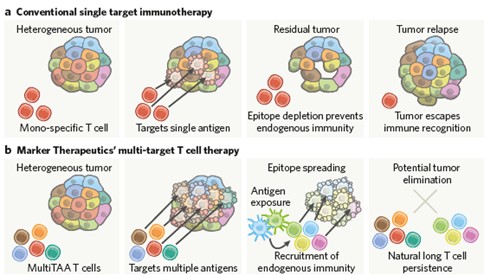
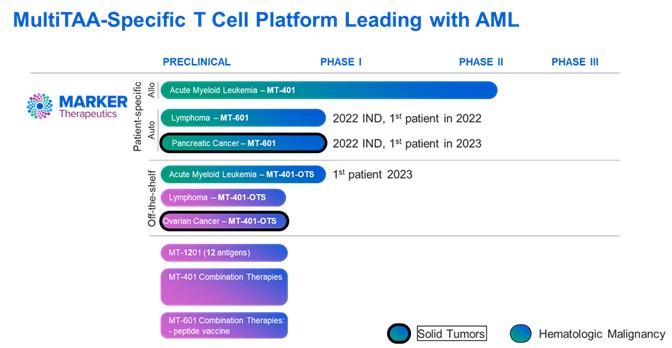
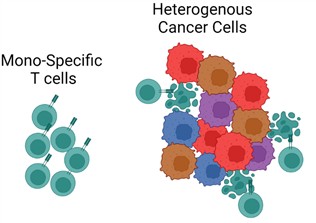
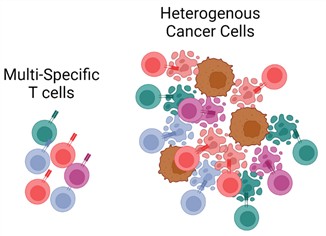
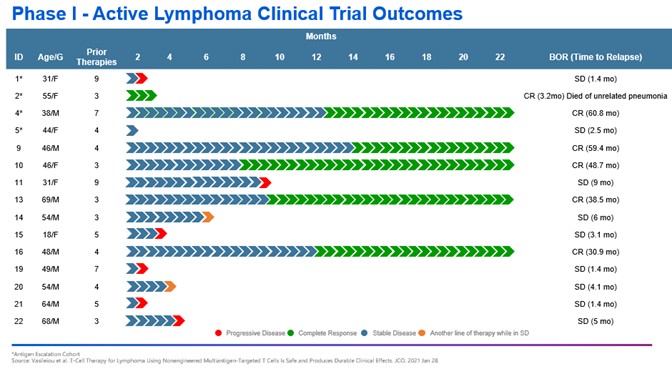
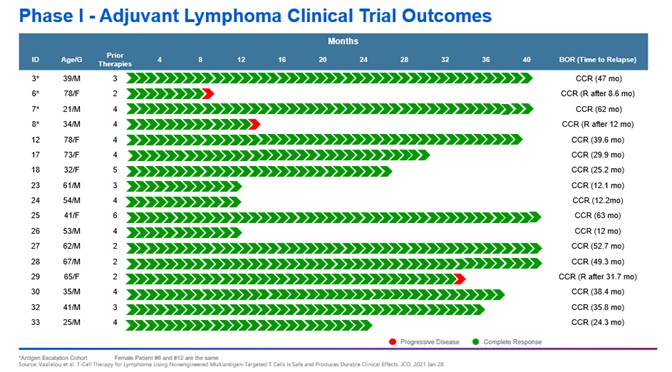
We are subject to stringent and changing laws, regulations, rules, contractual obligations, policies and other obligations related to data privacy and security. Our actual or perceived failure to comply with such obligations could lead to regulatory investigations or regulatory investigations or actions; litigation; fines and penalties; disruptions of our business operations; reputational harm; loss of revenue or profits; loss of customers or sales; and other adverse business consequences.
In the ordinary course of our business, we may collect, receive, store, process, generate, use, transmit, disclose, make accessible, protect, secure, dispose of, share (collectively, processing) personal data and other sensitive data, including proprietary and confidential business data, intellectual property, trade secrets, data regarding clinical trial subjects, and sensitive third-party data. We may rely on third parties (such as service providers) for our data processing-related activities. Our data processing activities subject us to numerous data privacy and security obligations, such as various laws, regulations, guidance, industry standards, external and internal privacy and security policies, contracts, and other obligations that govern the processing of personal data by us and on our behalf.
In the United States, federal, state, and local governments have enacted numerous data privacy and security laws, including data breach notification laws, personal data privacy laws, and consumer protection laws. For example, HIPAA, as amended by HITECH, imposes specific requirements relating to the privacy, security, and transmission of individually identifiable health information. Additionally, the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018, or CCPA, applies to personal data of consumers, business representatives, and employees, and requires businesses to provide specific disclosures in privacy notices and honor requests of California residents to exercise certain privacy rights. The CCPA provides for civil penalties of up to $7,500 per violation and allows private litigants affected by certain data breaches to recover significant statutory damages. Although the CCPA exempts some data processed in the context of clinical trials, the CCPA increases compliance costs and potential liability with respect to other personal data we maintain about California residents. In addition, California Privacy Rights Act of 2020, or CPRA, expands the CCPA’s requirements, including by adding a new right for individuals to correct their personal data and establishing a new regulatory agency to implement and enforce the law. Other states, such as Virginia and Colorado, have also passed comprehensive privacy laws, and similar laws are being considered in several other states, as well as at the federal and local levels. While these states, like the CCPA, also exempt some data processed in the context of clinical trials, these developments further complicate compliance efforts and increase legal risk and compliance costs for us and the third parties upon whom we rely. Outside the United States, an increasing number of laws, regulations, and industry standards apply to data privacy and security. For example, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (“EU GDPR”), the United Kingdom’s GDPR (“UK GDPR”), Brazil’s General Data Protection Law (Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados Pessoais, or “LGPD”) (Law No. 13,709/2018), and China’s Personal Information Protection Law (“PIPL”) impose strict requirements for processing personal data. For example, under the EU GDPR, companies may face temporary or definitive bans on data processing and other corrective actions, fines of up to 20 million euros or 4% of annual global revenue, whichever is greater, or private litigation related to processing of personal data brought by classes of data subjects or consumer protection organizations authorized at law to represent their interests.
We are also bound by contractual obligations related to data privacy and security, and our efforts to comply with such obligations may not be successful. For example, certain privacy laws, such as the CCPA, require our customers to impose specific contractual restrictions on their service providers. We publish privacy policies, marketing materials and other statements, regarding data privacy and security. If these policies, materials or statements are found to be deficient, lacking in transparency, deceptive, unfair, or misrepresentative of our practices, we may be subject to investigation, enforcement actions by regulators or other adverse consequences. Obligations related to data privacy and security are quickly changing, becoming increasingly stringent, and creating regulatory uncertainty. Additionally, these obligations may be subject to differing applications and interpretations, which may be inconsistent or conflict among jurisdictions. Preparing for and complying with these obligations requires us to devote significant resources, which may necessitate changes to our services, information technologies, systems, and practices and to those of any third parties that process personal data on our behalf.
We may at times fail (or be perceived to have failed) in our efforts to comply with our data privacy and security obligations. Moreover, despite our efforts, our personnel or third parties on whom we rely may fail to comply with such obligations, which could negatively impact our business operations. If we or the third parties on which we rely fail, or are perceived to have failed, to address or comply with applicable data privacy and security obligations, we could face significant consequences, including but not limited to: government enforcement actions (e.g., investigations, fines, penalties, audits, inspections, and similar); litigation (including class-action claims); additional reporting requirements and/or oversight; bans on processing personal data; and orders to destroy or not use personal data. Any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our reputation, business, or financial condition, including but not limited to: interruptions or stoppages in our business operations (including clinical trials); inability to process personal data or to operate in certain jurisdictions; limited ability to develop or commercialize our products; expenditure of time and resources to defend any claim or inquiry; adverse publicity; or substantial changes to our business model or operations.