. For taxable years beginning after December 31, 2021, “adjusted taxable income” is calculated by taking deductions allowable for depreciation, amortization, or depletion into account. This limitation, however, does not apply to an “electing real property trade or business.” As a REIT, Lamar Advertising would generally constitute a real property trade or businesses, and thus would retain the ability to fully deduct interest expenses if it makes such an election. However, an entity making such an election must use a longer depreciation cost recovery period for its property. Lamar Advertising has not made such election to date and has not yet determined whether it will make such election at a later date.
Legislative changes or other actions affecting REITs could have a negative effect on Lamar Advertising and its subsidiaries, including Lamar Media.
At any time, the U.S. federal income tax laws governing REITs or the administrative and judicial interpretations of those laws may be amended or interpreted in a different manner. Federal and state tax laws are constantly under review by persons involved in the legislative process, the IRS, the U.S. Department of the Treasury, and state taxing authorities. Additional changes to the tax laws, regulations and administrative and judicial interpretations, which may have retroactive application, could adversely affect Lamar Advertising and its subsidiaries. We cannot predict with certainty whether, when, in what forms, or with what effective dates, the tax laws, regulations and administrative and judicial interpretations applicable to Lamar Advertising may be changed. Accordingly, we cannot assure you that any such change will not significantly affect Lamar Advertising’s ability to qualify for taxation as a REIT or the U.S. federal income tax consequences to it of such qualification.
The ability of the board of directors of Lamar Advertising to revoke its REIT election, without stockholder approval, may cause adverse consequences to Lamar Media.
The Lamar Advertising charter provides that the board of directors may revoke or otherwise terminate the REIT election, without the approval of its stockholders, if the board determines that it is no longer in Lamar Advertising’s best interest to continue to qualify as a REIT. If Lamar Advertising ceases to be a REIT, it and certain of its subsidiaries, including Lamar Media, will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at regular corporate rates and applicable state and local corporate taxes.
32
Table of Contents
The exchange offer is intended to satisfy our obligations under the registration rights agreements. See “Registration Rights Agreements.” We will not receive any cash proceeds from the issuance of the exchange notes pursuant to the exchange offer. In consideration for issuing the exchange notes as contemplated in this prospectus, we will receive in exchange a like principal amount of outstanding notes. The form and terms of the exchange notes are identical in all respects to the form and terms of the outstanding notes, except the offer and exchange of the exchange notes have been registered under the Securities Act and the exchange notes will not have restrictions on transfer, registration rights or provisions for additional cash interest. The outstanding notes surrendered in exchange for the exchange notes will be retired and canceled and cannot be reissued. Accordingly, issuance of the exchange notes will not result in any change in our capitalization.
On February 6, 2020, we received approximately $987.0 million of net proceeds from our sale of the 2028 outstanding notes and the original 2030 outstanding notes, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and other offering expenses. We used the net proceeds of the offering to (i) redeem all of our outstanding $510.0 million aggregate principal amount 5 3/8% Senior Notes due 2024, (ii) repay the Term A loans under our senior credit facility, and (iii) repay certain outstanding amounts under the revolving portion of our senior credit facility.
On May 13, 2020, we received approximately $394.5 of net proceeds from our sale of the 2029 outstanding notes, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and other offering expenses. We used the net proceeds of the offering, together with cash on hand, (i) to repay the indebtedness outstanding under the revolving portion of our senior credit facility and (ii) the remainder, for general corporate purposes.
On August 19, 2020, we received approximately $146.9 of net proceeds from our sale of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, after deducting the initial purchasers’ discount and other offering expenses. We intend to use the net proceeds of the offering, together with cash on hand and borrowings under our senior credit facility, to effectuate the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption.
See “Description of Material Indebtedness” for a summary of the terms of our outstanding debt.
33
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth our capitalization at June 30, 2020, and our capitalization as of June 30, 2020 as adjusted to reflect the following:
| 1. | On August 19, 2020, we issued $150.0 million in aggregate principal amount of additional 2030 outstanding notes. |
| 2. | On August 31, 2020, we redeemed $267.5 million in aggregate principal amount of our 5% Subordinated Notes in the Partial 5% Notes Redemption. |
| 3. | We intend to use the proceeds from the issuance of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, together with cash on hand and borrowings under our senior credit facility, to effectuate the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption on September 16, 2020. |
You should read this table in conjunction with the information under the headings “Prospectus Summary—Recent Developments”, “Use of Proceeds”, “Summary Historical Consolidated Financial Data,” “Selected Historical Consolidated Financial Data” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements, including the notes thereto, which are included in this prospectus.
| As of June 30, 2020 | ||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | Actual (unaudited) | As adjusted for the Partial 5% Notes Redemption, the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption and the issuance of the additional 2030 notes (unaudited) | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 176,593 | $ | 10,000 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Current maturities of long term debt, net of deferred financing costs(1) | 9,120 | 131,620 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs, including current maturities: | ||||||||
Senior Credit Facility(2) | 585,642 | 689,155 | ||||||
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program(1) | (667 | ) | 121,833 | |||||
3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 | 591,606 | 591,606 | ||||||
4% Senior Notes due 2030(3) | 394,390 | 541,240 | ||||||
4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029 | 394,210 | 394,210 | ||||||
5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026 | 646,817 | 646,817 | ||||||
5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023(4) | 532,214 | — | ||||||
Other long-term debt | 11,687 | 11,687 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total long-term debt, including current maturities | 3,155,899 | 2,966,548 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total stockholder’s equity | 1,113,007 | 1,113,007 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total capitalization | 4,268,906 | 4,109,555 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| (1) | Includes borrowings under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, as adjusted. Additional borrowing capacity under Accounts Receivable Securitization Program as of June 30, 2020 is $171.8 million, actual, and $49.3 million, as adjusted. |
| (2) | Additional borrowing capacity under our revolving senior credit facility as of June 30, 2020 is $737.2 million, actual, and $633.7 million, as adjusted. |
| (3) | On February 6, 2020, we issued $400.00 million of aggregate principal amount of our original 2030 outstanding notes. On August 19, 2020, we issued the additional 2030 outstanding notes in an additional aggregate principal amount of $150.0 million. |
34
Table of Contents
| (4) | On July 30, 2020, we announced the Partial 5% Notes Redemption, whereby $267.5 million aggregate principal amount of the total $535.0 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of our 5% Subordinated Notes was redeemed on August 31, 2020. We funded the Partial 5% Notes Redemption with new borrowings under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, net of deferred financing costs, of $121.8 million and the remainder with cash on hand. |
We intend to use the proceeds from the offering of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, plus cash on hand and borrowings under our revolving credit facility to effectuate the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption, whereby we will redeem the remaining $267.5 million in aggregate outstanding principal amount of 5% Subordinated Notes.
Both the Partial 5% Notes Redemption occurred and the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption will occur at a redemption price equal to 100.833% of the principal amount of outstanding notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the applicable redemption date.
35
Table of Contents
SELECTED HISTORICAL CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL DATA
The following table contains our selected historical consolidated information and other operating data for the five years ended December 31, 2015, 2016, 2017, 2018 and 2019 and the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020. We have prepared this information from audited financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2015 through December 31, 2019 and the unaudited financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020. This information is only a summary. You should read it in conjunction with our historical financial statements and related notes thereto included in this prospectus.
In our opinion, the information for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020 reflects all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, necessary to fairly present our results of operations and financial condition. Results from interim periods should not be considered indicative of results for any other periods or for the year.
This information is only a summary. You should read it in conjunction with our historical financial statements and related notes included in this prospectus, as well as “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
| Year ended December 31, | Six months ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(dollars in thousands) | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Statement of operations data: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,353,396 | $ | 1,500,294 | $ | 1,541,260 | $ | 1,627,222 | $ | 1,753,644 | $ | 833,199 | $ | 754,221 | ||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses | 473,760 | 525,597 | 540,880 | 561,848 | 590,078 | 286,860 | 283,553 | |||||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 242,182 | 269,423 | 276,229 | 289,428 | 318,380 | 157,709 | 149,612 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses | 71,426 | 75,994 | 61,962 | 82,497 | 84,229 | 35,505 | 35,012 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 191,433 | 204,958 | 211,104 | 225,261 | 250,028 | 123,199 | 126,311 | |||||||||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | (8,765 | ) | (15,095 | ) | (4,664 | ) | 7,233 | (7,241 | ) | (5,161 | ) | (3,519 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Total operating expenses | 970,036 | 1,060,877 | 1,085,511 | 1,166,267 | 1,235,474 | 598,112 | 590,969 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Operating income | 383,360 | 439,417 | 455,749 | 460,955 | 518,170 | 235,087 | 163,252 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 98,399 | 123,682 | 128,390 | 129,198 | 149,852 | 75,532 | 71,621 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment | — | 3,198 | 71 | 15,429 | — | — | 18,184 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 284,961 | 312,537 | 327,288 | 316,328 | 368,318 | 159,555 | 73,447 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | 22,058 | 13,356 | 9,230 | 10,697 | (4,222 | ) | (10,292 | ) | 1,296 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 262,903 | $ | 299,181 | $ | 318,058 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 372,540 | $ | 169,847 | $ | 72,151 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||
Other data (as of end of period) (unaudited): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total billboard displays | 143,732 | 148,828 | 149,827 | 156,919 | 157,790 | 156,868 | 155,821 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total logo displays | 134,172 | 143,722 | 145,061 | 148,909 | 151,216 | 150,253 | 150,464 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Balance sheet data(1): | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 21,827 | $ | 35,030 | $ | 114,971 | $ | 20,994 | $ | 25,688 | $ | 16,754 | $ | 176,593 | ||||||||||||||
Working capital (deficit) | 48,882 | 39,691 | 98,033 | (86,699 | ) | (357,180 | ) | (297,269 | ) | 56,245 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total assets | 3,347,340 | 3,882,480 | 4,197,942 | 4,527,886 | 5,924,421 | 5,782,411 | 5,964,847 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs (including current maturities) | 1,893,404 | 2,349,183 | 2,556,690 | 2,888,688 | 2,980,118 | 2,972,502 | 3,155,899 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholder’s equity | 1,007,181 | 1,056,386 | 1,091,098 | 1,120,196 | 1,169,531 | 1,128,088 | 1,113,007 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Certain balance sheet reclassifications were made in order to be comparable to the current year presentation. |
36
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION
AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Overview
Our net revenues are derived primarily from the rental of advertising space on outdoor advertising displays that we own and operate. Revenue growth is based on many factors that include our ability to increase occupancy of our existing advertising displays; raise advertising rates; and acquire new advertising displays and our operating results are therefore affected by general economic conditions, as well as trends in the advertising industry. Advertising spending is particularly sensitive to changes in general economic conditions which affect the rates that we are able to charge for advertising on our displays and our ability to maximize advertising sales or occupancy on our displays.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The unprecedented and rapid spread of COVID-19 and the related government-imposed restrictions and social distancing measures implemented throughout the world have reduced demand for out-of-home advertising. Beginning in late March, large public events were cancelled, and governments began imposing restrictions on non-essential activities, which in turn lead to advertisers suspending, delaying or cancelling their advertising campaigns. The government-imposed restrictions have had an adverse impact on the volume of vehicles on roadways (particularly in larger markets), pedestrians in airports and riders on public transit and numerous advertising customer segments including, but not limited to, entertainment, retail, restaurant and automotive advertisers.
As a result, demand for billboard, transit and airport advertising declined, which has had an adverse impact on our revenues and financial position. The decrease in outdoor advertising demand during the three months ended June 30, 2020 resulted in a 22.5% decrease in our consolidated net revenues as compared to the same period in 2019. As revenues declined, we responded through a variety of cost saving and liquidity measures as discussed below. While we cannot predict the length and severity of the reduction in demand due to the pandemic, we observed an improvement in customer activity in June and July as the government-imposed restrictions on travel were eased. However, the exact timing and pace of the recovery remain uncertain given the continued impact of the pandemic on the overall U.S. and global economy, and new or renewed government-imposed restrictions on travel may be enacted in the future. Our liquidity measures and expense management initiatives may be modified as we monitor the timing of economic recovery.
In response to the ongoing pandemic, we have implemented measures to mitigate the impact on our financial position and operations. These measures include, but are not limited to, the following:
| • | issuing $400.0 million in 4 7/8% Senior Notes on May 13, 2020 which, along with cash on hand, were used to pay-down all outstanding balances under our revolving credit facility. Additionally, during the quarter ended June 30, 2020 we repaid all amounts outstanding under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. Our total liquidity was approximately $1.1 billion as of June 30, 2020; |
| • | reducing our consolidated operating costs (exclusive of depreciation and amortization and gain on disposition of assets) by $25.3 million or 10.4% for the three months ended June 30, 2020 over the same period in 2019 which included: |
| • | reductions in our transit and airport franchise costs and billboard lease costs; and |
| • | reducing our workforce by approximately 5% through attrition and selected layoffs; |
| • | sharply curtailing spending on capital projects, including new digital displays; |
| • | limiting acquisition activity; and |
37
Table of Contents
| • | utilizing portions of the CARES Act for deferral of employer portions of social security taxes through the end of 2020, with 50% of the deferral due December 31, 2021 and the remaining 50% due December 31, 2022. |
We will continue to evaluate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our business and we may access the debt and/or equity capital markets for additional liquidity, if necessary.
Lamar Advertising’s management and Board of Directors are continuing to evaluate our quarterly dividend plans for the remainder of 2020. This evaluation includes ensuring Lamar Advertising remains in compliance with its REIT dividend requirements for the year.
As of June 30, 2020 we did not incur any impairment charges related to goodwill or long-lived assets (including operating lease right of use assets). We also did not incur any significant credit losses for the three and six months ended June 30, 2020.
While some of our corporate, front office and sales workforce continues to work from home, a large majority have returned to their offices while adhering to the Center of Disease Control and Prevention and state and local governmental guidelines and recommendations. Due to the nature of their duties, our billboard operations employees, for the most part, continue to complete their tasks, while still adhering to social distancing measures. The impacts of working from home have been minimal on productivity. Also, while working from home has minimally impacted our processes, there have been no material impacts to our internal control environment.
We will continue to actively monitor the situation and may take further actions that alter our business operations as may be required by federal, state or local authorities, or that we determine are in the best interests of our employees, customers, partners and stockholders.
Acquisitions and capital expenditures
Historically, we have made strategic acquisitions of outdoor advertising assets to increase the number of outdoor advertising displays we operate in existing and new markets. We continue to evaluate and pursue strategic acquisition opportunities as they arise. We have financed our historical acquisitions and intend to finance any future acquisition activity from available cash, borrowings under our senior credit facility or the issuance of debt or equity securities. See “Liquidity and Capital Resources-Sources of Cash” for more information. During the six months ended June 30, 2020, we completed several acquisitions for a total cash purchase price of approximately $26.2 million. See Uses of Cash – Acquisitions for more information.
Our business requires expenditures for maintenance and capitalized costs associated with the construction of new billboard displays, the entrance into and renewal of logo sign and transit contracts, and the purchase of real estate and operating equipment. The following table presents a breakdown of capitalized expenditures for the three and six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019:
| Three months ended June 30, (in thousands) | Six months ended June 30, (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||
Total capital expenditures: | ||||||||||||||||
Billboard—traditional | $ | 1,503 | $ | 13,431 | $ | 8,023 | $ | 22,693 | ||||||||
Billboard—digital | 5,227 | 14,418 | 16,802 | 26,037 | ||||||||||||
Logos | 670 | 2,492 | 3,545 | 3,904 | ||||||||||||
Transit | 289 | 617 | 1,855 | 1,796 | ||||||||||||
Land and buildings | 1,022 | 1,208 | 2,258 | 1,696 | ||||||||||||
Operating equipment | 1,854 | 2,443 | 3,791 | 4,434 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Total capital expenditures | $ | 10,565 | $ | 34,609 | $ | 36,274 | $ | 60,560 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
38
Table of Contents
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
Our management reviews our performance by focusing on several key performance indicators not prepared in conformity with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United States (“GAAP”). We believe these non-GAAP performance indicators are meaningful supplemental measures of our operating performance and should not be considered in isolation of, or as a substitute for, their most directly comparable GAAP financial measures.
Included in our analysis of our results of operations are discussions regarding earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (“adjusted EBITDA”), funds from operations (“FFO”), as defined by the National Association of Real Estate Investment Trusts, adjusted funds from operations (“AFFO”) and acquisition-adjusted net revenue.
We define adjusted EBITDA as net income before income tax expense (benefit), interest expense (income), loss (gain) on extinguishment of debt and investments, stock-based compensation, depreciation and amortization, gain or loss on disposition of assets and investments, capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net and the impact of ASC 842 adoption.
FFO is defined as net income before gains or losses from the sale or disposal of real estate assets and investments and real estate related depreciation and amortization and including adjustments to eliminate unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest.
We define AFFO as FFO before (i) straight-line revenue and expense; (ii) impact of ASC 842 adoption; (iii) capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net (iv) stock-based compensation expense; (v) non-cash portion of tax provision; (vi) non-real estate related depreciation and amortization; (vii) amortization of deferred financing costs; (viii) loss on extinguishment of debt; (ix) non-recurring infrequent or unusual losses (gains); (x) less maintenance capital expenditures; and (xi) an adjustment for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest.
Acquisition-adjusted net revenue adjusts our net revenue for the prior period by adding to it the net revenue generated by the acquired assets before our acquisition of these assets for the same time frame that those assets were owned in the current period. In calculating acquisition-adjusted revenue, therefore, we include revenue generated by assets that we did not own in the period but acquired in the current period. We refer to the amount of pre-acquisition revenue generated by the acquired assets during the prior period that corresponds with the current period in which we owned the assets (to the extent within the period to which this report relates) as “acquisition net revenue”. In addition, we also adjust the prior period to subtract revenue generated by the assets that have been divested since the prior period and, therefore, no revenue derived from those assets is reflected in the current period.
Adjusted EBITDA, FFO, AFFO and acquisition-adjusted net revenue are not intended to replace net income or any other performance measures determined in accordance with GAAP. Neither FFO nor AFFO represent cash flows from operating activities in accordance with GAAP and, therefore, these measures should not be considered indicative of cash flows from operating activities as a measure of liquidity or of funds available to fund our cash needs, including our ability to make cash distributions. Rather, adjusted EBITDA, FFO, AFFO and acquisition-adjusted net revenue are presented as we believe each is a useful indicator of our current operating performance. We believe that these metrics are useful to an investor in evaluating our operating performance because (1) each is a key measure used by our management team for purposes of decision making and for evaluating our core operating results; (2) adjusted EBITDA is widely used in the industry to measure operating performance as depreciation and amortization may vary significantly among companies depending upon accounting methods and useful lives, particularly where acquisitions and non-operating factors are involved; (3) acquisition-adjusted net revenue is a supplement to net revenue to enable investors to compare period over period results on a more consistent basis without the effects of acquisitions and divestures, which reflects our
39
Table of Contents
core performance and organic growth (if any) during the period in which the assets were owned and managed by us; (4) adjusted EBITDA, FFO and AFFO each provides investors with a meaningful measure for evaluating our period-to-period operating performance by eliminating items that are not operational in nature; and (5) each provides investors with a measure for comparing our results of operations to those of other companies.
Our measurement of adjusted EBITDA, FFO, AFFO and acquisition-adjusted net revenue may not, however, be fully comparable to similarly titled measures used by other companies. Reconciliations of adjusted EBITDA, FFO, AFFO and acquisition-adjusted net revenue to net income, the most directly comparable GAAP measure, have been included herein.
Results of Operations
The following table presents certain items in our consolidated statements of operations as a percentage of net revenues for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 and the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019:
| Year Ended December 31, | Six Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2020 | 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses | 33.6 | 34.5 | 35.1 | 37.6 | 34.4 | |||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 18.2 | 17.8 | 17.9 | 19.8 | 18.9 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses | 4.8 | 5.1 | 4.0 | 4.6 | 4.3 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 14.3 | 13.8 | 13.7 | 16.7 | 14.8 | |||||||||||||||
Operating income | 29.5 | 28.3 | 29.6 | 21.6 | 28.2 | |||||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 0.9 | — | 2.4 | — | |||||||||||||||
Interest expense | 8.6 | 8.0 | 8.3 | 9.5 | 9.1 | |||||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense | (0.2 | ) | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.2 | (1.2 | ) | |||||||||||||
Net income | 21.2 | 18.8 | 20.6 | 9.6 | 20.4 | |||||||||||||||
Six Months ended June 30, 2020 compared to Six Months ended June 30, 2019
Net revenues decreased $79.0 million or 9.5% to $754.2 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 from $833.2 million for the same period in 2019. This decrease was primarily attributable to a decrease in billboard and transit net revenues of $62.6 million and $17.1 million, respectively, over the same period in 2019, which related to the ongoing pandemic. The decrease was offset slightly by an increase of $0.7 million in logo revenue.
For the six months ended June 30, 2020, there was an $89.2 million decrease in net revenues as compared to acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the six months ended June 30, 2019, which represents a decrease of 10.6%. See “Reconciliations” below. The $89.2 million decrease in revenue is primarily due to a $73.3 and $16.6 million decrease in billboard and transit net revenues, respectively, which are due to the effects of the ongoing pandemic. The decreases in outdoor and transit revenues were slightly offset by an increase of $0.7 million in logo revenue.
Total operating expenses, exclusive of depreciation and amortization and loss (gain) on disposition of assets, decreased $11.9 million, or 2.5% to $468.2 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 from $480.1 million in the same period in 2019. The $11.9 million decrease over the prior year is comprised of a $10.6 million decrease in total direct, general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding stock-based compensation) primarily related to the operations of our outdoor advertising assets, as well as a $1.3 million decrease in stock-based compensation.
Depreciation and amortization expense increased $3.1 million to $126.3 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 as compared to $123.2 million for the same period in 2019.
40
Table of Contents
For the six months ended June 30, 2020, we recognized a gain on disposition of assets of $3.5 million primarily resulting from transactions related to billboard locations.
Due to the above factors, operating income decreased by $71.8 million to $163.3 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 as compared to $235.1 million for the same period in 2019.
We recognized a loss on debt extinguishment of $18.2 million during the six months ended June 30, 2020, which relates to the early repayment of our 5 3/8% Senior Notes and refinancing of our senior credit facility.
Interest expense decreased $3.9 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020 to $72.0 million as compared to $75.9 million for the six months ended June 30, 2019.
The decrease in operating income, offset by the decrease in interest expense resulted in an $86.1 million decrease in net income before income taxes. The effective tax rate for the six months ended June 30, 2020 was 1.8%, which differs from the federal statutory rate primarily due to our qualification for taxation as a REIT and adjustments for foreign items.
As a result of the above factors, we recognized net income for the six months ended June 30, 2020 of $72.2 million, as compared to net income of $169.8 million for the same period in 2019.
Reconciliations:
Because acquisitions occurring after December 31, 2018 (the “acquired assets”) have contributed to our net revenue results for the periods presented, we provide 2019 acquisition-adjusted net revenue, which adjusts our 2019 net revenue for the six months ended June 30, 2019 by adding to or subtracting from it the net revenue generated by the acquired or divested assets prior to our acquisition or divestiture of these assets for the same time frame that those assets were owned in the six months ended June 30, 2020.
Reconciliations of 2019 reported net revenue to 2019 acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the six months ended June 30, as well as a comparison of 2019 acquisition-adjusted net revenue to 2020 reported net revenue for the six months ended June 30, are provided below:
Reconciliation and Comparison of Reported Net Revenue to Acquisition-Adjusted Net Revenue
| Six months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
Reported net revenue | $ | 754,221 | $ | 833,199 | ||||
Acquisition net revenue | — | 10,209 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Adjusted totals | $ | 754,221 | $ | 843,408 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
41
Table of Contents
Key Performance Indicators
Net Income/Adjusted EBITDA
(in thousands)
| Six Months Ended June 30, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 72,151 | $ | 169,847 | $ | (97,696 | ) | (57.5 | )% | |||||||
Income tax expense (benefit) | 1,296 | (10,292 | ) | 11,588 | ||||||||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment | 18,184 | — | 18,184 | |||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 71,621 | 75,532 | (3,911 | ) | ||||||||||||
Gain on disposition of assets | (3,519 | ) | (5,161 | ) | 1,642 | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 126,311 | 123,199 | 3,112 | |||||||||||||
Impact of ASC 842 adoption (lease accounting standard) | — | 1,930 | (1,930 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net | 1,036 | (8,304 | ) | 9,340 | ||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 6,162 | 7,506 | (1,344 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 293,242 | $ | 354,257 | $ | (61,015 | ) | (17.2 | )% | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA for the six months ended June 30, 2020 decreased 17.2% to $293.2 million. The decrease in adjusted EBITDA was primarily attributable to a decrease in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization, capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net and the impact of ASC 842 adoption) of $68.3 million, and was offset by a decrease in total general and administrative and corporate expenses of $7.2 million, excluding the impact of stock-based compensation expense.
Net Income/FFO/AFFO
(in thousands)
| Six Months Ended June 30, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 72,151 | $ | 169,847 | $ | (97,696 | ) | (57.5 | )% | |||||||
Depreciation and amortization related to real estate | 120,453 | 116,178 | 4,275 | |||||||||||||
Gain from sale or disposal of real estate, net of tax | (3,098 | ) | (4,884 | ) | 1,786 | |||||||||||
Non-cash tax benefit for REIT converted assets | — | (17,031 | ) | 17,031 | ||||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | 389 | 354 | 35 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
FFO | $ | 189,895 | $ | 264,464 | $ | (74,569 | ) | (28.2 | )% | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Straight line expense (income) | 1,733 | (216 | ) | 1,949 | ||||||||||||
Impact of ASC 842 adoption (lease accounting standard) | — | 1,930 | (1,930 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net | 1,036 | (8,304 | ) | 9,340 | ||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 6,162 | 7,506 | (1,344 | ) | ||||||||||||
Non-cash portion of tax provision | (1,313 | ) | 1,910 | (3,223 | ) | |||||||||||
Non-real estate related depreciation and amortization | 5,858 | 7,021 | (1,163 | ) | ||||||||||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs | 2,878 | 2,670 | 208 | |||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 18,184 | — | 18,184 | |||||||||||||
Capital expenditures – maintenance | (14,492 | ) | (23,396 | ) | 8,904 | |||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | (389 | ) | (354 | ) | (35 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
AFFO | $ | 209,552 | $ | 253,231 | $ | (43,679 | ) | (17.2 | )% | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
42
Table of Contents
FFO for the six months ended June 30, 2020 decreased from $264.5 million in 2019 to $189.9 million for the same period in 2020, a decrease of 28.2%. AFFO for the six months ended June 30, 2020 decreased 17.2% to $209.6 million as compared to $253.2 million for the same period in 2019. The decrease in AFFO was primarily attributable to the decrease in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization, capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net and the impact of ASC 842 adoption) offset by decreases in the total of general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding the effect of stock-based compensation expense).
Three Months ended June 30, 2020 compared to Three Months ended June 30, 2019
Net revenues decreased $101.1 million or 22.5% to $347.7 million for the three months ended June 30, 2020 from $448.7 million for the same period in 2019. This decrease was primarily attributable to a decrease in billboard and transit net revenues of $81.7 million and $18.6 million, respectively, over the same period in 2019, which related to the ongoing pandemic.
For the three months ended June 30, 2020, there was a $106.2 million decrease in net revenues as compared to acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2019, which represents a decrease of 23.4%. See “Reconciliations” below. The $106.2 million decrease in revenue is primarily due to an $87.0 million and $18.4 million decrease in billboard and transit net revenues, respectively, and are a result of the effects due to the ongoing pandemic.
Total operating expenses, exclusive of depreciation and amortization and loss (gain) on disposition of assets, decreased $25.3 million, or 10.4% to $218.1 million for the three months ended June 30, 2020 from $243.4 million in the same period in 2019. The $25.3 million decrease over the prior year is comprised of a $22.7 million decrease in total direct, general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding stock-based compensation) primarily related to the operations of our outdoor advertising assets, as well as a $2.5 million decrease in stock-based compensation.
Depreciation and amortization expense increased $2.3 million to $64.0 million for the three months ended June 30, 2020 as compared to $61.7 million for the same period in 2019.
For the three months ended June 30, 2020, we recognized a gain on disposition of assets of $1.0 million primarily resulting from transactions related to billboard locations.
Due to the above factors, operating income decreased by $77.6 million to $66.6 million for the three months ended June 30, 2020 as compared to $144.2 million for the same period in 2019.
Interest expense decreased $2.9 million for the three months ended June 30, 2020 to $35.4 million as compared to $38.3 million for the three months ended June 30, 2019.
The decrease in operating income, offset by the decrease in interest expense resulted in a $74.8 million decrease in net income before income taxes. The effective tax rate for the three months ended June 30, 2020 was (0.8)%, which differs from the federal statutory rate primarily due to our qualification for taxation as a REIT and adjustments for foreign items.
As a result of the above factors, we recognized net income for the three months ended June 30, 2020 of $31.5 million, as compared to net income of $118.5 million for the same period in 2019.
Reconciliations:
Because acquisitions occurring after December 31, 2018 (the “acquired assets”) have contributed to our net revenue results for the periods presented, we provide 2019 acquisition-adjusted net revenue, which adjusts our
43
Table of Contents
2019 net revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2019 by adding to or subtracting from it the net revenue generated by the acquired or divested assets prior to our acquisition or divestiture of these assets for the same time frame that those assets were owned in the three months ended June 30, 2020.
Reconciliations of 2019 reported net revenue to 2019 acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the three months ended June 30, as well as a comparison of 2019 acquisition-adjusted net revenue to 2020 reported net revenue for the three months ended June 30, are provided below:
Reconciliation and Comparison of Reported Net Revenue to Acquisition-Adjusted Net Revenue
| Three months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
Reported net revenue | $ | 347,652 | $ | 448,742 | ||||
Acquisition net revenue | — | 5,075 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Adjusted totals | $ | 347,652 | $ | 453,817 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Key Performance Indicators
Net Income/Adjusted EBITDA
(in thousands)
| Three Months Ended June 30, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 31,534 | $ | 118,485 | $ | (86,951 | ) | (73.4 | )% | |||||||
Income tax benefit | (240 | ) | (12,380 | ) | 12,140 | |||||||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment | 5 | — | 5 | |||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 35,258 | 38,090 | (2,832 | ) | ||||||||||||
Gain on disposition of assets | (1,015 | ) | (537 | ) | (478 | ) | ||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 63,998 | 61,693 | 2,305 | |||||||||||||
Impact of ASC 842 adoption (lease accounting standard) | — | 1,009 | (1,009 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net | 1,036 | (3,609 | ) | 4,645 | ||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 2,725 | 5,273 | (2,548 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 133,301 | $ | 208,024 | $ | (74,723 | ) | (35.9 | )% | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA for the three months ended June 30, 2020 decreased 35.9% to $133.3 million. The decrease in adjusted EBITDA was primarily attributable to a decrease in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization, capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net and the impact of ASC 842 adoption) of $85.1 million, and was offset by an decrease in total general and administrative and corporate expenses of $10.4 million, excluding the impact of stock-based compensation expense.
44
Table of Contents
Net Income/FFO/AFFO
(in thousands)
| Three Months Ended June 30, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 31,534 | $ | 118,485 | $ | (86,951 | ) | (73.4 | )% | |||||||
Depreciation and amortization related to real estate | 61,089 | 58,178 | 2,911 | |||||||||||||
Gain from sale or disposal of real estate, net of tax | (555 | ) | (410 | ) | (145 | ) | ||||||||||
Non-cash tax benefit for REIT converted assets | — | (17,031 | ) | 17,031 | ||||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | 140 | 156 | (16 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
FFO | $ | 92,208 | $ | 159,378 | $ | (67,170 | ) | (42.1 | )% | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Straight line expense | 679 | 20 | 659 | |||||||||||||
Impact of ASC 842 adoption (lease accounting standard) | — | 1,009 | (1,009 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net | 1,036 | (3,609 | ) | 4,645 | ||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 2,725 | 5,273 | (2,548 | ) | ||||||||||||
Non-cash portion of tax provision | (894 | ) | 1,118 | (2,012 | ) | |||||||||||
Non-real estate related depreciation and amortization | 2,909 | 3,515 | (606 | ) | ||||||||||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs | 1,500 | 1,338 | 162 | |||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 5 | — | 5 | |||||||||||||
Capital expenditures—maintenance | (3,863 | ) | (13,689 | ) | 9,826 | |||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | (140 | ) | (156 | ) | 16 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
AFFO | $ | 96,165 | $ | 154,197 | $ | (58,032 | ) | (37.6 | )% | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
FFO for the three months ended June 30, 2020 decreased from $159.4 million in 2019 to $92.2 million for the same period in 2020, a decrease of 42.1%. AFFO for the three months ended June 30, 2020 decreased 37.6% to $96.2 million as compared to $154.2 million for the same period in 2019. The decrease in AFFO was primarily attributable to the decrease in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization, capitalized contract fulfillment costs, net and the impact of ASC 842 adoption) offset by decreases in the total of general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding the effect of stock-based compensation expense).
Year ended December 31, 2019 compared to Year ended December 31, 2018
Net revenues increased $126.4 million or 7.8% to $1.754 billion for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $1.627 billion for the same period in 2018. This increase was attributable primarily to an increase in billboard net revenues of $124.6 million or 8.8% over the prior period, which is primarily related to the integration of outdoor assets acquired during 2018 and 2019, and the addition of approximately 330 digital displays during the year ended December 31, 2019. In addition, transit revenue increased $2.1 million, which represents an increase of 1.6% over the prior period.
Net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2019, as compared to acquisition-adjusted net revenues for the comparable period in 2018, increased $45.7 million, or 2.7%. The $45.7 million increase in revenue primarily consisted of a $41.7 million increase in billboard revenue primarily due to increases in digital revenue and a
45
Table of Contents
$4.1 million increase in transit revenue over the acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the comparable period in 2018. See “Reconciliations” below.
Total operating expenses, exclusive of depreciation and amortization and (gain) loss on disposition of assets, increased $58.9 million, or 6.3% to $992.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $933.8 million in the same period in 2018. The $58.9 million increase over the prior year is primarily comprised of an increase in total direct, general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding stock-based compensation) of $58.7 million primarily related to the operations of our outdoor advertising assets.
Depreciation and amortization expense increased $24.8 million to $250.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 as compared to $225.3 million for the same period in 2018, primarily related to the addition of approximately $516.2 million of depreciable assets acquired through acquisitions and $258.6 million in capitalized expenditures during fiscal years 2018 and 2019.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, we recognized a gain on disposition of assets of $7.2 million primarily resulting from an amendment of a transit contract in the first quarter of 2019. The gain in 2019 represents an increase of $14.5 million over the same period in 2018, largely due to the gain in 2019 coupled with our loss recognized in 2018 on the sale of our Puerto Rico assets in April of 2018 of $7.8 million.
Due primarily to the above factors, operating income increased $57.2 million to $518.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $461.0 million for the same period in 2018.
During the year ended December 31, 2018, we recorded a $15.4 million loss on debt extinguishment related to the prepayment of our 5 7/8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2022. The $15.4 million loss is comprised of a cash redemption premium of $9.8 million and a non-cash write off of unamortized deferred financing costs of approximately $5.6 million. See “Uses of Cash” for more information. There were no transactions resulting in a loss on debt extinguishment in fiscal year 2019.
Interest expense increased $20.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 to $150.6 million as compared to $129.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in interest expense is primarily related to the increased debt outstanding as compared to the same period in 2018.
The increase in operating income and decrease in loss on extinguishment of debt, offset by the increase in interest expense over the comparable period in 2018, resulted in a $52.0 million increase in net income before income taxes.
We recorded an income tax benefit of $4.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 as compared to income tax expense of $10.7 million for the same period in 2018. The $4.2 million benefit is comprised of a $17.0 million non-cash tax benefit resulting from REIT converted assets offset by income tax expense of $12.8 million. The $12.8 million tax expense equates to an effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2019 of approximately 3.5%, which differs from the federal statutory rate primarily due to Lamar Advertising’s qualification for taxation as a REIT and adjustments for foreign items.
As a result of the above factors, our recognized net income for the year ended December 31, 2019 of $372.5 million, as compared to net income of $305.6 million for the same period in 2018.
Reconciliations
Because acquisitions occurring after December 31, 2017 have contributed to our net revenue results for the periods presented, we provide 2018 acquisition-adjusted net revenue, which adjusts our 2018 net revenue for the year ended December 31, 2018 by adding to or subtracting from it the net revenue generated by the acquired or
46
Table of Contents
divested assets prior to our acquisition or divestiture of these assets for the same time frame that those assets were owned in the year ended December 31, 2019.
Reconciliations of 2018 reported net revenue to 2018 acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the year ended December 31, 2018 as well as a comparison of 2018 acquisition-adjusted net revenue to 2019 reported net revenue for the year ended December 31, 2019, are provided below:
Reconciliation and Comparison of Reported Net Revenue to Acquisition-Adjusted Net Revenue
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
Reported net revenue | $ | 1,753,644 | $ | 1,627,222 | ||||
Acquisition net revenue | — | 80,745 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Adjusted totals | $ | 1,753,644 | $ | 1,707,967 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Key Performance Indicators
Net Income/Adjusted EBITDA
(in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 372,540 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 66,909 | 21.9 | % | ||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense | (4,222 | ) | 10,697 | (14,919 | ) | |||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 15,429 | (15,429 | ) | ||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 149,852 | 129,198 | 20,654 | |||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | (7,241 | ) | 7,233 | (14,474 | ) | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 250,028 | 225,261 | 24,767 | |||||||||||||
Impact of ASC 842 adoption | (5,292 | ) | — | (5,292 | ) | |||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 29,647 | 29,443 | 204 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 785,312 | $ | 722,892 | $ | 62,420 | 8.6 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
47
Table of Contents
Adjusted EBITDA for the year ended December 31, 2019 increased 8.6% to $785.3 million. The increase in adjusted EBITDA was primarily attributable to the increase in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization and the impact of ASC 842 adoption) of $92.7 million, and was partially offset by an increase in general and administrative and corporate expenses of $30.3 million, excluding the impact of stock-based compensation expense and the impact of ASC 842 adoption.
Net Income/FFO/AFFO
(in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 372,540 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 66,909 | 21.9 | % | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization related to real estate | 235,802 | 212,457 | 23,345 | |||||||||||||
(Gain) loss from disposition of real estate assets and investments | (6,775 | ) | 8,689 | (15,464 | ) | |||||||||||
Non-cash tax benefit for REIT converted assets | (17,031 | ) | — | (17,031 | ) | |||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | 771 | 648 | 123 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
FFO | $ | 585,307 | $ | 527,425 | $ | 57,882 | 11.0 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Straight-line income | (361 | ) | (2,036 | ) | 1,675 | |||||||||||
Impact of ASC 842 adoption | (5,292 | ) | — | (5,292 | ) | |||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 29,647 | 29,443 | 204 | |||||||||||||
Non-cash portion of tax provision | 2,901 | 660 | 2,241 | |||||||||||||
Non-real estate related depreciation and amortization | 14,226 | 12,804 | 1,422 | |||||||||||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs | 5,365 | 4,920 | 445 | |||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 15,429 | (15,429 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capital expenditures—maintenance | (49,155 | ) | (43,108 | ) | (6,047 | ) | ||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | (771 | ) | (648 | ) | (123 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
AFFO | $ | 581,867 | $ | 544,889 | $ | 36,978 | 6.8 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
FFO for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $585.3 million as compared to FFO of $527.4 million for the same period in 2018. AFFO for the year ended December 31, 2019 increased 6.8% to $581.9 million as compared to $544.9 million for the same period in 2018. AFFO growth was primarily attributable to the increase in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization and the impact of ASC 842 adoption), offset by increases in general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding the effect of stock based compensation expense and the impact of ASC 842 adoption).
Year ended December 31, 2018 compared to Year ended December 31, 2017
Net revenues increased $86.0 million or 5.6% to $1.627 billion for the year ended December 31, 2018 from $1.541 billion for the same period in 2017. This increase was attributable primarily to an increase in billboard net revenues of $72.6 million or 5.4% over the prior period, which is primarily related to the integration of outdoor assets acquired during 2017 and 2018, and the addition of over 250 digital displays during the year ended December 31, 2018. In addition, logo sign revenue increased $1.5 million, which represents an increase of 1.8% over the prior period. Transit revenue increased $11.9 million, which represents an increase of 10.1% over the prior period, primarily due to several new transit and airport markets acquired in 2017 and 2018.
48
Table of Contents
Net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2018, as compared to acquisition-adjusted net revenues for the comparable period in 2017, increased $53.1 million, or 3.4%. The $53.1 million increase in revenue primarily consisted of a $45.1 million increase in billboard revenue primarily due to increases in digital and political revenue, a $1.1 million increase in logo revenue and a $6.8 million increase in transit revenue over the acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the comparable period in 2017. See “Reconciliations” below.
Total operating expenses, exclusive of depreciation and amortization and loss (gain) on disposition of assets, increased $54.7 million, or 6.2% to $933.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 from $879.1 million in the same period in 2017. The $54.7 million increase over the prior year is comprised of a $19.8 million increase in stock-based compensation expense and a $34.9 million increase in total direct, general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding stock-based compensation) primarily related to the operations of our outdoor advertising assets.
Depreciation and amortization expense increased $14.2 million to $225.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 as compared to $211.1 million for the same period in 2017, primarily related to the addition of approximately $774.7 million of assets acquired through acquisitions during fiscal years 2017 and 2018.
For the year ended December 31, 2018, we recognized a loss on disposition of assets of $7.2 million primarily related to the $7.8 million loss recognized on the sale of our Puerto Rico assets which closed on April 16, 2018.
Due primarily to the above factors, operating income increased $5.2 million to $461.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 compared to $455.7 million for the same period in 2017.
During the year ended December 31, 2018, we recorded a $15.4 million loss on debt extinguishment related to the prepayment of our 5 7/8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2022. The $15.4 million loss is comprised of a cash redemption premium of $9.8 million and a non-cash write off of unamortized deferred financing costs of approximately $5.6 million. See “Uses of Cash” for more information.
Interest expense increased $1.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2018 to $129.7 million as compared to $128.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. The increase in interest expense is primarily related to the increased debt outstanding as compared to the same period in 2017.
The increase in operating income offset by the increases in loss on extinguishment of debt and interest expense over the comparable period in 2017, resulted in a $11.0 million decrease in net income before income taxes. We recognized $10.7 million in income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2018. The effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2018 is approximately 3.4%, which differs from the federal statutory rate primarily due to Lamar Advertising’s qualification for taxation as a REIT and adjustments for foreign items.
As a result of the above factors, we recognized net income for the year ended December 31, 2018 of $305.6 million, as compared to net income of $318.1 million for the same period in 2017.
Reconciliations
Because acquisitions occurring after December 31, 2016 have contributed to our net revenue results for the periods presented, we provide 2017 acquisition-adjusted net revenue, which adjusts our 2017 net revenue for the year ended December 31, 2017 by adding to or subtracting from it the net revenue generated by the acquired or divested assets prior to our acquisition or divestiture of these assets for the same time frame that those assets were owned in the year ended December 31, 2018.
49
Table of Contents
Reconciliations of 2017 reported net revenue to 2017 acquisition-adjusted net revenue for the year ended December 31, 2017 as well as a comparison of 2017 acquisition-adjusted net revenue to 2018 reported net revenue for the year ended December 31, 2018, are provided below:
Reconciliation and Comparison of Reported Net Revenue to Acquisition-Adjusted Net Revenue
| Year-Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
Reported net revenue | $ | 1,627,222 | $ | 1,541,260 | ||||
Acquisition net revenue | — | 32,898 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Adjusted totals | $ | 1,627,222 | $ | 1,574,158 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Key Performance Indicators
Net Income/Adjusted EBITDA
(in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 305,631 | $ | 318,058 | $ | (12,427 | ) | (3.9 | )% | |||||||
Income tax expense | 10,697 | 9,230 | 1,467 | |||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 15,429 | 71 | 15,358 | |||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 129,198 | 128,390 | 808 | |||||||||||||
Loss (gain) on disposition of assets | 7,233 | (4,664 | ) | 11,897 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 225,261 | 211,104 | 14,157 | |||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 29,443 | 9,599 | 19,844 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 722,892 | $ | 671,788 | $ | 51,104 | 7.6 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Adjusted EBITDA for the year ended December 31, 2018 increased 7.6% to $722.9 million. The increase in adjusted EBITDA was primarily attributable to the increase in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization) of $65.0 million, and was partially offset by an increase in general and administrative and corporate expenses of $13.9 million, excluding the impact of stock-based compensation expense.
50
Table of Contents
Net Income/FFO/AFFO
(in thousands)
| Year Ended December 31, | Amount of Increase (Decrease) | Percent Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 305,631 | $ | 318,058 | $ | (12,427 | ) | (3.9 | )% | |||||||
Depreciation and amortization related to real estate | 212,457 | 198,630 | 13,827 | |||||||||||||
Loss (gain) from disposition of real estate assets and investments | 8,689 | (4,185 | ) | 12,874 | ||||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | 648 | 839 | (191 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
FFO | $ | 527,425 | $ | 513,342 | $ | 14,083 | 2.7 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Straight-line income | (2,036 | ) | (754 | ) | (1,282 | ) | ||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 29,443 | 9,599 | 19,844 | |||||||||||||
Non-cash portion of tax provision | 660 | 804 | (144 | ) | ||||||||||||
Non-real estate related depreciation and amortization | 12,804 | 12,474 | 330 | |||||||||||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs | 4,920 | 5,120 | (200 | ) | ||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 15,429 | 71 | 15,358 | |||||||||||||
Capital expenditures—maintenance | (43,108 | ) | (43,119 | ) | 11 | |||||||||||
Adjustments for unconsolidated affiliates and non-controlling interest | (648 | ) | (839 | ) | 191 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
AFFO | $ | 544,889 | $ | 496,698 | $ | 48,191 | 9.7 | % | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
FFO for the year ended December 31, 2018 was $527.4 million as compared to FFO of $513.3 million for the same period in 2017. AFFO for the year ended December 31, 2018 increased 9.7% to $544.9 million as compared to $496.7 million for the same period in 2017. AFFO growth was primarily attributable to the increase in our gross margin (net revenue less direct advertising expense, exclusive of depreciation and amortization), offset by increases in general and administrative and corporate expenses (excluding the effect of stock based compensation expense).
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
We have historically satisfied our working capital requirements with cash from operations and borrowings under our senior credit facility. We are the borrower under the senior credit facility and maintain all corporate operating cash balances. Any cash requirements of Lamar Advertising, therefore, must be funded by distributions from us.
Sources of Cash
Total Liquidity. As of June 30, 2020 we had approximately $1.086 billion of total liquidity, which is comprised of approximately $176.6 million in cash and cash equivalents and approximately $737.2 million of availability under the revolving portion of our senior credit facility and $171.8 million of availability under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. We expect the liquidity measures taken (as discussed above) and the remaining availability under the revolving credit facility and Accounts Receivable Securitization Program to be adequate in order for us to meet our operational requirements for the next twelve months as we continue to contend with the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic. We are currently in compliance with the maintenance covenant included in the senior credit facility and we would remain in compliance after giving effect to borrowing the full amount available to us under the revolving portion of the senior credit facility.
51
Table of Contents
As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, we had a working capital surplus (deficit) of $56.2 million and $(357.2) million, respectively. The increase in the working capital of $413.4 million is primarily due to our repayment of all outstanding balances under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program and increase in cash on hand as of June 30, 2020.
Cash Generated by Operations. For the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019 our cash provided by operating activities was $182.8 million and $214.3 million, respectively. The decrease in cash provided by operating activities for the six months ended June 30, 2020 over the same period in 2019 relates to a decrease in revenues offset by a decrease in operating expenses (excluding depreciation and amortization). Due to the adverse economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, we may not generate cash flows from operations during 2020 in excess of our cash needs for operations, capital expenditures and dividends, as described herein. However, we do expect to have sufficient cash on hand and availability under our revolving credit facility and Accounts Receivable Securitization Program to meet our operating cash needs for the next twelve months.
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. On December 18, 2018, we entered into the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. The Accounts Receivable Securitization Program provides up to $175.0 million in borrowing capacity, plus an accordion feature that would permit the borrowing capacity to be increased by up to $125.0 million. Borrowing capacity under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program is limited to the availability of eligible accounts receivable collateralizing the borrowings under the agreements governing the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. In connection with the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, we and certain of our subsidiaries (such subsidiaries, the “Subsidiary Originators”) sell and/or contribute their existing and future accounts receivable and certain related assets to one of two special purpose subsidiaries, Lamar QRS Receivables, LLC (the “QRS SPV”) and Lamar TRS Receivables, LLC (the “TRS SPV” and together with the QRS SPV the “Special Purpose Subsidiaries”), each of which is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Lamar Media. Existing and future accounts receivable relating to us and our qualified REIT subsidiaries will be sold and/or contributed to the QRS SPV and existing and future accounts receivable relating to our taxable REIT subsidiaries will be sold and/or contributed to the TRS SPV. Each of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries has granted the lenders party to the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program a security interest in all of its assets, which consist of the accounts receivable and related assets sold or contributed to them, as described above, in order to secure the obligations of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries under the agreements governing the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. Pursuant to the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, we have agreed to service the accounts receivable on behalf of the two Special Purpose Subsidiaries for a fee. We have also agreed to guaranty its performance in its capacity as servicer and originator, as well as the performance of the Subsidiary Originators, of their obligations under the agreements governing the Account Receivable Securitization Program. None of us, the Subsidiary Originators or the Special Purpose Subsidiaries guarantees the collectability of the receivables under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. In addition, each of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries is a separate legal entity with its own separate creditors who will be entitled to access the assets of such Special Purpose Subsidiary before the assets become available to us. Accordingly, the assets of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries are not available to pay creditors of Lamar Media or any of its subsidiaries, although collections from receivables in excess of the amounts required to repay the lenders and the other creditors of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries may be remitted to Lamar Media.
On June 30, 2020 we and the Special Purpose Subsidiaries entered into the Third Amendment of the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program which increased the maximum three month average Delinquency Ratio, Dilution Ratio, and Days’ Sales Outstanding to 11.00% (from 8.00%), 7.00% (from 4.00%) and 75 days (from 65 days), respectively. Additionally, the Amendment establishes a new Minimum Funding Threshold, which requires the Special Purpose Subsidiaries to maintain borrowings under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program on any day equal to the lesser of (i) 50.00% of the aggregate Commitment of all Lenders or (ii) the Borrowing Base, though the Special Purpose Subsidiaries have the right to borrow less than the Minimum Funding Threshold during certain periods prior to December 21, 2020, at their election.
52
Table of Contents
As of June 30, 2020 there were no outstanding aggregate borrowings under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. We had approximately $171.8 million of availability under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program as of June 30, 2020.
“At-the-Market” Offering Program. On May 1, 2018, Lamar Advertising entered into an equity distribution agreement (the “Sales Agreement”) with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Wells Fargo Securities LLC and SunTrust Robinson Humphrey, Inc. as our sales agents (each a “Sales Agent”, and collectively, the “Sales Agents”). Under the terms of the Sales Agreement, Lamar Advertising may, from time to time, issue and sell shares of its Class A common stock, having an aggregate offering price of up to $400.0 million through the Sales Agents as either agents or principals. Sales of the Class A common stock, if any, may be made in negotiated transactions or transactions that are deemed to be “at-the-market offerings” as defined in Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, including sales made directly on or through the Nasdaq Global Select Market and any other existing trading market for the Class A common stock, or sales made to or through a market maker other than on an exchange. Lamar Advertising has no obligation to sell any of the Class A common stock under the Sales Agreement and may at any time suspend solicitations and offers under the Sales Agreement. Lamar Advertising intends to use the net proceeds, if any, from the sale of the Class A common stock pursuant to the Sales Agreement for general corporate purposes, which may include the repayment, refinancing, redemption or repurchase of existing indebtedness, working capital, capital expenditures, acquisition of outdoor advertising assets and businesses and other related investments. During the six months ended June 30, 2020, Lamar Advertising did not issue any shares under this program.
Shelf Registration Statement. On August 6, 2018, Lamar Advertising filed an automatically effective shelf registration statement (No. 333-226614) that registered the offer and sale of an indeterminate amount of additional shares of its Class A common stock. During the six months ended June 30, 2020, Lamar Advertising did not issue any shares under this shelf registration, however, Lamar Advertising may issue additional shares under the shelf registration statement in the future in connection with future acquisitions or for other general corporate purposes.
Credit Facilities. On February 6, 2020, we entered into a Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement”) with certain of our subsidiaries as guarantors, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. as administrative agent and the lenders party thereto, under which the parties agreed to amend and restate our Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 15, 2017, as amended (the “Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement”).
The senior credit facility, as established by the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “senior credit facility”), consists of (i) a new $750.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility which will mature on February 6, 2025 (the “revolving credit facility”), (ii) a new $600.0 million Term B loan facility (the “Term B loans”) which will mature on February 6, 2027, and (iii) an incremental facility (the “Incremental Facility”) pursuant to which we may incur additional term loan tranches or increase our revolving credit facility subject to a pro forma secured debt ratio calculated as described under “Restrictions under Senior Credit Facility” of 4.50 to 1.00, as well as certain other conditions including lender approval. We borrowed all $600.0 million in Term B loans on February 6, 2020. The entire amount of the Term B loans will be payable at maturity. The net proceeds from the Term B loans, together with borrowing under the revolving credit facility and a portion of the proceeds of the issuance of the 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 and 4% Senior Notes due 2030 (both as described below), were used to repay all outstanding amounts under the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, and all revolving commitments under that facility were terminated. See Uses of Cash for more information.
As of June 30, 2020 the aggregate balance outstanding under the senior credit facility was $600.0 million, consisting of $600.0 million in Term B loans aggregate principal balance and no balance outstanding under our revolving credit facility. We had approximately $737.2 million of unused capacity under the revolving credit facility. We recorded a loss on debt extinguishment of approximately $5.6 million related to the refinancing of our senior credit facility.
53
Table of Contents
Note Offerings. On February 6, 2020, we issued, through an institutional private placement, $1.0 billion in aggregate principal amount of new senior notes consisting of $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding 2028 notes and $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the original 2030 outstanding notes. We used the proceeds of this offering to repay our existing Term A loans, redeem in full all $510.0 million in aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 5 3/8% Senior Notes due 2024 and partially repay borrowings under our revolving credit facility. We recorded a loss on debt extinguishment of approximately $12.6 million, of which $9.1 million was cash related to our redemption of the 5 3/8% Senior Notes. See Uses of Cash-Note Redemption for more information.
On May 13, 2020, we issued, through an institutional private placement, $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2029 outstanding notes. The issuance of the 2029 outstanding notes resulted in net proceeds to us of approximately $395.0 million. We used the proceeds of this offering to repay outstanding borrowings under our revolving credit facility and for general corporate purposes.
On August 19, 2020, we issued, through an institutional private placement, $150.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the additional 2030 outstanding notes. We intend to use the net proceeds of this offering, together with cash on hand and borrowings under our senior credit facility, to effectuate the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption.
Factors Affecting Sources of Liquidity
Internally Generated Funds. The key factors affecting internally generated cash flow are general economic conditions, specific economic conditions in the markets where we conduct our business and overall spending on advertising by advertisers. As a result of COVID-19, we incurred an adverse effect on our internally generated cash flows for the quarter ended June 30, 2020, and while we are uncertain of the severity and duration of the decline, we are anticipating an economic rebound in the second half of 2020 and into 2021.
Credit Facilities and Other Debt Securities. We must comply with certain covenants and restrictions related to the senior credit facility, our outstanding debt securities and our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program.
Restrictions Under Debt Securities. We must comply with certain covenants and restrictions related to our outstanding debt securities. Currently, we have outstanding the 5% Subordinated Notes (which were partially redeemed on August 31, 2020, and we expect will be fully redeemed on September 16, 2020), the $650.0 million 5 3/4% Senior Notes issued in January 2016 and February 2019 (the “5 3/4% Senior Notes”), the $600.0 million 2028 outstanding notes issued in February 2020, the $400.0 million 2029 outstanding notes issued in May 2020 and the $550.0 million 4% 2030 outstanding notes issued February 2020 and August 2020.
The indentures relating to our existing notes restrict our ability to incur additional indebtedness but permit the incurrence of indebtedness (including indebtedness under the senior credit facility), (i) if no default or event of default would result from such incurrence and (ii) if after giving effect to any such incurrence, the leverage ratio (defined as the sum of (x) total consolidated debt plus (y) the aggregate liquidation preference of any preferred stock of our restricted subsidiaries to trailing four fiscal quarter EBITDA (as defined in the indentures)) would be less than 7.0 to 1.0. Currently, we are not in default under the indentures of any of our outstanding notes and, therefore, would be permitted to incur additional indebtedness subject to the foregoing provision.
In addition to debt incurred under the provisions described in the preceding paragraph, the indentures relating to our outstanding notes permit us to incur indebtedness pursuant to the following baskets:
| • | up to $1.5 billion (or up to $2.0 billion in the case of the indentures governing the notes) of indebtedness under the senior credit facility; |
| • | indebtedness outstanding on the date of the indentures or debt incurred to refinance outstanding debt; |
| • | inter-company debt between us and our restricted subsidiaries or between restricted subsidiaries; |
54
Table of Contents
| • | certain purchase money indebtedness and capitalized lease obligations to acquire or lease property in the ordinary course of business that cannot exceed the greater of $50.0 million or 5% of our net tangible assets; |
| • | additional debt not to exceed $75.0 million; and |
| • | up to $500.0 million of permitted securitization financings, in the case of the indentures governing the notes. |
Restrictions Under Senior Credit Facility. We are required to comply with certain covenants and restrictions under the senior credit facility. If we or Lamar Advertising fails to comply with these tests, the lenders under the senior credit facility will be entitled to exercise certain remedies, including the termination of the lending commitments and the acceleration of the debt payments under the senior credit facility. At June 30, 2020 and currently, we are in compliance with all such tests under the senior credit facility.
We must maintain a secured debt ratio, defined as total consolidated secured debt of Lamar Advertising, us and our restricted subsidiaries (including capital lease obligations), minus the lesser of (x) $150.0 million and (y) the aggregate amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents of Lamar Advertising, us and our restricted subsidiaries (other than the Special Purpose Subsidiaries (as defined above under Sources of Cash – Accounts Receivable Securitization Program)) to EBITDA, as defined below, for the period of four consecutive fiscal quarters then ended, of less than or equal to 4.5 to 1.0.
We are restricted from incurring additional indebtedness subject to exceptions, one of which is that it may incur additional indebtedness not exceeding the greater of $250.0 million or 6% of our total assets.
We are also restricted from incurring additional unsecured senior indebtedness under certain circumstances unless, after giving effect to the incurrence of such indebtedness, it is in compliance with the secured debt ratio covenant and if, after giving effect to the incurrence of such indebtedness, we would have a total debt ratio, defined as (a) total consolidated debt (including subordinated debt) of Lamar Advertising, we and our restricted subsidiaries as of any date minus the lesser of (i) $150.0 million and (ii) the aggregate amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents of Lamar Advertising, us and our restricted subsidiaries (other than the Special Purpose Subsidiaries) to (b) EBITDA, as defined below, for the most recent four fiscal quarters then ended, is less than 7.0 to 1.0.
We are also restricted from incurring additional subordinated indebtedness under certain circumstances unless, after giving effect to the incurrence of such indebtedness, it is in compliance with the secured debt ratio covenant and our total debt ratio is less than 7.0 to 1.0.
Under the senior credit facility, “EBITDA” means, for any period, operating income for Lamar Advertising, us and our restricted subsidiaries (determined on a consolidated basis without duplication in accordance with GAAP) for such period (calculated (A) before (i) taxes, (ii) interest expense, (iii) depreciation, (iv) amortization, (v) any other non-cash income or charges accrued for such period, (vi) charges and expenses in connection with the senior credit facility, any actual or proposed acquisition, disposition or investment (excluding, in each case, purchases and sales of advertising space and operating assets in the ordinary course of business) and any actual or proposed offering of securities, incurrence or repayment of indebtedness (or amendment to any agreement relating to indebtedness), including any refinancing thereof, or recapitalization and (vii) any loss or gain relating to amounts paid or earned in cash prior to the stated settlement date of any swap agreement that has been reflected in operating income for such period) and (viii) any loss on sales of receivables and related assets to a Securitization Entity in connection with a Permitted Securitization Financing) and (B) after giving effect to the amount of cost savings, operating expense reductions and other operating improvements or synergies projected by us in good faith to be realized as a result of any acquisition, investment, merger, amalgamation or disposition within 18 months of any such acquisition, investment, merger, amalgamation or disposition, net of the amount of actual benefits realized during such period from such action; provided, (a) the aggregate amount for all such cost
55
Table of Contents
savings, operating expense reductions and other operating improvements or synergies will not exceed an amount equal to 15% of EBITDA for the applicable four quarter period and (b) any such adjustment to EBITDA may only take into account cost savings, operating expense reductions and other operating improvements or synergies that are (I) directly attributable to such acquisition, investment, merger, amalgamation or disposition, (II) expected to have a continuing impact on us and our restricted subsidiaries and (III) factually supportable, in each case all as certified by our chief financial officer) on behalf of us, and excluding (except to the extent received or paid in cash by Lamar Advertising, us or any of our restricted subsidiaries (other than the special purpose subsidiaries) income or loss attributable to equity in affiliates for such period), excluding any extraordinary and unusual gains or losses during such period, and excluding the proceeds of any casualty events and dispositions. For purposes hereof, the effect thereon of any adjustments required under Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141R shall be excluded. If during any period for which EBITDA is being determined, we have consummated any acquisition or disposition, EBITDA will be determined on a pro forma basis as if such acquisition or disposition had been made or consummated on the first day of such period.
We believe that our current level of cash on hand, availability under the senior credit facility and future cash flows from operations are sufficient to meet our operating needs for the next twelve months. All debt obligations are reflected on our balance sheet.
Restrictions under Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. The agreements governing the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program contain customary representations and warranties, affirmative and negative covenants, and termination event provisions, including but not limited to those providing for the acceleration of amounts owed under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program if, among other things, the Special Purpose Subsidiaries fail to make payments when due, we, the Subsidiary Originators or the Special Purpose Subsidiaries become insolvent or subject to bankruptcy proceedings or certain judicial judgments, breach certain representations and warranties or covenants or default under other material indebtedness, a change of control occurs, or if we fail to maintain the maximum secured debt ratio of 4.5 to 1.0 required under our senior credit facility.
Uses of Cash
Capital Expenditures. Capital expenditures, excluding acquisitions were approximately $36.3 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020. Due to the economic impacts of COVID-19 we have updated our anticipated 2020 total capital expenditures to be approximately $58.0 million.
Acquisitions. During the six months ended June 30, 2020, we completed acquisitions for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $26.2 million, which were financed using available cash on hand or borrowings under our revolving credit facility. Due to the economic impacts of COVID-19 we are limiting our acquisition activity.
Note Redemption. On August 31, 2020, we redeemed $267.5 million in aggregate principal amount of our outstanding 5% Subordinated Notes funded with a combination of cash on hand and availability under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. Following the redemption, $267.5 million of the original $535.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the 5% Subordinated Notes remained outstanding, which we intend to redeem on September 16, 2020 using proceeds from the offering of the additional 2030 outstanding notes, plus cash on hand and borrowings under our revolving credit facility.
On February 20, 2020, we used a portion of the proceeds from the 2028 outstanding notes and the original 2030 outstanding notes to redeem in full all $510.0 million in aggregate principal amount of our 5 3/8% Senior Notes. The 5 3/8% Senior Notes were redeemed at a redemption price equal to 101.792% of the aggregate principal amount of the outstanding 5 3/8% Senior Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest up to the redemption date. We recorded a loss on debt extinguishment of approximately $12.6 million related to the note redemption. See Sources of Cash-Note Offerings for more information.
56
Table of Contents
Senior Credit Facility. The Term B loans mature on February 6, 2027 and there are no required amortization payments related to the Term B loans. The Term B loans bear interest at rates based on the Adjusted LIBO Rate (“Eurodollar term loans”) or the Adjusted Base Rate (“Base Rate term loans”), at our option. Eurodollar Term B loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.50%. Base Rate Term B loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.50%. The revolving credit facility bears interest at rates based on the Adjusted LIBO Rate (“Eurodollar revolving loans”) or the Adjusted Base Rate (“Base Rate revolving loans”), at our option. Eurodollar revolving loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.50% (or the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.25% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1). Base Rate revolving loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.50% (or the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.25% at any time the total debt ratio is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1). The guarantees, covenants, events of default and other terms of the senior credit facility apply to the Term B loans and revolving credit facility.
Dividends. On February 27, 2020, Lamar Advertising’s Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $1.00 per share, paid on March 31, 2020 to its stockholders of record of its Class A common stock and Class B common stock on March 16, 2020. On May 28, 2020, Lamar Advertising’s Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.50 per share, paid on June 30, 2020 to its stockholders of record of its Class A common stock and Class B common stock on June 22, 2020. Lamar Advertising’s Board of Directors will evaluate our future dividend plans on a quarterly basis, giving consideration to our liquidity, our leverage and the anticipated operating environment. We intend to distribute at least 90% of our REIT taxable income and remain REIT qualified.
As a REIT, Lamar Advertising must annually distribute to its stockholders an amount equal to at least 90% of its REIT taxable income (determined before the deduction for distributed earnings and excluding any net capital gain). The amount, timing and frequency of future distributions will be at the sole discretion of the Board of Directors and will be declared based upon various factors, a number of which may be beyond Lamar Advertising’s control, including financial condition and operating cash flows, the amount required to maintain REIT status and reduce any income and excise taxes that Lamar Advertising otherwise would be required to pay, limitations on distributions in our existing and future debt instruments, Lamar Advertising’s ability to utilize NOLs to offset, in whole or in part, Lamar Advertising’s distribution requirements, limitations on its ability to fund distributions using cash generated through its Taxable REIT Subsidiaries (“TRSs”) and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem relevant.
Stock and Debt Repurchasing Program. On March 16, 2020, Lamar Advertising’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $250.0 million of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock. Additionally, the Board of Directors has authorized us to repurchase up to $250.0 million in outstanding senior or senior subordinated notes and other indebtedness outstanding from time to time under our senior credit facility. The repurchase program will expire on September 30, 2021 unless extended by the Board of Directors. There were no repurchases under the program as of June 30, 2020. Lamar Advertising’s and our management may opt not to make any repurchases under the program, or may make aggregate purchases less than the total amount authorized.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Our off-balance sheet commitments consist of guaranteed minimum payments to local transit municipalities and airport authorities for agreements which entitle us to rent advertising space to customers, in airports and on buses, benches or shelters. These agreements no longer meet the criteria of a lease under ASC 842, Leases, adopted on January 1, 2019 and are a result of our normal course of business.
57
Table of Contents
Commitments and Contingencies
As of June 30, 2020, we had outstanding debt of approximately $3.156 billion. In the future, we have principal revolver commitment reductions under the senior credit facility. In addition, we have fixed commercial commitments. These commitments are detailed on a contractual basis as follows:
| Total | Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||||||
Contractual Obligations | Less Than 1 Year | 1 - 3 Years | 3 - 5 Years | After 5 Years | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Long-Term Debt | $ | 3,155.9 | $ | 9.1 | $ | — | $ | 533.0 | $ | 2,613.8 | ||||||||||
Interest obligations on long term debt(1) | 880.0 | 134.1 | 274.7 | 223.3 | 247.9 | |||||||||||||||
Billboard site and other operating leases | 1,758.9 | 246.2 | 406.6 | 308.1 | 798.0 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total payments due | $ | 5,794.8 | $ | 389.4 | $ | 681.3 | $ | 1,064.4 | $ | 3,659.7 | ||||||||||
| (1) | Interest rates on our variable rate instruments are assuming rates at the June 2020 levels. |
| Total Amount Committed | Amount of Expiration Per Period | |||||||||||||||||||
Other Commercial Commitments | Less Than 1 Year | 1 - 3 Years | 3 - 5 Years | After 5 Years | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revolving Credit Facility(2) | $ | 750.0 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 750.0 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Standby Letters of Credit(3) | $ | 12.8 | $ | 12.3 | $ | 0.5 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| (2) | We had no amounts outstanding under the revolving credit facility as of June 30, 2020. |
| (3) | The standby letters of credit are issued under the revolving credit facility and reduce the availability of the facility by the same amount. |
Cash Flows
Our cash flows provided by operating activities increased by $67.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, primarily resulting from an increase in revenues of approximately $126.4 million and a decrease in operating net assets of $18.5 million, offset by increases in operating expenses (excluding stock-based compensation and depreciation and amortization) of approximately $58.7 million, as compared to the comparable period in 2018.
Cash flows used in investing activities decreased $222.1 million from $584.1 million in 2018 to $362.0 million in 2019 primarily due to a net decrease in the amount of assets acquired through acquisitions and capital expenditures of $227.8 million, as compared to the same period in 2018.
Our cash flows used in financing activities were $238.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 as compared to $45.8 million in 2018. This increase in cash used in financing activities of $192.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 is primarily due to financing transactions during the year, offset by decreases in cash paid for dividends to Lamar Advertising over the comparable period in 2018.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
Our discussion and analysis of our results of operations and liquidity and capital resources are based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments, including those related to intangible assets, goodwill impairment and asset retirement obligations. We base our estimates on historical and anticipated results and trends and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, including assumptions as to future events and, where applicable, established valuation
58
Table of Contents
techniques. These estimates form the basis for making judgments about carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. By their nature, estimates are subject to an inherent degree of uncertainty. Actual results may differ from our estimates. We believe that the following significant accounting policies and assumptions may involve a higher degree of judgment and complexity than others.
Goodwill Impairment. We have a significant amount of goodwill on its consolidated balance sheet and must perform an impairment test of goodwill annually or on a more frequent basis if events and circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. We have identified two reporting units (Logo operations and Billboard operations) in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 350 and no changes have been made to our reporting units from the prior period.
In our annual or interim measurement for impairment of goodwill, we conduct a qualitative assessment by examining relevant events and circumstances that could have a negative impact on our goodwill, which include macroeconomic conditions, industry and market conditions, cost factors, overall financial performance, reporting unit dispositions and acquisitions, our market capitalization and other relevant events specific to us. If, after assessing the totality of events or circumstances described above, we determine that it is more likely than not that the fair value of either of our reporting units is less than its carrying amount, we will perform a quantitative impairment test. If impairment is indicated as a result of the quantitative impairment test, a goodwill impairment charge would be recorded to write the goodwill down to its implied fair value. Based on the goodwill impairment analysis performed on December 31, 2019, we determined that the fair value of each reporting unit exceeded the carrying value and no impairment charge was recorded.
Asset Retirement Obligations. We had an asset retirement obligation of $226.1 million as of December 31, 2019. This liability relates to our obligation upon the termination or non-renewal of a lease to dismantle and remove its billboard structures from the leased land and to reclaim the site to its original condition. We record the present value of obligations associated with the retirement of tangible long-lived assets in the period in which they are incurred. The liability is capitalized as part of the related long-lived asset’s carrying amount. Over time, accretion of the liability is recognized as an operating expense and the capitalized cost is depreciated over the expected useful life of the related asset. In calculating the liability, we calculate the present value of the estimated cost to dismantle using an average cost to dismantle, adjusted for inflation and market risk.
This calculation includes 100% of our billboard structures on leased land (which currently consist of approximately 74,500 structures). We use a 15-year retirement period based on historical operating experience in its core markets, including the actual time that billboard structures have been located on leased land in such markets and the actual length of the leases in the core markets, which includes the initial term of the lease, plus consideration of any renewal period. Historical third-party cost information is used to estimate the cost of dismantling of the structures and the reclamation of the site. The interest rate used to calculate the present value of such costs over the retirement period is based on our historical credit-adjusted risk free rate.
Acquisitions. We account for transactions that meet the definition of a business and group asset purchases as acquisitions. For transactions that meet the definition of a business combination, we allocate the purchase price, including any contingent consideration, to the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed at their estimated fair values as of the date of the acquisition with any excess of the purchase price paid over the estimated fair value of net assets acquired recorded as goodwill. For transactions that meet the definition of a business, the determination of the final purchase price and the acquisition-date fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed may extend over more than one period and result in adjustments to the preliminary estimate recognized in the prior period financial statements. For transactions that meet the definition of asset group purchases, we allocate the purchase price to the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed at their estimated relative fair values as of the date of the acquisition. If a transaction is determined to be a group of assets, any direct acquisition costs are capitalized. Transaction costs for transactions determined to be a business combination are expensed as incurred.
59
Table of Contents
The fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed is typically determined by using either estimates of replacement costs or discounted cash flow valuation methods. When determining the fair value of tangible assets acquired, we must estimate the cost to replace the asset with a new asset, adjusted for an estimated reduction in fair value due to age of the asset, and the economic useful life. When determining the fair value of intangible assets acquired, we must estimate the applicable discount rate and the timing and amount of future cash flows.
Lease liabilities and right-of-use assets: On January 1, 2019, we adopted ASU No. 2016-02, “Leases (Codified as ASC 842),” which resulted in recording operating lease liabilities and right-of-use assets on our consolidated balance sheet. Our operating lease liabilities (including short-term liabilities) and right-of-use asset balances were $1.265 billion and $1.321 billion as of December 31, 2019, respectively. The balance is recorded based on the present value of the remaining minimum rental payments under the leasing standard for our existing operating leases. The key estimates for our leases include (1) the discount rate used to discount the unpaid lease payments to present value and (2) lease term. Our leases generally do not include a readily determinable implicit rate, therefore, using a portfolio approach, we determine our collateralized incremental borrowing rate to discount the lease payments based on the information available at lease commencement. Our lease terms include the noncancellable period of the lease plus any additional periods covered by either a Company option to extend (or not to terminate) the lease that we are reasonably certain to exercise, or an option to extend the lease controlled by the lessor. We have determined we are not reasonably certain to exercise renewals or termination options, and as a result we use the lease’s initial stated term as the lease term for our lease population.
Accounting Standards Update
Leases
In February 2016, the FASB established Topic 842, Leases, by issuing Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2016-02, which requires lessees to recognize leases on-balance sheet and disclose key information about leasing arrangements. Topic 842 was subsequently amended by ASU No. 2018-01, Land Easement Practical Expedient for Transition to Topic 842; ASU No. 2018-10 and ASU No. 2019-01, Codification Improvements to Topic 842, Leases; and ASU No. 2018-11, Targeted Improvements. The new standard establishes a right of use model (ROU) that requires a lessee to recognize an ROU asset and lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with a term longer than twelve months. Leases are classified as finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern and classification of expense recognition in the income statement.
We adopted the new standard effective January 1, 2019 using a modified retrospective transition approach, applying the new standard to all leases existing at the date of initial application. An entity was permitted to use either (1) its effective date or (2) the beginning of the earliest comparative period presented in the financial statements as its date of initial application. If an entity chooses the second option, the transition requirements for existing leases also apply to leases entered into between the date of initial application and the effective date. The entity must also recast its comparative period financial statements and provide the disclosures required by the new standard for the comparative periods. Consequently, financial information was not updated and the disclosures required under the new standard will not be provided for dates and periods before January 1, 2019.
The new standard provided a number of optional practical expedients in transition. We elected the ‘package of practical expedients’, which permitted us not to reassess under the new standard our prior conclusions about lease identification, lease classification and initial direct costs. We elected the practical expedient pertaining to land easements. We also elected the short-term lease recognition exemption for certain of our vehicle agreements. This means, for those leases that qualify, we will not recognize ROU assets or lease liabilities.
Upon adoption, we recognized additional operating liabilities of $1.2 billion, with corresponding ROU assets of the same amount based on the present value of the remaining minimum rental payments under current leasing standards for our existing operating leases. We did not have any changes to its opening balance of retained earnings for the adoption of this update.
60
Table of Contents
Other recently released pronouncements
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (Topic 326)—Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, and additional changes modifications, clarifications, or interpretations related to this guidance thereafter, which require a reporting entity to estimate credit losses on certain types of financial instruments, and present assets held at amortized cost and available-for-sale debt securities at the amount expected to be collected. The new guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019, and early adoption is permitted. Our adoption of this update did not have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements. As of June 30, 2020, our allowance for credit losses considered the current and future impacts caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, based on available information to date. We will continue to actively monitor the impact of COVID-19 on expected credit losses.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are exposed to interest rate risk in connection with variable rate debt instruments that we have issued. The information below summarizes our interest rate risk associated with our principal variable rate debt instruments outstanding at June 30, 2020, and should be read in conjunction with Note 10 of the Notes to Lamar Advertising’s Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
We have variable-rate debt outstanding under our senior credit facility and our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. Because interest rates may increase or decrease at any time, we are exposed to market risk as a result of the impact that changes in interest rates may have on the applicable borrowings outstanding. Increases in the interest rates applicable to these borrowings would result in increased interest expense and a reduction in our net income.
At June 30, 2020, there was approximately $598.3 million of indebtedness outstanding under our senior credit facility and our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, or approximately 18.7% of our outstanding long-term debt on that date, bearing interest at variable rates. The aggregate interest expense for 2020 with respect to borrowings under the senior credit facility and the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program was $13.9 million, and the weighted average interest rate applicable to these borrowings during 2020 was 2.6%. Assuming that the weighted average interest rate was 200 basis points higher (that is 4.6% rather than 2.6%), then our 2020 interest expense would have increased by approximately $10.4 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020.
We have attempted to mitigate the interest rate risk resulting from our variable interest rate long-term debt instruments by issuing fixed rate long-term debt instruments and maintaining a balance over time between the amount of our variable rate and fixed rate indebtedness. In addition, we have the capability under our senior credit facility to fix the interest rates applicable to our borrowings at an amount equal to Adjusted LIBO Rate or Adjusted Base Rate plus the applicable margin for periods of up to twelve months (in certain cases with the consent of the lenders), which would allow us to mitigate the impact of short-term fluctuations in market interest rates. In the event of an increase in interest rates, we may take further actions to mitigate our exposure. We cannot guarantee, however, that the actions that we may take to mitigate this risk will be feasible or that, if these actions are taken, that they will be effective.
61
Table of Contents
General
We are one of the largest outdoor advertising companies in the United States based on number of displays and have operated under the Lamar name since 1902. We operate in a single operating and reporting segment, advertising. We lease space for advertising on billboards, buses, shelters, benches, logo plates and in airport terminals. We offer our customers a fully integrated service, satisfying all aspects of their billboard display requirements from ad copy production to placement and maintenance.
Our Business
We operate three types of outdoor advertising displays: billboards, logo signs and transit advertising displays.
Billboards. As of June 30, 2020, we owned and operated over 155,800 billboard advertising displays in 45 states and Canada. We lease most of our advertising space on two types of billboards: bulletins and posters.
| • | Bulletins are generally large, illuminated advertising structures that are located on major highways and target vehicular traffic. |
| • | Posters are generally smaller advertising structures that are located on major traffic arteries and city streets and target vehicular and pedestrian traffic. |
In addition to these traditional billboards, we also lease advertising space on digital billboards, which are generally located on major traffic arteries and city streets. As of June 30, 2020, we owned and operated over 3,600 digital billboard advertising displays in 43 states and Canada.
Logo signs. We lease advertising space on logo signs located near highway exits.
| • | Logo signs generally advertise nearby gas, food, camping, lodging and other attractions. |
We are the largest provider of logo signs in the United States, currently operating 23 of the 26 privatized state logo sign contracts. As of June 30, 2020, we operated over 150,000 logo sign advertising displays in 24 states and Canada.
Transit advertising displays. We also lease advertising space on the exterior and interior of public transportation vehicles, in airport terminals, and on transit shelters and benches in over 75 markets. We operated over 51,000 transit advertising displays in 22 states and Canada as of June 30, 2020.
Corporate History
We have operated under the Lamar name since our founding in 1902 and have been publicly traded on NASDAQ under the symbol “LAMR” since 1996. We completed a reorganization on July 20, 1999 that created a holding company structure. At that time, the operating company (then called Lamar Advertising Company) was renamed Lamar Media Corp., and all of the operating company’s stockholders became stockholders of a new holding company. The new holding company then took the Lamar Advertising Company name, and Lamar Media Corp. became a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising Company.
During 2014, we completed a reorganization in order for Lamar Advertising to qualify as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. As part of the plan to reorganize our business operations so that Lamar Advertising could elect to qualify as a REIT for the taxable year ended December 31, 2014, Lamar Advertising completed a merger with its predecessor that was approved by its stockholders on November 17, 2014. At the time of the merger each outstanding share of Lamar Advertising’s predecessor’s Class A common stock, Class B common stock and Series AA preferred stock was converted into the right to receive an equal number of shares of Class A common
62
Table of Contents
stock, Class B common stock and Series AA preferred stock of the surviving corporation, respectively. Accordingly, references herein to Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock, Class B common stock and Series AA preferred stock refer to Lamar Advertising’s capital stock and the capital stock of Lamar Advertising’s predecessor, as applicable. We hold and operate certain assets through one or more taxable REIT subsidiaries (“TRSs”). The non-REIT qualified businesses that we hold through TRSs include most of our transit and foreign operations.
We may, from time to time, change the election of previously designated TRSs to be treated as qualified REIT subsidiaries or other disregarded entities (“QRSs”), and may reorganize and transfer certain assets or operations from our TRSs to other subsidiaries, including QRSs.
Operating Strategies
We strive to be a leading provider of outdoor advertising services in each of the markets that we serve, and our operating strategies for achieving that goal include:
Continuing to provide high quality local sales and service. We seek to identify and closely monitor the needs of our tenants and to provide them with a full complement of high quality advertising services. Local advertising constituted approximately 81% of our net revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2020, which management believes is higher than the industry average. We believe that the experience of our regional, territory and local managers has contributed greatly to our success. For example, our regional managers have been with us for an average of 34 years. In an effort to provide high quality sales and service at the local level, we employed over 1,000 local account executives as of June 30, 2020. Local account executives are typically supported by additional local staff and have the ability to draw upon the resources of our central office, as well as our offices in other markets, in the event business opportunities or tenants’ needs support such an allocation of resources.
Continuing a centralized control and decentralized management structure. Our management believes that, for our particular business, centralized control and a decentralized organization provide for greater economies of scale and are more responsive to local market demands. Therefore, we maintain centralized accounting and financial control over our local operations, but our local managers are responsible for the day-to-day operations in each local market and are compensated according to that market’s financial performance.
Continuing to focus on internal growth. Within our existing markets, we seek to increase our revenue and improve cash flow by employing highly-targeted local marketing efforts to improve our display occupancy rates and by increasing advertising rates where and when demand can absorb rate increases. Our local offices spearhead this effort and respond to local tenant demands quickly.
In addition, we routinely invest in upgrading our existing displays and constructing new displays. Since January 1, 2010, we invested approximately $1.1 billion in capitalized expenditures, which include improvements to our existing real estate portfolio and the construction of new locations. Our regular improvement and expansion of our advertising display inventory allows us to provide high quality service to our current tenants and to attract new tenants.
Continuing to pursue other outdoor advertising opportunities. We plan to renew existing logo sign contracts and pursue additional logo sign contracts. Logo sign opportunities arise periodically, both from states initiating new logo sign programs and states converting from government-owned and operated programs to privately-owned and operated programs. Furthermore, we plan to pursue additional tourist oriented directional sign programs in both the United States and Canada and also other motorist information signing programs as opportunities present themselves. In addition, in an effort to maintain market share, we continue to pursue attractive transit advertising opportunities as they become available.
Investing in capital expenditures including digital technology. We invested approximately $141.0 million in capital expenditures in fiscal 2019, of which approximately $57.5 million was spent on digital
63
Table of Contents
technology. We expect our 2020 capitalized expenditures to be approximately $58.0 million, as we have sharply curtailed spending on capital projects in response to the COVID-19 Pandemic. See “Recent developments—Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic”.
Capital Allocation Strategy
The objective of Lamar Advertising’s capital allocation strategy is to simultaneously increase adjusted funds from operations and its return on invested capital. To maintain its REIT status Lamar Advertising is required to distribute to its stockholders annually an amount equal to at least 90% of its REIT taxable income, excluding net capital gains. After complying with Lamar Advertising’s REIT distribution requirements, we plan to continue to allocate our available capital among investment alternatives that meet our return on investment criteria. During 2019, we generated $630.7 million of cash from operating activities, which was used to fund capital expenditures, dividends to Lamar Advertising’s shareholders and partially fund acquisitions.
Company Operations
Billboard Advertising
We lease most of our advertising space on two types of billboard advertising displays: bulletins and posters. As of June 30, 2020, we owned and operated approximately 155,800 billboard advertising displays in 45 states and Canada. In the six months ended June 30, 2020, we derived approximately 76% of our billboard advertising net revenues from bulletin rentals and 24% from poster rentals.
Bulletins are large, advertising structures (the most common size is fourteen feet high by forty-eight feet wide, or 672 square feet) consisting of panels on which advertising copy is displayed. We wrap advertising copy printed with computer-generated graphics on a single sheet of vinyl around the structure. To attract more attention, some of the panels may extend beyond the linear edges of the display face and may include three-dimensional embellishments. Because of their greater impact and higher cost, bulletins are usually located on major highways and target vehicular traffic. At June 30, 2020, we operated approximately 75,500 bulletin displays.
We generally lease individually-selected bulletin space to advertisers for the duration of the contract (ranging from 4 to 52 weeks). We also lease bulletins as part of a rotary plan under which we rotate the advertising copy from one bulletin location to another within a particular market at stated intervals (usually every sixty to ninety days) to achieve greater reach within that market.
Posters are smaller advertising structures (the most common size is eleven feet high by twenty-three feet wide, or 250 square feet; we also operate junior posters, which are five feet high by eleven feet wide, or 55 square feet). Poster panels utilize a single flexible sheet of polyethylene material that inserts onto the face of the panel. Posters are concentrated on major traffic arteries and target vehicular traffic, and junior posters are concentrated on city streets and target hard-to-reach pedestrian traffic and nearby residents. At June 30, 2020, we operated approximately 80,300 poster displays.
We generally lease poster space for 4 to 26 weeks; determined by the advertiser’s campaign needs. Posters are sold in packages of Target Rating Point (“TRP”) levels, which determine the percentage of a target audience an advertiser needs to reach. A package may include a combination of poster locations in order to meet reach and frequency campaign goals.
In addition to the traditional static displays, we also rent digital billboards. Digital billboards are large electronic light emitting diode (“LED”) displays (the most common sizes are fourteen feet high by forty-eight feet wide, or 672 square feet; ten and a half feet high by thirty six feet wide, or 378 square feet; and ten feet high by twenty-one feet wide, or 210 square feet) that are generally located on major traffic arteries and city streets. Digital billboards are capable of generating over one billion colors and vary in brightness based on ambient
64
Table of Contents
conditions. They display completely digital advertising copy from various advertisers in a slide show fashion, rotating each advertisement approximately every 6 to 8 seconds. At June 30, 2020, our inventory included over 3,600 digital display billboards in various markets. These 3,600 digital billboards generated approximately 25% of billboard advertising net revenue.
We own the physical structures on which the advertising copy is displayed. We build the structures on locations we either own or lease. In each local office, one employee typically performs site leasing activities for the markets served by that office.
In the majority of our markets, our local production staffs perform the full range of activities required to create and install billboard advertising displays. Production work includes creating the advertising copy design and layout, coordinating its printing and installing the designs on the displays. Our talented design staff uses state-of-the-art technology to prepare creative, eye-catching displays for our tenants. We can also help with the strategic placement of advertisements throughout an advertiser’s market by using software that allows us to analyze the target audience and its demographics. Our artists also assist in developing marketing presentations, demonstrations and strategies to attract new tenant advertisers.
In marketing billboard displays to advertisers, we compete with other forms of out-of-home advertising and other media. When selecting the media and provider through which to advertise, advertisers consider a number of factors and advertising providers, which are described in the section entitled “Competition” below.
Logo Sign Advertising
We entered the logo sign advertising business in 1988 and have become the largest provider of logo sign services in the United States, operating 24 of the 26 privatized state logo contracts as of June 30, 2020. We erect logo signs, which generally advertise nearby gas, food, camping, lodging and other attractions, and directional signs, which direct vehicle traffic to nearby services and tourist attractions, near highway exits. As of June 30, 2020, we operated approximately 46,150 logo sign structures containing over 150,000 logo advertising displays in the United States and Canada.
As of June 30, 2020, we operated the logo sign contracts in the province of Ontario, Canada and in the following states:
| Colorado | Georgia | Louisiana | Mississippi | Nebraska | New Mexico | Tennessee | ||||||
| Delaware | Kansas | Michigan | Missouri(1) | Nevada | Ohio | Utah | ||||||
| Florida | Kentucky | Minnesota | Montana | New Hampshire | Oklahoma | Virginia | ||||||
| New Jersey | South Carolina | Wisconsin |
| (1) | The logo sign contract in Missouri is operated by a 66 2/3% owned partnership. |
We also operate the tourist oriented directional signing (“TODS”) programs for the states of Colorado, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Michigan, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Jersey, Ohio, South Carolina, Utah, Virginia and the province of Ontario, Canada, providing approximately 26,600 advertising displays as of June 30, 2020.
Our logo and TODS operations are decentralized. Generally, each office is staffed with an experienced local general manager, local sales and office staff and a local signing sub-contractor. This decentralization allows the management staff of Interstate Logos, L.L.C. (the subsidiary that operates all of the logo and directional sign-related businesses) to travel extensively to the various operations and serve in a technical and management advisory capacity and monitor regulatory and contract compliance. We also run a silk screening operation in Baton Rouge, Louisiana and a display construction company in Atlanta, Georgia.
65
Table of Contents
State logo sign contracts represent the exclusive right to erect and operate logo signs within a state for a period of time. The terms of the contracts vary, but generally range from five to ten years, with additional renewal terms. Each logo sign contract generally allows the state to terminate the contract prior to its expiration and, in most cases, with compensation for the termination to be paid to us. When a logo sign contract expires, we transfer ownership of the advertising structures to the state. Depending on the contract, we may or may not be entitled to compensation at that time. Of our 24 logo sign contracts in place at June 30, 2020, four are subject to renewal or expiration in the next twelve months.
States usually award new logo sign contracts and renew expiring logo sign contracts through an open proposal process. In bidding for new and renewal contracts, we compete against other logo sign providers, as well as local companies based in the state soliciting proposals.
In marketing logo signs to advertisers, we compete with other forms of out-of-home advertising and other media. When selecting the media and provider through which to advertise, advertisers consider a number of factors and advertising providers which are described in the section entitled “Competition” below.
Transit Advertising
We entered into the transit advertising business in 1993 as a way to complement our existing business and maintain market share in certain markets. Transit contracts are generally with the local municipalities and airport authorities and allow us the exclusive right to rent advertising space to customers, in airports and on buses, benches or shelters. The terms of the contracts vary but generally range between 3-15 years, many with renewable options for contract extension. We rent transit advertising displays in airport terminals and on bus shelters, benches and buses in over 80 transit markets, and our production staff provides a full range of creative and installation services to our transit advertising tenants. As of June 30, 2020, we operated over 51,000 transit advertising displays in 22 states and Canada.
Municipalities usually award new transit advertising contracts and renew expiring transit advertising contracts through an open bidding process. In bidding for new and renewal contracts, we compete against national outdoor advertising providers and local, on-premise sign providers and sign construction companies. Transit advertising operators incur significant start-up costs to build and install the advertising structures (such as transit shelters) upon being awarded contracts.
In marketing transit advertising displays to advertisers, we compete with other forms of out-of-home advertising and other media. When selecting the media and provider through which to advertise, advertisers consider a number of factors and advertising providers which are described in the section entitled “Competition” below.
Competition
Although the outdoor advertising industry has encountered a wave of consolidation, the industry remains fragmented. The industry is comprised of several large outdoor advertising and media companies with operations in multiple markets, as well as smaller, local companies operating a limited number of structures in one or a few local markets.
Although we primarily focus on small to mid-size markets where we can attain a strong market share, in each of our markets, we compete against other providers of outdoor advertising and other types of media, including:
| • | Larger outdoor advertising providers, such as (i) Clear Channel Outdoor Holdings, Inc., which operates billboards, street furniture displays, transit displays and other out-of-home advertising displays and (ii) Outfront Media, Inc. (formerly CBS Outdoor), which operates traditional outdoor, street furniture and transit advertising properties. |
| • | Broadcast and cable television, radio, print media, direct mail marketing, the internet, social media and applications used in conjunction with wireless devices. |
66
Table of Contents
| • | An increasing variety of out-of-home advertising media, such as advertising displays in shopping centers, malls, airports, stadiums, movie theaters, supermarkets and advertising displays on taxis, trains and buses. |
In selecting the form of media through which to advertise, advertisers evaluate their ability to target audiences having a specific demographic profile, lifestyle, brand or media consumption or purchasing behavior or audiences located in, or traveling through, a particular geography. Advertisers also compare the relative costs of available media, evaluating the number of impressions (potential viewings), exposure (the opportunity for advertising to be seen) and circulation (traffic volume in a market), as well as potential effectiveness, quality of related services (such as advertising copy design and layout) and customer service. In competing with other media, we believe that outdoor advertising is relatively more cost-efficient than other media, allowing advertisers to reach broader audiences and target specific geographic areas or demographic groups within markets.
We believe that our strong emphasis on sales and customer service and our position as a major provider of advertising services in each of our primary markets enables us to compete effectively with the other outdoor advertising companies, as well as with other media, within those markets.
67
Table of Contents
Geographic Diversification
Our advertising displays are geographically diversified across the United States and Canada. The following table sets forth information regarding the geographic diversification of our advertising displays, which are listed in order of contributions to total revenue. Markets with less than 1% of total displays are grouped in the category “all other United States.”
| Percentage of Revenues for the year ended, December 31, 2019 | Number of Displays for the year ended, December 31, 2019 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Market | Static Billboard Displays | Digital Billboard Displays | Transit Displays | Logo Displays | Total Displays | Static Billboard Displays | Digital Billboard Displays | Transit Displays | Logo Displays | Total Displays | Percentage of Total Displays | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Las Vegas, NV | 1.8% | 2.6% | 15.0% | — | 3.0% | 837 | 64 | 1,498 | — | 2,399 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
New York, NY | 3.2% | 1.7% | — | — | 2.5% | 1,054 | 37 | — | — | 1,091 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pittsburgh, PA | 2.2% | 3.6% | 0.4% | — | 2.3% | 3,003 | 56 | 341 | — | 3,400 | 0.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Seattle, WA | 2.2% | 1.1% | 2.1% | — | 1.9% | 1,736 | 18 | 2,194 | — | 3,948 | 1.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cleveland, OH | 1.7% | 2.7% | 1.6% | — | 1.8% | 2,390 | 58 | 2,542 | — | 4,990 | 1.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gary, IN | 1.6% | 2.6% | — | — | 1.6% | 1,711 | 118 | — | — | 1,829 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
San Bernardino, CA | 1.6% | 1.9% | 1.1% | — | 1.5% | 782 | 33 | 1,273 | — | 2,088 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dallas, TX | 1.8% | 1.0% | 1.9% | — | 1.5% | 1,374 | 21 | 459 | — | 1,854 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nashville, TN | 1.4% | 2.2% | — | — | 1.4% | 1,735 | 61 | — | — | 1,796 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vancouver, Canada | — | — | 16.7% | — | 1.4% | — | — | 6,118 | — | 6,118 | 1.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Atlanta, GA | 1.2% | 2.5% | — | — | 1.3% | 771 | 56 | — | — | 827 | 0.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reading, PA | 1.1% | 2.1% | — | — | 1.2% | 1,244 | 101 | — | — | 1,345 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hartford, CT | 1.1% | 2.2% | 0.1% | — | 1.2% | 919 | 50 | 100 | — | 1,069 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Richmond, VA | 1.3% | 1.7% | — | — | 1.2% | 1,319 | 38 | — | — | 1,357 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Phoenix, AZ | 0.2% | 2.5% | 5.5% | — | 1.2% | 142 | 47 | 3,481 | — | 3,670 | 0.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Oklahoma City, OK | 1.4% | 1.4% | — | — | 1.2% | 2,209 | 33 | — | — | 2,242 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Knoxville, TN | 1.6% | 0.7% | — | — | 1.2% | 2,226 | 30 | — | — | 2,256 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Birmingham, AL | 1.2% | 1.2% | 0.3% | — | 1.1% | 1,581 | 32 | 318 | — | 1,931 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Raleigh, NC | 1.4% | 0.9% | — | — | 1.1% | 2,889 | 41 | — | — | 2,930 | 0.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Austin, TX | 1.5% | 0.4% | — | — | 1.0% | 952 | 5 | — | — | 957 | 0.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cincinnati, OH | 1.0% | 1.8% | — | — | 1.0% | 1,176 | 31 | — | — | 1,207 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Columbus, OH | 1.0% | 1.6% | — | — | 1.0% | 1,771 | 60 | — | — | 1,831 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Providence, RI | 1.0% | 1.7% | — | — | 1.0% | 582 | 31 | — | — | 613 | 0.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Baton Rouge, LA | 1.1% | 1.2% | — | — | 1.0% | 1,483 | 39 | — | — | 1,522 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Buffalo, NY | 0.9% | 1.1% | 2.4% | — | 1.0% | 933 | 28 | 1,690 | — | 2,651 | 0.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Indianapolis, IN | 1.2% | 0.9% | — | — | 1.0% | 2,395 | 20 | — | — | 2,415 | 0.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Greenville-Spartanburg, SC | 1.1% | 1.2% | — | — | 1.0% | 1,958 | 45 | — | — | 2,003 | 0.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All US Logo Programs* | — | — | — | 93.4% | 4.9% | — | — | — | 165,103 | 165,103 | 42.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All Other United States | 63.1% | 55.5% | 43.1% | — | 56.3% | 114,961 | 2,366 | 28,334 | — | 145,661 | 37.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All Other Canada* | 0.1% | — | 9.8% | 6.6% | 1.2% | 136 | 2 | 4,453 | 15,762 | 20,353 | 5.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 154,269 | 3,521 | 52,801 | 180,865 | 391,456 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total Revenue (in millions) | $ | 1,145.4 | $ | 392.1 | $ | 131.9 | $ | 84.2 | $ | 1,753.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * | Logo displays at December 31, 2019 include 29,649 displays related to the tourist oriented direction signing (“TODS”) programs. |
Taxable REIT Subsidiaries
We hold and operate certain of our assets that cannot be held and operated directly by a REIT through taxable REIT subsidiaries, or TRSs. A TRS is a subsidiary of a REIT that pays corporate taxes on its taxable income. The assets held in our TRSs primarily consist of our transit advertising business, advertising services business and our foreign operations. Our TRS assets and operations will continue to be subject, as applicable, to U.S. federal and
68
Table of Contents
state corporate income taxes. Furthermore, our assets and operations outside the United States will continue to be subject to foreign taxes in the jurisdictions in which those assets and operations are located. Net income from our TRSs will either be retained by our TRSs and used to fund their operations, or distributed to us, where it will be reinvested in our business or be available for distribution to Lamar Advertising’s stockholders. As of December 31, 2019, the annual revenue generated by our TRSs in the aggregate was approximately $323.7 million.
Advertising Tenants
Our tenant base is diverse. The table below sets forth the ten industries from which we derived most of our billboard advertising revenues for the six months ended June 30, 2020, as well as the percentage of billboard advertising revenues attributable to the advertisers in those industries. The individual advertisers in these industries accounted for approximately 77% of our billboard advertising net revenues in the six months ended June 30, 2020. No individual tenant accounted for more than 2.0% of our billboard advertising net revenues in that period.
Categories | Percentage of Net Billboard Advertising Revenues | |||
Service | 14 | % | ||
Health Care | 12 | % | ||
Restaurants | 11 | % | ||
Retailers | 8 | % | ||
Automotive | 6 | % | ||
Amusement | 5 | % | ||
Education | 5 | % | ||
Gaming | 5 | % | ||
Financial—Banks, Credit Unions | 4 | % | ||
Insurance | 4 | % | ||
Real Estate | 3 | % | ||
|
| |||
| 77 | % | |||
Regulation
Outdoor advertising is subject to governmental regulation at the federal, state and local levels. Regulations generally restrict the size, spacing, lighting and other aspects of advertising structures and pose a significant barrier to entry and expansion in many markets. Federal law, principally the Highway Beautification Act of 1965 (the “HBA”), regulates outdoor advertising on Federal—Aid Primary, Interstate and National Highway Systems roads. The HBA requires states, through the adoption of individual Federal/State agreements, to “effectively control” outdoor advertising along these roads, and mandates a state compliance program and state standards regarding size, spacing and lighting. These state standards, or their local and municipal equivalents, may be modified over time in response to legal challenges or otherwise, which may have an adverse effect on our business. The HBA requires any state or political subdivision that compels the removal of a lawful billboard along a Federal—Aid Primary or Interstate highway to pay just compensation to the billboard owner.
All states have passed billboard control statutes and regulations at least as restrictive as the federal requirements, including laws requiring the removal of illegal signs at the owner’s expense (and without compensation from the state). Although we believe that the number of our billboards that may be subject to removal as illegal is immaterial, and no state in which we operate has banned billboards entirely, from time to time governments have required us to remove signs and billboards legally erected in accordance with federal, state and local permit requirements and laws. Municipal and county governments generally also have sign controls as part of their
69
Table of Contents
zoning laws and building codes. We contest laws and regulations that we believe unlawfully restrict our constitutional or other legal rights and may adversely impact the growth of our outdoor advertising business.
Using federal funding for transportation enhancement programs, state governments have purchased and removed billboards for beautification, and may do so again in the future. Under the power of eminent domain, state or municipal governments have laid claim to property and forced the removal of billboards. Under a concept called amortization by which a governmental body asserts that a billboard operator has earned compensation by continued operation over time, local governments have attempted to force removal of legal but nonconforming billboards (i.e., billboards that conformed with applicable zoning regulations when built but which do not conform to current zoning regulations). Although the legality of amortization is questionable, it has been upheld in some instances. Often, municipal and county governments also have sign controls as part of their zoning laws, with some local governments prohibiting construction of new billboards or allowing new construction only to replace existing structures. Although we have generally been able to obtain satisfactory compensation for those of our billboards purchased or removed as a result of governmental action, there is no assurance that this will continue to be the case in the future.
We have also introduced and intend to continue to expand the deployment of digital billboards that display static digital advertising copy from various advertisers that change every 6 to 8 seconds. We have encountered some existing regulations that restrict or prohibit these types of digital displays but it has not yet materially impacted our digital deployment. Since digital billboards have been developed and introduced relatively recently into the market on a large scale, existing regulations that currently do not apply to them by their terms could be revised or new regulations could be enacted to impose greater restrictions. These regulations may impose greater restrictions on digital billboards due to alleged concerns over aesthetics or driver safety.
Relatively few large scale studies have been conducted to date regarding driver safety issues, if any, related to digital billboards. On December 30, 2013, the results of a study conducted by the U.S. Department of Transportation and the Federal Highway Administration that looked at the effect of digital billboards and conventional billboards on driver visual behavior were issued. The conclusions of the report indicated that the presence of digital billboards did not appear to be related to a decrease in looking toward the road ahead and were generally within acceptable thresholds. The report cautioned, however, that it adds to the knowledge base but does not present definitive answers to the research questions investigated. Accordingly, the results of future studies may result in regulations at the federal or state level that impose greater restrictions on digital billboards. Any new restrictions on digital billboards could have a material adverse effect on both our existing inventory of digital billboards and our plans to expand our digital deployment, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Legal Proceedings
From time to time, we are involved in litigation in the ordinary course of business, including disputes involving advertising contracts, site leases, employment claims and construction matters. We are also involved in routine administrative and judicial proceedings regarding billboard permits, fees and compensation for condemnations. We are not a party to any lawsuit or proceeding which, in the opinion of management, is likely to have a material adverse effect on us.
Real Estate Portfolio
Our management headquarters is located in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. We also own 126 local operating facilities with front office administration and sales office space connected to back-shop poster and bulletin production space. In addition, we lease an additional 130 operating facilities at an aggregate lease expense for 2019 of approximately $8.3 million.
We own over 8,900 parcels of property beneath our advertising displays. As of December 31, 2019, we leased over 74,300 outdoor sites, accounting for an annualized lease expense of approximately $287.6 million. This
70
Table of Contents
amount represented approximately 19% of billboard advertising net revenues for that period. These leases are for varying terms ranging from month-to-month to a term of over ten years, and many provide us with renewal options. Our lease agreements generally permit us to use the land for the construction, repair and relocation of outdoor advertising displays, including all rights necessary to access and maintain the site. Approximately 69% of our leases will expire or be subject to renewal in the next 5 years, 20% will expire or be subject to renewal in 6 to 10 years and 11% thereafter. There is no significant concentration of displays under any one lease or subject to negotiation with any one landlord. An important part of our management activity is to manage our lease portfolio and negotiate suitable lease renewals and extensions.
The following table illustrates the number of leased and owned sites by state as of December 31, 2019, which is sorted from greatest to least in number and percentage of leased sites. States in which we lease less than 2% of our portfolio are grouped in the category “All Other States.”
State | # of billboard leased sites | % of total | # of owned billboard sites | % of total | ||||||||||||
Texas | 5,669 | 7.6 | % | 962 | 10.7 | % | ||||||||||
Pennsylvania | 5,264 | 7.1 | % | 1,459 | 16.3 | % | ||||||||||
California | 4,564 | 6.1 | % | 130 | 1.5 | % | ||||||||||
Ohio | 4,511 | 6.1 | % | 533 | 6.0 | % | ||||||||||
North Carolina | 4,261 | 5.7 | % | 249 | 2.8 | % | ||||||||||
Tennessee | 3,252 | 4.4 | % | 415 | 4.6 | % | ||||||||||
Louisiana | 3,164 | 4.3 | % | 481 | 5.4 | % | ||||||||||
Alabama | 3,067 | 4.1 | % | 433 | 4.8 | % | ||||||||||
Wisconsin | 2,807 | 3.8 | % | 291 | 3.3 | % | ||||||||||
Georgia | 2,751 | 3.7 | % | 249 | 2.8 | % | ||||||||||
Florida | 2,652 | 3.6 | % | 376 | 4.2 | % | ||||||||||
South Carolina | 2,513 | 3.4 | % | 131 | 1.5 | % | ||||||||||
New York | 2,331 | 3.1 | % | 188 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||||
Missouri | 2,242 | 3.0 | % | 213 | 2.4 | % | ||||||||||
Michigan | 2,000 | 2.7 | % | 264 | 2.9 | % | ||||||||||
Mississippi | 1,949 | 2.6 | % | 358 | 4.0 | % | ||||||||||
Indiana | 1,859 | 2.5 | % | 266 | 3.0 | % | ||||||||||
Oklahoma | 1,827 | 2.5 | % | 129 | 1.4 | % | ||||||||||
Virginia | 1,651 | 2.2 | % | 160 | 1.8 | % | ||||||||||
Illinois | 1,560 | 2.1 | % | 311 | 3.5 | % | ||||||||||
All Other States | 14,470 | 19.4 | % | 1,355 | 15.0 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| 74,364 | 100.0 | % | 8,953 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||
Contract Expirations
We derive revenues primarily from renting advertising space to customers on our advertising displays. Our contracts with customers generally cover periods ranging from one week to one year and are generally billed every four weeks. Since contract terms are short-term in nature, we do not consider revenues by year of contract expiration to be meaningful.
Employees
We employed approximately 3,400 people as of June 30, 2020. Approximately 250 employees were engaged in overall management and general administration at our management headquarters in Baton Rouge, Louisiana, and the remainder, including approximately 1,000 local account executives, were employed in our operating offices.
Fifteen of our local offices employ billposters and construction personnel who are covered by collective bargaining agreements. We believe that our relationship with our employees, including approximately 110 unionized employees, is good, and we have never experienced a strike or work stoppage.
71
Table of Contents
Inflation
In the last three years, inflation has not had a significant impact on us.
Seasonality
Our revenues and operating results are subject to seasonality. Typically, we experience our strongest financial performance in the summer and fall, and our weakest financial performance in the first quarter of the calendar year, partly because retailers cut back their advertising spending immediately following the holiday shopping season. We expect this trend to continue in the future. Because a significant portion of our expenses is fixed, a reduction in revenues in any quarter is likely to result in a period-to-period decline in operating performance and net earnings.
72
Table of Contents
POLICIES WITH RESPECT TO CERTAIN ACTIVITIES
The following is a discussion of our policies with respect to distributions, investments, financing, lending and certain other activities of Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media. These policies have been determined and will be periodically hereafter amended, in a manner consistent with legal and contractual requirements, by the board of directors of Lamar Advertising without notice to, or a vote of, the stockholders of Lamar Advertising.
Investment Policies
Investments in Real Estate or Interests in Real Estate
We hold and operate substantially all of our domestic billboard advertising display business and logo sign advertising business directly and indirectly through non-TRS subsidiaries, and we hold substantially all of our domestic transit advertising business and our advertising services business, as currently structured and operated, and our operations in Canada through TRSs. Our investment objective is to seek the highest risk adjusted returns on invested capital for our stockholders by simultaneously increasing recurring free cash flow per share and our return on invested capital. To achieve this, we expect that we will continue to deploy our capital through our annual capital expenditure program and strategic acquisitions, subject to available funds and market conditions.
| • | Annual capital expenditures program. We will continue to reinvest in our existing assets and expand our existing outdoor advertising display portfolio. This includes capital expenditures associated with maintenance and capitalized costs associated with the construction of new billboard displays, the entrance into and renewal of logo sign and transit contracts, and the purchase of real estate and operating equipment. |
| • | Acquisitions. We will seek to pursue strategic acquisitions of outdoor advertising businesses and assets. This includes acquisitions in our existing markets and in new markets where we can meet our return on investment criteria. When evaluating investments in new markets, our return on investment criteria reflects the additional risks inherent to the particular geographic area. |
However, due to the economic impacts of COVID-19, we are temporarily curtailing capital expenditures and limiting our acquisition activity. See “Recent developments—Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic”.
Subject to certain asset tests that Lamar Advertising must satisfy to continue to qualify as a REIT, there are currently no limitations on (a) the percentage of our assets that may be invested in any one property, venture or type of security, (b) the number of properties in which we may invest, or (c) the concentration of investments in a single geographic region. The board of directors of Lamar Advertising may establish limitations, and other policies, as it deems appropriate from time to time.
Investments in Securities of or Interests in Persons Primarily Engaged in Real Estate Activities and Other Issuers
Generally speaking, we do not expect to engage in any significant investment activities with other entities, although we may consider joint venture investments with other investors. We may also invest in the securities of other issuers in connection with acquisitions of indirect interests in properties (normally general or limited partnership interests in special purpose partnerships owning properties). We may in the future acquire some, all or substantially all of the securities or assets of other REITs or similar entities where that investment would be consistent with our investment policies and the REIT qualification requirements. There are no limitations on the amount or percentage of our total assets that may be invested in any one issuer, other than those imposed by the gross income and asset tests that Lamar Advertising must satisfy to continue to qualify as a REIT. However, we do not currently anticipate investing in other issuers of securities for the purpose of exercising control or acquiring any investments primarily for sale in the ordinary course of business or holding any investments with a view to making short-term profits from their sale, but we may engage in these activities in the future.
73
Table of Contents
We do not intend that our investments in securities will require us to register as an “investment company” under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, and we intend to divest securities before any registration would be required. We do not intend to engage in trading, underwriting, agency distribution or sales of securities of other issuers.
Investments in Other Securities
We may in the future invest in additional securities such as bonds, preferred stock and common stock. We have no present intention to make any such investments, except as described above, or investments in cash equivalents in the ordinary course of business. Future investment activities in additional securities will not be limited to any specific percentage of our assets or to any specific type of securities or industry group.
Investments in Mortgages
We have not invested in, nor do we have any present intention to invest in, real estate mortgages, although we are not prohibited from doing so.
Dispositions
Subject to REIT qualification rules, we may dispose of some of our assets if, based upon management’s periodic review of our business, the board of directors of Lamar Advertising determines that such action would be in the best interests of Lamar Advertising and its stockholders.
Financing Policy
Our financing policies will largely depend on the nature and timeline of our investment opportunities and the prevailing economic and market conditions. If the board of directors of Lamar Advertising determines that additional funding is desirable, we may raise funds through the following means:
| • | debt financings, including but not limited to, accessing U.S. debt capital markets and drawing from the revolving portion of our senior credit facility; |
| • | equity offerings of securities; and |
| • | any combination of the above methods. |
We intend to retain the maximum possible cash flow to fund our investments, subject to provisions in the Code requiring distribution of REIT taxable income to maintain Lamar Advertising’s REIT status, and to minimize our income and excise tax liabilities. Further, as of June 30, 2020 we had approximately $1.086 billion of total liquidity, which is comprised of approximately $177.1 million in cash and cash equivalents and approximately $737.2 million of availability under the revolving portion of our senior credit facility and $171.8 million of availability under our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. We intend to utilize our cash on hand and availability under the revolving portion of our senior credit facility to fund future discretionary investments.
We expect our primary source of external funding will continue to be the debt capital markets. Currently, we have outstanding the 5% Subordinated Notes (which were partially redeemed on August 31, 2020, and we expect will be fully redeemed on September 16, 2020), the $650.0 million 5 3/4% Senior Notes issued in January 2016 and February 2019 (the “5 3/4% Senior Notes”), the $600.0 million 2028 outstanding notes issued in February 2020, the $400.0 million 2029 outstanding notes issued in May 2020 and the $550.0 million 2030 outstanding notes issued February 2020 and August 2020.
We do not have a formal policy limiting the amount of indebtedness that we may incur, but we are subject to certain restrictions in our indentures and senior credit facility with regard to permitted indebtedness. In the future,
74
Table of Contents
we may seek to extend, expand, reduce or renew our senior credit facility, obtain new credit facilities or lines of credit, or issue new unsecured or secured debt that may contain limitations on indebtedness. We will consider a number of factors when evaluating our level of indebtedness and when making decisions regarding the incurrence of indebtedness, including overall prudence, the purchase price of assets to be acquired with debt financing, the estimated market value of our assets upon refinancing, our ability to generate cash flow to cover our expected debt service and restrictions under our existing debt arrangements. For additional information, see the section entitled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
Equity Capital Policies
Subject to applicable law and the requirements for listed companies on the NASDAQ, the board of directors of Lamar Advertising may also authorize, without the approval of its stockholders, the obtaining of additional capital through the issuance of equity securities. Pursuant to Lamar Advertising’s charter, Lamar Advertising has authority to issue up to 362.5 million shares of Class A common stock, 37.5 million shares of Class B common stock and 100 million shares of undesignated preferred stock, of which 5,720 shares are designated Series AA preferred stock. Under Delaware law, the affirmative vote of the holders of a majority of the outstanding shares of any class of common stock is required to approve any amendment to the certificate of incorporation that would increase or decrease the par value of that class, or modify or change the powers, preferences or special rights of the shares of any class so as to affect that class adversely. Lamar Advertising’s charter, however, allows for amendments to increase or decrease the number of authorized shares of Class A common stock or Class B common stock without a separate vote of either class.
Existing stockholders will have no preemptive right to additional shares issued in any offering, and any offering might cause a dilution of investment. Lamar Advertising may in the future seek to offer equity securities as a source of discretionary investment funding when (a) it is a requirement of a seller, (b) the size of a strategic transaction would increase Lamar Advertising’s leverage beyond what the board of directors or management believes to be appropriate, or (c) it is otherwise determined appropriate by the board of directors.
The board of directors of Lamar Advertising may authorize the issuance of shares of preferred stock with terms and conditions that could have the effect of delaying, deterring or preventing a transaction or a change in control in Lamar Advertising that might involve a premium price for holders of shares of Lamar Advertising’s common stock or otherwise might be in their best interests. Additionally, shares of Lamar Advertising’s preferred stock could have distribution, voting, liquidation and other rights and preferences that are senior to those of shares of Lamar Advertising’s common stock.
Lamar Advertising may, under certain circumstances, purchase shares of its common stock in the open market or in private transactions with its stockholders, if those purchases are approved by its board of directors or a committee thereof. On March 16, 2020, Lamar Advertising’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $250.0 million of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock. Additionally, the Board of Directors has authorized us to repurchase up to $250.0 million in outstanding senior or senior subordinated notes and other indebtedness outstanding from time to time under our senior credit facility. The repurchase program will expire on September 30, 2021 unless extended by the Board of Directors. There were no repurchases under the program as of June 30, 2020. Lamar Advertising’s and our management may opt not to make any repurchases under the program, or may make aggregate purchases less than the total amount authorized. Any repurchases under the program would only be taken in conformity with applicable federal and state laws and the applicable requirements for Lamar Advertising to continue to qualify as a REIT.
Lending Policy
We expect that we will continue to make loans to our operating subsidiaries to the extent to which they require additional financing to fund growth through their discretionary capital programs and acquisitions.
75
Table of Contents
Reports to Stockholders
Lamar Advertising makes available to its stockholders its annual reports, including its audited financial statements. Lamar Advertising is subject to the information reporting provisions of the Exchange Act, which require it to file annual and periodic reports, proxy statements and other information, including audited financial statements, with the Commission.
Other Activities
At all times, we intend to operate and to invest so as to comply with the Code requirements related to Lamar Advertising’s continued REIT qualification unless, due to changing circumstances or changes to the Code or Treasury regulations, the board of directors of Lamar Advertising determines that it is no longer in the best interests of Lamar Advertising and its stockholders to qualify as a REIT.
76
Table of Contents
Our directors serve until the next annual meeting of stockholders and until their successors are elected and qualified. Our officers serve until the board meeting immediately following the next annual meeting of stockholders and until their successors are elected and qualified.
The following table sets forth the name, position and, as of June 30, 2020, age of each of our directors and executive officers.
Name | Age | Title | ||||
Sean E. Reilly | 59 | Chief Executive Officer, President and Director | ||||
Jay L. Johnson | 44 | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer and Director | ||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. | 66 | Director | ||||
Charles Brent McCoy | 69 | Director | ||||
Sean E. Reilly has served as our Chief Executive Officer and as Chief Executive Officer of Lamar Advertising since February 2011. Mr. Reilly has served as our President and as President of Lamar Advertising since February 2020. Prior to becoming Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Reilly served as our Chief Operating Officer and as Chief Operating Officer and President of Lamar Advertising’s Outdoor Division from November 2001 to February 2011. Mr. Reilly also held the position of Vice President of Mergers and Acquisitions. He began working with Lamar Advertising as Vice President of Mergers and Acquisitions in 1987 and served in that capacity until 1994. Mr. Reilly has served as our director since July 1999, and he also served as a director of Lamar Advertising from 1989 to 1996 and from 1999 until 2003. Mr. Reilly was the Chief Executive Officer of Wireless One, Inc., a wireless cable television company, from 1994 to 1997, after which he rejoined Lamar Advertising. Mr. Reilly received a B.A. from Harvard University in 1984 and a J.D. from Harvard Law School in 1989. Sean Reilly provides the board with valuable media industry experience from both inside and outside the company.
Jay L. Johnson has served as our Chief Financial Officer, Executive Vice President and Treasurer and as Chief Financial Officer, Executive Vice President and Treasurer of Lamar Advertising since October 2019. Prior to joining us, Mr. Johnson served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of DiamondRock Hospitality Company beginning in April 2018 and as Senior Vice President and Treasurer of Host Hotels & Resorts from 2015 to 2018. Prior to his role as Senior Vice President and Treasurer of Host, Mr. Johnson served from 2010 through 2015 in various roles within the corporate finance/treasury group at Host. Prior to Host, he served in a variety of banking roles at KeyBank Real Estate Capital and Bank of America. Prior these banking roles, he was in the management consulting practice of Deloitte & Touche LLP, the investment banking group at Prudential Securities and the industrial markets trading division of Enron Corporation. Mr. Johnson received an M.B.A. from Harvard Business School in 2004 and a B.A. in economics from Morehouse College in 1998. Jay Johnson brings extensive financial experience and a deep knowledge of our industry to the board.
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. was appointed as Executive Chairman of the board of Lamar Advertising in February 2020 and has served as one of our directors since February 1984. Mr. Reilly previously served as our President from July 1999 to February 2020 and as President of Lamar Advertising from February 1989 to February 2020. Mr. Reilly also served as our Chief Executive Officer from July 1999 to February 2011 and as Chief Executive Officer of Lamar Advertising from February 1989 to February 2011. He has served as our director since July 1999 and as a director of Lamar Advertising since February 1984. Prior to becoming President and Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Reilly served as the President of Lamar Advertising’s Outdoor Division from 1984 to 1989. Mr. Reilly, our employee since 1978, has also served as General Manager of the Baton Rouge Region and Vice President and General Manager of the Louisiana Region. Mr. Reilly received a B.A. from Harvard University in 1977. Kevin Reilly, with over 35 years of experience with us, has unparalleled knowledge of our business and operating history.
77
Table of Contents
Charles Brent McCoy has served as Executive Vice President of Business Development of Lamar Advertising since May 2004. Mr. McCoy has served as our director since January 2009. He currently serves on several other boards, including Blue Cross Blue Shield of Louisiana and the Baton Rouge Advisory Board of Iberia Bank. Mr. McCoy received a B.A. from Emory University in 1973 and an M.B.A. from Stanford University in 1976. Charles Brent McCoy brings extensive experience in business and the banking sector to the board.
Family Relationships
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Lamar Advertising’s Executive Chairman and our director, and Sean E. Reilly, Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer and President and our Chief Executive Officer, President and director, are siblings.
78
Table of Contents
The following discussion and tables set forth certain compensation information for our Chief Executive Officer and each of our other executive officers for their positions with Lamar Advertising. We do not pay any additional compensation for their positions with us.
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
Lamar Advertising’s Compensation Committee has responsibility for establishing, implementing and maintaining the compensation program for its executive officers. For the year ended December 31, 2019, Lamar Advertising’s executive officers consisted of Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Sean E. Reilly, Jay L. Johnson and Keith A. Istre, who are also referred to herein as the “named executive officers.” This Compensation Discussion and Analysis sets forth the objectives and material elements of the compensation paid to the named executive officers for fiscal 2019.
Executive Compensation Philosophy
The primary objective of Lamar Advertising’s executive compensation program is to retain and reward executive officers who contribute to our long-term success. We believe this requires a competitive compensation structure both as compared to similarly situated companies in the media industry and other companies that are our peers in terms of annual revenues. Additionally, we seek to align a significant portion of executive officer compensation to the achievement of specified Lamar Advertising performance goals. Incentive cash bonuses are included to drive executive performance by having pay at risk so that a significant portion of potential cash compensation is tied to goal achievement. We also include performance-based equity grants as a significant component of prospective executive compensation so that the value of a portion of executive compensation is tied directly to the performance of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock. In addition, discretionary bonuses may be made to executive officers based upon accomplishments outside the scope of the performance metrics used in Lamar Advertising’s incentive programs.
Use of Compensation Consultants and Peer Group Data
Lamar Advertising’s Compensation Committee did not consult with any compensation consultants in conjunction with its executive officer compensation determinations for fiscal 2019. The Compensation Committee did not set executive officer compensation to a specific percentile of the range of total compensation represented by a specified peer group when making its executive compensation determinations for fiscal 2019.
Material Elements of Executive Officer Compensation
The key elements of compensation for Lamar Advertising’s executive officers are base salaries, performance-based cash incentive awards and performance-based equity awards. Executives may also participate, on the same terms as all other employees, in a 401(k) retirement savings plan and health and welfare benefits.
Base Salary. Lamar Advertising pays a base salary to each of the named executive officers. The objective of base salary is to provide a fixed component of cash compensation to the executive that reflects the level of responsibility associated with the executive’s position and is competitive with the base compensation the executive could earn in a similar position at comparable companies. Base salary for Lamar Advertising’s named executive officers is reviewed annually in light of market compensation, tenure, individual performance, Lamar Advertising’s performance and other subjective considerations. Typically Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. makes recommendations to the Compensation Committee with regard to base salary for the executive officers that he believes are justified in light of these considerations.
79
Table of Contents
In March 2019, the Compensation Committee reviewed current base salaries in conjunction with Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. The Compensation Committee reviewed the roles and responsibilities of each executive officer and determined that no changes were warranted. In May 2019, when Lamar Advertising identified Jay L. Johnson as the successor to Keith A. Istre, the Compensation Committee approved Mr. Johnson’s base salary effective as of his start date.
Performance-Based Incentive Compensation. Lamar Advertising’s incentive compensation program consists of two types of awards that are granted under Lamar Advertising’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended: (i) a performance-based incentive cash bonus and (ii) a performance-based incentive equity award. This compensation program was designed by the Compensation Committee to link a significant portion of overall executive officer compensation to the achievement of enumerated performance targets. By including a fixed share equity award as a significant portion of executive compensation, the aggregate value of each executive officer’s compensation is dependent on the performance of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock.
Incentive Cash Bonus. In March 2019, the Compensation Committee set target amounts for incentive cash bonuses for each of Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Sean E. Reilly, and Keith A. Istre with corresponding performance goals. The Compensation Committee reviews those target amounts annually based the executive’s roles and responsibilities, Lamar Advertising’s performance, and the current economic environment. The Compensation Committee determined that the 2019 target incentive cash bonus of Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Sean E. Reilly, and Keith A. Istre, would remain unchanged at $250,000, $400,000, and $300,000, respectively. The Compensation Committee then approved the performance goals for 2019 pursuant to which any payout of incentive cash bonus awards would be based. The Compensation Committee also continued its practice of providing the possibility of higher payouts that provide incentives for superior performance above the 100% targeted levels of achievement, which can result in an incentive cash bonus in an amount that is up to 200% of the target amount.
When setting the performance goals for these executive officers’ incentive cash bonuses for fiscal 2019, the Compensation Committee met with management to review current operating budgets and financial projections along with any current initiatives that could impact Lamar Advertising’s anticipated 2019 results. The Compensation Committee determined that Lamar Advertising’s pro forma net revenue growth and pro forma earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization and adjusted for gain or loss on disposition of assets and investments (referred to herein as “EBITDA”) growth continue to be the appropriate measures on which to base incentive compensation as these measures are the primary measures used by both management and the investor community to evaluate Lamar Advertising’s performance.
The Compensation Committee’s goal when determining the specific performance thresholds is to set target (100%) goal achievement at a challenging but achievable level based on the 2019 operating budget in order to provide appropriate incentives for management in the context of the current fiscal year’s projected results and current business plan. To align Lamar Advertising’s performance and the level of award achievement, the Compensation Committee maintained a 65% threshold for minimum achievement of both cash incentive and equity incentive awards. The 2019 performance goals for incentive cash bonuses were based on achievement of pro forma revenue growth and pro forma EBITDA growth for fiscal 2019 over fiscal 2018 with 50% of the total bonus amount tied to each metric. Tables setting forth the actual performance thresholds for fiscal 2019 are set forth below.
80
Table of Contents
Following this review, the Compensation Committee certified that (i) Lamar Advertising’s pro forma net revenue growth resulted in attainment of 100% of each such named executive officer’s target cash incentive bonus for fiscal 2019 based on revenue, and (ii) Lamar Advertising’s pro forma EBITDA growth resulted in attainment of 95% of each such named executive officer’s target cash incentive bonus for fiscal 2019 based on EBITDA. The total 2019 cash incentive bonus for each of Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Sean E. Reilly, and Keith A. Istre is set forth below and is reflected in the Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation column of the 2019 Summary Compensation Table
Incentive Cash Bonus
| 2019 Awards | ||||||||||||
| Portion (50%) Based on Pro Forma Net Revenue Growth ($) | Portion (50%) Based on Pro Forma EBITDA Growth ($) | Total ($) | ||||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. | $ | 125,000 | $ | 118,750 | $ | 243,750 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Sean E. Reilly | $ | 200,000 | $ | 190,000 | $ | 390,000 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Keith A. Istre | $ | 150,000 | $ | 142,500 | $ | 292,500 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| * | In February 2020, Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. resigned as President and was appointed as Executive Chairman of the Board and Sean E. Reilly assumed the title of President in addition to Chief Executive Officer. |
Incentive Equity Awards. The Compensation Committee also determined the target amount of incentive equity awards for each of Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Sean E. Reilly, and Keith Istre at its March 2019 meeting. These target equity award amounts were set at 44,000 shares of Class A Common Stock for both Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and Sean E. Reilly, which amounts have remained unchanged since 2006. Keith A. Istre’s target equity incentive award of 34,000 shares of Class A common stock was also held constant. The Compensation Committee reaffirmed its belief that fixed share amounts provided appropriate incentives and alignment with interests of stockholders.
Under the terms of Lamar Advertising’s incentive equity award program, no shares of stock are issued unless and until the relevant performance goals have been met and certified by the Compensation Committee. Any earned shares are issued as soon as practicable following such certification and are fully vested at the time of issuance. The Compensation Committee feels that the use of stock awards as a part of its compensation program aligns executive compensation to the creation of stockholder value but not to such an extent that it would create incentives for executives to focus solely on short-term stock appreciation to the exclusion of long-term strategy.
The pro forma revenue growth and pro forma EBITDA growth metrics for fiscal 2019 over fiscal 2018 used in the context of the incentive cash awards were used to determine the achievement of incentive equity awards. Unlike incentive cash awards, there is no opportunity to achieve greater than 100% of the target equity awards.
On that basis, (i) Lamar Advertising’s pro forma net revenue growth resulted in attainment of 100% of each named executive officer’s target incentive equity award for 2019 based on revenue and (ii) Lamar Advertising’s pro forma EBITDA growth resulted in attainment of 95% of each named executive officer’s target incentive equity award for 2019 based on EBITDA. The total 2019 incentive equity awards earned by each executive is set forth below and reflected in the Stock Awards column of the 2019 Summary Compensation Table (see footnote 1
81
Table of Contents
to the 2019 Summary Compensation Table, which describes the assumptions underlying the calculation of the aggregate grant date fair value of these awards).
Incentive Equity Awards
| 2019 Awards | ||||||||||||
| Portion (50%) Based on Pro Forma Net Revenue Growth (#) | Portion (50%) Based on Pro Forma EBITDA Growth (#) | Total Shares Class A Common Stock (#) | ||||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. | 22,000 | 20,900 | 42,900 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Sean E. Reilly | 22,000 | 20,900 | 42,900 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Keith A. Istre | 17,000 | 16,150 | 33,150 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| * | In February 2020, Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. resigned as President and was appointed as Executive Chairman of the Board and Sean E. Reilly assumed the title of President in addition to Chief Executive Officer. |
The tables that follow set forth the level of pro forma net revenue and pro forma EBITDA growth required for fiscal 2019 over fiscal 2018 to achieve the stated percentage of target incentive awards for our named executive officers as set by the Compensation Committee in March 2019. These goals relate to achievement of both incentive cash and incentive equity awards, except that equity awards cannot exceed their target amount irrespective of goal achievement in excess of the 100% level.
2019 POTENTIAL INCENTIVE AWARDS*
Pro Forma Net Revenue Growth(1)—50%
Incentive Cash Bonus | ||||
Pro Forma Net Revenue Growth | Percentage of Target Bonus Earned | |||
Less than 1.6% | 0 | % | ||
At least 1.6% but less than 1.9% | 65 | % | ||
At least 1.9% but less than 2.0% | 70 | % | ||
At least 2.0% but less than 2.2% | 75 | % | ||
At least 2.2% but less than 2.3% | 80 | % | ||
At least 2.3% but less than 2.4% | 85 | % | ||
At least 2.4% but less than 2.6% | 90 | % | ||
At least 2.6% but less than 2.7% | 95 | % | ||
At least 2.7% but less than 4.0% | 100 | %* | ||
At least 4.0% but less than 4.5% | 125 | % | ||
At least 4.5% but less than 5.0% | 150 | % | ||
At least 5.0% but less than 5.5% | 175 | % | ||
At least 5.5% or greater | 200 | % | ||
Incentive Equity Award | ||||
Pro Forma Net Revenue Growth | Percentage of Target Bonus Earned | |||
Less than 1.6% | 0 | % | ||
At least 1.6% but less than 1.9% | 65 | % | ||
At least 1.9% but less than 2.0% | 70 | % | ||
At least 2.0% but less than 2.2% | 75 | % | ||
At least 2.2% but less than 2.3% | 80 | % | ||
At least 2.3% but less than 2.4% | 85 | % | ||
At least 2.4% but less than 2.6% | 90 | % | ||
At least 2.6% but less than 2.7% | 95 | % | ||
At least 2.7% or greater | 100 | %* | ||
| * | Denotes goal achieved for 2019 as certified by the Compensation Committee. |
| (1) | Pro forma net revenue growth is based on Lamar Advertising’s net revenue growth in 2019 over 2018 based on actual 2019 net revenue versus 2018 net revenue, as adjusted to reflect acquisitions and divestitures for the same time frame as actually owned in 2019. |
82
Table of Contents
2019 POTENTIAL INCENTIVE AWARDS*
Pro Forma EBITDA Growth(1)—50%
Incentive Cash Bonus | ||||
Pro Forma EBITDA Growth | Percentage of Target Bonus Earned | |||
Less than 2.3% | 0 | % | ||
At least 2.3% but less than 2.5% | 65 | % | ||
At least 2.5% but less than 2.6% | 70 | % | ||
At least 2.6% but less than 2.8% | 75 | % | ||
At least 2.8% but less than 3.0% | 80 | % | ||
At least 3.0% but less than 3.2% | 85 | % | ||
At least 3.2% but less than 3.3% | 90 | % | ||
At least 3.3% but less than 3.6% | 95 | %* | ||
At least 3.6% but less than 4.0% | 100 | % | ||
At least 4.0% but less than 4.5% | 125 | % | ||
At least 4.5% but less than 5.0% | 150 | % | ||
At least 5.0% but less than 5.5% | 175 | % | ||
At least 5.5% or greater | 200 | % | ||
Incentive Equity Award | ||||
Pro Forma EBITDA Growth | Percentage of Target Bonus Earned | |||
Less than 2.3% | 0 | % | ||
At least 2.3% but less than 2.5% | 65 | % | ||
At least 2.5% but less than 2.6% | 70 | % | ||
At least 2.6% but less than 2.8% | 75 | % | ||
At least 2.8% but less than 3.0% | 80 | % | ||
At least 3.0% but less than 3.2% | 85 | % | ||
At least 3.2% but less than 3.3% | 90 | % | ||
At least 3.3% but less than 3.6% | 95 | %* | ||
At least 3.6% or greater | 100 | % | ||
| * | Denotes goal achieved for 2019 as certified by the Compensation Committee. |
| (1) | Pro forma EBITDA growth is calculated in the same manner as pro forma net revenue growth with adjustments being made in the 2018 period to reflect acquisitions and divestitures for the same time frame as actually owned in 2019 and is also adjusted, solely with respect to calculation of incentive cash bonuses, to eliminate any expense in the period related to executive bonuses. |
Retirement of Keith A. Istre
Keith A. Istre resigned from his position as Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer of Lamar Advertising effective October 1, 2019 in connection with the start date of Jay L. Johnson. After this date, Mr. Istre assumed the title of Chief Financial Officer Emeritus. In consideration of his substantial contributions to Lamar Advertising and his assistance with the transition to Mr. Johnson through his retirement of December 31, 2019, Mr. Istre received the full amount of his agreed-upon 2019 compensation.
Compensation Paid to Jay L. Johnson
In addition to his base salary, Jay L. Johnson received a one-time discretionary stock grant, in consideration of compensation he forfeited as a result of resigning from his prior position, in an aggregate amount of 16,157 shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock, vesting in three equal installments on October 8, 2019 and the first and second anniversaries thereof. Mr. Johnson also received reimbursement of certain expenses incurred in connection with his relocation to Baton Rouge, Louisiana. Additionally, Lamar Advertising paid the following compensation to him in February 2020 in respect of his service in 2019: (i) an aggregate cash bonus payment of $315,000 and (ii) an aggregate of 6,303 shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock.
Beginning in 2020, Mr. Johnson became eligible to receive performance-based cash and stock bonuses consistent with the compensation paid to the other named executive officers. His initial annual target cash bonus amount is $300,000 and target stock bonus is 22,000 shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock. Lamar Advertising has agreed that he will receive the maximum stock bonus for the 2020 fiscal year. His cash bonus for the 2020 fiscal year will be payable based on the achievement of performance goals.
The Compensation Committee approved all amounts paid to Mr. Johnson, and such amounts were determined by the Compensation Committee to be advisable and appropriate in order to entice Mr. Johnson to accept his position with Lamar Advertising.
83
Table of Contents
Consideration of Prior Stockholder Advisory Vote on Executive Compensation
At Lamar Advertising’s 2020 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, over 96% of shares present at the meeting for purposes of the proposal were voted to approve, on an advisory basis, the compensation of Lamar Advertising’s named executive officers as disclosed in the proxy statement for that meeting, thus ratifying Lamar Advertising’s compensation philosophy and approach. Lamar Advertising’s board of directors and the Compensation Committee considered this overwhelming support, as well as Lamar Advertising’s past operating performance, in making the determination that the fundamental characteristics of Lamar Advertising’s executive compensation program should remain. The next advisory stockholder vote on executive compensation is scheduled to be held at Lamar Advertising’s 2023 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
Other Compensation Components
Discretionary Equity Awards. Lamar Advertising’s incentive compensation program permits the Compensation Committee to grant discretionary equity awards under its 1996 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended, that are not subject to achievement of performance criteria. Except as awarded to Jay L. Johnson, as described above, the named executive officers did not receive discretionary stock grants in 2019.
Perquisites. Lamar Advertising provides certain perquisites to the executive officers, including use of its aircraft and a company car. The executive officers are entitled to use Lamar Advertising’s aircraft, including for personal travel. These perquisites provide flexibility to the executives and increase travel efficiencies, allowing more productive use of executive time. More detail on these perquisites and other perquisites provided to Lamar Advertising’s executive officers may be found in the 2019 Summary Compensation Table.
Deferred Compensation. Lamar Advertising has a deferred compensation plan for certain officers, including the named executive officers. Under this plan, officers who meet certain criteria are eligible to receive company contributions into their accounts in the Lamar Deferred Compensation Plan. Officers do not have the option of deferring any portion of their earned cash compensation through additional voluntary contributions to the plan.
The deferred compensation plan is not funded by Lamar Advertising, and participants have an unsecured contractual commitment from Lamar Advertising to pay the amounts due under the deferred compensation plan. When payments under the plan are due, the funds are distributed from Lamar Advertising’s general assets. Lamar Advertising does not offer preferential earnings on deferred compensation. Deferred compensation is intended as a long-term savings vehicle for its officers in light of the fact that Lamar Advertising does not offer any traditional pension or defined benefit plan. The Compensation Committee does not consider deferred compensation accounts when setting executive pay levels, since this represents compensation that has previously been earned and individual accounts are a function of personal investment choices and market-based earnings.
Tax Implications
The Compensation Committee awards compensation to Lamar Advertising’s executive officers as it deems appropriate to meet its overall compensation objectives, even though it may not be fully deductible for the purposes of Section 162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”). In general, Section 162(m), prevents publicly held corporations from deducting, for federal income tax purposes, compensation paid in excess of $1,000,000 to certain executives. Historically, this deduction limitation did not apply, however, to compensation that constitutes “qualified performance-based compensation” within the meaning of Section 162(m) of the Code and the regulations promulgated thereunder.
For taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017, the exemption from Section 162(m)’s deduction limit for performance-based compensation has been repealed by legislation known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, such that compensation paid to Lamar Advertising’s named executive officers that is in excess of $1,000,000 will not be deductible by Lamar Advertising unless it qualifies for transition relief applicable to certain arrangements in place as of November 2, 2017 and not modified thereafter. Subject to the overall compensation objectives of Lamar Advertising, the Compensation Committee intends to administer any awards granted prior to November 2, 2017 which qualify as “performance-based compensation” under Section 162(m) of the Code, as amended by the Act, in accordance with the transition rules applicable to binding contracts in effect on November 2, 2017.
84
Table of Contents
Payments Upon Termination or Change–in–Control
Neither we nor Lamar Advertising have employment agreements or other agreements with any of our executive officers that entitle them to payments upon termination or in the event of a change-in-control, except that unvested shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock granted to Mr. Johnson on October 8, 2019 vest automatically upon his involuntary termination or death.
Compensation Policies and Practices as they Relate to Risk Management
Lamar Advertising’s management has reviewed its compensation policies and practices in conjunction with the Compensation Committee to determine if these policies and practices create risks that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on Lamar Advertising. Lamar Advertising’s basic compensation structure, as described above, includes base salaries, incentive cash bonuses and, for officers of Lamar Advertising (including certain non-executive officers), incentive equity compensation that primarily consists of annual performance-based equity awards. In light of this review of the compensation structure and its mix of both fixed and variable compensation, Lamar Advertising concluded that there are no risks arising from its compensation policies and practices for its employees that are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on Lamar Advertising.
85
Table of Contents
2019 Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth certain compensation information for Lamar Advertising’s named executive officers. The table reflects each officer’s position as of December 31, 2019.
Name and Principal Position | Year | Salary ($) | Bonus ($) | Stock Awards ($)(1) | Option Awards ($)(1) | Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation ($)(2) | All Other Compensation ($)(3)(4) | Total ($) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. Chairman of the Board and President* | 2019 | 100,000 | — | 3,422,320 | (5) | — | 243,750 | 157,508 | 3,923,578 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 100,000 | — | 3,864,836 | (6) | — | 343,750 | 243,622 | (8) | 4,552,208 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 100,000 | — | 3,331,680 | (7) | — | — | 280,243 | 3,711,923 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sean E. Reilly Chief Executive Officer* | 2019 | 700,000 | — | 3,422,320 | (5) | — | 390,000 | 453,790 | 4,966,110 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 700,000 | — | 3,864,836 | (6) | — | 550,000 | 444,274 | (8) | 5,559,110 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 700,000 | — | 3,331,680 | (7) | — | — | 385,119 | 4,416,799 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Jay L. Johnson Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer (Appointed October 1, 2019) | 2019 | 150,000 | — | 1,318,250 | (9) | — | — | 134,417 | 1,602,667 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Keith A. Istre Chief Financial | 2019 | 500,000 | — | 2,644,520 | (5) | — | 292,500 | 52,500 | 3,489,520 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 500,000 | — | 3,047,169 | (6) | — | 412,500 | 52,500 | 4,012,169 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 500,000 | — | 2,574,480 | (7) | — | — | 52,500 | 3,126,980 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * | In February 2020, Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. resigned as President and was appointed as Executive Chairman of Lamar Advertising’s Board and Sean E. Reilly assumed the title of President in addition to Chief Executive Officer. |
| (1) | Reflects the aggregate grant date fair value recognized for financial statement reporting purposes in accordance with ASC Topic 718. With respect to performance-based stock awards, the grant date fair value is calculated assuming the probable outcome of achievement, which on the grant date was expected to be 100% of the target equity incentive award amount, rather than the value of the actual award earned on the date when issued to the officer. For the assumptions underlying the valuation of these awards see Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Lamar Advertising’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019, filed with the Commission on February 20, 2020. With respect to discretionary stock grants, the grant date fair value is calculated as of the date of grant. |
| (2) | Amounts shown in the “Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation” column reflect the incentive cash awards granted at the beginning of each year, earned based on performance during that fiscal year and paid in the following fiscal year. The 2019 awards are described in further detail under the headings “Performance-Based Incentive Compensation” and “Incentive Cash Bonus” in the Compensation Discussion and Analysis and are also reflected in the table “Grants of Plan-Based Awards in Fiscal Year 2019” under the column “Estimated Future Payouts Under Non-Equity Incentive Plan Awards.” |
| (3) | Includes $94,986, $120,234, $202,893 for Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and $392,910, $338,437, and $323,903 for Mr. Sean E. Reilly for the personal use of the company aircraft in 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively, as further described below. Includes $81,817 for Mr. Johnson for relocation expenses in 2019. The amounts included in the “All Other Compensation” column also include the following perquisites provided to our named executive officers (except as otherwise indicated), which are valued at Lamar Advertising’s incremental cost, none of which individually exceeded $25,000: (a) personal use of a company car, |
86
Table of Contents
| (b) company-paid health insurance premiums and medical reimbursements, (c) personal use of a company-owned recreational facility by Mr. Sean E. Reilly and Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and (d) company-paid premiums for term life insurance for Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. Executives also have access to a country club at which the company has a membership, but each executive pays all fees related to such personal use, resulting in no additional incremental cost to Lamar Advertising. |
Lamar Advertising’s incremental cost for personal use of the corporate aircraft is based on the incremental cost to Lamar Advertising calculated based on the variable costs, related to the number of flight hours used, including fuel costs, landing/ramp fees, trip-related maintenance, crew travel expenses, supplies and catering, aircraft accrual expenses per hour of flight, any customs and foreign permit or similar fees. Our fixed costs that do not change based on usage, such as pilot salaries and the cost of maintenance not related to trips are excluded. The incremental cost to Lamar Advertising for personal use of a company car is calculated as a portion of the annual lease, mileage and fuel attributable to the personal use.
| (4) | Also includes employer contributions under Lamar Advertising’s deferred compensation plan of $50,000 for each of Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Mr. Sean E. Reilly and Mr. Istre for 2019, 2018 and 2017 and $50,000 for Mr. Johnson for 2019. |
| (5) | The ASC Topic 718 value of the shares actually earned based on achievement of performance goals for fiscal 2019, which awards were certified as earned by the Compensation Committee and issued on (i) February 19, 2020, for each of Mr. Sean E. Reilly and Mr. Istre, was $4,084,080 and $3,155,880 respectively and (ii) March 11, 2020, for Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., was $2,927,925. |
| (6) | Consists of performance-based stock awards in respect of 2018 performance and discretionary stock awards in respect of 2017 performance made in 2018. The ASC Topic 718 value of the performance-based stock awards was $2,878,040 for each of Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and Mr. Sean E. Reilly and $2,223,940 for Mr. Istre. They each earned 100% of their performance-based stock awards based on achievement of performance goals for fiscal 2018, which awards were certified as earned by the Compensation Committee and issued on February 18, 2019. Additionally, on February 26, 2018, the Compensation Committee approved discretionary stock grants to each of Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Mr. Sean E. Reilly and Mr. Istre for their 2017 contributions. The discretionary grant to Mr. Istre was made on February 26, 2018, and the ASC Topic 718 value of the discretionary shares awarded to Mr. Istre was $823,229. The discretionary grants to Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and Mr. Sean E. Reilly were made on March 9, 2018, after the receipt of necessary approvals under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976, as amended, and the ASC Topic 718 value of the discretionary shares awarded to each of Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and Mr. Sean E. Reilly was $986,796. |
| (7) | No shares were earned based on achievement of performance goals for fiscal 2017 for each of Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Mr. Sean E. Reilly and Mr. Istre. |
| (8) | Includes the payment of filing fees of $45,000 on behalf of each of Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and Mr. Sean E. Reilly in connection with filings made under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976, as amended (“HSR Act”). The Compensation Committee reviewed the legal requirements under the HSR Act and the triggering events for the filing requirement as a result of incentive equity awards granted to such executive officers. Based on this review, the Compensation Committee approved the payment by Lamar Advertising of the HSR Act filing fees otherwise payable by the executive officers. The Compensation Committee determined that these payments were appropriate because of the unavailability of an HSR Act exemption for receipt of stock by executive officers and because the filing obligation arose as a direct result of Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and Mr. Sean E. Reilly serving as officers of Lamar Advertising. The Compensation Committee further noted that the filing requirement was triggered by the cumulative holdings of the executive officers that were received over a long period of time during which they have made substantial contributions to Lamar Advertising and its growth. Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. and Mr. Sean E. Reilly each were responsible for taxes due as a result of Lamar Advertising paying the filing fees and they were not provided a tax gross-up payment related to the imputed compensation associated with this payment on their behalf. |
| (9) | Shares issued on October 8, 2019 in connection with Mr. Johnson’s start date. |
87
Table of Contents
Grants of Plan-Based Awards in Fiscal Year 2019
The following table sets forth certain compensation information for Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer and each of Lamar Advertising’s other executive officers (which are Lamar Media’s only executive officers).
Name | Grant Date | Estimated Future Payouts Under Non-Equity Incentive Plan Awards(1) | Estimated Future Payouts Under Equity Incentive Plan Awards(2) | All other stock awards: Number of shares of stock or units (#) | Grant Date Fair Value of Stock and Option Awards ($)(4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Threshold ($) | Target ($) | Maximum ($) | Threshold (#) | Target (#) | Maximum (#) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. | 3/15/2019 | 162,500 | 250,000 | 500,000 | 28,600 | 44,000 | 44,000 | — | 3,422,320 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sean E. Reilly | 3/15/2019 | 260,000 | 400,000 | 800,000 | 28,600 | 44,000 | 44,000 | — | 3,422,320 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Jay L. Johnson | 10/8/2019 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 16,157 | 1,318,250 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Keith A. Istre | 3/15/2019 | 195,000 | 300,000 | 600,000 | 22,100 | 34,000 | 34,000 | — | 2,644,520 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents the possible cash bonus granted under Lamar Advertising’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan that could be earned by achieving defined performance goals. Threshold amount assumes minimum attainment of both EBITDA and revenue levels to receive payment. |
| (2) | These awards constitute possible shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock issuable upon achievement of defined performance goals under Lamar Advertising’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan. Threshold amount assumes minimum attainment of both EBITDA and revenue levels to receive payment. |
| (3) | These awards constitute discretionary shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock issued under Lamar Advertising’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan. |
| (4) | Reflects the aggregate grant date fair value in accordance with ASC Topic 718 assuming the probable outcome of achievement, which for performance stock awards on the grant date was expected to be 100% of the target equity incentive award amount, rather than the value of the actual award earned on the date when issued to the officer. For the assumptions underlying the valuation of these awards see Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Lamar Advertising’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019, filed with the Commission on February 20, 2020. |
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End 2019
The following table sets forth certain compensation information for Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer and each of Lamar Advertising’s other executive officers (which are Lamar Media’s only executive officers).
| Option Awards | Stock Awards | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Name | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Exercisable | Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) Unexercisable | Option Exercise Price ($) | Option Expiration Date | Number of shares or units of stock that have not vested (#) | Market value of shares or units of stock that have not vested ($) | ||||||||||||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. | 100,000 | (1) | 0 | (1) | 42.21 | 1/24/2023 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Jay L. Johnson | — | — | — | — | 10,771 | (2) | $ | 961,419.46 | (3) | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | Granted on January 24, 2013. 20% of the award vested immediately upon grant, and an additional 20% vested on the next four anniversaries of the grant date. |
| (2) | Granted on October 8, 2019. 5,386 shares will vest on October 8, 2020 and 5,385 shares will vest on October 8, 2021. |
| (3) | Based on the closing price of $89.26 as of December 31, 2019. |
88
Table of Contents
Option Exercises and Stock Vested in Fiscal Year 2019
The following table sets forth certain compensation information for Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer and each of Lamar Advertising’s other executive officers (which are Lamar Media’s only executive officers).
| Option Awards | Stock Awards | |||||||||||||||
Name | Number of Shares Acquired on Exercise (#) | Value Realized on Exercise ($)(1) | Number of Shares Acquired on Vesting (#) | Value Realized on Vesting ($) | ||||||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Sean E. Reilly | 100,000 | 3,675,911.50 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Jay L. Johnson | — | — | 5,386 | 439,443.74 | ||||||||||||
Keith A. Istre | 4,209 | 148,914.42 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| (1) | Calculated as the product of (a) the number of shares of Lamar Advertising Class A common stock for which the stock options were exercised and (b) the excess of the closing price of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock on the NASDAQ Global Select Market on the date of the exercise over the applicable exercise price per share of the stock options. |
Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation for Fiscal Year 2019
The following table sets forth certain compensation information for Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer and each of Lamar Advertising’s other executive officers (which are Lamar Media’s only executive officers).
Name | Registrant Contributions in Last FY ($)(1) | Aggregate Earnings (Loss) in Last FY ($)(2) | Aggregate Balance at Last FYE ($)(3) | |||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. | 50,000 | 840,038.92 | 6,150,835.33 | |||||||||
Sean E. Reilly | 50,000 | 337,451.29 | 1,835,122.07 | |||||||||
Jay L. Johnson | 50,000 | — | — | |||||||||
Keith A. Istre | 50,000 | 94,994.92 | 1,149,730.80 | |||||||||
| (1) | Amounts in this column are included in the “All Other Compensation” column in the 2019 Summary Compensation Table. |
| (2) | Amounts in this column are not included in the 2019 Summary Compensation Table because they were not preferential or above market. |
| (3) | This column includes amounts in each named executive officer’s total deferred compensation account as of the last day of fiscal 2019, which includes (i) the following total previous contributions reported in each of Lamar Advertising’s previous proxy statements: Mr. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., $1,061,500; Mr. Sean E. Reilly, $765,000; and Mr. Keith A. Istre, $711,500; and (ii) aggregate earnings on all previously contributed amounts. This column does not include contributions for each officer for the 2019 fiscal year, which were made in January 2020 and reported in the first column. |
Lamar Advertising sponsors a deferred compensation plan for the benefit of certain of its board-elected officers who meet specific age, years of service and other criteria. Officers that met certain criteria are eligible for annual company contributions to the plan, depending on the employee’s length of service. Lamar Advertising’s contributions to the plan are maintained in a rabbi trust. Upon termination, death or disability, participating employees are eligible to receive an amount equal to the fair market value of the assets in the employee’s deferred compensation account either in a lump sum distribution or in twenty percent installments over a five-year period.
89
Table of Contents
Pay Ratio
Pursuant to the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the Commission adopted a rule requiring public companies to annually disclose the pay ratio between their median employee’s annual total compensation and the total compensation of the principal executive officer. Lamar Advertising’s principal executive officer is Mr. Sean E. Reilly, its Chief Executive Officer.
For 2019:
| • | the annual total compensation of the median of all Lamar Advertising employees (other than its Chief Executive Officer) was $59,550. |
| • | the annual total compensation of Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer, as reported in the Summary Compensation Table, was $4,966,110. |
Based on this information, for 2019 the ratio of the annual total compensation of Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer to the annual total compensation of its median employee, as required to be reported pursuant to Item 402 of Regulation S-K, was 83.4:1.
The annual total compensation of Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer as reported above is the amount reported in the Summary Compensation Table. As detailed in footnote 1 to the Summary Compensation Table, this amount includes the aggregate grant date fair value of a performance-based stock award assuming the probable outcome of achievement of performance targets, but does not reflect the actual performance-based stock award earned by Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer.
The median employee was identified using a listing of all employees as of December 31, 2019, and calculating the median amount of total 2019 compensation as it would be reported based on the IRS instructions for Box 5, Medicare wages and tips. Actual amounts reported on Box 5 for 2019 were used for all employees who were employed throughout the entire year. We further annualized pay for those individuals not employed for a full year in 2019. Once we identified Lamar Advertising’s median employee, we calculated such employee’s annual total compensation for 2019 in accordance with the requirements of Item 402(c)(2)(x) of Regulation S-K.
This pay ratio is a reasonable estimate calculated in a manner consistent with Commission rules based on Lamar Advertising’s payroll and employment records and the methodology described above. The Commission rules for identifying the median compensated employee and calculating the pay ratio based on that employee’s annual total compensation allow companies to adopt a variety of methodologies, to apply certain exclusions, and to make reasonable estimates and assumptions that reflect their compensation practices. As such, the pay ratio reported by other companies may not be comparable to the pay ratio reported above, as other companies may have different employment and compensation practices and may utilize different methodologies, exclusions, estimates and assumptions in calculating their own pay ratios.
Director Compensation in Fiscal Year 2019
All of our directors are employees and receive no additional compensation for their services as directors.
90
Table of Contents
EQUITY COMPENSATION PLAN INFORMATION
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2019 with respect to shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock that may be issued under its existing compensation plans.
Plan Category | (a) Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights | (b) Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights | (c) Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) | |||||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders(1) | | 887,491 | (2) | | 57.97 | (3) | | 3,107,905 | (4)(5) | |||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | n/a | n/a | n/a | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total | 887,491 | 57.97 | 3,107,905 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| (1) | Consists of Lamar Advertising’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended and 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, as amended. |
| (2) | Includes shares issuable upon achievement of outstanding performance-based awards under Lamar Advertising’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan. Does not include purchase rights accruing under Lamar Advertising’s 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan because the purchase price (and therefore the number of shares to be purchased) will not be determined until the end of the purchase period. |
| (3) | Does not take into account shares issuable upon achievement of outstanding performance-based awards, which will be issued for no consideration. |
| (4) | Includes shares available for future issuance under Lamar Advertising’s 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan. Under the evergreen formula of this plan, on the first day of each fiscal year beginning with 2020, the aggregate number of shares that may be purchased through the exercise of rights granted under the plan is increased by the lesser of (a) 500,000 shares, (b) one-tenth of one percent of the total number of shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock outstanding on the last day of the preceding fiscal year, and (c) a lesser amount determined by the board of directors. On January 1, 2020, 86,093 shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock were added to the 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan pursuant to the evergreen formula. |
91
Table of Contents
We are a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising Company, which owns all 100 shares of our outstanding common stock.
Lamar Advertising Company Common Stock
The following table sets forth certain information known to us as of July 31, 2020 with respect to the shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock and Class B common stock that are beneficially owned as of that date by: (i) each of Lamar Advertising’s directors; (ii) each of Lamar Advertising’s executive officers named in the 2019 Summary Compensation Table; (iii) all of Lamar Advertising’s directors and executive officers as a group; and (iv) each person known by Lamar Advertising to beneficially own more than 5% of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock or Class B common stock. Lamar Advertising’s Class B common stock is convertible into Class A common stock on a one-for-one basis. Except as otherwise indicated, we believe each beneficial owner named below has sole voting and sole investment power with respect to all shares beneficially owned by that holder. Percentage calculations of beneficial ownership are based on 86,406,356 shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class A common stock and 14,420,085 shares of Lamar Advertising’s Class B common stock outstanding on July 31, 2020.
Beneficial Owner | Title of Class | No. of Shares Owned | Percent of Class | |||||||
Directors, Nominees for Director and Executive Officers | ||||||||||
Kevin P. Reilly, Jr.○ | Class A Class B(2) | | 410,298 11,362,250 | (1) (3)(4) | | * 78.79% | (5) | |||
Sean E. Reilly | Class A Class B(2) | | 23,672 10,557,835 | (4)(6) | | * 73.22% | (7) | |||
Anna Reilly○ | Class A Class B(2) | | 154,646 10,000,000 | (8) (4)(9) | | * 69.35% | (10) | |||
Wendell Reilly○ | Class A Class B(2) | | 12,832 9,500,000 | (11) (4)(12) | | * 65.88% | (13) | |||
Jay L. Johnson | Class A | 17,207 | * | |||||||
Keith A. Istre§ | Class A | 126,618 | * | |||||||
Stephen P. Mumblow○ | Class A | 6,675 | (14) | * | ||||||
Thomas V. Reifenheiser○ | Class A | 46,611 | 15) | * | ||||||
John E. Koerner, III○ | Class A | 52,375 | (16) | * | ||||||
Marshall Loeb○ | Class A | 2,305 | * | |||||||
Elizabeth Thompson○ | Class A | 1,495 | * | |||||||
Nancy Fletcher○ | N/A | 2,303 | * | |||||||
All Current Directors and Executive Officers as a Group (10 Persons) | Class A & B | 15,150,504 | (17) | 15.03% | (18) | |||||
Five Percent Stockholders | ||||||||||
Reilly Family, LLC | Class B(2) | 9,000,000 | 62.41% | (19) | ||||||
The Vanguard Group 100 Vanguard Blvd. | Class A | 12,694,569 | (20) | 14.69% | ||||||
BlackRock, Inc. 55 East 52nd Street New York, NY 10055 | Class A | 8,925,903 | (21) | 10.33% | ||||||
Janus Henderson Group plc 201 Bishopsgate EC2M 3AE | Class A | 7,762,836 | (22) | 8.98% | ||||||
92
Table of Contents
| * | Less than 1%. |
| ○ | Current director of Lamar Advertising. |
| § | Former executive officer of Lamar Advertising and former executive officer and director of Lamar Media. |
| (1) | Includes 100,000 shares subject to stock options exercisable within 60 days of July 31, 2020. |
| (2) | Upon the sale of any shares of Class B common stock to a person other than to a Permitted Transferee, such shares will automatically convert into shares of Class A common stock. Permitted Transferees include (i) a descendant of Kevin P. Reilly, Sr.; (ii) a spouse or surviving spouse (even if remarried) of any individual named or described in (i) above; (iii) any estate, trust, guardianship, custodianship, curatorship or other fiduciary arrangement for the primary benefit of any one or more of the individuals named or described in (i) and (ii) above; and (iv) any corporation, partnership, limited liability company or other business organization controlled by and substantially all of the interests in which are owned, directly or indirectly, by any one or more of the individuals and entities named or described in (i), (ii), and (iii) above. Except for voting rights, the Class A common stock and Class B common stock are substantially identical. The holders of Class A common stock and Class B common stock vote together as a single class (except as may otherwise be required by Delaware law), with the holders of Class A common stock entitled to one vote per share and the holders of Class B common stock entitled to ten votes per share on all matters on which the holders of common stock are entitled to vote. |
| (3) | Includes 566,211 shares held by Ninemile, L.L.C., of which Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. is the managing member, all of which are pledged as collateral for a loan. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. has sole voting power over the shares held by Ninemile, L.L.C. but dispositions of the shares require the approval of 66% of the outstanding membership interests. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. disclaims beneficial ownership in the shares held by Ninemile, L.L.C., except to the extent of his pecuniary interest therein. |
| (4) | Includes 9,000,000 shares held by the Reilly Family, LLC (the “RFLLC”), of which Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. is the executive manager, 500,000 shares of which are pledged as collateral for a loan. Kevin P. Reilly, Jr.’s three siblings, Anna Reilly (a nominee for director), Sean E. Reilly (our Chief Executive Officer) and Wendell Reilly (a nominee for director) are the other managers of the RFLLC. The executive manager has sole voting power over the shares held by the RFLLC but dispositions of the shares require the approval of managers representing 75% of the limited liability company interests of the RFLLC. Anna Reilly, Sean E. Reilly, and Wendell Reilly disclaim beneficial ownership in the shares held by the RFLLC, except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. |
| (5) | Represents 11.27% of the Class A common stock if all shares of Class B common stock are converted into Class A common stock. |
| (6) | Includes 757,375 shares held by Jennifer and Sean Reilly Family, LLC. |
| (7) | Represents 10.47% of the Class A common stock if all shares of Class B common stock are converted into Class A common stock. |
| (8) | Includes 144,646 shares owned jointly by Anna Reilly and her spouse and 10,000 shares subject to stock options exercisable within 60 days of July 31, 2020. |
| (9) | Includes 1,000,000 shares owned jointly by Ms. Reilly and her spouse. |
| (10) | Represents 9.92% of the Class A common stock if all shares of Class B common stock are converted into Class A common stock. |
| (11) | Includes 5,000 shares held by his spouse and 4,000 shares subject to stock options exercisable within 60 days of July 31, 2020. |
| (12) | Includes 500,000 shares owned by Wendell Reilly individually. |
| (13) | Represents 9.42% of the Class A common stock if all shares of Class B common stock are converted into Class A common stock. |
| (14) | Includes 5,108 shares held in a brokerage margin account. The margin balance outstanding, if any, pursuant to such account may vary from time to time. |
| (15) | Includes 10,000 shares of Class A common stock subject to stock options exercisable within 60 days of July 31, 2020. |
| (16) | Includes 10,000 shares of Class A common stock subject to stock options exercisable within 60 days of July 31, 2020. |
| (17) | See Notes 1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, 15 and 16. |
93
Table of Contents
| (18) | Assumes the conversion of all shares of Class B common stock into shares of Class A common stock. |
| (19) | Represents 8.93% of the Class A common stock if all shares of Class B common stock are converted into Class A common stock. |
| (20) | As reported in the Schedule 13G/A filed on February 11, 2020 with the Commission for the year ended December 31, 2019, The Vanguard Group (“Vanguard”) has sole voting power with respect to 49,482 shares, shared voting power with respect to 16,626 shares, sole dispositive power with respect to 12,639,614 shares and shared dispositive power with respect to 54,955 shares. Includes 38,329 shares beneficially owned by Vanguard’s wholly-owned subsidiary Vanguard Fiduciary Trust Company (“VFTC”) as a result of VFTC’s serving as investment manager of collective trust accounts and 27,779 shares beneficially owned by Vanguard’s wholly-owned subsidiary Vanguard Investments Australia, Ltd. (“VIA”) as a result of VIA’s serving as investment manager of Australian investment offerings. |
| (21) | As reported in the Schedule 13G/A filed on January 10, 2020 with the Commission for the year ended December 31, 2019, BlackRock, Inc. has sole voting power with respect to 8,458,702 shares and sole dispositive power with respect to 8,925,903 shares. |
| (22) | As reported in the Schedule 13G filed on February 13, 2020 with the Commission for the year ended December 31, 2019, Janus Henderson Group plc (“Janus Henderson”) has an ownership stake in certain asset management entities, which furnish investment advice to various fund, individual and/or institutional clients (“Managed Portfolios”), including Janus Capital Management LLC (“Janus Capital”). Janus Henderson has shared voting and dispositive power with respect to all such shares. |
Preferred Stock
Lamar Advertising also has outstanding 5,719.49 shares of Series AA preferred stock. Holders of Series AA preferred stock are entitled to one vote per share. The Series AA preferred stock is held as follows: 3,134.8 shares (54.8%) by the RFLLC, of which Kevin P. Reilly, Jr. is the executive manager and Anna Reilly, Sean E. Reilly, and Wendell Reilly are managers; 1,500 shares (26.2%) by Charles W. Lamar III; 784.69 shares (13.7%) by Mary Lee Lamar Dixon; and 300 shares (5.3%) by the Josephine P. Lamar Test. Trust #1. The aggregate outstanding Series AA preferred stock represents less than 1% of the capital stock of Lamar Advertising.
94
Table of Contents
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
Related Person Transactions
RTC Holdings, LLC (“RTC”), a telecommunications company, is 100% owned by entities owned by members of the Reilly family. Entities owned by Sean E. Reilly, Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., and members of their respective immediate families hold a majority stake in RTC of approximately 89%. The RFLLC, which is owned by Sean E. Reilly, Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Anna Reilly and Wendell Reilly, and entities owned by each of them and members of their respective immediate families, holds the remaining minority stake in RTC of approximately 11%. On May 31, 2019, RTC acquired EATELCORP, LLC (“EATEL”) and its subsidiaries. EATEL provides phone and internet services to consumers and businesses in Louisiana. EATEL also provides data back-up and recovery services to businesses. During the year ended December 31, 2019, Lamar Advertising was a customer of EATEL for data back-up and recovery services. The aggregate amount paid by Lamar Advertising to EATEL for such services since during the year ended December 31, 2019 and six months ended June 30, 2020 was approximately $302,192 and $155,584, respectively. During the year ended December 31, 2019 and six months ended June 30, 2020, Lamar Advertising has been contracted by EATEL to provide advertising services in the aggregate amount of approximately $137,003 and $70,402, respectively.
Ross L. Reilly is the son of Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., the Executive Chairman of Lamar Advertising’s board of directors, and the nephew of Sean E. Reilly, Lamar Advertising’s Chief Executive Officer and President, and Lamar Adverting’s directors Wendell and Anna Reilly. Ross was employed as a General Manager of Lamar Advertising until March 31, 2020. Effective April 1, 2020, he assumed the role of Vice President of Mergers and Acquisitions and Business Analytics of Lamar Advertising. In connection with his employment during 2019, Ross’s aggregate compensation, including his base salary and bonus, did not exceed $120,000. He is eligible to participate in customary employee benefit programs for his position.
Policy on Related Person Transactions
Related persons include any of Lamar Advertising’s directors or executive officers, certain of Lamar Advertising’s stockholders and their immediate family members. A conflict of interest may occur when an individual’s private interest interferes, or appears to interfere, in any way with the interests of Lamar Advertising. Lamar Advertising’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics requires all directors, officers and employees to disclose to management any situations that may be, or appear to be, a conflict of interest. Once management receives notice of a conflict of interest, they will review and investigate the relevant facts and will then generally consult with Lamar Advertising’s General Counsel and the Audit Committee as appropriate.
Under Lamar Advertising’s Audit Committee’s charter, the Audit Committee is responsible for reviewing and pre-approving any related party transactions. Copies of Lamar Advertising’s Code of Business Conduct and Ethics and of Lamar Advertising’s Audit Committee charter are available on its website at www.lamar.com.
In addition to the reporting requirements under the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, each year Lamar Advertising’s directors and executive officers complete questionnaires identifying any transactions with Lamar Advertising in which the executive officers or directors or any immediate family members have an interest. Any such transactions or other related party transactions are reviewed and brought to the attention of the Audit Committee as appropriate.
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
The Compensation Committee of Lamar Advertising currently consists of Thomas V. Reifenheiser (Chairman), John E. Koerner, III and Stephen P. Mumblow. None of Lamar Advertising’s executive officers serves as a member of the board of directors or compensation committee of any other company that has one or more executive officers serving as a member of Lamar Advertising’s board of directors or Compensation Committee.
95
Table of Contents
Purpose and Effect of Exchange Offer
We sold the outstanding notes on February 6, 2020, May 13, 2020 and August 19, 2020 in unregistered private placements to certain initial purchasers. As part of those offerings, we entered into registration rights agreements with the respective initial purchasers. Under the registration rights agreements, we agreed to file the registration statement, of which this prospectus forms a part, to offer to exchange the outstanding notes for exchange notes in an offering registered under the Securities Act. This exchange offering satisfies that obligation. We also agreed to perform other obligations under those registration rights agreements. See “Registration Rights Agreements.”
By participating in the exchange offer, holders of outstanding notes will receive exchange notes that are freely tradable and not subject to restrictions on transfer, subject to the exceptions described under “—Resale of Exchange Notes” immediately below. In addition, holders of exchange notes generally will not be entitled to additional interest.
Resale of Exchange Notes
We believe that the exchange notes issued in exchange for the outstanding notes may be offered for resale, resold and otherwise transferred by any new noteholder without compliance with the registration and prospectus delivery provisions of the Securities Act if the conditions set forth below are met. We base this belief solely on interpretations of the federal securities laws by the staff of the Division of Corporation Finance of the Commission set forth in several no-action letters issued to third parties unrelated to us. A no-action letter is a letter from the staff of the Division of Corporation Finance of the Commission responding to a request for the staff’s views as to whether it would recommend any enforcement action to the Division of Enforcement of the Commission with respect to certain actions being proposed by the party submitting the request. We have not obtained, and do not intend to obtain, our own no-action letter from the Commission regarding the resale of the exchange notes. Instead, holders will be relying on the no-action letters that the Commission has issued to third parties in circumstances that we believe are similar to ours. Based on these no-action letters, the following conditions must be met:
| • | the holder must acquire the exchange notes in the ordinary course of its business; |
| • | the holder must have no arrangements or understanding with any person to participate in the distribution of the exchange notes within the meaning of the Securities Act; and |
| • | the holder must not be our “affiliate,” as that term is defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. |
Each holder of outstanding notes that wishes to exchange outstanding notes for exchange notes in the exchange offer must represent to us that it satisfies all of the above listed conditions. Any holder who tenders in the exchange offer who does not satisfy all of the above listed conditions:
| • | cannot rely on the position of the Commission set forth in the no-action letters referred to above; and |
| • | must comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with a resale of the exchange notes. |
The Commission considers broker-dealers that acquired outstanding notes directly from us, but not as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities, to be making a distribution of the exchange notes if they participate in the exchange offer. Consequently, these holders must comply with the registration and prospectus delivery requirements of the Securities Act in connection with a resale of the exchange notes.
Each broker-dealer that receives exchange notes for its own account in exchange for outstanding notes acquired by that broker-dealer as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities must deliver a prospectus in connection with a resale of the exchange notes and provide us with a signed acknowledgement of this
96
Table of Contents
obligation. A broker-dealer may use this prospectus, as amended or supplemented from time to time, in connection with resales of exchange notes received in exchange for outstanding notes where the broker-dealer acquired the outstanding notes as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities. The letter of transmittal states that by acknowledging and delivering a prospectus, a broker-dealer will not be considered to admit that it is an “underwriter” within the meaning of the Securities Act. We have agreed that for a period of 180 days after the expiration date of the exchange offer, we will make this prospectus available to broker-dealers for use in connection with any resale of the exchange notes.
Except as described in the prior paragraph, holders may not use this prospectus for an offer to resell, a resale or other retransfer of exchange notes. We are not making this exchange offer to, nor will we accept tenders for exchange from, holders of outstanding notes in any jurisdiction in which the exchange offer or the acceptance of it would not be in compliance with the securities or blue sky laws of that jurisdiction.
Terms of the Exchange
Upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in this prospectus and the accompanying letter of transmittal, which we refer to together in this prospectus as the “exchange offer,” we will accept any and all outstanding notes validly tendered and not withdrawn prior to 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on the expiration date. We will issue promptly after the expiration date, an aggregate principal amount of: (i) up to $600 million of 2028 exchange notes for a like principal amount of 2028 outstanding notes tendered and accepted in connection with the exchange offer; (ii) up to $400 million of 2029 exchange notes for a like principal amount of 2029 outstanding notes tendered and accepted in connection with the exchange offer; and (iii) up to $550 million of 2030 exchange notes for a like principal amount of 2030 outstanding notes tendered and accepted in connection with the exchange offer. Holders may tender some or all of their outstanding notes in connection with the exchange offer, but only in denominations of $2,000 and integral multiples of $1,000. The exchange offer is not conditioned upon any minimum amount of outstanding notes being tendered for exchange.
The terms of the 2028 exchange notes, 2029 exchange notes and 2030 exchange notes are identical in all material respects to the terms of the 2028 outstanding notes, 2029 outstanding notes and 2030 outstanding notes, respectively, except that:
| • | we have registered the exchange notes under the Securities Act and therefore these notes will not bear legends restricting their transfer; and |
| • | specified rights under the respective registration rights agreements, including the provisions providing for payment of additional interest in specified circumstances relating to the exchange offer, will be limited or eliminated. |
The exchange notes will evidence the same debt as the outstanding notes. The exchange notes will be issued under the same indentures and entitled to the same benefits under those indentures as the outstanding notes being exchanged. As of the date of this prospectus, $600 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 outstanding notes, $400 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2029 outstanding notes and $550 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2030 outstanding notes were outstanding. Outstanding notes accepted for exchange will be retired and cancelled and will not be reissued.
In connection with the issuance of the outstanding notes, we arranged for the outstanding notes originally purchased by qualified institutional buyers to be issued and transferable in book-entry form through the facilities of DTC, acting as depositary. Except as described under “–Book-Entry Transfer,” we will issue the exchange notes in the form of global notes registered in the name of DTC or its nominee, and each beneficial owner’s interest in it will be transferable in book-entry form through DTC.
Holders of outstanding notes do not have any appraisal or dissenters’ rights in connection with the exchange offer. We intend to conduct the exchange offer in accordance with the applicable requirements of the Exchange Act and the rules and regulations of the Commission.
97
Table of Contents
We will be considered to have accepted validly tendered outstanding notes if and when we have given written notice to that effect to the exchange agent. The exchange agent will act as agent for the tendering holders for the purposes of receiving the exchange notes from us.
If we do not accept any tendered outstanding notes for exchange because of an invalid tender, the occurrence of the other events described in this prospectus or otherwise, we will return these outstanding notes, without expense, to the tendering holder as quickly as possible after the expiration date of the exchange offer.
Holders who tender outstanding notes will not be required to pay brokerage commissions or fees or, subject to the instructions in the letter of transmittal, transfer taxes on exchange of outstanding notes in connection with the exchange offer. We will pay all charges and expenses, other than the applicable taxes described under “—Fees and Expenses” in connection with the exchange offer.
If we successfully complete the exchange offer, any outstanding notes which holders do not tender or which we do not accept in the exchange offer will remain outstanding and continue to accrue interest. The holders of outstanding notes after the exchange offer in general will not have further rights under the respective registration rights agreements, including registration rights and any rights to additional interest. Holders wishing to transfer the outstanding notes would have to rely on exemptions from the registration requirements of the Securities Act.
Expiration Date; Extensions; Amendments
The expiration date for the exchange offer is 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on October 15, 2020. We may extend this expiration date in our sole discretion, unless otherwise required by applicable law. If we so extend the expiration date, the term “expiration date” shall mean the latest date and time to which we extend the exchange offer.
We reserve the right, in our sole discretion:
| • | to delay accepting any outstanding notes, for example, in order to allow for the confirmation of tendered notes or for the rectification of any irregularity or defect in the tender of outstanding notes; |
| • | to extend the exchange offer; |
| • | to terminate the exchange offer if, in our sole judgment, any of the conditions described below shall not have been satisfied; or |
| • | to amend the terms of the exchange offer in any manner. |
We will give notice by press release or other written public announcement of any delay, extension or termination to the exchange agent. In addition, we will give, as promptly as practicable, written notice regarding any delay in acceptance, extension or termination of the offer to the registered holders of outstanding notes. If we amend the exchange offer in a manner that we determine to constitute a material change, or if we waive a material condition, we will promptly disclose the amendment or waiver in a manner reasonably calculated to notify the holders of outstanding notes of the amendment or waiver, and extend the offer as required by law to cause the exchange offer to remain open for at least five business days following such notice.
Without limiting the manner in which we may choose to make public announcements of any delay in acceptance, extension, termination, amendment or waiver regarding the exchange offer, we shall have no obligation to publish, advertise, or otherwise communicate any public announcement, other than by making a timely release to a financial news service.
Interest on the Exchange Notes
Interest on the 2028 exchange notes will accrue at the rate of 3.750% per annum on the principal amount, payable semiannually on January 15 and July 15. Interest on the 2028 exchange notes will accrue from July 15, 2020
98
Table of Contents
Interest on the 2029 exchange notes will accrue at the rate of 4.875% per annum on the principal amount, payable semiannually on March 15 and September 15. Interest on the 2029 exchange notes will accrue from May 13, 2020 or the date of the last periodic payment of interest on such outstanding notes, whichever is later.
Interest on the 2030 exchange notes will accrue at 4.000% per annum on the principal amount, payable semiannually on June 15 and December 15. Interest on the 2030 exchange notes will accrue from June 15, 2020.
Conditions to the Exchange Offer
Despite any other term of the exchange offer, we will not be required to accept for exchange, or exchange notes for, any outstanding notes and we may terminate the exchange offer as provided in this prospectus, if:
| • | the exchange offer, or the making of any exchange by a holder, violates, in our good faith determination, any applicable law, rule or regulation or any applicable interpretation of the staff of the Commission; |
| • | any action or proceeding shall have been instituted or threatened with respect to the exchange offer which, in our reasonable judgment, would impair our ability to proceed with the exchange offer; or |
| • | we have not obtained any governmental approval which we, in our sole discretion, exercised reasonably, consider necessary for the completion of the exchange offer as contemplated by this prospectus. |
The conditions listed above are for our sole benefit. We may assert them regardless of the circumstances giving rise to any of these conditions or waive them in our sole discretion in whole or in part. A failure on our part to exercise any of our rights under any of the conditions shall not constitute a waiver of that right, and that right shall be considered an ongoing right which we may assert at any time prior to the expiration of the exchange offer. All such conditions, other than those subject to governmental approval, will be satisfied or waived prior to the expiration of the exchange offer.
If we determine in our sole discretion, exercised reasonably, that any of the events listed above has occurred, we may, subject to applicable law:
| • | refuse to accept any outstanding notes and return all tendered outstanding notes to the tendering holders; |
| • | extend the exchange offer and retain all outstanding notes tendered before the expiration of the exchange offer, subject, however, to the rights of holders to withdraw these outstanding notes; or |
| • | waive unsatisfied conditions relating to the exchange offer and accept all properly tendered outstanding notes that have not been withdrawn. |
Any determination by us concerning the above events will be final and binding.
In addition, we reserve the right in our sole discretion, exercised reasonably, to:
| • | purchase or make offers for any outstanding notes that remain outstanding subsequent to the expiration date; and |
| • | to the extent permitted by applicable law, purchase outstanding notes in the open market, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. |
99
Table of Contents
The terms of any purchases or offers may differ from the terms of the exchange offer. Those purchases may require the consent of the lenders under our senior credit facility.
Procedures for Tendering
Except in limited circumstances, only a Euroclear participant, Clearstream participant or DTC participant listed on a DTC securities position listing with respect to the outstanding notes may tender outstanding notes in the exchange offer. To tender outstanding notes in the exchange offer:
| • | holders of outstanding notes that are DTC participants may follow the procedures for book-entry transfer as set forth under “—Book-Entry Transfer” and in the letter of transmittal; or |
| • | Euroclear participants and Clearstream participants on behalf of the beneficial owners of outstanding notes are required to use book-entry transfer pursuant to the standard operating procedures of Euroclear or Clearstream. These procedures include the transmission of a computer-generated message to Euroclear or Clearstream in lieu of a letter of transmittal. See the description of “agent’s message” under “—Book-Entry Transfer.” |
In addition, you must comply with one of the following:
| • | the exchange agent must receive, before expiration of the exchange offer, a timely confirmation of book-entry transfer of outstanding notes into the exchange agent’s account at DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream according to their respective standard operating procedures for electronic tenders and a properly transmitted agent’s message as described below; or |
| • | the exchange agent must receive any corresponding certificate or certificates representing outstanding notes along with the letter of transmittal; or |
| • | the holder must comply with the guaranteed delivery procedures described below. |
The tender by a holder of outstanding notes will constitute an agreement between the holder and us in accordance with the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in this prospectus and in the letter of transmittal. If less than all the outstanding notes held by a holder are tendered, the tendering holder should fill in the amount of outstanding notes being tendered in the specified box on the letter of transmittal. The entire amount of outstanding notes delivered or transferred to the exchange agent will be deemed to have been tendered unless otherwise indicated.
The method of delivery of outstanding notes, the letter of transmittal and all other required documents or transmission of an agent’s message, as described under “–Book-Entry Transfer,” to the exchange agent is at the election and risk of the holder. Instead of delivery by mail, we recommend that holders use an overnight or hand delivery service. In all cases, sufficient time should be allowed to assure timely delivery to the exchange agent prior to the expiration of the exchange offer. No letter of transmittal or outstanding notes should be sent to us, DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream. Delivery of documents to DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream in accordance with their respective procedures will not constitute delivery to the exchange agent.
Any beneficial holder whose outstanding notes are registered in the name of his or its broker, dealer, commercial bank, trust company or other nominee and who wishes to tender should contact the registered holder promptly and instruct it to tender on the beneficial holder’s behalf. If any beneficial holder wishes to tender on its own behalf, it must, prior to completing and executing the letter of transmittal and delivering its outstanding notes, either:
| • | make appropriate arrangements to register ownership of the outstanding notes in its name; or |
| • | obtain a properly completed bond power from the registered holder. |
The transfer of record ownership may take considerable time and may not be completed prior to the expiration date.
100
Table of Contents
Signatures on a letter of transmittal or a notice of withdrawal, as described in “Withdrawal of Tenders,” must be guaranteed by a member firm of a registered national securities exchange or of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc., a commercial bank or trust company having an office or correspondent in the United States or an “eligible guarantor institution,” within the meaning of Rule 17Ad-15 under the Exchange Act, which we refer to in this prospectus as an “eligible institution,” unless the outstanding notes are tendered:
| • | by a registered holder who has not completed the box entitled “Special Issuance Instructions” or “Special Delivery Instructions” on the letter of transmittal; or |
| • | for the account of an eligible institution. |
If the letter of transmittal is signed by a person other than the registered holder of any outstanding notes listed therein, the outstanding notes must be endorsed or accompanied by appropriate bond powers which authorize the person to tender the outstanding notes on behalf of the registered holder, in either case signed as the name of the registered holder or holders appears on the outstanding notes. If the letter of transmittal or any outstanding notes or bond powers are signed by trustees, executors, administrators, guardians, attorneys-in-fact, officers of corporations or others acting in a fiduciary or representative capacity, those persons should so indicate when signing and, unless waived by us, evidence satisfactory to us of their authority to so act must be submitted with the letter of transmittal.
We will determine in our sole discretion, exercised reasonably, all questions as to the validity, form, eligibility, including time of receipt, and acceptance and withdrawal of tendered outstanding notes. We reserve the absolute right to reasonably reject any and all outstanding notes not properly tendered or any outstanding notes whose acceptance by us would, in the opinion of our counsel, be unlawful. We also reserve the right to waive any defects or irregularities as to any particular outstanding notes. Our interpretation of the form and procedures for tendering outstanding notes in the exchange offer, including the instructions in the letter of transmittal, will be final and binding on all parties. Unless waived, holders must cure any defects or irregularities in connection with tenders of outstanding notes within a period we will determine. Although we intend to request the exchange agent to notify holders of defects or irregularities relating to tenders of outstanding notes, neither we, the exchange agent nor any other person will have any duty or incur any liability for failure to give this notification. We will not consider tenders of outstanding notes to have been made until these defects or irregularities have been cured or waived. The exchange agent will return any outstanding notes that are not properly tendered and as to which the defects or irregularities have not been cured or waived to the tendering holders, unless otherwise provided in the letter of transmittal, promptly following the expiration date.
In addition, we reserve the right, as set forth under “—Conditions to the Exchange Offer,” to terminate the exchange offer.
By tendering, each holder represents to us, among other things, that:
| • | the holder acquired exchange notes pursuant to the exchange offer in the ordinary course of its business; |
| • | the holder has no arrangement or understanding with any person to participate in the distribution of the exchange notes within the meaning of the Securities Act; and |
| • | the holder is not our “affiliate,” as defined in Rule 405 under the Securities Act. |
If the holder is a broker-dealer that will receive exchange notes for its own account in exchange for outstanding notes acquired by the broker-dealer as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities, the holder must acknowledge that it will deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of the exchange notes.
Book-Entry Transfer
We understand that the exchange agent will make a request promptly after the date of this prospectus to establish accounts with respect to the outstanding notes at DTC for the purpose of facilitating the exchange offer. Any
101
Table of Contents
financial institution that is a participant in DTC’s system may make book-entry delivery of outstanding notes by causing DTC to transfer the outstanding notes into the exchange agent’s DTC account in accordance with DTC’s Automated Tender Offer Program procedures for the transfer. Any participant in Euroclear or Clearstream may make book-entry delivery of outstanding notes by causing Euroclear or Clearstream to transfer the outstanding notes into the exchange agent’s account in accordance with established Euroclear or Clearstream procedures for transfer. The exchange of exchange notes for tendered outstanding notes will only be made after a timely confirmation of a book-entry transfer of the outstanding notes into the exchange agent’s account and timely receipt by the exchange agent of an agent’s message.
The term “agent’s message” means a message, transmitted by DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream, and received by the exchange agent and forming part of the confirmation of a book-entry transfer, which states that DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream has received an express acknowledgment from a participant tendering outstanding notes that the participant has received an appropriate letter of transmittal and agrees to be bound by the terms of the letter of transmittal, and that we may enforce the agreement against the participant. Delivery of an agent’s message will also constitute an acknowledgment from the tendering DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream participant that the representations contained in the letter of transmittal and described under “—Resale of Exchange Notes” are true and correct.
Guaranteed Delivery Procedures
The following guaranteed delivery procedures are intended for holders who wish to tender their outstanding notes but:
| • | their outstanding notes are not immediately available; |
| • | the holders cannot deliver their outstanding notes, the letter of transmittal, or any other required documents to the exchange agent prior to the expiration date; or |
| • | the holders cannot complete the procedure under the respective DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream standard operating procedures for electronic tenders before expiration of the exchange offer. |
The conditions that must be met to tender outstanding notes through the guaranteed delivery procedures are as follows:
| • | the tender must be made through an eligible institution; |
| • | before expiration of the exchange offer, the exchange agent must receive from the eligible institution either a properly completed and duly executed notice of guaranteed delivery in the form accompanying this prospectus, by facsimile transmission, mail or hand delivery, or a properly transmitted agent’s message in lieu of notice of guaranteed delivery: |
| • | setting forth the name and address of the holder, the certificate number or numbers of the outstanding notes tendered and the principal amount of outstanding notes tendered; |
| • | stating that the tender offer is being made by guaranteed delivery; |
| • | guaranteeing that, within three New York Stock Exchange trading days after expiration of the exchange offer, the letter of transmittal, or facsimile of the letter of transmittal, together with the outstanding notes tendered or a book-entry confirmation, and any other documents required by the letter of transmittal will be deposited by the eligible institution with the exchange agent; and |
| • | the exchange agent must receive the properly completed and executed letter of transmittal, or facsimile of the letter of transmittal, as well as all tendered outstanding notes in proper form for transfer or a book-entry confirmation, and any other documents required by the letter of transmittal, within three New York Stock Exchange trading days after expiration of the exchange offer; and |
102
Table of Contents
| • | upon request to the exchange agent, a notice of guaranteed delivery will be sent to holders who wish to tender their outstanding notes according to the guaranteed delivery procedures set forth above. |
Withdrawal of Tenders
Your tender of outstanding notes pursuant to the exchange offer is irrevocable except as otherwise provided in this section. You may withdraw tenders of outstanding notes at any time prior to 5:00 p.m., New York City time, on the expiration date.
For a withdrawal to be effective:
| • | the exchange agent must receive a written notice, which may be by facsimile transmission or letter, of withdrawal at the address set forth below under “Exchange Agent,” or |
| • | for DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream participants, holders must comply with their respective standard operating procedures for electronic tenders and the exchange agent must receive an electronic notice of withdrawal from DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream. |
Any notice of withdrawal must:
| • | specify the name of the person who tendered the outstanding notes to be withdrawn; |
| • | identify the outstanding notes to be withdrawn, including the certificate number or numbers and principal amount of the outstanding notes to be withdrawn; |
| • | include a statement that the person is withdrawing his election to have such outstanding notes exchanged; |
| • | be signed by the person who tendered the outstanding notes in the same manner as the original signature on the letter of transmittal, including any required signature guarantees; and |
| • | specify the name in which the outstanding notes are to be re-registered, if different from that of the withdrawing holder. |
If outstanding notes have been tendered pursuant to the procedure for book-entry transfer described above, any notice of withdrawal must specify the name and number of the account at DTC, Euroclear or Clearstream to be credited with the withdrawn outstanding notes and otherwise comply with the procedures of the applicable facility. We will determine in our sole discretion, exercised reasonably, all questions as to the validity, form and eligibility, including time of receipt, for the withdrawal notices, and our determination will be final and binding on all parties. Any outstanding notes so withdrawn will be deemed not to have been validly tendered for purposes of the exchange offer and no exchange notes will be issued with respect to them unless the outstanding notes so withdrawn are validly retendered. Any outstanding notes which have been tendered but which are not accepted for exchange will be returned to the holder without cost to the holder promptly after withdrawal, rejection of tender or termination of the exchange offer. Properly withdrawn outstanding notes may be re-tendered by following the procedures described under “—Procedures for Tendering” at any time prior to the expiration date.
Fees and Expenses
We will not make any payments to brokers, dealers or other persons soliciting acceptances of the exchange offer. We will, however, pay the exchange agent reasonable and customary fees for its services and its related reasonable out-of-pocket expenses, including accounting and legal fees. We may also pay brokerage houses and other custodians, nominees and fiduciaries the reasonable out-of-pocket expenses incurred by them in forwarding copies of this prospectus, letters of transmittal and related documents to the beneficial owners of the outstanding notes and in handling or forwarding tenders for exchange.
103
Table of Contents
Holders who tender their outstanding notes for exchange will not be obligated to pay any transfer taxes. If, however:
| • | exchange notes are to be delivered to, or issued in the name of, any person other than the registered holder of the outstanding notes tendered; or |
| • | tendered outstanding notes are registered in the name of any person other than the person signing the letter of transmittal; or |
| • | a transfer tax is imposed for any reason other than the exchange of outstanding notes in connection with the exchange offer; |
then the tendering holder must pay the amount of any transfer taxes due, whether imposed on the registered holder or any other persons. If the tendering holder does not submit satisfactory evidence of payment of these taxes or exemption from them with the letter of transmittal, the amount of these transfer taxes will be billed directly to the tendering holder.
Accounting Treatment
The exchange notes will be recorded at the same carrying value as the outstanding notes as reflected in our accounting records on the date of the exchange. Accordingly, we will not recognize any gain or loss for accounting purposes upon the completion of the exchange offer.
Consequences of Failures to Properly Tender Outstanding Notes in the Exchange
We will issue the exchange notes in exchange for the respective outstanding notes under the exchange offer only after timely receipt by the exchange agent of the outstanding notes, a properly completed and duly executed letter of transmittal and all other required documents. Therefore, holders of the outstanding notes desiring to tender outstanding notes in exchange for exchange notes should allow sufficient time to ensure timely delivery. We are under no duty to give notification of defects or irregularities of tenders of outstanding notes for exchange. Outstanding notes that are not tendered or that are tendered but not accepted by us will, following completion of the exchange offer, continue to be subject to the existing restrictions upon transfer under the Securities Act. If we successfully complete the exchange offer, specified rights under the registration rights agreements, including registration rights and any right to additional interest, will be either limited or eliminated.
Participation in the exchange offer is voluntary. In the event the exchange offer is completed, we will not be required to register the remaining outstanding notes. Remaining outstanding notes will continue to be subject to the following restrictions on transfer:
| • | holders may resell outstanding notes only if we register the outstanding notes under the Securities Act, if an exemption from registration is available, or if the transaction requires neither registration under nor an exemption from the requirements of the Securities Act; and |
| • | the remaining outstanding notes will bear a legend restricting transfer in the absence of registration or an exemption. |
We do not currently anticipate that we will register any remaining outstanding notes under the Securities Act. To the extent that outstanding notes are tendered and accepted in connection with the exchange offer, any trading market for remaining outstanding notes could be adversely affected.
104
Table of Contents
DESCRIPTION OF MATERIAL INDEBTEDNESS
The following is a description of our material indebtedness, other than the outstanding notes. The terms of the outstanding notes are substantially identical to the terms of the exchange notes. See “Description of Exchange Notes.” The following summaries are qualified in their entirety by reference to the credit and security agreements and indentures to which each summary relates, which are included or incorporated by reference into the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
Senior Credit Facility
Our senior credit facility currently consists of (i) a $750.0 million senior secured revolving credit facility which will mature on February 6, 2025, (ii) a $600.0 million Term B loan facility which will mature on February 6, 2027 (the “Term B loans”), and (iii) an incremental facility pursuant to which we may incur additional term loan tranches or increase our revolving credit facility subject to pro forma compliance with the secured debt ratio financial maintenance covenant described below. Lamar Media is the borrower under the senior credit facility and may also from time to time designate wholly owned subsidiaries as subsidiary borrowers under the incremental facility. Loans under the incremental facility may be in the form of additional term loan tranches or increases in the revolving credit facility. Our lenders have no obligation to make additional loans to us, or any designated subsidiary borrower, under the incremental facility, but may enter into such commitments in their sole discretion.
Our senior credit facility was entered into pursuant to the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated February 6, 2020 (as amended, the “senior credit facility”), for which JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. serves as administrative agent.
Under the senior credit facility, we borrowed all $600.0 million in Term B loans on February 6, 2020. The entire amount of the Term B loans will be payable at maturity. The net proceeds from the Term B loans, together with borrowing under the revolving credit facility and a portion of the proceeds of the issuance of the 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 and 4% Senior Notes due 2030 (both as described below), were used to repay all outstanding amounts under the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, and all revolving commitments under that facility were terminated.
Interest
The loans bear interest at rates based on the Adjusted LIBO Rate (“Eurodollar loans”) or the Adjusted Base Rate (“Base Rate loans”), at Lamar Media’s option.
| • | Eurodollar loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.50% (or, solely in the case of revolving loans, the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.25% at any time the Total Debt Ratio (as defined below) is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1.00). |
| • | Base Rate loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.50% (or, solely in the case of revolving loans, the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.25% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1.00). |
Total Debt Ratio is defined as total debt of Lamar Advertising and its restricted subsidiaries (other than Special Purpose Subsidiaries), minus the lesser of (x) $150 million and (y) the aggregate amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents of Lamar Advertising and its restricted subsidiaries (other than Special Purpose Subsidiaries) to EBITDA, as defined under “—Covenants” below, for the period of four consecutive fiscal quarters then ended.
Based on our trailing total leverage ratio at June 30, 2020, the spread applicable to borrowings under the revolving credit facility is 0.50% for Base Rate revolving loans and 1.50% for Eurodollar revolving loans and under the Term B loans is 0.50% for Base Rate term loans and 1.50% for Eurodollar term loans.
105
Table of Contents
Guarantees; security
Our obligations under our senior credit facility are guaranteed by Lamar Advertising and all of our domestic restricted subsidiaries, other than the Special Purpose Subsidiaries. Such obligations and guarantees are secured by a pledge of all of our capital stock, all of the capital stock of our domestic restricted subsidiaries, and 65% of the capital stock of our first-tier foreign subsidiaries, as well as a security interest in all of our assets and those of our domestic restricted subsidiaries (other than accounts receivable and certain related assets which secure our Accounts Receivable Securitization Program).
Covenants
Under the terms of the senior credit facility, we and our restricted subsidiaries are not permitted to incur any additional indebtedness at any one time outstanding in excess of the greater of (A) $250.0 million and (B) 6% of the total assets of Lamar Media and its subsidiaries on a consolidated basis, except:
| • | indebtedness created by the senior credit facility; |
| • | qualified debt securities so long as on a pro forma basis Lamar Advertising’s total debt to EBITDA ratio is less than 7.0 to 1.0; |
| • | existing indebtedness or, so long as no default would result therefrom, any extension, renewal, refunding or replacement of any existing indebtedness or indebtedness incurred by the issuance of notes as referred to in the paragraph above; |
| • | indebtedness in respect of secured or unsecured notes issued by us to extend, renew, refund or refinancing existing first lien indebtedness so long as no default would result from the issuance and the terms of the notes comply with certain conditions; |
| • | indebtedness under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program and similar financing arrangements; and |
| • | indebtedness of ours to any wholly owned subsidiary and of any wholly owned subsidiary to us. |
The senior credit facility also places certain restrictions upon our, and our restricted subsidiaries’, ability to, among other things:
| • | incur liens or guarantee obligations; |
| • | pay dividends and make other distributions including distributions to Lamar Advertising; |
| • | make investments and enter into joint ventures or hedging agreements; |
| • | dispose of assets; and |
| • | engage in transactions with affiliates except on an arms-length basis. |
In addition, so long as any commitments, loans or letters of credit remain outstanding under the revolving portion of our credit facility, we must maintain a secured debt ratio, defined as total consolidated secured debt (other than subordinated indebtedness and indebtedness under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program) of Lamar Advertising and its restricted subsidiaries, minus the lesser of (x) $150.0 million and (y) the aggregate amount of unrestricted cash and cash equivalents of Lamar Advertising and its restricted subsidiaries (other than Special Purpose Subsidiaries) to EBITDA, as defined below, for the period of four consecutive fiscal quarters then ended, of less than or equal to 4.50 to 1.0.
Under the senior credit facility, “EBITDA” means, for any period, operating income for Lamar Advertising, Lamar Media and its restricted subsidiaries (determined on a consolidated basis without duplication in accordance with GAAP) for such period (calculated (A) before (i) taxes, (ii) interest expense, (iii) depreciation, (iv) amortization, (v) any other non-cash income or charges accrued for such period, (vi) charges and expenses in connection with the senior credit facility, any actual or proposed acquisition, disposition or investment
106
Table of Contents
(excluding, in each case, purchases and sales of advertising space and operating assets in the ordinary course of business) and any actual or proposed offering of securities, incurrence or repayment of indebtedness (including, without limitation, pursuant to any Permitted Securitization Financing) or amendment to any agreement relating to indebtedness, including any refinancing thereof, or recapitalization, (vii) any loss or gain relating to amounts paid or earned in cash prior to the stated settlement date of any swap agreement that has been reflected in operating income for such period, and (viii) any loss on sales of receivables and related assets to a Securitization Entity in connection with a permitted securitization financing, and (B) after giving effect to the amount of cost savings, operating expense reductions and other operating improvements or synergies projected by Lamar Media in good faith to be realized as a result of any acquisition, investment, merger, amalgamation or disposition within 18 months of any such acquisition, investment, merger, amalgamation or disposition, net of the amount of actual benefits realized during such period from such action; provided, (a) the aggregate amount for all such cost savings, operating expense reductions and other operating improvements or synergies will not exceed an amount equal to 15% of EBITDA for the applicable four quarter period and (b) any such adjustment to EBITDA may only take into account cost savings, operating expense reductions and other operating improvements or synergies that are (I) directly attributable to such acquisition, investment, merger, amalgamation or disposition, (II) expected to have a continuing impact on Lamar Media and its restricted subsidiaries and (III) factually supportable, in each case all as certified by the chief financial officer of Lamar Media) on behalf of Lamar Media, and excluding (except to the extent received or paid in cash by Lamar Advertising, Lamar Media or any of its restricted subsidiaries income or loss attributable to equity in affiliates for such period), excluding any extraordinary and unusual gains or losses during such period, and excluding the proceeds of any casualty events and dispositions. For purposes hereof, the effect thereon of any adjustments required under Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141R shall be excluded. If during any period for which EBITDA is being determined, Lamar Media has consummated any acquisition or disposition, EBITDA will be determined on a pro forma basis as if such acquisition or disposition had been made or consummated on the first day of such period.
Events of default; change of control
The credit facility contains customary events of default (including payment defaults, cross-defaults to certain of our other indebtedness, breach of representations and covenants and change of control). The occurrence of an event of default under the credit facility would permit the lenders to accelerate the indebtedness and terminate the senior credit facility.
A change in control would occur if:
| • | we cease to be a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising; |
| • | Charles W. Lamar, III or Kevin P. Reilly, Sr. and their immediate family (including grandchildren) and entities under their control no longer hold sufficient voting stock of Lamar Advertising to elect at all times a majority of its board of directors; |
| • | anyone other than the holders specified in the preceding bullet acquire shares of Lamar Advertising representing more than 20% of the ordinary voting power or acquire control of Lamar Advertising; |
| • | a majority of the seats on Lamar Advertising’s board is occupied by persons who were neither nominated by the board of directors of Lamar Advertising nor appointed by directors so nominated; or |
| • | the occurrence of any “change of control” under and as defined in the indentures for our 5% Subordinated Notes, our 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026, the outstanding notes, the exchange notes being offered hereby or certain notes that may be hereinafter issued (including refunding indebtedness). |
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program
On December 18, 2018, we entered into a Receivables Financing Agreement as initial servicer with the Special Purpose Subsidiaries, as borrowers, PNC Bank, National Association as Administrative Agent, PNC Capital
107
Table of Contents
Markets LLC as Structuring Agent and certain lenders from time to time party thereto (such arrangement, the “Accounts Receivable Securitization Program”). Borrowing capacity under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program is limited to the availability of eligible accounts receivable collateralizing the borrowings under the agreements governing the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. The Accounts Receivable Securitization Program provides up to $175.0 million in borrowing capacity, plus an accordion feature that would permit the borrowing capacity to be increased by up to $125.0 million. In connection with the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, we and certain of our subsidiaries (such subsidiaries, the “Subsidiary Originators”) sell and/or contribute their existing and future accounts receivable and certain related assets to one of two Special Purpose Subsidiaries, Lamar QRS Receivables, LLC (the “QRS SPV”) and Lamar TRS Receivables, LLC (the “TRS SPV”), each of which is one of our wholly-owned subsidiaries. Existing and future accounts receivable relating to us and our qualified REIT subsidiaries will be sold and/or contributed to the QRS SPV and existing and future accounts receivable relating to our taxable REIT subsidiaries will be sold and/or contributed to the TRS SPV. Each of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries has granted the lenders party to the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program a security interest in all of its assets, which consist of the accounts receivable and related assets sold or contributed to them, as described above, in order to secure the obligations of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries under the agreements governing the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. Pursuant to the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, we have agreed service the accounts receivable on behalf of the two Special Purpose Subsidiaries for a fee. We have also agreed to guaranty our performance in our capacity as servicer and originator, as well as the performance of the Subsidiary Originators, of their obligations under the agreements governing the Account Receivable Securitization Program. Neither we, the Subsidiary Originators nor the Special Purpose Subsidiaries guarantees the collectability of the receivables under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. In addition, each of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries is a separate legal entity with its own separate creditors who will be entitled to access the assets of such Special Purpose Subsidiary before the assets become available to us. Accordingly, the assets of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries are not available to pay our or any of our subsidiaries’ creditors, although collections from receivables in excess of the amounts required to repay the lenders and the other creditors of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries may be remitted to us.
The agreements governing the Account Receivable Securitization Program contain customary representations and warranties, affirmative and negative covenants, and termination event provisions, including but not limited to those providing for the acceleration of amounts owed under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program if, among other things, the Special Purpose Subsidiaries fail to make payments when due, we, the Subsidiary Originators or the Special Purpose Subsidiaries become insolvent or subject to bankruptcy proceedings or certain judicial judgments, breach certain representations and warranties or covenants or default under other material indebtedness, a change of control occurs, or if we fail fails to maintain the maximum secured debt ratio of 4.50 to 1.0 required under our senior credit facility.
As of June 30, 2020, there were no outstanding borrowings under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. As described under “Summary—Recent developments—Redemption of 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023”, we partially funded the Partial 5% Notes Redemption with borrowings, net of deferred financing costs, under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program of approximately $121.8 million and the remainder with cash on hand.
5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023
On October 30, 2012, we issued $535.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 under an indenture among us, as issuer, certain of our subsidiaries, as guarantors, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee.
These notes are senior subordinated unsecured obligations, which are subordinated to indebtedness under the senior credit facility and our other senior indebtedness, including our 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026, the outstanding notes and the exchange notes being offered hereby. These notes rank senior to all of our other
108
Table of Contents
existing and future subordinated indebtedness. These notes bear interest at 5% per annum, payable twice a year on each of May 1 and November 1.
At any time prior to May 1, 2021, we may redeem some or all of these notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount plus a premium of 0.833%. The redemption premium is phased out on May 1, 2021.
Our obligations under these notes are guaranteed by all of our domestic subsidiaries, except Missouri Logos, a partnership, and the Special Purpose Subsidiaries. The guarantees under these notes are subordinated in right of payment to the guarantees under our senior credit facility and the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program, and under our 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026, the outstanding notes and the exchange notes being offered hereby.
The holders of these notes may force us to immediately repay the principal on these notes, including interest to the acceleration date, if, among other things, we fail to make payments on other indebtedness under which we have at least $20.0 million outstanding.
The indenture places certain restrictions upon our ability, and the ability of our subsidiaries, to, among other things:
| • | incur additional indebtedness; |
| • | issue preferred stock; |
| • | pay dividends or make other distributions or redeem capital stock; |
| • | incur liens or guarantee obligations; |
| • | dispose of assets; and |
| • | engage in transactions with affiliates except on an arms’ length basis. |
Upon a “change of control” (as defined in the indenture), we will be obligated to offer to purchase all of the outstanding notes at a purchase price of 101% of the principal amount plus accrued interest, if any. In addition, if we sell certain assets, we will be obligated to offer to purchase outstanding notes with the proceeds of the asset sale at a purchase price of 100% of the principal amount plus accrued interest, if any.
On August 31, 2020, we redeemed $267.5 million aggregate principal amount of the total $535.0 million aggregate principal amount outstanding of our 5% Subordinated Notes due 2023 in the Partial 5% Notes Redemption. On September 16, 2020, we intend to redeem the remaining $267.5 million aggregate principal amount of the 5% Subordinated Notes in the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption.
Both the Partial 5% Notes Redemption occurred and the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption will occur at a redemption price equal to 100.833% of the principal amount of the redeemed notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the applicable redemption date. Such redemption price will be due and payable on the redemption date upon surrender of the 5% Subordinated Notes at the applicable redemption date. Following the Partial 5% Notes Redemption and the Remaining 5% Notes Redemption, there will be no 5% Subordinated Notes outstanding.
5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026
On January 28, 2016, we issued $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026 under an indenture among us, as issuer, certain of our subsidiaries, as guarantors, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. On February 1, 2019, we issued an additional $250.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026.
These notes are general unsecured obligations, which are effectively subordinated to all of our secured debt (to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such debt), including the senior credit facility, and are
109
Table of Contents
structurally subordinated to all of the liabilities of any of our subsidiaries that do not guarantee the notes (including, without limitation, the liabilities of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program). These notes rank senior to all of our existing and future subordinated indebtedness, including our 5% Subordinated Notes. These notes rank equally with our outstanding notes and the exchange notes being offered hereby, and will rank equally with all of our existing and future senior debt. They are pari passu in right of payment to all of our existing and future senior indebtedness, including the notes offered hereby. These notes bear interest at 5 3/4% per annum, payable twice a year on February 1 and August 1.
At any time prior to February 1, 2021, we may redeem some or all of these notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon and a make-whole premium. This premium decreases annually from 2.875%% for a redemption between February 1, 2021 through February 1, 2022, to 1.917% for a redemption between February 1, 2022 through February 1, 2023 to 0.958% for a redemption on or after February 1, 2023 and is phased out completely after February 1, 2024.
Our obligations under these notes are guaranteed by all of our domestic subsidiaries, except Missouri Logos, a partnership, and the Special Purpose Subsidiaries. The guarantees under these notes are: pari passu in right of payment with our outstanding notes and the exchange notes being offered hereby and all other existing and future senior indebtedness of each guarantor; senior in right of payment of each guarantor’s guarantee of our 5% Subordinated Notes and any additional future senior subordinated or subordinated indebtedness of such guarantor; and effectively subordinated to any secured indebtedness of each guarantor to the extent of the value of the assets securing the indebtedness.
The holders of these notes may force us to immediately repay the principal on these notes, including interest to the acceleration date, if, among other things, we fail to make payments on other indebtedness under which we have at least $75.0 million outstanding.
The indenture places certain restrictions upon our ability, and the ability of our subsidiaries, to, among other things:
| • | incur additional debt and issue preferred stock; |
| • | make certain distributions, investments and other restricted payments; |
| • | create certain liens; |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
| • | agree to any restrictions on the ability of restricted subsidiaries to make payments to us; |
| • | merge, consolidate or sell substantially all of our assets; and |
| • | sell assets. |
Upon a “change of control” (as defined in the indenture), we will be obligated to purchase all of the outstanding notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the principal amount plus accrued interest, if any. In addition, if we sell certain assets, we will be obligated to offer to purchase outstanding notes with the proceeds of the asset sale at a purchase price of 100% of the principal amount plus accrued interest, if any.
3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028
On February 6, 2020, we issued $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 2028 outstanding notes under an indenture among us, as issuer, certain of our subsidiaries, as guarantors, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. The terms of these notes are substantially identical to the terms of the 2028 exchange notes. See “Description of Exchange Notes.”
110
Table of Contents
4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029
On May 13, 2020, we issued $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 2029 outstanding notes under an indenture among us, as issuer, certain of our subsidiaries, as guarantors, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. The terms of these notes are substantially identical to the terms of the 2029 exchange notes. See “Description of Exchange Notes.”
4% Senior Notes due 2030
On February 6, 2020, we issued $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the original 2030 outstanding notes under an indenture among us, as issuer, certain of our subsidiaries, as guarantors, and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. On August 19, 2020, we issued an additional $150.0 million in aggregate principal amount of additional 2030 outstanding notes. The terms of these notes are substantially identical to the terms of the 2030 exchange notes. See “Description of Exchange Notes.”
111
Table of Contents
The 2028 exchange notes (referred to in this section as the “2028 notes”) will be issued under an indenture (the “2028 notes indenture”), dated as of February 6, 2020, among Lamar Media, the Guarantors and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. The 2029 exchange notes (referred to in this section as the “2029 notes”) will be issued under an indenture (the “2029 notes indenture”), dated as of May 13, 2020, among Lamar Media, the Guarantors and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. The 2030 exchange notes (referred to in this section as the “2030 notes ”) will be issued under an indenture (the “2030 notes indenture”), dated as of February 6, 2020, among Lamar Media, the Guarantors and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as trustee. For purposes of this “Description of Exchange Notes,” the 2028 notes, together with the 2029 notes and the 2030 notes, are referred to as the “notes.” The 2028 notes indenture, together with the 2029 notes indenture and the 2030 notes indenture are referred to as the “notes indentures.”
The terms of the notes include those stated in the indentures and those made part of the indentures by reference to the Trust Indenture Act of 1939, as amended (the “Trust Indenture Act”), as in effect on the date of the indentures. The notes are subject to all such terms, and holders of each series of notes are referred to the applicable indenture and the Trust Indenture Act for a statement of the terms therein. The following is a summary of the material terms and provisions of the notes. A copy of each indenture and the notes are incorporated by reference as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. The definitions of certain capitalized terms are set forth under “—Certain definitions” or as otherwise defined throughout this description. For purposes of this description, references to “Lamar Media,” “we,” “us” or “our” include only Lamar Media Corp. and not its Subsidiaries and “Lamar Advertising” includes only Lamar Advertising Company and not its Subsidiaries.
General
The notes of each series will be:
| • | general unsecured obligations of Lamar Media; |
| • | pari passu in right of payment to all existing and future senior indebtedness of Lamar Media, including Lamar Media’s existing 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026 and the other series of notes; |
| • | senior in right of payment to Lamar Media’s existing 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (which will be fully redeemed on September 16, 2020) and any additional future senior subordinated Indebtedness of Lamar Media; |
| • | effectively subordinated to any secured Indebtedness of Lamar Media to the extent of the value of the assets securing such Indebtedness; and |
| • | structurally subordinated to all liabilities of the Subsidiaries of Lamar Media that are not Guarantors (including, without limitation, the liabilities of the Special Purpose Subsidiaries, or any other Securitization Entity, under any Permitted Securitization Financing). |
The notes will be unconditionally guaranteed by each of our existing Restricted Subsidiaries (other than Missouri Logos, a Partnership and the Special Purpose Subsidiaries) and certain of our future domestic Restricted Subsidiaries (other than any Securitization Entity).
The Guarantees will be:
| • | general unsecured obligations of each Guarantor; |
| • | pari passu in right of payment with all existing and future senior indebtedness of each Guarantor including each Guarantor’s guarantee of Lamar Media’s existing 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026 and the other series of notes; |
112
Table of Contents
| • | senior in right of payment to each Guarantor’s guarantee of Lamar Media’s existing 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 and any additional future senior subordinated or subordinated Indebtedness of such Guarantor; and |
| • | effectively subordinated to any secured Indebtedness of each Guarantor to the extent of the value of the assets securing such Indebtedness. |
The 2028 notes will be issued in an initial aggregate principal amount of $600,000,000. The 2029 notes will be issued in an initial aggregate principal amount of $400,000,000. The 2030 notes will be issued in an initial aggregate principal amount of $550,000,000. We may from time to time issue additional notes of any series pursuant to the applicable indenture having identical terms and conditions to the notes of such series we are currently offering (the “Additional Notes”). We will only be permitted to issue such Additional Notes if at the time of such issuance, and after giving effect thereto, we are in compliance with the covenants contained in the applicable indenture. Any Additional Notes of a series will be part of the same series as the notes of such series that we are currently offering and will vote on all matters with such notes. For purposes of this “Description of Exchange Notes,” except for the covenant described under “— Material covenants — Limitations on additional indebtedness and preferred stock of restricted subsidiaries,” references to the notes of any series include Additional Notes, if any. In addition, Lamar Media may incur additional indebtedness if at the time of such issuance, and after giving effect thereto, we are in compliance with the covenants contained in the indentures.
Maturity, interest and principal
The 2028 notes will mature on February 15, 2028. The 2028 notes will bear interest at a rate of 3 3/4% per year from July 15, 2020 until maturity. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on January 15 and July 15, commencing July 15, 2020, to holders of record of the 2028 notes at the close of business on the immediately preceding January 1 and July 1. Additionally, interest will be payable on the maturity date to holders of record on the maturity date. The 2028 notes will not be entitled to the benefit of any mandatory sinking fund.
The 2029 notes will mature on January 15, 2029. The 2029 notes will bear interest at a rate of 4.875 % per year from May 13, 2020 or the date of the last periodic payment of interest on the 2029 outstanding notes, whichever is later, until maturity. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on March 15 and September 15, commencing September 15, 2020, to holders of record of the 2029 notes at the close of business on the immediately preceding March 1 and September 1. Additionally, interest will be payable on the maturity date to holders of record on the maturity date. The 2029 notes will not be entitled to the benefit of any mandatory sinking fund.
The 2030 notes will mature on February 15, 2030. The 2030 notes will bear interest at a rate of 4% per year from June 15, 2020 until maturity. Interest is payable semi-annually in arrears on June 15 and December 15, commencing June 15, 2020, to holders of record of the 2030 notes at the close of business on the immediately preceding June 1 and December 1. Additionally, interest will be payable on the maturity date to holders of record on the maturity date. The 2030 notes will not be entitled to the benefit of any mandatory sinking fund.
The notes will be issued in registered form, without coupons, and in denominations of $2,000 and integral multiples of $1,000.
Optional redemption
The 2028 notes will be redeemable at the option of Lamar Media, in whole or in part, at any time on or after February 15, 2023, at the following redemption prices (expressed as a percentage of principal amount), together, in each case, with accrued and unpaid interest to (but not including) the redemption date, if redeemed during the twelve-month period beginning on February 15 of each year listed below:
Year | Percentage | |||
2023 | 101.875 | % | ||
2024 | 100.938 | % | ||
2025 and thereafter | 100.000 | % | ||
113
Table of Contents
The 2029 notes will be redeemable at the option of Lamar Media, in whole or in part, at any time on or after January 15, 2024, at the following redemption prices (expressed as a percentage of principal amount), together, in each case, with accrued and unpaid interest to (but not including) the redemption date, if redeemed during the twelve-month period beginning on January 15 of each year listed below:
Year | Percentage | |||
2024 | 102.438 | % | ||
2025 | 101.219 | % | ||
2026 and thereafter | 100.000 | % | ||
The 2030 notes will be redeemable at the option of Lamar Media, in whole or in part, at any time on or after February 15, 2025, at the following redemption prices (expressed as a percentage of principal amount), together, in each case, with accrued and unpaid interest to (but not including) the redemption date, if redeemed during the twelve-month period beginning on February 15 of each year listed below:
Year | Percentage | |||
2025 | 102.000 | % | ||
2026 | 101.333 | % | ||
2027 | 100.667 | % | ||
2028 and thereafter | 100.000 | % | ||
Notwithstanding the foregoing, Lamar Media may redeem in the aggregate up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of notes of a series at any time and from time to time prior to, (i) in the case of the 2028 notes, February 15, 2023 at a redemption price equal to 103.750% of the aggregate principal amount so redeemed, (ii) in the case of the 2029 notes, May 15, 2023 at a redemption price equal to 104.875% of the aggregate principal amount so redeemed and (iii) in the case of the 2030 notes, February 15, 2023 at a redemption price equal to 104.000% of the aggregate principal amount so redeemed, plus accrued interest to (but not including) the redemption date, out of the Net Proceeds of one or more Equity Offerings; provided, however, that at least 60% of the aggregate principal amount of notes of such series originally issued remains outstanding immediately after the occurrence of any such redemption and that any such redemption occurs within 120 days following the closing of any such Equity Offering.
In addition, at any time prior to (i) in the case of the 2028 notes, February 15, 2023, (ii) in the case of the 2029 notes, January 15, 2024 and (iii) in the case of the 2030 notes, February 15, 2025, Lamar Media may redeem all or any portion of any series of notes outstanding at a redemption price equal to:
| • | 100% of the aggregate principal amount of notes of such series to be redeemed, together with accrued and unpaid interest to such redemption date (subject to the rights of holders of record of the notes of such series on the relevant record date to receive payments of interest on the related interest payment date), plus |
| • | the Make Whole Amount. |
Furthermore, at Lamar Media’s option, it may condition any call for redemption on the receipt of financing to fund the redemption within the notice period. Any such condition will be expressly stated in the notice of redemption and in any press release or other public statement mentioning the call for redemption. If the financing condition is not satisfied during the notice period, the notes of such series will remain outstanding and Lamar Media will make a public statement to that effect.
The trustee shall have no duty to make any calculation in connection with the redemption of any series of notes.
Selection and notice
In the event of redemption of fewer than all of a series of notes (including for a partial redemption made with the proceeds of an Equity Offering) such notes shall be selected by lot for redemption (subject to applicable DTC
114
Table of Contents
procedures), unless such method is otherwise prohibited. The notes will be redeemable in whole or in part upon not less than 15 nor more than 60 days’ prior written notice, sent to a holder’s last address as it shall appear on the register maintained by the Registrar of the notes. On and after any redemption date, interest will cease to accrue on the notes of a series or portions thereof called for redemption unless Lamar Media shall fail to redeem any such note.
Guarantees
The notes will be guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by the Guarantors.
The obligations of each Guarantor will be limited to the maximum amount as will, after giving effect to all other contingent and fixed liabilities of such Guarantor and after giving effect to any collections from or payments made by or on behalf of any other Guarantor in respect of the obligations of such other Guarantor under its Guarantee or pursuant to its contribution obligations under the indentures, result in the obligations of such Guarantor under the Guarantee not constituting a fraudulent conveyance or fraudulent transfer under federal or state law. Each Guarantor that makes a payment or distribution under a Guarantee shall be entitled to a contribution from each other Guarantor in a pro rata amount based on the Adjusted Net Assets of each Guarantor. See “Risk factors—Federal and state statutes allow courts, under specific circumstances, to void the guarantees of the notes by our subsidiaries and require the holders of the notes to return payments received from the subsidiary guarantors.”
Upon (i) the release of all guarantees by a Guarantor of any Indebtedness of Lamar Media and the release of all Liens on the property and assets of such Guarantor securing such guarantees or (ii) the sale or disposition (whether by merger, sale of stock or otherwise) of a Guarantor (or substantially all of its assets) to an entity which is not a Subsidiary of Lamar Media which is otherwise in compliance with the indentures (and providing that the guarantee and Liens referred to in the foregoing clause (i) are also released at such time), such Guarantor shall be deemed released from all its obligations under the indentures and its Guarantee. In the event that a Restricted Subsidiary Guarantor ceases to be obligated to a Guarantor pursuant to the provisions under “—Material covenants—Limitation on Guarantees of material indebtedness,” as long as no Default or Event of Default is existing or will result therefrom, it shall be released from its obligations under the indentures and its Guarantee.
Material covenants
The indentures contain, among others, the following covenants:
Effectiveness of covenants
Following the first day:
(a) the notes have an Investment Grade Rating from both of the Ratings Agencies; and
(b) no Default has occurred and is continuing under the indentures; Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries will not be subject to the provisions of the indentures summarized under the headings below:
| • | “—Material covenants—Limitation on additional indebtedness and preferred stock of restricted subsidiaries”; |
| • | “—Material covenants—Limitation on restricted payments”; |
| • | “—Material covenants—Limitation on dividends and other payment restrictions affecting subsidiaries”; |
| • | “—Material covenants—Limitation on certain asset sales”; |
115
Table of Contents
| • | “—Material covenants—Limitation on transactions with affiliates”; and |
| • | clause (b) of “—Material covenants—Limitation on merger, consolidation or sale of assets” |
(collectively, the “Suspended Covenants”). If at any time the notes’ credit rating is downgraded from an Investment Grade Rating by any Rating Agency, then the Suspended Covenants will thereafter be reinstated as if such covenants had never been suspended (the “Reinstatement Date”) and be applicable pursuant to the terms of the indentures (including in connection with performing any calculation or assessment to determine compliance with the terms of the indentures), unless and until the notes subsequently attain an Investment Grade Rating and no Default or Event of Default is in existence (in which event the Suspended Covenants shall no longer be in effect for such time that the notes maintain an Investment Grade Rating); provided, however, that no Default, Event of Default or breach of any kind shall be deemed to exist or have occurred under the indentures, the notes or the Subsidiary Guarantees with respect to the Suspended Covenants based on, and none of Lamar Media or any of its Subsidiaries shall bear any liability for, any actions taken or events occurring during the Suspension Period (as defined below), or any actions taken at any time pursuant to any contractual obligation arising prior to the Reinstatement Date, regardless of whether such actions or events would have been permitted if the applicable Suspended Covenants remained in effect during such period. The period of time between the date of suspension of the covenants and the Reinstatement Date is referred to as the “Suspension Period.”
On the Reinstatement Date, all Indebtedness Incurred during the Suspension Period will be deemed to have been outstanding on the Issue Date, so that it is classified as permitted under clause (iii) of the definition of “Permitted Indebtedness.” Calculations made after the Reinstatement Date of the amount available to be made as Restricted Payments under “—Material covenants—Limitation on restricted payments” will be made as though the covenants described under “—Material covenants—Limitation on restricted payments” had been in effect since the Issue Date and throughout the Suspension Period. Accordingly, Restricted Payments made during the Suspension Period will reduce the amount available to be made as Restricted Payments under the first paragraph of “—Material covenants—Limitation on restricted payments” to the extent such Restricted Payments were not otherwise permitted to be made pursuant to clauses (i) through (ix) of the third paragraph under “—Material covenants—Limitation on restricted payments”; provided that the amount available to be made as Restricted Payments on the Reinstatement Date pursuant to the first paragraph shall not be reduced below zero solely as a result of such Restricted Payments under “—Material covenants—Limitation on restricted payments.” Additionally, upon any Reinstatement Date, the amount of Available Asset Sale Proceeds will be reset to zero.
During any period when the Suspended Covenants are suspended, the board of directors of Lamar Media may not designate any of Lamar Media’s Subsidiaries as Unrestricted Subsidiaries pursuant to the indentures.
Limitation on additional indebtedness and preferred stock of restricted subsidiaries
Lamar Media will not, and will not permit any Restricted Subsidiary to, directly or indirectly, incur any Indebtedness (including Acquired Indebtedness) other than Permitted Indebtedness, and will not permit any Restricted Subsidiary to issue any Preferred Stock, unless: after giving effect to the incurrence of such Indebtedness and the issuance of any such Preferred Stock and the receipt and application of the proceeds thereof, Lamar Media’s Leverage Ratio is less than 7.0 to 1.0.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, Preferred Stock may only be issued by a Restricted Subsidiary pursuant to the preceding sentence to the extent such Restricted Subsidiary is a Guarantor.
For purposes of determining compliance with this covenant (“—Limitations on additional indebtedness and preferred stock of restricted subsidiaries”), in the event that an item of proposed Indebtedness meets the criteria of more than one of the categories of Permitted Indebtedness, or is entitled to be incurred pursuant to the first sentence of this covenant, Lamar Media or the applicable Restricted Subsidiary shall be permitted to classify on the date of its incurrence, or later reclassify, all or a portion of such item of Indebtedness in any manner that complies with this covenant. Indebtedness permitted by this covenant need not be permitted solely by reference
116
Table of Contents
to one provision permitting such Indebtedness but may be permitted in part by one such provision and in part by another one or more other provisions of this covenant permitting such Indebtedness. Accrual of interest, accretion or amortization of original issue discount and the accretion of accreted value shall not be deemed to be an incurrence of Indebtedness for purposes of this covenant.
Limitation on restricted payments
Lamar Media will not make, and will not permit any of the Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly, make, any Restricted Payment unless:
(a) no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing at the time of or immediately after giving effect to such Restricted Payment;
(b) immediately after giving pro forma effect to such Restricted Payment, Lamar Media could incur $1.00 of additional Indebtedness (other than Permitted Indebtedness) under the covenant set forth under “— Limitation on additional indebtedness and preferred stock of restricted subsidiaries”; and
(c) immediately after giving effect to such Restricted Payment, the aggregate of all Restricted Payments declared or made after the Existing Notes Issue Date does not exceed the sum of (without duplication):
(1) 100% of Lamar Media’s Cumulative EBITDA minus 1.4 times Lamar Media’s Cumulative Consolidated Interest Expense, plus
(2) 100% of the aggregate Net Proceeds and the fair market value of securities or other property received by Lamar Media, after January 1, 2001, from (a) the issue or sale of Capital Stock (other than Disqualified Capital Stock or Capital Stock of Lamar Media issued to any Subsidiary of Lamar Media) of Lamar Media or any Indebtedness or other securities of Lamar Media convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for Capital Stock (other than Disqualified Capital Stock) of Lamar Media which has been so converted or exercised or exchanged, as the case may be, (b) any capital contribution to Lamar Media from Lamar Advertising (except as contemplated by clause (vi) of the following paragraph) and (c) any loans made to Lamar Media by Lamar Advertising prior to the Existing Notes Issue Date upon the cancellation of such loans by Lamar Advertising, plus
(3) the net reductions in Investments (other than reductions in Permitted Investments) in any Person resulting from payments of interest on Indebtedness, dividends, repayments of loans, partial or total releases or discharges of Guaranteed Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligations, or from designations of Unrestricted Subsidiaries as Restricted Subsidiaries, valued in each case at the fair market value thereof, not to exceed the amount of Investments previously made by Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries in such Person.
For purposes of determining under this clause (c) the amount expended for Restricted Payments, cash distributed shall be valued at the face amount thereof and property other than cash shall be valued at its fair market value as determined by the board of directors reasonably and in good faith. As of June 30, 2020, the total amount available for making Restricted Payments under this clause (c) was approximately $3.4 billion.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, Lamar Media and any of the Restricted Subsidiaries may pay any dividend or make any distribution to Lamar Advertising for the purpose of funding a payment of any dividend or making of any distribution on or in respect of shares of Lamar Advertising’s Capital Stock, in the case of each such dividend or distribution by Lamar Media or any of the Restricted Subsidiaries constituting a Restricted Payment, to the extent that Lamar Advertising believes in good faith that it qualifies as a “real estate investment trust” under Section 856 of the Code (or any successor provision) and that the declaration or payment of a dividend or making of a distribution in such amount is necessary to maintain Lamar Advertising’s status as a REIT for any taxable year with such dividend to be paid or distribution to be made as and when determined by Lamar Advertising, whether during or after the end of the relevant taxable year; provided, however, that (I) at the time of, and after giving effect to, any such dividend or distribution, no Event of Default of the type described in
117
Table of Contents
clauses (a), (b) (without giving effect to the grace period set forth therein) or (f) under the heading “Events of default” below shall have occurred and be continuing or would occur as a consequence thereof and the obligations in respect of the notes shall not otherwise have been accelerated and (II) two consecutive dividends or distributions pursuant to this paragraph shall not be permitted during the pendency of any single Event of Default.
The provisions of this covenant shall not prohibit:
(i) the payment of any distribution within 60 days after the date of declaration thereof, if at such date of declaration such payment would comply with the provisions of the indentures; provided, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” such amounts declared shall be included in the calculation but such amounts expended shall be excluded from the calculation;
(ii) the retirement of any shares of Capital Stock of Lamar Media or Indebtedness of Lamar Media subordinated or pari passu in right of payment to the notes by conversion into, or by or in exchange for, shares of Capital Stock (other than Disqualified Capital Stock), or out of, the Net Proceeds of the substantially concurrent sale (other than to a Subsidiary of Lamar Media) of other shares of Capital Stock of Lamar Media (other than Disqualified Capital Stock); provided, however, that the amount of any such Net Proceeds that are utilized for any such retirement shall be excluded from clause (c)(2) of the immediately preceding paragraph; provided, further, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (ii) shall be excluded from the calculation;
(iii) the redemption or retirement of Indebtedness of Lamar Media subordinated in right of payment to the notes in exchange for, by conversion into, or out of the Net Proceeds of, a substantially concurrent sale or incurrence of Indebtedness (it being understood that a redemption or retirement or irrevocable deposit for redemption or retirement of Indebtedness within 45 days of such sale or incurrence shall be deemed “substantially concurrent”) of Lamar Media (other than any Indebtedness owed to a Subsidiary of Lamar Media) that is, contractually subordinated in right of payment to the notes to at least the same extent as the subordinated Indebtedness being redeemed or retired and, (x) has a Stated Maturity no earlier than the final maturity date of the Indebtedness being redeemed or retired and (y) has an Average Life to Stated Maturity equal to or greater than the remaining Average Life to Stated Maturity of the Indebtedness being redeemed or retired; provided, however, that the amount of any such Net Proceeds that are utilized for any such redemption or retirement shall be excluded from clause (c)(2) of the immediately preceding paragraph; provided, further, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (iii) shall be excluded from the calculation;
(iv) the funding of loans (but not including the forgiveness of any such loan) to executive officers, directors and shareholders for relocation loans, bonus advances and other purposes consistent with past practices or the purchase, redemption or other acquisition for value of shares of Capital Stock of Lamar Advertising or Lamar Media (other than Disqualified Capital Stock) or options on such shares held by Lamar Advertising’s or Lamar Media’s or the Restricted Subsidiaries’ officers or employees or former officers or employees (or their estates or trusts or beneficiaries under their estates or trusts for the benefit of such beneficiaries) upon the death, disability, retirement or termination of employment of such current or former officers or employees pursuant to the terms of an employee benefit plan or any other agreement pursuant to which such shares of Capital Stock or options were issued or pursuant to a severance, buy-sell or right of first refusal agreement with such current or former officer or employee; provided that the aggregate amount of any such loans funded and cash consideration paid, or distributions made, pursuant to this clause (iv) do not in any one fiscal year exceed $7.0 million; provided, further, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (iv) shall be excluded from the calculation;
118
Table of Contents
(v) the making of Investments in Unrestricted Subsidiaries and joint ventures in an aggregate amount not to exceed since the Issue Date the greater of (A) $500.0 million and (B) 8% of Lamar Media’s Total Assets (plus, so long as the condition set forth in clause (b) of the first paragraph under the heading “Limitation on restricted payments” is satisfied at such time, an additional $50.0 million); provided, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments made subsequent to the Issue Date for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (v) shall be excluded in the calculation;
(vi) distributions by Lamar Media to Lamar Advertising to permit Lamar Advertising to pay obligations actually incurred by Lamar Advertising in respect of the payment of operating expenses of Lamar Media or the Restricted Subsidiaries in an aggregate amount in any fiscal year not to exceed 5% of the total operating expenses of Lamar Media and the Restricted Subsidiaries on a consolidated basis determined in accordance with GAAP and Tax Payments permitted by clause (v) of the covenant described under “— Limitation on transactions with affiliates”; provided, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (vi) shall be excluded from the calculation;
(vii) other Restricted Payments in an aggregate amount not to exceed $20.0 million in the aggregate; provided, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments made subsequent to the Issue Date for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (vii) shall be excluded in the calculation;
(viii) the repurchase, redemption or other acquisition or retirement for value of any Indebtedness that is contractually subordinated in right of payment to the notes and the Guarantees in accordance with the provisions similar to those described under the captions “Change of control” and “Limitation on certain asset sales”; provided, however, that all notes tendered in connection with a Change of Control Offer or Excess Proceeds Offer, as applicable, have been repurchased, redeemed or acquired for value prior to any Restricted Payment being made pursuant to this clause (viii); provided, further, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (viii) shall be excluded from the calculation;
(ix) the defeasance, redemption, repurchase, retirement or other acquisition or retirement for value of Indebtedness that is contractually subordinated in right of payment to the notes if, at the time of such defeasance, redemption, repurchase, retirement or other acquisition or retirement and after giving effect thereto, the Secured Leverage Ratio would be less than 4.50 to 1.0; provided, however, that in calculating the aggregate amount of Restricted Payments made for purposes of clause (c) of the first paragraph under this heading “Limitation on restricted payments,” amounts expended pursuant to this clause (ix) shall be excluded from the calculation; and
(x) any consideration, payment, dividend, distribution or other transfer in connection with a Permitted Securitization Financing.
Limitation on layering
Lamar Media will not, and will not permit any of the Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly incur, contingently or otherwise, any Indebtedness that is both (i) subordinate in right of payment to any Indebtedness of Lamar Media or any of the Subsidiary Guarantors, as the case may be, and (ii) pari passu in right of payment with the notes or any of the Guarantees, as the case may be.
Limitation on liens
Lamar Media will not, and will not permit any of the Restricted Subsidiaries to, create, incur or otherwise cause or suffer to exist or become effective any Liens of any kind (other than Permitted Liens) to secure Indebtedness
119
Table of Contents
upon any Property, assets, income or profit of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary or any shares of stock or debt of any Restricted Subsidiary (whether or not any of the foregoing is now owned or hereafter acquired) unless (i) if such Lien secures Indebtedness which is pari passu in right of payment with the notes, then the notes are secured on an equal and ratable basis with the obligations so secured until such time as such obligation is no longer secured by a Lien or (ii) if such Lien secures Indebtedness which is subordinated in right of payment to the notes, any such Lien shall be subordinated to a Lien granted to the holders of the notes in the same collateral as that securing such Lien to the same extent as such subordinated Indebtedness is subordinated to the notes.
Limitation on transactions with affiliates
Lamar Media will not, and will not permit any of the Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly, enter into or suffer to exist any transaction or series of related transactions with any Affiliate (an “Affiliate Transaction”) or extend, renew, waive or otherwise modify the terms of any Affiliate Transaction entered into prior to the Issue Date unless the terms of such Affiliate Transaction are fair and reasonable to Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be, or the terms of such Affiliate Transaction are at least as favorable as the terms which could be obtained by Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be, in a comparable transaction made on an arms’ length basis between unaffiliated parties. In any Affiliate Transaction involving an amount or having a value in excess of $20.0 million, Lamar Media must obtain a resolution of the board of directors approved by a majority of the members of the board of directors (and a majority of the disinterested members of the board of directors) certifying that such Affiliate Transaction complies with this “Limitation on transactions with affiliates” covenant. The foregoing provisions will not apply to:
(i) any Restricted Payment that is not prohibited by the provisions described under “— Limitation on restricted payments” (other than those described in clause (v) of the second paragraph thereunder),
(ii) any transaction between Lamar Media and any of its Restricted Subsidiaries or between Restricted Subsidiaries,
(iii) the payment of reasonable and customary regular fees to directors of Lamar Media who are not employees of Lamar Media and any employment and consulting arrangements entered into by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary with its executives or consultants in the ordinary course of business,
(iv) any transaction with a joint venture or similar entity which would constitute an Affiliate Transaction solely because Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary owns an equity interest in or otherwise controls such joint venture or similar entity; provided that no Affiliate of Lamar Media or any of its Subsidiaries other than Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary shall have a beneficial interest in such joint venture or similar entity,
(v) for so long as Lamar Media is a member of a group filing a consolidated or combined tax return with Lamar Advertising, payments to Lamar Advertising in respect of (A) an allocable portion of the tax liabilities of such group that is attributable to Lamar Media and its Subsidiaries, taking into account any carryovers and carrybacks of tax attributes (such as net operating losses) of Lamar Media and such Subsidiaries from other taxable years and (B) any cancellation of debt income in connection with any refinancing of Indebtedness of Lamar Advertising (collectively, “Tax Payments”); provided that any Tax Payments received from Lamar Media shall be paid over to the appropriate taxing authority within 30 days of Lamar Advertising’s receipt of such Tax Payments or refunded to Lamar Media,
(vi) any employment, indemnification, severance or other agreement or transactions relating to employee benefits or benefit plans with any employee, consultant or director of Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary that is entered into by Lamar Media or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries in the ordinary course of business, or
(vii) any transaction of Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries which would constitute a Permitted Securitization Financing.
120
Table of Contents
Limitation on guarantees of material indebtedness
Lamar Media will not permit any of the:
(A) domestic Restricted Subsidiaries (other than the Guarantors) to: (i) incur, guarantee or secure through the granting of Liens the payment of any Indebtedness of Lamar Media or any other Restricted Subsidiary; or (ii) pledge any intercompany notes representing obligations of any of the Restricted Subsidiaries to secure the payment of any Indebtedness of Lamar Media, or
(B) Restricted Subsidiaries that are not domestic Restricted Subsidiaries to guarantee the Senior Credit Facility,
in each case unless such Restricted Subsidiary, Lamar Media and the trustee execute and deliver a supplemental indenture evidencing such Restricted Subsidiary’s Guarantee under each indenture. Thereafter, such Restricted Subsidiary shall be a Guarantor for all purposes of the indentures.
Limitation on dividends and other payment restrictions affecting subsidiaries
Lamar Media will not, and will not permit any of the Restricted Subsidiaries to, directly or indirectly, create or otherwise cause or suffer to exist or become effective any encumbrance or restriction of any kind on the ability of any Restricted Subsidiary to:
(a) pay dividends or make any other distributions to Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary on its Capital Stock;
(b) pay any Indebtedness owed to Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(c) make loans or advances to Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(d) transfer any of its properties or assets to Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(e) grant liens or security interests on the assets of Lamar Media or the Restricted Subsidiaries in favor of the holders of the notes; or
(f) guarantee the notes or any renewals or refinancings thereof,
in each case, except for Permitted Dividend Encumbrances.
Limitation on certain asset sales
Lamar Media will not, and will not permit any of the Restricted Subsidiaries to, consummate an Asset Sale unless:
(i) Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be, receives consideration at the time of such sale or other disposition at least equal to the fair market value thereof (as determined in good faith by Lamar Media’s board of directors and evidenced by a board resolution);
(ii) not less than 75% of the consideration received by Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary, as the case may be, is in the form of cash or cash equivalents (those equivalents allowed under “Temporary Cash Investments”) or Replacement Assets (as defined below); provided, however, that the amount of (x) any liabilities of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiaries that are assumed by the transferee of such assets and for which Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries are released, including any such Indebtedness of a Restricted Subsidiary whose stock is purchased by the transferee and (y) any notes or other securities received by Lamar Media or any such Restricted Subsidiary which are converted into cash within 180 days after such Asset Sale (to the extent of cash received) shall be deemed to be cash for purposes of this provision; and
(iii) the Asset Sale Proceeds received by Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary are applied
121
Table of Contents
(a) first, to the extent Lamar Media elects, or is required, to permanently prepay, repay or purchase existing Indebtedness under the Senior Credit Facility or Purchase Money Indebtedness that ranks pari passu in right of payment with the notes solely to the extent that such Asset Sale involves property or assets securing such Purchase Money Indebtedness pursuant to a lien granted pursuant to clause (iv) of the definition of “Permitted Liens” within 360 days following the receipt of the Asset Sale Proceeds from any Asset Sale; provided, however, that any such repayment shall result in a permanent reduction of the commitments thereunder in an amount equal to the principal amount so repaid;
(b) second, to the extent of the balance of Asset Sale Proceeds after application as described above, to the extent Lamar Media elects, to an investment in assets (including Capital Stock or other securities purchased in connection with the acquisition of Capital Stock or property of another Person that is, or becomes, a Subsidiary of Lamar Media or that would constitute a Permitted Investment under clause (e) of the definition thereof) used or useful in businesses similar or ancillary to the business of Lamar Media and the Restricted Subsidiaries as conducted at the time of such Asset Sale (collectively, “Replacement Assets”); provided, however, that such investment occurs and such Asset Sale Proceeds are so applied within 360 days following the receipt of such Asset Sale Proceeds (the “Reinvestment Date”); and
(c) third, if on the Reinvestment Date with respect to any Asset Sale, the Available Asset Sale Proceeds exceed $50.0 million, Lamar Media shall apply an amount equal to such Available Asset Sale Proceeds to an offer to repurchase the notes, at a purchase price in cash equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of repurchase (an “Excess Proceeds Offer”); provided, however, that Lamar Media may, at the time that it makes any such Excess Proceeds Offer, also offer to purchase, at a price in cash equal to 100% of the outstanding principal amount thereof plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the purchase date, any Indebtedness which ranks pari passu in right of payment with the notes (a “Pari Passu Excess Proceeds Offer”) and to the extent Lamar Media so elects to make a Pari Passu Excess Proceeds Offer, notes and such pari passu Indebtedness shall be purchased pursuant to such Excess Proceeds Offer and Pari Passu Excess Proceeds Offer, respectively, on a pro rata basis based on the aggregate principal amount of such notes and pari passu Indebtedness then outstanding. To the extent that the aggregate principal amount of notes tendered pursuant to an Excess Proceeds Offer is less than the Available Asset Sale Proceeds, Lamar Media may use any remaining Excess Proceeds for any purpose not otherwise prohibited by the indentures. To the extent that the aggregate principal amount of pari passu Indebtedness tendered pursuant to a Pari Passu Excess Proceeds Offer is less than such pari passu Indebtedness’s pro rata share of such Available Asset Sale Proceeds, Lamar Media shall use such remaining Available Asset Sale Proceeds to purchase any notes validly tendered and not withdrawn pursuant to such Excess Proceeds Offer. If the aggregate principal amount of notes of a series validly tendered and not withdrawn by holders thereof exceeds the Available Asset Sale Proceeds or to the extent Lamar Media elects to make a Pari Passu Excess Proceeds Offer, exceeds such notes’ pro rata share of such Available Asset Sale Proceeds, then such notes to be purchased will be selected on a pro rata basis (subject to applicable DTC procedures). Upon completion of such Excess Proceeds Offer, the amount of Available Asset Sale Proceeds shall be reset to zero.
If Lamar Media is required to make an Excess Proceeds Offer, Lamar Media shall send, within 30 days following the Reinvestment Date, a notice to the holders stating, among other things:
(1) that such Holders have the right to require Lamar Media to apply the Available Asset Sale Proceeds to repurchase such notes at a purchase price in cash equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of repurchase;
(2) the repurchase date, which shall be no earlier than 30 days and not later than 60 days from the date such notice is mailed;
(3) the instructions, determined by Lamar Media, that each Holder must follow in order to have such notes repurchased; and
122
Table of Contents
(4) the calculations used in determining the amount of Available Asset Sale Proceeds to be applied to the repurchase of such notes.
Payments for consent
Neither Lamar Media nor any of its Subsidiaries shall, directly or indirectly, pay or cause to be paid any consideration, whether by way of interest, fee or otherwise, to any holder of any notes of a series for or as an inducement to any consent, waiver or amendment of any of the terms or provisions of the applicable indenture or such notes unless such consideration is offered to be paid or agreed to be paid to all holders of such notes which so consent, waive or agree to amend in the time frame set forth in the solicitation documents relating to such consent, waiver or agreement.
Reports to holders
Each indenture provides that, whether or not required by the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”), so long as any notes are outstanding under such indenture, Lamar Media will furnish the holders of notes:
(a) all quarterly and annual financial information that would be required to be contained in a filing with the Commission on Forms 10-Q and 10-K if Lamar Media were required to file such Forms, including a “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” that describes the financial condition and results of operations of Lamar Media and its consolidated Subsidiaries and, with respect to the annual information only, a report thereon by Lamar Media’s certified independent accountants; and
(b) all current reports that would be required to be filed with the Commission on Form 8-K if Lamar Media were required to file such reports, in each case within the time periods specified in the Commission’s rules and regulations.
In addition, whether or not required by the rules and regulations of the Commission, Lamar Media will file a copy of all such information and reports with the Commission for public availability within the time periods specified in the Commission’s rules and regulations (unless the Commission will not accept such a filing) and make such information available to securities analysts and prospective investors upon request. In addition, Lamar Media has agreed that, for so long as any notes remain outstanding, it will furnish to the holders and to securities analysts and prospective investors, upon their request, the information required to be delivered pursuant to Rule 144A(d)(4) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
Change of control
Upon the occurrence of a Change of Control, Lamar Media shall be obligated to make an offer to purchase (a “Change of Control Offer”), and shall purchase, on a business day (the “Change of Control Purchase Date”) not more than 60 nor less than 30 days following the occurrence of the Change of Control, all of the then outstanding notes of any series at a purchase price (the “Change of Control Purchase Price”) equal to 101% of the principal amount thereof plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the Change of Control Purchase Date. Lamar Media shall be required to purchase all notes of such series properly tendered pursuant to the Change of Control Offer and not withdrawn. The Change of Control Offer is required to remain open for at least 20 business days and until the close of business on the Change of Control Purchase Date. In order to effect such Change of Control Offer, Lamar Media shall, not later than the 30th day after the occurrence of the Change of Control, send to each holder of notes of such series notice of the Change of Control offer, which notice shall govern the terms of the Change of Control Offer and shall state, among other things, the procedures that holders of notes of such series must follow to accept the Change of Control Offer.
The occurrence of the events constituting a Change of Control under the indentures will result in an event of default under the Senior Credit Facility and, thereafter, the lenders will have the right to require repayment of the
123
Table of Contents
borrowings thereunder in full. There can be no assurance that Lamar Media will have adequate resources to repay or refinance all Indebtedness owing under the Senior Credit Facility or to fund the purchase of any notes upon a Change of Control.
In the event that a Change of Control occurs and the holders of notes of any series exercise their right to require Lamar Media to purchase notes of such series, if such purchase constitutes a “tender offer” for purposes of Rule 14e-1 under the Exchange Act at that time, Lamar Media will comply with the requirements of Rule 14e-1 as then in effect with respect to such repurchase.
Limitation on merger, consolidation or sale of assets
Lamar Media will not, directly or indirectly, in any transaction or series of transactions, merge or consolidate with or into, or sell, assign, convey, transfer, lease or otherwise dispose of all or substantially all of its properties and assets (as an entirety or substantially as an entirety in one transaction or a series of related transactions), to any person or persons, unless at the time of and after giving effect thereto:
(a) either (i) if the transaction or series of transactions is a merger or consolidation, Lamar Media shall be the surviving person of such merger or consolidation, or (ii) the person formed by such consolidation or into which Lamar Media is merged or to which the properties and assets of Lamar Media, are transferred (any such surviving person or transferee person being the “Surviving Entity”) shall be a corporation organized and existing under the laws of the United States of America, any state thereof or the District of Columbia and shall expressly assume by a supplemental indenture executed and delivered to the trustee, in form reasonably satisfactory to the trustee, all the obligations of Lamar Media under the applicable series of notes and the applicable indenture, and, in each case, such indenture shall remain in full force and effect; and
(b) immediately before and immediately after giving effect to such transaction or series of transactions on a pro forma basis (including, without limitation, any Indebtedness incurred or anticipated to be incurred in connection with or in respect of such transaction or series of transactions), no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing and Lamar Media or the Surviving Entity, as the case may be, after giving effect to such transaction or series of transactions on a pro forma basis (including, without limitation, any Indebtedness incurred or anticipated to be incurred in connection with or in respect of such transaction or series of transactions), (a) could incur $1.00 of additional Indebtedness pursuant to the first paragraph of the covenant described under “—Material covenants—Limitation on Additional Indebtedness and Preferred Stock of Restricted Subsidiaries” above (assuming a market rate of interest with respect to such additional Indebtedness) or (b) would have a Leverage Ratio that is no greater than the Leverage Ratio of Lamar Media immediately prior to such transaction.
In connection with any consolidation, merger or transfer of assets contemplated by this provision, Lamar Media shall deliver, or cause to be delivered, to the trustee, in form and substance reasonably satisfactory to the trustee, an Officers’ Certificate and an opinion of counsel, each stating that such consolidation, merger or transfer and the applicable supplemental indenture in respect thereto comply with this provision and that all conditions precedent herein provided for relating to such transaction or transactions have been complied with.
Any reference herein to a merger, transfer, consolidation, amalgamation, consolidation, assignment, sale, disposition or transfer, or similar term, shall be deemed to apply to a division of or by a limited liability company, or an allocation of assets to a series of a limited liability company (or the unwinding of such a division or allocation), as if it were a merger, transfer, consolidation, amalgamation, consolidation, assignment, sale, disposition or transfer, or similar term, as applicable, to, of or with a separate Person. Any division of a limited liability company shall constitute a separate Person hereunder (and each division of any limited liability company that is a Subsidiary, joint venture or any other like term shall also constitute such a Person or entity).
124
Table of Contents
Events of default
The following events are “Events of Default” for each series of notes:
(a) default in payment of any principal of, or premium, if any, on the notes of such series;
(b) default for 30 days in payment of any interest on the notes of such series;
(c) default by Lamar Media or any Guarantor in the observance or performance of any other covenant in such notes or the applicable indenture for 45 days (or in the case of the “Reports to holders” covenant, 120 days) after written notice from the trustee or the holders of not less than 25% in aggregate principal amount of the notes of such series then outstanding;
(d) default or defaults under one or more agreements, instruments, mortgages, bonds, debentures or other evidences of Indebtedness under which Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary of Lamar Media then has outstanding Indebtedness in excess of $100.0 million, individually or in the aggregate, and either (a) such Indebtedness is already due and payable in full or (b) such default or defaults have resulted in the acceleration of the maturity of such Indebtedness;
(e) any final judgment or judgments which can no longer be appealed for the payment of money in excess of $100.0 million (not covered by insurance) shall be rendered against Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary and shall not be discharged for any period of 60 consecutive days during which a stay of enforcement shall not be in effect; and
(f) certain events involving bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary.
The trustee may withhold notice to the holders of the notes of a series of any default (except in payment of principal of, premium, if any, or interest on the notes of such series) if the trustee considers it to be in the best interest of the holders of the notes of such series to do so.
If an Event of Default (other than an Event of Default resulting from certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization) shall have occurred and be continuing, then the trustee or the holders of not less than 25% in aggregate principal amount of the notes of a series then outstanding may declare to be immediately due and payable the entire principal amount of all the notes of such series then outstanding plus accrued interest to the date of acceleration, and such amounts shall become immediately due and payable; provided, however, that after such acceleration but before a judgment or decree based on acceleration is obtained by the trustee, the holders of a majority in aggregate principal amount of outstanding notes of a series may, under certain circumstances, rescind and annul such acceleration if all Events of Default, other than nonpayment of accelerated principal, premium or interest, have been cured or waived as provided in the applicable indenture. In case an Event of Default resulting from certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency or reorganization shall occur, the principal, premium and interest amount with respect to all of the notes of such series shall be due and payable immediately without any declaration or other act on the part of the trustee or the holders of the notes of such series.
The holders of a majority in principal amount of the notes of a series then outstanding shall have the right to waive any existing default or compliance with any provision of the applicable indenture or such notes and to direct the time, method and place of conducting any proceeding for any remedy available to the trustee, subject to certain limitations specified in the indentures. No holder of any note of a series will have any right to institute any proceeding with respect to the applicable indenture or for any remedy thereunder, unless such holder shall have previously given to the trustee written notice of a continuing Event of Default, unless the holders of at least 25% in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes of such series shall have made written request and provided indemnity satisfactory to the trustee to institute such proceeding as a trustee, unless the trustee shall have failed to institute such proceeding within 60 days and unless the trustee shall not have received from the holders of a majority in aggregate principal amount of the outstanding notes of such series a direction inconsistent with such request. However, such limitations do not apply to a suit instituted for payment on such note on or after the respective due dates expressed in such note.
125
Table of Contents
Defeasance and covenant defeasance
Lamar Media may elect either:
(a) to defease and be discharged from any and all obligations with respect to the notes of any series (except for the obligations to register the transfer or exchange of such notes, to replace temporary or mutilated, destroyed, lost or stolen notes, to maintain an office or agency in respect of such notes and to hold monies for payment in trust) (“defeasance”); or
(b) to be released from its obligations with respect to the notes of any series under certain covenants contained in the applicable indenture, some of which are described above under “—Material covenants” (“covenant defeasance”),
upon the deposit with the trustee (or other qualifying trustee), in trust for such purpose, of money and/or U.S. Government Obligations which through the payment of principal and interest in accordance with their terms will provide money, in an amount sufficient to pay the principal of, premium, if any, and interest on the notes of such series, on the scheduled due dates therefor or on a selected date of redemption in accordance with the terms of the applicable indenture. Such a trust may only be established if, among other things, Lamar Media has delivered to the trustee an opinion of counsel (as specified in the indenture) (i) to the effect that neither the trust nor the trustee will be required to register as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, and (ii) to the effect that holders of the notes of such series or persons in their positions will not recognize income, gain or loss for federal income tax purposes as a result of such deposit, defeasance and discharge and will be subject to federal income tax on the same amount and in the same manner and at the same times, as would have been the case if such deposit, defeasance and discharge had not occurred, which opinion, in the case of legal defeasance, shall be based on either a private ruling concerning the notes or a published ruling of the Internal Revenue Service.
Modification of indentures
From time to time, Lamar Media, the Guarantors and the trustee may, without the consent of holders of the notes, amend the indenture for any series of notes or the notes of such series or supplement the indenture for any series of notes for certain specified purposes, including, but not limited to, providing for uncertificated notes in addition to certificated notes, and curing any ambiguity, defect or inconsistency (including any amendment or supplement to conform the text of such indenture, the notes of such series or the Guarantees to any provision of this Description of notes), or making any other change that does not adversely affect the rights of any holder. Lamar Media, the Guarantors and the trustee, with the consent of holders of at least a majority in principal amount of the outstanding notes of a series, may amend the applicable indenture or such notes, except that no such modification shall, without the consent of each holder affected thereby:
(i) reduce the amount of notes of such series whose holders must consent to an amendment, supplement, or waiver to the applicable indenture or such notes;
(ii) reduce the rate of or change the time for payment of interest on any note of such series;
(iii) reduce the principal of or premium on or change the stated maturity of any note of such series;
(iv) make any note of such series payable in money other than that stated in the note;
(v) change the amount or time of any payment required by the notes of such series or reduce the premium payable upon any redemption of notes of such series, or change the time before which no such redemption may be made;
(vi) waive a default in the payment of the principal of, interest on, or redemption payment with respect to, any note of such series;
(vii) make any change in the provisions of the applicable indenture (a) protecting the right of each holder of a note of such series to receive payment of principal of, premium on and interest on such note on or after the
126
Table of Contents
due date thereof or to bring suit to enforce such payment, (b) permitting holders of a majority in principal amount of the notes of such series to waive any existing Default or Event of Default or compliance with any provision of the applicable indenture or such notes, or (c) changing this clause;
(viii) amend, alter, change or modify the obligation of Lamar Media to make and consummate a Change of Control Offer in the event of a Change of Control or make and consummate an Excess Proceeds Offer after such obligation has arisen or waive any Default in the performance of any such offers or modify any of the provisions or definitions with respect to any such offers; or
(ix) take any other action otherwise prohibited by the applicable indenture to be taken without the consent of each holder affected thereby.
Compliance certificate
Lamar Media will deliver to the trustee on or before 90 days after the end of Lamar Media’s fiscal year and on or before 45 days after the end of each of the first, second and third fiscal quarters in each year an Officers’ Certificate stating whether or not the signers know of any Default or Event of Default that has occurred. If they do, the certificate will describe the Default or Event of Default and its status. Lamar Media will also deliver to the trustee an Officers’ Certificate within five business days of becoming aware of any Default or Event of Default that has occurred.
The trustee
The trustee under the indentures will be the Registrar and Paying Agent with regard to the notes. Except during the continuance of an Event of Default, the trustee will perform only such duties as are specifically set forth in the indentures. During the existence of an Event of Default, the trustee will exercise such rights and powers vested in it under the indentures and use the same degree of care and skill in its exercise as a prudent person would exercise under the circumstances in the conduct of such person’s own affairs.
Governing law
The notes shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of the State of New York.
Certain definitions
Set forth below is a summary of certain of the defined terms used in the covenants contained in the indentures. Reference is made to the indentures for the full definition of all such terms as well as any other capitalized terms used herein for which no definition is provided.
“Acquired Indebtedness” means Indebtedness of a Person (including an Unrestricted Subsidiary) existing at the time such Person becomes a Restricted Subsidiary or assumed in connection with the acquisition of assets from such Person.
“Adjusted Net Assets” of a Guarantor at any date means the lesser of (x) the amount by which the fair value of the property of such Guarantor exceeds the total amount of liabilities, including, without limitation, contingent liabilities (after giving effect to all other fixed and contingent liabilities), but excluding liabilities under the Guarantee of such Guarantor at such date and (y) the amount by which the present fair salable value of the assets of such Guarantor at such date exceeds the amount that will be required to pay the probable liability of such Guarantor on its debts (after giving effect to all other fixed and contingent liabilities and after giving effect to any collection from any Subsidiary of such Guarantor in respect of the obligations of such Subsidiary under the Guarantee), excluding Indebtedness in respect of the Guarantee, as they become absolute and matured.
“Affiliate” of any specified Person means any other Person which directly or indirectly through one or more intermediaries controls, or is controlled by, or is under common control with, such specified Person. For the
127
Table of Contents
purposes of this definition, “control” (including, with correlative meanings, the terms “controlling,” “controlled by,” and “under common control with”), as used with respect to any Person, means the possession, directly or indirectly, of the power to direct or cause the direction of the management or policies of such Person, whether through the ownership of voting securities, by agreement or otherwise.
“Asset Acquisition” means:
(i) an Investment by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary in any other Person pursuant to which such Person shall become a Restricted Subsidiary or shall be consolidated or merged with Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary; or
(ii) the acquisition by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary of assets of any Person.
“Asset Sale” means the sale, transfer or other disposition (other than to Lamar Media or any of the Restricted Subsidiaries) in any single transaction or series of related transactions having a fair market value (as determined in good faith by Lamar Media) in excess of $15.0 million of:
(a) any Capital Stock of or other equity interest in any Restricted Subsidiary;
(b) all or substantially all of the assets of any business owned by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary or a division, line of business or comparable business segment of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary thereof; or
(c) any other assets or property of Lamar Media or of any Restricted Subsidiary (whether real or personal property).
For purposes of this definition, the term “Asset Sale” shall not include any sale, transfer or other disposition
(i) that is governed by and made in accordance with the provisions described under “—Material covenants—Limitation on merger, consolidation or sale of assets,”
(ii) to Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary that is a Guarantor,
(iii) involving obsolete, worn-out, excess or redundant equipment, or
(iv) involving Securitization Assets pursuant to a Permitted Securitization Financing.
“Asset Sale Proceeds” means, with respect to any Asset Sale:
(i) cash received by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary from such Asset Sale (including cash received as consideration for the assumption of liabilities incurred in connection with or in anticipation of such Asset Sale), after (a) provision for all income or other taxes measured by or resulting from such Asset Sale, (b) payment of all brokerage commissions, underwriting and other fees and expenses related to such Asset Sale (including, without limitation, reasonable attorneys’ fees and expenses), and (c) deduction of appropriate amounts to be provided by Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary as a reserve, in accordance with GAAP, against any liabilities associated with the assets sold or disposed of in such Asset Sale and retained by Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary after such Asset Sale, including, without limitation, pension and other post-employment benefit liabilities and liabilities related to environmental matters or against any indemnification obligations associated with the assets sold or disposed of in such Asset Sale; and
(ii) promissory notes and other noncash consideration received by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary from such Asset Sale or other disposition upon the liquidation or conversion of such notes or noncash consideration into cash.
“Available Asset Sale Proceeds” means, with respect to any Asset Sale, the aggregate Asset Sale Proceeds from such Asset Sale that have not been applied in accordance with clauses (iii)(a) or (iii)(b), and which have not been the basis for an Excess Proceeds Offer in accordance with clause (iii)(c), in each case, of the first paragraph of “—Material covenants—Limitation on certain asset sales.”
128
Table of Contents
“Average Life to Stated Maturity” means, with respect to any Indebtedness, as at any date of determination, the quotient obtained by dividing (i) the sum of the products of (a) the number of years (or any fraction thereof) from such date to the date or dates of each successive scheduled principal payment (including, without limitation, any sinking fund requirements) of such Indebtedness multiplied by (b) the amount of each such principal payment by (ii) the sum of all such principal payments.
“Capital Stock” means, with respect to any Person, any and all shares or other equivalents (however designated) of capital stock, partnership interests or any other participation, right or other interest in the nature of an equity interest in such Person or any option, warrant or other security convertible into any of the foregoing.
“Capitalized Lease Obligations” means Indebtedness represented by obligations under a lease that is required to be capitalized for financial reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP, and the amount of such Indebtedness shall be the capitalized amount of such obligations determined in accordance with GAAP.
“Change of Control” means the occurrence of any of the following events:
(a) any “person” or “group” (as such terms are used in Sections 13(d) and 14(d) of the Exchange Act), excluding Permitted Holders, is or becomes the “beneficial owner” (as defined in Rules 13d-3 and 13d-5 under the Exchange Act, except that a person or group shall be deemed to have “beneficial ownership” of all securities that such person or group has the right to acquire, whether such right is exercisable immediately or only after the passage of time, upon the happening of an event or otherwise), directly or indirectly, of more than 35% of the total voting power with respect to the total Voting Stock of Lamar Advertising; provided, however, that the Permitted Holders (i) “beneficially own” (as so defined) a lower percentage of such total voting power with respect to the Voting Stock than such other “person” or “group” and (ii) do not have the right or ability by voting power, contract or otherwise to elect or designate for election a majority of the board of directors of Lamar Advertising;
(b) Lamar Media or Lamar Advertising consolidates with, or merges with or into, another Person or sells, assigns, conveys, transfers, leases or otherwise disposes of all or substantially all of its assets to any person, or any Person consolidates with, or merges with or into, Lamar Media or Lamar Advertising, as the case may be, in any such event pursuant to a transaction in which the outstanding Voting Stock of Lamar Media or Lamar Advertising, as the case may be, is converted into or exchanged for cash, securities or other property, other than any such transaction where (i) the outstanding Voting Stock of Lamar Media or Lamar Advertising, as the case may be, is converted into or exchanged for (1) Voting Stock (other than Disqualified Capital Stock) of the surviving or transferee corporation or (2) cash, securities and other property in an amount which could then be paid by Lamar Media or Lamar Advertising, as the case may be, as a Restricted Payment under the applicable indenture, or a combination thereof, and (ii) immediately after such transaction no “person” or “group” (as such terms are used in Section 13(d) and 14(d) of the Exchange Act), excluding Permitted Holders, is the “beneficial owner” (as defined in Rules 13d-3 and 13d-5 under the Exchange Act, except that a person shall be deemed to have “beneficial ownership” of all securities that such person has the right to acquire, whether such right is exercisable immediately or only after the passage of time, upon the happening of an event or otherwise), directly or indirectly, of more than 50% of the total voting power with respect to the total Voting Stock of the surviving or transferee corporation;
(c) at any time during any consecutive two-year period, individuals who at the beginning of such period constituted the board of directors of Lamar Advertising (together with any new directors whose election by such board of directors or whose nomination for election by the stockholders of Lamar Advertising was approved by a vote of at least 66 2/3% of the directors then still in office who were either directors at the beginning of such period or whose election or nomination for election was previously so approved) cease for any reason to constitute a majority of the board of directors of Lamar Advertising then in office;
(d) Lamar Media is liquidated or dissolved or adopts a plan of liquidation; or
(e) at any time, Lamar Media ceases to be a direct or indirect wholly-owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising.
129
Table of Contents
“Common Stock” of any Person means all Capital Stock of such Person that is generally entitled to (i) vote in the election of directors of such Person or (ii) if such Person is not a corporation, vote or otherwise participate in the selection of the governing body, partners, managers or others that will control the management and policies of such Person.
“Consolidated Interest Expense” means, for any period, the aggregate amount of interest which, in conformity with GAAP, would be set forth opposite the caption “interest expense” or any like caption on an income statement for Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries on a consolidated basis (including, but not limited to, imputed interest included in Capitalized Lease Obligations, all commissions, discounts and other fees and charges owed with respect to letters of credit and bankers’ acceptance financing, the net costs associated with hedging obligations, the interest portion of any deferred payment obligation, amortization of discount or premium, if any, and all other noncash interest expense (other than interest amortized to cost of sales)) plus, without duplication, all net capitalized interest for such period and all interest incurred or paid under any guarantee of Indebtedness (including a guarantee of principal, interest or any combination thereof) of any Person, plus an amount equal to the product of (a) the aggregate dividends paid on Disqualified Capital Stock during such period and (b) a fraction, the numerator of which is one and the denominator of which is one minus Lamar Media’s then effective combined tax rate, to the extent paid; provided, however, that “Consolidated Interest Expense” shall exclude the amortization of deferred financing fees and exclude any and all interest accrued or paid or payable with respect thereto.
“Consolidated Net Income” means, for any period, the aggregate of the Net Income of Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries for such period, on a consolidated basis, determined in accordance with GAAP; provided, however, that:
(a) the Net Income of any Person (the “other Person”) in which Lamar Media or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries has less than a 100% interest (which interest does not cause the net income of such other Person to be consolidated into the net income of Lamar Media in accordance with GAAP) shall be included only to the extent of the amount of dividends or distributions paid to Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary;
(b) the Net Income of any Restricted Subsidiary (other than a Guarantor) that is subject to any restriction or limitation (assuming no waiver or satisfaction thereof shall have occurred) on the payment of dividends or the making of other distributions (other than pursuant to the notes or the indentures or under the Senior Credit Facility) shall be excluded to the extent of such restriction or limitation, except that, to the extent that any such restriction or limitation results solely from covenant limitations under any SBA Indebtedness, there shall not be deducted that portion of such Restricted Subsidiary’s Net Income which exceeds the outstanding aggregate principal amount of such SBA Indebtedness;
(c) any net gain (but not loss) resulting from an Asset Sale by Lamar Media or any of its Restricted Subsidiaries other than in the ordinary course of business shall be excluded; and
(d) extraordinary gains and losses shall be excluded.
“Consolidated Net Tangible Assets” means the book value of the assets of Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries (other than patents, patent rights, trademarks, trade names, franchises, copyrights, licenses, permits, goodwill and other intangible assets classified as such in accordance with GAAP) after all applicable deductions in accordance with GAAP (including, without limitation, reserves for doubtful receivables, obsolescence, depreciation and amortization) less all liabilities of Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries determined in accordance with GAAP.
“Cumulative Consolidated Interest Expense” means, as of any date of determination, Consolidated Interest Expense of Lamar Media from the Existing Notes Issue Date to the end of Lamar Media’s most recently ended full fiscal quarter prior to such date, taken as a single accounting period.
130
Table of Contents
“Cumulative EBITDA” means, as of any date of determination, EBITDA of Lamar Media from the Existing Notes Issue Date to the end of Lamar Media’s most recently ended full fiscal quarter prior to such date, taken as a single accounting period.
“Default” means any event that is, or with the passing of time or giving of notice or both would be, an Event of Default.
“Disqualified Capital Stock” means any Capital Stock of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary which, by its terms (or by the terms of any security into which it is convertible or for which it is exchangeable at the option of the holder thereof), or upon the happening of any event, matures or is mandatorily redeemable, pursuant to a sinking fund obligation or otherwise, or is redeemable at the option of the holder thereof, in whole or in part, on or prior to the maturity date of the notes, for cash or securities constituting Indebtedness.
“EBITDA” means, for any Person, for any period, an amount determined in accordance with GAAP equal to:
(a) the sum of, without duplication, (i) Consolidated Net Income for such period, plus (ii) the provision for taxes for such period based on income or profits to the extent such income or profits were included in computing Consolidated Net Income and any provision for taxes utilized in computing net loss under clause (i) hereof, plus (iii) to the extent it reduces Consolidated Net Income during such period, Consolidated Interest Expense for such period, plus (iv) depreciation for such period on a consolidated basis, plus (v) amortization of intangibles for such period on a consolidated basis, plus (vi) any other noncash items reducing Consolidated Net Income for such period, plus (vii) any reasonable fees and expenses in connection with any actual or proposed acquisition, Investment or financing to the extent such fees reduced Consolidated Net Income during such period (including as a result of the application of FASB 141R), plus (viii) any losses on a sale of receivables and related assets to the Securitization Entity in connection with a Permitted Securitization Financing, plus (ix) any cost savings, operating expense reductions, other operating improvements and initiatives and synergies projected in good faith to be reasonably anticipated to be realizable within 18 months of any investment, acquisition, merger, disposition or other action being given pro forma effect, net of the amount of actual benefits realized from such actions, subject to a cap for any period of four consecutive fiscal quarters of 15% of EBITDA; minus
(b) all noncash items increasing Consolidated Net Income for such period.
“Equity Offerings” means an offering by Lamar Advertising or Lamar Media of shares of its Capital Stock (however designated and whether voting or nonvoting but excluding Disqualified Capital Stock) and any and all rights, warrants or options to acquire such common stock pursuant to a registration statement registered pursuant to the Securities Act, in the case of such offerings by Lamar Advertising the proceeds of which are contributed to Lamar Media as common equity, other than (i) public offerings with respect to Capital Stock of Lamar Advertising registered on Form S-4 or Form S-8 or (ii) an issuance to any Subsidiary of Lamar Advertising or Lamar Media.
“Exchange Act” means the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
“Existing Notes Issue Date” means December 23, 2002.
“Financial Officer” means the chief financial officer, principal accounting officer, treasurer or controller of Lamar Media, as the case may be.
“GAAP” means generally accepted accounting principles consistently applied as in effect in the United States from time to time; provided, that for purposes of determining the accounting treatment for any lease, generally accepted accounting principles consistently applied in the United States as in effect on the Issue Date shall be applied (and without giving effect to FASB Accounting Standard Codification Topic 842).
“Guarantee” means each guarantee of the notes by each Guarantor.
131
Table of Contents
“Guaranteed Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligations” shall have the meaning set forth in the definition of “Investments.”
“Guarantor” means each domestic Subsidiary of Lamar Media in existence on the Issue Date (other than Missouri Logos, a Partnership) and each Subsidiary which thereafter guarantees payment of the notes pursuant to the covenant described under “Limitation on guarantees of material indebtedness.”
“incur” means, with respect to any Indebtedness or other obligation of any Person, to directly or indirectly create, issue, incur (by conversion, exchange or otherwise), assume, guarantee or otherwise become directly or indirectly liable with respect to (including as a result of an Asset Acquisition), or otherwise become responsible for, contingently or otherwise, any Indebtedness or other obligation or the recording, as required pursuant to GAAP or otherwise, of any such Indebtedness or other obligation on the balance sheet of such Person (and “incurrence,” “incurred,” “incurrable,” and “incurring” shall have meanings correlative to the foregoing); provided, however, that a change in GAAP that results in an obligation of such Person that exists at such time becoming Indebtedness shall not be deemed an incurrence of such Indebtedness.
“Indebtedness” means (without duplication), with respect to any Person, any indebtedness at any time outstanding, secured or unsecured, contingent or otherwise, which is for borrowed money (whether or not the recourse of the lender is to the whole of the assets of such Person or only to a portion thereof), or evidenced by bonds, notes, debentures or similar instruments or representing the balance deferred and unpaid of the purchase price of any property (excluding any balances that constitute accounts payable or trade payables, and other accrued liabilities arising in the ordinary course of business) if and to the extent any of the foregoing indebtedness would appear as a liability upon a balance sheet of such Person prepared in accordance with GAAP, and shall also include, to the extent not otherwise included:
(i) any Capitalized Lease Obligations of such Person;
(ii) obligations secured by a lien to which the property or assets owned or held by such Person is subject, whether or not the obligation or obligations secured thereby shall have been assumed (the amount of such obligation being deemed to be the lesser of the value of such property or asset or the amount of the obligations so secured);
(iii) guarantees of obligations of other Persons which would be included within this definition for such other Persons (whether or not such items would appear upon the balance sheet of the guarantor);
(iv) all obligations for the reimbursement of any obligor on any banker’s acceptance or for reimbursement of any obligor on any letter of credit with respect to drawings made thereunder and not yet reimbursed;
(v) in the case of Lamar Media, Disqualified Capital Stock of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(vi) obligations of any such Person under any Interest Rate Agreement applicable to any of the foregoing (if and to the extent such Interest Rate Agreement obligations would appear as a liability upon a balance sheet of such Person prepared in accordance with GAAP); and
(vii) the outstanding amount of any Guaranteed Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligations;
provided, however, that obligations in respect of performance and surety bonds and in respect of reimbursement obligations for undrawn letters of credit (whether or not secured by a lien) supporting insurance arrangements and performance and surety bonds, each incurred in the ordinary course of business and not as a part of a financing transaction, for the benefit of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary, shall not be considered Indebtedness for purposes of the indentures.
The amount of Indebtedness of any Person at any date shall be the outstanding balance at such date of all unconditional obligations as described above, provided, however, (i) that the amount outstanding at any time of any Indebtedness issued with original issue discount is the principal amount of such Indebtedness less the
132
Table of Contents
remaining unamortized portion of the original issue discount of such Indebtedness at such time as determined in conformity with GAAP and (ii) that Indebtedness shall not include any liability for federal, state, local or other taxes.
“Interest Rate Agreement” means, for any Person, any interest rate swap agreement, interest rate cap agreement, interest rate collar agreement or other similar agreement designed to protect the party indicated therein against fluctuations in interest rates.
“Investment Grade Rating” means a rating equal to or higher than Baa3 (or the equivalent) by Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. and BBB- (or the equivalent) by Standard & Poor’s Ratings Group, Inc., in each case, with a stable or better outlook; provided that a change in outlook shall not by itself cause Lamar Media to lose its Investment Grade Rating.
“Investments” means:
(i) directly or indirectly, any advance (other than a deposit of funds in connection with an acquisition, provided that either such acquisition is consummated by or through a Restricted Subsidiary or such deposit is returned to the Person that made it), account receivable (other than an account receivable arising in the ordinary course of business), loan or capital contribution to (by means of transfers of property to others, payments for property or services for the account or use of others or otherwise), the purchase of any stock, bonds, notes, debentures, partnership or joint venture interests or other securities of, or the acquisition, by purchase or otherwise, of all or substantially all of the business or assets or stock or other evidence of beneficial ownership of, any Person; and
(ii) any Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligation to the extent it is guaranteed by Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary or otherwise is recourse to or obligates Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary, directly or indirectly, contingently or otherwise, to the satisfaction thereof (“Guaranteed Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligations”).
Investments shall exclude extensions of trade credit on commercially reasonable terms in accordance with normal trade practices.
“Issue Date” means the date the notes of each series are first issued by Lamar Media and authenticated by the trustee under the applicable indenture.
“Leverage Ratio” means the ratio of (i) the sum of the aggregate outstanding amount of (x) Indebtedness of Lamar Media and the Restricted Subsidiaries and (y) except to the extent included in the previous clause (x), the aggregate liquidation preference of any Preferred Stock of Lamar Media’s Restricted Subsidiaries as of the date of determination on a consolidated basis in accordance with GAAP to (ii) Lamar Media’s EBITDA for the four full fiscal quarters (the “Four Quarter Period”) ending on or prior to the date of determination for which financial statements are available. For purposes of this definition, Lamar Media’s “EBITDA” shall be calculated on a pro forma basis after giving effect to any Asset Sales or Asset Acquisitions (including, without limitation, any Asset Acquisition giving rise to the need to make such calculation as a result of Lamar Media or one of the Restricted Subsidiaries (including any Person who becomes a Restricted Subsidiary as a result of such Asset Acquisition) incurring, assuming or otherwise becoming liable for Indebtedness and the application of Asset Sale Proceeds) at any time on or subsequent to the first day of the Four Quarter Period and on or prior to the date of determination, as if such Asset Sale or Asset Acquisition (including any EBITDA associated with such Asset Acquisition and including any pro forma expense and cost reductions determined in accordance with Article 11 of Regulation S-X relating to such Asset Acquisition) occurred on the first day of the Four Quarter Period.
“Lien” means, with respect to any property or assets of any Person, any mortgage or deed of trust, pledge, hypothecation, assignment, deposit arrangement, security interest, lien, charge, easement, encumbrance, preference, priority, or other security agreement or preferential arrangement of any kind or nature whatsoever on
133
Table of Contents
or with respect to such property or assets (including, without limitation, any Capitalized Lease Obligation, conditional sales, or other title retention agreement having substantially the same economic effect as any of the foregoing).
“Make Whole Amount” means, as determined by Lamar Media, with respect to any note at any redemption date, the excess, if positive, of:
(i) if such note is a 2028 note, (A) an amount, equal to the present value of (1) the redemption price of such note at February 15, 2023 (as set forth in the table in the first paragraph under “—Optional Redemption”) plus (2) the remaining scheduled interest that would accrue on the 2028 notes to be redeemed (subject to the right of holders on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date) to February 15, 2023 (other than interest accrued to the redemption date), computed using a discount rate equal to the Treasury Rate plus 50 basis points, over (B) the principal amount of the 2028 notes to be redeemed,
(ii) if such note is a 2029 note, (A) an amount, equal to the present value of (1) the redemption price of such note at January 15, 2024 (as set forth in the table in the first paragraph under “— Optional Redemption”) plus (2) the remaining scheduled interest that would accrue on the 2029 notes to be redeemed (subject to the right of holders on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date) to January 15, 2024 (other than interest accrued to the redemption date), computed using a discount rate equal to the Treasury Rate plus 50 basis points, over (B) the principal amount of the 2029 notes to be redeemed, and
(iii) if such note is a 2030 note, (A) an amount, equal to the present value of (1) the redemption price of such note at February 15, 2025 (as set forth in the table in the second paragraph under “—Optional Redemption”) plus (2) the remaining scheduled interest that would accrue on the 2030 notes to be redeemed (subject to the right of holders on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date) to February 15, 2025 (other than interest accrued to the redemption date), computed using a discount rate equal to the Treasury Rate plus 50 basis points, over (B) the principal amount of the 2030 notes to be redeemed.
“Moody’s” means Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. or any successor to the rating agency business thereof.
“Net Income” means, with respect to any Person for any period, the net income (loss) of such Person determined in accordance with GAAP.
“Net Proceeds” means:
(a) in the case of any sale of Capital Stock of or Indebtedness by Lamar Advertising or Lamar Media, the aggregate net cash proceeds received by Lamar Media, after payment of expenses, commissions and the like incurred in connection therewith; and
(b) in the case of any exchange, exercise, conversion or surrender of outstanding securities of any kind for or into shares of Capital Stock of Lamar Media which is not Disqualified Capital Stock, the net book value of such outstanding securities on the date of such exchange, exercise, conversion or surrender (plus any additional amount required to be paid by the holder to Lamar Media upon such exchange, exercise, conversion or surrender, less any and all payments made to the holders, e.g., on account of fractional shares and less all expenses incurred by Lamar Media in connection therewith).
“Officers’ Certificate” means, with respect to any Person, a certificate signed by the Chief Executive Officer, the President or any Vice President and the Chief Financial Officer or any Treasurer of such Person that shall comply with applicable provisions of the indentures.
“Outstanding Securitization Amount” means, at any time, without duplication (i) the sum of all then outstanding amounts advanced to Securitization Entities by lenders (other than Lamar Media or any Subsidiary) under Permitted Securitization Financings and (ii) the amount of accounts receivable disposed of in connection with any Permitted Securitization Financing (other than to a Securitization Entity) structured as a factoring arrangement that have stated due dates following such date of determination.
134
Table of Contents
“Permitted Business” means any business in which Lamar Media or its Restricted Subsidiaries are engaged on the date of the indentures and any other business related, incidental, complementary or ancillary thereto, and any unrelated business to the extent that it is not material in size as compared with Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries’ business as a whole.
“Permitted Dividend Encumbrances” means encumbrances or restrictions:
(a) existing on the Issue Date;
(b) arising by reason of Acquired Indebtedness of any Restricted Subsidiary existing at the time such Person became a Restricted Subsidiary; provided, however, that such encumbrances or restrictions were not created in anticipation of such Person becoming a Restricted Subsidiary and are not applicable to Lamar Media or any of the other Restricted Subsidiaries;
(c) arising under Indebtedness incurred under the Senior Credit Facility;
(d) arising under Refinancing Indebtedness; provided, however, that the terms and conditions of any such restrictions are no less favorable to the holders of notes than those under the Indebtedness being refinanced;
(e) customary provisions restricting the assignment of any contract or interest of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary;
(f) existing under an agreement relating to SBA Indebtedness and Permitted Securitization Financing;
(g) existing under an agreement relating to any Permitted Lien referred to in clause (iv) of the definition of Permitted Liens; provided, however, that such encumbrance or restriction only relates to the assets or property subject to such Permitted Lien;
(h) imposed by applicable law;
(i) imposed pursuant to a binding agreement which has been entered into for the sale or disposition of all or substantially all of the Capital Stock or of any assets of a Restricted Subsidiary; provided, however, such encumbrances and restrictions apply solely to such Capital Stock or assets of such Restricted Subsidiary which are the subject of such binding agreement;
(j) on cash or other deposits or net worth imposed pursuant to customer contracts entered into in the ordinary course of business;
(k) arising under Indebtedness (other than Indebtedness described in clause (b), (c), (d) or (f) above) permitted to be incurred pursuant to the indentures; provided, however, that the terms and conditions of any such encumbrances or restrictions are no more restrictive than the terms and conditions of any encumbrances or restrictions arising under the notes; and
(l) imposed with respect to the distribution or disposition of assets or property in joint venture agreements or other similar agreements entered into in the ordinary course of business.
“Permitted Holders” means (x) any of Charles Switzer, Charles W. Lamar, III, Kevin P. Reilly, Sr., members of their immediate families or any lineal descendant of any of the foregoing and the immediate families of any such lineal descendant, (y) any trust or partnership, to the extent it is for the benefit of any of the foregoing or (z) any Person or group of Persons controlled by any of the foregoing.
“Permitted Indebtedness” means:
(i) Indebtedness of Lamar Media and Restricted Subsidiaries which are Guarantors pursuant to the Senior Credit Facility in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $2.0 billion, less the aggregate amount of all permanent repayments thereunder made in accordance with “Limitation on certain asset sales,” and guarantees of such Indebtedness by Restricted Subsidiaries that are Guarantors;
(ii) Indebtedness under the notes (excluding any Additional Notes), the Guarantees and the Exchange Notes;
135
Table of Contents
(iii) Indebtedness not covered by any other clause of this definition which is outstanding on the date of the indentures;
(iv) Indebtedness of Lamar Media to any Wholly-Owned Restricted Subsidiary and Indebtedness of any Restricted Subsidiary to Lamar Media or another Restricted Subsidiary;
(v) Purchase Money Indebtedness and Capitalized Lease Obligations incurred by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary to acquire or lease property in the ordinary course of business; provided, however, that (a) the aggregate amount of such Purchase Money Indebtedness and Capital Lease Obligations outstanding at any time shall not exceed the greater of (x) 5% of Lamar Media’s Consolidated Net Tangible Assets at the time of the incurrence of any such Purchase Money Indebtedness or Capitalized Lease Obligations or (y) $50.0 million, and (b) in each case, such Purchase Money Indebtedness or Capitalized Lease Obligation, as the case may be, would not constitute more than 100% of the cost (determined in accordance with GAAP) of the property so purchased or leased plus reasonable fees and expenses incurred in connection therewith;
(vi) Interest Rate Agreements and any guarantees thereof;
(vii) Refinancing Indebtedness;
(viii) additional Indebtedness of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary that is a Guarantor not to exceed $75.0 million in principal amount outstanding at any time; and
(ix) Indebtedness pursuant to Permitted Securitization Financings, provided that the aggregate Outstanding Securitization Amount in respect of all Permitted Securitization Financings pursuant to this clause (ix) shall not exceed $500,000,000.
“Permitted Investments” means, for any Person, Investments made on or after the date of the indentures consisting of:
(a) Investments by Lamar Media or by a Restricted Subsidiary in Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary which is a Guarantor;
(b) Temporary Cash Investments;
(c) Investments by Lamar Media or by a Restricted Subsidiary in a Person, if as a result of such Investment (i) such Person becomes a Restricted Subsidiary which is a Guarantor or (ii) such Person is merged, consolidated or amalgamated with or into, or transfers or conveys substantially all of its assets to, or is liquidated into, Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary which is a Guarantor;
(d) an Investment that is made by Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary in the form of any stock, bonds, notes, debentures, partnership or joint venture interests or other securities that are issued by a third party to Lamar Media or such Restricted Subsidiary solely as partial consideration for the consummation of an Asset Sale that is otherwise permitted under the covenant described under “Limitation on certain asset sales”;
(e) Investments in Permitted Joint Ventures in an amount not to exceed $50.0 million; and
(f) Investments in Securitization Entities in connection with Permitted Securitization Financings.
“Permitted Joint Ventures” means a corporation, partnership or other entity (other than a Subsidiary) engaged in one or more Permitted Businesses in respect of which Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary (a) beneficially owns at least 5% of the shares of Capital Stock of such entity and (b) either is a party to an agreement empowering one or more parties to such agreement (which may or may not be Lamar Media or a Subsidiary), or is a member of a group that, pursuant to the constituent documents of the applicable corporation, partnership or other entity, has the power, to direct the policies, management and affairs of such entity.
“Permitted Liens” means:
(i) Liens existing on the Issue Date;
136
Table of Contents
(ii) Liens on property or assets of, or any shares of stock of, or interests in, or secured debt of, any Person existing at the time such Person becomes a Restricted Subsidiary or at the time such Person is merged into Lamar Media or any of the Restricted Subsidiaries; provided, however, that such Liens are not incurred in connection with, or in contemplation of, such Person becoming a Restricted Subsidiary or merging into Lamar Media or any of the Restricted Subsidiaries;
(iii) Liens in favor of Lamar Media or any of the Restricted Subsidiaries;
(iv) Liens to secure Purchase Money indebtedness that is otherwise permitted under the indentures; provided, however, that any such Lien is created solely for the purpose of securing such Purchase Money Indebtedness and does not extend to or cover any property other than such item of property and any improvements on such item;
(v) Liens for taxes, assessments or governmental charges that are being contested in good faith by appropriate proceedings;
(vi) Liens securing Indebtedness (x) permitted to be incurred by clause (i) of the definition of “Permitted Indebtedness” and (y) in addition to the amount permitted to be incurred by the foregoing subclause (x) so long as, in the case of this subclause (y), Indebtedness incurred pursuant to this subclause (y) (assuming any commitment therefor was fully drawn), when aggregated with any other Indebtedness of Lamar Media and the Guarantors which is secured by a Lien pursuant to this subclause (y), does not cause the Secured Leverage Ratio of Indebtedness incurred pursuant to this subclause (y) to exceed 4.5 to 1.0 as of the last day of the most recent quarter for which internal financial statements are available on the date such Indebtedness is incurred (or commitments therefor are obtained);
(vii) Permitted Dividend Encumbrances;
(viii) Liens on property of an Unrestricted Subsidiary at the time that it is designated as a Restricted Subsidiary pursuant to the definition of “Unrestricted Subsidiary”; provided that such Liens were not incurred in connection with, or contemplation of, such designation;
(ix) extensions, renewals or refundings of any Liens referred to in clauses (i), (ii) and (viii) above; provided that any such extension, renewal or refunding does not extend to any assets or secure any Indebtedness not securing or secured by the Liens being extended, renewed or refinanced;
(x) Liens securing Indebtedness in an aggregate principal amount not to exceed $1.0 million outstanding at any time; and
(xi) Liens on assets of a Securitization Entity and Securitization Assets, in each case, in connection with a Permitted Securitization Financing.
“Permitted Securitization Financing” means (i) any borrowing or factoring arrangement by a Securitization Entity with respect to Securitization Assets transferred to such Securitization Entity by Lamar Media or a Subsidiary or (ii) consisting of a factoring arrangement by the Lamar Media or a Subsidiary of Lamar Media pursuant to which Lamar Media or such Subsidiary sells Securitization Assets to a Person other than Lamar Media or a Subsidiary on a basis that is not recourse to Lamar Media or any Subsidiary except for Standard Securitization Undertakings.
“Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligations” shall have the meaning specified in the definition of “Unrestricted Subsidiary.”
“Person” or “person” means any individual, corporation, partnership, limited liability company, joint venture, association, joint-stock company, trust, unincorporated organization or government (including any agency or political subdivision thereof).
“Preferred Stock” means any Capital Stock of a Person, however designated, which entitles the holder thereof to a preference with respect to dividends, distributions or liquidation proceeds of such Person over the holders of other Capital Stock issued by such Person.
137
Table of Contents
“Property” of any Person means all types of real, personal, tangible, intangible or mixed property owned by such Person whether or not included in the most recent consolidated balance sheet of such Person and its Subsidiaries (Restricted Subsidiaries in the case of Lamar Media) under GAAP.
“Purchase Money Indebtedness” means any Indebtedness incurred by a Person to finance the cost (including the cost of construction or improvement and in the case of any Capitalized Lease Obligation, the lease) of any real or personal property, the principal amount of which indebtedness does not exceed the sum of (i) 100% of such cost and (ii) reasonable fees and expenses of such Person incurred in connection therewith.
“Rating Agencies” means S&P and Moody’s or if S&P or Moody’s or both shall not make a rating on any series of notes publicly available, a nationally recognized statistical Rating Agency or agencies, as the case may be, selected by Lamar Media (as certified by a resolution of the board of directors) which shall be substituted for S&P or Moody’s or both, as the case may be, for such series of notes.
“Refinancing Indebtedness” means Indebtedness that refunds, refinances or extends any Indebtedness of Lamar Media or the Restricted Subsidiaries outstanding on the Issue Date or other Indebtedness permitted to be incurred by Lamar Media or the Restricted Subsidiaries pursuant to the terms of the indentures (other than pursuant to clauses (i), (iv), (v) and (vi) of the definition of Permitted Indebtedness), but only to the extent that:
(i) the Refinancing Indebtedness is subordinated to the notes to at least the same extent, if at all, as the Indebtedness being refunded, refinanced or extended;
(ii) the Refinancing Indebtedness is scheduled to mature either (a) no earlier than the Indebtedness being refunded, refinanced or extended, or (b) after the maturity date of the applicable series of notes;
(iii) the portion of the Refinancing Indebtedness that is scheduled to mature on or prior to the maturity date of the applicable series of notes has a weighted average life to maturity at the time such Refinancing Indebtedness is incurred that is equal to or greater than the weighted average life to maturity of the portion of the Indebtedness being refunded, refinanced or extended that is scheduled to mature on or prior to the maturity date of the applicable series of notes;
(iv) such Refinancing Indebtedness is in an aggregate principal amount that is equal to or less than the sum of (a) the aggregate principal amount then outstanding under the Indebtedness being refunded, refinanced or extended, (b) the amount of any premium required to be paid in connection with such refunding, refinancing or extension pursuant to the terms of such Indebtedness or the amount of any premium reasonably determined by the board of directors of Lamar Media as necessary to accomplish such refunding, refinancing or extension by means of a tender offer or privately negotiated purchase and (c) the amount of customary fees, expenses and costs related to the incurrence of such Refinancing Indebtedness; and
(v) such Refinancing Indebtedness is incurred by the same Person that initially incurred the Indebtedness being refunded, refinanced or extended, except that Lamar Media may incur Refinancing Indebtedness to refund, refinance or extend Indebtedness of any Wholly-Owned Restricted Subsidiary.
“Restricted Payment” means any of the following:
(i) the declaration or payment of any dividend or any other distribution or payment on Capital Stock of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary or any payment made to the direct or indirect holders (in their capacities as such) of Capital Stock of Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary (other than (x) dividends or distributions payable solely in Capital Stock (other than Disqualified Stock) or in options, warrants or other rights to purchase Capital Stock (other than Disqualified Stock), and (y) in the case of Restricted Subsidiaries of Lamar Media, dividends or distributions payable to Lamar Media or to a Wholly-Owned Restricted Subsidiary);
(ii) the purchase, redemption or other acquisition or retirement for value of any Capital Stock of Lamar Media or any of the Restricted Subsidiaries (other than Capital Stock owned by Lamar Media or a Wholly-Owned Restricted Subsidiary);
138
Table of Contents
(iii) the making of any principal payment on, or the purchase, defeasance, repurchase, redemption or other acquisition or retirement for value, prior to any scheduled maturity, scheduled repayment or scheduled sinking fund payment, of any Indebtedness which is subordinated in right of payment to the notes that is outstanding on the Issue Date or any Refinancing Indebtedness that refinances such Indebtedness;
(iv) the making of any Investment or guarantee of any Investment in any Person other than a Permitted Investment;
(v) any designation of a Restricted Subsidiary as an Unrestricted Subsidiary to the extent set forth in the definition of Unrestricted Subsidiary; and
(vi) forgiveness of any Indebtedness of an Affiliate of Lamar Media (other than a Wholly-Owned Restricted Subsidiary) to Lamar Media or a Restricted Subsidiary.
For purposes of determining the amount expended for Restricted Payments, cash distributed or invested shall be valued at the face amount thereof and property other than cash shall be valued at its fair market value.
“Restricted Subsidiary” means a Subsidiary of Lamar Media other than an Unrestricted Subsidiary and includes all of the Subsidiaries of Lamar Media existing as of the Issue Date (other than Missouri Logos, a Partnership). The board of directors of Lamar Media may designate any Unrestricted Subsidiary or any Person that is to become a Subsidiary of Lamar Media as a Restricted Subsidiary if immediately after giving effect to such action (and treating any Acquired Indebtedness as having been incurred at the time of such action), Lamar Media could have incurred at least $1.00 of additional Indebtedness (other than Permitted Indebtedness) pursuant to the “Limitation on additional indebtedness and preferred stock of restricted subsidiaries” covenant and no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing.
“S&P” means S&P Global Ratings (a division of S&P Global Inc.) or any successor to the rating agency business thereof.
“SBA Indebtedness” means Indebtedness incurred pursuant to the United States Small Business Administration Disaster Relief Loan program or any similar loan program; provided, however, that such Indebtedness shall at all times be prepayable without penalty at the option of the obligor.
“Secured Indebtedness” means any Indebtedness secured by a Lien on any assets of Lamar Media or any Subsidiary that is a Restricted Subsidiary.
“Secured Leverage Ratio” means, as of any date of determination, the ratio of (1) the Total Secured Debt as of such date of determination to (2) EBITDA of Lamar Media for the period of the most recent four consecutive fiscal quarters for which internal financial statements are available, with such pro forma and other adjustments to each of Total Secured Debt and EBITDA as are appropriate and consistent with the pro forma and other adjustment provisions set forth in the definition of Leverage Ratio.
“Securitization Assets” means (a) accounts receivable and proceeds thereof, (b) contract rights, lockbox accounts and records with respect to such accounts receivable and any other assets customarily transferred together with accounts receivable in a receivables financing which is non-recourse to Lamar Media or any Subsidiary (other than Standard Securitization Undertakings) other than a Securitization Entity, as determined in good faith by a Financial Officer of Lamar Media and (c) any deposit account into which proceeds of accounts receivable are collected.
“Securitization Entity” means a Wholly Owned Restricted Subsidiary (or other Person formed in connection with Permitted Securitization Financings) of Lamar Media that engages in no activities other than Permitted Securitization Financings and any necessary related activities and owns no assets other than Securitization Assets, cash, cash equivalents and other assets relating to Permitted Securitization Financings and no portion of
139
Table of Contents
the Indebtedness (contingent or otherwise) of which is guaranteed by Lamar Advertising, Lamar Media or any Subsidiary (other than a Securitization Entity) of Lamar Media other than pursuant to Standard Securitization Undertakings.
“Senior Credit Facility” means the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of February 6, 2020 among Lamar Media, the guarantors party thereto, the several lenders from time to time party thereto and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and the other agents party thereto, and one or more other financing arrangements (including, without limitation, credit facilities or indentures) providing for revolving credit loans, term loans, letters of credit or other long-term indebtedness, together with the documents related thereto (including, without limitation, any guarantee agreements and security documents), in each case as such agreements may be amended (including any amendment and restatement thereof), supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time, including any agreement extending the maturity of, refinancing, replacing, consolidating or otherwise restructuring (including increasing the amount of available borrowings thereunder pursuant to incremental facilities or otherwise or adding Subsidiaries of Lamar Media as additional guarantors thereunder) all or any portion of the Indebtedness under any such agreement or any successor or replacement agreement and whether by the same or any other agent, lender or group of lenders and whether or not increasing the amount of Indebtedness that may be incurred thereunder.
“Special Purpose Subsidiaries” means Lamar QRS Receivables, LLC and Lamar TRS Receivables, LLC, newly-formed, special purpose entities and borrowers under that certain Receivables Financing Agreement dated as of December 18, 2018 among the Special Purpose Subsidiaries, PNC Bank, National Association as administrative agent, PNC Capital Markets LLC as structuring agent and certain lenders from time to time party thereto.
“Standard Securitization Undertakings” means representations, warranties, covenants, indemnities, performance guaranties and other obligations entered into in connection with a Permitted Securitization Financing that a Financial Officer of Lamar Media determines in good faith are customary for financings similar to a Permitted Securitization Financing.
“Stated Maturity” means, when used with respect to any note or any installment of interest thereon, the date specified in such note as the fixed date on which the principal of such note or such installment of interest is due and payable, and when used with respect to any other Indebtedness, means the date specified in the instrument governing such Indebtedness as the fixed date on which the principal of such Indebtedness, or any installment of interest thereon, is due and payable.
“Subsidiary” means, with respect to any Person:
(i) any corporation, association or other business entity of which more than 50% of the total voting power of shares of Capital Stock entitled (without regard to the occurrence of any contingency) to vote in the election of directors, managers or trustees thereof is at the time owned or controlled, directly or indirectly, by such Person or one or more of the other Subsidiaries of that Person (or a combination thereof); and
(ii) any partnership (a) the sole general partner or the managing general partner of which is such Person or a Subsidiary of such Person or (b) the only general partners of which are such Person or one or more Subsidiaries of such Person (or any combination thereof).
“Temporary Cash Investments” or “cash equivalents” means:
(i) United States dollars;
(ii) securities issued or directly and fully guaranteed or insured by the United States government or any agency or instrumentality thereof (provided that the full faith and credit of the United States is pledged in support thereof) having maturities of not more than one year from the date of acquisition;
(iii) certificates of deposit and eurodollar time deposits with maturities of one year or less from the date of acquisition, bankers’ acceptances with maturities not exceeding six months and overnight bank deposits, in
140
Table of Contents
each case, with any domestic commercial bank having capital and surplus in excess of $250.0 million and a Thomson BankWatch Rating of “B” or better;
(iv) repurchase obligations with a term of not more than ten days for underlying securities of the types described in clauses (ii) and (iii) above entered into with any financial institution meeting the qualifications specified in clause (iii) above;
(v) commercial paper or marketable direct obligations issued by any state of the United States of America or any political subdivision of any such state or any public instrumentality thereof, in each case, having one of the two highest ratings obtainable from Moody’s or S&P and in each case maturing within one year after the date of acquisition; and
(vi) money market funds at least 95% of the assets of which constitute cash equivalents of the kinds described in clauses (i) through (v) of this definition.
“Total Assets” means total assets of Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries on a consolidated basis, shown on the most recent balance sheet of Lamar Media and its Restricted Subsidiaries as may be expressly stated without giving effect to any amortization of the amount of intangible assets since the Issue Date, with such pro forma adjustments as are appropriate and consistent with the pro forma adjustment provisions set forth in the definition of “Leverage Ratio.”
“Total Secured Debt” means, as of any date of determination, the aggregate principal amount of Secured Indebtedness of Lamar Media and the Guarantors (other than cash management obligations and Interest Rate Agreements to the extent permitted by the indentures) outstanding on such date, determined on a consolidated basis.
“Treasury Rate” means, as of any applicable redemption date, the weekly average rounded to the nearest 1/100th of a percentage point (for the most recently completed week for which such information is available as of the date that is two business days prior to the applicable redemption date) of the yield to maturity of United States Treasury securities with a constant maturity (as compiled and published in the Federal Reserve Statistical Release H.15 with respect to each applicable day during such week or, if such Statistical Release is no longer published or available, any publicly available source of similar market data selected by Lamar Media) most nearly equal to the period from the applicable redemption date to (i) with respect to the 2028 notes, February 15, 2023; provided, however, that if the period from the applicable redemption date to February 15, 2023 is not equal to the constant maturity of a United States Treasury security for which such a yield is given, the Treasury Rate shall be obtained by linear interpolation (calculated to the nearest one twelfth of a year) from the weekly average yields of United States Treasury securities for which such yields are given, except that if the period from the applicable redemption date to February 15, 2023 is less than one year, the weekly average yield on actually traded United States Treasury securities adjusted to a constant maturity of one year will be used, (ii) with respect to the 2029 notes, January 15, 2024; provided, however, that if the period from the applicable redemption date to January 15, 2024 is not equal to the constant maturity of a United States Treasury security for which such a yield is given, the Treasury Rate shall be obtained by linear interpolation (calculated to the nearest one twelfth of a year) from the weekly average yields of United States Treasury securities for which such yields are given, except that if the period from the applicable redemption date to January 15, 2024 is less than one year, the weekly average yield on actually traded United States Treasury securities adjusted to a constant maturity of one year will be used and (iii) with respect to the 2030 notes, February 15, 2025; provided, however, that if the period from the applicable redemption date to February 15, 2025 is not equal to the constant maturity of a United States Treasury security for which such a yield is given, the Treasury Rate shall be obtained by linear interpolation (calculated to the nearest one twelfth of a year) from the weekly average yields of United States Treasury securities for which such yields are given, except that if the period from the applicable redemption date to February 15, 2025 is less than one year, the weekly average yield on actually traded United States Treasury securities adjusted to a constant maturity of one year will be used. The Treasury Rate shall be obtained by Lamar Media.
141
Table of Contents
“Unrestricted Subsidiary” means (a) any Subsidiary of an Unrestricted Subsidiary and (b) any Subsidiary of Lamar Media which is classified after the Issue Date as an Unrestricted Subsidiary by a resolution adopted by the board of directors of Lamar Media, but only so long as:
(i) no portion of the Indebtedness or any other obligation (contingent or otherwise) of such Unrestricted Subsidiary (other than obligations in respect of performance and surety bonds and in respect of reimbursement obligations for undrawn letters of credit supporting insurance arrangements and performance and surety bonds, each incurred in the ordinary course of business and not as part of a financing transaction (collectively, “Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligations”)) (A) is guaranteed by Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary, or (B) is recourse to or obligates Lamar Media or any Restricted Subsidiary of Lamar Media, directly or indirectly, contingently or otherwise, to satisfaction thereof;
(ii) such Unrestricted Subsidiary has no Indebtedness or any other obligation (other than Permitted Unrestricted Subsidiary Obligations) that, if in default in any respect (including a payment default), would permit (upon notice, lapse of time or both) any holder of any other Indebtedness of Lamar Media or its Restricted Subsidiaries to declare a default on such other Indebtedness or cause the payment thereof to be accelerated or payable prior to its stated maturity; and
(iii) no Default or Event of Default shall have occurred and be continuing.
Any designation of a Subsidiary as an Unrestricted Subsidiary shall be deemed a Restricted Payment in an amount equal to the fair market value of such Subsidiary (as determined in good faith by the board of directors of Lamar Media) and any such designation shall be permitted only if it complies with the provisions of “Limitation on restricted payments.” The trustee shall be given prompt notice by Lamar Media of each resolution adopted by the board of directors of Lamar Media under this provision, together with a copy of each such resolution adopted.
“U.S. Government Obligations” means direct non-callable obligations of, or non-callable obligations guaranteed by, the United States of America for the payment of which obligation or guarantee the full faith and credit of the United States of America is pledged.
“Voting Stock” means, with respect to any Person, securities of any class or classes of Capital Stock in such Person entitling the holders thereof to vote under ordinary circumstances in the election of members of the board of directors or other similar governing body of such Person.
“Wholly-Owned Restricted Subsidiary” means any Restricted Subsidiary, all of the outstanding Voting Stock (other than directors’ qualifying shares) of which are owned, directly or indirectly, by Lamar Media.
142
Table of Contents
REGISTRATION RIGHTS AGREEMENTS
We and our subsidiary guarantors entered into three registration rights agreements in connection with the closing of the private offerings of the outstanding notes, including: (i) with Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. and Citigroup Global Markets Inc., as representatives of the initial purchasers of the 2028 outstanding notes and original 2030 outstanding notes on February 6, 2020; (ii) with Wells Fargo Securities, LLC, as representative of the initial purchasers of the 2029 notes on May 13, 2020; and (iii) with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, as representative of the initial purchasers of the additional 2030 outstanding notes on August 19, 2020. In each agreement, we agreed for the benefit of the holders of the respective series of outstanding notes that we will use our reasonable best efforts to file with the Commission and cause to become effective a registration statement relating to an offer to exchange such notes for an issue of Commission-registered notes with terms identical to such notes (except that such exchange notes are not subject to restrictions on transfer or to any increase in annual interest rate as described below).
If applicable interpretations of the staff of the Commission do not permit us to effect the exchange offer, we are required to use our reasonable best efforts to cause to become effective a shelf registration statement relating to resales of the notes and to keep that shelf registration statement effective until the earlier of either (i) February 6, 2022, with respect to the 2028 notes and 2030 notes, or May 13, 2022, with respect to the 2029 notes, and (ii) the date on which all notes of a series covered by the shelf registration statement have been sold. We will, in the event of such a shelf registration, provide to each outstanding noteholder copies of the prospectus that is a part of the shelf registration statement, notify each noteholder when the shelf registration statement has become effective and take certain other actions to permit resales of the notes of each series. A noteholder that sells notes under the shelf registration statement generally will be required to be named as a selling security holder in the related prospectus and to deliver a prospectus to purchasers, will be subject to certain of the civil liability provisions under the Securities Act in connection with those sales and will be bound by the provisions of the applicable registration rights agreement that are applicable to such a noteholder (including certain indemnification obligations).
If this exchange offer is not completed (or, if required, the shelf registration statement is not declared effective) on or before November 2, 2020, with respect to the 2028 notes and the 2030 notes, or February 7, 2021, with respect to the 2029 notes (the “Target Registration Date”), the annual interest rate borne by notes of the applicable series will be increased (i) 0.25% per annum for the first 90-day period immediately following the Target Registration Date and (ii) an additional 0.25% per annum with respect to each subsequent 90-day period, in each case until the earlier of the second anniversary of the issue date of the notes and the date that such exchange offer is completed or, if required, the shelf registration statement is declared effective up to a maximum of 1.00% per annum of additional interest.
If we effect any exchange offer, we will be entitled to close such exchange offer not earlier than 20 business days after its commencement, provided that we have accepted all notes validly surrendered in accordance with the terms of such exchange offer. Notes of a series not tendered in the exchange offer shall bear interest at the rate set forth on the cover page of this prospectus and be subject to all the terms and conditions specified in the applicable indenture, including transfer restrictions.
The preceding is a summary of the material terms and provisions of each registration rights agreement. A copy of each registration rights agreement is incorporated by reference as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part.
143
Table of Contents
BOOK-ENTRY SETTLEMENT AND CLEARANCE
The Global Notes
Each series of exchange notes will be issued in the form of one or more registered notes in global form, without interest coupons, which are called, collectively, the global notes.
Upon issuance, each of the global notes will be deposited with the Trustee as custodian for The Depository Trust Company, or DTC, and registered in the name of Cede & Co., as nominee of DTC.
Ownership of beneficial interests in each global note will be limited to persons who have accounts with DTC, which are called DTC participants, or persons who hold interests through DTC participants. We expect that under procedures established by DTC:
| • | upon deposit of each global note with DTC’s custodian, DTC will credit portions of the principal amount of the global note to the accounts of the DTC participants designated by the initial purchasers; and |
| • | ownership of beneficial interests in each global note will be shown on, and transfer of ownership of those interests will be effected only through, records maintained by DTC (with respect to interests of DTC participants) and the records of DTC participants (with respect to other owners of beneficial interests in the global note). |
Beneficial interests in the global notes may not be exchanged for notes in physical, certificated form except in the limited circumstances described below.
Book-Entry Procedures for the Global Notes
All interests in the global notes will be subject to the operations and procedures of DTC, Euroclear and Clearstream. We provide the following summaries of those operations and procedures solely for the convenience of investors. The operations and procedures of each settlement system are controlled by that settlement system and may be changed at any time. We are not responsible for those operations or procedures.
DTC has advised us that it is:
| • | a limited purpose trust company organized under the laws of the State of New York; |
| • | a “banking organization” within the meaning of the New York State Banking Law; |
| • | a member of the Federal Reserve System; |
| • | a “clearing corporation” within the meaning of the Uniform Commercial Code; and |
| • | a “clearing agency” registered under Section 17A of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
DTC was created to hold securities for its participants and to facilitate the clearance and settlement of securities transactions between its participants through electronic book-entry changes to the accounts of its participants. DTC’s participants include securities brokers and dealers; banks and trust companies; clearing corporations and other organizations. Indirect access to DTC’s system is also available to others such as banks, brokers, dealers and trust companies; these indirect participants clear through or maintain a custodial relationship with a DTC participant, either directly or indirectly. Investors who are not DTC participants may beneficially own securities held by or on behalf of DTC only through DTC participants or indirect participants in DTC.
So long as DTC’s nominee is the registered owner of a global note, that nominee will be considered the sole owner or holder of the notes represented by that global note for all purposes under the indenture. Except as provided below, owners of beneficial interests in a global note:
| • | will not be entitled to have notes represented by the global note registered in their names; |
144
Table of Contents
| • | will not receive or be entitled to receive physical, certificated notes; and |
| • | will not be considered the owners or holders of the notes under the indenture for any purpose, including with respect to the giving of any direction, instruction or approval to the Trustee under the indenture. |
As a result, each investor who owns a beneficial interest in a global note must rely on the procedures of DTC to exercise any rights of a holder of notes under the indenture (and, if the investor is not a participant or an indirect participant in DTC, on the procedures of the DTC participant through which the investor owns its interest).
Payments of principal, premium (if any) and interest with respect to the notes represented by a global note will be made by the Trustee to DTC’s nominee as the registered holder of the global note. Neither we nor the Trustee will have any responsibility or liability for the payment of amounts to owners of beneficial interests in a global note, for any aspect of the records relating to or payments made on account of those interests by DTC, or for maintaining, supervising or reviewing any records of DTC relating to those interests.
Payments by participants and indirect participants in DTC to the owners of beneficial interests in a global note will be governed by standing instructions and customary industry practice and will be the responsibility of those participants or indirect participants and DTC.
Transfers between participants in DTC will be effected under DTC’s procedures and will be settled in same-day funds.
DTC has agreed to the above procedures to facilitate transfers of interests in the global notes among participants in its settlement systems. However, DTC is not obligated to perform these procedures and may discontinue or change these procedures at any time. Neither we nor the Trustee will have any responsibility for the performance by DTC or its participants or indirect participants of their obligations under the rules and procedures governing their operations.
Certificated Notes
Notes in physical, certificated form will be issued and delivered to each person that DTC identifies as a beneficial owner of the related notes only if:
| • | DTC is at any time unwilling, unable or ineligible to continue as depositary for the global notes or ceases to be registered as a clearing agency under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and a successor depositary is not appointed within 90 days of the date we are so informed in writing or become aware of same; or |
| • | an Event of Default has occurred and is continuing. |
145
Table of Contents
MATERIAL UNITED STATES FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following is a summary of certain United States federal income tax consequences of the exchange of outstanding notes for exchange notes and of the ownership and disposition of the exchange notes, but does not purport to be an analysis of all potential tax effects. This summary is based on the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), administrative pronouncements, judicial decisions and final, temporary and proposed regulations, all as in effect on the date hereof and all of which are subject to change, possibly with retroactive effect, or to different interpretations. Any such change or differing interpretations could affect the accuracy of the statements and consequences described below, possibly with adverse effect. We have not sought and will not seek any rulings from the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (the “IRS”) regarding the matters discussed below. There can be no assurance that the IRS or a court will not take a different position concerning the tax consequences of the exchange of the outstanding notes for the exchange notes or the ownership or disposition of the exchange notes or that any such position would be sustained.
This summary applies only to persons who hold the outstanding notes and the exchange notes as capital assets within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code (that is, for investment purposes) and does not address the tax consequences to subsequent purchasers of the notes. This summary does not discuss all aspects of United States federal income taxation that may be relevant to holders in light of their special circumstances or to holders subject to special tax rules (including, without limitation: financial institutions, corporations treated as personal holding companies, regulated insurance companies, insurance companies, real estate investment trusts, controlled foreign corporations, passive foreign investment companies, tax-exempt organizations, governmental organizations, dealers in securities or currencies, partnerships, S corporations and other pass-through entities and investors in such entities, persons subject to alternative minimum tax, persons holding the notes as a part of a hedge, straddle, conversion, constructive sale or other integrated transaction, U.S. holders (as defined below) whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar, or former U.S. citizens or long-term residents subject to taxation as expatriates under Section 877 of the Code). This summary also does not discuss any tax consequences arising under other United States federal tax laws (including estate and gift tax laws) or the law of any state, local, foreign or other taxing jurisdiction.
New Tax Legislation Enacted March 27, 2020
As noted above under “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Operations”, on March 27, 2020, the CARES Act was signed into law. Among other changes, the CARES Act modifies certain provisions of the Code, including those amended by the TCJA. Under the CARES Act, NOLs arising in taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017 and before January 1, 2021 may generally be carried back up to five taxable years preceding the tax year of such loss. However, this change under the CARES Act does not apply to REITs, so that NOLs of a REIT may not be carried back to any previous taxable year. The treatment of NOLs arising in taxable years beginning after December 31, 2020 is not affected by the CARES Act, and such losses may not be carried back to any prior taxable year. In addition, for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017, the TCJA had limited the deduction for NOLs to 80% of current year taxable income. The CARES Act eliminates this 80% limitation for taxable years beginning before January 1, 2021. Additionally, the TCJA limited the deductibility of net interest expense paid or accrued on debt properly allocable to a trade or business to 30% of “adjusted taxable income,” subject to certain exceptions. The CARES Act increases the maximum amount of interest expense that may be deducted to 50% of adjusted taxable income for taxable years beginning in 2019 or 2020. These changes impact us and our shareholders in various ways, and this summary of certain U.S. federal income tax considerations incorporates these changes where material.
YOU ARE URGED TO CONSULT YOUR OWN TAX ADVISOR REGARDING THE APPLICATION OF U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO YOUR PARTICULAR SITUATION AND THE CONSEQUENCES OF OTHER FEDERAL TAX LAWS (INCLUDING ESTATE AND GIFT TAX LAWS) AND THE LAWS OF ANY STATE, LOCAL, FOREIGN OR OTHER TAXING JURISDICTION OR UNDER ANY APPLICABLE TAX TREATY AND THE POSSIBLE EFFECT OF CHANGES IN THESE TAX LAWS.
146
Table of Contents
As used in this summary, the term “U.S. holder” means a beneficial owner of a note that is for United States federal income tax purposes (i) an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States, (ii) a corporation (including an entity treated as a corporation for United States federal income tax purposes) created or organized in or under the laws of the United States or of any political subdivision thereof, (iii) an estate, the income of which is subject to United States federal income tax regardless of its source, or (iv) a trust, if a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the administration of the trust and one or more United States persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust or if a valid election is in place to treat the trust as a United States person.
As used in this summary, the term “non-U.S. holder” means a beneficial owner of a note (other than a partnership) that is not a U.S. holder.
If a partnership (including any entity treated as a partnership for United States federal income tax purposes) is a beneficial owner of a note, the tax treatment of a partner in that partnership will generally depend on the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. Holders of notes that are partnerships and partners in those partnerships are urged to consult their tax advisors regarding the United States federal income tax consequences of the exchange of outstanding notes for exchange notes and of the ownership and disposition of the exchange notes.
Tax Consequences to U.S. Holders
Exchange Offer
The exchange of the outstanding notes for the exchange notes in connection with the exchange offer will not be treated as a taxable sale or exchange for United States federal income tax purposes. Accordingly,
| • | holders will not recognize taxable gain or loss as a result of the exchange; |
| • | the adjusted tax basis of an exchange note immediately after the exchange will be the same as the adjusted tax basis of the outstanding note exchanged therefor immediately before the exchange; |
| • | the holding period of the exchange note will include the holding period of the outstanding note; and |
| • | any original issue discount, acquisition premium, market discount or bond premium applicable to the outstanding notes will carry over to the exchange notes. |
Interest on the Notes
Stated interest on the notes will generally be taxable as ordinary interest income at the time the interest accrues or is received in accordance with a holder’s regular method of accounting for United States federal income tax purposes.
147
Table of Contents
Market Discount
If a holder acquires an exchange note (or purchased an outstanding note which such holder exchanges for an exchange note) for an amount that is less than its adjusted issue price, the difference will be treated as “market discount” (unless such difference is less than a statutorily defined de minimis amount), and the exchange note will be subject to the market discount rules. The holder of an exchange note that is subject to the market discount rules will be required to treat any full or partial principal payment or any gain recognized on the maturity, sale or other disposition of the note as ordinary income to the extent of the accrued market discount that has not previously been included in income. If a holder disposes of a note in certain otherwise nontaxable transactions, such holder must include accrued market discount as ordinary income as if the holder had sold the note at its then fair market value. The amount of market discount treated as having accrued will be determined either:
| • | on a straight-line basis by multiplying the market discount times a fraction, the numerator of which is the number of days the note was held by the holder and the denominator of which is the total number of days after the date such holder acquired the note up to, and including, the note’s maturity date; or |
| • | if the holder so elects, on the basis of a constant rate of compound interest. |
The holder of an exchange note subject to the market discount rules may elect to include market discount in income currently, through the use of either the straight-line inclusion method or the elective constant interest rate method, in lieu of recharacterizing gain upon disposition as ordinary income to the extent of accrued market discount at the time of disposition. Once made, this election will apply to all debt instruments with market discount acquired by the electing holder on or after the first day of the first taxable year to which the election applies and may not be revoked without the consent of the IRS. If an election is made to include market discount on a debt instrument in income currently, the basis of the debt instrument in the hands of the holder will be increased by the market discount thereon as it is included in income.
A holder who does not elect to include the market discount on an exchange note in income currently may be required to defer interest expense deductions for a portion of the interest paid on indebtedness incurred until the maturity of the note, its earlier disposition in a taxable transaction or, if the holder so elects, a subsequent taxable year in which sufficient income exists with respect to the exchange note.
Amortizable Bond Premium
If a holder purchases an exchange note (or purchased an outstanding note which such holder exchanges for an exchange note) for an amount in excess of all amounts payable on the note after the purchase date, other than payments of stated interest, such holder will be considered to have purchased the note with “amortizable bond premium” equal to the excess. Such holder will not be required to include in income any original issue discount with respect to the note. In general, a holder may elect to amortize bond premium by offsetting stated interest allocable to an accrual period with the premium allocable to that period at the time that the holder takes the interest into account under the holder’s regular method of accounting for United States federal income tax purposes. Bond premium is allocable to an accrual period on a constant yield basis. Because the exchange notes are redeemable at our option (see “Description of Exchange Notes—Optional Redemption”), special rules will apply which require a holder to determine the yield and maturity of the exchange notes for purposes of calculating and amortizing bond premium by assuming that we will exercise our option to redeem the holder’s notes in a manner that maximizes the holder’s yield. If we do not exercise our option to redeem the exchange note in the manner assumed, then solely for purposes of calculating and amortizing any remaining bond premium, the holder must treat the exchange note as retired and reissued on the deemed redemption date for its adjusted acquisition price as of that date. The adjusted acquisition price of the exchange note is the holder’s initial investment in the exchange note or the outstanding note, decreased by the amount of any payments, other than qualified stated interest payments, received with respect to such note and any bond premium previously amortized by the holder. Under Treasury regulations, the amount of amortizable bond premium that a holder may deduct in any accrual period is limited to the amount by which the holder’s total interest inclusions on the note in
148
Table of Contents
prior accrual periods exceed the total amount treated by the holder as a bond premium deduction in prior accrual periods. If any of the excess bond premium is not deductible, that amount is carried forward to the next accrual period.
A holder who elects to amortize bond premium must reduce the holder’s tax basis in the note by the amount of the premium used to offset interest income as set forth above. Once made, the election to amortize bond premium on a constant yield method applies to all debt instruments (other than debt instruments the interest on which is excludable from gross income) held or subsequently acquired by the holder on or after the first day of the first taxable year to which the election applies and may not be revoked without the consent of the IRS.
Sale, Redemption, Retirement or Other Taxable Disposition of the Notes
A holder of an exchange note will recognize gain or loss upon the sale, redemption, retirement or other taxable disposition of the note equal to the difference between (i) the amount of cash and the fair market value of any property received (except to the extent attributable to accrued interest) and (ii) the holder’s adjusted tax basis in the note. A holder’s adjusted tax basis in a note generally will equal such holder’s initial investment in the note, increased by the amount of original issue discount and any accrued market discount previously included in income and decreased by the amount of any payments, other than qualified stated interest payments, received with respect to such note and any amortized bond premium. If a holder disposes of a note between interest payment dates, a portion of the amount received represents stated interest accrued to the date of disposition and must be reported as ordinary interest income, and not as proceeds from the disposition, in accordance with the holder’s regular method of accounting for federal income tax purposes as described above under “—Interest on the Notes.” Subject to the market discount rules discussed above, any gain or loss recognized by a holder on the disposition of a note generally will be capital gain or loss and will be long-term capital gain or loss if the holder’s holding period is more than one year. The exchange of the outstanding notes for the exchange notes in connection with the exchange offer will not be a taxable sale or exchange for United States federal income tax purposes.
Medicare Tax
Certain U.S. holders that are individuals, estates, or trusts are subject to an additional 3.8% tax on their net investment income, which generally includes interest (including interest paid with respect to a note), dividends, annuities, royalties, rents, net gain attributable to the disposition of property not held in a trade or business (including net gain from the sale, exchange, redemption or other taxable disposition of a note) and certain other income, but will be reduced by any deductions properly allocable to such income or net gain. If you are a U.S. holder that is an individual, estate or trust, you are urged to consult your tax advisors regarding the applicability of the Medicare tax to your income and gains in respect of your investment in the notes.
Tax Consequences to Non-U.S. Holders
Exchange Offer
The exchange of the outstanding notes for the exchange notes in connection with the exchange offer will not be treated as a taxable sale or exchange for United States federal income tax purposes.
Interest on the Notes
Subject to the discussion below concerning effectively connected income, backup withholding, and FATCA, the 30% United States federal withholding tax should not apply to any payment of interest (including original issue discount) on the notes provided that: (i) the holder does not own actually or constructively 10% or more of the total combined voting power of Lamar Media Corp.; (ii) the holder is not a controlled foreign corporation related to Lamar Media Corp. through the actual or constructive stock ownership rules of the Code; (iii) the holder is not
149
Table of Contents
a bank whose receipt of interest on the notes is described in Section 881(c)(3)(A) of the Code; and (iv) either (a) the holder certifies, under penalties of perjury, to us or our paying agent on an IRS Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E, as applicable (or other applicable form), that the holder is not a United States person and provides certain other information or satisfies certain other certification requirements, or (b) a financial institution holding the notes on the holder’s behalf certifies, under penalty of perjury, that it has received an IRS Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E, as applicable (or other applicable form) from the beneficial owner and provides a copy or, in the case of certain foreign intermediaries, satisfies other certification requirements under the applicable United States Treasury regulations. Special certification requirements apply to certain non-U.S. holders that are entities.
If a non-U.S. holder cannot satisfy the requirements described above, payments of interest made to the holder will be subject to the 30% United States federal withholding tax, unless the holder provides us with either (i) a properly executed IRS Form W-8BEN or W-8BEN-E (or appropriate substitute form) claiming an exemption from or reduction in withholding under the benefit of an applicable income tax treaty or (ii) a properly executed IRS Form W-8ECI (or appropriate substitute form) stating that interest paid or accrued on the notes is not subject to withholding tax because it is effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business in the United States and is includible in such non-U.S. holder’s gross income.
A non-U.S. holder eligible for a reduced rate of United States withholding tax pursuant to an income tax treaty may obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld by filing an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS.
Sale, Redemption, Retirement or Other Taxable Disposition of the Notes
Subject to the discussion below concerning effectively connected income, backup withholding, and FATCA, a non-U.S. holder will not be subject to United States federal income tax on any gain realized on the sale, redemption, retirement or other taxable disposition of a note unless the non-U.S. holder is an individual who is present in the U.S. for at least 183 days during the year of disposition of the note and other conditions are satisfied. The exchange of the outstanding notes for exchange notes in connection with the exchange offer will not be a taxable sale or exchange for United States federal income tax purposes.
Effectively Connected Income
If a non-U.S. holder is engaged in a trade or business in the United States and the holder’s investment in a note is effectively connected with such trade or business, the holder will be exempt from the 30% withholding tax on interest (provided a certification requirement, generally on IRS Form W-8ECI, is met), but will instead generally be subject to regular United States federal income tax on a net income basis on any interest and gain with respect to the notes in the same manner as if the holder were a U.S. holder unless an applicable income tax treaty provides otherwise. In addition, if the non-U.S. holder is a foreign corporation, the holder may be subject to a branch profits tax of 30% (or the lower rate provided by an applicable income tax treaty) of the holder’s earnings and profits for the taxable year that are effectively connected with the holder’s conduct of a trade or business in the United States. If a non-U.S. holder is eligible for the benefits of a tax treaty, any effectively connected income or gain will generally be subject to United States federal income tax only if it is also attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by the holder in the United States.
Information Reporting and Backup Withholding
U.S. holders. Payments of interest (including original issue discount) and principal on, and proceeds received from a sale, exchange, retirement, redemption or other taxable disposition of, a note generally will be reported to U.S. holders, other than certain exempt recipients, such as corporations, on IRS Form 1099. In addition, a backup withholding tax may apply to such payments or proceeds if the U.S. holder fails to furnish the payor with a correct taxpayer identification number or other required certification or if it has been notified by the IRS that it is subject to backup withholding for failing to report interest or dividends required to be shown on the holder’s federal income tax returns. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup
150
Table of Contents
withholding rules will be allowed as a refund or credit against that U.S. holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability provided the required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
Non-U.S. holders. Payments of interest (including original issue discount) paid to a non-U.S. holder generally must be reported annually to the holder and the IRS. Copies of these information returns may also be made available under the provisions of a specific treaty or other agreement to the tax authorities of the country in which the non-U.S. holder resides. In general, a non-U.S. holder will not be subject to backup withholding with respect to interest or principal payments on the notes if such holder has provided the statement described above under “–United States Federal Income Tax Consequences to Non-U.S. Holders—Interest Payments on the Notes” and the payor does not have actual knowledge or reason to know that such holder is a U.S. person. In addition, a non-U.S. holder will not be subject to backup withholding with respect to the proceeds of the sale of a note (including on redemption or retirement) made within the United States or conducted through certain United States financial intermediaries if the payor receives the statement described above and does not have actual knowledge or reason to know that such holder is a United States person or such holder otherwise establishes an exemption. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. The amount of any backup withholding from a payment to a non-U.S. holder will be allowed as a credit against such holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, if any, and may entitle such holder to a refund, provided that the required information is timely furnished to the IRS. Non-U.S. holders should consult their tax advisors regarding the application of information reporting and backup withholding in their particular situations, the availability of exemptions and the procedure for obtaining such exemptions, if available.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance
The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act together with administrative guidance and certain intergovernmental agreements entered into thereunder (“FATCA”) generally imposes a 30% U.S. withholding tax on certain U.S. source payments, including interest (and original issue discount) on the exchange notes and on gross proceeds from a disposition of property of a type which can produce U.S. source interest (such as the exchange notes), paid to a foreign financial institution, or to a non-financial foreign entity, unless (a) the foreign financial institution agrees to comply with certain diligence, reporting and withholding obligations with respect to its U.S. accounts, (b) a non-financial foreign entity identifies and provides information relating to its 10% or greater U.S. owners (or confirms the absence of substantial U.S. owners), or (c) the foreign financial institution or non-financial foreign entity otherwise qualifies for an exemption from these rules. Certain countries have entered into, and other countries are expected to enter into, agreements with the United States to facilitate the type of information reporting required under FATCA. Such intergovernmental agreements may provide different rules with respect to non-U.S. financial institutions. The 30% withholding tax under FATCA applies regardless of whether the foreign financial institution or non-financial foreign entity receives payments as a beneficial owner or intermediary and whether the applicable payment otherwise is exempt from U.S. withholding (e.g., as “portfolio interest” or as capital gain upon the sale, exchange, redemption or other disposition of an exchange note).
As a result, holders may receive less interest or principal than expected with respect to the exchange notes. We will not pay any additional amounts with respect to any withholding tax imposed pursuant to FATCA. These rules were set to apply to gross proceeds from certain types of property as of January 1, 2019 but the IRS has released proposed regulations providing that these rules will not apply to any gross proceeds. The proposed regulations may presently be relied on and are likely to be finalized; as such these rules are unlikely to apply to any gross proceeds. Holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors with respect to these information reporting rules and due diligence requirements and the potential application of FATCA to them.
Taxation of Lamar Media
Our parent, Lamar Advertising, elected to be treated as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. We, Lamar Media, are treated as a qualified REIT subsidiary of Lamar Advertising that is disregarded as separate from its
151
Table of Contents
parent REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes. As discussed below under “Taxation of Lamar Advertising as a REIT,” REIT qualification involves the application of highly technical and complex provisions of the Code to Lamar Advertising’s assets and operations as well as various factual determinations concerning matters and circumstances not entirely within its control. There are limited judicial or administrative interpretations of these provisions. Although Lamar Advertising plans to operate in a manner consistent with the REIT qualification rules, we cannot assure you that it will so qualify or remain so qualified. If Lamar Advertising were to fail to qualify as a REIT, we, Lamar Media, would be classified as a taxable corporation and would be a member of Lamar Advertising’s consolidated group.
Taxation of Lamar Advertising as a REIT
Lamar Advertising elected to be taxed as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes beginning with its taxable year ended December 31, 2014, Lamar Advertising’s “first REIT taxable year.” A REIT generally is not subject to U.S. federal income tax on the income that it distributes to stockholders if it meets the applicable REIT distribution requirements and other requirements for qualification as a REIT. Lamar Advertising’s REIT election, assuming continuing compliance with the then applicable qualification tests, will continue in effect for subsequent taxable years.
We believe that Lamar Advertising’s form of organization and its operations have enabled and will enable it to continue to qualify as a REIT, beginning with its 2014 taxable year. Qualification and taxation as a REIT depend upon Lamar Advertising’s ability to meet, through actual annual (or in some cases quarterly) operating results, requirements relating to income, asset ownership, distribution levels and diversity of share ownership, and the various other REIT qualification requirements imposed under the Code, as in effect for each applicable taxable period. Given the complex nature of the REIT qualification requirements, the ongoing importance of factual determinations and the possibility of future changes in Lamar Advertising’s circumstances, we can provide no assurance that Lamar Advertising’s actual operating results will satisfy the requirements for taxation as a REIT under the Code for any particular taxable year.
So long as Lamar Advertising qualifies for taxation as a REIT, Lamar Advertising generally will not be subject to U.S. federal corporate income tax on its net income that is distributed currently to its stockholders. This treatment substantially eliminates “double taxation” (that is, taxation at both the corporate and stockholder levels) that generally results from an investment in a corporation. However, even if Lamar Advertising qualifies for taxation as a REIT, it will be subject to U.S. federal income tax as follows:
| • | Lamar Advertising will be taxed at regular corporate rates on any undistributed “REIT taxable income.” REIT taxable income is the taxable income of the REIT, subject to specified adjustments, including a deduction for dividends paid; |
| • | under some circumstances, Lamar Advertising may be subject to the “alternative minimum tax” on its items of tax preference although the “alternative minimum tax” applicable to corporations was repealed pursuant to the TCJA, effective for its 2018 taxable year and thereafter; |
| • | if Lamar Advertising has net income from the sale or other disposition of “foreclosure property” that is held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business, or other nonqualifying income from foreclosure property, it will be subject to tax at the highest corporate rate on this income; |
| • | Lamar Advertising’s net income from “prohibited transactions” will be subject to a 100% tax. In general, prohibited transactions are sales or other dispositions of property (other than foreclosure property) held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business unless such property has been held by Lamar Advertising for two years or more and certain other requirements are satisfied; |
| • | if Lamar Advertising fails to satisfy either the 75% gross income test or the 95% gross income test discussed below, but nonetheless maintains its qualification as a REIT because other requirements are met, it will be subject to a tax equal to the greater of (1) the amount by which 75% of Lamar |
152
Table of Contents
Advertising’s gross income exceeds the amount of its income qualifying under the 75% test for the taxable year or (2) the amount by which 95% of Lamar Advertising’s gross income exceeds the amount of its income qualifying for the 95% income test for the taxable year, multiplied by a fraction intended to reflect Lamar Advertising’s profitability; |
| • | if Lamar Advertising fails to satisfy any of the asset tests (other than a failure by a de minimis amount of the 5% or 10% asset tests) and it qualifies for and satisfies certain cure provisions, then Lamar Advertising will have to pay an excise tax equal to the greater of (1) $50,000 and (2) an amount determined by multiplying (x) the net income generated during a specified period by the assets that caused the failure by (y) the highest U.S. federal income tax rate applicable to corporations; |
| • | if Lamar Advertising fails to satisfy any REIT requirements other than the income test or asset test requirements and it qualifies for a reasonable cause exception, then Lamar Advertising may retain its REIT qualification, but it will have to pay a penalty equal to $50,000 for each such failure; |
| • | in each taxable year, Lamar Advertising will be subject to a nondeductible 4% excise tax to the extent of the sum of amounts actually distributed and amounts retained for which U.S. federal income tax was paid is less than the sum of: |
| • | 85% of its REIT ordinary income for the year; |
| • | 95% of its REIT capital gain net income for the year; and |
| • | any undistributed taxable income from prior taxable years; |
| • | Lamar Advertising will be subject to a 100% penalty tax on some payments it receives (or on certain expenses deducted by a TRS) if arrangements between Lamar Advertising and its TRSs are not comparable to similar arrangements among unrelated parties and it will incur such 100% excise tax if it is determined that it has been undercharged for certain services provided by a TRS.; |
| • | Lamar Advertising may elect to retain and pay U.S. federal income tax on its net long-term capital gain. In that case, a stockholder would include its proportionate share of Lamar Advertising’s undistributed long-term capital gain (to the extent we make a timely designation of such gain to the stockholder) in its income, would be deemed to have paid the tax Lamar Advertising paid on such gain, and would be allowed a credit for its proportionate share of the tax deemed to have been paid, and an adjustment would be made to increase the stockholder’s tax basis in Lamar Advertising’s stock; |
| • | if Lamar Advertising recognized gain on the disposition of assets held by it between January 1, 2014 and January 1, 2019, i.e. the five-year period after it became taxable as a REIT for U.S. federal income tax purposes, the lesser of (i) the amount of gain recognized on such disposition and (ii) the excess of the fair market value of such asset over Lamar Advertising’s basis in the asset on January 1, 2014, would be taxable at the highest regular corporate tax rate, which is currently 21%, on the lesser of the excess of the fair market value of the asset over Lamar Advertising’s basis in the asset on January 1, 2014, or the gain it realizes on the disposition. Such five-year period has expired but certain tax years for which this rule applied remain open such that additional taxes could be assessed with respect to sales in those tax years. |
| • | if after January 1, 2014, Lamar Advertising acquires an asset from a corporation in a transaction in which its basis in the asset is determined by reference to the basis of the asset in the hands of a present or former “C” corporation (including, for example, if it were to liquidate a wholly owned “C” corporation subsidiary), and if Lamar Advertising subsequently recognizes gain on the disposition of this asset during the five year period beginning on the date on which the asset ceased to be owned by the “C” corporation, then Lamar Advertising will pay tax at the highest regular corporate tax rate, which is currently 21%, on the lesser of the excess of the fair market value of the asset over the “C” corporation’s basis in the asset on the date the asset ceased to be owned by the “C” corporation, or the gain Lamar Advertising recognizes in the disposition; |
| • | income earned by Lamar Advertising’s TRSs will be subject to tax at regular corporate rates; and |
153
Table of Contents
| • | Lamar Advertising may be required to pay penalties to the IRS in certain circumstances, including if it fails to meet recordkeeping requirements intended to monitor Lamar Advertising’s compliance with rules relating to the composition of Lamar Advertising’s stockholders. |
Requirements for qualification as a REIT. In order to have so qualified, Lamar Advertising must have met and continue to meet the requirements discussed below, relating to Lamar Advertising’s organization, ownership, sources of income, nature of assets and distributions of income to stockholders.
The Code defines a REIT as a corporation, trust or association:
| (1) | that is managed by one or more trustees or directors; |
| (2) | the beneficial ownership of which is evidenced by transferable shares, or by transferable certificates of beneficial interest; |
| (3) | that would be taxable as a domestic corporation, but for Sections 856 through 859 of the Code; |
| (4) | that is neither a financial institution nor an insurance company subject to applicable provisions of the Code; |
| (5) | the beneficial ownership of which is held by 100 or more persons; |
| (6) | not more than 50% in value of the outstanding shares of which is owned during the last half of each taxable year, directly or indirectly, by five or fewer individuals, as defined in the Code to include specified entities; |
| (7) | that makes an election to be taxable as a REIT, or has made this election for a previous taxable year which has not been revoked or terminated, and satisfies all relevant filing and other administrative requirements established by the IRS that must be met to elect and maintain REIT status; |
| (8) | that uses a calendar year for U.S. federal income tax purposes and complies with the recordkeeping requirements of the Code and the Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder; and |
| (9) | that meets other applicable tests, described below, regarding the nature of its income and assets and the amount of its distributions. |
Conditions (1), (2), (3), (4), (7), (8), and (9) above must be met during the entire taxable year and condition (5) above must be met during at least 335 days of a taxable year of 12 months, or during a proportionate part of a taxable year of less than 12 months. Conditions (5) and (6) need not be satisfied during a corporation’s initial tax year as a REIT (which, in Lamar Advertising’s case, was 2014). For purposes of determining stock ownership under condition (6) above, a supplemental unemployment compensation benefits plan, a private foundation and a portion of a trust permanently set aside or used exclusively for charitable purposes generally are each considered an individual. A trust that is a qualified trust under Section 401(a) of the Code generally is not considered an individual, and beneficiaries of a qualified trust are treated as holding shares of a REIT in proportion to their actuarial interests in the trust for purposes of condition (6) above.
We believe that Lamar Advertising has outstanding sufficient shares of stock with sufficient diversity of ownership to allow it to satisfy conditions (5) and (6) above. In addition, Lamar Advertising’s charter provides restrictions regarding the transfer of shares of capital stock that are intended to assist it in satisfying the share ownership requirements described in conditions (5) and (6) above. These restrictions, however, may not ensure that Lamar Advertising will be able to satisfy these share ownership requirements.
To monitor its compliance with condition (6) above, a REIT is required to send annual letters to its stockholders requesting information regarding the actual ownership of its shares. If Lamar Advertising complies with the annual letters requirement and it does not know or, exercising reasonable diligence, would not have known of its failure to meet condition (6) above, then Lamar Advertising will be treated as having met condition (6) above.
For purposes of condition (8) above, Lamar Advertising will use a calendar year for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and it intends to comply with the applicable recordkeeping requirements.
154
Table of Contents
Lamar Advertising’s Non-REIT Accumulated Earnings and Profits. A REIT may not have any undistributed “C” corporation earnings and profits at the end of any taxable year. Thus, in order to qualify as a REIT, Lamar Advertising was required to distribute to its stockholders all of its undistributed earnings and profits accumulated through the end of 2013, prior to the end of Lamar Advertising’s first REIT taxable year.
Lamar Advertising retained accountants to compute the amount of Lamar Advertising’s accumulated E&P through December 31, 2013. Based on these calculations and projections, we believe that Lamar Advertising had no more than $40 million in accumulated E&P as of December 31, 2013. Lamar Advertising distributed this amount in full to its stockholders by the December 31, 2014 deadline. However, there can be no assurance that the IRS would not, upon subsequent examination, propose adjustments to Lamar Advertising’s calculation of the undistributed earnings and profits. If it is subsequently determined that Lamar Advertising had undistributed earnings and profits as of the end of its first taxable year as a REIT, Lamar Advertising may be eligible for a relief provision similar to the “deficiency dividends” procedure described below. To utilize this relief provision, Lamar Advertising would have to pay an interest charge for the delay in distributing the non-REIT accumulated E&P; in addition, Lamar Advertising would be required to distribute to its stockholders, in addition to Lamar Advertising’s other REIT distribution requirements, the amount of the non-REIT accumulated E&P less the interest charge paid.
Acquisitions of “C” Corporations. If Lamar Advertising acquires a corporation, liquidates a TRS or converts a TRS to a QRS, to preserve Lamar Advertising’s status as a REIT it must generally distribute all of the non-REIT accumulated E&P inherited in that transaction, if any, not later than the end of the taxable year in which the transaction occurred. The distribution of such non-REIT accumulated E&P may be eligible for taxation to noncorporate U.S. stockholders at the maximum 20% “qualified dividend” rate.
Ownership of Partnerships, LLCs and Qualified REIT Subsidiaries. In the case Lamar Advertising is a partner in a partnership or a member of a limited liability company or other entity that is treated as a partnership for United States federal income tax purposes, Treasury regulations provide that it is deemed to own its proportionate share of the partnership’s assets, and to earn its proportionate share of the partnership’s income, for purposes of the asset and gross income tests applicable to REITs, as described below. A REIT’s proportionate share of a partnership’s assets and income is based on its capital interests in the partnership. However, solely for purposes of the 10% value test, described below, the determination of Lamar Advertising’s interest in partnership assets is based on its proportionate interest in the equity and certain debt securities issued by the partnership. In addition, the assets and gross income of the partnership are deemed to retain the same character in its hands. Thus, its proportionate share of the assets and items of income of Lamar Advertising’s operating partnership and any of its subsidiaries treated as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes will be treated as its assets and items of income for purposes of applying the REIT requirements. As the sole general partner of the operating partnership, Lamar Advertising has direct control over it and indirect control over the subsidiaries in which its operating partnership or a subsidiary has a controlling interest. Lamar Advertising currently intends to operate these entities in a manner consistent with the requirements for its qualification as a REIT.
Under the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015, Congress revised the rules applicable to U.S. federal income tax audits of partnerships (such as certain of Lamar Advertising’s subsidiaries) and the collection of any tax resulting from any such audits or other tax proceedings, generally for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017. Under the new rules, the partnership itself may be liable for a hypothetical increase in partner-level taxes (including interest and penalties) resulting from an adjustment of partnership tax items on audit, regardless of changes in the composition of the partners (or their relative ownership) between the year under audit and the year of the adjustment. The new rules also include an elective alternative method under which the additional taxes resulting from the adjustment are assessed from the affected partners, subject to a higher rate of interest than otherwise would apply. Many questions remain as to how the new rules will apply, or if they will apply, especially with respect to partners that are REITs, and it is not clear at this time what effect this new legislation will have on Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media. However, these changes could increase the U.S. federal income tax, interest, and/or penalties otherwise borne by Lamar Advertising in the event of a U.S. federal income tax audit of a subsidiary partnership.
155
Table of Contents
If a REIT owns a corporate subsidiary that is a QRS, the separate existence of that subsidiary will be disregarded for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Generally, a QRS is a corporation, other than a TRS (discussed below), all of the stock of which is owned by the REIT. All assets, liabilities and items of income, deduction and credit of the QRS will be treated as assets, liabilities and items of income, deduction and credit of the REIT itself. A QRS will not be subject to federal corporate income taxation, although it may be subject to state and local taxation in some states.
Subsidiary REITs. Although Lamar Advertising does not expect to own interests in other REITs, it may find it necessary or advantageous in the future to do so. If any REIT in which Lamar Advertising holds an interest fails to qualify for taxation as a REIT in any taxable year, that failure could, depending on the circumstances, adversely affect Lamar Advertising’s ability to satisfy the various asset and gross income requirements applicable to REITs, including the requirement that REITs generally may not own, directly or indirectly, more than 10% of the securities of another corporation that is not a REIT or a TRS.
Taxable REIT Subsidiaries. A TRS is a corporation in which Lamar Advertising directly or indirectly owns stock and that elects, together with Lamar Advertising, to be treated as a TRS under Section 856(l) of the Code. In addition, if one of Lamar Advertising’s TRSs owns, directly or indirectly, securities representing more than 35% or more of the vote or value of a subsidiary corporation, that subsidiary will also be treated as Lamar Advertising’s TRS. A TRS is a corporation subject to U.S. federal income tax, and state and local income tax where applicable, as a regular “C” corporation. A TRS may be prevented from deducting interest on debt funded directly or indirectly by Lamar Advertising if certain tests are not satisfied, as described below in “New Interest Deduction Limitation Enacted by the TCJA.” Overall, no more than 20% (25% with respect to taxable years beginning before January 1, 2018) of the value of a REIT’s assets may consist of TRS securities.
Generally, a TRS can perform some impermissible tenant services without causing Lamar Advertising to receive impermissible tenant services income under the REIT income tests. A TRS also can recognize income that would be subject to the 100% prohibited transaction tax, or income that would be nonqualifying income under the gross income tests, if earned by a REIT, as described below. However, several provisions regarding the arrangements between a REIT and its TRSs ensure that a TRS will be subject to an appropriate level of U.S. federal income tax. For example, a TRS is limited in its ability to deduct interest payments made to Lamar Advertising in excess of a certain amount. In addition, Lamar Advertising will be obligated to pay a 100% penalty tax on some payments that it receives or on certain expenses deducted by the TRS if the economic arrangements among Lamar Advertising, its tenants and the TRS are not comparable to similar arrangements among unrelated parties and if it is determined that it has been undercharged for certain services provided by a TRS. Lamar Advertising owns and expects to continue to own interests in one or more TRSs that perform certain services for Lamar Advertising’s tenants, such as design and production of advertising copy and installations; holding certain property, such as the contracts and other assets related to Lamar Advertising’s transit business; and conducting other activities. Its TRSs may incur significant amounts of U.S. federal, state and local income taxes. Lamar Advertising also elected to treat its non-U.S. subsidiaries as its TRSs for REIT qualification purposes. Although Lamar Advertising’s non-U.S. subsidiaries are not expected to incur U.S. income taxes, they are subject to taxation in the jurisdictions where they operate and those taxes may be significant.
Income Tests Applicable to REITs. To qualify as a REIT, Lamar Advertising must satisfy two gross income tests annually. First, at least 75% of Lamar Advertising’s gross income, excluding gross income from prohibited transactions and certain other income and gains described below, for each taxable year must be derived directly or indirectly from investments relating to real property or mortgages on real property, including “rents from real property,” gains on the disposition of real estate assets other than certain debt instruments of publicly offered REITs, dividends paid by another REIT and interest on obligations secured by mortgages on real property or on interests in real property, income and gain derived from foreclosure property, or from some types of temporary investments. Second, at least 95% of Lamar Advertising’s gross income, excluding gross income from prohibited transactions and certain other income and gains described below, for each taxable year must be derived from any combination of income qualifying under the 75% test and dividends, interest, and gain from the sale or
156
Table of Contents
disposition of stock or securities. Lamar Advertising received a private letter ruling from the IRS confirming that the payments received from advertisers in respect of its billboards, logo signs and bus shelters will constitute rents from real property, provided certain conditions are met.
Rents received by Lamar Advertising will qualify as rents from real property for purposes of the REIT gross income tests described above only if several conditions are met. First, the amount of rent must not be based in whole or in part on the income or profits of any person. However, an amount received or accrued generally will not be excluded from the term “rents from real property” solely by reason of being based on a fixed percentage or percentages of receipts or sales. Second, rents received from a “related party tenant” (as defined below) will not qualify as rents from real property for purposes of the REIT gross income tests unless the tenant is a TRS and (1) at least 90% of the property is leased to unrelated tenants and the rent paid by the TRS is substantially comparable to the rent paid by the unrelated tenants for comparable space, or (2) the property leased to the TRS is a hotel or a health care facility and certain other requirements are satisfied. A tenant is a related party tenant if the REIT, or an actual or constructive owner of 10% or more of the stock of the REIT, actually or constructively owns 10% or more of the tenant. Third, if rent attributable to personal property, leased in connection with a lease of real property, is greater than 15% of the total rent received under the lease, then the portion of rent attributable to the personal property will not qualify as rents from real property.
Generally, for rents to qualify as rents from real property for purposes of the REIT gross income tests, Lamar Advertising may provide directly only an insignificant amount of services, unless those services are “customarily furnished or rendered” in connection with the rental of real property and not otherwise considered “rendered to the occupant.” Accordingly, Lamar Advertising may not provide “impermissible tenant services” (generally, services rendered to an occupant that are not customarily furnished in connection with the rental of real property) to tenants (except through an independent contractor from whom it derives no income and that meets other requirements or through a TRS) without giving rise to “impermissible tenant service income.” Impermissible tenant service income is deemed to be at least 150% of Lamar Advertising’s direct cost of providing the service. If the impermissible tenant service income exceeds 1% of Lamar Advertising’s total income from a property, then all of the income from that property will fail to qualify as rents from real property. If the total amount of impermissible tenant service income from a property does not exceed 1% of Lamar Advertising’s total income from the property, the services will not “taint” the other income from the property (that is, it will not cause the rent paid by tenants of that property to fail to qualify as rents from real property), but the impermissible tenant service income will not qualify as rents from real property.
Lamar Advertising has provided and expects to continue to provide certain services to its tenants. Lamar Advertising believes that the services with respect to its tenants that have been and will be provided by Lamar Advertising directly are usually or customarily rendered in connection with the use of advertising space only and are not otherwise rendered to particular tenants, or, if considered impermissible tenant services, income from the provision of such services with respect to a given property has not and will not jeopardize Lamar Advertising’s status as a REIT. Lamar Advertising believes that any services with respect to its tenants that may not be provided by Lamar Advertising directly without jeopardizing its status as a REIT have been, and, if applicable, will continue to be, performed by independent contractors or TRSs. In the private letter ruling issued to Lamar Advertising, the IRS confirmed that Lamar Advertising may directly provide leasing services, light and electricity to its sign structures and the routine maintenance of its sign structures. Currently, Lamar Advertising intends for its TRSs to provide certain other services, such as design, artwork and production related to advertising copy and logo plates, the installation, removal and/or replacement of advertising copy and logo plates on Lamar Advertising’s sign structures and certain other services and activities.
Lamar Advertising has, directly and indirectly through its subsidiaries, earned and will continue to earn amounts of nonqualifying income. For example, although its TRSs hold most of Lamar Advertising’s transit business contracts and assets and receive the income from Lamar Advertising’s transit business related to those contracts and assets, Lamar Advertising has retained a few of the transit contracts and the related assets in cases where it was impractical to transfer them and Lamar Advertising will continue to receive the nonqualifying income under
157
Table of Contents
those transit contracts. Also, Lamar Advertising is treating as nonqualifying income the payments it receives from the states under a few of Lamar Advertising’s logo contracts. If Lamar Advertising determines that the amount of nonqualifying income generated from these and certain other activities could affect its ability to meet the gross income tests Lamar Advertising may conduct these and other activities through a TRS.
If Lamar Advertising fails to satisfy one or both of the 75% or 95% gross income tests for any taxable year, Lamar Advertising may nevertheless qualify as a REIT for that year if it is entitled to relief under the Code. These relief provisions generally will be available if Lamar Advertising’s failure to meet the tests is due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect and, following Lamar Advertising’s identification of such failure for any taxable year, it files a schedule describing each item of its gross income for such taxable year described in the gross income tests in accordance with the applicable Treasury Regulations. It is not possible, however, to state whether in all circumstances Lamar Advertising would be entitled to the benefit of these relief provisions. For example, if Lamar Advertising fails to satisfy the gross income tests because nonqualifying income that it intentionally incurs exceeds the limits on nonqualifying income, the IRS could conclude that the failure to satisfy the tests was not due to reasonable cause. If Lamar Advertising is not entitled to relief under these provisions, Lamar Advertising will fail to qualify as a REIT. As discussed under “—Taxation of Lamar Advertising as a REIT” even if these relief provisions apply, Lamar Advertising would be subject to tax to the extent it fails to meet the REIT gross income tests.
Asset Tests Applicable to REITs. At the close of each quarter of Lamar Advertising’s taxable year, it must satisfy five tests relating to the nature of its assets:
| (1) | at least 75% of the value of Lamar Advertising’s total assets must be represented by real estate assets, cash, cash items and government securities. Real estate assets include, for this purpose, interests in real property (such as land, buildings, leasehold interest in real property and personal property leased with real property if the rents attributable to the personal property would be rents from real property under the income tests discussed above), interests in mortgages on real property or on interests in real property, shares in other qualifying REITs, stock or debt instruments held for less than one year that are purchased with the proceeds from an offering of Lamar Advertising’s shares or a public offering of its debt with a term of five years or more and, for taxable years beginning on or after January 1, 2016, debt instruments issued by publicly offered REITs; |
| (2) | not more than 25% of Lamar Advertising’s total assets may be represented by securities other than those in the 75% asset class; |
| (3) | except for cash, cash items, government securities and investments in QRSs, TRSs, equity interests in REITs or other securities that qualify as “real estate assets” for purposes of the test described in clause (1): the value of any one issuer’s securities owned by Lamar Advertising may not exceed 5% of the value of its total assets; Lamar Advertising may not own securities possessing more than 10% of the voting power of any one issuer’s outstanding securities; and it may not own more than 10% of the value of the outstanding securities of any one issuer; |
| (4) | not more than 20% (for taxable years beginning on or after January 1, 2018) or 25% (for taxable years beginning before January 1, 2018) of the value of Lamar Advertising’s total assets may be represented by securities of one or more TRSs; and |
| (5) | not more than 25% (for taxable years beginning on or after January 1, 2016) of the value of Lamar Advertising’s total assets may be represented by debt instruments of publicly offered REITs that are not secured by mortgages on real property or interests in real property. |
Securities for purposes of the asset tests may include debt securities. However, the 10% value test does not apply to certain “straight debt” and other excluded securities, as described in the Code, including, but not limited to, any loan to an individual or estate, any obligation to pay rents from real property and any security issued by a REIT. In addition, (1) a REIT’s interest as a partner in a partnership is not considered a security for purposes of
158
Table of Contents
applying the 10% value test to securities issued by the partnership; (2) any debt instrument issued by a partnership (other than straight debt or another excluded security) will not be considered a security issued by the partnership if at least 75% of the partnership’s gross income is derived from sources that would qualify for the 75% gross income test; and (3) any debt instrument issued by a partnership (other than straight debt or another excluded security) will not be considered a security issued by the partnership to the extent of the REIT’s interest as a partner in the partnership.
Debt will constitute “straight debt” if (a) neither Lamar Advertising, nor any of its controlled TRSs (that is, TRSs more than 50% of the vote or value of the outstanding stock of which is directly or indirectly owned by Lamar Advertising), own any of the issuer’s securities not described in the preceding paragraph that have an aggregate value greater than one percent of the issuer’s outstanding securities, as calculated under the Code; (b) the debt is a written unconditional promise to pay on demand or on a specified date a sum certain in money; (c) the debt is not convertible, directly or indirectly, into equity, and (d) the interest rate and the interest payment dates are not contingent on profits, the borrower’s discretion or similar factors. However, contingencies regarding time of payment of principal and interest are permissible for purposes of qualifying as straight debt if either (i) such contingency does not have the effect of changing the effective yield to maturity, as determined under the Code, other than a change in the annual yield to maturity that does not exceed the greater of (1) 5% of the annual yield to maturity or (2) 0.25%, or (ii) neither the aggregate issue price nor the aggregate face amount of the issuer’s debt instruments held by the REIT exceeds $1,000,000 and not more than 12 months of unaccrued interest can be required to be prepaid thereunder. In addition, debt will not be disqualified from being treated as “straight debt” solely because the time or amount of payment is subject to a contingency upon a default or the exercise of a prepayment right by the issuer of the debt, provided that such contingency is consistent with customary commercial practice.
Our Assets as Real Estate Assets. Treasury Regulations define “real property” for purposes of Section 856 of the Code to mean land or improvements thereon, such as buildings or other inherently permanent structures thereon, including items which are structural components of such buildings or structures. In addition, the term is defined recursively so that real property includes interests in real property. For these purposes, local law definitions are not controlling. By way of illustration, Treasury Regulations provide that real property includes wiring in a building, plumbing systems, central heating or central air-conditioning machinery, pipes or ducts, elevators or escalators installed in a building, and other items which are structural components of a building or other permanent structure; however, again by way of example, real property is defined to exclude assets accessory to the operation of a business such as machinery, printing presses, transportation equipment which is not a structural component of the building, office equipment, refrigerators, individual air-conditioning units, grocery counters, or furnishings of a motel, hotel, or office building. For purposes of Section 856 of the Code, real property includes real property outside of the United States as well as real property within the United States.
Treasury Regulations provide that, for purposes of Section 856 of the Code, the term “interests in real property” includes several types of interests that relate to real property such as (a) fee ownership and co-ownership of land or improvements thereon, leaseholds of land or improvements thereon, options to acquire land or improvements thereon, and options to acquire leaseholds of land or improvements thereon, (b) timeshare interests that represent an undivided fractional fee interest, or undivided leasehold interest, in real property, and that entitle the holders of the interests to the use and enjoyment of the property for a specified period of time each year, and (c) stock held by a person as a tenant-stockholder in a cooperative housing corporation (as those terms are defined in Section 216 of the Code). In several administrative pronouncements spanning almost four decades, the IRS has concluded that “interests in real property” properly include intangibles such as voting rights and goodwill that are inextricably and compulsorily tied to real property or otherwise inseparable from real property.
Although Lamar Advertising believes that its billboard sign structures (including the digital sign structures and displays), logo sign structures and bus shelters qualify as “real estate assets” under Section 856 and the Treasury Regulations thereunder, Lamar Advertising’s initial IRS ruling request included a request for a ruling on this issue. While Lamar Advertising’s request was pending, the IRS adopted the position that it will no longer issue
159
Table of Contents
private letter rulings addressing whether “outdoor advertising displays” for which an election under Section 1033(g)(3) of the Code (the “1033(g)(3) Election”) is available qualify as “real estate assets” under Code Section 856. Instead, the IRS advised Lamar Advertising to use the 1033(g)(3) Election to confirm the treatment of its outdoor advertising displays as real property. Since that time, the U.S. Treasury Department has issued regulations that explicitly provide that outdoor advertising displays for which a 1033(g)(3) Election has been properly made qualify as real property for REIT asset test purposes.
Treasury Regulations under Section 1033(g) of the Code define “outdoor advertising display” as “a rigidly assembled sign, display or device that constitutes, or is used to display, a commercial or other advertisement to the public and is permanently affixed to the ground or permanently attached to a building or other inherently permanent structure.” The 1033(g)(3) Election by its terms applies to treat an asset as “real property” for all purposes of the Code, including Section 856. Lamar Advertising believes that its billboard sign structures (including the digital sign structure and displays), logo sign structures and bus shelters qualify as “outdoor advertising displays” within the meaning of Section 1033(g) of the Code and the Treasury Regulations thereunder and Lamar Advertising made the 1033(g)(3) Election for its billboard sign structures, logo sign structures and bus shelters to be treated as “real property” for purposes of chapter 1 of the Code, including the REIT provisions, effective for its 2014 taxable year.
Lamar Advertising has received a private letter ruling from the IRS that Lamar Advertising’s intangible assets (including goodwill) that are associated with its outdoor advertising displays for which it makes a valid 1033(g)(3) Election also qualify as “real property” under the REIT rules. Lamar Advertising believes that any of its intangibles that do not so qualify either have no or minimal value or will be attributed to its TRSs.
Income and Asset Test Cure Provisions. After initially meeting the asset tests at the close of any quarter, Lamar Advertising will not lose its status as a REIT if it fails to satisfy any of the asset tests (other than the 10% voting limitation) at the end of a later quarter solely by reason of changes in the relative values of Lamar Advertising’s assets. If the failure to satisfy any such asset tests results from an acquisition of securities or other property during a quarter, the failure can be cured by disposition of sufficient non-qualifying assets within 30 days after the close of that quarter. Lamar Advertising has maintained and intends to continue to maintain adequate records of the value of its assets to ensure compliance with the asset tests and to take any available actions within 30 days after the close of any quarter as may be required to cure any noncompliance with the asset tests.
Moreover, if Lamar Advertising fails to satisfy any of the asset tests at the end of a calendar quarter during a taxable year and such failure is not cured within 30 days as described above, it will not lose its REIT status if one of the following additional exceptions applies: (1) the failure is due to a violation of the 5% or 10% asset tests and is “de minimis” (for this purpose, a “de minimis” failure is one that arises from Lamar Advertising’s ownership of assets the total value of which does not exceed the lesser of 1% of the total value of Lamar Advertising’s assets at the end of the quarter in which the failure occurred and $10 million) and Lamar Advertising either disposes of the assets that caused the failure or otherwise satisfies any of the asset tests within 6 months after the last day of the quarter in which its identification of the failure occurred; or (2) the failure is due to a violation of any of the asset tests (other than “de minimis” violations of the 5% or 10% asset tests) and all of the following requirements are satisfied: (i) the failure is due to reasonable cause and not willful neglect, (ii) Lamar Advertising files a schedule in accordance with Treasury Regulations providing a description of each asset that caused the failure, and (iii) Lamar Advertising either disposes of the assets that caused the failure or otherwise satisfy the asset tests within 6 months after the last day of the quarter in which Lamar Advertising’s identification of the failure occurred. If Lamar Advertising must rely on the reasonable cause exception for non-“de minimis” failures, it must pay an excise tax equal to the greater of (x) $50,000 and (y) an amount determined by multiplying the net income generated during a specified period by the assets that caused the failure by the highest U.S. federal income tax applicable to corporations.
Prohibited Transactions Tax. Any gain Lamar Advertising realizes on the sale of any property held as inventory or other property held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business will be treated as income
160
Table of Contents
from a prohibited transaction that is subject to a 100% penalty tax, unless such property has been held by Lamar Advertising for two years and certain other requirements are satisfied or the gain is realized in a TRS. Under existing law, whether property is held as inventory or primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of a trade or business is a question of fact that depends on all the facts and circumstances of a particular transaction. Lamar Advertising intends to hold, and, to the extent within its control, to have any joint venture to which Lamar Advertising’s operating partnership is a partner hold, properties for investment with a view to long-term appreciation, to engage in the business of acquiring, owning, operating and developing the properties, and to make sales of Lamar Advertising’s properties and other properties acquired subsequent to the date hereof as are consistent with Lamar Advertising’s investment objectives. Based upon Lamar Advertising’s investment objectives, it believes that overall, its properties should not be considered inventory or other property held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business. However, it may not always be practical to limit sales of properties and Lamar Advertising may be subject to the 100% penalty tax on the gain from dispositions of property if it is deemed to have held the property primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business.
The potential application of the prohibited transactions tax could cause Lamar Advertising to forego potential dispositions of other property or to forego other opportunities that might otherwise be attractive to it, or to undertake such dispositions or other opportunities through a TRS, which would generally result in corporate income taxes being incurred.
Foreclosure Property. Foreclosure property is real property (including interests in real property) and any personal property incident to such real property (1) that is acquired by a REIT as a result of the REIT having bid on the property at foreclosure, or having otherwise reduced the property to ownership or possession by agreement or process of law, after there was a default (or default was imminent) on a lease of the property or a mortgage loan held by the REIT and secured by the property, (2) for which the related loan or lease was made, entered into or acquired by the REIT at a time when default was not imminent or anticipated and (3) for which such REIT makes an election to treat the property as foreclosure property. REITs generally are subject to tax at the maximum corporate rate (currently 21%) on any net income from foreclosure property, including any gain from the disposition of the foreclosure property, other than income that would otherwise be qualifying income for purposes of the 75% gross income test. Any gain from the sale of property for which a foreclosure property election has been made will not be subject to the 100% tax on gains from prohibited transactions described above, even if the property is held primarily for sale to customers in the ordinary course of a trade or business.
Hedging Transactions and Foreign Currency Gains. Lamar Advertising may enter into hedging transactions with respect to one or more of its assets or liabilities. Hedging transactions could take a variety of forms, including interest rate swaps or cap agreements, options, futures contracts, forward rate agreements or similar financial instruments. Except to the extent as may be provided by future Treasury Regulations, any income from a hedging transaction which is clearly identified as such before the close of the day on which it was acquired, originated or entered into, including gain from the disposition or termination of such a transaction, will not constitute gross income for purposes of the 95% and 75% income tests (1) in the normal course of Lamar Advertising’s business primarily to manage risk of interest rate or price changes or currency fluctuations with respect to indebtedness incurred or to be incurred by Lamar Advertising to acquire or carry real estate assets or (2) primarily to manage the risk of currency fluctuations with respect to any item of income or gain that would be qualifying income under the 75% or 95% income tests (or any property which generates such income or gain), or, (3) for taxable years beginning on or after December 31, 2015, that hedges against transactions described in clause (1) or (2) and is entered into in connection with the extinguishment of debt or sale of property that is being hedged against by the transaction described in clause (1) or (2), and which complies with certain identification requirements, including gain from the disposition or termination of such a transaction, will not constitute gross income for purposes of the 95% gross income test and the 75% gross income test. To the extent Lamar Advertising enters into other types of hedging transactions, the income from those transactions is likely to be treated as nonqualifying income for purposes of both the 75% and 95% gross income tests. Lamar Advertising intends to structure any hedging transactions in a manner that does not jeopardize its ability to qualify as a REIT.
161
Table of Contents
In addition, certain foreign currency gains may be excluded from gross income for purposes of one or both of the REIT gross income tests, provided Lamar Advertising does not deal in or engage in substantial and regular trading in securities.
Annual Distribution Requirements Applicable to REITs. To qualify as a REIT, Lamar Advertising is required to distribute dividends, other than capital gain dividends, to its stockholders each year in an amount at least equal to (1) the sum of (a) 90% of Lamar Advertising’s REIT taxable income, computed without regard to the dividends paid deduction and Lamar Advertising’s net capital gain, and (b) 90% of the net income, after tax, from foreclosure property, minus (2) the sum of certain specified items of noncash income. For purposes of the distribution requirements, any built-in gain (net of the applicable tax) Lamar Advertising recognizes during the applicable recognition period that existed on an asset when it acquired it from a “C” corporation in a carry-over basis transaction (if disposed of prior to January 1, 2019) or that was held by Lamar Advertising as of January 1, 2014 will be included in Lamar Advertising’s REIT taxable income. These distributions must be paid either in the taxable year to which they relate, or in the following taxable year if declared before Lamar Advertising timely files its tax return for the prior year and if paid with or before the first regular dividend payment date after the declaration is made. In addition, if Lamar Advertising acquires a corporation by merger, acquire a corporation that becomes a QRS, Lamar Advertising liquidates a TRS or Lamar Advertising converts a TRS to a QRS, to preserve its status as a REIT, Lamar Advertising must generally distribute all of the non-REIT accumulated E&P inherited in that transaction, if any, not later than the end of Lamar Advertising’s taxable year in which the transaction occurred. See “—Taxation of Lamar Advertising as a REIT” for a discussion of the possible recognition of built-in gain as well as the distribution requirement. Furthermore, generally for taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017, subject to certain exceptions, generally Lamar Advertising must accrue income for U.S. federal income tax purposes no later than the time when such income is taken into account as revenue in its financial statements, which could create additional differences between REIT taxable income and the receipt of cash attributable to such income.
Lamar Advertising intends to make timely distributions sufficient to satisfy the annual distribution requirements.
Generally, Lamar Advertising anticipates having sufficient cash or liquid assets to enable it to satisfy the 90% distribution requirement. It is possible, however, that Lamar Advertising, from time to time, may choose to retain cash to fund capital projects or future operations or may not have sufficient cash or other liquid assets to meet this distribution requirement or to distribute such greater amount as may be necessary to avoid income and excise taxation, in part due to timing differences between (a) the actual receipt of income and the actual payment of deductible expenses and (b) the inclusion of such income and the deduction of such expenses in arriving at Lamar Advertising’s taxable income, or as a result of nondeductible expenses such as principal amortization or capital expenditures in excess of noncash deductions. In such event, Lamar Advertising may find it necessary to arrange for borrowings or pay taxable stock dividends in order to meet the distribution requirement.
Under some circumstances, Lamar Advertising may be able to rectify a failure to meet the distribution requirement for a year by paying dividends to stockholders in a later year, which may be included in its deduction for dividends paid for the earlier year. We will refer to such dividends as “deficiency dividends.” Thus, Lamar Advertising may be able to avoid being taxed on amounts distributed as deficiency dividends. Lamar Advertising will, however, be required to pay interest based upon the amount of any deduction taken for deficiency dividends. While the payment of a deficiency dividend will apply to a prior year for purposes of the REIT distribution requirements, it will be treated as an additional distribution to its stockholders in the year such dividend is paid.
To the extent that Lamar Advertising does not distribute all of its net capital gain or distribute at least 90%, but less than 100%, of Lamar Advertising’s REIT taxable income, as adjusted, it will be subject to tax on these retained amounts at regular corporate tax rates.
162
Table of Contents
Lamar Advertising will be subject to a nondeductible 4% excise tax to the extent the sum of amounts actually distributed and amounts retained for which U.S. federal income tax was paid is less than the sum of:
| (1) | 85% of its REIT ordinary income for the year; |
| (2) | 95% of its REIT capital gain net income for the year; and |
| (3) | any undistributed taxable income from prior taxable years. |
A REIT may elect to retain rather than distribute all or a portion of its net capital gains and pay tax on the gains. In that case, a REIT may elect to have its stockholders include their proportionate share of the undistributed net capital gains in income as long-term capital gains and receive a credit for their share of the tax paid by the REIT. For purposes of the 4% excise tax described above, any such retained amounts would be treated as having been distributed.
New Interest Deduction Limitation Enacted by the TCJA
Commencing in taxable years beginning after December 31, 2017, Section 163(j) of the Code, as amended by the TCJA, limits the deductibility of net interest expense paid or accrued on debt properly allocable to a trade or business to 30% of “adjusted taxable income” (increased by the CARES Act to 50% for tax years 2019 and 2020), subject to certain exceptions. Any amount paid or accrued in excess of the limitation is carried forward and may be deducted in a subsequent year, again subject to the 30% (or 50%, as applicable) limitation. Adjusted taxable income is determined without regard to certain deductions, including those for net interest expense, net operating loss carryforwards and, for taxable years beginning before January 1, 2022, depreciation, amortization and depletion. Provided the taxpayer makes a timely election (which is irrevocable), the 30% (or 50%, as applicable) limitation does not apply to a trade or business involving real property development, redevelopment, construction, reconstruction, rental, operation, acquisition, conversion, disposition, management, leasing or brokerage, within the meaning of Section 469(c)(7)(C) of the Code. If this election is made, depreciable real property (including certain improvements) held by the relevant trade or business must be depreciated under the alternative depreciation system under the Code, which generally is less favorable than the generally applicable system of depreciation under the Code. If Lamar Advertising does not make the election or if the election is determined not to be available with respect to all or certain of its business activities, the new interest deduction limitation could result in it having more REIT taxable income and thus increase the amount of distributions it must make in order to comply with the REIT requirements and avoid incurring corporate level income tax. Lamar Advertising has not made such an election at this time but may do so in the future.
Built-in Gains. As mentioned above, notwithstanding Lamar Advertising’s qualification and taxation as a REIT, Lamar Advertising may still be subject to corporate taxation in particular circumstances. As noted above, Lamar Advertising is subject to gain at corporate tax rates on assets held during the five year period after it elected to be taxed as a REIT (January 1, 2014) on the lesser of (1) the excess, if any, of the asset’s fair market value over Lamar Advertising’s basis in the asset, each determined as of January 1, 2014, or (2) Lamar Advertising’s gain recognized in the disposition. If Lamar Advertising recognized gain on the disposition of assets held by it between January 1, 2014 and January 1, 2019, i.e. the five-year period after it became taxable as a REIT, such gain would be taxable at the highest regular corporate tax rate, which is currently 21%, on the lesser of the excess of the fair market value of the asset over Lamar Advertising’s basis in the asset on January 1, 2014, or the gain it realizes on the disposition. Such five-year period has expired but certain tax years for which this rule applied remain open such that additional taxes could be assessed with respect to sales in those tax years.
In addition to the circumstances described above, Lamar Advertising will be subject to corporate taxation if it acquires an asset from a corporation in a transaction in which Lamar Advertising’s basis in the asset is determined by reference to the basis of the asset in the hands of a present or former “C” corporation (including, for example, if Lamar Advertising were to liquidate a TRS or convert a TRS to a QRS), and if Lamar Advertising subsequently recognizes gain on the disposition of this asset during the ten year period beginning on the date on
163
Table of Contents
which the asset ceased to be owned by the “C” corporation. In such case Lamar Advertising will generally pay tax at the highest regular corporate tax rate, currently 21%, on the lesser of (1) the excess, if any, of the asset’s fair market value over its adjusted tax basis, each determined as of the time the asset ceased to be owned by the “C” corporation, or (2) Lamar Advertising’s gain recognized in the disposition. Accordingly, any taxable disposition of an asset so acquired during the specified period could be subject to this built-in gains tax. To the extent attributable to Lamar Advertising’s gains in a taxable year that are subject to the built-in gains tax, net of any taxes paid on such gains with respect to that taxable year, Lamar Advertising’s dividends will be potentially eligible for taxation to noncorporate U.S. stockholders at the maximum 20% “qualified dividend” rate.
Record-Keeping Requirements. Lamar Advertising is required to comply with applicable record-keeping requirements. Failure to comply could result in monetary fines.
Failure of Lamar Advertising to Qualify as a REIT. If Lamar Advertising fails to satisfy any REIT requirements (other than the income test or asset test requirements, to which specific cure provisions apply), Lamar Advertising generally will avoid disqualification as a REIT if the failure is due to reasonable cause and not due to willful neglect and it pays a penalty of $50,000 with respect to such failure. It is not possible to state whether in all circumstances Lamar Advertising would be entitled to such statutory relief.
If Lamar Advertising fails to qualify for taxation as a REIT in any taxable year and the relief provisions do not apply, Lamar Advertising will be subject to tax on its taxable income at regular corporate rates, including any applicable alternative minimum tax (for taxable years beginning before January 1, 2018). Distributions to stockholders in any year in which Lamar Advertising fails to qualify will not be deductible by Lamar Advertising nor will they be required to be made. In such event, to the extent of current or accumulated earnings and profits, all distributions to stockholders will be taxable as dividend income. Subject to limitations of the Code, corporate stockholders may be eligible for the dividends-received deduction and non-corporate stockholders may be eligible to treat the dividends received from Lamar Advertising as qualified dividend income taxable as net capital gains under the provisions of Section 1(h)(11) of the Code. Unless Lamar Advertising is entitled to relief under specific statutory provisions, it also will be disqualified from electing to be taxed as a REIT for the four taxable years following the year during which qualification was lost.
Other Tax Consequences for Lamar Advertising
Lamar Advertising may be subject to state, local and foreign income, property, withholding and other tax in states, localities or foreign countries, including those in which Lamar Advertising transact business or reside. The state, local and foreign tax treatment of Lamar Advertising may not conform to the U.S. federal income tax consequences discussed above. To the extent that Lamar Advertising and its TRSs are required to pay federal, state, local or foreign income, property, withholding and other taxes, it will have less cash available to make payments on the notes.
Legislative or Other Actions Affecting REITs
The U.S. federal income tax rules are constantly under review by persons involved in the legislative process and by the IRS and the U.S. Treasury Department. We can provide no assurance as to whether, when, or in what form, the U.S. federal income tax laws applicable to Lamar Advertising may be enacted. Changes to the U.S. federal income tax laws and interpretations of U.S. federal income tax laws could adversely affect an investment in the notes.
164
Table of Contents
Each broker-dealer that receives exchange notes for its own account pursuant to the exchange offer must acknowledge that it will deliver a prospectus in connection with any resale of those exchange notes. A broker-dealer may use this prospectus, as amended or supplemented from time to time, in connection with resales of exchange notes received in exchange for outstanding notes where the broker-dealer acquired those outstanding notes as a result of market-making activities or other trading activities. We have agreed that for a period of 180 days after the expiration date of the exchange offer, we will make this prospectus, as amended or supplemented, available to any broker-dealer for use in connection with those resales.
We will not receive any proceeds from any sale of exchange notes by broker-dealers. Broker-dealers may sell exchange notes received by them for their own account pursuant to the exchange offer from time to time in one or more transactions in the over-the-counter market, in negotiated transactions, through the writing of options on the exchange notes or a combination of those methods of resale, at market prices prevailing at the time of resale, at prices related to prevailing market prices or negotiated prices. Any resale may be made directly to purchasers or to or through brokers or dealers who may receive compensation in the form of commissions or concessions from any broker-dealer or the purchasers of any exchange notes.
Any broker-dealer that resells exchange notes that were received by it for its own account pursuant to the exchange offer and any broker or dealer that participates in a distribution of those exchange notes may be deemed to be an “underwriter” within the meaning of the Securities Act. A profit on any resale of those exchange notes and any commissions or concessions received by any of those persons may be deemed to be underwriting compensation under the Securities Act. The letter of transmittal states that, by acknowledging that it will deliver and by delivering a prospectus, a broker-dealer will not be deemed to admit that it is an “underwriter” within the meaning of the Securities Act.
For a period of 180 days after the expiration date of the exchange offer, we will promptly send additional copies of this prospectus and any amendment or supplement to this prospectus to any broker-dealer that requests these documents in the letter of transmittal. We have agreed to pay all expenses incident to the exchange offer, including the expenses of one counsel for the holders of the outstanding notes, other than commissions or concessions of any brokers or dealers and will indemnify the holders of the outstanding notes, including any broker-dealers, against specified liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act.
You should be aware that the laws and practices of certain countries require investors to pay stamp taxes and other charges in connection with purchases of securities.
The trustee and its affiliates perform various financial advisory, investment banking and commercial banking services from time to time for us and our affiliates, for which they receive customary fees. The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. is the Trustee and exchange agent in connection with the exchange offer.
165
Table of Contents
The validity of the exchange notes offered hereby will be passed upon for us by Locke Lord LLP, Austin, Texas. Locke Lord LLP will deliver an opinion stating that the notes and the guarantees will be binding obligations of Lamar Media and the guarantors, respectively. In rendering its opinion, Locke Lord LLP will rely on the opinion of Kean Miller LLP with respect to certain matters pertaining to the subsidiaries guarantees.
The consolidated financial statements and schedules of Lamar Advertising Company and subsidiaries and Lamar Media Corp. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2019, and management’s assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 have been incorporated by reference herein and in the registration statement in reliance upon the reports of KPMG LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, incorporated by reference herein, and upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing. The audit reports covering the December 31, 2019 consolidated financial statements and schedules refers to a change in the method of accounting for revenue recognition and a change in the method of accounting for leases.
We have appointed The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A. as exchange agent in connection with the exchange offer. Holders should direct letters of transmittal or notices of guaranteed delivery to the exchange agent as follows:
The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A, as Exchange Agent
c/o The Bank of New York Mellon Corporation
Corporate Trust Operations- Reorganization Unit
111 Sanders Creek Parkway
East Syracuse, NY 13057
Attn: Tiffany Castor
Tel: 315-414-3034
Fax: 732-667-9408
Email: CT_Reorg_Unit_Inquiries@bnymellon.com
Delivery of a letter of transmittal to any address or facsimile number other than the one set forth above will not constitute a valid delivery.
166
Table of Contents
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
F-1
Table of Contents
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of Lamar Advertising Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act.
Lamar Advertising’s management assessed the effectiveness of Lamar Advertising’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013). Based on this assessment, Lamar Advertising’s management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2019, Lamar Advertising’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria. The effectiveness of Lamar Advertising’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 has been audited by KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report, which is included in Item 8 to this Annual Report.
F-2
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors
Lamar Advertising Company:
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Lamar Advertising Company and subsidiaries’ (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and financial statement schedules II to III (collectively, the consolidated financial statements), and our report dated February 20, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
F-3
Table of Contents
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ KPMG LLP |
| KPMG LLP |
Baton Rouge, Louisiana
February 20, 2020
F-4
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors
Lamar Advertising Company:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Lamar Advertising Company and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and financial statement schedules II to III (collectively, the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated February 20, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Change in Accounting Principle
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed its method of accounting for revenue recognition as of January 1, 2018, due to the adoption of Accounting Standards Codification Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers.
As discussed in Note 7 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed its method of accounting for leases as of January 1, 2019, due to the adoption of Accounting Standards Codification Topic 842, Leases.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
F-5
Table of Contents
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
Assessment of the accounting lease term for the portfolio of billboard land leases
As discussed in Note 7 to the consolidated financial statements, a lessee determines the lease term at the commencement date by identifying the non-cancellable period of the lease and then adding any periods for which it is reasonably certain to exercise a renewal option (or not to exercise a termination option). The Company has over 74,000 operating leases in which they determined the lease term using the portfolio approach.
We identified the assessment of the initial lease term for the portfolio of billboard land leases, which affects the discount rate for the lease as well as the measurement of the lease liability and right of use asset, as a critical audit matter. In the Company’s operating leases, the Company typically has both unilateral renewal and termination options. Determining the lease term involved a high degree of subjectivity as to whether the term should or should not include renewal period(s) (including periods after an optional termination date).
The primary procedures performed to address the critical audit matter included the following. We tested certain internal controls over the Company’s lease process, including determination of the stated initial lease term, reconciliation of inputs into the system, approval of operating lease contracts, and annual evaluation of the renewals and terminations exercised by the Company during the year. We evaluated the competence, capabilities, and objectivity of the Company’s real estate team that negotiates the operating lease terms, and that the team considers economic factors that are consistent with those enumerated in ASC 842 when negotiating the initial lease term and associated renewal and termination options. We inspected the Company’s assessment and conclusion of using the portfolio approach for its operating leases. We tested a sample of the Company’s operating lease population and obtained the underlying documentation used in the determination of the lease term to assess that the leases entered into are similar in relation to the lease agreement creation process, purpose, and considerations. We evaluated the impact of leases with early terminations and renewals beyond the stated initial term to assess the Company’s assertions about and use of the portfolio approach for the lease term.
Evaluating the fair value of site locations acquired in the Fairway Outdoor Advertising business combination
As discussed in Note 3 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company completed the acquisition of Fairway Outdoor Advertising on December 21, 2018, for an aggregate purchase price of $418.5 million. The Company finalized the fair value allocation in 2019. The Company acquired multiple intangible and tangible assets, the most significant of which was the site locations intangible asset. The acquisition date fair value allocation for the site locations asset was $153.4 million.
We identified the evaluation of the initial measurement of the site locations intangible asset acquired in the Fairway Outdoor Advertising transaction as a critical audit matter. There was a high degree of subjectivity in the forecasted financial data used in the discounted cash flow model to estimate the acquisition date fair value of the intangible asset. The discounted cash flow model included the following internally-developed assumptions for which there was limited observable market information, and the estimated fair value of such asset was sensitive to possible changes to these assumptions:
| • | Forecasted revenue; |
| • | Forecasted earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA); and |
| • | Company-specific risk premium utilized as an input to the discount rate. |
F-6
Table of Contents
The primary procedures we performed to address this critical audit matter included the following. We tested certain controls over the Company’s acquisition date valuation process to develop the relevant assumptions, as listed above, including controls related to the analysis of the assumptions based on market participants’ views. We compared the Company’s forecasted revenue and EBITDA assumptions to those of the Company’s peers using data publicly available. We assessed the assumptions for comparison to those of a market participant, including consideration of recent similar market transactions. We compared the Company’s forecasted revenue and EBITDA assumptions to both actual results and historical results to assess the Company’s ability to accurately forecast. We involved a valuation professional with specialized skills and knowledge to assist in the evaluation of the company-specific risk premium utilized as an input to the discount rate, considering the risk surrounding the forecasted revenue and EBITDA.
/s/ KPMG LLP |
| KPMG LLP |
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1999.
Baton Rouge, Louisiana
February 20, 2020
F-7
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Balance Sheets
December 31, 2019 and 2018
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 26,188 | $ | 21,494 | ||||
Receivables, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $13,185 and $11,161 as of 2019 and 2018, respectively | 254,930 | 235,576 | ||||||
Prepaid lease and contract expenses | — | 80,684 | ||||||
Other current assets | 29,051 | 25,915 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current assets | 310,169 | 363,669 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Property, plant and equipment (note 5) | 3,660,311 | 3,525,725 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (2,311,196 | ) | (2,230,677 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net property, plant and equipment | 1,349,115 | 1,295,048 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Operating lease right of use assets | 1,320,779 | — | ||||||
Goodwill (note 6) | 1,912,274 | 1,919,386 | ||||||
Intangible assets, net (note 6) | 992,244 | 915,453 | ||||||
Other assets | 56,574 | 51,085 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total assets | $ | 5,941,155 | $ | 4,544,641 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||
Trade accounts payable | $ | 14,974 | $ | 21,246 | ||||
Current maturities of long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $6,081 and $5,245 in 2019 and 2018, respectively (note 9) | 226,514 | 204,120 | ||||||
Current operating lease liabilities (note 7) | 196,841 | — | ||||||
Accrued expenses (note 8) | 107,225 | 122,467 | ||||||
Deferred income | 127,254 | 107,202 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current liabilities | 672,808 | 455,035 | ||||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $18,333 and $20,619 in 2019 and 2018, respectively (note 9) | 2,753,604 | 2,684,568 | ||||||
Operating lease liabilities (note 7) | 1,068,181 | — | ||||||
Deferred income tax liabilities (note 12) | 5,713 | 20,734 | ||||||
Asset retirement obligation (note 10) | 226,137 | 222,989 | ||||||
Other liabilities | 34,406 | 29,531 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities | 4,760,849 | 3,412,857 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholders’ equity (note 14): | ||||||||
Series AA preferred stock, par value $.001, $63.80 cumulative dividends, authorized 5,720 shares; 5,720 shares issued and outstanding at 2019 and 2018 | — | — | ||||||
Class A common stock, par value $.001, 362,500,000 shares authorized, 86,596,498 and 85,551,595 shares issued and 86,093,300 and 85,162,692 outstanding at 2019 and 2018, respectively | 87 | 86 | ||||||
Class B common stock, par value $.001, 37,500,000 shares authorized, 14,420,085 shares issued and outstanding at 2019 and 2018 | 14 | 14 | ||||||
Additional paid-in-capital | 1,922,222 | 1,852,421 | ||||||
Accumulated comprehensive income | 685 | 12 | ||||||
Accumulated deficit | (708,408 | ) | (695,337 | ) | ||||
Cost of shares held in treasury, 503,198 and 388,903 shares in 2019 and 2018, respectively | (34,294 | ) | (25,412 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholders’ equity | 1,180,306 | 1,131,784 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 5,941,155 | $ | 4,544,641 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-8
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Statements of Income | ||||||||||||
Net revenues (note 2) | $ | 1,753,644 | $ | 1,627,222 | $ | 1,541,260 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Operating expenses (income): | ||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 590,078 | 561,848 | 540,880 | |||||||||
General and administrative expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 318,380 | 289,428 | 276,229 | |||||||||
Corporate expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 84,658 | 82,896 | 62,344 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization (note 11) | 250,028 | 225,261 | 211,104 | |||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | (7,241 | ) | 7,233 | (4,664 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 1,235,903 | 1,166,666 | 1,085,893 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Operating income | 517,741 | 460,556 | 455,367 | |||||||||
Other expense (income): | ||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 15,429 | 71 | |||||||||
Interest income | (764 | ) | (534 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
Interest expense | 150,616 | 129,732 | 128,396 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 149,852 | 144,627 | 128,461 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Income before income tax expense | 367,889 | 315,929 | 326,906 | |||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense (note 12) | (4,222 | ) | 10,697 | 9,230 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Net income | 372,111 | 305,232 | 317,676 | |||||||||
Preferred stock dividends | 365 | 365 | 365 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Net income applicable to common stock | $ | 371,746 | $ | 304,867 | $ | 317,311 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Earnings per share: | ||||||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 3.71 | $ | 3.09 | $ | 3.24 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 3.71 | $ | 3.08 | $ | 3.23 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash dividends declared per share of common stock | $ | 3.84 | $ | 3.65 | $ | 3.32 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Weighted average common shares used in computing earnings per share: | ||||||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding basic | 100,130,721 | 98,817,525 | 97,930,555 | |||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding diluted | 100,320,574 | 99,086,160 | 98,369,865 | |||||||||
Statements of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 372,111 | $ | 305,232 | $ | 317,676 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | ||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | 673 | (1,290 | ) | 1,926 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 372,784 | $ | 303,942 | $ | 319,602 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-9
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Series AA PREF Stock | Class A CMN Stock | Class B CMN Stock | Treasury Stock | Add’l Paid in Capital | Accumulated Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2016 | $ | — | 83 | 15 | (12,303 | ) | 1,713,312 | (624 | ) | (630,955 | ) | 1,069,528 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | — | — | — | — | 4,012 | — | — | 4,012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 150,259 shares of common stock through stock awards | — | — | — | — | 18,491 | 18,491 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of 554,049 shares of stock options | — | — | — | — | 20,306 | — | — | 20,306 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 107,978 shares of common stock through employee purchase plan | — | — | — | — | 6,378 | — | — | 6,378 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of 190,280 shares of Class B common stock to Class A common stock | — | 1 | (1 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of 115,196 shares of treasury stock | — | — | — | (8,997 | ) | — | — | — | (8,997 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | — | 1,926 | — | 1,926 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 317,676 | 317,676 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends/distributions to common shareholders ($3.32 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (325,462 | ) | (325,462 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends ($63.80 per preferred share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (365 | ) | (365 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2017 | $ | — | 84 | 14 | (21,300 | ) | 1,762,499 | 1,302 | (639,106 | ) | 1,103,493 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | — | — | — | — | 4,012 | — | — | 4,012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 150,259 shares of common stock through stock awards | — | — | — | — | 11,012 | — | — | 11,012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of 361,618 shares of stock options | — | 1 | — | — | 13,432 | — | — | 13,433 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 126,012 shares of common stock through employee purchase plan | — | — | — | — | 7,115 | — | — | 7,115 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 576,002 shares of common stock for cash | — | 1 | — | — | 42,069 | — | — | 42,070 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 163,137 shares of common stock for purchase of assets | — | — | — | — | 12,282 | — | — | 12,282 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of 57,619 shares of treasury stock | — | — | — | (4,112 | ) | — | — | — | (4,112 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | — | (1,290 | ) | — | (1,290 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 305,232 | 305,232 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends/distributions to common shareholders ($3.65 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (361,098 | ) | (361,098 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends ($63.80 per preferred share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (365 | ) | (365 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2018 | $ | — | 86 | 14 | (25,412 | ) | 1,852,421 | 12 | (695,337 | ) | 1,131,784 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | — | — | — | — | 4,604 | 4,604 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 302,507 shares of common stock through stock awards | — | — | — | — | 20,956 | — | — | 20,956 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of 340,684 shares of stock options | — | — | — | — | 14,984 | — | — | 14,984 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 129,972 shares of common stock through employee purchase plan | — | — | — | — | 8,060 | — | — | 8,060 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 266,410 shares of common stock for cash | — | 1 | — | — | 21,197 | — | — | 21,198 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of 114,295 shares of treasury stock | — | — | — | (8,882 | ) | — | — | — | (8,882 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | — | 673 | — | 673 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 372,111 | 372,111 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends/distributions to common shareholders ($3.84 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (384,817 | ) | (384,817 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends ($63.80 per preferred share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (365 | ) | (365 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2019 | $ | — | 87 | 14 | (34,294 | ) | 1,922,222 | 685 | (708,408 | ) | 1,180,306 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-10
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 372,111 | $ | 305,232 | $ | 317,676 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 250,028 | 225,261 | 211,104 | |||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 29,647 | 29,443 | 9,599 | |||||||||
Amortization included in interest expense | 5,365 | 4,920 | 5,120 | |||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets and investments | (7,241 | ) | 7,233 | (4,664 | ) | |||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 15,429 | 71 | |||||||||
Deferred income tax (benefit) expense | (14,130 | ) | 1,538 | 804 | ||||||||
Provision for doubtful accounts | 10,608 | 7,985 | 6,762 | |||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
(Increase) decrease in: | ||||||||||||
Receivables | (28,357 | ) | (33,292 | ) | (17,524 | ) | ||||||
Prepaid expenses | 275 | (5,433 | ) | 309 | ||||||||
Other assets | (11,257 | ) | 2,828 | (8,410 | ) | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in: | ||||||||||||
Trade accounts payable | 700 | 1,366 | 309 | |||||||||
Accrued expenses | (1,597 | ) | (6,292 | ) | (9,508 | ) | ||||||
Operating lease liabilities | 9,102 | — | — | |||||||||
Other liabilities | 15,611 | 8,628 | (4,632 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows provided by operating activities | 630,865 | 564,846 | 507,016 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | (140,956 | ) | (117,638 | ) | (109,329 | ) | ||||||
Acquisitions | (226,278 | ) | (477,389 | ) | (297,305 | ) | ||||||
(Increase) decrease in notes receivable | (448 | ) | 9 | 515 | ||||||||
Proceeds received from property insurance claims | 210 | 4,222 | — | |||||||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | 5,438 | 6,648 | 6,053 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows used in investing activities | (362,034 | ) | (584,148 | ) | (400,066 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
Net proceeds from issuance of common stock | 44,262 | 62,662 | 26,684 | |||||||||
Cash used for purchase of treasury shares | (8,882 | ) | (4,112 | ) | (8,997 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 495,000 | 563,000 | 495,000 | |||||||||
Payments on revolving credit facility | (625,000 | ) | (481,000 | ) | (477,000 | ) | ||||||
Principal payments on long-term debt | (34,471 | ) | (27,328 | ) | (16,993 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds received from senior credit facility term loans | — | 599,250 | 450,000 | |||||||||
Proceeds received from accounts receivable securitization program | 9,000 | 175,000 | — | |||||||||
Payments on accounts receivable securitization program | (9,000 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Debt issuance costs | (4,463 | ) | (7,616 | ) | (4,941 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds received from note offering | 255,000 | — | — | |||||||||
Redemption of senior subordinated notes | — | (509,790 | ) | — | ||||||||
Payment on senior credit facility term loans | — | — | (247,500 | ) | ||||||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | (621 | ) | (541 | ) | (693 | ) | ||||||
Dividends/distributions | (385,182 | ) | (443,088 | ) | (244,201 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows used in financing activities | (264,357 | ) | (73,563 | ) | (28,641 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | 220 | (1,112 | ) | 1,632 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 4,694 | (93,977 | ) | 79,941 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 21,494 | 115,471 | 35,530 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 26,188 | $ | 21,494 | $ | 115,471 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | ||||||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 139,585 | $ | 136,711 | $ | 123,213 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash paid for state and federal income taxes | $ | 14,449 | $ | 8,563 | $ | 12,640 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-11
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(1) Significant Accounting Policies
(a) Nature of Business
Lamar Advertising Company (the Company) is engaged in the outdoor advertising business, operating approximately 157,800 billboard advertising displays in 45 states and Canada. The Company’s operating strategy is to be the leading provider of outdoor advertising services in the markets it serves.
In addition, the Company operates a logo sign business in 24 states throughout the United States and the province of Ontario, Canada and operates approximately 52,800 transit advertising displays in 22 states and Canada. Logo signs are erected pursuant to state-awarded service contracts on public rights-of-way near highway exits and deliver brand name information on available gas, food, lodging and camping services. Included in the Company’s logo sign business are tourism signing contracts. The Company provides transit advertising in airport terminals, on bus shelters, benches and buses in the markets it serves.
The Company operates as a Real Estate Investment Trust (“REIT”) for U.S. federal income tax purposes and generally will not be subject to federal income taxes on its income and gains that the Company distributes to its stockholders, including the income derived from advertising rental revenue. However, even as a REIT, the Company will remain obligated to pay income taxes on earnings from the assets of its taxable REIT subsidiaries (“TRSs”). In addition, the Company’s foreign assets and operations continue to be subject to taxation in the foreign jurisdictions where those assets are held or those operations are conducted.
(b) Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include Lamar Advertising Company, its wholly owned subsidiary, Lamar Media Corp. (Lamar Media), and its majority-owned subsidiaries. All inter-company transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
An operating segment is a component of an enterprise:
| • | that engages in business activities from which it may earn revenues and incur expenses; |
| • | whose operating results are regularly reviewed by the enterprise’s chief operating decision maker to make decisions about resources to be allocated to the segment and assess its performance; and |
| • | for which discrete financial information is available. |
We define the term ‘chief operating decision maker’ to be our executive management group, which consist of our Chief Executive Officer, President and Chief Financial Officer. Currently, all operations are reviewed on a consolidated basis for budget and business plan performance by our executive management group. Additionally, operational performance at the end of each reporting period is viewed in the aggregate by our management group. Any decisions related to changes in invested capital, personnel, operational improvement or training, or to allocate other company resources are made based on the combined results.
We operate in a single operating and reporting segment, advertising. We rent advertising space on billboards, buses, shelters, benches, logo plates and in airport terminals.
(c) Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets.
F-12
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(d) Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill is subject to an annual impairment test. The Company designated December 31 as the date of its annual goodwill impairment test. The Company is required to identify its reporting units and determine the carrying value of each reporting unit. The Company has identified two reporting units, Billboard operations and Logo operations, by assigning the assets and liabilities, including the existing goodwill and intangible assets, to those reporting units. The Company is required to determine the fair value of each reporting unit and compare it to the carrying amount of the reporting unit. To the extent the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds the fair value of the reporting unit, the Company would be required to book an impairment loss.
The Company conducts a qualitative assessment by examining relevant events and circumstances which could have a negative impact on the Company’s goodwill, which includes macroeconomic conditions, industry and market conditions, cost factors, overall financial performance, reporting unit dispositions and acquisitions, the market capitalization of the Company and other relevant events specific to the Company. If, after assessing the totality of events or circumstances described above, the Company determines that it is more likely than not that the fair value of either of the Company’s reporting units is less than its carrying amount, the Company will perform a quantitative impairment test. If industry and economic conditions deteriorate, the Company may be required to assess goodwill impairment before the next annual test, which could result in impairment charges.
The Company performed its annual measurement for impairment of the goodwill of its reporting units and concluded the fair value of each reporting unit exceeded its carrying amount at its annual impairment test date on December 31, 2019 and 2018; therefore, the Company was not required to recognize an impairment loss.
Intangible assets, consisting primarily of site locations, customer lists and contracts, and non-competition agreements are amortized using the straight-line method over the assets estimated useful lives, generally from 2 to 15 years.
(e) Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets, such as property, plant and equipment, and purchased intangibles subject to amortization, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset or asset group before interest expense. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset or asset group. Assets to be disposed of would be separately presented in the balance sheet and reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell, and are no longer depreciated. The assets and liabilities of a disposed group classified as held for sale would be presented separately in the appropriate asset and liability sections of the balance sheet.
(f) Acquisitions
The Company accounts for transactions that meet the definition of a business and group asset purchases as acquisitions. For transactions that meet the definition of a business combination, the Company allocates the purchase price, including any contingent consideration, to the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed at their estimated fair values as of the date of the acquisition with any excess of the purchase price paid over the estimated fair value of net assets acquired recorded as goodwill. The determination of the final purchase price
F-13
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
and the acquisition-date fair value of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed may extend over more than one period and result in adjustments to the preliminary estimate recognized in the prior period financial statements For transactions that meet the definition of asset group purchases, the Company allocates the purchase price to the assets acquired and the liabilities assumed at their estimated fair values as of the date of the acquisition. If a transaction is determined to be a group of assets, any direct acquisition costs are capitalized. Transaction costs for transactions determined to be a business combination are expensed as incurred.
The fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed is typically determined by using either estimates of replacement costs or discounted cash flow valuation methods. When determining the fair value of tangible assets acquired, the Company must estimate the cost to replace the asset with a new asset, adjusted for an estimated reduction in fair value due to age of the asset, and the economic useful life. When determining the fair value of intangible assets acquired, the Company must estimate the applicable discount rate and the timing and amount of future cash flows.
(g) Lease liabilities
On January 1, 2019, the Company adopted ASC 842, Leases, using a modified retrospective transition with January 1, 2019 as the effective date of our initial application. We also elected the package of practical expedients, which permitted us not to reassess under the new standard our prior conclusions about lease identification, lease classification and initial direct costs. We also elected the practical expedient pertaining to land easements, which allows the Company not to reassess its accounting treatment for our previously existing land easements as to whether they qualify as a lease under ASC 842.
The Company is party to various operating leases for production facilities, vehicles and sites upon which advertising structures are built, including our billboard land leases, leases of logo structures and leases of transit advertising space. The leases expire at various dates, have varying options to renew and cancel, and may contain escalation provisions. We expense our non-variable lease payments ratably over the lease term. Also, certain of our leases contain variable lease payments based on percentage of revenue or consumer price index or other inflation-based indices. The variable lease costs are expensed in the period incurred.
The key estimates for our leases include (1) the discount rate used to discount the unpaid lease payment to present value and (2) lease term. Our leases generally do not include a readily determinable implicit rate, therefore, using a portfolio approach, we determine our collateralized incremental borrowing rate to discount the lease payment based on the information available at lease commencement. Our lease terms include the noncancellable period of the lease plus any additional periods covered by either a Company option to extend (or not to terminate) the lease that the Company is reasonably certain to exercise, or an option to extend the lease controlled by the lessor. The Company has determined we are not reasonably certain to exercise renewals or termination options, and as a result we use the lease’s initial stated term as the lease term for our lease population.
(h) Deferred Income
Deferred income consists principally of advertising revenue invoiced in advance. Deferred advertising revenue is recognized in income over the term of the contract.
F-14
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(i) Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes outdoor advertising revenue on an accrual basis ratably over the term of the contracts. Production revenue and the related expense for the advertising copy are recognized upon satisfaction of its performance obligation.
The Company engages in barter transactions where the Company trades advertising space for goods and services. The Company recognizes revenues and expenses from barter transactions at fair value, which is determined based on the Company’s own historical practice of receiving cash for similar advertising space from buyers unrelated to the party in the barter transaction. The amount of revenue and expense recognized for advertising barter transactions is as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 9,636 | $ | 8,955 | $ | 8,469 | ||||||
Direct advertising expenses | $ | 3,982 | $ | 3,633 | $ | 3,603 | ||||||
General and administrative expenses | $ | 4,986 | $ | 4,758 | $ | 4,332 | ||||||
(j) Income Taxes
As a REIT, the Company is generally not subject to federal income taxes on income and gains distributed to the Company’s stockholders. However, the Company remains obligated to pay income taxes on earnings from domestic TRSs. In addition, the Company’s foreign assets and operations continue to be subject to taxation in the foreign jurisdictions where those assets are held or where those operations are conducted, including those designated as Qualified REIT Subsidiaries, or QRSs, for federal income tax purposes. Accordingly, the consolidated financial statements reflect provisions for federal, state, local and foreign income taxes. The Company recognizes deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis, as well as operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. The Company measures deferred tax assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences and carry forwards are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities as a result of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
(k) Dividends/Distributions
As a REIT, the Company must annually distribute to its stockholders an amount equal to at least 90% of its REIT taxable income (determined before the deduction for distributed earnings and excluding any net capital gain). During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company declared and paid distributions of its REIT taxable income of $384,817 or $3.84 per share. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company paid cash distributions of its REIT taxable income in an aggregate amount of $442,632 or $4.48 per share. The distributions paid during 2018 include distributions declared and accrued as of December 31, 2017 of $81,534 or $0.83 per share. During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company declared distributions of $325,462 or $3.32 per share, including paid distributions of $243,928 or $2.49 per share. The amount, timing and frequency of future distributions will be at the sole discretion of the Board of Directors and will be declared based upon various factors, a number of which may be beyond the Company’s control, including the financial condition and operating cash flows, the amount required to maintain REIT status and reduce any income and excise taxes that the Company otherwise would be required to pay, limitations on distributions in its existing and future debt instruments, the Company’s ability to utilize net operating losses (“NOLs”) to offset, in whole or in part, the
F-15
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Company’s distribution requirements, limitations on its ability to fund distributions using cash generated through its TRSs and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem relevant. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company paid dividend distributions to holders of its Series AA Preferred Stock of $365 or $63.80 per share. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company paid cash dividend distributions to holders of its Series AA Preferred Stock in an aggregate amount of $456 or $79.75 per share, including $91, or $15.95 per share, related to distributions accrued for in 2017. During the year ended December 31, 2017 the Company paid cash dividend distributions to holders of its Series AA Preferred Stock of $274 or $47.85 per share.
(l) Earnings Per Share
The calculation of basic earnings per share excludes any dilutive effect of stock options, while diluted earnings per share includes the dilutive effect of stock options. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 there were no dilutive shares excluded from the calculation.
(m) Stock Based Compensation
Compensation expense for share-based awards is recognized based on the grant date fair value of those awards. Stock-based compensation expense includes an estimate for pre-vesting forfeitures and is recognized over the requisite service periods of the awards on a straight-line basis, which is generally commensurate with the vesting term. Non-cash compensation expense recognized during the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018, and 2017 were $29,647, $29,443 and $9,599, respectively. The $29,647 expensed during the year ended December 31, 2019 consists of (i) $4,226 related to stock options and the employee stock purchase plan, (ii) $25,005 related to stock grants made under the Company’s performance-based stock incentive program in 2019 and (iii) $416 related to stock awards to directors. See Note 15 for information on the assumptions used to calculate the fair value of stock-based compensation.
(n) Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly-liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
(o) Foreign Currency Translation
Local currencies generally are considered the functional currencies outside the United States. Assets and liabilities for operations in local-currency environments are translated at year-end exchange rates. Income and expense items are translated at average rates of exchange prevailing during the year. Foreign currency translation adjustments are recorded as a component of other comprehensive income (loss) in the Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income and as a component of accumulated comprehensive income (loss) in the Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity.
(p) Asset Retirement Obligations
The Company is required to record the fair value of obligations associated with the retirement of tangible long-lived assets in the period in which it is incurred. The liability is capitalized as part of the related long-lived asset’s carrying amount. Over time, accretion of the liability is recognized as an operating expense and the capitalized cost is depreciated over the expected useful life of the related asset. The Company’s asset retirement obligations relate primarily to the dismantlement, removal, site reclamation and similar activities of its leased properties.
F-16
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(q) Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
(r) Comprehensive Income
Total comprehensive income is presented in the Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income and the components of accumulated comprehensive income (loss) are presented in the Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity. Comprehensive income (loss) is composed of foreign currency translation effects.
(s) Fair Value Measurements
The Company determines the fair value of its financial instruments using the fair value hierarchy, which requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value.
(t) Subsequent Events
The Company has performed an evaluation of subsequent events through the date on which the financial statements are issued.
(2) Revenue
On January 1, 2018, we adopted FASB Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-09 (Codified as ASC 606), Revenue from Contracts with Customers using the cumulative effect transition method applied to those contracts which were not completed as of January 1, 2018 and are not accounted for under ASC 840, Leases. Results for reporting periods beginning after January 1, 2018 are presented under ASC 606 or 840, while comparative information has not been adjusted and continues to be reported under ASC 605.
A majority of our billboard, logo, and transit space contracts are accounted for under ASC 840 and continued to be accounted for under the topic until January 1, 2019, our adoption date of ASU No. 2016-02 (Codified as ASC 842), Leases. Contracts which begin prior to January 1, 2019 and are accounted for under ASC 840 continued to be accounted for as a lease until the contract ends or is modified. Contracts beginning or modified on or after January 1, 2019 which do not meet the criteria of a lease under ASC 842 are accounted for under ASC 606, Revenue. The majority of our advertising space contracts do not meet the definition of a lease under ASC 842.
Due to the transition of our advertising space contracts into ASC 606 we are now required to capitalize our costs to fulfill a contract and expense the costs over the contract period. These costs include our costs to install advertising copy onto billboards. These costs were expensed as incurred under ASC 840. During the year ended December 31, 2019, we capitalized $24,920 of costs to fulfill a contract which is included in other current assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets, net of expensed costs of $15,734. The expensed costs are recorded in direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) in the Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income.
F-17
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Revenue Recognition
Advertising revenues: The majority of our revenues are derived from contracts for advertising space on billboard, logo and transit displays and were accounted for under ASC 840, Leases prior to January 1, 2019. Upon the Company’s adoption of ASC 842, Leases on January 1, 2019 the majority of our contracts for advertising space transitioned to being accounted for under ASC 606, Revenue. The contract revenues, under both ASC 840, Leases and ASC 606, Revenue, are recognized ratably over their contract life.
Other revenues: Our other component of revenue primarily consists of production services which includes creating and printing the advertising copy. On and after January 1, 2018 revenue for production contracts are recognized under ASC 606, Revenue. Contract revenues for production services are recognized upon satisfaction of the contract which is typically less than one week.
Arrangements with multiple performance obligations: Our contracts with customers may include multiple performance obligations. For such arrangements, we allocate revenue to each performance obligation based on the relative standalone selling price. We determine standalone selling prices based on the prices charged to customers using expected cost plus margin.
Deferred revenues: We record deferred revenues when cash payments are received or due in advance of our performance obligation. The term between invoicing and when a payment is due is not significant. For certain services we require payment before the product or services are delivered to the customer. The balance of deferred income is considered short-term and will be recognized in revenue within twelve months.
Practical expedients and exemptions: Upon our transition to ASC 606 from ASC 840, the Company utilized the following practical expedients and exemptions from ASC 606. We generally expense sales commissions when incurred because the amortization period is one year or less. These costs are recorded within direct advertising expense (exclusive of depreciation and amortization). We do not disclose the value of unsatisfied performance obligations as the majority of our contracts with customers have an original expected length of less than one year. For contracts with customers which exceed one year, the future amount to be invoiced to the customer corresponds directly with the value to be received by the customer.
The following table presents our disaggregated revenue by source including revenues accounted for under ASC 840, ASC 842 and ASC 606 for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017.
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Billboard Advertising | $ | 1,537,542 | $ | 1,412,978 | $ | 1,340,422 | ||||||
Logo Advertising | 84,201 | 84,424 | 82,936 | |||||||||
Transit Advertising | 131,901 | 129,820 | 117,902 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Net Revenues | $ | 1,753,644 | $ | 1,627,222 | $ | 1,541,260 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
(3) Acquisitions
Year Ended December 31, 2019
During the twelve months ended December 31, 2019, the Company completed several acquisitions of outdoor advertising assets for a total purchase price of $226,278, net of acquired cash of $1,508. This amount includes $227,588 of outdoor advertising assets purchased in 2019, offset by $1,310 in post-closing adjustments to acquired working capital related to the purchase of Fairway Outdoor Advertising (“Fairway”) in 2018.
F-18
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Each of these acquisitions was accounted for under the acquisition method of accounting, and, accordingly, the accompanying consolidated financial statements include the results of operations of each acquired entity from the date of acquisition. The acquisition purchase price has been allocated to assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on fair market value at the dates of acquisition.
The following is a summary of the allocation of the purchase price in the above transactions, which includes the final fair value allocation of the asset acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination completed on July 15, 2019, for an aggregate purchase price of $127,000.
| Total | ||||
Property, plant and equipment | $ | 37,988 | ||
Site locations | 131,208 | |||
Non-competition agreements | 240 | |||
Customer lists and contracts | 23,032 | |||
Asset acquisition costs | 756 | |||
Other intangibles | 3,115 | |||
Goodwill | 29,360 | |||
Current assets | 1,860 | |||
Current liabilities | (832 | ) | ||
Operating right of use assets | 23,934 | |||
Operating lease liabilities | (21,573 | ) | ||
Other liabilities | (1,500 | ) | ||
|
| |||
| $ | 227,588 | |||
|
| |||
Total acquired intangible assets for the year ended December 31, 2019 were $187,711, of which $29,360 was assigned to goodwill. Goodwill is not amortized for financial statement purposes, and no goodwill related to 2019 acquisitions is expected to be deductible for tax purposes. The remaining $158,351 of acquired intangible assets have a weighted average useful life of approximately 14 years. The intangible assets include customer lists and contracts of $23,032 (7 year weighted average useful life) and site locations of $131,208 (15 year weighted average useful life). The aggregate amortization expense related to the 2019 acquisitions for the year ended December 31, 2019 was approximately $7,570.
As of December 31, 2019, we have finalized our fair value allocation of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed from Fairway on December 21, 2018. Our updated fair value allocation of Fairway during 2019 includes property, plant and equipment, intangibles and goodwill of $96,840, $188,400 and $145,534, respectively. During the period ended December 31, 2019, goodwill was adjusted $36,583 due to updates from the original preliminary purchase price allocation provided as of December 31, 2018. The updated allocation resulted in prior and current period changes to depreciation and amortization. These changes were considered immaterial and recorded during the year ended December 31, 2019. During the year ended December 31, 2019, assets purchased from Fairway, which were initially placed into our taxable REIT subsidiary, were transferred to our qualifying REIT subsidiary. As a result, the Company recorded an income tax benefit of $17,031 in deferred tax liabilities assumed from our purchase.
The following unaudited pro forma financial information for the Company gives effect to the 2019 and 2018 acquisitions as if they had occurred on January 1, 2018. These pro forma results do not purport to be indicative of
F-19
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
the results of operations which actually would have resulted had the acquisitions occurred on such date or to project the Company’s results of operations for any future period.
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,764,493 | $ | 1,724,821 | ||||
Net income applicable to common stock | $ | 369,300 | $ | 292,012 | ||||
Net income per common share — basic | $ | 3.69 | $ | 2.96 | ||||
Net income per common share — diluted | $ | 3.68 | $ | 2.95 | ||||
Year Ended December 31, 2018
During the twelve months ended December 31, 2018, the Company completed several acquisitions of outdoor advertising assets for a total purchase price of $489,671, net of acquired cash of $8,554. The total purchase price consisted of the issuance of 163,137 shares of its Class A common stock for $12,282 and cash of $477,389. The purchases included the acquisition of assets in five U.S markets from Fairway Outdoor Advertising (“Fairway”) on December 21, 2018 for an aggregate purchase price of $418,500.
As of December 31, 2018, our fair value allocation of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed from Fairway was considered preliminary and subject to revision, which could result in adjustments to this allocation. In order to develop our preliminary fair values, the Company utilized asset information received from Fairway and fair value allocation benchmarks from similar completed transactions. Our preliminary allocation of Fairway included property, plant and equipment, intangibles and goodwill of $91,173, $156,319 and $182,117, respectively. As discussed above, we finalized the Fairway fair value allocation during 2019.
Each of these acquisitions was accounted for under the acquisition method of accounting, and, accordingly, the accompanying consolidated financial statements include the results of operations of each acquired entity from the date of acquisition. The acquisition costs have been allocated to assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on fair market value at the dates of acquisition.
The following is a summary of the allocation of the acquisition costs in the above transactions, excluding the preliminary allocation of Fairway.
| Total | ||||
Property, plant and equipment | $ | 8,648 | ||
Site locations | 57,105 | |||
Non-competition agreements | 342 | |||
Customer lists and contracts | 6,521 | |||
Asset acquisition costs | 336 | |||
Current assets | 1,041 | |||
Current liabilities | (355 | ) | ||
|
| |||
| $ | 73,638 | |||
|
| |||
Total acquired intangible assets for the year ended December 31, 2018 were $402,740, of which $182,117 was assigned to goodwill. Goodwill is not amortized for financial statement purposes, and no goodwill related to 2018 acquisitions is expected to be deductible for tax purposes. The remaining $220,623 of acquired intangible
F-20
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
assets have a weighted average useful life of approximately 14 years. The intangible assets include customer lists and contracts of $33,310 (7 year weighted average useful life) and site locations of $186,635 (15 year weighted average useful life). The aggregate amortization expense related to the 2018 acquisitions for the year ended December 31, 2018 was approximately $2,681.
The following unaudited pro forma financial information for the Company gives effect to the 2018 and 2017 acquisitions as if they had occurred on January 1, 2017. These pro forma results do not purport to be indicative of the results of operations which actually would have resulted had the acquisitions occurred on such date or to project the Company’s results of operations for any future period.
| 2018 | 2017 | |||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,699,052 | $ | 1,647,445 | ||||
Net income applicable to common stock | $ | 299,493 | $ | 306,900 | ||||
Net income per common share — basic | $ | 3.03 | $ | 3.13 | ||||
Net income per common share — diluted | $ | 3.02 | $ | 3.12 | ||||
(4) Non-cash Financing and Investing Activities
For the year ended December 31, 2019, there were no significant non-cash investing activities. For the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company had non-cash investing activities for the issuance of 163,137 shares of its Class A common stock related to acquisition purchases. The issuance had an approximate value of $12,282. For the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company had $2,879 non-cash investing activities related to acquisitions of outdoor advertising assets. There were no significant non-cash financing activities during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company had non-cash financing activities related to declared distributions of $81,625 which were paid to shareholders in January 2018.
(5) Property, Plant and Equipment
Major categories of property, plant and equipment at December 31, 2019 and 2018 are as follows:
| Estimated Life (Years) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||
Land | — | $ | 406,884 | $ | 384,264 | |||||||
Building and improvements | 10 — 39 | 181,797 | 173,306 | |||||||||
Advertising structures | 5 — 15 | 2,926,706 | 2,817,170 | |||||||||
Automotive and other equipment | 3 — 7 | 144,924 | 150,985 | |||||||||
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| $ | 3,660,311 | $ | 3,525,725 | |||||||||
|
|
|
| |||||||||
F-21
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(6) Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The following is a summary of intangible assets at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| Estimated Life (Years) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | |||||||||||||||||
Amortizable Intangible Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Customer lists and contracts | 7 — 10 | $ | 641,714 | $ | 539,405 | $ | 610,376 | $ | 514,928 | |||||||||||
Non-competition agreements | 3 — 15 | 66,014 | 64,379 | 65,771 | 64,119 | |||||||||||||||
Site locations | 15 | 2,384,520 | 1,509,335 | 2,228,767 | 1,422,794 | |||||||||||||||
Other | 2 — 15 | 49,864 | 36,749 | 45,992 | 33,612 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
| $ | 3,142,112 | $ | 2,149,868 | $ | 2,950,906 | $ | 2,035,453 | |||||||||||||
Unamortizable Intangible Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Goodwill | $ | 2,165,810 | $ | 253,536 | $ | 2,172,922 | $ | 253,536 | ||||||||||||
The changes in the gross carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 are as follows:
Balance as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 1,993,990 | ||
Goodwill acquired during the year | 182,117 | |||
Purchase price adjustments and other | (3,185 | ) | ||
Impairment losses | — | |||
|
| |||
Balance as of December 31, 2018 | $ | 2,172,922 | ||
Goodwill acquired during the year | 29,360 | |||
Purchase price adjustments and other | (36,472 | ) | ||
Impairment losses | — | |||
|
| |||
Balance as of December 31, 2019 | $ | 2,165,810 | ||
|
|
Amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017 was $113,679, $95,010 and $85,257, respectively. The following is a summary of the estimated amortization expense for future years:
2020 | $ | 108,323 | ||
2021 | 104,332 | |||
2022 | 99,480 | |||
2023 | 88,649 | |||
2024 | 84,835 | |||
Thereafter | 506,625 | |||
|
| |||
Total | $ | 992,244 | ||
|
|
(7) Leases
On January 1, 2019 the Company adopted ASC 842, Leases, using a modified retrospective transition with January 1, 2019 as the effective date of our initial application. We also elected the package of practical expedients, which permitted us not to reassess under the new standard our prior conclusions about lease
F-22
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
identification, lease classification and initial direct costs. We also elected the practical expedient pertaining to land easements, which allows the Company not to reassess its accounting treatment for our previously existing land easements as to whether they qualify as a lease under ASC 842.
The Company is party to various operating leases for production facilities, vehicles and sites upon which advertising structures are built, including our billboard land leases, leases of logo structures and leases of transit advertising space. The leases expire at various dates, have varying options to renew and cancel, and may contain escalation provisions. We expense our non-variable lease payments ratably over the lease term. Also, certain of our leases contain variable lease payments based on percentage of revenue or consumer price index or other inflation-based indices. The variable lease costs are expensed in the period incurred. Due to our election not to reassess conclusions about lease identification, as noted above, our transit agreements were accounted for as leases on January 1, 2019. As we enter into new or renew current transit agreements, those agreements will not likely meet the criteria of a lease under ASC 842, therefore they will no longer be accounted for as a lease.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, we had base operating lease costs of $312,883 and variable operating lease costs of $76,492, for a total operating lease cost of $389,375. During the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2017 we had total operating lease costs of $381,890 and $366,892, respectively. Our operating lease costs are recorded in direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization). Also, for the year ended December 31, 2019, we recorded a gain of $4,061 in (gain) loss of disposition of assets related to the amendment and termination of lease agreements. Cash payments of $316,527 were made reducing our operating lease liabilities for the year ended December 31, 2019 and are included in cash flows provided by operating activities in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
We elected the short-term lease exemption which applies to certain of our vehicle agreements. This election allows the Company to not recognize lease right of use assets (ROU assets) or lease liabilities for agreements with a term of twelve months or less. We recorded $4,691 in direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) for these agreements during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Our operating leases have a weighted-average remaining lease term of 12.0 years. The weighted-average discount rate of our operating leases is 4.8%. Also, during the year ended December 31, 2019, we obtained $35,813 of leased assets in exchange for new operating lease liabilities, which includes liabilities obtained through acquisitions.
The following is a summary of the maturities of our operating lease liabilities as of December 31, 2019:
2020 | $ | 240,438 | ||
2021 | 196,099 | |||
2022 | 175,598 | |||
2023 | 152,470 | |||
2024 | 135,234 | |||
Thereafter | 800,876 | |||
|
| |||
Total undiscounted operating lease payments | 1,700,715 | |||
Less: Imputed interest | (435,693 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Total operating lease liabilities | $ | 1,265,022 | ||
|
|
F-23
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
The following is a summary of minimum annual rental payments required under our operating lease that have original or remaining lease terms in excess of one year as of December 31, 2018:
2019 | $ | 254,866 | ||
2020 | $ | 188,138 | ||
2021 | $ | 165,642 | ||
2022 | $ | 144,814 | ||
2023 | $ | 122,814 | ||
Thereafter | $ | 819,004 |
(8) Accrued Expenses
The following is a summary of accrued expenses at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
Payroll | $ | 20,223 | $ | 20,667 | ||||
Interest | 32,734 | 27,067 | ||||||
Insurance benefits | 11,554 | 12,633 | ||||||
Accrued variable lease and contract expense | 12,559 | 36,158 | ||||||
Stock-based compensation | 23,297 | 19,211 | ||||||
Other | 6,858 | 6,731 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| $ | 107,225 | $ | 122,467 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
(9) Long-term Debt
Long-term debt consists of the following at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
Senior Credit Facility | $ | 1,127,069 | $ | 9,077 | $ | 1,117,992 | ||||||
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program | 175,000 | 846 | 174,154 | |||||||||
5% Senior Subordinated Notes | 535,000 | 3,237 | 531,763 | |||||||||
5 3/8% Senior Notes | 510,000 | 3,502 | 506,498 | |||||||||
5 3/4% Senior Notes | 654,345 | 7,752 | 646,593 | |||||||||
Other notes with various rates and terms | 3,118 | — | 3,118 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 3,004,532 | 24,414 | 2,980,118 | ||||||||||
Less current maturities | (232,595 | ) | (6,081 | ) | (226,514 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt, excluding current maturities | $ | 2,771,937 | $ | 18,333 | $ | 2,753,604 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
F-24
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
| December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
Senior Credit Facility | $ | 1,291,088 | $ | 11,576 | $ | 1,279,512 | ||||||
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program | 175,000 | 1,168 | 173,832 | |||||||||
5% Senior Subordinated Notes | 535,000 | 4,104 | 530,896 | |||||||||
5 3/8% Senior Notes | 510,000 | 4,262 | 505,738 | |||||||||
5 3/4% Senior Notes | 400,000 | 4,754 | 395,246 | |||||||||
Other notes with various rates and terms | 3,464 | — | 3,464 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 2,914,552 | 25,864 | 2,888,688 | ||||||||||
Less current maturities | (209,365 | ) | (5,245 | ) | (204,120 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt, excluding current maturities | $ | 2,705,187 | $ | 20,619 | $ | 2,684,568 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt contractual maturities are as follows:
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
2020 | $ | 232,595 | $ | 6,081 | $ | 226,514 | ||||||
2021 | $ | 74,487 | $ | 6,205 | $ | 68,282 | ||||||
2022 | $ | 426,971 | $ | 4,677 | $ | 422,294 | ||||||
2023 | $ | 541,989 | $ | 3,480 | $ | 538,509 | ||||||
2024 | $ | 517,008 | $ | 2,216 | $ | 514,792 | ||||||
Later years | $ | 1,211,482 | $ | 1,755 | $ | 1,209,727 | ||||||
Senior Credit Facility
Lamar Media’s Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 15, 2017 (as amended, the “senior credit facility”) originally consisted of (i) a $450,000 senior secured revolving credit facility which will mature on May 15, 2022 (the “revolving credit facility”), (ii) a $450,000 Term A loan facility (the “Term A loans”) which will mature on May 15, 2022, and (iii) an incremental facility pursuant to which Lamar Media may incur additional term loan tranches or increase its revolving credit facility subject to pro forma compliance with the secured debt ratio financial maintenance covenant (the “Incremental Facility”). Lamar Media borrowed all $450,000 in Term A loans on May 15, 2017. The net proceeds of the Term A loans, together with borrowing under the revolving portion of senior credit facility and cash on hand, were used to repay all outstanding amounts under the existing senior credit facility, and all revolving commitments under that facility were terminated.
On March 16, 2018, Lamar Media entered into Amendment No. 1 to the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated May 15, 2017, which amended the existing senior credit facility to establish a new $600,000 Term B Loan Facility (the “Term B loan”), which will mature on March 16, 2025. Lamar Media borrowed the full amount of the Term B loan on March 16, 2018. The proceeds from the Term B loan, together with available cash on hand were used to redeem in full Lamar Media’s 5 7/8% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2022.
F-25
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
On January 17, 2019, Lamar Media entered into an incremental amendment to the senior credit facility to include $100,000 in additional revolving commitments, thereby increasing the total borrowing capacity under the revolving credit facility to $550,000.
As of December 31, 2019, the senior credit facility consisted of (i) the revolving credit facility, (ii) the Term A loans, (iii) the Term B loans and (iv) the Incremental Facility.
The Term A loans mature on May 15, 2022 and the Term B loans mature on March 16, 2025. The remaining quarterly installments are scheduled to be paid on each March 31, June 30, September 30 and December 31 as follows:
Principal Payment Date | Term A | Term B | ||||||
March, 31 2020-June 30, 2020 | $ | 8,438 | $ | 1,500 | ||||
September 30, 2020-March 31, 2022 | $ | 16,875 | $ | 1,500 | ||||
Term A Loan Maturity May 15, 2022 | $ | 253,125 | $ | — | ||||
June 30, 2022-December 31, 2024 | $ | — | $ | 1,500 | ||||
Term B Loan Maturity March 16, 2025 | $ | — | $ | 559,500 | ||||
The Term loans bear interest at rates based on the Adjusted LIBO Rate (“Eurodollar term loans”) or the Adjusted Base Rate (“Base Rate term loans”), at Lamar Media’s option. Eurodollar term loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.75%; (or the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.50% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1 for Term A loans only). Base Rate term loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.75% (or the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.50% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1 for Term A loans only). The revolving credit facility bears interest at rates based on the Adjusted LIBO Rate (“Eurodollar revolving loans”) or the Adjusted Base Rate (“Base Rate revolving loans”), at Lamar Media’s option. Eurodollar revolving loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 2.25% (or the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 2.00% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 4.25 to 1; or the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.75% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 3.00 to 1). Base Rate revolving Loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted Base Rate plus 1.25% (or the Adjusted Base Rate plus 1.0% at any time the total debt ratio is less than or equal to 4.25 to 1, or the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.75% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 3.00 to 1). The guarantees, covenants, events of default and other terms of the senior credit facility apply to the Term A and B loans and revolving credit facility.
As of December 31, 2019, there was $150,000 outstanding under the revolving credit facility. Availability under the revolving facility is reduced by the amount of any letters of credit outstanding. Lamar Media had $12,709 letters of credit outstanding as of December 31, 2019 resulting in $387,291 of availability under its revolving facility. Revolving credit loans may be requested under the revolving credit facility at any time prior to its maturity on May 15, 2022.
The terms of Lamar Media’s senior credit facility and the indentures relating to Lamar Media’s outstanding notes restrict, among other things, the ability of Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media to:
| • | dispose of assets; |
| • | incur or repay debt; |
| • | create liens; |
F-26
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
| • | make investments; and |
| • | pay dividends. |
The senior credit facility contains provisions that would allow Lamar Media to conduct its affairs in a manner that would allow Lamar Advertising to qualify and remain qualified as a REIT, including by allowing Lamar Media to make distributions to Lamar Advertising required for the Company to qualify and remain qualified for taxation as a REIT, subject to certain restrictions.
Lamar Media’s ability to make distributions to Lamar Advertising is also restricted under the terms of these agreements. Under Lamar Media’s senior credit facility the Company must maintain a specified senior debt ratio at all times and in addition, must satisfy a total debt ratio in order to incur debt, make distributions or make certain investments.
Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media were in compliance with all of the terms of their indentures and the applicable senior credit agreement provisions during the periods presented.
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program
On December 18, 2018 Lamar Media entered into a $175,000 Receivable Financing Agreement (the “AR Program”) with its wholly-owned special purpose entities, Lamar QRS Receivables, LLC and Lamar TRS Receivables, LLC (the “Special Purpose Subsidiaries”) maturing on December 17, 2021. The AR Program is limited to the availability of eligible accounts receivable collateralizing the borrowings under the agreements governing the AR Program.
Pursuant to two separate Purchase and Sale Agreements dated December 18, 2018, each of which is among Lamar Media as initial Servicer, certain of Lamar Media’s subsidiaries and a Special Purpose Subsidiary, the subsidiaries sold substantially all of their existing and future accounts receivable balances to the Special Purpose Subsidiaries. The Special Purpose Subsidiaries use the accounts receivable balances to collateralize loans pursuant to the AR Program. Lamar Media retains the responsibility of servicing the accounts receivable balances pledged as collateral under the AR Program and provides a performance guaranty.
As of December 31, 2019 there was $175,000 outstanding on the AR Program bearing interest at approximately 3.3%. Proceeds from the AR Program were used primarily to repay outstanding amounts under our revolving credit facility. The commitment fee based on the amount of unused commitments under the AR Program was immaterial in 2019.
The AR Program is accounted for as a collateralized financing activity, rather than a sale of assets, and therefore: (i) accounts receivable balances pledged as collateral are presented as assets and the borrowings are presented as liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) our Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income reflect the associated charges for bad debt expense (a component of general and administrative expenses) related to the pledged accounts receivable and interest expense associated with the collateralized borrowings and (iii) receipts from customers related to the underlying accounts receivable are reflected as operating cash flows and borrowings and repayments under the collateralized loans are reflected as financing cash flows within our Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
5 7/8% Senior Subordinated Notes
On February 9, 2012, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $500,000 aggregate principal amount of 5 7/8% Senior Subordinated Notes, due 2022 (the “5 7/8% Senior Subordinated Notes”). The
F-27
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
institutional private placement resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $489,000. The Company used the proceeds from the Term B loans to redeem all of the 5 7/8% Notes on March 19, 2018 at a redemption price of 101.958% of the aggregate principal amount of the outstanding 5 7/8% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest up to but not including the redemption date. In conjunction with the redemption the Company recorded a loss on debt extinguishment of $15,429, of which $9,790 was cash, for the year ended December 31, 2018.
5% Senior Subordinated Notes
On October 30, 2012, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $535,000 aggregate principal amount of 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (the “5% Senior Subordinated Notes”). The institutional private placement resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $527,100.
Lamar Media may redeem the 5% Senior Subordinated Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 5% Senior Subordinated Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 5% Senior Subordinated Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 5% Senior Subordinated Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
5 3/8% Senior Notes
On January 10, 2014, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $510,000 aggregate principal amount of 5 3/8% Senior Notes due 2024 (the “5 3/8% Senior Notes”). The institutional private placement resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $502,300.
Lamar Media may redeem the 5 3/8% Senior Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 5 3/8% Senior Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 5 3/8% Senior Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 5 3/8% Senior Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
5 3/4% Senior Notes
On January 28, 2016, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $400,000 aggregate principal amount of 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026 (the “5 3/4 % Senior Notes”). The institutional private placement resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $394,500.
On February 1, 2019, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of an additional $250,000 aggregate principal amount under its 5 3/4% Notes (the “New Notes”). Other than with respect to the date of issuance, issue price and CUSIP number, the New Notes have the same terms as the 5 3/4% Notes. The net proceeds after underwriting fees and expenses, was approximately $251,500 and were used to repay a portion of the borrowings outstanding under the revolving credit facility.
At any time prior to February 1, 2021, Lamar Media may redeem some or all of the 5 3/4% Senior Notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon plus a make-whole premium. On or after February 1, 2021, Lamar Media may redeem the 5 3/4% Senior Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 5 3/4% Senior Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar
F-28
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 5 3/4% Senior Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 5 3/4% Senior Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
(10) Asset Retirement Obligation
The Company’s asset retirement obligation includes the costs associated with the removal of its structures, resurfacing of the land and retirement cost, if applicable, related to the Company’s outdoor advertising portfolio. The following table reflects information related to our asset retirement obligations:
Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | 215,089 | ||
Additions to asset retirement obligations | 7,583 | |||
Accretion expense | 4,404 | |||
Liabilities settled | (4,087 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 222,989 | ||
Additions to asset retirement obligations | 2,529 | |||
Accretion expense | 4,260 | |||
Liabilities settled | (3,641 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Balance at December 31, 2019 | $ | 226,137 | ||
|
|
(11) Depreciation and Amortization
The Company includes all categories of depreciation and amortization on a separate line in its Statements of Income. The amounts of depreciation and amortization expense excluded from the following operating expenses in its Statements of Income are:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Direct expenses | $ | 235,544 | $ | 212,585 | $ | 196,107 | ||||||
General and administrative expenses | 4,416 | 4,134 | 4,151 | |||||||||
Corporate expenses | 10,068 | 8,542 | 10,846 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| $ | 250,028 | $ | 225,261 | $ | 211,104 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
(12) Income Taxes
Commencing January 1, 2014, the Company began operating as a REIT for U.S. income tax purposes. Since operating as a REIT, the Company filed, and intends to continue to file, as a REIT, and its TRSs filed, and intend to continue to file, as C corporations. The Company also files tax returns in various states and countries. The Company’s state tax returns reflect different combinations of the Company’s subsidiaries and are dependent on the connection each subsidiary has with a particular state. The following information pertains to the Company’s income taxes on a consolidated basis.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (the “TCJA”) was signed into law, making significant changes to the Internal Revenue Code. As a result of the TCJA, a tax benefit of $3,372 and $466 was recorded to current tax expense and deferred tax expense, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2017.
F-29
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Income tax expense (benefit) consists of the following:
| Current | Deferred | Total | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2019: | ||||||||||||
U.S. federal | $ | 6,045 | $ | (13,450 | ) | $ | (7,405 | ) | ||||
State and local | 2,699 | (2,654 | ) | 45 | ||||||||
Foreign | 1,164 | 1,974 | 3,138 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| $ | 9,908 | $ | (14,130 | ) | $ | (4,222 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Year ended December 31, 2018: | ||||||||||||
U.S. federal | $ | 4,952 | $ | 435 | $ | 5,387 | ||||||
State and local | 2,615 | (123 | ) | 2,492 | ||||||||
Foreign | 1,592 | 1,226 | 2,818 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| $ | 9,159 | $ | 1,538 | $ | 10,697 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Year ended December 31, 2017: | ||||||||||||
U.S. federal | $ | 4,174 | $ | 359 | $ | 4,533 | ||||||
State and local | 2,706 | (170 | ) | 2,536 | ||||||||
Foreign | 1,546 | 615 | 2,161 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| $ | 8,426 | $ | 804 | $ | 9,230 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company had income taxes payable of $384 and $458, respectively.
The U.S. and foreign components of earnings before income taxes are as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
U.S. | $ | 357,445 | $ | 317,695 | $ | 332,607 | ||||||
Foreign | 10,444 | (1,766 | ) | (5,701 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Total | $ | 367,889 | $ | 315,929 | $ | 326,906 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
F-30
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
A reconciliation of significant differences between the reported amount of income tax expense and the expected amount of income tax expense that would result from applying the U.S. federal statutory income tax rate of 21 percent to income before taxes for the 2019 and 2018 tax years and 35 percent for the 2017 tax year, is as follows:
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Income tax expense at U.S. federal statutory rate | $ | 77,257 | $ | 66,345 | $ | 114,417 | ||||||
Tax adjustment related to REIT(a) | (70,619 | ) | (63,669 | ) | (109,294 | ) | ||||||
State and local income taxes, net of federal income tax benefit | 2,039 | 1,461 | 1,193 | |||||||||
Book expenses not deductible for tax purposes | 4,144 | 1,926 | 2,635 | |||||||||
Stock-based compensation | (1,177 | ) | 1,090 | (121 | ) | |||||||
Valuation allowance(b) | (1,032 | ) | 3,813 | 3,953 | ||||||||
Rate change(c) | — | (80 | ) | (466 | ) | |||||||
Undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries(d) | (102 | ) | (393 | ) | 1,363 | |||||||
Minimum tax credit refundable(e) | — | — | (4,108 | ) | ||||||||
Deferred tax adjustment due to REIT conversion(f) | (17,031 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Other differences, net(g) | 2,299 | 204 | (342 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Income tax expense | $ | (4,222 | ) | $ | 10,697 | $ | 9,230 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| (a) | Includes dividend paid deduction of $76,688, $69,818 and $110,442 for the tax years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. |
| (b) | For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, a non-cash valuation allowance of $(1,031), $3,813 and $3,953, respectively, was recorded to income tax expense due to our limited ability to utilize Puerto Rico deferred tax assets in future years. |
| (c) | Under the TCJA, the U.S. corporate income tax rate was lowered from 35% to 21%. As a result, a non-cash benefit of $466 to income tax expense was recorded for the reduction of the U.S. net deferred tax liability for the year ended December 31, 2017. |
| (d) | In periods prior to December 31, 2017, the undistributed earnings of our Canadian subsidiaries were designated as permanently reinvested. As of December 31, 2017, however, management did not assert that the undistributed earnings of our Canadian subsidiaries will be permanently reinvested. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, we recognized a deferred tax (benefit) charge of $(102), $(393) and $1,363, respectively, for future foreign withholding taxes related to undistributed earnings. |
| (e) | Under the TCJA, the corporate alternative minimum tax was repealed and any minimum tax carryforwards not utilized become fully refundable in 2021. The Company does not expect to utilize its minimum tax credit carryforward. As a result, a cash benefit of $4,108 to income tax expense was recorded for the year ended December 31, 2017. |
| (f) | The income tax provision for the year ended December 31, 2019 is net of the deferred tax benefit of $17,031, which relates to the transfer of assets purchased from Fairway into our qualifying REIT subsidiary on June 28, 2019. The Fairway assets were initially placed in the TRS. |
| (g) | Upon enactment, the TCJA includes a one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of cumulative foreign earnings, net of foreign tax credits. As a result, a cash charge of $736 to income tax expense was recorded for the year ended December 31, 2017. |
F-31
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
The tax effect of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and (liabilities) are presented below:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 499 | $ | 654 | ||||
Accrued liabilities not deducted for tax purposes | 3,431 | 7,022 | ||||||
Net operating loss carry forwards | 19,522 | 34,716 | ||||||
Tax credit carry forwards | 1,140 | 320 | ||||||
Charitable contributions carry forward | 5 | 47 | ||||||
Investment in partnerships | 382 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Gross deferred tax assets | 24,979 | 42,759 | ||||||
Less: valuation allowance | (22,902 | ) | (23,934 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net deferred tax assets | 2,077 | 18,825 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Deferred tax liabilities: | ||||||||
Intangibles | (5,898 | ) | (6,565 | ) | ||||
Investment in partnerships | — | (31,746 | ) | |||||
Property, plant and equipment | (701 | ) | (366 | ) | ||||
Undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries | (1,191 | ) | (882 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Gross deferred tax liabilities | (7,790 | ) | (39,559 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | (5,713 | ) | $ | (20,734 | ) | ||
|
|
|
| |||||
As of December 31, 2019, we have approximately $244,121 of U.S. net operating loss carry forwards to offset future taxable income. Of this amount, $47,358 is subject to Internal Revenue Code §382 limitation but will be available to be fully utilized by no later than 2027. These carry forwards expire between 2026 through 2037. In addition, we have $2,745 of various credits available to offset future U.S. federal income tax. Under the TCJA, the corporate alternative minimum tax was repealed and any minimum tax credit carryforwards not utilized become fully refundable in 2021. We do not expect to utilize our minimum tax credit of $2,054 before 2021.
As of December 31, 2019, we have approximately $831,791 of state net operating loss carry forwards before valuation allowances. These state net operating losses are available to reduce future taxable income and expire at various times and amounts. In addition, we have $135 of various credits available to offset future state income tax. There was no valuation allowance related to state net operating loss carry forwards as of December 31, 2019 and 2018. There were no net changes in the total state valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
As of December 31, 2019, we had approximately $48,135 of Puerto Rico net operating loss carry forwards before valuation allowances. These Puerto Rico net operating losses are available to offset future taxable income. These carry forwards expire between 2020 and 2028. In addition, we have $153 of alternative minimum tax credits available to offset future Puerto Rico income tax.
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income in those jurisdictions during the periods in
F-32
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
which those temporary differences become deductible. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities (including the impact of available carry back and carry forward periods), projected future taxable income, and tax-planning strategies in making this assessment. In order to fully realize the deferred tax assets, the Company will need to generate future taxable income before the expiration of the carry forwards governed by the tax code. Based on the current level of pretax earnings, the Company will not generate the minimum amount of future taxable income to support the realization of the deferred tax assets. As a result, management has determined that a valuation allowance related to Puerto Rico net operating loss carry forwards and other deferred tax assets is necessary. The valuation allowance for these deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 was $22,902 and $23,934, respectively. The net change in the total valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was an increase (decrease) of $(1,032) and $3,814, respectively. The amount of the deferred tax asset considered realizable, however, could be adjusted in the near term if estimates of future taxable income during the carry forward period increase.
As of December 31, 2019, the Company has accumulated undistributed earnings generated by our foreign subsidiaries of approximately $23,811. Management does not designate these earnings as permanently reinvested and has recognized a deferred tax liability of approximately $1,191 related to foreign withholding taxes on these earnings. We have recognized a current year tax expense of $180 related to 2019 earnings and a tax benefit of $(170) related to prior year earnings repatriated in 2019.
Under ASC 740 Income Taxes, we provide for uncertain tax positions, and the related interest, and adjust recognized tax benefits and accrued interest accordingly. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
Balance as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 2,067 | ||
Additions for tax positions related to current year | 932 | |||
Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 238 | |||
Reductions for tax positions related to prior years | — | |||
Lapse of statute of limitations | (30 | ) | ||
Settlements | — | |||
|
| |||
Balance as of December 31, 2018 | $ | 3,207 | ||
Additions for tax positions related to current year | 974 | |||
Additions for tax positions related to prior years | 386 | |||
Reductions for tax positions related to prior years | — | |||
Lapse of statute of limitations | (117 | ) | ||
Settlements | — | |||
|
| |||
Balance as of December 31, 2019 | $ | 4,450 | ||
|
|
Included in the balance of unrecognized benefits at December 31, 2019 is $4,450 of tax benefits that, if recognized in future periods, would impact our effective tax rate. During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, we recognized interest and penalties of $334 and $411, respectively, as a component of income tax expense in connection with our liabilities related to uncertain tax positions.
Within the next twelve months, we expect to decrease our unrecognized tax benefits by approximately $970 as a result of the expiration of statute of limitations.
We are subject to income taxes in the U.S. and nearly all states. In addition, the Company is subject to income taxes in Canada and the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. We are no longer subject to U.S federal income
F-33
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
tax examinations by tax authorities for years prior to 2016, or for any U.S. state income tax audit prior to 2013. With respect to Canada and Puerto Rico, we are no longer subject to income tax audits for years before 2016 and 2015, respectively.
(13) Related Party Transactions
Affiliates, as used within these statements, are persons or entities that are affiliated with Lamar Advertising Company or its subsidiaries through common ownership and directorate control.
The Company had receivables from employees of $80 at December 31, 2018. There were no receivables from employees at December 31, 2019. These receivables are primarily relocation loans for employees. The Company does not have any receivables from its current executive officers.
RTC Holdings, LLC (“RTC”), a telecommunications company, is 100% owned by entities owned by members of the Reilly family. Entities owned by Sean E. Reilly, Chief Executive Officer of the Company; Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., Chairman of the Board of Directors and President of the Company; and members of their respective immediate families hold a majority stake in RTC of approximately 89%. The Reilly Family, LLC, which is owned by Sean E. Reilly, Kevin P. Reilly, Jr., our directors Anna Reilly and Wendell Reilly, and entities owned by each of them and members of their respective immediate families, holds the remaining minority stake in RTC of approximately 11%. On May 31, 2019, RTC acquired EATELCORP, LLC (“EATEL”) and its subsidiaries. EATEL provides phone and internet services to consumers and businesses in Louisiana. EATEL also provides data back-up and recovery services to businesses. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company was a customer of EATEL for data back-up and recovery services. The aggregate amount paid by the Company to EATEL for such services was $302 for the year ended December 31, 2019. The Company was also contracted by EATEL to provide advertising services in the aggregate amount of $137 for the year ended December 31, 2019.
(14) Stockholders’ Equity
On July 16, 1999, the Board of Directors designated 5,720 shares of the 1,000,000 shares of previously undesignated preferred stock, par value $.001, as Series AA preferred stock, which shares were subsequently exchanged on a one for one basis in the REIT conversion. The Series AA preferred stock ranks senior to the Class A common stock and Class B common stock with respect to dividends and upon liquidation. Holders of Series AA preferred stock are entitled to receive, on a pari passu basis, dividends at the rate of $15.95 per share per quarter when, as and if declared by the Board of Directors. The Series AA preferred stock is entitled to receive, on a pari passu basis, $638 plus a further amount equal to any dividend accrued and unpaid to the date of distribution before any payments are made or assets distributed to the Class A common stock or Class B stock upon voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company. The liquidation value of the outstanding Series AA preferred stock at December 31, 2019 was $3,649. The Series AA preferred stock is entitled to one vote per share.
All of the outstanding shares of common stock are fully paid and nonassessable. In the event of the liquidation or dissolution of the Company, following any required distribution to the holders of outstanding shares of preferred stock, the holders of common stock are entitled to share pro rata in any balance of the corporate assets available for distribution to them. The Company may pay dividends if, when and as declared by the Board of Directors from funds legally available therefore, subject to the restrictions set forth in the Company’s existing indentures and the senior credit facility. Subject to the preferential rights of the holders of any class of preferred stock, holders of shares of common stock are entitled to receive such dividends as may be
F-34
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
declared by the Company’s Board of Directors out of funds legally available for such purpose. No dividend may be declared or paid in cash or property on any share of either class of common stock unless simultaneously the same dividend is declared or paid on each share of the other class of common stock, provided that, in the event of stock dividends, holders of a specific class of common stock shall be entitled to receive only additional shares of such class.
The rights of the Class A and Class B common stock are equal in all respects, except holders of Class B common stock have ten votes per share on all matters in which the holders of common stock are entitled to vote and holders of Class A common stock have one vote per share on such matters. The Class B common stock will convert automatically into Class A common stock upon the sale or transfer to persons other than permitted transferees (as defined in the Company’s certificate of incorporation, as amended).
On May 1, 2018, the Company entered into an equity distribution agreement (the “Sales Agreement”) with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Wells Fargo Securities LLC, and SunTrust Robinson Humphrey, Inc. as its sales agents (each a “Sales Agent”, and collectively, the “Sales Agents”). Under the terms of the Sales Agreement, the Company may, from time to time, issue and sell shares of its Class A common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Class A Common Stock”), having an aggregate offering price of up to $400,000, through the Sales Agents as either agents or principals. As of December 31, 2019, 842,412 shares of our Class A Common Stock have been sold under the Sales Agreement and accordingly $336,668 remains available to be sold under the Sales Agreement.
Sales of the Class A Common Stock, if any, may be made in negotiated transactions or transactions that are deemed to be “at-the-market offerings” as defined in Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, including sales made directly on or through the Nasdaq Global Select Market and any other existing trading market for the Class A Common Stock, or sales made to or through a market maker other than on an exchange. The Company has no obligation to sell any of the Class A Common Stock under the Sales Agreement and may at any time suspend solicitations and offers under the Sales Agreement.
On August 6, 2018, the Company filed an automatically effective shelf registration statement that registered the offer and sale of an indeterminate amount of additional shares of our Class A common stock. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued 163,137 shares of its Class A common stock in connection with acquisitions occurring during the period. The Company filed a prospectus supplement to the shelf registration statement relating to the offer and resale of such shares of Class A common stock. There were no shares issued under this shelf registration during the year ended December 31, 2019.
(15) Stock Compensation Plans
Equity Incentive Plan. Lamar’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended, (the “1996 Plan”) has reserved 17.5 million shares of common stock for issuance to directors and employees, including options granted and common stock reserved for issuance under its performance-based incentive program. Options granted under the 1996 Plan expire ten years from the grant date with vesting terms ranging from three to five years which primarily includes 1) options that vest in one-fifth increments beginning on the grant date and continuing on each of the first four anniversaries of the grant date and 2) options that cliff-vest on the fifth anniversary of the grant date. All grants are made at fair market value based on the closing price of our Class A common stock as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market on the date of grant.
In February 2013, the 1996 Plan was amended to eliminate the provision that limited the amount of Class A common stock, including shares retained from an award, that could be withheld to satisfy tax withholding
F-35
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
obligations to the minimum tax obligations required by law (except with respect to option awards). In accordance with ASC 718, Compensation – Stock Compensation, the Company is required to classify the awards affected by the amendment as liability-classified awards at fair value each period prior to their settlement. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company recorded a liability, in accrued expenses, of $23,297 and $19,211, respectively, related to its equity incentive awards affected by this amendment.
We use a Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model to estimate the fair value of share-based awards. The Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model incorporates various highly subjective assumptions, including expected term and expected volatility. We have reviewed our historical pattern of option exercises and have determined that meaningful differences in option exercise activity existed among vesting schedules. Therefore, for all stock options granted after January 1, 2006, we have categorized these awards into two groups of vesting 1) 5-year cliff vest and 2) 4-year graded vest, for valuation purposes. We have determined there were no meaningful differences in employee activity under our ESPP due to the nature of the plan.
We estimate the expected term of options granted using an implied life derived from the results of a hypothetical mid-point settlement scenario, which incorporates our historical exercise, expiration and post-vesting employment termination patterns, while accommodating for partial life cycle effects. We believe these estimates will approximate future behavior.
We estimate the expected volatility of our Class A common stock at the grant date using a blend of 90% historical volatility of our Class A common stock and 10% implied volatility of publicly traded options with maturities greater than six months on our Class A common stock as of the option grant date. Our decision to use a blend of historical and implied volatility was based upon the volume of actively traded options on our common stock and our belief that historical volatility alone may not be completely representative of future stock price trends.
Our risk-free interest rate assumption is determined using the Federal Reserve nominal rates for U.S. Treasury zero-coupon bonds with maturities similar to those of the expected term of the award being valued. We assumed an expected dividend yield of 5%.
We estimate option forfeitures at the time of grant and periodically revise those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. We record stock-based compensation expense only for those awards expected to vest using an estimated forfeiture rate based on our historical forfeiture data.
The fair value of each option grant is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following weighted-average assumptions used:
Grant Year | Dividend Yield | Expected Volatility | Risk Free Interest Rate | Expected Lives | ||||||||||||
2019 | 5 | % | 46 | % | 2 | % | 6 | |||||||||
2018 | 5 | % | 46 | % | 2 | % | 6 | |||||||||
2017 | 5 | % | 45 | % | 2 | % | 6 | |||||||||
F-36
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Information regarding the 1996 Plan for the year ended December 31, 2019 is as follows:
| Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Contractual Life | ||||||||||
Outstanding, beginning of year | 836,859 | $ | 49.65 | |||||||||
Granted | 117,000 | 76.92 | ||||||||||
Exercised | (340,684 | ) | 43.98 | |||||||||
Forfeited | (4,800 | ) | 61.23 | |||||||||
Expired | — | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Outstanding, end of year | 608,375 | 57.97 | 5.71 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Exercisable at end of year | 401,375 | 50.64 | 4.31 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
At December 31, 2019 there was $3,173 of unrecognized compensation cost related to stock options granted which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.77 years.
Shares available for future stock option and restricted share grants to employees and directors under existing plans were 2,669,471 at December 31, 2019. The aggregate intrinsic value of options outstanding as of December 31, 2019 was $19,034, and the aggregate intrinsic value of options exercisable was $15,502. Total intrinsic value of options exercised was $12,433 for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Stock Purchase Plan. Lamar Advertising’s 2009 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2009 ESPP”) was approved by our shareholders on May 28, 2009. The number of shares of Class A common stock available under the 2009 ESPP was automatically increased by 85,162 shares on January 1, 2019 pursuant to the automatic increase provisions of the 2009 ESPP. The 2009 ESPP expired by its terms on June 30, 2019. On May 30, 2019, our shareholders approved Lamar Advertising’s 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2019 ESPP”). The 2019 ESPP became effective upon the expiration of the 2009 ESPP. The number of shares of Class A common stock available for issuance under the 2019 ESPP consists of (1) 300,000 shares of Class A common stock and (2) any shares of Class A common stock available for future purchase under the 2009 ESPP at June 30, 2019.
The following is a summary of 2009 and 2019 ESPP share activity for the year ended December 31, 2019:
| Shares | ||||
Available for future purchases, January 1, 2019 | 183,244 | |||
Additional shares reserved under 2009 ESPP | 85,162 | |||
Additional shares reserved under 2019 ESPP | 300,000 | |||
Purchases | (129,972 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Available for future purchases, December 31, 2019 | 438,434 | |||
|
| |||
Performance-based compensation. Unrestricted shares of our Class A common stock may be awarded to key officers and employees under our 1996 Plan based on certain Company performance measures for fiscal year 2019. The number of shares to be issued, if any, are dependent on the level of achievement of these performance measures as determined by the Company’s Compensation Committee based on our 2019 results and were issued in the first quarter of 2020. The shares subject to these awards can range from a minimum of 0% to a maximum of 100% of the target number of shares depending on the level at which the goals are attained. Based on the
F-37
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Company’s performance measures achieved through December 31, 2019, the Company has accrued $22,838 as compensation expense related to these agreements.
(16) Benefit Plans
The Company sponsors a partially self-insured group health insurance program. The Company is obligated to pay all claims under the program, which are in excess of premiums, up to program limits. The Company is also self-insured with respect to its income disability benefits and against casualty losses on advertising structures. Amounts for expected losses, including a provision for losses incurred but not reported, is included in accrued expenses in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2019, the Company maintained $8,091 in letters of credit with a bank to meet requirements of the Company’s worker’s compensation and general liability insurance carrier.
Savings and Profit Sharing Plan
The Company sponsors The Lamar Corporation Savings and Profit Sharing Plan covering eligible employees who have completed one year of service and are at least 21 years of age. The Company has the option to match 50% of employees’ contributions up to 5% of eligible compensation. Employees can contribute up to 100% of compensation. Full vesting on the Company’s matched contributions occurs after three years for contributions made after January 1, 2002. Annually, at the Company’s discretion, an additional profit sharing contribution may be made on behalf of each eligible employee. The Company matched contributions of $5,688, $4,966 and $4,715 for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively.
Deferred Compensation Plan
The Company sponsors a Deferred Compensation Plan for the benefit of certain of its board-elected officers who meet specific age and years of service and other criteria. Officers that have attained the age of 30 and have a minimum of 10 years of service to the Company and satisfy additional eligibility guidelines are eligible for annual contributions to the plan generally ranging from $3 to $8, depending on the employee’s length of service. The Company’s contributions to the plan are maintained in a rabbi trust and, accordingly, the assets and liabilities of the plan are reflected in the balance sheet of the Company in other assets and other liabilities. Upon termination, death or disability, participating employees are eligible to receive an amount equal to the fair market value of the assets in the employee’s deferred compensation account. For the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, the Company contributed $1,675, $1,585 and $1,526, respectively.
On December 8, 2005, the Company’s Board of Directors approved an amendment to the Lamar Deferred Compensation Plan in order to (1) to comply with the requirements of Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code (“Section 409A”) applicable to deferred compensation and (2) to reflect changes in the administration of the plan. The Company’s Board of Directors also approved the adoption of a grantor trust pursuant to which amounts may be set aside, but remain subject to claims of the Company’s creditors, for payments of liabilities under the new plan, including amounts contributed under the old plan. The plan was further amended in August 2007 to make certain amendments to reflect Section 409A regulations issued on April 10, 2007. An additional clarifying amendment was made to the plan in December 2013.
F-38
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(17) Commitment and Contingencies
Off balance sheet arrangements
Our off-balance sheet commitments consist of guaranteed minimum payments to local transit municipalities and airport authorities for agreements which entitle us to rent advertising space to customers, in airports and on buses, benches or shelters. These agreements no longer meet the criteria of a lease under ASC 842, Leases, adopted on January 1, 2019 and are a result from our normal course of business. The following is a summary of the minimum payments related to these agreements.
2020 | $ | 20,621 | ||
2021 | $ | 16,965 | ||
2022 | $ | 16,702 | ||
2023 | $ | 15,614 | ||
2024 | $ | 14,624 | ||
Thereafter | $ | 1,289 |
Legal matters
The Company is involved in various claims and legal actions arising in the ordinary course of business. In the opinion of management, the ultimate disposition of these matters will not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations, or liquidity.
(18) Distribution Restrictions
Lamar Media’s ability to make distributions to Lamar Advertising is restricted under both the terms of the indentures relating to Lamar Media’s outstanding notes and by the terms of its senior credit facility. As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, Lamar Media was permitted under the terms of its outstanding senior subordinated and senior notes to make transfers to Lamar Advertising in the form of cash dividends, loans or advances in amounts up to $3,389,763 and $3,156,061, respectively.
As of December 31, 2019, Lamar Media’s senior credit facility allows it to make transfers to Lamar Advertising in any taxable year up to the amount of Lamar Advertising’s taxable income (without any deduction for dividends paid). In addition, as of December 31, 2019, transfers to Lamar Advertising are permitted under Lamar Media’s senior credit facility and as defined therein up to the available cumulative credit, as long as no default has occurred and is continuing and, after giving effect to such distributions, (i) the total debt ratio is less than 6.5 to 1 and (ii) the secured debt ratio does not exceed 3.5 to 1. As of December 31, 2019, the total debt ratio was less than 6.5 to 1 and Lamar Media’s secured debt ratio was less than 3.5 to 1, and the available cumulative credit was $2,140,441.
(19) Fair Value of Financial Instruments
At December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company’s financial instruments included cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, investments, accounts payable and borrowings. The fair values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and short-term borrowings and current portion of long-term debt approximated carrying values because of the short-term nature of these instruments. Investments and initial recognition of asset retirement obligations are reported at fair values. Fair values for investments held at cost are not readily available, but are estimated to approximate fair value. The estimated fair
F-39
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
value of the Company’s long term debt (including current maturities) was $3,064,068, which is greater than both the gross and carrying amount of $3,004,532 as of December 31, 2019. The majority of the fair value is determined using observed prices of publicly traded debt (level 1 in the fair value hierarchy) and the remaining is valued based on quoted prices for similar debt (level 2 in the fair value hierarchy).
(20) Information about Geographic Areas
Revenues from external customers attributable to foreign countries totaled $34,517, $35,146 and $33,424 for the years ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively. Net carrying value of long lived assets located in foreign countries totaled $4,549 and $2,387 as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. All other revenues from external customers and long lived assets relate to domestic operations.
(21) New Accounting Pronouncements
Leases
In February 2016, the FASB established Topic 842, Leases, by issuing Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2016-02, which requires lessees to recognize leases on-balance sheet and disclose key information about leasing arrangements. Topic 842 was subsequently amended by ASU No. 2018-01, Land Easement Practical Expedient for Transition to Topic 842; ASU No. 2018-10 and ASU No. 2019-01, Codification Improvements to Topic 842, Leases; and ASU No. 2018-11, Targeted Improvements. The new standard establishes a right-of-use model (ROU) that requires a lessee to recognize a ROU asset and lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with a term longer than 12 months. Leases are classified as finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern and classification of expense recognition in the income statement.
We adopted the new standard effective January 1, 2019 using a modified retrospective transition approach, applying the new standard to all leases existing at the date of initial application. An entity was permitted to use either (1) its effective date or (2) the beginning of the earliest comparative period presented in the financial statements as its date of initial application. If an entity chooses the second option, the transition requirements for existing leases also apply to leases entered into between the date of initial application and the effective date. The entity must also recast its comparative period financial statements and provide the disclosures required by the new standard for the comparative periods. Consequently, financial information was not updated and the disclosures required under the new standard will not be provided for dates and periods before January 1, 2019.
The new standard provided a number of optional practical expedients in transition. We elected the ‘package of practical expedients’, which permitted us not to reassess under the new standard our prior conclusions about lease identification, lease classification and initial direct costs. We elected the practical expedient pertaining to land easements. We also elected the short-term lease recognition exemption for certain of our vehicle agreements. This means, for those leases that qualify, we will not recognize ROU assets or lease liabilities.
Upon adoption, we recognized additional operating liabilities of $1.2 billion, with corresponding ROU assets of the same amount based on the present value of the remaining minimum rental payments under current leasing standards for our existing operating leases. In addition to the increase to the operating lease liabilities and right-of-use assets, Topic 842 also resulted in reclassifying the presentation of prepaid and deferred rent to operating lease right-of-use assets. The Company did not have any changes to its opening balance of retained earnings for the adoption of this update.
F-40
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Other recently released pronouncements
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-04, Intangibles – Goodwill and other (Topic 350): Simplifying the test for goodwill impairment. The update simplifies how a company completes its goodwill impairment test by eliminating the two-step process, which requires determining the fair value of assets acquired or liabilities assumed in a business combination. The update requires completing the goodwill impairment test by comparing the difference between the reporting unit’s carrying value and fair value. Goodwill charges, if any, would be determined by reducing the goodwill balance by the excess of the reporting unit’s carrying value over its fair value. The update is effective for annual and interim fiscal periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted for interim or annual goodwill impairment tests performed on or after January 1, 2017. The Company adopted this update beginning with its December 31, 2017 goodwill impairment test.
In November 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-18, Collaborative Arrangements (Topic 808). The update is to clarify when certain transactions between collaborative arrangement participants should be accounted for as revenue under Topic 606 and when the collaborative arrangement participant is a customer in the context of a unit of account. The update also adds unit-of-account guidance in Topic 808 and requires that a collaborative arrangement participant that is not directly related to sales to a third party, presenting the transaction together with revenue recognized under Topic 606 is precluded if the collaborative arrangement participant is not a customer. The update is effective for annual and interim fiscal periods beginning after December 15, 2019 with early adoption permitted. The adoption of this update did not have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326) Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments (“CECL”). The new guidance modifies how entities measure credit losses on most financial instruments. Topic 326 replaces the current “incurred loss” model with an “expected credit loss” model that requires consideration of a broader range of information to estimate expected credit losses over the lifetime of the asset. The new guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019, and early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2020 using the modified retrospective approach through a cumulative-effect adjustment to retained earnings as of the effective date. The adoption did not have a material impact to the consolidated financial statements.
(22) Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
The tables below represent the balances for the selected quarterly financial data of the Company for each reporting period in the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| Year 2019 Quarters | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 384,457 | $ | 448,742 | $ | 457,786 | $ | 462,659 | ||||||||
Net revenues less direct advertising expenses | $ | 243,987 | $ | 302,352 | $ | 308,940 | $ | 308,287 | ||||||||
Net income applicable to common stock | $ | 51,162 | $ | 118,305 | $ | 99,618 | $ | 102,661 | ||||||||
Net income per common share basic | $ | 0.51 | $ | 1.18 | $ | 0.99 | $ | 1.02 | ||||||||
Net income per common share diluted | $ | 0.51 | $ | 1.18 | $ | 0.99 | $ | 1.02 | ||||||||
F-41
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
| Year 2018 Quarters | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 361,026 | $ | 419,800 | $ | 418,498 | $ | 427,898 | ||||||||
Net revenues less direct advertising expenses | $ | 222,733 | $ | 279,016 | $ | 277,799 | $ | 285,826 | ||||||||
Net income applicable to common stock | $ | 14,961 | $ | 100,340 | $ | 93,965 | $ | 95,601 | ||||||||
Net income per common share basic | $ | 0.15 | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.95 | $ | 0.97 | ||||||||
Net income per common share diluted | $ | 0.15 | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.95 | $ | 0.96 | ||||||||
(23) Divestiture of Assets
On April 16, 2018 the Company sold its assets in Puerto Rico for $3,000 in cash and non-cash consideration consisting of a note receivable for $9,250 due April 2024. The Company recorded a loss on the sale of $7,809 for the year ended December 31, 2018. There were no significant divestitures of assets for the year ended December 31, 2019.
(24) Subsequent Events
On February 6, 2020, Lamar Media completed a refinancing transaction involving (i) the issuance of an additional $1,000,000 in aggregate principal amount of new senior notes, consisting of $600,000 in aggregate principal amount of 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 and $400,000 in aggregate principal amount of 4% Senior Notes due 2030 and (ii) the entry into the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, which amended and restated its existing senior credit facility. The new senior credit facility created under the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement consists of (i) a new $750,000 senior secured revolving credit facility, (ii) a new $600,000 Term B loan facility (the “new Term B loans”), and (iii) an incremental facility pursuant to which Lamar Media may incur additional term loan tranches or increase its revolving credit facility subject to a pro forma secured debt ratio. Lamar Media borrowed all $600,000 of the new Term B loans on February 6, 2020.
Proceeds from the refinancing transactions, after the payment of fees and expenses, were used to (1) redeem Lamar Media’s 5 3/8% Senior Notes on February 20, 2020 and (2) repay amounts outstanding under the Third Amended and Restated Senior Credit Agreement, including the existing Term A loans and Term B loans thereunder.
F-42
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands)
| Balance at Beginning of Period | Charged to Costs and Expenses | Deductions | Balance at End of Period | |||||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from trade accounts receivable: | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 11,161 | 11,608 | 9,584 | $ | 13,185 | ||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Valuation allowance | $ | 23,934 | — | 1,032 | $ | 22,902 | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from trade accounts receivable: | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 10,055 | 8,472 | 7,366 | $ | 11,161 | ||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Valuation allowance | $ | 20,120 | 3,814 | — | $ | 23,934 | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from trade accounts receivable: | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 9,356 | 6,762 | 6,063 | $ | 10,055 | ||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Valuation allowance | $ | 16,167 | 3,953 | — | $ | 20,120 | ||||||||||
F-43
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Schedule of Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation
December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands)
Description(1) | Encumbrances | Initial Cost(2) | Gross Carrying Amount(3) | Accumulated Depreciation | Construction Date | Acquisition Date | Useful Lives | |||||||||||||||||||||
391,456 Displays | — | — | $ | 3,333,590 | $ | (2,166,579 | ) | Various | Various | 5 to 20 years | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | No single asset exceeded 5% of the total gross carrying amount at December 31, 2019 |
| (2) | This information is omitted, as it would be impracticable to compile such information on a site-by-site basis |
| (3) | Includes sites under construction |
The following table summarizes activity for the Company’s real estate assets, which consists of advertising displays and the related accumulated depreciation.
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||
Gross real estate assets: | ||||||||||||
Balance at the beginning of the year | $ | 3,201,434 | $ | 3,074,046 | $ | 2,998,540 | ||||||
Capital expenditures on new advertising displays(4) | 59,604 | 54,151 | 49,946 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures on improvements/redevelopments of existing advertising displays | 25,025 | 12,781 | 6,265 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures other recurring | 36,354 | 34,758 | 32,523 | |||||||||
Land acquisitions(6) | 22,965 | 15,368 | 14,904 | |||||||||
Acquisition of advertising displays(5) (6) | 23,589 | 82,617 | 32,109 | |||||||||
Assets sold or written-off | (35,320 | ) | (70,494 | ) | (61,306 | ) | ||||||
Foreign exchange | (61 | ) | (1,793 | ) | 1,065 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Balance at the end of the year | $ | 3,333,590 | $ | 3,201,434 | $ | 3,074,046 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Accumulated depreciation: | ||||||||||||
Balance at the beginning of the year | $ | 2,082,335 | $ | 2,025,251 | $ | 1,973,958 | ||||||
Depreciation | 111,531 | 106,700 | 102,494 | |||||||||
Assets sold or written-off | (27,890 | ) | (48,488 | ) | (51,976 | ) | ||||||
Foreign exchange | 603 | (1,128 | ) | 775 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Balance at the end of the year | $ | 2,166,579 | $ | 2,082,335 | $ | 2,025,251 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| (4) | Includes non-cash amounts of $554, $446 and $921 at December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively |
| (5) | Includes non-cash amounts of $1,928, $7,199 and $3,043 at December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively |
| (6) | Includes preliminary allocation of assets acquired from Fairway at December 31, 2018 |
F-44
Table of Contents
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of Lamar Media Corp. is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act.
Lamar Media Corp.’s management assessed the effectiveness of Lamar Media Corp.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control –Integrated Framework (2013). Based on this assessment, Lamar Media Corp.’s management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2019, Lamar Media Corp.’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria. The effectiveness of Lamar Media Corp.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 has been audited by KPMG LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report, which is included in Item 8 to this Annual Report.
F-45
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors
Lamar Media Corp.:
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Lamar Media Corp. and subsidiaries’ (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, stockholder’s equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and financial statement schedules II to III (collectively, the consolidated financial statements), and our report dated February 20, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
F-46
Table of Contents
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ KPMG LLP |
| KPMG LLP |
Baton Rouge, Louisiana
February 20, 2020
F-47
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and Board of Directors
Lamar Media Corp.:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Lamar Media Corp. and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income, stockholder’s equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes and financial statement schedules II to III (collectively, the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated February 20, 2020 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Change in Accounting Principle
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, which refers to Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements of Lamar Advertising Company, the Company changed its method of accounting for revenue recognition as of January 1, 2018, due to the adoption of Accounting Standards Codification Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers.
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, which refers to Note 7 to the consolidated financial statements of Lamar Advertising Company, the Company changed its method of accounting for leases as of January 1, 2019, due to the adoption of Accounting Standards Codification Topic 842, Leases.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ KPMG LLP |
| KPMG LLP |
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 1992.
Baton Rouge, Louisiana
February 20, 2020
F-48
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Balance Sheets
December 31, 2019 and 2018
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 25,688 | $ | 20,994 | ||||
Receivables, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $13,185 and $11,161 as of 2019 and 2018, respectively | 254,930 | 235,576 | ||||||
Prepaid lease and contract expenses | — | 80,684 | ||||||
Other current assets | 29,051 | 25,915 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current assets | 309,669 | 363,169 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Property, plant and equipment | 3,660,311 | 3,525,725 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (2,311,196 | ) | (2,230,677 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net property, plant and equipment | 1,349,115 | 1,295,048 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Operating lease right of use assets | 1,320,779 | — | ||||||
Goodwill (note 3) | 1,902,123 | 1,909,235 | ||||||
Intangible assets, net (note 3) | 991,776 | 914,984 | ||||||
Other assets | 50,959 | 45,450 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total assets | $ | 5,924,421 | $ | 4,527,886 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||
Trade accounts payable | $ | 14,974 | $ | 21,246 | ||||
Current maturities of long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $6,081 and $5,245 in 2019 and 2018, respectively (note 5) | 226,514 | 204,120 | ||||||
Current operating lease liabilities | 196,841 | — | ||||||
Accrued expenses (note 4) | 101,266 | 117,300 | ||||||
Deferred income | 127,254 | 107,202 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current liabilities | 666,849 | 449,868 | ||||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $18,333 and $20,619 in 2019 and 2018, respectively (note 5) | 2,753,604 | 2,684,568 | ||||||
Operating lease liabilities | 1,068,181 | — | ||||||
Deferred income tax liabilities | 5,713 | 20,734 | ||||||
Asset retirement obligation | 226,137 | 222,989 | ||||||
Other liabilities | 34,406 | 29,531 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities | 4,754,890 | 3,407,690 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholder’s equity: | ||||||||
Common stock, $.01 par value, authorized 3,000 shares; 100 shares issued and outstanding at 2019 and 2018 | — | — | ||||||
Additional paid-in-capital | 2,992,729 | 2,922,907 | ||||||
Accumulated comprehensive income | 685 | 12 | ||||||
Accumulated deficit | (1,823,883 | ) | (1,802,723 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholder’s equity | 1,169,531 | 1,120,196 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity | $ | 5,924,421 | $ | 4,527,886 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-49
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Statements of Income | ||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,753,644 | $ | 1,627,222 | $ | 1,541,260 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Operating expenses (income): | ||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 590,078 | 561,848 | 540,880 | |||||||||
General and administrative expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 318,380 | 289,428 | 276,229 | |||||||||
Corporate expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 84,229 | 82,497 | 61,962 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 250,028 | 225,261 | 211,104 | |||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | (7,241 | ) | 7,233 | (4,664 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 1,235,474 | 1,166,267 | 1,085,511 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Operating income | 518,170 | 460,955 | 455,749 | |||||||||
Other expense (income): | ||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 15,429 | 71 | |||||||||
Interest income | (764 | ) | (534 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
Interest expense | 150,616 | 129,732 | 128,396 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 149,852 | 144,627 | 128,461 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Income before income tax expense | 368,318 | 316,328 | 327,288 | |||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense | (4,222 | ) | 10,697 | 9,230 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Net income | $ | 372,540 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 318,058 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Statements of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 372,540 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 318,058 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | ||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | 673 | (1,290 | ) | 1,926 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 373,213 | $ | 304,341 | $ | 319,984 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-50
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Stockholder’s Equity
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2016 | $ | — | 2,783,753 | (624 | ) | (1,726,743 | ) | 1,056,386 | ||||||||||||
Contribution from parent | — | 49,187 | — | — | 49,187 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translations | — | — | 1,926 | — | 1,926 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 318,058 | 318,058 | |||||||||||||||
Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (334,459 | ) | (334,459 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2017 | $ | — | 2,832,940 | 1,302 | (1,743,144 | ) | 1,091,098 | |||||||||||||
Contribution from parent | — | 89,967 | — | — | 89,967 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translations | — | — | (1,290 | ) | — | (1,290 | ) | |||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 305,631 | 305,631 | |||||||||||||||
Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (365,210 | ) | (365,210 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2018 | $ | — | 2,922,907 | 12 | (1,802,723 | ) | 1,120,196 | |||||||||||||
Contribution from parent | — | 69,822 | — | — | 69,822 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translations | — | — | 673 | — | 673 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 372,540 | 372,540 | |||||||||||||||
Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (393,700 | ) | (393,700 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2019 | $ | — | 2,992,729 | 685 | (1,823,883 | ) | 1,169,531 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-51
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands)
| 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | ||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 372,540 | $ | 305,631 | $ | 318,058 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 250,028 | 225,261 | 211,104 | |||||||||
Non-cash compensation | 29,647 | 29,443 | 9,599 | |||||||||
Amortization included in interest expense | 5,365 | 4,920 | 5,120 | |||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets and investments | (7,241 | ) | 7,233 | (4,664 | ) | |||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 15,429 | 71 | |||||||||
Deferred income tax (benefit) expense | (14,130 | ) | 1,538 | 804 | ||||||||
Provision for doubtful accounts | 10,608 | 7,985 | 6,762 | |||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
(Increase) decrease in: | ||||||||||||
Receivables | (28,357 | ) | (33,292 | ) | (17,524 | ) | ||||||
Prepaid expenses | 275 | (5,433 | ) | 309 | ||||||||
Other assets | (11,257 | ) | 3,270 | (8,410 | ) | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in: | ||||||||||||
Trade accounts payable | 700 | 1,366 | 309 | |||||||||
Accrued expenses | (1,597 | ) | (6,292 | ) | (9,416 | ) | ||||||
Operating lease liabilities | 9,102 | — | — | |||||||||
Other liabilities | (10,743 | ) | (19,974 | ) | (27,882 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows provided by operating activities | 604,940 | 537,085 | 484,240 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | (140,956 | ) | (117,638 | ) | (109,329 | ) | ||||||
Acquisitions | (226,278 | ) | (477,389 | ) | (297,305 | ) | ||||||
(Increase) decrease in notes receivable | (448 | ) | 9 | 515 | ||||||||
Proceeds received from property insurance claims | 210 | 4,222 | — | |||||||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | 5,438 | 6,648 | 6,053 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows used in investing activities | (362,034 | ) | (584,148 | ) | (400,066 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 495,000 | 563,000 | 495,000 | |||||||||
Payments on revolving credit facility | (625,000 | ) | (481,000 | ) | (477,000 | ) | ||||||
Principal payments on long-term debt | (34,471 | ) | (27,328 | ) | (16,993 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds received from senior credit facility term loans | — | 599,250 | 450,000 | |||||||||
Proceeds received from accounts receivable securitization program | 9,000 | 175,000 | — | |||||||||
Payments on accounts receivable securitization program | (9,000 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Debt issuance costs | (4,463 | ) | (7,616 | ) | (4,941 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds received from note offering | 255,000 | — | — | |||||||||
Redemption on senior subordinated notes | — | (509,790 | ) | — | ||||||||
Payment on senior credit facility term loans | — | — | (247,500 | ) | ||||||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | (621 | ) | (541 | ) | (693 | ) | ||||||
Dividends to parent | (393,700 | ) | (446,744 | ) | (252,925 | ) | ||||||
Contributions from parent | 69,822 | 89,967 | 49,187 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash flows used in financing activities | (238,433 | ) | (45,802 | ) | (5,865 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | 221 | (1,112 | ) | 1,632 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 4,694 | (93,977 | ) | 79,941 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 20,994 | 114,971 | 35,030 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 25,688 | $ | 20,994 | $ | 114,971 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | ||||||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 139,585 | $ | 136,711 | $ | 123,213 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Cash paid for state and federal income taxes | $ | 14,449 | $ | 8,563 | $ | 12,640 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-52
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(1) Significant Accounting Policies
(a) Nature of Business
Lamar Media Corp. (“Lamar Media”) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising Company. Lamar Media is engaged in the outdoor advertising business operating approximately 157,800 outdoor advertising displays in 45 states and Canada. Lamar Media’s operating strategy is to be the leading provider of outdoor advertising services in the markets it serves.
In addition, Lamar Media operates a logo sign business in 24 states throughout the United States as well as the province of Ontario, Canada. Logo signs are erected pursuant to state-awarded service contracts on public rights-of-way near highway exits and deliver brand name information on available gas, food, lodging and camping services. Included in the Company’s logo sign business are tourism signing contracts. The Company provides transit advertising in airport terminals, on bus shelters, benches and buses in the markets it serves.
Certain footnotes are not provided for the accompanying financial statements as the information in notes 2, 3, 5, 7, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 23 and 24 and portions of note 1 to the consolidated financial statements of Lamar Advertising Company included elsewhere in this filing are substantially equivalent to that required for the consolidated financial statements of Lamar Media Corp. Earnings per share data is not provided for the operating results of Lamar Media Corp. as it is a wholly owned subsidiary of Lamar Advertising Company.
(b) Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include Lamar Media, its wholly owned subsidiaries, The Lamar Company, L.L.C., Lamar Central Outdoor, LLC, Lamar TRS Holdings, LLC, Lamar Advertising Southwest, Inc., Interstate Logos, L.L.C., Lamar Obie Company, LLC, Lamar Canadian Outdoor Company, Lamar Advertising of Puerto Rico, Inc. and their majority-owned subsidiaries. All inter-company transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
(2) Non-cash Financing and Investing Activities
There were no significant non-cash investing activities for Lamar Media during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. For the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company had non-cash investing activities of $2,879 related to acquisitions of outdoor advertising assets. There were no significant non-cash financing activities during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. During the year ended December 31, 2017, Lamar Media had non-cash financing activities related to dividends to Lamar Advertising Company of $81,534 which were paid in January 2018.
F-53
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(3) Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The following is a summary of intangible assets at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| Estimated Life (Years) | 2019 | 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | |||||||||||||||||
Amortizable Intangible Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Customer lists and contracts | 7—10 | $ | 641,714 | $ | 539,405 | $ | 610,376 | $ | 514,928 | |||||||||||
Non-competition agreement | 3—15 | 66,014 | 64,379 | 65,771 | 64,119 | |||||||||||||||
Site locations | 15 | 2,384,520 | 1,509,335 | 2,228,767 | 1,422,794 | |||||||||||||||
Other | 2—15 | 49,318 | 36,671 | 45,446 | 33,535 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
| $ | 3,141,566 | $ | 2,149,790 | $ | 2,950,360 | $ | 2,035,376 | |||||||||||||
Unamortizable Intangible Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Goodwill | $ | 2,154,790 | $ | 252,667 | $ | 2,161,902 | $ | 252,667 | ||||||||||||
The changes in the gross carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 are as follows:
Balance as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 1,982,970 | ||
Goodwill acquired during the year | 182,117 | |||
Purchase price adjustments and other | (3,185 | ) | ||
Impairment losses | — | |||
|
| |||
Balance as of December 31, 2018 | $ | 2,161,902 | ||
Goodwill acquired during the year | 29,360 | |||
Purchase price adjustments and other | (36,472 | ) | ||
Impairment losses | — | |||
|
| |||
Balance as of December 31, 2019 | $ | 2,154,790 | ||
|
|
(4) Accrued Expenses
The following is a summary of accrued expenses at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
Payroll | $ | 20,223 | $ | 20,667 | ||||
Interest | 32,734 | 27,067 | ||||||
Accrued variable lease and contract expense | 12,559 | 36,158 | ||||||
Stock-based compensation | 23,297 | 19,211 | ||||||
Other | 12,453 | 14,197 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| $ | 101,266 | $ | 117,300 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
F-54
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(5) Long-term Debt
Long-term debt consists of the following at December 31, 2019 and 2018:
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
Senior Credit Facility | $ | 1,127,069 | $ | 9,077 | $ | 1,117,992 | ||||||
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program | 175,000 | 846 | 174,154 | |||||||||
5% Senior Subordinated Notes | 535,000 | 3,237 | 531,763 | |||||||||
5 3/8% Senior Notes | 510,000 | 3,502 | 506,498 | |||||||||
5 3/4% Senior Notes | 654,345 | 7,752 | 646,593 | |||||||||
Other notes with various rates and terms | 3,118 | — | 3,118 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 3,004,532 | 24,414 | 2,980,118 | ||||||||||
Less current maturities | (232,595 | ) | (6,081 | ) | (226,514 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt, excluding current maturities | $ | 2,771,937 | $ | 18,333 | $ | 2,753,604 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
Senior Credit Facility | $ | 1,291,088 | $ | 11,576 | $ | 1,279,512 | ||||||
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program | 175,000 | 1,168 | 173,832 | |||||||||
5% Senior Subordinated Notes | 535,000 | 4,104 | 530,896 | |||||||||
5 3/8% Senior Notes | 510,000 | 4,262 | 505,738 | |||||||||
5 3/4% Senior Notes | 400,000 | 4,754 | 395,246 | |||||||||
Other notes with various rates and terms | 3,464 | — | 3,464 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 2,914,552 | 25,864 | 2,888,688 | ||||||||||
Less current maturities | (209,365 | ) | (5,245 | ) | (204,120 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt, excluding current maturities | $ | 2,705,187 | $ | 20,619 | $ | 2,684,568 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt contractual maturities are as follows:
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
2020 | $ | 232,595 | $ | 6,081 | $ | 226,514 | ||||||
2021 | $ | 74,487 | $ | 6,205 | $ | 68,282 | ||||||
2022 | $ | 426,971 | $ | 4,677 | $ | 422,294 | ||||||
2023 | $ | 541,989 | $ | 3,480 | $ | 538,509 | ||||||
2024 | $ | 517,008 | $ | 2,216 | $ | 514,792 | ||||||
Later years | $ | 1,211,482 | $ | 1,755 | $ | 1,209,727 | ||||||
F-55
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
(6) Related Party Transactions
Affiliates, as used within these statements, are persons or entities that are affiliated with Lamar Media Corp. or its subsidiaries through common ownership and directorate control.
As of December 31, 2019 and 2018, there was a payable to Lamar Advertising Company, its parent, in the amount of $4,779 and $5,571, respectively.
Effective December 31, 2019 and 2018, Lamar Advertising Company contributed $69,822 and $89,967, respectively, to Lamar Media which resulted in an increase in Lamar Media’s additional paid-in capital.
(7) Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
The tables below represent the balances for the selected quarterly financial data of the Company for each reporting period in the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018.
| Year 2019 Quarters | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 384,457 | $ | 448,742 | $ | 457,786 | $ | 462,659 | ||||||||
Net revenues less direct advertising expenses | $ | 243,987 | $ | 302,352 | $ | 308,940 | $ | 308,287 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 51,362 | $ | 118,485 | $ | 99,832 | $ | 102,861 | ||||||||
| Year 2018 Quarters | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 361,026 | $ | 419,800 | $ | 418,498 | $ | 427,898 | ||||||||
Net revenues less direct advertising expenses | $ | 222,733 | $ | 279,016 | $ | 277,799 | $ | 285,826 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 15,158 | $ | 100,520 | $ | 94,165 | $ | 95,788 | ||||||||
(8) Summarized Financial Information of Subsidiaries
Separate condensed consolidating financial information for Lamar Media, subsidiary guarantors and non-guarantor subsidiaries are presented below. Lamar Media and its subsidiary guarantors have fully and unconditionally guaranteed Lamar Media’s obligations with respect to its publicly issued notes. All guarantees are joint and several. As a result of these guarantee arrangements, we are required to present the following condensed consolidating financial information. The following condensed consolidating financial information should be read in conjunction with the accompanying consolidated financial statements and notes. The condensed consolidating financial information is provided as an alternative to providing separate financial statements for guarantor subsidiaries. Separate financial statements of Lamar Media’s subsidiary guarantors are not included because the guarantees are full and unconditional and the subsidiary guarantors are 100% owned and jointly and severally liable for Lamar Media’s outstanding publicly issued notes. The accounts for all companies reflected herein are presented using the equity method of accounting for investments in subsidiaries.
F-56
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2019
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total current assets | $ | 13,859 | $ | 53,756 | $ | 242,054 | $ | — | $ | 309,669 | ||||||||||
Net property, plant and equipment | — | 1,340,675 | 8,440 | — | 1,349,115 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease right of use assets | — | 1,293,674 | 27,105 | — | 1,320,779 | |||||||||||||||
Intangibles and goodwill, net | — | 2,875,644 | 18,255 | — | 2,893,899 | |||||||||||||||
Other assets | 4,193,629 | 229,905 | 184,805 | (4,557,380 | ) | 50,959 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 4,207,488 | $ | 5,793,654 | $ | 480,659 | $ | (4,557,380 | ) | $ | 5,924,421 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 51,480 | $ | 34 | $ | 175,000 | $ | — | $ | 226,514 | ||||||||||
Current operating lease liabilities | — | 189,071 | 7,770 | — | 196,841 | |||||||||||||||
Other current liabilities | 26,960 | 196,689 | 19,845 | — | 243,494 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 78,440 | 385,794 | 202,615 | — | 666,849 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Long-term debt | 2,753,570 | 34 | — | — | 2,753,604 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease liabilities | — | 1,049,220 | 18,961 | — | 1,068,181 | |||||||||||||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 205,947 | 231,416 | 250,859 | (421,966 | ) | 266,256 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities | 3,037,957 | 1,666,464 | 472,435 | (421,966 | ) | 4,754,890 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Stockholders’ equity | 1,169,531 | 4,127,190 | 8,224 | (4,135,414 | ) | 1,169,531 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 4,207,488 | $ | 5,793,654 | $ | 480,659 | $ | (4,557,380 | ) | $ | 5,924,421 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-57
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2018
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total current assets | $ | 4,653 | $ | 121,549 | $ | 236,967 | $ | — | $ | 363,169 | ||||||||||
Net property, plant and equipment | — | 1,289,348 | 5,700 | — | 1,295,048 | |||||||||||||||
Intangibles and goodwill, net | — | 2,804,915 | 19,304 | — | 2,824,219 | |||||||||||||||
Other assets | 4,056,288 | 230,504 | 184,247 | (4,425,589 | ) | 45,450 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 4,060,941 | $ | 4,446,316 | $ | 446,218 | $ | (4,425,589 | ) | $ | 4,527,886 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 29,086 | $ | 34 | $ | 175,000 | $ | — | $ | 204,120 | ||||||||||
Other current liabilities | 27,067 | 204,103 | 14,578 | — | 245,748 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 56,153 | 204,137 | 189,578 | — | 449,868 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Long-term debt | 2,684,500 | 68 | — | — | 2,684,568 | |||||||||||||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 200,092 | 246,312 | 251,835 | (424,985 | ) | 273,254 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities | 2,940,745 | 450,517 | 441,413 | (424,985 | ) | 3,407,690 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Stockholders’ equity | 1,120,196 | 3,995,799 | 4,805 | (4,000,604 | ) | 1,120,196 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 4,060,941 | $ | 4,446,316 | $ | 446,218 | $ | (4,425,589 | ) | $ | 4,527,886 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-58
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income for the Year Ended December 31, 2019
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | — | $ | 1,709,691 | $ | 46,804 | $ | (2,851 | ) | $ | 1,753,644 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses(1) | — | 564,877 | 28,052 | (2,851 | ) | 590,078 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses(1) | — | 310,813 | 7,567 | — | 318,380 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses(1) | — | 82,652 | 1,577 | — | 84,229 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | — | 247,191 | 2,837 | — | 250,028 | |||||||||||||||
Gain on disposition of assets | — | (3,103 | ) | (4,138 | ) | — | (7,241 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| — | 1,202,430 | 35,895 | (2,851 | ) | 1,235,474 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating income | — | 507,261 | 10,909 | — | 518,170 | |||||||||||||||
Equity in (earnings) loss of subsidiaries | (517,516 | ) | — | — | 517,516 | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 144,976 | (149 | ) | 5,025 | — | 149,852 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Income (loss) before income tax expense | 372,540 | 507,410 | 5,884 | (517,516 | ) | 368,318 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense(2) | — | (7,360 | ) | 3,138 | — | (4,222 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 372,540 | $ | 514,770 | $ | 2,746 | $ | (517,516 | ) | $ | 372,540 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 372,540 | $ | 514,770 | $ | 2,746 | $ | (517,516 | ) | $ | 372,540 | |||||||||
Total other comprehensive income, net of tax | — | — | 673 | — | 673 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 372,540 | $ | 514,770 | $ | 3,419 | $ | (517,516 | ) | $ | 373,213 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Caption is exclusive of depreciation and amortization. |
| (2) | The income tax expense reflected in each column does not include any tax effect of the equity in earnings from subsidiaries. |
F-59
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income for the Year Ended December 31, 2018
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | — | $ | 1,579,619 | $ | 50,352 | $ | (2,749 | ) | $ | 1,627,222 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses(1) | — | 537,269 | 27,307 | (2,728 | ) | 561,848 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses(1) | — | 280,874 | 8,554 | — | 289,428 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses(1) | — | 80,861 | 1,636 | — | 82,497 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | — | 219,341 | 5,920 | — | 225,261 | |||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | — | (576 | ) | 7,809 | — | 7,233 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| — | 1,117,769 | 51,226 | (2,728 | ) | 1,166,267 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating income (loss) | — | 461,850 | (874 | ) | (21 | ) | 460,955 | |||||||||||||
Equity in (earnings) loss of subsidiaries | (450,791 | ) | — | — | 450,791 | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 129,731 | (99 | ) | (413 | ) | (21 | ) | 129,198 | ||||||||||||
Other expenses | 15,429 | — | — | — | 15,429 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Income (loss) before income tax expense | 305,631 | 461,949 | (461 | ) | (450,791 | ) | 316,328 | |||||||||||||
Income tax expense(2) | — | 7,879 | 2,818 | — | 10,697 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 305,631 | $ | 454,070 | $ | (3,279 | ) | $ | (450,791 | ) | $ | 305,631 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 305,631 | $ | 454,070 | $ | (3,279 | ) | $ | (450,791 | ) | $ | 305,631 | ||||||||
Total other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | (1,290 | ) | — | (1,290 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 305,631 | $ | 454,070 | $ | (4,569 | ) | $ | (450,791 | ) | $ | 304,341 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Caption is exclusive of depreciation and amortization. |
| (2) | The income tax expense reflected in each column does not include any tax effect of the equity in earnings from subsidiaries. |
F-60
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income for the Year Ended December 31, 2017
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | — | $ | 1,494,275 | $ | 51,332 | $ | (4,347 | ) | $ | 1,541,260 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses(1) | — | 512,247 | 31,277 | (2,644 | ) | 540,880 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses(1) | — | 266,798 | 9,431 | — | 276,229 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses(1) | — | 60,830 | 1,132 | — | 61,962 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | — | 201,424 | 9,680 | — | 211,104 | |||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | — | (5,704 | ) | 1,040 | — | (4,664 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| — | 1,035,595 | 52,560 | (2,644 | ) | 1,085,511 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating income (loss) | — | 458,680 | (1,228 | ) | (1,703 | ) | 455,749 | |||||||||||||
Equity in (earnings) loss of subsidiaries | (446,520 | ) | — | — | 446,520 | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 128,391 | (5 | ) | 1,707 | (1,703 | ) | 128,390 | |||||||||||||
Other expenses | 71 | — | — | — | 71 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Income (loss) before income tax expense | 318,058 | 458,685 | (2,935 | ) | (446,520 | ) | 327,288 | |||||||||||||
Income tax expense(2) | — | 7,069 | 2,161 | — | 9,230 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 318,058 | $ | 451,616 | $ | (5,096 | ) | $ | (446,520 | ) | $ | 318,058 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 318,058 | $ | 451,616 | $ | (5,096 | ) | $ | (446,520 | ) | $ | 318,058 | ||||||||
Total other comprehensive income, net of tax | — | — | 1,926 | — | 1,926 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 318,058 | $ | 451,616 | $ | (3,170 | ) | $ | (446,520 | ) | $ | 319,984 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Caption is exclusive of depreciation and amortization. |
| (2) | The income tax expense reflected in each column does not include any tax effect of the equity in earnings from subsidiaries. |
F-61
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows for the Year Ended December 31, 2019
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 469,907 | $ | 738,030 | $ | 6,660 | $ | (609,657 | ) | $ | 604,940 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | — | (136,696 | ) | (4,260 | ) | — | (140,956 | ) | ||||||||||||
Acquisitions | — | (226,278 | ) | — | — | (226,278 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | — | 5,438 | — | — | 5,438 | |||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from insurance claims | — | 210 | — | — | 210 | |||||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | (226,278 | ) | — | — | 226,278 | — | ||||||||||||||
Decrease in intercompany notes receivable | 3,787 | — | — | (3,787 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Increase in notes receivable | (448 | ) | — | — | — | (448 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (222,939 | ) | (357,326 | ) | (4,260 | ) | 222,491 | (362,034 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 495,000 | — | — | — | 495,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payment on revolving credit facility | (625,000 | ) | — | — | — | (625,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Principal payments on long-term debt | (34,471 | ) | — | — | — | (34,471 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds received from accounts receivable securitization program | — | — | 9,000 | — | 9,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payments on accounts receivable securitization program | — | — | (9,000 | ) | — | (9,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Debt issuance costs | (4,463 | ) | — | — | — | (4,463 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds received from note offering | 255,000 | — | — | — | 255,000 | |||||||||||||||
Intercompany loan proceeds (payments) | — | (702 | ) | (3,085 | ) | 3,787 | — | |||||||||||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | — | — | (621 | ) | — | (621 | ) | |||||||||||||
Dividends (to) from parent | (393,700 | ) | (609,657 | ) | — | 609,657 | (393,700 | ) | ||||||||||||
Contributions from (to) parent | 69,822 | 226,278 | — | (226,278 | ) | 69,822 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (237,812 | ) | (384,081 | ) | (3,706 | ) | 387,166 | (238,433 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | — | — | 221 | — | 221 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 9,156 | (3,377 | ) | (1,085 | ) | — | 4,694 | |||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 4,029 | 11,655 | 5,310 | — | 20,994 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 13,185 | $ | 8,278 | $ | 4,225 | $ | — | $ | 25,688 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-62
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows for the Year Ended December 31, 2018
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 430,896 | $ | 689,718 | $ | (17,143 | ) | $ | (566,386 | ) | $ | 537,085 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Acquisitions | — | (477,389 | ) | — | — | (477,389 | ) | |||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | — | (113,259 | ) | (4,379 | ) | — | (117,638 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | — | 3,839 | 2,809 | — | 6,648 | |||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from insurance claims | — | — | 4,222 | — | 4,222 | |||||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | (498,226 | ) | — | — | 498,226 | — | ||||||||||||||
Decrease in intercompany notes receivable | 30,034 | — | — | (30,034 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Decrease in notes receivable | 9 | — | — | — | 9 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (468,183 | ) | (586,809 | ) | 2,652 | 468,192 | (584,148 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 563,000 | — | — | — | 563,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payment on revolving credit facility | (481,000 | ) | — | — | — | (481,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Principal payments on long-term debt | (27,297 | ) | (31 | ) | — | — | (27,328 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds received from senior credit facility term loans | 599,250 | — | — | — | 599,250 | |||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from accounts receivable securitization program | — | — | 175,000 | — | 175,000 | |||||||||||||||
Debt issuance costs | (7,616 | ) | — | — | — | (7,616 | ) | |||||||||||||
Redemption on senior subordinated notes | (509,790 | ) | — | — | — | (509,790 | ) | |||||||||||||
Intercompany loan proceeds (payments) | 175,000 | (24,688 | ) | (180,346 | ) | 30,034 | — | |||||||||||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | — | — | (541 | ) | — | (541 | ) | |||||||||||||
Contributions from (to) parent | 89,967 | 498,226 | — | (498,226 | ) | 89,967 | ||||||||||||||
Dividends (to) from parent | (446,744 | ) | (566,386 | ) | — | 566,386 | (446,744 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (45,230 | ) | (92,879 | ) | (5,887 | ) | 98,194 | (45,802 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | — | — | (1,112 | ) | — | (1,112 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | (82,517 | ) | 10,030 | (21,490 | ) | — | (93,977 | ) | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 86,546 | 1,625 | 26,800 | — | 114,971 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 4,029 | $ | 11,655 | $ | 5,310 | $ | — | $ | 20,994 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-63
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Dollars in thousands, except share and per share data)
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows for the Year Ended December 31, 2017
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 383,370 | $ | 602,504 | $ | 2,174 | $ | (503,808 | ) | $ | 484,240 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Acquisitions | 3,750 | (298,901 | ) | (2,154 | ) | — | (297,305 | ) | ||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | — | (104,325 | ) | (5,004 | ) | — | (109,329 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | — | 6,053 | — | — | 6,053 | |||||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | (301,055 | ) | — | — | 301,055 | — | ||||||||||||||
(Increase) decrease in intercompany notes receivable | (7,624 | ) | — | — | 7,624 | — | ||||||||||||||
Decrease in notes receivable | 515 | — | — | — | 515 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (304,414 | ) | (397,173 | ) | (7,158 | ) | 308,679 | (400,066 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Principal payments on long-term debt | (16,993 | ) | — | — | — | (16,993 | ) | |||||||||||||
Payment on revolving credit facility | (477,000 | ) | — | — | — | (477,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 495,000 | — | — | — | 495,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payment on senior credit facility | (247,500 | ) | — | — | — | (247,500 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds received from senior credit facility | 450,000 | — | — | — | 450,000 | |||||||||||||||
Debt issuance costs | (4,941 | ) | — | — | — | (4,941 | ) | |||||||||||||
Intercompany loan proceeds (payments) | — | — | 7,624 | (7,624 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | — | — | (693 | ) | — | (693 | ) | |||||||||||||
Contributions from (to) parent | 49,187 | 298,901 | 2,154 | (301,055 | ) | 49,187 | ||||||||||||||
Dividends (to) from parent | (252,925 | ) | (503,808 | ) | — | 503,808 | (252,925 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (5,172 | ) | (204,907 | ) | 9,085 | 195,129 | (5,865 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | — | — | 1,632 | — | 1,632 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 73,784 | 424 | 5,733 | — | 79,941 | |||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 12,762 | 1,201 | 21,067 | — | 35,030 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 86,546 | $ | 1,625 | $ | 26,800 | $ | — | $ | 114,971 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-64
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
Years Ended December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands)
| Balance at Beginning of Period | Charged to Costs and Expenses | Deductions | Balance at End of Period | |||||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from trade accounts receivable: | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 11,161 | 11,608 | 9,584 | $ | 13,185 | ||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Valuation allowance | $ | 23,934 | — | 1,032 | $ | 22,902 | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from trade accounts receivable: | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 10,055 | 8,472 | 7,366 | $ | 11,161 | ||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Valuation allowance | $ | 20,120 | 3,814 | — | $ | 23,934 | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from trade accounts receivable: | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts | $ | 9,356 | 6,762 | 6,063 | $ | 10,055 | ||||||||||
Deducted in balance sheet from deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Valuation allowance | $ | 16,167 | 3,953 | — | $ | 20,120 | ||||||||||
F-65
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Schedule of Real Estate and Accumulated Depreciation
December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017
(In thousands)
Description(1) | Encumbrances | Initial Cost(2) | Gross Carrying Amount(3) | Accumulated Depreciation | Construction Date | Acquisition Date | Useful Lives | |||||||||||||||||||||
391,456 Displays | — | — | $ | 3,333,590 | $ | (2,166,579 | ) | Various | Various | 5 to 20 years | ||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | No single asset exceeded 5% of the total gross carrying amount at December 31, 2019 |
| (2) | This information is omitted, as it would be impracticable to compile such information on a site-by-site basis |
| (3) | Includes sites under construction |
The following table summarizes activity for the Company’s real estate assets, which consists of advertising displays and the related accumulated depreciation.
| December 31, 2019 | December 31, 2018 | December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||
Gross real estate assets: | ||||||||||||
Balance at the beginning of the year | $ | 3,201,434 | $ | 3,074,046 | $ | 2,998,540 | ||||||
Capital expenditures on new advertising displays(4) | 59,604 | 54,151 | 49,946 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures on improvements/redevelopments of existing advertising displays | 25,025 | 12,781 | 6,265 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures other recurring | 36,354 | 34,758 | 32,523 | |||||||||
Land acquisitions(6) | 22,965 | 15,368 | 14,904 | |||||||||
Acquisition of advertising displays(5)(6) | 23,589 | 82,617 | 32,109 | |||||||||
Assets sold or written-off | (35,320 | ) | (70,494 | ) | (61,306 | ) | ||||||
Foreign exchange | (61 | ) | (1,793 | ) | 1,065 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Balance at the end of the year | $ | 3,333,590 | $ | 3,201,434 | $ | 3,074,046 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Accumulated depreciation: | �� | |||||||||||
Balance at the beginning of the year | $ | 2,082,335 | $ | 2,025,251 | $ | 1,973,958 | ||||||
Depreciation | 111,531 | 106,700 | 102,494 | |||||||||
Assets sold or written-off | (27,890 | ) | (48,488 | ) | (51,976 | ) | ||||||
Foreign exchange | 603 | (1,128 | ) | 775 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Balance at the end of the year | $ | 2,166,579 | $ | 2,082,335 | $ | 2,025,251 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| (4) | Includes non-cash amounts of $554, $446 and $921 at December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively |
| (5) | Includes non-cash amounts of $1,928, $7,199 and $3,043 at December 31, 2019, 2018 and 2017, respectively |
| (6) | Includes preliminary allocation of assets acquired from Fairway at December 31, 2018 |
F-66
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| June 30, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 177,093 | $ | 26,188 | ||||
Receivables, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $17,661 and $13,185 in 2020 and 2019, respectively | 232,176 | 254,930 | ||||||
Other current assets | 34,968 | 29,051 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current assets | 444,237 | 310,169 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Property, plant and equipment | 3,666,749 | 3,660,311 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (2,346,274 | ) | (2,311,196 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net property, plant and equipment | 1,320,475 | 1,349,115 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Operating lease right of use assets | 1,292,917 | 1,320,779 | ||||||
Goodwill | 1,912,161 | 1,912,274 | ||||||
Intangible assets | 955,196 | 992,244 | ||||||
Other assets | 56,595 | 56,574 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total assets | $ | 5,981,581 | $ | 5,941,155 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||
Trade accounts payable | $ | 11,928 | $ | 14,974 | ||||
Current maturities of long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $0 and $6,081 in 2020 and 2019, respectively | 9,120 | 226,514 | ||||||
Current operating lease liabilities | 173,835 | 196,841 | ||||||
Accrued expenses | 73,071 | 107,225 | ||||||
Deferred income | 125,908 | 127,254 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current liabilities | 393,862 | 672,808 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $43,115 and $18,333 in 2020 and 2019, respectively | 3,146,779 | 2,753,604 | ||||||
Operating lease liabilities | 1,054,140 | 1,068,181 | ||||||
Deferred income tax liabilities | 4,406 | 5,713 | ||||||
Asset retirement obligation | 224,945 | 226,137 | ||||||
Other liabilities | 34,078 | 34,406 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities | 4,858,210 | 4,760,849 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholders’ equity: | ||||||||
Series AA preferred stock, par value $.001, $63.80 cumulative dividends, 5,720 shares authorized; 5,720 shares issued and outstanding at 2020 and 2019 | — | — | ||||||
Class A common stock, par value $.001, 362,500,000 shares authorized; 87,004,721 and 86,596,498 shares issued at 2020 and 2019, respectively; 86,389,807 and 86,093,300 outstanding at 2020 and 2019, respectively | 87 | 87 | ||||||
Class B common stock, par value $.001, 37,500,000 shares authorized, 14,420,085 shares issued and outstanding at 2020 and 2019 | 14 | 14 | ||||||
Additional paid-in capital | 1,955,612 | 1,922,222 | ||||||
Accumulated comprehensive (loss) income | (173 | ) | 685 | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (787,751 | ) | (708,408 | ) | ||||
Cost of shares held in treasury, 614,914 and 503,198 shares at 2020 and 2019, respectively | (44,418 | ) | (34,294 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholders’ equity | 1,123,371 | 1,180,306 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 5,981,581 | $ | 5,941,155 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-67
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Three months ended June 30, | Six months ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||
Statements of Income | ||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 347,652 | $ | 448,742 | $ | 754,221 | $ | 833,199 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Operating expenses (income) | ||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 134,059 | 146,390 | 283,553 | 286,860 | ||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 67,408 | 78,416 | 149,612 | 157,709 | ||||||||||||
Corporate expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 16,750 | 18,674 | 35,241 | 35,703 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 63,998 | 61,693 | 126,311 | 123,199 | ||||||||||||
Gain on disposition of assets | (1,015 | ) | (537 | ) | (3,519 | ) | (5,161 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| 281,200 | 304,636 | 591,198 | 598,310 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Operating income | 66,452 | 144,106 | 163,023 | 234,889 | ||||||||||||
Other expense (income) | ||||||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 5 | — | 18,184 | — | ||||||||||||
Interest income | (179 | ) | (232 | ) | (369 | ) | (385 | ) | ||||||||
Interest expense | 35,437 | 38,322 | 71,990 | 75,917 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| 35,263 | 38,090 | 89,805 | 75,532 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 31,189 | 106,016 | 73,218 | 159,357 | ||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense | (240 | ) | (12,380 | ) | 1,296 | (10,292 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net income | 31,429 | 118,396 | 71,922 | 169,649 | ||||||||||||
Cash dividends declared and paid on preferred stock | 91 | 91 | 182 | 182 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net income applicable to common stock | $ | 31,338 | $ | 118,305 | $ | 71,740 | $ | 169,467 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Earnings per share: | ||||||||||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 0.31 | $ | 1.18 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 1.70 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.31 | $ | 1.18 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 1.69 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Cash dividends declared per share of common stock | $ | 0.50 | $ | 0.96 | $ | 1.50 | $ | 1.92 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Weighted average common shares used in computing earnings per share: | ||||||||||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding basic | 100,765,681 | 100,012,827 | 100,677,510 | 99,862,452 | ||||||||||||
Weighted average common shares outstanding diluted | 100,861,881 | 100,222,082 | 100,818,347 | 100,058,054 | ||||||||||||
Statements of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 31,429 | $ | 118,396 | $ | 71,922 | $ | 169,649 | ||||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) | ||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | 740 | 287 | (858 | ) | 546 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 32,169 | $ | 118,683 | $ | 71,064 | $ | 170,195 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-68
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Series AA PREF Stock | Class A CMN Stock | Class B CMN Stock | Treasury Stock | Add’l Paid in Capital | Accumulated Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2019 | $ | — | 87 | 14 | (34,294 | ) | 1,922,222 | 685 | (708,408 | ) | $ | 1,180,306 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | — | — | — | — | 1,261 | — | — | 1,261 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 272,813 shares of common stock through performance stock awards | — | — | — | — | 24,956 | — | — | 24,956 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of 14,609 shares of stock options | — | — | — | — | 652 | — | — | 652 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 58,734 shares of common stock through employee purchase plan | — | — | — | — | 2,560 | — | — | 2,560 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of 110,520 shares of treasury stock | — | — | — | (10,068 | ) | — | — | — | (10,068 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | — | (1,598 | ) | — | (1,598 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 40,493 | 40,493 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends/distributions to common shareholders ($1.00 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (100,687 | ) | (100,687 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends ($15.95 per preferred share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (91 | ) | (91 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance, March 31, 2020 | $ | — | 87 | 14 | (44,362 | ) | 1,951,651 | (913 | ) | (768,693 | ) | $ | 1,137,784 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | — | — | — | — | 1,525 | — | — | 1,525 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of 13,642 shares of stock options | — | — | — | — | 671 | — | — | 671 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of shares 31,114 of common stock through employee purchase plan | — | — | — | — | 1,765 | — | — | 1,765 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of 1,196 shares of treasury stock | (56 | ) | (56 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | — | 740 | — | 740 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 31,429 | 31,429 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends/distributions to common shareholders ($0.50 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (50,396 | ) | (50,396 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends ($15.95 per preferred share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (91 | ) | (91 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2020 | $ | — | 87 | 14 | (44,418 | ) | 1,955,612 | (173 | ) | (787,751 | ) | $ | 1,123,371 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements
F-69
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Series AA PREF Stock | Class A CMN Stock | Class B CMN Stock | Treasury Stock | Add’l Paid in Capital | Accumulated Comprehensive Income | Accumulated Deficit | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2018 | $ | — | 86 | 14 | (25,412 | ) | 1,852,421 | 12 | (695,337 | ) | $ | 1,131,784 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | — | — | — | — | 1,178 | — | — | 1,178 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 286,350 shares of common stock through performance stock awards | — | — | — | — | 19,919 | — | — | 19,919 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of 186,521 shares of stock options | — | — | — | — | 7,352 | — | — | 7,352 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of 44,161 shares of common stock through employee purchase plan | — | — | — | — | 2,521 | — | — | 2,521 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of 111,835 shares of treasury stock | — | — | — | (8,682 | ) | — | — | — | (8,682 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | — | 259 | — | 259 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 51,253 | 51,253 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends/distributions to common shareholders ($0.96 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (95,915 | ) | (95,915 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends ($15.95 per preferred share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (91 | ) | (91 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance, March 31, 2019 | $ | — | 86 | 14 | (34,094 | ) | 1,883,391 | 271 | (740,090 | ) | $ | 1,109,578 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Non-cash compensation | — | — | — | — | 1,425 | — | — | 1,425 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of 85,379 shares of stock options | — | — | — | — | 3,943 | — | — | 3,943 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of shares 31,455 of common stock through employee purchase plan | — | — | — | — | 1,796 | — | — | 1,796 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation | — | — | — | — | — | 287 | — | 287 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | — | — | 118,396 | 118,396 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends/distributions to common shareholders ($0.96 per common share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (96,039 | ) | (96,039 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends ($15.95 per preferred share) | — | — | — | — | — | — | (91 | ) | (91 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2019 | $ | — | 86 | 14 | (34,094 | ) | 1,890,555 | 558 | (717,824 | ) | $ | 1,139,295 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements
F-70
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Unaudited)
(In thousands)
| Six months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 71,922 | $ | 169,649 | ||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 126,311 | 123,199 | ||||||
Stock-based compensation | 6,162 | 7,506 | ||||||
Amortization included in interest expense | 2,878 | 2,670 | ||||||
Gain on disposition of assets and investments | (3,519 | ) | (5,161 | ) | ||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 18,184 | — | ||||||
Deferred tax benefit | (1,313 | ) | (15,121 | ) | ||||
Provision for doubtful accounts | 8,331 | 4,657 | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities | ||||||||
Decrease (increase) in: | ||||||||
Receivables | 13,772 | (19,103 | ) | |||||
Prepaid lease expenses | 623 | 20,173 | ||||||
Other assets | (7,179 | ) | (11,108 | ) | ||||
(Decrease) increase in: | ||||||||
Trade accounts payable | (25 | ) | 1,520 | |||||
Accrued expenses | (12,012 | ) | (13,528 | ) | ||||
Operating lease liabilities | (8,735 | ) | (45,836 | ) | ||||
Other liabilities | (4,723 | ) | 17,532 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 210,677 | 237,049 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||
Acquisitions | (26,153 | ) | (78,141 | ) | ||||
Capital expenditures | (36,274 | ) | (60,560 | ) | ||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | 4,750 | 2,100 | ||||||
Increase of notes receivable | — | (544 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (57,677 | ) | (137,145 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||
Cash used for purchase of treasury stock | (10,124 | ) | (8,682 | ) | ||||
Net proceeds from issuance of common stock | 5,648 | 15,612 | ||||||
Principal payments on long term debt | (182 | ) | (14,421 | ) | ||||
Borrowings on long term debt | 8,750 | — | ||||||
Payments on revolving credit facility | (805,000 | ) | (375,000 | ) | ||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 655,000 | 220,000 | ||||||
Redemption of senior subordinated notes | (519,139 | ) | — | |||||
Proceeds received from note offering | 1,400,000 | 255,000 | ||||||
Proceeds received from accounts receivable securitization program | — | 9,000 | ||||||
Payments on accounts receivable securitization program | (175,000 | ) | (9,000 | ) | ||||
Proceeds received from senior credit facility term loans | 598,500 | — | ||||||
Payments on senior credit facility term loans | (978,097 | ) | — | |||||
Debt issuance costs | (30,112 | ) | (4,435 | ) | ||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | (882 | ) | (285 | ) | ||||
Dividends/distributions | (151,265 | ) | (192,136 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (1,903 | ) | (104,347 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | (192 | ) | 203 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 150,905 | (4,240 | ) | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 26,188 | 21,494 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 177,093 | $ | 17,254 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | ||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 68,784 | $ | 66,968 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash paid for foreign, state and federal income taxes | $ | 3,175 | $ | 9,260 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-71
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
(1) Significant Accounting Policies
The information included in the foregoing interim condensed consolidated financial statements is unaudited. In the opinion of management, all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair presentation of the Company’s financial position and results of operations for the interim periods presented have been reflected herein. The results of operations for interim periods are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the entire year. These interim condensed consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with the Company’s consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included in the 2019 Combined Form 10-K. Subsequent events, if any, are evaluated through the date on which the financial statements are issued.
The following are updates to our significant accounting policies from our 2019 Combined Form 10-K.
(a) Goodwill, intangibles and long-lived assets
Due to changes in relevant events and circumstances related to COVID-19, which could have a negative impact on the Company’s goodwill, the Company updated its goodwill qualitative assessment as of June 30, 2020. The update includes assessing macroeconomic conditions, industry and market conditions, cost factors, overall financial performance, reporting unit dispositions and acquisitions, the market capitalization of the Company and other relevant events specific to the Company. After assessing the totality of events and circumstances, the Company determined that it is not “more likely than not” that the fair value of either of the Company’s reporting units is less than its carrying amount. Therefore, management will not perform a quantitative impairment test and concluded its goodwill is not impaired as of June 30, 2020.
Management also reviewed the recoverability of our long-lived assets including intangibles, fixed assets and operating lease right of use assets and concluded there is no impairment loss as of June 30, 2020.
(b) Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expense during the reporting period. These estimates take into account historical and forward-looking factors that the Company believes are reasonable, including but not limited to the potential impacts arising from the COVID-19 pandemic, based on available information to date.
(2) Revenues
Advertising revenues: The majority of our revenues are derived from contracts for advertising space on billboard, logo and transit displays. Our contracts commencing prior to January 1, 2019 are accounted for under ASC 840, Leases. The majority of our contracts amended or commencing on or after January 1, 2019 are accounted for under ASC 606, Revenue. The contract revenues, under ASC 840, Leases and ASC 606, Revenue, are recognized ratably over their contract life. Costs to fulfill a contract, which include our costs to install advertising copy onto billboards, are capitalized and amortized to direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income.
F-72
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Other revenues: Our other component of revenue primarily consists of production services which includes creating and printing the advertising copy. Revenue for production contracts is recognized under ASC 606. Contract revenues for production services are recognized upon satisfaction of the contract which is typically less than one week.
Arrangements with multiple performance obligations: Our contracts with customers may include multiple performance obligations. For such arrangements, we allocate revenue to each performance obligation based on the relative standalone selling price. We determine standalone selling prices based on the prices charged to customers using expected cost plus margin.
Deferred revenues: We record deferred revenues when cash payments are received or due in advance of our performance obligation. The term between invoicing and when a payment is due is not significant. For certain services we require payment before the product or services are delivered to the customer. The balance of deferred income is considered short-term and will be recognized in revenue within twelve months.
Practical expedients and exemptions: The Company is utilizing the following practical expedients and exemptions from ASC 606. We generally expense sales commissions when incurred because the amortization period is one year or less. These costs are recorded within direct advertising expense (exclusive of depreciation and amortization). We do not disclose the value of unsatisfied performance obligations as the majority of our contracts with customers have an original expected length of less than one year. For contracts with customers which exceed one year, the future amount to be invoiced to the customer corresponds directly with the value to be received by the customer.
The following table presents our disaggregated revenue by source including both revenues accounted for under ASC 840 and ASC 606 for the three and six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019.
| Three months ended June 30, | Six months ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||
Billboard Advertising | $ | 312,095 | $ | 393,798 | $ | 667,400 | $ | 729,993 | ||||||||
Logo Advertising | 21,053 | 21,811 | 42,445 | 41,723 | ||||||||||||
Transit Advertising | 14,504 | 33,133 | 44,376 | 61,483 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net Revenues | $ | 347,652 | $ | 448,742 | $ | 754,221 | $ | 833,199 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
(3) Leases
During the three months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, we had operating lease costs of $78,331 and $77,816, respectively, and variable lease costs of $10,300 and $18,933, respectively. During the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, we had operating lease costs of $158,734 and $155,166, respectively, and variable lease costs of $27,744 and $36,017, respectively. These operating lease costs are recorded in direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization). Also, for the three months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, we recorded a loss of $266 and $193, respectively, in (gain) loss of disposition of assets related to the amendment and termination of lease agreements. For the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, we recorded a loss of $317 and a gain of $3,911, respectively, in (gain) loss of disposition of assets related to the amendment and termination of lease agreements. Cash payments of $161,460 and $180,487 were made reducing our operating lease liabilities for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, respectively, and are included in cash flows provided by operating activities in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
F-73
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
We elected the short-term lease exemption which applies to certain of our vehicle agreements. This election allows the Company to not recognize lease right of use assets (ROU assets) or lease liabilities for agreements with a term of twelve months or less. We recorded $1,249 and $1,097 in direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) for these agreements during the three months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, respectively. We recorded $2,507 and $2,226 in direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) for these agreements during the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Our operating leases have a weighted-average remaining lease term of 12.1 years. The weighted-average discount rate of our operating leases is 4.6%. Also, during the periods ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, we obtained $9,991 and $8,671, respectively, of leased assets in exchange for new operating lease liabilities, which includes liabilities obtained through acquisitions.
The following is a summary of the maturities of our operating lease liabilities as of June 30, 2020:
2020 | $ | 114,518 | ||
2021 | 206,414 | |||
2022 | 181,916 | |||
2023 | 158,968 | |||
2024 | 141,902 | |||
Thereafter | 854,924 | |||
|
| |||
Total undiscounted operating lease payments | 1,658,642 | |||
Less: Imputed interest | (430,667 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Total operating lease liabilities | $ | 1,227,975 | ||
|
|
(4) Stock-Based Compensation
Equity Incentive Plan. Lamar Advertising’s 1996 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended, (the “Incentive Plan”) has reserved 17.5 million shares of Class A common stock for issuance to directors and employees, including shares underlying granted options and common stock reserved for issuance under its performance-based incentive program. Options granted under the plan expire ten years from the grant date with vesting terms ranging from three to five years and include 1) options that vest in one-fifth increments beginning on the grant date and continuing on each of the first four anniversaries of the grant date and 2) options that cliff-vest on the fifth anniversary of the grant date. All grants are made at fair market value based on the closing price of our Class A common stock as reported on the Nasdaq Global Select Market on the date of grant.
We use a Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model to estimate the fair value of share-based awards. The Black-Scholes-Merton option pricing model incorporates various and highly subjective assumptions, including expected term and expected volatility. The Company granted options for an aggregate of 32,000 shares of its Class A common stock during the six months ended June 30, 2020. At June 30, 2020 a total of 2,470,063 shares were available for future grant.
Stock Purchase Plan. Lamar Advertising’s 2009 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2009 ESPP”), approved by our shareholders on May 28, 2009, expired by its terms on June 30, 2019. On May 30, 2019, our shareholders approved Lamar Advertising’s 2019 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “2019 ESPP”). The 2019 ESPP became effective upon the expiration of the 2009 ESPP. The number of shares of Class A common stock
F-74
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
available under the 2019 ESPP was automatically increased by 86,093 shares on January 1, 2020 pursuant to the automatic increase provisions of the 2019 ESPP.
The following is a summary of 2019 ESPP share activity for the six months ended June 30, 2020:
| Shares | ||||
Available for future purchases, January 1, 2020 | 438,434 | |||
Additional shares reserved under 2019 ESPP | 86,093 | |||
Purchases | (89,848 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Available for future purchases, June 30, 2020 | 434,679 | |||
|
| |||
Performance-based compensation. Unrestricted shares of our Class A common stock may be awarded to key officers, employees and directors under the Incentive Plan. The number of shares to be issued, if any, will be dependent on the level of achievement of performance measures for key officers and employees, as determined by the Company’s Compensation Committee based on our 2020 results. Any shares issued based on the achievement of performance goals will be issued in the first quarter of 2021. The shares subject to these awards can range from a minimum of 0% to a maximum of 100% of the target number of shares depending on the level at which the goals are attained. For the six months ended June 30, 2020, the Company has recorded $3,494 as stock-based compensation expense related to performance-based awards. In addition, each non-employee director automatically receives a restricted stock award of our Class A common stock upon election or re-election. The awards vest 50% on grant date and 50% on the last day of the directors’ one year term. The Company recorded $492 in stock-based compensation expense related to these awards for the six months ended June 30, 2020.
(5) Depreciation and Amortization
The Company includes all categories of depreciation and amortization on a separate line in its Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income. The amounts of depreciation and amortization expense excluded from the following operating expenses in its Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income are:
| Three months ended June 30, | Six months ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses | $ | 60,142 | $ | 58,200 | $ | 118,839 | $ | 116,315 | ||||||||
General and administrative expenses | 1,151 | 1,140 | 2,432 | 2,261 | ||||||||||||
Corporate expenses | 2,705 | 2,353 | 5,040 | 4,623 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| $ | 63,998 | $ | 61,693 | $ | 126,311 | $ | 123,199 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
F-75
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
(6) Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The following is a summary of intangible assets at June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019:
| Estimated | June 30, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Life (Years) | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | ||||||||||||||||
Amortizable intangible assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Customer lists and contracts | 7 — 10 | $ | 644,330 | $ | 551,309 | $ | 641,714 | $ | 539,405 | |||||||||||
Non-competition agreements | 3 — 15 | 66,101 | 64,512 | 66,014 | 64,379 | |||||||||||||||
Site locations | 15 | 2,399,355 | 1,550,917 | 2,384,520 | 1,509,335 | |||||||||||||||
Other | 2 — 15 | 49,974 | 37,826 | 49,864 | 36,749 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||
| $ | 3,159,760 | $ | 2,204,564 | $ | 3,142,112 | $ | 2,149,868 | |||||||||||||
Unamortizable intangible assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Goodwill | $ | 2,165,697 | $ | 253,536 | $ | 2,165,810 | $ | 253,536 | ||||||||||||
(7) Asset Retirement Obligations
The Company’s asset retirement obligations include the costs associated with the removal of its structures, resurfacing of the land and retirement cost, if applicable, related to the Company’s outdoor advertising portfolio. The following table reflects information related to our asset retirement obligations:
Balance at December 31, 2019 | $ | 226,137 | ||
Additions to asset retirement obligations | 421 | |||
Accretion expense | 2,129 | |||
Liabilities settled | (3,742 | ) | ||
|
| |||
Balance at June 30, 2020 | $ | 224,945 | ||
|
|
(8) Distribution Restrictions
Lamar Media’s ability to make distributions to Lamar Advertising is restricted under both the terms of the indentures relating to Lamar Media’s outstanding notes and by the terms of its senior credit facility. As of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, Lamar Media was permitted under the terms of its outstanding senior subordinated and senior notes to make transfers to Lamar Advertising in the form of cash dividends, loans or advances in amounts up to $3,429,654 and $3,389,763, respectively.
As of June 30, 2020, Lamar Media’s senior credit facility allows it to make transfers to Lamar Advertising in any taxable year up to the amount of Lamar Advertising’s taxable income (without any deduction for dividends paid). In addition, as of June 30, 2020, transfers to Lamar Advertising are permitted under Lamar Media’s senior credit facility and as defined therein up to the available cumulative credit, as long as no default has occurred and is continuing and, after giving effect to such distributions, (i) the total debt ratio is less than 7.0 to 1 and (ii) the secured debt ratio does not exceed 4.5 to 1. As of June 30, 2020, the total debt ratio was less than 7.0 to 1 and Lamar Media’s secured debt ratio was less than 4.5 to 1, and the available cumulative credit was $2,180,134.
F-76
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
(9) Earnings Per Share
The calculation of basic earnings per share excludes any dilutive effect of stock options, while diluted earnings per share includes the dilutive effect of stock options. There were no dilutive shares excluded from this calculation resulting from their anti-dilutive effect for the three and six months ended June 30, 2020 or 2019.
(10) Long-term Debt
Long-term debt consists of the following at June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019:
| June 30, 2020 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
Senior Credit Facility | $ | 598,339 | $ | 12,697 | $ | 585,642 | ||||||
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program | — | 667 | (667 | ) | ||||||||
5% Senior Subordinated Notes | 535,000 | 2,786 | 532,214 | |||||||||
5 3/4% Senior Notes | 653,988 | 7,171 | 646,817 | |||||||||
4 7/8% Senior Notes | 400,000 | 5,790 | 394,210 | |||||||||
4% Senior Notes | 400,000 | 5,610 | 394,390 | |||||||||
3 3/4% Senior Notes | 600,000 | 8,394 | 591,606 | |||||||||
Other notes with various rates and terms | 11,687 | — | 11,687 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 3,199,014 | 43,115 | 3,155,899 | ||||||||||
Less current maturities | (9,120 | ) | — | (9,120 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt, excluding current maturities | $ | 3,189,894 | $ | 43,115 | $ | 3,146,779 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||
| Debt | Deferred financing costs | Debt, net of deferred financing costs | ||||||||||
Senior Credit Facility | $ | 1,127,069 | $ | 9,077 | $ | 1,117,992 | ||||||
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program | 175,000 | 846 | 174,154 | |||||||||
5% Senior Subordinated Notes | 535,000 | 3,237 | 531,763 | |||||||||
5 3/8% Senior Notes | 510,000 | 3,502 | 506,498 | |||||||||
5 3/4% Senior Notes | 654,345 | 7,752 | 646,593 | |||||||||
Other notes with various rates and terms | 3,118 | — | 3,118 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| 3,004,532 | 24,414 | 2,980,118 | ||||||||||
Less current maturities | (232,595 | ) | (6,081 | ) | (226,514 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Long-term debt, excluding current maturities | $ | 2,771,937 | $ | 18,333 | $ | 2,753,604 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
Senior Credit Facility
On February 6, 2020, Lamar Media entered into a Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement”) with certain of Lamar Media’s subsidiaries as guarantors,
F-77
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. as administrative agent and the lenders party thereto, under which the parties agreed to amend and restate Lamar Media’s existing senior credit facility. The Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement amended and restated the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 15, 2017, as amended (the “Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement”).
The new senior credit facility, as established by the Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “senior credit facility”), consists of (i) a new $750,000 senior secured revolving credit facility which will mature on February 6, 2025 (the “revolving credit facility”), (ii) a new $600,000 Term B loan facility (the “Term B loans”) which will mature on February 6, 2027, and (iii) an incremental facility (the “Incremental Facility”) pursuant to which Lamar Media may incur additional term loan tranches or increase its revolving credit facility subject to a pro forma secured debt ratio of 4.50 to 1.00, as well as certain other conditions including lender approval. Lamar Media borrowed all $600,000 in Term B loans on February 6, 2020. The entire amount of the Term B loans will be payable at maturity. The net proceeds from the Term B loans, together with borrowing under the revolving portion of the senior credit facility and a portion of the proceeds of the issuance of the 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 and 4% Senior Notes due 2030 (both as described below), were used to repay all outstanding amounts under the Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, and all revolving commitments under that facility were terminated. As a result of refinancing our credit facility the Company incurred a loss on debt extinguishment of $5,608 for the six months ended June 30, 2020.
The Term B loans mature on February 6, 2027 with no required amortization payments. The Term B loans bear interest at rates based on the Adjusted LIBO Rate (“Eurodollar term loans”) or the Adjusted Base Rate (“Base Rate term loans”), at Lamar Media’s option. Eurodollar Term B loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.50%. Base Rate Term B loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.50%.
The revolving credit facility bears interest at rates based on the Adjusted LIBO Rate (“Eurodollar revolving loans”) or the Adjusted Base Rate (“Base Rate revolving loans”), at Lamar Media’s option. Eurodollar revolving loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.50% (or the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.25% at any time the Total Debt Ratio is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1). Base Rate revolving loans bear interest at a rate per annum equal to the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.50% (or the Adjusted Base Rate plus 0.25% at any time the total debt ratio is less than or equal to 3.25 to 1). The guarantees, covenants, events of default and other terms of the senior credit facility apply to the Term B loans and revolving credit facility.
As of June 30, 2020, there were no borrowings outstanding under the revolving credit facility. Availability under the revolving credit facility is reduced by the amount of any letters of credit outstanding. Lamar Media had $12,784 in letters of credit outstanding as of June 30, 2020 resulting in $737,216 of availability under its revolving credit facility. Revolving credit loans may be requested under the revolving credit facility at any time prior to its maturity on February 6, 2025.
The terms of Lamar Media’s senior credit facility and the indentures relating to Lamar Media’s outstanding notes restrict, among other things, the ability of Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media to:
| • | dispose of assets; |
| • | incur or repay debt; |
| • | create liens; |
F-78
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| • | make investments; and |
| • | pay dividends. |
The senior credit facility contains provisions that allow Lamar Media to conduct its affairs in a manner that allows Lamar Advertising to qualify and remain qualified as a REIT, including by allowing Lamar Media to make distributions to Lamar Advertising required for the Company to qualify and remain qualified for taxation as a REIT, subject to certain restrictions.
Lamar Media’s ability to make distributions to Lamar Advertising is also restricted under the terms of these agreements. Under Lamar Media’s senior credit facility, the Company must maintain a specified secured debt ratio as long as a revolving credit commitment, revolving loan or letter of credit remains outstanding, and in addition, must satisfy a total debt ratio in order to incur debt, make distributions or make certain investments.
Lamar Advertising and Lamar Media were in compliance with all of the terms of their indentures and the senior credit facility provisions during the periods presented.
Accounts Receivable Securitization Program
On December 18, 2018, Lamar Media entered into a $175,000 Receivable Financing Agreement (the “Accounts Receivable Securitization Program”) with its wholly-owned special purpose entities, Lamar QRS Receivables, LLC and Lamar TRS Receivables, LLC (the “Special Purpose Subsidiaries”) maturing on December 17, 2021. The Accounts Receivable Securitization Program is limited to the availability of eligible accounts receivable collateralizing the borrowings under the agreements governing the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program.
Pursuant to two separate Purchase and Sale Agreements dated December 18, 2018, each of which is among Lamar Media as initial Servicer, certain of Lamar Media’s subsidiaries and a Special Purpose Subsidiary, the subsidiaries sold substantially all of their existing and future accounts receivable balances to the Special Purpose Subsidiaries. The Special Purpose Subsidiaries use the accounts receivable balances to collateralize loans pursuant to the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. Lamar Media retains the responsibility of servicing the accounts receivable balances pledged as collateral under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program and provides a performance guaranty.
On June 30, 2020, Lamar Media and the Special Purpose Subsidiaries entered into the Third Amendment (the “Amendment”) to the Receivables Financing Agreement dated December 18, 2018. The Amendment increases the maximum three month average Delinquency Ratio, Dilution Ratio and Days’ Sales Outstanding to 11.00% (from 8.00%), 7.00% (from 4.00%) and 75 days (from 65 days), respectively, for each of the months of June, July and August 2020. The Amendment does not modify any other financial covenant. Additionally, the Amendment establishes a new Minimum Funding Threshold, which requires the Special Purpose Subsidiaries to maintain minimum borrowings under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program on any day equal to the lesser of (i) 50.00% of the aggregate Commitment of all Lenders or (ii) the Borrowing Base, though the Special Purpose Subsidiaries have the right to borrow less than the Minimum Funding Threshold during certain periods prior to December 21, 2020 at their election.
As of June 30, 2020 there was no outstanding aggregate borrowings under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program. Lamar Media had $171,810 available for borrowing under the Accounts Receivable
F-79
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Securitization Program as of June 30, 2020. The commitment fees based on the amount of unused commitments under the Accounts Receivable Securitization Program were immaterial during the six months ended June 30, 2020.
The Accounts Receivable Securitization Program is accounted for as a collateralized financing activity, rather than a sale of assets, and therefore: (i) accounts receivable balances pledged as collateral are presented as assets and the borrowings are presented as liabilities on our Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income reflect the associated charges for bad debt expense (a component of general and administrative expenses) related to the pledged accounts receivable and interest expense associated with the collateralized borrowings and (iii) receipts from customers related to the underlying accounts receivable are reflected as operating cash flows and borrowings and repayments under the collateralized loans are reflected as financing cash flows within our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
5% Senior Subordinated Notes
On October 30, 2012, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $535,000 aggregate principal amount of 5% Senior Subordinated Notes due 2023 (the “5% Notes”). The institutional private placement resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $527,100.
Lamar Media may redeem the 5% Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 5% Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 5% Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 5% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
5 3/8% Senior Notes
On January 10, 2014, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $510,000 aggregate principal amount of 5 3/8% Senior Notes due 2024 (the “5 3/8% Notes”). The institutional private placement resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $502,300. The Company used the proceeds from the 4% Senior Notes and 3 3/4% Senior Notes to redeem in full all of the 5 3/8% Notes on February 20, 2020 at a redemption price of 101% of the aggregate principal amounts of the outstanding 5 3/8% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest up to but not including the redemption date. In conjunction with the redemption, the Company recorded a loss on debt extinguishment of $12,576, of which $9,139 was cash, for the period ended June 30, 2020.
5 3/4% Senior Notes
On January 28, 2016, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $400,000 aggregate principal amount of 5 3/4% Senior Notes due 2026 (the “5 3/4% Notes”). The institutional private placement on January 28, 2016 resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $394,500.
On February 1, 2019, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of an additional $250,000 aggregate principal amount under its 5 3/4% Notes (the “New Notes”). Other than with respect to the date of issuance, issue price and CUSIP number, the New Notes have the same terms as the 5 3/4% Notes. The net proceeds after underwriting fees and expenses, was approximately $251,500 and were used to repay a portion of the borrowings outstanding under the revolving credit facility.
F-80
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
At any time prior to February 1, 2021, Lamar Media may redeem some or all of the 5 3/4% Notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon plus a make-whole premium. On or after February 1, 2021, Lamar Media may redeem the 5 3/4% Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 5 3/4% Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 5 3/4% Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 5 3/4% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
4% Senior Notes
On February 6, 2020, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $400,000 aggregate principal amount of 4% Senior Notes due 2030 (the “4% Notes”). The institutional private placement on February 6, 2020 resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $395,000.
Lamar Media may redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 4% Notes, at any time and from time to time, at a price equal to 104% of the aggregate principal amount redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, with the net cash proceeds of certain public equity offerings completed before February 15, 2023, provided that following the redemption, at least 60% of the 4% Notes that were originally issued remain outstanding and any such redemption occurs within 120 days following the closing of any such public equity offering. At any time prior to February 15, 2025, Lamar Media may redeem some or all of the 4% Notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon and a make-whole premium. On or after February 15, 2025, Lamar Media may redeem the 4% Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 4% Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 4% Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 4% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
3 3/4% Senior Notes
On February 6, 2020, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $600,000 aggregate principal amount of 3 3/4% Senior Notes due 2028 (the “3 3/4% Notes”). The institutional private placement on February 6, 2020 resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $592,500.
Lamar Media may redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of 3 3/4% Notes, at any time and from time to time, at a price equal to 103.75% of the aggregate principal amount redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, with the net cash proceeds of certain public equity offerings completed before February 15, 2023, provided that following the redemption, at least 60% of the 3 3/4% Notes that were originally issued remain outstanding and any such redemption occurs within 120 days following the closing of any such public equity offering. At any time prior to February 15, 2023, Lamar Media may redeem some or all of the 3 3/4% Notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon and a make-whole premium. On or after February 15, 2023, Lamar Media may redeem the 3 3/4% Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 3 3/4% Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 3 3/4% Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 3 3/4% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
F-81
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
4 7/8% Senior Notes
On May 13, 2020, Lamar Media completed an institutional private placement of $400,000 aggregate principal amount of 4 7/8% Senior Notes due 2029 (the “4 7/8% Notes”). The institutional private placement on May 13, 2020 resulted in net proceeds to Lamar Media of approximately $395,000.
Lamar Media may redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 4 7/8% Notes, at any time and from time to time, at a price equal to 104.875% of the aggregate principal amount redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, with the net cash proceeds of certain public equity offerings completed before May 15, 2023, provided that following the redemption, at least 60% of the 4 7/8% Notes that were originally issued remain outstanding and any such redemption occurs within 120 days following the closing of any such public equity offering. At any time prior to January 15, 2024, Lamar Media may redeem some or all of the 4 7/8% Notes at a price equal to 100% of the aggregate principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon and a make-whole premium. On or after January 15, 2024, Lamar Media may redeem the 4 7/8% Notes, in whole or in part, in cash at redemption prices specified in the 4 7/8% Notes. In addition, if the Company or Lamar Media undergoes a change of control, Lamar Media may be required to make an offer to purchase each holder’s 4 7/8% Notes at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount of the 4 7/8% Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, up to but not including the repurchase date.
Debt Repurchase Program
On March 16, 2020, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized Lamar Media to repurchase up to $250,000 outstanding senior or senior subordinated notes and other indebtedness outstanding from time to time under its Fourth Amended and Restated Credit Agreement. The repurchase program will expire on September 30, 2021 unless extended by the Board of Directors. There were no repurchases under the program as of June 30, 2020.
(11) Fair Value of Financial Instruments
At June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, the Company’s financial instruments included cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, investments, accounts payable and borrowings. The fair values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and short-term borrowings and current portion of long-term debt approximated carrying values because of the short-term nature of these instruments. Investment contracts are reported at fair values. Fair values for investments held at cost are not readily available, but are estimated to approximate fair value. The estimated fair value of the Company’s long-term debt (including current maturities) was $3,159,255 which does not exceed the carrying amount of $3,199,014 as of June 30, 2020. The majority of the fair value is determined using observed prices of publicly traded debt (level 1 in the fair value hierarchy) and the remaining is valued based on quoted prices for similar debt (level 2 in the fair value hierarchy).
(12) New Accounting Pronouncements
Leases
In February 2016, the FASB established Topic 842, Leases, by issuing Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2016-02, which requires lessees to recognize leases on-balance sheet and disclose key information about leasing arrangements. Topic 842 was subsequently amended by ASU No. 2018-01, Land Easement Practical
F-82
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Expedient for Transition to Topic 842; ASU No. 2018-10 and ASU No. 2019-01, Codification Improvements to Topic 842, Leases; and ASU No. 2018-11, Targeted Improvements. The new standard establishes a right of use model (ROU) that requires a lessee to recognize a ROU asset and lease liability on the balance sheet for all leases with a term longer than twelve months. Leases are classified as finance or operating, with classification affecting the pattern and classification of expense recognition in the income statement.
We adopted the new standard effective January 1, 2019 using a modified retrospective transition approach, applying the new standard to all leases existing at the date of initial application. An entity was permitted to use either (1) its effective date or (2) the beginning of the earliest comparative period presented in the financial statements as its date of initial application. If an entity chooses the second option, the transition requirements for existing leases also apply to leases entered into between the date of initial application and the effective date. The entity must also recast its comparative period financial statements and provide the disclosures required by the new standard for the comparative periods. Consequently, financial information was not updated and the disclosures required under the new standard will not be provided for dates and periods before January 1, 2019.
The new standard provided a number of optional practical expedients in transition. We elected the ‘package of practical expedients’, which permitted us not to reassess under the new standard our prior conclusions about lease identification, lease classification and initial direct costs. We elected the practical expedient pertaining to land easements. We also elected the short-term lease recognition exemption for certain of our vehicle agreements. This means, for those leases that qualify, we will not recognize ROU assets or lease liabilities.
Upon adoption, we recognized additional operating liabilities of $1.2 billion, with corresponding ROU assets of the same amount based on the present value of the remaining minimum rental payments under current leasing standards for our existing operating leases. In addition to the increase to the operating lease liabilities and right of use assets, Topic 842 also resulted in reclassifying the presentation of prepaid and deferred rent to operating lease right of use assets. The Company did not have any changes to its opening balance of retained earnings for the adoption of this update.
Other recently released pronouncements
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326) – Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, and additional changes modifications, clarifications, or interpretations related to this guidance thereafter, which require a reporting entity to estimate credit losses on certain types of financial instruments, and present assets held at amortized cost and available-for-sale debt securities at the amount expected to be collected. The new guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019. The Company adopted this guidance on January 1, 2020 and the impact of the adoption was not material to the Company’s consolidated financial statements. As of June 30, 2020, our allowance for credit losses considered the current and future impacts caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, based on available information to date. The Company will continue to actively monitor the impact of COVID-19 on expected credit losses.
(13) Dividends/Distributions
During the three months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, the Company declared and paid cash distributions in an aggregate amount of $50,396 or $0.50 per share and $96,039 or $0.96 per share, respectively. During the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, the Company declared and paid cash distributions in an aggregate
F-83
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
amount of $151,083 or $1.50 per share and $191,954 or $1.92 per share, respectively. The amount, timing and frequency of future distributions will be at the sole discretion of the Board of Directors and will be declared based upon various factors, a number of which may be beyond the Company’s control, including financial condition and operating cash flows, the amount required to maintain REIT status and reduce any income and excise taxes that the Company otherwise would be required to pay, limitations on distributions in our existing and future debt instruments, the Company’s ability to utilize net operating losses to offset, in whole or in part, the Company’s distribution requirements, limitations on its ability to fund distributions using cash generated through its taxable REIT subsidiaries (TRSs), the impact of COVID-19 on the Company’s operations and other factors that the Board of Directors may deem relevant. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, the Company paid cash dividend distributions to holders of its Series AA Preferred Stock in an aggregate amount of $91 or $15.95 per share and $182 or $31.90 per share for each period, respectively.
(14) Information about Geographic Areas
Revenues from external customers attributable to foreign countries totaled $11,022 and $17,057 for the six months ended June 30, 2020 and 2019, respectively. Net carrying value of long-lived assets located in foreign countries totaled $5,406 and $4,549 as of June 30, 2020 and December 31, 2019, respectively. All other revenues from external customers and long lived assets relate to domestic operations.
(15) Stockholders’ Equity
On May 1, 2018, the Company entered into an equity distribution agreement (the “Sales Agreement”) with J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Wells Fargo Securities LLC, and SunTrust Robinson Humphrey, Inc. as its sales agents (each a “Sales Agent”, and collectively, the “Sales Agents”). Under the terms of the Sales Agreement, the Company may, from time to time, issue and sell shares of its Class A common stock, having an aggregate offering price of up to $400,000, through the Sales Agents as either agents or principals. As of June 30, 2020, 842,412 shares of our Class A common stock have been sold under the Sales Agreement and accordingly $336,668 remained available to be sold under the Sales Agreement as of June 30, 2020.
Sales of the Class A common stock, if any, may be made in negotiated transactions or transactions that are deemed to be “at-the-market offerings” as defined in Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, including sales made directly on or through the Nasdaq Global Select Market and any other existing trading market for the Class A common stock, or sales made to or through a market maker other than on an exchange. The Company has no obligation to sell any of the Class A common stock under the Sales Agreement and may at any time suspend solicitations and offers under the Sales Agreement.
On August 6, 2018, the Company filed an automatically effective shelf registration statement that registered the offer and sale of an indeterminate amount of additional shares of our Class A common stock. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company issued 163,137 shares of its Class A common stock in connection with acquisitions occurring during the period. The Company filed a prospectus supplement to the shelf registration statement relating to the offer and resale of such shares of Class A common stock. There were no additional shares issued under this shelf registration during the year ended December 31, 2019 and the six months ended June 30, 2020.
On March 16, 2020, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $250,000 of the Company’s Class A common stock. The repurchase program will expire on September 30, 2021 unless extended by the Board of Directors. There were no repurchases under the program as of June 30, 2020.
F-84
Table of Contents
LAMAR ADVERTISING COMPANY
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
(16) Subsequent Event
On July 30, 2020, the Company announced that its wholly owned subsidiary, Lamar Media, intends to redeem $267,500 in aggregate principal amount of its outstanding 5% Notes on August 31, 2020. Following the redemption, $267,500 of the original $535,000 in aggregate principal amount of 5% Notes will remain outstanding under the indenture. The redemption will be made in accordance with the terms of the indenture governing the 5% Notes.
F-85
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except share data)
| June 30, 2020 | December 31, 2019 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | ||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
Current assets: | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 176,593 | $ | 25,688 | ||||
Receivables, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $17,661 and $13,185 in 2020 and 2019, respectively | 232,176 | 254,930 | ||||||
Other current assets | 34,968 | 29,051 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current assets | 443,737 | 309,669 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Property, plant and equipment | 3,666,749 | 3,660,311 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (2,346,274 | ) | (2,311,196 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net property, plant and equipment | 1,320,475 | 1,349,115 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Operating lease right of use assets | 1,292,917 | 1,320,779 | ||||||
Goodwill | 1,902,009 | 1,902,123 | ||||||
Intangible assets | 954,729 | 991,776 | ||||||
Other assets | 50,980 | 50,959 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total assets | $ | 5,964,847 | $ | 5,924,421 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||
Trade accounts payable | $ | 11,928 | $ | 14,974 | ||||
Current maturities of long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $0 and $6,081 in 2020 and 2019, respectively | 9,120 | 226,514 | ||||||
Current operating lease liabilities | 173,835 | 196,841 | ||||||
Accrued expenses | 66,701 | 101,266 | ||||||
Deferred income | 125,908 | 127,254 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total current liabilities | 387,492 | 666,849 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Long-term debt, net of deferred financing costs of $43,115 and $18,333 in 2020 and 2019, respectively | 3,146,779 | 2,753,604 | ||||||
Operating lease liabilities | 1,054,140 | 1,068,181 | ||||||
Deferred income tax liabilities | 4,406 | 5,713 | ||||||
Asset retirement obligation | 224,945 | 226,137 | ||||||
Other liabilities | 34,078 | 34,406 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities | 4,851,840 | 4,754,890 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholder’s equity: | ||||||||
Common stock, par value $.01, 3,000 shares authorized, 100 shares issued and outstanding at 2020 and 2019 | — | — | ||||||
Additional paid-in-capital | 3,026,120 | 2,992,729 | ||||||
Accumulated comprehensive income | (173 | ) | 685 | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (1,912,940 | ) | (1,823,883 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Stockholder’s equity | 1,113,007 | 1,169,531 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity | $ | 5,964,847 | $ | 5,924,421 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-86
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Three months ended June 30, | Six months ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | |||||||||||||
Statements of Income | ||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 347,652 | $ | 448,742 | $ | 754,221 | $ | 833,199 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Operating expenses (income) | ||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 134,059 | 146,390 | 283,553 | 286,860 | ||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 67,408 | 78,416 | 149,612 | 157,709 | ||||||||||||
Corporate expenses (exclusive of depreciation and amortization) | 16,645 | 18,585 | 35,012 | 35,505 | ||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 63,998 | 61,693 | 126,311 | 123,199 | ||||||||||||
Gain on disposition of assets | (1,015 | ) | (537 | ) | (3,519 | ) | (5,161 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| 281,095 | 304,547 | 590,969 | 598,112 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Operating income | 66,557 | 144,195 | 163,252 | 235,087 | ||||||||||||
Other expense (income) | ||||||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 5 | — | 18,184 | — | ||||||||||||
Interest income | (179 | ) | (232 | ) | (369 | ) | (385 | ) | ||||||||
Interest expense | 35,437 | 38,322 | 71,990 | 75,917 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
| 35,263 | 38,090 | 89,805 | 75,532 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 31,294 | 106,105 | 73,447 | 159,555 | ||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense | (240 | ) | (12,380 | ) | 1,296 | (10,292 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Net income | $ | 31,534 | $ | 118,485 | $ | 72,151 | $ | 169,847 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Statements of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 31,534 | $ | 118,485 | $ | 72,151 | $ | 169,847 | ||||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss) | ||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | 740 | 287 | (858 | ) | 546 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 32,274 | $ | 118,772 | $ | 71,293 | $ | 170,393 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-87
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Stockholder’s Equity
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2019 | $ | — | 2,992,729 | 685 | (1,823,883 | ) | $ | 1,169,531 | ||||||||||||
Contribution from parent | — | 29,429 | — | — | 29,429 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translations | — | — | (1,598 | ) | — | (1,598 | ) | |||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 40,617 | 40,617 | |||||||||||||||
Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (110,755 | ) | (110,755 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Balance, March 31, 2020 | $ | — | 3,022,158 | (913 | ) | (1,894,021 | ) | $ | 1,127,224 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Contribution from parent | — | 3,962 | — | — | 3,962 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translations | — | — | 740 | — | 740 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 31,534 | 31,534 | |||||||||||||||
Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (50,453 | ) | (50,453 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2020 | $ | — | 3,026,120 | (173 | ) | (1,912,940 | ) | $ | 1,113,007 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital | Accumulated Comprehensive Income | Accumulated Deficit | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2018 | $ | — | 2,922,907 | 12 | (1,802,723 | ) | $ | 1,120,196 | ||||||||||||
Contribution from parent | — | 30,970 | — | — | 30,970 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translations | — | — | 259 | — | 259 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 51,362 | 51,362 | |||||||||||||||
Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (104,597 | ) | (104,597 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Balance, March 31, 2019 | $ | — | 2,953,877 | 271 | (1,855,958 | ) | $ | 1,098,190 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Contribution from parent | — | 7,165 | — | — | 7,165 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translations | — | — | 287 | — | 287 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 118,485 | 118,485 | |||||||||||||||
Dividend to parent | — | — | — | (96,039 | ) | (96,039 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Balance, June 30, 2019 | $ | — | 2,961,042 | 558 | (1,833,512 | ) | $ | 1,128,088 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements
F-88
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Unaudited)
(In thousands)
| Six months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2020 | 2019 | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 72,151 | $ | 169,847 | ||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 126,311 | 123,199 | ||||||
Stock-based compensation | 6,162 | 7,506 | ||||||
Amortization included in interest expense | 2,878 | 2,670 | ||||||
Gain on disposition of assets and investments | (3,519 | ) | (5,161 | ) | ||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 18,184 | — | ||||||
Deferred tax benefit | (1,313 | ) | (15,121 | ) | ||||
Provision for doubtful accounts | 8,331 | 4,657 | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
Decrease (increase) in: | ||||||||
Receivables | 13,772 | (19,103 | ) | |||||
Prepaid lease expenses | 623 | 20,173 | ||||||
Other assets | (7,179 | ) | (11,108 | ) | ||||
(Decrease) increase in: | ||||||||
Trade accounts payable | (25 | ) | 1,520 | |||||
Accrued expenses | (12,012 | ) | (13,528 | ) | ||||
Operating lease liabilities | (8,735 | ) | (45,836 | ) | ||||
Other liabilities | (32,876 | ) | (5,371 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 182,753 | 214,344 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||
Acquisitions | (26,153 | ) | (78,141 | ) | ||||
Capital expenditures | (36,274 | ) | (60,560 | ) | ||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | 4,750 | 2,100 | ||||||
Increase of notes receivable | — | (544 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (57,677 | ) | (137,145 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||
Principal payments on long term debt | (182 | ) | (14,421 | ) | ||||
Borrowings on long term debt | 8,750 | — | ||||||
Payment on revolving credit facility | (805,000 | ) | (375,000 | ) | ||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 655,000 | 220,000 | ||||||
Redemption of senior subordinated notes | (519,139 | ) | — | |||||
Proceeds received from note offering | 1,400,000 | 255,000 | ||||||
Proceeds received from accounts receivable securitization program | — | 9,000 | ||||||
Payments on accounts receivable securitization program | (175,000 | ) | (9,000 | ) | ||||
Proceeds received from senior credit facility term loans | 598,500 | — | ||||||
Payments on senior credit facility term loans | (978,097 | ) | — | |||||
Debt issuance costs | (30,112 | ) | (4,435 | ) | ||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | (882 | ) | (285 | ) | ||||
Contributions from parent | 33,391 | 38,135 | ||||||
Dividend to parent | (161,208 | ) | (200,636 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 26,021 | (81,642 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | (192 | ) | 203 | |||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 150,905 | (4,240 | ) | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 25,688 | 20,994 | ||||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 176,593 | $ | 16,754 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | ||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 68,784 | $ | 66,968 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
Cash paid for foreign, state and federal income taxes | $ | 3,175 | $ | 9,260 | ||||
|
|
|
| |||||
See accompanying notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
F-89
Table of Contents
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
(1) Significant Accounting Policies
The information included in the foregoing interim condensed consolidated financial statements is unaudited. In the opinion of management all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair presentation of Lamar Media’s financial position and results of operations for the interim periods presented have been reflected herein. The results of operations for interim periods are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the entire year. These interim condensed consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with Lamar Media’s consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included in the 2019 Combined Form 10-K.
Certain notes are not provided for the accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements as the information in notes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 14, and 15 to the condensed consolidated financial statements of Lamar Advertising included elsewhere in this report is substantially equivalent to that required for the condensed consolidated financial statements of Lamar Media. Earnings per share data is not provided for Lamar Media, as it is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company.
(2) Summarized Financial Information of Subsidiaries
Separate condensed consolidating financial information for Lamar Media, subsidiary guarantors and non-guarantor subsidiaries are presented below. Lamar Media and its subsidiary guarantors have fully and unconditionally guaranteed Lamar Media’s obligations with respect to its publicly issued notes. All guarantees are joint and several. As a result of these guarantee arrangements, we are required to present the following condensed consolidating financial information. The following condensed consolidating financial information should be read in conjunction with the accompanying consolidated financial statements and notes. The condensed consolidating financial information is provided as an alternative to providing separate financial statements for guarantor subsidiaries. Separate financial statements of Lamar Media’s subsidiary guarantors are not included because the guarantees are full and unconditional and the subsidiary guarantors are 100% owned and jointly and severally liable for Lamar Media’s outstanding publicly issued notes. The accounts for all companies reflected herein are presented using the equity method of accounting for investments in subsidiaries.
F-90
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Balance Sheet as of June 30, 2020
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total current assets | $ | 164,644 | $ | 44,905 | $ | 234,188 | $ | — | $ | 443,737 | ||||||||||
Net property, plant and equipment | — | 1,311,329 | 9,146 | — | 1,320,475 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease right of use assets | — | 1,271,821 | 21,096 | — | 1,292,917 | |||||||||||||||
Intangibles and goodwill, net | — | 2,838,868 | 17,870 | — | 2,856,738 | |||||||||||||||
Other assets | 4,157,051 | 225,091 | 10,393 | (4,341,555 | ) | 50,980 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 4,321,695 | $ | 5,692,014 | $ | 292,693 | $ | (4,341,555 | ) | $ | 5,964,847 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | — | $ | 9,120 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 9,120 | ||||||||||
Current operating lease liabilities | — | 168,390 | 5,445 | — | 173,835 | |||||||||||||||
Other current liabilities | 33,062 | 158,005 | 13,470 | — | 204,537 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 33,062 | 335,515 | 18,915 | — | 387,492 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Long-term debt | 3,144,240 | 2,539 | — | — | 3,146,779 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease liabilities | — | 1,037,680 | 16,460 | — | 1,054,140 | |||||||||||||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 31,386 | 229,469 | 252,027 | (249,453 | ) | 263,429 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities | 3,208,688 | 1,605,203 | 287,402 | (249,453 | ) | 4,851,840 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Stockholder’s equity | 1,113,007 | 4,086,811 | 5,291 | (4,092,102 | ) | 1,113,007 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity | $ | 4,321,695 | $ | 5,692,014 | $ | 292,693 | $ | (4,341,555 | ) | $ | 5,964,847 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-91
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2019
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total current assets | $ | 13,859 | $ | 53,756 | $ | 242,054 | $ | — | $ | 309,669 | ||||||||||
Net property, plant and equipment | — | 1,340,675 | 8,440 | — | 1,349,115 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease right of use assets | — | 1,293,674 | 27,105 | — | 1,320,779 | |||||||||||||||
Intangibles and goodwill, net | — | 2,875,644 | 18,255 | — | 2,893,899 | |||||||||||||||
Other assets | 4,193,629 | 229,905 | 184,805 | (4,557,380 | ) | 50,959 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 4,207,488 | $ | 5,793,654 | $ | 480,659 | $ | (4,557,380 | ) | $ | 5,924,421 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDER’S EQUITY | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Current maturities of long-term debt | $ | 51,480 | $ | 34 | $ | 175,000 | $ | — | $ | 226,514 | ||||||||||
Current operating lease liabilities | — | 189,071 | 7,770 | — | 196,841 | |||||||||||||||
Other current liabilities | 26,960 | 196,689 | 19,845 | — | 243,494 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total current liabilities | 78,440 | 385,794 | 202,615 | — | 666,849 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Long-term debt | 2,753,570 | 34 | — | — | 2,753,604 | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease liabilities | — | 1,049,220 | 18,961 | — | 1,068,181 | |||||||||||||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 205,947 | 231,416 | 250,859 | (421,966 | ) | 266,256 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities | 3,037,957 | 1,666,464 | 472,435 | (421,966 | ) | 4,754,890 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Stockholder’s equity | 1,169,531 | 4,127,190 | 8,224 | (4,135,414 | ) | 1,169,531 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total liabilities and stockholder’s equity | $ | 4,207,488 | $ | 5,793,654 | $ | 480,659 | $ | (4,557,380 | ) | $ | 5,924,421 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-92
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income for the Three Months Ended June 30, 2020
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | — | $ | 341,664 | $ | 6,237 | $ | (249 | ) | $ | 347,652 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses (1) | — | 128,485 | 5,823 | (249 | ) | 134,059 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses(1) | — | 65,222 | 2,186 | — | 67,408 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses(1) | — | 16,521 | 124 | — | 16,645 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | — | 63,545 | 453 | — | 63,998 | |||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | — | (1,070 | ) | 55 | — | (1,015 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| — | 272,703 | 8,641 | (249 | ) | 281,095 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating income (loss) | — | 68,961 | (2,404 | ) | — | 66,557 | ||||||||||||||
Equity in (earnings) loss of subsidiaries | (66,370 | ) | — | — | 66,370 | — | ||||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 5 | — | — | — | 5 | |||||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 34,831 | (24 | ) | 451 | — | 35,258 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Income (loss) before income tax expense | 31,534 | 68,985 | (2,855 | ) | (66,370 | ) | 31,294 | |||||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit)(2) | — | 582 | (822 | ) | — | (240 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 31,534 | $ | 68,403 | $ | (2,033 | ) | $ | (66,370 | ) | $ | 31,534 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 31,534 | $ | 68,403 | $ | (2,033 | ) | $ | (66,370 | ) | $ | 31,534 | ||||||||
Total other comprehensive income, net of tax | — | — | 740 | — | 740 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 31,534 | $ | 68,403 | $ | (1,293 | ) | $ | (66,370 | ) | $ | 32,274 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Caption is exclusive of depreciation and amortization. |
| (2) | The income tax expense reflected in each column does not include any tax effect of the equity in earnings from subsidiaries. |
F-93
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income for the Three Months Ended June 30, 2019
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income | (unaudited) | |||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | — | $ | 437,074 | $ | 12,498 | $ | (830 | ) | $ | 448,742 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses(1) | — | 140,108 | 7,112 | (830 | ) | 146,390 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses(1) | — | 76,475 | 1,941 | — | 78,416 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses(1) | — | 18,274 | 311 | — | 18,585 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | — | 61,031 | 662 | — | 61,693 | |||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | — | (550 | ) | 13 | — | (537 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| — | 295,338 | 10,039 | (830 | ) | 304,547 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating income | — | 141,736 | 2,459 | — | 144,195 | |||||||||||||||
Equity in (earnings) loss of subsidiaries | (155,336 | ) | — | — | 155,336 | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 36,851 | (82 | ) | 1,321 | — | 38,090 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Income (loss) before income tax expense | 118,485 | 141,818 | 1,138 | (155,336 | ) | 106,105 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit) expense(2) | — | (13,231 | ) | 851 | — | (12,380 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 118,485 | $ | 155,049 | $ | 287 | $ | (155,336 | ) | $ | 118,485 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 118,485 | $ | 155,049 | $ | 287 | $ | (155,336 | ) | $ | 118,485 | |||||||||
Total other comprehensive income, net of tax | — | — | 287 | — | 287 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 118,485 | $ | 155,049 | $ | 574 | $ | (155,336 | ) | $ | 118,772 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Caption is exclusive of depreciation and amortization. |
| (2) | The income tax expense reflected in each column does not include any tax effect of the equity in earnings from subsidiaries. |
F-94
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2020
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | — | $ | 738,295 | $ | 16,689 | $ | (763 | ) | $ | 754,221 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses(1) | — | 271,537 | 12,779 | (763 | ) | 283,553 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses(1) | — | 145,750 | 3,862 | — | 149,612 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses(1) | — | 34,608 | 404 | — | 35,012 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | — | 125,450 | 861 | — | 126,311 | |||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on disposition of assets | — | (3,574 | ) | 55 | — | (3,519 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| — | 573,771 | 17,961 | (763 | ) | 590,969 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating income (loss) | — | 164,524 | (1,272 | ) | — | 163,252 | ||||||||||||||
Equity in (earnings) loss of subsidiaries | (160,584 | ) | — | — | 160,584 | — | ||||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 18,184 | — | — | — | 18,184 | |||||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 70,249 | (59 | ) | 1,431 | — | 71,621 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Income (loss) before income tax expense | 72,151 | 164,583 | (2,703 | ) | (160,584 | ) | 73,447 | |||||||||||||
Income tax expense (benefit)(2) | — | 1,924 | (628 | ) | — | 1,296 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 72,151 | $ | 162,659 | $ | (2,075 | ) | $ | (160,584 | ) | $ | 72,151 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 72,151 | $ | 162,659 | $ | (2,075 | ) | $ | (160,584 | ) | $ | 72,151 | ||||||||
Total other comprehensive loss, net of tax | — | — | (858 | ) | — | (858 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 72,151 | $ | 162,659 | $ | (2,933 | ) | $ | (160,584 | ) | $ | 71,293 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Caption is exclusive of depreciation and amortization. |
| (2) | The income tax expense reflected in each column does not include any tax effect of the equity in earnings from subsidiaries. |
F-95
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Statements of Income and Comprehensive Income for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2019
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | — | $ | 811,655 | $ | 23,024 | $ | (1,480 | ) | $ | 833,199 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Direct advertising expenses(1) | — | 274,858 | 13,482 | (1,480 | ) | 286,860 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses(1) | — | 154,132 | 3,577 | — | 157,709 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate expenses(1) | — | 34,897 | 608 | — | 35,505 | |||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | — | 121,864 | 1,335 | — | 123,199 | |||||||||||||||
Gain on disposition of assets | — | (1,010 | ) | (4,151 | ) | — | (5,161 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| — | 584,741 | 14,851 | (1,480 | ) | 598,112 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Operating income | — | 226,914 | 8,173 | — | 235,087 | |||||||||||||||
Equity in (earnings) loss of subsidiaries | (242,710 | ) | — | — | 242,710 | — | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net | 72,863 | (87 | ) | 2,756 | — | 75,532 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Income (loss) before income tax expense | 169,847 | 227,001 | 5,417 | (242,710 | ) | 159,555 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax expense(2) | — | (12,612 | ) | 2,320 | — | (10,292 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 169,847 | $ | 239,613 | $ | 3,097 | $ | (242,710 | ) | $ | 169,847 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| Statement of Comprehensive Income | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 169,847 | $ | 239,613 | $ | 3,097 | $ | (242,710 | ) | $ | 169,847 | |||||||||
Total other comprehensive income, net of tax | — | — | 546 | — | 546 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Total comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 169,847 | $ | 239,613 | $ | 3,643 | $ | (242,710 | ) | $ | 170,393 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
| (1) | Caption is exclusive of depreciation and amortization. |
| (2) | The income tax expense reflected in each column does not include any tax effect of the equity in earnings from subsidiaries. |
F-96
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2020
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 165,269 | $ | 238,800 | $ | 5,429 | $ | (226,745 | ) | $ | 182,753 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Acquisitions | 577 | (26,730 | ) | — | — | (26,153 | ) | |||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | — | (34,770 | ) | (1,504 | ) | — | (36,274 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | — | 4,750 | — | — | 4,750 | |||||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | (26,730 | ) | — | — | 26,730 | — | ||||||||||||||
(Increase) decrease in intercompany notes receivable | (181,089 | ) | — | — | 181,089 | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (207,242 | ) | (56,750 | ) | (1,504 | ) | 207,819 | (57,677 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 655,000 | — | — | — | 655,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payment on revolving credit facility | (805,000 | ) | — | — | — | (805,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Principal payments on long term debt | — | (182 | ) | — | — | (182 | ) | |||||||||||||
Borrowings on long term debt | — | 8,750 | — | — | 8,750 | |||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from note offering | 1,400,000 | — | — | — | 1,400,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payment on accounts receivable securitization program | — | — | (175,000 | ) | — | (175,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Redemption on senior subordinated notes | (519,139 | ) | — | — | — | (519,139 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds received from senior credit facility term loans | 598,500 | — | — | — | 598,500 | |||||||||||||||
Payments on senior credit facility term loans | (978,097 | ) | — | — | — | (978,097 | ) | |||||||||||||
Debt issuance costs | (30,112 | ) | — | — | — | (30,112 | ) | |||||||||||||
Intercompany loan proceeds | — | 3,808 | 177,281 | (181,089 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | — | — | (882 | ) | — | (882 | ) | |||||||||||||
Dividends (to) from parent | (161,208 | ) | (226,745 | ) | — | 226,745 | (161,208 | ) | ||||||||||||
Contributions from (to) parent | 33,391 | 26,730 | — | (26,730 | ) | 33,391 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 193,335 | (187,639 | ) | 1,399 | 18,926 | 26,021 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | — | — | (192 | ) | — | (192 | ) | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 151,362 | (5,589 | ) | 5,132 | — | 150,905 | ||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 13,185 | 8,278 | 4,225 | — | 25,688 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 164,547 | $ | 2,689 | $ | 9,357 | $ | — | $ | 176,593 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-97
Table of Contents
LAMAR MEDIA CORP.
AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
(Unaudited)
(In Thousands, Except for Share Data)
Condensed Consolidating Statement of Cash Flows for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2019
| Lamar Media Corp. | Guarantor Subsidiaries | Non- Guarantor Subsidiaries | Eliminations | Lamar Media Consolidated | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 158,778 | $ | 287,842 | $ | (2,208 | ) | $ | (230,068 | ) | $ | 214,344 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Acquisitions | — | (78,141 | ) | — | — | (78,141 | ) | |||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | — | (59,193 | ) | (1,367 | ) | — | (60,560 | ) | ||||||||||||
Proceeds from disposition of assets and investments | — | 2,100 | — | — | 2,100 | |||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from insurance claims | (78,141 | ) | — | — | 78,141 | — | ||||||||||||||
Investment in subsidiaries | 5,161 | — | — | (5,161 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Increase in intercompany notes receivable | (127 | ) | (417 | ) | — | — | (544 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (73,107 | ) | (135,651 | ) | (1,367 | ) | 72,980 | (137,145 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds received from revolving credit facility | 220,000 | — | — | — | 220,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payment on revolving credit facility | (375,000 | ) | — | — | — | (375,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Principal payments on long-term debt | (14,421 | ) | — | — | — | (14,421 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds received from note offering | 255,000 | — | — | — | 255,000 | |||||||||||||||
Payment on accounts receivable securitization program | — | — | (9,000 | ) | — | (9,000 | ) | |||||||||||||
Proceeds received from accounts receivable securitization program | — | — | 9,000 | — | 9,000 | |||||||||||||||
Debt issuance costs | (4,435 | ) | — | — | — | (4,435 | ) | |||||||||||||
Intercompany loan proceeds | — | (8,461 | ) | 3,300 | 5,161 | — | ||||||||||||||
Distributions to non-controlling interest | — | — | (285 | ) | — | (285 | ) | |||||||||||||
Dividends (to) from parent | (200,636 | ) | (230,068 | ) | — | 230,068 | (200,636 | ) | ||||||||||||
Contributions from (to) parent | 38,135 | 78,141 | — | (78,141 | ) | 38,135 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (81,357 | ) | (160,388 | ) | 3,015 | 157,088 | (81,642 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes in cash and cash equivalents | — | — | 203 | — | 203 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 4,314 | (8,197 | ) | (357 | ) | — | (4,240 | ) | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 4,029 | 11,655 | 5,310 | — | 20,994 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 8,343 | $ | 3,458 | $ | 4,953 | $ | — | $ | 16,754 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||||
F-98
Table of Contents
