| | | | | |
| Subject Selection for Clinical Study DAR-201 |
| • | | Key inclusion criteria |
| | | — | | Males and females age 35 to 85 years |
| | | — | | Resistant systolic hypertension as defined by the JNC 7 criteria (SBP³ 140 mm Hg for patients without compelling conditions; SBP³ 130 mm Hg for patients with diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or both) |
| | | — | | Treated with full doses of 3 or more antihypertensive drugs, including a diuretic |
| | | — | | Estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR)³ 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 |
| • | | Key exclusion criteria |
| | | — | | Average sitting SBP³ 180 mm Hg or DBP³ 110 mm Hg |
| | | — | | Symptomatic arrhythmias, unstable angina pectoris, symptomatic chronic heart failure, hemodynamically significant valvular heart disease, or significant pulmonary disease; or myocardial infarction, unstable angina, or cerebrovascular accident within 6 months of screening |
| | | — | | Abnormal laboratory parameters, including liver enzymes >2X the upper limit of normal (ULN) during the screening period |
| | | — | | Pregnant and/or nursing women |
| DAR-201 Study Design and Treatment |
| • | | DAR-201 was a 10-week study of escalating doses of darusentan versus placebo in 115 subjects with resistant systolic hypertension receiving combination therapy with full doses of 3 or more antihypertensive drugs, including a diuretic |
| • | | Following a 2-week placebo run-in period, subjects were randomized 2:1 to receive darusentan or placebo once daily in the morning for 10 weeks |
| | | — | | Darusentan was initiated at 10 mg and the dose was increased every 2 weeks through doses of 50, 100, and 150 mg until a maximum dose of 300 mg was achieved |
| | | — | | Subjects were withdrawn from darusentan or placebo over a 2-week period |
| DAR-201 Study Endpoints and Measures of Interest |
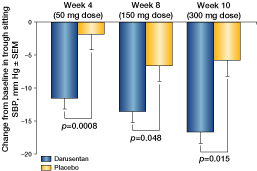
| • | | Changes from baseline to weeks 8 and 10 in trough sitting SBP were the co-primary endpoints |
| • | | Percentage of patients achieving SBP goal was a prespecified secondary endpoint |
| | | — | | JNC 7 SBP goals were <140 mm Hg in patients with no additional conditions and <130 mm Hg in patients with diabetes or chronic kidney disease |
| • | | Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring was performed at randomization and at the week 10 study visit or upon premature discontinuation from the study |
| | | — | | Trough BP was defined as the mean BP measured during the last 4 hours of ambulatory BP monitoring subsequent to Hour 18 postdose |
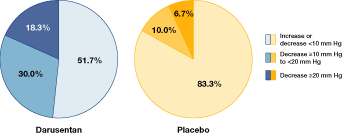
| • | | Additional analyses, including the percentage of patients who experienced a reduction in SBP of³ 10 or³ 20 mm Hg and the percentage of patients achieving SBP goal or a reduction of³ 10 mm Hg, were performed post hoc |
| Statistical Analyses |
| • | | The analysis for the primary endpoint (change in SBP) was a repeated measures analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) model, using all available data |
| • | | The analysis for proportion of responders was a logistic regression model for each timepoint, using the last available observation to impute missing data |
| • | | All subjects who received any dose of blinded study medication and had both a baseline and a postbaseline ambulatory blood pressure measurement were included in the efficacy analysis |
| • | | Presentedpvalues are adjusted for multiple comparisons unless otherwise indicated |