UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, DC 20549
Form 10-K
ANNUAL REPORT
PURSUANT TO SECTIONS 13 OR 15(d)
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
| þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008
or
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 0-29801
INTERMUNE, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | |
| Delaware | | 94-3296648 |
(State or other jurisdiction of
incorporation or organization) | | (IRS Employer identification No.) |
3280 Bayshore Boulevard
Brisbane, CA 94005
(Address of principal executive offices, including Zip Code)
(415) 466-2200
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | |
Title of Each Class | | Name of Exchange on which Registered |
| Common Stock, $0.001 par value | | The NASDAQ Stock Market Inc. |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | | Accelerated filer þ | | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
| | | | (Do not check if a smaller
reporting company) | | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No þ
As of June 30, 2008, the aggregate market value (based upon the closing sales price of such stock as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market on such date) of the voting and non-voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was $95,109,071, which excludes an aggregate of 32,020,139 shares of the registrant’s common stock held by officers and directors and by each person known by the registrant to own 5% or more of the registrant’s outstanding common stock as of June 30, 2008. Exclusion of shares held by any person should not be construed to indicate that such person possesses the power, direct or indirect, to direct or cause the direction of the management or policies of the registrant, or that such person is controlled by or under common control with the registrant. As of February 28, 2009, the number of outstanding shares of the registrant’s common stock was 43,364,648 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the 2009 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A not later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Form 10-K are incorporated by reference in Part III, Items 10-14 of this Form 10-K.
INTERMUNE, INC.
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2008
TABLE OF CONTENTS
2
PART I
Forward Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K (the “Report”) contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. These statements involve substantial risks and uncertainty. You can identify these statements by forward-looking words such as “may,” “will,” “expect,” “intend,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “plan,” “could,” “should” and “continue” or similar words. These forward-looking statements may also use different phrases.
We have based these forward-looking statements on our current expectations and projections about future events. These forward-looking statements, which are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions about us, may include, among other things, statements which address our strategy and operating performance and events or developments that we expect or anticipate will occur in the future, including, but not limited to, statements about:
| | • | | product and product candidate development; |
| | • | | the market or markets for our products or product candidates; |
| | • | | the ability of our products to treat patents in our markets; |
| | • | | timing and expectations of our clinical trials and when our products or product candidates may be marketed; |
| | • | | opportunities to establish development or commercial alliances; |
| | • | | governmental regulation and approval; |
| | • | | requirement of additional funding to complete research and development and commercialize products; |
| | • | | liquidity and sufficiency of our cash resources; |
| | • | | future revenue, including those from product sales and collaborations, adequacy of revenue reserve levels, future expenses, future financial performance and trends; |
| | • | | our future research and development expenses and other expenses; and |
| | • | | our operational and legal risks. |
You should also consider carefully the statements under “Item 1A. Risk Factors” below, which address additional factors that could cause our results to differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. Any forward-looking statements are qualified in their entirety by reference to the factors discussed in this Report, including those discussed in this Report under “Item 1A. Risk Factors” below. Because the factors referred to above, as well as the factors discussed in this Report under “Item 1A. Risk Factors” below, could cause actual results or outcomes to differ materially from those expressed in any forward-looking statements made by us or on our behalf, you should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statement. Further, any forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which it is made, and we undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statement to reflect events or circumstances after the date on which the statement is made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. New factors emerge from time to time, and it is not possible for us to predict which factors will arise. In addition, we cannot assess the impact of each factor on our business or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements. When used in this Report, unless otherwise indicated, “InterMune,” “we,” “our” and “us” refers to InterMune, Inc.
Overview
We are a biotech company focused on developing and commercializing innovative therapies in pulmonology and hepatology. Pulmonology is the field of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment
3
of lung conditions. Hepatology is the field of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the liver. We were incorporated in California in 1998 and reincorporated in Delaware in 2000 upon becoming a public company. During the past several years, we have reorganized our business by curtailing new investment in non-core areas and focusing our development and commercial efforts in pulmonology and hepatology. During 2005, we divested the Amphotec® (amphotericin B cholesteryl sulfate complex for injection) product as well as the oritavancin compound. Until December 2005, our revenue base was provided primarily from the sales of two products, Actimmune® (interferon gamma-1b) and Infergen® (consensus interferon alfacon-1). As part of our efforts to refocus our corporate strategy, we completed the sale of the Infergen product, including related intellectual property rights and inventory, to a wholly-owned subsidiary of Valeant Pharmaceuticals International (“Valeant”) in December 2005. Concurrent with the above transaction, we made the decision to significantly reduce our investment in field-based idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (“IPF”) disease awareness activities, which, when combined with the sale of our Infergen assets, led to a significant headcount reduction of approximately 160 full time equivalent employees. In October 2006, we entered into an Exclusive License and Collaboration Agreement (the “Collaboration Agreement”) with Hoffmann-LaRoche Inc. and F. Hoffmann-LaRoche Ltd. (collectively, “Roche”) to develop and commercialize products from our chronic hepatitis C virus (“HCV”) protease inhibitor program, including our lead candidate compound ITMN-191. In October 2006, we also reached a comprehensive settlement with the government concerning promotional activities for Actimmune by former employees during a period that ended in June 2003. The settlement resolved all outstanding government investigations of InterMune without criminal sanctions. As part of the settlement, we also entered into corporate integrity and deferred prosecution agreements with the government. Effective March 2007, as a result of disappointing clinical trial results and based upon the recommendation of the study’s independent data monitoring committee (“DMC”), we discontinued further development of Actimmune for IPF. Subsequent to the discontinuation of Actimmune for IPF, we now have the following key development programs in place: pirfenidone for IPF and the HCV protease inhibitor program. We have sustained losses in every year since inception and, as of December 31, 2008, we had an accumulated deficit of $755.4 million.
Our total revenue, loss from continuing operations and net loss for each of the years ended, and our total assets as of December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 are summarized in the following table:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
Total revenue | | $ | 48,152 | | | $ | 66,692 | | | $ | 90,784 | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (97,842 | ) | | | (94,596 | ) | | | (105,962 | ) |
Net loss | | | (97,739 | ) | | | (89,602 | ) | | | (107,206 | ) |
Total assets | | | 172,224 | | | | 262,445 | | | | 257,583 | |
Approved Product
Our sole approved product is Actimmune, approved for the treatment of patients with severe, malignant osteopetrosis and chronic granulomatous disease (“CGD”). During 2005, our three approved products were Actimmune, Infergen, approved for the treatment of patients with compensated liver disease who have chronic HCV infections, and Amphotec, approved for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis. In May 2005, we sold the Amphotec product to Three Rivers Pharmaceuticals, LLC (“Three Rivers”). In December 2005, we sold the Infergen product to Valeant. For the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, Actimmune accounted for all of our product revenue and substantially all of that revenue was derived from physicians’ prescriptions for the off-label use of Actimmune in the treatment of IPF.
Product Development
Drug development in the United States is a process that includes several steps required by the United States Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”). The process begins with the submission of an Investigational New Drug Application (“IND”) with the FDA, which if accepted by the FDA, allows for the opportunity for clinical study
4
of the potential new medicine. Clinical development typically involves three phases of clinical trials prior to approval: Phase I, II and III. Within the pharmaceutical industry, clinical development takes approximately seven years of a drug’s total development time. The FDA may require, or companies may pursue, additional clinical trials, known as Phase IV clinical trials, after a product is approved. The results of Phase IV clinical trials can confirm the effectiveness of a drug and can provide important safety information to supplement the FDA’s voluntary adverse drug reaction reporting system. The most significant costs associated with clinical development are Phase III clinical trials, as they tend to be the longest and largest studies conducted during the drug development process. It is possible for a drug that appears promising in a Phase II clinical trial to fail in a more rigorous Phase III clinical trial.
In responding to a New Drug Application (“NDA”), a Biologic License Application, (“BLA”), or an NDA or BLA supplement, the FDA may grant marketing approval (i.e., a license), request additional information or refuse to approve the application if it determines that the application does not provide an adequate basis for approval.
We have an advanced-stage development pipeline in the pulmonology area and a research and development-stage pipeline in the hepatology area.
In pulmonology, we are developing a single therapy for the treatment of IPF. IPF is a fatal disease characterized by progressive scarring, or fibrosis, of the lungs, which leads to the deterioration and destruction of lung function. There is no FDA approved therapy for IPF. Although conclusive data does not exist, it is estimated that approximately 100,000 people suffer from IPF in the United States, with approximately 30,000 new cases developing each year.
We are currently developing one clinically advanced compound for the treatment of IPF, pirfenidone. Pirfenidone is an orally available small molecule. It may have activity in multiple fibrotic indications, andin vitroexperiments show that it inhibits collagen synthesis, down-regulates profibrotic and proinflammatory cytokines and decreases fibroblast proliferation. In 2004, the FDA granted pirfenidone orphan drug status in the United States, and the European Medicines Agency (“EMEA”) granted pirfenidone orphan drug designation in the European Union, for the treatment of IPF. To develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, we have acquired from Marnac, Inc. (“Marnac”) and KDL GmbH (“KDL”) all of their remaining worldwide rights to the compound. Shionogi and Co. Ltd., or Shionogi, holds the rights to pirfenidone in Japan, Korea and Taiwan. Both we and Shionogi have undertaken clinical trials seeking to demonstrate that pirfenidone may positively affect lung function and disease progression in patients with IPF.
In December 2006, Shionogi reported positive results from its pivotal Phase III trial conducted in Japan evaluating pirfenidone for the treatment of patients with IPF. The trial was designed to evaluate a high-dose treatment regimen versus a placebo for 52 weeks. A low-dose treatment arm was also included. The Shionogi Phase III trial, in which 261 patients were enrolled and which used a measure of lung function called vital capacity, or VC, as the primary endpoint, showed that pirfenidone significantly slowed the worsening of the disease. Both the high-dose group and the low-dose group showed statistically significant positive results as compared to a placebo for the primary endpoint. Additionally, a statistically significant improvement was seen in progression-free survival, a key secondary endpoint, for the high-dose group compared to a placebo. In March 2007, Shionogi submitted an application to the Japanese Health Authorities for approval to market pirfenidone and on October 16, 2008 received regulatory approval to market pirfenidone for the treatment of patients with IPF in Japan.
Our CAPACITY trials for pirfenidone, which were initiated in April 2006, included two separate, concurrent Phase III trials conducted at 110 centers in North America and Europe. In May 2007, we completed enrollment of 779 patients with mild to moderate forms of IPF in the trials following our decision to refine and
5
expand the CAPACITY program to include an increase in the number of patients enrolled and a lengthening of the treatment duration. We made these refinements based on the data from the Shionogi Phase III trial and the knowledge gained from the unblinded placebo arm of our INSPIRE trial for Actimmune. We began our CAPACITY trials following Shionogi’s successful Phase II clinical trial in which pirfenidone was generally well tolerated, with the most frequent side effects reported being photosensitivity rash and gastrointestinal symptoms. The primary endpoint of our CAPACITY trials was lung function, as measured by change in forced vital capacity, or FVC, which is believed to be an important measure of disease progression in IPF. Our CAPACITY program was designed similarly to the Shionogi Phase III trial in that the maximum doses, on a mg/kg basis, were approximately the same and the primary endpoints (FVC versus VC) were expected to be clinically very similar. The CAPACITY trials were longer (72 weeks versus 52 weeks) than the Shionogi Phase III trial, which we anticipated would allow for better statistical power to demonstrate the efficacy of pirfenidone. On February 3, 2009, we announced results from the two Phase 3 CAPACITY studies. The primary endpoint of change in percent predicted Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) at Week 72 was met with statistical significance in CAPACITY 2 (p=0.001), along with the secondary endpoints of categorical change in FVC and progression-free survival (PFS). The primary endpoint was not met in CAPACITY 1 (p=0.501), but supportive evidence of a pirfenidone treatment effect was observed on a number of measures. Pirfenidone was safe and generally well tolerated in both CAPACITY studies. We are preparing a New Drug Application (NDA) for submission to the FDA, to be followed by a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) submission to the EMEA.
We initiated a second Phase III clinical trial of Actimmune for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate IPF (otherwise known as the “INSPIRE” trial) in December 2003. Effective March 2007, we discontinued the Phase III INSPIRE trial based upon the recommendation of the study’s independent DMC. In a planned interim analysis that included a total of 115 deaths, the DMC found the overall survival result crossed a predefined stopping boundary for lack of benefit of Actimmune relative to placebo. Among the 826 randomized patients, there was not a statistically significant difference between treatment groups in overall mortality (14.5% in the Actimmune group as compared to 12.7% in the placebo group). The adverse events associated with Actimmune therapy appeared generally consistent with prior clinical experience and most commonly involved constitutional symptoms. As a result of the negative INSPIRE trial results, we revised our estimates of inventory requirements as of December 31, 2006. Accordingly, we recorded a charge of $4.5 million in 2006 related to the prepayment of inventory that we had expected to receive in 2007 and 2008.
In hepatology, we are developing product candidates to provide expanded treatment options for patients suffering from HCV infection. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (“CDC”) an estimated 3.9 million Americans have been infected with HCV, of whom 2.7 million are chronically infected. It is estimated that there are 170 million people worldwide afflicted with this disease. The primary mode of transmission of HCV is through contaminated blood. Despite the currently available therapies, interferon alphas and ribavirin, there is considerable need for the development of novel therapeutic approaches since approximately 50% of patients are not cured with these currently available therapies. Patients who are not cured can develop cirrhosis, liver failure and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Our lead compound in hepatology is ITMN-191, an orally available HCV protease inhibitor. We are currently conducting a Phase Ib clinical trial of this compound. We have focused on HCV proteases because of their involvement in viral replication and suppressive effects on host response to viral infection. Our HCV protease inhibitor program is being conducted under our exclusive license and collaboration agreement with Roche.
Preclinical toxicology and pharmacokinetic studies in multiple species suggest that ITMN-191 has attractive therapeutic characteristics for the treatment of HCV, including significant liver exposure, slow dissociation from the NS3/4A protease and high in vitro potency and specificity. Our preclinical pharmacokinetic results also support the exploration of twice-daily oral dosing.
6
In May 2007, we reported that ITMN-191 had completed dosing in a Phase Ia single ascending-dose, or SAD, trial in 64 healthy volunteers. No serious adverse events were reported in the SAD trial. All adverse events were classified as mild (CTCAE Grade 1), and no volunteers were discontinued due to an adverse event. The most common adverse events were gastrointestinal-related, were all classified as mild (CTCAE Grade 1), occurred predominantly in the highest dose cohort, appeared to be attenuated in the presence of food and rapidly resolved without intervention. No clinically significant laboratory abnormalities or ECG changes were reported. Plasma exposure was observed in all dosage cohorts. The doses given in this SAD trial ranged from less than 10% to many-fold higher than those planned to be given in the Phase 1b multiple ascending dose, or MAD, trial which began in September 2007. Subjects who were administered ITMN-191 with a meal demonstrated significantly higher plasma levels of ITMN-191 compared to subjects given the same dose of ITMN-191 without a meal.
In early 2007, we designed a Phase Ib MAD trial of ITMN-191 based on the preliminary safety data from the SAD trial. We later amended our Clinical Trial Authorization, or CTA, for our planned Phase Ib trial to take into consideration new information on the dosing and side effect profiles of competitive protease inhibitors,in vitroand preclinical data on ITMN-191 and the food effect that was observed in the Phase Ia trial. In September 2007, European regulatory authorities approved our amended CTA related to the Phase Ib clinical trial of ITMN-191. The Phase Ib MAD trial was designed to assess the effect on viral kinetics, viral resistance, pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of multiple ascending doses of ITMN-191 given as a monotherapy both two and three times per day. The Phase Ib clinical trial began in September 2007, and we announced top-line viral kinetic and safety results from the first four treatment-naïve dose cohorts of the Phase Ib clinical trial in April 2008. In May 2008, we initiated a 14-day study of ITMN-191 with standard of care therapy and in January 2009 announced top-line results from all six completed dosage cohorts. Viral kinetic performance and safety results were reported for three cohorts each of ITMN-191 given every 12 hours (q12h) and every eight hours (q8h). This study demonstrated sufficient viral kinetic performance to warrant advancing ITMN-191 to a Phase 2b study, which will study both q12h and q8h regimens and both 12 and 24-week treatment durations. The Phase 2b study is anticipated to begin in the second quarter of 2009. ITMN-191 was generally safe and well tolerated. There were no serious adverse events (SAE) or Grade 4 adverse events (AEs) during treatment with ITMN-191.
In November 2008, we, together with Roche and Pharmasset, Inc. (“Pharmasset”) announced the initiation of INFORM-1, a dual combination clinical trial investigating the combination of two oral antiviral molecules in the absence of interferon. The initial study will evaluate the safety and combined antiviral activity of ITMN-191 and R7128, a polymerase inhibitor, in 14 days of combination therapy in treatment-naïve patients infected with HCV genotype 1.
Our oritavancin and Amphotec assets did not fit within our core focus areas of pulmonology and hepatology. Therefore, we divested these non-core assets during 2005.
Product Development Status
The following chart shows the status of our product development programs as of December 31, 2008:
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Preclinical | | Phase I | | Phase II | | Phase III |
Pulmonology | | | | | | | | |
Pirfenidone—Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (CAPACITY) | | | | | | | | X |
Anti-inflammatory/antifibrotic | | X | | | | | | |
| | | | |
Hepatology | | | | | | | | |
ITMN-191—Chronic hepatitis C program; protease inhibitor | | | | X | | | | |
Next generation protease inhibitor | | X | | | | | | |
7
Our Strategy
We intend to use our current capital resources and any potential revenue provided by sales of Actimmune to fund the development of our advanced-stage pulmonology pipeline and our research and development-stage hepatology pipeline.
Our strategy for achieving these objectives include:
Focusing our Development Efforts in the Areas of Pulmonology and Hepatology. Historically, we have pursued development opportunities in the areas of pulmonology, hepatology, infectious disease and oncology. During 2003 and 2004, we narrowed our focus to development and commercial efforts in pulmonology and hepatology in order to more effectively compete, manage our resources and sustain our business. During 2005, we further narrowed our focus to three core development programs: Actimmune in IPF (which, effective March 2007, has been discontinued), pirfenidone in IPF and our protease inhibitors in hepatology.
Investing in Preclinical and Applied Research. We have a preclinical and applied research group which focuses its research in pulmonology and hepatology. The hepatology research program includes our protease inhibitor program for the treatment of hepatitis C as well as a second small molecule program in hepatology. This group seeks to characterize mechanisms of action and biological, toxicology and pharmacology profiles of our product development candidates.
Obtaining FDA Approval for our Compounds in Pulmonology and Hepatology. We are developing pirfenidone and our protease inhibitors for diseases for which preclinical studies and clinical trials have shown evidence that they may be potentially effective treatments. We believe that pirfenidone may have potential as a treatment for IPF. We also believe that our protease inhibitors may have potential to treat patients with HCV infections.
Establishing Appropriate Alliances. We believe that we have significant opportunities to achieve additional revenue and to offset expenses by establishing appropriate development or commercial alliances in pulmonology and hepatology. Such alliances may help us accelerate our development efforts, offset our expenses and mitigate our risks. We have entered into a Collaboration Agreement with Roche to develop and commercialize products from our HCV protease inhibitor program, including our lead candidate compound ITMN-191.
Evaluating Appropriate Product Acquisition Candidates. We continue to evaluate appropriate product acquisition candidates that we believe could complement our existing pulmonology and hepatology portfolios.
Approved Product
Our sole approved product is Actimmune which is approved by the FDA only for the treatment of two rare congenital disorders: CGD and severe, malignant osteopetrosis. Actimmune is also approved for these indications by the health authorities in numerous other countries.
Chronic granulomatous disease. CGD is a life-threatening congenital disorder that causes patients, primarily children, to be vulnerable to severe, recurrent bacterial and fungal infections. This results in frequent and prolonged hospitalizations and commonly results in death. In 1990, Actimmune was approved by the FDA for reducing the frequency and the severity of serious infections associated with CGD, and is the only FDA approved drug for this disease.
Severe, malignant osteopetrosis. Severe, malignant osteopetrosis is a life-threatening, congenital disorder that primarily affects children. This disease results in increased susceptibility to infection and an overgrowth of bony structures that may lead to blindness and/or deafness. In 2000, Actimmune was approved by the FDA for delaying time to disease progression in patients with severe, malignant osteopetrosis, and is the only FDA approved drug for this disease.
8
We have the exclusive rights to develop and commercialize Actimmune for a broad range of diseases in the United States, Canada and Japan. We have an agreement with Boehringer Ingelheim (“BI”) in connection with the development and commercialization of interferon gamma-1b in Europe and the rest of the world under the trade name Imukin®. See “License and Other Agreements.” Substantially all of our revenue from sales of Actimmune has been derived from off-label uses of Actimmune rather than the treatment of osteopetrosis or CGD.
Development Programs
Pulmonology
We are developing pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF.
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
IPF is a disease characterized by progressive scarring, or fibrosis, of the lungs, which leads to their deterioration and destruction. The cause of IPF is unknown. The prognosis is poor for patients with IPF, which occurs primarily in persons 40 to 70 years old. Based on the published literature, median survival time from diagnosis is two to five years in patients with IPF, and most patients die from complications associated with IPF. Although conclusive data does not exist, it is estimated that approximately 100,000 people suffer from IPF in the United States, approximately one-half of whom have mild to moderate disease severity. There is no FDA approved therapy available for the treatment of IPF.
Actimmune for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. We were developing Actimmune for the treatment of IPF. We reported data from our first Phase III clinical trial of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF (GIPF-001) in August 2002. Although this trial failed to meet its primary and secondary endpoints, it provided us with information regarding the disease, appropriate clinical endpoints and the treatment effect of Actimmune on patients. Based on analysis of this data, we initiated a second Phase III clinical trial of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF (GIPF-007, or the “INSPIRE” trial) in December 2003. Effective March 2007, we discontinued the Phase III INSPIRE trial based upon the recommendation of the study’s independent DMC.
Pirfenidone for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
Pirfenidone, which may have activity in multiple fibrotic indications, is currently in clinical development for the treatment of IPF and for pulmonary fibrosis associated with Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome (“HPS”), a fatal, fibrotic lung disease caused by genetic factors for which there is no FDA approved therapy. Pirfenidone is an orally active, small molecule drug that appears to inhibit collagen synthesis, down-regulate production of multiple cytokines and block fibroblast proliferation and stimulation in response to cytokines. In May 2003, we concluded a 55-patient, proof-of-concept Phase II clinical trial of pirfenidone in IPF. We stopped this trial early to expedite the collection of preliminary safety and efficacy data and our assessment of whether these data support pirfenidone as a product candidate with potential benefits to IPF patients.
In 2004, we completed the data analysis and preclinical work necessary to design and conduct a pirfenidone registration program for IPF. In May 2005, the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine (AJRCCM) published results from a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled Phase II trial evaluating pirfenidone for the treatment of patients with IPF. This 107 patient study with a planned 12 month treatment period was conducted in Japan by Shionogi and was terminated after only nine months based on the recommendation of an independent Data Safety Monitoring Board following an interim analysis. This analysis suggested favorable effects of pirfenidone on acute exacerbations and other efficacy parameters. In December 2006, Shionogi reported positive results of their Phase III clinical trial of patients with IPF who were treated with pirfenidone. This Phase III clinical trial was conducted in Japan. In March 2007, Shionogi submitted an application to the Japanese Health Authorities for approval to market pirfenidone and on October 16, 2008 received regulatory approval to market pirfenidone for the treatment of patients with IPF in Japan.
9
Our CAPACITY trials, which were initiated in April 2006, included two separate, concurrent Phase III trials conducted at 110 centers in North America and Europe. In May 2007, we completed enrollment of 779 patients with mild to moderate forms of IPF in the trials following our decision to refine and expand the CAPACITY program to include an increase in the number of patients enrolled and a lengthening of the treatment duration. We made these refinements based on the data from the Shionogi Phase III trial and the knowledge gained from the unblinded placebo arm of our INSPIRE trial for Actimmune. We began our CAPACITY trials following Shionogi��s successful Phase II clinical trial in which pirfenidone was generally well tolerated, with the most frequent side effects reported being photosensitivity rash and gastrointestinal symptoms. The primary endpoint of our CAPACITY trials was lung function, as measured by change in forced vital capacity, or FVC, which is believed to be an important measure of disease progression in IPF. Our CAPACITY program was designed similarly to the Shionogi Phase III trial in that the maximum doses, on a mg/kg basis, were approximately the same and the primary endpoints (FVC versus VC) were expected to be clinically very similar. The CAPACITY trials were longer (72 weeks versus 52 weeks) than the Shionogi Phase III trial, which we anticipated would allow for better statistical power to detect the efficacy of pirfenidone. On February 3, 2009, we announced results from the two Phase 3 CAPACITY studies. The primary endpoint of change in percent predicted Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) at Week 72 was met with statistical significance in CAPACITY 2 (p=0.001), along with the secondary endpoints of categorical change in FVC and progression-free survival (PFS). The primary endpoint was not met in CAPACITY 1 (p=0.501), but supportive evidence of a pirfenidone treatment effect was observed on a number of measures. Pirfenidone was safe and generally well tolerated in both CAPACITY studies. We are preparing a New Drug Application (NDA) for submission to the FDA, to be followed by a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) submission to the EMEA.
In 2004, the FDA and the EMEA granted pirfenidone orphan drug designation for the treatment of IPF. Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan drug designation to drugs intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. This designation provides seven years of market exclusivity in the United States upon the FDA’s first approval of the product for the orphan designation provided that the sponsor complies with certain FDA specified conditions. EMEA orphan drug designation provides for ten years of market exclusivity in the European Union.
We are also supporting the development of pirfenidone for HPS by providing free pirfenidone drug product to the National Institute of Health (“NIH”) for its continuing Phase III clinical work on HPS.
Next-Generation Interferon Gamma
We had a license and collaboration agreement with Maxygen Holdings Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary of Maxygen, Inc. (“Maxygen”), to develop and commercialize novel, next-generation interferon gamma products that have enhanced pharmacokinetics and a potential for less frequent dosing regimens than Actimmune. Effective July 2007, we have terminated this agreement.
Hepatology
Our second area of focus is developing therapeutics in the area of hepatology. Our development efforts in hepatology are currently directed at expanding treatment options for patients suffering from HCV infections. Prior to the end of 2005, we were focusing our hepatology efforts on the pegylated interferon non-responder population. We have now decided to focus our investments on small molecules, the first of which is our protease inhibitor program which we believe could have a broad application in the overall HCV patient population.
Protease Inhibitor Program
We have a preclinical research program in the hepatology area. In September 2002, we entered into a drug discovery collaboration agreement with Array BioPharma, Inc. (“Array”) to discover novel small molecule protease inhibitors for the treatment of hepatitis C. In late 2004, we amended the Array agreement to provide for the acquisition of certain intellectual property rights from Array. In April 2005, we initiated a second research collaboration with Array with respect to a new hepatology target and have since terminated that agreement.
10
Results from scientific studies presented at the Digestive Disease Week medical conference in May 2005 have identified protease inhibitors as a promising therapeutic class. In 2005, we presented several abstracts demonstrating high potency, favorable pharmacokinetics, including uptake into the liver, and encouraging tolerability for our two lead oral HCV protease inhibitor compounds. In the third quarter of 2005, we chose “ITMN-191” (formerly known as ITMN B) as our lead compound and have advanced this compound through toxicology and other clinical trial authorization-enabling studies. We submitted a Clinical Trial Authorisation (“CTA”) with the French Medicinal and Biological Products Evaluation Directorate for this lead compound during the third quarter of 2006. In addition, we are pursuing research related to other small molecules for follow-on compounds to ITMN 191 as well as second-generation protease inhibitors. Under the Collaboration Agreement with Roche, we are collaborating to develop and commercialize products from our HCV protease inhibitor program, including our lead candidate compound ITMN-191, which entered Phase Ia clinical trials late in 2006 and Phase Ib clinical trials in September 2007 and May 2008, and novel second-generation HCV protease inhibitors.
In November 2008, we, together with Roche and Pharmasset announced the initiation of INFORM-1, a dual combination clinical trial investigating the combination of two oral antiviral molecules in the absence of interferon. The initial study will evaluate the safety and combined antiviral activity of ITMN-191 and R7128, a polymerase inhibitor, in 14 days of combination therapy in treatment-naïve patients infected with HCV genotype 1.
Other Assets
The oritavancin and Amphotec assets did not fit within our core focus areas of pulmonology and hepatology. Therefore, we divested these assets during 2005. We also discontinued our Phase III clinical trial of Actimmune for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Divesture of Oritavancin
Oritavancin is a semi-synthetic glycopeptide antibiotic in development for the treatment of a broad range of infections caused by gram-positive bacteria, including those resistant to other glycopeptides. Oritavancin has demonstrated the ability to kill most strains of gram-positive bacteria, while other glycopeptides and many other agents merely suppress them. Oritavancin may be effective in the treatment of a range of infections caused by gram-positive bacteria.
In two Phase III clinical trials with oritavancin for the treatment of complicated skin and skin-structure infections (“CSSSIs”), oritavancin achieved the primary efficacy endpoint and demonstrated that oritavancin was as effective as the comparator regimen of vancomycin followed by cephalexin, which is a commonly used regimen. However, the FDA requested an additional clinical safety study be completed prior to the submission of a New Drug Application, or NDA, for oritavancin for the treatment of CSSSIs. In December 2005, we sold our worldwide rights to oritavancin to Targanta Therapeutics (“Targanta”). The terms of the agreement included upfront and potential clinical related milestone payments of up to $9.0 million, of which $4.0 million has been received through December 31, 2008. We also received a convertible promissory note that, assuming certain clinical milestones were achieved, could have been valued at up to $25.0 million in principal amount from Targanta, which note was initially secured by the oritavancin assets. Upon the achievement by Targanta of certain corporate objectives, the notes were designed to convert into capital stock of Targanta, subject to certain limitations in the amount of voting stock that we may hold. Effective February 2007, these objectives were met by Targanta and, upon conversion of the promissory note, we received approximately 1.7 million shares of Targanta Series C preferred stock in exchange for the convertible promissory note. In October 2007, Targanta completed an initial public offering of its common stock at a price of $10.00 per share. Upon completion of the offering, our investment in Targanta was automatically converted into approximately 3.0 million shares of Targanta common stock and warrants to purchase approximately 0.1 million additional shares of Targanta common stock. These shares had been restricted for resale and were subject to a lock-up agreement that expired in April 2008. In connection with the 2005 sale of worldwide rights, Eli Lilly & Company (“Eli Lilly”) waived
11
its right to collect a $10.0 million milestone payment which had previously been accrued by us. We also received a seat on the Targanta board of directors from which we resigned effective December 31, 2007.
In January 2009, The Medicines Company announced its intent to acquire Targanta for $2.00 per share, or approximately $42.0 million and on January 27, 2009 commenced a tender offer to acquire all outstanding shares of Targanta. We have tendered our shares and received approximately $6.0 million in March 2009 upon closing of the transaction. We may also receive up to an additional $4.55 per share in contingent cash payments upon the achievement of specified regulatory and commercial milestones within certain time periods.
Divesture of Amphotec
Amphotec is an FDA approved lipid-form of amphotericin B indicated for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis in patients where renal impairment or unacceptable toxicity precludes the use of amphotericin B deoxycholate in effective doses, and in patients with invasive aspergillosis where prior amphotericin B deoxycholate has failed. Systemic fungal infections that do not respond to initial treatment with standard antifungal treatment regimens are typically treated with amphotericin B, the active ingredient in Amphotec. This product is approved in the United States under the name Amphotec and in more than 40 other countries under the name Amphocil. In 2004, we announced our intent to divest Amphotec and in May 2005, we sold Amphotec to Three Rivers for cash consideration. In accordance with our agreement with Three Rivers, we may receive contingent payments based on Three Rivers meeting future specified sales targets of Amphotec. These sales targets have since been met and we received an aggregate $1.5 million from Three Rivers, $0.5 million in 2007 and $1.0 million in 2008.
License and Other Agreements
Roche License and Collaboration Agreement (Protease Inhibitors)
In October 2006 we entered into a Collaboration Agreement with Roche. Under the Collaboration Agreement, we agreed to collaborate with Roche to develop and commercialize products from our HCV protease inhibitor program. The Collaboration Agreement includes our lead candidate compound ITMN-191, which entered Phase 1a clinical trials late in 2006 and phase 1b clinical trials during the third quarter of 2007. We also agreed to collaborate with Roche on a research program to identify, develop and commercialize novel second-generation HCV protease inhibitors.
Under the terms of the Collaboration Agreement, we agreed to conduct Phase I studies for ITMN-191, and thereafter Roche agreed to lead clinical development and commercialization. Upon closing, we received an upfront payment of $60.0 million from Roche. In addition, assuming successful development and commercialization of ITMN-191 in the United States and other countries, we could potentially receive up to an aggregate of $470.0 million in milestone payments. One milestone payment of $10.0 million was received in January 2007, which was not deemed to be substantially at risk at the execution of the Collaboration Agreement. Therefore, the upfront payment of $60.0 million and this $10.0 million milestone payment have been deferred and are being recognized ratably as collaboration revenue over the estimated life of the Collaboration Agreement and our continuing involvement. All further milestone payments have been assessed as substantially at-risk at the execution of the agreement and will be recognized as revenue when and if these milestones are achieved, as defined in the Collaboration Agreement. In June 2007 and September 2008, we received $10.0 million and $15.0 million milestone payments, respectively, which were recognized as revenue upon receipt as the milestones were deemed substantially at-risk at the execution of the agreement. Roche agreed to fund 67% of the global development costs of ITMN-191 and, if the product is approved for commercialization by the FDA, we agreed to co-commercialize the product in the United States and share profits on a 50-50 basis with Roche. We are entitled to receive royalties on any sales of the product outside of the United States. We have the right to opt-out of either co-development and/or co- commercialization of ITMN-191 in exchange for higher royalties on sales outside of the United States, and royalties instead of profit sharing in the United States. The economic terms for ITMN-191 could also apply to additional compounds that we and Roche develop under the Collaboration Agreement.
12
In November 2008, we amended the Collaboration Agreement among other things to extend the research program (and consequently the research exclusivity period whereby each party is prohibited from engaging in certain competitive research activities) for an additional amount of time and to provide for certain funding by Roche of activities taking place during such extended research period. Such research funding by Roche may be credited by Roche against certain future payments in connection with Roche’s inclusion of possible additional compounds as part of its license rights granted to it under the collaboration.
Genentech, Inc. License Agreement (Actimmune)
In 1998, we obtained a license from Genentech, Inc. (“Genentech”) for patents relating to Actimmune. The license from Genentech terminates on the later of May 5, 2018 or the date that the last of the patents licensed under the agreement expires. Our licensed Actimmune rights include exclusive and non-exclusive licenses. The exclusive licenses include the right to develop and commercialize Actimmune in the United States and Canada for the treatment and prevention of all human diseases and conditions, including infectious diseases, pulmonary fibrosis and cancer, but excluding arthritis and cardiac and cardiovascular diseases and conditions. The non-exclusive licenses include the right to make or have made Actimmune for clinical and commercial purposes within our field of use in the United States and Canada. In Japan, we have the exclusive license rights to commercialize Actimmune for the treatment and prevention of all infectious diseases caused by fungal, bacterial or viral agents, including in patients with CGD or osteopetrosis. We also have the opportunity, under specified conditions, to obtain further rights to Actimmune in Japan and other countries. In addition, we received an exclusive sublicense under certain of Genentech’s patents outside the United States, Canada and Japan under the BI agreement discussed below. Under the Genentech license, we pay Genentech royalties on the revenue from sales of Actimmune, and are required to make one-time payments to Genentech upon the occurrence of specified milestone events, which include the submission of a BLA with the FDA for approval to market Actimmune for the treatment of particular categories of diseases, the receipt of FDA approval to market Actimmune for the treatment of particular categories of diseases and the achievement of certain annual revenue targets for Actimmune. We had made royalty payments of approximately $79.3 million in the aggregate, but no milestone payments, under this agreement through December 31, 2008. If all of the milestones under this agreement are achieved, we would be required to make further milestone payments of $3.2 million, although we have no further development plans for Actimmune. We must satisfy specified diligence obligations under the agreement with Genentech to maintain our license from Genentech. Our rights to certain therapeutic uses for Actimmune under this agreement could revert to Genentech if we do not meet our diligence obligations or otherwise commit a material breach of the agreement.
Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH (Imukin)
In 2001, we formed a collaboration with BI to clinically develop and seek regulatory approval for interferon gamma-1b, the active ingredient in Actimmune, in certain diseases, and to commercialize a liquid formulation of interferon gamma-1b under one or more of BI’s trade names, including Imukin, in Europe and other major markets of the world (other than the United States, Canada and Japan). Under the agreement, the parties may seek to develop and obtain regulatory approval for the use of Imukin in the treatment of a variety of diseases, including IPF, ovarian cancer, CGD and osteopetrosis. The agreement provides that in return for our funding and managing clinical and regulatory development of interferon gamma-1b for these diseases in the countries covered by the agreement, BI will pay us royalties on sales of the product when it meets a specified minimum sales level. BI has an option to exclusively promote Imukin in all of the major market countries covered by the agreement, and we may opt to promote the product in those countries and for those new diseases for which BI does not do so. If we opt to promote the product in those countries or for those new diseases for which BI does not, we will pay royalties to BI on sales of the product in those countries and/or for those new diseases. We had neither paid nor received any royalties under this agreement through December 31, 2008, and there are no milestone payments under this agreement. The agreement will expire, on a country-by-country basis, upon expiration of the parties’ royalty obligations in each country covered by the agreement. Such royalty obligations generally expire fifteen years after regulatory approval of Imukin for certain specified indications in the relevant country. If no
13
such regulatory approvals are granted in a particular country, the royalty obligations in such country will expire in 2016. Prior to such expiration, either party can terminate the agreement for the uncured material breach of the other party or for the insolvency of the other party. In addition, we have the right to terminate the agreement with respect to certain countries at any time subsequent to regulatory approval for IPF.
Connetics Corporation (acquired by Stiefel Laboratories, Inc.) (Actimmune)
Through an assignment and option agreement with Connetics, we paid Connetics $5.7 million to acquire rights to Actimmune and are obligated to pay to Connetics a royalty of 0.25% of our net United States sales for Actimmune until our net United States sales cumulatively surpass $1.0 billion. Above $1.0 billion, we are obligated to pay a royalty of 0.5% of our net United States sales of Actimmune. Through a separate purchase agreement, we paid Connetics $0.4 million to acquire rights related to scleroderma and are obligated to pay Connetics a royalty of 4.0% on our net revenue from sales of Actimmune for the treatment of scleroderma. We had made royalty payments of approximately $1.7 million in the aggregate through December 31, 2008. There are no milestone payments pursuant to this agreement.
Amgen Inc. (Infergen, PEG-Alfacon-1 and Interferon Gamma)
In 2001, we entered into a licensing and commercialization agreement with Amgen through which we obtained an exclusive license in the United States and Canada to Infergen and the rights to an early stage program to develop a pegylated form of Infergen PEG-Alfacon-1. Infergen is currently approved in both the United States and Canada to treat chronic HCV infections. Under the agreement, we had the exclusive right to market Infergen and clinically develop it for other indications in the United States and Canada. In December 2004, we amended our licensing and commercialization agreement with Amgen to remove certain non-competition restrictions on Amgen with respect to alpha interferons in exchange for a specified reduction in the royalties payable by us to Amgen on Infergen sales should Amgen engage in certain competitive activities as well as Amgen’s consent to transfer the manufacturing of Infergen to a new supplier. (See section entitled “Manufacturing” below). We initially paid Amgen $29.0 million for up-front license and other fees and milestones with respect to our license, and had been obligated to pay royalties on sales of Infergen. In March 2003, we commenced a Phase I clinical trial for PEG-Alfacon-1, which required us to make a $1.5 million milestone payment to Amgen pursuant to the terms of the agreement. We had made royalty and milestone payments of approximately $41.0 million under this agreement in the aggregate through December 31, 2005. These rights and obligations with respect to Infergen under the agreement have been assumed by Valeant as part of our sale of the Infergen product to Valeant in December 2005. We have discontinued development of PEG-Alfacon-1.
Marnac, Inc./KDL GmbH (Pirfenidone)
In 2002, we licensed from Marnac and its co-licensor, KDL, their remaining worldwide rights to develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, including renal, liver and pulmonary fibrosis. Under the agreement terms, we received an exclusive license from Marnac and KDL in exchange for an up-front cash payment of $18.8 million and future milestone and up to 9% royalty payments. During the third quarter of 2007, we recorded a $7.5 million expense for such milestone payments, which were based on the progress of clinical development of pirfenidone. If all of the milestones under this agreement had been achieved, we would have been required to make milestone payments of $14.5 million. Effective November 21, 2007, we entered into asset purchase agreements with Marnac and KDL whereby we effectively terminated the prior license agreement by purchasing, among other things, the pirfenidone-related assets covered by such prior license agreement. Under the terms of the asset purchase agreements, we made acquisition payments of approximately $13.7 million, which includes the $7.5 million expense recorded in the third quarter of 2007 relating to the 2002 license agreement. Contingent acquisition payments of up to an additional $53.5 million would be made by us only if positive Phase III data and registration in the United States and European Union are achieved. The asset purchase agreements do not affect the rights to pirfenidone in Japan, Korea and Taiwan, which rights are licensed by Marnac and KDL to Shionogi. Since the original 2002 license agreement has been effectively terminated as a result of our acquisition of such pirfenidone-related assets from Marnac and KDL, we no longer have milestone or royalty obligations thereunder.
14
Novartis Corporation (Small Molecule Therapeutics)
In 2004, we entered into a license agreement with Chiron Corporation (which was acquired by Novartis Corporation) which granted us the right to discover, develop and commercialize small molecule therapeutic agents against certain HCV targets that are covered by patents owned by Novartis. In consideration for this license, we paid Novartis a nonrefundable fee of approximately $0.4 million in 2004 and are required to make milestone payments based on the clinical progress of ITMN-191. In 2006, we expensed $0.5 million upon initiation of the Phase Ia clinical trials for ITMN-191. Assuming that all of the remaining milestones under this agreement are achieved, we will be required to make milestone payments of $4.5 million. In addition, Novartis is entitled to receive royalties on future product sales.
Array BioPharma Inc. (Small Molecule Therapeutics)
In 2002, we entered into a drug discovery collaboration agreement to create small molecule therapeutics targeting hepatitis with Array. Under that agreement, we fund drug discovery research conducted by Array during the research term based on the number of Array scientists working on the research phase of the agreement and we are responsible for all development and commercialization. Though the research phase of the agreement expired in June 2007, Array will continue to be entitled to receive milestone payments under the agreement based on the selection and progress of clinical drug candidates, as well as low single-digit royalties on net sales of products derived from the collaborative efforts. In addition, in December 2004, the agreement was amended to provide a mechanism for us to purchase certain intellectual property rights arising from the collaboration. In April 2005, we initiated a second research collaboration with Array with respect to a new hepatology target and have since terminated that agreement.
Assuming that all of the remaining milestones under these agreements are achieved, we will be required to make milestone payments of $8.5 million. Total research and development expenses related to this agreement were $1.3 million and $10.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. We did not make any payments to Array in 2008. Included in the $10.2 million in 2006 is a $0.5 million milestone payment for the initiation of the Phase Ia clinical trial for ITMN-191.
Maxygen Holdings Ltd. (Next-Generation Interferon Gamma)
We had a license and collaboration agreement with Maxygen to develop and commercialize novel, next-generation interferon gamma products that have enhanced pharmacokinetics and a potential for less frequent dosing regimens than Actimmune. If preclinical data provided compelling proof of concept for a longer-acting interferon gamma compound, our plan would have been to take forward into clinical development selected protein-modified interferon gamma product candidates created by Maxygen that met these criteria. We had funded Maxygen’s optimization and development of these next-generation interferon gamma products and retained exclusive worldwide commercialization rights for all human therapeutic indications. Our diligence obligations included a minimum level of clinical development expenditures for an initial period of time, as well as the general obligation to use commercially reasonable efforts to clinically develop, seek regulatory approval for and commercialize a product in specified major market countries. The agreement terms included up-front license fees and full research funding, as well as development and commercialization milestone payments, which were payable based on the progress of our clinical development program for next-generation interferon gamma products and the achievement of certain sales targets with respect to such products. We had made payments of approximately $9.7 million under this agreement in the aggregate through December 31, 2008, including approximately $0.1 million in the last three years. Effective July 2007, we have terminated this agreement.
ALZA Corporation (Amphotec)
In 2001, we entered into a product acquisition agreement with ALZA Corporation, now a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, in which we acquired the rights to Amphotec. We had made royalty payments of
15
approximately $1.3 million, but no milestone payments, under this agreement in the aggregate through December 31, 2005. We assigned this agreement to Three Rivers in May 2005 in connection with Three Rivers’ purchase of the Amphotec product.
Manufacturing
We contract with qualified third-party manufacturers to produce our products and product candidates. This manufacturing strategy enables us to direct financial resources to the development and commercialization of products rather than diverting resources to establishing a manufacturing infrastructure.
Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH (Actimmune)
In January 2000, we entered into an agreement with BI for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune. The agreement, which had been amended from time to time, generally provided for the exclusive supply by BI and exclusive purchase by us of Actimmune. This contractual obligation to BI was denominated in euros. Prior to the failure of the INSPIRE trial, we had future purchase obligations of approximately $91.6 million. Given the fact that the Phase III INSPIRE trial was unsuccessful and was discontinued in March 2007, we entered into a termination agreement (“Termination Agreement”) with BI. The Termination Agreement provides for the termination of the existing supply agreement dated January 2000, as amended, for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune conditioned upon and coincident with the entry by us and BI into a new agreement for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune. In consideration of the entry into the Termination Agreement, we incurred approximately $6.8 million in termination expenses during the second quarter of 2007, which have been included in restructuring charges in our consolidated statement of operations. Pursuant to the Termination Agreement and new supply agreement, we eliminated $91.6 million in future purchase commitments for Actimmune for the years 2007 to 2012. On June 29, 2007, InterMune and BI entered into a new agreement for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune (“Supply Agreement”). Under the terms of the new Supply Agreement, we are not required to make any minimum annual purchase commitments and BI is not required to commit to reserving any minimum annual capacity for the manufacture of Actimmune. On a going forward basis, the product will be purchased based upon a rolling forecast. The new Supply Agreement is effective as of June 29, 2007 and will expire on December 31, 2012. If BI is not able to supply all of our requirements for Actimmune, we may choose an additional manufacturer. However, we are not entitled to seek such a secondary source until BI has informed us of its unwillingness or inability to meet our requirements. Either party has the right to terminate the Supply Agreement if the other party materially breaches its obligations thereunder. In addition, we have the right to terminate the Supply Agreement immediately in the event that health authorities prevent distribution of Actimmune for all indications.
Cardinal Health PTS, Inc. (oritavancin and pirfenidone)
In 2003, we entered into an agreement with Cardinal Health PTS, Inc. (“Cardinal Health”) to supply us with oritavancin drug product. We assigned this agreement to Targanta in December 2005 in connection with Targanta’s purchase of the oritavancin compound. Cardinal Health also formulates and encapsulates the active pharmaceutical ingredient (“API”) in the manufacturing process for pirfenidone.
ACIC Fine Chemical, Inc. and Signa C.V. (pirfenidone)
On May 13, 2004 we entered into a purchase agreement with ACIC Fine Chemicals Inc. (“ACIC”) to supply us with a finite amount of API for manufacturing of pirfenidone. Under a separate agreement with Signa C.V. (“Signa”), ACIC sub-contracted the actual manufacturing of this finite amount of API for pirfenidone to Signa. Under such purchase agreement, we would acquire the API for pirfenidone from ACIC on an ad hoc purchase order basis.
In January 2009, we entered into a definitive supply agreement with Signa and ACIC for the clinical and commercial supply of the API for pirfenidone, which agreement replaces and supersedes the purchase agreement
16
described above. The agreement generally provides for the exclusive supply by Signa and ACIC and the exclusive purchase (except in certain limited circumstances) by us of the API for pirfenidone with respect to the territories where we hold exclusive rights to pirfenidone. Under the terms of this supply agreement, we are not required to make any minimum annual purchases. The pirfenidone API will be purchased by us based upon a rolling forecast. The supply agreement was made effective as of December 17, 2008 and will continue for the longer of (i) 10 years thereafter and (ii) seven years from the date of approval of a finished product containing the API for pirfenidone. If Signa and ACIC are not able to supply all of our requirements for the API for pirfenidone, we may purchase the API from a second source third party supplier. Either party has the right to terminate the supply agreement if the other party materially breaches its obligations thereunder or in the event the manufacture, use, sale or importation of the API is found to be infringing of a third party’s intellectual property rights and such third party is unwilling to provide either Signa and ACIC or us with a license. In addition, we have the right to terminate the supply agreement in the event it is not commercially reasonable for us to sell or purchase the API or a finished product containing the API.
Patents and Proprietary Rights
Based on our own internal research efforts, we have filed numerous patents relating to the use of interferons to treat a variety of diseases in the areas of pulmonology, hepatology and oncology. In addition, we have filed for patents on a number of small molecules in hepatology and pulmonology.
Actimmune
We have acquired an exclusive license under certain Genentech patents to develop, use and sell interferon gamma-1b, the active ingredient in Actimmune, in particular fields in the United States, Canada and Japan under our license agreement with Genentech. This license agreement covers more than 12 United States patents and related foreign patents and/or patent applications filed in Japan and Canada. Certain of the United States patents covering DNA vectors and host cells relating to interferon gamma-1b have expired in 2005 and in 2006 without material impact to our business. In addition, a United States patent relating to the composition of interferon gamma-1b expires in 2014. Other material United States patents expire between 2009 and 2013. Under the Genentech license, we pay Genentech royalties on the sales of Actimmune, and are required to make one-time payments to Genentech upon the occurrence of specified milestone events, which include the submission of a BLA with the FDA for approval to market Actimmune for the treatment of particular categories of diseases, the receipt of FDA approval to market Actimmune for the treatment of particular categories of diseases and the achievement of certain annual revenue targets for Actimmune. Two United States composition-of-matter patents acquired from Amgen covering interferon-gamma analogs, including interferon gamma-1b, expire in 2022.
Pirfenidone
In 2002, we licensed from Marnac and its co-licensor KDL their worldwide rights, excluding Japan, Korea and Taiwan, to develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, including renal, liver and pulmonary fibrosis. Effective November 21, 2007, we entered into asset purchase agreements with Marnac and KDL whereby we effectively terminated the prior license agreement by purchasing, among other things, the pirfenidone-related assets covered by such prior license agreement. Among the patents we purchased under the asset purchase agreements are U.S. Patent Nos. 5,310,562; 5,962,478; 6,090,822, 6,300,349 and related foreign equivalents. When U.S. Patent No. 5,310,562 expires in 2011, we will not be able to use this patent to block others from marketing pirfenidone for the treatment of fibrotic disorders in the United States. For a description of certain intellectual property issues relating to this license, please see “Item 1A. Risk Factors-Over time, we will lose our ability to rely on the intellectual property we currently own to prevent competing products, which may impair our ability to generate revenue” below.
Protease Inhibitors
In late 2004, we purchased from Array certain co-ownership rights in patents relating to our protease inhibitor program such that we hold exclusive ownership rights in the patent applications and issued patents
17
covering the products arising out of our collaboration with Array. In February 2009, the United States Patent Office issued U.S. Patent No. 7,491,794 with claims covering the chemical structure of ITMN-191.
Competition
Actimmune for CGD and Severe Malignant Osteopetrosis
Actimmune is the only FDA approved therapy for CGD and severe, malignant osteopetrosis and we are not aware of any competitive products available or in development for these indications. However, in general, our products and product candidates face competition from other currently available or development-stage therapies.
Pirfenidone for IPF
There is no FDA approved therapy available for the treatment of IPF. We believe that the primary competition for pirfenidone, if approved by the FDA for the treatment of IPF, will initially consist of products that are approved for other indications and for which clinical development for IPF is contemplated or underway, such as Tracleer® (“bosentan”) and Letairis® (“ambrisentan”). In 2007, a Phase III clinical trial for bosentan has been initiated by Actelion Pharmaceuticals, Ltd. and in January 2009, Gilead Sciences, Inc. (“Gilead”) initiated a Phase III clinical trial of ambrisentan for the treatment of IPF.
Protease Inhibitor for HCV
In the field of hepatology there are multiple drug candidates in development for hepatitis C, including immunomodulators, synthetic interferons, ribavirin analogs, protease inhibitors, polymerase inhibitors, viral budding inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies and RNAi knockdown techniques. In the field of HCV protease inhibitors, several other companies have protease inhibitor drugs in development, including Schering-Plough Corporation, Gilead, Merck & Co., Pfizer, Inc., GlaxoSmithKline, Vertex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Tibotec, Inc. Many of these companies have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than we do, have a significant lead in terms of timing of clinical development, and are more experienced in the development of new drugs than we are.
Commercial Operations, Product Distribution and Medical Affairs
Reorganization of Commercial Operations
In connection with the divestiture of Infergen, we also made significant reductions in our commercial operations in late 2005, including a significant reduction in our field-based IPF disease awareness activities. We plan to rebuild a commercial presence in the future if and when Phase III data from the research and development pipeline warrant that investment. We continue to have a strategic marketing group that will continue to support the supply and reimbursement of Actimmune for its labeled indications, CGD and severe, malignant osteopetrosis. This group is also responsible for strategic planning in preparation for the potential launch of pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF.
Product Distribution
In the United States, Actimmune is sold primarily to distributors and specialty pharmacies who distribute directly to patients. During the year ended December 31, 2008, the primary specialty pharmacies and distributors for Actimmune were CuraScript, Inc. (formerly Priority Healthcare, Inc.), Nova Factor, Inc. and Caremark, Inc., which accounted for 39%, 29% and 17%, respectively, of our total net product sales.
Medical Affairs
We have a Medical Affairs Department that maintains current, scientific-based information about pulmonology and hepatology for the benefit of heath care providers, patients and caregivers, as well as our employees. Other functions of our Medical Affairs Department are medical education, medical information, publications and administration.
18
Sales by Geographic Region
Our total revenue by region for the years ended December 31, was as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
United States | | $ | 29,791 | | $ | 53,321 | | $ | 90,185 |
Rest of the world | | | 18,361 | | | 13,371 | | | 599 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Totals | | $ | 48,152 | | $ | 66,692 | | $ | 90,784 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Governmental Regulation and Product Approval
The FDA and comparable regulatory agencies in state and local jurisdictions and in foreign countries impose substantial requirements upon the clinical development, manufacture and marketing of pharmaceutical products. These agencies and other federal, state and local entities regulate research and development activities and the testing, manufacture, quality control, safety, effectiveness, labeling, storage, record keeping, approval, advertising and promotion of our products. We believe that our products will be regulated as biologics or drugs by the FDA.
The EMEA, or European Medicines Agency, is a centralized body of the European Union whose main responsibility is the protection and promotion of public health through the evaluation and supervision of medicines for human use. The EMEA coordinates the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products throughout the 25 European Union member states in a network of 42 national competent authorities.
The process required by the FDA before our potential products, or previously approved products to be marketed for the treatment of new diseases in the United States generally involves the following:
| | • | | preclinical laboratory and animal tests; |
| | • | | submission of an IND, which must become effective before clinical trials may begin; |
| | • | | adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of the proposed drug for its intended use; and |
| | • | | FDA approval of a new BLA, a new NDA, or a BLA or NDA supplement. |
The testing and approval process requires substantial time, effort and financial resources, and we cannot be certain that any new approvals for our products will be granted on a timely basis, if at all.
Prior to commencing a clinical trial in the United States, we must submit an IND to the FDA. The IND automatically becomes effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless the FDA, within the 30-day time period, raises concerns or questions about the application. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before the clinical trial can begin. Our submission of an IND may not result in FDA authorization to commence such a clinical trial. Further, an independent institutional review board (“IRB”) for each medical center proposing to conduct the clinical trial must review and approve the plan for any clinical trial before it commences.
For purposes of NDA or BLA approval, human clinical trials in the United States are typically conducted in three sequential phases that may overlap.
| | • | | Phase I: The drug is initially introduced into healthy human subjects or patients and tested for safety, dosage tolerance, absorption, metabolism, distribution and excretion. |
| | • | | Phase II: Studies are conducted in a limited patient population to identify possible adverse effects and safety risks, to determine the efficacy of the product for specific targeted diseases and to determine dosage tolerance, optimal dosage and dosage frequency. These Phase II clinical trials may be divided into early Phase II clinical trials, which are referred to as Phase IIa clinical trials, during which pilot |
19
| | studies are performed to determine initial activity and late Phase II clinical trials, which are referred to as Phase IIb clinical trials, that generally consist of controlled trials often involving several hundred patients in traditional drug development programs. |
| | • | | Phase III: When Phase II clinical trials demonstrate that a dosage range of the product is effective and has an acceptable safety profile, Phase III clinical trials are undertaken to further evaluate dosage, to provide statistically and clinically significant evidence of clinical efficacy and to further test for safety in an expanded patient population at multiple clinical study sites. It is possible for a drug that appears promising in a Phase II clinical trial to fail in a more rigorous and reliable Phase III clinical trial. For example, after Actimmune had shown promising results for the treatment of IPF in an investigator sponsored Phase II clinical trial, our initial Phase III study of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF failed to show significant effect on the primary endpoint of progression-free survival or on secondary endpoints of lung function and quality of life. |
In the case of products for severe or life-threatening diseases such as IPF, the initial human testing is often conducted in patients rather than in healthy volunteers. Because these patients already have the target disease, these studies may provide initial evidence of efficacy traditionally obtained in Phase II clinical trials, and thus these trials are frequently referred to as Phase I/II clinical trials.
We may not successfully complete Phase I, Phase II or Phase III clinical trial testing of our product candidates within any specific time period, if at all. Furthermore, the FDA or an IRB or the sponsor may suspend a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk.
The FDA may require, or companies may pursue, additional clinical trials after a product is approved. These are called Phase IV studies. The results of Phase IV studies can confirm the effectiveness of a drug and can provide important safety information to augment the FDA’s adverse drug reaction reporting system.
The results of product development, preclinical studies and clinical trials are submitted to the FDA as part of a BLA or NDA, or as part of a BLA or NDA supplement for approval as a treatment for a new disease if the product is already approved for a disease. The FDA may deny approval of a BLA, NDA or BLA or NDA supplement if the applicable regulatory criteria are not satisfied, or it may require additional clinical data. Even if such data are submitted, the FDA may ultimately decide that the BLA, NDA or BLA or NDA supplement does not satisfy the criteria for approval.
Once issued, the FDA may withdraw product approval if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. In addition, the FDA may require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the effect of approved products that have been commercialized, and the FDA has the power to prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of these post-marketing programs.
A company seeking approval of an abbreviated new drug application (“ANDA”), for the use of an approved drug that is subject to another company’s patent may have to certify to that patent and notify the owner of the NDA and patent for such drug that it is seeking approval. If the patent owner or licensee files a patent infringement lawsuit, FDA approval of the ANDA for which certification is made may be deferred pending the outcome of the lawsuit.
Satisfaction of FDA requirements or similar requirements of state, local and foreign regulatory agencies typically takes several years and the actual time required may vary substantially, based upon the type, complexity and novelty of the product or disease. Government regulation may delay or prevent marketing of potential products or of approved products for new diseases for a considerable period of time and impose costly procedures upon our activities. We cannot be certain that the FDA or any other regulatory agency will grant
20
approvals for our product candidates or for use of our approved products for new diseases on a timely basis, if at all. Success in early stage clinical trials does not ensure success in later stage clinical trials. Data obtained from clinical activities is not always conclusive and may be susceptible to varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. Even if a product receives regulatory approval, the approval may be significantly limited to specific diseases, patient subgroups and dosages. Further, even after regulatory approval is obtained, later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product may result in restrictions on the product or even complete withdrawal of the product from the market. Delays in obtaining, or failures to obtain, initial regulatory approval for any of our product candidates, or additional regulatory approvals for new indications of our approved products, would harm our business. In addition, we cannot predict what adverse governmental regulations may arise from future United States or foreign governmental action.
Any products we manufacture or distribute pursuant to FDA approvals are subject to continuing regulation by the FDA, including record-keeping requirements and reporting of adverse experiences with these products. Drug manufacturers and their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and other government agencies, and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and certain state agencies for compliance with good manufacturing practices, which impose certain procedural and documentation requirements upon us and our third-party manufacturers. We cannot be certain that we or our present or future suppliers will be able to comply with the good manufacturing practices regulations and other FDA regulatory requirements.
Physicians may prescribe legally available drugs for uses that are not described in the product’s labeling and that differ from those tested by us and approved by the FDA. Such off-label uses are common across medical specialties. For example, we are aware that physicians are prescribing Actimmune for the treatment of IPF, although we do not promote Actimmune for the treatment of IPF, and the FDA has not approved the use of Actimmune for the treatment of this disease. Substantially all of our Actimmune revenue is derived from physicians’ prescriptions for off-label use for IPF. The FDA does not regulate the behavior of physicians in their choice of treatments. The FDA does, however, restrict manufacturer’s communications on the subject of off-label use. Companies cannot promote FDA approved drugs for off-label uses. A company may engage in truthful, non-misleading, and non-promotional speech concerning its products. We may also educate physicians about a particular disease state and how that disease is properly diagnosed so that patients who qualify for the clinical trial might be identified. We also may survey physicians who are lawfully prescribing our products for off-label uses to monitor patients’ experiences, particularly as to whether safety issues have arisen. We may also, pursuant to FDA policies, respond to unsolicited requests from health care professionals and engage in appropriate scientific exchange of information about unapproved uses. We have engaged in these lawful activities in the past and continue to engage in some of them today. We have polices and procedures in place to regulate the lawful promotion of our marketed products within their labeled indications. Employees are trained to follow these policies and procedures and must certify that they will abide by them. The FDA actively enforces regulations prohibiting promotion of off-label uses and the promotion of products for which marketing approval has not been obtained. While we believe we are currently in compliance with the FDA’s regulations relating to off-label promotion, the regulations are subject to varying interpretations which continue to evolve. Failure to comply with these requirements in the past or with respect to future activities can result in regulatory enforcement action by the FDA and other governmental bodies, which would have an adverse effect on our revenue, business and financial prospects. On November 9, 2004 we received a subpoena from the U.S. Department of Justice requiring us to provide the Department of Justice with certain information relating to Actimmune, including information regarding the promotion and marketing of Actimmune. On October 25, 2006 we reached a comprehensive settlement with the government to resolve all claims without criminal sanctions relating to promotional activities for Actimmune for IPF by former InterMune employees during a period ending in June 2003. For a more complete description of this matter see “Item 3. Legal Proceedings” below.
The FDA’s policies may change and additional government regulations may be enacted which could prevent or delay regulatory approval of our potential products or approval of new diseases for our existing products. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of adverse governmental regulation that might arise from future legislative or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad.
21
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan drug designation to drugs intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States. Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting an NDA or BLA for that orphan indication. After the FDA grants orphan drug designation, the generic identity of the drug and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in or shorten the duration of the regulatory review and approval process. If a product that has orphan drug designation is the first to subsequently receive FDA approval for the disease for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to orphan drug exclusivity for seven years in the United States (i.e., the FDA may not approve any other applications to market the same drug for the same disease for seven years, except in very limited circumstances). Orphan drug designation exclusivity lasts for 10 years in the European Union. We have filed and intend to file for orphan drug designation for those diseases we target that meet the criteria for orphan drug exclusivity. For example, Actimmune has orphan drug exclusivity for severe, malignant osteopetrosis. Actimmune and pirfenidone have been granted orphan drug designation for the treatment of IPF by the FDA and EMEA. Although obtaining FDA and EMEA approval to market a product with orphan drug exclusivity can be advantageous, there can be no assurance that we will be able to maintain this designation for Actimmune or pirfenidone, nor can there be any assurance that we will be granted orphan drug designation for additional diseases or that orphan drug exclusivity will provide us with a material commercial advantage.
Research and Development
Our research and development expenses were $104.6 million, $105.9 million and $103.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006.
Facilities
All of our facilities and long-lived assets are located in the United States. Our facilities currently consist of 55,898 square feet of office space located at our headquarters at 3280 Bayshore Boulevard, Brisbane, California. In December 2000, we entered into a ten-year lease for this facility. In May 2006, we entered into an amendment to our existing lease to expand our existing office space by approximately 15,000 square feet. The lease expires concurrently with our existing facility lease in March 2011. We believe that our facilities are adequate for our current needs, and that suitable additional or substitute space will be available in the future to replace our existing facility, if necessary, or accommodate expansion of our operations.
Employees
As of February 28, 2009, we had 130 full-time employees. Of the full-time employees, 78 were engaged in research and development and 52 were engaged in general and administrative positions. In connection with the sale of the Infergen product to Valeant and the significant reduction in our field-based IPF disease awareness activities in 2005, we eliminated approximately 160 employee positions. As a result of our decision to discontinue the INSPIRE trial in March 2007, we eliminated approximately 70 additional positions over the course of 2007. We believe that our relations with our employees are good.
Available Information
We file electronically with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). We make available on our website at http://www.intermune.com, free of charge, copies of these reports as soon as reasonably practicable after filing these reports with, or furnishing them to, the SEC. You can also request copies of such documents by contacting our Investor Relations department at (415) 466-2242 or by sending an e-mail toir@intermune.com.
22
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The following table provides information regarding our executive officers and key employees as of February 28, 2009:
| | | | |
Name | | Age | | Title |
Daniel G. Welch | | 51 | | Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President |
Marianne T. Armstrong, Ph.D. | | 54 | | Chief Medical Affairs and Regulatory Officer |
Williamson Z. Bradford, M.D., Ph.D. | | 47 | | Senior Vice President, Clinical Science and Biometrics |
John C. Hodgman | | 54 | | Senior Vice President of Finance and Chief Financial Officer |
Steven B. Porter, M.D., Ph.D. | | 52 | | Chief Medical Officer |
Howard A. Simon, Esq., SPHR | | 50 | | Senior Vice President, Human Resources and Corporate Services and Associate General Counsel |
Robin J. Steele, Esq. | | 53 | | Senior Vice President of Legal Affairs, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary |
Daniel G. Welch. Mr. Welch has served as our Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President since May 2008. Prior to that, Mr. Welch served as our Chief Executive Officer and President and a member of our board of directors since September 2003. From March 2003 to September 2003, Mr. Welch served as a consultant to Warburg Pincus LLC, a global equity investor. From August 2002 to January 2003, Mr. Welch served as chairman and chief executive officer of Triangle Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a pharmaceutical company. From October 2000 to June 2002, Mr. Welch served as president of the pharmaceutical division of Elan Corporation, PLC, a pharmaceutical company. From September 1987 to August 2000, Mr. Welch served in various senior management roles at Sanofi-Synthelabo and its predecessor companies Sanofi and Sterling Winthrop, including vice president of worldwide marketing. From November 1980 to September 1987, Mr. Welch was with American Critical Care, a division of American Hospital Supply. He currently serves on the Board of Directors of one public company, Seattle Genetics, Inc. and is also a director of one private company. Mr. Welch holds a B.S. from the University of Miami and an MBA from the University of North Carolina.
Marianne T. Armstrong, Ph.D. Dr. Armstrong has served as our Chief Medical Affairs and Regulatory Officer since January 2006. From January 2004 to January 2006, Dr. Armstrong served as our Senior Vice President, Regulatory/Medical Affairs and Drug Safety. From April 2002 to January 2004, Dr. Armstrong served as our Senior Vice President of Global Regulatory Operations and Corporate Compliance. From December 1999 to April 2002, Dr. Armstrong served as senior director of clinical development/regulatory affairs at Genentech, Inc., a pharmaceutical company. From July 1998 to November 1999, Dr. Armstrong served as senior director of clinical development at PathoGenesis Corporation, a pharmaceutical company. From May 1995 to July 1998, Dr. Armstrong served as department head of clinical affairs for Amgen Inc., a pharmaceutical company. From January 1981 to April 1995, Dr. Armstrong held management positions in clinical development at Alcon Laboratories, Solvay Pharmaceuticals and Parke-Davis/Warner Lambert, each a pharmaceutical company, and was a regional sales representative at American McGaw, a division of American Hospital Supply. Dr. Armstrong holds a Ph.D. and M.S. from Florida State University.
Williamson Z. Bradford, M.D, Ph.D. Dr. Bradford has served as our Senior Vice President, Clinical Science and Biometrics since January 2008. From July 2001 to January 2008, Dr. Bradford held several positions including most recently Vice President of Clinical Science, responsible for our pulmonary development efforts. From 1999-2001, Dr. Bradford served as Director, Clinical Science at IntraBiotics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a pharmaceutical company, and from 1998-1999, Dr. Bradford served as Clinical Scientist at Genentech, Inc., a pharmaceutical company. Prior to 1998, Dr. Bradford held various academic and clinical positions including Assistant Professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). Dr. Bradford holds an M.D. from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, School of Medicine, a Ph.D. from the University of California, Berkeley, School of Public Health, and was trained in internal medicine and infectious diseases at UCSF. He is board-certified in infectious diseases and serves as an Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine in the Division of Infectious Diseases at UCSF.
23
John C. Hodgman. Mr. Hodgman has served as our Senior Vice President of Finance and Chief Financial Officer since August 2006. Prior to joining InterMune, Mr. Hodgman served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Aerogen, Inc. from June 2005 to October 2005 until its acquisition by Nektar. From August 1998 to December 2005, he served as Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer of Cygnus, Inc. Mr. Hodgman also served as Vice President of Finance, Chief Financial Officer of Cygnus from August 1994 to August 1998 in addition to serving as President of Cygnus’ Diagnostic Division. He currently serves on the Board of Directors of two public companies, Immersion Corporation and AVI BioPharma, Inc. Mr. Hodgman holds a B.S. from Brigham Young University and an M.B.A. from the University of Utah.
Steven B. Porter, M.D., Ph.D. Dr. Porter has served as our Chief Medical Officer since January 2006. Dr. Porter served as our Senior Vice President of Clinical Affairs from January 2004 to January 2006. From July 2001 to January 2004, Dr. Porter served as our Vice President of Clinical Research. From 1999 to June 2001, Dr. Porter was employed at IntraBiotics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a pharmaceutical company, most recently as Senior Director, Clinical Science and Clinical Affairs. From 1997 to 1999, Dr. Porter served as Senior Director, Clinical Affairs at Shaman Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a pharmaceutical company and from 1996 to 1997, Dr. Porter served as Associate Director, Clinical Research at Bayer Corporation. Dr. Porter received his M.D., and Ph.D. from Vanderbilt University School of Medicine. He completed his residency in internal medicine at the University of California, San Francisco and his fellowship in infectious diseases at the University of California, San Francisco and Stanford University.
Howard A. Simon, Esq, SPHR. Mr. Simon has served as our Senior Vice President, Human Resources and Corporate Services and Associate General Counsel since May 2004. Mr. Simon joined us from ABD Insurance and Financial Services, a financial services firm, where he was Senior Vice President, Human Resources & Associate Counsel from June 2003 to March 2004. Prior to ABD, Mr. Simon was the principal in HR & Employment Law Solutions, a consulting firm specializing in the biotechnology industry from February 2002 to June 2003. He served as Vice President, Human Resources at Maxygen, Inc. from 1999 to 2001. He holds an undergraduate degree from UC Berkeley, a law degree from the Boalt Hall School of Law (UC Berkeley), and a Master’s Degree from the Graduate Theological Union of Berkeley. Mr. Simon also is a certificated Senior Human Resources Professional.
Robin J. Steele, Esq. Ms. Steele has served as our Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary since May 2004. From 1998 to April 2003, Ms. Steele worked with Elan Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a global pharmaceutical company headquartered in Dublin, Ireland, most recently as Vice President, Commercial and Legal Affairs in San Diego. Prior to joining Elan, Ms. Steele was in private practice and served as outside counsel to a variety of life science and technology based companies in the Bay Area. Ms. Steele holds a B.A. in Biology from University of Colorado, Boulder, a J.D. from Hastings College of the Law, University of California, San Francisco, and a L.L.M. in Taxation from New York University School of Law.
24
An investment in our common stock is risky. Stockholders and potential purchasers of shares of our stock should carefully consider the following risk factors, which hereby update those risks contained in the “Risk Factors” section of our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q that was filed with the SEC on November 10, 2008, in addition to other information and risk factors in this Report. We are identifying these risk factors as important factors that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those contained in any written or oral forward-looking statements made by or on behalf of InterMune. We are relying upon the safe harbor for all forward-looking statements in this Report, and any such statements made by or on behalf of InterMune are qualified by reference to the following cautionary statements, as well as to those set forth elsewhere in this Report.
Risks Related to the Development of Our Products and Product Candidates
We may not succeed in our development efforts.
We commenced operations in 1998 and have incurred significant losses to date. Our revenue has been limited primarily to sales of Actimmune derived from physicians’ prescriptions for the off-label use of Actimmune in the treatment of IPF. In March 2007, we discontinued our development of Actimmune for treatment of IPF. Although we are developing pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF and have announced results for the CAPACITY trials in February 2009, pirfenidone will not be marketed for any diseases before late 2009 or early 2010, if at all.
We may fail to develop our products on schedule, or at all, for the reasons stated in “Risks Related to the Development of Our Products and Product Candidates.” If this were to occur, our costs would increase and our ability to generate revenue could be impaired.
Drug development is a long, expensive and uncertain process, and delay or failure can occur at any stage of any of our clinical trials.
To gain approval to market a product for the treatment of a specific disease, we must provide the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities with preclinical and clinical data that demonstrate the safety and statistically significant and clinically meaningful efficacy of that product for the treatment of the disease. Drug development is a long, expensive and uncertain process, and delay or failure can occur at any stage of any of our clinical trials. A number of companies in the pharmaceutical industry, including biotechnology companies, have suffered significant setbacks in clinical trials, even after promising results in earlier preclinical or clinical trials. These setbacks have been caused by, among other things, preclinical findings made while clinical studies were underway and safety or efficacy observations made in clinical studies. Success in preclinical testing and early clinical trials does not ensure that later clinical trials will be successful, and the results of clinical trials by other parties may not be indicative of the results in trials we may conduct. For example:
| | • | | The results from our CAPACITY trials differ in certain respects from the results of the Shionogi Phase III clinical trial for pirfenidone. In addition, pirfenidone failed to achieve statistical significance on the primary endpoint in one of our two pivotal CAPACITY clinical trials and there can be no assurance that the regulatory authorities in either the United States or Europe will grant regulatory approval based upon the efficacy data from a single pivotal trial, in combination with the other efficacy and safety results the company currently intends to submit in support of its NDA and MAA filings. Further analyses of the CAPACITY results will be conducted in the future and additional observations may be made which may lead to material change in our current regulatory strategy for pirfenidone, including a decision by us not to proceed with either or both of its regulatory submissions in the United States and Europe. |
| | • | | We terminated our development of Actimmune for patients with IPF as a result of our decision to discontinue the INSPIRE trial on the recommendation of the study’s independent DMC. We do not |
25
| | intend to conduct further development of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF. In addition, we reported that our exploratory Phase II clinical trial evaluating Actimmune for the potential treatment of advanced liver fibrosis caused by HCV in patients who have failed standard antiviral therapy failed to meet its primary endpoint. As a result, we do not intend to conduct further development of Actimmune for the treatment of liver fibrosis. |
| | • | | The positive results of the Phase Ia and Ib trials for ITMN-191 do not ensure that subsequent trials for ITMN-191 will be successful at any dosing level. |
We do not know whether our planned clinical trials will begin on time, or at all, or will be completed on schedule, or at all.
The commencement or completion of any of our clinical trials may be delayed or halted for numerous reasons, including, but not limited to, the following:
| | • | | the FDA or other regulatory authorities do not approve a clinical trial protocol or place a clinical trial on clinical hold; |
| | • | | patients do not enroll in clinical trials at the rate we expect; |
| | • | | patients experience adverse side effects; |
| | • | | patients withdraw or die during a clinical trial for a variety of reasons, including adverse events associated with the advanced stage of their disease and medical problems that may or may not be related to our products or product candidates; |
| | • | | the interim results of the clinical trial are inconclusive or negative; |
| | • | | our trial design, although approved, is inadequate to demonstrate safety and/or efficacy; |
| | • | | third-party clinical investigators do not perform our clinical trials on our anticipated schedule or consistent with the clinical trial protocol and good clinical practices, or other third-party organizations do not perform data collection and analysis in a timely or accurate manner; |
| | • | | our contract laboratories fail to follow good laboratory practices; or |
| | • | | sufficient quantities of the trial drug are not available. |
Our development costs will increase if we have material delays in our clinical trials or if we need to perform more or larger clinical trials than planned. If there are any significant delays for any of our other current or planned clinical trials, our financial results and the commercial prospects for our products and product candidates will be harmed, and our prospects for profitability will be impaired.
Preclinical development is a long, expensive and uncertain process, and we may terminate one or more of our current preclinical development programs.
We may determine that certain preclinical product candidates or programs do not have sufficient potential to warrant the allocation of resources toward them. Accordingly, we may elect to terminate our programs for and, in certain cases, our licenses to, such product candidates or programs. If we terminate a preclinical program in which we have invested significant resources, we will have expended resources on a program that will not provide a full return on our investment and missed the opportunity to have allocated those resources to potentially more productive uses. For example, we terminated our license and collaboration agreement with Maxygen for the development of next-generation interferon gamma products effective July 2007.
We currently depend upon one collaboration partner, Roche, for support in the development and commercialization of our HCV product candidates. If our Collaboration Agreement with Roche terminates, our business and, in particular, the development and commercialization of our HCV product candidates would be significantly harmed.
On October 16, 2006, we entered into the Collaboration Agreement with Roche. Under the Collaboration Agreement, we agreed to collaborate with Roche to develop and commercialize products from our HCV protease
26
inhibitor program. The Collaboration Agreement includes our lead candidate compound ITMN-191, which has completed Phase Ib clinical trials. We also agreed to collaborate with Roche on a research program to identify, develop and commercialize novel second-generation HCV protease inhibitors. Assuming that we continue to successfully develop and commercialize these product candidates, under the terms of the Collaboration Agreement we are entitled to receive reimbursement and sharing of expenses incurred in connection with the development of these product candidates and additional milestone payments from Roche. As a result, Roche is providing 67% of the development costs for ITMN-191. In addition, if any of the product candidates we have licensed to Roche are approved for commercialization, we anticipate receiving proceeds in connection with the sales of such products. Roche may terminate the Collaboration Agreement in its entirety, in any country, subject to certain limitations for major countries, or with respect to any product or product candidate licensed under the Collaboration Agreement for any reason on six months’ written notice. If the Collaboration Agreement is terminated in whole or in part and we are unable to enter into similar arrangements with other collaborators, our business could be materially adversely affected.
If Roche fails to perform its obligations under the Collaboration Agreement, we may not be able to successfully commercialize our product candidates licensed to Roche and the development and commercialization of our product candidates could be delayed, curtailed or terminated.
Under the Collaboration Agreement, if marketing authorization is obtained, we have the right to co-promote with Roche our lead candidate compound ITMN-191 and/or any other product candidates licensed to Roche, as applicable, in the United States and Roche has the right to market and sell ITMN-191 and/or any other product candidates licensed to Roche throughout the rest of the world. Roche is also responsible for the manufacturing of the global commercial supply for ITMN-191 and/or any other product candidates licensed to Roche. As a result, we will depend upon the success of the efforts of Roche to manufacture, market and sell ITMN-191 and/or any other product candidates, if approved. However, we have little to no control over the resources that Roche may devote to such manufacturing and commercialization efforts and, if Roche does not devote sufficient time and resources to such efforts, we may not realize the commercial benefits that we anticipate, and our results of operations may be adversely affected. In addition, if Roche were to terminate the Collaboration Agreement, we would not have manufacturing resources to manufacture ITMN-191, and we would need to develop those resources or contract with one or more third party manufacturers, which we may be unable to do at a favorable cost, or at all.
If we materially breach the representations and warranties we made to Roche under the Collaboration Agreement or any of our other contractual obligations, Roche has the right to seek indemnification from us for damages it suffers as a result of such breach. These amounts could be substantial.
We have agreed to indemnify Roche and its affiliates against losses suffered as a result of our material breach of representations and warranties and our other obligations in the Collaboration Agreement. If one or more of our representations and warranties were not true at the time we made them to Roche, we would be in breach of the Collaboration Agreement. In the event of a breach by us, Roche has the right to seek indemnification from us for damages suffered by Roche as a result of such breach. The amounts for which we could become liable to Roche may be substantial.
Roche has the right under certain circumstances to market and sell products that compete with our product candidates that we have licensed to Roche, and any competition by Roche could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Roche has agreed that, except as set forth in the Collaboration Agreement, it will not develop or commercialize certain specific competitive products during the exclusivity period, which extends until October 2011 at the latest. However if neither ITMN-191 nor any other product candidate is in clinical development, Roche may develop or commercialize such competitive products during the exclusivity period in accordance with the Collaboration Agreement. However, if they undertake such development or commercialization, we will have the right to terminate the Collaboration Agreement. Accordingly, despite the exclusivity period, Roche may
27
under certain circumstances develop or commercialize competitive products. Roche has significantly greater financial, technical and human resources than we have and they are better equipped to discover, develop, manufacture and commercialize products. In addition, Roche has more extensive experience than we have in preclinical studies and clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approvals and manufacturing and marketing pharmaceutical products. In the event that Roche competes with us, our business could be materially and adversely affected.
Risks Related to Government Regulation and Approval of our Products and Product Candidates
If we fail to comply or have in the past failed to comply with FDA or other government regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses and the promotion of products for which marketing approval has not been obtained, we could be subject to regulatory enforcement action by the FDA or other governmental authorities as well as follow-on actions filed by consumers and other end-payors, which actions could result in substantial fines, sanctions and damage awards against us, any of which could harm our business.
Physicians may prescribe commercially available drugs for uses that are not described in the product’s labeling and that differ from those uses tested by us and approved by the FDA. Such off-label uses are common across medical specialties. For example, even though the FDA has not approved the use of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF, we are aware that physicians are, and have in the past, prescribing Actimmune for the treatment of IPF. Substantially all of our Actimmune revenue is derived from physicians’ prescriptions for off-label use for IPF. The FDA does not regulate the behavior of physicians in their choice of treatments. The FDA and other governmental agencies do, however, restrict manufacturers’ communications on the subject of off-label use. Companies may not promote FDA approved drugs for off-label uses. Accordingly, we may not promote Actimmune for the treatment of IPF. The FDA and other governmental authorities actively enforce regulations prohibiting promotion of off-label uses. The federal government has levied large civil and criminal fines against manufacturers for alleged improper promotion, including us in October 2006 in connection with our reaching comprehensive settlement with the government to resolve all claims as it relates to our promotional activities with respect to Actimmune, and the FDA has enjoined several companies from engaging in off-label promotion. The FDA has also requested that companies enter into consent decrees or permanent injunctions under which certain promotional conduct is changed or curtailed. We are aware of many instances, including our own experience as it relates to Actimmune, in which the Office of the Inspector General of the FDA has sought and secured criminal penalties and/or a corporate integrity agreement against pharmaceutical manufacturers requiring payment of substantial fines and monitoring of certain promotional activities to ensure compliance with FDA regulations. We engage in medical education activities that are subject to scrutiny under the FDA’s regulations relating to off-label promotion. While we believe we are currently in compliance with these regulations, the regulations are subject to varying interpretations, which are evolving.
If the FDA or any other governmental agency initiates an enforcement action against us and it is determined that we violated prohibitions relating to off-label promotion in connection with past or future activities, we could be subject to civil and/or criminal fines and sanctions such as those noted above in this risk factor, any of which would have an adverse effect on our revenue, business and financial prospects. As a follow-on to such governmental enforcement actions, consumers and other end-payors of the product may initiate action against us claiming, among other things, fraudulent misrepresentation, civil RICO, unfair competition, violation of various state consumer protection statutes, and unjust enrichment. For example, as a follow-on to the subpoena we received from the U.S. Department of Justice with respect to our promotional and marketing activities in connection with Actimmune and the resulting settlement we reached with the government in October 2006, we have had various class action suits filed against us by consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune as discussed in more detail below in “Item 3. Legal Proceedings.” If the plaintiffs in such follow-on actions are successful , we could be subject to various damages, including compensatory damages, treble damages, punitive damages, restitution, disgorgement, prejudgment and post-judgment interest on any monetary award, and the reimbursement of the plaintiffs’ legal fees and costs, any of which would also have an adverse effect on our revenue, business and financial prospects.
28
In addition, some of the agreements pursuant to which we license our products, including our license agreement relating to Actimmune, contain provisions requiring us to comply with applicable laws and regulations, including the FDA’s restriction on the promotion of FDA approved drugs for off-label uses. As a result, if it were determined that we violated the FDA’s rules relating to off-label promotion in connection with our marketing of Actimmune, we may be in material breach of our license agreement for Actimmune. If we failed to cure a material breach of this license agreement, we could lose our rights to certain therapeutic uses for Actimmune under the agreement.
If the FDA imposes significant restrictions or requirements related to our products for any disease, or withdraws its approval of any of our products for any disease for which it has been approved, our revenue would decline.
The FDA and foreign regulatory authorities may impose significant restrictions on the use or marketing of our products or impose additional requirements for post-approval studies. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with any of our products or their manufacture may result in further restrictions, including withdrawal of the product from the market. In this regard, the FDA has conducted routine inspections of our manufacturing contractors, and some were issued a standard “notice of observations.” While we believe that all of these observations are being appropriately corrected, failure to correct any deficiency could result in manufacturing delays. Our existing approvals for diseases, and any new approval for any other disease that we target, if granted, could be withdrawn for failure to comply with regulatory requirements or to meet our post-approval commitments. For example, we have ongoing Phase IV post-marketing commitments to the FDA relating to Actimmune for the treatment of osteopetrosis. Our failure to adequately address these ongoing Phase IV commitments could result in a regulatory action or restriction, such as withdrawal of the relevant product’s approval by the FDA. If approval for a disease is withdrawn, we could no longer market the affected product for that disease. In addition, governmental authorities could seize our inventory of such product, or force us to recall any product already in the market, if we fail to comply with FDA or other governmental regulations.
For a description of restrictions relating to the off-label promotion of our products, please see the risk factor titled, “If we fail to comply or have in the past failed to comply with FDA or other government regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses and the promotion of products for which marketing approval has not been obtained, we could be subject to regulatory enforcement action by the FDA or other governmental authorities as well as follow-on actions filed by consumers and other end-payors, which actions could result in substantial fines, sanctions and damage awards against us, any of which could harm our business” above.
If our clinical trials fail to demonstrate to the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities that any of our products or product candidates are safe and effective for the treatment of particular diseases, the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities may require us to conduct additional clinical trials or may not grant us marketing approval for such products or product candidates for those diseases.
Our failure to adequately demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of any of our products or product candidates for the treatment of particular diseases may delay or prevent our receipt of the FDA’s and foreign regulatory authorities’ approval and, ultimately, may prevent commercialization of our products and product candidates for those diseases. The FDA and foreign regulatory authorities have substantial discretion in deciding whether, based on the benefits and risks in a particular disease, any of our products or product candidates should be granted approval for the treatment of that particular disease. Even if we believe that a clinical trial has demonstrated the safety and statistically significant efficacy of any of our products or product candidates for the treatment of a disease, the results may not be satisfactory to the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities. Preclinical and clinical data can be interpreted by the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities in different ways, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. Our CAPACITY trials are being conducted without a Special Protocol Assessment, so there can be no assurance that, even if we believe the results of the trials are favorable, the results will provide a sufficient basis in the view of the FDA for the FDA to grant regulatory approval of a new drug application for pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF. If regulatory delays are significant or regulatory
29
approval is limited or denied altogether, our financial results and the commercial prospects for those of our products or product candidates involved will be harmed, and our prospects for profitability will be impaired.
The pricing and profitability of our products may be subject to control by the government and other third-party payors.
The continuing efforts of governmental and other third-party payors to contain or reduce the cost of healthcare through various means may adversely affect our ability to successfully commercialize our products. For example, in most foreign markets, the pricing and/or profitability of prescription pharmaceuticals are subject to governmental control. In the United States, we expect that there will continue to be federal and state proposals to implement similar governmental controls. For example, federal legislation was enacted on December 8, 2003 that provides a new Medicare prescription drug benefit which began in 2006 and which mandates other reforms. Although we cannot predict the full effects on our business of the implementation of this program, it is possible that the new Medicare benefit, which will be managed by private health insurers, pharmacy benefit managers and other managed care organizations, will result in decreased reimbursement for prescription drugs, which may further exacerbate industry-wide pressure to reduce the prices charged for prescription drugs. In addition, increasing emphasis on managed care in the United States will continue to put pressure on the pricing of pharmaceutical products. These new and any future cost-control initiatives could decrease the price that we would receive for Actimmune or any other products that we may develop in the future, which would reduce our revenue and potential profitability.
Our failure or alleged failure to comply with anti-kickback and false claims laws could result in civil and/or criminal sanctions and/or harm our business.
We are subject to various federal and state laws pertaining to health care “fraud and abuse”, including anti-kickback laws and false claims laws. Subject to certain exceptions, the anti-kickback laws make it illegal for a prescription drug manufacturer to knowingly and willfully solicit, offer, receive or pay any remuneration in exchange for, or to induce, the referral of business, including the purchase or prescription of a particular drug. The federal government has published regulations that identify “safe harbors” or exemptions for certain payment arrangements that do not violate the anti-kickback statutes. Due to the breadth of the statutory provisions and the absence of guidance in the form of regulations or court decisions addressing some of our practices, it is possible that our practices might be challenged under anti-kickback or similar laws. False claims laws prohibit anyone from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, for payment to third party payors (including Medicare and Medicaid) claims for reimbursed drugs or services that are false or fraudulent, claims for items or services not provided as claimed or claims for medically unnecessary items or services. Our activities relating to the reporting of wholesaler or estimated retail prices for our products, the reporting of Medicaid rebate information and other information affecting federal and state and third-party payment for our products, and the sale and marketing of our products, could become subject to scrutiny under these laws.
In addition, pharmaceutical companies have been prosecuted under the False Claims Act in connection with their “off-label” promotion of drugs. For information regarding allegations with respect to “off-label” promotion by us, please see the risk factor titled “If we fail to comply or have in the past failed to comply with FDA or other government regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses and the promotion of products for which marketing approval has not been obtained, it could result in regulatory enforcement action by the FDA or other governmental authorities, including a substantial fine, either of which could harm our business” above.
If the government were to allege that we were, or convict us of, violating these laws, there could be a material adverse effect on us, including a substantial fine, decline in our stock price, or both. Our activities could be subject to challenge for the reasons discussed above and due to the broad scope of these laws and the increasing attention being given to them by law enforcement authorities.
30
Risks Related to Manufacturing and Our Dependence on Third Parties
The manufacturing and manufacturing development of our products and product candidates present technological, logistical and regulatory risks, each of which may adversely affect our potential revenue.
The manufacturing and manufacturing development of pharmaceuticals, and, in particular, biologicals, are technologically and logistically complex and heavily regulated by the FDA and other governmental authorities. The manufacturing and manufacturing development of our products and product candidates present many risks, including, but not limited to, the following:
| | • | | It may not be technically feasible to scale up an existing manufacturing process to meet demand or such scale-up may take longer than anticipated; and |
| | • | | Failure to comply with strictly enforced good manufacturing practices regulations and similar foreign standards may result in delays in product approval or withdrawal of an approved product from the market. For example, the FDA has conducted routine inspections of our manufacturing contractors, and some were issued a standard “notice of observations.” Failure to correct any deficiency could result in manufacturing delays. |
Any of these factors could delay clinical trials, regulatory submissions and/or commercialization of our products for particular diseases, interfere with current sales, entail higher costs and result in our being unable to effectively sell our products.
Our manufacturing strategy, which relies on third-party manufacturers, exposes us to additional risks as a result of which we may lose potential revenue.
We do not have the resources, facilities or experience to manufacture any of our products or product candidates ourselves. Completion of our clinical trials and commercialization of our products requires access to, or development of, manufacturing facilities that meet FDA standards to manufacture a sufficient supply of our products. The FDA must approve facilities that manufacture our products for commercial purposes, as well as the manufacturing processes and specifications for the product. We depend on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates for preclinical and clinical purposes, and we rely on third parties with FDA approved manufacturing facilities for the manufacture of Actimmune for commercial purposes. These third parties include BI, and Catalent Pharma Solutions, or Catalent. We have a long-term supply contract with BI for Actimmune, a long-term supply contract with Signa and ACIC for pirfenidone API and a contract with Catalent for the manufacture of the drug product for pirfenidone. In addition, under our Collaboration Agreement with Roche, we are dependent upon Roche for the manufacture of ITMN-191. However, if we do not perform our obligations under these agreements, these agreements may be terminated.
Our manufacturing strategy for our products and product candidates presents many risks, including, but not limited to, the following:
| | • | | If market demand for our products is less than our purchase obligations to our manufacturers, we may incur substantial penalties and substantial inventory write-offs. |
| | • | | Manufacturers of our products are subject to ongoing periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with strictly enforced good manufacturing practices regulations and similar foreign standards, and we do not have control over our third-party manufacturers’ compliance with these regulations and standards. |
| | • | | When we need to change third party manufacturers of a particular pharmaceutical product, the FDA and foreign regulatory authorities must approve the new manufacturers’ facilities and processes prior to our use or sale of products it manufactures for us. This requires demonstrated compatibility of product, process and testing and compliance inspections. Delays in transferring manufacturing technology between third parties could delay clinical trials, regulatory submissions and commercialization of our product candidates. |
31
| | • | | Our manufacturers might not be able or refuse to fulfill our commercial or clinical trial needs, which would require us to seek new manufacturing arrangements and may result in substantial delays in meeting market or clinical trial demands. For example, our current agreement with BI does not impose any obligation on BI to reserve a minimum annual capacity for the production of Actimmune, which could impair our ability to obtain product from them in a timely fashion. |
| | • | | We may not have intellectual property rights, or may have to share intellectual property rights, to any improvements in the manufacturing processes or new manufacturing processes for our products. |
| | • | | Our product costs may increase if our manufacturers pass their increasing costs of manufacture on to us. |
| | • | | If third-party manufacturers do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we will not be able to obtain or maintain regulatory approvals for our products and product candidates and will not be able to successfully commercialize our products and product candidates. In such event, we may not be able to locate any necessary acceptable replacement manufacturers or enter into favorable agreements with such replacement manufacturers in a timely manner, if at all. |
| | • | | If our agreement with a third-party manufacturer expires, we may not be able to renegotiate a new agreement with that manufacturer on favorable terms, if at all. If we cannot successfully complete such renegotiation, we may not be able to locate any necessary acceptable replacement manufacturers or enter into favorable agreements with such replacement manufacturers in a timely manner, if at all. |
Any of these factors could delay clinical trials, regulatory submissions or commercialization of our products for particular diseases, interfere with current sales, entail higher costs and result in our being unable to effectively sell our products.
We rely on third parties to conduct clinical trials for our products and product candidates, and those third parties may not perform satisfactorily.
If our third-party contractors do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may be delayed in or prevented from obtaining regulatory approvals for our products and product candidates, and may not be able to successfully commercialize our products and product candidates for targeted diseases. We do not have the ability to independently conduct clinical trials for all of our products and product candidates, and we rely on third parties such as contract research organizations, medical institutions and clinical investigators to perform this function. Our ability to monitor and audit the performance of these third parties is limited. If these third parties do not perform satisfactorily, our clinical trials may be extended or delayed, resulting in potentially substantial cost increases to us and other adverse impacts on our product development efforts. We may not be able to locate any necessary acceptable replacements or enter into favorable agreements with them, if at all.
Risks Related to the Commercialization of Our Products and Product Candidates
If the specialty pharmacies and distributors that we rely upon to sell our products fail to perform, our business may be adversely affected.
Our success depends on the continued customer support efforts of our network of specialty pharmacies and distributors. A specialty pharmacy is a pharmacy that specializes in the dispensing of injectable or infused medications for complex or chronic conditions, which often require a high level of patient education and ongoing management. The use of specialty pharmacies and distributors involves certain risks, including, but not limited to, risks that these specialty pharmacies and distributors will:
| | • | | not provide us with accurate or timely information regarding their inventories, the number of patients who are using Actimmune or Actimmune complaints; |
| | • | | not effectively sell or support Actimmune; |
32
| | • | | reduce their efforts or discontinue to sell or support Actimmune; |
| | • | | not devote the resources necessary to sell Actimmune in the volumes and within the time frames that we expect; |
| | • | | be unable to satisfy financial obligations to us or others; or |
Any such failure may result in decreased product sales and lower product revenue, which would harm our business.
Even if regulatory authorities approve our products or product candidates for the treatment of the diseases we are targeting, our products may not be marketed or commercially successful.
Our products and product candidates are expensive, and we anticipate that the annual cost for treatment for each of the diseases for which we are seeking approval will be significant. These costs will vary for different diseases based on the dosage and method of administration. Accordingly, we may decide not to market any of our products or product candidates for an approved disease because we believe that it may not be commercially successful. Market acceptance of and demand for our products and product candidates will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
| | • | | pricing and availability of alternative products; |
| | • | | ability to obtain third-party coverage or reimbursement for our products or product candidates to treat a particular disease; |
| | • | | perceived efficacy relative to other available therapies; |
| | • | | shifts in the medical community to new treatment paradigms or standards of care; |
| | • | | relative convenience and ease of administration; and |
| | • | | prevalence and severity of adverse side effects associated with treatment. |
If third-party payors do not provide coverage or reimburse patients for our products, our revenue and prospects for profitability will suffer.
Our ability to commercialize our products or product candidates for particular diseases is highly dependent on the extent to which coverage and reimbursement for our products is available from:
| | • | | private health insurers, including managed care organizations; |
| | • | | governmental payors, such as Medicaid, the U.S. Public Health Service Agency or the Veterans’ Administration; and |
| | • | | other third-party payors. |
Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of pharmaceutical products, particularly with respect to products that are prescribed by physicians for off-label use. If governmental and other third-party payors do not provide adequate coverage and reimbursement levels for our products, market acceptance of our products will be reduced, and our sales will suffer. Many third-party payors provide coverage or reimbursement only for FDA approved indications. If any large or many third-party payors decide to deny reimbursement for Actimmune used to treat IPF, sales of Actimmune would decline, and our revenue would suffer.
33
Often, third-party payors make the decision to reimburse an off-label prescription based on whether that product has a compendia listing. A drug compendia is produced by a compendia body, such as the United States Pharmacopoeia Drug Information, that lists approved indications that a product has received from the FDA. The compendia bodies also evaluate all of the clinical evidence to determine whether an off-label use of a product should be listed in the compendia as medically appropriate. A compendia listing of an off-label use is a condition typically required by third-party payors, such as Medicare and private payors, to cover that use. Applications for a compendia listing are often based upon the publication of certain data in peer reviewed journals whose publication is often outside the applicant’s control. We are not seeking to achieve acceptance by a compendia body for Actimmune for the treatment of IPF. As a result, additional third-party payors may decide to deny reimbursement for Actimmune for the treatment of IPF and fewer physicians may prescribe Actimmune for such treatment. If either of these were to occur, sales of Actimmune would decline and our revenue would suffer.
Some third-party payors have denied coverage for Actimmune for the treatment of IPF for a variety of reasons, including the cost of Actimmune, the fact that IPF is not an FDA approved indication for Actimmune or a third-party payor’s assessment that a particular patient’s case of IPF has advanced to a stage at which treatment with Actimmune would not have a significant effect. We believe that approximately 60-70% of the patients who seek coverage for Actimmune for the treatment of IPF from private third-party payors are able to obtain coverage. While coverage trends have not changed significantly in the last few years, major health plans could further restrict coverage or adopt a policy of no coverage since we have discontinued the INSPIRE trial and have no further development plans for Actimmune for the treatment of IPF.
Medicare generally does not provide coverage for drugs, like Actimmune, that are administered by injection in the home. Moreover, in connection with the Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003, Medicare has recently discussed the possibility of refusing to provide coverage for products for a specific indication unless the product has been approved by the FDA for that indication. If Medicare were to make a formal decision not to cover the off-label use of products, it may have a negative impact on the willingness of private third-party payors to provide coverage for the off-label use of products such as Actimmune.
Our supply agreement with BI may restrict our ability to establish alternative sources of Actimmune in a timely manner or at an acceptable cost, which may cause us to be unable to meet demand for Actimmune and to lose potential revenue.
Our new supply agreement with BI provides that BI is our exclusive source of supply for Actimmune, except under certain circumstances. Under the terms of the supply agreement, BI is not required to commit to reserving any minimum annual capacity for the manufacture of Actimmune and we cannot seek a secondary source to manufacture Actimmune until BI has indicated to us its inability or unwillingness to meet our requirements. If we are delayed in establishing a secondary supply source for Actimmune, or cannot do so at an acceptable cost, we may suffer a shortage of commercial supply of Actimmune or a higher cost of product, either of which would have a material and adverse effect on our revenue, business and financial prospects.
The activities of competitive drug companies, or others, may limit our products’ revenue potential or render them obsolete.
Our commercial opportunities will be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop or market products that, compared to our products or product candidates:
| | • | | have fewer or less severe adverse side effects; |
| | • | | have better patient compliance; |
34
| | • | | receive better reimbursement terms; |
| | • | | are more accepted by physicians; |
| | • | | are more adaptable to various modes of dosing; |
| | • | | have better distribution channels; |
| | • | | are easier to administer; or |
Even if we are successful in developing effective drugs, our products may not compete effectively with our competitors’ current or future products. We expect that pirfenidone, if approved, may compete with two products that are being developed for the treatment of IPF, although the products are currently-available and approved for other indications. Tracleer, marketed by Actelion, is in Phase III clinical trials for IPF and is the most advanced competitor to pirfenidone. Tracleer is currently approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Letairis, marketed by Gilead, is a product currently approved for pulmonary arterial hypertension that is in Phase III clinical trials for IPF. We expect that ITMN-191, if approved, may compete with telaprevir, which is being developed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals, SCH 503034, which is being developed by Schering-Plough, and TMC 435450, which is being developed by Tibotec Pharmaceuticals and Medivir. Telaprevir, SCH-503034 and TMC 435450 are in Phase II clinical trials. Our competitors include larger, more established, fully integrated pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology companies that have substantially greater capital resources, existing competitive products, larger research and development staffs and facilities, greater experience in drug development and in obtaining regulatory approvals and greater marketing capabilities than we do. For more information, see “Item 1. Business—Competition.”
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property Rights
We may not be able to obtain, maintain and protect certain proprietary rights necessary for the development and commercialization of our products or product candidates.
Our commercial success will depend in part on obtaining and maintaining patent protection on our products and product candidates and successfully defending these patents against third-party challenges. Our ability to commercialize our products will also depend in part on the patent positions of third parties, including those of our competitors. The patent positions of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies can be highly uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. No consistent policy regarding the breadth of claims allowed in biotechnology patents has emerged to date. Accordingly, we cannot predict with certainty the scope and breadth of patent claims that may be afforded to other companies’ patents. We could incur substantial costs in litigation if we are required to defend against patent suits brought by third parties, or if we initiate suits to protect our patent rights.
The degree of future protection for our proprietary rights is uncertain, and we cannot ensure that:
| | • | | we were the first to make the inventions covered by each of our pending patent applications; |
| | • | | we were the first to file patent applications for these inventions; |
| | • | | others will not independently develop similar or alternative technologies or duplicate any of our technologies; |
| | • | | any of our pending patent applications will result in issued patents; |
| | • | | any of our issued patents or those of our licensors will be valid and enforceable; |
| | • | | any patents issued to us or our collaborators will provide a basis for commercially viable products or will provide us with any competitive advantages or will not be challenged by third parties; |
| | • | | we will develop additional proprietary technologies that are patentable; or |
| | • | | the patents of others will not have a material adverse effect on our business. |
35
Others have filed and in the future may file patent applications covering uses and formulations of interferon gamma-1b, a pegylated version of this product, and other products in our development program. If a third party has been or is in the future issued a patent that blocked our ability to commercialize any of our products, alone or in combination, for any or all of the diseases that we are targeting, we would be prevented from commercializing that product or combination of products for that disease or diseases unless we obtained a license from the patent holder. We may not be able to obtain such a license to a blocking patent on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If we cannot obtain, maintain and protect the necessary proprietary rights for the development and commercialization of our products or product candidates, our business and financial prospects will be impaired.
Over time, we will lose our ability to rely upon the intellectual property we currently own to prevent competing products, and after 2011 pirfenidone may only be protected by orphan drug designation, which may impair our ability to generate revenue.
We have licensed certain patents relating to interferon gamma-1b, the active ingredient in Actimmune, from Genentech. A U.S. patent relating to the composition of interferon gamma-1b expires in 2014. Other material U.S. patents relating to interferon gamma-1b expire between 2009 and 2013. We also previously purchased certain patents relating to interferon gamma analogs from Amgen in 2002 including two U.S. patents that issued August 30, 2005 which will expire on August 30, 2022. When these various patents expire, we will be unable to use these patents to try to block others from marketing interferon gamma-1b in the United States.
In 2002, we licensed from Marnac and its co-licensor, KDL, their worldwide rights, excluding Japan, Korea and Taiwan, to develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, including the use of pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF. Effective November 21, 2007, we entered into asset purchase agreements with Marnac and KDL whereby we effectively terminated the prior license agreement by purchasing, among other things, the pirfenidone-related assets covered by such prior license agreement. Among the patents we purchased is U.S. Patent No. 5,310,562. After this U.S. patent expires in 2011, we will not be able to use this patent to block others from marketing pirfenidone for fibrotic disorders, including IPF. The FDA and the EMEA granted pirfenidone orphan drug designation for the treatment of IPF in 2004, which gives us seven years of market exclusivity for the use of pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF from the date that pirfenidone is approved, if it is approved. The pirfenidone molecule itself has no composition of matter patent protection in the United States or elsewhere. Therefore, we may have no ability to prevent others from commercializing pirfenidone for (i) IPF after the orphan drug designation exclusivity period ends, (ii) uses covered by other patents held by third parties, or (iii) other uses in the public domain for which there is no patent protection. We are primarily relying on exclusivity granted from orphan drug designation in IPF to protect pirfenidone from competitors in this indication. The exclusivity period in the United States begins on first NDA approval for this product in IPF and ends seven years thereafter. In addition, a third party could develop pirfenidone for another non-fibrotic disease that also qualifies for orphan drug designation and could be granted seven years exclusivity in that indication. Additionally, in the European Union we have been granted orphan drug designation for pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF by the EMEA, which provides for ten years of market exclusivity in the European Union following first marketing approval in the European Union. We cannot provide any assurance that we will be able to maintain this orphan drug designation.
Once our patents expire, we will be subject to competition from third parties who will be able to use the intellectual property covered by these patents, which could impair our ability to generate revenue.
If we breach our license agreement with Genentech, we may lose our ability to develop and market Actimmune.
We license certain patents and trade secrets relating to Actimmune from Genentech. If we breach this agreement with Genentech, they may be able to terminate the respective license, and we would have no further rights to utilize the licensed patents or trade secrets to develop and market Actimmune, which could adversely affect our revenue and financial prospects.
36
Since the pirfenidone molecule is in the public domain and the patents we acquired from Marnac and KDL are limited to specific methods of use of pirfenidone, we may be subject to competition from third party products with the same active pharmaceutical ingredients as our product candidate.
Composition of matter patent protection for pirfenidone molecule has expired in the United States and elsewhere. Others have obtained patents in the United States and elsewhere relating to methods of use of pirfenidone for the treatment of certain diseases. In 2002, we licensed from Marnac and its co-licensor, KDL, their worldwide rights, excluding Japan, Korea and Taiwan, to develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, including the use of pirfenidone for the treatment of IPF. Effective November 21, 2007, we entered into asset purchase agreements with Marnac and KDL whereby we effectively terminated the prior license agreement by purchasing, among other things, the pirfenidone-related assets covered by such prior license agreement. It is possible that a third party may develop pirfenidone for the treatment of certain diseases that are not covered by patents we had acquired. If such third party were to develop pirfenidone for a use that is not covered by any patents and such third parties successfully developed pirfenidone for non-fibrotic indications, we could face competition from third party products with the same active pharmaceutical ingredient as our product candidate. If a third party were to obtain FDA approval for the use of pirfenidone for an indication before we did, such third party would be first to market and could establish the price for pirfenidone. This could adversely impact our ability to implement our pricing strategy for the product and may limit our ability to maximize the commercial potential of pirfenidone. The presence of a lower priced competitive product with the same active pharmaceutical ingredients as our product could lead to use of the competitive product for our anti-fibrotic indications. This could lead to pricing pressure for pirfenidone, which would adversely affect our ability to generate revenue from the sale of pirfenidone for anti-fibrotic indications.
Litigation or third-party claims of intellectual property infringement could require us to spend substantial time and money and could adversely affect our ability to develop and commercialize products.
Our commercial success depends in part on our ability and the ability of our collaborators to avoid infringing patents and proprietary rights of third parties. Third parties may accuse us or our collaborators of employing their proprietary technology in our products, or in the materials or processes used to research or develop our products, without authorization. Any legal action against our collaborators or us claiming damages and/or seeking to stop our commercial activities relating to the affected products, materials and processes could, in addition to subjecting us to potential liability for damages, require our collaborators or us to obtain a license to continue to utilize the affected materials or processes or to manufacture or market the affected products. We cannot predict whether we, or our collaborators, would prevail in any of these actions or whether any license required under any of these patents would be made available on commercially reasonable terms, if at all. If we are unable to obtain such a license, we, or our collaborators, may be unable to continue to utilize the affected materials or processes or manufacture or market the affected products or we may be obligated by a court to pay substantial royalties and/or other damages to the patent holder. Even if we are able to obtain such a license, the terms of such a license could substantially reduce the commercial value of the affected product or products and impair our prospects for profitability. Accordingly, we cannot predict whether or to what extent the commercial value of the affected product or products or our prospects for profitability may be harmed as a result of any of the liabilities discussed above. Furthermore, infringement and other intellectual property claims, with or without merit, can be expensive and time-consuming to litigate and can divert management’s attention from our core business.
If the owners of the intellectual property we license fail to maintain the intellectual property, we may lose our rights to develop our products or product candidates.
We generally do not control the patent prosecution of technology that we license from others. Accordingly, we are unable to exercise the same degree of control over this intellectual property as we would exercise over technology that we own. For example, if Genentech fails to maintain the intellectual property licensed to us, we may lose our rights to develop and market certain therapeutic uses for Actimmune and may be forced to incur substantial additional costs to maintain or protect the intellectual property or to compel Genentech to do so.
37
If our employees, consultants and vendors do not comply with their confidentiality agreements or our trade secrets otherwise become known, our ability to generate revenue and profits may be impaired.
We rely on trade secrets to protect technology where it is possible that patent protection is not appropriate or obtainable. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect. We protect these rights mainly through confidentiality agreements with our corporate partners, employees, consultants and vendors. These agreements generally provide that all confidential information developed or made known to an individual or company during the course of their relationship with us will be kept confidential and will not be used or disclosed to third parties except in specified circumstances. In the case of employees and consultants, our agreements generally provide that all inventions made by the individual while engaged by us will be our exclusive property. We cannot be certain that these parties will comply with these confidentiality agreements, that we will have adequate remedies for any breach, or that our trade secrets will not otherwise become known or be independently discovered by our competitors. If our trade secrets become known, we may lose a competitive advantage and our ability to generate revenue may therefore be impaired.
By working with corporate partners, research collaborators and scientific advisors, we are subject to disputes over intellectual property, and our ability to obtain patent protection or protect proprietary information may be impaired.
Under some of our research and development agreements, inventions discovered in certain cases become jointly owned by our corporate partner and us and in other cases become the exclusive property of one of us. It can be difficult to determine who owns a particular invention, and disputes could arise regarding those inventions. These disputes could be costly and could divert management’s attention from our business. Our research collaborators and scientific advisors have some rights to publish our data and proprietary information in which we have rights. Such publications may impair our ability to obtain patent protection or protect our proprietary information, which could impair our ability to generate revenue.
Risks Related to Our Financial Results and Other Risks Related to Our Business
Revenue from the sale of Actimmune has been declining and is expected to decline further.
Physicians may choose not to prescribe Actimmune or provide fewer patient referrals for Actimmune for the treatment of IPF for a variety of reasons, some of which are because:
| | • | | Actimmune is not approved by the FDA for the treatment of IPF, and we therefore are unable to market or promote Actimmune for the treatment of IPF; |
| | • | | in our initial and Phase III INSPIRE clinical trials, Actimmune failed to meet the primary and secondary endpoints; |
| | • | | physicians prefer to enroll their patients in clinical trials for the treatment of IPF; |
| | • | | Actimmune does not have a drug compendia listing, often a criterion used by third-party payors to decide whether or not to reimburse off-label prescriptions; |
| | • | | physicians’ patients are unable to receive or lose reimbursement from a third-party reimbursement organization; |
| | • | | physicians are not confident that Actimmune has a clinically significant treatment effect for IPF; or |
| | • | | a competitor’s product shows a clinically significant treatment effect for IPF. |
Negative conditions in the global credit markets may impair the liquidity of a portion of our investment portfolio.
Our investment securities consist of high-grade auction rate securities, corporate debt securities and government agency securities. As of December 31, 2008, our long-term investments included $21.0 million at
38
par value (current carrying value of $17.5 million) of high-grade (AAA rated) auction rate securities issued by state municipalities. Our auction rate securities are debt instruments with a long-term maturity and an interest rate that is reset in short intervals through auctions. The recent conditions in the global credit markets have prevented some investors from liquidating their holdings of auction rate securities because the amount of securities submitted for sale has exceeded the amount of purchase orders for such securities. If there is insufficient demand for the securities at the time of an auction, the auction may not be completed and the interest rates may be reset to predetermined higher rates. Beginning February 2008, auctions failed for the entire $21.0 million of our auction rate securities and as a result our ability to liquidate our investment and fully recover the carrying value of our investment in the near term may be limited or not exist. In 2008, we recorded an impairment charge of $3.5 million for the writedown of the carrying value of these securities as we believe the decline in market value is other-than-temporary. If we attempt to liquidate a portion or all of our holdings in these securities in the near future, we may incur further losses.
If we fail to obtain the capital necessary to fund our operations, we will be unable to successfully execute our business plan.
We believe our existing cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities, anticipated cash flows from our sales of Actimmune and proceeds from our February 2009 public offering, will be sufficient to fund our operating expenses, settlement with the government, debt obligations and capital requirements under our current business plan through at least the end of 2009. However, our current plans and assumptions may change, and our capital requirements may increase in future periods. We have no committed sources of capital and do not know whether additional financing will be available when needed, or, if available, that the terms will be favorable to our stockholders or us. If additional funds are not available, we may be forced to delay or terminate clinical trials, curtail operations or obtain funds through collaborative and licensing arrangements that may require us to relinquish commercial rights or potential markets, or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us. If adequate funds are not available, we will not be able to successfully execute our business plan.
If we continue to incur net losses for an extended period of time, we may be unable to continue our business.
We have incurred net losses since inception, and our accumulated deficit was approximately $755.4 million at December 31, 2008. We expect to incur substantial additional net losses prior to achieving profitability, if ever. The extent of our future net losses and the timing of our profitability are highly uncertain, and we may never achieve profitable operations. We are planning to expand the number of diseases for which our products may be marketed, and this expansion will require significant expenditures. To date, we have generated revenue primarily through the sale of Actimmune. However, Actimmune sales have decreased in recent periods and we expect this trend to continue into the future. We have not generated operating profits to date from our products. If the time required for us to achieve profitability is longer than we anticipate, we may not be able to continue our business.
Failure to accurately forecast our revenue could result in additional charges for excess inventories or non-cancelable purchase obligations.
We base many of our operating decisions on anticipated revenue trends and competitive market conditions, which are difficult to predict. Based on past projected revenue trends, we acquired inventories and entered into non-cancelable purchase obligations in order to meet anticipated increases in demand for our products. However, more recent projected revenue trends resulted in us recording charges of $0.7 million, $1.6 million and $4.5 million in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively, for excess inventories from previous years’ contractual purchases. If revenue levels experienced in future quarters are substantially below our expectations, especially revenue from sales of Actimmune, we could be required to record additional charges for excess inventories and/or non-cancelable purchase obligations. For additional information relating to difficulties we have experienced forecasting revenue, see the risk factor titled “We may fail to meet our publicly announced revenue and/or expense projections and/or other financial guidance, which would cause our stock to decline in value” below.
39
If product liability lawsuits are brought against us, we may incur substantial liabilities.
The testing, marketing and sale of medical products entail an inherent risk of product liability. We have product liability risk for all of our product candidates and for all of the clinical trials we conduct, including our unsuccessful INSPIRE trial. If product liability costs exceed our liability insurance coverage, we may incur substantial liabilities. Whether or not we were ultimately successful in product liability litigation, such litigation would consume substantial amounts of our financial and managerial resources, and might result in adverse publicity, all of which would impair our business. While we believe that our clinical trial and product liability insurance currently provides adequate protection to our business, we may not be able to maintain our clinical trial insurance or product liability insurance at an acceptable cost, if at all, and this insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential claims or losses.
Our use of hazardous materials, chemicals, viruses and radioactive compounds exposes us to potential liabilities.
Our research and development activities involve the controlled use and disposal of hazardous materials, chemicals, infectious disease agents and various radioactive compounds. Although we believe that our safety procedures for handling and disposing of such materials comply with the standards prescribed by state and federal regulations, we cannot completely eliminate the risk of accidental contamination or injury from these materials. In the event of such an accident, we could be held liable for significant damages or fines, which may not be covered by or may exceed our insurance coverage.
If we fail to fulfill our obligations under the Deferred Prosecution Agreement with the U.S. Department of Justice or the Corporate Integrity Agreement with the Office of Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services it could have a material adverse effect on our business.
On October 26, 2006, we announced that we entered into a Deferred Prosecution Agreement with the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California and a Corporate Integrity Agreement with the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. Under the terms of the Deferred Prosecution Agreement, the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California filed an Information charging us with one count of off-label promotion of Actimmune for use with IPF, but has agreed to defer prosecution of such charge during the two year term of the Deferred Prosecution Agreement. The U.S. Attorney will seek dismissal of the Information after the two year period if we comply with the provisions of the Deferred Prosecution Agreement. Under the terms of the Corporate Integrity Agreement, the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services has agreed to waive any potential exclusion against us from participation in federal health care programs provided that we comply with the terms of the Corporate Integrity Agreement for a period of five years. If we do not satisfy our obligations under the Deferred Prosecution Agreement, the U.S. Attorney can proceed with the prosecution against us for actions involving the off-label promotion of Actimmune for use with IPF, as set forth in the Information, and may consider additional actions against us, which could have significant adverse effects on our operations and financial results. If we do not satisfy our obligations under the Corporate Integrity Agreement, the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services could potentially exclude us from participation in federal health care programs, which could have significant adverse effects on our operations and financial results.
We may be required to indemnify certain of our former officers and directors if any action is taken by the U.S. Attorney or other authorities with respect to those individuals in connection with the off-label promotion of Actimmune for use with IPF, and there can be no assurance that our directors’ and officers’ liability insurance will cover all of these indemnification obligations.
Insurance coverage is increasingly difficult to obtain or maintain.
While we currently maintain clinical trial and product liability insurance, directors’ and officers’ liability insurance, general liability insurance, property insurance and warehouse and transit insurance, first- and third- party
40
insurance is increasingly more costly and narrower in scope, and we may be required to assume more risk in the future. If we are subject to third-party claims or suffer a loss or damage in excess of our insurance coverage, we may be required to share that risk in excess of our insurance limits. Furthermore, any first- or third-party claims made on our insurance policies may impact our future ability to obtain or maintain insurance coverage at reasonable costs, if at all.
Budget or cash constraints may force us to delay our efforts to develop certain products in favor of developing others, which may prevent us from meeting our stated timetables and commercializing those products as quickly as possible.
Because we are an emerging company with limited resources, and because research and development is an expensive process, we must regularly assess the most efficient allocation of our research and development resources. Accordingly, we may choose to delay our research and development efforts for a promising product candidate to allocate those resources to another program, which could cause us to fall behind our initial timetables for development of certain product candidates. As a result, we may not be able to fully realize the value of some of our product candidates in a timely manner, since they will be delayed in reaching the market, or may not reach the market at all.
Failure to attract, retain and motivate skilled personnel and cultivate key academic collaborations will delay our product development programs and our business development efforts.
We had 130 full-time employees as of February 28, 2009, and our success depends on our continued ability to attract, retain and motivate highly qualified management and scientific personnel and on our ability to develop relationships with leading academic scientists. Competition for personnel and academic collaborations is intense. We are highly dependent on our current management and key scientific and technical personnel, including Daniel G. Welch, our Chief Executive Officer and President, as well as the other principal members of our management. None of our employees, including members of our management team, has a long-term employment contract, and any of our employees can leave at any time. Our success will depend in part on retaining the services of our existing management and key personnel and attracting and retaining new highly qualified personnel. In addition, we may need to hire additional personnel and develop additional academic collaborations if we expand our research and development activities. We do not know if we will be able to attract, retain or motivate personnel or cultivate academic collaborations. Our inability to hire, retain or motivate qualified personnel or cultivate academic collaborations would harm our business.
Risks Related to our Common Stock
We may fail to meet our publicly announced revenue and/or expense projections and/or other financial guidance, which would cause our stock to decline in value.
There are a number of reasons why we might fail to meet our revenue and/or expense projections and/or other financial guidance, including, but not limited to, the following:
| | • | | if only a subset of or no affected patients respond to therapy with any of our products or product candidates; |
| | • | | the actual dose or efficacy of the product for a particular condition may be different than currently anticipated; |
| | • | | negative publicity about the results of our clinical studies, such as the 2007 failure of INSPIRE to meet it’s primary endpoint and our resulting decision to discontinue the trial, or those of others with similar or related products may reduce demand for our products and product candidates; |
| | • | | the treatment regimen may be different in duration than currently anticipated; |
| | • | | treatment may be sporadic; |
41
| | • | | we may not be able to sell a product at the price we expect; |
| | • | | we may not be able to accurately calculate the number of patients using the product; |
| | • | | we may not be able to supply enough product to meet demand; |
| | • | | there may be current and future competitive products that have greater acceptance in the market than our products do; |
| | • | | we may decide to divest a product; |
| | • | | our development activities may proceed faster than planned; |
| | • | | we may decide to change our marketing and educational programs; |
| | • | | clinical trial participation may reduce product sales; or |
| | • | | physicians’ prescriptions or patient referrals for Actimmune may decline. |
If we fail to meet our revenue and/or expense projections and/or other financial guidance for any reason, our stock could decline in value.
Failure to maintain effective internal control over financial reporting in accordance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 could have a material adverse effect on our stock price.
Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the related rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission require an annual management assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting and a report by our independent registered public accounting firm attesting to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting at the end of the fiscal year. If we fail to maintain the adequacy of our internal control over financial reporting, as such standards are modified, supplemented or amended from time to time, we may not be able to ensure that we can conclude on an ongoing basis that we have effective internal control over financial reporting in accordance with Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the related rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission. If we cannot in the future favorably assess, or our independent registered public accounting firm is unable to provide an unqualified attestation report on, the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, investor confidence in the reliability of our financial reports may be adversely affected, which could have a material adverse effect on our stock price.
Our stock price may be volatile, and an investment in our stock could decline in value.
The trading price of our common stock has been and is likely to continue to be extremely volatile. During the twelve-month period ended December 31, 2008, the closing price of our common stock on the NASDAQ Global Select Market ranged from a high of $19.80 in April 2008 to a low of $9.73 in December 2008. Our stock price could be subject to wide fluctuations in response to a variety of factors, including, but not limited to any announcements made by Shionogi with respect to their pirfenidone product and all the factors discussed in this “Risk Factors” section.
In addition, the stock market in general, and the stock price of companies listed on the NASDAQ, and biotechnology companies in particular, have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of these companies. Broad market and industry factors may negatively affect the market price of our common stock, regardless of actual operating performance. Periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities frequently results in securities class action and shareholder derivative litigation against that company. This type of litigation can result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources.
42
If our officers, directors and certain stockholders choose to act together, they may be able to significantly influence our management and operations, acting in their own best interests and not necessarily those of other stockholders.
At December 31, 2008, our directors, executive officers and greater than 5% stockholders and their affiliates beneficially owned approximately 81% of our issued and outstanding common stock. Accordingly, they collectively may have the ability to significantly influence the election of all of our directors and to significantly influence the outcome of corporate actions requiring stockholder approval, such as mergers or a financing in which we sell more than 20% of our voting stock at a discount to market price. They may exercise this ability in a manner that advances their own best interests and not necessarily those of other stockholders. This concentration of ownership could also depress our stock price.
Substantial sales of shares may negatively impact the market price of our common stock.
If our stockholders sell substantial amounts of our common stock, including shares issued upon the exercise of outstanding options or conversion of our outstanding convertible notes the market price of our common stock may decline. In addition, the existence of our outstanding convertible notes may encourage short selling by market participants. These sales also might make it more difficult for us to sell equity or equity related securities in the future at a time and price that we deem appropriate. We are unable to predict the effect that sales may have on the then-prevailing market price of our common stock.
We have filed registration statements covering the approximately 10,994,802 shares of common stock that are either issuable upon the exercise of outstanding options or reserved for future issuance pursuant to our stock plans as of December 31, 2008. We have also filed a shelf registration statement covering the resale of our 0.25% convertible senior notes due in 2011 and the 3,929,505 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of those notes.
On October 29, 2004, we entered into an Amended and Restated Standstill Agreement with Warburg Pincus Equity Partners, L.P. and certain of its affiliates (“Warburg Pincus”) that permits Warburg Pincus to acquire up to 25% of our outstanding common stock in the open market. Under this agreement, Warburg Pincus may acquire up to 25% of our outstanding common stock and we have granted Warburg Pincus certain registration rights with respect to its holdings. The restriction on Warburg Pincus’ acquisition of additional shares of our common stock expired on October 29, 2007. In exchange for allowing Warburg Pincus to increase its ownership stake, Warburg Pincus has granted the independent members of our board of directors the right to vote the shares of InterMune common stock owned by Warburg Pincus in excess of 19.9%. In addition, Warburg Pincus has agreed to certain limitations on the manner in which it may dispose of its ownership interest in InterMune. In connection with this transaction, we also amended our stockholder Rights Plan to allow Warburg Pincus to acquire up to 25% of our outstanding common stock. Jonathan S. Leff, a member of our board of directors, is a managing director of Warburg Pincus LLC and a partner of Warburg Pincus & Co., which are affiliates of Warburg Pincus Equity Partners, L.P. In December 2006, we filed a shelf registration statement covering the sale of 7,357,549 shares held by Warburg Pincus and up to $175.0 million from any combination of debt securities, preferred stock, common stock or warrants that may be sold by us. In September 2007 and February 2009, we completed public offerings of 4,025,000 shares each of registered common stock under this shelf registration statement.
Management may invest or spend the proceeds of our February 2009 public offering in ways with which you may not agree and in ways that may not yield a return to our stockholders.
Management will retain broad discretion over the use of proceeds from our February 2009 public offering. Stockholders may not deem such uses desirable, and our use of the proceeds may not yield a significant return or any return at all for our stockholders. Management intends to use the proceeds from this offering for general corporate purposes, which may include funding research and development including the preparation and submission of an NDA and MAA for pirfenidone, increasing our working capital, reducing our indebtedness,
43
acquisitions or investments in businesses, products or technologies that are complementary to our own, and capital expenditures. Because of the number and variability of factors that determine our use of the proceeds from this offering, our actual uses of the proceeds of this offering may vary substantially from our currently planned uses. We intend to invest the net proceeds from this offering in short-term, investment-grade, interest-bearing securities until we are ready to use them.
Under the terms of our settlement with the U.S. Department of Justice concerning promotional activities for Actimmune by certain of our former employees, we may be required to apply a portion of the proceeds of our February 2009 public offering towards the making of an accelerated payment to the U.S. Department of Justice.
As part of the comprehensive settlement we entered into with the U.S. Department of Justice concerning promotional activities for Actimmune by certain of our former employees during a period that ended in June of 2003, we entered into a Civil Settlement Agreement that provides that if, after the effective date of the settlement, we receive over $150.0 million from in license fees and milestone payments from partnering (excluding any research and development contributions), external debt and equity financing during the term of the settlement, 20% of the amount over $150.0 million (subject to a cap of $10.0 million per year) must be applied to the acceleration of the $36.9 million in original scheduled principal payments under the settlement. We entered into the Civil Settlement Agreement on October 25, 2006 and it became effective on December 4, 2006, the date the settlement was approved by the United States District Court.
Since entering into the Civil Settlement Agreement, we have received approximately $35.0 million in license fees and milestone payments under our various partnering and collaboration agreements and approximately $136.9 million in equity financing. As a result, we have exceeded the aforementioned $150.0 million threshold by approximately $21.9 million and have made an accelerated payment to the U.S. Department of Justice of approximately $4.4 million in March 2009.
We have implemented anti-takeover provisions, which could discourage, prevent or delay a takeover, even if the acquisition would be beneficial to our stockholders, or frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management or Board of Directors.
The existence of our stockholder Rights Plan and provisions of our Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws, as well as provisions of Delaware law, could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire us, even if doing so would benefit our stockholders. In addition, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace members of our board of directors. Because our board of directors is responsible for appointing the members of our management team, these provisions could in turn affect any attempt by our stockholders to replace current members of our management team. These provisions:
| | • | | establish a classified board of directors so that not all members of our board may be elected at one time; |
| | • | | authorize the issuance of up to 5,000,000 shares of “blank check” preferred stock that could be issued by our board of directors to increase the number of outstanding shares and hinder a takeover attempt; |
| | • | | limit who may call a special meeting of stockholders; |
| | • | | prohibit stockholder action by written consent, thereby requiring all stockholder actions to be taken at a meeting of our stockholders; and |
| | • | | establish advance notice requirements for nominations for election to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon at stockholder meetings. |
44
In addition, Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibits business combinations between us and one or more significant stockholders unless specified conditions are met, may discourage, delay or prevent a third party from acquiring us.
We have never paid dividends on our capital stock, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
We have never declared or paid any dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain all of our future earnings, if any, to finance our operations and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our capital stock in the foreseeable future. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of our common stock will be the sole source of gain for investors in our common stock for the foreseeable future.
Risks Related to our Outstanding Notes
Our indebtedness and debt service obligations may adversely affect our cash flow.
As of December 31, 2008, our annual debt service obligation on the $85.0 million in aggregate principal amount of our 0.25% convertible senior notes due March 1, 2011 and $85.0 million in aggregate principal amount of our 5.00% convertible senior notes due March 1, 2015 was a combined $4.5 million. We intend to fulfill our current debt service obligations, including repayment of the principal, both from cash generated by our operations and from our existing cash and investments. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash to meet these obligations and need to use existing cash or liquidate investments in order to fund our current debt service obligations, including repayment of the principal, we may have to delay or curtail research and development programs.
We may add additional lease lines to finance capital expenditures and may obtain additional long-term debt and lines of credit. If we issue other debt securities in the future, our debt service obligations will increase further.
Our indebtedness could have significant additional negative consequences, including, but not limited to:
| | • | | requiring the dedication of a substantial portion of our expected cash flow from operations to service our indebtedness, thereby reducing the amount of our expected cash flow available for other purposes, including capital expenditures; |
| | • | | increasing our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions; |
| | • | | limiting our ability to obtain additional financing; |
| | • | | limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the industry in which we compete; and |
| | • | | placing us at a possible competitive disadvantage to less leveraged competitors and competitors that have better access to capital resources. |
We may not have the ability to raise the funds necessary to finance any required redemptions of our outstanding convertible notes, which might constitute a default by us.
If a designated event, such as the termination of trading of our common stock on the NASDAQ Global Select Market or a specified change of control transaction occurs prior to maturity, we may be required to redeem all or part of our 0.25% convertible senior notes due 2011 and 5.00% convertible senior notes due 2015. We may not have enough funds to pay the redemption price for all tendered notes. Although the indentures governing the 0.25% convertible senior notes due 2011 and 5.00% convertible senior notes due 2015 allow us in certain circumstances to pay the applicable redemption prices in shares of our common stock, if a designated event were to occur, we may not have sufficient funds to pay the redemption prices for all the notes tendered.
45
We have not established a sinking fund for payment of our outstanding notes, nor do we anticipate doing so. In addition, any future credit agreements or other agreements relating to our indebtedness may contain provisions prohibiting redemption of our outstanding notes under certain circumstances, or expressly prohibit our redemption of our outstanding notes upon a designated event or may provide that a designated event constitutes an event of default under that agreement. If a designated event occurs at a time when we are prohibited from purchasing or redeeming our outstanding notes, we could seek the consent of our lenders to redeem our outstanding notes or attempt to refinance this debt. If we do not obtain consent, we would not be permitted to purchase or redeem our outstanding notes. Our failure to redeem tendered notes would constitute an event of default under the indenture for the notes, which might constitute a default under the terms of our other indebtedness.
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
Our facilities currently consist of approximately 55,898 square feet of office space located at our headquarters at 3280 Bayshore Boulevard, Brisbane, California. In December 2000, we entered into a ten-year lease for this building. In May 2006, we entered into an amendment to our existing lease to expand our existing office and laboratory space by approximately 15,000 square feet on the first floor of 3260 Bayshore Boulevard, Brisbane, California 94005. The lease expires concurrently with our existing facility lease in March 2011. We believe that our facilities are adequate for our current needs, and that suitable additional or substitute space will be available in the future to replace our existing facility, if necessary, or accommodate expansion of our operations.
Class Action Lawsuits
On May 8, 2008, a complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledDeborah Jane Jarrett, Nancy Isenhower, and Jeffrey H. Frankel v. InterMune, Inc., W. Scott Harkonen, and Genentech, Inc., Case No. C-08-02376 (the “Jarrett Action”). Plaintiffs alleged that they were administered Actimmune, and they purported to sue on behalf of a class of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleged that the Company fraudulently misrepresented the medical benefits of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF and promoted Actimmune for IPF. The complaint asserted various claims against the Company, including civil RICO, unfair competition, violation of various state consumer protection statutes, and unjust enrichment. The complaint sought various damages in an unspecified amount, including compensatory damages, treble damages, punitive damages, restitution, disgorgement, prejudgment and post-judgment interest on any monetary award, and the reimbursement of the plaintiffs’ legal fees and costs. The complaint also sought equitable relief.
On June 11, 2008, a nearly identical complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledLinda K. Rybkoski v. InterMune, Inc., W. Scott Harkonen, and Genentech, Inc., Case No. CV-08-2916 (the “Rybkoski Action”). Plaintiff in this action alleged that she was administered Actimmune and purported to sue on behalf of a class of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleged virtually identical facts to those alleged in the Jarrett Action; it also asserted the same claims against the Company and sought the same relief. On July 23, 2008, the Rybkoski Action was ordered related to the Jarrett Action and is now pending before the same judge and is proceeding on the same schedule.
On August 8, 2008, a similar complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledZurich American Insurance Company v. Genentech, Inc., InterMune, Inc., and W.Scott Harkonen, Case No. CV-08-3797 (the “Zurich Action”). Plaintiff in the Zurich Action, which allegedly
46
provides health and pharmacy benefits to its insureds in the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and several U.S. territories, alleged that it paid for prescriptions of Actimmune and purported to sue on behalf of a class of third-party payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleged similar facts to those alleged in the Jarrett and Rybkoski Actions, and it also asserted civil RICO, unfair competition, various state consumer protection, and unjust enrichment claims against the Company. The complaint sought various damages in an unspecified amount, including compensatory damages, treble damages, punitive damages, prejudgment interest on all damages, and the reimbursement of the plaintiffs’ legal fees and costs. The complaint also sought a declaration that the conduct alleged was unlawful, as well as injunctive relief. On September 5, 2008, the Zurich Action was ordered related to the Jarrett Action and assigned to the same judge.
On September 26, 2008, Plaintiffs in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions filed an identical First Amended Class Action Complaint in all three actions. The First Amended Complaint, a putative nationwide class action on behalf of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune, is very similar to the first complaint that was filed in the Jarrett Action. It alleges the same basic facts, namely, that the Company fraudulently misrepresented the medical benefits of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF and promoted Actimmune for IPF. The First Amended Complaint asserts various claims against the Company, including civil RICO, unfair competition, violation of various state consumer protection statutes, and unjust enrichment. The First Amended Complaint seeks various damages in an unspecified amount, including the same categories of damages and other relief that were originally sought in the Jarrett Action.
On October 20, 2008, InterMune and the other defendants filed motions to dismiss the First Amended Complaint in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions.
On September 29, 2008, a similar complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledGovernment Employees Health Association, Inc. v. InterMune, Inc., W. Scott Harkonen and Genentech, Inc., Case No. CV-08-4531 (the “GEHA Action”). Plaintiff in the GEHA Action is allegedly a national health insurance plan serving federal employees and retirees, as well as their families. Plaintiff alleges that it paid for more than $4 million of Actimmune prescriptions during the class period, and it purports to sue on behalf of a class of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleges that the Company fraudulently misrepresented the medical benefits of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF and promoted Actimmune for IPF. The complaint asserts the same causes of action against the Company as the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions, including civil RICO, unfair competition, violation of various state consumer protection statutes, and unjust enrichment. The complaint seeks various damages in an unspecified amount, including compensatory damages, treble damages, punitive damages, restitution, disgorgement, prejudgment and post-judgment interest on any monetary award, and the reimbursement of the plaintiffs’ legal fees and costs. The complaint also seeks appropriate equitable relief. The GEHA action was subsequently related to the other actions, so that all four are pending before the same judge. By stipulation, the parties to the GEHA Action agreed that the briefing already submitted on the motions to dismiss in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions would constitute the briefing on a motion to dismiss in the GEHA Action.
The motions to dismiss in all four cases were heard on February 2, 2009, and the motions were taken under submission by the Court. We expect a ruling sometime in March or April 2009, although it may take longer. The court had stayed discovery until at least the time of the hearing on the motions to dismiss, and no party has sought to conduct discovery following the February 2, 2009 hearing. In the meantime, on February 24, 2009, the plaintiffs in all four actions sought to consolidate the four actions for purposes of pretrial proceedings; the defendants have not opposed this request, and the Court has not yet ruled on it.
The Company believes it has substantial factual and legal defenses to the claims at issue and intends to defend the above actions vigorously. We may enter into discussions regarding settlement of these matters, and may enter into settlement agreements, if we believe settlement is in the best interests of our shareholders. We cannot reasonably estimate the possible loss or range of loss that may arise from these lawsuits.
47
Department of Justice Settlement
On November 9, 2004, we received a subpoena from the U.S. Department of Justice requiring us to provide the Department of Justice with certain information relating to Actimmune, including information regarding the promotion and marketing of Actimmune. On October 25, 2006 we reached a comprehensive settlement with the government to resolve all claims without criminal sanctions relating to promotional activities for Actimmune for IPF by our former employees during a period ending in June 2003. As part of this comprehensive settlement, we entered into a Civil Settlement Agreement with the United States Department of Justice and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California. In addition, we entered into a Deferred Prosecution Agreement with the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California and a Corporate Integrity Agreement with the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services.
Under the terms of the Civil Settlement Agreement, we agreed to pay $36.9 million plus 5% interest on the then outstanding principal balance to the government over a period of five years, an amount to be shared between the Federal and participating State governments as per the agreement and the Medicaid Program. In October 2008, we entered into settlement and release agreements with the majority of the participating State governments pursuant to which the State portion of the aforementioned $36.9 million was distributed among such participating State governments. We recorded a $36.9 million charge during 2006 to reflect the final terms of the Civil Settlement Agreement. We paid $8.4 million, $4.1 million and $4.1 million in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively, and are required to make additional payments on the remaining settlement amount over the next three years in annual installments. The Civil Settlement Agreement contains a provision for the acceleration of certain of the $36.9 million in original scheduled principal payments if we receive over $150.0 million from partnering, license fees and milestone payments (excluding any research and development contributions), external debt and equity financing during the term of the Civil Settlement Agreement, subject to a cap on any acceleration of payment of $10.0 million in any one year. Since entering into the Civil Settlement Agreement, we have received $35.0 million in license fees and milestone payments under our various partnering and collaboration agreements and approximately $136.9 million in equity financing. As a result, we have exceeded the aforementioned $150.0 million threshold by approximately $21.9 million and have made an accelerated payment to the U.S. Department of Justice of approximately $4.4 million in March 2009.
Under the terms of the Deferred Prosecution Agreement, the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California will file an Information charging us with one count of off-label promotion of Actimmune for use with IPF, but will defer prosecution of such charge during the two year term of the Deferred Prosecution Agreement. The Deferred Prosecution Agreement became effective December 2006 when it was approved by the United States District Court for the Northern District of California. As a result, the two year term of such agreement expired December 2008 and the Information filed against us has since been dismissed.
Under the terms of the Corporate Integrity Agreement, the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services agreed to waive any potential exclusion of us from participation in federal health care programs provided that we comply with the terms of the Corporate Integrity Agreement for a period of five years. As part of the agreement, we agreed to retain an independent review organization to conduct periodic reviews of our promotional processes and policies as well as reviews of certain medical affairs group records.
Indemnity Agreement
On or about March 22, 2000, the Company entered into an Indemnity Agreement with W. Scott Harkonen M.D., who served as the Company’s chief executive officer until June 30, 2003. The Indemnity Agreement obligates the Company to hold harmless and indemnify Dr. Harkonen against expenses (including attorneys’ fees), witness fees, damages, judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement and any other amounts Dr. Harkonen becomes legally obligated to pay because of any claim or claims made against him in connection
48
with any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding , whether civil, criminal, arbitrational, administrative or investigative, to which Dr. Harkonen is a party by reason of the fact that he was a director, officer, employee or other agent of the Company. The Indemnity Agreement establishes exceptions to the Company’s indemnification obligation, including but not limited to claims “on account of [Dr. Harkonen’s] conduct that is established by a final judgment as knowingly fraudulent or deliberately dishonest or that constituted willful misconduct,” claims “on account of [Dr. Harkonen’s] conduct that is established by a final judgment as constituting a breach of [Dr. Harkonen’s] duty of loyalty to the Corporation or resulting in any personal profit or advantage to which [Dr. Harkonen] was not legally entitled,” and claims “for which payment is actually made to [Dr. Harkonen] under a valid and collectible insurance policy.” The Indemnity Agreement, however, obligates the Company to advance all expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred by Dr. Harkonen in connection with such proceedings, subject to an undertaking by Dr. Harkonen to repay said amounts if it shall be determined ultimately that he is not entitled to be indemnified by the Company.
Dr. Harkonen has been named as a defendant in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich and GEHA Actions described above. Dr. Harkonen also was a target of the investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice regarding the promotion and marketing of Actimmune. On March 18, 2008, a federal grand jury indicted Dr. Harkonen on two felony counts related to alleged improper promotion and marketing of Actimmune during the time Dr. Harkonen was employed by the Company. Trial in the criminal case (the “Criminal Action”) is set for June 2009.
Prior to December 2008, insurers that issued directors & officers (“D&O”) liability insurance to the Company had advanced all of Dr. Harkonen’s expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions. Those insurers included National Union Fire Insurance Company of Pittsburgh, PA (“AIG”), Underwriters at Lloyd’s, London (“Lloyd’s”), and Continental Casualty Company (“CNA”). On November 19, 2008, however, the insurer that issued a $5 million D&O insurance policy providing coverage excess of the monetary limits of coverage provided by AIG, Lloyd’s and CNA, Arch Specialty Insurance Company (“Arch”), advised the Company that the limits of the underlying coverage were expected to be depleted by approximately December 15, 2008; that Arch “disclaims coverage” based on misstatements and misrepresentations allegedly made by Dr. Harkonen in documents provided in the application for the Arch policy and the underlying Lloyd’s policy; and, based on that disclaimer, Arch would not be advancing any of Dr. Harkonen’s expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred in Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions.
As a result of Arch’s disclaimer of coverage and refusal to advance expenses, including attorneys’ fees, the Company has as of approximately December 15, 2008, become obligated to advance such expenses incurred by Dr. Harkonen in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions.
On January 13, 2009, the Company submitted to the American Arbitration Association (“AAA”) a Demand for Arbitration, InterMune, Inc. v. Arch Specialty Insurance Co., No. 74 194 01128 08 JEMO. Dr. Harkonen also is a party to the Arbitration. The Demand for Arbitration seeks an award compelling Arch to advance Dr. Harkonen’s legal fees and costs incurred in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions, and to advance other former officers’ legal fees and costs incurred in relation to the Department of Justice investigation. The AAA appointed a panel of three arbitrators on February 26, 2009. The parties to the Arbitration have until March 13, 2009, to move to disqualify any of the arbitrators. The Company expects that an initial hearing in the Arbitration will be scheduled shortly after the membership of the Arbitration panel is finalized.
| ITEM 4. | SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS |
None.
49
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Since the initial public offering of our common stock, $0.001 par value, on March 24, 2000, our common stock has traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol “ITMN.”
The following table sets forth the high and low closing sales prices of our common stock, as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market for the fiscal periods indicated:
| | | | | | |
Fiscal Year: | | High | | Low |
2008 | | | | | | |
First Quarter | | $ | 19.35 | | $ | 12.15 |
Second Quarter | | | 19.80 | | | 12.70 |
Third Quarter | | | 19.58 | | | 12.98 |
Fourth Quarter | | | 17.12 | | | 9.73 |
2007 | | | | | | |
First Quarter | | $ | 35.97 | | $ | 21.86 |
Second Quarter | | | 30.62 | | | 24.42 |
Third Quarter | | | 27.06 | | | 18.61 |
Fourth Quarter | | | 20.00 | | | 13.33 |
As of February 28, 2009, we had 71 stockholders of record. In addition, we believe that a significant number of beneficial owners of our common stock hold their shares in street name.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any dividends on our capital stock. We currently intend to retain all of our future earnings, if any, to finance our operations and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our capital stock in the foreseeable future.
50
Performance Graph
We show below the cumulative total return to our stockholders during the period from December 31, 2003 through December 31, 2008 in comparison to the cumulative return on the NASDAQ Composite and the AMEX Biotechnology Index during that same period. The results assume that $100 was invested on December 31, 2003.
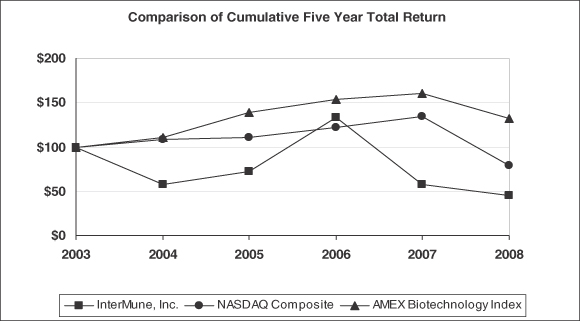
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Base period
December
2003 | | Years Ending December 31, |
Company/Index | | | 2004 | | 2005 | | 2006 | | 2007 | | 2008 |
InterMune, Inc. | | 100 | | $ | 57.25 | | $ | 72.54 | | $ | 132.77 | | $ | 57.56 | | $ | 45.68 |
NASDAQ Composite | | 100 | | | 108.41 | | | 110.79 | | | 122.16 | | | 134.29 | | | 79.25 |
AMEX Biotechnology Index | | 100 | | | 111.05 | | | 138.93 | | | 153.90 | | | 160.48 | | | 132.05 |
The information under “Performance Graph” is not soliciting material, is not deemed filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission and is not to be incorporated by reference in any filing of InterMune, Inc. under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, whether made before or after the filing date of this 10-K and irrespective of any general incorporation language in those filings.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
See the information incorporated by reference into Part III, Item 12 of this report for information regarding securities authorized for issuance under our equity compensation plans.
51
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
The selected consolidated financial data that appears below and on the following page has been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements. This historical data should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements and the related Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements contained in this Report, and with the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Item 7 of this Report. The selected consolidated statement of operations data for each of the three years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 are derived from the audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Report. The selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 are derived from audited financial statements not included in this Report.
In December 2005, we sold our Infergen product, including related intellectual property rights and inventory, to Valeant. The operating results of our Infergen activities, which include allocations of research and development and selling, general and administrative expenses, have been reclassified as discontinued operations for all periods presented.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | 2004 | |
| | | (In thousands, except per share data) | |
Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Actimmune | | $ | 29,880 | | | $ | 53,420 | | | $ | 90,317 | | | $ | 107,633 | | | $ | 124,980 | |
Other products | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,863 | | | | 3,700 | |
Collaboration revenue | | | 18,272 | | | | 13,272 | | | | 467 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenue, net | | | 48,152 | | | | 66,692 | | | | 90,784 | | | | 110,496 | | | | 128,680 | |
Costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | | 8,989 | | | | 14,109 | | | | 24,608 | | | | 35,022 | | | | 33,882 | |
Research and development | | | 104,581 | | | | 105,939 | | | | 103,849 | | | | 82,736 | | | | 75,683 | |
Acquired research and development and milestone (credits) payments (1) | | | — | | | | 13,725 | | | | — | | | | (10,000 | ) | | | — | |
General and administrative | | | 30,260 | | | | 29,577 | | | | 40,372 | | | | 58,854 | | | | 55,132 | |
Provision for government settlement | | | — | | | | — | | | | 36,944 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Restructuring charges | | | — | | | | 10,246 | | | | — | | | | 5,549 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total costs and expenses | | | 143,830 | | | | 173,596 | | | | 205,773 | | | | 172,161 | | | | 164,697 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations | | | (95,678 | ) | | | (106,904 | ) | | | (114,989 | ) | | | (61,665 | ) | | | (36,017 | ) |
Interest income | | | 5,616 | | | | 10,699 | | | | 9,512 | | | | 3,965 | | | | 3,490 | |
Interest and other income (expense) | | | (7,780 | ) | | | (666 | ) | | | (485 | ) | | | 52 | | | | (12,516 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations before income taxes | | | (97,842 | ) | | | (96,871 | ) | | | (105,962 | ) | | | (57,648 | ) | | | (45,043 | ) |
Income tax benefit | | | — | | | | (2,275 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (97,842 | ) | | | (94,596 | ) | | | (105,962 | ) | | | (57,648 | ) | | | (45,043 | ) |
Discontinued operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | 103 | | | | 4,994 | | | | (1,244 | ) | | | (32,925 | ) | | | (14,435 | ) |
Gain on sale of discontinued operations (net of transaction costs) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 85,338 | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | 103 | | | | 4,994 | | | | (1,244 | ) | | | 52,413 | | | | (14,435 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (97,739 | ) | | $ | (89,602 | ) | | $ | (107,206 | ) | | $ | (5,235 | ) | | $ | (59,478 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic and diluted loss per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | $ | (2.51 | ) | | $ | (2.67 | ) | | $ | (3.18 | ) | | $ | (1.79 | ) | | $ | (1.42 | ) |
Discontinued operations | | $ | — | | | $ | 0.15 | | | $ | (0.04 | ) | | $ | 1.63 | | | $ | (0.45 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share | | $ | (2.51 | ) | | $ | (2.52 | ) | | $ | (3.22 | ) | | $ | (0.16 | ) | | $ | (1.87 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares used in computing basic and diluted net loss per share | | | 38,982 | | | | 35,493 | | | | 33,277 | | | | 32,220 | | | | 31,760 | |
52
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | | | 2004 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
Balance sheet data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities (2) | | $ | 154,713 | | | $ | 235,292 | | | $ | 214,549 | | | $ | 215,525 | | | $ | 183,025 | |
Working capital | | | 96,680 | | | | 214,463 | | | | 201,924 | | | | 185,295 | | | | 185,133 | |
Total assets | | | 172,224 | | | | 262,445 | | | | 257,583 | | | | 266,242 | | | | 268,795 | |
Long-term obligations | | | 170,000 | | | | 170,000 | | | | 170,000 | | | | 170,000 | | | | 170,000 | |
Accumulated deficit | | | (755,428 | ) | | | (657,689 | ) | | | (568,087 | ) | | | (460,881 | ) | | | (455,646 | ) |
Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) | | | (124,872 | ) | | | (30,888 | ) | | | (39,797 | ) | | | 31,767 | | | | 32,791 | |
| (1) | These charges represent acquired research and development and milestone payments for projects that were in development, had not reached technical feasibility and had no foreseeable alternative future uses at the time of acquisition or when the milestone became payable. The 2005 balance reflects the reversal of the milestone liability in connection with the divestiture of oritavancin. Please see “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Results of Operations” and Note 5 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| (2) | Includes $17,494 of non-current available-for-sale securities as of December 31, 2008. |
53
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
Overview
For additional overview information relating to our business, including Actimmune, co-promotion and our product development programs, please see the discussion in “Item 1. Business—Overview,” which is incorporated herein by reference.
Significant License/Acquisition Agreements
We are highly dependent on technology we license or acquire from third parties. Actimmune, which is currently our sole marketed product, is subject to a license agreement with Genentech, Inc. The majority of our clinical development pipeline is also based on technology that we have licensed from third parties. Details of these agreements can be found elsewhere in this Report under “Item 1. Business—License and Other Agreements,” Notes 6 and 7 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, and under the heading “Results of Operations” below.
We will be required to make contingent milestone payments in accordance with all of our license and acquisition agreements in the aggregate amount of $70.9 million if all of the milestones defined in each of the agreements are achieved. These milestones include development, regulatory approval, commercialization and sales milestones. Of the $70.9 million in aggregate milestone payments, $53.5 million in contingent payments would be made by us only if positive Phase III data and registration in the United States and European Union are achieved for pirfenidone, of which $13.5 million has been paid in March 2009.
Our Need for Additional Capital
We commenced operations in 1998 and have incurred significant losses to date. Our revenue has been limited primarily to sales of Actimmune, which has been declining in recent years, derived from physicians’ prescriptions for the off-label use of Actimmune in the treatment of IPF. We expect to continue to incur net losses over the next several years as we continue the development of our advanced-stage pulmonology pipeline and our research-stage hepatology pipeline, apply for regulatory approvals for pirfenidone and grow our operations. Although we believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities, together with anticipated cash flows from sales of Actimmune and the proceeds from our February 2009 public offering, described below, will be sufficient to fund our operating expenses, settlement with the government, debt obligations and capital requirements under our current business plan through at least the end of 2009, we believe that we will continue to require substantial additional funding to complete the research and development activities currently contemplated and to commercialize pirfenidone. As a result, we may require additional funds and may attempt to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings, collaborative arrangements with corporate partners or from other sources. If additional capital is not available, we may be forced to curtail our development activities or cease operations.
Discontinuation of Actimmune Trial for IPF
Effective March 5, 2007, we made the decision to discontinue the Phase III INSPIRE clinical trial evaluating Actimmune in patients with IPF based upon the recommendation of the study’s independent DMC. As a result of the disappointing INSPIRE trial results, we revised our estimates of inventory requirements as of December 31, 2006. Accordingly, we recorded a charge of $4.5 million in 2006 related to the prepayment of inventory that we had expected to receive in 2007 and 2008. While we believe other Actimmune related assets are recoverable for at least their $1.4 million net carrying value, if sales decline below our revised estimates, we may incur additional asset impairment charges, including inventory writedowns in excess of the $1.6 million and $0.7 million recorded in 2007 and 2008, respectively, and impairment of acquired product rights, as well as product returns.
54
The following table reflects the asset balances as of December 31, 2008 which may be impacted (in thousands):
| | | |
Finished goods inventory | | $ | 1,249 |
Acquired product rights, net | | | 167 |
| | | |
Total | | $ | 1,416 |
| | | |
Critical Accounting Policies
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable. These estimates are the basis for our judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities, which in turn may impact our reported revenue and expenses. We have discussed the development, selection and disclosure of these estimates with the Audit Committee of our board of directors. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
An accounting policy is deemed to be critical if it requires an accounting estimate to be made based on assumptions about matters that are highly uncertain at the time the estimate is made, and if different estimates that reasonably could have been used, or changes in the accounting estimate that are reasonably likely to occur periodically, could materially change the financial statements. We believe that the following critical accounting policies affect our more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Stock-based Compensation
Beginning January 1, 2006, we account for stock-based compensation in accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards, or SFAS No. 123(R),Share-Based Payment. Under the fair value recognition provisions of this statement, stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized as expense over the vesting period. In order to estimate the value of share-based awards, we use the Black-Scholes model, which requires the use of certain subjective assumptions. The most significant assumptions are our estimates of the expected volatility and the expected term of the award. In addition, judgment is also required in estimating the amount of share-based awards that are expected to be forfeited. If actual results differ significantly from any of these estimates, stock-based compensation expense and our results of operations could be materially impacted.
If all of the remaining and outstanding restricted stock awards that were granted in 2006, 2007 and 2008 became vested, we would recognize approximately $3.9 million in compensation expense over a weighted average remaining period of 2.6 years. If all of the remaining nonvested and outstanding stock option awards that have been granted became vested, we would recognize approximately $12.8 million in compensation expense over a weighted average remaining period of 2.2 years. However, no compensation expense will be recognized for any stock awards that do not vest.
Revenue Recognition and Revenue Reserves
Revenue on product sales is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the price is fixed, and final delivery has occurred and there is a reasonable assurance of collectibility of the amounts receivable from the customer. Therefore, revenue is generally recognized upon delivery when title passes to a credit-worthy customer. Reserves are recorded at the time revenue is recognized for estimated returns, rebates,
55
chargebacks and cash discounts, if applicable. We sell to a limited number of customers, mainly specialty pharmacies and distributors. We obtain written purchase authorizations from our customers for a specified amount of product at a specified price. We are obligated to accept returns from customers if the pharmaceuticals they purchased have reached the expiration date. We have demonstrated the ability to make reasonable and reliable estimates of product returns based on historical experience. Due to the nature of our business model and based on historical experience, these estimates are not highly subjective. We review all sales transactions for potential rebates, chargebacks and discounts each month and monitor product ordering cycles and actual returns, product expiration dates and wholesale inventory levels to estimate potential product return rates. We believe that our reserves are adequate. For each of the periods presented below, we have not made any shipments as a result of incentives and/or in excess of our customers’ ordinary course of business inventory levels. Specialty wholesalers maintain low inventory levels and manage their inventory levels to optimize patient-based need (demand) and generally do not overstock Actimmune.
The tables below present the amounts reported as revenue reductions for the periods indicated (in thousands, except percentages):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
Reductions to Revenue | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Cash discounts | | $ | 666 | | | $ | 1,116 | | | $ | 1,887 | |
Product returns | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Chargebacks | | | 1,460 | | | | 1,222 | | | | 1,106 | |
Medicaid rebates | | | 1,279 | | | | 1,160 | | | | 2,032 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 3,405 | | | $ | 3,498 | | | $ | 5,025 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Gross product revenue | | $ | 33,285 | | | $ | 56,918 | | | $ | 95,342 | |
Revenue reductions as a % of gross product revenue | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash discounts | | | 2.0 | % | | | 2.0 | % | | | 2.0 | % |
Product returns | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Chargebacks | | | 4.4 | % | | | 2.1 | % | | | 1.2 | % |
Medicaid rebates | | | 3.8 | % | | | 2.0 | % | | | 2.1 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | 10.2 | % | | | 6.1 | % | | | 5.3 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
In 2008, chargebacks were approximately 4.4% of gross revenue, but historically have fallen within a range of 1.0% to 4.0% in any given year depending on the customer base. The increase in the current year is attributed to the TRICARE Pharmacy Program (“TRICARE”) which became effective January 2008 and is administered by the Department of Defense. Excluding TRICARE, chargebacks would have been approximately 3.7%, which would have increased reported revenue by approximately $0.2 million. In 2008, Medicaid rebates were approximately 3.8% of gross revenue, but could reasonably fall within a range of 2.0% to 4.0% in any given year. If Medicaid rebates had decreased to 3.0% during 2008, this would have increased our reported revenue by approximately $0.3 million. The ranges selected above are based on a review of historical trends and we believe they are reasonably likely to continue to be relevant in future periods. Chargebacks as a percentage of gross revenue increased in 2008 compared with 2007 and 2006 due to disappointing clinical trial results and our subsequent decision to discontinue further development of Actimmune in addition to the new TRICARE program. The increase in Medicaid rebate revenue reserves from 2.1% in 2006 and 2.0% in 2007 to 3.8% in 2008 is due to the price increase for Actimmune implemented midway through 2008 and the lack of a corresponding increase in the Medicaid reimbursement rate.
56
The source of information that we monitor in assisting us with computing chargebacks is from the Federal Supply Schedule, Veterans Administration and Public Health System pricing documents. These documents establish the maximum price allowable for the sale of our product to a government customer. The chargeback amount per unit is computed as the difference between our sales price to the wholesaler and the selling price from the wholesaler to a government customer. Chargebacks are processed directly by the wholesalers and are deducted from payments to us.
The source of information that we monitor in assisting us with computing Medicaid rebates is from each of the 50 states. Medicaid rebates are billed directly to us from each state. Billings from each of the states, which are based on end user reports submitted by pharmacies to the state agencies, are typically received within 45 days after the end of each calendar quarter. We use historical billing and payment trends made to the states to assist us in determining an estimated Medicaid rebate amount each period.
Clinical Trial Accruals
We accrue costs for clinical trial activities performed by contract research organizations based upon the estimated amount of work completed on each study. These estimates may or may not match the actual services performed by the organizations as determined by patient enrollment levels and related activities. We monitor patient enrollment levels and related activities to the extent possible through internal reviews, correspondence with contract research organizations and review of contractual terms. However, if we have incomplete or inaccurate information, we may overestimate or underestimate activity levels associated with various studies at a given point in time. In the event we underestimate, we could be required to record significant additional research and development expenses in future periods when the actual activity level becomes known. All such costs are charged to research and development expenses as incurred. To date, we have not experienced changes in estimates that have led to material research and development expense adjustments being recorded in future periods.
Inventory Reserves
Our inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market and our inventory costs are determined by the first-in first-out method. We enter into purchase obligations to purchase our inventory based upon sales forecasts to enable us to mitigate some of the risk associated with the long lead times required to manufacture our products.
We write off the cost of inventory and reserve for future minimum purchase commitments, if any, that we consider to be in excess of forecasted future demand. We define excess inventory as inventory that will expire before it can be sold, based on future sales forecasts. In making these assessments, we are required to make judgments as to the future demand for current or committed inventory purchase levels. We are also required to monitor the expiration dates of our products, since our products can no longer be used after their respective expiration dates. In 2004, in an effort to best manage the procurement and distribution of levels of Actimmune, we successfully completed the necessary testing to extend the expiration period of Actimmune from 30 months to a total of 36 months. As part of our excess inventory assessment for Actimmune, we also estimate the expiration date of any Actimmune to be manufactured in the future.
Projected revenue trends resulted in us recording charges during 2008 of $0.7 million to cost of goods sold for excess inventories. If Actimmune revenue levels experienced in future periods are substantially below our current expectations, we could be required to record additional charges for excess inventories. Please refer to the statements under “Item 1A. Risk Factors” in this Report to gain a better understanding of the possible reasons why actual results could differ from our estimates.
57
Results of Operations
Comparison of years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
Revenue
For the year ended December 31, 2008, we recorded total net revenue of $48.2 million, compared to $66.7 million for the same period in 2007, a decrease of 28%. This decrease was attributable to a decrease in sales of Actimmune of approximately $23.3 million, or 44%, partially offset by an increase in collaboration revenue of $5.0 million resulting from the agreement with Roche. In early March 2007, we announced that our Phase III INSPIRE program for Actimmune in IPF had been discontinued and that future Actimmune revenue was expected to decline. The $18.3 million and $13.3 million of collaboration revenue for 2008 and 2007, respectively, includes $15.0 million and $10.0 million milestones received in September 2008 and June 2007, respectively, each of which had been assessed as substantially at-risk at the initiation of the agreement and were therefore recognized as revenue when the milestones were achieved, as defined in the Collaboration Agreement. For each of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, Actimmune accounted for all of our product revenue. A substantial majority of these sales were derived from physicians’ prescriptions for the off-label use of Actimmune in the treatment of IPF. Collaboration revenue in 2008 and 2007 also includes approximately $3.2 million of amortization of the $70.0 million upfront payments received from Roche in 2006 and January 2007.
There are a number of variables that impact Actimmune revenue including, but not limited to, the discontinuation of the Phase III INSPIRE clinical trial in March 2007, the level of enrollment in IPF clinical trials of other companies, new patients started on therapy, average duration of therapy, new data on Actimmune or other products presented at medical conferences and publications in medical journals, reimbursement and patient referrals from physicians. In light of the failure of the INSPIRE clinical trial, we expect that net sales of Actimmune for the year ended December 31, 2009 will continue to decline.
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold included product manufacturing costs, royalties and distribution costs associated with our product revenue and inventory writedowns. Cost of goods sold for the year ended December 31, 2008 was $9.0 million, or approximately 30% of total product revenue, compared to $14.1 million, or approximately 26% of total product revenue, in the corresponding period of 2007. The decrease in cost of goods sold primarily reflects the decline in Actimmune revenue. Included in 2008 cost of goods sold is a charge of $0.7 million recorded for excess inventory. Included in 2007 cost of goods sold is a charge of approximately $1.6 million for excess inventories, recorded in connection with the impact of the Phase III INSPIRE trial results announced in March 2007. Excluding the $0.7 million and $1.6 million charges for excess inventory and purchase commitments in 2008 and 2007, respectively, cost of goods sold was approximately 28% and 23% of product revenue for each of the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. This increase can be attributed to a higher average cost per vial, reflecting a full year impact of the new supply agreement with BI entered into in June 2007 which stipulated a higher cost per vial charged to us.
Exchange rate fluctuations on inventory purchases may affect cost of goods sold on Actimmune inventory purchased from BI. In the past, we have utilized forward exchange contracts to partially offset the effect of exchange rate fluctuations, but we did not enter into any new contracts in 2007 or 2008.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development (“R&D”) expenses were $104.6 million and $105.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, representing a decrease of 1%. The decrease was primarily due to the discontinuation of the INSPIRE program, offset by the full enrollment in 2007 and completion of our two Phase III CAPACITY studies for pirfenidone late in 2008 and the conduct of the Phase 1a and 1b studies of ITMN-191.
The following table lists our current product development programs and the research and development expenses recognized in connection with each program during the indicated periods. The category titled
58
“Programs—Non-specific” is comprised of facilities and personnel costs that are not allocated to a specific development program or discontinued programs and $2.6 million and $6.0 million of stock-based compensation in 2008 and 2007, respectively. Our management reviews each of these program categories in evaluating our business. For a discussion of the risks and uncertainties associated with developing our products, as well as the risks and uncertainties associated with potential commercialization of our product candidates, see the specific sections under “Item 1A. Risk Factors” above.
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year ended December 31, |
Development Program | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
| | | (In thousands) |
Pulmonology | | $ | 60,641 | | $ | 56,169 | | $ | 50,065 |
Hepatology | | | 30,699 | | | 21,965 | | | 30,035 |
Oncology | | | — | | | — | | | 1,561 |
Programs—Non-specific | | | 13,241 | | | 27,805 | | | 22,188 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 104,581 | | $ | 105,939 | | $ | 103,849 |
| | | | | | | | | |
The largest component of our total operating expenses is our ongoing investments in research and development and, in particular, the clinical development of our product pipeline. The process of conducting the clinical research necessary to obtain FDA approval is costly and time consuming. Current FDA requirements for a new human drug to be marketed in the United States include:
| | • | | the successful conclusion of preclinical laboratory and animal tests, if appropriate, to gain preliminary information on the product’s safety; |
| | • | | the submission of an IND with the FDA to conduct human clinical trials for drugs; |
| | • | | the successful completion of adequate and well-controlled human clinical investigations to establish the safety and efficacy of the product for its recommended use; and |
| | • | | the submission by a company and acceptance and approval by the FDA of an NDA or BLA for a drug product to allow commercial distribution of the drug. |
In light of the factors mentioned above, we consider the active management and development of our clinical pipeline to be crucial to our long-term success. The actual probability of success for each candidate and clinical program may be impacted by a variety of factors, including, among others, the quality of the candidate, the validity of the target and disease indication, early clinical data, investment in the program, competition, manufacturing capability and commercial viability. Due to these factors, it is difficult to give accurate guidance on the anticipated proportion of our research and development investments or the future cash inflows from these programs.
Acquired Research and Development and Milestone Expense/(Credits)
In 2002, we licensed from Marnac and its co-licensor, KDL, their worldwide rights, excluding Japan, Korea and Taiwan, to develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, including renal, liver and pulmonary fibrosis. Effective November 21, 2007, we entered into asset purchase agreements with Marnac and KDL whereby we effectively terminated the prior license agreement by purchasing, among other things, the pirfenidone-related assets covered by such prior license agreement. Under the terms of the asset purchase agreements, we made acquisition payments of approximately $13.7 million in 2007. Contingent acquisition payments of up to an additional $53.5 million would be made by us only if positive Phase III data and registration in the United States and European Union are achieved. There were no charges for acquired research and development and milestone payments in the year ended December 31, 2008 under this, or any other, agreement.
59
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative (“G&A”) expenses were $30.3 million and $29.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, an increase of 2%. Headcount and cost reductions related to the closure of the INSPIRE trial for Actimmune in March 2007 were offset by increased legal expenses in connection with the lawsuits filed against the company earlier in 2008 and preparation costs related to the anticipated commercialization of pirfenidone.
Restructuring Charges
Effective March 5, 2007, we made the decision to discontinue the Phase III INSPIRE clinical trial evaluating Actimmune in patients with IPF based upon the recommendation of the study’s independent data monitoring committee. As a result of the disappointing INSPIRE trial results, we made the decision to reduce our workforce by approximately 50%, which has been completed as of September 30, 2007. As a result, we incurred approximately $3.4 million in personnel-related restructuring charges during 2007. The $3.4 million charge is comprised of approximately $2.9 million for cash severance and related benefits and $0.5 million of costs for the acceleration of options for approximately 66,000 shares of our common stock. We also incurred approximately $6.8 million in expenses in connection with the termination of our previous supply agreement with BI in the second quarter of 2007. See Note 15 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Interest Income
Interest income decreased to $5.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $10.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2007. The decrease in interest income for the year ended December 31, 2008 reflects a lower average balance on our invested cash and securities throughout 2008 compared to 2007 and relatively lower average interest rates in 2008 compared to 2007.
Interest Expense
Interest expense increased to $5.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $2.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2007. Each period reflects interest expense recorded in connection with our liability under the government settlement reached in October 2006. Interest expense for 2007 also includes interest on our $170.0 million 0.25% convertible notes due in March 2011 (the “2011 Notes”), including the amortization of related debt issuance costs. On June 24, 2008, we issued $85.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 5.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2015 (the “2015 Notes”) to certain holders of our existing 2011 Notes in exchange for $85.0 million in aggregate principal amount of their 2011 Notes. Remaining debt issuance costs of approximately $1.1 million, related to the extinguishment of $85.0 million of the existing 2011 Notes, were expensed during the second quarter of 2008 and have been included in interest expense.
Other Income (Expense)
Other income (expense) decreased to ($2.1) million of other expense for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $2.2 million of other income for 2007. Other expense for 2008 is comprised primarily of a $3.5 million impairment charge for the writedown of our long-term available-for-sale securities, partially offset by a $1.0 million contingent payment in connection with our divestiture of Amphotec in May 2005. Other income for 2007 includes $2.5 million in aggregate milestone payments from Targanta and Three Rivers in connection with our divestitures of oritavancin and Amphotec, respectively.
Income (loss) from Discontinued Operations
The income (loss) from discontinued operations reflects the divestiture of our Infergen product line to Valeant which was completed in December 2005. The income from discontinued operations of $0.1 million for
60
the year ended December 31, 2008 compares to income of $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2007. Discontinued operations in 2008 is comprised of adjustments to our initial product return estimates. Income from discontinued operations in 2007 reflects a clinical-related milestone received from Valeant. See Note 3 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Provision for Income Taxes
Due to our continuing operating losses and the uncertainty of our recognizing the potential future benefits from other non-operating losses, we recorded no provision for income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2008. The $2.3 million tax benefit recorded in 2007 primarily relates to net operating losses that we concluded are realizable based on our estimate of future taxable income resulting from future potential sales of our shares of Targanta common stock. As of December 31, 2008, we had federal net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $532.4 million. The net operating loss carryforwards will expire at various dates beginning in 2018 through 2028 if not utilized. We also have federal research and development tax credits of approximately $21.1 million that will expire in the years 2018 through 2028 and federal Orphan Drug tax credits of approximately $47.2 million that will expire in the years 2022 through 2028. In addition, we had net operating loss carryforwards for state income tax purposes of approximately $201.7 million that expire in the years 2012 through 2028 and state research and development tax credits of approximately $16.1 million that do not expire. Utilization of the net operating losses may be subject to a substantial annual limitation due to the “change in ownership” provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and similar state provisions. The annual limitation may result in the expiration of net operating losses before utilization.
We adopted the provisions of FIN 48 on January 1, 2007. Implementation of FIN 48 did not result in any adjustment to our Consolidated Statements of Operations or a cumulative adjustment to accumulated deficit.
Comparison of years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006
Revenue
For the year ended December 31, 2007, we recorded total net revenue of $66.7 million, compared to $90.8 million for the same period in 2006, a decrease of 27%. This decrease was attributable to a decrease in sales of Actimmune of approximately $36.9 million, or 41%, partially offset by an increase in collaboration revenue of $12.8 million resulting from the agreement with Roche. In early March 2007, we announced that our Phase III INSPIRE program for Actimmune in IPF had been discontinued and that future Actimmune revenue was expected to decline. The $13.3 million of collaboration revenue for 2007 includes a $10.0 million milestone received in June 2007, which had been assessed as substantially at-risk at the initiation of the agreement and was therefore recognized as revenue when the milestone was achieved, as defined in the Collaboration Agreement. For each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, Actimmune accounted for all of our product revenue. Substantially all of these sales were derived from physicians’ prescriptions for the off-label use of Actimmune in the treatment of IPF. Net revenue in 2006 includes approximately $0.5 million of collaboration revenue, which represents amortization of the $60.0 million upfront payment received from Roche during the fourth quarter of 2006.
Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold included product manufacturing costs, royalties and distribution costs associated with our product revenue and inventory writedowns. Cost of goods sold for the year ended December 31, 2007 was $14.1 million, or approximately 26% of total product revenue, compared to $24.6 million, or approximately 27% of total product revenue, in the corresponding period of 2006. The decrease in cost of goods sold primarily reflects the decline in Actimmune revenue. Included in 2007 cost of goods sold is a charge of $1.6 million recorded for excess inventory. Included in 2006 cost of goods sold is a charge of approximately $4.5 million for excess inventories, recorded in connection with the impact of the disappointing Phase III INSPIRE trial results
61
announced in March 2007. Excluding the $1.6 million and $4.5 million charges for excess inventory and purchase commitments in 2007 and 2006, respectively, cost of goods sold was approximately 23% and 22% of product revenue for each of the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Exchange rate fluctuations on inventory purchases may affect cost of goods sold on Actimmune inventory purchased from BI. In the past, we have utilized forward exchange contracts to partially offset the effect of exchange rate fluctuations, but we did not enter into any new contracts in 2006 or 2007.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development (“R&D”) expenses were $105.9 million and $103.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, representing an increase of 2%. The increase was primarily due to the full enrollment of our two Phase III CAPACITY studies for pirfenidone during 2007 and the conduct of the Phase 1a and 1b studies of ITMN-191, partially offset by reduced costs related to the discontinuation of the INSPIRE program and the full year reimbursement from Roche under our collaboration agreement. R&D expense also includes $6.0 million and $8.1 million of stock-based compensation in 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Acquired Research and Development and Milestone Expense/(Credits)
In 2002, we licensed from Marnac and its co-licensor, KDL, their worldwide rights, excluding Japan, Korea and Taiwan, to develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, including renal, liver and pulmonary fibrosis. Effective November 21, 2007, we entered into asset purchase agreements with Marnac and KDL whereby we effectively terminated the prior license agreement by purchasing, among other things, the pirfenidone-related assets covered by such prior license agreement. Under the terms of the asset purchase agreements, we made acquisition payments of approximately $13.7 million in 2007. Contingent acquisition payments of up to an additional $53.5 million would be made by us only if positive Phase III data and registration in the United States and European Union are achieved. There were no charges for acquired research and development and milestone payments in the year ended December 31, 2006.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative (“G&A”) expenses were $29.6 million and $40.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, representing a decrease of $10.8 million, or 27%. The decreased spending for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to the same period in 2006 reflects the impact of headcount and cost reductions related to the closure of the INSPIRE trial for Actimmune in March 2007.
Provision for Government Settlement
On November 9, 2004, we received a subpoena from the U.S. Department of Justice requiring us to provide the Department of Justice with certain information relating to Actimmune, including information regarding the promotion and marketing of Actimmune. On October 25, 2006, we reached a comprehensive settlement with the government concerning promotional activities for Actimmune by former employees during a period that ended in June 2003. A $36.9 million charge was recorded during 2006 to reflect the final terms of the civil settlement agreement. The settlement resolves without criminal sanctions, all outstanding government investigations of InterMune. We agreed to pay a total of $36.9 million, plus 5% interest on the then outstanding principal balance, over a period of five years. As part of the settlement, InterMune also entered into corporate integrity and deferred prosecution agreements with the government.
Restructuring Charges
Effective March 5, 2007, we made the decision to discontinue the Phase III INSPIRE clinical trial evaluating Actimmune in patients with IPF based upon the recommendation of the study’s independent data
62
monitoring committee. As a result of the disappointing INSPIRE trial results, we made the decision to reduce our workforce by approximately 50%, which has been completed as of September 30, 2007. As a result, we incurred approximately $3.4 million in personnel-related restructuring charges during 2007. The $3.4 million charge is comprised of approximately $2.9 million for cash severance and related benefits and $0.5 million of costs for the acceleration of options for approximately 66,000 shares of our common stock. We have also incurred approximately $6.8 million in expenses in connection with the termination of our previous supply agreement with BI. See Note 15 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Interest Income
Interest income increased to $10.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $9.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase in interest income for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to 2006 reflects a higher average balance on our invested cash and securities throughout 2007, including the proceeds of $73.4 million from our public offering which was completed in September 2007, and relatively higher average interest rates in 2007 compared to 2006.
Interest Expense
Interest expense increased to $2.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. The increase in interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2007 reflects a full year of interest incurred in connection with our liability under the government settlement reached in October 2006. Both 2007 and 2006 include interest on our $170.0 million principal amount 0.25% convertible senior notes, issued in February 2004 and the amortization of the related debt issuance costs.
Other Income
Other income increased to $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to $1.1 million for 2006. Other income for 2007 includes $2.5 million in aggregate milestone payments from Targanta and Three Rivers in connection with our divestitures of oritavancin and Amphotec, respectively. Other income for 2006 includes a $1.0 million cash payment received from Targanta in connection with the divestiture of oritavancin.
Income (loss) from Discontinued Operations
The income (loss) from discontinued operations reflects the divestiture of our Infergen product line to Valeant which was completed in December 2005. The income from discontinued operations of $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2007 compares to a loss of $1.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2006. Income from discontinued operations in 2007 reflects a clinical-related milestone received from Valeant. Discontinued operations in 2006 consist primarily of transition related services, including product returns, which were substantially completed at the end of 2006. See Note 3 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Provision for Income Taxes
The $2.3 million tax benefit recorded in 2007 primarily relates to net operating losses that we concluded are realizable based on our estimate of future taxable income resulting from future potential sales of our shares of Targanta common stock. Due to our continuing operating losses and the uncertainty of our recognizing the potential future benefits from the remaining non-operating losses, we recorded no provision for income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2006.
We adopted the provisions of FIN 48 on January 1, 2007. Implementation of FIN 48 did not result in any adjustment to our Consolidated Statements of Operations or a cumulative adjustment to accumulated deficit.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
At December 31, 2008, we had cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities of $154.7 million compared to $235.3 million at December 31, 2007. The decrease was primarily the result of operating losses,
63
partially offset by the receipt of $15.0 million from our collaboration partner Roche. Some of these available cash and cash equivalents are held in accounts managed by third party financial institutions and consist of invested cash and cash in our core operating accounts. The invested cash is invested in interest bearing funds managed by third party financial institutions. We can provide no assurances that access to our invested cash and cash equivalents will not be impacted by adverse conditions in the financial markets. In addition, at any point in time we maintain balances that exceed the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insurance limits. While we monitor the cash balances in our operating accounts on a regular basis, these cash balances could be impacted and we may be unable to access our cash if the underlying financial institutions fail or be subject to other adverse conditions in the financial markets. To date we have not experienced a lack of access to cash in any of our third party financial institution accounts.
Included in the $154.7 million of our cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities at December 31, 2008 is a portion of our investment in Targanta common stock which has a fair value of approximately $0.5 million, reflecting the fair market value of approximately 840,000 shares at the quoted market price on that date. The 840,000 shares of Targanta common stock represent the portion of our holdings estimated to qualify for resale within one year. Our total holdings of Targanta common stock had been approximately 3.0 million shares. In January 2009, The Medicines Company announced its intent to acquire Targanta for $2.00 per share, or approximately $42.0 million and on January 27, 2009 commenced a tender offer to acquire all outstanding shares of Targanta. We have tendered our shares and received approximately $6.0 million in March 2009 upon closing of the transaction. We may also receive up to an additional $4.55 per share in contingent cash payments upon the achievement of specified regulatory and commercial milestones within certain time periods. In February 2009, we completed a public offering of approximately 4.0 million shares of our registered common stock, at a price of $16.35 per share, and received net proceeds of approximately $63.5 million.
The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve principal while at the same time maximize yields without significantly increasing risk. To achieve this objective, we invest our excess cash in debt instruments of the U.S. federal and state governments and their agencies and high-quality corporate issuers, and, by policy, restrict our exposure by imposing concentration limits and credit worthiness requirements for all corporate issuers. At December 31, 2008, we held approximately $17.5 million of student loan auction rate securities (par value of $21.0 million), classified as long-term assets, which are substantially backed by the federal government. Beginning in February 2008, auctions failed for the entire $21.0 million of our auction rate securities and have continued to fail since. As a result, our ability to liquidate our investment and fully recover the carrying value of our investment in the near term may be limited or not exist. During the fourth quarter of 2008, we recorded an impairment charge of $3.5 million for the writedown of the carrying value of these securities as we believe the decline in market value is other-than-temporary in nature given the deteriorating credit and financial markets and specifically the auction rate securities market. All of our auction rate securities are currently rated AAA, the highest rating by a rating agency. If the issuers are unable to successfully close future auctions and their credit ratings deteriorate, we may in the future be required to record further impairment charges on these investments. Based on our expected operating cash flows, and our other sources of cash, including proceeds from our February 2009 public offering, and the recently announced results from our CAPACITY trials, we currently anticipate the need to liquidate these investments prior to maturity or estimated time to recovery in order to execute our current business plans. These investments were recorded at fair value as of December 31, 2008 based on a discounted cash flow analysis.
Operating Activities
Cash used in operating activities was $72.3 million during the year ended December 31, 2008, comprised primarily of a net loss of $97.7 million. Cash flows used in operating activities also reflects, among other things, stock-based compensation expense of $6.8 million, an increase in accounts payable and accrued compensation of $11.4 million and an increase in other accrued liabilities of approximately $5.0 million. The increase in accounts payable is primarily due to the amounts owed to Roche under the October 2006 Collaboration Agreement, which
64
increased $11.3 million in 2008. The increase in other accrued liabilities consists primarily of an increase in accrued clinical costs, reflecting the initiation of our RECAP clinical trial, the follow up to our recently completed CAPACITY trials. Details concerning the loss from operations can be found above in this Report under the heading “Results of Operations.”
Investing Activities
Investing activities provided $45.1 million in cash flows during the year ended December 31, 2008, primarily due to investment maturities and sales of available-for-sale securities totaling $167.0 million, partially offset by investment purchases of $119.8 million and purchases of property and equipment of $2.0 million.
Financing Activities
Cash provided by financing activities of $2.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 was due to the issuance of our common stock under our employee stock plans.
We believe that we will continue to require substantial additional funding to complete the research and development activities currently contemplated and to commercialize our product candidates. We believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities, together with anticipated cash flows from sales of Actimmune and proceeds from our February 2009 public offering, will be sufficient to fund our operating expenses, settlement with the government, debt obligations and capital requirements under our current business plan through at least the end of 2009. However, this forward-looking statement involves risks and uncertainties, and actual results could vary as a result of a number of factors, including the factors discussed under “Item 1A. Risk Factors.” This forward-looking statement is also based upon our current plans and assumptions, which may change, and our capital requirements, which may increase in future periods. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
| | • | | sales of Actimmune or any of our product candidates in development that receive commercial approval; |
| | • | | our ability to partner our programs or products; |
| | • | | the progress of our research and development efforts; |
| | • | | the scope and results of preclinical studies and clinical trials; |
| | • | | the costs, timing and outcome of regulatory reviews; |
| | • | | determinations as to the commercial potential of our product candidates in development; |
| | • | | the pace of expansion of administrative expenses; |
| | • | | the status of competitive products and competitive barriers to entry; |
| | • | | the establishment and maintenance of manufacturing capacity through third-party manufacturing agreements; |
| | • | | the establishment of collaborative relationships with other companies; |
| | • | | the payments of annual interest on our long-term debt; |
| | • | | the payments related to the Civil Settlement Agreement with the government; |
| | • | | the timing and size of the payments we may receive from Roche pursuant to the Collaboration Agreement; and |
| | • | | whether we must repay the principal in connection with our convertible debt obligations. |
As a result, we may require additional funds beyond the proceeds received from our February 2009 public offering and may attempt to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings, collaborative arrangements
65
with corporate partners or from other sources. We have no further commitments for such fund raising activities at this time. Additional funding may not be available to finance our operations when needed or, if available, the terms for obtaining such funds may not be favorable or may result in dilution to our stockholders.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any “special purpose” entities that are unconsolidated in our financial statements. We have no commercial commitments or loans with related parties.
Contractual Obligations
Contractual obligations represent future cash commitments and liabilities under agreements with third parties, and exclude contingent liabilities, such as milestone payments, for which we cannot reasonably predict future payments. The following chart represents our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2008, aggregated by type (in millions):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Contractual Obligations | | Total | | 2009 | | 2010-2011 | | 2012-2013 | | After 2013 |
Long-term debt obligations (1) | | $ | 198.2 | | $ | 4.5 | | $ | 93.8 | | $ | 8.5 | | $ | 91.4 |
Government settlement (2) | | | 26.0 | | | 7.0 | | | 19.0 | | | — | | | — |
Operating leases | | | 11.8 | | | 5.0 | | | 6.8 | | | — | | | — |
Non-cancelable purchase obligations—Other (3) | | | 1.7 | | | 1.7 | | | — | | | — | | | — |
Research and development commitments (4) | | | 6.3 | | | 4.9 | | | 1.4 | | | — | | | — |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total contractual cash obligations | | $ | 244.0 | | $ | 23.1 | | $ | 121.0 | | $ | 8.5 | | $ | 91.4 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (1) | These amounts include accrued interest and principal amounts of both the 0.25% convertible senior notes due 2011 and the 5.00% convertible senior notes due 2015. |
| (2) | These amounts do not reflect the impact of the $4.4 million accelerated payment made in March 2009 to the U.S. Department of Justice, though total obligation does not change. See Note 15 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
| (3) | These amounts consist of clinical related obligations. |
| (4) | These amounts consist of clinical, process development and other related obligations and are cancelable upon discontinuation of the trial. They do not include any amounts related to the collaboration agreement with Roche given the inherent difficulties in the estimation process. |
The operating leases for our facilities require letters of credit secured by a restricted cash balance with our bank. The amount of each letter of credit approximates six to twelve months of operating rent payable to the landlord of each facility.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On October 10, 2008, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Staff Position No. FAS 157-3,Determining the Fair Value of a Financial Asset When the Market for That Asset Is Not Active,(FSP FAS 157-3). This FSP, which was effective upon release, clarifies the application of FAS 157 in a market that is not active and provides guidance and examples to illustrate key considerations in determining the fair value of a financial asset when the market for that financial asset is not active. We considered the impact of FSP FAS 157-3 in evaluating the fair value of our auction rate securities.
In June 2008, the FASB ratified Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue No. 07-5,Determining Whether an Instrument (or Embedded Feature) is Indexed to an Entity’s Own Stock (“EITF 07-5”). EITF 07-5
66
provides guidance on how to determine if certain instruments (or embedded features) are considered indexed to our own stock, including instruments similar to our convertible senior notes. EITF 07-5 requires companies to use a two-step approach to evaluate an instrument’s contingent exercise provisions and settlement provisions in determining whether the instrument is considered to be indexed to its own stock and exempt from the application of SFAS No. 133,Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities. Although EITF 07-5 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, any outstanding instrument at the date of adoption will require a retrospective application of the accounting through a cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings upon adoption. We are currently evaluating the impact of adoption on our consolidated financial position and results of operations.
In May 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. APB 14-1,Accounting for Convertible Debt Instruments that May be Settled in Cash upon Conversion (Including Partial Cash Settlement) (FSP APB 14-1) that significantly impacts the accounting for convertible debt. The FSP requires cash settled convertible debt, such as our 0.25% convertible senior notes due March 2011 (the “2011 Notes”) that are currently outstanding, to be separated into debt and equity components at issuance and a value to be assigned to each component. The value assigned to the debt component would be the estimated fair value, as of the issuance date, of a similar bond without the conversion feature. The difference between the bond cash proceeds and this estimated fair value would be recorded as a debt discount and amortized to interest expense over the expected life of the bond. Although FSP APB 14-1 has no impact on our actual past or future cash flows, it requires us to record non-cash interest expense as the debt discount is amortized. FSP APB 14-1 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and interim periods within those fiscal years, and requires retrospective application to all periods presented. Early application is not permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact of adoption and based on our preliminary analysis of the requirements of FSP APB 14-1, we expect that the adoption of FSP APB 14-1 will have a material impact on our consolidated financial position and results of operations.
At its December 2007 meeting, the FASB ratified the consensus reached by the EITF in Issue No. 07-1,Accounting for Collaborative Arrangements Related to the Development and Commercialization of Intellectual Property. The EITF concluded that a collaborative arrangement is one in which the participants are actively involved and are exposed to significant risks and rewards that depend on the ultimate commercial success of the endeavor. Revenues and costs incurred with third parties in connection with collaborative arrangements would be presented gross or net based on the criteria in EITF 99-19,Reporting Revenue Gross as a Principal versus Net as an Agent, and other accounting literature. Payments to or from collaborators would be evaluated and presented based on the nature of the arrangement and its terms, the nature of the entity’s business and whether those payments are within the scope of other accounting literature. The nature and purpose of collaborative arrangements are to be disclosed along with the accounting policies and the classification and amounts of significant financial statement amounts related to the arrangements. Activities in the arrangement conducted in a separate legal entity should be accounted for under other accounting literature; however, required disclosure under EITF 07-1 applies to the entire collaborative agreement. This Issue is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and is to be applied retrospectively to all periods presented for all collaborative arrangements existing as of the effective date. We are in the process of evaluating the impact of adopting this pronouncement and have not determined whether it will have a material impact, but its adoption would not affect reported amounts of net loss.
In June 2007, the FASB ratified the consensus reached by the EITF on Issue No. 07-3 (“EITF 07-3”),Accounting for Nonrefundable Advance Payments for Goods or Services Received for Use in Future Research and Development Activities. Pursuant to EITF 07-3, nonrefundable advance payments for goods or services that will be used or rendered for future research and development activities should be deferred and capitalized. Such amounts should be recognized as an expense as the related goods are delivered or services are performed, or when the goods or services are no longer expected to be received. Effective January 1, 2008, we adopted EITF 07-3. The adoption did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
67
In February 2007, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 159 (“SFAS 159”),The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities. SFAS 159 permits an entity to measure certain financial assets and financial liabilities at fair value where entities will report unrealized gains and losses in earnings at each subsequent reporting date. The standard allows entities to elect fair value application on an instrument-by-instrument basis with certain exceptions. The fair value option election is irrevocable in most cases. Effective January 1, 2008, we adopted SFAS 159 and did not elect to adopt the fair value option under this Statement.
Effective January 1, 2008, we adopted SFAS No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements” (“SFAS 157”). In February 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. FAS 157-2, “Effective Date of FASB Statement No. 157”, which provides a one year deferral of the effective date of SFAS 157 for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed in the financial statements at fair value at least annually. Therefore, the Company has adopted the provisions of SFAS 157 with respect to its financial assets and liabilities only. SFAS 157 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value under generally accepted accounting principles and enhances disclosures about fair value measurements. Fair value is defined under SFAS 157 as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value under SFAS 157 must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The standard describes a fair value hierarchy based on three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable, that may be used to measure fair value which are the following:
| | • | | Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| | • | | Level 2—Inputs other than Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. |
| | • | | Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. |
The adoption of this statement did not have an impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Interest Rate and Market Risk
The securities in our investment portfolio are not leveraged, are classified as available-for-sale and are, due to their short-term nature, subject to minimal interest rate risk. We currently do not hedge interest rate exposure. Because of the short-term maturities of our investments, we do not believe that a change in market rates would have a significant negative impact on the value of our investment portfolio.
The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve principal while at the same time maximizing the income we receive from our investments without significantly increasing risk. To achieve this objective, we maintain our portfolio of cash equivalents and short-term and long-term investments in a variety of securities, including obligations of U.S. government-sponsored enterprises, municipal notes which may have an auction reset feature, corporate notes and bonds, commercial paper, and money market funds. These securities are classified as available for sale and consequently are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value with unrealized gains or losses reported as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income. Substantially all investments mature within approximately 2 years from the date of purchase. Our holdings of the securities of any one issuer, except obligations of U.S. government-sponsored enterprises, do not exceed 10% of the portfolio. If interest rates rise, the market value of our investments may decline, which could result in a realized loss if we are forced to sell an investment before its scheduled maturity. We do not utilize derivative financial instruments to manage our interest rate risks.
68
At December 31, 2008, we held approximately $21.0 million (at par) of municipal notes investments, classified as noncurrent assets, with an auction reset feature (“auction rate securities”) whose underlying assets are generally student loans which are substantially backed by the federal government. Commencing in February 2008 and continuing throughout the remainder of the year, auctions failed for the entire $21.0 million of our auction rate securities and as a result our ability to liquidate our investment and fully recover the carrying value of our investment in the near term may be limited or not exist. An auction failure means that the parties wishing to sell securities could not. All of our auction rate securities are currently rated AAA, the highest rating by a rating agency. If the issuers are unable to successfully close future auctions and their credit ratings deteriorate, we may in the future be required to record further impairment charges on these investments. Based on our expected operating cash flows, and our other sources of cash, including proceeds from our February 2009 public offering, and the recently announced results from our CAPACITY trials, we currently anticipate the need to liquidate these investments prior to maturity or estimated time to recovery in order to execute our current business plans. These investments were recorded at fair value as of December 31, 2008 based on a discounted cash flow analysis. The assumptions used in preparing the discounted cash flow model include estimates of, based on data available as of December 31, 2008, interest rates, timing and amount of cash flows, credit and liquidity premiums, and expected holding periods of these securities. Given the current market environment, these assumptions are volatile and subject to change, which could result in significant changes to the fair value of these securities in future periods. We used seven years as the expected holding period.
The following table presents hypothetical fair values of our auction rate securities had we used different underlying terms, including up to 30 years which approximates the actual maturity dates of the securities (in millions, except percentages):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expected term of cash flows (in years) | | Five | | | Seven | | | Ten | | | Thirty | |
Estimated Fair Value | | $ | 18.2 | | | $ | 17.5 | | | $ | 16.4 | | | $ | 10.7 | |
Percentage of original par value ($21.0 million) | | | 86.7 | % | | | 83.3 | % | | | 78.1 | % | | | 51.0 | % |
The table below presents the original principal amounts and weighted-average interest rates by year of maturity for our investment portfolio as of December 31, 2008 by effective maturity (in millions, except percentages):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2009 | | | 2010 | | | 2011 | | | 2012 | | 2013 and
beyond | | | Total | | | Fair value at
December 31,
2008 |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale securities | | $ | 120.0 | | | $ | 10.3 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | $ | 21.0 | | | $ | 151.3 | | | $ | 148.4 |
Average interest rate | | | 1.8 | % | | | 3.8 | % | | | — | | | | — | | | 2.3 | % | | | 2.0 | % | | | — |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
0.25% convertible senior notes due 2011 | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 85.0 | | | | — | | | — | | | $ | 85.0 | | | $ | 71.9 |
Average interest rate | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0.25 | % | | | — | | | — | | | | 0.25 | % | | | — |
5.00% convertible senior notes due 2015 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | $ | 85.0 | | | $ | 85.0 | | | $ | 86.3 |
Average interest rate | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | 5.00 | % | | | 5.00 | % | | | — |
69
The table below presents the original principal amounts and weighted-average interest rates by year of maturity for our investment portfolio as of December 31, 2007 by effective maturity (in millions, except percentages):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2009 | | | 2010 | | | 2011 | | | 2012 and
beyond | | Total | | | Fair value at
December 31,
2007 |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale securities | | $ | 211.7 | | | $ | 6.4 | | | $ | 2.9 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | $ | 221.0 | | | $ | 222.5 |
Average interest rate | | | 4.8 | % | | | 5.1 | % | | | 5.1 | % | | | — | | | | — | | | 4.8 | % | | | — |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
0.25% convertible senior notes due 2011 | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | $ | 170.0 | | | | — | | $ | 170.0 | | | $ | 159.5 |
Average interest rate | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0.25 | % | | | — | | | 0.25 | % | | | — |
Foreign Currency Market Risk
We purchase commercial and clinical products from BI and settle our obligations in a foreign currency. This exposes us to foreign currency exchange rate risk. To protect against currency exchange risks on forecasted foreign currency cash payments for the purchases of Actimmune from BI over the next year, we have considered instituting a foreign currency cash flow hedging program. In the past, we have hedged portions of our forecasted foreign currency cash payments with forward contracts. When the dollar strengthens significantly against the foreign currencies, the decline in the value of future foreign currency expenses is offset by losses in the value of the option or forward contracts designated as hedges. Conversely, when the dollar weakens, the increase in the value of future foreign currency expenses is offset by gains in the value of the forward contracts. In 2004, we used foreign currency forward contracts to partially mitigate this exposure, but have not entered into any new foreign currency forward contracts since that time. We regularly evaluate the cost-benefit of entering into such arrangements, and presently have no foreign currency hedge agreements outstanding.
Global Market and Economic Conditions
In the United States, recent market and economic conditions have been unprecedented and challenging with tighter credit conditions and slower growth through the fourth quarter of 2008. For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, continued concerns about the systemic impact of inflation, energy costs, geopolitical issues, the availability and cost of credit, the U.S. mortgage market, a declining real estate market in the U.S. and added concerns fueled by the federal government interventions in the U.S. financial and credit markets have contributed to instability in both United States and international capital and credit markets and diminished expectations for the U.S. and global economy. These conditions, combined with volatile energy prices, declining business and consumer confidence and increased unemployment have in recent weeks subsequent to the end of the year and afterward contributed to volatility of unprecedented levels and an economic slowdown.
As a result of these market conditions, the cost and availability of capital and credit has been and may continue to be adversely affected by illiquid credit markets and wider credit spreads. If volatile and adverse market conditions continue, they may limit our ability to timely borrow or access the capital and credit markets to meet liquidity needs, resulting in an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. The economic slowdown may lead to reduced opportunities to raise sufficient additional capital to enable us to fund future operations, which would have a negative impact on our business. In addition, the biotechnology industry has fluctuated significantly in the past and has experienced significant downturns in connection with, or in anticipation of, a deterioration in general economic conditions and we cannot accurately predict how severe and prolonged any downturn might be.
70
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
71
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of InterMune, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of InterMune, Inc. as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a). These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of InterMune, Inc. at December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), InterMune, Inc’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated March 10, 2009 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Palo Alto, California
March 10, 2009
72
INTERMUNE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 63,765 | | | $ | 88,946 | |
Available-for-sale securities | | | 73,454 | | | | 146,346 | |
Accounts receivable, net of allowances of $58 in 2008 and $44 in 2007 | | | 3,123 | | | | 3,117 | |
Inventories | | | 1,249 | | | | 1,776 | |
Deferred taxes | | | 205 | | | | 2,275 | |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | | | 3,195 | | | | 7,112 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total current assets | | | 144,991 | | | | 249,572 | |
Noncurrent available-for-sale securities | | | 17,494 | | | | — | |
Property and equipment, net | | | 6,582 | | | | 8,118 | |
Acquired product rights, net | | | 167 | | | | 667 | |
Other assets (includes restricted cash of $1,425) | | | 2,990 | | | | 4,088 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | $ | 172,224 | | | $ | 262,445 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 19,148 | | | $ | 7,392 | |
Accrued compensation | | | 6,939 | | | | 7,282 | |
Deferred taxes | | | 205 | | | | 2,275 | |
Other accrued liabilities | | | 22,019 | | | | 18,160 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total current liabilities | | | 48,311 | | | | 35,109 | |
Deferred rent | | | 1,426 | | | | 1,767 | |
Deferred collaboration revenue | | | 59,717 | | | | 62,989 | |
Liability under government settlement | | | 17,642 | | | | 23,468 | |
Convertible notes | | | 170,000 | | | | 170,000 | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 15) | | | | | | | | |
Stockholders’ deficit: | | | | | | | | |
Preferred stock, $0.001 par value; 5,000 shares authorized, no shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively | | | — | | | | — | |
Common stock, $0.001 par value, 70,000 shares authorized; 39,330 and 39,032 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively | | | 39 | | | | 39 | |
Additional paid-in capital | | | 631,932 | | | | 623,115 | |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | | (1,415 | ) | | | 3,647 | |
Accumulated deficit | | | (755,428 | ) | | | (657,689 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Total stockholders’ deficit | | | (124,872 | ) | | | (30,888 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit | | $ | 172,224 | | | $ | 262,445 | |
| | | | | | | | |
See Accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
73
INTERMUNE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | (In thousands, except per share amounts) | |
Revenue, net | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Actimmune | | $ | 29,880 | | | $ | 53,420 | | | $ | 90,317 | |
Collaboration revenue | | | 18,272 | | | | 13,272 | | | | 467 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenue, net | | | 48,152 | | | | 66,692 | | | | 90,784 | |
Costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | | 8,989 | | | | 14,109 | | | | 24,608 | |
Research and development | | | 104,581 | | | | 105,939 | | | | 103,849 | |
Acquired research and development and milestone expense | | | — | | | | 13,725 | | | | — | |
General and administrative | | | 30,260 | | | | 29,577 | | | | 40,372 | |
Restructuring charges | | | — | | | | 10,246 | | | | — | |
Provision for government settlement | | | — | | | | — | | | | 36,944 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total costs and expenses | | | 143,830 | | | | 173,596 | | | | 205,773 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations | | | (95,678 | ) | | | (106,904 | ) | | | (114,989 | ) |
Other income (expense): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest income | | | 5,616 | | | | 10,699 | | | | 9,512 | |
Interest expense | | | (5,693 | ) | | | (2,881 | ) | | | (1,542 | ) |
Other income (expense) | | | (2,087 | ) | | | 2,215 | | | | 1,057 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations before income taxes | | | (97,842 | ) | | | (96,871 | ) | | | (105,962 | ) |
Income tax benefit | | | — | | | | (2,275 | ) | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (97,842 | ) | | | (94,596 | ) | | | (105,962 | ) |
Discontinued operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | 103 | | | | 4,994 | | | | (1,244 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (97,739 | ) | | $ | (89,602 | ) | | $ | (107,206 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic and diluted loss per share | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | $ | (2.51 | ) | | $ | (2.67 | ) | | $ | (3.18 | ) |
Discontinued operations | | | — | * | | | 0.15 | | | | (0.04 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share | | $ | (2.51 | ) | | $ | (2.52 | ) | | $ | (3.22 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shares used in computing basic and diluted net loss per share | | | 38,982 | | | | 35,493 | | | | 33,277 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| * | Less than $0.01 per share |
See Accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
74
INTERMUNE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In
Capital | | | Deferred
Stock
Compensation | | | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income (Loss) | | | Accumulated
Deficit | | | Total
Stockholders’
Equity
(Deficit) | |
| | | Shares | | Amount | | | | | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
Balances at December 31, 2005 | | 32,589 | | $ | 33 | | $ | 493,953 | | | $ | (2,092 | ) | | $ | 754 | | | $ | (460,881 | ) | | $ | 31,767 | |
Net unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (7 | ) | | | — | | | | (7 | ) |
Change in unrealized gain on foreign currency cash flow hedge | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (607 | ) | | | — | | | | (607 | ) |
Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (107,206 | ) | | | (107,206 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (107,820 | ) |
Exercise of stock options | | 1,225 | | | 1 | | | 18,605 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18,606 | |
Stock issued under employee stock purchase plan | | 117 | | | — | | | 1,128 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,128 | |
Stock compensation related to the modification of stock options | | — | | | — | | | 253 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 253 | |
Issuance of restricted stock to employees, net of forfeitures | | 333 | | | — | | | 5,960 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5,960 | |
Reclassification of deferred compensation upon adoption of SFAS 123(R) | | — | | | — | | | (2,092 | ) | | | 2,092 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
Stock compensation related to employee stock benefit plans | | — | | | — | | | 10,309 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 10,309 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balances at December 31, 2006 | | 34,264 | | $ | 34 | | $ | 528,116 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 140 | | | $ | (568,087 | ) | | $ | (39,797 | ) |
Net unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities, net of taxes of $2,275 | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,719 | | | | — | | | | 3,719 | |
Change in unrealized gain on foreign currency cash flow hedge | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (212 | ) | | | — | | | | (212 | ) |
Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (89,602 | ) | | | (89,602 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (86,095 | ) |
Exercise of stock options | | 534 | | | 1 | | | 7,633 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 7,634 | |
Stock issued under employee stock purchase plan | | 111 | | | — | | | 1,257 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,257 | |
Issuance of common stock in a public offering at $19.50 per share, net of issuance costs of $5,092 | | 4,025 | | | 4 | | | 73,391 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 73,395 | |
Issuance of restricted stock to employees, net of forfeitures | | 98 | | | — | | | 2,694 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,694 | |
Stock compensation related to the modification of stock options | | — | | | — | | | 482 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 482 | |
Stock compensation related to employee stock benefit plans | | — | | | — | | | 9,542 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 9,542 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balances at December 31, 2007 | | 39,032 | | $ | 39 | | $ | 623,115 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 3,647 | | | $ | (657,689 | ) | | $ | (30,888 | ) |
Net unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | (5,062 | ) | | | — | | | | (5,062 | ) |
Net loss | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (97,739 | ) | | | (97,739 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (102,801 | ) |
Exercise of stock options | | 90 | | | — | | | 1,081 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,081 | |
Stock issued under employee stock purchase plan | | 71 | | | — | | | 939 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 939 | |
Issuance of restricted stock to employees, net of forfeitures | | 137 | | | — | | | 1,133 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,133 | |
Stock compensation related to employee stock benefit plans | | — | | | — | | | 5,664 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5,664 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balances at December 31, 2008 | | 39,330 | | $ | 39 | | $ | 631,932 | | | $ | — | | | $ | (1,415 | ) | | $ | (755,428 | ) | | $ | (124,872 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See Accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
75
INTERMUNE, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
| | | (In thousands) | |
Cash flows used for operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss | | $ | (97,739 | ) | | $ | (89,602 | ) | | $ | (107,206 | ) |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation expense | | | 6,797 | | | | 12,718 | | | | 16,522 | |
Amortization expense | | | 2,285 | | | | 1,336 | | | | 1,331 | |
Depreciation expense | | | 3,562 | | | | 3,511 | | | | 2,516 | |
Deferred taxes | | | — | | | | (2,275 | ) | | | — | |
Deferred rent | | | (341 | ) | | | (37 | ) | | | 161 | |
Net realized losses on sales and writedowns of available-for-sale securities | | | 3,170 | | | | — | | | | — | |
Change in unrealized gain on foreign currency cash flow hedge | | | — | | | | (212 | ) | | | (607 | ) |
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts receivable | | | (6 | ) | | | 8,682 | | | | 4,424 | |
Inventories | | | 527 | | | | 6,412 | | | | 4,249 | |
Prepaid expenses | | | 3,917 | | | | 579 | | | | (1,319 | ) |
Other assets | | | (687 | ) | | | 55 | | | | 927 | |
Accounts payable and accrued compensation | | | 11,413 | | | | (2,079 | ) | | | (24,090 | ) |
Other accrued liabilities | | | 5,010 | | | | (8,459 | ) | | | (5,816 | ) |
Liability under government settlement | | | (6,977 | ) | | | (2,474 | ) | | | 33,116 | |
Deferred collaboration revenue | | | (3,272 | ) | | | 6,727 | | | | 59,534 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in operating activities | | | (72,341 | ) | | | (65,118 | ) | | | (16,258 | ) |
Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Purchase of property and equipment | | | (2,026 | ) | | | (2,419 | ) | | | (4,452 | ) |
Purchases of available-for-sale securities | | | (119,805 | ) | | | (182,517 | ) | | | (130,434 | ) |
Maturities of available-for-sale securities | | | 81,801 | | | | 107,328 | | | | 41,396 | |
Sales of available-for-sale securities | | | 85,170 | | | | 40,000 | | | | 12,065 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | | | 45,140 | | | | (37,608 | ) | | | (81,425 | ) |
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Proceeds from issuance of common stock in a public offering, net of issuance costs | | | — | | | | 73,395 | | | | — | |
Proceeds from issuance of common stock under employee stock benefit plans, net | | | 2,020 | | | | 8,891 | | | | 19,734 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by financing activities | | | 2,020 | | | | 82,286 | | | | 19,734 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | | | (25,181 | ) | | | (20,440 | ) | | | (77,949 | ) |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | 88,946 | | | | 109,386 | | | | 187,335 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | | $ | 63,765 | | | $ | 88,946 | | | $ | 109,386 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest paid | | $ | 2,877 | | | $ | 1,733 | | | $ | 445 | |
Reclassification of deferred compensation upon adoption of SFAS 123(R) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 2,092 | |
See Accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
76
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Overview
We are an independent biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing innovative therapies in pulmonology and hepatology. Our revenue is provided from sales of Actimmune and our collaboration agreement with Roche. The pulmonology portfolio includes the Phase III program, CAPACITY, which is evaluating pirfenidone for the treatment of patients with IPF and a research program focused on small molecules for pulmonary disease. We announced results for the CAPACITY trials in February 2009 and intend to prepare regulatory filings for submission to the relevant authorities as soon as possible. The hepatology portfolio includes the HCV protease inhibitor compound ITMN-191 (referred to as R7227 at Roche) in Phase 1b, a second-generation HCV protease inhibitor research program and a research program evaluating a new target in hepatology.
| 2. | SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of InterMune and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, InterMune Canada Inc. and InterMune Ltd. (U.K.). All inter-company balances and transactions have been eliminated. To date, InterMune Canada Inc. and InterMune Ltd. (U.K.) have been dormant with no assets, liabilities or operations.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
We evaluate our estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis, including those related to our auction rate securities, reserves for doubtful accounts, returns, chargebacks, cash discounts and rebates; excess/obsolete inventories; the effects of inventory purchase commitments on inventory; and certain accrued clinical and preclinical expenses and contingent liabilities. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other specific assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources.
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Available-For-Sale Securities
Cash and cash equivalents consist of highly liquid investments with original maturities, when purchased, of less than three months. We classify all debt securities as available-for-sale. Cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities are carried at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses, reported as other comprehensive income (loss), a separate component of stockholders’ equity (deficit). We have estimated the fair value amounts by using quoted market prices or through a discounted cash flow analysis. The cost of securities sold is based on the specific identification method.
Fair Value of Other Financial Instruments
Other financial instruments, including accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities, are carried at historical cost, which we believe approximates fair value because of the short-term nature of these
77
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
instruments. The fair value of each of our $85.0 million convertible senior notes due 2011 and 2015 was $71.9 million and $86.3 million, respectively at December 31, 2008. As of December 31, 2007, the fair value of our $170.0 million convertible senior notes due 2011 was $159.5 million. For both 2008 and 2007, we determined the fair value of the outstanding balances of our notes using readily available market information.
Inventory Valuation
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost is determined by the specific identification method. Inventories were $1.2 million and $1.8 million at December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007, respectively, and consisted solely of Actimmune finished goods.
Because of the long lead times required to manufacture Actimmune, we enter into purchase obligations to satisfy our estimated inventory requirements. We evaluate the need to provide reserves for contractually committed future purchases of inventory that may be in excess of forecasted future demand. In making these assessments, we are required to make judgments as to the future demand for current as well as committed purchases. We are also required to make judgments as to the expiration dates of Actimmune, since Actimmune can no longer be used after its expiration date. As part of our excess inventory assessment for Actimmune, we also consider the expiration dates of Actimmune to be manufactured in the future under these purchase obligations.
During the years ended December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007, we charged $0.7 million and $1.6 million, respectively, to cost of goods sold for inventory write downs resulting from the estimated excess of inventory compared to forecasted inventory requirements. We did not incur any charges for excess inventory in 2006.
Concentration of Risks
Cash equivalents and investments are financial instruments that potentially subject us to concentration of risk to the extent recorded on the balance sheet. We have established guidelines for investing excess cash relative to diversification and maturities that we believe maintain safety and liquidity. The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve principal while at the same time maximizing yields without significantly increasing risk. To achieve this objective, we invest our excess cash in debt instruments of the U.S. federal and state governments and their agencies and high-quality corporate issuers, and, by policy, restrict our exposure to any single corporate issuer by imposing concentration limits. To reduce the exposure due to adverse shifts in interest rates we maintain investments with short effective maturities.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost and depreciated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows:
| | |
| | | Useful Lives |
Computer and laboratory equipment | | 3 to 5 years |
Office furniture and fixtures | | 3 to 5 years |
Leasehold improvements | | Length of lease |
Acquired Product Rights
Initial payments for the acquisition of products that, at the time of acquisition, are already marketed or are approved by the FDA for marketing are capitalized and amortized ratably over the estimated life of the products,
78
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
typically ten years. At the time of acquisition, the product life is estimated based upon the term of the agreement, the patent life of the product and our assessment of future sales and profitability of the product. We assess this estimate regularly during the amortization period and adjust the asset value or useful life when appropriate. Initial payments for the acquisition of products that, at the time of acquisition, are under development or are not approved by the FDA for marketing, have not reached technical feasibility and have no foreseeable alternative future uses are expensed as research and development costs. Acquired product rights consist of payments made for the acquisition of rights to interferon gamma (see Note 6). Accumulated amortization of this intangible asset was $3.3 million and $2.8 million at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Amortization expense for acquired product rights of $0.2 million is scheduled through April 2009 at which point the asset will be fully amortized.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
In accordance with SFAS No. 144, “Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets,” if indicators of impairment exist, we assess the recoverability of the affected long-lived assets by determining whether the carrying value of such assets can be recovered through undiscounted future operating cash flows. If impairment is indicated, we will measure the amount of such impairment by comparing the carrying value of the asset to the present value of the expected future cash flows associated with the use of the asset.
Revenue Recognition and Revenue Reserves
We recognize revenue generally upon delivery when title passes to a credit-worthy customer and record provisions for estimated returns, rebates, chargebacks and cash discounts against revenue. We are obligated to accept from customers the return of pharmaceuticals that have reached their expiration date. We believe that we are able to make reasonable and reliable estimates of product returns, rebates, chargebacks and cash discounts based on historical experience and other known or anticipated trends and factors. We review all sales transactions for potential rebates, chargebacks and discounts each month and believe that our reserves are adequate. We include shipping and handling costs in cost of goods sold.
Our revenue arrangements with multiple elements are divided into separate units of accounting if certain criteria are met, including whether the delivered element has stand-alone value to the customer and whether there is objective and reliable evidence of the fair value of the undelivered items. The consideration we receive is allocated among the separate units based on their respective fair values, and the applicable revenue recognition criteria are applied to each of the separate units. Advance payments received in excess of amounts earned are classified as deferred revenue until earned.
Collaboration revenue derived from our agreement with Roche generally includes upfront license fees and milestone payments. Nonrefundable upfront license fees that require our continuing involvement in the form of research, development, or other commercialization efforts by us are recognized as revenue ratably over the estimated term of our continuing involvement. Milestone payments received under our Roche collaboration agreement related to events that are substantively at risk of achievement at the initiation of the agreement are recognized as revenue when the milestones, as defined in the contract, are achieved and collectibility of the milestone is assured.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development (“R&D”) expenses include salaries, contractor and consultant fees, external clinical trial expenses performed by contract research organizations (“CRO”), licensing fees, acquired intellectual
79
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
property with no alternative future use and facility and administrative expense allocations. In addition, we fund R&D at research institutions under agreements that are generally cancelable at our option. Research costs typically consist of applied research and preclinical and toxicology work. Pharmaceutical manufacturing development costs consist of product formulation, chemical analysis and the transfer and scale-up of manufacturing at our contract manufacturers. Clinical development costs include the costs of Phase I, II and III clinical trials. These costs, along with the manufacturing scale-up costs, are a significant component of research and development expenses.
We accrue costs for clinical trial activities performed by contract research organizations and other third parties based upon the estimated amount of work completed on each study as provided by the CRO. These estimates may or may not match the actual services performed by the organizations as determined by patient enrollment levels and related activities. We monitor patient enrollment levels and related activities using available information; however, if we underestimate activity levels associated with various studies at a given point in time, we could be required to record significant additional R&D expenses in future periods when the actual activity level becomes known. We charge all such costs to R&D expenses.
Collaboration agreements with co-funding arrangements resulting in a net receivable or payable of R&D expenses are recognized as the related R&D expenses by both parties are incurred. The agreement with Roche resulted in a net payable of approximately $11.4 million at December 31, 2008 and a net payable of $0.1 million at December 31, 2007. See Note 7 below.
Advertising Costs
We expense advertising costs as incurred. Advertising costs were $42,000 and $285,000 for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. We did not incur advertising costs in 2008.
Income Taxes
In accordance with SFAS No. 109,“Accounting for Income Taxes,”we determine a deferred tax asset or liability based on the difference between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities as measured by the enacted tax rates, which will be in effect when these differences reverse. We provide a valuation allowance against net deferred tax assets unless, based upon the available evidence, it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized. Accordingly, the net deferred taxes have been fully offset by a valuation allowance.
We adopted the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109 (“FIN 48”) on January 1, 2007. FIN 48 requires companies to determine whether it is “more likely than not” that a tax position will be sustained upon examination by the appropriate taxing authorities before any tax benefit can be recorded in the financial statements. It also provides guidance on the recognition, measurement, classification and interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions. The adoption of FIN 48 did not have an impact on our results of operations or financial condition.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
SFAS No. 130, “Reporting Comprehensive Income,” requires components of other comprehensive income, including unrealized gains or losses on our available-for-sale securities, to be included in total comprehensive income (loss). Total comprehensive loss for each of the periods presented is disclosed in Note 11 below. Also,
80
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
other comprehensive income (loss) includes certain changes in stockholders’ equity (deficit) that are excluded from net loss. Specifically, we include in other comprehensive income (loss) changes in the fair value of our available-for-sale investments and derivatives designated as cash flow hedges.
Net Loss Per Share
We compute basic net loss per share by dividing the net loss for the period by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. We deduct shares subject to repurchase by us from the outstanding shares to arrive at the weighted average shares outstanding. We compute diluted net loss per share by dividing the net loss for the period by the weighted average number of common and potential common shares outstanding during the period. We exclude dilutive securities, composed of potential common shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options and common shares issuable on conversion of our convertible notes, from diluted net loss per share because of their anti-dilutive effect.
The securities excluded were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | As of December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Options | | 4,597 | | 4,671 | | 5,390 |
Shares issuable upon conversion of convertible notes | | 8,432 | | 7,859 | | 7,859 |
The calculation of basic and diluted net loss per share is as follows (in thousands, except per share data):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Net loss | | $ | (97,739 | ) | | $ | (89,602 | ) | | $ | (107,206 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic and diluted net loss per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average shares of common stock outstanding | | | 39,206 | | | | 35,743 | | | | 33,702 | |
Less: weighted-average shares subject to repurchase | | | (224 | ) | | | (250 | ) | | | (425 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average shares used in computing basic and diluted net loss per share | | | 38,982 | | | | 35,493 | | | | 33,277 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic and diluted net loss per share | | $ | (2.51 | ) | | $ | (2.52 | ) | | $ | (3.22 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-Based Compensation
On January 1, 2006, we adopted Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 123 (revised 2004), “Share-Based Payment,” (“SFAS 123(R)”) which requires the measurement and recognition of compensation expense for all share-based payment awards made to employees and directors including employee stock options, restricted stock and employee stock purchases related to the Amended and Restated 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) based on estimated fair values. In March 2005, the SEC issued Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107 (“SAB 107”) relating to SFAS 123(R). The Company has applied the provisions of SAB 107 as amended by SAB 110 in its adoption of SFAS 123(R).
SFAS 123(R) requires companies to estimate the fair value of share-based payment awards on the date of grant using an option-pricing model. The value of the portion of the award that is ultimately expected to vest is recognized as expense over the requisite service periods in our Consolidated Statement of Operations. Upon adoption of SFAS 123(R), we retained our method of valuation for share-based awards granted beginning in
81
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
fiscal 2006 with the use of the Black-Scholes option-pricing model (“Black-Scholes model”) which was previously used for our pro forma information required under SFAS 123. Our determination of fair value of share-based payment awards on the date of grant using an option-pricing model is affected by our stock price as well as assumptions regarding a number of highly complex and subjective variables. These variables include, but are not limited to our expected stock price volatility over the term of the awards, and actual and projected employee stock option exercise behaviors.
As stock-based compensation expense recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Operations for fiscal years 2008, 2007 and 2006 is based on awards ultimately expected to vest, it has been reduced for estimated forfeitures. SFAS 123(R) requires forfeitures to be estimated at the time of grant and adjusted, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. Stock-based compensation expense recognized under SFAS 123(R) for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 was $6.8 million, $12.7 million and $16.5 million, respectively. For additional information, see Note 13.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On October 10, 2008, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Staff Position No. FAS 157-3,Determining the Fair Value of a Financial Asset When the Market for That Asset Is Not Active,(FSP FAS 157-3). This FSP, which was effective upon release, clarifies the application of FAS 157 in a market that is not active and provides guidance and examples to illustrate key considerations in determining the fair value of a financial asset when the market for that financial asset is not active. We considered the impact of FSP FAS 157-3 in evaluating the fair value of our auction rate securities.
In June 2008, the FASB ratified Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue No. 07-5,Determining Whether an Instrument (or Embedded Feature) is Indexed to an Entity’s Own Stock (“EITF 07-5”). EITF 07-5 provides guidance on how to determine if certain instruments (or embedded features) are considered indexed to our own stock, including instruments similar to our convertible senior notes. EITF 07-5 requires companies to use a two-step approach to evaluate an instrument’s contingent exercise provisions and settlement provisions in determining whether the instrument is considered to be indexed to its own stock and exempt from the application of SFAS No. 133,Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities. Although EITF 07-5 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, any outstanding instrument at the date of adoption will require a retrospective application of the accounting through a cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings upon adoption. We are currently evaluating the impact of adoption on our consolidated financial position and results of operations.
In May 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. APB 14-1,Accounting for Convertible Debt Instruments that May be Settled in Cash upon Conversion (Including Partial Cash Settlement) (FSP APB 14-1) that significantly impacts the accounting for convertible debt. The FSP requires cash settled convertible debt, such as our 0.25% convertible senior notes due March 2011 (the “2011 Notes”) that are currently outstanding, to be separated into debt and equity components at issuance and a value to be assigned to each component. The value assigned to the debt component would be the estimated fair value, as of the issuance date, of a similar bond without the conversion feature. The difference between the bond cash proceeds and this estimated fair value would be recorded as a debt discount and amortized to interest expense over the expected life of the bond. Although FSP APB 14-1 has no impact on our actual past or future cash flows, it requires us to record non-cash interest expense as the debt discount is amortized. FSP APB 14-1 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008 and interim periods within those fiscal years, and requires retrospective application to all periods presented. Early application is not permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact of adoption and
82
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
based on our preliminary analysis of the requirements of FSP APB 14-1, we expect that the adoption of FSP APB 14-1 will have a material impact on our consolidated financial position and results of operations.
At its December 2007 meeting, the FASB ratified the consensus reached by the EITF in Issue No. 07-1,Accounting for Collaborative Arrangements Related to the Development and Commercialization of Intellectual Property. The EITF concluded that a collaborative arrangement is one in which the participants are actively involved and are exposed to significant risks and rewards that depend on the ultimate commercial success of the endeavor. Revenues and costs incurred with third parties in connection with collaborative arrangements would be presented gross or net based on the criteria in EITF 99-19,Reporting Revenue Gross as a Principal versus Net as an Agent, and other accounting literature. Payments to or from collaborators would be evaluated and presented based on the nature of the arrangement and its terms, the nature of the entity’s business and whether those payments are within the scope of other accounting literature. The nature and purpose of collaborative arrangements are to be disclosed along with the accounting policies and the classification and amounts of significant financial statement amounts related to the arrangements. Activities in the arrangement conducted in a separate legal entity should be accounted for under other accounting literature; however, required disclosure under EITF 07-1 applies to the entire collaborative agreement. This Issue is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2008, and is to be applied retrospectively to all periods presented for all collaborative arrangements existing as of the effective date. We are in the process of evaluating the impact of adopting this pronouncement and have not determined whether it will have a material impact, but its adoption would not affect reported amounts of net loss.
In June 2007, the FASB ratified the consensus reached by the EITF on Issue No. 07-3 (“EITF 07-3”),Accounting for Nonrefundable Advance Payments for Goods or Services Received for Use in Future Researchand Development Activities. Pursuant to EITF 07-3, nonrefundable advance payments for goods or services that will be used or rendered for future research and development activities should be deferred and capitalized. Such amounts should be recognized as an expense as the related goods are delivered or services are performed, or when the goods or services are no longer expected to be received. Effective January 1, 2008, we adopted EITF 07-3. The adoption did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In February 2007, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 159 (“SFAS 159”),The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities. SFAS 159 permits an entity to measure certain financial assets and financial liabilities at fair value where entities will report unrealized gains and losses in earnings at each subsequent reporting date. The standard allows entities to elect fair value application on an instrument-by-instrument basis with certain exceptions. The fair value option election is irrevocable in most cases. Effective January 1, 2008, we adopted SFAS 159 and did not elect to adopt the fair value option under this Statement.
Effective January 1, 2008, we adopted SFAS No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements” (“SFAS 157”). In February 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position No. FAS 157-2, “Effective Date of FASB Statement No. 157”, which provides a one year deferral of the effective date of SFAS 157 for non-financial assets and non-financial liabilities, except those that are recognized or disclosed in the financial statements at fair value at least annually. Therefore, the Company has adopted the provisions of SFAS 157 with respect to its financial assets and liabilities only. SFAS 157 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value under generally accepted accounting principles and enhances disclosures about fair value measurements. Fair value is defined under SFAS 157 as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value under
83
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
SFAS 157 must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The standard describes a fair value hierarchy based on three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable, that may be used to measure fair value which are the following:
| | • | | Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| | • | | Level 2—Inputs other than Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. |
| | • | | Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. |
The adoption of this statement did not have an impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
| 3. | DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS |
Product Acquisition Agreement
We entered into a Product Acquisition Agreement (the “Agreement”) with Valeant Pharmaceuticals International (“Valeant”) on November 28, 2005, whereby Valeant agreed to purchase all of the rights to Infergen from us. Valeant agreed to acquire certain assets, including intellectual property rights and inventory, as of December 30, 2005 for approximately $122.1 million, including a fixed payment of approximately $2.1 million in 2007. Of the $122.1 million, $6.5 million is related to the purchase of finished product inventory. The Agreement also states that we are entitled to receive approximately $20.0 million contingent upon Valeant achieving certain clinical related milestones beginning in 2007, of which $5.0 million was received in July 2007 and recorded in discontinued operations in the consolidated statement of operations.
Results of Discontinued Operations
Summary operating results for the discontinued operations are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Infergen revenue, net | | $ | 103 | | $ | (6 | ) | | $ | (1,024 | ) |
Contract (milestone) revenue | | | — | | | 5,000 | | | | — | |
Costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | | — | | | — | | | | 81 | |
Research and development | | | — | | | — | | | | (531 | ) |
Selling, general and administrative | | | — | | | — | | | | 230 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total costs and expenses | | | — | | | — | | | | (220 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Gain (loss) from discontinued operations | | $ | 103 | | $ | 4,994 | | | $ | (1,244 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Discontinued operations in 2008 is comprised of adjustments to our initial product return estimates and in 2007 consist primarily of the $5.0 million clinical related milestone received in July 2007. Discontinued operations in 2006 consist primarily of transition related services, including product returns.
84
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
| 4. | ASSET IMPAIRMENT AND RESTRUCTURING CHARGES |
Effective March 5, 2007, we made the decision to discontinue the Phase III INSPIRE clinical trial evaluating Actimmune in patients with IPF based upon the recommendation of the study’s independent DMC. As a result of the disappointing INSPIRE trial results, we revised our estimates of inventory requirements as of December 31, 2006. Accordingly, we recorded a charge of $4.5 million in 2006 related to the prepayment of inventory that we had expected to receive in 2007 and 2008. While we believe other Actimmune related assets are recoverable for at least their $1.4 million net carrying value, if sales decline below our revised estimates, we may incur additional asset impairment charges, including inventory writedowns in excess of the $1.6 million and $0.7 million recorded in 2007 and 2008, respectively, and impairment of acquired product rights, as well as product returns.
The following table reflects the asset balances as of December 31, 2008 which may be impacted (in thousands):
| | | |
| | | 2007 |
Finished goods inventory | | $ | 1,249 |
Acquired product rights, net | | | 167 |
| | | |
Total | | $ | 1,416 |
| | | |
We also incurred approximately $3.4 million in personnel-related restructuring charges during 2007, primarily consisting of severance related expenses to implement our announced plan to reduce the workforce by approximately 50%. This workforce reduction was completed as of September 30, 2007. The $3.4 million personnel-related restructuring charge was comprised of approximately $2.9 million for cash severance and related benefits and $0.5 million of costs for the acceleration of options for approximately 66,000 shares of our common stock. We also incurred approximately $6.8 million in expenses in connection with the termination of our previous supply agreement with BI in the second quarter of 2007. See Note 15 below.
The activity in the accrued restructuring balance, included within accounts payable and accrued compensation on the balance sheet, was as follows for 2007 and 2008 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Restructuring
Liabilities at
December 31,
2006 | | Charges | | Cash
Payments | | | Restructuring
Liabilities at
December 31,
2007 | | Charges | | Cash
Payments | | | Restructuring
Liabilities at
December 31,
2008 |
Workforce reduction | | $ | — | | $ | 2,984 | | $ | (2,780 | ) | | $ | 204 | | $ | — | | $ | (166 | ) | | $ | 38 |
Supply agreement termination | | | — | | | 6,779 | | | (6,779 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Totals | | $ | — | | $ | 9,763 | | $ | (9,559 | ) | | $ | 204 | | $ | — | | $ | (166 | ) | | $ | 38 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 5. | INVESTMENT IN TARGANTA COMMON STOCK |
In 2001, we entered into an asset purchase and license agreement with Eli Lilly pursuant to which we acquired worldwide rights to oritavancin. The agreement provided us with exclusive worldwide rights to develop, manufacture and commercialize oritavancin.
In December 2005, we sold the oritavancin compound to Targanta Therapeutics (“Targanta”). The terms of the agreement included upfront and clinical related contingent milestone payments of up to $9.0 million, of
85
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
which $4.0 million has been received through December 31, 2008. We also received a convertible promissory note that, assuming certain clinical milestones were achieved, could have been valued at up to $25.0 million in principal amount from Targanta, which note was initially secured by the oritavancin assets. Upon the achievement by Targanta of certain corporate objectives, the notes were designed to convert into capital stock of Targanta, subject to certain limitations in the amount of voting stock that we could hold. Effective February 2007, these objectives were met by Targanta and, upon conversion of the promissory note, we received approximately 1.7 million shares of Targanta Series C preferred stock in exchange for the convertible promissory note. In October 2007, Targanta completed an initial public offering of its common stock at a price of $10.00 per share. Upon completion of the offering, our investment in Targanta was automatically converted into approximately 3.0 million shares of Targanta common stock and warrants to purchase approximately 0.1 million additional shares of Targanta common stock. These shares had been restricted for resale and were subject to a lock-up agreement that expired in April 2008. We have recorded an unrealized loss, net of taxes, of $1.8 million on approximately 840,000 of those shares valued at approximately $0.5 million at December 31, 2008 representing the portion estimated to qualify for resale within one year in accordance with SFAS 115. At December 31, 2007, the unrealized gain, net of taxes, was $3.4 million on approximately 630,000 shares valued at $5.7 million.
In January 2009, The Medicines Company announced its intent to acquire Targanta for $2.00 per share, or approximately $42.0 million and on January 27, 2009 commenced a tender offer to acquire all outstanding shares of Targanta. We have tendered our shares and received approximately $6.0 million in March 2009 upon closing of the transaction. We may also receive up to an additional $4.55 per share in contingent cash payments upon the achievement of specified regulatory and commercial milestones within certain time periods.
| 6. | ACQUIRED PRODUCT RIGHTS |
Marnac, Inc./KDL GmbH (Pirfenidone)
In 2002, we licensed from Marnac and its co-licensor, KDL, their worldwide rights, excluding Japan, Korea and Taiwan, to develop and commercialize pirfenidone for all fibrotic diseases, including renal, liver and pulmonary fibrosis. Under the agreement terms, we received an exclusive license from Marnac and KDL in exchange for an up-front cash payment of $18.8 million and future milestone and up to 9% royalty payments. During the third quarter of 2007, we recorded a $7.5 million expense for such milestone payments, which are based on the progress of clinical development of pirfenidone. If all of the milestones under this agreement had been achieved, we would have been required to make milestone payments of $14.5 million. Effective November 21, 2007, we entered into asset purchase agreements with Marnac and KDL whereby we effectively terminated the prior license agreement by purchasing, among other things, the pirfenidone-related assets covered by such prior license agreement. Under the terms of the asset purchase agreements, we made acquisition payments of approximately $13.7 million, which includes the $7.5 million expense recorded in the third quarter of 2007 relating to the 2002 license agreement. These payments have been reported as acquired research and development in our consolidated statements of operations. Contingent acquisition payments of up to an additional $53.5 million would be made by us only if positive Phase III data and registration in the United States and European Union are achieved, of which $13.5 million has been paid in March 2009. The asset purchase agreements do not affect the rights to pirfenidone in Japan, Korea and Taiwan, which rights are licensed by Marnac and KDL to Shionogi. Since the original 2002 license agreement has been effectively terminated as a result of our acquisition of such pirfenidone-related assets from Marnac and KDL, we no longer have milestone or royalty obligations thereunder.
86
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Amgen Inc. (Interferon Gamma)
In 2002, we acquired certain pending patent applications relating to interferon gamma from Amgen in exchange for $3.5 million, of which $1.5 million was paid in June 2002, and the remaining $2.0 million was paid in January 2003. We are amortizing these product rights to operations over the expected useful product life of Actimmune. The net carrying value of this intangible asset was $0.2 million as of December 31, 2008.
Genentech, Inc. License Agreement (Actimmune)
In 1998, we obtained a license under Genentech’s patents relating to Actimmune. The license from Genentech terminates on the later of May 5, 2018 or the date that the last of the patents licensed under the agreement expires. Our licensed Actimmune rights include exclusive and non-exclusive licenses. The exclusive licenses include the right to develop and commercialize Actimmune in the United States and Canada for the treatment and prevention of all human diseases and conditions, including infectious diseases, pulmonary fibrosis and cancer, but excluding arthritis and cardiac and cardiovascular diseases and conditions. The non-exclusive licenses include the right to make or have made Actimmune for clinical and commercial purposes within our field of use in the United States and Canada. In Japan, we have the exclusive license rights to commercialize Actimmune for the treatment and prevention of all infectious diseases caused by fungal, bacterial or viral agents, including in patients with CGD or osteopetrosis. We also have the opportunity, under specified conditions, to obtain further rights to Actimmune in Japan and other countries. In addition, we received an exclusive sublicense under certain of Genentech’s patents outside the United States, Canada and Japan under the BI agreement discussed below. Under the Genentech license, we pay Genentech royalties on the revenue from sales of Actimmune and are required to make one-time payments to Genentech upon the occurrence of specified milestone events, which include the submission of a filing a BLA with the FDA for approval to market Actimmune for the treatment of particular categories of diseases, the receipt of FDA approval to market Actimmune for the treatment of particular categories of diseases and the achievement of certain annual revenue targets for Actimmune. We had made royalty payments of approximately $79.3 million, but no milestone payments, under this agreement in the aggregate through December 31, 2008. If all of the milestones under this agreement are achieved, we would be required to make milestone payments of $3.2 million, although we have no further development plans for Actimmune. We must satisfy specified diligence obligations under the agreement with Genentech to maintain our license from Genentech. Our rights to certain therapeutic uses for Actimmune under this agreement could revert to Genentech if we do not meet our diligence obligations or otherwise commit a material breach of the agreement.
Connetics Corporation (Actimmune)
Through an assignment and option agreement with Connetics, we paid Connetics $5.7 million to acquire rights to Actimmune and are obligated to pay to Connetics a royalty of 0.25% of our net United States sales for Actimmune until our net United States sales cumulatively surpass $1.0 billion. Above $1.0 billion, we are obligated to pay a royalty of 0.5% of our net United States sales of Actimmune. Through a separate purchase agreement, we paid Connetics $0.4 million to acquire rights related to scleroderma and are obligated to pay Connetics a royalty of 4.0% on our net revenue from sales of Actimmune for the treatment of scleroderma. We had made royalty payments of approximately $1.7 million in the aggregate through December 31, 2008. There are no milestone payments pursuant to this agreement.
87
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
| 7. | SPONSORED RESEARCH, LICENSE AND COLLABORATION AGREEMENTS |
Roche (Protease Inhibitors)
In October 2006 we entered into a Collaboration Agreement with Roche. Under the Collaboration Agreement, we agreed to collaborate with Roche to develop and commercialize products from our HCV protease inhibitor program. The Collaboration Agreement includes our lead candidate compound ITMN-191, which entered Phase 1a clinical trials late in 2006 and phase 1b clinical trials during the third quarter of 2007. We also agreed to collaborate with Roche on a research program to identify, develop and commercialize novel second-generation HCV protease inhibitors.
Under the terms of the Collaboration Agreement, we agreed to conduct Phase I studies for ITMN-191, and thereafter Roche agreed to lead clinical development and commercialization. Upon execution of the agreement, we received an upfront payment of $60.0 million from Roche. In addition, assuming successful development and commercialization of ITMN-191 in the United States and other countries, we could potentially receive up to an aggregate of $470.0 million in milestone payments. One milestone payment of $10.0 million was received in January 2007, which was not deemed to be substantially at risk at the execution of the Collaboration Agreement. Therefore, the upfront payment of $60.0 million and this $10.0 million milestone payment have been deferred and are being recognized ratably as collaboration revenue over the estimated period of our continuing involvement, currently expected to conclude approximately March 2028. All further milestone payments have been assessed as substantially at-risk at the execution of the agreement and will be recognized as revenue when and if these milestones are achieved, as defined in the Collaboration Agreement. In June 2007 and September 2008, we received $10.0 million and $15.0 million milestone payments, respectively, which were recognized as revenue upon receipt as the milestones were deemed substantially at-risk at the execution of the agreement. Roche agreed to fund 67% of the global development costs of ITMN-191 and, if the product is approved for commercialization by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, we agreed to co-commercialize the product in the United States and share profits on a 50-50 basis with Roche. We are entitled to receive royalties on any sales of the product outside of the United States. We have the right to opt-out of either co-development and/or co- commercialization of ITMN-191 in exchange for higher royalties on sales outside of the United States, and royalties instead of profit sharing in the United States. The economic terms for ITMN-191 could also apply to additional compounds that we and Roche develop under the Collaboration Agreement. In connection with this agreement with Roche, we have recorded a net payable of approximately $11.4 million at December 31, 2008 and a net payable of $0.1 million at December 31, 2007.
In November 2008, we amended the Collaboration Agreement among other things to extend the research program (and consequently the research exclusivity period whereby each party is prohibited from engaging in certain competitive research activities) for an additional amount of time and to provide for certain funding by Roche of activities taking place during such extended research period. Such research funding by Roche may be credited by Roche against certain future payments in connection with Roche’s inclusion of possible additional compounds as part of its license rights granted to it under the collaboration. In connection with this amendment and Roche’s funding of certain of our research activities, we have recorded a receivable from Roche of $1.4 million as of December 31, 2008, included within accounts receivable.
Novartis Corporation (Small Molecule Therapeutics)
In 2004, we entered into a license agreement with Chiron Corporation (which was acquired by Novartis) which granted us the right to discover, develop and commercialize small molecule therapeutic agents against certain HCV targets that are covered by patents owned by Novartis. In consideration for this license, we paid Novartis a nonrefundable fee of approximately $0.4 million in 2004 and are required to make milestone payments based on the clinical progress of ITMN-191. In 2006, we expensed $0.5 million upon initiation of the
88
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Phase Ia clinical trials for ITMN-191. Assuming that all of the remaining milestones under this agreement are achieved, we will be required to make milestone payments of $4.5 million. In addition, Novartis is entitled to receive royalties on future product sales.
Array BioPharma Inc. (Small Molecule Therapeutics)
In 2002, we entered into a drug discovery collaboration agreement to create small molecule therapeutics targeting hepatitis with Array. Under that agreement, we fund drug discovery research conducted by Array during the research term based on the number of Array scientists working on the research phase of the agreement and we are responsible for all development and commercialization. Though the research phase of the agreement expired in June 2007, Array will continue to be entitled to receive milestone payments under the agreement based on the selection and progress of clinical drug candidates, as well as low single-digit royalties on net sales of products derived from the collaborative efforts. In addition, in December 2004, the agreement was amended to provide a mechanism for us to purchase certain intellectual property rights arising from the collaboration. In April 2005, we initiated a second research collaboration with Array with respect to a new hepatology target and have since terminated that agreement.
Assuming that all of the remaining milestones under these agreements are achieved, we will be required to make milestone payments of $8.5 million. Total payments related to this agreement were $1.3 million and $10.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, and were recorded as research and development expenses. We did not record any research and development expense or make any payments related to Array in 2008. Included in the $10.2 million in 2006 is a $0.5 million milestone payment for the initiation of the Phase Ia clinical trial for ITMN-191.
In accordance with SFAS 157, the following table represents the Company’s fair value hierarchy for its financial assets (cash equivalents and investments, including accrued interest of approximately $0.8 million) measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2008 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
Money market funds | | $ | 33,952 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 33,952 |
Obligations of government-sponsored enterprises | | | — | | | 50,775 | | | — | | | 50,775 |
Obligations of United States government | | | — | | | 9,000 | | | — | | | 9,000 |
Corporate debt securities | | | — | | | 16,650 | | | — | | | 16,650 |
Commercial paper | | | — | | | 20,494 | | | — | | | 20,494 |
Targanta common stock | | | 512 | | | — | | | — | | | 512 |
Auction rate securities | | | — | | | — | | | 17,514 | | | 17,514 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 34,464 | | $ | 96,919 | | $ | 17,514 | | $ | 148,897 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Level 3 assets consist of municipal notes investments, classified as noncurrent assets, with an auction reset feature (“auction rate securities”) whose underlying assets are generally student loans which are substantially backed by the federal government. In February 2008, auctions began to fail for these securities and each auction since then has failed. Based on the overall failure rate of these auctions, the frequency of the failures, and the underlying maturities of the securities, a portion of which are greater than 30 years, and due to the uncertainty of when we will be able to dispose of these securities, we have classified auction rate securities as long-term assets on our balance sheet. During the fourth quarter of 2008, we recorded an impairment charge of approximately $3.5 million on these securities as we believe the losses are other-than-temporary in nature given the
89
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
deteriorating credit and financial markets and specifically the auction rate securities market, and our inability to hold such securities to their maturity or estimated recovery. Based on our expected operating cash flows, and our other sources of cash, including proceeds from our February 2009 public offering, and the recently announced results from our CAPACITY trials, we currently anticipate the need to liquidate these investments prior to maturity or estimated time to recovery in order to execute our current business plans. These investments were recorded at fair value as of December 31, 2008 based on a discounted cash flow analysis. The assumptions used in preparing the discounted cash flow model include estimates of, based on data available as of December 31, 2008, interest rates, timing and amount of cash flows, credit and liquidity premiums, and expected holding periods of these securities. Given the current market environment, these assumptions are volatile and subject to change, which could result in significant changes to the fair value of these securities in future periods. Since December 31, 2007, two of our auction rate securities with an aggregate fair value of $6.0 million were redeemed at par value. The following table provides a summary of changes in fair value of the Company’s Level 3 financial assets as of December 31, 2008 (in thousands):
| | | | |
| | | Auction rate
Securities | |
Balance at December 31, 2007 | | $ | 27,000 | |
Impairment charge included in other income (expense) | | | (3,506 | ) |
Net settlements | | | (6,000 | ) |
| | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2008 | | $ | 17,494 | |
| | | | |
| 9. | AVAILABLE-FOR-SALE INVESTMENTS |
The following is a summary of our available-for-sale investments as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value |
December 31, 2008 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of government-sponsored enterprises | | $ | 50,418 | | $ | 357 | | $ | — | | | $ | 50,775 |
Money market funds | | | 33,952 | | | — | | | — | | | | 33,952 |
Commercial paper | | | 20,477 | | | 17 | | | — | | | | 20,494 |
Corporate debt securities | | | 16,676 | | | 44 | | | (70 | ) | | | 16,650 |
Obligations of United States government | | | 9,000 | | | — | | | — | | | | 9,000 |
Targanta common stock | | | — | | | 512 | | | — | | | | 512 |
Auction rate securities | | | 17,514 | | | — | | | — | | | | 17,514 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 148,037 | | $ | 930 | | $ | (70 | ) | | $ | 148,897 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value |
Reported as: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash equivalents | | $ | 57,941 | | $ | 8 | | $ | — | | | $ | 57,949 |
Available-for-sale securities | | | 72,582 | | | 922 | | | (70 | ) | | | 73,434 |
Noncurrent available-for-sale securities | | | 17,514 | | | — | | | — | | | | 17,514 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 148,037 | | $ | 930 | | $ | (70 | ) | | $ | 148,897 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
90
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value |
December 31, 2007 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Obligations of government-sponsored enterprises | | $ | 135,813 | | $ | 181 | | $ | — | | | $ | 135,994 |
Corporate debt securities | | | 34,526 | | | 110 | | | (3 | ) | | | 34,633 |
Commercial paper | | | 12,815 | | | — | | | (53 | ) | | | 12,762 |
Targanta common stock | | | — | | | 5,687 | | | — | | | | 5,687 |
Auction rate securities and money market funds | | | 39,150 | | | — | | | — | | | | 39,150 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 222,304 | | $ | 5,978 | | $ | (56 | ) | | $ | 228,226 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | Gross
Unrealized
Gains | | Gross
Unrealized
Losses | | | Fair Value |
Reported as: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash equivalents | | $ | 81,861 | | $ | 20 | | $ | (1 | ) | | $ | 81,880 |
Available-for-sale securities | | | 140,443 | | | 5,958 | | | (55 | ) | | | 146,346 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 222,304 | | $ | 5,978 | | $ | (56 | ) | | $ | 228,226 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Realized gains and losses and declines in value, judged to be other than temporary, on available-for-sale securities are included in other income (expense) for the years 2008, 2007 and 2006. Realized gains and losses were calculated based on the specific identification method and were approximately ($3.2) million in 2008 and $0 in both 2007 and 2006. During the fourth quarter of 2008, we recorded an impairment charge of approximately $3.5 million related to the writedown of our auction rate securities as we believe the losses are other-than-temporary in nature given the deteriorating credit and financial markets and specifically the auction rate securities market. Unrealized holding gains and losses on securities classified as available-for-sale are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax. Our investment in Targanta common stock consisted of approximately 3.0 million shares of which we have recorded an unrealized gain on approximately 840,000 of those shares representing the portion estimated to qualify for resale within one year. See Note 5 above.
The following is a summary of the amortized cost and estimated fair value of available-for-sale securities at December 31, by contractual maturity (excludes Targanta common stock) (in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2008 |
| | | Amortized
Cost | | Fair Value |
Mature in less than one year | | $ | 120,133 | | $ | 120,537 |
Mature in one to three years | | | 10,390 | | | 10,333 |
Mature in over three years | | | 17,514 | | | 17,514 |
| | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 148,037 | | $ | 148,384 |
| | | | | | |
91
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Property and equipment and related accumulated depreciation and amortization is as follows at December 31 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
Computer and laboratory equipment | | $ | 12,966 | | | $ | 11,060 | |
Office furniture and fixtures | | | 3,721 | | | | 3,710 | |
Leasehold improvements | | | 9,816 | | | | 9,839 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 26,503 | | | | 24,609 | |
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | (19,921 | ) | | | (16,491 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 6,582 | | | $ | 8,118 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Other accrued liabilities consist of the following at December 31 (in thousands):
| | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 |
Accrued clinical trial costs | | $ | 8,186 | | $ | 4,624 |
Liability under government settlement—current | | | 6,023 | | | 7,174 |
Deferred collaboration revenue—current | | | 3,272 | | | 3,272 |
Accrued interest | | | 1,487 | | | 142 |
Royalties payable | | | 709 | | | 884 |
Medicaid rebates | | | 365 | | | 256 |
Provision for returns and rebates | | | 294 | | | 378 |
Accrued research and development | | | 733 | | | 812 |
Other accrued liabilities | | | 950 | | | 618 |
| | | | | | |
Total other accrued liabilities | | $ | 22,019 | | $ | 18,160 |
| | | | | | |
| 11. | COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) |
Comprehensive income (loss) is comprised of net loss and other comprehensive income (loss). We include in other comprehensive income (loss) changes in the fair value of derivatives designated as foreign currency cash flow hedges and unrealized gains and losses on our available-for-sale securities, including approximately 840,000 shares of Targanta common stock, which represents the portion of our holdings that are estimated to qualify for resale within one year. The activity in other comprehensive income (loss) is as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Net loss | | $ | (97,739 | ) | | $ | (89,602 | ) | | $ | (107,206 | ) |
Change in unrealized gain/(loss) on available-for-sale securities, net of tax benefit of $2,275 in 2007 | | | (5,062 | ) | | | 3,719 | | | | (7 | ) |
Change in realized and unrealized gain on foreign currency hedge | | | — | | | | (212 | ) | | | (607 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss | | $ | (102,801 | ) | | $ | (86,095 | ) | | $ | (107,820 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
92
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) consists of the following at (in thousands):
| | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 |
Net unrealized gain (loss) on available-for-sale securities, net of tax of $2,275 at December 31, 2008 and December 31, 2007, (including ($1,763) and $3,412, respectively, related to Targanta shares) | | $ | (1,415 | ) | | $ | 3,647 |
| | | | | | | |
In February 2004, we issued 0.25% convertible senior notes due March 1, 2011 in an aggregate principal amount of $170.0 million (the “2011 Notes”). The 2011 Notes are convertible into our common stock at the option of the holder at a conversion price of approximately $21.63 per share, subject to adjustment in certain circumstances. Interest on the 2011 Notes is payable semiannually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year. The 2011 Notes are unsecured and rank on parity with all existing and future senior unsecured debt and prior to all subordinated indebtedness. In addition, the 2011 Notes are effectively subordinated to any existing and future secured debt to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such debt. Offering expenses of $5.8 million (subject to adjustment for the extinguishment described below) related to the sale of the 2011 Notes were recorded in other assets and are being amortized to interest expense using the effective interest method over the term of the 2011 Notes, which is seven years from the date of issuance.
On June 24, 2008, we issued $85.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 5.00% Convertible Senior Notes due 2015 (the “2015 Notes”) to certain holders (the “Holders”) of our existing 2011 Notes in exchange for $85.0 million in aggregate principal amount of their 2011 Notes. The 2015 Notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and rank equally in right of payment with all of our existing and future senior debt, including the 2011 Notes, and rank senior in right of payment to all of our existing and future subordinated debt. The 2015 Notes were exchanged by us with the Holders exclusively and solely for the 2011 Notes in a transaction exempt from registration under Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
The terms of the 2015 Notes are substantially similar to the 2011 Notes, except, among other things, the following: (i) the 2015 Notes will mature on March 1, 2015 as opposed to March 1, 2011; (ii) the 2015 Notes bear interest at a rate of 5.00% per annum as opposed to .25% per annum; (iii) holders of the 2015 Notes may convert their 2015 Notes into shares of our common stock at a conversion rate of 52.9661 shares per $1,000 principal amount of notes (representing a conversion price of approximately $18.88 per share), subject to adjustment, whereas holders of the 2011 Notes may convert their 2011 Notes into shares of common stock at a conversion rate of 46.2283 shares per $1,000 principal amount of notes (representing a conversion price of approximately $21.63 per share), subject to adjustment; (iv) the conversion rate for the 2015 Notes will be increased in certain circumstances that constitute a fundamental change of the Company and in connection with a withholding tax redemption; and (v) we can only settle conversion of the 2015 Notes by delivery of shares of common stock as opposed to our ability to settle conversion of the 2011 Notes by delivery of cash (or a combination of cash and shares) in lieu of shares.
In accordance with the provisions of Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) 96-19,Debtor’s Accounting for a Modification or Exchange of Debt Instruments, (“EITF 96-19”), the exchange was treated as the extinguishment of the original debt and issuance of new debt. Accordingly, we recorded a non-cash loss on debt extinguishment of $1.1 million during the second quarter of fiscal 2008 which loss was entirely comprised of unamortized debt issuance costs related to the 2011 Notes that were exchanged. This non-cash loss has been included in interest expense in our consolidated statements of operations. Debt issuance costs of approximately
93
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
$0.6 million related to the sale of the 2015 Notes were recorded in other assets and are being amortized to interest expense using the effective interest method over the term of the 2015 Notes, which is approximately seven years from the date of issuance. The remaining $85.0 million in principal amount of the 2011 Notes have not been modified or extinguished.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
To provide employees with an opportunity to purchase our common stock through payroll deductions, our board of directors adopted the 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”). Under the ESPP, employees, subject to certain restrictions, may purchase shares of common stock at 85% of the fair market value at either the date of eligibility for enrollment or the date of purchase, whichever is less. Purchases are limited to the lesser of 15% of each employee’s eligible annual compensation or $25,000. Through the end of December 2008, we issued a cumulative total of 771,776 shares under the ESPP, including 71,833 issued in 2008, and 1,616,734 shares remained available for future issuance at December 31, 2008. Beginning January 1, 2001 and continuing through and including January 1, 2006, the amount of common stock reserved for issuance under the ESPP increased annually on that date by the lesser of (i) one percent (1%) of the total number of shares of common stock outstanding on such January 1, (ii) 400,000 shares of common stock, or (iii) a number of shares as determined by the board of directors prior to January 1, which shall be lesser than (i) or (ii) above.
Restricted Stock Awards
In May 2008 and May 2007, we granted employees restricted stock awards for approximately 151,000 shares and 128,000 shares of our common stock, respectively, with weighted-average fair values of $15.34 and $25.50 per share, respectively, that vest annually over a four year period. In January 2006 we granted employees restricted stock awards for 404,450 shares of our common stock with a weighted-average fair value of $19.30 per share that became fully vested in January 2008 upon the Company’s achievement of the fourth of four different performance-based milestones. Vesting occurred at the rate of twenty-five percent each for the four different milestones over the two-year period. In May 2006, the first of the four milestones was met and in January and March 2007, the second and third milestones were met, respectively. Grants made in 2004 (none were granted in 2005) vested annually over a four-year period, thirty percent in each of the first three years and the final ten percent in 2008. Restricted stock awards are shares of common stock which are forfeited if the employee leaves the Company prior to vesting. As a result of all of these restricted stock awards, we recognized $1.1 million in compensation expense during the year ended December 31, 2008, compared to $2.7 million and $6.0 million in the years ended December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. As all of the restricted stock awards vest through 2009 and beyond, we will continue to recognize stock based compensation expense related to the grants of these restricted awards. These stock awards offer employees the opportunity to earn shares of our stock over time, rather than options that give the employee the right to purchase stock at a set price. If all of the remaining restricted stock awards that were granted in 2006, 2007 and 2008 vest, we will recognize approximately $3.9 million in compensation expense over a weighted average remaining period of 2.6 years. However, no compensation expense will be recognized for stock awards that do not vest.
94
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
A summary of our restricted stock activity is presented in the following table:
| | | | | | |
Restricted Stock Awards | | Shares | | | Weighted-Average
Grant Date Fair
Value |
Nonvested at December 31, 2005 | | 175,651 | | | $ | 16.02 |
Granted | | 424,450 | | | | 19.43 |
Vested | | (161,959 | ) | | | 18.08 |
Forfeited | | (92,774 | ) | | | 17.77 |
| | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2006 | | 345,368 | | | $ | 18.78 |
Granted | | 128,077 | | | | 25.50 |
Vested | | (233,258 | ) | | | 18.54 |
Forfeited | | (30,478 | ) | | | 19.27 |
| | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2007 | | 209,709 | | | $ | 23.08 |
Granted | | 150,748 | | | | 15.34 |
Vested | | (88,280 | ) | | | 20.56 |
Forfeited | | (13,924 | ) | | | 21.38 |
| | | | | | |
Nonvested at December 31, 2008 | | 258,253 | | | $ | 19.51 |
| | | | | | |
Stock Compensation Plans
In 1999, we adopted the 1999 Equity Incentive Plan (“1999 Plan”). The 1999 Plan provided for the granting of options to purchase common stock and the issuance of shares of common stock, subject to repurchase rights, to directors, employees and consultants. Certain options were immediately exercisable, at the discretion of our board of directors. Shares issued pursuant to the exercise of an unvested option are subject to the right of repurchase which lapses over periods specified by the board of directors, generally four years from the date of grant. In 2000, we terminated all remaining unissued shares under the 1999 Plan amounting to 121,584 shares. Under the 1999 Plan, 46,550 shares have been granted to employees that are subject to repurchase as of December 31, 2008.
In 2000, our board of directors adopted the 2000 Equity Incentive Plan, which was most recently amended and approved by stockholders in 2007 and re-named the Amended and Restated 2000 Equity Incentive Plan (“2000 Plan”). In 2000, a total of 2.0 million shares of common stock were initially reserved for issuance under the 2000 Plan. In 2002, 2004 and 2007 an additional 2.5 million, 1.0 million and 1.5 million shares of common stock, respectively, were reserved for issuance under the 2000 Plan. The 2000 Plan provides for the granting of options to purchase common stock and the issuance of shares of common stock, subject to repurchase rights, to directors, employees and consultants. Shares issued pursuant to the exercise of an unvested option are subject to our right of repurchase which lapses over periods specified by the board of directors, generally four years from the date of grant. Options not immediately exercisable generally vest up to a maximum of four years. Options previously granted under the 2000 Plan had a maximum term of 10 years. Effective May 15, 2007, new option grants have a maximum term of 7 years.
In 2000, our board of directors adopted the 2000 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Option Plan, which was most recently amended in 2007 and re-named the Amended and Restated 2000 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Option Plan (“Directors’ Plan”). In 2000, a total of 180,000 shares of common stock were initially reserved for issuance under the Directors’ Plan. From 2001 through 2004, an additional 1,090,000 shares of common stock were reserved for issuance under the Director’s Plan. The Directors’ Plan provides for the granting of options to purchase common stock and the issuance of shares of common stock, subject to repurchase rights, to directors of InterMune.
95
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Shares issued pursuant to the exercise of an unvested option are subject to our right of repurchase which lapses over periods specified by the board of directors, generally one year from the date of grant for annual grants and three years from the date of grant for initial grants made to new directors. Options not immediately exercisable generally vest over four years. Options granted under the Directors’ Plan have a maximum term of 10 years.
The stock option and related activity under all of our stock option plans is summarized as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Outstanding Options |
| | | Shares Available
for Grant | | | Number of Options | | | Weighted
Average Exercise
Price per Share |
Balance at December 31, 2005 | | 1,700,906 | | | 6,449,030 | | | $ | 19.22 |
Stock options granted | | (1,406,716 | ) | | 1,406,716 | | | $ | 16.15 |
Restricted shares granted | | (424,450 | ) | | — | | | | — |
Forfeited stock options | | 1,240,435 | | | (1,240,435 | ) | | $ | 25.10 |
Restricted shares forfeited | | 92,774 | | | — | | | | — |
Stock options exercised | | — | | | (1,225,763 | ) | | $ | 15.18 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2006 | | 1,202,949 | | | 5,389,548 | | | $ | 17.99 |
Stock options granted | | (515,700 | ) | | 515,700 | | | $ | 25.37 |
Restricted shares granted | | (128,077 | ) | | — | | | | — |
Forfeited stock options | | 699,972 | | | (699,972 | ) | | $ | 19.77 |
Restricted shares forfeited | | 30,478 | | | — | | | | — |
Stock options exercised | | — | | | (534,008 | ) | | $ | 14.30 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2007 | | 1,289,622 | | | 4,671,268 | | | $ | 18.96 |
Stock options granted | | (670,725 | ) | | 670,725 | | | $ | 15.62 |
Restricted shares granted | | (150,748 | ) | | — | | | | — |
Forfeited stock options | | 655,651 | | | (655,651 | ) | | $ | 19.45 |
Restricted shares forfeited | | 13,924 | | | — | | | | — |
Stock options exercised | | — | | | (89,783 | ) | | $ | 12.04 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2008 | | 1,137,724 | | | 4,596,559 | | | $ | 18.54 |
| | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2008, the weighted average remaining contractual term for the outstanding options was 5.8 years and the aggregate intrinsic value was approximately $0.5 million on that date. The total intrinsic value of options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2008 was approximately $0.4 million. Intrinsic value for stock options is defined as the difference between the market value and the exercise price on the date of exercise.
The following table summarizes information about options outstanding at December 31, 2008:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options Outstanding | | Options Exercisable |
Range of
Exercise Prices | | Number of
Shares | | Weighted
Average
Remaining
Contractual Life | | Weighted
Average
Exercise Price | | Number of
Shares | | Weighted
Average
Exercise Price |
| $ 4.50 – $12.74 | | 1,151,364 | | 5.92 | | $ | 11.21 | | 1,071,998 | | $ | 11.12 |
| $13.26 – $15.40 | | 1,276,152 | | 6.99 | | $ | 15.17 | | 549,835 | | $ | 15.06 |
| $15.41 – $21.51 | | 1,150,205 | | 5.41 | | $ | 19.30 | | 977,442 | | $ | 19.54 |
| $22.02 – $49.26 | | 1,018,838 | | 4.53 | | $ | 30.18 | | 786,554 | | $ | 31.59 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 4,596,559 | | 5.78 | | $ | 18.54 | | 3,385,829 | | $ | 18.95 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
96
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
At December 31, 2008, the weighted average remaining contractual term for options exercisable is 5.5 years and the aggregate intrinsic value for those shares is approximately $0.5 million. If all of the remaining nonvested and outstanding stock option awards that have been granted became vested, we will recognize approximately $12.8 million in compensation expense over a weighted average remaining period of 2.2 years. However, no compensation expense will be recognized for any stock awards that do not vest.
Stockholder Rights Agreement
In July 2001, our board of directors approved the adoption of a stockholder Rights Agreement, which provided for the distribution of one preferred share purchase right (a “Right”) for each outstanding share of our common stock. The dividend was paid on August 3, 2001 to the stockholders of record on that date. Each Right entitles the registered holder to purchase one one-hundredth of a share of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Preferred Shares”), at a price of $390.00 per one one-hundredth of a Preferred Share (the “Purchase Price”), subject to adjustment. The Rights will be exercisable upon the earlier of: (i) the date of a public announcement that a person, entity or group of affiliated or associated persons have acquired beneficial ownership of 20% or more of the outstanding common shares (an “Acquiring Person”), or (ii) ten business days (or such later date as may be determined by action of the board of directors prior to such time as any person or entity becomes an Acquiring Person) following the commencement of, or announcement of an intention to commence, a tender offer or exchange offer the consummation of which would result in any person or entity becoming an Acquiring Person. In October 2004, the Rights Agreement was amended to allow Warburg Pincus Equity Partners, L.P. and certain of its affiliates (“Warburg Pincus”) to acquire ownership of up to 25% of our issued and outstanding common stock in open market purchases without becoming an Acquiring Person. Jonathan S. Leff, a member of our board of directors, is a managing director of Warburg Pincus LLC and a partner of Warburg Pincus & Co., which are affiliates of Warburg Pincus Equity Partners, L.P.
In the event that any person, entity or group of affiliated or associated persons become an Acquiring Person, each holder of a Right will have the right to receive, upon exercise, the number of common shares having a market value of two times the exercise price of the Right. In the event that we are acquired in a merger or other business combination transaction or 50% or more of our consolidated assets or earning power are sold to an Acquiring Person, its associates or affiliates or certain other persons in which such persons have an interest, each holder of a Right will have the right to receive, upon the exercise at the then-current exercise price of the Right, that number of shares of common stock of the acquiring company which at the time of such transaction will have a market value of two times the exercise price of the Right. At any time after an Acquiring Person becomes an Acquiring Person and prior to the acquisition by such Acquiring Person of 50% or more of the outstanding common shares, our board of directors may exchange the Rights (other than Rights owned by such person or group which have become void), in whole or in part, at an exchange ratio of one common share, or one one-hundredth of a Preferred Share, per Right (or, at our election, we may issue cash, debt, stock or a combination thereof in exchange for the Rights), subject to adjustment. The Rights will expire on August 3, 2011, unless we redeem or exchange them.
Public Offering
On September 26, 2007, we completed a public offering of approximately 4.0 million shares of registered common stock, at a price of $19.50 per share. We received net proceeds of approximately $73.4 million after deducting underwriting fees of $4.7 million and other related expenses of $0.4 million.
97
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Reserved Shares
At December 31, 2008, common stock subject to future issuance is as follows:
| | |
Common stock issuable upon conversion of convertible senior notes | | 8,431,524 |
Outstanding common stock options | | 4,596,559 |
Common stock available for grant under stock option plans | | 1,137,724 |
Common stock available for grant under the 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan | | 1,616,734 |
| | |
Total | | 15,782,541 |
| | |
Valuation and Expense Information under SFAS 123(R)
The following table reflects stock-based compensation expense recognized under SFAS 123(R) for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Research and development | | $ | 2,627 | | $ | 6,012 | | $ | 8,127 |
General and administrative | | | 4,170 | | | 6,224 | | | 8,395 |
Restructuring charges | | | — | | | 482 | | | — |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total stock-based compensation expense | | $ | 6,797 | | $ | 12,718 | | $ | 16,522 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Approximately $0.3 million has been included in G&A expense for the year ended December 31, 2006 in connection with the amendment to our Amended and Restated 2000 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Option Plan, which allows the board of directors to specify in a directors’ stock option agreement a longer or shorter period of time by which a director must exercise the option before the option terminates.
Our method of valuation for share-based awards is based on the Black-Scholes model . Our determination of fair value of share-based payment awards on the date of grant using an option-pricing model is affected by our stock price as well as assumptions regarding a number of highly complex and subjective variables. These variables include, but are not limited to our expected stock price volatility over the term of the awards, and actual and projected employee stock option exercise behaviors. A description of the assumptions follows:
| | • | | We estimated expected volatility using a blend of implied volatility based on market-traded options on our common stock and historical volatility of our common stock over the contractual life of the options. |
| | • | | The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for periods within the contractual life of the option. |
| | • | | The expected life of options granted represents the period of time the options are expected to be outstanding. The Company has applied the provisions of SAB 107 as amended by SAB 110 to determine the expected term. |
| | • | | The expected dividend yield is based on our current dividend yield as the best estimate of projected dividend yield for periods within the contractual life of the option. |
98
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
We estimated the fair value of each option grant on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Expected stock price volatility | | 78 | % | | 58 | % | | 56 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | 3.3 | % | | 4.8 | % | | 5.0 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | 4.6 | | | 4.9 | | | 6.0 | |
Expected dividend yield | | — | | | — | | | — | |
The weighted-average fair value per share of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 was $9.78, $13.72 and $9.30, respectively.
We estimated the fair value of the employees’ stock purchase rights using the Black-Scholes model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Expected stock price volatility | | 77 | % | | 56 | % | | 65 | % |
Risk-free interest rate | | 1.8 | % | | 4.5 | % | | 4.1 | % |
Expected term (in years) | | 0.5 | | | 1.0 | | | 1.8 | |
Expected dividend yield | | — | | | — | | | — | |
The weighted-average fair value for purchase rights granted under the employee stock purchase plan for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 was $6.02, $7.25 and $6.21, respectively.
As stock-based compensation expense recognized in the Consolidated Statement of Operations for fiscal years 2008, 2007 and 2006 is based on awards ultimately expected to vest, each has been reduced for estimated forfeitures. SFAS 123(R) requires forfeitures to be estimated at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates.
The Company’s benefit for income taxes consists of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Deferred: | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | — | | $ | 1,934 | | $ | — |
State | | | — | | | 341 | | | — |
| | | | | | | | | |
Totals | | $ | — | | $ | 2,275 | | $ | — |
| | | | | | | | | |
The tax benefit recorded in 2007 primarily relates to net operating losses that we concluded are realizable based on our estimate of future taxable income resulting from future potential sales of our shares of Targanta common stock.
99
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
A reconciliation of the Company’s recorded income tax benefit to the U.S. statutory rate follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
Federal tax benefit at statutory rate | | $ | (33,231 | ) | | $ | (31,238 | ) | | $ | (36,450 | ) |
Increase (reduction) in tax resulting from: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
State taxes, net of federal benefits | | | (6,626 | ) | | | (700 | ) | | | (10,890 | ) |
Change in valuation allowance | | | 52,860 | | | | 12,821 | | | | 57,602 | |
Research and development and orphan drug credits | | | (14,168 | ) | | | (10,728 | ) | | | (2,038 | ) |
Change in deferreds | | | (5,095 | ) | | | 26,037 | | | | (20,180 | ) |
Stock options | | | 610 | | | | (2,668 | ) | | | (636 | ) |
Government settlement | | | — | | | | — | | | | 12,561 | |
Other | | | 5,650 | | | | 4,201 | | | | 31 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Totals | | $ | — | | | $ | (2,275 | ) | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting and the amount used for income tax purposes.
Significant components of our deferred taxes are as follows at December 31 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | | | |
Net operating loss carryforwards | | $ | 201,000 | | | $ | 162,000 | |
Research and development credits | | | 63,000 | | | | 50,000 | |
Capitalized research and development costs | | | 12,000 | | | | 15,000 | |
Deferred revenue | | | 25,000 | | | | 23,000 | |
Other, net | | | 18,000 | | | | 16,000 | |
| | | | | | | | |
Total deferred tax assets | | | 319,000 | | | | 266,000 | |
Valuation allowance | | | (318,795 | ) | | | (263,725 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net deferred tax assets | | $ | 205 | | | $ | 2,275 | |
| | |
Deferred tax liability: | | | | | | | | |
Unrealized gain on investments, including Targanta common stock | | | (205 | ) | | | (2,275 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
Net deferred tax | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
| | | | | | | | |
Realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon future earnings, if any, the timing and amount of which are uncertain. The valuation allowance increased by $55.1 million, $11.7 million, and $58.0 million during the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
Deferred tax assets related to carryforwards at December 31, 2008 include approximately $10.0 million associated with stock option activity for which any subsequently recognized tax benefits will be credited directly to stockholders equity.
As of December 31, 2008, we had federal net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $532.4 million. The net operating loss carryforwards will expire at various dates beginning in 2018 through 2028 if not utilized. We also have federal research and development tax credits of approximately $21.1 million that will expire in the years 2018 through 2028 and federal Orphan Drug tax credits of approximately $47.2 million that will expire in
100
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
the years 2022 through 2028. In addition, we had net operating loss carryforwards for state income tax purposes of approximately $201.7 million that expire in the years 2012 through 2028 and state research and development tax credits of approximately $16.1 million that do not expire.
Utilization of the net operating losses may be subject to a substantial annual limitation due to the “change in ownership” provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and similar state provisions. The annual limitation may result in the expiration of net operating losses before utilization.
We adopted the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Interpretation No. 48,Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109 (“FIN 48”) on January 1, 2007. FIN 48 requires companies to determine whether it is “more likely than not” that a tax position will be sustained upon examination by the appropriate taxing authorities before any tax benefit can be recorded in the financial statements. It also provides guidance on the recognition, measurement, classification and interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions. The following table summarizes the activity related to the Company’s gross unrecognized tax benefits:
| | | | |
| | | Gross
Unrecognized
Tax Benefits | |
Balance at January 1, 2007 | | $ | 10,415 | |
Increases related to current year tax positions | | | 2,954 | |
| | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2007 | | $ | 13,369 | |
Decreases related to prior year tax positions | | | (340 | ) |
Increases related to current year tax positions | | | 3,852 | |
| | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2008 | | $ | 16,881 | |
| | | | |
At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the Company had unrecognized tax benefits of approximately $16.9 million and $13.4 million, respectively. The unrecognized tax benefits, if recognized, would not have an impact on the Company’s effective tax rate. The Company does not expect a significant change to its unrecognized tax benefits over the next twelve months. The unrecognized tax benefits may increase or change during the next year for items that arise in the ordinary course of business.
We file income tax returns in the U.S. federal and various state and local jurisdictions. The 2005 tax year which we had previously been under examination by the Internal Revenue Service has been reviewed and accepted. Remaining tax years from 1998 through 2007 remain open to examination by the major taxing authorities to which we are subject. Our policy is to record interest related to uncertain tax positions as interest and any penalties as other expense in our consolidated statement of operations. As of the date of adoption of FIN 48 and through December 31, 2008, we did not have any interest or penalties associated with unrecognized tax benefits.
| 15. | COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
Leases
We have a non-cancelable lease for facilities, which expires in 2011. Total rent expense was approximately $4.1 million, $4.1 million and $4.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
101
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
The following is a schedule by year of future minimum lease payments of all leases at December 31, 2008 (in thousands):
| | | |
Year | | Operating Leases |
2009 | | $ | 4,981 |
2010 | | | 5,153 |
2011 | | | 1,712 |
| | | |
| | $ | 11,846 |
| | | |
The operating lease for our facility requires a letter of credit secured by a restricted cash balance with our bank. The amount of the letter of credit approximates 6-12 months of operating rent payable to the landlord of the facility and is effective until we reach profitability. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, restricted cash under this letter of credit amounted to $1.4 million.
Purchase Commitments
In January 2000, we entered into an agreement with BI for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune. The agreement, which had been amended from time to time, generally provided for the exclusive supply by BI and exclusive purchase by us of Actimmune. This contractual obligation to BI was denominated in euros. Prior to the failure of the INSPIRE trial, we had future purchase obligations of approximately $91.6 million. Given the fact that the Phase III INSPIRE trial was unsuccessful and was discontinued in March 2007, we entered into a termination agreement (“Termination Agreement”) with BI. The Termination Agreement provides for the termination of the existing supply agreement dated January 2000, as amended, for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune conditioned upon and coincident with the entry by us and BI into a new agreement for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune. In consideration of the entry into the Termination Agreement, we incurred approximately $6.8 million in termination expenses during the second quarter of 2007, which have been included in restructuring charges in our consolidated statement of operations. Pursuant to the Termination Agreement and new supply agreement, we eliminated $91.6 million in future purchase commitments for Actimmune for the years 2007 to 2012. On June 29, 2007, InterMune and BI entered into a new agreement for the clinical and commercial supply of Actimmune (“Supply Agreement”). Under the terms of the new Supply Agreement, we are not required to make any minimum annual purchase commitments and BI is not required to commit to reserving any minimum annual capacity for the manufacture of Actimmune. On a going forward basis, the product will be purchased based upon a rolling forecast. The new Supply Agreement is effective as of June 29, 2007 and will expire on December 31, 2012. If BI is not able to supply all of our requirements for Actimmune, we may choose an additional manufacturer. However, we are not entitled to seek such a secondary source until BI has informed us of its unwillingness or inability to meet our requirements. Either party has the right to terminate the Supply Agreement if the other party materially breaches its obligations thereunder. In addition, we have the right to terminate the Supply Agreement immediately in the event that health authorities prevent distribution of Actimmune for all indications.
Contingent Payments
We may be required to make contingent milestone payments to the owners of our licensed products or the suppliers of our drug compounds in accordance with our license, commercialization and collaboration agreements in the aggregate amount of $70.9 million if all of the milestones per the agreements are achieved. These milestones include development, regulatory approval, commercialization and sales milestones. Of the $70.9 million in aggregate milestone payments, $53.5 million in contingent payments would be made by us only if positive Phase III data and registration in the United States and European Union are achieved for pirfenidone,
102
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
of which $13.5 million has been paid in March 2009. Potential milestone payments of $3.2 million are related to the further development of Actimmune, which we have no current plan to do, and therefore we do not expect to pay these amounts.
Department of Justice Settlement
On November 9, 2004, we received a subpoena from the U.S. Department of Justice requiring us to provide the Department of Justice with certain information relating to Actimmune, including information regarding the promotion and marketing of Actimmune. On October 25, 2006 we reached a comprehensive settlement with the government to resolve all claims without criminal sanctions relating to promotional activities for Actimmune for IPF by our former employees during a period ending in June 2003. As part of this comprehensive settlement, we entered into a Civil Settlement Agreement with the United States Department of Justice and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California. In addition, we entered into a Deferred Prosecution Agreement with the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California and a Corporate Integrity Agreement with the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services.
Under the terms of the Civil Settlement Agreement, we agreed to pay $36.9 million plus 5% interest on the then outstanding principal balance to the government over a period of five years, an amount to be shared between the Federal and participating State governments as per the agreement and the Medicaid Program. In October 2008, we entered into settlement and release agreements with the majority of the participating State governments pursuant to which the State portion of the aforementioned $36.9 million was distributed among such participating State governments. We recorded a $36.9 million charge during 2006 to reflect the final terms of the Civil Settlement Agreement. We paid $8.4 million, $4.1 million and $4.1 million in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively, and are required to make additional payments on the remaining settlement amount over the next three years in annual installments. The Civil Settlement Agreement contains a provision for the acceleration of certain of the $36.9 million in original scheduled principal payments if we receive over $150.0 million from partnering, license fees and milestone payments (excluding any research and development contributions), external debt and equity financing during the term of the Civil Settlement Agreement, subject to a cap on any acceleration of payment of $10.0 million in any one year. Since entering into the Civil Settlement Agreement, we have received $35.0 million in license fees and milestone payments under our various partnering and collaboration agreements and approximately $136.9 million in equity financing. As a result, we have exceeded the aforementioned $150.0 million threshold by approximately $21.9 million and have made an accelerated payment to the U.S. Department of Justice of approximately $4.4 million in March 2009.
The following table reflects the schedule of payments due under the settlement as of December 31, 2008 and does not reflect the impact of the $4.4 million accelerated payment described above (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
Year | | Principal | | Interest | | Total |
2009 | | | 5,826 | | | 1,174 | | | 7,000 |
2010 | | | 8,118 | | | 882 | | | 9,000 |
2011 | | | 9,524 | | | 476 | | | 10,000 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 23,468 | | $ | 2,532 | | $ | 26,000 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Under the terms of the Deferred Prosecution Agreement, the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California will file an Information charging us with one count of off-label promotion of Actimmune for use with IPF, but will defer prosecution of such charge during the two year term of the Deferred Prosecution Agreement. The Deferred Prosecution Agreement became effective December 2006 when it was
103
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
approved by the United States District Court for the Northern District of California. As a result, the two year term of such agreement expired December 2008 and the Information filed against us has since been dismissed.
Under the terms of the Corporate Integrity Agreement, the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services agrees to waive any potential exclusion of us from participation in federal health care programs provided that we comply with the terms of the Corporate Integrity Agreement for a period of five years. As part of the agreement, we agreed to retain an independent review organization to conduct periodic reviews of our promotional processes and policies as well as reviews of certain medical affairs group records.
Legal Proceedings
On May 8, 2008, a complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledDeborah Jane Jarrett, Nancy Isenhower, and Jeffrey H. Frankel v. InterMune, Inc., W. Scott Harkonen, and Genentech, Inc., Case No. C-08-02376 (the “Jarrett Action”). Plaintiffs alleged that they were administered Actimmune, and they purported to sue on behalf of a class of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleged that the Company fraudulently misrepresented the medical benefits of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF and promoted Actimmune for IPF. The complaint asserted various claims against the Company, including civil RICO, unfair competition, violation of various state consumer protection statutes, and unjust enrichment. The complaint sought various damages in an unspecified amount, including compensatory damages, treble damages, punitive damages, restitution, disgorgement, prejudgment and post-judgment interest on any monetary award, and the reimbursement of the plaintiffs’ legal fees and costs. The complaint also sought equitable relief.
On June 11, 2008, a nearly identical complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledLinda K. Rybkoski v. InterMune, Inc., W. Scott Harkonen, and Genentech, Inc., Case No. CV-08-2916 (the “Rybkoski Action”). Plaintiff in this action alleged that she was administered Actimmune and purported to sue on behalf of a class of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleged virtually identical facts to those alleged in the Jarrett Action; it also asserted the same claims against the Company and sought the same relief. On July 23, 2008, the Rybkoski Action was ordered related to the Jarrett Action and is now pending before the same judge and is proceeding on the same schedule.
On August 8, 2008, a similar complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledZurich American Insurance Company v. Genentech, Inc., InterMune, Inc., and W. Scott Harkonen, Case No. CV-08-3797 (the “Zurich Action”). Plaintiff in the Zurich Action, which allegedly provides health and pharmacy benefits to its insureds in the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and several U.S. territories, alleged that it paid for prescriptions of Actimmune and purported to sue on behalf of a class of third-party payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleged similar facts to those alleged in the Jarrett and Rybkoski Actions, and it also asserted civil RICO, unfair competition, various state consumer protection, and unjust enrichment claims against the Company. The complaint sought various damages in an unspecified amount, including compensatory damages, treble damages, punitive damages, prejudgment interest on all damages, and the reimbursement of the plaintiffs’ legal fees and costs. The complaint also sought a declaration that the conduct alleged was unlawful, as well as injunctive relief. On September 5, 2008, the Zurich Action was ordered related to the Jarrett Action and assigned to the same judge.
On September 26, 2008, Plaintiffs in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions filed an identical First Amended Class Action Complaint in all three actions. The First Amended Complaint, a putative nationwide class action on behalf of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune, is very similar to the first complaint that was filed in the Jarrett Action. It alleges the same basic facts, namely, that the Company fraudulently misrepresented
104
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
the medical benefits of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF and promoted Actimmune for IPF. The First Amended Complaint asserts various claims against the Company, including civil RICO, unfair competition, violation of various state consumer protection statutes, and unjust enrichment. The First Amended Complaint seeks various damages in an unspecified amount, including the same categories of damages and other relief that were originally sought in the Jarrett Action.
On October 20, 2008, InterMune and the other defendants filed motions to dismiss the First Amended Complaint in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions. On September 29, 2008, a similar complaint was filed in the United States District Court for the Northern District of California entitledGovernment Employees Health Association, Inc. v. InterMune, Inc., W. Scott Harkonen and Genentech, Inc., Case No. CV-08-4531 (the “GEHA Action”). Plaintiff in the GEHA Action is allegedly a national health insurance plan serving federal employees and retirees, as well as their families. Plaintiff alleges that it paid for more than $4 million of Actimmune prescriptions during the class period, and it purports to sue on behalf of a class of consumers and other end-payors of Actimmune. The complaint alleges that the Company fraudulently misrepresented the medical benefits of Actimmune for the treatment of IPF and promoted Actimmune for IPF. The complaint asserts the same causes of action against the Company as the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions, including civil RICO, unfair competition, violation of various state consumer protection statutes, and unjust enrichment. The complaint seeks various damages in an unspecified amount, including compensatory damages, treble damages, punitive damages, restitution, disgorgement, prejudgment and post-judgment interest on any monetary award, and the reimbursement of the plaintiffs’ legal fees and costs. The complaint also seeks appropriate equitable relief. The GEHA action was subsequently related to the other actions, so that all four are pending before the same judge. By stipulation, the parties to the GEHA Action agreed that the briefing already submitted on the motions to dismiss in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, and Zurich Actions would constitute the briefing on a motion to dismiss in the GEHA Action.
The motions to dismiss in all four cases were heard on February 2, 2009, and the motions were taken under submission by the Court. We expect a ruling sometime in March or April 2009, although it may take longer. The court had stayed discovery until at least the time of the hearing on the motions to dismiss, and no party has sought to conduct discovery following the February 2, 2009 hearing. In the meantime, on February 24, 2009, the plaintiffs in all four actions sought to consolidate the four actions for purposes of pretrial proceedings; the defendants have not opposed this request, and the Court has not yet ruled on it.
The Company believes it has substantial factual and legal defenses to the claims at issue and intends to defend the actions vigorously. We may enter into discussions regarding settlement of these matters, and may enter into settlement agreements, if we believe settlement is in the best interests of our shareholders. We cannot reasonably estimate the possible loss or range of loss that may arise from these lawsuits.
Indemnity Agreement
On or about March 22, 2000, the Company entered into an Indemnity Agreement with W. Scott Harkonen M.D., who served as the Company’s chief executive officer until June 30, 2003. The Indemnity Agreement obligates the Company to hold harmless and indemnify Dr. Harkonen against expenses (including attorneys’ fees), witness fees, damages, judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement and any other amounts Dr. Harkonen becomes legally obligated to pay because of any claim or claims made against him in connection with any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding , whether civil, criminal, arbitrational, administrative or investigative, to which Dr. Harkonen is a party by reason of the fact that he was a director, officer, employee or other agent of the Company. The Indemnity Agreement establishes exceptions to the Company’s indemnification obligation, including but not limited to claims “on account of [Dr. Harkonen’s] conduct that is established by a final judgment as knowingly fraudulent or deliberately dishonest or that
105
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
constituted willful misconduct,” claims “on account of [Dr. Harkonen’s] conduct that is established by a final judgment as constituting a breach of [Dr. Harkonen’s] duty of loyalty to the Corporation or resulting in any personal profit or advantage to which [Dr. Harkonen] was not legally entitled,” and claims “for which payment is actually made to [Dr. Harkonen] under a valid and collectible insurance policy.” The Indemnity Agreement, however, obligates the Company to advance all expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred by Dr. Harkonen in connection with such proceedings, subject to an undertaking by Dr. Harkonen to repay said amounts if it shall be determined ultimately that he is not entitled to be indemnified by the Company.
Dr. Harkonen has been named as a defendant in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich and GEHA Actions described above. Dr. Harkonen also was a target of the investigation by the U.S. Department of Justice regarding the promotion and marketing of Actimmune. On March 18, 2008, a federal grand jury indicted Dr. Harkonen on two felony counts related to alleged improper promotion and marketing of Actimmune during the time Dr. Harkonen was employed by the Company. Trial in the criminal case (the “Criminal Action”) is set for June 2009.
Prior to December 2008, insurers that issued directors & officers (“D&O”) liability insurance to the Company had advanced all of Dr. Harkonen’s expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions. Those insurers included National Union Fire Insurance Company of Pittsburgh, PA (“AIG”), Underwriters at Lloyd’s, London (“Lloyd’s”), and Continental Casualty Company (“CNA”). On November 19, 2008, however, the insurer that issued a $5 million D&O insurance policy providing coverage excess of the monetary limits of coverage provided by AIG, Lloyd’s and CNA, Arch Specialty Insurance Company (“Arch”), advised the Company that the limits of the underlying coverage were expected to be depleted by approximately December 15, 2008; that Arch “disclaims coverage” based on misstatements and misrepresentations allegedly made by Dr. Harkonen in documents provided in the application for the Arch policy and the underlying Lloyd’s policy; and, based on that disclaimer, Arch would not be advancing any of Dr. Harkonen’s expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred in Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions.
As a result of Arch’s disclaimer of coverage and refusal to advance expenses, including attorneys’ fees, the Company has as of approximately December 15, 2008, become obligated to advance such expenses incurred by Dr. Harkonen in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions.
On January 13, 2009, the Company submitted to the American Arbitration Association (“AAA”) a Demand for Arbitration,InterMune, Inc. v. Arch Specialty Insurance Co., No. 74 194 01128 08 JEMO. Dr. Harkonen also is a party to the Arbitration. The Demand for Arbitration seeks an award compelling Arch to advance Dr. Harkonen’s legal fees and costs incurred in the Jarrett, Rybkoski, Zurich, GEHA and Criminal Actions, and to advance other former officers’ legal fees and costs incurred in relation to the Department of Justice investigation. The AAA appointed a panel of three arbitrators on February 26, 2009. The parties to the Arbitration have until March 13, 2009, to move to disqualify any of the arbitrators. The Company expects that an initial hearing in the Arbitration will be scheduled shortly after the membership of the Arbitration panel is finalized.
| 16. | DISCLOSURES ABOUT SEGMENTS OF AN ENTERPRISE AND RELATED INFORMATION |
We have determined that, in accordance with SFAS No. 131, we operate in one segment, because operating results are reported only on an aggregate basis to our chief operating decision makers. We currently market Actimmune in the United States for the treatment of chronic granulomatous disease and severe, malignant osteopetrosis.
106
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Our net revenue for the years ended December 31, are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
Actimmune | | $ | 29,880 | | $ | 53,420 | | $ | 90,317 |
Collaboration revenue | | | 18,272 | | | 13,272 | | | 467 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Totals | | $ | 48,152 | | $ | 66,692 | | $ | 90,784 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Our net revenue by region for the years ended December 31, are as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 |
United States | | $ | 29,791 | | $ | 53,321 | | $ | 90,185 |
Rest of world | | | 18,361 | | | 13,371 | | | 599 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Totals | | $ | 48,152 | | $ | 66,692 | | $ | 90,784 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Our revenue and trade receivables are concentrated with a few customers. We perform credit evaluations on our customers’ financial condition and limit the amount of credit extended. However, we generally do not require collateral on accounts receivable. Concentrations of credit risk, with respect to accounts receivable, exist to the extent of amounts presented in the financial statements. Two customers represented 38% and 32%, respectively, of total accounts receivable at December 31, 2008, and four customers represented 43%, 25%, 11% and 10%, respectively, of total accounts receivable at December 31, 2007. No other customer represented more than 10% of accounts receivable at December 31, 2008 or December 31, 2007.
Revenue from customers representing 10% or more of total product revenue during the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
Customer | | 2008 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
CuraScript, Inc (formerly Priority Healthcare) | | 39 | % | | 48 | % | | 57 | % |
Caremark | | 17 | % | | 23 | % | | 22 | % |
Nova Factor | | 29 | % | | 7 | % | | 4 | % |
Merck Medco | | 1 | % | | 12 | % | | 11 | % |
| 17. | RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS |
On October 29, 2004 we entered into an Amended and Restated Standstill Agreement with Warburg Pincus Equity Partners, L.P. and certain of its affiliates (“Warburg Pincus”) that permits Warburg Pincus to acquire up to 25% of our outstanding common stock in the open market. Under this agreement, Warburg Pincus may acquire up to 25% of our outstanding common stock and we have granted Warburg Pincus certain registration rights with respect to its holdings. In exchange for allowing Warburg Pincus to increase its ownership stake, Warburg Pincus has granted the independent members of our board of directors the right to vote the shares of InterMune common stock owned by Warburg Pincus in excess of 19.9%. In addition, Warburg Pincus has agreed to certain limitations on the manner in which it may dispose of its ownership interest in InterMune. In connection with this transaction, we have also amended our stockholder Rights Plan to allow Warburg Pincus to acquire up to 25% of our outstanding common stock in open market purchases. Jonathan S. Leff, a member of our board of directors, is a managing director of Warburg Pincus LLC and a partner of Warburg Pincus & Co., which are affiliates of Warburg Pincus Equity Partners, L.P. As of December 31, 2008, Warburg Pincus held approximately 19% of our outstanding common stock.
107
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
On May 1, 1999, we adopted a 401(k) defined contribution plan that covers all full time employees, as defined, who fulfill certain length-of-service requirements. Employees may contribute up to the maximum limit imposed by federal tax law. Beginning in 2005, we began matching employee contributions at a rate of 50% of the first $6,000 per employee contributed each year. In 2007, we increased our matching contribution rate to 50% of the first $8,000 per employee contributed each year and in 2008 increased the contribution rate to 50% of the first $10,000 per employee. Our total matching contributions were $0.5 million, $0.6 million and $0.5 million in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively.
| 19. | GUARANTEES AND INDEMNIFICATIONS |
In November 2002, the FASB issued Interpretation No. 45,“Guarantor’s Accounting and Disclosure Requirements for Guarantees, including Indirect Guarantees of Indebtedness of Others”(“FIN 45”). FIN 45 requires that upon issuance of a guarantee, the guarantor must recognize a liability for the fair value of the obligations it assumes under that guarantee.
As permitted under Delaware law and in accordance with our Bylaws, we indemnify our officers and directors for certain events or occurrences, subject to certain limits, while the officer or director is or was serving at our request in such capacity. We terminate the indemnification agreements with our officers and directors upon the termination of their employment, but the termination will not affect claims for indemnification relating to events occurring prior to the effective date of termination. The maximum amount of potential future indemnification is unlimited; however, our director and officer insurance policy limits our exposure and may enable us to recover a portion of any future amounts paid. Accordingly, we believe the fair value of these indemnification agreements is minimal. Therefore, we have not recorded any liabilities for these agreements as of December 31, 2008.
On February 19, 2009, we completed a public offering of approximately 4.0 million shares of registered common stock, at a price of $16.35 per share. We received net proceeds of approximately $63.5 million after deducting underwriting fees of $2.0 million and other related expenses of $0.3 million. As a result of this transaction, we have made an accelerated payment to the U.S. Department of Justice of approximately $4.4 million in March 2009. See Note 15.
108
INTERMUNE, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
| 21. | QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (Unaudited) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | First
Quarter | | | Second
Quarter | | | Third
Quarter | | | Fourth
Quarter | | | Total Year | |
| | | (In thousands, except per share amounts) | |
2008 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Actimmune | | $ | 8,496 | | | $ | 7,296 | | | $ | 7,505 | | | $ | 6,583 | | | $ | 29,880 | |
Collaboration revenue | | | 818 | | | | 818 | | | | 15,818 | | | | 818 | | | | 18,272 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenue, net | | $ | 9,314 | | | $ | 8,114 | | | $ | 23,323 | | | $ | 7,401 | | | $ | 48,152 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 3,186 | | | $ | 2,398 | | | $ | 1,692 | | | $ | 1,713 | | | $ | 8,989 | |
Loss from operations | | | (28,520 | ) | | | (26,864 | ) | | | (11,913 | ) | | | (28,381 | ) | | | (95,678 | ) |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (26,425 | ) | | | (26,515 | ) | | | (12,528 | ) | | | (32,374 | ) | | | (97,842 | ) |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | 78 | | | | (4 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | 32 | | | | 103 | |
Net loss | | | (26,347 | ) | | | (26,519 | ) | | | (12,531 | ) | | | (32,342 | ) | | | (97,739 | ) |
Basic and diluted loss per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | $ | (0.68 | ) | | $ | (0.68 | ) | | $ | (0.32 | ) | | $ | (0.83 | ) | | $ | (2.51 | ) |
Discontinued operations | | | — | * | | | — | * | | | — | * | | | — | * | | | — | * |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share | | $ | (0.68 | ) | | $ | (0.68 | ) | | $ | (0.32 | ) | | $ | (0.83 | ) | | $ | (2.51 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
2007 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Actimmune | | $ | 19,525 | | | $ | 14,533 | | | $ | 10,553 | | | $ | 8,809 | | | $ | 53,420 | |
Collaboration revenue | | | 818 | | | | 10,818 | | | | 818 | | | | 818 | | | | 13,272 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenue, net | | $ | 20,343 | | | $ | 25,351 | | | $ | 11,371 | | | $ | 9,627 | | | $ | 66,692 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | $ | 5,284 | | | $ | 3,276 | | | $ | 3,491 | | | $ | 2,058 | | | $ | 14,109 | |
Restructuring charges | | | 1,333 | | | | 8,596 | | | | 317 | | | | — | | | | 10,246 | |
Loss from operations | | | (25,209 | ) | | | (21,567 | ) | | | (29,755 | ) | | | (30,373 | ) | | | (106,904 | ) |
Loss from continuing operations | | | (20,661 | ) | | | (19,808 | ) | | | (28,167 | ) | | | (25,960 | ) | | | (94,596 | ) |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | (144 | ) | | | 16 | | | | 5,043 | | | | 79 | | | | 4,994 | |
Net loss | | | (20,805 | ) | | | (19,792 | ) | | | (23,124 | ) | | | (25,881 | ) | | | (89,602 | ) |
Basic and diluted loss per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | $ | (0.61 | ) | | $ | (0.58 | ) | | $ | (0.81 | ) | | $ | (0.67 | ) | | $ | (2.67 | ) |
Discontinued operations | | | — | * | | | — | * | | | 0.15 | | | | — | * | | | 0.15 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share | | $ | (0.61 | ) | | $ | (0.58 | ) | | $ | (0.66 | ) | | $ | (0.67 | ) | | $ | (2.52 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| * | Less than $0.01 per share |
109
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURES |
Not Applicable.
| ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. We maintain “disclosure controls and procedures,” as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act, that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met. Additionally, in designing disclosure controls and procedures, our management necessarily was required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible disclosure controls and procedures. The design of any disclosure controls and procedures also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions.
Based on their evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
We assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission inInternal Control—Integrated Framework. Based on our assessment using those criteria, we concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2008.
Our independent registered public accounting firm has expressed an opinion on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting which is included below.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting. There have been no changes to our internal controls over financial reporting during the three months ended December 31, 2008 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Limitations on the Effectiveness of Controls. Our management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, does not expect that our disclosure controls and procedures or our internal control over financial reporting will prevent all error and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within the company have been detected.
110
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of InterMune, Inc.
We have audited InterMune, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the COSO criteria). InterMune, Inc.’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, InterMune, Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of InterMune, Inc. as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008 of InterMune, Inc. and our report dated March 10, 2009 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Palo Alto, California
March 10, 2009
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION. |
Not applicable.
111
PART III
Certain information required by Part III is omitted from this Annual Report on Form 10-K because we expect to file with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission a definitive proxy statement pursuant to Regulation 14A in connection with the solicitation of proxies for our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held at 10:00 a.m. on May 5, 2009 (the “Proxy Statement”) not later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and certain information included therein is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
Identification of Directors and Executive Officers
The information required by this Item with respect to Executive Officers may be found under the caption, “Executive Officers of the Registrant” at the end of Item 1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The information required by this Item with respect to Directors, including information with respect to our audit committee financial expert and the identification of our audit committee, is incorporated herein by reference from the information under the caption “Proposal 1—Election of Directors” contained in the Proxy Statement.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
The information required by this Item with respect to compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act is incorporated herein by reference from the section captioned “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” contained in the Proxy Statement.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
The information required by this Item with respect to our code of ethics is incorporated herein by reference from the section captioned “Proposal 1—Election of Directors—Code of Business Ethics and Conduct” contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the information under the sections entitled “Executive Compensation” and “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the information under the captions “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the information under the caption “Executive Compensation—Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the information from the Proxy Statement under the section entitled “Proposal 2—Ratification of Selection of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.”
112
PART IV
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(a) The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K:
(1)Financial Statements
See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
(2) Financial Statement Schedules
The following financial statement schedule is filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. All other financial statement schedules have been omitted because they are either not applicable or the required information has been included in the consolidated financial statements or the notes thereto.
Schedule II
InterMune, Inc.
Valuation and Qualifying Accounts and Reserves
Years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Description | | Balance at
Beginning of
Year | | Charged to
Revenue or
Expense | | Utilizations | | | Balance at
End of Year |
Allowance for cash discounts: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year ended December 31, 2008 | | $ | 44 | | $ | 666 | | $ | (652 | ) | | $ | 58 |
Year ended December 31, 2007 | | | 164 | | | 1,116 | | | (1,236 | ) | | | 44 |
Year ended December 31, 2006 | | | 337 | | | 1,887 | | | (2,060 | ) | | | 164 |
| | | | |
Allowance for doubtful accounts: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year ended December 31, 2008 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | | | $ | — |
Year ended December 31, 2007 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — |
Year ended December 31, 2006 | | | 108 | | | — | | | (108 | ) | | | — |
(3) Exhibits
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
1.1 | | Underwriting Agreement, dated September 20, 2007, among Registrant, Goldman, Sachs & Co., Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. and CIBC World Markets Corp. (24) |
| |
1.2 | | Underwriting Agreement, dated February 12, 2009, between Registrant and UBS Securities LLC. (28) |
| |
3.1 | | Certificate of Incorporation of Registrant. (1) |
| |
3.2 | | Certificate of Ownership and Merger, dated April 26, 2001. (8) |
| |
3.3 | | Bylaws of Registrant. (1) |
| |
3.4 | | Certificate of Amendment of Certificate of Incorporation of Registrant. (12) |
| |
3.5 | | Certificate of Amendment of Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Registrant. (15) |
| |
3.6 | | Registrant’s Certificate of Designation of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock. (7) |
| |
4.1 | | Specimen Common Stock Certificate. (1) |
113
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
4.6 | | Indenture, dated as of February 17, 2004, between Registrant and The Bank of New York. (14) |
| |
4.7 | | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of February 17, 2004, among Registrant, Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated, Banc of America Securities LLC, Credit Suisse First Boston LLC, Harris Nesbitt Corp. and RBC Capital Markets Corporation. (14) |
| |
4.8 | | Indenture, dated as of June 24, 2008, between Registrant and The Bank of New York Trust Company, N.A. (27) |
| |
4.9 | | Form of 5.00% Convertible Senior Note due 2015 (included in Exhibit 4.8). (27) |
| |
10.1+ | | Form of Indemnity Agreement. (1) |
| |
10.2+ | | 1999 Equity Incentive Plan and related documents. (1) |
| |
10.3+ | | Amended and Restated 2000 Equity Incentive Plan and related documents. (26) |
| |
10.4+ | | Amended and Restated 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan and related documents. (26) |
| |
10.5+ | | Amended and Restated 2000 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Option Plan and related documents. (26) |
| |
10.6 | | Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated January 7, 2000, between Registrant and certain holders of the common stock. (1) |
| |
10.7 | | Rights Agreement, dated July 17, 2001, between Registrant and Mellon Investor Services LLC. (7) |
| |
10.8 | | Preliminary Stipulation of Settlement Agreement, dated May 6, 2005. (17) |
| |
10.9+ | | Form of Change of Control Provisions for Officers. (2) |
| |
10.10 | | Assignment and Option Agreement, dated June 23, 2000, between Registrant and Connetics Corporation. (3) |
| |
10.11 | | Consent to Assignment Agreement, dated June 23, 2000, between Registrant, Connetics Corporation and Genentech, Inc. (3) |
| |
10.12 | | Notice re: Return of Rights to Gamma Interferon for Treatment of Infectious Diseases in Japan, dated July 25, 2000, between Registrant and Genentech, Inc. (3) |
| |
10.13 | | Form of Common Stock Purchase Agreement, dated August 11, 2000, between the Company and Investors. (4) |
| |
10.14 | | Lease Agreement, dated December 18, 2000, between Registrant and GAL-BRISBANE, L.P. (5) |
| |
10.15 | | First Amendment to Brisbane Technology Park Lease, effective as of December 18, 2000, between Registrant and GAL-BRISBANE, L.P. (5) |
| |
10.16* | | Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (6) |
| |
10.17 | | Amendment No. 5, dated January 25, 2001, to License Agreement, dated May 5, 1998, between Registrant and Genentech, Inc. (6) |
| |
10.18 | | Letter Amendment, dated August 1, 2001, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (8) |
| |
10.19+ | | Employment Offer Letter, dated April 5, 2002, between Registrant and Marianne Armstrong, Ph.D. (9) |
| |
10.20+ | | Bonus Plan Memorandum, dated April 18, 2002, from Registrant to Marianne Armstrong, Ph.D. (9) |
114
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
10.21 | | Letter Amendment, dated May 28, 2002, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (9) |
| |
10.22 | | Letter Amendment, dated July 1, 2002, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (9) |
| |
10.23* | | Amendment No. 4, dated January 28, 2003, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (10) |
| |
10.24+ | | Employment Offer Letter, dated April 30, 2002, between Registrant and Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. (11) |
| |
10.25+ | | Bonus Plan Memorandum, dated May 22, 2002, from Registrant to Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. (11) |
| |
10.26+ | | Employment Offer Letter, dated September 24, 2003, between Registrant and Daniel G. Welch. (12) |
| |
10.27+ | | Stock Bonus Award Agreement, dated November 5, 2003, between Registrant and William R. Ringo, Jr. (13) |
| |
10.28 | | Amended and Restated Standstill Agreement, dated October 29, 2004, among Registrant, Warburg Pincus & Co. and certain affiliates of Warburg Pincus & Co. (16) |
| |
10.29 | | Registration Rights Agreement, dated October 29, 2004, among Registrant, Warburg Pincus & Co. and certain affiliates of Warburg Pincus & Co. (16) |
| |
10.30 | | Amendment, dated October 29, 2004 to Rights Agreement, dated July 17, 2001, between Registrant and Mellon Investor Services LLC. (16) |
| |
10.31+ | | Employment Offer Letter Agreement, dated June 13, 2001, between Registrant and Williamson Bradford, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.32+ | | Employment Offer Letter Agreement, dated June 1, 2001, between Registrant and Steven Porter, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.33+ | | Employment Offer Letter Agreement, dated August 9, 2004, between Registrant and Robin Steele. (18) |
| |
10.34+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated August 18, 2004, between Registrant and Marianne Armstrong, Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.35+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated August 18, 2004, between Registrant and Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.36+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated July 27, 2004, between Registrant and Williamson Bradford, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.37+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated July 26, 2004, between Registrant and Steven Porter, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.38+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated July 27, 2004, between Registrant and Howard A. Simon, Esq. (18) |
| |
10.39* | | Product Acquisition Agreement, dated November 28, 2005, between Registrant and Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America. (19) |
| |
10.40* | | Asset Purchase Agreement dated December 23, 2005, between Registrant and Targanta Therapeutics Corporation. (20) |
| |
10.41+ | | Severance Agreement and General Release, dated January 6, 2006, between Registrant and Roger L. Hawley. (20) |
115
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
10.42* | | Amendment No. 6, dated February 27, 2006, to License Agreement dated May 5, 1998, between Registrant and Genentech, Inc. (20) |
| |
10.43* | | Exclusive License and Collaboration Agreement dated October 16, 2006 between Registrant and Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (21) |
| |
10.44 | | Deferred Prosecution Agreement between Registrant and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California (21) |
| |
10.45 | | Civil Settlement Agreement between Registrant and the United States Department of Justice and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California (21) |
| |
10.46 | | Corporate Integrity Agreement between Registrant and the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (21) |
| |
10.47+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Howard Simon. (22) |
| |
10.48+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Robin Steele. (22) |
| |
10.49+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and John Hodgman. (22) |
| |
10.50+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Bill Bradford. (22) |
| |
10.51+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Steve Porter. (22) |
| |
10.52+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Marianne Armstrong. (22) |
| |
10.53+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Lawrence Blatt. (22) |
| |
10.54+ | | Separation Agreement and Release of Claims dated July 3, 2007 between Registrant and Thomas Kassberg. (23) |
| |
10.55+ | | Separation Agreement and Release of Claims dated July 3, 2007 between Registrant and Cynthia Robinson. (23) |
| |
10.56* | | Termination Agreement dated June 6, 2007 between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH. (25) |
| |
10.57* | | Supply Agreement dated June 29, 2007 between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH. (25) |
| |
10.58 | | Letter Amendment dated December 19, 2007 to Product Acquisition Agreement dated November 28, 2005 between Registrant and Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America. (26) |
| |
10.59* | | Asset Purchase Agreement, dated November 19, 2007, among Registrant, Marnac, Inc., and Dr. Solomon B. Margolin. (26) |
| |
10.60* | | Asset Purchase Agreement, dated November 21, 2007, among Registrant, KDL GmbH, and Dr. Shitotomo Yamauchi. (26) |
| |
10.61* | | License Agreement, dated August 24, 2004, between Registrant and Chiron Corporation. (26) |
| |
10.62* | | Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.63* | | Amendment No. 1, dated May 8, 2003, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.64* | | Amendment No. 2, dated January 7, 2004, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
116
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
10.65* | | Amendment No. 3, dated September 10, 2004, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.66* | | Amendment No. 4, dated December 7, 2004, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.67* | | Letter Agreement, dated March 10, 2005, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.68* | | Amendment No. 5, dated June 30, 2005, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.69* | | Amendment No. 6, dated February 3, 2006, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.70* | | Amendment No. 7, dated June 28, 2006, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.71** | | First Amendment to Exclusive License and Collaboration Agreement effective October 16, 2008 between Registrant and Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (29) |
| |
10.72** | | API Supply Agreement dated December 17, 2008 among Registrant, on the one hand, and Signa S.A. de C.V., ACIC Fine Chemicals Inc., and ACIC Europe Limited, on the other hand. (29) |
| |
10.73 | | Form of State Settlement Agreement and Release with various states in connection with Deferred Prosecution Agreement between Registrant and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California (29) |
| |
21.1 | | List of Subsidiaries. (29) |
| |
23.1 | | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. (29) |
| |
24.1 | | Power of Attorney (included on the signature pages hereto) |
| |
31.1 | | Certification required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a). (29) |
| |
31.2 | | Certification required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a). (29) |
| |
32.1† | | Certification required by Rule 13a-14(b) or Rule 15d-14(b) and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code (18 U.S.C. §1350). (29) |
| * | Confidential treatment has been granted with respect to certain portions of this exhibit. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| ** | Confidential treatment has been requested with respect to certain portions of this exhibit. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| + | Management contract or compensation plan or arrangement. |
| † | This certification accompanies the Periodic Report pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and shall not be deemed “filed” by the Company for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. |
| (1) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 2, 2000 (No. 333-96029), as amended by Amendment No. 1 filed with the Commission on February 18, 2000, as amended by Amendment No. 2 filed with the Commission on March 6, 2000, as amended by Amendment No. 3 filed with the Commission on March 22, 2000, as amended by Amendment No. 4 filed with the Commission on March 23, 2000 and as amended by Amendment No. 5 filed with the Commission on March 23, 2000. |
| (2) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2000. |
| (3) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2000. |
| (4) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on August 23, 2000. |
| (5) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2000. |
117
| (6) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2001. |
| (7) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on July 18, 2001. |
| (8) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2001. |
| (9) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended June 30, 2002. |
| (10) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended March 31, 2003. |
| (11) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended June 30, 2003. |
| (12) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended September 30, 2003. |
| (13) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003. |
| (14) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s amended Annual Report on Form 10-K/A (Amendment No. 2) for the year ended December 31, 2003. |
| (15) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s amended Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q/A (Amendment No. 1) filed for the quarter ended June 30, 2004. |
| (16) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on November 4, 2004. |
| (17) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended March 31, 2005. |
| (18) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004. |
| (19) | Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of Form 8-K (File No. 001-11397) filed by Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, the parent company of Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America on January 5, 2006. |
| (20) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. |
| (21) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006. |
| (22) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on May 25, 2007. |
| (23) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on July 10, 2007. |
| (24) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on September 21, 2007. |
| (25) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2007. |
| (26) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007. |
| (27) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on June 24, 2008. |
| (28) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on February 17, 2009. |
(c) Exhibits
See Item 15(a) above.
(d) Financial Statement Schedules
See Item 15(a) above.
118
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | |
| INTERMUNE, INC. |
| |
By: | | /s/ JOHN C. HODGMAN |
| | John C. Hodgman Senior Vice President of Finance Administration and Chief Financial Officer |
Dated: March 13, 2009
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints John C. Hodgman and Daniel G. Welch, and each of them, as his true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of substitution for him, and in his name in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and any of them or his substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated have signed this Report below:
| | | | |
Signatures | | Title | | Date |
| | |
/s/ DANIEL G. WELCH Daniel G. Welch | | Chairman of the Board of Directors, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | | March 13, 2009 |
| | |
/s/ JOHN C. HODGMAN John C. Hodgman | | Senior Vice President of Finance Administration and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | | March 13, 2009 |
| | |
/s/ BRUCE W. TOMLINSON Bruce W. Tomlinson | | Vice President, Controller and Principal Accounting Officer | | March 13, 2009 |
| | |
/s/ LOUIS DRAPEAU Louis Drapeau | | Director | | March 13, 2009 |
| | |
/s/ LARS EKMAN Lars Ekman | | Lead Independent Director | | March 13, 2009 |
| | |
/s/ JAMES I. HEALY James I. Healy | | Director | | March 13, 2009 |
| | |
/s/ DAVID S. KABAKOFF David S. Kabakoff | | Director | | March 13, 2009 |
| | |
/s/ JONATHAN S. LEFF Jonathan S. Leff | | Director | | March 13, 2009 |
119
EXHIBIT INDEX
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
1.1 | | Underwriting Agreement, dated September 20, 2007, among Registrant, Goldman, Sachs & Co., Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. and CIBC World Markets Corp. (24) |
| |
1.2 | | Underwriting Agreement, dated February 12, 2009, between Registrant and UBS Securities LLC. (28) |
| |
3.1 | | Certificate of Incorporation of Registrant. (1) |
| |
3.2 | | Certificate of Ownership and Merger, dated April 26, 2001. (8) |
| |
3.3 | | Bylaws of Registrant. (1) |
| |
3.4 | | Certificate of Amendment of Certificate of Incorporation of Registrant. (12) |
| |
3.5 | | Certificate of Amendment of Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Registrant. (15) |
| |
3.6 | | Registrant’s Certificate of Designation of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock. (7) |
| |
4.1 | | Specimen Common Stock Certificate. (1) |
| |
4.6 | | Indenture, dated as of February 17, 2004, between Registrant and The Bank of New York. (14) |
| |
4.7 | | Registration Rights Agreement, dated as of February 17, 2004, among Registrant, Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated, Banc of America Securities LLC, Credit Suisse First Boston LLC, Harris Nesbitt Corp. and RBC Capital Markets Corporation. (14) |
| |
4.8 | | Indenture, dated as of June 24, 2008, between Registrant and The Bank of New York Trust Company, N.A. (27) |
| |
4.9 | | Form of 5.00% Convertible Senior Note due 2015 (included in Exhibit 4.8). (27) |
| |
10.1+ | | Form of Indemnity Agreement. (1) |
| |
10.2+ | | 1999 Equity Incentive Plan and related documents. (1) |
| |
10.3+ | | Amended and Restated 2000 Equity Incentive Plan and related documents. (26) |
| |
10.4+ | | Amended and Restated 2000 Employee Stock Purchase Plan and related documents. (26) |
| |
10.5+ | | Amended and Restated 2000 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Option Plan and related documents. (26) |
| |
10.6 | | Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated January 7, 2000, between Registrant and certain holders of the common stock. (1) |
| |
10.7 | | Rights Agreement, dated July 17, 2001, between Registrant and Mellon Investor Services LLC. (7) |
| |
10.8 | | Preliminary Stipulation of Settlement Agreement, dated May 6, 2005. (17) |
| |
10.9+ | | Form of Change of Control Provisions for Officers. (2) |
| |
10.10 | | Assignment and Option Agreement, dated June 23, 2000, between Registrant and Connetics Corporation. (3) |
| |
10.11 | | Consent to Assignment Agreement, dated June 23, 2000, between Registrant, Connetics Corporation and Genentech, Inc. (3) |
| |
10.12 | | Notice re: Return of Rights to Gamma Interferon for Treatment of Infectious Diseases in Japan, dated July 25, 2000, between Registrant and Genentech, Inc. (3) |
| |
10.13 | | Form of Common Stock Purchase Agreement, dated August 11, 2000, between the Company and Investors. (4) |
| |
10.14 | | Lease Agreement, dated December 18, 2000, between Registrant and GAL-BRISBANE, L.P. (5) |
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
10.15 | | First Amendment to Brisbane Technology Park Lease, effective as of December 18, 2000, between Registrant and GAL-BRISBANE, L.P. (5) |
| |
10.16* | | Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (6) |
| |
10.17 | | Amendment No. 5, dated January 25, 2001, to License Agreement, dated May 5, 1998, between Registrant and Genentech, Inc. (6) |
| |
10.18 | | Letter Amendment, dated August 1, 2001, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (8) |
| |
10.19+ | | Employment Offer Letter, dated April 5, 2002, between Registrant and Marianne Armstrong, Ph.D. (9) |
| |
10.20+ | | Bonus Plan Memorandum, dated April 18, 2002, from Registrant to Marianne Armstrong, Ph.D. (9) |
| |
10.21 | | Letter Amendment, dated May 28, 2002, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (9) |
| |
10.22 | | Letter Amendment, dated July 1, 2002, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (9) |
| |
10.23* | | Amendment No. 4, dated January 28, 2003, to Development and Marketing Agreement, dated March 23, 2001, between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. (10) |
| |
10.24+ | | Employment Offer Letter, dated April 30, 2002, between Registrant and Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. (11) |
| |
10.25+ | | Bonus Plan Memorandum, dated May 22, 2002, from Registrant to Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. (11) |
| |
10.26+ | | Employment Offer Letter, dated September 24, 2003, between Registrant and Daniel G. Welch. (12) |
| |
10.27+ | | Stock Bonus Award Agreement, dated November 5, 2003, between Registrant and William R. Ringo, Jr. (13) |
| |
10.28 | | Amended and Restated Standstill Agreement, dated October 29, 2004, among Registrant, Warburg Pincus & Co. and certain affiliates of Warburg Pincus & Co. (16) |
| |
10.29 | | Registration Rights Agreement, dated October 29, 2004, among Registrant, Warburg Pincus & Co. and certain affiliates of Warburg Pincus & Co. (16) |
| |
10.30 | | Amendment, dated October 29, 2004 to Rights Agreement, dated July 17, 2001, between Registrant and Mellon Investor Services LLC. (16) |
| |
10.31+ | | Employment Offer Letter Agreement, dated June 13, 2001, between Registrant and Williamson Bradford, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.32+ | | Employment Offer Letter Agreement, dated June 1, 2001, between Registrant and Steven Porter, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.33+ | | Employment Offer Letter Agreement, dated August 9, 2004, between Registrant and Robin Steele. (18) |
| |
10.34+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated August 18, 2004, between Registrant and Marianne Armstrong, Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.35+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated August 18, 2004, between Registrant and Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.36+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated July 27, 2004, between Registrant and Williamson Bradford, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
10.37+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated July 26, 2004, between Registrant and Steven Porter, M.D., Ph.D. (18) |
| |
10.38+ | | Amendment to Offer Letter re Severance Pay and Change in Control, dated July 27, 2004, between Registrant and Howard A. Simon, Esq. (18) |
| |
10.39* | | Product Acquisition Agreement, dated November 28, 2005, between Registrant and Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America. (19) |
| |
10.40* | | Asset Purchase Agreement dated December 23, 2005, between Registrant and Targanta Therapeutics Corporation. (20) |
| |
10.41+ | | Severance Agreement and General Release, dated January 6, 2006, between Registrant and Roger L. Hawley. (20) |
| |
10.42* | | Amendment No. 6, dated February 27, 2006, to License Agreement dated May 5, 1998, between Registrant and Genentech, Inc. (20) |
| |
10.43* | | Exclusive License and Collaboration Agreement dated October 16, 2006 between Registrant and Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (21) |
| |
10.44 | | Deferred Prosecution Agreement between Registrant and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California. (21) |
| |
10.45 | | Civil Settlement Agreement between Registrant and the United States Department of Justice and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California. (21) |
| |
10.46 | | Corporate Integrity Agreement between Registrant and the Office of the Inspector General of the United States Department of Health and Human Services. (21) |
| |
10.47+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Howard Simon. (22) |
| |
10.48+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Robin Steele. (22) |
| |
10.49+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and John Hodgman. (22) |
| |
10.50+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Bill Bradford. (22) |
| |
10.51+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Steve Porter. (22) |
| |
10.52+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Marianne Armstrong. (22) |
| |
10.53+ | | Retention Payment Agreement dated May 24, 2007 between Registrant and Lawrence Blatt. (22) |
| |
10.54+ | | Separation Agreement and Release of Claims dated July 3, 2007 between Registrant and Thomas Kassberg. (23) |
| |
10.55+ | | Separation Agreement and Release of Claims dated July 3, 2007 between Registrant and Cynthia Robinson. (23) |
| |
10.56* | | Termination Agreement dated June 6, 2007 between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH. (25) |
| |
10.57* | | Supply Agreement dated June 29, 2007 between Registrant and Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH. (25) |
| |
10.58 | | Letter Amendment dated December 19, 2007 to Product Acquisition Agreement dated November 28, 2005 between Registrant and Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America. (26) |
| |
10.59* | | Asset Purchase Agreement, dated November 19, 2007, among Registrant, Marnac, Inc., and Dr. Solomon B. Margolin. (26) |
| |
10.60* | | Asset Purchase Agreement, dated November 21, 2007, among Registrant, KDL GmbH, and Dr. Shitotomo Yamauchi. (26) |
| |
10.61* | | License Agreement, dated August 24, 2004, between Registrant and Chiron Corporation. (26) |
| | |
Number | | Description of Document |
10.62* | | Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.63* | | Amendment No. 1, dated May 8, 2003, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.64* | | Amendment No. 2, dated January 7, 2004, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.65* | | Amendment No. 3, dated September 10, 2004, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.66* | | Amendment No. 4, dated December 7, 2004, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.67* | | Letter Agreement, dated March 10, 2005, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.68* | | Amendment No. 5, dated June 30, 2005, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.69* | | Amendment No. 6, dated February 3, 2006, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.70* | | Amendment No. 7, dated June 28, 2006, to the Drug Discovery Collaboration Agreement, dated September 13, 2002, between Registrant and Array BioPharma Inc. (26) |
| |
10.71** | | First Amendment to Exclusive License and Collaboration Agreement effective October 16, 2008 between Registrant and Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (29) |
| |
10.72** | | API Supply Agreement dated December 17, 2008 among Registrant, on the one hand, and Signa S.A. de C.V., ACIC Fine Chemicals Inc., and ACIC Europe Limited, on the other hand. (29) |
| |
10.73 | | Form of State Settlement Agreement and Release with various states in connection with Deferred Prosecution Agreement between Registrant and the United States Attorney’s Office for the Northern District of California. (29) |
| |
21.1 | | List of Subsidiaries. (29) |
| |
23.1 | | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. (29) |
| |
24.1 | | Power of Attorney (included on the signature pages hereto) |
| |
31.1 | | Certification required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a). (29) |
| |
31.2 | | Certification required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a). (29) |
| |
32.1† | | Certification required by Rule 13a-14(b) or Rule 15d-14(b) and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code (18 U.S.C. §1350). (29) |
| * | Confidential treatment has been granted with respect to certain portions of this exhibit. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| ** | Confidential treatment has been requested with respect to certain portions of this exhibit. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| + | Management contract or compensation plan or arrangement. |
| † | This certification accompanies the Periodic Report pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and shall not be deemed “filed” by the Company for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. |
| (1) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 2, 2000 (No. 333-96029), as amended by Amendment No. 1 filed with the Commission on February 18, 2000, as amended by Amendment No. 2 filed with the Commission on March 6, 2000, as amended by Amendment No. 3 filed with the Commission on March 22, 2000, as amended by Amendment No. 4 filed with the Commission on March 23, 2000 and as amended by Amendment No. 5 filed with the Commission on March 23, 2000. |
| (2) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2000. |
| (3) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2000. |
| (4) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on August 23, 2000. |
| (5) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2000. |
| (6) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2001. |
| (7) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on July 18, 2001. |
| (8) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2001. |
| (9) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended June 30, 2002. |
| (10) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended March 31, 2003. |
| (11) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended June 30, 2003. |
| (12) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended September 30, 2003. |
| (13) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003. |
| (14) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s amended Annual Report on Form 10-K/A (Amendment No. 2) for the year ended December 31, 2003. |
| (15) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s amended Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q/A (Amendment No. 1) filed for the quarter ended June 30, 2004. |
| (16) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on November 4, 2004. |
| (17) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed for the quarter ended March 31, 2005. |
| (18) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004. |
| (19) | Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 of Form 8-K (File No. 001-11397) filed by Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, the parent company of Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America on January 5, 2006. |
| (20) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. |
| (21) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006. |
| (22) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on May 25, 2007. |
| (23) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on July 10, 2007. |
| (24) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on September 21, 2007. |
| (25) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2007. |
| (26) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2007. |
| (27) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on June 24, 2008. |
| (28) | Filed as an exhibit to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K on February 17, 2009. |
